- USC Libraries
- Research Guides

Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- 8. The Discussion
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
The purpose of the discussion section is to interpret and describe the significance of your findings in relation to what was already known about the research problem being investigated and to explain any new understanding or insights that emerged as a result of your research. The discussion will always connect to the introduction by way of the research questions or hypotheses you posed and the literature you reviewed, but the discussion does not simply repeat or rearrange the first parts of your paper; the discussion clearly explains how your study advanced the reader's understanding of the research problem from where you left them at the end of your review of prior research.
Annesley, Thomas M. “The Discussion Section: Your Closing Argument.” Clinical Chemistry 56 (November 2010): 1671-1674; Peacock, Matthew. “Communicative Moves in the Discussion Section of Research Articles.” System 30 (December 2002): 479-497.
Importance of a Good Discussion
The discussion section is often considered the most important part of your research paper because it:
- Most effectively demonstrates your ability as a researcher to think critically about an issue, to develop creative solutions to problems based upon a logical synthesis of the findings, and to formulate a deeper, more profound understanding of the research problem under investigation;
- Presents the underlying meaning of your research, notes possible implications in other areas of study, and explores possible improvements that can be made in order to further develop the concerns of your research;
- Highlights the importance of your study and how it can contribute to understanding the research problem within the field of study;
- Presents how the findings from your study revealed and helped fill gaps in the literature that had not been previously exposed or adequately described; and,
- Engages the reader in thinking critically about issues based on an evidence-based interpretation of findings; it is not governed strictly by objective reporting of information.
Annesley Thomas M. “The Discussion Section: Your Closing Argument.” Clinical Chemistry 56 (November 2010): 1671-1674; Bitchener, John and Helen Basturkmen. “Perceptions of the Difficulties of Postgraduate L2 Thesis Students Writing the Discussion Section.” Journal of English for Academic Purposes 5 (January 2006): 4-18; Kretchmer, Paul. Fourteen Steps to Writing an Effective Discussion Section. San Francisco Edit, 2003-2008.
Structure and Writing Style
I. General Rules
These are the general rules you should adopt when composing your discussion of the results :
- Do not be verbose or repetitive; be concise and make your points clearly
- Avoid the use of jargon or undefined technical language
- Follow a logical stream of thought; in general, interpret and discuss the significance of your findings in the same sequence you described them in your results section [a notable exception is to begin by highlighting an unexpected result or a finding that can grab the reader's attention]
- Use the present verb tense, especially for established facts; however, refer to specific works or prior studies in the past tense
- If needed, use subheadings to help organize your discussion or to categorize your interpretations into themes
II. The Content
The content of the discussion section of your paper most often includes :
- Explanation of results : Comment on whether or not the results were expected for each set of findings; go into greater depth to explain findings that were unexpected or especially profound. If appropriate, note any unusual or unanticipated patterns or trends that emerged from your results and explain their meaning in relation to the research problem.
- References to previous research : Either compare your results with the findings from other studies or use the studies to support a claim. This can include re-visiting key sources already cited in your literature review section, or, save them to cite later in the discussion section if they are more important to compare with your results instead of being a part of the general literature review of prior research used to provide context and background information. Note that you can make this decision to highlight specific studies after you have begun writing the discussion section.
- Deduction : A claim for how the results can be applied more generally. For example, describing lessons learned, proposing recommendations that can help improve a situation, or highlighting best practices.
- Hypothesis : A more general claim or possible conclusion arising from the results [which may be proved or disproved in subsequent research]. This can be framed as new research questions that emerged as a consequence of your analysis.
III. Organization and Structure
Keep the following sequential points in mind as you organize and write the discussion section of your paper:
- Think of your discussion as an inverted pyramid. Organize the discussion from the general to the specific, linking your findings to the literature, then to theory, then to practice [if appropriate].
- Use the same key terms, narrative style, and verb tense [present] that you used when describing the research problem in your introduction.
- Begin by briefly re-stating the research problem you were investigating and answer all of the research questions underpinning the problem that you posed in the introduction.
- Describe the patterns, principles, and relationships shown by each major findings and place them in proper perspective. The sequence of this information is important; first state the answer, then the relevant results, then cite the work of others. If appropriate, refer the reader to a figure or table to help enhance the interpretation of the data [either within the text or as an appendix].
- Regardless of where it's mentioned, a good discussion section includes analysis of any unexpected findings. This part of the discussion should begin with a description of the unanticipated finding, followed by a brief interpretation as to why you believe it appeared and, if necessary, its possible significance in relation to the overall study. If more than one unexpected finding emerged during the study, describe each of them in the order they appeared as you gathered or analyzed the data. As noted, the exception to discussing findings in the same order you described them in the results section would be to begin by highlighting the implications of a particularly unexpected or significant finding that emerged from the study, followed by a discussion of the remaining findings.
- Before concluding the discussion, identify potential limitations and weaknesses if you do not plan to do so in the conclusion of the paper. Comment on their relative importance in relation to your overall interpretation of the results and, if necessary, note how they may affect the validity of your findings. Avoid using an apologetic tone; however, be honest and self-critical [e.g., in retrospect, had you included a particular question in a survey instrument, additional data could have been revealed].
- The discussion section should end with a concise summary of the principal implications of the findings regardless of their significance. Give a brief explanation about why you believe the findings and conclusions of your study are important and how they support broader knowledge or understanding of the research problem. This can be followed by any recommendations for further research. However, do not offer recommendations which could have been easily addressed within the study. This would demonstrate to the reader that you have inadequately examined and interpreted the data.
IV. Overall Objectives
The objectives of your discussion section should include the following: I. Reiterate the Research Problem/State the Major Findings
Briefly reiterate the research problem or problems you are investigating and the methods you used to investigate them, then move quickly to describe the major findings of the study. You should write a direct, declarative, and succinct proclamation of the study results, usually in one paragraph.
II. Explain the Meaning of the Findings and Why They are Important
No one has thought as long and hard about your study as you have. Systematically explain the underlying meaning of your findings and state why you believe they are significant. After reading the discussion section, you want the reader to think critically about the results and why they are important. You don’t want to force the reader to go through the paper multiple times to figure out what it all means. If applicable, begin this part of the section by repeating what you consider to be your most significant or unanticipated finding first, then systematically review each finding. Otherwise, follow the general order you reported the findings presented in the results section.
III. Relate the Findings to Similar Studies
No study in the social sciences is so novel or possesses such a restricted focus that it has absolutely no relation to previously published research. The discussion section should relate your results to those found in other studies, particularly if questions raised from prior studies served as the motivation for your research. This is important because comparing and contrasting the findings of other studies helps to support the overall importance of your results and it highlights how and in what ways your study differs from other research about the topic. Note that any significant or unanticipated finding is often because there was no prior research to indicate the finding could occur. If there is prior research to indicate this, you need to explain why it was significant or unanticipated. IV. Consider Alternative Explanations of the Findings
It is important to remember that the purpose of research in the social sciences is to discover and not to prove . When writing the discussion section, you should carefully consider all possible explanations for the study results, rather than just those that fit your hypothesis or prior assumptions and biases. This is especially important when describing the discovery of significant or unanticipated findings.
V. Acknowledge the Study’s Limitations
It is far better for you to identify and acknowledge your study’s limitations than to have them pointed out by your professor! Note any unanswered questions or issues your study could not address and describe the generalizability of your results to other situations. If a limitation is applicable to the method chosen to gather information, then describe in detail the problems you encountered and why. VI. Make Suggestions for Further Research
You may choose to conclude the discussion section by making suggestions for further research [as opposed to offering suggestions in the conclusion of your paper]. Although your study can offer important insights about the research problem, this is where you can address other questions related to the problem that remain unanswered or highlight hidden issues that were revealed as a result of conducting your research. You should frame your suggestions by linking the need for further research to the limitations of your study [e.g., in future studies, the survey instrument should include more questions that ask..."] or linking to critical issues revealed from the data that were not considered initially in your research.
NOTE: Besides the literature review section, the preponderance of references to sources is usually found in the discussion section . A few historical references may be helpful for perspective, but most of the references should be relatively recent and included to aid in the interpretation of your results, to support the significance of a finding, and/or to place a finding within a particular context. If a study that you cited does not support your findings, don't ignore it--clearly explain why your research findings differ from theirs.
V. Problems to Avoid
- Do not waste time restating your results . Should you need to remind the reader of a finding to be discussed, use "bridge sentences" that relate the result to the interpretation. An example would be: “In the case of determining available housing to single women with children in rural areas of Texas, the findings suggest that access to good schools is important...," then move on to further explaining this finding and its implications.
- As noted, recommendations for further research can be included in either the discussion or conclusion of your paper, but do not repeat your recommendations in the both sections. Think about the overall narrative flow of your paper to determine where best to locate this information. However, if your findings raise a lot of new questions or issues, consider including suggestions for further research in the discussion section.
- Do not introduce new results in the discussion section. Be wary of mistaking the reiteration of a specific finding for an interpretation because it may confuse the reader. The description of findings [results section] and the interpretation of their significance [discussion section] should be distinct parts of your paper. If you choose to combine the results section and the discussion section into a single narrative, you must be clear in how you report the information discovered and your own interpretation of each finding. This approach is not recommended if you lack experience writing college-level research papers.
- Use of the first person pronoun is generally acceptable. Using first person singular pronouns can help emphasize a point or illustrate a contrasting finding. However, keep in mind that too much use of the first person can actually distract the reader from the main points [i.e., I know you're telling me this--just tell me!].
Analyzing vs. Summarizing. Department of English Writing Guide. George Mason University; Discussion. The Structure, Format, Content, and Style of a Journal-Style Scientific Paper. Department of Biology. Bates College; Hess, Dean R. "How to Write an Effective Discussion." Respiratory Care 49 (October 2004); Kretchmer, Paul. Fourteen Steps to Writing to Writing an Effective Discussion Section. San Francisco Edit, 2003-2008; The Lab Report. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Sauaia, A. et al. "The Anatomy of an Article: The Discussion Section: "How Does the Article I Read Today Change What I Will Recommend to my Patients Tomorrow?” The Journal of Trauma and Acute Care Surgery 74 (June 2013): 1599-1602; Research Limitations & Future Research . Lund Research Ltd., 2012; Summary: Using it Wisely. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Schafer, Mickey S. Writing the Discussion. Writing in Psychology course syllabus. University of Florida; Yellin, Linda L. A Sociology Writer's Guide . Boston, MA: Allyn and Bacon, 2009.
Writing Tip
Don’t Over-Interpret the Results!
Interpretation is a subjective exercise. As such, you should always approach the selection and interpretation of your findings introspectively and to think critically about the possibility of judgmental biases unintentionally entering into discussions about the significance of your work. With this in mind, be careful that you do not read more into the findings than can be supported by the evidence you have gathered. Remember that the data are the data: nothing more, nothing less.
MacCoun, Robert J. "Biases in the Interpretation and Use of Research Results." Annual Review of Psychology 49 (February 1998): 259-287; Ward, Paulet al, editors. The Oxford Handbook of Expertise . Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press, 2018.
Another Writing Tip
Don't Write Two Results Sections!
One of the most common mistakes that you can make when discussing the results of your study is to present a superficial interpretation of the findings that more or less re-states the results section of your paper. Obviously, you must refer to your results when discussing them, but focus on the interpretation of those results and their significance in relation to the research problem, not the data itself.
Azar, Beth. "Discussing Your Findings." American Psychological Association gradPSYCH Magazine (January 2006).
Yet Another Writing Tip
Avoid Unwarranted Speculation!
The discussion section should remain focused on the findings of your study. For example, if the purpose of your research was to measure the impact of foreign aid on increasing access to education among disadvantaged children in Bangladesh, it would not be appropriate to speculate about how your findings might apply to populations in other countries without drawing from existing studies to support your claim or if analysis of other countries was not a part of your original research design. If you feel compelled to speculate, do so in the form of describing possible implications or explaining possible impacts. Be certain that you clearly identify your comments as speculation or as a suggestion for where further research is needed. Sometimes your professor will encourage you to expand your discussion of the results in this way, while others don’t care what your opinion is beyond your effort to interpret the data in relation to the research problem.
- << Previous: Using Non-Textual Elements
- Next: Limitations of the Study >>
- Last Updated: May 25, 2024 4:09 PM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
- U.S. Department of Health & Human Services

- Virtual Tour
- Staff Directory
- En Español
You are here
Science, health, and public trust.
September 8, 2021
Explaining How Research Works
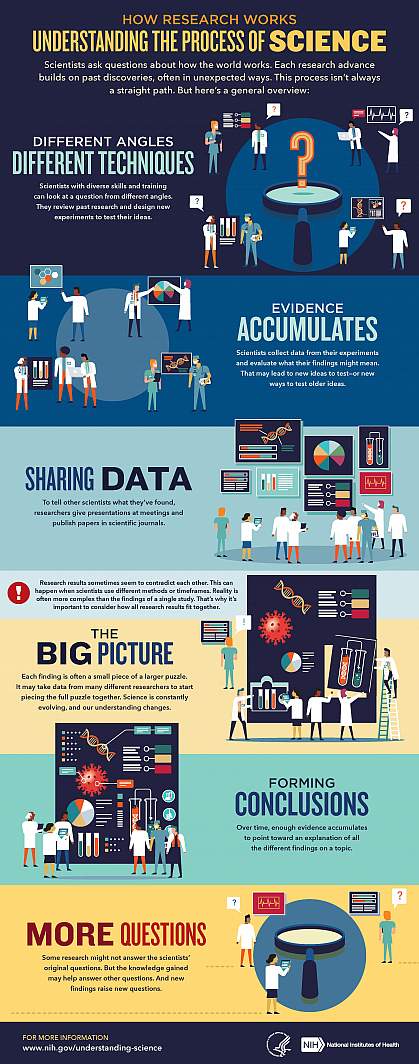
We’ve heard “follow the science” a lot during the pandemic. But it seems science has taken us on a long and winding road filled with twists and turns, even changing directions at times. That’s led some people to feel they can’t trust science. But when what we know changes, it often means science is working.

Explaining the scientific process may be one way that science communicators can help maintain public trust in science. Placing research in the bigger context of its field and where it fits into the scientific process can help people better understand and interpret new findings as they emerge. A single study usually uncovers only a piece of a larger puzzle.
Questions about how the world works are often investigated on many different levels. For example, scientists can look at the different atoms in a molecule, cells in a tissue, or how different tissues or systems affect each other. Researchers often must choose one or a finite number of ways to investigate a question. It can take many different studies using different approaches to start piecing the whole picture together.
Sometimes it might seem like research results contradict each other. But often, studies are just looking at different aspects of the same problem. Researchers can also investigate a question using different techniques or timeframes. That may lead them to arrive at different conclusions from the same data.
Using the data available at the time of their study, scientists develop different explanations, or models. New information may mean that a novel model needs to be developed to account for it. The models that prevail are those that can withstand the test of time and incorporate new information. Science is a constantly evolving and self-correcting process.
Scientists gain more confidence about a model through the scientific process. They replicate each other’s work. They present at conferences. And papers undergo peer review, in which experts in the field review the work before it can be published in scientific journals. This helps ensure that the study is up to current scientific standards and maintains a level of integrity. Peer reviewers may find problems with the experiments or think different experiments are needed to justify the conclusions. They might even offer new ways to interpret the data.
It’s important for science communicators to consider which stage a study is at in the scientific process when deciding whether to cover it. Some studies are posted on preprint servers for other scientists to start weighing in on and haven’t yet been fully vetted. Results that haven't yet been subjected to scientific scrutiny should be reported on with care and context to avoid confusion or frustration from readers.
We’ve developed a one-page guide, "How Research Works: Understanding the Process of Science" to help communicators put the process of science into perspective. We hope it can serve as a useful resource to help explain why science changes—and why it’s important to expect that change. Please take a look and share your thoughts with us by sending an email to [email protected].
Below are some additional resources:
- Discoveries in Basic Science: A Perfectly Imperfect Process
- When Clinical Research Is in the News
- What is Basic Science and Why is it Important?
- What is a Research Organism?
- What Are Clinical Trials and Studies?
- Basic Research – Digital Media Kit
- Decoding Science: How Does Science Know What It Knows? (NAS)
- Can Science Help People Make Decisions ? (NAS)
Connect with Us
- More Social Media from NIH

Biomedical Beat Blog – National Institute of General Medical Sciences
Follow the process of discovery
Search this blog
How research works: understanding the process of science.
Have you ever wondered how research works? How scientists make discoveries about our health and the world around us? Whether they’re studying plants, animals, humans, or something else in our world, they follow the scientific method. But this method isn’t always—or even usually—a straight line, and often the answers are unexpected and lead to more questions. Let’s dive in to see how it all works.
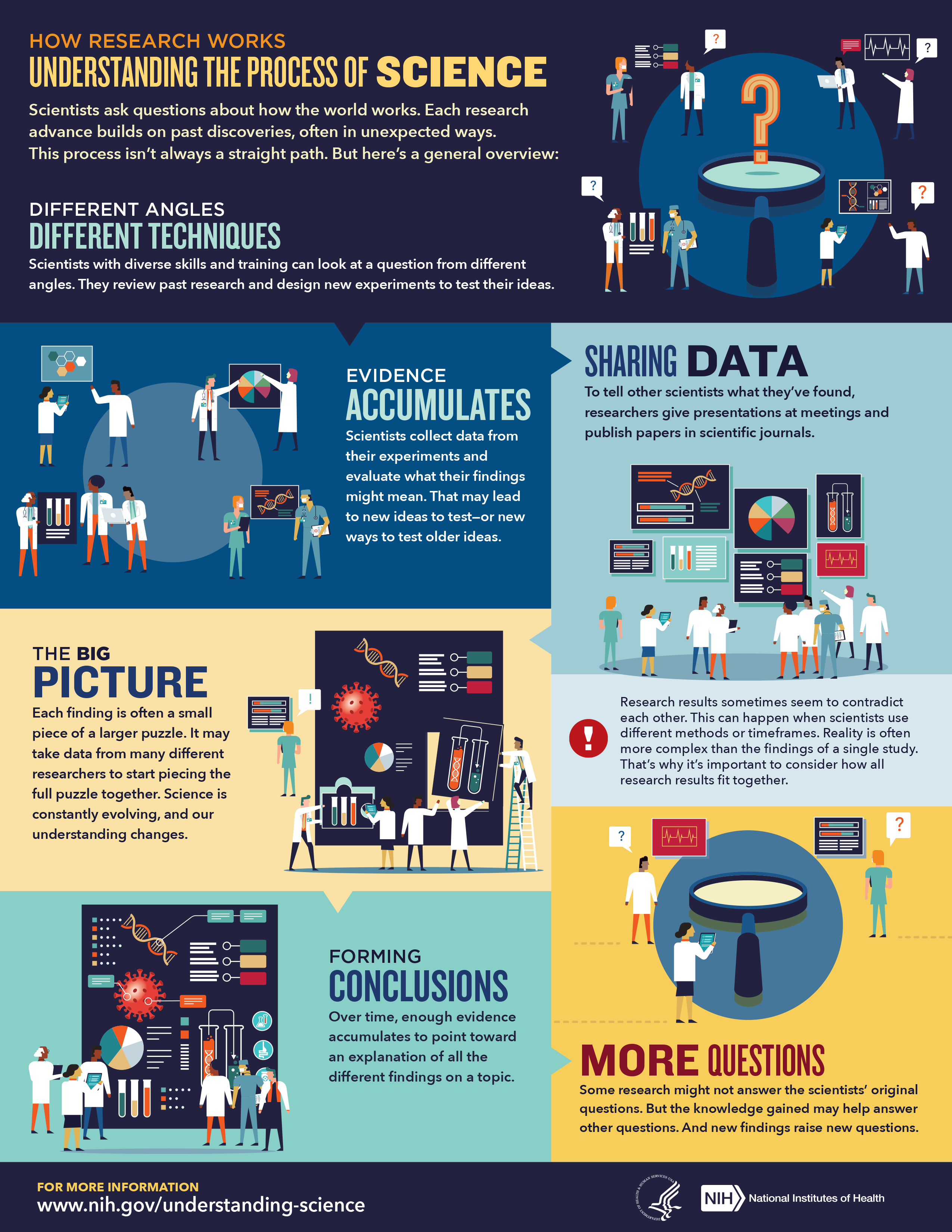
The Question Scientists start with a question about something they observe in the world. They develop a hypothesis, which is a testable prediction of what the answer to their question will be. Often their predictions turn out to be correct, but sometimes searching for the answer leads to unexpected outcomes.
The Techniques To test their hypotheses, scientists conduct experiments. They use many different tools and techniques, and sometimes they need to invent a new tool to fully answer their question. They may also work with one or more scientists with different areas of expertise to approach the question from other angles and get a more complete answer to their question.
The Evidence Throughout their experiments, scientists collect and analyze their data. They reach conclusions based on those analyses and determine whether their results match the predictions from their hypothesis. Often these conclusions trigger new questions and new hypotheses to test.
Researchers share their findings with one another by publishing papers in scientific journals and giving presentations at meetings. Data sharing is very important for the scientific field, and although some results may seem insignificant, each finding is often a small piece of a larger puzzle. That small piece may spark a new question and ultimately lead to new findings.
Sometimes research results seem to contradict each other, but this doesn’t necessarily mean that the results are wrong. Instead, it often means that the researchers used different tools, methods, or timeframes to obtain their results. The results of a single study are usually unable to fully explain the complex systems in the world around us. We must consider how results from many research studies fit together. This perspective gives us a more complete picture of what’s really happening.
Even if the scientific process doesn’t answer the original question, the knowledge gained may help provide other answers that lead to new hypotheses and discoveries.
Learn more about the importance of communicating how this process works in the NIH News in Health article, “ Explaining How Research Works .”

This post is a great supplement to Pathways: The Basic Science Careers Issue.
Pathways introduces the important role that scientists play in understanding the world around us, and all scientists use the scientific method as they make discoveries—which is explained in this post.
Learn more in our Educator’s Corner .
2 Replies to “How Research Works: Understanding the Process of Science”
Nice basic explanation. I believe informing the lay public on how science works, how parts of the body interact, etc. is a worthwhile endeavor. You all Rock! Now, we need to spread the word ‼️❗️‼️ Maybe eith a unique app. And one day, with VR and incentives to read & answer a couple questions.
As you know, the importance of an informed population is what will keep democracy alive. Plus it will improve peoples overall wellness & life outcomes.
Thanks for this clear explanation for the person who does not know science. Without getting too technical or advanced, it might be helpful to follow your explanation of replication with a reference to meta-analysis. You might say something as simple as, “Meta-analysis is a method for doing research on all the best research; meta-analytic research confirms the overall trend in results, even when the best studies show different results.”
Comments are closed.
Subscribe to Biomedical Beat
Get our latest blog posts delivered straight to your inbox! Sign Up Here
2.1 Why Is Research Important?
Learning objectives.
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Explain how scientific research addresses questions about behavior
- Discuss how scientific research guides public policy
- Appreciate how scientific research can be important in making personal decisions
Scientific research is a critical tool for successfully navigating our complex world. Without it, we would be forced to rely solely on intuition, other people’s authority, and blind luck. While many of us feel confident in our abilities to decipher and interact with the world around us, history is filled with examples of how very wrong we can be when we fail to recognize the need for evidence in supporting claims. At various times in history, we would have been certain that the sun revolved around a flat earth, that the earth’s continents did not move, and that mental illness was caused by possession ( Figure 2.2 ). It is through systematic scientific research that we divest ourselves of our preconceived notions and superstitions and gain an objective understanding of ourselves and our world.
The goal of all scientists is to better understand the world around them. Psychologists focus their attention on understanding behavior, as well as the cognitive (mental) and physiological (body) processes that underlie behavior. In contrast to other methods that people use to understand the behavior of others, such as intuition and personal experience, the hallmark of scientific research is that there is evidence to support a claim. Scientific knowledge is empirical : It is grounded in objective, tangible evidence that can be observed time and time again, regardless of who is observing.
While behavior is observable, the mind is not. If someone is crying, we can see behavior. However, the reason for the behavior is more difficult to determine. Is the person crying due to being sad, in pain, or happy? Sometimes we can learn the reason for someone’s behavior by simply asking a question, like “Why are you crying?” However, there are situations in which an individual is either uncomfortable or unwilling to answer the question honestly, or is incapable of answering. For example, infants would not be able to explain why they are crying. In such circumstances, the psychologist must be creative in finding ways to better understand behavior. This chapter explores how scientific knowledge is generated, and how important that knowledge is in forming decisions in our personal lives and in the public domain.
Use of Research Information
Trying to determine which theories are and are not accepted by the scientific community can be difficult, especially in an area of research as broad as psychology. More than ever before, we have an incredible amount of information at our fingertips, and a simple internet search on any given research topic might result in a number of contradictory studies. In these cases, we are witnessing the scientific community going through the process of reaching a consensus, and it could be quite some time before a consensus emerges. For example, the explosion in our use of technology has led researchers to question whether this ultimately helps or hinders us. The use and implementation of technology in educational settings has become widespread over the last few decades. Researchers are coming to different conclusions regarding the use of technology. To illustrate this point, a study investigating a smartphone app targeting surgery residents (graduate students in surgery training) found that the use of this app can increase student engagement and raise test scores (Shaw & Tan, 2015). Conversely, another study found that the use of technology in undergraduate student populations had negative impacts on sleep, communication, and time management skills (Massimini & Peterson, 2009). Until sufficient amounts of research have been conducted, there will be no clear consensus on the effects that technology has on a student's acquisition of knowledge, study skills, and mental health.
In the meantime, we should strive to think critically about the information we encounter by exercising a degree of healthy skepticism. When someone makes a claim, we should examine the claim from a number of different perspectives: what is the expertise of the person making the claim, what might they gain if the claim is valid, does the claim seem justified given the evidence, and what do other researchers think of the claim? This is especially important when we consider how much information in advertising campaigns and on the internet claims to be based on “scientific evidence” when in actuality it is a belief or perspective of just a few individuals trying to sell a product or draw attention to their perspectives.
We should be informed consumers of the information made available to us because decisions based on this information have significant consequences. One such consequence can be seen in politics and public policy. Imagine that you have been elected as the governor of your state. One of your responsibilities is to manage the state budget and determine how to best spend your constituents’ tax dollars. As the new governor, you need to decide whether to continue funding early intervention programs. These programs are designed to help children who come from low-income backgrounds, have special needs, or face other disadvantages. These programs may involve providing a wide variety of services to maximize the children's development and position them for optimal levels of success in school and later in life (Blann, 2005). While such programs sound appealing, you would want to be sure that they also proved effective before investing additional money in these programs. Fortunately, psychologists and other scientists have conducted vast amounts of research on such programs and, in general, the programs are found to be effective (Neil & Christensen, 2009; Peters-Scheffer, Didden, Korzilius, & Sturmey, 2011). While not all programs are equally effective, and the short-term effects of many such programs are more pronounced, there is reason to believe that many of these programs produce long-term benefits for participants (Barnett, 2011). If you are committed to being a good steward of taxpayer money, you would want to look at research. Which programs are most effective? What characteristics of these programs make them effective? Which programs promote the best outcomes? After examining the research, you would be best equipped to make decisions about which programs to fund.
Link to Learning
Watch this video about early childhood program effectiveness to learn how scientists evaluate effectiveness and how best to invest money into programs that are most effective.
Ultimately, it is not just politicians who can benefit from using research in guiding their decisions. We all might look to research from time to time when making decisions in our lives. Imagine that your sister, Maria, expresses concern about her two-year-old child, Umberto. Umberto does not speak as much or as clearly as the other children in his daycare or others in the family. Umberto's pediatrician undertakes some screening and recommends an evaluation by a speech pathologist, but does not refer Maria to any other specialists. Maria is concerned that Umberto's speech delays are signs of a developmental disorder, but Umberto's pediatrician does not; she sees indications of differences in Umberto's jaw and facial muscles. Hearing this, you do some internet searches, but you are overwhelmed by the breadth of information and the wide array of sources. You see blog posts, top-ten lists, advertisements from healthcare providers, and recommendations from several advocacy organizations. Why are there so many sites? Which are based in research, and which are not?
In the end, research is what makes the difference between facts and opinions. Facts are observable realities, and opinions are personal judgments, conclusions, or attitudes that may or may not be accurate. In the scientific community, facts can be established only using evidence collected through empirical research.
NOTABLE RESEARCHERS
Psychological research has a long history involving important figures from diverse backgrounds. While the introductory chapter discussed several researchers who made significant contributions to the discipline, there are many more individuals who deserve attention in considering how psychology has advanced as a science through their work ( Figure 2.3 ). For instance, Margaret Floy Washburn (1871–1939) was the first woman to earn a PhD in psychology. Her research focused on animal behavior and cognition (Margaret Floy Washburn, PhD, n.d.). Mary Whiton Calkins (1863–1930) was a preeminent first-generation American psychologist who opposed the behaviorist movement, conducted significant research into memory, and established one of the earliest experimental psychology labs in the United States (Mary Whiton Calkins, n.d.).
Francis Sumner (1895–1954) was the first African American to receive a PhD in psychology in 1920. His dissertation focused on issues related to psychoanalysis. Sumner also had research interests in racial bias and educational justice. Sumner was one of the founders of Howard University’s department of psychology, and because of his accomplishments, he is sometimes referred to as the “Father of Black Psychology.” Thirteen years later, Inez Beverly Prosser (1895–1934) became the first African American woman to receive a PhD in psychology. Prosser’s research highlighted issues related to education in segregated versus integrated schools, and ultimately, her work was very influential in the hallmark Brown v. Board of Education Supreme Court ruling that segregation of public schools was unconstitutional (Ethnicity and Health in America Series: Featured Psychologists, n.d.).
Although the establishment of psychology’s scientific roots occurred first in Europe and the United States, it did not take much time until researchers from around the world began to establish their own laboratories and research programs. For example, some of the first experimental psychology laboratories in South America were founded by Horatio Piñero (1869–1919) at two institutions in Buenos Aires, Argentina (Godoy & Brussino, 2010). In India, Gunamudian David Boaz (1908–1965) and Narendra Nath Sen Gupta (1889–1944) established the first independent departments of psychology at the University of Madras and the University of Calcutta, respectively. These developments provided an opportunity for Indian researchers to make important contributions to the field (Gunamudian David Boaz, n.d.; Narendra Nath Sen Gupta, n.d.).
When the American Psychological Association (APA) was first founded in 1892, all of the members were White males (Women and Minorities in Psychology, n.d.). However, by 1905, Mary Whiton Calkins was elected as the first female president of the APA, and by 1946, nearly one-quarter of American psychologists were female. Psychology became a popular degree option for students enrolled in the nation’s historically Black higher education institutions, increasing the number of Black Americans who went on to become psychologists. Given demographic shifts occurring in the United States and increased access to higher educational opportunities among historically underrepresented populations, there is reason to hope that the diversity of the field will increasingly match the larger population, and that the research contributions made by the psychologists of the future will better serve people of all backgrounds (Women and Minorities in Psychology, n.d.).
The Process of Scientific Research
Scientific knowledge is advanced through a process known as the scientific method . Basically, ideas (in the form of theories and hypotheses) are tested against the real world (in the form of empirical observations), and those empirical observations lead to more ideas that are tested against the real world, and so on. In this sense, the scientific process is circular. The types of reasoning within the circle are called deductive and inductive. In deductive reasoning , ideas are tested in the real world; in inductive reasoning , real-world observations lead to new ideas ( Figure 2.4 ). These processes are inseparable, like inhaling and exhaling, but different research approaches place different emphasis on the deductive and inductive aspects.
In the scientific context, deductive reasoning begins with a generalization—one hypothesis—that is then used to reach logical conclusions about the real world. If the hypothesis is correct, then the logical conclusions reached through deductive reasoning should also be correct. A deductive reasoning argument might go something like this: All living things require energy to survive (this would be your hypothesis). Ducks are living things. Therefore, ducks require energy to survive (logical conclusion). In this example, the hypothesis is correct; therefore, the conclusion is correct as well. Sometimes, however, an incorrect hypothesis may lead to a logical but incorrect conclusion. Consider this argument: all ducks are born with the ability to see. Quackers is a duck. Therefore, Quackers was born with the ability to see. Scientists use deductive reasoning to empirically test their hypotheses. Returning to the example of the ducks, researchers might design a study to test the hypothesis that if all living things require energy to survive, then ducks will be found to require energy to survive.
Deductive reasoning starts with a generalization that is tested against real-world observations; however, inductive reasoning moves in the opposite direction. Inductive reasoning uses empirical observations to construct broad generalizations. Unlike deductive reasoning, conclusions drawn from inductive reasoning may or may not be correct, regardless of the observations on which they are based. For instance, you may notice that your favorite fruits—apples, bananas, and oranges—all grow on trees; therefore, you assume that all fruit must grow on trees. This would be an example of inductive reasoning, and, clearly, the existence of strawberries, blueberries, and kiwi demonstrate that this generalization is not correct despite it being based on a number of direct observations. Scientists use inductive reasoning to formulate theories, which in turn generate hypotheses that are tested with deductive reasoning. In the end, science involves both deductive and inductive processes.
For example, case studies, which you will read about in the next section, are heavily weighted on the side of empirical observations. Thus, case studies are closely associated with inductive processes as researchers gather massive amounts of observations and seek interesting patterns (new ideas) in the data. Experimental research, on the other hand, puts great emphasis on deductive reasoning.
We’ve stated that theories and hypotheses are ideas, but what sort of ideas are they, exactly? A theory is a well-developed set of ideas that propose an explanation for observed phenomena. Theories are repeatedly checked against the world, but they tend to be too complex to be tested all at once; instead, researchers create hypotheses to test specific aspects of a theory.
A hypothesis is a testable prediction about how the world will behave if our idea is correct, and it is often worded as an if-then statement (e.g., if I study all night, I will get a passing grade on the test). The hypothesis is extremely important because it bridges the gap between the realm of ideas and the real world. As specific hypotheses are tested, theories are modified and refined to reflect and incorporate the result of these tests Figure 2.5 .
To see how this process works, let’s consider a specific theory and a hypothesis that might be generated from that theory. As you’ll learn in a later chapter, the James-Lange theory of emotion asserts that emotional experience relies on the physiological arousal associated with the emotional state. If you walked out of your home and discovered a very aggressive snake waiting on your doorstep, your heart would begin to race and your stomach churn. According to the James-Lange theory, these physiological changes would result in your feeling of fear. A hypothesis that could be derived from this theory might be that a person who is unaware of the physiological arousal that the sight of the snake elicits will not feel fear.
A scientific hypothesis is also falsifiable , or capable of being shown to be incorrect. Recall from the introductory chapter that Sigmund Freud had lots of interesting ideas to explain various human behaviors ( Figure 2.6 ). However, a major criticism of Freud’s theories is that many of his ideas are not falsifiable; for example, it is impossible to imagine empirical observations that would disprove the existence of the id, the ego, and the superego—the three elements of personality described in Freud’s theories. Despite this, Freud’s theories are widely taught in introductory psychology texts because of their historical significance for personality psychology and psychotherapy, and these remain the root of all modern forms of therapy.
In contrast, the James-Lange theory does generate falsifiable hypotheses, such as the one described above. Some individuals who suffer significant injuries to their spinal columns are unable to feel the bodily changes that often accompany emotional experiences. Therefore, we could test the hypothesis by determining how emotional experiences differ between individuals who have the ability to detect these changes in their physiological arousal and those who do not. In fact, this research has been conducted and while the emotional experiences of people deprived of an awareness of their physiological arousal may be less intense, they still experience emotion (Chwalisz, Diener, & Gallagher, 1988).
Scientific research’s dependence on falsifiability allows for great confidence in the information that it produces. Typically, by the time information is accepted by the scientific community, it has been tested repeatedly.
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/psychology-2e/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Rose M. Spielman, William J. Jenkins, Marilyn D. Lovett
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Psychology 2e
- Publication date: Apr 22, 2020
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/psychology-2e/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/psychology-2e/pages/2-1-why-is-research-important
© Jan 6, 2024 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.

- Joyner Library
- Laupus Health Sciences Library
- Music Library
- Digital Collections
- Special Collections
- North Carolina Collection
- Teaching Resources
- The ScholarShip Institutional Repository
- Country Doctor Museum
Presentations: Oral Presentations
- Poster Design
- Poster Content
- Poster Presentation
- Oral Presentations
- Printing & Archiving
Oral Presentations Purpose
An Oral Research Presentation is meant to showcase your research findings. A successful oral research presentation should: communicate the importance of your research; clearly state your findings and the analysis of those findings; prompt discussion between researcher and audience. Below you will find information on how to create and give a successful oral presentation.
Creating an Effective Presentation
Who has a harder job the speaker? Or, the audience?
Most people think speaker has the hardest job during an oral presentation, because they are having to stand up in a room full of people and give a presentation. However, if the speaker is not engaging and if the material is way outside of the audiences knowledge level, the audience can have a difficult job as well. Below you will find some tips on how to be an effective presenter and how to engage with your audience.
Organization of a Presentation
Introduction/Beginning
How are you going to begin? How are you going to get the attention of your audience? You need to take the time and think about how you are going to get started!
Here are some ways you could start:
- Ask the audience a question
- make a statement
- show them something
No matter how you start your presentation it needs to relate to your research and capture the audiences attention.
Preview what you are going to discuss . Audiences do not like to be manipulated or tricked. Tell the audience exactly what you are going to discuss, this will help them follow along. *Do not say you are going to cover three points and then try to cover 8 points.
At the end of your introduction, the audience should feel like they know exactly what you are going to discuss and exactly how you are going to get there.
Body/Middle
Conclusion/End
Delivery and Communication
Eye Contact
Making eye contact is a great way to engage with your audience. Eye contact should be no longer than 2-3 seconds per person. Eye contact for much longer than that can begin to make the audience member feel uncomfortable.
Smiling lets attendees know you are happy to be there and that you are excited to talk with them about your project.
We all know that body language says a lot, so here are some things you should remember when giving your presentation.
- Stand with both feet on the floor, not with one foot crossed over the other.
- Do not stand with your hands in your pockets, or with your arms crossed.
- Stand tall with confidence and own your space (remember you are the expert).
Abbreviated Notes
Having a written set of notes or key points that you want to address can help prevent you from reading the poster.
Speak Clearly
Sometimes when we get nervous we begin to talk fast and blur our words. It is important that you make sure every word is distinct and clear. A great way to practice your speech is to say tongue twisters.
Ten tiny tots tottered toward the shore
Literally literary. Literally literary. Literally literary.
Sally soon saw that she should sew some sheets.
Avoid Fillers
Occasionally we pick up fillers that we are not aware of, such as um, like, well, etc. One way to get rid of fillers is to have a friend listen to your speech and every time you say a "filler" have that friend tap you on the arm or say your name. This will bring the filler to light, then you can practice avoiding that filler.
Manage Anxiety
Many people get nervous when they are about to speak to a crowd of people. Below are ways that you can manage your anxiety levels.
- Practice, Practice, Practice - the more prepared you are the less nervous you will be.
- Recognize that anxiety is just a big shot of adrenalin.
- Take deep breaths before your presentation to calm you down.
Components of an Oral Research Presentation
Introduction
The introduction section of your oral presentation should consist of 3 main parts.
Part 1: Existing facts
In order to give audience members the "full picture", you first need to provide them with information about past research. What facts already exist? What is already known about your research area?
Part 2: Shortcomings
Once you have highlighted past research and existing facts. You now need to address what is left to be known, or what shortcomings exist within the current information. This should set the groundwork for your experiment. Keep in mind, how does your research fill these gaps or help address these questions?
Part 3: Purpose or Hypothesis
After you have addressed past/current research and have identified shortcomings/gaps, it is now time to address your research. During this portion of the introduction you need to tell viewers why you are conducting your research experiement/study, and what you hope to accomplish by doing so.
In this section you should share with your audience how you went about collecting and analyzing your data
Should include:
- Participants: Who or what was in the study?
- Materials/ measurements: what did you measure?
- Procedures: How did you do the study?
- Data-analysis: What analysis were conducted?
This section contains FACTS – with no opinion, commentary or interpretation. Graphs, charts and images can be used to display data in a clear and organized way.
Keep in mind when making figures:
- Make sure axis, treatments, and data sets are clearly labeled
- Strive for simplicity, especially in figure titles.
- Know when to use what kind of graph
- Be careful with colors.
Interpretation and commentary takes place here. This section should give a clear summary of your findings.
You should:
- Address the positive and negative aspects of you research
- Discuss how and if your research question was answered.
- Highlight the novel and important findings
- Speculate on what could be occurring in your system
Future Research
- State your goals
- Include information about why you believe research should go in the direction you are proposing
- Discuss briefly how you plan to implement the research goals, if you chose to do so.
Why include References?
- It allows viewers to locate the material that you used, and can help viewers expand their knowledge of your research topic.
- Indicates that you have conducted a thorough review of the literature and conducted your research from an informed perspective.
- Guards you against intellectual theft. Ideas are considered intellectual property failure to cite someone's ideas can have serious consequences.
Acknowledgements
This section is used to thank the people, programs and funding agencies that allowed you to perform your research.
Questions
Allow for about 2-3 minutes at the end of your presentation for questions.
It is important to be prepared.
- Know why you conducted the study
- Be prepared to answer questions about why you chose a specific methodology
If you DO NOT know the answer to a question
Visual Aids
PowerPoints and other visual aids can be used to support what you are presenting about.
Power Point Slides and other visual aids can help support your presentation, however there are some things you should consider:
- Do not overdo it . One big mistake that presenters make is they have a slide for every single item they want to say. One way you can avoid this is by writing your presentation in Word first, instead of making a Power Point Presentation. By doing this you can type exactly what you want to say, and once your presentation is complete, you can create Power Point slides that help support your presentation.
Formula for number of visual aids : Length of presentation divided by 2 plus 1
example: 12 minute presentation should have no more than 7 slides.
- Does it add interest?
- Does it prove?
- Does it clarify?
- Do not read the text . Most people can read, and if they have the option of reading material themselves versus listen to you read it, they are going to read it themselves and then your voice becomes an annoyance. Also, when you are reading the text you are probably not engaging with the audience.
- No more than 4-6 lines on a slide and no more than 4-6 words in a line.
- People should be able to read your slide in 6 seconds.
- << Previous: Poster Presentation
- Next: Printing & Archiving >>
- Last Updated: Apr 11, 2024 9:02 AM
- URL: https://libguides.ecu.edu/c.php?g=637469
- What is New
- Download Your Software
- Behavioral Research
- Software for Consumer Research
- Software for Human Factors R&D
- Request Live Demo
- Contact Sales
Sensor Hardware

We carry a range of biosensors from the top hardware producers. All compatible with iMotions
iMotions for Higher Education
Imotions for business.

Can You Build Your Own Eye Tracking Glasses?
Morten Pedersen

Managing and Measuring Cognitive Performance
News & events.
- iMotions Lab
- iMotions Online
- Eye Tracking
- Eye Tracking Screen Based
- Eye Tracking VR
- Eye Tracking Glasses
- Eye Tracking Webcam
- FEA (Facial Expression Analysis)
- Voice Analysis
- EDA/GSR (Electrodermal Activity)
- EEG (Electroencephalography)
- ECG (Electrocardiography)
- EMG (Electromyography)
- Respiration
- iMotions Lab: New features
- iMotions Lab: Developers
- EEG sensors
- Sensory and Perceptual
- Consumer Inights
- Human Factors R&D
- Work Environments, Training and Safety
- Customer Stories
- Published Research Papers
- Document Library
- Customer Support Program
- Help Center
- Release Notes
- Contact Support
- Partnerships
- Mission Statement
- Ownership and Structure
- Executive Management
- Job Opportunities
Publications
- Newsletter Sign Up
The Importance of Research Design: A Comprehensive Guide

Research design plays a crucial role in conducting scientific studies and gaining meaningful insights. A well-designed research enhances the validity and reliability of the findings and allows for the replication of studies by other researchers. This comprehensive guide will provide an in-depth understanding of research design, its key components, different types, and its role in scientific inquiry. Furthermore, it will discuss the necessary steps in developing a research design and highlight some of the challenges that researchers commonly face.
Table of Contents
Understanding research design.
Research design refers to the overall plan or strategy that outlines how a study is conducted. It serves as a blueprint for researchers, guiding them in their investigation, and helps ensure that the study objectives are met. Understanding research design is essential for researchers to effectively gather and analyze data to answer research questions.
When embarking on a research study, researchers must carefully consider the design they will use. The design determines the structure of the study, including the research questions, data collection methods, and analysis techniques. It provides clarity on how the study will be conducted and helps researchers determine the best approach to achieve their research objectives. A well-designed study increases the chances of obtaining valid and reliable results.
Definition and Purpose of Research Design
Research design is the framework that outlines the structure of a study, including the research questions, data collection methods, and analysis techniques. It provides a systematic approach to conducting research and ensures that all aspects of the study are carefully planned and executed.
The purpose of research design is to provide a clear roadmap for researchers to follow. It helps them define the research questions they want to answer and identify the variables they will study. By clearly defining the purpose of the study, researchers can ensure that their research design aligns with their objectives.
Key Components of Research Design
A research design consists of several key components that influence the study’s validity and reliability. These components include the research questions, variables and operational definitions, sampling techniques, data collection methods, and statistical analysis procedures.
The research questions are the foundation of any study. They guide the entire research process and help researchers focus their efforts. By formulating clear and concise research questions, researchers can ensure that their study addresses the specific issues they want to investigate.

Variables and operational definitions are also crucial components of research design. Variables are the concepts or phenomena that researchers want to measure or study. Operational definitions provide a clear and specific description of how these variables will be measured or observed. By clearly defining variables and their operational definitions, researchers can ensure that their study is consistent and replicable.
Sampling techniques play a vital role in research design as well. Researchers must carefully select the participants or samples they will study to ensure that their findings are generalizable to the larger population. Different sampling techniques, such as random sampling or purposive sampling, can be used depending on the research objectives and constraints.
Data collection methods are another important component of research design. Researchers must decide how they will collect data, whether through surveys, interviews, observations, or experiments. The choice of data collection method depends on the research questions and the type of data needed to answer them.
Finally, statistical analysis procedures are used to analyze the collected data and draw meaningful conclusions. Researchers must determine the appropriate statistical tests or techniques to use based on the nature of their data and research questions. The choice of statistical analysis procedures ensures that the data is analyzed accurately and that the results are valid and reliable.
Types of Research Design
Research design encompasses various types that researchers can choose depending on their research goals and the nature of the phenomenon being studied. Understanding the different types of research design is essential for researchers to select the most appropriate approach for their study.
When embarking on a research project, researchers must carefully consider the design they will employ. The design chosen will shape the entire study, from the data collection process to the analysis and interpretation of results. Let’s explore some of the most common types of research design in more detail.
Experimental Design
Experimental design involves manipulating one or more variables to observe their effect on the dependent variable. This type of design allows researchers to establish cause-and-effect relationships between variables by controlling for extraneous factors. Experimental design often relies on random assignment and control groups to minimize biases.
Imagine a group of researchers interested in studying the effects of a new teaching method on student performance. They could randomly assign students to two groups: one group would receive instruction using the new teaching method, while the other group would receive instruction using the traditional method. By comparing the performance of the two groups, the researchers can determine whether the new teaching method has a significant impact on student learning.
Experimental design provides a strong foundation for making causal claims, as it allows researchers to control for confounding variables and isolate the effects of the independent variable. However, it may not always be feasible or ethical to manipulate variables, leading researchers to explore alternative designs.
Free 44-page Experimental Design Guide
For Beginners and Intermediates
- Introduction to experimental methods
- Respondent management with groups and populations
- How to set up stimulus selection and arrangement

Non-Experimental Design
Non-experimental design is used when it is not feasible or ethical to manipulate variables. This design relies on naturally occurring variations in data and focuses on observing and describing relationships between variables. Non-experimental design can be useful for exploratory research or when studying phenomena that cannot be controlled, such as human behavior.
For instance, researchers interested in studying the relationship between socioeconomic status and health outcomes may collect data from a large sample of individuals and analyze the existing differences. By examining the data, they can determine whether there is a correlation between socioeconomic status and health, without manipulating any variables.
Non-experimental design allows researchers to study real-world phenomena in their natural setting, providing valuable insights into complex social, psychological, and economic processes. However, it is important to note that non-experimental designs cannot establish causality, as there may be other variables at play that influence the observed relationships.
Quasi-Experimental Design
Quasi-experimental design resembles experimental design but lacks the element of random assignment. In situations where random assignment is not possible or practical, researchers can utilize quasi-experimental designs to gather data and make inferences. However, caution must be exercised when drawing causal conclusions from quasi-experimental studies.
Consider a scenario where researchers are interested in studying the effects of a new drug on patient recovery time. They cannot randomly assign patients to receive the drug or a placebo due to ethical considerations. Instead, they can compare the recovery times of patients who voluntarily choose to take the drug with those who do not. While this design allows for data collection and analysis, it is important to acknowledge that other factors, such as patient motivation or severity of illness, may influence the observed outcomes.
Quasi-experimental designs are valuable when experimental designs are not feasible or ethical. They provide an opportunity to explore relationships and gather data in real-world contexts. However, researchers must be cautious when interpreting the results, as causal claims may be limited due to the lack of random assignment.
By understanding the different types of research design, researchers can make informed decisions about the most appropriate approach for their study. Each design offers unique advantages and limitations, and the choice depends on the research question, available resources, and ethical considerations. Regardless of the design chosen, rigorous methodology and careful data analysis are crucial for producing reliable and valid research findings.
The Role of Research Design in Scientific Inquiry
A well-designed research study enhances the validity and reliability of the findings. Research design plays a crucial role in ensuring the scientific rigor of a study and facilitates the replication of studies by other researchers. Understanding the role of research design in scientific inquiry is vital for researchers to conduct impactful and robust research.
Ensuring Validity and Reliability
Research design plays a critical role in ensuring the validity and reliability of the study’s findings. Validity refers to the degree to which the study measures what it intends to measure, while reliability pertains to the consistency and stability of the results. Through careful consideration of the research design, researchers can minimize potential biases and increase the accuracy of their measurements.
Facilitating Replication of Studies
A robust research design allows for the replication of studies by other researchers. Replication plays a vital role in the scientific process as it helps confirm the validity and generalizability of research findings. By clearly documenting the research design, researchers enable others to reproduce the study and validate the results, thereby contributing to the cumulative knowledge in a field.
Steps in Developing a Research Design
Developing a research design involves a systematic process that includes several important steps. Researchers need to carefully consider each step to ensure that their study is well-designed and capable of addressing their research questions effectively.
Identifying Research Questions
The first step in developing a research design is to identify and define the research questions or hypotheses. Researchers need to clearly articulate what they aim to investigate and what specific information they want to gather. Clear research questions provide guidance for the subsequent steps in the research design process.
Selecting Appropriate Design Type
Once the research questions are identified, researchers need to select the most appropriate type of research design. The choice of design depends on various factors, including the research goals, the nature of the research questions, and the available resources. Careful consideration of these factors is crucial to ensure that the chosen design aligns with the study objectives.
Determining Data Collection Methods
After selecting the research design, researchers need to determine the most suitable data collection methods. Depending on the research questions and the type of data required, researchers can utilize a range of methods, such as surveys, interviews, observations, or experiments. The chosen methods should align with the research objectives and allow for the collection of high-quality data.
One of the most important considerations when designing a study in human behavior research is participant recruitment. We have written a comprehensive guide on best practices and pitfalls to be aware of when recruiting participants, which can be read here.
Enhancing Research Design with iMotions and Biosensors
Introduction to enhanced research design.
In the realm of scientific studies, especially within human cognitive-behavioral research, the deployment of advanced technologies such as iMotions software and biosensors has revolutionized research design. This chapter delves into how these technologies can be integrated into various research designs, improving the depth, accuracy, and reliability of scientific inquiries.
Integrating iMotions in Research Design
Imotions software: a key to multimodal data integration.
The iMotions platform stands as a pivotal tool in modern research design. It’s designed to integrate data from a plethora of biosensors, providing a comprehensive analysis of human behavior. This software facilitates the synchronizing of physiological, cognitive, and emotional responses with external stimuli, thus enriching the understanding of human behavior in various contexts.
Biosensors: Gateways to Deeper Insights
Biosensors, including eye trackers, EEG, GSR, ECG, and facial expression analysis tools, provide nuanced insights into the subconscious and conscious aspects of human behavior. These tools help researchers in capturing data that is often unattainable through traditional data collection methods like surveys and interviews.
Application in Different Research Designs
- Eye Tracking : In experimental designs, where the impact of visual stimuli is crucial, eye trackers can reveal how subjects interact with these stimuli, thereby offering insights into cognitive processes and attention.
- EEG : EEG biosensors allow researchers to monitor brain activity in response to controlled experimental manipulations, offering a window into cognitive and emotional responses.
- Facial Expression Analysis : In observational studies, analyzing facial expressions can provide objective data on emotional responses in natural settings, complementing subjective self-reports.
- GSR/EDA : These tools measure physiological arousal in real-life scenarios, giving researchers insights into emotional states without the need for intrusive measures.
- EMG : In studies where direct manipulation isn’t feasible, EMG can indicate subtle responses to stimuli, which might be overlooked in traditional observational methods.
- ECG/PPG : These sensors can be used to understand the impact of various interventions on physiological states such as stress or relaxation.
Streamlining Research Design with iMotions
The iMotions platform offers a streamlined process for integrating various biosensors into a research design. Researchers can easily design experiments, collect multimodal data, and analyze results in a unified interface. This reduces the complexity often associated with handling multiple streams of data and ensures a cohesive and comprehensive research approach.
Integrating iMotions software and biosensors into research design opens new horizons for scientific inquiry. This technology enhances the depth and breadth of data collection, paving the way for more nuanced and comprehensive findings.
Whether in experimental, non-experimental, or quasi-experimental designs, iMotions and biosensors offer invaluable tools for researchers aiming to uncover the intricate layers of human behavior and cognitive processes. The future of research design is undeniably intertwined with the advancements in these technologies, leading to more robust, reliable, and insightful scientific discoveries.
Challenges in Research Design
Research design can present several challenges that researchers need to overcome to conduct reliable and valid studies. Being aware of these challenges is essential for researchers to address them effectively and ensure the integrity of their research.
Ethical Considerations
Research design must adhere to ethical guidelines and principles to protect the rights and well-being of participants. Researchers need to obtain informed consent, ensure participant confidentiality, and minimize potential harm or discomfort. Ethical considerations should be carefully integrated into the research design to promote ethical research practices.
Practical Limitations
Researchers often face practical limitations that may impact the design and execution of their studies. Limited resources, time constraints, access to participants or data, and logistical challenges can pose obstacles during the research process. Researchers need to navigate these limitations and make thoughtful choices to ensure the feasibility and quality of their research.
Research design is a vital aspect of conducting scientific studies. It provides a structured framework for researchers to answer their research questions and obtain reliable and valid results. By understanding the different types of research design and following the necessary steps in developing a research design, researchers can enhance the rigor and impact of their studies.
However, researchers must also be mindful of the challenges they may encounter, such as ethical considerations and practical limitations, and take appropriate measures to address them. Ultimately, a well-designed research study contributes to the advancement of knowledge and promotes evidence-based decision-making in various fields.
Last edited
About the author
See what is next in human behavior research
Follow our newsletter to get the latest insights and events send to your inbox.
Related Posts

Can you use HTC VIVE Pro Eye for eye tracking research?

Top 5 Publications of 2023
Laila Mowla

Understanding Cognitive Workload: What Is It and How Does It Affect Us?
The Best Neuroscience Software
You might also like these.

The World Runs on Behavioral Insights
Consumer Insights

New OSM Reference System from iMotions
Human Factors and UX

How to Measure Stress
Work and Safety
Case Stories
Explore Blog Categories
Best Practice
Collaboration, product guides, product news, research fundamentals, research insights, 🍪 use of cookies.
We are committed to protecting your privacy and only use cookies to improve the user experience.
Chose which third-party services that you will allow to drop cookies. You can always change your cookie settings via the Cookie Settings link in the footer of the website. For more information read our Privacy Policy.
- gtag This tag is from Google and is used to associate user actions with Google Ad campaigns to measure their effectiveness. Enabling this will load the gtag and allow for the website to share information with Google. This service is essential and can not be disabled.
- Livechat Livechat provides you with direct access to the experts in our office. The service tracks visitors to the website but does not store any information unless consent is given. This service is essential and can not be disabled.
- Pardot Collects information such as the IP address, browser type, and referring URL. This information is used to create reports on website traffic and track the effectiveness of marketing campaigns.
- Third-party iFrames Allows you to see thirdparty iFrames.

Significance of the Study
Ai generator.
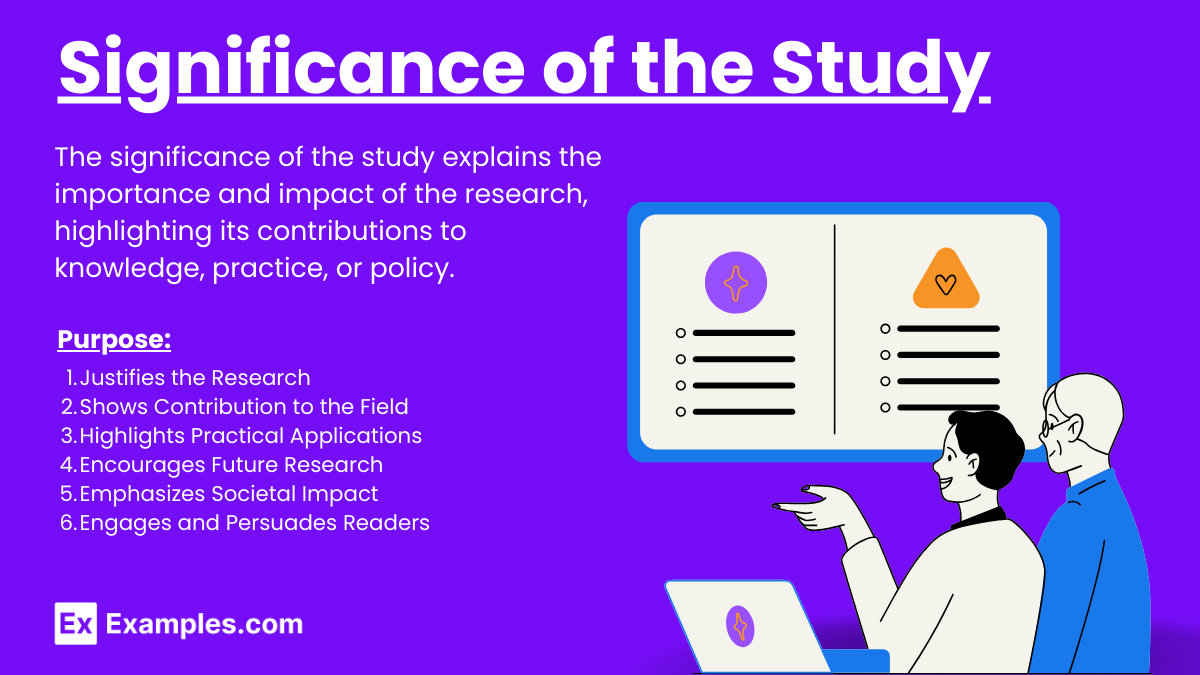
The significance of the study underscores the research’s importance, illustrating its impact on existing knowledge and potential applications. It highlights how the findings address gaps, resolve problems, or contribute to advancements in a specific field. By emphasizing the study’s relevance, it demonstrates the broader implications for society, academia, or industry, justifying the research effort and investment.
What is the Significance of the Study?
The significance of the study illustrates the research’s importance, highlighting its impact on existing knowledge and potential applications. It addresses gaps, resolves problems, or contributes to advancements in a specific field. Emphasizing the study’s relevance, it demonstrates broader implications for society, academia, or industry, justifying the research effort and investment.
Significance of the Study Format
When writing the “Significance of the Study” section in a research paper , follow this format to ensure clarity and impact:
1. Introduction
- Contextual Background: Provide a brief background of the research topic.
- Research Problem: State the problem the study addresses.
2. Purpose of the Study
- Objective Statement: Clearly define the main objective of the study.
- Scope of the Study: Outline what the study covers.
3. Importance to the Field
- Contribution to Knowledge: Explain how the study will add to existing knowledge.
- Theoretical Significance: Discuss the study’s theoretical implications.
4. Practical Implications
- Real-world Application: Describe how the findings can be applied in practical setting .
- Beneficiaries: Identify who will benefit from the research (e.g., policymakers, practitioners, educators).
5. Advancement of Future Research
- Foundation for Future Studies: Indicate how the study can serve as a basis for further research.
- Research Gaps: Highlight any gaps the study aims to fill.
6. Societal Impact
- Broader Implications: Discuss the potential societal benefits or changes resulting from the study.
- Public Awareness: Explain how the study can raise awareness or understanding of the issue.
7. Conclusion
- Summary of Significance: Recap the main points that underline the importance of the study.
- Call to Action: Encourage specific actions or further studies based on the research findings.
Significance of the Study on Impact of Remote Work on Employee Productivity in the Tech Industry 1. Introduction The rapid shift to remote work due to the COVID-19 pandemic has fundamentally changed the dynamics of workplace productivity, especially within the tech industry. This study aims to examine how remote work influences employee productivity compared to traditional office settings. 2. Purpose of the Study The primary objective of this research is to evaluate the productivity levels of tech employees working remotely versus those working in office environments. The study analyzes various productivity metrics, such as task completion rates, quality of work, and employee satisfaction. 3. Importance to the Field This research contributes significantly to the existing body of knowledge by providing empirical data on the productivity impacts of remote work. It refines theoretical models of workplace productivity and offers new insights into remote work dynamics specific to the tech sector. Understanding these dynamics helps scholars and practitioners alike in shaping effective productivity strategies in the evolving work landscape. 4. Practical Implications The findings from this study have crucial practical implications for tech companies aiming to optimize their remote work policies. By understanding how remote work affects productivity, managers and HR departments can develop strategies to enhance employee performance and well-being in remote settings. These insights can also assist in designing training programs that equip employees with the skills needed for effective remote work. 5. Advancement of Future Research This study sets the stage for future research on long-term remote work trends and their impacts across various industries. It addresses existing gaps by providing a detailed analysis of how remote work influences productivity in the tech sector. Future researchers can build on this work to explore remote work dynamics in other fields and under different conditions. 6. Societal Impact The study highlights the broader societal implications of remote work, such as promoting work-life balance, reducing urban congestion, and lowering environmental pollution. By demonstrating the potential benefits of remote work, this research can influence public policy and corporate strategies towards more sustainable and flexible working conditions, ultimately contributing to societal well-being. 7. Conclusion Understanding the impact of remote work on productivity is essential for developing effective work policies and creating healthier work environments. This study provides valuable insights that can guide tech companies in optimizing their remote work strategies. Future research should explore the long-term effects of remote work across different sectors to provide a comprehensive understanding of its benefits and challenges.
Significance of the Study Examples
- Significance of the Study: Research Paper
- Significance of the Study: Qunatitive Research
- Significance of the Study: Qualitative Research
Research Paper

Qunatitive Research


Qualitative Research

More Significance of the Study Examples
- Educational Resources and Student Performance
- Business Innovation and Competitive Advantage
- Social Media Influencers and Brand Loyalty
- Mental Health Benefits of Physical Activ ity
- Sustainable Food Practices and Consumer Behavior
- Green Building and Energy Efficiency
- Technology in Healthcare
- Employee Engagement and Job Performance
- Business Strategies and Market Adaptation
- Mindfulness at Work
Purpose of Writing the Significance of a Study
When writing academic research or scholarly articles, one critical section is the significance of the study . This part addresses the importance and impact of the research, both theoretically and practically. Here are the main purposes of writing the significance of a study:
1. Establishing Relevance
The primary purpose is to explain why the study is relevant. It connects the research to existing literature, highlighting gaps or deficiencies that the current study aims to fill. This helps to justify the research problem and demonstrates the necessity of the study.
2. Highlighting Contributions
This section outlines the contributions the study will make to the field. It discusses how the findings can advance knowledge, theory, or practice. The significance emphasizes new insights, innovative approaches, or advancements that the study will provide.
3. Guiding Further Research
The significance of the study often includes suggestions for future research. By identifying limitations and unexplored areas, it encourages other researchers to pursue related questions. This helps to build a foundation for continuous inquiry and discovery.
4. Demonstrating Practical Applications
Beyond theoretical contributions, the significance of the study highlights practical applications. It shows how the research can solve real-world problems, improve practices, or influence policy-making. This connects academic research to practical outcomes that benefit society.
5. Engaging Stakeholders
Writing the significance of a study engages various stakeholders, including scholars, practitioners, policymakers, and funders. It communicates the value of the research to different audiences, making it easier to garner support, funding, or collaboration.
6. Enhancing Research Impact
A well-articulated significance section enhances the overall impact of the research. It underscores the importance and potential influence of the study, increasing its visibility and recognition in the academic community and beyond.
Benefits of Significance of the Study
Writing the significance of a study offers several benefits that enhance the research’s value and impact. Here are the key benefits:
1. Clarifies Research Value
The significance section clarifies the value of the research by explaining its importance and relevance. It helps readers understand why the study matters and what contributions it aims to make to the field.
2. Justifies the Research Problem
This section provides a rationale for the study by highlighting the research problem’s importance. It justifies the need for the study by identifying gaps in existing literature and explaining how the research will address these gaps.
3. Engages and Motivates Readers
A well-articulated significance section engages and motivates readers, including scholars, practitioners, and policymakers. It draws their interest by showcasing the study’s potential impact and benefits.
4. Secures Funding and Support
Explaining the significance of the study can help secure funding and support from stakeholders. Funding agencies and institutions are more likely to invest in research that demonstrates clear value and potential impact.
5. Guides Research Focus
The significance section helps guide the research focus by clearly defining the study’s contributions and goals. This clarity ensures that the research stays on track and aligns with its intended purpose.
6. Enhances Academic Credibility
Demonstrating the significance of a study enhances the researcher’s academic credibility. It shows a deep understanding of the field and the ability to identify and address important research questions.
7. Encourages Further Research
By identifying gaps and suggesting future research directions, the significance section encourages other researchers to build on the study’s findings. This fosters a continuous cycle of inquiry and discovery in the field.
8. Highlights Practical Applications
The significance section highlights practical applications of the research, showing how it can solve real-world problems. This makes the study more appealing to practitioners and policymakers who are interested in practical solutions.
9. Increases Research Impact
A clear and compelling significance section increases the overall impact of the research. It enhances the study’s visibility and recognition, leading to broader dissemination and application of the findings.
10. Supports Academic and Professional Goals
For researchers, writing a strong significance section supports academic and professional goals. It can contribute to career advancement, publication opportunities, and recognition within the academic community.
How to Write the Significance of the Study

Writing the significance of a study involves explaining the importance and impact of your research. This section should clearly articulate why your study matters, how it contributes to the field, and what practical applications it may have. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you write an effective significance of the study:
Start with the Context
Begin by providing a brief overview of the research context. This sets the stage for understanding the importance of your study. Example : “In today’s digital age, digital literacy has become a critical skill for students. As technology continues to integrate into education, understanding its impact on academic performance is essential.”
Identify the Research Gap
Explain the gap in existing literature or the problem your study aims to address. Highlighting this gap justifies the need for your research. Example: “Despite the growing importance of digital literacy, there is limited empirical evidence on its direct impact on high school students’ academic performance. This study seeks to fill this gap by investigating this relationship.”
Explain the Theoretical Contributions
Discuss how your study will contribute to existing theories or knowledge in the field. This shows the academic value of your research. Example : “The findings of this study will contribute to educational theory by providing new insights into how digital literacy skills influence student learning outcomes. It will expand the current understanding of the role of technology in education.”
Highlight Practical Implications
Describe the practical applications of your research. Explain how the findings can be used in real-world settings. Example : “Practically, the results of this study can inform educators and policymakers about the importance of incorporating digital literacy programs into the curriculum. It will help design more effective teaching strategies that enhance students’ digital competencies.”
Mention the Beneficiaries
Identify who will benefit from your study. This could include scholars, practitioners, policymakers, or specific groups affected by the research problem. Example: “This research will benefit educators, school administrators, and policymakers by providing evidence-based recommendations for integrating digital literacy into educational practices. Additionally, students will benefit from improved learning outcomes and better preparedness for the digital world.”
Suggest Future Research
Point out areas for future research that stem from your study. This shows the ongoing relevance and potential for further inquiry. Example : “Future research could explore the long-term effects of digital literacy on career readiness and job performance. Additionally, studies could examine the impact of specific digital literacy interventions on diverse student populations.”
Use Clear and Concise Language
Ensure your writing is clear and concise. Avoid jargon and overly complex sentences to make your significance easily understandable.
What is the significance of a study?
The significance explains the importance, contributions, and impact of the research, highlighting why the study is necessary and how it benefits the field and society.
Why is the significance of a study important?
It justifies the research, engages readers, secures funding, guides the research focus, and highlights practical and theoretical contributions, enhancing the study’s impact and visibility.
How do you identify the significance of a study?
Identify gaps in existing literature, potential contributions to theory and practice, and practical applications that address real-world problems, demonstrating the study’s relevance and importance.
What should be included in the significance of a study?
Include the research context, identified gaps, theoretical contributions, practical applications, beneficiaries, and suggestions for future research to comprehensively explain the study’s importance.
How long should the significance of a study be?
Typically, the significance section should be concise, around 1-2 paragraphs, providing enough detail to clearly convey the study’s importance and contributions.
Can the significance of a study influence funding decisions?
Yes, a well-articulated significance section can attract funding by demonstrating the study’s potential impact and relevance to funding agencies and stakeholders.
How does the significance of a study benefit researchers?
It clarifies the research focus, enhances credibility, guides the research process, and supports academic and professional goals by highlighting the study’s contributions and importance.
Should the significance of a study mention future research?
Yes, mentioning future research directions shows the ongoing relevance of the study and encourages further inquiry, contributing to continuous advancement in the field.
How does the significance of a study relate to the research problem?
The significance justifies the research problem by explaining its importance, highlighting gaps in existing knowledge, and showing how the study addresses these issues.
Can practical applications be part of the significance of a study?
Yes, practical applications are crucial, showing how the research can solve real-world problems, influence practices, and benefit specific groups or society overall.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting

Promoting research Why research is important to the counselling professions
Research is important for clients, for practitioners and politically to continue to demonstrate that counselling changes lives. Research provides evidence for the range of issues where therapy can be effective and the positive outcomes for clients.
Research matters
... for clients.
The prime importance of research is for client welfare. We have a duty to clients to evidence the benefits of therapy, and also to recognise its potential adverse effects.
Using routine outcomes to give clients feedback on their progress in therapy is helpful to both the client and the practitioner and may improve outcomes. Research can also support client choice by identifying a range of therapies which may be beneficial for them.
... for practitioners
Research is a vital part of therapeutic practice. The BACP Ethical Framework for the Counselling Professions values research for 'enhancing our professional knowledge and providing an evidence-base for practice in ways that benefit our clients' (Good practice point 84). It commits members to 'keeping accurate and appropriate records' (Commitment 2e) and to 'monitoring how clients experience our work together and the effects of our work with them' (Commitment 6d).
While it may feel that incorporating research into routine practice can interfere with the therapeutic process, studies show that therapists who monitor their clients’ progress using tools such as outcome measures are better able to meet their client’s needs.
... for commissioners
Evidence that counselling and psychotherapy are effective and cost effective is essential for commissioning of services. The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) develops its guidelines based on research. If no research is available on a particular therapy, or if other research is considered to be of a higher standard, then the therapy may not be recommended, even if there is no evidence that it is less effective than more widely researched alternatives. An example of this is the commissioning of IAPT services where Cognitive Behaviour Therapy (CBT) has the largest body of research and is most often commissioned.
All of our research activities are driven by our r esearch strategy and we undertake specific activities to support, encourage and generate research. We support, encourage and undertake research across the counselling professions by:
- providing a research enquiry service and guidance documents for those starting out in research or who wish to refresh their skills
- running practice research networks (PRNs) to bring together practitioners, trainers and researchers to engage in research and evaluation
- providing non-monetary and in-kind support for collaborative research projects such as: administrative input project promotion and recruitment support practical research support
- undertaking research ourselves, and in partnership with others, to help build the evidence base for the counselling professions. Recent work includes: a research study with the University of Sheffield which looked at the effectiveness of counselling and CBT in treating depression a three year trial evaluated the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of school-based counselling working with a consortium of university and college counselling services to create a shared routine outcomes database and build evidence for the sector
Funding of research
We provide some financial support for research by:
- offering research grant funding in the areas of collaborative research and secondary data analysis
- PhD studentships to fund research that supports our work in promoting the counselling professions
Disseminate research
We support the dissemination of research by:
- organising an annual, peer-reviewed conference to showcase the latest research in the counselling professions
- providing members with access to peer-reviewed research papers through our Counselling and Psychotherapy Research Journal and the EBSCO database
Supporting the work of the policy and professional standards teams at BACP
We support the work of many internal departments, but particularly the work of the policy and professional standards teams by:
- providing research evidence to support responses to policy and practice consultations, such as the NICE guideline for treating depression in adults
- undertaking and advising on scoping and systematic reviews to support the development of competency frameworks and curricula
Current projects

Research resources
Resources to inform your practice, help you undertake research and update you on our research activities.

Research awards and grants
Encouraging research into counselling and psychotherapy

BACP Research Conference
A leading international event for researchers and practitioners
Further reading
- Barlow DH. Negative Effects From Psychological Treatments: A Perspective American Psychologist, 2010:65(1):13-20.
- Lambert MJ, Whipple JL, Smart DM, Vermeersch DA, Nielson SL, Hawkins EJ. The Effects of Providing Therapists With Feedback on Patient Progress During Psychotherapy: Are Outcomes Enhanced? Psychotherapy Research. 2001:11(1):49-68
- Reese RJ, Norsworthy LA, and Rowlands SR. Does a continuous feedback system improve psychotherapy outcome? Psychotherapy Theory, Research, Practice, Training. 2009:46(4):418–431
- Stanhope V, Barrenger SL, Salzer MS and Marcus SC. Examining the Relationship between Choice, Therapeutic Alliance and Outcomes in Mental Health Services. Journal of personal medicine. 2013:3(3): 191-202
- Lambert MJ. Presidential address: What we have learned from a decade of research aimed at improving psychotherapy outcome in routine care, Psychotherapy Research. 2006:17(1):1-14
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Depression in adults: recognition and management Clinical guideline [CG90]. 2009
Animal research
BACP focuses on evaluating the effectiveness and cost effectiveness of counselling and psychotherapy for people of all ages, so we do not fund research using animals. However, as a member of the Association of Medical Research Charities (AMRC) we adhere to the AMRC's principles as outlined in its statement on animal research .
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Behav Anal Pract
- v.8(2); 2015 Oct
The Importance of Research—A Student Perspective
Rachel arena.
grid.252546.20000000122978753Department of Psychology, Auburn University, Magnolia Street and Duncan Drive and West Thatch Ave, Auburn, AL 36849 USA
Sheridan Chambers
Angelyn rhames, katherine donahoe.
As students, we will focus on the importance of an objective ranking system, research, and mentorship to an applicant. We will address points raised in the (Behavior Analysis In Practice 8(1):7–15, 2015) article as well as debate the usefulness of proposed standards of objective ranking.
A Student’s Perspective on Research
A little more than a year ago each of us was madly scrambling to negotiate the process of graduate program admissions. Like many people who go to graduate school, each of us had some history of viewing academic efforts through the lens of “too much is never enough,” and we applied our obsessive habits to the challenge of gathering information about graduate programs. We pored over Web sites and printed brochures. We stalked program faculty at conferences, via email and phone, and during campus visits. We talked to trusted mentors about the programs they respected. When in professional settings, we tried to find out where people who impressed us had attended graduate school, and we sometimes eavesdropped on strangers’ conversations for potentially valuable tidbits about the graduate programs they were considering.
Based on this chaotic and exhausting experience, we agree with Dixon et al. ( 2015 ) that consumers in our field need standardized information about the relative merits of graduate programs in applied behavior analysis (ABA). When we began the process of screening graduate programs, we knew that we were uninformed but we were less sure about what we needed to learn to become better consumers. We suspect that, like us, most college seniors find it difficult to know what aspects of a graduate program are crucial to the training of highly qualified ABA practitioners. To us, the most important contribution of Dixon et al. ( 2015 ) was to emphasize that our field should not abandon students to an uncertain process of self-education.
We agree with Dixon et al. ( 2015 ) that our field is better equipped than outside bodies (e.g., U.S. News & World Report ) to determine what constitutes top-quality graduate training. We were aware that the Behavior Analysis Certification Board publishes the rates at which graduates of various programs pass its certification exam, and we considered this information during our respective searches. Even as undergraduates, however, we knew that there is more to being a capable practitioner than simply passing the certification exam, and we would have appreciated much more guidance from our field than we received.
In the absence of standardized, objective information about graduate programs, prospective graduate students have to rely heavily on hearsay. As we gathered information on program reputations from mentors and colleagues, it occurred to us that this information sometimes says as much about the person providing it as about graduate programs themselves. We learned that some people are impressed by graduate programs that have a reputation for highly selective admissions, but we were not sure how or whether this predicted the quality of training that we could hope to receive. We learned that certain mentors thought highly of certain programs, but different people thought highly of different programs, and it was not always obvious how these opinions related to specific features of the training offered by the programs. We weren’t always sure whether the opinions were generic or had been offered with our individual needs and interests in mind.
Among the features of graduate programs that interested us was the type and degree of emphasis on research. Here, a few words of explanation will provide context for our perspective. As undergraduates, we learned to value evidence-based practices, data-based case management, and the science-based critical thinking that should guide clinical case management. But each of us decided to seek graduate training not just to apply current best practices; we also wanted to contribute to clinical innovation (e.g., Critchfield 2015 ). For various reasons, none of us wished to conduct research for a living, and we chose our program at Auburn University in part because its accelerated, 12-month, non-thesis curriculum would get us swiftly into the workplace where we knew, from past field experiences, our main reinforcers are to be found. Still, program research emphasis was important to us.
Unfortunately, far too much time and effort was required for us to understand that different programs have different types of research emphases. “Research training” comprises not a single repertoire but many. One involves conducting research. Another involves locating and consuming available research on a topic of interest. Yet, another involves translating from research findings in order to develop innovative interventions (Critchfield 2015 ; Critchfield & Reed, 2005 ). It is here that we would quibble with the position of Dixon et al. ( 2015 ), which suggests a one-size-fits-all approach to assessing the research climate at ABA graduate programs.
In order to gain insight about the research environment in graduate programs, undergraduates often compare their own research interests to those of faculty as described on program web sites and as illustrated in published articles. This comparison is most relevant to students who seek to become independent researchers. Our own goal is to become life-long consumers of research. It may not be the full-time job of Masters-level practitioners to conduct research, but in a field that is growing quickly it is pivotal that people like us not be limited to the state of our field’s knowledge at the time we take a certification exam. We need skills for tracking scholarly developments across the full breath of our careers.
We agree with Dixon et al. ( 2015 ) that it is helpful for ABA program faculty to maintain active research programs, but our concern is with what program graduates are able to do with the fruits of research, not how many articles a faculty member can publish. It has been suggested that the process of developing effective and transportable interventions from research findings requires a skill set that is independent of either conducting research or implementing existing interventions (e.g., Critchfield 2015 ; Critchfield and Reed, 2005 ). No skill set seems more relevant to our lifelong professional development.
Yes, we want to learn how to read and critically evaluate research, but we want to learn to do this from faculty who know how to translate and who care about helping us to become translators. Our ideal ABA program faculty member will have the time and inclination to focus on this. We want mentors who can conduct research, but more importantly who will discuss research with us on a regular basis and explore with us how research findings relate to the behavioral processes operating in practice settings. We want mentors whose skills and schedules allow them to provide on-site clinical supervision through which the connections between research and practice can be drawn explicitly.
While we applaud the efforts of Dixon et al. ( 2015 ) to rank ABA graduate programs in terms of program research climate, we stress that this climate has multiple facets. We represent a category of consumer who cares very much about our field’s research foundations, but we wish to harness rather than add to those foundations. Faculty publication counts may not be the best measure of a program’s ability to help us to this. Unfortunately, the program attributes that we particularly value are hard to quantify and thus will be difficult to incorporate into an objective system for ranking programs. Yet, if the purpose of rankings is to assist consumers (Dixon et al., 2015 ), then the needs of consumers like us should not be ignored.
Contributor Information
Rachel Arena, Email: ude.nrubua@0200azr .
Sheridan Chambers, Email: ude.nrubua@5400cms .
Angelyn Rhames, Email: ude.nrubua@7400rza .
Katherine Donahoe, Email: ude.nrubua@4200drk .
- Critchfield TS. What counts as high-quality practitioner training in applied behavior analysis? Behavior Analysis In Practice. 2015; 8 (1):3–6. doi: 10.1007/s40617-015-0049-0. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Critchfield TS, Reed DD. Conduits of translation in behavior-science bridge research. In: Burgos JE, Ribes E, editors. Theory, basic and applied research, and technological applications in behavior science: Conceptual and methodological issues. Guadalajara, Mexico: University of Guadalajara Press; 2005. pp. 45–84. [ Google Scholar ]
- Dixon MR, Reed DD, Smith T, Belisle J, Jackson RE. Research rankings of behavior analytic graduate training programs and their faculty. Behavior Analysis In Practice. 2015; 8 (1):7–15. doi: 10.1007/s40617-015-0057-0. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
Predicting medical waste generation and associated factors using machine learning in the Kingdom of Bahrain
- Research Article
- Published: 27 May 2024
Cite this article

- Khadija Al-Omran ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-3658-1938 1 , 2 &
- Ezzat Khan 1 , 3
Effective planning and managing medical waste necessitate a crucial focus on both the public and private healthcare sectors. This study uses machine learning techniques to estimate medical waste generation and identify associated factors in a representative private and a governmental hospital in Bahrain. Monthly data spanning from 2018 to 2022 for the private hospital and from 2019 to February 2023 for the governmental hospital was utilized. The ensemble voting regressor was determined as the best model for both datasets. The model of the governmental hospital is robust and successful in explaining 90.4% of the total variance.
Similarly, for the private hospital, the model variables are able to explain 91.7% of the total variance. For the governmental hospital, the significant features in predicting medical waste generation were found to be the number of inpatients, population, surgeries, and outpatients, in descending order of importance. In the case of the private hospital, the order of feature importance was the number of inpatients, deliveries, personal income, surgeries, and outpatients. These findings provide insights into the factors influencing medical waste generation in the studied hospitals and highlight the effectiveness of the ensemble voting regressor model in predicting medical waste quantities.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions

Data availability
Data pertaining to this article is included in the main body. However, for further queries, the authors may be contacted, if needed.
Abbasi M, El Hanandeh A (2016) Forecasting municipal solid waste generation using artificial intelligence modelling approaches. Waste Manage 56:13–22
Article Google Scholar
Abbasi M, Abduli M, Omidvar B, Baghvand A (2013) Forecasting municipal solid waste generation by hybrid support vector machine and partial least square model. Int J Environ Res 7(1):27–38
Google Scholar
Adamović VM, Antanasijević DZ, Ristić MĐ, Perić-Grujić AA, Pocajt VV (2018) An optimized artificial neural network model for the prediction of rate of hazardous chemical and healthcare waste generation at the national level. J Mater Cycles Waste Manage 20(3):1736–1750
Ahmad M, Kamiński P, Olczak P, Alam M, Iqbal MJ, Ahmad F, Khan BJ (2021) Development of prediction models for shear strength of rockfill material using machine learning techniques. Appl Sci 11(13):6167
Article CAS Google Scholar
Alhumoud JM, Alhumoud HM (2007) An analysis of trends related to hospital solid wastes management in Kuwait. Manag Environ Qual 18(5):502–513. https://doi.org/10.1108/14777830710778274
Ali Abdoli M, Falah Nezhad M, Salehi Sede R, Behboudian S (2012) Longterm forecasting of solid waste generation by the artificial neural networks. Environ Prog Sustainable Energy 31(4):628–636
Al-Omran K, Khan E, Ali N, Bilal M (2021) Estimation of COVID-19 generated medical waste in the Kingdom of Bahrain. Sci Total Environ 801:149642
Al-Omran K, Abahussain A, Khan E (2023a) Integrated environmental assessment of medical waste management in the Kingdom of Bahrain. Sustainability 15(3):2397
Al-Omran K, Khan E, Perna S, Ali N (2023b) Factors associated with medical waste under pandemic situation: a case study of the Kingdom of Bahrain. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag 25(5):2951–2963
Al-Shallash, K., & Shereif, M. (2007). Healthcare waste management in Saudi Arabia. A case study . Paper presented at the Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology, Kos island, Greece, September 5–7, 2007, 24 - 27
Altin FG, Budak İ, Özcan F (2023) Predicting the amount of medical waste using kernel-based SVM and deep learning methods for a private hospital in Turkey. Sustain Chem Pharm 33:101060
Arabgol S, Ko HS (2013) Application of artificial neural network and genetic algorithm to healthcarewaste prediction. J Artif Intell Soft Comput Res 3(4):243–250
Basith S, Manavalan B, Shin TH, Lee G (2018) iGHBP: computational identification of growth hormone binding proteins from sequences using extremely randomised tree. Comput Struct Biotechnol J 16:412–420
Bdour A, Altrabsheh B, Hadadin N, Al-Shareif M (2007) Assessment of medical wastes management practice: a case study of the northern part of Jordan. Waste Manage 27(6):746–759
Breiman L (1996) Bagging predictors. Mach Learn 24:123–140
Byeon H (2021) Exploring factors for predicting anxiety disorders of the elderly living alone in South Korea using interpretable machine learning: a population-based study. Int J Environ Res Public Health 18(14):7625
Carbonell JG, Michalski RS, Mitchell TM (1983) An overview of machine learning. Mach Learn 1:3–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-051054-5.50005-4
CBB. (2023). Publications & data-financial stability report. Retrieved from https://www.cbb.gov.bh/publications/
Ceylan Z, Bulkan S, Elevli S (2020) Prediction of medical waste generation using SVR, GM (1, 1) and ARIMA models: a case study for megacity Istanbul. J Environ Health Sci Eng 18(2):687–697
Chakraborty D, Mondal J, Barua HB, Bhattacharjee A (2023) Computational solar energy–ensemble learning methods for prediction of solar power generation based on meteorological parameters in Eastern India. Renew Energy Focus 44:277–294
Chen T, Guestrin C (2016) Xgboost: a scalable tree boosting system . Paper presented at the Proceedings of the 22nd acm sigkdd international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining, 785–794
Coskuner G, Jassim MS, Zontul M, Karateke S (2021) Application of artificial intelligence neural network modeling to predict the generation of domestic, commercial and construction wastes. Waste Manage Res 39(3):499–507
deHaan E, Moon JR, Shipman JE, Swanquist QT, Whited RL (2023) Control variables in interactive models. J Financ Report 8(2):77–85
Devi A, Ravindra K, Kaur M, Kumar R (2019) Evaluation of biomedical waste management practices in public and private sector of health care facilities in India. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:26082–26089
EPA. (2022). Medical waste. Retrieved from https://www.epa.gov/rcra/medical-waste
Erdebilli B, Devrim-İçtenbaş B (2022) Ensemble voting regression based on machine learning for predicting medical waste: a case from Turkey. Mathematics 10(14):2466
Géron A (2022) Hands-on machine learning with Scikit-Learn, Keras, and TensorFlow: Concepts, Tools, and Techniques to Build Intelligent Systems (Third ed.). O’Reilly Media, USA
Geurts P, Ernst D, Wehenkel L (2006) Extremely randomized trees. Mach Learn 63:3–42
Gheyas IA, Smith LS (2010) A neural network-based framework for the reconstruction of incomplete data sets. Neurocomputing 73(16–18):3039–3065
Golbaz S, Nabizadeh R, Sajadi HS (2019) Comparative study of predicting hospital solid waste generation using multiple linear regression and artificial intelligence. J Environ Health Sci Eng 17(1):41–51
Gutierrez, G. (2020). Artificial intelligence in the intensive care unit. Annual Update in Intensive Care and Emergency Medicine 2020, 667-681
Hao H, Zhang J, Zhang Q, Yao L, Sun Y (2021) Improved gray neural network model for healthcare waste recycling forecasting. J Comb Optim 42:813–830
Heddam S (2021) Intelligent data analytics approaches for predicting dissolved oxygen concentration in river: extremely randomized tree versus random forest, MLPNN and MLR (T. G, Sitharam. Springer Singapore, Singapore
Information & eGovernment Authority. (2022). Bahrain open data portal. Retrieved from https://www.data.gov.bh/pages/homepage/
Jahandideh S, Jahandideh S, Asadabadi EB, Askarian M, Movahedi MM, Hosseini S, Jahandideh M (2009) The use of artificial neural networks and multiple linear regression to predict rate of medical waste generation. Waste Manage 29(11):2874–2879
Jassim MS, Coskuner G, Zontul M (2022) Comparative performance analysis of support vector regression and artificial neural network for prediction of municipal solid waste generation. Waste Manage Res 40(2):195–204
Jassim MS, Coskuner G, Sultana N, Hossain SZ (2023) Forecasting domestic waste generation during successive COVID-19 lockdowns by bidirectional LSTM super learner neural network. Appl Soft Comput 133:109908
Karpušenkaitė A, Ruzgas T, Denafas G (2016) Forecasting medical waste generation using short and extra short datasets: case study of Lithuania. Waste Manage Res 34(4):378–387
Ke G, Meng Q, Finley T, Wang T, Chen W, Ma W, . . . Liu T-Y (2017) Lightgbm: a highly efficient gradient boosting decision tree . Paper presented at the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, p 30
Kilimci ZH (2022) Ensemble regression-based gold price (XAU/USD) prediction. J Emerg Com Tech 2(1):7–12
Kokol P, Kokol M, Zagoranski S (2022) Machine learning on small size samples: a synthetic knowledge synthesis. Sci Prog 105(1):1–16
Komilis D, Fouki A, Papadopoulos D (2012) Hazardous medical waste generation rates of different categories of health-care facilities. Waste Manage 32(7):1434–1441
Korkut EN (2018) Estimations and analysis of medical waste amounts in the city of Istanbul and proposing a new approach for the estimation of future medical waste amounts. Waste Manage 81:168–176
Kwak SK, Kim JH (2017) Statistical data preparation: management of missing values and outliers. Korean J Anesthesiol 70(4):407–411
Lai, C.-H., Yang, C.-T., Kristiani, E., Liu, J.-C., & Chan, Y.-W. (2020). Using xgboost for cyberattack detection and analysis in a network log system with elk stack . Paper presented at the Frontier Computing: Theory, Technologies and Applications (FC 2019) 8, 302–311, Singapore
Li Y, Chen W (2020) A comparative performance assessment of ensemble learning for credit scoring. Mathematics 8(10):1756
Li S, Zhang X (2020) Research on orthopedic auxiliary classification and prediction model based on XGBoost algorithm. Neural Comput Appl 32:1971–1979
Lindahl JF, Grace D (2015) The consequences of human actions on risks for infectious diseases: a review. Infect Ecol Epidemiol 5(1):30048
Mahesh B (2020) Machine learning algorithms-a review. Int J Sci Res 9:381–386
Matsuto T, Tanaka N (1993) Data analysis of daily collection tonnage of residential solid waste in Japan. Waste Manage Res 11(4):333–343
Medium. (2019). Stats series #1 — elastic net. Retrieved from https://medium.com/@konark145/stats-series-1-elastic-net-655786810be7
Microsoft. (2023a). Explore automated machine learning in Azure ML. Retrieved from https://microsoftlearning.github.io/AI-900-AIFundamentals/instructions/02-module-02.html
Microsoft. (2023b). LightGBM. Retrieved from https://github.com/microsoft/LightGBM
MOH. (2023). Salmaniya Medical Complex. Retrieved from https://www.moh.gov.bh/HealthInstitution/SalmaniyaMedicalComplex?lang=en
Mohamed L, Ebrahim S, Al-Thukair A (2009) Hazardous healthcare waste management in the Kingdom of Bahrain. Waste Manage 29(8):2404–2409
Murphy KP (2012) Machine learning: a probabilistic perspective. MIT Press, London, England
Nattee C, Khamsemanan N, Lawtrakul L, Toochinda P, Hannongbua S (2017) A novel prediction approach for antimalarial activities of Trimethoprim, Pyrimethamine, and Cycloguanil analogues using extremely randomized trees. J Mol Graph Model 71:13–27
Neves AC, Maia CC, de Castro e Silva ME, Vimieiro GV, Gomes Mol MP (2022) Analysis of healthcare waste management in hospitals of Belo Horizonte Brazil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(60):90601–90614
Nguyen, X. C., Nguyen, T. T. H., La, D. D., Kumar, G., Rene, E. R., Nguyen, D. D., . . . Nguyen, V. K. (2021). Development of machine learning-based models to forecast solid waste generation in residential areas: a case study from Vietnam. Resour Conserv Recycl 167:105381
NHRA. (2020). Annual report 2020. Retrieved from https://www.nhra.bh/About/AnnualReport/MediaHandler/ImageHandler/documents/About/Annual%20Report/NHRA%20Annual%20Report%202020n.pdf
Noori R, Abdoli M, Ghasrodashti AA, Jalili Ghazizade M (2009) Prediction of municipal solid waste generation with combination of support vector machine and principal component analysis: a case study of Mashhad. Environ Prog Sustain Energ 28(2):249–258
Park J, Moon J, Jung S, Hwang E (2020) Multistep-ahead solar radiation forecasting scheme based on the light gradient boosting machine: a case study of Jeju Island. Remote Sens 12(14):2271
Portal, KOBSN. (2022). Public health sector. Retrieved from https://www.bahrain.bh/new/en/health-public_en.html
Ramírez-Gallego S, Krawczyk B, García S, Woźniak M, Herrera F (2017) A survey on data preprocessing for data stream mining: current status and future directions. Neurocomputing 239:39–57
Rashid, H. M. M., Yatim, S. R. M., Abdullah, S., Pejabat, M. Y. A. F., Nazim, I. A., & Ahmad, Z. (2022). Forecasting medical waste generation in Hospital Taiping, Perak using nonlinear autoregressive (NAR) neural network method . Paper presented at the 2022 3rd International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Data Sciences (AiDAS), September 7, 243–247, IPOH, Malaysia
Sabour MR, Mohamedifard A, Kamalan H (2007) A mathematical model to predict the composition and generation of hospital wastes in Iran. Waste Manage 27(4):584–587. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2006.05.010
Scribbr. (2021). Control variables | What are they & why do they matter? Retrieved from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/control-variable/
Sengupta D, Agrahari S (2017) Modelling trends in solid and hazardous waste management, 1st edn. Springer, Singapore
Book Google Scholar
Shahhosseini M, Hu G, Pham H (2022) Optimizing ensemble weights and hyperparameters of machine learning models for regression problems. Machine Learning with Applications 7:100251
Tesfahun E, Kumie A, Beyene A (2016) Developing models for the prediction of hospital healthcare waste generation rate. Waste Manage Res 34(1):75–80. https://doi.org/10.1177/0734242X15607422
Thakur V, Ramesh A (2018) Analyzing composition and generation rates of biomedical waste in selected hospitals of Uttarakhand, India. J Mater Cycles Waste Manage 20:877–890
The Word Bank. (2023). DataBank-WDI database archives. Retrieved from https://databank.worldbank.org/source/wdi-database-archives
Tofallis C (2015) A better measure of relative prediction accuracy for model selection and model estimation. J Oper Res Soc 66:1352–1362. https://doi.org/10.1057/jors.2014.103
Vinayak, R. K., & Gilad-Bachrach, R. (2015). Dart: dropouts meet multiple additive regression trees . Paper presented at the Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, February 21, 489–497, San Diego, CA, USA
Wang W, Liang J, Liu R, Song Y, Zhang M (2022) A robust variable selection method for sparse online regression via the elastic net penalty. Mathematics 10(16):2985. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10162985
Wei Y, Cui M, Ye Z, Guo Q (2021) Environmental challenges from the increasing medical waste since SARS outbreak. J Clean Prod 291:125246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.125246
WHO. (2014). Safe management of wastes from health-care activities: World Health Organization
Zou H, Hastie T (2005) Regularization and variable selection via the elastic net. J R Stat Soc Ser B Stat Methodol 67(2):301–320
Download references
Acknowledgements
Research Committee for Government Hospitals, Kingdom of Bahrain, through approval No. 57300522, is highly acknowledged. The management and dedicated officials of SMC and PH are highly acknowledged for their unwavering support and cooperation in providing essential data for this research.
The authors express their appreciation to Bahrain Polytechnic-BP for the support that made the publication of this article successful.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Environment and Sustainable Development, College of Science, University of Bahrain, Sakhir, 32038, Kingdom of Bahrain
Khadija Al-Omran & Ezzat Khan
School of Logistics and Maritime Studies, Faculty of Business and Logistics, Bahrain Polytechnic, Isa Town, 33349, Kingdom of Bahrain
Khadija Al-Omran
Department of Chemistry, University of Malakand, Lower Dir, Chakdara, 18800, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
KA: conceptualization, writing–original draft, methodology, writing–review and editing; EK: conceptualization, supervision, writing–review and editing.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Khadija Al-Omran .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Consent for publication, additional information.
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file1 (DOCX 31 KB)
Rights and permissions.
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Al-Omran, K., Khan, E. Predicting medical waste generation and associated factors using machine learning in the Kingdom of Bahrain. Environ Sci Pollut Res (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-33773-1
Download citation
Received : 28 November 2023
Accepted : 19 May 2024
Published : 27 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-33773-1
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Medical waste prediction
- Machine learning
- Ensemble voting regression
- Kingdom of Bahrain
- Sustainability
- Associated factors
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

COMMENTS
Qualitative Findings. Qualitative research is an exploratory research method used to understand the complexities of human behavior and experiences. Qualitative findings are non-numerical and descriptive data that describe the meaning and interpretation of the data collected. Examples of qualitative findings include quotes from participants ...
For most research papers in the social and behavioral sciences, there are two possible ways of organizing the results. Both approaches are appropriate in how you report your findings, but use only one approach. Present a synopsis of the results followed by an explanation of key findings. This approach can be used to highlight important findings.
• Explain the concept of qualitative analysis. • Explain how to analyze and interpret the findings of your research. • Explain the concept of synthesis as an ongoing process. • Describe how to go about presenting a final synthesis. Section II: Application • Presentation of a completed analysis and interpretation chapter based on
(whether the study is quantitative, qualitative, or mixed-methods), the findings are presented in order of importance, beginning with the answer to the primary research question(s). In his instructions for writing journal articles, Daryl Bem writes, "The general rule in reporting your findings is to give the forest first and then the trees.
Discuss how scientific research guides public policy. Appreciate how scientific research can be important in making personal decisions. Scientific research is a critical tool for successfully navigating our complex world. Without it, we would be forced to rely solely on intuition, other people's authority, and blind luck.
The discussion section is often considered the most important part of your research paper because it: Most effectively demonstrates your ability as a researcher to think critically about an issue, to develop creative solutions to problems based upon a logical synthesis of the findings, and to formulate a deeper, more profound understanding of the research problem under investigation;
Placing research in the bigger context of its field and where it fits into the scientific process can help people better understand and interpret new findings as they emerge. A single study usually uncovers only a piece of a larger puzzle. Questions about how the world works are often investigated on many different levels.
research always involves communication with others. Learning can occur at an individual, intuitive level, but research requires the sym-bolisation and transmission of these understandings in the public domain. 5 Research findings are judged according to criteria of validity, truth-fulness or authenticity. To make a claim that a statement is ...
Learning to evaluate and use research findings in daily practice is an important and lifelong part of professional development. This requires not only changes in educational programmes, but also a realignment of institutions so that management structures can support changes in knowledge and the implementation of changes in procedures.
Why you should communicate and share your research findings 1. What you have found in your study could make a difference to our population staying well and healthy. 2. Sharing research findings makes a difference to our understanding of different conditions and treatments. 3. Research should be open to scrutiny to ensure it is high quality and ...
Researchers share their findings with one another by publishing papers in scientific journals and giving presentations at meetings. Data sharing is very important for the scientific field, and although some results may seem insignificant, each finding is often a small piece of a larger puzzle. ... That small piece may spark a new question and ...
Discuss how scientific research guides public policy. Appreciate how scientific research can be important in making personal decisions. Scientific research is a critical tool for successfully navigating our complex world. Without it, we would be forced to rely solely on intuition, other people's authority, and blind luck.
Abstractspiepr Abs1. Every day people do research as they gather information to learn about something of interest. In the scientific world, however, research means something different than simply gathering information. Scientific research is characterized by its careful planning and observing, by its relentless efforts to understand and explain ...
Research is a rigorous problem-solving process whose ultimate goal is the discovery of new knowledge. Research may include the description of a new phenomenon, definition of a new relationship, development of a new model, or application of an existing principle or procedure to a new context. Research is systematic, logical, empirical, reductive, replicable and transmittable, and generalizable.
Oral Presentations Purpose. An Oral Research Presentation is meant to showcase your research findings. A successful oral research presentation should: communicate the importance of your research; clearly state your findings and the analysis of those findings; prompt discussion between researcher and audience. Below you will find information on ...
INTRODUCTION. The definition of research varies among studies and scholars, and it is difficult to devise a single definition. The Oxford English Dictionary defines research as "a careful study of a subject, especially in order to discover new facts or information about it" [], while Webster's Dictionary defines research as "studious inquiry or examination - especially: investigation ...
The previous chapter reviewed the value of privacy, while this chapter examines the value and importance of health research. As noted in the introduction to Chapter 2, the committee views privacy and health research as complementary values. Ideally, society should strive to facilitate both for the benefit of individuals as well as the public.
Research design plays a crucial role in conducting scientific studies and gaining meaningful insights. A well-designed research enhances the validity and reliability of the findings and allows for the replication of studies by other researchers. This comprehensive guide will provide an in-depth understanding of research design, its key ...
Education in research ethics is can help people get a better understanding of ethical standards, policies, and issues and improve ethical judgment and decision making. Many of the deviations that occur in research may occur because researchers simply do not know or have never thought seriously about some of the ethical norms of research.
Why Research Is Necessary and Valuable in Our Daily Lives. It's a tool for building knowledge and facilitating learning. It's a means to understand issues and increase public awareness. It helps us succeed in business. It allows us to disprove lies and support truths. It is a means to find, gauge, and seize opportunities.
Another important dimension of relevance is the extent to which findings can be generalised beyond the setting in which they were generated" . The work of Mays and Pope positions research relevance amidst the longstanding tension between internal and external validity.
Describe the practical applications of your research. Explain how the findings can be used in real-world settings. Example: "Practically, the results of this study can inform educators and policymakers about the importance of incorporating digital literacy programs into the curriculum. It will help design more effective teaching strategies ...
The prime importance of research is for client welfare. We have a duty to clients to evidence the benefits of therapy, and also to recognise its potential adverse effects. Using routine outcomes to give clients feedback on their progress in therapy is helpful to both the client and the practitioner and may improve outcomes. Research can also ...
Abstract. As students, we will focus on the importance of an objective ranking system, research, and mentorship to an applicant. We will address points raised in the (Behavior Analysis In Practice 8 (1):7-15, 2015) article as well as debate the usefulness of proposed standards of objective ranking. Keywords: Graduate school, Graduate training ...
These findings demonstrate the large variability of GSI soil base cation concentrations and the relative importance of soil, climate, and landscape drivers of base cation dynamics. High variability in GSI soil data is commonly observed and further research is needed to reduce uncertainties for modeling studies and design.
Environmental Science and Pollution Research - Effective planning and managing medical waste necessitate a crucial focus on both the public and private healthcare sectors. ... In the case of the private hospital, the order of feature importance was the number of inpatients, deliveries, personal income, surgeries, and outpatients. These findings ...