An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Front Psychol

Academic Stress and Mental Well-Being in College Students: Correlations, Affected Groups, and COVID-19
Georgia barbayannis.
1 Department of Neurology, Rutgers New Jersey Medical School, Newark, NJ, United States
Mahindra Bandari
Xiang zheng.
2 Rutgers New Jersey Medical School, Newark, NJ, United States
Humberto Baquerizo
3 Office for Diversity and Community Engagement, Rutgers New Jersey Medical School, Newark, NJ, United States
Keith W. Pecor
4 Department of Biology, The College of New Jersey, Ewing, NJ, United States
Associated Data
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Academic stress may be the single most dominant stress factor that affects the mental well-being of college students. Some groups of students may experience more stress than others, and the coronavirus disease 19 (COVID-19) pandemic could further complicate the stress response. We surveyed 843 college students and evaluated whether academic stress levels affected their mental health, and if so, whether there were specific vulnerable groups by gender, race/ethnicity, year of study, and reaction to the pandemic. Using a combination of scores from the Perception of Academic Stress Scale (PAS) and the Short Warwick-Edinburgh Mental Well-Being Scale (SWEMWBS), we found a significant correlation between worse academic stress and poor mental well-being in all the students, who also reported an exacerbation of stress in response to the pandemic. In addition, SWEMWBS scores revealed the lowest mental health and highest academic stress in non-binary individuals, and the opposite trend was observed for both the measures in men. Furthermore, women and non-binary students reported higher academic stress than men, as indicated by PAS scores. The same pattern held as a reaction to COVID-19-related stress. PAS scores and responses to the pandemic varied by the year of study, but no obvious patterns emerged. These results indicate that academic stress in college is significantly correlated to psychological well-being in the students who responded to this survey. In addition, some groups of college students are more affected by stress than others, and additional resources and support should be provided to them.
Introduction
Late adolescence and emerging adulthood are transitional periods marked by major physiological and psychological changes, including elevated stress (Hogan and Astone, 1986 ; Arnett, 2000 ; Shanahan, 2000 ; Spear, 2000 ; Scales et al., 2015 ; Romeo et al., 2016 ; Barbayannis et al., 2017 ; Chiang et al., 2019 ; Lally and Valentine-French, 2019 ; Matud et al., 2020 ). This pattern is particularly true for college students. According to a 2015 American College Health Association-National College Health Assessment survey, three in four college students self-reported feeling stressed, while one in five college students reported stress-related suicidal ideation (Liu, C. H., et al., 2019 ; American Psychological Association, 2020 ). Studies show that a stressor experienced in college may serve as a predictor of mental health diagnoses (Pedrelli et al., 2015 ; Liu, C. H., et al., 2019 ; Karyotaki et al., 2020 ). Indeed, many mental health disorders, including depression, anxiety, and substance abuse disorder, begin during this period (Blanco et al., 2008 ; Pedrelli et al., 2015 ; Saleh et al., 2017 ; Reddy et al., 2018 ; Liu, C. H., et al., 2019 ).
Stress experienced by college students is multi-factorial and can be attributed to a variety of contributing factors (Reddy et al., 2018 ; Karyotaki et al., 2020 ). A growing body of evidence suggests that academic-related stress plays a significant role in college (Misra and McKean, 2000 ; Dusselier et al., 2005 ; Elias et al., 2011 ; Bedewy and Gabriel, 2015 ; Hj Ramli et al., 2018 ; Reddy et al., 2018 ; Pascoe et al., 2020 ). For instance, as many as 87% of college students surveyed across the United States cited education as their primary source of stress (American Psychological Association, 2020 ). College students are exposed to novel academic stressors, such as an extensive academic course load, substantial studying, time management, classroom competition, financial concerns, familial pressures, and adapting to a new environment (Misra and Castillo, 2004 ; Byrd and McKinney, 2012 ; Ekpenyong et al., 2013 ; Bedewy and Gabriel, 2015 ; Ketchen Lipson et al., 2015 ; Pedrelli et al., 2015 ; Reddy et al., 2018 ; Liu, C. H., et al., 2019 ; Freire et al., 2020 ; Karyotaki et al., 2020 ). Academic stress can reduce motivation, hinder academic achievement, and lead to increased college dropout rates (Pascoe et al., 2020 ).
Academic stress has also been shown to negatively impact mental health in students (Li and Lin, 2003 ; Eisenberg et al., 2009 ; Green et al., 2021 ). Mental, or psychological, well-being is one of the components of positive mental health, and it includes happiness, life satisfaction, stress management, and psychological functioning (Ryan and Deci, 2001 ; Tennant et al., 2007 ; Galderisi et al., 2015 ; Trout and Alsandor, 2020 ; Defeyter et al., 2021 ; Green et al., 2021 ). Positive mental health is an understudied but important area that helps paint a more comprehensive picture of overall mental health (Tennant et al., 2007 ; Margraf et al., 2020 ). Moreover, positive mental health has been shown to be predictive of both negative and positive mental health indicators over time (Margraf et al., 2020 ). Further exploring the relationship between academic stress and mental well-being is important because poor mental well-being has been shown to affect academic performance in college (Tennant et al., 2007 ; Eisenberg et al., 2009 ; Freire et al., 2016 ).
Perception of academic stress varies among different groups of college students (Lee et al., 2021 ). For instance, female college students report experiencing increased stress than their male counterparts (Misra et al., 2000 ; Eisenberg et al., 2007 ; Evans et al., 2018 ; Lee et al., 2021 ). Male and female students also respond differently to stressors (Misra et al., 2000 ; Verma et al., 2011 ). Moreover, compared to their cisgender peers, non-binary students report increased stressors and mental health issues (Budge et al., 2020 ). The academic year of study of the college students has also been shown to impact academic stress levels (Misra and McKean, 2000 ; Elias et al., 2011 ; Wyatt et al., 2017 ; Liu, C. H., et al., 2019 ; Defeyter et al., 2021 ). While several studies indicate that racial/ethnic minority groups of students, including Black/African American, Hispanic/Latino, and Asian American students, are more likely to experience anxiety, depression, and suicidality than their white peers (Lesure-Lester and King, 2004 ; Lipson et al., 2018 ; Liu, C. H., et al., 2019 ; Kodish et al., 2022 ), these studies are limited and often report mixed or inconclusive findings (Liu, C. H., et al., 2019 ; Kodish et al., 2022 ). Therefore, more studies should be conducted to address this gap in research to help identify subgroups that may be disproportionately impacted by academic stress and lower well-being.
The coronavirus disease 19 (COVID-19) pandemic is a major stressor that has led to a mental health crisis (American Psychological Association, 2020 ; Dong and Bouey, 2020 ). For college students, the COVID-19 pandemic has resulted in significant changes and disruptions to daily life, elevated stress levels, and mental and physical health deterioration (American Psychological Association, 2020 ; Husky et al., 2020 ; Patsali et al., 2020 ; Son et al., 2020 ; Clabaugh et al., 2021 ; Lee et al., 2021 ; Lopes and Nihei, 2021 ; Yang et al., 2021 ). While any college student is vulnerable to these stressors, these concerns are amplified for members of minority groups (Salerno et al., 2020 ; Clabaugh et al., 2021 ; McQuaid et al., 2021 ; Prowse et al., 2021 ; Kodish et al., 2022 ). Identifying students at greatest risk provides opportunities to offer support, resources, and mental health services to specific subgroups.
The overall aim of this study was to assess academic stress and mental well-being in a sample of college students. Within this umbrella, we had several goals. First, to determine whether a relationship exists between the two constructs of perceived academic stress, measured by the Perception of Academic Stress Scale (PAS), and mental well-being, measured by the Short Warwick-Edinburgh Mental Well-Being Scale (SWEMWBS), in college students. Second, to identify groups that could experience differential levels of academic stress and mental health. Third, to explore how the perception of the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic affected stress levels. We hypothesized that students who experienced more academic stress would have worse psychological well-being and that certain groups of students would be more impacted by academic- and COVID-19-related stress.
Materials and Methods
Survey instrument.
A survey was developed that included all questions from the Short Warwick-Edinburgh Mental Well-Being (Tennant et al., 2007 ; Stewart-Brown and Janmohamed, 2008 ) and from the Perception of Academic Stress Scale (Bedewy and Gabriel, 2015 ). The Short Warwick-Edinburgh Mental Well-Being Scale is a seven-item scale designed to measure mental well-being and positive mental health (Tennant et al., 2007 ; Fung, 2019 ; Shah et al., 2021 ). The Perception of Academic Stress Scale is an 18-item scale designed to assess sources of academic stress perceived by individuals and measures three main academic stressors: academic expectations, workload and examinations, and academic self-perceptions of students (Bedewy and Gabriel, 2015 ). These shorter scales were chosen to increase our response and study completion rates (Kost and de Rosa, 2018 ). Both tools have been shown to be valid and reliable in college students with Likert scale responses (Tennant et al., 2007 ; Bedewy and Gabriel, 2015 ; Ringdal et al., 2018 ; Fung, 2019 ; Koushede et al., 2019 ). Both the SWEMWBS and PAS scores are a summation of responses to the individual questions in the instruments. For the SWEMWBS questions, a higher score indicates better mental health, and scores range from 7 to 35. Similarly, the PAS questions are phrased such that a higher score indicates lower levels of stress, and scores range from 18 to 90. We augmented the survey with demographic questions (e.g., age, gender, and race/ethnicity) at the beginning of the survey and two yes/no questions and one Likert scale question about the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic at the end of our survey.
Participants for the study were self-reported college students between the ages of 18 and 30 years who resided in the United States, were fluent in English, and had Internet access. Participants were solicited through Prolific ( https://prolific.co ) in October 2021. A total of 1,023 individuals enrolled in the survey. Three individuals did not agree to participate after beginning the survey. Two were not fluent in English. Thirteen individuals indicated that they were not college students. Two were not in the 18–30 age range, and one was located outside of the United States. Of the remaining individuals, 906 were full-time students and 96 were part-time students. Given the skew of the data and potential differences in these populations, we removed the part-time students. Of the 906 full-time students, 58 indicated that they were in their fifth year of college or higher. We understand that not every student completes their undergraduate studies in 4 years, but we did not want to have a mixture of undergraduate and graduate students with no way to differentiate them. Finally, one individual reported their age as a non-number, and four individuals did not answer a question about their response to the COVID-19 pandemic. This yielded a final sample of 843 college students.
Data Analyses
After reviewing the dataset, some variables were removed from consideration due to a lack of consistency (e.g., some students reported annual income for themselves and others reported family income) or heterogeneity that prevented easy categorization (e.g., field of study). We settled on four variables of interest: gender, race/ethnicity, year in school, and response to the COVID-19 pandemic ( Table 1 ). Gender was coded as female, male, or non-binary. Race/ethnicity was coded as white or Caucasian; Black or African American; East Asian; Hispanic, Latino, or of Spanish origin; or other. Other was used for groups that were not well-represented in the sample and included individuals who identified themselves as Middle Eastern, Native American or Alaskan Native, and South Asian, as well as individuals who chose “other” or “prefer not to answer” on the survey. The year of study was coded as one through four, and COVID-19 stress was coded as two groups, no change/neutral response/reduced stress or increased stress.
Characteristics of the participants in the study.
Our first goal was to determine whether there was a relationship between self-reported academic stress and mental health, and we found a significant correlation (see Results section). Given the positive correlation, a multivariate analysis of variance (MANOVA) with a model testing the main effects of gender, race/ethnicity, and year of study was run in SPSS v 26.0. A factorial MANOVA would have been ideal, but our data were drawn from a convenience sample, which did not give equal representation to all groupings, and some combinations of gender, race/ethnicity, and year of study were poorly represented (e.g., a single individual). As such, we determined that it would be better to have a lack of interaction terms as a limitation to the study than to provide potentially spurious results. Finally, we used chi-square analyses to assess the effect of potential differences in the perception of the COVID-19 pandemic on stress levels in general among the groups in each category (gender, race/ethnicity, and year of study).
In terms of internal consistency, Cronbach's alpha was 0.82 for the SMEMWBS and 0.86 for the PAS. A variety of descriptors have been applied to Cronbach's alpha values. That said, 0.7 is often considered a threshold value in terms of acceptable internal consistency, and our values could be considered “high” or “good” (Taber, 2018 ).
The participants in our study were primarily women (78.5% of respondents; Table 1 ). Participants were not equally distributed among races/ethnicities, with the majority of students selecting white or Caucasian (66.4% of responders; Table 1 ), or years of study, with fewer first-year students than other groups ( Table 1 ).
Students who reported higher academic stress also reported worse mental well-being in general, irrespective of age, gender, race/ethnicity, or year of study. PAS and SWEMWBS scores were significantly correlated ( r = 0.53, p < 0.001; Figure 1 ), indicating that a higher level of perceived academic stress is associated with worse mental well-being in college students within the United States.

SWEMWBS and PAS scores for all participants.
Among the subgroups of students, women, non-binary students, and second-year students reported higher academic stress levels and worse mental well-being ( Table 2 ; Figures 2 – 4 ). In addition, the combined measures differed significantly between the groups in each category ( Table 2 ). However, as measured by partial eta squared, the effect sizes were relatively small, given the convention of 0.01 = small, 0.06 = medium, and 0.14 = large differences (Lakens, 2013 ). As such, there were only two instances in which Tukey's post-hoc tests revealed more than one statistical grouping ( Figures 2 – 4 ). For SWEMWBS score by gender, women were intermediate between men (high) and non-binary individuals (low) and not significantly different from either group ( Figure 2 ). Second-year students had the lowest PAS scores for the year of study, and first-year students had the highest scores. Third- and fourth-year students were intermediate and not statistically different from the other two groups ( Figure 4 ). There were no pairwise differences in academic stress levels or mental well-being among racial/ethnic groups.
Results of the MANOVA.

SWEMWBS and PAS scores according to gender (mean ± SEM). Different letters for SWEMWBS scores indicate different statistical groupings ( p < 0.05).

SWEMWBS and PAS scores according to year in college (mean ± SEM). Different letters for PAS scores indicate different statistical groupings ( p < 0.05).

SWEMWBS and PAS scores according to race/ethnicity (mean ± SEM).
The findings varied among categories in terms of stress responses due to the COVID-19 pandemic ( Table 3 ). For gender, men were less likely than women or non-binary individuals to report increased stress from COVID-19 (χ 2 = 27.98, df = 2, p < 0.001). All racial/ethnic groups responded similarly to the pandemic (χ 2 = 3.41, df = 4, p < 0.49). For the year of study, first-year students were less likely than other cohorts to report increased stress from COVID-19 (χ 2 = 9.38, df = 3, p < 0.03).
Impact of COVID-19 on stress level by gender, race/ethnicity, and year of study.
Our primary findings showed a positive correlation between perceived academic stress and mental well-being in United States college students, suggesting that academic stressors, including academic expectations, workload and grading, and students' academic self-perceptions, are equally important as psychological well-being. Overall, irrespective of gender, race/ethnicity, or year of study, students who reported higher academic stress levels experienced diminished mental well-being. The utilization of well-established scales and a large sample size are strengths of this study. Our results extend and contribute to the existing literature on stress by confirming findings from past studies that reported higher academic stress and lower psychological well-being in college students utilizing the same two scales (Green et al., 2021 ; Syed, 2021 ). To our knowledge, the majority of other prior studies with similar findings examined different components of stress, studied negative mental health indicators, used different scales or methods, employed smaller sample sizes, or were conducted in different countries (Li and Lin, 2003 ; American Psychological Association, 2020 ; Husky et al., 2020 ; Pascoe et al., 2020 ; Patsali et al., 2020 ; Clabaugh et al., 2021 ; Lee et al., 2021 ; Lopes and Nihei, 2021 ; Yang et al., 2021 ).
This study also demonstrated that college students are not uniformly impacted by academic stress or pandemic-related stress and that there are significant group-level differences in mental well-being. Specifically, non-binary individuals and second-year students were disproportionately impacted by academic stress. When considering the effects of gender, non-binary students, in comparison to gender-conforming students, reported the highest stress levels and worst psychological well-being. Although there is a paucity of research examining the impact of academic stress in non-binary college students, prior studies have indicated that non-binary adults face adverse mental health outcomes when compared to male and female-identifying individuals (Thorne et al., 2018 ; Jones et al., 2019 ; Budge et al., 2020 ). Alarmingly, Lipson et al. ( 2019 ) found that gender non-conforming college students were two to four times more likely to experience mental health struggles than cisgender students (Lipson et al., 2019 ). With a growing number of college students in the United States identifying as as non-binary, additional studies could offer invaluable insight into how academic stress affects this population (Budge et al., 2020 ).
In addition, we found that second-year students reported the most academic-related distress and lowest psychological well-being relative to students in other years of study. We surmise this may be due to this group taking advanced courses, managing heavier academic workloads, and exploring different majors. Other studies support our findings and suggest higher stress levels could be attributed to increased studying and difficulties with time management, as well as having less well-established social support networks and coping mechanisms compared to upperclassmen (Allen and Hiebert, 1991 ; Misra and McKean, 2000 ; Liu, X et al., 2019 ). Benefiting from their additional experience, upperclassmen may have developed more sophisticated studying skills, formed peer support groups, and identified approaches to better manage their academic stress (Allen and Hiebert, 1991 ; Misra and McKean, 2000 ). Our findings suggest that colleges should consider offering tailored mental health resources, such as time management and study skill workshops, based on the year of study to improve students' stress levels and psychological well-being (Liu, X et al., 2019 ).
Although this study reported no significant differences regarding race or ethnicity, this does not indicate that minority groups experienced less academic stress or better mental well-being (Lee et al., 2021 ). Instead, our results may reflect the low sample size of non-white races/ethnicities, which may not have given enough statistical power to corroborate. In addition, since coping and resilience are important mediators of subjective stress experiences (Freire et al., 2020 ), we speculate that the lower ratios of stress reported in non-white participants in our study (75 vs. 81) may be because they are more accustomed to adversity and thereby more resilient (Brown, 2008 ; Acheampong et al., 2019 ). Furthermore, ethnic minority students may face stigma when reporting mental health struggles (Liu, C. H., et al., 2019 ; Lee et al., 2021 ). For instance, studies showed that Black/African American, Hispanic/Latino, and Asian American students disclose fewer mental health issues than white students (Liu, C. H., et al., 2019 ; Lee et al., 2021 ). Moreover, the ability to identify stressors and mental health problems may manifest differently culturally for some minority groups (Huang and Zane, 2016 ; Liu, C. H., et al., 2019 ). Contrary to our findings, other studies cited racial disparities in academic stress levels and mental well-being of students. More specifically, Negga et al. ( 2007 ) concluded that African American college students were more susceptible to higher academic stress levels than their white classmates (Negga et al., 2007 ). Another study reported that minority students experienced greater distress and worse mental health outcomes compared to non-minority students (Smith et al., 2014 ). Since there may be racial disparities in access to mental health services at the college level, universities, professors, and counselors should offer additional resources to support these students while closely monitoring their psychological well-being (Lipson et al., 2018 ; Liu, C. H., et al., 2019 ).
While the COVID-19 pandemic increased stress levels in all the students included in our study, women, non-binary students, and upperclassmen were disproportionately affected. An overwhelming body of evidence suggests that the majority of college students experienced increased stress levels and worsening mental health as a result of the pandemic (Allen and Hiebert, 1991 ; American Psychological Association, 2020 ; Husky et al., 2020 ; Patsali et al., 2020 ; Son et al., 2020 ; Clabaugh et al., 2021 ; Lee et al., 2021 ; Yang et al., 2021 ). Our results also align with prior studies that found similar subgroups of students experience disproportionate pandemic-related distress (Gao et al., 2020 ; Clabaugh et al., 2021 ; Hunt et al., 2021 ; Jarrett et al., 2021 ; Lee et al., 2021 ; Chen and Lucock, 2022 ). In particular, the differences between female students and their male peers may be the result of different psychological and physiological responses to stress reactivity, which in turn may contribute to different coping mechanisms to stress and the higher rates of stress-related disorders experienced by women (Misra et al., 2000 ; Kajantie and Phillips, 2006 ; Verma et al., 2011 ; Gao et al., 2020 ; Graves et al., 2021 ). COVID-19 was a secondary consideration in our study and survey design, so the conclusions drawn here are necessarily limited.
The implications of this study are that college students facing increased stress and struggling with mental health issues should receive personalized and specific mental health services, resources, and support. This is particularly true for groups that have been disproportionately impacted by academic stress and stress due to the pandemic. Many students who experience mental health struggles underutilize college services due to cost, stigma, or lack of information (Cage et al., 2020 ; Lee et al., 2021 ). To raise awareness and destigmatize mental health, colleges can consider distributing confidential validated assessments, such as the PAS and SWEMWBS, in class and teach students to self-score (Lee et al., 2021 ). These results can be used to understand how academic stress and mental well-being change over time and allow for specific and targeted interventions for vulnerable groups. In addition, teaching students healthy stress management techniques has been shown to improve psychological well-being (Alborzkouh et al., 2015 ). Moreover, adaptive coping strategies, including social and emotional support, have been found to improve the mental well-being of students, and stress-reduction peer support groups and workshops on campus could be beneficial in reducing stress and improving the self-efficacy of students (Ruthig et al., 2009 ; Baqutayan, 2011 ; Bedewy and Gabriel, 2015 ; Freire et al., 2020 ; Green et al., 2021 ; Suresh et al., 2021 ). Other interventions that have been effective in improving the coping skills of college students include cognitive-behavioral therapy, mindfulness mediation, and online coping tools (Kang et al., 2009 ; Regehr et al., 2013 ; Molla Jafar et al., 2015 ; Phang et al., 2015 ; Houston et al., 2017 ; Yusufov et al., 2019 ; Freire et al., 2020 ). Given that resilience has also been shown to help mediate stress and improve mental well-being during the COVID-19 pandemic, interventions focusing on enhancing resilience should be considered (Surzykiewicz et al., 2021 ; Skalski et al., 2022 ). Telemental health resources across colleges can also be implemented to reduce stigma and improve at-risk students' access to care (Toscos et al., 2018 ; Hadler et al., 2021 ). University campuses, professors, and counselors should consider focusing on fostering a more equitable and inclusive environment to encourage marginalized students to seek mental health support (Budge et al., 2020 ).
Limitations
While our study has numerous strengths, including using standardized instruments and a large sample size, this study also has several limitations due to both the methodology and sample. First, the correlational study design precludes making any causal relationships (Misra and McKean, 2000 ). Thereby, our findings should be taken in the context of academic stress and mental well-being, and recognize that mental health could be caused by other non-academic factors. Second, the PAS comprised only the perception of responses to academic stress, but stress is a multi-factorial response that encompasses both perceptions and coping mechanisms to different stressors, and the magnitude of stress varies with the perception of the degree of uncontrollability, unpredictability, or threat to self (Miller, 1981 ; Hobfoll and Walfisch, 1984 ; Lazarus and Folkman, 1984 ; Wheaton, 1985 ; Perrewé and Zellars, 1999 ; Schneiderman et al., 2005 ; Bedewy and Gabriel, 2015 ; Schönfeld et al., 2016 ; Reddy et al., 2018 ; Freire et al., 2020 ; Karyotaki et al., 2020 ). Third, the SWEMSBS used in our study and the data only measured positive mental health. Mental health pathways are numerous and complex, and are composed of distinct and interdependent negative and positive indicators that should be considered together (Margraf et al., 2020 ). Fourth, due to the small effect sizes and unequal representation for different combinations of variables, our analysis for both the PAS and SWEMSBS included only summed-up scales and did not examine group differences in response to the type of academic stressors or individual mental health questions.
An additional limitation is that the participants in our study were a convenience sample. The testing service we used, prolific.co, self-reports a sample bias toward young women of high levels of education (i.e., WEIRD bias) (Team Prolific, 2018 ). The skew toward this population was observed in our data, as 80% of our participants were women. While we controlled for these factors, the possibility remains that the conclusions we draw for certain groups, such as nonbinary students, ethnic/racial minorities, and men, may not be as statistically powerful as they should be. Moreover, our pre-screening was designed to recruit undergraduate level, English-speaking, 18–30-year-olds who resided in the United States. This resulted in our participant demographics being skewed toward the WEIRD bias that was already inherent in the testing service we used. Future research will aim to be more inclusive of diverse races/ethnicities, sexual orientations, languages, educational backgrounds, socioeconomic backgrounds, and first-generation college students.
Another limitation of our study is the nature of satisficing. Satisficing is a response strategy in which a participant answers a question to satisfy its condition with little regard to the quality or accuracy of the answer (Roberts et al., 2019 ). Anonymous participants are more likely to satisfice than respondents who answer the question face-to-face (Krosnick et al., 2002 ). We sought to mitigate satisficing by offering financial incentives to increase response rates and decrease straight-lining, item skipping, total missing items, and non-completion (Cole et al., 2015 ). Concerns of poor data quality due to surveys offering financial incentives found little evidence to support that claim and may do the opposite (Cole et al., 2015 ). On the other hand, social desirability bias may have influenced the participant's self-reported responses, although our anonymous survey design aimed to reduce this bias (Joinson, 1999 ; Kecojevic et al., 2020 ).
Future Studies
Future studies should replicate our study to validate our results, conduct longitudinal cohort studies to examine well-being and perceived academic stress over time, and aim for a more representative student sample that includes various groups, including diverse races/ethnicities, sexual orientations, socioeconomic backgrounds, languages, educational levels, and first-generation college students. Additionally, these studies should consider examining other non-academic stressors and students' coping mechanisms, both of which contribute to mental health and well-being (Lazarus and Folkman, 1984 ; Freire et al., 2020 ). Further explorations of negative and other positive indicators of mental health may offer a broader perspective (Margraf et al., 2020 ). Moreover, future research should consider extending our work by exploring group differences in relation to each factor in the PAS (i.e., academic expectations, workload and examinations, and self-perception of students) and SWEMBS to determine which aspects of academic stress and mental health were most affected and allow for the devising of targeted stress-reduction approaches. Ultimately, we hope our research spurs readers into advocating for greater academic support and access to group-specific mental health resources to reduce the stress levels of college students and improve their mental well-being.
Utilizing two well-established scales, our research found a statistically significant correlation between the perceived academic stress of university students and their mental well-being (i.e., the higher the stress, the worse the well-being). This relationship was most apparent among gender and grade levels. More specifically, non-binary and second-year students experienced greater academic burden and lower psychological well-being. Moreover, women, non-binary students, and upper-level students were disproportionately impacted by stress related to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Studies regarding broad concepts of stress and well-being using a questionnaire are limited, but our study adds value to the understanding of academic stress as a contributor to the overall well-being of college students during this specific point in time (i.e., the COVID-19 pandemic). Competition both for admission to college (Bound et al., 2009 ) and during college (Posselt and Lipson, 2016 ) has increased over time. Further, selective American colleges and universities draw applicants from a global pool. As such, it is important to document the dynamics of academic stress with renewed focus. We hope that our study sparks interest in both exploring and funding in-depth and well-designed psychological studies related to stress in colleges in the future.
Data Availability Statement
Ethics statement.
The studies involving human participants were reviewed and approved by Institutional Review Board at Rutgers University. The patients/participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author Contributions
GB and MB contributed to conceptualization, study design, IRB application, manuscript drafting, and revision. XZ participated in the conceptualization and design of the questionnaires. HB participated in subject recruitment and questionnaire collection. KP contributed to data analysis, table and figure preparation, manuscript drafting, and revision. XM contributed to conceptualization, study design, IRB application, supervision of the project, manuscript drafting, and revision. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
This study was made possible by a generous donation from the Knights of Columbus East Hanover Chapter in New Jersey.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Shivani Mehta and Varsha Garla for their assistance with the study. We also thank all the participants for their efforts in the completion of the study.
- Acheampong C., Davis C., Holder D., Averett P., Savitt T., Campbell K. (2019). An exploratory study of stress coping and resiliency of black men at one medical school: a critical race theory perspective . J. Racial Ethnic Health Disparit. 6 , 214–219. 10.1007/s40615-018-0516-8 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Alborzkouh P., Nabati M., Zainali M., Abed Y., Shahgholy Ghahfarokhi F. (2015). A review of the effectiveness of stress management skills training on academic vitality and psychological well-being of college students . J. Med. Life 8 , 39–44. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Allen S., Hiebert B. (1991). Stress and coping in adolescents . Can. J. Counsel. 25 , 19–32. [ Google Scholar ]
- American Psychological Association . (2020). Stress in AmericaTM2020: A National Mental Health Crisis . Washington, DC: American Psychological Association. [ Google Scholar ]
- Arnett J. J.. (2000). Emerging adulthood. A theory of development from the late teens through the twenties . Am. Psychol. 55 , 469–480. 10.1037/0003-066X.55.5.469 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Baqutayan S.. (2011). Stress and social support . Indian J. Psychol. Med. 33 , 29–34. 10.4103/0253-7176.85392 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Barbayannis G., Franco D., Wong S., Galdamez J., Romeo R. D., Bauer E. P. (2017). Differential effects of stress on fear learning and activation of the amygdala in pre-adolescent and adult male rats . Neuroscience 360 , 210–219. 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2017.07.058 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bedewy D., Gabriel A. (2015). Examining perceptions of academic stress and its sources among university students: the perception of academic stress scale . Health Psychol. Open 2 , 1–9. 10.1177/2055102915596714 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Blanco C., Okuda M., Wright C., Hasin D. S., Grant B. F., Liu S. M., et al.. (2008). Mental health of college students and their non-college-attending peers: results from the National Epidemiologic Study on Alcohol and Related Conditions . Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 65 , 1429–1437. 10.1001/archpsyc.65.12.1429 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bound J., Hershbein B., Long B. T. (2009). Playing the admissions game: student reactions to increasing college competition . J. Econ. Perspect. 23 , 119–146. 10.1257/jep.23.4.119 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Brown D. L.. (2008). African American resiliency: examining racial socialization and social support as protective factors . J. Black Psychol. 34 , 32–48. 10.1177/0095798407310538 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Budge S. L., Domínguez S., Jr., Goldberg A. E. (2020). Minority stress in nonbinary students in higher education: the role of campus climate and belongingness . Psychol. Sex. Orient. Gender Divers. 7 , 222–229. 10.1037/sgd0000360 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Byrd D. R., McKinney K. J. (2012). Individual, interpersonal, and institutional level factors associated with the mental health of college students . J. Am. Coll. Health 60 , 185–193. 10.1080/07448481.2011.584334 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cage E., Stock M., Sharpington A., Pitman E., Batchelor R. (2020). Barriers to accessing support for mental health issues at university . Stud. High. Educ. 45 , 1637–1649. 10.1080/03075079.2018.1544237 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chen T., Lucock M. (2022). The mental health of university students during the COVID-19 pandemic: an online survey in the UK . PLoS ONE 17 , e0262562. 10.1371/journal.pone.0262562 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chiang J. J., Ko A., Bower J. E., Taylor S. E., Irwin M. R., Fuligni A. J. (2019). Stress, psychological resources, and HPA and inflammatory reactivity during late adolescence . Dev. Psychopathol. 31 , 699–712. 10.1017/S0954579418000287 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Clabaugh A., Duque J. F., Fields L. J. (2021). Academic stress and emotional well-being in United States college students following onset of the COVID-19 pandemic . Front. Psychol. 12 , 628787. 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.628787 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cole J. S., Sarraf S. A., Wang X. (2015). Does Use of Survey Incentives Degrade Data Quality? Chicago, IL: Association for Institutional Research Annual Forum. [ Google Scholar ]
- Defeyter M. A., Stretesky P. B., Long M. A., Furey S., Reynolds C., Porteous D., et al.. (2021). Mental well-being in UK higher education during Covid-19: do students trust universities and the government? Front. Public Health 9 , 646916. 10.3389/fpubh.2021.646916 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Dong L., Bouey J. (2020). Public mental health crisis during COVID-19 Pandemic, China . Emerging Infect. Dis. 26 , 1616–1618. 10.3201/eid2607.200407 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Dusselier L., Dunn B., Yongyi W., Shelley M., II, Whalen D. (2005). Personal, health, academic, and environmental predictors of stress in residence halls . J. Am. Coll. Health 54 , 15–24. 10.3200/JACH.54.1.15-24 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Eisenberg D., Golberstein E., Hunt J. B. (2009). Mental health and academic success in college . B.E. J Econ Anal Policy 9 , 1–35. 10.2202/1935-1682.2191 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Eisenberg D., Gollust S. E., Golberstein E., Hefner J. L. (2007). Prevalence and correlates of depression, anxiety, and suicidality among university students . Am. J. Orthopsychiatry 77 , 534–542. 10.1037/0002-9432.77.4.534 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ekpenyong C. E., Daniel N. E., Aribo E. O. (2013). Associations between academic stressors, reaction to stress, coping strategies and musculoskeletal disorders among college students . Ethiop. J. Health Sci. 23 , 98–112. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Elias H., Ping W. S., Abdullah M. C. (2011). Stress and academic achievement among undergraduate students in Universiti Putra Malaysia . Proc. Soc. Behav. Sci. 29 , 646–655. 10.1016/j.sbspro.2011.11.288 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Evans T. M., Bira L., Gastelum J. B., Weiss L. T., Vanderford N. L. (2018). Evidence for a mental health crisis in graduate education . Nat. Biotechnol . 36 , 282–284. 10.1038/nbt.4089 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Freire C., Ferradás M., Regueiro B., Rodríguez S., Valle A., Núñez J. C. (2020). Coping strategies and self-efficacy in university students: a person-centered approach . Front. Psychol. 11 , 841. 10.3389/fpsyg.2020.00841 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Freire C., Ferradás M. D., Valle A., Núñez J. C., Vallejo G. (2016). Profiles of psychological well-being and coping strategies among university students . Front. Psychol. 7 , 1554. 10.3389/fpsyg.2016.01554 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Fung S.. (2019). Psychometric evaluation of the Warwick-Edinburgh Mental Well-being Scale (WEMWBS) with Chinese University Students . Health Qual. Life Outcomes 17 , 46. 10.1186/s12955-019-1113-1 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Galderisi S., Heinz A., Kastrup M., Beezhold J., Sartorius N. (2015). Toward a new definition of mental health . World Psychiatry 14 , 231–233. 10.1002/wps.20231 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gao W., Ping S., Liu X. (2020). Gender differences in depression, anxiety, and stress among college students: a longitudinal study from China . J. Affect. Disord. 263 , 292–300. 10.1016/j.jad.2019.11.121 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Graves B. S., Hall M. E., Dias-Karch C., Haischer M. H., Apter C. (2021). Gender differences in perceived stress and coping among college students . PLoS ONE 16 , e0255634. 10.1371/journal.pone.0255634 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Green Z. A., Faizi F., Jalal R., Zadran Z. (2021). Emotional support received moderates academic stress and mental well-being in a sample of Afghan university students amid COVID-19 . Int. J. Soc. Psychiatry . 207640211057729. 10.1177/00207640211057729. [Epub ahead of print]. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hadler N. L., Bu P., Winkler A., Alexander A. W. (2021). College student perspectives of telemental health: a review of the recent literature . Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 23 , 6. 10.1007/s11920-020-01215-7 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hj Ramli N. H., Alavi M., Mehrinezhad S. A., Ahmadi A. (2018). Academic stress and self-regulation among university students in Malaysia: mediator role of mindfulness . Behav. Sci. 8 , 12. 10.3390/bs8010012 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hobfoll S. E., Walfisch S. (1984). Coping with a threat to life: a longitudinal study of self-concept, social support, and psychological distress . Am. J. Community Psychol. 12 , 87–100. 10.1007/BF00896930 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hogan D. P., Astone N. M. (1986). The transition to adulthood . Annu. Rev. Sociol. 12 , 109–130. 10.1146/annurev.so.12.080186.000545 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Houston J. B., First J., Spialek M. L., Sorenson M. E., Mills-Sandoval T., Lockett, et al.. (2017). Randomized controlled trial of the Resilience and Coping Intervention (RCI) with undergraduate university students . J Am. Coll. Health 65 , 1–9. 10.1080/07448481.2016.1227826 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Huang C. Y., Zane N. (2016). Cultural influences in mental health treatment . Curr. Opin. Psychol. 8 , 131–136. 10.1016/j.copsyc.2015.10.009 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hunt C., Gibson G. C., Vander Horst A., Cleveland K. A., Wawrosch C., Granot M., et al.. (2021). Gender diverse college students exhibit higher psychological distress than male and female peers during the novel coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic . Psychol. Sex. Orient. Gender Divers. 8 , 238–244. 10.1037/sgd0000461 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Husky M. M., Kovess-Masfety V., Swendsen J. D. (2020). Stress and anxiety among university students in France during Covid-19 mandatory confinement . Compr. Psychiatry 102 :152191. 10.1016/j.comppsych.2020.152191 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Jarrett B. A., Peitzmeier S. M., Restar A., Adamson T., Howell S., Baral S., et al.. (2021). Gender-affirming care, mental health, and economic stability in the time of COVID-19: a multi-national, cross-sectional study of transgender and nonbinary people . PLoS ONE 16 , e0254215. 10.1371/journal.pone.0254215 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Joinson A.. (1999). Social desirability, anonymity, and Internet-based questionnaires . Behav. Res. Methods Instrum. Comput. 31 , 433–438. 10.3758/BF03200723 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Jones B. A., Pierre Bouman W., Haycraft E., Arcelus J. (2019). Mental health and quality of life in non-binary transgender adults: a case control study . Int. J. Transgender. 20 , 251–262. 10.1080/15532739.2019.1630346 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kajantie E., Phillips D. I. (2006). The effects of sex and hormonal status on the physiological response to acute psychosocial stress . Psychoneuroendocrinology 31 , 151–178. 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2005.07.002 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kang Y. S., Choi S. Y., Ryu E. (2009). The effectiveness of a stress coping program based on mindfulness meditation on the stress, anxiety, and depression experienced by nursing students in Korea . Nurse Educ. Today 29 , 538–543. 10.1016/j.nedt.2008.12.003 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Karyotaki E., Cuijpers P., Albor Y., Alonso J., Auerbach R. P., Bantjes J., et al.. (2020). Sources of stress and their associations with mental disorders among college students: results of the World Health Organization World Mental Health Surveys International College Student Initiative . Front. Psychol. 11 , 1759. 10.3389/fpsyg.2020.01759 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kecojevic A., Basch C. H., Sullivan M., Davi N. K. (2020). The impact of the COVID-19 epidemic on mental health of undergraduate students in New Jersey, cross-sectional study . PLoS ONE 15 , e0239696. 10.1371/journal.pone.0239696 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ketchen Lipson S., Gaddis S. M., Heinze J., Beck K., Eisenberg D. (2015). Variations in student mental health and treatment utilization across US Colleges and Universities . J Am. Coll. Health 63 , 388–396. 10.1080/07448481.2015.1040411 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kodish T., Lau A. S., Gong-Guy E., Congdon E., Arnaudova I., Schmidt M., et al.. (2022). Enhancing racial/ethnic equity in college student mental health through innovative screening and treatment . Adm. Policy Ment. Health 49 , 267–282. 10.1007/s10488-021-01163-1 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kost R. G., de Rosa J. C. (2018). Impact of survey length and compensation on validity, reliability, and sample characteristics for ultrashort-, short-, and long-research participant perception surveys . J. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2 , 31–37. 10.1017/cts.2018.18 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Koushede V., Lasgaard M., Hinrichsen C., Meilstrup C., Nielsen L., Rayce S. B., et al.. (2019). Measuring mental well-being in Denmark: validation of the original and short version of the Warwick-Edinburgh mental well-being scale (WEMWBS and SWEMWBS) and cross-cultural comparison across four European settings . Psychiatry Res. 271 , 502–509. 10.1016/j.psychres.2018.12.003 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Krosnick J. A., Holbrook A. L., Berent M. K., Carson R. T., Michael Hanemann W., Kopp R. J., et al.. (2002). The impact of “no opinion” response options on data quality: non-attitude reduction or an invitation to satisfice? Public Opin. Q. 66 , 371–403. 10.1086/341394 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lakens D.. (2013). Calculating and reporting effect sizes to facilitate cumulative science: a practical primer for t-tests and ANOVAs . Front. Psychol. 4 , 863. 10.3389/fpsyg.2013.00863 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lally M., Valentine-French S. (2019). Chapter 7: Emerging and Early Adulthood. Lifespan Development: A Psychological Perspective. 2nd Edn. p.246-306). [E-book] San Francisco: Creative Commons . Available online at: http://dept.clcillinois.edu/psy/LifespanDevelopment.pdf (accessed February 6, 2022).
- Lazarus R. S., Folkman S. (1984). Stress, Appraisal, and Coping . New York, NY: Springer. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lee J., Jeong H. J., Kim S. (2021). Stress, anxiety, and depression among undergraduate students during the COVID-19 pandemic and their use of mental health services . Innovat. High. Educ. 1–20. 10.1007/s10755-021-09552-y [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lesure-Lester G. E., King N. (2004). Racial-ethnic differences in social anxiety among college students . J. Coll. Stud. Retent. Res. Theory Pract. 6 , 359–367. 10.2190/P5FR-CGAH-YHA4-1DYC [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Li H., Lin C. (2003). College stress and psychological well-being of Chinese college students . Acta Psychol. Sinca 25 , 222–230. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lipson S. K., Kern A., Eisenberg D., Breland-Noble A. M. (2018). Mental health disparities among college students of color . J. Adolesc. Health 63 , 348–356. 10.1016/j.jadohealth.2018.04.014 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lipson S. K., Raifman J., Abelson S., Reisner S. L. (2019). Gender minority mental health in the U.S.: results of a National Survey on College Campuses . Am. J. Prev. Med. 57 , 293–301. 10.1016/j.amepre.2019.04.025 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Liu C. H., Stevens C., Wong S., Yasui M., Chen J. A. (2019). The prevalence and predictors of mental health diagnoses and suicide among U.S. college students: implications for addressing disparities in service use . Depress. Anxiety 36 , 8–17. 10.1002/da.22830 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Liu X., Ping S., Gao W. (2019). Changes in undergraduate students' psychological well-being as they experience University Life . Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 16 , 2864. 10.3390/ijerph16162864 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lopes A. R., Nihei O. K. (2021). Depression, anxiety and stress symptoms in Brazilian university students during the COVID-19 pandemic: predictors and association with life satisfaction, psychological well-being and coping strategies . PLoS ONE 16 , e0258493. 10.1371/journal.pone.0258493 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Margraf J., Zhang X. C., Lavallee K. L., Schneider S. (2020). Longitudinal prediction of positive and negative mental health in Germany, Russia, and China . PLoS ONE 15 , e0234997. 10.1371/journal.pone.0234997 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Matud M. P., Díaz A., Bethencourt J. M., Ibáñez I. (2020). Stress and psychological distress in emerging adulthood: a gender analysis . J. Clin. Med. 9 , 2859. 10.3390/jcm9092859 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- McQuaid R. J., Cox S., Ogunlana A., Jaworska N. (2021). The burden of loneliness: implications of the social determinants of health during COVID-19 . Psychiatry Res. 296 , 113648. 10.1016/j.psychres.2020.113648 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Miller S. M.. (1981). Predictability and human stress: toward a clarification of evidence and theory . Adv. Exp. Soc. Psychol. 14 , 203–256. 10.1016/S0065-2601(08)60373-1 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Misra R., Castillo L. G. (2004). Academic stress among college students: comparison of American and International Students . Int. J. Stress Manag. 11 , 132–148. 10.1037/1072-5245.11.2.132 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Misra R., McKean M. (2000). College students' academic stress and its relation to their anxiety, time management, and leisure satisfaction . Am. J. Health Stud. 16 , 41–51. [ Google Scholar ]
- Misra R., McKean M., West S., Russo T. (2000). Academic stress of college students: Comparison of student and faculty perceptions . Coll. Stud. J. 34 , 236–245. [ Google Scholar ]
- Molla Jafar H., Salabifard S., Mousavi S. M., Sobhani Z. (2015). The effectiveness of group training of CBT-based stress management on anxiety, psychological hardiness and general self-efficacy among university students . Glob. J. Health Sci. 8 , 47–54. 10.5539/gjhs.v8n6p47 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Negga F., Applewhite S., Livingston I. (2007). African American college students and stress: school racial composition, self-esteem and social support . Coll. Stud. J. 41 , 823. [ Google Scholar ]
- Pascoe M. C., Hetrick S. E., Parker A. G. (2020). The impact of stress on students in secondary school and higher education . Int. J. Adolesc. Youth 25 , 104–112. 10.1080/02673843.2019.1596823 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Patsali M. E., Mousa D. V., Papadopoulou E., Papadopoulou K., Kaparounaki C. K., Diakogiannis I., et al.. (2020). University students' changes in mental health status and determinants of behavior during the COVID-19 lockdown in Greece . Psychiatry Res. 292 , 113298. 10.1016/j.psychres.2020.113298 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pedrelli P., Nyer M., Yeung A., Zulauf C., Wilens T. (2015). College students: mental health problems and treatment considerations . Acad. Psychiatry 39 , 503–511. 10.1007/s40596-014-0205-9 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Perrewé P. L., Zellars K. L. (1999). An examination of attributions and emotions in the transactional approach to the organizational stress process . J. Org. Behav. 20 , 739–752. 10.1002/(SICI)1099-1379(199909)20:5<739::AID-JOB1949>3.0.CO;2-C [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Phang C. K., Mukhtar F., Ibrahim N., Keng S. L., Mohd Sidik S. (2015). Effects of a brief mindfulness-based intervention program for stress management among medical students: the Mindful-Gym randomized controlled study . Adv. Health Sci. Educ. Theory Pract. 20 , 1115–1134. 10.1007/s10459-015-9591-3 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Posselt J. R., Lipson S. K. (2016). Competition, anxiety, and depression in the college classroom: variations by student identity and field of study . J. Coll. Stud. Dev. 57 , 973–989. 10.1353/csd.2016.0094 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Prowse R., Sherratt F., Abizaid A., Gabrys R. L., Hellemans K., Patterson Z. R., et al.. (2021). Coping with the COVID-19 pandemic: examining gender differences in stress and mental health among university students . Front. Psychiatry 12 , 650759. 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.650759 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Reddy K. J., Menon K. R., Thattil A. (2018). Academic stress and its sources among university students . Biomed Pharmacol J 11 , 1. 10.13005/bpj/1404 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Regehr C., Glancy D., Pitts A. (2013). Interventions to reduce stress in university students: a review and meta-analysis . J. Affect. Disord. 148 , 1–11. 10.1016/j.jad.2012.11.026 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ringdal R., Bradley Eilertsen M. E., Bjørnsen H. N., Espnes G. A., Moksnes U. K. (2018). Validation of two versions of the Warwick-Edinburgh Mental Well-Being Scale among Norwegian adolescents . Scand. J. Public Health 46 , 718–725. 10.1177/1403494817735391 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Roberts C., Gilbert E., Allum N., Eisner L. (2019). Research synthesis: Satisficing in surveys: a systematic review of the literature . Public Opin. Q. 83 , 598–626. 10.1093/poq/nfz035 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Romeo R. D., Patel R., Pham L., So V. M. (2016). Adolescence and the ontogeny of the hormonal stress response in male and female rats and mice . Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 70 , 206–216. 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2016.05.020 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ruthig J. C., Haynes T. L., Stupnisky R. H., Perry R. P. (2009). Perceived Academic Control: mediating the effects of optimism and social support on college students' psychological health . Soc. Psychol. Educ. 12 , 233–249. 10.1007/s11218-008-9079-6 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ryan R. M., Deci E. L. (2001). On happiness and human potentials: a review of research on hedonic and eudaimonic well-being . Annu. Rev. Psychol. 52 , 141–166. 10.1146/annurev.psych.52.1.141 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Saleh D., Camart N., Romo L. (2017). Predictors of stress in college students . Front. Psychol. 8 , 19. 10.3389/fpsyg.2017.00019 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Salerno J. P., Williams N. D., Gattamorta K. A. (2020). LGBTQ populations: psychologically vulnerable communities in the COVID-19 pandemic . Psychol. Trauma 12 , S239–S242. 10.1037/tra0000837 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Scales P. C., Benson P. L., Oesterle S., Hill K. G., Hawkins J. D., Pashak T. J. (2015). The dimensions of successful young adult development: a conceptual and measurement framework . Appl. Dev. Sci. 20 , 150–174. 10.1080/10888691.2015.1082429 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Schneiderman N., Ironson G., Siegel S. D. (2005). Stress and health: psychological, behavioral, and biological determinants . Annu. Rev. Clin. Psychol. 1 , 607–628. 10.1146/annurev.clinpsy.1.102803.144141 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Schönfeld P., Brailovskaia J., Bieda A., Zhang X. C., Margraf J. (2016). The effects of daily stress on positive and negative mental health: mediation through self-efficacy . Int. J. Clin. Health Psychol. 16 , 1–10. 10.1016/j.ijchp.2015.08.005 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Shah N., Cader M., Andrews B., McCabe R., Stewart-Brown S. L. (2021). Short Warwick-Edinburgh Mental Well-being Scale (SWEMWBS): performance in a clinical sample in relation to PHQ-9 and GAD-7 . Health Qual. Life Outcomes 19 , 260. 10.1186/s12955-021-01882-x [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Shanahan M. J.. (2000). Pathways to adulthood in changing societies: variability and mechanisms in life course perspective . Annu. Rev. Sociol. 26 , 667–692. 10.1146/annurev.soc.26.1.667 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Skalski S. B., Konaszewski K., Büssing A., Surzykiewicz J. (2022). Resilience and mental well-being during the COVID-19 pandemic: serial mediation by persistent thinking and anxiety about coronavirus . Front. Psychiatry 12 , 810274. 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.810274 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Smith K. M., Chesin M. S., Jeglic E. L. (2014). Minority college student mental health: does majority status matter? Implications for college counseling services . J. Multicult. Counsel. Dev. 42 , 77–92. 10.1002/j.2161-1912.2014.00046.x [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Son C., Hegde S., Smith A., Wang X., Sasangohar F. (2020). Effects of COVID-19 on college students' mental health in the United States: interview survey study . J. Med. Internet Res. 22 , e21279. 10.2196/21279 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Spear L. P.. (2000). The adolescent brain and age-related behavioral manifestations . Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 24 , 417–463. 10.1016/S0149-7634(00)00014-2 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Stewart-Brown S., Janmohamed K. (2008). Warwick-Edinburgh mental well-being scale. User guide. Version, 1 . 10.1037/t80221-000 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Suresh R., Karkossa Z., Richard J., Karia M. (2021). Program evaluation of a student-led peer support service at a Canadian university . Int. J. Ment. Health Syst. 15 , 54. 10.1186/s13033-021-00479-7 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Surzykiewicz J., Konaszewski K., Skalski S., Dobrakowski P. P., Muszyńska J. (2021). Resilience and mental health in the polish population during the COVID-19 lockdown: a mediation analysis . J. Clin. Med. 10 , 4974. 10.3390/jcm10214974 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Syed N. B.. (2021). Impact of levels of education on perceived academic stress and mental wellbeing: an investigation into online mode of learning during pandemic . J. Psychol. Res. 3 , 12–18. 10.30564/jpr.v3i2.3032 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Taber K. S.. (2018). The use of Cronbach's alpha when developing and reporting research instruments in science education . Res. High. Educ. 48 , 1273–1296. 10.1007/s11165-016-9602-2 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Team Prolific (2018). What Are the Advantages and Limitations of an Online Sample? Prolific Researcher Help Centre . Available online at: https://researcher-help.prolific.co/hc/en-gb/articles/360009501473-What-are-the-advantages-and-limitations-of-an-online-sample-#:~:text=Limitations%20Rapid-responder%20bias.%20Prolific%20predominantly%20uses%20convenience%20sampling%2C,and%20fairly%20distribute%20study%20places%20among%20active%20participants (accessed February 22, 2022).
- Tennant R., Hiller L., Fishwick R., Platt S., Joseph S., Weich S., et al.. (2007). The Warwick-Edinburgh Mental Well-being Scale (WEMWBS): development and UK validation . Health Qual. Life Outcomes 5 , 63. 10.1186/1477-7525-5-63 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Thorne N., Witcomb G. L., Nieder T., Nixon E., Yip A., Arcelus J. (2018). A comparison of mental health symptomatology and levels of social support in young treatment seeking transgender individuals who identify as binary and non-binary . Int. J. Transgender. 20 , 241–250. 10.1080/15532739.2018.1452660 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Toscos T., Carpenter M., Drouin M., Roebuck A., Kerrigan C., Mirro M. (2018). College students' experiences with, and willingness to use, different types of telemental health resources: do gender, depression/anxiety, or stress levels matter? Telemed. J. E Health 24 , 998–1005. 10.1089/tmj.2017.0243 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Trout I. Y., Alsandor D. J. (2020). Graduate student well-being: learning and living in the US during the COVID-19 pandemic . Int. J. Multidiscipl. Perspect. High. Educ. 5 , 150–155 10.32674/jimphe.v5i1.2576 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Verma R., Balhara Y. P., Gupta C. S. (2011). Gender differences in stress response: role of developmental and biological determinants . Ind. Psychiatry J. 20 , 4–10. 10.4103/0972-6748.98407 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wheaton B.. (1985). Models for the stress-buffering functions of coping resources . J. Health Soc. Behav. 26 , 352–364. 10.2307/2136658 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wyatt T. J., Oswalt S. B., Ochoa Y. (2017). Mental health and academic performance of first-year college students . Int. J. High. Educ. 6,178–187. 10.5430/ijhe.v6n3p178 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Yang C., Chen A., Chen Y. (2021). College students' stress and health in the COVID-19 pandemic: the role of academic workload, separation from school, and fears of contagion . PLoS ONE 16 , e0246676. 10.1371/journal.pone.0246676 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Yusufov M., Nicoloro-SantaBarbara J., Grey N. E., Moyer A., Lobel M. (2019). Meta-analytic evaluation of stress reduction interventions for undergraduate and graduate students . Int. J. Stress Mang . 26 , 132–145. 10.1037/str0000099 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]

Popular Searches
- Back to school
- Why do I feel weird
- School programs
- Managing stress
- When you’re worried about a friend who doesn’t want help
Understanding Academic Stress in College
How can you tell if your college stress is unhealthy, signs you may need professional support, get more academic stress tips.
Share this resource

If you’re like most college students, you experience school-related stress. Stress isn’t always a bad thing. At manageable levels, it’s necessary and healthy because it keeps you motivated and pushes you to stay on track with studying and classwork.
But when stress, worry, and anxiety start to overwhelm you, it makes it harder to focus and get things done. National studies of college students have repeatedly found that the biggest stumbling blocks to academic success are emotional health challenges including:
- Not getting enough sleep
- Depression
Many things can create stress in college. Maybe you’re on a scholarship and you need to maintain certain grades to stay eligible. Maybe you’re worried about the financial burden of college on your family. You may even be the first person in your family to attend college, and it can be a lot of pressure to carry the weight of those expectations.
Stress seems like it should be typical, so it’s easy to dismiss it. You may even get down on yourself because you feel like you should handle it better. But research shows that feeling overwhelming school-related stress actually reduces your motivation to do the work, impacts your overall academic achievement, and increases your odds of dropping out.
Stress can also cause health problems such as depression, poor sleep, substance abuse, and anxiety.
For all those reasons—and just because you deserve as much balance in your life as possible—it’s important to figure out if your stress is making things harder than they need to be, affecting your health, or getting in the way of your life.
Then you can get help and learn ways to reduce the impact of stress on your life.
First identify what’s causing your stress.
- Is it a particular class or type of work?
- Is it an issue of time management and prioritization?
- Do you have too much on your plate?
- Is it due to family expectations or financial obligations?
Next think about how college stress affects you overall.
- Does it prevent you from sleeping?
- Does it make it take longer to do your work or paralyze you from even starting?
- Does it cause you to feel anxious, unwell, or depressed?
If any of that feels familiar, it’s time to find support to ease your stress and help you feel better. Check out these tips to figure out the best support and approach for you.
It’s important to be able to recognize when stress starts to become all-encompassing, affecting your overall mental health and well-being. Here are some signs you might need to get help:
- Insomnia or chronic trouble sleeping
- Inability to motivate
- Anxiety that results in physical symptoms such as hair loss, nail biting, or losing weight
- Depression, which may manifest as not wanting to spend time with friends, making excuses, or sleeping excessively
- Mood swings, such as bursting into tears or bouts of anger
Learn how to find professional mental health support at your school or elsewhere.
If you need help right now, text HOME to 741-741 for a free, confidential conversation with a trained counselor any time of day, or text or call 988 or use the chat function at 988lifeline.org .
If this is a medical emergency or there is immediate danger of harm, call 911 and explain that you need support for a mental health crisis.
Tips for Managing Academic Stress in College
How to Reduce Stress by Prioritizing and Getting Organized
5 Ways to Stay Calm When You’re Stressed About School
6 Ways to Take Care of Yourself During Exam Time
Related resources
3 steps to make it easier to ask for mental health support, how to identify and talk about your feelings, election stress: tips to manage anxious feelings about politics, search resource center.
If you or someone you know needs to talk to someone right now, text, call, or chat 988 for a free confidential conversation with a trained counselor 24/7.
You can also contact the Crisis Text Line by texting HOME to 741-741.
If this is a medical emergency or if there is immediate danger of harm, call 911 and explain that you need support for a mental health crisis.
- Our Mission
The Science Behind Student Stress
A new study shows how a growth mindset helps students cope with academic setbacks.

A new study finds that when students experience an academic setback such as a bad grade, the amount of cortisol—the so-called stress hormone—in their bodies typically spikes. For most students it drops back down to normal levels a day later, but for some it stays high. These students remain fixated on the setback and have difficulty moving forward.
The researchers analyzed the stress levels of students at two high schools in central Texas during an especially stressful time—the transition into high school. Students completed daily surveys asking about the stress they experienced, and daily saliva samples were collected to measure their cortisol levels.
A majority of these students—68 percent—experienced a drop in grades in the first semester and reported feeling stressed as a result. In how they handled that stress, two clear groups emerged. Students who believed that intelligence can be developed—a growth mindset—were more likely to see setbacks as temporary, and not only had lower overall cortisol levels but were able to return to lower levels shortly after a setback. Students who believed that intelligence is fixed, on the other hand, maintained high cortisol level for longer, said researchers—a stress response that tends to depress problem solving and intellectual flexibility.
“Declining grades may get ‘under the skin,’ as it were, for first-year high school students who believe intelligence is a fixed trait,” explains Hae Yeon Lee, the study’s lead author. “But believing, instead, that intelligence can be developed—or having what is called a growth mindset—may buffer the effects of academic stress.” The researchers speculate that students with a growth mindset may be more likely to seek out "resources to help them cope—such as talking with teachers, peers, or parents about how to study more effectively."
Stress isn’t always bad. Cortisol increases blood sugar, metabolism, and memory function, providing a temporary boost to physical and cognitive ability, and positive stress—called eustress —can boost motivation and decision-making, helping students achieve goals. The stress experienced over an upcoming test is a reminder to study, a way of raising the stakes so that students recognize the importance of being prepared.
But with chronic stress , high cortisol levels can instead impair brain functioning and suppress the immune system, causing long-term damage. During childhood, the neural circuits for dealing with stress are malleable, and chronic stress can rewire the brain to become overly reactive or slow to shut down when faced with threats. So too much stress can disrupt normal brain development and increase the risk of diseases even into adulthood, according to a 2014 Harvard report .
What can schools do to help? “For many young people, the transition to high school can seem like the start of a stressful, seemingly endless marathon,” the researchers write. They recommend that in addition to helping students develop a growth mindset, schools pay closer attention to the demands that students face in ninth grade, and provide more academic and emotional support during this transition year.
The takeaway: Stressed-out students aren’t thinking about solutions. If you want students to learn from their mistakes and overcome obstacles, think about ways to encourage them to adopt a growth mindset .
- Future Students
- Current Students
- Faculty/Staff

News and Media
- News & Media Home
- Research Stories
- School's In
- In the Media
You are here
Student stress during the pandemic.

High school students are experiencing rising stress levels and lower engagement with learning since the start of the COVID-19 pandemic, according to a new study by NBC News and Challenge Success, a nonprofit affiliated with Stanford Graduate School of Education (GSE).
Kids feel that “they are more stressed than they were before the pandemic, they have more work, they are less engaged in school, and their relationships with teachers and [other] kids are strained,” says Denise Pope, a senior lecturer at Stanford GSE and co-founder of Challenge Success.
On this episode of School’s In , Pope talks with show co-host and GSE Dean Dan Schwartz about the study – one of the largest national research projects to shed light on the pandemic’s impact on student connection, engagement and mental health. She also shares what parents and educators might take from its findings in the days and years ahead.
In addition to grades, workload and time management, the study found that one of the top sources of stress for students was lack of sleep. This surprised Pope, who thought remote learning would give students more flexibility and time to sleep. But 43 percent of the students reported sleeping less, and about 5 percent said they were getting less than four hours a night.
Other sources of stress included college and the future, finances and a lack of time to play and relax. Females and students of color in particular experienced high levels of stress and pressure.
Some good news: “People are now much more aware of these problems,” says Pope. “I think more teachers recognize the importance of checking in on mental health and how it’s connected to academics, and how it’s part of their job.”
You can listen to School's In on SiriusXM , Apple Podcasts , Google Podcasts , Spotify , Stitcher and Soundcloud .
⟵ Go to all School's In
Get the Educator
Subscribe to our monthly newsletter.
Stanford Graduate School of Education
482 Galvez Mall Stanford, CA 94305-3096 Tel: (650) 723-2109
- Contact Admissions
- GSE Leadership
- Site Feedback
- Web Accessibility
- Career Resources
- Faculty Open Positions
- Explore Courses
- Academic Calendar
- Office of the Registrar
- Cubberley Library
- StanfordWho
- StanfordYou
Improving lives through learning

- Stanford Home
- Maps & Directions
- Search Stanford
- Emergency Info
- Terms of Use
- Non-Discrimination
- Accessibility
© Stanford University , Stanford , California 94305 .
College students’ stress levels are ‘bubbling over.’ Here’s why, and how schools can help

John Yang John Yang

Claire Mufson Claire Mufson
Leave your feedback
- Copy URL https://www.pbs.org/newshour/show/college-students-stress-levels-are-bubbling-over-heres-why-and-how-schools-can-help
College is a time of major transition and of stress. During the pandemic, students have been struggling to cope with ever-increasing levels of mental distress among students. A recent study by The American College Health Association found that one in four students had considered suicide. John Yang looks at the problem and solutions, on and off campus, for NewsHour's “Rethinking College” series.
Read the Full Transcript
Notice: Transcripts are machine and human generated and lightly edited for accuracy. They may contain errors.
Judy Woodruff:
College is a time of major transition and of stress. Add in the pandemic, and colleges are left struggling to cope with ever-increasing levels of mental distress among students.
John Yang looks at the problem and what can done on and off campus for our series Rethinking College.
Judy, a study this year by the American College Health Association found that 48 percent of college students reported moderate or severe psychological stress, 53 percent reported being lonely, and one in four had considered suicide.
Many college campuses are scrambling to expand and rethink the ways they help students cope with mental health concerns.
Riana Elyse Anderson is an assistant professor of health behavior and health education at the University of Michigan.
Thanks for being with us.
This issue, I think, really got a lot of attention nationally when the University of North Carolina had sort of a mental health break for students after there were two apparent suicides. But you study this issue. You teach young people on a college campus. What do you see? Talk about your personal experience to sort of give our viewers a sense of this issue.
Riana Elyse Anderson, University of Michigan: Sure.
So, we know, over the past year, we have watched stress, anxiety and depression go up about fourfold for everyone. And that absolutely includes our young folks. So, whether these are pediatric populations or the collegiate population, we're watching this number just balloon, and that's on top of what we saw even as a pattern before COVID.
So we're watching college students really get impacted by the comparison that they're seeing in their classmates online, in social media. They're using comparison and they're feeling particularly anxious about it for themselves.
What were the factors before the pandemic?
Riana Elyse Anderson:
Social media is one thing that has really ballooned in this past decade, where children and adolescents are now college students who have been utilizing those strategies for the past several years now are starting to see, oh, that person got into college, this person scored this on this exam, whereas before you could only look as far as the cafeteria, right?
You didn't know what was happening nationwide. But now you have this greater comparison, and it's really impacting one's well-being.
Is there a sense of the — of a generational difference, that young people now are perhaps more concerned about mental health issues?
A wonderful article just came out looking at even the generation like myself, which is just one above the millennials, who really started thinking about mental health a bit differently than our generation before us.
We're starting to see now that generational divide in the Gen Z'ers, who are really staking a claim and saying, not only am I noticing it, but I want to take those days like the UNC students demanded, or I have to see a counselor, rather than go to class, rather than go to work.
And that's something our generation or those above never thought to do, never thought possible. So, on the one hand, what a wonderful thing to do and have that autonomy to say. It's another thing, though, when collegiate professors like myself are now saying, what do we do? How do we contend with teaching, with meeting, with doing the things we have to do for school to continue and meeting the needs of our students?
So, it's just challenging now for us to contend with that.
Are there differences along sort of racial, ethnic, socioeconomic lines? Thinking particularly first-generation college students whose families may not be prepared to help them through this.
Certainly, COVID has impacted that.
So we're seeing this dual impact of not only the resources that have been impacted by COVID, but the socioeconomic and racial disparities. So you're watching folks who perhaps didn't have the access or the tablets, the technology to do the work from home, or perhaps they didn't want to show their screens.
And so that's lessening the amount of time that they're on screen. They're feeling less connected to folks. And now that they're back into a college setting, that year has really impacted them. And they're trying to understand, how do they find community? How are they now exposed to some of the things that they weren't exposed to last year, including discrimination or rejection?
So they're contending with a lot of things that are unique for them relative to their classmates.
Talk about how colleges and universities can address this. How can they help students deal with this?
And, also, you talk about students being more willing to seek help. Are they finding — or are they being a little overwhelmed or finding greater demand than they have the supply for?
Absolutely. So, you said it well.
And the ways that we can combat that are prevention and intervention strategies. So, with respect to what you just said, the CAP services, or counseling and psych services, that most universities have, if we know what these numbers are, we can plan accordingly. We can make sure that we have referrals in the community.
We can expand the number of people on staff. So intervention strategies, once we know that mental health problems are bubbling over, can be something that we can do. But we can also engage in prevention strategies. That is, can we reduce the amount of assignments that we're giving? Can we take more days, like UNC did, as a community, so that no one's e-mailing, no one — it's not just who is saying, I'm going to take an individual day.
Your professors, your administration, no one is e-mailing or expecting anything of you, so that we can prevent some of those problems that we're seeing in the first place.
Riana Elyse Anderson from the University of Michigan, thank you very much.
Listen to this Segment

Watch the Full Episode
John Yang is the anchor of PBS News Weekend and a correspondent for the PBS NewsHour. He covered the first year of the Trump administration and is currently reporting on major national issues from Washington, DC, and across the country.
Support Provided By: Learn more
More Ways to Watch
- PBS iPhone App
- PBS iPad App
Educate your inbox
Subscribe to Here’s the Deal, our politics newsletter for analysis you won’t find anywhere else.
Thank you. Please check your inbox to confirm.
Home — Essay Samples — Nursing & Health — Psychiatry & Mental Health — Stress
Essays About Stress
Hook examples for stress essays, "the modern epidemic: unmasking stress's grip" hook.
"In our fast-paced world, stress has become an epidemic, silently gripping lives. Unmask the hidden turmoil it causes and its far-reaching consequences on mental and physical health."
"Stress: The Silent Health Menace" Hook
"Stress may not always be visible, but its impact on our health is undeniable. Explore the physiological and psychological toll that stress takes on the human body."
"From Chaos to Calm: Strategies for Stress Management" Hook
"Amidst life's chaos, discover effective strategies for managing stress. Delve into mindfulness, relaxation techniques, and ways to regain a sense of calm amidst the storm."
"Workplace Stress: Balancing Ambition and Well-Being" Hook
"Balancing career ambitions with well-being is a constant challenge. Examine the sources of workplace stress and discuss how individuals and organizations can foster a healthier work environment."
"The Domino Effect: Stress's Impact on Relationships" Hook
"Stress doesn't only affect individuals; it ripples through relationships. Analyze how stress can strain personal connections and explore ways to strengthen bonds under pressure."
"A Stress-Free Tomorrow: Shaping a Resilient Future" Hook
"Imagine a future with less stress. Discuss the importance of resilience and mental health awareness in building a society that can withstand the pressures of modern life."
"Beyond Coping: Thriving in the Face of Stress" Hook
"It's not just about coping; it's about thriving. Share stories of individuals who have turned adversity into opportunities for growth and empowerment."
Narrative Essay on Stress
Managing stress: causes, effects, and coping mechanisms, made-to-order essay as fast as you need it.
Each essay is customized to cater to your unique preferences
+ experts online
Population Density and Mental Health
Stress - a universal problem, effects of stress on the mind and body, stress management: what is stress and how to overcome it, let us write you an essay from scratch.
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Effects of Stress on The Body: How It Affects Physical and Psychological Health
Stress: definition, types and impact, "good" stress vs "bad" stress, stress is not always a bad thing, get a personalized essay in under 3 hours.
Expert-written essays crafted with your exact needs in mind
Coping Up with Stress
How to reduce your stress levels, the problem of anxiety and stress and its treatment, the importance of stress management, sources of stress in youth, a calm mind is a healthy mind, the impact of stress on academic success in college students, stress and its main sources, overview of biological predispositions and risk factors associated with depression, stress and its role in our life, work/life balance and stress management, the influence that arousal, stress, and anxiety can have on sport performance, work stress, health and employees, stress related to job and ways to manage it, comparison of stress rates among children and adults, hypnotherapeutic treatments for stress, anxiety and phobias, stress and anxiety as the distractors of an athlete’s attention, psychological wellbeing and psychology distress, stress in our lives: effective communication in workplace under pressure.
Stress, in psychology and biology, is any environmental or physical pressure that elicits a response from an organism.
Stress may be acute, chronic, or traumatic. Acute stress is characterized by immediate danger that occurs within a short span of time. Chronic stress is characterized by the persistent presence of sources of frustration or anxiety that a person encounters every day. Traumatic stress is characterized by the occurrence of a life-threatening event that evokes fear and helplessness.
In psychology, researchers generally classify the different types of stressors into four categories: 1) crises/catastrophes, 2) major life events, 3) daily hassles/microstressors, and 4) ambient stressors.
Stress causes muscular aches and tightness. Stress can impact mental performance. Women appear more prone to stress than men. Chronic stress can cause substance abuse.
Relevant topics
- Mental Health
- Eating Disorders
- Drug Addiction
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Bibliography
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
Celebrating 150 years of Harvard Summer School. Learn about our history.
Managing Stress in High School
Our reasons may vary, but everyone experiences stress. Here are some of the common reasons high school students feel stressed, and what they can do about it.
Pamela Reynolds
Exams. Choosing a college. Figuring out what to do with your life.
No doubt, high school can be a high-pressure time in life. And high school students, as a result, get stressed out.
In fact, according to the American Psychological Association’s Stress in America 2020 survey, teens who are already under stress due to the normal pressures of high school have felt even more stress in recent years, thanks to the pandemic. About 43 percent of teens surveyed in 2020 said their stress levels had gone up, and 45 percent said they had a hard time concentrating on schoolwork. Many reported feeling less motivated.
Although life has mostly returned back to normal, that doesn’t mean the stress that high school students feel has disappeared.
The typical challenges that anyone faces in high school continue as they always have, and, in some cases, have grown more complicated. Consequently, surveys suggest, many teens continue to experience a decline in mental and physical health.
If you’re in high school and stressed, we get it. In this blog, we’ll talk about what stress is, what triggers it, and how you can manage it.
What is Stress?
“Stress” is a term we use constantly in conversation, but what does it really mean?
Stress can be defined as our physical and mental responses to some external event. The event might be considered “good” like preparing to go to the prom, or bad, like feeling tense after an illness, an argument with a friend, or while preparing for an upcoming test.
The good thing about most stress is that it usually goes away once the external event causing the stress is over.
Alternatively, there is a type of stress that results more from an internal dialogue than an external event. We call this “anxiety.” It involves persistent feelings of dread or apprehension that interfere with your daily life, even after the test, the argument, or prom, are just a distant memory.
Why Are Teens So Stressed?
Simply being a teenager can be hard. Your body is changing. You may be grappling with your sexuality or gender identity. Add to that the academic demands of high school and throw in the pressures of social media, and the tension mounts.
“Some of the common triggers of stress in teens might be anxiety to perform well in academics such as getting into a good college, peer pressure, interpersonal relationships, or body image issues,” says Sakshi Khurana, Research Fellow at Harvard’s Weisz Lab for Youth Mental Health. “Other larger issues that the world is going through — for example, climate change or war— might also act as stressors for teens as they are learning about the world.”
The most common source of stress for high school students, according to the 2017 APA Stress survey , is school itself, with about 83 percent of teens identifying school as a major stressor. The second biggest source of student stress, (according to 69 percent of students), was getting into a good college or deciding what to do after high school. The third biggest teen stress was financial concerns for the family (65 percent of students).
Here’s a quick breakdown of broad categories of factors that may stress you out:
- Academics. In high school, not only are you worried about next week’s English, History or Calculus exam, but you’re also worried about applying to college and taking the SAT tests, too. It can all feel overwhelming, and you may feel pressure to please your parents and teachers.
- Social Stress. Even without the pressures of academics, life in high school can be demanding. Dealing with friends and classmates, starting new romantic relationships, handling bullies and peer pressure both online and off, can be a lot to handle.
- Family Issues. If your parents are divorcing, if your family is experiencing financial problems, or even if you just have trouble getting along with siblings, your stress levels can go up.
- Trauma . Dramatic life events ranging from a death in the family, to an accident, to emotional and physical abuse, can cause stress. Also in this category, you can include the collective trauma of such global events such as school shootings, terrorism, and natural disasters.
- Big Life Changes . Changes like moving and starting a new school can be a major stress for teens.
Explore College Programs for High School Students at Harvard Summer School
What are Signs of Stress in High School Students?
If you’re a high school student feeling stressed, you may not even recognize the symptoms.
In fact, many symptoms of stress might be considered normal for teens who are also dealing with natural hormonal and physical changes. For that reason, it’s important to consider whether behavioral changes can be linked in time to an external event.
Signs of stress include:
- Feeling more agitated, anxious, short-tempered, or depressed
- Getting sick more often
- Having more headaches, stomachaches, or other aches and pains
- Feeling more tired than usual
- Not being able to sleep, or sleeping too much
- Skipping meals or overeating
- Neglecting chores or hobbies
- Trouble concentrating and forgetfulness
- High blood pressure
According to the APA 2017 survey, the most common symptoms of stress among teens were insomnia, overeating or eating unhealthy foods, skipping meals, feeling angry, nervous, or anxious, feeling fatigued, and snapping at friends and classmates.
Why is Stress so Problematic for Teens?
Let’s be clear, a little bit of stress is a normal part of life, and sometimes even desirable.
Stress can act as a motivator, getting us to do things we might not otherwise. Good stress is called “eustress” and can help get you excited and energized about that first date or taking the stage in your first musical.
But too much unrelieved stress can lead to mental and physical health issues.
Your body reacts to stress by releasing a hormone called cortisol which regulates blood pressure and immune function. If you’re stressed all the time and your body produces too much cortisol, it can lower your immunity, raise your blood pressure, and impair your cognitive performance.
In teens, the part of the brain regulating the stress response is less developed than in adults, meaning that if you’re a stressed-out teen, you may experience stress longer than an adult.
“In the teen years, due to hormonal changes, stress tends to influence the emotional functioning of the brain, which in turn impacts the cognitive and executive functioning,” says Khurana.
You might not be able to sleep, you may overeat, or develop digestive, cardiovascular, or immune problems. Stress can even put you at a higher risk for developing mental illnesses like anxiety or depression .
What are the Best Techniques to Help Students Manage Stress?
Since too much stress is not a good thing for your mind or body, you should think about incorporating a few stress management techniques into your daily life.
“A few techniques that might help teens manage stress are relaxation through deep breathing, meditation, or mindfulness, channeling energy into sports or creative pursuits such as music, art, theater, and forming meaningful relationships or friendships,” says Khurana. “Additionally, every culture has its own way of enabling young people to manage stress, so drawing from those traditions might be helpful as well.”
Here are few ideas of how high school students can learn how to deal with stress at school:
- Keeping a journal
- Getting plenty of exercise
- Eating healthy, regular meals
- Making sure you get enough sleep
- Downloading an app that provides relaxation exercises (such as deep breathing or visualization) or tips for practicing mindfulness
- Limiting excess caffeine in soft drinks or coffee
- Reaching out to friends or family members who help you cope in a positive way
- Making time to do fun things
- Learning to recognize and prepare for stressful periods by doing all of the above
With so many big life decisions ahead, getting through high school happy and whole can definitely feel challenging at times. It’s easy to see why so many high school students feel stressed. The good news is that there are solutions. Adopt the strategies above, take a deep breath, and remember, it’s not forever!
Join our mailing list for important updates about college programs for high school students at Harvard.
About the Author
Pamela Reynolds is a Boston-area feature writer and editor whose work appears in numerous publications. She is the author of “Revamp: A Memoir of Travel and Obsessive Renovation.”
Prepare for College
How to Build Your Personal Brand in High School
Building your personal brand is all about telling the world who you are.
Harvard Division of Continuing Education
The Division of Continuing Education (DCE) at Harvard University is dedicated to bringing rigorous academics and innovative teaching capabilities to those seeking to improve their lives through education. We make Harvard education accessible to lifelong learners from high school to retirement.


- ACADEMIC ADVICE
The Effects of Stress on College Students & Ways to Overcome it
- June 1, 2022
Table of Contents
What is academic stress, physical effects of stress, psychological effects of stress, relationships or lack of friends, homesickness, tips to overcome stress during college, avoid procrastinating, on-campus mental health services, off-campus centers and hotlines.
We have all heard at least one person being nostalgic about the great time they had in college. And it’s true. Being on your own for the first time ever, pursuing a degree, meeting new people, and living in a new city can give you a new purpose and perspective in life. But we also have to admit that college can be stressful too. While all these great new opportunities might be a dream come true for some, they can be overwhelming for many others. And this overwhelming feeling might go away when you get settled in after a week or might stick around in the form of academic stress.
To understand academic stress, we first need to understand what the term “stress” really means. In simple terms, stress refers to a distressed state of mind caused by various factors. Mental stress manifests differently based on the person or level of stress.
Now that we have clarified what “stress” is, it will be pretty easy to understand what academic stress is. We use the term “academic stress” to refer to the kind of psychological distress caused by factors pertaining to one’s academic performance. The stressors that cause academic stress vary depending on the student, but they all have in common the fear of failure in some way or another.
How Stress Affects College Students & Their Mental Health
While virtually everyone has experienced stress at some point in their lives, its intensity and the way we deal with it differs with every person. For some people, it’s just jitters before a presentation, and that’s it, but for others who don’t know how to deal with or manage it, stress can be a serious problem in their everyday lives. High levels of stress concerning academic performance have a negative impact on one’s mental and physical health. Ironically, academic stress also negatively affects a student’s academic performance.
Though we have stated that stress is related to the mind, you may easily detect someone with higher stress levels due to the physical manifestations of academic stress. While physically, the signs of stress may differ from person to person, there are some more prevalent physical symptoms among students:
Muscle pain & headache
Many of us usually attribute headaches and muscle pain to factors such as dehydration, physical activity, etc. The truth is that muscle pain and headaches are also widespread symptoms of academic stress. When you are stressed, muscles in your body tense up; and when these muscles are tensed for a more extended period, it results in aches and pains in your body.
Nausea & stomach aches
Other common symptoms of academic stress in students include stomach aches and digestive issues like diarrhea or constipation. In even more extreme cases, academic stress manifests itself in the form of nausea and vomiting.
As we have already established, academic stress originates from the need to perform well academically for various reasons. The fear of failure in academic challenges can seriously strain students psychologically. Here are some of the most prevalent psychological symptoms that derive from academic stress:
Anxiety & depression
It is no news that academic stress can worsen symptoms for those that already have an anxiety disorder or depression. According to a survey conducted by the Anxiety & Depression Association of America (ADAA) , 30% of students admitted that stress had a negative impact on their academic performance .
Sleep disorder
High levels of stress can disrupt your sleep schedule or quality. Whether in quantity or quality, less sleep pushes the body to produce more stress hormones like cortisol. And while it is normal for the body to produce cortisol, this particular hormone negatively affects your memory, metabolic rate, and blood glucose regulation when at high levels. This, in turn, will put a student on a vicious cycle where academic stress negatively affects your sleep, and the lack of sleep negatively affects your academic performance.
Causes of Stress During College
Academic stress may affect students of all educational levels, one way or another: whether they are performing in front of an audience, entering an exam, or some other way. However, it is essential to note that college students have some additional stressors that set them apart from students of other levels of education. College students experience stress due to external or internal factors. Here are some of the most common stress-causing factors in college students:
There are a few reasons why some people choose not to pursue a college degree, and the cost of tuition is one of them. Many of those who enroll in college have problems making ends meet due to tuition and other college-related expenses. Simultaneously working and studying can put a strain on the mental health of many students as they try to balance personal, academic, and work life. One possible solution to this problem may be to apply for scholarships, grants, or even loans.
One of the main challenges for many college students is actually making time for themselves or socializing with others. This is especially difficult when they need to work to be able to afford college. Lack of quality time with friends or absence of a social life altogether has a negative effect on a student’s mental health as there is virtually no time to “recharge.”
Think about this: One day, you are a carefree 17-year-old, eating home-cooked meals every day and having the best time of your life in high school. A few months later, you are legally an adult, getting your first job and probably moving thousands of miles away from everything you have ever known to go to college. Even the mere thought of such a transition is enough to stress you out. College students are now far away from their families and responsible for everything that concerns their own lives.
The transition from high school to college can be tough on many students for various reasons. One of the main stressors for college students is the coursework. Students usually struggle to meet deadlines or handle the increased workload that comes with enrolling in college.
Ending the Stigma
The best thing to do in order to help students deal with academic stress is to end the stigma. This can be done by spreading awareness of the effects of academic stress on students’ mental, physical, and emotional health. Only by continually and persistently addressing this issue and educating each other can we overcome or at least learn how to manage academic stress.
✅ Request information on BAU's programs TODAY!
If you or someone you know are experiencing academic stress and its adverse effects on your mental and physical health and your academic performance, it is time to take action . Learning what to do to prevent becoming stressed due to academic workload or even how to manage your academic stress is extremely important for many reasons we have already discussed. Here are some tips on how to overcome academic stress when in college:
Maintain a healthy diet
A healthy diet is a well-balanced diet that includes vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and a regular eating schedule and daily exercise. While maintaining a healthy diet should be a priority for everyone, a healthy diet can also help with overcoming academic stress. Eating healthy will keep your blood pressure and glucose stable, both of which may fluctuate when a person is in a stressful situation. While many students make it a habit of drinking caffeinated drinks to stay focused on their studies, it is best to opt for water or milk. This is because caffeinated drinks raise cortisol levels in the body, similar to what stress does.
Remain physically active
Being physically active does not mean you need to be all closed up in a gym sweating away. Any sport or physical activity counts as exercise as long as it increases your heart rate. When exercising or taking part in physical activity, your body releases hormones (endorphins) that, among other benefits, reduce stress.
Make sure you spend time outdoors
Sometimes just being in a room by yourself you will associate with stress and anxiety and hence stress out. College students can also deal with academic stress by spending time outdoors. Leaving your dorm room or library and simply going outside for a walk can do wonders for your focus. Being surrounded by nature and greenery significantly reduces your cortisol levels.
The change in workload is one of the leading causes of academic stress in college students. By learning how to manage your time better, you make sure to always meet your deadlines. By avoiding procrastination, you spread out the workload, so you don’t have to worry about working under pressure when the deadlines approach.
Seeking Medical Support
While totally manageable for a lot of people, academic stress can have powerful adverse effects on others. Some of the negative effects of academic stress may be too exhausting to deal with on your own. That is why it is always essential to know places to seek help if needed:
Lately, there has been an increase in awareness surrounding mental health issues, including academic stress. That is why many institutions offer on-campus health services for their students. You can learn more about these services by visiting your college’s website.
If you feel that on-campus mental health services won’t do for you personally, you can always seek help in off-campus centers. Another great source that offers support is the hotlines available 24/7. Check the number for suicide prevention lifelines to consult with specialists on anything you might be dealing with, including anxiety, depression, stress, etc. You can contact the National Suicide Prevention Lifeline at 1-800-273-8255 .
Though there has been some progress in awareness regarding mental health, specifically the effects of stress on mental and physical health, there is still so much to do. There are a few steps students can take to better deal with academic pressure, like eating healthy, exercising, managing their time better, consulting with loved ones and specialists, etc. As academic stress can have serious negative effects on one’s health, everyone should take it seriously and work towards overcoming it the best they can.
Bay Atlantic University
Leave a reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
You May Also Like
- 4 minute read
8 Ways to Pay Off Student Loans
- September 23, 2022
What is the Academic Achievement Gap and How Can It Be Closed?
- July 13, 2020
- 7 minute read
How to Write a Cover Letter for an Internship (With Examples)
- October 14, 2022
- 8 minute read
How Long You Can Stay in the U.S. on a Student Visa?
- May 17, 2022
- 8 shares 8 0 0
Master of Public Health: Roles, Job Outlook & Salaries
- February 22, 2022
- 5 minute read
Top 10 Things That Look Good on College Applications
- September 29, 2022
Navigate the Levels of English as a Second Language
- April 24, 2024
- 6 minute read
Learning English as A Second Language: A Comprehensive Guide
Mastering esl teacher skills: a comprehensive guide to success, esl vs. efl: what is the difference, request information on bau's programs today.
Essay on Stress Management
500 words essay on stress management.
Stress is a very complex phenomenon that we can define in several ways. However, if you put them together, it is basically the wear and tear of daily life. Stress management refers to a wide spectrum of techniques and psychotherapies for controlling a person’s stress level, especially chronic stress . If there is effective stress management, we can help one another break the hold of stress on our lives. The essay on stress management will throw light on the very same thing.

Identifying the Source of Stress
The first step of stress management is identifying the source of stress in your life. It is not as easy as that but it is essential. The true source of stress may not always be evident as we tend to overlook our own stress-inducing thoughts and feelings.
For instance, you might constantly worry about meeting your deadline. But, in reality, maybe your procrastination is what leads to this stress than the actual deadline. In order to identify the source of stress, we must look closely within ourselves.
If you explain away stress as temporary, then it may be a problem. Like if you yourself don’t take a breather from time to time, what is the point? On the other hand, is stress an integral part of your work and you acknowledging it like that?
If you make it a part of your personality, like you label things as crazy or nervous energy, you need to look further. Most importantly, do you blame the stress on people around you or the events surrounding you?
It is essential to take responsibility for the role one plays in creating or maintaining stress. Your stress will remain outside your control if you do not do it.
Strategies for Stress Management
It is obvious that we cannot avoid all kinds of stress but there are many stressors in your life which you can definitely eliminate. It is important to learn how to say no and stick to them. Try to avoid people who stress you out.
Further, if you cannot avoid a stressful situation, try altering it. Express your feelings don’t bottle them up and manage your time better. Moreover, you can also adapt to the stressor if you can’t change it.
Reframe problems and look at the big picture. Similarly, adjust your standards and focus on the positive side. Never try to control the uncontrollable. Most importantly, make time for having fun and relaxing.
Spend some time with nature, go for a walk or call a friend, whatever pleases you. You can also try working out, listening to music and more. As long as it makes you happy, never give up.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Conclusion of the Essay on Stress Management
All in all, we can control our stress levels with relaxation techniques that evoke the relaxation response of our body. It is the state of restfulness that is the opposite of the stress response. Thus, when you practice these techniques regularly, you can build your resilience and heal yourself.

FAQ of Essay on Stress Management
Question 1: What is the importance of stress management?
Answer 1: Stress management is very efficient as it helps in breaking the hold which stress has on our lives. Moreover, you can also become happy, healthy and more productive because of it. The ultimate goal should be to live a balanced life and have the resilience to hold up under pressure.
Question 2: Give some stress management techniques.
Answer 2: There are many stress management techniques through which one can reduce stress in their lives. One can change their situation or their reaction to it. We can try by altering the situation. If not, we can change our attitudes towards it. Remember, accept things that you cannot change.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

Essay Sample on Causes and Effects of Stress on Students, With Outline
Published by gudwriter on January 4, 2021 January 4, 2021
Cause and Effects Essay Outline About Stress Among Students
Introduction.
Stress in students may have serious harmful effects and thus needs to be addressed.
Elevate Your Writing with Our Free Writing Tools!
Did you know that we provide a free essay and speech generator, plagiarism checker, summarizer, paraphraser, and other writing tools for free?
Paragraph 1:
One of the causes of stress in students is poor sleeping habits.
- Students who do not get enough sleep at night or lack healthy sleeping habits are likely to develop stress.
- Enough sleep allows the brain and body of a student to relax and recharge.
- Lack of it can limit a student’s ability to learn, concentrate and solve problems.
Paragraph 2:
Student stress is caused by academic pressure.
- They are given homework assignments.
- They have classroom assignments and term papers that are supposed to be completed and submitted in strict deadlines.
- Pressure to do well from those close to them such as family, friends, and teachers.
Paragraph 3:
Student stress may result from poor nutrition and unhealthy eating habits.
- Stress-inducing foods are those that have high refined carbohydrates, sugar, caffeine, and fat.
- A stress-reducing diet is made up of foods that are high in complex carbohydrates and fiber and low in fat content.
Paragraph 4:
High stress levels could make students develop physical symptoms that could negatively affect their academic performance.
- When a student experiences these symptoms, they might not feel the motivation they once felt about doing their best on academic tasks.
- The symptoms are detrimental to the health of students.
Paragraph 5:
Stress makes students to have poor management skills.
- A student could become disorganized and uncertain about their priorities and goals.
- They become incapable of effectively budgeting and managing their time.
- They develop a tendency of procrastinating and neglecting responsibilities.
Paragraph 6:
Stress leads to self-defeating thoughts.
- A student under stress may consistently think about the adversity or negative situation in which they are.
- They could constantly focus on their weaknesses and failures.
Paragraph 7:
There are various stress management strategies students may take to reduce stress.
- Get regular physical activity and practice.
- Spend quality time with friends and family, and keeping a sense of humor.
- Find time for such hobbies as listening to music, playing football, and reading a book.
- Get enough sleep and consume balanced diet.
- Stress in students cause serious negative effects, both physical and academic.
- It results from poor sleeping habits, academic pressure, and poor nutrition and unhealthy eating habits.
- It results into physical symptoms, poor management skills, and self-defeating thoughts.
- Parents and teachers should work together to ensure that students do not experience much stress.
Looking for cheap speech writing services for phd? Hire a reliable essay writer who will create a 100% original paper and deliver it on time. Gudwriter has a pool of professionals who understand how to write quality cause and effect essays from suitable selected topics.
A Cause and Effect Essay on Stress in Students
Stress is the natural response the human body gives to challenges. Students are exposed to stress by various factors. When a student undergoes chronic stress or high stress levels, their ability to learn, memorize, and post good academic performances can be interfered with regardless of their age or grade. Stress can also make a student experience poor mental, emotional, and physical health. Teachers and parents may help students avoid chronic stress in their lives if they learn about and develop a good understanding of common stressors. Stress in students may have serious harmful effects and thus needs to be addressed.
One of the causes of stress in students is poor sleeping habits. Compared to students who get plenty of sleep, students who do not get enough sleep at night or lack healthy sleeping habits are likely to develop stress. Enough sleep allows the brain and body of a student to relax and recharge. It also helps in ensuring that the immune system remains strong. On the other hand, lack of enough sleep can limit a student’s ability to learn, concentrate, and solve problems and can also make them more aggressive. According to Hales and Hales (2016), it is recommended by the National Sleep Foundation that young people, especially students, should maintain a regular sleep schedule and that they should sleep for between 8.5 and 9.25 hours per night.
Another major cause of student stress is academic pressure. As teachers prepare students for standardized tests, they give them homework even if the students are as young as six only. In addition to these homework assignments, there are classroom assignments and term papers that are supposed to be completed and submitted in strict deadlines. The pressure that comes from these assignments coupled with the desire by students to succeed academically culminates into stress. Students also experience pressure to do well in their academic work from those close to them such as family, friends, and even teachers (Raju, 2009). They therefore feel so much pushed that they even resort to academic dishonesty such as cheating in exams so as to match these high expectations.
A student’s stress levels can also increase due to poor nutrition and unhealthy eating habits. Foods that are associated with high stress levels in students include those that have high refined carbohydrates, sugar, caffeine, and fat. This is the case with many types of fast, processed, and convenience foods. Examples of foods that induce stress include French fries, white bread, processed snack foods, candy bars, donuts, energy drinks, and sodas (Kumar, 2015). A healthy stress-reducing diet is made up of foods that are high in complex carbohydrates and fiber and low in fat content. Examples of such foods include lean proteins, nuts, whole grains, vegetables, and fruits.
It is noteworthy that high stress levels can make students develop physical symptoms that could negatively affect their academic performance. These signs and symptoms include chest pain, elevated blood pressure, stomach upset, mumbled or rapid speech, nervous habits such as fidgeting, back and neck pains, tremors and trembling of lips, and frequent headaches (Kumar, 2015). When a student experiences these symptoms, they might not feel the motivation they once felt about doing their best in such academic tasks as completing assignments or preparing for tests. Moreover, the symptoms are detrimental to the health of students, a factor which may father make their academic fortunes to dwindle.
Stress also makes students to have poor management skills. A student could become disorganized and uncertain about their priorities and goals as a result of suffering from high levels of stress. This could further make them incapable of effectively budgeting and managing their time. Moreover, highly stressed students have the tendency to procrastinate and neglect such important responsibilities as meeting deadlines and completing assignments (Hales & Hales, 2016). This, of course, negatively impacts the quality of their academic work and study skills.
High stress levels could further lead to self-defeating thoughts among students. While undergoing stress, it is likely that a student may consistently think about the adversity or negative situation in which they find themselves. In addition, they could constantly focus on their weaknesses and failures while ignoring their strengths and achievements. These are self-defeating thoughts that not only deal a blow to their self-esteem but also affect how they behave and how they feel both as humans and as students (Patel, 2016). They result into a student lacking confidence in their abilities and this negatively impacts their success in school since they cannot perform to their highest potential.
There are various stress management strategies students may take to reduce stress. One of these is to get regular physical activity and practice such relaxation techniques as massage, tai chi, yoga, meditation, and deep breathing. Students may also keep stress away by spending quality time with friends and family, and keeping a sense of humor. Another strategy may be to find time for such hobbies as listening to music, playing football, and reading a book. It is also important that one gets enough sleep and consumes balanced diet (Mayo Clinic Staff, 2019). These strategies may both alleviate and prevent stress among students.
Stress in students cause serious negative effects, both physical and academic. Students may experience stress due to poor sleeping habits, academic pressure, and poor nutrition and unhealthy eating habits. Students need enough sleep and less pressure for their brain to relax and recharge for it to function well. They also need to avoid stress-inducing foods such as fries and sodas. As has been seen, high stress levels could lead to physical symptoms, poor management skills, and self-defeating thoughts among students. As such, parents and teachers should work together in ensuring that students do not experience much stress because it is not good for their health and academic ability.
Hales, D., & Hales, J. (2016). Personal stress management: surviving to thriving . Boston, MA: Cengage Learning.
Kumar, N. (2015). Psychological stress among science students . New York, NY: Springer.
Mayo Clinic Staff. (2019). “Stress symptoms: effects on your body and behavior”. Mayo Clinic . Retrieved March 27, 2020 from https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/stress-management/in-depth/stress-symptoms/art-20050987
Patel, G. (2016). An achievement motivation and academic anxiety of school going students . Lunawada: Red’shine Publication. Inc.
Raju, M. V. (2009). Health psychology and counselling . Delhi, India: Discovery Publishing House.
Do you need help with homework and wondering where you can seek help? Request help me write my paper and get help from qualified tutors who will write your paper following all the guidelines provided. At Gudwriter, our papers are 100% original and only customized for you. Contact us today to save your time and grade.
Dive into the complex web of stressors and their consequences for students in our comprehensive essay. To amplify the impact of your talk, use our innovative speech generator to craft engaging speeches.
More essays and articles to explore;
- Free cause and effect essay on smoking
- Environmental sciences and causes of climate change
- Essay sample on importance of reading
- 85 cause and effect essay topics to investigate
- How to write a cause and effect essay
- Demonstration speech ideas and topics

Special offer! Get 20% discount on your first order. Promo code: SAVE20
Related Posts
Free essays and research papers, artificial intelligence argumentative essay – with outline.
Artificial Intelligence Argumentative Essay Outline In recent years, Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become one of the rapidly developing fields and as its capabilities continue to expand, its potential impact on society has become a topic Read more…
Synthesis Essay Example – With Outline
The goal of a synthesis paper is to show that you can handle in-depth research, dissect complex ideas, and present the arguments. Most college or university students have a hard time writing a synthesis essay, Read more…

Examples of Spatial Order – With Outline
A spatial order is an organizational style that helps in the presentation of ideas or things as is in their locations. Most students struggle to understand the meaning of spatial order in writing and have Read more…

Essay on Examination Stress on Students
Students are often asked to write an essay on Examination Stress on Students in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Examination Stress on Students
Understanding examination stress.
Examination stress is a common issue among students. It refers to the anxiety and nervousness students feel before and during exams.
Causes of Examination Stress
The main causes of exam stress include high expectations from parents, fear of failure, and lack of preparation.
Effects on Students
Examination stress can lead to health problems like headaches, sleep issues, and even depression. It also affects a student’s concentration and performance.
In conclusion, it’s vital to manage exam stress for overall well-being and academic success.
250 Words Essay on Examination Stress on Students
Introduction.
Examinations are an integral part of the academic system, designed to assess students’ understanding and knowledge of subjects. However, they often induce a significant amount of stress among students, which can adversely affect their performance and overall well-being.
The Origin of Examination Stress
Examination stress primarily originates from the pressure to perform well. This pressure can stem from various sources such as high personal expectations, fear of failure, or societal and parental expectations. The competitive nature of the academic system, along with the perception that success in examinations equates to success in life, further exacerbates this stress.
Impacts of Examination Stress
Examination stress can have profound psychological and physiological impacts on students. It can lead to anxiety, depression, sleep disorders, and even physical health problems like headaches and fatigue. Moreover, it can impair students’ cognitive functions, thus negatively affecting their academic performance.
Managing Examination Stress
Effective stress management strategies are crucial for students to navigate through examination stress. Regular exercise, adequate sleep, and a balanced diet can help maintain physical health and reduce stress levels. Psychological strategies such as mindfulness, positive affirmations, and relaxation techniques can also be beneficial.
While examinations are necessary for academic evaluation, it’s essential to address the stress they cause. A balanced approach, focusing on both academic excellence and mental well-being, can help students manage examination stress effectively, thus leading to a healthier and more productive academic life.
500 Words Essay on Examination Stress on Students
Examinations are an integral part of the educational system, designed to evaluate a student’s understanding and knowledge of the subjects studied. However, they often bring with them a significant amount of stress, causing a negative impact on the mental and physical health of students. This essay delves into the phenomenon of examination stress, its causes, effects, and possible solutions.
Examination stress is a psychological condition in which students experience extreme distress and anxiety in the period leading up to, during, and even after examinations. It is characterized by feelings of fear, self-doubt, and apprehension about one’s performance in the exams. While a certain level of stress can be motivational, excessive stress can hinder performance and well-being.
The causes of examination stress are multifaceted. The pressure to perform well, high expectations from parents and teachers, competition amongst peers, and fear of failure are common triggers. Additionally, the lack of effective study habits, poor time management, and the absence of relaxation or recreational activities can exacerbate the stress. The modern educational system, with its emphasis on grades and rankings, often overlooks the individual learning pace and capabilities of students, further contributing to this stress.
Effects of Examination Stress
Examination stress can have severe implications on a student’s mental and physical health. It can lead to anxiety disorders, depression, and in extreme cases, suicidal thoughts. Physically, it can cause headaches, sleep disorders, loss of appetite, and a weakened immune system. Moreover, it can negatively impact a student’s academic performance and hinder the learning process, creating a vicious cycle of stress and poor performance.
Addressing Examination Stress
Addressing examination stress necessitates a multi-pronged approach. Firstly, a change in perspective towards examinations is required. They should be perceived as a part of the learning process rather than a do-or-die situation. Secondly, students should be encouraged to adopt effective study habits and time management techniques, which can reduce last-minute cramming and associated stress.
Moreover, the importance of physical exercise and recreational activities in maintaining mental health should be emphasized. Regular breaks, balanced diet, and adequate sleep are crucial for stress management. Counseling services should also be made available in educational institutions to help students cope with stress.
In conclusion, examination stress is a prevalent and severe issue faced by students. It is crucial to address this problem to ensure the holistic development of students and foster a healthy learning environment. By altering our perspectives, improving study habits, and prioritizing mental health, we can mitigate the effects of examination stress and transform the educational experience into a more enjoyable and less stressful journey.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
- Essay on Telephone for Students
- Essay on Student Politics
- Essay on My Strength as a Student
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

420 Stress Essay Topic Ideas & Examples
To write a stress essay, you’ll need a good idea to start your research and writing process. We have some for you to check.
📑 Aspects to Cover in a Stress Essay
🏆 best stress topic ideas & essay examples, 🥇 most interesting stress topics to write about, 🎓 simple & easy stress essay topics, 📌 research titles about stress, 👍 good stress essay topics, 💡 interesting topics to write about stress, ❓ stress research questions.
As a student, you’re likely familiar with the subject already. Yet, you may struggle to choose between composing about stress management or mental health issues. That’s why our team has prepared this list of stress essay topics. Look through them to consider every possible title and pick the most suitable one.
Stress has become one of the most common problem individuals experience today. It is possible to say that everyone has felt stressed out at least once in their life.
Stress essays are challenging and engaging assignments that can help students to learn more about the issue. We are here to help you write an outstanding essay on stress.
Let us start by choosing the subject for your paper. We would suggest choosing one of the following stress essay topics and titles:
- Stress management techniques and their significance
The effects of stress on the body
- How bullying increases stress among students
- Causes and symptoms of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) (you can choose another mental health disorder, too)
- Benefits of leisure activities to reduce the level of stress
- The link between nutrition and stress
- Consequences of workplace stress
- Common causes of stress among students
Note that you can select one of the other stress essay titles, too. You can search for them online. Remember to only use online examples as an inspiration for your paper and avoid copying the information you will find.
Once you have chosen one of the topics, you are ready to work on your outstanding essay. Here are the aspects you should cover in your paper on stress:
- Think about what you already know about the subject you had selected. Check out stress essay examples online if you are not sure that your topic is relevant. Research the information about the issue, using credible sources (Wikipedia is not one of them!).
- Select the sources that you cite in your paper. The general rule is that you should use peer-reviewed articles and scholarly books. Ask your professor about the sources in advance.
- A well-developed stress essay outline is important. Include an introductory paragraph, several body paragraphs (we would recommend writing at least three), and a conclusion.
- Think about the purpose of your paper. Do you want to help the reader to minimize stress? Should your essay provide statistical data? Do you want to address workplace stress or school-related stress? Consider these questions while working on the essay.
A thesis statement is a must. Generally, it should be present in the last sentence of your introduction. Here is how a thesis can look like:
Nutrition is directly linked to the level of stress in an individual. / Workplace stress can lead to depression among employees.
- Define stress. Provide a dictionary definition of stress or select one from the articles you have studied. Your reader should understand the concept of stress clearly. Remember that there are different types of stress based on its causes.
- Discuss the consequences of stress, referring to the sources you have selected. Address the physical and emotional outcomes of stress.
- Discuss the potential ways of dealing with stress. According to the purpose of your paper, address one or several methods in detail. What are the positive changes an individual can feel after these interventions? Reflect on this question, too.
- Remember to support your claims with evidence from the sources you have studied. Cite the literature properly using the citation style guide.
- Your concluding paragraph should restate the main arguments of the paper. Avoid adding new information or in-text citations in this section.
Please feel free to analyze our free samples and get the best ideas for your essay!
- Time Management and Its Effect in Reducing Stress among Students One of the causes of stress among high school students and college students is the difficulty in interacting with a completely new set of students and an even larger social group within the body of […]
- Effects of Stress on Human Health There are numerous theories and researches on stress and health, they all agree that stress has an adverse effect on human health; the statement goes “a stressed man is an unhealthy man”.
- How to Manage Stress at Work Essay Work stress is one of the ailments that are acknowledged worldwide to be affecting the healthiness of the organization and the health or workers.
- Stress Among College Students: Causes, Effects and Overcomes Due to stress, college students may experience such adverse outcomes as the decreased levels of cognitive functioning, the impaired ability to study, and, consequently, lower academic performance.
- Stress Management While undertaking the survey on management of stress in organizations, I came to realize that the sources of stress to employees are many and vary from one employee to another.
- Yoga for Stress Management For instance, Karma yoga, which is one of Yoga types, aids in controlling stress through the development of appropriate attitudes in relation to work environment coupled with enhancing the ability to respond positively to professional […]
- Work Stress and Its Effects on Individuals Managers of leading companies have long realized that this phenomenon is dangerous to both employees and companies, and one of their priorities is to remove the causes of work stress and or at least minimize […]
- Stress: Definition and Different Types of Stress Many believe that individual or team performance is susceptible to the effects of stress as there is a requirement for teams to maintain acceptable performance.
- Frustration and Stress Managing The stress that is a result of waiting and anticipation is a kind of stress that can be controlled. Humor is one of the many forms that can be used to blow up stress.
- How to Beat Stress? Stress seems to follow us everywhere and every minute, so that it is not always possible for people to find the time and think of the ways to beat stress and live quietly with no […]
- How to Cope with Stress Essay The identification of the stressor also opens a window for an individual to explore other adaptation methods, which can be of help in the future such as avoidance.
- Factors and Consequences of a Plane Crash: Traumatic Stress The effects from air crash are determined by among other things, the cause of the crash, the altitude and its speed at the time of crash.
- Teen Stress: How to Help Them Manage It? The physiologic changes of the body, the first steps are taken in search of the individuality, examinations, and tests in school or college, the pressure from the parent’s side, the issues in the relationships, diffidence, […]
- Working Conditions That Lead to Stress at Amazon For example, among the methods for evaluating the efficiency of warehouse employees is the indicator of the number of processed packages per hour.
- How Does Stress Affect the Body? Especially after the pandemic of COVID-19 has made the levels of stress in people worldwide skyrocket, the significance of studying the levels of stress on the human body has grown tremendously.
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder: Case Conceptualization Samuel, an 8-year-old black male, lives in an adopted white family consisting of the father, incarcerated for domestic violence charges, the mother, the primary caretaker and the only home provider, and the older sibling.
- Comparison of Stress Level Among Traditional Learning and Online Learning College Students The distance learners have been perceived to be enjoying a suitable environment of learning as opposed to the traditional classroom learners who experience high levels of stress.
- Improving Stress Resistance in Agricultural Crops The biotechnology involved in producing such crops faces many difficulties and there are a lot of considerations of the methods used to improve the crop’s resistance that need to be assessed.
- People Should Consider Owning a Pet Because Doing So Can Relieve Stress These are great techniques, but the issue of having a pet as a best friend is unique and one of the recently discovered best practices of relieving work-related strains or stress.
- Emotions, Stress and Ways to Cope with Them This means that strong emotions will trigger complex brain patterns and physiological responses due to the nature of hormones the body releases.
- Pre-Stressed Concrete The aim of this paper is to discuss the historical developments of pre-stressed concrete, the basic concepts of pre-stressed concrete, and the manufacturing of the pre-stressed concrete.
- Posttraumatic Stress Disorders: Psychological Assessment PTSD was adopted by experts in the third revision of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual for Mental Disorders to replace terms like “shell shock, nervous shock, and combat fatigue” that described the response to traumatic […]
- Academic Stress and Its Impact on Teenagers Another possible solution is raising awareness about the harms of stress to human health to educate students and their parents on the risks associated with stress.
- Stress and Its Effects on Health The effects of stress on the cardiovascular system are explained in a review by Kivimaki & Steptoe to determine the impact of stress on the development and progression of cardiovascular diseases.
- Burnout Stress in Nursing Related With Lazarus and Folkman’s Theory According to Lazarus and Folkman, stress is the relationship existing between a person and the environment that compels the individual beyond resources and consequently endangering life. The theory of stress and coping helps individuals to […]
- Transactional Model of Stress and Coping in Intravenous Drug Users The purpose of this paper is to explain how the transactional model of stress and coping can be used to explain and assess the process of coping in a group of intravenous users at risk […]
- The Relationship Between Self-Efficacy and Perceived Stress The last hypothesis is that there is a significant gender difference in the measures of self-efficacy, emotional intelligence, and perceived stress.
- Stress and Burnout in the Workplace This paper investigates the causes of stress and burnout in the workplace and suggests ways of minimizing stress and burnout. This will also result in stress and burnout, ultimately affecting the performance of the workers.
- Time and Stress Management for Better Productivity Procrastination is the forwarding of events that have to be done at a specific time to another time in the future.
- Stress Management in Work Environment Leka, Griffiths and Cox are of the opinion that work related stress arises from the disparity between the demands of the job and the pressure on the employee on one hand and the mismatch between […]
- Stress and Burnout in Organizations Stress may refer to a state of psychological and physical discomfort of an individual, which is derivative of the interaction of external and biological factors. This paper discusses the organizations’ and workers’ challenges related to […]
- The Relationship between Stress Management and Criminal Recidivism Employment tends to increase the social capital of individuals, what is usually referred to as the networks of shared norms and values, which augments the access to the much-needed necessities.
- Understanding and Addressing Family Stress: Parental Responses and Impact on Children The spousal relationship, employment, a lack of structure in the household, and psychological suffering all contribute to stress. They are regarded as potent mediators, and therefore, offending elders indicates disrespecting the father and may lead […]
- Stress Reduction Among College Students In conclusion, “Calm” is useful in mindfulness meditation to decrease stress and enhance self-compassion and mindfulness among students. However, there is constrained information regarding the palatability and effectiveness of delivering mindfulness meditation interventions through mobile […]
- ANOVA Analysis: The Influence of Physical Activity on Stress Levels The independent variable of this research is the degree of physical activity, while the independent variable is the level of stress.
- Stress Management in the Adulthood To effectively handle stress, an individual must be able to recognize the symptoms of stress and understand the possible cause which is easy as stress changes an individual’s happiness level, health, and behavior.
- Defining The Stress Response Across Scientific Disciplines To capture the varying levels of stress among different patients, Holmes and Rahe use percentages to explain the different degrees of a person’s stress level.
- Stress Management in the Hospitality Industry In the event of such aspects the body tries to bring its system to a balance by building adequate energy as well as staying alert to face any possibility of the threat happening.
- Stresses of Being a Student Eustress is a form of stress which is normally thrilling and fun and a good example of this is when one is rushing to meet a deadline for an assignment submission.
- Social Impact of Stress in Childhood Stress in childhood can profoundly affect the cognitive and social development of a person. They can have a life-long impact on the behavior and identify of a person.
- The Problem of Workplace Stress Stress at work can be defined as “the harmful physical and emotional responses that occur when the requirements of a job do not match the capabilities, resources or needs of the worker”. A variety of […]
- Post Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) as a Health Issue in the Society The treatment is aimed at relieving the symptoms that the patient seems to be experiencing so that the individual can be able to deal with the traumatic experience.
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder and Substance Use Disorder The hypothesis of self-medication is one of the mechanisms that can expound the comorbidity between post-traumatic stress disorder and anxiety illness.
- A Healthy Way To Cope With Stress According to Seaward, stress is “the experience of a perceived threat to one’s mental, physical or spiritual well-being, resulting from a series of physiological responses and adaptations”.
- Organisational Stress and Its Possible Transformations The main problem is the inability to understand how organisational stress could influence the work of teachers and if it is necessary to cope with it or neglect its possibility.
- Exam Stress: Effective Management It is important for a child to get enough rest for the relaxation of the mind and body. In line with Hemmings, it is important for parents to analyze the mood of a child who […]
- Positive Psychology and Academic Stress With the rising cases of academic stress among students in the United States, the federal government has introduced positive psychology programs in schools across the country.
- Stress, Its Causes and Effects Relationship Understanding the diverse nature of the causes of the stress is crucial to the effective elimination of its effects, as these two factors heavily depend on each other.
- Definition of Fiscal Stress The state government and local authorities may use different services they provide to the public to measure the level of fiscal stress.
- Problem Solving: What Can We Do About Our Stress? Since we can decide on what to believe or think, we posses the aptitude on how we can respond to the exigent events and circumstances in our daily lives.
- Stress in College Students, Its Causes and Effects Recognizing the cause and effect of stress in college students is an important aspect in college management and leadership as it will lead to a better understanding and development of the appropriate methods for intervention.
- Acute Stress and Attachment Theory At the point of stress, the person will feel vulnerable or in danger and will need something to offer them security.
- Stress Among Criminal Justice Workers The criminal justice system is aware of the seriousness of the current problem and is trying to adapt to the emerging trend.
- Stress Management Skills of Student-Athletes Their responses will then be categorized as “low perceived stress,” “moderate perceived stress,” and “high perceived stress”. The students will then be qualified as possessing superior, above-average, average, or below-average stress management skills.
- Stress Management for Patients With Arthritis The study’s primary objectives were to substantiate the hypothesis of the relation between RA activity and stress and find the evidence for the basis of further decisions.
- “Stress: How It Affects Us”: Critical Analysis As the name suggests, the article is related to stress and how it affects our day-to-day workings as well as our health in general.
- Anger, Stress and Aggression in Violent Offenders The intentions of the aggressor and the nature of the aggression offer the description of that form of aggression. Thus, understanding the relationship between anger, stress and aggression is important to the practitioners involved in […]
- Stress: causes and effects This is due to the research methods used in the process of analyzing and finding solutions to the global psychological challenges and problems.
- Effect of Stress on Relations and Marriage Therefore, this paper had the aim of discussing the effects of stress on a marriage and relationships and how the stress can be reduced and controlled.
- Stress related to workplace conditions Physical factors are those related to the ability of the body to function correctly in the work environment. Unpredictability and uncertainty of work situations are recognized as the main causes of stress in the workplace.
- Early-Life Stress and Adult Inflammation: Fagundes & Way’s Study In the article, “Early-Life Stress and Adult Inflammation,” the authors provide a literature synopsis of the relationship between early-life stress and inflammation in adulthood.
- Stress Management and Work Performance in the United Kingdom In this society, it is very important for the management of various firms and governmental organizations to take care of the interests of the employees.
- Stress Reduction Programs in an Organization There are different approaches to reducing stress levels in an organization. To choose the appropriate program, it is necessary to assess the available options based on a range of criteria.
- The Effect of Stress on the Immunity With an increase in the concentration of glucocorticoids, the thymus decreases in size and the formation of immune cells is disrupted.
- Mindfulness Meditation to Reduce Nursing Stress Levels This project will discuss nurse stress and the implementation of mindfulness meditation sessions as a main intervention for its reduction. Nurse stress should no longer be ignored, and the effect of mindfulness meditation may be […]
- Relationship Between Stress and Greying of the Hair The main topic of this study was the study of the influence of a negative psychological state of a person on the increase in the number of gray hairs.
- Stress and Its Influence on Human Body Prolonged exposure to stress worsens the body’s resistance and the immune and vegetative systems of a person and disrupts the functioning of hormonal glands and metabolism.
- Aspects of the Posttraumatic Stress Disorder They include direct or indirect exposure to stressors, intrusion symptoms, the persistent avoidance of trauma-related stressors, negative alterations in mood and the development of mental health comorbidities, aggression, and self-destructive behavior, the duration for not […]
- Family Health Assessment: Child Poverty, Toxic Stress Because of the nature of their work, and the fact that the two were working even during the pandemic, the father was at one point exposed to Covid-19. The model that will help the family […]
- Dogs: The Stress Coping Mechanisms When the arousal level increases, it helps the body prepare for action and deal with the cause of the stress. The hormone helps them to cope with the stress and to recover from it more […]
- Self-Reported PTSD (Posttraumatic Stress) Symptoms and Social Support At the same time, multiple authors prove that social support and connectedness with family members, relatives, friends, and other members of the community contribute to PTG and the minimization of the signs of PTSD in […]
- Coronary Heart Disease Caused by Stress It is essential to study the degree of influence of stress on the development of coronary heart disease since, in this way, it will be possible to prevent it more successfully.
- Self SWOT: Stress Resistance as the Main Strength However, the irrationality of my organization of time and schedule is a big threat that I will begin to lose control over my studies, which may affect my future career and its trajectory.
- Stress and Its Adverse Health Effects The article’s topic is Stress and Health: A Review of Psychobiological Processes. For instance, when stress increases or is prolonged, the dangers of mental health challenges and medical complications arise.
- Stress Management in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients The study also covered the epidemiological and pathophysiology of RA and looked at data linking psychological trauma to the emergence and aggravation of the clinical disease.
- The Effect of Emotional Freedom Techniques on Nurses’ Stress The objectives for each of the three criteria are clearly stated, with the author explaining the aims to the reader well throughout the content in the article’s title, abstract, and introduction.
- Pathophysiology of Stress, Processed Foods, and Risky Alcohol Consumption The body starts to see the fats, sugars, and salt in ultra-processed foods as rewards, which leads to increased cravings and overeating.
- Teachers Wellbeing: Becoming Aware of Work-Relate Stress Teachers who are aware of these stressors early in their careers may be able to minimize their risk of burnout and experience a sense of well-being.
- The Traumas from Post Traumatic Stress Disorder Measuring the prevalence and incidence of PTSD requires excellent knowledge of epidemiology and biostatistics. The prevalence and incidence of PTSD have increased since 2000.
- Stress and Related Risks in Vulnerable Communities The case study family is between the ages of five and thirty-five years and consists of a father, a mother, and two male children. My rationale behind the ranking is the impact of the risks […]
- COVID-19, Secondary Traumatic Stress and Burnout The second part of the hypothesis states that the levels of STS and BO among caretakers during the pandemic will be higher than before it.
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder: Preliminary Care Coordination The personal character of trauma and how the patient reacts to it justifies the need to design patient-centered interventions to address this healthcare problem.
- Circumstances Causing Stress in Adolescence Hold one’s breath for many seconds and gently exhale via the mouth to evacuate the lungs, hence easing the body of stress. The more one is stressed, the more difficult and nervous it is to […]
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder: Causes and Symptoms The article by Smith entitled Posttraumatic Stress Disorder is valuable because it offers important information on the causes and symptoms of PTSD and ways of recognizing and treating the condition.
- Mishele’s Theory Applied to Pediatric Medical Traumatic Stress In other words, the theory addresses the problem of the subjective perception of the treatment outcomes and diseases under the prism of uncertainty.
- Major Depressive Disorder and Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Her sleep is turbulent, she has rape nightmares, her mood is depressed, and her affect is congruent and constrained. Her mental process is rational and linear, and her mental faculties are largely intact.
- Meditation Effects on Anxiety and Stress My goal in this exercise was to use meditation to manage anxiety and stress and improve my general mental well-being. I am not accustomed to meditation and had to turn to YouTube for guidance.
- Stress and Deviance in College Education The other concept of the connection between deviance and stress is the stress factors. Management of stressors and the consequent effects on deviance among college students is yet to be investigated.
- Posttraumatic Stress Disorder: Case Presentation Report Date of initial assessment: N/A PSEUDO Name: Ana Ana is a self-referred and re-occurring client who entered counseling after the case of domestic violence. As a result, Ana expressed feelings of anxiety and fear […]
- Panel: Women’s Stress and COVID-19 It is vital to examine what is known about the connection of women’s stress to COVID-19. Overall, the link between COVID-19 and women’s stress is apparent.
- Effects of Support on Stress in School Principals Threats to living standards and wellbeing, the strain on families and the escalation of injustices, changes in teaching techniques and the role of technology, and the disruption of higher learning and scholarship are among the […]
- The DSM-5 Criteria for Posttraumatic Stress Disorder The inference is backed by the fact that Victor’s traumatic situation is persistently manifesting intrusion symptoms such as nightmares, flashbacks, unwanted upsetting memories, and a lack of willingness to share previous hurtful events. Victor displays […]
- Early Life Stress: Resilience Development in Children For their own and the children’s sake, school counselors may be assigned to a particular institution in primary schools. An attempt to harness the unique qualities and capabilities that evolve in a high-stress setting is […]
- Posttraumatic Stress Disorder Treatment Research Therefore, the advantage of qualitative research, in this case, relates to the ability to investigate patients’ PTSD treatment experiences and uncover their meanings.
- Coping with Stress in Clinical Neuropsychiatry Joseph should be able to identify what is stressing him most, which in this case it is financial issues and the fact that his wife is always annoyed with him because he is always around, […]
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Misapprehension A significant proportion of civilians are affected by post-traumatic stress but ignore the symptoms and fail to seek early interventions influenced by misconceptions about how PTSD develops and its symptoms.
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder and Opioid Use in Veterans This study examined the proportion of United States veterans who had PTSD and engaged in the use of illegal opioids to cope with it or had done so in the past.
- The Impact of Chronic Stress on Pathological Conditions Long-term stress is hazardous, as it damages the mechanisms of self-regulation of the body, leading to constant fluctuations in the level of hormones and unhealthy rhythms of breathing and heartbeat.
- Toxic Stress and Its Negative Effects The experience of toxic stress in the early years of life also negatively affects school performance and the physical development of children.
- Sex-Specific Effects of Music Listening on Couples’ Stress in Everyday Life Wuttke-Linnemann et al.also highlight the presence of gender-specific differences as to how specifically music listening can impact stress among men and women.
- Stress as an Important Psychological Issue The ability to complete work on time, learn new skills at the first request of the bosses, and the need to work overtime – all this is among the constant needs of a modern working […]
- Traumatic Stress Disorders & Treatment It will be based on the hypothesis that trauma has a detrimental impact on a person’s identity and is likely to result in adverse consequences in the future.
- Smoking and Stress Among Veterans The topic is significant to explore because of the misconception that smoking can alleviate the emotional burden of stress and anxiety when in reality, it has an exacerbating effect on emotional stress.
- Post Traumatic Stress Disorder in A Journal for Jordan Considering the loss of her husband in the war, Dana had not recovered, and the expression of irate reaction is a symptom of PTSD.
- Stress Management Benefits for Health Therefore, stress management strategies are crucial to eliminating the adverse impact of tension and anxiety. Physical activity and socializing are the techniques I have successfully applied to manage stress.
- Nurses’ Mental Health and Stress at Workplace This is the first research to present the viewpoints of mental health nurses on a resilience program. Theoretical ideas of resilience and understanding of mental health nurses’ resilience emerged through constant comparative study and integration […]
- The Relationship Between Stress and Health: Article Summary The implications of the study allow for stating that the increased exposure to stress at work leads to worsened health of the stressed individuals.
- Improving Nurses’ Stress Response During the COVID-19 The article is dedicated to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the overall health of nurses. It is necessary to study the mental health of nurses further and develop ways to level the negative […]
- Coping with Stress and Physical Health Problems In this regard, Julie, first of all, needs to accept the situation as it is, to appreciate the things and the context that she is no longer able to change.
- A Theorist View of Stress, Human Body and Mind As one can see, both K bler-Ross and Frankl focus on human stress as a form of suffering in the face of insurmountable life troubles, such as death or suffering.
- Employee Stress and Burnout at the Workplace This is done by giving outbreaks to those actively involved in the manufacture of the products and giving leaves for some time; the company has also created shift sessions that allow specified workers to take […]
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Development Avoidance of objects that remind you of the traumatic incident is another symptom of PTSD. Identifying erroneous and unreasonable beliefs about the incident and replacing them with a more balanced image is also part of […]
- Stress Management Techniques for Students: Yoga Yoga’s most major benefits are its capacity to relieve stress and exhaustion, to stimulate and revive, and to be used for anti-aging and calming treatment.
- Sexual Aversion and Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder This aspect causes difficulties in prescribing therapy, since the latter requires a thorough study of the psychological nature of the problems. In the treatment of sexual aversion disorder, a doctor needs to investigate a complex […]
- Thoughts on Stress Management and Happiness Although she has all her financial needs met overwhelmingly, her failure to proceed with her studies and get employment makes her feel unsatisfied.
- Workplace Stress Among American Nurses During the Coronavirus Pandemic In this systematic review paper, the researcher seeks to discuss workplace stress among American nurses during the peak of the coronavirus pandemic in the country.
- Secondary Post Traumatic Stress Disorder in Children The relationship between parents’ experiences and interactions with the onset of PTSD in children will be explored. There is vast information on the management of treatment and prevention of PTSD in children.
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder and Parenting Style On a scale of 1 to 10, with 1 being lowest and 10 being highest, how much do you believe that kids need to learn early who the boss is in the family?
- Heat Stress at Provincial, Federal, and International Levels It formulates the purpose of the report, namely the comparison of norms and regulations for safe work at the provincial, federal and international levels.
- Durations of Vowels: Effect of Stress, Lexical Focus, and Segmental Focus The article in question addresses the correlation between the duration of a vowel and the type of focus or stress. De Jong and Zawaydeh address this phonetic issue on the basis of the Arabic language, […]
- Healthcare Workers’ Stress Coping Strategies This is especially relevant for the mental health domain, as the major flows of resources in the healthcare sectors all over the globe are directed towards combating the main adverse physical consequences of the infection.
- Stress and Depression Among Nursing Students The study aims to determine how different the manifestations of stress and depression are among American nursing students compared to students of other disciplines and what supports nursing students in continuing their education.
- The Stress of Working with Families There is an intricate shared history that is interpreted in different ways by different members, and the boundaries, psychological distances, and roles within and between family subsystems are constantly shifting.
- Coping with Stress: Stress and Health In terms of physical, emotional, and behavioral signs, Julia is experiencing severe stress, which requires the help of specialists and the introduction of various techniques that contribute to the normalization of all aspects of life.
- “Poverty, Toxic Stress, and Education…” Study by Kelly & Li Kelly and Li are concerned with the lack of research about poverty and toxic stress affecting the neurodevelopment of preterm children.
- Prefrontal Cortex and Effects of Stress Exposure However, the inability to control the stressor can reduce the prefrontal cortex’s capacity to regulate stress responses. Exposure to stress noticeably weakens the effectiveness of the prefrontal cortex while stimulating more primitive responses of the […]
- Stress as a Result of Combining Work and Family At the same time, it is difficult to say that such a life on a constant clear schedule contributes to the psychological health of a person.
- Analysis of Stress Management Aspects In the science of stress management, there are a number of practices aimed at strengthening the mental health of the student, thus improving their response to potentially stressful events.
- Phonetics and Phonology of English Word Stress People have trouble pronouncing some words in their L2 due to the influence of their L1 accent. Many students find it challenging to accurately pronounce words in their second language due to the influence of […]
- Adaptation to Stress of Endocrine and Sympathetic Nervous System Stress is a non-specific body reaction that occurs under the action of various extreme factors that threaten the violation of homeostasis and is characterized by stereotypical changes in the function of the nervous and endocrine […]
- The Resilience Handbook: Approaches to Stress and Trauma I was surprised to learn that music is not just the words but also the lyrics in the heart and mind.
- Assessing the Personal Stress Levels To ascertain the levels of stress in my everyday life, I have used several assessment tools. Implementing the “Symptoms of Stress” methodology, I have discovered that the occurrence of stress in my life is quite […]
- Stress Management Techniques The proposed strategies and examples should help students to understand different situations and overcome stress disregarding settings and external factors.
- Occupational Health: Workplace Stress To avoid noise-related stress, Ruth handles her job with a positive attitude and this makes it easy to enjoy work. In conclusion, work-related stress is a major cause of poor performance by employees due to […]
- Humor as the Leading Strategy of Stress Relief The purpose of this paper is to discuss the importance of humor as one of the leading stress management strategies. In other words, it does not suffice to know the sources of stress, as the […]
- Workplace Stress and Absenteeism in the Ship-Repair Industry: A Case Study This qualitative exploratory case study sought to discover techniques that production and project managers of a ship-repair company in the maritime industry use to minimize.
- Stress Patterns in Police Work: A Longitudinal Study The research problem identified by the investigator relates to the prevalence of distress in the police occupation. The primary variable of the study was the mean stress measure, which was derived from the Langner-22 list […]
- Occupational Stress: Patient Teaching Plan Physical exercise is helpful for the patients with work-related stress and anxiety. Physical exercise helps alleviate work and stress-related pains in different parts of the body.
- Stress Among Secondary and Tertiary Students The results of the study by Pascoe et al.demonstrate that the majority of students report high levels of stress and negative effects on their mental and physical health.
- Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction in the Workplace What are the weakness of the study and how can it be improved. According to I/O psychologist work is done to obtain productivity and to improve the quality of life of the clients.
- Free Radicals, Oxidative Stress, and Antioxidants The presence of ROS in excess causes oxidative stress in the body, leading to the oxidation of proteins and lipids and the transformation of their structures and roles in the body.
- Stress From a Biblical Perspective The Bible, in that case, provides a sense of hope and relief which leads to relaxation. In 1 Samuel 30:1-31, Amalekites exploited the opportunity of David and his men’s absence in the south city of […]
- Dealing With Stress: What Makes One’s Life Complete Carrying the burden of stress, I became rather reserved and unwilling to socialize, which led to certain misconceptions among my friends and me.
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Pathophysiology Sakellariou and Stefanatou, further link threat responsiveness and fear regulation with the signalling of 5-HT within the amygdala; this is an area within the brain deemed essential in comprehending the reaction to fear and aetiology […]
- Workplace Yoga Reducing Stress in Employees Since the key idea of a project is to sell the yoga and meditation practice program to the other departments of a firm, it is important to understand the expected benefits.
- Cross-National Job Stress: A Quantitative and Qualitative Study That is why, in order to fill the substantial research gap, the exploratory study of Liu et al.examines the perceptions of job stress in two culturally dissimilar countries the United States and China using both […]
- The Effectiveness of Occupational Stress Management However, as it relates to analyzing the shipbuilding and ship-repair industries, the level of occupational stress is higher in comparison to other sectors of the economy, and the effectiveness of managing the problem is lower.
- Coping With Stress in Breast Cancer Patients Therefore, it is important for research experts to ensure and guarantee adherence to methodologies and guidelines that define scientific inquiry. However, various discrepancies manifest with regard to the initiation and propagation of research studies.
- Changes in Life and Psychological Stress Assessment The vagueness of the evaluation system and the lack of precision in terms of results assessment, however, beg the question whether psychological assessments can be trusted.
- Nursing Work Stress Level During Pandemics In the case of this project, the DNP student was able to review at length the issue of occupational stress in nursing.
- Stress Management Through Transcendental Meditation Thus, to improve productivity and the general wellbeing of its employees, a company ought to offer stress management program. However, transcendental meditation seems to be the most beneficial as it enables people to deal with […]
- Stress Analysis of Thin Walled Structures and Results This consideration takes the priority of the passengers’ safety to ensure they do not experience the effects of either deformation or heat dissipated by the parts involved in the impact.”At the same time other structural […]
- Advanced Stress Analysis – Characteristic of Model The choice of approach is done in the preliminary stages of structural design of shapes. 893Kg/mm3 The density of the envelope is 1.
- The Unified Trauma Theory of High-Stress Level Fatigue a Case of Loyola University The steps of this process are outlined, concluding with definitions and a description of the middle range theory of unified trauma theory of high-stress fatigue, which was developed.
- Stress Sources in a Detective’s Life One of the morale issues that can result from the behavior of the detective is the segregation of the detective by his workmates and none of them might want to work with him.
- Effects of Obesity on Neuroendocrine, and Immune Cell Responses to Stress All the participants of the experiment including obese and non-obese women were scheduled to days one to ten by their menstrual cycle. Statistic and comparative analyses were performed to compare the results of obese and […]
- Health and Wellness: Stress, Diabetes and Tobacco Related Problems Emotional health and well being refers to our ability to deal with our emotions as well as the emotions of those around us.
- Effective Use of Prazosin for Posttraumatic Stress Disorder All the traditional agents have shown to have several side effects and cannot be fully relied on in treatment of PTSD.
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Diagnostics and Screening Do you observe a headache from the early morning? Do you have a headache when you sleep well?
- Effect of Stress Hormones on Brain Cells Cortisol hormone is responsible for the shrinking of the hippocampal volume that controls the formation of new neurons in the brain cells, and it may lead to depression.
- BMI and Stress Levels Among Students in the US
- Conger’s Stress and Family With Children
- Posttraumatic Stress Disorder
- Dealing With Grief – Stress Factors
- Stress at Work: Creating Healthy Organisations
- Wholeness Meeting to Deal With Stress in School
- Family Nursing and Stress Theory
- Adult Life Stress: Assessment Tools Analysis
- Personal Stress Management and Relaxation Techniques
- Relation Work – Stress – Health
- Stress, Emotional Intelligence, and Job Performance Correlation in Nursing
- Managing Stress Through Communication Skills in Nursing
- The Effectiveness of ICU Nurses in Reducing Stress among Family Members
- Mindfulness-Based Stress and Burnout Reduction in Nurses
- Stress-Strain Relation of Stainless Steel After Exposure to Fire
- Identifying Causes of Stress among Nurses
- Definition and Concept of Stress in Nursing
- Nursing Burnout: Increased Stress Experienced by Nurses
- Emotions and Stress on the Job
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) Among Vets
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder: Overview
- Nurses and Stress: Mindfulness Meditation Program
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Treatment in Intellectually Disabled Patients: The Promise of Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing Therapy
- Stress Management in University Students
- Women in the West Who Are Put Under Stress Due to Social Media
- Stress in the Teaching Fraternity
- Work Related Stress: Symptoms and Management
- Stress at Work: Main Aspects, Globalization Influence
- Client Diagnosis: Posttraumatic Stress Disorder
- Stress Test Process to a Community Issue
- Employees’ Stress and Burnout
- Disaster Crisis: Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Symptoms
- Yoga and Stress Reduction
- Managing Stress: A Reflection of Personal Experience
- Personal & Professional Development: Managing Stress
- Stress Symptoms and Management
- Living With Post Traumatic Stress Disorder
- How Stress Affects Learning in Middle School
- Motivation, Emotion, Stress, Health and Work
- The Role of Stress in Our Everyday Life
- Employee Stress Causes in Different Countries
- Socio-Cultural and Stress Models in Diagnosis
- Posttraumatic Stress Disorder After Rape Attempt
- Post Traumatic Stress Disorder: Causes and Consequences
- Posttraumatic Stress Symptom Disease
- Stress, Depression and Psychoneuroimmunology
- How Can College Students Cope With Stress
- Stress, Its Effects on Health
- Causes and Effects of Marital Stress on the Health of Women
- Academic Related Sicknesses: Stress in Medical Students
- Stress Management and Wellness Programs by Corporate Sector
- Work Stress: Coping Through Work-Life Programs
- The Relationship Between Emotion Regulation Suppression and the Academic and Life Stress Levels
- Health and Stress in College Students
- Stress: Causes, Sources and Symptoms
- Sources of Stress Among African American Students
- Stress and Medical Students’ Lifes
- Impact of Stress on Intimate Relationship
- Stress of Police Officers and How They Cope With It
- Educational Psychology: Student Learning and Stress
- Acute and Post Traumatic Stress Disorders
- Impacts of High Stress Levels on Teachers
- Stress Management Under Organizational Psychology
- Stress and Higher Education Student: A Critical Review
- Post Traumatic Stress Disorder: German Researches
- Preventing Burnout in Preschool Teachers
- Can Stress Be Fattening: Discussion
- Sports Demands and Stress Management in Athletics
- Holmes and Rahe Stress Test and Coping Strategies
- Reducing Nurses’ Stress: A Web-Based Management Program
- Depression and Anxiety Due to School and Work-Related Stress
- Mental Healthcare in Louisiana: Growth in Stress Rates
- Student Loans and Financial Stress
- How Nurses Cope with Job Stress
- Family Stress and Crisis: We Got Through It
- Stress Among African American College Students
- Stress Can Affect Future Generations’ Genes
- Posttraumatic Stress Disorder in Veteran Community
- Evidence-Based Procedures That Reduce Stress and Promote Health
- UAE: Stress Management and Organizational Performance
- Organizational Concern: Job Stress and Burnout
- “Emotional Freedom Technique and Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder” by Rebecca L. Fahey
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder and Treatment Effectiveness
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder in Missouri Veterans
- Posttraumatic Stress Disorder Management in Children
- College Student Work Habits, Interruptions, and Stress
- Stress Factors in the Queer Community
- Chronobiology and Stress in Horses
- Horse Transportation and Stress-Reducing Strategies
- Newly Graduated Nurses and Stress: Study Analysis
- Heat Stress in Flight Cockpits in the Desert Climate
- Employment and Stress Management
- Spiritual Life: Avoiding Stress Burnout
- Interviewing the Patient: Stress and Anxiety Reasons
- Productivity and Work-Related Stress in the UAE
- Workplace Stress and Labor Law in the United Kingdom
- Stress Management: Personal Success Plan
- Does Locus of Control and Motivation Predict Occupational Stress?
- Modern Workplace Issues: Stress, Conflict, Quality
- Occupational Stress in the Maritime Industry
- Racial Disparities in Posttraumatic Stress Disorder Treatment
- Posttraumatic Stress Disorder in Hispanic Teenager
- Posttraumatic Stress Disorder Treatment in Soldier
- Stress Impact on Self-Esteam and Personal Growth
- Employee Motivation, Termination, and Work Stress
- Posttraumatic Stress Disorder: Modality Treatment Plan
- Anxiety Disorder: Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction
- Crisis Intervention Model and Critical Stress Management
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder and Its Theories
- Emotion Regulation and Posttraumatic Stress Disorder
- Workplace Stress and Mitigating Measures
- Stress Factors in the Fire Service
- Stress, Conflict and Misunderstandings in the Workplace
- Stress Increases the Desire to Eat Sweets
- How Coffee Affects Stress?
- Burnout, Compassion Fatigue and Stress at Workplace
- Stress Assessment Questionnaire Ethical Usage
- Stress in Policing: Reasons and Effects
- Meditation as a Way to Alleviate Stress
- Stress Management for Life
- Sexual Harassment and Psychological Stress
- Prenatal Maternal Stress Outcomes
- Discretion, Job Stress, and Other Policing Issues
- Workplace Stress Management Programs
- Kant’s and Mill’s Ideas for Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder
- Intimate Partner Violence and Maternal Stress
- Stress Statistics, Definition, and Perception
- Physiological Mechanism of Stress
- Post-Traumatic Stress and Evidence-Based Practice
- Stress as a Risk Factor for Inflammation
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Assets and Facilities
- Minority Stress and Health: Societal Issues
- Housewives’ Compensation and Stress Factors
- Stress and Eating Behavior
- Ways to Manage Stress and Enhance Well-Being for Students
- Police Stress Within Law Enforcement
- To Better Cope With Stress, Listen to Your Body
- “Stress” Video and “A Natural Fix for ADHD” Article
- Organizational Stress and Job Satisfaction Relationships
- The Effect Job Stress on Satisfaction with Life
- Ethics Code for Human Participation in Stress Reduction
- Office 2010 Transformation: Stress Management Plan
- Post Traumatic Stress Disorder or Combat Fatigue
- Genentech Inc.’s Workplace Stress Management
- Stress, Depression, and Responses to Them
- Post Traumatic Stress Disorder: Caucasian Girl’ Case
- Students’ Stress Levels in Kean University
- Acute Stress Disorder: Cynthia’s Treatment Case
- Great Recession Impact on Workplace Stress
- Food and Stress Relationship: Psychological Factor
- Stress Management Strategies in Applied Psychology
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder in Soldiers
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder: Gender Variations
- Stress Impacts on the Human Development
- Stress Levels and Stress Management Methods
- Post Traumatic Stress Disorder: Joseph Wolpe Treatment Theory
- Reducing Stress: Cognitive Patterns and Behaviors Changing
- Stress: Effects and Management Proposal
- Health Psychology: Eating and Stress’ Relations
- Stress and Recovery After Rape
- The Holmes-Rahe Life Stress Inventory – Psychology
- Mood and Stress Psychology: Causes, Effects and Treatments
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder – Psychology
- Managing Stress and Depression at Work Places – Psychology
- Job’ Stress and Depression
- Stress and Burnout in Law Enforcement
- Police and Corrections Officers’ Stress – Psychology
- Stress and Strains in the Renaissance Society
- Infidelity as a Cause of Divorce and Stress Disorder
- Walmart Company: Reducing Employee Stress
- Stress Reduction at Work
- Stress’ Definition and Effects
- Suggestions on Stress Management
- Correlation Study of the Relationship Between Individual Resilience, Hope, Stress and Humour
- Stress & Its Effects on the Brain and Body
- Ability to Manage Stress as the Most Important Skill of Effective Communicators
- Stress Management and Work Performance in the UK
- The Relationship Between Employee Productivity and Work Related Stress
- The Caregiver Burnout and Long-Term Stress
- Post Traumatic Stress Disorder Principles and Types
- Solutions for Students to Reduce Stress in University Life
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder in Veterans
- The Effects of Forgiveness Therapy on Depression, Anxiety and Posttraumatic Stress for Women After Spousal Emotional Abuse
- Critical Evaluation of Stress Management Approaches
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder: Causes, Symptoms and Treatments
- Critical Review of a Mental Disorder: The Post Traumatic Stress Disorder in DSM-IV-TR
- Post Traumatic Stress Disorder and Its Treatment
- Underlying Issues Associated with Sleep Disorders and Stress
- How College Athletes Deal with Stress and Manage Time
- Impact and Strategies of Fiscal Stress on States and Municipalities
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder and Abused Women
- Acute Stress Reaction and Acute Stress Disorder
- Post Traumatic Stress Disorder: History and Symptoms
- Biological Factors Involved in Stress
- Posttraumatic stress. The Case of Mary
- Stress Management among Customer Service Employees: Antecedents & Interventions
- Depression: Law Enforcement Officers and Stress
- The Impact of Stress & Unpleasant Feelings on People
- The Causes of Stress in the Contemporary Society
- Earthquakes as a Cause of the Post Traumatic Stress Disorder
- Workplace Stress Problem
- Reducing Stress in Al-Khobar
- Post Traumatic Stress Disorder Developed in Repeated War Zones Deployment
- Towards Understanding Stress-Related Issues Affecting First Year Students on Their Transition Into University Culture
- Stress and Injury in Sports
- Family, Stress and Delinquency among Adolescent
- Effects of stress on physical health
- Stress at the Workplace for Correctional Officers
- Human Stress and Dale Carnegie
- “Denial: A Memoir” a Book by Jessica Stern
- Adjustment in Psychology: Stress
- Reaction to Stress: Flight or Fight
- Conflict and Stress: Their Potential Impact on a Project
- How Stress Affects Different Personality Types
- Abnormal Psychology: Posttraumatic Stress Disorder
- Diverse Effects of the Work Related Stress
- Problems of the Employee Stress in Organizations
- Managing Time and Stress
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder in Tim O’Brien’s “In the Lake of Woods”
- Randomized Trial of Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy for Chronic Post-Traumatic Stress Disorders in Adult Female Survivors of Childhood Sexual Abuse
- How Stress Affects Your Physical Health?
- The Experiment to Prove the Fact That Psychological Stress Causes Headache
- Post Traumatic Stress Disorder: Assessment and Treatment Strategies
- Controlling Stress and Tension
- Research Application of How College Athletes Deal with Stress and Manage Time
- Post Traumatic Stress Disorder in Veterans and How Family Relationships Are Affected
- Self Efficacy, Stress & Coping, and Headspace Program
- Characteristics and Treatments of Post Traumatic Stress Disorder
- Analysis of Posttraumatic Stress Disorder in Military Personnel
- Work-Related Stress: Impeding Organization’s Success
- Does Cardiorespiratory Fitness Buffer Stress Reactivity and Stress Recovery in Police Officers?
- What Does Stress Really Stress?
- Where Does Stress Come From and How Does It Affect a Pregnant Mother and Her Unborn Child?
- Can Stress Cause Severe Headache?
- Does Compressing High School Duration Affect Students’ Stress and Mental Health?
- Does Regular Exercise Reduce Stress Levels?
- How Long Does Birth Trauma Last?
- Does Telework Stress Employees Out?
- Can Detox Tea Relieve Stress?
- Are Posttraumatic Stress Symptoms and Avoidant Coping Inhibitory Factors?
- What makes Stress and Burnout?
- Can Stress Cause Coronary Heart Disease?
- Can Local Stress Enhancement Induce Stability in Fracture Processes?
- What Cause Students Stress?
- Does Practical Parenting Stress You Out?
- What Does Posttraumatic Stress Disorder Truly Mean?
- Does Elevated Job Stress Affect Smoking Levels?
- What Causes Psychological Stress?
- Does Prolonged Stress Increase the Likelihood of a Stroke?
- Can Music Therapy Improve Stress Anxiety?
- Does Emotional Intelligence Buffer the Effects of Acute Stress?
- Whether Stress Have Any Effect on the Productivity of Employees in an Organization?
- Can Simulated Green Exercise Improve Recovery From Acute Mental Stress?
- Can Social Support Alleviate Stress While Shopping in Crowded Retail Environments?
- Can the Attention Training Technique Reduce Stress in Students?
- Are Certain Personalities More Prone to Stress?
- Can Stress Trigger Diseases?
- Does Acute Stress Impact Declarative and Procedural Learning?
- Does Prenatal Stress Shape Postnatal Resilience?
- Are Quebecers More Stressed Out at Work Than Others?
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, February 29). 420 Stress Essay Topic Ideas & Examples. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/stress-essay-examples/
"420 Stress Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." IvyPanda , 29 Feb. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/stress-essay-examples/.
IvyPanda . (2024) '420 Stress Essay Topic Ideas & Examples'. 29 February.
IvyPanda . 2024. "420 Stress Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." February 29, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/stress-essay-examples/.
1. IvyPanda . "420 Stress Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." February 29, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/stress-essay-examples/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "420 Stress Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." February 29, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/stress-essay-examples/.
- Mental Illness Research Topics
- Human Development Research Ideas
- Abnormal Psychology Paper Topics
- Cognitive Development Essay Ideas
- Depression Essay Topics
- Health Promotion Research Topics
- Mindfulness Research Ideas
- Positive Psychology Titles
- MEMBER LOGIN
- MEDIA RELATIONS
Military Stress

- ASSESSMENTS
- DOCUMENTARIES

How Can Students Release Stress and Improve Concentration?
- October 4, 2023

In the rat race of trying to achieve excellent grades and get admitted into a good college, students often forget that they need not just their mental faculties but also their emotional and spiritual sides to be successful. One way of nurturing all these three aspects is through the practice of meditation. While it has been around for centuries, meditation is now being recognized as an essential means of promoting mental and emotional well-being. It can be a powerful tool for reducing stress and improving focus.
What is meditation?
In simple terms, meditation is the art of doing nothing, staying still, and letting go of thoughts, cares, and worries to relax in your true nature, stirring love, joy, and peace.
How can meditation help you succeed in school?
Here are some of the ways that meditation can help you succeed in school:
-> Meditation can help you deal with stress and anxiety and manage it better. When you feel overwhelmed or stressed, meditating for a few minutes might help you relax and focus on the task at hand.
-> Meditation can improve your concentration. When you are able to focus better, you will be able to complete schoolwork more quickly and efficiently.
-> Meditation can help you learn new information. By improving your focus and concentration, meditation can help you absorb and remember information more effectively.
-> Meditation can make you feel more relaxed and at ease. This can help you feel more confident in social situations and be less likely to experience anxiety or stress.
If you are looking for a way to reduce stress and improve your academic performance, consider giving meditation a try. It may just be the boost you need to succeed in school!
How can meditation specifically help students?
Stress Relief : One of the main reasons students turn to meditation is because of the stress and anxiety that comes with academics. The pressure to get good grades, prepare for exams and meet deadlines can be difficult at times. In such situations, taking a few minutes out to meditate can help clear the mind and calm down. Meditation has been shown to increase gray matter density in some regions of the brain, which is associated with better stress management.
Concentration Improvement : When studying or working on assignments, it is crucial to be able to focus and concentrate on the task at hand. Unfortunately, this can be difficult for students who are constantly bombarded with distractions. Meditation has been shown to improve focus and concentration, thereby helping students get more work done in a shorter period of time.
Information absorption : To do well in academics, students need to be able to absorb and remember the information they are studying. But with numerous distractions and a busy lifestyle, many students find it challenging to focus on the task at hand. Meditation has been shown to improve information absorption and memory retention, thereby helping students to learn and remember information more effectively.
Emotional Well-being : A balanced emotional state is critical for students as it allows them to deal with stress and anxiety healthily. When students are feeling mental strain and stress, meditation can help restore balance and promote a healthy state of mind. Meditation has been shown to increase positive emotions such as joy, happiness, contentment, and love. It also decreases negative emotions such as anger, anxiety, stress, and depression.
How can you meditate?
There are many different ways to meditate, and the best way to find out what works for you is to experiment a bit. However, to begin with, here are a few tips that can help you get started:
-> Find a quiet place where you can sit or recline in comfort.
-> Sit with your spine straight, your eyes closed, and your hands resting in your lap with your palms up.
-> Take a few deep breaths and let go of all thoughts and distractions.
-> When you are ready, focus on your breath and count each inhale and exhale.
-> If you find your mind wandering, gently guide it back to your breath.
-> Meditate for as long as you like, starting with just a few minutes and building up to at least 20 minutes or more.
Remember, there is no wrong way to meditate, so experiment until you find a method that works best for you. And above all, be patient – the benefits of meditation often take time to manifest. But, with practice, you will soon find that meditation can help you achieve greater peace and calmness, both mentally and emotionally.
What are the alternatives to meditation?
Besides meditation, there are several ways to reduce stress and improve your focus and concentration. Some popular alternatives to meditation include:
-> Yoga : Yoga is a physical and mental exercise that combines breathing exercises, meditation, and postures. It is often used to improve flexibility, strength, balance, and posture.
-> Tai Chi : Tai Chi is a form of martial arts that combines deep breathing and relaxation with slow, gentle movements. It is often used to improve balance, flexibility, and strength.
-> Qi Gong : Qi Gong is a form of martial arts and meditation that combines deep breathing with slow, gentle movements and visualization. It is often used to improve balance, flexibility, strength, and energy levels.
-> Mindfulness : Mindfulness is a form of meditation that focuses on the present moment and accepts thoughts and feelings without judgment. It is often used to improve focus, concentration, stress relief, and emotional well-being.
So, if you are feeling hardship by academics and looking for a way to reduce stress and improve your academic performance, consider giving meditation or one of its alternatives a try for a few minutes and see how you feel; you may just be surprised at the positive difference it makes! It is possible that you will be amazed at how much of a difference it makes and be the boost you need to succeed in school!
Photo by cottonbro studio
Photo by Kelvin Valerio
By Cynthia Sullivan
Original post OnlineMastersColleges.com
More Articles

Post-Traumatic Growth Finding Hope in Adversity

New research reveals stress hormones trigger white blood cells to create pathways for cancer metastasis.

Workplace Stress and Painkiller Dependency: A Hidden Crisis

How to thrive under stress, according to a former Navy SEAL and FBI Agent

7 Ways to Ease Work Stress — Including the Desktop Decoration That Can Dial Down Tension Fast

Combating Workplace Stress with Online Therapy: A Modern Solution for Busy Professionals

Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder and Traumatic Brain Injury, TESI Statistical Analysis. Operations Iraqi and Enduring Freedom.

What Are the Signs of PTSD? 4 Ways to Tell

How Stress-Dumping Can Threaten a Relationship

Northamptonshire Mind revolutionises mental health support with innovative Alpha-Stim partnership
- Open access
- Published: 16 May 2024
Procrastination, depression and anxiety symptoms in university students: a three-wave longitudinal study on the mediating role of perceived stress
- Anna Jochmann 1 ,
- Burkhard Gusy 1 ,
- Tino Lesener 1 &
- Christine Wolter 1
BMC Psychology volume 12 , Article number: 276 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
148 Accesses
Metrics details
It is generally assumed that procrastination leads to negative consequences. However, evidence for negative consequences of procrastination is still limited and it is also unclear by which mechanisms they are mediated. Therefore, the aim of our study was to examine the harmful consequences of procrastination on students’ stress and mental health. We selected the procrastination-health model as our theoretical foundation and tried to evaluate the model’s assumption that trait procrastination leads to (chronic) disease via (chronic) stress in a temporal perspective. We chose depression and anxiety symptoms as indicators for (chronic) disease and hypothesized that procrastination leads to perceived stress over time, that perceived stress leads to depression and anxiety symptoms over time, and that procrastination leads to depression and anxiety symptoms over time, mediated by perceived stress.
To examine these relationships properly, we collected longitudinal data from 392 university students at three occasions over a one-year period and analyzed the data using autoregressive time-lagged panel models.
Procrastination did lead to depression and anxiety symptoms over time. However, perceived stress was not a mediator of this effect. Procrastination did not lead to perceived stress over time, nor did perceived stress lead to depression and anxiety symptoms over time.
Conclusions
We could not confirm that trait procrastination leads to (chronic) disease via (chronic) stress, as assumed in the procrastination-health model. Nonetheless, our study demonstrated that procrastination can have a detrimental effect on mental health. Further health outcomes and possible mediators should be explored in future studies.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
“Due tomorrow? Do tomorrow.”, might be said by someone who has a tendency to postpone tasks until the last minute. But can we enjoy today knowing about the unfinished task and tomorrow’s deadline? Or do we feel guilty for postponing a task yet again? Do we get stressed out because we have little time left to complete it? Almost everyone has procrastinated at some point when it came to completing unpleasant tasks, such as mowing the lawn, doing the taxes, or preparing for exams. Some tend to procrastinate more frequently and in all areas of life, while others are less inclined to do so. Procrastination is common across a wide range of nationalities, as well as socioeconomic and educational backgrounds [ 1 ]. Over the last fifteen years, there has been a massive increase in research on procrastination [ 2 ]. Oftentimes, research focuses on better understanding the phenomenon of procrastination and finding out why someone procrastinates in order to be able to intervene. Similarly, the internet is filled with self-help guides that promise a way to overcome procrastination. But why do people seek help for their procrastination? Until now, not much research has been conducted on the negative consequences procrastination could have on health and well-being. Therefore, in the following article we examine the effect of procrastination on mental health over time and stress as a possible facilitator of this relationship on the basis of the procrastination-health model by Sirois et al. [ 3 ].
Procrastination and its negative consequences
Procrastination can be defined as the tendency to voluntarily and irrationally delay intended activities despite expecting negative consequences as a result of the delay [ 4 , 5 ]. It has been observed in a variety of groups across the lifespan, such as students, teachers, and workers [ 1 ]. For example, some students tend to regularly delay preparing for exams and writing essays until the last minute, even if this results in time pressure or lower grades. Procrastination must be distinguished from strategic delay [ 4 , 6 ]. Delaying a task is considered strategic when other tasks are more important or when more resources are needed before the task can be completed. While strategic delay is viewed as functional and adaptive, procrastination is classified as dysfunctional. Procrastination is predominantly viewed as the result of a self-regulatory failure [ 7 ]. It can be understood as a trait, that is, as a cross-situational and time-stable behavioral disposition [ 8 ]. Thus, it is assumed that procrastinators chronically delay tasks that they experience as unpleasant or difficult [ 9 ]. Approximately 20 to 30% of adults have been found to procrastinate chronically [ 10 , 11 , 12 ]. Prevalence estimates for students are similar [ 13 ]. It is believed that students do not procrastinate more often than other groups. However, it is easy to examine procrastination in students because working on study tasks requires a high degree of self-organization and time management [ 14 ].
It is generally assumed that procrastination leads to negative consequences [ 4 ]. Negative consequences are even part of the definition of procrastination. Research indicates that procrastination is linked to lower academic performance [ 15 ], health impairment (e.g., stress [ 16 ], physical symptoms [ 17 ], depression and anxiety symptoms [ 18 ]), and poor health-related behavior (e.g., heavier alcohol consumption [ 19 ]). However, most studies targeting consequences of procrastination are cross-sectional [ 4 ]. For that reason, it often remains unclear whether an examined outcome is a consequence or an antecedent of procrastination, or whether a reciprocal relationship between procrastination and the examined outcome can be assumed. Additionally, regarding negative consequences of procrastination on health, it is still largely unknown by which mechanisms they are mediated. Uncovering such mediators would be helpful in developing interventions that can prevent negative health consequences of procrastination.
The procrastination-health model
The first and only model that exclusively focuses on the effect of procrastination on health and the mediators of this effect is the procrastination-health model [ 3 , 9 , 17 ]. Sirois [ 9 ] postulates three pathways: An immediate effect of trait procrastination on (chronic) disease and two mediated pathways (see Fig. 1 ).
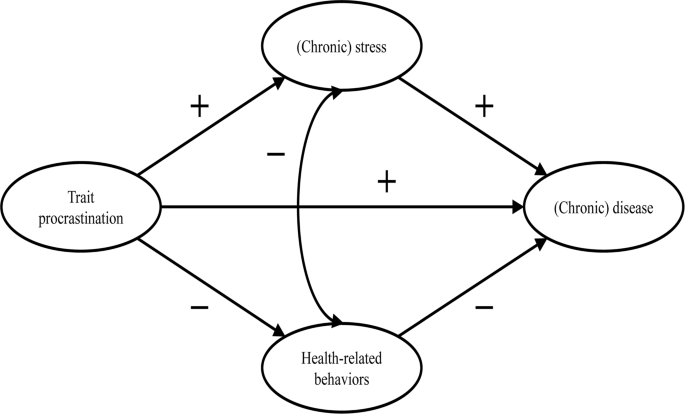
Adopted from the procrastination-health model by Sirois [ 9 ]
The immediate effect is not further explained. Research suggests that procrastination creates negative feelings, such as shame, guilt, regret, and anger [ 20 , 21 , 22 ]. The described feelings could have a detrimental effect on mental health [ 23 , 24 , 25 ].
The first mediated pathway leads from trait procrastination to (chronic) disease via (chronic) stress. Sirois [ 9 ] assumes that procrastination creates stress because procrastinators are constantly aware of the fact that they still have many tasks to complete. Stress activates the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenocortical (HPA) system, increases autonomic nervous system arousal, and weakens the immune system, which in turn contributes to the development of diseases. Sirois [ 9 ] distinguishes between short-term and long-term effects of procrastination on health mediated by stress. She believes that, in the short term, single incidents of procrastination cause acute stress, which leads to acute health problems, such as infections or headaches. In the long term, chronic procrastination, as you would expect with trait procrastination, causes chronic stress, which leads to chronic diseases over time. There is some evidence in support of the stress-related pathway, particularly regarding short-term effects [ 3 , 17 , 26 , 27 , 28 ]. However, as we mentioned above, most of these studies are cross-sectional. Therefore, the causal direction of these effects remains unclear. To our knowledge, long-term effects of trait procrastination on (chronic) disease mediated by (chronic) stress have not yet been investigated.
The second mediated pathway leads from trait procrastination to (chronic) disease via poor health-related behavior. According to Sirois [ 9 ], procrastinators form lower intentions to carry out health-promoting behavior or to refrain from health-damaging behavior because they have a low self-efficacy of being able to care for their own health. In addition, they lack the far-sighted view that the effects of health-related behavior only become apparent in the long term. For the same reason, Sirois [ 9 ] believes that there are no short-term, but only long-term effects of procrastination on health mediated by poor health-related behavior. For example, an unhealthy diet leads to diabetes over time. The findings of studies examining the behavioral pathway are inconclusive [ 3 , 17 , 26 , 28 ]. Furthermore, since most of these studies are cross-sectional, they are not suitable for uncovering long-term effects of trait procrastination on (chronic) disease mediated by poor health-related behavior.
In summary, previous research on the two mediated pathways of the procrastination-health model mainly found support for the role of (chronic) stress in the relationship between trait procrastination and (chronic) disease. However, only short-term effects have been investigated so far. Moreover, longitudinal studies are needed to be able to assess the causal direction of the relationship between trait procrastination, (chronic) stress, and (chronic) disease. Consequently, our study is the first to examine long-term effects of trait procrastination on (chronic) disease mediated by (chronic) stress, using a longitudinal design. (Chronic) disease could be measured by a variety of different indicators (e.g., physical symptoms, diabetes, or coronary heart disease). We choose depression and anxiety symptoms as indicators for (chronic) disease because they signal mental health complaints before they manifest as (chronic) diseases. Additionally, depression and anxiety symptoms are two of the most common mental health complaints among students [ 29 , 30 ] and procrastination has been shown to be a significant predictor of depression and anxiety symptoms [ 18 , 31 , 32 , 33 , 34 ]. Until now, the stress-related pathway of the procrastination-health model with depression and anxiety symptoms as the health outcome has only been analyzed in one cross-sectional study that confirmed the predictions of the model [ 35 ].
The aim of our study is to evaluate some of the key assumptions of the procrastination-health model, particularly the relationships between trait procrastination, (chronic) stress, and (chronic) disease over time, surveyed in the following analysis using depression and anxiety symptoms.
In line with the key assumptions of the procrastination-health model, we postulate (see Fig. 2 ):
Procrastination leads to perceived stress over time.
Perceived stress leads to depression and anxiety symptoms over time.
Procrastination leads to depression and anxiety symptoms over time, mediated by perceived stress.
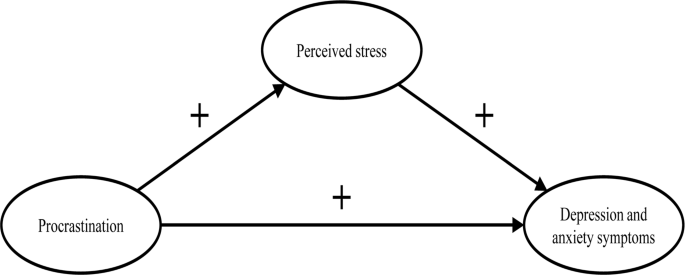
The section of the procrastination-health model we examined
Materials and methods
Our study was part of a health monitoring at a large German university Footnote 1 . Ethical approval for our study was granted by the Ethics Committee of the university’s Department of Education and Psychology. We collected the initial data in 2019. Two occasions followed, each at an interval of six months. In January 2019, we sent out 33,267 invitations to student e-mail addresses. Before beginning the survey, students provided their written informed consent to participate in our study. 3,420 students took part at the first occasion (T1; 10% response rate). Of these, 862 participated at the second (T2) and 392 at the third occasion (T3). In order to test whether dropout was selective, we compared sociodemographic and study specific characteristics (age, gender, academic semester, number of assessments/exams) as well as behavior and health-related variables (procrastination, perceived stress, depression and anxiety symptoms) between the participants of the first wave ( n = 3,420) and those who participated three times ( n = 392). Results from independent-samples t-tests and chi-square analysis showed no significant differences regarding sociodemographic and study specific characteristics (see Additional file 1: Table S1 and S2 ). Regarding behavior and health-related variables, independent-samples t-tests revealed a significant difference in procrastination between the two groups ( t (3,409) = 2.08, p < .05). The mean score of procrastination was lower in the group that participated in all three waves.
The mean age of the longitudinal respondents was 24.1 years ( SD = 5.5 years), the youngest participants were 17 years old, the oldest one was 59 years old. The majority of participants was female (74.0%), 7 participants identified neither as male nor as female (1.8%). The respondents were on average enrolled in the third year of studying ( M = 3.9; SD = 2.3). On average, the students worked about 31.2 h ( SD = 14.1) per week for their studies, and an additional 8.5 h ( SD = 8.5) for their (part-time) jobs. The average income was €851 ( SD = 406), and 4.9% of the students had at least one child. The students were mostly enrolled in philosophy and humanities (16.5%), education and psychology (15.8%), biology, chemistry, and pharmacy (12.5%), political and social sciences (10.6%), veterinary medicine (8.9%), and mathematics and computer science (7.7%).
We only used established and well evaluated instruments for our analyses.
- Procrastination
We adopted the short form of the Procrastination Questionnaire for Students (PFS-4) [ 36 ] to measure procrastination. The PFS-4 assesses procrastination at university as a largely stable behavioral disposition across situations, that is, as a trait. The questionnaire consists of four items (e.g., I put off starting tasks until the last moment.). Each item was rated on a 5-point scale ((almost) never = 1 to (almost) always = 5) for the last two weeks. All items were averaged, with higher scores indicating a greater tendency to procrastinate. The PFS-4 has been proven to be reliable and valid, showing very high correlations with other established trait procrastination scales, for example, with the German short form of the General Procrastination Scale [ 37 , 38 ]. We also proved the scale to be one-dimensional in a factor analysis, with a Cronbach’s alpha of 0.90.
Perceived stress
The Heidelberger Stress Index (HEI-STRESS) [ 39 ] is a three-item measure of current perceived stress due to studying as well as in life in general. For the first item, respondents enter a number between 0 (not stressed at all) and 100 (completely stressed) to indicate how stressed their studies have made them feel over the last four weeks. For the second and third item, respondents rate on a 5-point scale how often they feel “stressed and tense” and as how stressful they would describe their life at the moment. We transformed the second and third item to match the range of the first item before we averaged all items into a single score with higher values indicating greater perceived stress. We proved the scale to be one-dimensional and Cronbach’s alpha for our study was 0.86.
Depression and anxiety symptoms
We used the Patient Health Questionnaire-4 (PHQ-4) [ 40 ], a short form of the Patient Health Questionnaire [ 41 ] with four items, to measure depression and anxiety symptoms. The PHQ-4 contains two items from the Patient Health Questionnaire-2 (PHQ-2) [ 42 ] and the Generalized Anxiety Disorder Scale-2 (GAD-2) [ 43 ], respectively. It is a well-established screening scale designed to assess the core criteria of major depressive disorder (PHQ-2) and generalized anxiety disorder (GAD-2) according to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5). However, it was shown that the GAD-2 is also appropriate for screening other anxiety disorders. According to Kroenke et al. [ 40 ], the PHQ-4 can be used to assess a person’s symptom burden and impairment. We asked the participants to rate how often they have been bothered over the last two weeks by problems, such as “Little interest or pleasure in doing things”. Response options were 0 = not at all, 1 = several days, 2 = more than half the days, and 3 = nearly every day. Calculated as the sum of the four items, the total scores range from 0 to 12 with higher scores indicating more frequent depression and anxiety symptoms. The total scores can be categorized as none-to-minimal (0–2), mild (3–5), moderate (6–8), and severe (9–12) depression and anxiety symptoms. The PHQ-4 was shown to be reliable and valid [ 40 , 44 , 45 ]. We also proved the scale to be one-dimensional in a factor analysis, with a Cronbach’s alpha of 0.86.
Data analysis
To test our hypotheses, we performed structural equation modelling (SEM) using R (Version 4.1.1) with the package lavaan. All items were standardized ( M = 0, SD = 1). Due to the non-normality of some study variables and a sufficiently large sample size of N near to 400 [ 46 ], we used robust maximum likelihood estimation (MLR) for all model estimations. As recommended by Hu and Bentler [ 47 ], we assessed the models’ goodness of fit by chi-square test statistic, root mean square error of approximation (RMSEA), standardized root mean square residual (SRMR), Tucker-Lewis index (TLI), and comparative fit index (CFI). A non-significant chi-square indicates good model fit. Since chi-square is sensitive to sample size, we also evaluated fit indices less sensitive to the number of observations. RMSEA and SRMR values of 0.05 or lower as well as TLI and CFI values of 0.97 or higher indicate good model fit. RMSEA values of 0.08 or lower, SRMR values of 0.10 or lower, as well as TLI and CFI values of 0.95 or higher indicate acceptable model fit [ 48 , 49 ]. First, we conducted confirmatory factor analysis for the first occasion, defining three factors that correspond to the measures of procrastination, perceived stress, and depression and anxiety symptoms. Next, we tested for measurements invariance over time and specified the measurement model, before testing our hypotheses.
Measurement invariance over time
To test for measurement invariance over time, we defined one latent variable for each of the three occasions, corresponding to the measures of procrastination, perceived stress, and depression and anxiety symptoms, respectively. As recommended by Geiser and colleagues [ 50 ], the links between indicators and factors (i.e., factor loadings and intercepts) should be equal over measurement occasions; therefore, we added indicator specific factors. A first and least stringent step of testing measurement invariance is configural invariance (M CI ). It was examined whether the included constructs (procrastination, perceived stress, depression and anxiety symptoms) have the same pattern of free and fixed loadings over time. This means that the assignment of the indicators to the three latent factors over time is supported by the underlying data. If configural invariance was supported, restrictions for the next step of testing measurement invariance (metric or weak invariance; M MI ) were added. This means that each item contributes to the latent construct to a similar degree over time. Metric invariance was tested by constraining the factor loadings of the constructs over time. The next step of testing measurement invariance (scalar or strong invariance; M SI ) consisted of checking whether mean differences in the latent construct capture all mean differences in the shared variance of the items. Scalar invariance was tested by constraining the item intercepts over time. The constraints applied in the metric invariance model were retained [ 51 ]. For the last step of testing measurement invariance (residual or strict invariance; M RI ), the residual variables were also set equal over time. If residual invariance is supported, differences in the observed variables can exclusively be attributed to differences in the variances of the latent variables.
We used the Satorra-Bentler chi-square difference test to evaluate the superiority of a more stringent model [ 52 ]. We assumed the model with the largest number of invariance restrictions – which still has an acceptable fit and no substantial deterioration of the chi-square value – to be the final model [ 53 ]. Following previous recommendations, we considered a decrease in CFI of 0.01 and an increase in RMSEA of 0.015 as unacceptable to establish measurement invariance [ 54 ]. If a more stringent model had a significant worse chi-square value, but the model fit was still acceptable and the deterioration in model fit fell within the change criteria recommended for CFI and RMSEA values, we still considered the more stringent model to be superior.
Hypotheses testing
As recommended by Dormann et al. [ 55 ], we applied autoregressive time-lagged panel models to test our hypotheses. In the first step, we specified a model (M 0 ) that only included the stabilities of the three variables (procrastination, perceived stress, depression and anxiety symptoms) over time. In the next step (M 1 ), we added the time-lagged effects from procrastination (T1) to perceived stress (T2) and from procrastination (T2) to perceived stress (T3) as well as from perceived stress (T1) to depression and anxiety symptoms (T2) and from perceived stress (T2) to depression and anxiety symptoms (T3). Additionally, we included a direct path from procrastination (T1) to depression and anxiety symptoms (T3). If this path becomes significant, we can assume a partial mediation [ 55 ]. Otherwise, we can assume a full mediation. We compared these nested models using the Satorra-Bentler chi-square difference test and the Akaike information criterion (AIC). The chi-square difference value should either be non-significant, indicating that the proposed model including our hypotheses (M 1 ) does not have a significant worse model fit than the model including only stabilities (M 0 ), or, if significant, it should be in the direction that M 1 fits the data better than M 0 . Regarding the AIC, M 1 should have a lower value than M 0 .
Table 1 displays the means, standard deviations, internal consistencies (Cronbach’s alpha), and stabilities (correlations) of all study variables. The alpha values of procrastination, perceived stress, and depression and anxiety symptoms are classified as good (> 0.80) [ 56 ]. The correlation matrix of the manifest variables used for the analyses can be found in the Additional file 1: Table S3 .
We observed the highest test-retest reliabilities for procrastination ( r ≥ .74). The test-retest reliabilities for depression and anxiety symptoms ( r ≥ .64) and for perceived stress ( r ≥ .54) were a bit lower (see Table 1 ). The pattern of correlations shows a medium to large but positive relationship between procrastination and depression and anxiety symptoms [ 57 , 58 ]. The association between procrastination and perceived stress was small, the one between perceived stress and depression and anxiety symptoms very large (see Table 1 ).
Confirmatory factor analysis showed an acceptable to good fit (x 2 (41) = 118.618, p < .001; SRMR = 0.042; RMSEA = 0.071; TLI = 0.95; CFI = 0.97). When testing for measurement invariance over time for each construct, the residual invariance models with indicator specific factors provided good fit to the data (M RI ; see Table 2 ), suggesting that differences in the observed variables can exclusively be attributed to differences of the latent variables. We then specified and tested the measurement model of the latent constructs prior to model testing based on the items of procrastination, perceived stress, and depression and anxiety symptoms. The measurement model fitted the data well (M M ; see Table 3 ). All items loaded solidly on their respective factors (0.791 ≤ β ≤ 0.987; p < .001).
To test our hypotheses, we analyzed the two models described in the methods section.
The fit of the stability model (M 0 ) was acceptable (see Table 3 ). Procrastination was stable over time, with stabilities above 0.82. The stabilities of perceived stress as well as depression and anxiety symptoms were somewhat lower, ranging from 0.559 (T1 -> T2) to 0.696 (T2 -> T3) for perceived stress and from 0.713 (T2 -> T3) to 0.770 (T1 -> T2) for depression and anxiety symptoms, respectively.
The autoregressive mediation model (M 1 ) fitted the data significantly better than M 0 . The direct path from procrastination (T1) to depression and anxiety symptoms (T3) was significant (β = 0.16; p < .001), however, none of the mediated paths (from procrastination (T1) to perceived stress (T2) and from perceived stress (T2) to depression and anxiety symptoms (T3)) proved to be substantial. Also, the time-lagged paths from perceived stress (T1) to depression and anxiety symptoms (T2) and from procrastination (T2) to perceived stress (T3) were not substantial either (see Fig. 3 ).
To examine whether the hypothesized effects would occur over a one-year period rather than a six-months period, we specified an additional model with paths from procrastination (T1) to perceived stress (T3) and from perceived stress (T1) to depression and anxiety symptoms (T3), also including the stabilities of the three constructs as in the stability model M 0 . The model showed an acceptable fit (χ 2 (486) = 831.281, p < .001; RMSEA = 0.048; SRMR = 0.091; TLI = 0.95; CFI = 0.95), but neither of the two paths were significant.
Therefore, our hypotheses, that procrastination leads to perceived stress over time (H1) and that perceived stress leads to depression and anxiety symptoms over time (H2) must be rejected. We could only partially confirm our third hypothesis, that procrastination leads to depression and anxiety over time, mediated by perceived stress (H3), since procrastination did lead to depression and anxiety symptoms over time. However, this effect was not mediated by perceived stress.
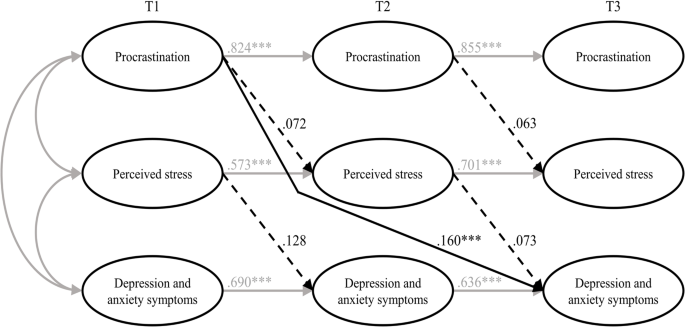
Results of the estimated model including all hypotheses (M 1 ). Note Non-significant paths are dotted. T1 = time 1; T2 = time 2; T3 = time 3. *** p < .001
To sum up, we tried to examine the harmful consequences of procrastination on students’ stress and mental health. Hence, we selected the procrastination-health model by Sirois [ 9 ] as a theoretical foundation and tried to evaluate some of its key assumptions in a temporal perspective. The author assumes that trait procrastination leads to (chronic) disease via (chronic) stress. We chose depression and anxiety symptoms as indicators for (chronic) disease and postulated, in line with the key assumptions of the procrastination-health model, that procrastination leads to perceived stress over time (H1), that perceived stress leads to depression and anxiety symptoms over time (H2), and that procrastination leads to depression and anxiety symptoms over time, mediated by perceived stress (H3). To examine these relationships properly, we collected longitudinal data from students at three occasions over a one-year period and analyzed the data using autoregressive time-lagged panel models. Our first and second hypotheses had to be rejected: Procrastination did not lead to perceived stress over time, and perceived stress did not lead to depression and anxiety symptoms over time. However, procrastination did lead to depression and anxiety symptoms over time – which is in line with our third hypothesis – but perceived stress was not a mediator of this effect. Therefore, we could only partially confirm our third hypothesis.
Our results contradict previous studies on the stress-related pathway of the procrastination-health model, which consistently found support for the role of (chronic) stress in the relationship between trait procrastination and (chronic) disease. Since most of these studies were cross-sectional, though, the causal direction of these effects remained uncertain. There are two longitudinal studies that confirm the stress-related pathway of the procrastination-health model [ 27 , 28 ], but both studies examined short-term effects (≤ 3 months), whereas we focused on more long-term effects. Therefore, the divergent findings may indicate that there are short-term, but no long-term effects of trait procrastination on (chronic) disease mediated by (chronic) stress.
Our results especially raise the question whether trait procrastination leads to (chronic) stress in the long term. Looking at previous longitudinal studies on the effect of procrastination on stress, the following stands out: At shorter study periods of two weeks [ 27 ] and four weeks [ 28 ], the effect of procrastination on stress appears to be present. At longer study periods of seven weeks [ 59 ], three months [ 28 ], six months, and twelve months, as in our study, the effect of procrastination on stress does not appear to be present. There is one longitudinal study in which procrastination was a significant predictor of stress symptoms nine months later [ 34 ]. The results of this study should be interpreted with caution, though, because the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic fell within the study period, which could have contributed to increased stress symptoms [ 60 ]. Unfortunately, Johansson et al. [ 34 ] did not report whether average stress symptoms increased during their study. In one of the two studies conducted by Fincham and May [ 59 ], the COVID-19 pandemic outbreak also fell within their seven-week study period. However, they reported that in their study, average stress symptoms did not increase from baseline to follow-up. Taken together, the findings suggest that procrastination can cause acute stress in the short term, for example during times when many tasks need to be completed, such as at the end of a semester, but that procrastination does not lead to chronic stress over time. It seems possible that students are able to recover during the semester from the stress their procrastination caused at the end of the previous semester. Because of their procrastination, they may also have more time to engage in relaxing activities, which could further mitigate the effect of procrastination on stress. Our conclusions are supported by an early and well-known longitudinal study by Tice and Baumeister [ 61 ], which compared procrastinating and non-procrastinating students with regard to their health. They found that procrastinators experienced less stress than their non-procrastinating peers at the beginning of the semester, but more at the end of the semester. Additionally, our conclusions are in line with an interview study in which university students were asked about the consequences of their procrastination [ 62 ]. The students reported that, due to their procrastination, they experience high levels of stress during periods with heavy workloads (e.g., before deadlines or exams). However, the stress does not last, instead, it is relieved immediately after these periods.
Even though research indicates, in line with the assumptions of the procrastination-health model, that stress is a risk factor for physical and mental disorders [ 63 , 64 , 65 , 66 ], perceived stress did not have a significant effect on depression and anxiety symptoms in our study. The relationship between stress and mental health is complex, as people respond to stress in many different ways. While some develop stress-related mental disorders, others experience mild psychological symptoms or no symptoms at all [ 67 ]. This can be explained with the help of vulnerability-stress models. According to vulnerability-stress models, mental illnesses emerge from an interaction of vulnerabilities (e.g., genetic factors, difficult family backgrounds, or weak coping abilities) and stress (e.g., minor or major life events or daily hassles) [ 68 , 69 ]. The stress perceived by the students in our sample may not be sufficient enough on its own, without the presence of other risk factors, to cause depression and anxiety symptoms. However, since we did not assess individual vulnerability and stress factors in our study, these considerations are mere speculation.
In our study, procrastination led to depression and anxiety symptoms over time, which is consistent with the procrastination-health model as well as previous cross-sectional and longitudinal evidence [ 18 , 21 , 31 , 32 , 33 , 34 ]. However, it is still unclear by which mechanisms this effect is mediated, as perceived stress did not prove to be a substantial mediator in our study. One possible mechanism would be that procrastination impairs affective well-being [ 70 ] and creates negative feelings, such as shame, guilt, regret, and anger [ 20 , 21 , 22 , 62 , 71 ], which in turn could lead to depression and anxiety symptoms [ 23 , 24 , 25 ]. Other potential mediators of the relationship between procrastination and depression and anxiety symptoms emerge from the behavioral pathway of the procrastination-health model, suggesting that poor health-related behaviors mediate the effect of trait procrastination on (chronic) disease. Although evidence for this is still scarce, the results of one cross-sectional study, for example, indicate that poor sleep quality might mediate the effect of procrastination on depression and anxiety symptoms [ 35 ].
In summary, we found that procrastination leads to depression and anxiety symptoms over time and that perceived stress is not a mediator of this effect. We could not show that procrastination leads to perceived stress over time, nor that perceived stress leads to depression and anxiety symptoms over time. For the most part, the relationships between procrastination, perceived stress, and depression and anxiety symptoms did not match the relationships between trait procrastination, (chronic) stress, and (chronic) disease as assumed in the procrastination-health model. Explanations for this could be that procrastination might only lead to perceived stress in the short term, for example, during preparations for end-of-semester exams, and that perceived stress may not be sufficient enough on its own, without the presence of other risk factors, to cause depression and anxiety symptoms. In conclusion, we could not confirm long-term effects of trait procrastination on (chronic) disease mediated by (chronic) stress, as assumed for the stress-related pathway of the procrastination-health model.
Limitations and suggestions for future research
In our study, we tried to draw causal conclusions about the harmful consequences of procrastination on students’ stress and mental health. However, since procrastination is a trait that cannot be manipulated experimentally, we have conducted an observational rather than an experimental study, which makes causal inferences more difficult. Nonetheless, a major strength of our study is that we used a longitudinal design with three waves. This made it possible to draw conclusions about the causal direction of the effects, as in hardly any other study targeting consequences of procrastination on health before [ 4 , 28 , 55 ]. Therefore, we strongly recommend using a similar longitudinal design in future studies on the procrastination-health model or on consequences of procrastination on health in general.
We chose a time lag of six months between each of the three measurement occasions to examine long-term effects of procrastination on depression and anxiety symptoms mediated by perceived stress. However, more than six months may be necessary for the hypothesized effects to occur [ 72 ]. The fact that the temporal stabilities of the examined constructs were moderate or high (0.559 ≤ β ≤ 0.854) [ 73 , 74 ] also suggests that the time lags may have been too short. The larger the time lag, the lower the temporal stabilities, as shown for depression and anxiety symptoms, for example [ 75 ]. High temporal stabilities make it more difficult to detect an effect that actually exists [ 76 ]. Nonetheless, Dormann and Griffin [ 77 ] recommend using shorter time lags of less than one year, even with high stabilities, because of other influential factors, such as unmeasured third variables. Therefore, our time lags of six months seem appropriate.
It should be discussed, though, whether it is possible to detect long-term effects of the stress-related pathway of the procrastination-health model within a total study period of one year. Sirois [ 9 ] distinguishes between short-term and long-term effects of procrastination on health mediated by stress, but does not address how long it might take for long-term effects to occur or when effects can be considered long-term instead of short-term. The fact that an effect of procrastination on stress is evident at shorter study periods of four weeks or less but in most cases not at longer study periods of seven weeks or more, as we mentioned earlier, could indicate that short-term effects occur within the time frame of one to three months, considering the entire stress-related pathway. Hence, it seems appropriate to assume that we have examined rather long-term effects, given our study period of six and twelve months. Nevertheless, it would be beneficial to use varying study periods in future studies, in order to be able to determine when effects can be considered long-term.
Concerning long-term effects of the stress-related pathway, Sirois [ 9 ] assumes that chronic procrastination causes chronic stress, which leads to chronic diseases over time. The term “chronic stress” refers to prolonged stress episodes associated with permanent tension. The instrument we used captures perceived stress over the last four weeks. Even though the perceived stress of the students in our sample was relatively stable (0.559 ≤ β ≤ 0.696), we do not know how much fluctuation occurred between each of the three occasions. However, there is some evidence suggesting that perceived stress is strongly associated with chronic stress [ 78 ]. Thus, it seems acceptable that we used perceived stress as an indicator for chronic stress in our study. For future studies, we still suggest the use of an instrument that can more accurately reflect chronic stress, for example, the Trier Inventory for Chronic Stress (TICS) [ 79 ].
It is also possible that the occasions were inconveniently chosen, as they all took place in a critical academic period near the end of the semester, just before the examination period began. We chose a similar period in the semester for each occasion for the sake of comparability. However, it is possible that, during this preparation periods, stress levels peaked and procrastinators procrastinated less because they had to catch up after delaying their work. This could have introduced bias to the data. Therefore, in future studies, investigation periods should be chosen that are closer to the beginning or in the middle of a semester.
Furthermore, Sirois [ 9 ] did not really explain her understanding of “chronic disease”. However, it seems clear that physical illnesses, such as diabetes or cardiovascular diseases, are meant. Depression and anxiety symptoms, which we chose as indicators for chronic disease, represent mental health complaints that do not have to be at the level of a major depressive disorder or an anxiety disorder, in terms of their quantity, intensity, or duration [ 40 ]. But they can be viewed as precursors to a major depressive disorder or an anxiety disorder. Therefore, given our study period of one year, it seems appropriate to use depression and anxiety symptoms as indicators for chronic disease. At longer study periods, we would expect these mental health complaints to manifest as mental disorders. Moreover, the procrastination-health model was originally designed to be applied to physical diseases [ 3 ]. Perhaps, the model assumptions are more applicable to physical diseases than to mental disorders. By applying parts of the model to mental health complaints, we have taken an important step towards finding out whether the model is applicable to mental disorders as well. Future studies should examine additional long-term health outcomes, both physical and psychological. This would help to determine whether trait procrastination has varying effects on different diseases over time. Furthermore, we suggest including individual vulnerability and stress factors in future studies in order to be able to analyze the effect of (chronic) stress on (chronic) diseases in a more differentiated way.
Regarding our sample, 3,420 students took part at the first occasion, but only 392 participated three times, which results in a dropout rate of 88.5%. At the second and third occasion, invitation e-mails were only sent to participants who had indicated at the previous occasion that they would be willing to participate in a repeat survey and provided their e-mail address. This is probably one of the main reasons for our high dropout rate. Other reasons could be that the students did not receive any incentives for participating in our study and that some may have graduated between the occasions. Selective dropout analysis revealed that the mean score of procrastination was lower in the group that participated in all three waves ( n = 392) compared to the group that participated in the first wave ( n = 3,420). One reason for this could be that those who have a higher tendency to procrastinate were more likely to procrastinate on filling out our survey at the second and third occasion. The findings of our dropout analysis should be kept in mind when interpreting our results, as lower levels of procrastination may have eliminated an effect on perceived stress or on depression and anxiety symptoms. Additionally, across all age groups in population-representative samples, the student age group reports having the best subjective health [ 80 ]. Therefore, it is possible that they are more resilient to stress and experience less impairment of well-being than other age groups. Hence, we recommend that future studies focus on other age groups as well.
It is generally assumed that procrastination leads to lower academic performance, health impairment, and poor health-related behavior. However, evidence for negative consequences of procrastination is still limited and it is also unclear by which mechanisms they are mediated. In consequence, the aim of our study was to examine the effect of procrastination on mental health over time and stress as a possible facilitator of this relationship. We selected the procrastination-health model as a theoretical foundation and used the stress-related pathway of the model, assuming that trait procrastination leads to (chronic) disease via (chronic) stress. We chose depression and anxiety symptoms as indicators for (chronic) disease and collected longitudinal data from students at three occasions over a one-year period. This allowed us to draw conclusions about the causal direction of the effects, as in hardly any other study examining consequences of procrastination on (mental) health before. Our results indicate that procrastination leads to depression and anxiety symptoms over time and that perceived stress is not a mediator of this effect. We could not show that procrastination leads to perceived stress over time, nor that perceived stress leads to depression and anxiety symptoms over time. Explanations for this could be that procrastination might only lead to perceived stress in the short term, for example, during preparations for end-of-semester exams, and that perceived stress may not be sufficient on its own, that is, without the presence of other risk factors, to cause depression and anxiety symptoms. Overall, we could not confirm long-term effects of trait procrastination on (chronic) disease mediated by (chronic) stress, as assumed for the stress-related pathway of the procrastination-health model. Our study emphasizes the importance of identifying the consequences procrastination can have on health and well-being and determining by which mechanisms they are mediated. Only then will it be possible to develop interventions that can prevent negative health consequences of procrastination. Further health outcomes and possible mediators should be explored in future studies, using a similar longitudinal design.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
University Health Report at Freie Universität Berlin.
Abbreviations
Comparative fit index
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition
Generalized Anxiety Disorder Scale-2
Heidelberger Stress Index
Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenocortical
Robust maximum likelihood estimation
Short form of the Procrastination Questionnaire for Students
Patient Health Questionnaire-2
Patient Health Questionnaire-4
Root mean square error of approximation
Structural equation modeling
Standardized root mean square residual
Tucker-Lewis index
Lu D, He Y, Tan Y, Gender S, Status. Cultural differences, Education, family size and procrastination: a sociodemographic Meta-analysis. Front Psychol. 2021. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.719425 .
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Yan B, Zhang X. What research has been conducted on Procrastination? Evidence from a systematical bibliometric analysis. Front Psychol. 2022. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2022.809044 .
Sirois FM, Melia-Gordon ML, Pychyl TA. I’ll look after my health, later: an investigation of procrastination and health. Pers Individ Dif. 2003;35:1167–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0191-8869(02)00326-4 .
Article Google Scholar
Grunschel C. Akademische Prokrastination: Eine qualitative und quantitative Untersuchung von Gründen und Konsequenzen [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]: Universität Bielefeld; 2013.
Steel P. The Nature of Procrastination: a Meta-Analytic and Theoretical Review of Quintessential Self-Regulatory failure. Psychol Bull. 2007;133:65–94. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.133.1.65 .
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Corkin DM, Yu SL, Lindt SF. Comparing active delay and procrastination from a self-regulated learning perspective. Learn Individ Differ. 2011;21:602–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lindif.2011.07.005 .
Balkis M, Duru E. Procrastination, self-regulation failure, academic life satisfaction, and affective well-being: underregulation or misregulation form. Eur J Psychol Educ. 2016;31:439–59. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10212-015-0266-5 .
Schulz N. Procrastination und Planung – Eine Untersuchung zum Einfluss von Aufschiebeverhalten und Depressivität auf unterschiedliche Planungskompetenzen [Doctoral dissertation]: Westfälische Wilhelms-Universität Münster; 2007.
Sirois FM. Procrastination, stress, and Chronic Health conditions: a temporal perspective. In: Sirois FM, Pychyl TA, editors. Procrastination, Health, and well-being. London: Academic; 2016. pp. 67–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-802862-9.00004-9 .
Harriott J, Ferrari JR. Prevalence of procrastination among samples of adults. Psychol Rep. 1996;78:611–6. https://doi.org/10.2466/pr0.1996.78.2.611 .
Ferrari JR, O’Callaghan J, Newbegin I. Prevalence of Procrastination in the United States, United Kingdom, and Australia: Arousal and Avoidance delays among adults. N Am J Psychol. 2005;7:1–6.
Google Scholar
Ferrari JR, Díaz-Morales JF, O’Callaghan J, Díaz K, Argumedo D. Frequent behavioral Delay tendencies by adults. J Cross Cult Psychol. 2007;38:458–64. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022022107302314 .
Day V, Mensink D, O’Sullivan M. Patterns of academic procrastination. JCRL. 2000;30:120–34. https://doi.org/10.1080/10790195.2000.10850090 .
Höcker A, Engberding M, Rist F, Prokrastination. Ein Manual Zur Behandlung Des Pathologischen Aufschiebens. 2nd ed. Göttingen: Hogrefe; 2017.
Kim KR, Seo EH. The relationship between procrastination and academic performance: a meta-analysis. Pers Individ Dif. 2015;82:26–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2015.02.038 .
Khalid A, Zhang Q, Wang W, Ghaffari AS, Pan F. The relationship between procrastination, perceived stress, saliva alpha-amylase level and parenting styles in Chinese first year medical students. Psychol Res Behav Manag. 2019;12:489–98. https://doi.org/10.2147/PRBM.S207430 .
Sirois FM. I’ll look after my health, later: a replication and extension of the procrastination–health model with community-dwelling adults. Pers Individ Dif. 2007;43:15–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2006.11.003 .
Reinecke L, Meier A, Aufenanger S, Beutel ME, Dreier M, Quiring O, et al. Permanently online and permanently procrastinating? The mediating role of internet use for the effects of trait procrastination on psychological health and well-being. New Media Soc. 2018;20:862–80. https://doi.org/10.1177/1461444816675437 .
Westgate EC, Wormington SV, Oleson KC, Lindgren KP. Productive procrastination: academic procrastination style predicts academic and alcohol outcomes. J Appl Soc Psychol. 2017;47:124–35. https://doi.org/10.1111/jasp.12417 .
Feyzi Behnagh R, Ferrari JR. Exploring 40 years on affective correlates to procrastination: a literature review of situational and dispositional types. Curr Psychol. 2022;41:1097–111. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-021-02653-z .
Rahimi S, Hall NC, Sticca F. Understanding academic procrastination: a longitudinal analysis of procrastination and emotions in undergraduate and graduate students. Motiv Emot. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11031-023-10010-9 .
Patrzek J, Grunschel C, Fries S. Academic procrastination: the perspective of University counsellors. Int J Adv Counselling. 2012;34:185–201. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10447-012-9150-z .
Watson D, Clark LA, Carey G. Positive and negative affectivity and their relation to anxiety and depressive disorders. J Abnorm Psychol. 1988;97:346–53. https://doi.org/10.1037//0021-843x.97.3.346 .
Cândea D-M, Szentagotai-Tătar A. Shame-proneness, guilt-proneness and anxiety symptoms: a meta-analysis. J Anxiety Disord. 2018;58:78–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.janxdis.2018.07.005 .
Young CM, Neighbors C, DiBello AM, Traylor ZK, Tomkins M. Shame and guilt-proneness as mediators of associations between General Causality orientations and depressive symptoms. J Soc Clin Psychol. 2016;35:357–70. https://doi.org/10.1521/jscp.2016.35.5.357 .
Stead R, Shanahan MJ, Neufeld RW. I’ll go to therapy, eventually: Procrastination, stress and mental health. Pers Individ Dif. 2010;49:175–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2010.03.028 .
Dow NM. Procrastination, stress, and sleep in tertiary students [Master’s thesis]: University of Canterbury; 2018.
Sirois FM, Stride CB, Pychyl TA. Procrastination and health: a longitudinal test of the roles of stress and health behaviours. Br J Health Psychol. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjhp.12658 .
Hofmann F-H, Sperth M, Holm-Hadulla RM. Psychische Belastungen Und Probleme Studierender. Psychotherapeut. 2017;62:395–402. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00278-017-0224-6 .
Liu CH, Stevens C, Wong SHM, Yasui M, Chen JA. The prevalence and predictors of mental health diagnoses and suicide among U.S. college students: implications for addressing disparities in service use. Depress Anxiety. 2019;36:8–17. https://doi.org/10.1002/da.22830 .
Aftab S, Klibert J, Holtzman N, Qadeer K, Aftab S. Schemas mediate the Link between Procrastination and Depression: results from the United States and Pakistan. J Rat-Emo Cognitive-Behav Ther. 2017;35:329–45. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10942-017-0263-5 .
Flett AL, Haghbin M, Pychyl TA. Procrastination and depression from a cognitive perspective: an exploration of the associations among Procrastinatory Automatic thoughts, rumination, and Mindfulness. J Rat-Emo Cognitive-Behav Ther. 2016;34:169–86. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10942-016-0235-1 .
Saddler CD, Sacks LA. Multidimensional perfectionism and academic procrastination: relationships with Depression in University students. Psychol Rep. 1993;73:863–71. https://doi.org/10.1177/00332941930733pt123 .
Johansson F, Rozental A, Edlund K, Côté P, Sundberg T, Onell C, et al. Associations between procrastination and subsequent Health outcomes among University students in Sweden. JAMA Netw Open. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.49346 .
Gusy B, Jochmann A, Lesener T, Wolter C, Blaszcyk W. „Get it done – schadet Aufschieben Der Gesundheit? Präv Gesundheitsf. 2023;18:228–33. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11553-022-00950-4 .
Glöckner-Rist A, Engberding M, Höcker A, Rist F. Prokrastinationsfragebogen für Studierende (PFS): Zusammenstellung sozialwissenschaftlicher items und Skalen. ZIS - GESIS Leibniz Institute for the Social Sciences; 2014.
Klingsieck KB, Fries S. Allgemeine Prokrastination: Entwicklung Und Validierung Einer Deutschsprachigen Kurzskala Der General Procrastination Scale (Lay, 1986). Diagnostica. 2012;58:182–93. https://doi.org/10.1026/0012-1924/a000060 .
Lay CH. At last, my research article on procrastination. J Res Pers. 1986;20:474–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/0092-6566(86)90127-3 .
Schmidt LI, Obergfell J. Zwangsjacke Bachelor?! Stressempfinden Und Gesundheit Studierender: Der Einfluss Von Anforderungen Und Entscheidungsfreiräumen Bei Bachelor- Und Diplomstudierenden Nach Karaseks Demand-Control-Modell. Saarbrücken: VDM Verlag Dr. Müller; 2011.
Kroenke K, Spitzer RL, Williams JB, Löwe B. An Ultra-brief Screening Scale for anxiety and depression: the PHQ-4. Psychosomatics. 2009;50:613–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0033-3182(09)70864-3 .
Spitzer RL, Kroenke K, Williams JB. Validation and utility of a self-report version of PRIME-MD: the PHQ Primary Care Study. JAMA. 1999;282:1737–44. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.282.18.1737 .
Kroenke K, Spitzer RL, Williams JB. The Patient Health Questionnaire-2: validity of a two-item Depression Screener. Med Care. 2003;41:1284–92.
Kroenke K, Spitzer RL, Williams JB, Monahan PO, Löwe B. Anxiety disorders in Primary Care: prevalence, impairment, Comorbidity, and detection. Ann Intern Med. 2007;146:317–25. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-146-5-200703060-00004 .
Khubchandani J, Brey R, Kotecki J, Kleinfelder J, Anderson J. The Psychometric properties of PHQ-4 depression and anxiety screening scale among College Students. Arch Psychiatr Nurs. 2016;30:457–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apnu.2016.01.014 .
Löwe B, Wahl I, Rose M, Spitzer C, Glaesmer H, Wingenfeld K, et al. A 4-item measure of depression and anxiety: validation and standardization of the Patient Health Questionnaire-4 (PHQ-4) in the general population. J Affect Disorders. 2010;122:86–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2009.06.019 .
Boomsma A, Hoogland JJ. The robustness of LISREL modeling revisited. In: Cudeck R, Du Toit S, Sörbom D, editors. Structural equation modeling: Present and Future: a festschrift in honor of Karl Jöreskog. Lincolnwood: Scientific Software International; 2001. pp. 139–68.
Hu L, Bentler PM. Fit indices in Covariance structure modeling: sensitivity to Underparameterized Model Misspecification. Psychol Methods. 1998;3:424–53. https://doi.org/10.1037/1082-989X.3.4.424 .
Schermelleh-Engel K, Moosbrugger H, Müller H. Evaluating the fit of structural equation models: test of significance and descriptive goodness-of-fit measures. MPR. 2003;8:23–74.
Hu L, Bentler PM. Cutoff criteria for fit indexes in Covariance structure analysis: conventional criteria Versus New Alternatives. Struct Equ Model. 1999;6:1–55. https://doi.org/10.1080/10705519909540118 .
Geiser C, Eid M, Nussbeck FW, Courvoisier DS, Cole DA. Analyzing true change in Longitudinal Multitrait-Multimethod studies: application of a Multimethod Change Model to Depression and anxiety in children. Dev Psychol. 2010;46:29–45. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0017888 .
Putnick DL, Bornstein MH. Measurement invariance conventions and reporting: the state of the art and future directions for psychological research. Dev Rev. 2016;41:71–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dr.2016.06.004 .
Satorra A, Bentler PM. A scaled difference chi-square test statistic for moment structure analysis. Psychometrika. 2001;66:507–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02296192 .
Geiser C. Datenanalyse Mit Mplus: Eine Anwendungsorientierte Einführung. Wiesbaden: VS Verlag für Sozialwissenschaften; 2010.
Book Google Scholar
Chen F, Curran PJ, Bollen KA, Kirby J, Paxton P. An empirical evaluation of the use of fixed cutoff points in RMSEA Test Statistic in Structural equation models. Sociol Methods Res. 2008;36:462–94. https://doi.org/10.1177/0049124108314720 .
Dormann C, Zapf D, Perels F. Quer- und Längsschnittstudien in der Arbeitspsychologie [Cross-sectional and longitudinal studies in occupational psychology.]. In: Kleinbeck U, Schmidt K-H,Enzyklopädie der Psychologie [Encyclopedia of psychology]:, Themenbereich D, Serie III, Band 1, Arbeitspsychologie [Subject Area, Series D. III, Volume 1, Industrial Psychology]. Göttingen: Hogrefe Verlag; 2010. pp. 923–1001.
Nunnally JC, Bernstein IH. Psychometric theory. 3rd ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 1994.
Gignac GE, Szodorai ET. Effect size guidelines for individual differences researchers. Pers Indiv Differ. 2016;102:74–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2016.06.069 .
Funder DC, Ozer DJ. Evaluating effect size in Psychological Research: sense and nonsense. Adv Methods Practices Psychol Sci. 2019;2:156–68. https://doi.org/10.1177/2515245919847202 .
Fincham FD, May RW. My stress led me to procrastinate: temporal relations between perceived stress and academic procrastination. Coll Stud J. 2021;55:413–21.
Daniali H, Martinussen M, Flaten MA. A Global Meta-Analysis of Depression, anxiety, and stress before and during COVID-19. Health Psychol. 2023;42:124–38. https://doi.org/10.1037/hea0001259 .
Tice DM, Baumeister RF. Longitudinal study of procrastination, performance, stress, and Health: the costs and benefits of Dawdling. Psychol Sci. 1997;8:454–8. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9280.1997.tb00460.x .
Schraw G, Wadkins T, Olafson L. Doing the things we do: a grounded theory of academic procrastination. J Educ Psychol. 2007;99:12–25. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.99.1.12 .
Slavich GM. Life Stress and Health: a review of conceptual issues and recent findings. Teach Psychol. 2016;43:346–55. https://doi.org/10.1177/0098628316662768 .
Phillips AC, Carroll D, Der G. Negative life events and symptoms of depression and anxiety: stress causation and/or stress generation. Anxiety Stress Coping. 2015;28:357–71. https://doi.org/10.1080/10615806.2015.1005078 .
Hammen C. Stress and depression. Annu Rev Clin Psychol. 2005;1:293–319. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.clinpsy.1.102803.143938 .
Blazer D, Hughes D, George LK. Stressful life events and the onset of a generalized anxiety syndrome. Am J Psychiatry. 1987;144:1178–83. https://doi.org/10.1176/ajp.144.9.1178 .
Southwick SM, Charney DS. The Science of Resilience: implications for the Prevention and Treatment of Depression. Science. 2012;338:79–82. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1222942 .
Ingram RE, Luxton DD. Vulnerability-stress models. In: Hankin BL, Abela JR, editors. Development of psychopathology: a vulnerability-stress perspective. Thousand Oaks: Sage; 2005. pp. 32–46.
Chapter Google Scholar
Maercker A. Modelle Der Klinischen Psychologie. In: Petermann F, Maercker A, Lutz W, Stangier U, editors. Klinische psychologie – Grundlagen. Göttingen: Hogrefe; 2018. pp. 13–31.
Krause K, Freund AM. Delay or procrastination – a comparison of self-report and behavioral measures of procrastination and their impact on affective well-being. Pers Individ Dif. 2014;63:75–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2014.01.050 .
Grunschel C, Patrzek J, Fries S. Exploring reasons and consequences of academic procrastination: an interview study. Eur J Psychol Educ. 2013;28:841–61. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10212-012-0143-4 .
Dwyer JH. Statistical models for the social and behavioral sciences. New York: Oxford University Press; 1983.
Cohen JA, Power Primer. Psychol Bull. 1992;112:155–9. https://doi.org/10.1037//0033-2909.112.1.155 .
Ferguson CJ. An effect size primer: a Guide for clinicians and Researchers. Prof Psychol Res Pr. 2009;40:532–8. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0015808 .
Hinz A, Berth H, Kittel J, Singer S. Die zeitliche Stabilität (Test-Retest-Reliabilität) Von Angst Und Depressivität Bei Patienten Und in Der Allgemeinbevölkerung. Z Med Psychol. 2011;20:24–31. https://doi.org/10.3233/ZMP-2010-2012 .
Adachi P, Willoughby T. Interpreting effect sizes when controlling for stability effects in longitudinal autoregressive models: implications for psychological science. Eur J Dev Psychol. 2015;12:116–28. https://doi.org/10.1080/17405629.2014.963549 .
Dormann C, Griffin M. Optimal time lags in Panel studies. Psychol Methods. 2015;20:489–505. https://doi.org/10.1037/met0000041 .
Weckesser LJ, Dietz F, Schmidt K, Grass J, Kirschbaum C, Miller R. The psychometric properties and temporal dynamics of subjective stress, retrospectively assessed by different informants and questionnaires, and hair cortisol concentrations. Sci Rep. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-37526-2 .
Schulz P, Schlotz W, Becker P. TICS: Trierer Inventar Zum chronischen stress. Göttingen: Hogrefe; 2004.
Heidemann C, Scheidt-Nave C, Beyer A-K, Baumert J, Thamm R, Maier B, et al. Health situation of adults in Germany - results for selected indicators from GEDA 2019/2020-EHIS. J Health Monit. 2021;6:3–25. https://doi.org/10.25646/8459 .
Download references
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Open Access Funding provided by Freie Universität Berlin.
Open Access funding enabled and organized by Projekt DEAL.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Division of Prevention and Psychosocial Health Research, Department of Education and Psychology, Freie Universität Berlin, Habelschwerdter Allee 45, 14195, Berlin, Germany
Anna Jochmann, Burkhard Gusy, Tino Lesener & Christine Wolter
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Conceptualization: A.J., B.G., T.L.; methodology: B.G., A.J.; validation: B.G.; formal analysis: A.J., B.G.; investigation: C.W., T.L., B.G.; data curation: C.W., T.L., B.G.; writing–original draft preparation: A.J., B.G.; writing–review and editing: A.J., T.L., B.G., C.W.; visualization: A.J., B.G.; supervision: B.G., T.L.; project administration: C.W., T.L., B.G.; All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Corresponding authors
Correspondence to Anna Jochmann or Burkhard Gusy .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
This study was performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Ethical approval was obtained from the Ethics Committee of the Department of Education and Psychology, Freie Universität Berlin. All methods were carried out in accordance with relevant guidelines and regulations. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Material 1
Selective dropout analysis and correlation matrix of the manifest variables
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Jochmann, A., Gusy, B., Lesener, T. et al. Procrastination, depression and anxiety symptoms in university students: a three-wave longitudinal study on the mediating role of perceived stress. BMC Psychol 12 , 276 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40359-024-01761-2
Download citation
Received : 25 May 2023
Accepted : 02 May 2024
Published : 16 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s40359-024-01761-2
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Student health
- Longitudinal study
BMC Psychology
ISSN: 2050-7283
- General enquiries: [email protected]

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Survey Instrument. A survey was developed that included all questions from the Short Warwick-Edinburgh Mental Well-Being (Tennant et al., 2007; Stewart-Brown and Janmohamed, 2008) and from the Perception of Academic Stress Scale (Bedewy and Gabriel, 2015).The Short Warwick-Edinburgh Mental Well-Being Scale is a seven-item scale designed to measure mental well-being and positive mental health ...
Effects of Stress. Due to stress, college students may experience such adverse outcomes as the decreased levels of cognitive functioning, the impaired ability to study, and, consequently, lower academic performance (Abdulghani et al. 516). First of all, the fact that a student is experiencing stress might have a considerable adverse effect on ...
National studies of college students have repeatedly found that the biggest stumbling blocks to academic success are emotional health challenges including: Stress. Anxiety. Not getting enough sleep. Depression. Many things can create stress in college. Maybe you're on a scholarship and you need to maintain certain grades to stay eligible.
Student stress is a serious issue that can impact their physical and mental health, as well as their academic performance. By recognizing the signs of stress and learning effective coping strategies, students can take control of their stress and improve their overall well-being. 250 Words Essay on Stress On Students Stress On Students
The Science Behind Student Stress. A new study shows how a growth mindset helps students cope with academic setbacks. A new study finds that when students experience an academic setback such as a bad grade, the amount of cortisol—the so-called stress hormone—in their bodies typically spikes. For most students it drops back down to normal ...
original definition of stress formulated by Selye (1983) was, "Stress is a non-specific response of the body". Stress is an. unavoidable phenomenon in all aspects of human life. Stress. is an ...
High school students are experiencing rising stress levels and lower engagement with learning since the start of the COVID-19 pandemic, according to a new study by NBC News and Challenge Success, a nonprofit affiliated with Stanford Graduate School of Education (GSE). Kids feel that "they are more stressed than they were before the pandemic, they have more work, they are less
Two recent and popular theories of student success, Angela Duckworth's grit theory and Carol Dweck's mind-set theory, further coalesce around the idea that stress sits at the core of persistence decisions. Grit theory argues that some students better manage the trials and travails of life; they're grittier by nature.
College is a time of major transition and of stress. During the pandemic, students have been struggling to cope with ever-increasing levels of mental distress among students. A recent study by The ...
Methods. A single author (MP) searched PubMed and Google Scholar for peer-reviewed articles published at any time in English. Search terms included academic, school, university, stress, mental health, depression, anxiety, youth, young people, resilience, stress management, stress education, substance use, sleep, drop-out, physical health with a combination of any and/or all of the preceding terms.
Essay grade: Excellent. 3 pages / 1401 words. Stress, as defined in the Longman Dictionary, is the continuous feeling of worry about your work or personal life that prevents one from relaxing or feeling at ease. Every student and adult faces stress at one point or another in their life.
No doubt, high school can be a high-pressure time in life. And high school students, as a result, get stressed out. In fact, according to the American Psychological Association's Stress in America 2020 survey, teens who are already under stress due to the normal pressures of high school have felt even more stress in recent years, thanks to the pandemic.
Stress is an unavoidable part of life, but research has found that increased daily stressors put college-aged young adults at a higher risk for stress than other age groups. Making new friends, handling a more challenging workload, feeling pressured to succeed, being without parental support, and navigating the stresses of more independent ...
Stress is the body's emotional, physical, or behavioral response to environmental change. Stress can be a short-term reaction in response to an upcoming event, such as homework deadlines, an upcoming exam, or speaking in front of the class. Stress can also result from traumatic or ongoing experiences, such as coping with parents' divorce ...
Stress management for kids and teens. Facing stressors is a fact of life, for children and adults. These strategies can help keep stress in check: Sleep well. Sleep is essential for physical and emotional well-being. Experts recommend nine to 12 hours of sleep a night for 6- to 12-year olds.
Coursework. Ending the Stigma. Tips to Overcome Stress During College. Avoid procrastinating. Seeking Medical Support. On-campus mental health services. Off-campus centers and hotlines. Conclusion. We have all heard at least one person being nostalgic about the great time they had in college.
By nearly every metric, student mental health is worsening. During the 2020-2021 school year, more than 60% of college students met the criteria for at least one mental health problem, according to the Healthy Minds Study, which collects data from 373 campuses nationwide (Lipson, S. K., et al., Journal of Affective Disorders, Vol. 306, 2022).In another national survey, almost three quarters ...
Question 2: Give some stress management techniques. Answer 2: There are many stress management techniques through which one can reduce stress in their lives. One can change their situation or their reaction to it. We can try by altering the situation. If not, we can change our attitudes towards it. Remember, accept things that you cannot change.
Among the subgroups of students, women, non-binary students, and second-year students reported higher academic stress levels and worse mental well-being (Table 2; Figures 2-4).In addition, the combined measures differed significantly between the groups in each category ().However, as measured by partial eta squared, the effect sizes were relatively small, given the convention of 0.01 = small ...
Stress is just one of the many hurdles college students face. Short-term stress can help learners raise a grade , polish an essay, or pursue a coveted career opportunity. But long-term stress, if left unaddressed, can have detrimental side effects.
A Cause and Effect Essay on Stress in Students Introduction. Stress is the natural response the human body gives to challenges. Students are exposed to stress by various factors. When a student undergoes chronic stress or high stress levels, their ability to learn, memorize, and post good academic performances can be interfered with regardless ...
500 Words Essay on Examination Stress on Students Introduction. Examinations are an integral part of the educational system, designed to evaluate a student's understanding and knowledge of the subjects studied. However, they often bring with them a significant amount of stress, causing a negative impact on the mental and physical health of ...
Stress essays are challenging and engaging assignments that can help students to learn more about the issue. We are here to help you write an outstanding essay on stress. Let us start by choosing the subject for your paper. We would suggest choosing one of the following stress essay topics and titles: Stress management techniques and their ...
Here are some of the ways that meditation can help you succeed in school: -> Meditation can help you deal with stress and anxiety and manage it better. When you feel overwhelmed or stressed, meditating for a few minutes might help you relax and focus on the task at hand. -> Meditation can improve your concentration.
For example, some students tend to regularly delay preparing for exams and writing essays until the last minute, even if this results in time pressure or lower grades. Procrastination must be distinguished from strategic delay ... we tried to examine the harmful consequences of procrastination on students' stress and mental health. Hence, ...
A recent national college health survey revealed that 10% of college students had been diagnosed with depression, underscoring the urgent need for effective stress management strategies. Conclusion In conclusion, while stress is an inevitable part of life, its impact on college students is substantial and warrants attention.