

6 Tips For Giving a Fabulous Academic Presentation
6-tips-for-giving-a-fabulous-academic-presentation.
Tanya Golash-Boza, Associate Professor of Sociology, University of California
January 11, 2022
One of the easiest ways to stand out at an academic conference is to give a fantastic presentation.
In this post, I will discuss a few simple techniques that can make your presentation stand out. Although, it does take time to make a good presentation, it is well worth the investment.
Tip #1: Use PowerPoint Judiciously
Images are powerful. Research shows that images help with memory and learning. Use this to your advantage by finding and using images that help you make your point. One trick I have learned is that you can use images that have blank space in them and you can put words in those images.
Here is one such example from a presentation I gave about immigration law enforcement.
PowerPoint is a great tool, so long as you use it effectively. Generally, this means using lots of visuals and relatively few words. Never use less than 24-point font. And, please, never put your presentation on the slides and read from the slides.
Tip #2: There is a formula to academic presentations. Use it.
Once you have become an expert at giving fabulous presentations, you can deviate from the formula. However, if you are new to presenting, you might want to follow it. This will vary slightly by field, however, I will give an example from my field – sociology – to give you an idea as to what the format should look like:
- Introduction/Overview/Hook
- Theoretical Framework/Research Question
- Methodology/Case Selection
- Background/Literature Review
- Discussion of Data/Results
Tip #3: The audience wants to hear about your research. Tell them.
One of the most common mistakes I see in people giving presentations is that they present only information I already know. This usually happens when they spend nearly all of the presentation going over the existing literature and giving background information on their particular case. You need only to discuss the literature with which you are directly engaging and contributing. Your background information should only include what is absolutely necessary. If you are giving a 15-minute presentation, by the 6 th minute, you need to be discussing your data or case study. At conferences, people are there to learn about your new and exciting research, not to hear a summary of old work.
Tip #4: Practice. Practice. Practice.
You should always practice your presentation in full before you deliver it. You might feel silly delivering your presentation to your cat or your toddler, but you need to do it and do it again. You need to practice to ensure that your presentation fits within the time parameters. Practicing also makes it flow better. You can’t practice too many times.
Tip #5: Keep To Your Time Limit
If you have ten minutes to present, prepare ten minutes of material. No more. Even if you only have seven minutes, you need to finish within the allotted time. If you write your presentation out, a general rule of thumb is two minutes per typed, double-spaced page. For a fifteen-minute talk, you should have no more than 7 double-spaced pages of material.
Tip #6: Don’t Read Your Presentation
Yes, I know that in some fields reading is the norm. But, can you honestly say that you find yourself engaged when listening to someone read their conference presentation? If you absolutely must read, I suggest you read in such a way that no one in the audience can tell you are reading. I have seen people do this successfully, and you can do it too if you write in a conversational tone, practice several times, and read your paper with emotion, conviction, and variation in tone.
What tips do you have for presenters? What is one of the best presentations you have seen? What made it so fantastic? Let us know in the comments below.
Want to learn more about the publishing process? The Wiley Researcher Academy is an online author training program designed to help researchers develop the skills and knowledge needed to be able to publish successfully. Learn more about Wiley Researcher Academy .
Image credit: Tanya Golash-Boza
Read the Mandarin version here .

Watch our Webinar to help you get published
Please enter your Email Address
Please enter valid email address
Please Enter your First Name
Please enter your Last Name
Please enter your Questions or Comments.
Please enter the Privacy
Please enter the Terms & Conditions

How research content supports academic integrity

Finding time to publish as a medical student: 6 tips for Success

Software to Improve Reliability of Research Image Data: Wiley, Lumina, and Researchers at Harvard Medical School Work Together on Solutions

Driving Research Outcomes: Wiley Partners with CiteAb

ISBN, ISSN, DOI: what they are and how to find them

Image Collections for Medical Practitioners with TDS Health

How do you Discover Content?

Writing for Publication for Nurses (Mandarin Edition)

Get Published - Your How to Webinar

Finding time to publish as a medical student: 6 tips for success
Related articles.
Learn how Wiley partners with plagiarism detection services to support academic integrity around the world
Medical student Nicole Foley shares her top tips for writing and getting your work published.
Wiley and Lumina are working together to support the efforts of researchers at Harvard Medical School to develop and test new machine learning tools and artificial intelligence (AI) software that can
Learn more about our relationship with a company that helps scientists identify the right products to use in their research
What is ISBN? ISSN? DOI? Learn about some of the unique identifiers for book and journal content.
Learn how medical practitioners can easily access and search visual assets from our article portfolio
Explore free-to-use services that can help you discover new content
Watch this webinar to help you learn how to get published.

How to Easily Access the Most Relevant Research: A Q&A With the Creator of Scitrus
Atypon launches Scitrus, a personalized web app that allows users to create a customized feed of the latest research.

Effectively and Efficiently Creating your Paper
FOR INDIVIDUALS
FOR INSTITUTIONS & BUSINESSES
WILEY NETWORK
ABOUT WILEY
Corporate Responsibility
Corporate Governance
Leadership Team
Cookie Preferences
Copyright @ 2000-2024 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc., or related companies. All rights reserved, including rights for text and data mining and training of artificial technologies or similar technologies.
Rights & Permissions
Privacy Policy
Terms of Use

Princeton Correspondents on Undergraduate Research
How to Make a Successful Research Presentation
Turning a research paper into a visual presentation is difficult; there are pitfalls, and navigating the path to a brief, informative presentation takes time and practice. As a TA for GEO/WRI 201: Methods in Data Analysis & Scientific Writing this past fall, I saw how this process works from an instructor’s standpoint. I’ve presented my own research before, but helping others present theirs taught me a bit more about the process. Here are some tips I learned that may help you with your next research presentation:
More is more
In general, your presentation will always benefit from more practice, more feedback, and more revision. By practicing in front of friends, you can get comfortable with presenting your work while receiving feedback. It is hard to know how to revise your presentation if you never practice. If you are presenting to a general audience, getting feedback from someone outside of your discipline is crucial. Terms and ideas that seem intuitive to you may be completely foreign to someone else, and your well-crafted presentation could fall flat.
Less is more
Limit the scope of your presentation, the number of slides, and the text on each slide. In my experience, text works well for organizing slides, orienting the audience to key terms, and annotating important figures–not for explaining complex ideas. Having fewer slides is usually better as well. In general, about one slide per minute of presentation is an appropriate budget. Too many slides is usually a sign that your topic is too broad.

Limit the scope of your presentation
Don’t present your paper. Presentations are usually around 10 min long. You will not have time to explain all of the research you did in a semester (or a year!) in such a short span of time. Instead, focus on the highlight(s). Identify a single compelling research question which your work addressed, and craft a succinct but complete narrative around it.
You will not have time to explain all of the research you did. Instead, focus on the highlights. Identify a single compelling research question which your work addressed, and craft a succinct but complete narrative around it.
Craft a compelling research narrative
After identifying the focused research question, walk your audience through your research as if it were a story. Presentations with strong narrative arcs are clear, captivating, and compelling.
- Introduction (exposition — rising action)
Orient the audience and draw them in by demonstrating the relevance and importance of your research story with strong global motive. Provide them with the necessary vocabulary and background knowledge to understand the plot of your story. Introduce the key studies (characters) relevant in your story and build tension and conflict with scholarly and data motive. By the end of your introduction, your audience should clearly understand your research question and be dying to know how you resolve the tension built through motive.
- Methods (rising action)
The methods section should transition smoothly and logically from the introduction. Beware of presenting your methods in a boring, arc-killing, ‘this is what I did.’ Focus on the details that set your story apart from the stories other people have already told. Keep the audience interested by clearly motivating your decisions based on your original research question or the tension built in your introduction.
- Results (climax)
Less is usually more here. Only present results which are clearly related to the focused research question you are presenting. Make sure you explain the results clearly so that your audience understands what your research found. This is the peak of tension in your narrative arc, so don’t undercut it by quickly clicking through to your discussion.
- Discussion (falling action)
By now your audience should be dying for a satisfying resolution. Here is where you contextualize your results and begin resolving the tension between past research. Be thorough. If you have too many conflicts left unresolved, or you don’t have enough time to present all of the resolutions, you probably need to further narrow the scope of your presentation.
- Conclusion (denouement)
Return back to your initial research question and motive, resolving any final conflicts and tying up loose ends. Leave the audience with a clear resolution of your focus research question, and use unresolved tension to set up potential sequels (i.e. further research).
Use your medium to enhance the narrative
Visual presentations should be dominated by clear, intentional graphics. Subtle animation in key moments (usually during the results or discussion) can add drama to the narrative arc and make conflict resolutions more satisfying. You are narrating a story written in images, videos, cartoons, and graphs. While your paper is mostly text, with graphics to highlight crucial points, your slides should be the opposite. Adapting to the new medium may require you to create or acquire far more graphics than you included in your paper, but it is necessary to create an engaging presentation.
The most important thing you can do for your presentation is to practice and revise. Bother your friends, your roommates, TAs–anybody who will sit down and listen to your work. Beyond that, think about presentations you have found compelling and try to incorporate some of those elements into your own. Remember you want your work to be comprehensible; you aren’t creating experts in 10 minutes. Above all, try to stay passionate about what you did and why. You put the time in, so show your audience that it’s worth it.
For more insight into research presentations, check out these past PCUR posts written by Emma and Ellie .
— Alec Getraer, Natural Sciences Correspondent
Share this:
- Share on Tumblr

Reference management. Clean and simple.
How to make a scientific presentation

Scientific presentation outlines
Questions to ask yourself before you write your talk, 1. how much time do you have, 2. who will you speak to, 3. what do you want the audience to learn from your talk, step 1: outline your presentation, step 2: plan your presentation slides, step 3: make the presentation slides, slide design, text elements, animations and transitions, step 4: practice your presentation, final thoughts, frequently asked questions about preparing scientific presentations, related articles.
A good scientific presentation achieves three things: you communicate the science clearly, your research leaves a lasting impression on your audience, and you enhance your reputation as a scientist.
But, what is the best way to prepare for a scientific presentation? How do you start writing a talk? What details do you include, and what do you leave out?
It’s tempting to launch into making lots of slides. But, starting with the slides can mean you neglect the narrative of your presentation, resulting in an overly detailed, boring talk.
The key to making an engaging scientific presentation is to prepare the narrative of your talk before beginning to construct your presentation slides. Planning your talk will ensure that you tell a clear, compelling scientific story that will engage the audience.
In this guide, you’ll find everything you need to know to make a good oral scientific presentation, including:
- The different types of oral scientific presentations and how they are delivered;
- How to outline a scientific presentation;
- How to make slides for a scientific presentation.
Our advice results from delving into the literature on writing scientific talks and from our own experiences as scientists in giving and listening to presentations. We provide tips and best practices for giving scientific talks in a separate post.
There are two main types of scientific talks:
- Your talk focuses on a single study . Typically, you tell the story of a single scientific paper. This format is common for short talks at contributed sessions in conferences.
- Your talk describes multiple studies. You tell the story of multiple scientific papers. It is crucial to have a theme that unites the studies, for example, an overarching question or problem statement, with each study representing specific but different variations of the same theme. Typically, PhD defenses, invited seminars, lectures, or talks for a prospective employer (i.e., “job talks”) fall into this category.
➡️ Learn how to prepare an excellent thesis defense
The length of time you are allotted for your talk will determine whether you will discuss a single study or multiple studies, and which details to include in your story.
The background and interests of your audience will determine the narrative direction of your talk, and what devices you will use to get their attention. Will you be speaking to people specializing in your field, or will the audience also contain people from disciplines other than your own? To reach non-specialists, you will need to discuss the broader implications of your study outside your field.
The needs of the audience will also determine what technical details you will include, and the language you will use. For example, an undergraduate audience will have different needs than an audience of seasoned academics. Students will require a more comprehensive overview of background information and explanations of jargon but will need less technical methodological details.
Your goal is to speak to the majority. But, make your talk accessible to the least knowledgeable person in the room.
This is called the thesis statement, or simply the “take-home message”. Having listened to your talk, what message do you want the audience to take away from your presentation? Describe the main idea in one or two sentences. You want this theme to be present throughout your presentation. Again, the thesis statement will depend on the audience and the type of talk you are giving.
Your thesis statement will drive the narrative for your talk. By deciding the take-home message you want to convince the audience of as a result of listening to your talk, you decide how the story of your talk will flow and how you will navigate its twists and turns. The thesis statement tells you the results you need to show, which subsequently tells you the methods or studies you need to describe, which decides the angle you take in your introduction.
➡️ Learn how to write a thesis statement
The goal of your talk is that the audience leaves afterward with a clear understanding of the key take-away message of your research. To achieve that goal, you need to tell a coherent, logical story that conveys your thesis statement throughout the presentation. You can tell your story through careful preparation of your talk.
Preparation of a scientific presentation involves three separate stages: outlining the scientific narrative, preparing slides, and practicing your delivery. Making the slides of your talk without first planning what you are going to say is inefficient.
Here, we provide a 4 step guide to writing your scientific presentation:
- Outline your presentation
- Plan your presentation slides
- Make the presentation slides
- Practice your presentation

Writing an outline helps you consider the key pieces of your talk and how they fit together from the beginning, preventing you from forgetting any important details. It also means you avoid changing the order of your slides multiple times, saving you time.
Plan your talk as discrete sections. In the table below, we describe the sections for a single study talk vs. a talk discussing multiple studies:
Introduction | Introduction - main idea behind all studies |
Methods | Methods of study 1 |
Results | Results of study 1 |
Summary (take-home message ) of study 1 | |
Transition to study 2 (can be a visual of your main idea that return to) | |
Brief introduction for study 2 | |
Methods of study 2 | |
Results of study 2 | |
Summary of study 2 | |
Transition to study 3 | |
Repeat format until done | |
Summary | Summary of all studies (return to your main idea) |
Conclusion | Conclusion |
The following tips apply when writing the outline of a single study talk. You can easily adapt this framework if you are writing a talk discussing multiple studies.
Introduction: Writing the introduction can be the hardest part of writing a talk. And when giving it, it’s the point where you might be at your most nervous. But preparing a good, concise introduction will settle your nerves.
The introduction tells the audience the story of why you studied your topic. A good introduction succinctly achieves four things, in the following order.
- It gives a broad perspective on the problem or topic for people in the audience who may be outside your discipline (i.e., it explains the big-picture problem motivating your study).
- It describes why you did the study, and why the audience should care.
- It gives a brief indication of how your study addressed the problem and provides the necessary background information that the audience needs to understand your work.
- It indicates what the audience will learn from the talk, and prepares them for what will come next.
A good introduction not only gives the big picture and motivations behind your study but also concisely sets the stage for what the audience will learn from the talk (e.g., the questions your work answers, and/or the hypotheses that your work tests). The end of the introduction will lead to a natural transition to the methods.
Give a broad perspective on the problem. The easiest way to start with the big picture is to think of a hook for the first slide of your presentation. A hook is an opening that gets the audience’s attention and gets them interested in your story. In science, this might take the form of a why, or a how question, or it could be a statement about a major problem or open question in your field. Other examples of hooks include quotes, short anecdotes, or interesting statistics.
Why should the audience care? Next, decide on the angle you are going to take on your hook that links to the thesis of your talk. In other words, you need to set the context, i.e., explain why the audience should care. For example, you may introduce an observation from nature, a pattern in experimental data, or a theory that you want to test. The audience must understand your motivations for the study.
Supplementary details. Once you have established the hook and angle, you need to include supplementary details to support them. For example, you might state your hypothesis. Then go into previous work and the current state of knowledge. Include citations of these studies. If you need to introduce some technical methodological details, theory, or jargon, do it here.
Conclude your introduction. The motivation for the work and background information should set the stage for the conclusion of the introduction, where you describe the goals of your study, and any hypotheses or predictions. Let the audience know what they are going to learn.
Methods: The audience will use your description of the methods to assess the approach you took in your study and to decide whether your findings are credible. Tell the story of your methods in chronological order. Use visuals to describe your methods as much as possible. If you have equations, make sure to take the time to explain them. Decide what methods to include and how you will show them. You need enough detail so that your audience will understand what you did and therefore can evaluate your approach, but avoid including superfluous details that do not support your main idea. You want to avoid the common mistake of including too much data, as the audience can read the paper(s) later.
Results: This is the evidence you present for your thesis. The audience will use the results to evaluate the support for your main idea. Choose the most important and interesting results—those that support your thesis. You don’t need to present all the results from your study (indeed, you most likely won’t have time to present them all). Break down complex results into digestible pieces, e.g., comparisons over multiple slides (more tips in the next section).
Summary: Summarize your main findings. Displaying your main findings through visuals can be effective. Emphasize the new contributions to scientific knowledge that your work makes.
Conclusion: Complete the circle by relating your conclusions to the big picture topic in your introduction—and your hook, if possible. It’s important to describe any alternative explanations for your findings. You might also speculate on future directions arising from your research. The slides that comprise your conclusion do not need to state “conclusion”. Rather, the concluding slide title should be a declarative sentence linking back to the big picture problem and your main idea.
It’s important to end well by planning a strong closure to your talk, after which you will thank the audience. Your closing statement should relate to your thesis, perhaps by stating it differently or memorably. Avoid ending awkwardly by memorizing your closing sentence.
By now, you have an outline of the story of your talk, which you can use to plan your slides. Your slides should complement and enhance what you will say. Use the following steps to prepare your slides.
- Write the slide titles to match your talk outline. These should be clear and informative declarative sentences that succinctly give the main idea of the slide (e.g., don’t use “Methods” as a slide title). Have one major idea per slide. In a YouTube talk on designing effective slides , researcher Michael Alley shows examples of instructive slide titles.
- Decide how you will convey the main idea of the slide (e.g., what figures, photographs, equations, statistics, references, or other elements you will need). The body of the slide should support the slide’s main idea.
- Under each slide title, outline what you want to say, in bullet points.
In sum, for each slide, prepare a title that summarizes its major idea, a list of visual elements, and a summary of the points you will make. Ensure each slide connects to your thesis. If it doesn’t, then you don’t need the slide.
Slides for scientific presentations have three major components: text (including labels and legends), graphics, and equations. Here, we give tips on how to present each of these components.
- Have an informative title slide. Include the names of all coauthors and their affiliations. Include an attractive image relating to your study.
- Make the foreground content of your slides “pop” by using an appropriate background. Slides that have white backgrounds with black text work well for small rooms, whereas slides with black backgrounds and white text are suitable for large rooms.
- The layout of your slides should be simple. Pay attention to how and where you lay the visual and text elements on each slide. It’s tempting to cram information, but you need lots of empty space. Retain space at the sides and bottom of your slides.
- Use sans serif fonts with a font size of at least 20 for text, and up to 40 for slide titles. Citations can be in 14 font and should be included at the bottom of the slide.
- Use bold or italics to emphasize words, not underlines or caps. Keep these effects to a minimum.
- Use concise text . You don’t need full sentences. Convey the essence of your message in as few words as possible. Write down what you’d like to say, and then shorten it for the slide. Remove unnecessary filler words.
- Text blocks should be limited to two lines. This will prevent you from crowding too much information on the slide.
- Include names of technical terms in your talk slides, especially if they are not familiar to everyone in the audience.
- Proofread your slides. Typos and grammatical errors are distracting for your audience.
- Include citations for the hypotheses or observations of other scientists.
- Good figures and graphics are essential to sustain audience interest. Use graphics and photographs to show the experiment or study system in action and to explain abstract concepts.
- Don’t use figures straight from your paper as they may be too detailed for your talk, and details like axes may be too small. Make new versions if necessary. Make them large enough to be visible from the back of the room.
- Use graphs to show your results, not tables. Tables are difficult for your audience to digest! If you must present a table, keep it simple.
- Label the axes of graphs and indicate the units. Label important components of graphics and photographs and include captions. Include sources for graphics that are not your own.
- Explain all the elements of a graph. This includes the axes, what the colors and markers mean, and patterns in the data.
- Use colors in figures and text in a meaningful, not random, way. For example, contrasting colors can be effective for pointing out comparisons and/or differences. Don’t use neon colors or pastels.
- Use thick lines in figures, and use color to create contrasts in the figures you present. Don’t use red/green or red/blue combinations, as color-blind audience members can’t distinguish between them.
- Arrows or circles can be effective for drawing attention to key details in graphs and equations. Add some text annotations along with them.
- Write your summary and conclusion slides using graphics, rather than showing a slide with a list of bullet points. Showing some of your results again can be helpful to remind the audience of your message.
- If your talk has equations, take time to explain them. Include text boxes to explain variables and mathematical terms, and put them under each term in the equation.
- Combine equations with a graphic that shows the scientific principle, or include a diagram of the mathematical model.
- Use animations judiciously. They are helpful to reveal complex ideas gradually, for example, if you need to make a comparison or contrast or to build a complicated argument or figure. For lists, reveal one bullet point at a time. New ideas appearing sequentially will help your audience follow your logic.
- Slide transitions should be simple. Silly ones distract from your message.
- Decide how you will make the transition as you move from one section of your talk to the next. For example, if you spend time talking through details, provide a summary afterward, especially in a long talk. Another common tactic is to have a “home slide” that you return to multiple times during the talk that reinforces your main idea or message. In her YouTube talk on designing effective scientific presentations , Stanford biologist Susan McConnell suggests using the approach of home slides to build a cohesive narrative.
To deliver a polished presentation, it is essential to practice it. Here are some tips.
- For your first run-through, practice alone. Pay attention to your narrative. Does your story flow naturally? Do you know how you will start and end? Are there any awkward transitions? Do animations help you tell your story? Do your slides help to convey what you are saying or are they missing components?
- Next, practice in front of your advisor, and/or your peers (e.g., your lab group). Ask someone to time your talk. Take note of their feedback and the questions that they ask you (you might be asked similar questions during your real talk).
- Edit your talk, taking into account the feedback you’ve received. Eliminate superfluous slides that don’t contribute to your takeaway message.
- Practice as many times as needed to memorize the order of your slides and the key transition points of your talk. However, don’t try to learn your talk word for word. Instead, memorize opening and closing statements, and sentences at key junctures in the presentation. Your presentation should resemble a serious but spontaneous conversation with the audience.
- Practicing multiple times also helps you hone the delivery of your talk. While rehearsing, pay attention to your vocal intonations and speed. Make sure to take pauses while you speak, and make eye contact with your imaginary audience.
- Make sure your talk finishes within the allotted time, and remember to leave time for questions. Conferences are particularly strict on run time.
- Anticipate questions and challenges from the audience, and clarify ambiguities within your slides and/or speech in response.
- If you anticipate that you could be asked questions about details but you don’t have time to include them, or they detract from the main message of your talk, you can prepare slides that address these questions and place them after the final slide of your talk.
➡️ More tips for giving scientific presentations
An organized presentation with a clear narrative will help you communicate your ideas effectively, which is essential for engaging your audience and conveying the importance of your work. Taking time to plan and outline your scientific presentation before writing the slides will help you manage your nerves and feel more confident during the presentation, which will improve your overall performance.
A good scientific presentation has an engaging scientific narrative with a memorable take-home message. It has clear, informative slides that enhance what the speaker says. You need to practice your talk many times to ensure you deliver a polished presentation.
First, consider who will attend your presentation, and what you want the audience to learn about your research. Tailor your content to their level of knowledge and interests. Second, create an outline for your presentation, including the key points you want to make and the evidence you will use to support those points. Finally, practice your presentation several times to ensure that it flows smoothly and that you are comfortable with the material.
Prepare an opening that immediately gets the audience’s attention. A common device is a why or a how question, or a statement of a major open problem in your field, but you could also start with a quote, interesting statistic, or case study from your field.
Scientific presentations typically either focus on a single study (e.g., a 15-minute conference presentation) or tell the story of multiple studies (e.g., a PhD defense or 50-minute conference keynote talk). For a single study talk, the structure follows the scientific paper format: Introduction, Methods, Results, Summary, and Conclusion, whereas the format of a talk discussing multiple studies is more complex, but a theme unifies the studies.
Ensure you have one major idea per slide, and convey that idea clearly (through images, equations, statistics, citations, video, etc.). The slide should include a title that summarizes the major point of the slide, should not contain too much text or too many graphics, and color should be used meaningfully.

10 Ways to Make Academic Presentations More Interesting

If you’ve ever sat through an academic presentation, you know how quickly you can fall asleep, become bored, confused, or overwhelmed. If you’re given the task of presenting an academic topic, you know the challenges you face in keeping your audience engaged and interested. Applying the 10 tips below will help you overcome the obstacles academic presenters face:
Use less text and even less numbers
We always recommend using visuals as opposed to text when giving a presentation; this advice particularly applies to academic topics because there is a great temptation to mix in a lot of words, numbers, or codes to inform the audience. This may work for speeches but with academic subjects you want to support and interpret words and numbers with visuals and not repeat them. Regardless of the subject being discussed, slides are intended to engage the audience with clear and colorful graphics, graphs, and tables—not as a teleprompter for the speaker. Even an audience of PhD students are like any other human being: highly visual.
Avoid information overload
Whether presenting templates, words, graphs, or figures, the rule of thumb is K.I.S.S—keep it short and simple. Your audience can only take so much information. Divide the body of your presentation into the three main points you want the audience to recall and process and limit your diagrams to a maximum of seven components.
Employ nonverbal cues
Experienced presenters know that how something is presented can be more crucial than what is being presented. And presenting important academic material is no exception. Aside from using visual aids, engage the audience’s senses. Establish eye contact, vary your tone of voice, make the appropriate facial expressions and natural gestures, and convey a high level of energy and confidence—in most cases these are more important than the words you say. As long as these nonverbal cues are not distracting, your audience will stay interested and actually believe what you’re saying.
Know your audience
Understand their learning style and knowledge level before giving your presentation including what information they need to know. Most guidelines recommend presenting the bigger picture first before drilling down the details but some actually learn faster the opposite way. Many academia professionals also make the mistake of establishing a rapport with a select group of people in the audience, such as those in the more advanced level, even if the majority of the listeners are unfamiliar with the subject at hand.
Engage your audience
It’s important to check if your audience understands your message every now and then, especially for academic topics. Get your audience to participate by engaging them in a discussion rather than just talking to them.
Employ humor, surprises, and practical examples
Just because an academic topic is serious and complex doesn’t mean you can’t do what presenters of other subjects do to keep their audience interested and awake like telling a joke or structuring your presentation as a unique story . Move beyond PowerPoint slides while speaking, especially when you need your audience to totally focus on the matter at hand.
Go back to the basics
This is another common mistake in presenting academic matters. Many people have a tendency to use complex jargon to make them appear intellectual, credible, or sophisticated but this only makes your topic incomprehensible. Again, the presentation is for the audience so you want to inform the audience about a topic they don’t know, not simply inform them that you know something they don’t.
Practice, practice, practice
There is truth to the saying “practice makes perfect.” Rehearse the presentation, including any jokes or stories, multiple times until it becomes so natural you no longer need a script and will only have to establish rapport with your audience come presentation day. Try recording your presentation to make a realistic assessment.
End your presentation with a summary
Have your audience leave the room with a clear understanding of your message or what they have to do with a brief conclusion using large and readable fonts or graphics. When using fonts for technical matters , avoid using comic sans or fonts smaller than 28 points.
Don’t make your presentation your handout
An academic presentation is a talk about an idea and not the paper itself; your presentation should support rather than document the paper. Hence, prepare a separate handout, if necessary, containing essential words and visuals for the audience.
Indeed, with the right techniques and approach, you can turn even the most boring topic into something interesting, useful, and exciting.
Do you have other ways to perk up your audience during an academic presentation? Let us know by commenting below.
Create professional presentations online
Other people also read
9 Ideas For Your Next PowerPoint Presentation

10 Tips to Make Your PowerPoint Presentation Effective

5 Design Principles of Improving your Presentation Style
How to Prepare and Give a Scholarly Oral Presentation
- First Online: 01 January 2020
Cite this chapter

- Cheryl Gore-Felton 2
1259 Accesses
Building an academic reputation is one of the most important functions of an academic faculty member, and one of the best ways to build a reputation is by giving scholarly presentations, particularly those that are oral presentations. Earning the reputation of someone who can give an excellent talk often results in invitations to give keynote addresses at regional and national conferences, which increases a faculty member’s visibility along with their area of research. Given the importance of oral presentations, it is surprising that few graduate or medical programs provide courses on how to give a talk. This is unfortunate because there are skills that can be learned and strategies that can be used to improve the ability to give an interesting, well-received oral presentation. To that end, the aim of this chapter is to provide faculty with best practices and tips on preparing and giving an academic oral presentation.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others

Strategies for the Preparation and Delivery of Oral Presentation

Graduate Students and Learning How to Get Published
Pashler H, McDaniel M, Rohrer D, Bjork R. Learning styles: concepts and evidence. Psychol Sci Public Interest. 2009;9:105–19.
Article Google Scholar
Newsam JM. Out in front: making your mark with a scientific presentation. USA: First Printing; 2019.
Google Scholar
Ericsson AK, Krampe RT, Tesch-Romer C. The role of deliberate practice in the acquisition of expert performance. Psychol Rev. 1993;100:363–406.
Seaward BL. Managing stress: principles and strategies for health and well-being. 7th ed. Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC: Burlington; 2012.
Krantz WB. Presenting an effective and dynamic technical paper: a guidebook for novice and experienced speakers in a multicultural world. Philadelphia: Elsevier; 2017.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences, Stanford University School of Medicine, Stanford, CA, USA
Cheryl Gore-Felton
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Cheryl Gore-Felton .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Laura Weiss Roberts
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Gore-Felton, C. (2020). How to Prepare and Give a Scholarly Oral Presentation. In: Roberts, L. (eds) Roberts Academic Medicine Handbook. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-31957-1_42
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-31957-1_42
Published : 01 January 2020
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-030-31956-4
Online ISBN : 978-3-030-31957-1
eBook Packages : Medicine Medicine (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

Ten smart ways to ace your next academic presentation
Using examples and practical tips, Dorsa Amir explains the techniques that ensure your presentation communicates its message effectively – from slide design to structuring your talk

You may also like

Popular resources
.css-1txxx8u{overflow:hidden;max-height:81px;text-indent:0px;} The secrets to success as a provost
Using non verbal cues to build rapport with students, emotionally challenging research and researcher well-being, augmenting the doctoral thesis in preparation for a viva, how hard can it be testing ai detection tools.
As a presenter, your main job is to guide the audience through your argument in the clearest, most engaging, most efficient way possible. You must respect the audience’s time and attention. This means being mindful of how long your presentation is, what you’re including in your slides, and importantly, how it is all packaged and presented.
A great presenter is one who is intentional: each element in the presentation serves a clear function and is intended to support the audience’s understanding of the content.
Here are 10 tips to keep in mind to ensure your presentation hits the mark
1. Any time you put something on your slides, its primary purpose is to help the audience, not you
Many presenters will add copious text or other elements to help themselves remember points they want to make. However, this is usually less helpful for the audience (most of this information belongs in presenter notes, and not on the slides). Think of yourself like a director of a movie. What do you want the audience to focus on at any given moment? What features on your slides will enhance the verbal point you are making and which will distract from it? Be intentional about what you include on your slides, and only include elements that serve a clear and helpful function for the audience.
2. Condense text to the main question or key points of the slide
It may be tempting to write out snippets of the script wholesale and add them to the slides, but this often results in PowerPoint karaoke, where the audience is simply watching you read the text out loud to them. While text is certainly useful for helping to concretise points or make slides more accessible, be judicious about what you include. Each slide should make one or two clear points. It’s better to have more slides with less content than fewer slides that are jam-packed. Of course, the amount of text you include will also be determined by the type of presentation you are giving. If students will be using your slides as a study aid, for example, you may want to include more information than if you are creating a research talk for a conference.

3. Avoid using too many colours, fonts or animations
Consider elements such as fonts, colours and animations as tools in your presentation toolkit. These elements should be used sparingly and only when they serve a clear purpose. I’m sure you’ve all attended a talk with colours bright enough to burn your retinas or crammed with “fun” fonts such as Comic Sans. Try to refrain from doing that. Animations that allow certain elements to appear or disappear along with your presentation — such as bullet points that appear as you say them — can help direct the attention of the audience. Colour contrasts are primarily helpful for visual segmentation or bringing attention to particular elements. Fonts, colours or flashy animations that are purely decorative are more distracting than helpful.

4. Avoid colour combinations that are hard to read
Be mindful of how colours interact with each other to either facilitate or inhibit comprehension. White text on black (or the reverse) is often a safe bet. Don’t overdecorate! (See above).
5. If you’re showing a graph, orient the audience to the axes before plotting the data and make sure they can actually see all of it
I typically show the axes and labels first, making sure to orient everyone to the variables and how they are going to be visualised, and then I reveal the data. This ensures that everyone understands how to interpret the visualisation they are about to see. It is also helpful to restate the key prediction and tell the audience what they should expect to see if the prediction is true, and then plot the data. Use large sizes and clear fonts. I’ve heard way too many people say things like: “You probably can’t read this but…” To that, I want to say: “But you’re the one making the slide! You did this to us!” Don’t be that person.
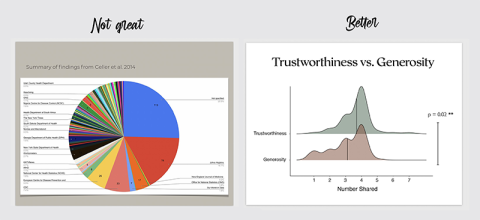
6. Use high-resolution images or videos
This is especially true for presentations that will be projected onto a larger surface. If it’s fuzzy on your computer screen, it will look even fuzzier when magnified and projected. Try to integrate high-resolution images and vector graphics to avoid this. When your images contain text, delete those portions and re-enter the text in text boxes that will scale up much more clearly when magnified.
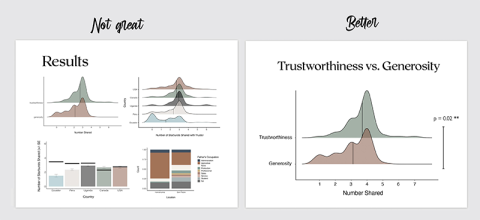
7. When illustrating results, identify one or two key graphs to make your point
The temptation is often to show the audience every single result you found, but this dilutes the overall message you are trying to send. There’s no need to visualise everything: you should focus on the key graphs that tell most or all of the story. If you have built up the presentation in the right way, when the audience see your data visualisation, they will immediately understand what you found and whether it supports your hypothesis. That’s how clear and accessible the graph should be.
8. Don’t overload the audience with unnecessary complex jargon or acronyms
Every time you introduce a new term or a brand new acronym (BNA), you are asking the audience to do you a favour and commit this new item to working memory. The audience doesn’t know your presentation; they don’t know what’s going to be important later and what isn’t. They’re trusting that you are only presenting information to them that is relevant and they’re doing their best to follow along. Make this process as easy and enjoyable as possible for them. Be judicious with what you ask them to remember or commit to memory. If you can explain a concept without jargon, avoid the jargon!
9. Enhance accessibility
The Web Accessibility Initiative has a great set of guidelines that I will summarise here. Use easy-to-read fonts in large sizes. Make sure there is enough contrast between colours to make them discernible. When giving virtual talks, consider turning on automatic closed captioning. If it’s feasible, provide annotated slide handouts. During the presentation itself, speak clearly and loudly, avoiding unnecessarily complex vocabulary or culturally specific idioms. Where possible, use a microphone. You should also try to verbally describe pertinent parts of visual information on your slides, such as graphics or videos.
10. Use outline slides and marker slides to segment information
Research shows that we understand and remember information better when it comes in bite-size pieces; think of chapters in a book. To incorporate this structure into your talk, break apart the presentation into smaller pieces. Always incorporate an outline slide that previews the structure of the talk and gives the audience a sense of what to expect. Also, use marker slides to communicate that a new section is beginning. And make sure to wrap up each section with a summary slide.

Dorsa Amir is a postdoc in the department of psychology at the University of California, Berkeley.
If you would like advice and insight from academics and university staff delivered direct to your inbox each week, sign up for the Campus newsletter .
The secrets to success as a provost
Emotions and learning: what role do emotions play in how and why students learn, the podcast: bringing an outsider’s eye to primary sources, a diy guide to starting your own journal, formative, summative or diagnostic assessment a guide, harnessing the power of data to drive student success.
Register for free
and unlock a host of features on the THE site
Academic presentations: Structure
- Presentation Design
- Slide design
- Conferences
- Group presentations
Jump to content on this page:
“A solid structure is the foundation of a coherent presentation, and shows the relationship between the parts and whole.” Nancy Duarte, Resonate
A presentation that has a strong, clear structure is a presentation that is easy to follow. Without structure, a presentation can be confusing to an audience. How do they know if you are going to cover what they need to know? How can they tell which slides contain the most important points? This page considers some ways that you can organise your slides to give shape to your presentation as a whole.
Basic presentation structure
Every presentation should flow like a good story. It should involve the audience directly.
- The beginning section is where you hook them. Start with the general picture then explain the specific problem and how by listening to your presentation you can solve it for them.
- The middle section should contain the main detail of your presentation, and can be organised in a number of ways (two good ones are explained below).
- Finally your end section should summarise the presentation and lead the audience to the next step.
Design your slides so that these sections look distinctive and any key points stand out.
Beginning section
This section is all about drawing the audience in; giving them a reason to want to listen to the main part of your presentation.
You can include any or all of the following:
- A really well designed title slide that grabs the attention
- A slide that gives the audience the big picture
- A slide that shows what you will be focusing on
- A slide that uses the word 'you' or 'your' in the title to connect with the audience
- A slide that tells the audience what is to come in your presentation (its structure)

After your title slide, you need slides covering these areas
Middle section structure option 1 - key points
Several authors suggest using a structure that involves an introduction followed by a middle section containing key point slides (usually 3).
The ideas is that there is a hierarchy of slides so that after each key point you have other slides that explain or add detail to that key point.
Cliff Atkinson (writer of the book Beyond Bullet Points ) suggested using a table in MSWord (similar to the one in the template that is available to download at the bottom of this page) to help you structure and plan your presentation before you even open PowerPoint. This means you can concentrate on your story before getting distracted by design and content issues. We have copy of the book in our library: Beyond Bullet Points: Beyond Bullet Points .
Middle section option 2 - sparkline
For her book Resonate Nancy Duarte looked in detail at the structure of successful presentations throughout history (even back to Lincoln's Gettysburg Address). She discovered that many have the same structural form which she calls a 'sparkline'.

This structure makes a clear distinction between what is (the position before the presentation is seen and acted upon) and what could be (the position after the presentation is seen and acted upon). The audience is introduced to the what is state at the beginning of the presentation and then switched back and forth between what could be and what is several times before ending in the what could be condition, which she calls Reward:New Bliss .
Nancy explains this better here: Sparkline Overview .
In terms of academic work the what is is the current level of knowledge or previous thinking on a subject and the what could be is the new knowledge or new thinking. The new bliss is what the audience could do or learn next now that they are aware of the change.
End section
The end of your presentation is a very powerful part because it contains your final words, the ones that the audience will take away with them. After you have finished your middle section, have at least one slide that summarises your main points and one slide that leaves the audience with the most important point of your presentation - the one you would like them to remember even if they forget everything else.

Include slides that show these in your end section
DO NOT finish with a slide that says Any Questions? or Thanks for Listening as this a waste of your final slide and does not need a visual image to help the audience understand your words. This slide could potentially be viewed longer than any other slide (whilst you answer your questions or receive feedback) and so you want to make sure it contains something that is important to both you and the audience.

These slides are a waste of your last slide - use the final slide for your most important point not a throwaway.
Template for structuring an academic presentation

This MSWord document is a template for structuring a typical academic presentation, it can be adapted and changed if necessary depending on how long the presentation you need to give is. Try to fill it in using full sentences as these will become your slide titles .
The blue sections are optional. The NEED and TASK sections are most suited to research presentations.
This is designed for a presentation between 20-30 minutes long. Shorter presentations will have no explanatory points and longer presentations will need more explanatory points.
This is adapted from Cliff Atkinson's Beyond Bullet Points template. See the link to the book above.
- << Previous: Home
- Next: Presentation Design >>
- Last Updated: Nov 29, 2023 11:42 AM
- URL: https://libguides.hull.ac.uk/present
- Login to LibApps
- Library websites Privacy Policy
- University of Hull privacy policy & cookies
- Website terms and conditions
- Accessibility
- Report a problem
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Academic Module 3: Giving Academic Presentations
17 Giving Academic Presentations: Talks, Power Points, and Posters
As mentioned earlier, students enrolled in college courses, especially in the U.S., are often required to demonstrate their knowledge and perspectives on a given topic in the form of oral presentations. Before we look at the different formats these presentations may occur in, let’s first look at the tasks of preparing and giving presentations through the lens of audience, purpose, and parameters, or APP.
Audience, Purpose, and Parameters (APP)
Let’s start with the first criterion–the audience.
- When you present information orally, whether informally (e.g. while participating in a discussion in the class) or formally (e.g. a graded individual or group presentation on a topic assigned by the professor), who is the target audience? Generally, students present ideas and information to the members of the classroom community, which include both the professor and other students. In this case, you would again need to decide about the language(s) and the appropriate tone or register you would need to use. In other words, who your audience is informs what you say and what you write in a college course. Therefore, it is very helpful to identify clearly who the target audience is for any academic assignment, especially presentations.
Now, let’s look at the second criterion–the purpose.
- The purpose of a presentation, individual or group, may vary. Some presentations are informative, others are descriptive, and some tend to be persuasive. Some presentations combine all of these elements. The patterns that are used in composing an essay are used in oral presentations as well. To ensure that the presentation matches the assignment, read the assignment guidelines carefully to gauge what the purpose of the presentation is and then ensure that the information is appropriately crafted.
The final criterion of a good presentation is the parameters.
- As you read the guidelines of the presentation, make sure to note what the parameters are: what format are you required to use (speech, Power Point, poster, and so forth); what is the length allowed (how many minutes, for instance); what language(s) and register are you expected to use (e.g. academic English); and so on. In some presentations, there may be time set aside for questions and answers (Q&A) or discussion. Make sure to prepare for that as well, if required.
Common Presentation Formats
The three most common ways in which students formally present information in college courses are as talks/speeches, through Power Points, and with posters.
Talks and Speeches
Many students find the idea of giving a speech or a talk intimidating. That is understandable, but know that all good orators use certain skills and strategies to give interesting and relevant oral presentations. These skills and strategies may vary from one country/culture/context to another. As you adapt your presentation styles to the U.S. college context, think about how a ‘good talk’ is perceived as here.
Watch this video of Chris Anderson, the founder of TedTalk, as he explains how to give great talks. As you watch, try to take notes about strategies that you could use in your talks and presentations in this course and beyond.
Power Points
Students have to often given presentations using such tools as Power Point in college courses. Montgomery College’s Digital Learning Centers offer a helpful workshop titled ‘Power Point Basics’ multiple times in a year. [1]
Another format that is often used to give a presentation is with posters. In academic conferences, for instance, special times and spaces are regularly set aside for poster presentations. In college courses, students may have to work individually or in groups to create and present posters. Some workplaces, as well, may require these skills. A well-organized poster presentation showcases the presenter’s deep understanding of the topic. Convincing facts are provided, and there are many details and explanations — both in the poster and in the presentation itself. A good poster also contains the right balance of graphics and text, and the presenter remains mindful of the audience, purpose, and parameters provided by the instructor.
- There are many other similar or more interactive formats available for giving presentations, such as Google Slides and Prezi. Explore these formats in your free time and become more familiar with them. They may come in handy in your future academic and professional presentations. ↵
Demystifying Academic English Copyright © by Rashi Jain is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Popular Templates
- Accessibility
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog Beginner Guides How To Make a Good Presentation [A Complete Guide]
How To Make a Good Presentation [A Complete Guide]
Written by: Krystle Wong Jul 20, 2023

A top-notch presentation possesses the power to drive action. From winning stakeholders over and conveying a powerful message to securing funding — your secret weapon lies within the realm of creating an effective presentation .
Being an excellent presenter isn’t confined to the boardroom. Whether you’re delivering a presentation at work, pursuing an academic career, involved in a non-profit organization or even a student, nailing the presentation game is a game-changer.
In this article, I’ll cover the top qualities of compelling presentations and walk you through a step-by-step guide on how to give a good presentation. Here’s a little tip to kick things off: for a headstart, check out Venngage’s collection of free presentation templates . They are fully customizable, and the best part is you don’t need professional design skills to make them shine!
These valuable presentation tips cater to individuals from diverse professional backgrounds, encompassing business professionals, sales and marketing teams, educators, trainers, students, researchers, non-profit organizations, public speakers and presenters.
No matter your field or role, these tips for presenting will equip you with the skills to deliver effective presentations that leave a lasting impression on any audience.
Click to jump ahead:
What are the 10 qualities of a good presentation?
Step-by-step guide on how to prepare an effective presentation, 9 effective techniques to deliver a memorable presentation, faqs on making a good presentation, how to create a presentation with venngage in 5 steps.
When it comes to giving an engaging presentation that leaves a lasting impression, it’s not just about the content — it’s also about how you deliver it. Wondering what makes a good presentation? Well, the best presentations I’ve seen consistently exhibit these 10 qualities:
1. Clear structure
No one likes to get lost in a maze of information. Organize your thoughts into a logical flow, complete with an introduction, main points and a solid conclusion. A structured presentation helps your audience follow along effortlessly, leaving them with a sense of satisfaction at the end.
Regardless of your presentation style , a quality presentation starts with a clear roadmap. Browse through Venngage’s template library and select a presentation template that aligns with your content and presentation goals. Here’s a good presentation example template with a logical layout that includes sections for the introduction, main points, supporting information and a conclusion:

2. Engaging opening
Hook your audience right from the start with an attention-grabbing statement, a fascinating question or maybe even a captivating anecdote. Set the stage for a killer presentation!
The opening moments of your presentation hold immense power – check out these 15 ways to start a presentation to set the stage and captivate your audience.
3. Relevant content
Make sure your content aligns with their interests and needs. Your audience is there for a reason, and that’s to get valuable insights. Avoid fluff and get straight to the point, your audience will be genuinely excited.
4. Effective visual aids
Picture this: a slide with walls of text and tiny charts, yawn! Visual aids should be just that—aiding your presentation. Opt for clear and visually appealing slides, engaging images and informative charts that add value and help reinforce your message.
With Venngage, visualizing data takes no effort at all. You can import data from CSV or Google Sheets seamlessly and create stunning charts, graphs and icon stories effortlessly to showcase your data in a captivating and impactful way.

5. Clear and concise communication
Keep your language simple, and avoid jargon or complicated terms. Communicate your ideas clearly, so your audience can easily grasp and retain the information being conveyed. This can prevent confusion and enhance the overall effectiveness of the message.
6. Engaging delivery
Spice up your presentation with a sprinkle of enthusiasm! Maintain eye contact, use expressive gestures and vary your tone of voice to keep your audience glued to the edge of their seats. A touch of charisma goes a long way!
7. Interaction and audience engagement
Turn your presentation into an interactive experience — encourage questions, foster discussions and maybe even throw in a fun activity. Engaged audiences are more likely to remember and embrace your message.
Transform your slides into an interactive presentation with Venngage’s dynamic features like pop-ups, clickable icons and animated elements. Engage your audience with interactive content that lets them explore and interact with your presentation for a truly immersive experience.

8. Effective storytelling
Who doesn’t love a good story? Weaving relevant anecdotes, case studies or even a personal story into your presentation can captivate your audience and create a lasting impact. Stories build connections and make your message memorable.
A great presentation background is also essential as it sets the tone, creates visual interest and reinforces your message. Enhance the overall aesthetics of your presentation with these 15 presentation background examples and captivate your audience’s attention.
9. Well-timed pacing
Pace your presentation thoughtfully with well-designed presentation slides, neither rushing through nor dragging it out. Respect your audience’s time and ensure you cover all the essential points without losing their interest.
10. Strong conclusion
Last impressions linger! Summarize your main points and leave your audience with a clear takeaway. End your presentation with a bang , a call to action or an inspiring thought that resonates long after the conclusion.
In-person presentations aside, acing a virtual presentation is of paramount importance in today’s digital world. Check out this guide to learn how you can adapt your in-person presentations into virtual presentations .
Preparing an effective presentation starts with laying a strong foundation that goes beyond just creating slides and notes. One of the quickest and best ways to make a presentation would be with the help of a good presentation software .
Otherwise, let me walk you to how to prepare for a presentation step by step and unlock the secrets of crafting a professional presentation that sets you apart.
1. Understand the audience and their needs
Before you dive into preparing your masterpiece, take a moment to get to know your target audience. Tailor your presentation to meet their needs and expectations , and you’ll have them hooked from the start!
2. Conduct thorough research on the topic
Time to hit the books (or the internet)! Don’t skimp on the research with your presentation materials — dive deep into the subject matter and gather valuable insights . The more you know, the more confident you’ll feel in delivering your presentation.
3. Organize the content with a clear structure
No one wants to stumble through a chaotic mess of information. Outline your presentation with a clear and logical flow. Start with a captivating introduction, follow up with main points that build on each other and wrap it up with a powerful conclusion that leaves a lasting impression.
Delivering an effective business presentation hinges on captivating your audience, and Venngage’s professionally designed business presentation templates are tailor-made for this purpose. With thoughtfully structured layouts, these templates enhance your message’s clarity and coherence, ensuring a memorable and engaging experience for your audience members.
Don’t want to build your presentation layout from scratch? pick from these 5 foolproof presentation layout ideas that won’t go wrong.

4. Develop visually appealing and supportive visual aids
Spice up your presentation with eye-catching visuals! Create slides that complement your message, not overshadow it. Remember, a picture is worth a thousand words, but that doesn’t mean you need to overload your slides with text.
Well-chosen designs create a cohesive and professional look, capturing your audience’s attention and enhancing the overall effectiveness of your message. Here’s a list of carefully curated PowerPoint presentation templates and great background graphics that will significantly influence the visual appeal and engagement of your presentation.
5. Practice, practice and practice
Practice makes perfect — rehearse your presentation and arrive early to your presentation to help overcome stage fright. Familiarity with your material will boost your presentation skills and help you handle curveballs with ease.
6. Seek feedback and make necessary adjustments
Don’t be afraid to ask for help and seek feedback from friends and colleagues. Constructive criticism can help you identify blind spots and fine-tune your presentation to perfection.
With Venngage’s real-time collaboration feature , receiving feedback and editing your presentation is a seamless process. Group members can access and work on the presentation simultaneously and edit content side by side in real-time. Changes will be reflected immediately to the entire team, promoting seamless teamwork.
7. Prepare for potential technical or logistical issues
Prepare for the unexpected by checking your equipment, internet connection and any other potential hiccups. If you’re worried that you’ll miss out on any important points, you could always have note cards prepared. Remember to remain focused and rehearse potential answers to anticipated questions.

8. Fine-tune and polish your presentation
As the big day approaches, give your presentation one last shine. Review your talking points, practice how to present a presentation and make any final tweaks. Deep breaths — you’re on the brink of delivering a successful presentation!
In competitive environments, persuasive presentations set individuals and organizations apart. To brush up on your presentation skills, read these guides on how to make a persuasive presentation and tips to presenting effectively .

Whether you’re an experienced presenter or a novice, the right techniques will let your presentation skills soar to new heights!
From public speaking hacks to interactive elements and storytelling prowess, these 9 effective presentation techniques will empower you to leave a lasting impression on your audience and make your presentations unforgettable.
1. Confidence and positive body language
Positive body language instantly captivates your audience, making them believe in your message as much as you do. Strengthen your stage presence and own that stage like it’s your second home! Stand tall, shoulders back and exude confidence.
2. Eye contact with the audience
Break down that invisible barrier and connect with your audience through their eyes. Maintaining eye contact when giving a presentation builds trust and shows that you’re present and engaged with them.
3. Effective use of hand gestures and movement
A little movement goes a long way! Emphasize key points with purposeful gestures and don’t be afraid to walk around the stage. Your energy will be contagious!
4. Utilize storytelling techniques
Weave the magic of storytelling into your presentation. Share relatable anecdotes, inspiring success stories or even personal experiences that tug at the heartstrings of your audience. Adjust your pitch, pace and volume to match the emotions and intensity of the story. Varying your speaking voice adds depth and enhances your stage presence.

5. Incorporate multimedia elements
Spice up your presentation with a dash of visual pizzazz! Use slides, images and video clips to add depth and clarity to your message. Just remember, less is more—don’t overwhelm them with information overload.
Turn your presentations into an interactive party! Involve your audience with questions, polls or group activities. When they actively participate, they become invested in your presentation’s success. Bring your design to life with animated elements. Venngage allows you to apply animations to icons, images and text to create dynamic and engaging visual content.
6. Utilize humor strategically
Laughter is the best medicine—and a fantastic presentation enhancer! A well-placed joke or lighthearted moment can break the ice and create a warm atmosphere , making your audience more receptive to your message.
7. Practice active listening and respond to feedback
Be attentive to your audience’s reactions and feedback. If they have questions or concerns, address them with genuine interest and respect. Your responsiveness builds rapport and shows that you genuinely care about their experience.

8. Apply the 10-20-30 rule
Apply the 10-20-30 presentation rule and keep it short, sweet and impactful! Stick to ten slides, deliver your presentation within 20 minutes and use a 30-point font to ensure clarity and focus. Less is more, and your audience will thank you for it!
9. Implement the 5-5-5 rule
Simplicity is key. Limit each slide to five bullet points, with only five words per bullet point and allow each slide to remain visible for about five seconds. This rule keeps your presentation concise and prevents information overload.
Simple presentations are more engaging because they are easier to follow. Summarize your presentations and keep them simple with Venngage’s gallery of simple presentation templates and ensure that your message is delivered effectively across your audience.

1. How to start a presentation?
To kick off your presentation effectively, begin with an attention-grabbing statement or a powerful quote. Introduce yourself, establish credibility and clearly state the purpose and relevance of your presentation.
2. How to end a presentation?
For a strong conclusion, summarize your talking points and key takeaways. End with a compelling call to action or a thought-provoking question and remember to thank your audience and invite any final questions or interactions.
3. How to make a presentation interactive?
To make your presentation interactive, encourage questions and discussion throughout your talk. Utilize multimedia elements like videos or images and consider including polls, quizzes or group activities to actively involve your audience.
In need of inspiration for your next presentation? I’ve got your back! Pick from these 120+ presentation ideas, topics and examples to get started.
Creating a stunning presentation with Venngage is a breeze with our user-friendly drag-and-drop editor and professionally designed templates for all your communication needs.
Here’s how to make a presentation in just 5 simple steps with the help of Venngage:
Step 1: Sign up for Venngage for free using your email, Gmail or Facebook account or simply log in to access your account.
Step 2: Pick a design from our selection of free presentation templates (they’re all created by our expert in-house designers).
Step 3: Make the template your own by customizing it to fit your content and branding. With Venngage’s intuitive drag-and-drop editor, you can easily modify text, change colors and adjust the layout to create a unique and eye-catching design.
Step 4: Elevate your presentation by incorporating captivating visuals. You can upload your images or choose from Venngage’s vast library of high-quality photos, icons and illustrations.
Step 5: Upgrade to a premium or business account to export your presentation in PDF and print it for in-person presentations or share it digitally for free!
By following these five simple steps, you’ll have a professionally designed and visually engaging presentation ready in no time. With Venngage’s user-friendly platform, your presentation is sure to make a lasting impression. So, let your creativity flow and get ready to shine in your next presentation!
Discover popular designs

Infographic maker

Brochure maker

White paper online

Newsletter creator

Flyer maker

Timeline maker

Letterhead maker

Mind map maker

Ebook maker
8 Tips to Give a Memorable Academic Presentation
If you’ve ever been in the audience of an academic presentation, you know that many, if not most, are a bit… well, dull. And when an audience is bored , they tend to forget everything the presenter has said.
To ensure this doesn’t happen to you, here are 8 tips to help you make your academic presentation memorable.
1. Understand the Goal of Your Presentation
In order to structure your presentation correctly it’s important that you understand the overall goal of the presentation. For academic presentations , there are actually 2 potential goals presenters might have:
- Inspire the audience to WANT to read your paper. Most conferences give speakers just 10 minutes to present. Reading your paper will most likely take closer to 30 minutes. So the goal here is to cover just enough to entice your listeners to want to read your paper. Treat your presentation a bit like a movie trailer – it’s a tease of what’s to come.
- Make connections with others in your field of study. If your goal is to have something to discuss with audience members after your presentation as a way to make introductions, then you’ll want to emphasize the kind of feedback you want. You may want to ask the audience what you should do next or what might explain the results that you got. In this way, you are inviting the audience to find you after the presentation to continue the discussion.
2. Keep Your Data Current
There can be a lot of lag time between when a paper is submitted and when you present it at conference. Sometimes 6 to 12 months may pass by in the interim. You will most likely have done more work and research during that time.
Some of the best and most memorable presentations are the ones where the presenter shares new data that has been discovered since their paper’s publishing. So don’t think you have to stick to what your paper shares. The idea here is to share real value with the audience.
3. Use a Proven Framework
When you’re just getting started, it’s important to use a framework that can guide you on the creation and development of your presentation. While each presentation might deviate slightly based on a specific field, they all tend to follow the same framework, which looks something like this:
- Introduction/Overview/Hook
- Theoretical Framework/Research Question
- Methodology/Case Selection
- Background/Literature Review
- Discussion of Data/Results
When you become better at giving these academic presentations, you can feel free to play around with this structure. But for now, stick to it.
4. Practice
It’s important to be prepared for your presentation . Getting up there and winging it is a recipe for disaster. So make sure you take the time to practice. Ask friends, family and/or colleagues if they would listen and give feedback. If you can’t find anyone to help you, then record yourself giving your presentation and watch with your audience members’ point of view in mind.
Did you talk too fast ? Were you looking down the entire time? Were you interested or bored in what you had to say?
Don’t feel the need or even attempt to memorize your presentation. You simply want to become very familiar with the flow and structure of what you’re going to say so it feels natural coming out of your mouth.
5. Stick to Your Time Limit
It’s important to develop your presentation with your allotted timeframe in mind. If you’ve only been given 10 minutes, then be sure your presentation isn’t 14 minutes or 6 minutes.
A good rule of thumb is that each typed, double-spaced page takes roughly 2 minutes to speak. So for a 10-minute talk, you should have no more than 5 double-spaced pages of material prepared.
6. Don’t Load Your Presentation Slides
Remember, your slides are there to supplement your presentation. Do not fill your slides with so much text that the audience spends your entire presentation reading your slides instead of listening to you.
Be sure to use images . Research suggests that images help with learning and memory, so if you want your presentation to be memorable, be sure to include images into your slides.
7. Don’t Read Your Own Slides
To keep your audience engaged , you want to consistently make eye contact with them throughout your presentation. You can’t do this if you are looking down at notes or up at your own slides. Again, you don’t have to memorize all of the exact words you are going to say, but KNOW what you want to say so you can speak and look out at your audience at the same time.
8. Be Open to Questions
There will most likely be a Q&A at the end of your presentation, and often this is where you can make the biggest impact on your audience. Don’t make the mistake of assuming a question is a challenge to you when it is just a question.
For instance, someone may ask, “Why did you use methodology A instead of B?” To your ear this may sound like they are saying “B” would have been the better choice. But what they are really doing is trying to learn more about what you were thinking and how you came to certain conclusions.
Giving academic presentations can be challenging and nerve-wracking. But if you follow these 8 tips, you will be able to give a memorable presentation every time.
Thank you so much! This worked well for me and now, I have a happy audience!
Leave a Response Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Please enter an answer in digits: one + 15 =
Ashish Arora
You might also like.

Essential Tips to Find the Right Audience for Your Next Presentation

Expert Tips to Handle Distractions When You Speak on Stage

9 Tips to Craft the Perfect Title for Your Next PowerPoint Presentation
Unleash the Power of Agile Communication in the Fast-Changing Digital Realm
Effective Academic Presentation Tips Your Students Need to Know
.jpg)
Delivering information in a manner that is clear, concise and insightful while providing an audience with great learning opportunities are important components for successful presentations. Today, presentation skills are a basic requirement of every field, and students must practise and aim for mastery in preparation for the workplace. It is integral to students’ academic and career success to learn how to properly present and demonstrate their knowledge while ensuring that their peers are well engaged in the material. Apart from solely providing information, presentations should stimulate interactive learning through a pleasing audio and visual experience for the audience.
Having students do presentations on a regular basis is an effective way of learning by teaching which is proven to improve knowledge retention and overall comprehension. Not only that, but students get to practice their research, communication and leadership skills. Furthermore, presentations enable students to develop their creativity by implementing innovative ways of adding value to their peers’ education in a way that captures their attention and interests.
Presentations provide learning benefits to both the presenter and the audience. In order to extrapolate these benefits, the experience must be authentic and well-delivered. This blog post will show you how to do just that!
Pro Tips for Effective Academic Presentation
- Stay passionate to connect with your audience
- Focus on your main topic
- Maintain eye contact
- Use your voice creatively
- Keep a fluent body language
- Stay calm and confident
- Do not read from your slides
- Maintain your time limit while presenting [1]
Presentation Skills Students can Acquire and Develop
- Using PowerPoint Effectively
Students must learn how to use PowerPoint presentations to create a visual representation of the information that is being shared with the rest of the group. Being well-versed in the software allows for more impactful information delivery. Students can add high-quality images, diagrams and highlight the important elements of their research in bullet points. This allows students to present both qualitative and quantitative information in a digestible manner. [1]
- Adapting to your Audience
One of the most common mistakes many presenters make is to under or overestimate their target audience. Students should thoroughly research their audience to understand where they stand and draft an engaging presentation accordingly. Presenters must question themselves about what their audience may already be aware of and what new information can the presenter share with them. To eliminate confusion, conducting a brief question and answer session where the presenter can address all the points of concern throughout the presentation can be helpful to keep everyone on the same page and allow the audience to absorb the content more thoroughly.
- Time Management
Most academic presentations have a specified time allotted for each student to showcase his/her work. Students must prepare the material for their presentation, keeping it relevant to the time they have been given. If you're writing your presentation out, 2 minutes per double-spaced page is a good rule of thumb to follow. Make sure you don’t have over 7 double-spaced pages of material for a fifteen-minute talk. [2]
Most students who drift away from their central point of focus in the presentation are seen with long ineffective presentations that bore your audience. Keeping the presentation short and to the point helps outline your presentation's purpose and highlights prominent aspects of the topic.
- Keeping your Audience Engaged
Students must understand the essence behind presenting in front of others. It is essential to capture an audience’s attention and share your knowledge with them. Having an impactful opening sentence/slide at the beginning of your presentation prevents the rapid deterioration of your audience’s attention which is common in presentations that feel irrelevant, confusing or generic right from the start.
- Effective Preparation
Lastly, with good preparation, a student must have enough practice to present their work with confidence and in an organized manner. Students must be comfortable with their material and slides and practice their presentation both alone and in front of an audience. One can also practice using a laser pointer or props if they will use them during the presentation.
Keep in mind that you and your research are the stars of the show, and therefore one must avoid adding any unnecessary information or images that will take the attention away from your work. Practicing in front of a mirror allows students to assess their body language and how it compliments what they are saying in their presentation. [3]
Mediums for Academic Presentations
Irrespective of the presentation quality in front of an audience, the way it is being presented also impacts the target audience. Specific mediums play a significant role in setting the dynamics with the audience. Different platforms that students can use to give a presentation are as follows:
- PowerPoint Presentation
A popular way of presenting in front of an audience includes using a creative slideshow that aids your audience’s greater attention towards you. This also allows a visual representation of both qualitative and quantitative data. This medium allows you to observe your audience’s changing expressions towards your slides and respond accordingly to effectively solidify their learning by complimenting what they see on the screen with verbalized information. It is highly recommended for informative presentations.
- Video Conferencing
Living in a digitally advanced era, individuals commonly conduct presentations online. Remote learning today encourages individuals to update their learning style and even present their knowledge in a technologically advanced manner. Video conferencing allows students to present anywhere and participate in the class. With different third-party apps like Zoom and Google Meet, students can also share their screen and share a PPT while they speak.
A simple way to present in front of an audience is to speak to them as is. In this type of presentation, your own body language and dressing play a vital role in setting the right dynamics from the very beginning of your presentation. It is important to start with a creative, open line and remain audibly clear for the audience to understand. It is highly recommended for persuasive presentations.
How to Present in an Online Class?
Remote learning has gained much popularity in recent years, and the pandemic also made it clear for teachers to start adopting various teaching methods and strategies that complement online learning. [4] Educators have started coming up with innovative methods to conduct online classes and encourage their students to participate through class presentations. There are a bunch of ways a student can present in online classes, including:
Your laptop or computer device’s camera can be used to get face to face with your audience. Different platforms like Zoom, Google Meet and Skype can be used to connect with a group of students online and give a live presentation. In such presentations, students need to find a neutral background with minimal disturbance so that their audience does not get distracted during the presentation and focuses on what the presenter has to say. These presentations can be taken to another level as the presenter can also share their screen and support their words with facts, figures and diagrams on their screen.
For this, you must find a quiet place to conduct a presentation with minimum background noise as it can create a lot of chaos during your presentation. As much as possible, students should use good quality headphones with a microphone that only picks up close-range sounds to eliminate further noise from being heard by the audience. It is also highly recommended that students consider dressing appropriately to appear professional in front of their peers.
- Pre-Recorded Video
With multiple screen recording options, you can record a complete video clip and add written or oral narrations for your audience. An advantage of this setting is that it allows students to edit their presentations and share the best quality results. With pre-recorded videos, you cannot answer live questions therefore, you must cover the topic comprehensively. A complete breakdown of detailed concepts through step-by-step presentations is recommended for a better understanding of the audience.
- Asynchronous Presentations
In this type of presentation, the recorded file is viewed later by the audience. This allows greater access to a wider audience with no time constraints. This is ideal for students who have anxiety and fear public speaking as they can easily keep taking takes until they have the perfect one. However, the audience cannot immediately ask any questions related to the presentations and they have to go through leaving a comment or email and wait for a response. [5]
How Kritik Improves Students' Presentation Skills
Presentations are an effective way of developing several skills that are required for professional growth and academic success. By presenting, students learn by teaching which is an efficient way of consolidating knowledge. Given that presentations play a key role in providing students great learning opportunities, it is important to consider the platform wherein students can present their knowledge and interact with one another. With Kritik, students have the ability to present individually or work with teammates and present as a group. The added benefit of Kritik’s peer-evaluation in presentations is that students can provide structured, professional feedback to the presenter(s) using effective, customized rubrics. Students can upload multiple files of various formats such as audio, video and PPT slides which ensures that students can still deliver information in a manner that is interactive and informative despite the remote learning environment. Here at Kritik, we closely work with hundreds of professors who put an emphasis on developing students’ presentation skills. Kritik provides a great platform for an audience to not just listen but to also provide regular constructive criticism back to the presenter. By using Kritik, your students are empowered to become better presenters through an interactive platform that focuses on rubric-based assessments to facilit
[1] James, C. J., & Linte, C. A. (2014). Improve Your Next Presentation: Tips on Effective Presentation Design and Delivery [Continuing Education]. IEEE Pulse , 5 (3), 78-81.
[2] Golash-Boza, T. (2018). 6 Tips for Giving a Fabulous Academic Presentation. Wiley. Retrieved from https://www.wiley.com/network/researchers/promoting-your-article/6-tips-for-giving-a-fabulous-academic-presentation
[3] University of Birmingham. (2021). Tips for effective presentation. Retrieved from https://www.birmingham.ac.uk/schools/metallurgy-materials/about/cases/tips-advice/presentation.aspx
[4] Despite Covid-19, education continues thanks to online learning. ACCA Think Ahead. Retrieved from https://yourfuture.accaglobal.com/global/en/blog/online-learning.html
[5] OWL. (2021). Sharing and Presenting Work in Remote Classrooms. Purdue University. Retrieved from https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/teacher_and_tutor_resources/teaching_resources/remote_teaching_resources/sharing_and_presenting_work_in_remote_classrooms.html

Get Started Today
Related blogposts.
- Assistant Professor / Lecturer
- PhD Candidate
- Senior Researcher / Group Leader
- Researcher / Analyst
- Research Assistant / Technician
- Administration
- Executive / Senior Industry Position
- Mid-Level Industry Position
- Junior Industry Position
- Graduate / Traineeship
- Remote/Hybrid Jobs
- Summer / Winter Schools
- Online Courses
- Professional Training
- Supplementary Courses
- All Courses
- PhD Programs
- Master's Programs
- MBA Programs
- Bachelor's Programs
- Online Programs
- All Programs
- Fellowships
- Postgraduate Scholarships
- Undergraduate Scholarships
- Prizes & Contests
- Financial Aid
- Research/Project Funding
- Other Funding
- All Scholarships
- Conferences
- Exhibitions / Fairs
- Online/Hybrid Conferences
- All Conferences
- Economics Terms A-Z
- Career Advice
- Study Advice
- Work Abroad
- Study Abroad
- Campus Reviews
- Recruiter Advice
- Study Guides - For Students
- Educator Resource Packs
- All Study-Guides
- University / College
- Graduate / Business School
- Research Institute
- Bank / Central Bank
- Private Company / Industry
- Consulting / Legal Firm
- Association / NGO
- All EconDirectory
- 📖 INOMICS Handbook
All Categories
All disciplines.
- Scholarships
- All Economics Terms A-Z
- Study-Guides
- EconDirectory
- All 📖 INOMICS Handbook

Make it Count
How to give a great academic presentation.
Read a summary or generate practice questions using the INOMICS AI tool
Whether you’re a graduate student giving a presentation for a course or a researcher presenting at a conference, being able to give an engaging and well-prepared presentation is a valuable skill for anyone in academia – in COVID times it is invaluable . Today, hardly a talk is given without an accompanying PowerPoint presentation full of flashy graphs, images, exploding sub-titles, and often far too many bullet points.
In this post, we will offer you specific tips on how to hone your presentation and sharpen your speech in order to give an interesting, memorable and overall successful academic presentation. Building on past blog articles including Dress Code for Academic Conferences and How to Write a Cover Letter , this post will offer you advice that can be applied across a range of situations that you will face time and again throughout your career. So, without further ado.
1. Tailor your talk to your audience
Although you never want to underestimate the intelligence and experience of your audience, you also need to be aware of the specific crowd to which you are speaking. If you are at a highly technical conference for researchers in your subfield, going into great detail and skipping over any basic background research would be a good idea. If you are attending an interdisciplinary seminar the following month, however, simply adapting the same presentation is not a good idea.
Take the time to make sure your presentation reflects the education level, interests and general make-up of your audience, and your talk will necessarily have a better reception.
2. Keep text to a minimum
The idea of a visual aid is that it should accompany your presentation, not replace it. Thus, your slides should offer complementary information, rather than forcing your audience to try to simultaneously read and listen to you talk.
Always use a font that is easy to read and keep the size large enough so that even those at the back of the room or lecture hall can see every word. However, images and graphs are always better than words – a simple slide accompanied by a great verbal description is your best option. Check out more tips for designing a persuasive presentation .
3. Practice, practice, practice
Even if you feel completely confident in your presentation skills, it’s always a good idea to rehearse in order to give the best talk possible. Through practice you become more comfortable each element of your presentation and are less likely to forget small but important things such as an introduction of who you are and where you work or study.
By practicing you can make sure that your slides are organized in such a way as to create a good flow for your points, you become more comfortable with all of the transition points and you have the chance to make any necessary changes before you find yourself on stage.
4. Harness your nerves
Even if you’ve practiced like crazy, it’s normal to still feel nervous. If you make the conscious choice to channel that nervous energy into enthusiasm, you can actually boost your own performance and simultaneously build confidence. Taking long pauses and deep breaths are fine practices, and if done in a controlled manner they can add emphasis to specific points within your talk while also calming you down.

5. Respect your time limit
It is natural to get caught up in your talk and forget to keep track of time. A presentation that drags on forever invariably loses favor with the audience, however, so it’s important to keep to the schedule. Setting a watch or clock on the podium is one way to give yourself a physical reminder of the time without being too obvious about it.
Another option is to ask a friend or colleague to give you a reminder when you’ve hit the halfway point or when you only have five minutes remaining of your allotted time. If you choose to use a reminder, remember not to speed up or rush even if you feel like you’re running out of time and still have lots to say. Prepare for this scenario ahead of time and choose which slides you could skip if need be. Regardless of whether you’ve had to skip certain sections, always have a strong conclusion planned. People tend to remember the beginning and end of events the best, so going out strong is important. Finally, always thank your audience and your host before leaving the stage.
Currently trending in Russia
- Professor Job
- Posted 2 weeks ago
Two Professorships (W2) for Economics with a focus on International Economics

- Professional Training Course, Summer School, Course
- Posted 4 days ago
Monitoring and Forecasting Macroeconomic and Financial Risk: SoFiE European Summer School (Brussels)

- PhD Program, Supplementary Course, Program
- (Partially Online)
International Doctoral Courses and Seminars in Health Economics and Policy

- presentation
- conferences
Related Items

Call for application to the PhD in Economics 2024-25

MSc Economics and Finance

RSEP & SRH Dresden School of Management International Conference on Economics, Finance and Business
Featured announcements, doctoral programme in economics (mres+phd), difference-in-differences and event studies for panel data and…, mitarbeiter*innen für die banken- und finanzaufsicht, monitoring and forecasting macroeconomic and financial risk: sofie…, 36th rsep international conference on economics, finance and business, tinbergen institute summer school, upcoming deadlines.
- Jun 24, 2024 HEMAP – Two-year Master programme in Health Economics, Management and Policy
- Jun 24, 2024 PAE – Two-year Master's program in Policy Analysis and Evaluation – Alma Mater Sturdiorum - Università di Bologna
- Jun 27, 2024 LMAEM – Two year Master's program in Applied Economics and Markets – Alma Mater Studiorum - Università di Bologna
- Jun 28, 2024 Qatar Centre for Global Banking & Finance, 4th Annual Conference
- Jun 30, 2024 MSc/PhD in Quantitative Economics - University of Alicante
INOMICS AI Tools
The INOMICS AI can generate an article summary or practice questions related to the content of this article. Try it now!
An error occured
Please try again later.
3 Practical questions, generated by our AI model
For more questions on economics study topics, with practice quizzes and detailed answer explanations, check out the INOMICS Study Guides.
Login to your account
Email Address
Forgot your password? Click here.

- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
How to Make a “Good” Presentation “Great”
- Guy Kawasaki

Remember: Less is more.
A strong presentation is so much more than information pasted onto a series of slides with fancy backgrounds. Whether you’re pitching an idea, reporting market research, or sharing something else, a great presentation can give you a competitive advantage, and be a powerful tool when aiming to persuade, educate, or inspire others. Here are some unique elements that make a presentation stand out.
- Fonts: Sans Serif fonts such as Helvetica or Arial are preferred for their clean lines, which make them easy to digest at various sizes and distances. Limit the number of font styles to two: one for headings and another for body text, to avoid visual confusion or distractions.
- Colors: Colors can evoke emotions and highlight critical points, but their overuse can lead to a cluttered and confusing presentation. A limited palette of two to three main colors, complemented by a simple background, can help you draw attention to key elements without overwhelming the audience.
- Pictures: Pictures can communicate complex ideas quickly and memorably but choosing the right images is key. Images or pictures should be big (perhaps 20-25% of the page), bold, and have a clear purpose that complements the slide’s text.
- Layout: Don’t overcrowd your slides with too much information. When in doubt, adhere to the principle of simplicity, and aim for a clean and uncluttered layout with plenty of white space around text and images. Think phrases and bullets, not sentences.
As an intern or early career professional, chances are that you’ll be tasked with making or giving a presentation in the near future. Whether you’re pitching an idea, reporting market research, or sharing something else, a great presentation can give you a competitive advantage, and be a powerful tool when aiming to persuade, educate, or inspire others.
- Guy Kawasaki is the chief evangelist at Canva and was the former chief evangelist at Apple. Guy is the author of 16 books including Think Remarkable : 9 Paths to Transform Your Life and Make a Difference.
Partner Center

How To Make Your Academic Presentations More Engaging
- Post author By Kay Woot
- Post date August 10, 2022
- No Comments on How To Make Your Academic Presentations More Engaging
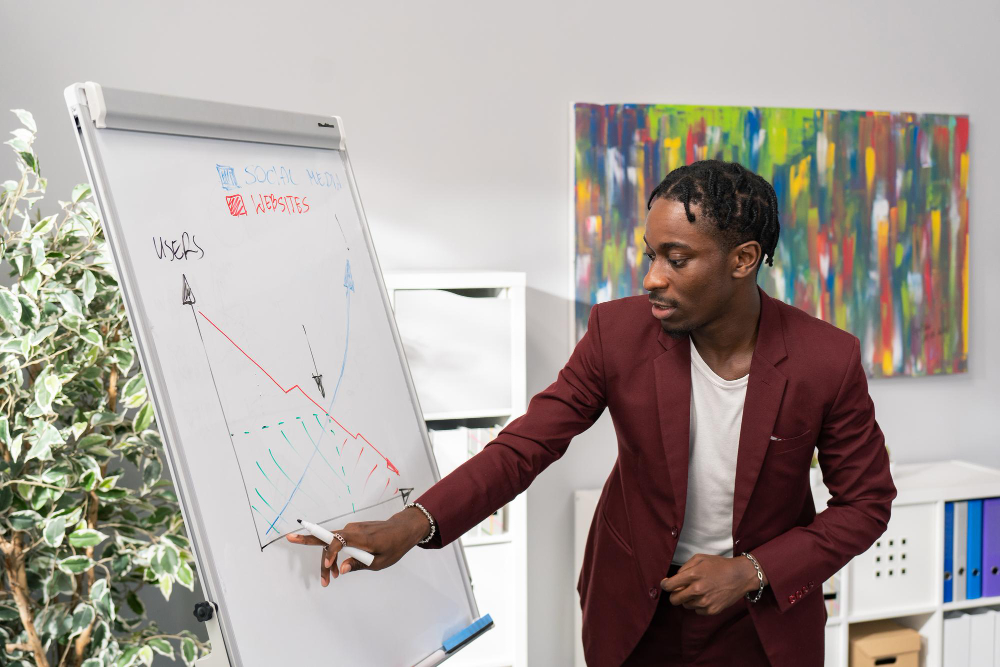

Are you tired of making dry, boring academic presentations? Do your audiences seem to lose interest halfway through your talk? If so, it might be time to try some new strategies to make your presentations more engaging. In this blog post, we will discuss five ways to make your presentations more interesting and engaging for your listeners. Keep reading to learn more!
Table of contents
How to make your academic presentations more engaging
1. Start with a bang
The first few minutes of your presentation are crucial in setting the tone and grabbing your audience’s attention. So make sure you start strong! An engaging opening anecdote, an interesting statistic or a thought-provoking question are all great ways to get your audience’s attention from the get-go.
2. Keep it relevant
Your audience wants to know why your presentation is relevant to them. So make sure you explain early on in your talk how your research relates to their interests, work or lives. By doing this, you’ll ensure that your audience stays engaged throughout your talk.
3. Make it visual
People are more likely to remember information if it is presented visually. So incorporating images, diagrams and charts into your presentation can be a great way to engage your audience and help them to understand and remember your key points.
4. Use stories
Stories are a powerful way to engage an audience. If you can weave a personal story or case study into your presentation, you’ll not only engage your audience but also make your points more memorable.
5. Keep it simple
Don’t try to pack too much information into your presentation. Instead, focus on delivering a few key messages that you want your audience to remember. By keeping your presentation concise and to-the-point, you’ll engage your audience more effectively.
6. Leave time for questions
Make sure you leave plenty of time at the end of your presentation for questions from your audience. This not only shows that you’re open to feedback and discussion, but also gives your audience a chance to further engage with your research.
Ways to make your speeches or papers more interesting for your audience
1. Use strong language:
Use powerful words and phrases to convey your message clearly and effectively. Avoid using filler words or platitudes that will make your audience tune out.
2. Be engaging:
Make sure to keep your audience engaged by making eye contact, using facial expressions, and speaking with enthusiasm. You want people to be interested in what you’re saying, so it’s important to appear engaged yourself.
3. Use examples:
Providing concrete examples will help your audience to understand your points more clearly. Whether you’re using real-life examples or hypothetical ones, make sure they’re relatable and easy to follow.
4. Be concise:
Don’t try to cram too much information into your speech or paper. Be clear and concise in your delivery, and focus on the most important points that you want to get across.
5. End with a bang:
Just as you start your presentation with an attention-grabbing opening, you’ll want to finish strong as well. Leave your audience with something memorable, whether it’s a thought-provoking question or a powerful call to action.
Tips for delivering an engaging and effective presentation
1. Start with a strong opening.
Your opening should grab your audience’s attention and give them a sense of what your presentation will be about. A good way to do this is to start with a story, joke, or interesting statistic.
2. Make sure your slide deck is visually appealing.
Your slides should be clear, concise, and easy on the eyes. Avoid using too much text or putting too much information on each slide.
3. Use PowerPoint (or another presentation software) wisely.
PowerPoint (or another presentation software) can be a great way to add visual interest to your presentation and help you deliver your message more effectively. However, it’s important to use PowerPoint wisely. Overusing animation and transitions can be distracting, and using too many slides can make your presentation seem like a sales pitch.
4. Practice, practice, practice.
One of the best ways to ensure that your presentation is engaging and effective is to practice it several times before you deliver it. This will help you become more comfortable with your material and help you make any necessary adjustments.
5. Be prepared for questions.
Questions from the audience can be a great way to engage them in your presentation. However, they can also be scary if you’re not prepared for them. It’s important to anticipate questions that your audience may have and to have answers prepared.
The importance of eye contact and body language in presentations
Some people may think that the most important thing when giving a presentation is the verbal content. However, research has shown that nonverbal cues, such as eye contact and body language, are actually more important in conveying your message.
Eye contact is essential in making sure that your audience is engaged with what you’re saying. It helps to create a connection and builds trust. Additionally, it allows you to gauge the reactions of your audience and make any necessary adjustments to your presentation.
Your body language is also important in making sure that your presentation is effective. Make sure that you use open and confident body language. This will help to make your audience feel more comfortable and will make it more likely that they will pay attention to what you’re saying.
How to use humor effectively in academic presentations
Some academics believe that humor should never be used in presentations, while others believe that it can be useful in certain situations. However, there is no one-size-fits-all answer to this question – it depends on the audience, the topic, and the presenter’s personal style.
If you do decide to use humor in your presentation, there are a few things to keep in mind. First, make sure that your jokes are appropriate for the audience. If you’re presenting to a group of scholars, avoid using toilet humor or crude jokes. Second, don’t use humor as a crutch – if your presentation is weak, adding a few jokes won’t make it better. Finally, be aware of your own personal style – some people are naturally funny, while others are not. If you’re not sure whether you can pull off a joke, it’s probably best to avoid it.
Overcoming stage fright when giving academic presentations
Firstly, it is important to understand what is causing your stage fright. Once you know what is triggering your anxiety, you can start to address it. Common causes of stage fright include worries about the content of your presentation, fears of public speaking, and nervousness about being judged by your peers. Once you know what is causing your stage fright, you can begin to work on overcoming it.
The role of audience interaction in making academic presentations more engaging
Academic presentations can often be seen as dry and dull, with little interaction between the presenter and the audience. However, research has shown that incorporating audience interaction into your presentation can make it more engaging and interesting for both the presenter and the audience.
There are a few different ways that you can incorporate audience interaction into your presentation. One way is to ask the audience questions throughout the presentation and then encourage them to discuss the answers amongst themselves. This not only gets the audience more involved in the presentation, but it also allows you to gauge their understanding of the material.
Another way to incorporate audience interaction is to use group work or activities during your presentation. This can be something as simple as having the audience brainstorm solutions to a problem or discuss a controversial topic. By involving the audience in these activities, you will again get them more engaged with the presentation and ensure that they are taking something away from it.
Making use of technology to enhance engagement in academic presentations
Academic presentations can often be quite dry and boring, especially if they are simply a lecture format. However, by making use of technology, you can easily engage your audience and make your presentation more interactive.
There are a few different ways that you can use technology to engage your audience. One way is to use PowerPoint or another presentation software to create slides that are interactive. For example, you can insert questions into your slides and ask your audience to answer them. You can also use PowerPoint or another presentation software to create polls and surveys that your audience can participate in.
Another way to engage your audience is to use social media. You can live tweet during your presentation or post updates to Facebook or another social media platform. You can also use social media to ask your audience questions or get their feedback on your presentation.
Finally, you can use technology to create an interactive experience for your audience by using virtual reality or augmented reality.
Considerations for designing engaging and visually appealing PowerPoint slides
1. Use high-quality images
When selecting images for your PowerPoint slides, it’s important to choose ones that are high quality and visually appealing. Blurry or low-resolution images will make your slides look unprofessional, so be sure to use images that are crisp and clear. Additionally, try to use images that are relevant to the topic of your presentation.
2. Use slide templates
One way to make sure your PowerPoint slides look professional is to use slide templates. There are many different templates available online, or you can create your own. Using a template will help ensure that your slides have a consistent look and feel.
3. Limit the text on each slide
If you have too much text on a slide, it can be overwhelming for your audience. Try to limit the amount of text on each slide, and use bullet points instead of long paragraphs. Additionally, make sure the font size is large enough to be easily readable.
4. Use colors wisely
When choosing colors for your PowerPoint slides, it’s important to use them wisely. Using too many colors can be distracting, so try to limit yourself to two or three colors. Additionally, make sure the colors you use are easy to read and not too bright.
5. Use animations and transitions sparingly
Animations and transitions can be a great way to add interest to your PowerPoint slides. However, it’s important to use them sparingly. Too many animations and transitions can be distracting and make your presentation seem cluttered.
6. Proofread your slides
Before you finalize your PowerPoint slides, be sure to proofread them for any typos or grammatical errors. Nothing will make your presentation look more unprofessional than errors in your slides.
Best practices for structuring and delivering an engaging academic presentation
– Start with a strong introduction that will grab the attention of your audience and give them an overview of what you will be talking about.
– Organize your presentation in a logical way, using signposting to help guide your audience through your argument.
– Use a variety of delivery methods throughout your presentation, such as slides, video, or interactive activities, to keep things interesting.
– Make sure to practice your presentation beforehand so that you are familiar with the material and can delivery it confidently.
Have you tried any of these tips to make your academic presentations more engaging? What worked well for you? Let us know in the comments below.
Related posts:
- How To Ace Your Exams: Study Skills And Human Psychology
- How To Optimize Your Human Resources Department For Maximum Efficiency
- 125 Amazing Statistics About Luxury Products & Services
HSLU Master Service Design
The behind-the-scenes blog [still in beta]
How to create an excellent final presentation without presentation skills
In this article I will share with you 5 practical tips you can implement to improve the chances that the project you spend days, months and even years working on lands well with the people who evaluate it. Even if you suck at making slides, storytelling or selling yourself. These tips are focused on students in a master program but they can easily apply to the professional world too.
- Know the evaluation criteria
- Use the evaluation criteria as a checkin tool
- Dry run your presentation dozen of times
- Test the presentation with your evaluators
- Do some healthy and transparent lobbying
- Bonus one: Respect the deadlines and timing
As I’m writing this article, I’m in the train coming back from hours of listening to final diploma presentations of the students from the Master Design of the HSLU.
There were some great presentations and I want to share here a few ingredients that I think helped make these presentation a success.
I’m sharing these tips here to help next year students and people outside of the program benefit from these learnings
The tips in detail
For these tips I’m not focused on how to make the slides of a presentation, that’s something that today is pretty easily solved with templates ( hello Canva ), help from peers or even freelancers.
Tip 1: Know the evaluation criteria
Most of the times, both in studies and in professional work their are clear expectations. These expectations can take the form of a briefing or contract (in the professional world) or a list of evaluation criteria (in the academic world).
As the people who evaluate your work (a client, a boss, or a teacher) will use these tools to make sure that you delivered what was expected these tools should be essential.
You should:
- Have access to them
- Know them in details
- Have asked questions about how they are used
In a previous article I’ve talked about How do we grade academic work within the master Service Design of the HSLU? In it I showed that in the academic world and especially in the Master Design of the HSLU:
- Evaluation criteria are given at the start of the projects
- The same exact criteria are used by teachers and experts
Tip 2: Use the evaluation criteria as a checkin tool
Many people working in the design world are used to principles and critieria that can help check the quality of the work as we are doing the work (like the 10 Usability Heuristics for User Interface Design by Jakob Nielsen or the 15 Principles of Good Service Design by Lou Downe).
Instead of waiting the end of the project to evaluate how good it is, the evaluation criteria given at the start of the project can be used every month or during each coaching session to see where there is the biggest blind spot that needs more attention and love.
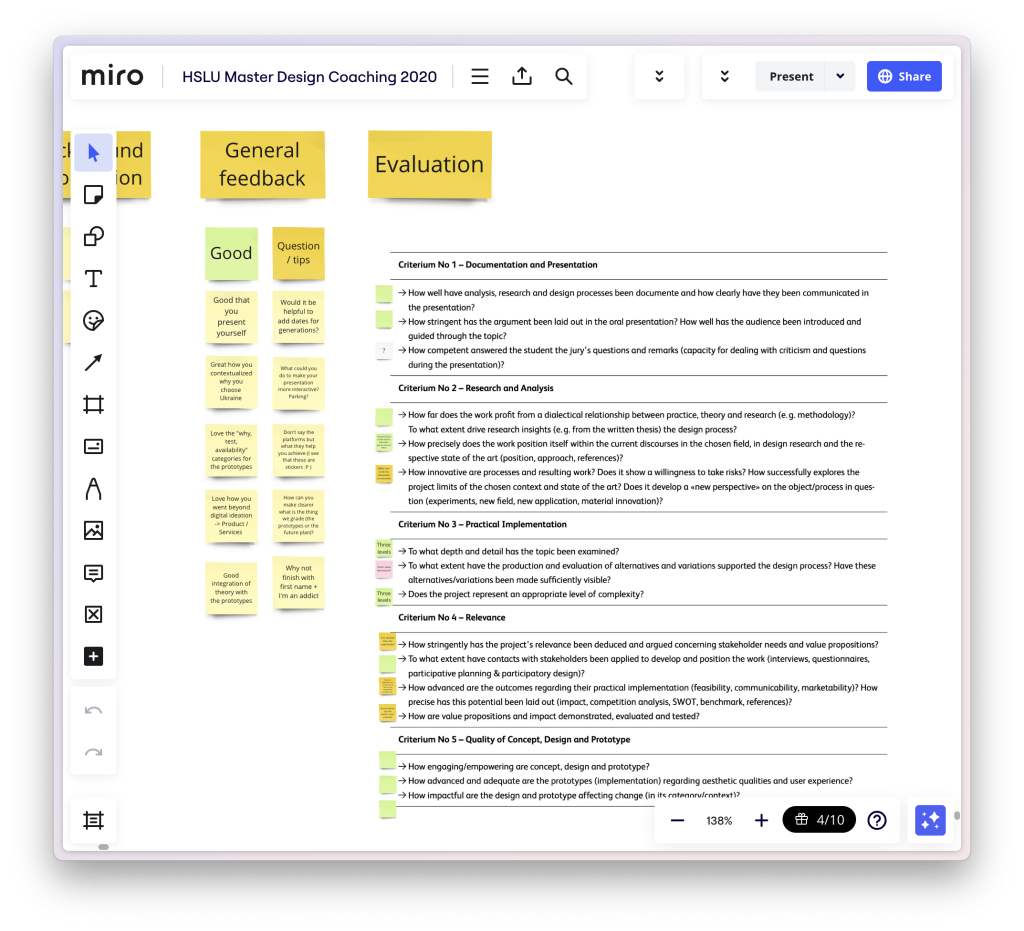
I’ve seen smart students do that even alone and don’t wait for a coach or teacher to do a mid-project evaluation. That’s why in the future, as a coach in the master Service Design program, I’ll push more students to do these self evaluations.
Tip 3: Dry run your presentation dozen of times
When we look at a comedian we feel: wow this guy is naturally funny. What we don’t see is that before this comedian did a big show in front of hundreds of people, he tested his material in tiny cafés, cut elements, reworked them for a very long time. Comedians know that to land a perfect joke you have to get everything right, timing, content, expression, etc. And they test that over and over.
That’s why it’s smart to do dozens of dry run presentations. These are presentations that have low stakes: they can be done:
- Alone just recording yourself with a camera
- With family members and friends who know nothing about your work
- With peers (work colleagues, other students)
Back in the days when I worked as a consultant, with my mate and partner in crime Patrizia Lamprecht we had a rule of thumb for our pitch presentations:
Each time we do a mistake in the dry run, with fix the issue and start over from the beginning.
This meant that we repeated a pitch up to the moment it felt like a theater piece we knew by heart. We improved every detail in the presentation. And to the audience it felt effortless as we were some kid of wizards.
This is a simple piece of advice, but one that gets overlooked so often. And one that makes a huge difference in feeling comfortable when presenting your work.
Tip 4: Test the presentation with your evaluators multiple times
Whenever you’re working with other humans lobbying and politics are part of the game. So it’s smart to not only test your presentation alone, with friends and peers but also to do it with the people that will evaluate you. And don’t stop there, engage with these people (when allowed in the rules as in some case you might be allowed to engage in advance with a supervisor but not the outside expert).
Why should you do dry runs with your evaluators?
- They will be the ones grading you, so it’s smart to know how they think. In some way they are one of your clients.
- It helps you adresse all the critical things during your presentation, so that during the question time people don’t have to try to save your presentation by asking question so that you reveal the information they need to grade you well. This makes then the question time after your presentation more interesting.
- It’s easier to evaluate something that you don’t discover for the first time and that you have seen progress over time
Tip 5: Do some healthy and transparent lobbying
Asking your evaluator to do a dry run of your presentation is just the first part of your political and lobbying playbook. Which again works perfectly also in the professional world.
Make sure that you understand the viewpoint, needs, etc. of your evaluator. How do you do that? Ask questions, ask to spend time around a coffee to discuss your profession. Show curiosity and interest.
It’s hard to evaluate curiosity and interest in a 20 minute presentation. It’s much easier to do it when you’ve already met the person before.
Bonus tip: Respect the deadlines and timing
This might be a Swiss cultural aspect but respecting deadlines and timing will help put your evaluators in the right mood.
As someone who has to evaluate diploma presentations, I read them in detail in advance and take detailled notes in advance. So that during the presentation I’m not trying to understand but I’m deepening my understanding.
This means that as a student you have to respect the deadline for submitting your PDF presentation. If you don’t:
- As the person who grades you, I come unprepared
- During your presentation I’ll have to spend a lot of energy in my note taking instead of only listening (because it’s required that evaluators justify and comment the grades).
- It’s making me feel less respected as you didn’t respect the rules and made my life harder
The same goes with respecting the time you have to present orally. Make sure to even finish earlier than the time you have. This ensures that:
- As the person who grades you, I feel I have enough time to ask you questions
- I don’t feel rushed or frustrated because there was no time to ask you a question
- You and me aren’t frustrated because you couldn’t show everything you wanted
You might also like

How do we grade academic work within the master Service Design of the HSLU?
A new chapter: Why we’re relaunching the microsite of the Master Service Design
By continuing to browse the site you are agreeing to our use of cookies and similar tracking technologies described in our privacy policy .
Supporting Educators & Students
Teaching & learning.
As part of its broad-based teaching mission, the AHA develops and shares resources for educators and students. From regional teaching conferences and online programs to pathbreaking research projects, AHA initiatives foster a community grounded in our shared commitment to understanding the past. We support and convene people who share a love of history and historical thinking.
Resources for Educators & Students

K–12 Education
The AHA strives to ensure that every K–12 student has access to high quality history instruction. We create resources for the classroom, advise on state and federal policy, and advocate for the vital importance of history in public education.

Undergraduate Education
Teaching and learning are at the foundation of the AHA’s mission to promote historical thinking in public life. What do students learn in undergraduate history courses? How and why are history majors so successful in a variety of careers?

Graduate Education
Many historians will pursue graduate training at some stage in their career. To meet the needs of both students and graduate programs, the AHA creates resources, provides platforms, and convenes conversations about student success from application to completion.
For Academic Departments
History department chairs are on the front lines of the discipline, defending historians’ work and supporting their professional lives at all stages of their academic careers. The AHA strives to strengthen this work and provide resources and opportunities that make chairs’ work easier and valued. The AHA provides resources and hosts a variety of events and opportunities to benefit department chairs and build community, including webinars, sessions at the annual meeting, and an in-person workshop.
Current Events in Historical Context
Essential, carefully researched resources by historians providing context for conversations about current events.
Regional Conferences on Introductory History Courses
What do students learn in introductory history courses? How can historical thinking support student learning and success across the curriculum? Our regional conferences endeavor to strengthen the community of practice focused on introductory history courses, both in secondary and higher education.
Standards & Guidelines

June 10, 2024
Guidelines for Academic Tenure-Track Job Offers in History
June 9, 2024
Statement on Age Discrimination
Aha historical collections.
The AHA has made primary sources available for research purposes, along with AHA archival reports and documents.
Vetted Resources
Vetted Resources compiles in a central location materials and tools that have been professionally vetted by historians, offering instructors access to high-quality materials that meet professional standards
AHA Resource Library

June 20, 2024
16 Months to Sumter: Newspaper Editorials on the Path to Secession

June 16, 2024
The History of Racism and Racist Violence: International Contexts and Comparisons
The history of racism and racist violence: monuments and museums, join the aha.
The AHA brings together historians from all specializations and all work contexts, embracing the breadth and variety of activity in history today.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Tip #1: Use PowerPoint Judiciously. Images are powerful. Research shows that images help with memory and learning. Use this to your advantage by finding and using images that help you make your point. One trick I have learned is that you can use images that have blank space in them and you can put words in those images.
How to improve your PPT slides for an academic presentation at university. It discusses design, fonts, structure, animation, pictures, graphs, and referencin...
How to Make Academic Presentations Berthold Herrendorf (Arizona State University) August 23, 2016 I prepared the first version of these slides as an introduction to a presentation class for advanced PhD students at ASU in 2015/6. I have since updated them taking into account comments and suggestions from Georg Duernecker, Edward Prescott, B ...
Presentations with strong narrative arcs are clear, captivating, and compelling. Orient the audience and draw them in by demonstrating the relevance and importance of your research story with strong global motive. Provide them with the necessary vocabulary and background knowledge to understand the plot of your story.
Related Articles. This guide provides a 4-step process for making a good scientific presentation: outlining the scientific narrative, preparing slide outlines, constructing slides, and practicing the talk. We give advice on how to make effective slides, including tips for text, graphics, and equations, and how to use rehearsals of your talk to ...
Be neat. 2. Avoid trying to cram too much into one slide. y Don't be a slave to your slides. 3. Be brief. y use keywords rather than long sentences. 4. Avoid covering up slides.
Practice, practice, practice. There is truth to the saying "practice makes perfect.". Rehearse the presentation, including any jokes or stories, multiple times until it becomes so natural you no longer need a script and will only have to establish rapport with your audience come presentation day.
Academic presentation tip #10: Prepare PPT presentation and PDF backup copy to reduce anxiety . A final tip that I'd like to share with you here is about the format of your presentation. I remember that I was delivering a presentation at an academic conference couple of years ago. Halfway through the presentation, I realised that my figures ...
To assist the audience, a speaker could start by saying, "Today, I am going to cover three main points.". Then, state what each point is by using transitional words such as "First," "Second," and "Finally.". For research focused presentations, the structure following the overview is similar to an academic paper.
A great presenter is one who is intentional: each element in the presentation serves a clear function and is intended to support the audience's understanding of the content. Here are 10 tips to keep in mind to ensure your presentation hits the mark. 1. Any time you put something on your slides, its primary purpose is to help the audience, not ...
Newcastle University. Academic Skills Kit. 1 10 Top Tips for Academic Presentations . Practice in different situations . It's normal to feel nervous before giving a presentation and you may not be able to get rid of your nerves entirely, but that isn't necessarily a bad thing. The adrenaline
Creating Successful Presentations. A. Content. Using Visual Aids to Communicate Your Content. watch for repetitiveness. make sure your content doesn't repeat things you've already said. organize your content so that you're clearly adding "something new". avoid redundancy. try not to repeat yourself.
Learn the 10 steps for creating and delivering a PowerPoint or Keynote presentation on the graduate and undergraduate levels.
This MSWord document is a template for structuring a typical academic presentation, it can be adapted and changed if necessary depending on how long the presentation you need to give is. Try to fill it in using full sentences as these will become your slide titles. The blue sections are optional.
Making a PowerPoint. Follow these step-by-step guides on how to add certain elements to your PowerPoint presentation: Select a Design Theme. Add or Delete a Slide. Add an Image to a Slide. Add Notes to Your Slides. Add Animations.
☛ For English subtitles, click on subtitles/closed captions.Need more help with your English? How can the ELC help YOU!☛ Check out the ELC: https://www.polyu...
Common Presentation Formats. The three most common ways in which students formally present information in college courses are as talks/speeches, through Power Points, and with posters. Talks and Speeches. Many students find the idea of giving a speech or a talk intimidating. That is understandable, but know that all good orators use certain ...
Apply the 10-20-30 rule. Apply the 10-20-30 presentation rule and keep it short, sweet and impactful! Stick to ten slides, deliver your presentation within 20 minutes and use a 30-point font to ensure clarity and focus. Less is more, and your audience will thank you for it! 9. Implement the 5-5-5 rule. Simplicity is key.
To ensure this doesn't happen to you, here are 8 tips to help you make your academic presentation memorable. 1. Understand the Goal of Your Presentation. In order to structure your presentation correctly it's important that you understand the overall goal of the presentation. For academic presentations, there are actually 2 potential goals ...
Students must prepare the material for their presentation, keeping it relevant to the time they have been given. If you're writing your presentation out, 2 minutes per double-spaced page is a good rule of thumb to follow. Make sure you don't have over 7 double-spaced pages of material for a fifteen-minute talk. [2]
Focus on the content of your presentation and your audience will too. 5. Respect your time limit. It is natural to get caught up in your talk and forget to keep track of time. A presentation that drags on forever invariably loses favor with the audience, however, so it's important to keep to the schedule. Setting a watch or clock on the ...
Summary. A strong presentation is so much more than information pasted onto a series of slides with fancy backgrounds. Whether you're pitching an idea, reporting market research, or sharing ...
1. Use strong language: Use powerful words and phrases to convey your message clearly and effectively. Avoid using filler words or platitudes that will make your audience tune out. 2. Be engaging: Make sure to keep your audience engaged by making eye contact, using facial expressions, and speaking with enthusiasm.
Check out our 10 top student tips for presenting at university. Further help available on our website: http://libguides.hull.ac.uk/present___________This vid...
Say it with your body. In face-to-face conversation, body language plays an important role. Communication is 55 percent non-verbal, 38 percent vocal (tone and inflection), and 7 percent words, according to Albert Mehrabian, a researcher who pioneered studies on body language [].Up to 93 percent of communication, then, does not involve what you are actually saying.
Even if you suck at making slides, storytelling or selling yourself. These tips are focused on students in a master program but they can easily apply to the professional world too. In summary. Know the evaluation criteria; Use the evaluation criteria as a checkin tool; Dry run your presentation dozen of times; Test the presentation with your ...
Resources for Educators & Students K-12 Education The AHA strives to ensure that every K-12 student has access to high quality history instruction. We create resources for the classroom, advise on state and federal policy, and advocate for the vital importance of history in public education. Learn More Undergraduate Education…
#LIVE | Watch #CruxofTheMatter: Row over @NCERT's syllabus purge: 'Course' correction justified? with Rahul Shivshankar