How to write an effective introduction for your research paper
Last updated
20 January 2024
Reviewed by
However, the introduction is a vital element of your research paper . It helps the reader decide whether your paper is worth their time. As such, it's worth taking your time to get it right.
In this article, we'll tell you everything you need to know about writing an effective introduction for your research paper.
- The importance of an introduction in research papers
The primary purpose of an introduction is to provide an overview of your paper. This lets readers gauge whether they want to continue reading or not. The introduction should provide a meaningful roadmap of your research to help them make this decision. It should let readers know whether the information they're interested in is likely to be found in the pages that follow.
Aside from providing readers with information about the content of your paper, the introduction also sets the tone. It shows readers the style of language they can expect, which can further help them to decide how far to read.
When you take into account both of these roles that an introduction plays, it becomes clear that crafting an engaging introduction is the best way to get your paper read more widely. First impressions count, and the introduction provides that impression to readers.
- The optimum length for a research paper introduction
While there's no magic formula to determine exactly how long a research paper introduction should be, there are a few guidelines. Some variables that impact the ideal introduction length include:
Field of study
Complexity of the topic
Specific requirements of the course or publication
A commonly recommended length of a research paper introduction is around 10% of the total paper’s length. So, a ten-page paper has a one-page introduction. If the topic is complex, it may require more background to craft a compelling intro. Humanities papers tend to have longer introductions than those of the hard sciences.
The best way to craft an introduction of the right length is to focus on clarity and conciseness. Tell the reader only what is necessary to set up your research. An introduction edited down with this goal in mind should end up at an acceptable length.
- Evaluating successful research paper introductions
A good way to gauge how to create a great introduction is by looking at examples from across your field. The most influential and well-regarded papers should provide some insights into what makes a good introduction.

Dissecting examples: what works and why
We can make some general assumptions by looking at common elements of a good introduction, regardless of the field of research.
A common structure is to start with a broad context, and then narrow that down to specific research questions or hypotheses. This creates a funnel that establishes the scope and relevance.
The most effective introductions are careful about the assumptions they make regarding reader knowledge. By clearly defining key terms and concepts instead of assuming the reader is familiar with them, these introductions set a more solid foundation for understanding.
To pull in the reader and make that all-important good first impression, excellent research paper introductions will often incorporate a compelling narrative or some striking fact that grabs the reader's attention.
Finally, good introductions provide clear citations from past research to back up the claims they're making. In the case of argumentative papers or essays (those that take a stance on a topic or issue), a strong thesis statement compels the reader to continue reading.
Common pitfalls to avoid in research paper introductions
You can also learn what not to do by looking at other research papers. Many authors have made mistakes you can learn from.
We've talked about the need to be clear and concise. Many introductions fail at this; they're verbose, vague, or otherwise fail to convey the research problem or hypothesis efficiently. This often comes in the form of an overemphasis on background information, which obscures the main research focus.
Ensure your introduction provides the proper emphasis and excitement around your research and its significance. Otherwise, fewer people will want to read more about it.
- Crafting a compelling introduction for a research paper
Let’s take a look at the steps required to craft an introduction that pulls readers in and compels them to learn more about your research.
Step 1: Capturing interest and setting the scene
To capture the reader's interest immediately, begin your introduction with a compelling question, a surprising fact, a provocative quote, or some other mechanism that will hook readers and pull them further into the paper.
As they continue reading, the introduction should contextualize your research within the current field, showing readers its relevance and importance. Clarify any essential terms that will help them better understand what you're saying. This keeps the fundamentals of your research accessible to all readers from all backgrounds.
Step 2: Building a solid foundation with background information
Including background information in your introduction serves two major purposes:
It helps to clarify the topic for the reader
It establishes the depth of your research
The approach you take when conveying this information depends on the type of paper.
For argumentative papers, you'll want to develop engaging background narratives. These should provide context for the argument you'll be presenting.
For empirical papers, highlighting past research is the key. Often, there will be some questions that weren't answered in those past papers. If your paper is focused on those areas, those papers make ideal candidates for you to discuss and critique in your introduction.
Step 3: Pinpointing the research challenge
To capture the attention of the reader, you need to explain what research challenges you'll be discussing.
For argumentative papers, this involves articulating why the argument you'll be making is important. What is its relevance to current discussions or problems? What is the potential impact of people accepting or rejecting your argument?
For empirical papers, explain how your research is addressing a gap in existing knowledge. What new insights or contributions will your research bring to your field?
Step 4: Clarifying your research aims and objectives
We mentioned earlier that the introduction to a research paper can serve as a roadmap for what's within. We've also frequently discussed the need for clarity. This step addresses both of these.
When writing an argumentative paper, craft a thesis statement with impact. Clearly articulate what your position is and the main points you intend to present. This will map out for the reader exactly what they'll get from reading the rest.
For empirical papers, focus on formulating precise research questions and hypotheses. Directly link them to the gaps or issues you've identified in existing research to show the reader the precise direction your research paper will take.
Step 5: Sketching the blueprint of your study
Continue building a roadmap for your readers by designing a structured outline for the paper. Guide the reader through your research journey, explaining what the different sections will contain and their relationship to one another.
This outline should flow seamlessly as you move from section to section. Creating this outline early can also help guide the creation of the paper itself, resulting in a final product that's better organized. In doing so, you'll craft a paper where each section flows intuitively from the next.
Step 6: Integrating your research question
To avoid letting your research question get lost in background information or clarifications, craft your introduction in such a way that the research question resonates throughout. The research question should clearly address a gap in existing knowledge or offer a new perspective on an existing problem.
Tell users your research question explicitly but also remember to frequently come back to it. When providing context or clarification, point out how it relates to the research question. This keeps your focus where it needs to be and prevents the topic of the paper from becoming under-emphasized.
Step 7: Establishing the scope and limitations
So far, we've talked mostly about what's in the paper and how to convey that information to readers. The opposite is also important. Information that's outside the scope of your paper should be made clear to the reader in the introduction so their expectations for what is to follow are set appropriately.
Similarly, be honest and upfront about the limitations of the study. Any constraints in methodology, data, or how far your findings can be generalized should be fully communicated in the introduction.
Step 8: Concluding the introduction with a promise
The final few lines of the introduction are your last chance to convince people to continue reading the rest of the paper. Here is where you should make it very clear what benefit they'll get from doing so. What topics will be covered? What questions will be answered? Make it clear what they will get for continuing.
By providing a quick recap of the key points contained in the introduction in its final lines and properly setting the stage for what follows in the rest of the paper, you refocus the reader's attention on the topic of your research and guide them to read more.
- Research paper introduction best practices
Following the steps above will give you a compelling introduction that hits on all the key points an introduction should have. Some more tips and tricks can make an introduction even more polished.
As you follow the steps above, keep the following tips in mind.
Set the right tone and style
Like every piece of writing, a research paper should be written for the audience. That is to say, it should match the tone and style that your academic discipline and target audience expect. This is typically a formal and academic tone, though the degree of formality varies by field.
Kno w the audience
The perfect introduction balances clarity with conciseness. The amount of clarification required for a given topic depends greatly on the target audience. Knowing who will be reading your paper will guide you in determining how much background information is required.
Adopt the CARS (create a research space) model
The CARS model is a helpful tool for structuring introductions. This structure has three parts. The beginning of the introduction establishes the general research area. Next, relevant literature is reviewed and critiqued. The final section outlines the purpose of your study as it relates to the previous parts.
Master the art of funneling
The CARS method is one example of a well-funneled introduction. These start broadly and then slowly narrow down to your specific research problem. It provides a nice narrative flow that provides the right information at the right time. If you stray from the CARS model, try to retain this same type of funneling.
Incorporate narrative element
People read research papers largely to be informed. But to inform the reader, you have to hold their attention. A narrative style, particularly in the introduction, is a great way to do that. This can be a compelling story, an intriguing question, or a description of a real-world problem.
Write the introduction last
By writing the introduction after the rest of the paper, you'll have a better idea of what your research entails and how the paper is structured. This prevents the common problem of writing something in the introduction and then forgetting to include it in the paper. It also means anything particularly exciting in the paper isn’t neglected in the intro.
Should you be using a customer insights hub?
Do you want to discover previous research faster?
Do you share your research findings with others?
Do you analyze research data?
Start for free today, add your research, and get to key insights faster
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 11 January 2024
Last updated: 15 January 2024
Last updated: 17 January 2024
Last updated: 25 November 2023
Last updated: 12 May 2023
Last updated: 30 April 2024
Last updated: 13 May 2024
Latest articles
Related topics, .css-je19u9{-webkit-align-items:flex-end;-webkit-box-align:flex-end;-ms-flex-align:flex-end;align-items:flex-end;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-flex-direction:row;-ms-flex-direction:row;flex-direction:row;-webkit-box-flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-box-pack:center;-ms-flex-pack:center;-webkit-justify-content:center;justify-content:center;row-gap:0;text-align:center;max-width:671px;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}}@media (max-width: 799px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}} decide what to .css-1kiodld{max-height:56px;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-1kiodld{display:none;}} build next, decide what to build next.

Users report unexpectedly high data usage, especially during streaming sessions.

Users find it hard to navigate from the home page to relevant playlists in the app.

It would be great to have a sleep timer feature, especially for bedtime listening.

I need better filters to find the songs or artists I’m looking for.
Log in or sign up
Get started for free
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- 4. The Introduction
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
The introduction leads the reader from a general subject area to a particular topic of inquiry. It establishes the scope, context, and significance of the research being conducted by summarizing current understanding and background information about the topic, stating the purpose of the work in the form of the research problem supported by a hypothesis or a set of questions, explaining briefly the methodological approach used to examine the research problem, highlighting the potential outcomes your study can reveal, and outlining the remaining structure and organization of the paper.
Key Elements of the Research Proposal. Prepared under the direction of the Superintendent and by the 2010 Curriculum Design and Writing Team. Baltimore County Public Schools.
Importance of a Good Introduction
Think of the introduction as a mental road map that must answer for the reader these four questions:
- What was I studying?
- Why was this topic important to investigate?
- What did we know about this topic before I did this study?
- How will this study advance new knowledge or new ways of understanding?
According to Reyes, there are three overarching goals of a good introduction: 1) ensure that you summarize prior studies about the topic in a manner that lays a foundation for understanding the research problem; 2) explain how your study specifically addresses gaps in the literature, insufficient consideration of the topic, or other deficiency in the literature; and, 3) note the broader theoretical, empirical, and/or policy contributions and implications of your research.
A well-written introduction is important because, quite simply, you never get a second chance to make a good first impression. The opening paragraphs of your paper will provide your readers with their initial impressions about the logic of your argument, your writing style, the overall quality of your research, and, ultimately, the validity of your findings and conclusions. A vague, disorganized, or error-filled introduction will create a negative impression, whereas, a concise, engaging, and well-written introduction will lead your readers to think highly of your analytical skills, your writing style, and your research approach. All introductions should conclude with a brief paragraph that describes the organization of the rest of the paper.
Hirano, Eliana. “Research Article Introductions in English for Specific Purposes: A Comparison between Brazilian, Portuguese, and English.” English for Specific Purposes 28 (October 2009): 240-250; Samraj, B. “Introductions in Research Articles: Variations Across Disciplines.” English for Specific Purposes 21 (2002): 1–17; Introductions. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; “Writing Introductions.” In Good Essay Writing: A Social Sciences Guide. Peter Redman. 4th edition. (London: Sage, 2011), pp. 63-70; Reyes, Victoria. Demystifying the Journal Article. Inside Higher Education.
Structure and Writing Style
I. Structure and Approach
The introduction is the broad beginning of the paper that answers three important questions for the reader:
- What is this?
- Why should I read it?
- What do you want me to think about / consider doing / react to?
Think of the structure of the introduction as an inverted triangle of information that lays a foundation for understanding the research problem. Organize the information so as to present the more general aspects of the topic early in the introduction, then narrow your analysis to more specific topical information that provides context, finally arriving at your research problem and the rationale for studying it [often written as a series of key questions to be addressed or framed as a hypothesis or set of assumptions to be tested] and, whenever possible, a description of the potential outcomes your study can reveal.
These are general phases associated with writing an introduction: 1. Establish an area to research by:
- Highlighting the importance of the topic, and/or
- Making general statements about the topic, and/or
- Presenting an overview on current research on the subject.
2. Identify a research niche by:
- Opposing an existing assumption, and/or
- Revealing a gap in existing research, and/or
- Formulating a research question or problem, and/or
- Continuing a disciplinary tradition.
3. Place your research within the research niche by:
- Stating the intent of your study,
- Outlining the key characteristics of your study,
- Describing important results, and
- Giving a brief overview of the structure of the paper.
NOTE: It is often useful to review the introduction late in the writing process. This is appropriate because outcomes are unknown until you've completed the study. After you complete writing the body of the paper, go back and review introductory descriptions of the structure of the paper, the method of data gathering, the reporting and analysis of results, and the conclusion. Reviewing and, if necessary, rewriting the introduction ensures that it correctly matches the overall structure of your final paper.
II. Delimitations of the Study
Delimitations refer to those characteristics that limit the scope and define the conceptual boundaries of your research . This is determined by the conscious exclusionary and inclusionary decisions you make about how to investigate the research problem. In other words, not only should you tell the reader what it is you are studying and why, but you must also acknowledge why you rejected alternative approaches that could have been used to examine the topic.
Obviously, the first limiting step was the choice of research problem itself. However, implicit are other, related problems that could have been chosen but were rejected. These should be noted in the conclusion of your introduction. For example, a delimitating statement could read, "Although many factors can be understood to impact the likelihood young people will vote, this study will focus on socioeconomic factors related to the need to work full-time while in school." The point is not to document every possible delimiting factor, but to highlight why previously researched issues related to the topic were not addressed.
Examples of delimitating choices would be:
- The key aims and objectives of your study,
- The research questions that you address,
- The variables of interest [i.e., the various factors and features of the phenomenon being studied],
- The method(s) of investigation,
- The time period your study covers, and
- Any relevant alternative theoretical frameworks that could have been adopted.
Review each of these decisions. Not only do you clearly establish what you intend to accomplish in your research, but you should also include a declaration of what the study does not intend to cover. In the latter case, your exclusionary decisions should be based upon criteria understood as, "not interesting"; "not directly relevant"; “too problematic because..."; "not feasible," and the like. Make this reasoning explicit!
NOTE: Delimitations refer to the initial choices made about the broader, overall design of your study and should not be confused with documenting the limitations of your study discovered after the research has been completed.
ANOTHER NOTE : Do not view delimitating statements as admitting to an inherent failing or shortcoming in your research. They are an accepted element of academic writing intended to keep the reader focused on the research problem by explicitly defining the conceptual boundaries and scope of your study. It addresses any critical questions in the reader's mind of, "Why the hell didn't the author examine this?"
III. The Narrative Flow
Issues to keep in mind that will help the narrative flow in your introduction :
- Your introduction should clearly identify the subject area of interest . A simple strategy to follow is to use key words from your title in the first few sentences of the introduction. This will help focus the introduction on the topic at the appropriate level and ensures that you get to the subject matter quickly without losing focus, or discussing information that is too general.
- Establish context by providing a brief and balanced review of the pertinent published literature that is available on the subject. The key is to summarize for the reader what is known about the specific research problem before you did your analysis. This part of your introduction should not represent a comprehensive literature review--that comes next. It consists of a general review of the important, foundational research literature [with citations] that establishes a foundation for understanding key elements of the research problem. See the drop-down menu under this tab for " Background Information " regarding types of contexts.
- Clearly state the hypothesis that you investigated . When you are first learning to write in this format it is okay, and actually preferable, to use a past statement like, "The purpose of this study was to...." or "We investigated three possible mechanisms to explain the...."
- Why did you choose this kind of research study or design? Provide a clear statement of the rationale for your approach to the problem studied. This will usually follow your statement of purpose in the last paragraph of the introduction.
IV. Engaging the Reader
A research problem in the social sciences can come across as dry and uninteresting to anyone unfamiliar with the topic . Therefore, one of the goals of your introduction is to make readers want to read your paper. Here are several strategies you can use to grab the reader's attention:
- Open with a compelling story . Almost all research problems in the social sciences, no matter how obscure or esoteric , are really about the lives of people. Telling a story that humanizes an issue can help illuminate the significance of the problem and help the reader empathize with those affected by the condition being studied.
- Include a strong quotation or a vivid, perhaps unexpected, anecdote . During your review of the literature, make note of any quotes or anecdotes that grab your attention because they can used in your introduction to highlight the research problem in a captivating way.
- Pose a provocative or thought-provoking question . Your research problem should be framed by a set of questions to be addressed or hypotheses to be tested. However, a provocative question can be presented in the beginning of your introduction that challenges an existing assumption or compels the reader to consider an alternative viewpoint that helps establish the significance of your study.
- Describe a puzzling scenario or incongruity . This involves highlighting an interesting quandary concerning the research problem or describing contradictory findings from prior studies about a topic. Posing what is essentially an unresolved intellectual riddle about the problem can engage the reader's interest in the study.
- Cite a stirring example or case study that illustrates why the research problem is important . Draw upon the findings of others to demonstrate the significance of the problem and to describe how your study builds upon or offers alternatives ways of investigating this prior research.
NOTE: It is important that you choose only one of the suggested strategies for engaging your readers. This avoids giving an impression that your paper is more flash than substance and does not distract from the substance of your study.
Freedman, Leora and Jerry Plotnick. Introductions and Conclusions. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Introduction. The Structure, Format, Content, and Style of a Journal-Style Scientific Paper. Department of Biology. Bates College; Introductions. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Introductions. The Writer’s Handbook. Writing Center. University of Wisconsin, Madison; Introductions, Body Paragraphs, and Conclusions for an Argument Paper. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; “Writing Introductions.” In Good Essay Writing: A Social Sciences Guide . Peter Redman. 4th edition. (London: Sage, 2011), pp. 63-70; Resources for Writers: Introduction Strategies. Program in Writing and Humanistic Studies. Massachusetts Institute of Technology; Sharpling, Gerald. Writing an Introduction. Centre for Applied Linguistics, University of Warwick; Samraj, B. “Introductions in Research Articles: Variations Across Disciplines.” English for Specific Purposes 21 (2002): 1–17; Swales, John and Christine B. Feak. Academic Writing for Graduate Students: Essential Skills and Tasks . 2nd edition. Ann Arbor, MI: University of Michigan Press, 2004 ; Writing Your Introduction. Department of English Writing Guide. George Mason University.
Writing Tip
Avoid the "Dictionary" Introduction
Giving the dictionary definition of words related to the research problem may appear appropriate because it is important to define specific terminology that readers may be unfamiliar with. However, anyone can look a word up in the dictionary and a general dictionary is not a particularly authoritative source because it doesn't take into account the context of your topic and doesn't offer particularly detailed information. Also, placed in the context of a particular discipline, a term or concept may have a different meaning than what is found in a general dictionary. If you feel that you must seek out an authoritative definition, use a subject specific dictionary or encyclopedia [e.g., if you are a sociology student, search for dictionaries of sociology]. A good database for obtaining definitive definitions of concepts or terms is Credo Reference .
Saba, Robert. The College Research Paper. Florida International University; Introductions. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina.
Another Writing Tip
When Do I Begin?
A common question asked at the start of any paper is, "Where should I begin?" An equally important question to ask yourself is, "When do I begin?" Research problems in the social sciences rarely rest in isolation from history. Therefore, it is important to lay a foundation for understanding the historical context underpinning the research problem. However, this information should be brief and succinct and begin at a point in time that illustrates the study's overall importance. For example, a study that investigates coffee cultivation and export in West Africa as a key stimulus for local economic growth needs to describe the beginning of exporting coffee in the region and establishing why economic growth is important. You do not need to give a long historical explanation about coffee exports in Africa. If a research problem requires a substantial exploration of the historical context, do this in the literature review section. In your introduction, make note of this as part of the "roadmap" [see below] that you use to describe the organization of your paper.
Introductions. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; “Writing Introductions.” In Good Essay Writing: A Social Sciences Guide . Peter Redman. 4th edition. (London: Sage, 2011), pp. 63-70.
Yet Another Writing Tip
Always End with a Roadmap
The final paragraph or sentences of your introduction should forecast your main arguments and conclusions and provide a brief description of the rest of the paper [the "roadmap"] that let's the reader know where you are going and what to expect. A roadmap is important because it helps the reader place the research problem within the context of their own perspectives about the topic. In addition, concluding your introduction with an explicit roadmap tells the reader that you have a clear understanding of the structural purpose of your paper. In this way, the roadmap acts as a type of promise to yourself and to your readers that you will follow a consistent and coherent approach to addressing the topic of inquiry. Refer to it often to help keep your writing focused and organized.
Cassuto, Leonard. “On the Dissertation: How to Write the Introduction.” The Chronicle of Higher Education , May 28, 2018; Radich, Michael. A Student's Guide to Writing in East Asian Studies . (Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Writing n. d.), pp. 35-37.
- << Previous: Executive Summary
- Next: The C.A.R.S. Model >>
- Last Updated: May 20, 2024 8:18 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
How to Write the Introduction to a Scientific Paper?
- Open Access
- First Online: 24 October 2021
Cite this chapter
You have full access to this open access chapter

- Samiran Nundy 4 ,
- Atul Kakar 5 &
- Zulfiqar A. Bhutta 6
65k Accesses
142 Altmetric
An Introduction to a scientific paper familiarizes the reader with the background of the issue at hand. It must reflect why the issue is topical and its current importance in the vast sea of research being done globally. It lays the foundation of biomedical writing and is the first portion of an article according to the IMRAD pattern ( I ntroduction, M ethodology, R esults, a nd D iscussion) [1].
I once had a professor tell a class that he sifted through our pile of essays, glancing at the titles and introductions, looking for something that grabbed his attention. Everything else went to the bottom of the pile to be read last, when he was tired and probably grumpy from all the marking. Don’t get put at the bottom of the pile, he said. Anonymous
You have full access to this open access chapter, Download chapter PDF
Similar content being viewed by others

The Introduction Section


Abstract and Keywords

Writing and publishing a scientific paper
1 what is the importance of an introduction.
An Introduction to a scientific paper familiarizes the reader with the background of the issue at hand. It must reflect why the issue is topical and its current importance in the vast sea of research being done globally. It lays the foundation of biomedical writing and is the first portion of an article according to the IMRAD pattern ( I ntroduction, M ethodology, R esults, a nd D iscussion) [ 1 ].
It provides the flavour of the article and many authors have used phrases to describe it for example—'like a gate of the city’ [ 2 ], ‘the beginning is half of the whole’ [ 3 ], ‘an introduction is not just wrestling with words to fit the facts, but it also strongly modulated by perception of the anticipated reactions of peer colleagues’, [ 4 ] and ‘an introduction is like the trailer to a movie’. A good introduction helps captivate the reader early.

2 What Are the Principles of Writing a Good Introduction?
A good introduction will ‘sell’ an article to a journal editor, reviewer, and finally to a reader [ 3 ]. It should contain the following information [ 5 , 6 ]:
The known—The background scientific data
The unknown—Gaps in the current knowledge
Research hypothesis or question
Methodologies used for the study
The known consist of citations from a review of the literature whereas the unknown is the new work to be undertaken. This part should address how your work is the required missing piece of the puzzle.
3 What Are the Models of Writing an Introduction?
The Problem-solving model
First described by Swales et al. in 1979, in this model the writer should identify the ‘problem’ in the research, address the ‘solution’ and also write about ‘the criteria for evaluating the problem’ [ 7 , 8 ].
The CARS model that stands for C reating A R esearch S pace [ 9 , 10 ].
The two important components of this model are:
Establishing a territory (situation)
Establishing a niche (problem)
Occupying a niche (the solution)
In this popular model, one can add a fourth point, i.e., a conclusion [ 10 ].
4 What Is Establishing a Territory?
This includes: [ 9 ]
Stating the general topic and providing some background about it.
Providing a brief and relevant review of the literature related to the topic.
Adding a paragraph on the scope of the topic including the need for your study.
5 What Is Establishing a Niche?
Establishing a niche includes:
Stating the importance of the problem.
Outlining the current situation regarding the problem citing both global and national data.
Evaluating the current situation (advantages/ disadvantages).
Identifying the gaps.
Emphasizing the importance of the proposed research and how the gaps will be addressed.
Stating the research problem/ questions.
Stating the hypotheses briefly.
Figure 17.1 depicts how the introduction needs to be written. A scientific paper should have an introduction in the form of an inverted pyramid. The writer should start with the general information about the topic and subsequently narrow it down to the specific topic-related introduction.
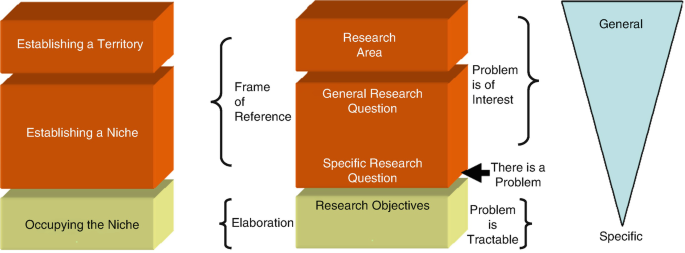
Flow of ideas from the general to the specific
6 What Does Occupying a Niche Mean?
This is the third portion of the introduction and defines the rationale of the research and states the research question. If this is missing the reviewers will not understand the logic for publication and is a common reason for rejection [ 11 , 12 ]. An example of this is given below:
Till date, no study has been done to see the effectiveness of a mesh alone or the effectiveness of double suturing along with a mesh in the closure of an umbilical hernia regarding the incidence of failure. So, the present study is aimed at comparing the effectiveness of a mesh alone versus the double suturing technique along with a mesh.
7 How Long Should the Introduction Be?
For a project protocol, the introduction should be about 1–2 pages long and for a thesis it should be 3–5 pages in a double-spaced typed setting. For a scientific paper it should be less than 10–15% of the total length of the manuscript [ 13 , 14 ].
8 How Many References Should an Introduction Have?
All sections in a scientific manuscript except the conclusion should contain references. It has been suggested that an introduction should have four or five or at the most one-third of the references in the whole paper [ 15 ].
9 What Are the Important Points Which Should be not Missed in an Introduction?
An introduction paves the way forward for the subsequent sections of the article. Frequently well-planned studies are rejected by journals during review because of the simple reason that the authors failed to clarify the data in this section to justify the study [ 16 , 17 ]. Thus, the existing gap in knowledge should be clearly brought out in this section (Fig. 17.2 ).
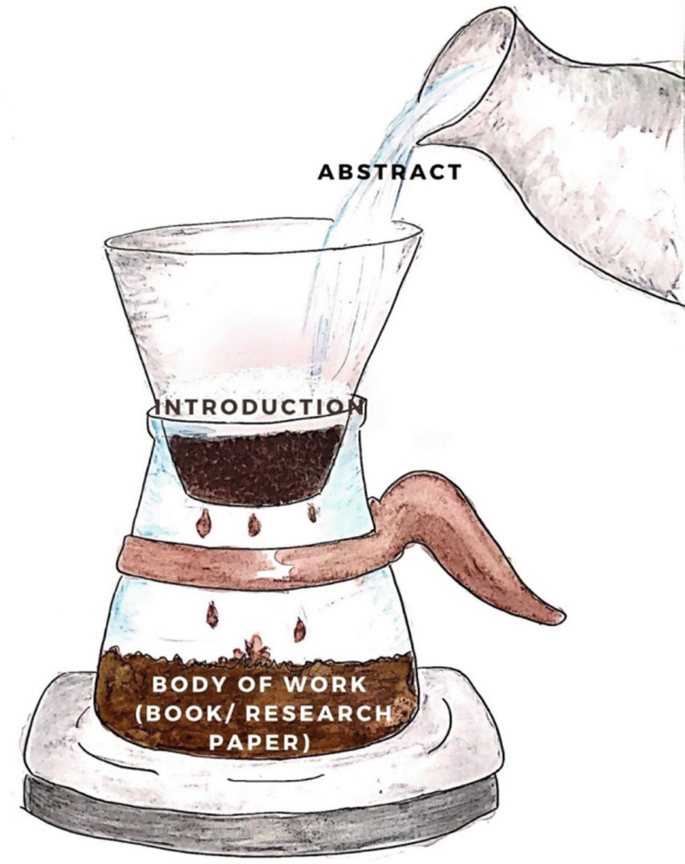
How should the abstract, introduction, and discussion look
The following points are important to consider:
The introduction should be written in simple sentences and in the present tense.
Many of the terms will be introduced in this section for the first time and these will require abbreviations to be used later.
The references in this section should be to papers published in quality journals (e.g., having a high impact factor).
The aims, problems, and hypotheses should be clearly mentioned.
Start with a generalization on the topic and go on to specific information relevant to your research.
10 Example of an Introduction

11 Conclusions
An Introduction is a brief account of what the study is about. It should be short, crisp, and complete.
It has to move from a general to a specific research topic and must include the need for the present study.
The Introduction should include data from a literature search, i.e., what is already known about this subject and progress to what we hope to add to this knowledge.
Moore A. What’s in a discussion section? Exploiting 2-dimensionality in the online world. Bioassays. 2016;38(12):1185.
Article Google Scholar
Annesley TM. The discussion section: your closing argument. Clin Chem. 2010;56(11):1671–4.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Bavdekar SB. Writing the discussion section: describing the significance of the study findings. J Assoc Physicians India. 2015;63(11):40–2.
PubMed Google Scholar
Foote M. The proof of the pudding: how to report results and write a good discussion. Chest. 2009;135(3):866–8.
Kearney MH. The discussion section tells us where we are. Res Nurs Health. 2017;40(4):289–91.
Ghasemi A, Bahadoran Z, Mirmiran P, Hosseinpanah F, Shiva N, Zadeh-Vakili A. The principles of biomedical scientific writing: discussion. Int J Endocrinol Metab. 2019;17(3):e95415.
Swales JM, Feak CB. Academic writing for graduate students: essential tasks and skills. Ann Arbor, MI: University of Michigan Press; 2004.
Google Scholar
Colombo M, Bucher L, Sprenger J. Determinants of judgments of explanatory power: credibility, generality, and statistical relevance. Front Psychol. 2017;8:1430.
Mozayan MR, Allami H, Fazilatfar AM. Metadiscourse features in medical research articles: subdisciplinary and paradigmatic influences in English and Persian. Res Appl Ling. 2018;9(1):83–104.
Hyland K. Metadiscourse: mapping interactions in academic writing. Nordic J English Stud. 2010;9(2):125.
Hill AB. The environment and disease: association or causation? Proc Royal Soc Med. 2016;58(5):295–300.
Alpert JS. Practicing medicine in Plato’s cave. Am J Med. 2006;119(6):455–6.
Walsh K. Discussing discursive discussions. Med Educ. 2016;50(12):1269–70.
Polit DF, Beck CT. Generalization in quantitative and qualitative research: myths and strategies. Int J Nurs Stud. 2010;47(11):1451–8.
Jawaid SA, Jawaid M. How to write introduction and discussion. Saudi J Anaesth. 2019;13(Suppl 1):S18–9.
Jawaid SA, Baig M. How to write an original article. In: Jawaid SA, Jawaid M, editors. Scientific writing: a guide to the art of medical writing and scientific publishing. Karachi: Published by Med-Print Services; 2018. p. 135–50.
Hall GM, editor. How to write a paper. London: BMJ Books, BMJ Publishing Group; 2003. Structure of a scientific paper. p. 1–5.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Surgical Gastroenterology and Liver Transplantation, Sir Ganga Ram Hospital, New Delhi, India
Samiran Nundy
Department of Internal Medicine, Sir Ganga Ram Hospital, New Delhi, India
Institute for Global Health and Development, The Aga Khan University, South Central Asia, East Africa and United Kingdom, Karachi, Pakistan
Zulfiqar A. Bhutta
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Rights and permissions
Open Access This chapter is licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ ), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license and indicate if changes were made.
The images or other third party material in this chapter are included in the chapter's Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the chapter's Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder.
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s)
About this chapter
Nundy, S., Kakar, A., Bhutta, Z.A. (2022). How to Write the Introduction to a Scientific Paper?. In: How to Practice Academic Medicine and Publish from Developing Countries?. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-5248-6_17
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-5248-6_17
Published : 24 October 2021
Publisher Name : Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN : 978-981-16-5247-9
Online ISBN : 978-981-16-5248-6
eBook Packages : Medicine Medicine (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
- Research Papers
How to Write a Research Introduction
Last Updated: December 6, 2023 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Megan Morgan, PhD . Megan Morgan is a Graduate Program Academic Advisor in the School of Public & International Affairs at the University of Georgia. She earned her PhD in English from the University of Georgia in 2015. There are 7 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 2,653,396 times.
The introduction to a research paper can be the most challenging part of the paper to write. The length of the introduction will vary depending on the type of research paper you are writing. An introduction should announce your topic, provide context and a rationale for your work, before stating your research questions and hypothesis. Well-written introductions set the tone for the paper, catch the reader's interest, and communicate the hypothesis or thesis statement.
Introducing the Topic of the Paper

- In scientific papers this is sometimes known as an "inverted triangle", where you start with the broadest material at the start, before zooming in on the specifics. [2] X Research source
- The sentence "Throughout the 20th century, our views of life on other planets have drastically changed" introduces a topic, but does so in broad terms.
- It provides the reader with an indication of the content of the essay and encourages them to read on.

- For example, if you were writing a paper about the behaviour of mice when exposed to a particular substance, you would include the word "mice", and the scientific name of the relevant compound in the first sentences.
- If you were writing a history paper about the impact of the First World War on gender relations in Britain, you should mention those key words in your first few lines.

- This is especially important if you are attempting to develop a new conceptualization that uses language and terminology your readers may be unfamiliar with.

- If you use an anecdote ensure that is short and highly relevant for your research. It has to function in the same way as an alternative opening, namely to announce the topic of your research paper to your reader.
- For example, if you were writing a sociology paper about re-offending rates among young offenders, you could include a brief story of one person whose story reflects and introduces your topic.
- This kind of approach is generally not appropriate for the introduction to a natural or physical sciences research paper where the writing conventions are different.
Establishing the Context for Your Paper

- It is important to be concise in the introduction, so provide an overview on recent developments in the primary research rather than a lengthy discussion.
- You can follow the "inverted triangle" principle to focus in from the broader themes to those to which you are making a direct contribution with your paper.
- A strong literature review presents important background information to your own research and indicates the importance of the field.

- By making clear reference to existing work you can demonstrate explicitly the specific contribution you are making to move the field forward.
- You can identify a gap in the existing scholarship and explain how you are addressing it and moving understanding forward.

- For example, if you are writing a scientific paper you could stress the merits of the experimental approach or models you have used.
- Stress what is novel in your research and the significance of your new approach, but don't give too much detail in the introduction.
- A stated rationale could be something like: "the study evaluates the previously unknown anti-inflammatory effects of a topical compound in order to evaluate its potential clinical uses".
Specifying Your Research Questions and Hypothesis

- The research question or questions generally come towards the end of the introduction, and should be concise and closely focused.
- The research question might recall some of the key words established in the first few sentences and the title of your paper.
- An example of a research question could be "what were the consequences of the North American Free Trade Agreement on the Mexican export economy?"
- This could be honed further to be specific by referring to a particular element of the Free Trade Agreement and the impact on a particular industry in Mexico, such as clothing manufacture.
- A good research question should shape a problem into a testable hypothesis.

- If possible try to avoid using the word "hypothesis" and rather make this implicit in your writing. This can make your writing appear less formulaic.
- In a scientific paper, giving a clear one-sentence overview of your results and their relation to your hypothesis makes the information clear and accessible. [10] X Trustworthy Source PubMed Central Journal archive from the U.S. National Institutes of Health Go to source
- An example of a hypothesis could be "mice deprived of food for the duration of the study were expected to become more lethargic than those fed normally".

- This is not always necessary and you should pay attention to the writing conventions in your discipline.
- In a natural sciences paper, for example, there is a fairly rigid structure which you will be following.
- A humanities or social science paper will most likely present more opportunities to deviate in how you structure your paper.
Research Introduction Help

Community Q&A
- Use your research papers' outline to help you decide what information to include when writing an introduction. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 1
- Consider drafting your introduction after you have already completed the rest of your research paper. Writing introductions last can help ensure that you don't leave out any major points. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

- Avoid emotional or sensational introductions; these can create distrust in the reader. Thanks Helpful 50 Not Helpful 12
- Generally avoid using personal pronouns in your introduction, such as "I," "me," "we," "us," "my," "mine," or "our." Thanks Helpful 31 Not Helpful 7
- Don't overwhelm the reader with an over-abundance of information. Keep the introduction as concise as possible by saving specific details for the body of your paper. Thanks Helpful 24 Not Helpful 14
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://library.sacredheart.edu/c.php?g=29803&p=185916
- ↑ https://www.aresearchguide.com/inverted-pyramid-structure-in-writing.html
- ↑ https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/introduction
- ↑ https://writing.wisc.edu/Handbook/PlanResearchPaper.html
- ↑ https://dept.writing.wisc.edu/wac/writing-an-introduction-for-a-scientific-paper/
- ↑ https://writing.wisc.edu/handbook/assignments/planresearchpaper/
- ↑ http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3178846/
About This Article

To introduce your research paper, use the first 1-2 sentences to describe your general topic, such as “women in World War I.” Include and define keywords, such as “gender relations,” to show your reader where you’re going. Mention previous research into the topic with a phrase like, “Others have studied…”, then transition into what your contribution will be and why it’s necessary. Finally, state the questions that your paper will address and propose your “answer” to them as your thesis statement. For more information from our English Ph.D. co-author about how to craft a strong hypothesis and thesis, keep reading! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Abdulrahman Omar
Oct 5, 2018
Did this article help you?
May 9, 2021
Lavanya Gopakumar
Oct 1, 2016
Dengkai Zhang
May 14, 2018
Leslie Mae Cansana
Sep 22, 2016

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
How long should the research paper introduction be? The length of the research paper introduction can vary across journals and disciplines. While there are no strict word limits for writing the research paper introduction, an ideal length would be one page, with a maximum of 400 words over 1-4 paragraphs.
Table of contents. Step 1: Introduce your topic. Step 2: Describe the background. Step 3: Establish your research problem. Step 4: Specify your objective (s) Step 5: Map out your paper. Research paper introduction examples. Frequently asked questions about the research paper introduction.
Dr. Michelle Harris, Dr. Janet Batzli,Biocore. This section provides guidelines on how to construct a solid introduction to a scientific paper including background information, study question, biological rationale, hypothesis, and general approach. If the Introduction is done well, there should be no question in the reader's mind why and on ...
Step 2: Building a solid foundation with background information. Including background information in your introduction serves two major purposes: It helps to clarify the topic for the reader. It establishes the depth of your research. The approach you take when conveying this information depends on the type of paper.
After you've done some extra polishing, I suggest a simple test for the introductory section. As an experiment, chop off the first few paragraphs. Let the paper begin on, say, paragraph 2 or even page 2. If you don't lose much, or actually gain in clarity and pace, then you've got a problem. There are two solutions.
When to Write Research Paper Introduction. The introduction of a research paper is typically written after the research has been conducted and the data has been analyzed. This is because the introduction should provide an overview of the research problem, the purpose of the study, and the research questions or hypotheses that will be investigated.
In general, your introductions should contain the following elements: Orienting Information. When you're writing an essay, it's helpful to think about what your reader needs to know in order to follow your argument. Your introduction should include enough information so that readers can understand the context for your thesis.
Step 1: Hook your reader. Step 2: Give background information. Step 3: Present your thesis statement. Step 4: Map your essay's structure. Step 5: Check and revise. More examples of essay introductions. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about the essay introduction.
To help guide your reader, end your introduction with an outline of the structure of the thesis or dissertation to follow. Share a brief summary of each chapter, clearly showing how each contributes to your central aims. However, be careful to keep this overview concise: 1-2 sentences should be enough. Note.
The median introduction was 553 words long (equivalent to 21 sentences, or 4 paragraphs), and 90% of the introductions were between 245 and 1,245 words. 2. The introduction is the shortest section of the research paper (14.6% of the total word count), approximately half the length of other sections (Methods, Results, and Discussion).
When writing your research paper introduction, there are several key elements you should include to ensure it is comprehensive and informative. A hook or attention-grabbing statement to capture the reader's interest. It can be a thought-provoking question, a surprising statistic, or a compelling anecdote that relates to your research topic.
The introduction leads the reader from a general subject area to a particular topic of inquiry. It establishes the scope, context, and significance of the research being conducted by summarizing current understanding and background information about the topic, stating the purpose of the work in the form of the research problem supported by a hypothesis or a set of questions, explaining briefly ...
Steps to write a research paper introduction. By following the steps below, you can learn how to write an introduction for a research paper that helps readers "shake hands" with your topic. In each step, thinking about the answers to key questions can help you reach your readers. 1. Get your readers' attention
The 4-step approach to writing the Introduction section. As a rule of thumb, this section accounts for about 10% of the total word count of the body of a typical research paper, or about 400 words spread over three paragraphs in a 4000-word paper.1 With that, let us now understand how to write the Introduction section step-by-step: 1.
An Introduction to a scientific paper familiarizes the reader with the background of the issue at hand. It must reflect why the issue is topical and its current importance in the vast sea of research being done globally. ... the introduction should be about 1-2 pages long and for a thesis it should be 3-5 pages in a double-spaced typed ...
Start with a general overview of your topic. Narrow the overview until you address your paper's specific subject. Then, mention questions or concerns you had about the case. Note that you will address them in the publication. Prior research. Your introduction is the place to review other conclusions on your topic.
Abstract. An article primarily includes the following sections: introduction, materials and methods, results, discussion, and conclusion. Before writing the introduction, the main steps, the heading and the familiarity level of the readers should be considered. Writing should begin when the experimental system and the equipment are available.
Download Article. 1. Announce your research topic. You can start your introduction with a few sentences which announce the topic of your paper and give an indication of the kind of research questions you will be asking. This is a good way to introduce your readers to your topic and pique their interest.
Create a research paper outline. Write a first draft of the research paper. Write the introduction. Write a compelling body of text. Write the conclusion. The second draft. The revision process. Research paper checklist. Free lecture slides.
How long is the introduction in a research paper? AThe introduction takes up about 30-40% of the entire paper since the context and research background should be specified and further discussed. For a general academic paper with 4000 words, the introduction must be approximately 1500 words. You can do the math for the rest!
You can adjust this outline to fit your research findings better and ensure that your paper remains well-organized and focused. 5. Write a Rough Draft. Once your outline is in place, you can begin the writing process. Remember, when you write a rough draft, it isn't meant to be perfect.
introduction for any paper will contain some common elements. You can see these common elements in the sample introductions on this page. In general, your introductions should contain the following elements: • Orienting information When you're writing an essay, it's helpful to think about what your reader needs to know in order to follow ...
Even a Little Bit of Expertise Can Go a Long Way. My usual approach to helping students get past this floundering stage is to tell them to avoid thinking up a study altogether. Instead, I tell ...
Step 2: Conduct Thorough Research. Once you've chosen your topic, it's time to collect information and data to create insightful content that delivers actual value. You can use both internal and external sources to gather information for your white paper.
INTRODUCTION Stem cell research combines biology, medicine, and technology, promising to alter health care and the understanding of human development. ... and Reconstructionist movements, are open to supporting ESC use or research as long as it is for saving a life.[64] Within Judaism, the Talmud, or study, gives personhood to the child at ...