Doctor of Philosophy in Education


Additional Information
- Download the Doctoral Viewbook
- Admissions & Aid
The Harvard Ph.D. in Education trains cutting-edge researchers who work across disciplines to generate knowledge and translate discoveries into transformative policy and practice.
Offered jointly by the Harvard Graduate School of Education and the Harvard Kenneth C. Griffin Graduate School of Arts and Sciences, the Ph.D. in Education provides you with full access to the extraordinary resources of Harvard University and prepares you to assume meaningful roles as university faculty, researchers, senior-level education leaders, and policymakers.
As a Ph.D. candidate, you will collaborate with scholars across all Harvard graduate schools on original interdisciplinary research. In the process, you will help forge new fields of inquiry that will impact the way we teach and learn. The program’s required coursework will develop your knowledge of education and your expertise in a range of quantitative and qualitative methods needed to conduct high-quality research. Guided by the goal of making a transformative impact on education research, policy, and practice, you will focus on independent research in various domains, including human development, learning and teaching, policy analysis and evaluation, institutions and society, and instructional practice.
Curriculum Information
The Ph.D. in Education requires five years of full-time study to complete. You will choose your individual coursework and design your original research in close consultation with your HGSE faculty adviser and dissertation committee. The requirements listed below include the three Ph.D. concentrations: Culture, Institutions, and Society; Education Policy and Program Evaluation; and Human Development, Learning and Teaching .
We invite you to review an example course list, which is provided in two formats — one as the full list by course number and one by broad course category . These lists are subject to modification.
Ph.D. Concentrations and Examples
Summary of Ph.D. Program
Doctoral Colloquia In year one and two you are required to attend. The colloquia convenes weekly and features presentations of work-in-progress and completed work by Harvard faculty, faculty and researchers from outside Harvard, and Harvard doctoral students. Ph.D. students present once in the colloquia over the course of their career.
Research Apprenticeship The Research Apprenticeship is designed to provide ongoing training and mentoring to develop your research skills throughout the entire program.
Teaching Fellowships The Teaching Fellowship is an opportunity to enhance students' teaching skills, promote learning consolidation, and provide opportunities to collaborate with faculty on pedagogical development.
Comprehensive Exams The Written Exam (year 2, spring) tests you on both general and concentration-specific knowledge. The Oral Exam (year 3, fall/winter) tests your command of your chosen field of study and your ability to design, develop, and implement an original research project.
Dissertation Based on your original research, the dissertation process consists of three parts: the Dissertation Proposal, the writing, and an oral defense before the members of your dissertation committee.
Culture, Institutions, and Society (CIS) Concentration
In CIS, you will examine the broader cultural, institutional, organizational, and social contexts relevant to education across the lifespan. What is the value and purpose of education? How do cultural, institutional, and social factors shape educational processes and outcomes? How effective are social movements and community action in education reform? How do we measure stratification and institutional inequality? In CIS, your work will be informed by theories and methods from sociology, history, political science, organizational behavior and management, philosophy, and anthropology. You can examine contexts as diverse as classrooms, families, neighborhoods, schools, colleges and universities, religious institutions, nonprofits, government agencies, and more.
Education Policy and Program Evaluation (EPPE) Concentration
In EPPE, you will research the design, implementation, and evaluation of education policy affecting early childhood, K–12, and postsecondary education in the U.S. and internationally. You will evaluate and assess individual programs and policies related to critical issues like access to education, teacher effectiveness, school finance, testing and accountability systems, school choice, financial aid, college enrollment and persistence, and more. Your work will be informed by theories and methods from economics, political science, public policy, and sociology, history, philosophy, and statistics. This concentration shares some themes with CIS, but your work with EPPE will focus on public policy and large-scale reforms.
Human Development, Learning and Teaching (HDLT) Concentration
In HDLT, you will work to advance the role of scientific research in education policy, reform, and practice. New discoveries in the science of learning and development — the integration of biological, cognitive, and social processes; the relationships between technology and learning; or the factors that influence individual variations in learning — are transforming the practice of teaching and learning in both formal and informal settings. Whether studying behavioral, cognitive, or social-emotional development in children or the design of learning technologies to maximize understanding, you will gain a strong background in human development, the science of learning, and sociocultural factors that explain variation in learning and developmental pathways. Your research will be informed by theories and methods from psychology, cognitive science, sociology and linguistics, philosophy, the biological sciences and mathematics, and organizational behavior.
Program Faculty
The most remarkable thing about the Ph.D. in Education is open access to faculty from all Harvard graduate and professional schools, including the Harvard Graduate School of Education, the Faculty of Arts and Sciences, the Harvard Kennedy School, the Harvard Law School, Harvard Medical School, and the Harvard School of Public Health. Learn about the full Ph.D. Faculty.
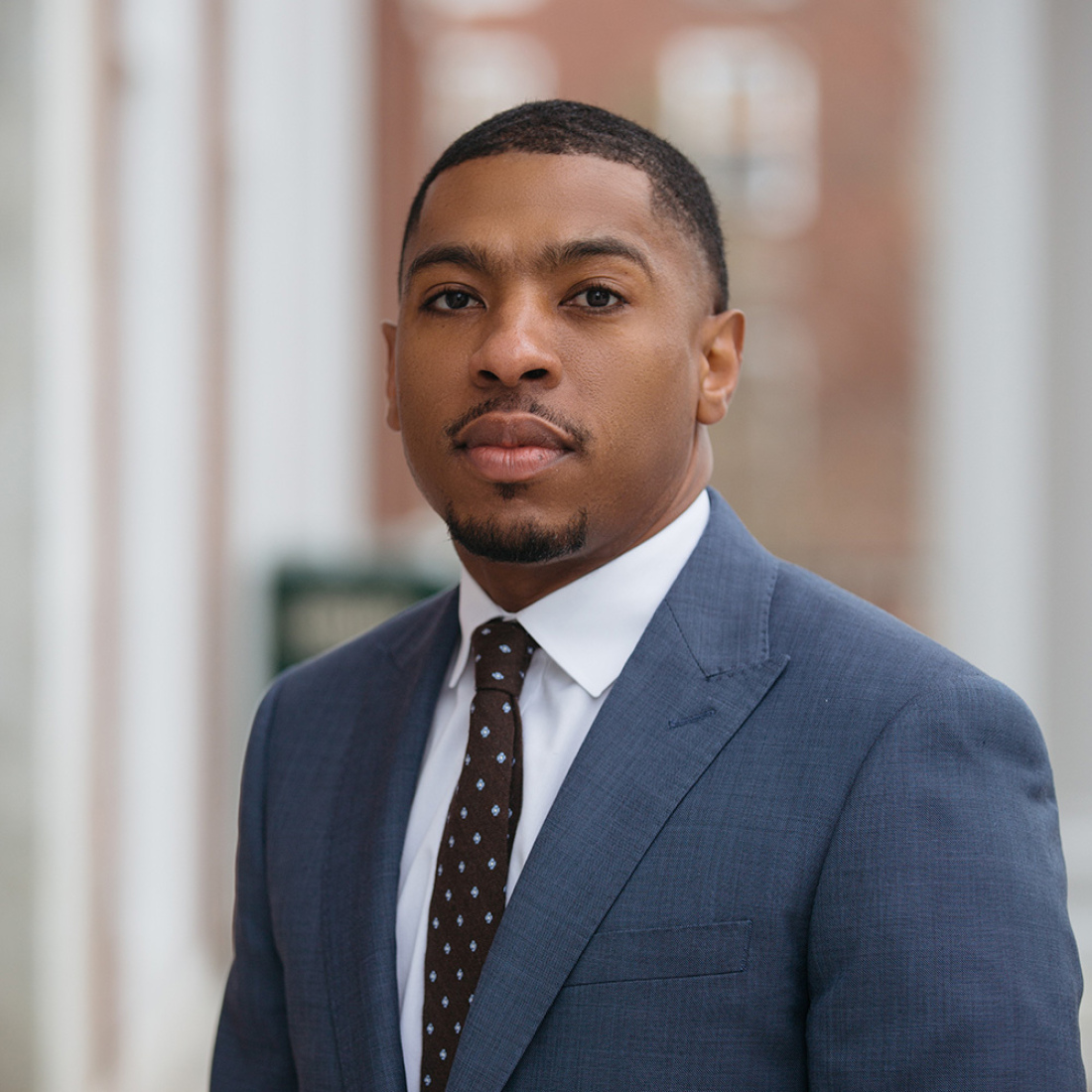

Jarvis R. Givens
Jarvis Givens studies the history of American education, African American history, and the relationship between race and power in schools.
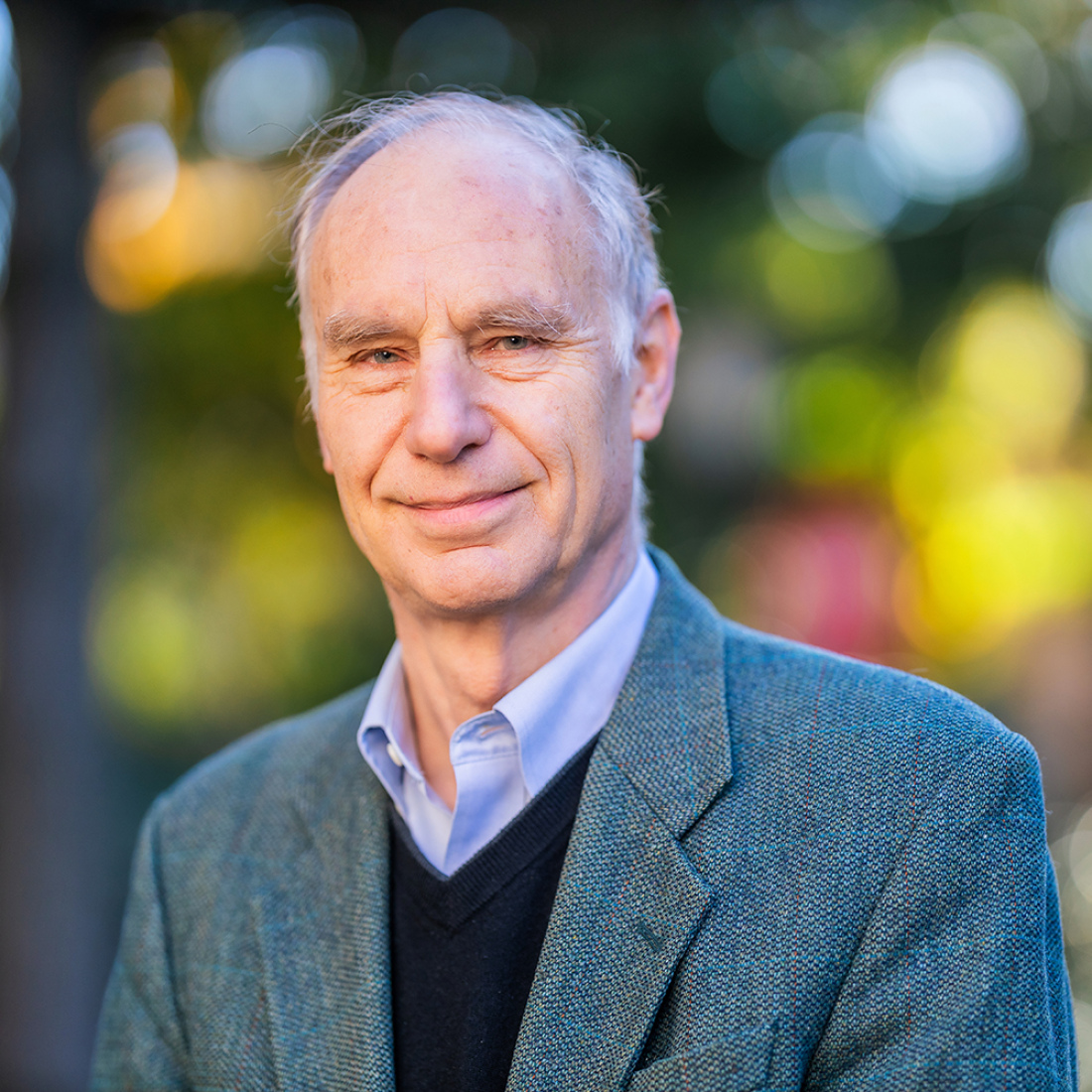

Paul L. Harris
Paul Harris is interested in the early development of cognition, emotion, and imagination in children.
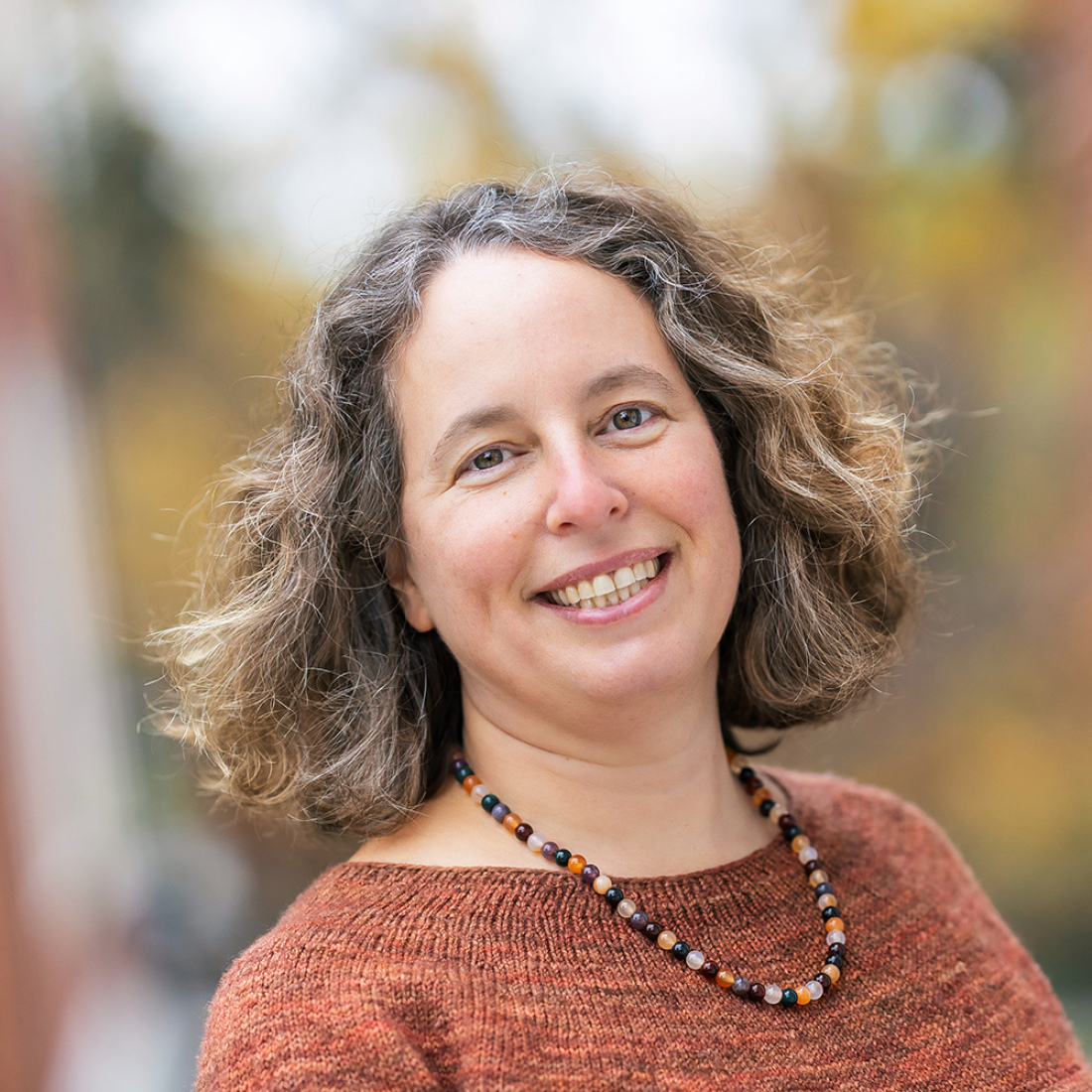

Meira Levinson
Meira Levinson is a normative political philosopher who works at the intersection of civic education, youth empowerment, racial justice, and educational ethics.
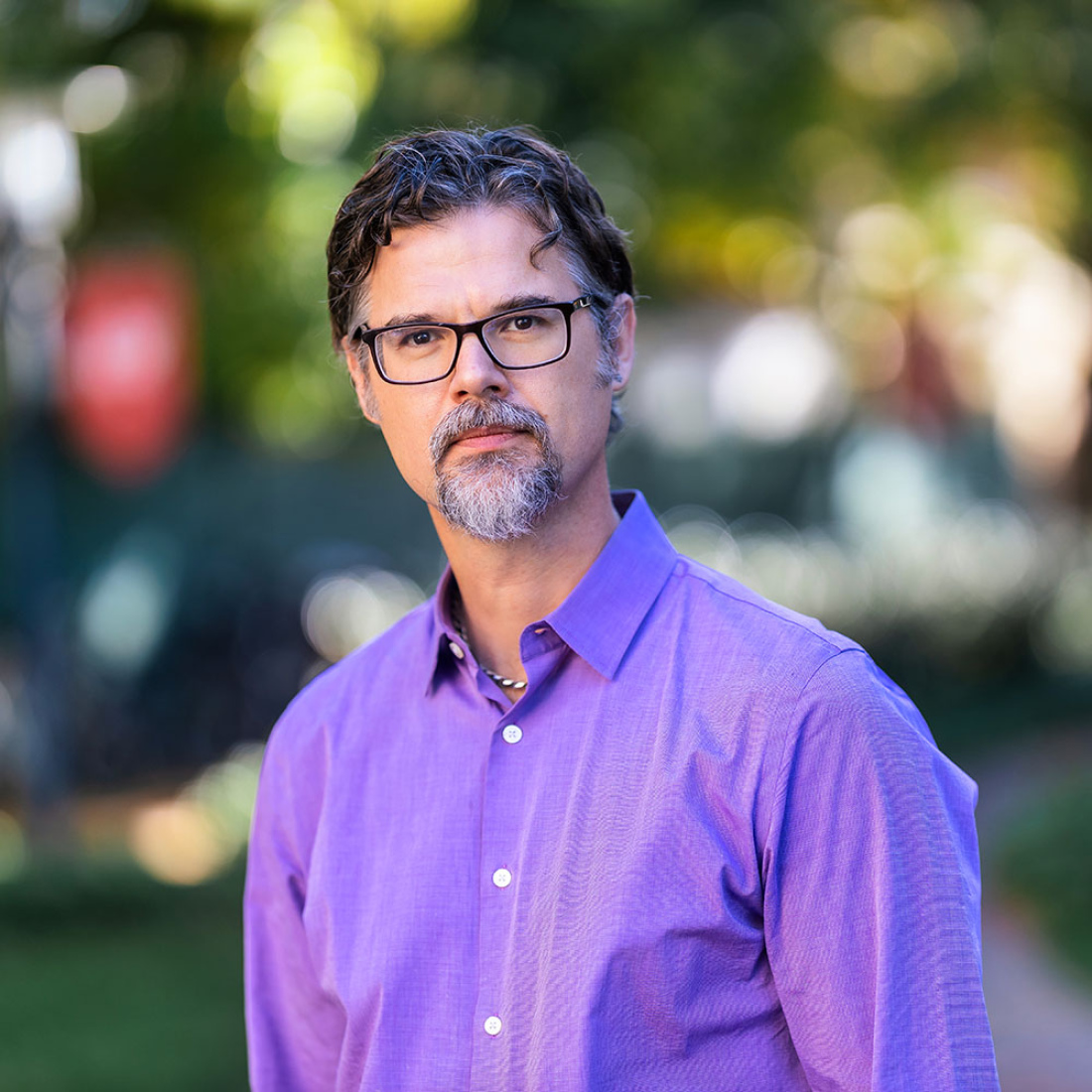

Luke W. Miratrix
Luke Miratrix is a statistician who explores how to best use modern statistical methods in applied social science contexts.
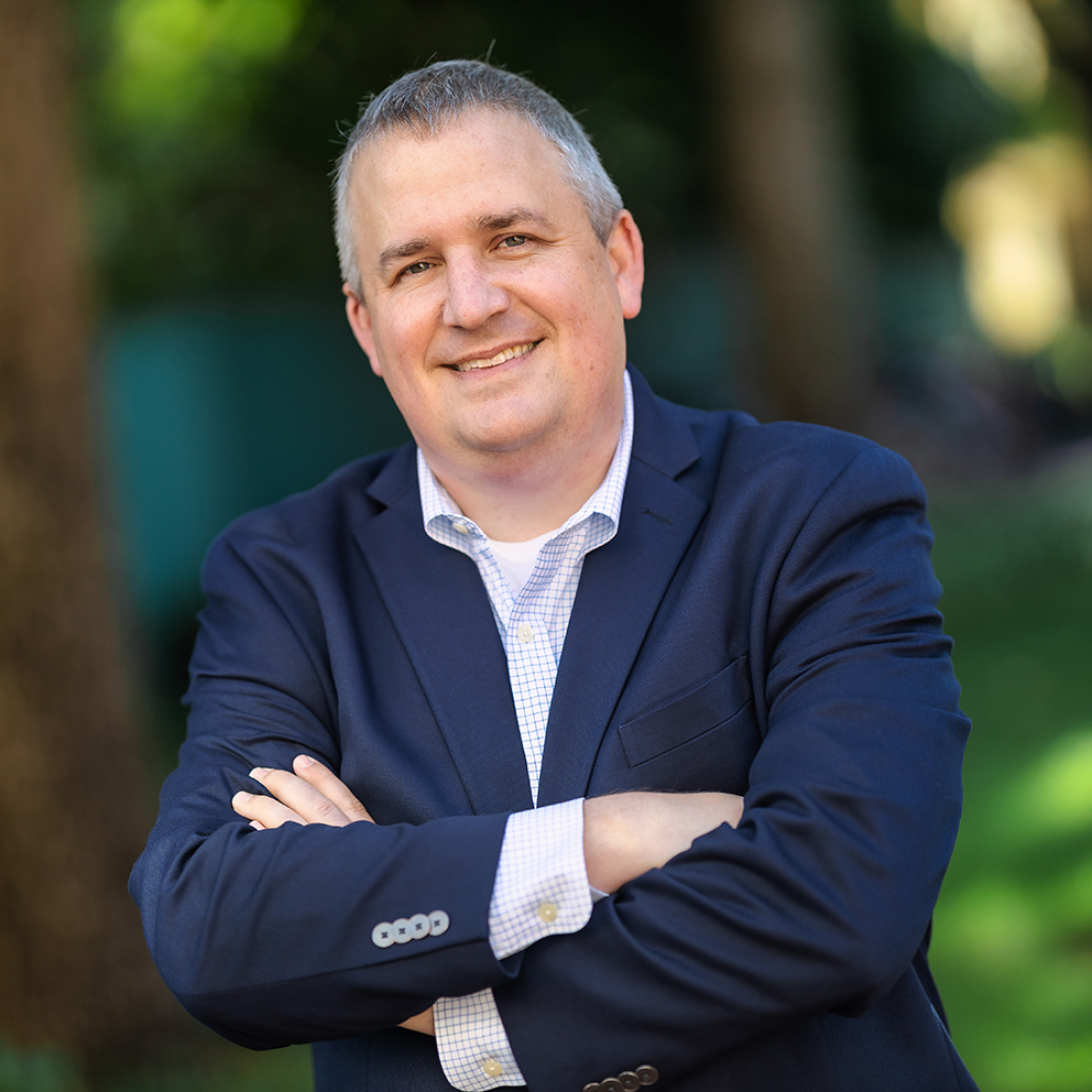

Eric Taylor
Eric Taylor studies the economics of education, with a particular interest in employer-employee interactions between schools and teachers hiring and firing decisions, job design, training, and performance evaluation.
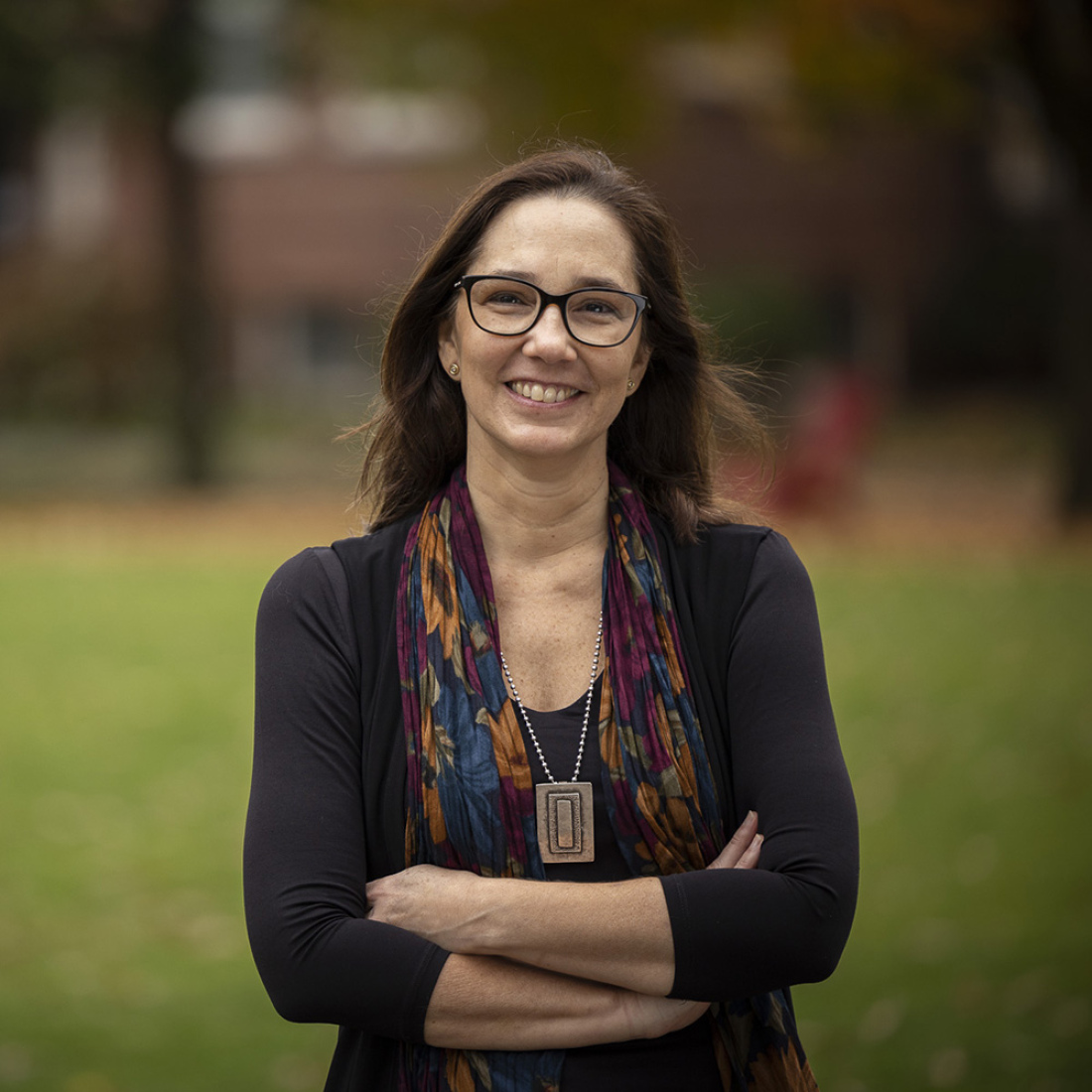

Paola Uccelli
Paola Ucelli studies socio-cultural and individual differences in the language development of multilingual and monolingual students.

View Ph.D. Faculty
Dissertations.
The following is a complete listing of successful Ph.D. in Education dissertations to-date. Dissertations from November 2014 onward are publicly available in the Digital Access to Scholarship at Harvard (DASH) , the online repository for Harvard scholarship.
- 2022 Graduate Dissertations (265 KB pdf)
- 2021 Graduate Dissertations (177 KB pdf)
- 2020 Graduate Dissertations (121 KB pdf)
- 2019 Graduate Dissertations (68.3 KB pdf)
Student Directory
An opt-in listing of current Ph.D. students with information about their interests, research, personal web pages, and contact information:
Doctor of Philosophy in Education Student Directory
Introduce Yourself
Tell us about yourself so that we can tailor our communication to best fit your interests and provide you with relevant information about our programs, events, and other opportunities to connect with us.
Program Highlights
Explore examples of the Doctor of Philosophy in Education experience and the impact its community is making on the field:
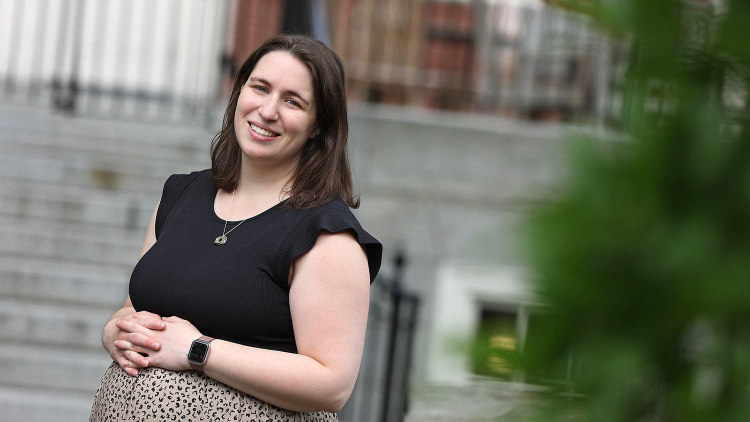

Improving the Teacher Workforce
With her research work, doctoral marshal Mary Laski, Ph.D.'24, is trying to make teaching in K–12 schools more sustainable and attractive

Building The ‘Bridge’ Between Research and Practice
Marshal Doug Mosher, Ph.D.'24, reflects on his journey to the Ed. School and the lessons — musical and teaching — learned along the way

How to Become a College Professor: Degrees & Requirements
By Jon Konen, District Superintendent

The truth is, most of that is probably in your head.
The goal of your professors is not to judge you, but to help you learn and expand your potential. It’s a job that comes with a lot of control and freedom, but also involves a real commitment.
Professors are dedicated to knowledge and education. They thrive on teaching and intellectual reasoning and discovery.
Becoming a professor is a dream job if you thrive in the world of theory and knowledge. If your dream is to expand the bounds of human knowledge, to share what you have learned, and to change lives, then a professorship is right up your alley.
Many college professors don’t set out to join that profession. It’s a job that sneaks up on some people. After years studying or working in a field, suddenly the option to teach in that field becomes a viable option. It offers up new opportunities to explore and innovate. Maybe just as important, it’s an opportunity to pass along what you have learned to the next generation of professionals. You can shape your industry, and the world.
Although college professors are definitely educators, that doesn’t mean they need a degree in education. In fact, they flip the script for teaching on its head. They are expected first and foremost to be experts in their own field, and learn pedagogical techniques and principles later on.
This means that becoming a professor doesn’t always follow a straight path, but in a basic sense the process will almost always include these five steps.
How to Become a College Professor in 5 Steps

One unique thing about getting started down the path to learning how to become a college professor is that you don’t really need to take the prescribed steps in order.
Sure, some of them have to come before others—you need an undergraduate degree before anyone will admit you to a PhD program, for example—but otherwise it’s a list of requirements you can check off at almost any stage of your career.
There is enormous competition for these jobs, though. The further you go along to path, the harder each step will become. You’ll need brains, dedication, and a lot of luck to make it all the way to becoming a college professor.
How long does it take to become a college professor?
For the typical pathway to professorship, you can expect a minimum of 8 to 11 years from high school graduation to the front of the lecture hall. But this depends a great deal on your field of study.
Fields that require real-world work experience can add another five years to a decade to your journey. And most professors find their calling along the way, not necessarily pursuing a straight path to the job. Those years of gaining experience and sharpening your skills can add decades to the process.
1. Get a Four-Year Bachelor’s Degree
If you want to teach college, you had better be a college graduate. In every case, that starts with earning a four-year bachelor’s degree.
Because becoming a professor is a long process, with a lot of different paths that can lead to it, your bachelor’s doesn’t necessarily have to be in the field you want to teach in. Many people shift interests through the course of their academic career.
It is important to lay the groundwork for developing your knowledge through education over the long-term. As you’ll see, becoming a professor requires a lot of advanced research and study. Your undergraduate program should equip you with the kind of skills you need to branch out into further learning and research.
Just about any bachelor’s major relevant to your general area of interest can lay the foundation for more advanced study if becoming a professor is your long-term goal.
Want to become a professor of education? Then it’s going to take a degree in education to get you started down the right path. Ready to take the next step? Find teaching degree programs near you!
2. Earn an Advanced Degree in Your Area of Expertise
To teach any material at the college level, you need a deep understanding of the theory and concepts behind it. That’s always going to mean earning an advanced degree in the subject.
Research can be an important part of professorial work, and master’s and doctoral level programs are exactly where you learn how to do that work.
The research required as part of your studies, and eventually your thesis and dissertation projects, are also a primary way for you to develop an advanced understanding of your field.
This is also an important time to cultivate mentors and relationships in your field. When you get to the point where you are applying for positions, you’ll find that the academic field is a pretty small community, so who you know matters.
Your professors in grad school will know people on the hiring committees at the colleges and universities where you will be interviewing later on. If you impressed them, you can expect a good word in the right ears.
What degree do you need to be a college professor? … Does a college professor need a PhD?
The PhD, or Doctor of Philosophy, has long been the standard degree requirement for college professors. Many community colleges and other two-year schools may require only a master’s degree, however. There are also certain areas of study where a PhD is not considered necessary, such as acting and music. Almost all traditional academic departments at four-year universities definitely prefer to higher doctoral graduates as professors, however.
For example, you’ll want to earn a doctorate in education if you plan to become a professor of education.
Can you be a professor with a master’s degree?
It’s most common to find professors teaching with only a master’s degree at the community college level, or working as adjunct faculty at four-year colleges. Adjuncts are the academic version of temps, but they make up the majority of faculty in American universities. According to NCES, in 2018, 54 percent of instructors at degree-granting post-secondary institutions were adjunct faculty.
In many fields, however, there is a surplus of PhD graduates, which makes competition stiff even for adjunct positions. In these fields, a master’s-level professor position is rare.
3. Build Real-world Experience in Your Field

But if you’re aiming to be a professor in journalism, medicine, engineering, or just about any other field with practical applications, most colleges want to see that you have what it takes to do what you will teach . That means holding down a job and racking up some accomplishments to build up that CV you’ll be submitting to the hiring committee.
Colleges and universities actively seek out professors who have expertise in cutting-edge subjects in their field. You’ll want to look for jobs that will give you experience in the kinds of topics that will be most important to the future of your field. That’s exactly what students are going to come to school to learn.
How To Be a College Professor Without a PhD
The drive to be the school with the most cutting-edge curriculum in a given field is one that can push hiring committees away from that PhD standard. If you can develop the right expertise, and a reputation to match, then it’s possible you can meet the college professor requirements without having a doctorate.
If there is big demand for professors in a particular field, you can sometimes find temporary work with only a master’s degree. If you earn a master’s degree in education , for example, you might be able to get a job instructing teachers as an adjunct professor.
It’s also much easier to become a professor without a PhD if you want to teach in a field where PhDs aren’t the standard mark of expertise. Arts programs, for example, generally show preference to instructors with experience and expertise over those with impressive academic credentials who may not have a lot of experience because the paths to those industries often don’t run through college.
4. Get Hired as a College Professor
Once you have the experience and the education to become qualified, you can start hunting for jobs teaching in college classrooms.
At first, you’ll almost certainly start as an adjunct, teaching part-time or in a visiting position at community colleges or small universities. Since there are no real professional pedagogical standards in college instruction, this serves as a sort of apprenticeship where you cut your teeth learning how to actually transfer your knowledge to students.
At the entry level, college professors don’t have a lot of options in the job market. You will very likely have to relocate to an area with a school willing to hire you. You’ll go through a lot of interviews and apply to a lot of positions to get your foot in the door.
The process and timing will vary from field to field. Many have specialized publications, like PhilJobs.org for philosophy positions, where openings are posted.
Your qualifications and specialties are very important. Schools are often looking for very specific areas of expertise to shore up their existing faculty range. Frequently, the pedigree of your education will matter. A degree from a big-name school gets you further than a small state college no one has ever heard of.
Different colleges and different departments within those colleges have different priorities when it comes to hiring. At research driven institutions, your record of exploration and publication may be all-important. At schools that value teaching, your classroom expertise will be more valued.
What qualifications do you need to be a professor?
Though a master’s to start, and then eventually earning a doctorate, is the general rule for full-time tenure positions, here are no state or national standards for teaching college. The question is only truly answered by college hiring committees. Every school is different. They value different qualities ranging from research experience to real-world know-how. And it can differ from job to job or even year to year.
The most important quality you need when figuring out how to become a college professor may be your desire to learn. If you want to get your students interested in the material, you need to live and breathe it yourself. Academia is all about the process of expanding and understanding new knowledge. You’ll never fit into the field if you don’t have a passion for that.
5. Earn Tenure at Your University

Tenure is the end of the line for college professors. While almost any other kind of job can fire you with or without cause, once a professor has tenure, they are all but assured a position for life. Tenure insulates the academic community from trends and fads, allowing unpopular opinions to be expressed and unusual lines of research to be pursued. These are the hallmarks of liberal thinking and a liberal education.
But you have to earn that kind of freedom.
That first involves getting a fixed-term contract that offers possible tenure. It probably won’t be your first professorship, so you can expect to jump around between a few schools before it comes up.
That contract will mark you as an assistant professor, starting the long road to tenure. You will teach for a few years at that level, being observed by your department and undergoing evaluation by both students and other professors.
Assuming you survive that process, you will earn promotion to associate professor. This means a salary bump but also increased scrutiny for several more years. Your teaching, research, and publication accomplishments will all be weighed during this period. You may also take on additional administrative responsibilities in your department, and be evaluated in your performance.
In the end, a tenure committee of other faculty will decide whether or not you are worthy of becoming a full tenured professor.
Do professors make good money?
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, in 2020 the median salary for postsecondary teachers, the category that college professors are included in, was $80,790 per year.
But that also includes educators at vocational schools and other training academies outside of traditional colleges. The top ten percent of the group make excellent money, over $180,360 per year. The field you teach in can also affect your salary, with in-demand areas like law, economics, and engineering commanding six-figure median salaries.
Is a college professor a good career?
Like any career, becoming a college professor can be great if it delivers what you are looking for in a job. It’s perfect for people who enjoy exploring intellectual ideas, passing them on to students, engaging in cutting-edge research, and discussing it with other academics. Professors have tremendous flexibility in their personal schedules and in their freedom to teach topics that interest them. They have to be self-motivated and enjoy engaging with students. The opportunity to take long sabbaticals without risk of losing your job is also a big benefit that many enjoy.
Do You Need a PhD to Be a Professor?
If you want to work in higher education, you may be wondering, “Do you need a PhD to be a professor?”

Professors are experts in their fields who teach courses, conduct research, and support their academic institutions.
Editorial Listing ShortCode:
The type of degree that’s required to work as a professor depends on where you work and what types of courses you want to teach. Learning how to become a college professor is vital if you hope to serve as a faculty member at a college or university.

You don’t necessarily need a PhD to become a professor. Colleges and universities often hire professors with other types of degrees. In that case, what degree do you need to be a professor?
Graduates of master’s programs are often qualified to work as professors, particularly at two-year institutions. These professionals may have more limited responsibilities than professors with PhDs, and they are sometimes limited to teaching introductory courses.
Schools that require professors to hold a doctoral degree may accept another type of professor degree from an accredited university. These are some of the professional doctorate degrees that prospective employers may consider in place of a PhD:
- Doctor of Education
- Doctor of Arts
- Doctor of Business Administration
- Doctor of Public Health
- Doctor of Science
- Doctor of Chemistry
- Doctor of Medicine
Job candidates who don’t hold a PhD may be able to strengthen their candidacy for a position with professional experience. Publishing articles or books that contribute to the field is also beneficial, as it reflects a high level of expertise.
The education requirement for a career as a professor differs between colleges, so it’s essential to review each institution’s policy before applying for a position.
How to Become a Professor

Becoming a professor requires a series of academic and professional steps, including:
- Earning a bachelor’s degree . The pursuit of a professor position begins with a bachelor’s degree. Although it’s helpful to select a field that’s related to your career goal, bachelors programs are an opportunity to explore your interests, and many master’s programs accept students with various degrees.
- Entering graduate school . Some students complete separate master’s and PhD programs. Others enroll in accelerated programs and earn their master’s degree while also working toward their PhD.
- Taking comprehensive exams . Once you have completed your coursework, you will take a series of exams covering the material you studied. The exam may take the form of a written or oral test, portfolio, or research paper.
- Completing a dissertation . Most PhD programs require students to complete a dissertation, an extensive project that may require several years of research and writing. The final stage of a dissertation is typically the oral defense, during which you present your paper and findings to a committee of faculty and answer their questions.
- Gaining experience . It may be beneficial to work as a lecturer or adjunct instructor prior to becoming a professor. This offers evidence of your teaching skills to prospective employers.
- Applying for positions . Even if your doctoral degree is not yet completed, you can begin applying for professor positions while working on your dissertation. The hiring process generally includes submitting an application, a curriculum vitae, and letters of recommendation as well as participating in an interview and presentation or teaching demonstration.
It can be competitive to find a position as a professor, so it may be necessary to apply for positions at multiple schools before finding the right role.
Are All Professors Doctors?
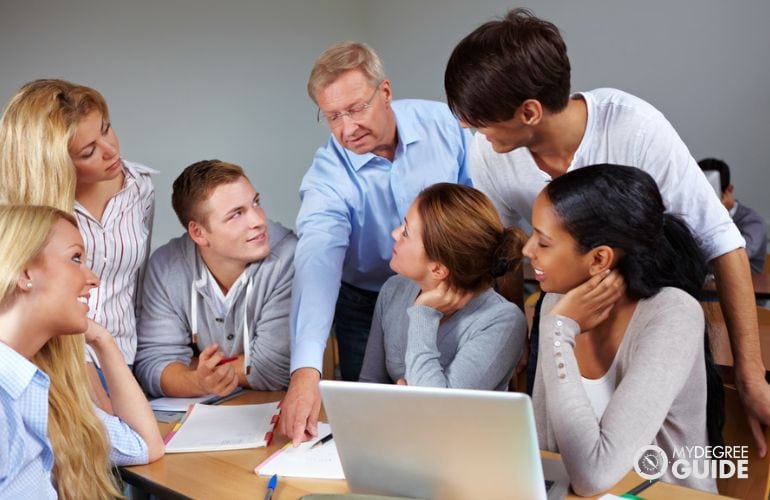

Not all professors are doctors, but many are. Professors are only considered doctors if they hold a doctoral degree, such as a PhD or professional doctorate.
Professors with masters degrees are not classified or addressed as doctors. Because professors need a high level of knowledge and experience in their field, a PhD is a common requirement for this type of position. Many prominent schools only hire graduates of PhD programs for full-time roles as professors.
Is a PhD a Doctor?
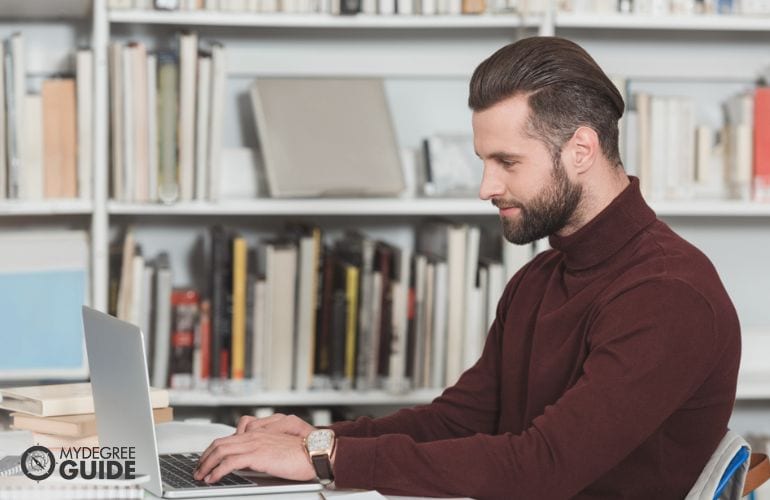

A person who holds a PhD is a doctor , but they hold a Doctor of Philosophy rather than a Doctor of Medicine. Medical doctors, or MDs, treat patients, diagnose health conditions, and study diseases, and they complete their degrees at medical schools.
Some PhDs specialize in medicine or health care, but PhDs can also be members of many other fields. For example, a student might obtain a PhD in Sociology, Business Administration, or Higher Education. Online PhD programs are available at a variety of colleges and universities.
What Can You Get a PhD In?
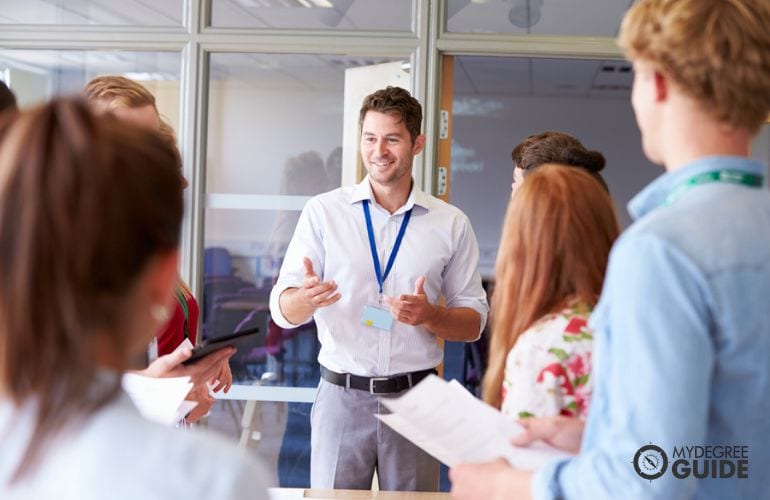

Doctoral degrees are offered in many disciplines, including:
- Sciences . Students can pursue degrees in subjects such as physics, chemistry, and engineering.
- Health care . Physical therapy and audiology are potential areas of study for students hoping to work in health care.
- Education . A PhD in Education may help you advance in your teaching career or become a school administrator.
- Psychology . Programs in psychology are ideal for students who want to work as psychologists or researchers.
- English . Many schools offer English PhDs focused on literature, while others emphasize writing and rhetoric.
When choosing what PhD you can get in , it helps to consider your academic background and interests.
Can You Be a Professor with a Masters?
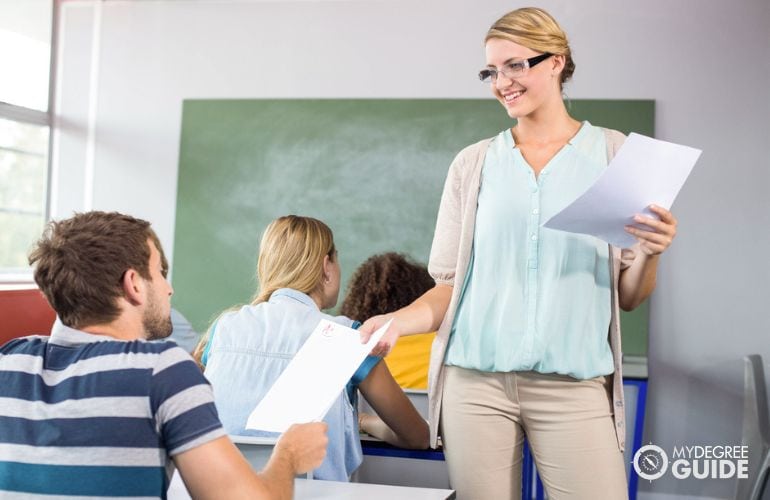

Yes, you can be a professor with a master’s degree. Many schools hire professionals with master’s degrees to serve as entry-level instructors.
Community colleges and two-year institutions are especially popular employers for graduates of master’s programs. Four year colleges may also hire job candidates with master’s degrees, but they often work as adjuncts rather than as full-time employees. Adjuncts have temporary positions and may not receive benefits.
Because of the high level of competition for academic positions in certain disciplines, it may be easier to get a job as a professor with a Ph.D. rather than a master’s degree.
What Does a Professor Do?

Professors have a wide range of responsibilities. Most people in this role are responsible for teaching several courses within their discipline. They may also develop or update curriculum and assessments for their departments.
In addition to teaching, professors usually offer advising to students and supervise their graduate research projects, such as dissertations. They often join college committees that focus on improving practices and policies within the institution.
Many professors also conduct original research and write journal articles for publication. These contributions are often a requirement for receiving tenure.
How Much Do College Professors Make?

The salary for a postsecondary teacher can differ based on your location, the specific school where you work, your level of experience, and your discipline or specialization.
For example, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics , the median annual salary for engineering professors is $103,550. This is higher than the median wage for business professors, which is $88,790. Some professors who want to work outside of the classroom become instructional coordinators. Professionals in this area earn median salaries of $66,490 per year.
A career as a professor may eventually lead to a job as a postsecondary education administrator. The median salary for this type of position is $99,940.
What’s the Difference Between an Assistant vs. Associate Professor?
Although they both teach courses at the college level, assistant and associate professors have separate roles with notable differences.
Many professors are initially hired as assistant professors and progress to become associate professors.
Becoming a Professor

Do you need a doctorate to be a professor? The answer to this question changes based on the requirements of each specific academic institution.
No matter where you hope to work, certain steps are necessary before you can work as a professor. The path generally begins with a bachelor’s degree and culminates with a master’s degree or a doctoral degree, such as a PhD.
Whether you’re considering different bachelors degrees or are ready to enroll in a PhD program, you can begin your journey toward becoming a professor by researching accredited colleges and universities.

You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience.

Health & Nursing
Courses and certificates.
- Bachelor's Degrees
- View all Business Bachelor's Degrees
- Business Management – B.S. Business Administration
- Healthcare Administration – B.S.
- Human Resource Management – B.S. Business Administration
- Information Technology Management – B.S. Business Administration
- Marketing – B.S. Business Administration
- Accounting – B.S. Business Administration
- Finance – B.S.
- Supply Chain and Operations Management – B.S.
- Accelerated Information Technology Bachelor's and Master's Degree (from the School of Technology)
- Health Information Management – B.S. (from the Leavitt School of Health)
Master's Degrees
- View all Business Master's Degrees
- Master of Business Administration (MBA)
- MBA Information Technology Management
- MBA Healthcare Management
- Management and Leadership – M.S.
- Accounting – M.S.
- Marketing – M.S.
- Human Resource Management – M.S.
- Master of Healthcare Administration (from the Leavitt School of Health)
- Data Analytics – M.S. (from the School of Technology)
- Information Technology Management – M.S. (from the School of Technology)
- Education Technology and Instructional Design – M.Ed. (from the School of Education)
Certificates
- Supply Chain
- Accounting Fundamentals
- View all Business Degrees
Bachelor's Preparing For Licensure
- View all Education Bachelor's Degrees
- Elementary Education – B.A.
- Special Education and Elementary Education (Dual Licensure) – B.A.
- Special Education (Mild-to-Moderate) – B.A.
- Mathematics Education (Middle Grades) – B.S.
- Mathematics Education (Secondary)– B.S.
- Science Education (Middle Grades) – B.S.
- Science Education (Secondary Chemistry) – B.S.
- Science Education (Secondary Physics) – B.S.
- Science Education (Secondary Biological Sciences) – B.S.
- Science Education (Secondary Earth Science)– B.S.
- View all Education Degrees
Bachelor of Arts in Education Degrees
- Educational Studies – B.A.
Master of Science in Education Degrees
- View all Education Master's Degrees
Curriculum and Instruction – M.S.
Educational Leadership – M.S.
- Education Technology and Instructional Design – M.Ed.
Master's Preparing for Licensure
- Teaching, Elementary Education – M.A.
- Teaching, English Education (Secondary) – M.A.
- Teaching, Mathematics Education (Middle Grades) – M.A.
- Teaching, Mathematics Education (Secondary) – M.A.
- Teaching, Science Education (Secondary) – M.A.
- Teaching, Special Education (K-12) – M.A.
Licensure Information
- State Teaching Licensure Information
Master's Degrees for Teachers
- Mathematics Education (K-6) – M.A.
- Mathematics Education (Middle Grade) – M.A.
- Mathematics Education (Secondary) – M.A.
- English Language Learning (PreK-12) – M.A.
- Endorsement Preparation Program, English Language Learning (PreK-12)
- Science Education (Middle Grades) – M.A.
- Science Education (Secondary Chemistry) – M.A.
- Science Education (Secondary Physics) – M.A.
- Science Education (Secondary Biological Sciences) – M.A.
- Science Education (Secondary Earth Science)– M.A.
- View all Technology Bachelor's Degrees
- Cloud Computing – B.S.
- Computer Science – B.S.
- Cybersecurity and Information Assurance – B.S.
- Data Analytics – B.S.
- Information Technology – B.S.
- Network Engineering and Security – B.S.
- Software Engineering – B.S.
- Accelerated Information Technology Bachelor's and Master's Degree
- Information Technology Management – B.S. Business Administration (from the School of Business)
- View all Technology Master's Degrees
- Cybersecurity and Information Assurance – M.S.
- Data Analytics – M.S.
- Information Technology Management – M.S.
- MBA Information Technology Management (from the School of Business)
- Full Stack Engineering
- Web Application Deployment and Support
- Front End Web Development
- Back End Web Development
3rd Party Certifications
- IT Certifications Included in WGU Degrees
- View all Technology Degrees
- View all Health & Nursing Bachelor's Degrees
- Nursing (RN-to-BSN online) – B.S.
- Nursing (Prelicensure) – B.S. (Available in select states)
- Health Information Management – B.S.
- Health and Human Services – B.S.
- Psychology – B.S.
- Health Science – B.S.
- Healthcare Administration – B.S. (from the School of Business)
- View all Nursing Post-Master's Certificates
- Nursing Education—Post-Master's Certificate
- Nursing Leadership and Management—Post-Master's Certificate
- Family Nurse Practitioner—Post-Master's Certificate
- Psychiatric Mental Health Nurse Practitioner —Post-Master's Certificate
- View all Health & Nursing Degrees
- View all Nursing & Health Master's Degrees
- Nursing – Education (BSN-to-MSN Program) – M.S.
- Nursing – Leadership and Management (BSN-to-MSN Program) – M.S.
- Nursing – Nursing Informatics (BSN-to-MSN Program) – M.S.
- Nursing – Family Nurse Practitioner (BSN-to-MSN Program) – M.S. (Available in select states)
- Nursing – Psychiatric Mental Health Nurse Practitioner (BSN-to-MSN Program) – M.S. (Available in select states)
- Nursing – Education (RN-to-MSN Program) – M.S.
- Nursing – Leadership and Management (RN-to-MSN Program) – M.S.
- Nursing – Nursing Informatics (RN-to-MSN Program) – M.S.
- Master of Healthcare Administration
- MBA Healthcare Management (from the School of Business)
- Business Leadership (with the School of Business)
- Supply Chain (with the School of Business)
- Accounting Fundamentals (with the School of Business)
- Back End Web Development (with the School of Technology)
- Front End Web Development (with the School of Technology)
- Web Application Deployment and Support (with the School of Technology)
- Full Stack Engineering (with the School of Technology)
- Single Courses
- Course Bundles
Apply for Admission
Admission requirements.
- New Students
- WGU Returning Graduates
- WGU Readmission
- Enrollment Checklist
- Accessibility
- Accommodation Request
- School of Education Admission Requirements
- School of Business Admission Requirements
- School of Technology Admission Requirements
- Leavitt School of Health Admission Requirements
Additional Requirements
- Computer Requirements
- No Standardized Testing
- Clinical and Student Teaching Information
Transferring
- FAQs about Transferring
- Transfer to WGU
- Transferrable Certifications
- Request WGU Transcripts
- International Transfer Credit
- Tuition and Fees
- Financial Aid
- Scholarships
Other Ways to Pay for School
- Tuition—School of Business
- Tuition—School of Education
- Tuition—School of Technology
- Tuition—Leavitt School of Health
- Your Financial Obligations
- Tuition Comparison
- Applying for Financial Aid
- State Grants
- Consumer Information Guide
- Responsible Borrowing Initiative
- Higher Education Relief Fund
FAFSA Support
- Net Price Calculator
- FAFSA Simplification
- See All Scholarships
- Military Scholarships
- State Scholarships
- Scholarship FAQs
Payment Options
- Payment Plans
- Corporate Reimbursement
- Current Student Hardship Assistance
- Military Tuition Assistance
WGU Experience
- How You'll Learn
- Scheduling/Assessments
- Accreditation
- Student Support/Faculty
- Military Students
- Part-Time Options
- Virtual Military Education Resource Center
- Student Outcomes
- Return on Investment
- Students and Gradutes
- Career Growth
- Student Resources
- Communities
- Testimonials
- Career Guides
- Skills Guides
- Online Degrees
- All Degrees
- Explore Your Options
Admissions & Transfers
- Admissions Overview
Tuition & Financial Aid
Student Success
- Prospective Students
- Current Students
- Military and Veterans
- Commencement
- Careers at WGU
- Advancement & Giving
- Partnering with WGU
EDUCATION CAREER GUIDES
College Professor Career
What is a college professor.
A college professor is a highly educated individual who holds a doctoral degree or a master's degree and has a wealth of knowledge in their area of expertise. They are not only responsible for instructing students but also for conducting research in their field. College professors play a crucial role in shaping the minds of future generations, which is why they are held in high regard. They are skilled communicators who are adept at explaining complex ideas in a way that students can easily comprehend. In addition to their teaching responsibilities, professors also advise students, mentor aspiring academics, publish research papers, and attend academic conferences. It takes years of hard work and dedication to become a college professor, but the rewards of helping students and advancing knowledge make it a very fulfilling career.

RESPONSIBILITIES
What Does a College Professor Do?
Some of the day-to-day responsibilities of professors include:
- Preparing lectures: College professors are responsible for preparing lectures and other teaching materials for their classes. This includes researching the topics they will be discussing, writing lecture notes, and developing activities that students can do to learn the material. Professors also need to stay up to date on new developments in their field so that they can incorporate them into their instruction.
- Grading assignments: Professors are expected to grade assignments, such as tests and essays, that students submit throughout the semester. Professors must read each assignment carefully and provide feedback to help students understand what they did well and what areas they need to improve in.
- Advising students: Professors often serve as advisors to students who are majoring or minoring in their department. This includes meeting with students one-on-one to discuss course selection, career plans, research, and other academic matters. Professors may also provide recommendations for internships or research opportunities that could help a student further their studies.
- Serving on committees: Professors are regularly asked to serve on committees at their institution. These committees typically focus on issues such as curriculum development, faculty hiring, and budgeting decisions that affect the entire college or university.
- Attending conferences: Professors are expected to attend conferences related to their field of study or teaching discipline. At these conferences, professors have the opportunity to network with other professionals in their field and exchange ideas about new developments in research or pedagogy that could benefit their students or department back home.
- Conducting research: Many college professors also engage in research projects related to their field of study while teaching at an institution of higher learning. This allows them to stay up to date on new developments in their field while also contributing original work that could benefit future generations of scholars and practitioners alike.
- Publishing their work: A professor may choose to publish writings related to their research projects or teaching experiences while working in a college or university setting. These writings can take many forms, including books, journal articles, book chapters, white papers, blog posts, and more. Writing these publications is an important way for professors to share their knowledge with others both inside and outside of academia.
Where Does a College Professor Work?
College professors work in a variety of settings , from large research universities to small liberal arts colleges. Some may even work at community colleges or online schools. Their work environments may range from traditional classroom settings to research labs or even international fieldwork. Regardless of where they work, college professors play an integral role in higher education by shaping the minds of the next generation of leaders and contributing to the advancement of knowledge in their respective fields.

EDUCATION & BEST DEGREES
How do i become a college professor.
Educational requirements for professors can vary by state and institution. If you want to teach part-time as an adjunct professor at a community college, you might only need to obtain your master’s degree . On the other hand, if you’d like to teach at a four-year university or college and follow a tenure track, you’ll likely need a Ph.D. You should gain teaching experience through assistantships, fellowships, tutoring, or other opportunities while earning your degree. Networking with professors and colleagues in your field can also be beneficial, as they may have information about job openings or can provide letters of recommendation.
Once you have your degree and significant career experience, you can begin applying to open positions at universities or other academic institutions. Keep in mind that competition for these jobs can be quite high, so it's important to be persistent and patient.

Best Degrees for a College Professors
An online master's degree for current teachers looking to move into a...
An online master's degree for current teachers looking to move into a school or district leadership position, like principal, vice principal, or administrator.
- Time: 60% of grads earned this degree within 23 months.
- Tuition: $3,975 per 6-month term.
- Courses: 13 total courses in this program.
This program is for licensed teachers who are ready to take the next step in their education career.
Skills for your résumé included in this program:
- School Financial Leadership
- People & Talent
- School Operations and Management
- Leadership Ethics
Put your leadership skills to good use—in the service of America's children—with this education master's degree.
States that do not accept this program: Alabama, Connecticut, Georgia, Hawaii, Iowa, Kansas, and Minnesota.
An online master's degree for those who have educational experience and...
An online master's degree for those who have educational experience and are looking to further their careers with a graduate program focused on curriculum development and design.
- Time: 62% of students earn this degree within 12 months.
- Tuition: $3,975 per 6-month term.
- Courses: 10 total courses in this program.
- Differentiated Instruction
- Curriculum and Instruction Design
- Educational Research
Help schools create engaging, meaningful, and memorable learning experiences to improve learning outcomes for all students with this M.S. degree.

How Much Does a College Professor Make?
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor and Statistics (BLS), the median annual pay for college professors is $80,840 . Some of the factors that may influence how much a professor earns include:
Their level of education
Which subjects they teach
Whether they are adjunct or tenured
If they work at a community college or a four-year university
If they work at a public or private university
Years of relevant job experience
What Is the Job Outlook for a College Professor?
According to the BLS, the job outlook for professors and postsecondary teachers is positive. Between 2022 and 2032, the field is expected to grow by 8% . Factors driving this change include:
An increase in students pursuing higher education
State and local government budgets
An increased number of open positions for part-time, rather than full-time, professors

What Skills Does a College Professor Need?
Some of the core skills you’ll need to successfully work as a professor include:
- Strong communication skills: A college professor needs strong communication skills to effectively convey information to their students. This includes being able to clearly explain concepts, answer questions, and engage in meaningful dialogue with students.
- Organizational skills: Organizational skills are essential for any college professor as their role demands planning lectures, grading assignments, and managing student records. Professors must also be able to organize their own time effectively to ensure that all of their tasks are completed on time.
- Critical thinking skills: Professors need to analyze complex topics and determine how best to present them in clear and understandable ways for their students. They must also be able to think critically when evaluating student work and providing feedback that will help the students improve their understanding of the material.
- Adaptability: As the educational landscape is constantly changing due to advances in technology and new research findings, adaptability is key. Professors must stay up to date on these changes and adjust their teaching methods accordingly to ensure that their students have access to the most current information available.
- Interpersonal skills: Professors will often need to interact with students both inside and outside of the classroom. Professors should have excellent interpersonal skills to foster positive relationships with students and create an environment where everyone feels comfortable asking questions or expressing opinions without fear of judgment or criticism.
- Patience: There will always be times when some students may struggle more than others with certain concepts or assignments. Professors should remain patient while helping those students understand the material better so that everyone can succeed together in the classroom environment.
- Passion for teaching: A passion for teaching is essential for any successful college professor as it will motivate them when they face challenging tasks or difficult decisions related to their job duties. This motivation can also help inspire enthusiasm for research, learning, and writing among students, which can lead them to greater success.
Our Online University Degree Programs Start on the First of Every Month, All Year Long
No need to wait for spring or fall semester. It's back-to-school time at WGU year-round. Get started by talking to an Enrollment Counselor today, and you'll be on your way to realizing your dream of a bachelor's or master's degree—sooner than you might think!
Next Start Date {{startdate}}
Interested in Becoming a College Professor?
Learn more about degree programs that can prepare you for this meaningful career.
The University
For students.
- Student Portal
- Alumni Services
Most Visited Links
- Business Programs
- Student Experience
- Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion
- Student Communities

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, the 19 steps to becoming a college professor.
Other High School , College Info

Do you love conducting research and engaging with students? Can you envision yourself working in academia? Then you're probably interested in learning how to become a college professor. What are the basic requirements for becoming a college professor? What specific steps should you take in order to become one?
In this guide, we start with an overview of professors, taking a close look at their salary potential and employment growth rate. We then go over the basic college professor requirements before giving you a step-by-step guide on how to become one.
Feature Image: Georgia Southern /Flickr
Becoming a College Professor: Salary and Job Outlook
Before we dive into our discussion of salaries and employment growth rates, it's important to be aware of the incredible challenge of becoming a college professor.
These days, it is unfortunately well known that the number of people qualified to be professors far outnumbers the availability of professor job openings , which means that the job market is extremely competitive. Even if you do all the steps below, the chances of your actually becoming a college professor are slim —regardless of whether you want to teach in the humanities or sciences .
Now that we've gone over the current status of the professor job market, let's take a look at some hard figures for salary and employment growth rate.
Salary Potential for Professors
First, what is the salary potential for college professors? The answer to this question depends a lot on what type of professor you want to be and what school you end up working at .
In general, though, here's what you can expect to make as a professor. According to a recent study conducted by the American Association of University Professors , the average salaries for college professors are as follows :
- Full professors: $140,543
- Associate professors: $95,828
- Assistant professors: $83,362
- Part-time faculty members: $3,556 per standard course section
As you can see, there's a pretty huge range in professors' salaries , with full professors typically making $40,000-$50,000 more per year than what associate and assistant professors make.
For adjunct professors (i.e., part-time teachers), pay is especially dismal . Many adjunct professors have to supplement their incomes with other jobs or even public assistance, such as Medicaid, just to make ends meet.
One study notes that adjuncts make less than minimum wage when taking into account non-classroom work, including holding office hours and grading papers.
All in all, while it's possible to make a six-figure salary as a college professor, this is rare, especially considering that 73% of college professors are off the tenure track .
Employment Rates for Professors
Now, what about employment rates for professor jobs? According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), the projected growth rate for postsecondary teachers in the years 2020-2030 is 12% —that's 4% higher than the average rate of growth of 8%.
That said, most of this employment growth will be in part-time (adjunct) positions and not full-time ones. This means that most professor job openings will be those with the lowest salaries and lowest job security .
In addition, this job growth will vary a lot by field (i.e., what you teach). The chart below shows the median salaries and projected growth rates for a variety of fields for college professors (arranged alphabetically):
Source: BLS.gov
As this chart indicates, depending on the field you want to teach in, your projected employment growth rate could range from 0% to as high as 21% .
The fastest growing college professor field is health; by contrast, the slowest growing fields are social sciences, mathematical science, atmospheric and earth sciences, computer science, and English language and literature. All of these are growing at a slower-than-average pace (less than 5%).
Law professors have the highest salary , with a median income of $116,430. On the opposite end, the lowest-earning field is criminal justice and law enforcement, whose professors make a median salary of $63,560—that's over $50,000 less than what law professors make.
College Professor Requirements and Basic Qualifications
In order to become a college professor, you'll need to have some basic qualifications. These can vary slightly among schools and fields, but generally you should expect to need the following qualifications before you can become a college professor .
#1: Doctoral Degree in the Field You Want to Teach In
Most teaching positions at four-year colleges and universities require applicants to have a doctoral degree in the field they wish to teach in.
For example, if you're interested in teaching economics, you'd likely need to get a PhD in economics. Or if you're hoping to teach Japanese literature, you'd get a PhD in a relevant field, such as Japanese studies, Japanese literature, or comparative literature.
Doctoral programs usually take five to seven years and require you to have a bachelor's degree and a master's degree. (Note, however, that many doctoral programs do allow you to earn your master's along the way.)
But is it possible to teach college-level classes without a doctoral degree? Yes—but only at certain schools and in certain fields.
As the BLS notes, some community colleges and technical schools allow people with just a master's degree to teach classes ; however, these positions can be quite competitive, so if you've only got a master's degree and are up against applicants with doctorates, you'll likely have a lower chance of standing out and getting that job offer .
In addition, some fields let those with just master's degrees teach classes. For example, for creative writing programs, you'd only need a Master of Fine Arts.
#2: Teaching Experience
Another huge plus for those looking to become professors is teaching experience. This means any experience with leading or instructing classes or students.
Most college professors gain teaching experience as graduate students. In many master's and doctoral programs, students are encouraged (sometimes even required) to either lead or assist with undergraduate classes.
At some colleges, such as the University of Michigan, graduate students can get part-time teaching jobs as Graduate Student Instructors (GSIs) . For this position, you'll usually teach undergraduate classes under the supervision of a full-time faculty member.
Another college-level teaching job is the Teaching Assistant or Teacher's Aide (TA) . TAs assist the main professor (a full-time faculty member) with various tasks, such as grading papers, preparing materials and assignments, and leading smaller discussion-based classes.
#3: Professional Certification (Depending on Field)
Depending on the field you want to teach in, you might have to obtain certification in something in addition to getting a doctoral degree. Here's what the BLS says about this:
"Postsecondary teachers who prepare students for an occupation that requires a license, certification, or registration, may need to have—or they may benefit from having—the same credential. For example, a postsecondary nursing teacher might need a nursing license or a postsecondary education teacher might need a teaching license."
Generally speaking, you'll only need certification or a license of some sort if you're preparing to teach in a technical or vocational field , such as health, education, or accounting.
Moreover, while you don't usually need any teaching certification to be able to teach at the college level, you will need it if you want to teach at the secondary level (i.e., middle school or high school).

#4: Publications and Prominent Academic Presence
A high number of publications is vital to landing a job as a professor. Since full-time college-level teaching jobs are extremely competitive, it's strongly encouraged (read: basically required!) that prospective professors have as many academic publications as possible .
This is particularly important if you're hoping to secure a tenure-track position, which by far offers the best job security for professors. Indeed, the famous saying " publish or perish " clearly applies to both prospective professors and practicing professors.
And it's not simply that you'll need a few scholarly articles under your belt— you'll also need to have big, well-received publications , such as books, if you want to be a competitive candidate for tenure-track teaching positions.
Here's what STEM professor Kirstie Ramsey has to say about the importance of publications and research when applying for tenure-track jobs:
"Many colleges and universities are going through a transition from a time when research was not that important to a time when it is imperative. If you are at one of these institutions and you were under the impression that a certain amount of research would get you tenure, you should not be surprised if the amount of research you will need increases dramatically before you actually go up for tenure. At first I thought that a couple of peer-reviewed articles would be enough for tenure, especially since I do not teach at a research university and I am in a discipline where many people do not go into academe. However, during my first year on the tenure track at my current institution, I realized that only two articles would not allow me to jump through the tenure hoop."
To sum up, it's not just a doctorate and teaching experience that make a professor, but also lots and lots of high-quality, groundbreaking research .
How to Become a Professor: 19-Step Guide
Now that we've gone over the basic college professor requirements, what specific steps should you take to become one? What do you need to do in high school? In college? In graduate school?
Here, we introduce to you our step-by-step guide on how to become a college professor . We've divided the 19 steps into four parts:
- High School
- Graduate School (Master's Degree)
- Graduate School (Doctorate)
Part 1: High School
It might sound strange to start your path to becoming a professor in high school, but doing so will make the entire process go a lot more smoothly for you. Here are the most important preliminary steps you can take while still in high school.
- Step 1: Keep Up Your Grades
Although all high school students should aim for strong GPAs , because you're specifically going into the field of education, you'll need to make sure you're giving a little extra attention to your grades . Doing this proves that you're serious about not only your future but also education as a whole—the very field you'll be entering!
Furthermore, maintaining good grades is important for getting into a good college . Attending a good college could, in turn, help you get into a more prestigious graduate school and obtain a higher-paying teaching job .
If you already have an idea of what subject you'd like to teach, try to take as many classes in your field as possible . For example, if you're a lover of English, you might want to take a few electives in subjects such as journalism or creative writing. Or if you're a science whiz, see whether you can take extra science classes (beyond the required ones) in topics such as marine science, astronomy, or geology.
Again, be sure that you're getting high marks in your classes , particularly in the ones that are most relevant to the field you want to teach in.
- Step 2: Tutor in Your Spare Time
One easy way of gaining teaching experience as a high school student is to become a tutor. Pick a subject you're strong at—ideally, one you might want to eventually teach—and consider offering after-school or weekend tutoring services to your peers or other students in lower grades.
Tutoring will not only help you decide whether teaching is a viable career path for you, but it'll also look great on your college applications as an extracurricular activity .

- Step 3: Get a High SAT/ACT Score
Since you'll need to go to graduate school to become a professor, it'll be helpful if you can get into a great college. To do this, you'll need to have an impressive SAT/ACT score .
Ideally, you'll take your first SAT or ACT around the beginning of your junior year. This should give you enough time to take the test again in the spring, and possibly a third time during the summer before or the autumn of your senior year.
The SAT/ACT score you'll want to aim for depends heavily on which colleges you apply to.
For more tips on how to set a goal score, check out our guides to what a great SAT / ACT score is .
- Step 4: Submit Impressive College Applications
Though it's great to attend a good college, where you go doesn't actually matter too much—just as long as it offers an academic program in the (broad) field or topic you're thinking of teaching in.
To get into the college of your choice, however, you'll still want to focus on putting together a great application , which will generally include the following:
- A high GPA and evidence of rigorous coursework
- Impressive SAT/ACT scores
- An effective personal statement/essay
- Strong letters of recommendation (if required)
Be sure to give yourself plenty of time to work on your applications so you can submit the best possible versions of them before your schools' deadlines .
If you're aiming for the Ivy League or other similarly selective institutions, check out our expert guide on how to get into Harvard , written by a real Harvard alum.
Part 2: College
Once you get into college, what can you do to help your chances of getting into a good grad school and becoming a college professor? Here are the next steps to take.
- Step 5: Declare a Major in the Field You Want to Teach
Perhaps the most critical step is to determine what exactly you want to teach in the future—and then major in it (or a related field) . For instance, if after taking some classes in computer science you decide that you really want to teach this subject, then go ahead and declare it as your major.
If you're still not sure what field you'll want to teach in, you can always change your major later on or first declare your field of interest as a minor (and then change it to a major if you wish). If the field you want to teach is not offered as a major or minor at your college, try to take as many relevant classes as possible.
Although it's not always required for graduate school applicants to have majored in the field they wish to study at the master's or doctoral level, it's a strong plus in that it shows you've had ample experience with the subject and will be able to perform at a high level right off the bat.
- Step 6: Observe Your Professors in Action
Since you're thinking of becoming a college professor, this is a great time to sit down and observe your professors to help you determine whether teaching at the postsecondary level is something you're truly interested in pursuing.
In your classes, evaluate how your professors lecture and interact with students . What kinds of tools, worksheets, books, and/or technology do they use to effectively engage students? What sort of atmosphere do they create for the class?
It's also a good idea to look up your professors' experiences and backgrounds in their fields . What kinds of publications do they have to their name? Where did they get their master's and doctoral degrees? Are they tenured or not? How long have they been teaching?
If possible, I recommend meeting with a professor directly (ideally, one who's in the same field you want to teach in) to discuss a career in academia. Most professors will be happy to meet with you during their office hours to talk about your career interests and offer advice.
Doing all of this will give you an inside look at what the job of professor actually entails and help you decide whether it's something you're passionate about.
- Step 7: Maintain Good Grades
Because you'll need to attend graduate school after college, it's important to maintain good grades as an undergraduate, especially in the field you wish to teach. This is necessary because most graduate programs require a minimum 3.0 undergraduate GPA for admission .
Getting good grades also ensures that you'll have a more competitive application for grad school, and indicates that you take your education seriously and are passionate about learning.

- Step 8: Get to Know Your Professors
Aside from watching how your professors teach, it's imperative to form strong relationships with them outside of class , particularly with those who teach in the field you want to teach as well.
Meet with professors during their office hours often. Consult them whenever you have questions about assignments, papers, projects, or your overall progress. Most importantly, don't be afraid to talk to them about your future goals!
You want to build a strong rapport with your professors, which is basically the same thing as networking. This way, you'll not only get a clearer idea of what a professor does, but you'll also guarantee yourself stronger, more cogent letters of recommendation for graduate school .
- Step 9: Gain Research and/or Publication Experience
This isn't an absolute necessity for undergraduates, but it can certainly be helpful for your future.
If possible, try to gain research experience through your classes or extracurricular projects . For instance, you could volunteer to assist a professor with research after class or get a part-time job or internship as a research assistant.
If neither option works, consider submitting a senior thesis that involves a heavy amount of research . Best case scenario, all of your research will amount to a publication (or two!) with your name on it.
That being said, don't fret too much about getting something published as an undergraduate . Most students don't publish anything in college yet many go on to graduate school, some of whom become college professors. Rather, just look at this as a time to get used to the idea of researching and writing about the results of your research.
- Step 10: Take the GRE and Apply to Grad School
If you're hoping to attend graduate school immediately after college, you'll need to start working on your application by the fall of your senior year .
One big part of your graduate school application will be GRE scores , which are required for many graduate programs. The GRE is an expensive test , so it's best if you can get away with taking it just once (though there's no harm in taking it twice).
Although the GRE isn't necessarily the most important feature of your grad school application , you want to make sure you're dedicating enough time to it so that it's clear you're really ready for grad school.
Other parts of your grad school application will likely include the following:
- Undergraduate transcripts
- Personal statement / statement of purpose
- Curriculum vitae (CV) / resume
- Letters of recommendation
For more tips on the GRE and applying to grad school, check out our GRE blog .

Part 3: Graduate School (Master's Degree)
Once you've finished college, it's time to start thinking about graduate school. I'm breaking this part into two sections: master's degree and doctorate .
Note that although some doctoral programs offer a master's degree along the way, others don't or prefer applicants who already have a master's degree in the field.
- Step 11: Continue to Keep Up Your Grades
Again, one of your highest priorities should be to keep up your grades so you can get into a great doctoral program once you finish your master's program. Even more important, many graduate programs require students to get at least Bs in all their classes , or else they might get kicked out of the program! So definitely focus on your grades.
- Step 12: Become a TA
One great way to utilize your graduate program (besides taking classes!) is to become a Teaching Assistant, or TA, for an undergraduate class. As a TA, you will not only receive a wage but will also gain lots of firsthand experience as a teacher at the postsecondary level .
Many TAs lead small discussion sections or labs entirely on their own, offering a convenient way to ease into college-level teaching.
TAs' duties typically involve some or all of the following:
- Grading papers and assignments
- Leading small discussion or lab sections of a class (instead of its large lecture section)
- Performing administrative tasks for the professor
- Holding office hours for students
The only big negative with being a TA is the time commitment ; therefore, be sure you're ready and willing to dedicate yourself to this job without sacrificing your grades and academic pursuits.

- Step 13: Research Over the Summer
Master's programs in the US typically last around two years, giving you at least one summer during your program. As a result, I strongly recommend using this summer to conduct some research for your master's thesis . This way you can get a head start on your thesis and won't have to cram in all your research while also taking classes.
What's more, using this time to research will give you a brief taste of what your summers might look like as a professor , as college professors are often expected to perform research over their summer breaks .
Many graduate programs offer summer fellowships to graduate students who are hoping to study or conduct research (in or outside the US). My advice? Apply for as many fellowships as possible so you can give yourself the best chance of getting enough money to support your academic plans.
- Step 14: Write a Master's Thesis
Even if your program doesn't require a thesis, you'll definitely want to write one so you can have proof that you're experienced with high-level research . This type of research could help your chances of getting into a doctoral program by emphasizing your commitment to the field you're studying. It will also provide you with tools and experiences that are necessary for doing well in a doctoral program and eventually writing a dissertation.
Step 15: Apply to Doctoral Programs OR Apply for Teaching Jobs
This step has two options depending on which path you'd rather take.
If you really want to teach at a four-year college or university, then you must continue on toward a doctorate . The application requirements for doctoral programs are similar to those for master's programs . Read our guide for more information about grad school application requirements .
On the other hand, if you've decided that you don't want to get a doctorate and would be happy to teach classes at a community college or technical school, it's time to apply for teaching jobs .
To start your job hunt, meet with some of your current or past professors who teach in the field in which you'll also be teaching and see whether they know of any job openings at nearby community colleges or technical schools. You might also be able to use some professors as references for your job applications (just be sure to ask them before you write down their names!).
If you can't meet with your professors or would rather look for jobs on your own, try browsing the career pages on college websites or looking up teaching jobs on the search engine HigherEdJobs .
Part 4: Graduate School (Doctorate)
The final part of the process (for becoming a college professor at a four-year institution) is to get your doctoral degree in the field you wish to teach . Here's what you'll need to do during your doctoral program to ensure you have the best chance of becoming a college professor once you graduate.
- Step 16: Build Strong Relationships With Professors
This is the time to really focus on building strong relationships with professors—not just with those whose classes you've taken but also with those who visit the campus to give talks, hold seminars, attend conferences, etc. This will give you a wider network of people you know who work in academia, which will (hopefully) make it a little easier for you to later land a job as a professor.
Make sure to maintain a particularly strong relationship with your doctoral advisor . After all, this is the professor with whom you'll work the most closely during your time as a doctoral student and candidate. Be open with your advisor : ask her for advice, meet with her often, and check that you're making satisfactory progress toward both your doctorate and your career goals.
- Step 17: Work On Getting Your Research Published
This is also the time to start getting serious about publishing your research.
Remember, it's a huge challenge to find a job as a full-time professor , especially if all you have is a PhD but no major publications. So be sure to focus on not only producing a great dissertation but also contributing to essays and other research projects .
As an article in The Conversation notes,
"By far the best predictor of long-term publication success is your early publication record—in other words, the number of papers you've published by the time you receive your PhD. It really is first in, best dressed: those students who start publishing sooner usually have more papers by the time they finish their PhD than do those who start publishing later."
I suggest asking your advisor for advice on how to work on getting some of your research published if you're not sure where to start.
- Step 18: Write a Groundbreaking Dissertation
You'll spend most of your doctoral program working on your dissertation—the culmination of your research. In order to eventually stand out from other job applicants, it's critical to come up with a highly unique dissertation . Doing this indicates that you're driven to conduct innovative research and make new discoveries in your field of focus.
You might also consider eventually expanding your dissertation into a full-length book .
- Step 19: Apply for Postdoc/Teaching Positions
Once you've obtained your doctorate, it's time to start applying for college-level teaching jobs!
One option you have is to apply for postdoctoral (postdoc) positions . A postdoc is someone who has a doctorate and who temporarily engages in "mentored scholarship and/or scholarly training." Postdocs are employed on a short-term basis at a college or university to help them gain further research and teaching experience.
While you can theoretically skip the postdoc position and dive straight into applying for long-term teaching jobs, many professors have found that their postdoc work helped them build up their resumes/CVs before they went on to apply for full teaching positions at colleges .
In an article for The Muse , Assistant Professor Johanna Greeson at Penn writes the following about her postdoc experience:
"Although I didn't want to do a post-doc, it bought me some time and allowed me to further build my CV and professional identity. I went on the market a second time following the first year of my two-year post-doc and was then in an even stronger position than the first time."
Once you've completed your postdoc position, you can start applying for full-time faculty jobs at colleges and universities. And what's great is that you'll likely have a far stronger CV/resume than you had right out of your doctoral program .
Conclusion: How to Become a College Professor
Becoming a college professor takes years of hard work, but it's certainly doable as long as you know what you'll need to do in order to prepare for the position and increase your chances of securing a job as a professor.
Overall, it's extremely difficult to become a professor. Nowadays, there are many more qualified applicants than there are full-time, college-level teaching positions , making tenure-track jobs in particular highly competitive.
Although the employment growth rate for professors is a high 11%, this doesn't mean that it'll be easy to land a job as a professor . Additionally, salaries for professors can vary a lot depending on the field you teach in and the institution you work at; you could make as little as minimum wage (as an adjunct/part-time professor) or as much as $100,000 or higher (as a full professor).
For those interested in becoming a professor, the basic college professor requirements are as follows :
- A doctoral degree in the field you want to teach in
- Teaching experience
- Professional certification (depending on your field)
- Publications and prominent academic presence
In terms of the steps needed for becoming a college professor, I will list those again briefly here. Feel free to click on any steps you'd like to reread!
- Step 15: Apply to Doctoral Programs or Apply for Teaching Jobs
Good luck with your future teaching career!
What's Next?
Considering other career paths besides teaching? Then check out our in-depth guides to how to become a doctor and how to become a lawyer .
No matter what job (or jobs!) you end up choosing, you'll likely need a bachelor's degree—ideally, one from a great school. Get tips on how to submit a memorable college application , and learn how to get into Harvard and other Ivy League schools with our expert guide.
Need help finding jobs? Take a look at our picks for the best job search websites to get started.

Hannah received her MA in Japanese Studies from the University of Michigan and holds a bachelor's degree from the University of Southern California. From 2013 to 2015, she taught English in Japan via the JET Program. She is passionate about education, writing, and travel.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
- Harvard Business School →
- Doctoral Programs →
PhD Programs
- Accounting & Management
- Business Economics
- Health Policy (Management)
- Organizational Behavior
- Technology & Operations Management
Students in our PhD programs are encouraged from day one to think of this experience as their first job in business academia—a training ground for a challenging and rewarding career generating rigorous, relevant research that influences practice.
Our doctoral students work with faculty and access resources throughout HBS and Harvard University. The PhD program curriculum requires coursework at HBS and other Harvard discipline departments, and with HBS and Harvard faculty on advisory committees. Faculty throughout Harvard guide the programs through their participation on advisory committees.
How do I know which program is right for me?
There are many paths, but we are one HBS. Our PhD students draw on diverse personal and professional backgrounds to pursue an ever-expanding range of research topics. Explore more here about each program’s requirements & curriculum, read student profiles for each discipline as well as student research , and placement information.
The PhD in Business Administration grounds students in the disciplinary theories and research methods that form the foundation of an academic career. Jointly administered by HBS and GSAS, the program has five areas of study: Accounting and Management , Management , Marketing , Strategy , and Technology and Operations Management . All areas of study involve roughly two years of coursework culminating in a field exam. The remaining years of the program are spent conducting independent research, working on co-authored publications, and writing the dissertation. Students join these programs from a wide range of backgrounds, from consulting to engineering. Many applicants possess liberal arts degrees, as there is not a requirement to possess a business degree before joining the program
The PhD in Business Economics provides students the opportunity to study in both Harvard’s world-class Economics Department and Harvard Business School. Throughout the program, coursework includes exploration of microeconomic theory, macroeconomic theory, probability and statistics, and econometrics. While some students join the Business Economics program directly from undergraduate or masters programs, others have worked in economic consulting firms or as research assistants at universities or intergovernmental organizations.
The PhD program in Health Policy (Management) is rooted in data-driven research on the managerial, operational, and strategic issues facing a wide range of organizations. Coursework includes the study of microeconomic theory, management, research methods, and statistics. The backgrounds of students in this program are quite varied, with some coming from public health or the healthcare industry, while others arrive at the program with a background in disciplinary research
The PhD program in Organizational Behavior offers two tracks: either a micro or macro approach. In the micro track, students focus on the study of interpersonal relationships within organizations and the effects that groups have on individuals. Students in the macro track use sociological methods to examine organizations, groups, and markets as a whole, including topics such as the influence of individuals on organizational change, or the relationship between social missions and financial objectives. Jointly administered by HBS and GSAS, the program includes core disciplinary training in sociology or psychology, as well as additional coursework in organizational behavior.
Accounting & Management
Business economics , health policy (management) , management , marketing , organizational behavior , strategy , technology & operations management .
Smart. Open. Grounded. Inventive. Read our Ideas Made to Matter.
Which program is right for you?

Through intellectual rigor and experiential learning, this full-time, two-year MBA program develops leaders who make a difference in the world.
A rigorous, hands-on program that prepares adaptive problem solvers for premier finance careers.
A 12-month program focused on applying the tools of modern data science, optimization and machine learning to solve real-world business problems.
Earn your MBA and SM in engineering with this transformative two-year program.
Combine an international MBA with a deep dive into management science. A special opportunity for partner and affiliate schools only.
A doctoral program that produces outstanding scholars who are leading in their fields of research.
Bring a business perspective to your technical and quantitative expertise with a bachelor’s degree in management, business analytics, or finance.
A joint program for mid-career professionals that integrates engineering and systems thinking. Earn your master’s degree in engineering and management.
An interdisciplinary program that combines engineering, management, and design, leading to a master’s degree in engineering and management.
Executive Programs
A full-time MBA program for mid-career leaders eager to dedicate one year of discovery for a lifetime of impact.
This 20-month MBA program equips experienced executives to enhance their impact on their organizations and the world.
Non-degree programs for senior executives and high-potential managers.
A non-degree, customizable program for mid-career professionals.
PhD Program
Program overview.
Now Reading 1 of 4
Rigorous, discipline-based research is the hallmark of the MIT Sloan PhD Program. The program is committed to educating scholars who will lead in their fields of research—those with outstanding intellectual skills who will carry forward productive research on the complex organizational, financial, and technological issues that characterize an increasingly competitive and challenging business world.
Start here.
Learn more about the program, how to apply, and find answers to common questions.
Admissions Events
Check out our event schedule, and learn when you can chat with us in person or online.
Start Your Application
Visit this section to find important admissions deadlines, along with a link to our application.
Click here for answers to many of the most frequently asked questions.
PhD studies at MIT Sloan are intense and individual in nature, demanding a great deal of time, initiative, and discipline from every candidate. But the rewards of such rigor are tremendous: MIT Sloan PhD graduates go on to teach and conduct research at the world's most prestigious universities.
PhD Program curriculum at MIT Sloan is organized under the following three academic areas: Behavior & Policy Sciences; Economics, Finance & Accounting; and Management Science. Our nine research groups correspond with one of the academic areas, as noted below.
MIT Sloan PhD Research Groups
Behavioral & policy sciences.
Economic Sociology
Institute for Work & Employment Research
Organization Studies
Technological Innovation, Entrepreneurship & Strategic Management
Economics, Finance & Accounting
Accounting
Management Science
Information Technology
System Dynamics
Those interested in a PhD in Operations Research should visit the Operations Research Center .

PhD Program Structure
Additional information including coursework and thesis requirements.

MIT Sloan Predoctoral Opportunities
MIT Sloan is eager to provide a diverse group of talented students with early-career exposure to research techniques as well as support in considering research career paths.
Rising Scholars Conference
The fourth annual Rising Scholars Conference on October 25 and 26 gathers diverse PhD students from across the country to present their research.
Now Reading 2 of 4
The goal of the MIT Sloan PhD Program's admissions process is to select a small number of people who are most likely to successfully complete our rigorous and demanding program and then thrive in academic research careers. The admission selection process is highly competitive; we aim for a class size of nineteen students, admitted from a pool of hundreds of applicants.
What We Seek
- Outstanding intellectual ability
- Excellent academic records
- Previous work in disciplines related to the intended area of concentration
- Strong commitment to a career in research
MIT Sloan PhD Program Admissions Requirements Common Questions
Dates and Deadlines
Admissions for 2024 is closed. The next opportunity to apply will be for 2025 admission. The 2025 application will open in September 2024.
More information on program requirements and application components
Students in good academic standing in our program receive a funding package that includes tuition, medical insurance, and a fellowship stipend and/or TA/RA salary. We also provide a new laptop computer and a conference travel/research budget.
Funding Information
Throughout the year, we organize events that give you a chance to learn more about the program and determine if a PhD in Management is right for you.
PhD Program Events
June phd program overview.
During this webinar, you will hear from the PhD Program team and have the chance to ask questions about the application and admissions process.
July PhD Program Overview
August phd program overview, september 12 phd program overview.
Complete PhD Admissions Event Calendar
Unlike formulaic approaches to training scholars, the PhD Program at MIT Sloan allows students to choose their own adventure and develop a unique scholarly identity. This can be daunting, but students are given a wide range of support along the way - most notably having access to world class faculty and coursework both at MIT and in the broader academic community around Boston.
Now Reading 3 of 4

Profiles of our current students
MIT Sloan produces top-notch PhDs in management. Immersed in MIT Sloan's distinctive culture, upcoming graduates are poised to innovate in management research and education. Here are the academic placements for our PhDs graduating in May and September 2024. Our 2024-2025 job market candidates will be posted in early June 2024.
Academic Job Market
Doctoral candidates on the current academic market
Academic Placements
Graduates of the MIT Sloan PhD Program are researching and teaching at top schools around the world.
view recent placements
MIT Sloan Experience
Now Reading 4 of 4
The PhD Program is integral to the research of MIT Sloan's world-class faculty. With a reputation as risk-takers who are unafraid to embrace the unconventional, they are engaged in exciting disciplinary and interdisciplinary research that often includes PhD students as key team members.
Research centers across MIT Sloan and MIT provide a rich setting for collaboration and exploration. In addition to exposure to the faculty, PhD students also learn from one another in a creative, supportive research community.
Throughout MIT Sloan's history, our professors have devised theories and fields of study that have had a profound impact on management theory and practice.
From Douglas McGregor's Theory X/Theory Y distinction to Nobel-recognized breakthroughs in finance by Franco Modigliani and in option pricing by Robert Merton and Myron Scholes, MIT Sloan's faculty have been unmatched innovators.
This legacy of innovative thinking and dedication to research impacts every faculty member and filters down to the students who work beside them.
Faculty Links
- Accounting Faculty
- Economic Sociology Faculty
- Finance Faculty
- Information Technology Faculty
- Institute for Work and Employment Research (IWER) Faculty
- Marketing Faculty
- Organization Studies Faculty
- System Dynamics Faculty
- Technological Innovation, Entrepreneurship, and Strategic Management (TIES) Faculty
Student Research
“MIT Sloan PhD training is a transformative experience. The heart of the process is the student’s transition from being a consumer of knowledge to being a producer of knowledge. This involves learning to ask precise, tractable questions and addressing them with creativity and rigor. Hard work is required, but the reward is the incomparable exhilaration one feels from having solved a puzzle that had bedeviled the sharpest minds in the world!” -Ezra Zuckerman Sivan Alvin J. Siteman (1948) Professor of Entrepreneurship
Sample Dissertation Abstracts - These sample Dissertation Abstracts provide examples of the work that our students have chosen to study while in the MIT Sloan PhD Program.
We believe that our doctoral program is the heart of MIT Sloan's research community and that it develops some of the best management researchers in the world. At our annual Doctoral Research Forum, we celebrate the great research that our doctoral students do, and the research community that supports that development process.
The videos of their presentations below showcase the work of our students and will give you insight into the topics they choose to research in the program.
Attention To Retention: The Informativeness of Insiders’ Decision to Retain Shares
2024 PhD Doctoral Research Forum Winner - Gabriel Voelcker
Watch more MIT Sloan PhD Program Doctoral Forum Videos

Keep Exploring
Ask a question or register your interest
Faculty Directory
Meet our faculty.

What is a Professor?
Bruce Macfarlane, the author of Intellectual Leadership in Higher Education , describes ‘professor’ as ‘a slippery term’. That’s because in the UK it means something quite different from what it denotes in North America. In North America ‘professor’ and ‘professorship’ are generic labels applied to all academics employed to research and teach in universities. In the UK, much of Europe (and, for the most part, in Australasia and South Africa), ‘professorship’ denotes distinction: a professor is someone who has been promoted to the highest academic grade – usually on the basis of her or his scholarly achievements. It’s the equivalent to what, in North America, is known as full professorship.
Some people are unclear about how someone known as ‘Dr’ is different from someone whose title is ‘Professor’. ‘Dr’ denotes someone who has studied for, and been awarded, a PhD, so it denotes an academic qualification: the holder of the highest university degree. It’s the equivalent of writing ‘PhD’ after someone’s name. Most professors will be PhD-holders, but so will be many – if not most – other academics employed as university teachers and researchers. ‘Professor’ doesn’t denote a qualification but an academic staff grade – the most senior one. So, in the UK, an academic whose title is ‘Dr’ is someone who’s got a PhD, but hasn’t been promoted to the highest academic grade, while an academic whose title is ‘Professor’ is someone who probably (but not necessarily) has a PhD, but who has been promoted to the highest grade on the university pay scale. Professorship therefore denotes seniority and status. If we make a comparison with medical doctors working in a hospital, all will have medical degrees, but they are employed at different levels of seniority, with consultants being the most senior doctors. We may think of professors as the equivalent of hospital consultants.
On this website the UK interpretation of ‘professor’, ‘professorship’ and the ‘professoriate’ apply.
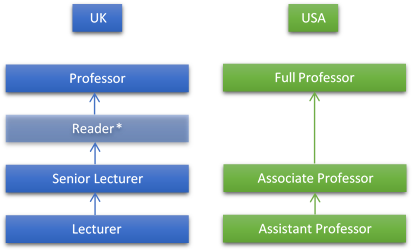
Main academic grades in the UK, shown alongside the North American equivalents (* some universities do not use the reader grade).
This diagram represents the core grading system used in most UK universities. Some UK universities have adopted North American nomenclature, but in such contexts the title ‘professor’ remains reserved, for the most part, to denoting only the most senior grade; associate and assistant professors tend not to be referred to or addressed as professors.
Academic grading systems used in the UK’s post-1992 university sector may include additional grades, such as principal lecturer.
How do people get to be professors?
In several European countries – such as France, Germany and, more recently, Italy – an academic who wishes to be promoted to a professorship must first write a lengthy academic document that indicates what contribution s/he has made to knowledge, through her or his research. The document is similar in length and nature to a PhD thesis, and its quality is judged by a panel of professors who are experts in the applicant’s research field. This process of seeking approval from the academic community of one’s academic credentials for professorship is called habilitation . If the panel judges the academic to be worthy of professorship, s/he is then eligible to apply for vacant professorships, but is not guaranteed to be appointed to one.
In the UK promotion to professorship doesn’t depend upon habilitation . Each university has its own policy on promotions at any level, and decides whom it promotes or appoints to professorship, against its own criteria, and academics who wish to be considered for promotion must submit an application that indicates how they meet the university’s criteria. A different route to professorship in the UK involves academics simply applying for any vacant professorships that are advertised, and undergoing the selection process.
What proportion of university academics are professors?
In the UK, around one in ten university academics is a professor. Data provided by the UK’s Higher Education Statistics Agency numbers professors employed in UK higher education institutions in 2015-2016 at 19,975, representing 9.9% of all academic staff. The UK-based professoriate suffers from gender imbalance; of the 19,970 academics who, in 2015-16 were categorised by their institutions as professors, only 4,775 are recorded as female.
PhD, Professor, and Postdoc Salaries in the United States
The United States is home to several of the world’s best universities making it a top destination for international researchers. Here’s a breakdown of the most common American job titles and their associated average annual salaries. All salary statistics in this article are in American Dollars (USD) and are pre-tax.
PhD Student
A Master’s degree is not always required to do a PhD in the US. Several top universities offer direct entry PhD programs. An American PhD begins with two to three years of coursework in order to pass qualifying exams. During this time doctoral students are able to develop their research interests and hone in on their thesis topic. They will then write a thesis proposal which must be approved before they can start their dissertation. Most programs require PhD students to gain two to three years of teaching experience as well, either by leading their own class or as teaching assistants for a professor. It takes an average of six years to earn a PhD in the US.
Unlike some European countries, there is no mandated minimum salary or national salary scale for PhD students in the US. PhD students ear n between $ 15,000 and $30,000 a year depending on their institution, field of study, and location. This stipend can be tax-free (if it is a fellowship award) or taxable (if it is a salary e.g from a teaching position). American PhD students are usually only paid for nine months of the year but many programs offer summer funding opportunities. A PhD funding package will also include a full or partial tuition waiver.
After earning a PhD, many researchers go on to a postdoc. A postdoc is a continuation of the researcher’s training that allows them to further specialize in a particular field and learn new techniques. Postdoc positions are usually two to three years and it is not unusual to do more than one postdoc. There is no limit on the number of years you can be a postdoc in the US. The average salary (2023 ) for postdocs in the US is $61,143 per year.
A lecturer is a non-tenure-track teaching position. They often have a higher teaching load than tenure track-faculty and no research obligations. These positions are more common in the humanities or as foreign language instructors. Lecturers hold advanced degrees, though not always PhDs. The average salary for a full time lecturer in 2021-2022 according to the American Association of University Professors was $69,499.
Assistant Professor
This is the start of the tenure track. An assistant professor is responsible for teaching, research, and service to the institution (committee membership). Assistant professors typically teach two to four courses per semester while also supervising graduate students. They are also expected to be active researchers and publish books, monographs, papers, and journal articles to meet their tenure requirements. The average salary for assistant professors in 2021-2022 was $85,063 according to the American Association of University Professors .
Associate Professor
An assistant professor who has been granted tenure is then promoted to an associate professor. An associate professor often has a national reputation and is involved in service activities beyond their university. The average salary for associate professors in 2021-2022 was $97,734 according to the American Association of University Professors .
This is the final destination of the tenure track. Five to seven years after receiving tenure, associate professors go through another review. If they are successful, they are promoted to the rank of professor (sometimes called full professor). Professors usually have a record of accomplishment that has established them as an international or national leader in their field. The average salary for professors in 2021-2022 according to the American Association of University Professors was $143,823.
Discover related jobs
Discover similar employers
Accelerate your academic career
Why Academics Should Use Twitter
Twitter has a lot of value for academics as a professional social networ...
The 5 Most Important Questions You’ll Be Asked During a PhD Interview
These are the five most important questions you will be asked in a PhD i...
PhD, Postdoc, and Professor Salaries in France
France has a strong academic tradition and is committed to investing in ...
UK Academic Job Titles Explained
What's the difference between a Lecturer and a Reader? Here's a breakdow...
Dutch Academic Job Titles Explained
What's the difference between a universitair docent and a hoogleraar? Wh...
Moving to Belgium to Research or Study
Belgium is a great place to work and study. Here are some practical thin...
Jobs by field
- Electrical Engineering 162
- Machine Learning 154
- Artificial Intelligence 142
- Programming Languages 139
- Molecular Biology 127
- Mechanical Engineering 124
- Cell Biology 113
- Materials Engineering 103
- Materials Chemistry 101
- Electronics 97
Jobs by type
- Postdoc 336
- Assistant / Associate Professor 141
- Researcher 115
- Professor 110
- Research assistant 88
- Lecturer / Senior Lecturer 68
- Engineer 67
- Management / Leadership 51
- Tenure Track 47
Jobs by country
- Belgium 282
- Netherlands 165
- Morocco 112
- Switzerland 110
- Luxembourg 56
Jobs by employer
- KU Leuven 119
- Mohammed VI Polytechnic Unive... 112
- KTH Royal Institute of Techno... 69
- Ghent University 67
- ETH Zürich 57
- University of Luxembourg 55
- University of Twente 45
- Eindhoven University of Techn... 43
- Manchester Metropolitan Unive... 31
This website uses cookies
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Computers and Electronics
- Online Communications
How to Address a PhD in Email
Last Updated: May 12, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Shannon O'Brien, MA, EdM and by wikiHow staff writer, Eric McClure . Shannon O'Brien is the Founder and Principal Advisor of Whole U. (a career and life strategy consultancy based in Boston, MA). Through advising, workshops and e-learning Whole U. empowers people to pursue their life's work and live a balanced, purposeful life. Shannon has been ranked as the #1 Career Coach and #1 Life Coach in Boston, MA by Yelp reviewers. She has been featured on Boston.com, Boldfacers, and the UR Business Network. She received a Master's of Technology, Innovation, & Education from Harvard University. There are 8 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 54,443 times.
Writing an email to a college professor with a Ph.D.? Do you call someone with a Ph.D. a doctor? Figuring out the right way to address someone with a doctorate is a lot easier than it may seem, and we’re going to break this down so that you can get it right. In this article, we’ll walk you through everything you need to know about how to address someone with a Ph.D.
Do you address someone with a Ph.D. as a doctor?

How to Address an Email to Multiple Professors

- “Dear Professor Jones, Professor Smith, and Professor Ali.”
- “Dr. Jones, Dr. Smith, and Professor Ali,”
- “Dr. Jones and Professor Smith,”
What is the proper way to write a name with Ph.D.?

- You may have seen Ph.D. holders put “Ph.D.” at the end of their name. This is something authors do, but you shouldn’t need to write it this way.
Do you call a professor a doctor?

- You’re very unlikely to get into any trouble by referring to your college teacher as “professor,” even if they are a doctor. At worst, they’ll kindly correct you.
- In the United States, it is generally seen by most educators as socially acceptable to address a doctor who is also a professor as “professor.” It’s not technically correct, but you’re unlikely to offend any of your educators. As such, you can usually call a doctor a professor or Dr. in email. [4] X Research source
How do you address Ph.D. students?

- A Ph.D. student is not a doctor yet, but they may still be a professor.
- “Professor” traditionally refers to tenure-track educators at the collegiate level, but there’s no harm or risk of offense by calling an adjunct instructor, lecturer, or TA, “professor.” [6] X Research source
- “Miss” has historically been used to address unmarried women, while “Mrs.” has referred to married women. These titles are going out of style since many people find them offensive, so you’re best off skipping these.
Do the rules for addressing Ph.D. holders ever change?

- For example, in Canada, you are not “officially” allowed to refer to non-medical doctors as “Dr.” You would address them as “Mr. Jones, Doctor of Mathematics.”
- This also applies to the “Jimmy Jones, Ph.D.” form, too. In the United Kingdom, for example, you don’t use any periods. Someone in the UK would write, “Jimmy Jones, PhD” without the punctuation.
Expert Q&A
- It doesn’t matter if someone has a Ph.D. is in philosophy, education, biology, math, or any other discipline. If a person has obtained a doctorate degree, they’re a doctor—even if they don’t see patients. [8] X Research source Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- Ph.D. is shorthand for doctor of philosophy. The word “doctor” comes from the Latin word “docere,” which means “to teach.” In ancient times, “Philosophy” was used to refer to any academic field. [9] X Research source Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- The only exception, at least in the United States, are people with a law degree (they are technically “Juris Doctors”, or J.Ds). You do not use a special title or honorific to address someone with a law degree. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://www.btb.termiumplus.gc.ca/tpv2guides/guides/wrtps/index-fra.html?lang=fra&lettr=indx_catlog_p&page=9e-8ycfVZx-4.html
- ↑ https://www.purdue.edu/advisors/students/email.php
- ↑ https://www.minotstateu.edu/careers/pages/cover-letter-salutation.shtml
- ↑ https://writingcenter.gmu.edu/writing-resources/different-genres/sending-email-to-faculty-and-administrators
- ↑ https://www.universityaffairs.ca/career-advice/career-advice-article/what-should-i-call-my-professor/
- ↑ https://healthenews.mcgill.ca/use-of-dr-doctor-in-quebec-and-updating-your-honorific-in-mcgills-systems/
- ↑ https://www.cmaj.ca/content/re-who-entitled-be-called-doctor
- ↑ https://www.franklin.edu/blog/doctorate-vs-ph-d-what-are-the-differences
About This Article

- Send fan mail to authors
Is this article up to date?

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Level up your tech skills and stay ahead of the curve

How to Properly Address a PhD
By: Author Dr. Patrick Capriola
Posted on Published: February 5, 2021
Honorifics play an important role in the English language. Not only do honorifics signify rank, but they help to convey courtesy and respect. In academia, honorifics are especially important, so it’s vital to address someone correctly. Many people wonder if they should address a PhD as doctor.
You should address a PhD with the honorific term “Doctor,” followed by their name in both spoken and written situations. The term strictly applies to anyone who has obtained a PhD degree, MD (Doctor of Medicine), or JD (Doctor of Law). English derives the honorific “Doctor” from the Latin word docere, which means “to teach,” and it applies to a PhD because they have reached a level where they can teach others.
Honorifics exist across all languages and cultures and are significant when using and understanding a language. Who should have the title of “Doctor” is widely debated by the academic world, revealing just how important honorifics are in modern-day English.
What Is a PhD?
A PhD is also known as a Doctor of Philosophy. A PhD is considered a terminal degree in the academic world, which means that the person has obtained the highest formal degree in a specific field ( source ).
A Doctor of Philosophy is considered to be the traditional doctoral degree. However, over the years, many other types of doctoral degrees have been introduced. Examples of these include the EdD, a Doctor of Education, and DBA, a Doctor of Business ( source ).
Furthermore, a Doctor of Philosophy is considered an academic degree, while other types of doctorates are deemed professional degrees.
If you are considering pursuing a PhD, then you may be interested in exploring this article, “ How to Set and Follow Through on Academic Goals; Examples for Success .”
How and When to Use the Honorific “Dr.”
The honorific “Doctor” or “Dr.” should be used when addressing someone with a PhD, whether via written or verbal correspondence, and it applies to both males and females.
People working towards a PhD, also known as an ABD (All but Dissertation), should not be given the title of “Doctor.” Instead, you should refer to them as “Mr.” or “Ms.” until they have officially completed their PhD.
Undoubtedly, the candidate who has earned their doctorate has worked hard, so it is understandable why they deserve to be addressed correctly.
The Prenominal and Postnominal
When discussing the subject of addressing someone with a PhD, it’s vital to consider the prenominal “Dr.” and the postnominal “PhD.”
Dr . Douglas Ferguson (Dr. is the pronominal)
Douglas Ferguson, PhD (PhD is the postnominal)
When someone earns the title of “Dr.,” they lose the previous honorifics they may have carried, such as “Mr.” or “Ms.”
A postnominal and pronominal are never used together at the same time.
Furthermore, when discussing these terms grammatically, the prenominal is used in the third person, while the postnominal is most often used in the first person. However, this may change depending on the context.
Written
In academic circles, a considerable amount of correspondence is done via email and the written word. If you want to send a letter addressed to someone with a PhD, such as a cover letter, you use the prenominal “Dr.”
When writing in a formal or professional context, you do not need to include the first name.
Dear Dr. Fergsuon, I hope this email finds you well.
In written correspondence, if you are receiving an email from someone with a PhD, they may choose to sign off with either the prenominal or the postnominal.
Regards, Dr . Douglas Ferguson
Regards, Douglas Ferguson, PhD
If you are uncertain, check your previous correspondence with them. Most people will have a footer at the end of their email, which tells you their qualifications.

When addressing a person with a PhD verbally, you never use the postnominal.
Good morning Dr . Ferguson
Dr . Ferguson, I have a question regarding the upcoming exams.
That was an interesting lecture today, Dr . Ferguson.
When Is It “Dr.” and When Is It “Professor?”
Whether to use the term “Dr.” or “Prof.” will depend on several factors. “Professor” is a higher rank than “Dr.”
However, the title only exists within a university context. Someone with a PhD will always hold the title of “Doctor”; however, they would still have to meet other commitments to become a Professor.
It is important to remember that not all those with the title “Professor” have a PhD, so the terms aren’t always exchangeable.
Often the person lecturing you will indicate how they wish to be addressed. They may want you to call them “Dr.” or “Prof.” or even by their first names. However, it is not recommended to call someone by their first name unless requested to do so.
If a person has a doctorate, the general rule is to call them “Dr.,” whether they are lecturing you or not.
When it is appropriate to use the term ‘Professor’ differs from country to country. In America and Canada, anyone lecturing is generally granted the name “Professor” despite factors such as seniority and tenure.
However, in countries such as the UK and Germany, only full-time professors may be called “Professor.”
The list of academic ranks changes from country to country, but we can examine three examples to get a general idea.
United States
- Distinguished, Endowed, or University Professor
- Associate Professor
- Assistant Professor
- Master Instructor
- Senior Instructor
- Lecturer/Research Associate
- Part-time Lecturer
United Kingdom
- Distinguished Professor/Chair
- Full Professor/Reader
- Senior Lecturer/Associate Professor
- Assistant Lecturer/Clinical Lecturer
- Associate Lecturer/Teaching Assistant/Departmental lecturer
South Africa
- Full Professor
- Senior Lecturer
- Junior Lecturer
Honorifics in English
An English honorific refers to a prefix that occurs before a person’s name ( source ). Honorifics are not considered to be positions or titles that can appear without the person’s name, for example, the Queen or the President.
In English, honorifics are also often used to distinguish between males and females. However, some honorifics, such as “Dr.” and “General,” apply to both males and females.
This is because when these honorifics were first used, only males were able to obtain said titles.
Honorifics are an essential part of the English Language and must be used when formally addressing people, whether it be verbal or written.
Who Should Be Called “Doctor”?
In the Canadian Medical Association Journal, Dr. James P. Winter, a professor at the University of Windsor, argues that those with a PhD are the only ones who are entitled to be called “Doctor.”
In his argument, Winter poses some interesting questions concerning the evolution of the word “Doctor” and how it has changed over the last 700 years.
Winter argues that due to inappropriate use, the term “Doctor” has become overused and underappreciated.
Winters stated that in many countries, such as Canada, healthcare professionals who don’t have a medical degree, such as pharmacists, are allowed to call themselves “Doctor.”

Winters looks at the term from both a historical and linguistic point of view to support his argument. As the term “Doctor” is adopted from the Latin word docere, meaning “to teach,” those with the title should be teaching others. He argues that teaching others is not common practice outside of academia.
Furthermore, he argues that the title of “Doctor” originated in the 1300s when it was only used to describe distinguished scholars.
Winter goes on to state that PhDs are the highest degree that anyone can obtain from a university, while many health professionals only achieve undergraduate degrees. He considers MDs to be professional degrees and not truly doctorates.
He concludes that PhDs are the only “real” doctors as dictated by linguists and history. Many academics share Winter’s feelings, with many PhD holders feeling that they have earned the right to be called “Doctor.”
Dr. Fern Riddle, a historian and author, started a debate on Twitter in 2018 when she claimed she wanted only to be referred to only as “Doctor” rather than “Ms.” or “Miss” because she had earned her authority ( source ).
Her opinions received backlash when people called her arrogant and entitled. Yet, many female PhD holders prefer to be called “Doctor.”This is because it illustrates their achievement and status irrespective of whether they are married.
Those in the medical field argue that the term “Doctor” is significant because it makes patients feel at ease. As such, any health professional who is helping someone should be allowed to bear the honorific ( source ).
Who should rightfully be called “Doctor” is a topic that is continuously debated.
The reality is that the term “Doctor” has changed over the years to encompass a much wider circle of people. This includes not only professionals and academics but males and females.
Whatever your perspective, it is clear that the title of “Doctor” is still much sought after and revered, and that is not likely to change anytime soon.
Final Thoughts
Those who have obtained a PhD have done so by working hard and dedicating years of their life to academia. As such, it is important when dealing with someone who has a PhD that you address them correctly.
The term “Doctor” and to whom it is applied is constantly changing from country to country. It remains to be seen who else will be awarded the title in the future and how those who hold the title will react to its evolution.
Universities vs. University’s: Understanding the Difference between Plural and Possessive
Sunday 21st of February 2021
[…] For an article on how to properly address a Ph.D., make sure you read our article on this subject. […]

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The Harvard Ph.D. in Education trains cutting-edge researchers who work across disciplines to generate knowledge and translate discoveries into transformative policy and practice. Offered jointly by the Harvard Graduate School of Education and the Harvard Kenneth C. Griffin Graduate School of Arts and Sciences, the Ph.D. in Education provides ...
Earn a Bachelor's Degree. The first step to becoming a college professor is completing an undergraduate degree in a discipline that interests you. As most postsecondary teaching positions ...
According to NCES, in 2018, 54 percent of instructors at degree-granting post-secondary institutions were adjunct faculty. In many fields, however, there is a surplus of PhD graduates, which makes competition stiff even for adjunct positions. In these fields, a master's-level professor position is rare. 3. Build Real-world Experience in Your ...
The path generally begins with a bachelor's degree and culminates with a master's degree or a doctoral degree, such as a PhD. Whether you're considering different bachelors degrees or are ready to enroll in a PhD program, you can begin your journey toward becoming a professor by researching accredited colleges and universities.
Earn a Doctorate Degree. The most critical step in how to become a professor - earning your doctorate. In addition to required coursework, most programs require a dissertation, which is your own work of original research. It serves as a demonstration of your abilities to add new knowledge to your field, and your abilities to train future ...
Educational requirements for professors can vary by state and institution. If you want to teach part-time as an adjunct professor at a community college, you might only need to obtain your master's degree. On the other hand, if you'd like to teach at a four-year university or college and follow a tenure track, you'll likely need a Ph.D.
For those interested in becoming a professor, the basic college professor requirements are as follows: A doctoral degree in the field you want to teach in. Teaching experience. Professional certification (depending on your field) Publications and prominent academic presence.
A Doctor of Philosophy (PhD, Ph.D., or DPhil; Latin: philosophiae doctor or doctor philosophiae) is the most common degree at the highest academic level, awarded following a course of study and research. The degree is abbreviated PhD and sometimes, especially in the U.S., as Ph.D. It is derived from the Latin Philosophiae Doctor, pronounced as three separate letters (/ p iː eɪ tʃ ˈ d iː ...
Here are nine steps you can take to become a professor: 1. Earn a bachelor's degree. Professors usually need multiple degrees before they can start teaching students, as they're typically experts in a certain subject. This means that most professors start their careers by earning bachelor's degrees.
Academic rank (also scientific rank) is the rank of a scientist or teacher in a college, high school, university or research establishment.The academic ranks indicate relative importance and power of individuals in academia. The academic ranks are specific for each country, there is no worldwide-unified ranking system.Among the common ranks are professor, associate professor (), assistant ...
Individuals with an EdD can become a professor at a college or university, but they typically also have several years of work experience. For instance, a superintendent of a school district may retire and become a professor of education at a university. It is recommended that if your career goal is to become a professor, that you pursue a PhD ...
Use this step-by-step guide to help you become a philosophy professor: 1. Earn a bachelor's degree. Complete a bachelor's degree to help prepare you for a career as a philosophy professor. While not required, a major in philosophy and religious studies can be helpful to learn about related topics and prepare you for further education.
Learn more about whether earning a PhD could benefit your career. A Doctor of Philosophy, often known as a PhD, is a terminal degree —or the highest possible academic degree you can earn in a subject. While PhD programs (or doctorate programs) are often structured to take between four and five years, some graduate students may take longer as ...
The candidates have to adapt to the culture, Ethos, standards, and reputation of the University. Countries like Canada, Australia and the USA and so provide PhD and master courses. Work experience is required to become a Professor abroad. Read More: PhD Abroad. How to Become a Professor in the USA. Studying a PhD course in the USA has its perks.
Students in our PhD programs are encouraged from day one to think of this experience as their first job in business academia—a training ground for a challenging and rewarding career generating rigorous, relevant research that influences practice. Our doctoral students work with faculty and access resources throughout HBS and Harvard University.
MIT Sloan PhD Program graduates lead in their fields and are teaching and producing research at the world's most prestigious universities. Rigorous, discipline-based research is the hallmark of the MIT Sloan PhD Program. The program is committed to educating scholars who will lead in their fields of research—those with outstanding ...
Some people are unclear about how someone known as 'Dr' is different from someone whose title is 'Professor'. 'Dr' denotes someone who has studied for, and been awarded, a PhD, so it denotes an academic qualification: the holder of the highest university degree. It's the equivalent of writing 'PhD' after someone's name.
A PhD is a terminal academic degree students typically pursue when they're interested in an academic or research career. A PhD is the highest possible academic degree a student can obtain. PhD stands for "Doctor of Philosophy," which refers to the immense knowledge a student gains when earning the degree. While you can actually get a PhD in ...
PhD students earn between $15,000 and $30,000 a year depending on their institution, field of study, and location. This stipend can be tax-free (if it is a fellowship award) or taxable (if it is a salary e.g from a teaching position). American PhD students are usually only paid for nine months of the year but many programs offer summer funding ...
The two most common types of graduate degrees are master's and doctoral degrees: A master's is a 1-2 year degree that can prepare you for a multitude of careers. A PhD, or doctoral degree, takes 3-7 years to complete (depending on the country) and prepares you for a career in academic research. A master's is also the necessary first ...
Adress a professor as "doctor" only if they have a Ph.D. You usually need a doctoral degree to be hired as a college professor, so many higher educators are indeed doctors. If you know that a college professor is a doctor, opt for "Dr." instead of "professor" when you address them via email.
Professor Albert Einstein as a professor Occupation Names Professor Occupation type Education, research, teaching Activity sectors Academics Description Competencies Academic knowledge, research, writing journal articles or book chapters, teaching Education required Master's degree, doctoral degree (e.g., PhD), professional degree, or other terminal degree Fields of employment Academics ...
You should address a PhD with the honorific term "Doctor," followed by their name in both spoken and written situations. The term strictly applies to anyone who has obtained a PhD degree, MD (Doctor of Medicine), or JD (Doctor of Law). English derives the honorific "Doctor" from the Latin word docere, which means "to teach," and it ...