How has technology changed - and changed us - in the past 20 years?

Remember this? Image: REUTERS/Stephen Hird

.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo{-webkit-transition:all 0.15s ease-out;transition:all 0.15s ease-out;cursor:pointer;-webkit-text-decoration:none;text-decoration:none;outline:none;color:inherit;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:hover,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-hover]{-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:focus,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-focus]{box-shadow:0 0 0 3px rgba(168,203,251,0.5);} Madeleine Hillyer

.chakra .wef-9dduvl{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-9dduvl{font-size:1.125rem;}} Explore and monitor how .chakra .wef-15eoq1r{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-size:1.25rem;color:#F7DB5E;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-15eoq1r{font-size:1.125rem;}} Digital Communications is affecting economies, industries and global issues

.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;color:#2846F8;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{font-size:1.125rem;}} Get involved with our crowdsourced digital platform to deliver impact at scale
Stay up to date:, technological transformation.
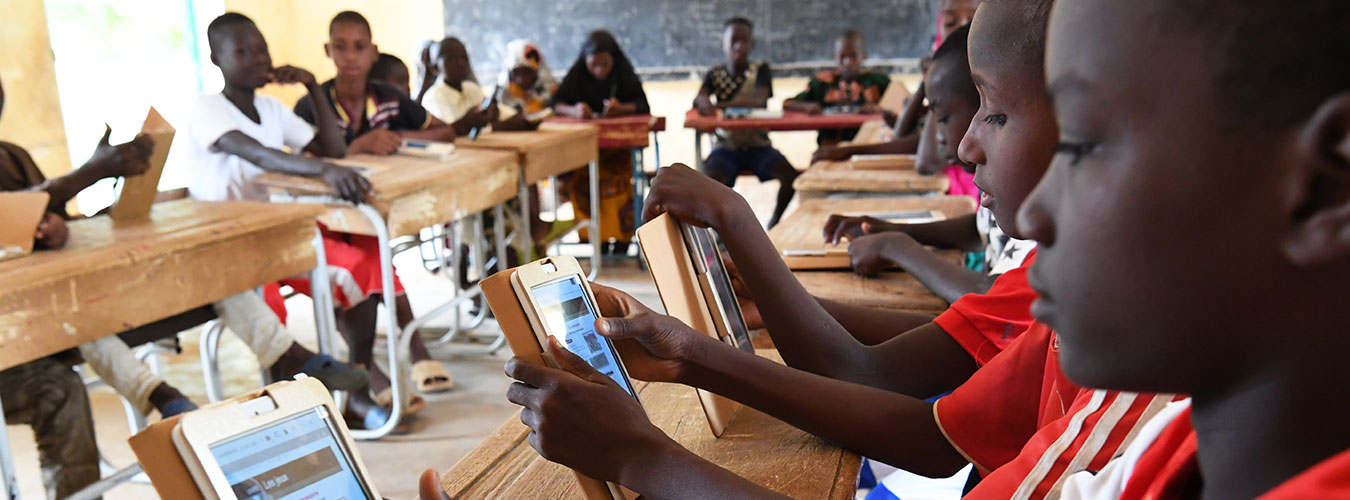
- Since the dotcom bubble burst back in 2000, technology has radically transformed our societies and our daily lives.
- From smartphones to social media and healthcare, here's a brief history of the 21st century's technological revolution.
Just over 20 years ago, the dotcom bubble burst , causing the stocks of many tech firms to tumble. Some companies, like Amazon, quickly recovered their value – but many others were left in ruins. In the two decades since this crash, technology has advanced in many ways.
Many more people are online today than they were at the start of the millennium. Looking at broadband access, in 2000, just half of Americans had broadband access at home. Today, that number sits at more than 90% .

This broadband expansion was certainly not just an American phenomenon. Similar growth can be seen on a global scale; while less than 7% of the world was online in 2000, today over half the global population has access to the internet.
Similar trends can be seen in cellphone use. At the start of the 2000s, there were 740 million cell phone subscriptions worldwide. Two decades later, that number has surpassed 8 billion, meaning there are now more cellphones in the world than people
Have you read?
The future of jobs report 2023, how to follow the growth summit 2023.
At the same time, technology was also becoming more personal and portable. Apple sold its first iPod in 2001, and six years later it introduced the iPhone, which ushered in a new era of personal technology. These changes led to a world in which technology touches nearly everything we do.
Technology has changed major sectors over the past 20 years, including media, climate action and healthcare. The World Economic Forum’s Technology Pioneers , which just celebrated its 20th anniversary, gives us insight how emerging tech leaders have influenced and responded to these changes.
Media and media consumption
The past 20 years have greatly shaped how and where we consume media. In the early 2000s, many tech firms were still focused on expanding communication for work through advanced bandwidth for video streaming and other media consumption that is common today.
Others followed the path of expanding media options beyond traditional outlets. Early Tech Pioneers such as PlanetOut did this by providing an outlet and alternative media source for LGBTQIA communities as more people got online.
Following on from these first new media options, new communities and alternative media came the massive growth of social media. In 2004 , fewer than 1 million people were on Myspace; Facebook had not even launched. By 2018, Facebook had more 2.26 billion users with other sites also growing to hundreds of millions of users.

While these new online communities and communication channels have offered great spaces for alternative voices, their increased use has also brought issues of increased disinformation and polarization.
Today, many tech start-ups are focused on preserving these online media spaces while also mitigating the disinformation which can come with them. Recently, some Tech Pioneers have also approached this issue, including TruePic – which focuses on photo identification – and Two Hat , which is developing AI-powered content moderation for social media.
Climate change and green tech
Many scientists today are looking to technology to lead us towards a carbon-neutral world. Though renewed attention is being given to climate change today, these efforts to find a solution through technology is not new. In 2001, green tech offered a new investment opportunity for tech investors after the crash, leading to a boom of investing in renewable energy start-ups including Bloom Energy , a Technology Pioneer in 2010.
In the past two decades, tech start-ups have only expanded their climate focus. Many today are focuses on initiatives far beyond clean energy to slow the impact of climate change.
Different start-ups, including Carbon Engineering and Climeworks from this year’s Technology Pioneers, have started to roll out carbon capture technology. These technologies remove CO2 from the air directly, enabling scientists to alleviate some of the damage from fossil fuels which have already been burned.
Another expanding area for young tech firms today is food systems innovation. Many firms, like Aleph Farms and Air Protein, are creating innovative meat and dairy alternatives that are much greener than their traditional counterparts.
Biotech and healthcare
The early 2000s also saw the culmination of a biotech boom that had started in the mid-1990s. Many firms focused on advancing biotechnologies through enhanced tech research.
An early Technology Pioneer, Actelion Pharmaceuticals was one of these companies. Actelion’s tech researched the single layer of cells separating every blood vessel from the blood stream. Like many other biotech firms at the time, their focus was on precise disease and treatment research.
While many tech firms today still focus on disease and treatment research, many others have been focusing on healthcare delivery. Telehealth has been on the rise in recent years , with many young tech expanding virtual healthcare options. New technologies such as virtual visits, chatbots are being used to delivery healthcare to individuals, especially during Covid-19.
Many companies are also focusing their healthcare tech on patients, rather than doctors. For example Ada, a symptom checker app, used to be designed for doctor’s use but has now shifted its language and interface to prioritize giving patients information on their symptoms. Other companies, like 7 cups, are focused are offering mental healthcare support directly to their users without through their app instead of going through existing offices.
The past two decades have seen healthcare tech get much more personal and use tech for care delivery, not just advancing medical research.
The World Economic Forum was the first to draw the world’s attention to the Fourth Industrial Revolution, the current period of unprecedented change driven by rapid technological advances. Policies, norms and regulations have not been able to keep up with the pace of innovation, creating a growing need to fill this gap.
The Forum established the Centre for the Fourth Industrial Revolution Network in 2017 to ensure that new and emerging technologies will help—not harm—humanity in the future. Headquartered in San Francisco, the network launched centres in China, India and Japan in 2018 and is rapidly establishing locally-run Affiliate Centres in many countries around the world.
The global network is working closely with partners from government, business, academia and civil society to co-design and pilot agile frameworks for governing new and emerging technologies, including artificial intelligence (AI) , autonomous vehicles , blockchain , data policy , digital trade , drones , internet of things (IoT) , precision medicine and environmental innovations .
Learn more about the groundbreaking work that the Centre for the Fourth Industrial Revolution Network is doing to prepare us for the future.
Want to help us shape the Fourth Industrial Revolution? Contact us to find out how you can become a member or partner.
In the early 2000s, many companies were at the start of their recovery from the bursting dotcom bubble. Since then, we’ve seen a large expansion in the way tech innovators approach areas such as new media, climate change, healthcare delivery and more.
At the same time, we have also seen tech companies rise to the occasion of trying to combat issues which arose from the first group such as internet content moderation, expanding climate change solutions.
The Technology Pioneers' 2020 cohort marks the 20th anniversary of this community - and looking at the latest awardees can give us a snapshot of where the next two decades of tech may be heading.
Don't miss any update on this topic
Create a free account and access your personalized content collection with our latest publications and analyses.
License and Republishing
World Economic Forum articles may be republished in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International Public License, and in accordance with our Terms of Use.
The views expressed in this article are those of the author alone and not the World Economic Forum.
The Agenda .chakra .wef-n7bacu{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-weight:400;} Weekly
A weekly update of the most important issues driving the global agenda
.chakra .wef-1dtnjt5{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;} More on Forum Institutional .chakra .wef-17xejub{-webkit-flex:1;-ms-flex:1;flex:1;justify-self:stretch;-webkit-align-self:stretch;-ms-flex-item-align:stretch;align-self:stretch;} .chakra .wef-nr1rr4{display:-webkit-inline-box;display:-webkit-inline-flex;display:-ms-inline-flexbox;display:inline-flex;white-space:normal;vertical-align:middle;text-transform:uppercase;font-size:0.75rem;border-radius:0.25rem;font-weight:700;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;line-height:1.2;-webkit-letter-spacing:1.25px;-moz-letter-spacing:1.25px;-ms-letter-spacing:1.25px;letter-spacing:1.25px;background:none;padding:0px;color:#B3B3B3;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;box-decoration-break:clone;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;}@media screen and (min-width:37.5rem){.chakra .wef-nr1rr4{font-size:0.875rem;}}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-nr1rr4{font-size:1rem;}} See all

Day 2 #SpecialMeeting24: Key insights and what to know
Gayle Markovitz
April 28, 2024

Day 1 #SpecialMeeting24: Key insights and what just happened
April 27, 2024

#SpecialMeeting24: What to know about the programme and who's coming
Mirek Dušek and Maroun Kairouz

Climate finance: What are debt-for-nature swaps and how can they help countries?
Kate Whiting
April 26, 2024

What to expect at the Special Meeting on Global Collaboration, Growth and Energy for Development
Spencer Feingold and Gayle Markovitz
April 19, 2024

From 'Quit-Tok' to proximity bias, here are 11 buzzwords from the world of hybrid work
April 17, 2024

Essay on Modern Technology 1000+ Words
In today’s fast-paced world, modern technology plays an essential role in our lives. It surrounds us in the form of smartphones, computers, smart homes, and more. These advancements have transformed the way we communicate, work, and live. This essay will explore the many reasons why modern technology is a boon for society.
Improved Communication
Modern technology has revolutionized communication. With the advent of smartphones, people can connect with friends and family no matter where they are. According to recent statistics, 81% of people use smartphones for messaging and social media, making it easier to stay in touch.
Learning Made Fun
In the classroom, modern technology has made learning more engaging and interactive. Educational apps and online resources provide students with a wealth of knowledge at their fingertips. For instance, Khan Academy offers free online lessons in various subjects, helping students grasp complex concepts with ease.
Medical Breakthroughs
Technology has also transformed the field of medicine. With the help of advanced machines, doctors can diagnose illnesses more accurately and treat patients more effectively. For example, robotic surgery has reduced the risk of complications during operations.
Increased Productivity
In the workplace, technology has boosted productivity. Computers and software tools allow employees to streamline their tasks, reducing the time spent on repetitive work. A study by the Bureau of Labor Statistics found that technology has contributed to a 69% increase in productivity in the past two decades.
Environmental Benefits
Modern technology has the potential to help us combat environmental challenges. Electric cars, for instance, produce fewer emissions than traditional gasoline vehicles, contributing to cleaner air. Additionally, smart home systems can help us reduce energy consumption, leading to a more sustainable future.
Accessibility for All
One of the remarkable aspects of modern technology is its ability to make life more accessible for individuals with disabilities. Screen-reading software, voice recognition technology, and mobility aids have empowered people with disabilities to lead more independent lives.
Innovation and Creativity
The world of technology continually pushes the boundaries of human innovation and creativity. Think about the imaginative video games, stunning visual effects in movies, and groundbreaking virtual reality experiences. These creations were all made possible through modern technology.
Global Connectivity
The internet, a product of modern technology, has connected people from all corners of the globe. It fosters cross-cultural understanding, enables international collaboration, and allows us to access information from diverse perspectives.
Conclusion of Essay on Modern Technology
In conclusion, modern technology has become an integral part of our lives, offering countless benefits to society. It enhances communication, facilitates learning, advances medical practices, boosts productivity, and addresses environmental concerns. Additionally, it promotes accessibility, fuels innovation, and connects us on a global scale. As we continue to embrace and develop modern technology, we must harness its potential for the betterment of humanity. It’s clear that the marvels of modern technology have transformed our world for the better and hold the promise of an even brighter future.
Also Check: The Essay on Essay: All you need to know

Technology over the long run: zoom out to see how dramatically the world can change within a lifetime
It is easy to underestimate how much the world can change within a lifetime. considering how dramatically the world has changed can help us see how different the world could be in a few years or decades..
Technology can change the world in ways that are unimaginable until they happen. Switching on an electric light would have been unimaginable for our medieval ancestors. In their childhood, our grandparents would have struggled to imagine a world connected by smartphones and the Internet.
Similarly, it is hard for us to imagine the arrival of all those technologies that will fundamentally change the world we are used to.
We can remind ourselves that our own future might look very different from the world today by looking back at how rapidly technology has changed our world in the past. That’s what this article is about.
One insight I take away from this long-term perspective is how unusual our time is. Technological change was extremely slow in the past – the technologies that our ancestors got used to in their childhood were still central to their lives in their old age. In stark contrast to those days, we live in a time of extraordinarily fast technological change. For recent generations, it was common for technologies that were unimaginable in their youth to become common later in life.
The long-run perspective on technological change
The big visualization offers a long-term perspective on the history of technology. 1
The timeline begins at the center of the spiral. The first use of stone tools, 3.4 million years ago, marks the beginning of this history of technology. 2 Each turn of the spiral represents 200,000 years of history. It took 2.4 million years – 12 turns of the spiral – for our ancestors to control fire and use it for cooking. 3
To be able to visualize the inventions in the more recent past – the last 12,000 years – I had to unroll the spiral. I needed more space to be able to show when agriculture, writing, and the wheel were invented. During this period, technological change was faster, but it was still relatively slow: several thousand years passed between each of these three inventions.
From 1800 onwards, I stretched out the timeline even further to show the many major inventions that rapidly followed one after the other.
The long-term perspective that this chart provides makes it clear just how unusually fast technological change is in our time.
You can use this visualization to see how technology developed in particular domains. Follow, for example, the history of communication: from writing to paper, to the printing press, to the telegraph, the telephone, the radio, all the way to the Internet and smartphones.
Or follow the rapid development of human flight. In 1903, the Wright brothers took the first flight in human history (they were in the air for less than a minute), and just 66 years later, we landed on the moon. Many people saw both within their lifetimes: the first plane and the moon landing.
This large visualization also highlights the wide range of technology’s impact on our lives. It includes extraordinarily beneficial innovations, such as the vaccine that allowed humanity to eradicate smallpox , and it includes terrible innovations, like the nuclear bombs that endanger the lives of all of us .
What will the next decades bring?
The red timeline reaches up to the present and then continues in green into the future. Many children born today, even without further increases in life expectancy, will live well into the 22nd century.
New vaccines, progress in clean, low-carbon energy, better cancer treatments – a range of future innovations could very much improve our living conditions and the environment around us. But, as I argue in a series of articles , there is one technology that could even more profoundly change our world: artificial intelligence (AI).
One reason why artificial intelligence is such an important innovation is that intelligence is the main driver of innovation itself. This fast-paced technological change could speed up even more if it’s driven not only by humanity’s intelligence but also by artificial intelligence. If this happens, the change currently stretched out over decades might happen within a very brief time span of just a year. Possibly even faster. 4
I think AI technology could have a fundamentally transformative impact on our world. In many ways, it is already changing our world, as I documented in this companion article . As this technology becomes more capable in the years and decades to come, it can give immense power to those who control it (and it poses the risk that it could escape our control entirely).
Such systems might seem hard to imagine today, but AI technology is advancing quickly. Many AI experts believe there is a real chance that human-level artificial intelligence will be developed within the next decades, as I documented in this article .
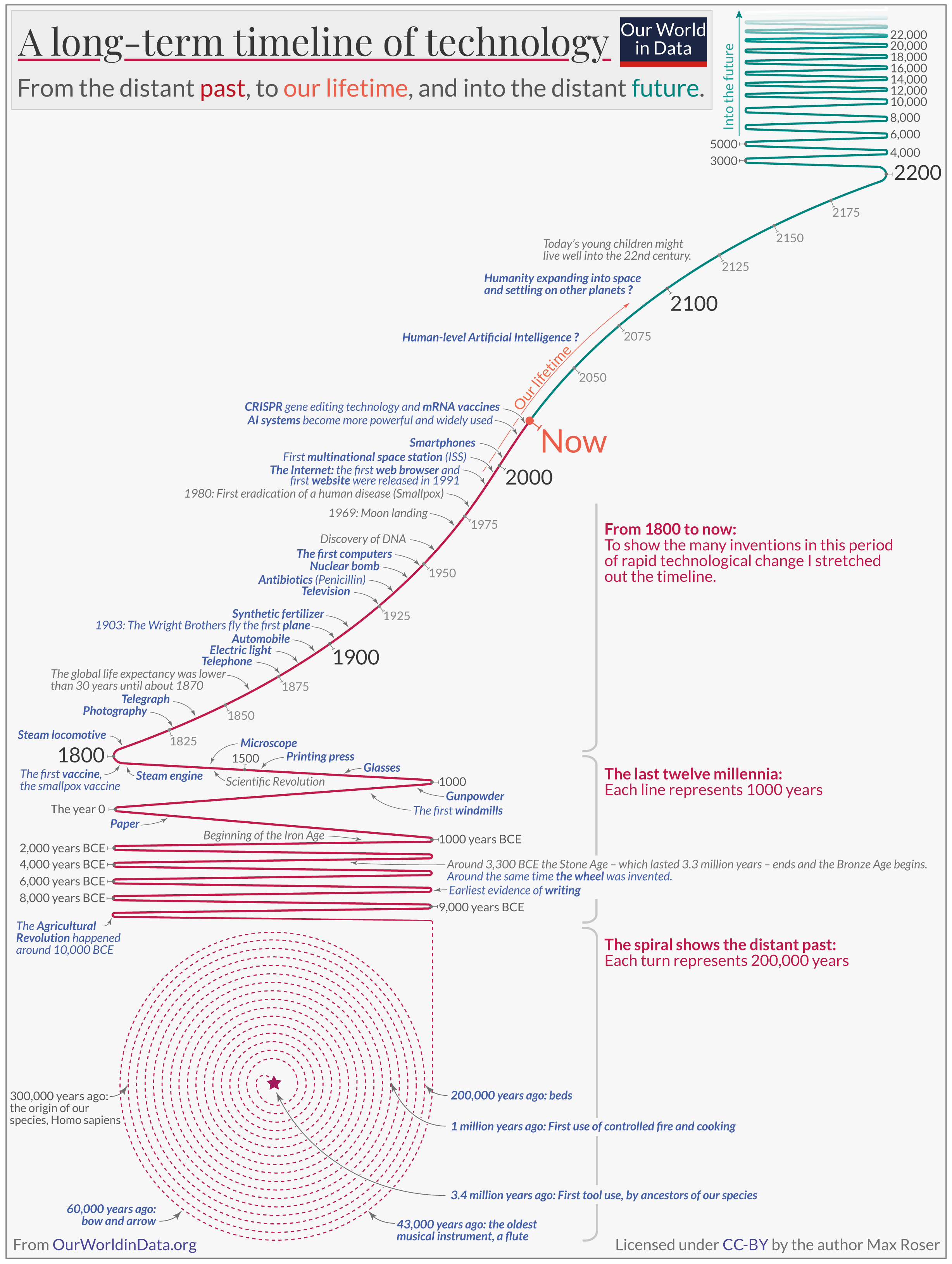
Technology will continue to change the world – we should all make sure that it changes it for the better
What is familiar to us today – photography, the radio, antibiotics, the Internet, or the International Space Station circling our planet – was unimaginable to our ancestors just a few generations ago. If your great-great-great grandparents could spend a week with you, they would be blown away by your everyday life.
What I take away from this history is that I will likely see technologies in my lifetime that appear unimaginable to me today.
In addition to this trend towards increasingly rapid innovation, there is a second long-run trend. Technology has become increasingly powerful. While our ancestors wielded stone tools, we are building globe-spanning AI systems and technologies that can edit our genes.
Because of the immense power that technology gives those who control it, there is little that is as important as the question of which technologies get developed during our lifetimes. Therefore, I think it is a mistake to leave the question about the future of technology to the technologists. Which technologies are controlled by whom is one of the most important political questions of our time because of the enormous power these technologies convey to those who control them.
We all should strive to gain the knowledge we need to contribute to an intelligent debate about the world we want to live in. To a large part, this means gaining knowledge and wisdom on the question of which technologies we want.
Acknowledgments: I would like to thank my colleagues Hannah Ritchie, Bastian Herre, Natasha Ahuja, Edouard Mathieu, Daniel Bachler, Charlie Giattino, and Pablo Rosado for their helpful comments on drafts of this essay and the visualization. Thanks also to Lizka Vaintrob and Ben Clifford for the conversation that initiated this visualization.
Appendix: About the choice of visualization in this article
The recent speed of technological change makes it difficult to picture the history of technology in one visualization. When you visualize this development on a linear timeline, then most of the timeline is almost empty, while all the action is crammed into the right corner:

In my large visualization here, I tried to avoid this problem and instead show the long history of technology in a way that lets you see when each technological breakthrough happened and how, within the last millennia, there was a continuous acceleration of technological change.
The recent speed of technological change makes it difficult to picture the history of technology in one visualization. In the appendix, I show how this would look if it were linear.
It is, of course, difficult to assess when exactly the first stone tools were used.
The research by McPherron et al. (2010) suggested that it was at least 3.39 million years ago. This is based on two fossilized bones found in Dikika in Ethiopia, which showed “stone-tool cut marks for flesh removal and percussion marks for marrow access”. These marks were interpreted as being caused by meat consumption and provide the first evidence that one of our ancestors, Australopithecus afarensis, used stone tools.
The research by Harmand et al. (2015) provided evidence for stone tool use in today’s Kenya 3.3 million years ago.
References:
McPherron et al. (2010) – Evidence for stone-tool-assisted consumption of animal tissues before 3.39 million years ago at Dikika, Ethiopia . Published in Nature.
Harmand et al. (2015) – 3.3-million-year-old stone tools from Lomekwi 3, West Turkana, Kenya . Published in Nature.
Evidence for controlled fire use approximately 1 million years ago is provided by Berna et al. (2012) Microstratigraphic evidence of in situ fire in the Acheulean strata of Wonderwerk Cave, Northern Cape province, South Africa , published in PNAS.
The authors write: “The ability to control fire was a crucial turning point in human evolution, but the question of when hominins first developed this ability still remains. Here we show that micromorphological and Fourier transform infrared microspectroscopy (mFTIR) analyses of intact sediments at the site of Wonderwerk Cave, Northern Cape province, South Africa, provide unambiguous evidence—in the form of burned bone and ashed plant remains—that burning took place in the cave during the early Acheulean occupation, approximately 1.0 Ma. To the best of our knowledge, this is the earliest secure evidence for burning in an archaeological context.”
This is what authors like Holden Karnofsky called ‘Process for Automating Scientific and Technological Advancement’ or PASTA. Some recent developments go in this direction: DeepMind’s AlphaFold helped to make progress on one of the large problems in biology, and they have also developed an AI system that finds new algorithms that are relevant to building a more powerful AI.
Cite this work
Our articles and data visualizations rely on work from many different people and organizations. When citing this article, please also cite the underlying data sources. This article can be cited as:
BibTeX citation
Reuse this work freely
All visualizations, data, and code produced by Our World in Data are completely open access under the Creative Commons BY license . You have the permission to use, distribute, and reproduce these in any medium, provided the source and authors are credited.
The data produced by third parties and made available by Our World in Data is subject to the license terms from the original third-party authors. We will always indicate the original source of the data in our documentation, so you should always check the license of any such third-party data before use and redistribution.
All of our charts can be embedded in any site.
Our World in Data is free and accessible for everyone.
Help us do this work by making a donation.

Essay on Modern Technology
Students are often asked to write an essay on Modern Technology in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Modern Technology
Introduction to modern technology.
Modern technology refers to the recent advancements and innovations that have made our lives easier. It includes computers, smartphones, the internet, and many more.
Benefits of Modern Technology
Modern technology has numerous benefits. It helps us communicate with people worldwide, provides information at our fingertips, and makes learning fun and interactive.
Challenges of Modern Technology
Despite the benefits, modern technology also poses some challenges. It can lead to addiction and loss of privacy. It’s crucial to use technology wisely to avoid these issues.
In conclusion, modern technology has changed our lives significantly. It’s our responsibility to use it responsibly and reap its benefits.
Also check:
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Modern Technology
- Paragraph on Modern Technology
- Speech on Modern Technology
250 Words Essay on Modern Technology
The advent of modern technology.
Modern technology, an offshoot of the ceaseless human quest for innovation, has become an integral part of our lives. It has not only revolutionized communication and information dissemination but also transformed the way we live, work, and play.
Impact on Communication and Information
The advent of the Internet and smartphones has democratized information, making it accessible to everyone, everywhere. Social media platforms have given a voice to the voiceless, enabling a global dialogue that transcends geographical boundaries. Additionally, the emergence of artificial intelligence and machine learning has opened up new frontiers in data analysis and decision-making processes.
Transforming Daily Life
Modern technology has also significantly altered our daily routines. Smart homes, equipped with automated devices, have enhanced comfort and convenience. Wearable technology monitors our health, encouraging proactive wellness. Furthermore, e-commerce platforms and digital payment systems have streamlined shopping and financial transactions.
Work and Play in the Digital Age
In the workspace, technology has automated repetitive tasks, freeing up time for creative and strategic thinking. Remote working, made possible by digital tools, has blurred the lines between office and home. Meanwhile, in the realm of entertainment, virtual and augmented reality technologies have redefined our concept of play, immersing us in interactive digital worlds.
The Double-edged Sword
However, this technological revolution is a double-edged sword. While it brings countless benefits, it also presents challenges such as privacy concerns, cybercrime, and digital addiction. It is, therefore, crucial to navigate this digital landscape with caution, leveraging its advantages while mitigating its potential risks.
In conclusion, modern technology, with its profound impact on communication, daily life, work, and play, is an undeniable force shaping the 21st-century human experience.
500 Words Essay on Modern Technology
In the contemporary era, modern technology has emerged as a significant facet of human life. It has revolutionized the way we communicate, learn, work, and entertain ourselves. The rapid evolution of technology, from the advent of the internet to the development of artificial intelligence, has had profound implications on society, economy, and culture.
The Impact of Modern Technology on Communication
Modern technology has drastically transformed the realm of communication. The rise of social media platforms and instant messaging apps has made it possible to connect with people across the globe in real time. Emails and video conferences have replaced traditional letters and face-to-face meetings, making communication faster and more efficient. However, this digital revolution has also raised concerns about privacy and the authenticity of information disseminated online.
Modern Technology in Education
The education sector has also benefited immensely from modern technology. E-learning platforms and virtual classrooms have made education accessible to a wider audience, breaking geographical barriers. Advanced technologies like virtual reality and augmented reality are being used to create immersive learning experiences. Nonetheless, the digital divide and the lack of digital literacy pose challenges in harnessing the full potential of technology in education.
Modern Technology in the Workplace
Modern technology has reshaped the workplace as well. Automation and artificial intelligence have streamlined operations, increased productivity, and reduced human error. Remote working has become a reality, thanks to cloud computing and collaborative tools. However, the fear of job displacement due to automation and the need for constant upskilling to keep up with technological advancements are issues that need to be addressed.
Modern Technology and Entertainment
In the realm of entertainment, modern technology has given rise to new forms of media and has changed the way we consume content. Streaming platforms have challenged traditional television, and online gaming has become a global phenomenon. While these advancements have democratized entertainment, they have also raised questions about digital addiction and mental health.
Conclusion: The Future of Modern Technology
In conclusion, modern technology, despite its potential drawbacks, is an integral part of our lives. It has the power to drive societal change, foster economic growth, and enhance the quality of life. As we navigate the digital age, it is crucial to strike a balance between leveraging technology and mitigating its adverse impacts. The future of modern technology lies in ethical, responsible, and inclusive innovation.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
- Essay on Save Nature Save Life
- Essay on Nature and Its Importance
- Essay on Save Nature
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.


Search the United Nations
- Issue Briefs
- Commemoration
- Branding Package
- Our Common Agenda
- Press Releases

The Impact of Digital Technologies
Technologies can help make our world fairer, more peaceful, and more just. Digital advances can support and accelerate achievement of each of the 17 Sustainable Development Goals – from ending extreme poverty to reducing maternal and infant mortality, promoting sustainable farming and decent work, and achieving universal literacy. But technologies can also threaten privacy, erode security and fuel inequality. They have implications for human rights and human agency. Like generations before, we – governments, businesses and individuals – have a choice to make in how we harness and manage new technologies.
A DIGITAL FUTURE FOR ALL?
Digital technologies have advanced more rapidly than any innovation in our history – reaching around 50 per cent of the developing world’s population in only two decades and transforming societies. By enhancing connectivity, financial inclusion, access to trade and public services, technology can be a great equaliser.
In the health sector, for instance, AI-enabled frontier technologies are helping to save lives, diagnose diseases and extend life expectancy. In education, virtual learning environments and distance learning have opened up programmes to students who would otherwise be excluded. Public services are also becoming more accessible and accountable through blockchain-powered systems, and less bureaucratically burdensome as a result of AI assistance.Big data can also support more responsive and accurate policies and programmes.
However, those yet to be connected remain cut off from the benefits of this new era and remain further behind. Many of the people left behind are women, the elderly, persons with disabilities or from ethnic or linguistic minorities, indigenous groups and residents of poor or remote areas. The pace of connectivity is slowing, even reversing, among some constituencies. For example, globally, the proportion of women using the internet is 12 per cent lower than that of men. While this gap narrowed in most regions between 2013 and 2017, it widened in the least developed countries from 30 per cent to 33 per cent.
The use of algorithms can replicate and even amplify human and systemic bias where they function on the basis of data which is not adequately diverse. Lack of diversity in the technology sector can mean that this challenge is not adequately addressed.
THE FUTURE OF WORK
Throughout history, technological revolutions have changed the labour force: creating new forms and patterns of work, making others obsolete, and leading to wider societal changes. This current wave of change is likely to have profound impacts. For example, the International Labour Organization estimates that the shift to a greener economy could create 24 million new jobs globally by 2030 through the adoption of sustainable practices in the energy sector, the use of electric vehicles and increasing energy efficiency in existing and future buildings.
Meanwhile, reports by groups such as McKinsey suggest that 800 million people could lose their jobs to automation by 2030 , while polls reveal that the majority of all employees worry that they do not have the necessary training or skills to get a well-paid job.
There is broad agreement that managing these trends will require changes in our approach to education, for instance, by placing more emphasis on science, technology, engineering, and maths; by teaching soft skills, and resilience; and by ensuring that people can re-skill and up-skill throughout their lifetimes. Unpaid work, for example childcare and elderly care in the home, will need to be better supported, especially as with the shifting age profile of global populations, the demands on these tasks are likely to increase.
THE FUTURE OF DATA
Today, digital technologies such as data pooling and AI are used to track and diagnose issues in agriculture, health, and the environment, or to perform daily tasks such as navigating traffic or paying a bill. They can be used to defend and exercise human rights – but they can also be used to violate them, for example, by monitoring our movements, purchases, conversations and behaviours. Governments and businesses increasingly have the tools to mine and exploit data for financial and other purposes.
However, personal data would become an asset to a person, if there were a formula for better regulation of personal data ownership. Data-powered technology has the potential to empower individuals, improve human welfare, and promote universal rights, depending on the type of protections put in place.
THE FUTURE OF SOCIAL MEDIA
Social media connects almost half of the entire global population . It enables people to make their voices heard and to talk to people across the world in real time. However, it can also reinforce prejudices and sow discord, by giving hate speech and misinformation a platform, or by amplifying echo chambers.
In this way, social media algorithms can fuel the fragmentation of societies around the world. And yet they also have the potential to do the opposite.
THE FUTURE OF CYBERSPACE
How to manage these developments is the subject of much discussion – nationally and internationally – at a time when geopolitical tensions are on the rise. The UN Secretary-General has warned of a ‘great fracture’ between world powers, each with their own internet and AI strategy, as well as dominant currency, trade and financial rules and contradictory geopolitical and military views. Such a divide could establish a digital Berlin Wall. Increasingly, digital cooperation between states – and a universal cyberspace that reflects global standards for peace and security, human rights and sustainable development – is seen as crucial to ensuring a united world. A ‘global commitment for digital cooperation’ is a key recommendation by the Secretary-General’s High-level Panel on Digital Cooperation .
FOR MORE INFORMATION
The Sustainable Development Goals
The Age of Digital Interdependence: Report of the UN Secretary-General’s High-level Panel on Digital Cooperation
ILO | Global Commission on the Future of Work
Secretary General’s Address to the 74th Session of the UN General Assembly
Secretary General’s Strategy on New Technology
PDF VERSION
Download the pdf version
Greater Good Science Center • Magazine • In Action • In Education
Relationships Articles & More
What makes technology good or bad for us, how technology affects our well-being partly depends on whether it strengthens our relationships..
Everyone’s worried about smartphones. Headlines like “ Have smartphones destroyed a generation? ” and “ Smartphone addiction could be changing your brain ” paint a bleak picture of our smartphone addiction and its long-term consequences. This isn’t a new lament—public opinion at the advent of the newspaper worried that people would forego the stimulating pleasures of early-morning conversation in favor of reading the daily .
Is the story of technology really that bad? Certainly there’s some reason to worry. Smartphone use has been linked to serious issues, such as dwindling attention spans , crippling depression , and even increased incidence of brain cancer . Ultimately, though, the same concern comes up again and again: Smartphones can’t be good for us, because they’re replacing the real human connection of the good old days.
Everyone’s heard how today’s teens just sit together in a room, texting, instead of actually talking to each other. But could those teenagers actually be getting something meaningful and real out of all that texting?
The science of connection

A quick glance at the research on technology-mediated interaction reveals an ambivalent literature. Some studies show that time spent socializing online can decrease loneliness , increase well-being , and help the socially anxious learn how to connect to others. Other studies suggest that time spent socializing online can cause loneliness , decrease well-being , and foster a crippling dependence on technology-mediated interaction to the point that users prefer it to face-to-face conversation.
It’s tempting to say that some of these studies must be right and others wrong, but the body of evidence on both sides is a little too robust to be swept under the rug. Instead, the impact of social technology is more complicated. Sometimes, superficially similar behaviors have fundamentally different consequences. Sometimes online socialization is good for you, sometimes it’s bad, and the devil is entirely in the details.
This isn’t a novel proposition; after all, conflicting results started appearing within the first few studies into the internet’s social implications, back in the 1990s. Many people have suggested that to understand the consequences of online socialization, we need to dig deeper into situational factors and circumstances. But what we still have to do is move beyond recognition of the problem to provide an answer: When, how, and why are some online interactions great, while others are dangerous?
The interpersonal connection behaviors framework
As a scientist of close relationships, I can’t help but see online interactions differently from thinkers in other fields. People build relationships by demonstrating their understanding of each other’s needs and perspectives, a cyclical process that brings them closer together. If I tell you my secrets, and you respond supportively, I’m much more likely to confide in you again—and you, in turn, are much more likely to confide in me.
This means that every time two people talk to each other, an opportunity for relationship growth is unfolding. Many times, that opportunity isn’t taken; we aren’t about to have an in-depth conversation with the barista who asks for our order. But connection is always theoretically possible, and that’s true whether we’re interacting online or face-to-face.
Close relationships are the bread and butter of happiness—and even health. Being socially isolated is a stronger predictor of mortality than is smoking multiple cigarettes a day . If we want to understand the role technology plays in our well-being, we need to start with the role it plays in our relationships.
And it turns out that the kind of technology-mediated interactions that lead to positive outcomes are exactly those that are likely to build stronger relationships. Spending your time online by scheduling interactions with people you see day in and day out seems to pay dividends in increased social integration . Using the internet to compensate for being lonely just makes you lonelier; using the internet to actively seek out connection has the opposite effect .
“The kind of technology-mediated interactions that lead to positive outcomes are exactly those that are likely to build stronger relationships”
On the other hand, technology-mediated interactions that don’t really address our close relationships don’t seem to do us any good—and might, in fact, do us harm. Passively scrolling through your Facebook feed without interacting with people has been linked to decreased well-being and increased depression post-Facebook use.
That kind of passive usage is a good example of “ social snacking .” Like eating junk food, social snacking can temporarily satisfy you, but it’s lacking in nutritional content. Looking at your friends’ posts without ever responding might make you feel more connected to them, but it doesn’t build intimacy.
Passive engagement has a second downside, as well: social comparison . When we compare our messy lived experiences to others’ curated self-presentations, we are likely to suffer from lowered self-esteem , happiness, and well-being. This effect is only exacerbated when we consume people’s digital lives without interacting with them, making it all too easy to miss the less photogenic moments of their lives.
Moving forward
The interpersonal connection behaviors framework doesn’t explain everything that might influence our well-being after spending time on social media. The internet poses plenty of other dangers—for two examples, the sense of wasting time or emotional contagion from negative news. However, a focus on meaningful social interaction can help explain decades of contradictory findings. And even if the framework itself is challenged by future work, its central concept is bound to be upheld: We have to study the details of how people are spending their time online if we want to understand its likely effects.
In the meantime, this framework has some practical implications for those worried about their own online time. If you make sure you’re using social media for genuinely social purposes, with conscious thought about how it can improve your life and your relationships, you’ll be far more likely to enjoy your digital existence.
This article was originally published on the Behavioral Scientist . Read the original article .
About the Author

Jenna Clark
Jenna Clark, Ph.D. , is a senior behavioral researcher at Duke University's Center for Advanced Hindsight, where she works to help people make healthy decisions in spite of themselves. She's also interested in how technology contributes to our well-being through its effect on our close personal relationships.
You May Also Enjoy

This article — and everything on this site — is funded by readers like you.
Become a subscribing member today. Help us continue to bring “the science of a meaningful life” to you and to millions around the globe.
Tech at the edge: Trends reshaping the future of IT and business
It is easy to become numb to the onslaught of new technologies hitting the market, each with its own promise of changing (more often “revolutionizing”) the business world. But our analysis of some of the more meaningful tech trends lays out a convincing case that something significant is happening. 1 Michael Chui, Roger Roberts, and Lareina Yee, “ McKinsey Technology Trends Outlook 2022 ,” McKinsey, August 24, 2022.
These tech trends are generally accelerating the primary characteristics that have defined the digital era: granularity, speed, and scale. But it’s the magnitude of these changes—in computing power, bandwidth, and analytical sophistication—that is opening the door to new innovations, businesses, and business models.
The emergence of cloud and 5G , for example, exponentially increases compute power and network speeds that can enable greater innovation. Developments in the metaverse of augmented and virtual reality open the doors to virtual R&D via digital twins , for example, and immersive learning. Advances in AI, machine learning, and software 2.0 (machine-written code) bring a range of new services and products, from autonomous vehicles to connected homes, well within reach.
Much ink has been spilled on identifying tech trends, but less attention has been paid to the implications of those changes. To help understand how management will need to adapt in the face of these technology trends in the next three to five years, we spoke to business leaders and leading thinkers on the topic. We weren’t looking for prognostications; we wanted to explore realistic scenarios, their implications, and what senior executives might do to get ready.
The discussions pinpointed some broad, interrelated shifts, such as how technology’s radically increasing power is exerting a centrifugal force on the organization, pushing innovation to expert networks at the edges of the company; how the pace and proliferation of these innovations calls for radical new approaches to continuous learning built around skills deployed at points of need; how these democratizing forces mean that IT can no longer act as a centralized controller of technology deployment and operations but instead needs to become a master enabler and influencer; and how these new technologies are creating more data about, and touchpoints with, customers, which is reshaping the boundaries of trust and requiring a much broader understanding of a company’s security responsibilities.
1. Innovation at the edge
Key tech trends.
We estimate that 70 percent of companies will employ hybrid or multicloud management technologies, tools, and processes . 2 “ The top trends in tech ,” McKinsey, June 15, 2021. At the same time, 5G will deliver network speeds that are about ten times faster than current speeds on 4G LTE networks, 3 Irina Ivanova, “What consumers need to know about this week’s AT&T–Verizon 5G rollout,” CBS News, January 20, 2022. with expectations of speeds that are up to 100 times faster with 40 times faster latency. 4 “5G speed: 5G vs. 4G performance compared,” Tom’s Guide, June 1, 2021. By 2024, more than 50 percent of user touches will be augmented by AI-driven speech, written word, or computer-vision algorithms , 5 “ The top trends in tech ,” June 15, 2021. while global data creation is projected to grow to more than 180 zettabytes by 2025, up from 64.2 zettabytes in 2020. 6 “Amount of data created, consumed, and stored 2010–2025,” Statista Research Department, May 23, 2022. The low-code development platform market‘s compound annual growth rate (CAGR) is projected at about 30 percent through 2030. 7 “Global $187 billion low-code development platform market to 2030,” GlobeNewswire, November 10, 2020.
Shift: Innovation develops around personal networks of experts at the porous edge of the organization and is supported by capabilities that scale the benefits across the business.
These technologies promise access to virtually unlimited compute power and massive data sets, as well as a huge leap in bandwidth at low cost, making it cheaper and easier to test, launch, and scale innovations quickly. The resulting acceleration in innovation will mean that companies can expect more disruptions from more sources. Centralized strategic and innovation functions cannot hope to keep pace on their own. Companies will need to be much more involved in networks outside their organizations to spot, invest in, and even acquire promising opportunities.
Corporate venture-capital (VC) funds with centralized teams have looked to find and fund innovation, but their track record has been spotty, often because the teams lack the requisite skills and are simply too far removed from the constantly evolving needs of individual business units. Instead, companies will need to figure out how to tap their front lines, particularly business domain experts and technologists, to enable them to act, in effect, as the business’s VC arm. That’s because the people who are writing code and building solutions are often well plugged into strong external networks in their fields and have the expertise to evaluate new developments. One pharma company, for example, taps its own expert researchers in various fields, such as gene expression, who know well the people outside the company who are leaders in the field.
While companies will need to create incentives and opportunities for engineers to build up and engage with their networks, the key focus must be on empowering teams so they can spend their allocated budget as they see fit—for example, experimenting and failing without penalty (within boundaries) and deciding on technologies to meet their goals (within prescribed guidelines).
The IT organization of the future can play an important role in building up a scaling capability to make that innovation work for the business, something that has traditionally been a challenge. Individual developers or small teams working fast don’t tend to naturally think about how to scale an application. That issue is likely to be exacerbated as nontechnical users working in pockets across organizations use low-code/no-code (LC/NC) applications to design and build programs with point-and-click or pull-down-menu interfaces.
One pharma company has taken this idea to heart by giving local business units the flexibility to run with a nonstandard idea when it has proven to be better than what the company is already doing. In return for that flexibility, the business unit must commit to helping the rest of the organization use the new idea, and IT builds it into the company’s standards.
In considering how this scaling capability might work, companies could, for example, assign advanced developers to “productize” applications by refactoring code so they can scale. IT leadership can provide tools and platforms, reusable-code libraries that are easily accessible, and flexible, standards-based architecture so that innovations can be scaled across the business more easily.
Questions for leadership
- What incentives will best encourage engineers and domain experts to develop, maintain, and tap into their networks?
- What processes are in place for tracking and managing VC activity at the edge?
- What capabilities do you need to identify innovation opportunities and “industrialize” the best ones so they can be shared across the organization?
For more on how to empower workers at the edge, see “ Tech companies innovate at the edge. Legacy companies can too ,” in Harvard Business Review.
Would you like to learn more about McKinsey Digital ?
2. a perpetual-learning culture.
Advances in AI, machine learning, robotics, and other technologies have increased the pace of change tenfold . By 2025, we estimate that 50 billion devices will be connected to the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), while 70 percent of manufacturers are expected to be using digital twins regularly (by 2022). 8 “ The top trends in tech ,” June 15, 2021. Some 70 percent of new applications will use LC/NC technologies by 2025, up from less than 25 percent in 2020. 9 “Gartner says cloud will be the centerpiece of new digital experiences,” Gartner, November 10, 2021. The global metaverse revenue opportunity could approach $800 billion in 2024, up from about $500 billion in 2020. 10 Bloomberg Intelligence, “Metaverse may be $800 billion market, next tech platform,” Bloomberg, December 1, 2021. This proliferation of technological innovations means we can expect to experience more progress in the next decade than in the past 100 years combined, according to entrepreneur and futurist Peter Diamandis. 11 Peter Diamandis and Steven Kotler, The Future Is Faster than You Think: How Converging Technologies Are Transforming Business, Industries, and Our Lives , New York: Simon & Schuster, 2020.
Shift: Tech literacy becomes core to every role, requiring learning to be continuous and built at the level of individual skills that are deployed at the point of need.
With the pace and proliferation of technologies pushing innovation to the edge of the organization, businesses need to be ready to incorporate the most promising options from across the front lines. This will create huge opportunities, but only for those companies that develop true tech intelligence through a perpetual-learning culture. The cornerstone of this effort includes training all levels of personnel, from “citizen developers” working with easy-to-use LC/NC tools or in entirely new environments such as the metaverse, to full-stack developers and engineers, who will need to continually evolve their skills to keep up with changing technologies. We’re already seeing situations where poorly trained employees use LC/NC to churn out suboptimal products.
While there will always be a need for more formalized paths for foundational learning, we anticipate an acceleration in the shift from teaching curricula periodically to continuous learning that can deliver varying technical skills across the entire organization. In practice, that will mean orienting employee development around delivering skills. This requires breaking down a capability into its smallest sets of composite skills. One large tech company, for example, created 146,000 skills data points for the 1,200 technical skills it was assessing.
The key point is that these skills “snippets”—such as a block of code or a video of a specific negotiating tactic—need to be integrated into the workflow so that they’re delivered when needed. This might be called a “LearnOps” approach, where learning is built into the operations. This integration mentality is established at Netflix, where data scientists partner directly with product managers, engineering teams, and other business units to design, execute, and learn from experiments. 12 Netflix Technology Blog , “Experimentation is a major focus of data science across Netflix,” blog entry by Martin Tingley et al., January 11, 2022.
As important as being able to deploy learning is building a learning culture by making continuous learning expected and easy to do. The way top engineers learn can be instructive. This is a community that is highly aware of the need to keep their skills up to date. They have ingrained habits of sharing code, and they gravitate to projects where they can learn. One advantage of using open source, for example, is the built-in community that constantly updates and reviews code. In the same spirit, we’re seeing companies budget extra time to allow people to try new tools or technologies when they’re building a product. Other companies are budgeting for “learning buffers” to allow for setbacks in product development that teams can learn from. 13 “ The big boost: How incumbents successfully scale their new businesses ,” McKinsey, August 27, 2020.
Netflix, which makes broad, open, and deliberate information sharing a core value, built the Netflix experimentation platform as an internal product that acts as a repository of solutions for future teams to reuse. It has a product manager and innovation road map, with the goal of making experimentation a simple and integrated part of the product life cycle. 14 Netflix Technology Blog , “Netflix: A culture of learning,” blog entry by Martin Tingley et al., January 25, 2022.
To support this kind of continuous learning and experimentation, companies will need to accept mistakes. The art will be in limiting the impact of potentially costly mistakes, such as the loss or misuse of customer data. IT will need to architect protocols, incentives, and systems to encourage good behaviors and reduce bad ones. Many companies are beginning to adopt practices such as automated testing to keep mistakes from happening in the first place ; creating spaces where mistakes won’t affect other applications or systems, such as isolation zones in cloud environments ; and building in resiliency protocols.
- Do you have a list of the most important skills your business needs?
- What is the minimum level of learning needed for advanced users of analytics and manipulators of data?
- How do you track what people are learning and whether that learning is effective and translating into better performance?
3. IT as a service
It is estimated that the global cloud microservices platform market will generate $4.2 billion in revenue by 2028, up from $952 million in 2020. 15 Cloud microservice platform market report , Research Dive, November 2021. GitHub has more than 200 million code repositories and expects 100 million software developers by 2025. 16 Paul Krill, “GitHub expects more than 100 million software developers by 2025,” InfoWorld, December 3, 2020. Nearly 90 percent of developers already use APIs. 17 Christina Voskoglou, “APIs have taken over software development,” Nordic APIs, October 27, 2020. Software 2.0 creates new ways of writing software and reduces complexity. Software sourced by companies from cloud-service platforms, open repositories, and software as a service (SaaS) is growing at a CAGR of 27.5 percent from 2021 to 2028. 18 Software as a service (SaaS) market, 2021–2028 , Fortune Business Insights, January 2022.
Shift: IT becomes the enabler of product innovation by serving small, interoperable blocks of code.
When innovation is pushed to the edge and a perpetual-learning culture permeates an organization, the role of IT shifts dramatically. IT can’t support this dynamic environment by sticking to its traditional role as a controlling entity managing technology at the center. The premium will now be on IT’s ability to enable innovation, requiring a shift in its traditional role as protector of big tech assets to a purveyor of small blocks of code. The gold standard of IT effectiveness will be its ability to help people stitch together snippets of code into a useful product.
We are already seeing what that might look like. Employees at G&J Pepsi-Cola Bottlers with little to no experience at software development created an app that examines images of a store shelf to identify the number and type of bottles on it, then automatically restocks it based on historic trends. 19 Adam Burden, “Low code/no code could reshape business innovation,” VentureBeat, February 5, 2022. One pharmaceutical company grew its low-code platform base from eight users to 1,400 in just one year . Business users outside of IT are now building applications with thousands of monthly sessions. 20 Shivam Srivastava, Kartik Trehan, Dilip Wagle, and Jane Wang, “ Developer Velocity: How software excellence fuels business performance ,” McKinsey, April 20, 2020. Companies that empower “citizen developers” score 33 percent higher on innovation compared with bottom-quartile companies that don’t provide that level of support, according to a McKinsey survey. 21 Shivam Srivastava, Kartik Trehan, Dilip Wagle, and Jane Wang, “ Developer Velocity: How software excellence fuels business performance ,” McKinsey, April 20, 2020.
These developments point toward much more of a “buffet” approach to technology, where IT builds useful blocks of reusable code, sometimes assembles them into specific products, and makes them available through a user-friendly cataloging system for the business to use to create the products it needs. IT provides guiderails, such as API standards and directives on the environments in which the code might be most useful; protects the most sensitive information, such as customer data and financial records; and tracks their adoption. This tracking capability will become particularly crucial as bots, AI, algorithms, and APIs proliferate. Transparency isn’t sufficient. IT will need to make sense of all the activity through advanced tech performance and management capabilities and the development of new roles, such as data diagnosticians and bot managers.
This IT-as-a-service approach puts the product at the center of the operating model, requiring a commitment to organizing IT around product management . Some companies have been moving in this direction. But reaching the scale needed to support fast-paced and more diffuse innovation will require a deeper commitment to product owners, working with leaders in the business side of the house, to run teams with real P&L responsibility. Many organizations, from traditional enterprises to digital natives, have found that putting in place product leaders who set overall product and portfolio strategy, drive execution, and empower product owners to drive innovation aligned with business outcomes and P&L metrics can increase the return on the funding that flows to technology delivery and quicken the pace of innovation.
- Do you have a vision for how the role of the IT organization will change to enable democratization of technology?
- How will you elevate the role of the technology product manager, and do you have a road map for developing that role?
- What systems will you need to put in place to manage and track the use, reuse, and performance of code?

McKinsey Technology Trends Outlook 2022
4. expanded trust boundaries.
It was estimated that almost 100 percent of biometrics-capable devices (such as smartphones) will be using biometrics for transactions by 2022. 22 “Usage of biometric technology in transactions with mobile devices worldwide 2016–2022”, Statista Research Department, June 13, 2022. The effectiveness of these technologies has advanced dramatically, with the best facial-identification algorithms having improved 50 times since 2014. 23 William Crumpler, “How accurate are facial recognition systems—and why does it matter?” Center for Strategies and International Studies (CSIS), April 14, 2020. These developments are contributing to profound unease in the relationship between technology and consumers of technology. The Pearson Institute and the Associated Press-NORC Center for Public Affairs Research shows that “about two-thirds of Americans are very or extremely concerned about hacking that involves their personal information, financial institutions, government agencies, or certain utilities.” 24 Chuck Brooks, “More alarming cybersecurity stats for 2021!” Forbes , October 24, 2021.
Shift: Trust expands to cover a broader array of stakeholder concerns and become an enterprise-wide responsibility.
These enormous shifts in technology power and capacity will create many more touchpoints with customers and an exponential wave of new data about customers. Even as IT’s role within the organization becomes more that of an enabler, the expanding digital landscape means that IT must broaden its trust capabilities around security, privacy, and cyber . To date, consumers have largely embraced the convenience that technology provides, from ordering a product online to adjusting the temperature in their homes remotely to monitoring their health through personal devices. In exchange for these conveniences, consumers have traditionally been willing to provide some personal information. But a steady undercurrent of privacy and trust concerns around these ever-more-sophisticated conveniences is raising the stakes on the broad topic of trust. Consumers are becoming more aware of their identity rights, making decisions based on values, and demanding the ethical use of data and responsible AI .
The most obvious concern is around cybersecurity , an ongoing issue that is already on the board-level agenda. But tech-driven trust issues are much broader and are driven by three characteristics. One is the sheer quantity of personal data, such as biometrics, that companies and governments collect, creating concerns about privacy and data misuse. The second is that personal security issues are becoming more pervasive in the physical world. Wired homes, connected cars, and the Internet of Medical Things, for example, are all vectors for attack that can affect people’s well-being. Third is the issue that advanced analytics seem too complex to be understood and controlled, leading to deep unease about people’s relationship with technology. This issue is driving the development of “ explainable AI ” and the movement to debias AI.
Adding to the complexity is the frequent need to manage and secure trust across an entire ecosystem of technologies. Take the wired home, for example. The proliferation of devices—think virtual assistants, security, communications, power management, and entertainment systems—means that a large group of providers will need to agree on standards for managing, in effect, an interconnected security net in the home.
These developments require a complex extension of the boundaries of trust. The significant advantages that many incumbents enjoy—existing relationships with customers and proprietary data—are at risk unless businesses rethink how they manage and nurture that trust. Companies need to consider putting identity and trust management at the core of their customer experience and business processes. That can happen effectively only when companies assign a dedicated leader with real power and board-level prioritization with enterprise-wide responsibility across the entire trust and security landscape. Given the tech underpinnings of this trust environment, IT will need to play a key role in monitoring and remediating, such as assessing the impact of new legislation on AI algorithms, tracking incidents, identifying the number and nature of high-risk data-processing activities and automated decisions, and—perhaps most important—monitoring consumer trust levels and the issues that affect them.
- Who is responsible for the enterprise-wide trust and risk landscape?
- How have you integrated your efforts around customer trust with overall cybersecurity processes?
- What privacy, trust, and security processes are in place to manage the entire life cycle of your data?
It is inevitable that the pace of technological change will continue to accelerate. The successful technology leader of the future will not simply need to adopt new technologies but to build capabilities to absorb continuous change and make it a source of competitive advantage.
Steve Van Kuiken is a senior partner in McKinsey’s New Jersey office.
Explore a career with us
Related articles.

Digital twins: From one twin to the enterprise metaverse

Why digital trust truly matters

IoT value set to accelerate through 2030: Where and how to capture it
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Technology Essay


Essay on Technology
The word "technology" and its uses have immensely changed since the 20th century, and with time, it has continued to evolve ever since. We are living in a world driven by technology. The advancement of technology has played an important role in the development of human civilization, along with cultural changes. Technology provides innovative ways of doing work through various smart and innovative means.
Electronic appliances, gadgets, faster modes of communication, and transport have added to the comfort factor in our lives. It has helped in improving the productivity of individuals and different business enterprises. Technology has brought a revolution in many operational fields. It has undoubtedly made a very important contribution to the progress that mankind has made over the years.
The Advancement of Technology:
Technology has reduced the effort and time and increased the efficiency of the production requirements in every field. It has made our lives easy, comfortable, healthy, and enjoyable. It has brought a revolution in transport and communication. The advancement of technology, along with science, has helped us to become self-reliant in all spheres of life. With the innovation of a particular technology, it becomes part of society and integral to human lives after a point in time.
Technology is Our Part of Life:
Technology has changed our day-to-day lives. Technology has brought the world closer and better connected. Those days have passed when only the rich could afford such luxuries. Because of the rise of globalisation and liberalisation, all luxuries are now within the reach of the average person. Today, an average middle-class family can afford a mobile phone, a television, a washing machine, a refrigerator, a computer, the Internet, etc. At the touch of a switch, a man can witness any event that is happening in far-off places.
Benefits of Technology in All Fields:
We cannot escape technology; it has improved the quality of life and brought about revolutions in various fields of modern-day society, be it communication, transportation, education, healthcare, and many more. Let us learn about it.
Technology in Communication:
With the advent of technology in communication, which includes telephones, fax machines, cellular phones, the Internet, multimedia, and email, communication has become much faster and easier. It has transformed and influenced relationships in many ways. We no longer need to rely on sending physical letters and waiting for several days for a response. Technology has made communication so simple that you can connect with anyone from anywhere by calling them via mobile phone or messaging them using different messaging apps that are easy to download.
Innovation in communication technology has had an immense influence on social life. Human socialising has become easier by using social networking sites, dating, and even matrimonial services available on mobile applications and websites.
Today, the Internet is used for shopping, paying utility bills, credit card bills, admission fees, e-commerce, and online banking. In the world of marketing, many companies are marketing and selling their products and creating brands over the internet.
In the field of travel, cities, towns, states, and countries are using the web to post detailed tourist and event information. Travellers across the globe can easily find information on tourism, sightseeing, places to stay, weather, maps, timings for events, transportation schedules, and buy tickets to various tourist spots and destinations.
Technology in the Office or Workplace:
Technology has increased efficiency and flexibility in the workspace. Technology has made it easy to work remotely, which has increased the productivity of the employees. External and internal communication has become faster through emails and apps. Automation has saved time, and there is also a reduction in redundancy in tasks. Robots are now being used to manufacture products that consistently deliver the same product without defect until the robot itself fails. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technology are innovations that are being deployed across industries to reap benefits.
Technology has wiped out the manual way of storing files. Now files are stored in the cloud, which can be accessed at any time and from anywhere. With technology, companies can make quick decisions, act faster towards solutions, and remain adaptable. Technology has optimised the usage of resources and connected businesses worldwide. For example, if the customer is based in America, he can have the services delivered from India. They can communicate with each other in an instant. Every company uses business technology like virtual meeting tools, corporate social networks, tablets, and smart customer relationship management applications that accelerate the fast movement of data and information.
Technology in Education:
Technology is making the education industry improve over time. With technology, students and parents have a variety of learning tools at their fingertips. Teachers can coordinate with classrooms across the world and share their ideas and resources online. Students can get immediate access to an abundance of good information on the Internet. Teachers and students can access plenty of resources available on the web and utilise them for their project work, research, etc. Online learning has changed our perception of education.
The COVID-19 pandemic brought a paradigm shift using technology where school-going kids continued their studies from home and schools facilitated imparting education by their teachers online from home. Students have learned and used 21st-century skills and tools, like virtual classrooms, AR (Augmented Reality), robots, etc. All these have increased communication and collaboration significantly.
Technology in Banking:
Technology and banking are now inseparable. Technology has boosted digital transformation in how the banking industry works and has vastly improved banking services for their customers across the globe.
Technology has made banking operations very sophisticated and has reduced errors to almost nil, which were somewhat prevalent with manual human activities. Banks are adopting Artificial Intelligence (AI) to increase their efficiency and profits. With the emergence of Internet banking, self-service tools have replaced the traditional methods of banking.
You can now access your money, handle transactions like paying bills, money transfers, and online purchases from merchants, and monitor your bank statements anytime and from anywhere in the world. Technology has made banking more secure and safe. You do not need to carry cash in your pocket or wallet; the payments can be made digitally using e-wallets. Mobile banking, banking apps, and cybersecurity are changing the face of the banking industry.
Manufacturing and Production Industry Automation:
At present, manufacturing industries are using all the latest technologies, ranging from big data analytics to artificial intelligence. Big data, ARVR (Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality), and IoT (Internet of Things) are the biggest manufacturing industry players. Automation has increased the level of productivity in various fields. It has reduced labour costs, increased efficiency, and reduced the cost of production.
For example, 3D printing is used to design and develop prototypes in the automobile industry. Repetitive work is being done easily with the help of robots without any waste of time. This has also reduced the cost of the products.
Technology in the Healthcare Industry:
Technological advancements in the healthcare industry have not only improved our personal quality of life and longevity; they have also improved the lives of many medical professionals and students who are training to become medical experts. It has allowed much faster access to the medical records of each patient.
The Internet has drastically transformed patients' and doctors’ relationships. Everyone can stay up to date on the latest medical discoveries, share treatment information, and offer one another support when dealing with medical issues. Modern technology has allowed us to contact doctors from the comfort of our homes. There are many sites and apps through which we can contact doctors and get medical help.
Breakthrough innovations in surgery, artificial organs, brain implants, and networked sensors are examples of transformative developments in the healthcare industry. Hospitals use different tools and applications to perform their administrative tasks, using digital marketing to promote their services.
Technology in Agriculture:
Today, farmers work very differently than they would have decades ago. Data analytics and robotics have built a productive food system. Digital innovations are being used for plant breeding and harvesting equipment. Software and mobile devices are helping farmers harvest better. With various data and information available to farmers, they can make better-informed decisions, for example, tracking the amount of carbon stored in soil and helping with climate change.
Disadvantages of Technology:
People have become dependent on various gadgets and machines, resulting in a lack of physical activity and tempting people to lead an increasingly sedentary lifestyle. Even though technology has increased the productivity of individuals, organisations, and the nation, it has not increased the efficiency of machines. Machines cannot plan and think beyond the instructions that are fed into their system. Technology alone is not enough for progress and prosperity. Management is required, and management is a human act. Technology is largely dependent on human intervention.
Computers and smartphones have led to an increase in social isolation. Young children are spending more time surfing the internet, playing games, and ignoring their real lives. Usage of technology is also resulting in job losses and distracting students from learning. Technology has been a reason for the production of weapons of destruction.
Dependency on technology is also increasing privacy concerns and cyber crimes, giving way to hackers.

FAQs on Technology Essay
1. What is technology?
Technology refers to innovative ways of doing work through various smart means. The advancement of technology has played an important role in the development of human civilization. It has helped in improving the productivity of individuals and businesses.
2. How has technology changed the face of banking?
Technology has made banking operations very sophisticated. With the emergence of Internet banking, self-service tools have replaced the traditional methods of banking. You can now access your money, handle transactions, and monitor your bank statements anytime and from anywhere in the world. Technology has made banking more secure and safe.
3. How has technology brought a revolution in the medical field?
Patients and doctors keep each other up to date on the most recent medical discoveries, share treatment information, and offer each other support when dealing with medical issues. It has allowed much faster access to the medical records of each patient. Modern technology has allowed us to contact doctors from the comfort of our homes. There are many websites and mobile apps through which we can contact doctors and get medical help.
4. Are we dependent on technology?
Yes, today, we are becoming increasingly dependent on technology. Computers, smartphones, and modern technology have helped humanity achieve success and progress. However, in hindsight, people need to continuously build a healthy lifestyle, sorting out personal problems that arise due to technological advancements in different aspects of human life.
Essay on Technology – A Boon or Bane for Students
500+ words essay on technology for students.
In this essay on technology, we are going to discuss what technology is, what are its uses, and also what technology can do? First of all, technology refers to the use of technical and scientific knowledge to create, monitor, and design machinery. Also, technology helps in making other goods that aid mankind.
Essay on Technology – A Boon or Bane?
Experts are debating on this topic for years. Also, the technology covered a long way to make human life easier but the negative aspect of it can’t be ignored. Over the years technological advancement has caused a severe rise in pollution . Also, pollution has become a major cause of many health issues. Besides, it has cut off people from society rather than connecting them. Above all, it has taken away many jobs from the workers class.

Familiarity between Technology and Science
As they are completely different fields but they are interdependent on each other. Also, it is due to science contribution we can create new innovation and build new technological tools. Apart from that, the research conducted in laboratories contributes a lot to the development of technologies. On the other hand, technology extends the agenda of science.
Vital Part of our Life
Regularly evolving technology has become an important part of our lives. Also, newer technologies are taking the market by storm and the people are getting used to them in no time. Above all, technological advancement has led to the growth and development of nations.
Negative Aspect of Technology
Although technology is a good thing, everything has two sides. Technology also has two sides one is good and the other is bad. Here are some negative aspects of technology that we are going to discuss.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
With new technology the industrialization increases which give birth to many pollutions like air, water, soil, and noise. Also, they cause many health-related issues in animals, birds, and human beings.
Exhaustion of Natural Resources
New technology requires new resources for which the balance is disturbed. Eventually, this will lead to over-exploitation of natural resources which ultimately disturbs the balance of nature.
Unemployment
A single machine can replace many workers. Also, machines can do work at a constant pace for several hours or days without stopping. Due to this, many workers lost their job which ultimately increases unemployment .
Types of Technology
Generally, we judge technology on the same scale but in reality, technology is divided into various types. This includes information technology, industrial technology , architectural technology, creative technology and many more. Let’s discuss these technologies in brief.
Industrial Technology
This technology organizes engineering and manufacturing technology for the manufacturing of machines. Also, this makes the production process easier and convenient.
Creative Technology
This process includes art, advertising, and product design which are made with the help of software. Also, it comprises of 3D printers , virtual reality, computer graphics, and other wearable technologies.
Information Technology
This technology involves the use of telecommunication and computer to send, receive and store information. Internet is the best example of Information technology.

FAQs on Essay on Technology
Q.1 What is Information technology?
A – It is a form of technology that uses telecommunication and computer systems for study. Also, they send, retrieve, and store data.
Q.2 Is technology harmful to humans?
A – No, technology is not harmful to human beings until it is used properly. But, misuses of technology can be harmful and deadly.
Download Toppr – Best Learning App for Class 5 to 12
Toppr provides free study materials, last 10 years of question papers, 1000+ hours of video lectures, live 24/7 doubts solving, and much more for FREE! Download Toppr app for Android and iOS or signup for free.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

Feb 13, 2023
200-500 Word Example Essays about Technology
Got an essay assignment about technology check out these examples to inspire you.
Technology is a rapidly evolving field that has completely changed the way we live, work, and interact with one another. Technology has profoundly impacted our daily lives, from how we communicate with friends and family to how we access information and complete tasks. As a result, it's no surprise that technology is a popular topic for students writing essays.
But writing a technology essay can be challenging, especially for those needing more time or help with writer's block. This is where Jenni.ai comes in. Jenni.ai is an innovative AI tool explicitly designed for students who need help writing essays. With Jenni.ai, students can quickly and easily generate essays on various topics, including technology.
This blog post aims to provide readers with various example essays on technology, all generated by Jenni.ai. These essays will be a valuable resource for students looking for inspiration or guidance as they work on their essays. By reading through these example essays, students can better understand how technology can be approached and discussed in an essay.
Moreover, by signing up for a free trial with Jenni.ai, students can take advantage of this innovative tool and receive even more support as they work on their essays. Jenni.ai is designed to help students write essays faster and more efficiently, so they can focus on what truly matters – learning and growing as a student. Whether you're a student who is struggling with writer's block or simply looking for a convenient way to generate essays on a wide range of topics, Jenni.ai is the perfect solution.
The Impact of Technology on Society and Culture
Introduction:.
Technology has become an integral part of our daily lives and has dramatically impacted how we interact, communicate, and carry out various activities. Technological advancements have brought positive and negative changes to society and culture. In this article, we will explore the impact of technology on society and culture and how it has influenced different aspects of our lives.
Positive impact on communication:
Technology has dramatically improved communication and made it easier for people to connect from anywhere in the world. Social media platforms, instant messaging, and video conferencing have brought people closer, bridging geographical distances and cultural differences. This has made it easier for people to share information, exchange ideas, and collaborate on projects.
Positive impact on education:
Students and instructors now have access to a multitude of knowledge and resources because of the effect of technology on education . Students may now study at their speed and from any location thanks to online learning platforms, educational applications, and digital textbooks.
Negative impact on critical thinking and creativity:
Technological advancements have resulted in a reduction in critical thinking and creativity. With so much information at our fingertips, individuals have become more passive in their learning, relying on the internet for solutions rather than logic and inventiveness. As a result, independent thinking and problem-solving abilities have declined.
Positive impact on entertainment:
Technology has transformed how we access and consume entertainment. People may now access a wide range of entertainment alternatives from the comfort of their own homes thanks to streaming services, gaming platforms, and online content makers. The entertainment business has entered a new age of creativity and invention as a result of this.
Negative impact on attention span:
However, the continual bombardment of information and technological stimulation has also reduced attention span and the capacity to focus. People are easily distracted and need help focusing on a single activity for a long time. This has hampered productivity and the ability to accomplish duties.
The Ethics of Artificial Intelligence And Machine Learning
The development of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) technologies has been one of the most significant technological developments of the past several decades. These cutting-edge technologies have the potential to alter several sectors of society, including commerce, industry, healthcare, and entertainment.
As with any new and quickly advancing technology, AI and ML ethics must be carefully studied. The usage of these technologies presents significant concerns around privacy, accountability, and command. As the use of AI and ML grows more ubiquitous, we must assess their possible influence on society and investigate the ethical issues that must be taken into account as these technologies continue to develop.
What are Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning?
Artificial Intelligence is the simulation of human intelligence in machines designed to think and act like humans. Machine learning is a subfield of AI that enables computers to learn from data and improve their performance over time without being explicitly programmed.
The impact of AI and ML on Society
The use of AI and ML in various industries, such as healthcare, finance, and retail, has brought many benefits. For example, AI-powered medical diagnosis systems can identify diseases faster and more accurately than human doctors. However, there are also concerns about job displacement and the potential for AI to perpetuate societal biases.
The Ethical Considerations of AI and ML
A. Bias in AI algorithms
One of the critical ethical concerns about AI and ML is the potential for algorithms to perpetuate existing biases. This can occur if the data used to train these algorithms reflects the preferences of the people who created it. As a result, AI systems can perpetuate these biases and discriminate against certain groups of people.
B. Responsibility for AI-generated decisions
Another ethical concern is the responsibility for decisions made by AI systems. For example, who is responsible for the damage if a self-driving car causes an accident? The manufacturer of the vehicle, the software developer, or the AI algorithm itself?
C. The potential for misuse of AI and ML
AI and ML can also be used for malicious purposes, such as cyberattacks and misinformation. The need for more regulation and oversight in developing and using these technologies makes it difficult to prevent misuse.
The developments in AI and ML have given numerous benefits to humanity, but they also present significant ethical concerns that must be addressed. We must assess the repercussions of new technologies on society, implement methods to limit the associated dangers, and guarantee that they are utilized for the greater good. As AI and ML continue to play an ever-increasing role in our daily lives, we must engage in an open and frank discussion regarding their ethics.
The Future of Work And Automation
Rapid technological breakthroughs in recent years have brought about considerable changes in our way of life and work. Concerns regarding the influence of artificial intelligence and machine learning on the future of work and employment have increased alongside the development of these technologies. This article will examine the possible advantages and disadvantages of automation and its influence on the labor market, employees, and the economy.
The Advantages of Automation
Automation in the workplace offers various benefits, including higher efficiency and production, fewer mistakes, and enhanced precision. Automated processes may accomplish repetitive jobs quickly and precisely, allowing employees to concentrate on more complex and creative activities. Additionally, automation may save organizations money since it removes the need to pay for labor and minimizes the danger of workplace accidents.
The Potential Disadvantages of Automation
However, automation has significant disadvantages, including job loss and income stagnation. As robots and computers replace human labor in particular industries, there is a danger that many workers may lose their jobs, resulting in higher unemployment and more significant economic disparity. Moreover, if automation is not adequately regulated and managed, it might lead to stagnant wages and a deterioration in employees' standard of life.
The Future of Work and Automation
Despite these difficulties, automation will likely influence how labor is done. As a result, firms, employees, and governments must take early measures to solve possible issues and reap the rewards of automation. This might entail funding worker retraining programs, enhancing education and skill development, and implementing regulations that support equality and justice at work.
IV. The Need for Ethical Considerations
We must consider the ethical ramifications of automation and its effects on society as technology develops. The impact on employees and their rights, possible hazards to privacy and security, and the duty of corporations and governments to ensure that automation is utilized responsibly and ethically are all factors to be taken into account.
Conclusion:
To summarise, the future of employment and automation will most certainly be defined by a complex interaction of technological advances, economic trends, and cultural ideals. All stakeholders must work together to handle the problems and possibilities presented by automation and ensure that technology is employed to benefit society as a whole.
The Role of Technology in Education
Introduction.
Nearly every part of our lives has been transformed by technology, and education is no different. Today's students have greater access to knowledge, opportunities, and resources than ever before, and technology is becoming a more significant part of their educational experience. Technology is transforming how we think about education and creating new opportunities for learners of all ages, from online courses and virtual classrooms to instructional applications and augmented reality.
Technology's Benefits for Education
The capacity to tailor learning is one of technology's most significant benefits in education. Students may customize their education to meet their unique needs and interests since they can access online information and tools.
For instance, people can enroll in online classes on topics they are interested in, get tailored feedback on their work, and engage in virtual discussions with peers and subject matter experts worldwide. As a result, pupils are better able to acquire and develop the abilities and information necessary for success.
Challenges and Concerns
Despite the numerous advantages of technology in education, there are also obstacles and considerations to consider. One issue is the growing reliance on technology and the possibility that pupils would become overly dependent on it. This might result in a lack of critical thinking and problem-solving abilities, as students may become passive learners who only follow instructions and rely on technology to complete their assignments.
Another obstacle is the digital divide between those who have access to technology and those who do not. This division can exacerbate the achievement gap between pupils and produce uneven educational and professional growth chances. To reduce these consequences, all students must have access to the technology and resources necessary for success.
In conclusion, technology is rapidly becoming an integral part of the classroom experience and has the potential to alter the way we learn radically.
Technology can help students flourish and realize their full potential by giving them access to individualized instruction, tools, and opportunities. While the benefits of technology in the classroom are undeniable, it's crucial to be mindful of the risks and take precautions to guarantee that all kids have access to the tools they need to thrive.
The Influence of Technology On Personal Relationships And Communication
Technological advancements have profoundly altered how individuals connect and exchange information. It has changed the world in many ways in only a few decades. Because of the rise of the internet and various social media sites, maintaining relationships with people from all walks of life is now simpler than ever.
However, concerns about how these developments may affect interpersonal connections and dialogue are inevitable in an era of rapid technological growth. In this piece, we'll discuss how the prevalence of digital media has altered our interpersonal connections and the language we use to express ourselves.
Direct Effect on Direct Interaction:
The disruption of face-to-face communication is a particularly stark example of how technology has impacted human connections. The quality of interpersonal connections has suffered due to people's growing preference for digital over human communication. Technology has been demonstrated to reduce the usage of nonverbal signs such as facial expressions, tone of voice, and other indicators of emotional investment in the connection.
Positive Impact on Long-Distance Relationships:
Yet there are positives to be found as well. Long-distance relationships have also benefited from technological advancements. The development of technologies such as video conferencing, instant messaging, and social media has made it possible for individuals to keep in touch with distant loved ones. It has become simpler for individuals to stay in touch and feel connected despite geographical distance.
The Effects of Social Media on Personal Connections:
The widespread use of social media has had far-reaching consequences, especially on the quality of interpersonal interactions. Social media has positive and harmful effects on relationships since it allows people to keep in touch and share life's milestones.
Unfortunately, social media has made it all too easy to compare oneself to others, which may lead to emotions of jealousy and a general decline in confidence. Furthermore, social media might cause people to have inflated expectations of themselves and their relationships.
A Personal Perspective on the Intersection of Technology and Romance
Technological advancements have also altered physical touch and closeness. Virtual reality and other technologies have allowed people to feel physical contact and familiarity in a digital setting. This might be a promising breakthrough, but it has some potential downsides.
Experts are concerned that people's growing dependence on technology for intimacy may lead to less time spent communicating face-to-face and less emphasis on physical contact, both of which are important for maintaining good relationships.
In conclusion, technological advancements have significantly affected the quality of interpersonal connections and the exchange of information. Even though technology has made it simpler to maintain personal relationships, it has chilled interpersonal interactions between people.
Keeping tabs on how technology is changing our lives and making adjustments as necessary is essential as we move forward. Boundaries and prioritizing in-person conversation and physical touch in close relationships may help reduce the harm it causes.
The Security and Privacy Implications of Increased Technology Use and Data Collection
The fast development of technology over the past few decades has made its way into every aspect of our life. Technology has improved many facets of our life, from communication to commerce. However, significant privacy and security problems have emerged due to the broad adoption of technology. In this essay, we'll look at how the widespread use of technological solutions and the subsequent explosion in collected data affects our right to privacy and security.
Data Mining and Privacy Concerns
Risk of Cyber Attacks and Data Loss
The Widespread Use of Encryption and Other Safety Mechanisms
The Privacy and Security of the Future in a Globalized Information Age
Obtaining and Using Individual Information
The acquisition and use of private information is a significant cause for privacy alarm in the digital age. Data about their customers' online habits, interests, and personal information is a valuable commodity for many internet firms. Besides tailored advertising, this information may be used for other, less desirable things like identity theft or cyber assaults.
Moreover, many individuals need to be made aware of what data is being gathered from them or how it is being utilized because of the lack of transparency around gathering personal information. Privacy and data security have become increasingly contentious as a result.
Data breaches and other forms of cyber-attack pose a severe risk.
The risk of cyber assaults and data breaches is another big issue of worry. More people are using more devices, which means more opportunities for cybercriminals to steal private information like credit card numbers and other identifying data. This may cause monetary damages and harm one's reputation or identity.
Many high-profile data breaches have occurred in recent years, exposing the personal information of millions of individuals and raising serious concerns about the safety of this information. Companies and governments have responded to this problem by adopting new security methods like encryption and multi-factor authentication.
Many businesses now use encryption and other security measures to protect themselves from cybercriminals and data thieves. Encryption keeps sensitive information hidden by encoding it so that only those possessing the corresponding key can decipher it. This prevents private information like bank account numbers or social security numbers from falling into the wrong hands.
Firewalls, virus scanners, and two-factor authentication are all additional security precautions that may be used with encryption. While these safeguards do much to stave against cyber assaults, they are not entirely impregnable, and data breaches are still possible.
The Future of Privacy and Security in a Technologically Advanced World
There's little doubt that concerns about privacy and security will persist even as technology improves. There must be strict safeguards to secure people's private information as more and more of it is transferred and kept digitally. To achieve this goal, it may be necessary to implement novel technologies and heightened levels of protection and to revise the rules and regulations regulating the collection and storage of private information.
Individuals and businesses are understandably concerned about the security and privacy consequences of widespread technological use and data collecting. There are numerous obstacles to overcome in a society where technology plays an increasingly important role, from acquiring and using personal data to the risk of cyber-attacks and data breaches. Companies and governments must keep spending money on security measures and working to educate people about the significance of privacy and security if personal data is to remain safe.
In conclusion, technology has profoundly impacted virtually every aspect of our lives, including society and culture, ethics, work, education, personal relationships, and security and privacy. The rise of artificial intelligence and machine learning has presented new ethical considerations, while automation is transforming the future of work.
In education, technology has revolutionized the way we learn and access information. At the same time, our dependence on technology has brought new challenges in terms of personal relationships, communication, security, and privacy.
Jenni.ai is an AI tool that can help students write essays easily and quickly. Whether you're looking, for example, for essays on any of these topics or are seeking assistance in writing your essay, Jenni.ai offers a convenient solution. Sign up for a free trial today and experience the benefits of AI-powered writing assistance for yourself.
Try Jenni for free today
Create your first piece of content with Jenni today and never look back
Impact of Technology on Communication Essay
Introduction, advancement of technology in communication, media technology and online communication, the impacts of mobile phone on communication, reference list.
The realm of technology is ever-changing. New advances in applied science have forever transformed the way people interact. Exploring the impact of technology on communication and debating whether people connect with others differently seems to be the topic of the day.
Technology has allowed people to keep in touch no matter the distance. One is able to communicate 24 hours around the clock, seven days a week, 365 days on an interpersonal level.
What are the real impacts of technology on communication? How do electronics mediate and change the ways in which humans interact? How has the emergence of the Internet, mobile phones, and social networks affected society and businesses?
In order to reveal the importance of technology in communication, the essay tries to find answers to these questions. It explores how everything has changed over the years and discusses the connection between technology and communication.
To begin this examination and find answers to these questions, we begin by defining media and communication and outlining the stages of technological advancement from old age to the present day in the field of communication. The paper will highlight the use of the Internet, newspapers, radio, and other media, but it mostly dwells on the use of mobile telephony.
Communication is “the imparting or exchange of information by speaking, writing or using some other medium” (Daniel & Rod, 2011). On the other hand, media is defined as “the main means of mass communication (television, radio, and newspapers) regarded collectively.”
Technology has changed everything in the modern society. The way we communicate has been revolutionized by the advancement of new innovations in the telecommunication sector. Connecting with other people with ease is more feasible in today’s world, and this is due to speed.
Several centuries ago, books and newspapers reigned as the only choice of communication. Then later, innovators brought the radio and television before innovation was taken a notch higher with the coming of the personal computer (Johnson, 1997, p.3).
With every new innovation, the reliance on books and newspapers as the mass medium of communication continued to reduce. With time, human culture has come to understand the power and the mechanisms involved in technology and invention. In today’s world, information has permeated the cycles of change and development.
The world today, past and present, can be studied at ease with the growing information technology. Technology has advanced with sheer velocity allowing different media to shape our thinking and habits. The people who were born during the television era thought that it was the climax of innovation, but they suddenly found themselves acclimating to a new medium, the World Wide Web.
Every time a new medium rolls out, the perceptions towards the previous media you were used to change (Johnson, 1997 p5). Technology proved to be powerful in the sense that no human being can predict what will change and what won’t with certainty.
The irony of it all is the fact that the influence of technology extends beyond generations to come. It is with no doubt that technology has changed the lives of human beings; information and entertainment are being received in a more convenient way.
The innovation of having a conversation using a device called the telephone changed everything in communication. This became magical, and one couldn’t believe such innovation would exist (Tofts, 1997, p.40).
With the emergence of new media technologies, consumers have been empowered to ‘filter’ the information they want to receive. This allows them to have a choice of which news to watch or what information to listen to (Palmer, 2003, p.161).
Media consumption has been made an engaging experience with marketers studying the preferences of the consumers in order to reflect broader social changes in society. In today’s world, the computer is seen as a multi-purpose machine with work and leisure functions, therefore, creating more value.
The rise of the Internet has also made it possible to have virtual offices where the user can work from home or any convenient location. The flow of information from different media has greatly changed the social structures of society at different levels (Barry, 1999).
Digital media has enabled news and event to be channeled in real-time. The combination of the Internet and commerce has given birth to e-commerce sites providing huge potential for marketers to reach out to virtual communities.
In the world today, there are numerous media screens within our surroundings. This ranges from the television sets in our houses, computer monitors at the office, mobile phones and MP3 players in our pockets and handbag.
Even when shopping or waiting to board a plane, you’re most probably staring at screens with entertainment media (Soukup, 2008, p.5). Heavy marketing has been adopted by producers of mobile technologies targeting consumers who possess mobile phones with picture and video capacity (Goggin, 2006, p.170).
Media texts producers have termed mobile media as a “third screen,” a device that consumers carry around with much ease. Unlike television screens, broader communication networks have been integrated into personal computers and mobile phones (Goggin, 2006, p.9).
Train, buses, and airplanes have been dominated by mobile screens providing passengers with entertainment as well as other media content, especially advertisements (Caron & Carona, 2007, p.17). With a lot of commercial media content, the preferences of people change in their everyday lives.
The world of popular media has become chaotic, with hundreds of television channels to choose from, thousands of songs ready for download, and not forgetting millions of web pages to surf.
The emergence of social media like Facebook and Twitter has enabled people to manage interactions and relationships with many friends. Technologies have impacted interpersonal communication enabling people to interact more often than before.
In addition to reducing the distance between people, online communication with tools like Facebook and Twitter enables people to keep track of their contacts with friends and are more aware of the last time they interacted with them. Online communication now incorporates more than one mode of contact, including text, voice, and body language.
A mobile phone is a device that has always been seen as connecting people who are far apart, thus overcoming the geographical distance between them. The number of mobile phone users has continued to increase substantially. The mobile phone has been integrated as part of people’s lives in the sense that it’s available and easy to use, keeping us connected to our families, friends, and business people (Ling, 2004, p.21-24).
The how and when the way we use our mobile phones impacts our communication not only with those we’re communicating with but also with the people within our proximity. At this point, it is paramount to note the changes that have taken place and that have allowed the adoption of mobile phones. The tremendous proliferation of this device has drastically changed the traditional communication model.
Who are the users of mobile phones, and for what purposes do they use them? Has there been any change in the way mobile phone facilitates communication? How has the face to face interaction been affected by mobile calls? Has mobile communication enhanced relationships?
These are some of the questions that arise when we try to fathom the way communication has affected our personal and professional lives. There are sentiments that mobile phones have reduced humans to emotionless beings.
There is no doubt that the revolution brought about the use of mobile phones in the way we communicate. There have been different perceptions among individuals and social levels in society in regard to mobile usage.
When we had fixed telephone lines that were put in a booth, telephones were seen as business tools only and were placed in a fixed, quiet environment. There was restriction when it came to teenagers using these phones (Agar, 2003). The ‘birth’ of mobile phones brought changes, and phone calls became a habit to many irrespective of age or location.
Today, people can use mobile phones wherever they are in private or in public. People have been addicted to their mobile phones more than any other gadget known to man, with the device remaining on throughout. Its portability enables people to carry it wherever they go (Castells, 1996).
A personal virtual network has been created whereby users can be available at all times to communicate with friends, family, and colleagues. The geographical barrier has been destroyed, making people feel close to one another, and the face to face communication has been rendered rather less important with this mediated communication (Richard, 2004, p.22).
Meetings and briefings have become obsolete, with communication being mediated by a computer or a phone. Mobile SMS (short messaging service) service and the Internet has become the preferable communication channels for most teenagers and young people all over the world (Plant, 2000, p.23).
There are places where mobile phones have become taboo devices, places like churches and crucial corporate meetings. At such places, the mobile ring is seen as a nuisance. In other scenarios, it is seen as a destructive device by acting as a third party and especially for dating couples who want to have a private conversation.
Any phone ring is seen as an ‘intruder,’ and this harms the relationship between the partners (Plant, 2000, p.29). In his research, Plant observes that there are those people who use mobile as ’a means of managing privacy where calls are carefully selected’. He categorizes this group of people as ‘hedgehogs.’
The other category is those people who use mobile phones as the key central part of their life. They become so attached to the device and cannot do without it. Plant referred to this group as ‘fox.’ They are regular users who need to feel connected with their families and friend. Their life will be dreadful if they lack the device (2000, p.32).
Telephones have promoted the use of text messaging and modernization since it’s allowing people to communicate more both verbally and by texting in a more convenient and efficient way. SMS has made communication to be more immediate, and users can customize the message at ease with the various applications installed on their mobiles (Richard, 2004, p. 100).
The advanced phones have email support as well as multimedia messages making chatting become a lifestyle for many who conduct business and those initiating intimate communication. It has emerged that SMS has made people become more united.
Users have developed abbreviated messages, which are now universally accepted as an appropriate language. The initial purpose of the phone to make calls has even lost taste with many people, especially the young generation.
According to Reid &Reid, more than 85% of teenagers prefer texting to talking on their mobile usage (Reid & Reid, 2004, p.1). There is ease of communication when it comes to texting in the sense that some formalities are eliminated, making communication more personal.
Texting has helped introverts who may lack the skills to have phone conversations allowing them to express their true self to other people leading to greater understanding and stronger relationships (Reid & Reid, 2004, p.8).
The use of mobile technology has affected the personalities of people to a great extent. Today, more people are hiding their feelings and whereabouts behind mobile phones, and this has raised suspicions among families, friends, and couples.
People go through text messages of others just to find out more about the individual who might even have no clue about what is happening. Contrary to this, most people believe that mobile is so crucial in enhancing the relationship between people no matter the distance and that it bonds us together more than it separates us (Plant, 2000, p.58).
The usage of mobile phones by children and teenagers has changed the way parents bring up their kids. Parenting has really changed as parents try to increase their surveillance and monitor their children’s mobile usage.
Their concern is to know who communicates with their kind and the kind of conversations they normally have. They are worried about the kind of social network the children create in their contact lists.
With the emergence of virtual communities, the influence of mobile phones has spilled over and affects parenting in general. Nonetheless, the primary purpose of mobile phones to facilitate communication has not changed.
There is no doubt that technology has changed the way humans communicate. Great impacts can be seen in the way communication has changed the social structures of our society at all levels. Even in years to come, technology remains the driving force of the way people interact.
The advancement of technology ensures that communication is quicker and that more people remain connected. There has been an evolution in interpersonal skills with the advancement of technology, and users should always be keen on adapting to new ways of communication.
Technology has continually brought new methods of communication leading to the expansion of mediated communication. The reality of having one message shared across a huge audience (mass communication) is now with us. A situation where neither time nor geography can limit the accessibility of information.
We have seen the merging together of newspapers and books with computer technology so that the frequency and ease of reporting information and advertisements can be increased. The exposure of both individuals and society to mediated communication has therefore affected our daily lives, particularly in our culture and the way we communicate.
Agar, J., 2003. Constant Touch: A Global History of the Mobile Phone . Cambridge: Icon Books.
Barry, W., 1999. Networks in the Global Village . Boulder Colo: Westview Press.
Caron, A, & Caronia, L., 2007. Moving cultures: mobile communication in everyday life. Montreal: McGill-Queen’s University Press.
Castells, M., 1996. The Information Age: Economy, Society and Culture, Volume 1. The Rise of the Network Society . Oxford: Blackwell.
Daniel, C., & Rod, M., 2011.The Dictionary of Media and Communications . Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Goggin, G., 2006. Cell phone culture mobile technology in everyday life. New York: Routledge.
Palmer, D., 2003. The Paradox of User Control’. 5 th Annual Digital Arts and Culture Conference (Proceedings), pp.160-164.
Plant, S., 2000. On the Mobile: the effects of mobile telephones on social and individual life . Web.
Postman, N., 1992. Technopoly: The surrender of culture to technology . New York: Vintage Books.
Reid, D. J. & Reid F. J. M., 2004. Insights into the Social and Psychological Effects of SMS Text Messaging . Web.
Richard, L., 2004. The Mobile Connection: The Cell Phone’s Impact on Society . San Francisco Morgan: Kaufmann.
Soukup, C., 2008. ‘Magic Screens: Everyday Life in an Era of Ubiquitous and Mobile Media Screens’, presented at 94 th annual Convention . San Diego .
Stephen, J., 1997. Interface Culture: How New Technology Transforms the Way We Create and Communicate . San Francisco: Basic Books.
Tofts, D., 1997. ‘ The technology within’ in memory trade: A Prehistory of Cyberculture, North Ryde: 21C Books.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2023, October 28). Impact of Technology on Communication Essay. https://ivypanda.com/essays/impact-of-technology-on-communication/
"Impact of Technology on Communication Essay." IvyPanda , 28 Oct. 2023, ivypanda.com/essays/impact-of-technology-on-communication/.
IvyPanda . (2023) 'Impact of Technology on Communication Essay'. 28 October.
IvyPanda . 2023. "Impact of Technology on Communication Essay." October 28, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/impact-of-technology-on-communication/.
1. IvyPanda . "Impact of Technology on Communication Essay." October 28, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/impact-of-technology-on-communication/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Impact of Technology on Communication Essay." October 28, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/impact-of-technology-on-communication/.
- Texting's Importance for the Society
- Texting as a Valuable Way of Communication
- Drunk Driving vs. Texting While Driving
- Dangers of Texting while Driving
- The South Dakota Legislature on Texting and Driving
- Texting in Modern Society
- Banning Texting while Driving Saves Lives
- LG Mobile Teen Texting Campaign
- Texting While Driving Should Be Illegal
- Tougher Punishment for Texting While Driving
- Electronic Communication
- The Role of Communication in Society
- Public Relations and Ethical Decisions
- Social Network Communication
- Modern Day Communication
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
How Pew Research Center will report on generations moving forward
Journalists, researchers and the public often look at society through the lens of generation, using terms like Millennial or Gen Z to describe groups of similarly aged people. This approach can help readers see themselves in the data and assess where we are and where we’re headed as a country.
Pew Research Center has been at the forefront of generational research over the years, telling the story of Millennials as they came of age politically and as they moved more firmly into adult life . In recent years, we’ve also been eager to learn about Gen Z as the leading edge of this generation moves into adulthood.
But generational research has become a crowded arena. The field has been flooded with content that’s often sold as research but is more like clickbait or marketing mythology. There’s also been a growing chorus of criticism about generational research and generational labels in particular.
Recently, as we were preparing to embark on a major research project related to Gen Z, we decided to take a step back and consider how we can study generations in a way that aligns with our values of accuracy, rigor and providing a foundation of facts that enriches the public dialogue.
A typical generation spans 15 to 18 years. As many critics of generational research point out, there is great diversity of thought, experience and behavior within generations.
We set out on a yearlong process of assessing the landscape of generational research. We spoke with experts from outside Pew Research Center, including those who have been publicly critical of our generational analysis, to get their take on the pros and cons of this type of work. We invested in methodological testing to determine whether we could compare findings from our earlier telephone surveys to the online ones we’re conducting now. And we experimented with higher-level statistical analyses that would allow us to isolate the effect of generation.
What emerged from this process was a set of clear guidelines that will help frame our approach going forward. Many of these are principles we’ve always adhered to , but others will require us to change the way we’ve been doing things in recent years.
Here’s a short overview of how we’ll approach generational research in the future:
We’ll only do generational analysis when we have historical data that allows us to compare generations at similar stages of life. When comparing generations, it’s crucial to control for age. In other words, researchers need to look at each generation or age cohort at a similar point in the life cycle. (“Age cohort” is a fancy way of referring to a group of people who were born around the same time.)
When doing this kind of research, the question isn’t whether young adults today are different from middle-aged or older adults today. The question is whether young adults today are different from young adults at some specific point in the past.
To answer this question, it’s necessary to have data that’s been collected over a considerable amount of time – think decades. Standard surveys don’t allow for this type of analysis. We can look at differences across age groups, but we can’t compare age groups over time.
Another complication is that the surveys we conducted 20 or 30 years ago aren’t usually comparable enough to the surveys we’re doing today. Our earlier surveys were done over the phone, and we’ve since transitioned to our nationally representative online survey panel , the American Trends Panel . Our internal testing showed that on many topics, respondents answer questions differently depending on the way they’re being interviewed. So we can’t use most of our surveys from the late 1980s and early 2000s to compare Gen Z with Millennials and Gen Xers at a similar stage of life.
This means that most generational analysis we do will use datasets that have employed similar methodologies over a long period of time, such as surveys from the U.S. Census Bureau. A good example is our 2020 report on Millennial families , which used census data going back to the late 1960s. The report showed that Millennials are marrying and forming families at a much different pace than the generations that came before them.
Even when we have historical data, we will attempt to control for other factors beyond age in making generational comparisons. If we accept that there are real differences across generations, we’re basically saying that people who were born around the same time share certain attitudes or beliefs – and that their views have been influenced by external forces that uniquely shaped them during their formative years. Those forces may have been social changes, economic circumstances, technological advances or political movements.
When we see that younger adults have different views than their older counterparts, it may be driven by their demographic traits rather than the fact that they belong to a particular generation.
The tricky part is isolating those forces from events or circumstances that have affected all age groups, not just one generation. These are often called “period effects.” An example of a period effect is the Watergate scandal, which drove down trust in government among all age groups. Differences in trust across age groups in the wake of Watergate shouldn’t be attributed to the outsize impact that event had on one age group or another, because the change occurred across the board.
Changing demographics also may play a role in patterns that might at first seem like generational differences. We know that the United States has become more racially and ethnically diverse in recent decades, and that race and ethnicity are linked with certain key social and political views. When we see that younger adults have different views than their older counterparts, it may be driven by their demographic traits rather than the fact that they belong to a particular generation.
Controlling for these factors can involve complicated statistical analysis that helps determine whether the differences we see across age groups are indeed due to generation or not. This additional step adds rigor to the process. Unfortunately, it’s often absent from current discussions about Gen Z, Millennials and other generations.
When we can’t do generational analysis, we still see value in looking at differences by age and will do so where it makes sense. Age is one of the most common predictors of differences in attitudes and behaviors. And even if age gaps aren’t rooted in generational differences, they can still be illuminating. They help us understand how people across the age spectrum are responding to key trends, technological breakthroughs and historical events.
Each stage of life comes with a unique set of experiences. Young adults are often at the leading edge of changing attitudes on emerging social trends. Take views on same-sex marriage , for example, or attitudes about gender identity .
Many middle-aged adults, in turn, face the challenge of raising children while also providing care and support to their aging parents. And older adults have their own obstacles and opportunities. All of these stories – rooted in the life cycle, not in generations – are important and compelling, and we can tell them by analyzing our surveys at any given point in time.
When we do have the data to study groups of similarly aged people over time, we won’t always default to using the standard generational definitions and labels. While generational labels are simple and catchy, there are other ways to analyze age cohorts. For example, some observers have suggested grouping people by the decade in which they were born. This would create narrower cohorts in which the members may share more in common. People could also be grouped relative to their age during key historical events (such as the Great Recession or the COVID-19 pandemic) or technological innovations (like the invention of the iPhone).
By choosing not to use the standard generational labels when they’re not appropriate, we can avoid reinforcing harmful stereotypes or oversimplifying people’s complex lived experiences.
Existing generational definitions also may be too broad and arbitrary to capture differences that exist among narrower cohorts. A typical generation spans 15 to 18 years. As many critics of generational research point out, there is great diversity of thought, experience and behavior within generations. The key is to pick a lens that’s most appropriate for the research question that’s being studied. If we’re looking at political views and how they’ve shifted over time, for example, we might group people together according to the first presidential election in which they were eligible to vote.
With these considerations in mind, our audiences should not expect to see a lot of new research coming out of Pew Research Center that uses the generational lens. We’ll only talk about generations when it adds value, advances important national debates and highlights meaningful societal trends.
- Age & Generations
- Demographic Research
- Generation X
- Generation Z
- Generations
- Greatest Generation
- Methodological Research
- Millennials
- Silent Generation

Kim Parker is director of social trends research at Pew Research Center
How Teens and Parents Approach Screen Time
Who are you the art and science of measuring identity, u.s. centenarian population is projected to quadruple over the next 30 years, older workers are growing in number and earning higher wages, teens, social media and technology 2023, most popular.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Economy & Work
- Family & Relationships
- Gender & LGBTQ
- Immigration & Migration
- International Affairs
- Internet & Technology
- News Habits & Media
- Non-U.S. Governments
- Other Topics
- Politics & Policy
- Race & Ethnicity
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Copyright 2024 Pew Research Center
Terms & Conditions
Privacy Policy
Cookie Settings
Reprints, Permissions & Use Policy
Samsung says AI to drive technology demand in second half after strong Q1
- Medium Text
- Memory chip sales nearly double from prior year
- Operating profit highest since Q3 2022
- Plans to increase HBM supply 3-fold in 2024

MEMORY CHIP PROFIT
Sign up here.
Reporting by Joyce Lee and Heekyong Yang; Editing by Miyoung Kim and Jamie Freed
Our Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. New Tab , opens new tab

Technology Chevron

Super Micro forecasts quarterly revenue above estimates as AI powers server demand
Super Micro Computer forecast fourth-quarter revenue above estimates on Tuesday as it expects continued demand for its servers used in artificial intelligence applications.

Advertisement
Supported by
In Race to Build A.I., Tech Plans a Big Plumbing Upgrade
The spending that the industry’s giants expect artificial intelligence to require is starting to come into focus — and it is jarringly large.
- Share full article

By Karen Weise
Karen Weise covers technology from Seattle.
If 2023 was the tech industry’s year of the A.I. chatbot, 2024 is turning out to be the year of A.I. plumbing. It may not sound as exciting, but tens of billions of dollars are quickly being spent on behind-the-scenes technology for the industry’s A.I. boom.
Companies from Amazon to Meta are revamping their data centers to support artificial intelligence. They are investing in huge new facilities, while even places like Saudi Arabia are racing to build supercomputers to handle A.I. Nearly everyone with a foot in tech or giant piles of money, it seems, is jumping into a spending frenzy that some believe could last for years.
Microsoft, Meta, and Google’s parent company, Alphabet, disclosed this week that they had spent more than $32 billion combined on data centers and other capital expenses in just the first three months of the year. The companies all said in calls with investors that they had no plans to slow down their A.I. spending.
In the clearest sign of how A.I. has become a story about building a massive technology infrastructure, Meta said on Wednesday that it needed to spend billions more on the chips and data centers for A.I. than it had previously signaled.
“I think it makes sense to go for it, and we’re going to,” Mark Zuckerberg, Meta’s chief executive, said in a call with investors.
The eye-popping spending reflects an old parable in Silicon Valley: The people who made the biggest fortunes in California’s gold rush weren’t the miners — they were the people selling the shovels. No doubt Nvidia, whose chip sales have more than tripled over the last year, is the most obvious A.I. winner.
The money being thrown at technology to support artificial intelligence is also a reminder of spending patterns of the dot-com boom of the 1990s. For all of the excitement around web browsers and newfangled e-commerce websites, the companies making the real money were software giants like Microsoft and Oracle, the chipmaker Intel, and Cisco Systems, which made the gear that connected those new computer networks together.
But cloud computing has added a new wrinkle: Since most start-ups and even big companies from other industries contract with cloud computing providers to host their networks, the tech industry’s biggest companies are spending big now in hopes of luring customers.
Google’s capital expenditures — largely the money that goes into building and outfitting data centers — almost doubled in the first quarter, the company said. Microsoft’s were up 22 percent . Amazon, which will report earnings on Tuesday, is expected to add to that growth.
Meta’s investors were unhappy with Mr. Zuckerberg, sending his company’s share price down more than 16 percent after the call. But Mr. Zuckerberg, who just a few years ago was pilloried by shareholders for a planned spending spree on augmented and virtual reality, was unapologetic about the money that his company is throwing at A.I. He urged patience, potentially for years.
“Our optimism and ambitions have just grown quite a bit,” he said.
Investors had no problem stomaching Microsoft’s spending. Microsoft is the only major tech company to report financial details of its generative A.I. business, which it said had contributed to more than a fifth of the growth of its cloud computing business. That amounted to $1 billion in three months, analysts estimated.
Microsoft said its generative A.I. business could have been even bigger — if the company had enough data center supply to meet the demand, underscoring the need to keep on building.
The A.I. investments are creating a halo for Microsoft’s core cloud computing offering, Azure, helping it draw new customers. “Azure has become a port of call for pretty much anybody who is doing any A.I. project,” Satya Nadella, Microsoft’s chief executive, said on Thursday.
(The New York Times sued Microsoft and its partner, OpenAI, in December, claiming copyright infringement of news content related to their A.I. systems.)
Google said sales from its cloud division were up 28 percent, including “an increasing contribution from A.I.”
In a letter to shareholders this month, Andy Jassy, Amazon’s chief executive, said that much attention had been paid to A.I. applications, like ChatGPT, but that the opportunity for more technical efforts, around infrastructure and data, was “gigantic.”
For the computing infrastructure, “the key is the chip inside it,” he said, emphasizing that bringing down costs and wringing more performance out of the chips is key to Amazon’s effort to develop its own A.I. chips .
Infrastructure demands generally fall into two buckets: First, there is building the largest, cutting-edge models, which some A.I. developers say could soon top $1 billion for each new round. Chief executives said that being able to work on developing cutting-edge systems, either directly or with partners, was essential for remaining at the forefront of A.I.
And then there is what’s called inferencing, or querying the models to actually use them. This can involve customers tapping into the systems, like an insurer using generative A.I. to summarize a customer complaint, or the companies themselves putting A.I. directly into their own products, as Meta recently did by embedding a chatbot assistant in Facebook and Instagram. That’s also expensive.
Data centers take time to build and outfit. Chips face supply shortages and costly fabrication. With such long-term bets, Susan Li, Meta’s finance chief, said the company was building with “fungibility.” It wants wiggle room to change how it uses the infrastructure, if the future turns out to be not exactly what it expects.
Karen Weise writes about technology and is based in Seattle. Her coverage focuses on Amazon and Microsoft, two of the most powerful companies in America. More about Karen Weise
Explore Our Coverage of Artificial Intelligence
News and Analysis
Saudi Arabia is plowing money into glitzy events, computing power and artificial intelligence research, putting it in the middle of an escalating U.S.-China struggle for technological influence.
Microsoft gave more signs that its hefty investments in A.I. were beginning to bear fruit, as it reported a 17 percent jump in revenue and a 20 percent increase in profit for the first three months of the year.
Meta projected that revenue for the current quarter would be lower than what Wall Street anticipated and said it would spend billions of dollars more on its artificial intelligence efforts, even as it reported robust revenue and profits for the first three months of the year.
The Age of A.I.
A new category of apps promises to relieve parents of drudgery, with an assist from A.I . But a family’s grunt work is more human, and valuable, than it seems.
Despite Mark Zuckerberg’s hope for Meta’s A.I. assistant to be the smartest , it struggles with facts, numbers and web search.
Much as ChatGPT generates poetry, a new A.I. system devises blueprints for microscopic mechanisms that can edit your DNA.
Could A.I. change India’s elections? Avatars are addressing voters by name, in whichever of India’s many languages they speak. Experts see potential for misuse in a country already rife with disinformation.
Which A.I. system writes the best computer code or generates the most realistic image? Right now, there’s no easy way to answer those questions, our technology columnist writes .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A crucial part of understanding how technology has created global change and, in turn, how global changes have influenced the development of new technologies is understanding the technologies themselves in all their richness and complexity—how they work, the limits of what they can do, what they were designed to do, how they are actually used.
Madeleine Hillyer. This article is part of: Pioneers of Change Summit. Since the dotcom bubble burst back in 2000, technology has radically transformed our societies and our daily lives. From smartphones to social media and healthcare, here's a brief history of the 21st century's technological revolution. Just over 20 years ago, the dotcom ...
Article by Kocielnik et al. (2018) Modern technologies allow people to collect a lot of data about their activities, for example, distance traveled and similar information. However, a gap remains in analyzing and using this data for personal learning. Therefore, it is necessary to involve users in reflection, which expands self-knowledge ...
Introduction. Modern technology has changed the world beyond recognition. Thanks to technology in the twentieth and twenty-first centuries, advances have been made that have revolutionized our lives. Modern man can hardly imagine his life without machines. Every day, new devices either appear, or existing ones are improved.
In conclusion, modern technology has become an integral part of our lives, offering countless benefits to society. It enhances communication, facilitates learning, advances medical practices, boosts productivity, and addresses environmental concerns. Additionally, it promotes accessibility, fuels innovation, and connects us on a global scale.
New vaccines, progress in clean, low-carbon energy, better cancer treatments - a range of future innovations could very much improve our living conditions and the environment around us. But, as I argue in a series of articles, there is one technology that could even more profoundly change our world: artificial intelligence (AI).
The debate of modern technology is one that reaches out to almost everyone in the modern era living in the United States, since it is a first world country, everybody living in the country at one point has interacted with a piece of modern technology. The evolution of technology in the last two decades has been exponentially fast, changing ...
In conclusion, modern technology, with its profound impact on communication, daily life, work, and play, is an undeniable force shaping the 21st-century human experience. 500 Words Essay on Modern Technology Introduction to Modern Technology. In the contemporary era, modern technology has emerged as a significant facet of human life.
Digital advances can support and accelerate achievement of each of the 17 Sustainable Development Goals - from ending extreme poverty to reducing maternal and infant mortality, promoting ...
7. Scott Gelber. By Sarah Bures. May 6, 2020. Times Insider explains who we are and what we do, and delivers behind-the-scenes insights into how our journalism comes together. For years ...
A quick glance at the research on technology-mediated interaction reveals an ambivalent literature. Some studies show that time spent socializing online can decrease loneliness, increase well-being, and help the socially anxious learn how to connect to others. Other studies suggest that time spent socializing online can cause loneliness, decrease well-being, and foster a crippling dependence ...
The disadvantages of modern technology involve numerous risks related to people's cognitive intelligence and children's healthy development. Nowadays, even pre-school children have access to gadgets and some online sources, which helps them to learn "by modeling the adult world" (Given et al., 2016, p. 350). This "world" may involve ...
PDF | On Aug 13, 2020, Zhuldizay T. Kulzhanova and others published Impact of Technology on Modern Society—A Philosophical Analysis of the Formation of Technogenic Environment | Find, read and ...
Yet even for a recent English word 'technology' has come to embrace often conflicting meanings. In this essay review I have three aims. First, I will offer a summary of Eric Schatzberg's important new opus Technology, which untangles and clarifies the history of 'technology' and its cognates as actors' categories. Second, I will ...
It is easy to become numb to the onslaught of new technologies hitting the market, each with its own promise of changing (more often "revolutionizing") the business world. But our analysis of some of the more meaningful tech trends lays out a convincing case that something significant is happening. 1 Michael Chui, Roger Roberts, and Lareina Yee, "McKinsey Technology Trends Outlook 2022 ...
Essay on Technology. The word "technology" and its uses have immensely changed since the 20th century, and with time, it has continued to evolve ever since. We are living in a world driven by technology. The advancement of technology has played an important role in the development of human civilization, along with cultural changes.
A - It is a form of technology that uses telecommunication and computer systems for study. Also, they send, retrieve, and store data. Q.2 Is technology harmful to humans? A - No, technology is not harmful to human beings until it is used properly. But, misuses of technology can be harmful and deadly.
The World Health Organization (WHO) defines health technology as the application of organised knowledge and skills in the form of medicines, medical devices, vaccines, procedures and systems developed to solve a health problem and improve quality of life (World Health Organization, Health technology assessment).The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) defines health ...
Task 2 or the essay writing test of the IELTS writing section needs to be completed within 40 minutes, and the minimum word count is 250 words. The questions around general interest topics are mostly repeated by changing the question pattern and wording. Essays on modern technology have been frequently included as a part of task 2 over the years.
Direct Effect on Direct Interaction: The disruption of face-to-face communication is a particularly stark example of how technology has impacted human connections. The quality of interpersonal connections has suffered due to people's growing preference for digital over human communication.
Importance of technolog y in education. The role of technology in the field of education is four-. fold: it is included as a part of the curriculum, as an. instructional delivery system, as a ...
The current relationship between technology and mental health is, understandably, mainly portrayed pejoratively. The word "technology" is often associated with personal devices, media and the internet and criticized for its direct impact on attention span, addiction and self-esteem as it provides an aperture on others' lives enabling for ...
Project Maven was meant to revolutionize modern warfare. But the conflict in Ukraine has underscored how difficult it is to get 21st-century data into 19th-century trenches. By David E. Sanger ...
Much as ChatGPT generates poetry, a new A.I. system devises blueprints for microscopic mechanisms that can edit your DNA. The physical structure of OpenCRISPR-1, a gene editor created by A.I ...
The advancement of technology ensures that communication is quicker and that more people remain connected. There has been an evolution in interpersonal skills with the advancement of technology, and users should always be keen on adapting to new ways of communication. Technology has continually brought new methods of communication leading to ...
The tricky part is isolating those forces from events or circumstances that have affected all age groups, not just one generation. These are often called "period effects." An example of a period effect is the Watergate scandal, which drove down trust in government among all age groups.
Alphabet-owned Google has agreed to pay News Corp , owner of the Wall Street Journal, between $5 million and $6 million annually to develop new AI-related content and products, the Information ...
, opens new tab increased its sales during its fourth quarter, the computer peripherals maker said on Tuesday, snapping two-and-a-half years of sales downturns after a pandemic-driven boom.
The upbeat outlook from the world's largest memory chip maker sent its shares 1.8% higher on Tuesday after it reported a more than 10-fold rise in first-quarter operating profit.
If 2023 was the tech industry's year of the A.I. chatbot, 2024 is turning out to be the year of A.I. plumbing. It may not sound as exciting, but tens of billions of dollars are quickly being ...