- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to content

- Home – AI for Research


The Ultimate Guide to Case Study Analysis
Welcome to a comprehensive exploration of the realm where real-world scenarios meet analytical prowess. In academia and business, the art of dissecting situations, identifying key issues, and formulating strategic recommendations is paramount. This guide is designed to equip you with the skills needed to navigate the complexities of case study analysis effectively. Whether you are a student honing your problem-solving abilities or a professional seeking to enhance your decision-making skills, this resource is tailored to meet your requirements. Through practical advice, real-life examples, and expert perspectives, you will gain the expertise to extract valuable insights from cases and apply them in various contexts. Prepare to embark on a journey that will elevate your analytical thinking and empower you to make informed decisions. Let’s delve into the world of analytical exploration together!
Key Steps in Conducting a Case Study Analysis
Case studies are an integral part of various academic and professional fields, providing a detailed examination of a particular subject. Conducting a case study analysis involves several key steps that help in understanding the complexities of the case and deriving meaningful insights. Here are the essential steps to effectively conduct a case study analysis:.
Preparing for Analysis: The first step in conducting a case study analysis is to thoroughly read and understand the case study. Identify the key stakeholders, relevant facts, and any other pertinent information that will aid in the analysis. It is essential to create a timeline of events and gather all necessary data to ensure a comprehensive understanding of the case.
Identifying Key Problems and Issues: Once you have a good grasp of the case study, identify the main problems or issues that the subject is facing. This step involves critically analyzing the information presented and determining the root causes of the problems. Conduct interviews, surveys, or additional research to delve deeper into the identified issues and gain multiple perspectives.
Formulating a Thesis Statement: Based on the identified problems, formulate a clear and concise thesis statement that summarizes the main issue or challenge faced by the subject of the case study. The thesis statement will guide the rest of your analysis. Ensure that your thesis statement is specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) to effectively address the problem.
Recommendations and Further Actions: After analyzing the case study and developing a thesis statement, it is crucial to provide recommendations and suggest further actions that can address the identified problems. These recommendations should be practical, feasible, and supported by evidence from the case study. Consider the implications of your recommendations and propose a detailed action plan with clear steps and responsibilities.
Implementation and Evaluation: Once recommendations are made, focus on the implementation phase. Develop a monitoring and evaluation plan to track the progress of the proposed solutions. Regularly assess the outcomes and make adjustments as needed to ensure the effectiveness of the implemented strategies.
By following these key steps in conducting a case study analysis, you can effectively analyze complex cases, draw meaningful conclusions, and propose actionable recommendations for addressing the issues at hand. Remember, a well-executed case study analysis can provide valuable insights and contribute to informed decision-making processes.
Writing a Comprehensive Case Study Analysis
Case studies are an essential tool for understanding real-world scenarios and applying theoretical knowledge to practical situations. A well-crafted case study analysis can provide valuable insights and recommendations for businesses, organizations, and individuals. To ensure that your case study analysis is thorough and effective, consider the following points:.
Structuring Your Analysis: Begin by outlining the key issues or problems presented in the case study. Identify the main stakeholders involved and their interests. Then, develop a logical structure for your analysis, including an introduction, background information, analysis of key issues, recommendations, and a conclusion.
Incorporating Supporting Evidence: Back up your analysis with relevant data, facts, and examples from the case study. Use charts, graphs, and other visual aids to illustrate your points. Make sure to cite your sources properly and provide a clear rationale for your conclusions.
Proofreading and Editing: Before finalizing your case study analysis, review it carefully for errors in grammar, punctuation, and spelling. Ensure that your writing is clear, concise, and free of jargon. Consider seeking feedback from peers or mentors to improve the quality of your analysis.
In addition to the above points, it is crucial to delve deeper into the case study context. Understand the industry trends, competitive landscape, and any external factors that may influence the situation. Conduct a SWOT analysis to identify strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats relevant to the case. This strategic analysis can provide a holistic view and help in formulating more robust recommendations.
Furthermore, consider the ethical implications of the decisions proposed in your analysis. Evaluate the potential impact on various stakeholders, including employees, customers, and the community. Addressing ethical considerations demonstrates a comprehensive understanding of the case study and showcases your commitment to responsible decision-making.
Lastly, consider the implementation aspects of your recommendations. Outline a detailed action plan with clear steps, responsibilities, and timelines. Discuss potential challenges that may arise during implementation and propose mitigation strategies to ensure successful execution.
By incorporating these additional elements into your case study analysis, you can elevate the depth and quality of your insights, making your analysis a valuable resource for strategic planning and problem-solving.
Enhancing Your Case Study Analysis
When it comes to conducting a case study analysis, there are various strategies that can be employed to enhance the quality and effectiveness of the study. Two key approaches that can significantly improve your case study analysis are utilizing templates for structuring your case studies and incorporating visual elements to increase reader engagement.
Utilizing Templates for Effective Case Studies:
Templates can serve as a valuable tool in organizing and presenting your case study in a clear and structured manner. By using a template, you can ensure that all essential components of the case study are included, such as the background information, problem statement, methodology, results, and conclusions. Templates can also help maintain consistency across multiple case studies, making it easier for readers to navigate and understand the content.
Incorporating Visual Elements for Engagement:
In addition to well-structured content, incorporating visual elements can greatly enhance the engagement level of your case study. Visual elements such as charts, graphs, images, and infographics can help break down complex information into more digestible formats, making it easier for readers to grasp key insights and findings. Visuals can also make your case study more visually appealing and memorable, increasing the likelihood of reader retention and understanding.
Moreover, when incorporating visual elements, it is essential to ensure that they are relevant and complement the textual content. Visual aids should not only enhance understanding but also add value by providing additional context or highlighting critical points within the case study.
Furthermore, consider the target audience when selecting visual elements. Different types of visuals may resonate better with specific audiences. For instance, a business-oriented audience might prefer data-driven charts and graphs, while a more general audience might respond better to illustrative images or real-life examples.
Additionally, interactive elements such as clickable graphics or embedded multimedia can further enhance reader engagement and interactivity with the case study content. These interactive features can create a more immersive experience for the audience, allowing them to explore the information in a more dynamic and personalized way.
By incorporating a combination of well-structured templates, relevant visual elements, and interactive features, you can not only improve the overall quality of your case study analysis but also create a more engaging and impactful experience for your audience.
Citing Sources and Appendices
When writing any academic or research-based content, it is crucial to properly cite all external sources used in your work. This not only gives credit to the original authors but also helps readers locate the sources for further reference. There are various citation styles that one can follow, such as APA (American Psychological Association), MLA (Modern Language Association), or Harvard style. Each style has its own set of rules regarding how to cite different types of sources like books, journals, websites, etc. It is essential to be consistent in applying the chosen citation style throughout the document.
In addition to citing external sources, including appendices can also enhance the quality and credibility of your work
Appendices are used to provide supplementary information that is not essential to the main text but can offer valuable context or data. This could include raw data, detailed technical information, questionnaires used in research, or any additional material that supports the main content of the document. When including appendices, it is important to clearly label each one and refer to them within the main text when necessary. This ensures that readers can easily navigate through the document and access the supplementary information as needed.
Referencing External Sources
When citing external sources, it is important to follow the guidelines of the chosen citation style. In addition to the basic information like author name, publication year, and title, some citation styles may require additional details such as page numbers, URLs, or DOI (Digital Object Identifier). It is crucial to accurately record these details to provide a complete and accurate reference.
Using Citation Styles like APA, MLA, or Harvard
Each citation style has its own unique format for citing sources. For example, in APA style, in-text citations typically include the author’s last name and the publication year, while MLA style uses the author’s last name and page number. Understanding the specific requirements of each style is essential to ensure proper citation throughout the document.
Including Appendices for Original Data
Appendices are a valuable tool for including supplementary information that supports the main content of your work. When including original data in an appendix, it is important to present the information in a clear and organized manner. This could involve creating tables, charts, or graphs to present the data visually, along with a brief explanation to help readers interpret the information effectively.
Overall, citing external sources and including appendices are essential components of academic and research writing. By following the guidelines of the chosen citation style and providing relevant supplementary information in the appendices, you can enhance the credibility and clarity of your work.
Mastering the art of case study analysis is a valuable skill that can greatly benefit students and professionals alike. By following the steps outlined in this guide, individuals can enhance their critical thinking abilities and problem-solving skills. Additionally, honing the ability to dissect and analyze case studies effectively can lead to improved decision-making and strategic planning in various fields. For further guidance on crafting concise and engaging summaries of research studies, check out the detailed tips provided in the article ‘How to Write a Scientific Abstract’ at Avidnote . Strengthen your academic writing skills and enhance your research capabilities today!.
Privacy Overview
Adding {{itemName}} to cart
Added {{itemName}} to cart

How to Write a Case Study: The Compelling Step-by-Step Guide

Is there a poignant pain point that needs to be addressed in your company or industry? Do you have a possible solution but want to test your theory? Why not turn this drive into a transformative learning experience and an opportunity to produce a high-quality business case study? However, before that occurs, you may wonder how to write a case study.
You may also be thinking about why you should produce one at all. Did you know that case studies are impactful and the fifth most used type of content in marketing , despite being more resource-intensive to produce?
Below, we’ll delve into what a case study is, its benefits, and how to approach business case study writing:
Definition of a Written case study and its Purpose
A case study is a research method that involves a detailed and comprehensive examination of a specific real-life situation. It’s often used in various fields, including business, education, economics, and sociology, to understand a complex issue better.
It typically includes an in-depth analysis of the subject and an examination of its context and background information, incorporating data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and existing literature.
The ultimate aim is to provide a rich and detailed account of a situation to identify patterns and relationships, generate new insights and understanding, illustrate theories, or test hypotheses.
Importance of Business Case Study Writing
As such an in-depth exploration into a subject with potentially far-reaching consequences, a case study has benefits to offer various stakeholders in the organisation leading it.
- Business Founders: Use business case study writing to highlight real-life examples of companies or individuals who have benefited from their products or services, providing potential customers with a tangible demonstration of the value their business can bring. It can be effective for attracting new clients or investors by showcasing thought leadership and building trust and credibility.
- Marketers through case studies and encourage them to take action: Marketers use a case studies writer to showcase the success of a particular product, service, or marketing campaign. They can use persuasive storytelling to engage the reader, whether it’s consumers, clients, or potential partners.
- Researchers: They allow researchers to gain insight into real-world scenarios, explore a variety of perspectives, and develop a nuanced understanding of the factors that contribute to success or failure. Additionally, case studies provide practical business recommendations and help build a body of knowledge in a particular field.
How to Write a Case Study – The Key Elements

Considering how to write a case study can seem overwhelming at first. However, looking at it in terms of its constituent parts will help you to get started, focus on the key issue(s), and execute it efficiently and effectively.
Problem or Challenge Statement
A problem statement concisely describes a specific issue or problem that a written case study aims to address. It sets the stage for the rest of the case study and provides context for the reader.
Here are some steps to help you write a case study problem statement:
- Identify the problem or issue that the case study will focus on.
- Research the problem to better understand its context, causes, and effects.
- Define the problem clearly and concisely. Be specific and avoid generalisations.
- State the significance of the problem: Explain why the issue is worth solving. Consider the impact it has on the individual, organisation, or industry.
- Provide background information that will help the reader understand the context of the problem.
- Keep it concise: A problem statement should be brief and to the point. Avoid going into too much detail – leave this for the body of the case study!
Here is an example of a problem statement for a case study:
“ The XYZ Company is facing a problem with declining sales and increasing customer complaints. Despite improving the customer experience, the company has yet to reverse the trend . This case study will examine the causes of the problem and propose solutions to improve sales and customer satisfaction. “
Solutions and interventions

Business case study writing provides a solution or intervention that identifies the best course of action to address the problem or issue described in the problem statement.
Here are some steps to help you write a case study solution or intervention:
- Identify the objective , which should be directly related to the problem statement.
- Analyse the data, which could include data from interviews, observations, and existing literature.
- Evaluate alternatives that have been proposed or implemented in similar situations, considering their strengths, weaknesses, and impact.
- Choose the best solution based on the objective and data analysis. Remember to consider factors such as feasibility, cost, and potential impact.
- Justify the solution by explaining how it addresses the problem and why it’s the best solution with supportive evidence.
- Provide a detailed, step-by-step plan of action that considers the resources required, timeline, and expected outcomes.
Example of a solution or intervention for a case study:
“ To address the problem of declining sales and increasing customer complaints at the XYZ Company, we propose a comprehensive customer experience improvement program. “
“ This program will involve the following steps:
- Conducting customer surveys to gather feedback and identify areas for improvement
- Implementing training programs for employees to improve customer service skills
- Revising the company’s product offerings to meet customer needs better
- Implementing a customer loyalty program to encourage repeat business “
“ These steps will improve customer satisfaction and increase sales. We expect a 10% increase in sales within the first year of implementation, based on similar programs implemented by other companies in the industry. “
Possible Results and outcomes

Writing case study results and outcomes involves presenting the impact of the proposed solution or intervention.
Here are some steps to help you write case study results and outcomes:
- Evaluate the solution by measuring its effectiveness in addressing the problem statement. That could involve collecting data, conducting surveys, or monitoring key performance indicators.
- Present the results clearly and concisely, using graphs, charts, and tables to represent the data where applicable visually. Be sure to include both quantitative and qualitative results.
- Compare the results to the expectations set in the solution or intervention section. Explain any discrepancies and why they occurred.
- Discuss the outcomes and impact of the solution, considering the benefits and drawbacks and what lessons can be learned.
- Provide recommendations for future action based on the results. For example, what changes should be made to improve the solution, or what additional steps should be taken?
Example of results and outcomes for a case study:
“ The customer experience improvement program implemented at the XYZ Company was successful. We found significant improvement in employee health and productivity. The program, which included on-site exercise classes and healthy food options, led to a 25% decrease in employee absenteeism and a 15% increase in productivity . “
“ Employee satisfaction with the program was high, with 90% reporting an improved work-life balance. Despite initial costs, the program proved to be cost-effective in the long run, with decreased healthcare costs and increased employee retention. The company plans to continue the program and explore expanding it to other offices .”
Case Study Key takeaways

Key takeaways are the most important and relevant insights and lessons that can be drawn from a case study. Key takeaways can help readers understand the most significant outcomes and impacts of the solution or intervention.
Here are some steps to help you write case study key takeaways:
- Summarise the problem that was addressed and the solution that was proposed.
- Highlight the most significant results from the case study.
- Identify the key insights and lessons , including what makes the case study unique and relevant to others.
- Consider the broader implications of the outcomes for the industry or field.
- Present the key takeaways clearly and concisely , using bullet points or a list format to make the information easy to understand.
Example of key takeaways for a case study:
- The customer experience improvement program at XYZ Company successfully increased customer satisfaction and sales.
- Employee training and product development were critical components of the program’s success.
- The program resulted in a 20% increase in repeat business, demonstrating the value of a customer loyalty program.
- Despite some initial challenges, the program proved cost-effective in the long run.
- The case study results demonstrate the importance of investing in customer experience to improve business outcomes.
Steps for a Case Study Writer to Follow

If you still feel lost, the good news is as a case studies writer; there is a blueprint you can follow to complete your work. It may be helpful at first to proceed step-by-step and let your research and analysis guide the process:
- Select a suitable case study subject: Ask yourself what the purpose of the business case study is. Is it to illustrate a specific problem and solution, showcase a success story, or demonstrate best practices in a particular field? Based on this, you can select a suitable subject by researching and evaluating various options.
- Research and gather information: We have already covered this in detail above. However, always ensure all data is relevant, valid, and comes from credible sources. Research is the crux of your written case study, and you can’t compromise on its quality.
- Develop a clear and concise problem statement: Follow the guide above, and don’t rush to finalise it. It will set the tone and lay the foundation for the entire study.
- Detail the solution or intervention: Follow the steps above to detail your proposed solution or intervention.
- Present the results and outcomes: Remember that a case study is an unbiased test of how effectively a particular solution addresses an issue. Not all case studies are meant to end in a resounding success. You can often learn more from a loss than a win.
- Include key takeaways and conclusions: Follow the steps above to detail your proposed business case study solution or intervention.
Tips for How to Write a Case Study
Here are some bonus tips for how to write a case study. These tips will help improve the quality of your work and the impact it will have on readers:
- Use a storytelling format: Just because a case study is research-based doesn’t mean it has to be boring and detached. Telling a story will engage readers and help them better identify with the problem statement and see the value in the outcomes. Framing it as a narrative in a real-world context will make it more relatable and memorable.
- Include quotes and testimonials from stakeholders: This will add credibility and depth to your written case study. It also helps improve engagement and will give your written work an emotional impact.
- Use visuals and graphics to support your narrative: Humans are better at processing visually presented data than endless walls of black-on-white text. Visual aids will make it easier to grasp key concepts and make your case study more engaging and enjoyable. It breaks up the text and allows readers to identify key findings and highlights quickly.
- Edit and revise your case study for clarity and impact: As a long and involved project, it can be easy to lose your narrative while in the midst of it. Multiple rounds of editing are vital to ensure your narrative holds, that your message gets across, and that your spelling and grammar are correct, of course!
Our Final Thoughts
A written case study can be a powerful tool in your writing arsenal. It’s a great way to showcase your knowledge in a particular business vertical, industry, or situation. Not only is it an effective way to build authority and engage an audience, but also to explore an important problem and the possible solutions to it. It’s a win-win, even if the proposed solution doesn’t have the outcome you expect. So now that you know more about how to write a case study, try it or talk to us for further guidance.
Are you ready to write your own case study?
Begin by bookmarking this article, so you can come back to it. And for more writing advice and support, read our resource guides and blog content . If you are unsure, please reach out with questions, and we will provide the answers or assistance you need.
Categorised in: Resources
This post was written by Premier Prose
© 2024 Copyright Premier Prose. Website Designed by Ubie

- Privacy Overview
- Strictly Necessary Cookies
- Cookie Policy
This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
Strictly Necessary Cookie should be enabled at all times so that we can save your preferences for cookie settings.
If you disable this cookie, we will not be able to save your preferences. This means that every time you visit this website you will need to enable or disable cookies again.
More information about our Cookie Policy

- Research Process
What is a Problem Statement? [with examples]
- 5 minute read
Table of Contents
The statement of the problem is one of the first things that a colleague or potential client will read. With the vastness of the information available at one’s fingertips in the online9 world, your work may have just a few seconds to draw in a reader to take a deeper look at your proposal before moving on to the next option. It explains quickly to the reader, the problem at hand, the need for research, and how you intend to do it.
A strong, clear description of the problem that drew you to your research has to be straightforward, easy to read and, most important, relevant. Why do you care about this problem? How can solving this problem impact the world? The problem statement is your opportunity to explain why you care and what you propose to do in the way of researching the problem.
A problem statement is an explanation in research that describes the issue that is in need of study . What problem is the research attempting to address? Having a Problem Statement allows the reader to quickly understand the purpose and intent of the research. The importance of writing your research proposal cannot be stressed enough. Check for more information on Writing a Scientific Research Project Proposal .
It is expected to be brief and concise , and should not include the findings of the research or detailed data . The average length of a research statement is generally about one page . It is going to define the problem, which can be thought of as a gap in the information base. There may be several solutions to this gap or lack of information, but that is not the concern of the problem statement. Its purpose is to summarize the current information and where a lack of knowledge may be presenting a problem that needs to be investigated .
The purpose of the problem statement is to identify the issue that is a concern and focus it in a way that allows it to be studied in a systematic way . It defines the problem and proposes a way to research a solution, or demonstrates why further information is needed in order for a solution to become possible.
What is Included in a Problem Statement?
Besides identifying the gap of understanding or the weakness of necessary data, it is important to explain the significance of this lack.
-How will your research contribute to the existing knowledge base in your field of study?
-How is it significant?
-Why does it matter?
Not all problems have only one solution so demonstrating the need for additional research can also be included in your problem statement. Once you identify the problem and the need for a solution, or for further study, then you can show how you intend to collect the needed data and present it.
How to Write a Statement of Problem in Research Proposal
It is helpful to begin with your goal. What do you see as the achievable goal if the problem you outline is solved? How will the proposed research theoretically change anything? What are the potential outcomes?
Then you can discuss how the problem prevents the ability to reach your realistic and achievable solution. It is what stands in the way of changing an issue for the better. Talk about the present state of affairs and how the problem impacts a person’s life, for example.
It’s helpful at this point to generally layout the present knowledge and understanding of the subject at hand, before then describing the gaps of knowledge that are currently in need of study. Your problem statement is a proposed solution to address one of these gaps.
A good problem statement will also layout the repercussions of leaving the problem as it currently stands. What is the significance of not addressing this problem? What are the possible future outcomes?
Example of Problem Statement in Research Proposal
If, for example , you intended to research the effect of vitamin D supplementation on the immune system , you would begin with a review of the current knowledge of vitamin D’s known function in relation to the immune system and how a deficiency of it impacts a person’s defenses.
You would describe the ideal environment in the body when there is a sufficient level of vitamin D. Then, begin to identify the problems associated with vitamin D deficiency and the difficulty of raising the level through supplementation, along with the consequences of that deficiency. Here you are beginning to identify the problem of a common deficiency and the current difficulty of increasing the level of vitamin D in the blood.
At this stage, you may begin to identify the problem and narrow it down in a way that is practical to a research project. Perhaps you are proposing a novel way of introducing Vitamin D in a way that allows for better absorption by the gut, or in a combination with another product that increases its level in the blood.
Describe the way your research in this area will contribute to the knowledge base on how to increase levels of vitamin D in a specific group of subjects, perhaps menopausal women with breast cancer. The research proposal is then described in practical terms.
How to write a problem statement in research?
Problem statements differ depending on the type and topic of research and vary between a few sentences to a few paragraphs.
However, the problem statement should not drag on needlessly. Despite the absence of a fixed format, a good research problem statement usually consists of three main parts:
Context: This section explains the background for your research. It identifies the problem and describes an ideal scenario that could exist in the absence of the problem. It also includes any past attempts and shortcomings at solving the problem.
Significance: This section defines how the problem prevents the ideal scenario from being achieved, including its negative impacts on the society or field of research. It should include who will be the most affected by a solution to the problem, the relevance of the study that you are proposing, and how it can contribute to the existing body of research.
Solution: This section describes the aim and objectives of your research, and your solution to overcome the problem. Finally, it need not focus on the perfect solution, but rather on addressing a realistic goal to move closer to the ideal scenario.
Here is a cheat sheet to help you with formulating a good problem statement.
1. Begin with a clear indication that the problem statement is going to be discussed next. You can start with a generic sentence like, “The problem that this study addresses…” This will inform your readers of what to expect next.
2. Next, mention the consequences of not solving the problem . You can touch upon who is or will be affected if the problem continues, and how.
3. Conclude with indicating the type of research /information that is needed to solve the problem. Be sure to reference authors who may have suggested the necessity of such research.
This will then directly lead to your proposed research objective and workplan and how that is expected to solve the problem i.e., close the research gap.
Language Editing Plus
Elsevier Language Editing Plus service will provide you with a thorough language review of your thesis, article or presentation. It offers review of logic and flow, reference checks, document formatting, a customized cover letter and more.

- Manuscript Preparation
What is and How to Write a Good Hypothesis in Research?

How to Use Tables and Figures effectively in Research Papers
You may also like.

Descriptive Research Design and Its Myriad Uses

Five Common Mistakes to Avoid When Writing a Biomedical Research Paper

Making Technical Writing in Environmental Engineering Accessible

To Err is Not Human: The Dangers of AI-assisted Academic Writing

When Data Speak, Listen: Importance of Data Collection and Analysis Methods

Choosing the Right Research Methodology: A Guide for Researchers

Why is data validation important in research?

Writing a good review article
Input your search keywords and press Enter.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- Case Study | Definition, Examples & Methods
Case Study | Definition, Examples & Methods
Published on 5 May 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 30 January 2023.
A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organisation, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research.
A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods , but quantitative methods are sometimes also used. Case studies are good for describing , comparing, evaluating, and understanding different aspects of a research problem .
Table of contents
When to do a case study, step 1: select a case, step 2: build a theoretical framework, step 3: collect your data, step 4: describe and analyse the case.
A case study is an appropriate research design when you want to gain concrete, contextual, in-depth knowledge about a specific real-world subject. It allows you to explore the key characteristics, meanings, and implications of the case.
Case studies are often a good choice in a thesis or dissertation . They keep your project focused and manageable when you don’t have the time or resources to do large-scale research.
You might use just one complex case study where you explore a single subject in depth, or conduct multiple case studies to compare and illuminate different aspects of your research problem.
| Research question | Case study |
|---|---|
| What are the ecological effects of wolf reintroduction? | Case study of wolf reintroduction in Yellowstone National Park in the US |
| How do populist politicians use narratives about history to gain support? | Case studies of Hungarian prime minister Viktor Orbán and US president Donald Trump |
| How can teachers implement active learning strategies in mixed-level classrooms? | Case study of a local school that promotes active learning |
| What are the main advantages and disadvantages of wind farms for rural communities? | Case studies of three rural wind farm development projects in different parts of the country |
| How are viral marketing strategies changing the relationship between companies and consumers? | Case study of the iPhone X marketing campaign |
| How do experiences of work in the gig economy differ by gender, race, and age? | Case studies of Deliveroo and Uber drivers in London |
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Once you have developed your problem statement and research questions , you should be ready to choose the specific case that you want to focus on. A good case study should have the potential to:
- Provide new or unexpected insights into the subject
- Challenge or complicate existing assumptions and theories
- Propose practical courses of action to resolve a problem
- Open up new directions for future research
Unlike quantitative or experimental research, a strong case study does not require a random or representative sample. In fact, case studies often deliberately focus on unusual, neglected, or outlying cases which may shed new light on the research problem.
If you find yourself aiming to simultaneously investigate and solve an issue, consider conducting action research . As its name suggests, action research conducts research and takes action at the same time, and is highly iterative and flexible.
However, you can also choose a more common or representative case to exemplify a particular category, experience, or phenomenon.
While case studies focus more on concrete details than general theories, they should usually have some connection with theory in the field. This way the case study is not just an isolated description, but is integrated into existing knowledge about the topic. It might aim to:
- Exemplify a theory by showing how it explains the case under investigation
- Expand on a theory by uncovering new concepts and ideas that need to be incorporated
- Challenge a theory by exploring an outlier case that doesn’t fit with established assumptions
To ensure that your analysis of the case has a solid academic grounding, you should conduct a literature review of sources related to the topic and develop a theoretical framework . This means identifying key concepts and theories to guide your analysis and interpretation.
There are many different research methods you can use to collect data on your subject. Case studies tend to focus on qualitative data using methods such as interviews, observations, and analysis of primary and secondary sources (e.g., newspaper articles, photographs, official records). Sometimes a case study will also collect quantitative data .
The aim is to gain as thorough an understanding as possible of the case and its context.
In writing up the case study, you need to bring together all the relevant aspects to give as complete a picture as possible of the subject.
How you report your findings depends on the type of research you are doing. Some case studies are structured like a standard scientific paper or thesis, with separate sections or chapters for the methods , results , and discussion .
Others are written in a more narrative style, aiming to explore the case from various angles and analyse its meanings and implications (for example, by using textual analysis or discourse analysis ).
In all cases, though, make sure to give contextual details about the case, connect it back to the literature and theory, and discuss how it fits into wider patterns or debates.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, January 30). Case Study | Definition, Examples & Methods. Scribbr. Retrieved 9 June 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/case-studies/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, correlational research | guide, design & examples, a quick guide to experimental design | 5 steps & examples, descriptive research design | definition, methods & examples.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- What Is a Case Study? | Definition, Examples & Methods
What Is a Case Study? | Definition, Examples & Methods
Published on May 8, 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on November 20, 2023.
A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research.
A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods , but quantitative methods are sometimes also used. Case studies are good for describing , comparing, evaluating and understanding different aspects of a research problem .
Table of contents
When to do a case study, step 1: select a case, step 2: build a theoretical framework, step 3: collect your data, step 4: describe and analyze the case, other interesting articles.
A case study is an appropriate research design when you want to gain concrete, contextual, in-depth knowledge about a specific real-world subject. It allows you to explore the key characteristics, meanings, and implications of the case.
Case studies are often a good choice in a thesis or dissertation . They keep your project focused and manageable when you don’t have the time or resources to do large-scale research.
You might use just one complex case study where you explore a single subject in depth, or conduct multiple case studies to compare and illuminate different aspects of your research problem.
| Research question | Case study |
|---|---|
| What are the ecological effects of wolf reintroduction? | Case study of wolf reintroduction in Yellowstone National Park |
| How do populist politicians use narratives about history to gain support? | Case studies of Hungarian prime minister Viktor Orbán and US president Donald Trump |
| How can teachers implement active learning strategies in mixed-level classrooms? | Case study of a local school that promotes active learning |
| What are the main advantages and disadvantages of wind farms for rural communities? | Case studies of three rural wind farm development projects in different parts of the country |
| How are viral marketing strategies changing the relationship between companies and consumers? | Case study of the iPhone X marketing campaign |
| How do experiences of work in the gig economy differ by gender, race and age? | Case studies of Deliveroo and Uber drivers in London |
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Once you have developed your problem statement and research questions , you should be ready to choose the specific case that you want to focus on. A good case study should have the potential to:
- Provide new or unexpected insights into the subject
- Challenge or complicate existing assumptions and theories
- Propose practical courses of action to resolve a problem
- Open up new directions for future research
TipIf your research is more practical in nature and aims to simultaneously investigate an issue as you solve it, consider conducting action research instead.
Unlike quantitative or experimental research , a strong case study does not require a random or representative sample. In fact, case studies often deliberately focus on unusual, neglected, or outlying cases which may shed new light on the research problem.
Example of an outlying case studyIn the 1960s the town of Roseto, Pennsylvania was discovered to have extremely low rates of heart disease compared to the US average. It became an important case study for understanding previously neglected causes of heart disease.
However, you can also choose a more common or representative case to exemplify a particular category, experience or phenomenon.
Example of a representative case studyIn the 1920s, two sociologists used Muncie, Indiana as a case study of a typical American city that supposedly exemplified the changing culture of the US at the time.
While case studies focus more on concrete details than general theories, they should usually have some connection with theory in the field. This way the case study is not just an isolated description, but is integrated into existing knowledge about the topic. It might aim to:
- Exemplify a theory by showing how it explains the case under investigation
- Expand on a theory by uncovering new concepts and ideas that need to be incorporated
- Challenge a theory by exploring an outlier case that doesn’t fit with established assumptions
To ensure that your analysis of the case has a solid academic grounding, you should conduct a literature review of sources related to the topic and develop a theoretical framework . This means identifying key concepts and theories to guide your analysis and interpretation.
There are many different research methods you can use to collect data on your subject. Case studies tend to focus on qualitative data using methods such as interviews , observations , and analysis of primary and secondary sources (e.g., newspaper articles, photographs, official records). Sometimes a case study will also collect quantitative data.
Example of a mixed methods case studyFor a case study of a wind farm development in a rural area, you could collect quantitative data on employment rates and business revenue, collect qualitative data on local people’s perceptions and experiences, and analyze local and national media coverage of the development.
The aim is to gain as thorough an understanding as possible of the case and its context.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
In writing up the case study, you need to bring together all the relevant aspects to give as complete a picture as possible of the subject.
How you report your findings depends on the type of research you are doing. Some case studies are structured like a standard scientific paper or thesis , with separate sections or chapters for the methods , results and discussion .
Others are written in a more narrative style, aiming to explore the case from various angles and analyze its meanings and implications (for example, by using textual analysis or discourse analysis ).
In all cases, though, make sure to give contextual details about the case, connect it back to the literature and theory, and discuss how it fits into wider patterns or debates.
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Normal distribution
- Degrees of freedom
- Null hypothesis
- Discourse analysis
- Control groups
- Mixed methods research
- Non-probability sampling
- Quantitative research
- Ecological validity
Research bias
- Rosenthal effect
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Selection bias
- Negativity bias
- Status quo bias
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, November 20). What Is a Case Study? | Definition, Examples & Methods. Scribbr. Retrieved June 8, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/case-study/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, primary vs. secondary sources | difference & examples, what is a theoretical framework | guide to organizing, what is action research | definition & examples, what is your plagiarism score.

Research Writing and Analysis
- NVivo Group and Study Sessions
- SPSS This link opens in a new window
- Statistical Analysis Group sessions
- Using Qualtrics
- Dissertation and Data Analysis Group Sessions
- Defense Schedule - Commons Calendar This link opens in a new window
- Research Process Flow Chart
- Research Alignment Chapter 1 This link opens in a new window
- Step 1: Seek Out Evidence
- Step 2: Explain
- Step 3: The Big Picture
- Step 4: Own It
- Step 5: Illustrate
- Annotated Bibliography
- Literature Review This link opens in a new window
- Systematic Reviews & Meta-Analyses
- How to Synthesize and Analyze
- Synthesis and Analysis Practice
- Synthesis and Analysis Group Sessions
- Problem Statement
- Purpose Statement
- Conceptual Framework
- Theoretical Framework
- Locating Theoretical and Conceptual Frameworks This link opens in a new window
- Quantitative Research Questions
- Qualitative Research Questions
- Trustworthiness of Qualitative Data
- Analysis and Coding Example- Qualitative Data
- Thematic Data Analysis in Qualitative Design
- Dissertation to Journal Article This link opens in a new window
- International Journal of Online Graduate Education (IJOGE) This link opens in a new window
- Journal of Research in Innovative Teaching & Learning (JRIT&L) This link opens in a new window
Writing a Case Study

What is a case study?

A Case study is:
- An in-depth research design that primarily uses a qualitative methodology but sometimes includes quantitative methodology.
- Used to examine an identifiable problem confirmed through research.
- Used to investigate an individual, group of people, organization, or event.
- Used to mostly answer "how" and "why" questions.
What are the different types of case studies?

| Descriptive | This type of case study allows the researcher to: | How has the implementation and use of the instructional coaching intervention for elementary teachers impacted students’ attitudes toward reading? |
| Explanatory | This type of case study allows the researcher to: | Why do differences exist when implementing the same online reading curriculum in three elementary classrooms? |
| Exploratory | This type of case study allows the researcher to:
| What are potential barriers to student’s reading success when middle school teachers implement the Ready Reader curriculum online? |
| Multiple Case Studies or Collective Case Study | This type of case study allows the researcher to: | How are individual school districts addressing student engagement in an online classroom? |
| Intrinsic | This type of case study allows the researcher to: | How does a student’s familial background influence a teacher’s ability to provide meaningful instruction? |
| Instrumental | This type of case study allows the researcher to: | How a rural school district’s integration of a reward system maximized student engagement? |
Note: These are the primary case studies. As you continue to research and learn
about case studies you will begin to find a robust list of different types.
Who are your case study participants?

|
|
This type of study is implemented to understand an individual by developing a detailed explanation of the individual’s lived experiences or perceptions.
|
|
| This type of study is implemented to explore a particular group of people’s perceptions. |
|
| This type of study is implemented to explore the perspectives of people who work for or had interaction with a specific organization or company. |
|
| This type of study is implemented to explore participant’s perceptions of an event. |
What is triangulation ?
Validity and credibility are an essential part of the case study. Therefore, the researcher should include triangulation to ensure trustworthiness while accurately reflecting what the researcher seeks to investigate.

How to write a Case Study?
When developing a case study, there are different ways you could present the information, but remember to include the five parts for your case study.

|
|
|
|
|
|

Was this resource helpful?
- << Previous: Thematic Data Analysis in Qualitative Design
- Next: Journal Article Reporting Standards (JARS) >>
- Last Updated: May 29, 2024 8:05 AM
- URL: https://resources.nu.edu/researchtools

Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Assignments
- Annotated Bibliography
- Analyzing a Scholarly Journal Article
- Group Presentations
- Dealing with Nervousness
- Using Visual Aids
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
- Types of Structured Group Activities
- Group Project Survival Skills
- Leading a Class Discussion
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Works
- Writing a Case Analysis Paper
- Writing a Case Study
- About Informed Consent
- Writing Field Notes
- Writing a Policy Memo
- Writing a Reflective Paper
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Generative AI and Writing
- Acknowledgments
A case study research paper examines a person, place, event, condition, phenomenon, or other type of subject of analysis in order to extrapolate key themes and results that help predict future trends, illuminate previously hidden issues that can be applied to practice, and/or provide a means for understanding an important research problem with greater clarity. A case study research paper usually examines a single subject of analysis, but case study papers can also be designed as a comparative investigation that shows relationships between two or more subjects. The methods used to study a case can rest within a quantitative, qualitative, or mixed-method investigative paradigm.
Case Studies. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Mills, Albert J. , Gabrielle Durepos, and Eiden Wiebe, editors. Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010 ; “What is a Case Study?” In Swanborn, Peter G. Case Study Research: What, Why and How? London: SAGE, 2010.
How to Approach Writing a Case Study Research Paper
General information about how to choose a topic to investigate can be found under the " Choosing a Research Problem " tab in the Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper writing guide. Review this page because it may help you identify a subject of analysis that can be investigated using a case study design.
However, identifying a case to investigate involves more than choosing the research problem . A case study encompasses a problem contextualized around the application of in-depth analysis, interpretation, and discussion, often resulting in specific recommendations for action or for improving existing conditions. As Seawright and Gerring note, practical considerations such as time and access to information can influence case selection, but these issues should not be the sole factors used in describing the methodological justification for identifying a particular case to study. Given this, selecting a case includes considering the following:
- The case represents an unusual or atypical example of a research problem that requires more in-depth analysis? Cases often represent a topic that rests on the fringes of prior investigations because the case may provide new ways of understanding the research problem. For example, if the research problem is to identify strategies to improve policies that support girl's access to secondary education in predominantly Muslim nations, you could consider using Azerbaijan as a case study rather than selecting a more obvious nation in the Middle East. Doing so may reveal important new insights into recommending how governments in other predominantly Muslim nations can formulate policies that support improved access to education for girls.
- The case provides important insight or illuminate a previously hidden problem? In-depth analysis of a case can be based on the hypothesis that the case study will reveal trends or issues that have not been exposed in prior research or will reveal new and important implications for practice. For example, anecdotal evidence may suggest drug use among homeless veterans is related to their patterns of travel throughout the day. Assuming prior studies have not looked at individual travel choices as a way to study access to illicit drug use, a case study that observes a homeless veteran could reveal how issues of personal mobility choices facilitate regular access to illicit drugs. Note that it is important to conduct a thorough literature review to ensure that your assumption about the need to reveal new insights or previously hidden problems is valid and evidence-based.
- The case challenges and offers a counter-point to prevailing assumptions? Over time, research on any given topic can fall into a trap of developing assumptions based on outdated studies that are still applied to new or changing conditions or the idea that something should simply be accepted as "common sense," even though the issue has not been thoroughly tested in current practice. A case study analysis may offer an opportunity to gather evidence that challenges prevailing assumptions about a research problem and provide a new set of recommendations applied to practice that have not been tested previously. For example, perhaps there has been a long practice among scholars to apply a particular theory in explaining the relationship between two subjects of analysis. Your case could challenge this assumption by applying an innovative theoretical framework [perhaps borrowed from another discipline] to explore whether this approach offers new ways of understanding the research problem. Taking a contrarian stance is one of the most important ways that new knowledge and understanding develops from existing literature.
- The case provides an opportunity to pursue action leading to the resolution of a problem? Another way to think about choosing a case to study is to consider how the results from investigating a particular case may result in findings that reveal ways in which to resolve an existing or emerging problem. For example, studying the case of an unforeseen incident, such as a fatal accident at a railroad crossing, can reveal hidden issues that could be applied to preventative measures that contribute to reducing the chance of accidents in the future. In this example, a case study investigating the accident could lead to a better understanding of where to strategically locate additional signals at other railroad crossings so as to better warn drivers of an approaching train, particularly when visibility is hindered by heavy rain, fog, or at night.
- The case offers a new direction in future research? A case study can be used as a tool for an exploratory investigation that highlights the need for further research about the problem. A case can be used when there are few studies that help predict an outcome or that establish a clear understanding about how best to proceed in addressing a problem. For example, after conducting a thorough literature review [very important!], you discover that little research exists showing the ways in which women contribute to promoting water conservation in rural communities of east central Africa. A case study of how women contribute to saving water in a rural village of Uganda can lay the foundation for understanding the need for more thorough research that documents how women in their roles as cooks and family caregivers think about water as a valuable resource within their community. This example of a case study could also point to the need for scholars to build new theoretical frameworks around the topic [e.g., applying feminist theories of work and family to the issue of water conservation].
Eisenhardt, Kathleen M. “Building Theories from Case Study Research.” Academy of Management Review 14 (October 1989): 532-550; Emmel, Nick. Sampling and Choosing Cases in Qualitative Research: A Realist Approach . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2013; Gerring, John. “What Is a Case Study and What Is It Good for?” American Political Science Review 98 (May 2004): 341-354; Mills, Albert J. , Gabrielle Durepos, and Eiden Wiebe, editors. Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010; Seawright, Jason and John Gerring. "Case Selection Techniques in Case Study Research." Political Research Quarterly 61 (June 2008): 294-308.
Structure and Writing Style
The purpose of a paper in the social sciences designed around a case study is to thoroughly investigate a subject of analysis in order to reveal a new understanding about the research problem and, in so doing, contributing new knowledge to what is already known from previous studies. In applied social sciences disciplines [e.g., education, social work, public administration, etc.], case studies may also be used to reveal best practices, highlight key programs, or investigate interesting aspects of professional work.
In general, the structure of a case study research paper is not all that different from a standard college-level research paper. However, there are subtle differences you should be aware of. Here are the key elements to organizing and writing a case study research paper.
I. Introduction
As with any research paper, your introduction should serve as a roadmap for your readers to ascertain the scope and purpose of your study . The introduction to a case study research paper, however, should not only describe the research problem and its significance, but you should also succinctly describe why the case is being used and how it relates to addressing the problem. The two elements should be linked. With this in mind, a good introduction answers these four questions:
- What is being studied? Describe the research problem and describe the subject of analysis [the case] you have chosen to address the problem. Explain how they are linked and what elements of the case will help to expand knowledge and understanding about the problem.
- Why is this topic important to investigate? Describe the significance of the research problem and state why a case study design and the subject of analysis that the paper is designed around is appropriate in addressing the problem.
- What did we know about this topic before I did this study? Provide background that helps lead the reader into the more in-depth literature review to follow. If applicable, summarize prior case study research applied to the research problem and why it fails to adequately address the problem. Describe why your case will be useful. If no prior case studies have been used to address the research problem, explain why you have selected this subject of analysis.
- How will this study advance new knowledge or new ways of understanding? Explain why your case study will be suitable in helping to expand knowledge and understanding about the research problem.
Each of these questions should be addressed in no more than a few paragraphs. Exceptions to this can be when you are addressing a complex research problem or subject of analysis that requires more in-depth background information.
II. Literature Review
The literature review for a case study research paper is generally structured the same as it is for any college-level research paper. The difference, however, is that the literature review is focused on providing background information and enabling historical interpretation of the subject of analysis in relation to the research problem the case is intended to address . This includes synthesizing studies that help to:
- Place relevant works in the context of their contribution to understanding the case study being investigated . This would involve summarizing studies that have used a similar subject of analysis to investigate the research problem. If there is literature using the same or a very similar case to study, you need to explain why duplicating past research is important [e.g., conditions have changed; prior studies were conducted long ago, etc.].
- Describe the relationship each work has to the others under consideration that informs the reader why this case is applicable . Your literature review should include a description of any works that support using the case to investigate the research problem and the underlying research questions.
- Identify new ways to interpret prior research using the case study . If applicable, review any research that has examined the research problem using a different research design. Explain how your use of a case study design may reveal new knowledge or a new perspective or that can redirect research in an important new direction.
- Resolve conflicts amongst seemingly contradictory previous studies . This refers to synthesizing any literature that points to unresolved issues of concern about the research problem and describing how the subject of analysis that forms the case study can help resolve these existing contradictions.
- Point the way in fulfilling a need for additional research . Your review should examine any literature that lays a foundation for understanding why your case study design and the subject of analysis around which you have designed your study may reveal a new way of approaching the research problem or offer a perspective that points to the need for additional research.
- Expose any gaps that exist in the literature that the case study could help to fill . Summarize any literature that not only shows how your subject of analysis contributes to understanding the research problem, but how your case contributes to a new way of understanding the problem that prior research has failed to do.
- Locate your own research within the context of existing literature [very important!] . Collectively, your literature review should always place your case study within the larger domain of prior research about the problem. The overarching purpose of reviewing pertinent literature in a case study paper is to demonstrate that you have thoroughly identified and synthesized prior studies in relation to explaining the relevance of the case in addressing the research problem.
III. Method
In this section, you explain why you selected a particular case [i.e., subject of analysis] and the strategy you used to identify and ultimately decide that your case was appropriate in addressing the research problem. The way you describe the methods used varies depending on the type of subject of analysis that constitutes your case study.
If your subject of analysis is an incident or event . In the social and behavioral sciences, the event or incident that represents the case to be studied is usually bounded by time and place, with a clear beginning and end and with an identifiable location or position relative to its surroundings. The subject of analysis can be a rare or critical event or it can focus on a typical or regular event. The purpose of studying a rare event is to illuminate new ways of thinking about the broader research problem or to test a hypothesis. Critical incident case studies must describe the method by which you identified the event and explain the process by which you determined the validity of this case to inform broader perspectives about the research problem or to reveal new findings. However, the event does not have to be a rare or uniquely significant to support new thinking about the research problem or to challenge an existing hypothesis. For example, Walo, Bull, and Breen conducted a case study to identify and evaluate the direct and indirect economic benefits and costs of a local sports event in the City of Lismore, New South Wales, Australia. The purpose of their study was to provide new insights from measuring the impact of a typical local sports event that prior studies could not measure well because they focused on large "mega-events." Whether the event is rare or not, the methods section should include an explanation of the following characteristics of the event: a) when did it take place; b) what were the underlying circumstances leading to the event; and, c) what were the consequences of the event in relation to the research problem.
If your subject of analysis is a person. Explain why you selected this particular individual to be studied and describe what experiences they have had that provide an opportunity to advance new understandings about the research problem. Mention any background about this person which might help the reader understand the significance of their experiences that make them worthy of study. This includes describing the relationships this person has had with other people, institutions, and/or events that support using them as the subject for a case study research paper. It is particularly important to differentiate the person as the subject of analysis from others and to succinctly explain how the person relates to examining the research problem [e.g., why is one politician in a particular local election used to show an increase in voter turnout from any other candidate running in the election]. Note that these issues apply to a specific group of people used as a case study unit of analysis [e.g., a classroom of students].
If your subject of analysis is a place. In general, a case study that investigates a place suggests a subject of analysis that is unique or special in some way and that this uniqueness can be used to build new understanding or knowledge about the research problem. A case study of a place must not only describe its various attributes relevant to the research problem [e.g., physical, social, historical, cultural, economic, political], but you must state the method by which you determined that this place will illuminate new understandings about the research problem. It is also important to articulate why a particular place as the case for study is being used if similar places also exist [i.e., if you are studying patterns of homeless encampments of veterans in open spaces, explain why you are studying Echo Park in Los Angeles rather than Griffith Park?]. If applicable, describe what type of human activity involving this place makes it a good choice to study [e.g., prior research suggests Echo Park has more homeless veterans].
If your subject of analysis is a phenomenon. A phenomenon refers to a fact, occurrence, or circumstance that can be studied or observed but with the cause or explanation to be in question. In this sense, a phenomenon that forms your subject of analysis can encompass anything that can be observed or presumed to exist but is not fully understood. In the social and behavioral sciences, the case usually focuses on human interaction within a complex physical, social, economic, cultural, or political system. For example, the phenomenon could be the observation that many vehicles used by ISIS fighters are small trucks with English language advertisements on them. The research problem could be that ISIS fighters are difficult to combat because they are highly mobile. The research questions could be how and by what means are these vehicles used by ISIS being supplied to the militants and how might supply lines to these vehicles be cut off? How might knowing the suppliers of these trucks reveal larger networks of collaborators and financial support? A case study of a phenomenon most often encompasses an in-depth analysis of a cause and effect that is grounded in an interactive relationship between people and their environment in some way.
NOTE: The choice of the case or set of cases to study cannot appear random. Evidence that supports the method by which you identified and chose your subject of analysis should clearly support investigation of the research problem and linked to key findings from your literature review. Be sure to cite any studies that helped you determine that the case you chose was appropriate for examining the problem.
IV. Discussion
The main elements of your discussion section are generally the same as any research paper, but centered around interpreting and drawing conclusions about the key findings from your analysis of the case study. Note that a general social sciences research paper may contain a separate section to report findings. However, in a paper designed around a case study, it is common to combine a description of the results with the discussion about their implications. The objectives of your discussion section should include the following:
Reiterate the Research Problem/State the Major Findings Briefly reiterate the research problem you are investigating and explain why the subject of analysis around which you designed the case study were used. You should then describe the findings revealed from your study of the case using direct, declarative, and succinct proclamation of the study results. Highlight any findings that were unexpected or especially profound.
Explain the Meaning of the Findings and Why They are Important Systematically explain the meaning of your case study findings and why you believe they are important. Begin this part of the section by repeating what you consider to be your most important or surprising finding first, then systematically review each finding. Be sure to thoroughly extrapolate what your analysis of the case can tell the reader about situations or conditions beyond the actual case that was studied while, at the same time, being careful not to misconstrue or conflate a finding that undermines the external validity of your conclusions.
Relate the Findings to Similar Studies No study in the social sciences is so novel or possesses such a restricted focus that it has absolutely no relation to previously published research. The discussion section should relate your case study results to those found in other studies, particularly if questions raised from prior studies served as the motivation for choosing your subject of analysis. This is important because comparing and contrasting the findings of other studies helps support the overall importance of your results and it highlights how and in what ways your case study design and the subject of analysis differs from prior research about the topic.
Consider Alternative Explanations of the Findings Remember that the purpose of social science research is to discover and not to prove. When writing the discussion section, you should carefully consider all possible explanations revealed by the case study results, rather than just those that fit your hypothesis or prior assumptions and biases. Be alert to what the in-depth analysis of the case may reveal about the research problem, including offering a contrarian perspective to what scholars have stated in prior research if that is how the findings can be interpreted from your case.
Acknowledge the Study's Limitations You can state the study's limitations in the conclusion section of your paper but describing the limitations of your subject of analysis in the discussion section provides an opportunity to identify the limitations and explain why they are not significant. This part of the discussion section should also note any unanswered questions or issues your case study could not address. More detailed information about how to document any limitations to your research can be found here .
Suggest Areas for Further Research Although your case study may offer important insights about the research problem, there are likely additional questions related to the problem that remain unanswered or findings that unexpectedly revealed themselves as a result of your in-depth analysis of the case. Be sure that the recommendations for further research are linked to the research problem and that you explain why your recommendations are valid in other contexts and based on the original assumptions of your study.
V. Conclusion
As with any research paper, you should summarize your conclusion in clear, simple language; emphasize how the findings from your case study differs from or supports prior research and why. Do not simply reiterate the discussion section. Provide a synthesis of key findings presented in the paper to show how these converge to address the research problem. If you haven't already done so in the discussion section, be sure to document the limitations of your case study and any need for further research.
The function of your paper's conclusion is to: 1) reiterate the main argument supported by the findings from your case study; 2) state clearly the context, background, and necessity of pursuing the research problem using a case study design in relation to an issue, controversy, or a gap found from reviewing the literature; and, 3) provide a place to persuasively and succinctly restate the significance of your research problem, given that the reader has now been presented with in-depth information about the topic.
Consider the following points to help ensure your conclusion is appropriate:
- If the argument or purpose of your paper is complex, you may need to summarize these points for your reader.
- If prior to your conclusion, you have not yet explained the significance of your findings or if you are proceeding inductively, use the conclusion of your paper to describe your main points and explain their significance.
- Move from a detailed to a general level of consideration of the case study's findings that returns the topic to the context provided by the introduction or within a new context that emerges from your case study findings.
Note that, depending on the discipline you are writing in or the preferences of your professor, the concluding paragraph may contain your final reflections on the evidence presented as it applies to practice or on the essay's central research problem. However, the nature of being introspective about the subject of analysis you have investigated will depend on whether you are explicitly asked to express your observations in this way.
Problems to Avoid
Overgeneralization One of the goals of a case study is to lay a foundation for understanding broader trends and issues applied to similar circumstances. However, be careful when drawing conclusions from your case study. They must be evidence-based and grounded in the results of the study; otherwise, it is merely speculation. Looking at a prior example, it would be incorrect to state that a factor in improving girls access to education in Azerbaijan and the policy implications this may have for improving access in other Muslim nations is due to girls access to social media if there is no documentary evidence from your case study to indicate this. There may be anecdotal evidence that retention rates were better for girls who were engaged with social media, but this observation would only point to the need for further research and would not be a definitive finding if this was not a part of your original research agenda.
Failure to Document Limitations No case is going to reveal all that needs to be understood about a research problem. Therefore, just as you have to clearly state the limitations of a general research study , you must describe the specific limitations inherent in the subject of analysis. For example, the case of studying how women conceptualize the need for water conservation in a village in Uganda could have limited application in other cultural contexts or in areas where fresh water from rivers or lakes is plentiful and, therefore, conservation is understood more in terms of managing access rather than preserving access to a scarce resource.
Failure to Extrapolate All Possible Implications Just as you don't want to over-generalize from your case study findings, you also have to be thorough in the consideration of all possible outcomes or recommendations derived from your findings. If you do not, your reader may question the validity of your analysis, particularly if you failed to document an obvious outcome from your case study research. For example, in the case of studying the accident at the railroad crossing to evaluate where and what types of warning signals should be located, you failed to take into consideration speed limit signage as well as warning signals. When designing your case study, be sure you have thoroughly addressed all aspects of the problem and do not leave gaps in your analysis that leave the reader questioning the results.
Case Studies. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Gerring, John. Case Study Research: Principles and Practices . New York: Cambridge University Press, 2007; Merriam, Sharan B. Qualitative Research and Case Study Applications in Education . Rev. ed. San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass, 1998; Miller, Lisa L. “The Use of Case Studies in Law and Social Science Research.” Annual Review of Law and Social Science 14 (2018): TBD; Mills, Albert J., Gabrielle Durepos, and Eiden Wiebe, editors. Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010; Putney, LeAnn Grogan. "Case Study." In Encyclopedia of Research Design , Neil J. Salkind, editor. (Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010), pp. 116-120; Simons, Helen. Case Study Research in Practice . London: SAGE Publications, 2009; Kratochwill, Thomas R. and Joel R. Levin, editors. Single-Case Research Design and Analysis: New Development for Psychology and Education . Hilldsale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, 1992; Swanborn, Peter G. Case Study Research: What, Why and How? London : SAGE, 2010; Yin, Robert K. Case Study Research: Design and Methods . 6th edition. Los Angeles, CA, SAGE Publications, 2014; Walo, Maree, Adrian Bull, and Helen Breen. “Achieving Economic Benefits at Local Events: A Case Study of a Local Sports Event.” Festival Management and Event Tourism 4 (1996): 95-106.
Writing Tip
At Least Five Misconceptions about Case Study Research
Social science case studies are often perceived as limited in their ability to create new knowledge because they are not randomly selected and findings cannot be generalized to larger populations. Flyvbjerg examines five misunderstandings about case study research and systematically "corrects" each one. To quote, these are:
Misunderstanding 1 : General, theoretical [context-independent] knowledge is more valuable than concrete, practical [context-dependent] knowledge. Misunderstanding 2 : One cannot generalize on the basis of an individual case; therefore, the case study cannot contribute to scientific development. Misunderstanding 3 : The case study is most useful for generating hypotheses; that is, in the first stage of a total research process, whereas other methods are more suitable for hypotheses testing and theory building. Misunderstanding 4 : The case study contains a bias toward verification, that is, a tendency to confirm the researcher’s preconceived notions. Misunderstanding 5 : It is often difficult to summarize and develop general propositions and theories on the basis of specific case studies [p. 221].
While writing your paper, think introspectively about how you addressed these misconceptions because to do so can help you strengthen the validity and reliability of your research by clarifying issues of case selection, the testing and challenging of existing assumptions, the interpretation of key findings, and the summation of case outcomes. Think of a case study research paper as a complete, in-depth narrative about the specific properties and key characteristics of your subject of analysis applied to the research problem.
Flyvbjerg, Bent. “Five Misunderstandings About Case-Study Research.” Qualitative Inquiry 12 (April 2006): 219-245.
- << Previous: Writing a Case Analysis Paper
- Next: Writing a Field Report >>
- Last Updated: Jun 3, 2024 9:44 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/assignments

How it works
Transform your enterprise with the scalable mindsets, skills, & behavior change that drive performance.
Explore how BetterUp connects to your core business systems.
We pair AI with the latest in human-centered coaching to drive powerful, lasting learning and behavior change.
Build leaders that accelerate team performance and engagement.
Unlock performance potential at scale with AI-powered curated growth journeys.
Build resilience, well-being and agility to drive performance across your entire enterprise.
Transform your business, starting with your sales leaders.
Unlock business impact from the top with executive coaching.
Foster a culture of inclusion and belonging.
Accelerate the performance and potential of your agencies and employees.
See how innovative organizations use BetterUp to build a thriving workforce.
Discover how BetterUp measurably impacts key business outcomes for organizations like yours.
A demo is the first step to transforming your business. Meet with us to develop a plan for attaining your goals.

- What is coaching?
Learn how 1:1 coaching works, who its for, and if it's right for you.
Accelerate your personal and professional growth with the expert guidance of a BetterUp Coach.
Types of Coaching
Navigate career transitions, accelerate your professional growth, and achieve your career goals with expert coaching.
Enhance your communication skills for better personal and professional relationships, with tailored coaching that focuses on your needs.
Find balance, resilience, and well-being in all areas of your life with holistic coaching designed to empower you.
Discover your perfect match : Take our 5-minute assessment and let us pair you with one of our top Coaches tailored just for you.

Research, expert insights, and resources to develop courageous leaders within your organization.
Best practices, research, and tools to fuel individual and business growth.
View on-demand BetterUp events and learn about upcoming live discussions.
The latest insights and ideas for building a high-performing workplace.
- BetterUp Briefing
The online magazine that helps you understand tomorrow's workforce trends, today.
Innovative research featured in peer-reviewed journals, press, and more.
Founded in 2022 to deepen the understanding of the intersection of well-being, purpose, and performance
We're on a mission to help everyone live with clarity, purpose, and passion.
Join us and create impactful change.
Read the buzz about BetterUp.
Meet the leadership that's passionate about empowering your workforce.
For Business
For Individuals
3 Problem statement examples and steps to write your own
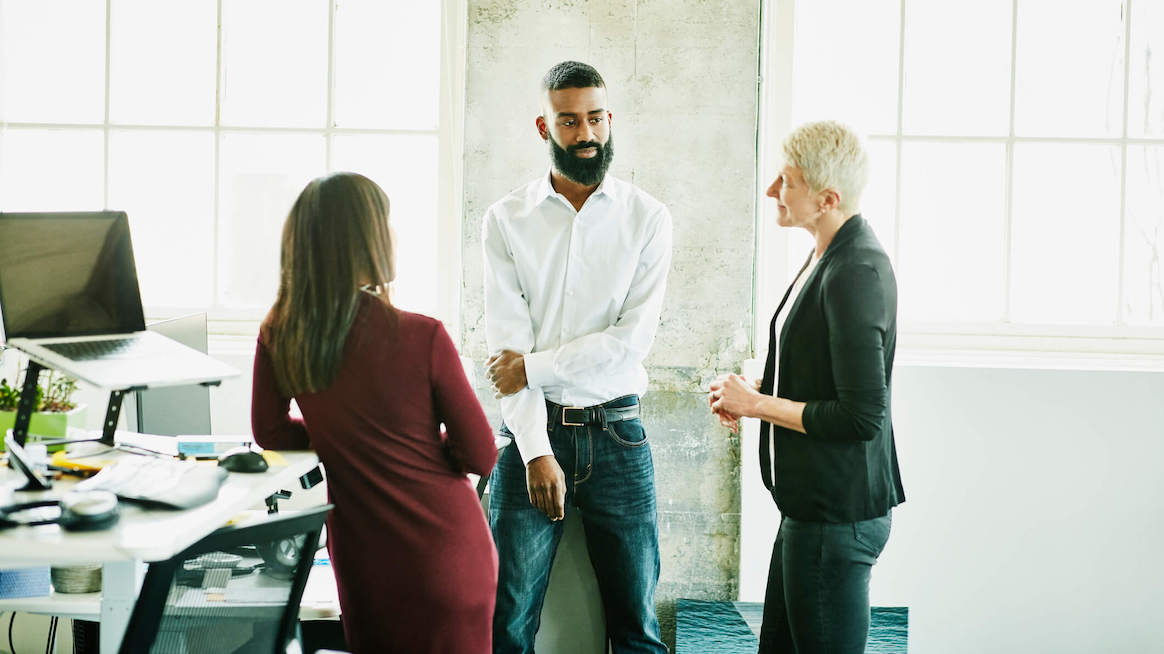

We’ve all encountered problems on the job. After all, that’s what a lot of work is about. Solving meaningful problems to help improve something.
Developing a problem statement that provides a brief description of an issue you want to solve is an important early step in problem-solving .
It sounds deceptively simple. But creating an effective problem statement isn’t that easy, even for a genius like Albert Einstein. Given one hour to work on a problem, he’d spend 55 minutes thinking about the problem and five minutes finding solutions. (Or so the story goes.)
Einstein was probably exaggerating to make a point. But considering his success in solving complex problems, we think he was on to something.
As humans, we’re wired to jump past the problem and go directly to the solution stage. In emergencies, this behavior can be lifesaving, as in leaping out of the way of a speeding car. But when dealing with longer-range issues in the workplace, this can lead to bad decisions or half-baked solutions.
That’s where problem statements come in handy. They help to meaningfully outline objectives to reach effective solutions. Knowing how to develop a great problem statement is also a valuable tool for honing your management skills .
But what exactly is a problem statement, when should you use one, and how do you go about writing one? In this article, we'll answer those questions and give you some tips for writing effective problem statements. Then you'll be ready to take on more challenges large and small.
What is a problem statement?
First, let’s start by defining a problem statement.
A problem statement is a short, clear explanation of an issue or challenge that sums up what you want to change. It helps you, team members, and other stakeholders to focus on the problem, why it’s important, and who it impacts.
A good problem statement should create awareness and stimulate creative thinking . It should not identify a solution or create a bias toward a specific strategy.
Taking time to work on a problem statement is a great way to short-circuit the tendency to rush to solutions. It helps to make sure you’re focusing on the right problem and have a well-informed understanding of the root causes. The process can also help you take a more proactive than reactive approach to problem-solving . This can help position you and your team to avoid getting stuck in constant fire-fighting mode. That way, you can take advantage of more growth opportunities.
When to use a problem statement
The best time to create a problem statement is before you start thinking of solutions. If you catch yourself or your team rushing to the solution stage when you’re first discussing a problem, hit the brakes. Go back and work on the statement of the problem to make sure everyone understands and agrees on what the real problem is.
Here are some common situations where writing problem statements might come in handy:
- Writing an executive summary for a project proposal or research project
- Collaborating on a cross-functional project with several team members
- Defining the customer issue that a proposed product or service aims to solve
- Using design thinking to improve user experience
- Tackling a problem that previous actions failed to solve
How to identify a problem statement
Like the unseen body of an iceberg, the root cause of a specific problem isn’t always obvious. So when developing a problem statement, how do you go about identifying the true, underlying problem?
These two steps will help you uncover the root cause of a problem :
- Collect information from the research and previous experience with the problem
- Talk to multiple stakeholders who are impacted by the problem
People often perceive problems differently. Interviewing stakeholders will help you understand the problem from diverse points of view. It can also help you develop some case studies to illustrate the problem.
Combining these insights with research data will help you identify root causes more accurately. In turn, this methodology will help you craft a problem statement that will lead to more viable solutions.
What are problem statements used for?
You can use problem statements for a variety of purposes. For an organization, it might be solving customer and employee issues. For the government, it could be improving public health. For individuals, it can mean enhancing their own personal well-being . Generally, problem statements can be used to:
- Identify opportunities for improvement
- Focus on the right problems or issues to launch more successful initiatives – a common challenge in leadership
- Help you communicate a problem to others who need to be involved in finding a solution
- Serve as the basis for developing an action plan or goals that need to be accomplished to help solve the problem
- Stimulate thinking outside the box and other types of creative brainstorming techniques
3 examples of problem statements
When you want to be sure you understand a concept or tool, it helps to see an example. There can also be some differences in opinion about what a problem statement should look like. For instance, some frameworks include a proposed solution as part of the problem statement. But if the goal is to stimulate fresh ideas, it’s better not to suggest a solution within the problem statement.
In our experience, an effective problem statement is brief, preferably one sentence. It’s also specific and descriptive without being prescriptive.
Here are three problem statement examples. While these examples represent three types of problems or goals, keep in mind that there can be many other types of problem statements.
Example Problem Statement 1: The Status Quo Problem Statement
Example:
The average customer service on-hold time for Example company exceeds five minutes during both its busy and slow seasons.
This can be used to describe a current pain point within an organization that may need to be addressed. Note that the statement specifies that the issue occurs during the company’s slow time as well as the busy season. This is helpful in performing the root cause analysis and determining how this problem can be solved.
The average customer service on-hold time for Example company exceeds five minutes during both its busy and slow seasons. The company is currently understaffed and customer service representatives are overwhelmed.
Background:
Example company is facing a significant challenge in managing their customer service on-hold times. In the past, the company had been known for its efficient and timely customer service, but due to a combination of factors, including understaffing and increased customer demand, the on-hold times have exceeded five minutes consistently. This has resulted in frustration and dissatisfaction among customers, negatively impacting the company's reputation and customer loyalty.
Reducing the on-hold times for customer service callers is crucial for Example company. Prolonged waiting times have a detrimental effect on customer satisfaction and loyalty, leading to potential customer churn and loss of revenue. Additionally, the company's declining reputation in terms of customer service can have a lasting impact on its competitive position in the market. Addressing this problem is of utmost importance to improve customer experience and maintain a positive brand image.
Objectives:
The primary objective of this project is to reduce the on-hold times for customer service callers at Example company. The specific objectives include:
- Analyzing the current customer service workflow and identifying bottlenecks contributing to increased on-hold times.
- Assessing the staffing levels and resource allocation to determine the extent of understaffing and its impact on customer service.
- Developing strategies and implementing measures to optimize the customer service workflow and reduce on-hold times.
- Monitoring and evaluating the effectiveness of the implemented measures through key performance indicators (KPIs) such as average on-hold time, customer satisfaction ratings, and customer feedback.
- Establishing a sustainable approach to maintain reduced on-hold times, taking into account both busy and slow seasons, through proper resource planning, training, and process improvements.
Example Problem Statement 2: The Destination Problem Statement
Leaders at Example company want to increase net revenue for its premium product line of widgets by 5% for the next fiscal year.
This approach can be used to describe where an organization wants to be in the future. This type of problem statement is useful for launching initiatives to help an organization achieve its desired state.
Like creating SMART goals , you want to be as specific as possible. Note that the statement specifies “net revenue” instead of “gross revenue." This will help keep options open for potential actions. It also makes it clear that merely increasing sales is not an acceptable solution if higher marketing costs offset the net gains.
Leaders at Example company aim to increase net revenue for its premium product line of widgets by 5% for the next fiscal year. However, the company currently lacks the necessary teams to tackle this objective effectively. To achieve this growth target, the company needs to expand its marketing and PR teams, as well as its product development teams, to prepare for scaling.
Example company faces the challenge of generating a 5% increase in net revenue for its premium product line of widgets in the upcoming fiscal year. Currently, the company lacks the required workforce to drive this growth. Without adequate staff in the marketing, PR, and product development departments, the company's ability to effectively promote, position, and innovate its premium product line will be hindered. To achieve this kind of growth, it is essential that Example company expands teams, enhances capabilities, and strategically taps into the existing pool of loyal customers.
Increasing net revenue for the premium product line is crucial for Example company's overall business success. Failure to achieve the targeted growth rate can lead to missed revenue opportunities and stagnation in the market. By expanding the marketing and PR teams, Example company can strengthen its brand presence, effectively communicate the value proposition of its premium product line, and attract new customers.
Additionally, expanding the product development teams will enable the company to introduce new features and innovations, further enticing existing and potential customers. Therefore, addressing the workforce shortage and investing in the necessary resources are vital for achieving the revenue growth objective.
The primary objective of this project is to increase net revenue for Example company's premium product line of widgets by 5% in the next fiscal year. The specific objectives include:
- Assessing the current workforce and identifying the gaps in the marketing, PR, and product development teams.
- Expanding the marketing and PR teams by hiring skilled professionals who can effectively promote the premium product line and engage with the target audience.
- Strengthening the product development teams by recruiting qualified individuals who can drive innovation, enhance product features, and meet customer demands.
- Developing a comprehensive marketing and PR strategy to effectively communicate the value proposition of the premium product line and attract new customers.
- Leveraging the existing base of loyal customers to increase repeat purchases, referrals, and brand advocacy.
- Allocating sufficient resources, both time and manpower, to support the expansion and scaling efforts required to achieve the ambitious revenue growth target.
- Monitoring and analyzing key performance indicators (KPIs) such as net revenue, customer acquisition, customer retention, and customer satisfaction to measure the success of the growth initiatives.
- Establishing a sustainable plan to maintain the increased revenue growth beyond the next fiscal year by implementing strategies for continuous improvement and adaptation to market dynamics.
Example Problem Statement 3 The Stakeholder Problem Statement
In the last three quarterly employee engagement surveys , less than 30% of employees at Eample company stated that they feel valued by the company. This represents a 20% decline compared to the same period in the year prior.
This strategy can be used to describe how a specific stakeholder group views the organization. It can be useful for exploring issues and potential solutions that impact specific groups of people.
Note the statement makes it clear that the issue has been present in multiple surveys and it's significantly worse than the previous year. When researching root causes, the HR team will want to zero in on factors that changed since the previous year.
In the last three quarterly employee engagement surveys, less than 30% of employees at the Example company stated that they feel valued by the company. This indicates a significant decline of 20% compared to the same period in the previous year.
The company aspires to reduce this percentage further to under 10%. However, achieving this goal would require filling specialized roles and implementing substantial cultural changes within the organization.
Example company is facing a pressing issue regarding employee engagement and perceived value within the company. Over the past year, there has been a notable decline in the percentage of employees who feel valued. This decline is evident in the results of the quarterly employee engagement surveys, which consistently show less than 30% of employees reporting a sense of value by the company.
This decline of 20% compared to the previous year's data signifies a concerning trend. To address this problem effectively, Example company needs to undertake significant measures that go beyond superficial changes and necessitate filling specialized roles and transforming the company culture.
Employee engagement and a sense of value are crucial for organizational success. When employees feel valued, they tend to be more productive, committed, and motivated. Conversely, a lack of perceived value can lead to decreased morale, increased turnover rates, and diminished overall performance.
By addressing the decline in employees feeling valued, Example company can improve employee satisfaction, retention, and ultimately, overall productivity. Achieving the desired reduction to under 10% is essential to restore a positive work environment and build a culture of appreciation and respect.
The primary objective of this project is to increase the percentage of employees who feel valued by Example company, aiming to reduce it to under 10%. The specific objectives include:
- Conducting a comprehensive analysis of the factors contributing to the decline in employees feeling valued, including organizational policies, communication practices, leadership styles, and cultural norms.
- Identifying and filling specialized roles, such as employee engagement specialists or culture change agents, who can provide expertise and guidance in fostering a culture of value and appreciation.
- Developing a holistic employee engagement strategy that encompasses various initiatives, including training programs, recognition programs, feedback mechanisms, and communication channels, to enhance employee value perception.
- Implementing cultural changes within the organization that align with the values of appreciation, respect, and recognition, while fostering an environment where employees feel valued.
- Communicating the importance of employee value and engagement throughout all levels of the organization, including leadership teams, managers, and supervisors, to ensure consistent messaging and support.
- Monitoring progress through regular employee surveys, feedback sessions, and key performance indicators (KPIs) related to employee satisfaction, turnover rates, and overall engagement levels.
- Providing ongoing support, resources, and training to managers and supervisors to enable them to effectively recognize and appreciate their teams and foster a culture of value within their respective departments.
- Establishing a sustainable framework for maintaining high employee value perception in the long term, including regular evaluation and adaptation of employee engagement initiatives to address evolving needs and expectations.

What are the 5 components of a problem statement?
In developing a problem statement, it helps to think like a journalist by focusing on the five Ws: who, what, when, where, and why or how. Keep in mind that every statement may not explicitly include each component. But asking these questions is a good way to make sure you’re covering the key elements:
- Who: Who are the stakeholders that are affected by the problem?
- What: What is the current state, desired state, or unmet need?
- When: When is the issue occurring or what is the timeframe involved?
- Where: Where is the problem occurring? For example, is it in a specific department, location, or region?
- Why: Why is this important or worth solving? How is the problem impacting your customers, employees, other stakeholders, or the organization? What is the magnitude of the problem? How large is the gap between the current and desired state?
How do you write a problem statement?
There are many frameworks designed to help people write a problem statement. One example is outlined in the book, The Conclusion Trap: Four Steps to Better Decisions, ” by Daniel Markovitz. A faculty member at the Lean Enterprise Institute, the author uses many case studies from his work as a business consultant.
To simplify the process, we’ve broken it down into three steps:
1. Gather data and observe
Use data from research and reports, as well as facts from direct observation to answer the five Ws: who, what, when, where, and why.
Whenever possible, get out in the field and talk directly with stakeholders impacted by the problem. Get a firsthand look at the work environment and equipment. This may mean spending time on the production floor asking employees questions about their work and challenges. Or taking customer service calls to learn more about customer pain points and problems your employees may be grappling with.
2. Frame the problem properly
A well-framed problem will help you avoid cognitive bias and open avenues for discussion. It will also encourage the exploration of more options.
A good way to test a problem statement for bias is to ask questions like these:
| Question | Action |
| Does the problem appear to have only one possible solution? | Look for ways to rephrase it to open up more possibilities. |
| Does the statement describe a symptom instead of the problem? | Dig deeper for the root cause. |
| Does the statement suggest the problem is that you don’t have enough time, money, or people? | Find a way to pose the problem that will lead to more creative solutions. |
| Does the problem statement lack an obvious solution? | Great! You’re probably ready to start exploring solutions. |
| Does the statement stimulate brainstorming and discussion? | Good job! Keep the discussion going by asking why. |
3. Keep asking why (and check in on the progress)
When it comes to problem-solving, stay curious. Lean on your growth mindset to keep asking why — and check in on the progress.
Asking why until you’re satisfied that you’ve uncovered the root cause of the problem will help you avoid ineffective band-aid solutions.
What to avoid when writing a problem statement
When crafting a problem statement, it's essential to communicate the issue clearly and effectively. A well-formulated problem statement sets the stage for understanding and addressing the challenge at hand. However, there are common pitfalls that can undermine its clarity and purpose. Here's what you should avoid:
- Vagueness : Be specific about the problem and its context.
- Complexity : Keep the language simple and direct.
- Overgeneralization : Avoid broad statements that don’t address specific issues.
- Assumptions : Don’t presume solutions or causes without evidence.
- Jargon : Use clear, accessible language that can be understood by all stakeholders.
Refining your problem statements
When solving any sort of problem, there’s likely a slew of questions that might arise for you. In order to holistically understand the root cause of the problem at hand, your workforce needs to stay curious.
An effective problem statement creates the space you and your team need to explore, gain insight, and get buy-in before taking action.
If you have embarked on a proposed solution, it’s also important to understand that solutions are malleable. There may be no single best solution. Solutions can change and adapt as external factors change, too. It’s more important than ever that organizations stay agile . This means that interactive check-ins are critical to solving tough problems. By keeping a good pulse on your course of action, you’ll be better equipped to pivot when the time comes to change.
BetterUp can help. With access to virtual coaching , your people can get personalized support to help solve tough problems of the future.
Enhance your problem-solving skills
Discover effective strategies and personalized guidance to tackle complex challenges with confidence.
Madeline Miles
Madeline is a writer, communicator, and storyteller who is passionate about using words to help drive positive change. She holds a bachelor's in English Creative Writing and Communication Studies and lives in Denver, Colorado. In her spare time, she's usually somewhere outside (preferably in the mountains) — and enjoys poetry and fiction.

18 excellent educational podcasts to fuel your love of learning
The future of ai: where does your job stand, 6 ai prompt generator tools to boost your creativity, 4 benefits of ai and 4 potential disadvantages, 20 ai tools to help boost productivity in 2023, how to use 100% of your brain: is it possible, experimentation brings innovation: create an experimental workplace, can dreams help you solve problems 6 ways to try, applications of ai: 10 common examples, similar articles, 10 problem-solving strategies to turn challenges on their head, writing a value statement: your guide to keeping your team aligned, how to write an executive summary in 10 steps, create smart kpis to strategically grow your business, stand out to your hiring panel with a personal value statement, what’s a project scope, and how do you write one, contingency planning: 4 steps to prepare for the unexpected, what is a career statement, and should you write one, how to craft an impactful company mission statement, stay connected with betterup, get our newsletter, event invites, plus product insights and research..
3100 E 5th Street, Suite 350 Austin, TX 78702
- Platform Overview
- Integrations
- Powered by AI
- BetterUp Lead™
- BetterUp Manage™
- BetterUp Care®
- Sales Performance
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Case Studies
- Why BetterUp?
- About Coaching
- Find your Coach
- Career Coaching
- Communication Coaching
- Life Coaching
- News and Press
- Leadership Team
- Become a BetterUp Coach
- BetterUp Labs
- Center for Purpose & Performance
- Leadership Training
- Business Coaching
- Contact Support
- Contact Sales
- Privacy Policy
- Acceptable Use Policy
- Trust & Security
- Cookie Preferences
How to Write a Case Study Analysis
Before writing a case study analysis, it is important to identify a relevant subject and research problem. While preparing to write, the author should critically assess the potential problem and the need for in-depth analysis. For example, hidden problems, outdated information, or a feasible recommendation are all indications that a problem lends itself to a case study. The introduction should not only include a problem statement but should also note its importance, provide background information, supply a rationale for applying a case study method, and suggest potential advancement of knowledge in the given field.
Literature Review
The key purpose of the literature review in a case study analysis is to present the historical context of a problem and its background based on academic evidence. Synthesis of existing studies contributes to the subsequent substantial aspects that should be taken into account:
- Identify the context of the problem under consideration and locate related studies, showing the link between them. Each of the academic pieces used to write a case study should make a particular contribution to understanding or resolving the target problem.
- Connect all the studies together and provide a critical appraisal. One of the most common mistakes is to merely present existing evidence without any analysis or clarification of how one or another research investigation relates to the problem.
- Discover and discuss any gaps in the literature, demonstrating how the case study adds more value and credibility to the available evidence. For example, if the case study focuses on strategies used to promote feminism, it is possible to explore the gap of how this movement is developing in the Middle East, where it is not as evident as in Western countries.
- Identify conflicts and contradictory issues that can be found in the literature. This helps in coming closer to the resolution of the problem. If, for example, two different approaches are regarded as mutually exclusive in one study, and the same approaches are considered compatible in another, it is an evident conflict. A discussion of such contradictory issues should be placed in the case study to suggest feasible solutions.
- Locate the case study in the context of the literature and within the larger scale. More to the point, by synthesizing the pertinent literature and indicating the role of the case study, the researcher shows that he or she has made essential efforts toward addressing the problem.
In this section, it is important to clarify why a specific subject and problem were chosen for study. A range of subjects is possible, and the type chosen will impact how the method will be described. The key types of subjects include phenomena, places, persons, and events.
- The investigation of a phenomenon as a target of a case study implies that certain facts or circumstances exist and require change and improvement. The behavioral and social sciences often require the study of challenging issues such as the causes of high employee turnover or a low level of motivation on the part of managers. In such a case, cause-and-effect relationships should be established to evaluate the environment.
- If an accident or event composes the basis of the case study, its time and place will set the specifics of the research. A rare or critical event as well as any one of a number of common situations may be selected; in any case, a rationale should be provided to support the choice. As a rule, rare events require forging a new way of thinking regarding the occurrence, while dealing with a commonly encountered situation is associated with challenging existing hypotheses. In both types of cases, the following elements should be included in the case analysis: timeframe, circumstances, and consequences.
- A focus on a person as the subject of a study refers to scrutinizing the individual’s experience, relationships, and behaviors. For example, a discussion of Mark Zuckerberg as the creator of Facebook requires identifying the background, conflicts, and positive and negative consequences of his contributions to society.
- A place as the subject of a case study should be special, and it should be clear to readers why a particular area or neighborhood was chosen. What is, for example, the aim of focusing on China and Japan instead of the United States when exploring homelessness issues?
An important part of case study research or development in the field of the social and behavioral sciences involves discussing and interpreting findings. Therefore, after a thorough literature review, it is necessary to compare, reiterate, and revise the findings based on the experiences reported in previous studies along with the writer’s personal understanding of the subject studied.
- The discussion section may start with a brief summary of the findings that are of the greatest importance and particularly thought-provoking.
- The results should be assessed in terms of the hypothesis and objectives of the research. Briefly reiterating these, indicate whether the data obtained have confirmed the hypothesis, the goal has been achieved, and the research tasks have been addressed.
- The researcher should indicate how the findings are consistent with the conclusions of other researchers and theories described in the literature review. Comparing and contrasting the findings with the articles mentioned in the literature review will be beneficial as this will support the importance of the new study.
- To identify the possibilities and ways of applying the results to solve practical problems, recommendations for practical implementation should be as specific as possible and describe actions that organizations or individuals can take to put the findings into practice.
- The advantages of the research methodology used and the limitations of the generalization of the results obtained should be clarified. Such a discussion is especially necessary in a case study since it demonstrates an understanding of methodological nuances.
- It is advantageous to outline the prospects and suggestions for further research on the given problem to expand the scope of application of the results. It is also crucial to point out possible ways to improve the methodology and organization of a case study analysis.
In the conclusion, restating the key findings and noting their importance is essential to allow readers to understand the key points of the case study report. The conclusion should be written concisely, including a description of the problem and elaborating on solutions while presenting the expected future effect of the actions proposed for practical implementation. While the body of the case study paper focuses on details, the conclusion contains a generalized scope of the research problem. However, overgeneralization as well as failure to specify limitations should be avoided. Only the documentary evidence serves as a basis for assumptions, and the statement of limitations will help preclude unjustified conclusions.
Unfortunately, your browser is too old to work on this site.
For full functionality of this site it is necessary to enable JavaScript.
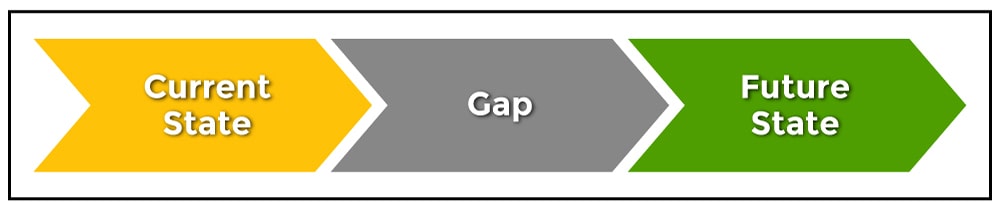
How to Write an Effective Problem Statement
Published: April 9, 2018 by Rod Morgan

Continuous improvement specialists are challenged to solve problems for their organizations or clients. They have acquired a wide array of tools, methods and techniques for that purpose.
If continuous improvement practitioners are able to establish the winning conditions for change, they can look forward to successful outcomes. However, the devil is in the details, making continuous improvement jobs interesting and challenging.
One of those “little devils” that often gets overlooked is the need to construct an effective problem statement at the start of any improvement project.
What Is a Problem Statement?
Adapted from an article by Alan Bryman in the International Journal of Social Research Methodology : A problem is a statement about an area of concern, a condition to be improved upon, a difficulty to be eliminated, or a troubling question that exists in theory or in practice that points to the need for meaningful understanding and deliberate investigation.
Why Is It So Hard to Write an Effective Problem Statement?
One of the challenges in writing a great problem statement is the distractions that can come from a variety of sources.
- Symptoms associated with the problem add to the confusion when trying to describe a problem. For example, arriving at the physician’s office and stating, “Doctor, I am experiencing pain in the back of my thigh down to the lower part of my leg! I need you to ‘fix’ my leg!” It is only after a thoughtful evaluation that the doctor concludes that your problem lies with your sciatic nerve and originates in your lower back.
- Solutions are often an early consideration when wrestling with a problem. When one is faced with a problem, alleviating that pain as quickly as possible is a natural, almost reflexive, action. It is, however, extremely important to avoid jumping to solutions until a profound understanding of the current state is achieved.
- The search for causes of your pain is a natural reaction that also needs to be avoided when first describing a problem. Establishing root cause will be a part of the ensuing investigative procedure but should be reserved for the appropriate time in the lifecycle of the problem-solving method.
- Blame is also a natural reflex when one is afflicted with a problem. A quote attributed to John Burroughs, American naturalist and nature essayist, may be all that needs to be said on this subject: “You can get discouraged many times, but you are not a failure until you begin to blame somebody else and stop trying.”
In short, a great problem statement must be free of causes, solutions and blame, and careful consideration must be given to ensure symptoms do not become a distraction.
What Is in a Problem Statement?
A problem statement should describe an undesirable gap between the current-state level of performance and the desired future-state level of performance. A problem statement should include absolute or relative measures of the problem that quantify that gap, but should not include possible causes or solutions!

Key elements of an effective problem statement include:
- Gap : Identify the gap (pain) that exists today.
- Timeframe, location and trend : Describe when and where the problem was first observed and what kind of trend it is following.
- Impact : Quantify the gap (cost, time, quality, environmental, personal, etc.)
- Importance : To the organization, the individual, etc. to better understand the urgency.
What Method Can I Employ to Author a Great Problem Statement?
The ability to articulate an effective problem statement is not simply a business skill – it is a life skill. How can children, youth and adults begin to solve problems if they haven’t been able to adequately describe them? This holds true for continuous improvement specialists.
The 5W2H (what, when, where, why, who, how, how much) method is deceptively simple. Ask the right questions in the right order and let the answers lead you to a great problem statement.
Example of Developing a Problem Statement
Let’s walk through the 5W2H method for manufacturing and call center examples.
Question 1 : What is the problem that needs to be solved?
- Manufacturer : Window frames and parts are ending up in the assembly department missing required weep holes or slots.
- Call center : The assessment call is too complex, time consuming and administratively heavy, resulting in a diminished experience for the client as well as the staff member performing the work.
Question 2 : Why is it a problem? (highlight the pain)
- Manufacturer : If identified (visual inspection), the affected parts must be sent back for rework, thereby increasing the overall cost of manufacturing, creating higher inventory levels (WIP) and increasing risk since some of the defects may not be detected until later in the process, or worse, they may end up being incorrectly shipped to the job sites.
- Call center : This results in higher variability and length of call handling time, clients having to repeat their “story” as the move through the assessment and downstream case worker (meeting) process, clients providing more information than may be required, increased workload for the assessment worker and increased wait times in the (telephone) queue. The overall impact is reduced service levels as well as diminished client and assessment worker experience.
Question 3 : Where is the problem observed? (location, products)
- Manufacturer : This problem is observed in the assembly department, downstream departments as well as ultimately in the field with customer complaints and costly field repairs and replacements.
- Call center : This problem is observed in all assessment calls but will vary in magnitude depending on the client (needs and circumstance), assessment worker (experience) and other factors that contribute to variation in the handling of assessment calls.
Question 4 : Who is impacted? (customers, businesses, departments)
- Manufacturer : This problem affects the assembly department that is tasked with trying to inspect for the error and react accordingly, rework occurring in the department/work cell responsible for weep holes and slots, the company as a whole in terms of cost, brand and reputation, and, most importantly, the customer who is affected by this problem if it makes it to the field.
- Call center : This affects the client associated with the call, clients waiting in the queue, client’s families, and the organization and employers in the community being served.
Question 5 : When was the problem first observed?
- Manufacturer : This has been an ongoing issue going back as far as memory serves in the long-term employees, but with increased volume and more customization and higher complexity in design, the impact and severity of this problem has increased rapidly over the last two years.
- Call center : This is a latent problem that has always existed but has become more evident with recent changes, including changes in funding, legislation, demand for services, client demographics and recent integration efforts in the organization as part of their ongoing commitment to continuous improvement of service pathways and client experience.
Question 6 : How is the problem observed? (symptoms)
- Manufacturer : Customer (in-field installation and service) complaints, increased warranty costs, manufacturing non-conformance reports (NCR), complaints from assembly department team and increased costs in fabrication.
- Call center : This problem is observed in the variation in call-handling times, wait times in the telephone queue, call abandon rates, increased stress in front-line staff (workload and client anxiety/dissatisfaction) and ambiguity in call handling protocols.
Question 7 : How often is the problem observed? (error rate, magnitude, trend)
- Manufacturer : There is an observed 62,000 parts per million (PPM) for this specific defect, taking into consideration rework completed in-house and observed defects in the field. The PPM is derived from the number of weeping holes and slots required per unit assembly versus the actual number of deficiencies overall observed for the same number of units.
- Call center : This is a daily operational occurrence but increases in call complexity related to changes in the knowledge base – multiple programs and changes in the environment (client demographics and needs/circumstances, legislation, etc.) – have resulted in an increase in severity and stress on the system.
Think of a problem you have encountered in your personal or professional life, or a problem you are currently tasked to solve. Employ the preceding method of asking seven simple questions and see where it takes you.
Teach this simple and effective method to your friends, colleagues and family. Writing problem statements truly is a life skill and, when employed correctly, will place anyone in good stead to start solving the problem.
About the Author

- Richard G. Trefry Library
- Course-Specific
Q. Need help with writing a case study analysis?
- Textbooks & Course Materials
- Tutoring & Classroom Help
- Writing & Citing
Answered By: Coleen Neary Last Updated: Jun 02, 2023 Views: 267246
A case study analysis requires you to investigate a business problem, examine the alternative solutions, and propose the most effective solution using supporting evidenc e.
Before you begin writing, follow these guidelines to help you prepare and understand the case study:
- Take notes, highlight relevant facts, and underline key problems.
- Identify two to five key problems
- Why do they exist?
- How do they impact the organization?
- Who is responsible for them?
- Review course readings, discussions, outside research, and your experience.
- Consider strong supporting evidence, pros, and cons: is this solution realistic?
Once you have gathered the necessary information, a draft of your analysis should include these sections:
- Identify the key problems and issues in the case study.
- Formulate and include a thesis statement, summarizing the outcome of your analysis in 1–2 sentences.
- Set the scene: background information, relevant facts, and the most important issues.
- Demonstrate that you have researched the problems in this case study.
- Outline possible alternatives (not necessarily all of them)
- Explain why alternatives were rejected
- Constraints/reasons
- Why are alternatives not possible at this time?
- Provide one specific and realistic solution
- Explain why this solution was chosen
- Support this solution with solid evidence
- Concepts from class (text readings, discussions, lectures)
- Outside research
- Personal experience (anecdotes)
- Determine and discuss specific strategies for accomplishing the proposed solution.
- If applicable, recommend further action to resolve some of the issues
- What should be done and who should do it?
After you have composed the first draft of your case study analysis, read through it to check for any gaps or inconsistencies in content or structure: Is your thesis statement clear and direct? Have you provided solid evidence? Is any component from the analysis missing?
Source : University of Arizona Writing Center. (n.d.). Writing a case study analysis . URL: https://writingcenter.uagc.edu/writing-case-study-analysis
- For additional help with the final draft on revisions and editing, please refer to Writing@APUS, The Final Product for tips on proofreading,
- Looking for other business writing resources? See: How to Find Business Communication & Writing Resources
Questions? Contact the library .
- How do I find case studies about my research topic?
- How can I find case study articles about metaphors in organizations?
- Analyze a case study (Cenage)
- Write a case study analysis (Cenage)
- How to Write and Format a Business Case Study (ThoughtCo,)
- Boston Univerity Libguide | Open Access Business Case Studies
- Free Management Library | Basics of Developing Case Studies
- Share on Facebook
Was this helpful? Yes 104 No 8
Need personalized help? Librarians are available 365 days/nights per year! See our schedule.

Learn more about how librarians can help you succeed.
Useful Links
3+ SAMPLE Case Analysis Problem Statement in PDF| MS Word
Case analysis problem statement | ms word, 3+ sample case analysis problem statement, what is a case analysis problem statement, components of a case analysis problem statement, how to write a case analysis problem statement, how do you write a problem statement, what makes a good problem statement, what is a problem statement.

Case Study Analysis Problem Statement

Business Case Analysis Problem Statement

Case-Control Analysis Problem Statement
Case Analysis Team Problem Statement
1. define how certain things should work, 2. state the problem and emphasize why it matters, 3. explain the financial costs of the problem, 4. back up the claims and propose a clear solution, 5. highlight the benefits of the proposed solutions, 6. conclude the problem statement.
- What is the problem?
- Who has the problem?
- Where and when does the problem happen?
- How often does the problem happen?
- What are the causes?
- What is its impact?
Share This Post on Your Network
File formats, word templates, google docs templates, excel templates, powerpoint templates, google sheets templates, google slides templates, pdf templates, publisher templates, psd templates, indesign templates, illustrator templates, pages templates, keynote templates, numbers templates, outlook templates, you may also like these articles, 20+ sample nursing personal statements in pdf | ms word.

Since the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic, everyone began to realize just how critical the job of nurses was. Of course, even in the pre-pandemic era, nurses already played…
14+ SAMPLE Talent Statement in PDF

“Talent is cheaper than table salt. What separates the talented individual from the successful one is a lot of hard work,” Stephen King quotes. Talent acquisition specialists are often…
browse by categories
- Questionnaire
- Description
- Reconciliation
- Certificate
- Spreadsheet
Information
- privacy policy
- Terms & Conditions
Case Study Research Method in Psychology
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
Case studies are in-depth investigations of a person, group, event, or community. Typically, data is gathered from various sources using several methods (e.g., observations & interviews).
The case study research method originated in clinical medicine (the case history, i.e., the patient’s personal history). In psychology, case studies are often confined to the study of a particular individual.
The information is mainly biographical and relates to events in the individual’s past (i.e., retrospective), as well as to significant events that are currently occurring in his or her everyday life.
The case study is not a research method, but researchers select methods of data collection and analysis that will generate material suitable for case studies.
Freud (1909a, 1909b) conducted very detailed investigations into the private lives of his patients in an attempt to both understand and help them overcome their illnesses.
This makes it clear that the case study is a method that should only be used by a psychologist, therapist, or psychiatrist, i.e., someone with a professional qualification.
There is an ethical issue of competence. Only someone qualified to diagnose and treat a person can conduct a formal case study relating to atypical (i.e., abnormal) behavior or atypical development.
Famous Case Studies
- Anna O – One of the most famous case studies, documenting psychoanalyst Josef Breuer’s treatment of “Anna O” (real name Bertha Pappenheim) for hysteria in the late 1800s using early psychoanalytic theory.
- Little Hans – A child psychoanalysis case study published by Sigmund Freud in 1909 analyzing his five-year-old patient Herbert Graf’s house phobia as related to the Oedipus complex.
- Bruce/Brenda – Gender identity case of the boy (Bruce) whose botched circumcision led psychologist John Money to advise gender reassignment and raise him as a girl (Brenda) in the 1960s.
- Genie Wiley – Linguistics/psychological development case of the victim of extreme isolation abuse who was studied in 1970s California for effects of early language deprivation on acquiring speech later in life.
- Phineas Gage – One of the most famous neuropsychology case studies analyzes personality changes in railroad worker Phineas Gage after an 1848 brain injury involving a tamping iron piercing his skull.
Clinical Case Studies
- Studying the effectiveness of psychotherapy approaches with an individual patient
- Assessing and treating mental illnesses like depression, anxiety disorders, PTSD
- Neuropsychological cases investigating brain injuries or disorders
Child Psychology Case Studies
- Studying psychological development from birth through adolescence
- Cases of learning disabilities, autism spectrum disorders, ADHD
- Effects of trauma, abuse, deprivation on development
Types of Case Studies
- Explanatory case studies : Used to explore causation in order to find underlying principles. Helpful for doing qualitative analysis to explain presumed causal links.
- Exploratory case studies : Used to explore situations where an intervention being evaluated has no clear set of outcomes. It helps define questions and hypotheses for future research.
- Descriptive case studies : Describe an intervention or phenomenon and the real-life context in which it occurred. It is helpful for illustrating certain topics within an evaluation.
- Multiple-case studies : Used to explore differences between cases and replicate findings across cases. Helpful for comparing and contrasting specific cases.
- Intrinsic : Used to gain a better understanding of a particular case. Helpful for capturing the complexity of a single case.
- Collective : Used to explore a general phenomenon using multiple case studies. Helpful for jointly studying a group of cases in order to inquire into the phenomenon.
Where Do You Find Data for a Case Study?
There are several places to find data for a case study. The key is to gather data from multiple sources to get a complete picture of the case and corroborate facts or findings through triangulation of evidence. Most of this information is likely qualitative (i.e., verbal description rather than measurement), but the psychologist might also collect numerical data.
1. Primary sources
- Interviews – Interviewing key people related to the case to get their perspectives and insights. The interview is an extremely effective procedure for obtaining information about an individual, and it may be used to collect comments from the person’s friends, parents, employer, workmates, and others who have a good knowledge of the person, as well as to obtain facts from the person him or herself.
- Observations – Observing behaviors, interactions, processes, etc., related to the case as they unfold in real-time.
- Documents & Records – Reviewing private documents, diaries, public records, correspondence, meeting minutes, etc., relevant to the case.
2. Secondary sources
- News/Media – News coverage of events related to the case study.
- Academic articles – Journal articles, dissertations etc. that discuss the case.
- Government reports – Official data and records related to the case context.
- Books/films – Books, documentaries or films discussing the case.
3. Archival records
Searching historical archives, museum collections and databases to find relevant documents, visual/audio records related to the case history and context.
Public archives like newspapers, organizational records, photographic collections could all include potentially relevant pieces of information to shed light on attitudes, cultural perspectives, common practices and historical contexts related to psychology.
4. Organizational records
Organizational records offer the advantage of often having large datasets collected over time that can reveal or confirm psychological insights.
Of course, privacy and ethical concerns regarding confidential data must be navigated carefully.
However, with proper protocols, organizational records can provide invaluable context and empirical depth to qualitative case studies exploring the intersection of psychology and organizations.
- Organizational/industrial psychology research : Organizational records like employee surveys, turnover/retention data, policies, incident reports etc. may provide insight into topics like job satisfaction, workplace culture and dynamics, leadership issues, employee behaviors etc.
- Clinical psychology : Therapists/hospitals may grant access to anonymized medical records to study aspects like assessments, diagnoses, treatment plans etc. This could shed light on clinical practices.
- School psychology : Studies could utilize anonymized student records like test scores, grades, disciplinary issues, and counseling referrals to study child development, learning barriers, effectiveness of support programs, and more.
How do I Write a Case Study in Psychology?
Follow specified case study guidelines provided by a journal or your psychology tutor. General components of clinical case studies include: background, symptoms, assessments, diagnosis, treatment, and outcomes. Interpreting the information means the researcher decides what to include or leave out. A good case study should always clarify which information is the factual description and which is an inference or the researcher’s opinion.
1. Introduction
- Provide background on the case context and why it is of interest, presenting background information like demographics, relevant history, and presenting problem.
- Compare briefly to similar published cases if applicable. Clearly state the focus/importance of the case.
2. Case Presentation
- Describe the presenting problem in detail, including symptoms, duration,and impact on daily life.
- Include client demographics like age and gender, information about social relationships, and mental health history.
- Describe all physical, emotional, and/or sensory symptoms reported by the client.
- Use patient quotes to describe the initial complaint verbatim. Follow with full-sentence summaries of relevant history details gathered, including key components that led to a working diagnosis.
- Summarize clinical exam results, namely orthopedic/neurological tests, imaging, lab tests, etc. Note actual results rather than subjective conclusions. Provide images if clearly reproducible/anonymized.
- Clearly state the working diagnosis or clinical impression before transitioning to management.
3. Management and Outcome
- Indicate the total duration of care and number of treatments given over what timeframe. Use specific names/descriptions for any therapies/interventions applied.
- Present the results of the intervention,including any quantitative or qualitative data collected.
- For outcomes, utilize visual analog scales for pain, medication usage logs, etc., if possible. Include patient self-reports of improvement/worsening of symptoms. Note the reason for discharge/end of care.
4. Discussion
- Analyze the case, exploring contributing factors, limitations of the study, and connections to existing research.
- Analyze the effectiveness of the intervention,considering factors like participant adherence, limitations of the study, and potential alternative explanations for the results.
- Identify any questions raised in the case analysis and relate insights to established theories and current research if applicable. Avoid definitive claims about physiological explanations.
- Offer clinical implications, and suggest future research directions.
5. Additional Items
- Thank specific assistants for writing support only. No patient acknowledgments.
- References should directly support any key claims or quotes included.
- Use tables/figures/images only if substantially informative. Include permissions and legends/explanatory notes.
- Provides detailed (rich qualitative) information.
- Provides insight for further research.
- Permitting investigation of otherwise impractical (or unethical) situations.
Case studies allow a researcher to investigate a topic in far more detail than might be possible if they were trying to deal with a large number of research participants (nomothetic approach) with the aim of ‘averaging’.
Because of their in-depth, multi-sided approach, case studies often shed light on aspects of human thinking and behavior that would be unethical or impractical to study in other ways.
Research that only looks into the measurable aspects of human behavior is not likely to give us insights into the subjective dimension of experience, which is important to psychoanalytic and humanistic psychologists.
Case studies are often used in exploratory research. They can help us generate new ideas (that might be tested by other methods). They are an important way of illustrating theories and can help show how different aspects of a person’s life are related to each other.
The method is, therefore, important for psychologists who adopt a holistic point of view (i.e., humanistic psychologists ).
Limitations
- Lacking scientific rigor and providing little basis for generalization of results to the wider population.
- Researchers’ own subjective feelings may influence the case study (researcher bias).
- Difficult to replicate.
- Time-consuming and expensive.
- The volume of data, together with the time restrictions in place, impacted the depth of analysis that was possible within the available resources.
Because a case study deals with only one person/event/group, we can never be sure if the case study investigated is representative of the wider body of “similar” instances. This means the conclusions drawn from a particular case may not be transferable to other settings.
Because case studies are based on the analysis of qualitative (i.e., descriptive) data , a lot depends on the psychologist’s interpretation of the information she has acquired.
This means that there is a lot of scope for Anna O , and it could be that the subjective opinions of the psychologist intrude in the assessment of what the data means.
For example, Freud has been criticized for producing case studies in which the information was sometimes distorted to fit particular behavioral theories (e.g., Little Hans ).
This is also true of Money’s interpretation of the Bruce/Brenda case study (Diamond, 1997) when he ignored evidence that went against his theory.
Breuer, J., & Freud, S. (1895). Studies on hysteria . Standard Edition 2: London.
Curtiss, S. (1981). Genie: The case of a modern wild child .
Diamond, M., & Sigmundson, K. (1997). Sex Reassignment at Birth: Long-term Review and Clinical Implications. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine , 151(3), 298-304
Freud, S. (1909a). Analysis of a phobia of a five year old boy. In The Pelican Freud Library (1977), Vol 8, Case Histories 1, pages 169-306
Freud, S. (1909b). Bemerkungen über einen Fall von Zwangsneurose (Der “Rattenmann”). Jb. psychoanal. psychopathol. Forsch ., I, p. 357-421; GW, VII, p. 379-463; Notes upon a case of obsessional neurosis, SE , 10: 151-318.
Harlow J. M. (1848). Passage of an iron rod through the head. Boston Medical and Surgical Journal, 39 , 389–393.
Harlow, J. M. (1868). Recovery from the Passage of an Iron Bar through the Head . Publications of the Massachusetts Medical Society. 2 (3), 327-347.
Money, J., & Ehrhardt, A. A. (1972). Man & Woman, Boy & Girl : The Differentiation and Dimorphism of Gender Identity from Conception to Maturity. Baltimore, Maryland: Johns Hopkins University Press.
Money, J., & Tucker, P. (1975). Sexual signatures: On being a man or a woman.
Further Information
- Case Study Approach
- Case Study Method
- Enhancing the Quality of Case Studies in Health Services Research
- “We do things together” A case study of “couplehood” in dementia
- Using mixed methods for evaluating an integrative approach to cancer care: a case study
Related Articles

Research Methodology
Qualitative Data Coding

What Is a Focus Group?

Cross-Cultural Research Methodology In Psychology

What Is Internal Validity In Research?

Research Methodology , Statistics
What Is Face Validity In Research? Importance & How To Measure

Criterion Validity: Definition & Examples

How to Build a Compelling Problem Statement (+Case Study)

Your pipeline’s ‘Closed Lost’ column is filled with prospects who expressed the exact same pain points as your customers.
Both of these groups started from the same place — a list of pains that align with your product. But they ended their buying journey in two different places.
So what gives? How does a picture-perfect deal, with a prospect whose problems are a match for your product, fall through?
Nobody cared (enough).
Really. Sometimes, a competitor steals the deal. Others times, a budget gets re-allocated. But more often than not, your deal just slipped down the priority list. Your champion couldn’t get their team interested. The decider didn’t take the time to take a look.
That’s because your champion didn’t tell a compelling story that cut through the clutter .
Some champions are natural storytellers. They hit all the high notes. They know how to make their team lean in a little closer. But other buyers need your help.
They need a specific, compelling problem statement that grabs and holds attention.
Here’s how to create one.
The Formula for Compelling Problem Statements
First, I’ll give you the formula. Then, we’ll break down each of its parts.
Costs Every [Frequency], at least [Reach] are [Pain], costing us [Impact].
Consequences That means [Implication #2]. If that’s not addressed by [Timeline], then [Implication #3].
Part 1: Focus on Costs
We all feel more upset if we lose $10, than we feel happy if we find $10.
That’s the basic idea of “Loss Aversion.” We feel a greater pressure to avoid losses than we do to acquire the equivalent gain. It’s also why you should build your problem statement around losses.
Highlight active or immanent losses first, before calling out new opportunities.

To make the loss compelling, be specific. And to be specific, quantify the impact of your buyer’s problem whenever possible. A simple way to estimate the impact is:

Don’t give your best guess. Ask your buyer what their guess is. Then, write it down with them. Here are a few examples, with some made up numbers:

Once you’ve quantified the problem, don’t assume the loss is meaningful .
For example, if you’re selling to the enterprise, beware of The Law of Large Numbers. Pointing out a $1M loss is pointing out 0.0001% in a business that does $10B in annual revenue.
Instead, ask questions like:
- How does this estimate of [X] compare to what you expected to see?
- How do you think [decision maker] would react to seeing this number?
- Are there other problems your team’s facing that are more pressing than this?
Part 2: Highlight Consequences
You’d be surprised what overwhelm and burnout can force us to live with. We grow numb to our problems, and apathy becomes a perfectly acceptable solution.
But often, that’s because we can’t see the full consequences of our inaction. So once you’ve quantified the loss (above), press into its implications. There are three levels of consequences you’ll want to speak to:
- Functional Problems: “It takes a long time to build customer surveys and analyze the data.”
- Strategic Problems: “We’re not sure which customers are a churn risk before their renewal date.”
- Personal Problems: “Me, or someone on my team, may lose our job if renewal revenue declines.”
Now, nobody likes talking consequences. So generally, it’s best to lead your buyers to them with questions — not statements. Questions that start by asking:
- What happens if...
- What does this mean for...
- How will that affect...
Bringing It All Together
If your head is spinning with “math” right now, your buyer’s will be too.
While you’ll quickly become fluent in problem statements using this framework, your champion will need some help. So from here, make sure to:
- Put their story to the test. After you’ve drawn out all the component parts with your champion, ask them to play back the story. Is it compelling? Is their delivery confident?
- Write it out for them. Give them something to refer back to during a conversation, and to send around to their team afterwards.
- Develop a problem statement process. Getting the data you need to turn a minor-annoyance into a can’t-ignore mega issue may require some creativity. Here’s a case study on that, below.
[Case Study] “My board definitely needs to see this.”
The breakthrough that let one my past sales teams cross the chasm from $500K, to $5M, in ARR was the process for enabling our champions with a can’t-ignore problem statement.
Here’s the full story.
Creating Context
We sold marketing and fundraising software to nonprofits. CRM, landing pages, payments, email, text, video, all-in-one. For context, our market was the 1.2M nonprofits raising close to $500 B every year.
A portion of this funding comes from foundations. Foundations are organizations that exist to give out large chunks of money to nonprofits called “grants.” These grants are great when you get them, but they’re not sustainable.
For example, a $500K grant needs to be replaced with a wider group of individual donors before it’s fully spent. Otherwise, the nonprofit can’t keep funding their programs and payroll.
When nonprofits don’t raise money from individuals, that’s a problem. Think of it like investing in a startup. If the startup doesn’t find customers to generate cash — aside from raising more venture funding — the investment was for nothing. There’s no revenue to keep the show going.
Collecting the Right Data
I had created a champion out of the Head of Grantmaking at one of the nation’s largest family foundations. They grant out more than $50M to nonprofits every year, and she saw the problem we were solving.
She knew our software could help her nonprofits raise more funding, but buying software for 20 nonprofits would be a significant, six-figure deal — which needed board approval. What’s more, her board had never funded a for-profit company’s software before. Generally, nonprofits are skeptical of for-profits, regardless of their social good.
We were rolling a boulder uphill, and needed a compelling story. We were chatting one day when I said, “This may be crazy. But what if we asked all your nonprofits for their fundraising data, to show your board?”
She was up to give it a shot. So next, I:
- Wrote a three-part email campaign requesting her nonprofits help her out with a survey.
- Signed up for Typeform and built out a simple survey to collect fundraising data.
- Opened up a free Mailchimp account and built out the survey campaign.
- Recorded a Loom video that showed my champion how to upload a list of emails and hit “send.”
- Downloaded all the survey responses a week later and crunched the data in Excel.
- Put together a short, 2-page report for the next board meeting packet.
Crafting the Problem Statement
That report shared this statement:
Every year, at least 200 of the Foundation’s nonprofits raise less than 20% of their annual budget from individual donors, which is costing the Foundation more than $10M in follow-on funding to keep them operational. This means the programs we support are at risk of closing, if we don’t continue to fund them. If that’s not addressed inside this fiscal year, we’ll be unable to allocate this funding to new initiatives outlined in the strategic plan we’re voting on today.
When my champion saw this, she immediately said, “ My board needs to see this .”
Here’s the end of the story.
This paragraph — not a case study, deck, or demo — helped my champion closed the deal.
That deal not only pushed us over quota for the month, it opened up a whole new market segment. We could now point to their foundation, and the 20 nonprofits they brought with them, as one of our customers. That gave us credibility to start engaging with other foundations.
In fact, we hired on a new FTE for our sales enablement team, who built out and perfected that survey process. It became a “free assessment” we gave to every champion in our pipeline.
FLUINT RESOURCES
Check out our library of free resources and templates.
Our readers are using our frameworks to close more deals, and faster than ever. How? They are selling with their buyers. You can too.
Get the latest posts and frameworks on selling with your buyers, not to them.
Delivered to your inbox 2X per month. Sometimes 3X if we're on a roll.

- Business Templates
- Sample Statements
FREE 10+ Case Study Problem Statement Samples in PDF | DOC

A case study is an in-depth and specific study of a certain yet relevant person, group, or event. In a case study involving psychology and its related disciplines, nearly every aspect of the subject’s life and history is analyzed to understand the human mind through seeking and unveiling patters of behavior. This type of academic study can be used in a variety of fields including psychology, medicine, education, anthropology, political science, social science, law related studies, and social work. With the importance of this study, it is very much recommended to have this Case Study Problem Statement available anytime. In making this possible and convenient for the one that’s going to make all these problem statements, our site is offering you free, available, ready-made but very open to be customized templates that you can choose from. Just look into these templates throughout the article and choose the template that could help you achieve your problem statement goals.
Case Study Problem Statement
10+ case study problem statement samples, 1. data case study problem statement, 2. exploratory case study problem statement, 3. case study development problem statement, 4. case study sales problem statement, 5. dell case study problem statement, 6. sample case study problem statement, 7. standard case study problem statement, 8. case study analysis problem statement, 9. qualitative case study problem statement, 10. restorative case study problem statement, 11. case study scope of problem statement, what is a case study, benefits and limitations, types of case study, what exactly is a case study, when should you do a case study.
For other problem statement template needs, our site also offers you templates like Graduate School Personal Statement, Subcontractor Statement , Freelance Statement, High School Statement, Interior Design Statement, Short Research Statement , Scientific Research Statement, Copyright Disclaimer Statement and more in the storage just for you and your convenience. Our article does not only give you utilizable templates that you can choose from, but also relevant and important information that you might want to consider as you go along with your project and its processes.

Size: 46 KB

Size: 699 KB

Size: 127 KB

Size: 207 KB

Size: 505 KB

Size: 294 KB

Size: 67 KB

Size: 81 KB

Size: 609 KB

Size: 54 KB
The aim is that learning gained from studying one case can be generalized to many others, so putting it into simpler terms is the most effective way to achieve this goal. On the contrary, case studies tend to be highly subjective, specific, deep and it is sometimes difficult to generalize results to the larger population of common good. Case studies focus on a single individual or group cases, but somehow, they follow a format that is similar to other types of psychology writing.
A case study can have both strengths and weaknesses, just like any other type of academic writing. Researchers must take into consideration these advantages and disadvantages before deciding if this type of study is appropriate for their needs. One of the greatest advantages of a case study is that it allows researchers to investigate, imagine and scrutinize that are often difficult to impossible to replicate or studied in a laboratory. Some other benefits of a case study that are important to be tackled with are:
- Makes it possible for researchers to collect a great deal of information
- Provide researchers the chance to gather or collect information on rare or unusual cases
- Allows the researchers to develop hypotheses that can be explored and studied in depth in experimental research
- Don’t need to be generalized to the larger population
- Cannot demonstrate cause and effect
- May not be scientifically rigorous
- Can lead to bias
Researchers may choose to perform a case study if they are interested in exploring a unique or revise and improvise, somehow develop a recently discovered phenomenon. The insights gained from such research can then help the researchers develop additional ideas, critical insights and generalizations and study questions that might then be explored in future studies.
There are the many different types of case studies that psychologists and other researchers might use:
- Collective case studies : These talks about the studying of a group of individuals. Researchers might decide on studying a group of people in a certain setting or look at an entire community of people.
- Descriptive case studies : These usually starts with a descriptive theory. The subjects or respondent’s statements should be well-observed and the information gathered is compared to the pre-existing theory.
- Explanatory case studies : These are often used to do causal case studies. In other words, researchers are interested in looking at factors that may have actually caused certain yet common everyday-life-things to occur.
- Exploratory case studies : These are sometimes used as a prelude and continue to further, more in-depth research. This allows researchers to gather more information first before then use it in developing their research questions and hypotheses.
- Instrumental case studies : These happens when the individual or group allows researchers to understand more than what is initially obvious to observers, this is done through careful observations and focused group discussions.
- Intrinsic case studies : This type of case study is when the researcher has a personal motive or interest that he would like to answer by making the study. Jean Piaget’s deep and focused observations of his own children are great examples of how an intrinsic case study can contribute to the development of a psychological theory, further then becoming a great information that is spread to those who are practicing in the field.
A case study is a research strategy and an empirical inquiry that investigates a phenomenon within its real-life context. Case studies are based on an in-depth investigation of a single individual, group or event to explore the causes of underlying principles.
Understand how other companies have coped when faced with a challenging dilemma. Apply lessons learned from other organizations to your own company. Master and implement new ways of working. Obtain digestible information through brief but focused content.
You might find yourself getting difficulties in making the form or the project from scratch, as in zero. To help you in this matter, you are highly encouraged to avail the resources that are legally utilizable. Avail our great templates in SampleTemplates now!
Related Posts
Free 10+ research proposal problem statement samples in pdf | doc, free 10+ engineering problem statement samples [ software, mechanical, civil ], free 30+ information statement samples in pdf | ms word, free 50+ policy statement samples in ms word | google docs | pdf, free 50+ summary statement samples in pdf | ms word, free 10+ nursing school personal statement in pdf, free 20+ sworn statement samples in pdf | ms word, free 9+ mortgage statement samples and templates in pdf, free 10+ independent subcontractor statement samples in ms word | google docs | apple pages | pdf, free 10+ trust distribution statement samples in pdf, free 13+ sample personal statement templates in pdf | ms word, free 14+ compliance statement samples & templates in pdf | ms word, free 10+ extension impact statement samples in pdf | doc, free 10+ bank reconciliation statement samples and templates in pdf | ms word, free 10+ diversity mission statement samples in ms word | pdf, free 36+ statement examples & templates, free 31+ analysis templates, free 29+ statement samples, free 14+ compliance statement samples.
Create powerful business content together.

BONUS : Read the case study how-to guide .
Case Study Template
Good case studies tell a compelling story to potential clients of how your company rose to the occasion. The Case Study Template will help you showcase your company’s credibility in solving a particularly challenging client problem and prove to potential clients that you have what it takes to perform well. Specifically, case studies can help you:
- Highlight your expertise in delivering measurable results based on KPIs.
- Position your brand as an authority in your industry to attract potential customers.
- Provide visual proof of your skills, experience, and expertise as a company.
- Showcase your perseverance in handling difficult projects or campaigns.
Xtensio is your team space for beautiful living documents. Create , manage and share business collateral, easily. Join the 256,643 changemakers.
Other Case Study Templates

How to create an effective Case Study with Xtensio
- Click and start editing, no account or credit card required. Follow along with the instructional copy. Add charts, graphs, images, and videos to customize your case study. Drag & drop. Resize. It’s the easiest editor ever.
- Customize everything to match your brand. Define your style guide; Add your (or your client’s) brand fonts and colors. You can even pull colors directly from a website to easily brand your case studies.
- Work on the key details of your case study together on the cloud. Add colleagues (or clients) to collaborate on the case study template. Changes automatically save and sync across all devices, in real-time.
- Share a link. Present a slideshow. Embed. Download a PDF/PNG. Your case study seamlessly adapts to your workflow. No more jumping from tool-to-tool to create different types of deliverables.
- Reuse and repurpose. Save your own custom case study templates. Or copy and merge into other documents.
Follow along step-by-step with the Case Study how-to guide .
What is a case study?
An effective case study is a great way to show potential clients, customers, and stakeholders how valuable your product or service is by explaining how your business solved a particularly challenging client problem.
Marketing case studies examine a single client situation in-depth and provide a detailed analysis of how your organization resolved the challenge.
The best case studies not only tell a story about your company but also contain some hard measurable metrics. This allows you to highlight your successes in a way that will make an ideal potential customer become your customer. Essentially, a case study is an effective way to learn about your business and a great marketing tool.
When looking for potential projects to use for a case study, look for ones that:
- Involved a particular challenge that required a unique set of skills that your company possesses
- Received special awards, press coverage or accolades
- Involved a high profile project
- Involved a well-known (preferably Fortune 500) brand or company
The most important element of your case study is that it must show a real-life example to relate to your target client. While a good case study showcases your company, a great case study makes the reader want to start a conversation with you.
What information should be included in a case study?
The first thing to consider is who will be reading your case studies. Messages and their delivery resonate differently, depending on who is on the receiving end. For example, a thirty-something software entrepreneur will measure success differently than a fifty-something CEO of a large corporation. Understanding your target audience will help you tell your case study in a way that will effectively speak to them.
When gathering information for your case study, interview happy customers and ask questions to your potential case study subject that align with the story you are trying to tell. No case study will be the same, and your questions will vary from client to client.
Before you contact the customer, consider interview questions so you have an idea of what you need to produce a compelling case study demonstrating your potential to succeed.
At the end of the information-gathering process, you should have a solid understanding of the following to outline how your product was the best solution for the customers’ particular challenge:
- The client’s initial challenge
- Why did the client choose your company
- Your company’s approach to the problem
- The solution and implementation process
- The results and final measures of success
Some questions to ask your client during the initial interview:
- Can you give a brief description of your company?
- How did you first hear about our product or service?
- What challenges or pain points prompted using our product?
- What were you looking for in a solution to your problem?
- Did you have any roadblocks while using our product?
Don’t forget to talk to your colleagues and get their perspectives on the project when writing your case study. You may also want to include some quotes from internal stakeholders or project leads to make an even more compelling case study.
How do you write a case study?
When writing a case study, make sure you know who you’re talking to. Your audience, i.e. who would be interested in your product or service, should be your main focus when you create a case study. Once you’ve compiled your facts, format the story so that it will appeal to potential customers.
The format and content of case study templates vary, but in general, your business case study should look like a strong landing page: brief, pictorial, and engaging.
Xtensio’s case study template includes instructional copy to show you everything you need to know to create a real-life example of your company’s strengths. The template is organized into sections and modules designed to make your case study flow like a well-planned story and we’ve broken the template into three main sections: the snapshot, the body and the footer.
The Snapshot
This section is designed to give a quick overview of your story and prompt readers to want to learn more. Consider it an executive summary, a book cover, or a brief description in an online store. It should have enough information to grab a potential customer’s attention, but not so much that they will stop reading. Include client details, the project name, and a brief description of the problem, as well as quantitative metrics that demonstrate your accomplishment.
You can also include the date the case study was originally published here to help potential customers identify if your product or service is a good fit for them right now.
This section is the meat of your case study and will focus on customer results. Like any good story, it will have a beginning, a middle and an end. Classic western storytelling uses a pretty standard formula that includes a problem, the approach taken to solve it, the solution and the end results. The body of Xtensio’s case study template is divided into four key areas that align to these story elements: the Challenge, the Approach, the Solution and the Results. Here, make sure you explain using your product for a certain use case and describe how your service helped the client.
To close your case study, end with a short paragraph about who your company is, as well as your contact information. This is handy if your business case study becomes separated from your company’s website information somehow.
If you plan on sharing the case study online, make sure to add the links to your website and social media handles, using our social media module. If you are planning to print, then don’t forget to spell out the name of your website and/or add a contact phone number and email address.
Invite feedback and participation by your colleagues and the client by inviting them to collaborate on the case study template in real-time. Once you are satisfied with your case study, you can add it to your website, share it on your social channels, use it in presentations, or send out emails to potential clients. You can also download a pdf version that can be printed and shared.

Design, manage and share beautiful living documents… easily, together. Explore Xtensio
- Click and edit anything… together.
- Customize to match your branding.
- Share with a link, present, embed or download.
Related to the Case Study Template
Fully customizable templates that you can make your own.
See All Templates
Teams use Xtensio to craft and share beautiful living documents .
256,643 users and counting..
Jerome Katz
Professor of Entrepreneurship @
St. Louis University

Jake Peters

Robin Bramman
Founder and Chief Brand Mixologist @

Olakunle Oladehin
Executive Director @
Everybody Dance Now!

Aaron Friedland
The Walking School Bus

Trailblazer360

Stephen Paterson
Chief Product Officer @
AND Digital
Teamspace for beautiful living documents .

256,643 users and counting…
- Book a Demo
Fact sheets
- Facts in pictures
- Publications
- Questions and answers
- Tools and toolkits
- HIV and AIDS
- Hypertension
- Mental disorders
- Top 10 causes of death
- All countries
- Eastern Mediterranean
- South-East Asia
- Western Pacific
- Data by country
- Country presence
- Country strengthening
- Country cooperation strategies
- News releases
- Feature stories
- Press conferences
- Commentaries
- Photo library
- Afghanistan
- Cholera
- Coronavirus disease (COVID-19)
- Greater Horn of Africa
- Israel and occupied Palestinian territory
- Disease Outbreak News
- Situation reports
- Weekly Epidemiological Record
- Surveillance
- Health emergency appeal
- International Health Regulations
- Independent Oversight and Advisory Committee
- Classifications
- Data collections
- Global Health Estimates
- Mortality Database
- Sustainable Development Goals
- Health Inequality Monitor
- Triple Billion
- Data collection tools
- Global Health Observatory
- Insights and visualizations
- COVID excess deaths
- World Health Statistics
- Partnerships
- Committees and advisory groups
- Collaborating centres
- Technical teams
- Organizational structure
- Initiatives
- General Programme of Work
- WHO Academy
- Investment case
- WHO Foundation
- External audit
- Financial statements
- Internal audit and investigations
- Programme Budget
- Results reports
- Governing bodies
- World Health Assembly
- Executive Board
- Member States Portal
COVID-19 pandemic triggers 25% increase in prevalence of anxiety and depression worldwide
Wake-up call to all countries to step up mental health services and support.
In the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic, global prevalence of anxiety and depression increased by a massive 25%, according to a scientific brief released by the World Health Organization (WHO) today. The brief also highlights who has been most affected and summarizes the effect of the pandemic on the availability of mental health services and how this has changed during the pandemic.
Concerns about potential increases in mental health conditions had already prompted 90% of countries surveyed to include mental health and psychosocial support in their COVID-19 response plans, but major gaps and concerns remain.
“The information we have now about the impact of COVID-19 on the world’s mental health is just the tip of the iceberg,” said Dr Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, WHO Director-General. “This is a wake-up call to all countries to pay more attention to mental health and do a better job of supporting their populations’ mental health.”
Multiple stress factors
One major explanation for the increase is the unprecedented stress caused by the social isolation resulting from the pandemic. Linked to this were constraints on people’s ability to work, seek support from loved ones and engage in their communities.
Loneliness, fear of infection, suffering and death for oneself and for loved ones, grief after bereavement and financial worries have also all been cited as stressors leading to anxiety and depression. Among health workers, exhaustion has been a major trigger for suicidal thinking.
Young people and women worst hit
The brief, which is informed by a comprehensive review of existing evidence about the impact of COVID-19 on mental health and mental health services, and includes estimates from the latest Global Burden of Disease study, shows that the pandemic has affected the mental health of young people and that they are disproportionally at risk of suicidal and self-harming behaviours. It also indicates that women have been more severely impacted than men and that people with pre-existing physical health conditions, such as asthma, cancer and heart disease, were more likely to develop symptoms of mental disorders.
Data suggests that people with pre-existing mental disorders do not appear to be disproportionately vulnerable to COVID-19 infection. Yet, when these people do become infected, they are more likely to suffer hospitalization, severe illness and death compared with people without mental disorders. People with more severe mental disorders, such as psychoses, and young people with mental disorders, are particularly at risk.
Gaps in care
This increase in the prevalence of mental health problems has coincided with severe disruptions to mental health services, leaving huge gaps in care for those who need it most. For much of the pandemic, services for mental, neurological and substance use conditions were the most disrupted among all essential health services reported by WHO Member States. Many countries also reported major disruptions in life-saving services for mental health, including for suicide prevention.
By the end of 2021 the situation had somewhat improved but today too many people remain unable to get the care and support they need for both pre-existing and newly developed mental health conditions.
Unable to access face-to-face care, many people have sought support online, signaling an urgent need to make reliable and effective digital tools available and easily accessible. However, developing and deploying digital interventions remains a major challenge in resource-limited countries and settings.
WHO and country action
Since the early days of the pandemic, WHO and partners have worked to develop and disseminate resources in multiple languages and formats to help different groups cope with and respond to the mental health impacts of COVID-19. For example, WHO produced a story book for 6-11-year-olds, My Hero is You, now available in 142 languages and 61 multimedia adaptations, as well as a toolkit for supporting older adults available in 16 languages.
At the same time, the Organization has worked with partners, including other United Nations agencies, international nongovernmental organizations and the Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies, to lead an interagency mental health and psychosocial response to COVID-19. Throughout the pandemic, WHO has also worked to promote the integration of mental health and psychosocial support across and within all aspects of the global response.
WHO Member States have recognized the impact of COVID-19 on mental health and are taking action. WHO’s most recent pulse survey on continuity of essential health services indicated that 90% of countries are working to provide mental health and psychosocial support to COVID-19 patients and responders alike. Moreover, at last year’s World Health Assembly, countries emphasized the need to develop and strengthen mental health and psychosocial support services as part of strengthening preparedness, response and resilience to COVID-19 and future public health emergencies. They adopted the updated Comprehensive Mental Health Action Plan 2013-2030, which includes an indicator on preparedness for mental health and psychosocial support in public health emergencies.
Step up investment
However, this commitment to mental health needs to be accompanied by a global step up in investment. Unfortunately, the situation underscores a chronic global shortage of mental health resources that continues today. WHO’s most recent Mental Health Atlas showed that in 2020, governments worldwide spent on average just over 2% of their health budgets on mental health and many low-income countries reported having fewer than 1 mental health worker per 100 000 people.
Dévora Kestel, Director of the Department of Mental Health and Substance Use at WHO, sums up the situation: ”While the pandemic has generated interest in and concern for mental health, it has also revealed historical under-investment in mental health services. Countries must act urgently to ensure that mental health support is available to all.”
Media Contacts
Alison Brunier
Communications Officer World Health Organization
Carla Drysdale
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
4 takeaways from the historic felony conviction of Donald Trump

Domenico Montanaro

Former President Donald Trump sits in Manhattan Criminal Court in New York on May 20. A jury found Trump guilty of all 34 felony counts on Thursday. Dave Sanders/The New York Times via AP, Pool hide caption
For the first time in American history, a former president has been found guilty of a crime.
A jury of his peers in New York unanimously found Donald Trump guilty on all 34 counts of falsifying business records in order to influence the 2016 presidential election.
Remarkably, this is taking place in an election year in which said former president is running for his old job back, and it will undoubtedly have political consequences.

Former President Trump is found guilty in historic New York criminal case
“The real verdict is going to be Nov. 5 by the people,” Trump said outside the New York courtroom after the verdict.
“There is still only one way to keep Donald Trump out of the Oval Office: at the ballot box,” Michael Tyler, a Biden campaign spokesman, said in a statement.
Well, they agree on one thing.
So what will the political fallout from all of this be? Let’s dive in with these takeaways from a momentous day in American history:
1. Donald Trump is still going to be the Republican nominee.
Technically, the Republican Party’s nominating convention hasn’t happened yet, so it could, in theory , select another candidate.
But that’s not happening. Republicans are lining up behind Trump, from the speaker of the House to the cadre of Trump allies auditioning to be his vice presidential running mate.
Trump has full control over the Republican National Committee. He has installed loyalists in state parties across the country, and because of that, he’s in a stronger position with the Republican Party than in 2016 when he beat back a convention coup attempt from Texas Sen. Ted Cruz and allies.
This is Trump’s party. Full stop. He’s going to be nominated by the party. It will take place, incredibly, just days after he’s scheduled to be sentenced in this case (July 11).
And he’s going to be on the ballot this November.

See where the big Trump cases stand in the months leading to the election
Also, to be clear: Trump is not going to prison, legal experts believe, because he does not have a prior criminal record. This crime is punishable by anything from probation to a degree of house arrest, and up to four years in prison.
It’s also not at all clear that Trump will lose his voting rights in Florida, despite the felony conviction.
Plus, Trump is going to appeal, so any real consequences, if the verdict is upheld, potentially won’t come for months.
2. Yes, Trump’s base is likely to stick with him, but this isn’t the primary anymore.
Trump was able to raise gobs of money during the primary off indictments, and he only grew stronger during that time — with Republicans.
Now the real test comes, and that’s with a general-election audience. There are some key questions:
- Will this conviction resonate with persuadable voters in key swing states?
- Does this do anything to rally support to President Biden’s side with voters he’s been struggling with, like younger voters, Black voters and Latinos? They’ve been lukewarm toward Biden, in part, because of affordability, housing costs and his age, but will they want to vote for a “convicted felon” or will they sit it out or support a third-party candidate?
- Especially important in a year that’s expected to have lower turnout than four years ago, will this verdict rally or suppress turnout among some rank-and-file potential Trump voters, especially white voters without college degrees? They make up a core part of Trump’s base, but they are a group whose participation rates have been lower than others through the years. Republicans would say absolutely not, that this will only galvanize his base.
The latest NPR/PBS NewsHour/Marist poll suggests most voters will not be swayed either way. It showed that some, including younger voters, might be moved at the margins, but this may be a reset moment in the campaign.
It’s a historic moment in American history. Many Americans are likely going to be just tuning in now to learn about the conviction. And the bottom line is: The last thing Trump wanted was “Trump” and “convicted felon” in the same headline. And barring an overturn on appeal before the election, that’s what will be attached to him as voters weigh their choices.

Trump is found guilty on 34 felony counts. Read the counts here
3. the ball is in biden’s court to see if he can capitalize on this politically..
The president has been very cautious about speaking out about Trump’s legal woes. With Trump continuing to dominate the news with wall-to-wall coverage of the trials, it’s been hard for the Biden campaign to break through.
It makes sense in a very important respect that Biden, up until the verdict, did not hammer Trump on his legal problems. He is president, and he didn’t want to show any hint of impropriety and has not wanted to appear, in any way, to be influencing the Justice Department’s federal investigations of Trump or and state prosecutors.
That hasn’t stopped Trump and conservative media from saying exactly that, though — and worse. But now, with this verdict, and with this likely to be the only trial Trump faces before the election — despite three other major, election-related cases against him — expect Biden to lean into this.
The line Biden has to toe is between being president and being a candidate. The White House counsel’s office essentially said no comment, but Biden’s campaign has weighed in, noting that the New York case shows “no one is above the law.”
Now, Biden has to choose. And right now, he’s slightly behind in the race. So the question isn’t really whether Biden will talk about the conviction, but whether he’s capable of delivering and capitalizing on it.
4. The verdict raises the stakes for big moments coming up in the campaign.
There will be challenges for both Biden and Trump now with how to spin this to their respective advantages.
The attempts started fast and furious. Trump and his surrogates denounced the legitimacy of the verdict immediately afterward, and both campaigns were quickly out with statements and fundraising appeals.

RFK's voters know they're not electing the next president. They're with him anyway
It’s indicative of the fact that this is a presidential campaign year, and every turn will get heightened focus.
There are going to be some big moments coming up that will provide opportunities and risks for the candidates on this:
- June 27: First, there’s the very early debate both candidates agreed to, taking place in less than a month. Can Biden use this to his advantage effectively? Can Trump defend himself in a way that doesn’t alienate middle-of-the-road voters?
- July 15-18: The next signposts are the conventions. The Republicans are up first in Milwaukee, just days after Trump’s scheduled sentencing in this case. Expect Trump and his team to try to use that week to rally the base, unify and make sure there are no cracks in the foundation.
- Aug. 19-22: Then, it's the Democrats' turn in Chicago. Can Biden use the conviction to shore up his coalition, which is showing some gaping holes right now, and assure voters who continue to question his mental fitness that he’s up for the job? Remember, Democrats are also fretting about potential protests that could make the party look divided.
- Sept. 10: It’s the last debate, which kicks off the sprint to the finish and perhaps the last, big chance for either candidate to make their case. Early voting begins not long after.
The campaigns will be trying hard to turn out every last voter they think should vote for them to show up — and Trump’s conviction is likely to be a very large piece of the campaign going forward.
The state of AI in early 2024: Gen AI adoption spikes and starts to generate value
If 2023 was the year the world discovered generative AI (gen AI) , 2024 is the year organizations truly began using—and deriving business value from—this new technology. In the latest McKinsey Global Survey on AI, 65 percent of respondents report that their organizations are regularly using gen AI, nearly double the percentage from our previous survey just ten months ago. Respondents’ expectations for gen AI’s impact remain as high as they were last year , with three-quarters predicting that gen AI will lead to significant or disruptive change in their industries in the years ahead.
About the authors
This article is a collaborative effort by Alex Singla , Alexander Sukharevsky , Lareina Yee , and Michael Chui , with Bryce Hall , representing views from QuantumBlack, AI by McKinsey, and McKinsey Digital.
Organizations are already seeing material benefits from gen AI use, reporting both cost decreases and revenue jumps in the business units deploying the technology. The survey also provides insights into the kinds of risks presented by gen AI—most notably, inaccuracy—as well as the emerging practices of top performers to mitigate those challenges and capture value.
AI adoption surges
Interest in generative AI has also brightened the spotlight on a broader set of AI capabilities. For the past six years, AI adoption by respondents’ organizations has hovered at about 50 percent. This year, the survey finds that adoption has jumped to 72 percent (Exhibit 1). And the interest is truly global in scope. Our 2023 survey found that AI adoption did not reach 66 percent in any region; however, this year more than two-thirds of respondents in nearly every region say their organizations are using AI. 1 Organizations based in Central and South America are the exception, with 58 percent of respondents working for organizations based in Central and South America reporting AI adoption. Looking by industry, the biggest increase in adoption can be found in professional services. 2 Includes respondents working for organizations focused on human resources, legal services, management consulting, market research, R&D, tax preparation, and training.
Also, responses suggest that companies are now using AI in more parts of the business. Half of respondents say their organizations have adopted AI in two or more business functions, up from less than a third of respondents in 2023 (Exhibit 2).
Gen AI adoption is most common in the functions where it can create the most value
Most respondents now report that their organizations—and they as individuals—are using gen AI. Sixty-five percent of respondents say their organizations are regularly using gen AI in at least one business function, up from one-third last year. The average organization using gen AI is doing so in two functions, most often in marketing and sales and in product and service development—two functions in which previous research determined that gen AI adoption could generate the most value 3 “ The economic potential of generative AI: The next productivity frontier ,” McKinsey, June 14, 2023. —as well as in IT (Exhibit 3). The biggest increase from 2023 is found in marketing and sales, where reported adoption has more than doubled. Yet across functions, only two use cases, both within marketing and sales, are reported by 15 percent or more of respondents.
Gen AI also is weaving its way into respondents’ personal lives. Compared with 2023, respondents are much more likely to be using gen AI at work and even more likely to be using gen AI both at work and in their personal lives (Exhibit 4). The survey finds upticks in gen AI use across all regions, with the largest increases in Asia–Pacific and Greater China. Respondents at the highest seniority levels, meanwhile, show larger jumps in the use of gen Al tools for work and outside of work compared with their midlevel-management peers. Looking at specific industries, respondents working in energy and materials and in professional services report the largest increase in gen AI use.
Investments in gen AI and analytical AI are beginning to create value
The latest survey also shows how different industries are budgeting for gen AI. Responses suggest that, in many industries, organizations are about equally as likely to be investing more than 5 percent of their digital budgets in gen AI as they are in nongenerative, analytical-AI solutions (Exhibit 5). Yet in most industries, larger shares of respondents report that their organizations spend more than 20 percent on analytical AI than on gen AI. Looking ahead, most respondents—67 percent—expect their organizations to invest more in AI over the next three years.
Where are those investments paying off? For the first time, our latest survey explored the value created by gen AI use by business function. The function in which the largest share of respondents report seeing cost decreases is human resources. Respondents most commonly report meaningful revenue increases (of more than 5 percent) in supply chain and inventory management (Exhibit 6). For analytical AI, respondents most often report seeing cost benefits in service operations—in line with what we found last year —as well as meaningful revenue increases from AI use in marketing and sales.
Inaccuracy: The most recognized and experienced risk of gen AI use
As businesses begin to see the benefits of gen AI, they’re also recognizing the diverse risks associated with the technology. These can range from data management risks such as data privacy, bias, or intellectual property (IP) infringement to model management risks, which tend to focus on inaccurate output or lack of explainability. A third big risk category is security and incorrect use.
Respondents to the latest survey are more likely than they were last year to say their organizations consider inaccuracy and IP infringement to be relevant to their use of gen AI, and about half continue to view cybersecurity as a risk (Exhibit 7).
Conversely, respondents are less likely than they were last year to say their organizations consider workforce and labor displacement to be relevant risks and are not increasing efforts to mitigate them.
In fact, inaccuracy— which can affect use cases across the gen AI value chain , ranging from customer journeys and summarization to coding and creative content—is the only risk that respondents are significantly more likely than last year to say their organizations are actively working to mitigate.
Some organizations have already experienced negative consequences from the use of gen AI, with 44 percent of respondents saying their organizations have experienced at least one consequence (Exhibit 8). Respondents most often report inaccuracy as a risk that has affected their organizations, followed by cybersecurity and explainability.
Our previous research has found that there are several elements of governance that can help in scaling gen AI use responsibly, yet few respondents report having these risk-related practices in place. 4 “ Implementing generative AI with speed and safety ,” McKinsey Quarterly , March 13, 2024. For example, just 18 percent say their organizations have an enterprise-wide council or board with the authority to make decisions involving responsible AI governance, and only one-third say gen AI risk awareness and risk mitigation controls are required skill sets for technical talent.
Bringing gen AI capabilities to bear
The latest survey also sought to understand how, and how quickly, organizations are deploying these new gen AI tools. We have found three archetypes for implementing gen AI solutions : takers use off-the-shelf, publicly available solutions; shapers customize those tools with proprietary data and systems; and makers develop their own foundation models from scratch. 5 “ Technology’s generational moment with generative AI: A CIO and CTO guide ,” McKinsey, July 11, 2023. Across most industries, the survey results suggest that organizations are finding off-the-shelf offerings applicable to their business needs—though many are pursuing opportunities to customize models or even develop their own (Exhibit 9). About half of reported gen AI uses within respondents’ business functions are utilizing off-the-shelf, publicly available models or tools, with little or no customization. Respondents in energy and materials, technology, and media and telecommunications are more likely to report significant customization or tuning of publicly available models or developing their own proprietary models to address specific business needs.
Respondents most often report that their organizations required one to four months from the start of a project to put gen AI into production, though the time it takes varies by business function (Exhibit 10). It also depends upon the approach for acquiring those capabilities. Not surprisingly, reported uses of highly customized or proprietary models are 1.5 times more likely than off-the-shelf, publicly available models to take five months or more to implement.
Gen AI high performers are excelling despite facing challenges
Gen AI is a new technology, and organizations are still early in the journey of pursuing its opportunities and scaling it across functions. So it’s little surprise that only a small subset of respondents (46 out of 876) report that a meaningful share of their organizations’ EBIT can be attributed to their deployment of gen AI. Still, these gen AI leaders are worth examining closely. These, after all, are the early movers, who already attribute more than 10 percent of their organizations’ EBIT to their use of gen AI. Forty-two percent of these high performers say more than 20 percent of their EBIT is attributable to their use of nongenerative, analytical AI, and they span industries and regions—though most are at organizations with less than $1 billion in annual revenue. The AI-related practices at these organizations can offer guidance to those looking to create value from gen AI adoption at their own organizations.
To start, gen AI high performers are using gen AI in more business functions—an average of three functions, while others average two. They, like other organizations, are most likely to use gen AI in marketing and sales and product or service development, but they’re much more likely than others to use gen AI solutions in risk, legal, and compliance; in strategy and corporate finance; and in supply chain and inventory management. They’re more than three times as likely as others to be using gen AI in activities ranging from processing of accounting documents and risk assessment to R&D testing and pricing and promotions. While, overall, about half of reported gen AI applications within business functions are utilizing publicly available models or tools, gen AI high performers are less likely to use those off-the-shelf options than to either implement significantly customized versions of those tools or to develop their own proprietary foundation models.
What else are these high performers doing differently? For one thing, they are paying more attention to gen-AI-related risks. Perhaps because they are further along on their journeys, they are more likely than others to say their organizations have experienced every negative consequence from gen AI we asked about, from cybersecurity and personal privacy to explainability and IP infringement. Given that, they are more likely than others to report that their organizations consider those risks, as well as regulatory compliance, environmental impacts, and political stability, to be relevant to their gen AI use, and they say they take steps to mitigate more risks than others do.
Gen AI high performers are also much more likely to say their organizations follow a set of risk-related best practices (Exhibit 11). For example, they are nearly twice as likely as others to involve the legal function and embed risk reviews early on in the development of gen AI solutions—that is, to “ shift left .” They’re also much more likely than others to employ a wide range of other best practices, from strategy-related practices to those related to scaling.
In addition to experiencing the risks of gen AI adoption, high performers have encountered other challenges that can serve as warnings to others (Exhibit 12). Seventy percent say they have experienced difficulties with data, including defining processes for data governance, developing the ability to quickly integrate data into AI models, and an insufficient amount of training data, highlighting the essential role that data play in capturing value. High performers are also more likely than others to report experiencing challenges with their operating models, such as implementing agile ways of working and effective sprint performance management.
About the research
The online survey was in the field from February 22 to March 5, 2024, and garnered responses from 1,363 participants representing the full range of regions, industries, company sizes, functional specialties, and tenures. Of those respondents, 981 said their organizations had adopted AI in at least one business function, and 878 said their organizations were regularly using gen AI in at least one function. To adjust for differences in response rates, the data are weighted by the contribution of each respondent’s nation to global GDP.
Alex Singla and Alexander Sukharevsky are global coleaders of QuantumBlack, AI by McKinsey, and senior partners in McKinsey’s Chicago and London offices, respectively; Lareina Yee is a senior partner in the Bay Area office, where Michael Chui , a McKinsey Global Institute partner, is a partner; and Bryce Hall is an associate partner in the Washington, DC, office.
They wish to thank Kaitlin Noe, Larry Kanter, Mallika Jhamb, and Shinjini Srivastava for their contributions to this work.
This article was edited by Heather Hanselman, a senior editor in McKinsey’s Atlanta office.
Explore a career with us
Related articles.

Moving past gen AI’s honeymoon phase: Seven hard truths for CIOs to get from pilot to scale

A generative AI reset: Rewiring to turn potential into value in 2024

Implementing generative AI with speed and safety

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Identify the key problems and issues in the case study. Formulate and include a thesis statement, summarizing the outcome of your analysis in 1-2 sentences. Background. Set the scene: background information, relevant facts, and the most important issues. Demonstrate that you have researched the problems in this case study. Evaluation of the Case
Conducting a case study analysis involves several key steps that help in understanding the complexities of the case and deriving meaningful insights. Here are the essential steps to effectively conduct a case study analysis:. ... problem statement, methodology, results, and conclusions. Templates can also help maintain consistency across ...
Step 3: Set your aims and objectives. Finally, the problem statement should frame how you intend to address the problem. Your goal here should not be to find a conclusive solution, but rather to propose more effective approaches to tackling or understanding it. The research aim is the overall purpose of your research.
A problem statement concisely describes a specific issue or problem that a written case study aims to address. It sets the stage for the rest of the case study and provides context for the reader. Here are some steps to help you write a case study problem statement: Identify the problem or issue that the case study will focus on.
1. Begin with a clear indication that the problem statement is going to be discussed next. You can start with a generic sentence like, "The problem that this study addresses…". This will inform your readers of what to expect next. 2. Next, mention the consequences of not solving the problem.
Multiple case studies can be used in a research study; case analysis involves examining a single scenario. Case study research can use two or more cases to examine a problem, often for the purpose of conducting a comparative investigation intended to discover hidden relationships, document emerging trends, or determine variations among ...
Case studies tend to focus on qualitative data using methods such as interviews, observations, and analysis of primary and secondary sources (e.g., newspaper articles, photographs, official records). Sometimes a case study will also collect quantitative data. Example: Mixed methods case study. For a case study of a wind farm development in a ...
Case studies are good for describing, comparing, evaluating and understanding different aspects of a research problem. Table of contents. When to do a case study. Step 1: Select a case. Step 2: Build a theoretical framework. Step 3: Collect your data. Step 4: Describe and analyze the case.
How to Write a Case Analysis Generally, organize your essay around 1. A definition or position statement (your conclusion) - answers the question what? 2. An argument (your evidence - quantitative and/or qualitative) - answers why? 3. A chronological action plan (steps to solve a problem, implement a decision, improve
A Case study is: An in-depth research design that primarily uses a qualitative methodology but sometimes includes quantitative methodology. Used to examine an identifiable problem confirmed through research. Used to investigate an individual, group of people, organization, or event. Used to mostly answer "how" and "why" questions.
The purpose of a paper in the social sciences designed around a case study is to thoroughly investigate a subject of analysis in order to reveal a new understanding about the research problem and, in so doing, contributing new knowledge to what is already known from previous studies. In applied social sciences disciplines [e.g., education, social work, public administration, etc.], case ...
Example Problem Statement 1: The Status Quo Problem Statement. Example: The average customer service on-hold time for Example company exceeds five minutes during both its busy and slow seasons. This can be used to describe a current pain point within an organization that may need to be addressed.
How to Write a Case Study Analysis. Before writing a case study analysis, it is important to identify a relevant subject and research problem. While preparing to write, the author should critically assess the potential problem and the need for in-depth analysis. For example, hidden problems, outdated information, or a feasible recommendation ...
Key elements of an effective problem statement include: Gap: Identify the gap (pain) that exists today. Timeframe, location and trend: Describe when and where the problem was first observed and what kind of trend it is following. Impact: Quantify the gap (cost, time, quality, environmental, personal, etc.) Importance: To the organization, the ...
Introduction. Identify the key problems and issues in the case study. Formulate and include a thesis statement, summarizing the outcome of your analysis in 1-2 sentences. Background. Set the scene: background information, relevant facts, and the most important issues. Demonstrate that you have researched the problems in this case study.
Best, worst, and most likely scenarios can also be insightful. Step 5: Decision. Students propose their solution to the problem. This decision is justified based on an in-depth analysis. Explain why the recommendation made is the best fit for the criteria. Step 6: Implementation plan.
A case study is one of the most commonly used methodologies of social research. This article attempts to look into the various dimensions of a case study research strategy, the different epistemological strands which determine the particular case study type and approach adopted in the field, discusses the factors which can enhance the effectiveness of a case study research, and the debate ...
2. State the Problem and Emphasize Why It Matters. The case analysis problem statement must address what the problem is, why the organization considers it a problem, and why it is necessary to find a resolution. It wraps all the other 'w' questions that follow, in most cases.
Feb 21, 2021. --. 1. Solving a Data Science case study means analyzing and solving a problem statement intensively. Solving case studies will help you show unique and amazing data science use ...
The case study is not a research method, but researchers select methods of data collection and analysis that will generate material suitable for case studies. Freud (1909a, 1909b) conducted very detailed investigations into the private lives of his patients in an attempt to both understand and help them overcome their illnesses.
Uber: Product Case Study. Parth Batra · Follow. 9 min read · Sep 18, 2019--1. Listen. Share. Problem Statement: ... This use case is based on market analysis data totally. Miscellaneous (brute ...
Here's a case study on that, below. [Case Study] "My board definitely needs to see this." The breakthrough that let one my past sales teams cross the chasm from $500K, to $5M, in ARR was the process for enabling our champions with a can't-ignore problem statement. Here's the full story. Creating Context
If problem statements are, in general, used to fix issues, then examining a business problem is the purpose of Case Analysis Problem Statements. Alongside this, this kind of problem statements look for solutions to the problem, and with the help of back-up data, propose the best one for the respective circumstances.
10+ Case Study Problem Statement Samples. 1. Data Case Study Problem Statement. 2. Exploratory Case Study Problem Statement. 3. Case Study Development Problem Statement. 4. Case Study Sales Problem Statement.
Case Study Template. Used 9813 times Share | Updated May 15, 2024. Good case studies tell a compelling story to potential clients of how your company rose to the occasion. The Case Study Template will help you showcase your company's credibility in solving a particularly challenging client problem and prove to potential clients that you have what it takes to perform well.
Español. In the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic, global prevalence of anxiety and depression increased by a massive 25%, according to a scientific brief released by the World Health Organization (WHO) today. The brief also highlights who has been most affected and summarizes the effect of the pandemic on the availability of mental health ...
Former President Trump is found guilty in historic New York criminal case. "The real verdict is going to be Nov. 5 by the people," Trump said outside the New York courtroom after the verdict ...
If 2023 was the year the world discovered generative AI (gen AI), 2024 is the year organizations truly began using—and deriving business value from—this new technology. In the latest McKinsey Global Survey on AI, 65 percent of respondents report that their organizations are regularly using gen AI, nearly double the percentage from our ...
Open the Page Thumbnails side panel. Select a page thumbnail, and choose Page Properties from the Options menu . In the Page Properties dialog, select Tab Order, and then select the tab order. Use Row Order. Moves through rows from left to right, or right to left for pages with a right-to-left binding. Use Column Order.