Class 6 Science Chapter 8 Case Based Questions - Light, Shadow and Reflections
Sarah is conducting an experiment with different objects to understand the properties of light. She has a wooden box, a glass pane, and a candle. She is using a source of light to observe the behavior of these objects.
Q1: What type of object is the wooden box in this scenario, and why? Ans: The wooden box is an opaque object because it does not allow light to pass through it. Q2: If Sarah observes that she can see through the glass pane clearly, what type of object is it, and why? Ans: The glass pane is a transparent object because it allows light to pass through it clearly. Q3: How does the behavior of the candle differ from the wooden box and the glass pane in terms of emitting light? Ans: The candle is a luminous object because it emits its own light. Q4: Which of the following objects is an example of a translucent object? (a) Wooden box (b) Glass pane (c) Candle Ans: (b) Q5: What is the primary characteristic that distinguishes a luminous object from a non-luminous object? (a) Color (b) Shape (c) Ability to emit light Ans: (c)
Mark is using a pinhole camera to capture images. He is experimenting with the camera's focus and understanding the principles behind it.
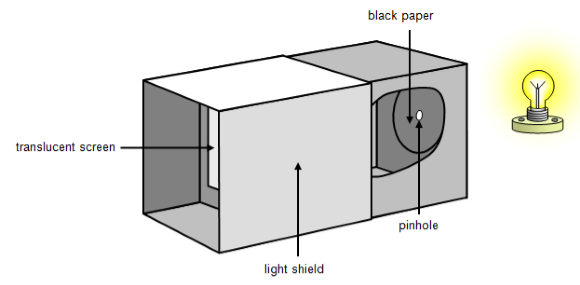
Q6: Explain how the image formed by Mark's pinhole camera is different from the actual object in terms of size and orientation. Ans: The image formed by Mark's pinhole camera is inverted and smaller in size compared to the actual object. Q7: Describe the steps Mark should follow to make a pinhole camera. Ans: Steps to make a pinhole camera:
- Take two rectangular boxes that fit into one another without any gap.
- Cut open one side of each box.
- Make a small hole in the larger box at the center of the closed end opposite the side that has been cut open.
- Cut a square of side five centimeters in the smaller box in the closed end opposite the side that has been cut open.
- Cover this square with tracing paper.
- Slide the smaller box into the larger box, ensuring that the pinhole and the tracing paper are in line with one another but at opposite ends.
- Slide the smaller box to adjust the focus.
Q8: Why is it mentioned that "the image is not clear" in the context of a pinhole camera? Ans: The image is not clear because the pinhole camera uses a small hole to form the image, resulting in limited light and reduced clarity. Q9: What is the principle on which a pinhole camera works? (a) The principle of reflection of light. (b) The principle of refraction of light. (c) The principle of straight-line propagation of light. Ans: (c) Q10: Which type of surface reflects the entire light incident on it? (a) Transparent surface (b) Opaque surface (c) Plane mirror surface Ans: (c)
A group of students is discussing the difference between shadows and images. They are using a mirror and a flashlight to observe and learn about these phenomena.
Q11: Explain the similarities and differences between shadows and images. Ans: Similarities:
- Both shadows and images require a source of light.
- They are formed when light interacts with objects.
Differences:
- Shadows are black and have no color, while images can be colorful.
- Shadows change in length with the position of the sun, while images in a mirror remain the same size.
Q12: Describe the setup and conditions required to observe a shadow and an image. Ans: To observe a shadow, you need a source of light, an opaque object, and a screen. To observe an image in a mirror, you need a reflective surface and an object in front of it. Q13: Why do shadows change in length throughout the day, while images in a mirror do not? Ans: Shadows change in length throughout the day because of the changing angle and position of the sun. Images in a mirror do not change size. Q14: Which of the following statements is true regarding shadows and images? (a) Shadows are always colorful. (b) Images change in size with the position of the sun. (c) Shadows can be seen without the need for a screen. Ans: (c) Q15: What is the main reason behind the formation of shadows? (a) Reflection of light (b) Bending of light (c) Blocking of light Ans: (b)
A group of students is visiting an observatory, where they encounter a two-way mirror. They are curious about its functionality.
Q16: Explain how a two-way mirror works and its practical applications. Ans: A two-way mirror, also known as a one-way mirror, allows one side to act as a mirror (reflective) and the other side as plain glass (transparent). It is used for observing people without them knowing, such as in police stations or psychological institutions. Q17: Compare and contrast the behavior of a two-way mirror with a regular plane mirror. Ans: Comparison with a regular plane mirror:
- A plane mirror is always reflective, whereas a two-way mirror can switch between reflective and transparent properties.
Q18: In what situations might a two-way mirror be used for observation without detection? Ans: A two-way mirror might be used for covert observation without detection. Q19: A two-way mirror acts as: (a) A transparent medium (b) A translucent medium (c) A combination of a mirror and plain glass Ans: (c) Q20: What type of surface is a smooth plane mirror? (a) Transparent surface (b) Opaque surface (c) Reflective surface Ans: (c)
Tom is studying the concept of reflection and its importance in our daily lives. He is experimenting with various reflective surfaces.
Q21: Explain the concept of reflection of light and how it plays a role in forming images. Ans: The concept of reflection of light involves the bouncing back of light when it encounters a smooth shiny surface. Reflection plays a role in forming images by redirecting light rays. Q22: Describe the behavior of light when it is incident on a smooth shiny surface. Ans: When light is incident on a smooth shiny surface, it reflects back into the same medium following the laws of reflection. Q23: Provide examples of everyday situations where reflection of light is essential. Ans: Examples of everyday situations with reflection of light: Mirrors, shiny metal surfaces, glass windows, and still water surfaces. Q24: Which term best describes the likeness of an object carried and formed by light in a mirror? (a) Image (b) Shadow (c) Reflection Ans: (a) Q25: What is the primary characteristic that distinguishes a plane mirror from other reflective surfaces? (a) Color (b) Smoothness (c) Size of reflection Ans: (b)

Top Courses for Class 6
Extra questions, video lectures, semester notes, class 6 science chapter 8 case based questions - light, shadow and reflections, mock tests for examination, previous year questions with solutions, shortcuts and tricks, past year papers, viva questions, study material, objective type questions, sample paper, practice quizzes, important questions.

Case Based Questions: Light, Shadows & Reflections Free PDF Download
Importance of case based questions: light, shadows & reflections, case based questions: light, shadows & reflections notes, case based questions: light, shadows & reflections class 6, study case based questions: light, shadows & reflections on the app, welcome back, create your account for free.
Forgot Password
Unattempted tests, change country, practice & revise.
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Light, Shadows and Reflections Class 6 Notes CBSE Science Chapter 11 (Free PDF Download)
- Revision Notes

Revision Notes for CBSE Class 6 Science Chapter 11 - Free PDF Download
Free PDF download of Class 6 Science Chapter 11 - Light, Shadows and Reflections Revision Notes & Short Key-notes prepared by expert Science teachers from latest edition of CBSE(NCERT) books. R egister Online for NCERT Solutions Class 6 Science tuition on Vedantu.com to score more marks in your examination . Vedantu is a platform that provides free CBSE Solutions (NCERT) and other study materials for students. Maths Students who are looking for the better solutions ,they can download Class 6 Maths NCERT Solutions to help you to revise complete syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Download CBSE Class 6 Science Revision Notes 2024-25 PDF
Also, check CBSE Class 6 Science revision notes for All chapters:
Access Class 6 Science Chapter 11 – Light, Shadows and Reflection Notes
Definition of light.
Light is a form of invisible energy, perceived by eyes when scattered by small dust particles that stimulate sight and makes things visible.
Due to the scattering of light, other objects are visible.
Light and the eyes both are necessary to see things.
The sensation caused by light that helps us to see things is called sight or vision.
Sources of Light
Natural: sources that have their own energy to create light.
For example Sun, stars, candle flames etc.
Artificial: The man-made sources of light are called artificial sources of light.
For example light bulbs, tube lights, torch etc.
Classification of Light: On the Basis of Its Emission.
Luminous Objects: Objects which emit light of their own are called luminous objects.
For example sun, torch, candle flame.
Non-Luminous Objects: Objects which do not have the light of their own and are visible due to reflection or scattering of light are called non-luminous objects.
Example: moon, rainbow, table etc.
Optical media and its types
Optical Media: Any substance through which light travels is called optical media.
Transparent Object: a substance through which light passes without any obstruction is called a transparent object. Objects seen through them are clearly visible. For example glass, water, air etc.
Translucent Object: a substance that obstructs some part of the light and the light cannot pass through them completely is called a translucent object.
For example butter paper, etched glass etc.
Opaque Object: a substance that does not allow light to pass through it is called an opaque object.
For example wood, metal etc.
Definition of Shadow
A shadow is the 'region of the absence of light' caused by an object which does not allow light to pass. As light travels in a straight line, the light obstructed by the object causes a dark region with no light.
A shadow is formed in the presence of a light source.
Opaque and translucent objects which restrict the light to pass through them form a shadow, transparent objects do not produce a shadow.
Properties of a shadow
Due to Size of Light Source:
A. Due to the smaller (point) light source: Only one dark shadow is formed. This is known as the umbra.
B. Due to larger(extended) light source: number of shadows formed are two, a dark one in the centre and a light one on the of the direction of propagation of light;
A dark shadow is called the umbra.
A faint or lighter shadow is called a penumbra.
The size of these shadows depends upon the positioning of the screen with respect to the object. The size of the umbra decreases and the penumbra increases as the screen is moved away from the object and vice-versa.
Colour of Shadow:
The colour of the shadow is black due to the absence of light, irrespective of the colour of the object.
Length of the Shadow:
The length of the shadow depends on the angle at which light is incident on an object. For example, the length of a person's shadow decreases as the sun rises overhead.
Eclipse:
A shadow is formed in space which makes the sun or the moon invisible for some duration. Eclipse is the phenomenon of overshading a bright object with another object.
Types of the Eclipse:
Solar Eclipse: The moon comes between the sun and the earth during its revolution around the earth, which causes darkness on the earth (in the shadow) during the day.
Lunar Eclipse: The sun, moon and the earth are in a straight line such that the earth comes in between the sun and the moon and obstructs the light of the sun to reach the moon, that is, the shadow of the earth falls on the moon and the moon is not visible.
Definition of Reflection of Light:
The bouncing back of a light ray after striking an object at some angle is known as reflection. We see our image in a mirror after reflection. The objects around us are visible due to the reflection of light.
Significance of Light, Shadows and Reflections Class 6 Notes CBSE Science Chapter 11 (Free PDF Download)
The significance of "Light, Shadows, and Reflections" Class 6 CBSE Science Chapter 11 notes, available as free PDF downloads, is paramount in the realm of science education. These notes simplify intricate scientific concepts related to the behavior of light, shadows, and reflections, making them accessible and comprehensible for young learners.
They provide clarity and depth to the subject, helping students grasp the fundamental principles that govern the fascinating world of optics. Moreover, these notes stimulate curiosity and critical thinking by presenting real-life examples and practical applications. Being available as free PDF downloads ensures that educational resources are easily accessible to all students, promoting equitable learning opportunities. In essence, these notes enrich the learning experience, nurturing both scientific knowledge and a sense of wonder about the mysteries of light, shadows, and reflections in our daily lives.
How Do Light, Shadows and Reflections Affect Our Daily Life?
Light, shadows, and reflections play a significant and often unnoticed role in our daily lives, influencing several aspects of our experiences and interactions with the world.
1. Visibility: Light is essential for visibility. It enables us to see our surroundings, recognize objects, and navigate safely, whether it's daylight illuminating the streets or artificial light in our homes.
2. Time Management: Shadows are vital indicators of time, helping us determine the time of day. Sundials, for instance, rely on the movement of shadows to tell time accurately.
3. Safety: Light and shadows are critical for safety. Reflectors, road signs, and traffic lights utilize the principles of reflection and shadows to guide and protect motorists and pedestrians.
4. Art and Aesthetics: In art and architecture, the interplay of light and shadows is used to create depth, texture, and atmosphere. Lighting design in homes, theaters, and public spaces is an essential aspect of aesthetics.
5. Technology: Light is the basis of technologies like cameras, projectors, and optical fibers, which have revolutionized communication, entertainment, and healthcare.
6. Scientific Exploration: In scientific research, light and its properties are crucial. Microscopes, telescopes, and spectrometers rely on the behavior of light for various scientific observations.
In summary, light, shadows, and reflections are integral to our daily existence, affecting our perception, safety, aesthetics, technology, and scientific understanding. They demonstrate the profound impact that scientific principles can have on our everyday lives.
Conclusion
The Class 6 CBSE Science Chapter 11 notes on "Light, Shadows, and Reflections," available as free PDF downloads, are invaluable educational resources. These notes simplify the complex concepts of optics, making them accessible to young learners. They provide comprehensive coverage of the chapter, ensuring a well-rounded understanding of the subject matter. Moreover, these notes foster critical thinking and practical application of scientific principles. Being accessible as free PDF downloads ensures equitable access to quality educational materials. Ultimately, these notes enrich the learning experience, instilling a profound appreciation for the intriguing phenomena of light, shadows, and reflections that shape our world and our understanding of it.

FAQs on Light, Shadows and Reflections Class 6 Notes CBSE Science Chapter 11 (Free PDF Download)
1. What is Chapter 11 of Class 6 Science based on?
Chapter 11 “Light, Shadows and Reflections” of Class 6 Science, as the name suggests, is based on the concepts of light, shadows and reflection. The NCERT book simply describes and defines the concepts and gives an insight on the topics like sources of light and their types and functions, types of optical media and it further explains the concept of shadows along with its properties. It provides easy to understand notes, making it easier for students to learn these concepts.
2. What are the characteristics of light according to Science Chapter 11 Class 6?
Light is said to be the natural mechanism that enables one's sight and makes things visible. It is an invisible form of energy and its path is seen through scattered dust particles in the atmosphere. Light itself is not visible but it makes other things visible. There are many sources of light, some natural and some man-made that enable sight. The main source of light in the universe is the sun. Other sources of light include stars, candles, and electric torches.
3. How are shadows formed as given in Class 6 Science Chapter 11?
The NCERT book provides an easy definition of the concept of shadow. It explains the formation of shadow and the types and characteristics of shadow formed. According to the definition, any obstacle in the way of light casts a shadow, it is the region of the absence of light. When any obstacle cuts off the light coming from a source, a shadow is cast. Shadows can be classified as umbra and penumbra, based on the extent of the source. To know more students can visit the Vedantu app or website.
4. What are optical media?
Light is known to enable sight and make objects visible to us. Optical media are defined as objects that enable light to pass through them completely or partially. There are three types of optical media. The first is a transparent medium, which allows light to pass through it completely. The second type is translucent medium, which allows light to pass through it partially. The third type is an opaque medium that does not let light pass through it at all.
5. What is an eclipse as given in Chapter 11 of Class 6 Science?
Chapter 11 “Light, Shadows and Reflection” of Class 6 Science is based on the concept of light and shadows and everything regarding that. An eclipse is defined as the overshadowing of a bright object, or a shadow in space that renders the sun and the moon invisible for a while. An eclipse is of two types - solar and lunar. A solar eclipse occurs on a new moon day and a lunar eclipse occurs on a full moon day. To know more about this chapter, students can download the revision notes free of cost from the Vedantu website.
NCERT Solutions
Study materials for class 6.
CBSE Class 6 Science Notes Chapter 11 Light Shadows and Reflections
CBSE Class 6 Science Notes Chapter 11 Light Shadows and Reflections are given below. Our notes are designed by the subject experts and are as per the NCERT guidelines. These notes include all the important points of the chapter in detailed way, so you can refer to this whenever required. Study Path provides CBSE Class 6 Science Notes Chapter 11 that are easy to understand and also free downloadable PDF format, so students can practice it for their studies and get good marks in their examinations.
Light Shadows and Reflections Class 6 Notes Science Chapter 11
Introduction
Light is a form of energy which helps us in seeing objects. When light falls on an object, some of the light gets reflected. The reflected light comes to our eyes and we are able to see an object.
Sources of Light
Objects that produce their own light are called Luminous Objects. Example, Sun, Fire
Objects that do not produce their own light but are visible when reflect light falling on them are called Non-Luminous Objects. Example – Table, planets.
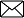
Rectilinear propagation of light
Light takes the quickest path between any two points. Therefore, light travels in a straight line. This is known as a rectilinear propagation of light.
Transparent, Opaque and Translucent Objects
Luminous & Non-luminous objects
- Objects that emit light and heat are known as luminous objects. E.g.: Sun and other stars
- Objects that do not produce their own light but reflect the light emitted by luminous objects are known as non-luminous objects. E.g.: Earth, trees
Objects can be classified based on their interaction with light.
- Transparent objects allow light to pass through them without getting scattered. E.g.: glass
- Translucent objects allow light to pass through them partially. E.g.: Butter paper
- Opaque objects do not allow any light to pass through them. E.g.: a table, a book, etc
Shadows are dark regions formed when an opaque object blocks the path of light. This formation is possible only because light only travels in a straight line.
Shadow formation
- A shadow is formed when an opaque object comes in the path of light.
- A shadow needs a screen where it is formed, for example, the ground, or walls of a room or even the surfaces of buildings.
- Shadows give us an idea about the shapes of different objects. Or, it can even mislead us about the shape of different objects. E.g. the shadow of a cone appears to be a triangle on the screen.

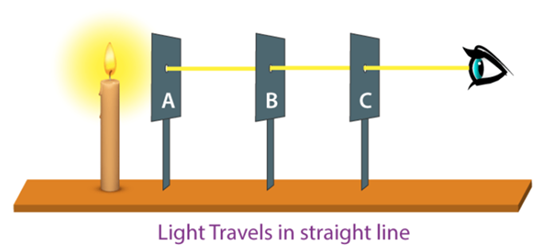
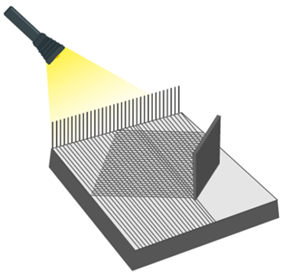
The Pinhole Camera
Formation of image by pinhole camera
- A pinhole camera is a simple camera that consists of a light-proof box, a thin film for a screen and a small aperture or hole to allow the passage of light rays.
- The light from outside enters through the small hole and forms an image on the screen that is inverted.
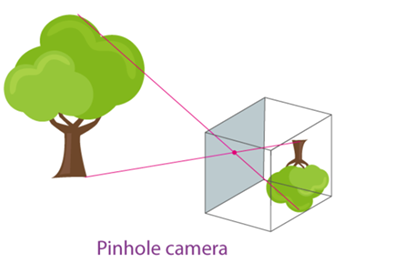
How to make a Pinhole Camera?
Step 1: Take two cardboard boxes one larger than the other such that one box slides into the other without any gap.
Step 2: Cut out open one side of each box. On the opposite side of the larger box cut a small hole in the centre.
Step 3: On the opposite side of the smaller box cut a square of about 5 cm and cover this open area with a tracing paper.
Step 4: Slide the smaller box inside the larger one such that the side with the tracing paper is on the inside.
Step 5: Cover the camera and your head with a black cloth and then get ready to observe the distant objects.
Natural Pin-hole Camera
When we pass under a tree covered with large number of leaves, we notice that small patches of sun light under it. These circular images are, in fact, pin hole images of the Sun. The gaps between the leaves, act as the pin holes. These gaps are all kinds of irregular shapes, but, we can see circular images of the Sun. This is called Natural Pin-Hole Camera
Mirrors and Reflection
A mirror is a surface usually consisting of a glass that reflects light incident on it to form clear erect images.
When light is incident on a surface, it gets reflected or it bounces back. Any surface that is really well polished or shiny acts like a mirror. The phenomenon of light bouncing off surfaces is called reflection.
Characteristics of images
- Images have colour, unlike shadows. They are formed due to the converging rays of light that comes after reflecting from objects.
- A real image is formed by actual convergence of light rays. Real images always form on a screen.
- A virtual image is the apparent convergence of diverging light rays. Virtual images cannot be obtained on a screen.
Plane mirrors and images formed by them
A plane mirror changes the direction of light that falls on it.
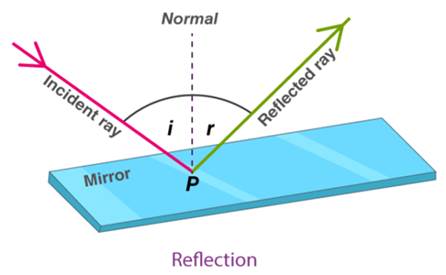
This enables us to see images. Take the example of a comb placed in front of a mirror over a dark coloured paper. Let a beam of light pass through the comb on the mirror using a torch. Then an image is observed similar to the one given:
We observe that the light gets reflected from this mirror and it travels in straight lines.
Revision Notes for CBSE Class 6 Science Chapter 11 – Free PDF Download
Our Class 6 Revision Notes will provide a quick glimpse of the chapter and improve the learning experience. We have made these revision notes keeping the convenience of students in mind so that it proves more effective. You can easily read these Class 6 notes just by clicking on the chapter names provided above.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.


Notes of Ch 11 Light, Shadows and Reflections Class 6th Science
Revision notes of ch 11 light, shadows and reflections class 6th science.
- Luminous objects
- Non-Luminous objects
- Transparent, Opaque and Translucent Objects
- Characteristics of light
- Shadow and its properties
- Pinhole camera
- Mirror and types of mirror
Contact Form
The Site is down as we are performing important server maintenance, during which time the server will be unavailable for approximately 24 hours. Please hold off on any critical actions until we are finished. As always your feedback is appreciated.

- Study Packages
- NCERT Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Online Test

- Questions Bank
- Light, Shadows and Reflections
- Test Series
- Ncert Solutions
- Solved Papers
- Current Affairs
- JEE Main & Advanced
- Pre-Primary
- MP State Exams
- UP State Exams
- Rajasthan State Exams
- Jharkhand State Exams
- Chhattisgarh State Exams
- Bihar State Exams
- Haryana State Exams
- Gujarat State Exams
- MH State Exams
- Himachal State Exams
- Delhi State Exams
- Uttarakhand State Exams
- Punjab State Exams
- J&K State Exams
6th Class Science Light, Shadows and Reflections Question Bank
Done light total questions - 100.

question_answer 1) Light is a form of energy produced by a
A) luminous object done clear
B) non-luminous object done clear
C) transparent object done clear
D) opaque object done clear
question_answer 2) Planets are example of
C) translucent object done clear
D) transparent object done clear
question_answer 3) Which of these conditions is/are essential for a shadows to be produced?
A) A light source done clear
B) An opaque object done clear
C) A screen/surface done clear
D) All of the above done clear
question_answer 4) An artificial source of light is
A) sun done clear
B) firefly done clear
C) jellyfish done clear
D) electric bulb done clear
question_answer 5) Which of these materials could produce a shadow?
A) A clear glass slab done clear
B) A milky white plastic done clear
C) Clear water done clear
D) A piece of wood done clear
question_answer 6) A.......... image can be obtained on a screen.
A) real done clear
B) virtual done clear
C) eract done clear
D) inverted done clear
question_answer 7) When a person sees himself in a mirror, what do his eyes observe?
A) A virtual image whose rays originate at the person. done clear
B) A virtual image formed from light that originate behind the mirror. done clear
C) Areal image whose rays appear to originate at the person. done clear
D) A real image whose rays originate behind the mirror. done clear
question_answer 8) The objects that cast shadow are
A) transparent done clear
B) translucent done clear
C) opaque done clear
D) luminous done clear
question_answer 9) What happen to light rays when they strike an uneven surface from same direction?
A) They are reflected in the same direction done clear
B) They are reflected in many directions done clear
C) They are absorbed by the surface done clear
D) They pass through the surface and are diffracted done clear
question_answer 10) If a student stand 3 m in front of a mirror, what is the distance between he and his image?
A) 1.5m done clear
B) 3m done clear
C) 6m done clear
D) 7.5m done clear
question_answer 11) Which of the following is/are the example(s) of a light reflector? 1. Fluorescent tube 2. A mirror 3. The moon
A) (1) only done clear
B) (3) only done clear
C) (1) and (2) only done clear
D) (2) and (3) only done clear
question_answer 12) Select the one that is a natural source of light.
A) Lighted fluorescent tube done clear
B) Red hot iron bar done clear
C) Sun done clear
D) Trees done clear
question_answer 13) Which of the following is a non-luminous body?
A) Sun done clear
B) Moon done clear
C) Stars done clear
D) All of these done clear
question_answer 14) To see a non-luminous object we need
A) light done clear
B) eyes done clear
C) Both of these done clear
D) None of these done clear
question_answer 15) Which of the following is a transparent substance?
A) Wooden blackboard done clear
B) Mirror done clear
C) A sheet of glass done clear
question_answer 16) Which of the following is translucent?
A) Oily paper done clear
B) Aluminium sheet done clear
C) Glass done clear
question_answer 17) "Speed of light is the same, no matter how it is measured" was first contemplated by
A) A.A. Michelson done clear
B) John Dalton done clear
C) Albert Einstein done clear
question_answer 18) If an object placed in the path of light allowed almost the whole of the light falling on it to pass through it, then the object is classified as
A) transparent done clear
B) translucent done clear
C) opaque done clear
question_answer 19) A shining star is
A) a natural source of light done clear
B) an artificial source of light done clear
C) a luminous body done clear
D) Both (a) and (c) done clear
question_answer 20) A translucent substance
A) allows most of light to pass through it done clear
B) allows a part of light to pass through it done clear
C) does not allow light to pass through it done clear
D) None of the above is correct done clear
question_answer 21) An image is formed on a screen when
A) a transparent object is placed between the screen and the source of light done clear
B) an opaque object is placed between the screen and the source of light done clear
C) Both the above are correct done clear
question_answer 22) In a pinhole camera, the image formed is
A) erect done clear
B) inverted done clear
C) smaller done clear
D) larger done clear
question_answer 23) Moon is a
A) luminous body done clear
B) non-luminous body done clear
C) neither luminous nor non-luminious done clear
question_answer 24) Which of the following are needed for formation of a shadow?
A) Source of light done clear
C) Screen done clear
question_answer 25) Does the shadow of an object always provide us correct information about the shape of the object?
A) Yes done clear
B) No done clear
C) Can't say done clear
D) All are incorrect done clear
question_answer 26) Which of the following will form a shadow similar to that formed by a thin note-book?
A) A rectangular box done clear
B) A circular box done clear
C) Both the above done clear
question_answer 27) Thick black paper is
A) transparent done clear
C) opaque done clear
question_answer 28) Following are some sources of light. Which of them is natural?
A) Moon done clear
B) Flame of candle done clear
C) Bulb done clear
D) Sun done clear
question_answer 29) Which tiny particles can be observed in a ray of light entering from a small gap of a window?
A) Oxygen done clear
B) Nitrogen done clear
C) Dust done clear
D) Water Vapours done clear
question_answer 30) Which of the following materials is most suitable for a solar electrical cell?
A) Iron done clear
B) Silicon done clear
C) Steel done clear
D) Aluminium done clear
question_answer 31) A solar cell converts ______
A) chemical Energy to light energy done clear
B) light energy to electrical energy done clear
C) electrical energy to light energy done clear
D) light energy to chemical energy done clear
question_answer 32) Tube light glass : Semi transparent :: Mirror glass: ______
A) Non-Luminous done clear
B) Transparent done clear
C) Reflector done clear
D) Opaque done clear
question_answer 33) Which of the following statement(s) is/are correct?
A) An oily paper is translucent done clear
B) The shadow formed by a coloured object will be coloured done clear
C) Black thick paper is transparent done clear
question_answer 34) Which of the following statement(s) is/are correct?
A) Light travels in straight lines done clear
B) Luminous objects emit their own light done clear
D) None of above done clear
question_answer 35) Which of the following statement(s) is/are correct?
A) The image formed in a pin hole camera is erect done clear
B) The image formed in a pin hole camera is not erect done clear
C) If we place a transparent object in the path of light the shadow formed will be much clearer done clear
D) None of these is correct done clear
question_answer 36) For the formation of shadow, essential conditions
A) There should be a source of light done clear
B) There should be a screen done clear
C) An opaque substance should be placed between the source of light and screen done clear
question_answer 37) An object that emits light of its own is
A) a luminous object done clear
B) a non-luminous object done clear
C) a source of light done clear
question_answer 38) Luminous objects
A) emit light during night time done clear
B) emit light during day time done clear
C) emit light of their own during day and night done clear
D) None of the above is correct. done clear
A) \[A\to (s);B\to (p);C\to (r);D\to (q)\] done clear
B) \[A\to (p);B\to (q);C\to (r);D\to (s)\] done clear
C) \[A\to (s);B\to (r);C\to (q);D\to (p)\] done clear
D) \[A\to (s);B\to (r);C\to (p);D\to (q)\] done clear
A) \[A\to (p);B\to (q);C\to (r);D\to (s)\] done clear
B) \[A\to (q);B\to (p);C\to (s);D\to (r)\] done clear
C) \[A\to (p);B\to (r);C\to (q);D\to (s)\] done clear
D) \[A\to (p);B\to (s);C\to (q);D\to (r)\] done clear
question_answer 41) DIRECTIONS: Read the passage (s) given below and answer the questions that follow. Passage-1 Luminous objects give off their own light, such as the sun and stars. Fireflies and glow-worms are luminous. Non-luminous object do not give off light or glow. Sun is a
A) non-luminous object done clear
B) luminous object done clear
C) transparent object done clear
question_answer 42) DIRECTIONS: Read the passage (s) given below and answer the questions that follow. Passage-1 Luminous objects give off their own light, such as the sun and stars. Fireflies and glow-worms are luminous. Non-luminous object do not give off light or glow. Fireflies is
A) a glowing object done clear
B) a deep sea fish done clear
C) both (a) and (b) done clear
D) neither (a) nor (b) done clear
question_answer 43) DIRECTIONS: Read the passage (s) given below and answer the questions that follow. Passage-1 Luminous objects give off their own light, such as the sun and stars. Fireflies and glow-worms are luminous. Non-luminous object do not give off light or glow. Non-luminous objects
A) have their own light done clear
B) are visible when they reflect the light fallen them from luminous objects done clear
C) do not give off light done clear
D) both (b) and (c) done clear
question_answer 44) DIRECTIONS: Read the passage (s) given below and answer the questions that follow. Passage-2 Take a comb in your right hand and bring it to your hair and look at yourself in mirror. You can see your own face in the mirror. This is your mirror image. In your mirror image you appear to be holding the comb in your
A) left hand done clear
B) right hand done clear
C) comb is not visible done clear
question_answer 45) DIRECTIONS: Read the passage (s) given below and answer the questions that follow. Passage-2 Take a comb in your right hand and bring it to your hair and look at yourself in mirror. You can see your own face in the mirror. This is your mirror image. The images of an object formed in a pin hole camera and that in a mirror are
A) quite similar done clear
B) quite different done clear
C) can't say done clear
question_answer 46) DIRECTIONS: Read the passage (s) given below and answer the questions that follow. Passage-2 Take a comb in your right hand and bring it to your hair and look at yourself in mirror. You can see your own face in the mirror. This is your mirror image. The image formed in a mirror is due to
A) reflection of light done clear
B) bending of light done clear
D) None of these done clear
question_answer 47) DIRECTIONS: The questions in this segment consists of two statements, one labelled as "Assertion" and the other labelled as "Reason R ". You are to examine these two statements carefully and decide if the Assertion A and Reason R are individually true and if so, whether the reason is a correct explanation of the assertion. Select your answers to these items using codes given below. Assertion: Shadow forms when light falls on a wooden block. Reason: Light is reflected when it bounces off surface.
A) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A. done clear
B) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A. done clear
C) A is true but R is false. done clear
D) A is false but R is true. done clear
question_answer 48) DIRECTIONS: The questions in this segment consists of two statements, one labelled as "Assertion" and the other labelled as "Reason R ". You are to examine these two statements carefully and decide if the Assertion A and Reason R are individually true and if so, whether the reason is a correct explanation of the assertion. Select your answers to these items using codes given below. Assertion: Solar and lunar eclipses are results of shadow formation. Reason: Sun is essential for shadow formation.
question_answer 49) DIRECTIONS: The questions in this segment consists of two statements, one labelled as "Assertion" and the other labelled as "Reason R ". You are to examine these two statements carefully and decide if the Assertion A and Reason R are individually true and if so, whether the reason is a correct explanation of the assertion. Select your answers to these items using codes given below. Assertion: Shadow is formed when an opaque object comes in the path of light. Reason: An opaque body does not allow any light to pass through it.
question_answer 50) DIRECTIONS: The questions in this segment consists of two statements, one labelled as "Assertion" and the other labelled as "Reason R ". You are to examine these two statements carefully and decide if the Assertion A and Reason R are individually true and if so, whether the reason is a correct explanation of the assertion. Select your answers to these items using codes given below. Assertion: When we look into the mirror, we see our own face inside the mirror. Reason: Mirror is made of a transparent substance that allows the light to pass through it.
question_answer 51) DIRECTIONS: The questions in this segment consists of two statements, one labelled as "Assertion" and the other labelled as "Reason R ". You are to examine these two statements carefully and decide if the Assertion A and Reason R are individually true and if so, whether the reason is a correct explanation of the assertion. Select your answers to these items using codes given below. Assertion: When the light from a source falls on a mirror it gets reflected. Reason: On being reflected there is no change in the direction of light.
question_answer 52) DIRECTIONS: The questions in this segment consists of two statements, one labelled as "Assertion" and the other labelled as "Reason R ". You are to examine these two statements carefully and decide if the Assertion A and Reason R are individually true and if so, whether the reason is a correct explanation of the assertion. Select your answers to these items using codes given below. Assertion: Mirror reflection gives clear images. Reason: Images are quite similar to shadows.
question_answer 53) DIRECTIONS: Read the following two statements carefully and choose the correct options. Statement-1: Light travels in a straight line. Statement-2: Light requires a medium to travel.
A) Statement (1) is correct while statement (2) is incorrect. done clear
B) Statement (2) is correct while statement (1) is incorrect. done clear
C) Both statements are correct done clear
D) Both statements are incorrect. done clear
A) erect and enlarged done clear
B) inverted and enlarged done clear
C) erect and diminished done clear
D) inverted and diminished done clear
A) Light Energy\[\to \]Chemical Energy\[\to \]Potential Energy done clear
B) Potential Energy\[\to \]Chemical Energy\[\to \]Kinetic Energy done clear
C) Solar Energy\[\to \] Chemical Energy\[\to \]Kinetic Energy done clear
D) Heat Energy\[\to \]Electrical Energy\[\to \]Mechanical Energy done clear
question_answer 57) What happens to a light beam when it passes through a translucent material such as waxed paper?
A) Most of the light passes through done clear
B) Light is reflected in its incident path done clear
C) Most of the light is absorbed and very little is reflected done clear
D) Light is not allowed to pass through done clear
question_answer 58) A boy of length 10 m, to see his own complete image, requires a plane mirror at least equal to:
A) 10m done clear
B) 5m done clear
C) 3.33m done clear
D) 2m done clear
question_answer 59) A plane mirror is in front of you in which you can see your image. It is approaching towards you at a speed of 10 cm/sec then at what speed will your image approach you?
A) 10 cm/sec done clear
B) 5 cm/sec done clear
C) 20 cm/sec done clear
D) 15 cm/sec done clear
question_answer 60) What kind of eclipse do we see when the moon is entirely within the Earth's umbral shadow?
A) Partial lunar done clear
B) Partial solar done clear
C) Total lunar done clear
D) Total solar done clear
question_answer 61) The size of a shadow of an opaque object close to the screen and away from the source of light
A) increases done clear
B) decreases done clear
C) remains the same done clear
D) first decreases then increases done clear
question_answer 62) What happens to the image produced by a pinhole camera when you move the back wall farther from the pinhole? It becomes
A) larger and fainter done clear
B) smaller and fainter done clear
C) larger and brighter done clear
D) smaller and brighter done clear
question_answer 63) A girl holding a ball in her right hand is standing in front of a mirror. The ball will seems to be in her
A) right hand done clear
B) left hand done clear
C) depend on distance between girl and mirror done clear
D) depend on size of mirror done clear
question_answer 64) Non-luminous bodies become visible when they..........light.
A) reflect done clear
B) radiate done clear
C) refract done clear
D) none of these done clear
question_answer 65) Which is the safest way to view a solar eclipse?
A) Using a solar filter done clear
B) A pinhole filter done clear
C) Binoculars or telescope done clear
question_answer 66) What is the correct alignment during a solar eclipse?
A) Sun, Moon, Earth done clear
B) Moon, Sun, Earth done clear
C) Sun, Earth, Moon done clear
question_answer 67) Select the objects that use reflection of light
A) a mirror fixed on your dressing table done clear
B) the side mirror of your car done clear
C) a periscope done clear
question_answer 68) We can classify fog as
A) transparent substance done clear
B) opaque substance done clear
C) translucent substance done clear
question_answer 69) If we stand in front of a mirror with comb in our right hand, we will see that the image formed shows the comb in our
C) either right hand or left hand done clear
D) sometimes in right hand and sometimes in left hand done clear
question_answer 70) Select the one that gives a clear reflection of ourselves
A) stationary surface of clear water done clear
B) well polished surface of shoes done clear
C) smooth cushion surface done clear
question_answer 71) A student was asked to observe the night sky and note down various objects observed by him in his note book. He listed the following objects (i) Stars (ii) Moon (iii) Clouds From amongst the above the sources of light in night sky are
A) only done clear
B) (ii) only done clear
C) (iii) only done clear
D) and (ii) done clear
question_answer 72) When light falls on an opaque object
A) it gets reflected and reaches our eye done clear
B) it passes through the object done clear
C) the opaque object sends a signal to our eye that enables us to see the object done clear
question_answer 73) A tracing paper is a
B) transluscent substance done clear
C) opaque substance done clear
D) can't say done clear
question_answer 74) I have kept an object in my hand and through it tried to look at a lighted torch held against it. Nothing except a faint glow out lining the object is visible. The object in my hand is
A) transparent done clear
B) transluscent done clear
C) opaque done clear
question_answer 75) Periscope, a device used in U-boats, makes use of
A) reflection of light done clear
B) refraction of light done clear
C) shadow formation by opaque objects done clear
question_answer 76) What happens when lightning occurs?
A) Light comes from sun to cloud done clear
B) Light comes from cloud to earth done clear
C) Electric current flows in atmosphere done clear
D) Electric current flows from sun to cloud done clear
question_answer 77) Which of the following statement(s) is/are correct?
A) Shadows are formed on the same side as the light source done clear
B) Shadows are formed on the opposite side to the light source done clear
C) Shadows give us an exact idea of the shape of the object done clear
question_answer 78) Which of the following statement(s) is/are correct?
A) A shadow is formed when an opaque object comes in the path of light done clear
B) For the formation of shadow we need and opaque object and a source of light only done clear
C) The colour of shadow of an object will be different when seen in light coming from different sources done clear
D) All the above are correct. done clear
question_answer 79) An object that does not emit light of its own but is visible due to the light from a source of light falling on it, is
C) either luminous or non-luminous done clear
question_answer 80) Moon is considered a non-luminous object as
A) it emits light only during night done clear
B) it does not emit its own light done clear
C) it is visible during night only done clear
D) All the above are correct done clear
question_answer 81) Transluscent body is one that
A) allows almost whole of light to pass through it done clear
B) allows light to pass through it only partly done clear
C) through which we can see objects clearly done clear
question_answer 82) The image formed by a pinhole camera is inverted because
A) light travels in straight lines done clear
B) on passing through a pin hole camera there occurs a lateral inversion in the rays of light done clear
C) light rays get reflected in a pin hole camera done clear
question_answer 83) For making a periscope, the number of mirrors needed is
A) 1 done clear
B) 2 done clear
C) 3 done clear
D) 4 done clear
question_answer 84) A handicapped person has three fingers and has no thumb in his left hand but his right hand has four fingers as also the thumb. He holds a mirror in his right hand and looks at this own image in a mirror. In the mirror image he will appear as holding his comb with
A) three fingers done clear
B) four fingers done clear
C) none of these done clear
D) can't say done clear
A) \[A\to (p);B\to (q);C\to (r);D\to (s)\] done clear
B) \[A\to (p);B\to (r);C\to (s);D\to (q)\] done clear
C) \[A\to (q);B\to (p);C\to (r);D\to (s)\] done clear
D) \[A\to (s);B\to (p);C\to (q);D\to (r)\] done clear
B) \[A\to (q);B\to (r);C\to (s);D\to (p)\] done clear
C) \[A\to (q);B\to (s);C\to (p);D\to (r)\] done clear
D) \[A\to (r);B\to (p);C\to (q);D\to (s)\] done clear
A) umbra done clear
B) penumbra done clear
C) source done clear
D) curved path done clear
A) umbra done clear
A) Moon done clear
B) Sun done clear
C) Earth done clear
A) used in U-boats done clear
B) that makes use of reflection of light done clear
A) that uses reflections to see around corners done clear
B) that uses the property of light that light travels in straight lines done clear
A) Kaleidoscope done clear
B) Periscope done clear
C) Both of the above done clear
question_answer 93) DIRECTIONS: The questions in this segment consists of two statements, one labelled as "Assertion A" and the other labelled as "Reason R". You are to examine these two statements carefully and decide if the Assertion A and Reason Rare individually true and if so, whether the reason is a correct explanation of the assertion. Select your answers to these items using codes given below. Assertion: Shadow is always black. Reason: A shadow only shows the outline of an object.
question_answer 94) DIRECTIONS: The questions in this segment consists of two statements, one labelled as "Assertion A" and the other labelled as "Reason R". You are to examine these two statements carefully and decide if the Assertion A and Reason Rare individually true and if so, whether the reason is a correct explanation of the assertion. Select your answers to these items using codes given below. Assertion: Image has the colour of the object. Reason: Image gives only the outline of the object.
question_answer 95) DIRECTIONS: The questions in this segment consists of two statements, one labelled as "Assertion A" and the other labelled as "Reason R". You are to examine these two statements carefully and decide if the Assertion A and Reason Rare individually true and if so, whether the reason is a correct explanation of the assertion. Select your answers to these items using codes given below. Assertion: In cars the windshields made of glass are used. Reason: Those substances through which things can be seen clearly are called transparent substances.
question_answer 96) DIRECTIONS: Read the following three statements carefully and choose the correct option. Statement - 1: The length of shadow formed by sunlight remains constant with time. Statement - 2: The speed of light in air is \[3\times {{10}^{8}}\text{m/s}\text{.}\]. Statement - 3: Speed of light remains same in all medium.
A) Statement (1) and (3) are incorrect while statement (2) is correct. done clear
B) Statement (1) and (2) are incorrect while (3) is correct. done clear
C) All the statements are correct. done clear
D) All the statements are incorrect. done clear
A) Regular reflection done clear
B) Diffuse reflection done clear
C) Dispersion done clear
D) Refraction done clear
A) umbra done clear
C) dark region done clear
D) None of these done clear
A) Become large done clear
B) Remain same done clear
C) Become small done clear
D) Get distorted done clear
A) The source of light is not a strong source done clear
B) It is not night time done clear
C) The tumbler is made of transparent material done clear
Study Package

Question - Light
Related question.

Reset Password.
OTP has been sent to your mobile number and is valid for one hour
Mobile Number Verified
Your mobile number is verified.

- Book Solutions
- State Boards
Class 6 Science Case Study Question
Case study question class 6 science (cbse / ncert board).
Class 6 Science Case Study Question and Answer: CBSE / NCERT Board Class 6 Science Case Study Question prepared by expert Science Teacher. Students can learn Case Based Question / Paragraph Type Question for NCERT Class 6 Science.
There are total 16 chapter Food Where Does It Come From, Components of Food, Fibre to Fabric, Sorting Materials Into Groups, Separation of Substances, Changes Around Us, Getting to Know Plants, Body Movements, The Living Organisms and Their Surroundings, Motion and Measurement of Distances, Light Shadows and Reflection, Electricity and Circuits, Fun with Magnets, Water, Air Around Us, Garbage In Garbage Out.
For any problem during learning any Case or any doubts please comment us. We are always ready to help You.
CBSE Class 6 Science Case Study Question
Chapter 1 Food Where Does It come From Case Study Question
Chapter 2 Components of Food Case Study Question
Chapter 3 Fibre to Fabric Case Study Question
Chapter 4 Sorting Materials Into Groups Case Study Question
Chapter 5 Separation of Substances Case Study Question
Chapter 6 Changes Around Us Case Study Question
Chapter 7 Getting to Know Plants Case Study Question
Chapter 8 Body Movements Case Study Question
Chapter 9 The Living Organisms – Characteristics and Habitats Case Study Question
Chapter 10 Motion and Measurement of Distances Case Study Question
Chapter 11 Light Shadows and Reflection Case Study Question
Chapter 12 Electricity and Circuits Case Study Question
Chapter 13 Fun with Magnets Case Study Question
Chapter 14 Water Case Study Question
Chapter 15 Air Around Us Case Study Question
Chapter 16 Garbage In Garbage Out Case Study Question
What is Case Study Question?
Ans. At case Study there will one paragraph and on the basis of that concept some question will made. Students have to solve that question.
How many marks will have at case based question?
Most of time 5 questions will made from each case. There will 1 or 2 marks for each question.
Important links:
- Lakhmir Singh Class 6 Book Solution
- NCERT Solution Class 6 Science
Sign in to your account
Username or Email Address
Remember Me
Question and Answer forum for K12 Students

MCQ Questions for Class 6 Science Chapter 11 Light Shadows and Reflection with Answers
We have compiled the NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 6 Science Chapter 11 Light Shadows and Reflection with Answers Pdf free download covering the entire syllabus. Practice MCQ Questions for Class 6 Science with Answers on a daily basis and score well in exams. Refer to the Light Shadows and Reflection Class 6 MCQs Questions with Answers here along with a detailed explanation.
Light Shadows and Reflection Class 6 MCQs Questions with Answers
Choose the correct option.
Question 1. Which one of the following is the natural source of light? (a) Electric bulb (b) Sun (c) Tube light (d) Moon
Answer: (b) Sun

Question 2. The object which does not have light of its own is (a) shining mirror (b) light bulb (c) star (d) lighted match box
Answer: (a) shining mirror

Question 3. Stars are (a) luminous (b) non-luminous (c) both of these (d) none of these
Answer: (a) luminous
Question 4. A torch is a (a) luminous (b) non-luminous (c) both of these (d) none of these
Question 5. Which of the following is a non-luminous object? (a) Torch (b) Sun (c) Electric light (d) Chair
Answer: (d) Chair
Question 6. Objects that do not give out or emit light of their own are called (a) luminous (b) non-luminous (c) opaque (d) translucent
Answer: (b) non-luminous
Question 7. Which of the following is a luminous object? (a) Pencil (b) Chair (c) Sun (d) Table
Answer: (c) Sun
Question 8. The objects which allow light to pass through them are called (a) transparent (b) opaque (c) translucent (d) none of these
Answer: (a) transparent
Question 9. Air is (a) transparent (b) translucent (c) both of these (d) none of these
Question 10. Glass sheet is a/an (a) transparent object (b) opaque object (c) transparent object (d) none of these
Answer: (c) translucent
Question 11. Substances through which light can pass partially and things cannot be seen clearly through them are (a) transparent (b) opaque (c) translucent (d) none of these
Question 12. Which of the following are transparent or allows light to pass through it? (a) Rubber (b) Glass (c) Copper (d) Wood
Answer: (b) Glass
Question 13. Solid wax is (a) transparent (b) translucent (c) opaque (d) none of these
Answer: (c) opaque
Question 14. Objects which does not allow light to pass through them are called (a) opaque objects (b) transparent objects (c) translucent objects (d) none of these
Answer: (a) opaque objects
Question 15. A mirror is an example of (a) transparent object (b) opaque object (c) translucent (d) none of these
Answer: (b) opaque object
Question 16. Which is an example of a translucent object? (a) A thin glass sheet (b) A thin paper sheet (c) A thin iron sheet (d) A thin wooden sheet
Question 17. Light travels in (a) a curved line (b) a random way (c) a straight line (d) a zig-zag line
Answer: (c) a straight line
Question 18. Which types of objects do not allow light to pass through them? (a) Transparent (b) Translucent (c) Opaque (d) None of these
Answer: (c) Opaque
Question 19. When an opaque object comes in the way of light it makes (a) a shadow (b) a coloured image (c) a black and white image (d) no image
Answer: (a) a shadow
Question 20. The image formed in water is (a) inverted (b) erect (c) long (d) diminished
Answer: (b) erect
Question 21. The shape of shadow depends upon the (a) shape of the object (b) size of the object (c) size of source of light (d) colour of the source light
Answer: (a) shape of the object
Question 22. The position of the shadow changes with (a) the position of the light source (b) the movement of the light source (c) both (a) and (b) (d) none of these
Answer: (c) both (a) and (b)
Question 23. Image formed by plane mirror is (a) inverted (b) erect (c) erect but laterally inverted (d) none of these
Answer: (c) erect but laterally inverted
Question 24. Image formed by a pinhole camera is (a) erect (b) inverted (c) sometimes erect, sometimes inverted (d) none of these
Answer: (b) inverted
Question 25. The pinhole image of the sun is (a) circular (b) long (c) sometimes long sometime circular (d) none of these
Answer: (a) circular
Question 26. Shadow of an object is (a) dark (black) (b) blue (c) red (d) depends on the colour of object
Answer: (a) dark (black)
Question 27. Shadow gives information about (a) shape of the light source (b) size of object (c) surface (d) shape of object
Answer: (d) shape of object
Question 28. The formation of shadow of one celestial body on the other is known as (a) image (b) reflection (c) eclipse (d) none of these
Answer: (c) eclipse
Question 29. The ray of light that falls on a plane mirror is called (a) reflected ray (b) incident ray (c) both (a) and (b) (d) none of these
Answer: (b) incident ray
Question 30. When a light ray returns back after striking the surface of the plane mirror is called (a) reflected ray (b) incident ray (c) both (a) and (b) (d) none of these
Answer: (a) reflected ray
Question 31. Air and water are (a) transparent objects (b) translucent objects (c) opaque objects (d) none of these
Answer: (a) transparent objects
Question 32. Stars are (a) luminous (b) non-luminous (c) both of these (d) none of these
Question 33. The material which allows light to pass through it is (a) copper (b) wood (c) rubber (d) glass
Answer: (d) glass
Question 34. Shadow of an object is always (a) blue (b) red (c) white (d) black
Answer: (d) black
Question 35. The object that does not give out light on its own is the (a) star (b) lighted match-stick (c) light bulb (d) shining mirror
Answer: (d) shining mirror
Question 36. Light travels in a (a) curved line (b) straight line (c) circle (d) none of these
Answer: (b) straight line
Question 37. Natural luminous object among the following is (a) planets (b) moon (c) sun (d) all of these
Answer: (c) sun
Question 38. Shadows give us information about the (a) size of object (b) shape of object (c) surface (d) all of these
Answer: (b) shape of object
Question 39. Plywood sheet is a/an (a) transparent object (b) translucent object (c) opaque object (d) none of these
Answer: (c) opaque object
Question 40. The ray of light that falls on a plane mirror is called (a) reflection (b) reflected ray (c) incident ray (d) beam of ray
Answer: (c) incident ray
Fill in the Blanks
Question 1. __________ helps us to see objects.
Answer: Light
Question 2. Objects that give out or emit light of their own are called __________ objects.
Answer: luminous
Question 3. Objects that do not have light of their own are called __________ objects.
Answer: non-luminous
Question 4. Substances which allow light to pass through them are called _________ objects.
Answer: transparent
Question 5. The darkness that an object cause when it prevents light to pass through is called _________
Answer: shadow
Question 6. Image formed by a plane mirror is _________
Answer: erect
Question 7. Image formed by a pinhole camera is _________ down.
Answer: upside
Question 8. Light travels in a _________ line.
Answer: straight
Question 9. Plastic is opaque but glass is _________
Question 10. The image formed by a mirror is due to _________ of light.
Answer: reflection
Question 11. Shadows are formed when an _________ object comes in the path of light.
Answer: opaque
Question 12. The phenomenon due to which light returns back after striking a highly polished surface is called _________ of light.
Question 13. The working of a pinhole camera is based on the property of _________ propagation of light.
Answer: rectilinear
Question 14. A shadow is always __________ while the image shows true colours of the object.
Answer: black
Question 15. The size of a shadow is relative to the __________ of source of light with respect to the object.
Answer: position
Question 16. In a plane mirror our left hand looks like right hand. This phenomenon is known as _________
Answer: lateral inversion
Question 17. We are able to see the things around us due to …………………….
Answer: light
Question 18. Butter paper is a ……………………. object.
Answer: translucent
Question 19. ……………………. objects do not allow light to pass through them.
Question 20. The position of the shadow changes with the ……………………. of the object.
Answer: movement
Question 21. All shadows caused by the sun are made of ……………………. and …………………….
Answer: umbra, penumbra
Question 22. In pinhole camera, the image is free from spherical and ……………………. aberrations.
Answer: chromatic
Question 23. The glass sheet of plane mirror offers a ……………………. surface.
Answer: smooth
Question 24. The image which cannot be projected on to a screen is called ……………………. image.
Answer: virtual
Question 25. Cellophane sheet is ……………………. while tracing paper is …………………….
Answer: transparent, translucent
Question 26. All the planets and the moon are the ……………………. of light.
Answer: reflectors
True or False
Question 1. A mirror reflects a beam of light.
Answer: True
Question 2. A blackboard is a luminous object.
Answer: False
Question 3. The image formed by a pinhole camera is erect.
Question 4. The moon is a non-luminous body.
Question 5. Wax paper is a transparent object.
Question 6. Torch is a luminous object.
Question 7. Black thick paper is translucent.
Question 8. The shadow of a coloured object is also coloured.
Question 9. Mirror does not change the direction of light that falls on it.
Question 10. A shadow is formed when a transparent object comes in the way of light.
Question 11. The image formed by a plane mirror is erect but laterally inverted.
Question 12. The pinhole image of the sun is rectangular.
Question 13. All opaque objects do not cast shadows.
Question 14. A firefly is a luminous body.
Question 15. The dark patches formed behind an opaque object when it does not allow light to pass through it are called shadows.
Question 16. The objects which do not allow light to pass through them are called translucent objects.
Question 17. Shadows do not give us any information about the shapes of objects.
Question 18. The colour of opaque objects affect the dark colour of the shadow.
Question 19. Light travels in a curved line. This property of light is called rectilinear propagation of light.
Question 20. The light ray which returns after striking a smooth surface is called incident ray.
Question 21. Moon has its own light.
Question 22. Air and water are translucent objects.
Question 23. Dark patches are produced when light is stopped by opaque objects.
Question 24. The formation of shadow shows that light travels in a straight line.
Question 25. The part of the shadow which occurs in the centre is called penumbra.
Question 26. Sun rays falling on a flying bird form shadow in space.
Question 27. Focusing in required in a pinhole camera.
Question 28. Pinhole camera is used to study the moving objects also.
Question 29. The plane mirror shines due to the silver coating.
Question 30. A pinhole camera uses a lens to form a real and inverted image.
Match the items given in column I suitably with those given in column II.
Hope the information shed above regarding NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 6 Science Chapter 11 Light Shadows and Reflection with Answers Pdf free download has been useful to an extent. If you have any other queries of CBSE Class 6 Science Light Shadows and Reflection MCQs Multiple Choice Questions with Answers, feel free to reach us so that we can revert back to us at the earliest possible.
- NCERT SOLUTIONS
- CHAPTER NOTES
- PRIVACY POLICY

- RD SHARMA SOLUTIONS
- IIT JEE SOLVED QUESTIONS
Class 6th Science Chapter 11 Light Shadows and Reflection

About STUDYGUIDE360 STUDYGUIDE360 is a student centric educational web portal which provides quality test papers and study materials for the students preparing for CBSE or targeting various entrance exams. During past few years, a number of surveys on students were made to better understand their problems regarding their studies and their basic requirement.
LIKE US ON FACEBOOK
Contact form.
- NCERT Exemplar
- NCERT Exemplar Class 6
- NCERT Exemplar Class 6 Science
- Class 6 Science Chapter 11
NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 11 - Light
NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 11 Light help students understand all the important concepts covered in the chapter easily and clearly, which helps in building a strong foundation in the subject. From the exam point of view, the solutions are provided in a simple manner where students can secure excellent scores by practising the NCERT Exemplar Class 6 Science solutions. To know more about these concepts, students can download the solutions in PDF and practise offline as well.
Chapter 11 – Light provides answers to all the questions related to each and every concept covered in this chapter. This chapter deals with light and the reflection of an object. Students can prepare for their examinations in a more effective manner using these NCERT Exemplar Class 6 Science solutions, as they help to crack twisted questions easily. The solutions are available in PDF, which can be easily downloaded for free from the link given below.
Download the PDF of NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 11 – Light

Access answers to NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 11 – Light
Multiple-choice Questions:
1. Observe the picture given in fig 11.1 carefully.

A patch of light is obtained at B, when the torch is lighted, as shown. Which of the following is kept at position A to get this patch of light? (b) A glass sheet (c) A mirror (d) A sheet of white paper, Solution:
(c): Mirror
Only a mirror can reflect a patch of light and change its direction.
2. A student observes a tree given in figure through a pinhole camera. Which of the diagrams given in figures (a) to (d) depicts the image seen by her correctly?

(b): Option (b) depicts the image seen by the student correctly
She will observe the upside-down image of the tree with lateral inversion.
3. Four students, A, B, C and D, looked through pipes of different shapes to see a candle flame as shown in fig 11.4.

Who will be able to see the candle flame clearly? (a) A (b) B (c) C (d) D Solution:
Light travels in a straight line.
4. Which of the following is/are not always necessary to observe a shadow? (a) Sun (b) Screen (c) Source of light (d) Opaque object Solution:
Sun is not always necessary to observe a shadow.
Sun is a source of light. Any source of light can replace it like, torch etc.
5. Paheli observed the shadow of a tree at 8:00 a.m., 12:00 noon and 3:00 p.m. Which of the following statements is closest to her observation about the shape and size of the shadow? (a) The shape of the shadow of the tree changes, but the size remains the same. (b) The size of the shadow of the tree changes, but the shape remains the same. (c) Both the size and shape of the shadow of the tree change. (d) Neither the shape nor the size of the shadow changes. Solution:
(c): Both the size and shape of the shadow of the tree change.
The Sun being the source of light, changes its position at different points of time. So, accordingly, the size and shape of the shadow of the tree change.
6. Which of the following can never form a circular shadow? (a) A ball (b) A flat disc (c) A shoe box (d) An ice cream cone Solution:
(c): A shoe box
A shoebox is either rectangle or square in shape.
7. Two students, while sitting across a table, looked down on its top surface. They noticed that they could see their own and each other’s image. The table top is likely to be made of (a) Unpolished wood (b) Red stone (c) Glass sheet (d) Wood top covered with cloth Solution:
(c): Glass sheet
Only the glass sheet can reflect light properly in order to form their images.
Very Short Answer Questions:
8. You have 3 opaque strips with very small holes of different shapes, as shown in fig 11.5. If you obtain an image of the sun on a wall through these holes, will the image formed by these holes be the same or different?

All these three objects form the same images. These opaque strips will act as pinholes and image of the sun will be obtained on the wall.
9. Observe the picture given in fig 11.6. A sheet of some material is placed at position ‘P’, still the patch of light is obtained on the screen. What is the type of material of this sheet?

Light passes through only transparent material hence, sheet P must be of transparent material as it allows light to pass through it.
10. Three torches A, B and C, shown in fig 11.7 are switched on one by one. The light from which of the torches will not form a shadow of the ball on the screen.

We know that light travels in a straight line. The light from torch C will not form a shadow of the ball on the screen. Since torch C is placed parallel to the screen light cannot pass through the screen.
11. Look at the given figure.

Will there be any difference in the shadow formed on the screen in A and B? Solution:
No, shadows formed on screens A and B will be the same.
12. Correct the following statements. (i) The colour of the shadow of an object depends on the colour of the object. (ii) Transparent objects allow light to pass through them partially. Solution:
(i) No, the colour of the object does not depend on the colour of the shadow since the shadow is usually dark in colour.
(ii) Transparent objects allow most of the light to pass through them. Translucent objects allow light to pass through them partially.
13. Suggest a situation where we obtain more than one shadow of an object at a time. Solution:
At a time, we can obtain more than one shadow of an object if the light from more than one source falls on it.
For example: In a cricket stadium, we can observe multiple shadows of players since the light falls on them from different directions.
14. On a sunny day, does a bird or an aeroplane flying high in the sky cast its shadow on the ground? Under what circumstances can we see their shadow on the ground? Solution:
No, a bird or an aeroplane flying high in the sky cannot cast its shadow on the ground even on a sunny day because they are flying at a higher altitude where the object cannot obtain its shadow.
We can only see their shadow on the ground if they are flying very close to the ground.
15. You are given a transparent glass sheet. Suggest any two ways to make it translucent without breaking it. Solution:
A transparent glass sheet can be made into a translucent glass sheet without breaking it by:
(i) Applying oil, grease, butter on it or pasting a butter paper on it.
(ii) Rubbing the surface of the glass by any abrasive material like sandpaper on it.
16. A torch is placed at two different positions A and B, one by one, as shown in fig. 11.9.

The shape of the shadow obtained in two positions is shown in fig. 11.10.

Match the position of the torch and shape of the shadow of the ball. Solution:
Position A will form the shadow ‘a’.
Position B will form the shadow ‘b’.
As the position of torch changes, we can observe the change in the shape of the shadow.
17. A student covered a torch with red cellophane sheet to obtain red light. Using the red light, she obtains a shadow of an opaque object. She repeats this activity with green and blue light. Will the colour of the light affect the shadow? Explain. Solution:
No, the colour of light will not affect the shadow because the shadow is usually dark or black patch formed when an object obstructs the path of light and hence no light reaches in the shadow region.
18. Is the air around us always transparent? Discuss. Solution:
Yes, the air around us is transparent, which makes things visible to our eyes. When thick smoke/ thick clouds, etc. are present in the air it does not remain transparent it makes visibility difficult.
19. Three identical towels of red, blue and green colours are hanging on a clothes line in the sun. What would be the colour of shadows of these towels? Solution:
Shadow is usually dark or black in colour. Hence, the colour of shadows of all the three towels will remain same as no light passes through them.
20. Using a pinhole camera a student observes the image of two of his friends, standing in sunlight, wearing yellow and red shirt respectively. What will be the colours of the shirts in the image? Solution:
Pinhole camera does not change the colour of the image. The colours of the shirts in the image will remain the same as the colour of the shirt. But the image of the person will be inverted when seeing through a pinhole camera.
21. In fig 11.11, a flower made of thick coloured paper has been pasted on the transparent glass sheet. What will be the shape and colour of shadow seen on the screen?

The shadow formed will be of the shape of a flower along with the stalk and the shadow will be dark in colour.
Long Answer Questions:
22. A football match is being played at night in a stadium with floodlights ON. You can see the shadow of a football kept at the ground but cannot see its shadow when it is kicked high in the air. Explain. Solution:
We can see the shadow of football lying on the ground because the ground acts as a screen for it. However, when the football is kicked high into the air it will be away from the ground, the shadow disappears with height hence we cannot see the shadow of the football when it is in air.
23. A student had a ball, a screen and a torch in working condition. He tried to form a shadow of the ball on the screen by placing them in different positions. Sometimes the shadow was not obtained. Explain. Solution:
Some of the reasons why shadow was not obtained can be
(i) The screen is far away from the ball.
(ii) The beam of light from the torch is falling parallel to the screen on the ball.
(iii) The torch is kept away from the ball.
24. A sheet of plywood, a piece of muslin cloth and that of a transparent glass, all of the same size and shape were placed at A one by one in the arrangement shown in fig 11.12. Will the shadow be formed in each case? If yes, how will the shadow on the screen be different in each case? Give reasons for your answer.

Shadow will not be formed in any of the cases. Only the piece of muslin cloth and the sheet of plywood will cast a shadow on the screen.
(i) The piece of muslin cloth will form a lighter shadow as it allows light to pass through it partially.
(ii) The sheet of plywood will form a dark shadow as it blocks the path of light completely.
(iii) The transparent glass will allow most of the light to pass through it. So, no shadow will be obtained on the screen.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

Have an account?

Class 6 - Light, Shadows & Reflection
20 questions

Introducing new Paper mode
No student devices needed. Know more
Which of the following does not have light of its own?
When the Sun is behind you, your shadow is ...
in front of you
at the side of you
12.Translucent is?
When light bounces off an object
Material that only allows a little light to pass through
Our main source of light
Material that allows light to pass through
Light made by nature
Material that allows no light to pass through
What is the main source of light?
When an object moves closer to a light source, its shadow...
Gets smaller
Gets bigger
Changes shape
Stays the same size
Why do shadows made by the Sun move throughout the day?
Because the weather changes
Because someone moves the objects
Because the sun appears to move across the sky
Because it's magic!
Shadows are longest during _______.
morning and evening
Where will the tree's shadow be?
- 10. Multiple Choice Edit 30 seconds 1 pt Which is NOT a source of light? firefly ball sun falshlight
- 11. Multiple Choice Edit 30 seconds 1 pt Which source of light is natural? firworks lightbulb lightning headlights
We can see things around us because of light reflecting off the object and into our eyes?
- 14. Multiple Choice Edit 1 minute 1 pt Which will make the darkest shadow? Light shining on a... sheet of thin tissue paper glass window wooden chopping board none of the above
- 15. Multiple Choice Edit 1 minute 1 pt What does reflection mean? Light bouncing off an object. Light is bending around an object. Light is moving through and object. This is no light.
Which colours reflect more light?
Bright colours
Dark colours
Why does the cat form a shadow?
It reflects light
It blocks light
What is the best explanation for Mickey seeing himself in the mirror?
There is light on the Earth even on a dark, cloudy day. This is because clouds are:
Transparent
Translucent
- 20. Multiple Choice Edit 30 seconds 1 pt Which source of light is natural? firworks lightbulb lightning headlights
Explore all questions with a free account

Continue with email
Continue with phone

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
[Download] Case Study Questions for Class 6 Science Chapter 11 Light Shadow and Reflection. Here we are providing case study or passage-based questions for class 6 science chapter 11 Light Shadow and Reflection. Case Study/Passage Based Questions. Passage-1. Take a comb in your right hand and bring it to your hair and look at yourself in mirror.
The Case Based Questions: Light, Shadows & Reflections is an invaluable resource that delves deep into the core of the Class 6 exam. These study notes are curated by experts and cover all the essential topics and concepts, making your preparation more efficient and effective.
Answer: (a) The shadow of the pencil will be small when the pencil is taken close to the wall and away from the candle. (b) The shadow will be big in size when the pencil is taken closer to the candle. (c) To get the same sized shadow as the pencil is, adjust the distance between the wall, pencil and candle at equal distances. CBSE Class 6 ...
NCERT Extra Questions for Class 6 Science Chapter 11 Light Shadows and Reflection. Transparent Opaque And Transculent Objects. Question 1. Define luminous body. Answer: The objects which emit light of their own are called luminous bodies, e.g., the sun, the stars, etc. Question 2.
1. Used as a rear mirror 2. Security mirrors 3. Surveillance mirror. Light, Shadows and Reflections Class 6 Chapter 11 Science Notes help students to understand the concepts in an easier way and it also includes important questions on the exam point of view.
NCERT Exemplar Problems Class 6 Science Chapter 11 Light Shadows and Reflection. Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) ... the East directions, respectively. However, at 12:00 noon, the sun will be high in the sky just above the tree, so the shadow of tree will be short. Question 6: ... Most of the light in case of muslin cloth will be reflected. So ...
The object must be placed in the path of light. Then shadow is formed on the screen. 7. Define reflection of light. Ans: When light rays after striking the smooth and shiny surface return to same medium, this phenomenon is called reflection of light. 8. Write difference between shadow and image. Ans: 9.
The object must be placed in the path of light. Then shadow is formed on the screen. 7. Define reflection of light. Answer: When light rays after striking the smooth and shiny surface return to same medium, this phenomenon is called reflection of light. 8. Write difference between shadow and image.
Light shadow and reflection Class 6 PDF is now available for Class 6 Science Chapter 11. The PDF file contains proper explanations, images, questions and answers of Chapter 11, Light Shadow & Reflection. The explanation of the subjects has been provided in a way students receive teachings from his/her private tutors.
Study Important Questions for Class 6 Science Chapter 11 - Light Shadows and Reflections. Very Short Answer Questions: 1 Mark. Define the following: 1. Luminous objects. Ans: Luminous items are those that can produce their own light. Luminous items include the sun, star, moon, lit candle, and so on. 2.
Match the position of the torch and shape of the shadow of the ball. Solution: A → a; B → b. As the position of torch changes, we can observe the change in shape of shadow. Question 17. A student covered a torch with red cellophane sheet to obtain red light. Using the red light she obtains a shadow of an opaque object.
Chapter 11 "Light, Shadows and Reflection" of Class 6 Science is based on the concept of light and shadows and everything regarding that. An eclipse is defined as the overshadowing of a bright object, or a shadow in space that renders the sun and the moon invisible for a while. An eclipse is of two types - solar and lunar.
Light Shadows and Reflections Class 6 Notes Science Chapter 11. Introduction. Light is a form of energy which helps us in seeing objects. When light falls on an object, some of the light gets reflected. The reflected light comes to our eyes and we are able to see an object. Sources of Light.
Access Answers of NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 11 Light, Shadows and Reflections. Exercise Questions. 1. Rearrange the boxes given below to make a sentence that helps us understand opaque objects. Solution: The given boxes can be rearranged to form 'Opaque Objects Make Shadows' as shown below. 2.
Revision Notes of Ch 11 Light, Shadows and Reflections Class 6th Science. → It is a form of energy which is responsible for seeing objects. → When light falls on an object, some light get reflected, this reflected light come to our eyes and we are able to see an object. (i) Luminous object: The objects which emit their own light is called ...
question_answer 95) DIRECTIONS: The questions in this segment consists of two statements, one labelled as "Assertion A" and the other labelled as "Reason R". You are to examine these two statements carefully and decide if the Assertion A and Reason Rare individually true and if so, whether the reason is a correct explanation of the assertion.
Chapter 6 Changes Around Us Case Study Question. Chapter 7 Getting to Know Plants Case Study Question. Chapter 8 Body Movements Case Study Question. Chapter 9 The Living Organisms - Characteristics and Habitats Case Study Question. Chapter 10 Motion and Measurement of Distances Case Study Question. Chapter 11 Light Shadows and Reflection Case ...
Refer to the Light Shadows and Reflection Class 6 MCQs Questions with Answers here along with a detailed explanation. ... When an opaque object comes in the way of light it makes (a) a shadow (b) a coloured image (c) a black and white image (d) no image. ... Question 28. Pinhole camera is used to study the moving objects also. Answer. Answer ...
CBSE Class 6 Science Notes Chapter 11 Light, Shadows and Reflection. Source of light: An object which emits light, is called a source of light. For example, sun, torch, etc. Non-luminous objects: These are the objects which do not emit light of their own. Such a body becomes visible when light falls on it. For example, the moon, the planets, etc.
Answer: An object which does not have its own light is called a non-luminous object, e.g., chair, moon, etc. Question 4. Name some luminous objects. Answer: Torch, bulb, sun, firefly and a burning candle. Question 5. Give four examples of non-luminous objects. Answer:
LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS 1. What is reflection of light? Explain reflection of light with the help of an activity. Ans: When light rays fall on a highly polished (e.g. mirror) smooth surface and return to the same medium, it is called reflection of light. Activity to show reflection of light: This activity should be done at night or in a dark ...
To know more about these concepts, students can download the solutions in PDF and practise offline as well. Chapter 11 - Light provides answers to all the questions related to each and every concept covered in this chapter. This chapter deals with light and the reflection of an object. Students can prepare for their examinations in a more ...
Class 6 - Light, Shadows & Reflection quiz for 6th grade students. Find other quizzes for Science and more on Quizizz for free!