An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Perspect Clin Res
- v.2(2); Apr-Jun 2011

Good documentation practice in clinical research
Chitra bargaje.
Department of Clinical Trials and Safety, Global Quality and Regulatory Compliance, Bristol Myers Squibb, Mumbai, India
One of the most common inspection findings in investigator site inspections is lack of reliable, accurate and adequate source documentation. This also happens to be the most common pitfall identified during sponsor audits. The importance of good documentation practice needs to be emphasized to investigator sites to ensure that the study results are built on the foundation of credible and valid data. This article focuses on the key principles of good documentation practice and offers suggestions for improvement.
INTRODUCTION
Inadequate/inaccurate case histories form the second most commonly cited deficiency in US-FDA inspections of clinical investigator sites.
Similarly, source documentation issues ranked 5th among the top 10 findings from European Medicines Agency (EMA) inspections of investigator sites in 2009[ 1 ] and in some instances the findings were classified ‘critical’. Not surprisingly, clinical trial monitors and auditors also report documentation issues as a frequent area of GCP concern.
I would like to share an experience at a recent investigator site audit.
During the audit opening meeting we were informed that all the source data is on paper and no electronic documentation is used. The site was actually using MS word to document the data collected during the study. In normal practice the site did not use MS word to generate medical records. This method was adopted only for clinical trial subjects. For the trial subjects there were no other hand-written progress notes which the site would normally use for routine patients.
There were two underlying potential issues here:
- First, the site was following a different practice for documenting progress for clinical research subjects. Were the subjects’ records missing any elements of standard care because of the deviation from routine practice?
- Second, the site thought they had no electronic documentation, although MS word was used to record all subject data.
This example, illustrates a common occurrence in clinical trial research where a lack of understanding of basic GCP principles may have a negative impact on the quality of the study.
WHAT IS THE PURPOSE OF SOURCE DOCUMENTATION?
To understand the importance of good source documentation we should first review the purpose of source documentation. The most important purpose of source documentation in a clinical trial is to reconstruct the trial as it happened. It should enable an independent observer to reconfirm the data. Documentation should be such that it is able to provide audit trail to permit investigation if and when required.
Source documentation is the medical record of the subject before, during and after the trial.
It is the tool which confirms the eligibility criteria of the subject in the given trial.
It documents the progress of the subject from consenting till the subject completes the study. It records the accountability of the investigational product dispensed, consumed and returned by the subject. It serves as the complete medical record of the subject as the reference to the treating physician at any point of time.
Finally it forms a strong foundation for the data that gets transcribed into a CRF which ultimately gets translated into a clinical study report.
Irrespective of clinical trial, accurate documentation supports the fundamental principle of protecting subject’s rights, safety and well-being.
There can not be two thoughts to emphasize the need for reliable and quality documentation.
PRINCIPLES OF GOOD DOCUMENTATION PRACTICE
So, what does it mean when we say ‘Good Documentation’ and how do we practice it?
Any basic training in clinical research will definitely include these phrases:
‘What is not documented is not done!’
‘Document what is done as well as what is not done!’
Roots of good documentation principles are in the ICH-GCP where source data and source document is first defined.
ICH E6 1.51 source data
All information in original records and certified copies of original records of clinical findings, observations, or other activities in a clinical trial necessary for the reconstruction and evaluation of the trial. Source data are contained in source documents (original records or certified copies).
The words in italics describe some inherent qualities of source data.
ICH E6 1.52 source documents
Original documents, data and records (e.g., hospital records, clinical and office charts, laboratory notes, memoranda, subjects’ diaries or evaluation checklists, pharmacy dispensing records, recorded data from automated instruments, copies or transcriptions certified after verification as being accurate copies, microfiches, photographic negatives, microfilm or magnetic media, X-rays, subject files, and records kept at the pharmacy, at the laboratories and at medico-technical departments involved in the clinical trial).
This definition describes the various types of documents which collectively form the source document.
Key attributes for good documentation were first described by US-FDA in the form of ALCOA -attributable, legible, contemporaneous, original and accurate. These are also adapted by World Health Organization (WHO). These criteria evolved with time. EMA has added some more ‘letters’ to describe qualities of good source documentation particularly for electronic documentation.[ 2 – 4 ]
Let‘s look at these attributes described by different authorities collectively.
Attributable
It should be clear who has documented the data.
Readable and signatures identifiable.
Contemporaneous
The information should be documented in the correct time frame along with the flow of events. If a clinical observation cannot be entered when made, chronology should be recorded. Acceptable amount of delay should be defined and justified.[ 4 ]
Original, if not original should be exact copy; the first record made by the appropriate person. The investigator should have the original source document.
Accurate, consistent and real representation of facts.
Long-lasting and durable.
Available and accessible
Easily available for review of treating physicians and during audits/inspections. The documents should be retrievable in reasonable time.
Complete till that point in time.
Demonstrate the required attributes consistently.
Based on real and reliable facts.
Corroborated
The data should be backed up by evidence.
Interestingly, it should be noted that the Drug Controller General India (DCGI) would emphasize on the condition in addition to the completeness, legibility and accessibility of investigator source data file as noted in DCGI’s guidance document for inspections.[ 5 ] My understanding of ‘condition’ is the state of the source documents, in terms of filing, storing and readability.
The degree to which the data fulfills the data quality criteria establishes acceptability of the data. It also determines the degree of excellence of the data quality. Qualities like consistency, credibility and corroboration help establish data integrity along with the data quality.
These are the expectations from clinical trial documentation however in reality many issues are observed in terms of quality of source documentation.
COMMON FINDINGS WITH RESPECT TO SOURCE DOCUMENTATION
‘Failure to maintain adequate and accurate case histories that record all observations and other data pertinent to the investigation on each individual administered the investigational drug or employed as a control in the investigation’ is cited in 6 out of the 10 warning letters issued by US-FDA to clinical investigators in 2010.[ 6 ]
At one investigator site source documents were not available because the computer ‘crashed’ . So in the absence of availability, adequacy of the records could not be evaluated. The investigator was warned for ‘failure to retain records required to be maintained for the required timeframe per regulations’ .
I would like to highlight some of the findings from the warning letters in detail here. These findings give an idea of regulatory expectations and lacunae in documentation noted during inspections. I am sure readers would be able to relate to some of these findings with their personal experience.
- Eligibility criteria could not be confirmed. For e.g., (a)IVRS user manual states “Complete call worksheets prior to contacting the IVRS; then file completed worksheets with each subject’s source documentation.” The IVRS worksheets were not kept in the subjects’ files or maintained at the site and as such it could not be confirmed that patients were stratified in the right arm and received the medication they were assigned to. (b) All the items in the exclusion criteria checklist are checked except for the exclusion criterion related to the history of thrombocytopenia, including heparin-induced thrombocytopenia, or a platelet count <100,000 cells/microliter. In the absence of lab report this exclusion criteria could not be confirmed on the basis of the incomplete checklists.
- Multiple records for same data points making it unable to determine which served as the accurate source record, for e.g., multiple versions of visual analog scales completed for same visit with different values.
- Discrepancies in records to confirm primary efficacy endpoint of the study, for e.g., the total administered dose of morphine, as reflected in hospital records was different from the Case Report Form. The primary efficacy endpoint of the protocol was to measure the reduction in the requirement for morphine use in the 24 hours following surgery measured by total morphine usage compared to placebo.
- Clinical significance for out of range lab values not documented on the lab reports or conflicting information found in the source documentation-e.g., significant high glucose value marked as clinically nonsignificant on the lab report although the subject was referred to for primary physician for further follow-up.
- Missing pages from subject interview scales, numerous unexplained corrections months after the initial entries and conflicting information; incorrect subject identifiers, incorrect date e.g., same date on screening visit, visit week 1 and week 4.
- Numerous AEs not reported in CRFs, delays in transcribing data in CRFs, discrepancies between source and the CRF. Lack of timely reporting of AEs in eCRFs jeopardizes subject safety and reliability and integrity of data captured at the site.
- Incorrect/incomplete documentation regarding the disposition of drugs-dates, quantity and use by subjects.
Although some of these issues may appear minor prima facie such as some checkboxes not checked, a lab report not marked for significance for out of range value, some discrepancies in source and CRF, unexplained corrections, these issues point toward lack of understanding of good documentation requirements. For an independent observer such data would fail to provide confidence and assurance of data quality and safety of the subjects enrolled. The data may be deemed unfit for use. All exposure of patients to new drugs and the efforts and time spent by the investigator team would be wasted.
Systematic deficiencies in documentation can lead to questions about the integrity of the data, potentially resulting in health authority decisions to exclude the data from analysis.
In essence, we can definitely say that the quality of documentation can make or break the study at a given site.
WHAT ARE THE POSSIBLE ROOT CAUSES FOR REPEATED DEFICIENCIES IN SOURCE DOCUMENTATION?
Clinical research documentation involves a variety of documents from various sources and is often completed by several people. Thus rendering this process to be complicated and posing challenges to meet requirements. Moreover clinical research happens over a long period of time which adds to the challenge of maintaining continuity in the documentation practice.
Inadequacies in documentation could be the result of lack of training and experience in good understanding of clinical research and documentation requirements. As a result the principal investigator (PI) and staff may continue documentation per the routine medical practice. In India, the documentation in routine medical practice may not be as extensive as what would be expected for clinical research.
Additional unmonitored medical records are discovered at the time of audits/inspections. Such as: Diaries of coordinator, inpatient records of the hospital, electronic records, etc., for the simple reason that the staff does not realize that these form a part of source record. These unmonitored records may have important data which do not find its way to the CRF. This would have an impact on the availability of important information in CRFs. Reliability and integrity of data might me affected as a result.
In many FDA warning letters one can observe that inadequate case histories, consenting or drug disposal records are often attributed to the lack of investigator’s supervision in ensuring compliance. The PI delegates responsibilities to the study team and may not provide adequate time to review the source data due to lack of time or commitment. The study documentation is completely left on the shoulders of study coordinator’s.
Various tools are used for data collection. At times sponsor provides source document worksheets to ensure complete documentation. If these worksheets are not designed accurately to align with the protocol and CRF source data quality is directly impacted. These worksheets are often completed as checkboxes without any additional notes, comments or supporting documents. Source document worksheets sometimes also result in multiple records. The sites continue to maintain the clinical practice routine documentation and worksheets are completed in addition for the study. As such, these worksheets are no longer a primary source and thus no source document.
Workload of the existing staff can be another important reason leading to poor documentation. This may cause errors like source data for one subject entered in another subject record, pages misfiled, use of incorrect consent forms and similar issues.
Study coordinator/PI work with various sponsors/CROs at a time. These different sponsors/CROs communicate different level of expectations regarding source documentation. If the site is not experienced enough and they do not have a standard procedure to follow they may get confused with variations in guidance they receive. This may negatively impact the quality of data.
Certain technical inadequacies may also lead to poor source documentation. For e.g., the ECG machine is old and does not print the date, time and subject identifiers, printer or fax machine does not work. If the fax is not working it may result in not receiving important data i.e., lab reports, data queries, investigational product allocation confirmations, SAE transmission confirmations, etc. Important email correspondence with sponsor/CROs if not printed and archived may get lost.
HOW CAN THE DOCUMENTATION BE IMPROVED?
Based on the various causes noted above, I would like to offer some suggestions to improve the quality of source documentation at sites.
- PI should delegate responsibilities to staff adequately trained in protocol and GCP. Particular training should be provided on ALCOA and other good documentation practice requirements. Medical decisions should be delegated to medically qualified staff. Training of site staff should be repeated at defined frequency. New hires should be adequately trained before trial participation.
- PI should commit for involvement, and supervision throughout the entire duration of the study. There should be an agreed and documented procedure for PI to ensure supervision of the study by meetings with site staff, monitors; review of documentation, timely resolution of medical, ethical or GCP issues. The PI or designated subinvestigators should validate the medical data. The PI should also supervise the work of SMO staff and external facilities if used. In case there are performance issues with SMO staff or external facility PI should immediately inform the supervisor as well as sponsor.
- Site should develop a SOP for good documentation. This SOP should be shared with the sponsor/CRO and agreed upon before the start of the trial. This SOP should address aspects including but not limited to consenting process, verifying eligibility, use of right tools such as diaries, source document worksheets, OPD papers, copies of prescriptions, etc; ways to avoid multiple records and in case of multiple records should define the source for the study, method of corrections, review of safety labs and other reports. Documented procedure at site level should encompass management, maintenance, archival and retrieval of source documentation. Sites should have measures for continuous improvement and maintaining high-quality data. Sites should develop process for quality control.
- Before the trial commences all technical aspects such as for e-CRFs, fax, printers, etc. should be clarified and issues resolved. In case of any difficulties during the trial, sponsor should be informed and back-up plans agreed upon till the issue is resolved. In case when original lab records or investigational records are sent to central location for assessment, process should be in place to ensure a duplicate copy or certified copy is available in the site source records.
- Sponsor/CRO also plays an important role in ensuring quality of source documentation. Sponsor/CRO should ensure PI’s commitment and involvement throughout the study. Sponsor/CRO should assess the site’s documentation practice during pre-study visit and during the study; provide training to the site staff to reinforce expectations. Time spent effectively during pre-study evaluation on source documentation would help a great deal to minimize documentation issues later. The source data and their respective capture methods should be clearly defined prior to trial recruitment i.e. in the protocol or study specific source data agreement.
CONCLUSIONS
Source documentation should demonstrate the ALCOA and other attributes as described by regulatory authorities and GCP. Source documentation related findings are the most commonly cited during inspections and audits. PI’s commitment and involvement in the trial makes a huge difference. Efforts to train the sites, understand the sites practices right from the pre-study visit and continuous monitoring and training would definitely help in improving and maintaining the quality of site source documentation practices.
Ultimately the source document should speak for itself. It should narrate the medical journey of the patient as it happened to an independent observer-an auditor or inspector and thus form a strong foundation for a good clinical research.
Acknowledgments
I would like to thank Jessica Parchman (Group Director) and Kristel Van De Voorde (Director) from Global Quality and Regulatory Compliance, Bristol Myers Squibb for reviewing the article and providing valuable suggestions in shaping this article.
- Skip to main content
- Skip to ChatBot Assistant
- Academic Writing
- What is a Research Paper?
- Steps in Writing a Research Paper
- Critical Reading and Writing
- Punctuation
- Writing Exercises
- ELL/ESL Resources
Documenting Sources
Documenting means showing where you got source information that's not your own. Remember, a research paper blends your ideas with ideas and information from other sources. Documentation shows the reader what ideas are yours and what information and ideas you've taken from a source to support your point of view.
Why Document?
- By correctly documenting, you establish your credibility as a writer and researcher. You're letting your reader know that you've consulted experts whose ideas and information back up your own thoughts and ideas. Consequently, you make your viewpoint or argument more believable.
- When you don't document correctly, your academic integrity can be called into question, because it may seem as though you're passing off others' ideas as your own.
- If you don't document, you could inadvertently plagiarize, which is grounds for dismissal from college.
Academic Integrity
Academic integrity involves not only acknowledging your sources, but also creating your own ideas. Academic integrity, explained in this way, sounds relatively simple. But the particular applications are a bit more tricky. The most common academic integrity problems that most students encounter are these:
- relying too heavily on others' information in a research paper
- relying too heavily on others' words in a paraphrase or summary
- citing and documenting sources incorrectly
- relying too heavily on help from other sources
The most egregious violation of academic integrity is when a student uses a writing assignment for more than one course, or when a student "borrows" a paper and passes it off as his or her own work.
What to Document
The basic rule for documentation is this: Document any specific ideas, opinions, and facts that are not your own. The only thing you don't have to document is common knowledge.
For example: you do have to document the fact that 103 cities in New York state were originally settled by English settlers because this is a specific fact that is not common knowledge. You do not have to document the information that New York state has places named for British cities, since this is common knowledge.
There are two categories of common knowledge:
- information that's known to the general public
- information that is agreed upon by most people in a professional field
Tip: Sometimes common knowledge can be tricky to define. A good rule is this: if in doubt, document.
Can You Document Too Much?
If you find yourself needing to document almost every sentence, then it means you have not thought enough about your topic to develop your own ideas. A paper should not be just a collection of others' ideas and facts. Sources should only support or substantiate your ideas.
Tip: The rule of thumb is that whenever you use information from sources you should comment on the information. Your comment should be approximately the same length as the source itself.
Where to Document
You must identify your sources in two places in your research paper:
- in your paper as you use direct quotations or paraphrases and summaries of ideas and information from the sources you've researched
Citing at the end of the paper: Put your notecards with the source information on them in alphabetical order according to the authors' last names, then follow the correct format for providing the essential source information.
Documenting your sources within the text of your paper: Most current research papers insert the basic source information inside parentheses within the text of the paper either at the end of the sentence, or group of sentences, that contain the source's information.
Tip: Footnotes are out of date.
Merely documenting paraphrases and summaries at the end of paragraphs leaves your reader confused. Does the documentation refer to the last sentence? the whole paragraph? part of a paragraph? So you also need to show where the source's information starts as well as ends. The easiest way to do this is to use a phrase such as "According to Dr. James Watts …" or "Carly Simon maintains that…"
According to the "American Heritage Dictionary," plagiarism means "to steal and use [the ideas and writings of another] as one's own. To appropriate passages or ideas from [another] and use them as one's own."
Plagiarism is a serious offense within the academic community. You plagiarize whether you intend to or not when you don't credit others' ideas within/at the end of your paper. Even though you may have rewritten ideas and information using your own words in a paraphrase or summary, the ideas and information are not yours. You must cite your source.
Read more information about plagiarism .
Need Assistance?
If you would like assistance with any type of writing assignment, learning coaches are available to assist you. Please contact Academic Support by emailing [email protected].
Questions or feedback about SUNY Empire's Writing Support?
Contact us at [email protected] .
Smart Cookies
They're not just in our classes – they help power our website. Cookies and similar tools allow us to better understand the experience of our visitors. By continuing to use this website, you consent to SUNY Empire State University's usage of cookies and similar technologies in accordance with the university's Privacy Notice and Cookies Policy .
Source Documents and Source Data
Study documentation serves as evidence to demonstrate the conduct of the research, the quality of the data collected and the compliance of the Investigator with applicable regulatory and institutional requirements.
One type of study documentation that study teams need to maintain is documentation to support protocol adherence (reference study documentation requirements and OHSP Policy 901: Investigator Responsibilities ).
This type of study documentation should demonstrate:
- that you completed the procedures defined in approved protocol, in the manner defined by the approved protocol; and
- the integrity of the data collected.
This responsibility is typically met through that maintenance of ‘source documents’ and data collection tools (also referred to as case report forms).
Definitions: Source documents and source data
Source documents are ‘ original documents, data and records’ and include documents such as hospital records, laboratory reports, academic records, memoranda, subject diaries, assessment measures, and pharmacy dispensing records. Source data is the information recorded in a source document, such as clinical findings and observations. [1]
examples of source documents and corresponding source data
What’s the difference between a source document and a data collection tool.
Data collection tools (also referred to as Case Report Forms [CRF]) are paper or electronic forms/instruments that are used to facilitate the collection of data. Depending on the nature of the research, you might use a data collection tool to:
A. Record original data, e.g., an investigator measures a subject’s grip strength using a hand dynamometer and records the measurement;
B. Record data that was originally collected for another purpose (outside the context of the research), e.g., a study coordinator records a blood pressure measurement from the medical record; or
C. Record data that was collected for study purposes from another study-specific source, e.g., a research assistant records the total carbohydrate, fat and protein grams consumed by a subject based on what the subject recorded in their the food diary.
Depending on how a data collection tool is used, it may or may not be considered a source document.
In Item A above, where the investigator records the subject’s grip strength, the data collection tool is the original (first) source of documentation of the data. Therefore the data collection tool would also be considered the source document.
Whereas in Items B and C, the data collection tool would not be consider the source because it is not where the data was originally documented (respectively, the medical record and food diary are the source documents).
Why does it matter?
A key attributes of ‘ good’ study documentation , as identified in the ALCOAC standard, is maintaining original documentation (i.e., source documentation). This is because original documentation provides accurate information (accuracy being another key attribute of study documentation), which ultimately effects the precision with which a study team is able to test hypotheses and meet the aims of the research.
Therefore, during the planning phase of the research, study teams need to carefully consider:
- How study procedures will be documented; and
- How the data flows from the subject to the study database.
Generally, it is best practice to consider each data point(s) from each study procedure independently and determine what each corresponding source document is.
Some procedures, by virtue of their conduct, will result in corresponding source documentation–e.g., a blood sample that gets sent to a certified laboratory for analysis will result in a lab report or a survey/assessment form gets completed. The same is true when pre-existing data is collected from routine procedures performed outside the context of the research–e.g., collecting current medications maintained in the medical record or a standardized test score maintained in an academic record.
Some procedures, on the other hand, will require the creation of study-specific records in order to document the conduct of the procedures and resulting data. It is best practice to make maximum use of original source documentation (i.e., documentation that exists by virtue of the conduct of the procedure) and create study-specific documentation only for:
- procedures lacking an original source (e.g., verbal assessments of eligibility criteria, interviews, or other study-specific procedures); or
- to support compliance (e.g., study checklists).
Study teams should also try to avoid unnecessary duplication of documentation (e.g., recording the results from a lab report into additional CRFs and then into an electronic database) when possible in order to avoid transcription and data entry errors. [3]
Additional details
The ‘good’ documentation attributes identified above (original and accurate) are specifically identified as investigator responsibilities related to the maintenance of study records in guidance applicable to research regulated by the Food & Drug Administration (FDA). FDA (2018) and International Council for Harmonization (ICH) Good Clinical Practice (2016) guidance specifically states:
- “The investigator/institution should maintain adequate and accurate source documents and trial records that include all pertinent observations on each of the site’s trial subjects. Source data should be attributable, legible, contemporaneous, original, accurate, and complete…” (Section 4.9.0)
- “Data reported on the CRF, that are derived from source documents, should be consistent with the source documents or the discrepancies should be explained.” (Section 4.9.2)
- “When a copy is used to replace an original document (e.g., source documents, CRF), the copy should fulfill the requirements for certified copies .” (Section 8.1) [1,2]
This means that Investigators conducting FDA-regulated research should ensure that source documents (inclusive of data collection tools or CRFs that act as source documentation as well as any other type of source document–e.g., components of a medical record and subject-completed measures/diaries) should be maintained by the site. Doing so validates the existence of the subject and the integrity of the data.
The FDA’s Bioresearch Monitoring Program (BIMO) Compliance Program Manual for Clinical Investigators and Sponsor-Investigators (i.e., the FDA inspection site manual) further reinforces this requirement, noting that “when an inspection occurs… it will include a comparison of the data submitted to FDA with source documents…” for the purposes of data verification.
- International Council for Harmonization of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH) – Integrated Addendum to ICH E6(R1): Guideline for Good Clinical Practice E6(R2). (2016, November 9). Retrieved March 30, 2020 from the ICH
- Food & Drug Administration (FDA) Guidance for Industry – E6(R2) Good Clinical Practice: Integrated Addendum to ICH E6(R2). (2018, March). Retrieved March 30, 2020 from the FDA
- Mathieu, M (ed.). (2009, May). Good Clinical Practice: A Question & Answer Reference Guide. Needham, MA: Barnett International.
Related resources
Good documentation practices (gdp), study documentation faqs, study documentation requirements, recorded training sessions.
Archived UR-HRPP Educational Forums are available. To access recordings listed below, follow our Blackboard Self-Enrollment Instructions and enroll in the course titled ‘UR-HRPP Educational Materials’:
- 12/9/2021: Essential Study Documentation – Part 1
- 1/21/2022: Essential Study Documentation – Part 2
Source Documentation
Source Data is defined as all information in original records and certified copies of original records of clinical findings, observations, or other activities (in a clinical investigation) used for the reconstruction and evaluation of the trial. This typically comes down to the first place that a data point is recorded. The Investigator and designated research personnel are responsible for clearly identifying the data and documents that will be maintained as source data and documentation for the research at the start of and throughout the trial.
Source documentation should meet ALCOA-C standards. Source data should be attributable, legible, contemporaneous, original, accurate, and complete.
- A ttributable: It should be obvious who wrote or did what.
- L egible: Can it be read? Never use pencils to record source documents, use dark colored ink. Avoid abbreviations.
- C ontemporaneous: The information should be current and documented in the correct time frame.
- O riginal: Original or a certified copy or a printout from an electronic data source.
- A ccurate: Are conflicting data recorded elsewhere? Content should precisely reflect the event being recorded.
- C omplete: Source documents should be complete and not missing any information.
Source Documents may include: hospital records, subject diaries, pharmacy dispensing lists, test results, x-rays, lab records, etc.
If source documentation is incorrect, incomplete, or otherwise deficient, research personnel may correct and/or complete by making an additional entry or addendum to the source documentation. The late entry must be signed or initialed and dated in present time by the person making the entry.
Research personnel must NOT modify past-dated source documentation in research records in an attempt to resolve deficiencies. Altering past-dated records is potentially fraudulent.
If it is noted in the research record that data are missing and those data are then obtained or found at a later date, study personnel will ensure that its incorporation in the research record is noted. The notation must be signed or initialed and dated.
With Sponsor approval, study personnel may use Case Report Forms (CRFs) as source documents if they were used to initially record data and they accurately represent data collected for the study.

Choosing & Using Sources: A Guide to Academic Research
(48 reviews)
Cheryl Lowry, Ohio State University
Copyright Year: 2016
Publisher: Ohio State University Libraries
Language: English
Formats Available
Conditions of use.
Learn more about reviews.
Reviewed by Elbert Davis, Assistant Professor, Marshall University on 10/24/21
The author does an incredible job in explaining the research process, from choosing a research question to how to search for sources (and citing those sources), and more. There are relevant self-check quizzes throughout the book to check for... read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 5 see less
The author does an incredible job in explaining the research process, from choosing a research question to how to search for sources (and citing those sources), and more. There are relevant self-check quizzes throughout the book to check for understanding, along with other supplemental resources. As the book was published through The Ohio State University, some of the sources are only available to OSU students, but the author makes it clear when this is the case.
Content Accuracy rating: 5
The author did an excellent job with the accuracy of the book, Two specific examples that stood out: taking care to mention that Wikipedia is a great as a starting point, but not as an endpoint for research. Lowry also clearly explained that educational use did not automatically mean fair use, which seems to be an issue with students and faculty alike.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 5
The book should remain relevant in years to come, as academic research seems to follow the same basic pattern. The only issue would be if The Ohio State University changes the links used in the book, although I expect these to be easy to update. The book would still be able to be used without the supplemental links though.
Clarity rating: 5
The book seems to be targeting an introductory audience. Lowry does a great job of breaking down the jargon of academic research into plain English for the beginning researcher.
Consistency rating: 5
I thought the author used approprate terminology for a student learning about academic research.
Modularity rating: 5
The book is designed into specific chapters for the different aspects of choosing a source. While there are specific sections devoted to The Ohio State University library, I would not expect to have any trouble assigning the other chapters in my courses.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 5
The author started at the beginning, with how to design a research question before going into choosing a source, which gave good background knowledge.
Interface rating: 5
The contents of the book were clean and crisp. No distortions were noted. Navigation from the table of contents was easy.
Grammatical Errors rating: 5
No grammatical errors were noted.
Cultural Relevance rating: 5
Nothing offensive was in the book.
I have a difficult time in getting beginning graduate student to understand the different types of sources and fair use. I think using most chapters of this book would help a great deal in that comprehension.
Reviewed by Kelly LeFave, Instructor, Portland Community College on 6/15/21
This student friendly overview of academic research, including a strong focus on information literacy, covers many of the salient points that college level writing and writing for research classes curricula contain, making it a strong choice as a... read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 4 see less
This student friendly overview of academic research, including a strong focus on information literacy, covers many of the salient points that college level writing and writing for research classes curricula contain, making it a strong choice as a comprehensive and useful overview. Chapters include enough depth of coverage to make the leap from information to practice for students; self-directed activities are provided to check knowledge, work through concept applications, and offer more specifics. The book provides an easy-to-navigate Table of Contents, but an Index and Glossary do not seem to be available.
Content Accuracy rating: 4
Some errors appear that a thorough proofread would catch. Some resources may need to be updated since information practices and modes change so quickly; some references and links direct students to OSU information that would not apply to all readers.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 4
The book’s topic – academic research – necessarily demands constant updating given our fast-changing digital landscape and the shifting paradigms we are witnessing for locating and evaluating information in our times. Resources can become obsolete fairly quickly in this environment. The book’s content is largely up-to-date, though a thorough review of linked resources, perhaps annually, would be beneficial. For instance, a video on RSS mentioned a Google feature that looks to be no longer available, though finding alternatives proves simple when searched online. The book’s organization makes updating or replacing linked resources easy, so keeping the content relevant would be straightforward with regular review.
Content is presented in a style engaging for students, using the “you” pronoun address to walk readers through a thinking process that applies and links ideas to practice; this effective approach is used for many of the book’s concepts. The writing strikes a good stylistic balance between engaging the student reader and informing/challenging that same reader by modeling research brainstorming or methods. The style seems appropriate for college level readers and college level curricula. The topic of academic research does include some technical terms at times, but the book’s approach is to define and explain such terms a part of its content.
Stylistically and organizationally, the content is consistent and easy-to-follow. A user begins to anticipate knowledge check activities or “try it out” activities at particular points in each section. The knowledge check quizzes, which are simplified multiple choice questions, seem at odds with the highly contextualized concept explanations in much of the book’s prose; perhaps a different approach to knowledge check quizzing, which as an element can be helpful, would work better.
Modularity rating: 4
Headings and subheadings follow a logical organization and are easy to navigate in the book. Some sections do refer to—and link to—other book sections, but most would work as stand-alone modules. An instructor or course designer could pick and choose sections and adapt them for their own purposes. As a whole, the book remains self-referential to the context of a specific university, which limits the easy adaptation of the book, and perhaps even sections, for faculty and course designers at other educational institutions.
The book’s organization is easy to navigate and coheres with the overall focus on presenting academic research and information literacy in a way that invites students toward a practical and fuller understanding. Topic order makes sense and is organized via headings and subheadings well.
Overall, no significant navigation issues or interface distractions.
A few errors that look like typos remain in the book. Otherwise, grammatical errors are not an issue for readability.
Cultural Relevance rating: 4
A more nuanced and inclusive awareness of cultural relevance and diversity is worth considering for the book. The choice of some example topics, such as school shootings, might be distracting or traumatic for some student populations, while adding more examples that showcase interests or topics related to non-dominant cultural ideas would widen the sense of inclusivity throughout the book. Choices might be contingent on the demographics of the Ohio State University population, but more awareness of this aspect of the book might also make it more appealing as a resource for others to adapt
Reviewed by Nell McCabe, Associate Professor, Berkshire Community College on 6/15/21
This text is very-student friendly and covers all aspects of writing a student research paper, including steps that students frequently overlook such as the value of preliminary research and the different ways to incorporate different kinds of... read more
This text is very-student friendly and covers all aspects of writing a student research paper, including steps that students frequently overlook such as the value of preliminary research and the different ways to incorporate different kinds of information in a paper.
This text provides a well-balanced, research-driven approach to guiding students through the process of writing an academic research paper. Spelling mistakes, flaw grammar and usage, and factual errors are few and far between (as in I didn't find any during the course of this review).
Kinds of sources and the means of evaluating them are broad enough to be long-lasting, but the examples and other supporting details are timely and relevant.
This text uses student-friendly language and avoids jargon and other symptoms of academia run amok, while still maintaining high standards and expectations for students. Connections between the different stages of conducting research and developing an argument are well laid out and clear.
Terms associated with locating, evaluating, and incorporating a range of different kinds of sources are clear and consistent throughout the text.
The chapters do stand alone and I could image someone using bits and pieces or leaving out bits and pieces, but since the text is primarily focused on supporting the needs of a college research throughout the research process, it is hard to image much need for separating it into discrete modules. You could certainly rearrange the order of the chapters too if that worked better for your approach to teaching student research.
The flow of one chapter into the next is well-integrated and smooth. The order of the chapters
I had no issues with the interface; everything worked as expected.
Cultural Relevance rating: 3
The book does not go out of its way to make obviously inclusive examples. Increasing the cultural perspectives represented in the examples would enhance the overall value of this text.
Reviewed by Darci Adolf, Director of Library & Media Services, Oregon Coast Community College on 6/11/21
I found "Choosing and Using Sources" to be quite comprehensive and included the major areas that I cover in my LIB 101 Research skills class. In my class I like to cover each area of Eisenberg's Big6 Research model: Task definition, information... read more
I found "Choosing and Using Sources" to be quite comprehensive and included the major areas that I cover in my LIB 101 Research skills class. In my class I like to cover each area of Eisenberg's Big6 Research model: Task definition, information seeking strategies, location and access, use of information, synthesis, and evaluation. I was pleased to find the subject of synthesis covered under the writing chapter-- many research textbooks leave this out. I did not find anything that talked about Evaluation of the process and product. Also, I would've liked to have seen social justice and equity issues in information publishing and access addressed as a chapter or portion of a chapter. The textbook has a great Table of Contents, but no index.
This textbook seems to contain accurate and error-free content. I spot-checked most of the chapters and didn't find anything I didn't believe to be true, and links weren't broken. Because this book is mostly factual in nature, there aren't areas where an author's opinion was used over facts, and opinions seem to be be appropriate and unbiased. For example, the author remarks on the use of blogs in research: "Blogs – Frequently updated websites that do not necessarily require extensive technical skills and can be published by virtually anyone for no cost to themselves other than the time they devote to content creation." This is a wide-held belief among librarians.
The content appeared to be up-to-date throughout the book. The area that might change the quickest is the types of sources, Chapter 2 in the book. They did a good job including an overview of all of the major source types and should stay relevant for a good period of time. Because they've listed these source types in a single chapter, updates to the text should be fairly straight forward and easy to do without disturbing much of the rest of the book.
Clarity rating: 4
The text was clear to me, a seasoned librarian. But I think there were terms used throughout the textbook that might not be familiar to a student first starting out in library research. So I would add some clarification around some of the language if I were using this textbook for a lower-level class. For example: There are several types of specialized databases listed including: Bibliographic, Full-text, Multimedia, etc. Many first year students wouldn't know those terms, or others such as "circulation, World-cat, discharge, InterLibrary Loan" and so forth.
The text was consistent throughout in terms of terminology and the overall frame. As I mentioned previously, some of the terms might need to be defined for the first-year student, either in-text or in a separate glossary. The framework is well-done, with clear chapters and sections--it was definitely written by those who teach research at the college level.
The textbook has 13 chapters that are again sub-divided into six or more sub-topics. This makes it very easy for an instructor to pick and choose which topics to cover. The thirteen broader subjects makes it easy to use the entire textbook for a term-- or just choose the pieces you want to use. For example, I would use the "Ethical Use and Citing Sources" chapter if I were doing a one-shot in a classroom, but might choose to use most of the chapters for an online class.
The structure was easy to follow. If I were setting it up myself, I'd probably combine the chapters on Ethical Use of Sources (Ethical Use and Citing Sources, Why Cite Sources, and Challenges in Citing Sources) with the chapter on "How to Cite Sources," but it's easier to have them separate and combine them for a class than to have a big block of text that would make it difficult to work through.
The textbook online version was done in Wordpress, and was easy to view and navigate. There were several other choices for students, including a PDF that could be viewed off line. There were charts, graphs, and links throughout that added to the content, but not so much as to be distracting. Any visuals were simple and enough white space was left as to not overwhelm, with colors that were contrasting visually.
I spot-checked throughout the text in each chapter and did not find any grammatical errors.
The textbook seemed to be inclusive of all races, ethnicities, and backgrounds.
Ohio State University has included a lot of links to their own pages, handouts, and resources that would need to be changed or omitted by a new user. For example, they have a handout from the OSU Writing Center, and they link to the OSU World Cat platform. These would need to be changed by the adopter.
Reviewed by Kaia Henrickson, Assistant Professor of Library & Information Science, Information Literacy Librarian, University of Alaska, Southeast on 11/4/20, updated 12/16/20
This text does a good job highlighting the steps in the research process, from formulating a strong research question, to finding and evaluating sources, to incorporating ideas from research into writing, and finally, to citing and using sources... read more
This text does a good job highlighting the steps in the research process, from formulating a strong research question, to finding and evaluating sources, to incorporating ideas from research into writing, and finally, to citing and using sources properly. Each chapter can stand on its own as useful content for a research-based course, or the entire text could be used to walk students through the entire research and writing process. Based on tutorials created for Ohio State University Libraries, some sections, like Chapter 5 on search tools as well as some of the activities, are fairly specific to OSU. Still, much of the text and many of the activities are applicable to all student researchers. This would be a great base text for someone who wanted to remix and add in information from their own university library and student service supports to replace the OSU-focused sections.
The material is accurate overall.
Text content, as well as videos and activities, are fairly current. Sections are small, so making updates should be fairly easy.
While the text is generally clear, there are sections that are a bit cumbersome or wordy. The Evaluating Sources section, especially, seems overly complicated.
References and links to other helpful sections within the text are appropriate and useful. Key concepts and ideas are repeated and built upon as the text progresses.
Each chapter is divided into manageable sections, and there are few sections which require a lot of scrolling. Those that are longer are broken up by subheadings. Embedded video content, visuals, and boxes are used to break up the text for easier reading and more visual appeal.
The text clearly progresses through the steps in the research and writing process from start to finish, but it can also be accessed by section if a particular subtopic is all that is needed. Each chapter stands on its own, as well as being integrated into the whole.
Interface rating: 3
The web version of the text has no paragraph indents or lines of space between paragraphs, which makes it a bit difficult to read, especially when there are longer blocks of text. There are many videos included that only have automatically-created closed captions (and a few with no closed captions available at all). A few of the graphics are blurry, but most visual and audiovisual content is clear and easy to read. With some of the linked activities, it is unclear what to do when you have selected an incorrect answer, and there is not much feedback for students who answer questions incorrectly.
Grammatical Errors rating: 4
There are a few typos and other minor issues here and there in the text. Some of the linked activities have more significant errors.
The text is not culturally insensitive, but it also doesn't present much in the way of diversity in examples or ideas. In addition, there is a noticeable amount content that is focused on Ohio State University resources and students, and this may not be relevant for readers from other universities.
Reviewed by Marybeth Beller, Associate Professor, Marshall University on 3/13/20
The book provides a thorough review of the research process; that said, a professor will have to add discipline-specific information and requirements, such as expected citation practices and research methods. read more
The book provides a thorough review of the research process; that said, a professor will have to add discipline-specific information and requirements, such as expected citation practices and research methods.
I found no errors in the text.
I will use this book for my undergraduate research course as it gives a very good introduction to research, from narrowing the topic to turning questions into hypotheses.
The book is very clear and provides graphs, links and videos for the reader to have additional information as needed.
Each chapter is organized similarly to the others and is written in the same easy-to-follow, technical-free language. It removes any inhibitions a reader might have.
Each chapter section has its own heading and link. The entire book could be assigned or sections of the book could be just as easily assigned. A drop-down table of contents menu allows the reader to move freely between topics.
This guide is beautifully organized for the beginning researcher but can easily be followed through the table of contents for students needed refreshers on particular elements of research.
I found no interface issues at all in navigating the book.
There were no grammatical errors in the text.
I believe the book would be welcomed by a diverse group of people. There is no insensitive language or use of poor examples in the book.
I really enjoyed the organization of the book and that the author takes the time to include links to additional information as well as videos for students who want to spend more time with a particular concept.
Reviewed by Racheal Rothrock, Assistant Professor, Miami University on 2/28/20
The text is comprehensive in its covering of topics related to choosing and using sources, though it does not go into great depth for each topic. Rather this text provides a broad overview around the topic of sources. This text seems to be written... read more
The text is comprehensive in its covering of topics related to choosing and using sources, though it does not go into great depth for each topic. Rather this text provides a broad overview around the topic of sources. This text seems to be written for an upper-level, undergraduate student audience. No glossary is provided.
This information is presented in an unbiased way that informs on the topic rather than presenting a strong bias or slant toward a particular type of source (though, there is cultural bias—see review comments in “cultural” section). The text does provide details on what approaches might be more helpful in certain situations. This provides a balance of usefulness for students trying to determine which sources to use, while also not assigning value to some sources over others or create a hierarchy.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 3
The text demonstrates a current understanding around the topic of sources, taking into account the shift away from paper and toward digital sources. While overall this text should be useful for several years, there are some areas that may require updating (e.g. links, OSU policies or statements, specifics about various citation styles, software options available, copyright laws, etc.). Throughout the text, the authors do depend on examples that are specific to OSU (e.g. a section on “WorldCat@OSU”), and this might provide less useful for non-OSU students.
The text is written with simple language and explanations are given for more technical terminology (e.g. peer-reviewed, quantitative, qualitative, etc.).
Little specialized terminology is used throughout the text, however, the language and terminology used is consistent throughout. The format, structure, and approach the authors use, is also consistent throughout the text and forms a cohesive narrative.
The text is broken up by main topics and then within each topic, subtopics are provided to support the main topic. The length of each subtopic is fairly brief and examples are provided throughout with graphical separation for clarity. While the topics and subtopics support each other, each subtopic could be assigned individually and would maintain usefulness.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 4
Overall, the organization is logical and clear. There are a few topics that might be shifted in their order, but this is not a critical need. For instance, moving the information about copyright closer to the section on ethical use of sources might make sense, but does not overly disrupt the general flow of the text.
There are no significant issues. A fixed bar at the bottom of the screen allows for navigation to pages directly preceding and proceeding the current page and a clickable contents button at the top right side of the page allows further navigation between sections. Overall, visuals do not appear to be distorted, however, many of the visuals are quite large, taking up the majority of the screen, and could be reduced in size without losing effectiveness. Additionally, on pages 9 and 11, a graphic is presented that contains text that is too small to read. While it is not necessary to read the text in the visual in order to understand the lesson of the section, because it is provided, it would be reasonable to make this large enough to be legible.
The text seems to be free of any major grammatical errors.
This text is written from an academic, western cultural perspective that is relevant to the particular topic and audience (i.e. “A guide to academic research”), but does not take into other ontological or epistemological scholarly perspectives (e.g. testimonios or oral histories as significant sources). The visuals and examples do privilege the U.S. and mainstream cultures, such as through a photo of a White woman using her Mac computer in a library, a photo of a football team, an illustration with the U.S. flag in it, an example question of “How has NASA helped America,” an example opinion of “George Clooney is the sexiest actor alive,” etc. The text is not overtly insensitive or offensive, but it also does not appear to take up or address non-dominant perspectives and cultures in any substantive way.
Reviewed by Audrey Besch, Temporary Faculty , East Tennessee State University on 10/31/19
This text is very comprehensive! From choosing sources to the final research project, this book does a wonderful job of providing all the steps. read more
This text is very comprehensive! From choosing sources to the final research project, this book does a wonderful job of providing all the steps.
Information is accurate for the purposes of writing research and using sources.
Up-to-date and relevant, this text does a good job of outlining various types of sources that can be used and the appropriate ways in which to use them.
Very easy to read content that would be great for students, especially those who are just starting the academic writing process for research.
The text remained consistent in it's use of terminology and framework.
Text has an appropriate use of subheadings and includes activity sections that focus on concepts. Material was broken into easy to grasp ways that didn't seem too lengthy.
Content is well organized and in a logical format for the content provided.
Book did not have any navigation issues and all images were appropriately used for content.
To the extent of my knowledge, there were no grammatical errors in this text.
There were no culturally insensitive issues or offensive language in this text that I could find.
Reviewed by Kris Frykman, Community Faculty, Minnesota State University System on 10/18/19
Comprehensive overview, with examples, to punctuate learning. read more
Comprehensive overview, with examples, to punctuate learning.
Clear, accurate process in showcasing academic research.
Appropriate book for researchers of all levels.
Chapter follow-up questions and videos are included to further enhance clarity.
Terminology and examples are included to further make the content accessible for the reader.
The book is divided in sections so that students can study and apply one concept at a time.
Content is clearly organized.
Charts, diagrams, examples, and videos are highlighted to exemplify key contents.
No discernable grammatical errors.
Appropriately culturally sensitive.
Reviewed by TyRee Jenks, Research Librarian & Library Instruction Coordinator, Montana State University - Billings on 7/31/19
The text is very comprehensive and covers all the necessary aspects of information literacy and student research. There is no index or glossary included, but terms are well explained within the text. The extensive coverage of topics, like types... read more
The text is very comprehensive and covers all the necessary aspects of information literacy and student research. There is no index or glossary included, but terms are well explained within the text. The extensive coverage of topics, like types of sources and copyright, was thorough while not being so in-depth as to bore students. The activities, quizzes, and short videos reinforce the concepts covered in the chapters and add interest, however some quizzes would benefit from additional explanation as to why answers are right or wrong.
The content of the text seems to be accurate. Very minor spelling errors and a copy/paste duplicate. No apparent bias.
Content is up to date and relevant for students while being broad enough to be useful for a longer period of time. Updating information would be easy. The text contains a lot of hyperlinks that an instructor would need to stay on top of to keep the links current. In some cases the links were to very reliable sources that will remain stable for a long time (i.e. Purdue OWL) while others are more transient (i.e. YouTube videos).
In general the text is clear, including good explanations of terms and concepts. It contains very little jargon and the prose is accessible. In “The Details Are Tricky” section, the finer points of primary, secondary, or tertiary information could be confusing to students who are trying to comprehend the basics. The author’s inclusion of informative tables with sample responses as well as the blank template for students to use was helpful.
There is consistent use of terminology and layout throughout the text.
The book has good modularity, excellent graphics, and the text and/or activities can easily be used at the point of need in an information literacy class or one that is discipline specific. Chapters can be used individually or rearranged as needed.
Overall the organizational flow worked well, however the chapters on copyright and fair use might make more sense when grouped with the chapters on the ethical use of sources and how to cite sources.
The EPUB and web versions of the text are easy to navigate with a clickable table of contents and left/right arrow navigation at the bottom of each page. Other than some images that could be resized, the formatting lent itself to consistency throughout the text giving students a uniform experience. In some cases the URL links were just written text instead of hyperlinked which was a little inconsistent. Pleasant graphics added value, explained concepts, balanced out the text, and added visual interest. The inclusion of links that lead out to further explanations of concepts (i.e. the peer review process or how to read a scholarly article) are a nice addition.
There are no major grammatical errors that would be distracting to the reader.
The text is applicable to students in all disciplines, and there are no concerns about cultural relevance or insensitivity. The text is heavily OSU centric (i.e. referencing the OSU code of conduct and requiring students to log in to OSU resources for some activities and examples) and requires effort on the part of instructors at other institutions to make the necessary changes making the content applicable at their institution.
With modifications this text could be incorporated into a three credit information literacy course for undergraduates or into other disciplines. The fair use and copyright sections could be useful to instructors as well as students. Could easily integrate with the ACRL Framework. There is some great general information on writing and making an argument that are applicable across disciplines.
Reviewed by Eric Bradley, Research and Instruction Librarian, Goshen College on 5/31/19
The focus of the book is on published sources for college level research and writing. In this area it is comprehensive. It does not address other areas of academic research. read more
The focus of the book is on published sources for college level research and writing. In this area it is comprehensive. It does not address other areas of academic research.
The content is accurate, error-free, and politically neutral. The last piece makes this a excellent source in the current United States political climate.
Content reflects the current realities of the information landscape. Several of the chapters use up-to-date wording that may need to be updated more frequently, but the excellent modularity of the text allows for accommodation.
The book is straight forward and uses contemporary language of the information and academic landscapes.
The text follows a consistent framework throughout the book.
The text is divided in a way to teach across a course. While the text builds upon itself, many of the chapters stand alone well. I have skipped several chapters of the text and it has not caused any disruption with students.
Excellent organization. The text guides the reader step by step through the research process.
Interface rating: 4
The overall interface is strong. The images and charts are excellent, although the use of branded logos in some of the images may become dated.
No grammatical errors noted.
The text is focused on academic research practices for a North American context. While not culturally insensitive or offensive in any way, it does not take into consideration research practices of other cultures.
I use this text as a replacement of Booth et al.’s Craft of Research. Beside the benefits of being a open textbook, this text provides a more relevant guide to finding sources in the current academic environment.
Reviewed by Kathleen Murphy, Coordinator and Assistant Professor of Music Thearpy, Loyola University-New Orleans on 4/30/19
This book includes all relevant information to help students choose appropriate sources for an academic research paper. It clearly defines different types of sources that can be used, and the difference between primary and secondary sources. It... read more
This book includes all relevant information to help students choose appropriate sources for an academic research paper. It clearly defines different types of sources that can be used, and the difference between primary and secondary sources. It gives an overview of how to search various databases, and defines and describes boolean operators. The chapter on ethical uses of sources clearly defines plagiarism and how and when to cite so as to avoid plagiarizing. The chapter on copyright is an excellent addition; that information is not common in many texts related to academic writing. Each chapter contains extra activities students can work on independently to help with understanding and application of the material covered.
Overall, I found the book to be accurate. I did find one error in Chapter 7. In the section titled "Challenges in Citing Sources" the entry labeled "Running out of Time" was repeated. In regards to bias--I did not find the content to be biased; however, the majority of links where students could go to get extra information were connected to Ohio State University. The one notable exception were the links to the Perdue Online Writing Lab.
The content is up-to-date and relevant. Choosing and using sources for an academic paper has not changed much. What has changed is how to access and find the sources to choose and use. This book does a nice job of explaining how to find sources--databases, google scholar, and search engines. My only concern is the frequent suggestion to search Wikipedia. As an academic, I find this a little troubling. To the author's credit, they did not that one should not cite Wikipedia or use information from Wikipedia in an academic paper. I am not able to comment on ease of updating information, as that is a technical issue.
The book is written in clear, accessible language, with limited "jargon." At times I found the writing to be too simple, written more for high school students than college students. Definitions are provided for all relevant terms.
The book is internally consistent. It moves through the process of choosing and using sources in a linear fashion. However, to their credit, the authors note that writing an academic research paper is not always a linear process.
Each chapter is broken up into smaller units that cover a topic relevant to the chapter theme. Sections of this book could be assigned as individual assignments based on areas of difficultly students seem to be having. Alternatively, a professor could develop a class session or two around each of the chapters. These book seems to be very versatile; there are links to previous chapters that readers can click on to refresh their memories.
The topics in the text are presented in a logical and clear way. The book moves through each topic associated with choosing and using sources in sequence that most researchers would follow. The table of contents, with main headings and subtopics provide a step-by-step guide to help undergraduate students through the research process.
There are many links in throughout the book that students can click on to get more information or to practice skills. Navigation back to the main text is a little trickier. Sometimes, clicking on the back arrow will get the reader back to the page s/he was studying before clicking on the hyperlink. More often, however, the back arrow will take the reader back to the Table of Contents, or front cover of the book. Not all the links worked when I went through the book
I did not fine any grammatical or mechanical errors. I think the book is well-written and appropriate for high school students. I think the language may be too simplistic for most college students.
I did not come across anything that was culturally insensitive or offensive in any way.
I think this book is an excellent resource for high school students, and maybe college freshman who need help in choosing and using sources for an academic paper. The book is logical, gives an overview of the process and provides excellent examples and extra activities to enhance learning. I think it also could be used as a self-study guide.
Reviewed by Miguel Valderrama, Adjunct Assistant Professor, New York City College of Technology on 4/7/19
This book is a great resource of all steps needed to be taken in an academic research process. The book's index clearly displays a suggested methodology to follow and makes it easier to comeback for the review of previous chapters. In general the... read more
This book is a great resource of all steps needed to be taken in an academic research process. The book's index clearly displays a suggested methodology to follow and makes it easier to comeback for the review of previous chapters. In general the book is easy to read and every time a new world or a particular terminology related to the topic comes up, it is clearly defined and put into context.
This book collects a series of methodologies that have been proven to be efficient when they are put into use during the process of academic research. These techniques are not only presented and described to the readers, they are also actively used in the various examples, pretty much in every chapter in the book. These techniques may not be the only way a person can start and develop a research process but they are certainly a clear and convenient way to do so for beginners. There may be complex terminology entered to the discussion which may slow down the reading process. However, this is effectively addressed by separated easy to access links; This provide more in detail definitions and exercises from a particular section.
This book is a guide that presents many particularities of research methods and techniques that have been used for long time. These methodologies have been proven to be very effective in academic research. This book not only collects many of these techniques but carefully relate them to new searching tools that are part of the communication era we live in nowadays. This was not the case just couple of decades ago. I anticipate long life to the methodologies presented in this text with years or decades before they could become obsolete. Within this context, the searching tools may keep changing but the methodologies that are used here could keep working efficiently; at least as a way to approach to a research process for an undergrad student.
The author uses a clear and easy way to understand the language and terminology that makes part of a research process. Without getting too deep into technical terminology the book marks clearly words that deserve more understanding and usually provides separate links which connects the reader with a deeper explanation. The text doesn't have very large paragraphs all around which to me allows readers to keep a good and dynamic paste. Links to previous discussed topics presents a quick way to review previous content without loosing the paste.
Consistency rating: 4
Through out the entire text it is consistent that at the beginning of every chapter there's a statement related to what the previous set of contents was, also in several parts of the book this first paragraph makes a point about how this relates to what it is about to be presented in that chapter. This is why several words allusive to the subject of research are reuse constantly in different chapters. This makes lots of sense to me as a way to keep the reader's familiarity with these terms which will also ended up increasing retentivity levels in the subject. Since the book is clearly broken down into steps they all seemed to be well placed in order to present a cohesive structure that guides the process of research.
Academic research it is a process that should be flexible by nature in many ways. Even though some parts of the process could be done simultaneously to others, this will definitely not apply to all of them. This book brings up an interesting way to order this process which even though may look rigid at times it tries to make sure that some parts are developed before others in the research. It is presented that way so that there's enough understanding of the bases before there can be any progression or even conclusions. This is mostly reflected in the techniques that are presented, where some of then have as their main job to detonate creative thinking. For example: the importance of the set of questions that are asked at the beginning is that the answers will be used mostly to clarify the end goals of a research.
This text is organized following a clear and efficient way to develop an academic research process. It is well distributed in chapters that are all connected to each other in one or other way. The book is efficient at establishing this connections, specially at the beginning and end of every chapter where there's mentioning of the previous and following topic's main ideas. This helps readers to keep track with the overall content.
This book presents an excellent graphic approach to expose its content. The electronic version has the really nice feature of having the index accessible at any point of the reading process. This text is full of links that are either deeper explanations of a particular topic or a set of exercises that are directly related to what the reader is learning. If the idea was to present the information in a format that doesn't look congested to the eyes and that it is not distracting the reader from the important ideas, the editors made an excellent job. This book can't be easier to read, follow through and understand.
Besides a couple of punctuation spaces here and then I was not able to perceive any major grammatical errors. The book is well written all around. Punctuation is pretty much excellent and its composition keeps the reader in track with the content effectible.
Particularly the topics used as examples were very diverse in therms of gender allusion, cultural backgrounds and specialized fields. Research is a process that apply to all disciplines and the professionals working in them. This makes the research process a particularly broad one. The book makes efforts to present this idea by using numerous examples that connect with different segments of the population at numerous levels.
This books is an excellent tool available to anyone who wishes to start a serious research process in almost any particular professional area or field, even amateur researchers can benefit from its content. The book was written to merge the topic content with a series of exercises, tests and examples using a cohesive testing dynamic that helps to increase retention. This dynamic becomes the most efficient way to understand what it takes to start a professional research. The steps to follow the process are laid out clearly in this guide and the important things that need to be taking in account during the research process are highlighted and deconstructed to obtain a deeper overall understanding by the reader or researcher. The fact that the reader is being quizzed constantly during the entire book generates a stronger connection with the important subjects and a good way to evaluate the reader's understanding in real time as well. Highly recommended to undergrad and graduate students and perhaps even amateur researchers becoming familiar with the process of research as well.
Reviewed by Cindy Gruwell, Professor/Research Librarian, Minnesota State on 1/11/19
Choosing and Using Sources does a very good job of covering the topic of Academic Research. Each chapter focuses on an aspect of the research process and thoroughly covers the content with easy to read text and examples/activities for student... read more
Choosing and Using Sources does a very good job of covering the topic of Academic Research. Each chapter focuses on an aspect of the research process and thoroughly covers the content with easy to read text and examples/activities for student practice. Most importantly first-year students through seniors should find the content informative and presented in a collegial format.
All of the content is accurate and explained in a manner that is easy to grasp. There are some minor typos in some of the activities, but they do not confuse the reader. The text is bias-free and includes interesting examples that students can relate to.
The overall content is highly relevant and will age very well. Updates would definite be easy to handle and manipulate. By breaking down each chapter into a variety of content areas, readers will be able to focus and review areas of concern.
Having read several print and online texts of a similar nature, it was a pleasure to come across a text that is clean, consistent, and concise. Each topic has an appropriate amount of information to get the point across as well as tips that lead the reader to additional information. The presentation is consistent throughout without any bloating often found in print texts.
The authors of the text did an excellent job of producing an online text that is consistent and easy to use. No tricks that make it difficult to navigate or confusing to read.
One aspect of the text that I especially like is the modularity that allows for the use of a particular chapter or page(s). Too often texts have chapters that make readers feel like there is no end in sight. The concise nature of this work blends extremely well with the modularity of the complete text.
What makes this text easy to adapt is the layout from beginning to end. Each chapter and section scaffolds upon the other which will allow students to build their skills in a natural manner. Knowledge attained will easily transfer from one topic to another as they move through the book.
While I believe that the text is excellent and I have adopted it for my class, I do find myself frustrated by not being able to move from one section to another within a chapter without having to go back to the contents list. This surprised me because most books and tutorials have forward and backward links, especially within chapters.
There are a few grammatical (spelling) errors in several of the exercises, however, they do not interfere or confuse the reader.
This is definitely a professional work that has no cultural issues and is an excellent example of a non-biased text.
While looking for an OER text I was delighted to come across this book. The content and flow fit in with my class content extremely well and is an excellent resources for courses in the liberal arts, general research, and library-centric classes.
Reviewed by Kathy Moss, Clinical Professor, University of Missouri on 11/27/18
The hyperlinks and examples include a wide range of topics that include cooking, surgery, architecture and sports. read more
The hyperlinks and examples include a wide range of topics that include cooking, surgery, architecture and sports.
Credit is given to an editor, production and design specialists, as well as several content contributors. No additional information is provided to support inference regarding author credibility.
The open textbook Choosing & Using Sources: A Guide to Academic Research presented material that is relevant to my current issues course, including Background reading, Developing a complex research question, Classifying sources, and Evaluating sources.
The topics are presented clearly, using an engaging conversational style and frequent tips and activities. A reader who has no background in information science may be hampered by some terms used in the book (e.g., blog, podcast, Wikipedia, browser, database, Gawker, Reddit). The book does give intentional attention to the technology-naïve audience with some skills (Control-F) and topics (brief description of LexisNexis Academic, Lantern Online).
Terms and organizational framework are consistent throughout the text.
I plan to assign particular chapters of this text that are most relevant to my course's goals. The consistency of the text's terminology and organization should permit this reading plan with minimal distraction to the reader.
The information is clearly organized with a contents listing, chapter numbers and section headers. This organization facilitates easy access for learners with a specific interest in a single topic.
The author’s frequent use of hyperlinks invites students to explore topics more in-depth.
I note a few minor typographical errors that did not adversely affect my ability to comprehend the text.
The book includes examples of non-Western sources such as the allAfrica news database. Some of the links and examples are only available to individuals who have accounts with The Ohio State University. Though the book includes examples in audio and video formats, it could be improved by giving specific attention to topics related to accessibility.
The book provides the opportunity for readers to apply the topics by analyzing its frequent examples.
Reviewed by Lori Meier, Associate Professor, East Tennessee State University on 11/8/18
This text is exceedingly comprehensive. It addresses all elements of academic research (i.e. choosing questions, exploring and selecting sources, searching strategies, citation issues, copyright) as well as providing abundant links for student... read more
This text is exceedingly comprehensive. It addresses all elements of academic research (i.e. choosing questions, exploring and selecting sources, searching strategies, citation issues, copyright) as well as providing abundant links for student use. It is lacking an index or glossary - although many concepts are defined in the various chapters.
This book is accurate and comprehensive. I would not hesitate to use this resource with undergraduate or graduate students as a beginning primer for research.
The book is relevant and timely in regards to the various resources and tech tools it mentions (Google Scholar, EndNote, Ref Works). Given the subject matter I suspect that this book will have longevity to users.
The text is clear and provides definitions for jargon/technical terminology that is used. It is very comprehensive which might be a bit intimidating for the first time reader, but all elements needed for cogent research are included and therefore necessary. I appreciate the use of student scenarios as a way to step-by-step show the thinking process of choosing research questions.
Very consistent and thorough.
This text would be ideal for use as single chapters in courses where the content is needed. While the content is crafted with Ohio State University students in mind it is still very relevant for use by students and scholars. I am already thinking how I might use this next semester with an undergraduate honor's thesis student - both as modules to be read but also as a reference source.
The book is organized in a logical manner but spends only a brief amount of time about qualitative and quantitative research as peer-reviewed sources and only gives basic definitions for those two terms. I would perhaps suggest an additional section on qual/quant/mixed methods research methodology and perhaps a quick overview of research methods or samples via discipline. Additionally, a mention of the common IRB process for Human Subject Research might be helpful to those students using academic sources that discuss that process. It is a very clear text and this could be added with just a few pages of information that might be beneficial to students.
Navigation links worked well for me. The book is easy to read and the display features are not troublesome to me.
Grammatically sound.
Appropriate and is accessible to a wide audience.
Reviewed by Kathy Lamb, ELL Specialist/ English Instructor, Miami University on 8/2/18
The text covers most areas of academic research, and has a table of contents but no glossary, which is much needed. Topics are clear and concise, transitioning smoothly from general to more specific, such as “What is a Research Question?” to... read more
The text covers most areas of academic research, and has a table of contents but no glossary, which is much needed. Topics are clear and concise, transitioning smoothly from general to more specific, such as “What is a Research Question?” to “Narrowing Topics” and finding “Related Terms”. Perfect for college freshmen.
The content is accurate, error-free and unbiased.
The source is up-to-date and it would be relatively easy to update information.
The text is easily understand and flows in a clear manner. Ideas and topics progress easily and examples are used to offer context.
Ideas build one upon another and academic vocabulary is repeated throughout.
Some parts of the book seem a little “text heavy”, but overall it is well organized with efficient flow. The embedded links in the text connect earlier concepts
One problematic is that there lacks a glossary. The table of contents is very long, but broken down so that one is able to easily reference topics. Chapters are concise enough to be read in a timely manner and effectively used.
For some of the online activities it was confusing to discern which answers were correct or incorrect. And, after clicking on and completing an activity one must go back to the former page in order to navigate further. On the other hand, being able to access other information about the chapter topics via link is a handy tool.
There are no grammatical errors.
This book is culturally relevant and not offensive or insensitive in any way.
Reviewed by Sara Abrahamson, Faculty, Minneosta West Community and Technical College on 8/2/18
This text is very comprehensive. The complete research process is broken down from start to finish. read more
This text is very comprehensive. The complete research process is broken down from start to finish.
Very accurate information.
The content is very relative to today's researchers and does a fine job of detailing types of sources.
Very easy to read with content that is easily understood by even a first-time researcher.
The content was very consistent and easy to follow because if it.
LOVED the easy of reading because of the small, digestible informational pieces!
The flow of the text was perfect, following the research process from beginning to end.
I enjoyed the hyperlinked Activities, however, they did not all work for me.
No grammatical errors found.
Very culturally unbiased.
Excellent text that I wished I had years ago!
Reviewed by Justin Megahan, Librarian / Associate Professor, Fontbonne University on 6/19/18
The text does a good job covering academic research. There is a table of contents, but I feel like a glossary and index would be helpful for this book. read more
The text does a good job covering academic research. There is a table of contents, but I feel like a glossary and index would be helpful for this book.
The content is accurate. I did not notice any errors.
The content is up-to-date. There are many databases and websites referred to in the text so it is important to check those relevant links on occasion. It would be straightforward to update the text as needed.
The text clearly steps the reader through the research process. The process is discussed in detail over the 13 chapters.
The text is consistent.
The book is modular. Chapters can be rearranged without confusion. The Copyright Chapter is a good example of a component that can be used separately as a supplemental reading in another course.
The book is organized logically. The addition of a glossary and index could help navigation.
The book has images, charts, and videos that are useful. There are quick activity questions that tests the students’ knowledge on the current topic. These activities do link out to OSU’s site so it is important to make sure those links continue to stay active.
The text contains no grammatical errors.
This book does not have cultural concerns.
Many links direct the reader to OSU resources that have restricted access. The discussion of OSU resources and tools needs to be modified to fit the reader’s institutional resources. “ACTIVITY: Quantitative vs. Qualitative” has a link that is no longer working.
Reviewed by Jane Theissen, Reference Librarian/Professor, Fontbonne University on 5/21/18
The research process is explained in detail, from how to develop a research question to where and how to research through the application of copyright, fair use and citation styles. read more
The research process is explained in detail, from how to develop a research question to where and how to research through the application of copyright, fair use and citation styles.
The content is accurate and unbiased. Most of the links, which are plentiful and well placed, are either broken or link to resources at OSU's library, which I could not access. Use of this book would require time to correct this.
The content is stable. Other than updating the links, little would need to be done to use this text.
Very clearly written; jargon is appropriately explained. Self-checks allow students to make sure they understand the material.
Each section logically builds on the previous, and tone is consistent throughout.
The text has a great deal of modularity. Each section is listed in the Table of Contents and covers a few pages or less. There is no index. It is easy to find and move to sections quickly. the structure allows one to pull sections out for other courses (which I have done).
The research process is explained step-by-step with appropriate detail and excellent graphics.
Images, charts, and diagrams serve to explain and support the text. Many seem rather large and I found them a bit distracting. Additionally, there are page breaks in strange places, leaving large blocks of white space on pages while the narrative continued on the next page. This was very confusing. It would also be helpful if the links would open in a new window.
It seemed inclusive where applicable.
This text impressed me as appropriate for high school students or college freshmen.
Reviewed by Laura Heinz, Librarian, Texas Tech University on 3/27/18
This book provides beginning student researchers with a clear and complete path to the research process for class assignments and undergraduate research projects. read more
This book provides beginning student researchers with a clear and complete path to the research process for class assignments and undergraduate research projects.
The content is presented is accurate and in an unbiased manner for students to easily grasp the process and concepts.
This book was written in 2016 and may need some minor updates. The material is presented in a logical manner that leads students through the process as they begin their research. Each chapter can be used independently as the instructor fits the chapters into course content.
This book is easily understood by an undergraduate and doesn't require extra readings or content to be understood. It is concise and clear which will be appreciated by the student as they conduct research.
This book is consistent in it's framework which leads the student to each step logically avoiding confusion or frustration.
The chapters can easily be used independently and refer students to other chapters with supporting information.
The book is written to lead students in a logical manner through the research process. The length of the chapters allows a student to easily read the chapter for that step in their research, apply it and refer to it easily.
The book downloads easily onto a laptop or e-reader. The graphics display nicely on either size screen and enhance the text.
No grammatical errors were noticed.
This book is not culturally insensitive or offensive in any way. Examples used are appropriate.
This book introduces beginning student researchers to the academic research process in a thoughtful and deliberate manner. The books lack of jargon and abbreviations will help international students learn how to better navigate an academic library for research. Instructors in all disciplines should consider this book as an additional textbook for their classes requiring research for assignments, class projects and/or papers.
Reviewed by Hilary Johnson, Learning & Teaching Librarian, The Open University on 3/27/18
The text does not include an index or glossary. However, it covers a complex (and dry) subject in an economical and stimulating fashion. Each reader would learn about the subject from the basic text but the authors have enriched the text by... read more
The text does not include an index or glossary. However, it covers a complex (and dry) subject in an economical and stimulating fashion. Each reader would learn about the subject from the basic text but the authors have enriched the text by embedding audio-visual resources, download-and-keep checklists and formative activities of excellent quality.Chapter 9 'Making an Argument' is particularly strong and complements Chapter 1's analysis of research questions well. It is an excellent resource for undergraduates, post-graduates and beyond, and could also be useful for professionals researching topics to support evidence-based practice protocols.
More tips about applying facets to search results on services like Summon, EDS or Primo would be a useful addiition. I was surprised the authors did not employ language to frame the skill development in the language of 'employability' and life-skills, which might hook readers who are not planning to engage in academic research in the long-term.
The accuracy of the book was excellent, My score would have been 5, except the advice about copyright legislation and fair use is only applicable to students of Ohio State or elsewhere in the USA; so an institution in the Britain, Ireland or Europe would not be able to use or recommend chapters 11 or 12. However, these chapters are well-judged for the intended audience; succinct and comprehensible, where so many guides are too woolly or arcane to be useful to a general readership.
Chapter 1 had a dead link to an audio-visual resource. The explanation of how to use Wikipedia for academic study was nuanced, classic and practical. The explanation of how to use truncation and wildcards were similarly time- (and platform-) proof. There is much current interest in 'fake news' and the manipulation of Facebook and Google algorithms. So it could be timely to add a section on the known issues and some practical strategies to compensate for them.
The authors use excellent, clear English that should be comprehensible to anyone with academic english reading proficiency. My only qualms related to an ambiguous use of the term "poster" (this word has a particular meaning in an academic setting which was not explained) and more extensively around the slightly simplistic and dated language used for the university library catalogue and abstract & indexing databases. One of the activity sheets is structured like a decision-tree and starts with the question "are you working from a database"; with modern resource discovery platforms and other aggregating tools, students may not be able to tell whether they are looking at results from a single database, all the databases from one supplier or multiple databases from a variety of suppliers.
The stylesheet and planning of content is elegant and the quality is consistent throughout the text.
Each chapter is split into useful subsections, with clear formatting to demarcate between topics, tips and activities. The authors have also helpfully embedded hyperlinks to relevant chapters or sections earlier or later in the book.The length of individual subsections is consistent to make reading online easy (balancing scrolling and page turning). However, the length of embedded audio-visual materials varies so a student planning their time might be surprised in places.
The text has a sensible progression of topics, with hyperlinks back and forwards to connect relevant topics. And the final chapter, 'Roles of Research Sources', pulls together the lessons learnt with a useful acronym (BEAM), giving the book a strong ending.
I accessed the text on a variety of browsers, screen sizes and operating systems without any problems with the interface.
I only spotted two minor errors - site instead of cite and White's definition (page 186) without an apostrophe.
Not all the video materials embedded are captioned making them inaccessible to some categories of disabled users.
Reviewed by Lydia Bales, Academic Skills Tutor & Librarian, Staffordshire University on 2/1/18
Considering the book is not overly large, the guide manages to be very through and comprehensive guide to locating sources and using them correctly. It even goes further in giving some great information on making an argument and writing out the... read more
Considering the book is not overly large, the guide manages to be very through and comprehensive guide to locating sources and using them correctly. It even goes further in giving some great information on making an argument and writing out the research. The chapters are in easily digestible chunks covering the process of searching and evaluating resources in a useful and cross-discipline manner. It covers the source search process of research in an easily digestible manner.
The topics are accurate and have been written in a way that they will not date too much. The links and examples of the services provided may need updating to keep them accurate but the nature of the online format makes this easily possible. The Copyright chapter is obviously only applicable to those studying in the US. Having a version of this chapter available discussing copyright law in the UK could be useful any access the course for a different location.
The topics, examples and videos used are relevant and useful and should not date too much. The links and examples of the services provided may need updating to keep them accurate but the nature of the online format makes this easily possible. Some of the examples and links are specific to Ohio State and America and this can limit the relevance for students who do not have the ability to access Ohio State resources or are not based in America. Also the copyright section specfically is obviously only US copyright law limiting it's usefulness for students based in other locations.
The writing style is straightforward and easy to follow. It is sometimes slightly repetitive but overall the information is clearly presented and the vocabulary used is not too advanced. The style is informal and it makes a weighty topic much easier to process. I think it would be useful to have a glossary in the resource for students who maybe have not come across some of the topic specific words before and need them defining.
I was impressed with the consistency considering the work is made up of different author’s contributions. I could not identify different voices within the text, which helped improve the flow of the work. The arrangement of the contents tab is very useful to help navigate to specific sections of chapters as well as the overall chapter.
The layout of the book makes this modular. You can choose which sections to look at in any order and they read clearly and separately well. The other sections are signposted throughout the text and you can link back through to these using the hyperlinks provided. I think the order could be slightly improved by moving the citing and copyright information after the information on argument and writing but because you can choose how to read the book then it is not really an issue. I think it is important to note that if you cannot play the video content or the links in the book are Ohio State Specific the book does lose some of its positive features.
Overall, the structure is straightforward and logical. It flows in a manner that is easy to read and to process. Using the navigation you can work your way through the book in any order you feel is appropriate. As I stated I feel the referencing and copyright information could be in a different place but because you can choose to read this in a different order, it does not really matter.
Having read the online version on both a PC and a tablet I found the interface both easy to use and accessible. The page and chapter length worked well on both platforms and it was easy to access the links and activities contained within the resource. I could not access the videos on the PC due to not having Adobe Flash and it would be useful to have known I would require this to access the resource in its entirety. The video content is a refreshing change to just text and the images used are overall relevant. The videos do not all include a text version and this would be useful for accessibility. A few of them do have this option. Some of the images in the text viewed blurry on my PC and tablet. I am not sure if this was an issue with my own software or an error in the book.
I did not notice any errors during this read through. In some places, the text was a bit repetitive but this not disrupt the flow too drastically.
The examples used are not offensive and are diverse in their range. They have not given examples that define the guide for specific subset of students, which makes it more applicable.
Just for accessibility purposes, I think all the videos need a text version not just some. In addition, the RefWorks program has now been updated and it is called New Refworks with a changed logo and this could be updated in the book along with the guide to setting up Refworks if your institution subscribes. I feel that there are many links that you could not access unless you were an Ohio State user and this could disrupt the flow of the book for some users.
Reviewed by Lori Jacobson, Associate Director, Curriculum Development, William & Mary Writing Resources Center on 2/1/18
The book provides a comprehensive introduction to the use of sources in academic writing. read more
The book provides a comprehensive introduction to the use of sources in academic writing.
The book is a polished, professional and appropriate tool to help students improve their information literacy.
The content is relevant for undergraduate students and their instructors. It focuses primarily on fundamental approaches to finding, evaluating, and deploying sources in order to enter the scholarly conversation. While the authors occasionally mention a specific tool, or insert links to outside sources, these are placed within "Tip" boxes that can easily be updated.
Because this book was created for students at Ohio State University, it is sometimes quite specific about tools or processes that are unique to OSU. Instructors using this book at other institutions may sometimes need to suggest their own's institution's available tools to keep the text relevant for their students.
The book is well-crafted for an undergraduate audience, taking an easy-going, friendly tone and clearly defining key terms and concepts. It is also accessibly structured, making it fairly easy for users to jump between topics, rather than requiring a linear read. Links between related sections are provided wherever it is appropriate.
The book uses a consistent design scheme and structure. Features that appear in each chapter include graphics, tip boxes, examples, activities, and summaries.
Each unit of the text stands on its own and could be easily assigned as an individual reading. Rather than being self-referential, the text will suggest that more information on a related topic can be found in one of the other modules.
The text is organized to flow in roughly the same sequence as a typical research project. Students who are reading the text while working on a project should find individual sections logically presented and relevant. This is clearly not a text designed as background reading; rather it functions best as "just in time" information for students working through the research process.
I found the text quite easy to use in it its online form. It is visually appealing, easy to navigate, and thoughtfully arranged.
I noticed a couple of typos, but no significant grammatical errors.
The examples provided are of broad interest, and most readers will have some familiarity with them. There were no insensitive or offensive comments or examples.
Choosing & Using Sources: A Guide to Academic Research is a practical tool for novice researchers. It asks students to begin the process with a research question, and then provides a step-by-step approach to creating the question. All the other chapters flow from this effective beginning, and should increase students' information literacy by helping them understand types of sources available to researchers, the relationship between sources and information needs, how sources should be evaluated, and how they can be deployed effectively and ethically. Additional chapters on argumentation and copyright round out the book's overall usefulness to students engaged in a research project. This book could be easily paired with a staged research project, and would provide students with the "just-in-time" information they need to successfully complete the assignment.
Reviewed by Kristin Green, Reference and Instruction Librarian, Penn State Worthington Scranton on 2/1/18
The aspects of academic research that are prudent to cover within the first year of any undergraduate student's general education are all covered within this textbook. From an introduction to the ethics of source use to crafting basic Boolean... read more
The aspects of academic research that are prudent to cover within the first year of any undergraduate student's general education are all covered within this textbook. From an introduction to the ethics of source use to crafting basic Boolean search strings, all facets of entering scholarly discourse are addressed in brief chapters that feel modern and accessible. While instructors may wish to supplement or replace some of the exercise sets in the text with their own assessments, the content of the text provides ample coverage if selected to serve as a primary textbook for a foundational information literacy course.
The book is accurate in addressing the current state of the information landscape as encountered in the realm of academic research, as well as the legalities of copyright and fair use.
All content within this book is current and the content within chapters sections are written in a style that today's undergraduate students will be able to learn easily from. Many of the concepts, processes, and principles that are covered in the text have an inherent longevity that will prolong the relevance of this text past its initial publication date. However some chapter sections, tutorials, and videos are institution-specific reducing the overall relevancy of using the entire text at other locations.
The text is written in a clear and concise style that current students will find very accessible. The authors consciously defined any technical terminology or jargon as it was introduced throughout the chapters. Furthermore, the technical concepts that were more complex to define are often accompanied by visuals to help convey what is being defined.
The terminology and format of the book, along with the linked exercise sets and visualizations, provide a solid consistency that will helps students focus on learning the content rather than being bogged down with understanding the textbook format.
Instructors could easily parse different chapters of this book to use for modular instruction, especially in "one-shot" or other limited instructional scenarios. Some of the chapters are a bit self-referential which may generate a minor degree of confusion if used out of the holistic context.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 3
While there is a logical flow to most of the chapters, some seem a little out of place such as the "Making an Argument" chapter. I would have preferred a division of chapters into sections, where the writing-related chapters were separated from the source-related chapters. I also think the chapters that covered Copyright, Fair Use, ethical source use, and citations would have a stronger flow if organized together in their own section.
The ability to navigate through the book from the table of contents page is a great feature for students, especially when the instructor is choosing to assign only particular chapters or work through some of the chapters in a different sequence. The linked exercise sets are also easy to navigate through, allowing students to focusing on applying learned concepts rather than learning new interfaces. However, throughout my review some of the linked external content would not open for me and links to external materials always have the possibility of changing which may result in future inaccessibility
No grammatical errors were detected when reviewing this book.
This book is not offensive nor culturally insensitive in any manner.
For any instructor looking for an open textbook to orient undergraduate students to the basics of the academic research and writing processes while simultaneously providing context of contemporary issues surrounding these scholarly activities, this is a comprehensive and accessible choice!
Reviewed by Anne Behler, Information Literacy Librarian & Instruction Coordinator, The Pennsylvania State University on 2/1/18
This text offers a comprehensive breakdown of the academic research process, with special effort made to demystify jargon that may present itself in either the classroom or library environment. Beginning with establishing a research question and... read more
This text offers a comprehensive breakdown of the academic research process, with special effort made to demystify jargon that may present itself in either the classroom or library environment. Beginning with establishing a research question and carrying through to integrating and citing sources, the text includes practical tools for students to use in their own research, as well as links to supplemental information. If anything, the text errs on the side of providing too much information, such that a novice researcher may feel overloaded.
The text offers an accurate articulation of the research process, and avoids bias by covering a wide variety of potential information sources, including the use of web search engines other than Google.
Because the information landscape is constantly shifting, the text will require fairly frequent review. This is particularly important when it comes to how web sources are addressed. For example, the book does not address fake news and/or dealing with problematic web resources, and it glosses over use of social media as an information source. However, the concepts related to the research process itself change very little, and the information presented about them has staying power.
The text is written in accessible language, and works to address uses of jargon that are typical within the academic environment by providing explanations for what professors typically want when they request a particular item in the research process. This is an effective way to establish relevance with students, as well as clarify academic expectations.
The language within the text is consistent and accessible, with helpful insertions of definitions and/or links to explanatory supplementary information online.
The text's sections are clearly and logically labeled, and could very easily be plugged into a course in part or whole.
The order of topics in the text follow the research assignment process, from point of assignment decoding through to writing and source citation. Given the audience for the text and its intended purpose, this makes great sense.
The text contains links to many outside web sources that may provide helpful supplemental information for the reader; however many of these links were found to be dead. Comprehensive review of all links is highly recommended. In addition, I recommend continuing review of available videos related to the topics, as many selected are either rudimentary or contain dated material.
The writing and grammatical quality of this text are of the highest quality.
The text is culturally relevant and inclusive in its examples.
As stated, this book holds great utility and relevance, but requires updating for links to external web resources. It will also need to be adapted to keep up with the changing landscape of information sources themselves.
Reviewed by Craig Larson, Librarian, North Hennepin Community College on 2/1/18
The book is very comprehensive, sometimes almost too much so (sections on copyright seem to be more detailed than the average college student would need or perhaps be interested in; the section on the lifecycle of information, while interesting,... read more
The book is very comprehensive, sometimes almost too much so (sections on copyright seem to be more detailed than the average college student would need or perhaps be interested in; the section on the lifecycle of information, while interesting, also is a bit questionable as to its overall relevance). Instructors who choose this book for a one- or two-credit information literacy course will have much more material at their hands than they can reasonably cover in a semester. This book would make a good companion volume to just about any course involving research.
The content is accurate and unbiased. As an example, I was interested to find that the author actually recommends that students use Wikipedia, at least in the very early stages of research, to get an overall picture of their topic. So many college instructors, regardless of the subject, seem to have a strong aversion to Wikipedia. Here, the author actually goes into some detail on how using the references in an entry can lead the researcher to additional sources he/she might not find through other means. Some of the activities are a bit misleading or written in such a way that there could be more than one right answer, which isn't necessarily an error, but could be tightened up a bit.
The content is largely relevant and up-to-date, though I was a bit surprised to not find a section addressing "fake news," which has become such a watchword over the past year. I was also a bit surprised that, although the author has a section talking about which "neighborhood" certain types of information "hangs out," there wasn't a discussion of different domain names, such as ".edu," ".org," and ".com" and what they indicate to readers. Also hampering the book's relevance somewhat is an overabundance of examples and activities that require an Ohio State student ID to log-in. Many of these would have to be re-worked or re-written for the book to be useful at other schools.
In large part, the book is clearly written and new ideas are clearly explained. The writer does a pretty good job of avoiding jargon and technical terminology or where it can't be avoided, of providing examples and clear definitions of terms. Some of the activities aren't so clearly written that there is one obviously correct answer. Also, some of the scoring of activities isn't clear enough to indicate to the user what was wrong and why it was wrong or even the correct answer that should have been chosen. Not every concept is adequately explained or thoroughly developed (for instance, the crucial process of moving from an initial reading to a research question could use further clarification and development). Another area that could use further discussion and development would be how to use databases.
The book is largely consistent, though there are occasions where the consistency falls through. For example, most of the accompanying activities will open in a new window, but not all. There were several occasions where this reader closed out an activity window and closed out the entire book as well. This is an area that someone really should take a look at, as it can be confusing and irritating for the user. Also, the fact that many of the book's activities require an Ohio State student ID effectively locks out users from other institutions.
The book is largely modular, with sections that can easily be broken apart and assigned at different points in the course. There is a very useful table of contents, broken down by subject into smaller pieces that can easily be accessed. As mentioned previously, the book is very comprehensive, almost too much so at times, so having this table of contents is very helpful.
The book is fairly-well organized, though there are things placed in odd locations that could be touched on earlier or later, as the case may be. For instance, there is a good discussion fairly late in the book about deciding whether to quote, paraphrase, or summarize, which would have been much more useful if it was placed in the section of the book that directly addresses each of those activities. Instead, it is placed in a section on academic integrity (which, again, is very Ohio State-specific, too much so, really). I also question the relevance of a chapter on creating an academic argument, which if it is to be included at all, would seem to make much more sense earlier in the book, when students are learning the basics of research and how to apply it to their writing.
The book is largely free of significant issues, although as mentioned previously, many of the activities require an Ohio State student ID to log-in and use, which makes them useless to students from other institutions. Also, the activities are sometimes difficult to follow--one doesn't know why one answered incorrectly or what the correct answer even is in some instances. And the fact that some activities open a new browser window and some don't can also be confusing. There are a few activities that lead to broken links.
There are the occasional run-on sentences and spelling mistakes in the text. It's almost impossible not to have some issues in this area. However, the infrequent errors don't detract from the book or its overall usefulness, though it might be a good idea for someone to go through the text and try to clear some of these up.
The book does a good job of avoiding being culturally insensitive or offensive. Activities and examples are written in such a way as to be inclusive. Many of the examples link directly to sites that deal with minority themes and issue.
I think, on the whole, this is a very useful book and one that could be put to immediate use in many instances. However, the number of activities and examples that require an Ohio State student ID to access make this less relevant than it could be if the author had striven for more universal examples.
Reviewed by Mairéad Hogan, Lecturer, National University of Ireland, Galway on 2/1/18
This book covers the subject matter in a comprehensive and detailed way. The way in which the material is presented is very suitable for students who have not previously been involved in academic research as it starts at the very beginning and... read more
This book covers the subject matter in a comprehensive and detailed way. The way in which the material is presented is very suitable for students who have not previously been involved in academic research as it starts at the very beginning and assumes no prior knowledge. It has additional features that help to reinforce the material, such as activities and MCQs. These help to reinforce the learning and test the reader’s understanding. Additionally, the examples used are very useful and helpful in gaining understanding of the subject matter.
It goes into the material in depth and not only tells students how to progress their research but also explains clearly why they should be doing it this way. For example, it explains to students how to differentiate between good and bad sources. However, I have one small concern with this aspect. They do not tell students how to differentiate between different standards of peer-reviewed journals. They do mention looking at citation count but state that is not a useful measure for very recent articles. Some discussion on determining the quality of the journal itself would be helpful. For example, looking at citation counts for the journal, rather than the article would be one example, as would looking at rankings.
Overall, I would see this as an excellent reference book to last students through their academic careers.
The material itself is accurate. However, many of the links to additional material either do not work or are inaccessible to those without OSU credentials.
The material is mainly presented in a way that will last. However, many of the links no longer work so these should be checked and alternatives put in on a regular basis. Additionally, there are links to videos that may not be there in the future, although all I clicked on were available. However, the text description of the videos did not work. Many of the activities (MCQ’s etc) have a dated feel about them in terms of layout and interaction. The design of them could do with some updating.
The writing itself is very clear and easy to understand. Diagrams are used to good effect to clarify concepts (e.g. use of Venn diagrams to explain Boolean concepts). However, some of the terminology is not as clearly defined as it could be. While terms are generally explained clearly in the text, it would be nice to have a glossary of terms. Additionally, the MCQs are not always clear as if the reader gets an answer wrong it is not always apparent which is the correct one.
The book is consistent in writing style and interface.
The book is structured in a modular format whereby the reader can dip in and out of different sections, as they need to. Equally, for a student starting out, it is structured in a way that is likely to follow the steps in the same order as the student, making it a good companion to their research projects.
The book was organised in a very natural and sensible way and flowed smoothly from one topic to another. Links were provided to related sections of the book where relevant so that if the reader forgot what was meant by a particular topic, they could easily hop back and forth. The book started at the very beginning with good coverage of developing a research question and then progressed through tools and sources to help with this. The additional activities were all web based, which works fine if you have easy access. However, I was using a kindle with poor broadband so struggled to access it at times. It also felt a bit disruptive leaving the book to do the activities. It’s also not always clear whether links lead to another part of the book or to an external site. The tips are a useful addition. The stand out when flicking through the book and help to reinforce the important points. It is also useful the ways steps are clearly broken down into sub-steps.
I downloaded it to Kindle, and found a number of issues. It struggled to deal with larger fonts, resulting in some text not being visible.. There were also references to “the bottom of the page” but the bottom of the page varies depending on font size. Not all of the activities worked. Some of the activities required OSU credentials to access them, which was frustrating.
There were some minor grammatical and typographical errors but nothing major.
The book is very US centric in its use of examples. For example, there is an American football example and news sources referred to are US based generally. Additionally, copyright discussion is US centric.
Overall, I found this to be an excellent book that will help students in their research projects. I think it is a book that they will use for a number of years as it is has sufficient depth to help at different levels. The one main change I would make would be to broaden OSU references and activities so they are referring to databases in general, for example, rather than simply talking about the OSU one. Much of the material is relevant regardless of institution but a reader unfamiliar with databases would not be aware of this and might skip over some very useful information.
Reviewed by Anthony Patterson, Assistant Professor, North Carolina Central University on 2/1/18
Choosing and Using Sources is an extremely thorough text taking readers through the research process from formulating research questions to fair use and copy right issues. I particularly liked the online examples and resources including quizzes... read more
Choosing and Using Sources is an extremely thorough text taking readers through the research process from formulating research questions to fair use and copy right issues. I particularly liked the online examples and resources including quizzes and videos. The table of contents is thorough but there is not a glossary. While this is a strong text some discussion of theory and how theoretical frameworks are used in academic writing.
While the text could have addressed additional areas, the authors were accurate and detailed. Chapter 8 - How to Cite Sources is well done and accurately takes novel researchers through when they should and should not provide citations.
The authors present how to develop, approach, and conduct sound research in a well thought out format. This text is up-to-date addressing issues like Wikipedia and Google Scholar. While issues around these information sources will change, the way this text is set up, it can easily be updated in the future.
The book is well written, clear, and easy to follow. Jargon such as primary, secondary, and tertiary sources were explained clearly with appropriate examples. This text will be accessible for my students and most others pursuing advanced degrees.
The authors are consistent throughout the text when discussing topics like presenting arguments and the relationship this has with concepts like research questions and the sources researcher select. While consistency is expected is difficult to do especially when writing as a team. More impressively is the consistency of supplemental materials throughout the text.
The book has long chapters and occasionally I had some difficulty knowing where one section ended and another began but overall it is readily divisible. Another important aspect of the text are the supplemental materials like online quizzes and videos which are also clearly align with the sections in the text.
I was skeptical at first when I began reading but the overall organization of this text is good. Even though the text is about writing and sources, a section of theory and incorporating theoretical frameworks would have strengthen the book. However the topics selected flowed well and led potential researchers through a logical process.
A few problems linking to sum supplemental materials but overall I was impressed by the quality of the graphics as well as the links to quizzes and videos that were provided.
I did not come across any grammatical or typographical issues.
I did not see any cultural insensitive examples or information provided. However I also did not see a lot of racial or ethnic diversity in examples throughout this text. Overall, I feel the authors approached the subject matter appropriately.
Reviewed by Rachelle Savitz, Assistant Professor, Clemson University on 2/1/18
The text is quite comprehensive regarding finding, using, and understanding sources. It provides the process of sourcing from start to finish with examples and activities provided throughout to support the reader. Various ways to find sources... read more
The text is quite comprehensive regarding finding, using, and understanding sources. It provides the process of sourcing from start to finish with examples and activities provided throughout to support the reader. Various ways to find sources are described. There is a focus throughout on software and databases for the students at the authors institution and that can be confusing to readers from other institutions. The information provided regarding citing, ethics and copyright, and fair use was informative and would be beneficial to the reader. There were sections throughout that could have been more in depth and more specific. For instance, when going over the various ways to cite sources, additional examples could be provided and the version/edition should be listed. For instance, was the APA citation in APA 6th edition format? Also, make sure to address citing from secondary sources as students do this often and tend to cite what they read even if they read it from another text. The TOC was helpful and allowed ease of understanding what was to be covered in each section. One main complain that I have was regarding the additional information provided to help the reader in writing a paper. This information would be helpful for basic college writing but not for academic writing, thesis or dissertation writing. The sections required for some of these papers are not discussed and the text eludes that the sections provided regarding writing an argumentative piece would be appropriate for all. Also, synthesizing information could be explained a bit more and with more depth. Synthesizing includes more than critiquing and summarizing. All in all, the sourcing information is spectacular and the additional information could be expanded upon.
Accuracy of sourcing was spot on. Some of the additional categories discussed, as mentioned in the first section of this review, could be expanded upon to fully explain that category, if it is to be included in the book. The examples and activities provided were quite good and would be very beneficial for students to apply what they are learning in real-life contexts. Links were provided for extending information. I did not attempt to open every link but making sure they are up-to-date will be important as time goes forward. I also feel that the section on popular texts can be misleading. Stating that the Washington Post is "popular" eludes that it is not reliable or valid. This is not necessarily true as many experts in various fields write sections in "popular" newspapers.
As previously stated, a lot of links go to OSU resources. This could be problematic for any reader that is not at OSU. More information should be provided to support any student in the world as that part would be confusing to many students.
The text is easy to read and follow. All new information is explained and then examples and activities are provided. This is student friendly and allows any reader to quickly follow along and understand what is being stated, especially regarding the sourcing elements. As stated above, there are some sections that could/should be expanded upon for clarity and this might be best for beginning university students but the text was easy to understand in regards to sourcing, citing, and fair use. More information on how to use the sources and sections of papers would be beneficial to all students.
Each chapter seemed to follow a similar structure that followed the TOC.
Modularity rating: 3
Reading the book online provides ability to chunk the text based on assignments and can be read chapter by chapter, entirety or starting at different places. Due to the extensive amount of outside links and examples, this would be quite different if read in paper format. This book truly has to be read online to ensure benefit from all of the additional activities, links, examples, sources, etc. In addition, the many links specific to OSU would not be helpful for other students.
The organization is consistent from chapter to chapter. Information is explained and then examples and activities are provided to further knowledge. This works well for readers that needs examples.
Using a laptop provided no issues. However, when using a smartphone, the pages changed in size and various display features did not load properly or at all.
Very few grammatical errors were noticed.
No cultural issues noticed other than the many OSU references and sources. This could be offensive to other institutions as they will not be able to access many of the links.
Reviewed by Scott Rice, Associate Professor, Appalachian State University on 2/1/18
The book is very comprehensive which sometimes detracted from its usefulness. There were a few units that may be superfluous, but I did appreciate that the author seemed to err on the side of inclusivity, leaving it to other adoptees how much... read more
The book is very comprehensive which sometimes detracted from its usefulness. There were a few units that may be superfluous, but I did appreciate that the author seemed to err on the side of inclusivity, leaving it to other adoptees how much content they might use and repurpose.
The book is error-free and appears to be free of bias.
The book is pitched to an Ohio State University audience, so some of the resources pointed to would not be the same as a potential adopter's institution might select. In addition, the book needs some updating regarding the impact of social media on the information cycle. Social media formats are mentioned, but a fuller treatment of how they fit into the information climate would be a good addition.
The text was clear and easy to read, and provided numerous examples for its points. It also did not rely on jargon in its explanations, which makes it much more accessible.
The text was consistent in its use of terms. I found its tone consistent, as well as the level of explanation for the wide variety of concepts explored.
The organization of the text into units makes it very easy to break the content apart into smaller units and use it for a variety of purposes. I could see using the content for different parts of several courses, as well as incorporating it into e-learning content.
The topics are presented in a logical fashion, following the path that a typical research assignment might take. This will also make it easier to fit within the flow of a course that uses the textbook to teach about the process of academic research.
The interface of the text itself works appropriately, but some of the ancillary quizzes and extra material did not work so well. Many of the graphics did not work as well within the pdf format as they do in the web format.
The textbook was free of grammatical errors and was easy to read.
The text did not appear to be culturally insensitive.
I am exploring the creation of a for-credit information literacy class at my institution and this book is a possible candidate for adoption for the course.
Reviewed by Bryan Gattozzi, Lecturer, General Studies Writing, Bowling Green State University on 2/1/18
I was impressed how the text began helping students understand the benefits of leading a research project by writing research question(s), following with assessment of research methods, and thinking about research writing as an avenue to test a... read more
I was impressed how the text began helping students understand the benefits of leading a research project by writing research question(s), following with assessment of research methods, and thinking about research writing as an avenue to test a hypothesis instead of one simply confirming a previous, and perhaps uninformed, belief.
The book didn't seem to dismiss any possible research method. Instead it provided suggestions of how and when any individual research method may be relevant.
The book was published last academic year and the content included is still relevant, mostly because best-practices in research (and research writing) haven't changed much.
The volume of research methods students can use given the internet's power is ever increasing, yet the book does well to isolate a handful of long standing tenets that academic writers have used for decades while allowing for discussion of web-based writing and multi-modal presentation methods instructors may increasingly require students to use.
Each section is concise, clear, and easy to follow . . . for me.
I assume students will be capable of reading the text, performing quizzes provided, and plotting out a research path to complete their assignment(s).
Then again, as an academic I obsess over these issues. I can see a student yawning while reading this text.
The content isn't especially fun to read yet the information provided in relevant and time-saving if students are willing to relax, read actively, and apply the material to the assignment their instructor has given.
I don't imagine many students would seek the book out and read about research methods, yet an instructor can pair excerpts from the book with specific assignments along a student's research path to help the student retain and apply the helpful suggestions in the book.
The text does well to allow students to name the process they're going through when composing a research question then deciding on what research path fits their question. Students are guided to consider what blend of qualitative / quantitative, primary / secondary / tertiary, or public / professional / scholarly research will fit their research and writing goals.
The book refers back to the same terms throughout and provides students with active learning worksheets to plot a research AND writing plan to complete their work, one they could conceivably follow throughout their academic and professional career.
Each subheading contains, on average, not more than a page of content allowing instructors the ability to easily limit reading assignments from the book to concise, focused sections.
The book is very process-based, and follows the workflow necessary to write a successful academic researched assignment.
The limit of this strategy might be students being overwhelmed with so much discussion of process they'd be paralyzed to inaction.
An instructor, then, would have to be direct in assigning reading materials relevant to a student's immediate research goal.
I like how the text follows the path a student would follow: from narrowing a research question, selecting and reviewing research materials, then choosing how to implement them ethically in writing.
It also details how to process research considerations students may not consider including how to archive research results, to respect copyright law when publishing blog posts or submitting student work to an online repository.
The text contains many online activities, sample research artifacts, and instructional handouts. Some require on Ohio State student authentication. The text is still useful without access to these materials, though an instructor would have to alert students to this issue.
Text was proofread well.
Didn't see any culturally insensitive content.
Reviewed by Jonathan Grunert, Assistant Professor of Library Services: Information Literacy Coordinator, Colorado State University - Pueblo on 2/1/18
This textbook covers the concepts found in the ACRL frameworks in a way that is meaningful and accessible to academic researchers at all levels. It adequately provides a discussion of the complete research process, with clear signposts as to which... read more
This textbook covers the concepts found in the ACRL frameworks in a way that is meaningful and accessible to academic researchers at all levels. It adequately provides a discussion of the complete research process, with clear signposts as to which steps writers might need to revisit to improve their work.
The content appears to be accurate to 2016, with some acknowledgement that finding sources is an activity that has seen many changes in the past few decades, and will likely seem more, and rapidly.
Information discovery and retrieval is a rapidly changing process in a changing field. But much of the content in this textbook—as far as general advice and instruction for finding resources and the ways to use them—remains relevant. As information processes change and as information uses change, I have no doubt that librarians will be at the forefront of maintaining the relevance of a textbook like this one through various edition changes.
This textbook is clear, and accessible to researchers at all levels. Jargon, where present, is well-explained, and the contexts for the various components of the textbook are provided.
The text and frameworks in this book are consistent with ACRL frameworks as well as with the ways librarians tend to talk about finding and using sources. Furthermore, the book consistently uses the same terminologies to clearly explain sometimes difficult practices.
I would be very comfortable using any chapter of this book to teach a component of the academic research process. The chapters are discrete, with well-defined boundaries. The modularity of this textbook helps reinforce the overarching idea in this book: the iterative research process. Students might read the chapters in virtually any order, and come away with a valuable understanding of the research process.
This textbook presents the research process in the way that many students and faculty think about the process—from the perspective of the end goal, and through the organizational structure of an academic paper. But, it also indicates throughout the process places when the researcher needs to revisit an earlier step, to modify the project, or to make the end product more meaningful.
No issues in the interface; nothing distracting from the content.
Some minor punctuation errors, but no grammatical errors that distract from the content.
This textbook comes from an American perspective for ways of searching for, retrieving, and using information, as well as the traditionally American ways of constructing arguments. Though there is not discussion of other cultural ways of arguing academically, this textbook does not dismiss or otherwise denigrate other cultures; nor is it insensitive in any way.
Many examples are university-specific to the libraries at Ohio State University, as should be expected from a textbook such as this. As such, this book will be most helpful to students using the book at OSU. However, instructors using this book need to be aware of this focus, and must prepare to supplement with materials accessible by researchers outside OSU.
Reviewed by Susan Nunamaker, Lecturer, Clemson University on 2/1/18
This textbook is comprehensive. It goes in-depth covering the topics of research questions (specifically how to narrow down topics), types of sources, sources and information needs, precision searching, search tools, evaluating sources, ethical... read more
This textbook is comprehensive. It goes in-depth covering the topics of research questions (specifically how to narrow down topics), types of sources, sources and information needs, precision searching, search tools, evaluating sources, ethical use of sources, how to cite sources, making an argument, writing tips, copyright basics, fair use, and roles of resource sources. The textbook hits all of the topics that I plan to cover in my upcoming classroom-based research course with the exception of techniques for completing and writing a literature review. The textbook touches on the topic through a section on "background reading", but does not go in-depth. Otherwise, the textbook covers every aspect of academic research.
I found no errors or bias issues in my initial first read of the textbook.
The information and techniques provided within this textbook are up-to-date and relevant for academic research. I reviewed several textbooks before choosing this one for my upcoming masters-level classroom-based research course. I chose this book because of its relevance in regard to the practical skills needed in order to complete research assignments within the course, as well as, writing a capstone research paper.
This textbook is clear and exceptionally readable. It is organized by research skills in an order that makes sense to the reader. For example, the book begins with a chapter on choosing one's research question. Verbiage is clear and concise for all levels of academia to be able to effectively utilize this text.
This textbook is consistent in terms of terminology and framework. Each chapter of the textbook builds on the last. The reader is not necessarily expected to have prior knowledge of research before reading chapter one, but should easily be able to have a good frame of reference for academic research by the end of the textbook due to its high-quality framework for scaffolding knowledge with each chapter.
This textbook does a great job of sectioning academic research into small bites for the reader. It was easy for me to create modules from the textbook's chapters, spreading the information within the text over an 8-week course. The modularity of this textbook was a selling point for utilizing the textbook with students.
This is a well-organized textbook. Each chapter builds on prior chapters. Chapters are organized in a logical manner. The first chapter begins with the purpose of research questions and builds content to assist the reader in narrowing down options for research questions. The textbook progresses to assist the reader in building skills as an academic researcher throughout the textbook.
No interface issues were discovered during my initial exposure to the online format. I printed the PDF (because I still love paper) and all display features printed properly. The online navigation is easy to use and pleasing to the eye, as well.
No grammar issues were detected during my initial review of the textbook.
This text is not culturally insensitive or offensive in my opinion.
This is an excellent textbook if you are looking to utilize it to introduce students to the academic research and writing process. Its layout and design and conducive to module-based instruction, and the content is well thought out and beneficial.
Reviewed by Diane Kauppi, Library Faculty, Technical Services & Systems, Ruth A Myers Library at Fond du Lac Tribal & Community College on 2/1/18
The text did a great job of covering the subject and the table of contents were laid out well. The content was well thought out. read more
The text did a great job of covering the subject and the table of contents were laid out well. The content was well thought out.
I found the accuracy to be good. The content is a good representation of what a student needs to know in order better understanding library research.
The content itself is good & should stand the test of time for the near future. The only exception is that even though it's only one year from the publishing date (2016) many of the links are broken. And I would have preferred a OER text that was geared more generally for application to any institution vs. the inclusion of OSU specific references, links, resources.
For a text written to a 4-year university/college audience the text was good. For a 2-year community college audience some of the terminology would need to be defined.
I found the consistency to be good. It followed through each section with including tips, activities, etc.
I think the modularity was good. And the text could easily be broken down into smaller sections to be used as units by themselves or refresher units. The only issue would be where there are links within a module that link to other modules. Add to this that these links didn't work-- I rec'd errors each time I tried a module link.
The overall organization and flow as great. As stated on p 6 ("... as though you are conducting a research project while reading them [the sections]...") this made my logical side happy.
I like the links to activities for students to practice the skills being taught. The problem though was that many of the links no longer work. Additionally, many of the links are to areas not available to users who are not affiliated with OSU. And as mentioned in another review section, module links to other modules didn't work either.
I found the grammar to be quite good with only a few exceptions or where it was clunky at times.
I thought the text was neutral in this area. Nothing that blatantly jumped out at me.
I appreciated the link to application of research to other areas of our lives outside of academic research. I try to get this point across to students, especially when they are hesitant and resistant to library research. I found the "tips" & "summaries" to be a nice added 'pop' & easy for referring back to later. I liked the bold letters/words for emphasis. And the suggestion to "brush up" on p 31 was a nice touch vs outwardly assuming they don't know. The downloadable templates are a great resource for students. Overall, I found the text to be a good resource.
Reviewed by Kristine Roshau, Instructional Technology Specialist and PT Faculty Librarian, Central Oregon Community College on 8/15/17
This text is extensive! Like the title suggests, it truly is a full guide to academic research, from developing a topic, finding sources, and using them appropriately. It also follows the logical order of the search process, from identifying an... read more
This text is extensive! Like the title suggests, it truly is a full guide to academic research, from developing a topic, finding sources, and using them appropriately. It also follows the logical order of the search process, from identifying an information need, evaluating source quality (and purpose), and how to perform complex searches. It also highlights several common areas where academic research can be performed, from the college library catalog to specialized databases and how to find academic sources on the free web.
The book also covers what to do once sources have been found, including the importance of properly citing sources, ethical use of source material, and how to cite unusual or non-standard source material. It then moves into addressing the writing process: developing an argument and idea, writing tips, and a large section on copyright, fair use, creative commons, and public domain.
The table of contents is very granular, which is helpful. The sections vary in length, but given the overall size of the book (190 pages) having a very specific TOC is useful when returning to the text as a reference source.
I did not find any objectionable or questionable content. The authors have done a good job of selecting examples for each section (often with associated online activities or examples linked out to the web) that are varied and unbiased, but also represent realistic examples of what students might be encountering during their research process. I was really pleased when looking through the section on citing sources - styles can change, but the book is written in such a way as to be comprehensive about the purpose of citing sources, and links out to many helpful web sources, citation tools, etc so the information will remain accurate in the textbook even if the style guides themselves are updated in the future.
The section on copyright is similarly done.
See previous note - it is clear the authors have taken care to include examples that will remain relevant, not evaporate into popular culture, and provide flexibility where the content may be updated or changes (such as copyright law and citation style guides). They do provide a LOT of external links and activities, not all produced by Ohio State. So it's possible that some of their links may break in the future. It does appear that they have made an effort to either link to open sources they control, or which are unlike to change significantly (ie: government websites).
If I were using this text, I would probably modify some of the resource sections (eg: databases) to reflect those that the students at my institution have access to, though the writers do make a point of identifying OSU access-only resources where applicable. I would also update the copyright/plagiarism section to include our college's student handbook blurbs, etc.
The tone is extremely approachable in all of the areas I checked. This is extremely important in academic research where there are a lot of areas of possible legal entanglement, and the authors have done a credible job of breaking down complex concepts into approachable prose and examples.
The textbook is consistent in both writing and structure; however, I do with the table of contents was split into sections in the same way the content is. Page numbers are given though, so that's not really a big deal. There were one or two places where I saw formatting errors, but nothing overly distracting - it did not adversely effect the content.
It is visually appealing and for the most part, easy to navigate. No huge blocks of text, and it also intersperses activities, tips, and examples. The text is also organized in such a way that it can be used as a reference, without needing to be read from start to finish in order to make sense, which is helpful for the researcher who may need to pop in for just pieces of the work.
However, there is a strong presence of external sources (often OSU library webpages) and activities that are linked out of the text. The writing itself is certainly standalone, but the book would lose a lot of its character if it were printed and not viewed digitally. I would have liked a References or bibliographic section that listed some of these resources, but there wasn't one, meaning the user would not be able to search for the resource if the linked text didn't work.
I can see the potential for too many asides for activities to be distracting, but they are generally held to the end of their relevant sections, so it wasn't too overwhelming. The organization follows a logical research process, walking the reader through from beginning to end.
As mentioned before, there are a few places where it looks like images have distorted the intended formatting, pushing items to empty pages, etc. But these instances are rare. A few of the images could be higher resolution, but they were certainly legible (and I was viewing this text at 125% zoom on a larger screen, so my experience is probably not representative of every reader).
It is long though, and I would have loved to be able to jump to sections through anchor bookmarks in the content page - that would be a nice touch.
I also found a few broken links, which is not totally surprising, given the volume of them in this book.
None noticed in this review.
No objectionable content found - the authors have chosen inclusive examples wherever possible, while remaining realistic about subjects students might be researching.
Not all of the links to activities are self-describing (there are no plain URLs, but many of the activity links contain the same 'Open Activity in Web Browser' text, which would be confusing if a user was navigating with a screen reader.
Reviewed by Deborah Finkelstein, Adjunct Professor, George Mason University on 6/20/17
The book is very comprehensive. The authors consistently explain concepts well and provide easy-to-understand examples that are approachable for the undergraduate audience. For example, the authors don’t just say, “narrow down your source,” they... read more
The book is very comprehensive. The authors consistently explain concepts well and provide easy-to-understand examples that are approachable for the undergraduate audience. For example, the authors don’t just say, “narrow down your source,” they go through steps to narrow it down, walking students through the process. (p 9) Very thorough. They also spend a page and a half giving examples of “Regular Question” vs. “Research Question.” (p 13-14) This ensures that students will understand the difference. They also do well with explaining fact vs. option, objective vs. subjective, primary vs. secondary vs. tertiary sources, popular vs. professional vs. scholarly magazines, when to quote vs. paraphrase vs. summarize, and other concepts that are critical to performing research.
The book does not have an index. The table of contents is quite thorough and very useful in understanding the breakdown of the book or locating certain topics.
The book is error-free.
There are many digital examples in the text. As long as authors make updates as technology inevitably changes in the future, the book should remain relevant.
The book has a conversational tone that is connective, trustworthy, and approachable for the undergraduate audience. This makes it easy to read and easy to understand.
The book is very consistent with tone, and terminology.
In the introduction, the book encourages students to “jump around a bit in this guide to meet your needs.” (p 5). The book stays true to this idea. Students could read the book straight through, but it is well-designed for “jumping around.” The sections stand alone, and instructors could easily assign sections in the book out of order. This book could be used as the only textbook in a classroom, or an instructor could use these modules to supplement an existing textbook. Topics are easily found in the book thanks to an excellent table of contents, a clear organizational structure, and a great use of headers.
The book is well-organized and follows a logical structure. Individual topics are also well-organized. The authors break processes into step-by-step, making is easy for students to learn.
Great use of visual aids. For example, there is a chart on how to narrow down research topic (p 9), and a chart on the roles of resources in research (p 179). These items are great for visual learners, and they make the text come alive while emphasizing important concepts.
The book shares links to outside sources. This provides students that would like more information that is beyond the book with resources. It additionally provides students links to activities, such as one that asks them if a source is primary, secondary, or tertiary (p 34). On occasion, it links to outside companies, such as citation management software, news outlets, and social media, making the book a resource. In this way, the book utilizes the medium of a digital book.
The book is free of grammatical errors.
The book is culturally sensitive. The book is designed for Ohio University students. Examples given occasionally apply to Ohio, such as when the authors are providing examples of newspapers, they list two out of six that are from Ohio, including the campus newspaper (p 43) There is also a link to the OSU Libraries’ newspaper database (p 44), and when talking about citation management software, they mention the three that are available at OSU. It’s not a large enough issue that one should not use the book; it’s still easy to understand, but it is a limitation and worth mentioning to students.
I teach a 300-level English class on performing research and writing research papers. I plan to utilize this book next semester due to the excellent organization of modules, the approachable tone, and the great explanations and examples.
Reviewed by Constance Chemay, Head of Public Services, Library Services; Asst. Professor, User Instruction, River Parishes Community College, Gonzales, LA on 6/20/17
The book does an excellent job covering the subject, and even goes beyond what its title suggests, with chapters on writing and formulating an argument. The chapters on copyright and fair use are exceptional. However, it lacks both a glossary and... read more
The book does an excellent job covering the subject, and even goes beyond what its title suggests, with chapters on writing and formulating an argument. The chapters on copyright and fair use are exceptional. However, it lacks both a glossary and an index. Some terms are defined in their appropriate chapters, but not all. Some students, particularly first-year or those who may be enrolled in developmental courses, would benefit greatly from a glossary. The activities, while appropriate for their contexts, are mixed in their effectiveness; some provide good feedback with clarification, but most offer little more than a smiley face for a correct answer or an “x” for a wrong answer with no other feedback.
For the most part, this book is accurate and unbiased, but one area where I noticed discrepancies is the chapter on citing sources. MLA released its 8th edition in April 2016, yet the examples provided are 7th edition. I also noticed errors in the example for APA; only the first word, proper nouns, and those following major punctuation marks are to be capitalized in article titles following APA formating guidelines. Regarding bias, the book is unbiased; however, I disagree with the discussion of news sources regarding mainstream versus non-mainstream (or mainline as used in the text); main-stream media includes "traditional" sources, e.g., television, newspapers, and radio, as opposed to online sources, especially social media. The authors’ inclusion of Fox News, a right-leaning national television news network, a contemporary of CBS, NBC, and ABC, as non-mainline rather than mainline shows bias, in my opinion. It’s difficult to find news from any news source, mainstream or not, right, left or center, that doesn’t have some bias or opinions in its reporting.
This textbook itself is written so that it will be relevant for a long time. However, there are some exceptions. The discussion of citation styles uses examples for MLA that reflect the 7th edition rather than the 8th, which was released in April 2016. The book covers this discrepancy somewhat with its tip regarding choosing a citation style, with its remarks that styles do change and its recommendation to check with one’s instructors. Another issue is the potential for link rot regarding external websites; in fact there are a few dead links in the text and activities already. A couple of online resources mentioned and linked to, IPL2 and the Statistical Abstracts of the US, have been retired for at least a couple of years, which makes me wonder about when the book was actually last reviewed edited.
The book is well-written, easy to read, conversational. Most technical language is defined and used appropriately.
This book is consistent in terms of its terminology and framework.
This book is extremely modular in its organization at the chapter level and within the chapters. It can be easily reordered to meet specific course or instructor needs. It does refer to other sections of the text, but these references are appropriate, emphasizing more in-depth information elsewhere in the book. Sections that are unique to OSU can be replaced/revised to make the text relevant to other institutions as needed.
It is well organized and reflects the processes and stages of research. While the research process is not linear, the topics are presented in a logical manner that guides students through the process. I did note that a couple of sections in chapter 7, on ethical use of sources don’t really seem to fit there, however. The paragraphs on page 118 discussing a lack of understanding of the materials and lack of time might fit better in other chapters.
While the online version works well, the PDF format has issues. Some of the in-text navigation links work (the TOC links) while others found throughout the text don’t, often giving an “error: unknown export format” message. There are also a few dead links in both the online and PDF formats, as well as in some of the online activities. Some links direct users to OSU Libraries’ resources, either their catalog or their licensed databases, but not all such links are clearly identified as such.
Grammatical Errors rating: 3
For the most part, this text is well-written, grammatically; however, it does have a few grammatical/typographical errors, possibly more than one might expect from a text of this length, and assuming that the author is most likely a committee rather than an individual, more eyes reviewing the text should catch such errors. There are also instances of tense inconsistencies, shifting from present to past in the same sentence. Two paragraphs on page 47, under “Finding Data in Articles . . .,” repeat the same four sentences verbatim in different order. This occurs again on page 88. While these are not grammatical errors, they are certainly editorial errors. Most of the online activities have typos, as well, more so than the textbook.
This textbook is not culturally insensitive or offensive.
I do like this book. I think it puts the topic in terms that students can readily use and understand. I'd even recommend the chapters on copyright and fair use to faculty! I do think that it could benefit from the inclusion of a glossary and an index, as well as regular and frequent review, especially in regards to the linked resources. The PDF version definitely needs revisions since it seems that most of the in-text referral links throughout the text don’t work. Since it is tailored to OSU’s library resources, any instruction librarian using the book can substitute content relevant to his/her institution; non-library faculty using the text can consult their own librarians for help with this.
Reviewed by Dawn Kennedy, Ed.S, Health Education, Anoka-Ramsey Community College on 4/11/17
Choosing & Using Sources: A Guide to Academic Research serves as an excellent guide for teaching the research process. It takes the learner through the process of academic research and writing in an easy to understand manner. As an educator... read more
Choosing & Using Sources: A Guide to Academic Research serves as an excellent guide for teaching the research process. It takes the learner through the process of academic research and writing in an easy to understand manner. As an educator in a community college setting, I am working with students who are new to the research process. This text will be useful when working with students to start developing the appropriate process of research writing. The text has neither a back-of-the-book index nor a glossary. It is beneficial that key terms are defined throughout the chapters.
The information presented in the text is accurate at this point in time and unbiased. One concern is that some of The information presented in the text is accurate at this point in time and unbiased. One concern is that some of the links do not work.
Content is up-to-date at this point in time. Most examples and exercises are arranged separately from the main text and can be updated as needed. Some of the content links to the Ohio State University Libraries databases which may not be assessable to students outside that institution.
This text is clearly written, well-illustrated, and user-friendly for the undergraduate audience. It avoids technical jargon and provides definitions where appropriate.
Choosing & Using Sources: A Guide to Academic Research is consistent in terms of terminology and framework.
Regarding the book’s modularity, users of this text can be selective in chapter choice. In this sense the text is useful to instructors and students who wish to focus on a single component and /or use the text as a reference. For a better understanding of the research process in its entirety, reading the text in the order written may prove to be more beneficial.
The text's organization mirrors the research process in a logical, clear manner. Chapters 1-8 lead the reader through the basics of research literacy and research skills; chapters nine and ten explain the process for making an argument and writing tips; Subsequent chapters zero in on copyright and Fair Use information. Key concepts and points are supported with highlights, examples and colorful illustrations.
The text displays generous use of visuals which are clear and free of distortion. The activities provided support the concepts and skills being addressed and are easy to navigate. One concern is the activities which are linked to Ohio State University may not provide access to all, resulting in limited access of information and frustration for the reader.
• The text is not culturally insensitive or offensive in any way.
This is a text does an excellent job of explaining the research process in a logical manner. The text uses examples, illustrations, and skill practice to support the learning process. I recommend this text for use in it's entirely for teaching and learning the research process and as a resource for the rest of us.
Reviewed by Scott Miller, Reference and Instruction Librarian, Rogue Community College on 4/11/17
The book is very comprehensive and even goes beyond what might be expected in this kind of textbook. Along with choosing and using sources, the authors include a section on making an argument. Topics are dealt with appropriately and the text... read more
The book is very comprehensive and even goes beyond what might be expected in this kind of textbook. Along with choosing and using sources, the authors include a section on making an argument. Topics are dealt with appropriately and the text employs tests and activities along the way. I found some of the activities were not particularly well designed and sometimes answers to questions were based on assumptions by the authors as to context that in real life may or may not be appropriate. For instance, they claim that the periodical/journal title "Coral Reefs" is a scholarly journal, but judging by the title alone in a real life exercise there is no way to know whether it is scholarly or popular in nature.
There could have been more discussion about context and how it defines whether a sources is primary, secondary or tertiary. '
What the this textbook does not have is any kind of index or glossary, which I found disappointing.
I did not find any instances of inaccuracies in the text. I did find, however, some assumptions in the text that were not always warranted. I took issue with the assumption that mainline news sources are objective (p. 42). It is very clear that news articles are often biased. I think telling students that mainline news sources are objective effectively disarms instead of promotes critical thinking by students doing research.
On page 126 there is a discussion about using quotations where the authors say that all quotes are to be put within quotation marks. This is not true of block quotes in MLA or APA style and they omit any mention of it.
This textbook should retain its relevancy for several years, but it will lose its effectiveness very soon, since many of the dozens and dozens of links in the text will surely break before long. In the short term the links are a great feature, but they do severely limit the longevity of the book. I also found them annoyingly pervasive.
It should also be noted that the MLA citation example on page 122 uses the outdated MLA 7th edition guidelines.
Overall, I thought the book was very clearly written and easy to follow. The one section I struggled reading was the section on sources and information need. It seemed to want much more editing and was often wordy and almost obscure.
I did not notice any lack of consistency in terminology or framework.
This is one the book's strengths. It was clearly organized into topics and subtopics which sometimes could be addressed in an order chosen by an instructor. There were, however, occasional self-references to earlier sections or previously used external sources.
Moving from the simpler aspects of choosing and evaluating sources to the more complex uses of them and how arguments are constructed made good sense.
Interface rating: 2
I found the interface to have significant problems. At least a dozen links would not work from the PDF text when opened in Firefox. I often got the message, "error: unknown export format." The links seemed to work when viewing the text online, however.
The textbook's usefulness outside of Ohio State is severely limited by the frequent use of sources only available through OSU student logins. The textbook was written for OSU students, but it really fails as a textbook for any other institution unless it is significantly modified.
I found a few missing punctuation marks, and only two missing or wrong words in sentences. For a textbook this long, that's very good.
The textbook used interesting and non-offensive examples.
While it's a good textbook for choosing and using information sources it suffers from being too specifically written for OSU students, as well as including an overabundance of links that will reduce its longevity. Not including any kind of index or glossary is also a drawback.
Reviewed by Vanessa Ruccolo, Advanced Instructor of English, Virginia Tech on 2/8/17
Ch. 1 has a great overview of regular versus research questions and the difference between qualitative and quantitative research. Ch. 2 covers primary, secondary, and tertiary sources as well as popular, professional, and scholarly. Ch. 3... read more
Ch. 1 has a great overview of regular versus research questions and the difference between qualitative and quantitative research. Ch. 2 covers primary, secondary, and tertiary sources as well as popular, professional, and scholarly. Ch. 3 includes a source plan (i.e. what do you need the sources for and what is your plan). Ch. 4 gives tips and hints for searching on a library database. Ch. 5 gives different search options, like the library or Google Scholar. Ch. 6 is all about evaluating the sources you find, including clues about sussing out bias and thoroughness, as well as discussing currency of topic. Ch. 7 discusses why you should cite sources. Ch. 8 discusses ways to cite sources. Ch. 9 is looking at argument as dialog and what is necessary in that exchange and a recommended order of components. Ch. 10 covers quoting, paraphrasing,and summarizing and signal phrases. Ch. 11, 12 are copyright and fair use. Ch. 13 covers the roles or research.
I will use Ch. 1 and 2 in my classes, as I think the breakdown of research is useful and clear. Ch. 3 also has useful imbedded tools that will help students plan; Ch. 4 and 5 might be used as references post-library visit. I will also use Ch. 6 and Ch. 10.
I think the information provided for distinguishing scholarly, popular, and professional is helpful and I hope the resources help students understand good, reliable sources a bit better. The same is true for searching for sources, and I think the sections on search engines and evaluation of sources are going to be quite useful.
While the information on copyright, fair use, and why and ways to cite sources is fine, I won't be using these for my English classes as I find them not as helpful or relevant.
I think the book is quite accurate in terms of information provided. They use sources that both I and my students use, so clearly the book is addressing real needs in the classroom. It also makes suggestions that reinforce the concepts our librarians share with the students and instructors, so I find this to be extremely helpful.
The book suggests Purdue OWL, a source I also use; however, I realized this year that OWL was behind in updating some of the MLA citation changes. So that's something maybe for the book authors to note or address when recommending websites.
With that said, I think the book covers key specifics like university library websites, Google Scholar, and search engines, in broad enough terms to keep it relevant. Also, the graphics are simple and not dated, and there is one drawing of the "outernet" that shows what social media, Youtube, etc. would look like in the "real, outer" world. This drawing is the only thing I saw that might be dated soon, but its point is still solid.
Very easy to read, clear terminology and explanation of terms, and lists are also provided to help break up each page's prose, which means the information is presented in a visually clear form as well.
I think the consistency of terminology as well as the scaffolding makes sense on the whole. I didn't seem places where the language changed or seemed to have several writers or definitions.
Perhaps one of the best parts of this book is how each chapter is contained, succinct, includes an activity, but still builds on and with the other chapters. Each chapter is stand-alone and clear and easy to read online, or if you chose to print it. The creators clearly had the online reader in mind, however, and the chapter lengths and fonts are comfortable.
Overall, I like the organization, specifically for chapters 10-6. I would change the order of the final chapters so that Ch. 9 and 10 come before Ch. 7, 8, 11, 12. I would also move Ch. 13 "The Roles of Research" to earlier in the book, perhaps around Ch. 3 or Ch. 6. If I use these materials, I will reorder some of the chapters for my class so that the scaffolding and explanations work a bit more side by side.
Again, comfortable, easy-to-read pages, simple graphics and the charts used are helpful and appropriate. I especially appreciated that the authors didn't use images that showed people or figures that could both date the book and also make students feel talked down to - I hate images like this and refuse to use textbooks that incorporate them, so kudos!
Additional resources are easy to access.
I wish the email option (for sending yourself a page) pulled up a screen in which I could type the email I wanted it sent to. Instead, it pulls up Messenger, which I don't use.
The Table of Contents didn't let me jump to the chapter when I pulled down the menu. Was that just my computer/browser?
Now, I didn't read through as though I was grading (it is winter break, after all!) but nothing jumped off the page. If something had, if there had been a mistake, I would still use the text; if there had been several, I would have considered abandoning it for class. However, the information is still so good I i might have told my students to find the grammar mistakes as part of an assignment just so that I could use the research parts still; however, I didn't not see any.
No, nothing. Perhaps if the authors include more examples for citations they could pull from culturally different sources then, but the material here was so broad in terms of textual sources it was in no way exclusive.
I will be using parts of this book in my English classes. Well done to the authors - a helpful, free supplement.
Reviewed by Dale Jenkins, Advanced Instructor, Virginia Polytechnic Institute & State University (Virginia Tech) on 2/8/17
Having taught freshmen how to write college research papers for the past 18 years, I gave the text high marks on addressing all of the key elements college students need to engage in academic research. read more
Having taught freshmen how to write college research papers for the past 18 years, I gave the text high marks on addressing all of the key elements college students need to engage in academic research.
The text implements content from a host of sources which is extremely useful, but the grammar needs a few tweaks.
This represents a strong aspect of the text. The writers did a good job of winnowing out unnecessary components of the research process, although my freshmen would not delve into the Fair Use and Copyright chapters.
The book gets outstanding marks on clarity. Students will find this to be a definite strength of the text.
The authors did a good job with consistency. I kept my students in mind as I evaluated this aspect of the text.
Students would find this book extremely accessible in terms of modularity. I don't see them being overwhelmed by the text or high-brow jargon.
I noted a logical progression to all thirteen of the chapters. Students in upper-level classes would find the chapters on Fair Use and Copyright more significant in their academic studies.
The hyperlinks and the interactive elements of the book will be extremely appealing to students as well as being substantive.
The book still needs some work in this regard. Pronouns don't always agree with the antecedents, and I noted several shifts in voice in the text.
The text doesn't have any instances of cultural insensitivity, and I pay close attention to this aspect of textbooks when I peruse them for potential use in my courses.
The hyperlinks, using different types of media, and the chapters on "Why Precision Searching?" and the discussion of plagiarism proved to be well-crafted and accessible for students. I also commend the authors for the lack of jargon that would leave students in its wake.
Reviewed by Jarrod Dunham, Instructor - English Composition, Portland Community College on 2/8/17
A very comprehensive guide to the writing of the research paper. I've taught research writing for several years, and this book covers all the material I'd typically cover in a class. Previously I've not used a textbook in that class, but I'm... read more
A very comprehensive guide to the writing of the research paper. I've taught research writing for several years, and this book covers all the material I'd typically cover in a class. Previously I've not used a textbook in that class, but I'm teaching an online section this term and find that the book offers a very effective substitute for the lectured and activities I'd otherwise be presenting in class.
This text is accurate and up-to-date with the most recent developments and issues in the field.
This text is very much up-to-date. It shows an awareness of changing conventions in academic writing, and emphasizes the latest technological tools for researching and managing citations. It frequently links to outside resources, which could be problematic in the event those resources were removed or relocated, but in practice I never encountered such an issue.
Clarity is one of the book's strengths. It is written in clear, simple, and concise prose, resisting the kind of "academese" that is frequently employed in textbooks and gives students a false impression of what academic writing should look like. I found all of the content very easy to understand, and, although it's intended for slightly more advanced classes, accessible for Freshman writing students.
The text is highly consistent, both in terms of the terminology it employs, its organizational structure, and its systematic incorporation of tips, learning activities, and quizzes.
The book is divided into 13 chapters, each of which addresses particular aspects of research writing and can be employed on its own, or in conjunction with other related chapters. I found that assigning chapters in order was generally perfectly appropriate, although there was no issue with assigning the odd chapter out of order - links to previous or later content are provided where appropriate, so students can easily navigate to other relevant sections of the text.
This text is very nicely organized. It moves from the beginning stages of the pre-writing process - choosing a topic and identifying appropriate guiding questions - through the research to the writing of the paper itself. I found that the organizational structure of the text very closely mirrored the structure I use myself in teaching research writing. As such, adopting this text for the course (and adapting the course to the text) was a delightfully straightforward exercise.
The interface of the text is excellent. It is very easy to navigate, very attractive, and all tools work as intended. Some features are only available to those with Ohio State University log-ins, which yields a handful of frustrating moments, but in general I didn't find this to be a significant issue.
The text is error free and written in a simple, accessible, and engaging style. It's not merely an easy read, but one that effectively models clear and concise academic prose for writing students.
To the extent such issues come into play, the text is inclusive and culturally sensitive. The content of the text is mostly neutral on such issues - they simply tend not to come into play - but I was pleased to find a comprehensive chapter on the ethical use of sources, which introduces an ethical dimension to the research and writing process that many students may not anticipate or otherwise be prepared to navigate.
Overall I was quite pleased with this text. In my online section of Research Paper Writing, I have assigned nine of the thirteen chapters, and am very pleased with the breadth of content covered thereby. With one exception, I've been able to assign those chapters in the order they appear in the book, which simplified the planning process for myself, and offers a structure to the course that will be more readily apparent to my students as well. Late chapters on Copyrights Basics and Fair Use struck me as unnecessary and a little off topic, but it is of course easy to simply not assign those chapters, and since this is not a print book they have no bearing on materials costs.
For an online class like the one I am currently teaching, this is an excellent primary text. Even in a face-to-face class it could prove to be a very useful supplemental text. Normally I resist the use of supplemental texts in face-to-face classes, but since this one is free it is ideal for that purpose: instructors and students can simply rely on it to whatever extent feels useful.
Reviewed by Jennifer Lantrip, Reference Librarian, Umpqua Community College on 2/8/17
This book is an excellent source for guiding undergraduate students through the research process, from understanding the purposes for doing research and writing a research question, to composing a thesis and contributing to a scholarly... read more
This book is an excellent source for guiding undergraduate students through the research process, from understanding the purposes for doing research and writing a research question, to composing a thesis and contributing to a scholarly conversation. Students learn where and how to find relevant sources and how to evaluate and use them ethically. The main text is supplemented with links to useful resources, videos, worksheets, examples, and exercises. These are all high quality sources, making this a comprehensive resource for teaching information literacy and the research process. While no index or glossary is provided, terms are well defined within the text. Links are provided to other sections within the text where terms are further discussed.
The content is error-free, unbiased, and accurate. Ideas and concepts are in accordance with the Association of College and Research Libraries’ “Framework for Information Literacy for Higher Education,” with the exception of several small sections that could easily be clarified or adapted.
The opening section of Chapter 3 states that researchers should find sources in order to meet their information needs. However, it states that one information need is “to convince your audience that your answer is correct or, at least, the most reasonable answer.” This should be clarified for students so that they understand that they should start their research with an open mind as opposed to looking for sources which support their predetermined thesis.
The section “The Sources to Meet Needs” in Chapter 3 states that convincing one’s audience is an information need and that students should find sources based upon what their audience would be convinced by. Researchers should not choose their sources based upon what would convince their audience, but rather upon what sources best answer their research question. The most relevant and highest quality sources should not be omitted from the research process because the researcher does not think that his/her audience would be convinced by them. It is part of the researcher’s job to educate and convince his/her audience why the chosen sources and the research are relevant and of high quality.
Chapter 13 mentions briefly, “Putting your sources to work for you in these roles can help you write in a more powerful, persuasive way—to, in fact, win your argument.” It is very important for researchers to make convincing arguments through using quality sources, doing quality research, and presenting the information in an understandable way. Students should understand that the goal of scholarly conversation is not to “win” arguments, but rather to contribute to the world’s shared knowledge. While one argument may hold for a time, it will most likely be refined in some way by future researchers.
The main content of each chapter is current and does not contain terms that will soon be outdated. Specific examples and exercises are arranged separately from the main chapter text and can be updated independently. Some of the content discusses and links to Ohio State University Libraries databases which are unavailable to students at other institutions. While some of this knowledge is transferable, the specific information about these databases is unique to OSU Libraries. It would be useful if this information could be generalized in the main flow of the text so that it would be applicable for students at other institutions.
This text is very readable and easy to understand. Concepts are explained clearly. Exercises and examples are provided to help students grasp each new concept. It is written in a casual tone that appears to make an effort to put its readers at ease while giving solid information about how to complete research and writing assignments successfully.
The terminology used in this book and its framework are consistent. Each chapter, chapter sections, examples, and exercises are organized in a consistent manner throughout the book, making it easy to follow. Students can refer to specific sections of the book or read it straight through. Because links are provided to sections of the book where important terms are defined or discussed further, students can easily jump to relevant sections of the book.
The book is divided into chapters and subsections which lead the reader seamlessly and logically through the research process. The book could easily be assigned to be read linearly, but it would also work well for instructors to assign specific chapters as applicable to the course content.
This book takes students through the research process in logical steps, from choosing and refining research questions, to producing and sharing what they have learned. For students who are unfamiliar with the research process, it would be most useful to read the book linearly as each chapter prepares students for future chapters.
This text is easy to navigate in both the PDF and online versions. Images are clear. There are currently no broken links. The contents in the PDF version could be made clearer by making a greater distinction between the main chapter and chapter section titles.
The text has negligible grammatical errors.
This text is not culturally insensitive or offensive.
I highly recommend this book for teaching information literacy and the research process to undergraduates.
Reviewed by Patricia Akhimie, Asst. Prof of English, Rutgers University-Newark on 2/8/17
This textbook does not include an index or glossary but is full-text searchable, returning a an easy to read and access menu of clickable search results to take readers directly to the desired information. In addition, an expandable Table of... read more
This textbook does not include an index or glossary but is full-text searchable, returning a an easy to read and access menu of clickable search results to take readers directly to the desired information. In addition, an expandable Table of Contents for the book is available as a tab so that readers can view an overview of topics and jump to other sections at any time. This textbook offers a review of research methods that is certainly comprehensive. Instructors will likely find that individual sections, rather than the whole work, are most useful in planning lessons and constructing student assignments in research based and writing intensive courses at the undergraduate level.
This textbook is accurate in its representation of research methods and of the reasoning behind these approaches. In addition, details about citation styles, and search tools, seem error-free. Treatments of the more complex aspects of research, such as constructing an argument, are unbiased and thorough.
The textbook should be useful to students and instructors for some time. It should be noted, however, that research software and citation styles are updated, though infrequently. Thus, the video walkthroughs of particular databases, for example, may be obsolete or misleading after some time.
This textbook is remarkably lucid and approachable for undergraduate readers. Discussions of complex ideas are illustrated with useful graphics that readers and instructors will find particularly helpful. The video walkthroughs are perhaps the most attractive illustrations for instructors. These guides will be appealing and easy to use for students intimidated by large databases and their idiosyncrasies.
The textbook is immanently usable. It is consistent in its tone as well as in its use of terms.
It is clear that this textbook has been designed with modularity in mind. Individual sections will be more useful than others, depending on the type and level of the class. In addition, sections can easily be assigned at different points over the course of a semester. For example, sections might be assigned at intervals that reflect the stages of the development of undergraduate student’s independent research paper. The section on formulating research questions might appear early in the semester, the section on citation styles toward the end.
The organization of the book reflects the stages of research. This means that navigating the textbook will be intuitive.
Navigating this textbook will be intuitive, the Table of Contents tab makes moving between sections very easy.
Readers will find the textbook free of simple typos and errors.
Readers will find the textbook inclusive. Some readers may find that the attempt made in the textbook to speak to research in the humanities, social sciences and sciences has meant that discussions can be vague at times but this is to be expected in a textbook on this topic aimed at a broad range of readers and researchers.
Reviewed by Heather Jerónimo, Assistant Professor, University of Northern Iowa on 2/8/17
This text is a comprehensive review of the various types of sources one might need to complete a research project or paper. The book begins with a clear explanation of how to formulate a research question, while the majority of the chapters focus... read more
This text is a comprehensive review of the various types of sources one might need to complete a research project or paper. The book begins with a clear explanation of how to formulate a research question, while the majority of the chapters focus on finding and evaluating sources. The topics in this text are well-chosen and reflect several aspects of academic writing in which beginning researchers might struggle, such as how to do a precision search, understanding biased versus unbiased sources, and how to decide between quoting or paraphrasing. This book is written at a level that undergraduates should easily be able to comprehend, while the content of the chapters gets increasingly detailed and complex throughout the book. There is no index or glossary at the back of the book, but there is a very complete table of contents at the beginning of the text. Readers might find it useful if the chapter titles in the table of contents were in bold, as the detailed breakdown of sections—while helpful—can be overwhelming when one is looking for the main categories of the book.
The text provides helpful and unbiased examples for how to do research in many different areas. The practice activities relate quite well to the content of the chapters, although some links do not work. One of the strengths of the text is its applicability in a general sense to many different types of research.
In most chapters the information is kept very general, allowing the text to enjoy relative longevity, as the process of how to conduct academic research, cite quotes, etc., likely will not change drastically in the near future. For example, in the section on databases, different types of databases are explained, but the author does not reference many specific databases to which students may or may not have access. With an understanding of the concept, students then are equipped to find the databases that pertain to their field and that are offered by their institutions. There are several references to Ohio State throughout the text that will not be helpful to all readers, but they do not impede the reader’s comprehension of the text.
It is a very readable text, written at a level that makes it easily accessible to undergraduate students. The author has avoided jargon that would be confusing to the readers.
Even though the book gives examples of various types of research and sources, it maintains a high level of consistency throughout.
The chapters are clearly divided in a way that allows the reader the option to skip between chapters or to read the chapters in succession. This text could be put to a variety of uses within the classroom. As an instructor, one could use it as a primary text for a Research Methods or Composition class. One could also suggest that students read only certain sections in a class that was not primarily focused on the writing of research papers but that had a research component. This text is a valuable how-to manual that students can reference throughout their academic journey.
The text has a logical organization and flow. The book transitions from more basic information at the beginning to more specialized knowledge in later chapters, allowing students to gradually become more immersed in the topic. The structure permits students to read the text from cover to cover, or to read only the information and chapters about which they are curious. The activities serve as good checkpoints to assess students’ knowledge and break up longer readings.
The interface of the text is easy to manage and does not distract from the content. The placement and accessibility of the activities provide quick and easy checks to assess whether students have understood the concepts of the chapters. The images support the text and are linked closely to the message.
There are few grammatical errors in this text.
The text is not culturally insensitive or offensive. Like many textbooks, it could be more intentional in its inclusion of a variety of races, ethnicities, and backgrounds, perhaps in the examples or practice activities.
Reviewed by Dr. William Vann, Information Studies Faculty, Minneapolis Community and Technical College on 12/5/16
While there is neither a back-of-the-book index nor a compiled glossary in this outstanding textbook (key terms are defined, however, throughout the chapters), one cannot deny its comprehensiveness. In fact, this text covers so much ground it is... read more
While there is neither a back-of-the-book index nor a compiled glossary in this outstanding textbook (key terms are defined, however, throughout the chapters), one cannot deny its comprehensiveness. In fact, this text covers so much ground it is unlikely to be used in its entirety for any single college course. Information literacy and research skills courses will find the first eight chapters to be a robust introduction to their subject matter, replete with interactive activities and auto-graded assessments. Composition courses engaged in research-based writing will likely work through the first eight chapters selectively, but then dwell on chapters nine and ten on argument formation and writing. Such courses may also benefit from the excellent chapter thirteen on Joseph Bizup's BEAM method of deploying research sources in scholarly communication. Chapters eleven and twelve on copyright and fair use, respectively, are likely to be used only by advanced undergraduates, faculty, and professional librarians, but they do serve as a handy reference nonetheless.
All of the chapters of this textbook contain authoritative and accurate information, in line with national information literacy standards and sound pedagogical methods for composition and critical thinking. The only section of the text I took issue with was the "Fact or Opinion" part of the second chapter, where the authors try to distinguish between fact, opinion, subjective information, and objective information. The authors' attempt results in claims like "the death penalty is wrong" being rendered as opinions, while claims like "women should stock up on calcium to ensure strong bones" are judged to be subjective information. Facts and objective information are superior, on this way of thinking, because they are the result of research studies, particularly empirical, quantitative ones.
I suspect that this way of drawing the distinction would do little to challenge the naive relativism most undergraduates bring to the classroom. (How many of us, when analyzing a text with beginning undergraduates, have had to entertain the question "Isn't that just the author's opinion though?") A better approach would be to talk about claims that are empirically justified (facts), claims that are justified, but not empirically (value judgments - "x is wrong", prescriptive claims - "women should do x"), and claims that are not adequately justified by any means (opinions). In this way, answering a research question like "Is the death penalty unjust?" is not merely an exercise in subjective opinion-making, but rather an exploration of reasoned argumentation, only some of which may be empirical or based on research studies.
The text is current and will likely be so for some time. Examples, activities, and tips are marked off from the main chapter prose, so will be easy to refresh when necessary.
There is no lack of technical terms in the world of information studies, but this textbook does a fine job of providing definitions where appropriate in each chapter. Concepts and methods are explained in context, and illustrative, easy-to-follow examples adorn each chapter.
The only area of the text that falls a little short on clarity is the interactive activities. These are usually multiple choice or matching questions, but some of the word choice in questions left this reader confused, and in some cases the instructions could have been more explicit.
Being authored by committee, we might expect this textbook to suffer in the consistency category. Yet it does not, thanks again to the fine editing job by Cheryl Lowry. Perhaps the book's provenance as a series of online tutorials put together by librarians and faculty at OSU is partly responsible for this.
As the authors suggest on the first page, the research process isn't always linear. So reading a text modeled on the research process oughtn't to be a straightforward chapter-by-chapter march either. Consequently, faculty and students can comfortably read this text selectively and skip chapters as needed. For the most holistic understanding of the research process, however, it would be sensible to work through at least chapters one through eight in their entirety.
I appreciate how the text's organization mirrors the research process itself. The first chapter takes on research questions, exactly where student researchers need to begin their projects. Subsequent chapters explore types of information sources, how to find and evaluate them, and finally how to deploy them in a well-argued scholarly product. The writing in each chapter is clear and crisp, with important concepts amplified by colorful visualizations.
As mentioned above, the chapters on copyright and fair use which occur near the end of the book feel like a logical interruption to the book's flow, and they might well fit more comfortably as appendices for occasional reference by advanced undergraduates, faculty, and librarians.
The "look and feel" of this textbook is clean and very intuitive to navigate through. The design strikes a pleasing balance between prose, graphics, and special formatting features like the explanatory, grey-background "TIPS" found in each chapter. Subheadings, bulleted and ordered lists, and judicious font choices make the text easy to read in all its online file formats.
One weakness of the interface is that several of the linked activities point to OSU Libraries' resources, thus requiring OSU authentication to be accessed. While it is understandable that the authors wanted to include their libraries' proprietary information sources in the activities - these are the sources their students and faculty will be using in actual practice, after all - this obviously makes this text less of an "open" textbook. Those outside of the OSU community who would like to adopt this textbook will therefore have to come up with their own replacement activities in such cases, or do without.
A few of the links in the text did lead me to a curious OSU server error message: "Error: Unknown export format", but I expect these links will be repaired as they are reported to the authors.
This textbook has clearly been edited with careful eyes by Cheryl Lowry, as grammatical errors are few to none. The grammatical hygiene of the text can probably also be attributed to its collective authorship - over a dozen librarians and faculty of the Ohio State University Libraries developed the content, which was born out of a series of online tutorials.
This textbook is culturally relevant in its use of examples and depictions of college students.
This text is a substantial contribution to the open textbook movement, and its quality easily meets or exceeds anything comparable in the commercial publishing arena. Highly recommended.
Reviewed by Kelly McKenna, Assistant Professor, Colorado State University on 12/5/16
The book provides a thorough introduction and how to regarding sources in academic writing. With the exception of the first chapter on writing research questions, the rest of the book is focused on sources, which is relevant for any type of... read more
The book provides a thorough introduction and how to regarding sources in academic writing. With the exception of the first chapter on writing research questions, the rest of the book is focused on sources, which is relevant for any type of academic writing not just research papers. The information is relevant across disciplines and readable to a wide audience. It is clearly written for and geared towards undergraduate students, particularly from Ohio State University. The index is detailed making it easy to locate specific information and includes hyperlinks for clear navigation. A slightly altered index format would make the chapter topics more readily available and accessed. All subjects and chapters are aligned rather than clearly indicating each of the chapters found within the text.
Content throughout the book is accurate and clearly written. There does not appear to bias in reading the material. The book includes numerous resources linked throughout the text, however some are no longer active resulting in error messages.
Due to the significant number of links throughout the book, it is likely updates will be necessary on a consistent basis. These links are extremely beneficial, so ensuring they are accurate and up to date is essential to the content of this book. Much of the book reads as a "how to" regarding sources, so although practices for scholarly writing will likely not become obsolete the sources and technology used to locate the sources will evolve.
The informal tone of the text is engaging and applicable for the intended audience. The writers are aware of their audience, avoiding technical jargon. Also, throughout the book they provide numerous examples, resources, activities, and tips to provide insight and relevancy to students.
The structure of the book is clear and well organized with each chapter providing scaffolding for the next. Although the text is internally consistent regarding terminology there are formatting differences between and within some chapters. Blue boxes throughout the text contain tips, examples, answers, etc. Organization, readability, and consistency could be improved if these were constant throughout the text similar to the presentation of activities in the text.
Sections of the book could be easily assigned and read in isolation. Subsections of material are clearly marked and chapters are presented in organized fashion with clear delineation between segments. The inclusion of numerous activities, examples, resources, and tips improve modularity.
The book is created as a tool for students completing academic writing and follows this course. Topics contained in the book are presented in a clear and logical structure. As mentioned above, with exception of the first chapter, the material is relevant to all undergraduate academic writing, not just research.
The layout and display work well as a PDF or electronic book. Numerous visuals are included throughout and are free of distortion or other distracting or confusing issues. As mentioned above, the index could be improved by clearly articulating the subheadings as within a chapter.
The book contains minimal to no grammatical errors.
The book is not culturally insensitive or offensive in any way.
Some sections of the book are specific to Ohio State University potentially limiting its relevancy and audience in specific chapters or sections.
Table of Contents
- 1. Research Questions
- 2. Types of Sources
- 3. Sources and Information Needs
- 4. Precision Searching
- 5. Search Tools
- 6. Evaluating Sources
- 7. Ethical Use of Sources
- 8. How to Cite Sources
- 9. Making an Argument
- 10. Writing Tips
- 11. Copyright Basics
- 12. Fair Use
- 13. Roles of Research Sources
Ancillary Material
About the book.
Choosing & Using Sources presents a process for academic research and writing, from formulating your research question to selecting good information and using it effectively in your research assignments. Additional chapters cover understanding types of sources, searching for information, and avoiding plagiarism. Each chapter includes self-quizzes and activities to reinforce core concepts and help you apply them. There are also appendices for quick reference on search tools, copyright basics, and fair use.
What experts are saying about Choosing & Using Sources: A Guide to Academic Research :
“…a really fantastic contribution that offers a much needed broadened perspective on the process of research, and is packed to the brim with all kinds of resources and advice on how to effectively use them. The chapter on plagiarism is really excellent, and the chapter on searching for sources is utterly brilliant.”
– Chris Manion, PhD Coordinator of Writing Across the Curriculum at Ohio State University
“… an excellent resource for students, with engaging content, graphics, and examples—very compelling. The coverage of copyright is outstanding.”
– J. Craig Gibson Co-chair of ACRL's Task Force on Information Literacy Competency Standards for Higher Education
About the Contributors
Cheryl Lowry , training and education specialist, Ohio State University Libraries.
Contribute to this Page
Source Document Binder
Per ICH GCP guideline E6 section 5.1 source data is identified as “all information in original records of clinical findings, observations, or other activities in a clinical trial necessary for the reconstruction and evaluation of the trial.” This is the first recording of subject-related information. According to 21 CFR 312.62(b) , and investigator is required to prepare and maintain adequate and accurate case histories that record all observations and other data pertinent to the investigation on each individual. Source documents must be complete, accurate, and valid. The regulatory authorities consider source documents to be the basis for al trial data and the adjudication of the outcome of events. The purpose of source documents/patient record binder:
- To document the existence of the participant and substantiate integrity of trial data collected.
- To include original documents related to the trial, medical treatment, history of participant, and participant’s condition while on-study or in follow-up. To provide an auditable link in the chain from the study database back to the original source (visit worksheet).
- To collect data for transfer to CRFs and then to the study database.
- To instruct study coordinators and other site personnel on what data to collect and information necessary to answer data queries.
These can be electronic media, original documents or certified copies. The following Source Document Binder Table of Contents is adopted from Partners Healthcare.
- Primary Sources
- Definitions
- Documents - Printed & Published
- Objects and Artifacts
- Sound Recordings
- Visual Materials
- Digitized Sources
- Locating Sources
- Sources By Subject
- Evaluating Sources
- Documenting Sources / Copyright
- Research Tips
- Using Archives This link opens in a new window
Primary Sources Definition
What are primary sources .
Primary sources enable the researcher to get as close as possible to the truth of what actually happened during an historical event or time period. Primary source is a term used in a number of disciplines to describe source material that is closest to the person, information, period, or idea being studied. A primary source (also called original source ) is a document, recording, artifact, or other source of information that was created at the time under study, usually by a source with direct personal knowledge of the events being described. It serves as an original source of information about the topic.
Similar definitions are used in library science , and other areas of scholarship. In journalism, a primary source can be a person with direct knowledge of a situation, or a document created by such a person. Primary sources are distinguished from secondary sources , which cite, comment on, or build upon primary sources, though the distinction is not a sharp one.
Newspaper Research
- Historical Newspapers (ProQuest) This link opens in a new window Includes the New York Times, Chicago Tribune, LA Times, Christian Science Monitor, and more. Newspapers are in PDF format and provide a visual representation of the newspaper.
- ProQuest Central This link opens in a new window Includes both newspapers and scholarly journals
- Historical Newspapers The Guardian and The Observer Search The Guardian (1821-2003) and its sister paper, The Observer (1791-2003)
- New York Newspaper Archive This link opens in a new window Access New York Newspaper Archives and discover stories of the past with NewspaperArchive.com. The archive covers New York history from 1753-2023, with lots of content from smaller, local newspapers. Articles have been scanned as PDFs and include images and advertisements, and are full text searchable.
- America's Historical Newspapers This link opens in a new window America's Historical Newspapers includes articles from local and regional American and Hispanic American newspapers from all 50 states. Coverage dates from 1690 to the early 20th century. Articles have been scanned as PDFs and include images and advertisements, and are full text searchable.
- American Periodicals Series Online This link opens in a new window includes digitized images of the pages of American magazines and journals published from colonial days to the dawn of the 20th century, 1740-1940.
- Times Digital Archive (London) This link opens in a new window Provides full-text access to back issues of The Times newspaper. Dates of coverage: 1785 to 2006.
- Hispanic American Newspapers, 1808-1980 This link opens in a new window Hispanic American Newspapers, 1808-1980 provides access to searchable digitized copies of newspapers printed in the U.S. during the 19th and 20th centuries for a Hispanic readership. It features hundreds of monolingual and bilingual newspapers in Spanish and English, including many obscure titles from the 19th century.
- Global Newsstream This link opens in a new window Full text of 300+ U.S. and international news sources. Includes coverage of 150+ major U.S. and international newspapers such as The New York Times and the Times of London, plus hundreds of other news sources and news wires.
- Gale Newspaper Sources This link opens in a new window The Gale NewsVault is a portal to several historical collections of British newspapers and periodicals. It enables full-text searching across several titles simultaneously, including the Times of London, Financial Times, and Times Literary Supplement, along with aggregate newspaper and periodical collections covering the 17th, 18th, and 19th centuries.
- Access World News This link opens in a new window Access World News provides the html full text and, for some titles, the pdf "as printed" visual representation, of articles from a variety of national and international news sources, including newspapers, digital-native news websites, television and radio transcripts, blogs, college and university newspapers, journals, magazines, and some audio and video. Most international titles are English language. Dates of coverage vary from title to title, but primarily span the late 20th century to present.
The Billy Rose Theatre Collection
TITLE: [Scene from Othello with Paul Robeson as Othello and Uta Hagen as Desdemona, Theatre Guild Production, Broadway, 1943-44] http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Robeson_Hagen_Othello.jpg SOURCE:Prints and Photographs Division Washington, D.C. 20540
The Billy Rose Theatre Collection of The New York Public Library is one of the largest and most comprehensive archives devoted to the theatrical arts. This image is a work of an employee of the United States Farm Security Administration or Office of War Information domestic photographic units, created during the course of the person's official duties. As a work of the U.S. federal government, the image is in the public domain.
- Billy Rose Collection NYPL The Billy Rose Theatre Division of The New York Public Library is one of the largest and most comprehensive archives devoted to the theatrical arts.
- New York Public Library Archives & Manuscripts On this site, you can search The New York Public Library's vast holdings, initiate a research visit, submit a query to an archivist, and access digitized material. Most Broadway shows can be viewed in the special collections. You will need a NYPL library card to view them.
- ArchiveGrid This link opens in a new window Thousands of libraries, museums, and archives have contributed nearly a million collection descriptions to ArchiveGrid.
- WorldCat - FirstSearch (OCLC) This link opens in a new window Search for books and more in libraries in the U.S. and around the world. Indicates when NYU Libraries holds a copy of a book and shows you nearby libraries with holdings.
- Internet Archive Internet Archive is a non-profit digital library offering free universal access to books, movies & music, as well as 456 billion archived web pages.
- Archives Unbound This link opens in a new window NYU is currently subscribing 14 collections:African America, Communists, and the National Negro Congress; Federal Response to Radicalism; Federal Surveillance of African Americans; Feminism in Cuba - 19th through 20th century archival document; Global Missions and Theology; India from Crown Rule to Republic; Testaments to the Holocaust (Documents and Rare Printed Materials from the Wiener Library, London); The Hindu Conspiracy Cases (Activities of the Indian Independence Movement in the U.S., 1908-1933); The Indian Army and Colonial Warfare on the Frontiers of India; The International Women’s Movement (The Pan Pacific Southeast Asia Women’s Association of the USA, 1950-1985); The Middle East Online - Arab-Israeli Relations; The Middle East Online - Iraq; U.S. and Iraqi Relations: U.S. Technical Aid; and, Witchcraft in Europe.
Historical Databases
An advert for P.T. Barnum's "Feejee Mermaid" in 1842 or thereabout. Author: P. T. Barnum or an employee, Source: Newspaper advert commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/File:Barnum_mermai... This image (or other media file) is in the public domain because its copyright has expired.
- America: History and Life with Full Text This link opens in a new window ndexes literature covering the history and culture of the United States and Canada, from prehistory to the present. The database indexes 1,700 journals and also includes citations and links to book and media reviews. Strong English-language journal coverage is balanced by an international perspective on topics and events, including abstracts in English of articles published in more than 40 languages. Publication dates of coverage: 1964 to present.
- Historical Abstracts with Full Text (EBSCO) This link opens in a new window Covers the history of the world (excluding the United States and Canada) from 1450 to the present, including world history, military history, women's history, history of education, and more. Indexes more than 1,700 academic historical journals in over 40 languages. Publication dates of coverage: 1955 to present.
- Theatre in Context Collection This link opens in a new window O’Dell’s Annals of the New York Stage, the Oxford University Press Companion series, and Greenwood’s American Theatre Companies series are just a few of the many in-copyright sources included in the Theatre in Context Collection. Placed alongside thousands of playbills, posters, photographs, and related theatrical ephemera, users will be able to paint a more comprehensive picture of the life and evolution of dramatic works.
- Shakespeare Collection This link opens in a new window The Shakespeare Collection provides access to general reference data, full-text scholarly periodicals, reprinted criticism, facsimile primary source material and the full-text annotated works from The Arden Shakespeare. Users can view page images of the First Folio, key Quartos, and major editions and adaptations of Shakespeare's works, plus works by Shakespeare's contemporaries and promptbooks from the 17th to the 20th century.
- Black Thought and Culture This link opens in a new window Contains 1297 sources with 1100 authors, covering the non-fiction published works of leading African-Americans. Particular care has been taken to index this material so that it can be searched more thoroughly than ever before. Where possible the complete published non-fiction works are included, as well as interviews, journal articles, speeches, essays, pamphlets, letters and other fugitive material.
- Periodicals Archive Online This link opens in a new window Provides full-text and full-image access to hundreds of journals published in the arts, humanities, social sciences, and areas of general popular interest. Each periodical is covered back to its first issue, regardless of when it began publication. International in scope, PAO covers periodicals in a number of Western languages.
- Accessible Archives This link opens in a new window Includes the following collections: African American Newspapers, The Civil War Part I. A Newspaper Perspective, The Pennsylvania Genealogical Catalog, Pennsylvania Newspaper Record, South Carolina Newspapers, and The Liberator. ** Within these collections are papers such as The Charleston Mercury, The Christian Recorder, The Colored American, Douglass Monthly, Frederick, Douglass Paper, Freedom's Journal, Godey's Lady's Book, The Liberator, The National Era, The New York Herald, The North Star, The Pennsylvania Gazette, The Pennsylvania Packet, The Maryland Gazette, Provincial Freeman, Richmond Enquirer, The South Carolina Gazette, The Gazette of the State of South Carolina, The South Carolina Gazette and Country Journal, The South Carolina and American General Gazette, Weekly Advocate.
- Early English Books Online (EEBO) This link opens in a new window Early English Books Online (EEBO) contains digital facsimile page images of virtually every work printed in England, Ireland, Scotland, Wales and British North America and works in English printed elsewhere from 1473-1700. Searchable full text is also available for a subset of the collection.
- Eighteenth Century Journals This link opens in a new window Eighteenth Century Journals brings together rare journals printed between 1685 and 1835, primarily in the British Isles (with some publications from India, the Caribbean, and Europe). Users can view and download page images and search transcribed full text for all journals in the collection.
- C19: The 19th Century Index This link opens in a new window C19: The 19th Century Index provides bibliographic coverage of nineteenth-century books, periodicals, official documents, newspapers and archives from the English-speaking world. This database includes the Wellesley Index to Victorian Periodicals (1824-1900), Poole's Index to Periodical Literature, Palmer's Index to The Times, the Nineteenth Century Short Title Catalogue, and more.
- Sixties: Primary Documents and Personal Narratives 1960 - 1974 This link opens in a new window This resource consists of diaries, letters, autobiographies and other memoirs, written and oral histories, manifestos, government documents, memorabilia, and scholarly commentary. With 150,000 pages of material at completion, this searchable collection is a resource for students and scholars researching this period in American history, culture, and politics.
- African American Archives (via Fold3) This link opens in a new window This full text resource offers access to original documents that reveal a side of the African American story that few have seen before.
- African American Experience This link opens in a new window Full-text digital resource exploring the history and culture of African Americans, as well as the greater Black Diaspora. Features access to full-text content from more than 400 titles, 3,000 slave narratives, over 2000 images, 5,000 primary sources, and 250 vetted Web sites.
Letters & Diaries /Oral Histories
- Oral History Online This link opens in a new window Provides in-depth indexing to more than 2,700 collections of Oral History in English from around the world. The collection provides keyword searching of almost 281,000 pages of full-text by close to 10,000 individuals from all walks of life.
- American Civil War: Letters and Diaries This link opens in a new window This database contains 2,009 authors and approximately 100,000 pages of diaries, letters and memoirs. Includes 4,000 pages of previously unpublished manuscripts such as the letters of Amos Wood and his wife and the diary of Maryland Planter William Claytor. The collection also includes biographies, an extensive bibliography of the sources in the database, and material licensed from The Civil War Day-by-Day by E.B. Long.
- British and Irish Women's Letters and Diaries This link opens in a new window Includes 10,000 pages of diaries and letters revealing the experiences of approximately 500 women. The collection now includes primary materials spanning more than 300 years. The collection also includes biographies and an extensive annotated bibliography of the sources in the database.
- North American Immigrant Letters, Diaries and Oral Histories This link opens in a new window North American Immigrant Letters, Diaries and Oral Histories includes 2,162 authors and approximately 100,000 pages of information, so providing a unique and personal view of what it meant to immigrate to America and Canada between 1800 and 1950. Contains contemporaneous letters, diaries, oral histories, interviews, and other personal narratives.
- North American Women's Letters and Diaries This link opens in a new window North American Women's Letters and Diaries includes the immediate experiences of 1,325 women and 150,000 pages of diaries and letters.
Gale Primary Sources
- Gale Primary Sources This link opens in a new window Gale Artemis is a groundbreaking research environment that integrates formerly disparate digital collections to enable innovative research. Gale Artemis provides an unprecedented, seamless research experience that helps students find a starting point, search across a wide array of materials and points in time, and discover new ways to analyze information.
Victorian Popular Culture
- Victorian Popular Culture This link opens in a new window An essential resource for the study of popular entertainment in the nineteenth and early twentieth centuries. This innovative portal invites users into the darkened halls, small backrooms and travelling venues that hosted everything from spectacular shows and bawdy burlesque, to the world of magic and spiritualist séances. ** The resource is divided into four self-contained sections: Moving Pictures, Optical Entertainments and the Advent of Cinema; Music Hall, Theatre and Popular Entertainment; Circuses, Sideshows and Freaks; Spiritualism, Sensation and Magic
Historical Image Collections
commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/File:Cushman_in_Ha... , The American actress Charlotte Cushman advertised in William Shakespeare's Hamlet at the Washington Theater in 1861. Author:Washington Theater, SOURCE:Public Library of Congress. this image (or other media file) is in the public domain because its copyright has expired.
- American Broadsides and Ephemera This link opens in a new window American Broadsides and Ephemera offers fully searchable images of approximately 15,000 broadsides printed between 1820 and 1900 and 15,000 pieces of ephemera printed between 1760 and 1900. The remarkably diverse subjects of these broadsides range from contemporary accounts of the Civil War, unusual occurrences and natural disasters to official government proclamations, tax bills and town meeting reports. Featuring many rare items, the pieces of ephemera include clipper ship sailing cards, early trade cards, bill heads, theater and music programs, stock certificates, menus and invitations documenting civic, political and private celebrations.
- Early American Imprints, Series I. Evans, 1639-1800 This link opens in a new window Search or browse the books, pamphlets, broadsides and other imprints listed in the renowned bibliography by Charles Evans.
- Early American Imprints, Series II. Shaw-Shoemaker, 1801-1819 This link opens in a new window Search or browse the books, pamphlets, broadsides and other imprints listed in the distinguished bibliography by Ralph R. Shaw and Richard H. Shoemaker. 1801-1819
- American Antiquarian Society (AAS) Historical Periodicals Collection (EBSCO) This link opens in a new window Provide digital access to the most comprehensive collection of American periodicals published between 1691 and 1877. Included digitized images of American magazines and journals never before available outside the walls of the American Antiquarian Society. The collection is available in five series: Series 1 (1691-1820) - Series 2 (1821-1837) - Series 3 (1838-1852) - Series 4 (1853-1865) - Series 5 (1866-1877)
Link to Bobst Special Collections
- NYU Special Collections Bobst Library's Special Collections department houses significant archival resources including materials from the Downtown Collection, which documents New York City's downtown arts scene from the 1970s through the early 1990s. Maria Irene Fornés and Richard Foreman are among the many artists whose materials are housed in the Downtown Collection.
- Fales It is especially strong in English literature from the middle of the 18th century to the present, documenting developments in the novel. The Downtown Collection documents the downtown New York art, performance, and literary scenes from 1975 to the present and is extremely rich in archival holdings, including extensive film and video objects.
- Tamiment One of the finest research collections in the country documenting the history of radical politics: socialism, communism, anarchism, utopian experiments, the cultural left, the New Left, and the struggle for civil rights and civil liberties.
Guide to International Collections
- SIBMAS International Directory of Performing Arts Collections and Institutions
Books Containing Primary Source Documents
- The mediaeval stage by Chambers, E. K. (Edmund Kerchever), 1866-1954 Call Number: Online versions avail.
- The Elizabethan stage by Chambers, E. K. (Edmund Kerchever), 1866-1954 Call Number: PN2589 .C4 1965 4 vol. plus online version avail
- The diary of Samuel Pepys by Pepys, Samuel, 1633-1703 Call Number: Avail. online
- A history of theatrical art in ancient and modern times. by Mantzius, Karl, 1860-1921 Call Number: PN2106 .M313 1970 4 vol. also internet access
- Ben Jonson by Ben Jonson Call Number: online access
- << Previous: Visual Materials
- Next: Digitized Sources >>
- Last Updated: May 22, 2024 3:19 PM
- URL: https://guides.nyu.edu/primary
Document Analysis
- First Online: 02 January 2023
Cite this chapter

- Benjamin Kutsyuruba 4
Part of the book series: Springer Texts in Education ((SPTE))
2 Citations
This chapter describes the document analysis approach. As a qualitative method, document analysis entails a systematic procedure for reviewing and evaluating documents through finding, selecting, appraising (making sense of), and synthesizing data contained within them. This chapter outlines the brief history, method and use of document analysis, provides an outline of its process, strengths and limitations, and application, and offers further readings, resources, and suggestions for student engagement activities.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others

Qualitative Text Analysis: A Systematic Approach

Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis: A Guide for Beginners

Qualitative Content Analysis: Theoretical Background and Procedures
Altheide, D. L. (1987). Ethnographic content analysis. Qualitative Sociology, 10 (1), 65–77.
Article Google Scholar
Altheide, D. L. (1996). Qualitative media analysis . SAGE.
Google Scholar
Altheide, D. L. (2000). Tracking discourse and qualitative document analysis. Poetics, 27 , 287–299.
Atkinson, P. A., & Coffey, A. (1997). Analysing documentary realities. In D. Silverman (Ed.), Qualitative research: Theory, method and practice (pp. 45–62). SAGE.
Berg, B. L. (2001). Qualitative research methods for social sciences . Allyn and Bacon.
Bowen, G. A. (2009). Document analysis as a qualitative research method. Qualitative Research Journal, 9 (2), 27–40. https://doi.org/10.3316/qrj0902027
Bryman, A. (2003). Research methods and organization studies . Routledge.
Book Google Scholar
Cardno, C. (2018). Policy document analysis: A practical educational leadership tool and a qualitative research method. Educational Administration: Theory and Practice , 24 (4), 623–640. https://doi.org/10.14527/kuey.2018.016
Caulley, D. N. (1983). Document analysis in program evaluation. Evaluation and Program Planning, 6 , 19–29.
Corbin, J., & Strauss, A. (2008). Basics of qualitative research: Techniques and procedures for developing grounded theory (3rd ed.). SAGE.
Derrida, J. (1978). Writing and difference . Routledge & Kegan Paul.
Glaser, B. G., & Strauss, A. L. (1967). The discovery of grounded theory: Strategies for qualitative research . Aldine De Gruyter.
Glesne, C., & Peshkin, A. (1992). Becoming qualitative researchers (2nd ed.). Longman.
Goode, W. J., & Hatt, P. K. (1952). Methods in social research . McGraw-Hill.
Hodder, I. (2000). The interpretation of documents and material culture. In N. K. Denzin & Y. S. Lincoln (Eds.), Handbook of qualitative research (2nd ed., pp. 703–715). SAGE.
Krippendorff, K. (1980). Content analysis: An introduction to its methodology. SAGE.
Lombard, M., Snyder-Duch, J., & Bracken, C. C. (2002). Content analysis in mass communication: Assessment and reporting of intercoder reliability. Human Communication Research, 28 , 587–604.
Lombard, M., Snyder-Duch, J., & Bracken, C. C. (2010). Practical resources for assessing and reporting intercoder reliability in content analysis research projects . Retrieved March 20, 2011, from http://matthewlombard.com/reliability/index_print.html
Mayring, P. (2000). Qualitative content analysis. Forum: Qualitative social research (Vol. 1(2)). Retrieved March 22, 2011, from http://www.qualitative-research.net/index.php/fqs/article/viewArticle/1089/2385
McMillan, J. H., & Schumacher, S. (2010). Research in education: Evidence-based inquiry (7th ed.). Pearson.
Merriam, S. B. (1988a). Case study research in education: A qualitative approach . Jossey-Bass.
Merriam, S. B. (1998b). Case study research in education . Jossey-Bass.
Miller, F. A., & Alvarado, K. (2005). Incorporating documents into qualitative nursing research. Journal of Nursing Scholarship, 37 (4), 348–353.
Neuendorf, K. A. (2002). The content analysis guidebook . SAGE.
O’Leary, Z. (2014). The essential guide to doing your research project (2nd ed.). SAGE.
Patton, M. Q. (2002). Qualitative research & evaluation methods (3rd ed.). SAGE.
Prior, L. (2003). Using documents in social research . SAGE.
Prior, L. (2008a). Document analysis. In L. Given (Ed.), The SAGE encyclopaedia of qualitative research methods (pp. 231–232). SAGE. https://doi.org/10.4135/9781412963909
Prior, L. (2008b). Repositioning documents in social research. Sociology, 42 (5), 821–836. https://doi.org/10.1177/0038038508094564
Prior, L. (2012). The role of documents in social research. In S. Delamont (Ed.), Handbook of qualitative research in education (pp. 426–438). Edward Elgar.
Salminen, A., Kauppinen, K., & Lehtovaara, M. (1997). Towards a methodology for document analysis. Journal of the American Society for Information Science, 48 (7), 644–655.
Stake, R. E. (1995). The art of case study research . SAGE.
Wharton, C. (2006). Document analysis. In V. Jupp (Ed.), The SAGE dictionary of social research methods (pp. 80–81). SAGE. https://doi.org/10.4135/9780857020116
Yin, R. K. (2009). Case study research, design and methods (4th ed.). SAGE.
Additional Reading
Kutsyuruba, B. (2017). Examining education reforms through document analysis methodology. In I. Silova, A. Korzh, S. Kovalchuk, & N. Sobe (Eds.), Reimagining Utopias: Theory and method for educational research in post-socialist contexts (pp. 199–214). Sense.
Kutsyuruba, B., Christou, T., Heggie, L., Murray, J., & Deluca, C. (2015). Teacher collaborative inquiry in Ontario: An analysis of provincial and school board policies and support documents. Canadian Journal of Educational Administration and Policy, 172 , 1–38.
Kutsyuruba, B., Godden, L., & Tregunna, L. (2014). Curbing the early-career attrition: A pan-Canadian document analysis of teacher induction and mentorship programs. Canadian Journal of Educational Administration and Policy, 161 , 1–42.
Segeren, A., & Kutsyuruba, B. (2012). Twenty years and counting: An examination of the development of equity and inclusive education policy in Ontario (1990–2010). Canadian Journal of Educational Administration and Policy, 136 , 1–38.
Online Resources
Document Analysis: A How To Guide (12:27 min) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vOsE9saR_ck
Document Analysis with Philip Adu (1:16:40 min) https://youtu.be/bLKBffW5JPU
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Queen’s University, Kingston, Canada
Benjamin Kutsyuruba
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Benjamin Kutsyuruba .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Department of Educational Administration, College of Education, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, SK, Canada
Janet Mola Okoko
Scott Tunison
Department of Educational Administration, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, SK, Canada
Keith D. Walker
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Kutsyuruba, B. (2023). Document Analysis. In: Okoko, J.M., Tunison, S., Walker, K.D. (eds) Varieties of Qualitative Research Methods. Springer Texts in Education. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-04394-9_23
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-04394-9_23
Published : 02 January 2023
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-031-04396-3
Online ISBN : 978-3-031-04394-9
eBook Packages : Education Education (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
Sign in to your site’s geographic location:
3 tips to create outstanding clinical trial source documents.

Creating exceptional clinical research source documents is crucial for successful clinical trials. The best way to ensure that your source documents are ready is to know and understand the Clinical Study Protocol (CSP), which serves as the basis for your source documents. Use the CSP as your primary reference when creating source documents. This is because it explains exactly what happens in each step of the clinical trial.
First, read the CSP. Once you have a general idea of what each source document should contain, dig a little deeper. Use these three targeted sections in the CSP to gather crucial information needed to write an outstanding clinical trial source document.
1. Clinical Trial Participant Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria in your Source Documents

The Inclusion & Exclusion Criteria section has some of the most valuable information needed to reach study endpoints. It’s also included in every CSP. That said, write your source documents to collect information about a patient. You can ask them directly, or collect information through observation from clinical trial staff. To use this section of the CSP to your advantage, go through each of the inclusion and exclusion criteria and make sure that there is a question in your source documents that confirms each criterion.
For example, if an exclusion criterion in a particular study omits a patient who has a BMI that is >=31, include a BMI question in the demographic source document(s). Note that not all criterion are explicitly stated in the study activities portion of the CSP. So, if you want to make an extremely valuable source document, try writing a note in italics. Include the note under the question that states the exclusionary value and include the criteria number.
2. Use Study Endpoints in Your Source Documents

Study endpoints explain why the clinical trial is being conducted. Thus, during source document create, you’ll answer most of your questions in the study endpoints section of the CSP.
To create great source documents, use a similar process for study endpoints that you did for the inclusion and exclusion criterion. Find the endpoints in the CSP and look for specific values, queues, or milestones that need to be monitored throughout the study.
One way to include information about a desired outcome is to write a note about the endpoint in a source question. Or, you can include it in the “details and directions” section of a source document.
Here’s an example. One study endpoint measures a Six Minute Walk Test in patients at 30 days post treatment, and again at 1 year. Within the source, create a question that asks for the difference between the walk tests at the two dates. This allows the investigator or staff to assess if there is a change from baseline.
3. Don’t Forget Appendices & Tables in Your Clinical Trial Source
At this point, almost all of the source documents for the clinical trial have been written and polished. However, if you want to create a truly outstanding source document, don’t forget the appendices and tables section of the CSP.
The appendices and tables section may also include information to further explain the study, its purposes, and detailed information about specific procedures.
Here’s an example. An appendix in a study called Appendix B: Definitions offers all definitions for terms used throughout the study. Include these specific definitions within the relevant source document.
From the example above, in the Six Minute Walk Test (6MWT), include a definition from the appendices and table section, links to resources, and CSP reference information.
While there are many tricks to the trade, make sure you know what is being written, why, and for whom. Get to know the clinical study protocol to create great source documents.
Here at Team CRIO, our study designers create well-written digitized documents that include alerts for protocol and regulatory deviations. These handy features take the guesswork out of deviations and help to keep you organized. We strive to get the most out of a clinical study protocol in our eSource and CTMS digital documents.

21 CFR Part 11 Regulation Compliance Update
Compliance Update: The 21 CFR Part 11 Regulation is a cornerstone of conducting clinical trials in today’s world. The release of the regulation 1997 established guidelines for the use of electronic records and electronic signatures in FDA-regulated industries and had a significant impact on the pharmaceutical and medical device industries. The FDA began working on...

The Current State of Clinical Trials in Ukraine—A Conversation with Dr. Roman Fishchuk
Meet Dr. Roman Fishchuk, an esteemed otorhinolaryngologist (ENT) whose journey in the healthcare field has been marked by a commitment to providing medical care and innovative treatment options through clinical trials in his native Ukraine. Having graduated from Ivano-Frankivsk National Medical University, Dr. Fishchuk specialized in otolaryngology and completed a Master’s degree at the University...

Transitioning to CRIO? How to Get Your Data Ready for Migration
You have just signed on to use CRIO and you are excited to get started. Even if you are moving primarily from paper, you may have data that you want to migrate into CRIO rather than having to re-enter it. For many of our new clients, they have a wealth of information available in spreadsheets...

Get articles delivered to your inbox, every week
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Types of Sources

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
This section lists the types of sources most frequently used in academic research and describes the sort of information that each commonly offers.
Print Sources
Books and Textbooks: Odds are that at least one book has been written about virtually any research topic you can imagine (and if not, your research could represent the first steps toward a best-selling publication that addresses the gap!). Because of the time it takes to publish a book, books usually contain more dated information than will be found in journals and newspapers. However, because they are usually much longer, they can often cover topics in greater depth than more up-to-date sources.
Newspapers: Newspapers contain very up-to-date information by covering the latest events and trends. Newspapers publish both factual information and opinion-based articles. However, due to journalistic standards of objectivity, news reporting will not always take a “big picture” approach or contain information about larger trends, instead opting to focus mainly on the facts relevant to the specifics of the story. This is exacerbated by the rapid publication cycles most newspapers undergo: new editions must come out frequently, so long, in-depth investigations tend to be rarer than simple fact-reporting pieces.
Academic and Trade Journals: Academic and trade journals contain the most up-to-date information and research in industry, business, and academia. Journal articles come in several forms, including literature reviews that overview current and past research, articles on theories and history, and articles on specific processes or research. While a well-regarded journal represents the cutting-edge knowledge of experts in a particular field, journal articles can often be difficult for non-experts to read, as they tend to incorporate lots of technical jargon and are not written to be engaging or entertaining.
Government Reports and Legal Documents: The government regularly releases information intended for internal and/or public use. These types of documents can be excellent sources of information due to their regularity, dependability, and thoroughness. An example of a government report would be any of the reports the U.S. Census Bureau publishes from census data. Note that most government reports and legal documents can now be accessed online.
Press Releases and Advertising: Companies and special interest groups produce texts to help persuade readers to act in some way or inform the public about some new development. While the information they provide can be accurate, approach them with caution, as these texts' publishers may have vested interests in highlighting particular facts or viewpoints.
Flyers, Pamphlets, Leaflets: While some flyers or pamphlets are created by reputable sources, because of the ease with which they can be created, many less-than-reputable sources also produce these. Pamphlets and leaflets can be useful for quick reference or very general information, but beware of pamphlets that spread propaganda or misleading information.
Digital and Electronic Sources
Multimedia: Printed material is certainly not the only option for finding research. You might also consider using sources such as radio and television broadcasts, interactive talks, and recorded public meetings. Though we often go online to find this sort of information today, libraries and archives offer a wealth of nondigitized media or media that is not available online.
Websites: Most of the information on the Internet is distributed via websites. Websites vary widely in terms of the quality of information they offer. For more information, visit the OWL's page on evaluating digital sources.
Blogs and personal websites: Blogs and personal sites vary widely in their validity as sources for serious research. For example, many prestigious journalists and public figures may have blogs, which may be more credible than most amateur or personal blogs. Note, however, that there are very few standards for impartiality or accuracy when it comes to what can be published on personal sites.
Social media pages and message boards: These types of sources exist for all kinds of disciplines, both in and outside of the university. Some may be useful, depending on the topic you are studying, but, just like personal websites, the information found on social media or message boards is not always credible.
What Is a Primary Source?
Glossary of Grammatical and Rhetorical Terms - Definition and Examples
Diane Diederich / Getty Images
- An Introduction to Punctuation
- Ph.D., Rhetoric and English, University of Georgia
- M.A., Modern English and American Literature, University of Leicester
- B.A., English, State University of New York
In research and academics, a primary source refers to information collected from sources that witnessed or experienced an event firsthand. These can be historical documents , literary texts, artistic works, experiments, journal entries, surveys, and interviews. A primary source, which is very different from a secondary source , is also called primary data.
The Library of Congress defines primary sources as "the raw materials of history—original documents and objects which were created at the time under study," in contrast to secondary sources , which are "accounts or interpretations of events created by someone without firsthand experience," ("Using Primary Sources").
Secondary sources are often meant to describe or analyze a primary source and do not give firsthand accounts; primary sources tend to provide more accurate depictions of history but are much harder to come by.
Characteristics of Primary Sources
There are a couple of factors that can qualify an artifact as a primary source. The chief characteristics of a primary source, according to Natalie Sproull, are: "(1) [B]eing present during the experience, event or time and (2) consequently being close in time with the data. This does not mean that data from primary sources are always the best data."
Sproull then goes on to remind readers that primary sources are not always more reliable than secondary sources. "Data from human sources are subject to many types of distortion because of such factors as selective recall, selective perceptions, and purposeful or nonpurposeful omission or addition of information. Thus data from primary sources are not necessarily accurate data even though they come from firsthand sources," (Sproull 1988).
Original Sources
Primary sources are often called original sources, but this is not the most accurate description because you're not always going to be dealing with original copies of primary artifacts. For this reason, "primary sources" and "original sources" should be considered separate. Here's what the authors of "Undertaking Historical Research in Literacy," from Handbook of Reading Research , have to say about this:
"The distinction also needs to be made between primary and original sources . It is by no means always necessary, and all too often it is not possible, to deal only with original sources. Printed copies of original sources, provided they have been undertaken with scrupulous care (such as the published letters of the Founding Fathers), are usually an acceptable substitute for their handwritten originals." (E. J. Monaghan and D. K. Hartman, "Undertaking Historical Research in Literacy," in Handbook of Reading Research , ed. by P. D. Pearson et al. Erlbaum, 2000)
When to Use Primary Sources
Primary sources tend to be most useful toward the beginning of your research into a topic and at the end of a claim as evidence, as Wayne Booth et al. explain in the following passage. "[Primary sources] provide the 'raw data' that you use first to test the working hypothesis and then as evidence to support your claim . In history, for example, primary sources include documents from the period or person you are studying, objects, maps, even clothing; in literature or philosophy, your main primary source is usually the text you are studying, and your data are the words on the page. In such fields, you can rarely write a research paper without using primary sources," (Booth et al. 2008).
When to Use Secondary Sources
There is certainly a time and place for secondary sources and many situations in which these point to relevant primary sources. Secondary sources are an excellent place to start. Alison Hoagland and Gray Fitzsimmons write: "By identifying basic facts, such as year of construction, secondary sources can point the researcher to the best primary sources , such as the right tax books. In addition, a careful reading of the bibliography in a secondary source can reveal important sources the researcher might otherwise have missed," (Hoagland and Fitzsimmons 2004).
Finding and Accessing Primary Sources
As you might expect, primary sources can prove difficult to find. To find the best ones, take advantage of resources such as libraries and historical societies. "This one is entirely dependent on the assignment given and your local resources; but when included, always emphasize quality. ... Keep in mind that there are many institutions such as the Library of Congress that make primary source material freely available on the Web," (Kitchens 2012).
Methods of Collecting Primary Data
Sometimes in your research, you'll run into the problem of not being able to track down primary sources at all. When this happens, you'll want to know how to collect your own primary data; Dan O'Hair et all tell you how: "If the information you need is unavailable or hasn't yet been gathered, you'll have to gather it yourself. Four basic methods of collecting primary data are field research, content analysis, survey research, and experiments. Other methods of gathering primary data include historical research, analysis of existing statistics, ... and various forms of direct observation," (O'Hair et al. 2001).
- Booth, Wayne C., et al. The Craft of Research . 3rd ed., University of Chicago Press, 2008.
- Hoagland, Alison, and Gray Fitzsimmons. "History." Recording Historic Structures. 2nd. ed., John Wiley & Sons, 2004.
- Kitchens, Joel D. Librarians, Historians, and New Opportunities for Discourse: A Guide for Clio's Helpers . ABC-CLIO, 2012.
- Monaghan, E. Jennifer, and Douglas K. Hartman. "Undertaking Historical Research in Literacy." Handbook of Reading Research. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, 2002.
- O'Hair, Dan, et al. Business Communication: A Framework for Success . South-Western College Pub., 2001.
- Sproull, Natalie L. Handbook of Research Methods: A Guide for Practitioners and Students in the Social Sciences. 2nd ed. Scarecrow Press, 1988.
- "Using Primary Sources." Library of Congress .
- Secondary Sources in Research
- Primary and Secondary Sources in History
- Research in Essays and Reports
- How to Prove Your Family Tree Connections
- Five Steps to Verifying Online Genealogy Sources
- Pros and Cons of Secondary Data Analysis
- Understanding Secondary Data and How to Use It in Research
- Documentation in Reports and Research Papers
- What Is a Research Paper?
- How to Use Libraries and Archives for Research
- 6 Skills Students Need to Succeed in Social Studies Classes
- How to Cite Genealogy Sources
- Definition and Examples of Quotation in English Grammar
- Glossary of Historical Terms
- How to Determine a Reliable Source on the Internet
- Fashion Throughout History
- Harvard Library
- Research Guides
- Faculty of Arts & Sciences Libraries
Library Research Guide for the History of Science: Introduction
- What is a Primary Source?
- Senior Theses 2023
- Background and Context/Biography
- Exploring Your Topic
- Using HOLLIS
- What is a Secondary Source?
Page Contents
Knowing a primary source when you see one, kinds of primary sources, find primary sources in hollis, using digital libraries and collections online, using bibliographies.
- Exploring the Special Collections at Harvard
- Citing Sources & Organizing Research
Primary sources provide first-hand testimony or direct evidence concerning a topic under investigation. They are created by witnesses or recorders who experienced the events or conditions being documented.
Often these sources are created at the time when the events or conditions are occurring, but primary sources can also include autobiographies, memoirs, and oral histories recorded later.
Primary sources are characterized by their content, regardless of the format available. (Handwritten notes could be published; the published book might be digitized or put on microfilm, but those notes are still primary sources in any format).
Some types of primary sources:
- Original documents (excerpts or translations acceptable): Diaries, speeches, manuscripts, letters, interviews, news film footage, contemporary newspaper articles, autobiographies, official records, pamphlets, meeting notes, photographs, contemporary sketches
- Creative works : Poetry, drama, novels, music, art
- Relics or artifacts : Furniture, clothing, buildings
Examples of primary sources include:
- A poster from the Brotherhood of Sleeping Car Porters' 1962 strike
- The papers of William James
- A 1970 U.S. State Dept document updating Nixon on U.S.-Soviet space cooperation activities (Harvard login)
- A British pamphlet: "Electric Lighting for Country Houses," 1898
- Phineas Gage's skull
- The text of J. Robert Oppenheimer's "Atomic Weapons" presentation to the American Philosophical Society
Outline of Primary Sources for History
Archives and Manuscripts
Archives and manuscripts are the unpublished records of persons (letters, notes, diaries, etc.) and organizations. What are Archives? Usually each archival collection has a (short) catalog record and a detailed finding aid (which is often available online).
- "Catalog record” refers to the kind of record found in library online catalogs, similar to those for books, although often a bit longer. Example of an Archive record .
- “Finding aid” (sometimes called an inventory) generally refers to a list of the folder labels for the collection, accompanied by a brief collection overview (scope and contents note) and a biographical (or institutional) note on the creator of the collection. Finding aids may be as long as needed given the size of the collection. They vary considerably according to the practices of individual repositories. Example of a Finding aid .
To find Archives and manuscripts at Harvard, go to HOLLIS Advanced search . Search your keywords or Subject terms (see the HOLLIS page of this guide ) in the Library Catalog, limiting to Resource Type: Archives/Manuscripts. You can choose the library at the right (Search Scope). Countway Medicine has abundant medical archives, and Schlesinger has many archives of women activists, many in health and reproductive rights fields. Sample search on Subject: Women health .
Library Research Guide for Finding Manuscripts and Archival Collections explains
- How to find archives and manuscripts at Harvard
- How to find archives and manuscripts elsewhere in US via search tools and via subject guides .
- How to find archives and manuscripts in Europe and elsewhere.
- Requesting digitization of archival material from Harvard and from other repositories .
For digitized archival material together with other kinds of primary sources:
- Finding Primary Sources Online offers general instructions for finding primary sources online and a list of resources by region and country
- Online Primary Source Collections for the History of Science lists digital collections at Harvard and beyond by topic.
- Online Primary Source Collections for History lists digital collections at Harvard and beyond by topic.
Methods for finding books are described under the HOLLIS page of this guide and in the Finding Primary Sources in HOLLIS box on this page.
- Book Reviews may give an indication as to how a scientific work was received. See: Finding Book Reviews .
- Numerous, especially pre-1923 books (as well as periodicals and other sources) can be found and full text searched in several digital libraries (see box on this page).
Periodicals
Scientific articles :
Web of Science Citation Indexes (Harvard Login) (1900- ) articles in all areas of science. Includes medical articles not in PubMed. You can use the Cited Reference search in the Web of Science to find primary source articles that cite a specified article, thus getting an idea of its reception. More information on the Web of Science .
PubMed (1946- ) covers, usually with abstracts, periodical articles on all areas of medicine. - --Be sure to look at the MeSH (Medical Subject Headings) at the bottom of pertinent records. Very recent articles may not as yet received their MeSH terms. So look at older records to find the MeSH terms, and use a variety of keywords as well as MeSH terms to find the new records. --The MeSH terms are the same as the Medical Subject terms found in HOLLIS. --Hit Free article or Try Harvard Library, not the publisher's name to see full text
JSTOR (Harvard Login) offers full-text of complete runs (up to about 5 years ago) of over 400 journals. JSTOR allows simultaneous or individual searching, full-text searching optional, numerous journals in a variety of fields of science and medicine. See the list at the bottom of the Advanced search screen. JSTOR searches the "Notes and News" sections of journals ( Science is especially rich in this material). In Advanced Search choose Item Type: Miscellaneous to limit largely to "Notes and News".
PsycINFO) (Harvard Login) (1872- ) indexes the professional and academic literature in psychology and related disciplines
Many more scientific periodical indexes are listed in the Library Research Guide for the History of Science .
General interest magazines and periodicals see:
American Periodicals Series Online (Harvard Login) (1740-1900) offers full text of about 1100 American periodicals. Includes several scientific and medical journals including the American Journal of Science and the Medical Repository. In cases where a periodical started before 1900, coverage is included until 1940.
British Periodicals (Harvard Login) (1681-1920) offers full text for several hundred British periodicals.
Ethnic NewsWatch (Harvard Login) (1959- ) is a full text database of the newspapers, magazines, and journals of the ethnic, minority and native press.
Periodicals Index Online (Harvard Login) indexes contents of thousands of US and European journals in the humanities and social sciences, from their first issues to 1995.
Reader's Guide Retrospective (WilsonWeb) (Harvard Login) (1890-1982) indexes many American popular periodicals.
Many more general periodical indexes are listed in Finding Articles in General and Popular Periodicals (North America and Western Europe) .
Articles in non-science fields (religion, public policy): see the list in the Library Research Guide for History .
Professional/Trade : Aimed at particular trades or professions. See the Library Research Guide for History
Newspaper articles : see the Guide to Newspapers and Newspaper Indexes .
Personal accounts . These are first person narratives recalling or describing a person’s life and opinions. These include Diaries, memoirs, autobiographies, and when delivered orally and recorded: Oral histories and Interviews.
National Library of Medicine Oral Histories
Regulatory Oral History Hub (Kenan Institute for Ethics, Duke University) offers links to digital collections containing interviews with regulators, lawyers, and judges. Mainly U.S.
Visual sources :
Records for many, but by no means all, individual Harvard University Library images are available in HOLLIS Images , an online catalog of images. Records include subjects and a thumbnail image. HOLLIS Images is included in HOLLIS searches.
Science & Society Picture Library offers over 50,000 images from the Science Museum (London), the National Museum of Photography, Film & Television and the National Railway Museum.
Database of Scientific Illustrators (DSI) includes over 12500 illustrators in natural history, medicine, technology and various sciences worldwide, c.1450-1950. Living illustrators excluded.
NYPL Digital Gallery Pictures of Science: 700 Years of Scientific and Medical Illustration
Images from the History of Medicine (IHM) includes prints and photographs from the U.S. National Library of Medicine. (The IHM is contained within a larger NLM image database, so this link goes to a specialized search).
Images From the History of the Public Health Service: a Photographic Exhibit .
Wellcome Images
Films/Videos
To find films in HOLLIS , search your topic keywords, then on the right side of the results screen, look at Resource Type and choose video/film.
To find books about films about your topic, search your topic keywords AND "in motion pictures" (in "")
Film Platform offers numerous documentary films on a wide variety of subjects. There are collections on several topics. Searches can be filtered by topic, country of production, and language.
A list of general sources for images and film is available in the Library Research Guide for History and additional sources for the history of science in Library Research Guide for the History of Science .
Government documents often concern matters of science and health policy. For Congressional documents, especially committee reports, see ProQuest Congressional (Harvard Login ).
HathiTrust Digital Library . Each full text item is linked to a standard library catalog record, thus providing good metadata and subject terms. The catalog can be searched separately. Many government documents are full text viewable. Search US government department as Author.
More sources are listed in the Library Research Guide for History
For artifacts and other objects , the Historic Scientific Instruments Collection in the Science Center includes over 15,000 instruments, often with contemporary documentation, from 1450 through the 20th century worldwide.
Waywiser, online database of the Collection of Historical Scientific Instruments .
Warren Anatomical Museum of the Center for the History of Medicine in the Countway Library of Medicine has a rich collection of medical artifacts and specimens.
Peabody Museum of Archaeology and Ethnology
Fall 2020: these collections are closed during the pandemic. Check out their links above to see what they have available online.
Primary Source Terms :
You can limit HOLLIS searches to your time period, but sources may be published later, such as a person's diary published posthumously. Find these with these special Subject terms.
You can use the following terms to search HOLLIS for primary sources:
- Correspondence
- Description and travel
- Manuscripts
- Notebooks, sketchbooks, etc.
- Personal narratives (refers to accounts of wars and diseases only)
- Pictorial works
- Sources (usually refers to collections of published primary sources)
Include these terms with your topical words in HOLLIS searches. For example: tuberculosis personal narratives
Online Primary Source Collections for the History of Science lists digital collections at Harvard and beyond by topic
Google Book Search, HathiTrust Digital Library and Internet Archives offer books and periodicals digitized from numerous libraries. Only out-of-copyright, generally post-1923, books are fully viewable. Each of these three digital libraries allows searching full text over their entire collections.
Google Book Search
HathiTrust Digital Library . Each full text item is linked to a standard library catalog record, thus providing good metadata and subject terms. The catalog can be searched separately. Many post-1923 out-of-copyright books, especially government documents, are full text viewable. You can search within copyright books to see what page your search term is on.
Internet Archive now offers a beta full text search. Put your terms (phrases or personal names, in quotation marks (""), work best) in the search box.
The Online Books Page arranges electronic texts by Library of Congress call numbers and is searchable (but not full text searchable). Includes books not in Google Books, HathiTrust, or Internet Archive. Has many other useful features.
Medical Heritage Library . Information about the Medical Heritage Library. Now searchable full text.
UK Medical Heritage Library
Biodiversity Heritage Library
Contagion: Historical Views of Diseases and Epidemics (1493-1922) provides digitized historical, manuscript, and image resources selected from Harvard University libraries and archives.
Expeditions and Discoveries (1626-1953) features nine expeditions in anthropology and archaeology, astronomy, botany, and oceanography in which Harvard University played a significant role. Includes manuscripts and records, published materials, visual works, and maps from 14 Harvard repositories.
Defining Gender Online: Five Centuries of Advice Literature for Men and Women (1450-1910).
Twentieth Century Advice Literature: North American Guides on Race, Sex, Gender, and the Family.
Many more general History digital libraries and collections: Library Research Guide for History
More History of Science digital libraries: Library Research Guide for the History of Science .
There may already be a detailed list of sources (a bibliography) for your topic.
For instance:
A bibliography of eugenics , by Samuel J. Holmes ... Berkeley, Calif., University of California press, 1924, 514 p. ( University of California publications in zoology . vol. XXV) Full text online .
Look for specialized subject bibliographies in HOLLIS Catalog . Example . WorldCat can do similar searches in the Subject Keyword field for non-Harvard holdings.
- << Previous: What is a Secondary Source?
- Next: Exploring the Special Collections at Harvard >>
- Last Updated: Apr 14, 2024 9:25 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.harvard.edu/HistSciInfo
Harvard University Digital Accessibility Policy
- Thought Leadership
SOURCE DOCUMENT VERIFICATION AND SOURCE DATA REVIEW: WHAT'S THE DIFFERENCE AND WHY WE SHOULD CARE
- Source Data Verification
- Source Data Review
- Clinical Operations Services
The thinking on monitoring of clinical studies has been changing over the past several years, so now is a good time to reassess the place of SDV and SDR in the operation of clinical trials .
Now hold on, 100% SDV has been the industry standard for years, and what, even, is this SDR thing?
While source document verification (SDV) aims to compare recorded data against the source documents to ensure a match, the purpose of source document review (SDR) is to ensure the quality of the source documentation itself. This encompasses reviewing source documentation for completeness, digging further into the processes by which source is generated and checking for patterns of deviations, among other things. Think of SDR as making sure that you have the building blocks needed to get clean data in the first place.
That sounds all well and good, but with so many companies doing 100% SDV, isn’t that some sort of requirement anyway?
Well, no. Federal regulations on clinical research don’t define a minimum or maximum amount of SDV ( Oversight of Clinical Investigations — A Risk-Based Approach to Monitoring, Guidance for Industry, August 2013 ). The thrust of the regulation is that there should be processes in place to monitor the study to ensure that it is run according to GCP principals, and that it generates high quality data, so that the outcomes of the research can be trusted. In this sense, the traditional idea of monitoring as having a person on-site verifying CRF data is only a small part of the picture.
But if we’re talking about data quality, it would make sense that verifying all CRFs would ensure the cleanest data.
On first pass, that would seem to be true, but there is a good body of literature to indicate this is not the case, such as Cheetz N, et al., Thera Innov & Reg Sci. 2014 or Andersen JP, et al., Brit Clin Pharm. 2015 . In short, 100% SDV is unlikely to catch much of importance that would not have been identified by data review or other means that can be done centrally and remotely; there is minimal return for the degree of monitor time and effort required by 100% SDV. Wouldn’t it be better for the monitor to use some of those hours on other critical tasks? Important monitoring steps like reviewing the completeness of the investigator study file or ensuring the pharmacy is handling study drug correctly often get displaced by the need to get through just a few more CRFs.
That’s a fair point. So, what is there beyond 100% SDV?
Quite a bit, and certainly more than we can cover here, but as mentioned earlier, monitoring (including SDV and SDR) is only part of the bigger picture of ensuring the quality of a study and its data. To reduce the risk of data discrepancies, protocol deviations, and other potential errors, the key is to create study specific processes and systems to minimize the chance of events that negatively impact the study. These processes may include some degree of SDV, SDR and other risk management strategies. There also should be periodic reassessments of how these strategies are working, to allow for the adjustments needed to maintain or improve the overall quality of the study.
Would monitors also be happier for not having to grind through every CRF?
Probably! Though I haven’t seen published research on that just yet!
“While source document verification (SDV) aims to compare recorded data against the source documents to ensure a match, the purpose of source document review (SDR) is to ensure the quality of the source documentation itself.”
Share This Article
10 Ways On How To Find Sources For A Research Paper
Declan Gessel
May 27, 2024

If you are struggling to find credible sources for your research paper, you are in the right place. Utilizing academic sources gives your paper credibility and makes your arguments more compelling. This guide will teach you to gather academic sources to elevate your research paper. The importance of academic sources cannot be stressed enough. By utilizing academic sources, you add value to your work.
Including academic sources in your research paper makes your argument more compelling and credible. Focusing on academic resources elevates your work and resonates with your readers. In the digital age, finding sources has never been easier. By leveraging technology, you can access an array of academic resources. Although finding sources may seem daunting, you can discover academic resources quickly and efficiently.
In this guide, we detail various strategies for finding academic resources. As you gather resources, assessing each source's credibility is crucial. In the digital age, anyone can publish information, regardless of its validity. By utilizing the CRAAP Test , you can evaluate the credibility of your sources. This tool assesses a source's currency, relevance, authority, accuracy, and purpose.
By determining these factors, you can ensure that your sources are trustworthy and reliable. Each source you use in your research paper should pass the CRAAP Test. By utilizing this tool, you enhance the credibility of your work and make your arguments more compelling. By following the strategies outlined in this guide, you can easily gather academic sources for your research paper.
Table of Contents
What are credible research sources, characteristics of a reliable source, how to evaluate source credibility, write smarter with jotbot — start writing for free today.

Credible sources are essential for providing accurate, reliable, and verifiable information in research papers. When I say "credible sources," I mean sources authored by experts and published in reputable journals, books, or websites. The integrity and reliability of your research depend on these sources. Credible sources ensure your research findings' accuracy and provide detailed and reliable information. Strengthening the foundation of your argument is critical. It supports and validates your claims. Using respected sources enhances the authority and legitimacy of your work. Credible sources prevent the dissemination of false or misleading information. They also improve the overall quality and credibility of your paper. These sources contribute to the scholarly quality and trustworthiness of your research.
Related Reading
• how to know if an article is peer reviewed • semantic scholar • what are scholarly sources • credible sources for research • how to use google scholar • craap method • evaluating sources • 10 examples of reliable sources • academic search engines

When I evaluate a source's credibility, accuracy is critical. I always check to see if the information presented can be verified. I look for sources that cite their sources and avoid making misleading claims. The best sources have been fact-checked and reviewed by editors.
Objectivity
I make sure the source remains objective and neutral in its presentation of information. I avoid sources with a clear agenda or relying on emotional manipulation rather than facts. A trustworthy source should present information unbiasedly and provide substantial evidence to back up its claims.
Before considering a source credible, I check the author or publisher's credibility. I look for recognized experts or authorities in the field, as scholarly articles are typically written by researchers or academics with relevant qualifications. I also check for credentials, and affiliations with reputable institutions, or established publishers.
Finally, I ensure the information is up-to-date and relevant to the topic at hand. I always check the source's publication date to ensure it aligns with current knowledge or research in the field. Keeping up with the most current and relevant information helps to ensure the quality and credibility of the source.
Jotbot is your personal document assistant. Jotbot does AI note-taking, AI video summarizing, AI citation/source finder, writes AI outlines for essays, and even writes entire essays with Jotbot’s AI essay writer. Join 500,000+ writers, students, teams, and researchers worldwide to write more, write better, and write faster with Jotbot. Write smarter, not harder with Jotbot. Start writing for free with Jotbot today — sign in with Google and get started in seconds.
• Best Databases for Research • How to Find Peer Reviewed Articles on Google Scholar • ChatPDF Alternative • Best Databases for Research • Scholarly vs Popular Sources • Google Scholar Alternative • Best AI for Writing Research Papers • Peer-Reviewed Sources • How to Find Research Papers • Best Websites for Research Papers Free • Databases Like JSTOR • AI That Cites Sources • How to Tell if a Source Is Scholarly

1. Dive Deep into Scholarly Articles and Journals
Academic Databases offer a plethora of resources that allow you to research numerous topics from a scholarly perspective. I suggest databases such as JSTOR, ScienceDirect, and EBSCOhost, which provide up-to-date and well-vetted information.
2. Utilize the Wealth of Your University Library
The university library is a hidden gem, offering resources that may not be available elsewhere. The library has academic journals, e-books, and print materials that are invaluable for research. Don't forget to ask the librarian for help!
3. Government Websites: A Treasure Trove of Information
Government websites (those that end in .gov) are rich in trustworthy data, reports, and statistics. They offer a broad spectrum of topics, from health to environmental science.
4. Sink Your Teeth Into Educational Websites
Educational websites ending in .edu are another great resource. These sites often contain research findings from universities and institutions, providing a solid foundation for your research.
5. Turn to Established News Outlets
Reputable news organizations are perfect for acquiring information on current events and analysis. Hunt for websites that differentiate between news and opinion, with a strong emphasis on fact-checking and integrity.
6. Delve into Peer-Reviewed Journals
Information from peer-reviewed journals is backed by experts in the field, guaranteeing credibility and supporting evidence. This makes it an excellent source of research material.
7. Explore Books by Credible Authors
You should include books by reliable authors published by university presses or reputable publishing houses on your list. The author's expertise and credentials significantly improve the validity of the information.
8. Reports from Reputable Organizations
Organizations such as research institutes think tanks, and NGOs can provide a wealth of information on various topics. Search for organizations renowned for their credibility and transparent funding sources.
9. Trustworthy Documentary Films
While not the conventional source, documentary films can provide unique insights and perspectives on social and historical issues. Ensure that the documentaries have a solid factual basis and have minimal bias.
10. Published Interviews with Experts
Interviews with professionals in relevant fields can offer firsthand accounts and valuable insights. Look for interviews conducted by reputable journalists or published by credible sources to enhance the credibility of your research.

Author Expertise
When evaluating a source, the first thing I look at is who wrote it. I want to see if the author is a professor in the field, a researcher with relevant experience, or someone with no credentials. An author with credentials from reputable institutions or organizations is likelier to publish accurate and reliable information.
Currency of Information
The next thing I consider is the currency of information. I look to see if the information is fresh and relevant to my research needs. I understand that the publication date is crucial and should align with my research requirements. For some fields, like fast-moving scientific fields, recent publications are essential, while for others, historical accuracy might be more important.
Objectivity and Bias
Then, I check for objectivity and bias in the source. A credible source should present a balanced, unbiased view, acknowledging opposing viewpoints and avoiding sensationalized language. I am wary of sources with a clear agenda or those heavily promoting a particular perspective.
Evidence and Citations
Lastly, I consider the evidence and citations provided by the source. I look for supporting evidence that backs up the claims made. Sources that cite reputable publications and include references to credible sources demonstrate stronger credibility.
When it comes to writing research papers, finding credible sources can be a challenging task. Jotbot is an artificial intelligence-powered document assistant that can help you with this aspect of your paper. Jotbot takes note-taking to the next level by providing AI summaries of videos and analyzing texts to produce outlines.
It can even help you find citations and sources for your research, streamlining your writing process and making it more efficient. By leveraging Jotbot’s AI capabilities , you can write better, write faster, and write smarter. Start writing with Jotbot today by signing in with Google and experiencing a new level of writing efficiency.
• Are Blogs Scholarly Sources • How to Find Scientific Articles • How to Find Sources for an Essay • Sourcely AI • Finding Sources • Vetting Sources • Types of Scholarly Sources

Trusted by 500,000+ Students
Your documents, supercharged with AI.
Once you write with JotBot, you'll never want to write without it.
Start writing for free
Your personal document assistant.
Start for free
Press enquiries
Influencer Program
Affiliate Program
Terms & Conditions
Privacy policy
AI Essay Writer
AI Source Finder
AI Outline Generator
How to Use JotBot AI
AI Note Taker
AI Video Summarizer
AI YouTube Video Summarizer
© 2023 JotBot AI by SLAM Ventures, LLC all rights reserved
© 2023 SLAM Ventures, LLC

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

5.6: Finding and Evaluating Research Sources
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 58153

- Anne Eidenmuller
- Columbia Basin College
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
Introduction
In order to create rhetorically effective and engaging pieces, research writers must be able to find appropriate and diverse sources and to evaluate those sources for usefulness and credibility. This chapter discusses how to locate such sources and how to evaluate them. On the one hand, this is a chapter about the nuts and bolts of research. If you have written research papers before, searching for sources and citing them in your paper may, at times, have appeared to you as purely mechanical processes, chores necessary to produce a paper. On the other hand, when writers work with research sources, first finding and then evaluating them, they do rhetorical work. Finding good sources and using them effectively helps you to create a message and a persona that your readers are more likely to accept, believe, and be interested in than if unsuitable and unreliable sources are used. This chapter covers the various kinds of research sources available to writers. It discusses how to find, evaluate, and use primary and secondary sources, printed and online ones.
Types of Research Sources
It is a well-known cliché: we live in an information age. Information has become a tangible commodity capable of creating and destroying wealth, influencing public opinion and government policies, and effecting social change. As writers and citizens, we have unprecedented access to different kinds of information from different sources. Writers who hope to influence their audiences need to know what research sources are available, where to find them, and how to use them.
Primary and Secondary Sources
Definition of primary sources.
Let us begin with the definition of primary and secondary sources. A primary research sources is one that allows you to learn about your subject “firsthand.” Primary sources provide direct evidence about the topic under investigation. They offer us “direct access” to the events or phenomena we are studying. For example, if you are researching the history of World War II and decide to study soldiers’ letters home or maps of battlefields, you are working with primary sources. Similarly, if you are studying the history of your hometown in a local archive that contains documents pertaining to that history, you are engaging in primary research. Among other primary sources and methods are interviews, surveys, polls, observations, and other similar “firsthand” investigative techniques. The fact that primary sources allow us “direct access” to the topic does not mean that they offer an objective and unbiased view of it. It is therefore important to consider primary sources critically and, if possible, gather multiple perspectives on the same event, time period, or questions from multiple primary sources.
Definition of Secondary Sources
Secondary sources describe, discuss, and analyze research obtained from primary sources or from other secondary sources. Using the previous example about World War II, if you read other historians’ accounts of it, government documents, maps, and other written documents, you are engaging in secondary research. Some types of secondary sources with which you are likely to work include books, academic journals, popular magazines and newspapers, websites, and other electronic sources. The same source can be both primary and secondary, depending on the nature and purpose of the project. For example, if you study a culture or group of people by examining texts they produce, you are engaging in primary research. On the other hand, if that same group published a text analyzing some external event, person, or issue and if your focus is not on the text’s authors but on their analysis, you would be doing secondary research. Secondary sources often contain descriptions and analyses of primary sources. Therefore, accounts, descriptions, and interpretations of research subjects found in secondary sources are at least one step further removed from what can be found in primary sources about the same subject. And while primary sources do not give us a completely objective view of reality, secondary sources inevitably add an extra layer of opinion and interpretation to the views and ideas found in primary sources. All texts are rhetorical creations, and writers make choices about what to include and what to omit. As researchers, we need to understand that and not rely on either primary or secondary sources blindly.
Writing Activity: Examining the Same Topic through Primary and Secondary Sources
Primary and secondary sources can offer writers different views of the same topic. This activity invites you to explore the different perspectives that you may get after investigating the same subject through primary and secondary sources. It should help us see how our views of different topics depend on the kinds of sources we use. Find several primary sources on a topic that interests you. Include archival documents, first- hand accounts, lab experiment results, interviews, surveys, and so on. Depending on how much time you have for this project, you may or may not be able to consult all of the above source types. In either case, try to consult sources of three or four different kinds. Next, write a summary of what you learned about your subject as a result of your primary-source investigation. Mention facts, dates, important people, opinions, theories, and anything that seems important or interesting. Now, conduct a brief secondary-source search on the same subject. Use books, journals, popular magazines and newspapers, Internet sites, and so on. Write a summary of your findings. Finally, compare the two summaries. What differences do you see? What new ideas, perspectives, ideas, or opinions did your secondary-source search yield? As a result of these two searches, have you obtained different accounts of the same research subject? Pay special attention to the differences in descriptions, accounts, or interpretations of the same subject. Notice what secondary sources add to the treatment of the subject and what they take away, compared to the primary sources.
Print and Electronic Sources
Researcher have at their disposal both printed and electronic sources. Before the advent of the Internet, most research papers were written with the use of printed sources only. Until fairly recently, one of the main stated goals of research writing instruction was to give students practice in the use of the library. Libraries are venerable institutions, and therefore printed sources have traditionally been seen (with good reason, usually,) as more solid and reliable than those found on the Internet. With the growing popularity of the Internet and other computerized means of storing and communicating information, traditional libraries faced serious competition for clients. It has become impractical if not impossible for researchers to ignore the massive amount of information available to them on the Internet or from other online sources. As a result, it is not uncommon for many writers beginning a research project to begin searching online rather than at a library or a local archive. For example, several times in the process of writing this essay, when I found myself in need of information fast, I opened my Web browser and researched online. With the popularity of the Internet ever increasing, it has become common practice for many student writers to limit themselves to online research and to ignore the library. While there are some cases when a modified version of such an approach to searching may be justifiable (more about that later), it is clear that by using only online research sources, a writer severely limits his or her options. This section covers three areas. First, we will discuss the various types of printed and online sources as well the main similarities and differences between them. Next, I’d like to offer some suggestions on using your library effectively and creatively. Finally, we will examine the topic of conducting online searches, including methods of evaluating information found on the Internet.
Know Your Library
It is likely that your college or university library consists of two parts. One is the brick and mortar building, often at a central location on campus, where you can go to look for books, magazines, newspapers, and other publications. The other part is online. Most good libraries keep a collection of online research databases that are supported, at least in part, by your tuition and fees, and to which only people who are affiliated with the college or the university that subscribes to these databases have access. Let us begin with the brick and mortar library. If you have not yet been to your campus library, visit it soon. Larger colleges and universities usually have several libraries that may specialize in different academic disciplines. As you enter the library, you are likely to find a circulation desk (place where you can check out materials) and a reference desk. Behind the reference desk you will find reference librarians. Instead of wandering around the library alone, hoping to hit the research sources that you need for your project, it is a good idea to talk to a reference librarian at the beginning of every research project, especially if you are at a loss for a topic or research materials. Your brick and mortar campus library is likely to house the following types of materials:
- Books (these include encyclopedias, dictionaries, indexes, and so on)
- Academic Journals
- Popular magazines
- Government documents
- A music and film collection (on CDs, VHS tapes, and DVDs)
- A CD-Rom collection
- A microfilm and microfiche collection
- Special collections, such as ancient manuscripts or documents related to local history and culture.
According to librarian Linda M. Miller, researchers need to “gather relevant information about a topic or research question thoroughly and efficiently. To be thorough, it helps to be familiar with the kinds of resources that the library holds, and the services it provides to enable access to the holdings of other libraries” (2001, 61). Miller’s idea is a simple one, yet it is amazing how many inexperienced writers prefer to use the first book or journal they come across in the library as the basis for their writing and do not take the time to learn what the library has to offer. Here are some practical steps that will help you learn about your library:
Take a tour of the library with your class or other groups if such tours are available. While such group tours are generally less effective than conducting your own searches of a topic that interests you, they will give you a good introduction to the library and, perhaps, give you a chance to talk to a librarian.
Check your library’s website to see if online “virtual” tours are available. At James Madison University where I work, the librarians have developed a series of interactive online activities and quizzes which anyone wishing to learn about the JMU libraries can take in their spare time.
Talk to reference librarians! They are truly your best source of information. They will not get mad at you if you ask them too many questions. Not only are they paid to answer your questions, but most librarians love what they do and are eager to share their expertise with others.
Go from floor to floor and browse the shelves. Learn where different kinds of materials are located and what they look like.
Pay attention to the particulars of your campus library’s architecture. I am an experienced library user, but it look me some time, after I arrived at my university for the first time, to figure out that our library building has an annex that can only be accessed by taking a different elevator from the one leading to the main floors.
Use the library not only as a source of knowledge but as a source of entertainment and diversion. I like going to the library to browse through new fiction acquisitions. Many campus libraries also have excellent film and music collections.
The items on the list above will help you to acquire a general understanding of your campus library. However, the only way to gain an in-depth and meaningful knowledge of your library is to use it for specific research and writing projects. No matter how attentive you are during a library tour or while going from floor to floor and learning about all the different resources your library has to offer, it is during searchers that you conduct for your research projects that you will become most interested and involved in what you are doing. Here, therefore, is an activity that combines the immediate goal of finding research sources for a research project with the more long-term goal of knowing what your campus library has to offer.
Activity: Conducting a Library Search for a Writing Project
If you have a research and writing topic in mind for your next project, head for your brick-and-mortar campus library. As soon as you enter the building, go straight to the reference desk and talk to a reference librarian. Be aware that some of the people behind the reference desk may be student assistants working there. As a former librarian assistant myself and as a current library user, I know that most student assistants know their job rather well, but sometimes they need help from the professionals. So, don’t be surprised if the first person you approach refers you to someone else. Describe your research interests to the librarian. Be proactive. The worst disservice you can do yourself at this point is to look, sound, and act disinterested. Remember that the librarian can be most helpful if you are passionate about the subject of your research and if—this is very important—the paper you are writing is not due the next day. So, before you go to the library, try to narrow your topic or formulate some specific research questions. For example, instead of saying that you are interested in dolphins, you might explain that you are looking for information about people who train dolphins to be rescue animals. If the librarian senses that you have a rather vague idea about what to research and write about, he or she may point you to general reference sources such as indexes, encyclopedias, and research guides. While those may prove to be excellent thought-triggering publications, use them judiciously and don’t choose the first research topic you find just because your library has a lot of resources on it. After all, your research and writing will be successful only when you are deeply interested in and committed to your investigation. If you have a more definite idea about what you would like to research and write about, the reference librarian will likely point you to the library’s online catalog. I have often seen librarians working alongside students to help them identify or refine a writing topic. Find several different types of materials pertaining to your topic. Include books and academic articles. Don’t forget popular magazines and newspapers—the popular press covers just about any subject, event, or phenomena, and such articles may bring a unique perspective not found in academic sources. Also, don’t neglect to look in the government documents section to see if there has been any legislation or government regulation relevant to your research subject. Remember that at this stage your goal is to learn as much as you can about your topic by casting your research net as far and wide as you can. So, do not limit yourself to the first few sources you will find. Keep looking, and remember that your goal is to find the best information available. You will probably have to look in a variety of sources. If you are pressed for time you may not be able to study the books dedicated to your topic in detail. In this case, you may decide to focus your research entirely on shorter texts, such as journal and magazine articles, websites, government documents, and so on. However it is always a good idea to at least browse through the books on your topic to see whether they contain any information or leads worth investigating further.
Cyber Library
Besides the brick and mortar buildings, nearly all college and university libraries have a Web space that is a gateway to more documents, resources, and information than any library building can house. From your library’s website, you can not only search the library’s holdings but also access millions of articles, electronic books, and other resources available on the Internet. It is a good idea to conduct a search from your campus library page rather than from your favorite search engine. There are three reasons for that. First, most of the materials you will find through your library site are accessible to paying subscribers only and cannot be found via any search engine. Second, online library searches return organized and categorized results, complete with the date of publication and source—something that cannot be said about popular search engines. Finally, by searching online library databases you can be reasonably sure that the information you retrieve is reliable.
So, what might you expect to find on your library’s website? The site of the library at James Madison University where I work offers several links. In addition to the link to the library catalog, there is a Quick Reference link, a link called Research Databases, a Periodical Locator, Research Guides, and Internet Search. There are also links to special collections and to the featured or new electronic databases to which the library has recently subscribed. While your school library may use other names for these links, the kinds of resources they offer will be similar to what JMU’s library has to offer. Most of these links are self-explanatory. Obviously, the link to the library catalog allows you to search your brick and mortar library’s collection. A periodical locator search will tell you what academic journals, popular magazines, and newspapers are available at your library. The Internet search option will allow you to search the World Wide Web, except that your library’s Internet searching function will probably allow you to conduct meta-searches—i.e., searches using many search engines simultaneously. Where a link like Research Databases or Research Guides will take you is a little less obvious. Therefore I will cover these two types of library resources in some detail. Let us start with the research databases. An average-size college or university subscribes to hundreds, if not thousands, of online databases on just about every subject. These databases contain, at a minimum, information about titles, authors, and sources of relevant newspaper and journal articles, government documents, online archive materials, and other research sources. Most databases provide readers with abstracts (short summaries) of those materials, and a growing number of online databases offer full texts of articles. From the research-database home page, it is possible to search for a specific database or by subject. Research-guide websites are similar to the database home pages, except that, in addition to database links, they often offer direct connections to academic journals and other relevant online resources on the research subject. Searching online is a skill that can only be learned through frequent practice and critical reflection. Therefore, in order to become a proficient user of your library’s electronic resources, you will need to visit the library’s website often and conduct many searches. Although most library websites are organized according to similar principles and offer similar types of resources, it will be up to you as a researcher and learner to find out what your school library has to offer and to learn to use those resources. I hope that the following activities will help you in that process.
Activity: Exploring your Cyber Library
Go to your school library’s website and explore the kinds of resources it has to offer.
Conduct searches on a subject you are currently investigating or interested in investigating in the future, using the a periodical locator resource (if your library has one). Then, conduct similar searches of electronic databases and research guides.
Summarize, whether in an oral presentation or in writing, your search process and the kinds of sources you have found. Pay attention to particular successes and failures that occurred as you searched.
Print Sources or Electronic?
In the early years of the Internet, there was widespread mistrust of the World Wide Web and the information it had to offer. While some of this mistrust is still present (and justifiable), the undeniable fact is that the authority of the Internet as a legitimate and reliable source of information has increased considerably in recent years. For example, academic journals in almost every discipline complement their printed volumes with Web versions, and some are now only available online. These online journals employ the same rigorous submission review processes as their printed counterparts. Complete texts of academic and other books are sometimes available on the Internet. Respected specialized databases and government document collections are published entirely and exclusively online. Print and electronic sources are not created equal, and although online and other electronic texts are gaining ground as legitimate research resources, there is still a widespread and often justified opinion among academics and other writers that printed materials make better research sources. Some materials available in some libraries simply cannot be found online and vice versa. For example, if you are a Shakespeare scholar wishing to examine manuscripts from the Elizabethan times, you will not find them online. To get to them, you will have to visit the Folger Shakespeare Library in Washington, DC, or a similar repository of Elizabethan manuscripts. On the other hand, if you are researching the Creative Commons movement, which is a community dedicated to reforming copyright laws in this country, then your best bet is to begin your search on the Internet at http://www.creativecommons.org/ . Surely, after reading the website, you will need to augment your research by reading other related materials, both online and in print, but in this case, starting online rather than in the library is a reasonable idea. As a researching writer, you should realize that printed and electronic sources are not inherently bad or good. Either type can be reliable or unreliable; either can be appropriate or inappropriate for a specific research project. It is up to researchers and writers to learn how to select both print and electronic sources judiciously and how to evaluate them for their reliability and appropriateness for particular purposes.
Determining the Suitability and Reliability of Research Sources
Much of the discussion about the relative value of printed and electronic—especially Internet—sources revolves around the issue of reliability. When it comes to libraries, the issue is more or less clear. Libraries keep books, journals, ands other publications that usually undergo a rigorous pre- and post-publication review process. It is reasonable to assume that your campus library contains very few or no materials that are blatantly unreliable or false, unless those materials are kept there precisely to demonstrate their unreliability and falsehood. As a faculty member, I am sometimes asked by my university librarians to recommend titles in my academic field that our university library should own. Of course my opinion (or that of another faculty member) does not completely safeguard against the library acquiring materials that contain errors and or misleading information; we use our experience and knowledge in the field to recommend certain titles and omit certain others. Faculty recommendations are the last stage of long process before a publication gets to a campus library. Before that, every book, journal article, or other material undergoes a stringent review from the publisher’s editors and other readers. And while researchers still need to use sound judgment in deciding which library sources to use in their project, the issue is usually one of relevance and suitability for a specific research project and specific research questions rather than one of whether the information presented in the source is truthful or not. The same is true of some electronic sources. Databases and other research sources published on CD-ROMs, as well as various online research websites that accompany many contemporary writing textbooks, for example, are subject to the same strict review process as their printed counterparts. Information contained in specialized academic and professional databases is also screened for reliability and accuracy. If, as we have established, most of the materials you are likely to encounter in your campus library are generally trustworthy, then your task as a researcher is to determine the relevance of the information contained in books, journals, and other materials for your particular research project. It is a simple question, really: will my research sources help me answer the research questions that I am posing in my project? Will they help me learn as much as I can about my topic and create a rhetorically effective and interesting text for my readers? Consider the following example. Recently, the topic of the connection between certain antidepressant drugs and suicidal tendencies among teenagers who take those drugs has received a lot of media coverage. Suppose you are interested in researching this topic further. Suppose, too, that you want not only to give statistical information about the problem in your paper but also to study firsthand accounts of the people who have been negatively affected by the antidepressants. When you come to your campus library, you have no trouble locating the latest reports and studies that give you a general overview of your topic, including rates of suicidal behavior in teenagers who took the drugs, tabulated data on the exact relationships between the dosage of the drugs and the changes in the patients’ moods, and so on. All this may be useful information, and there is a good chance that, as a writer, you will still find a way to use it in your paper. You could, for example, provide the summary of the statistics in order to introduce the topic to your readers. However, this information does not fulfill your research purpose completely. You want to understand what it is like to be a teenager whose body and mind have been affected by the antidepressants, yet the printed materials you have found so far offer no such insight. They fulfill your goal only partially. To find such firsthand accounts, then, you will either have to keep looking in the library or conduct interviews with people who have been affected by these drugs.
Suitability of Sources
Determine how suitable a particular source is for your current research project. To do this, consider the following factors:
- Scope: What topics and subtopics does the source cover? Is it a general overview of your subject or it is a specialized resource?
- Audience: Who is the intended audience for the text? If the text itself is too basic or too specialized, it may not match the expectations and needs of your own target audience.
- Timeliness: When was the source published? Does it represent the latest information, theories, and views? Bear in mind, though, that if you are conducting a historical investigation, you will probably need to consult older materials, too.
What are credentials of the author(s)? This may be particularly important when you use Internet sources, since there are so few barriers to publishing online. One needn’t have an academic degree or credentials to make one’s writing publicly available. As part of your evaluation of the source’s authority, you should also pay attention to the kinds of external sources that were used during its creation. Look through the bibliography or list of works cited attached to the text. Not only will it help you determine how reliable and suitable the source is, but it may also provide you with further leads for your own research. Try asking the above questions of any source you are using for a research project you are currently conducting.
Reliability of Internet Sources
Charles Lowe, the author of the essay “The Internet Can Be a Wonderful Place, but . . .” offers the following opinion of the importance of the Internet as a research source for contemporary researchers:
To a generation raised in the electronic media culture, the Internet is an environment where you feel more comfortable, more at home than the antiquated libraries and research arenas of the pre-electronic, print culture. To you, instructors just don’t get it when they advise against using the Internet for research or require the bulk of the sources for a research paper to come from the library (129-130).
Indeed, the Internet has become the main source of information not only for college students, but also for many people outside academia. And while I do not advise you to stay away from the Internet when researching and I generally do not require my own students to use only printed sources, I do know that working with Internet sources places additional demands on the researcher and the writer. Because much of the Internet is a democratic, open space, and because anyone with a computer can post materials online, evaluating online sources is not always easy. A surprisingly large number of people believe much of the information on the Internet, even if this information is blatantly misleading or its authors have a self-serving agenda. I think many students uncritically accept information they find on the Internet because some of the sites on which this information appears look and sound very authoritative. Used to believing the published word, inexperienced writers often fall for such information as legitimate research data. So, what are some of strategies you can use to determine that reliability? The key to successful evaluation of Internet research sources, as any other research sources, is application of your critical reading and thinking skills. In order to determine the reliability of any source, including online sources, it is advisable to conduct a basic rhetorical analysis of that source. When deciding whether to use a particular website as a research source, every writer should ask and answer the following questions:
- Who is the author (or, authors) of the website and the materials presented on it? What is known about the site’s author(s) and its publishers and their agendas and goals?
- What is the purpose of the website?
- Who is the target audience of the website
- How do the writing style and the design of the website contribute to (or detract from) its meaning?
Website Authors and Publishers
As with a printed source, first we need to consider the author and the publisher of a website. Lowe suggests that we start by looking at the tag in the website’s URL. Whether it is a “.com,” an “.org,” a “.net, “or an “.edu” site can offer useful clues about the types and credibility of materials located on the site. In addition to the three most common URL tags listed above, websites of military organizations use the extension “.mil” while websites hosted in other countries have other tags that are usually abbreviations of those countries’ names. Sites of government agencies end in “.gov.” For example, most sites hosted in Great Britain have the tag “.uk,” which stands for “United Kingdom.” Websites based in Italy usually have the tag “.it,” and so on. Typically, a “.com” site is set up to sell or promote a product or service. Therefore, if you are researching Nike shoes, you will probably not want to rely on http://www.nike.com/ if you want to get a more objective review of the product. While Nike’s website may provide some useful information about the products it sells, the site’s main purpose is to sell Nike’s goods, playing up the advantages of their products. Keep in mind that not all “.com” websites try to sell something. Sometimes academics and other professionals obtain “.com” addresses because they are easy to obtain. For example, the professional website of Charles Lowe (cited above) is located at http://www.cyberdash.com/ . Political candidates running for office often also choose “.com” addresses for their campaign websites. In every case, you need to apply your critical reading skills and your judgment when evaluating a website. The “.org” sites usually belong to organizations, including political groups. These sites can present some specific challenges to researchers trying to evaluate their credibility and usefulness. To understand these challenges, let us consider the “.org” sites of two political research organizations, also known as “think tanks.” One is the conservative Heritage Foundation ( http://www.heritage.org ), and the other is the traditionally liberal Center for National Policy ( http://www.cnponline.org ). Both sites have “About” pages intended to explain to their readers the goals and purposes of the organizations they represent. The Heritage Foundation’s site contains the following information:
. . . The Heritage Foundation is a research and educational institute—a think tank—whose mission is to formulate and promote conservative public policies based on the principles of free enterprise, limited government, individual freedom, traditional American values, and a strong national defense. ( http://www.heritage.org/about )
This statement can tell a researcher a lot about the research articles and other materials contained in the site. It tells us that the authors of the site are not neutral, nor do they pretend to be. Instead, they are advancing a particular political agenda, so, when used as research sources, the writings on the site should not be seen as unbiased “truths” but as arguments. The same is true of the Center for National Policy’s website, although its authors use a different rhetorical strategy to explain their political commitments. They write:
The Center for National Policy (CNP) is a nonprofit, nonpartisan public policy organization located in Washington, DC. Founded in 1981, the center’s mission is to engage national leaders with new policy options and innovative programs designed to advance progressive ideas in the interest of all Americans ( http://www.cnponline.org/people_and_programs.html )
It takes further study of the center’s website, as well as sure knowledge of the American political scene, to realize that the organization leans toward the left of the political spectrum. The websites of both organizations contain an impressive amount of research, commentary, and other materials designed to advance the groups’ causes. When evaluating “.org” sites, it is important to realize that they belong to organizations, and each organization has a purpose or a cause. Therefore, each organizational website will try to advance that cause and fulfill that purpose by publishing appropriate materials. Even if the research and arguments presented on those sites are solid (and they often are), there is no such thing as an unbiased and disinterested source. This is especially true of political and social organizations whose sole purpose is to promote agendas. The Internet addresses ending in “.edu” are rather self-evident—they belong to universities and other educational institutions. On these sites we can expect academic articles and other writings, as well as papers and other works created by students. These websites are also useful resources if you are looking for information on a specific college or university. Be aware, though, that typically any college faculty member or student can obtain Web space from their institution and publish materials of their own choosing there. Thus some of the texts that appear on “.edu” sites may be personal rather than academic. In recent years, some political research organizations have begun to use Web addresses with the “.edu” tag. One of these organizations is The Brookings Institution, whose address is http://www.brookings.edu . Government websites that end in “.gov” can be useful sources of information on the latest legislation and other regulatory documents. The website with a “.net” extension can belong to commercial organizations or online forums.
Website Content
Now that we have established principles for evaluating the authors and publishers of Web materials, let us look at the content of the writing. As I have stated above, like all writing, Web writing is argumentative; therefore it is important to recognize that authors of Web texts work to promote their agendas or highlight the events, organizations, and opinions that they consider right, important, and worthy of public attention. Different writers work from different assumptions and try to reach different audiences. Websites of political organizations are prime examples of that.
Activity: Evaluating Website Content
Go to one of the following websites: The Heritage Foundation ( http://www.heritage.org ), The Center for National Policy ( http://www.cnponline.org ), The Brookings Institution ( http://www.brookings.edu ), or The American Enterprise Institute ( http://www.aei.org ). Or choose another website suggested by your instructor. Browse through the site’s content and consider the following questions:
- What is the purpose of the site?
- What is its intended audience? How do we know?
- What are the main subjects discussed on the sites?
- What assumptions and biases do the authors of the publications on the site seem to have? How do we know?
- What research methods and sources do the authors of these materials use? How does research help the writers of the site state their case?
Apply the same analysis to any online sources you are using for one of your research projects.
Website Design and Style
The style and layout of any text is a part of that text’s message, and online research sources are no exception. Well-designed and written websites add to the ethos (credibility) of their authors while badly designed and poorly written ones detract from it. Sometimes, however, a website with a good-looking design can turn out to be an unreliable or unsuitable research source.
In Place of a Conclusion: Do Not Accept A Source Just Because It Sounds or Looks Authoritative
Good writers try to create authoritative texts. Having authority in their writing helps them advance their arguments and influence their audiences. To establish such authority, writers use a variety of methods. As has been discussed throughout this essay, it is important for any researcher to recognize authoritative and credible research sources. On the other hand, it is also important not to accept authoritative sources without questioning them. After all, the purpose of every researched piece of writing is to create new views and new theories on the subject, not to repeat the old ones, however good and well presented those old theories may be. Therefore, when working with reliable and suitable research sources, consider them solid foundations that will help you to achieve a new understanding of your subject, which will be your own. Applying the critical source-evaluation techniques discussed in this essay will help you to accomplish this goal.
- Finding and Evaluating Research Sources. Authored by : Pavel Zemliansky. Located at : http://www.saylor.org/site/wp-content/uploads/2011/01/ENGL002-Chapter-4-Research-Writing.pdf . License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
The Macroeconomic Impact of Climate Change: Global vs. Local Temperature
This paper estimates that the macroeconomic damages from climate change are six times larger than previously thought. We exploit natural variability in global temperature and rely on time-series variation. A 1°C increase in global temperature leads to a 12% decline in world GDP. Global temperature shocks correlate much more strongly with extreme climatic events than the country-level temperature shocks commonly used in the panel literature, explaining why our estimate is substantially larger. We use our reduced-form evidence to estimate structural damage functions in a standard neoclassical growth model. Our results imply a Social Cost of Carbon of $1,056 per ton of carbon dioxide. A business-as-usual warming scenario leads to a present value welfare loss of 31%. Both are multiple orders of magnitude above previous estimates and imply that unilateral decarbonization policy is cost-effective for large countries such as the United States.
Adrien Bilal gratefully acknowledges support from the Chae Family Economics Research Fund at Harvard University. The views expressed herein are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Bureau of Economic Research.
MARC RIS BibTeΧ
Download Citation Data
Mentioned in the News
More from nber.
In addition to working papers , the NBER disseminates affiliates’ latest findings through a range of free periodicals — the NBER Reporter , the NBER Digest , the Bulletin on Retirement and Disability , the Bulletin on Health , and the Bulletin on Entrepreneurship — as well as online conference reports , video lectures , and interviews .

ACLU and Coalition Oppose Impacts of Restrictions on "Open Source" AI on Transparency, Civil Rights, and Research
Related issues.
- Privacy & Technology
Stay Informed
Sign up to be the first to hear about how to take action.
By completing this form, I agree to receive occasional emails per the terms of the ACLU’s privacy statement.

14 Top Outstanding Open Source LLMs For Research and Commercial Use
Large Language Models (or LLMs) are machine learning models ( built on top of transformer neural network ) that aim to solve language problems like auto-completion, text classification, text generation, and more. It is a subset of Deep Learning.
The "large" refers to the model being pre-trained by a massive set of data (could be in sizes of petabytes), accompanied by millions or billions of parameters and further fine-tuned for a specific use-case.
While LLMs made projects like ChatGPT and Google Gemini possible, they are proprietary. So, there's a lack of transparency, and the entire control of the LLM (and its usage) is at the discretion of the company that owns it. So, what's the solution to this? Open source LLMs .
With an open-source LLM, you can have multiple benefits like transparency, no vendor lock-in, free to use for commercial purposes, and total control over customization of the model (in terms of performance, carbon footprint, and more) .
Similar reasons why we need open-source ChatGPT chatbot alternatives:

Now that you know why we need open-source LLMs, let me highlight some of the best ones available.
1. Falcon 180B
The Technology Innovation Institute (TII) in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) launched an open LLM, which performs close to its proprietary competitors.
The model includes 180 billion parameters and was trained on 3.5 trillion tokens.
In the Falcon AI model family, there are smaller/newer models like Falcon 2 11B, which is a scalable solution, and outperforms similar models from Meta and Google.
2. Dolly 2.0
Dolly 2.0 is one of the most prominent open-source LLM models developed by Databricks, fine-tuned on a human-generated instruction dataset. Unlike its predecessor, the dataset is its original, generated by more than 5000 employees of the company.
It includes 12 billion parameters, and is geared towards summarization, QA, classification, and some brainstorming. Dolly 2.0 does not aim to compete with existing models, but the focus was more on providing a human-generated dataset along with an LLM. They claimed it to be the first of its kind back then that tried to mimic ChatGPT's interaction.
3. Cerebras-GPT
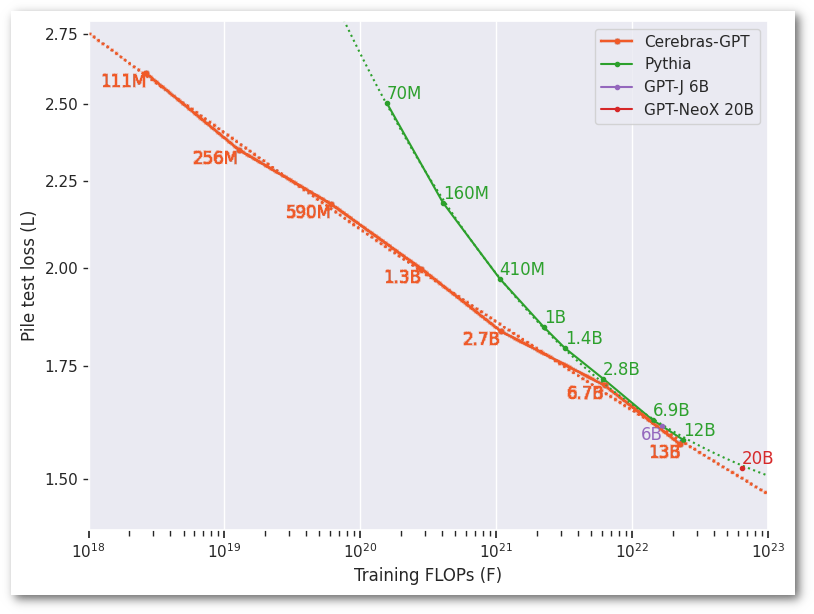
Cerebras-GPT is a family of seven GPT-3 open-source LLM models ranging from 111 million to 13 billion parameters.
These models aim for higher accuracy with a faster training times, lower cost, and consume less energy. It is trained using DeepMind's Chinchilla formula.
Bloom is an open-access multilingual LLM model that is trained to continue text from prompts, and can be trained for other text-based tasks.
The model includes 176 billion parameters, and can output in 46 different languages and 13 programming languages.
5. DLite V2
DLite by AI Squared aims to present lightweight LLMs that you can use almost anywhere.
The family of model includes variations ranging from 123 million to 1.5 billion parameters. It utilizes the same database built by Databricks for Dolly 2.0. Hence, it is tuned for the same use-case.

MPT-7B is another prominent open-source model by Databricks . Unlike Dolly 2.0, it competes and surpasses Meta's LLaMA-7B in many ways.
The model was trained using a mixed set of data from various sources, including 6.7 billion parameters. It also aims to be an affordable alternative to the closed source LLM models available.
XGen 7B is an LLM model by Salesforce , one of the leading companies in its industry. The model has been trained for text generation and code tasks, claiming performance benefits over similar models like MPT.
8. OpenLLaMA
OpenLLaMA is a reproduction of Meta's popular LLaMa model trained with a different dataset to make it available under a permissive license, when compared to Meta's custom commercial license.
Currently, you can find OpenLLaMA 7Bv2 and a 3Bv3 model, with all of them trained using a mixture of datasets.
You can learn more about it on its GitHub page.
9. StarCoder
StarCoder is an interesting open-source LLM trained using data from GitHub (commits, issues etc) fine-tuned for coding tasks.
It includes 15 billion parameters and trained on 80+ programming languages. Considering the data is from GitHub, you will need to add attribution wherever necessary when you use the model.
Another open-source from Salesforce, fine-tuned for coding tasks and code generation. CodeT5 is one of the most competing code LLMs that features 16 billion parameters, and claims to outperform OpenAI's code-cushman001 model.
Yi-1.5 is an exciting open-source LLM featuring a whopping 34.4 billion parameters.
It is fine-tuned for coding, math, reasoning, and instruction-following capability. Originally, this model wasn't open-source, but later it was. And, that's a good thing.
12. SOLAR-10.7B
SOLAR-10.7B is a pre-trained open-source LLM by Upstage.ai that just generates random text. You need to fine-tune it to adapt to your particular requirements.
When compared to models with larger parameters, it promises to provide a good model performance efficiency and scalability even with 10.7 billion parameters. It is an incredibly popular adaptable language model.
13. Mistral 7B
Mistral 7B is a powerful language model that claims to outperform LLaMa 1/2 in various ways. The large language model is capable of math, reasoning, word knowledge, QA, and more.
It is a pre-trained generative text model with 7 billion parameters. Hence, it does not have any moderation mechanisms. So, you need to fine-tune it to output moderated results.
14. OLMo-7B

OLMo-7B is yet another open language model pre-trained with Dolma dataset featuring three trillion token open corpus. The entire training data, model weights, and the code is open-source, and available to use without restriction.
💬 What is your favorite open-source LLM? Have you tried running any of them? Share your thoughts in the comments below!
A passionate technophile who also happens to be a Computer Science graduate. You will usually see cats dancing to the beautiful tunes sung by him.
8 Best Linux Tools For Digital Artists
Ten blogs every ubuntu user must follow, running ai locally using ollama on ubuntu linux, 8 open source second brain knowledge base tools, run llms locally on raspberry pi using ollama ai, become a better linux user.
With the FOSS Weekly Newsletter, you learn useful Linux tips, discover applications, explore new distros and stay updated with the latest from Linux world

Great! You’ve successfully signed up.
Welcome back! You've successfully signed in.
You've successfully subscribed to It's FOSS.
Your link has expired.
Success! Check your email for magic link to sign-in.
Success! Your billing info has been updated.
Your billing was not updated.
Healthy Eating Pyramid

Generations of Americans are accustomed to the food pyramid design, and it’s not going away. In fact, the Healthy Eating Pyramid and the Healthy Eating Plate (as well as the Kid’s Healthy Eating Plate ) complement each other.
Consumers can think of the Healthy Eating Pyramid as a grocery list:
- Vegetables , fruits , whole grains , healthy oils , and healthy proteins like nuts , beans , fish , and chicken should make it into the shopping cart every week, along with a little yogurt or other dairy foods if desired.
- The Healthy Eating Pyramid also addresses other aspects of a healthy lifestyle— exercise , weight control , vitamin D , and multivitamin supplements , and moderation in alcohol for people who drink—so it’s a useful tool for health professionals and health educators.

Translating nutrition advice into a colorful pyramid is great way to illustrate what foods make up a healthy diet. The shape immediately suggests that some foods are good and should be eaten often, and that others aren’t so good and should be eaten only occasionally. The layers represent major food groups that contribute to the total diet. The problem with the US government’s original Food Guide Pyramid, released in 1992, was that it conveyed the wrong dietary advice. And MyPyramid, its 2005 replacement, was vague and confusing.
MyPyramid, unveiled in 2005, was essentially the Food Guide Pyramid turned on its side, without any explanatory text. Six swaths of color swept from the apex of MyPyramid to the base: orange for grains, green for vegetables, red for fruits, a teeny band of yellow for oils, blue for milk, and purple for meat and beans. The widths suggested how much food a person should choose from each group. A band of stairs running up the side of the Pyramid, with a little stick figure chugging up it, served as a reminder of the importance of physical activity.

Permission of use
The Healthy Eating Pyramid image on this Web site is owned by Harvard University. It may be downloaded and used without permission for educational and other non-commercial uses with proper attribution, including the following copyright notification and credit line:
Copyright © 2008. For more information about The Healthy Eating Pyramid, please see The Nutrition Source, Department of Nutrition, Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, www.thenutritionsource.org , and Eat, Drink, and Be Healthy, by Walter C. Willett, M.D., and Patrick J. Skerrett (2005), Free Press/Simon & Schuster Inc.”
Any other use, including commercial reuse or mounting on other systems, requires permission from the Department of Nutrition at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health. Please contact us to request permission.
Terms of Use
The contents of this website are for educational purposes and are not intended to offer personal medical advice. You should seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this website. The Nutrition Source does not recommend or endorse any products.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The most important purpose of source documentation in a clinical trial is to reconstruct the trial as it happened. It should enable an independent observer to reconfirm the data. Documentation should be such that it is able to provide audit trail to permit investigation if and when required.
Documenting Sources. Documenting means showing where you got source information that's not your own. Remember, a research paper blends your ideas with ideas and information from other sources. Documentation shows the reader what ideas are yours and what information and ideas you've taken from a source to support your point of view.
A source document is a document in which data collected for a clinical trial is first recorded. This data is usually later entered in the case report form. The International Conference on Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH-GCP) guidelines define source documents as "original documents ...
Medical Record vs. Research Record There are some documents that serve as source documents that are not allowed to be placed in a medical record. However, they need to be maintained as source documents. Creating a research record allows you to save these types of source documents.
Source documents are ' original documents, data and records' and include documents such as hospital records, laboratory reports, academic records, memoranda, subject diaries, assessment measures, and pharmacy dispensing records. Source data is the information recorded in a source document, such as clinical findings and observations.
Source Documents may include: hospital records, subject diaries, pharmacy dispensing lists, test results, x-rays, lab records, etc. If source documentation is incorrect, incomplete, or otherwise deficient, research personnel may correct and/or complete by making an additional entry or addendum to the source documentation.
Source Documentation 101. Our Clinical Research 101 series takes an in-depth look at key steps and tips for navigating the clinical research process. The twentieth installment in our Clinical Research 101 series is by Leslie Love, Senior Project Manager at CHÉOS. The following is a brief discussion of source documentation, and why it is ...
Choosing & Using Sources presents a process for academic research and writing, from formulating your research question to selecting good information and using it effectively in your research assignments. Additional chapters cover understanding types of sources, searching for information, and avoiding plagiarism. Each chapter includes self-quizzes and activities to reinforce core concepts and ...
Purpose. The purpose of this standard operating procedure (SOP) is to provide guidance to research personnel when a system of records is established. Documentation of source data is necessary for the reconstruction, evaluation, and validation of clinical findings, observations, and other activities during a clinical trial.
Source documents are medical records providing documentation prior to, during, and following the clinical trial [17]. These should be detailed, documenting the trial and providing enough ...
Source Document Binder. Per ICH GCP guideline E6 section 5.1 source data is identified as "all information in original records of clinical findings, observations, or other activities in a clinical trial necessary for the reconstruction and evaluation of the trial.". This is the first recording of subject-related information.
Throughout the research process, you'll likely use various types of sources. The source types commonly used in academic writing include: Academic journals. Books. Websites. Newspapers. Encyclopedias. The type of source you look for will depend on the stage you are at in the writing process.
Primary source is a term used in a number of disciplines to describe source material that is closest to the person, information, period, or idea being studied. A primary source (also called original source ) is a document, recording, artifact, or other source of information that was created at the time under study, usually by a source with ...
The origins of document analysis as a social science research method can be traced back to Goode and Hatt (), who recommended that scholars screen, count, and code documents content and use it as appropriate evidence.Later, Glaser and Strauss argued that documents should be considered in social investigation similar to "anthropologist's informant or a sociologist's interviewee" (p. 163).
Primary sources provide raw information and first-hand evidence. Examples include interview transcripts, statistical data, and works of art. Primary research gives you direct access to the subject of your research. Secondary sources provide second-hand information and commentary from other researchers. Examples include journal articles, reviews ...
So, if you want to make an extremely valuable source document, try writing a note in italics. Include the note under the question that states the exclusionary value and include the criteria number. 2. Use Study Endpoints in Your Source Documents. Study endpoints explain why the clinical trial is being conducted.
For more information, contact Naila Ganatra at (215) 413-2471. Adequate and accurate source documentation in clinical research is critical to ensuring subject safety, data integrity, and investigators meeting regulatory expectations. Appropriate monitoring of source data is also vital for the sponsor stakeholder performance.
Print Sources. Books and Textbooks: Odds are that at least one book has been written about virtually any research topic you can imagine (and if not, your research could represent the first steps toward a best-selling publication that addresses the gap!).Because of the time it takes to publish a book, books usually contain more dated information than will be found in journals and newspapers.
In research and academics, a primary source refers to information collected from sources that witnessed or experienced an event firsthand. These can be historical documents, literary texts, artistic works, experiments, journal entries, surveys, and interviews. A primary source, which is very different from a secondary source, is also called ...
A list of general sources for images and film is available in the Library Research Guide for History and additional sources for the history of science in Library Research Guide for the History of Science. Government documents often concern matters of science and health policy.
While source document verification (SDV) aims to compare recorded data against the source documents to ensure a match, the purpose of source document review (SDR) is to ensure the quality of the source documentation itself. ... Well, no. Federal regulations on clinical research don't define a minimum or maximum amount of SDV ...
Source Documents . Source Data is defined as all information in original records and certified copies of original records of clinical findings, observations, or other activities (in a clinical investigation) used for the ... used to document key research data elements. If data are entered directly into a computer system, the electronic record ...
What Are Credible Research Sources? Credible sources are essential for providing accurate, reliable, and verifiable information in research papers. When I say "credible sources," I mean sources authored by experts and published in reputable journals, books, or websites. The integrity and reliability of your research depend on these sources.
Secondary sources describe, discuss, and analyze research obtained from primary sources or from other secondary sources. Using the previous example about World War II, if you read other historians' accounts of it, government documents, maps, and other written documents, you are engaging in secondary research.
This paper estimates that the macroeconomic damages from climate change are six times larger than previously thought. We exploit natural variability in global temperature and rely on time-series variation. A 1°C increase in global temperature leads to a 12% decline in world GDP. Global temperature ...
By completing this form, I agree to receive occasional emails per the terms of the ACLU's privacy statement.
Project 2025, also known as the Presidential Transition Project, is a collection of policy proposals to fundamentally reshape the U.S. federal government in the event of a Republican victory in the 2024 U.S. presidential election. Established in 2022, the project aims to recruit tens of thousands of conservatives to the District of Columbia to replace existing federal civil servants—whom ...
MPT-7B is another prominent open-source model by Databricks. Unlike Dolly 2.0, it competes and surpasses Meta's LLaMA-7B in many ways. The model was trained using a mixed set of data from various sources, including 6.7 billion parameters. It also aims to be an affordable alternative to the closed source LLM models available.
The Nutrition Source does not recommend or endorse any products. Help us improve The Nutrition Source! Take our quick survey to share your experience using the website, and offer any suggestions that may help us improve The Nutrition Source. Explore: Use healthy oils (like olive and canola oil) for cooking, on salad, and at the table. ...