Search the Holocaust Encyclopedia
- Animated Map
- Discussion Question
- Media Essay
- Oral History
- Timeline Event
- Clear Selections
- Bahasa Indonesia
- Português do Brasil
Featured Content
Find topics of interest and explore encyclopedia content related to those topics
Find articles, photos, maps, films, and more listed alphabetically
For Teachers
Recommended resources and topics if you have limited time to teach about the Holocaust
Explore the ID Cards to learn more about personal experiences during the Holocaust
Timeline of Events
Explore a timeline of events that occurred before, during, and after the Holocaust.

Introduction to the Holocaust
- Antisemitism
- How Many People did the Nazis Murder?
- Book Burning
- German Invasion of Western Europe, May 1940
- Voyage of the St. Louis
- Genocide of European Roma (Gypsies), 1939–1945
- The Holocaust and World War II: Key Dates
Liberation of Nazi Camps
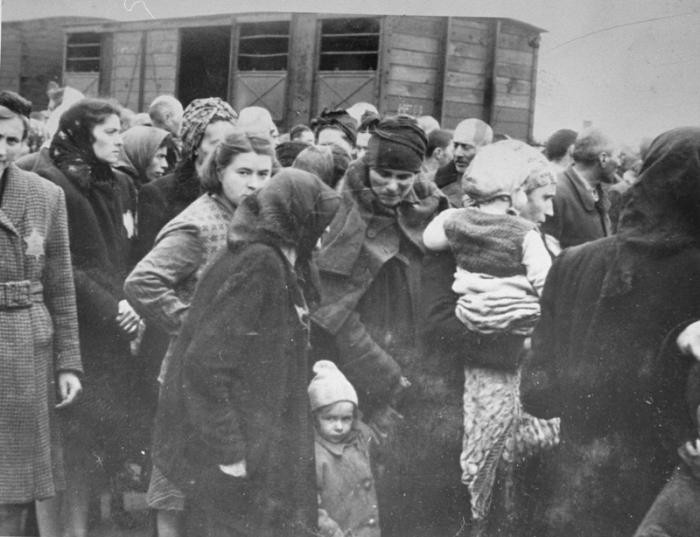

The Holocaust was the systematic, state-sponsored persecution and murder of six million European Jews by the Nazi German regime and its allies and collaborators. The Holocaust was an evolving process that took place throughout Europe between 1933 and 1945.
Antisemitism was at the foundation of the Holocaust. Antisemitism, the hatred of or prejudice against Jews, was a basic tenet of Nazi ideology. This prejudice was also widespread throughout Europe.
Nazi Germany’s persecution of Jews evolved and became increasingly more radical between 1933 and 1945. This radicalization culminated in the mass murder of six million Jews.
During World War II, Nazi Germany and its allies and collaborators killed nearly two out of every three European Jews using deadly living conditions, brutal mistreatment, mass shootings and gassings, and specially designed killing centers.
- Final Solution
- Third Reich
- World War II
This content is available in the following languages
[caption=941bfca8-4244-4f75-b763-6f84201310d3] - [credit=941bfca8-4244-4f75-b763-6f84201310d3]
The Holocaust (1933–1945) was the systematic, state-sponsored persecution and murder of six million European Jews by the Nazi German regime and its allies and collaborators. 1 In addition to perpetrating the Holocaust, Nazi Germany also persecuted and murdered millions of other victims .
What was the Holocaust?
The United States Holocaust Memorial Museum defines the years of the Holocaust as 1933–1945. The Holocaust era began in January 1933 when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party came to power in Germany. It ended in May 1945, when the Allied Powers defeated Nazi Germany in World War II. The Holocaust is also sometimes referred to as “the Shoah,” the Hebrew word for “catastrophe.”
By the end of the Holocaust, the Nazi German regime and their allies and collaborators had murdered six million European Jews.
Why did the Nazis target Jews?
The Nazis targeted Jews because the Nazis were radically antisemitic. This means that they were prejudiced against and hated Jews. In fact, antisemitism was a basic tenet of their ideology and at the foundation of their worldview.
The Nazis falsely accused Jews of causing Germany’s social, economic, political, and cultural problems. In particular, they blamed them for Germany’s defeat in World War I (1914–1918). Some Germans were receptive to these Nazi claims. Anger over the loss of the war and the economic and political crises that followed contributed to increasing antisemitism in German society. The instability of Germany under the Weimar Republic (1918–1933), the fear of communism , and the economic shocks of the Great Depression also made many Germans more open to Nazi ideas, including antisemitism.
However, the Nazis did not invent antisemitism. Antisemitism is an old and widespread prejudice that has taken many forms throughout history. In Europe, it dates back to ancient times. In the Middle Ages (500–1400), prejudices against Jews were primarily based in early Christian belief and thought, particularly the myth that Jews were responsible for the death of Jesus. Suspicion and discrimination rooted in religious prejudices continued in early modern Europe (1400–1800). At that time, leaders in much of Christian Europe isolated Jews from most aspects of economic, social, and political life. This exclusion contributed to stereotypes of Jews as outsiders. As Europe became more secular, many places lifted most legal restrictions on Jews. This, however, did not mean the end of antisemitism. In addition to religious antisemitism, other types of antisemitism took hold in Europe in the 18th and 19th centuries. These new forms included economic, nationalist, and racial antisemitism. In the 19th century, antisemites falsely claimed that Jews were responsible for many social and political ills in modern, industrial society. Theories of race, eugenics , and Social Darwinism falsely justified these hatreds. Nazi prejudice against Jews drew upon all of these elements, but especially racial antisemitism . Racial antisemitism is the discriminatory idea that Jews are a separate and inferior race.
Where did the Holocaust take place?
The Holocaust was a Nazi German initiative that took place throughout German- and Axis-controlled Europe. It affected nearly all of Europe’s Jewish population, which in 1933 numbered 9 million people.
The Holocaust began in Germany after Adolf Hitler was appointed chancellor in January 1933. Almost immediately, the Nazi German regime (which called itself the Third Reich ) excluded Jews from German economic, political, social, and cultural life. Throughout the 1930s, the regime increasingly pressured Jews to emigrate.
But the Nazi persecution of Jews spread beyond Germany. Throughout the 1930s, Nazi Germany pursued an aggressive foreign policy . This culminated in World War II, which began in Europe in 1939. Prewar and wartime territorial expansion eventually brought millions more Jewish people under German control.
Nazi Germany’s territorial expansion began in 1938–1939. During this time, Germany annexed neighboring Austria and the Sudetenland and occupied the Czech lands. On September 1, 1939, Nazi Germany began World War II (1939–1945) by attacking Poland . Over the next two years, Germany invaded and occupied much of Europe, including western parts of the Soviet Union . Nazi Germany further extended its control by forming alliances with the governments of Italy , Hungary , Romania , and Bulgaria . It also created puppet states in Slovakia and Croatia. Together these countries made up the European members of the Axis alliance , which also included Japan.
By 1942—as a result of annexations, invasions, occupations, and alliances—Nazi Germany controlled most of Europe and parts of North Africa. Nazi control brought harsh policies and ultimately mass murder to Jewish civilians across Europe.
The Nazis and their allies and collaborators murdered six million Jews.
Geography of the Holocaust
How did Nazi Germany and its allies and collaborators persecute Jewish people?
Between 1933 and 1945, Nazi Germany and its allies and collaborators implemented a wide range of anti-Jewish policies and measures. These policies varied from place to place. Thus, not all Jews experienced the Holocaust in the same way. But in all instances, millions of people were persecuted simply because they were identified as Jewish.
Throughout German-controlled and aligned territories, the persecution of Jews took a variety of forms:
- Legal discrimination in the form of antisemitic laws . These included the Nuremberg Race Laws and numerous other discriminatory laws.
- Various forms of public identification and exclusion. These included antisemitic propaganda , boycotts of Jewish-owned businesses , public humiliation , and obligatory markings (such as the Jewish star badge worn as an armband or on clothing).
- Organized violence. The most notable example is Kristallnacht . There were also isolated incidents and other pogroms (violent riots).
- Physical Displacement. Perpetrators used forced emigration, resettlement, expulsion, deportation, and ghettoization to physically displace Jewish individuals and communities.
- Internment. Perpetrators interned Jews in overcrowded ghettos , concentration camps , and forced-labor camps, where many died from starvation, disease, and other inhumane conditions.
- Widespread theft and plunder. The confiscation of Jews’ property, personal belongings, and valuables was a key part of the Holocaust.
- Forced labor . Jews had to perform forced labor in service of the Axis war effort or for the enrichment of Nazi organizations, the military, and/or private businesses.
Many Jews died as a result of these policies. But before 1941, the systematic mass murder of all Jews was not Nazi policy. Beginning in 1941, however, Nazi leaders decided to implement the mass murder of Europe’s Jews. They referred to this plan as the “Final Solution to the Jewish Question.”
What was the “Final Solution to the Jewish Question”?
The Nazi “Final Solution to the Jewish Question” (“ Endlösung der Judenfrage ”) was the deliberate and systematic mass murder of European Jews. It was the last stage of the Holocaust and took place from 1941 to 1945. Though many Jews were killed before the "Final Solution" began, the vast majority of Jewish victims were murdered during this period.
Mass Shootings
The Nazi German regime perpetrated mass shootings of civilians on a scale never seen before. After Germany invaded the Soviet Union in June 1941, German units began to carry out mass shootings of local Jews. At first, these units targeted Jewish men of military age. But by August 1941, they had started massacring entire Jewish communities. These massacres were often conducted in broad daylight and in full view and earshot of local residents.
Mass shooting operations took place in more than 1,500 cities, towns, and villages across eastern Europe. German units tasked with murdering the local Jewish population moved throughout the region committing horrific massacres. Typically, these units would enter a town and round up the Jewish civilians. They would then take the Jewish residents to the outskirts of the town. Next, they would force them to dig a mass grave or take them to mass graves prepared in advance. Finally, German forces and/or local auxiliary units would shoot all of the men, women, and children into these pits. Sometimes, these massacres involved the use of specially designed mobile gas vans. Perpetrators would use these vans to suffocate victims with carbon monoxide exhaust.
Germans also carried out mass shootings at killing sites in occupied eastern Europe. Typically these were located near large cities. These sites included Fort IX in Kovno (Kaunas), the Rumbula and Bikernieki Forests in Riga , and Maly Trostenets near Minsk . At these killing sites, Germans and local collaborators murdered tens of thousands of Jews from the Kovno, Riga, and Minsk ghettos. They also shot tens of thousands of German, Austrian, and Czech Jews at these killing sites. At Maly Trostenets, thousands of victims were also murdered in gas vans.
The German units that perpetrated the mass shootings in eastern Europe included Einsatzgruppen (special task forces of the SS and police), Order Police battalions, and Waffen-SS units. The German military ( Wehrmacht ) provided logistical support and manpower. Some Wehrmacht units also carried out massacres. In many places, local auxiliary units working with the SS and police participated in the mass shootings. These auxiliary units were made up of local civilian, military, and police officials.
As many as 2 million Jews were murdered in mass shootings or gas vans in territories seized from Soviet forces.
Killing Centers
German authorities, with the help of their allies and collaborators, transported Jews from across Europe to these killing centers. They disguised their intentions by calling the transports to the killing centers “resettlement actions” or “evacuation transports.” In English, they are often referred to as “deportations.” Most of these deportations took place by train. In order to efficiently transport Jews to the killing centers, German authorities used the extensive European railroad system , as well as other means of transportation. In many cases the railcars on the trains were freight cars; in other instances they were passenger cars.
The conditions on deportation transports were horrific. German and collaborating local authorities forced Jews of all ages into overcrowded railcars. They often had to stand, sometimes for days, until the train reached its destination. The perpetrators deprived them of food, water, bathrooms, heat, and medical care. Jews frequently died en route from the inhumane conditions.
The vast majority of Jews deported to killing centers were gassed almost immediately after their arrival. Some Jews whom German officials believed to be healthy and strong enough were selected for forced labor.
My mother ran over to me and grabbed me by the shoulders, and she told me "Leibele, I'm not going to see you no more. Take care of your brother." — Leo Schneiderman describing arrival at Auschwitz, selection, and separation from his family
At all five killing centers, German officials forced some Jewish prisoners to assist in the killing process. Among other tasks, these prisoners had to sort through victims’ belongings and remove victims’ bodies from the gas chambers. Special units disposed of the millions of corpses through mass burial, in burning pits, or by burning them in large, specially designed crematoria .
Nearly 2.7 million Jewish men, women, and children were murdered at the five killing centers.
What were ghettos and why did German authorities create them during the Holocaust?
Ghettos were areas of cities or towns where German occupiers forced Jews to live in overcrowded and unsanitary conditions. German authorities often enclosed these areas by building walls or other barriers. Guards prevented Jews from leaving without permission. Some ghettos existed for years, but others existed only for months, weeks, or even days as holding sites prior to deportation or murder.
German officials first created ghettos in 1939–1940 in German-occupied Poland. The two largest were located in the occupied Polish cities of Warsaw and Lodz (Łódź). Beginning in June 1941, German officials also established them in newly conquered territories in eastern Europe following the German attack on the Soviet Union. German authorities and their allies and collaborators also established ghettos in other parts of Europe. Notably, in 1944, German and Hungarian authorities created temporary ghettos to centralize and control Jews prior to their deportation from Hungary.
The Purpose of the Ghettos
German authorities originally established the ghettos to isolate and control the large local Jewish populations in occupied eastern Europe. Initially, they concentrated Jewish residents from within a city and the surrounding area or region. However, beginning in 1941, German officials also deported Jews from other parts of Europe (including Germany) to some of these ghettos.
Jewish forced labor became a central feature of life in many ghettos. In theory, it was supposed to help pay for the administration of the ghetto as well as support the German war effort. Sometimes, factories and workshops were established nearby in order to exploit the imprisoned Jews for forced labor. The labor was often manual and grueling.
Life in the Ghettos

Jews in the ghettos sought to maintain a sense of dignity and community. Schools, libraries, communal welfare services, and religious institutions provided some measure of connection among residents. Attempts to document life in the ghettos, such as the Oneg Shabbat archive and clandestine photography, are powerful examples of spiritual resistance . Many ghettos also had underground movements that carried out armed resistance. The most famous of these is the Warsaw ghetto uprising in 1943.
Liquidating the Ghettos
Beginning in 1941–1942, Germans and their allies and collaborators murdered ghetto residents en masse and dissolved ghetto administrative structures. They called this process “liquidation.” It was part of the “Final Solution to the Jewish Question.” The majority of Jews in the ghettos were murdered either in mass shootings at nearby killing sites or after deportation to killing centers. Most of the killing centers were deliberately located near the large ghettos of German-occupied Poland or on easily-accessible railway routes.
Who was responsible for carrying out the Holocaust and the Final Solution?
Many people were responsible for carrying out the Holocaust and the Final Solution.
At the highest level, Adolf Hitler inspired, ordered, approved, and supported the genocide of Europe’s Jews. However, Hitler did not act alone. Nor did he lay out an exact plan for the implementation of the Final Solution. Other Nazi leaders were the ones who directly coordinated, planned, and implemented the mass murder. Among them were Hermann Göring , Heinrich Himmler , Reinhard Heydrich , and Adolf Eichmann .
However, millions of Germans and other Europeans participated in the Holocaust. Without their involvement, the genocide of the Jewish people in Europe would not have been possible. Nazi leaders relied upon German institutions and organizations; other Axis powers; local bureaucracies and institutions; and individuals.
German Institutions, Organizations, and Individuals
As members of these institutions, countless German soldiers , policemen , civil servants , lawyers, judges , businessmen , engineers, and doctors and nurses chose to implement the regime’s policies. Ordinary Germans also participated in the Holocaust in a variety of ways. Some Germans cheered as Jews were beaten or humiliated. Others denounced Jews for disobeying racist laws and regulations. Many Germans bought, took, or looted their Jewish neighbors' belongings and property. These Germans’ participation in the Holocaust was motivated by enthusiasm, careerism, fear, greed, self-interest, antisemitism, and political ideals, among other factors.
Non-German Governments and Institutions
Nazi Germany did not perpetrate the Holocaust alone. It relied on the help of its allies and collaborators. In this context, “allies” refers to Axis countries officially allied with Nazi Germany. “Collaborators” refers to regimes and organizations that cooperated with German authorities in an official or semi-official capacity. Nazi Germany’s allies and collaborators included:
- The European Axis Powers and other collaborationist regimes (such as Vichy France ). These governments passed their own antisemitic legislation and cooperated with German goals.
- German-backed local bureaucracies, especially local police forces. These organizations helped round up, intern, and deport Jews even in countries not allied with Germany, such as the Netherlands .
- Local auxiliary units made up of military and police officials and civilians. These German-backed units participated in massacres of Jews in eastern Europe (often voluntarily).
The terms “allies” and “collaborators” can also refer to individuals affiliated with these governments and organizations.
Individuals across Europe
Throughout Europe, individuals who had no governmental or institutional affiliation and did not directly participate in murdering Jews also contributed to the Holocaust.
One of the deadliest things that neighbors, acquaintances, colleagues, and even friends could do was denounce Jews to Nazi German authorities. An unknown number chose to do so. They revealed Jews’ hiding places, unmasked false Christian identities, and otherwise identified Jews to Nazi officials. In doing so, they brought about their deaths. These individuals’ motivations were wide-ranging: fear, self-interest, greed, revenge, antisemitism, and political and ideological beliefs.
Individuals also profited from the Holocaust. Non-Jews sometimes moved into Jews’ homes, took over Jewish-owned businesses, and stole Jews’ possessions and valuables. This was part of the widespread theft and plunder that accompanied the genocide.
Most often individuals contributed to the Holocaust through inaction and indifference to the plight of their Jewish neighbors. Sometimes these individuals are called bystanders .
Who were the other victims of Nazi persecution and mass murder?
The Holocaust specifically refers to the systematic, state-sponsored persecution and murder of six million Jews. However, there were also millions of other victims of Nazi persecution and murder . In the 1930s, the regime targeted a variety of alleged domestic enemies within German society. As the Nazis extended their reach during World War II, millions of other Europeans were also subjected to Nazi brutality.
The Nazis classified Jews as the priority “enemy.” However, they also targeted other groups as threats to the health, unity, and security of the German people. The first group targeted by the Nazi regime consisted of political opponents . These included officials and members of other political parties and trade union activists. Political opponents also included people simply suspected of opposing or criticizing the Nazi regime. Political enemies were the first to be incarcerated in Nazi concentration camps . Jehovah’s Witnesses were also incarcerated in prisons and concentration camps. They were arrested because they refused to swear loyalty to the government or serve in the German military.
The Nazi regime also targeted Germans whose activities were deemed harmful to German society. These included men accused of homosexuality , persons accused of being professional or habitual criminals, and so-called asocials (such as people identified as vagabonds, beggars, prostitutes, pimps, and alcoholics). Tens of thousands of these victims were incarcerated in prisons and concentration camps. The regime also forcibly sterilized and persecuted Afro-Germans .
People with disabilities were also victimized by the Nazi regime. Before World War II, Germans considered to have supposedly unhealthy hereditary conditions were forcibly sterilized. Once the war began, Nazi policy radicalized. People with disabilities, especially those living in institutions, were considered both a genetic and a financial burden on Germany. These people were targeted for murder in the so-called Euthanasia Program .
The Nazi regime employed extreme measures against groups considered to be racial, civilizational, or ideological enemies. This included Roma (Gypsies) , Poles (especially the Polish intelligentsia and elites), Soviet officials , and Soviet prisoners of war . The Nazis perpetrated mass murder against these groups.
How did the Holocaust end?
But liberation did not bring closure. Many Holocaust survivors faced ongoing threats of violent antisemitism and displacement as they sought to build new lives. Many had lost family members, while others searched for years to locate missing parents, children, and siblings.
How did some Jews survive the Holocaust?
Despite Nazi Germany’s efforts to murder all the Jews of Europe, some Jews survived the Holocaust. Survival took a variety of forms. But, in every case, survival was only possible because of an extraordinary confluence of circumstances, choices, help from others (both Jewish and non-Jewish), and sheer luck.
Survival outside of German-Controlled Europe
Some Jews survived the Holocaust by escaping German-controlled Europe. Before World War II began, hundreds of thousands of Jews emigrated from Nazi Germany despite significant immigration barriers. Those who immigrated to the United States, Great Britain, and other areas that remained beyond German control were safe from Nazi violence. Even after World War II began, some Jews managed to escape German-controlled Europe. For example, approximately 200,000 Polish Jews fled the German occupation of Poland. These Jews survived the war under harsh conditions after Soviet authorities deported them further east into the interior of the Soviet Union.
Survival in German-Controlled Europe
A smaller number of Jews survived inside German-controlled Europe. They often did so with the help of rescuers. Rescue efforts ranged from the isolated actions of individuals to organized networks, both small and large. Throughout Europe, there were non-Jews who took grave risks to help their Jewish neighbors, friends, and strangers survive. For example, they found hiding places for Jews, procured false papers that offered protective Christian identities, or provided them with food and supplies. Other Jews survived as members of partisan resistance movements . Finally, some Jews managed, against enormous odds, to survive imprisonment in concentration camps, ghettos, and even killing centers.
In the aftermath of the Holocaust, those Jews who survived were often confronted with the traumatic reality of having lost their entire families and communities. Some were able to go home and chose to rebuild their lives in Europe. Many others were afraid to do so because of postwar violence and antisemitism . In the immediate postwar period, those who could not or would not return home often found themselves living in displaced persons camps . There, many had to wait years before they were able to immigrate to new homes.
In the aftermath of the Holocaust, the world has struggled to come to terms with the horrors of the genocide, to remember the victims, and to hold perpetrators responsible . These important efforts remain ongoing.
Series: After the Holocaust

The Aftermath of the Holocaust: Effects on Survivors

Displaced Persons

About Life after the Holocaust

Postwar Trials

What is Genocide?
Genocide timeline, series: the holocaust.

"Final Solution": Overview

Forced Labor: An Overview

Mass Shootings of Jews during the Holocaust

Gassing Operations

Deportations to Killing Centers

Killing Centers: An Overview
Switch series, critical thinking questions.
What can we learn from the massive size and scope of the Holocaust?
Across Europe, the Nazis found countless willing helpers who collaborated or were complicit in their crimes. What motives and pressures led so many individuals to persecute, to murder, or to abandon their fellow human beings?
Were there warning signs of what was to come before the Nazis came to power in 1933? Before the start of mass killing in 1941?
In this context, “allies” refers to Axis countries officially allied with Nazi Germany. “Collaborators” refers to regimes and organizations that cooperated with German authorities in an official or semi-official capacity. These German-backed collaborators included some local police forces, bureaucracies, and paramilitary units. The terms “allies” and “collaborators” can also refer to individuals affiliated with these governments and organizations.
Thank you for supporting our work
We would like to thank Crown Family Philanthropies and the Abe and Ida Cooper Foundation for supporting the ongoing work to create content and resources for the Holocaust Encyclopedia. View the list of all donors .
Nazi Germany (1933-1945)
Second edition by S. Jonathan Wiesen, Pamela Swett First edition by Richard Breitman
- Volume (3/6)
Introduction
Bibliography, party and state, policing the reich, racism and biopolitics, economy and consumer politics, gender, youth, and sexuality, arts and culture, science, technology, and nature, military, foreign policy, and war, the holocaust, survival, resistance and rescue, transnational connections, book burnings across germany (1933), germany: territorial expansion (1935-1939), administrative structure under national socialism (1941), europe at the beginning of december 1941, concentration and extermination camps and major “euthanasia” centers, forced laborers by national origin (1944), europe in april 1944, jewish victims of the holocaust by country, sept. 1, 1939–may 7, 1945, estimated fatalities during the second world war by country (1939-1945).
The Holocaust and Nazi Germany Research Paper
Hitler was one of the most notorious dictators the world has ever seen. He engineered the most horrific activities in the history of humankind, the holocaust. The rise of the Nazis to power in 1933 led to the establishment of thousands of concentration camps, which were centers of mass murders of Jews. Most Germans supported the ideology that led to the persecution of the Jews.
The Nazis viewed the Jews as a foreign race that was in an eternal battle for dominance with the Aryans. Hitler’s book, Mein Kampf, is a clear illustration of his contempt towards the Jews. The book regards the Jews as an inferior race that should not take part in Germany’s political, cultural, and intellectual life.
The book, which was a best seller, during his time as Germany’s leader, brainwashed Germans into conforming to his ideas. Therefore, Hitler had millions of ardent followers who were willing to persecute Jews. In fact, there is no record of coercion of civilians by the Nazis to persecute Jews.
Civilians did so out of their own free will. Even German intellectuals conformed to the Nazi ideology. Doctors used Jews as guinea pigs for undertaking various medical tests (Fishel, 1998).
During the holocaust, there was institutionalization of persecution of the Jews. All institutions helped in the persecution of the Jews. The intellectual society did not raise a finger to prevent the mass murder of the Jews. In fact, it aided the mass murders. Dr. Josef Mengele was one of the most notorious intellectuals who supported the persecution of the Jews.
Dr. Mengele carried out medical experiment using human subjects from various concentration camps. Some of the experiments included testing of drugs, surgeries, and amputations. This inhuman treatment inflicted great suffering to the people. In most instances, it culminated in the death of the human subjects. This is despite the fact the medical profession requires doctors to obtain consent from the patients before using them in undertaking any experiments.
Dr. Mengele killed and dissected most of the patients who did not die from the experiments (Fishel, 1998). However, not all intellectuals supported Hitler and his ideologies after he ascended to power. Hitler gained the support of the intellectuals gradually. When Hitler ascended to power, he attacked several groups that had opposed him gradually and systematically.
Hitler first attacked members of parties that did not support him. Afterwards he attacked intellectuals at universities. Hitler then attacked prominent church leaders. Finally, Hitler turned to his main targets, the Jews. Hitler attacked each of the above groups as minority groups (Zassenhaus, 1974). Gradual attack and isolation of the groups reduced the resistance of the groups.
These groups were the only institutions in the society that were capable of mobilizing people against Hitler’s ideologies, which advocated for mass murder of Jews. Therefore, removal of these obstacles facilitated the propagation of Hitler’s ideologies by the masses.
During the holocaust, pogroms were common within the regions that were under the control of the Germans. Pogrom refers to mob attacks by civilians against Jews. Pogroms usually led to the killing of Jews and destruction of property and religious centers of the Jews. Authorities usually condoned the persecution of the Jews during the pogroms.
Pogroms may also target certain ethnic groups in the society. In the Nazi Germany, pogroms were very common. Civilians killed thousands of Jews in the streets of various towns. Various scholars trace the beginning the holocaust to an anti-Jewish riot in 1938 – Kristallnacht (the Night of Broken Glass). During the riot, civilians attacked Jews and vandalized their property.
The riots led to the killing of nearly 100 Jews. In addition, the Nazis sent approximately 30,000 Jews to various concentration camps. The Jews stayed in the concentration camps for several weeks. The government granted the Jews freedom on condition that they would transfer their property to the Nazis or if they proved that they would emigrate in the near future. During the pogrom, civilians destroyed approximately 7,000 Jewish businesses and more than 1,600 synagogues.
The riots took place simultaneously in Germany and Austria. The major cause of the pogrom was the assassination of a German diplomat by a Jewish minor in Paris. The Nazis took advantage of this event to instigate civilians to undertake widespread persecution of Jews (Zassenhaus, 1974). The fact that the Nazi party could mobilize people to undertake widespread persecution of the Jews is a clear indication that many people prescribed to the ideals of the Nazi party.
Not all pogroms occurred at the hands of the Germans. Citizens of other countries also persecuted Jews. One such pogrom was the Iasi Pogrom, which was one of the deadliest pogroms during the holocaust. The pogrom occurred in Romania. It resulted in the death of more than 13,000 Jews. Civilians, police, and military officials carried out the mass murder of the Jews (Frank, 2001).
Between June and July of 1941, the Nazis and Ukrainian police organized two large pogroms in the Ukrainian city of Lwow. The pogroms resulted in the death of approximately 6,000 Jews. The pogrom was a retribution for the alleged collaboration of the Jews with the Soviet government. Poland was one the regions that had the largest number of Jews in Europe.
As a result, there was widespread persecution of the Jews by both the civilians and the Nazis. The holocaust resulted in the death of more than three million Jews in Poland. The Jedwabne pogrom, which occurred in July 1941, is one of the many pogroms that took place in Poland. During the pogrom, non-Jewish Poles burned more than 300 Jews in a barn house.
The non-Jewish Poles undertook the killing of the Jews under the supervision of the police (Herzog, 2006). In Lithuania, anti-Jewish pogroms in Kaunas resulted in the killing of approximately 3,800 Jews and the burning of Jewish settlements and synagogues. The Nazis and the Lithuanian police led the anti-Jewish pogroms in Kaunas (Fishel, 1998).
In all the pogroms that took place in various parts of the German territory, the Nazis did not use coercion to instigate civilians to kill Jews. Civilians killed Jews out of their own free will. In addition, the Nazis did not impose punishments on people who did not take part in the killings. Most attacks involved unarmed Jews and heavily armed civilians.
The police usually supervised the killings of the Jews by the civilians. This made it difficult for the Jews to defend themselves. However, the number of the Jews killed by civilians during the anti-Jewish pogroms is only a small fraction of the total number of Jews who died during the holocaust. Millions of Jews died in the extermination camps.
Fishel, J. (1998). The holocaust . Westport, CT: Greenwood Publishing.
Frank, B.G. (2001). A travel guide to Jewish Europe , Third edition. Gretna, LA: Pelican Publishing.
Herzog, D. (2006). Lessons and legacies vii: The holocaust in international perspective . Evanston, IL: Northwestern University Press.
Zassenhaus, H. (1974). Walls: Resisting the third Reich- one woman’s story . Boston, MA: Beacon Press.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2019, April 15). The Holocaust and Nazi Germany. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-holocaust-and-nazi-germany/
"The Holocaust and Nazi Germany." IvyPanda , 15 Apr. 2019, ivypanda.com/essays/the-holocaust-and-nazi-germany/.
IvyPanda . (2019) 'The Holocaust and Nazi Germany'. 15 April.
IvyPanda . 2019. "The Holocaust and Nazi Germany." April 15, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-holocaust-and-nazi-germany/.
1. IvyPanda . "The Holocaust and Nazi Germany." April 15, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-holocaust-and-nazi-germany/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "The Holocaust and Nazi Germany." April 15, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-holocaust-and-nazi-germany/.
- Conduction of The Holocaust
- 1942-1945 Holocaust: Nazi Germany’s Political Reasons
- Holocaust: Nazi Anti-Jewish Policies and Actions
- The Holocaust: Analysis of Life in the Kovno, Warsaw and Lodz Ghettos
- The Holocaust and Jews Extermination
- Leni Riefenstahl’s Triumph of the Will
- The Burden of Hitler’s Legacy
- The Nazi Holocaust’s Effects
- Society and Politics
- Art and Culture
- Biographies
- Publications

History Grade 11 - Topic 3 Essay Questions

Essay Question
To what extent did Australian government policies and legislation succeed in perpetuating racism and the dehumanization of the Aborigines in the 19th and 20th centuries? Present an argument in support of your answer using relevant historical evidence. [1]
Introduction :
A number of scholars agree that race was part of the Enlightenment project that resulted from the desire to classify people into distinct categories. [2] Racial classification certainly existed before this period, but the ‘modern’ application of race has much to do with Europe’s interaction with the ‘rest of the world’. [3] Thus, central to the project of European colonialism was the crystallization of Eugenics policies and an array of social Darwinist theories in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. These theories which later transformed government policy and law rendered non-European peoples as subhuman and biologically inferior and thus should be dispossessed of their land and other vital resources and ultimately exterminated in society. Therefore, and relevant to this essay, we will focus on the implementation of Eugenics policies and Social Darwinism in Australia in order to evaluate the extent to which these policies impacted on the Aboriginal people of Australia.
British colonisation and occupation of Australia
After the British colonised Australia in the 18th century, the first one hundred and forty years of Australian colonial history was marked by conflict and dispossession. [4] The arrival of Lieutenant James Cook and then Arthur Philip in 1788 marked the beginning of ‘white settlement’. [5] From 1788, Australia was treated by the British as a colony of settlement, not of conquest. Aboriginal land was expropriated by the British colonists on the premise that the land was empty (the terra nullius theory) and that the British colonists discovered it. This myth was applied across the colonial world to perpetuate and justify indigenous dispossession and genocide. [6]
Colonists viewed the indigenous Australians as inferior and scarcely human. Their way of life was seen as ‘primitive and uncivilised’, and colonialists believed that their culture would eventually die out. [7] This view justified colonial conquest of the Aboriginal people. Social anthropologists from universities who ‘studied’ the way of life of the Aborigines reinforced this view. [8] Firstly, this view added some ‘scientific’ credibility to observations about this ‘primitive’ society with the lowest level of kinship and the most ‘primitive’ form of religion. Secondly, it also added to the views of Australian eugenicists without deeply analysing the complexities of Aboriginal life. [9]
Application of eugenics policies on the Aborigines
Eugenics associations were established in many states, e.g., New South Wales and Victoria. In 1960 the Racial Hygiene Association, based in Sydney, became the Family Planning Association. [10] A prominent eugenicist in Melbourne was Prof Richard Berry who believed the Aborigines to be the most primitive form of humans. Berry studied and measured people’s heads to prove his theory that white, educated people were the smartest, while the poor, criminals and Aboriginal Australian were the least so. Berry proposed a euthanasia chamber for so-called mental defectives. [11] Ideas of racial decay and racial suicide were aimed at strengthening the number of whites in society, especially in the north where Asian populations were expanding. [12] In 1901 the Immigration Restriction Act was passed (known as the White Australia Policy). White racial unity was promoted as a form of racial purity.
Immigration was encouraged from the UK in 1922 to swell European numbers and thousands of children were sent to keep Australia white. 1912: white mothers offered £5 childbirth bounty in order to grow the size of wealthy middle -class families, which tended to have fewer children than poorer, pauper families in society. [13] This was partly in response to the debate around ‘racial suicide’. It was thought that the middle class would die out because they were not having enough children. [14] Decrease in the number of middle-class whites led to notions of ‘racial decay’. It was assumed that ‘racial poisons’ (e.g., TB, venereal disease, prostitution, alcoholism and criminality) would decimate whites with good stock (middle class). Plans were made to deal with ‘racially contaminated’ and misfits to keep middle class ‘pure’. [15]
Australia Immigration Policies
The White Australian policy of 1901 aimed at cohesion among the white population in the country. [16] It enshrined discrimination and white superiority. Between 1920 and 1967 thousands of British children between the ages of 3 and 14 were sent to Australia and Canada to boost the size of the white population. These children came from poor backgrounds and were mostly in social care. Many of these children were cut off from their families and were often told they were orphans. [17] In addition, a number of these children stayed in orphanages in Australia or became unpaid cheap labour on farms and in some instances were physically and sexually abused. The children who were forcibly migrated under the system became known as the Lost Generation. Catholic Church established homes to accommodate and assist migrant children. In 1987 the Child Migrant Trust under the leadership of Margaret Humphreys began to publicise the abuse of child migrants. [18]
The lost generation?
Children of mixed race were either viewed as inferior by some or as slightly more superior than other Aborigines. [19] However, at the beginning of the 20th century, these ‘half-caste’ children were viewed as a threat to the future of the white race in Australia. In 1913, W. Baldwin Spencer set up 13 proposals to manage the half-caste populations in and around the towns, mining housing and other sites of contact between ‘races’. These included: segregated living areas in certain towns, limits set on the employment of indigenous population by white Australians, the removal of Aboriginal people to a compound, the construction of a half-caste home in one area, a ban on interracial contact and authority given to protectors in some areas to remove ‘half-caste’ children from their families and place them in homes.
By 1930s the number of part-Aboriginal population increased. Dr Cecil Cook and A.O. Neville believed that the white race was headed for extinction. They were responsible for assimilation programmes for ‘breeding blackness out.’ About 100 000 ‘mixed-race’ children were taken from their parents between 1910 and 1970 to breed out Aboriginal blood. Cook encouraged lighter-skinned women to marry white men and in this way ‘breed out their colour’. In 1951, the new Minister for Territories, Paul Hasluck, claimed that assimilation would be the new policy to deal with the indigenous people and motivated this on the grounds of looking after the child’s welfare. Policemen or government officials often took children from their sobbing mothers, they were raised as orphans. Many of these children experienced abuse and neglect. Labels were used, e.g., quadroon, octaroon, to indicate how much ‘white’ blood they had. This policy only ended in 1971. These children are known today as the Stolen Generation. [20]
Reparations?
The practice of removing Aboriginal children from their families was not spoken about until 1997. An official enquiry revealed consistent abuse, exploitation in the labour market, social dislocation that led to alcoholism, violence, and early death. [21] In 2009 Prime Minister Kevin Rudd apologised in parliament for the laws and policies that inflicted grief, suffering and loss on them. He particularly mentioned the ‘Stolen Generation’ who had been removed from their families. In 2010 Rudd apologised to the ‘Lost Generation’ of children who were held in orphanages and other institutions between 1930 and 1970. [22]
Racial ideologies were not simply advanced by a conglomeration of nationalism, imperialism, Darwinism and Eugenics. In the early Twentieth Century, there became evidence strands of simply cultural racism that can be seen as running alongside the biological determinism that was largely prevalent. From this perspective, individuals were suspicious or negative towards to other races not solely on the basis on racial differences, but because those differences represented a divergence in cultural values. This can be seen in the number of miscegenation laws that prevailed in Australia and elsewhere in the colonial world in this context, which have been interpreted as founded on notions of biological mixing. This therefore was an attempt to assert the supremacy of the white race over all other races. Therefore, the development of the sciences of evolutionary Darwinism and Eugenics provided further scientific validity to these views, justifying unequal power relationships either by pinpointing the inability of certain races to develop, or by suggesting the more advanced races had a personal benevolence to the others.

Nazi Germany and the Holocaust
Hitlers consolidation of power from 1933 to 1934 :
The Great Depression had severe economic effects which increased support for political parties that were extremists such as the NSDAP (Nationalsozialistische Deutsche Arbeiterpartei = National Socialist German Workers’ Party, which is popularly known as the Nazi party in English) on the right and the Communist Party on the left. [23] In 1993, Hitler was appointed as Chancellor by the then President Von Hindenburg. [24] This was a significant appointment as Hitler used his position as head of government to consolidate Nazi control. In power, the Nazis dominated the police force by utilizing them to break up meetings that opposition parties had and outlawed all forms of public meetings by justifying that these posed a ‘threat’ to public safety. on the 27th of February 1993, an arson attack occurred which burned the building which housed the German parliament, and this attack became known as the Reichstag Fire. After the Reichstag fire, Hitler got Von Hindenburg to pass a decree which suspended all articles in the constitution that guaranteed peoples key freedoms and liberty. [25] This meant that political opposition were arrested and subsequently sent to concentration camps. The Nazis did not win a clear majority in the elections despite rigorous intimidation and propaganda. As a result, Hitler banned the Communists from the Reichstag party which was supported by the Centre Party- a lay Catholic Party in Germany. [26] Hitler then arranged to get the Reichstag to agree to pass the Enabling Act which allowed him to make laws by decree. This made it possible for Hitler to centralise the government by taking away powers of the state governments. In addition, Hitler destroyed the free trade union movements and banned the Social Democrats and the Communist Party. [27] However, in 1934, an increasing number of left-wing elements within the Nazi Party were opposing Hitlers authority. [28] The Sturmabteilung- Nazi Party’s paramilitary wing, which was led by Ernst Rohm was interested in the socialistic elements of Nazism. [29] In short, they wanted Germany to be a full socialistic state. However, the German Wehrmacht- unified armed forces of Nazi Germany opposed the Sturmabteilung’s stance. On the 30th of June 1934, Hitler’s Schutzstaffel (SS)- a major paramilitary organization under Adolf Hitler got rid of the Sturmabteilung in which 400 of their murders were murdered including Rohm their leader. [30] The SS was now the new elite force which aligned itself with the Hitlers Nazi Party. Following the death of Von Hindenburg in 1934, Hitler merged the positions of president and chancellor and became known as the Führer- leader. Within this new leadership structure, total loyalty was demanded from all Germans. This also led to Germany becoming police state- a totalitarian state controlled by a political police force that secretly supervises the citizens' activities. The SS were led by Heinrich Himmler who was a ruthless and brutal leader who ran the labour and concentration camps, including the Gestapo- secrete state police. [31] Most Germans understood that to resist the rule of the Nazis would be futile.
The creation of a racial state in Germany: defining the German nation in relation to the ‘other’:
In Germany, the ‘perfect German race’ came to be known as the Aryan race which was perceived as the master race by the Nazi Party. [32] The ‘other’ was other races which were perceived to be unproductive, asocial and undesirables such as the gypsies and the Jews which were viewed as coming from impure blood. These groups of people were thought to be inferior and therefore marginalised, treated as sub-human by segregating them and thus dehumanising them. [33] The Aryan race were considered superior because of their ancestry, survival instinct, ‘pure blood’, intellect and perception that they had the capacity to work hard. In Hitlers Nazi state, antisemitism was blamed on race. Hitler hated Jewish people and thus, this hatred shaped his political philosophy. As a result, Jews became a scapegoat for Germanies problems and were thus hunted down in order to eradicate them. To identify ‘others’, stereotyping was used to judge and isolate them. [34] This led to prejudice and gross discrimination which sometimes even meant death. The Nazi Parties promotion of the idea to cleanse Germany of all its ‘enemies’ and because Hitler hated Jews, this led to the mass killing of Millions of Jews.

Applying racial and eugenic laws and policies- Purifying the nation:
Positive eugenics- Refers to efforts which are directed and expanding desirable traits. Positive eugenic Nazi programmes thus encouraged the breeding of pure Aryans since they were viewed as the master race. [35] In these programmes, women were central in creating this perceived pure nation. What this meant practically was that breeding between ‘Aryan’ women and genetically suitable ‘Aryan’ men such as those who were part of the SS were heavily encouraged. In 1936, the Lebensborn programme was established in which SS couples who were deemed to be biologically, racially and hereditarily valuable families were selected to adopt suitable Aryan children. [36]
Negative eugenics- refers to effort which are directed to eliminate through sterilisation, segregation or other means those who are perceived or deemed to be physically, mentally or morally ‘undesirable’. Negative eugenics programmes and laws were passed to eliminate ‘contaminating’ elements of German society. These took many different forms such as sterilisation programmes. [37] In July 1933, the Sterilisation law was passed which gave Nazis the power to sterilise any person who suffered from diseases or hereditary conditions such as schizophrenia or feeblemindedness. Approximately 350 000 people were sterilised as a result of this programme including teenagers of mixed race. In 1933, the Department of Gene and Race Care was establish and Genetic health courts helped enforce these laws. Concentration camps were established and by 1936, these camps were filled with prostitutes, alcoholics, beggars, homosexuals and juvenile delinquents. [38] By 1938, around 11 000 were sent to these camps. Euthanasia (intentionally ending life to relieve pain and suffering) programmes were established. At the beginning of WWII, Hitler signed a decree which allowed for the systematic killing (euthanasia) in institutions of handicapped patients who were considered incurable. [39] The name of the programme was called Operation T4. These killings were secretly carried out in order to prevent a negative reaction from the Catholic Church. These killings were ordered by doctors in special committees who decided who was going to be killed. Initially, these killings were done by lethal injection, however, carbon monoxide was later used. [40] Nazi records show that 70 273 deaths were carried out by gassing at six different euthanasia centres. These euthanasia programmes were just the testing for Jewish extermination later on.
Groups targeted by the Nazis:
Under Hitler, policies in Germany were based on anti-Semitism as he regarded Jews as a separate race who were un-Godly and evil. At first, discrimination made life very uncomfortable for Jews in Germany. However, as the Nazi Party grew in power by having less and less opposition in Germany, Hitlers Party introduced stricter laws against Jews. [41] Most German people chose to be bystanders when these atrocities were being committed. As a result of these laws, Jewish people were Segregated from political, economic, social and educational life in Germany. Between the years 1933 to 1934, Jewish professions and buisinesses were being targeted which resulted in them being excluded from civil services. In 1935, the Nuremburg Laws (antisemitic and racist laws that were enacted in Germany by the Nazi Party) were passed. [42] The Nuremburg Laws meant that Jewish people were not considered German citizens and they forbade marriages between German citizens and Jewish Germans. However, these anti-Semitic laws were relaxed in 1936 because Germany hosted the Olympic games, and thus had many visitors. [43] The following year in 1937 ‘Aryanisation’ began again. When the Nazi Party annexed (The concept in international law in which one state forcibly acquires another states territory) Austria in 1938, anti-Semitism spread there as well. On November 1938, a German diplomat was murdered in Paris, and as retaliation, Jewish shops, buisineses, homes and places of worship were targeted throughout Germany. 20 000 Jews were sent to concentration camps, majority of whom were killed. [44] This event came to be known as Kristallnacht (Violent, state-mandated actions against Jews). This led to Jewish pupils being expelled from schools, Jewish businessmen forced to close their shops, Jewish valuables to be confiscated and in 1939 a curfew was introduced for Jews.
Sinti and Roma:
Gypsies in Germany, like the Jews were targeted for extermination. At first, many were deported as the ‘undesirables.’ However, later there were sterilisation laws against the gypsies. A new law termed “Fight against the Gypsy Menace” required that all gypsies register with the police. [45] They were then forced into concentration camps and ghettos. In Europe, thousands of gypsy women and children were killed in various campaigns. A separate ‘Gypsy family camp’ was set up at Auschwitz-Birkenau which saw many inmates die of exhaustion from hard labour, disease, malnutrition and gassing of children which were done by a Dr called Mengele. [46] Alex Bandy, a Hungarian journalist termed this campaign the ‘forgotten holocaust’.
Other groups targeted by the Nazis:
Political opponents such as Social Democrats, Communists and Trade union leaders were targeted by the Nazis. [47] In addition, Religious opponents such as Jehovah’s Witnesses and Dissident priests (Catholic resistance to Nazi Germany) were also targeted by the Nazis. Those accused of ‘asocial’ crimes such as criminals or homosexuals were also targeted by the Nazi Party. [48]
Choices that people made:
Perpetrators:
Some of the perpetrators of the Nazi regime were secretaries, train drivers, bureaucrats while others actively took part in the killings. [49] Others perpetrators were in the Einsatzgruppen (Extermination squads) while others ran the concentration camps. However, many Nazi Party official denied complicity and said that they were merely following orders. Some perpetrators even claimed that they were negatively affected by their violent actions. [50]
Bystanders:
The vast majority of people not just in Germany but were the world were bystanders. By choosing this stance of being a bystander and be different and passive witnesses, bystanders affirmed the perpetrators. Within the group of bystanders, others chose to become the perpetrators, while others chose to be resisters or rescuers. [51]
Rescuers under the Nazi regime chose to courageously speak out against the regime or actively rescue victims. Many of these rescuers attributed their actions to their convictions and morality to resist evil. Many of them acted courageously based on their faith. Many hid Jews or smuggled them out of occupied areas. [52]
Responses of the persecuted: exile, accommodation, defiance:
Responses from being persecuted by the Nazi Party took many forms such as partisan activities such as smuggling of secret messages, exchanging of food and weapons which sabotaged the Nazis attempt to persecute those they deemed undesirable. In addition, those persecuted responded by military engagement with the Nazi Party despite being heavily suppressed by Nazi troops. Victims continued with their way of life such as cultural traditions, religious practices, creating music and art such as poetry inside the concentration camps and ghettos. In addition, some of the victims managed to escape or go into exile. This caused underground resistance movements aimed at countering Nazi propaganda with anti-Nazi propaganda. The determination for survival was also a form of resistance by victims.
From persecution to mass murder: The Final solution:
The Holocaust (Was the genocide of European Jews during WWII) was carried out as the ‘Final Solution’ under the guise of war. The Einsatzgruppen followed German soldiers into invading other territories. They arrested everyone who resisted and killed those they thought could resist. The Nazis carried out forced removals of those they deemed sub-human or undesirables and carried out mass murders. [53] In Poland, thousand of Polish citizens were sent to labour and concentration camps. Jews were forcibly put in overcrowded ghettos were many would die of inhumane conditions and starvation.
Labour and extermination camps:
In 1941, the Einsatzgruppen followed invading troops into Russia where thousands of Jews were rounded up in preparation to send them to concentration camps. 700 Jews were gassed in vans in Chelmo. This reinforced Hitler’s desire for a ‘Final Solution’ to the Jewish question. The death camps under the SS were established for this reason. [54] In addition, extermination centre sites were purposely located near railway lines so that there was efficient transportation. In 1942, there were mass deportations of Jews from the ghettos. A lot of them died along the way due to the unhygienic conditions, lack of food and heat in transportation. Gas chambers were created for the purposes of mass gassing of Jews using Zyklon-B pellets. Jewish bodies were cremated, and their ashes and bones were intended for fertilisers. Approximately 6 million Jews were killed during the Holocaust. [55]
Forms of justice: The Nuremburg Trials:
Allied forces decided that the main perpetrators of the Holocaust should be put on trial. [56] An international military tribunal was set up at Nuremburg where 22 Nazi leaders were put on trial for crimes against humanity in addition to their other war crimes. [57] Nazi records provided a much of the evidence and details of the crimes the leaders and committed. The accused did not deny having committed these crimes but were claiming that these crimes were not against humanity. Others argued that they were simply following orders. 13 different trials were set up in Nuremburg between the years 1945 and 1950 and 12 defendants were sentenced to dead. In total 199 Nazis were put on trial. This type of justice is called punitive justice where the perpetrators get punished for their crimes. [58]
Shortcomings of the process:
These trials did not come without their shortcomings, some of which included small perpertrators not being called and held accountable for their actions as they could deny their complicity for what had happened. In addition, victorious allies carried out the trials and as a result, Germany and German people never faced what they had done. For many years there was a culture of silence and this could be regarded as a denial of responsibility. [59]
Positive outcomes of these trials:
These trials did come with some positives such as giving people new ways of thinking about how to tackle gross human rights violations. Restorative justice and mechanism such as truth and reconciliation commissions could be formed in the future. Examples of such truth and reconciliation commissions around the world are the Liberian Truth and Reconciliation Commission and South Africa’s Truth and Reconciliation Commission. [60]
This content was originally produced for the SAHO classroom by Ayabulela Ntwakumba and Thandile Xesi
[1] National Senior Certificate. “Grade 11 November History Paper 1 Exam,” National Senior Certificate, November 2018.
[2] Cohen, William B. "Literature and Race: Nineteenth Century French Fiction, Blacks and Africa 1800-1880." Race 16, no. 2 (1974): 181-205.
[3] Macdonald, Ian. "The Capitalist Way to Curb Discrimination." Race Today (1973): 241.
[4] http://www.workingwithindigenousaustralians.info/content/History_3_Colo…
[7] https://australianstogether.org.au/discover/indigenous culture/kinship.
[8] Moses, A. Dirk. "An antipodean genocide? The origins of the genocidal moment in the colonization of Australia." Journal of Genocide Research 2, no. 1 (2000): 89-106.
[9] Genger, Peter. "The British Colonization of Australia: An Exposé of the Models, Impacts and Pertinent Questions." Peace and Conflict Studies 25, no. 1 (2018): 4.
[10] Barta, Tony. "Relations of genocide: land and lives in the colonization of Australia." Genocide and the modern age: etiology and case studies of mass death 2 (1987): 237-253.
[11] Foley, Gary. "Eugenics, Melbourne University and me." Tracker: be informed, be involved, be inspired (2012).
[12] Ibid.,
[13] Banner, Stuart. "Why Terra Nullius-Anthropology and Property Law in Early Australia." Law & Hist. Rev. 23 (2005): 95.
[14] Ibid.,
[15] Lester, Alan, and Nikita Vanderbyl. "The Restructuring of the British Empire and the Colonization of Australia, 1832–8." In History Workshop Journal, vol. 90, pp. 165-188. Oxford Academic, 2021.
[16] Hunter, Ernest, and Desley Harvey. "Indigenous suicide in australia, new zealand, canada and the united states." Emergency Medicine 14, no. 1 (2002): 14-23.
[17] Wakefield, Edward Gibbon. A view of the art of colonization, with present reference to the British Empire. JW Parker, 1849.
[18] Hollinsworth, David. Race and racism in Australia. Thomson Learning Australia, 2006.
[19] Ibid.,
[20] Hume, Lynne. "The dreaming in contemporary aboriginal Australia." Indigenous religions: a companion. London: Cassell (2000): 125-138.
[21] Read, Peter. Belonging: Australians, place and Aboriginal ownership. Cambridge University Press, 2000.
[22] Ibid.,
[23] King, Gary, Ori Rosen, Martin Tanner, and Alexander F. Wagner. "Ordinary economic voting behavior in the extraordinary election of Adolf Hitler." The Journal of Economic History 68, no. 4 (2008): 951-996.
[24] Caldwell, Peter. "National Socialism and Constitutional Law: Carl Schmitt, Otto Koellreutter, and the Debate over the Nature of the Nazi State, 1993-1937." Cardozo L. Rev. 16 (1994): 399
[25] Bessel, Richard. "The Nazi capture of power." journal of Contemporary History 39, no. 2 (2004): 169-188.
[26] Evans, Richard. "Hitler's Dictatorship." History Review 51 (2005): 20.
[27] Ibid.,
[28] Britannica, T. Editors of Encyclopaedia. "SA." Encyclopedia Britannica, November 11, 2020. https://www.britannica.com/topic/SA-Nazi-organization .
[29] Ibid.,
[30] Ibid.,
[31] Power, Jonathan. "Heinrich Himmler, Hitler’s Deputy–From Boyhood to Chief Murderer of the Jews." In Ending War Crimes, Chasing the War Criminals, pp. 13-18. Brill Nijhoff, 2017.
[32] https://encyclopedia.ushmm.org/content/en/article/aryan-1
[33] Ibid.,
[34] Ibid.,
[35] Grodin, Michael A., Erin L. Miller, and Johnathan I. Kelly. "The Nazi physicians as leaders in eugenics and “euthanasia”: Lessons for today." American journal of public health 108, no. 1 (2018): 53-57.
[36] Ibid.,
[37] Kevles, Daniel J. "Eugenics and human rights." Bmj 319, no. 7207 (1999): 435-438.
[38] Ibid.,
[39] Benedict, Susan, and Jochen Kuhla. "Nurses’ participation in the euthanasia programs of Nazi Germany." Western Journal of Nursing Research 21, no. 2 (1999): 246-263.
[40] ibid.,
[41] Johnson, Mary, and Carol Rittner. "Circles of Hell: Jewish and non-Jewish victims of the Nazis." The Annals of the American Academy of Political and Social Science 548, no. 1 (1996): 123-137.
[42] Kroslak, Daniel. "Nuremberg Laws." The Lawyer Quarterly.-ISSN 8396 (1805): 184-194.
[43] Rippon, Anton. Hitler's Olympics: The Story of the 1936 Nazi Games. Pen and Sword, 2006.
[44] Fitzgerald, Stephanie. Kristallnacht. Capstone, 2017.
[45] Lutz, Brenda Davis. "Gypsies as Victims of the Holocaust." Holocaust and Genocide Studies 9, no. 3 (1995): 346-359.
[46] Ibid.,
[47] Evans, Richard. "Hitler's Dictatorship." History Review 51 (2005): 20.
[48] Ibid.,
[49] O’Byrne, Darren. "Perpetrators? Political civil servants in the Third Reich." In Perpetrators and Perpetration of Mass Violence, pp. 83-98. Routledge, 2018.
[50] Ibid.,
[51] Monroe, Kristen Renwick. "Cracking the code of genocide: The moral psychology of rescuers, bystanders, and Nazis during the Holocaust." Political Psychology 29, no. 5 (2008): 699-736.
[52] Ibid.,
[53] Breitman, Richard. "Plans for the final solution in early 1941." German Studies Review 17, no. 3 (1994): 483-493.
[54] Pohl, Dieter. "The Holocaust and the concentration camps." In Concentration Camps in Nazi Germany, pp. 161-178. Routledge, 2009.
[55] Ibid.,
[56] Steinacher, Gerald J. "The Betrayal: The Nuremberg Trials and German Divergence Kim Christian Priemel." (2018): 123-124.
[57] https://www.history.com/topics/world-war-ii/nuremberg-trials
[58] Ibid.,
[59] Ibid.,
[60] Adam, Heribert, and Kanya Adam. "Merits and shortcomings of the South African Truth and Reconciliation Commission." In Remembrance and Forgiveness, pp. 34-46. Routledge, 2020.
- Adam, Heribert, and Kanya Adam. "Merits and shortcomings of the South African Truth and Reconciliation Commission." In Remembrance and Forgiveness, pp. 34-46. Routledge, 2020.
- Bessel, Richard. "The Nazi capture of power." journal of Contemporary History 39, no. 2 (2004): 169-188.
- Benedict, Susan, and Jochen Kuhla. "Nurses’ participation in the euthanasia programs of Nazi Germany." Western Journal of Nursing Research 21, no. 2 (1999): 246-263.
- Breitman, Richard. "Plans for the final solution in early 1941." German Studies Review 17, no. 3 (1994): 483-493.
- Britannica, T. Editors of Encyclopaedia. "SA." Encyclopedia Britannica, November 11, 2020. https://www.britannica.com/topic/SA-Nazi-organization.
- Bunker, Raymond. "Systematic colonization and town planning in Australia and New Zealand." Planning Perspectives 3, no. 1 (1988): 59-80.
- Caldwell, Peter. "National Socialism and Constitutional Law: Carl Schmitt, Otto Koellreutter, and the Debate over the Nature of the Nazi State, 1993-1937." Cardozo L. Rev. 16 (1994): 399
- Dunn, Kevin M., James Forrest, Ian Burnley, and Amy McDonald. "Constructing racism in Australia." Australian journal of social issues 39, no. 4 (2004): 409-430.
- Docker, John. "A plethora of intentions: genocide, settler colonialism and historical consciousness in Australia and Britain." The International Journal of Human Rights 19, no. 1 (2015): 74-89.
- Fitzgerald, Stephanie. Kristallnacht. Capstone, 2017.
- Grodin, Michael A., Erin L. Miller, and Johnathan I. Kelly. "The Nazi physicians as leaders in eugenics and “euthanasia”: Lessons for today." American journal of public health 108, no. 1 (2018): 53-57.
- Hollinsworth, David. Race and racism in Australia. Thomson Learning Australia, 2006.
- Howard-Wagner, Deirdre. "Colonialism and the science of race difference." In TASA and SAANZ 2007 Joint Conference Refereed Conference Proceedings–Public Sociologies: Lessons and Trans-Tasman Comparisons, The Australian Sociological Association. 2007.
- Jalata, Asafa. "The impacts of English colonial terrorism and genocide on Indigenous/Black Australians." Sage Open 3, no. 3 (2013): 2158244013499143.
- Johnson, Mary, and Carol Rittner. "Circles of Hell: Jewish and non-Jewish victims of the Nazis." The Annals of the American Academy of Political and Social Science 548, no. 1 (1996): 123-137.
- Kevles, Daniel J. "Eugenics and human rights." Bmj 319, no. 7207 (1999): 435-438.
- King, Gary, Ori Rosen, Martin Tanner, and Alexander F. Wagner. "Ordinary economic voting behavior in the extraordinary election of Adolf Hitler." The Journal of Economic History 68, no. 4 (2008): 951-996.
- Kroslak, Daniel. "Nuremberg Laws." The Lawyer Quarterly.-ISSN 8396 (1805): 184-194.
- Lutz, Brenda Davis. "Gypsies as Victims of the Holocaust." Holocaust and Genocide Studies 9, no. 3 (1995): 346-359.
- Monroe, Kristen Renwick. "Cracking the code of genocide: The moral psychology of rescuers, bystanders, and Nazis during the Holocaust." Political Psychology 29, no. 5 (2008): 699-736.
- Moses, A. Dirk. "An antipodean genocide? The origins of the genocidal moment in the colonization of Australia." Journal of Genocide Research 2, no. 1 (2000): 89-106.
- Moses, D., & Stone, D. (Eds.). (2013). Colonialism and genocide. Routledge.
- O’Byrne, Darren. "Perpetrators? Political civil servants in the Third Reich." In Perpetrators and Perpetration of Mass Violence, pp. 83-98. Routledge, 2018.
- Pohl, Dieter. "The Holocaust and the concentration camps." In Concentration Camps in Nazi Germany, pp. 161-178. Routledge, 2009.
- Power, Jonathan. "Heinrich Himmler, Hitler’s Deputy–From Boyhood to Chief Murderer of the Jews." In Ending War Crimes, Chasing the War Criminals, pp. 13-18. Brill Nijhoff, 2017.
- Rippon, Anton. Hitler's Olympics: The Story of the 1936 Nazi Games. Pen and Sword, 2006.
- Robinson, Shirleene, and Jessica Paten. "The question of genocide and Indigenous child removal: the colonial Australian context." Journal of Genocide Research 10, no. 4 (2008): 501-518.
- Rogers, Thomas James, and Stephen Bain. "Genocide and frontier violence in Australia." Journal of Genocide Research 18, no. 1 (2016): 83-100.
- Short, Doctor Damien. Redefining genocide: Settler colonialism, social death and ecocide. Zed Books Ltd., 2016.
- Steinacher, Gerald J. "The Betrayal: The Nuremberg Trials and German Divergence Kim Christian Priemel." (2018): 123-124.
- Torrens, Robert. Colonization of south Australia. Longman, Rees, Orme, Brown, Green, and Longman, 1836.
- Wakefield, Edward Gibbon. A view of the art of colonization, with present reference to the British Empire. JW Parker, 1849.
Return to topic: Ideas of Race in the 19th and 20th Centuries
Return to SAHO Home
Return to History Classroom
Collections in the Archives
Know something about this topic.
Towards a people's history
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser or activate Google Chrome Frame to improve your experience.
24 German Essay Phrases
We need to talk about your German essays.
Essay writing is a skill that you can learn in any language.
All you need is to brush up your vocabulary and follow a few simple strategies, and you’ll be well on your way to writing your first masterpiece.
This post will provide you with a list of useful German words and phrases to include in your next essay, plus the different types of German essays, a few writing strategies and even a sample essay at the end.
German Essay Phrases
General explaining, ordering facts and ideas, demonstrating contrast, expressing your opinion, summarizing and concluding, what are german essays like, the different types of german essays, how to write an essay in german in 4 steps, 1. write down a list of words , 2. do your research, 3. make an outline using transition words, 4. write directly in german, an example of a german essay, and one more thing....
Download: This blog post is available as a convenient and portable PDF that you can take anywhere. Click here to get a copy. (Download)
Let’s start with the words and phrases themselves. As you’ll see, they’re grouped according to how and when you’ll use them. Let’s start off with some that will help you explain your arguments.
1. Weil (Because)
Daniel muss lernen, weil er morgen einen Test hat.
(Daniel has to study because he has a test tomorrow.)
2. Da (Because)
Daniel muss lernen, da er morgen einen Test hat.
3. Denn (Because)
Daniel muss lernen, denn er hat morgen einen Test.
(Daniel has to study because tomorrow he has a test.)
A quick note: Weil, da and denn are generally interchangeable. Keep in mind though that denn requires a different word order.
4. Damit (In order to; So that)
Lisa lernt viel, damit sie den Test besteht.
(Lisa is studying a lot in order to pass the test.)
5. Um (To; In order to)
Lisa lernt viel, um den Test zu bestehen.
(Lisa is studying a lot to pass the test.)
6. Im Grunde (Basically; Fundamentally)
Im Grunde ist Deutsch keine schwierige Sprache.
(Fundamentally, German is not a difficult language.)
7. Eigentlich (Actually)
Eigentlich ist Deutsch nicht so schwierig, wie es scheint.
(Actually, German is not as difficult as it seems.)
8. Ein Beispiel anführen (To give an example)
Ich möchte ein Beispiel anführen .
(I would like to give an example.)
9. Dieses Beispiel zeigt, dass… (This example shows that…)
Dieses Beispiel zeigt, dass das Lernen einer Fremdsprache beim Reisen viele Vorteile hat.
(This example shows that studying a foreign language has many advantages when traveling.)
10. Erstens… zweitens… (Firstly… secondly…)
Erstens kann man sich auf Reisen besser verständigen und zweitens lernt man viele neue Leute kennen.
(Firstly, you can communicate better while traveling, and secondly, you meet many new people.)
11. Das Wichtigste ist… (T he most important thing is…)
Das Wichtigste ist , die Angst vor der Sprache zu verlieren.
(The most important thing is to lose your fear of the language.)
12. Außer dem (Furthermore)
Außerdem kann man beim Reisen seine Sprachkenntnisse verbessern.
(Furthermore, you can improve your language knowledge while traveling.)
13. Nicht nur… sondern auch… (Not only… but also…)
Nicht nur im Unterricht, sondern auch im Alltag kann man viel Deutsch lernen.
(Not only in class, but also in everyday life you can learn a lot of German.)
14. Obwohl (Even though)
Obwohl Anna viel lernt, hat sie Probleme mit der deutschen Grammatik.
(Even though Anna studies a lot, she has problems with German grammar.)
15. Allerdings (However)
Anna lernt gerne Deutsch, allerdings hat sie Probleme mit der Grammatik.
(Anna enjoys studying German; however, she has problems with the grammar.)
16. Trotz (Despite)
Trotz ihrer Probleme mit der Grammatik lernt Anna gerne Deutsch.
(Despite her problems with German grammar, Anna enjoys studying German.)
17. Im Vergleich zu (In comparison to)
Im Vergleich zu Russisch ist Deutsch eine einfache Sprache.
In comparison to Russian, German is an easy language.
18. Im Gegensatz zu (In contrast to; Unlike)
Im Gegensatz zu Anna lernt Paul gerne neue Vokabeln.
Unlike Anna, Paul enjoys learning new vocabulary.
19. Meiner Meinung nach (In my opinion)
Meiner Meinung nach sollte jeder eine Fremdsprache lernen.
(In my opinion, everybody should study a foreign language.)
20. Ich bin der Ansicht, dass… (I believe that…)
Ich bin der Ansicht, dass jeder eine Fremdsprache lernen sollte.
(I believe that everybody should study a foreign language.)
21. Ich finde es schade, dass… (I think it’s a pity that…)
Ich finde es schade, dass die Schulen keine anderen Fremdsprachen unterrichten.
(I think it’s a pity that schools don’t teach other foreign languages.)
22. Alles in Allem (Overall)
Alles in allem ist Deutsch nicht so schwierig, wie es scheint.
(Overall, German isn’t as difficult as it seems.)
23. Im Großen und Ganzen (Overall)
Im Großen und Ganzen ist Deutsch keine schwierige Sprache.
(Overall, German isn’t a difficult language.)
24. Zusammenfassend kann man sagen, dass… (In summary, it can be said that…)
Zusammenfassend kann man sagen, dass Sprachen beim Reisen sehr hilfreich sein können.
(In summary, it can be said that languages can be very helpful when traveling.)
Ok, let’s get a little deeper into the actual essays themselves. How do they compare to the essays that you’re probably used to writing?
- They have a similar structure to English essays. Remember how English essays have a beginning, middle and end? Good news: German essays contain those same parts. When you’re writing a German essay, you’ll want to include an opening paragraph with your argument, three supporting paragraphs that further your argument and a conclusion. German and English are often surprisingly similar, and essay structure is no exception.
- German essays are more to the point. Although German essays and English essays are structured similarly, German essays—just like German speakers—tend to be more blunt and to the point. You won’t need to dance around your conclusions or obfuscate in German: just say what you mean.
- German punctuation is different. Germans have different rules for punctuation than English speakers. For example, Germans introduce a direct quote with a colon instead of a comma. They use quotes instead of italics for the names of books, movies and newspapers. And they set off relative clauses beginning with dass (that) with a comma, unlike in American English. Understanding these differences between English and German punctuation will ensure you don’t give yourself away as a non-native speaker through punctuation marks alone!
Before you get started on your essay, make sure you know what type of essay you’re going to write. If it’s a school essay, be sure to read and understand the instructions.
Here are a few notes about the most common kinds of essays in German.
- An Erzählung is a narrative essay that tells a story. Your teacher might give you some keywords or pictures and ask you to create a story around it. An Erlebniserzählung (“experience story”) is about a personal experience and can be written in the first person.
- An Erörterung is an argumentative essay, a writing piece meant to persuade someone to think the way you do. This writing genre requires you to investigate your topic well and provide evidence to prove your point.
- In a Nacherzählung you summarize and recount a book, a film or an article you have read, from an objective perspective. Depending on the essay instructions, you might be asked for your personal opinion in the conclusion.
Are you ready to start writing? Use these four strategies to wow your teachers and write the perfect German essay.
You should look at any new activity as an opportunity to learn and master new vocabulary . Instead of using the same words that you use in your everyday German speech, use this essay as an opportunity to introduce new words into your German lexicon.
Besides, incorporating academic words that help you craft and shape your argument can make your essay sound more professional and polished. So before you start writing, write down a list of the German words you’d like to incorporate in your essay.
As with everything else, you should look at the research portion of the essay-writing process as an opportunity to learn more about Germany—this time, about German culture, history , politics or travel .
Chances are if you’re writing your essay for a language-learning class, you’ll be assigned a topic pertaining to one of these aspects of German life, so use this as a chance to learn more about Deutschland.
For example, Deutsche Welle offers information and resources about German history. Other newspapers such as Berliner Zeitung and Frankfurter Allgemeine Zeitung offer another perspective on politics and daily life in Germany.
There’s nothing clunkier than an essay that doesn’t flow naturally from one point to the next. Besides, thinking about how your arguments and points interact with each other will help you organize your essay and make sure you get your point across. (Do they support each other? Counter each other? How exactly do they function to further your argument?)
Examples of transition words:
- Vorher (prior)
- zur gleichen Zeit (at the same time)
- dann (then)
- trotzdem (nevertheless)
- noch (still)
Writing an essay in English and then translating it into German often results in stilted, poorly formed sentences and unnatural constructions.
For example, remember that German word order is different from English. If you write “He didn’t read the book,” a one-to-one literal translation would be Er hat gelesen nicht das Buch . But the correct translation is actually Er hat nicht das Buch gelesen. In this example, translating word for word leads to errors.
There’s another, less tangible reason why it’s not a good idea to write in English and translate to German. Sure, you could just remember that you need to change the word order when translating into German. But isn’t it better to adapt your brain so that German word order seems fluid and natural?
Learning to think and write off-the-cuff in German is an essential step towards fluency, and devising sentences in German, instead of sentences in translation, will help you learn to do that.
One good way to learn to think in a language is to hear it spoken in natural contexts. You can hear German spoken naturally in German language TV shows , movies and YouTube videos .
FluentU takes authentic videos—like music videos, movie trailers, news and inspiring talks—and turns them into personalized language learning lessons.
You can try FluentU for free for 2 weeks. Check out the website or download the iOS app or Android app.
P.S. Click here to take advantage of our current sale! (Expires at the end of this month.)
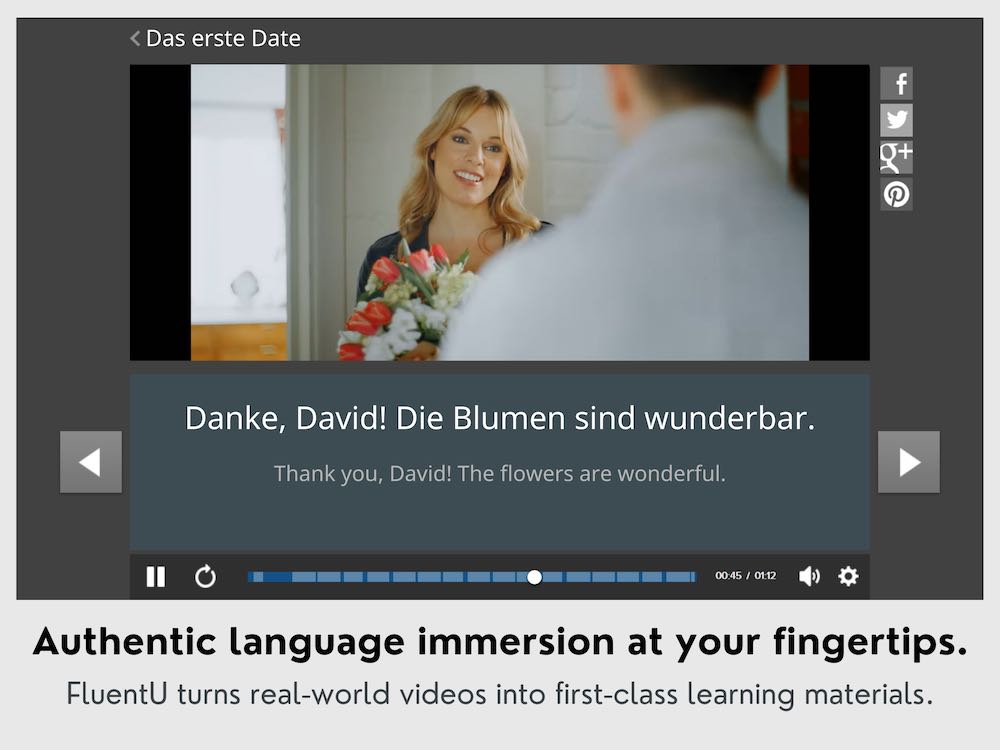
Try FluentU for FREE!
Listening to German spoken at a natural speed and native accent will help get you thinking in the language in real time. This will help get you to the point where you can come up with your own sentences in German, rather than thinking in English sentences first and then translating them in your head before you speak or write. That will greatly improve your speed and fluency when writing in German.
So, simply start writing the essay in German. Look up any words you’re not sure of and double-check any grammatical constructions that you’re not familiar with. After you finish writing, ask a German-speaking friend to look over the essay to make sure it sounds natural.
Now that we’ve explored strategies and phrases for writing top-notch German essays, let’s take a look at an example.
World War I doesn’t get as much coverage in the States as World War II (where it was more directly involved). But for Europe, World War I was a devastating example of the dangers of modern technological warfare and the horrors of violence.
Let’s take a look at an example opening paragraph and outline of an essay about the effect of World War I on German government and life.
Opening paragraph:
Der Erste Weltkrieg war ein totaler Krieg, der Deutschland völlig veränderte. Dieser Krieg hat 1914 angefangen, und 1918, als der Krieg zu Ende kam, waren die deutsche Gesellschaft, Regierung und Kultur nicht mehr erkennbar. Am Anfang hat der Erste Weltkrieg altväterliche Ideen und Systeme verstärkt. Am Ende hat dieser Krieg dagegen diese altväterlichen Dinge zerstört.
(The First World War was a total war that completely changed Germany. This war began in 1914 and in 1918, when the war came to an end, German society, government and culture were no longer recognizable. At the beginning, the First World War strengthened old-fashioned ideas and systems. However, by the end, this war destroyed these old-fashioned things.)
Notice that this opening paragraph is not very different at all from the first paragraph of an English essay. You can use the same structure you’ve always used to write your German essay, leaving you free to focus on grammar and vocabulary.
Notice also the use of phrases such as Am Anfang (at the beginning) and Dagegen (however). Words like these can help you make a point and counterpoint in your opening paragraph (or anywhere in your essay, for that matter).
I. Am Anfang (at the beginning):
– Dieser Krieg hat Deutschland vereint . (This war united Germany.) – Menschen hatten ein patriotisches Gefühl. (People had a patriotic feeling.) – Menschen dachten, dass der Krieg bald zu Ende kommen würde. (People thought that the war would soon come to an end.)
Notice that these points employ words like dachten (thought). Written German often relies on Präteritum , a form of the past tense that’s rarely used in spoken Deutsch. It’s often called “literary past tense” for this reason. Check out this guide to the Präteritum to include this tense in your essay.
II. Andrerseits (on the other hand):
– Bald gab es kein Essen mehr . (Soon there was no more food.) – Menschen wurden krank und desillusioniert . (People became sick and disillusioned.) – Es gab Proteste und Unruhen. (There was protest and unrest.)
Like in an English essay, your second and third paragraphs can include supporting points or counterpoints that contribute to the overall theme of your piece. The word Andrerseits (on the other hand) is an ideal transition word to show that you’re moving into another section of your essay.
Also notice that this essay will rely on vocabulary words that the average language learner might not have come across in his or her learning. After all, who learns the words for “disillusioned” and “unrest” in their intermediate German class? But don’t be daunted by the fact that your essay might include eclectic vocabulary. Instead, use this as an opportunity for more learning.
III. zum Schluss (in conclusion):
– Der Kaiser hat abgedankt . (The Emperor abdicated.) – Eine Republik wurde geboren. (A Republic was born.) – Die alten Werte waren weg. (The old values were gone.)
Once again, abgedankt (abdicated) is an example of the literary past tense (and an example of a word that you probably haven’t come across in your previous German studies!)
IV. Schließlich (finally)
– Der Erste Weltkrieg hat Deutschland verändert . (The First World War completely changed Germany.)
Again, like in an English essay, you should use this paragraph to summarize your main point.
Feeling a bit more confident about your next German essay now?
Just make a great essay plan, write down some new words and phrases that you want to include and off you go!
By sprinkling these bits of flair into your German essays, you’re sure to make your writing better and more effective.
Enjoy writing!
Want to know the key to learning German effectively?
It's using the right content and tools, like FluentU has to offer ! Browse hundreds of videos, take endless quizzes and master the German language faster than you've ever imagine!
Watching a fun video, but having trouble understanding it? FluentU brings native videos within reach with interactive subtitles.
You can tap on any word to look it up instantly. Every definition has examples that have been written to help you understand how the word is used. If you see an interesting word you don't know, you can add it to a vocabulary list.
And FluentU isn't just for watching videos. It's a complete platform for learning. It's designed to effectively teach you all the vocabulary from any video. Swipe left or right to see more examples of the word you're on.
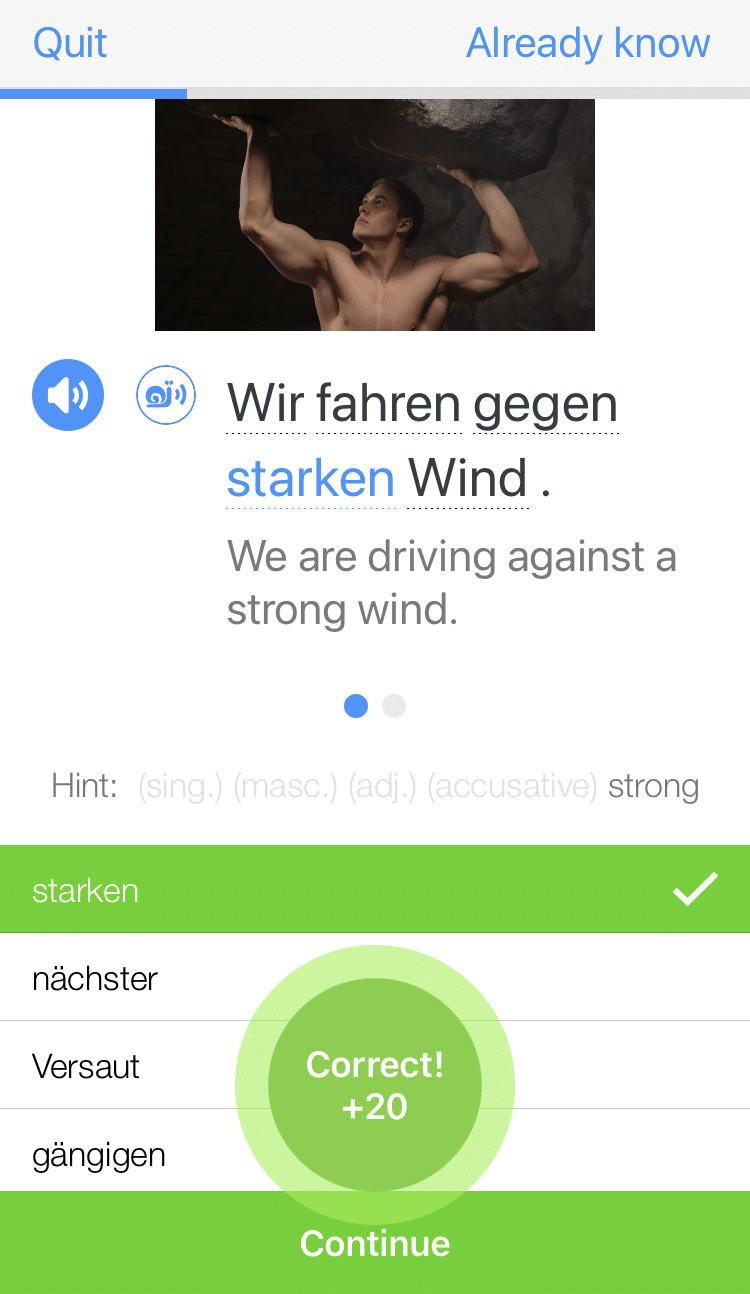
The best part is that FluentU keeps track of the vocabulary that you're learning, and gives you extra practice with difficult words. It'll even remind you when it’s time to review what you’ve learned.
Start using the FluentU website on your computer or tablet or, better yet, download the FluentU app from the iTunes or Google Play store. Click here to take advantage of our current sale! (Expires at the end of this month.)
Enter your e-mail address to get your free PDF!
We hate SPAM and promise to keep your email address safe


50 Useful German Essay Words and Phrases
by fredo21
January 9, 2019
2 Comments
Essay-writing is in itself already a difficult endeavor. Now writing an essay in a foreign language like German ---that’s on a different plane of difficulty.
To make it easier for you, here in this article, we’ve compiled the most useful German essay phrases. Feel free to use these to add a dash of pizzazz into your essays. It will add just the right amount of flourish into your writing---enough to impress whoever comes across your work!

You can also download these phrases in PDF format by clicking the button below.

Now here’s your list!
What other German vocabulary list would you like to see featured here? Please feel free to leave a message in the comment section and we’ll try our best to accommodate your requests soon!
Once again, you can download your copy of the PDF by subscribing using the button below!
For an easier way to learn German vocabulary, check out German short stories for beginners!

A FUN AND EFFECTIVE WAY TO LEARN GERMAN
- 10 entertaining short stories about everyday themes
- Practice reading and listening with 90+ minutes of audio
- Learn 1,000+ new German vocabulary effortlessly!
About the author
Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked
Thank you for the good writeup. It in fact was a amusement account it. Look advanced to far added agreeable from you! By the way, how can we communicate?
Asking questions are genuinely good thing if you are not understanding anything completely, except this piece of writing provides nice understanding yet.
You might also like
Learning Method
Sentence Structure and Word Order in German
German declension: the four grammatical cases in detail, prepositions with dative, accusative, and mixed, learn all about german two-way prepositions: what they are and how to use them, sign up below ... and get instant access to the freebie.

German Essay Phrases: 24 Useful Expressions to Write an Essay in German
As we often think in English first, translating our ideas into useful German phrases can be tricky.
This handy blog post includes 24 essential German essay phrases to help make your writing flow more smoothly and sound more natural. Whether you’re preparing for the Goethe exam, a GCSE test, or just want to improve your written German for real-life situations, these chunks and phrases will help you. Easy German has a great video on useful German expression:
From organizing your thoughts with transitions like “ zudem ” and “ außerdem “, to expressing your opinion with phrases like “ meiner Meinung nach ” and “ ich denke, dass… “, this post has you covered.
Write an essay with German essay phrases: learn how to structure your story
Goethe tests love a clear and logical format. They follow the same structure throughout the different levels. The good news is, when you’re learning a language, you can use these German essay phrases with these structures even in your real-life dialogues. Then, gradually, you can shift your focus to a more natural-sounding speaking.
First, begin with an engaging introduction to get the reader’s attention. This intro paragraph should also include a short thesis statement that outlines the central argument you’ll be taking.
In the body of your essay, organize your thoughts into separate paragraphs. Use transitional phrases like “ außerdem ” (furthermore) and “ zudem ” (moreover) to connect your paragraphs and create a flow.
After that, summarize your main points and restate your thesis. But! Avoid introducing new information. Leave the reader with a compelling final thought or even a call to action that makes your central argument stronger.
If you’re not certain enough, check the following list and learn about the must-have go-to German essay phrases now!

1. Erstens – Firstly
This German essay phrase is used to introduce the first point in your essay.
Erstens werden wir die Hauptargumente diskutieren. [Firstly, we will discuss the main arguments.]

2. Zweitens – Secondly
Normally, this phrase is there for you when you want to introduce the second point in a structured manner.
Zweitens betrachten wir einige Gegenbeispiele. [Secondly, we will look at some counterexamples.]
3. Drittens – Thirdly
Used to signal the third point for clarity in your argument.
Drittens ziehen wir eine Schlussfolgerung. [Thirdly, we will draw a conclusion.]
4. Einleitend muss man sagen… – To begin with, one has to say…
Start your essay with this phrase to introduce your key points.
Einleitend muss man sagen, dass dieses Thema komplex ist. [To begin with, one has to say that this topic is complex.]
5. Man muss … in Betracht ziehen – One needs to take … into consideration
When you want to consider a specific aspect in your discussion.
Man muss den historischen Kontext in Betracht ziehen. [One needs to take the historical context into consideration.]
6. Ein wichtiger Aspekt von X ist … – An important aspect of X is …
To highlight an important part…
Ein wichtiger Aspekt von Nachhaltigkeit ist die Ressourcenschonung. [An important aspect of sustainability is resource conservation.]
7. Man muss erwähnen, dass… – One must mention that …
Used to emphasize a point that need acknowledgement.
Man muss erwähnen, dass es verschiedene Ansichten gibt. [One must mention that there are different viewpoints.]
8. Im Vergleich zu – In comparison to…
To compare different elements in your essay.
Im Vergleich zu konventionellen Autos sind Elektrofahrzeuge umweltfreundlicher. [In comparison to conventional cars, electric vehicles are more eco-friendly.]
9. Im Gegensatz zu – In contrast to…
When you want to present an alternative viewpoint or argument.
Im Gegensatz zu optimistischen Prognosen ist die Realität ernüchternd. [In contrast to optimistic forecasts, reality is sobering.]
10. Auf der einen Seite – On the one hand
To add a new perspective.
Auf der einen Seite gibt es finanzielle Vorteile. [On the one hand, there are financial benefits.]

11. Auf der anderen Seite – On the other hand
Present an alternative viewpoint.
Auf der anderen Seite bestehen ethische Bedenken. [On the other hand, ethical concerns exist.]
12. Gleichzeitig – At the same time
When you want to show a simultaneous relationship between ideas.
Gleichzeitig müssen wir Kompromisse eingehen. [At the same time, we must make compromises.]
13. Angeblich – Supposedly
If you want to add information that is claimed but not confirmed.
Angeblich wurde der Konflikt beigelegt. [Supposedly, the conflict was resolved.]
14. Vermutlich – Presumably
Used when discussing something that is presumed but not certain.
Vermutlich wird sich die Situation verbessern. [Presumably, the situation will improve.]
15. In der Tat – In fact
To add a fact or truth in your essay.
In der Tat sind die Herausforderungen groß. [In fact, the challenges are great.]
16. Tatsächlich – Indeed
Emphasize a point or a fact.
Tatsächlich haben wir Fortschritte gemacht. [Indeed, we have made progress.]
17. Im Allgemeinen – In general
When discussing something in a general context.
Im Allgemeinen ist das System reformbedürftig. [In general, the system needs reform.]
18. Möglicherweise – Possibly
Spice your essay with a possibility or potential scenario.
Möglicherweise finden wir einen Konsens. [Possibly, we will find a consensus.]
19. Eventuell – Possibly
To suggest a potential outcome or situation.
Eventuell müssen wir unsere Strategie überdenken. [Possibly, we need to rethink our strategy.]
20. In jedem Fall / Jedenfalls – In any case
Used to emphasize a point regardless of circumstances.
In jedem Fall müssen wir handeln. [In any case, we must take action.]
21. Das Wichtigste ist – The most important thing is
If you want to highlight the most important thing in your saying.
Das Wichtigste ist, dass wir zusammenarbeiten. [The most important thing is that we cooperate.]
22. Ohne Zweifel – Without a doubt
To introduce a statement that is unquestionably trues.
Ohne Zweifel ist Bildung der Schlüssel zum Erfolg. [Without a doubt, education is the key to success.]
23. Zweifellos – Doubtless
Just as the previous one, when you want say something that is, without a doubt, true.
Zweifellos gibt es noch viel zu tun. [Doubtless, there is still a lot to be done.]
24. Verständlicherweise – Understandably
If you want to add a thing that is understandable in the given context.
Verständlicherweise sind einige Menschen besorgt. [Understandably, some people are concerned.]
Practice the most important German essay phrases
Practice the German essay phrases now!
This is just part of the exercises. There’s many more waiting for you if you click the button below!
Learn the language and more German essay words and sentences with Conversation Based Chunking
Conversation Based Chunking represents a powerful approach to learning language skills. It’s especially useful for productive purposes like essay writing.
By learning phrases and expressions used in natural discourse, students internalize vocabulary and grammar in context rather than as isolated rules. This method helps you achieve fluency and helps you develop a ‘feel’ for a an authentic patterns.
Chunking common multi-word units accelerates progress by reducing cognitive load compared to consciously constructing each sentence from individual words. Sign up now to get access to your German Conversation Based Chunking Guide.
Lukas is the founder of Effortless Conversations and the creator of the Conversation Based Chunking™ method for learning languages. He's a linguist and wrote a popular book about learning languages through "chunks". He also co-founded the language education company Spring Languages, which creates online language courses and YouTube content.
Similar Posts

5 Different Ways to Say Good Afternoon in German – Guten Tag & Schönen Nachmittag
Afternoons in German-speaking regions are a little bit different than in the rest of Europe: while others are still working hard, Spanish speaking people are…

Everything you need to know about German articles: der, die, das + 6 Tips to memorize them!
I know, I know… Learning the intricacies of German grammar can be a challenge. Articles hold a huge importance in the German language. Mastering these…

How to Think in German: 8 Tips to Make Your Brain a German Speaker
Imagine waking up every morning and having your thoughts flow effortlessly (pun intended, haha!) in German. You open your eyes and the first words that…

How to Learn with German Flashcards: 3 Tips for German Vocabulary Learning & the Best Flashcard Apps
You’re at a business meeting in Berlin, trying to explain your company’s latest product to potential German clients. But as you struggle to find the…

Learn German Shadowing: A Language Learning Method to Get Fluent Faster (2024)
Beyond traditional study methods for learning languages, there is an innovative technique that promises to fast-track your speaking abilities – speech shadowing. You can immediately…

Talk about Animals in German: 100+ German Animal Names and Phrases
Do you have pets? Or just love the outdoors, and want to know more about the wildlife? It doesn’t matter! Learning about animals in German…
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
What are you looking for?
Enter the 2024 annual essay contest.
Schreiben, © Colourbox
It's time for the Annual Essay Contest! Students from Grades 3-12 are invited to enter. This year's topics are currywurst and climate neutrality.
The essay contest is open to students from Grades 3-12 and the deadline for entries is May 1, 2024. Students must choose and write about one of the following topics. Detailed rules and information about submission guidelines can be found below. We enourage all participants to read them.
Herta Heuwer had a street food booth in Berlin and it is said that on September 4, 1949, it was there that she invented currywurst. The sauce with sliced sausage was a hit and currywurst was on its way to becoming an iconic street food. Today there are a number of street food booths offering currywurst all over Germany and the food is closely associated with Berlin with the dish one of the newer traditions in the country. Have you heard of or ever tasted currywurst?
Think about food that you associated with people, events or places. Is there a traditional food that your family must make or eat during certain times of the year? Are there local foods that you think all visitors must try? Describe your family’s and town’s food traditions, including examples of specific foods. Why are they important to you and what makes them important? Would they be the same without the traditional foods? Are there traditions that you plan to continue as an adult?
Topic B Climate-Neutral Industrial Nation
Germany plans to become a climate-neutral industrial nation by 2045. In order to achieve this, changes must take place on every level of society. From the continued development of sources for renewable energy to production facilities using different materials to towns and cities working with residents to reduce their carbon footprint – it must all work together in order to accomplish the goal.
Picture yourself as mayor of a small town and you are looking for ways to become climate-neutral. You’ve examined the buildings, transportation and personal habits of your residents. There are many places you could start. What are some ideas the first ideas you can think of to start making changes? Do you have ways that each person could contribute to the effort? Describe your ideas, giving specific examples, and why they will help with the climate-neutral goal and how people will help. Are there examples in your real town that you think should be done in other places?
Additional content
About the Essay Contest
The German Information Center USA fulfills the public diplomacy mission of the German Embassy in Washington, D.C. To encourage American students to get to know modern Germany, the German Embassy…
Detailed Rules and Guidelines
Students must choose and write about one the following topics: Topic A Currywurst Herta Heuwer had a street food booth in Berlin and it is said that on September 4, 1949, it was there that she…
Criteria for Judging
Winners will be determined by a panel of judges from the German Embassy Washington. Entries will be judged based on their content, style and grammar. Successful entries will: Follow the…
Amazon.com gift e-certificates will be awarded to the national 1st place winners in each age group. 1st place – grades 3 – 5: $100 gift certificate 1st place – grades 6 – 8: $150 gift…
- Top of page
- Application process for Germany VISA
- Germany Travel Health Insurance
- Passport Requirements
- Visa Photo Requirements
- Germany Visa Fees
- Do I need a Visa for short stays in Germany?
- How to Get Flight Itinerary and Hotel Booking for Visa Application
- Germany Airport Transit Visa
- Germany Business VISA
- Guest Scientist VISA
- Germany Job Seeker Visa
- Medical Treatment VISA
- Tourist & Visitor Visa
- Trade Fair & Exhibitions VISA
- Training or Internship VISA
- Study Visa for Germany
- Working (Employment) VISA
- German Pronunciation
- German Volabulary
- Requirements
- Health Insurance
- Trend & Living
- Free Assessment Form
- Privacy Policy
Easy German Essays for Beginners: 8 Examples to Practice Your Language Skills

Are you a beginner in learning German and looking for ways to practice your language skills? One great way to do so is by writing essays in German. Writing essays not only improves your grammar and vocabulary but also helps you express your thoughts and ideas in the target language. In this article, we will provide you with eight easy German essays for Beginners with English translation and vocabulary to help you get started.
- Meine Familie (My family) – Write about your family, including their names, occupations, and hobbies.
- Mein Haus (My house) – Describe your house or apartment, including the number of rooms, furniture, and decorations.
- Meine Hobbys (My hobbies) – Talk about your favorite hobbies, such as playing sports, reading books, or listening to music.
- Meine Schule (My school) – Write about your school, including its location, teachers, and subjects you study.
- Meine Freunde (My friends) – Discuss your friends, including how you met them, their personalities, and what you like to do together.
- Meine Stadt (My city) – Describe your city or town, including its population, tourist attractions, and cultural events.
- Meine Reise (My trip) – Write about a recent trip you took, including the destination, transportation, and activities you did there.
- Meine Lieblingsessen (My favorite food) – Talk about your favorite foods, including traditional German dishes and other international cuisines.
Remember to use simple vocabulary and sentence structures while writing the essays. Good luck with your German learning journey!
Table of Contents
Meine familie (my family).
Ich heiße Maria und ich möchte euch gerne meine Familie vorstellen. Wir sind insgesamt vier Personen in meiner Familie. Mein Vater heißt Klaus und er arbeitet als Ingenieur. Meine Mutter heißt Petra und sie ist Hausfrau. Mein Bruder heißt Jan und er geht noch zur Schule.
(My name is Maria, and I would like to introduce you to my family. We are a family of four. My father’s name is Klaus, and he works as an engineer. My mother’s name is Petra, and she is a homemaker. My brother’s name is Jan, and he still goes to school.)
Vocabulary:
- Ich heiße Maria (My name is Maria)
- insgesamt (altogether)
- vier Personen (four persons)
- der Vater (father)
- arbeiten (to work)
- der Ingenieur (engineer)
- die Mutter (mother)
- Hausfrau (homemaker)
- der Bruder (brother)
- noch zur Schule gehen (still go to school)
Mein Vater arbeitet in einem großen Unternehmen als Ingenieur. Er ist sehr fleißig und verbringt viel Zeit im Büro. In seiner Freizeit geht er gerne joggen oder spielt Golf. Meine Mutter kümmert sich um den Haushalt und verbringt viel Zeit damit, leckere Mahlzeiten zu kochen. Sie liest auch gerne Bücher und geht regelmäßig zum Yoga.
(My father works in a large company as an engineer. He is very hardworking and spends a lot of time in the office. In his free time, he likes to go jogging or play golf. My mother takes care of the household and spends a lot of time cooking delicious meals. She also likes to read books and regularly attends yoga classes.)
- in einem großen Unternehmen (in a large company)
- sehr fleißig (very hardworking)
- viel Zeit (a lot of time)
- im Büro (in the office)
- in seiner Freizeit (in his free time)
- joggen (to go jogging)
- Golf spielen (to play golf)
- sich kümmern um (to take care of)
- der Haushalt (household)
- leckere Mahlzeiten kochen (cook delicious meals)
- gerne lesen (like to read)
- regelmäßig (regularly)
- zum Yoga gehen (go to yoga)
Mein Bruder Jan geht noch zur Schule und ist sehr sportlich. Er spielt Fußball im Verein und geht regelmäßig ins Fitnessstudio. In seiner Freizeit hört er gerne Musik und schaut Filme.
(My brother Jan still goes to school and is very sporty. He plays soccer in a club and regularly goes to the gym. In his free time, he likes to listen to music and watch movies.)
- sehr sportlich (very sporty)
- Fußball spielen (to play soccer)
- im Verein (in a club)
- ins Fitnessstudio gehen (to go to the gym)
- Musik hören (listen to music)
- Filme schauen (watch movies)
Ich studiere im Moment an der Universität und meine Hobbys sind Lesen, Reisen und Yoga. In meiner Freizeit gehe ich gerne in die Natur und genieße die frische Luft.
(I am currently studying at the university, and my hobbies are reading, traveling, and yoga. In my free time, I like to go into nature and enjoy the fresh air.)
- studieren (to study)
- an der Universität (at the university)
- die Hobbys (hobbies)
- Lesen (reading)
- Reisen (traveling)
- Yoga (yoga)
- die Freizeit (free time)
- in die Natur gehen (go into nature)
- genießen (enjoy)
- frische Luft (fresh air)
Das ist meine Familie. Wir haben viele verschiedene Hobbys und Interessen, aber wir verbringen auch gerne gemeinsam Zeit miteinander.
(This is my family. We have many different hobbies and interests, but we also enjoy spending time together.)
- das ist (this is)
- verschiedene Hobbys und Interessen (different hobbies and interests)
- gerne Zeit miteinander verbringen (enjoy spending time together)
Top reasons why Berlin is the best city for Expats!
Mein Haus (My House)
Ich lebe in einem Haus mit drei Schlafzimmern und zwei Bädern. Das Haus ist zweistöckig und hat auch einen Keller. Im Erdgeschoss befinden sich das Wohnzimmer, die Küche und ein Esszimmer. Im Wohnzimmer haben wir ein bequemes Sofa und einen großen Fernseher. In der Küche gibt es eine Spülmaschine, einen Herd, einen Backofen und einen Kühlschrank. Das Esszimmer hat einen Esstisch mit sechs Stühlen.
(I live in a house with three bedrooms and two bathrooms. The house is two stories and also has a basement. On the ground floor, there is the living room, kitchen, and a dining room. In the living room, we have a comfortable sofa and a large television. In the kitchen, there is a dishwasher, stove, oven, and refrigerator. The dining room has a dining table with six chairs.)
- das Haus (house)
- die Schlafzimmer (bedrooms)
- die Bäder (bathrooms)
- zweistöckig (two-storied)
- der Keller (basement)
- das Erdgeschoss (ground floor)
- das Wohnzimmer (living room)
- die Küche (kitchen)
- das Esszimmer (dining room)
- ein bequemes Sofa (a comfortable sofa)
- ein großer Fernseher (a large television)
- eine Spülmaschine (a dishwasher)
- ein Herd (a stove)
- ein Backofen (an oven)
- ein Kühlschrank (a refrigerator)
- ein Esstisch (a dining table)
- sechs Stühle (six chairs)
Im Obergeschoss befinden sich die Schlafzimmer und die Bäder. Mein Schlafzimmer hat ein großes Bett, einen Schreibtisch und einen Kleiderschrank. Das Badezimmer hat eine Badewanne und eine Dusche. In den anderen Schlafzimmern gibt es auch Betten und Schränke für Kleidung.
(Upstairs, there are the bedrooms and bathrooms. My bedroom has a large bed, a desk, and a closet. The bathroom has a bathtub and a shower. In the other bedrooms, there are also beds and closets for clothes.)
- das Obergeschoss (upper floor)
- das Schlafzimmer (bedroom)
- der Schreibtisch (desk)
- der Kleiderschrank (closet)
- das Badezimmer (bathroom)
- die Badewanne (bathtub)
- die Dusche (shower)
- die anderen Schlafzimmer (the other bedrooms)
Im Keller haben wir eine Waschmaschine und einen Trockner. Wir nutzen den Keller auch als Lager für Dinge, die wir nicht oft brauchen.
(In the basement, we have a washing machine and dryer. We also use the basement as a storage area for things we don’t need often.)
- die Waschmaschine (washing machine)
- der Trockner (dryer)
- als Lager nutzen (use as storage area)
- Dinge (things)
Wir haben auch einige Dekorationen im Haus. Im Wohnzimmer haben wir ein großes Gemälde an der Wand und im Esszimmer steht eine Vase mit Blumen auf dem Tisch.
(We also have some decorations in the house. In the living room, we have a large painting on the wall, and in the dining room, there is a vase of flowers on the table.)
- die Dekorationen (decorations)
- das Gemälde (painting)
- die Wand (wall)
- die Vase (vase)
- die Blumen (flowers)
- der Tisch (table)
Wir haben auch ein paar Teppiche im Haus, um den Boden zu bedecken. Das Wohnzimmer hat einen braunen Teppich, während die Schlafzimmer jeweils einen unterschiedlichen Farbton haben. Mein Schlafzimmer hat einen blauen Teppich, während das andere Schlafzimmer einen roten Teppich hat.
(We also have some carpets in the house to cover the floor. The living room has a brown carpet, while the bedrooms have a different color tone each. My bedroom has a blue carpet, while the other bedroom has a red carpet.)
- der Teppich (carpet)
- den Boden bedecken (to cover the floor)
- unterschiedliche Farbton (different color tone)
Insgesamt bin ich sehr glücklich mit meinem Haus. Es ist gemütlich und hat genug Platz für meine Familie und mich.
(Overall, I am very happy with my house. It is cozy and has enough space for my family and me.)
- insgesamt (overall)
- glücklich (happy)
- gemütlich (cozy)
- genug Platz (enough space)
Difference between ein, eine, einen, and einem in the German Language
Meine hobbys (my hobbies).
Ich habe einige Hobbys, die ich sehr gerne mache. Eines meiner Lieblingshobbys ist es, Sport zu treiben. Insbesondere mag ich es, Basketball zu spielen und Laufen zu gehen. Ich liebe es, im Freien zu sein und Sport zu treiben, weil es mir hilft, mich fit und gesund zu halten.
(I have some hobbies that I really enjoy doing. One of my favorite hobbies is doing sports. In particular, I like to play basketball and go running. I love being outdoors and doing sports because it helps me stay fit and healthy.)
- das Hobby (hobby)
- Sport treiben (to do sports)
- Basketball spielen (to play basketball)
- Laufen gehen (to go running)
- im Freien sein (to be outdoors)
- fit und gesund (fit and healthy)
Ein weiteres Hobby von mir ist das Lesen von Büchern. Ich lese gerne Romane und Sachbücher, besonders über Geschichte und Wissenschaft. Lesen ist für mich eine Möglichkeit, zu lernen und meine Vorstellungskraft zu erweitern.
(Another hobby of mine is reading books. I enjoy reading novels and non-fiction books, especially about history and science. Reading is a way for me to learn and expand my imagination.)
- das Lesen (reading)
- das Buch (book)
- der Roman (novel)
- das Sachbuch (non-fiction book)
- die Geschichte (history)
- die Wissenschaft (science)
- die Vorstellungskraft (imagination)
Außerdem höre ich gerne Musik. Ich mag viele verschiedene Genres wie Pop, Rock und Klassik. Musik kann meine Stimmung beeinflussen und mich entspannen.
(Additionally, I like to listen to music. I enjoy many different genres like pop, rock, and classical. Music can influence my mood and help me relax.)
- die Musik (music)
- das Genre (genre)
- Pop, Rock, Klassik (pop, rock, classical)
- die Stimmung (mood)
- sich entspannen (to relax)
Insgesamt bin ich sehr dankbar für meine Hobbys. Sie helfen mir, meinen Geist und Körper gesund zu halten und mich zu entspannen.
(Overall, I am very grateful for my hobbies. They help me keep my mind and body healthy and help me relax.)
- dankbar (grateful)
- der Geist (mind)
- der Körper (body)
German Essays on My Family: Meine Familie
Meine schule (my school).
Ich besuche eine Schule in der Nähe meines Hauses. Die Schule ist relativ groß und hat viele Schülerinnen und Schüler. Wir haben viele Lehrerinnen und Lehrer, die alle sehr nett und hilfsbereit sind.
(I attend a school near my house. The school is relatively large and has many students. We have many teachers who are all very kind and helpful.)
- besuchen (to attend)
- die Nähe (proximity)
- relativ (relatively)
- die Schülerin (female student)
- der Schüler (male student)
- viele (many)
- die Lehrerin (female teacher)
- der Lehrer (male teacher)
- nett (kind)
- hilfsbereit (helpful)
Die Schule bietet viele verschiedene Fächer an, einschließlich Mathematik, Geschichte, Englisch, Naturwissenschaften und Fremdsprachen. Mein Lieblingsfach ist Englisch, weil ich gerne Geschichten lese und schreibe. Ich denke, dass es wichtig ist, eine gute Ausbildung zu haben, um im Leben erfolgreich zu sein.
(The school offers many different subjects, including mathematics, history, English, science, and foreign languages. My favorite subject is English because I enjoy reading and writing stories. I believe that having a good education is important to be successful in life.)
- das Fach (subject)
- einschließlich (including)
- Mathematik (mathematics)
- Geschichte (history)
- Englisch (English)
- Naturwissenschaften (science)
- Fremdsprachen (foreign languages)
- das Lieblingsfach (favorite subject)
- die Geschichte (story)
- die Ausbildung (education)
- erfolgreich (successful)
Unsere Schule hat auch viele außerschulische Aktivitäten, wie zum Beispiel Sportmannschaften und Musikgruppen. Ich bin Mitglied des Schulfußballteams und wir haben viele Spiele gegen andere Schulen in der Gegend. Es macht mir viel Spaß und ich habe viele Freunde durch das Team kennengelernt.
(Our school also has many extracurricular activities, such as sports teams and music groups. I am a member of the school soccer team and we have many games against other schools in the area. It’s a lot of fun and I have made many friends through the team.)
- außerschulisch (extracurricular)
- die Aktivitäten (activities)
- die Sportmannschaften (sports teams)
- die Musikgruppen (music groups)
- das Mitglied (member)
- das Schulfußballteam (school soccer team)
- das Spiel (game)
- die Gegend (area)
- der Spaß (fun)
- der Freund (friend)
Insgesamt bin ich sehr glücklich auf meiner Schule und ich denke, dass ich hier eine gute Ausbildung bekomme. Ich hoffe, dass ich in Zukunft noch mehr von den vielen Möglichkeiten, die die Schule bietet, profitieren kann.
(Overall, I am very happy at my school and I think that I am getting a good education here. I hope that in the future, I can take advantage of even more of the many opportunities that the school offers.)
- die Möglichkeit (opportunity)
- profitieren (to take advantage of)
List of German adjectives with English meaning
Meine Freunde (My friends)
Ich habe viele Freunde, aber ich möchte über meine drei engsten Freunde sprechen. Wir haben uns alle in der Grundschule kennengelernt und sind seitdem unzertrennlich.
(I have many friends, but I want to talk about my three closest friends. We all met in elementary school and have been inseparable ever since.)
- die Freunde (friends)
- unzertrennlich (inseparable)
Mein erster Freund heißt Max. Er ist sehr sportlich und spielt gerne Fußball und Basketball. Max ist auch sehr lustig und hat immer eine positive Einstellung. Wir lieben es, zusammen Sport zu treiben oder Videospiele zu spielen.
(My first friend is Max. He is very athletic and likes to play soccer and basketball. Max is also very funny and always has a positive attitude. We love to exercise or play video games together.)
- sportlich (athletic)
- Fußball (soccer)
- Basketball (basketball)
- die Einstellung (attitude)
- lustig (funny)
- zusammen (together)
- Videospiele (video games)
Meine Freundin Anna ist sehr künstlerisch und liebt es zu malen und zu zeichnen. Sie hat auch ein großes Herz und ist immer bereit, anderen zu helfen. Anna und ich machen oft zusammen Kunstprojekte oder gehen ins Kino.
(My friend Anna is very artistic and loves to paint and draw. She also has a big heart and is always willing to help others. Anna and I often do art projects together or go to the movies.)
- künstlerisch (artistic)
- malen (to paint)
- zeichnen (to draw)
- das Herz (heart)
- bereit (willing)
- helfen (to help)
- das Kunstprojekt (art project)
- ins Kino gehen (to go to the movies)
Mein Freund Tom ist sehr intelligent und liebt es, neue Dinge zu lernen. Er ist auch sehr abenteuerlustig und geht gerne auf Reisen. Tom und ich haben viele spannende Abenteuer erlebt, wie zum Beispiel Campingausflüge oder Klettertouren.
(My friend Tom is very smart and loves to learn new things. He is also very adventurous and likes to travel. Tom and I have had many exciting adventures, such as camping trips or climbing expeditions.)
- intelligent (smart)
- abenteuerlustig (adventurous)
- die Reise (travel)
- die Abenteuer (adventures)
- der Campingausflug (camping trip)
- die Klettertour (climbing expedition)
Insgesamt bin ich sehr dankbar für meine Freunde und bin froh, dass ich sie habe. Wir haben so viele schöne Erinnerungen zusammen gemacht und ich freue mich auf viele weitere Abenteuer mit ihnen.
(Overall, I am very grateful for my friends and am glad to have them. We have made so many beautiful memories together and I look forward to many more adventures with them.)
- froh (glad)
- die Erinnerungen (memories)
Meine Stadt (My city)
Ich lebe in einer Stadt namens Hamburg in Deutschland. Hamburg ist die zweitgrößte Stadt Deutschlands und hat eine Bevölkerung von etwa 1,8 Millionen Menschen. Es ist eine Hafenstadt und liegt an der Elbe.
(I live in a city called Hamburg in Germany. Hamburg is the second largest city in Germany and has a population of about 1.8 million people. It is a port city and located on the river Elbe.)
- die Bevölkerung (population)
- der Hafen (port)
- die Elbe (river Elbe)
Hamburg ist bekannt für seine vielen Touristenattraktionen. Eines der bekanntesten ist der Hamburger Hafen, der einer der größten Häfen Europas ist. Es gibt auch den Fischmarkt, auf dem man frischen Fisch kaufen und lokale Spezialitäten probieren kann.
(Hamburg is known for its many tourist attractions. One of the most famous is the Port of Hamburg, which is one of the largest ports in Europe. There is also the Fish Market, where you can buy fresh fish and try local specialties.)
- die Touristenattraktionen (tourist attractions)
- bekannt (known)
- der Fischmarkt (fish market)
- frisch (fresh)
- lokale Spezialitäten (local specialties)
Außerdem gibt es viele kulturelle Veranstaltungen in Hamburg. Jedes Jahr findet das Hamburger Domfest statt, das größte Volksfest im Norden Deutschlands. Es gibt auch das Internationale Filmfest Hamburg, bei dem Filme aus der ganzen Welt gezeigt werden.
(Additionally, there are many cultural events in Hamburg. Every year, the Hamburg Dom Festival takes place, which is the largest folk festival in northern Germany. There is also the Hamburg International Film Festival, where films from all over the world are shown.)
- kulturelle Veranstaltungen (cultural events)
- das Domfest (folk festival)
- das Internationale Filmfest (international film festival)
- aus der ganzen Welt (from all over the world)
Insgesamt ist Hamburg eine lebendige und vielfältige Stadt, die für jeden etwas zu bieten hat.
(Overall, Hamburg is a vibrant and diverse city that has something to offer for everyone.)
- lebendig (vibrant)
- vielfältig (diverse)
- etwas zu bieten haben (to have something to offer)
My trip (Meine Reise)
Ich bin vor Kurzem mit meiner Familie nach Paris gereist. Wir sind direkt von unserer Stadt aus geflogen und kamen früh am Morgen in Paris an.
(I recently went on a trip to Paris with my family. We took a direct flight from our city and arrived in Paris early in the morning.)
- Vor Kurzem (recently)
- Die Reise (trip)
- Meine Familie (my family)
- Fliegen (to fly)
- Direkt (direct)
- Unsere Stadt (our city)
- Ankommen (to arrive)
- Früh (early)
- Am Morgen (in the morning)
Wir haben in einem Hotel im Herzen der Stadt gewohnt, in der Nähe vieler beliebter Sehenswürdigkeiten. Unser Hotelzimmer hatte eine tolle Aussicht auf den Eiffelturm, der nur einen kurzen Spaziergang entfernt war.
(We stayed in a hotel in the heart of the city, close to many popular tourist attractions. Our hotel room had a great view of the Eiffel Tower, which was just a short walk away.)
- das Hotel (hotel)
- die Stadt (city)
- die Nähe (proximity, closeness)
- die Sehenswürdigkeiten (tourist attractions)
- das Hotelzimmer (hotel room)
- die Aussicht (view)
- der Eiffelturm (Eiffel Tower)
- der Spaziergang (walk)
Während unseres Aufenthalts haben wir viele berühmte Wahrzeichen der Stadt besucht, darunter das Louvre-Museum und die Kathedrale Notre-Dame. Wir haben auch eine Bootsfahrt auf der Seine gemacht, was eine großartige Möglichkeit war, die Stadt aus einer anderen Perspektive zu sehen.
(During our stay, we visited many of the city’s famous landmarks, including the Louvre Museum and Notre-Dame Cathedral. We also went on a boat tour of the Seine River, which was a great way to see the city from a different perspective.)
- der Aufenthalt (stay)
- berühmte Wahrzeichen (famous landmarks)
- das Louvre-Museum (the Louvre Museum)
- die Kathedrale Notre-Dame (Notre-Dame Cathedral)
- die Bootsfahrt (boat tour)
- die Seine (the Seine River)
- aus einer anderen Perspektive (from a different perspective)
Eines der Highlights unserer Reise war das Probieren der köstlichen französischen Küche. Wir haben in vielen verschiedenen Restaurants und Cafés gegessen und alles von Croissants bis Escargots ausprobiert.
(One of the highlights of our trip was trying the delicious French cuisine. We ate at many different restaurants and cafes, and tried everything from croissants to escargots.)
- das Highlight (the highlight)
- die Reise (the trip)
- das Probieren (the trying/tasting)
- die köstliche französische Küche (the delicious French cuisine)
- das Restaurant (the restaurant)
- das Café (the café)
- alles (everything)
- der Croissant (the croissant)
- die Escargots (the escargots (snails))
Insgesamt war unser Trip nach Paris eine wunderbare Erfahrung. Wir haben die schönen Sehenswürdigkeiten, das leckere Essen und die reiche Kultur der Stadt genossen. Es war eine großartige Gelegenheit, Zeit mit meiner Familie zu verbringen und bleibende Erinnerungen zu schaffen.
(Overall, our trip to Paris was a wonderful experience. We enjoyed the beautiful sights, delicious food, and rich culture of the city. It was a great opportunity to spend time with my family and create lasting memories.)
- Insgesamt (Overall)
- Trip (trip)
- Paris (Paris)
- Eine wunderbare Erfahrung (A wonderful experience)
- Wir haben genossen (We enjoyed)
- Die schönen Sehenswürdigkeiten (The beautiful sights)
- Das leckere Essen (The delicious food)
- Die reiche Kultur der Stadt (The rich culture of the city)
- Eine großartige Gelegenheit (A great opportunity)
- Zeit mit meiner Familie zu verbringen (To spend time with my family)
- Bleibende Erinnerungen zu schaffen (To create lasting memories)
Meine Lieblingsessen (My favorite food)
Ich esse gerne viele verschiedene Arten von Essen und habe viele Lieblingsspeisen. Einige meiner Favoriten sind traditionelle deutsche Gerichte wie Schnitzel und Spätzle, Sauerkraut und Bratwurst.
(I like to eat many different types of food and have many favorite dishes. Some of my favorites are traditional German dishes like Schnitzel and Spätzle, Sauerkraut, and Bratwurst.)
- Lieblingsspeisen (favorite dishes)
- traditionelle deutsche Gerichte (traditional German dishes)
- Schnitzel (breaded and fried meat cutlets)
- Spätzle (soft egg noodles)
- Sauerkraut (fermented cabbage)
- Bratwurst (grilled or fried sausage)
Ich mag auch viele internationale Küchen, wie zum Beispiel italienische Pizza und Pasta, thailändisches Curry, indische Masala und japanisches Sushi.
(I also enjoy many international cuisines, such as Italian pizza and pasta, Thai curry, Indian masala, and Japanese sushi.)
- internationale Küchen (international cuisines)
Ein weiteres meiner Lieblingsessen ist mexikanisches Essen wie Tacos, Quesadillas und Guacamole. Die Kombination aus scharfen Gewürzen und frischen Zutaten macht das Essen zu einer Geschmacksexplosion.
(Another one of my favorite foods is Mexican cuisine like tacos, quesadillas, and guacamole. The combination of spicy seasonings and fresh ingredients makes the food a flavor explosion.)
- scharfe Gewürze (spicy seasonings)
- frische Zutaten (fresh ingredients)
- Geschmacksexplosion (flavor explosion)
- mexikanisches Essen (Mexican cuisine)
- Tacos (filled tortillas)
- Quesadillas (stuffed and grilled tortillas)
- Guacamole (dip made from mashed avocado)
Insgesamt genieße ich es, neue Gerichte und Küchen auszuprobieren und verschiedene Aromen und Texturen zu entdecken. Essen ist eine große Leidenschaft von mir und ich liebe es, zu kochen und neue Rezepte zu kreieren.
(Overall, I enjoy trying new dishes and cuisines and discovering different flavors and textures. Food is a big passion of mine, and I love to cook and create new recipes.)
- Aromen und Texturen (flavors and textures)
- Leidenschaft (passion)
- Rezepte (recipes)
- kochen (to cook)
- kreieren (to create)
Some Travel hacks when travelling in Europe
Conclusion:
In conclusion, writing essays in German can be a fun and effective way to improve your language skills. The eight essay examples provided in this article (Easy German Essays for Beginners) offer a range of topics that will help you practice your writing skills, expand your vocabulary, and gain confidence in your ability to express yourself in German. So why not try writing one of these essays today and see how much progress you can make in your German language journey?
More articles
From lyrics to pronunciation: learn the german national anthem, deutschlandlied, navigating the german language: a comprehensive starter vocabulary, 150+ common german phrases to sound like a native speaker, leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Some cheap and expensive things in Germany
German universities where we can apply, without uni-assist, latest article, 56 tuition free master’s programs in computer science in germany – explore your options today, your gateway to germany: 20 universities where you can apply without uni-assist, expanding your software company in germany: a step-by-step guide.

Plan For Germany
© Plan for Germany. All rights reserved.
Sister Sites
Popular category.
- German Language 40
- Lifestyle 35
- Trend & Living 30
- Level A1 23
Editor Picks

COMMENTS
The Nazi Party, led by Adolf Hitler, dictated over Germany from (1933-45). Germany suffering defeat in World War I, provoked the rise of a powerful united Nazi country which in turn led to World War II, the Holocaust, and great influence left on the next generation of German youth. The rise of the notoriously known Nazi Party was caused by ...
If your students are studying World War II or European history, understanding Nazi Germany is essential. Use the following essay topics to help them research and write about Nazi Germany.
Introduction to the Holocaust. The Holocaust was the systematic, state-sponsored persecution and murder of six million European Jews by the Nazi German regime and its allies and collaborators. The Holocaust was an evolving process that took place throughout Europe between 1933 and 1945. Antisemitism was at the foundation of the Holocaust.
Germany - Totalitarianism, Nazis, WW2: The main purpose and goal of the Nazi revolution was to establish a Volksgemeinschaft. Its creation required the purification and increase of the German "race" as well as its biological separation from the Jews, whose infusion of evil into the German bloodstream, the Nazis said, served to pollute and undermine Germany's well-being.
Germany in 1933 following a series of electoral victories by the Nazi Party. He ruled absolutely until his death by suicide in April 1945. Upon achieving power, Hitler smashed the nation's democratic institutions and transformed Germany into a war state intent on conquering Europe for the benefit of the so-called Aryan race.
4 Life in Nazi Germany. Nazi ideology. 1. Describe the life of Adolf Hitler between 1905 and 1918. How might Hitler's experiences in this period have shaped his political views and ideas? 2. Identify and discuss five key elements of Nazi ideology. What did the Nazis believe and what were their objectives?
This visual essay includes a selection of Nazi propaganda images, both "positive" and "negative.". It focuses on posters that Germans would have seen in newspapers like Der Stürmer and passed in the streets, in workplaces, and in schools. Some of these posters were advertisements for traveling exhibits—on topics like "The Eternal ...
Teachers, students, and other users will discover images, documents, videos, and audio clips that will spark debates about power structures in the Third Reich, Nazi Germany's relationship with other countries, and the experiences and behaviors of Germans from all walks of life—women and men, industrial workers, farmers, middle-class ...
Introduction This volume on Nazi Germany offers a variety of primary sources to students, educators, and other researchers. In working with a time period that has been documented extensively, we editors were able to put together a wealth of materials that lend themselves to classroom use, independent or guided primary-source research, and general interest reading.
Extract. From Central European History 's founding in 1968, Nazism commanded a great deal of attention in the journal, but it was only after many years that this was also true of the Holocaust. A quick search on JSTOR shows that, of the articles and reviews mentioning the Holocaust, less than 10 percent were published in the journal's first ...
The Nazi-Soviet pacts: a half-century later 14. Germany and the United States, 1917-1949 15. Germany and Pearl Harbour 16. Global conflict: relations between the European and Pacific theatres in World War II 17. The Holocaust and the war in 1943 18. The German resistance to Hitler 19. D-Day after 50 years 20. German plans for victory 21.
He engineered the most horrific activities in the history of humankind, the holocaust. The rise of the Nazis to power in 1933 led to the establishment of thousands of concentration camps, which were centers of mass murders of Jews. Most Germans supported the ideology that led to the persecution of the Jews. We will write a custom essay on your ...
In the first four lessons of the unit, students explore questions about identity, stereotyping, and group membership. This assessment step introduces students to a writing prompt that builds on these important themes and connects them to the history students explore later in this unit. The prompt is designed to serve as both a thematic frame ...
However, the German Wehrmacht- unified armed forces of Nazi Germany opposed the Sturmabteilung's stance. On the 30th of June 1934, Hitler's Schutzstaffel (SS)- a major paramilitary organization under Adolf Hitler got rid of the Sturmabteilung in which 400 of their murders were murdered including Rohm their leader.
The Holocaust and Nazi Germany Essay. The Holocaust is most well-known for the organized and inhumane extermination of more than six million Jews. The death total of the Jews is this most staggering; however, other groups such as Gypsies, Poles, Russians, political groups, Jehovah's witnesses, and homosexuals were targeted as well (Holocaust ...
Germany was a dictatorship, with all power in the hands of Adolf Hitler. According to this document, how did the Nazis use their power of controlling the media? Check all that apply. A,C,E. Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Which characteristics of totalitarian rule does this document describe? Check all that ...
The Different Types of German Essays. How to Write an Essay in German in 4 Steps. 1. Write down a list of words. 2. Do your research. 3. Make an outline using transition words. 4.
This resource comprises an essay on each of three prescribed works for A-level German, Paper 2 (7662). Each essay is accompanied by the relevant mark scheme extract and by a commentary to explain the marks awarded. This resource aims to exemplify to teachers the way the mark scheme is applied to students' essays.
This graphic organizer shows facts and details about Nazi Germany. The organizer could be best used for an essay on. Nazi Germany as an example of a totalitarian state. Read a sentence from the first draft of a document-based essay on the persecution of Jews in Nazi Germany. Hitler announced a boycott of Jewish-owned businesses.
50 Useful German Essay Words and Phrases. Essay-writing is in itself already a difficult endeavor. Now writing an essay in a foreign language like German ---that's on a different plane of difficulty. To make it easier for you, here in this article, we've compiled the most useful German essay phrases. Feel free to use these to add a dash of ...
1. Erstens - Firstly. This German essay phrase is used to introduce the first point in your essay. Erstens werden wir die Hauptargumente diskutieren. [Firstly, we will discuss the main arguments.] 2. Zweitens - Secondly. Normally, this phrase is there for you when you want to introduce the second point in a structured manner.
This year's topics are currywurst and climate neutrality. The essay contest is open to students from Grades 3-12 and the deadline for entries is May 1, 2024. Students must choose and write about one of the following topics. Detailed rules and information about submission guidelines can be found below. We enourage all participants to read them.
In conclusion, writing essays in German can be a fun and effective way to improve your language skills. The eight essay examples provided in this article (Easy German Essays for Beginners) offer a range of topics that will help you practice your writing skills, expand your vocabulary, and gain confidence in your ability to express yourself in ...