PhD Interview Questions and Answers (13 Questions + Answers)

Most PhD applications include an interview. This allows your university (and perhaps even your prospective supervisor) to discuss the PhD with you in more detail.
This article lists some of the most common PhD interview questions along with their answers. The goal is to help you prepare for a PhD interview and pass with flying colors.

1) How did you develop this proposal?

When responding to this question, demonstrate your thought process, research skills, and the evolution of your ideas. Let's choose the subject of "Renewable Energy Integration in Urban Planning" as an example.
Sample answer:
"My proposal on 'Renewable Energy Integration in Urban Planning' originated from my undergraduate thesis on sustainable cities. Intrigued by the potential of renewable energy in urban environments, I conducted a literature review to identify gaps in current research. This review highlighted a lack of comprehensive strategies for integrating renewable technologies at a city-wide level. I then consulted with experts in urban planning and renewable energy, which provided practical insights into the challenges and opportunities in this field. I designed a methodology that combines spatial analysis with energy modeling to explore optimal renewable energy integration in urban landscapes. This proposal represents an amalgamation of academic research, expert consultation, and innovative methodology development."
This answer is effective because it mentions a literature review demonstrates the ability to conduct thorough research and identify gaps in existing knowledge.
2) Why do you wish to pursue a PhD?
For this question, it's important to articulate your passion for the subject, your long-term career goals, and how the PhD program aligns with these aspects.
Let's choose the subject of "Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare" for this example.
"I am passionate about leveraging technology to improve healthcare outcomes, and pursuing a PhD in Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare aligns perfectly with this passion. During my Master's, I was fascinated by the potential of AI to revolutionize diagnostic processes and personalized medicine. I believe a PhD will provide me with the deep technical knowledge and research skills necessary to contribute significantly to this field. My goal is to develop AI systems that enhance medical diagnostics, ultimately improving patient care and treatment efficiency. This PhD program, known for its pioneering research in AI and strong healthcare collaborations, is the ideal environment for me to develop these innovations and achieve my career aspirations in healthcare technology."
This is a great answer because you clearly state that the PhD will provide the necessary skills and knowledge, indicating a clear understanding of the purpose of the program.
3) Why do you think you are the right candidate for this PhD program?
Discuss how your research interests align with the program's strengths and the faculty's expertise. Explain how the program's resources, courses, and research opportunities can help you achieve your academic and career goals.
"I am deeply passionate about environmental science, particularly in the area of sustainable urban development. This passion was ignited during my master's program in Environmental Studies at XYZ University, where I completed a thesis on urban green spaces and their impact on city microclimates. This research not only honed my skills in data analysis and GIS mapping but also highlighted the importance of interdisciplinary approaches to environmental issues. I am drawn to your PhD program at ABC University because of its innovative research on sustainable urban planning and the renowned work of Professor Jane Smith in this field. Her research aligns with my interest in integrating green infrastructure into urban planning to mitigate climate change effects. My perseverance, attention to detail, and ability to synthesize complex data make me an ideal candidate for this challenging program. Pursuing this PhD is integral to my goal of becoming an environmental consultant, where I plan to develop strategies for cities to reduce their environmental footprint."
This response is effective because it mentions particular aspects of your experience and the program, avoiding generic statements. It also outlines how the PhD fits into your career path.
4) What do you plan to do after you have completed your PhD?
Be specific about the type of career you aspire to, whether it's in academia, industry, research, etc. Explain how the PhD will equip you with the skills and knowledge for your chosen career path.
"After completing my PhD in Computational Neuroscience, I plan to pursue a career in academia as a university professor. My doctoral research on neural network modeling will provide a strong foundation for teaching and conducting further research in this area. I aim to develop innovative courses that bridge computer science and neuroscience, addressing the growing demand for interdisciplinary knowledge in these fields. Additionally, I intend to continue my research on applying machine learning techniques to understand brain function, which has potential implications for developing new treatments for neurological disorders. This academic pathway allows me to contribute significantly to both education and research in Computational Neuroscience."
This is a great answer because it connects the PhD research directly to future career plans.
It also articulates how your work can impact both academia and the broader field of Computational Neuroscience.
5) Why have you chosen this specific PhD program?
Mention specific aspects of the program that attracted you, such as the curriculum, research facilities, faculty expertise, or reputation.
Explain how the program aligns with your research interests or academic background.
"I chose the PhD program in Artificial Intelligence at MIT because of its cutting-edge research and interdisciplinary approach, which perfectly aligns with my academic background in computer science and my passion for machine learning. The program's emphasis on both theoretical foundations and practical applications in AI is particularly appealing. Additionally, the opportunity to work under the guidance of Professor [Name], whose work in [specific area, e.g., neural networks or AI ethics] has deeply influenced my own research interests, is a significant draw. This program is an ideal fit for me to further develop my skills and contribute to the field of AI, ultimately aiming for a career in AI research and development in the tech industry."
This answer connects your background and goals to the program's offerings.
Including a specific professor's name shows detailed knowledge about the program and faculty.
6) What impact would you like your PhD project to have?
When answering this question, convey both the academic significance and the potential real-world applications of your research. Let's choose a project focused on developing eco-friendly battery technologies for electric vehicles for this example.
"My PhD project aims to develop new eco-friendly battery technologies for electric vehicles (EVs), addressing both the environmental impact of battery production and the efficiency of energy storage. I hope my research will contribute to the academic field by advancing our understanding of sustainable materials for energy storage, potentially leading to publications and patents. Beyond academia, I envision this project significantly impacting the EV industry by providing a more sustainable and efficient battery alternative. This innovation could play a crucial role in reducing the carbon footprint of transportation and supporting global efforts towards a greener future. Ultimately, I aspire for my work to not only advance scientific knowledge but also drive real-world changes in how we approach energy sustainability in transportation."
This is an excellent answer because it connects the project to larger environmental goals and societal benefits. It also reflects a forward-thinking approach, demonstrating your understanding of the project's potential long-term implications.
7) What difficulties would you expect to encounter during this project?
It's important to demonstrate awareness of potential challenges and convey a proactive mindset toward problem-solving. Let's choose a project focused on the development of a novel AI-driven diagnostic tool for early detection of neurological diseases for this example.
"In developing an AI-driven diagnostic tool for early detection of neurological diseases, I anticipate several challenges. Firstly, the accuracy and reliability of the tool depend heavily on the quality and diversity of the data used for training the AI algorithms. Obtaining a comprehensive dataset that adequately represents the population can be difficult due to privacy concerns and data availability. Secondly, ensuring the AI model's interpretability to be clinically useful while maintaining high performance is another challenge, given the complexity of neurological diseases. To address these, I plan to collaborate with interdisciplinary teams, including data privacy experts and neurologists, to source and utilize data ethically and effectively. I also intend to continuously refine the AI model, focusing on both its predictive accuracy and clinical applicability. These challenges, while significant, present valuable opportunities for innovation and interdisciplinary collaboration."
This response is effective because it clearly outlines realistic challenges specific to the AI diagnostic tool project. It also presents a proactive approach to overcoming these challenges, showing problem-solving skills.
8) How will you fund this project?
When answering this question, show that you've thought about the financial aspects of your research and are aware of funding sources that are available and applicable to your project.
"I have identified multiple funding sources to support my renewable energy research project at Stanford University. Firstly, I plan to apply for the DOE Office of Science Graduate Student Research (SCGSR) Program, which offers substantial support for projects focusing on sustainable energy. My proposal for this grant is already in progress, highlighting how my project aligns with the DOE's priorities in advancing clean energy technologies. Additionally, I'm exploring departmental fellowships at Stanford, particularly those aimed at renewable energy research. I am also keen on establishing industry partnerships, given the project's relevance to current energy challenges and the potential for collaborative funding and technological exchange. Last but not least, I will seek conference grants to present my research findings, which can lead to further academic collaborations and additional funding opportunities."
Notice how this answer mentions funding sources that align with the renewable energy focus of the project and the resources available at Stanford University.
9) Tell us about a time you experienced a setback
Focus on a situation relevant to your academic or research experience. Let's use a real-world example where a research experiment failed due to unexpected variables.
"During my Master’s thesis on the effects of soil composition on plant growth, I faced a major setback. My initial experiments, which involved growing plants in different soil types, failed to produce consistent results due to unanticipated environmental variations in the greenhouse. This was disheartening, especially as the deadline approached. However, I responded by reassessing my experimental setup. I consulted with my supervisor and decided to control more variables, such as humidity and temperature. I also refined my data collection methods to include more frequent soil and plant measurements. These adjustments led to more reliable results, and I successfully completed my thesis. This experience taught me the importance of adaptability in research and reinforced the value of meticulous experimental design."
This is a great answer because it shows how you’ve encountered and overcame a specific problem, demonstrating resilience and adaptability.
10) What are your strengths and weaknesses?
When answering this question, it's important to present a balanced view of yourself, showing self-awareness and a commitment to personal development. Choose strengths that are relevant to a PhD program and weaknesses that you're actively working to improve.
"One of my key strengths is my analytical thinking, which I demonstrated during my Master's project where I developed a novel algorithm for data analysis. This required me to not only understand complex theories but also apply them creatively to solve real-world problems. As for weaknesses, I sometimes struggle with overcommitment, taking on too many projects at once. This occasionally led to stress during my undergraduate studies. However, I am actively working on this by improving my time management skills and learning to prioritize tasks more effectively. I've started using project management tools and setting clear boundaries, which has already shown improvements in my workflow and stress levels."
This answer maintains a good balance between strengths and weaknesses. It also shows self-awareness, demonstrating a proactive approach to personal development.
11) Why have you chosen to study for a PhD at this university?
Mention specific aspects of the PhD program that attracted you. Explain how your research interests align with the work being done at the university.
"I am drawn to the PhD program in Astrophysics at Caltech due to its outstanding reputation in space research and the unparalleled resources available at the Owens Valley Radio Observatory. My research interest lies in the study of exoplanets, and Caltech's active projects in this area, such as the Zwicky Transient Facility, align perfectly with my academic goals. The opportunity to work under the guidance of Professor [Name], known for pioneering work in exoplanetary atmospheres, is particularly exciting. Additionally, Caltech's collaborative environment and emphasis on interdisciplinary research are conducive to my professional growth, providing a platform to engage with experts from various fields in astrophysics."
This response directly connects your research interests with ongoing projects and facilities at Caltech. It also shows you’ve done your research on faculty members and their work.
12) What can you bring to this research group?
Focus on your unique skills, experiences, and perspectives that will contribute to the research group's success. Let's choose the field of Biomedical Engineering at Johns Hopkins University for this example.
"As a prospective member of the Biomedical Engineering research group at Johns Hopkins University, I bring a unique combination of skills and experiences. My expertise in microfluidics, honed during my Master’s research, aligns well with the group’s focus on developing lab-on-a-chip devices for medical diagnostics. I have also co-authored two papers in this field, demonstrating my ability to contribute to high-impact research. Additionally, my experience in a start-up environment, where I worked on developing portable diagnostic tools, has equipped me with a practical understanding of translating research into applications. I thrive in collaborative settings, often bringing interdisciplinary insights that foster innovative problem-solving. I am excited about the prospect of contributing to the group’s ongoing projects and introducing fresh perspectives to advance our understanding and application of biomedical technology."
This response shows your relevant expertise, ability to work in a team, and the unique perspectives you can offer, positioning you as a valuable addition to the research group.
13) Do you have any questions for us?
Asking good questions demonstrates your motivation. It also shows that you’ve given some genuine consideration to the project and/or program you’re applying to.
Some questions you can ask the interviewer include:
- What will the supervision arrangements be for the project?
- What kind of training and skills sessions are offered as part of the PhD program?
- How many other PhD students has this supervisor seen to completion?
- Are there any major developments or partnerships planned for the department?
- Are there likely to be any changes to the funding arrangements for the project?
- What opportunities will I have for presenting my research?
Remember: you’re a good student, with lots of potential. You’re considering at least three years of hard work with this university. You need to know that you’ll get on with your supervisor, that your work will be appreciated and that there are good prospects for your project.
What to wear to a PhD interview
Wear formal attire for a PhD interview. Your best bet is to wear a suit. A navy blue suit is the best and most versatile option. No matter your gender, a suit is always very professional.
For men, wear a suit with a tie, dress shirt, and dress shoes. For women, wear a suit (pantsuit or skirt suit) with a blouse, or conservative dress, and closed-toe shoes.
When in doubt, it’s better to be slightly overdressed than underdressed. The goal is to make a professional impression and feel confident, without your attire distracting from the conversation.
What to expect from a PhD interview
At its core, a PhD interview will consist of questions that allow your potential supervisors to get to know you better and have an understanding of what you’d like to study, why you’ve chosen your field of study, and whether you’d be a good fit for the PhD program.
You should expect general questions to help the interviewer get a sense of your likes and dislikes, and your overall personality.
Next, expect questions about your personal motivations for studying a PhD. Your interviewer will also be interested in any relevant experience you have to qualify you to study this PhD.
In the next section, expect questions about your PhD project. You should be prepared to discuss your project idea in detail and demonstrate to the interviewer that you are the ideal candidate.
Last but not least, the interviewer will discuss your future ambitions and give you an opportunity to ask questions. Remember that this interview goes both ways.
It’s important to ask the interviewer relevant questions to show your engagement and the serious consideration you are giving their program.
You are preparing to spend several years of your life at this school. Think about what is important to you and what would make or break your decision to attend this university.
Prepare a list of questions ahead of the interview.
Understanding the interviewer’s point of view
During a PhD interview, interviewers are typically looking for a range of traits that indicate whether you are well-suited for the rigors of a doctoral program and a research career.
These traits include:
Intellectual Curiosity and Passion: A strong enthusiasm for the subject area and a desire to contribute to and expand knowledge in the field.
Research Skills and Experience: Demonstrable skills in conducting research, including designing experiments, collecting and analyzing data, and interpreting results. Prior research experience relevant to the PhD topic is often a plus.
Resilience and Perseverance: The capacity to handle setbacks and challenges, which are common in research, and to persist in the face of difficulties.
Collaboration and Teamwork: Although PhD research can be quite independent, the ability to work well with others, including advisors, faculty, and other students, is crucial.
Self-Motivation and Independence: The drive to work independently, manage one's own project, and stay motivated over the long term.
Fit with the Program: Alignment of the candidate’s research interests and goals with the strengths and focus of the PhD program and faculty.
These traits not only indicate your readiness for a PhD program but also your potential to contribute meaningfully to their field of study and succeed in a research-oriented career.
Related posts:
- University Interview Questions (16 Questions + Answers)
- Project Manager Interview Questions (14 Specific Questions + Answers)
- Strength-Based Interview Questions (21 Questions + Answers)
- Engineering Interview Questions (15 Questions + Answers)
- Business Analyst Interview Questions (17 Questions + Answers)
Reference this article:
About The Author

PracticalPie.com is a participant in the Amazon Associates Program. As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
Follow Us On:
Youtube Facebook Instagram X/Twitter
Psychology Resources
Developmental
Personality
Relationships
Psychologists
Serial Killers
Psychology Tests
Personality Quiz
Memory Test
Depression test
Type A/B Personality Test
© PracticalPsychology. All rights reserved
Privacy Policy | Terms of Use

The Plagiarism Checker Online For Your Academic Work
Start Plagiarism Check
Editing & Proofreading for Your Research Paper
Get it proofread now
Online Printing & Binding with Free Express Delivery
Configure binding now
- Academic essay overview
- The writing process
- Structuring academic essays
- Types of academic essays
- Academic writing overview
- Sentence structure
- Academic writing process
- Improving your academic writing
- Titles and headings
- APA style overview
- APA citation & referencing
- APA structure & sections
- Citation & referencing
- Structure and sections
- APA examples overview
- Commonly used citations
- Other examples
- British English vs. American English
- Chicago style overview
- Chicago citation & referencing
- Chicago structure & sections
- Chicago style examples
- Citing sources overview
- Citation format
- Citation examples
- College essay overview
- Application
- How to write a college essay
- Types of college essays
- Commonly confused words
- Definitions
- Dissertation overview
- Dissertation structure & sections
- Dissertation writing process
- Graduate school overview
- Application & admission
- Study abroad
- Master degree
- Harvard referencing overview
- Language rules overview
- Grammatical rules & structures
- Parts of speech
- Punctuation
- Methodology overview
- Analyzing data
- Experiments
- Observations
- Inductive vs. Deductive
- Qualitative vs. Quantitative
- Types of validity
- Types of reliability
- Sampling methods
- Theories & Concepts
- Types of research studies
- Types of variables
- MLA style overview
- MLA examples
- MLA citation & referencing
- MLA structure & sections
- Plagiarism overview
- Plagiarism checker
- Types of plagiarism
- Printing production overview
- Research bias overview
- Types of research bias
- Example sections
- Types of research papers
- Research process overview
- Problem statement
- Research proposal
- Research topic
- Statistics overview
- Levels of measurment
- Frequency distribution
- Measures of central tendency
- Measures of variability
- Hypothesis testing
- Parameters & test statistics
- Types of distributions
- Correlation
- Effect size
- Hypothesis testing assumptions
- Types of ANOVAs
- Types of chi-square
- Statistical data
- Statistical models
- Spelling mistakes
- Tips overview
- Academic writing tips
- Dissertation tips
- Sources tips
- Working with sources overview
- Evaluating sources
- Finding sources
- Including sources
- Types of sources
Your Step to Success
Plagiarism Check within 10min
Printing & Binding with 3D Live Preview
Dissertation Interview – A Short Guide With Helpful Tips
How do you like this article cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

A dissertation interview is a vital tool in academic research, often serving as a primary source in data collection . These structured, semi-structured, or unstructured dialogues provide detailed and firsthand insights into the research topic, supplementing or extending other research methods. The design, execution, and analysis of dissertation interviews require careful planning and a clear understanding of the research question to ensure they contribute effectively to the overarching thesis. This guide aims to guide students with helpful tips for dissertation interviews.
Inhaltsverzeichnis
- 1 Dissertation Interview – In a Nutshell
- 2 Definition: Dissertation interview
- 3 Including a dissertation interview
- 4 Referring to a dissertation interview
- 5 Quoting a dissertation interview
- 6 Using the name of the interviewee from the dissertation interview
Dissertation Interview – In a Nutshell
- Transcribe the interview accurately for inclusion in the dissertation.
- Situations in which you cannot include a dissertation interview transcript in your appendix.
- How to quote a dissertation interview in your dissertation
- What to consider when using the name of the interviewee.
Definition: Dissertation interview
A dissertation interview is a method of primary data collection used in academic research, typically undertaken for a dissertation or thesis. It can be in the form of a structured, semi-structured, or unstructured interview between the researcher and the interviewee(s), with the goal of gaining detailed, firsthand insights into the research topic. The interview questions are formulated based on the research objectives, and the responses are used to support or explore the thesis argument in depth. The information derived from such interviews often complements secondary data or may serve as the primary basis for the research findings.
- Closed questions only allow for a limited number of predetermined answers.
- Open questions encourage individuals to contribute details of their thoughts and feelings.
Including a dissertation interview
You have conducted interviews as part of your descriptive study for your dissertation. How do you incorporate them? There is a high possibility you do not know what is anticipated since no one ever told you.
Transcribing interviews is a condition for using them in dissertations. This may be accomplished with the use of transcribing software. The transcripts of the interviews might be included as an appendix. Due to the length of the appendix, it may be necessary to submit it as a separate document after discussing your dissertation interview with your supervisor. It is essential to have proof that interviews were conducted.

Referring to a dissertation interview
Include the transcripts of the interviews in an appendix, and then refer to them throughout your dissertation via paraphrasing. This is how paraphrasing works:
- Interviewee A claims that (Appendix 1).
- Through conversation with B, it became apparent that (Appendix 1)
There may be cases when you cannot include a dissertation interview transcript in your appendix. If we cannot make any references to the interview, it may be cited in the following way if you are using the APA format .
- Person A claims that (Individual conversation, December 24th, 2012).
Quoting a dissertation interview
You must use quotation marks if you take someone else’s statements in a dissertation interview. Finding fascinating quotations will be much simpler if you understand how to pull useful data out of the individual during the dissertation interview. It’s important to maintain professionalism throughout the dissertation interview.
Using the name of the interviewee from the dissertation interview
Do not copy down the interviewee’s name without considering these two things:
If the identity is important to the study and you have obtained the interviewee’s consent to use it, then you can go ahead. You may use a description instead if you are not authorized to use the name.
How is an interview included in a dissertation?
Use a transitional phrase like “according to” or another reference when introducing your interview in the piece. Likewise, tailor your responses to the particular dissertation interview format you are using. Doing so will give your paper a more credible and convincing character.
Is there a certain number of questions posed in a dissertation interview?
Use two or three queries to get started. Research may become overwhelming in scope if excessive questions are asked. For this reason, you should begin with no more than two or three research topics, but some studies may have more.
When writing a dissertation, how long should an interview last?
They normally take 30 minutes to a few hours to complete and are only done once. It’s common practice in many fields to conduct interviews to gather information.
How likely is it that a dissertation interview will be turned down?
The truth is that defending a dissertation is tough and that some students have theirs turned down. All the academics showing you the ropes on how to write a dissertation that will get you accepted have been rejected at some time in their careers.
We use cookies on our website. Some of them are essential, while others help us to improve this website and your experience.
- External Media
Individual Privacy Preferences
Cookie Details Privacy Policy Imprint
Here you will find an overview of all cookies used. You can give your consent to whole categories or display further information and select certain cookies.
Accept all Save
Essential cookies enable basic functions and are necessary for the proper function of the website.
Show Cookie Information Hide Cookie Information
Statistics cookies collect information anonymously. This information helps us to understand how our visitors use our website.
Content from video platforms and social media platforms is blocked by default. If External Media cookies are accepted, access to those contents no longer requires manual consent.
Privacy Policy Imprint
Introduce yourself in a PhD interview (4 simple steps + examples)
The opening of an application interview for a PhD position usually starts with short introductions of everyone participating in the conversation. Many applicants wonder how to best introduce themselves in a PhD interview. Four simple steps (including examples) help you to develop a powerful self-introduction .
What to do in a PhD interview introduction
What not to do in a phd interview introduction, introductions in a phd interview.
Interviewing for a PhD position can be nerve-wrecking.
On the one hand, the interview is an advanced stage in the PhD application process and a reason to celebrate having come so far.
On the other hand, you may feel much more vulnerable during an interview than when sending a carefully crafted application letter.
A PhD application interview requires you to react quickly to questions, and you will never know what exactly the admissions committee will ask. Nonetheless, you can properly prepare for a PhD interview. One of the elements is preparing a powerful introduction of yourself.
A self-introduction summarises who you are and why you want the PhD position. A powerful self-introduction can set the tone for the whole interview.
If you are unprepared, there is a risk of going in all directions when it is your turn to introduce yourself. It may throw you off and make you extra nervous for the remainder of the interview.
You may also like: How to strategically prepare for a PhD application
Several things are pivotal in PhD interview introductions:
- Keep it short: A good self-introduction is not too long. Of course, it should be longer than simply stating “ My name is … and I would like this position because I love doing research .” However, when introducing yourself, you should avoid speaking for longer than 3-4 minutes.
- Don’t take away all answers to potential questions: Some applicants try to predict all possible interview questions in advance. Then they try to answer all of them as part of their self-introduction. Don’t! There will be plenty of time in the interview to go into details. In a self-introduction, stick to a handful of key points that you want to bring across.
- Take non-verbal cues into account: Non-verbal cues include facial expressions, gestures and body language. During a self-introduction, you should make sure to come across excited about the interview instead of scared and defensive. Smile. Pause. You should also try to read the body language of the interviewer/s: Leaning forward, moving, or hand gestures are cues to wrap up your self-introduction.
Several things are best to be avoided when you introduce yourself in a PhD interview:
- Don’t start babbling: Many PhD applicants start babbling when they are nervous. Babbling means they talk rapidly and incomprehensively. They may repeat information and go in all directions. The easiest way to prevent babbling is by preparing the self-introduction in advance. The four steps explained below can help you with this preparation.
- Don’t provide too detailed information: A self-introduction in a PhD interview serves one purpose: introducing yourself at the start of the interview. Nothing more and nothing less. Hence, there is no need to go into detail about every single aspect. For instance, it is enough to explain what bachelor’s degree you earned. No need to list all individual courses that you followed.
- Don’t already ask questions: It is advisable not to end your self-introduction with several questions that you have. Rest assured that there will likely be a time when the interviewers ask whether you have any questions about the PhD programme that you applied to. However, most interviews will begin with questions to the applicant and not the other way around. So be mindful of this general structure of PhD interviews, and don’t create an awkward situation by immediately bombarding your interviewer/s with your own questions.
Step 1: State your full name
The first step is easy-peasy: State your full name. Why?
Not all names can be intuitively pronounced. So help your interviewer/s by saying out loud your whole name. In that way, they will be more comfortable addressing you by name throughout the interview.
Step 2: Give a brief overview of your educational (and professional) background
Your educational background has a lot of weight in the decision of the application committee on whether you are a good match for a PhD programme or not.
Therefore, it is useful to provide a brief summary of your educational background. Those who have work experience also benefit from including it.
Step 3: Explain why you are interested in the PhD position
The next step is to justify your interest in the PhD position. There are several powerful ways to explain why you want to do a PhD.
What is important in this next step, however, is to link your motivation to the specific PhD position that you are interviewing for. Remember to keep it relatively short!
Step 4: Thank everyone for the opportunity to be interviewed
The final step is to thank everyone for the opportunity to be interviewed. Be gracious and polite, and express your enthusiasm for the interview. This will create a comfortable atmosphere in which questions can be freely asked and answered.
Master Academia
Get new content delivered directly to your inbox.
Subscribe and receive Master Academia's quarterly newsletter.
10 key skills of successful master's students
Clever strategies to keep up with the latest academic research, related articles.

How to write effective cover letters for a paper submission

17 strong academic phrases to write your literature review (+ real examples)

How to organize and structure academic panel discussions

How to deal with a desk-rejected paper
Newly Launched - World's Most Advanced AI Powered Platform to Generate Stunning Presentations that are Editable in PowerPoint

Researched by Consultants from Top-Tier Management Companies

Powerpoint Templates
Icon Bundle
Kpi Dashboard
Professional
Business Plans
Swot Analysis
Gantt Chart
Business Proposal
Marketing Plan
Project Management
Business Case
Business Model
Cyber Security
Business PPT
Digital Marketing
Digital Transformation
Human Resources
Product Management
Artificial Intelligence
Company Profile
Acknowledgement PPT
PPT Presentation
Reports Brochures
One Page Pitch
Interview PPT
All Categories
Top 10 Ph.D. Interview Presentation Templates With Samples and Examples
Mayuri Gangwal
Do you know that only 56 % of students complete their Ph.D.? Factors such as students' age, department, and lack of a good mentor sometimes contribute to the non-completion rate. Indeed, the journey to earning a doctoral degree is challenging. It involves years of research and extensive writing. However, most students find a lack of focus and motivation to be the primary reason for their failure.
If you prepare for the PhD interview, PhD presentation slides can benefit you in several ways. For instance, templates save considerable time and effort and allow to focus on content delivery. Furthermore, for amateurs creating presentations, templates help them to organize content effectively.
At the same time, candidates often face several challenges regarding content creation and delivery. Templates can help streamline the process, but being aware of potential pitfalls is essential. Here are some common challenges associated with using presentation templates for PhD interviews:
In a recent survey, 6 out of 10 students feel nervous and anxious before the final presentation. It is because they find it challenging to communicate the importance of their research effectively. Crafting visually appealing slides can be tricky, especially for those without a design background. Did you find this relatable? Yes, our PhD interview templates can be a valuable solution for you.
They serve as valuable tools for creating well-structured presentations and assist students in delivering a solid defense for their Doctoral theses. Let's dive in and learn more about these templates and see how they can be valuable resources in your academic journey.
Template 1: Thesis Research Paper Proposal Template
This template can elevate your academic presentations to the next level. It is tailored specially for scholars, researchers, and students. It helps them embark on the rigorous journey of thesis proposal development and ensures that their research proposals are remembered. This template's uniqueness is its visually appealing designs. It integrates text, graphs, and tables and provides a solid structure to your presentation. Whether it's for your academic review or seminars, this template empowers you with confidence and clarity.

Download this template and make your proposal more impactful.
Template 2: Research Proposal Steps Template
Use this template to streamline your research proposal creation process. It is a comprehensive resource covering every crucial aspect of a research proposal. You can use this template to craft an engaging cover letter for your proposal. Thus, this template ensures that your proposal is compelling and professionally presented. Additionally, this template simplifies the process of conveying complex research plans. This template is structured to guide you through the essential steps of the research proposal. It will help you present your research coherently and persuasively. Download now!

Download this template today and embark on a seamless journey of crafting your thesis proposal.
Template 3: Research Proposal for Thesis Template
This template can help you effectively present your thesis proposal. It also ensures that you get sponsors for your project by providing a professional look at your proposal. So, this template is a must for someone presenting their hypothesis, as it provides a solid foundation for the presentation. The template encompasses a variety of crucial elements, from the thesis statement to the project stages.

Download and leverage this template today to focus on critical market components.
Template 4: Abstract for Thesis Research Proposal Template
This PPT Set helps streamline the complex process of crafting compelling research proposals by providing a structured and intuitive design. The template is divided into two parts. The first consists of six sections briefly describing the thesis. The second part includes a summary and description of the content. Thus, it empowers users to articulate their research objectives and methodologies precisely so that their proposal not only meets but also exceeds expectations.

Download this template today and elevate your academic work to new heights.
Template 5: Research Method Overview Template
This template is designed for ambitious scholars to help them dive into the essence of academic precision. This template helps researchers by providing them with a robust and logical roadmap for their research. This not only increases their efficiency but also helps them select the best research method. This template provides a clear picture of the target audience and how to conduct the study. Thus, this template acts as a catalyst for boosting the proposal's effectiveness. Want to transform your proposal into a compelling narrative that commands attention and respect?

Download this template today.
Template 6: Method of Data Collection for Thesis Research Paper Proposal
It is the best template for someone looking to elevate their data collection methods. This template provides a clear and professional way to collect data for academic brilliance. It provides a structured framework to articulate the rationale behind the chosen manner. Thus, it is a template and a strategic tool for showcasing your research and methodology. It ensures that your proposal stands out to provide a deep understanding of your work. Additionally, this template helps you communicate complex methodologies in an accessible manner and develop a deeper connection with your audience.

Download this template today and transform your thesis proposal into a masterpiece.
Template 7: Work Plan with Timetable Template
It is a versatile template that is designed to help professionals across industries. It helps them organize and present their project plans clearly and precisely. The template is divided into three sub-templates to simplify the entire planning phase. The first template includes various activities associated with a specific completion month. It helps you stay organized by outlining different tasks and actions. The second template delves deeper into project activities by outlining a detailed weekly work plan. This way, it provides better visibility and time management. Additionally, it helps you allocate your resources efficiently and prioritize activities. The third and the last templates provide different stages with their names and timeframes, adding to the level of detail and enhancing the proposed research's feasibility.
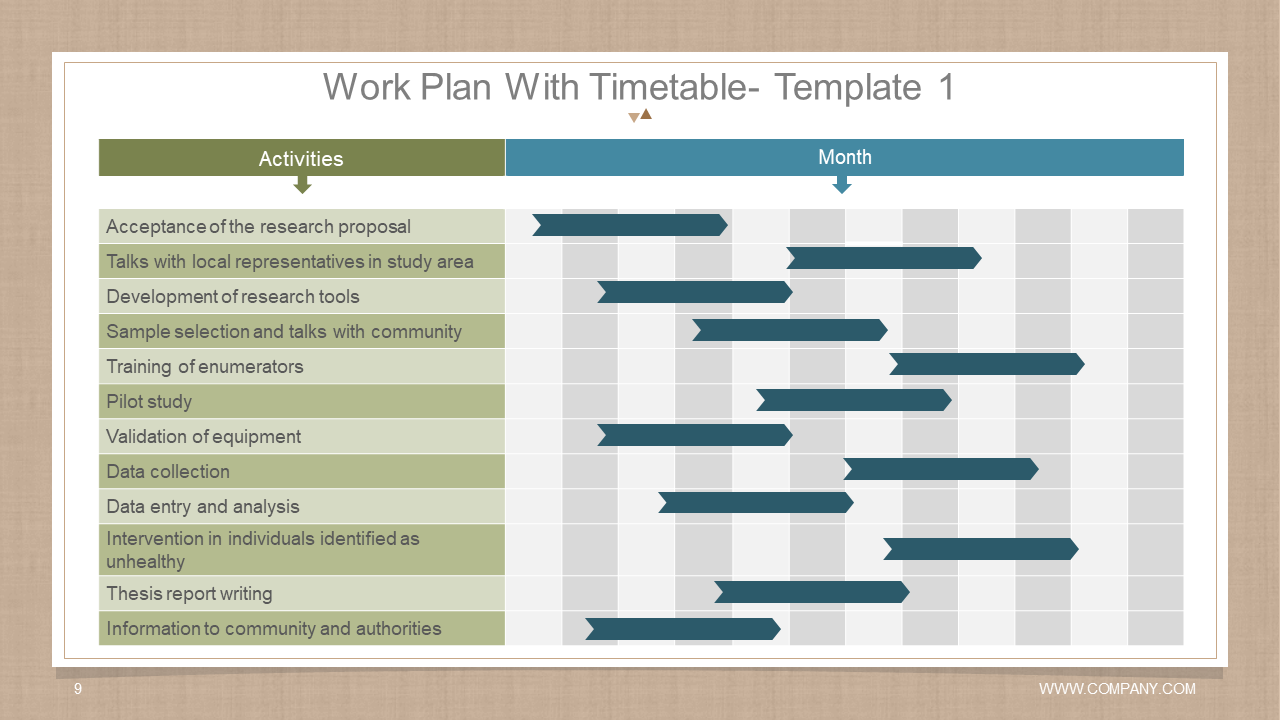
Download this template today to take the first step toward achieving project excellence.
Template 8: Implication of Research Template
This professional template helps you unlock the full potential of your research findings. It is a cornerstone for scholars and professionals eager to convey the significance of their research. The template is Structured as a four-stage process to help students present their research implications. The template's design not only presents data in a captive and visually appealing manner. But it also narrates the story behind your findings and their relevance in real-world applications. Further, this template gives the researcher the chance to explore a variety of angles and helps them consider different aspects of the issue, making research more comprehensive. It further makes research more versatile and applicable to various contexts, which makes it relevant to a broader audience.
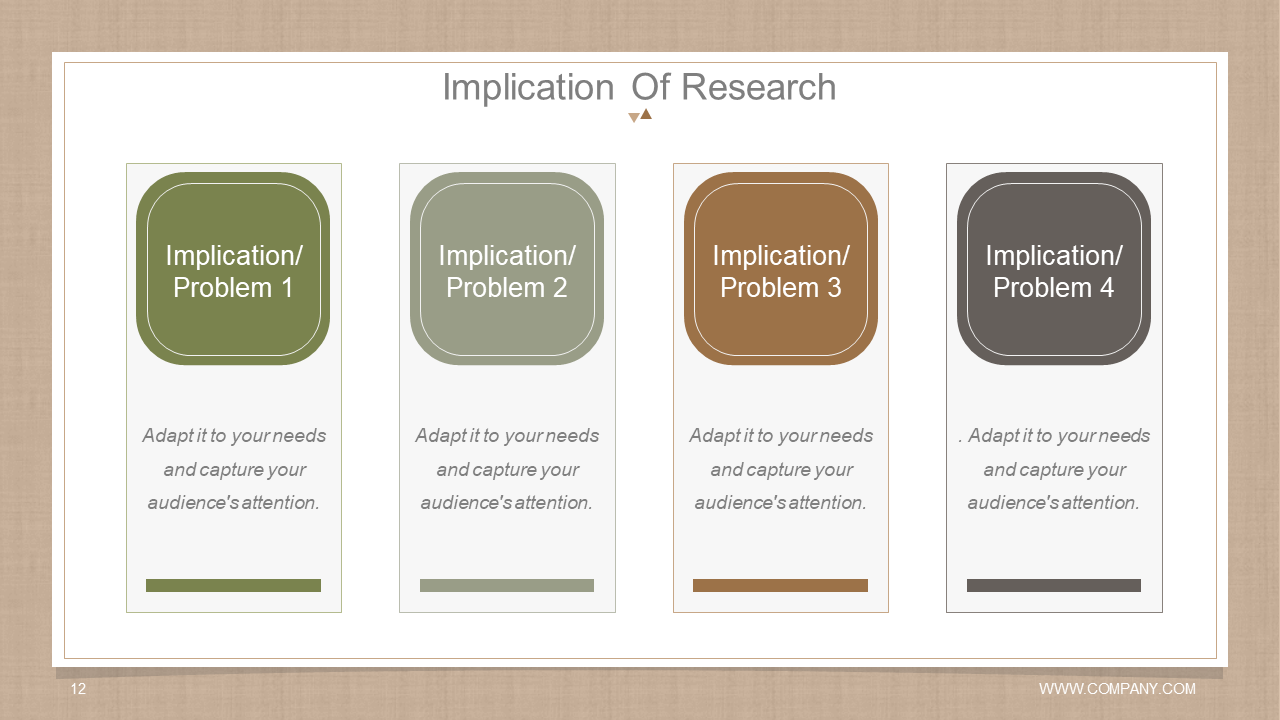
Download this template today and bridge the gap between academic research and applications.
Template 9: Aims and Objective of Research Proposal for Thesis Template (Slide 5)
This template is the blueprint for academic success. It is designed to elevate your doctoral thesis proposal. It helps you create a concise and compelling presentation outlining your research objectives. On one side, it highlights the study's objectives, while on the other, it highlights the expected outcome. This way, it ensures that your academic goals are understood easily because lack of clarity may confuse the audience. So, this template sets the stage by explaining what the study aims to achieve.

Download this template today to embark on a journey of research excellence.
Template 10: Dissertation Methodology Template
This comprehensive template can assist students through the complexities of the research approach. It can be their ultimate guide in structuring and presenting their methodology. This template subdivides the entire process into four distinguished subheadings to streamline the process. The first subheading outlines the resources that can be instrumental in research. The second subheading highlights the diversity of the research inputs and helps categorize and organize the gathered data. The following subheading details the analytical techniques for validating your findings. The last, but not least, subheadings discuss the various collection methods and illustrate the strategic approach for gathering comprehensive data.

Download this template to set a solid foundation for your dissertation.
Conclusion
A student takes 4 to 7 years to complete his Ph.D., requiring strategic planning, dedication, and dedication. Additionally, writing and publishing journals is not a cakewalk. It needs exceptional scholars' writing skills along with critical thinking. Our thesis-dissertation templates can open doors to various opportunities and establish you as a credible and competent researcher.
Additionally, our thesis timeline templates help you streamline your project planning. It also bridges the gap between academic reading and research with real-world applications.
Download these templates today and pave the way for a successful and impactful career.
Related posts:
- How to Design the Perfect Service Launch Presentation [Custom Launch Deck Included]
- Quarterly Business Review Presentation: All the Essential Slides You Need in Your Deck
- [Updated 2023] How to Design The Perfect Product Launch Presentation [Best Templates Included]
- 99% of the Pitches Fail! Find Out What Makes Any Startup a Success
Liked this blog? Please recommend us

Must-Have Software Migration Plan Templates with Examples and Samples

Top 10 Hedge Fund Pitch Deck Templates with Samples and Examples
This form is protected by reCAPTCHA - the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

Digital revolution powerpoint presentation slides

Sales funnel results presentation layouts
3d men joinning circular jigsaw puzzles ppt graphics icons

Business Strategic Planning Template For Organizations Powerpoint Presentation Slides

Future plan powerpoint template slide

Project Management Team Powerpoint Presentation Slides

Brand marketing powerpoint presentation slides

Launching a new service powerpoint presentation with slides go to market

Agenda powerpoint slide show

Four key metrics donut chart with percentage

Engineering and technology ppt inspiration example introduction continuous process improvement

Meet our team representing in circular format

How To Write The Methodology Chapter
The what, why & how explained simply (with examples).
By: Jenna Crossley (PhD) | Reviewed By: Dr. Eunice Rautenbach | September 2021 (Updated April 2023)
So, you’ve pinned down your research topic and undertaken a review of the literature – now it’s time to write up the methodology section of your dissertation, thesis or research paper . But what exactly is the methodology chapter all about – and how do you go about writing one? In this post, we’ll unpack the topic, step by step .
Overview: The Methodology Chapter
- The purpose of the methodology chapter
- Why you need to craft this chapter (really) well
- How to write and structure the chapter
- Methodology chapter example
- Essential takeaways
What (exactly) is the methodology chapter?
The methodology chapter is where you outline the philosophical underpinnings of your research and outline the specific methodological choices you’ve made. The point of the methodology chapter is to tell the reader exactly how you designed your study and, just as importantly, why you did it this way.
Importantly, this chapter should comprehensively describe and justify all the methodological choices you made in your study. For example, the approach you took to your research (i.e., qualitative, quantitative or mixed), who you collected data from (i.e., your sampling strategy), how you collected your data and, of course, how you analysed it. If that sounds a little intimidating, don’t worry – we’ll explain all these methodological choices in this post .

Why is the methodology chapter important?
The methodology chapter plays two important roles in your dissertation or thesis:
Firstly, it demonstrates your understanding of research theory, which is what earns you marks. A flawed research design or methodology would mean flawed results. So, this chapter is vital as it allows you to show the marker that you know what you’re doing and that your results are credible .
Secondly, the methodology chapter is what helps to make your study replicable. In other words, it allows other researchers to undertake your study using the same methodological approach, and compare their findings to yours. This is very important within academic research, as each study builds on previous studies.
The methodology chapter is also important in that it allows you to identify and discuss any methodological issues or problems you encountered (i.e., research limitations ), and to explain how you mitigated the impacts of these. Every research project has its limitations , so it’s important to acknowledge these openly and highlight your study’s value despite its limitations . Doing so demonstrates your understanding of research design, which will earn you marks. We’ll discuss limitations in a bit more detail later in this post, so stay tuned!
Need a helping hand?
How to write up the methodology chapter
First off, it’s worth noting that the exact structure and contents of the methodology chapter will vary depending on the field of research (e.g., humanities, chemistry or engineering) as well as the university . So, be sure to always check the guidelines provided by your institution for clarity and, if possible, review past dissertations from your university. Here we’re going to discuss a generic structure for a methodology chapter typically found in the sciences.
Before you start writing, it’s always a good idea to draw up a rough outline to guide your writing. Don’t just start writing without knowing what you’ll discuss where. If you do, you’ll likely end up with a disjointed, ill-flowing narrative . You’ll then waste a lot of time rewriting in an attempt to try to stitch all the pieces together. Do yourself a favour and start with the end in mind .
Section 1 – Introduction
As with all chapters in your dissertation or thesis, the methodology chapter should have a brief introduction. In this section, you should remind your readers what the focus of your study is, especially the research aims . As we’ve discussed many times on the blog, your methodology needs to align with your research aims, objectives and research questions. Therefore, it’s useful to frontload this component to remind the reader (and yourself!) what you’re trying to achieve.
In this section, you can also briefly mention how you’ll structure the chapter. This will help orient the reader and provide a bit of a roadmap so that they know what to expect. You don’t need a lot of detail here – just a brief outline will do.
Section 2 – The Methodology
The next section of your chapter is where you’ll present the actual methodology. In this section, you need to detail and justify the key methodological choices you’ve made in a logical, intuitive fashion. Importantly, this is the heart of your methodology chapter, so you need to get specific – don’t hold back on the details here. This is not one of those “less is more” situations.
Let’s take a look at the most common components you’ll likely need to cover.
Methodological Choice #1 – Research Philosophy
Research philosophy refers to the underlying beliefs (i.e., the worldview) regarding how data about a phenomenon should be gathered , analysed and used . The research philosophy will serve as the core of your study and underpin all of the other research design choices, so it’s critically important that you understand which philosophy you’ll adopt and why you made that choice. If you’re not clear on this, take the time to get clarity before you make any further methodological choices.
While several research philosophies exist, two commonly adopted ones are positivism and interpretivism . These two sit roughly on opposite sides of the research philosophy spectrum.
Positivism states that the researcher can observe reality objectively and that there is only one reality, which exists independently of the observer. As a consequence, it is quite commonly the underlying research philosophy in quantitative studies and is oftentimes the assumed philosophy in the physical sciences.
Contrasted with this, interpretivism , which is often the underlying research philosophy in qualitative studies, assumes that the researcher performs a role in observing the world around them and that reality is unique to each observer . In other words, reality is observed subjectively .
These are just two philosophies (there are many more), but they demonstrate significantly different approaches to research and have a significant impact on all the methodological choices. Therefore, it’s vital that you clearly outline and justify your research philosophy at the beginning of your methodology chapter, as it sets the scene for everything that follows.

Methodological Choice #2 – Research Type
The next thing you would typically discuss in your methodology section is the research type. The starting point for this is to indicate whether the research you conducted is inductive or deductive .
Inductive research takes a bottom-up approach , where the researcher begins with specific observations or data and then draws general conclusions or theories from those observations. Therefore these studies tend to be exploratory in terms of approach.
Conversely , d eductive research takes a top-down approach , where the researcher starts with a theory or hypothesis and then tests it using specific observations or data. Therefore these studies tend to be confirmatory in approach.
Related to this, you’ll need to indicate whether your study adopts a qualitative, quantitative or mixed approach. As we’ve mentioned, there’s a strong link between this choice and your research philosophy, so make sure that your choices are tightly aligned . When you write this section up, remember to clearly justify your choices, as they form the foundation of your study.
Methodological Choice #3 – Research Strategy
Next, you’ll need to discuss your research strategy (also referred to as a research design ). This methodological choice refers to the broader strategy in terms of how you’ll conduct your research, based on the aims of your study.
Several research strategies exist, including experimental , case studies , ethnography , grounded theory, action research , and phenomenology . Let’s take a look at two of these, experimental and ethnographic, to see how they contrast.
Experimental research makes use of the scientific method , where one group is the control group (in which no variables are manipulated ) and another is the experimental group (in which a specific variable is manipulated). This type of research is undertaken under strict conditions in a controlled, artificial environment (e.g., a laboratory). By having firm control over the environment, experimental research typically allows the researcher to establish causation between variables. Therefore, it can be a good choice if you have research aims that involve identifying causal relationships.
Ethnographic research , on the other hand, involves observing and capturing the experiences and perceptions of participants in their natural environment (for example, at home or in the office). In other words, in an uncontrolled environment. Naturally, this means that this research strategy would be far less suitable if your research aims involve identifying causation, but it would be very valuable if you’re looking to explore and examine a group culture, for example.
As you can see, the right research strategy will depend largely on your research aims and research questions – in other words, what you’re trying to figure out. Therefore, as with every other methodological choice, it’s essential to justify why you chose the research strategy you did.
Methodological Choice #4 – Time Horizon
The next thing you’ll need to detail in your methodology chapter is the time horizon. There are two options here: cross-sectional and longitudinal . In other words, whether the data for your study were all collected at one point in time (cross-sectional) or at multiple points in time (longitudinal).
The choice you make here depends again on your research aims, objectives and research questions. If, for example, you aim to assess how a specific group of people’s perspectives regarding a topic change over time , you’d likely adopt a longitudinal time horizon.
Another important factor to consider is simply whether you have the time necessary to adopt a longitudinal approach (which could involve collecting data over multiple months or even years). Oftentimes, the time pressures of your degree program will force your hand into adopting a cross-sectional time horizon, so keep this in mind.
Methodological Choice #5 – Sampling Strategy
Next, you’ll need to discuss your sampling strategy . There are two main categories of sampling, probability and non-probability sampling.
Probability sampling involves a random (and therefore representative) selection of participants from a population, whereas non-probability sampling entails selecting participants in a non-random (and therefore non-representative) manner. For example, selecting participants based on ease of access (this is called a convenience sample).
The right sampling approach depends largely on what you’re trying to achieve in your study. Specifically, whether you trying to develop findings that are generalisable to a population or not. Practicalities and resource constraints also play a large role here, as it can oftentimes be challenging to gain access to a truly random sample. In the video below, we explore some of the most common sampling strategies.
Methodological Choice #6 – Data Collection Method
Next up, you’ll need to explain how you’ll go about collecting the necessary data for your study. Your data collection method (or methods) will depend on the type of data that you plan to collect – in other words, qualitative or quantitative data.
Typically, quantitative research relies on surveys , data generated by lab equipment, analytics software or existing datasets. Qualitative research, on the other hand, often makes use of collection methods such as interviews , focus groups , participant observations, and ethnography.
So, as you can see, there is a tight link between this section and the design choices you outlined in earlier sections. Strong alignment between these sections, as well as your research aims and questions is therefore very important.
Methodological Choice #7 – Data Analysis Methods/Techniques
The final major methodological choice that you need to address is that of analysis techniques . In other words, how you’ll go about analysing your date once you’ve collected it. Here it’s important to be very specific about your analysis methods and/or techniques – don’t leave any room for interpretation. Also, as with all choices in this chapter, you need to justify each choice you make.
What exactly you discuss here will depend largely on the type of study you’re conducting (i.e., qualitative, quantitative, or mixed methods). For qualitative studies, common analysis methods include content analysis , thematic analysis and discourse analysis . In the video below, we explain each of these in plain language.
For quantitative studies, you’ll almost always make use of descriptive statistics , and in many cases, you’ll also use inferential statistical techniques (e.g., correlation and regression analysis). In the video below, we unpack some of the core concepts involved in descriptive and inferential statistics.
In this section of your methodology chapter, it’s also important to discuss how you prepared your data for analysis, and what software you used (if any). For example, quantitative data will often require some initial preparation such as removing duplicates or incomplete responses . Similarly, qualitative data will often require transcription and perhaps even translation. As always, remember to state both what you did and why you did it.
Section 3 – The Methodological Limitations
With the key methodological choices outlined and justified, the next step is to discuss the limitations of your design. No research methodology is perfect – there will always be trade-offs between the “ideal” methodology and what’s practical and viable, given your constraints. Therefore, this section of your methodology chapter is where you’ll discuss the trade-offs you had to make, and why these were justified given the context.
Methodological limitations can vary greatly from study to study, ranging from common issues such as time and budget constraints to issues of sample or selection bias . For example, you may find that you didn’t manage to draw in enough respondents to achieve the desired sample size (and therefore, statistically significant results), or your sample may be skewed heavily towards a certain demographic, thereby negatively impacting representativeness .
In this section, it’s important to be critical of the shortcomings of your study. There’s no use trying to hide them (your marker will be aware of them regardless). By being critical, you’ll demonstrate to your marker that you have a strong understanding of research theory, so don’t be shy here. At the same time, don’t beat your study to death . State the limitations, why these were justified, how you mitigated their impacts to the best degree possible, and how your study still provides value despite these limitations .
Section 4 – Concluding Summary
Finally, it’s time to wrap up the methodology chapter with a brief concluding summary. In this section, you’ll want to concisely summarise what you’ve presented in the chapter. Here, it can be a good idea to use a figure to summarise the key decisions, especially if your university recommends using a specific model (for example, Saunders’ Research Onion ).
Importantly, this section needs to be brief – a paragraph or two maximum (it’s a summary, after all). Also, make sure that when you write up your concluding summary, you include only what you’ve already discussed in your chapter; don’t add any new information.

Methodology Chapter Example
In the video below, we walk you through an example of a high-quality research methodology chapter from a dissertation. We also unpack our free methodology chapter template so that you can see how best to structure your chapter.
Wrapping Up
And there you have it – the methodology chapter in a nutshell. As we’ve mentioned, the exact contents and structure of this chapter can vary between universities , so be sure to check in with your institution before you start writing. If possible, try to find dissertations or theses from former students of your specific degree program – this will give you a strong indication of the expectations and norms when it comes to the methodology chapter (and all the other chapters!).
Also, remember the golden rule of the methodology chapter – justify every choice ! Make sure that you clearly explain the “why” for every “what”, and reference credible methodology textbooks or academic sources to back up your justifications.
If you need a helping hand with your research methodology (or any other component of your research), be sure to check out our private coaching service , where we hold your hand through every step of the research journey. Until next time, good luck!

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
You Might Also Like:

51 Comments
highly appreciated.
This was very helpful!
This was helpful
Thanks ,it is a very useful idea.
Thanks ,it is very useful idea.
Thank you so much, this information is very useful.
Thank you very much. I must say the information presented was succinct, coherent and invaluable. It is well put together and easy to comprehend. I have a great guide to create the research methodology for my dissertation.
Highly clear and useful.
I understand a bit on the explanation above. I want to have some coach but I’m still student and don’t have any budget to hire one. A lot of question I want to ask.
Thank you so much. This concluded my day plan. Thank you so much.
Thanks it was helpful
Great information. It would be great though if you could show us practical examples.
Thanks so much for this information. God bless and be with you
Thank you so so much. Indeed it was helpful
This is EXCELLENT!
I was totally confused by other explanations. Thank you so much!.
justdoing my research now , thanks for the guidance.
Thank uuuu! These contents are really valued for me!
This is powerful …I really like it
Highly useful and clear, thank you so much.
Highly appreciated. Good guide
That was helpful. Thanks
This is very useful.Thank you
Very helpful information. Thank you
This is exactly what I was looking for. The explanation is so detailed and easy to comprehend. Well done and thank you.
Great job. You just summarised everything in the easiest and most comprehensible way possible. Thanks a lot.
Thank you very much for the ideas you have given this will really help me a lot. Thank you and God Bless.
Such great effort …….very grateful thank you
Please accept my sincere gratitude. I have to say that the information that was delivered was congruent, concise, and quite helpful. It is clear and straightforward, making it simple to understand. I am in possession of an excellent manual that will assist me in developing the research methods for my dissertation.
Thank you for your great explanation. It really helped me construct my methodology paper.
thank you for simplifieng the methodoly, It was realy helpful
Very helpful!
Thank you for your great explanation.
The explanation I have been looking for. So clear Thank you
Thank you very much .this was more enlightening.
helped me create the in depth and thorough methodology for my dissertation
Thank you for the great explaination.please construct one methodology for me
I appreciate you for the explanation of methodology. Please construct one methodology on the topic: The effects influencing students dropout among schools for my thesis
This helped me complete my methods section of my dissertation with ease. I have managed to write a thorough and concise methodology!
its so good in deed
wow …what an easy to follow presentation. very invaluable content shared. utmost important.
Peace be upon you, I am Dr. Ahmed Khedr, a former part-time professor at Al-Azhar University in Cairo, Egypt. I am currently teaching research methods, and I have been dealing with your esteemed site for several years, and I found that despite my long experience with research methods sites, it is one of the smoothest sites for evaluating the material for students, For this reason, I relied on it a lot in teaching and translated most of what was written into Arabic and published it on my own page on Facebook. Thank you all… Everything I posted on my page is provided with the names of the writers of Grad coach, the title of the article, and the site. My best regards.
A remarkably simple and useful guide, thank you kindly.
I real appriciate your short and remarkable chapter summary
Bravo! Very helpful guide.
Only true experts could provide such helpful, fantastic, and inspiring knowledge about Methodology. Thank you very much! God be with you and us all!
highly appreciate your effort.
This is a very well thought out post. Very informative and a great read.
THANKS SO MUCH FOR SHARING YOUR NICE IDEA
I love you Emma, you are simply amazing with clear explanations with complete information. GradCoach really helped me to do my assignment here in Auckland. Mostly, Emma make it so simple and enjoyable
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly

Community Blog
Keep up-to-date on postgraduate related issues with our quick reads written by students, postdocs, professors and industry leaders.
Thesis and Dissertation Appendicies – What to Include
- By DiscoverPhDs
- August 12, 2020

An appendix is a section at the end of a dissertation that contains supplementary information. An appendix may contain figures, tables, raw data, and other additional information that supports the arguments of your dissertation but do not belong in the main body.
It can be either a long appendix or split into several smaller appendices. Each appendix should have its own title and identification letters, and the numbering for any tables or figures in them should be reset at the beginning of each new appendix.
Purpose of an Appendix
When writing the main body of your dissertation, it is important to keep it short and concise in order to convey your arguments effectively.
Given the amount of research you would have done, you will probably have a lot of additional information that you would like to share with your audience.
This is where appendices come in. Any information that doesn’t support your main arguments or isn’t directly relevant to the topic of your dissertation should be placed in an appendix.
This will help you organise your paper, as only information that adds weight to your arguments will be included; it will also help improve your flow by minimising unnecessary interruptions.
Note, however, that your main body must be detailed enough that it can be understood without your appendices. If a reader has to flip between pages to make sense of what they are reading, they are unlikely to understand it.
For this reason, appendices should only be used for supporting background material and not for any content that doesn’t fit into your word count, such as the second half of your literature review .
What to Include in a Dissertation Appendix
A dissertation appendix can be used for the following supplementary information:
Research Results
There are various ways in which research results can be presented, such as in tables or diagrams.
Although all of your results will be useful to some extent, you won’t be able to include them all in the main body of your dissertation. Consequently, only those that are crucial to answering your research question should be included.
Your other less significant findings should be placed in your appendix, including raw data, proof of control measures, and other supplemental material.
Details of Questionnaires and Interviews
You can choose to include the details of any surveys and interviews you have conducted. This can include:
- An interview transcript,
- A copy of any survey questions,
- Questionnaire results.
Although the results of your surveys, questionnaires or interviews should be presented and discussed in your main text, it is useful to include their full form in the appendix of a dissertation to give credibility to your study.
Tables, Figures and Illustrations
If your dissertation contains a large number of tables, figures and illustrative material, it may be helpful to insert the less important ones in your appendix. For example, if you have four related datasets, you could present all the data and trend lines (made identifiable by different colours) on a single chart with a further breakdown for each dataset in your appendix.
Letters and Correspondence
If you have letters or correspondence, either between yourself and other researchers or places where you sought permission to reuse copyrighted material, they should be included here. This will help ensure that your dissertation doesn’t become suspected of plagiarism.
List of Abbreviations
Most researchers will provide a list of abbreviations at the beginning of their dissertation, but if not, it would be wise to add them as an appendix.
This is because not all of your readers will have the same background as you and therefore may have difficulty understanding the abbreviations and technical terms you use.
Note: Some researchers refer to this as a ‘glossary’, especially if it is provided as an appendix section. For all intended purposes, this is the same as a list of abbreviations.
Finding a PhD has never been this easy – search for a PhD by keyword, location or academic area of interest.
How to Format a Dissertation Appendix
In regards to format, you can include one lengthy appendix or structure it into several smaller appendices.
Although the choice is yours, it is usually better to opt for several different appendices as it allows you to organise your supplementary information into different categories based on what they are.
The following guidelines should be observed when preparing your dissertation appendices section:
- Each appendix should start on a new page and be given a unique title and identifying letter, such as “Appendix A – Raw Data”. This allows you to more easily refer to appendix headings in the text of your main body should you need to.
- Each appendix should have its own page numbering system, comprising the appendix identification letter and the corresponding page number. The appendix identification letter should be reset for each appendix, but the page number should remain continuous. For example, if ‘Appendix A’ has three pages and ‘Appendix B’ two pages, the page numbers should be A-1, A-2, A-3, B-4, B-5.
- The numbering of tables and figures should be reset at the beginning of each new appendix. For example, if ‘Appendix A’ contains two tables and ‘Appendix B’ one table, the table number within Appendix B should be ‘Table 1’ and not ‘Table 3’.
- If you have multiple appendices instead of a single longer one, insert a ‘List of Appendices’ in the same way as your contents page.
- Use the same formatting (font size, font type, spacing, margins, etc.) as the rest of your report.
Example of Appendices
Below is an example of what a thesis or dissertation appendix could look like.
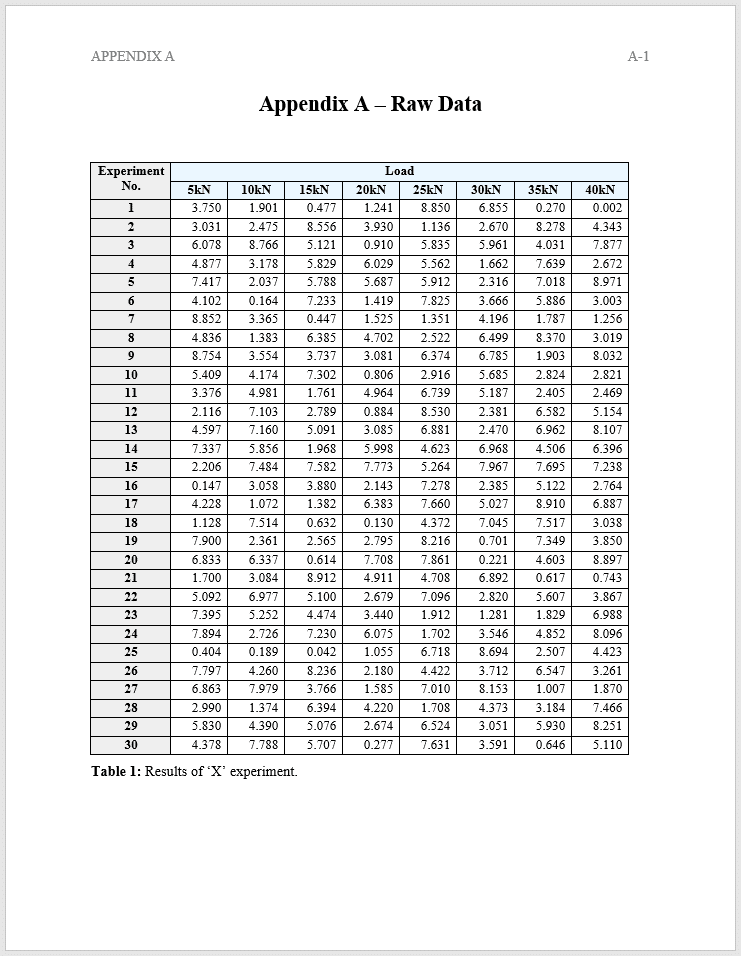
Referring to an Appendix In-Text
You must refer to each appendix in the main body of your dissertation at least once to justify its inclusion; otherwise, the question arises as to whether they are really needed.
You can refer to an appendix in one of three ways:
1. Refer to a specific figure or table within a sentence, for example: “As shown in Table 2 of Appendix A, there is little correlation between X and Y”.
2. Refer to a specific figure or table in parentheses, for example: “The results (refer to Table 2 of Appendix A) show that there is little correlation between X and Y”.
3. Refer to an entire appendix, for example: “The output data can be found in Appendix A”.
Appendices vs Appendixes
Both terms are correct, so it is up to you which one you prefer. However, it is worth noting that ‘appendices’ are used more frequently in the science and research community, so we recommend using the former in academic writing if you have no preferences.
Where Does an Appendix Go?
For a dissertation, your appendices should be inserted after your reference list.
Some people like to put their appendices in a standalone document to separate it from the rest of their report, but we only recommend this at the request of your dissertation supervisor, as this isn’t common practice.
Note : Your university may have its own requirements or formatting suggestions for writing your dissertation or thesis appendix. As such, make sure you check with your supervisor or department before you work on your appendices. This will especially be the case for any students working on a thesis.

Multistage sampling is a more complex form of cluster sampling for obtaining sample populations. Learn their pros and cons and how to undertake them.

An In Press article is a paper that has been accepted for publication and is being prepared for print.

An academic transcript gives a breakdown of each module you studied for your degree and the mark that you were awarded.
Join thousands of other students and stay up to date with the latest PhD programmes, funding opportunities and advice.

Browse PhDs Now

Learn more about using cloud storage effectively, video conferencing calling, good note-taking solutions and online calendar and task management options.

Stay up to date with current information being provided by the UK Government and Universities about the impact of the global pandemic on PhD research studies.

Julia’s in her final year of her PhD at University College London. Her research is helping to better understand how Alzheimer’s disease arises, which could lead to new successful therapeutics.

Freya’s in the final year of her PhD at the University of Leeds. Her project is about improving the precision of observations between collocated ground-based weather radar and airborne platforms.
Join Thousands of Students

How to write a PhD thesis: a step-by-step guide
A draft isn’t a perfect, finished product; it is your opportunity to start getting words down on paper, writes Kelly Louise Preece
Kelly Louise Preece

Created in partnership with

You may also like

Popular resources
.css-1txxx8u{overflow:hidden;max-height:81px;text-indent:0px;} The secrets to success as a provost
Using non verbal cues to build rapport with students, emotionally challenging research and researcher well-being, augmenting the doctoral thesis in preparation for a viva, how hard can it be testing ai detection tools.
Congratulations; you’ve finished your research! Time to write your PhD thesis. This resource will take you through an eight-step plan for drafting your chapters and your thesis as a whole.

Organise your material
Before you start, it’s important to get organised. Take a step back and look at the data you have, then reorganise your research. Which parts of it are central to your thesis and which bits need putting to one side? Label and organise everything using logical folders – make it easy for yourself! Academic and blogger Pat Thomson calls this “Clean up to get clearer” . Thomson suggests these questions to ask yourself before you start writing:
- What data do you have? You might find it useful to write out a list of types of data (your supervisor will find this list useful too.) This list is also an audit document that can go in your thesis. Do you have any for the “cutting room floor”? Take a deep breath and put it in a separate non-thesis file. You can easily retrieve it if it turns out you need it.
- What do you have already written? What chunks of material have you written so far that could form the basis of pieces of the thesis text? They will most likely need to be revised but they are useful starting points. Do you have any holding text? That is material you already know has to be rewritten but contains information that will be the basis of a new piece of text.
- What have you read and what do you still need to read? Are there new texts that you need to consult now after your analysis? What readings can you now put to one side, knowing that they aren’t useful for this thesis – although they might be useful at another time?
- What goes with what? Can you create chunks or themes of materials that are going to form the basis of some chunks of your text, perhaps even chapters?
Once you have assessed and sorted what you have collected and generated you will be in much better shape to approach the big task of composing the dissertation.
Decide on a key message
A key message is a summary of new information communicated in your thesis. You should have started to map this out already in the section on argument and contribution – an overarching argument with building blocks that you will flesh out in individual chapters.
You have already mapped your argument visually, now you need to begin writing it in prose. Following another of Pat Thomson’s exercises, write a “tiny text” thesis abstract. This doesn’t have to be elegant, or indeed the finished product, but it will help you articulate the argument you want your thesis to make. You create a tiny text using a five-paragraph structure:
- The first sentence addresses the broad context. This locates the study in a policy, practice or research field.
- The second sentence establishes a problem related to the broad context you have set out. It often starts with “But”, “Yet” or “However”.
- The third sentence says what specific research has been done. This often starts with “This research” or “I report…”
- The fourth sentence reports the results. Don’t try to be too tricky here, just start with something like: “This study shows,” or “Analysis of the data suggests that…”
- The fifth and final sentence addresses the “So What?” question and makes clear the claim to contribution.
Here’s an example that Thomson provides:
Secondary school arts are in trouble, as the fall in enrolments in arts subjects dramatically attests. However, there is patchy evidence about the benefits of studying arts subjects at school and this makes it hard to argue why the drop in arts enrolments matters. This thesis reports on research which attempts to provide some answers to this problem – a longitudinal study which followed two groups of senior secondary students, one group enrolled in arts subjects and the other not, for three years. The results of the study demonstrate the benefits of young people’s engagement in arts activities, both in and out of school, as well as the connections between the two. The study not only adds to what is known about the benefits of both formal and informal arts education but also provides robust evidence for policymakers and practitioners arguing for the benefits of the arts. You can find out more about tiny texts and thesis abstracts on Thomson’s blog.
- Writing tips for higher education professionals
- Resource collection on academic writing
- What is your academic writing temperament?
Write a plan
You might not be a planner when it comes to writing. You might prefer to sit, type and think through ideas as you go. That’s OK. Everybody works differently. But one of the benefits of planning your writing is that your plan can help you when you get stuck. It can help with writer’s block (more on this shortly!) but also maintain clarity of intention and purpose in your writing.
You can do this by creating a thesis skeleton or storyboard , planning the order of your chapters, thinking of potential titles (which may change at a later stage), noting down what each chapter/section will cover and considering how many words you will dedicate to each chapter (make sure the total doesn’t exceed the maximum word limit allowed).
Use your plan to help prompt your writing when you get stuck and to develop clarity in your writing.
Some starting points include:
- This chapter will argue that…
- This section illustrates that…
- This paragraph provides evidence that…
Of course, we wish it werethat easy. But you need to approach your first draft as exactly that: a draft. It isn’t a perfect, finished product; it is your opportunity to start getting words down on paper. Start with whichever chapter you feel you want to write first; you don’t necessarily have to write the introduction first. Depending on your research, you may find it easier to begin with your empirical/data chapters.
Vitae advocates for the “three draft approach” to help with this and to stop you from focusing on finding exactly the right word or transition as part of your first draft.

This resource originally appeared on Researcher Development .
Kelly Louse Preece is head of educator development at the University of Exeter.
If you would like advice and insight from academics and university staff delivered direct to your inbox each week, sign up for the Campus newsletter .
The secrets to success as a provost
Emotions and learning: what role do emotions play in how and why students learn, the podcast: bringing an outsider’s eye to primary sources, a diy guide to starting your own journal, formative, summative or diagnostic assessment a guide, harnessing the power of data to drive student success.
Register for free
and unlock a host of features on the THE site
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Welcome to the Purdue Online Writing Lab

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The Online Writing Lab at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service of the Writing Lab at Purdue. Students, members of the community, and users worldwide will find information to assist with many writing projects. Teachers and trainers may use this material for in-class and out-of-class instruction.
The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives. The Purdue OWL offers global support through online reference materials and services.
A Message From the Assistant Director of Content Development
The Purdue OWL® is committed to supporting students, instructors, and writers by offering a wide range of resources that are developed and revised with them in mind. To do this, the OWL team is always exploring possibilties for a better design, allowing accessibility and user experience to guide our process. As the OWL undergoes some changes, we welcome your feedback and suggestions by email at any time.
Please don't hesitate to contact us via our contact page if you have any questions or comments.
All the best,
Social Media
Facebook twitter.
PPOL PhD Dissertations and Job Placements
In this section.
- Economics Track
- Judgment and Decision Making Track
- Politics and Institutions Track
- Science, Technology and Policy Studies Track
- Current Students
- Doctoral Student Handbook
- Dissertations & Job Placements
- PhD Student Life
- Faculty & Research
Learn about the dissertations of our PhD in Public Policy graduates and their job placements directly following graduation.
2021-present
Jiahua liu (economics track).
Dissertation Title: Essays on International Trade and Firm Growth in Developing Countries Advisor: Gordon Hanson Job Placement: Economist, Cornerstone Research
kristen McCormack (economics track)
Dissertation Title: Essays in Environmental Economics Advisor: David Cutler Job Placement: Economist, U.S. Treasury
dayea oh (economics track)
Dissertation Title: Essays on Applied Microeconomics Advisor: Will Dobbie Job Placement: Assistant Professor, School of Public Policy, Pepperdine University
lauren russell (economics track)
Dissertation Title: Essays on the U.S. Criminal Legal System and Black-White Inequality Advisor: David Deming Job Placement: Economist, Labor Markets Section, Federal Reserve Board
Samuel stemper (economics track)
Dissertation Title: Essays on the Economics of Education Advisor: Christopher Avery Job Placement: Assistant Professor, Department of Economics, University of Auckland
Amy wickett (economics track)
Dissertation Title: Essays on Diversity Advisor: Desmond Ang Job Placement: to be confirmed
Shweta Bhogale
Dissertation Title: Essays on Agriculture and Rural Development in Developing Countries Advisor: Rema Hanna Job Placement: Post-Doctoral Fellow, King Climate Action Initiative, J-PAL
Kevin Carney
Dissertation Title: Essays in Development and Behavioral Economics Advisor: Gautam Rao Job Placement:
- Post-Doctoral Fellow (one year), Department of Economics, University of Chicago
- Assistant Professor, Department of Economics, University of Michigan
Dissertation Title: Two Essays on Legal Entanglements and One Essay on Worker Voice Advisor: Will Dobbie Job Placement: Research Director, People Lab, University of California, Berkeley
Stuart Iler
Dissertation Title: Essays on Shock Propagation in Economic Production Networks: Applications to U.S. Oil Price Episodes and Green Jobs Advisor: Joseph Aldy Job Placement: Consultant, Resources for the Future
frina Lin (economics track)
Dissertation Title: Essays on Health Care and Inequality Advisor: Marcella Alsan Job Placement: to be confirmed
Grace McCormack
Dissertation Title: Three Essays in Applied Microeconomics Advisor: David Cutler Job Placement: Post-Doctoral Researcher, University of Southern California
José Morales-Arilla
Dissertation Title: Essays on the Political Economy of Development Advisor: Edward Glaeser Job Placement: Assistant Professor, Bush School of Government and Public Service, Texas A&M University
Felix Owusu (Economics track)
Dissertation Title: Policy and Inequality in the Criminal Legal System Advisor: David Deming Job Placement: Assistant Professor of Public Policy, Goldman School of Public Policy, University of California, Berkeley
James Reisinger
Dissertation Title: Social Spillovers in Beliefs, Preferences, and Well-being Advisor: Michela Carlana Job Placement: Post-Doctoral Fellowship, Furman Center, New York University
Elizabeth Spink (economics track)
Dissertation Title: Essays on Water Utility Quality and Access Advisor: Rema Hanna Job Placement: Economist, Environmental Protection Agency
Yazan Al-Karablieh
Dissertation Title: Essays on Corporate Taxation Advisor: Stefanie Stantcheva Job Placement: Economist, Economist Program, International Monetary Fund
Sebastián Bustos
Dissertation Title: Essays in International Economics, Development, and Globalization Advisor: Ricardo Hausmann Job Placement: Senior Fellow, Growth Lab , Center for International Development , Harvard Kennedy School
Holly Dykstra
Dissertation Title: Essays in Behavioral Economics Advisor: Brigitte C. Madrian Job Placement: Junior Professor, Department of Economics, University of Konstanz
Marie-Pascale Grimon
Dissertation Title: Essays in Labor Economics and Child Welfare Advisor: Amanda Pallais Job Placement: Assistant Professor, Swedish Institute for Social Research, Stockholm University
Blake Heller
Dissertation Title: Essays on Late Investment in Human Capital Advisor: Joshua Goodman Job Placement:
- Assistant Professor, Hobby School of Public Affairs, University of Houston
- Post-Doctoral Fellow 2021-2022, Peabody College of Education and Human Development, Vanderbilt University
Shefali Khanna
Dissertation Title: Essays in Energy and Development Economics Advisor: Rema Hanna Job Placement: Post-Doctoral Fellow, Economics and Public Policy Department, Imperial College London
Kunal Mangal
Dissertation Title: Essays on the Economics of Public Sector Recruitment in India Advisor: Asim Khwaja Job Placement: Visiting Fellow, Azim Premji University
Niharika Singh
Dissertation Title: Essays in Development Economics Advisor: Asim Khwaja Job Placement: Assistant Professor, Department of Economics, University of Notre Dame
Daniel Stuart
Dissertation Title: Essays in Energy and Environmental Economics Advisor: Joseph Aldy Job Placement: Associate, Analysis Group
Andrew Bacher-HicKs
Dissertation Title: Essays on the Economics of Education Advisor: Christopher Avery Job Placement: Assistant Professor of Education Policy, Boston University
Megan Bailey
Dissertation Title: Essays in Climate Policy and Innovation Advisor: Joseph Aldy Job Placement: Assistant Professor, University of Calgary
Patrick Behrer
Dissertation Title: Three Essays in Environmental and Development Economics Advisor: Rema Hanna Job Placement: Post-Doctoral Fellow, Center on Food Security and the Environment, Stanford University
Elijah de la Campa
Dissertation Title: Three Essays on the Provision of Local Public Goods Advisor: Jeffrey Liebman Job Placement: Senior Research Associate in Economics and Urban Analytics, Bloomberg Harvard City Leadership Initiative
Charlie Dorison
Dissertation Title: Essays on Emotion and Decision Making Advisor: Jennifer Lerner Job Placement: Post-Doctoral Fellow, Dispute Resolution Research Center, Management and Operations Department, Northwestern University
Madeleine Gelblum
Dissertation Title: Essays on Labor and Personnel Economics Advisor: David Deming Job Placement: Labor Market Analyst, Facebook
Guthrie Gray-Lobe
Dissertation Title: Essays in Development Economics Advisor: Michael Kremer Job Placement: Post-Doctoral Fellow, Harvard University
Asad Liaqat
Dissertation Title: Essays in Development Economics and Political Economy Advisor: Asim Khwaja Job Placement: Research Scientist, Novi Economics team, Facebook
Heidi Liu
Dissertation Title: Essays in Behavioral Economics, Gender and Employment Advisor: Iris Bohnet Job Placement: Sharswood Fellow, University of Pennsylvania School of Law
Sharan Mamidipudi
Dissertation Title: Essays in Development Economics and Political Economy Advisor: Gautam Rao Job Placement: Assistant Professor, Department of Agricultural and Resource Economics, University of Maryland
Aroop Mukharji
Dissertation Title: Sea Change: McKinley, Roosevelt, and the Expansion of U.S. Foreign Policy 1897-1909 Advisor: Fredrik Logevall Job Placement: Post-Doctoral Fellow, The Fletcher School of Law and Diplomacy, Tufts University
Christine Mulhern
Dissertation Title: Personalized Information and College Choices: The Role of School Counselors, Technology, and Siblings Advisor: Christopher Avery Job Placement: Associate Policy Research, RAND
Dissertation Title: Essays in Energy and Development Economics Advisor: Rohini Pande Job Placement: Applied Scientist, Uber
Rebecca Sachs
Dissertation Title: Essays on Health Care Markets and the Safety Net Advisor: David Cutler Job Placement: Analyst, Health Studies Unit, Congressional Budget Office
Chris Umphres
Dissertation Title: Essays on Judgement and Decision Making Advisor: Jennifer Lerner Job Placement: United States Air Force
Bradley DeWees
Dissertation Title: Essays on Judgment and Decision Making Advisors: Jennifer Lerner , Julia Minson Job Placement: Assistant Director of Operations, United States Air Force
Abraham Holland
Dissertation Title: Essays in Development Economics Advisors: Edward Glaeser , Rohini Pande Job Placement: Research Staff Member, Institute for Defense Analyses

Ariella Kahn-Lang
Dissertation Title: Essays in Labor Market Inequality Advisors: Christopher Avery , Lawrence Katz Job Placement: Researcher, Human Services, Mathematica
Jennifer Kao
Dissertation Title: Essays in the Economics of Health and Innovation Advisors: Pierre Azoulay , Amitabh Chandra , David Cutler Job Placement: Assistant Professor, Strategy Unit, UCLA Anderson School of Management
Stephanie Majerowicz
Dissertation Title: Essays in Education and Development Economics Advisors: Asim Khwaja , Michael Kremer Job Placement: Assistant Professor of Government, Universidad de los Andes, Colombia (Post-Doctoral Research Fellow, briq Institute on Behavior & Inequality)
Emily Mower
Dissertation Title: Algorithms and Applied Econometrics in the Digital Economy Advisors: Kris Johnson Ferreira , Joshua Goodman , Shane Greenstein Job Placement: Senior Data Scientist, edX
Gabriel Tourek
Dissertation Title: Essays in Development and Public Economics Advisors: Nathaniel Hendren , Asim Khwaja Job Placement: Post-Doctoral Associate, Abdul Latif Jameel Poverty Action Lab (J-PAL)
Daniel Velez-Lopez
Dissertation Title: Essays in Environmental Economics Advisor: Joseph Aldy Job Placement: Lead Analyst, Venture Fellowship Program, National Grid Partners
Rohit Chandra
Dissertation Title: Adaptive State Capitalism in the Indian Coal Industry Advisor: José A. Gómez-Ibáñez
Juan Pablo Chauvin
Dissertation Title: Essays in Urban Economics and Development Advisor: Edward Glaeser Job Placement: Research Economist, Inter-American Development Bank
Cuicui Chen
Dissertation Title: Essays on Environmental Economics and Industrial Organization Advisors: Joseph Aldy , Ariél Pakes Job Placement: Assistant Professor, Department of Economics, State University of New York at Albany
Stephen Coussens
Dissertation Title: Essays in Health and Behavioral Economics Advisors: David Cutler , Brigitte Madrian Job Placement: Assistant Professor of Health Policy and Management, Mailman School of Public Health, Columbia University
Raissa Fabregas
Dissertation Title: Essays in Development Economics and Education Advisors: Michael Kremer , Rohini Pande Job Placement: Assistant Professor, Lyndon B. Johnson School of Public Affairs, University of Texas at Austin
Todd Gerarden
Dissertation Title: Essays in Environmental Economics and Industrial Organization Advisors: Ariél Pakes , Robert Stavins Job Placement: Assistant Professor, Charles H. Dyson School of Applied Economics and Management, Cornell University
Sarika Gupta
Dissertation Title: Essays in Development Economics and Governance Advisor: Rohini Pande Job Placement: Young Professionals Program, The World Bank
Alicia Harley
Dissertation Title: Why Does Technology Fail to Benefit the Poorest Farmers? A Sociotechnical Approach to the Study of Innovation and Poverty Advisor: William Clark Job Placement: Post-Doctoral Research Fellow, Sustainability Science Program, Harvard Kennedy School
Janhavi Nilekani
Dissertation Title: Essays at the Intersection of Environmental and Development Economics Advisors: Rema Hanna , Rohini Pande Job Placement: Founder, Aastar
Dissertation Title: Essays on Structural Transformation and Trade Advisors: Melissa Dell , Martin Rotemberg Job Placement: Harvard Graduate Students Union, United Auto Workers
Martin Abel
Dissertation Title: Essays on Labor Markets in Developing Countries Advisors: Rema Hanna , Lawrence Katz Job Placement: Assistant Professor, Department of Economics, Middlebury College
Jonathan Baker
Dissertation Title: Essays in Water Conservation and Water Quality Programs Advisor: Robert Stavins Job Placement: Economist, Analysis Group
Tomoko Harigaya
Dissertation Title: Delivering Financial Services to the Poor: Constraints on Access, Take-up, and Usage Advisor: Rohini Pande Job Placement: Research Associate, Precision Agriculture for Development
Laura Quinby
Dissertation Title: Compensation and Employment Policies in the U.S. Public Sector Advisor: Lawrence Katz Job Placement: Research Economist, Center for Retirement Research, Boston College
Dissertation Title: State Strategies Under Global Rules: Chinese Industrial Policy in the WTO Era Advisor: Peter A. Hall Job Placement: Assistant Professor, Department of Political Science, University of Oregon
Samura Atallah
Dissertation Title: Studies in Labor Economics, Organizational Economics, and Development Advisor: Ellen J. Langer Job Placement: Associate, McKinsey & Company
Tara Grillos
Dissertation Title: Participation, Power, and Preferences in International Development Advisor: William Clark Job Placement: Assistant Professor, Department of Political Science, Purdue University
Nils Hägerdal
Dissertation Title: Ethnic Cleansing as Military Strategy: Lessons From Lebanon, 1975-1990 Advisor: Robert H. Bates Job Placement: Junior Research Fellow, Brandeis University
Elizabeth Linos
Dissertation Title: Three Essays on Human Capital in the Public Sector Advisor: Jeffrey Liebman Job Placement: Assistant Professor, Goldman School of Public Policy, University of California, Berkeley
Dissertation Title: Essays in Optimizing Social Policy for Different Populations: Education, Targeting, and Impact Evaluation Advisor: Lant Pritchett Job Placement: Founder and CEO, StellarEmploy
Yusuf Neggers
Dissertation Title: Essays in Economic Development and Political Economy Advisor: Rohini Pande Job Placement: Watson Post-Doctoral Fellow, Brown University
Oyebola Okunogbe
Dissertation Title: Essays in Political Economy and Development Advisor: Asim Khwaja Job Placement: Economist, Development Research Group, The World Bank
Trisha Shrum
Dissertation Title: Behavioral and Experimental Insights on Consumer Decisions and the Environment Advisors: Joseph Aldy , David Laibson Job Placement: Post-Doctoral Fellow, Earth Lab, University of Colorado
Samuel Stolper
Dissertation Title: Oil and Water: Essays on the Economics of Natural Resource Usage Advisors: Joseph Aldy , Robert Stavins Job Placement:
- Fall 2016 > Post-Doctoral Fellow, Energy Initiative, Center for Energy and Environmental Policy Research, Department of Economics, Massachusetts Institute of Technology
- Fall 2017 > Assistant Professor, School of Natural Resources and Environment, University of Michigan
Maria Cecilia Acevedo
Dissertation Title: Essays in the Political Economy of Conflict and Development Advisors: Rohini Pande , James Robinson Job Placement: Consultant, Poverty Global Practice Division, The World Bank
Natalie Bau
Dissertation Title: Essays at the Intersection of Development and Education Advisors: Asim Khwaja , Nathan Nunn Job Placement: Assistant Professor, Department of Economics, University of Toronto
Syon Bhanot
Dissertation Title: Field Experiments in Behavioral and Public Economics Advisors: Brigitte Madrian , Richard Zeckhauser Job Placement: Assistant Professor, Department of Economics, Swarthmore College
Gabriel Chan
Dissertation Title: Essays on Energy Technology Innovation Policy Advisors: William Clark , Laura Díaz Anadón Job Placement: Assistant Professor, Department of Science, Technology and Policy, Humphrey School of Public Affairs, University of Minnesota
Sarah Cohodes
Dissertation Title: Essays on the Economics of Education Advisor: Christopher Avery Job Placement: Assistant Professor, Department of Education Policy and Social Analysis, Teachers College, Columbia University
A. Nilesh Fernando
Dissertation Title: Land, Labor and Technology: Essays in Development Economics Advisors: Lawrence Katz , Asim Khwaja Job Placement: Assistant Professor, Department of Economics, University of Notre Dame (Post-Doc at Harvard University)
Daniel Honig
Dissertation Title: Navigating by Judgment: Organizational Structure, Autonomy, and Country Context in Delivering Foreign Aid Advisor: Peter A. Hall Job Placement: Assistant Professor, School of Advanced International Studies, Johns Hopkins University
Mahnaz Islam
Dissertation Title: Essays on Development Economics Advisors: Rema Hanna , Rohini Pande Job Placement: Economist, Amazon
joo Julia A. lee
Dissertation Title: Essays in Organizational Behavior Advisor: Francesca Gino Job Placement: Post-Doctoral Fellow, Institutional Corruption Program, Edmond J. Safra Center for Ethics, Harvard University
Andry Liscovich
Dissertation Title: Essays in Experimental and Labor Economics Advisor: Nicholas A. Christakis Job Placement: Director of Technology, RA Capital Management
Richard Sweeney
Dissertation Title: Essays on Industry Response to Energy and Environmental Policy Advisors: Ariél Pakes , Robert Stavins Job Placement: Assistant Professor, Department of Economics, Boston College
Elizabeth Walker
Dissertation Title: Essays at the Intersection of Environment and Development Economics Advisor: Rema Hanna Job Placement: Consultant, Energy, Environment, and Network Industries Practice, NERA Economic Consulting
Dissertation Title: Essays on the Transmission and Diffusion of Productive Knowledge in International Economics Advisor: Elhanan Helpman Job Placement: Senior Associate Economist, Inter-American Development Bank
Ariel Dora Stern
Dissertation Title: Essays in the Economics of Health Care and the Regulation of Medical Technology Advisor: Amitabh Chandra Job Placement: Assistant Professor, Technology and Operations Management Unit, Harvard Business School
Alexandra van Geen
Dissertation Title: Essays in Experimental Economics and the Improvement of Judgment and Decision Making Advisor: Iris Bohnet Job Placement: Assistant Professor, Department of Finance, Erasmus School of Economics
Clara Monika Zverina
Dissertation Title: Essays in Public and Labor Economics Advisor: Jeffrey Liebman Job Placement: Post-Doctoral Fellow in Disability Research, National Bureau of Economic Research (NBER)
Will Dobbie
Dissertation Title: Essays in Labor Economics Advisor: Roland G. Fryer, Jr. Job Placement: Assistant Professor of Economics and Public Affairs, Department of Economics, Woodrow Wilson School, Princeton University
Jeffrey Friedman
Dissertation Title: Cumulative Dynamics and Strategic Assessment: U.S. Military Decision Making in Iraq, Vietnam, and the American Indian Wars Advisor: Stephen Walt Job Placement: Post-Doctoral Fellow in International Security and U.S. Foreign Policy, John Sloan Dickey Center for International Understanding, Dartmouth College
Marie E. Newhouse
Dissertation Title: Kant's Typo, and the Limits of Law Advisor: Arthur Applbaum Job Placement: Residential Lab Fellow, Edmond J. Safra Center for Ethics, Harvard Law School
Olga Rostapshova
Dissertation Title: Pushing a Troika of Development: Promoting Investment, Curbing Corruption, and Enhancing Public Good Provision Advisor: Richard Zeckhauser Job Placement: Post-Doctoral Fellow, Specialist, Social Impact, Social Science Genetics Association Consortium, National Bureau of Economic Research (NBER) and Senior Evaluations
Laurence Tai
Dissertation Title: Hierarchical Game-Theoretic Models of Transparency in the Administrative State Advisor: Daniel Carpenter Job Placement: Residential Lab Fellow, Edmond J. Safra Center for Ethics, Harvard Law School
Christopher Carrigan
Dissertation Title: Structured to Fail? Explaining Regulatory Performance Under Completing Mandates Advisor: Daniel Carpenter Job Placement: Assistant Professor, Trachtenberg School of Public Policy and Public Administration, George Washington University
Souman Hong
Dissertation Title: Online Institutions, Markets, and Democracy Advisor: Matthew Baum Job Placement: Assistant Professor, Yonsei University
Avinash Kishore
Dissertation Title: Essays on Economics of Indoor and Outdoor Air Pollution in India Advisor: Dale Jorgenson Job Placement: Post-Doctoral Fellow, International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI), New Delhi, India
Robyn Meeks
Dissertation Title: Essays on the Economics of Household Water Access in Developing Countries Advisor: Rohini Pande Job Placement: Assistant Professor in Environmental Economics, School of Natural Resources and Environment, University of Michigan
Karl Neumar
Dissertation Title: Essays on Optimal Management of Portfolios Advisor: Richard Zeckhauser Job Placement:, Founding Partner, HNC Advisors
Philip Osafo-Kwaako
Dissertation Title: Essays in Economic History and Development Advisor: James Robinson Job Placement: Post-Doctoral Fellow, Institute for Quantitative Social Sciences at Harvard
Matthew Ransom
Dissertation Title: Essays on the Economics of Climate Change Advisor: Richard Zeckhauser Job Placement: Senior Analyst, Health and Environment Division, Abt Associates
Christopher Robert
Dissertation Title: Wealth, Welfare, and Well-being: Essays in Indebtedness and Normative Analysis Advisor: Richard Zeckhauser Job Placement: President and CEO, Dobility; Adjunct Lecturer, Harvard Kennedy School
William Skimmyhorn
Dissertation Title: Essays in Behavioral Household Finance Advisor: Brigitte Madrian Job Placement: Assistant Professor, United States Military Academy (West Point)
Maoliang Ye
Dissertation Title: Gradualism in Coordination and Trust Building Advisors: Raj Chetty , Brigitte Madrian Job Placement: Assistant Professor, Remin University of China
Tristan Zajonc
Dissertation Title: Essays on Causal Inference for Public Policy Advisor: Guido Imbens Job Placement: Visiting Fellow, Institute for Quantitative Social Science at Harvard; Co-founder and CEO, Sense, Inc.
Ina Ganguli
Dissertation Title: Labor Markets in Transition: Science and Migration After the Collapse of the Soviet Union Advisor: Richard B. Freeman Job Placement:
- 2011–2012 > Post-Doctoral Fellow, Harvard Business School, Harvard Medical School
- 2012 > Assistant Professor, Stockholm School of Economics
John Horton
Dissertation Title: Online Labor Markets Advisor: Richard Zeckhauser Job Placement: Economist, Odesk
Victoria Levin
Dissertation Title: Choices and Consequences: Decisions on Health, Wealth, and Employment Advisor: Brigitte Madrian Job Placement: Economist, The World Bank
Suerie Moon
Dissertation Title: Embedding Neoliberalism: Global Health and the Evolution of the Global Intellectual Property Regime (1995-2009) Advisor: John Ruggie Job Placement: Non-academic offers—undecided
Gary Reinbold
Dissertation Title: Essays on Child Mortality and Growth Faltering in Bangladesh and Kenya Advisor: Mary Jo Bane Job Placement: Assistant Professor, Department of Public Administration, University of Illinois Springfield
Abigail Fisher Williamson
Dissertation Title: Beyond the Passage of Time: Local Government Response in New Immigrant Destinations Advisor: Robert D. Putnam Job Placement: Preceptor, Harvard College Writing Program
Andrés Zahler
Dissertation Title: Essays on Export Dynamics Advisor: Ricardo Hausmann Job Placement: Assistant Professor, Department of Economics, Public Policy Institute, Diego Portales University
Mohamad Al-Ississ
Dissertation Title: The Role of Beliefs in Financial Markets: Three Essays on Violence, Trust and Religion Advisor: Iris Bohnet Job Placement: Assistant Professor, University of Cairo, Joint appointment with Business School and School of Global Affairs
Sharon Barnhardt
Dissertation Title: Essays on the Impact of Residential Location on Networks, Attitudes and Cooperation: Experimental Evidence from India Advisor: Rohini Pande Job Placement: Institute for Financial Management and Research, Chennai, India
David Deming
Dissertation Title: Long-Term Impacts of Educational Interventions Advisor: Lawrence Katz Job Placement: Assistant Professor, Heinz School of Public Health, Carnegie Mellon University
Brooke Kelsey Jack
Dissertation Title: Essays on Developing Country Markets in Environment and Health Advisor: Christopher Avery Job Placement:
- 2010–2011 > Post-Doctoral Fellow, Department of Economics, Massachusetts Institute of Technology
- 2011 > Assistant Professor, Department of Economics, Tufts University
David J. Lynch
Dissertation Title: Does Analogical Reasoning Affect Political Attitudes? Evidence from Survey Experiments Advisor: Gary King Job Placement: Consultant, RWS Advisory
Santitarn Sathirathai
Dissertation Title: Loyal Friends and Fickle Lenders: The Behavior of Financial Institutions During Financial Crises Advisor: Asim Khwaja Job Placement: Credit Suisse, Singapore
Dissertation Title: Essays on the Economics of Education Advisor: Lawrence Katz Job Placement: Institute of Education Sciences, (National Center for Education Evaluation), U.S. Department of Education
Hunt Allcott
Dissertation Title: Consumer Behavior and Firm Strategy in Energy Markets Advisor: Robert Stavins Job Placement:
- 2009–2011 > Post-Doctoral Fellow, Department of Economics, Massachusetts Institute of Technology
- 2011 > Assistant Professor of Economics, New York University
Jeffrey Bielicki
Dissertation Title: Integrated Systems Analysis and Technological Findings for Carbon Capture and Storage Deployment Advisor: John Holdren Job Placement: Weinberg Fellow, Research Scientist, Oak Ridge National Laboratory
Jonathan Borck
Dissertation Title: Beyond Compliance: Three Essays on Voluntary Corporate Environmentalism Advisor: Richard Zeckhauser Job Placement: Economist, Analysis Group, Boston
Warigia Bowman
Dissertation Title: Digital Development: Technology, Governance, and the Quest for Modernity in East Africa Advisor: Sheila Jasanoff Job Placement: Assistant Professor, Department of Public Policy Leadership, University of Mississippi
Jennifer Bulkeley
Dissertation Title: Perspectives on Power: Chinese Strategies to Measure and Manage China’s Rise Advisor: Ashton Carter Job Placement: Special Assistant for Asian and Pacific Security Affairs, Office of the Secretary of Defense
Oeindrila Dube
Dissertation Title: Essays in the Political Economy of Conflict and Development Advisor: Sendhil Mullainathan Job Placement: 2009–2010 > Post-Doctoral Fellow, Assistant Professor of Political Science, Center for Global Development, New York University
Allan Friedman
Dissertation Title: Privacy, Security, and the Dynamics of Networked Information Sharing Advisor: David Lazer Job Placement:
- 2009–2010 > Post-Doctoral Fellowship, School of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Center for Research on Computation and Society, Harvard University
- 2010 > Brookings Institution
Felipe Kast
Dissertation Title: Essays on Poverty Dynamics and Social Policy Advisor: Alberto Abadie Job Placement: Abdul Latif Jameel Poverty Action Lab (J-PAL), Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile
Dissertation Title: Green Chemistry: A Study of Innovation for Sustainable Development Advisor: William Clark Job Placement: Senior Policy Analyst, Center for Green Chemistry and Green Engineering, Yale University
Holly Ho Ming
Dissertation Title: Growing Up in the Urban Shadow: Realities and Dreams of Migrant Workers’ Children in Beijing and Shanghai Advisor: Anthony Saich Job Placement: Breakthrough, Ltd, Hong Kong, Youth Foundation, Beijing and Shanghai
Tatsuya Nishida
Dissertation Title: Incomplete Alliances: A Comparative Analysis of the Hub-and Spoke System in the Asia-Pacific Advisor: Stephen Walt Job Placement: Post-Doc at a Japanese university
Jason Richwine
Dissertation Title: IQ and Immigration Policy Advisor: George Borjas Job Placement: Research Fellow, American Enterprise Institute
Juan Saavedra
Dissertation Title: The Role of Resources and Incentives in Education Production Advisor: Lawrence Katz Job Placement: Assistant Professor of Public Policy, School of Government, Universidad de los Andes, Colombia
Judith Scott-Clayton
Dissertation Title: Understanding America's Unfinished Transformation: Three Essays on the Economics of Higher Education Advisor: Christopher Jencks Job Placement: Assistant Professor of Economics and Education, Teachers College, Columbia University
Sandra Sequeira
Dissertation Title: On the Waterfront: An Empirical Study of Corruption in Ports Advisor: Sendhil Mullainathan Job Placement:
- 2009 > Post-Doctoral Fellow, New York Law School
- 2010 > Lecturer in Development Economics, London School of Economics and Political Science
Yuhki Tajima
Dissertation Title: Order and Violence in Authoritarian Breakdowns: How Institutions Explain Communal Violence in Indonesia Advisor: Robert H. Bates Job Placement: Assistant Professor of Political Science, University of California, Riverside
Ngoc Anh Tran
Dissertation Title: Corruption, Ranking and Competition Advisor: Richard Zeckhauser Job Placement: Assistant Professor of Public Policy, University of Indiana
Dissertation Title: Three Essays in Environmental Economics Advisor: Robert Stavins Job Placement: Assistant Professor of Economics, Mount Holyoke College
Fotini Christia
Dissertation Title: The Closest of Enemies: Alliance Formation in the Afghan and Bosnian Civil Wars Advisor: Robert H. Bates Job Placement: Assistant Professor, Department of Political Science, Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Kessely Corea Hong
Dissertation Title: Group Differences in Preferences, Beliefs, and Perceptions? Advisor: Iris Bohnet On family leave
Sebastian S. James
Dissertation Title: Essays on Tax Policy and Tax Compliance Advisor: Caroline M. Hoxby Job Placement: Senior Economist on Tax Policy, The World Bank
Bailey W. Klinger
Dissertation Title: Discovering New Export Activities in Developing Countries: Uncertainty, Linkages, and the Product Space Advisor: Ricardo Hausmann Job Placement: Director, Center for International Development (CID) Research Lab, Harvard Kennedy School
Carolyn M. Kousky
Dissertation Title: Responding to Risk: Information and Decision Making in the Floodplains of St. Louis County, Missouri Advisor: Richard Zeckhauser Job Placement: Fellow, Resources for the Future
Elta C. Smith
Dissertation Title: Governing Rice: The Politics of Experimentation in Global Agriculture Advisor: Sheila Jasanoff Job Placement: Post-Doctoral Fellow, Department of Environment and Political Economy, University of California, Berkeley
Nicole A. Szlezak
Dissertation Title: Global Health in the Making: China, HIV/AIDS and the Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis and Malaria Advisor: Sheila Jasanoff Job Placement: Consultant, McKinsey & Company
Adam T. Thomas
Dissertation Title: Forgotten Fathers: A Collection of Essays on Low-Skilled Men and Marriage Advisor: William Julius Wilson Job Placement: Research Director, Economic Studies, Brookings Institution
Dissertation Title: Nonparametric Methods for Inference After Variable Selection, Comparisons of Survival Distributions, and Random Effects Meta-Analysis, and Reporting of Subgroup Analyses (Department of Biostatistics) Advisor: Stephen Lagakos Job Placement: Assistant Professor, Department of Urban Planning, University of California, Los Angeles
Blair s. Williams
Dissertation Title: Essays in Legislative Behavior Advisor: David King Job Placement: Assistant Professor, Department of Social Sciences, United States Military Academy (West Point)
Naomi Calvo
Dissertation Title: How Parents Choose Schools: A Mixed-Methods Study of Public School Choice in Seattle Advisor: Christopher Jencks Job Placement: Principal Associate, Education Resource Strategies
Dissertation Title: Essays on Environmental Tax Policy Analysis: Dynamic Computable General Equilibrium Approaches Applied to China Advisor: Dale Jorgenson Job Placement: Assistant Professor, Department of Economics, School of Economics and Management, Tsinghua University
Andrew Feldman
Dissertation Title: What Works in Work-First Welfare? Advisor: Jeffrey Liebman Job Placement: Post-Doctoral Fellow, Harvard Kennedy School
Fiona Greig
Dissertation Title: Barriers to Advancement: Perspectives from Behavioral Economics, Negotiation and Gender Analysis Advisor: Iris Bohnet Job Placement: Consultant, McKinsey & Company
Dissertation Title: Essays on Education Production in China and the U.S. Advisor: Anthony Saich Job Placement: Policy Specialist, Human Development Report Office, UN Development Programme
Beau Kilmer
Dissertation Title: Essays on the Consequences of Drug Use and Drug Testing Advisor: Mark Moore Job Placement: Associate Policy Researcher, RAND
Indhira Santos
Dissertation Title: Essays on Natural Disasters and Household Income Advisor: Jeffrey Liebman Job Placement: Research Fellow, Bruegel
Dissertation Title: Essays on Environmental, Energy, and Natural Resource Economics Advisor: William Hogan Job Placement: Assistant Professor in Energy Economics and Policy, Department of Energy and Geo-Environmental Engineering, Penn State University
Pelin Berkmen
Dissertation Title: Essays on Monetary Policy and Debt Accumulation Advisor: Andrés Velasco Job Placement: Research Economist, International Monetary Fund
Eduardo Cavallo
Dissertation Title: Living as a Debtor in a World of Sudden Stops: The Roles of Exposure to Trade and Commitment Advisor: Jeffrey Frankel Job Placement: Research Economist, Inter-American Development Bank
Dissertation Title: Household Behavior and Energy Demand: Evidence from Peru Advisor: Mark Rosenzweig Job Placement: Post-Doctoral Fellow, The Earth Institute, Columbia University
Dissertation Title: The Economic Interdependence of China and the World Advisor: Robert Lawrence Job Placement: Private Sector Consultant
Jenny Schuetz
Dissertation Title: Land, Money and Politics: Essays on Government Intervention in Housing Markets Advisor: José A. Gómez-Ibáñez Job Placement: Post-Doctoral Fellow, Furman Center for Real Estate and Urban Policy, New York University
Jong-Sung You
Dissertation Title: A Comparative Study of Income Inequality, Corruption, and Social Trust Advisor: Robert D. Putnam Job Placement: Assistant Professor, Graduate School of International Relations and Pacific Studies, University of California, San Diego
Chad b. steinberg
Dissertation Title: Does the Neighborhood Matter? Three Essays in International Economics Advisor: Dani Rodrik Job Placement: Economist, International Monetary Fund
Khuong Minh Vu
Dissertation Title: ICT and Global Economic Growth: Contribution, Impact, and Policy Implications Advisor: Dale Jorgenson Job Placement: Visiting Professor, Sawyer School of Management, Suffolk University
Steven c. Anderson
Dissertation Title: Analyzing Strategic Interaction in Multi-Settlement Electricity Markets: A Closed-Loop Supply Function Equilibrium Model Advisor: William Hogan Job Placement: Post-Doctoral Fellow, Harvard Electricity Policy Group
Dissertation Title: Essays in Environmental Economics and Policy Advisor: Robert Stavins Job Placement: Visiting Professor, University of Texas at Dallas
Andrew k. Leigh
Dissertation Title: Essays in Poverty and Inequality Advisor: Christopher Jencks Job Placement: Fellow, Research School of Social Sciences, Australian National University
Gavin Samms
Dissertation Title: Essay in Education Policy Advisor: Christopher Jencks Job Placement: Post-Doctoral Fellow, Harvard Graduate School of Education
Sheryl Winston Smith
Dissertation Title: Innovation and Globalization in Four High-Technology Industries in the United States: One Size Does Not Fit All Advisor: Lewis Branscomb Job Placement: Research Associate in Economics and Management, Gustavus Adolphus College
Lori d. Snyder
Dissertation Title: Essays on Facility-Level Response to Environmental Regulations Advisor: Robert Stavins Job Placement: Assistant Professor of Environmental Economics and Policy, Nicholas School of Environmental and Earth Sciences, Duke University
Carolyn Gideon
Dissertation Title: Sustainable Competition or Inevitable Monopoly? The Potential for Competition in Network Communications Industries Advisor: Lewis Branscomb Job Placement: Assistant Professor of International Communications and Communications Technology, Tufts University
Gabriel Kaplan
Dissertation Title: Between Politics and Markets: The Institutional Allocation of Resources in Higher Education Advisor: Joseph Kalt Job Placement: Assistant Professor of Public Affairs, University of Colorado Denver
Tuan Minh Le
Dissertation Title: Analysis of Tax and Trade Incentives for Foreign Direct Investment: The Case of Vietnam Advisor: Dwight H. Perkins Job Placement: Public Finance Economist, The World Bank
Pierre LeBlanc
Dissertation Title: Essays on Tax-Deferred Saving in Canada Advisor: David Wise Job Placement: Economist, Department of Finance, Government of Canada
Dorina Bekoe
Dissertation Title: After the Peace Agreement: Lessons for Implementation from Mozambique, Angola, and Liberia Advisor: Robert H. Bates Job Placement: Associate, International Peace Academy
Sheila Cavanagh
Dissertation Title: Essays in Environmental Economics and Policy Advisor: Robert Stavins Job Placement: Assistant Professor of Economics, School of Forestry and Environmental Studies, Yale University
Ajay Chaudry
Dissertation Title: Child Care Arrangements Among Low-Income Families: A Qualitative Approach Advisor: Mary Jo Bane Job Placement: Faculty Member, The New School
Dissertation Title: Money and Mission: How Non-Profit Organizations Finance Their Charitable Activities Advisor: Richard Zeckhauser Job Placement: Public Finance Associate, UBS Paine Webber
R. Karl Rethemeyer
Dissertation Title: Centralization or Democratization: Assessing the Internet's Impact on Policy Networks Advisor: Jane Fountain Job Placement: Assistant Professor of Public Affairs and Policy, Nelson A. Rockefeller College of Public Policy, State University of New York at Albany
Lisa Sanbonmatsu
Dissertation Title: Child Neglect in a Changing Economic and Social Policy Context Advisor: Mary Jo Bane Job Placement: Post-Doctoral Fellow, National Bureau of Economic Research
Andres Vinelli
Dissertation Title: The Management and Performance of Microfinance Organizations Advisor: Mark Moore Job Placement: Special Assistant to the Chairman, National Association of Securities Dealers
Alix Peterson Zwane
Dissertation Title: Essays in Environment and Development Advisor: Robert Stavins Job Placement: Cooperative Extension Specialist, Department of Agriculture and Resource Economics, University of California, Berkeley
Dissertation Title: Integrating Information and Decision Making in a Multi-Level World: Cross-scale Environmental Science and Management Advisor: William Clark Job Placement: Research Associate, Sustainability Systems Project, Belfer Center for Science and International Affairs
RicHARD Doblin
Dissertation Title: Regulation of the Medical Use of Psychedelics and Marijuana Advisor: F.M. Scherer Job Placement: President, Multi-Disciplinary Association for Psychedelic Studies
Judith Kelley
Dissertation Title: Norms and Membership Conditionality: The Role of European Institutions in Ethnic Politics in Latvia, Estonia, Slovakia and Romania Advisor: Lisa Martin Job Placement: Assistant Professor of Public Policy, Duke University
Anthony Patt
Dissertation Title: Strategy and Psychology in Environmental Assessment Advisor: William Clark Job Placement: Assistant Professor, Center for Energy and Environmental Studies, Boston University
Sasha Pivovarsky
Dissertation Title: Essays on Institutions and Finance Advisor: Benjamin Sachs Job Placement: Economist, International Monetary Fund
David Skilling
Dissertation Title: Policy Coordination, Political Structure, and Public Debt: The Political Economy of Public Debt Accumulation in OECD Countries Since 1960 Advisor: Richard Zeckhauser Job Placement: Economist, New Zealand Treasury
Marcus Stanley
Dissertation Title: Essays in Program Evaluation Advisor: Claudia Goldin Job Placement: Assistant Professor of Economics, Case Western Reserve University
Robert Taliercio
Dissertation Title: Administrative Reform as Credible Commitment: The Design, Sustainability, and Performance of Semi-Autonomous Revenue Authorities in Latin America Advisor: Merilee Grindle Job Placement: Fellow, Young Professionals Program, The World Bank
Todd Olmstead
Dissertation Title: The Effects of Freeway Management Systems and Motorist Assistance Patrols on the Frequency of Reported Motor Vehicle Crashes Advisor: José A. Gómez-Ibáñez Job Placement: Consultant, McKinsey & Company
Gustavo Merino-Juarez
Dissertation Title: Federalism and the Policy Process: Using Basic Education as a Test-Case of Decentralization in Mexico Advisor: John Donahue Job Placement: Assistant Professor of Economics, Instituto Tecnológico Autónomo de México
Carlos Rufin
Dissertation Title: The Political Economy of Institutional Change in the Electricity Supply Industry Advisor: William Hogan Job Placement: Assistant Professor of Business Strategy, Babson College
Howard Shatz
Dissertation Title: The Location of U.S. Multinational Affiliates Advisor: Benjamin Sachs Job Placement: Research Fellow, Public Policy Institute of California
David Snelbecker
Dissertation Title: Pension Reform in Economies with Large Informal Sectors: The Case of the Ukraine Advisor: William Hogan Job Placement: Manager, The Services Group
David Autor
Dissertation Title: Essays on the Changing Labor Market: Computerization, Inequality, and the Development of the Contingent Work Force Advisor: Lawrence Katz Job Placement: Assistant Professor, Department of Economics, Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Alison Earle
Dissertation Title: Keeping the Job You Find: Understanding Job Turnover Among Welfare Recipients Who Obtain Work Advisor: David Ellwood Job Placement: Research Scientist, Department of Health and Social Behavior, Harvard School of Public Health
Karen Eggleston
Dissertation Title: Incentives in Health Care Payment Systems Advisor: Joseph P. Newhouse Job Placement: Assistant Professor of Economics, Tufts University
Karen Fisher-Vanden
Dissertation Title: Structural Change and Technological Diffusion in Transition Economies: Implications for Energy Use and Carbon Emissions in China Advisor: Dale Jorgenson Job Placement: Assistant Professor, Environmental Studies Program, Dartmouth College
WooChan Kim
Dissertation Title: Essays in International Capital Markets Advisor: Wei Job Placement: Deputy Director, Ministry of Finance and Economy, Republic of Korea
Chang-Yang Lee
Dissertation Title: A Theory of the Determinants of R&D: Consumer Characteristics and Technological Competence Advisor: F.M. Scherer Job Placement: Director, Ministry of Commerce, Industry and Energy, Republic of Korea
Steven Todd Schatzki
Dissertation Title: A Theoretical and Empirical Examination of Land Use Change Under Uncertainty Advisor: Robert Stavins Job Placement: Senior Analyst, National Economic Research Associates
Stuart Orin Shapiro
Dissertation Title: Speed Bumps and Road Blocks: Procedural Controls and Regulatory Change Advisor: Cary Coglianese Job Placement: Policy Analyst, Office of Information and Regulatory Affairs, U.S. Office of Management and Budget
Tay Keong Tan
Dissertation Title: Silence, Sacrifice, and Shoofly Pies: An Inquiry into the Social Capital and Organizational Structures of the Amish Community in Lancaster County, Pennsylvania Advisor: Katherine S. Newman Job Placement: Assistant Professor, National University of Singapore
Kathryn p. Boudett
Dissertation Title: In Search of a Second Chance: The Consequences of GED Certification, Education and Training for Young Women Without Traditional High School Diplomas Advisor: Thomas Kane Job Placement: Research Fellow, Harvard Project on Schooling and Children
Bryan c. Hassel
Dissertation Title: Designed to Fail? Charter School Programs and the Politics of Structural Choice Advisor: Paul E. Peterson Job Placement: Consultant, Private Company
Christopher e. Herbert
Dissertation Title: Limited Choices: The Effect of Residential Segregation on Homeownership Among Blacks Advisor: Kain Job Placement: Senior Analyst, Abt Associates
Jason c. Snipes
Dissertation Title: Skill Mismatch, Turnover, and the Development of Young Workers’ Careers Advisor: Ronald Ferguson Job Placement: Research Associate, Manpower Demonstration Research Corporation
John d. Chapman
Dissertation Title: Biased Enrollment and Risk Adjustment for Health Plans Advisor: Joseph P. Newhouse Job Placement: Vice President, Health Care Information Systems
Ingrid gould Ellen
Dissertation Title: Sharing America's Neighborhoods: The Changing Prospects for Stable, Racial Integration Advisor: Richard Zeckhauser Job Placement: Assistant Professor, Robert F. Wagner Graduate School of Public Service, New York University
Tae Yun Kim
Dissertation Title: An Analysis of Defense Procurement Policy in Korea: Selection, Cost Accounting, and Profit Policies Advisor: F.M. Scherer Job Placement: Government Official, Republic of Korea
Dara e. Menashi
Dissertation Title: Making Public/Private Collaboration Productive: Lessons for Creating Social Capital Advisor: Ronald Ferguson Job Placement: Consultant, Private Company
Richard g. Newell, Jr.
Dissertation Title: Environmental Policy and Technological Change: The Effect of Economic Incentives and Direct Regulation on Energy-Saving Innovation Advisor: Robert Stavins Job Placement: Fellow, Resources for the Future
Vicki Norberg-Bohm
Dissertation Title: Technological Change for Sustainable Development: Lessons from the Mexican Electric Power Sector Advisor: William Clark Job Placement: Assistant Professor of Environmental Policy and Planning, Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Michael a. Santoro
Dissertation Title: Trade Investment and Human Rights: A Moral Framework for Foreign Relations with China Advisor: Frederick Schauer Job Placement: Assistant Professor, Graduate School of Management, Rutgers University

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Including interviews in your dissertation. To present interviews in a dissertation, you first need to transcribe your interviews. You can use transcription software for this. You can then add the written interviews to the appendix. If you have many or long interviews that make the appendix extremely long, the appendix (after consultation with ...
To ace your Ph.D. program interviews, prepare to answer—and ask—these key questions. You've made it to the last step of the Ph.D. application process: the interview. Congratulations! But amid the excitement and butterflies, don't neglect the crucial next step: preparation. Grad school interviews—in which aspiring graduate students meet ...
Depending on the format for your PhD interview it could involve: A formal question and answer session in front of a postgraduate recruitment panel. A presentation, based on your research proposal or area of expertise. A one-to-one discussion with your prospective supervisor.
5. Not keeping your golden thread front of mind. We touched on this a little earlier, but it is a key point that should be central to your entire research process. You don't want to end up with pages and pages of data after conducting your interviews and realize that it is not useful to your research aims.
Here is a curated list of ten top-notch tools to aid you in your PhD thesis interviews: · Qualaroo: Simplify survey development and target specific demographics with ease, ensuring accurate data ...
Be honest about the things you find challenging, but identify them as training needs and discuss how you expect to improve upon them as part of your PhD. Do answer: I feel that I'm a good written communicator. My existing academic and professional work demonstrates an ability to put forward ideas clearly and concisely.
Common PhD Interview Questions. In this guide, we'll share 11 common PhD interview questions and our suggestions on how to answer them. A PhD interview is an essential step in securing a doctorate position. This is because it enables the prospective supervisor to get to know you better and determine whether you'd be a good fit for the project.
This article lists some of the most common PhD interview questions along with their answers. The goal is to help you prepare for a PhD interview and pass with flying colors. ... "During my Master's thesis on the effects of soil composition on plant growth, I faced a major setback. My initial experiments, which involved growing plants in ...
Most dissertations are 100 to 300 pages in length. All dissertations should be divided into appropriate sections, and long dissertations may need chapters, main divisions, and even subdivisions. Students should keep in mind that GSAS and many departments deplore overlong and wordy dissertations.
A PhD interviewer commonly asks for the interviewee to create a short presentation (3-5 slides) to bring the supervisors up to date with what relevant experience you have, to learn a bit about you as a person and to see your motivation for taking their project. It usually only takes up the first few minutes of the interview.
However, all Ph.D. interviews will include questions that concern your academic achievements, field of research, motivation for applying and goals. Here are 10 questions you may encounter in a Ph.D. interview with example answers: 1. Why do you think you are the right candidate for this Ph.D. program?
Northcott, Joy (2011) 'Teaching English as a Foreign Language: Perceptions of an In-service Diploma Course'. Unpublished EdD thesis, Open University. Sudajit-apa, Melada (2008) 'Systematising EAP materials development: Design, evaluation and revision in a Thai undergraduate reading course'. Unpublished PhD thesis, University of Edinburgh.
3. I was selected for an interview for a PhD scholarship and asked to give a 10-minute presentation consisting of 10 slides including "summarising both your research experience and your research plan for the project". How should I set up the PPT? Is this way ok? How much detail should I go into when describing my thesis?
A dissertation interview is a method of primary data collection used in academic research, typically undertaken for a dissertation or thesis. It can be in the form of a structured, semi-structured, or unstructured interview between the researcher and the interviewee(s), with the goal of gaining detailed, firsthand insights into the research topic.
Step 1: State your full name. Example. Step 2: Give a brief overview of your educational (and professional) background. Example. Step 3: Explain why you are interested in the PhD position. Example. Step 4: Thank everyone for the opportunity to be interviewed. Example.
The process for conducting in-depth interviews follows the same general process as is followed for other research: plan, develop instruments, collect data, analyze data, and disseminate findings. More detailed steps are given below. 1. Plan. • Identify stakeholders who will be involved.
The results chapter in a dissertation or thesis (or any formal academic research piece) is where you objectively and neutrally present the findings of your qualitative analysis (or analyses if you used multiple qualitative analysis methods ). This chapter can sometimes be combined with the discussion chapter (where you interpret the data and ...
Prize-Winning Thesis and Dissertation Examples. Published on September 9, 2022 by Tegan George.Revised on July 18, 2023. It can be difficult to know where to start when writing your thesis or dissertation.One way to come up with some ideas or maybe even combat writer's block is to check out previous work done by other students on a similar thesis or dissertation topic to yours.
A dissertation is a long-form piece of academic writing based on original research conducted by you. It is usually submitted as the final step in order to finish a PhD program. Your dissertation is probably the longest piece of writing you've ever completed. It requires solid research, writing, and analysis skills, and it can be intimidating ...
Yes, our PhD interview templates can be a valuable solution for you. ... Template 1: Thesis Research Paper Proposal Template. This template can elevate your academic presentations to the next level. It is tailored specially for scholars, researchers, and students. It helps them embark on the rigorous journey of thesis proposal development and ...
Do yourself a favour and start with the end in mind. Section 1 - Introduction. As with all chapters in your dissertation or thesis, the methodology chapter should have a brief introduction. In this section, you should remind your readers what the focus of your study is, especially the research aims. As we've discussed many times on the blog ...
An interview transcript, A copy of any survey questions, Questionnaire results. Although the results of your surveys, questionnaires or interviews should be presented and discussed in your main text, it is useful to include their full form in the appendix of a dissertation to give credibility to your study. Tables, Figures and Illustrations
It often starts with "But", "Yet" or "However". The third sentence says what specific research has been done. This often starts with "This research" or "I report…". The fourth sentence reports the results. Don't try to be too tricky here, just start with something like: "This study shows," or "Analysis of the data ...
saturation is ideal, some give numerical guidance. For example, Adler and Adler advise graduate students to sample between 12 and 60, with 30 being the mean; and Ragin suggests that a glib answer is '20 for an M.A. thesis and 50 for a Ph.D. dissertation'.
Mission. The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives.
2020 Andrew Bacher-HicKs. Dissertation Title: Essays on the Economics of Education Advisor: Christopher Avery Job Placement: Assistant Professor of Education Policy, Boston University. Megan Bailey. Dissertation Title: Essays in Climate Policy and Innovation Advisor: Joseph Aldy Job Placement: Assistant Professor, University of Calgary