Outside USA: +1‑607‑330‑3200

Critical Thinking Cornell Certificate Program
Overview and courses.
Have you ever known a very intelligent person who made a very bad decision?
Critical problem solving is both a discipline and a skill; one that even very smart people can benefit from learning. Careful thought around decisions can help your teams and organizations thrive. And in today’s age of automation, it’s never been a more essential mindset to develop at every level of a company.
In this certificate program, you will practice a disciplined, systematic approach to problem solving. You will learn how to deeply analyze a problem, assess possible solutions and associated risks, and hone your strategic decision-making skills by following a methodology based on tested actions and sound approaches. Whether you’re interested in preparing for a management role or already lead an execution function, you’ll come away better equipped to confidently tackle any decision large or small, make a compelling business case, and apply influence in your organization in a way that creates the optimal conditions for success.
The courses in this certificate program are required to be completed in the order that they appear.
This program includes a year of free access to Symposium! These events feature several days of live, highly participatory virtual Zoom sessions with Cornell faculty and experts to explore the most pressing leadership topics. Symposium events are held several times throughout the year. Once enrolled in your program, you will receive information about upcoming events.
Throughout the year, you may participate in as many sessions as you wish. Attending Symposium sessions is not required to successfully complete the certificate program.
Course list
Problem-solving using evidence and critical thinking.
Have you ever known a very intelligent person who made a very bad decision? If so, you know that having a high IQ does not guarantee that you automatically make critically thoughtful decisions. Critically thoughtful problem-solving is a discipline and a skill—one that allows you to make decisions that are the product of careful thought, and the results of those decisions help your team and organization thrive.
In this course you will practice a disciplined, systematic approach to problem solving that helps ensure that your analysis of a problem is comprehensive, is based on quality, credible evidence, and takes full and fair account of the most probable counterarguments and risks. The result of this technique is a thoroughly defensible assessment of what the problem is, what is causing it, and the most effective plan of action to address it. Finally, you will identify and frame a problem by assessing its context and develop a well-reasoned and implementable solution that addresses the underlying causes.
Making a Convincing Case for Your Solution
When trying to persuade someone, the tendency is to begin in advocacy mode—for example: “Here's something I want you to agree to.” Most people do not react positively to the feeling of being sold something. The usual reaction is to literally or figuratively start backing up. To make a convincing case, it is more effective to engage with the decision maker as a partner in problem-solving. This makes your counterpart feel less like someone is trying to get them to buy something and more like you are working together to bring about an outcome that is desirable to both parties. Begin by asking yourself: “What is the problem you and the decision maker are solving together?”
By the end of this course, you will have learned how to deeply analyze a problem, possible solutions, and the associated risks as well as the most persuasive and efficient ways of presenting your proposal.
You are required to have completed the following course or have equivalent experience before taking this course:
- Solve Problems Using Evidence and Critical Thinking
Strategic Decision Making
The ability to make effective and timely decisions is an essential skill for successful executives. Mastery of this skill influences all aspects of day-to-day operations as well as strategic planning. In this course, developed by Professor Robert Bloomfield, Ph.D. of Cornell University's Johnson Graduate School of Management, you will hone your decision-making skills by following a methodology based on tested actions and sound organizational approaches. You will leave this course better equipped to confidently tackle any decision large or small, and you'll do so in a way that creates the optimal conditions for success.
Navigating Power Relationships
Leaders at every level need to be able to execute on their ideas. In virtually every case, this means that leaders need to be able to persuade others to join in this execution. In order to do so, understanding how to create and utilize power in an organization is critical.
In this course, developed by Professor Glen Dowell, Ph.D., of Cornell University's Johnson Graduate School of Management, students will focus on their personal relationship with power as well as how power works in their organization and social network.
Project Management Institute (PMI ® ) Continuing Certification : Participants who successfully complete this course will receive 6 Professional Development Units (PDUs) from PMI ® . Please contact PMI ® for details about professional project management certification or recertification.
Interpreting the Behavior of Others
Applying strategic influence.
Being able to influence others is the most fundamental characteristic of an effective leader, but many people in positions of power don't know specifically how they are influencing others' behavior in positive directions. They let it happen by chance or use their formal authority—getting people to do things because “the boss said so.” But as leaders gets promoted within their organization, using formal authority becomes less effective as they not only need to influence subordinates, but also peers, external stakeholders, and superiors. In this course, Professor Filipowicz explores the three complementary levels of influence. First, you will explore heuristics, or rules of thumb, that people use in order to make decisions. Next, you will learn how to influence through reciprocity by uncovering what the person you want to influence wants and needs. Lastly, you will learn how to alter the social and physical environment in order to get the change in behavior you want. By the end of this course, you'll have the skills to consistently draw out the desired behaviors from your team and from those around you.
Leadership Symposium LIVE
Symposium sessions feature three days of live, highly interactive virtual Zoom sessions that will explore today’s most pressing topics. The Leadership Symposium offers you a unique opportunity to engage in real-time conversations with peers and experts from the Cornell community and beyond. Using the context of your own experiences, you will take part in reflections and small-group discussions to build on the skills and knowledge you have gained from your courses.
Join us for the next Symposium in which we’ll discuss the ways that leaders across industries have continued engaging their teams over the past two years while pivoting in strategic ways. You will support your coursework by applying your knowledge and experiences to relevant topics for leaders. Throughout this Symposium, you will examine different areas of leadership, including innovation, strategy, and engagement. By participating in relevant and engaging discussions, you will discover a variety of perspectives and build connections with your fellow participants from various industries.
Upcoming Symposium: June 4-6, 2024 from 11am – 1pm ET
- Building a Culture of Collaboration
- Identifying Common Barriers to Performance
- Setting Yourself Up For Successful Buy-in
All sessions are held on Zoom.
Future dates are subject to change. You may participate in as many sessions as you wish. Attending Symposium sessions is not required to successfully complete any certificate program. Once enrolled in your courses, you will receive information about upcoming events. Accessibility accommodations will be available upon request.
How It Works
- View slide #1
- View slide #2
- View slide #3
- View slide #4
- View slide #5
- View slide #6
- View slide #7
- View slide #8
- View slide #9
Faculty Authors

- Certificates Authored
Risa Mish is professor of practice of management at the Johnson Graduate School of Management. She designed and teaches the MBA Core course in Critical and Strategic Thinking, in addition to teaching courses in leadership and serving as faculty co-director of the Johnson Leadership Fellows program.
She has been the recipient of the MBA Core Faculty Teaching Award, selected by the residential program MBA class to honor the teacher who “best fosters learning through lecture, discussion and course work in the required core curriculum”; the Apple Award for Teaching Excellence, selected by the MBA graduating classes to honor a faculty member who “exemplifies outstanding leadership and enduring educational influence”; the “Best Teacher Award”, selected by the graduating class of the Cornell-Tsinghua dual degree MBA/FMBA program offered by Johnson at Cornell and the PBC School of Finance at Tsinghua University; the Stephen Russell Distinguished Teaching Award, selected by the five-year MBA reunion class to honor a faculty member whose “teaching and example have continued to influence graduates five years into their post-MBA careers”; and the Globe Award for Teaching Excellence, selected by the Executive MBA graduating class to honor a faculty member who “demonstrates a command of subject matter and also possesses the creativity, dedication, and enthusiasm essential to meet the unique challenges of an EMBA education.”
Mish serves as a keynote speaker and workshop leader at global, national, and regional conferences for corporations and trade associations in the consumer products, financial services, health care, high tech, media, and manufacturing industries, on a variety of topics, including critical thinking and problem solving, persuasion and influence, and motivating optimal employee performance. Before returning to Cornell, Mish was a partner in the New York City law firm of Collazo Carling & Mish LLP (now Collazo Florentino & Keil LLP), where she represented management clients on a wide range of labor and employment law matters, including defense of employment discrimination claims in federal and state courts and administrative agencies, and in labor arbitrations and negotiations under collective bargaining agreements. Prior to CC&M, Mish was a labor and employment law associate with Simpson Thacher & Bartlett in New York City, where she represented Fortune 500 clients in the financial services, consumer products, and manufacturing industries. She is admitted to practice before the U.S. Supreme Court and state and federal courts in New York and Massachusetts.
Mish is a member of the board of directors of SmithBucklin Corporation, the world’s largest trade association management company, headquartered in Chicago and TheraCare Corporation, headquartered in New York City. She formerly served as a Trustee of the Tompkins County Public Library, Vice Chair of the board of directors of the Community Foundation of Tompkins County, and member of the board of directors of the United Way of Tompkins County.
- Omnichannel Leadership Program
- Corporate Communication
- Intrapreneurship
- Management 360
Critical Thinking
- Performance Leadership
- Executive Leadership
- Change Management

Glen Dowell is an Associate Professor of Management and Organizations at the Johnson Graduate School of Management, Cornell University. He researches in the area of corporate sustainability, with a focus on firm environmental performance. Recent projects have investigated the effect of local demographic factors on changes in pollution levels, the role of corporate merger and acquisition in facilitating changes in facility environmental performance, and the relative influence of financial return and disruption on the commercial adoption of energy savings initiatives.
Professor Dowell’s research has been published in Management Science, Organization Studies, Advances in Strategic Management, Strategic Management Journal, Organization Science, Journal of Management, Industrial and Corporate Change, Journal of Business Ethics, and Administrative Science Quarterly. He is senior editor at Organization Science and co-editor of Strategic Organization, is on the editorial boards of Strategic Management Journal and Administrative Science Quarterly, and represents Cornell on the board of the Alliance for Research in Corporate Sustainability (ARCS). He is also the Division Chair for the Organizations and Natural Environment Division of the Academy of Management.
Professor Dowell teaches Sustainable Global Enterprise and Critical and Strategic Thinking. He is a faculty affiliate for the Center for Sustainable Global Enterprise and a faculty fellow at the Atkinson Center for a Sustainable Future.
- Sustainable Business
- Hotel Management and Owner Relations
- Strategic Healthcare Leadership
- Executive Healthcare Leadership

Since coming to the Johnson Graduate School of Management in 1991, Robert J. Bloomfield has used laboratory experiments to study financial markets and investor behavior. He has also published in all major business disciplines, including finance, accounting, marketing, organizational behavior, and operations research. Professor Bloomfield served as director of the Financial Accounting Standards Research Initiative (FASRI), an activity of the Financial Accounting Standards Board, and is an editor of a special issue of Journal of Accounting Research dedicated to Registered Reports of empirical research. Professor Bloomfield has recently taken on editorship of Journal of Financial Reporting, which is pioneering an innovative editorial process intended to broaden the range of research methods used in accounting, improve the quality of research execution, and encourage the honest reporting of findings.
- Management Accounting for Leaders
- Management Accounting

Allan Filipowicz is clinical professor of management and organizations at the Samuel Curtis Johnson Graduate School of Management at Cornell University. Professor Filipowicz’s research focuses on how emotions drive or impede leadership effectiveness, at both the intrapersonal and interpersonal levels. Within this domain, he studies the relationship between emotions and risky decision making; the influence of humor on both leadership and negotiation effectiveness; the impact of emotional transitions in negotiations; and the relationship between genes, chronotype (morningness–eveningness) and performance. His work has been published in the Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, Journal of Behavioral Decision Making, Journal of Operations Management, International Journal of Forecasting, Creativity Research Journal, Journal of Circadian Rhythms, and Scientific Reports.
Professor Filipowicz teaches Managing and Leading Organizations (recently winning a Best Core Faculty Award), Negotiations, Executive Leadership and Development, Leading Teams, and Critical and Strategic Thinking. He has taught executives across the globe, from Singapore to Europe to the US, with recent clients including Medtronic, Bayer, Google, Pernod Ricard, and Harley-Davidson. Professor Filipowicz received his PhD from Harvard University. He holds an MBA from The Wharton School, an MA in International Affairs from the University of Pennsylvania, and degrees in electrical engineering (MEng, BS) and economics (BA) from Cornell University. His professional experience includes banking (Bankers Trust, New York) and consulting, including running his own boutique consulting firm and four years with The Boston Consulting Group in Paris.
- Adaptive Healthcare Strategy
- Negotiation Mastery
- Psychology of Leadership
Key Course Takeaways
- Respond decisively and consistently when faced with situations that require a decision
- Assess the context of the problem
- Summarize your analysis of the problem
- Analyze potential solutions from multiple perspectives
- Build a compelling business case for your solution
- Improve your ability to exercise influence in your organization and activate your network to achieve goals
- Establish responsibilities and accountabilities to ensure effective follow-through on decisions made

Download a Brochure

What You'll Earn
- Critical Thinking Certificate from Cornell Johnson Graduate School of Management
- 60 Professional Development Hours (6 CEUs)
- 38 Professional Development Units (PDUs) toward PMI recertification
- 30 Professional Development Credits (PDCs) toward SHRM-CP and SHRM-SCP recertification
- 30 Credit hours towards HRCI recertification
Watch the Video
Who should enroll.
- C-level executives, VPs, managers
- Industry leaders with 2-10+ years experience
- Mid-level professionals looking to move into leadership roles
- Engineers and designers leading projects
- Consultants or analysts
- Anyone whose work involves devising, proposing, and defending evidence-based solutions

“eCornell puts you in control of your education entrepreneurship. It allows you to choose what you need to learn and how you need to learn it at the right time.”
Request information now by completing the form below..

Enter your information to get access to a virtual open house with the eCornell team to get your questions answered live.
- ADEA Connect
- Communities
- Career Opportunities
- New Thinking
- ADEA Governance
- House of Delegates
- Board of Directors
- Advisory Committees
- Sections and Special Interest Groups
- Governance Documents and Publications
- Dental Faculty Code of Conduct
- ADEAGies Foundation
- About ADEAGies Foundation
- ADEAGies Newsroom
- Gies Awards
- Press Center
- Strategic Directions
- 2023 Annual Report
- ADEA Membership
- Institutions
- Faculty and Staff
- Individuals
- Corporations
- ADEA Members
- Predoctoral Dental
- Allied Dental
- Nonfederal Advanced Dental
- U.S. Federal Dental
- Students, Residents and Fellows
- Corporate Members
- Member Directory
- Directory of Institutional Members (DIM)
- 5 Questions With
- ADEA Member to Member Recruitment
- Students, Residents, and Fellows
- Information For
- Deans & Program Directors
- Current Students & Residents
- Prospective Students
- Educational Meetings
- Upcoming Events
- 2025 Annual Session & Exhibition
- eLearn Webinars
- Past Events
- Professional Development
- eLearn Micro-credentials
- Leadership Institute
- Leadership Institute Alumni Association (LIAA)
- Faculty Development Programs
- ADEA Scholarships, Awards and Fellowships
- Academic Fellowship
- For Students
- For Dental Educators
- For Leadership Institute Fellows
- Teaching Resources
- ADEA weTeach®
- MedEdPORTAL
Critical Thinking Skills Toolbox
- Resources for Teaching
- Policy Topics
- Task Force Report
- Opioid Epidemic
- Financing Dental Education
- Holistic Review
- Sex-based Health Differences
- Access, Diversity and Inclusion
- ADEA Commission on Change and Innovation in Dental Education
- Tool Resources
- Campus Liaisons
- Policy Resources
- Policy Publications
- Holistic Review Workshops
- Leading Conversations Webinar Series
- Collaborations
- Summer Health Professions Education Program
- Minority Dental Faculty Development Program
- Federal Advocacy
- Dental School Legislators
- Policy Letters and Memos
- Legislative Process
- Federal Advocacy Toolkit
- State Information
- Opioid Abuse
- Tracking Map
- Loan Forgiveness Programs
- State Advocacy Toolkit
- Canadian Information
- Dental Schools
- Provincial Information
- ADEA Advocate
- Books and Guides
- About ADEA Publications
- 2023-24 Official Guide
- Dental School Explorer
- Dental Education Trends
- Ordering Publications
- ADEA Bookstore
- Newsletters
- About ADEA Newsletters
- Bulletin of Dental Education
- Charting Progress
- Subscribe to Newsletter
- Journal of Dental Education
- Subscriptions
- Submissions FAQs
- Data, Analysis and Research
- Educational Institutions
- Applicants, Enrollees and Graduates
- Dental School Seniors
- ADEA AADSAS® (Dental School)
- AADSAS Applicants
- Health Professions Advisors
- Admissions Officers
- ADEA CAAPID® (International Dentists)
- CAAPID Applicants
- Program Finder
- ADEA DHCAS® (Dental Hygiene Programs)
- DHCAS Applicants
- Program Directors
- ADEA PASS® (Advanced Dental Education Programs)
- PASS Applicants
- PASS Evaluators
- DentEd Jobs
- Information For:

- Introduction
- Overview of Critical Thinking Skills
- Teaching Observations
- Avenues for Research
CTS Tools for Faculty and Student Assessment
- Critical Thinking and Assessment
- Conclusions
- Bibliography
- Helpful Links
- Appendix A. Author's Impressions of Vignettes
A number of critical thinking skills inventories and measures have been developed:
Watson-Glaser Critical Thinking Appraisal (WGCTA) Cornell Critical Thinking Test California Critical Thinking Disposition Inventory (CCTDI) California Critical Thinking Skills Test (CCTST) Health Science Reasoning Test (HSRT) Professional Judgment Rating Form (PJRF) Teaching for Thinking Student Course Evaluation Form Holistic Critical Thinking Scoring Rubric Peer Evaluation of Group Presentation Form
Excluding the Watson-Glaser Critical Thinking Appraisal and the Cornell Critical Thinking Test, Facione and Facione developed the critical thinking skills instruments listed above. However, it is important to point out that all of these measures are of questionable utility for dental educators because their content is general rather than dental education specific. (See Critical Thinking and Assessment .)
Table 7. Purposes of Critical Thinking Skills Instruments
Reliability and Validity
Reliability means that individual scores from an instrument should be the same or nearly the same from one administration of the instrument to another. The instrument can be assumed to be free of bias and measurement error (68). Alpha coefficients are often used to report an estimate of internal consistency. Scores of .70 or higher indicate that the instrument has high reliability when the stakes are moderate. Scores of .80 and higher are appropriate when the stakes are high.
Validity means that individual scores from a particular instrument are meaningful, make sense, and allow researchers to draw conclusions from the sample to the population that is being studied (69) Researchers often refer to "content" or "face" validity. Content validity or face validity is the extent to which questions on an instrument are representative of the possible questions that a researcher could ask about that particular content or skills.
Watson-Glaser Critical Thinking Appraisal-FS (WGCTA-FS)
The WGCTA-FS is a 40-item inventory created to replace Forms A and B of the original test, which participants reported was too long.70 This inventory assesses test takers' skills in:
(a) Inference: the extent to which the individual recognizes whether assumptions are clearly stated (b) Recognition of assumptions: whether an individual recognizes whether assumptions are clearly stated (c) Deduction: whether an individual decides if certain conclusions follow the information provided (d) Interpretation: whether an individual considers evidence provided and determines whether generalizations from data are warranted (e) Evaluation of arguments: whether an individual distinguishes strong and relevant arguments from weak and irrelevant arguments
Researchers investigated the reliability and validity of the WGCTA-FS for subjects in academic fields. Participants included 586 university students. Internal consistencies for the total WGCTA-FS among students majoring in psychology, educational psychology, and special education, including undergraduates and graduates, ranged from .74 to .92. The correlations between course grades and total WGCTA-FS scores for all groups ranged from .24 to .62 and were significant at the p < .05 of p < .01. In addition, internal consistency and test-retest reliability for the WGCTA-FS have been measured as .81. The WGCTA-FS was found to be a reliable and valid instrument for measuring critical thinking (71).
Cornell Critical Thinking Test (CCTT)
There are two forms of the CCTT, X and Z. Form X is for students in grades 4-14. Form Z is for advanced and gifted high school students, undergraduate and graduate students, and adults. Reliability estimates for Form Z range from .49 to .87 across the 42 groups who have been tested. Measures of validity were computed in standard conditions, roughly defined as conditions that do not adversely affect test performance. Correlations between Level Z and other measures of critical thinking are about .50.72 The CCTT is reportedly as predictive of graduate school grades as the Graduate Record Exam (GRE), a measure of aptitude, and the Miller Analogies Test, and tends to correlate between .2 and .4.73
California Critical Thinking Disposition Inventory (CCTDI)
Facione and Facione have reported significant relationships between the CCTDI and the CCTST. When faculty focus on critical thinking in planning curriculum development, modest cross-sectional and longitudinal gains have been demonstrated in students' CTS.74 The CCTDI consists of seven subscales and an overall score. The recommended cut-off score for each scale is 40, the suggested target score is 50, and the maximum score is 60. Scores below 40 on a specific scale are weak in that CT disposition, and scores above 50 on a scale are strong in that dispositional aspect. An overall score of 280 shows serious deficiency in disposition toward CT, while an overall score of 350 (while rare) shows across the board strength. The seven subscales are analyticity, self-confidence, inquisitiveness, maturity, open-mindedness, systematicity, and truth seeking (75).
In a study of instructional strategies and their influence on the development of critical thinking among undergraduate nursing students, Tiwari, Lai, and Yuen found that, compared with lecture students, PBL students showed significantly greater improvement in overall CCTDI (p = .0048), Truth seeking (p = .0008), Analyticity (p =.0368) and Critical Thinking Self-confidence (p =.0342) subscales from the first to the second time points; in overall CCTDI (p = .0083), Truth seeking (p= .0090), and Analyticity (p =.0354) subscales from the second to the third time points; and in Truth seeking (p = .0173) and Systematicity (p = .0440) subscales scores from the first to the fourth time points (76). California Critical Thinking Skills Test (CCTST)
Studies have shown the California Critical Thinking Skills Test captured gain scores in students' critical thinking over one quarter or one semester. Multiple health science programs have demonstrated significant gains in students' critical thinking using site-specific curriculum. Studies conducted to control for re-test bias showed no testing effect from pre- to post-test means using two independent groups of CT students. Since behavioral science measures can be impacted by social-desirability bias-the participant's desire to answer in ways that would please the researcher-researchers are urged to have participants take the Marlowe Crowne Social Desirability Scale simultaneously when measuring pre- and post-test changes in critical thinking skills. The CCTST is a 34-item instrument. This test has been correlated with the CCTDI with a sample of 1,557 nursing education students. Results show that, r = .201, and the relationship between the CCTST and the CCTDI is significant at p< .001. Significant relationships between CCTST and other measures including the GRE total, GRE-analytic, GRE-Verbal, GRE-Quantitative, the WGCTA, and the SAT Math and Verbal have also been reported. The two forms of the CCTST, A and B, are considered statistically significant. Depending on the testing, context KR-20 alphas range from .70 to .75. The newest version is CCTST Form 2000, and depending on the testing context, KR-20 alphas range from .78-.84.77
The Health Science Reasoning Test (HSRT)
Items within this inventory cover the domain of CT cognitive skills identified by a Delphi group of experts whose work resulted in the development of the CCTDI and CCTST. This test measures health science undergraduate and graduate students' CTS. Although test items are set in health sciences and clinical practice contexts, test takers are not required to have discipline-specific health sciences knowledge. For this reason, the test may have limited utility in dental education (78).
Preliminary estimates of internal consistency show that overall KR-20 coefficients range from .77 to .83.79 The instrument has moderate reliability on analysis and inference subscales, although the factor loadings appear adequate. The low K-20 coefficients may be result of small sample size, variance in item response, or both (see following table).
Table 8. Estimates of Internal Consistency and Factor Loading by Subscale for HSRT
Professional Judgment Rating Form (PJRF)
The scale consists of two sets of descriptors. The first set relates primarily to the attitudinal (habits of mind) dimension of CT. The second set relates primarily to CTS.
A single rater should know the student well enough to respond to at least 17 or the 20 descriptors with confidence. If not, the validity of the ratings may be questionable. If a single rater is used and ratings over time show some consistency, comparisons between ratings may be used to assess changes. If more than one rater is used, then inter-rater reliability must be established among the raters to yield meaningful results. While the PJRF can be used to assess the effectiveness of training programs for individuals or groups, the evaluation of participants' actual skills are best measured by an objective tool such as the California Critical Thinking Skills Test.
Teaching for Thinking Student Course Evaluation Form
Course evaluations typically ask for responses of "agree" or "disagree" to items focusing on teacher behavior. Typically the questions do not solicit information about student learning. Because contemporary thinking about curriculum is interested in student learning, this form was developed to address differences in pedagogy and subject matter, learning outcomes, student demographics, and course level characteristic of education today. This form also grew out of a "one size fits all" approach to teaching evaluations and a recognition of the limitations of this practice. It offers information about how a particular course enhances student knowledge, sensitivities, and dispositions. The form gives students an opportunity to provide feedback that can be used to improve instruction.
Holistic Critical Thinking Scoring Rubric
This assessment tool uses a four-point classification schema that lists particular opposing reasoning skills for select criteria. One advantage of a rubric is that it offers clearly delineated components and scales for evaluating outcomes. This rubric explains how students' CTS will be evaluated, and it provides a consistent framework for the professor as evaluator. Users can add or delete any of the statements to reflect their institution's effort to measure CT. Like most rubrics, this form is likely to have high face validity since the items tend to be relevant or descriptive of the target concept. This rubric can be used to rate student work or to assess learning outcomes. Experienced evaluators should engage in a process leading to consensus regarding what kinds of things should be classified and in what ways.80 If used improperly or by inexperienced evaluators, unreliable results may occur.
Peer Evaluation of Group Presentation Form
This form offers a common set of criteria to be used by peers and the instructor to evaluate student-led group presentations regarding concepts, analysis of arguments or positions, and conclusions.81 Users have an opportunity to rate the degree to which each component was demonstrated. Open-ended questions give users an opportunity to cite examples of how concepts, the analysis of arguments or positions, and conclusions were demonstrated.
Table 8. Proposed Universal Criteria for Evaluating Students' Critical Thinking Skills
Aside from the use of the above-mentioned assessment tools, Dexter et al. recommended that all schools develop universal criteria for evaluating students' development of critical thinking skills (82).
Their rationale for the proposed criteria is that if faculty give feedback using these criteria, graduates will internalize these skills and use them to monitor their own thinking and practice (see Table 4).

- Application Information
- ADEA GoDental
- ADEA AADSAS
- ADEA CAAPID
- Events & Professional Development
- Scholarships, Awards & Fellowships
- Publications & Data
- Official Guide to Dental Schools
- Data, Analysis & Research
- Follow Us On:
- ADEA Privacy Policy
- Terms of Use
- Website Feedback
- Website Help
- Numerical Reasoning
- Verbal Reasoning
- Inductive Reasoning
- Diagrammatic Reasoning
- Logical Reasoning
- Mechanical Reasoning
- Situational Judgement
- Deductive reasoning
- Critical thinking
- Spatial reasoning
- Error checking
- Verbal comprehension
- Reading comprehension
- Psychometric tests
- Personality test
- In-Tray exercise
- E-Tray exercise
- Group exercise
- Roleplay exercise
- Presentation exercise
- Analysis exercise
- Case study exercise
- Game based assessments
- Competency based assessment
- Strengths based assessment
- Strengths based interview
- Video interview
- Saville Assessment
- Talent Q / Korn Ferry
- Watson Glaser
- Test Partnership
- Clevry (Criterion)
- Criteria Corp
- Aon / Cut-e
- Sova Assessment
- For Practice
- For Business
Watson Glaser Critical Thinking Tests
Complex and challenging critical thinking tests, including the Watson-Glaser, are used mostly by law firms.
Page contents:
About critical thinking tests and how they work, free practice critical thinking tests, the watson glaser critical thinking appraisal, what is measured by a watson glaser critical thinking test, what should i know before taking a watson glaser critical thinking test, major publishers' critical thinking tests, advice for all critical thinking tests, assessmentday's practice tests can help you to prepare for a critical thinking test, one final point, other test publishers.
Updated: 08 September 2022
Critical thinking tests, or critical reasoning tests, are psychometric tests used in recruitment at all levels, graduate, professional and managerial, but predominantly in the legal sector. However, it is not uncommon to find companies in other sectors using critical thinking tests as part of their selection process. This is an intense test, focusing primarily on your analytical, or critical thinking, skills. Some tests are still conducted by paper and pen, but, just like other psychometric tests, critical thinking tests are mostly administered online at home or on a computer at a testing center.
The questions are multiple choice, and these choices and the style of questions are explained in more detail further down the page. The tests will often follow these two common timings:
- 30 questions with a 40 minute time limit
- 80 questions with a 60 minute time limit
Critical Thinking can be defined in many ways and an exact description is disputed, however, most agree on a broad definition of critical thinking, that 'critical thinking involves rational, purposeful, and goal-directed thinking...by using certain cognitive skills and strategies.' An absence or lack of critical thinking skills at times may lead us to believe things which aren't true, because we haven't sufficiently analysed and criticized the information we've received or used this to formulate and independently test our own theories, arguments and ideas. These are all examples of critical thinking skills put into practice. Glaser (An Experiment in the Development of Critical Thinking, 1941) stated that to think critically involved three key parts:
- An attitude of being disposed to consider in a thoughtful way the problems and subjects that come within the range of one's experiences
- Knowledge of the methods of logical inquiry and reasoning
- Some skill in applying those methods
Note: AssessmentDay and its products are not affiliated with Pearson or TalentLens. Our practice tests are for candidates to prepare for the Watson Glaser Critical Thinking Appraisal; we do not sell tests for employers to select candidates.
Free Critical Thinking Test
Here, we have a full critical thinking test for you to practice for free. You can dive straight in and practice the full test (in blue at the bottom), or tackle each individual section one at a time.
All answers and explanations are included at the end of the test, or alternatively you can download the Solutions PDF. Each test has been given a generous time limit.
Critical Thinking Test 1
- 40 questions
Critical Thinking Test 2
Critical thinking test 3, critical thinking test 4.
TalentLens' Watson Glaser Critical Thinking Appraisal (WGCTA) is the most common critical thinking test. You can visit their official site here: Watson Glaser . Most other critical thinking tests are based on the Watson Glaser format. More than 90 years' of experience have led to many modifications and improvements in the test.
The Watson Glaser Critical Thinking Appraisal is widely regarded as a good predictor of work productivity and at identifying candidates with a good potential to become managers and occupy other positions as a senior member of staff. The latest edition of the Watson Glaser Critical Thinking Test has improved its validity, appealed more to businesses by focusing on business-relevant topics, switched to the Item Response Theory (IRT) for its scoring, updated norm groups, and integrated anti-cheat measures by having an online retest, which can be used to validate results.
Developed by Goodwin Watson and Edward Glaser, the Watson Glaser test is favored by law firms , keen to measure people's abilities to reason, reach conclusions and know when leaps in logic have been made. Skills which are required in the legal sector. The questions in each of the 5 sections aims to evaluate the candidate's ability to:
- 1. Arrive at correct inferences
- 2. Identify when an assumption has been made
- 3. Use deductive reasoning
- 4. Reach logical conclusions
- 5. Evaluate the effectiveness of arguments
Did You Know
The most recent revision of the W-GCTA was published in 2011 with notable improvements being better face validity and business-relevant items, scoring based on Item Response Theory (IRT), updated norm groups, and an online retest which can be used to validate a paper and pencil test result.
A Critical thinking tests assesses your ability in 5 key areas mentioned above; assumptions, arguments, deductions, inferences and interpreting information. Often in this order. A short paragraph of text a few sentences long or a single sentence is used as a starting point. This passage will contain information which you will base your answer to the question on. Another sentence is then presented to you and you will be asked to judge something about this sentence based on the information in the short paragraph. The five sections are explained in more detail here:
- Assumptions - You are being asked to state whether the information in the second set of text you are presented is an assumption made in the first paragraph. Quite a tricky concept to get your head around at first. In a nutshell, when people speak or make arguments, there are underlying assumptions in those arguments. Here you are presented with some assumptions and are asked to judge if that is being made in the original statement. For example in the statement "only people earning a high salary can afford a fast car," what's being assumed is that fast cars are expensive because only people who are earning a lot of money can buy one, however, what's not being assumed is that people without high salaries aren't legally allowed to buy a fast car. You are asked to choose whether an assumption has been made or has not been made.
- Arguments - You are presented with an argument, such as "Should college fees be abolished?" Regardless of your own opinions and thoughts on the argument, you are then presented with statements related to this original argument. You are asked to say whether the responses to the original argument of "Should college fees be abolished?" make for strong or weak arguments. Arguments are considered strong if they are related to the topic such as, "Yes, many people who would benefit from a college education do not because they cannot afford it. This hurts the country's economic growth." The argument presented is sound, related to the original question. Compare this with a weak argument, "No, I do not trust people who read a lot of books." It is clear that the second argument bears very little relation to the subject of the abolition of college tuition fees. This is not to say that an argument against the original argument will always be a weak one, or that an argument in favor will always be a strong one. For example, "Yes, I like people that read books," is in favor of the abolition as indicated by "yes," but that person's like or dislike of others that read books isn't related, or hasn't been explained how it's related to removing the fees. Carefully considering what is being said, remove it from your own personal opinions and political views to objectively analyse what someone else has put forward.
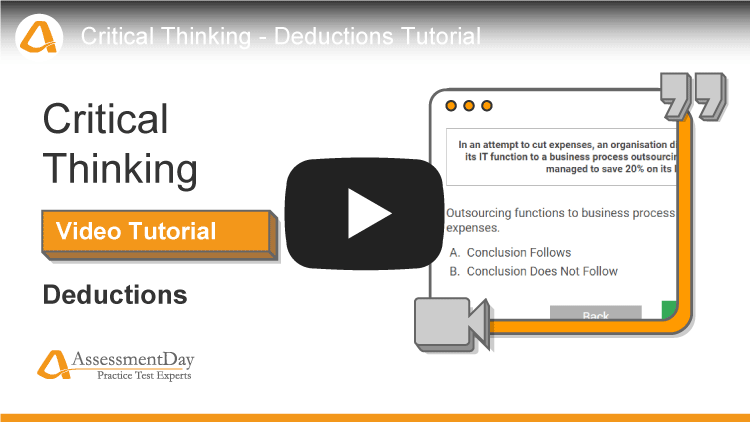
- Deductions - A few sentences of information are presented to you. Another separate short statement will also be shown to you, which is supposed to represent a conclusion that someone has reached. You will have to determine whether this conclusion logically follows from the information given to you. Can the statement be deduced from the information available>? If so, and without a doubt, then the conclusion follows, if not, then the conclusion does not follow. Your decision must be based on the information given and not from your own knowledge.
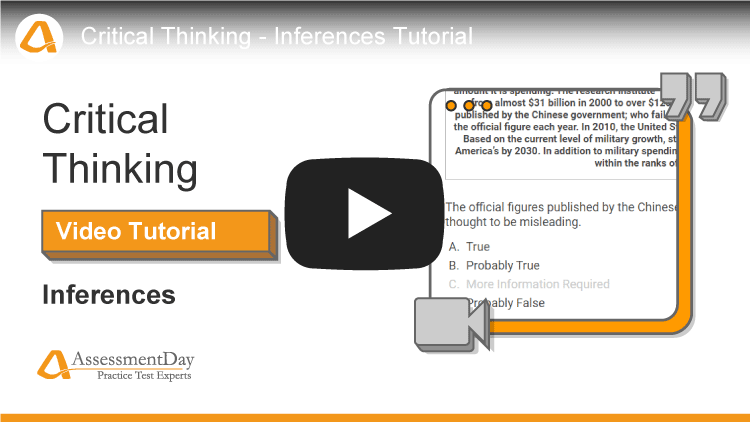
- Inferences - A short scenario is described to you, followed by possible inferences. The inferences are short statements. Imagine that these are what people have said is inferred from the scenario. Use your judgement and the short scenario to assess whether what's being said has actually been inferred from the passage and the likelihood of this inference. You are asked to rank each inference as either 'true,' 'false,' 'possibly true,' 'possibly false.' For some proposed inferences there isn't enough information to say either 'true' or 'false' so a fifth option is included; 'more information required.' You can only select one option from the five.
- Interpreting Information - Following a similar format to the previous four sections, a short passage of information and then a series of statements are shown to you. You are asked to judge whether the information in the passage can be interpreted as the statements suggest. The answer options are straightforward here; you either select 'conclusion follows,' or 'conclusion does not follow,' depending on whether or not you believe that the statement can be logically reached from the information given. Again, for this section and all others, you are to base your choice of answer on what you're given, not on any specialized knowledge you might have.
If a watson glaser critical thinking test is used in the early stages of the application process it's likely to be used as a screening tool. This puts some pressure on candidates to meet a minimum pass mark, which will allow them to be selected to go on to the next stage of the selection process. If it's used at a later stage in the process, the results from this will be combined with performance in other assessments, tests, exercises and interviews. All the information you need to answer the questions will be in the test. Below the details of a few companies' critical thinking tests are pointed out.
Here is a list of critical reasoning tests on the market at present, which candidates may be likely to encounter for recruitment, selection or development.
- W-GCTA - The Watson Glaser Critical Thinking Appraisal as it is formally called is the most ubiquitous critical thinking test out there. This is the one that you are most likely to encounter.
- GMAT - The general management aptitude test, used by business schools and colleges test students' critical thinking ability. The critical thinking questions are written in a business or finance context.
- SHL - SHL have produced the Critical Reasoning Test Battery composed of 60 critical reasoning questions with a strict time limit of 30 minutes.
- Cornell - Cornell have developed a critical thinking test to be used in educational environments. The two levels, X and Z, are aimed at children and adults, respectively.
- Area-specific - There are tests which focus on either numerical critical reasoning skills and verbal critical reasoning skills. These tests will ask only numerical or only verbal questions to assess your skills in a specific area.
Here is some general advice to help you perform to the best of your ability for your critical reasoning test.
- No prior knowledge - The key point here is that critical reasoning tests are measuring your ability to think, or the method that you use to reach a conclusion. You should therefore not rely on prior knowledge to answer the question. Questions will be written so that you do not need to know any specialist knowledge to answer the question. For example, you will not be expected to know mathematical formulas or laws of nature and to answer questions with that information. If you are given the formula and its description in the questions, you are expected to use that information to reach the answer.
- Carefully read the instructions - There are 5 sections to most critical thinking tests and each will assess a slightly different skill. Make sure you have read the instructions and understand what it is you are expected to do to answer the questions for this section. There is quite a difference between the Assumptions section and the Deductions section for example. Applying the rules of one to the other would lead to just guessing the answers and making many mistakes.
- Keep your eye on the timer - These tests are complex. You might find yourself fixated on answering one question and taking up a lot of the time you are allowed. Checking how much time you have every so often can help you to more evenly distribute your time between the questions. This is done to avoid spending too much time on one question when that time would be better spent answering more or checking your answers. This time management applies to all tests, but is particularly important with Critical Thinking tests, as many people believe they have such a large amount of time, but underestimate the number of questions they have to answer.
- Logical fallacies - Identifying logical fallacies is key to many parts of this test, and researching the difference between sound and fallacious logic will prove helpful in a critical reasoning test. A fallacy is an error in reasoning due to a misconception or a presumption, and an argument which employs a formal fallacy, logical fallacy or a deductive fallacy in its reasoning becomes an invalid argument. Researching the different types of fallacy (i.e. red herring argument, straw man argument, confusing correlation and causation etc.) can help you spot these in the test and correctly answer the question.
The practice tests that we have cover all of the sections of the Watson Glaser Critical Thinking test and these overlap with many of the variations in Critical Thinking tests produced by major publishers. practice helps to increase your confidence, gives you a chance to learn from your mistakes in a risk-free environment, and can reduce stress before an exam.
The best place to get advice on taking a critical thinking tests is the test publisher's website, for example this one for the Watson Glaser .
If you have already successfully passed a few initial stages of the application process, it's unlikely that companies will focus solely on your results in the Watson Glaser Critical Thinking test when deciding whether or not to hire you. This type of selection by results on one test is more likely if it is part of the early stages of the process. However, towards the later stages the company will look at your results across interviews, group exercises, other aptitude tests and your résumé and will collate all of this information before reaching a decision. If you have been invited to undertake a critical reasoning test then the organisation clearly has an interest in hiring you, let that fact inspire confidence and perform to the best of your ability on your test, good luck!
You may also be interested in these popular tests sections.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The Test Manual, Booklets, and Specimen Sets are available for purchase at www.CriticalThinking.com. The Cornell Critical Thinking Tests are typically administered in a classroom, and the school will purchase the test. A set of ten individual test booklets costs $29.99, the manual costs $8.99, and licenses can be purchased for $3.99 per test.
Cornell Critical Thinking Test Specimen Set. Grade (s): 4-12+. Cornell sets the standard for all critical thinking tests. This is a test that a parent can administer at home and get a valid score. Specimen set contains two tests, one bubble sheet and an administration manual. Our Price: $19.99.
Cornell Critical Thinking Tests Grades: 5-12+ Critical Thinking, Tests These tests develop a clear picture of your students' critical thinking abilities. They can be used to teach critical thinking skills, to predict students' performance on your state prociency exam, for honors/AP programs, critical thinking courses, college admissions ...
The Critical Thinking Co.™ 800-458-4849 The Cornell Critical Thinking Tests develop a clear picture of critical thinking abilities. The tests can be used to teach critical thinking skills, to predict performance on state proficiency exams or for honors/AP programs.
Cornell critical thinking test. The Cornell critical thinking test was made to test students and first developed in 1985. It is an American system that helps teachers, parents and administrators to confidently predict future performance for college admission, gifted and advanced placement programs, and even career success.
05503GBN. Cornell Critical Thinking Tests Levels X & Z Administration Manual. 5-12+. Paperback Book. $8.99. Add to Cart. The Cornell Critical Thinking Tests develop a clear picture of your students' critical thinking abilities. The tests can be used to teach critical thinking skills, to predict students' performance on your state ...
In this certificate program, you will practice a disciplined, systematic approach to problem solving. You will learn how to deeply analyze a problem, assess possible solutions and associated risks, and hone your strategic decision-making skills by following a methodology based on tested actions and sound approaches.
For a sample of 138 eighth and ninth grade students a principal factors solution of the intercorrelations among 71 items of the Cornell Critical Thinking Test (CCTT), Level X revealed five identifiable dimensions following a varimax rotation: (a) Relevance, (b) Irrelevance, (c) Differentiating Levels of Reliability of Observations or of Authorities, (d) Accuracy of Deduction, and (e ...
An unresolved issue in the measurement of critical thinking is the underlying factor structure of available instruments. The Cornell Critical Thinking Tests Level X (Ennis, Millman, & Tomko, 2005) is a widely used assessment of critical thinking in educational settings for students in grades 4−14. Perhaps due to the scale's intentional complex factor structure with overlapping dimensions ...
Cornell Critical Thinking Test Series THE CORNELL CONDITIONAL-REASONING TEST, FORM X by Robert H. Ennis William L. Gardiner John Guzzetta Richard Morrow ... You will see that you already do some of this kind of thinking. The sample questions make clear what is expected. DO NOT GUESS WlLDLY. There is a scoring penalty for guessing wrong. If you ...
Cornell Critical Thinking Test (CCTT): The CCTT is a multiple-choice test designed to measure critical thinking skills in students from grades 5 through 12, as well as adults. It assesses skills such as induction, deduction, credibility, identification of assumptions, and definition of terms.
© 2005 The Critical Thinking Co. • www.CriticalThinking.com • 800-458-4849 1 MANUAL CORNELL TEST X ANd Z I. INTROdUCTION This-manual-provides-information-concerning-
Follow a regular study schedule. Use quality study materials: text books, flashcards, study guides, practice tests, etc. Highlight key points in your notes. Utilize discussion groups. Take a timed practice test. Tab and highlight for open book tests. Study with friends. Don't study the night before the test. more.
An unresolved issue in the measurement of critical thinking is the underlying factor structure of available instruments. The Cornell Critical Thinking Tests Level X (Ennis, Millman, & Tomko, 2005) is a widely used assessment of critical thinking in educational settings for students in grades 4−14.Perhaps due to the scale's intentional complex factor structure with overlapping dimensions ...
Cornell Critical Thinking Test (CCTT) There are two forms of the CCTT, X and Z. Form X is for students in grades 4-14. Form Z is for advanced and gifted high school students, undergraduate and graduate students, and adults. Reliability estimates for Form Z range from .49 to .87 across the 42 groups who have been tested.
The Cornell Tests still provide probably the best models of what can be done to test critical thinking using multiple-choice questions. Their joint manual is also an excellent model of what such a manual should provide in the way of evidence and cautionary advise.Experience suggests that the Cornell Tests also make excellent teaching materials (students find it very instructive to discuss the ...
The Physics Lab Inventory of Critical thinking (PLIC) is a closed-response survey designed to assess how students critically evaluate experimental methods, data, and models. We define critical thinking as the ways in which you make decisions about what to do and what to trust. In a scientific context, this decision-making is based in evidence ...
Cornell - Cornell have developed a critical thinking test to be used in educational environments. The two levels, X and Z, are aimed at children and adults, respectively. ... AssessmentDay's practice tests can help you to prepare for a Critical Thinking test. The practice tests that we have cover all of the sections of the Watson Glaser ...
An unresolved issue in the measurement of critical thinking is the underlying factor structure of available instruments. The Cornell Critical Thinking Tests Level X (Ennis, Millman, & Tomko, 2005) is a widely used assessment of critical thinking in educational settings for students in grades 4−14.Perhaps due to the scale's intentional complex factor structure with overlapping dimensions ...
Critical thinking tests provide companies valuable insight into the leadership, reasoning, and overall capabilities of candidates. Because strong critical thinking skills are highly sought after, the critical thinking test can be applicable to any field and discipline across multiple levels of expertise from recent graduate to executive.
The Five Critical Thinking Skills Explained. 1. Recognition of Assumption. You'll be presented with a statement. The statement is then followed by several proposed assumptions. When answering, you must work out if an assumption was made or if an assumption was not made in the statement.