Reported Speech
Perfect english grammar.

Reported Statements
Here's how it works:
We use a 'reporting verb' like 'say' or 'tell'. ( Click here for more about using 'say' and 'tell' .) If this verb is in the present tense, it's easy. We just put 'she says' and then the sentence:
- Direct speech: I like ice cream.
- Reported speech: She says (that) she likes ice cream.
We don't need to change the tense, though probably we do need to change the 'person' from 'I' to 'she', for example. We also may need to change words like 'my' and 'your'. (As I'm sure you know, often, we can choose if we want to use 'that' or not in English. I've put it in brackets () to show that it's optional. It's exactly the same if you use 'that' or if you don't use 'that'.)
But , if the reporting verb is in the past tense, then usually we change the tenses in the reported speech:
- Reported speech: She said (that) she liked ice cream.
* doesn't change.
- Direct speech: The sky is blue.
- Reported speech: She said (that) the sky is/was blue.
Click here for a mixed tense exercise about practise reported statements. Click here for a list of all the reported speech exercises.
Reported Questions
So now you have no problem with making reported speech from positive and negative sentences. But how about questions?
- Direct speech: Where do you live?
- Reported speech: She asked me where I lived.
- Direct speech: Where is Julie?
- Reported speech: She asked me where Julie was.
- Direct speech: Do you like chocolate?
- Reported speech: She asked me if I liked chocolate.
Click here to practise reported 'wh' questions. Click here to practise reported 'yes / no' questions. Reported Requests
There's more! What if someone asks you to do something (in a polite way)? For example:
- Direct speech: Close the window, please
- Or: Could you close the window please?
- Or: Would you mind closing the window please?
- Reported speech: She asked me to close the window.
- Direct speech: Please don't be late.
- Reported speech: She asked us not to be late.
Reported Orders
- Direct speech: Sit down!
- Reported speech: She told me to sit down.
- Click here for an exercise to practise reported requests and orders.
- Click here for an exercise about using 'say' and 'tell'.
- Click here for a list of all the reported speech exercises.

Hello! I'm Seonaid! I'm here to help you understand grammar and speak correct, fluent English.

Read more about our learning method

Reported Speech – Rules, Examples & Worksheet
| Candace Osmond
Candace Osmond
Candace Osmond studied Advanced Writing & Editing Essentials at MHC. She’s been an International and USA TODAY Bestselling Author for over a decade. And she’s worked as an Editor for several mid-sized publications. Candace has a keen eye for content editing and a high degree of expertise in Fiction.
They say gossip is a natural part of human life. That’s why language has evolved to develop grammatical rules about the “he said” and “she said” statements. We call them reported speech.
Every time we use reported speech in English, we are talking about something said by someone else in the past. Thinking about it brings me back to high school, when reported speech was the main form of language!
Learn all about the definition, rules, and examples of reported speech as I go over everything. I also included a worksheet at the end of the article so you can test your knowledge of the topic.
What Does Reported Speech Mean?
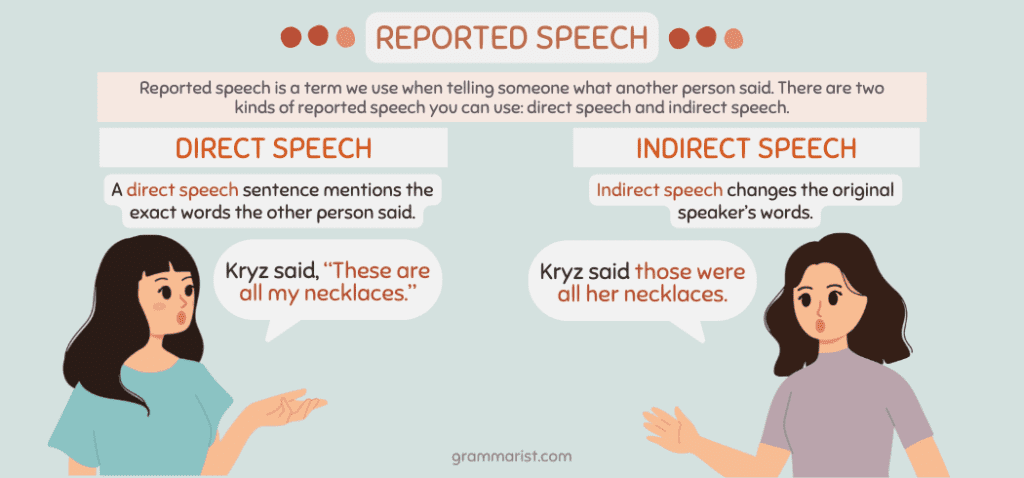
Reported speech is a term we use when telling someone what another person said. You can do this while speaking or writing.
There are two kinds of reported speech you can use: direct speech and indirect speech. I’ll break each down for you.
A direct speech sentence mentions the exact words the other person said. For example:
- Kryz said, “These are all my necklaces.”
Indirect speech changes the original speaker’s words. For example:
- Kryz said those were all her necklaces.
When we tell someone what another individual said, we use reporting verbs like told, asked, convinced, persuaded, and said. We also change the first-person figure in the quotation into the third-person speaker.
Reported Speech Examples
We usually talk about the past every time we use reported speech. That’s because the time of speaking is already done. For example:
- Direct speech: The employer asked me, “Do you have experience with people in the corporate setting?”
Indirect speech: The employer asked me if I had experience with people in the corporate setting.
- Direct speech: “I’m working on my thesis,” I told James.
Indirect speech: I told James that I was working on my thesis.
Reported Speech Structure
A speech report has two parts: the reporting clause and the reported clause. Read the example below:
- Harry said, “You need to help me.”
The reporting clause here is William said. Meanwhile, the reported clause is the 2nd clause, which is I need your help.
What are the 4 Types of Reported Speech?
Aside from direct and indirect, reported speech can also be divided into four. The four types of reported speech are similar to the kinds of sentences: imperative, interrogative, exclamatory, and declarative.
Reported Speech Rules
The rules for reported speech can be complex. But with enough practice, you’ll be able to master them all.
Choose Whether to Use That or If
The most common conjunction in reported speech is that. You can say, “My aunt says she’s outside,” or “My aunt says that she’s outside.”
Use if when you’re reporting a yes-no question. For example:
- Direct speech: “Are you coming with us?”
Indirect speech: She asked if she was coming with them.
Verb Tense Changes
Change the reporting verb into its past form if the statement is irrelevant now. Remember that some of these words are irregular verbs, meaning they don’t follow the typical -d or -ed pattern. For example:
- Direct speech: I dislike fried chicken.
Reported speech: She said she disliked fried chicken.
Note how the main verb in the reported statement is also in the past tense verb form.
Use the simple present tense in your indirect speech if the initial words remain relevant at the time of reporting. This verb tense also works if the report is something someone would repeat. For example:
- Slater says they’re opening a restaurant soon.
- Maya says she likes dogs.
This rule proves that the choice of verb tense is not a black-and-white question. The reporter needs to analyze the context of the action.
Move the tense backward when the reporting verb is in the past tense. That means:
- Present simple becomes past simple.
- Present perfect becomes past perfect.
- Present continuous becomes past continuous.
- Past simple becomes past perfect.
- Past continuous becomes past perfect continuous.
Here are some examples:
- The singer has left the building. (present perfect)
He said that the singers had left the building. (past perfect)
- Her sister gave her new shows. (past simple)
- She said that her sister had given her new shoes. (past perfect)
If the original speaker is discussing the future, change the tense of the reporting verb into the past form. There’ll also be a change in the auxiliary verbs.
- Will or shall becomes would.
- Will be becomes would be.
- Will have been becomes would have been.
- Will have becomes would have.
For example:
- Direct speech: “I will be there in a moment.”
Indirect speech: She said that she would be there in a moment.
Do not change the verb tenses in indirect speech when the sentence has a time clause. This rule applies when the introductory verb is in the future, present, and present perfect. Here are other conditions where you must not change the tense:
- If the sentence is a fact or generally true.
- If the sentence’s verb is in the unreal past (using second or third conditional).
- If the original speaker reports something right away.
- Do not change had better, would, used to, could, might, etc.
Changes in Place and Time Reference
Changing the place and time adverb when using indirect speech is essential. For example, now becomes then and today becomes that day. Here are more transformations in adverbs of time and places.
- This – that.
- These – those.
- Now – then.
- Here – there.
- Tomorrow – the next/following day.
- Two weeks ago – two weeks before.
- Yesterday – the day before.
Here are some examples.
- Direct speech: “I am baking cookies now.”
Indirect speech: He said he was baking cookies then.
- Direct speech: “Myra went here yesterday.”
Indirect speech: She said Myra went there the day before.
- Direct speech: “I will go to the market tomorrow.”
Indirect speech: She said she would go to the market the next day.
Using Modals

If the direct speech contains a modal verb, make sure to change them accordingly.
- Will becomes would
- Can becomes could
- Shall becomes should or would.
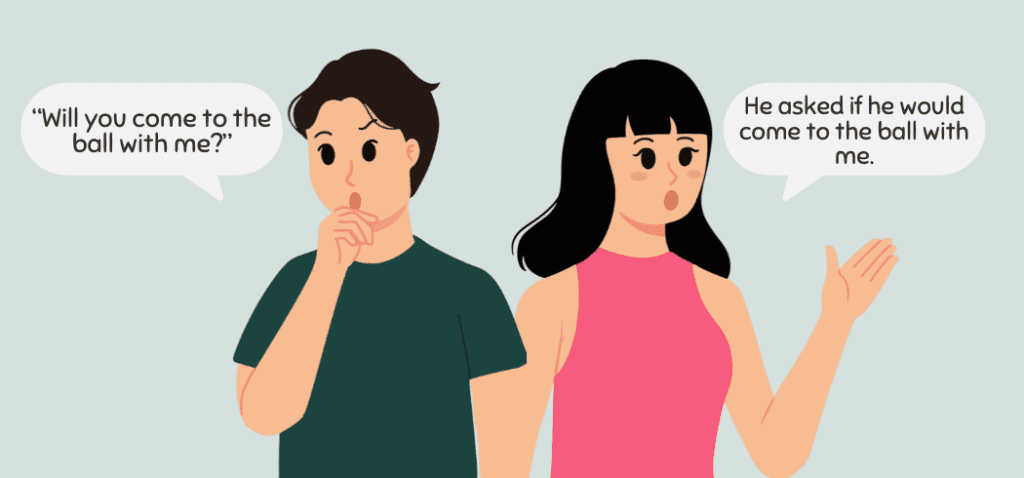
- Direct speech: “Will you come to the ball with me?”
Indirect speech: He asked if he would come to the ball with me.
- Direct speech: “Gina can inspect the room tomorrow because she’s free.”
Indirect speech: He said Gina could inspect the room the next day because she’s free.
However, sometimes, the modal verb should does not change grammatically. For example:
- Direct speech: “He should go to the park.”
Indirect speech: She said that he should go to the park.
Imperative Sentences
To change an imperative sentence into a reported indirect sentence, use to for imperative and not to for negative sentences. Never use the word that in your indirect speech. Another rule is to remove the word please . Instead, say request or say. For example:
- “Please don’t interrupt the event,” said the host.
The host requested them not to interrupt the event.
- Jonah told her, “Be careful.”
- Jonah ordered her to be careful.
Reported Questions
When reporting a direct question, I would use verbs like inquire, wonder, ask, etc. Remember that we don’t use a question mark or exclamation mark for reports of questions. Below is an example I made of how to change question forms.
- Incorrect: He asked me where I live?
Correct: He asked me where I live.
Here’s another example. The first sentence uses direct speech in a present simple question form, while the second is the reported speech.
- Where do you live?
She asked me where I live.
Wrapping Up Reported Speech
My guide has shown you an explanation of reported statements in English. Do you have a better grasp on how to use it now?
Reported speech refers to something that someone else said. It contains a subject, reporting verb, and a reported cause.
Don’t forget my rules for using reported speech. Practice the correct verb tense, modal verbs, time expressions, and place references.
Grammarist is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon.com. When you buy via the links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission at no cost to you.
2024 © Grammarist, a Found First Marketing company. All rights reserved.
- English Grammar
- Reported Speech
Reported Speech - Definition, Rules and Usage with Examples
Reported speech or indirect speech is the form of speech used to convey what was said by someone at some point of time. This article will help you with all that you need to know about reported speech, its meaning, definition, how and when to use them along with examples. Furthermore, try out the practice questions given to check how far you have understood the topic.

Table of Contents
Definition of reported speech, rules to be followed when using reported speech, table 1 – change of pronouns, table 2 – change of adverbs of place and adverbs of time, table 3 – change of tense, table 4 – change of modal verbs, tips to practise reported speech, examples of reported speech, check your understanding of reported speech, frequently asked questions on reported speech in english, what is reported speech.
Reported speech is the form in which one can convey a message said by oneself or someone else, mostly in the past. It can also be said to be the third person view of what someone has said. In this form of speech, you need not use quotation marks as you are not quoting the exact words spoken by the speaker, but just conveying the message.
Now, take a look at the following dictionary definitions for a clearer idea of what it is.
Reported speech, according to the Oxford Learner’s Dictionary, is defined as “a report of what somebody has said that does not use their exact words.” The Collins Dictionary defines reported speech as “speech which tells you what someone said, but does not use the person’s actual words.” According to the Cambridge Dictionary, reported speech is defined as “the act of reporting something that was said, but not using exactly the same words.” The Macmillan Dictionary defines reported speech as “the words that you use to report what someone else has said.”
Reported speech is a little different from direct speech . As it has been discussed already, reported speech is used to tell what someone said and does not use the exact words of the speaker. Take a look at the following rules so that you can make use of reported speech effectively.
- The first thing you have to keep in mind is that you need not use any quotation marks as you are not using the exact words of the speaker.
- You can use the following formula to construct a sentence in the reported speech.
- You can use verbs like said, asked, requested, ordered, complained, exclaimed, screamed, told, etc. If you are just reporting a declarative sentence , you can use verbs like told, said, etc. followed by ‘that’ and end the sentence with a full stop . When you are reporting interrogative sentences, you can use the verbs – enquired, inquired, asked, etc. and remove the question mark . In case you are reporting imperative sentences , you can use verbs like requested, commanded, pleaded, ordered, etc. If you are reporting exclamatory sentences , you can use the verb exclaimed and remove the exclamation mark . Remember that the structure of the sentences also changes accordingly.
- Furthermore, keep in mind that the sentence structure , tense , pronouns , modal verbs , some specific adverbs of place and adverbs of time change when a sentence is transformed into indirect/reported speech.
Transforming Direct Speech into Reported Speech
As discussed earlier, when transforming a sentence from direct speech into reported speech, you will have to change the pronouns, tense and adverbs of time and place used by the speaker. Let us look at the following tables to see how they work.
Here are some tips you can follow to become a pro in using reported speech.
- Select a play, a drama or a short story with dialogues and try transforming the sentences in direct speech into reported speech.
- Write about an incident or speak about a day in your life using reported speech.
- Develop a story by following prompts or on your own using reported speech.
Given below are a few examples to show you how reported speech can be written. Check them out.
- Santana said that she would be auditioning for the lead role in Funny Girl.
- Blaine requested us to help him with the algebraic equations.
- Karishma asked me if I knew where her car keys were.
- The judges announced that the Warblers were the winners of the annual acapella competition.
- Binsha assured that she would reach Bangalore by 8 p.m.
- Kumar said that he had gone to the doctor the previous day.
- Lakshmi asked Teena if she would accompany her to the railway station.
- Jibin told me that he would help me out after lunch.
- The police ordered everyone to leave from the bus stop immediately.
- Rahul said that he was drawing a caricature.
Transform the following sentences into reported speech by making the necessary changes.
1. Rachel said, “I have an interview tomorrow.”
2. Mahesh said, “What is he doing?”
3. Sherly said, “My daughter is playing the lead role in the skit.”
4. Dinesh said, “It is a wonderful movie!”
5. Suresh said, “My son is getting married next month.”
6. Preetha said, “Can you please help me with the invitations?”
7. Anna said, “I look forward to meeting you.”
8. The teacher said, “Make sure you complete the homework before tomorrow.”
9. Sylvester said, “I am not going to cry anymore.”
10. Jade said, “My sister is moving to Los Angeles.”
Now, find out if you have answered all of them correctly.
1. Rachel said that she had an interview the next day.
2. Mahesh asked what he was doing.
3. Sherly said that her daughter was playing the lead role in the skit.
4. Dinesh exclaimed that it was a wonderful movie.
5. Suresh said that his son was getting married the following month.
6. Preetha asked if I could help her with the invitations.
7. Anna said that she looked forward to meeting me.
8. The teacher told us to make sure we completed the homework before the next day.
9. Sylvester said that he was not going to cry anymore.
10. Jade said that his sister was moving to Los Angeles.
What is reported speech?
What is the definition of reported speech.
Reported speech, according to the Oxford Learner’s Dictionary, is defined as “a report of what somebody has said that does not use their exact words.” The Collins Dictionary defines reported speech as “speech which tells you what someone said, but does not use the person’s actual words.” According to the Cambridge Dictionary, reported speech is defined as “the act of reporting something that was said, but not using exactly the same words.” The Macmillan Dictionary defines reported speech as “the words that you use to report what someone else has said.”
What is the formula of reported speech?
You can use the following formula to construct a sentence in the reported speech. Subject said that (report whatever the speaker said)
Give some examples of reported speech.
Given below are a few examples to show you how reported speech can be written.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
Reported Speech: Rules, Examples, Exceptions

👉 Quiz 1 / Quiz 2
Advanced Grammar Course
What is reported speech?
“Reported speech” is when we talk about what somebody else said – for example:
- Direct Speech: “I’ve been to London three times.”
- Reported Speech: She said she’d been to London three times.
There are a lot of tricky little details to remember, but don’t worry, I’ll explain them and we’ll see lots of examples. The lesson will have three parts – we’ll start by looking at statements in reported speech, and then we’ll learn about some exceptions to the rules, and finally we’ll cover reported questions, requests, and commands.

So much of English grammar – like this topic, reported speech – can be confusing, hard to understand, and even harder to use correctly. I can help you learn grammar easily and use it confidently inside my Advanced English Grammar Course.
In this course, I will make even the most difficult parts of English grammar clear to you – and there are lots of opportunities for you to practice!

Backshift of Verb Tenses in Reported Speech
When we use reported speech, we often change the verb tense backwards in time. This can be called “backshift.”
Here are some examples in different verb tenses:
Reported Speech (Part 1) Quiz
Exceptions to backshift in reported speech.
Now that you know some of the reported speech rules about backshift, let’s learn some exceptions.
There are two situations in which we do NOT need to change the verb tense.
No backshift needed when the situation is still true
For example, if someone says “I have three children” (direct speech) then we would say “He said he has three children” because the situation continues to be true.
If I tell you “I live in the United States” (direct speech) then you could tell someone else “She said she lives in the United States” (that’s reported speech) because it is still true.
When the situation is still true, then we don’t need to backshift the verb.

He said he HAS three children
But when the situation is NOT still true, then we DO need to backshift the verb.
Imagine your friend says, “I have a headache.”
- If you immediately go and talk to another friend, you could say, “She said she has a headache,” because the situation is still true
- If you’re talking about that conversation a month after it happened, then you would say, “She said she had a headache,” because it’s no longer true.
No backshift needed when the situation is still in the future
We also don’t need to backshift to the verb when somebody said something about the future, and the event is still in the future.
Here’s an example:
- On Monday, my friend said, “I ‘ll call you on Friday .”
- “She said she ‘ll call me on Friday”, because Friday is still in the future from now.
- It is also possible to say, “She said she ‘d (she would) call me on Friday.”
- Both of them are correct, so the backshift in this case is optional.
Let’s look at a different situation:
- On Monday, my friend said, “I ‘ll call you on Tuesday .”
- “She said she ‘d call me on Tuesday.” I must backshift because the event is NOT still in the future.

Review: Reported Speech, Backshift, & Exceptions
Quick review:
- Normally in reported speech we backshift the verb, we put it in a verb tense that’s a little bit further in the past.
- when the situation is still true
- when the situation is still in the future
Reported Requests, Orders, and Questions
Those were the rules for reported statements, just regular sentences.
What about reported speech for questions, requests, and orders?
For reported requests, we use “asked (someone) to do something”:
- “Please make a copy of this report.” (direct speech)
- She asked me to make a copy of the report. (reported speech)
For reported orders, we use “told (someone) to do something:”
- “Go to the bank.” (direct speech)
- “He told me to go to the bank.” (reported speech)
The main verb stays in the infinitive with “to”:
- She asked me to make a copy of the report. She asked me make a copy of the report.
- He told me to go to the bank. He told me go to the bank.
For yes/no questions, we use “asked if” and “wanted to know if” in reported speech.
- “Are you coming to the party?” (direct)
- He asked if I was coming to the party. (reported)
- “Did you turn off the TV?” (direct)
- She wanted to know if I had turned off the TV.” (reported)
The main verb changes and back shifts according to the rules and exceptions we learned earlier.
Notice that we don’t use do/does/did in the reported question:
- She wanted to know did I turn off the TV.
- She wanted to know if I had turned off the TV.
For other questions that are not yes/no questions, we use asked/wanted to know (without “if”):
- “When was the company founded?” (direct)
- She asked when the company was founded.” (reported)
- “What kind of car do you drive?” (direct)
- He wanted to know what kind of car I drive. (reported)
Again, notice that we don’t use do/does/did in reported questions:
- “Where does he work?”
- She wanted to know where does he work.
- She wanted to know where he works.
Also, in questions with the verb “to be,” the word order changes in the reported question:
- “Where were you born?” ([to be] + subject)
- He asked where I was born. (subject + [to be])
- He asked where was I born.

Reported Speech (Part 2) Quiz
Learn more about reported speech:
- Reported speech: Perfect English Grammar
- Reported speech: BJYU’s
If you want to take your English grammar to the next level, then my Advanced English Grammar Course is for you! It will help you master the details of the English language, with clear explanations of essential grammar topics, and lots of practice. I hope to see you inside!
I’ve got one last little exercise for you, and that is to write sentences using reported speech. Think about a conversation you’ve had in the past, and write about it – let’s see you put this into practice right away.
Master the details of English grammar:

More Espresso English Lessons:
About the author.
Shayna Oliveira
Shayna Oliveira is the founder of Espresso English, where you can improve your English fast - even if you don’t have much time to study. Millions of students are learning English from her clear, friendly, and practical lessons! Shayna is a CELTA-certified teacher with 10+ years of experience helping English learners become more fluent in her English courses.
Reported Speech

If we want to say what somebody has said, we basically have two options:
- We can use the person's exact words - in quotation marks "..." if we are writing ( direct speech ).
- We can change the person's words into our own words ( reported speech ).
In this lesson we learn about reported speech , the structure that we use when we report what another person has said, and reported speech rules.
Now we will look at:
- Reported Statements
- Time and Place
- Reported Questions
- Reported Requests
- Reported Orders And then you can check your understanding of reported speech with...
- Reported Speech Quiz
Reported speech is called "indirect speech" by some people. Other people regard reported speech simply as one form of indirect speech. Other forms are, for example:
- questions-within-questions: Can you tell me if they are expensive?
- mental processes: He believes that politics is a dirty game.
Search form
- B1-B2 grammar
Reported speech
Daisy has just had an interview for a summer job.
Instructions
As you watch the video, look at the examples of reported speech. They are in red in the subtitles. Then read the conversation below to learn more. Finally, do the grammar exercises to check you understand, and can use, reported speech correctly.
Sophie: Mmm, it’s so nice to be chilling out at home after all that running around.
Ollie: Oh, yeah, travelling to glamorous places for a living must be such a drag!
Ollie: Mum, you can be so childish sometimes. Hey, I wonder how Daisy’s getting on in her job interview.
Sophie: Oh, yes, she said she was having it at four o’clock, so it’ll have finished by now. That’ll be her ... yes. Hi, love. How did it go?
Daisy: Well, good I think, but I don’t really know. They said they’d phone later and let me know.
Sophie: What kind of thing did they ask you?
Daisy: They asked if I had any experience with people, so I told them about helping at the school fair and visiting old people at the home, that sort of stuff. But I think they meant work experience.
Sophie: I’m sure what you said was impressive. They can’t expect you to have had much work experience at your age.
Daisy: And then they asked me what acting I had done, so I told them that I’d had a main part in the school play, and I showed them a bit of the video, so that was cool.
Sophie: Great!
Daisy: Oh, and they also asked if I spoke any foreign languages.
Sophie: Languages?
Daisy: Yeah, because I might have to talk to tourists, you know.
Sophie: Oh, right, of course.
Daisy: So that was it really. They showed me the costume I’ll be wearing if I get the job. Sending it over ...
Ollie: Hey, sis, I heard that Brad Pitt started out as a giant chicken too! This could be your big break!
Daisy: Ha, ha, very funny.
Sophie: Take no notice, darling. I’m sure you’ll be a marvellous chicken.
We use reported speech when we want to tell someone what someone said. We usually use a reporting verb (e.g. say, tell, ask, etc.) and then change the tense of what was actually said in direct speech.
So, direct speech is what someone actually says? Like 'I want to know about reported speech'?
Yes, and you report it with a reporting verb.
He said he wanted to know about reported speech.
I said, I want and you changed it to he wanted .
Exactly. Verbs in the present simple change to the past simple; the present continuous changes to the past continuous; the present perfect changes to the past perfect; can changes to could ; will changes to would ; etc.
She said she was having the interview at four o’clock. (Direct speech: ' I’m having the interview at four o’clock.') They said they’d phone later and let me know. (Direct speech: ' We’ll phone later and let you know.')
OK, in that last example, you changed you to me too.
Yes, apart from changing the tense of the verb, you also have to think about changing other things, like pronouns and adverbs of time and place.
'We went yesterday.' > She said they had been the day before. 'I’ll come tomorrow.' > He said he’d come the next day.
I see, but what if you’re reporting something on the same day, like 'We went yesterday'?
Well, then you would leave the time reference as 'yesterday'. You have to use your common sense. For example, if someone is saying something which is true now or always, you wouldn’t change the tense.
'Dogs can’t eat chocolate.' > She said that dogs can’t eat chocolate. 'My hair grows really slowly.' > He told me that his hair grows really slowly.
What about reporting questions?
We often use ask + if/whether , then change the tenses as with statements. In reported questions we don’t use question forms after the reporting verb.
'Do you have any experience working with people?' They asked if I had any experience working with people. 'What acting have you done?' They asked me what acting I had done .
Is there anything else I need to know about reported speech?
One thing that sometimes causes problems is imperative sentences.
You mean like 'Sit down, please' or 'Don’t go!'?
Exactly. Sentences that start with a verb in direct speech need a to + infinitive in reported speech.
She told him to be good. (Direct speech: 'Be good!') He told them not to forget. (Direct speech: 'Please don’t forget.')
OK. Can I also say 'He asked me to sit down'?
Yes. You could say 'He told me to …' or 'He asked me to …' depending on how it was said.
OK, I see. Are there any more reporting verbs?
Yes, there are lots of other reporting verbs like promise , remind , warn , advise , recommend , encourage which you can choose, depending on the situation. But say , tell and ask are the most common.
Great. I understand! My teacher said reported speech was difficult.
And I told you not to worry!
Check your grammar: matching
Check your grammar: error correction, check your grammar: gap fill, worksheets and downloads.
What was the most memorable conversation you had yesterday? Who were you talking to and what did they say to you?

Sign up to our newsletter for LearnEnglish Teens
We will process your data to send you our newsletter and updates based on your consent. You can unsubscribe at any time by clicking the "unsubscribe" link at the bottom of every email. Read our privacy policy for more information.
Reported Speech (Indirect Speech)
Exercises on reported speech.
If we report what another person has said, we usually do not use the speaker’s exact words (direct speech), but reported (indirect) speech. Therefore, you need to learn how to transform direct speech into reported speech. The structure is a little different depending on whether you want to transform a statement, question or request.
When transforming statements, check whether you have to change:
- present tense verbs (3rd person singular)
- place and time expressions
- tenses (backshift)
→ more on statements in reported speech
When transforming questions, check whether you have to change:
Also note that you have to:
- transform the question into an indirect question
- use the interrogative or if / whether
→ more on questions in reported speech
→ more on requests in reported speech
Additional Information and Exeptions
Apart from the above mentioned basic rules, there are further aspects that you should keep in mind, for example:
- main clauses connected with and / but
- tense of the introductory clause
- reported speech for difficult tenses
- exeptions for backshift
- requests with must , should , ought to and let’s
→ more on additional information and exeptions in reported speech
Statements in Reported Speech
- no backshift – change of pronouns
- no backshift – change of pronouns and places
- with backshift
- with backshift and change of place and time expressions
Questions in Reported Speech
Requests in reported speech.
- Exercise 1 – requests (positive)
- Exercise 2 – requests (negative)
- Exercise 3 – requests (mixed)
Mixed Exercises on Reported Speech
- Exercise on reported speech with and without backshift
Grammar in Texts
- „ The Canterville Ghost “ (highlight direct speech and reported speech)
Reported Speech in English Grammar
Direct speech, changing the tense (backshift), no change of tenses, question sentences, demands/requests, expressions with who/what/how + infinitive, typical changes of time and place.
- Lingolia Plus English
Introduction
In English grammar, we use reported speech to say what another person has said. We can use their exact words with quotation marks , this is known as direct speech , or we can use indirect speech . In indirect speech , we change the tense and pronouns to show that some time has passed. Indirect speech is often introduced by a reporting verb or phrase such as ones below.
Learn the rules for writing indirect speech in English with Lingolia’s simple explanation. In the exercises, you can test your grammar skills.
When turning direct speech into indirect speech, we need to pay attention to the following points:
- changing the pronouns Example: He said, “ I saw a famous TV presenter.” He said (that) he had seen a famous TV presenter.
- changing the information about time and place (see the table at the end of this page) Example: He said, “I saw a famous TV presenter here yesterday .” He said (that) he had seen a famous TV presenter there the day before .
- changing the tense (backshift) Example: He said, “She was eating an ice-cream at the table where you are sitting .” He said (that) she had been eating an ice-cream at the table where I was sitting .
If the introductory clause is in the simple past (e.g. He said ), the tense has to be set back by one degree (see the table). The term for this in English is backshift .
The verbs could, should, would, might, must, needn’t, ought to, used to normally do not change.
If the introductory clause is in the simple present , however (e.g. He says ), then the tense remains unchanged, because the introductory clause already indicates that the statement is being immediately repeated (and not at a later point in time).
In some cases, however, we have to change the verb form.
When turning questions into indirect speech, we have to pay attention to the following points:
- As in a declarative sentence, we have to change the pronouns, the time and place information, and set the tense back ( backshift ).
- Instead of that , we use a question word. If there is no question word, we use whether / if instead. Example: She asked him, “ How often do you work?” → She asked him how often he worked. He asked me, “Do you know any famous people?” → He asked me if/whether I knew any famous people.
- We put the subject before the verb in question sentences. (The subject goes after the auxiliary verb in normal questions.) Example: I asked him, “ Have you met any famous people before?” → I asked him if/whether he had met any famous people before.
- We don’t use the auxiliary verb do for questions in indirect speech. Therefore, we sometimes have to conjugate the main verb (for third person singular or in the simple past ). Example: I asked him, “What do you want to tell me?” → I asked him what he wanted to tell me.
- We put the verb directly after who or what in subject questions. Example: I asked him, “ Who is sitting here?” → I asked him who was sitting there.
We don’t just use indirect questions to report what another person has asked. We also use them to ask questions in a very polite manner.
When turning demands and requests into indirect speech, we only need to change the pronouns and the time and place information. We don’t have to pay attention to the tenses – we simply use an infinitive .
If it is a negative demand, then in indirect speech we use not + infinitive .
To express what someone should or can do in reported speech, we leave out the subject and the modal verb and instead we use the construction who/what/where/how + infinitive.
Say or Tell?
The words say and tell are not interchangeable. say = say something tell = say something to someone
How good is your English?
Find out with Lingolia’s free grammar test
Take the test!
Maybe later
EnglishPost.org
Reported Speech: Structures and Examples
Reported speech (Indirect Speech) is how we represent the speech of other people or what we ourselves say.
Reported Speech focuses more on the content of what someone said rather than their exact words
The structure of the independent clause depends on whether the speaker is reporting a statement, a question, or a command.
Table of Contents
Reported Speech Rules and Examples
Present tenses and reported speech, past tenses and reported speech, reported speech examples, reported speech and the simple present, reported speech and present continuous, reported speech and the simple past, reported speech and the past continuous, reported speech and the present perfect, reported speech and the past perfect, reported speech and ‘ can ’ and ‘can’t’, reported speech and ‘ will ’ and ‘ won’t ’, reported speech and could and couldn’t, reported speech and the future continuous, reported questions exercises online.
To turn sentences into Indirect Speech, you have to follow a set of rules and this is what makes reported speech difficult for some.
To make reported speech sentences, you need to manage English tenses well.
- Present Simple Tense changes into Past Simple Tense
- Present Progressive Tense changes into Past Progressive Tense
- Present Perfect Tense changes into Past Perfect Tense
- Present Perfect Progressive Tense changes into Past Perfect Tense
- Past Simple Tense changes into Past Perfect Tense
- Past Progressive Tense changes into Perfect Continuous Tense
- Past Perfect Tense doesn’t change
- Past Perfect Progressive Tense doesn’t change
- Future Simple Tense changes into would
- Future Progressive Tense changes into “would be”
- Future Perfect Tense changes into “would have·
- Future Perfect Progressive Tense changes into “would have been”
These are some examples of sentences using indirect speech
The present simple tense usually changes to the past simple
The present continuous tense usually changes to the past continuous.
The past simple tense usually changes to the past perfect
The past continuous tense usually changes to the past perfect continuous.
The present perfect tense usually changes to the past perfect tense
The past perfect tense does not change
‘ Can ’ and ‘can’t’ in direct speech change to ‘ could ’ and ‘ couldn’t ’
‘ Will ’ and ‘ won’t ’ in direct speech change to ‘ would ’ and ‘ wouldn’t ’
Could and couldn’t doesn’t change
Will ’ and ‘ won’t ’ in direct speech change to ‘ would ’ and ‘ wouldn’t ’
These are some online exercises to learn more about reported questions
- Present Simple Reported Yes/No Question Exercise
- Present Simple Reported Wh Question Exercise
- Mixed Tense Reported Question Exercise
- Present Simple Reported Statement Exercise
- Present Continuous Reported Statement Exercise
I am Jose Manuel, English professor and creator of EnglishPost.org, a blog whose mission is to share lessons for those who want to learn and improve their English
Related Posts

Sentences with Would: Guide & Examples

Second Conditional Sentences and Questions

100 Present Perfect Continuous Examples

100 Reported Speech Examples: How To Change Direct Speech Into Indirect Speech
Reported speech, also known as indirect speech, is a way of communicating what someone else has said without quoting their exact words. For example, if your friend said, “ I am going to the store ,” in reported speech, you might convey this as, “ My friend said he was going to the store. ” Reported speech is common in both spoken and written language, especially in storytelling, news reporting, and everyday conversations.
Reported speech can be quite challenging for English language learners because in order to change direct speech into reported speech, one must change the perspective and tense of what was said by the original speaker or writer. In this guide, we will explain in detail how to change direct speech into indirect speech and provide lots of examples of reported speech to help you understand. Here are the key aspects of converting direct speech into reported speech.
Reported Speech: Changing Pronouns
Pronouns are usually changed to match the perspective of the person reporting the speech. For example, “I” in direct speech may become “he” or “she” in reported speech, depending on the context. Here are some example sentences:
- Direct : “I am going to the park.” Reported : He said he was going to the park .
- Direct : “You should try the new restaurant.” Reported : She said that I should try the new restaurant.
- Direct : “We will win the game.” Reported : They said that they would win the game.
- Direct : “She loves her new job.” Reported : He said that she loves her new job.
- Direct : “He can’t come to the party.” Reported : She said that he couldn’t come to the party.
- Direct : “It belongs to me.” Reported : He said that it belonged to him .
- Direct : “They are moving to a new city.” Reported : She said that they were moving to a new city.
- Direct : “You are doing a great job.” Reported : He told me that I was doing a great job.
- Direct : “I don’t like this movie.” Reported : She said that she didn’t like that movie.
- Direct : “We have finished our work.” Reported : They said that they had finished their work.
- Direct : “You will need to sign here.” Reported : He said that I would need to sign there.
- Direct : “She can solve the problem.” Reported : He said that she could solve the problem.
- Direct : “He was not at home yesterday.” Reported : She said that he had not been at home the day before.
- Direct : “It is my responsibility.” Reported : He said that it was his responsibility.
- Direct : “We are planning a surprise.” Reported : They said that they were planning a surprise.
Reported Speech: Reporting Verbs
In reported speech, various reporting verbs are used depending on the nature of the statement or the intention behind the communication. These verbs are essential for conveying the original tone, intent, or action of the speaker. Here are some examples demonstrating the use of different reporting verbs in reported speech:
- Direct: “I will help you,” she promised . Reported: She promised that she would help me.
- Direct: “You should study harder,” he advised . Reported: He advised that I should study harder.
- Direct: “I didn’t take your book,” he denied . Reported: He denied taking my book .
- Direct: “Let’s go to the cinema,” she suggested . Reported: She suggested going to the cinema .
- Direct: “I love this song,” he confessed . Reported: He confessed that he loved that song.
- Direct: “I haven’t seen her today,” she claimed . Reported: She claimed that she hadn’t seen her that day.
- Direct: “I will finish the project,” he assured . Reported: He assured me that he would finish the project.
- Direct: “I’m not feeling well,” she complained . Reported: She complained of not feeling well.
- Direct: “This is how you do it,” he explained . Reported: He explained how to do it.
- Direct: “I saw him yesterday,” she stated . Reported: She stated that she had seen him the day before.
- Direct: “Please open the window,” he requested . Reported: He requested that I open the window.
- Direct: “I can win this race,” he boasted . Reported: He boasted that he could win the race.
- Direct: “I’m moving to London,” she announced . Reported: She announced that she was moving to London.
- Direct: “I didn’t understand the instructions,” he admitted . Reported: He admitted that he didn’t understand the instructions.
- Direct: “I’ll call you tonight,” she promised . Reported: She promised to call me that night.
Reported Speech: Tense Shifts
When converting direct speech into reported speech, the verb tense is often shifted back one step in time. This is known as the “backshift” of tenses. It’s essential to adjust the tense to reflect the time elapsed between the original speech and the reporting. Here are some examples to illustrate how different tenses in direct speech are transformed in reported speech:
- Direct: “I am eating.” Reported: He said he was eating.
- Direct: “They will go to the park.” Reported: She mentioned they would go to the park.
- Direct: “We have finished our homework.” Reported: They told me they had finished their homework.
- Direct: “I do my exercises every morning.” Reported: He explained that he did his exercises every morning.
- Direct: “She is going to start a new job.” Reported: He heard she was going to start a new job.
- Direct: “I can solve this problem.” Reported: She said she could solve that problem.
- Direct: “We are visiting Paris next week.” Reported: They said they were visiting Paris the following week.
- Direct: “I will be waiting outside.” Reported: He stated he would be waiting outside.
- Direct: “They have been studying for hours.” Reported: She mentioned they had been studying for hours.
- Direct: “I can’t understand this chapter.” Reported: He complained that he couldn’t understand that chapter.
- Direct: “We were planning a surprise.” Reported: They told me they had been planning a surprise.
- Direct: “She has to complete her assignment.” Reported: He said she had to complete her assignment.
- Direct: “I will have finished the project by Monday.” Reported: She stated she would have finished the project by Monday.
- Direct: “They are going to hold a meeting.” Reported: She heard they were going to hold a meeting.
- Direct: “I must leave.” Reported: He said he had to leave.
Reported Speech: Changing Time and Place References
When converting direct speech into reported speech, references to time and place often need to be adjusted to fit the context of the reported speech. This is because the time and place relative to the speaker may have changed from the original statement to the time of reporting. Here are some examples to illustrate how time and place references change:
- Direct: “I will see you tomorrow .” Reported: He said he would see me the next day .
- Direct: “We went to the park yesterday .” Reported: They said they went to the park the day before .
- Direct: “I have been working here since Monday .” Reported: She mentioned she had been working there since Monday .
- Direct: “Let’s meet here at noon.” Reported: He suggested meeting there at noon.
- Direct: “I bought this last week .” Reported: She said she had bought it the previous week .
- Direct: “I will finish this by tomorrow .” Reported: He stated he would finish it by the next day .
- Direct: “She will move to New York next month .” Reported: He heard she would move to New York the following month .
- Direct: “They were at the festival this morning .” Reported: She said they were at the festival that morning .
- Direct: “I saw him here yesterday.” Reported: She mentioned she saw him there the day before.
- Direct: “We will return in a week .” Reported: They said they would return in a week .
- Direct: “I have an appointment today .” Reported: He said he had an appointment that day .
- Direct: “The event starts next Friday .” Reported: She mentioned the event starts the following Friday .
- Direct: “I lived in Berlin two years ago .” Reported: He stated he had lived in Berlin two years before .
- Direct: “I will call you tonight .” Reported: She said she would call me that night .
- Direct: “I was at the office yesterday .” Reported: He mentioned he was at the office the day before .
Reported Speech: Question Format
When converting questions from direct speech into reported speech, the format changes significantly. Unlike statements, questions require rephrasing into a statement format and often involve the use of introductory verbs like ‘asked’ or ‘inquired’. Here are some examples to demonstrate how questions in direct speech are converted into statements in reported speech:
- Direct: “Are you coming to the party?” Reported: She asked if I was coming to the party.
- Direct: “What time is the meeting?” Reported: He inquired what time the meeting was.
- Direct: “Why did you leave early?” Reported: They wanted to know why I had left early.
- Direct: “Can you help me with this?” Reported: She asked if I could help her with that.
- Direct: “Where did you buy this?” Reported: He wondered where I had bought that.
- Direct: “Who is going to the concert?” Reported: They asked who was going to the concert.
- Direct: “How do you solve this problem?” Reported: She questioned how to solve that problem.
- Direct: “Is this the right way to the station?” Reported: He inquired whether it was the right way to the station.
- Direct: “Do you know her name?” Reported: They asked if I knew her name.
- Direct: “Why are they moving out?” Reported: She wondered why they were moving out.
- Direct: “Have you seen my keys?” Reported: He asked if I had seen his keys.
- Direct: “What were they talking about?” Reported: She wanted to know what they had been talking about.
- Direct: “When will you return?” Reported: He asked when I would return.
- Direct: “Can she drive a manual car?” Reported: They inquired if she could drive a manual car.
- Direct: “How long have you been waiting?” Reported: She asked how long I had been waiting.
Reported Speech: Omitting Quotation Marks
In reported speech, quotation marks are not used, differentiating it from direct speech which requires them to enclose the spoken words. Reported speech summarizes or paraphrases what someone said without the need for exact wording. Here are examples showing how direct speech with quotation marks is transformed into reported speech without them:
- Direct: “I am feeling tired,” she said. Reported: She said she was feeling tired.
- Direct: “We will win the game,” he exclaimed. Reported: He exclaimed that they would win the game.
- Direct: “I don’t like apples,” the boy declared. Reported: The boy declared that he didn’t like apples.
- Direct: “You should visit Paris,” she suggested. Reported: She suggested that I should visit Paris.
- Direct: “I will be late,” he warned. Reported: He warned that he would be late.
- Direct: “I can’t believe you did that,” she expressed in surprise. Reported: She expressed her surprise that I had done that.
- Direct: “I need help with this task,” he admitted. Reported: He admitted that he needed help with the task.
- Direct: “I have never been to Italy,” she confessed. Reported: She confessed that she had never been to Italy.
- Direct: “We saw a movie last night,” they mentioned. Reported: They mentioned that they saw a movie the night before.
- Direct: “I am learning to play the piano,” he revealed. Reported: He revealed that he was learning to play the piano.
- Direct: “You must finish your homework,” she instructed. Reported: She instructed that I must finish my homework.
- Direct: “I will call you tomorrow,” he promised. Reported: He promised that he would call me the next day.
- Direct: “I have finished my assignment,” she announced. Reported: She announced that she had finished her assignment.
- Direct: “I cannot attend the meeting,” he apologized. Reported: He apologized for not being able to attend the meeting.
- Direct: “I don’t remember where I put it,” she confessed. Reported: She confessed that she didn’t remember where she put it.
Reported Speech Quiz
Thanks for reading! I hope you found these reported speech examples useful. Before you go, why not try this Reported Speech Quiz and see if you can change indirect speech into reported speech?


Reported Speech with Examples and Test (PDF)
Reported speech is used when we want to convey what someone else has said to us or to another person. It involves paraphrasing or summarising what has been said , often changing verb tenses , pronouns and other elements to suit the context of the report.
*doesn’t change

Formula of Reported Speech
The formula for reported speech involves transforming direct speech into an indirect form while maintaining the meaning of the original statement. In general, the formula includes:
- Choosing an appropriate reporting verb (e.g., say, tell, mention, explain).
- Changing pronouns and time expressions if necessary.
- Shifting the tense of the verb back if the reporting verb is in the past tense.
- Using reporting clauses like “that” or appropriate conjunctions.
- Adjusting word order and punctuation to fit the structure of the reported speech.
Here’s a simplified formula:
Reporting Verb + Indirect Object + Conjunction + Reported Clause
For example:
- She said (reporting verb) to me (indirect object) that (conjunction) she liked ice cream (reported clause).

Here’s how we use reported speech:
Reporting Verbs: We use verbs like ‘say’ or ‘tell’ to introduce reported speech. If the reporting verb is in the present tense, the tense of the reported speech generally remains the same.
If the reporting verb is in the past tense , the tense of the reported speech often shifts back in time.
Tense Changes: Tense changes are common in reported speech. For example, present simple may change to past simple, present continuous to past continuous, etc. However, some verbs like ‘would’, ‘could’, ‘should’, ‘might’, ‘must’, and ‘ought to’ generally don’t change.
Reported Questions: When reporting questions, we often change them into statements while preserving the meaning. Question words are retained, and the tense of the verbs may change.
Reported Requests and Orders: Requests and orders are reported similarly to statements. Reported requests often use ‘asked me to’ + infinitive, while reported orders use ‘told me to’ + infinitive.
Time Expressions: Time expressions may need to change depending on when the reported speech occurred in relation to the reporting moment. For instance, ‘today’ may become ‘that day’ or ‘yesterday’, ‘yesterday’ might become ‘the day before’, and so forth.
Reported Speech with Examples PDF
Reported Speech PDF – download
Reported Speech Test
Reported Speech A2 – B1 Test – download
You May Also Like

English Level Tests For A1 & A2 PDF (download)

20+ Example Sentences in the Past Progressive Tense (PDF)

Virtual Data Rooms: What they Are, and Their Uses and Benefits
- I would like books for studying.

What is Reported Speech and how to use it? with Examples
Published by
Olivia Drake
Reported speech and indirect speech are two terms that refer to the same concept, which is the act of expressing what someone else has said.
On this page:
Reported speech is different from direct speech because it does not use the speaker’s exact words. Instead, the reporting verb is used to introduce the reported speech, and the tense and pronouns are changed to reflect the shift in perspective. There are two main types of reported speech: statements and questions.
1. Reported Statements: In reported statements, the reporting verb is usually “said.” The tense in the reported speech changes from the present simple to the past simple, and any pronouns referring to the speaker or listener are changed to reflect the shift in perspective. For example, “I am going to the store,” becomes “He said that he was going to the store.”
2. Reported Questions: In reported questions, the reporting verb is usually “asked.” The tense in the reported speech changes from the present simple to the past simple, and the word order changes from a question to a statement. For example, “What time is it?” becomes “She asked what time it was.”
It’s important to note that the tense shift in reported speech depends on the context and the time of the reported speech. Here are a few more examples:
- Direct speech: “I will call you later.”Reported speech: He said that he would call me later.
- Direct speech: “Did you finish your homework?”Reported speech: She asked if I had finished my homework.
- Direct speech: “I love pizza.”Reported speech: They said that they loved pizza.
When do we use reported speech?
Reported speech is used to report what someone else has said, thought, or written. It is often used in situations where you want to relate what someone else has said without quoting them directly.
Reported speech can be used in a variety of contexts, such as in news reports, academic writing, and everyday conversation. Some common situations where reported speech is used include:
News reports: Journalists often use reported speech to quote what someone said in an interview or press conference.
Business and professional communication: In professional settings, reported speech can be used to summarize what was discussed in a meeting or to report feedback from a customer.
Conversational English: In everyday conversations, reported speech is used to relate what someone else said. For example, “She told me that she was running late.”
Narration: In written narratives or storytelling, reported speech can be used to convey what a character said or thought.
How to make reported speech?
1. Change the pronouns and adverbs of time and place: In reported speech, you need to change the pronouns, adverbs of time and place to reflect the new speaker or point of view. Here’s an example:
Direct speech: “I’m going to the store now,” she said. Reported speech: She said she was going to the store then.
In this example, the pronoun “I” is changed to “she” and the adverb “now” is changed to “then.”
2. Change the tense: In reported speech, you usually need to change the tense of the verb to reflect the change from direct to indirect speech. Here’s an example:
Direct speech: “I will meet you at the park tomorrow,” he said. Reported speech: He said he would meet me at the park the next day.
In this example, the present tense “will” is changed to the past tense “would.”
3. Change reporting verbs: In reported speech, you can use different reporting verbs such as “say,” “tell,” “ask,” or “inquire” depending on the context of the speech. Here’s an example:
Direct speech: “Did you finish your homework?” she asked. Reported speech: She asked if I had finished my homework.
In this example, the reporting verb “asked” is changed to “said” and “did” is changed to “had.”
Overall, when making reported speech, it’s important to pay attention to the verb tense and the changes in pronouns, adverbs, and reporting verbs to convey the original speaker’s message accurately.
How do I change the pronouns and adverbs in reported speech?
1. Changing Pronouns: In reported speech, the pronouns in the original statement must be changed to reflect the perspective of the new speaker. Generally, the first person pronouns (I, me, my, mine, we, us, our, ours) are changed according to the subject of the reporting verb, while the second and third person pronouns (you, your, yours, he, him, his, she, her, hers, it, its, they, them, their, theirs) are changed according to the object of the reporting verb. For example:
Direct speech: “I love chocolate.” Reported speech: She said she loved chocolate.
Direct speech: “You should study harder.” Reported speech: He advised me to study harder.
Direct speech: “She is reading a book.” Reported speech: They noticed that she was reading a book.
2. Changing Adverbs: In reported speech, the adverbs and adverbial phrases that indicate time or place may need to be changed to reflect the perspective of the new speaker. For example:
Direct speech: “I’m going to the cinema tonight.” Reported speech: She said she was going to the cinema that night.
Direct speech: “He is here.” Reported speech: She said he was there.
Note that the adverb “now” usually changes to “then” or is omitted altogether in reported speech, depending on the context.
It’s important to keep in mind that the changes made to pronouns and adverbs in reported speech depend on the context and the perspective of the new speaker. With practice, you can become more comfortable with making these changes in reported speech.
How do I change the tense in reported speech?
In reported speech, the tense of the reported verb usually changes to reflect the change from direct to indirect speech. Here are some guidelines on how to change the tense in reported speech:
Present simple in direct speech changes to past simple in reported speech. For example: Direct speech: “I like pizza.” Reported speech: She said she liked pizza.
Present continuous in direct speech changes to past continuous in reported speech. For example: Direct speech: “I am studying for my exam.” Reported speech: He said he was studying for his exam.
Present perfect in direct speech changes to past perfect in reported speech. For example: Direct speech: “I have finished my work.” Reported speech: She said she had finished her work.
Past simple in direct speech changes to past perfect in reported speech. For example: Direct speech: “I visited my grandparents last weekend.” Reported speech: She said she had visited her grandparents the previous weekend.
Will in direct speech changes to would in reported speech. For example: Direct speech: “I will help you with your project.” Reported speech: He said he would help me with my project.
Can in direct speech changes to could in reported speech. For example: Direct speech: “I can speak French.” Reported speech: She said she could speak French.
Remember that the tense changes in reported speech depend on the tense of the verb in the direct speech, and the tense you use in reported speech should match the time frame of the new speaker’s perspective. With practice, you can become more comfortable with changing the tense in reported speech.
Do I always need to use a reporting verb in reported speech?
No, you do not always need to use a reporting verb in reported speech. However, using a reporting verb can help to clarify who is speaking and add more context to the reported speech.
In some cases, the reported speech can be introduced by phrases such as “I heard that” or “It seems that” without using a reporting verb. For example:
Direct speech: “I’m going to the cinema tonight.” Reported speech with a reporting verb: She said she was going to the cinema tonight. Reported speech without a reporting verb: It seems that she’s going to the cinema tonight.
However, it’s important to note that using a reporting verb can help to make the reported speech more formal and accurate. When using reported speech in academic writing or journalism, it’s generally recommended to use a reporting verb to make the reporting more clear and credible.
Some common reporting verbs include say, tell, explain, ask, suggest, and advise. For example:
Direct speech: “I think we should invest in renewable energy.” Reported speech with a reporting verb: She suggested that they invest in renewable energy.
Overall, while using a reporting verb is not always required, it can be helpful to make the reported speech more clear and accurate
How to use reported speech to report questions and commands?
1. Reporting Questions: When reporting questions, you need to use an introductory phrase such as “asked” or “wondered” followed by the question word (if applicable), subject, and verb. You also need to change the word order to make it a statement. Here’s an example:
Direct speech: “What time is the meeting?” Reported speech: She asked what time the meeting was.
Note that the question mark is not used in reported speech.
2. Reporting Commands: When reporting commands, you need to use an introductory phrase such as “ordered” or “told” followed by the person, to + infinitive, and any additional information. Here’s an example:
Direct speech: “Clean your room!” Reported speech: She ordered me to clean my room.
Note that the exclamation mark is not used in reported speech.
In both cases, the tense of the reported verb should be changed accordingly. For example, present simple changes to past simple, and future changes to conditional. Here are some examples:
Direct speech: “Will you go to the party with me?”Reported speech: She asked if I would go to the party with her. Direct speech: “Please bring me a glass of water.”Reported speech: She requested that I bring her a glass of water.
Remember that when using reported speech to report questions and commands, the introductory phrases and verb tenses are important to convey the intended meaning accurately.
How to make questions in reported speech?
To make questions in reported speech, you need to use an introductory phrase such as “asked” or “wondered” followed by the question word (if applicable), subject, and verb. You also need to change the word order to make it a statement. Here are the steps to make questions in reported speech:
Identify the reporting verb: The first step is to identify the reporting verb in the sentence. Common reporting verbs used to report questions include “asked,” “inquired,” “wondered,” and “wanted to know.”
Change the tense and pronouns: Next, you need to change the tense and pronouns in the sentence to reflect the shift from direct to reported speech. The tense of the verb is usually shifted back one tense (e.g. from present simple to past simple) in reported speech. The pronouns should also be changed as necessary to reflect the shift in perspective from the original speaker to the reporting speaker.
Use an appropriate question word: If the original question contained a question word (e.g. who, what, where, when, why, how), you should use the same question word in the reported question. If the original question did not contain a question word, you can use “if” or “whether” to introduce the reported question.
Change the word order: In reported speech, the word order of the question changes from the inverted form to a normal statement form. The subject usually comes before the verb, unless the original question started with a question word.
Here are some examples of reported questions:
Direct speech: “Did you finish your homework?”Reported speech: He wanted to know if I had finished my homework. Direct speech: “Where are you going?”Reported speech: She wondered where I was going.
Remember that when making questions in reported speech, the introductory phrases and verb tenses are important to convey the intended meaning accurately.
Here you can find more examples of direct and indirect questions
What is the difference between reported speech an indirect speech?
In reported or indirect speech, you are retelling or reporting what someone said using your own words. The tense of the reported speech is usually shifted back one tense from the tense used in the original statement. For example, if someone said, “I am going to the store,” in reported speech you would say, “He/she said that he/she was going to the store.”
The main difference between reported speech and indirect speech is that reported speech usually refers to spoken language, while indirect speech can refer to both spoken and written language. Additionally, indirect speech is a broader term that includes reported speech as well as other ways of expressing what someone else has said, such as paraphrasing or summarizing.
Examples of direct speech to reported
- Direct speech: “I am hungry,” she said. Reported speech: She said she was hungry.
- Direct speech: “Can you pass the salt, please?” he asked. Reported speech: He asked her to pass the salt.
- Direct speech: “I will meet you at the cinema,” he said. Reported speech: He said he would meet her at the cinema.
- Direct speech: “I have been working on this project for hours,” she said. Reported speech: She said she had been working on the project for hours.
- Direct speech: “What time does the train leave?” he asked. Reported speech: He asked what time the train left.
- Direct speech: “I love playing the piano,” she said. Reported speech: She said she loved playing the piano.
- Direct speech: “I am going to the grocery store,” he said. Reported speech: He said he was going to the grocery store.
- Direct speech: “Did you finish your homework?” the teacher asked. Reported speech: The teacher asked if he had finished his homework.
- Direct speech: “I want to go to the beach,” she said. Reported speech: She said she wanted to go to the beach.
- Direct speech: “Do you need help with that?” he asked. Reported speech: He asked if she needed help with that.
- Direct speech: “I can’t come to the party,” he said. Reported speech: He said he couldn’t come to the party.
- Direct speech: “Please don’t leave me,” she said. Reported speech: She begged him not to leave her.
- Direct speech: “I have never been to London before,” he said. Reported speech: He said he had never been to London before.
- Direct speech: “Where did you put my phone?” she asked. Reported speech: She asked where she had put her phone.
- Direct speech: “I’m sorry for being late,” he said. Reported speech: He apologized for being late.
- Direct speech: “I need some help with this math problem,” she said. Reported speech: She said she needed some help with the math problem.
- Direct speech: “I am going to study abroad next year,” he said. Reported speech: He said he was going to study abroad the following year.
- Direct speech: “Can you give me a ride to the airport?” she asked. Reported speech: She asked him to give her a ride to the airport.
- Direct speech: “I don’t know how to fix this,” he said. Reported speech: He said he didn’t know how to fix it.
- Direct speech: “I hate it when it rains,” she said. Reported speech: She said she hated it when it rained.
Share this:
Leave a reply cancel reply, i’m olivia.

Welcome to my virtual classroom! Join me on a journey of language and learning, where we explore the wonders of English together. Let’s discover the joy of words and education!
Let’s connect
Join the fun!
Stay updated with our latest tutorials and ideas by joining our newsletter.
Type your email…
Recent posts
Present perfect vs past perfect exercises with answers, present perfect negative sentences exercises with answers, present perfect questions exercises with answers, present perfect simple exercises with answers, third conditional negative form exercises, third conditional question form exercises, discover more from fluent english grammar.
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Continue reading
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
At Morehouse, Biden says dissent should be heard because democracy is 'still the way'

Stephen Fowler
Jeongyoon Han

President Biden speaks to graduating students at the Morehouse College commencement Sunday in Atlanta. Alex Brandon/AP hide caption
President Biden speaks to graduating students at the Morehouse College commencement Sunday in Atlanta.
President Biden told Morehouse College's graduating class of 2024 that he's committed to serving Black voters while defending freedom and democracy in the face of "extremist forces" that he says threaten the soul of the nation.
With just six months until the general election, the speech, which was filled with religious themes of struggle and resilience, also served as a continuation of Biden's warning to his supporters of what he thinks the country would look like if Donald Trump is elected again.
"They don't see you in the future of America, but they're wrong," he said. "To me, we make history, not erase it. We know Black history is American history."
The president's commencement address at Morehouse, a historically Black school in Atlanta, also comes as polling shows potentially lower support for his reelection efforts among Black voters and young voters, and as campus protests over conflict in Gaza have disrupted graduations around the country.
Biden said he understood angst over the direction of the country, acknowledged "dissent about America's role in the world" and said that those who have different views should have their voices heard in the name of democracy.
"That's my commitment to you," he said. "To show you: democracy, democracy democracy — it's still the way."

Graduating students at the Morehouse College commencement bow their heads Sunday in Atlanta. President Biden addressed the graduating class of 2024 and warned about "extremist forces" he says threaten the soul of the nation. Alex Brandon/AP hide caption
Graduating students at the Morehouse College commencement bow their heads Sunday in Atlanta. President Biden addressed the graduating class of 2024 and warned about "extremist forces" he says threaten the soul of the nation.
His speech is also one of many events on his recent trip aimed at speaking to Black voters, following events with plaintiffs in the historic Brown v. Board Supreme Court case, meetings with Black Greek Letter Organizations, often known as the Divine Nine, and before he headlines an NAACP dinner in Detroit.
For weeks, several college and university campuses around the country have been roiled with student protests and encampments expressing opposition against Biden and U.S. policies and involvement around conflict in Gaza.

Biden will cap off a week of outreach to Black Americans with Morehouse commencement

Biden is set for the Morehouse graduation. Students are divided
Morehouse has seen student demonstrations, but not occupation of campus spaces or clashes with law enforcement. Outside of the ceremony, a small number of protesters gathered while the commencement itself did not see any major disruptions.
Last week, Morehouse College President David Thomas said he would rather halt proceedings than have students escorted away for protesting.
"If my choice is 20 people being arrested on national TV on the Morehouse campus, taken away in zip ties during our commencement, before we would reach that point, I would conclude the ceremony," he said on NPR's Weekend Edition .

An attendee stands in protest with their back to President Biden as Biden speaks to graduating students at the Morehouse College commencement Sunday in Atlanta. John Bazemore/AP hide caption
An attendee stands in protest with their back to President Biden as Biden speaks to graduating students at the Morehouse College commencement Sunday in Atlanta.
Those concerns did not come to pass. Apart from the heightened security and increased media presence, Biden's speech was met with a similar response to a typical college graduation ceremony.
More than 400 graduating students walked across the stage Sunday, and during Biden's speech a handful of students, some wearing keffiyehs , turned their chairs around to face away from the president.
After the ceremony, Morehouse issued a statement praising the graduating class and their intentionally muted response to Biden.
"It is fitting that a moment of organized, peaceful activism would occur on our campus while the world is watching to continue a critical conversation," the statement reads. "We are proud of the resilient class of 2024's unity in silent protest, showing their intentionality in strategy, communication, and coordination as a 414-person unit."
DeAngelo Fletcher, Morehouse College's valedictorian, closed his address to his classmates by addressing global conflict, particularly the Israel-Hamas war.
"For the first time in our lives, we've heard the global community sing one harmonious song that transcends language and culture," he said. "It is my sense as a Morehouse Man, nay — as a human being — to call for an immediate and a permanent ceasefire in the Gaza Strip."
Biden's speech at Morehouse comes with intense scrutiny as many presidential horse race polls show the president lagging with young voters, Black voters and other nonwhite groups that helped propel him to a narrow victory against Trump in 2020.
Those polls — for now — signal a drop in support for Biden but not necessarily an equal shift toward Trump. There are also signs that some of the displeasure with Biden is more pronounced among people who aren't as likely to vote in November.
While facing a nominal challenge in the Democratic presidential primary, Biden's best-performing areas have often come in places with a large share of Black voters. For example, in Georgia's primary contest 95% of Black voters pulled a Democratic ballot, and Biden won 95% of the overall vote.
While some students, faculty and alumni expressed opposition to Biden's selection as the commencement speaker, reaction on campus during the graduation ceremony was largely positive.
Dr. Tiffany Johnson, a 50-year-old who came to the campus green at 4:30 a.m. to see her son graduate, was also excited to see Biden.
"He is the leader of the free world, the most important job in the world, and for him to come to speak to [Morehouse] graduates, to inspire them, is phenomenal," Johnson said.
Johnson said Black voters who might not support Biden are part of a "bandwagon" that do not understand what he has done for the community, and said his speech would be an ideal opportunity to share his accomplishments.
In the speech, Biden touted a track record that he says makes key investments in Black communities, including a record $16 billion funding package toward historically Black colleges and universities, protecting voting rights, and creating economic policies that strengthens Black businesses.
- commencement address
- graduation ceremony
- morehouse college
- young voters
- Donald Trump
- black voters
Harrison Butker’s commencement speech: Wives should stay at home. His mom’s a medical physicist

- Show more sharing options
- Copy Link URL Copied!
Harrison Butker is a three-time Super Bowl champion and one of the most accurate field-goal kickers in NFL history.
As such, the Kansas City Chiefs kicker was given a platform to express his views as the commencement speaker at Benedictine College .
The devout Christian used the opportunity to give some radical thoughts and controversial opinions during a 20-minute speech delivered at the ceremony honoring the 485 students graduating from the Catholic private liberal arts school in Atchison, Kan., on Saturday.
Butker took shots at gender roles, abortion, President Biden and Pride month during his Benedictine address. Now the NFL appears to be distancing itself from the 28-year-old.
“Harrison Butker gave a speech in his personal capacity,” Jonathan Beane, NFL senior vice president and chief diversity and inclusion officer, said in a statement emailed to The Times. “His views are not those of the NFL as an organization. The NFL is steadfast in our commitment to inclusion, which only makes our league stronger.”
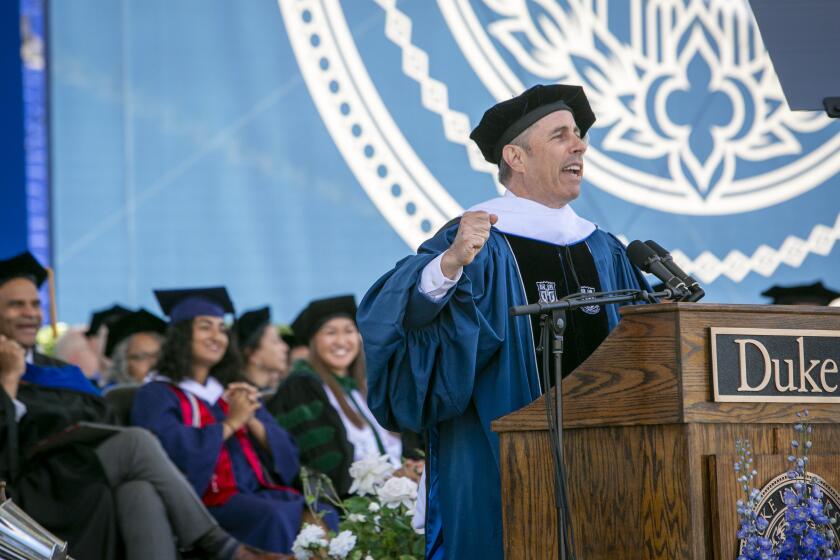

Entertainment & Arts
What’s the deal with Jerry Seinfeld? His Duke University address sparks student walkout
Duke University enlisted Jerry Seinfeld to deliver its 2024 commencement speech, but a group of pro-Palestinian student protesters refused to stay for his punchline.
May 13, 2024
At Benedictine, Butker told the male graduates to “be unapologetic in your masculinity” and congratulated the female graduates on their “amazing accomplishment.” He went on to tell the women that he “would venture to guess that the majority of you are most excited about your marriage and the children you will bring into this world.”
Butker then told those women that “my beautiful wife, Isabelle, would be the first to say her life truly started when she began living her vocation as a wife and as a mother. I’m on this stage today and able to be the man I am because I have a wife who leans into her vocation.”
Butker — whose mother, Elizabeth Keller Butker, is a medical physicist at Emory University’s Winship Cancer Institute in Atlanta, where she’s worked since 1988 — then started getting choked up.
“I’m beyond blessed with the many talents God has given me,” Butker said, “but it cannot be overstated that all my success is made possible because a girl I met in band class back in middle school would convert to the faith, become my wife and embrace one of the most important titles of all: homemaker.”
That statement was met with 18 seconds of enthusiastic cheers and applause. Butker continued praising his wife and her role in their family.
“She’s the primary educator to our children. She’s the one who ensures I never let football or my business become a distraction from that of a husband and a father. She is the person that knows me best at my core and it is through our marriage that, Lord willing, we both will attain salvation.”

Silenced USC valedictorian walked the stage and the crowd reaction was anything but silent
Diplomas will be handed out Friday during individual school events for graduating seniors at USC.
May 10, 2024
During his opening remarks, Butker stated that “things like abortion , in vitro fertilization , surrogacy , euthanasia, as well as a growing support for the degenerate cultural values and media, all stem from the pervasiveness of disorder.”
He also said that Biden “has been so vocal in his support for the murder of innocent babies that I’m sure to many people it appears you can be both Catholic and pro-choice.”
At one point, Butker mentioned the word “pride” — then clarified that he wasn’t talking about “the deadly sins sort of Pride that has an entire month dedicated to it, but the true God-centered pride that is cooperating with the Holy Ghost to glorify Him.”
The comment, a jab at the LGBTQ+ community that celebrates Pride month every June, received a few chuckles from the audience.
When Butker finished his address, the crowd rose for an ovation. Susannah Leisegang , a former Benedictine track and field athlete who graduated Saturday with a degree in graphic design, said she was among the handful of people who did not stand.
“Some of us did boo — me and my roommate definitely did,” Leisegang said in a video she posted on TikTok . “There was a standing ovation from everyone in the room, except from me, my roommate and about 10 to 15 other women. You also have to keep in mind this was at a Catholic and conservative college, so a lot of the men were like, ‘F— yeah!’ They were excited. But it was horrible. Most of the women were looking back and forth at each other like, ‘What the f— is going on?’”

Supreme Court to pregnant women: Good luck with that
Forget the ‘split court’ garbage. This Supreme Court is not going to protect even emergency abortions. Here’s what you need to know.
April 25, 2024
Leisegang pointed out that she is 21 and has a job lined up in her field.
“Getting married and having kids is not my ideal situation right now,” she said. “So, yeah, it was definitely horrible and it definitely made graduation feel a little less special, knowing I had to sit through that and get told I’m nothing but a homemaker.”
Other members of the graduating class who participated in the ceremony have shared a variety of opinions on Butker’s speech. Elle Wilbers, 22, a future medical school student, told the Associated Press she thought Butker’s reference to the LGBTQ+ community was “horrible.”
“We should have compassion for the people who have been told all their life that the person they love is like, it’s not OK to love that person,” she said.
Kassidy Neuner, 22, who plans to teach for a year before going to law school, told the AP that being a stay-at-home parent is “a wonderful decision” but “it’s also not for everybody.”
“I think that he should have addressed more that it’s not always an option,” she said. “And, if it is your option in life, that’s amazing for you. But there’s also the option to be a mother and a career woman.”

Company Town
Hollywood’s stunt-driving industry is dominated by men. These women are fighting for change
Olivia Summers and Dee Bryant are building a team of all-women stunt drivers to make the stunt-driving industry more inclusive.
April 10, 2024
ValerieAnne Volpe, 20, who graduated with an art degree, told the AP she thought Butker said things that “people are scared to say.”
“You can just hear that he loves his wife,” Volpe said. “You can hear that he loves his family,” she said.
Butker has not commented publicly since the address. His previous social media posts are being used by people leaving comments both blasting and supporting his remarks. Heavy.com reports that all images of Isabelle Butker have been removed from her husband’s X and Instagram feeds in recent days.
Benedictine has not publicly addressed Butker’s controversial statements and did not immediately respond to multiple messages from The Times. The college’s social media feeds have been flooded with angry comments regarding Butker’s speech, and the comment section for the YouTube video of it has been disabled.
An article on Benedictine’s website about the commencement ceremony had initially referred to Butker’s speech as “inspiring.” The uncredited piece includes a reworked version of Butker’s “homemaker” quote that does not include that word, with no indication that the quote had been altered.

California high school football team refuses to play against girls, even after settling Title IX lawsuit
Despite settling a Title IX lawsuit, Santa Maria Valley Christian Academy again didn’t allow its high school football team to play against an opponent with female players.
Oct. 5, 2023
The Chiefs did not respond to a request for comment from The Times. Tavia Hunt, wife of Chiefs owner Clark Hunt , appeared to express her support for Butker in a lengthy Instagram post Thursday.
“Countless highly educated women devote their lives to nurturing and guiding their children,” she wrote. “Someone disagreeing with you doesn’t make them hateful; it simply means they have a different opinion. Let’s celebrate families, motherhood and fatherhood.”
Gracie Hunt, 25, one of Clark and Tavia Hunt’s three children was asked about Butker’s speech Friday on “ Fox & Friends .”
“I can only speak from my own experience, which is I had the most incredible mom who had the ability to stay home and be with us as kids growing up,” Gracie Hunt said. “And I understand that there are many women out there who can’t make that decision but for me in my life, I know it was really formative in shaping me and my siblings to be who we are.”
Asked if she understood what Butker was talking about, Hunt said, “For sure, and I really respect Harrison and his Christian faith and what he’s accomplished on and off the field.”
A change.org petition calling for the team to release the kicker because of his comments has received more than 185,000 signatures. Eight petitions supporting Butker appear on the site as well. One has more than 11,000 signatures while the rest have fewer than 800 each.
The Chargers poked fun at Butker on Wednesday in their schedule-release video, which is modeled after “The Sims” video game. In the video, Butker’s likeness is shown baking a pie, scrubbing a kitchen counter and arranging flowers.
should we REALLY make our schedule release video in the sims? yes yes yesyes yesyes yes yes yes yes yes yes yes yes yes yesyes yes yes yes yesye yes yes yes yes yesyes pic.twitter.com/MXzfAPyhe8 — Los Angeles Chargers (@chargers) May 16, 2024
The official X account for Kansas City also appeared to attempt putting a humorous spin on the matter, posting a “reminder” that Butker lives in a different city Wednesday night before deleting it and posting an apology .
Earlier in the week on X, Kansas City Mayor Quinton Lucas appeared to defend Butker’s right to express his views .
Grown folks have opinions, even if they play sports. I disagree with many, but I recognize our right to different views. Nobody should have to stick to anything. Varied and shall I say—diverse—viewpoints help the world go round. — Mayor Q (@QuintonLucasKC) May 14, 2024
I think he holds a minority viewpoint, even in this state and the bordering one. I also believe more athletes, if freer to speak, would stand up for the voices of many marginalized communities. I hate “stick to sports” when used to muzzle Black athletes. I’m with consistency. — Mayor Q (@QuintonLucasKC) May 14, 2024
Last year, Butker gave the commencement address at his alma mater, Georgia Tech, advising the graduates to “ get married and start a family .”

The fight to move the Catholic Church in America to the right — and the little-known O.C. lawyer behind it
As Pope Francis nudges the Roman Catholic Church to the left globally, layman Tim Busch of Irvine is pushing American Catholicism to the right.
Dec. 18, 2023
More to Read

Granderson: A football player said something stupid about women. Let it go
May 17, 2024

Biden’s Morehouse College graduation invitation draws backlash
April 24, 2024

L.A. Affairs: I went to USC. He went to UCLA. Could I fight on in the name of love?
April 12, 2024
Get our high school sports newsletter
Prep Rally is devoted to the SoCal high school sports experience, bringing you scores, stories and a behind-the-scenes look at what makes prep sports so popular.
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the Los Angeles Times.

Chuck Schilken is a sports reporter on the Fast Break team. He spent more than 18 years with the Los Angeles Times’ Sports Department in a variety of roles. Before joining The Times, he worked for more than a decade as a sports reporter and editor at newspapers in Virginia and Maryland.
More From the Los Angeles Times

DEA, LAPD launch criminal investigation into Matthew Perry’s fatal ketamine use

Police lower the boom on Pasadena man accused of setting off over 150 explosions in two years

California Supreme Court to hear oral arguments on Uber, Lyft-backed Prop. 22
![reported for speech Stephanie Lazarus, a Los Angeles police detective charged with capital murder in the 1986 slaying of her ex-boyfriend's wife pleaded not guilty during her arraignment in Los Angeles Superior Court Monday morning, July 6, 2009. (AP Photo/Al Seib ,Pool)]](https://ca-times.brightspotcdn.com/dims4/default/516ae7b/2147483647/strip/true/crop/2400x1600+0+79/resize/840x560!/quality/75/?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcalifornia-times-brightspot.s3.amazonaws.com%2F65%2Fe0%2F8228b5b44c0da5be07c48647ce71%2Fdetective-killing.JPEG)
Many pushed to free ‘kind’ LAPD cop who murdered ex-boyfriend’s wife. Victim’s family fought back
- Cambridge Dictionary +Plus
Reported speech: indirect speech
Indirect speech focuses more on the content of what someone said rather than their exact words. In indirect speech , the structure of the reported clause depends on whether the speaker is reporting a statement, a question or a command.
Indirect speech: reporting statements
Indirect reports of statements consist of a reporting clause and a that -clause. We often omit that , especially in informal situations:
The pilot commented that the weather had been extremely bad as the plane came in to land. (The pilot’s words were: ‘The weather was extremely bad as the plane came in to land.’ )
I told my wife I didn’t want a party on my 50th birthday. ( that -clause without that ) (or I told my wife that I didn’t want a party on my 50th birthday .)
Indirect speech: reporting questions
Reporting yes-no questions and alternative questions.
Indirect reports of yes-no questions and questions with or consist of a reporting clause and a reported clause introduced by if or whether . If is more common than whether . The reported clause is in statement form (subject + verb), not question form:
She asked if [S] [V] I was Scottish. (original yes-no question: ‘Are you Scottish?’ )
The waiter asked whether [S] we [V] wanted a table near the window. (original yes-no question: ‘Do you want a table near the window? )
He asked me if [S] [V] I had come by train or by bus. (original alternative question: ‘Did you come by train or by bus?’ )
Questions: yes-no questions ( Are you feeling cold? )
Reporting wh -questions
Indirect reports of wh -questions consist of a reporting clause, and a reported clause beginning with a wh -word ( who, what, when, where, why, how ). We don’t use a question mark:
He asked me what I wanted.
Not: He asked me what I wanted?
The reported clause is in statement form (subject + verb), not question form:
She wanted to know who [S] we [V] had invited to the party.
Not: … who had we invited …
Who , whom and what
In indirect questions with who, whom and what , the wh- word may be the subject or the object of the reported clause:
I asked them who came to meet them at the airport. ( who is the subject of came ; original question: ‘Who came to meet you at the airport?’ )
He wondered what the repairs would cost. ( what is the object of cost ; original question: ‘What will the repairs cost?’ )
She asked us what [S] we [V] were doing . (original question: ‘What are you doing?’ )
Not: She asked us what were we doing?
When , where , why and how
We also use statement word order (subject + verb) with when , where, why and how :
I asked her when [S] it [V] had happened (original question: ‘When did it happen?’ ).
Not: I asked her when had it happened?
I asked her where [S] the bus station [V] was . (original question: ‘Where is the bus station?’ )
Not: I asked her where was the bus station?
The teacher asked them how [S] they [V] wanted to do the activity . (original question: ‘How do you want to do the activity?’ )
Not: The teacher asked them how did they want to do the activity?
Questions: wh- questions
Indirect speech: reporting commands
Indirect reports of commands consist of a reporting clause, and a reported clause beginning with a to -infinitive:
The General ordered the troops to advance . (original command: ‘Advance!’ )
The chairperson told him to sit down and to stop interrupting . (original command: ‘Sit down and stop interrupting!’ )
We also use a to -infinitive clause in indirect reports with other verbs that mean wanting or getting people to do something, for example, advise, encourage, warn :
They advised me to wait till the following day. (original statement: ‘You should wait till the following day.’ )
The guard warned us not to enter the area. (original statement: ‘You must not enter the area.’ )
Verbs followed by a to -infinitive
Indirect speech: present simple reporting verb
We can use the reporting verb in the present simple in indirect speech if the original words are still true or relevant at the time of reporting, or if the report is of something someone often says or repeats:
Sheila says they’re closing the motorway tomorrow for repairs.
Henry tells me he’s thinking of getting married next year.
Rupert says dogs shouldn’t be allowed on the beach. (Rupert probably often repeats this statement.)
Newspaper headlines
We often use the present simple in newspaper headlines. It makes the reported speech more dramatic:
JUDGE TELLS REPORTER TO LEAVE COURTROOM
PRIME MINISTER SAYS FAMILIES ARE TOP PRIORITY IN TAX REFORM
Present simple ( I work )
Reported speech
Reported speech: direct speech
Indirect speech: past continuous reporting verb
In indirect speech, we can use the past continuous form of the reporting verb (usually say or tell ). This happens mostly in conversation, when the speaker wants to focus on the content of the report, usually because it is interesting news or important information, or because it is a new topic in the conversation:
Rory was telling me the big cinema in James Street is going to close down. Is that true?
Alex was saying that book sales have gone up a lot this year thanks to the Internet.
‘Backshift’ refers to the changes we make to the original verbs in indirect speech because time has passed between the moment of speaking and the time of the report.
In these examples, the present ( am ) has become the past ( was ), the future ( will ) has become the future-in-the-past ( would ) and the past ( happened ) has become the past perfect ( had happened ). The tenses have ‘shifted’ or ‘moved back’ in time.
The past perfect does not shift back; it stays the same:
Modal verbs
Some, but not all, modal verbs ‘shift back’ in time and change in indirect speech.
We can use a perfect form with have + - ed form after modal verbs, especially where the report looks back to a hypothetical event in the past:
He said the noise might have been the postman delivering letters. (original statement: ‘The noise might be the postman delivering letters.’ )
He said he would have helped us if we’d needed a volunteer. (original statement: ‘I’ll help you if you need a volunteer’ or ‘I’d help you if you needed a volunteer.’ )
Used to and ought to do not change in indirect speech:
She said she used to live in Oxford. (original statement: ‘I used to live in Oxford.’ )
The guard warned us that we ought to leave immediately. (original statement: ‘You ought to leave immediately.’ )
No backshift
We don’t need to change the tense in indirect speech if what a person said is still true or relevant or has not happened yet. This often happens when someone talks about the future, or when someone uses the present simple, present continuous or present perfect in their original words:
He told me his brother works for an Italian company. (It is still true that his brother works for an Italian company.)
She said she ’s getting married next year. (For the speakers, the time at the moment of speaking is ‘this year’.)
He said he ’s finished painting the door. (He probably said it just a short time ago.)
She promised she ’ll help us. (The promise applies to the future.)
Indirect speech: changes to pronouns
Changes to personal pronouns in indirect reports depend on whether the person reporting the speech and the person(s) who said the original words are the same or different.
Indirect speech: changes to adverbs and demonstratives
We often change demonstratives ( this, that ) and adverbs of time and place ( now, here, today , etc.) because indirect speech happens at a later time than the original speech, and perhaps in a different place.
Typical changes to demonstratives, adverbs and adverbial expressions
Indirect speech: typical errors.
The word order in indirect reports of wh- questions is the same as statement word order (subject + verb), not question word order:
She always asks me where [S] [V] I am going .
Not: She always asks me where am I going .
We don’t use a question mark when reporting wh- questions:
I asked him what he was doing.
Not: I asked him what he was doing?

Word of the Day
to fasten the belt that keeps you in your seat in a car or a plane

Searching out and tracking down: talking about finding or discovering things

Learn more with +Plus
- Recent and Recommended {{#preferredDictionaries}} {{name}} {{/preferredDictionaries}}
- Definitions Clear explanations of natural written and spoken English English Learner’s Dictionary Essential British English Essential American English
- Grammar and thesaurus Usage explanations of natural written and spoken English Grammar Thesaurus
- Pronunciation British and American pronunciations with audio English Pronunciation
- English–Chinese (Simplified) Chinese (Simplified)–English
- English–Chinese (Traditional) Chinese (Traditional)–English
- English–Dutch Dutch–English
- English–French French–English
- English–German German–English
- English–Indonesian Indonesian–English
- English–Italian Italian–English
- English–Japanese Japanese–English
- English–Norwegian Norwegian–English
- English–Polish Polish–English
- English–Portuguese Portuguese–English
- English–Spanish Spanish–English
- English–Swedish Swedish–English
- Dictionary +Plus Word Lists
To add ${headword} to a word list please sign up or log in.
Add ${headword} to one of your lists below, or create a new one.
{{message}}
Something went wrong.
There was a problem sending your report.
Eddie Vedder Calls Harrison Butker a ‘F—ing P—y’ Mid-Concert Over Sexist Speech: ‘There’s Nothing More Masculine Than a Strong Man Supporting a Strong Woman’
By Zack Sharf
Digital News Director
- Nikki Glaser Rips Ben Affleck for Bombing at Netflix’s Tom Brady Roast: ‘He Didn’t Prepare’ and ‘Probably Thinks It’s Beneath Him to Do This’ 4 hours ago
- ‘The Smashing Machine’ First Look: Dwayne Johnson Transforms Into MMA Icon Mark Kerr in Benny Safdie’s A24 Drama 5 hours ago
- Jeff Daniels Says Agents Wanted Him Off ‘Dumb and Dumber’; He Feared Toilet Scene Might End His Career Until Jim Carrey Said: ‘It’s Going to Be Great … Go All the Way With It’ 22 hours ago

Pearl Jam played the MGM Grand in Las Vegas on May 18, and frontman Eddie Vedder couldn’t resist eviscerating Kansas City Chiefs kicker Harrison Butker for his controversial commencement speech at Benedictine College (via BroBible ). Butker has received enormous backlash for the speech, in which he attacked Pride Month and shared his belief that women belong in the kitchen. He said “one of the most important titles” a woman could have is homemaker.
Popular on Variety
“There should be pride in homemaking if you’re a man or a woman … it’s one of the hardest jobs and you should definitely take pride in it, but you’re going to benefit by giving up your dreams?” the frontman asked. “I couldn’t understand the logic, so I’m questioning it in public right now … It’s not a graduation speech.”
Vedder then took direct aim at Butker, telling the crowd: “The irony was that the football player — well, kicker … You see the kicker doesn’t have the pads because he doesn’t tackle anybody or get tackled — but he started telling men, ‘Don’t forget to puff up your chest and be more masculine. Don’t lose your masculinity.’ The irony was that when he was saying that, he looked like such a fucking pussy.”
“There’s nothing more masculine than a strong man supporting a strong woman,” Vedder said as the audience roared with applause and cheers.
Vedder is far from the only one publicly condemning Butker’s commencement speech. The Benedictine Sisters of Mount St. Scholastica recently denounced his comments, saying they “reject a narrow definition of what it means to be Catholic.”
Even the NFL got involved when Jonathan Beane, the organization’s senior vice president and chief diversity and inclusion officer, said Butker’s “views are not those of the NFL as an organization. The NFL is steadfast in our commitment to inclusion, which only makes our league stronger.”
More From Our Brands
Streaming hack: here’s how to get a max subscription on the house, exclusive: inside the world’s first 3-d printed neighborhood in marfa, texas, georgia qb’s fraud lawsuit poised to shake up nil collectives, the best loofahs and body scrubbers, according to dermatologists, 9-1-1 recap: a deadly crisis unearths another traumatic secret from bobby’s past — plus, look who’s home, verify it's you, please log in.
Biden delivers Morehouse commencement speech as some on campus express pro-Palestinian messages
ATLANTA — President Joe Biden delivered the commencement address at Morehouse College on Sunday morning, his most direct engagement with college students since the start of the Israel-Hamas war and a key opportunity for him to engage with a group of voters that data suggests is softening on him: young, Black men.
In his remarks, Biden ticked through his administration's policies that he said have aided Black Americans, including a record $16 billion in new aid for historically Black colleges and universities.
And, in a nod to the pro-Palestinian sentiment among Morehouse students and faculty, Biden reiterated his calls for an immediate cease-fire in Gaza, more humanitarian aid in the region and support for a two-state solution that would lead to the creation of a Palestinian state.
“We’ve been working on a deal as we speak. Working around the clock to lead an international effort to get more aid into Gaza, rebuild Gaza. I’m also working around the clock for more than just one cease-fire. I’m working to bring the region together. Working to build a lasting, durable peace,” he said.
As Biden spoke, roughly six students in the crowd sat turned away from him. Though Biden did not reference the action directly, his remarks touched on the “anger and frustration” felt by many Americans over the war, including by members of his own family.
“I know it breaks your heart. It breaks mine as well,” Biden said. “Leadership is about fighting through the most intractable problems. It’s about challenging anger, frustration and heartbreak. To find a solution. It’s about doing what you believe is right, even when it’s hard and lonely.”
Following the speech, Morehouse President David Thomas praised Biden for a “thought-provoking speech” he said was reflective of the president “listening.”
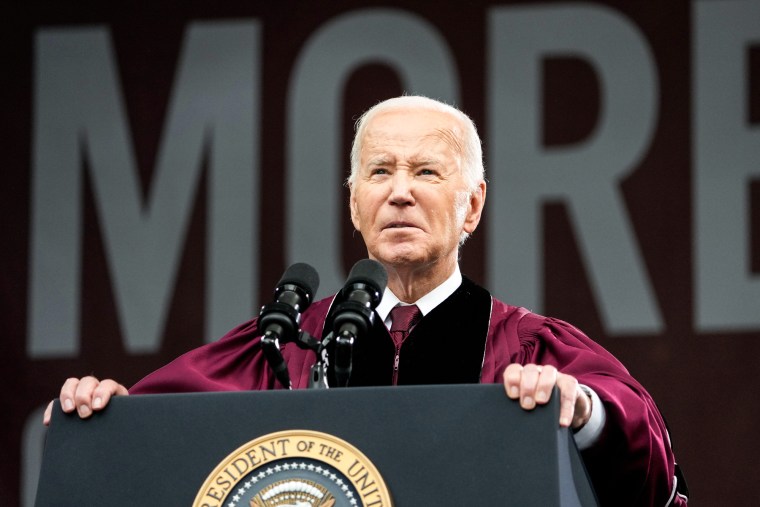

“You spoke to the hard issues confronting our nation and the world at this moment,” Thomas said before conferring an honorary doctorate degree onto Biden.
No significant, disruptive protests materialized, but some students and faculty members still expressed their support for Gaza during the ceremony.
Pro-Palestinian demonstrations began even before Biden took the stage Sunday morning. As graduates and faculty entered the ceremony, at least eight students and three staff members wore pro-Palestinian garb, some adorned in Palestinian flags and others wearing keffiyeh scarves.
An opening prayer by the Rev. Claybon Lea Jr. urged those in power to be “accountable for valuing human life” across the globe.
“Whether they live in Israel or Palestine, Ukraine or Russia, the Congo or Haiti, God give us men that will value life and call us to accountability. Give us men who require all of us to live the golden rule and even follow the edicts of that Palestinian Jew named Jesus,” Lea said as Biden sat inches behind him.
In the most direct call to action of the ceremony, valedictorian DeAngelo Jeremiah Fletcher concluded his remarks by calling for an immediate cease-fire in Gaza, framing his decision to speak on the conflict as a moral duty in line with the legacy of fellow Morehouse alumnus Martin Luther King Jr.
“It is important to recognize that both sides have suffered heavy casualties in the wake of Oct. 7,” Fletcher said. “From the comfort of our homes, we watch an unprecedented number of civilians mourn the loss of men, women and children while calling for a release of all hostages. For the first time in our lives, we’ve heard the global community sing one harmonious song that transcends language and culture. It is my stance as a Morehouse man named as a human being to call for an immediate and a permanent cease-fire in the Gaza Strip.”
As Biden took the stage, graduating students remained seated and silent, even as older alumni nearby cheered.
And during his remarks, faculty member Samuel Livingston held up the flag of the Democratic Republic of Congo, in an effort to bring attention to ongoing conflict in the region.
Sebastian Gordon, a graduating senior from Washington, D.C., was satisfied with Biden's remarks. “I know one concern that my class had was actions and words didn’t line up,” Gordon told NBC News. “I’m happy with his words that he said. I’m just going to continue to watch to make sure his actions line up with that.”
The protests during the commencement were largely peaceful, following instructions Thomas, the school president, gave to faculty and students across at least three meetings: The right to protest would be honored as long as they’re not disruptive.
Ahead of the commencement, Thomas told CNN that though he would not ask police to intervene should protests occur during Biden’s remarks, he would immediately bring the commencement to a halt.
“I have also made a decision that we will also not ask police to take individuals out of commencement in zip ties. If faced with the choice, I will cease the ceremonies on the spot if we were to reach that position,” Thomas said.
Even the most vocal student protesters at Morehouse predicted that protests during the commencement ceremony would likely not be disruptive, partially due to the volatility a police response would likely incite.
“I think that whatever happens on Sunday on the part of the people and the people who want to see some change is going to be peaceful,” sophomore Anwar Karim said. “I don’t see it erupting like it has at some of the other campuses, because we at HBCUs here are also just mindful of the fact of how interactions with police often go.”
White House press secretary Karine Jean-Pierre said Friday that Biden spent several days working on the speech, tapping into a brain trust of senior advisers, including some Morehouse alums, to craft his message to the 415 Black men graduating from the school.
Biden previewed the tone of his remarks during a speech Thursday to commemorate the 70th anniversary of the Supreme Court’s Brown v. Board of Education decision.
“Morehouse was founded after our nation’s Civil War to help prepare Black Americans who were formerly enslaved to enter the ministry, earn an education and usher them from slavery to freedom,” Biden said before announcing $16 billion in new investments for historically Black colleges and universities. “The founders of Morehouse understood something fundamental. Education is linked to freedom. Because to be free means to have something that no one can ever take away from you.”
Biden’s speech at Morehouse came against the backdrop of protests on college campuses nationwide over his handling over the war in Gaza, with many students and faculty members voicing opposition to the White House’s continued financial and military support for Israel. Some at Morehouse hoped Biden would speak directly to those concerns during his commencement remarks.
“I hope that we don’t get boilerplate language. I hope that we get something we haven’t heard before. I hope that his ethical, moral conscience trump any politics,” Morehouse professor Stephane Dunn said at a protest Friday.
Morehouse has also had pro-Palestinian protests on campus, though the HBCU did not see the same scale or escalation of demonstrations as some larger universities.
The school’s decision to host Biden as commencement speaker and award him an honorary doctorate degree almost immediately sparked protests among faculty and students, some continuing into the days leading up to the commencement ceremony.
“This is one big distraction on a day to celebrate the class of 2024 following Covid-19, but this is also an opportunity for students to make their voices heard during a time of increasing war and genocide in the Middle East,” Morehouse senior Calvin Bell said in reaction to Biden’s visit.
“We as students, faculty and alums who are standing on the right side of history do not stand with Biden,” Karim said. “We do not align ourselves with all of the clear and avid support that he’s had for a genocidal campaign on the part of the Israelis for the last over 200-plus days.”
Most recently, Morehouse faculty were split over the decision to award Biden an honorary doctorate degree at the ceremony. A letter circulated among staff members in protest of the decision got more that two dozen signatures in support, and the vote to award the degree passed 50-38, with roughly 12 faculty members abstaining.
The White House deployed its allies to Morehouse, both formally and informally, to assuage concerns and lower tensions over Biden’s visit.
Steve Benjamin, who heads the White House Office of Public Engagement, met with a small group of Morehouse students and faculty this month following a push from the school’s leadership for “direct engagement” from the White House.
During the meeting, some students expressed concerns about Biden overshadowing their graduation, while others implored Benjamin to ensure Biden’s speech doesn’t double as a campaign stump speech — frustrated with the idea of the commencement address being a vehicle for Biden to bolster support among Black voters.
That sentiment was shared by other Morehouse students critical of Biden’s visit.
“I don’t think it’s a coincidence that he only accepted the invitation after Trump was already in [Atlanta’s] West End, trying to make gains and failing to make gains with our students here,” Morehouse student Malik Poole said at a campus protest ahead of Biden’s visit. “And this is coming at a time where voters of color are fleeing from Biden at record pace.”
But still, Biden’s Morehouse visit came amid a concerted effort by his administration and campaign in the past week to sharpen his message to Black voters .
On Thursday, Biden met with plaintiffs and their family members from the historic Brown v. Board of Education case. The following day, he met with leaders of the Divine Nine, a group of historically Black sororities and fraternities, alongside Vice President Kamala Harris, a member of the Alpha Kappa Alpha sorority herself. During his trip to Georgia, Biden attended an event Saturday focused on engaging Black voters. And following his commencement address, Biden will close out the weekend by delivering the keynote address at the NAACP Freedom Fund dinner in Detroit, where he plans to tout his administration’s accomplishments for Black Americans.
As data suggests that Black voters — particularly young Black voters — are souring on Biden, some at Morehouse recognized the “opportunity” Biden had to make his case to members of that voting bloc during his address.
“If you want ... these students to vote in the fall for you, you have to give them something that shows that you are hearing them,” Dunn said. “That you are trying to do something we haven’t heard about. This is the opportunity.”
Nnamdi Egwuonwu is a 2024 NBC News campaign embed.
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
N.F.L. Player Draws Rebukes (and Trolling) for Graduation Speech
Kansas City’s Harrison Butker quoted Taylor Swift lyrics while telling men to be “unapologetic in your masculinity” and women to focus on being homemakers.

By Scott Cacciola and Benjamin Hoffman
Harrison Butker of the Kansas City Chiefs is one of the best place-kickers in the N.F.L. That is enough to make him somewhat famous in the football world, but players of his position aren’t typically known by more casual observers — unless they do something especially great or terrible on the field.
Last weekend, with the N.F.L. solidly in its off-season, Mr. Butker found himself at the center of a great deal of vitriol on social media, and it had nothing to do with his job.
On Saturday, Mr. Butker delivered a 20-minute commencement address to the graduates of Benedictine College, a conservative Catholic school in Atchison, Kan., about 50 miles northwest of Kansas City. He packed his speech full of conservative political discourse, railing against “degenerative cultural values and media.” He rebuked President Biden for his stance as a Catholic who supports abortion rights, and urged women to forgo careers so that they could support their husbands.
“I can tell you that my beautiful wife, Isabelle, would be the first to say that her life truly started when she began living her vocation as a wife and as a mother,” Mr. Butker said. “I’m on this stage today and able to be the man I am because I have a wife who leans into her vocation.”
He added: “It cannot be overstated that all of my success is made possible because a girl I met in band class back in middle school would convert to the faith, become my wife and embrace one of the most important titles of all: homemaker.”
Mr. Butker, who appeared to be choking up, was greeted by a round of applause that lasted for nearly 20 seconds before he was able to continue. At the end of his speech, the crowd gave him a standing ovation.
The reaction online, however, was not nearly as receptive, with his comments being picked apart by posters on TikTok, Instagram and X.
Team officials did not immediately respond to a request for comment, but the views Mr. Butker expressed prompted the N.F.L. to issue a statement saying the speech did not match the league’s values, and resulted in a rival team, the Los Angeles Chargers, trolling Mr. Butker on social media. More than 125,000 people, as of Thursday afternoon, had signed a petition on Change.org calling for Kansas City to cut ties with its star kicker.
Mr. Butker, 28, who describes himself as a devout Catholic, has won three Super Bowls with Kansas City since joining the team as a rookie in 2017. He converted all 11 of his field-goal attempts in the team’s most recent playoff run, and set a record for the longest field goal in Super Bowl history (57 yards) in the team’s championship-clinching victory over the San Francisco 49ers in February.
But on a team full of stars — Patrick Mahomes is widely considered the best quarterback in the N.F.L., and the team’s tight end, Travis Kelce, is among the best to ever play his position and is dating Taylor Swift — Mr. Butker had never really stood out. His speech on Saturday may have changed all that.
In the speech, Mr. Butker encouraged men to be “unapologetic in your masculinity,” referenced “the deadly sins” of homosexuality, and criticized Catholic priests for deriving “their happiness from the adulation they receive from their parishioners.” In attempting to drive home his point, Mr. Butker invoked lyrics from Ms. Swift’s song “ Bejeweled ” without mentioning her or Mr. Kelce by name.
“This undue familiarity will prove to be problematic every time,” Mr. Butker said, “because as my teammate’s girlfriend says, ‘familiarity breeds contempt.’”
Quoting Ms. Swift’s lyrics in such a speech was unusual, considering her status as an entertainment mogul who speaks frequently of empowering women and is believed to have a net worth of more than $1 billion .
Mr. Butker had also weighed in on Ms. Swift earlier this year, in an interview with the Eternal Word Television Network, describing her as “so humble and so gracious.” He added, in a nod to the values he discussed in Saturday’s speech, that he hoped that she and Mr. Kelce would “get married and start a family.”
The views expressed during Mr. Butker’s commencement speech at Benedictine drew swift condemnation. Justice Horn, a former Kansas City commissioner, wrote : “Harrison Butker doesn’t represent Kansas City nor has he ever. Kansas City has always been a place that welcomes, affirms and embraces our LGBTQ+ community members.”
Jessica Valenti, a feminist author, addressed the speech in her “Abortion, Every Day” newsletter , saying “So let’s be very clear about this commencement speech: Butker’s remarks weren’t ‘fringe’ or radical — they’re the law. He was simply saying out loud what Republicans have already codified: that women’s role in this country is to bear children and support men, who are the actual stars of the show.” She said bans on abortion, like the ones Mr. Butker is advocating, are “the embodiment of the smallest men’s biggest wishes.”
The N.F.L.’s response was to issue a statement from Jonathan Beane, the league’s chief diversity and inclusion officer, in which he said that Mr. Butker’s “views are not those of the N.F.L. as an organization. The N.F.L. is steadfast in our commitment to inclusion, which only makes our league stronger.”
The Chargers, a rival team of the Chiefs, went a step beyond that, poking fun at Mr. Butker during a video announcing the team’s 2024 schedule. In the video, a Sims character with a striking resemblance to Mr. Butker was shown working in the kitchen.
As the week has unfolded, the discussion of Mr. Butker has expanded to looking into other aspects of his life. Among the details discussed by many on social media: Despite his stance on women in the workplace, his mother, Elizabeth Keller Butker, has a distinguished career. She is a medical physicist in the department of radiation oncology at the Emory University School of Medicine in Atlanta.
Scott Cacciola writes features and profiles of people in the worlds of sports and entertainment for the Styles section of The Times. More about Scott Cacciola
Benjamin Hoffman is a senior editor who writes, assigns and edits stories primarily on the intersection between sports, lifestyle and culture. More about Benjamin Hoffman
Inside the World of Sports
Dive deeper into the people, issues and trends shaping professional, collegiate and amateur athletics..
Testing the W.N.B.A.’s TV Limits: The docuseries “Full Court Press” closely tracked college stars like Caitlin Clark and Kamilla Cardoso. Fans who want to follow elite W.N.B.A. rookies could have a tougher time .
Competing for Olympic Spots: Two friends had run side by side for more than 10,000 miles. Both vied for a place in the marathon at the Paris Games .
Captivating New York: It has been 50 years since the Knicks last won the N.B.A. championship. Now, a freshly promising team has enthralled the city .
Americanizing English Soccer: U.S. investors are gobbling up the storied teams of the English Premier League — and changing the stadium experience in ways that soccer fans resent.
Wild World of Sports: Surprisingly often, animals show up uninvited at sporting events. Sometimes, it gets a little weird .
VCU students walk out of commencement during Youngkin address
VCU students who walked out said they were demonstrating support for Palestinians and protesting some of the Republican governor’s crusade against efforts to promote racial equity in education.
RICHMOND — Dozens of Virginia Commonwealth University students walked out of their graduation ceremony Saturday morning as Gov. Glenn Youngkin delivered the commencement address, demonstrating support for Palestinians and protesting some of the Republican’s crusade against efforts to promote racial equity in education.
The selection of Youngkin as speaker drew criticism from some ahead of the ceremony. The university’s chapter of the NAACP this week urged VCU officials to rescind the invitation, and some students in recent days said they would hold a walkout during the ceremony.
College protests over Gaza war

On Saturday, attendees at the commencement were given cards congratulating the graduating class but warning that anyone who disrupted the ceremony was subject to removal.
As Youngkin began his speech, dozens of the graduates in attendance filed out of the Greater Richmond Convention Center, mostly in silence, some holding kaffiyeh scarves and signs aloft. “Teach Black history,” one read. “Book bans [do not equal] respect for learning,” read another.
The protest did not disrupt the program, though an initial burst of applause for the protesters briefly drowned out the governor’s speech. Youngkin pressed on with his address, which included a tribute to his late mother and an extended symphony metaphor.
“The world needs your music,” he said.
Spokesmen for VCU and the governor’s office declined to comment on the walkout.
More than 4,700 VCU students graduated this spring, about 3,000 of them undergraduates. It is a diverse student body, representing 40 countries. More than 900 were first-generation college students, VCU said ahead of the ceremony.
Adding to tensions on Saturday, the ceremony came about two weeks after police used pepper spray to disperse a crowd at a pro-Palestinian demonstration on VCU’s campus. Thirteen people, including six students, were arrested.
The event was among the demonstrations spreading on college campuses around the country, with more than 2,800 arrested as campus officials and protesters facing off in recent weeks. In Virginia, more than 80 people were arrested at Virginia Tech in Blacksburg , a dozen at the University of Mary Washington in Fredericksburg and more than 25 at the University of Virginia .
VCU, in downtown Richmond just a mile west of the state Capitol, has a long tradition of hosting the sitting governor as commencement speaker. Terry McAuliffe (D) gave the address in 2015, as did Robert F. McDonnell (R) in 2011, Tim Kaine (D) in 2008, Mark R. Warner (D) in 2004, Jim Gilmore (R) in 1999 and George Allen (R) in 1997, according to the university.
The VCU chapter of the NAACP sent a letter to university President Michael Rao and the board of visitors Wednesday demanding that the university revoke the governor’s invitation to speak. “Since becoming Governor of Virginia, Youngkin has worked to intimidate and silence educators with anti-racist pedagogies,” the letter stated, citing a short-lived tip line for parents to report the teaching of “divisive concepts” and the reversal of protections for transgender youth.
Asked about the calls to cancel his appearance, Youngkin said Tuesday he hoped the focus would be on the students and their achievements. “I think that anyone who thinks they’re going to disrupt this for their own personal goals, I think it’s misguided,” Youngkin told reporters at an event in Richmond. “Let’s celebrate the students. Let’s honor the students.”
Opposition to Youngkin was due, in part, to the governor’s objections to a proposal to require VCU students to take a course in racial literacy. The school conceived the plan amid the racial reckoning that followed the 2020 murder of George Floyd by Minneapolis police and was still working to implement it when Youngkin raised concerns early this year.
In March, a Youngkin spokesman said the governor was concerned that such a mandate would promote leftist “groupthink.” “Virginia’s public institutions should be teaching our students how to think, not what to think and not advancing ideological conformity,” spokesman Christian Martinez told Virginia Public Media .
On Friday, VCU’s governing board voted against requiring the racial literacy course, but will still make some courses available for interested students.
“Central to the board’s deliberations was a commitment to upholding academic freedom while empowering students with flexibility and autonomy in their educational journey,” VCU said in a written statement after the vote. “The discussion clearly expressed support for the racial literacy classes, and these courses are accessible to students who wish to explore them.”
Outside the convention center, Taya Coates, a mass communications graduate, said she was on the fence about walking out until the students around her started to rise. She decided that she, too, wanted to stand against the governor, who she said didn’t reflect her values.
“It just doesn’t represent our university,” Coates, 23, said of Youngkin’s appearance. Around her, friends embraced and cried. Families cheered for their graduates, posing for photos and remarking about how proud they were of the display.
A smaller group of graduates joined a group of demonstrators outside the convention center. The group marched through the streets chanting “Free Palestine” until they reached Abner Clay Park, about a half mile from the commencement ceremony.
A handful of graduates, still in their caps and gowns, spoke about why they walked out.
Arrington Evans, a political science graduate and member of the NAACP at VCU, said the governor’s actions, particularly his opposition to equity initiatives in education, was in opposition to the kind of work she had been advocating for at VCU.
“This matters more to me, doing right by your classmates and the people in your community, than sitting there doing nothing,” Evans said. “Actions speak louder than words. And that’s what this was.”
In his speech, Youngkin did not acknowledge the protest or make any reference to the politically strife moment. He highlighted some members of the graduating class, including an immigrant from Uganda and another who had overcome cancer. Youngkin advised graduates to “make tomorrow better than today,” choose their “life partner” wisely and be slow to anger.
Before the walkout, Saturday’s graduation began like any other, with robed and smiling graduates waving to relatives and snapping selfies as they marched into the ceremony.
The ceremony wrapped in ordinary fashion two hours later, with black and gold balloons dropping from the ceiling and getting batted around like beach balls.
The walkout was for many a forgettable blip in an otherwise celebratory day. That was a relief to attendees who’d arrived wary of potential disruptions or even violence.
“I’m just hoping that doesn’t happen and we can be here and celebrate these graduates in peace,” LaKeyda Robinson, 45, of Alexandria, said as she watched her “firstborn niece,” Dhasia Allen, walk into the ceremony.
Marcos Chavez, a 54-year-old Bolivian immigrant who works as carpenter in Herndon, was not giving a thought to Gaza or Youngkin. For him, the day was all about his daughter, Natalia. Already the first person in the family to earn a college degree, on Saturday she graduated from VCU’s school of dentistry.
“Right now my focus is on my daughter,” he said. “That’s it.”


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Time Expressions with Reported Speech Sometimes when we change direct speech into reported speech we have to change time expressions too. We don't always have to do this, however. It depends on when we heard the direct speech and when we say the reported speech. For example: It's Monday. Julie says "I'm leaving today".
Reported speech - English Grammar Today - a reference to written and spoken English grammar and usage - Cambridge Dictionary
The four types of reported speech are similar to the kinds of sentences: imperative, interrogative, exclamatory, and declarative. Reported Speech Rules. The rules for reported speech can be complex. But with enough practice, you'll be able to master them all. Choose Whether to Use That or If. The most common conjunction in reported speech is ...
Reported speech: He asked if he would see me later. In the direct speech example you can see the modal verb 'will' being used to ask a question. Notice how in reported speech the modal verb 'will' and the reporting verb 'ask' are both written in the past tense. So, 'will' becomes 'would' and 'ask' becomes 'asked'.
Reported speech is the form in which one can convey a message said by oneself or someone else, mostly in the past. It can also be said to be the third person view of what someone has said. In this form of speech, you need not use quotation marks as you are not quoting the exact words spoken by the speaker, but just conveying the message. Q2.
👉 Quiz 1 / Quiz 2. Advanced Grammar Course. What is reported speech? "Reported speech" is when we talk about what somebody else said - for example: Direct Speech: "I've been to London three times." Reported Speech: She said she'd been to London three times. There are a lot of tricky little details to remember, but don't worry, I'll explain them and we'll see lots of ...
Reported speech is called "indirect speech" by some people. Other people regard reported speech simply as one form of indirect speech. Other forms are, for example: questions-within-questions: Can you tell me if they are expensive? mental processes: He believes that politics is a dirty game.
Yes, and you report it with a reporting verb. He said he wanted to know about reported speech. I said, I want and you changed it to he wanted. Exactly. Verbs in the present simple change to the past simple; the present continuous changes to the past continuous; the present perfect changes to the past perfect; can changes to could; will changes ...
Exercises on Reported Speech. If we report what another person has said, we usually do not use the speaker's exact words (direct speech), but reported (indirect) speech. Therefore, you need to learn how to transform direct speech into reported speech. The structure is a little different depending on whether you want to transform a statement ...
Reported speech: He said he would meet me at the park the next day. In this example, the present tense "will" is changed to the past tense "would." 3. Change reporting verbs: In reported speech, you can use different reporting verbs such as "say," "tell," "ask," or "inquire" depending on the context of the speech.
Introduction. In English grammar, we use reported speech to say what another person has said. We can use their exact words with quotation marks, this is known as direct speech, or we can use indirect speech. In indirect speech, we change the tense and pronouns to show that some time has passed. Indirect speech is often introduced by a reporting ...
March 29, 2024. Reported speech (Indirect Speech) is how we represent the speech of other people or what we ourselves say. Reported Speech focuses more on the content of what someone said rather than their exact words. The structure of the independent clause depends on whether the speaker is reporting a statement, a question, or a command.
What is indirect speech or reported speech? When we tell people what another person said or thought, we often use reported speech or indirect speech. To do that, we need to change verb tenses (present, past, etc.) and pronouns (I, you, my, your, etc.) if the time and speaker are different.For example, present tenses become past, I becomes he or she, and my becomes his or her, etc.
Reported speech, also known as indirect speech, is a way of communicating what someone else has said without quoting their exact words. For example, if your friend said, "I am going to the store," in reported speech, you might convey this as, "My friend said he was going to the store." Reported speech is common in both spoken and written language, especially in storytelling, news ...
Formula of Reported Speech. The formula for reported speech involves transforming direct speech into an indirect form while maintaining the meaning of the original statement. In general, the formula includes: Choosing an appropriate reporting verb (e.g., say, tell, mention, explain). Changing pronouns and time expressions if necessary.
Reported speech: She said she was going to the store then. In this example, the pronoun "I" is changed to "she" and the adverb "now" is changed to "then.". 2. Change the tense: In reported speech, you usually need to change the tense of the verb to reflect the change from direct to indirect speech. Here's an example:
Biden's speech at Morehouse comes with intense scrutiny as many presidential horse race polls show the president lagging with young voters, Black voters and other nonwhite groups that helped ...
Harrison Butker is a three-time Super Bowl champion and one of the most accurate field-goal kickers in NFL history. As such, the Kansas City Chiefs kicker was given a platform to express his views ...
Reported speech - English Grammar Today - a reference to written and spoken English grammar and usage - Cambridge Dictionary
Reported speech: indirect speech - English Grammar Today - a reference to written and spoken English grammar and usage - Cambridge Dictionary
Eddie Vedder Calls Harrison Butker a 'F—ing P—y' Mid-Concert Over Sexist Speech: 'There's Nothing More Masculine Than a Strong Man Supporting a Strong Woman'. Pearl Jam played the ...
House GOP Conference Chair Elise Stefanik delivered remarks at the Israeli Knesset Sunday, saying victory for Israel in the war against Hamas starts with "wiping" those responsible for the ...
Biden's speech at Morehouse came against the backdrop of protests on college campuses nationwide over his handling over the war in Gaza, with many students and faculty members voicing opposition ...
N.F.L. Player Draws Rebukes (and Trolling) for Graduation Speech. Kansas City's Harrison Butker quoted Taylor Swift lyrics while telling men to be "unapologetic in your masculinity" and ...
When Governor Glenn Youngkin (R-Va.) began his speech at Virginia Commonwealth University's commencement, graduates walked out in protest. (Video: The Washington Post) More than 4,700 VCU students ...