

Assignment 5.2 | Week-7 | Programming for Everybody (Getting Started with Python) By Coursera

Coursera Programming for Everybody (Getting Started with Python) Week 5 Assignment 5.2
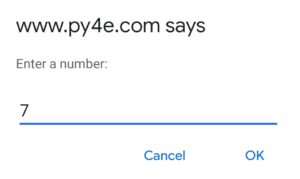
Question: 5.2 Write a program that repeatedly prompts a user for integer numbers until the user enters ‘done’. Once ‘done’ is entered, print out the largest and smallest of the numbers. If the user enters anything other than a valid number catch it with a try/except and put out an appropriate message and ignore the number. Enter 7, 2, bob, 10, and 4 and match the output below.
Do Not Only Use These Quizzes For Getting Certificates.You Can Take Help From These Quizzes Answer. All Quizzes & Contents Are Free Of Charge. ✅ If You Want Any Quiz Answers Then Please Contact Us
Related Questions & Answers:
- Programming for Everybody (Getting Started with Python) – Coursera Quiz Answers Programming for Everybody (Getting Started with Python) – Coursera 4.8 Stars (167,402 ratings) Instructor: Charles Russell Severance Enroll Now This Programming ... Read more...
- Assignment 2.2 | Week-4 | Programming for Everybody (Getting Started with Python) By Coursera Coursera Programming for Everybody (Getting Started with Python) Week 4 Assignment 2.2 Question: 2.2 Write a program that uses input to prompt ... Read more...
- Chapter 5 (Quiz Answers) | Week-7 | Programming for Everybody (Getting Started with Python) By Coursera Coursera Programming for Everybody (Getting Started with Python) Week 7 Chapter 5 Graded Quiz • 30 min 1. What is ... Read more...
- Chapter 4 (Quiz Answers) | Week-6 | Programming for Everybody (Getting Started with Python) By Coursera Coursera Programming for Everybody (Getting Started with Python) Week 6 Chapter 4 Graded Quiz • 30 min 1. Which Python ... Read more...
- Chapter 3 (Quiz Answers) | Week-5 | Programming for Everybody (Getting Started with Python) By Coursera Coursera Programming for Everybody (Getting Started with Python) Week 5 Chapter 3 Graded Quiz • 30 min 1. What do ... Read more...
- Chapter 2 (Quiz Answers) | Week-4 | Programming for Everybody (Getting Started with Python) By Coursera Coursera Programming for Everybody (Getting Started with Python) Week 4 Chapter 2 Graded Quiz • 30 min 1. Which of ... Read more...
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Please Enable JavaScript in your Browser to Visit this Site.


Community Support (Archived) — Edward Lundqvist asked a question.
I need help with the assignment 5.2 in Python for everybody. Somebody that could help me?
- Learner Support

𝗠𝗮𝗿𝘆𝗮𝗺 (Community Guide) 💡
Hi @Edward Lundqvist,
You may find the threads in the discussion forums of your course helpful. Here are 2 examples:
1. Assignment 5.2
2. Assignment 5.2
If not, feel free to get help from the teaching staff. They are very active there, answering learners' questions.

User16924707185781139090
Related Questions
© 2021 Coursera Inc. All rights reserved.
Instantly share code, notes, and snippets.
initiatorvaibhav / 5.2 Write a program that repeatedly prompts a user for integer numbers until the user enters 'done'. Once 'done' is entered, print out the largest and smallest of the numbers. If the user enters anything other than a valid number catch it with a try,
- Download ZIP
- Star ( 0 ) 0 You must be signed in to star a gist
- Fork ( 0 ) 0 You must be signed in to fork a gist
- Embed Embed this gist in your website.
- Share Copy sharable link for this gist.
- Clone via HTTPS Clone using the web URL.
- Learn more about clone URLs
- Save initiatorvaibhav/3758f116f237ef60e9c5ca4e8b18f788 to your computer and use it in GitHub Desktop.

initiatorvaibhav commented Feb 21, 2022
newer update
Sorry, something went wrong.
- Table of Contents
- Course Home
- Assignments
- Peer Instruction (Instructor)
- Peer Instruction (Student)
- Change Course
- Instructor's Page
- Progress Page
- Edit Profile
- Change Password
- Scratch ActiveCode
- Scratch Activecode
- Instructors Guide
- About Runestone
- Report A Problem
- This Chapter
- 1. Why Program?' data-toggle="tooltip" >
Python for Everybody - Interactive ¶
Assignments ¶, table of contents ¶.
- 1.1. Why should you learn to write programs?
- 1.2. Creativity and motivation
- 1.3. Computer hardware architecture
- 1.4. Understanding programming
- 1.5. Words and sentences in Python
- 1.6. Conversing with Python
- 1.7. Terminology: Interpreter and compiler
- 1.8. Writing a program
- 1.9. What is a program?
- 1.10. The building blocks of programs
- 1.11. What could possibly go wrong?
- 1.12. Debugging
- 1.13. The learning journey
- 1.14. Glossary
- 1.15. Exercises
- 2.1. Values and types
- 2.2. Variables
- 2.3. Variable names and keywords
- 2.4. Statements
- 2.5. Operators and operands
- 2.6. Expressions
- 2.7. Order of operations
- 2.8. Modulus operator
- 2.9. String operations
- 2.10. Asking the user for input
- 2.11. Comments
- 2.12. Choosing mnemonic variable names
- 2.13. Debugging
- 2.14. Glossary
- 2.15. Multiple Choice Questions
- 2.16. Mixed-up Code Questions
- 2.17. Write Code Questions
- 3.1. How to be a Successful Programmer
- 3.2. How to Avoid Debugging
- 3.3. Beginning tips for Debugging
- 3.4.1. ParseError
- 3.4.2. TypeError
- 3.4.3. NameError
- 3.4.4. ValueError
- 3.5. Summary
- 3.6. Exercises
- 4.1. Boolean expressions
- 4.2. Logical operators
- 4.3. Conditional execution
- 4.4. Alternative execution
- 4.5. Chained conditionals
- 4.6. Nested conditionals
- 4.7. Catching exceptions using try and except
- 4.8. Short-circuit evaluation of logical expressions
- 4.9. Debugging
- 4.10. Glossary
- 4.11. Multiple Choice Questions
- 4.12. Mixed-up Code Questions
- 4.13. Write Code Questions
- 4.14.1. Comparison Operators
- 4.14.2. if/else Statements
- 4.14.3. Boolean Operations
- 5.1. Function calls
- 5.2. Built-in functions
- 5.3. Type conversion functions
- 5.4. Math functions
- 5.5. Random numbers
- 5.6. Adding new functions
- 5.7. Definitions and uses
- 5.8. Flow of execution
- 5.9. Parameters and arguments
- 5.10. Fruitful functions and void functions
- 5.11. Why functions?
- 5.12. Debugging
- 5.13. Glossary
- 5.14. Multiple Choice Questions
- 5.15. Mixed-up Code Questions
- 5.16. Write Code Questions
- 5.17.1. Print and Function Basics
- 5.17.2. Parts of a Function and Function Calls
- 5.17.3. Writing Function Calls
- 5.17.4. Function Order
- 5.17.5. Special Characters and Keywords
- 5.18. Functions Multiple Choice Questions
- 5.19. Functions Mixed-Up Code Questions
- 5.20. Functions Write Code Questions
- 5.21.1. String Indices
- 5.21.2. String Slices
- 5.21.3. Input and Converting Between Strings and Numbers
- 5.21.4. String Methods
- 5.22. Functions and Strings Multiple Choice Questions
- 5.23. Functions and Strings Mixed-Up Code Questions
- 5.24. Functions and Strings Write Code Questions
- 5.25.1. Basic Conditionals and Tests
- 5.25.2. Logical Operators and Complex Conditionals
- 5.26. Functions and Conditionals Multiple Choice Questions
- 5.27. Functions and Conditionals Mixed-Up Code Questions
- 5.28. Functions and Conditionals Write Code Questions
- 5.29.1. List Indexing
- 5.29.2. Built-in Functions That Work on Lists
- 5.29.3. List Methods
- 5.29.4. Using the Slice Operator
- 5.30. Functions with Lists Multiple Choice Questions
- 5.31. Functions and Lists Mixed-Up Code Questions
- 5.32. Functions and Lists Write Code Questions
- 5.33.1. The For-Each Loop
- 5.33.2. Range and For
- 5.33.3. While Loops
- 5.34. Functions with Loops Multiple Choice Questions
- 5.35. Functions and Loops Mixed-Up Code Questions
- 5.36. Functions and Loops Write Code Questions
- 5.37.1. Tuples
- 5.37.2. Tuples are Immutable
- 5.37.3. Dictionaries
- 5.38. Functions with Tuples and Dictionaries Multiple Choice Questions
- 5.39. Functions with Tuples and Dictionaries Mixed-Up Code Questions
- 5.40. Functions with Tuples and Dictionaries Write Code Questions
- 5.41.1. Function Example
- 5.41.2. String Definition
- 5.41.3. String Indices
- 5.41.4. String Slices
- 5.41.5. Basic Conditionals and Tests
- 5.41.6. Logical Operators and Complex Conditionals
- 5.42.1. List Indexing and Slicing
- 5.42.2. Built-in Functions That Work on Lists
- 5.42.3. List Methods
- 5.42.4. The For-Each Loop
- 5.42.5. Range and For
- 5.42.6. While Loops
- 6.1. Updating variables
- 6.2. The while statement
- 6.3. Infinite loops
- 6.4. Finishing iterations with continue
- 6.5. Definite loops using for
- 6.6.1. Counting and summing loops
- 6.6.2. Maximum and minimum loops
- 6.7. Debugging
- 6.8. Glossary
- 6.9. Multiple Choice Questions
- 6.10. Mixed-up code Questions
- 6.11. Write Code Questions
- 6.12.1. for Statements
- 6.12.2. The range Function
- 6.12.3. while Statements
- 7.1. A string is a sequence
- 7.2. Getting the length of a string using len()
- 7.3. Traversal through a string with a loop
- 7.4. String slices
- 7.5. Strings are immutable
- 7.6. Looping and counting
- 7.7. The in operator
- 7.8. String comparison
- 7.9. String methods
- 7.10. Parsing strings
- 7.11. Format operator
- 7.12. Debugging
- 7.13. Glossary
- 7.14. Multiple Choice Questions
- 7.15. Mixed-up Code Questions
- 7.16. Write-code questions
- 7.17.1. Indexing and Slicing
- 7.17.2. Common String Methods
- 8.1. Persistence
- 8.2. Opening files
- 8.3. Text files and lines
- 8.4. Reading files
- 8.5. Searching through a file
- 8.6. Letting the user choose the file name
- 8.7. Using try, except, and open
- 8.8. Writing files
- 8.9. Debugging
- 8.10. Summary
- 8.11. Glossary
- 8.12. Multiple Choice Questions
- 8.13. Mixed-up Code Questions
- 8.14. Write Code Questions
- 8.15.1. Reading from Files
- 8.16.1. Comma-Separated Values (CSV) Files
- 8.16.2. Nested dictionaries
- 8.16.3. Comma-Separated Values (CSV) Files with a Header Row
- 8.17.1. CSV Reader
- 8.17.2. Reading Comma-Separated Values (CSV) Files with a Header Row
- 8.17.3. Writing a Comma-Separated Values (CSV) File with CSV Writer
- 9.1. A list is a sequence
- 9.2. Lists are mutable
- 9.3. Traversing a list
- 9.4. List operations
- 9.5. List slices
- 9.6. List methods
- 9.7. Deleting elements
- 9.8. Lists and functions
- 9.9. Lists and strings
- 9.10. Parsing lines
- 9.11. Objects and values
- 9.12. Aliasing
- 9.13. List arguments
- 9.14. Debugging
- 9.15. Glossary
- 9.16. Multiple Choice Questions
- 9.17. Mixed-Up Code Questions
- 9.18. Write Code Questions
- 9.19. Group Work: Lists
- 10.1. Dictionaries
- 10.2. Dictionary as a Set of Counters
- 10.3. Dictionaries and Files
- 10.4. Looping and Dictionaries
- 10.5. Advanced Text Parsing
- 10.6. Debugging
- 10.7. Glossary
- 10.8. Multiple Choice Questions
- 10.9. Mixed-Up Code Questions
- 10.10. Write Code Questions
- 11.1. Tuples are Immutable
- 11.2. Comparing Tuples
- 11.3. Tuple Assignment
- 11.4. Dictionaries and Tuples
- 11.5. Multiple Assignment with Dictionaries
- 11.6. The Most Common Words
- 11.7. Using Tuples as Keys in Dictionaries
- 11.8. Sequences: Strings, Lists, and Tuples - Oh My!
- 11.9. Debugging
- 11.10. Glossary
- 11.11. Multiple Choice Questions
- 11.12. Tuples Mixed-Up Code Questions
- 11.13. Write Code Questions
- 12.1. Regular Expressions
- 12.2. Character Matching in Regular Expressions
- 12.3. Extracting Data Using Regular Expressions
- 12.4. Combining Searching and Extracting
- 12.5. Escape Character
- 12.6. Summary
- 12.7. Bonus section for Unix / Linux users
- 12.8. Debugging
- 12.9. Glossary
- 12.10. Multiple Choice Questions
- 12.11. Practice Problems - Regular Expressions
- 12.12. Mixed-Up Code Questions
- 12.13. Write Code Questions
- 12.14.1. Regex Methods
- 12.14.2. Quantifiers
- 12.14.3. Character Sets
- 12.14.4. Character Ranges
- 12.14.5. Character Classes
- 12.14.6. Escaping Special Characters
- 12.14.7. Greedy and Non-Greedy Matching
- 12.15.1. Using a logical “or”
- 12.15.2. Specifying What to Extract - Matching Groups
- 12.15.3. Specifying What to Extract - Non-Matching Groups
- 12.15.4. Boundary or Anchor Characters
- 12.15.5. Negating a Character Set
- 13.1. Networked programs
- 13.2. HyperText Transfer Protocol - HTTP
- 13.3. The world’s simplest web browser
- 13.4. Retrieving an image over HTTP
- 13.5. Retrieving web pages with urllib
- 13.6. Reading binary files using urllib
- 13.7.1. Start and End Tags
- 13.7.2. List Tags
- 13.7.3. Tag Relationships: Parent, Child, Sibling
- 13.8. Mixed-Up Code Questions
- 13.9.1. Table Tags
- 13.9.2. Link Tag
- 13.9.3. Image Tag
- 13.9.4. Attributes
- 13.9.5. Div and Span tags
- 13.9.6. Using CSS Classes
- 13.10. Parsing HTML and scraping the web
- 13.11. Parsing HTML using regular expressions
- 13.12. Parsing HTML using BeautifulSoup
- 13.13.1. Getting a tag from a soup object
- 13.13.2. Getting text from a tag
- 13.13.3. Getting data from tags with attributes
- 13.13.4. How to Find Tags Inside of Tags
- 13.14. Bonus section for Unix / Linux users
- 13.15. Glossary
- 13.16. Multiple Choice Questions
- 13.17. Mixed-Up Code Questions
- 13.18. Write Code Exercises
- 14.1. Scrape all the Cottage Inn Pizza locations
- 14.2. Get news links from faculty webpages
- 14.3.1. Plan 2: Example
- 14.3.2. Plan 2: When to use this plan
- 14.3.3. Plan 2: How to use this plan
- 14.3.4. Plan 2: Exercises
- 14.4.1. Plan 3: Example
- 14.4.2. Plan 3: When to use this plan
- 14.4.3. Plan3: How to use this plan
- 14.4.4. Plan 3: Exercises
- 14.5.1. Plan 4: Example
- 14.5.2. Plan 4: When to use it
- 14.5.3. Plan 4: How to use it
- 14.5.4. Plan 4: Exercises
- 14.6.1. Looking closer at a tag
- 14.6.2. Plan 5: Example
- 14.6.3. Plan 5: How to use it
- 14.6.4. Plan 5: Exercises
- 14.7.1. Plan 9: Example
- 14.7.2. Plan 9: Exercises
- 14.8.1. Plan 10: Outline
- 14.9. Code writing activity part 1
- 14.10. Code writing activity part 2
- 14.11. Code writing activity part 3
- 14.12. Code debugging activity
- 14.13.1. Relevant tags
- 14.14.1. Plan 1
- 14.14.2. Plan 2
- 14.14.3. Plan 3
- 14.14.4. Plan 4
- 14.14.5. Plan 5
- 14.14.6. Plan 6
- 14.14.7. Plan 9
- 14.14.8. Plan 10
- 14.15. Multiple Choice Questions
- 14.16. Mixed-Up Code Questions
- 14.17. Write Code Questions
- 15.1.1. Properly Formatted XML
- 15.2.1. Using get to get the value of an attribute
- 15.2.2. Getting Data from the First Element of a Type in XML
- 15.2.3. Fixing Errors in XML
- 15.2.4. Write Code to Process XML
- 15.3. Looping through nodes
- 15.4.1. List of Dictionaries
- 15.5.1. Converting a JSON String into a Python Object
- 15.5.2. Converting a Python object into a JSON string
- 15.6.1. Getting JSON Data From an API
- 15.6.2. Using a Dictionary for URL Parameters
- 15.7. Security and API usage
- 15.8. Glossary
- 15.9. Multiple Choice Questions
- 15.10. Mixed-Up Code Questions
- 15.11. Write Code Questions
- 15.12. Application 1: Google geocoding web service
- 15.13. Application 2: Twitter
- 16.1. Managing larger programs
- 16.2. Getting started
- 16.3. Using objects
- 16.4. Starting with programs
- 16.5. Subdividing a problem
- 16.6. Our first Python object
- 16.7. Classes as types
- 16.8. Object lifecycle
- 16.9. Multiple instances
- 16.10. Inheritance
- 16.11. Summary
- 16.12. Glossary
- 16.13. Multiple Choice Questions
- 16.14. Mixed-Up Code Exercises
- 16.15. Write Code Exercises
- 16.16.1. A Book Class
- 16.16.2. Create More Book Objects
- 16.16.3. Add a Method to a Class
- 16.17.1. Inheritance
- 16.17.2. Overriding an Inherited Method
- 17.1.1. What does a left turn of 90 mean?
- 17.2. Practice with Turtles
- 17.3. Turtle Methods
- 17.4. Single and Multiple Turtles
- 17.5. Using Repetition with Turtles
- 17.6. Teacher Note: Turtle Geometry
- 17.7. Total Turtle Trip Theorem
- 17.8. Making Patterns within Patterns
- 17.9. The Turtle Stamp Procedure
- 17.10. Creating Functions with Turtles
- 17.11.1. Summary of Turtle Methods
- 17.11.2. Summary of Screen Methods
- 17.12. Multiple Choice Questions
- 17.13. Mixed-Up Code Questions
- 17.14. Write Code Questions
- 18.1. Using Repetition with Images
- 18.2. Understanding Image Representation
- 18.3. A Pattern for Image Processing
- 18.4. Changing Step 5: Increasing and decreasing color values
- 18.5. Changing Step 6: Changing where we put the colors
- 18.6. Changing Step 3: Changing which data we use
- 18.7. Image Chaper Summary
- 18.8. Multiple Choice Questions
- 18.9. Mixed-Up Code Exercises
- 18.10. Write Code Exercises
- 19.1. Object-oriented programming
- 19.2. A change of perspective
- 19.3. Objects Revisited
- 19.4. User Defined Classes
- 19.5. Improving our Constructor
- 19.6. Adding Other Methods to our Class
- 19.7. Objects as Arguments and Parameters
- 19.8. Converting an Object to a String
- 19.9. Instances as Return Values
- 19.10.1. Multiple Classes
- 19.10.2. Object-Oriented Analysis and Design
- 19.10.3. UML Diagrams
- 19.11. Multiple Classes Practice
- 19.12. Multiple Choice Questions for Multiple Classes
- 19.13. Glossary
- 19.14. Multiple Choice Questions
- 19.15. Mixed-Up Code Exercises
- 19.16. Exercises
- 20.1. Pillars of OOP
- 20.2. Introduction to Inheritance - Point and LabeledPoint
- 20.3. Call a Parent Method
- 20.4. Reuse Through Association
- 20.5. Class Diagrams
- 20.6. Association vs. Inheritance
- 20.7.1. Storing Postal Addresses
- 20.7.2. Storing International Addresses
- 20.7.3. Inheritance Applied
- 20.7.4. A List of Addresses
- 20.7.5. Using isinstance
- 20.8.1. Testing your Code
- 20.8.2. Creating Test Cases
- 20.8.3. Understanding Unit Tests
- 20.8.4. Writing Unit Tests
- 20.9.1. Assert methods
- 20.9.2. Writing Unit Tests
- 20.10. Multiple Choice Questions
- 20.11. Mixed-Up Code Questions
- 20.12. Write Code Questions
- 21.1. What is a database?
- 21.2. Database concepts
- 21.3. Database Browser for SQLite
- 21.4. Creating a database table
- 21.5. Structured Query Language summary
- 21.6. More SELECT Keywords
- 21.7. Spidering Twitter using a database
- 21.8. Basic data modeling
- 21.9.1. Constraints in database tables
- 21.9.2. Retrieve and/or insert a record
- 21.9.3. Storing the friend relationship
- 21.10. Three kinds of keys
- 21.11. Using JOIN to retrieve data
- 21.12. Summary
- 21.13. Debugging
- 21.14. Glossary
- 21.15. Multiple Choice Questions
- 21.16. Mixed-Up Code Questions
- 21.17. Write Code Questions
- 22.1. Visualizing data
- 22.2. Building a Google map from geocoded data
- 22.3. Visualizing networks and interconnections
- 22.4. Visualizing mail data
- 22.5. Multiple Choice Questions
- 22.6. Mixed-Up Code Questions
Acknowledgements ¶
Acknowledgements, Contributors, License, and Preface
- Contributions
- Copyright Detail for Python for Everybody
- Credits for Python for Everybody
- Printing History for for Python for Everybody
- Copyright Details for for Python for Everybody
- Remixing an Open Book
Search Page

- View Active Threads
- View Today's Posts
- View New Posts
- My Discussions
- Unanswered Posts
- Unread Posts
- Active Threads
- Mark all forums read
- Member List
- Interpreter
[split] Python for Everybody 5.2 assignment
- Python Forum
- Python Coding
- 0 Vote(s) - 0 Average
- View a Printable Version
User Panel Messages
Announcements.

Login to Python Forum
Python for Everybody
- Coursera: Python for Everybody Specialization
- edX: Python for Everybody
- FutureLearn: Programming for Everybody (Getting Started with Python)
- FreeCodeCamp
- Free certificates for University of Michigan students and staff
If you log in to this site you have joined a free, global open and online course. You have a grade book, autograded assignments, discussion forums, and can earn badges for your efforts.
We take your privacy seriously on this site, you can review our Privacy Policy for more details.
If you want to use these materials in your own classes you can download or link to the artifacts on this site, export the course material as an IMS Common Cartridge®, or apply for an IMS Learning Tools Interoperability® (LTI®) key and secret to launch the autograders from your LMS.
The code for this site including the autograders, slides, and course content is all available on GitHub . That means you could make your own copy of the course site, publish it and remix it any way you like. Even more exciting, you could translate the entire site (course) into your own language and publish it. I have provided some instructions on how to translate this course in my GitHub repository.
And yes, Dr. Chuck actually has a race car - it is called the SakaiCar . He races in a series called 24 Hours of Lemons .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Fork 5 5. [Coursera] Python for everybody 5.2 Assignment. Raw. 5.2 Write a program that repeatedly prompts a user for integer numbers until the user enters 'done'. Once 'done' is entered, print out the largest and smallest of the numbers. If the user enters anything other than a valid number catch it with a try,except and put out an appropriate ...
5.2 Write a program that repeatedly prompts a user for integer numbers until the user enters 'done'. Once 'done' is entered, print out the largest and smallest of the numbers. If the user enters anything other than a valid number catch it with a try/except and put out an appropriate message and ignore the number.
I have been taking Coursera's course, Programming for Everybody with Python. But one of the assignment 5.2 on week 7 got my attention. The objective is to make the user enter some numbers and enter done, when he entered all the numbers he wanted. After that, the output should be the biggest number and smallest number he entered. Here is the ...
Hi guys, in this video I solved the assignment 5.2 of Coursera Python for Everybody. Hope you find it useful.If you're new, Subscribe! https://www.youtube....
This contains all the practices for the lectures, custom answers to the assignments and additional inline notes for "Python for Everybody Specialization" on Coursera by the University of Michigan. 41 stars 54 forks Branches Tags Activity
Coursera: Programming For Everybody Assignment 5.2 program solution Answer | Python for Everybody Assignment 5.2 program solution.IF YOUR PROGRAM IS WORKING...
Code link:https://drive.google.com/file/d/1HDYJ1BNgLPGk4P3sZRqcQvXuDNBuN1jK/view?usp=sharingCoursera: Python For Everybody Assignment 5.2 program solution | ...
Raw. Exercise 5.2 - Python for Everybody. Write another program that prompts for a list of numbers. as above and at the end prints out both the maximum and minimum of. the numbers instead of the average. largest = None. smallest = None. count = 0.
CourseraProgramming for Everybody (Getting Started with Python)Week 5 Assignment 5.2 Question: 5.2 Write a program that repeatedly prompts a user for integer numbers until the user enters 'done'. Once 'done' is entered, print out the largest and smallest of the numbers. If the user enters anything other than a valid number catch it…
This is the requirement 5.2 Write a program that repeatedly prompts a user for integer numbers until the user enters 'done'. Once 'done' is entered, print out the largest and smallest of the numbers. If the user enters anything other than a valid number catch it with a try/except and put out an appropriate message and ignore the number.
This is the first part of videos of solutions for python for everybody courses on Coursera, for more information go to my git-hub pagehttps://github.com/Akhi...
Joined: Oct 2017. Reputation: 1. #1. Oct-07-2017, 03:58 PM. Hey guys- I'm on my last assignment for Python and I need some expert assistance please. This is the assignment: 5.2 Write a program that repeatedly prompts a user for integer numbers until the user enters 'done'. Once 'done' is entered, print out the largest and smallest of the numbers.
The video is about the solution of the mentioned assignment of the python course named 'PYTHON FOR EVERYBODY' on coursera by Dr. Chuck
Help with the assignment 5.2 in Python for everybody. Community Support (Archived) — Edward Lundqvist asked a question. March 8, 2021 at 6:45 AM. Help with the assignment 5.2 in Python for everybody. I need help with the assignment 5.2 in Python for everybody. Somebody that could help me?
Assignment solutions for python for everybody. Contribute to sweehors/python-for-everybody development by creating an account on GitHub.
Fork 0. [Coursera] Python for everybody 5.2 Assignment. Raw. 5.2 Write a program that repeatedly prompts a user for integer numbers until the user enters 'done'. Once 'done' is entered, print out the largest and smallest of the numbers. If the user enters anything other than a valid number catch it with a try,except and put out an appropriate ...
Python for Everybody - Interactive¶ Assignments¶ Assignments; Table of Contents ...
Python for Everybody 3.3 assignment: ramadan2099: 7: 31,905: Apr-08-2020, 06:49 AM Last Post: DeaD_EyE : Python for everyone course assignment 5.2: ofekx: 3: 8,600: Dec-23-2019, 08:41 PM Last Post: nilamo: Users browsing this thread: 1 Guest(s) View a Printable Version;
Coursera: Python for Everybody Specialization; edX: Python for Everybody; FreeCodeCamp; Free certificates for University of Michigan students and staff; If you log in to this site you have joined a free, global open and online course. You have a grade book, autograded assignments, discussion forums, and can earn badges for your efforts.
this contains all the answers to the quizes and asssignments for "Programming for Everybody (Getting Started with Python)" on Coursera by the University of Michigan. - Coursera---Programming-for-Everybody-Getting-Started-with-Python-/Week 7- Assignment 5.2 at master · Ritik2703/Coursera---Programming-for-Everybody-Getting-Started-with-Python-
Hello friends, In this video we discussed about Coursera programming for everybody Assignment 5.2 answer other way it's known as Python for everybody Exercise 5.2 Complete program In this course Assignment (Exercise) are available in week 7 part.
We read every piece of feedback, and take your input very seriously.