22 Logic Puzzle Questions To Challenge Your Mind!
Jane Ng • 31 August, 2023 • 8 min read
Looking for Logic puzzle questions to challenge your logic skills without breaking a sweat? You’re in the right place! In this blog post, we’ll provide a list of 22 delightful logic puzzle questions that will make you think, and ponder as you find their right answers. So, gather ’round, get comfy, and let’s embark on a journey into the world of riddles and brain teasers!

Table Of Contents
Level #1 – easy logic puzzle questions, level #2 – logic puzzle questions in math , level #3 – logic puzzle questions for adults, key takeaways.
1/ Question: If an electric train is moving north at 100 mph and the wind is blowing to the west at 10 mph, which way does the smoke from the train go? Answer: Electric trains don’t produce smoke.
2/ Question: Three friends – Alex, Phil Dunphy, and Claire Pritchett – went to a movie. Alex sat next to Phil, but not next to Claire. Who sat next to Claire? Answer: Phil sat next to Claire.
3/ Question: There are six glasses in a row. The first three are filled with milk, and the next three are empty. Can you rearrange six glasses so that the full and empty glasses are in alternating order by moving only one glass?
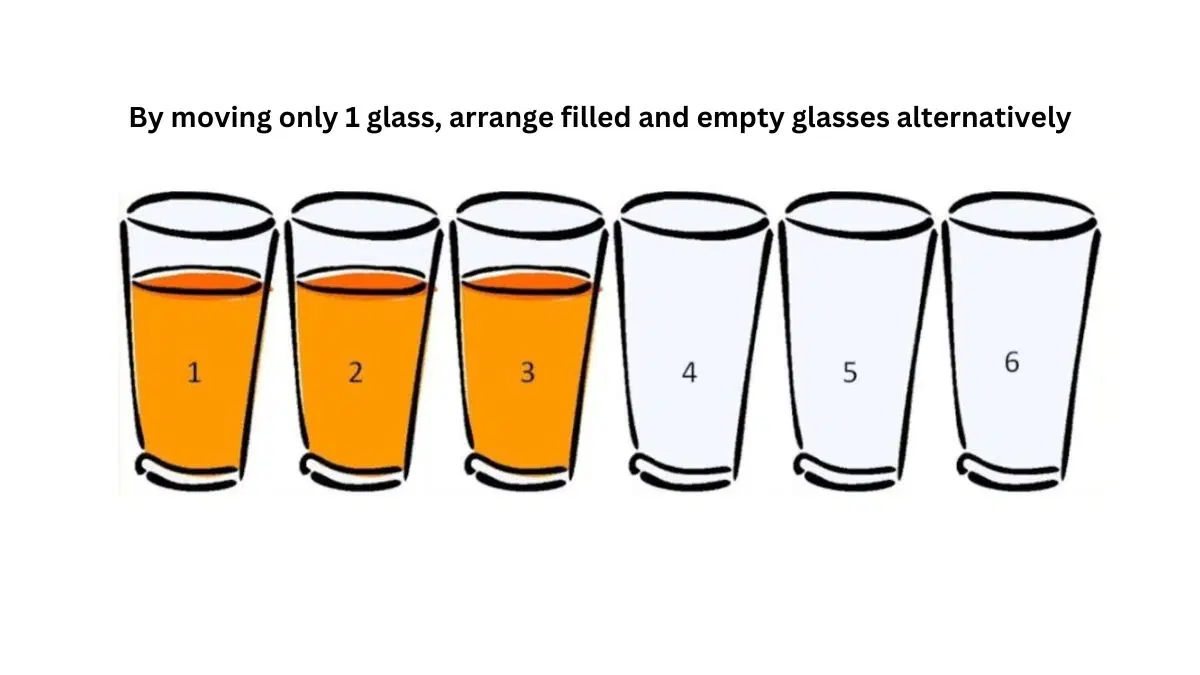
Answer: Yes, pour milk from the second glass into the fifth glass.
4/ Question: A man stands on one side of a river, his dog on the other. A man calls his dog, who immediately traverses the river without getting wet. How did the dog do it? Answer: The river was frozen, so the dog walked across the ice.
5/ Question: Sara is twice as old as Mike. If Mike is 8 years old, how old is Sara? Answer: Sara is 16 years old.
6/ Question: Four people need to cross a rickety bridge at night. They have only one flashlight and the bridge can only hold two people at a time. The four people walk at different speeds: one can cross the bridge in 1 minute, another in 2 minutes, the third in 5 minutes, and the slowest in 10 minutes. When two people cross the bridge together, they must go at the slower person’s pace. The speed of two people crossing a bridge together is limited by the speed of the slower person.
Answer: 17 minutes. First, the two fastest cross together (2 minutes). Then, the fastest returns with the flashlight (1 minute). The two slowest cross together (10 minutes). Finally, the second fastest returns with the flashlight (2 minutes).
7/ Question: A man gave one son 10 cents and another son was given 15 cents. What time is it? Answer: The time is 1:25 (a quarter past one).
8/ Question: If you multiply my age by 2, add 10, and then divide by 2, you’ll get my age. How old am I? Answer: You are 10 years old.
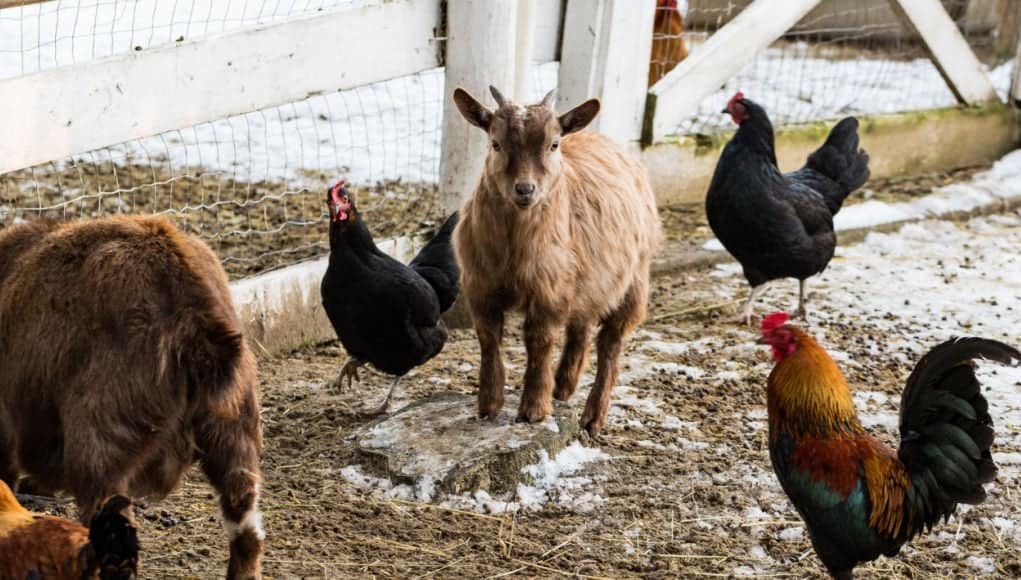
9/ Question: What is the weight of the three animals in the photo?
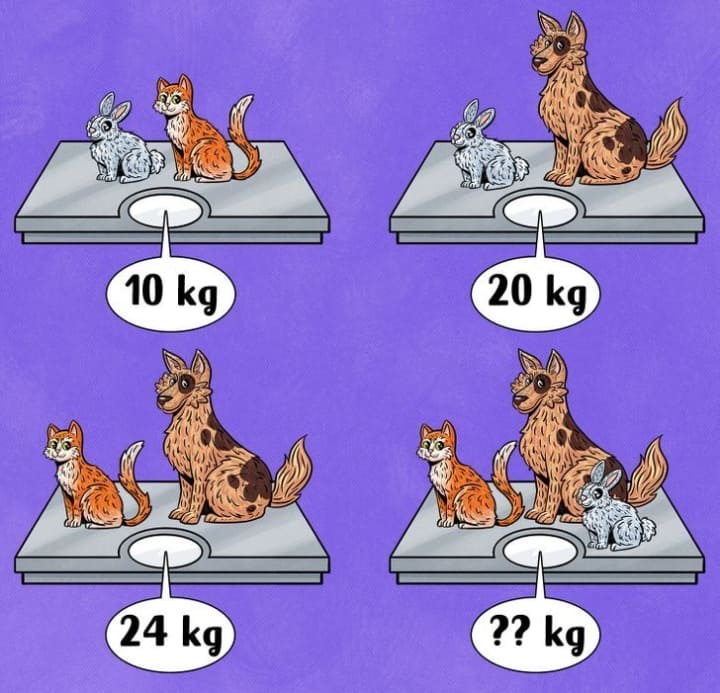
Answer: 27kg
10/ Question: If a snail climbs up a 10-foot pole during the day and then slips down 6 feet during the night, how many days will it take for the snail to reach the top?
Answer: 4 days. (On the first day, the snail climbs 10 feet during the day and then slips 6 feet during the night, leaving it at 4 feet. On the second day, it climbs another 10 feet, reaching 14 feet. On the third day, it climbs another 10 feet, reaching 24 feet. Finally, on the fourth day, it climbs the remaining 6 feet to reach the top.)
11/ Question: If you have 8 red balls, 5 blue balls, and 3 green balls in a bag, what is the probability of drawing a blue ball on the first try? Answer: The probability is 5/16. (There are a total of 8 + 5 + 3 = 16 balls. There are 5 blue balls, so the probability of drawing a blue ball is 5/16.)
12/ Question: A farmer has chickens and goats. There are 22 heads and 56 legs. What is the number of each animal that the farmer has? Answer: The farmer has 10 chickens and 12 goats.

13/ Question: How many times can you subtract 5 from 25? Answer : Once. (After subtracting 5 once, you’d be left with 20, and you can’t subtract 5 from 20 without going into negative numbers.)
14/ Question: What three positive numbers give the same answer when multiplied and added together? Answer: 1, 2, and 3. (1 * 2 * 3 = 6, and 1 + 2 + 3 = 6.)
15/ Question: If a pizza is cut into 8 slices and you eat 3, what percentage of the pizza have you consumed? Answer: You have consumed 37.5% of the pizza. (To calculate the percentage, divide the number of slices you’ve eaten by the total number of slices and multiply by 100: (3 / 8) * 100 = 37.5%.)
16/ Question: Which of the four pictures a, b, c, d, is the correct answer?
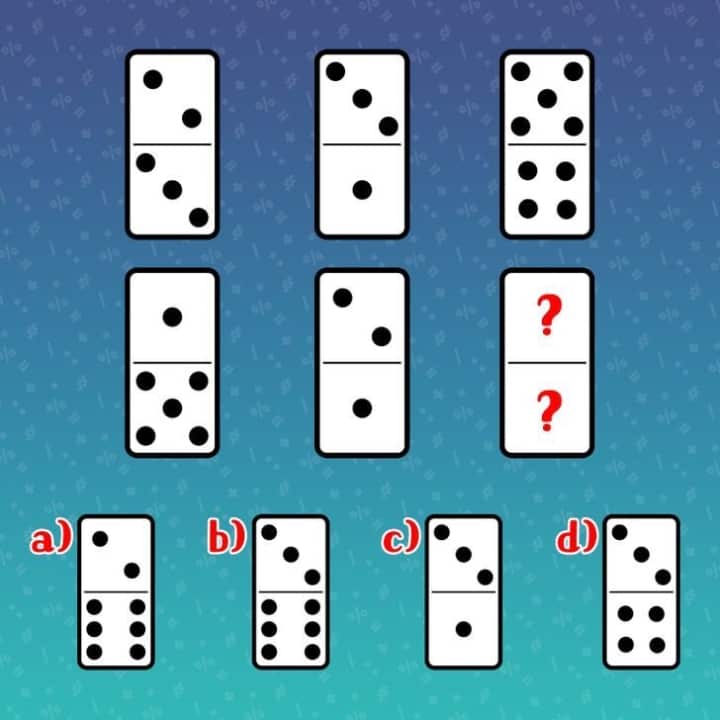
Answer: Picture b
17/ Question: If three people check into a hotel room that costs $30, they each contribute $10. Later, the hotel manager realized there was a mistake and the room should have cost $25. The manager gives $5 to the bellboy and asks him to return it to the guests. The bellboy, however, keeps $2 and gives each guest $1. Now, each guest has paid $9 (totaling $27) and the bellboy has $2, which makes $29. What became of the $1 that was missing?
Answer: The missing dollar riddle is a trick question. The $27 that the guests paid includes the $25 for the room and the $2 that the bellboy kept.
18/ Question: A man is pushing his car along a road when he comes to a hotel. He shouts, “I’m bankrupt!” Why? Answer: He’s playing a game of Monopoly.
19/ Question: If a man buys a shirt for $20 and sells it for $25, is this a 25% profit?
Answer: No. (The cost price of the shirt is $20, and the selling price is $25. The profit is $25 – $20 = $5. To calculate the profit percentage, you divide the profit by the cost price and then multiply by 100: (5 / 20) * 100 = 25%. The profit percentage is 25%, not the profit amount.)
20/ Question: If a car’s speed increases from 30 mph to 60 mph, how much does the speed increase in terms of a percentage? Answer: The speed increases by 100%.
21/ Question: If you have a rectangular garden that is 4 feet long and 5 feet wide, what is the perimeter? Answer: The perimeter is 18 feet. (The formula for the perimeter of a rectangle is P = 2 * (length + width). In this case, P = 2 * (4 + 5) = 2 * 9 = 18 feet.)
22/ Question: If two hours ago, it was as long after one o’clock as it was before one o’clock, what time is it now? Answer: It’s 2 o’clock.
In the world of logic puzzles, every twist and turn unveils a new challenge for our minds to conquer. To elevate your puzzle experience and add an interactive touch, check out AhaSlide’s features . With AhaSlides, you can turn these puzzles into shared adventures, sparking friendly competitions and lively discussions. Ready to dive in? Visit our templates and bring an extra layer of fun to your logic puzzle journey!
What is an example of a logic puzzle?
Example of a Logic Puzzle: If two hours ago, it was as long after one o’clock as it was before one o’clock, what time is it now? Answer: It’s 2 o’clock.
Where can I find logic puzzles?
You can find logic puzzles in books, puzzle magazines, online puzzle websites, mobile apps, and AhaSlides dedicated to puzzles and brain teasers.
What is a logic puzzle meaning?
A logic puzzle is a type of game or activity that challenges your reasoning and problem-solving skills. It involves using logical deductions to analyze given information and arrive at a correct solution.
Ref: Parade | Buzzfeed

A writer who wants to create practical and valuable content for the audience
Tips to Engage with Polls & Trivia
More from AhaSlides

- IBPS RRB Exam 2023 - Free Course
- Current Affairs
- General Knowledge
- SSC CGL Pre.Yrs.Papers
- SSC CGL Practice Papers
- SBI Clerk PYQ
- IBPS PO PYQ
- IBPS Clerk PYQ
- SBI PO Practice Paper
Logical Reasoning Questions and Answers
- Number Series Reasoning Questions and Answers
- Alphanumeric Series Reasoning Questions and Answers
- Analogy Reasoning Questions and Answers
- Making Judgements: Reasoning Questions
- Course of Action: Logical Reasoning Questions
- Statement and Conclusion Logical Reasoning
- Cause and Effect: Logical Reasoning Questions and Answers
- Statement and Argument-Analytical Reasoning
- Logical Deduction Questions and Answers (2023)
- HCL Placement Paper | Verbal Reasoning Set - 2
- Reasoning Tricks to Solve Coding -Decoding and Calendar Problems
- Statement and Assumption in Logical Reasoning
- Venn Diagram
Logical Reasoning _ Verbal Reasoning
- Verbal Reasoning: Logical Arrangement Of Words
- Placement | Reasoning | Blood Relationship
- Syllogism: Verbal Reasoning Questions and Answers
- Cubes: Verbal Reasoning Questions and Answers
- Seating Arrangement : Aptitude Questions and Answers
- Direction Sense test
- Data Sufficiency in Logical Reasoning
Logical Reasoning _ Non-Verbal Reasoning
- Mirror Image: Verbal Reasoning
- Picture Analogies Questions - Non Verbal Reasoning
Logical Reasoning involves the ability to use and understand logical connections between facts or ideas.
- In verbal reasoning , questions are expressed in words or statements and require the reader to think critically about the language used in order to choose the correct answer from the given options.
- Non-verbal reasoning meanwhile involves questions presented as images and figures, requiring the reader to comprehend how one element relates to another before selecting the right answer out of a list of potential answers.
Logical Reasoning is a key component of many competitive and reasoning ability-testing exams in India and abroad. Reasoning questions allow organizations to assess a candidate’s problem-solving skills, critical thinking capabilities, and capacity for logical and analytical thinking.
Aptitude Questions such as Quantitative Aptitude and Logical Reasoning are considered essential skills for success in a wide range of competitive exams worldwide. These two sections often form the backbone of entrance exams, whether it’s for a public sector job in India or a university admission test in the United States.

Go through the following article to learn more about the various types of reasoning ability queries generally included in competitive tests.
Logical Reasoning Topics
Logical Reasoning is a crucial section in various competitive exams, and aspirants must study these topics to improve their problem-solving abilities and score better.
Types of Questions included in logical reasoning:
- Verbal Questions
- Puzzle Questions
- Image-Based Questions
- Sequence Questions
Topic-wise practice questions on logical reasoning:
- Number Series
- Letter and Symbol Series
- Verbal Classification
- Essential Part
- Artificial Language
- Matching Definitions
- Making Judgments
- Logical Problems
- Logical Games
- Analyzing Arguments
- Course of Action
- Statement and Conclusion
- Theme Detection
- Cause and Effect
- Statement and Argument
- Logical Deduction
- Letter Series
- Verification of the Truth of the Statement
- Coding Decoding
- Assertion and Reason
- Statement and Assumptions
- Logical Venn Diagram
Verbal Reasoning
Verbal reasoning is the cognitive ability to understand and interpret information presented in written or spoken language and apply logical reasoning to draw conclusions and solve problems.
It involves analyzing and evaluating information, making inferences and deductions, and identifying relationships between concepts and ideas. Verbal reasoning often tests a candidate’s language comprehension, critical thinking, and analytical skills and is commonly used in aptitude tests, job interviews, and higher education admissions.
A strong grasp of verbal reasoning can help individuals communicate effectively, think critically, and make informed decisions in their personal and professional lives.
Verbal Reasoning Questions and Answers Topics
- Logical Sequence of Words
- Blood Relation Test
- Series Completion
- Cube and Cuboid
- Seating Arrangement
- Character Puzzles
- Direction Sense Test
- Classification
- Data Sufficiency
- Arithmetic Reasoning
- Verification of Truth
Non-Verbal Reasoning
Non-verbal reasoning is the cognitive ability that involves questions presented as images and figures, requiring the reader to comprehend how one element relates to another before selecting the right answer out of a list of potential answers.
Non-verbal reasoning often tests a candidate’s ability to think creatively, solve problems, and make quick decisions, and is commonly used in aptitude tests, job interviews, and higher education admissions.
A strong grasp of non-verbal reasoning can help individuals develop their creativity, spatial awareness, and problem-solving abilities, making them more effective at tackling complex challenges in their personal and professional lives.
If you are a government exam aspirant or a student preparing for college placements, the reasoning is the topic that you need to practice thoroughly. Below are some topics that need to be practiced well for the reasoning section of the exam. So, let’s go through the following article to learn more about the various types of reasoning queries generally included in competitive tests.
Non-Verbal Reasoning Questions and Answers Topics
- Analytical Reasoning
- Mirror Images
- Water Images
- Embedded Images
- Pattern Completion
- Figure Matrix
- Paper Folding
- Paper Cutting
- Rule Detection
- Grouping of Images
- Dot Situation
- Shape Construction
- Image Analysis
- Cubes and Dice
- Picture Analogies
Logical reasoning is an important assessment tool for a wide range of competitive examinations. Questions in this section are designed to judge a candidate’s analytical and logical thinking abilities. Various types of reasoning questions are included in this section to test the student’s capacity for problem-solving, deduction, and inference.
Practicing questions is the only way to prepare for the reasoning test section. This way, even those who may struggle in this section can have an equal chance at success during exams or applications. The article contains concepts, questions, and topics of the reasoning section from the competitive exams and the placement exams’ point of view.
FAQs – Logical Reasoning
Q1. what is logical reasoning .
Logical reasoning involves the ability to use and understand logical connections between facts or ideas. The reasoning is a critical component of many tests and interviews. In order to perform well, it can be beneficial to practice doing reasoning questions with solutions available.
Q2. What are logical reasoning questions?
Logical reasoning questions can be both verbal and non-verbal: In verbal logical reasoning questions, questions are expressed in words or statements and require the reader to think critically about the language used in order to choose the correct answer from the given options and in non-verbal logical reasoning questions, it involves questions presented as images and figures, requiring the reader to comprehend how one element relates to another before selecting the right answer out of a list of potential answers.
Q3. What is the approach to solving reasoning questions?
Follow the steps given below for preparation: 1. Practice with a timer and solve questions within the time limit. 2. Read the question carefully and try to understand the logic behind it. 3. Practice as many questions as you can and brush up on your skills.
Q4. Which book is good for the preparation of reasoning question sets?
Students can practice from the following books: 1. A Modern Approach to Verbal & Non-Verbal Reasoning by R.S. Agarwal 2. Shortcuts in Reasoning (Verbal, Non-Verbal, Analytical & Critical) for Competitive Exams by Disha Experts 3. How to Crack Test of Reasoning by Arihant Experts
Q5. What is the syllabus of the Reasoning Aptitude section for competitive exams?
Reasoning Aptitude covers a wide range of topics. Those topics are already given in the article. Aspirants must go through the article to learn about those topics and practice them thoroughly.
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- SSC/Banking
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
Reset password New user? Sign up
Existing user? Log in
- Number Theory
- Probability
- Everyday Math
- Classical Mechanics
- Electricity and Magnetism
- Computer Science
- Quantitative Finance
Take a guided, problem-solving based approach to learning Logic. These compilations provide unique perspectives and applications you won't find anywhere else.
What's inside
- Introduction
- Puzzles and Riddles
- Multi-Level Thinking
- The Rational Detective
- Syllogisms and Sets
- Logic Machines
- Arithmetic With Logic Gates
- Propositional Logic
- First-Order Logic
Joy of Problem Solving
- Intro to Problem Solving
- Coin Rearrangements
- Truth Tellers and Liars
- Operator Searches
- Matchstick Puzzles
Community Wiki
Browse through thousands of Logic wikis written by our community of experts.
- Truth-Tellers and Liars
- Cryptogram - Problem Solving
- Solving Propositional Logic Word Problem
- Mind Reading with Math
- Information Compression
- K-level thinking
- Chess Puzzles
- Arithmetic Puzzles - Operator Search
- Arithmetic Puzzles - Fill in the Blanks
- Elimination Grids
- Grid Puzzles
- Combinatorial Games - Definition
- Combinatorial Games - Winning Positions
- Tic Tac Toe
- Sprague Grundy Theorem
- Chess Puzzles - Reduced Games
- Chess Puzzles - Opening Strategies
- Chess Puzzles - Rook Strategies
- Rook Polynomial
- Game Theory
- Nash Equilibrium
- Zero-Sum Games
- Prisoner's Dilemma
- Braess' Paradox
- Utility Functions
- Cognitive Bias
- Monty Hall Problem
- Birthday Problem
- Two-Envelope Paradox
- Simpson's Paradox
- Berkson's Paradox
- Newcomb's Paradox
- Benford's Law
- Mathematics of Voting
- Survivorship Bias
- Russell's Paradox
- Zeno's Paradox
- Gabriel's Horn
- Truth Tables
- Proof by Contradiction
- Mathematical Logic and Computability
- Mathematical Logic and Computability II (continuation)
- Propositional Logic Using Algebra
- Venn Diagram
- Predicate Logic
Problem Loading...
Note Loading...
Set Loading...
40+Logical Thinking Questions: To test your logical skills
welcome to our Logic Challenge!
In this Logic Questions Post, we're diving deep into the world of logical thinking questions. Get ready for a thrilling journey as we explore brain-teasing puzzles designed to test your reasoning skills. Whether you're a seasoned puzzle enthusiast or new to the game, these challenges are sure to entertain and challenge you. So, let's dive in and embark on this exciting adventure of logical thinking questions!
1. Question: A bat and a ball cost $1.10 in total. The bat costs $1.00 more than the ball. How much does the ball cost
Answer: The ball costs $0.05. (If the ball costs $0.05, then the bat costs $1.05, totaling $1.10.)
2. Question: There are six eggs in a basket. Six people each take one egg. How can it be that one egg is left in the basket?
Answer: The last person took the basket with the egg still inside.
3. Question: If you rearrange the letters "CIFAIPC," you would get the name of ?
Answer: Pacific.
4. Question: A man builds a house with four sides of rectangular construction, each side having a southern exposure. A big bear comes along. What color is the bear?
Answer: White. (The house is built on the North Pole, so it faces south. Polar bears are the only bears that live in the North Pole, and they are white.)
5. Question: A farmer has 17 sheep. All but 9 die. How many sheep are left?
Answer: Nine sheep. (All but 9 die implies that 9 are left.)
6. Question: Mary's father has five daughters: 1. Nana, 2. Nene, 3. Nini, 4. Nono. What is the name of the fifth daughter?
Answer: Mary. (The question says "Mary's father has five daughters.")
7. Question: How many squares are there on a chessboard?
Answer: There are 204 squares on a chessboard.
8. Question: If there are 3 apples and you take away 2, how many do you have?
Answer: You have 2 apples. (You took them, so they are in your possession.)
9. Question: Which is heavier, a pound of feathers or a pound of bricks?
Answer: Neither. They both weigh a pound.
10. Question: How can you divide 10 oranges between 11 people evenly?
Answer: Make orange juice and distribute it.
11. Question: If a plane crashes on the border of the United States and Mexico, where do they bury the survivors?
Answer: You don't bury survivors.
12. Question: If it takes 5 machines 5 minutes to make 5 widgets, how long would it take 100 machines to make 100 widgets?
Answer: It would still take 5 minutes. Each machine is making one widget in 5 minutes, regardless of the number of machines.
13. Question: You see a boat filled with people. It has not sunk, but when you look again, you don't see a single person on the boat. Why?
Answer: All the people were married, so there are no single people on the boat.
14. Question: I have keys but no locks. I have space but no room. You can enter, but can't go outside. What am I?
Answer: A keyboard.
15. Question: A man is found hanging in a room with 53 bicycles. How did he die?
Answer: He stood on a block of ice with a noose around his neck. When the ice melted, he was left hanging.
16. Question: You are in a room with no doors or windows. The only items in the room are a mirror and a table. How do you escape?
Answer: Look in the mirror to see what you "saw." Use the saw to cut the table in half. Two halves make a 'hole' which you can use to escape.
17. Question: You have a fox, a chicken, and a sack of grain. You must cross a river with only one of them at a time. If you leave the fox with the chicken, the fox will eat the chicken. If you leave the chicken with the grain, the chicken will eat the grain. How do you get all three across safely?
Answer: Take the chicken across first, then go back for the fox. Leave the fox on the other side and take the chicken back. Leave the chicken and take the grain across. Finally, go back alone for the chicken.
18. Question: You are driving a bus. At the first stop, 4 people get on. At the second stop, 8 people get on and 3 get off. At the third stop, 2 people get on and 5 get off. The bus is grey, the driver is old, and it's raining outside. What color is the bus driver's hair?
Answer: You are the bus driver, so the color of the bus driver's hair is whatever your hair color is.
19. Question: How many times can you subtract 10 from 100?
Answer: Only once, because after you subtract it once, it becomes 90, not 100 anymore.
20. Question: What is the next number in the sequence: 1, 11, 21, 1211, 111221?
Answer: The next number is 312211. This is known as the Look and Say sequence, where each term describes the previous term.
Share this daily riddles on

Writer Name : Lipika Lajwani
Date : 2024-4-13
daily riddles

15 Challenging Riddles for Adults with Answers | Mind Your Logic Riddles
"Daily Brain Teasers for Adults: Enjoy Easy Riddles, Test Your Wits, and Uncover Answers for a Great...

10 Mind-Bending Riddles to Challenge Your Wits: Can You Solve Them All?
Put your problem-solving skills to the test with these ten mind-bending riddles. Challenge your thin...

15 Fun and Challenging English Riddles for Kids: Test Their Wits and Creativity
Engage your kids' minds with these 15 exciting English riddles. These riddles for kids are designed ...

Fun and Challenging English Riddles: Test Your Brain with 20 Brain Teasers
Enjoy the thrill of solving 20 new and exciting English riddles. Challenge your problem-solving skil...

10 Fun and Challenging Riddles for Kids: Exercise Their Minds with Brain-Teasing Puzzles
Engage your kids' minds with these 10 exciting riddles. These kid-friendly brain teasers will entert...
Get 25% off all test packages.
Get 25% off all test packages!
Click below to get 25% off all test packages.
Analytical Reasoning Tests
- 538 questions
Analytical reasoning tests examine an individual’s ability to apply logic to solve problems. The questions vary depending on the type of analytical reasoning test you’re taking: from extracting key information from complex passages of text (verbal reasoning), to looking for patterns in a series of images (non-verbal reasoning), or using given information to draw conclusions or make predictions (inductive and deductive reasoning).
What is an analytical reasoning test?
An analytical reasoning test is a type of aptitude test that is often used by employers to assess a job candidate’s ability to think critically and solve complex problems.
As well as these skills, employers want to see evidence that you can keep calm under pressure and work quickly against the clock.
The test is nearly always timed, meaning you don’t have long to work through each question to find the correct answer.
Depending on which type of job you’re applying for, the test you take may be in the style of verbal reasoning , non-verbal reasoning , inductive reasoning or deductive reasoning . As such, it’s worth practicing as many different types of tests as you can to familiarise yourself with the questions.
The analytical reasoning test is widely used because it looks for skills that are sought after in almost every industry. It helps employers find candidates who will be quick to learn, adapt and solve problems.
Why do use analytical reasoning tests?
Employers use analytical reasoning tests to assess candidates’ ability to analyze complex information, make logical deductions, and solve problems effectively. These tests help employers evaluate candidates’ critical thinking skills, decision-making abilities, and aptitude for handling challenging situations. By administering analytical reasoning tests, employers can identify candidates who possess the cognitive abilities necessary for success in roles that require analytical thinking, such as management, finance, engineering, and data analysis. Additionally, these tests provide employers with valuable insights into candidates’ problem-solving approaches and their capacity to navigate intricate scenarios, aiding in the selection of the most suitable candidates for the job.
As applicants have to work harder and harder to make their CV stand out, an aptitude test like this is a good way of ensuring candidates possess the necessary skills.
It’s common for employers or recruiters to set the analytical reasoning test before the interview stage, so they can select candidates based on their test performance. The test therefore acts as a filter, ensuring employers get to meet the people they believe are most likely to excel.
Completing a good analytical reasoning test gives an indication that you’re a strong critical thinker who can rise to the challenge – an attractive proposition for any employer.
How do analytical reasoning tests work?
An employer will select the type of analytical reasoning test (verbal, non-verbal, inductive or deductive) based on the skills they want to examine.
Finding out exactly which type of test you’ll be taking is helpful so you can focus your preparation, but if you don’t know we recommend trying out all of the different mock tests to familiarise yourself with the individual question styles and formats.
When you take the test, you’ll normally have around one minute to answer each question – which is yet another reason to familiarise yourself with the kinds of questions you’re likely to be asked.
Here’s a brief overview of the four different test types:
- Verbal reasoning – requires you to read through long passages of text and showcase your comprehension and analysis skills by answering a series of questions on what you’ve just read.
- Non-verbal reasoning – presents you with images such as graphs, pictures and patterns, and requires you to use your logic and problem-solving skills to decipher the rule that connects the sequence.
- Inductive reasoning – equips you with certain facts or information, and then asks you to make predictions or assumptions based on that evidence.
- Deductive reasoning – will ask you to use the statements given to you to make further statements of fact.
After the test, your score will be calculated and compared to those of the other individuals who took the same test, or a normative group (which can help an employer see how well you fared compared to previous candidates).
Analytical test formats
Verbal Reasoning Tests
Verbal reasoning tests examine your ability to draw out key information from long, often complex passages of text, to form a conclusion. Very often this takes the form of questions to which you would select ‘true’, ‘false’ or ‘cannot say’ as the response.
No prior knowledge of the subject matter is required, but it is important to practice verbal reasoning tests as it can take a while to get used to the question format.
You will need to be able to distinguish between what’s fact and what’s merely being inferred when you’re reading through the passages of text. This shows an employer that you have the comprehension, logic and analytical skills they’re looking for.
Practising verbal reasoning tests before you take the one that really matters is vital if you want to showcase the best of your abilities to a potential employer. The more mock tests you take, the better you’ll get at sifting through the passages of text for evidence, quickly assimilating the information and confidently deciding what’s true, false or uncertain.
You’ll normally have around one minute to answer each question on the verbal reasoning test (although it’s always worth checking this is the case with your test when you begin). It’s important you don’t spend ages on a challenging problem, as you could end up not answering other questions that you might have easily been able to answer.
At the end, if you have time left you can always go back to anything you weren’t sure about and have another go.
The verbal reasoning test is most commonly used by employers or recruiters hiring for roles where strong communication skills are critical – which applies to most jobs, hence their popularity.
Non-Verbal Reasoning Tests
Non-verbal reasoning tests comprise graphs, tables and data, and the accompanying questions will assess how adept you are at drawing conclusions from limited information, finding connecting patterns and working quickly under considerable time pressure.
These types of analytical reasoning tests are often part of the application process for roles in industries such as finance, engineering and HR.
The best way you can prepare for a non-verbal reasoning test is to take as many mock tests as you can. After you’ve completed a test, it’s important to look back through your answers and identify your weaker areas, so you know where you need to direct your focus.
Not only will practising ensure you get quicker and better, it’ll also help you familiarise yourself with the different graphs, tables and images you’re likely to be confronted with on a non-verbal reasoning test.
As with the verbal reasoning test, you normally get around one minute to answer each question, so finding the right balance between speed and accuracy is really important – something that you’ll find a lot easier if you’ve put the practice time in beforehand.
A successful non-verbal reasoning test will prove to an employer that you have the critical thinking, reasoning and logical skills needed to cope with the demands of the job you’re applying for.
Inductive / Deductive Reasoning Tests
If you’re asked to take an inductive test or deductive test , you’re essentially being asked to show how well you can identify patterns and use your logic. Although the overall skills you’ll demonstrate are very similar, the two tests are slightly different.
Inductive reasoning test – you’ll need to identify relationships between statements, images or facts and figures, and use this analysis to show, logically, what should come next.
Deductive reasoning test – you’ll be given a statement of fact and you’ll need to use this information to deduce another factually correct statement.
These aptitude tests are most commonly used in the hiring of science, tech and IT roles, as the type of skills they seek to showcase – logical thinking, identifying patterns, problem solving and critical thinking – are all valuable in these industries.
So even if you have the type of brain that finds these kinds of problems easier than most, it’s always worth practising inductive/deductive reasoning tests beforehand to familiarise yourself with the specific style of question, and what’s required of you in a short amount of time.
Prepare yourself for leading employers

5 Free Example Analytical Reasoning Questions
Here are five example analytical questions to try out. Answers for all five are below the tests. If you need further practice, try out our full free tests.
Verbal Question 1

Statement : A derivative could be used by an airline to secure the price of oil now, which it won’t use until six months time.
Verbal Question 2

Statement : More people taking early retirement is the major contributory factor to the public sector pension deficit.
Diagrammatic Question 1

Which is the next logical image in the sequence?
Numerical Question 1

What was the ratio of the cost of a Google click in April compared to the cost of a Facebook and Yahoo click in February?
Abstract Question 1

Which of the boxes comes next in the sequence?
Verbal Question 1 : True – “to secure the price of a commodity which is to be “bought” at a future date, but at a price that is set today.”
Verbal Question 2 : Cannot tell – the passage refers to both this fact, extended life expectancy, and that the value of pension fund assets has fallen.
Diagrammatic Question 1 : There is a central figure and four figures with one in each corner: (i) The central figure firstly increases in size over a series of three, then decreases in the same fashion; (ii) The central figure changes from white, to having a dotted outline, to black; and (iii) The four figures rotate around the four corners, moving two corners at a time. So the correct answer is F.
Numerical Question 1 : Step 1. Extract the relevant figures from the graph Cost of per click in April. Google 18 cents : Facebook + Yahoo (14 + 6 = 20 cents). Step 2. Divide 20 by 18 to calculate the ratio. 20 ÷18 = 1.11 Step 3. Present as a ratio 1 : 1.11
Abstract Question 1 : Arrow changes direction from pointing up, to pointing down, with each turn. 2. Triangle moves from top left corner in an anti-clockwise direction around the frame with each turn. So the answer is B.
Sample Analytical Reasoning Tests question Test your knowledge!

Consider a set of figures where the size of shapes increases with each subsequent figure. If the sequence starts with a small triangle and each figure adds two centimeters to each side of the shape, what size would the fifth shape be?
When analyzing a series of processes in a diagram, you notice that there is a cyclical pattern. If a process starts with A, continues to B, followed by C, and then starts over, what would be the fourth step after starting over twice?
- The process ends.
If a premise states that 'All managers can handle stress' and 'Susan is a manager', what conclusion can you draw?
- Susan cannot handle stress.
- Not all managers can handle stress.
- Susan can handle stress.
- The ability to handle stress is not important for managers.
You are given a dataset where the sales of a company have increased by 5% every month for the past 4 months. If the sales in the first month were $200,000, what should be the sales in the fifth month?
After reading the following passage, determine the main argument presented by the author. 'Many companies focus on short-term gains rather than long-term stability. This can lead to decisions that are profitable in the immediate future but may jeopardize the company's longevity. It is essential for businesses to balance immediate profits with sustainable growth.'
- Short-term gains are more important than long-term stability.
- Companies should consider long-term stability over short-term profits.
- Decisions should balance immediate profits and sustainable growth.
- Long-term stability is impossible to achieve for most companies.
Start your success journey
Access one of our Analytical Reasoning tests for FREE.
After using the platform for two weeks, I’ve never felt more prepared for an Aptitude test.
Ethan used Practice Aptitude Tests to improve his situational judgement scores.

Hire better talent
At Neuroworx we help companies build perfect teams

Analytical Reasoning Tests Tips
1 background research.
Get as much background information as possible on the test you’ll be taking from the employer or recruiter, so you know which areas to focus on.
2 Prepare with mock tests
Preparation is key – take mock tests in a quiet, distraction-free area and always make sure you go back through your answers at the end to identify any areas you need to work harder at.
3 Tips for test day
On the test day itself, make sure you have everything you need to complete the test. When you start, ensure you know roughly how long you’ve got to answer each question, as although you’ll always need to work quickly, it’s important to read the question thoroughly and ensure you’ve understood it before getting started.
4 Stay positive
Try and remain positive. The tests are designed to be challenging, since employers want to push you. If you’ve put the time and effort into practising aptitude tests, you should feel confident you’ve given yourself the best chance possible to succeed.
Analytical Reasoning Video Tutorials

Rotated Views
Similar Shapes

Prepare for your Analytical Reasoning Test
Immediate access. Cancel anytime.
- 30 Numerical reasoning tests
- 30 Verbal reasoning tests
- 30 Diagrammatic reasoning tests
- 30 Situational judgement tests
- 34 Publisher packages e.g. Watson Glaser
- 252 Employer packages e.g. HSBC
- 29 Extra packages e.g Mechanical
- Dashboard performance tracking
- Full solutions and explanations
- Tips, tricks, guides and resources
- Access to free tests
- Basic performance tracking
- Solutions & explanations
- Tips and resources
Analytical Reasoning Tests FAQs
What is this test used for.
Analytical reasoning tests are a go-to tool for employers looking to gauge a candidate’s problem-solving prowess. Organizations across a myriad of industries use these assessments to get a handle on the analytical skills that are crucial in the modern workplace.
What do these tests involve?
Dive into questions that challenge your problem-solving abilities across verbal, non-verbal, inductive, and deductive reasoning areas. Whether it’s deciphering complex texts, spotting trends in images, or making predictions, these tests are your all-in-one gym to flex those analytical muscles.
What do these tests measure?
Our tests aren’t just a bunch of random questions; they are refined and updated using cutting-edge tech. They’re designed to measure your logical and analytical acumen, ensuring you’re tested against the latest industry benchmarks for analytical reasoning.
Where can I practice these tests?
Ready to put your analytical skills to the test? Practice Aptitude Tests is your one-stop shop for simulating real-world analytical reasoning exams. Here, you’ll find a treasure trove of practice material to get you test-ready!
Which employers use these tests?
Analytical reasoning tests aren’t just popular; they’re a staple in the hiring toolkit for a vast array of organizations looking to identify top talent who can navigate complex problem-solving tasks with ease.
Reviews of our Analytical Reasoning tests
What our customers say about our Analytical Reasoning tests
Bob Gautier
United States of America
October 23, 2023
I really do not think negatively in any way about this test. It dies what it’s supposed to do, and designed to do what it does.
Andrew Smith
United Kingdom
October 05, 2023
A good range of alternating patterns, some repeat themselves on several questions, while others are one-offs.
Caramel Teoh
The seqence
I like how convenient it was to answer to question. I dislike that all the question is almost all the same
Juan Garcera
August 06, 2023
Interesting
It is a good first immersion on the complexity of analytical reasoning and a good first step to get into more demanding exercises.
Stephanie Scalzo
July 25, 2023
Find patterns, but attack each question individually
I have not had the opportunity to take a test like this in years! It was really cool to use my brain in this kind of way again and to work through each individual problem while also finding patterns throughout the test.
MemeLord 29
July 13, 2023
Understanding the sequences
I liked the fact you had to use logical thinking and process of elimination sometimes, to figure the answer
Simulation Aeronautics
July 09, 2023
Attention to detail
The shapes in the pattern have changes which require sharp attention to detail to select the next sequence.
Marco Cavallari
June 03, 2023
My 1st ever psychometric test
It was quite challenging at first, but after a while it became more and more easier to find patterns.
Elizabeth M.Calinawan
Philippines
May 31, 2023
The refreshing abstract reasoning
i like the test very much. Refreshing the next sequence, need enough time to think it over but with the time limit. Yeah, very interesting this test too. Well, when.this test refer to a real life of course anticipation in the area may prevail have a swift solution in every conce
khadijah Ansari
May 16, 2023
My brain had a hard time focusing and differentiating between them, trying to recognise a pattern was difficult.
By using our website you agree with our Cookie Policy.
- AON Hewitt G.A.T.E.
- PI Cognitive Assessment (PLI Test)
- Korn Ferry Leadership Assessment
- Berke Assessment
- Ergometrics
- Thomas International
- Predictive Index (PI)
- NEO Personality Inventory
- Leadership Assessment
- Gallup’s CliftonStrengths
- Sales Personality Tests
- Personality Management Tests
- Saville Wave
- McQuaig Word Survey
- Bell Personality Test
- Myers Briggs Personality Test
- DISC Personality Test
- Management SJT
- Supervisory SJT
- Administrative SJT
- Call Center SJT
- Customer Service SJT
- Firefighter SJT
- Numerical Reasoning Tests
- Verbal Reasoning Tests
- Logical Reasoning Tests
- Cognitive Ability Tests
- Technical Aptitude Tests
- Spatial Reasoning Tests
- Abstract Reasoning Test
- Deductive Reasoning Tests
- Inductive Reasoning Tests
- Mechanical Reasoning Tests
- Diagrammatic Reasoning Tests
- Fault Finding Aptitude Tests
- Mathematical Reasoning Tests
- Critical Thinking Tests
- Analytical Reasoning Tests
- Raven’s Progressive Matrices Test
- Criteria’s CCAT
- Matrigma Test
- Air Traffic Controller Test
- Administrative Assistant Exam
- Clerical Ability Exam
- School Secretary Tests
- State Trooper Exam
- Probation Officer Exam
- FBI Entrance Exam
- Office Assistant Exam
- Clerk Typist Test
- Police Records Clerk Exam
- Canada’s Public Service Exams
- Firefighter Exams
- Police Exams
- Army Aptitude Tests
- USPS Postal Exams
- Hiring Process by Professions
Select Page
Practice Logical Reasoning Test Example Questions – 2024

- Logical Tests
- Free Example Questions
One of the most popular, and perhaps most dreaded, type of psychometric test is the logical reasoning test. These screening questions won’t ask you for formulas or equations. You’ll have to rely solely on your own ingenuity to solve these problems.
You’ll need a great deal of concentration to succeed on a logic test. Logic tests are really designed to assess your intelligence. Similar to I.Q. tests in design, these aptitude assessments test your problem-solving skills, your critical thinking skills, and your creativity.
Below, we’ll explain a little bit more about the logic test questions you can expect on logic pre-employment exams and how you should approach them. We’ll also discuss some of our best tips for logic tests, so make sure to take notes! When you’re done, click over to the second tab and try your hand at our logical reasoning sample questions.
What Is a Logical Reasoning Test?
A logical reasoning test, as opposed to a numerical or verbal reasoning test , requires solely your reasoning ability. While you will have to know how to read, you won’t need to know any grammar, and you certainly won’t need to know how to multiply numbers.
Based on deductive and inductive reasoning, logical thinking questions will take one of two forms. Either you’ll be presented with a series of shapes and asked about the patterns they make, or you’ll be given a series of statements and asked to state what you know to be certain. We’ll go through both of these types of questions.
Why Do I Need to Take Logical Reasoning Tests?
Employers want to know, first and foremost, that you know how to analyze information and learn new skills quickly. These so-called “soft skills” are really far more important to a company than you might imagine, and they’re nearly impossible to really measure in an interview.
Logical questions help employers to see how well applicants recognize patterns, overcome adversity, and concentrate for extended periods of time. The skills you’ll need to pass a logical reasoning test are the same ones that will help you anticipate pitfalls, develop winning strategies, and start new initiatives.
Logical aptitude tests are designed, very simply, to test for intelligence. In fact, you’ll probably see a lot of the same questions on an I.Q. test. As it turns out, intelligence and success are very closely linked. The more intelligent someone is, the more quickly he learns and masters new skills, the better he remembers information told to him, and the more easily he overcomes problems.
How to Answer Logical Reasoning Questions:
Every logical reasoning question is different, and while you should be able to recognize patterns after a while, there are no shortcuts or one-size-fits-all responses. Here we have a few principles you should keep in mind. However, if you find that you’re still struggling with logic, then make sure to check out the free logic examples we have printed in our questions tab.
- Identify a Major Pattern: Whenever dealing with diagrams, you’ll want to focus on patterns. The series or matrix will be assembled of various sequences, and it’s your job to figure out what they are. Once you’ve identified a major pattern, you’ll want to see if you can also identify a minor pattern. Typically, series and matrices use at least two different patterns.
For example, if Jenny’s coat is both long and blue, we can logically assume that any red or green coats we may find do not belong to Jenny. On the other hand, if Jenny’s coat is either long or blue, we have a different set of criteria.
Logic also makes use of if–>then statements. For example, “If Jenny buys a new coat, she’ll buy one that is long and blue.” In that case, we know that Jenny can only buy a long, blue coat if, in fact, she buys a new coat. If her brother buys a coat for her, she won’t have bought a long, blue coat. These facts may seem redundant if you’ve never studied logic before, but they become quite significant when programming computers, for instance.
Diagrammatic Abstract Reasoning
This non-verbal form of logical reasoning usually involves series or matrices made up of shapes or figures arranged in a certain pattern.
To solve these questions, you’re going to use inductive reasoning. Your goal as the job-seeker is to identify the pattern and complete the task. Here are the four different kinds of tasks you can expect on non-verbal logic test questions.
- Series In a series question, you’ll be shown 4-6 pictures and asked to choose the next figure in the series from several choices. You might also find that one of the figures in the middle of the series has been left out, and you’ll have to choose which picture best completes the pattern.
- Matrices Matrices are very similar to series except they extend in two directions. While a series only goes from left to right, a matrix has patterns both horizontally and vertically. Not only will you have to make sure that the figure you choose completes the pattern in its row, but you’ll also have to check to see whether it agrees with the figures above and below it.
- Odd One Out Sometimes you’ll be given a set of figures and asked to identify the outlier. While the figures won’t be lined up in a series, they will have something in common. It will be your job determine which characteristics are relevant and to group the pictures based on these similarities.
- A/B Groups In A/B grouping questions, you’ll be given two groups of figures and one figure on its own. You’ll have to decide why the figures were grouped the way they were. You’ll then have to place the single figure in one of the two groups.
Verbal Logical Reasoning
While diagrammatic questions require inductive reasoning, verbal questions call for deductive reasoning. On a verbal question, you’ll be given a series of statements, premises, said to be true, and you’ll have to determine whether the conclusion necessarily follows from those statements.
- All men are mortal.
- Socrates is a man.
- Therefore, Socrates is mortal
- If it rains, the school will cancel the picnic.
- If the school cancels the picnic, the children will watch a film instead.
- Therefore, if it rains, the children will watch a film.
- Either I will go swimming or hiking.
- I will go swimming.
- I will not go hiking.
- Order Other deductive questions will ask you to put a set of people or items in order based on certain descriptions. For instance, they might tell you that “Sam is not last,” or that “Jaimie is before Paul,” but it will be up to you to figure out exactly where they are in line.
Logical Reasoning Test Tips:
Make sure you read our top tips for logical aptitude tests before heading out to the assessment center.
- Write Everything Down: Logic questions are particularly tricky. Instead of trying to keep everything straight in your head, try to write down the details on a piece of paper. Diagrams can be especially helpful when recording important facts.
For example, if the grass is wet, we can assume it probably rained. Logically, though, we can’t state for certain that it rained if we have no proof. It could have been the gardener who left the sprinklers on overnight.
- Focus on Truth Values: Make sure you know the difference between words like some, many, and all or words like sometimes, always, and never. These qualifying words can completely change the truth value of a statement.
- Pay Attention to All Details: When completing diagrammatic tests, be very careful to pay attention to all relevant details. A pattern may be based on multiple dots and lines, and if you rush, you’ll miss subtle aspects of the pattern.
Final Thoughts on Logical Questioning:
While most of us study science and history in school, very few of us ever study formal logic. In fact, unless you went to graduate school for law, engineering, philosophy, or abstract mathematics, logic as a concept in and of itself is probably pretty foreign to you.
If this is the case, then don’t fret. Logic is, not coincidentally, fairly logical. As long as you’re familiar with some of the basic fundamentals, you shouldn’t have too much trouble. Click over to the second tab to prepare with some of our online practice questions. Then read the answer explanations to see whether or not your reasoning was on track.
Free Logical Reasoning Practice Test
Practice4Me’s experts designed an example test for your needs to get you familiarized with various question types and to improve your chances of scoring high. This free test is a printable PDF file that includes questions and answers.
Download our free logical reasoning practice test PDF here .
Free Example Questions to Practice
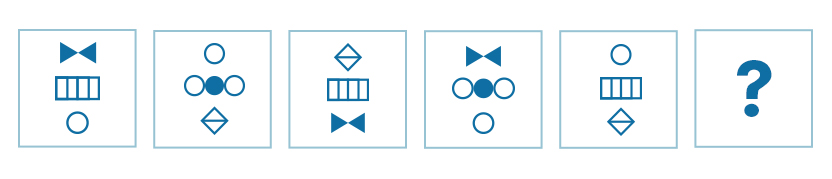
Questions 4 and 5 deal with the following information:
Given the following premises, state whether the conclusions are true, false, or unknown:
All athletes are coaches, but not all coaches are athletes. All coaches live in Chicago. No students are athletes, but all students are coaches. Some teachers are both athletes and students. Some parents are teachers, but no parents are students or athletes.
Explained Answers:
- B: Notice how the middle shape alternates between the three dots and the stripes. The figures on either side are in a three-way rotation with a circle, a bow, and a diamond.
- C: Picture C is the odd picture out because it’s the only one in which the bars don’t dip down below the line.
- C: Deanna—the order is: Clayton, Billy, Deanna, Annie, Elise
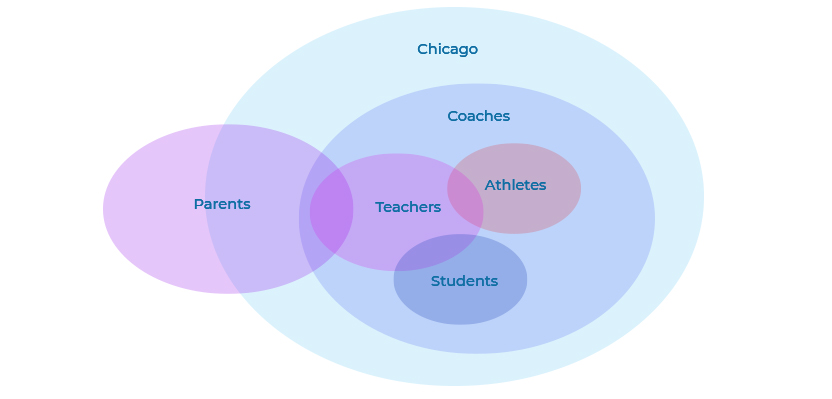
- B: All students are coaches, but as you can see in the picture, there may be many coaches who are not students. So, the answer is false.

Aptitude Tests
- Aptitude Tests Guide
- Numerical Reasoning Test
- Verbal Reasoning Test
- Cognitive Ability Test
- Critical Thinking Test
- Logical Reasoning Test
- Spatial Reasoning Test
- Technical Aptitude Test
- Inductive Reasoning Test
- Analytical Reasoning Test
- Deductive Reasoning Test
- Mechanical Reasoning Test
- Non-Verbal Reasoning Tests
- Diagrammatic Reasoning Test
- Concentration Assessment Test
- Finance Reasoning Aptitude Test
- Fault Finding (Fault Diagnosis) Test
- Senior Management Aptitude Tests
- Error Checking Tests
- In-Basket Exercise
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
Course: LSAT > Unit 1
Getting started with logical reasoning.
- Introduction to arguments
- Catalog of question types
- Types of conclusions
- Types of evidence
- Types of flaws
- Identify the conclusion | Quick guide
- Identify the conclusion | Learn more
- Identify the conclusion | Examples
- Identify an entailment | Quick guide
- Identify an entailment | Learn more
- Strongly supported inferences | Quick guide
- Strongly supported inferences | Learn more
- Disputes | Quick guide
- Disputes | Learn more
- Identify the technique | Quick guide
- Identify the technique | Learn more
- Identify the role | Quick guide
- Identify the role | learn more
- Identify the principle | Quick guide
- Identify the principle | Learn more
- Match structure | Quick guide
- Match structure | Learn more
- Match principles | Quick guide
- Match principles | Learn more
- Identify a flaw | Quick guide
- Identify a flaw | Learn more
- Match a flaw | Quick guide
- Match a flaw | Learn more
- Necessary assumptions | Quick guide
- Necessary assumptions | Learn more
- Sufficient assumptions | Quick guide
- Sufficient assumptions | Learn more
- Strengthen and weaken | Quick guide
- Strengthen and weaken | Learn more
- Helpful to know | Quick guide
- Helpful to know | learn more
- Explain or resolve | Quick guide
- Explain or resolve | Learn more
Logical Reasoning overview
- Two scored sections with 24-26 questions each
- Logical Reasoning makes up roughly half of your total points .
Anatomy of a Logical Reasoning question
- Passage/stimulus: This text is where we’ll find the argument or the information that forms the basis for answering the question. Sometimes there will be two arguments, if two people are presented as speakers.
- Question/task: This text, found beneath the stimulus, poses a question. For example, it may ask what assumption is necessary to the argument, or what must be true based on the statements above.
- Choices: You’ll be presented with five choices, of which you may select only one. You’ll see us refer to the correct choice as the “answer” throughout Khan Academy’s LSAT practice.
What can I do to tackle the Logical Reasoning section most effectively?
Dos and don’ts.
- Don’t panic: You’re not obligated to do the questions in any order, or even to do a given question at all. Many students find success maximizing their score by skipping a select handful of questions entirely, either because they know a question will take too long to solve, or because they just don’t know how to solve it.
- Don’t be influenced by your own views, knowledge, or experience about an issue or topic: The LSAT doesn’t require any outside expertise. All of the information that you need will be presented in the passage. When you add your own unwarranted assumptions, you’re moving away from the precision of the test’s language and toward more errors. This is one of the most common mistakes that students make on the LSAT!
- Don’t time yourself too early on: When learning a new skill, it’s good policy to avoid introducing time considerations until you’re ready. If you were learning piano, you wouldn’t play a piece at full-speed before you’d practiced the passages very slowly, and then less slowly, and then less slowly still. Give yourself time and room to build your skill and confidence. Only when you’re feeling good about the mechanics of your approach should you introduce a stopwatch.
- Do read with your pencil: Active reading strategies can help you better understand logical reasoning arguments and prevent you from “zoning out” while you read. Active readers like to underline or bracket an argument’s conclusion when they find it. They also like to circle keywords, such as “however”, “therefore”, “likely”, “all”, and many others that you’ll learn throughout your studies with us. If you’re reading with your pencil, you’re much less likely to wonder what you just read in the last minute.
- Do learn all of the question types: An effective approach to a necessary assumption question is very different from an effective approach to an explain question, even though the passage will look very similar in both. In fact, the same argument passage could theoretically be used to ask you a question about the conclusion, its assumptions or vulnerabilities to criticism, its technique, the role of one of its statements, a principle it displays, or what new info might strengthen or weaken it!
- Do spend time on the fundamentals: The temptation to churn through a high volume of questions can be strong, but strong LSAT-takers carefully and patiently learn the basics. For example, you’ll need to be able to identify a conclusion quickly and accurately before you’ll be able to progress with assumptions or flaws (identifying gaps in arguments). Similarly, a firm understanding of basic conditional reasoning will be invaluable as you approach many challenging questions. Be patient with yourself!
Want to join the conversation?
- Upvote Button navigates to signup page
- Downvote Button navigates to signup page
- Flag Button navigates to signup page
What is the Critical Thinking Test?
Critical thinking practice test, take a free practice critical thinking test, practice critical thinking test.
Updated November 16, 2023

The Critical Thinking Test is a comprehensive evaluation designed to assess individuals' cognitive capacities and analytical prowess.
This formal examination, often referred to as the critical thinking assessment, is a benchmark for those aiming to demonstrate their proficiency in discernment and problem-solving.
In addition, this evaluative tool meticulously gauges a range of skills, including logical reasoning, analytical thinking, and the ability to evaluate and synthesize information.
This article will embark on an exploration of the Critical Thinking Test, elucidating its intricacies and elucidating its paramount importance. We will dissect the essential skills it measures and clarify its significance in gauging one's intellectual aptitude.
We will examine examples of critical thinking questions, illuminating the challenging scenarios that candidates encounter prompting them to navigate the complexities of thought with finesse.
Before going ahead to take the critical thinking test, let's delve into the realm of preparation. This segment serves as a crucible for honing the skills assessed in the actual examination, offering candidates a chance to refine their analytical blades before facing the real challenge. Here are some skills that will help you with the critical thinking assessment: Logical Reasoning: The practice test meticulously evaluates your ability to deduce conclusions from given information, assess the validity of arguments, and recognize patterns in logic. Analytical Thinking: Prepare to dissect complex scenarios, identify key components, and synthesize information to draw insightful conclusions—a fundamental aspect of the critical thinking assessment. Problem-Solving Proficiency: Navigate through intricate problems that mirror real-world challenges, honing your capacity to approach issues systematically and derive effective solutions. What to Expect: The Critical Thinking Practice Test is crafted to mirror the format and complexity of the actual examination. Expect a series of scenarios, each accompanied by a set of questions that demand thoughtful analysis and logical deduction. These scenarios span diverse fields, from business and science to everyday scenarios, ensuring a comprehensive evaluation of your critical thinking skills. Examples of Critical Thinking Questions Scenario: In a business context, analyze the potential impacts of a proposed strategy on both short-term profitability and long-term sustainability. Question: What factors would you consider in determining the viability of the proposed strategy, and how might it affect the company's overall success? Scenario: Evaluate conflicting scientific studies on a pressing environmental issue.
Question: Identify the key methodologies and data points in each study. How would you reconcile the disparities to form an informed, unbiased conclusion?
Why Practice Matters
Engaging in the Critical Thinking Practice Test familiarizes you with the test format and cultivates a mindset geared towards agile and astute reasoning. This preparatory phase allows you to refine your cognitive toolkit, ensuring you approach the assessment with confidence and finesse.
We'll navigate through specific examples as we proceed, offering insights into effective strategies for tackling critical thinking questions. Prepare to embark on a journey of intellectual sharpening, where each practice question refines your analytical prowess for the challenges ahead.
This is a practice critical thinking test.
The test consists of three questions .
After you have answered all the questions, you will be shown the correct answers and given full explanations.
Make sure you read and fully understand each question before answering. Work quickly, but don't rush. You cannot afford to make mistakes on a real test .
If you get a question wrong, make sure you find out why and learn how to answer this type of question in the future.
Six friends are seated in a restaurant across a rectangular table. There are three chairs on each side. Adam and Dorky do not have anyone sitting to their right and Clyde and Benjamin do not have anyone sitting to their left. Adam and Benjamin are not sitting on the same side of the table.
If Ethan is not sitting next to Dorky, who is seated immediately to the left of Felix?

You might also be interested in these other PRT articles:

- Numerical Reasoning
- Verbal Reasoning
- Inductive Reasoning
- Logical Reasoning
- Situational Judgement
- Mechanical Reasoning
- Watson Glaser Critical thinking
- Deductive reasoning
- Abstract reasoning
- Spatial reasoning
- Error checking
- Verbal comprehension
- Reading comprehension
- Diagrammatic Reasoning
- Psychometric tests
- Personality test
- In-Tray exercise
- E-Tray exercise
- Competency based assessment
- Game based assessments
- Analysis exercise
- Group exercise
- Presentation exercise
- Video interview
- Strengths based assessment
- Strengths based interviews
- Saville Assessment
- Talent Q / Korn Ferry
- Watson Glaser
- Criterion Partnership
- Test Partnership
- Cut-e / Aon
- Team Focus PFS
- Sova Assessment
Logical Reasoning Tests
Practice tests, solutions, and tips to help you pass employers' logical reasoning tests.
- Buy logical tests
- Start for free
Updated: 08 April 2024
- What is a logical reasoning test?
A logical reasoning test is used measure a candidate’s problem solving ability. They assess the ability to come to conclusions based on logic. You are presented with a series of shapes and are required to find patterns and rules to help you find the correct answer. These tests may be encountered for any position at any level of recruitment, but they may be particularly common when recruiting for positions which require significant problem solving ability or higher use of logic.
What is an example of logical reasoning?
Here are screenshots of our logical reasoning tests to understand what an example question involves:
Page contents:
- How we can help with logical tests
- Logical reasoning tutorial - Part 1
- Free logical reasoning tests
- Logical reasoning tutorial - Part 2
Different types of logical reasoning
- Most common logical reasoning tests
- Logical reasoning test advice
Logical reasoning FAQs
How assessmentday can help with logical reasoning tests.
AssessmentDay offer numerous types of logical reasoning test which can help you perform to your best in the real thing. Practising logical reasoning tests is an ideal method of preparation as it allows you to learn from your mistakes, improving performance with every practice trial. Similarly experiencing time limits, the test layout and the overall test experience can help ease worries and anxieties about the test by familiarising yourself with them. It goes without saying that a candidate that has undertaken a logical reasoning test numerous times and seen their prior mistakes, and learned from them will be less nervous than a first time test candidate.
Logical Reasoning Video Tutorial - Part 1
Free practice logical reasoning tests
Free logical reasoning test 1.
This free logical reasoning test contains 10 questions and has a time limit of 70 seconds per question .
Free Logical Reasoning Test 2
Logical reasoning test 1.
- 12 questions
Logical Reasoning Test 2
Logical reasoning test 3, logical reasoning test 4, logical reasoning video tutorial - part 2.
There are numerous types of logical reasoning test, and many of these are used interchangeably. These tests tend to be similar in their layout and methodology, but with subtle and important differences.
Survey results
We analysed a sample of logic-based tests, to find the most common terms/most popular type was: Inductive reasoning
Here is a breakdown of the most common logical ability tests:
- Inductive reasoning: - Inductive reasoning is the ability to reach general conclusion based on perceived patterns observed in specific events. Inductive logic is often used in everyday life and is therefore practical to a work place environment. In these tests candidates will be provided with a series of diagrams with an evident pattern. Candidates will need to identify the pattern in the sequence of diagrams and select the next diagram in the sequence.
- Deductive reasoning: - Deductive reasoning involves a general rule or principle that leads to a specific conclusion. These tests will evaluate and measure a candidate's ability to make logical arguments and draw sound conclusions based on provided data, as well as identify flaws in a piece of information. As a result this is a useful tool in selection procedures as this type of reasoning will be used in the workplace. This type of reasoning will often be used in verbal reasoning tests and numerical tests, and is therefore very likely to be encountered in recruitment processes.
- Abstract reasoning: - Abstract reasoning, also known as conceptual reasoning measures your lateral thinking ability. In these tests candidates will be tested on their ability to identify relationships, patterns and trends. Candidates will be provided with a series of images that follow a logical sequence or underlying rules. This may include following a rule in a sequence, identifying a code or finding a missing diagram.
- Diagrammatic reasoning: - Diagrammatic reasoning is a specific form of abstract reasoning. Tests which assess this ability will typically show a flowchart of diagrams and symbols, with an input and an output. Candidates will need to identify which inputs effect diagrams, and therefore generate a specific output based on those rules.
- Critical thinking: - Critical thinking tests are a type of verbal critical reasoning task which assesses various different types of logical reasoning in arguments, assumptions and conclusions. Typical logical abilities tested include analysing arguments, making inferences and evaluating conclusions.
The most common logical reasoning tests used by employers
Did you know.
Different test publishers use different names for their assessments. The term logical reasoning is used by TalentQ. Other companies may call their test abstract, inductive, or diagrammatic reasoning. It is good advice when being asked to sit a logical reasoning test to speak to the person who invited you and ask for a bit more detail; they may even give you a few example questions so you know what to expect.
Our 2020 study asked candidates about their logical reasoning test experience, in doing so we managed to find the most popular test publishers from our sample:
- 1. Talent Q Elements Logical Ability - the important feature of these tests is that they are adaptive. That is to say the difficulty of each question is automatically determined by your performance in the previous question. So the questions become more difficult as you progress in order to quickly find your level of logical reasoning ability. There are typically 12 questions to these TalentQ logical tests and a time limit of 75 seconds per question.
- 2. Kenexa Logical Reasoning - this test published by Kenexa is actually very similar in style to what SHL call an inductive reasoning test. They are effectively the same thing; the candidate is asked to select which diagram fits within the given series from a choice of five options. Typically Kenexa will give the candidate 20 minutes for 24 questions for their logical reasoning test.
- 3. Ravens Progressive Matricies (Ravens APM / Ravens SPM) - The grid-style of symbols each following a pattern is also used in the Ravens Progressive Matrices assessments. With Raven's logical test, there are two levels of this test: Advanced Progressive Matrices (23 questions, 42 minutes) and Standard Progressive Matrices (28 questions, 47 minutes). Our logical tests are suitable for Raven's APM-III and Raven's SPM tests, you can alter the time limit with of our tests to create a more authentic experience.
Master aptitude tests and become the #1 candidate
Get a completely free starter account
- Over 20 tests
- Track your progress
General logical reasoning test advice
Although all tests evaluate a specific logical ability, or set of abilities, there are general strategies which can be applied to ensure maximum performance in a logical reasoning test.
Here is a list of useful tips and advice for logical reasoning tests:
- 1. Stay calm: - Logical reasoning tests of all kinds can be nerve racking, particularly ones which are time limited. As a result it is important to stay calm as to allow optimum performance during your exam. A small amount of anxiety can be a performance booster, maximise focus and therefore performance. However, serious test anxiety can severely hamper performance. Proper practice, enough sleep the night before and deep and regular breathing can all help settle your nerves, and perform to your best on the day of your test.
- 2. Research the type of test: - Learning as much about the test beforehand can help you dive straight into the test once you have received it, saving you time. Similarly after researching the test, and the logical abilities which it assesses, can help you hone these skills and ensure you demonstrate the particular aptitude required for the test, optimising your performance.
- 3. Clarify what type of test: - If an employer states that you will need to undertake a logical reasoning test, it is important to gauge what type of logical reasoning will be tested due to the broad nature of logical reasoning. Don’t be afraid to ask for clarification to identify which logical reasoning test will be used, and which logical reasoning skill will be tested as this information will be invaluable for your pre test preparation.
- 4. Figure out the answer first: - A general tip for logical reasoning tests is to figure out the correct answer/sequence/rule before looking at the multiple choices. This way once you have an idea in your head of the correct answer, you can simply pick it out. If you look at the multiple choice answers first, you will be more inclined to pick the answer which best looks like the correct answer, rather than take the time to evaluate it logically. Your logic will be subject to more bias if you base your answer on which answer seems correct on face value, instead of evaluating it using the logical skills being tested.
- For more advice on logical reasoning tests, check out our logical reasoning tips where we go through an example question and give you advice on how to pass logical tests.
Yes, logical reasoning is a skill just like numerical reasoning which can be developed and practised. Some people will naturally be talented with logical reasoning and be able to solve logical puzzles much easier than others. Logical reasoning involves being able to solve logic puzzles and draw conclusions from patterns.
Logical reasoning is important for your ability to solve problems and generate creative ideas. It's this reason that many employers use logical reasoning tests in their application process.
The best way to practise logic skills is by using logical reasoning tests. These will provide the best practise as they directly involve all the skills needed in solving logic problems. You can also practise things like word puzzles or any kind of puzzle that requires you to identify patterns to find answers.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
7 Module 7: Thinking, Reasoning, and Problem-Solving
This module is about how a solid working knowledge of psychological principles can help you to think more effectively, so you can succeed in school and life. You might be inclined to believe that—because you have been thinking for as long as you can remember, because you are able to figure out the solution to many problems, because you feel capable of using logic to argue a point, because you can evaluate whether the things you read and hear make sense—you do not need any special training in thinking. But this, of course, is one of the key barriers to helping people think better. If you do not believe that there is anything wrong, why try to fix it?
The human brain is indeed a remarkable thinking machine, capable of amazing, complex, creative, logical thoughts. Why, then, are we telling you that you need to learn how to think? Mainly because one major lesson from cognitive psychology is that these capabilities of the human brain are relatively infrequently realized. Many psychologists believe that people are essentially “cognitive misers.” It is not that we are lazy, but that we have a tendency to expend the least amount of mental effort necessary. Although you may not realize it, it actually takes a great deal of energy to think. Careful, deliberative reasoning and critical thinking are very difficult. Because we seem to be successful without going to the trouble of using these skills well, it feels unnecessary to develop them. As you shall see, however, there are many pitfalls in the cognitive processes described in this module. When people do not devote extra effort to learning and improving reasoning, problem solving, and critical thinking skills, they make many errors.
As is true for memory, if you develop the cognitive skills presented in this module, you will be more successful in school. It is important that you realize, however, that these skills will help you far beyond school, even more so than a good memory will. Although it is somewhat useful to have a good memory, ten years from now no potential employer will care how many questions you got right on multiple choice exams during college. All of them will, however, recognize whether you are a logical, analytical, critical thinker. With these thinking skills, you will be an effective, persuasive communicator and an excellent problem solver.
The module begins by describing different kinds of thought and knowledge, especially conceptual knowledge and critical thinking. An understanding of these differences will be valuable as you progress through school and encounter different assignments that require you to tap into different kinds of knowledge. The second section covers deductive and inductive reasoning, which are processes we use to construct and evaluate strong arguments. They are essential skills to have whenever you are trying to persuade someone (including yourself) of some point, or to respond to someone’s efforts to persuade you. The module ends with a section about problem solving. A solid understanding of the key processes involved in problem solving will help you to handle many daily challenges.
7.1. Different kinds of thought
7.2. Reasoning and Judgment
7.3. Problem Solving
READING WITH PURPOSE
Remember and understand.
By reading and studying Module 7, you should be able to remember and describe:
- Concepts and inferences (7.1)
- Procedural knowledge (7.1)
- Metacognition (7.1)
- Characteristics of critical thinking: skepticism; identify biases, distortions, omissions, and assumptions; reasoning and problem solving skills (7.1)
- Reasoning: deductive reasoning, deductively valid argument, inductive reasoning, inductively strong argument, availability heuristic, representativeness heuristic (7.2)
- Fixation: functional fixedness, mental set (7.3)
- Algorithms, heuristics, and the role of confirmation bias (7.3)
- Effective problem solving sequence (7.3)
By reading and thinking about how the concepts in Module 6 apply to real life, you should be able to:
- Identify which type of knowledge a piece of information is (7.1)
- Recognize examples of deductive and inductive reasoning (7.2)
- Recognize judgments that have probably been influenced by the availability heuristic (7.2)
- Recognize examples of problem solving heuristics and algorithms (7.3)
Analyze, Evaluate, and Create
By reading and thinking about Module 6, participating in classroom activities, and completing out-of-class assignments, you should be able to:
- Use the principles of critical thinking to evaluate information (7.1)
- Explain whether examples of reasoning arguments are deductively valid or inductively strong (7.2)
- Outline how you could try to solve a problem from your life using the effective problem solving sequence (7.3)
7.1. Different kinds of thought and knowledge
- Take a few minutes to write down everything that you know about dogs.
- Do you believe that:
- Psychic ability exists?
- Hypnosis is an altered state of consciousness?
- Magnet therapy is effective for relieving pain?
- Aerobic exercise is an effective treatment for depression?
- UFO’s from outer space have visited earth?
On what do you base your belief or disbelief for the questions above?
Of course, we all know what is meant by the words think and knowledge . You probably also realize that they are not unitary concepts; there are different kinds of thought and knowledge. In this section, let us look at some of these differences. If you are familiar with these different kinds of thought and pay attention to them in your classes, it will help you to focus on the right goals, learn more effectively, and succeed in school. Different assignments and requirements in school call on you to use different kinds of knowledge or thought, so it will be very helpful for you to learn to recognize them (Anderson, et al. 2001).
Factual and conceptual knowledge
Module 5 introduced the idea of declarative memory, which is composed of facts and episodes. If you have ever played a trivia game or watched Jeopardy on TV, you realize that the human brain is able to hold an extraordinary number of facts. Likewise, you realize that each of us has an enormous store of episodes, essentially facts about events that happened in our own lives. It may be difficult to keep that in mind when we are struggling to retrieve one of those facts while taking an exam, however. Part of the problem is that, in contradiction to the advice from Module 5, many students continue to try to memorize course material as a series of unrelated facts (picture a history student simply trying to memorize history as a set of unrelated dates without any coherent story tying them together). Facts in the real world are not random and unorganized, however. It is the way that they are organized that constitutes a second key kind of knowledge, conceptual.
Concepts are nothing more than our mental representations of categories of things in the world. For example, think about dogs. When you do this, you might remember specific facts about dogs, such as they have fur and they bark. You may also recall dogs that you have encountered and picture them in your mind. All of this information (and more) makes up your concept of dog. You can have concepts of simple categories (e.g., triangle), complex categories (e.g., small dogs that sleep all day, eat out of the garbage, and bark at leaves), kinds of people (e.g., psychology professors), events (e.g., birthday parties), and abstract ideas (e.g., justice). Gregory Murphy (2002) refers to concepts as the “glue that holds our mental life together” (p. 1). Very simply, summarizing the world by using concepts is one of the most important cognitive tasks that we do. Our conceptual knowledge is our knowledge about the world. Individual concepts are related to each other to form a rich interconnected network of knowledge. For example, think about how the following concepts might be related to each other: dog, pet, play, Frisbee, chew toy, shoe. Or, of more obvious use to you now, how these concepts are related: working memory, long-term memory, declarative memory, procedural memory, and rehearsal? Because our minds have a natural tendency to organize information conceptually, when students try to remember course material as isolated facts, they are working against their strengths.
One last important point about concepts is that they allow you to instantly know a great deal of information about something. For example, if someone hands you a small red object and says, “here is an apple,” they do not have to tell you, “it is something you can eat.” You already know that you can eat it because it is true by virtue of the fact that the object is an apple; this is called drawing an inference , assuming that something is true on the basis of your previous knowledge (for example, of category membership or of how the world works) or logical reasoning.
Procedural knowledge
Physical skills, such as tying your shoes, doing a cartwheel, and driving a car (or doing all three at the same time, but don’t try this at home) are certainly a kind of knowledge. They are procedural knowledge, the same idea as procedural memory that you saw in Module 5. Mental skills, such as reading, debating, and planning a psychology experiment, are procedural knowledge, as well. In short, procedural knowledge is the knowledge how to do something (Cohen & Eichenbaum, 1993).
Metacognitive knowledge
Floyd used to think that he had a great memory. Now, he has a better memory. Why? Because he finally realized that his memory was not as great as he once thought it was. Because Floyd eventually learned that he often forgets where he put things, he finally developed the habit of putting things in the same place. (Unfortunately, he did not learn this lesson before losing at least 5 watches and a wedding ring.) Because he finally realized that he often forgets to do things, he finally started using the To Do list app on his phone. And so on. Floyd’s insights about the real limitations of his memory have allowed him to remember things that he used to forget.
All of us have knowledge about the way our own minds work. You may know that you have a good memory for people’s names and a poor memory for math formulas. Someone else might realize that they have difficulty remembering to do things, like stopping at the store on the way home. Others still know that they tend to overlook details. This knowledge about our own thinking is actually quite important; it is called metacognitive knowledge, or metacognition . Like other kinds of thinking skills, it is subject to error. For example, in unpublished research, one of the authors surveyed about 120 General Psychology students on the first day of the term. Among other questions, the students were asked them to predict their grade in the class and report their current Grade Point Average. Two-thirds of the students predicted that their grade in the course would be higher than their GPA. (The reality is that at our college, students tend to earn lower grades in psychology than their overall GPA.) Another example: Students routinely report that they thought they had done well on an exam, only to discover, to their dismay, that they were wrong (more on that important problem in a moment). Both errors reveal a breakdown in metacognition.
The Dunning-Kruger Effect
In general, most college students probably do not study enough. For example, using data from the National Survey of Student Engagement, Fosnacht, McCormack, and Lerma (2018) reported that first-year students at 4-year colleges in the U.S. averaged less than 14 hours per week preparing for classes. The typical suggestion is that you should spend two hours outside of class for every hour in class, or 24 – 30 hours per week for a full-time student. Clearly, students in general are nowhere near that recommended mark. Many observers, including some faculty, believe that this shortfall is a result of students being too busy or lazy. Now, it may be true that many students are too busy, with work and family obligations, for example. Others, are not particularly motivated in school, and therefore might correctly be labeled lazy. A third possible explanation, however, is that some students might not think they need to spend this much time. And this is a matter of metacognition. Consider the scenario that we mentioned above, students thinking they had done well on an exam only to discover that they did not. Justin Kruger and David Dunning examined scenarios very much like this in 1999. Kruger and Dunning gave research participants tests measuring humor, logic, and grammar. Then, they asked the participants to assess their own abilities and test performance in these areas. They found that participants in general tended to overestimate their abilities, already a problem with metacognition. Importantly, the participants who scored the lowest overestimated their abilities the most. Specifically, students who scored in the bottom quarter (averaging in the 12th percentile) thought they had scored in the 62nd percentile. This has become known as the Dunning-Kruger effect . Many individual faculty members have replicated these results with their own student on their course exams, including the authors of this book. Think about it. Some students who just took an exam and performed poorly believe that they did well before seeing their score. It seems very likely that these are the very same students who stopped studying the night before because they thought they were “done.” Quite simply, it is not just that they did not know the material. They did not know that they did not know the material. That is poor metacognition.
In order to develop good metacognitive skills, you should continually monitor your thinking and seek frequent feedback on the accuracy of your thinking (Medina, Castleberry, & Persky 2017). For example, in classes get in the habit of predicting your exam grades. As soon as possible after taking an exam, try to find out which questions you missed and try to figure out why. If you do this soon enough, you may be able to recall the way it felt when you originally answered the question. Did you feel confident that you had answered the question correctly? Then you have just discovered an opportunity to improve your metacognition. Be on the lookout for that feeling and respond with caution.
concept : a mental representation of a category of things in the world
Dunning-Kruger effect : individuals who are less competent tend to overestimate their abilities more than individuals who are more competent do
inference : an assumption about the truth of something that is not stated. Inferences come from our prior knowledge and experience, and from logical reasoning
metacognition : knowledge about one’s own cognitive processes; thinking about your thinking
Critical thinking
One particular kind of knowledge or thinking skill that is related to metacognition is critical thinking (Chew, 2020). You may have noticed that critical thinking is an objective in many college courses, and thus it could be a legitimate topic to cover in nearly any college course. It is particularly appropriate in psychology, however. As the science of (behavior and) mental processes, psychology is obviously well suited to be the discipline through which you should be introduced to this important way of thinking.
More importantly, there is a particular need to use critical thinking in psychology. We are all, in a way, experts in human behavior and mental processes, having engaged in them literally since birth. Thus, perhaps more than in any other class, students typically approach psychology with very clear ideas and opinions about its subject matter. That is, students already “know” a lot about psychology. The problem is, “it ain’t so much the things we don’t know that get us into trouble. It’s the things we know that just ain’t so” (Ward, quoted in Gilovich 1991). Indeed, many of students’ preconceptions about psychology are just plain wrong. Randolph Smith (2002) wrote a book about critical thinking in psychology called Challenging Your Preconceptions, highlighting this fact. On the other hand, many of students’ preconceptions about psychology are just plain right! But wait, how do you know which of your preconceptions are right and which are wrong? And when you come across a research finding or theory in this class that contradicts your preconceptions, what will you do? Will you stick to your original idea, discounting the information from the class? Will you immediately change your mind? Critical thinking can help us sort through this confusing mess.
But what is critical thinking? The goal of critical thinking is simple to state (but extraordinarily difficult to achieve): it is to be right, to draw the correct conclusions, to believe in things that are true and to disbelieve things that are false. We will provide two definitions of critical thinking (or, if you like, one large definition with two distinct parts). First, a more conceptual one: Critical thinking is thinking like a scientist in your everyday life (Schmaltz, Jansen, & Wenckowski, 2017). Our second definition is more operational; it is simply a list of skills that are essential to be a critical thinker. Critical thinking entails solid reasoning and problem solving skills; skepticism; and an ability to identify biases, distortions, omissions, and assumptions. Excellent deductive and inductive reasoning, and problem solving skills contribute to critical thinking. So, you can consider the subject matter of sections 7.2 and 7.3 to be part of critical thinking. Because we will be devoting considerable time to these concepts in the rest of the module, let us begin with a discussion about the other aspects of critical thinking.
Let’s address that first part of the definition. Scientists form hypotheses, or predictions about some possible future observations. Then, they collect data, or information (think of this as making those future observations). They do their best to make unbiased observations using reliable techniques that have been verified by others. Then, and only then, they draw a conclusion about what those observations mean. Oh, and do not forget the most important part. “Conclusion” is probably not the most appropriate word because this conclusion is only tentative. A scientist is always prepared that someone else might come along and produce new observations that would require a new conclusion be drawn. Wow! If you like to be right, you could do a lot worse than using a process like this.
A Critical Thinker’s Toolkit
Now for the second part of the definition. Good critical thinkers (and scientists) rely on a variety of tools to evaluate information. Perhaps the most recognizable tool for critical thinking is skepticism (and this term provides the clearest link to the thinking like a scientist definition, as you are about to see). Some people intend it as an insult when they call someone a skeptic. But if someone calls you a skeptic, if they are using the term correctly, you should consider it a great compliment. Simply put, skepticism is a way of thinking in which you refrain from drawing a conclusion or changing your mind until good evidence has been provided. People from Missouri should recognize this principle, as Missouri is known as the Show-Me State. As a skeptic, you are not inclined to believe something just because someone said so, because someone else believes it, or because it sounds reasonable. You must be persuaded by high quality evidence.
Of course, if that evidence is produced, you have a responsibility as a skeptic to change your belief. Failure to change a belief in the face of good evidence is not skepticism; skepticism has open mindedness at its core. M. Neil Browne and Stuart Keeley (2018) use the term weak sense critical thinking to describe critical thinking behaviors that are used only to strengthen a prior belief. Strong sense critical thinking, on the other hand, has as its goal reaching the best conclusion. Sometimes that means strengthening your prior belief, but sometimes it means changing your belief to accommodate the better evidence.
Many times, a failure to think critically or weak sense critical thinking is related to a bias , an inclination, tendency, leaning, or prejudice. Everybody has biases, but many people are unaware of them. Awareness of your own biases gives you the opportunity to control or counteract them. Unfortunately, however, many people are happy to let their biases creep into their attempts to persuade others; indeed, it is a key part of their persuasive strategy. To see how these biases influence messages, just look at the different descriptions and explanations of the same events given by people of different ages or income brackets, or conservative versus liberal commentators, or by commentators from different parts of the world. Of course, to be successful, these people who are consciously using their biases must disguise them. Even undisguised biases can be difficult to identify, so disguised ones can be nearly impossible.
Here are some common sources of biases:
- Personal values and beliefs. Some people believe that human beings are basically driven to seek power and that they are typically in competition with one another over scarce resources. These beliefs are similar to the world-view that political scientists call “realism.” Other people believe that human beings prefer to cooperate and that, given the chance, they will do so. These beliefs are similar to the world-view known as “idealism.” For many people, these deeply held beliefs can influence, or bias, their interpretations of such wide ranging situations as the behavior of nations and their leaders or the behavior of the driver in the car ahead of you. For example, if your worldview is that people are typically in competition and someone cuts you off on the highway, you may assume that the driver did it purposely to get ahead of you. Other types of beliefs about the way the world is or the way the world should be, for example, political beliefs, can similarly become a significant source of bias.
- Racism, sexism, ageism and other forms of prejudice and bigotry. These are, sadly, a common source of bias in many people. They are essentially a special kind of “belief about the way the world is.” These beliefs—for example, that women do not make effective leaders—lead people to ignore contradictory evidence (examples of effective women leaders, or research that disputes the belief) and to interpret ambiguous evidence in a way consistent with the belief.
- Self-interest. When particular people benefit from things turning out a certain way, they can sometimes be very susceptible to letting that interest bias them. For example, a company that will earn a profit if they sell their product may have a bias in the way that they give information about their product. A union that will benefit if its members get a generous contract might have a bias in the way it presents information about salaries at competing organizations. (Note that our inclusion of examples describing both companies and unions is an explicit attempt to control for our own personal biases). Home buyers are often dismayed to discover that they purchased their dream house from someone whose self-interest led them to lie about flooding problems in the basement or back yard. This principle, the biasing power of self-interest, is likely what led to the famous phrase Caveat Emptor (let the buyer beware) .
Knowing that these types of biases exist will help you evaluate evidence more critically. Do not forget, though, that people are not always keen to let you discover the sources of biases in their arguments. For example, companies or political organizations can sometimes disguise their support of a research study by contracting with a university professor, who comes complete with a seemingly unbiased institutional affiliation, to conduct the study.
People’s biases, conscious or unconscious, can lead them to make omissions, distortions, and assumptions that undermine our ability to correctly evaluate evidence. It is essential that you look for these elements. Always ask, what is missing, what is not as it appears, and what is being assumed here? For example, consider this (fictional) chart from an ad reporting customer satisfaction at 4 local health clubs.
Clearly, from the results of the chart, one would be tempted to give Club C a try, as customer satisfaction is much higher than for the other 3 clubs.
There are so many distortions and omissions in this chart, however, that it is actually quite meaningless. First, how was satisfaction measured? Do the bars represent responses to a survey? If so, how were the questions asked? Most importantly, where is the missing scale for the chart? Although the differences look quite large, are they really?
Well, here is the same chart, with a different scale, this time labeled:
Club C is not so impressive any more, is it? In fact, all of the health clubs have customer satisfaction ratings (whatever that means) between 85% and 88%. In the first chart, the entire scale of the graph included only the percentages between 83 and 89. This “judicious” choice of scale—some would call it a distortion—and omission of that scale from the chart make the tiny differences among the clubs seem important, however.
Also, in order to be a critical thinker, you need to learn to pay attention to the assumptions that underlie a message. Let us briefly illustrate the role of assumptions by touching on some people’s beliefs about the criminal justice system in the US. Some believe that a major problem with our judicial system is that many criminals go free because of legal technicalities. Others believe that a major problem is that many innocent people are convicted of crimes. The simple fact is, both types of errors occur. A person’s conclusion about which flaw in our judicial system is the greater tragedy is based on an assumption about which of these is the more serious error (letting the guilty go free or convicting the innocent). This type of assumption is called a value assumption (Browne and Keeley, 2018). It reflects the differences in values that people develop, differences that may lead us to disregard valid evidence that does not fit in with our particular values.
Oh, by the way, some students probably noticed this, but the seven tips for evaluating information that we shared in Module 1 are related to this. Actually, they are part of this section. The tips are, to a very large degree, set of ideas you can use to help you identify biases, distortions, omissions, and assumptions. If you do not remember this section, we strongly recommend you take a few minutes to review it.
skepticism : a way of thinking in which you refrain from drawing a conclusion or changing your mind until good evidence has been provided
bias : an inclination, tendency, leaning, or prejudice
- Which of your beliefs (or disbeliefs) from the Activate exercise for this section were derived from a process of critical thinking? If some of your beliefs were not based on critical thinking, are you willing to reassess these beliefs? If the answer is no, why do you think that is? If the answer is yes, what concrete steps will you take?
7.2 Reasoning and Judgment
- What percentage of kidnappings are committed by strangers?
- Which area of the house is riskiest: kitchen, bathroom, or stairs?
- What is the most common cancer in the US?
- What percentage of workplace homicides are committed by co-workers?
An essential set of procedural thinking skills is reasoning , the ability to generate and evaluate solid conclusions from a set of statements or evidence. You should note that these conclusions (when they are generated instead of being evaluated) are one key type of inference that we described in Section 7.1. There are two main types of reasoning, deductive and inductive.
Deductive reasoning
Suppose your teacher tells you that if you get an A on the final exam in a course, you will get an A for the whole course. Then, you get an A on the final exam. What will your final course grade be? Most people can see instantly that you can conclude with certainty that you will get an A for the course. This is a type of reasoning called deductive reasoning , which is defined as reasoning in which a conclusion is guaranteed to be true as long as the statements leading to it are true. The three statements can be listed as an argument , with two beginning statements and a conclusion:
Statement 1: If you get an A on the final exam, you will get an A for the course
Statement 2: You get an A on the final exam
Conclusion: You will get an A for the course
This particular arrangement, in which true beginning statements lead to a guaranteed true conclusion, is known as a deductively valid argument . Although deductive reasoning is often the subject of abstract, brain-teasing, puzzle-like word problems, it is actually an extremely important type of everyday reasoning. It is just hard to recognize sometimes. For example, imagine that you are looking for your car keys and you realize that they are either in the kitchen drawer or in your book bag. After looking in the kitchen drawer, you instantly know that they must be in your book bag. That conclusion results from a simple deductive reasoning argument. In addition, solid deductive reasoning skills are necessary for you to succeed in the sciences, philosophy, math, computer programming, and any endeavor involving the use of logic to persuade others to your point of view or to evaluate others’ arguments.
Cognitive psychologists, and before them philosophers, have been quite interested in deductive reasoning, not so much for its practical applications, but for the insights it can offer them about the ways that human beings think. One of the early ideas to emerge from the examination of deductive reasoning is that people learn (or develop) mental versions of rules that allow them to solve these types of reasoning problems (Braine, 1978; Braine, Reiser, & Rumain, 1984). The best way to see this point of view is to realize that there are different possible rules, and some of them are very simple. For example, consider this rule of logic:
therefore q
Logical rules are often presented abstractly, as letters, in order to imply that they can be used in very many specific situations. Here is a concrete version of the of the same rule:
I’ll either have pizza or a hamburger for dinner tonight (p or q)
I won’t have pizza (not p)
Therefore, I’ll have a hamburger (therefore q)
This kind of reasoning seems so natural, so easy, that it is quite plausible that we would use a version of this rule in our daily lives. At least, it seems more plausible than some of the alternative possibilities—for example, that we need to have experience with the specific situation (pizza or hamburger, in this case) in order to solve this type of problem easily. So perhaps there is a form of natural logic (Rips, 1990) that contains very simple versions of logical rules. When we are faced with a reasoning problem that maps onto one of these rules, we use the rule.
But be very careful; things are not always as easy as they seem. Even these simple rules are not so simple. For example, consider the following rule. Many people fail to realize that this rule is just as valid as the pizza or hamburger rule above.
if p, then q
therefore, not p
Concrete version:
If I eat dinner, then I will have dessert
I did not have dessert
Therefore, I did not eat dinner
The simple fact is, it can be very difficult for people to apply rules of deductive logic correctly; as a result, they make many errors when trying to do so. Is this a deductively valid argument or not?
Students who like school study a lot
Students who study a lot get good grades
Jane does not like school
Therefore, Jane does not get good grades
Many people are surprised to discover that this is not a logically valid argument; the conclusion is not guaranteed to be true from the beginning statements. Although the first statement says that students who like school study a lot, it does NOT say that students who do not like school do not study a lot. In other words, it may very well be possible to study a lot without liking school. Even people who sometimes get problems like this right might not be using the rules of deductive reasoning. Instead, they might just be making judgments for examples they know, in this case, remembering instances of people who get good grades despite not liking school.
Making deductive reasoning even more difficult is the fact that there are two important properties that an argument may have. One, it can be valid or invalid (meaning that the conclusion does or does not follow logically from the statements leading up to it). Two, an argument (or more correctly, its conclusion) can be true or false. Here is an example of an argument that is logically valid, but has a false conclusion (at least we think it is false).
Either you are eleven feet tall or the Grand Canyon was created by a spaceship crashing into the earth.
You are not eleven feet tall
Therefore the Grand Canyon was created by a spaceship crashing into the earth
This argument has the exact same form as the pizza or hamburger argument above, making it is deductively valid. The conclusion is so false, however, that it is absurd (of course, the reason the conclusion is false is that the first statement is false). When people are judging arguments, they tend to not observe the difference between deductive validity and the empirical truth of statements or conclusions. If the elements of an argument happen to be true, people are likely to judge the argument logically valid; if the elements are false, they will very likely judge it invalid (Markovits & Bouffard-Bouchard, 1992; Moshman & Franks, 1986). Thus, it seems a stretch to say that people are using these logical rules to judge the validity of arguments. Many psychologists believe that most people actually have very limited deductive reasoning skills (Johnson-Laird, 1999). They argue that when faced with a problem for which deductive logic is required, people resort to some simpler technique, such as matching terms that appear in the statements and the conclusion (Evans, 1982). This might not seem like a problem, but what if reasoners believe that the elements are true and they happen to be wrong; they will would believe that they are using a form of reasoning that guarantees they are correct and yet be wrong.
deductive reasoning : a type of reasoning in which the conclusion is guaranteed to be true any time the statements leading up to it are true
argument : a set of statements in which the beginning statements lead to a conclusion
deductively valid argument : an argument for which true beginning statements guarantee that the conclusion is true
Inductive reasoning and judgment
Every day, you make many judgments about the likelihood of one thing or another. Whether you realize it or not, you are practicing inductive reasoning on a daily basis. In inductive reasoning arguments, a conclusion is likely whenever the statements preceding it are true. The first thing to notice about inductive reasoning is that, by definition, you can never be sure about your conclusion; you can only estimate how likely the conclusion is. Inductive reasoning may lead you to focus on Memory Encoding and Recoding when you study for the exam, but it is possible the instructor will ask more questions about Memory Retrieval instead. Unlike deductive reasoning, the conclusions you reach through inductive reasoning are only probable, not certain. That is why scientists consider inductive reasoning weaker than deductive reasoning. But imagine how hard it would be for us to function if we could not act unless we were certain about the outcome.
Inductive reasoning can be represented as logical arguments consisting of statements and a conclusion, just as deductive reasoning can be. In an inductive argument, you are given some statements and a conclusion (or you are given some statements and must draw a conclusion). An argument is inductively strong if the conclusion would be very probable whenever the statements are true. So, for example, here is an inductively strong argument:
- Statement #1: The forecaster on Channel 2 said it is going to rain today.
- Statement #2: The forecaster on Channel 5 said it is going to rain today.
- Statement #3: It is very cloudy and humid.
- Statement #4: You just heard thunder.
- Conclusion (or judgment): It is going to rain today.
Think of the statements as evidence, on the basis of which you will draw a conclusion. So, based on the evidence presented in the four statements, it is very likely that it will rain today. Will it definitely rain today? Certainly not. We can all think of times that the weather forecaster was wrong.
A true story: Some years ago psychology student was watching a baseball playoff game between the St. Louis Cardinals and the Los Angeles Dodgers. A graphic on the screen had just informed the audience that the Cardinal at bat, (Hall of Fame shortstop) Ozzie Smith, a switch hitter batting left-handed for this plate appearance, had never, in nearly 3000 career at-bats, hit a home run left-handed. The student, who had just learned about inductive reasoning in his psychology class, turned to his companion (a Cardinals fan) and smugly said, “It is an inductively strong argument that Ozzie Smith will not hit a home run.” He turned back to face the television just in time to watch the ball sail over the right field fence for a home run. Although the student felt foolish at the time, he was not wrong. It was an inductively strong argument; 3000 at-bats is an awful lot of evidence suggesting that the Wizard of Ozz (as he was known) would not be hitting one out of the park (think of each at-bat without a home run as a statement in an inductive argument). Sadly (for the die-hard Cubs fan and Cardinals-hating student), despite the strength of the argument, the conclusion was wrong.
Given the possibility that we might draw an incorrect conclusion even with an inductively strong argument, we really want to be sure that we do, in fact, make inductively strong arguments. If we judge something probable, it had better be probable. If we judge something nearly impossible, it had better not happen. Think of inductive reasoning, then, as making reasonably accurate judgments of the probability of some conclusion given a set of evidence.
We base many decisions in our lives on inductive reasoning. For example:
Statement #1: Psychology is not my best subject
Statement #2: My psychology instructor has a reputation for giving difficult exams
Statement #3: My first psychology exam was much harder than I expected
Judgment: The next exam will probably be very difficult.
Decision: I will study tonight instead of watching Netflix.
Some other examples of judgments that people commonly make in a school context include judgments of the likelihood that:
- A particular class will be interesting/useful/difficult
- You will be able to finish writing a paper by next week if you go out tonight
- Your laptop’s battery will last through the next trip to the library
- You will not miss anything important if you skip class tomorrow
- Your instructor will not notice if you skip class tomorrow
- You will be able to find a book that you will need for a paper
- There will be an essay question about Memory Encoding on the next exam
Tversky and Kahneman (1983) recognized that there are two general ways that we might make these judgments; they termed them extensional (i.e., following the laws of probability) and intuitive (i.e., using shortcuts or heuristics, see below). We will use a similar distinction between Type 1 and Type 2 thinking, as described by Keith Stanovich and his colleagues (Evans and Stanovich, 2013; Stanovich and West, 2000). Type 1 thinking is fast, automatic, effortful, and emotional. In fact, it is hardly fair to call it reasoning at all, as judgments just seem to pop into one’s head. Type 2 thinking , on the other hand, is slow, effortful, and logical. So obviously, it is more likely to lead to a correct judgment, or an optimal decision. The problem is, we tend to over-rely on Type 1. Now, we are not saying that Type 2 is the right way to go for every decision or judgment we make. It seems a bit much, for example, to engage in a step-by-step logical reasoning procedure to decide whether we will have chicken or fish for dinner tonight.
Many bad decisions in some very important contexts, however, can be traced back to poor judgments of the likelihood of certain risks or outcomes that result from the use of Type 1 when a more logical reasoning process would have been more appropriate. For example:
Statement #1: It is late at night.
Statement #2: Albert has been drinking beer for the past five hours at a party.
Statement #3: Albert is not exactly sure where he is or how far away home is.
Judgment: Albert will have no difficulty walking home.
Decision: He walks home alone.
As you can see in this example, the three statements backing up the judgment do not really support it. In other words, this argument is not inductively strong because it is based on judgments that ignore the laws of probability. What are the chances that someone facing these conditions will be able to walk home alone easily? And one need not be drunk to make poor decisions based on judgments that just pop into our heads.
The truth is that many of our probability judgments do not come very close to what the laws of probability say they should be. Think about it. In order for us to reason in accordance with these laws, we would need to know the laws of probability, which would allow us to calculate the relationship between particular pieces of evidence and the probability of some outcome (i.e., how much likelihood should change given a piece of evidence), and we would have to do these heavy math calculations in our heads. After all, that is what Type 2 requires. Needless to say, even if we were motivated, we often do not even know how to apply Type 2 reasoning in many cases.
So what do we do when we don’t have the knowledge, skills, or time required to make the correct mathematical judgment? Do we hold off and wait until we can get better evidence? Do we read up on probability and fire up our calculator app so we can compute the correct probability? Of course not. We rely on Type 1 thinking. We “wing it.” That is, we come up with a likelihood estimate using some means at our disposal. Psychologists use the term heuristic to describe the type of “winging it” we are talking about. A heuristic is a shortcut strategy that we use to make some judgment or solve some problem (see Section 7.3). Heuristics are easy and quick, think of them as the basic procedures that are characteristic of Type 1. They can absolutely lead to reasonably good judgments and decisions in some situations (like choosing between chicken and fish for dinner). They are, however, far from foolproof. There are, in fact, quite a lot of situations in which heuristics can lead us to make incorrect judgments, and in many cases the decisions based on those judgments can have serious consequences.
Let us return to the activity that begins this section. You were asked to judge the likelihood (or frequency) of certain events and risks. You were free to come up with your own evidence (or statements) to make these judgments. This is where a heuristic crops up. As a judgment shortcut, we tend to generate specific examples of those very events to help us decide their likelihood or frequency. For example, if we are asked to judge how common, frequent, or likely a particular type of cancer is, many of our statements would be examples of specific cancer cases:
Statement #1: Andy Kaufman (comedian) had lung cancer.
Statement #2: Colin Powell (US Secretary of State) had prostate cancer.
Statement #3: Bob Marley (musician) had skin and brain cancer
Statement #4: Sandra Day O’Connor (Supreme Court Justice) had breast cancer.
Statement #5: Fred Rogers (children’s entertainer) had stomach cancer.
Statement #6: Robin Roberts (news anchor) had breast cancer.
Statement #7: Bette Davis (actress) had breast cancer.
Judgment: Breast cancer is the most common type.
Your own experience or memory may also tell you that breast cancer is the most common type. But it is not (although it is common). Actually, skin cancer is the most common type in the US. We make the same types of misjudgments all the time because we do not generate the examples or evidence according to their actual frequencies or probabilities. Instead, we have a tendency (or bias) to search for the examples in memory; if they are easy to retrieve, we assume that they are common. To rephrase this in the language of the heuristic, events seem more likely to the extent that they are available to memory. This bias has been termed the availability heuristic (Kahneman and Tversky, 1974).
The fact that we use the availability heuristic does not automatically mean that our judgment is wrong. The reason we use heuristics in the first place is that they work fairly well in many cases (and, of course that they are easy to use). So, the easiest examples to think of sometimes are the most common ones. Is it more likely that a member of the U.S. Senate is a man or a woman? Most people have a much easier time generating examples of male senators. And as it turns out, the U.S. Senate has many more men than women (74 to 26 in 2020). In this case, then, the availability heuristic would lead you to make the correct judgment; it is far more likely that a senator would be a man.
In many other cases, however, the availability heuristic will lead us astray. This is because events can be memorable for many reasons other than their frequency. Section 5.2, Encoding Meaning, suggested that one good way to encode the meaning of some information is to form a mental image of it. Thus, information that has been pictured mentally will be more available to memory. Indeed, an event that is vivid and easily pictured will trick many people into supposing that type of event is more common than it actually is. Repetition of information will also make it more memorable. So, if the same event is described to you in a magazine, on the evening news, on a podcast that you listen to, and in your Facebook feed; it will be very available to memory. Again, the availability heuristic will cause you to misperceive the frequency of these types of events.
Most interestingly, information that is unusual is more memorable. Suppose we give you the following list of words to remember: box, flower, letter, platypus, oven, boat, newspaper, purse, drum, car. Very likely, the easiest word to remember would be platypus, the unusual one. The same thing occurs with memories of events. An event may be available to memory because it is unusual, yet the availability heuristic leads us to judge that the event is common. Did you catch that? In these cases, the availability heuristic makes us think the exact opposite of the true frequency. We end up thinking something is common because it is unusual (and therefore memorable). Yikes.
The misapplication of the availability heuristic sometimes has unfortunate results. For example, if you went to K-12 school in the US over the past 10 years, it is extremely likely that you have participated in lockdown and active shooter drills. Of course, everyone is trying to prevent the tragedy of another school shooting. And believe us, we are not trying to minimize how terrible the tragedy is. But the truth of the matter is, school shootings are extremely rare. Because the federal government does not keep a database of school shootings, the Washington Post has maintained their own running tally. Between 1999 and January 2020 (the date of the most recent school shooting with a death in the US at of the time this paragraph was written), the Post reported a total of 254 people died in school shootings in the US. Not 254 per year, 254 total. That is an average of 12 per year. Of course, that is 254 people who should not have died (particularly because many were children), but in a country with approximately 60,000,000 students and teachers, this is a very small risk.
But many students and teachers are terrified that they will be victims of school shootings because of the availability heuristic. It is so easy to think of examples (they are very available to memory) that people believe the event is very common. It is not. And there is a downside to this. We happen to believe that there is an enormous gun violence problem in the United States. According the the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, there were 39,773 firearm deaths in the US in 2017. Fifteen of those deaths were in school shootings, according to the Post. 60% of those deaths were suicides. When people pay attention to the school shooting risk (low), they often fail to notice the much larger risk.
And examples like this are by no means unique. The authors of this book have been teaching psychology since the 1990’s. We have been able to make the exact same arguments about the misapplication of the availability heuristics and keep them current by simply swapping out for the “fear of the day.” In the 1990’s it was children being kidnapped by strangers (it was known as “stranger danger”) despite the facts that kidnappings accounted for only 2% of the violent crimes committed against children, and only 24% of kidnappings are committed by strangers (US Department of Justice, 2007). This fear overlapped with the fear of terrorism that gripped the country after the 2001 terrorist attacks on the World Trade Center and US Pentagon and still plagues the population of the US somewhat in 2020. After a well-publicized, sensational act of violence, people are extremely likely to increase their estimates of the chances that they, too, will be victims of terror. Think about the reality, however. In October of 2001, a terrorist mailed anthrax spores to members of the US government and a number of media companies. A total of five people died as a result of this attack. The nation was nearly paralyzed by the fear of dying from the attack; in reality the probability of an individual person dying was 0.00000002.
The availability heuristic can lead you to make incorrect judgments in a school setting as well. For example, suppose you are trying to decide if you should take a class from a particular math professor. You might try to make a judgment of how good a teacher she is by recalling instances of friends and acquaintances making comments about her teaching skill. You may have some examples that suggest that she is a poor teacher very available to memory, so on the basis of the availability heuristic you judge her a poor teacher and decide to take the class from someone else. What if, however, the instances you recalled were all from the same person, and this person happens to be a very colorful storyteller? The subsequent ease of remembering the instances might not indicate that the professor is a poor teacher after all.
Although the availability heuristic is obviously important, it is not the only judgment heuristic we use. Amos Tversky and Daniel Kahneman examined the role of heuristics in inductive reasoning in a long series of studies. Kahneman received a Nobel Prize in Economics for this research in 2002, and Tversky would have certainly received one as well if he had not died of melanoma at age 59 in 1996 (Nobel Prizes are not awarded posthumously). Kahneman and Tversky demonstrated repeatedly that people do not reason in ways that are consistent with the laws of probability. They identified several heuristic strategies that people use instead to make judgments about likelihood. The importance of this work for economics (and the reason that Kahneman was awarded the Nobel Prize) is that earlier economic theories had assumed that people do make judgments rationally, that is, in agreement with the laws of probability.
Another common heuristic that people use for making judgments is the representativeness heuristic (Kahneman & Tversky 1973). Suppose we describe a person to you. He is quiet and shy, has an unassuming personality, and likes to work with numbers. Is this person more likely to be an accountant or an attorney? If you said accountant, you were probably using the representativeness heuristic. Our imaginary person is judged likely to be an accountant because he resembles, or is representative of the concept of, an accountant. When research participants are asked to make judgments such as these, the only thing that seems to matter is the representativeness of the description. For example, if told that the person described is in a room that contains 70 attorneys and 30 accountants, participants will still assume that he is an accountant.
inductive reasoning : a type of reasoning in which we make judgments about likelihood from sets of evidence
inductively strong argument : an inductive argument in which the beginning statements lead to a conclusion that is probably true
heuristic : a shortcut strategy that we use to make judgments and solve problems. Although they are easy to use, they do not guarantee correct judgments and solutions
availability heuristic : judging the frequency or likelihood of some event type according to how easily examples of the event can be called to mind (i.e., how available they are to memory)
representativeness heuristic: judging the likelihood that something is a member of a category on the basis of how much it resembles a typical category member (i.e., how representative it is of the category)
Type 1 thinking : fast, automatic, and emotional thinking.
Type 2 thinking : slow, effortful, and logical thinking.
- What percentage of workplace homicides are co-worker violence?
Many people get these questions wrong. The answers are 10%; stairs; skin; 6%. How close were your answers? Explain how the availability heuristic might have led you to make the incorrect judgments.
- Can you think of some other judgments that you have made (or beliefs that you have) that might have been influenced by the availability heuristic?
7.3 Problem Solving
- Please take a few minutes to list a number of problems that you are facing right now.
- Now write about a problem that you recently solved.
- What is your definition of a problem?
Mary has a problem. Her daughter, ordinarily quite eager to please, appears to delight in being the last person to do anything. Whether getting ready for school, going to piano lessons or karate class, or even going out with her friends, she seems unwilling or unable to get ready on time. Other people have different kinds of problems. For example, many students work at jobs, have numerous family commitments, and are facing a course schedule full of difficult exams, assignments, papers, and speeches. How can they find enough time to devote to their studies and still fulfill their other obligations? Speaking of students and their problems: Show that a ball thrown vertically upward with initial velocity v0 takes twice as much time to return as to reach the highest point (from Spiegel, 1981).
These are three very different situations, but we have called them all problems. What makes them all the same, despite the differences? A psychologist might define a problem as a situation with an initial state, a goal state, and a set of possible intermediate states. Somewhat more meaningfully, we might consider a problem a situation in which you are in here one state (e.g., daughter is always late), you want to be there in another state (e.g., daughter is not always late), and with no obvious way to get from here to there. Defined this way, each of the three situations we outlined can now be seen as an example of the same general concept, a problem. At this point, you might begin to wonder what is not a problem, given such a general definition. It seems that nearly every non-routine task we engage in could qualify as a problem. As long as you realize that problems are not necessarily bad (it can be quite fun and satisfying to rise to the challenge and solve a problem), this may be a useful way to think about it.
Can we identify a set of problem-solving skills that would apply to these very different kinds of situations? That task, in a nutshell, is a major goal of this section. Let us try to begin to make sense of the wide variety of ways that problems can be solved with an important observation: the process of solving problems can be divided into two key parts. First, people have to notice, comprehend, and represent the problem properly in their minds (called problem representation ). Second, they have to apply some kind of solution strategy to the problem. Psychologists have studied both of these key parts of the process in detail.
When you first think about the problem-solving process, you might guess that most of our difficulties would occur because we are failing in the second step, the application of strategies. Although this can be a significant difficulty much of the time, the more important source of difficulty is probably problem representation. In short, we often fail to solve a problem because we are looking at it, or thinking about it, the wrong way.
problem : a situation in which we are in an initial state, have a desired goal state, and there is a number of possible intermediate states (i.e., there is no obvious way to get from the initial to the goal state)
problem representation : noticing, comprehending and forming a mental conception of a problem
Defining and Mentally Representing Problems in Order to Solve Them
So, the main obstacle to solving a problem is that we do not clearly understand exactly what the problem is. Recall the problem with Mary’s daughter always being late. One way to represent, or to think about, this problem is that she is being defiant. She refuses to get ready in time. This type of representation or definition suggests a particular type of solution. Another way to think about the problem, however, is to consider the possibility that she is simply being sidetracked by interesting diversions. This different conception of what the problem is (i.e., different representation) suggests a very different solution strategy. For example, if Mary defines the problem as defiance, she may be tempted to solve the problem using some kind of coercive tactics, that is, to assert her authority as her mother and force her to listen. On the other hand, if Mary defines the problem as distraction, she may try to solve it by simply removing the distracting objects.
As you might guess, when a problem is represented one way, the solution may seem very difficult, or even impossible. Seen another way, the solution might be very easy. For example, consider the following problem (from Nasar, 1998):
Two bicyclists start 20 miles apart and head toward each other, each going at a steady rate of 10 miles per hour. At the same time, a fly that travels at a steady 15 miles per hour starts from the front wheel of the southbound bicycle and flies to the front wheel of the northbound one, then turns around and flies to the front wheel of the southbound one again, and continues in this manner until he is crushed between the two front wheels. Question: what total distance did the fly cover?
Please take a few minutes to try to solve this problem.
Most people represent this problem as a question about a fly because, well, that is how the question is asked. The solution, using this representation, is to figure out how far the fly travels on the first leg of its journey, then add this total to how far it travels on the second leg of its journey (when it turns around and returns to the first bicycle), then continue to add the smaller distance from each leg of the journey until you converge on the correct answer. You would have to be quite skilled at math to solve this problem, and you would probably need some time and pencil and paper to do it.
If you consider a different representation, however, you can solve this problem in your head. Instead of thinking about it as a question about a fly, think about it as a question about the bicycles. They are 20 miles apart, and each is traveling 10 miles per hour. How long will it take for the bicycles to reach each other? Right, one hour. The fly is traveling 15 miles per hour; therefore, it will travel a total of 15 miles back and forth in the hour before the bicycles meet. Represented one way (as a problem about a fly), the problem is quite difficult. Represented another way (as a problem about two bicycles), it is easy. Changing your representation of a problem is sometimes the best—sometimes the only—way to solve it.
Unfortunately, however, changing a problem’s representation is not the easiest thing in the world to do. Often, problem solvers get stuck looking at a problem one way. This is called fixation . Most people who represent the preceding problem as a problem about a fly probably do not pause to reconsider, and consequently change, their representation. A parent who thinks her daughter is being defiant is unlikely to consider the possibility that her behavior is far less purposeful.
Problem-solving fixation was examined by a group of German psychologists called Gestalt psychologists during the 1930’s and 1940’s. Karl Dunker, for example, discovered an important type of failure to take a different perspective called functional fixedness . Imagine being a participant in one of his experiments. You are asked to figure out how to mount two candles on a door and are given an assortment of odds and ends, including a small empty cardboard box and some thumbtacks. Perhaps you have already figured out a solution: tack the box to the door so it forms a platform, then put the candles on top of the box. Most people are able to arrive at this solution. Imagine a slight variation of the procedure, however. What if, instead of being empty, the box had matches in it? Most people given this version of the problem do not arrive at the solution given above. Why? Because it seems to people that when the box contains matches, it already has a function; it is a matchbox. People are unlikely to consider a new function for an object that already has a function. This is functional fixedness.
Mental set is a type of fixation in which the problem solver gets stuck using the same solution strategy that has been successful in the past, even though the solution may no longer be useful. It is commonly seen when students do math problems for homework. Often, several problems in a row require the reapplication of the same solution strategy. Then, without warning, the next problem in the set requires a new strategy. Many students attempt to apply the formerly successful strategy on the new problem and therefore cannot come up with a correct answer.
The thing to remember is that you cannot solve a problem unless you correctly identify what it is to begin with (initial state) and what you want the end result to be (goal state). That may mean looking at the problem from a different angle and representing it in a new way. The correct representation does not guarantee a successful solution, but it certainly puts you on the right track.
A bit more optimistically, the Gestalt psychologists discovered what may be considered the opposite of fixation, namely insight . Sometimes the solution to a problem just seems to pop into your head. Wolfgang Kohler examined insight by posing many different problems to chimpanzees, principally problems pertaining to their acquisition of out-of-reach food. In one version, a banana was placed outside of a chimpanzee’s cage and a short stick inside the cage. The stick was too short to retrieve the banana, but was long enough to retrieve a longer stick also located outside of the cage. This second stick was long enough to retrieve the banana. After trying, and failing, to reach the banana with the shorter stick, the chimpanzee would try a couple of random-seeming attempts, react with some apparent frustration or anger, then suddenly rush to the longer stick, the correct solution fully realized at this point. This sudden appearance of the solution, observed many times with many different problems, was termed insight by Kohler.
Lest you think it pertains to chimpanzees only, Karl Dunker demonstrated that children also solve problems through insight in the 1930s. More importantly, you have probably experienced insight yourself. Think back to a time when you were trying to solve a difficult problem. After struggling for a while, you gave up. Hours later, the solution just popped into your head, perhaps when you were taking a walk, eating dinner, or lying in bed.
fixation : when a problem solver gets stuck looking at a problem a particular way and cannot change his or her representation of it (or his or her intended solution strategy)
functional fixedness : a specific type of fixation in which a problem solver cannot think of a new use for an object that already has a function
mental set : a specific type of fixation in which a problem solver gets stuck using the same solution strategy that has been successful in the past
insight : a sudden realization of a solution to a problem
Solving Problems by Trial and Error
Correctly identifying the problem and your goal for a solution is a good start, but recall the psychologist’s definition of a problem: it includes a set of possible intermediate states. Viewed this way, a problem can be solved satisfactorily only if one can find a path through some of these intermediate states to the goal. Imagine a fairly routine problem, finding a new route to school when your ordinary route is blocked (by road construction, for example). At each intersection, you may turn left, turn right, or go straight. A satisfactory solution to the problem (of getting to school) is a sequence of selections at each intersection that allows you to wind up at school.
If you had all the time in the world to get to school, you might try choosing intermediate states randomly. At one corner you turn left, the next you go straight, then you go left again, then right, then right, then straight. Unfortunately, trial and error will not necessarily get you where you want to go, and even if it does, it is not the fastest way to get there. For example, when a friend of ours was in college, he got lost on the way to a concert and attempted to find the venue by choosing streets to turn onto randomly (this was long before the use of GPS). Amazingly enough, the strategy worked, although he did end up missing two out of the three bands who played that night.
Trial and error is not all bad, however. B.F. Skinner, a prominent behaviorist psychologist, suggested that people often behave randomly in order to see what effect the behavior has on the environment and what subsequent effect this environmental change has on them. This seems particularly true for the very young person. Picture a child filling a household’s fish tank with toilet paper, for example. To a child trying to develop a repertoire of creative problem-solving strategies, an odd and random behavior might be just the ticket. Eventually, the exasperated parent hopes, the child will discover that many of these random behaviors do not successfully solve problems; in fact, in many cases they create problems. Thus, one would expect a decrease in this random behavior as a child matures. You should realize, however, that the opposite extreme is equally counterproductive. If the children become too rigid, never trying something unexpected and new, their problem solving skills can become too limited.
Effective problem solving seems to call for a happy medium that strikes a balance between using well-founded old strategies and trying new ground and territory. The individual who recognizes a situation in which an old problem-solving strategy would work best, and who can also recognize a situation in which a new untested strategy is necessary is halfway to success.
Solving Problems with Algorithms and Heuristics
For many problems there is a possible strategy available that will guarantee a correct solution. For example, think about math problems. Math lessons often consist of step-by-step procedures that can be used to solve the problems. If you apply the strategy without error, you are guaranteed to arrive at the correct solution to the problem. This approach is called using an algorithm , a term that denotes the step-by-step procedure that guarantees a correct solution. Because algorithms are sometimes available and come with a guarantee, you might think that most people use them frequently. Unfortunately, however, they do not. As the experience of many students who have struggled through math classes can attest, algorithms can be extremely difficult to use, even when the problem solver knows which algorithm is supposed to work in solving the problem. In problems outside of math class, we often do not even know if an algorithm is available. It is probably fair to say, then, that algorithms are rarely used when people try to solve problems.
Because algorithms are so difficult to use, people often pass up the opportunity to guarantee a correct solution in favor of a strategy that is much easier to use and yields a reasonable chance of coming up with a correct solution. These strategies are called problem solving heuristics . Similar to what you saw in section 6.2 with reasoning heuristics, a problem solving heuristic is a shortcut strategy that people use when trying to solve problems. It usually works pretty well, but does not guarantee a correct solution to the problem. For example, one problem solving heuristic might be “always move toward the goal” (so when trying to get to school when your regular route is blocked, you would always turn in the direction you think the school is). A heuristic that people might use when doing math homework is “use the same solution strategy that you just used for the previous problem.”
By the way, we hope these last two paragraphs feel familiar to you. They seem to parallel a distinction that you recently learned. Indeed, algorithms and problem-solving heuristics are another example of the distinction between Type 1 thinking and Type 2 thinking.
Although it is probably not worth describing a large number of specific heuristics, two observations about heuristics are worth mentioning. First, heuristics can be very general or they can be very specific, pertaining to a particular type of problem only. For example, “always move toward the goal” is a general strategy that you can apply to countless problem situations. On the other hand, “when you are lost without a functioning gps, pick the most expensive car you can see and follow it” is specific to the problem of being lost. Second, all heuristics are not equally useful. One heuristic that many students know is “when in doubt, choose c for a question on a multiple-choice exam.” This is a dreadful strategy because many instructors intentionally randomize the order of answer choices. Another test-taking heuristic, somewhat more useful, is “look for the answer to one question somewhere else on the exam.”
You really should pay attention to the application of heuristics to test taking. Imagine that while reviewing your answers for a multiple-choice exam before turning it in, you come across a question for which you originally thought the answer was c. Upon reflection, you now think that the answer might be b. Should you change the answer to b, or should you stick with your first impression? Most people will apply the heuristic strategy to “stick with your first impression.” What they do not realize, of course, is that this is a very poor strategy (Lilienfeld et al, 2009). Most of the errors on exams come on questions that were answered wrong originally and were not changed (so they remain wrong). There are many fewer errors where we change a correct answer to an incorrect answer. And, of course, sometimes we change an incorrect answer to a correct answer. In fact, research has shown that it is more common to change a wrong answer to a right answer than vice versa (Bruno, 2001).
The belief in this poor test-taking strategy (stick with your first impression) is based on the confirmation bias (Nickerson, 1998; Wason, 1960). You first saw the confirmation bias in Module 1, but because it is so important, we will repeat the information here. People have a bias, or tendency, to notice information that confirms what they already believe. Somebody at one time told you to stick with your first impression, so when you look at the results of an exam you have taken, you will tend to notice the cases that are consistent with that belief. That is, you will notice the cases in which you originally had an answer correct and changed it to the wrong answer. You tend not to notice the other two important (and more common) cases, changing an answer from wrong to right, and leaving a wrong answer unchanged.
Because heuristics by definition do not guarantee a correct solution to a problem, mistakes are bound to occur when we employ them. A poor choice of a specific heuristic will lead to an even higher likelihood of making an error.
algorithm : a step-by-step procedure that guarantees a correct solution to a problem
problem solving heuristic : a shortcut strategy that we use to solve problems. Although they are easy to use, they do not guarantee correct judgments and solutions
confirmation bias : people’s tendency to notice information that confirms what they already believe
An Effective Problem-Solving Sequence
You may be left with a big question: If algorithms are hard to use and heuristics often don’t work, how am I supposed to solve problems? Robert Sternberg (1996), as part of his theory of what makes people successfully intelligent (Module 8) described a problem-solving sequence that has been shown to work rather well:
- Identify the existence of a problem. In school, problem identification is often easy; problems that you encounter in math classes, for example, are conveniently labeled as problems for you. Outside of school, however, realizing that you have a problem is a key difficulty that you must get past in order to begin solving it. You must be very sensitive to the symptoms that indicate a problem.
- Define the problem. Suppose you realize that you have been having many headaches recently. Very likely, you would identify this as a problem. If you define the problem as “headaches,” the solution would probably be to take aspirin or ibuprofen or some other anti-inflammatory medication. If the headaches keep returning, however, you have not really solved the problem—likely because you have mistaken a symptom for the problem itself. Instead, you must find the root cause of the headaches. Stress might be the real problem. For you to successfully solve many problems it may be necessary for you to overcome your fixations and represent the problems differently. One specific strategy that you might find useful is to try to define the problem from someone else’s perspective. How would your parents, spouse, significant other, doctor, etc. define the problem? Somewhere in these different perspectives may lurk the key definition that will allow you to find an easier and permanent solution.
- Formulate strategy. Now it is time to begin planning exactly how the problem will be solved. Is there an algorithm or heuristic available for you to use? Remember, heuristics by their very nature guarantee that occasionally you will not be able to solve the problem. One point to keep in mind is that you should look for long-range solutions, which are more likely to address the root cause of a problem than short-range solutions.
- Represent and organize information. Similar to the way that the problem itself can be defined, or represented in multiple ways, information within the problem is open to different interpretations. Suppose you are studying for a big exam. You have chapters from a textbook and from a supplemental reader, along with lecture notes that all need to be studied. How should you (represent and) organize these materials? Should you separate them by type of material (text versus reader versus lecture notes), or should you separate them by topic? To solve problems effectively, you must learn to find the most useful representation and organization of information.
- Allocate resources. This is perhaps the simplest principle of the problem solving sequence, but it is extremely difficult for many people. First, you must decide whether time, money, skills, effort, goodwill, or some other resource would help to solve the problem Then, you must make the hard choice of deciding which resources to use, realizing that you cannot devote maximum resources to every problem. Very often, the solution to problem is simply to change how resources are allocated (for example, spending more time studying in order to improve grades).
- Monitor and evaluate solutions. Pay attention to the solution strategy while you are applying it. If it is not working, you may be able to select another strategy. Another fact you should realize about problem solving is that it never does end. Solving one problem frequently brings up new ones. Good monitoring and evaluation of your problem solutions can help you to anticipate and get a jump on solving the inevitable new problems that will arise.
Please note that this as an effective problem-solving sequence, not the effective problem solving sequence. Just as you can become fixated and end up representing the problem incorrectly or trying an inefficient solution, you can become stuck applying the problem-solving sequence in an inflexible way. Clearly there are problem situations that can be solved without using these skills in this order.
Additionally, many real-world problems may require that you go back and redefine a problem several times as the situation changes (Sternberg et al. 2000). For example, consider the problem with Mary’s daughter one last time. At first, Mary did represent the problem as one of defiance. When her early strategy of pleading and threatening punishment was unsuccessful, Mary began to observe her daughter more carefully. She noticed that, indeed, her daughter’s attention would be drawn by an irresistible distraction or book. Fresh with a re-representation of the problem, she began a new solution strategy. She began to remind her daughter every few minutes to stay on task and remind her that if she is ready before it is time to leave, she may return to the book or other distracting object at that time. Fortunately, this strategy was successful, so Mary did not have to go back and redefine the problem again.
Pick one or two of the problems that you listed when you first started studying this section and try to work out the steps of Sternberg’s problem solving sequence for each one.
a mental representation of a category of things in the world
an assumption about the truth of something that is not stated. Inferences come from our prior knowledge and experience, and from logical reasoning
knowledge about one’s own cognitive processes; thinking about your thinking
individuals who are less competent tend to overestimate their abilities more than individuals who are more competent do
Thinking like a scientist in your everyday life for the purpose of drawing correct conclusions. It entails skepticism; an ability to identify biases, distortions, omissions, and assumptions; and excellent deductive and inductive reasoning, and problem solving skills.
a way of thinking in which you refrain from drawing a conclusion or changing your mind until good evidence has been provided
an inclination, tendency, leaning, or prejudice
a type of reasoning in which the conclusion is guaranteed to be true any time the statements leading up to it are true
a set of statements in which the beginning statements lead to a conclusion
an argument for which true beginning statements guarantee that the conclusion is true
a type of reasoning in which we make judgments about likelihood from sets of evidence
an inductive argument in which the beginning statements lead to a conclusion that is probably true
fast, automatic, and emotional thinking
slow, effortful, and logical thinking
a shortcut strategy that we use to make judgments and solve problems. Although they are easy to use, they do not guarantee correct judgments and solutions
udging the frequency or likelihood of some event type according to how easily examples of the event can be called to mind (i.e., how available they are to memory)
judging the likelihood that something is a member of a category on the basis of how much it resembles a typical category member (i.e., how representative it is of the category)
a situation in which we are in an initial state, have a desired goal state, and there is a number of possible intermediate states (i.e., there is no obvious way to get from the initial to the goal state)
noticing, comprehending and forming a mental conception of a problem
when a problem solver gets stuck looking at a problem a particular way and cannot change his or her representation of it (or his or her intended solution strategy)
a specific type of fixation in which a problem solver cannot think of a new use for an object that already has a function
a specific type of fixation in which a problem solver gets stuck using the same solution strategy that has been successful in the past
a sudden realization of a solution to a problem
a step-by-step procedure that guarantees a correct solution to a problem
The tendency to notice and pay attention to information that confirms your prior beliefs and to ignore information that disconfirms them.
a shortcut strategy that we use to solve problems. Although they are easy to use, they do not guarantee correct judgments and solutions
Introduction to Psychology Copyright © 2020 by Ken Gray; Elizabeth Arnott-Hill; and Or'Shaundra Benson is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- Brain Development
- Childhood & Adolescence
- Diet & Lifestyle
- Emotions, Stress & Anxiety
- Learning & Memory
- Thinking & Awareness
- Alzheimer's & Dementia
- Childhood Disorders
- Immune System Disorders
- Mental Health
- Neurodegenerative Disorders
- Infectious Disease
- Neurological Disorders A-Z
- Body Systems
- Cells & Circuits
- Genes & Molecules
- The Arts & the Brain
- Law, Economics & Ethics
- Neuroscience in the News
- Supporting Research
- Tech & the Brain
- Animals in Research
- BRAIN Initiative
- Meet the Researcher
- Neuro-technologies
- Tools & Techniques
- Core Concepts
- For Educators
- Ask an Expert
- The Brain Facts Book

Test Your Problem-Solving Skills
Personalize your emails.
Personalize your monthly updates from BrainFacts.org by choosing the topics that you care about most!
Find a Neuroscientist
Engage local scientists to educate your community about the brain.
Image of the Week
Check out the Image of the Week Archive.

SUPPORTING PARTNERS
- Privacy Policy
- Accessibility Policy
- Terms and Conditions
- Manage Cookies
Some pages on this website provide links that require Adobe Reader to view.
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Critical Thinking Is About Asking Better Questions
- John Coleman

Six practices to sharpen your inquiry.
Critical thinking is the ability to analyze and effectively break down an issue in order to make a decision or find a solution. At the heart of critical thinking is the ability to formulate deep, different, and effective questions. For effective questioning, start by holding your hypotheses loosely. Be willing to fundamentally reconsider your initial conclusions — and do so without defensiveness. Second, listen more than you talk through active listening. Third, leave your queries open-ended, and avoid yes-or-no questions. Fourth, consider the counterintuitive to avoid falling into groupthink. Fifth, take the time to stew in a problem, rather than making decisions unnecessarily quickly. Last, ask thoughtful, even difficult, follow-ups.
Are you tackling a new and difficult problem at work? Recently promoted and trying to both understand your new role and bring a fresh perspective? Or are you new to the workforce and seeking ways to meaningfully contribute alongside your more experienced colleagues? If so, critical thinking — the ability to analyze and effectively break down an issue in order to make a decision or find a solution — will be core to your success. And at the heart of critical thinking is the ability to formulate deep, different, and effective questions.
- JC John Coleman is the author of the HBR Guide to Crafting Your Purpose . Subscribe to his free newsletter, On Purpose , follow him on Twitter @johnwcoleman, or contact him at johnwilliamcoleman.com.
Partner Center
The service you are accessing is either under high load or has detected unusual activity from your network location.
To protect this service from abuse please complete the challenge below to continue.
What code is in the image? submit
Your unique support ID for this request is: 15816054534512002597.
If you see this challenge frequently or believe you are seeing it in error please record this ID and contact the Deakin University IT Service Desk . Additional information is available from the IT Knowledge Base .
Logical Reasoning Questions and Answers
Logical reasoning interview questions and answers.
Here you can find Logical Reasoning interview questions and answers for your placement interviews and entrance exam preparation.
Why should I learn to solve Logical Reasoning questions?
Learn and practise solving Logical Reasoning questions to enhance your skills so that you can clear interviews, competitive examinations, and various entrance tests (CAT, GATE, GRE, MAT, bank exams, railway exams, etc.) with full confidence.
Where can I get Logical Reasoning questions and answers with explanations?
IndiaBIX provides you with numerous Logical Reasoning questions and answers with explanations. Fully solved problems with detailed answer descriptions and explanations are given and will be easy to understand.
Where can I get Logical Reasoning MCQ interview questions and answers (objective type, multiple choice)?
Here you can find multiple-choice-type Logical Reasoning questions and answers for your interviews and entrance examinations. Objective-type and true-or-false-type questions are also given here.
How do I download Logical Reasoning questions in PDF format?
You can download Logical Reasoning quiz questions and answers as PDF files or eBooks.
How do I solve Logical Reasoning quiz problems?
You can easily solve all kinds of quiz questions based on Logical Reasoning by practising the given exercises, including shortcuts and tricks.
- Number Series
- Letter and Symbol Series
- Verbal Classification
- Essential Part
- Artificial Language
- Matching Definitions
- Making Judgments
- Verbal Reasoning
- Logical Problems
- Logical Games
- Analyzing Arguments
- Statement and Assumption
- Course of Action
- Statement and Conclusion
- Theme Detection
- Cause and Effect
- Statement and Argument
- Logical Deduction
Current Affairs
Interview questions, group discussions.
- Data Interpretation
- Verbal Ability
- Verbal Test
- C Programming
- Technical Interview
- Placement Papers
- Submit Paper

- Search Search Search …
- Search Search …
Critical thinking puzzles for adults (with answers)

Critical thinking can help to better navigate the information-dense and complex world we live in. By thinking critically we can better identify priorities, take a sensible approach to problem-solving and reach conclusions logically in line with evidence. Puzzles are an excellent way both to learn and practice critical thinking skills.
If you’d like to learn more about critical thinking or simply practice your skills with some puzzles, then this is the article for you. Read a little bit more about critical thinking skills and how to apply them first, or just skip straight to the puzzles and see how you get on.
What is critical thinking?
Critical thinking is a broad approach to problem solving and analysis based on logic and evidence. It brings together a wide range of intellectual competences and the ability to combine and cross-reference them. Some of the most important elements of a critical thinking approach include:
Analytical skills:
- understanding of questions and concepts
- differentiation of relevant / irrelevant evidence and information
- identification of similarities, connections and differences
- use of metaphors or analogies to communicate ideas
Powers of inference:
- extraction of meaning from data using inductive or deductive reasoning
- extrapolation of data or abstraction into concepts and patterns
- correct identification and deployment of analogies and assumptions
- grasp of causal relationships, allowing development of conclusions and theories.
Data and theory evaluation:
- assessment of how strong, important or credible a theory might be
- taking on board new data and new arguments which alter understanding of ideas and theory
Rational decision-making:
– application of all the skills and competences above in order to come to a rational conclusion.
Problem-solving attitude: In addition to being able to think critically, you must also be personally inclined to think critically when facing a difficult or complex challenge. Developing qualities including curiosity and fairness, while distancing yourself from ideologies and group-think, should all help to create the kind of psychological landscape where critical thinking can flourish.
How can I learn critical thinking?
Critical thinking skills are hard to develop from only reading books or listening to lectures. The most effective way to sharpen and deepen critical thinking faculties is to practice critical thinking . Critical thinking puzzles offer a fun way to learn and the eight critical thinking puzzles we’ve chosen for this article should help you make a good start.

The aMAZEing PuzzleBox
Level 7 sequential discovery puzzle box
Made from original LEGO® bricks
Find the GOLDEN BAR to complete the challenge
CAN YOU HANDLE IT?..
Eight critical thinking puzzles – with answers
Puzzle 1 – letter puzzles.
What common feature do the following words share?
Answer: All of these words begin with a vowel. This type of puzzle may send your mind off in the wrong direction, thinking about the objects or concepts described by the words, and the properties they might share. In fact, the solution lies in a far more simple consideration of the alphabet. Puzzle 1 is a simple example of a common type of letter or word puzzle.
Puzzle 2 – Commonalities and differences
What do the following items have in common and which is the odd one out?
Orange Juice
Answer: These items are all liquids and the odd one out is petrol, since all the others are drinkable liquids.
Puzzle 3 – Falling on his feet
A man who lives in a high-rise building decides to exit through the window one morning rather than using the door. Somehow he survives the fall without a scratch and walks away to work. How did this happen?
Answer: The man lived on the ground or first floor and merely stepped or jumped down to the pavement outside. By stating early on that the building in question was a high-rise building, it’s easy for someone reading quickly to assume that the man jumped from a window on a high store but this it s not necessarily the case.
Puzzle 4 – Walk this way
A group of five people enter a windowless meeting room together. An hour later when the meeting ends, four walk out of the door, leaving the room empty. What has happened to the fifth member of the group?
Answer: The fifth person was in a wheelchair and wheeled out of the room rather than walked. Solving this puzzle requires you to think laterally about the question and the possible solutions. The answer can be found by asking yourself whether the emphasis of the question is on the emptiness of the room or the means by which the other four people left.
Puzzle 5 – Shapes and symbols
When lying on my side, I am everything, but when cut in half, I am nothing. What am I?
Answer: The number 8. This puzzle requires that you think about a shape being repositioned or cut in a way that can change it to “everything” or “nothing”. Number 8 on its side is the mathematical symbol for infinity (i.e. everything) and also shaped like two small number 0s put together.
Puzzle 6 – Three hard options
The hero is escaping the lair of an evil super-villain and is faced with three possible exits:
- Door A leads into a pit of bubbling lava
- Door B leads to a room housing a deadly hitman
- Door C leads to the den full of lions that haven’t had a meal for a year.
Which door should the hero choose?
Answer: Door C. If the lion hasn’t eaten in a year, it will definitely be dead by now. This type of puzzle requires you to consider the full implications of the information given, rather than being drawn into a comparison of the relative dangers of lava, hitmen and lions…
Puzzle 7 – The bus driver’s eyes
You are a bus driver. Today the bus is empty at the start of your route but at the first stop, four people get onto the bus. Eight people get on at the second stop, while three alight. When the bus reaches the third stop, one more gets off, and three get on.
At the fourth stop, two people get off the bus and one gets on. The bus is traveling at an average speed of 30mph and its tires are new. What color are the bus driver’s eyes?
Answer: You are the bus driver so the color will be the color of your own eyes. This type of puzzle tries to confuse you and obscure the single piece of relevant information by presenting large quantities of irrelevant information.
Puzzle 8 – Losing weight
A man walks into a room, closes the doors behind him and presses a button. In a matter of seconds the man is 20lb lighter. Despite this, he leaves the room at the same weight he entered it.
Answer: The room in question is actually an elevator. When the man gets in and presses the button, the elevator moves downwards with an acceleration that reduces the effect of gravity and makes the man temporarily 20lb lighter. Once the lift stops moving, the man’s weight is subject to normal gravity, just the same as before. Solving this puzzle requires a small piece of general physics knowledge.
A final word…
We hope you’ve enjoyed our critical thinking puzzles for adults and that your critical thinking skills are feeling refreshed and sharpened after reading our article. Whether at school, in the workplace, or in general life, critical thinking can be a valuable tool for success and anyone can learn to use it.
Get more critical thinking puzzles on our Youtube channel:
20 Challenging Lateral Thinking Puzzles That Are Harder Than They Seem
You may also like

Does Personality Matter When Choosing A Career?
Take a look at the different departments of a company and see if you can spot certain characteristics unique to each: The […]

Parents Teaching Critical Thinking: Effective Strategies for Raising Independent Thinkers
Parents play a vital role in fostering the cognitive development of their children, and one of the most essential skills they can […]

Unlocking the Power of Critical Thinking (Questioning Assumptions)
In the quest for personal and professional growth, critical thinking is a fundamental skill that can revolutionize one’s problem-solving abilities, decision-making processes, […]

Unleashing Your Creativity: Associative Thinking Techniques Explained
Creativity is a valuable asset in today’s world, and many people strive to unleash their creative potential. Associative thinking is a technique […]
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience.
3 Great Examples of Problem-Solving and Reasoning Questions (and One Bad One)

Great problem-solving and reasoning questions (PSR) are those that provoke students into thinking. We want them to care about the problems they’re solving, and to do that, we have to tickle their fancies, pique their interest, and stock the embers of curiosity burning deep within.
You’ll see reactions to intriguing PSR questions. Students will pause before they make decisions – that’s a sure sign their minds are working on the ‘reasoning’ part of the exercise.
Lastly, there should be opportunities for diverse thinking and for students to explain or model their approach to the problem. Everyone thinks differently and thinking needs to be justified (and rewarded!).
We’ve put together 3 great examples of PSR questions and 1 bad one. See if you can spot which is which!
How many hats and socks?

Strand: Number & Algebra
Sub-strand: Fractions
Purpose of the task:
Students add fractions with the same denominator up to 1 whole to solve a real-life problem.
Mrs Yarn bought 1 large ball of blue wool. To make a hat she needs 2/7ths of a ball. To make a scarf she needs 3/7ths and to make a pompom she needs 1/7ths.
What could she make that would use the entire ball of wool?
What other combination of hats, scarves and pompoms could she make that would use the entire ball of wool?
Work with a partner to find all the possibilities.
A revolution in ratios
Strand: Number & Algebra
Sub-strand: Rates and ratios
Solve a word problem identifying equivalent ratios with regards to the revolutions of cogs. Involves using multiple two-part ratios.The diagram shows 4 cogs that form part of a simple machine.
The number of full revolutions that each cog completes is related by the ratios:
A : C = 2 : 1
B : D = 3 : 8
A : D = 1 : 2
What is the ratio of cogs A, B, C and D in its simplest form?
Simplified ratio of cog A: ____
Simplified ratio of cog B: ____
Simplified ratio of cog C: ____
Simplified ratio of cog D: ____
Cog A completes 24 revolutions.
How many revolutions does cog B complete in the same time?
Number of revolutions: ____
Broken calculator

Strand: Number & Algebra
Sub-strand: Operations
Use a broken calculator to make values between -20 and 20. Students explore the arithmetic properties of integers.
A broken calculator has only some keys working (shown in green).
Use the calculator keys to make all whole number values between -20 and 20.
Show your workings.
Is it possible to make the same values without the use of the division key? Explain your answer.
Do this sum
What is 2 x 5 x 7?
Answer: ____

Get access to 900+ unique problem solving activities with a free trial of our mathematics programs
You might like....

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Then working backward and dividing 25 by five, we get five minutes for one cat to catch each mouse. 18. Logic Puzzle: There is a barrel with no lid and some wine in it. "This barrel of wine is ...
1/ Question: If an electric train is moving north at 100 mph and the wind is blowing to the west at 10 mph, which way does the smoke ... A logic puzzle is a type of game or activity that challenges your reasoning and problem-solving skills. It involves using logical deductions to analyze given information and arrive at a correct solution. Ref ...
Logical reasoning is an important assessment tool for a wide range of competitive examinations. Questions in this section are designed to judge a candidate's analytical and logical thinking abilities. Various types of reasoning questions are included in this section to test the student's capacity for problem-solving, deduction, and inference.
Practice realistic logical reasoning tests, with questions & answers written by experts. Try a free logical test now and get tips & solutions. Get 25% off all test packages. ... Logical reasoning tests are a type of psychometric test used to measure your problem-solving skills. They come in various forms, but all have the underlying purpose of ...
Take a guided, problem-solving based approach to learning Logic. These compilations provide unique perspectives and applications you won't find anywhere else.
So, let's dive in and embark on this exciting adventure of logical thinking questions! 1. Question: A bat and a ball cost $1.10 in total. The bat costs $1.00 more than the ball. How much does the ball cost. Show Answer. 2. Question: There are six eggs in a basket. Six people each take one egg.
Logical reasoning, often referred to as logical thinking or critical thinking, is a cognitive process that involves the ability to analyze information, identify patterns, make sound judgments and draw valid conclusions. It is a fundamental skill that plays a crucial role in problem-solving, decision-making and rational thinking.
Learn what an analytical reasoning test is, plus the skills required. Then practice example analytical reasoning questions with answers fully explained. Get 25% off all test packages. Get my discount now ... Dive into questions that challenge your problem-solving abilities across verbal, non-verbal, inductive, and deductive reasoning areas ...
Free Example Questions. One of the most popular, and perhaps most dreaded, type of psychometric test is the logical reasoning test. These screening questions won't ask you for formulas or equations. You'll have to rely solely on your own ingenuity to solve these problems. You'll need a great deal of concentration to succeed on a logic test.
Exercise : Logical Problems - Type 1. Each problem consists of three statements. Based on the first two statements, the third statement may be true, false, or uncertain. 1. Tanya is older than Eric. Cliff is older than Tanya. Eric is older than Cliff. 2. Blueberries cost more than strawberries.
A Logical Reasoning question is made up of these parts: Passage/stimulus: This text is where we'll find the argument or the information that forms the basis for answering the question. Sometimes there will be two arguments, if two people are presented as speakers. Question/task: This text, found beneath the stimulus, poses a question.
Learn what logical reasoning is and its types, and understand how to use logic to solve a problem. Explore logical problem-solving strategies, and see examples.
This formal examination, often referred to as the critical thinking assessment, is a benchmark for those aiming to demonstrate their proficiency in discernment and problem-solving. In addition, this evaluative tool meticulously gauges a range of skills, including logical reasoning, analytical thinking, and the ability to evaluate and synthesize ...
A logical reasoning test is used measure a candidate's problem solving ability. They assess the ability to come to conclusions based on logic. ... There are typically 12 questions to these TalentQ logical tests and a time limit of 75 seconds per question. 2. Kenexa Logical Reasoning - this test published by Kenexa is actually very similar in ...
Problem Solving Reasoning is a logical reasoning part where candidates will be given various questions and they need to perform various operations such as addition, division, greater than, lesser than, etc are interchanged or substituted to find the correct answer. Almost all the government examinations ask questions on the problem solving reasoning section.
Module 7: Thinking, Reasoning, and Problem-Solving. This module is about how a solid working knowledge of psychological principles can help you to think more effectively, so you can succeed in school and life. You might be inclined to believe that—because you have been thinking for as long as you can remember, because you are able to figure ...
Test Your Problem-Solving Skills. Personalize Your Emails Personalize your monthly updates from BrainFacts.org by choosing the topics that you care about most! Sign Up Find a Neuroscientist Engage local scientists to educate your community about the brain. ...
Summary. Critical thinking is the ability to analyze and effectively break down an issue in order to make a decision or find a solution. At the heart of critical thinking is the ability to ...
The term "lateral thinking" was coined in 1967 by physician and inventor Edward de Bono, to describe a kind of out-of-the-box reasoning and critical analysis of scenarios that call for more than just typical step-by-step logic to solve. Lateral thinking is related to creative problem solving and critical thinking, all valuable skills to have, and […]
Quiz: test your logical thinking skills. Do you consider yourself a logical thinker? Perhaps you're the type of person who thrives on quizzes and the opportunity to solve a tricky problem. Or you might find logical thinking a real struggle at times, and realise you need to give your skills a rev-up. Like it or not, the art of thinking ...
Statement and Assumption. Course of Action. Statement and Conclusion. Theme Detection. Cause and Effect. Statement and Argument. Logical Deduction. Take an Online Logical Reasoning Test Now! Logical Reasoning questions and answers with explanations are provided for your competitive exams, placement interviews, and entrance tests.
Critical thinking is a broad approach to problem solving and analysis based on logic and evidence. It brings together a wide range of intellectual competences and the ability to combine and cross-reference them. Some of the most important elements of a critical thinking approach include: Analytical skills: understanding of questions and concepts
Purpose of the task: Solve a word problem identifying equivalent ratios with regards to the revolutions of cogs. Involves using multiple two-part ratios.The diagram shows 4 cogs that form part of a simple machine. The number of full revolutions that each cog completes is related by the ratios: A : C = 2 : 1. B : D = 3 : 8. A : D = 1 : 2. Part A.
This booklet contains over 40 reasoning and problem solving questions suitable for KS2 and KS3 classes. These are the questions that we have been putting out each day in March 2016 on Twitter in the run up to SATS. The answers are provided with some simple notes at the back of the booklet and for some questions ...
Navigating the realms of creativity often requires a departure from the rigid pathways of logical thinking. While logic forms the backbone of problem-solving in many fields, creative endeavors ...
4 Problem-Solving Paths. Creative problem solving often involves exploring multiple paths to find the best solution. Logical thinking comes into play by helping you map out these paths and ...
Creative problem solving is a valuable skill that allows you to find innovative solutions to complex challenges. However, when you rely solely on logical thinking, it can sometimes put a damper on ...