

How to Write a Purpose Statement (Templates, Examples)
By Status.net Editorial Team on September 30, 2023 — 15 minutes to read
- Key Elements of a Purpose Statement Part 1
- How to Write a Purpose Statement Step-by-Step Part 2
- Identifying Your Goals Part 3
- Defining Your Audience Part 4
- Outlining Your Methods Part 5
- Stating the Expected Outcomes Part 6
- Purpose Statement Example for a Research Paper Part 7
- Purpose Statement Example For Personal Goals Part 8
- Purpose Statement Example For Business Objectives Part 9
- Purpose Statement Example For an Essay Part 10
- Purpose Statement Example For a Proposal Part 11
- Purpose Statement Example For a Report Part 12
- Purpose Statement Example For a Project Part 13
- Purpose Statement Templates Part 14
A purpose statement is a vital component of any project, as it sets the tone for the entire piece of work. It tells the reader what the project is about, why it’s important, and what the writer hopes to achieve.
Part 1 Key Elements of a Purpose Statement
When writing a purpose statement, there are several key elements that you should keep in mind. These elements will help you to create a clear, concise, and effective statement that accurately reflects your goals and objectives.
1. The Problem or Opportunity
The first element of a purpose statement is the problem or opportunity that you are addressing. This should be a clear and specific description of the issue that you are trying to solve or the opportunity that you are pursuing.
2. The Target Audience
The second element is the target audience for your purpose statement. This should be a clear and specific description of the group of people who will benefit from your work.
3. The Solution
The third element is the solution that you are proposing. This should be a clear and specific description of the action that you will take to address the problem or pursue the opportunity.
4. The Benefits
The fourth element is the benefits that your solution will provide. This should be a clear and specific description of the positive outcomes that your work will achieve.
5. The Action Plan
The fifth element is the action plan that you will follow to implement your solution. This should be a clear and specific description of the steps that you will take to achieve your goals.
Part 2 How to Write a Purpose Statement Step-by-Step
Writing a purpose statement is an essential part of any research project. It helps to clarify the purpose of your study and provides direction for your research. Here are some steps to follow when writing a purpose statement:
- Start with a clear research question: The first step in writing a purpose statement is to have a clear research question. This question should be specific and focused on the topic you want to research.
- Identify the scope of your study: Once you have a clear research question, you need to identify the scope of your study. This involves determining what you will and will not include in your research.
- Define your research objectives: Your research objectives should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound. They should also be aligned with your research question and the scope of your study.
- Determine your research design: Your research design will depend on the nature of your research question and the scope of your study. You may choose to use a qualitative, quantitative, or mixed-methods approach.
- Write your purpose statement: Your purpose statement should be a clear and concise statement that summarizes the purpose of your study. It should include your research question, the scope of your study, your research objectives, and your research design.
Research question: What are the effects of social media on teenage mental health?
Scope of study: This study will focus on teenagers aged 13-18 in the United States.
Research objectives: To determine the prevalence of social media use among teenagers, to identify the types of social media used by teenagers, to explore the relationship between social media use and mental health, and to provide recommendations for parents, educators, and mental health professionals.
Research design: This study will use a mixed-methods approach, including a survey and interviews with teenagers and mental health professionals.
Purpose statement: The purpose of this study is to examine the effects of social media on teenage mental health among teenagers aged 13-18 in the United States. The study will use a mixed-methods approach, including a survey and interviews with teenagers and mental health professionals. The research objectives are to determine the prevalence of social media use among teenagers, to identify the types of social media used by teenagers, to explore the relationship between social media use and mental health, and to provide recommendations for parents, educators, and mental health professionals.
Part 3 Section 1: Identifying Your Goals
Before you start writing your purpose statement, it’s important to identify your goals. To do this, ask yourself the following questions:
- What do I want to achieve?
- What problem do I want to solve?
- What impact do I want to make?
Once you have a clear idea of your goals, you can start crafting your purpose statement. Your purpose statement should be a clear and concise statement that outlines the purpose of your work.
For example, if you’re writing a purpose statement for a business, your statement might look something like this:
“Our purpose is to provide high-quality products and services that improve the lives of our customers and contribute to the growth and success of our company.”
If you’re writing a purpose statement for a non-profit organization, your statement might look something like this:
“Our purpose is to improve the lives of underserved communities by providing access to education, healthcare, and other essential services.”
Remember, your purpose statement should be specific, measurable, and achievable. It should also be aligned with your values and goals, and it should inspire and motivate you to take action.
Part 4 Section 2: Defining Your Audience
Once you have established the purpose of your statement, it’s important to consider who your audience is. The audience for your purpose statement will depend on the context in which it will be used. For example, if you’re writing a purpose statement for a research paper, your audience will likely be your professor or academic peers. If you’re writing a purpose statement for a business proposal, your audience may be potential investors or clients.
Defining your audience is important because it will help you tailor your purpose statement to the specific needs and interests of your readers. You want to make sure that your statement is clear, concise, and relevant to your audience.
To define your audience, consider the following questions:
- Who will be reading your purpose statement?
- What is their level of knowledge or expertise on the topic?
- What are their needs and interests?
- What do they hope to gain from reading your purpose statement?
Once you have a clear understanding of your audience, you can begin to craft your purpose statement with their needs and interests in mind. This will help ensure that your statement is effective in communicating your goals and objectives to your readers.
For example, if you’re writing a purpose statement for a research paper on the effects of climate change on agriculture, your audience may be fellow researchers in the field of environmental science. In this case, you would want to make sure that your purpose statement is written in a way that is clear and concise, using technical language that is familiar to your audience.
Or, if you’re writing a purpose statement for a business proposal to potential investors, your audience may be less familiar with the technical aspects of your project. In this case, you would want to make sure that your purpose statement is written in a way that is easy to understand, using clear and concise language that highlights the benefits of your proposal.
The key to defining your audience is to put yourself in their shoes and consider what they need and want from your purpose statement.
Part 5 Section 3: Outlining Your Methods
After you have identified the purpose of your statement, it is time to outline your methods. This section should describe how you plan to achieve your goal and the steps you will take to get there. Here are a few tips to help you outline your methods effectively:
- Start with a general overview: Begin by providing a brief overview of the methods you plan to use. This will give your readers a sense of what to expect in the following paragraphs.
- Break down your methods: Break your methods down into smaller, more manageable steps. This will make it easier for you to stay organized and for your readers to follow along.
- Use bullet points: Bullet points can help you organize your ideas and make your methods easier to read. Use them to list the steps you will take to achieve your goal.
- Be specific: Make sure you are specific about the methods you plan to use. This will help your readers understand exactly what you are doing and why.
- Provide examples: Use examples to illustrate your methods. This will make it easier for your readers to understand what you are trying to accomplish.
Part 6 Section 4: Stating the Expected Outcomes
After defining the problem and the purpose of your research, it’s time to state the expected outcomes. This is where you describe what you hope to achieve by conducting your research. The expected outcomes should be specific and measurable, so you can determine if you have achieved your goals.
It’s important to be realistic when stating your expected outcomes. Don’t make exaggerated or false claims, and don’t promise something that you can’t deliver. Your expected outcomes should be based on your research question and the purpose of your study.
Here are some examples of expected outcomes:
- To identify the factors that contribute to employee turnover in the company.
- To develop a new marketing strategy that will increase sales by 20% within the next year.
- To evaluate the effectiveness of a new training program for improving customer service.
- To determine the impact of social media on consumer behavior.
When stating your expected outcomes, make sure they align with your research question and purpose statement. This will help you stay focused on your goals and ensure that your research is relevant and meaningful.
In addition to stating your expected outcomes, you should also describe how you will measure them. This could involve collecting data through surveys, interviews, or experiments, or analyzing existing data from sources such as government reports or industry publications.
Part 7 Purpose Statement Example for a Research Paper
If you are writing a research paper, your purpose statement should clearly state the objective of your study. Here is an example of a purpose statement for a research paper:
The purpose of this study is to investigate the effects of social media on the mental health of teenagers in the United States.
This purpose statement clearly states the objective of the study and provides a specific focus for the research.
Part 8 Purpose Statement Example For Personal Goals
When writing a purpose statement for your personal goals, it’s important to clearly define what you want to achieve and why. Here’s a template that can help you get started:
“I want to [goal] so that [reason]. I will achieve this by [action].”
Example: “I want to lose 10 pounds so that I can feel more confident in my body. I will achieve this by going to the gym three times a week and cutting out sugary snacks.”
Remember to be specific and realistic when setting your goals and actions, and to regularly review and adjust your purpose statement as needed.
Part 9 Purpose Statement Example For Business Objectives
If you’re writing a purpose statement for a business objective, this template can help you get started:
[Objective] [Action verb] [Target audience] [Outcome or benefit]
Here’s an example using this template:
Increase online sales by creating a more user-friendly website for millennial shoppers.
This purpose statement is clear and concise. It identifies the objective (increase online sales), the action verb (creating), the target audience (millennial shoppers), and the outcome or benefit (a more user-friendly website).
Part 10 Purpose Statement Example For an Essay
“The purpose of this essay is to examine the causes and consequences of climate change, with a focus on the role of human activities, and to propose solutions that can mitigate its impact on the environment and future generations.”
This purpose statement clearly states the subject of the essay (climate change), what aspects will be explored (causes, consequences, human activities), and the intended outcome (proposing solutions). It provides a clear roadmap for the reader and sets the direction for the essay.
Part 11 Purpose Statement Example For a Proposal
“The purpose of this proposal is to secure funding and support for the establishment of a community garden in [Location], aimed at promoting sustainable urban agriculture, fostering community engagement, and improving local access to fresh, healthy produce.”
Why this purpose statement is effective:
- The subject of the proposal is clear: the establishment of a community garden.
- The specific goals of the project are outlined: promoting sustainable urban agriculture, fostering community engagement, and improving local access to fresh produce.
- The overall objective of the proposal is evident: securing funding and support.
Part 12 Purpose Statement Example For a Report
“The purpose of this report is to analyze current market trends in the electric vehicle (EV) industry, assess consumer preferences and buying behaviors, and provide strategic recommendations to guide [Company Name] in entering this growing market segment.”
- The subject of the report is provided: market trends in the electric vehicle industry.
- The specific goals of the report are analysis of market trends, assessment of consumer preferences, and strategic recommendations.
- The overall objective of the report is clear: providing guidance for the company’s entry into the EV market.
Part 13 Purpose Statement Example For a Project
“The purpose of this project is to design and implement a new employee wellness program that promotes physical and mental wellbeing in the workplace.”
This purpose statement clearly outlines the objective of the project, which is to create a new employee wellness program. The program is designed to promote physical and mental wellbeing in the workplace, which is a key concern for many employers. By implementing this program, the company aims to improve employee health, reduce absenteeism, and increase productivity. The purpose statement is concise and specific, providing a clear direction for the project team to follow. It highlights the importance of the project and its potential benefits for the company and its employees.
Part 14 Purpose Statement Templates
When writing a purpose statement, it can be helpful to use a template to ensure that you cover all the necessary components:
Template 1: To [action] [target audience] in order to [outcome]
This template is a straightforward way to outline your purpose statement. Simply fill in the blanks with the appropriate information:
- The purpose of […] is
- To [action]: What action do you want to take?
- [Target audience]: Who is your target audience?
- In order to [outcome]: What outcome do you hope to achieve?
For example:
- The purpose of our marketing campaign is to increase brand awareness among young adults in urban areas, in order to drive sales and revenue growth.
- The purpose of our employee training program is to improve customer service skills among our frontline staff, in order to enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- The purpose of our new product launch is to expand our market share in the healthcare industry, by offering a unique solution to the needs of elderly patients with chronic conditions.
Template 2: This [project/product] is designed to [action] [target audience] by [method] in order to [outcome].
This template is useful for purpose statements that involve a specific project or product. Fill in the blanks with the appropriate information:
- This [project/product]: What is your project or product?
- Is designed to [action]: What action do you want to take?
- By [method]: What method will you use to achieve your goal?
- This app is designed to provide personalized nutrition advice to athletes by analyzing their training data in order to optimize performance.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key elements of a purpose statement.
A purpose statement should clearly communicate the main goal or objective of your writing. It should be concise and specific, providing a clear direction for your work. The key elements of a purpose statement include the topic or subject matter, the intended audience, and the overall goal or objective of your writing.
How can a purpose statement benefit your writing?
A purpose statement can help you stay focused and on track when writing. It can also help you to avoid going off-topic or getting bogged down in unnecessary details. By clearly identifying the main goal or objective of your writing, a purpose statement can help you to stay organized and ensure that your writing is effective and impactful.
What are some common mistakes to avoid when writing a purpose statement?
One common mistake is being too vague or general in your purpose statement. Another mistake is making your purpose statement too long or complex, which can make it difficult to understand. Additionally, it’s important to avoid including unnecessary information or details that are not directly relevant to your main goal or objective.
How can you tailor your purpose statement to your audience?
When writing a purpose statement, it’s important to consider your audience and their needs. You should tailor your purpose statement to your audience by using language and terminology that they will understand. You should also consider their level of knowledge or expertise on the subject matter and adjust your purpose statement accordingly.
What are some effective templates for writing a purpose statement?
There are many effective templates for writing a purpose statement, but one common approach is to use the following structure: “The purpose of this writing is to [insert goal or objective] for [insert audience] regarding [insert topic or subject matter].”
Can you provide examples of successful purpose statements?
- “The purpose of this report is to provide an analysis of the current market trends and make recommendations for future growth strategies for our company.”
- “The purpose of this essay is to explore the impact of social media on modern communication and its implications for society.”
- “The purpose of this proposal is to secure funding for a new community center that will provide educational and recreational opportunities for local residents.”
- How to Write a Personal Mission Statement (20 Examples)
- How to Write a Letter of Employment (Templates, Examples)
- How to Ask for a Letter of Recommendation [Examples]
- Individual Development Plan [Examples & Templates]
- How to Write a Two-Week Notice [Effective Examples]
- Job Application Email (Templates, Examples)
- The Grossman Group Difference
- Internal Communications
- Leadership Communication
- Change Management
- Organizational Culture Change
- Resource Center
- Heart First Giveaway
- Case Studies

How to Write a Purpose Statement That Serves Its Purpose (With 10 Examples)

If you had 5 minutes – or better yet, 5 seconds, could you describe WHY your organization exists? Would your colleagues describe it in the same way? And more importantly, would they FEEL a strong connection to the company's purpose?
Companies with a clear business purpose statement, and that use their purpose statement to connect with employees, customers, and key stakeholders at a deeper level, have an edge.
Why Company Purpose Matters Even More Today
It’s not a new concept: we tend to feel a bit better going to work or buying a product or service when we know there’s a greater reason for being behind it. It’s often a deciding factor between choosing one brand or company over another. What is new, though, is that the world we live and work in today calls for even more of a spotlight on purpose.
According to a 2021 McKinsey study , nearly 70% of employees are reflecting on purpose because of the pandemic. And, based on a PwC survey , 83% of employees rated “meaning in day-to-day work” as important to them. This has a downstream impact on hiring, morale, retention, and performance.
Your purpose statement is the foundation for how you can attract and retain talent, differentiate your culture, accelerate performance in a competitive, crowded marketplace, and re-energize employees who may be fatigued, apathetic, or skeptical.
The same McKinsey study found that employees who say that they live their purpose at work are:
- 6.5 times more likely to report higher resilience,
- 4 times more likely to report better health,
- 6 times more likely to want to stay at the company, and
- 1.5 times more likely to go above and beyond to contribute to the company (which is the employee engagement outcome many leaders and teams try to achieve).
For these reasons and more, our team believes that every organization should have a purpose statement and should know how to use it to tell your story on the inside and out for business impact so employees, customers, investors, shareholders, potential employees, and customers, and your many other stakeholders and partners see that they have a place in your company’s purpose.
What the Purpose Statement Is
A company purpose statement is its reason for being. It should answer these questions: Why do we exist beyond making money? What would the world lose if we didn’t exist? It goes beyond who you are and what you do. It’s your why and the impact your organization has on others.
Here are six characteristics of great purpose statements:
- Articulate the movement they’re ultimately championing and/or why the company is on the journey they are
- Are grand and aspirational while also believable
- Are differentiated so when viewed together with the mission, vision, and values of your company they are unique to your organization
- Are specific and create clarity, so they mean something to your company
- Are memorable and repeatable
- Have a tone and content that reflects the culture of the organization and fits them like a glove
Done right, company purpose statements are an important aspect of decision-making inside an organization so that it’s consistent with the company’s purpose.
10 Company Purpose Statement Examples
Here are 10 purpose statement examples across a variety of industries with a few thoughts on what makes them strong:
- AT&T: We create connection. This is both aspirational and ties to the company and its products and services over the years – which makes it believable. While it isn’t specific to a product, it creates clarity about what the company sees as its ultimate reason for being – to create connection. This is what we mean by “fitting like a glove”.
- Charles Schwab Corporation: To champion every client's goals with passion and integrity. It speaks to the larger reason for being a company in the financial services industry. It is specific to the movement it focuses on (championing clients’ goals) and it reflects the culture of the organization (passion and integrity). It’s both aspirational and believable.
- CVS Health: Bringing our heart to every moment of your health™ This captures the essence of the company’s focus around people’s lives and health. It’s memorable and repeatable and is used as a tagline. It ties in its brand as well (the heart), which also speaks to company culture and its intended service experience.
- Kellogg’s: Creating better days and a place at the table for everyone through our trusted food brands. You see the statement, company name, think of the products, and know that they go hand in hand. It speaks to the movement the company is championing (better days and a place at the table for everyone). It is grand and aspirational while also being believable. It’s specific and speaks to its industry (trusted food brand).
- Ford Motor Company: To help build a better world, where every person is free to move and pursue their dreams. This is grand and aspirational as well as entirely believable. If you run the screen of “what would be at risk if the company didn’t exist?” the mind goes to images of people not being able to get to their jobs, school, to travel, and be where they want to be. In reading this purpose statement, you learn quite a bit about the company and what it stands for (build a better world, be free to move, help people pursue their dreams).
- Virgin Atlantic: Everyone can take on the world. It speaks to the culture of the company, is easy to remember, and is memorable. It’s aspirational and yet feels believable in the sense that its products and services actually help people “take on the world”. There’s a swagger to this phrase that exudes confidence, feels empowering, and feels right at home with the brand. When you see this purpose statement and think about the company and what it’s all about, you can see (and almost feel) how they belong together.
- McDonald’s: To feed and foster communities. It’s memorable, repeatable, and naturally ties to the business it is in. It also signals in a believable way that its aspirations go beyond food and are also about building communities.
- NIKE: To move the world forward through the power of sport. It’s clear, easy to remember, and specific to the business. You know the industry right away which helps differentiate them (power of sport). It’s aspirational (moving the world forward) and also believable. When you read the purpose statement, you can visualize the essence of the company and its products that help people move.
- Novartis: To reimagine medicine to improve and extend people's lives. It’s specific to the industry (healthcare) and speaks to why the company exists (reimagine medicine) and its higher level reason for being (improve and extend people’s lives). It’s clear and easy to remember.
- Kroger: To feed the human spirit™ This speaks to its industry and focus as a business (food). It’s easy to remember and repeat, reading like a slogan. It’s also aspirational in that it speaks to feeding more than the “person” but also the “human spirit”.
How a Purpose Statement Fits Into Your Company’s Mission, Vision, and Values
Purpose is one of several elements of your organization’s DNA that make your company uniquely you. Together, these define who you are as a company and what you stand for. They serve as your North Star for your business – what you do, why you do it, and how you do it.
- Purpose statement: An organization’s reason for being (beyond making a profit) and how the products/services benefit people. It answers the questions for your customers and employees: why do we exist and what would the world lose if we didn’t exist? It has an external focus and remains constant over time. Purpose statements could be centered on society, customers, or community. All the other elements of the DNA tie back to the purpose statement.
- Mission statement: The mission states what the company will do to realize its business purpose. It comes from the perspective of inside the organization. The key elements to the mission statement are that it states the type of business/work you do today, is forward-looking, and speaks to your capabilities. It focuses on what you do and how you do it. A mission statement guides decision-making and informs business strategy, and it could evolve over time while your organization’s purpose remains the same.
- Vision statement: Paints a picture of what our company’s future looks like if we’re successful. It answers the question. It’s a statement of where the organization is heading. It’s future-oriented and aspirational. It’s also connected to the hearts and minds of people and captures hopes and dreams.
- Values and behaviors: These make up the desired ways of work (or culture) that employees need to live to advance the purpose, mission, and vision. Values describe the principles that are expected of employees, and behaviors are the tangible, observable, measurable elements that can be implemented. Both values and behaviors are intended to help employees know what’s expected of them and to guide how they show up at work. They define the company’s culture and personality, and answer the question: What does our company look like in action? Values and behaviors can happen in pockets but are aspirational for others.
Put another way…
- The purpose GUIDES you.
- The mission FOCUSES you.
- The vision INSPIRES you.
- The values ALIGN you.
- The behaviors MEASURE you.
These elements of a company’s DNA form a strategic framework that helps employees know what matters most for the organization, and how day-to-day business plans and tasks fit into the larger whole and greater good. It’s also an important way for employees to see how their sense of purpose fits (or doesn’t) with the place they work.
It’s like a stack of jigsaw puzzle pieces that fit together to form a cohesive picture for everyone to see and share in common.
How to Know When You Need to Update Your Purpose Statement
Because the purpose statement guides your company, it’s important to regularly calibrate between your purpose statement and changing dynamics to ensure they stay connected in all the right ways. Here are some defining moments in a company that signal when it’s time to review your purpose statement and determine whether it’s time to update it:
- New CEO / leadership team: With new leadership comes new perspective on the business. It’s a time when leaders are evaluating the business, weighing options, and setting new directions for the company that will make an impact. It’s important to also evaluate the purpose statement of the company and line it up.
- Merger and/or acquisition: This is a major change to your company that warrants a calibration to your purpose statement (and mission, vision, and values) as new entities, teams, products, and services are at play. It’s a good time to evaluate whether the purpose statement remains true to the company in its new state. At a minimum, it’s critical to drive awareness of your company’s purpose with employees, customers, and other stakeholders so they fully understand and appreciate it.
- New strategy: Purpose statements and company strategy must go hand in hand so if your company has a new strategy (or is working on a new strategy ), check that the purpose statement is still consistent and relevant.
- Significant transformation: Congruency between the company’s purpose and actions is essential. When big changes are happening in a company it’s key to calibrate so the transformation efforts continue to sync and support the company’s purpose and strategic direction. And, if the transformation is changing direction for a company, then the purpose statement (and mission, vision, and values) may need to evolve.
- Recruitment, retention issues, or other people-related issues: More than ever, employees want to work for companies that share a common sense of purpose and values. If your organization is struggling to recruit and retain employees, check your purpose statement and see if it’s as relevant and compelling as it needs to be.
- Heightened competition: Employees, customers, and investors look for differentiation and companies with an edge. Your purpose statement says a lot about your company – who you are, what you stand for, why you exist, and what’s at risk if you’re not there. When competition is fierce, it’s time to look at your purpose statement to see if it defines you accurately, speaks to your aspirations, and helps you stand out.
- Annual strategic planning: Make it a habit to check your purpose statement (along with your vision, mission, and values) annually in the context of your company’s strategic planning, so the most important elements of your organization guide decision-making for key priorities and plans for the year. It’s the ultimate litmus test to see that priorities and plans support your company’s purpose statement (and overall DNA). And, if they don’t line up, to have strategic conversations about what’s changing and why and whether it warrants updating your purpose statement.
How to Write a Purpose Statement
Apply these principles as you consider your approach to developing your company’s purpose statement:
- Make it a strategic business exercise – that sets the direction for your vision, mission, values, and strategy and is the foundation for how people know you as a company. Keep it from being a word-smithing exercise.
- Be intentional – Dig deep to understand the origin of the company and follow that thread through to who you are today, and why you will continue to exist in the future.
- Let leaders set the tone and involve others with purpose – The purpose statement should be shaped by the leadership team and key influencers in the company and then vetted and fine-tuned with employees so that they have shared meaning and ownership. This is bigger than any one person or team writing the purpose statement.
- Iterate – Work a smart process and let the process work so as people’s thinking evolves, the purpose statement captures it.
- Connect to your culture – Let the essence of your culture come through in how you describe the essence of your company.
- Go beyond the ordinary – If you lined up your purpose statement with others in your industry (or even other industries), check that it stands out from the rest.
- Have a plan – This is how you’re going to create the purpose statement and what you’ll do to introduce it to your key stakeholders inside and outside the company.
Steps to Writing Your Purpose Statement
Whether creating a purpose statement from scratch or refreshing an existing one, follow these steps to guide you. How you approach writing your purpose statement may vary depending on where you are as an organization, your starting point, and your culture.
- Intake Compare your current purpose statement with how your organization shows up in internal and external artifacts to see what’s consistent and what’s not. Ask: What’s similar and what’s different that we should consider for the new purpose statement?
- Develop Your Roadmap Determine your plan of action to get to a purpose statement that your organization is fully aligned around. Ask: What are the key steps and milestones to drive toward?
- Identify Your Stakeholders and Engagement Plan Map your plan for who and how you’ll engage people from across your organization in the process. Consider who your champions will be, who will be hands-on in co-creation, and who you want to involve along the way to preview or test concepts. If there are many stakeholders, consider a working group or committee of representatives to advance the work in a more manageable way. And then involve others to preview and test the committee’s work. Ask: When the purpose statement is drafted, who do we need to have on board so they support it and what’s the best way to get those people involved?
- Conduct Stakeholder Listening Based on your engagement plan, hold listening sessions with key stakeholders to understand their thoughts on the business and how that translates to the company’s purpose. Summarize what you’re hearing. Ask: What are the common themes and where are there different points of view that warrant more conversation and alignment?
- Co-create the Purpose Statement Gather all the key stakeholders to co-create the purpose statement together in a hands-on, interactive way. Have a facilitator lead the session and leverage all the work done in Steps 1 through 4. You can walk out with a solid draft of the purpose statement that the group is aligned around and that’s ready to test drive with others. Ask: Do we have a purpose statement that we all understand, believe in, and can champion?
- Test the Purpose Statement Involve other stakeholders for input and buy-in. Get the draft purpose statement in front of employee groups and see what they say. You can also have key groups of leaders and working group members test drive the purpose statement with their teams. Ask: What resonates, where is further clarification needed, and in what ways do we see this purpose statement being lived in the company?
- Discuss and Refine the Purpose Statement Use the learnings as fodder for discussion with your core working group and champions about what changes to make in the purpose statement and to inform your communications before you revise and finalize the purpose statement. Ask: What feedback warrants changes to the purpose statement? What concepts will require more communication to help people understand?
Key Learnings from Developing Purpose Statements
We’ve worked with many clients to create their purpose statement (and their mission, vision, and values as well). Here are four things to keep in mind:
- The process is as important as the statement – How you engage people and bring them along on the journey is just as important as what the final words are of your company’s purpose statement. You need a purpose statement that will guide the company – and its people – for years to come and that requires involvement from people.
- Involve skeptics – Some may think of this work as a word-smithing activity or that culminates in posters that no one ever reads. To those people, we say … let’s get you involved in this process so we can make sure that doesn’t happen. Build a plan that is skeptic-proof. I’ve heard from many leaders as they go through this process that they were skeptical about this work at first and then became the biggest advocates of the purpose statement they created and the process that was taken to build it.
- Avoid shortcuts that may cause shortcomings – On paper, a purpose statement is just a few words but getting a room full of people (let alone a whole company) to align around the meaning behind the words looks easier than it is. We believe in a “go slow to go fast” approach that by working a smart process you’ll get to a better outcome faster and that will have lasting power. Watch out for shortcuts that can cause shortcomings – for example, skipping listening or testing may save a few days, but you lose out on important insights and cut people out of being involved who could have become champions.
- Embrace input – It can be nerve-wracking to draft a purpose statement and then take it to pockets of the organization for input not knowing if it will be liked or overhauled. However, it’s better to bring people along on the journey and get input before things are finalized for prime time. In addition, when people are engaged earlier, they tend to be more positive. We worked with a client to preview their company’s DNA (including the purpose statement) with more than 1,000 people. The reception was extremely positive and where there was feedback, it was hugely helpful. Most importantly, when it came time to roll out the final content, people were on board and ready to champion it because they had been a part of the process.
You’ve Crafted Your Purpose Statement – Now What?
Having a clear purpose statement is a big step to celebrate. It’s also just the beginning as you think about how to embed it into the organization. Consider these next steps:
- Define your terms – A purpose statement is just a few words, but every single word matters and needs to mean something. Have specific definitions for each word so people in your organization know what it means and use the terms consistently.
- Align the rest of the strategy to the purpose statement – The purpose statement anchors many other components of your company’s strategic framework so everything needs to ladder back to it, including the mission, vision, values, culture, business plans and priorities, and KPIs and metrics. Identify where there are connections to make and/or disconnects to address. Create a strategic framework that shows visually how all the pieces connect together.
- Plan the rollout and activation – Have a plan for how to communicate the company’s purpose across the organization. Think of it in terms of launching, activating, and sustaining so you can embed the purpose in how people think and work. Make it part of the everyday storytelling inside and outside the company. This takes time, consistency across voices and channels, and purposeful communication.
Case Study: A Purpose-Driven Function
We worked recently with a large function in a global organization through these steps. The function originally needed help to roll out and embed their new strategy to its 7,500 employees, but early on it became clear that before employees could align around a strategy, they first needed to come together with one shared purpose. Working these steps led to many defining moments, including:
- During discovery, an employee survey led to useful insights that guided the leadership team’s focus and helped them address some opportunities, and it served as a follow-up loop for communicating the purpose and strategy.
- Leader listening uncovered a wide range of perspectives on the organization’s purpose and path forward. This was critical to uncover early on, so the work to follow could bridge the gaps and bring the leaders together as one aligned team.
- The process of co-creating the purpose statement worked. It got some grumbles at first. “Really, we need to break up into groups and do flip chart exercises?” Yes... and did they ever rise to the occasion. In a few short hours, the group co-created a purpose statement and started using it in the same meeting to make some critical business decisions. It was an instant payoff and the leadership team knew it. They later described that as a defining moment for their leadership team and their company.
- Leaders played an active role in talking about the purpose statement with their teams and ensuring a common understanding of the meaning of each element of the purpose.
- Next-level leaders (directors and above in this case) became immersed in their purpose, mission, vision, values, and strategy at an offsite meeting where every moment of the day was designed purposefully to bring the company’s DNA to life in ways that made it real, relevant, and actionable for them, so they could take the same experience and energy back to their teams to get them grounded in it.
- The purpose statement took on a life of its own as leaders enrolled their teams in it. They held rallies, decorated their sites with signage, gave employees swag, made it part of everyday conversation, and even got teams writing songs about the purpose statement. It took hold because people got inspired and excited about it.
To learn how we helped another organization define its new DNA following a merger of equals, check out this case study .
Final Thoughts
Be purposeful when creating your company’s purpose statement so that it’s strategic, you have organizational buy-in, and it’s tied to business goals for the best outcome. Follow these steps so that your organization has a purpose statement that effortlessly describes why you exist and guides your company for the future in a way that sets you apart, and that employees, customers, and other key stakeholders know and believe in.
As you reflect on your company’s purpose statement, would it benefit from being updated?
—Kate Bushnell
This quick guide covers a methodology you can use to co-create your purpose statement and maximize leader and employee buy-in. Download Maximizing Strategy Development & Rollout with Top Leaders today!

Comments on this post
Other posts you might be interested in, 4 steps to harness the power of purpose and drive business transformation – guest blogger, tapestry's jennifer leemann, 4 ways leaders can take control of the great resignation, show you care: 4 must-have strategies to build feedback channels in your organization, subscribe to the leadercommunicator blog.
Get new blog posts delivered directly to your inbox.
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience.

Health & Nursing
Courses and certificates.
- Bachelor's Degrees
- View all Business Bachelor's Degrees
- Business Management – B.S. Business Administration
- Healthcare Administration – B.S.
- Human Resource Management – B.S. Business Administration
- Information Technology Management – B.S. Business Administration
- Marketing – B.S. Business Administration
- Accounting – B.S. Business Administration
- Finance – B.S.
- Supply Chain and Operations Management – B.S.
- Accelerated Information Technology Bachelor's and Master's Degree (from the School of Technology)
- Health Information Management – B.S. (from the Leavitt School of Health)
Master's Degrees
- View all Business Master's Degrees
- Master of Business Administration (MBA)
- MBA Information Technology Management
- MBA Healthcare Management
- Management and Leadership – M.S.
- Accounting – M.S.
- Marketing – M.S.
- Human Resource Management – M.S.
- Master of Healthcare Administration (from the Leavitt School of Health)
- Data Analytics – M.S. (from the School of Technology)
- Information Technology Management – M.S. (from the School of Technology)
- Education Technology and Instructional Design – M.Ed. (from the School of Education)
Certificates
- View all Business Degrees
Bachelor's Preparing For Licensure
- View all Education Bachelor's Degrees
- Elementary Education – B.A.
- Special Education and Elementary Education (Dual Licensure) – B.A.
- Special Education (Mild-to-Moderate) – B.A.
- Mathematics Education (Middle Grades) – B.S.
- Mathematics Education (Secondary)– B.S.
- Science Education (Middle Grades) – B.S.
- Science Education (Secondary Chemistry) – B.S.
- Science Education (Secondary Physics) – B.S.
- Science Education (Secondary Biological Sciences) – B.S.
- Science Education (Secondary Earth Science)– B.S.
- View all Education Degrees
Bachelor of Arts in Education Degrees
- Educational Studies – B.A.
Master of Science in Education Degrees
- View all Education Master's Degrees
- Curriculum and Instruction – M.S.
- Educational Leadership – M.S.
- Education Technology and Instructional Design – M.Ed.
Master's Preparing for Licensure
- Teaching, Elementary Education – M.A.
- Teaching, English Education (Secondary) – M.A.
- Teaching, Mathematics Education (Middle Grades) – M.A.
- Teaching, Mathematics Education (Secondary) – M.A.
- Teaching, Science Education (Secondary) – M.A.
- Teaching, Special Education (K-12) – M.A.
Licensure Information
- State Teaching Licensure Information
Master's Degrees for Teachers
- Mathematics Education (K-6) – M.A.
- Mathematics Education (Middle Grade) – M.A.
- Mathematics Education (Secondary) – M.A.
- English Language Learning (PreK-12) – M.A.
- Endorsement Preparation Program, English Language Learning (PreK-12)
- Science Education (Middle Grades) – M.A.
- Science Education (Secondary Chemistry) – M.A.
- Science Education (Secondary Physics) – M.A.
- Science Education (Secondary Biological Sciences) – M.A.
- Science Education (Secondary Earth Science)– M.A.
- View all Technology Bachelor's Degrees
- Cloud Computing – B.S.
- Computer Science – B.S.
- Cybersecurity and Information Assurance – B.S.
- Data Analytics – B.S.
- Information Technology – B.S.
- Network Engineering and Security – B.S.
- Software Engineering – B.S.
- Accelerated Information Technology Bachelor's and Master's Degree
- Information Technology Management – B.S. Business Administration (from the School of Business)
- View all Technology Master's Degrees
- Cybersecurity and Information Assurance – M.S.
- Data Analytics – M.S.
- Information Technology Management – M.S.
- MBA Information Technology Management (from the School of Business)
- Full Stack Engineering
- Web Application Deployment and Support
- Front End Web Development
- Back End Web Development
3rd Party Certifications
- IT Certifications Included in WGU Degrees
- View all Technology Degrees
- View all Health & Nursing Bachelor's Degrees
- Nursing (RN-to-BSN online) – B.S.
- Nursing (Prelicensure) – B.S. (Available in select states)
- Health Information Management – B.S.
- Health and Human Services – B.S.
- Psychology – B.S.
- Health Science – B.S.
- Healthcare Administration – B.S. (from the School of Business)
- View all Nursing Post-Master's Certificates
- Nursing Education—Post-Master's Certificate
- Nursing Leadership and Management—Post-Master's Certificate
- Family Nurse Practitioner—Post-Master's Certificate
- Psychiatric Mental Health Nurse Practitioner —Post-Master's Certificate
- View all Health & Nursing Degrees
- View all Nursing & Health Master's Degrees
- Nursing – Education (BSN-to-MSN Program) – M.S.
- Nursing – Leadership and Management (BSN-to-MSN Program) – M.S.
- Nursing – Nursing Informatics (BSN-to-MSN Program) – M.S.
- Nursing – Family Nurse Practitioner (BSN-to-MSN Program) – M.S. (Available in select states)
- Nursing – Psychiatric Mental Health Nurse Practitioner (BSN-to-MSN Program) – M.S. (Available in select states)
- Nursing – Education (RN-to-MSN Program) – M.S.
- Nursing – Leadership and Management (RN-to-MSN Program) – M.S.
- Nursing – Nursing Informatics (RN-to-MSN Program) – M.S.
- Master of Healthcare Administration
- MBA Healthcare Management (from the School of Business)
- Business Leadership (with the School of Business)
- Supply Chain (with the School of Business)
- Back End Web Development (with the School of Technology)
- Front End Web Development (with the School of Technology)
- Web Application Deployment and Support (with the School of Technology)
- Full Stack Engineering (with the School of Technology)
- Single Courses
- Course Bundles
Apply for Admission
Admission requirements.
- New Students
- WGU Returning Graduates
- WGU Readmission
- Enrollment Checklist
- Accessibility
- Accommodation Request
- School of Education Admission Requirements
- School of Business Admission Requirements
- School of Technology Admission Requirements
- Leavitt School of Health Admission Requirements
Additional Requirements
- Computer Requirements
- No Standardized Testing
- Clinical and Student Teaching Information
Transferring
- FAQs about Transferring
- Transfer to WGU
- Transferrable Certifications
- Request WGU Transcripts
- International Transfer Credit
- Tuition and Fees
- Financial Aid
- Scholarships
Other Ways to Pay for School
- Tuition—School of Business
- Tuition—School of Education
- Tuition—School of Technology
- Tuition—Leavitt School of Health
- Your Financial Obligations
- Tuition Comparison
- Applying for Financial Aid
- State Grants
- Consumer Information Guide
- Responsible Borrowing Initiative
- Higher Education Relief Fund
FAFSA Support
- Net Price Calculator
- FAFSA Simplification
- See All Scholarships
- Military Scholarships
- State Scholarships
- Scholarship FAQs
Payment Options
- Payment Plans
- Corporate Reimbursement
- Current Student Hardship Assistance
- Military Tuition Assistance
WGU Experience
- How You'll Learn
- Scheduling/Assessments
- Accreditation
- Student Support/Faculty
- Military Students
- Part-Time Options
- Virtual Military Education Resource Center
- Student Outcomes
- Return on Investment
- Students and Gradutes
- Career Growth
- Student Resources
- Communities
- Testimonials
- Career Guides
- Skills Guides
- Online Degrees
- All Degrees
- Explore Your Options
Admissions & Transfers
- Admissions Overview
Tuition & Financial Aid
Student Success
- Prospective Students
- Current Students
- Military and Veterans
- Commencement
- Careers at WGU
- Advancement & Giving
- Partnering with WGU
How to Develop Your Company’s Purpose Statement
- See More Tags

If you aspire to lead or start a company, you’ll play a crucial role in driving its vision, goals, and plan for success. A purpose statement establishes the foundation you need to do that effectively.
While some degree programs touch on the topic of purpose statements, you might not realize how this concept can apply to your future career .
Here’s how you can take the skills you’ve learned from your business degree and use them while writing an effective company purpose statement.
What is a Purpose Statement?
The first step to understanding a purpose statement is to distinguish it from a mission statement because each plays a different role in your business plan .
Mission Statement vs. Purpose Statement
A purpose statement is a single statement that defines the reason your company exists—beyond simply making a profit. It also illustrates how your product or service positively impacts the people you serve. Once your purpose is established, you’ll need a series of goals to drive that purpose. That’s where the mission statement comes in.
First and foremost, a mission statement is actionable. It explains the path you need to take to reach your purpose. So, while a purpose statement is focused on the future, a mission statement is rooted in the present.
Unlike a company mission, your company purpose isn’t something that can be completed or checked off a list. A purpose statement illustrates the ongoing pursuit to push your company forward.
What Does a Purpose Statement Do?
A purpose statement sets expectations, both internally (for leadership and employees) and externally (for customers and investors). It acts as your company’s blueprint for the future and helps guide all the decisions you make—from how you manufacture your products to the words you use in your marketing.
Your purpose also influences your customer. In fact, 63% of global consumers prefer to purchase products and services from companies that stand for a purpose, according to recent research.
The study found that companies that stand for something bigger than what they sell, communicate their purpose, and demonstrate commitment are more likely to attract consumers and influence purchasing decisions.
Leaders around the world are taking note of the rise of purpose-driven companies , too. Lise Kingo, CEO and executive director of the UN Global Compact, stated, “The idea of business as an agent of change and a purveyor of positive values is gaining traction and legitimacy around the world. With a growing number of companies taking steps to be more responsible in how they treat employees, communities, and the planet, we are seeing business emerge as a real player and solution-provider in the quest to put our world on a better course.”
Beyond attracting customers and increasing your bottom line, clarifying your company purpose is important for these reasons:
1. Distinguishes Your Business from Competitors
One important role of your purpose statement is to define what makes your company unique. After all, your competitors might be able to replicate your product or service, but they’d be hard pressed to duplicate your unique purpose.
People can be genuinely inspired if your company has a solid purpose. When customers and employees understand what drives your passion and ignites your purpose, they’re more likely to get on board with it.
2. Helps Meet Goals
A strong purpose statement sets a path for how your company will move forward, which will help you see and set clear goals. These goals should go beyond financial performance; they should also measure how your purpose is progressing toward the social impact you’re trying to make.
3. Informs Company Culture
A recent employee survey by Harvard Business Review found that only 28% of employees felt connected to their company’s purpose, and 34% thought they were contributing to their company’s success. According to the article, a lack of purpose among employees can create a negative company culture where employees feel unmotivated and unaligned.
So how do you avoid this?
Creating a purpose-driven culture starts with clear communication between employees and leadership—as well as listening and being open to feedback. When everyone understands and supports the company's purpose, it creates a united front where everyone from the top down is working toward the same goals.
Furthermore, multiple studies show a purpose-driven culture is a positive one. This is because employees feel more engaged and motivated when they can connect the work they do with how it contributes to the organization’s purpose .

How Do I Write a Purpose Statement?
Creating a company purpose statement is no small task. It requires a deep understanding of why your company exists and where it hopes to go in the future. If you’re still feeling stuck, here are some steps to take as you're developing your company's purpose.
Step #1: Define what you do.
But more specifically, lay out what your company does to solve a particular problem for your customers.
Step #2: Pinpoint your passion.
Think about what inspires the work you do. For example, are you passionate about creating sustainable products? Do you strive to be the most innovative? Are you focused on serving local communities?
Step #3: List your values.
Understanding the things your company is passionate about will help you come up with specific values that align with your purpose. Those values might include things like sustainability, innovation, integrity, quality, etc.
Step #4: Create a draft.
Once you’ve defined what you do and why you do it, take pen to paper and start drafting ideas for your purpose statement.
As you’re writing, make sure your purpose statement is:
- Short (about 1-2 sentences)
- Easy to understand
- Aspirational (but not vague)
Step #5: Get feedback.
Ask others in your organization to review what you’ve written and consider their feedback as you hone your purpose statement.
Step #6: Leave room for growth.
Keep in mind that a purpose statement is a constant work in progress, and changes will happen as your business evolves.
Examples of Effective Purpose Statements
Use these company purpose statements to draw inspiration from:
- Southwest Airlines lets its personality shine through in its purpose statement: “Connect people to what's important in their lives through friendly, reliable, and low-cost air travel.”
- Kellogg’s and Coke keep it short and sweet: “Nourishing families so they can flourish and thrive.” – Kellogg’s, “Refresh the world. Make a difference.” – Coke
- If you’re looking for an example of an empowering purpose statement, here’s Dove’s: “Discovering the value of 'real' beauty and improving self-esteem worldwide.”
- Both The Red Cross and Whole Foods have purpose statements that make an emotional connection: “Our deepest purpose as an organization is helping support the health, well-being, and healing of both people—customers, Team Members, and business organizations in general—and the planet.” – Whole Foods, “To protect life and health and to ensure respect for the human being .” – The Red Cross
- Crayola and Lego lean on their ability to inspire: “Encouraging children to be creative, and enabling parents to inspire them.” – Crayola, “To inspire and develop the builders of tomorrow.” - Lego
Now that you know what a company purpose statement is, why it’s important, and how to develop your own, you’ll be ready to put this important business skill into practice in your own organization.
Ready to Start Your Journey?
HEALTH & NURSING
Recommended Articles
Take a look at other articles from WGU. Our articles feature information on a wide variety of subjects, written with the help of subject matter experts and researchers who are well-versed in their industries. This allows us to provide articles with interesting, relevant, and accurate information.
{{item.date}}
{{item.preTitleTag}}
{{item.title}}
The university, for students.
- Student Portal
- Alumni Services
Most Visited Links
- Business Programs
- Student Experience
- Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion
- Student Communities
- Start A Project
How to Write a Purpose Statement for Your Company (+31 Examples)

Looking for tips on how to write a purpose statement for your company? Curious about what a purpose statement is, why it’s important, or even how it’s different than a mission statement?
Wherever you are in the process of understanding, identifying, or writing your company’s purpose statement, we have the information and insight you need to take the next step.
Articulating your business’s purpose in a clear, concise purpose statement is key to creating a more impactful brand . This is because purpose gets right to the heart of why you do what you do as a business. It speaks to profound reasons why employees and customers want to be associated with your brand.
In what follows, we’ll take a look why a purpose is so critical to your business’s success. We’ll unpack a purpose statement definition, look at purpose statement examples in the world’s most successful brands, and see how you can define a powerful purpose statement for your own brand.
What is a Purpose Statement?
The difference between a purpose statement and a mission statement, the benefits of a strong purpose statement, 5 qualities of a strong purpose statement, how to write a purpose statement, 31 purpose statement examples, the takeaway.
A purpose statement is a short sentence that describes the reason a company exists beyond making money. It is the singular answer to the most fundamental question an organization faces: “Why?”
Why does your business exist? What drives you to get out of bed in the morning to go to work? Why do you work long hours or make sacrifices to keep your business moving forward?
Purpose is the primary driver that motivates an organization, especially during difficult or challenging times. It is the impetus behind the action that leads to the impact .
Also known as a core purpose, business purpose, or company purpose, a purpose statement is an essential component of the brand compass , a strategic messaging system that also includes vision , mission , and values .

So, what’s the difference between a purpose statement and a mission statement?
The answer is fairly straightforward. Where a purpose statement describes the simple, profound idea behind why an organization exists, a mission statement is a more detailed account. Your mission statement outlines what you plan to do as an organization, how you plan to achieve it, and whom you’re doing it for.
You can think of your purpose statement as describing the emotional or philosophical motivation behind your business, while your mission statement is a strategic roadmap for your business’s success.

Organizational purpose isn’t just for environmentally or socially conscious brands, either. A well-crafted purpose statement that powerfully communicates your organization’s raison d’être is one of the best ways to connect with those you serve on a more profound, human level.
As we’ll see below, connections like these are a powerful way to boost brand loyalty among customers and employees alike. Let’s take a closer look some of the most immediate benefits of a strong purpose statement.
Attract & Retain Top Talent
Today’s employees are looking for more than competitive salaries and attractive benefits packages. The best talent out there wants to work for purpose-driven companies. This makes purpose an indispensable component to effective employer branding .
This fact has been borne out by multiple studies of late. Take the findings from Porter Novelli’s Purpose Perception Study , which surveyed 1,200 adults ranging in age from 18 to 69.
The study found that:
- 78% of employees are more likely to want to work a purpose-driven company
- 72% are more likely to be loyal to that company
- 72% are more likely to forgive that company if it makes a misstep
Not only does clearly defining and communicating your company purpose put your business in a more competitive position in the labor market, it also ensures that the employees you do hire will stick around longer. Reduced turnover means more cohesive company culture and better brand alignment . It also means the investments you make in your workforce will have larger, longer-term dividends.

The Brand Compass Course
Learn the secret to defining your company's Purpose, Vision, Mission & Values.
Improve Productivity
The benefits of a clearly articulated purpose don’t end with attracting talent and building culture. Business purpose is a powerful driver when it comes to employee productivity.
The simple truth is that inspired employees are more productive employees. As we’ve already seen, purpose gives your team motivation that goes beyond a paycheck and a benefits package. It gives them a reason to get out of bed in the morning.
When workers have a purposeful reason for putting in long hours that goes beyond mere financial compensation, they are more likely to see personal sacrifices as worth it. A more cohesive company culture filled with more motivated employees naturally leads to a more inspired, more productive team.
Inspire Your Customers
Where employees want to work for purpose-driven brands, customers want to buy from them. We see evidence of this fact borne out in study after study.
Porter Novelli found that purpose matters in important ways to vast majorities of consumers:
- 66% of customers consider a company’s purpose when making purchase decisions
- 78% are more likely to remember a company with a strong purpose
In today’s marketplace, it’s simply no longer good enough to compete on the basis of cost or quality alone. Today’s customers expect more from the businesses they engage with. They want to align themselves with brands that share their values. That starts with purpose.
Brands with a clearly defined, authentic sense of purpose will always have an edge in our increasingly socially conscious consumer landscape.
Meaningfully Differentiate Yourself from the Competition
Speaking of competition, your core purpose is one of the most profound ways to set your brand apart from similar brands in your industry.
Not only are customers more likely to recognize, remember, and engage with a purpose-driven brand, they’re also more likely to purchase it over the competition. In fact, 71% of customers say they would purchase from a purpose-driven company over the alternative when cost and quality are equal.
The fact is, if you haven’t clearly defined your purpose statement, you can’t very well build a purpose-driven brand. And if you haven’t built a purpose-driven brand, you’re missing out on a fundamental opportunity to create meaningful competitive differentiation , connect with customers, and gain market share.
The numbers don’t lie. Both internally and externally, business purpose is an essential ingredient of business growth.
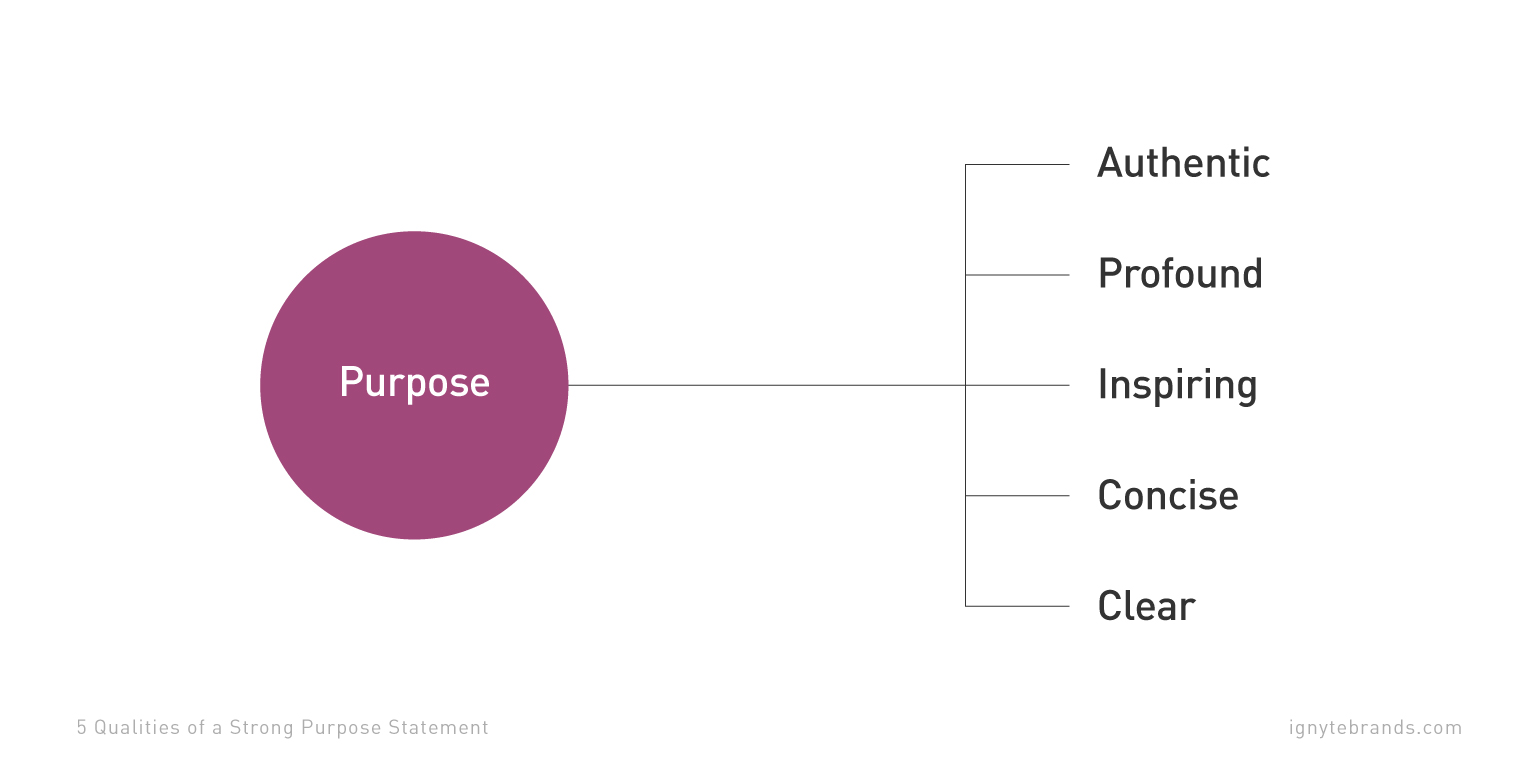
So, what separates a strong purpose statement from a less effective one? There are five qualities that every good business purpose statement should have.
A strong purpose statement is:
Purpose starts first and foremost with authenticity. The two ideas are inextricably linked. So, what does it mean for a company purpose to be authentic?
An authentic purpose statement is one that is borne from an honest accounting of who you are as an organization, where you started, and where you’re headed. It is a genuine sentiment that reflects your true character and values and that’s aligned with your brand positioning .
An authentic purpose is ultimately also a human idea. It isn’t about your own business’s growth but about the change you hope to affect in the world. Which is a good segue to our next essential quality of every strong purpose statement.
A strong corporate purpose isn’t just honest and genuine, it’s also deep and meaningful. Your purpose should mean something—both to those within your organization and to those you serve.
A profound purpose is an idea that makes people think. It should convince both your customers and your employees that you stand for something beyond quarterly reports and balance sheet figures.
Many brands find profound purpose in environmental and/or social impact, but not every purpose has to be centered on an ESG-oriented value proposition . A profound purpose can be as simple as making the world a happier, safer, or more enriching place.
The best purpose statements aren’t just authentic and profound, they are also inspiring. Your purpose, remember, is the reason you do what you do as an organization. It is by its very definition a motivational idea.
Describing that motivation in a way that inspires people to act is the best way to get the most mileage out of your purpose statement—and build brand equity in the process. Your purpose statement should inspire your employees to find deeper meaning in the work they do, giving them the impetus they need to push through challenging times.
Your business purpose statement should also inspire your customers. Not just to buy your products and services (although, as we’ve seen, that’s one of the most tangible benefits of a well-crafted purpose), but also to associate themselves with your brand. Customers inspired by purpose will always be your best brand advocates.
A quick Google search will turn up business purpose examples of all shapes and sizes. This includes long, run-on sentences that unpack not just why a company does what it does, but also what, how, and for whom. As is the case with nearly all writing, however, the best of the bunch are the shortest ones.
A purpose statement should be as concise as possible for two reasons. One, your organizational purpose is the answer to one question and one question only: why? Second, the shorter the statement, the more powerful it becomes.
You’ll see this firsthand in the purpose statement examples we’ve collected below. While we limited our list to the best purpose statements we could find, you’ll see that even among these highlights, the shortest and simplest statements outshine the others.
Take Netflix’s “To entertain the world” or Kroger’s “To feed the human spirit.” Both leave little room for doubt when it comes to the profound reasons why these companies exist—and do so in as few words as possible.
The final quality of a strong purpose statement is clarity. After all, your corporate purpose can be as authentic and concise as possible, but if it’s vague or ambiguous it won’t be very meaningful or inspiring to those who hear it.
A clearly stated core purpose is one that isn’t too abstract or philosophical. It doesn’t beat around the bush when it comes to plainly answering the question “why?”
We’ll explore more about how to craft a clear, concise purpose statement in our next section, but suffice it to say that when it comes to communicating the singular reason your business exists, clarity is kind.
Think of the five essential qualities above as the ultimate criteria for the final draft of your purpose statement. But one of the keys to writing a strong purpose statement is not to worry too much about checking all of the boxes when you first get started.
Let’s take a closer look at what the process looks like when you’re ready to write your company purpose statement.

So how do you write a business purpose statement of your own? We’ve boiled it down to three simple steps that are sure to result in an effective and impactful statement.
1. Identify Your Purpose
The first step in the process is brainstorming and ideation. This is the “no bad ideas” phase, where the goal isn’t to worry about conciseness or clarity, but rather to come up with a handful of ideas to choose from.
Put together a small team of your most creative minds in front of a whiteboard and start by asking yourself the following questions:
- Why do we exist as an organization?
- Why do we do what we do as a business (beyond making money or increasing shareholder value)?
- What positive change are we looking to affect in the world?
- Why do we get out of bed in the morning to go to work (beyond a paycheck)?
- What is it that drives us to put in extra effort or push through challenging times?
- Why do we work long hours or put up with the occasional unruly customer or make any of the sacrifices we do to keep our business moving forward?
Once you have a handful of ideas, try to identify a single idea or theme that is behind them all. The goal is to get to the heart of why you do what you do.
Pro tip: if you think you’ve put your finger on it, ask “why?” again. Is it to better your community? To make people happy? To make the world a safer place? You’re looking for a central, profound idea behind everything you do.
Imagine yourself as the precocious, insatiably curious kid, who keeps asking why until you get to the heart of the matter.
2. Articulate Your Purpose
Once you think you’ve hit on the idea that is at the root of why you do what you do, the next step is to craft it into a purpose statement.
Now, because purpose statements are essentially answers to the question “why?” most of them take a similar format.
So, “Why do you do X?”
“We do X to Y”
Or, more simply:
Purpose statements that start with an infinite verb like this are by nature actively oriented. And actively oriented statements will always be more inspiring and motivational than passively oriented statements.
Try following a similar format with your purpose statement. In the sentence, “We do X to Y,” what are your X and Y?
Maybe you “sell electric vehicles to keep people moving.” Or maybe you “design cutting-edge apps to navigate the world.” Or perhaps you “produce fertilizer to make the world a greener place.”
Whatever your answer might be, whittle it down to just the Y:
To keep people moving.
To navigate the world.
To make the world a greener place.
Remember, when it comes to purpose statements, the shorter the better. Try to boil it down to a single idea and aim for no more than 6 or 7 words. Don’t worry about the “what” or “how.” The goal is not a statement that says “To do X because of Z so that Y.” You’re just looking for “To Y.”
3. Communicate Your Purpose
The final step of any good purpose statement is to use it as inspiration throughout your business. As we’ve already seen, purpose should be at the very heart of everything you do as an organization.
From your business model to your branding to your marketing and beyond—all of it makes more sense and is more impactful when you start with “why.”
Internally, your purpose statement should be an integral part of brand compass messaging that your entire team is familiar with. It should be documented in your brand guidelines and be used as a cornerstone of internal communications.
Externally, your organizational purpose should be the starting point for your brand story . As we’ll see in out next section, the world’s most compelling brands are those with purpose-driven brand experiences .
Customers instinctually gravitate towards brands with an authentic sense of purpose that shines through in everything from their brand messaging to their brand design .

Purpose has become increasingly more important to Fortune 500 brands like those listed here. Let’s take a look at how these brands have articulated their purpose statements—and leveraged them to build more meaningful connections with those they serve.
AT&T’s Purpose: “To connect people to greater possibility – with expertise, simplicity, and inspiration.”
BlackRock’s Purpose: “To help more and more people experience financial well-being.”
Coca-Cola’s Purpose: “Refresh the world. Make a difference.”
CVS’s Purpose: “Bringing our heart to every moment of your health.”
Intel’s Purpose: “To create world-changing technology that improves the life of every person on the planet.”
Kohl’s Purpose: “To inspire and empower families to lead fulfilled lives.”
Kroger’s Purpose: “To feed the human spirit.”
MetLife’s Purpose: “To help our customers navigate life’s twists and turns.”
Ralph Lauren’s Purpose: “To inspire the dream of a better life through authenticity and timeless style.”
Target’s Purpose: “To help all families discover the joy of everyday life.”
Verizon’s Purpose: “To give people the ability to do more.”
Walgreens’ Purpose: “More joyful lives through better health.”
Walmart’s Purpose: “To help people save money so they can live better.”
REI’s Purpose: “To awaken a life-long love of the outdoors.”
Amazon’s Purpose: “To be Earth’s most customer-centric company.”
Netflix’s Purpose: “To entertain the world”
Disney’s Purpose: “To entertain, inform and inspire people around the globe through the power of unparalleled storytelling.”
Google’s Purpose: “To organize the world’s information”
Zappos’s Purpose: “To deliver WOW.”
Red Bull’s Purpose: “To give wings to people and ideas”
Lyft’s Purpose: “To improve people’s lives with the world’s best transportation.”
Adidas’s Purpose: “Through sport, we have the power to change lives.”
Apple’s Purpose: “To empower creative exploration and self-expression.”
Chobani’s Purpose: “To make better food for more people.”
IKEA’s Purpose: “To create a better everyday life for the many people.”
Lego’s Purpose: “To inspire and develop the builders of tomorrow.”
SAP’s Purpose: “To help the world run better and improve people’s lives.”
Microsoft’s Purpose: “To empower every person and organization on this planet to achieve more.”
Airbnb’s Purpose: “To help people to belong anywhere.”
Tesla’s Purpose: “To accelerate the planet’s transition to sustainable energy.”
Patagonia’s Purpose: “To save our home planet.”
A powerful purpose statement is one of the best ways to foster brand loyalty and build brand equity. By identifying your organization’s reason for existing beyond making money and articulating a clear, concise, and authentic statement that communicates that reason, you can set the stage for creating deeper connections with customers and employees alike.
Take inspiration from the growing list of Fortune 500 brands, whose business purpose examples are listed above. Few things are more powerful than purpose when it comes to creating a profound brand experience that speaks to audiences on a deeply human level.

The Ultimate Guide to Rebranding
Everything you need to know about rebranding your business-and avoiding costly mistakes.
Brian Lischer

The Ultimate Guide To Rebranding
Everything you need to know about rebranding your business - and avoiding costly mistakes.
About Ignyte
We help businesses grow by transforming their brands into valuable business assets that inspire employees, motivate customers, and generate lasting economic value.
Subscribe to Brand Thinking
Get our latest posts delivered straight to your inbox.

Brand Coaching
Fuel Your Brand’s Growth with 1-on-1 Coaching from Ignyte Founder, Brian Lischer.

What Is a Brand?

5 Ways to Recession-Proof Your Brand

4 Surefire Ways to Align Your Brand Internally
- QUICK LINKS
- How to enroll
- Career services
How to write an effective business statement of purpose

By Michael Feder
This article has been vetted by University of Phoenix's editorial advisory committee. Read more about our editorial process.
This article has been reviewed by Kathryn Uhles, MIS, MSP , Dean, College of Business and IT
At a glance
- A purpose statement is a one- or two-sentence statement that defines a company’s purpose and goals.
- A purpose statement is similar to a mission statement or vision statement , but whereas those exist primarily for internal employees and stakeholders, purpose statements are designed for customers as well.
- Want to learn how to write an effective purpose statement and other business skills? Check out online business degree programs at University of Phoenix.
What is a purpose statement?
Every business, regardless of size, industry or revenue structure, needs a purpose statement. The statement should capture a company’s purpose, vision and values and summarize its main goal in one or two sentences.
A purpose statement is a single, concise, declarative statement that identifies why a company exists. It is shared with customers and helps inform business decisions by outlining a business’s direction and how it aims to inspire and positively impact others.
Just like social capital , a purpose statement can cultivate goodwill with customers . People may prefer buying from, or partnering with, companies that maintain a high moral standard . It’s important for companies to maintain those high standards, both for customer visibility and to drive operations forward.

Purpose statement vs. mission statement vs. vision statement
A mission statement, vision statement and purpose statement sound similar, but they actually fulfill different roles. A mission statement best describes a company’s overarching goal . A vision statement is a declarative statement about a company’s purpose . Both statements are often only shared internally with employees or key stakeholders.
Mission statements should describe an organization’s reason for existing. They might describe the mindset of a business’s leaders, list and define core values, or describe how a company inspires to improve or change the world.
A purpose statement, meanwhile, defines a company’s purpose as a means to direct activities . It is meant to be shared not only internally but also with potential customers or brand participants.
To this end, purpose statements should address customers and connect what the business does with whom it does it for. Consider this a person-first version of the mission statement , with customers at the center of a business’s objectives.
What makes a purpose statement effective?
Several elements go into writing an effective purpose statement. When creating one for your company, make sure you prioritize elements like clarity, honesty and an understanding of your business’s sector .
Even if potential customers aren’t familiar with your brand, they should be able to understand what you do just by reading your statement. Make it concise, use active verbs and eliminate unnecessary details so you can focus on your main, customer-focused goals .
Exaggerating or including false information can harm your business. Misrepresentations of your company can lead to overpromising and underdelivering — two of the quickest ways to alienate customers.
For best results, be transparent and accurate .
Positioning
An honest purpose statement should also highlight what makes your company stand out from the competition. This element requires an understanding of your industry and a strong competitive analysis .
Try to help potential customers choose your business over the competition by highlighting your organization’s advantages, all while being careful not to belittle other companies.
read similar articles

What is a business model? Components, types and examples
How to write a purpose statement.
When writing a purpose statement for your organization, address your target audience while emphasizing elements that make your company different from the rest. You will need to decide who writes and contributes, and who can provide feedback about how the statement resonates with employees.
1. Decide who will write the purpose statement
First and foremost, decide who will write the statement. This may not be easy, particularly for companies with large marketing departments and multiple executives. Some companies might have several employees who want to write or contribute. In other cases, it might be difficult to find anyone to volunteer.
For best results, make sure someone with a business background writes your organization’s purpose statement. Ideally, this person should have a business degree that included course content in operations, communication and business management.
The best purpose statements are sometimes written by employees with a master’s degree in business . These individuals can leverage executive-level business leadership and administration skills to create something that resonates with all company representatives.
If your company can’t agree on one person, consider making the statement a collaborative effort . Schedule a meeting or two when everyone can share their thoughts. You can use the ideas to form the initial draft before distributing it throughout the company for feedback.
2. Address your audience
Your purpose statement should be all about your audience. Keep it directed toward your potential customers and describe the elements of your organization that might appeal to them.
This is an opportunity to describe your company’s reason for existence , with customers as your direct audience. Craft the messaging with the recipients in mind, and don’t be afraid to emphasize how important customers are to the company’s continued success.
3. Consider what makes your company stand out
Your company is unique no matter how many other competitors might be in your field. Your statement should highlight your company’s unique features as compared to every other company operating in your sector and should align with your overall business plan.
Focus on the goods and services that make you a better fit for customers than other providers. To do this, you’ll need consider everything that makes your company stand out. This step is vital when starting a new business since it will help you focus on your organization’s best qualities.
4. Get feedback
No matter how confident your company might be in the first draft of your purpose statement, it’s still a great idea to get feedback . Give internal employees the chance to read the statement, and remain open to what they have to say about it.
Getting feedback while drafting your purpose statement can help you gain a fresh perspective on your business. You’ll learn to view your company through other employees’ eyes. You’ll also achieve a more complete definition of your company’s purpose.

Examples of strong purpose statements
So, how do you pull it all together? Indeed.com has some examples , including:
- “We strive to protect wildlife through education about endangered species.”
- “Our purpose is to bring awareness to the need for medical supplies in overpopulated cities.”
- “We work toward building a safe and secure community by implementing emergency calling systems.”
Joseph Aranyosi, associate dean of the College of Business and Information Technology at University of Phoenix, offered a few more:
- “Our purpose is to provide sustainable food alternatives that can help to minimize greenhouse gases and reduce global warming.”
- “We offer affordable healthcare options for low-income patients to proactively address medical issues and reduce healthcare costs.”
- “We develop automated customer service solutions and custom-built social media apps to promote small business growth.”
Gain critical business skills with an online degree
University of Phoenix offers several business degrees that prepare students with skills for a variety of career paths. Whether you’re looking to build the fundamentals or advance your skill set, there’s a degree program for you. Here are just a few online business programs at University of Phoenix to consider:
- Associate of Arts with a concentration in Business Fundamentals — From management to accounting, the skills learned in this program are essential for anyone looking to advance their business education.
- Bachelor of Science in Accounting — Businesses around the world rely on skilled accountants to manage their finances and make profitable business decisions.
- Bachelor of Science in Business — Knowledge of the ins and outs of running a business can spell the difference between success and failure in a competitive business world.
- Bachelor of Science in Communication — It’s one thing to have a great idea, it’s another to properly communicate that idea to a large audience. Develop skills to be a media relations specialist, copywriter and more in this degree program.
- Master of Business Administration — Advance your business skills beyond the fundamentals and prepare yourself for higher leadership roles. This degree program can prepare graduates for careers as business managers, operations directors and more.
- Master of Management — Take your understanding of business organization and management to an advanced level. This degree program is perfect for those with experience in the workforce who are looking to take on greater leadership roles.
- Doctor of Business Administration — Expand your understanding of organizations, work environments and industry. This program invites participants to delve into cutting-edge research in the field of business and develop skills for solving complex organizational problems.

ABOUT THE AUTHOR
Michael Feder is a content marketing specialist at University of Phoenix, where he researches and writes on a variety of topics, ranging from healthcare to IT. He is a graduate of the Johns Hopkins University Writing Seminars program and a New Jersey native!
want to read more like this?

What Is Design Thinking and Why It Matters
Career support.
June 16, 2022 • 12 minutes

UNPUBLISHED Why Future Leaders Need to Understand Learning Styles
June 15, 2022 • 5 Minutes

What Can You Do With a Finance Degree?
Online degrees.
September 14, 2023 • 11 minutes
Search the site:
- WordPress Retainers
- Enterprise Development
- Maintenance & Support
The Essentials of Writing a Powerful Business Purpose Statement
Businesses today share fundamental corporate and social commitments. They seek to inspire the community, attract talent, and out-originate competition. And more and more of them have a purpose that goes beyond profit.
Crafting your Business Purpose Statement is a pivotal step in the early stages of identifying your enterprise’s core values and objectives. It’s the single line that encapsulates the very reason for your company’s existence, serving as a testament to your branding efforts.
A business’s purpose statement mirrors the connection between your core products and services and the positive impact they have on people’s lives. This statement acts as a compass for your company’s daily decisions, guiding your go-to-market strategies and initiatives.
In this article, we have prepared a few tips to help you write a powerful business purpose statement as well as practical guidelines on how to craft it well.
The Differences between Purpose, Mission, and Vision
Before we walk you through the specifics, we would like to make some important distinctions. Namely the differences between vision, mission, and purpose.
- A vision statement describes what your business is looking forward to and working towards. It’s the what of your organization.
- A mission statement outlines the process of turning your vision into a reality. It’s the how of your company.
- A purpose statement sets your reason for doing what you do. The why of your venture’s existence.
The three types of statements reflect different aspects of your organization’s operations and differ in the questions they answer. However, they are closely related plans of action that can help you deliver what your company is ultimately fighting for.
Without further ado, let’s get into the nitty-gritty of how to make your brand stand out with a strong and well-defined purpose statement.
1. It Should Inspire and Show Personality
Defining your purpose statement is a process. Adding the right words to correctly depict the reason for your company’s existence is a bit harder than you may imagine. The answer to your business’s “why” may seem obvious to you, but the key is to ground it in reality and communicate it to your audience successfully.
Start by reflecting on how your company came to be – the reason for creating it, the challenges you’ve overcome, the lessons you’ve learnt and the values you’ve adopted.
If you are an emerging entrepreneur with a completely new venture you can also apply this approach, but in a more personal context. Look back at the significant turning point that prompted you to become a business owner.
If you’re an established business with a long history of success, you can acknowledge the milestones of your firm’s growth. You can identify and define your business heritage and pin-point the specific characteristics of your brand that made it stand out all these years.
Make sure your purpose statement doesn’t include buzzwords or jargon. Use simple and clear language to directly communicate what your company’s here to accomplish.
2. It Should Play a Role with an Outcome
Since your purpose statement answers your company’s why it should set the outcome of what your business ultimately wishes to achieve and see out there.
Start your research by talking to your leadership. Ask them various questions and summarize the recurring themes.
Here are some examples:
- Why are you in this business?
- What do you like the most about working in the company?
- What image do you think the company conveys to the outside world?
- How do you feel about this image? What do you like and dislike about it?
- What specific challenges does the company solve?
- What do you think the purpose of the company is?
- What makes this business different from competitors’?
- Who are the target customers?
- What do you think they value most about this company?
- How do you think the company’s products and services reach their business goals? Do you think it’s effective? Would you say they reflect the business’s purpose?
- What are five words you would describe the company and its culture with?
- What underlying principles and philosophies shaped your responses to the previous questions?
Make sure you involve every leadership member . Think carefully about what you want to ask them. Form clear questions and take detailed notes.
Word your company’s purpose in a way that inspires room for thoughts while directly underlining your organization’s value proposition.
3. It Should Be Short, Yet Powerful
Your business purpose should be credible and easy to remember, especially by your employees. They are your most important resource and every one of them can influence how your organization is represented outside your office walls.
Your employees provide an essential link between you and your customers. Their energy can be a powerful asset to ensure that the entire organization leads with purpose. If they are happy, motivated and find a sense of fulfilment, they can be strong ambassadors of everything your brand stands for.
To find out how your employees feel about the purpose of your company you can ask them questions like:
- What inspired you to apply to this company?
- What do you like the most about working there? What makes you feel proud about it?
- How do you think the company’s products/services help customers?
- In what ways do you identify yourself with the company?
- What do you think is the company’s purpose? How would you put it in a few words?
- Do you think the purpose is reflected in the company culture?
Being in sync with your employees can help you make your business more agile and more responsive to challenges.
Always remember that your employees bring to light your purpose. The better it sticks in their minds the more natural it will be for them to communicate through their work.
4. It Should Create Space for Innovation and Growth
You’ve reflected back on how your organization has matured. You’ve sought and gained employee and leadership insights. Now, it’s important to identify the events and trends that can affect the social, political, economic and technological contexts that your brand operates in.
Maintaining a clear understanding of the present and the ability to anticipate and study future trends can set you apart. Align your Business Purpose Statement with real-world contexts to give it tangible meaning. This clarity allows you to understand opportunities more deeply, challenge the usual way of doing things, find the best solutions, and build on ideas. Hence, a compelling purpose statement may sometimes be wrestling with conflicting tensions all for the sake of fostering innovation and growth.
Purpose statements that fall into this category include:
With this statement, Workday showcases that there’s a possibility of instilling the human aspect into software and that it’s what they strive for.
With this statement, JetBlue deals with the tension that there are no boundaries to great customer experience.
5. It Should Be Aspirational and Precise
Your purpose statement should give a sort of tingle – a burst of inspiration and excitement. It should make your company want to strive to grow, to innovate, and to set an example. So, adding a pinch of emotion helps everyone involved to embrace it as their own.
The purpose of your business should reflect rational reasons for which it can supercharge your brand, culture, and business strategy as well as your organization’s ethics. Simply stating something, doesn’t make it come to life. Hence, a meaningful purpose statement should be able to influence a good purpose in practice. It should be aspirational and precise, expanding your organization’s opportunities for growth.
A vague example goes like this: “To make the world a better place”. A good example is more like this:
Additionally, your purpose statement can have a general or a social focus. Some companies have a more general statement, which doesn’t necessarily involve a social or environmental aspect.
An example of this is Airbnb’s statement:
It’s precise and showcases the company’s commitment to helping people travel like locals and experience a sense of community they wouldn’t be able to find in a hotel
This doesn’t mean that Airbnb doesn’t care about social or environmental issues. It simply means that it’s not at the very core of their existence.
To show you the difference, a business with a good social purpose is Patagonia:
6. It Should Evolve with Time
Purpose isn’t something that can be achieved once and for all. Companies grow, the business and social contexts change and your purpose statement should stretch along with these. It should always push your team further and it should set the stage for an inexhaustible series of new goals.
Let’s take Tesla as an example. Their original statement was:
But their current statement is:
The change from transportation to energy reflects also the shift in Tesla’s priority from an electric vehicle company to developing technology that makes sustainable energy more accessible.
Benefits of a Powerful Purpose Statement
Your company’s purpose statement establishes your business´s unique and inimitable attributes. It provides your brand with a competitive advantage and it acts as a guide for overcoming unprecedented challenges. It sets the tone that moves your organization forward, but it’s meaningless if not backed by solid and measurable commitments.
We hope our guide can help you create a defined and powerful business purpose statement for your organization. In fact, we would love to see what you’ve crafted, so don’t hesitate to share it with us in the comments below.
Realizing Your Business Idea
DevriX is a full-service WordPress development agency. We are not only offering web development services but rather an expert team of specialists that can advise you through every step of building your online presence.

Team DevriX
This article is crafted by DevriX's seasoned marketing team, boasting over four decades of collective expertise in crafting sophisticated marketing funnels, devising comprehensive content frameworks and pillars, implementing engaging email campaigns, and creating impactful social media content designed for scalability.
Our marketing experts specialize in the complete spectrum of inbound marketing strategies. As an accredited HubSpot Agency Partner and a Semrush Partner, we engage in meticulous research, blending our extensive experience with the unique insights of our highly skilled team.
We set benchmarks in content creation by incorporating cutting-edge marketing trends, leveraging in-depth industry research, and utilizing state-of-the-art AI tools for data segmentation and captivating content hooks. Our proficiency extends across a diverse range of sectors, including working with SMEs, Fortune 1000 companies, global B2B brands, major publishing entities, WooCommerce platforms, business directories, and affiliate networks.

The Poetry of Purpose: Inspirational Purpose Statement Examples
Discover what an effective purpose statement is, read insightful purpose statement examples, and learn how to drive your career, projects, or business.

Directing a business, a project, or even your own career can be an uphill battle if you lack a central point of focus and purpose.
What do you hold onto when priorities seem muddled? How do you lead your team toward shared goals? How do you assure clients that you’re on the same page as them?
That’s what a well-crafted and clearly defined purpose statement is for.
Whether you’re drafting a purpose statement for personal development, a project, or a business, this guide is made for you. Dive in to get a sharper understanding of what a purpose statement is and how to write one — plus, inspiration from insightful examples.
What are purpose statements?
A purpose statement or vision statement explains your “why.” It helps others understand why you do what you do.
However, a purpose statement isn’t just about setting goals or making plans — it’s also about giving those goals and plans real meaning. It’s what adds soul to the process.
There are three main kinds of purpose statements: personal (for you), project (for a specific task), and business (for a company). Each of these is crafted to address the unique needs, challenges, and aspirations of its particular area, but they all share the same aim: to bring about clarity, direction, and motivation.
Personal purpose statement
A personal purpose statement highlights what drives you, your goals, and what you truly care about. It covers not only where you want to go but also why you want to go there and the principles you’ll honor along the way.
A personal purpose statement has transformative power, bringing clarity to the chaos, direction amid distractions, and an unwavering foundation when life’s storms hit.
A helpful tip to help you craft your purpose statement is to reflect on moments in the past when you felt most fulfilled or when you made a difference, no matter how small.
With a personal vision statement, every choice and step you take is anchored to something bigger. Crafting one can improve your quality of life, filling your days with purpose, depth, and contentment.
Project purpose statement
A project purpose statement includes a clear declaration of the intent and goals of a project. It provides detailed information about the project objectives, the method that will be used to achieve them, and the values the project aspires to uphold.
Clearly defined objectives lay out the expected outcome of the project. Whether it’s the development of a new software solution or the unveiling of a new product line, these objectives need to be communicated so everyone involved has a clear understanding of what to aim for.
The method, or the plan of action, is where the project scope is defined. The scope outlines the specific steps, the extent of the work to be done, and the limits of the project. Defining the project scope helps manage expectations and ensures that resources are used efficiently and the project remains on track.
Values serve as the ethical cornerstone of a project. They set the guiding principles for decision-making so that the project upholds its integrity in the face of challenges.
One of the main benefits of a project purpose statement is its ability to bring clarity and alignment, which increases team engagement. In fact, 78% of adults are more likely to want to work for a company that leads with purpose. A project purpose statement ensures all involved stakeholders are on the same page, which is essential for building trust and motivating team members.
Business purpose statement
A business purpose statement defines a company’s core values, goals, and mission. It goes beyond profit margins and product lines to capture the overarching ethos and culture that the business champions.
A business purpose statement is instrumental in integrating strategies for team collaboration . Having a clear vision and values ensures that everyone in the company, regardless of their position, shares the same objectives. This unified approach fosters a more cohesive, efficient, and motivated work environment in which everyone feels they are contributing to a shared goal.
Moreover, when a company is clear about its purpose, this resonates with customers. Notably, 71% of consumers prefer to buy from a company with a strong purpose.
Purpose statement vs. value statement vs. mission statement
“Purpose statement,” “value statement,” and “mission statement” are common buzzwords in the workplace. But how do they differ? Let’s take a quick look at each of them, using the golden arches of McDonald’s as our guide.
Purpose statement
A purpose statement addresses the reason a company exists. It is the driving force for what a company hopes to ultimately achieve. McDonald’s purpose is “to feed and foster communities,” which emphasizes its commitment to not just serving food but also positively impacting communities.
Mission statement
A mission statement is about the present moment and how the company operates day-to-day to fulfill its purpose. It’s more specific and action-oriented than the purpose statement. McDonald’s mission , “Making delicious feel-good moments easy for everyone,” shows that its daily objective is to provide enjoyable and convenient meals.
Value statement
A value statement articulates the principles and beliefs that guide a company’s actions and decisions. It represents the company’s core ethics.
Here is McDonald’s value statement:
Serve: We put our guests and people first.
Inclusion: We open our doors to everyone.
Integrity: We do the right thing.
Community: We are good neighbors.
Family: We get better together.
These values outline the principles that dictate how Mcdonald’s conducts business and interacts with stakeholders.
Purpose statement examples
Ever stumbled upon a phrase or slogan from a brand that made you nod in agreement or even see the company in a new light?
That’s the power of an inspirational purpose statement. Looking at purpose statement examples is like window shopping for ideas and inspirations. It can guide you in finding your own words and direction.
Moreover, reading the purpose statements of businesses you admire can help you consider your own priorities and goals.
Personal purpose statements
A personal purpose statement offers a clear view of what fuels your passion and shapes your choices. Merging this clarity into your work can lead to more meaningful experiences and connections.
Here are some examples:
- “I am committed to maximizing my daily output and making the most of my day doing productive tasks.”
- “Building bridges, not walls, in teamwork is my mantra; I believe in harnessing collective strength through collaboration.”
- “Every challenge is a stepping stone, and I aim to achieve success by facing every obstacle head-on.”
- “Clear, open, and effective communication is the foundation of all my interactions, as I value clarity and mutual respect.”
- “I prioritize meaningful relationships, nurturing trust, understanding, and growth in every personal and professional connection.”
Why are personal purpose statements effective?
These statements provide clear direction and intent. They’re concise yet powerful because they convey the individual’s core values and principles in each respective domain.
Project purpose statements
A project purpose statement explains the core objectives and values of your initiative. It paves the way for more structured, impactful, and meaningful outcomes.
Here are some guidelines for writing your statement:
- Productivity: “Our goal is to work smarter and boost our daily output by 20% by optimizing existing workflows.”
- Delivery: “We aim to deliver our products on time, making sure 95% of our orders get to our clients when promised.”
- Time management: “With meticulous planning and execution, we will reduce turnaround time by 15%.”
- Teamwork/collaboration: “Our project should include the contributions of every team member, leading to a collective achievement of our goals.”
- Innovation: “To drive forward-thinking solutions in the 21st century, we will push the boundaries of what’s possible and encourage continuous improvement.”
Why are project purpose statements effective?
When employees understand a project’s value, they feel a heightened sense of purpose and are more committed.
Business purpose statements
A well-written business purpose statement inspires trust, loyalty, and motivation within not just the team but also customers. Sixty-three percent of employees say that they feel motivated in companies that clearly define and communicate value to customers.
Take a look at these real-world examples:
- Satisfying customers: Amazon’s vision is “to be Earth’s most customer-centric company, where customers can find and discover anything they might want to buy online.”
- Business values: Patagonia believes in “building the best product, causing no unnecessary harm, and using business to inspire and implement solutions to the environmental crisis.”
- Taking care of employees: Starbucks promises “to nurture and inspire the human spirit — one person, one cup, and one neighborhood at a time.”
- Commercial success: Apple aims “to bring the best user experience to its customers through its innovative hardware, software, and services.”
- Innovation: Tesla, the pioneer of electric vehicles, is on a mission “to accelerate the world’s transition to sustainable energy.”
Why are purpose statements effective?
Purpose statements like these resonate deeply with both employees and consumers. With 66% of consumers factoring in a business’s purpose during purchase decisions, clear objectives and values hold great sway.
How to utilize purpose statements
While crafting a powerful purpose statement is important, you need to weave it into the very fabric of your organization to maximize its impact. It’s not enough to simply have a purpose statement — the real magic happens when it’s applied and practiced daily.
As we dive deeper into this section, we’ll explore practical ways to breathe life into your purpose statement and make it a tangible force that drives your business.
Using personal purpose statements
Personal purpose statements can give you daily motivation and guidance in the workplace. Here are some strategies you can implement to integrate your personal purpose statement into your professional life:
1. Mindful morning rituals
Win the morning, win the day.
Start your day off by reflecting on your purpose statement. Use Motion to set a recurring reminder each morning, prompting you to read and meditate on your statement. This practice will help set the tone for the day and align you with your core purpose.
2. Task prioritization
Every task carries its own weight and significance. So move the ones that align most closely with your purpose statement to the top of your to-do list.
Motion can help you automatically prioritize your daily tasks based on your goals so you’re consistently focused on what matters most to you.
3. Reflective reviews
At the end of the week, use Motion to track and review the progress you’ve made. This is an easy way to reflect on your accomplishments and assess how they fit into your personal purpose statement. It not only gives you a sense of achievement but also provides insights into areas that need improvement.
Using project purpose statements
Having a well-defined project purpose statement and integrating it into the way you manage your teams, tasks, and workflows can help you stay aligned with your core purpose.
Seventy percent of employees say that their sense of purpose is defined by their work. This makes an effective project purpose statement essential for getting your team on board and improving their sense of purpose.
Here are some strategies you can use to integrate a purpose statement into your projects:
1. Frequent reiteration
At the beginning of each meeting or brainstorming session, revisit the project’s purpose statement. A brief reminder can keep everyone focused and on track.
2. Visual displays
Incorporate your purpose statement into project documentation, dashboards, or even as a pinned note in a collaboration tool.
For example, Motion lets you attach documents, spreadsheets, pictures, and more to a project or task. Having your project purpose statement visible can serve as a constant touchstone on which to base your decision-making.
3. Communication alignment
Leverage communication tools, like Motion, to announce your purpose statement and gather feedback.
Open and public communication ensures that everyone understands and buys into the purpose, fostering a collective commitment.
Using business purpose statements
Implementing an effective business purpose statement means aligning all employees, directing the company, and sharing the vision with clients and potential customers.
Consider the following strategies to integrate your business’ purpose statement:
1. Employee onboarding and training
From day one, introduce new hires to the company’s purpose statement. Make it a central part of their onboarding orientation.
Use Motion’s meeting assistant to schedule regular training sessions with the team. Doing this can help emphasize your business purpose statement’s significance and help everyone uphold it.
2. Marketing and branding
Your external communications, whether advertising, PR, or social media, should reflect your purpose statement. This not only attracts customers that agree with it but also reinforces your commitment to it. Once it’s out in the open, there’s an added responsibility to consistently deliver on it.
3. Regular feedback
Set aside times during quarterly or annual reviews to revisit the purpose statement. Encourage feedback on how well it’s being integrated, and identify where improvements can be made. This process helps refine its application over time.
Motion helps you realize your purpose
A strong, clear, and tailored purpose is essential to have at every level.
With tools like Motion, you can ensure that your purpose statement comes to life in your everyday life and professional life, projects, and every aspect of your business.
If you can remember your priorities, integrate them into your actions, and communicate them clearly, your purpose statement can be your true North Star.
At Motion, our purpose is to empower individuals like you to navigate the complexities of life with confidence and clarity. We believe that everyone has the potential to achieve greatness, and it starts with harnessing the power of productivity.
Put your purpose statement into action by signing up for our 7-day free trial .

Related articles

The Secrets to Effective Sprint Planning

What Are Long-Term Goals? (+50 Examples & Tips to Achieve Them)
6 Best AI Calendar Assistants for Easy Organization
Put motion to the test., tech and media companies are talking about motion.

How to Write a Business Purpose Statement
by Danielle Smyth
Published on 22 Jan 2019
A business purpose statement is an essential part of forming a new business. In some states, it is even a legally required aspect of your business filing. Whether mandatory or not, having a business purpose statement can help you to identify your mission, define your goals and ultimately find the success you crave.
Writing a business purpose statement comes down to answering one important question: why is your company in business?
What Does Business Purpose Mean?
Business purpose differs from mission or vision in that it illustrates the organization’s impact on customers. The purpose of your company is to provide a certain service or product to your clients. The statement of purpose should, therefore, illustrate how you will improve the lives of those you serve. Not only is a business purpose statement a good thing to have, but it can also provide a competitive advantage over companies without such a statement. Also, the purpose can be used as a guide to dictate company actions. If a certain decision does not align with the business’s statement of purpose, it shouldn’t be acted on.
To write a business purpose statement, you need to be able to answer one important question: why is your company in business? If you are forming an LLC, it is required by law that you provide a statement of purpose. For many other business structures, it is still advisable that you have a documented statement of this kind, whether required or not.
A business purpose statement should be short, at just one to a few sentences. While it should be specific to the type of work you plan to do, you should also leave some room for ambiguity to provide your company room to grow and develop over time. Depending on your jurisdiction, statements that are too vague may not be accepted for business filing purposes.
Vision vs. Mission vs. Purpose
Mission, vision, purpose – what’s the difference? Your mission statement should define your company’s objective and its approach to reach these goals. Vision, on the other hand, describes your business’s goals for the future and outlines how you will get there. Meanwhile, a statement of purpose explains the type of work you do and how it will benefit your customers. These distinctions are minor, but it’s important to have a clearly defined vision, mission and purpose as a business owner.
How to Write a Business Mission Statement
To write an effective business mission statement, you must be able to articulate your company’s strategy. A mission statement should concisely answer four questions, as follows:
- What does my company do?
- How do we do it?
- Who do we provide this service for?
- What value do we provide?
Even if you are a solo entrepreneur or run a small, seemingly self-explanatory business, you should develop a mission statement to provide a framework for running your company.
Statements of Purpose for Businesses
- Small Business
- Business Technology & Customer Support
- Market Businesses on the Internet
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Pinterest" aria-label="Share on Pinterest">
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Reddit" aria-label="Share on Reddit">
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Flipboard" aria-label="Share on Flipboard">
The Importance of Setting Goals for a Business
List of objectives when starting a business, policy statement guidelines.
- Objectives in Awareness Advertising
- What Is a Statement of Purpose for a Restaurant?
A statement of purpose is an integral component of your small business's overall strategic operation plan. This document contains your company's core philosophy and values, from which you measure the worth of all business decisions and strategies. Crafting an understandable and attainable statement of purpose helps you and your management team to create policies and measure the success of your company as a whole.
Statement of Purpose Definition
The statement of purpose for your small business defines your company's core goals and purpose. According to Web Marketing Today, an Internet marketing website, the statement also forms the basis for your small business's brand and the promises your company intends to make to consumers. A statement of purpose isn't as broad as a mission statement, which seeks to incorporate business strategies and procedures into the document. Instead, a statement of purpose focuses primarily on the short message that will guide your company in formulating its business practices and procedures, without spelling out what those methods will look like when your business opens its doors.
Avoid Vague Statements
Just because your small business's statement of purpose doesn't include your company's plans for business operations, doesn't mean you should be vague in crafting its language. Your company's statement of purpose shouldn't simply be "make money." The statement of purpose should describe the way in which your small business wants to become successful while carving out a place in the local business community. Focusing the statement with specific language can help your management team come up with strategies and methods to accomplish the goals your statement of purpose sets.
Think About Customer Need
Thinking about the needs your small business is fulfilling for customers can help you craft a statement of purpose that positions your company strategically, as opposed to functionally, according to Web Marketing Today. This allows your mission statement to transcend just creating products and instead focus on providing services for customers. A statement of purpose focused on function allows your business the flexibility to meet consumer needs regardless of the products your company currently offers for sale.
Creating Attainable Goals
An unattainable ideal, including the pursuit of perfection, doesn't make for a good statement of purpose because your employees and management team can't adequately judge if its practices are working towards that goal. It's perfectly acceptable to create a lofty goal for your small business, but this goal should also be within the realm of possibility. This allows your management personnel to gauge the worthiness of proposed business plans and the success of current business strategies.
- Web Marketing Today: Building Your Brand
- Cambridge Rindge & Latin School Research Guide: Writing a Statement of Purpose
Jonathan Lister has been a writer and content marketer since 2003. His latest book publication, "Bullet, a Demos City Novel" is forthcoming from J Taylor Publishing in June 2014. He holds a Bachelor of Arts in English from Shippensburg University and a Master of Fine Arts in writing and poetics from Naropa University.
Related Articles
Example of a corporate web strategy statement, the advantages of having a mission statement, how important is having a philosophy to a corporation, 9 characteristics of an effective mission statement, business strategies of companies, what information should be on a mission statement, what is the business difference between objectives & goals, what is a creative strategy statement, importance of mission vision in organizational strategy, most popular.
- 1 Example of a Corporate Web Strategy Statement
- 2 The Advantages of Having a Mission Statement
- 3 How Important Is Having a Philosophy to a Corporation?
- 4 9 Characteristics of an Effective Mission Statement
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is a Business Plan?
Understanding business plans, how to write a business plan, common elements of a business plan, how often should a business plan be updated, the bottom line, business plan: what it is, what's included, and how to write one.
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
A business plan is a document that details a company's goals and how it intends to achieve them. Business plans can be of benefit to both startups and well-established companies. For startups, a business plan can be essential for winning over potential lenders and investors. Established businesses can find one useful for staying on track and not losing sight of their goals. This article explains what an effective business plan needs to include and how to write one.
Key Takeaways
- A business plan is a document describing a company's business activities and how it plans to achieve its goals.
- Startup companies use business plans to get off the ground and attract outside investors.
- For established companies, a business plan can help keep the executive team focused on and working toward the company's short- and long-term objectives.
- There is no single format that a business plan must follow, but there are certain key elements that most companies will want to include.
Investopedia / Ryan Oakley
Any new business should have a business plan in place prior to beginning operations. In fact, banks and venture capital firms often want to see a business plan before they'll consider making a loan or providing capital to new businesses.
Even if a business isn't looking to raise additional money, a business plan can help it focus on its goals. A 2017 Harvard Business Review article reported that, "Entrepreneurs who write formal plans are 16% more likely to achieve viability than the otherwise identical nonplanning entrepreneurs."
Ideally, a business plan should be reviewed and updated periodically to reflect any goals that have been achieved or that may have changed. An established business that has decided to move in a new direction might create an entirely new business plan for itself.
There are numerous benefits to creating (and sticking to) a well-conceived business plan. These include being able to think through ideas before investing too much money in them and highlighting any potential obstacles to success. A company might also share its business plan with trusted outsiders to get their objective feedback. In addition, a business plan can help keep a company's executive team on the same page about strategic action items and priorities.
Business plans, even among competitors in the same industry, are rarely identical. However, they often have some of the same basic elements, as we describe below.
While it's a good idea to provide as much detail as necessary, it's also important that a business plan be concise enough to hold a reader's attention to the end.
While there are any number of templates that you can use to write a business plan, it's best to try to avoid producing a generic-looking one. Let your plan reflect the unique personality of your business.
Many business plans use some combination of the sections below, with varying levels of detail, depending on the company.
The length of a business plan can vary greatly from business to business. Regardless, it's best to fit the basic information into a 15- to 25-page document. Other crucial elements that take up a lot of space—such as applications for patents—can be referenced in the main document and attached as appendices.
These are some of the most common elements in many business plans:
- Executive summary: This section introduces the company and includes its mission statement along with relevant information about the company's leadership, employees, operations, and locations.
- Products and services: Here, the company should describe the products and services it offers or plans to introduce. That might include details on pricing, product lifespan, and unique benefits to the consumer. Other factors that could go into this section include production and manufacturing processes, any relevant patents the company may have, as well as proprietary technology . Information about research and development (R&D) can also be included here.
- Market analysis: A company needs to have a good handle on the current state of its industry and the existing competition. This section should explain where the company fits in, what types of customers it plans to target, and how easy or difficult it may be to take market share from incumbents.
- Marketing strategy: This section can describe how the company plans to attract and keep customers, including any anticipated advertising and marketing campaigns. It should also describe the distribution channel or channels it will use to get its products or services to consumers.
- Financial plans and projections: Established businesses can include financial statements, balance sheets, and other relevant financial information. New businesses can provide financial targets and estimates for the first few years. Your plan might also include any funding requests you're making.
The best business plans aren't generic ones created from easily accessed templates. A company should aim to entice readers with a plan that demonstrates its uniqueness and potential for success.
2 Types of Business Plans
Business plans can take many forms, but they are sometimes divided into two basic categories: traditional and lean startup. According to the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) , the traditional business plan is the more common of the two.
- Traditional business plans : These plans tend to be much longer than lean startup plans and contain considerably more detail. As a result they require more work on the part of the business, but they can also be more persuasive (and reassuring) to potential investors.
- Lean startup business plans : These use an abbreviated structure that highlights key elements. These business plans are short—as short as one page—and provide only the most basic detail. If a company wants to use this kind of plan, it should be prepared to provide more detail if an investor or a lender requests it.
Why Do Business Plans Fail?
A business plan is not a surefire recipe for success. The plan may have been unrealistic in its assumptions and projections to begin with. Markets and the overall economy might change in ways that couldn't have been foreseen. A competitor might introduce a revolutionary new product or service. All of this calls for building some flexibility into your plan, so you can pivot to a new course if needed.
How frequently a business plan needs to be revised will depend on the nature of the business. A well-established business might want to review its plan once a year and make changes if necessary. A new or fast-growing business in a fiercely competitive market might want to revise it more often, such as quarterly.
What Does a Lean Startup Business Plan Include?
The lean startup business plan is an option when a company prefers to give a quick explanation of its business. For example, a brand-new company may feel that it doesn't have a lot of information to provide yet.
Sections can include: a value proposition ; the company's major activities and advantages; resources such as staff, intellectual property, and capital; a list of partnerships; customer segments; and revenue sources.
A business plan can be useful to companies of all kinds. But as a company grows and the world around it changes, so too should its business plan. So don't think of your business plan as carved in granite but as a living document designed to evolve with your business.
Harvard Business Review. " Research: Writing a Business Plan Makes Your Startup More Likely to Succeed ."
U.S. Small Business Administration. " Write Your Business Plan ."
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps 1 of 25
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example 2 of 25
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, and How to Create One 3 of 25
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained 4 of 25
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One 5 of 25
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills 6 of 25
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One 7 of 25
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact 8 of 25
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan 9 of 25
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details 10 of 25
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks 11 of 25
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons 12 of 25
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites 13 of 25
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin 14 of 25
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit 15 of 25
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons 16 of 25
- Best Startup Business Loans for May 2024 17 of 25
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros and Cons, and Differences From an LLC 18 of 25
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types 19 of 25
- What Is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined 20 of 25
- Corporation: What It Is and How To Form One 21 of 25
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide 22 of 25
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide 23 of 25
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips 24 of 25
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide 25 of 25
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-1456193345-2cc8ef3d583f42d8a80c8e631c0b0556.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
How to Write a Business Plan: Step-by-Step Guide + Examples

Noah Parsons
24 min. read
Updated May 7, 2024
Writing a business plan doesn’t have to be complicated.
In this step-by-step guide, you’ll learn how to write a business plan that’s detailed enough to impress bankers and potential investors, while giving you the tools to start, run, and grow a successful business.
- The basics of business planning
If you’re reading this guide, then you already know why you need a business plan .
You understand that planning helps you:
- Raise money
- Grow strategically
- Keep your business on the right track
As you start to write your plan, it’s useful to zoom out and remember what a business plan is .
At its core, a business plan is an overview of the products and services you sell, and the customers that you sell to. It explains your business strategy: how you’re going to build and grow your business, what your marketing strategy is, and who your competitors are.
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow.
A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It’s also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals.
After completing your plan, you can use it as a management tool to track your progress toward your goals. Updating and adjusting your forecasts and budgets as you go is one of the most important steps you can take to run a healthier, smarter business.
We’ll dive into how to use your plan later in this article.
There are many different types of plans , but we’ll go over the most common type here, which includes everything you need for an investor-ready plan. However, if you’re just starting out and are looking for something simpler—I recommend starting with a one-page business plan . It’s faster and easier to create.
It’s also the perfect place to start if you’re just figuring out your idea, or need a simple strategic plan to use inside your business.
Dig deeper : How to write a one-page business plan
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
- What to include in your business plan
Executive summary
The executive summary is an overview of your business and your plans. It comes first in your plan and is ideally just one to two pages. Most people write it last because it’s a summary of the complete business plan.
Ideally, the executive summary can act as a stand-alone document that covers the highlights of your detailed plan.
In fact, it’s common for investors to ask only for the executive summary when evaluating your business. If they like what they see in the executive summary, they’ll often follow up with a request for a complete plan, a pitch presentation , or more in-depth financial forecasts .
Your executive summary should include:
- A summary of the problem you are solving
- A description of your product or service
- An overview of your target market
- A brief description of your team
- A summary of your financials
- Your funding requirements (if you are raising money)
Dig Deeper: How to write an effective executive summary
Products and services description
This is where you describe exactly what you’re selling, and how it solves a problem for your target market. The best way to organize this part of your plan is to start by describing the problem that exists for your customers. After that, you can describe how you plan to solve that problem with your product or service.
This is usually called a problem and solution statement .
To truly showcase the value of your products and services, you need to craft a compelling narrative around your offerings. How will your product or service transform your customers’ lives or jobs? A strong narrative will draw in your readers.
This is also the part of the business plan to discuss any competitive advantages you may have, like specific intellectual property or patents that protect your product. If you have any initial sales, contracts, or other evidence that your product or service is likely to sell, include that information as well. It will show that your idea has traction , which can help convince readers that your plan has a high chance of success.
Market analysis
Your target market is a description of the type of people that you plan to sell to. You might even have multiple target markets, depending on your business.
A market analysis is the part of your plan where you bring together all of the information you know about your target market. Basically, it’s a thorough description of who your customers are and why they need what you’re selling. You’ll also include information about the growth of your market and your industry .
Try to be as specific as possible when you describe your market.
Include information such as age, income level, and location—these are what’s called “demographics.” If you can, also describe your market’s interests and habits as they relate to your business—these are “psychographics.”
Related: Target market examples
Essentially, you want to include any knowledge you have about your customers that is relevant to how your product or service is right for them. With a solid target market, it will be easier to create a sales and marketing plan that will reach your customers. That’s because you know who they are, what they like to do, and the best ways to reach them.
Next, provide any additional information you have about your market.
What is the size of your market ? Is the market growing or shrinking? Ideally, you’ll want to demonstrate that your market is growing over time, and also explain how your business is positioned to take advantage of any expected changes in your industry.
Dig Deeper: Learn how to write a market analysis
Competitive analysis
Part of defining your business opportunity is determining what your competitive advantage is. To do this effectively, you need to know as much about your competitors as your target customers.
Every business has some form of competition. If you don’t think you have competitors, then explore what alternatives there are in the market for your product or service.
For example: In the early years of cars, their main competition was horses. For social media, the early competition was reading books, watching TV, and talking on the phone.
A good competitive analysis fully lays out the competitive landscape and then explains how your business is different. Maybe your products are better made, or cheaper, or your customer service is superior. Maybe your competitive advantage is your location – a wide variety of factors can ultimately give you an advantage.
Dig Deeper: How to write a competitive analysis for your business plan
Marketing and sales plan
The marketing and sales plan covers how you will position your product or service in the market, the marketing channels and messaging you will use, and your sales tactics.
The best place to start with a marketing plan is with a positioning statement .
This explains how your business fits into the overall market, and how you will explain the advantages of your product or service to customers. You’ll use the information from your competitive analysis to help you with your positioning.
For example: You might position your company as the premium, most expensive but the highest quality option in the market. Or your positioning might focus on being locally owned and that shoppers support the local economy by buying your products.
Once you understand your positioning, you’ll bring this together with the information about your target market to create your marketing strategy .
This is how you plan to communicate your message to potential customers. Depending on who your customers are and how they purchase products like yours, you might use many different strategies, from social media advertising to creating a podcast. Your marketing plan is all about how your customers discover who you are and why they should consider your products and services.
While your marketing plan is about reaching your customers—your sales plan will describe the actual sales process once a customer has decided that they’re interested in what you have to offer.
If your business requires salespeople and a long sales process, describe that in this section. If your customers can “self-serve” and just make purchases quickly on your website, describe that process.
A good sales plan picks up where your marketing plan leaves off. The marketing plan brings customers in the door and the sales plan is how you close the deal.
Together, these specific plans paint a picture of how you will connect with your target audience, and how you will turn them into paying customers.
Dig deeper: What to include in your sales and marketing plan
Business operations
The operations section describes the necessary requirements for your business to run smoothly. It’s where you talk about how your business works and what day-to-day operations look like.
Depending on how your business is structured, your operations plan may include elements of the business like:
- Supply chain management
- Manufacturing processes
- Equipment and technology
- Distribution
Some businesses distribute their products and reach their customers through large retailers like Amazon.com, Walmart, Target, and grocery store chains.
These businesses should review how this part of their business works. The plan should discuss the logistics and costs of getting products onto store shelves and any potential hurdles the business may have to overcome.
If your business is much simpler than this, that’s OK. This section of your business plan can be either extremely short or more detailed, depending on the type of business you are building.
For businesses selling services, such as physical therapy or online software, you can use this section to describe the technology you’ll leverage, what goes into your service, and who you will partner with to deliver your services.
Dig Deeper: Learn how to write the operations chapter of your plan
Key milestones and metrics
Although it’s not required to complete your business plan, mapping out key business milestones and the metrics can be incredibly useful for measuring your success.
Good milestones clearly lay out the parameters of the task and set expectations for their execution. You’ll want to include:
- A description of each task
- The proposed due date
- Who is responsible for each task
If you have a budget, you can include projected costs to hit each milestone. You don’t need extensive project planning in this section—just list key milestones you want to hit and when you plan to hit them. This is your overall business roadmap.
Possible milestones might be:
- Website launch date
- Store or office opening date
- First significant sales
- Break even date
- Business licenses and approvals
You should also discuss the key numbers you will track to determine your success. Some common metrics worth tracking include:
- Conversion rates
- Customer acquisition costs
- Profit per customer
- Repeat purchases
It’s perfectly fine to start with just a few metrics and grow the number you are tracking over time. You also may find that some metrics simply aren’t relevant to your business and can narrow down what you’re tracking.
Dig Deeper: How to use milestones in your business plan
Organization and management team
Investors don’t just look for great ideas—they want to find great teams. Use this chapter to describe your current team and who you need to hire . You should also provide a quick overview of your location and history if you’re already up and running.
Briefly highlight the relevant experiences of each key team member in the company. It’s important to make the case for why yours is the right team to turn an idea into a reality.
Do they have the right industry experience and background? Have members of the team had entrepreneurial successes before?
If you still need to hire key team members, that’s OK. Just note those gaps in this section.
Your company overview should also include a summary of your company’s current business structure . The most common business structures include:
- Sole proprietor
- Partnership
Be sure to provide an overview of how the business is owned as well. Does each business partner own an equal portion of the business? How is ownership divided?
Potential lenders and investors will want to know the structure of the business before they will consider a loan or investment.
Dig Deeper: How to write about your company structure and team
Financial plan
Last, but certainly not least, is your financial plan chapter.
Entrepreneurs often find this section the most daunting. But, business financials for most startups are less complicated than you think, and a business degree is certainly not required to build a solid financial forecast.
A typical financial forecast in a business plan includes the following:
- Sales forecast : An estimate of the sales expected over a given period. You’ll break down your forecast into the key revenue streams that you expect to have.
- Expense budget : Your planned spending such as personnel costs , marketing expenses, and taxes.
- Profit & Loss : Brings together your sales and expenses and helps you calculate planned profits.
- Cash Flow : Shows how cash moves into and out of your business. It can predict how much cash you’ll have on hand at any given point in the future.
- Balance Sheet : A list of the assets, liabilities, and equity in your company. In short, it provides an overview of the financial health of your business.
A strong business plan will include a description of assumptions about the future, and potential risks that could impact the financial plan. Including those will be especially important if you’re writing a business plan to pursue a loan or other investment.
Dig Deeper: How to create financial forecasts and budgets
This is the place for additional data, charts, or other information that supports your plan.
Including an appendix can significantly enhance the credibility of your plan by showing readers that you’ve thoroughly considered the details of your business idea, and are backing your ideas up with solid data.
Just remember that the information in the appendix is meant to be supplementary. Your business plan should stand on its own, even if the reader skips this section.
Dig Deeper : What to include in your business plan appendix
Optional: Business plan cover page
Adding a business plan cover page can make your plan, and by extension your business, seem more professional in the eyes of potential investors, lenders, and partners. It serves as the introduction to your document and provides necessary contact information for stakeholders to reference.
Your cover page should be simple and include:
- Company logo
- Business name
- Value proposition (optional)
- Business plan title
- Completion and/or update date
- Address and contact information
- Confidentiality statement
Just remember, the cover page is optional. If you decide to include it, keep it very simple and only spend a short amount of time putting it together.
Dig Deeper: How to create a business plan cover page
How to use AI to help write your business plan
Generative AI tools such as ChatGPT can speed up the business plan writing process and help you think through concepts like market segmentation and competition. These tools are especially useful for taking ideas that you provide and converting them into polished text for your business plan.
The best way to use AI for your business plan is to leverage it as a collaborator , not a replacement for human creative thinking and ingenuity.
AI can come up with lots of ideas and act as a brainstorming partner. It’s up to you to filter through those ideas and figure out which ones are realistic enough to resonate with your customers.
There are pros and cons of using AI to help with your business plan . So, spend some time understanding how it can be most helpful before just outsourcing the job to AI.
Learn more: 10 AI prompts you need to write a business plan
- Writing tips and strategies
To help streamline the business plan writing process, here are a few tips and key questions to answer to make sure you get the most out of your plan and avoid common mistakes .
Determine why you are writing a business plan
Knowing why you are writing a business plan will determine your approach to your planning project.
For example: If you are writing a business plan for yourself, or just to use inside your own business , you can probably skip the section about your team and organizational structure.
If you’re raising money, you’ll want to spend more time explaining why you’re looking to raise the funds and exactly how you will use them.
Regardless of how you intend to use your business plan , think about why you are writing and what you’re trying to get out of the process before you begin.
Keep things concise
Probably the most important tip is to keep your business plan short and simple. There are no prizes for long business plans . The longer your plan is, the less likely people are to read it.
So focus on trimming things down to the essentials your readers need to know. Skip the extended, wordy descriptions and instead focus on creating a plan that is easy to read —using bullets and short sentences whenever possible.
Have someone review your business plan
Writing a business plan in a vacuum is never a good idea. Sometimes it’s helpful to zoom out and check if your plan makes sense to someone else. You also want to make sure that it’s easy to read and understand.
Don’t wait until your plan is “done” to get a second look. Start sharing your plan early, and find out from readers what questions your plan leaves unanswered. This early review cycle will help you spot shortcomings in your plan and address them quickly, rather than finding out about them right before you present your plan to a lender or investor.
If you need a more detailed review, you may want to explore hiring a professional plan writer to thoroughly examine it.
Use a free business plan template and business plan examples to get started
Knowing what information to include in a business plan is sometimes not quite enough. If you’re struggling to get started or need additional guidance, it may be worth using a business plan template.
There are plenty of great options available (we’ve rounded up our 8 favorites to streamline your search).
But, if you’re looking for a free downloadable business plan template , you can get one right now; download the template used by more than 1 million businesses.
Or, if you just want to see what a completed business plan looks like, check out our library of over 550 free business plan examples .
We even have a growing list of industry business planning guides with tips for what to focus on depending on your business type.
Common pitfalls and how to avoid them
It’s easy to make mistakes when you’re writing your business plan. Some entrepreneurs get sucked into the writing and research process, and don’t focus enough on actually getting their business started.
Here are a few common mistakes and how to avoid them:
Not talking to your customers : This is one of the most common mistakes. It’s easy to assume that your product or service is something that people want. Before you invest too much in your business and too much in the planning process, make sure you talk to your prospective customers and have a good understanding of their needs.
- Overly optimistic sales and profit forecasts: By nature, entrepreneurs are optimistic about the future. But it’s good to temper that optimism a little when you’re planning, and make sure your forecasts are grounded in reality.
- Spending too much time planning: Yes, planning is crucial. But you also need to get out and talk to customers, build prototypes of your product and figure out if there’s a market for your idea. Make sure to balance planning with building.
- Not revising the plan: Planning is useful, but nothing ever goes exactly as planned. As you learn more about what’s working and what’s not—revise your plan, your budgets, and your revenue forecast. Doing so will provide a more realistic picture of where your business is going, and what your financial needs will be moving forward.
- Not using the plan to manage your business: A good business plan is a management tool. Don’t just write it and put it on the shelf to collect dust – use it to track your progress and help you reach your goals.
- Presenting your business plan
The planning process forces you to think through every aspect of your business and answer questions that you may not have thought of. That’s the real benefit of writing a business plan – the knowledge you gain about your business that you may not have been able to discover otherwise.
With all of this knowledge, you’re well prepared to convert your business plan into a pitch presentation to present your ideas.
A pitch presentation is a summary of your plan, just hitting the highlights and key points. It’s the best way to present your business plan to investors and team members.
Dig Deeper: Learn what key slides should be included in your pitch deck
Use your business plan to manage your business
One of the biggest benefits of planning is that it gives you a tool to manage your business better. With a revenue forecast, expense budget, and projected cash flow, you know your targets and where you are headed.
And yet, nothing ever goes exactly as planned – it’s the nature of business.
That’s where using your plan as a management tool comes in. The key to leveraging it for your business is to review it periodically and compare your forecasts and projections to your actual results.
Start by setting up a regular time to review the plan – a monthly review is a good starting point. During this review, answer questions like:
- Did you meet your sales goals?
- Is spending following your budget?
- Has anything gone differently than what you expected?
Now that you see whether you’re meeting your goals or are off track, you can make adjustments and set new targets.
Maybe you’re exceeding your sales goals and should set new, more aggressive goals. In that case, maybe you should also explore more spending or hiring more employees.
Or maybe expenses are rising faster than you projected. If that’s the case, you would need to look at where you can cut costs.
A plan, and a method for comparing your plan to your actual results , is the tool you need to steer your business toward success.
Learn More: How to run a regular plan review
Free business plan templates and examples
Kickstart your business plan writing with one of our free business plan templates or recommended tools.

Free business plan template
Download a free SBA-approved business plan template built for small businesses and startups.
Download Template

One-page plan template
Download a free one-page plan template to write a useful business plan in as little as 30-minutes.

Sample business plan library
Explore over 500 real-world business plan examples from a wide variety of industries.
View Sample Plans
How to write a business plan FAQ
What is a business plan?
A document that describes your business , the products and services you sell, and the customers that you sell to. It explains your business strategy, how you’re going to build and grow your business, what your marketing strategy is, and who your competitors are.
What are the benefits of a business plan?
A business plan helps you understand where you want to go with your business and what it will take to get there. It reduces your overall risk, helps you uncover your business’s potential, attracts investors, and identifies areas for growth.
Having a business plan ultimately makes you more confident as a business owner and more likely to succeed for a longer period of time.
What are the 7 steps of a business plan?
The seven steps to writing a business plan include:
- Write a brief executive summary
- Describe your products and services.
- Conduct market research and compile data into a cohesive market analysis.
- Describe your marketing and sales strategy.
- Outline your organizational structure and management team.
- Develop financial projections for sales, revenue, and cash flow.
- Add any additional documents to your appendix.
What are the 5 most common business plan mistakes?
There are plenty of mistakes that can be made when writing a business plan. However, these are the 5 most common that you should do your best to avoid:
- 1. Not taking the planning process seriously.
- Having unrealistic financial projections or incomplete financial information.
- Inconsistent information or simple mistakes.
- Failing to establish a sound business model.
- Not having a defined purpose for your business plan.
What questions should be answered in a business plan?
Writing a business plan is all about asking yourself questions about your business and being able to answer them through the planning process. You’ll likely be asking dozens and dozens of questions for each section of your plan.
However, these are the key questions you should ask and answer with your business plan:
- How will your business make money?
- Is there a need for your product or service?
- Who are your customers?
- How are you different from the competition?
- How will you reach your customers?
- How will you measure success?
How long should a business plan be?
The length of your business plan fully depends on what you intend to do with it. From the SBA and traditional lender point of view, a business plan needs to be whatever length necessary to fully explain your business. This means that you prove the viability of your business, show that you understand the market, and have a detailed strategy in place.
If you intend to use your business plan for internal management purposes, you don’t necessarily need a full 25-50 page business plan. Instead, you can start with a one-page plan to get all of the necessary information in place.
What are the different types of business plans?
While all business plans cover similar categories, the style and function fully depend on how you intend to use your plan. Here are a few common business plan types worth considering.
Traditional business plan: The tried-and-true traditional business plan is a formal document meant to be used when applying for funding or pitching to investors. This type of business plan follows the outline above and can be anywhere from 10-50 pages depending on the amount of detail included, the complexity of your business, and what you include in your appendix.
Business model canvas: The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea.
One-page business plan: This format is a simplified version of the traditional plan that focuses on the core aspects of your business. You’ll typically stick with bullet points and single sentences. It’s most useful for those exploring ideas, needing to validate their business model, or who need an internal plan to help them run and manage their business.
Lean Plan: The Lean Plan is less of a specific document type and more of a methodology. It takes the simplicity and styling of the one-page business plan and turns it into a process for you to continuously plan, test, review, refine, and take action based on performance. It’s faster, keeps your plan concise, and ensures that your plan is always up-to-date.
What’s the difference between a business plan and a strategic plan?
A business plan covers the “who” and “what” of your business. It explains what your business is doing right now and how it functions. The strategic plan explores long-term goals and explains “how” the business will get there. It encourages you to look more intently toward the future and how you will achieve your vision.
However, when approached correctly, your business plan can actually function as a strategic plan as well. If kept lean, you can define your business, outline strategic steps, and track ongoing operations all with a single plan.
See why 1.2 million entrepreneurs have written their business plans with LivePlan
Noah is the COO at Palo Alto Software, makers of the online business plan app LivePlan. He started his career at Yahoo! and then helped start the user review site Epinions.com. From there he started a software distribution business in the UK before coming to Palo Alto Software to run the marketing and product teams.

Table of Contents
- Use AI to help write your plan
- Common planning mistakes
- Manage with your business plan
- Templates and examples
Related Articles

1 Min. Read
How to Calculate Return on Investment (ROI)

7 Min. Read
How to Write a Bakery Business Plan + Sample

5 Min. Read
How To Write a Business Plan for a Life Coaching Business + Free Example

3 Min. Read
What to Include in Your Business Plan Appendix
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software

How to Write a Stand-Out Purpose Statement + Examples

The success of a nonprofit organization depends on a number of factors, but one of the most important is having a clearly defined purpose. A well-crafted statement of purpose can help guide your nonprofit’s decisions and keep you focused on your goals. In this article, we’ll discuss what goes into a great nonprofit purpose statement and provide some examples for inspiration.
Why Is a Purpose Statement Important?
A nonprofit purpose statement is important because it articulates the organization’s goals and values. It can also be used as a marketing tool to attract donors and volunteers. A clear purpose statement can help your nonprofit stay focused and make decisions that align with your goals in creating a nonprofit communication plan .
How To Write a Stand-Out Purpose Statement
When writing a purpose statement, it’s important to keep the following elements in mind:
-Define your mission: What is your “reason for being” a nonprofit? What problem or need are you trying to solve? What do you hope to change?
– Articulate your values: What guiding principles will inform your nonprofit’s decisions?
– Keep it short and to the point: A purpose statement should be concise. It can be just a few sentences long.
– Be specific: Avoid general statements like “to help people.” Instead, focus on a specific population or issue that your non-profit highlights.
– Focus on the future: A great purpose statement should inspire people to support the work of your nonprofit.
– Use positive language: Language that is optimistic and uplifting is more likely to resonate with people.
-Avoid jargon: Use language that can be understood by everyone.
-Focus on what your nonprofit does, not who you serve: For example, “to provide shelter for homeless families” is more clear than “to help families in need.”
-Create a few drafts: Don’t be afraid to revise your purpose statement until you’re happy with it.
-Get feedback: Once you’ve written a few drafts, ask others for their input. This can help fine-tune your statement and ensure it’s clear and concise.
Examples of Stand-Out Purpose Statements
Still struggling to come up with a great purpose statement for your nonprofit? Here are some examples of clear, strong purpose statements to inspire you:
- To provide shelter and support for homeless families.
- To inspire and empower young people to achieve their potential.
- To promote racial equality and social justice.
- To provide food and clothing to those in need.
- To protect the environment and wildlife.
A nonprofit purpose statement is a vital part of your organization’s success. It should be concise, specific, and inspiring. By following these tips, you can write a great purpose statement that will guide your nonprofit’s work and attract supporters.
MBA Statement of Purpose Examples
Featured Expert: Srikanth Raghavan, MBA
MBA statement of purpose examples can be beneficial when you are trying to write one yourself or just wanting to understand exactly what they are. That’s why we’ve provided a couple of them for you in this blog. In addition to that, we’ll be going over everything you need to know about grad school statements of purpose , such as the MBA statement of purpose. You will learn about their importance, content, format, and how to use them to contextualize your other application components, such as your reference letters or MBA personal statement .
>> Want us to help you get accepted? Schedule a free strategy call here . <<
Article Contents 12 min read
What is an mba statement of purpose.
An MBA statement of purpose (SoP) is a short academic essay often required for graduate school applications. It’s an essential part of your application that is supposed to tell the admissions committee why you are interested in their MBA program and why you are the perfect fit for it. Furthermore, it gives you the chance to contextualize the statistics and numbers in your application and present yourself to the graduate program in a more well-rounded way. The admissions committee already knows about your work experience from your MBA resume and your academic performance from your transcripts. The statement of purpose allows them to assess your suitability for their institution, and more importantly, their program.
Every school is different, so you need to check the specific requirements of the program you are interested in. Some schools may require a statement of purpose in addition to other essays. In contrast, other schools like the Wharton School of Business for example, may not ask specifically for a statement of purpose but have a prompt that essentially asks why you are a good fit for the school. Either way, you will need to respond with a strong and compelling essay to improve your chances of getting in.
How to write a strong MBA statement of purpose
The format and content.
You should always check the specific requirements of the program you are applying to, as each school is different. Your chosen program could have an exact word count, a page limit, or a prompting question that you need to answer. If your program has given any instructions, it is imperative that you follow them. Unless otherwise specified, your statement of purpose should:
- Follow the general structure of an academic essay
- Be between 500 and 1000 words
- Be grammatically correct
- Be organized and easy to read
Give yourself time : Writing a strong statement of purpose isn’t unlike preparing the rest of your application; the key is preparation. We recommend giving yourself at least six weeks to write your statement. Give yourself enough time to thoroughly research the program or faculty, gather all the information that could be helpful to you, and draft, redraft and finalize your statement.
Research the program : The purpose of your statement is to convince the admissions committee that you are the perfect fit for their program in particular and to do that, you need to know what kind of candidate they are looking for. You should spend time on the institution’s website and talk to alumni if possible. Try to get a sense of the school’s academic culture. Take some time to familiarize yourself with the research specialties of various faculty members, and keep track of those whose research interests align with yours.
The more you know about the school and the MBA program, the better equipped you will be to write a strong letter that showcases the values or qualities that the school is looking for. For instance, if you are preparing an application to Kellogg business school , your research will probably lead you to find out that their MBA program aims to create leaders who are not afraid to challenge the status quo and find creative solutions. In that case, you might want to make sure your statement of purpose showcases your creative problem-solving skills.
Seek expert advice : You may also want to consider investing in a graduate school admissions consultant or MBA admissions consulting . Preparing an MBA application is no easy feat, especially the essay portions. The truth is that admissions consultants have more experience reading and writing these types of essays so they can see things that you can’t. Their constructive feedback might just be what you need to write a statement of purpose that will stand out.
Being too impersonal : Your statement of purpose is supposed to put the rest of your application into context. You should avoid just listing your accomplishments or your reasons for wanting to attend the school. People are more likely to remember a story, so instead, focus on creating a narrative around your experiences and why they make you a perfect fit for the program. Additionally, research-intensive MBA programs may require you to discuss your research interests. In these cases, many students confuse the statement of purpose and research interest statement . Both essays are about the candidate’s relevant past academic & professional experiences, long-term goals in the field, and research interests when applicable. However, while a research interest statement is a formal academic document, a statement of purpose is more of a personal essay meant to describe your journey and overall suitability for a program.
Jargon-heavy statements : Even if you are applying to a business school, you should try to avoid jargon and acronyms that are not well known outside of your field of study. The admissions committee will read your statement, and they might not be experts in your particular field. We understand that you want to come across as knowledgeable, but it is equally important that your statement be easy to follow and read.
Generic statements : We highly recommend that you write multiple statements of purpose and tailor them to the MBA programs you are applying to. A common mistake that applicants make is writing one generic statement of purpose and sending it to all the business schools they are applying to. This usually backfires because each school and each program is different. First, various schools may have different format requirements for the statement of purpose. Secondly, the academic culture and the kind of candidate each school is looking for can be very different.
For example, a student might send the same letter to Harvard business school and Stanford business school , assuming that they have similar requirements because they are both prestigious institutions that aim to form tomorrow’s business leaders. However, Harvard business school makes it clear that they look for candidates with an analytical aptitude and desire to be engaged in the community. If these qualities are not showcased in the letter to Harvard, the candidate might not get called for an interview (so don't forget to review MBA interview questions as well). This is why it's so important to review Harvard MBA personal statement examples - you must understand what the admissions committee of this renowned institution expects.
Ignoring guidelines : This tip is quite self-explanatory, but we feel it is worth mentioning again because it’s a very common pitfall. Many institutions will give clear instructions for the application documents, including the statement of purpose. It is crucial that you follow these instructions. If there is a word count, stick to it. If there is a prompt, answer the question in the prompt and stay on topic. Do not use your essay to address something in your application that is completely unrelated to the question that you were asked. Following the guidelines set by the program will show the admissions committee that you take your application seriously and that you know how to follow instructions.
Need to work on your MBA resume too? Check out this infographic:
Now that you know what is expected from a strong MBA statement of purpose, here are a few examples that can help inspire your own.
MBA statement of purpose sample 1
I often joke that I speak three languages: English, French, and consumer. I have been saying this since I took an introduction to marketing class while completing my undergraduate degree and learned about talking to customers in a language they understand. It resonated with me because I practically grew up in my mother's small dry-cleaning store. I watched her relay the same information to different people from various walks of life in many different ways. It was always in English, but her word choice and tone would change so much that my siblings and I would joke about it. Since then, I have been fascinated by communication. The effect that it has on people and businesses. This fascination led to my dual degree in business management and psychology, and today, it is one of the things that drive me to apply to the X business school MBA program.
Over the past five years, I have used what I learned at university to expand our family business and help grow many others in my community. The experience taught me that no matter how good your product or service is, introducing it to the market is indeed half the battle when it comes to business. My goal is to create a marketing firm that will help small local businesses maximize their reach and full potential. I understand that a big part of this is marketing, and that is why I want to study it further.
The X MBA program is uniquely suited to help me achieve this goal. In today's Business landscape, small businesses need different strategies to survive and compete in the world of big companies that can deliver things overnight. The X MBA program is one of the very few curriculums that offer courses specifically designed for small businesses and the latest marketing strategies, such as social media as a marketing tool.
As a person with ambitions to become an entrepreneur, there are also many other aspects of business management that I wish to understand better, such as accounting Tools, Logistics, and Supply-Chain. My initial assumption was that I would need to find two separate programs to be completely immersed in the two fields that I wish to study. However, your holistic approach to business management would actually allow me to master marketing and communications while learning to be a better business owner.
Beyond the fact that this curriculum is perfect for what I want to learn and eventually use in my career, X business school is also as community-focused as I am. In Undergrad, I spent two years working with other members of the Student Union Association to organize and help with the green initiative that the school was launching. I noticed that the X student union has a branch dedicated to something similar, and I would love to be a part of it if given the opportunity.
My passion for community building and marketing makes me a perfect fit for this program. Furthermore, my academic background and practical experience have given me the tools to succeed in this MBA program and beyond. I am hardworking, dedicated, and eager to learn. I hope you give me a chance to do so at X University.
This statement is particularly strong because it clearly communicates the applicant’s fit for the program. Notice the fact that the applicant gives clear examples of the claims that they make about themselves. For example, they mention that they are very community focused and make it evident by sharing that they volunteered in college and that their long-term goal is to work for the businesses in their local community.
MBA statement of purpose sample 2
X university prompt: Why have you chosen to pursue an MBA program and why have you chosen to do it at X institution? (Max 600 words)
I was a writer before I was a businesswoman, and studying business isn’t a life-long dream that I harbor. Still, it has become a necessity at this juncture of my professional career.
I was born in a liberal and educated family that stressed the importance of following one’s dreams and passions. I can appreciate how amazing that is now that I am an adult, but as a confused teenager who had no dream and didn’t seem to have a hobby, let alone a passion - it was a nightmare. I attempted many different things, from team sports to theatre, but nothing ever really stuck until I discovered my love for the written word in high school. I am grateful for that journey today because it has taught me to be comfortable with change and given me the ability to adapt quickly. These abilities have served me well in my professional career so far, and I hope that they will continue to do so if I am given the opportunity to attend X business school for your MBA program.
I’m sure you’re wondering why a person who seemingly has no interest in business wants to attend a reputable business school such as yours. Most people do not associate a Master of Business Administration degree with the writing profession. When one thinks about an MBA, more often than not, the first thought that comes to mind would be that a person who undertakes an MBA aspires to get a better job in banking, finance, or business consulting. However, business actually affects many different areas of a writer’s profession. I have come to the conclusion that to succeed as a writer, I must gain systematic knowledge about the workings of a business, and your program is the perfect place for me to do so.
Whether you are a freelance writer like I have been in the past or an author like I am now, you are essentially an entrepreneur with a product to sell: your art. The holistic approach of the X MBA program is designed for entrepreneurs like myself who are ready to take their business to the next level. I am particularly interested in learning all about the statistical and programming tools used in the Business Analytics domain. These tools will help me make generalized sense of data and gain valuable insights to help me figure out who my target audience is and how I can better reach them.
I fervently believe that my communication skills, academic background, and entrepreneurial spirit have prepared me for success in this rigorous MBA program. Additionally, as a person who was born and raised in X city, I have seen the significant impact that the school and its alumni have had on our great city and would love to be a part of it. I am particularly passionate about making tertiary education more accessible to the less fortunate and would love to join the group of students and alumni who coordinate the fundraising efforts of your Access Tuition Fund.
In short, I believe that this program is uniquely suited to help me gain a holistic understanding of the functioning of entrepreneurial businesses and mold me into a well-rounded professional. My hope is that you will see that my academic background, work experience, as well as my passion for my craft, and how it interacts with business logistics make me the perfect candidate for your MBA program.
Pay particular attention to the fact that this statement of purpose manages to communicate fit and provide a few details about the applicant’s abilities but it does not stray from the question that was asked by the prompt.
Wondering what kind of courses you should take during your MBA? This video has some helpful advice:
After you write
Before you go, we just want to remind you of a few questions that you should ask yourself before submitting your statement of purpose.
Once you have your final draft, step away from it for a little while and come back to look at it with fresh eyes. You should ask yourself the questions above as you read and make the necessary adjustments. You can also opt to use an application review process where an expert would go over your statement of purpose draft and work with you to get it to the best version possible.
It’s a short essay that tells an admission committee why you are a perfect fit for their MBA program.
An MBA statement of purpose should tell the admissions board why you are interested in an MBA, why you’ve chosen their program in particular, why you’d be a good addition to the program, and how the MBA will help you achieve your career goals.
Unless otherwise specified by the business school you are applying to, you should keep your statement between 500 and 1000 words.
The beginning of your statement needs to be attention-grabbing. We recommend starting with a quote, an anecdote, or an interesting personal fact.
Your statement should be structured like a general academic essay with an introduction, main body, and conclusion.
In short, no! You should always tailor your MBA statement of purpose to the school you are applying to. One generic statement for many different schools will not be enough to make your application stand out.
Your statement of purpose is meant to show the admissions board that you are a good fit for their program and your ambitions are part of who you are. In other words, your plans tell the school a little bit more about who you are.
The best way to make your statement more compelling is to research the school you are applying to thoroughly, find out what kind of candidate they are looking for, and ensure that your statement of purpose reflects the qualities that the school seeks. It is also best to give clear examples for every claim you make about yourself.
Want more free tips? Subscribe to our channels for more free and useful content!
Apple Podcasts
Like our blog? Write for us ! >>
Have a question ask our admissions experts below and we'll answer your questions, get started now.
Talk to one of our admissions experts
Our site uses cookies. By using our website, you agree with our cookie policy .
FREE Training Webclass:
How to make your mba application stand out.
And Avoid the Top 5 Mistakes That Get Most Rejected
Time Sensitive. Limited Spots Available:
We guarantee you'll get into your dream MBA program or you don't pay.
Swipe up to see a great offer!
Testimonials
Free Resources
PrepScholar GRE Prep
Gre prep online guides and tips, 7 successful statement of purpose examples.
Not sure what graduate schools are looking for in a statement of purpose? Looking at successful graduate school statement of purpose samples can help! In this guide, we’ll orient you to what makes a great statement of purpose or letter of intent for graduate school. Then we’ll provide you with four successful statement of purpose examples from our graduate school experts. We’ll also provide analysis of what makes them successful. Finally, we’ll direct you to even more helpful examples that you can find online!
The Graduate School Statement of Purpose: An Overview
A statement of purpose (also called a letter of intent or a research statement) introduces your interests and experience to the admissions committee. For research-focused programs, like most PhDs and many master’s degrees, your statement of purpose will focus primarily on your past research experience and plans. For more professionally-focused graduate programs, your statement of purpose will primarily discuss how your pursuit of this professional program relates to your past experiences, and how you will use the skills from the program in your future career.
A statement of purpose for grad school is also where you sell the admissions committee on why you belong in their program specifically. Why do you fit there, and how does what they offer fit your interests?

What’s in a Great Grad School Statement of Purpose?
Here are the essential elements of a strong graduate school statement of purpose:
Clear Articulation of Goals and Interests
A strong statement of purpose will clearly and specifically lay out your goals in undertaking the program and what you hope to accomplish with the degree. Again, for a research-focused program, this will focus primarily on the research project(s) you want to undertake while you are there. For a more professional program, discuss what interests you within the professional field and what skills/knowledge you hope to gain through the program.
Quick side note: we've created the world's leading online GRE prep program that adapts to you and your strengths and weaknesses. Not sure what to study? Confused by how to improve your score? We give you minute by minute guide.
You don't NEED a prep program to get a great GRE score. But we believe PrepScholar is the best GRE prep program available right now , especially if you find it hard to organize your study schedule and don't know what to study .
Click here to learn how you can improve your GRE score by 7 points, guaranteed .
You should be as specific as possible in discussing what interests you. Use examples of particular phenomena, tools, or situations that you find exciting. If you are vague or say that everything in the field interests you, you run the risk of seeming unfocused or not actually that passionate.
Don’t worry that being too specific will box you into a particular research area or subfield during your entire tenure in graduate school. Your program understands that interests change—they won’t be pulling out your research statement to cross-reference with your dissertation proposal!
Evidence of Past Experience and Success
A great graduate school statement of purpose will also show programs that you have already been successful. They want applicants that will be able to follow through on their research/professional plans!
To this end, you’ll need to provide evidence of how your background qualifies you to pursue this program and your specific interests in the field. You’ll probably discuss your undergraduate studies and any professional experience you have. But be sure to draw on specific, vivid examples. You might draw on your thesis, major projects you’ve worked on, papers you have written/published, presentations you’ve given, mentors you’ve worked with, and so on. This gives admissions committees concrete evidence that you are qualified to undertake graduate study!

Interest and Fit With the Program
The third essential ingredient to a great statement of purpose is to clearly lay out why you and the program are a good fit. You should be able to identify both specific reasons why your work fits with the program and why the program suits your work/interests! Are there particular professors you’d like to work with? Does the department have a strong tradition in a certain methodology or theory you’re interested in? Is there a particular facet to the curriculum that you’d like to experience?
Showing that you and the program are a match shows that you chose the program thoughtfully and have genuine interest in it. Programs want to admit students who aren’t just passionate about the field. They want students who are genuinely enthused about their specific program and positioned to get the most out of what they have to offer.
Strong Writing
The final essential piece of a strong statement of purpose or letter of intent is strong writing. Writing skills are important for all graduate programs. You’ll need to demonstrate that you can clearly and effectively communicate your ideas in a way that flows logically. Additionally, you should show that you know how to write in a way that is descriptive but concise. A statement of purpose shouldn’t ever be longer than two pages, even without a hard word limit.
Admissions committees for humanities programs may be a little more focused on writing style than admissions officers for STEM programs. But even in quantitative and science-focused fields, written communication skills are an essential part of graduate school. So a strong statement of purpose will always be effectively written. You’ll see this in our statement of purpose for graduate school samples.

Real, Successful Statement of Purpose Samples
In this section, we’ll present four successful graduate school statement of purpose examples from our graduate school experts, along with a brief commentary on each statement. These statements come from a diverse selection of program types to show you how the core essentials of a statement of purpose can be implemented differently for different fields.
Note: identifying information for these statements have been changed—except for example four, which is my statement.
- Statement of Purpose Sample One: Japanese Studies MA

This statement of purpose is notable for its great use of space and its vivid descriptions. The author is able to cram a lot into about a page. She discusses how she came to her two primary research interests (and how they are connected). She integrates this discussion of her interests with information on her past experiences and qualifications for pursuing the course of study. Finally, she includes details on her goals in pursuing the program and components of the program that interest her. Her examples are specific and fleshed-out. There’s a lot very cleverly included in a small amount of page space!
Additionally, the language is very vivid. Phrases like “evocative and visceral” and “steadily unraveling,” are eye-catching and intriguing. They demonstrate that she has the writing skills necessary to pursue both graduate study and her interest in translation.
- Statement of Purpose Sample Two: Music MM
This sample is fairly long, although at 12 point Times New Roman it’s under two pages single-spaced. The length of this statement is partially due to the somewhat expansive nature of the prompt, which asks what role music has played in the applicant’s life “to date.” This invites applicants to speak more about experiences further in the past (in the childhood and teen years) than is typical for a statement of purpose. Given that this is for a master’s degree in music, this is logical; musical study is typically something that is undertaken at a fairly young age.
This statement does an excellent job describing the student’s past experiences with music in great detail. The descriptions of the student’s past compositions and experiences performing new music are particularly vivid and intriguing.
This statement also lays out and elaborates on specific goals the student hopes to pursue through the program, as well as features particular to the program that interest the student (like particular professors).

- Statement of Purpose Sample Three: Economics PhD

One of the first things you’ll likely notice about this statement is that it’s a little on the longer side. However, at 12 point Times New Roman font and single-spaced, it still comes in under 2 pages (excluding references). It makes sense for a PhD statement of purpose sample to be longer than a master’s degree statement of purpose—there’s more to lay out in terms of research interests!
The writing style is fairly straightforward—there’s definitely a stronger focus on delivering content than flashy writing style. As Economics is a more quantitative-focused field, this is fine. But the writing is still well-organized, clear, and error-free.
The writer also gives numerous examples of their past work and experience, and shows off their knowledge of the field through references, which is a nice touch.
- Statement of Purpose Sample Four: History of the Book MA
This is actually my statement of purpose. It was for a program that I got accepted to but did not end up attending, for a Master’s in the History of the Book. You’ll notice that the two essay prompts essentially asked us to split our statement of purpose into two parts: the first prompt asked about our research interests and goals, and the second prompt asked about our relevant experience and qualifications.
I’ll keep my comments on this graduate school statement of purpose sample brief because I’ll do a deep dive on it in the next section. But looking back at my statement of purpose, I do a good job outlining what within the field interests me and clearly laying out how my past experiences have qualified me for the program.
Obviously this statement did its job, since I was accepted to the program. However, if I were to improve this statement, I’d change the cliche beginning (“since I was a child”) and provide more specificity in what about the program interested me.

Deep Dive Analysis of a Sample Statement of Purpose for Graduate School
Next, we’ll do a paragraph by paragraph analysis of my statement, statement of purpose sample four. I’ll analyze its strengths and suggest ways I could shore up any weaknesses to make it even stronger.
Essay 1: Academic Interests
To refresh, here’s the first prompt: Please give a short statement that describes your academic interests, purpose, objectives and motivation in undertaking this postgraduate study. (max 3500 chars – approx. 500 words)
Want to improve your GRE score by 7 points? We have the industry's leading GRE prep program. Built by world-class instructors with 99th percentile GRE scores , the program learns your strengths and weaknesses through machine learning data science, then customizes your prep program to you so you get the most effective prep possible.
Try our 5-day full access trial for free:
Paragraph 1
Since I was a child, my favorite thing has always been a book. Not just for the stories and information they contain, although that is a large part of it. Mostly, I have been fascinated by the concept of book as object—a tangible item whose purpose is to relate intangible ideas and images. Bookbindings and jackets, different editions, the marginalia in a used book—all of these things become part of the individual book and its significance, and are worth study and consideration. Books and their equivalent forms—perfect bound, scrolled, stone tablets, papyrus—have long been an essential part of material culture and are also one of our most significant sources of information about the human historical past. Through both the literal object of the book, the words contained thereon, and its relationship to other books—forms of context, text and intertext—we are able to learn and hopefully manage layers of information with which we would otherwise have no familiarity.
First, the good: this paragraph does a good job introducing my academic interest in the book-as-object, and shows off pre-existing knowledge both of the study of material culture and literary theory. Additionally, the language is engaging: the juxtaposition of “tangible” and “intangible” in the beginning and phrases like “perfect bound, scrolled, stone tablets, papyrus” lend life to the writing and keep the reader engaged.
If I were to go back and improve this paragraph, first, I would absolutely change the first sentence to something less cliche than talking about my childhood. I might try something like “My love of books is a multifaceted thing. I don’t only love them for the stories and….” Second, I would chill out on the em dashes a little bit. Three sets in one paragraph is a little excessive. Finally, I might actually cut this paragraph down slightly to make more room word-wise later in the statement to discuss what specific things about the program interest me.

Paragraph 2
Furthermore, blogs, webcomics, digital archives, e-readers, and even social media sites like tumblr and Facebook have revolutionized the concept of the book by changing how we share and transmit ideas and information, just as the Gutenberg printing press revolutionized the book all those years ago in the fifteenth century. Once again there has been an explosion both in who can send out information and who can receive it.
This paragraph briefly and effectively introduces my other main academic interest: how new technology has changed the concept of the book-as-object. The tie-back to the printing press is a nice touch; it’s a vivid example that shows that I’m aware of important historical moments in book history.
Paragraph 3
I am deeply interested in the preservation of the physical book, as I think it is an important part of human history (not to mention a satisfying sensory experience for the reader). However I am also very concerned with the digitization and organization of information for the modern world such that the book, in all of its forms, stays relevant and easy to access and use. Collections of books, archives, and information as stored in the world’s servers, libraries and museums are essential resources that need to be properly organized and administered to be fully taken advantage of by their audiences. My purpose in applying to the University of Edinburgh’s Material Culture and History of the Book is to gain the skills necessary to keep all forms of the book relevant and functional in an age when information can move more radically than ever before.
This paragraph actually has a focus problem. Since it covers two topics, I should split it into two paragraphs: one on the integration of my two interests, and one on my goals and interests in the program. I could also stand to expand on what features the program has that interest me: professors I’d like to work with, particular aspects of the curriculum, etc.
In spite of these things, however, this paragraph does a good job clearly integrating the two academic interests related to the book I introduced in the first two paragraphs. And the language is still strong —“satisfying sensory experience” is a great phrase. However, I’ve been using the word “information,” a lot; I might try to replace with appropriate synonyms (like “knowledge”) in a couple of places.
Paragraph 4
Additionally, I intend on pursuing a PhD in Library and Information Sciences upon completion of my master’s and I feel that this program while make me uniquely suited to approach library science from a highly academic and interdisciplinary perspective.
This final paragraph offers just quick touch on my future goals beyond the program. It’s typically fine for this to be relatively brief, as it is here, just so long as you can clearly identify some future goals.

Essay 2: Relevant Experience
The second prompt just asked me to describe my relevant knowledge, training, and skills.
As a folklore and mythology student, I have gained a robust understanding of material culture and how it relates to culture as a whole. I have also learned about the transmission of ideas, information, stories and pieces of lore among and between populations, which is an important component of book history. Folklore is also deeply concerned with questions of the literary vs. oral lore and the tendency for text to “canonize” folklore, and yet text can also question or invert canonized versions; along with this my studies in my focus field of religion and storytelling have been deeply concerned with intertextuality. One of my courses was specifically concerned with the Heian-period Japanese novel The Tale of Genji and questions of translation and representation in post-Heian picture scrolls and also modern translations and manga. In addition to broader cultural questions concerned with gender and spirituality both in historical Japan and now, we considered the relationships between different Genji texts and images.
This is a strong, focused paragraph. I relate my academic background in Folklore and Mythology to my interests in studying the book, as well as showing off some of my knowledge in the area. I also chose and elaborated on a strong example (my class on the Tale of Genji ) of my relevant coursework.
I also have work experience that lends itself to the study of the book. After my freshman year of college I interned at the Chicago History Museum. Though I was in the visitor services department I was exposed to the preservation and archival departments of the museum and worked closely with the education department, which sparked my interest in archival collections and how museums present collection information to the public. After my sophomore year of college and into my junior year, I worked at Harvard’s rare books library, Houghton. At Houghton I prepared curated collections for archival storage. These collections were mostly comprised of the personal papers of noteworthy individuals, categorized into alphabetical folders. This experience made me very process-oriented and helped me to understand how collections come together on a holistic basis.
This paragraph also has a clear focus: my past, relevant work experience. Discussing archival collections and presenting information to the public links the interests discussed in my first statement with my qualifications in my second statement. However, if I were to revise this paragraph, I would add some specific examples of the amazing things I worked on and handled at Houghton Library. In that job, I got to touch Oliver Cromwell’s death mask! An interesting example would make this paragraph really pop even more.
Finally, in my current capacity as an education mentor in Allston, a suburb of Boston, I have learned the value of book history and material culture from an educational perspective. As a mentor who designs curriculum for individual students and small groups, I have learned to highly value clearly organized and useful educational resources such as websites, iPad apps, and books as tools for learning. By managing and organizing collections in a way that makes sense we are making information accessible to those who need it.
This final paragraph discusses my current (at the time) work experience in education and how that ties into my interest in the history of the book. It’s an intriguing connection and also harkens back to my discussion of information availability in the paragraph three of the first statement. Again, if I were to amp up this statement even more, I might include a specific example of a book-based (or book technology-based) project I did with one of my students. I worked on things like bookbinding and making “illuminated manuscripts” with some of my students; those would be interesting examples here.
This statement is split into two parts by virtue of the two-prompt format. However, if I were to integrate all of this information into one unified statement of purpose, I would probably briefly introduce my research interests, go in-depth on my background, then circle back around to speak more about my personal interests and goals and what intrigues me about the program. There’s not really one correct way to structure a statement of purpose just so long as it flows well and paragraphs are structured in a logical way: one topic per paragraph, with a clear topic and concluding sentence.

More Statement of Purpose Examples
We’ve provided you with four great graduate school statement of purpose examples from our graduate school experts. However, if you’re looking for more, there are other sample letters of intent and statements of purpose for graduate school online. We’ve rounded up the best ones here, along with some strengths and weaknesses about each example.
Majortests Statement of Purpose Sample
This is a fairly straightforward, clearly written statement of purpose sample for a biology program. It includes useful commentary after each paragraph about what this statement of purpose is accomplishing.
- This statement of purpose sample is well-organized, with clear topic sentences and points made in each paragraph.
- The student clearly identifies what interests her about the program.
- The student proactively addresses questions about why she hasn’t gone directly to graduate school, and frames her professional research experience as a positive thing.
- She gives a tiny bit of color about her personality in a relevant way by discussing her involvement with the Natural History Society.
- In general, discussing high school interests is too far back in time unless the anecdote is very interesting or unusual. The detail about The Theory of Evolution is intriguing; the information about the high school teacher seems irrelevant. The student should have condensed this paragraph into a sentence or two.
- While this statement is cogently written and makes the candidate sound competent and well-qualified, it’s not exactly the most scintillating piece of writing out there. Some of the constructions are a little awkward or cliche. For example, the “many people have asked me” sentence followed by “the answer is” is a little bit clunky. This is probably fine for a STEM program. But just be aware that this statement is not a paragon of writing style.
Want to improve your GRE score by 7+ points?
Check out our best-in-class online GRE prep program . We guarantee your money back if you don't improve your GRE score by 7 points or more.
PrepScholar GRE is entirely online, and it customizes your prep program to your strengths and weaknesses . We also feature 2,000 practice questions , official practice tests, 150 hours of interactive lessons, and 1-on-1 scoring and feedback on your AWA essays.
Check out our 5-day free trial now:
UC Berkeley History Statement of Purpose Sample
This is a graduate school statement of purpose example from the UC Berkeley History department’s PhD program, with annotations from a professor as to why it’s a successful statement.
- The author is able to very clearly and articulately lay out her research interests and link them to past work she has successfully completed, namely, her thesis.
- She is able to identify several things about the program and Berkeley that indicate why it is a good fit for her research interests.
- She addresses the time she spent away from school and frames it as a positive, emphasizing that her use of time was well-considered and productive.
- Her writing is very vivid, with excellent word choice and great imagery.
While very well-written and engaging, this sample statement of purpose for graduate school is a little bit on the long side! It’s a little over two single-spaced pages, which is definitely pushing the limits of acceptable length. Try to keep yours at 2 pages or less. Some of the information on the thesis (which comprises over half of the statement of purpose) could be condensed to bring it down to two pages.

Pharmacy Residency Letter of Intent Sample
This is not technically a sample letter of intent for graduate school because it’s actually for a pharmacy residency program. However, this example still provides illumination as to what makes a decent graduate school letter of intent sample.
- This is a serviceable letter of intent: the writer clearly lays out their own goals within the field of pharmacy, what qualifications they have and how they’ve arrived at their interests, and how the program fits their needs.
- The writing is clearly structured and well-organized.
- The main weakness is that some of the writer’s statements come across as fairly generic. For example, “The PGY-1 Residency Program at UO Hospitals will provide me with the opportunity to further develop my clinical knowledge, critical thinking, teaching, research, and leadership skills” is a generic statement that could apply to any residency program. A punchier, more program-specific conclusion would have amped up this letter.
- While the writer does a decent job providing examples of their activities, like working as a tutor and attending the APhA conference, more specificity and detail in these examples would make the statement more memorable.
- There’s a typo in the last paragraph —a “to” that doesn’t belong! This is an unprofessional blip in an otherwise solid letter. Read you own letter of intent aloud to avoid this!
NIU Bad Statement of Purpose Example
This is an ineffective graduate school statement of purpose example, with annotations on why it doesn’t work.
As you might imagine, the main strength in this document is as an example of what not to do. Otherwise, there is little to recommend it.
- The annotations quite clearly detail the weaknesses of this statement. So I won’t address them exhaustively except to point out that this statement of purpose fails at both content and style. The author includes irrelevant anecdotes and lists without offering a decisive picture of interests or any particular insight into the field. Additionally, the statement is riddled with grammatical mistakes, awkward sentence structures, and strange acronyms.
- You’ll note that the commentary advises you to “never start with a quote.” I agree that you should never start with a freestanding quote as in this example. However, I do think starting with a quote is acceptable in cases like the Berkeley history example above, where the quote is brief and then directly linked to the research interest.

Graduate School Statement of Purpose Examples: 4 Key Points
Graduate programs ask for statement of purpose to hear about your interests and goals and why you think you and the program would be a good fit.
There are four key elements to a successful statement of purpose:
- A clear articulation of your goals and interests
- Evidence of past experiences and success
- Interest and fit with the program
- Strong writing
We’ve provided you with four successful statement of purpose samples from our graduate school experts!
We also provided additional statement of purpose samples (and a sample letter of intent) for graduate school from other sources on the internet. Now you have all kinds of guidance!
What’s Next?
If you’re looking for more information on graduate school , see our guide to what makes a good GPA for grad school .
Not sure if you need to take the GRE ? See if you can get into graduate school without GRE scores .
Want more information about the GRE? We can help you figure out when to take the GRE , how to make a GRE study plan , and how to improve your GRE score .
Ready to improve your GRE score by 7 points?
Author: Ellen McCammon
Ellen is a public health graduate student and education expert. She has extensive experience mentoring students of all ages to reach their goals and in-depth knowledge on a variety of health topics. View all posts by Ellen McCammon

Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Welcome to the Purdue Online Writing Lab

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The Online Writing Lab at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service of the Writing Lab at Purdue. Students, members of the community, and users worldwide will find information to assist with many writing projects. Teachers and trainers may use this material for in-class and out-of-class instruction.
The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives. The Purdue OWL offers global support through online reference materials and services.
A Message From the Assistant Director of Content Development
The Purdue OWL® is committed to supporting students, instructors, and writers by offering a wide range of resources that are developed and revised with them in mind. To do this, the OWL team is always exploring possibilties for a better design, allowing accessibility and user experience to guide our process. As the OWL undergoes some changes, we welcome your feedback and suggestions by email at any time.
Please don't hesitate to contact us via our contact page if you have any questions or comments.
All the best,
Social Media
Facebook twitter.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The business purpose statement is about serving your customers and addressing their needs. The best way to identify what your customer desires is by asking them through surveys or polls and researching your customer base as a whole. 3. Consider your short- and long-term goals.
The first element of a purpose statement is the problem or opportunity that you are addressing. This should be a clear and specific description of the issue that you are trying to solve or the opportunity that you are pursuing. 2. The Target Audience. The second element is the target audience for your purpose statement.
10 Company Purpose Statement Examples. Here are 10 purpose statement examples across a variety of industries with a few thoughts on what makes them strong: AT&T: We create connection. This is both aspirational and ties to the company and its products and services over the years - which makes it believable.
A personal purpose statement is your internal compass; More subjective and reflects the unique motivations and aspirations of a person. Mainly written for yourself, explaining your life goals and motivations. Company purpose statements. A company purpose statement is the guiding principle of the entire organization.
If you're still feeling stuck, here are some steps to take as you're developing your company's purpose. Step #1: Define what you do. But more specifically, lay out what your company does to solve a particular problem for your customers. Step #2: Pinpoint your passion. Think about what inspires the work you do.
IKEA's Purpose: "To create a better everyday life for the many people.". Lego's Purpose: "To inspire and develop the builders of tomorrow.". SAP's Purpose: "To help the world run better and improve people's lives.". Microsoft's Purpose: "To empower every person and organization on this planet to achieve more.".
A purpose statement is a single, concise, declarative statement that identifies why a company exists. It is shared with customers and helps inform business decisions by outlining a business's direction and how it aims to inspire and positively impact others. Just like social capital, a purpose statement can cultivate goodwill with customers.
Form clear questions and take detailed notes. Word your company's purpose in a way that inspires room for thoughts while directly underlining your organization's value proposition. 3. It Should Be Short, Yet Powerful. Your business purpose should be and easy to remember, especially by your employees.
The method, or the plan of action, ... Implementing an effective business purpose statement means aligning all employees, directing the company, and sharing the vision with clients and potential customers. Consider the following strategies to integrate your business' purpose statement: 1. Employee onboarding and training
A business purpose statement should be short, one to a few sentences. Business purpose differs from vision or mission statements. While it should be specific to the type of work you plan to do, your business purpose statement should leave room for growth as well.
A statement of purpose is an integral component of your small business's overall strategic operation plan. This document contains your company's core philosophy and values, from which you measure ...
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
Business Plan: A business plan is a written document that describes in detail how a business, usually a new one, is going to achieve its goals. A business plan lays out a written plan from a ...
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow. A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It's also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals. After completing your plan, you can ...
A Purpose Statement is an explanation of the company's motivations and reasons for being, and why it works the way it does. A Mission Statement is a definition of the company's business, who it serves, what it does, its objectives, and its approach to reaching those objectives. A Vision Statement is a description of the desired future state ...
3. Capture your why. Think about why you started your business in the first place, and what impact you hope to make. Customers want to know the backstory for a brand and why they should feel ...
Statement of Purpose Outline Template. Introduction. 1.1 Briefly introduce yourself: [Your Name, Your Profession or Current Status] 1.2 Indicate why you are writing this statement of purpose: [Specific Purpose, e.g. applying for a job, graduate program, research grant, etc.]
It can be just a few sentences long. - Be specific: Avoid general statements like "to help people.". Instead, focus on a specific population or issue that your non-profit highlights. - Focus on the future: A great purpose statement should inspire people to support the work of your nonprofit. - Use positive language: Language that is ...
The statement of purpose (also known as a statement of intent or motivation letter) is your chance to stand out from the crowd and showcase your motivation, skills and potential. It should: Outline your academic or professional interests and goals. Discuss relevant skills, experience and achievements. Demonstrate why you'd be a good fit for ...
MBA statement of purpose sample 1. I often joke that I speak three languages: English, French, and consumer. I have been saying this since I took an introduction to marketing class while completing my undergraduate degree and learned about talking to customers in a language they understand.
A statement of purpose (SOP) is a critical component of most graduate school applications, and are often required for various types of graduate level programs, including Graduate Certificates and Master's Degrees. An SOP offers you the opportunity to showcase your motivations, qualifications, and aspirations to a school's Office of Admissions.
Tips for writing a successful MBA statement of purpose. As you write your SOP, here are a few things to keep in mind that can help your writing stand out: Clearly state your goals: Openly communicate your short-term and long-term goals in earning your MBA. Clear statements around this crucial element of your SOP can help you avoid any potential ...
We've provided you with four successful statement of purpose samples from our graduate school experts! Statement of Purpose Sample One: Japanese Studies MA. Statement of Purpose Sample Two: Music MM. Statement of Purpose Sample Three: Economics PhD. Statement of Purpose Sample Four: History of the Book MA.
The Online Writing Lab at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service of the Writing Lab at Purdue.
United Airlines - Airline Tickets, Travel Deals and Flights If you're seeing this message, that means JavaScript has been disabled on your browser, please enable JS ...