- Harvard Business School →
- Faculty & Research →
- January 2014 (Revised June 2020)
- HBS Case Collection

The Rise and Fall of Nokia
- Format: Print
- | Language: English
- | Pages: 26
About The Authors
Juan Alcacer
Tarun Khanna
Related work.
- Faculty Research
- November 2020
The Rise and Fall of Nokia (Abridged)
- The Rise and Fall of Nokia By: Juan Alcácer
- The Rise and Fall of Nokia By: Juan Alcacer, Tarun Khanna and Christine Snively
- The Rise and Fall of Nokia (Abridged) By: Juan Alcácer and Tarun Khanna
Brought to you by:

Nokia: The Inside Story of the Rise and Fall of a Technology Giant
By: Quy Huy, Timo O. Vuori, Lisa Duke
The case examines the downward spiral of Nokia, the mobile technology giant that once conquered the world, seen from the perspective of 'insiders' - based on interviews with Nokia executives at top…
- Length: 15 page(s)
- Publication Date: Sep 26, 2016
- Discipline: General Management
- Product #: IN1289-PDF-ENG
What's included:
- Teaching Note
- Educator Copy
$4.95 per student
degree granting course
$8.95 per student
non-degree granting course
Get access to this material, plus much more with a free Educator Account:
- Access to world-famous HBS cases
- Up to 60% off materials for your students
- Resources for teaching online
- Tips and reviews from other Educators
Already registered? Sign in
- Student Registration
- Non-Academic Registration
- Included Materials
The case examines the downward spiral of Nokia, the mobile technology giant that once conquered the world, seen from the perspective of 'insiders' - based on interviews with Nokia executives at top and middle management level. They describe the emotional undercurrents of the innovation process that caused temporal myopia - an excessive focus on short-term innovation at the expense of longer-term more beneficial activities. Nokia's once-stellar performance was undermined by misaligned collective fear: top managers were afraid of competition from rival products, while middle managers were afraid of their bosses and even their peers. It was their reluctance to share negative information with top managers - who thus remained overly optimistic about the organisation's capabilities - that generated inaccurate feedback and poorly adapted organizational responses that led to the company's downfall. The case covers the period from the early 2000s to 2010, with a focus on 2007 (the introduction of the iPhone) to 2010, when the CEO left.
Learning Objectives
After reading and analysing the case, students will understand (i) how emotional dynamics influence hard technological and strategic decisions in organizations as they translate into challenges for innovation, (ii) how emotional dynamics can undermine innovation and performance.
Sep 26, 2016 (Revised: Dec 12, 2022)
Discipline:
General Management
IN1289-PDF-ENG
We use cookies to understand how you use our site and to improve your experience, including personalizing content. Learn More . By continuing to use our site, you accept our use of cookies and revised Privacy Policy .
Case Study 4: The Collapse of Nokia’s Mobile Phone Business
- First Online: 30 July 2018
Cite this chapter

- Tuomo Peltonen 2
2153 Accesses
3 Citations
14 Altmetric
This chapter provides a wisdom-oriented reading of one of the most spectacular business failures of recent times: the collapse of Nokia mobile phones between 2007 and 2015. Using executive biographies and other published accounts of Nokia’s organisational patterns, the chapter attempts to offer a more balanced explanation of the processes behind Nokia’s inability to respond to the changing industry circumstances. The following analysis pays attention to the shaping of Nokia’s organisational culture. Company and its new leadership adopted a professional, no-nonsense approach in the aftermath of the problems of the late 1980s and early 1990s. The new generation of managers believed in a rational mindset supported by a bureaucratic organisational form. Leaning on a superior technological competence within the mobile phone sector, Nokia was capable of ultimately becoming the market leader. However, in 2007, with two major players, Apple and Google, joining the business, the established rules of competitive dynamics were irrevocably changed. Focus shifted to software and applications. Nokia’s risk-aversive and closed organisational culture could not respond in a situation where an open search for new innovations and a cooperative internal working mode were needed. An analysis of the development of Nokia’s organisational psyche following the emergence of a new generation of managers and executives highlights the role of local beliefs in using philosophical wisdom in critical circumstances. Nokia and its leadership were not able to abandon the outmoded habits and structures, as these had become integrated with the very identity of the company.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Bibliography
Agarwal, R., & Helfat, C. E. (2009). Strategic renewal of organizations. Organization Science, 20 (2), 281–293. https://doi.org/10.1287/orsc.1090.0423 .
Article Google Scholar
Alahuhta, M. (2015). Johtajuus [Leadership]. Helsinki: Bookwell.
Google Scholar
Borden, M. (2009, January 9). Nokia rocks the world: The phone King’s plan to redefine its business. Fast Company . https://www.fastcompany.com/1325729/nokia-rocks-world-phone-kings-plan-redefine-its-business . (read 1.4.2018).
Brannen, M. Y., & Doz, Y. L. (2012). Corporate languages and strategic agility: Trapped in your jargon or lost in translation? California Management Review, 54 (3), 77–97. https://doi.org/10.1525/cmr.2012.54.3.77 .
Bryman, A. (2015). Social research methods . Oxford University Press. https://doi.org/10.4135/9781849209939 .
Cooper, R. (1986). Organization/Disorganization. Social Science Information, 25 (2), 299–335.
Cooper, R. (1997). The visibility of social systems. In K. Hetherington & R. Mundo (Eds.), Ideas of difference (pp. 32–41). Oxford: Blackwell.
Cord, D. J. (2014). The decline and fall of Nokia . Helsingfors: Schildt & Söderström.
Donaldson, L. (2001). The contingency theory of organizations . Thousand Oaks: Sage.
Book Google Scholar
Häikiö, M. (2009). Nokia – matka maailman huipulle [Nokia – the journey to the top of the world] (in Finnish). Helsinki: Edita.
Heikkinen, M.-P. (2010). Mokia. Helsingin Sanomat , April 27, 2011. http://www.hs.fi/kuukausiliite/a1305875065676 (read 1.4.2018).
Insead. (2014). The decline of Nokia: Interview with former CEO Olli-Pekka Kallasvuo. Insead Knowledge , April 12, 2013. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jR5a_DBYSmI
Isaacson, W. (2011). Steve Jobs . Helsinki: Otava.
Kärppä, H. (2016). Tässä ovat 2000-luvun suurimmat irtisanomiset – kärkisijoilla Nokia ja Microsoft [The biggest layoffs during the 2000’s] (in Finnish). Helsingin Sanomat. http://www.hs.fi/talous/a1459916372158 (read 1.4.2018).
Kortteinen, M. (1992). Kunnian kenttä: suomalainen palkkatyö kulttuurisena muotona [Field of honor: Finnish work as a cultural form] (in Finnish). Hämeenlinna: Karisto.
Laamanen, T., Lamberg, J. A., & Vaara, E. (2016). Explanations of success and failure in management learning: What can we learn from Nokia’s rise and fall? Academy of Management Learning & Education, 15 (1), 2–25.
Linden, C.-G. (2015). Nokia och Finland [Nokia and Finland] (in Swedish). Helsinki: Schildt & Söderström.
March, J. G., & Sutton, R. I. (1997). Organizational performance as a dependent variable. Organization Science, 8 (6), 698–706 http://doi.org/Article .
Milne, R. (2009, March 23). Jorma Ollila: Champion of Nordic capitalism. Financial Times . http://royaldutchshellplc.com/2009/03/23/jorma-ollila-champion-of-nordic-capitalism/ (read 1.4.2018).
Nykänen, M., & Salminen, M. (2014). Operaatio Elop [Operation Elop] (in Finnish). Helsinki: Teos.
Ollila, J. (2016, Augest 29). Tervetuliaispuhe Etlan 70-vuotisjuhlaseminaarissa [Welcome speech in the 70th anniversary of Etla] (in Finnish). https://www.etla.fi/wp-content/uploads/Jorma-Ollila-Etla70.pdf (read 1.4.2018).
Ollila, J., & Saukkomaa, H. (2013). Mahdoton menestys: kasvun paikkana Nokia [Impossible success: Nokia as a place for growth] (in Finnish). Helsinki: Otava.
Ollila, J., & Saukkomaa, H. (2016). Against all odds: Leading nokia from near catastrophe to global success . Palmyra, VA: Maven House.
Palmu-Joroinen, A.-L. (2009). Nokia-vuodet [Nokia years]. Helsinki: Atena.
Ristimäki, M. (2006, October 13). Nokian ex-pomo: nykyjohtajilta puuttuu yleissivistys [Ex-Nokia boss: Current leaders are lacking general education]. Taloussanomat . http://www.iltasanomat.fi/taloussanomat/art-2000001477674.html (read 1.4.2018).
Taleb, N. N. (2007). The black swan: The impact of the highly improbable . New York: Random house.
The Editorial Staff of Ylioppilaslehti. (2004, April 9). Tuhannen ja yhden yön taistolaisuus [The Stalinism of thousand and one nights]. Ylioppilaslehti . http://ylioppilaslehti.fi/2004/04/274/ (read 1.4.2018).
Virtanen, J. (2013). Näin Nokia on irtisanonut Suomessa [This is the way Nokia has laid off employees in Finland]. Yle Uutiset . http://yle.fi/uutiset/3-6455026 (read 1.4.2018).
Vuori, T. O., & Huy, Q. N. (2016). Distributed attention and shared emotions in the innovation process: How Nokia lost the smartphone battle. Administrative Science Quarterly, 61 (1), 9–51. https://doi.org/10.1177/0001839215606951 .
Weber, M. (1976). Protestant ethic and the spirit of capitalism (4th ed., T. Parsons, Trans.). London: Allen & Unwin (Original work published 1930).
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Business, Aalto University, Helsinki, Finland
Tuomo Peltonen
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 The Author(s)
About this chapter
Peltonen, T. (2019). Case Study 4: The Collapse of Nokia’s Mobile Phone Business. In: Towards Wise Management. Palgrave Macmillan, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-91719-1_6
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-91719-1_6
Published : 30 July 2018
Publisher Name : Palgrave Macmillan, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-319-91718-4
Online ISBN : 978-3-319-91719-1
eBook Packages : Business and Management Business and Management (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
How Nokia Embraced the Emotional Side of Strategy
- Timo O. Vuori

Don’t dismiss the “soft stuff.”
How do emotions shape strategy making? A pair of researchers investigated this topic by doing a close analysis of Nokia’s severe strategic challenges between 2007 and 2013. As part of this research, they conducted 120 interviews, including nine with board members and 19 with top managers. They found that while emotions are often dismissed as the “soft stuff,” they have profound effects on strategy. To avoid emotions having a negative effect on strategic decision-making, managers can do three things. First, increase trust by setting clear, and healthy, conversational norms. Second, reduce emotional attachment to a failing strategy by generating many new options — not just one alternative. And third, nudge top managers to pay attention to data that conflicts with their gut feelings.
How do emotions shape strategy making? We investigated this topic when we studied how Nokia executives dealt with the company’s severe strategic challenges between 2007 and 2013. As part of this research, we conducted 120 interviews, including nine with board members and 19 with top managers.
- TV Timo O. Vuori is an assistant professor in strategic management at Aalto University in Finland.
- QH Quy Huy is the Solvay Chaired Professor of Technological Innovation at INSEAD and Academic Director of the INSEAD China Initiative.
Partner Center
Nokia Change Management Case Study
Nokia is a company that has undergone significant change over the years, transforming itself from a mobile phone manufacturer to a leading player in the telecommunications infrastructure market.
This transformation was driven by a range of factors, including changes in market conditions, advancements in technology, and shifting customer needs and preferences.
However, perhaps the most important factor in Nokia’s successful transformation was its approach to change management.
In this blog post of Nokia’s change management case study, we’ll examine key strategies and tactics that the company employed to drive its successful transformation.
By examining the lessons learned from Nokia’s experience, we can gain valuable insights into effective change management and the critical factors that are required for a successful organizational transformation.
Let’s start reading.
Brief History of Nokia Journey of Change
Nokia was a Finnish company that produced a wide range of products, including paper, rubber, and cables. It was not until the 1980s that Nokia started focusing on telecommunications equipment, but even then, it was still a relatively small player in the industry.
In the late 1990s, Nokia made a strategic decision to focus solely on mobile phones, which at the time were rapidly growing in popularity. Nokia recognized the potential of the mobile phone market early on and invested heavily in research and development to create innovative and user-friendly devices.
Nokia’s decision to focus on mobile phones paid off, and by the early 2000s, the company had become the world’s largest mobile phone manufacturer, with a dominant market share. Nokia’s success was due to its ability to offer a wide range of phones at different price points and to develop cutting-edge technology such as the first mobile phones with built-in cameras and internet connectivity.
However, Nokia’s dominance in the mobile phone market was short-lived. The company struggled to keep up with the rapid pace of technological innovation and the rise of new competitors, such as Apple and Samsung. As a result, Nokia’s market share declined sharply in the late 2000s and early 2010s, and the company eventually sold its mobile phone business to Microsoft in 2014.
Nokia refocused on telecommunications infrastructure and services. It was a again a success story. In 2015 Nokia acquires French telecommunications equipment company Alcatel-Lucent.
What are those external and internal factors that caused change?
There were several external and internal factors that led to Nokia’s change management and transformation from a mobile phone producer to a telecommunication infrastructure service provider. Here are some of the key factors:
External factors:
- Increased competition: The rise of new competitors such as Apple and Samsung in the mobile phone market put pressure on Nokia’s mobile phone business, leading to declining market share and profits.
- Rapid technological change: The rapid pace of technological innovation in the mobile phone industry made it difficult for Nokia to keep up and remain competitive.
- Shift towards smartphones: The shift towards smartphones and the decline of feature phones also contributed to Nokia’s decline in the mobile phone market.
- Opportunities in telecommunication infrastructure: The growing demand for 5G networks and other telecommunications infrastructure services presented an opportunity for Nokia to diversify and expand its business.
Internal factors:
- Strategic decision-making : Nokia’s leadership recognized the need to adapt to changing market conditions and made the strategic decision to shift its focus towards telecommunications infrastructure services.
- Strengths in telecommunications: Nokia had a strong history and expertise in the telecommunications industry, which gave it a foundation to build on in expanding its business.
- Investment in research and development: Nokia continued to invest in research and development, allowing it to develop new products and services in the telecommunications infrastructure market.
- Acquisitions and partnerships: Nokia made strategic acquisitions and partnerships to expand its capabilities in telecommunications infrastructure services, such as the acquisition of Alcatel-Lucent and the partnership with Xiaomi.

07 Key Drivers of successful change management of Nokia
The successful change management of Nokia from a mobile phone manufacturer to a telecommunications infrastructure provider was driven by several key factors. Here are some of the most important drivers:
1. Clear Strategic Direction
Nokia’s clear strategic direction helped guide decision-making at all levels of the organization, ensuring that all stakeholders were aligned towards common goals and objectives. This helped Nokia to allocate resources more effectively, ensuring that investments were directed towards initiatives that supported the company’s long-term goals.
The leadership and employees focused its efforts on key priorities, such as developing new products and services in the telecommunications infrastructure market, and helped to minimize distractions from other activities that were not aligned with the company’s strategic objectives.
2. Agility and Adaptability
Agility and adaptability are important characteristics for organizations looking to succeed in a rapidly changing market environment. Nokia’s ability to demonstrate both agility and adaptability was key to its successful transformation from a mobile phone manufacturer to a telecommunications infrastructure provider. Nokia was able to quickly recognize and respond to changing market conditions and pivot its business towards new opportunities, such as the growing demand for telecommunications infrastructure services.
3. Research and Development
Nokia’s continued investment in R&D played a critical role in its successful transformation from a mobile phone manufacturer to a telecommunications infrastructure provider. By investing in R&D, Nokia was able to develop new products and services in the telecommunications infrastructure market and stay ahead of its competitors. This allowed the company to offer innovative and cutting-edge solutions that met the evolving needs of its customers. Additionally, Nokia’s investment in R&D helped the company to build a strong intellectual property portfolio, which further strengthened its competitive advantage in the market.
4. Operational Excellence
Nokia’s focus on operational efficiency and continuous improvement was a critical factor in its successful transformation from a mobile phone manufacturer to a telecommunications infrastructure provider. By streamlining its operations and reducing costs, Nokia was able to improve its competitiveness and profitability in the highly competitive telecommunications infrastructure market. This focus on operational excellence helped the company to optimize its production processes, reduce waste, and improve product quality, which in turn helped it to deliver products and services to its customers more efficiently and at a lower cost.
5. Strong Leadership
Nokia’s success in transforming itself from a mobile phone manufacturer to a telecommunications infrastructure provider was due in part to the strong and experienced leadership of CEO Rajeev Suri, who played a key role in leading the company through the transformation process. Suri’s leadership was critical in rallying employees around the new strategic direction and ensuring that all stakeholders were aligned towards common goals and objectives. Suri also provided clear direction and guidance to the organization, helping to steer the company through the challenges and uncertainties of the transformation process.
6. Cultural Change
Nokia’s success in transformation is also due to cultural change. Nokia encouraged employees to be more innovative and agile in their work, fostering a culture of experimentation and continuous improvement. The company also emphasized the importance of collaboration and teamwork, encouraging employees to work together to solve complex problems and achieve common goals. Nokia invested in employee development and training, helping to foster a culture of continuous learning and development. This cultural shift helped to create a more flexible, innovative, and agile organization that was better able to adapt to changing market conditions and drive the company’s successful transformation.
7. Acquisition and Partnerships
Acquisitions and partnerships are critical tools that Nokia used to expand its capabilities and build a competitive advantage. By acquiring companies with complementary products and services, Nokia was able to expand its capabilities in telecommunications infrastructure services, giving the company a competitive advantage and helping it to build a comprehensive portfolio of products and services. Additionally, by partnering with other companies in the industry, Nokia was able to leverage the strengths of its partners to deliver innovative solutions that met the evolving needs of its customers.
Final Words
Nokia’s successful transformation from a mobile phone manufacturer to a leading player in the telecommunications infrastructure market is a powerful case study in effective change management. By adopting a clear strategic direction, investing in research and development, focusing on operational excellence, fostering a culture of innovation and collaboration, and pursuing strategic acquisitions and partnerships, Nokia was able to adapt to changing market conditions and pivot its business towards new opportunities. Ultimately, Nokia’s transformation serves as a powerful example of how organizations can successfully adapt and evolve in response to changing market conditions, leveraging their strengths and capabilities to drive growth and success in new markets and industries.
About The Author
Tahir Abbas
Related posts.
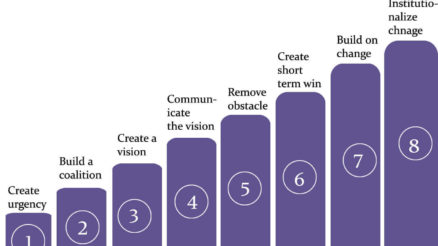
Kotter’s 8 Steps Model of Change Management

08 Ways Change Managers Benefit from Resistance to Change

Change Management Storytelling Examples, Types, and Techniques
To read this content please select one of the options below:
Please note you do not have access to teaching notes, strategic management of business model transformation: lessons from nokia.
Management Decision
ISSN : 0025-1747
Article publication date: 3 May 2011
This paper aims to offer a conceptualization of how and why corporate level strategic change may build on historical differentiation at business unit level.
Design/methodology/approach
Methodologically, an historical case study of Nokia Corporation's drastic business model transformation between the years 1987 and 1995 is reported.
The conceptual and historical work results in a process model of business model change, demonstrating how central business units feed strategic alternatives and capabilities to the corporate‐level transformation process.
Practical implications
The results highlight the importance of corporate level “market mechanisms' that allow promising strategic alternatives to emerge and select out inferior options. In this process, a key mechanism is the exchange of executives and cognitive mindsets between business units and corporate headquarters (CHQ).
Originality/value
The reported research offers an original contribution by showing the dynamic interplay of cognitive and organizational change processes, and highlighting the importance of building on existing capabilities and competencies despite the pressure to demonstrate strong turnaround activities.
- Business planning
- Organizational change
- Business history
- Telecommunications
- Corporate strategy
Aspara, J. , Lamberg, J. , Laukia, A. and Tikkanen, H. (2011), "Strategic management of business model transformation: lessons from Nokia", Management Decision , Vol. 49 No. 4, pp. 622-647. https://doi.org/10.1108/00251741111126521
Emerald Group Publishing Limited
Copyright © 2011, Emerald Group Publishing Limited
Related articles
We’re listening — tell us what you think, something didn’t work….
Report bugs here
All feedback is valuable
Please share your general feedback
Join us on our journey
Platform update page.
Visit emeraldpublishing.com/platformupdate to discover the latest news and updates
Questions & More Information
Answers to the most commonly asked questions here
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Nokia case study

Related Papers
ramanajaneyulu pokathota
Nokia was a synonym for the mobile phone industry for a long time; however, when it came into the era of smart phones, the former leader was under an awkward situation. Nokia sold its mobile phone business to Microsoft on September 3, 2013. A company following Kodak with the legendary color failed in the impact of the new technology revolution. This was a typical case of the subversion of an industry; therefore, the author believed that it was necessary to analyze the process. This paper studied Nokia's decline mainly from the three parts. First of all, looking back Nokia's development process from the glory to the decline, it can be divided into three stages: the transition period, the peak period and the decline period, followed by analyzing the reasons of its decline from three parts: Nokia executives' grasp for the market, the company's business strategy and business cooperation, and finally analyzing its inspiration for modern enterprises from the marketing perspective.
In this paper, we study the changing explanations of success and failure over the course of a firm’s history. We build on a discursive approach that highlights the role of narrative attributions in making sense of corporate performance. Specifically, we analyze how the Nokia Corporation was framed first as a success and later as a failure and how these dimensions of performance were explained in various actors’ narrative accounts. In both the success and failure accounts, our analysis revealed a striking black-and-white picture that resulted in the institutionalization of Nokia’s metanarratives of success and failure. Our findings also reveal a number of discursive attributional tendencies; and thus warn of the cognitive and politically motivated biases that are likely to characterize management literature. Keywords: strategic management; causal attribution; sense-making; discourse analysis; narrative; management history
Mathematics Education Research Group of Australasia
Debra Panizzon
Polymer Degradation and Stability
johan sarazin
Materiality and Visuality in North East India
rakhee kalita moral
European Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology and Reproductive Biology
David J Torpy
2006 HPCMP Users Group Conference (HPCMP-UGC'06)
Nikhil Bhatia
ALIMO PHILIP
Background: The textile industry generates a large volume of waste due to the increasing demand for clothing for daily use and fashion. To reduce waste, reverse logistics (RL) has been proposed to ensure the recycling and reuse of waste textiles in the value chain. RL has been broadly examined in several manufacturing supply chains but less explored in the textile industry. The absence of a systematic review on textile reverse logistics (TRL) makes it difficult to identify existing knowledge gaps and research opportunities. Methods: Using the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) framework, this paper contributes a systematic literature review of 28 relevant papers published on TRL between 1999 and August 2022. Results: Overall, there is a shortage of recycling facilities in developing economies. There is a need for quantitative models that assess the location and potential disruptions and aversion of the resulting risks of TRL. Investigating consumers’ perspectives on the desire to sort and transport old textiles to collection sites would be helpful to manufacturers. Additionally, system optimization to reduce emissions that emerge through the TRL production line would help reduce costs. It is also found that incentivizing clothing businesses that adhere to TRL practices would encourage more participation. Conclusions: This study discusses research opportunities in TRL that are beneficial to the clothing and textiles industry and researchers in developing new waste management strategies.
如何购买贝德福特大学毕业证 bedfordhire毕业证学历证书学历学位认证原版一模一样
留信网入网《英国斯特林大学diploma文凭防伪底纹》《Q微信/1954292140》斯特林大学毕业证书学位证书办理【英国成绩单电子版英国斯特林大学学历证书硕士毕业证书英文、《斯特林大学Offer录取通知书文凭证书》、《英国原版文凭-斯特林大学毕业证学位证购买》、英国文凭和毕业证书制作英国斯特林大学毕业证翻译、斯特林大学成绩单电子版办理急速办理英国英国斯特林大学 Degree斯特林大学Bachelor Diploma。 留学生买斯特林大学毕业证文凭、学历认证请联系【Q/微信1954 292 140】英国文凭证书设计急速办理斯特林大学毕业证书复印件。专业为留学生办理斯特林大学毕业证、成绩单、使馆留学回国人员证明、教育部学历学位认证、斯特林大学录取通知书、Offer、在读证明、雅思托福成绩单、网上存档永久可! 为留学生提供以下服务: 一、斯特林大学毕业证#成绩单等全套材料《英国文凭证书设计急速办理斯特林大学毕业证书复印件》【Q/微1954292140】《永久可查斯特林大学成绩单电子版》,从防伪到印刷,从水印到钢印烫金,跟学校原版100%相同. 二、真实教育部认证,教育部存档,中国教育部留学服务中心认证(即教育部留服认证)网站100%可查. 三、真实使馆认证(即留学人员回国证明),使馆存档可通过大使馆查询确认. 四、真实留信网认证,国家专业人才认证中心颁发入库证书,留信网永久存档可查. 文凭学历证书办理流程《英国文凭证书设计急速办理斯特林大学毕业证书复印件》《Q微1954292140》: 1、客户提供办理信息:姓名、生日、专业、学位、毕业时间等(如信息不确定可以咨询顾问:微信1954292140我们有专业老师帮你查询); 2、客户付定金下单; 3、公司确认到账转制作点做电子图; 4、电子图做好发给客户确认; 5、电子图确认好转成品部做成品; 6、成品做好拍照或者视频确认再付余款; 7、快递给客户(国内顺丰,国外DHL)。 【公司采用定金+余款的付款流程,以最大化保障您的利益,让您放心无忧】 #澳洲文凭毕业证 #美国毕业证 #英国文凭 #加拿大文凭毕业证 #新西兰毕业证 #法国毕业证 #德国毕业证、铸就十年品质!信誉!实体公司!可以视频看办公环境样板,如需办理真实可查《办理斯特林大学毕业证书复印件》【Q/微1954292140】《英国斯特林大学成绩单电子版永久可查》可以先到公司面谈,勿轻信小中介黑作坊! 注:上述高仿材料,随时都可以安排办理《英国文凭证书设计急速办理斯特林大学毕业证书复印件》【Q/微1954292140】《永久可查斯特林大学成绩单电子版》毕业证成绩单,专业,学位,毕业时间都可以根据客户要求安排。 斯特林大学文凭学历证书办理流程《Q微1954292140》: 1、客户提供办理信息:姓名、生日、专业、学位、毕业时间等(如信息不确定可以咨询顾问:微信1954292140我们有专业老师帮你查询); 2、客户付定金下单; 3、公司确认到账转制作点做电子图; 4、电子图做好发给客户确认; 5、电子图确认好转成品部做成品; 6、成品做好拍照或者视频确认再付余款; 7、快递给客户(国内顺丰,国外DHL)。 真实教育部学历认证 ★ 教育部学历学位认证《英国文凭证书设计急速办理斯特林大学毕业证书复印件》【Q/微1954292140】《永久可查斯特林大学成绩单电子版》,留服官网真实存档可查,永久存档。 ★ 留学回国人员证明(使馆认证),使馆网站真实存档可查。 ★ 真实教育部认证,教育部存档,中国教育部留学服务中心认证(即教育部留服认证)网站100%可查。 ★ 真实使馆认证(即留学人员回国证明),使馆存档可通过大使馆查询确认。 ★ 留信网认证,国家专业人才认证中心颁发入库证书,留信网永久存档可查。 留信网认证《办理斯特林大学毕业证书复印件》【Q/微1954 292 140】《英国斯特林大学成绩单电子版永久可查》国内认可度怎么样?可以用来入职吗?总体来说,留信网的认证一定程度上也能协助刚归国的留学生找工作。让企业更为直观的了解留学生个人的专业能力,及其对工作的胜任能力。显示认可度是比前几年更高了。留信网作为在中国学位认证评定的另一个平台,对比传统的认证更为现代化、综合性,并且许多就业企业和单位也认可留信网认证出的结果,为企业在筛选专业人才时提供了一个不错的参考,总体上还是要看企业对于人才选拔上的要求,如果留服认证没办法正常申请办理《英国文凭证书设计急速办理斯特林大学毕业证书复印件》【Q/微1954 292 140】《永久可查斯特林大学成绩单电子版》,这种情况下,就可以考虑申请办理留信认证《英国斯特林大学毕业证书复印件办理》【Q/微1954 292 140】《急速办理斯特林大学文凭证书设计》。
RELATED PAPERS
Altamir Guilherme Wagner
Lecture Notes in Computer Science
Florin Teodorescu
Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry
stewart frescas
Rocznik Teologii Katolickiej
Leszek Marius Jakoniuk
jadranka garmaz
WHO South-East Asia Journal of Public Health
Rosete Pescador
Ecological Applications
Stephen Carpenter
Education in the Knowledge Society (EKS)
Miguel Ángel Ruiz Hernández
Milena Parent
Iskandar Hailani
Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions®
Tingquan Wu
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
- Today's news
- Reviews and deals
- Climate change
- 2024 election
- Fall allergies
- Health news
- Mental health
- Sexual health
- Family health
- So mini ways
- Unapologetically
- Buying guides
Entertainment
- How to Watch
- My Portfolio
- Latest News
- Stock Market
- Biden Economy
- Stocks: Most Actives
- Stocks: Gainers
- Stocks: Losers
- Trending Tickers
- World Indices
- US Treasury Bonds
- Top Mutual Funds
- Highest Open Interest
- Highest Implied Volatility
- Stock Comparison
- Advanced Charts
- Currency Converter
- Basic Materials
- Communication Services
- Consumer Cyclical
- Consumer Defensive
- Financial Services
- Industrials
- Real Estate
- Mutual Funds
- Credit Cards
- Balance Transfer Cards
- Cash-back Cards
- Rewards Cards
- Travel Cards
- Student Loans
- Personal Loans
- Car Insurance
- Mortgage Calculator
- Morning Brief
- Market Domination
- Market Domination Overtime
- Asking for a Trend
- Opening Bid
- Stocks in Translation
- Lead This Way
- Good Buy or Goodbye?
- Fantasy football
- Pro Pick 'Em
- College Pick 'Em
- Fantasy baseball
- Fantasy hockey
- Fantasy basketball
- Download the app
- Daily fantasy
- Scores and schedules
- GameChannel
- World Baseball Classic
- Premier League
- CONCACAF League
- Champions League
- Motorsports
- Horse racing
- Newsletters
New on Yahoo
- Privacy Dashboard
Yahoo Finance
Global autonomous networks market report 2024-2029, with case studies of vejthani hospital, university of oxford and heilongjiang international university green campus network.
Global Autonomous Networks Market
Dublin, June 07, 2024 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- The "Global Autonomous Networks Market by Offering (Solutions and Services), End User (Service Providers and Verticals (Hospitality, Education, Government, Healthcare, Transportation & Logistics)) and Region - Forecast to 2029" report has been added to ResearchAndMarkets.com's offering. The autonomous networks market is estimated at USD 7 billion in 2024 to USD 17.5 billion by 2029, at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 20.1%. These networks enhance efficiency and reliability in network management for service providers by enabling real-time monitoring, automated troubleshooting, and predictive maintenance, which reduces operational costs and improves service quality. They also allow for seamless scalability, dynamic adaptation to changing demands, and enhanced security through automatic threat detection and mitigation. Additionally, the integration of AI and machine learning supports continuous optimization and innovation, ensuring that autonomous networks remain at the forefront of technological advancements.
By offering, the solutions segment is expected to register the largest market share during the forecast period. Within the projected 2024-2029 forecast period, the solutions segment is anticipated to hold a most significant market share in the autonomous networks market due to several factors. The increasing complexity of network infrastructures necessitates comprehensive solutions that can autonomously manage and optimize operations, integrating advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning to adapt to evolving network conditions and demands. This demand is further boosted by the growing adoption of automation across industries, driven by the need for efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Additionally, the rise of emerging technologies like 5G, IoT, and edge computing requires robust and adaptive network management systems, enhancing the relevance and uptake of autonomous network solutions. Furthermore, regulatory pressures and the need for improved cybersecurity also drive organizations to invest in comprehensive autonomous network solutions to ensure compliance and protect sensitive data. Overall, the solutions segment is set to lead the market due to its ability to address the challenges of modern network management effectively. By end user, service providers are expected to hold the largest market share during the forecast period. The service providers segment is expected to dominate the autonomous networks market from 2024 to 2029 due to their significant role in driving the adoption and implementation of advanced networking technologies. Service providers are at the forefront of integrating autonomous networks to enhance their operational efficiency, reduce costs, and improve service delivery. These entities are heavily investing in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and automation to manage the increasing demand for high-speed, reliable connectivity and to support the production of IoT devices, 5G networks, and cloud services. Additionally, service providers are under constant pressure to offer differentiated services and maintain competitive advantage, making the adoption of autonomous networks a strategic priority. As a result, their continuous efforts to innovate and optimize their network infrastructure are expected to lead to the largest market share within this segment. North America is estimated to have the largest market size during the forecast period. North America possesses a highly developed telecommunications infrastructure, with widespread adoption of advanced technologies such as 5G. This technological advancement creates a fertile ground for implementing autonomous networks, which rely on robust connectivity and low latency. Moreover, the region is home to many leading technology companies, and startups focused on innovation in networking and automation, fostering a competitive landscape that drives rapid advancements in autonomous network solutions. Additionally, North America has a conducive regulatory environment that encourages investment in emerging technologies, further stimulating growth in the autonomous networks market. Lastly, the region's large and diverse consumer base, coupled with increasing demand for seamless connectivity and digital services, provides a substantial market opportunity for autonomous network providers to thrive and expand their operations. The report provides insights on the following pointers:
Analysis of critical drivers (Rise of internet of things (IoT) devices, Increased need for real-time data processing & analysis), restraints (High initial investment required to adopt this technology, Lack of standardization, Cybersecurity risks), opportunities (Edge computing optimization, Network slicing), and challenges (Customer requirement interaction, Service provider requirement interaction, Automation by maximizing utility) influencing the growth of the autonomous networks market.
Product Development/Innovation: Detailed insights on upcoming technologies, research & development activities, and new product & service launches in the autonomous networks market.
Market Development: The report provides comprehensive information about lucrative markets and analyses the autonomous networks market across various regions.
Market Diversification: Exhaustive information about new products & services, untapped geographies, recent developments, and investments in the autonomous networks market.
Competitive Assessment: In-depth assessment of market shares, growth strategies and service offerings of leading companies including Ericsson (Sweden), Nokia (Finland), NEC Corporation (Japan), Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd (China), Hewlett Packard Enterprise (US), Cisco Systems (US), IBM Corporation (US), Ciena (US), Extreme Networks (US), Arista Networks (US), Broadcom (US), ZTE Corporation (China), Allied Telesis (Japan), Logic Monitor (US), SolarWinds Worldwide(US), BMC Software (US), Drivenets (Israel), Versa Networks (US), Arrcus (US), Intraway (Argentina), Augtera (US), Auvik Networks (Canada), Infovista (France), and Innovile (Turkey).
Key Attributes:
Key Topics Covered: Executive Summary
Autonomous Networks Market to Witness Significant Growth During Forecast Period
Autonomous Networks Market: Regional Snapshot
Premium Insights
Attractive Opportunities for Key Players in Autonomous Networks Market - Aging Network Infrastructure and Rising Demand for Network Efficiency and Automation to Drive Market
Autonomous Networks Market: Top Growing Segments - Top Growing Segments in Autonomous Networks Market in 2024
Autonomous Networks Market, by Offering - Services Segment to Hold Higher Growth Rate During Forecast Period
Autonomous Networks Market, by End-user - Service Providers Segment to Account for Larger Market Share in 2024
North America: Autonomous Networks Market, by Offering and End-user - Solutions and Service Providers Segments to Account for Largest Market Shares in North America in 2024
Market Dynamics
Rise of IoT Devices
Increased Need for Real-Time Data Processing & Analysis
High Initial Investment
Lack of Standardization
Increased Connectivity and Automation Elevating Potential for Cybersecurity Risks
Opportunities
Edge Computing Optimization
Network Slicing
Difficulties in Comprehending Customers' Requirements
Challenges Regarding Alignment of Network Configurations with Business Objectives
Case Study Analysis
Vejthani Hospital Used Huawei's Wi-Fi 6 Network to Become Smart Hospital
AI-Driven Networking from Juniper Improved Network Visibility and Control for University of Oxford
China Mobile Communications Company Enhanced Broadband Experience with Nokia Ava AI and Analytics
Heilongjiang International University Built Green Campus Network with Huawei's Imaster NCE-Campusinsight
Companies Featured
Hewlett Packard Enterprise
Cisco Systems, Inc.
Arista Networks
NEC Corporation
Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd.
IBM Corporation
Ciena Corporation
Extreme Networks
ZTE Corporation
Allied Telesis
Logic Monitor
Solarwinds Worldwide
BMC Software
Versa Networks
Arrcus Inc.
Augtera Networks
Auvik Networks
For more information about this report visit https://www.researchandmarkets.com/r/wlh0te
About ResearchAndMarkets.com ResearchAndMarkets.com is the world's leading source for international market research reports and market data. We provide you with the latest data on international and regional markets, key industries, the top companies, new products and the latest trends.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
I found this article on the strategic decisions behind Nokia's failure incredibly insightful! 📉 As someone interested in business strategy and management, understanding the factors that led to Nokia's downfall provides valuable lessons for avoiding similar pitfalls in the future. 💡 The analysis of Nokia's missteps, from failing to adapt to changing market trends to underestimating the ...
1 INTRODUCTION. The widespread emergence of digital platforms has important strategic implications for incumbent firms that go beyond traditional strategy making at disruptions (Altman et al., 2022; Kretschmer et al., 2020; McIntyre et al., 2021).This is partly because "digital platforms and their associated ecosystems are fundamentally transforming the competitive landscape and boundaries ...
Case Study 4: The Collapse of Nokia's Mobile Phone Business: Wisdom and Stupidity in Strategic Decision-making. ... exemplary management started to look like a textbook case of failed strat-
Historical research is relatively distinct from theory-motivated case studies in the management field (Decker, Kipping, ... was appointed as the new CEO of Nokia. The strategic intent of Elop's new top management team was to regain product leadership in the smartphone market and to retain the market leader position in low-end mobile phones.
The Real Cause of Nokia's Crisis. by. Michael Schrage. February 15, 2011. Nokia's technology isn't a root cause of its current crisis. Don't blame its engineers and designers either. The ...
Abstract. In 2013, Nokia sold its Device and Services business to Microsoft for €5.4 billion. For decades Nokia had led the telecommunications (telecom) industry in handsets and networking. By the late 2000s, however, Nokia's position as market leader in mobile devices was threatened by competition from new lower-cost Asian manufacturers.
Strategy. Who Killed Nokia? Nokia Did. Quy Huy , INSEAD and Timo Vuori , Aalto University. 22 Sep 2015 31. Despite being an exemplar of strategic agility, the fearful emotional climate prevailing at Nokia during the rise of the iPhone froze coordination between top and middle managers terrified of losing status and resources from management.
The case examines the downward spiral of Nokia, the mobile technology giant that once conquered the world, seen from the perspective of 'insiders' - based on interviews with Nokia executives at top and middle management level. They describe the emotional undercurrents of the innovation process that caused temporal myopia - an excessive focus on short-term innovation at the expense of longer ...
The case describes Nokia's spectacular rise and fall, shedding light on the combination of external factors and internal decisions that resulted in the company's handset business being sold to Microsoft in 2010. During the successful period of growth (roughly 1990 through to 2006), Nokia's focus on design and functionality gained it a worldwide reputation. It was acknowledged as the first ...
Abstract. This chapter provides a wisdom-oriented reading of one of the most spectacular business failures of recent times: the collapse of Nokia mobile phones between 2007 and 2015. Using executive biographies and other published accounts of Nokia's organisational patterns, the chapter attempts to offer a more balanced explanation of the ...
To avoid emotions having a negative effect on strategic decision-making, managers can do three things. First, increase trust by setting clear, and healthy, conversational norms. Second, reduce ...
Nokia Change Management Case Study. Tahir Abbas March 3, 2023. Nokia is a company that has undergone significant change over the years, transforming itself from a mobile phone manufacturer to a leading player in the telecommunications infrastructure market. This transformation was driven by a range of factors, including changes in market ...
In this case study, we will examine the factors that contributed to Nokia's decline and explore what we can learn from the company's failure. The Rise of Nokia: In the early 2000s, Nokia was the ...
Design/methodology/approach Methodologically, an historical case study of Nokia Corporation's drastic business model transformation between the years 1987 and 1995 is reported.
Nokia Case Study Introduction: The fundamental question in the field of strategic management is how organisations achieve and sustain competitive advantage (Teece, et al, 1997) and therefore attain above industry-average profit. However, since both the business environment and individual firms are dynamic systems, continuously in flux, it is a ...
Nokia (or any other corporation) remains tentative. This is not a problem if we realise the limits of our research, but most of the similar case studies published even in top management journals ignore these limitations when seeking theoretical explanations, contributions and 'being interesting' (Barley, 2016; Davis, 1971).
Methodologically, an historical case study of Nokia Corporation's drastic business model transformation between the years 1987 and 1995 is reported. Findings The conceptual and historical work results in a process model of business model change, demonstrating how central business units feed strategic alternatives and capabilities to the ...
The fundamental question in the field of strategic management is how organisations achieve and sustain competitive advantage (Teece, et al, 1997) and therefore attain above industry-average profit. However, since both the business environment and individual firms are dynamic systems, continuously in flux, it is a big challenge to achieve a fit between these two systems (de Wit B and Meyer R ...
Strategic Management Journal, 2022, 43(2): 340-369. [10] Aspara J, Lamberg J A, Laukia A, et al. Strategic management of business model transformation: lessons from Nokia. Management Decision, 2011. [11] Bhutto A. Managing interindustry differences through dynamic capabilities: The case study of Nokia.
3.1.1. Strategy Diagnosis I. Product differentiation and positive network effects:The reason behind Nokia's new strategy in the smart phone market was given by Nokia's CEO and is based on the belief thatthe battle of devices has now become a war of ecosystems.
Nokia Strategic Management Case Studies With Solution Petter Gottschalk Nokia Case Study: How Can Nokia Maintain Its Market Position in the Mature European Market? Anonym,2008-02 Seminar paper from the year 2006 in the subject Business economics - Marketing, Corporate Communication, CRM, Market
Keywords: strategic management; causal attribution; sense-making; discourse analysis; narrative; management history. Download Free PDF View PDF. ... Nokia Case Study Introduction: The fundamental question in the field of strategic management is how organisations achieve and sustain competitive advantage (Teece, et al, 1997) and therefore attain ...
Essay on Strategic management - Nokia Nokia Mission Nokia's mission is simple: "Connecting People. Our goal is to build great mobile products that enable billions of people worldwide to enjoy ... Sustainable innovation- Nokia case study Introduction: The technology offers a promise of a better world through the improvements in standards of ...
These networks enhance efficiency and reliability in network management for service providers by enabling real-time monitoring, automated troubleshooting, and predictive maintenance, which reduces ...
The autonomous networks market is estimated at USD 7 billion in 2024 to USD 17.5 billion by 2029, at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 20.1%. These networks enhance efficiency and ...