Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- How to Write a Strong Hypothesis | Guide & Examples

How to Write a Strong Hypothesis | Guide & Examples
Published on 6 May 2022 by Shona McCombes .
A hypothesis is a statement that can be tested by scientific research. If you want to test a relationship between two or more variables, you need to write hypotheses before you start your experiment or data collection.
Table of contents
What is a hypothesis, developing a hypothesis (with example), hypothesis examples, frequently asked questions about writing hypotheses.
A hypothesis states your predictions about what your research will find. It is a tentative answer to your research question that has not yet been tested. For some research projects, you might have to write several hypotheses that address different aspects of your research question.
A hypothesis is not just a guess – it should be based on existing theories and knowledge. It also has to be testable, which means you can support or refute it through scientific research methods (such as experiments, observations, and statistical analysis of data).
Variables in hypotheses
Hypotheses propose a relationship between two or more variables . An independent variable is something the researcher changes or controls. A dependent variable is something the researcher observes and measures.
In this example, the independent variable is exposure to the sun – the assumed cause . The dependent variable is the level of happiness – the assumed effect .
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Step 1: ask a question.
Writing a hypothesis begins with a research question that you want to answer. The question should be focused, specific, and researchable within the constraints of your project.
Step 2: Do some preliminary research
Your initial answer to the question should be based on what is already known about the topic. Look for theories and previous studies to help you form educated assumptions about what your research will find.
At this stage, you might construct a conceptual framework to identify which variables you will study and what you think the relationships are between them. Sometimes, you’ll have to operationalise more complex constructs.
Step 3: Formulate your hypothesis
Now you should have some idea of what you expect to find. Write your initial answer to the question in a clear, concise sentence.
Step 4: Refine your hypothesis
You need to make sure your hypothesis is specific and testable. There are various ways of phrasing a hypothesis, but all the terms you use should have clear definitions, and the hypothesis should contain:
- The relevant variables
- The specific group being studied
- The predicted outcome of the experiment or analysis
Step 5: Phrase your hypothesis in three ways
To identify the variables, you can write a simple prediction in if … then form. The first part of the sentence states the independent variable and the second part states the dependent variable.
In academic research, hypotheses are more commonly phrased in terms of correlations or effects, where you directly state the predicted relationship between variables.
If you are comparing two groups, the hypothesis can state what difference you expect to find between them.
Step 6. Write a null hypothesis
If your research involves statistical hypothesis testing , you will also have to write a null hypothesis. The null hypothesis is the default position that there is no association between the variables. The null hypothesis is written as H 0 , while the alternative hypothesis is H 1 or H a .
Hypothesis testing is a formal procedure for investigating our ideas about the world using statistics. It is used by scientists to test specific predictions, called hypotheses , by calculating how likely it is that a pattern or relationship between variables could have arisen by chance.
A hypothesis is not just a guess. It should be based on existing theories and knowledge. It also has to be testable, which means you can support or refute it through scientific research methods (such as experiments, observations, and statistical analysis of data).
A research hypothesis is your proposed answer to your research question. The research hypothesis usually includes an explanation (‘ x affects y because …’).
A statistical hypothesis, on the other hand, is a mathematical statement about a population parameter. Statistical hypotheses always come in pairs: the null and alternative hypotheses. In a well-designed study , the statistical hypotheses correspond logically to the research hypothesis.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2022, May 06). How to Write a Strong Hypothesis | Guide & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 6 May 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/hypothesis-writing/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, operationalisation | a guide with examples, pros & cons, what is a conceptual framework | tips & examples, a quick guide to experimental design | 5 steps & examples.
Science Fair Wizard
- Pick a topic
- Determine a problem
- Investigate your problem
- Formulate a hypothesis
Experimenting
- Define the problem
- Select your variables
- Draft your hypothesis
- Write your procedure
- Get permissions
- Test your hypothesis
- Compile your data
- Write your research paper
- Construct your exhibit
- Prepare your presentation
- Show Time! Pre-science fair checklist
- Submit your paperwork

Step 5C: Draft your hypothesis
Your draft hypothesis statement should include the following:
- the question or problem you are trying to answer;
- how the independent variable will be changed;
- the measurable or testable effect it will have on the dependent variable ;
- and your best guess as to what you think the outcome will be.
Use the space on the Experiment Design Worksheet to draft your hypothesis statement.
Tip: A hypothesis problem can be stated in different ways. Here are some examples:
As a question: Does temperature affect the rate of plant growth? As a statement: Temperature may affect the rate of plant growth. As an if/then statement: If temperature is related to the rate of plant growth, then changing the temperature will change the rate of plant growth.
A hypothesis is a statement that predicts the outcome of your experiment, and is informed by the research you have done on your topic.
The digital library project

- Manuscript Preparation
What is and How to Write a Good Hypothesis in Research?
- 4 minute read
- 309.3K views
Table of Contents
One of the most important aspects of conducting research is constructing a strong hypothesis. But what makes a hypothesis in research effective? In this article, we’ll look at the difference between a hypothesis and a research question, as well as the elements of a good hypothesis in research. We’ll also include some examples of effective hypotheses, and what pitfalls to avoid.
What is a Hypothesis in Research?
Simply put, a hypothesis is a research question that also includes the predicted or expected result of the research. Without a hypothesis, there can be no basis for a scientific or research experiment. As such, it is critical that you carefully construct your hypothesis by being deliberate and thorough, even before you set pen to paper. Unless your hypothesis is clearly and carefully constructed, any flaw can have an adverse, and even grave, effect on the quality of your experiment and its subsequent results.
Research Question vs Hypothesis
It’s easy to confuse research questions with hypotheses, and vice versa. While they’re both critical to the Scientific Method, they have very specific differences. Primarily, a research question, just like a hypothesis, is focused and concise. But a hypothesis includes a prediction based on the proposed research, and is designed to forecast the relationship of and between two (or more) variables. Research questions are open-ended, and invite debate and discussion, while hypotheses are closed, e.g. “The relationship between A and B will be C.”
A hypothesis is generally used if your research topic is fairly well established, and you are relatively certain about the relationship between the variables that will be presented in your research. Since a hypothesis is ideally suited for experimental studies, it will, by its very existence, affect the design of your experiment. The research question is typically used for new topics that have not yet been researched extensively. Here, the relationship between different variables is less known. There is no prediction made, but there may be variables explored. The research question can be casual in nature, simply trying to understand if a relationship even exists, descriptive or comparative.
How to Write Hypothesis in Research
Writing an effective hypothesis starts before you even begin to type. Like any task, preparation is key, so you start first by conducting research yourself, and reading all you can about the topic that you plan to research. From there, you’ll gain the knowledge you need to understand where your focus within the topic will lie.
Remember that a hypothesis is a prediction of the relationship that exists between two or more variables. Your job is to write a hypothesis, and design the research, to “prove” whether or not your prediction is correct. A common pitfall is to use judgments that are subjective and inappropriate for the construction of a hypothesis. It’s important to keep the focus and language of your hypothesis objective.
An effective hypothesis in research is clearly and concisely written, and any terms or definitions clarified and defined. Specific language must also be used to avoid any generalities or assumptions.
Use the following points as a checklist to evaluate the effectiveness of your research hypothesis:
- Predicts the relationship and outcome
- Simple and concise – avoid wordiness
- Clear with no ambiguity or assumptions about the readers’ knowledge
- Observable and testable results
- Relevant and specific to the research question or problem
Research Hypothesis Example
Perhaps the best way to evaluate whether or not your hypothesis is effective is to compare it to those of your colleagues in the field. There is no need to reinvent the wheel when it comes to writing a powerful research hypothesis. As you’re reading and preparing your hypothesis, you’ll also read other hypotheses. These can help guide you on what works, and what doesn’t, when it comes to writing a strong research hypothesis.
Here are a few generic examples to get you started.
Eating an apple each day, after the age of 60, will result in a reduction of frequency of physician visits.
Budget airlines are more likely to receive more customer complaints. A budget airline is defined as an airline that offers lower fares and fewer amenities than a traditional full-service airline. (Note that the term “budget airline” is included in the hypothesis.
Workplaces that offer flexible working hours report higher levels of employee job satisfaction than workplaces with fixed hours.
Each of the above examples are specific, observable and measurable, and the statement of prediction can be verified or shown to be false by utilizing standard experimental practices. It should be noted, however, that often your hypothesis will change as your research progresses.
Language Editing Plus
Elsevier’s Language Editing Plus service can help ensure that your research hypothesis is well-designed, and articulates your research and conclusions. Our most comprehensive editing package, you can count on a thorough language review by native-English speakers who are PhDs or PhD candidates. We’ll check for effective logic and flow of your manuscript, as well as document formatting for your chosen journal, reference checks, and much more.

- Research Process
Systematic Literature Review or Literature Review?

What is a Problem Statement? [with examples]
You may also like.

Make Hook, Line, and Sinker: The Art of Crafting Engaging Introductions

Can Describing Study Limitations Improve the Quality of Your Paper?

A Guide to Crafting Shorter, Impactful Sentences in Academic Writing

6 Steps to Write an Excellent Discussion in Your Manuscript

How to Write Clear and Crisp Civil Engineering Papers? Here are 5 Key Tips to Consider

The Clear Path to An Impactful Paper: ②

The Essentials of Writing to Communicate Research in Medicine

Changing Lines: Sentence Patterns in Academic Writing
Input your search keywords and press Enter.

Introduction
1. get your idea and do some research, 2. ask a testable question, 3. design and conduct your experiment, 4. examine your results, 5. communicate your experiment and results.
Learning Space
Teachable Moments
Stay Connected

How to Do a Science Fair Project
To get started on your science fair project, you'll learn to observe the world around you and ask questions about the things you observe.
Observe the world around you and ask questions about the things you observe.
Develop your idea into a question you can test. Your question should follow the format, "How does [input] affect [output]?"
Design your experiment and keep track of the results. Remember to only change one variable and conduct your experiment multiple times for each trial. Each trial should be repeated in exactly the same way.
Now that your experiment is done, it's time to examine your results. You want to look for trends in your results and draw conclusions from those trends. You also want to examine your data for possible influences from factors you didn't consider at first.
Make a poster display that summarizes your experiment so you can share your results. Be sure to include the question you were trying to answer (your hypothesis), the steps you took to answer that question, your results and any factors that may have influenced your results. Your poster should be visually appealing, but also clear about what you did and why people should care.

- Science Notes Posts
- Contact Science Notes
- Todd Helmenstine Biography
- Anne Helmenstine Biography
- Free Printable Periodic Tables (PDF and PNG)
- Periodic Table Wallpapers
- Interactive Periodic Table
- Periodic Table Posters
- How to Grow Crystals
- Chemistry Projects
- Fire and Flames Projects
- Holiday Science
- Chemistry Problems With Answers
- Physics Problems
- Unit Conversion Example Problems
- Chemistry Worksheets
- Biology Worksheets
- Periodic Table Worksheets
- Physical Science Worksheets
- Science Lab Worksheets
- My Amazon Books
Hypothesis Examples

A hypothesis is a prediction of the outcome of a test. It forms the basis for designing an experiment in the scientific method . A good hypothesis is testable, meaning it makes a prediction you can check with observation or experimentation. Here are different hypothesis examples.
Null Hypothesis Examples
The null hypothesis (H 0 ) is also known as the zero-difference or no-difference hypothesis. It predicts that changing one variable ( independent variable ) will have no effect on the variable being measured ( dependent variable ). Here are null hypothesis examples:
- Plant growth is unaffected by temperature.
- If you increase temperature, then solubility of salt will increase.
- Incidence of skin cancer is unrelated to ultraviolet light exposure.
- All brands of light bulb last equally long.
- Cats have no preference for the color of cat food.
- All daisies have the same number of petals.
Sometimes the null hypothesis shows there is a suspected correlation between two variables. For example, if you think plant growth is affected by temperature, you state the null hypothesis: “Plant growth is not affected by temperature.” Why do you do this, rather than say “If you change temperature, plant growth will be affected”? The answer is because it’s easier applying a statistical test that shows, with a high level of confidence, a null hypothesis is correct or incorrect.
Research Hypothesis Examples
A research hypothesis (H 1 ) is a type of hypothesis used to design an experiment. This type of hypothesis is often written as an if-then statement because it’s easy identifying the independent and dependent variables and seeing how one affects the other. If-then statements explore cause and effect. In other cases, the hypothesis shows a correlation between two variables. Here are some research hypothesis examples:
- If you leave the lights on, then it takes longer for people to fall asleep.
- If you refrigerate apples, they last longer before going bad.
- If you keep the curtains closed, then you need less electricity to heat or cool the house (the electric bill is lower).
- If you leave a bucket of water uncovered, then it evaporates more quickly.
- Goldfish lose their color if they are not exposed to light.
- Workers who take vacations are more productive than those who never take time off.
Is It Okay to Disprove a Hypothesis?
Yes! You may even choose to write your hypothesis in such a way that it can be disproved because it’s easier to prove a statement is wrong than to prove it is right. In other cases, if your prediction is incorrect, that doesn’t mean the science is bad. Revising a hypothesis is common. It demonstrates you learned something you did not know before you conducted the experiment.
Test yourself with a Scientific Method Quiz .
- Mellenbergh, G.J. (2008). Chapter 8: Research designs: Testing of research hypotheses. In H.J. Adèr & G.J. Mellenbergh (eds.), Advising on Research Methods: A Consultant’s Companion . Huizen, The Netherlands: Johannes van Kessel Publishing.
- Popper, Karl R. (1959). The Logic of Scientific Discovery . Hutchinson & Co. ISBN 3-1614-8410-X.
- Schick, Theodore; Vaughn, Lewis (2002). How to think about weird things: critical thinking for a New Age . Boston: McGraw-Hill Higher Education. ISBN 0-7674-2048-9.
- Tobi, Hilde; Kampen, Jarl K. (2018). “Research design: the methodology for interdisciplinary research framework”. Quality & Quantity . 52 (3): 1209–1225. doi: 10.1007/s11135-017-0513-8
Related Posts

Do a Science Fair Project!
How do you do a science fair project.

Ask a parent, teacher, or other adult to help you research the topic and find out how to do a science fair project about it.
Test, answer, or show?
Your science fair project may do one of three things:
Test an idea (or hypothesis.)
Answer a question.
Show how nature works.
Topic ideas:
Space topics:.
How do the constellations change in the night sky over different periods of time?
How does the number of stars visible in the sky change from place to place because of light pollution?
Learn about and demonstrate the ancient method of parallax to measure the distance to an object, such as stars and planets.
Study different types of stars and explain different ways they end their life cycles.
Earth topics:
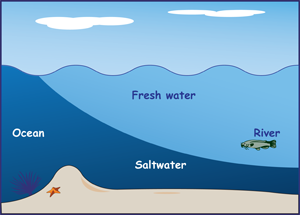
How do the phases of the Moon correspond to the changing tides?
Demonstrate what causes the phases of the Moon?
How does the tilt of Earth’s axis create seasons throughout the year?
How do weather conditions (temperature, humidity) affect how fast a puddle evaporates?
How salty is the ocean?
Solar system topics:

How does the size of a meteorite relate to the size of the crater it makes when it hits Earth?
How does the phase of the Moon affect the number of stars visible in the sky?
Show how a planet’s distance from the Sun affects its temperature.
Sun topics:
Observe and record changes in the number and placement of sun spots over several days. DO NOT look directly at the Sun!
Make a sundial and explain how it works.
Show why the Moon and the Sun appear to be the same size in the sky.
How effective are automobile sunshades?
Study and explain the life space of the sun relative to other stars.

Pick a topic.
Try to find out what people already know about it.
State a hypothesis related to the topic. That is, make a cause-and-effect-statement that you can test using the scientific method .
Explain something.
Make a plan to observe something.
Design and carry out your research, keeping careful records of everything you do or see.
Create an exhibit or display to show and explain to others what you hoped to test (if you had a hypothesis) or what question you wanted to answer, what you did, what your data showed, and your conclusions.
Write a short report that also states the same things as the exhibit or display, and also gives the sources of your initial background research.
Practice describing your project and results, so you will be ready for visitors to your exhibit at the science fair.
Follow these steps to a successful science fair entry!
If you liked this, you may like:
Writing an Introduction for a Scientific Paper
Dr. michelle harris, dr. janet batzli, biocore.
This section provides guidelines on how to construct a solid introduction to a scientific paper including background information, study question , biological rationale, hypothesis , and general approach . If the Introduction is done well, there should be no question in the reader’s mind why and on what basis you have posed a specific hypothesis.
Broad Question : based on an initial observation (e.g., “I see a lot of guppies close to the shore. Do guppies like living in shallow water?”). This observation of the natural world may inspire you to investigate background literature or your observation could be based on previous research by others or your own pilot study. Broad questions are not always included in your written text, but are essential for establishing the direction of your research.
Background Information : key issues, concepts, terminology, and definitions needed to understand the biological rationale for the experiment. It often includes a summary of findings from previous, relevant studies. Remember to cite references, be concise, and only include relevant information given your audience and your experimental design. Concisely summarized background information leads to the identification of specific scientific knowledge gaps that still exist. (e.g., “No studies to date have examined whether guppies do indeed spend more time in shallow water.”)
Testable Question : these questions are much more focused than the initial broad question, are specific to the knowledge gap identified, and can be addressed with data. (e.g., “Do guppies spend different amounts of time in water <1 meter deep as compared to their time in water that is >1 meter deep?”)
Biological Rationale : describes the purpose of your experiment distilling what is known and what is not known that defines the knowledge gap that you are addressing. The “BR” provides the logic for your hypothesis and experimental approach, describing the biological mechanism and assumptions that explain why your hypothesis should be true.
The biological rationale is based on your interpretation of the scientific literature, your personal observations, and the underlying assumptions you are making about how you think the system works. If you have written your biological rationale, your reader should see your hypothesis in your introduction section and say to themselves, “Of course, this hypothesis seems very logical based on the rationale presented.”
- A thorough rationale defines your assumptions about the system that have not been revealed in scientific literature or from previous systematic observation. These assumptions drive the direction of your specific hypothesis or general predictions.
- Defining the rationale is probably the most critical task for a writer, as it tells your reader why your research is biologically meaningful. It may help to think about the rationale as an answer to the questions— how is this investigation related to what we know, what assumptions am I making about what we don’t yet know, AND how will this experiment add to our knowledge? *There may or may not be broader implications for your study; be careful not to overstate these (see note on social justifications below).
- Expect to spend time and mental effort on this. You may have to do considerable digging into the scientific literature to define how your experiment fits into what is already known and why it is relevant to pursue.
- Be open to the possibility that as you work with and think about your data, you may develop a deeper, more accurate understanding of the experimental system. You may find the original rationale needs to be revised to reflect your new, more sophisticated understanding.
- As you progress through Biocore and upper level biology courses, your rationale should become more focused and matched with the level of study e ., cellular, biochemical, or physiological mechanisms that underlie the rationale. Achieving this type of understanding takes effort, but it will lead to better communication of your science.
***Special note on avoiding social justifications: You should not overemphasize the relevance of your experiment and the possible connections to large-scale processes. Be realistic and logical —do not overgeneralize or state grand implications that are not sensible given the structure of your experimental system. Not all science is easily applied to improving the human condition. Performing an investigation just for the sake of adding to our scientific knowledge (“pure or basic science”) is just as important as applied science. In fact, basic science often provides the foundation for applied studies.
Hypothesis / Predictions : specific prediction(s) that you will test during your experiment. For manipulative experiments, the hypothesis should include the independent variable (what you manipulate), the dependent variable(s) (what you measure), the organism or system , the direction of your results, and comparison to be made.
If you are doing a systematic observation , your hypothesis presents a variable or set of variables that you predict are important for helping you characterize the system as a whole, or predict differences between components/areas of the system that help you explain how the system functions or changes over time.
Experimental Approach : Briefly gives the reader a general sense of the experiment, the type of data it will yield, and the kind of conclusions you expect to obtain from the data. Do not confuse the experimental approach with the experimental protocol . The experimental protocol consists of the detailed step-by-step procedures and techniques used during the experiment that are to be reported in the Methods and Materials section.
Some Final Tips on Writing an Introduction
- As you progress through the Biocore sequence, for instance, from organismal level of Biocore 301/302 to the cellular level in Biocore 303/304, we expect the contents of your “Introduction” paragraphs to reflect the level of your coursework and previous writing experience. For example, in Biocore 304 (Cell Biology Lab) biological rationale should draw upon assumptions we are making about cellular and biochemical processes.
- Be Concise yet Specific: Remember to be concise and only include relevant information given your audience and your experimental design. As you write, keep asking, “Is this necessary information or is this irrelevant detail?” For example, if you are writing a paper claiming that a certain compound is a competitive inhibitor to the enzyme alkaline phosphatase and acts by binding to the active site, you need to explain (briefly) Michaelis-Menton kinetics and the meaning and significance of Km and Vmax. This explanation is not necessary if you are reporting the dependence of enzyme activity on pH because you do not need to measure Km and Vmax to get an estimate of enzyme activity.
- Another example: if you are writing a paper reporting an increase in Daphnia magna heart rate upon exposure to caffeine you need not describe the reproductive cycle of magna unless it is germane to your results and discussion. Be specific and concrete, especially when making introductory or summary statements.
Where Do You Discuss Pilot Studies? Many times it is important to do pilot studies to help you get familiar with your experimental system or to improve your experimental design. If your pilot study influences your biological rationale or hypothesis, you need to describe it in your Introduction. If your pilot study simply informs the logistics or techniques, but does not influence your rationale, then the description of your pilot study belongs in the Materials and Methods section.
How will introductions be evaluated? The following is part of the rubric we will be using to evaluate your papers.
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
How to Create a Science Fair Project
Last Updated: December 6, 2022 References
This article was co-authored by Bess Ruff, MA . Bess Ruff is a Geography PhD student at Florida State University. She received her MA in Environmental Science and Management from the University of California, Santa Barbara in 2016. She has conducted survey work for marine spatial planning projects in the Caribbean and provided research support as a graduate fellow for the Sustainable Fisheries Group. There are 11 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been viewed 142,930 times.
The science fair is an integral part of education. Science fairs allow you to understand and practice the scientific method on any topic that you are interested in. Make sure you have lots of time to complete your project so that it can be well researched and executed. There are many aspects to the science fair project including researching the topic, designing the experiment, analyzing the data, and making an eye-catching display board.
Choosing a Science Fair Project

- Do some brainstorming. Write down any ideas you have or problems that you’d like to solve. [1] X Research source
- Pick a topic that is appropriate for your age level. It’s okay to be ambitious, but make sure you have enough time to finish everything by the deadline.
- Keep track of all of your sources so you can cite them in your final report.

- Spend at least 1 week researching your topic and gathering information. Spend another week analyzing data, writing the report, and designing the board.
- Choose an experiment that fits within your time constraints. Some experiments can take at least 1 week, including gathering materials.

- If you will need to use any mathematical formulas or equations to answer your question, research these as well so that you understand them before you begin.
- Research experiments that may have already addressed some aspect of your question. Designing the experiment will be easier if you have a previous framework to build upon.
- Ask your teacher or a parent to help you better understand the topic you’ve chosen by asking them if it looks like you have any gaps in your knowledge.

- The independent variable is the condition that the scientist changes. You should only have 1 independent variable.
- The dependent variable is the condition that's measured in response to the changes in the independent variable. It's the one that gets observed throughout the experiment.
- The controlled variables are all of the conditions in an experiment that remain constant throughout the duration of the experiment.
Performing the Experiment

- For example, in an experiment about the growth height of a plant in different light levels, your hypothesis might be: If plants need light to grow, then they will not grow as high in low light or no light conditions.

- Answering these questions will help you make a materials list and develop a clear procedure.
- Make sure your experiment can be performed safely or with adult supervision. [5] X Research source

- Write the steps with an action verb at the beginning, such as “Open the container.”
- Avoid statements such as, “I opened the container.”
- Let a parent, sibling, or classmate read your procedure and see if they have any questions. Add more steps if necessary.

- If an item is particularly cheap or fragile, you might want to gather extras just in case you need them.
- Take all of the necessary safety precautions before starting the experiment.

- Make a note if you altered the procedure in any way during the actual experiment.
- Take pictures during the experiment to use on your display board.

- Keep all of your observations and data in your lab notebook.
- For long-term experiments, date each observation so you know exactly when you made it.

- For example, start an experiment with 3 plants in different light conditions. Use plants with the same starting height or just subtract the original height at the end.
Analyzing the Data

- You might be able to glance at your data and see if it supports or disproves your hypothesis, but understand that you can’t make any firm conclusions until the data has been properly analyzed.

- For example, your 3 plants in low light may have grown 3.0 inches (7.6 cm), 4.0 inches (10 cm), and 3.5 inches (8.9 cm), respectively. The average growth height for low light is (3+4+3.5)/3 = 3.5 in.

- Bar graphs and line graphs are a great way to visualize your data.
- You can draw a graph by hand, but it looks much cleaner and more professional to make it on the computer.
- For our example, graph the light levels on the x-axis and the growth height on the y-axis.

- Give the graph a title that tells you exactly which data are represented.
- For example, “Plant Growth Height in Various Levels of Light.”

- At the high school level, you might be able to run some statistics on your data to see if there truly are significant differences between the independent variables.
Presenting Your Project

- Some reports may require an abstract, which is just a short summary of the entire project.
- Proofread your entire report before turning it in.
- Cite all of the sources used for your report. Do not copy and paste information from sources, but summarize it in your own words.

- Make subheadings that are bold and large enough to read at a distance of 2–3 feet (0.61–0.91 m).
- Too many colors on the board can be overwhelming and look chaotic. Stick to 1 or 2 colors to make everything pop.
- Print the necessary information on white paper and then layer the colored construction paper underneath.
- Avoid using wrinkled paper and leaving glue marks on the board.
- Make sure your fonts and font sizes are consistent throughout each section.

- Include pictures that were taken during the experiment to show exactly what you did.
- Avoid using giant blocks of text. If you do have some that are large, break them up with pictures or figures.

- Write some note cards with key points in case you need to refer back to them when speaking with someone.
Expert Q&A

- Don't be too critical on yourself; it leads to frustration. Thanks Helpful 2 Not Helpful 0
- Pick a topic that is interesting to you so you will enjoy working on it. Thanks Helpful 2 Not Helpful 0
- Generally, volcanoes are overused and should be avoided. Thanks Helpful 3 Not Helpful 0

- Always use gloves and goggles when handling chemicals. Thanks Helpful 80 Not Helpful 25
- Be sure to cite your sources: plagiarism is a guaranteed F. Thanks Helpful 83 Not Helpful 27
- Seek adult help when using sharp objects. Thanks Helpful 6 Not Helpful 1
- Know that the Internet is not always truthful. Thanks Helpful 6 Not Helpful 3
You Might Also Like

- ↑ http://www.kidsciencechallenge.com/year-four/create.php
- ↑ http://www.sciencebuddies.org/science-fair-projects/project_background_research_plan.shtml
- ↑ http://www.sciencebuddies.org/science-fair-projects/project_variables.shtml
- ↑ http://www.sciencebuddies.org/science-fair-projects/project_hypothesis.shtml
- ↑ http://www.kidsciencechallenge.com/year-four/teachers_projects.php
- ↑ http://www.sciencebuddies.org/science-fair-projects/project_experimental_procedure.shtml
- ↑ http://www.sciencebuddies.org/science-fair-projects/project_materials_list.shtml
- ↑ http://www.sciencebuddies.org/science-fair-projects/project_experiment.shtml#overview
- ↑ http://www.sciencebuddies.org/science-fair-projects/project_data_analysis.shtml#overview
- ↑ http://www.sciencebuddies.org/science-fair-projects/project_conclusions.shtml
- ↑ http://www.opencolleges.edu.au/informed/teacher-resources/science-fair-projects/
About This Article

- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Jan 7, 2020

Did this article help you?
Jenna Vasquez
Feb 23, 2017
Samruddhi Chikhalikar
Sep 8, 2016
Oct 30, 2018
Summer Miller
Sep 16, 2016

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter

How to Develop a Good Research Hypothesis
The story of a research study begins by asking a question. Researchers all around the globe are asking curious questions and formulating research hypothesis. However, whether the research study provides an effective conclusion depends on how well one develops a good research hypothesis. Research hypothesis examples could help researchers get an idea as to how to write a good research hypothesis.
This blog will help you understand what is a research hypothesis, its characteristics and, how to formulate a research hypothesis
Table of Contents
What is Hypothesis?
Hypothesis is an assumption or an idea proposed for the sake of argument so that it can be tested. It is a precise, testable statement of what the researchers predict will be outcome of the study. Hypothesis usually involves proposing a relationship between two variables: the independent variable (what the researchers change) and the dependent variable (what the research measures).
What is a Research Hypothesis?
Research hypothesis is a statement that introduces a research question and proposes an expected result. It is an integral part of the scientific method that forms the basis of scientific experiments. Therefore, you need to be careful and thorough when building your research hypothesis. A minor flaw in the construction of your hypothesis could have an adverse effect on your experiment. In research, there is a convention that the hypothesis is written in two forms, the null hypothesis, and the alternative hypothesis (called the experimental hypothesis when the method of investigation is an experiment).
Characteristics of a Good Research Hypothesis
As the hypothesis is specific, there is a testable prediction about what you expect to happen in a study. You may consider drawing hypothesis from previously published research based on the theory.
A good research hypothesis involves more effort than just a guess. In particular, your hypothesis may begin with a question that could be further explored through background research.
To help you formulate a promising research hypothesis, you should ask yourself the following questions:
- Is the language clear and focused?
- What is the relationship between your hypothesis and your research topic?
- Is your hypothesis testable? If yes, then how?
- What are the possible explanations that you might want to explore?
- Does your hypothesis include both an independent and dependent variable?
- Can you manipulate your variables without hampering the ethical standards?
- Does your research predict the relationship and outcome?
- Is your research simple and concise (avoids wordiness)?
- Is it clear with no ambiguity or assumptions about the readers’ knowledge
- Is your research observable and testable results?
- Is it relevant and specific to the research question or problem?

The questions listed above can be used as a checklist to make sure your hypothesis is based on a solid foundation. Furthermore, it can help you identify weaknesses in your hypothesis and revise it if necessary.
Source: Educational Hub
How to formulate a research hypothesis.
A testable hypothesis is not a simple statement. It is rather an intricate statement that needs to offer a clear introduction to a scientific experiment, its intentions, and the possible outcomes. However, there are some important things to consider when building a compelling hypothesis.
1. State the problem that you are trying to solve.
Make sure that the hypothesis clearly defines the topic and the focus of the experiment.
2. Try to write the hypothesis as an if-then statement.
Follow this template: If a specific action is taken, then a certain outcome is expected.
3. Define the variables
Independent variables are the ones that are manipulated, controlled, or changed. Independent variables are isolated from other factors of the study.
Dependent variables , as the name suggests are dependent on other factors of the study. They are influenced by the change in independent variable.
4. Scrutinize the hypothesis
Evaluate assumptions, predictions, and evidence rigorously to refine your understanding.
Types of Research Hypothesis
The types of research hypothesis are stated below:
1. Simple Hypothesis
It predicts the relationship between a single dependent variable and a single independent variable.
2. Complex Hypothesis
It predicts the relationship between two or more independent and dependent variables.
3. Directional Hypothesis
It specifies the expected direction to be followed to determine the relationship between variables and is derived from theory. Furthermore, it implies the researcher’s intellectual commitment to a particular outcome.
4. Non-directional Hypothesis
It does not predict the exact direction or nature of the relationship between the two variables. The non-directional hypothesis is used when there is no theory involved or when findings contradict previous research.
5. Associative and Causal Hypothesis
The associative hypothesis defines interdependency between variables. A change in one variable results in the change of the other variable. On the other hand, the causal hypothesis proposes an effect on the dependent due to manipulation of the independent variable.
6. Null Hypothesis
Null hypothesis states a negative statement to support the researcher’s findings that there is no relationship between two variables. There will be no changes in the dependent variable due the manipulation of the independent variable. Furthermore, it states results are due to chance and are not significant in terms of supporting the idea being investigated.
7. Alternative Hypothesis
It states that there is a relationship between the two variables of the study and that the results are significant to the research topic. An experimental hypothesis predicts what changes will take place in the dependent variable when the independent variable is manipulated. Also, it states that the results are not due to chance and that they are significant in terms of supporting the theory being investigated.
Research Hypothesis Examples of Independent and Dependent Variables
Research Hypothesis Example 1 The greater number of coal plants in a region (independent variable) increases water pollution (dependent variable). If you change the independent variable (building more coal factories), it will change the dependent variable (amount of water pollution).
Research Hypothesis Example 2 What is the effect of diet or regular soda (independent variable) on blood sugar levels (dependent variable)? If you change the independent variable (the type of soda you consume), it will change the dependent variable (blood sugar levels)
You should not ignore the importance of the above steps. The validity of your experiment and its results rely on a robust testable hypothesis. Developing a strong testable hypothesis has few advantages, it compels us to think intensely and specifically about the outcomes of a study. Consequently, it enables us to understand the implication of the question and the different variables involved in the study. Furthermore, it helps us to make precise predictions based on prior research. Hence, forming a hypothesis would be of great value to the research. Here are some good examples of testable hypotheses.
More importantly, you need to build a robust testable research hypothesis for your scientific experiments. A testable hypothesis is a hypothesis that can be proved or disproved as a result of experimentation.
Importance of a Testable Hypothesis
To devise and perform an experiment using scientific method, you need to make sure that your hypothesis is testable. To be considered testable, some essential criteria must be met:
- There must be a possibility to prove that the hypothesis is true.
- There must be a possibility to prove that the hypothesis is false.
- The results of the hypothesis must be reproducible.
Without these criteria, the hypothesis and the results will be vague. As a result, the experiment will not prove or disprove anything significant.
What are your experiences with building hypotheses for scientific experiments? What challenges did you face? How did you overcome these challenges? Please share your thoughts with us in the comments section.
Frequently Asked Questions
The steps to write a research hypothesis are: 1. Stating the problem: Ensure that the hypothesis defines the research problem 2. Writing a hypothesis as an 'if-then' statement: Include the action and the expected outcome of your study by following a ‘if-then’ structure. 3. Defining the variables: Define the variables as Dependent or Independent based on their dependency to other factors. 4. Scrutinizing the hypothesis: Identify the type of your hypothesis
Hypothesis testing is a statistical tool which is used to make inferences about a population data to draw conclusions for a particular hypothesis.
Hypothesis in statistics is a formal statement about the nature of a population within a structured framework of a statistical model. It is used to test an existing hypothesis by studying a population.
Research hypothesis is a statement that introduces a research question and proposes an expected result. It forms the basis of scientific experiments.
The different types of hypothesis in research are: • Null hypothesis: Null hypothesis is a negative statement to support the researcher’s findings that there is no relationship between two variables. • Alternate hypothesis: Alternate hypothesis predicts the relationship between the two variables of the study. • Directional hypothesis: Directional hypothesis specifies the expected direction to be followed to determine the relationship between variables. • Non-directional hypothesis: Non-directional hypothesis does not predict the exact direction or nature of the relationship between the two variables. • Simple hypothesis: Simple hypothesis predicts the relationship between a single dependent variable and a single independent variable. • Complex hypothesis: Complex hypothesis predicts the relationship between two or more independent and dependent variables. • Associative and casual hypothesis: Associative and casual hypothesis predicts the relationship between two or more independent and dependent variables. • Empirical hypothesis: Empirical hypothesis can be tested via experiments and observation. • Statistical hypothesis: A statistical hypothesis utilizes statistical models to draw conclusions about broader populations.
Wow! You really simplified your explanation that even dummies would find it easy to comprehend. Thank you so much.
Thanks a lot for your valuable guidance.
I enjoy reading the post. Hypotheses are actually an intrinsic part in a study. It bridges the research question and the methodology of the study.
Useful piece!
This is awesome.Wow.
It very interesting to read the topic, can you guide me any specific example of hypothesis process establish throw the Demand and supply of the specific product in market
Nicely explained
It is really a useful for me Kindly give some examples of hypothesis
It was a well explained content ,can you please give me an example with the null and alternative hypothesis illustrated
clear and concise. thanks.
So Good so Amazing
Good to learn
Thanks a lot for explaining to my level of understanding
Explained well and in simple terms. Quick read! Thank you
It awesome. It has really positioned me in my research project
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Reporting Research
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for data interpretation
In research, choosing the right approach to understand data is crucial for deriving meaningful insights.…

Comparing Cross Sectional and Longitudinal Studies: 5 steps for choosing the right approach
The process of choosing the right research design can put ourselves at the crossroads of…

- Industry News
COPE Forum Discussion Highlights Challenges and Urges Clarity in Institutional Authorship Standards
The COPE forum discussion held in December 2023 initiated with a fundamental question — is…

- Career Corner
Unlocking the Power of Networking in Academic Conferences
Embarking on your first academic conference experience? Fear not, we got you covered! Academic conferences…

Research Recommendations – Guiding policy-makers for evidence-based decision making
Research recommendations play a crucial role in guiding scholars and researchers toward fruitful avenues of…
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for…
Comparing Cross Sectional and Longitudinal Studies: 5 steps for choosing the right…
How to Design Effective Research Questionnaires for Robust Findings

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
Steps in a Science Fair Project
What are the steps in a science fair project.
- Pick a topic
- Construct an exhibit for results
- Write a report
- Practice presenting
Some science fair projects are experiments to test a hypothesis . Other science fair projects attempt to answer a question or demonstrate how nature works or even invent a technology to measure something.
Before you start, find out which of these are acceptable kinds of science fair projects at your school. You can learn something and have fun using any of these approaches.
- First, pick a topic. Pick something you are interested in, something you'd like to think about and know more about.
- Then do some background research on the topic.
- Decide whether you can state a hypothesis related to the topic (that is, a cause and effect statement that you can test), and follow the strict method listed above, or whether you will just observe something, take and record measurements, and report.
- Design and carry out your research, keeping careful records of everything you do or see and your results or observations.
- Construct an exhibit or display to show and explain to others what you hoped to test (if you had a hypothesis) or what question you wanted to answer, what you did, what your data showed, and your conclusions.
- Write a short report that also states the same things as the exhibit or display, and also gives the sources of your initial background research.
- Practice describing your project and results, so you will be ready for visitors to your exhibit at the science fair.
Learn STEM by Doing (and having fun)!

The Ultimate Science Fair Project Guide – From Start to Finish
When our daughter entered her first science fair, we kept seeing references to the Internet Public Library Science Fair Project Resource Guide . However, the IPL2 permanently closed… taking the guide with it. Bummer ! After now participating in over a half-dozen elementary school science fairs (including a first-place finish!), we created our own guide to help other students go from start to finish in their next science fair project. If this is your first science fair, have fun! If you’ve done it before, we hope this is your best one! Let’s science!
*Images from Unsplash
How to Use the STEMium Science Fair Project Ultimate Guide?

If you are just starting off and this is your first science fair, here’s how to get started:
- Start with the STEMium Science Fair Project Roadmap . This is an infographic that “maps” out the process from start to finish and shows all the steps in a visual format.
- Getting Started – Why Do a Science Fair Project . Besides walking through some reasons to do a project, we also share links to examples of national science fair competitions, what’s involved and examples of winning science fair experiments . *Note: this is where you’ll get excited!!
- The Scientific Method – What is It and What’s Involved . One of the great things about a science fair project is that it introduces students to an essential process/concept known as the scientific method. This is simply the way in which we develop a hypothesis to test.
- Start the Process – Find an Idea . You now have a general idea of what to expect at the science fair, examples of winning ideas, and know about the scientific method. You’re ready to get started on your own project. How do you come up with an idea for a science fair project? We have resources on how to use a Google tool , as well as some other strategies for finding an idea.
- Experiment and Build the Project . Time to roll up those sleeves and put on your lab coat.
- Other Resources for the Fair. Along the way, you will likely encounter challenges or get stuck. Don’t give up – it’s all part of the scientific process. Check out our STEMium Resources page for more links and resources from the web. We also have additional experiments like the germiest spot in school , or the alka-seltzer rocket project that our own kids used.
Getting Started – Why Do a Science Fair Project
For many students, participating in the science fair might be a choice that was made FOR you. In other words, something you must do as part of a class. Maybe your parents are making you do it. For others, maybe it sounded like a cool idea. Something fun to try. Whatever your motivation, there are a lot of great reasons to do a science fair project.
- Challenge yourself
- Learn more about science
- Explore cool technology
- Make something to help the world! (seriously!)
- Win prizes (and sometimes even money)
- Do something you can be proud of!
Many students will participate in a science fair at their school. But there are also national competitions that include 1000s of participants. There are also engineering fairs, maker events, and hackathons. It’s an exciting time to be a scientist!! The list below gives examples of national events.
- Regeneron Science Talent Search
- Regeneron International Science and Engineering Fair
- Google Science Fair
- Conrad Challenge
- Microsoft Imagine Cup
- JSHS Program
- Exploravision
What’s the Scientific Method?
Before we jump into your project, it’s important to introduce a key concept: The Scientific Method . The scientific method is the framework scientists use to answer their questions and test their hypothesis. The figure below illustrates the steps you’ll take to get to the end, but it starts with asking a question (you’ve already finished the first step!).

After we find a problem/idea to tackle, and dig into some background research, we create a guess on a potential solution. This is known as our hypothesis.
Example of a Hypothesis
My brother can hold his breath underwater longer than I can (“our problem”) –> how can I hold my breath longer? (“our question”) –> if I drink soda with caffeine before I hold my breath, I will be able to stay underwater longer (“our solution”). Our hypothesis is that using caffeine before we go underwater will increase the time we hold our breath. We’re not sure if that is a correct solution or not at this stage – just taking a guess.
Once we have a hypothesis, we design an experiment to TEST our hypothesis. First, we will change variables/conditions one at a time while keeping everything else the same, so we can compare the outcomes.
Experimental Design Example
Using our underwater example, maybe we will test different drinks and count how long I can hold my breath. Maybe we can also see if someone else can serve as a “control” – someone who holds their breath but does not drink caffeine. For the underwater experiment, we can time in seconds how long I hold my breath before I have a drink and then time it again after I have my caffeine drink. I can also time how long I stay underwater when I have a drink without caffeine.
Then, once we finish with our experiment, we analyze our data and develop a conclusion.
- How many seconds did I stay underwater in the different situations?
- Which outcome is greater? Did caffeine help me hold my breath longer?
Finally, (and most important), we present our findings. Imagine putting together a poster board with a chart showing the number of seconds I stayed underwater in the different conditions.
Hopefully you have a better sense of the scientific method. If you are completing a science fair project, sticking with these steps is super important. Just in case there is any lingering confusion, here are some resources for learning more about the scientific method:
- Science Buddies – Steps of the Scientific Method
- Ducksters – Learn About the Scientific Method
- Biology4kids – Scientific Method
- National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences – Scientific Method
What Science Fair Project Should I Do?

And science is no different.
Just know that if you can get through the idea part, the rest of the science fair is relatively smooth sailing. Remember to keep an open mind and a positive outlook . Each year 100s of 1000s of kids, teenagers and college students come up with new projects and ideas to test. You’ve got this!
What Makes a Great Science Fair Project? Start with a Problem To Solve

As we discuss below, good science experiments attempt to answer a QUESTION. Why is the sky blue? Why does my dog bark at her reflection? First, we will step through some ways to find TESTABLE QUESTIONS. These questions that you create will be what you work on for your science fair project. Pick something fun, something interesting and something that you are excited about. Not sure what that looks like? Step through some of the tips below for help.
Use the Google Science Fair Idea Generator
Are you surprised Google made a tool for science fair projects?? Our post called the low-stress way to find a science fair project gives a more in-depth overview about how to use it. It’s a great first stop if you’re early in the brainstorming process.
Answer your own questions

- What type of music makes you run faster?
- Can boys hold their breath underwater longer than girls?
- How can I be sure the sandwich I bought is gluten free?
- If we plant 100 trees in our neighborhood, will the air be cleaner?
Still stuck? Get inspiration from other science fair projects

Check out the Getting Started section and look at some of the winning science project ideas, our STEMium experiments and our Resource page. We’ve presented a ton of potential idea starters for you – take time to run through some of these, but our suggestion is to give yourself a deadline to pick an idea . Going through the lists could take you longer than you think, and in many cases sometimes it’s just better to pick something and go for it! The next section will take you through how to create testable questions for your project.
Starting Your Project: Find A Testable Question
The best experiments start with a question. Taking that a step further, the questions you useyou’re your science fair project should be ones that are TESTABLE. That means something you can measure. Let’s look at an example. Let’s say I’m super excited about baking. OH YEA!! I love baking. Specifically, baking cakes. In fact, I love baking cakes so much that I want to do a science project related to cakes. We’ve got two questions on cakes that we created. Which question below could be most useful for a science fair project:
1) Can eating cake before a test improve your score?
2) Why isn’t carrot cake more popular than chocolate cake?
The second question isn’t necessarily a bad question to pick. You could survey people and perhaps tackle the question that way. However, chances are you will get a lot of different answers and it will probably take a lot of surveys to start to pick up a trend.
Although, the first question might be a little easier. How would you test this? Maybe you pick one type of cake and one test that you give people. If you can get five people to take the test after eating cake and five people take the test with no cake, you can compare the test results. There might be other variables beyond cake that you could test (example: age, sex, education). But you can see that the first question is probably a little easier to test. The first question is also a little easier to come up with a hypothesis.
At this point, you’ve got an idea. That was the hard part! Now it’s time to think a little more about that idea and focus it into a scientific question that is testable and that you can create a hypothesis around .
What makes a question “testable”?
Testable questions are ones that can be measured and should focus on what you will change. In our first cake question, we would be changing whether or not people eat cake before a test. If we are giving them all the same test and in the same conditions, you could compare how they do on the test with and without cake. As you are creating your testable question, think about what you WILL CHANGE (cake) and what you are expecting to be different (test scores). Cause and effect. Check out this reference on testable questions for more details.
Outline Your Science Project – What Steps Should I Take?

Do Background Research / Create Hypothesis
Science experiments typically start with a question (example: Which cleaning solution eliminates more germs?). The questions might come up because of a problem. For example, maybe you’re an engineer and you are trying to design a new line of cars that can drive at least 50 mph faster. Your problem is that the car isn’t fast enough. After looking at what other people have tried to do to get the car to go faster, and thinking about what you can change, you try to find a solution or an answer. When we talk about the scientific method, the proposed answer is referred to as the HYPOTHESIS.

- Science Buddies
- National Geographic
The information you gather to answer these research questions can be used in your report or in your board. This will go in the BACKGROUND section. For resources that you find useful, make sure you note the web address where you found it, and save in a Google Doc for later.
Additional Research Tips
For your own science fair project, there will likely be rules that will already be set by the judges/teachers/school. Make sure you get familiar with the rules FOR YOUR FAIR and what needs to be completed to participate . Typically, you will have to do some research into your project, you’ll complete experiments, analyze data, make conclusions and then present the work in a written report and on a poster board. Make a checklist of all these “to do” items. Key things to address:
- Question being answered – this is your testable question
- Hypothesis – what did you come up with and why
- Experimental design – how are you going to test your hypothesis
- Conclusions – why did you reach these and what are some alternative explanations
- What would you do next? Answering a testable question usually leads to asking more questions and judges will be interested in how you think about next steps.
Need more help? Check out these additional resources on how to tackle a science fair project:
- Developing a Science Fair Project – Wiley
- Successful Science Fair Projects – Washington University
- Science Fair Planning Guide – Chattahoochee Elementary
Experiment – Time to Test That Hypothesis
Way to go! You’ve found a problem and identified a testable question. You’ve done background research and even created a hypothesis. It’s time to put it all together now and start designing your experiment. Two experiments we have outlined in detail – germiest spot in school and alka-seltzer rockets – help show how to set up experiments to test variable changes.
The folks at ThoughtCo have a great overview on the different types of variables – independent, dependent and controls. You need to identify which ones are relevant to your own experiment and then test to see how changes in the independent variable impacts the dependent variable . Sounds hard? Nope. Let’s look at an example. Let’s say our hypothesis is that cold weather will let you flip a coin with more heads than tails. The independent variable is the temperature. The dependent variable is the number of heads or tails that show up. Our experiment could involve flipping a coin fifty times in different temperatures (outside, in a sauna, in room temperature) and seeing how many heads/tails we get.
One other important point – write down all the steps you take and the materials you use!! This will be in your final report and project board. Example – for our coin flipping experiment, we will have a coin (or more than one), a thermometer to keep track of the temperature in our environment. Take pictures of the flipping too!
Analyze Results – Make Conclusions
Analyzing means adding up our results and putting them into pretty pictures. Use charts and graphs whenever you can. In our last coin flipping example, you’d want to include bar charts of the number of heads and tails at different temperatures. If you’re doing some other type of experiment, take pictures during the different steps to document everything.
This is the fun part…. Now we get to see if we answered our question! Did the weather affect the coin flipping? Did eating cake help us do better on our test?? So exciting! Look through what the data tells you and try to answer your question. Your hypothesis may / may not be correct. It’s not important either way – the most important part is what you learned and the process. Check out these references for more help:
- How to make a chart or graph in Google Sheets
- How to make a chart in Excel
Presentation Time – Set Up Your Board, Practice Your Talk
Personally, the presentation is my favorite part! First, you get to show off all your hard work and look back at everything you did! Additionally, science fair rules should outline the specific sections that need to be in the report, and in the poster board – so, be like Emmett from Lego Movie and read the instructions. Here’s a loose overview of what you should include:
- Title – what is it called.
- Introduction / background – here’s why you’re doing it and helping the judges learn a bit about your project.
- Materials/Methods – what you used and the steps in your experiment. This is so someone else could repeat your experiment.
- Results – what was the outcome? How many heads/tails? Include pictures and graphs.
- Conclusions – was your hypothesis correct? What else would you like to investigate now? What went right and what went wrong?
- References – if you did research, where did you get your information from? What are your sources?
The written report will be very similar to the final presentation board. The board that you’ll prepare is usually a three-panel board set up like the picture shown below.

To prepare for the presentation, you and your partner should be able to talk about the following:
- why you did the experiment
- the hypothesis that was tested
- the data results
- the conclusions.
It’s totally OK to not know an answer. Just remember this is the fun part!
And that’s it! YOU DID IT!!
Science fair projects have been great opportunities for our kids to not only learn more about science, but to also be challenged and push themselves. Independent projects like these are usually a great learning opportunity. Has your child completed a science fair project that they are proud of? Include a pic in the comments – we love to share science!! Please also check out our STEMium Resources page for more science fair project tips and tricks .
STEMomma is a mother & former scientist/educator. She loves to find creative, fun ways to help engage kids in the STEM fields (science, technology, engineering and math). When she’s not busy in meetings or carpooling kids, she loves spending time with the family and dreaming up new experiments or games they can try in the backyard.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
Notify me of new posts by email.

Science & Quantitative Reasoning Education
Yale undergraduate research, how to write a proposal.
The abstract should summarize your proposal. Include one sentence to introduce the problem you are investigating, why this problem is significant, the hypothesis to be tested, a brief summary of experiments that you wish to conduct and a single concluding sentence. (250 word limit)
Introduction
The introduction discusses the background and significance of the problem you are investigating. Lead the reader from the general to the specific. For example, if you want to write about the role that Brca1 mutations play in breast cancer pathogenesis, talk first about the significance of breast cancer as a disease in the US/world population, then about familial breast cancer as a small subset of breast cancers in general, then about discovery of Brca1 mutations in familial breast cancer, then Brca1’s normal functions in DNA repair, then about how Brca1 mutations result in damaged DNA and onset of familial breast cancer, etc. Definitely include figures with properly labeled text boxes (designated as Figure 1, Figure 2, etc) here to better illustrate your points and help your reader wade through unfamiliar science. (3 pages max)
Formulate a hypothesis that will be tested in your grant proposal. Remember, you are doing hypothesis-driven research so there should be a hypothesis to be tested! The hypothesis should be focused, concise and flow logically from the introduction. For example, your hypothesis could be “I hypothesize that overexpressing wild type Brca1 in Brca1 null tumor cells will prevent metastatic spread in a mouse xenograph model.” Based on your hypothesis, your Specific Aims section should be geared to support it. The hypothesis is stated in one sentence in the proposal.
Specific Aims (listed as Specific Aim 1, Specific Aim 2)
This is where you will want to work with your mentor to craft the experimental portion of your proposal. Propose two original specific aims to test your hypothesis. Don’t propose more than two aims-you will NOT have enough time to do more. In the example presented, Specific Aim 1 might be “To determine the oncogenic potential of Brca1 null cell lines expressing wild type Brca1 cDNA”. Specific aim 2 might be “To determine the metastatic potential of Brca1 null cells that express WT Brca1”. You do not have to go into extensive technical details, just enough for the reader to understand what you propose to do. The best aims yield mechanistic insights-that is, experiments proposed address some mechanisms of biology. A less desirable aim proposes correlative experiments that does not address mechanistically how BRCA1 mutations generate cancer. It is also very important that the two aims are related but NOT interdependent. What this means is that if Aim 1 doesn’t work, Aim 2 is not automatically dead. For example, say you propose in Aim 1 to generate a BRCA1 knockout mouse model, and in Aim 2 you will take tissues from this mouse to do experiments. If knocking out BRCA1 results in early embryonic death, you will never get a mouse that yields tissues for Aim 2. You can include some of your mentor’s data here as “Preliminary data”. Remember to carefully cite all your sources. (4 pages max; 2 pages per Aim)
Potential pitfalls and alternative strategies
This is a very important part of any proposal. This is where you want to discuss the experiments you propose in Aims 1 and 2. Remember, no experiment is perfect. Are there any reasons why experiments you proposed might not work? Why? What will you do to resolve this? What are other possible strategies you might use if your experiments don’t work? If a reviewer spots these deficiencies and you don’t propose methods to correct them, your proposal will not get funded. You will want to work with your mentor to write this section. (1/2 page per Aim)
Cite all references, including unpublished data from your mentor. Last, First, (year), Title, Journal, volume, pages.
*8 page proposal limit (not including References), 1.5 spacing, 12pt Times New Roman font
- View an example of a research proposal submitted for the Yale College First-Year Summer Research Fellowship (PDF).
- View an example of a research proposal submitted for the Yale College Dean’s Research Fellowship and the Rosenfeld Science Scholars Program (PDF) .
VanCleave's Science Fun
Your Guide to Science Projects, Fun Experiments, and Science Research
Crystal Project: Hypothesis
By Janice VanCleave

The science fair project question is: How does the type of dissolved salt effect the appearance of the evaporite crystals formed?
So, what do you think?
Will using different kinds of salt affect the physical appearance of the crystals formed?
Your guess about the answer to the science fair question is called your hypothesis, and it can be written like this:
Since crystals are made of chemicals, then using different kinds of salt (will or will not) result in evaporite crystals with different physical appearances.
Back to Halite Crystal Index
Share this:

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A hypothesis is the best answer to a question based on what is known. Scientists take that best answer and do experiments to see if it still makes sense or if a better answer can be made. When a scientist has a question they want to answer, they research what is already known about the topic. Then, they come up with their best answer to the ...
Developing a hypothesis (with example) Step 1. Ask a question. Writing a hypothesis begins with a research question that you want to answer. The question should be focused, specific, and researchable within the constraints of your project. Example: Research question.
Step 5: Phrase your hypothesis in three ways. To identify the variables, you can write a simple prediction in if … then form. The first part of the sentence states the independent variable and the second part states the dependent variable. If a first-year student starts attending more lectures, then their exam scores will improve.
Keep in mind that writing the hypothesis is an early step in the process of doing a science project. The steps below form the basic outline of the Scientific Method: Ask a Question. Do Background Research. Construct a Hypothesis. Test Your Hypothesis by Doing an Experiment. Analyze Your Data and Draw a Conclusion.
1. Select a topic. Pick a topic that interests you, and that you think it would be good to know more about. [2] If you are writing a hypothesis for a school assignment, this step may be taken care of for you. 2. Read existing research. Gather all the information you can about the topic you've selected.
A hypothesis is a statement that predicts the outcome of your experiment, and is informed by the research you have done on your topic.. A testable question is one that allows you to make a comparison. In scientific inquiry, this is done by setting up a test in which you will change one factor of your experiment and observe its effect on the rest of your experiment.
An effective hypothesis in research is clearly and concisely written, and any terms or definitions clarified and defined. Specific language must also be used to avoid any generalities or assumptions. Use the following points as a checklist to evaluate the effectiveness of your research hypothesis: Predicts the relationship and outcome.
Get your idea and do some research. DIY Space: How to Do a Science Fair Project - Step 1. Watch on. Observe the world around you and ask questions about the things you observe. 2. Ask a testable question. DIY Space: How to Do a Science Fair Project - Step 2. Watch on. Develop your idea into a question you can test.
Here are some research hypothesis examples: If you leave the lights on, then it takes longer for people to fall asleep. If you refrigerate apples, they last longer before going bad. If you keep the curtains closed, then you need less electricity to heat or cool the house (the electric bill is lower). If you leave a bucket of water uncovered ...
Make a plan to observe something. Design and carry out your research, keeping careful records of everything you do or see. Create an exhibit or display to show and explain to others what you hoped to test (if you had a hypothesis) or what question you wanted to answer, what you did, what your data showed, and your conclusions.
research and create breakthroughs in knowledge. These brief statements are what form the basis of entire research experiments. Thus, a flaw in the formulation of a hypothesis may cause a flaw in the design of an entire experiment. Flaws in experimental design may lead to the use of unreliable information in the field
Dr. Michelle Harris, Dr. Janet Batzli,Biocore. This section provides guidelines on how to construct a solid introduction to a scientific paper including background information, study question, biological rationale, hypothesis, and general approach. If the Introduction is done well, there should be no question in the reader's mind why and on ...
Prepare yourself for the project. Discuss possible topics and plans with your teacher. Note any guidelines they give for the assignment, and keep these requirements in mind while designing your project. If your teacher hands out any worksheets regarding the science fair, keep them together in a folder. 2.
The steps to write a research hypothesis are: 1. Stating the problem: Ensure that the hypothesis defines the research problem. 2. Writing a hypothesis as an 'if-then' statement: Include the action and the expected outcome of your study by following a 'if-then' structure. 3.
Research. Hypothesis. Experiment. Construct an exhibit for results. Write a report. Practice presenting. Some science fair projects are experiments to test a hypothesis. Other science fair projects attempt to answer a question or demonstrate how nature works or even invent a technology to measure something. Before you start, find out which of ...
A hypothesis is a tentative, testable answer to a scientific question. Once a scientist has a scientific question she is interested in, the scientist reads up to find out what is already known on the topic. Then she uses that information to form a tentative answer to her scientific question. Sometimes people refer to the tentative answer as "an ...
After now participating in over a half-dozen elementary school science fairs (including a first-place finish!), we created our own guide to help other students go from start to finish in their next science fair project. If this is your first science fair, have fun! If you've done it before, we hope this is your best one!
This is where you will want to work with your mentor to craft the experimental portion of your proposal. Propose two original specific aims to test your hypothesis. Don't propose more than two aims-you will NOT have enough time to do more. In the example presented, Specific Aim 1 might be "To determine the oncogenic potential of Brca1 null ...
Crystal Project: Hypothesis. By Janice VanCleave. A hypothesis is your best prediction about the answer to your science fair project question. The science fair project question is: How does the type of dissolved salt effect the appearance of the evaporite crystals formed?