Solver Title

Generating PDF...
- Pre Algebra Order of Operations Factors & Primes Fractions Long Arithmetic Decimals Exponents & Radicals Ratios & Proportions Percent Modulo Number Line Expanded Form Mean, Median & Mode
- Algebra Equations Inequalities System of Equations System of Inequalities Basic Operations Algebraic Properties Partial Fractions Polynomials Rational Expressions Sequences Power Sums Interval Notation Pi (Product) Notation Induction Logical Sets Word Problems
- Pre Calculus Equations Inequalities Scientific Calculator Scientific Notation Arithmetics Complex Numbers Polar/Cartesian Simultaneous Equations System of Inequalities Polynomials Rationales Functions Arithmetic & Comp. Coordinate Geometry Plane Geometry Solid Geometry Conic Sections Trigonometry
- Calculus Derivatives Derivative Applications Limits Integrals Integral Applications Integral Approximation Series ODE Multivariable Calculus Laplace Transform Taylor/Maclaurin Series Fourier Series Fourier Transform
- Functions Line Equations Functions Arithmetic & Comp. Conic Sections Transformation
- Linear Algebra Matrices Vectors
- Trigonometry Identities Proving Identities Trig Equations Trig Inequalities Evaluate Functions Simplify
- Statistics Mean Geometric Mean Quadratic Mean Average Median Mode Order Minimum Maximum Probability Mid-Range Range Standard Deviation Variance Lower Quartile Upper Quartile Interquartile Range Midhinge Standard Normal Distribution
- Physics Mechanics
- Chemistry Chemical Reactions Chemical Properties
- Finance Simple Interest Compound Interest Present Value Future Value
- Economics Point of Diminishing Return
- Conversions Roman Numerals Radical to Exponent Exponent to Radical To Fraction To Decimal To Mixed Number To Improper Fraction Radians to Degrees Degrees to Radians Hexadecimal Scientific Notation Distance Weight Time Volume
- Pre Algebra
- Pre Calculus
- Linear Algebra
- Trigonometry
- Geometric Mean
- Quadratic Mean
- Probability
- Standard Deviation
- Lower Quartile
- Upper Quartile
- Interquartile Range
- Standard Normal Distribution
- Conversions

Most Used Actions
Number line.
- arithmetic\:mean\:1,\:2,\:3,\:4,\:5,\:6
- geometric\:mean\:\left\{0.42,\:0.52,\:0.58,\:0.62\right\}
- quadratic\:mean\:-4,\:5,\:6,\:9
- median\:\:\left\{1,\:7,\:-3,\:4,\:9\right\}
- mode\:\left\{90,\:94,\:53,\:68,\:79,\:94,\:87,\:90,\:70,\:69,\:65,\:89,\:85\right\}
- minimum\:-4,\:5,\:6,\:9
- maximum\:\frac{31}{100},\:\frac{23}{105},\:\frac{31}{205},\:\frac{54}{205}
- mid\:range\:1,\:2,\:3,\:4,\:5,\:6
- range\:\:\left\{1,\:7,\:-3,\:4,\:9\right\}
- standard\:deviation\:\:\left\{1,\:7,\:-3,\:4,\:9\right\}
- variance\:1,\:2,\:3,\:4,\:5,\:6
- lower\:quartile\:-4,\:5,\:6,\:9
- upper\:quartile\:\left\{0.42,\:0.52,\:0.58,\:0.62\right\}
- interquartile\:range\:1,\:2,\:3,\:4,\:5,\:6
- midhinge\:\left\{90,\:94,\:53,\:68,\:79,\:84,\:87,\:72,\:70,\:69,\:65,\:89,\:85\right\}
- What is the best calculator for statistics?
- Symbolab offers an online calculator specifically for statistics that can perform a wide range of calculations, including standard deviation, variance, range and normal distribution. It also provides detailed step-by-step solutions.
- What is statistics?
- Statistics is the branch of mathematics that deals with the collection, analysis, interpretation, presentation, and organization of data. There are two main branches of statistics: descriptive statistics, and inferential statistics.
- What is descriptive statistics?
- Descriptive statistics is a branch of statistics that deals with summarizing, organizing and describing data. Descriptive statistics uses measures such as central tendency (mean, median, and mode) and measures of variability (range, standard deviation, variance) to give an overview of the data.
- What is inferential statistics?
- Inferential statistics is a branch of statistics that deals with making predictions and inferences about a population based on a sample of data. Inferential statistics uses probability theory and statistical models to make predictions and inferences about a population.
- What is the difference between statistics and probability?
- Statistics is the branch of mathematics dealing with the collection, analysis, interpretation, presentation, and organization of data, while probability is the branch of mathematics dealing with the likelihood of occurrence of different events.
statistics-calculator
- Lies, Damned Lies, and Statistics Statistics is about analyzing data, for instance the mean is commonly used to measure the “central tendency” of...
Please add a message.
Message received. Thanks for the feedback.
Teach yourself statistics
Statistics Problems
One of the best ways to learn statistics is to solve practice problems. These problems test your understanding of statistics terminology and your ability to solve common statistics problems. Each problem includes a step-by-step explanation of the solution.
- Use the dropdown boxes to describe the type of problem you want to work on.
- click the Submit button to see problems and solutions.
Main topic:
Problem description:
In one state, 52% of the voters are Republicans, and 48% are Democrats. In a second state, 47% of the voters are Republicans, and 53% are Democrats. Suppose a simple random sample of 100 voters are surveyed from each state.
What is the probability that the survey will show a greater percentage of Republican voters in the second state than in the first state?
The correct answer is C. For this analysis, let P 1 = the proportion of Republican voters in the first state, P 2 = the proportion of Republican voters in the second state, p 1 = the proportion of Republican voters in the sample from the first state, and p 2 = the proportion of Republican voters in the sample from the second state. The number of voters sampled from the first state (n 1 ) = 100, and the number of voters sampled from the second state (n 2 ) = 100.
The solution involves four steps.
- Make sure the sample size is big enough to model differences with a normal population. Because n 1 P 1 = 100 * 0.52 = 52, n 1 (1 - P 1 ) = 100 * 0.48 = 48, n 2 P 2 = 100 * 0.47 = 47, and n 2 (1 - P 2 ) = 100 * 0.53 = 53 are each greater than 10, the sample size is large enough.
- Find the mean of the difference in sample proportions: E(p 1 - p 2 ) = P 1 - P 2 = 0.52 - 0.47 = 0.05.
σ d = sqrt{ [ P1( 1 - P 1 ) / n 1 ] + [ P 2 (1 - P 2 ) / n 2 ] }
σ d = sqrt{ [ (0.52)(0.48) / 100 ] + [ (0.47)(0.53) / 100 ] }
σ d = sqrt (0.002496 + 0.002491) = sqrt(0.004987) = 0.0706
z p 1 - p 2 = (x - μ p 1 - p 2 ) / σ d = (0 - 0.05)/0.0706 = -0.7082
Using Stat Trek's Normal Distribution Calculator , we find that the probability of a z-score being -0.7082 or less is 0.24.
Therefore, the probability that the survey will show a greater percentage of Republican voters in the second state than in the first state is 0.24.
See also: Difference Between Proportions

Statistical Thinking for Industrial Problem Solving
A free online statistics course.
Back to Course Overview
Statistical Thinking and Problem Solving
Statistical thinking is vital for solving real-world problems. At the heart of statistical thinking is making decisions based on data. This requires disciplined approaches to identifying problems and the ability to quantify and interpret the variation that you observe in your data.
In this module, you will learn how to clearly define your problem and gain an understanding of the underlying processes that you will improve. You will learn techniques for identifying potential root causes of the problem. Finally, you will learn about different types of data and different approaches to data collection.
Estimated time to complete this module: 2 to 3 hours

Statistical Thinking and Problem Solving Overview (0:36)

Specific topics covered in this module include:
Statistical thinking.
- What is Statistical Thinking
Problem Solving
- Overview of Problem Solving
- Statistical Problem Solving
- Types of Problems
- Defining the Problem
- Goals and Key Performance Indicators
- The White Polymer Case Study
Defining the Process
- What is a Process?
- Developing a SIPOC Map
- Developing an Input/Output Process Map
- Top-Down and Deployment Flowcharts
Identifying Potential Root Causes
- Tools for Identifying Potential Causes
- Brainstorming
- Multi-voting
- Using Affinity Diagrams
- Cause-and-Effect Diagrams
- The Five Whys
- Cause-and-Effect Matrices
Compiling and Collecting Data
- Data Collection for Problem Solving
- Types of Data
- Operational Definitions
- Data Collection Strategies
- Importing Data for Analysis
- Engineering
The Partner of Choice for Engineers Across the Globe
SOLUTION TOPICS
Quality engineering, process engineering, chemical engineering, biomedical engineering, electrical engineering, reliability engineering, mechanical engineering, solutions built for engineers.
Minitab provides a multitude of solutions for engineers to aid in problem solving and analytics. Attack problems with brainstorming tools, plan projects and process improvements through visual tools, and then collect data and analyze it, all within the Minitab ecosystem. Our solutions can help you find the answers you need using graphical tools, statistics, and predictive analytics.

For quality professionals, it is crucial to quickly and clearly identify the root cause when customers are experiencing problems with services or products. Minitab is the ideal partner for quality professionals who want to take on additional projects, or lead the development of a formal continuous improvement or operational excellence program.

Watch the webinar to explore a step-by-step project roadmap to effectively investigate, improve, and maintain a process.
Process engineers need to understand their processes. Minitab is the expert in process improvement, with solutions designed to identify areas of improvement, measure processes outcomes, and monitor them. See an example of how Minitab can help with capability statistics that tell you how well your process is meeting the specifications that you have.

Statistics plays a big role in all engineering professions and has become even more important for chemical engineers. Because of the proliferation of inexpensive instrumentation, an engineer working in a modern plant has access to a tremendous amount of data. As a result, chemical engineers are dealing with more, and more complex, data than ever before. Learning data analysis and data science skills will enable you to provide unique and in-depth insights from your data that can create significant value for your organization today.

Applying the principles of biology, medicine, and engineering create life-saving solutions. That’s why Minitab works closely with biomedical engineers to ensure they are creating the safest and highest quality products. Learn how Boston Scientific leveraged Minitab solutions to improve manufacturing and as a result, drove significant savings.
Minitab provides solutions to enable electrical engineers to design, develop, test, and supervise the manufacture of electrical equipment. With different analytical and problem-solving tools, Minitab is the partner of choice for electrical engineers. Learn more about how one electronics maker used one of Minitab’s tools to find better specifications for suppliers and realize significant cost savings.
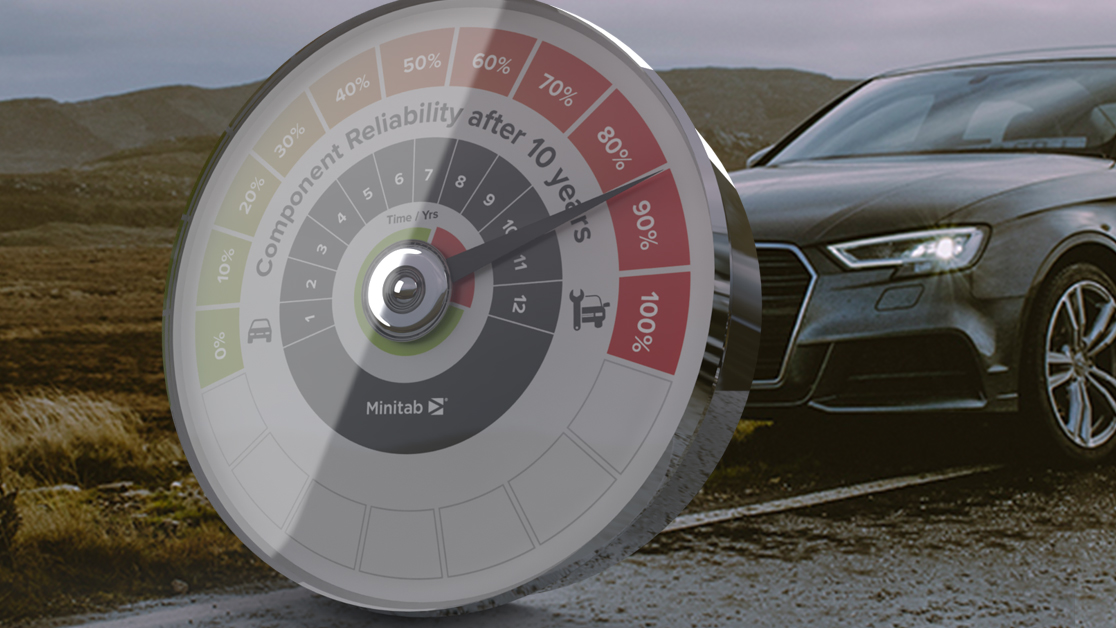
Imagine your new car breaks down after driving 60 miles. The engine light turns on and your vehicle must now be towed to be serviced. This is not only a warranty issue but also a field problem, due to lack of product reliability. Minitab partners with engineers to both optimize the design of products and ensure reliability to prevent this happening to you.
Mechanical engineers work on a wide range of projects from creating detailed designs to conducting simulations and analyses. Mechanical engineers must not only collaborate with multidisciplinary teams to ensure projects are completed successfully and on schedule, but they also play a key role in troubleshooting and resolving technical issues, conducting research, and improving mechanical systems and devices. Minitab provides mechanical engineers the broadest solutions and resources needed to perform their duties better, faster and easier.
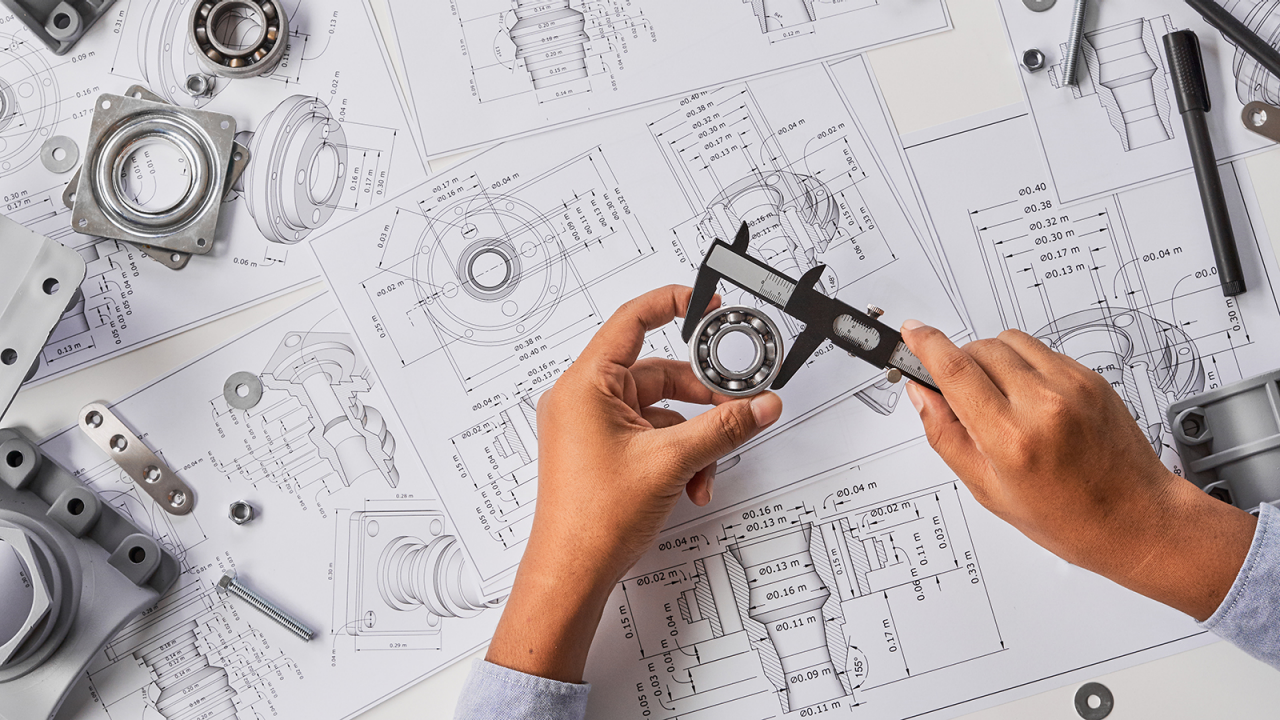
The Partner of Choice for Engineers Around the Globe
When there is a problem, engineers are tasked to solve it. As if that isn’t challenging enough, working without proper tools and solutions makes problem-solving more difficult. To truly be successful, engineers need access to data, solutions to integrate and analyze it, project management skills, and templates to improve the process and ensure continuous improvement.
That’s why Minitab created an ecosystem that tackles problem-solving the way engineers do. Need structured problem-solving tools to brainstorm? Check! Want to standardize forms like FMEAs, PPAP, or House of Quality? We have them! Looking to pull data from different sources to analyze on one platform? You’ve come to the right place!
Whether you’re an engineer in quality or process improvement, or in product development, we understand the day-to-day challenges of properly designing and testing. That’s because we’ve been doing it for over 50 years. We provide solutions to collect, monitor, and measure data with an eye toward improvement. Plus, with our services, training, and education, we can help you do your job better and even expand your skillset. We can help solve your problems, so that you can solve them for your organization.
OUR CUSTOMERS
“Minitab [is] the best tool for quality management. I use Minitab to run time series plots, charts, and control charts, as well as Pareto charts, fish bone charts…all the quality data was presented to upper management using Minitab. I would recommend it without hesitation!”
Jose Luis P. Quality Chief
“I deal with a few projects at a time and Minitab really helps me in understanding the failure points and relations within sub activities of a process. I can do a better root cause analysis to find the origin of a problem and also use the FMEA tool to weigh the severity, occurrence, and detection. I can tell with confidence that we have saved a whole lot of time compared to the hours of discussions and calculations we would have spent if we didn't invest in this software. The efficiency of our team has gone up significantly.”
Rahul V. Senior Development Engineer

“Minitab has made it so easy to analyze [my] data... from creating graphs, statistical analysis, and forming reports, it is the best thing an engineer can ask for. You don't need to be an expert to use it.”
Maria M. Industrial & Manufacturing Engineer
- Trust Center
© 2024 Minitab, LLC. All Rights Reserved.
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Notice
- Cookie Settings
You are now leaving minitab.com.
Click Continue to proceed to:
Have questions? Contact us at (770) 518-9967 or [email protected]

Statistical Problem Solving (SPS)

- Statistical Problem Solving
Problem solving in any organization is a problem. Nobody wants to own the responsibility for a problem and that is the reason, when a problem shows up fingers may be pointing at others rather than self.

This is a natural human instinctive defense mechanism and hence cannot hold it against any one. However, it is to be realized the problems in industry are real and cannot be wished away, solution must be sought either by hunch or by scientific methods. Only a systematic disciplined approach for defining and solving problems consistently and effectively reveal the real nature of a problem and the best possible solutions .
A Chinese proverb says, “ it is cheap to do guesswork for solution, but a wrong guess can be very expensive”. This is to emphasize that although occasional success is possible trough hunches gained through long years of experience in doing the same job, but a lasting solution is possible only through scientific methods.
One of the major scientific method for problem solving is through Statistical Problem Solving (SPS) this method is aimed at not only solving problems but may be used for improvement on existing situation. It involves a team armed with process and product knowledge, having willingness to work together as a team, can undertake selection of some statistical methods, have willingness to adhere to principles of economy and willingness to learn along the way.
Statistical Problem Solving (SPS) could be used for process control or product control. In many situations, the product would be customer dictated, tried, tested and standardized in the facility may involve testing at both internal to facility or external to facility may be complex and may require customer approval for changes which could be time consuming and complex. But if the problem warrants then this should be taken up.
Process controls are lot simpler than product control where SPS may be used effectively for improving profitability of the industry, by reducing costs and possibly eliminating all 7 types of waste through use of Kaizen and lean management techniques.
The following could be used as 7 steps for Statistical Problem Solving (SPS)
- Defining the problem
- Listing variables
- Prioritizing variables
- Evaluating top few variables
- Optimizing variable settings
- Monitor and Measure results
- Reward/Recognize Team members
Defining the problem: Source for defining the problem could be from customer complaints, in-house rejections, observations by team lead or supervisor or QC personnel, levels of waste generated or such similar factors.
Listing and prioritizing variables involves all features associated with the processes. Example temperature, feed and speed of the machine, environmental factors, operator skills etc. It may be difficult to try and find solution for all variables together. Hence most probable variables are to be selected based on collective wisdom and experience of the team attempting to solve the problem.
Collection of data: Most common method in collecting data is the X bar and R charts. Time is used as the variable in most cases and plotted on X axis, and other variables such as dimensions etc. are plotted graphically as shown in example below.
Once data is collected based on probable list of variables, then the data is brought to the attention of the team for brainstorming on what variables are to be controlled and how solution could be obtained. In other words , optimizing variables settings . Based on the brainstorming session process control variables are evaluated using popular techniques like “5 why”, “8D”, “Pareto Analysis”, “Ishikawa diagram”, “Histogram” etc. The techniques are used to limit variables and design the experiments and collect data again. Values of variables are identified from data which shows improvement. This would lead to narrowing down the variables and modify the processes, to achieve improvement continually. The solutions suggested are to be implemented and results are to be recorded. This data is to be measured at varying intervals to see the status of implementation and the progress of improvement is to be monitored till the suggested improvements become normal routine. When results indicate resolution of problem and the rsults are consistent then Team memebres are to be rewarded and recognized to keep up their morale for future projects.

Who Should Pursue SPS
- Statistical Problem Solving can be pursued by a senior leadership group for example group of quality executives meeting weekly to review quality issues, identify opportunities for costs saving and generate ideas for working smarter across the divisions
- Statistical Problem solving can equally be pursued by a staff work group within an institution that possesses a diversity of experience that can gather data on various product features and tabulate them statistically for drawing conclusions
- The staff work group proposes methods for rethinking and reworking models of collaboration and consultation at the facility
- The senior leadership group and staff work group work in partnership with university faculty and staff to identify research communications and solve problems across the organization
Benefits of Statistical Problem Solving
- Long term commitment to organizations and companies to work smarter.
- Reduces costs, enhances services and increases revenues.
- Mitigating the impact of budget reductions while at the same time reducing operational costs.
- Improving operations and processes, resulting in a more efficient, less redundant organization.
- Promotion of entrepreneurship intelligence, risk taking corporations and engagement across interactions with business and community partners.
- A culture change in a way a business or organization collaborates both internally and externally.
- Identification and solving of problems.
- Helps to repetition of problems
- Meets the mandatory requirement for using scientific methods for problem solving
- Savings in revenue by reducing quality costs
- Ultimate improvement in Bottom -Line
- Improvement in teamwork and morale in working
- Improvement in overall problem solving instead of harping on accountability
Business Impact
- Scientific data backed up problem solving techniques puts the business at higher pedestal in the eyes of the customer.
- Eradication of over consulting within businesses and organizations which may become a pitfall especially where it affects speed of information.
- Eradication of blame game
QSE’s Approach to Statistical Problem Solving
By leveraging vast experience, it has, QSE organizes the entire implementation process for Statistical Problem Solving in to Seven simple steps
- Define the Problem
- List Suspect Variables
- Prioritize Selected Variables
- Evaluate Critical Variables
- Optimize Critical Variables
- Monitor and Measure Results
- Reward/Recognize Team Members
- Define the Problem (Vital Few -Trivial Many):
List All the problems which may be hindering Operational Excellence . Place them in a Histogram under as many categories as required.
Select Problems based on a simple principle of Vital Few that is select few problems which contribute to most deficiencies within the facility
QSE advises on how to Use X and R Charts to gather process data.
- List Suspect Variables:
QSE Advises on how to gather data for the suspect variables involving cross functional teams and available past data
- Prioritize Selected Variables Using Cause and Effect Analysis:
QSE helps organizations to come up prioritization of select variables that are creating the problem and the effect that are caused by them. The details of this exercise are to be represented in the Fishbone Diagram or Ishikawa Diagram

- Evaluate Critical Variables:
Use Brain Storming method to use critical variables for collecting process data and Incremental Improvement for each selected critical variable
QSE with its vast experiences guides and conducts brain storming sessions in the facility to identify KAIZEN (Small Incremental projects) to bring in improvements. Create a bench mark to be achieved through the suggested improvement projects
- Optimize Critical Variable Through Implementing the Incremental Improvements:
QSE helps facilities to implement incremental improvements and gather data to see the results of the efforts in improvements
- Monitor and Measure to Collect Data on Consolidated incremental achievements :
Consolidate and make the major change incorporating all incremental improvements and then gather data again to see if the benchmarks have been reached
QSE educates and assists the teams on how these can be done in a scientific manner using lean and six sigma techniques
QSE organizes verification of Data to compare the results from the original results at the start of the projects. Verify if the suggestions incorporated are repeatable for same or better results as planned
Validate the improvement project by multiple repetitions
- Reward and Recognize Team Members:
QSE will provide all kinds of support in identifying the great contributors to the success of the projects and make recommendation to the Management to recognize the efforts in a manner which befits the organization to keep up the morale of the contributors.
Need Certification?
Quality System Enhancement has been a leader in global certification services for the past 30 years . With more than 800 companies successfully certified, our proprietary 10-Step Approach™ to certification offers an unmatched 100% success rate for our clients.
Recent Posts
Cdfa proposition 12 – farm animal confinement.

ISO 27001 Flyer

ISO 27701 Flyer
Have a question, sign up for our newsletter.
Hear about the latest industry trends from the QSE team of experts. Receive special offers for training services and invitations to free webinars.
ISO Standards
- ISO 9001:2015
- ISO 10993-1:2018
- ISO 13485:2016
- ISO 14001:2015
- ISO 15189:2018
- ISO 15190:2020
- ISO 15378:2017
- ISO/IEC 17020:2012
- ISO/IEC 17025:2017
- ISO 20000-1:2018
- ISO 22000:2018
- ISO 22301:2019
- ISO 27001:2015
- ISO 27701:2019
- ISO 28001:2007
- ISO 37001:2016
- ISO 45001:2018
- ISO 50001:2018
- ISO 55001:2014
Telecommunication Standards
- TL 9000 Version 6.1
Automotive Standards
- IATF 16949:2016
- ISO/SAE 21434:2021
Aerospace Standards
Forestry standards.
- FSC - Forest Stewardship Council
- PEFC - Program for the Endorsement of Forest Certification
- SFI - Sustainable Forest Initiative
Steel Construction Standards
Food safety standards.
- FDA Gluten Free Labeling & Certification
- Hygeine Excellence & Sanitation Excellence
GFSI Recognized Standards
- BRC Version 9
- FSSC 22000:2019
- Hygeine Excellent & Sanitation Excellence
- IFS Version 7
- SQF Edition 9
- All GFSI Recognized Standards for Packaging Industries
Problem Solving Tools
- Corrective & Preventative Actions
- Root Cause Analysis
- Supplier Development
Excellence Tools
- Bottom Line Improvement
- Customer Satisfaction Measurement
- Document Simplification
- Hygiene Excellence & Sanitation
- Lean & Six Sigma
- Malcom Baldridge National Quality Award
- Operational Excellence
- Safety (including STOP and OHSAS 45001)
- Sustainability (Reduce, Reuse, & Recycle)
- Total Productive Maintenance
Other Standards
- California Transparency Act
- Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS)
- Hemp & Cannabis Management Systems
- Recycling & Re-Using Electronics
- ESG - Environmental, Social & Governance
- CDFA Proposition 12 Animal Welfare
Simplification Delivered™
QSE has helped over 800 companies across North America achieve certification utilizing our unique 10-Step Approach ™ to management system consulting. Schedule a consultation and learn how we can help you achieve your goals as quickly, simply and easily as possible.

COMMENTS
Free math problem solver answers your statistics homework questions with step-by-step explanations. Mathway. Visit Mathway on the web. Start 7-day free trial on the app. Start 7-day free trial on the app. Download free on Amazon. Download free in Windows Store. get Go. Statistics. Basic Math. Pre-Algebra. Algebra. Trigonometry. Precalculus.
Reach out to us at [email protected] or click the Help beacon in the bottom right corner of the screen if you're still having trouble! Calculate statistics for free with the first AI-powered stats solver. Compute p-values, calculate sample sizes, and get step-by-step statistics homework help in seconds.
Welcome! Here, you will find all the help you need to be successful in your statistics class. Check out our statistics calculators to get step-by-step solutions to almost any statistics problem. Choose from topics such as numerical summary, confidence interval, hypothesis testing, simple regression and more.
There are 10 modules in this course. Statistical Thinking for Industrial Problem Solving is an applied statistics course for scientists and engineers offered by JMP, a division of SAS. By completing this course, students will understand the importance of statistical thinking, and will be able to use data and basic statistical methods to solve ...
Discover the key steps to effectively solve statistical challenges: define the problem, gather data, select the appropriate model, use tools like R or Python, and validate results. Dive into the world of DataCamp for interactive statistical learning experiences. Stewart Kaplan. November 17, 2023. blog.
Free Statistics Calculator - find the mean, median, standard deviation, variance and ranges of a data set step-by-step
This website provides training and tools to help you solve statistics problems quickly, easily, and accurately - without having to ask anyone for help. Online Tutorials ... We are indebted to Ian Smith for alerting us to a problem with the chi square calculator and for his practical suggestions to fix the problem. We are grateful to ...
Statistical Thinking and Problem Solving. Statistical thinking is about understanding, controlling and reducing process variation. Learn about process maps, problem-solving tools for defining and scoping your project, and understanding the data you need to solve your problem.
Statistics As Problem Solving. Consider statistics as a problem-solving process and examine its four components: asking questions, collecting appropriate data, analyzing the data, and interpreting the results. This session investigates the nature of data and its potential sources of variation. Variables, bias, and random sampling are introduced.
A statistics problem typically contains four components: 1. Ask a Question. Asking a question gets the process started. It's important to ask a question carefully, with an understanding of the data you will use to find your answer. 2, Collect Data. Collecting data to help answer the question is an important step in the process.
Module 1: Statistical Thinking and Problem Solving; Statistical thinking is about understanding, controlling and reducing process variation. Learn about process maps, problem-solving tools for defining and scoping your project, and understanding the data you need to solve your problem. Module 2A: Exploratory Data Analysis, Part 1
The Shainin System™ (SS) is defined as a problem-solving system designed for medium- to high-volume processes where data are cheaply available, statistical methods are widely used, and intervention into the process is difficult. ... Converge executes the strategies by applying statistical tools in a series of tactical cycles where each cycle ...
In this article we explored three techniques that can be applied to any problem to help find its solution. Please read on to part two to discover 3 further problem solving tools as well as the answer to the initial problem presented in this article. References: World Economic Forum 2023 future of jobs report
Problem 1. In one state, 52% of the voters are Republicans, and 48% are Democrats. In a second state, 47% of the voters are Republicans, and 53% are Democrats. Suppose a simple random sample of 100 voters are surveyed from each state. What is the probability that the survey will show a greater percentage of Republican voters in the second state ...
This one-day seminar provides training on the seven statistical tools. These tools are used in problem solving and continual improvement endeavors. The seven statistical tools were first introduced by Dr. Ishikawa when he introduced problem solving in Japan. Dr. Ishikawa put together seven simple tools that were already available for use.
Six Sigma tools are defined as the problem-solving tools used to support Six Sigma and other process improvement efforts. The Six Sigma expert uses qualitative and quantitative techniques to drive process improvement. ... Some of the statistical and graphical tools commonly used in improvement projects are: DMAIC: The define, measure, analyze ...
Statistical Thinking and Problem Solving. Statistical thinking is vital for solving real-world problems. At the heart of statistical thinking is making decisions based on data. This requires disciplined approaches to identifying problems and the ability to quantify and interpret the variation that you observe in your data.
The seven basic tools stand in contrast to more advanced statistical methods such as survey sampling, acceptance sampling, statistical hypothesis testing, design of experiments, multivariate analysis, and various methods developed in the field of operations research. See also. A3 problem solving - Structured problem improvement approach
Statistical process control (SPC) is defined as the use of statistical techniques to control a process or production method. SPC tools and procedures can help you monitor process behavior, discover issues in internal systems, and find solutions for production issues. Statistical process control is often used interchangeably with statistical ...
Minitab provides a multitude of solutions for engineers to aid in problem solving and analytics. Attack problems with brainstorming tools, plan projects and process improvements through visual tools, and then collect data and analyze it, all within the Minitab ecosystem. Our solutions can help you find the answers you need using graphical tools ...
It involves a team armed with process and product knowledge, having willingness to work together as a team, can undertake selection of some statistical methods, have willingness to adhere to principles of economy and willingness to learn along the way. Statistical Problem Solving (SPS) could be used for process control or product control.
The Six Sigma approach is a truly powerful problem-solving tool. By working from a practical problem to a statistical problem, a statistical solution and finally a practical solution, you will be assured that you have identified the correct root cause of the problem which affects the quality of your products.
Quality Glossary Definition: Seven tools of quality "The Old Seven." "The First Seven." "The Basic Seven." Quality pros have many names for these seven basic tools of quality, first emphasized by Kaoru Ishikawa, a professor of engineering at Tokyo University and the father of "quality circles."Start your quality journey by mastering these tools, and you'll have a name for them too: indispensable.
The 5 Whys technique is one of the most commonly used Lean Six Sigma tools for problem-solving. It involves asking "why" at least five times to get to the root cause of a particular issue or problem. ... Regression analysis is a powerful statistical process control tool used in Lean Six Sigma to understand the relationship between variables ...