- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips

Because, Because, Because (How to Prevent Repetition)
3-minute read
- 24th September 2016
When Dorothy, the Tin Man, the Scarecrow and the Cowardly Lion head off to see the Wizard of Oz , they do so ‘because, because, because, because, because, because, because of the wonderful things he does.’
This is undeniably a catchy tune to hum while walking a yellow brick road. From a proofreading perspective , however, it’s hard to get past the unnecessary repetition of ‘because’.
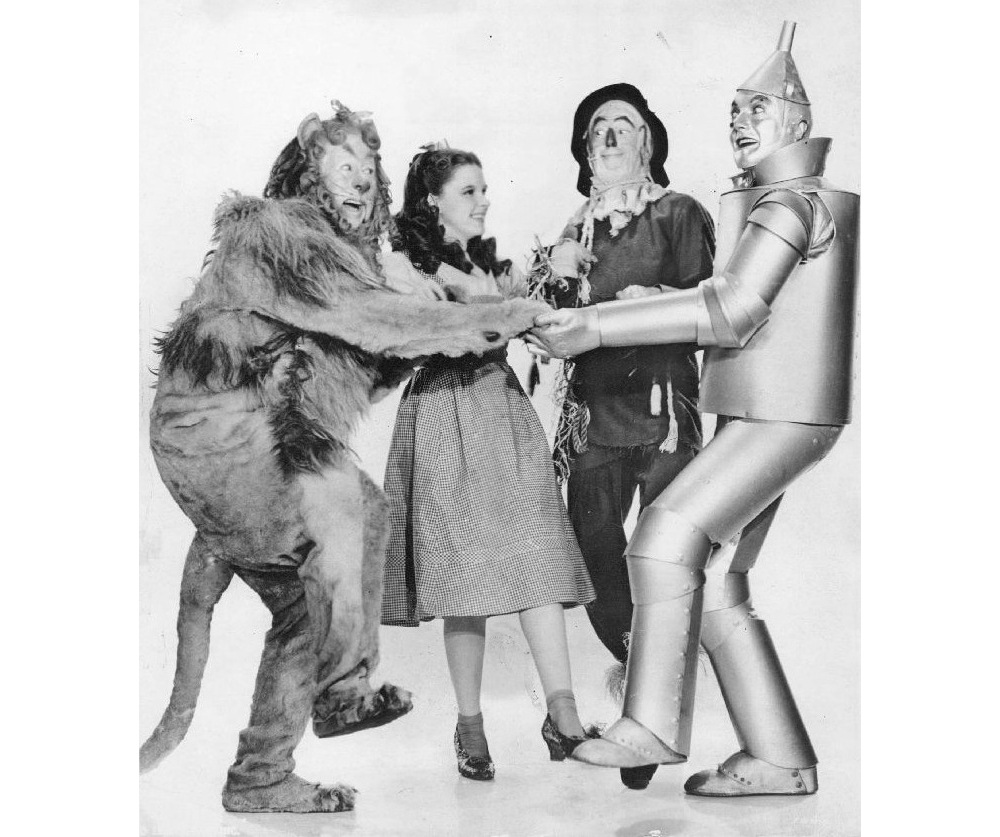

If Dorothy had used ‘because’ that often in an essay, we’d definitely suggest she make a few changes, as repetition can make your work seem monotonous. And since ‘because’ is a common term in academic writing , we recommend learning a few alternatives.
Synonyms for ‘Because’
There are plenty of words and phrases you can use in place of ‘because’ when introducing an explanation or justification in an essay. To demonstrate, we’ll work with this example sentence:
I went to see The Wizard of Oz because I love musical theatre.
Single words that can replace ‘because’ here include ‘as’, ‘since’ and ‘for’ (note that some terms require adding a comma to avoid ambiguity):
I went to see The Wizard of Oz , as I love musical theatre.
I went to see The Wizard of Oz since I love musical theatre.
I went to see The Wizard of Oz , for I love musical theatre.
However, ‘as’ and ‘since’ are both sometimes considered informal, while ‘for’ is quite old-fashioned. Thus, in academic writing, you may want to use a phrase instead:
I went to see The Wizard of Oz due to my love of musical theatre.
I went to see The Wizard of Oz as a result of my love for musical theatre.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
I went to see The Wizard of Oz on account of my love for musical theatre.
I went to see The Wizard of Oz in view of my love of musical theatre.
Many of these are actually replacements for the phrase ‘because of’ rather than just ‘because’, which is why the sentence is slightly changed in some cases.

Rearranging Sentences
Alternatively, you could get around overusing ‘because’ by rearranging sentences. For instance, we could say:
The Wizard of Oz was cancelled because the theatre burned down.

However, we could restructure the sentence to remove the ‘because’:
The theatre burned down, so The Wizard of Oz was cancelled.
Here, the conjunction ‘so’ is used to indicate that the second clause (‘ The Wizard of Oz was cancelled’) results from the first clause (‘the theatre burned down’). It thereby explains the situation without using ‘because’. Other possibilities include:
The theatre burned down; thus, The Wizard of Oz was cancelled.
The theatre burned down, which meant that The Wizard of Oz was cancelled.
There are, in fact, dozens of ways you could express the same idea without using ‘because’. The crucial thing is maintaining the sense of explaining or justifying something. Keep this in mind and it should be easy to avoid overusing words like ‘because’!
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Get help from a language expert. Try our proofreading services for free.
9-minute read
How to Use Infographics to Boost Your Presentation
Is your content getting noticed? Capturing and maintaining an audience’s attention is a challenge when...
8-minute read
Why Interactive PDFs Are Better for Engagement
Are you looking to enhance engagement and captivate your audience through your professional documents? Interactive...
7-minute read
Seven Key Strategies for Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization is rapidly shaping the digital landscape, requiring content professionals to adapt their...
How to Ace Slack Messaging for Contractors and Freelancers
Effective professional communication is an important skill for contractors and freelancers navigating remote work environments....
How to Insert a Text Box in a Google Doc
Google Docs is a powerful collaborative tool, and mastering its features can significantly enhance your...
2-minute read
How to Cite the CDC in APA
If you’re writing about health issues, you might need to reference the Centers for Disease...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
Word Choice: Alternatives to ‘Said’ and ‘Because’
3-minute read
- 29th November 2015
Our research shows that ‘said’ and ‘because’ are two of the most overused words in academic writing . This is understandable, as both are useful for explaining research and the results of studies.
However, excessive repetition of common words can detract from the flow of your written work, so it helps to know a few alternatives.
Alternatives to ‘Said’
The word ‘said’ is mostly used when reporting speech. This includes quoting research (e.g. in you literature review) or reporting what participants have said in an interview or survey. For example:
One respondent said that the process was ‘too complicated’.
There are lots of alternatives to ‘said’, all of which attribute the thought being reported to the person named. These include ‘claimed’, ‘suggested’ and ‘remarked’:
One respondent claimed that the process was ‘too complicated’.
One respondent suggested that the process was ‘too complicated’.
One respondent remarked that the process was ‘too complicated’.
There are also words you can use in place of ‘said’ when the person you’re quoting is doing something specific, such as arguing or clarifying a point:
Jones (1994, p.16) argues that ‘previous policies are now outdated’.
The CEO clarified that ‘company policy has changed since the incident’.
With these, make sure the word you use fits the context: it would not make sense, for instance, to say that ‘the CEO argued that company policy has changed’ as this is a factual claim (i.e. either policy has changed or it hasn’t), not an argument.
Alternatives to ‘Because’
The word ‘because’ means ‘due to the fact that’. As such, it’s handy for explaining your reasoning and commonly used when describing the consequences of something.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
There are two main ways to use ‘because’. One is as a conjunction, where ‘because’ is followed by a subject and a verb:
A qualitative approach was chosen because it enables collection of in-depth data.
In these cases, alternatives include ‘since’ and ‘as’, both of which are also conjunctions:
A qualitative approach was chosen since it enables collection of in-depth data.
A qualitative approach was chosen as it enables collection of in-depth data.
The phrase ‘because of’, meanwhile, is a preposition, so needs to be followed by a noun phrase or an ‘-ing’ verb:
The results are unreliable because of the limited sample size.
The business failed because of falling prices.
In this case, your alternatives include phrases like ‘due to’ and ‘as a result of’:
The results are unreliable due to the limited sample size.
The business failed as a result of falling prices.
Remember to check whether you’re using ‘because’ or ‘because of’ before selecting an alternative word.
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Get help from a language expert. Try our proofreading services for free.
9-minute read
How to Use Infographics to Boost Your Presentation
Is your content getting noticed? Capturing and maintaining an audience’s attention is a challenge when...
8-minute read
Why Interactive PDFs Are Better for Engagement
Are you looking to enhance engagement and captivate your audience through your professional documents? Interactive...
7-minute read
Seven Key Strategies for Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization is rapidly shaping the digital landscape, requiring content professionals to adapt their...
How to Ace Slack Messaging for Contractors and Freelancers
Effective professional communication is an important skill for contractors and freelancers navigating remote work environments....
How to Insert a Text Box in a Google Doc
Google Docs is a powerful collaborative tool, and mastering its features can significantly enhance your...
2-minute read
How to Cite the CDC in APA
If you’re writing about health issues, you might need to reference the Centers for Disease...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
- Daily Crossword
- Word Puzzle
- Word Finder
- Word of the Day
- Synonym of the Day
- Word of the Year
- Language stories
- All featured
- Gender and sexuality
- All pop culture
- Writing hub
- Grammar essentials
- Commonly confused
- All writing tips
- Pop culture
- Writing tips
Advertisement
conjunction as in on account of
Weak matches
- as a result of
- as things go
- by cause of
- by reason of
- by virtue of
- considering
- for the reason that
- for the sake of
- in as much as
- in behalf of
- in the interest of
- on the grounds that
preposition as in on account of
Discover More
Example sentences.
Because he's joined the colors—he's not dead!Because he's found his duty—he's not lost!
I will drive you over-because it is rather a lonesome walk for you.
He was silent; and presently she said: "I—the reason of it—my crying—is b-b-because I don't wish you to be unhappy."
Can you picture a room where the portires are all of different lengths?because the decorator had no sense of line value?
At length she stammered: "I did not come b-because I simply couldn't stand it!"
Related Words
Words related to because are not direct synonyms, but are associated with the word because . Browse related words to learn more about word associations.
conjunction as in because
- inasmuch as
- seeing that
adjective as in taking everything in mind
- all things considered
- everything being equal
- forasmuch as
- in consideration of
- in light of
- insomuch as
- taking into account
conjunction as in in consequence of the fact that
conjunction as in in view of the fact that
- making allowance for
adverb as in to such an extent
Viewing 5 / 11 related words
When To Use
What are other ways to say because .
The conjunction because introduces a direct reason for an occurrence or action: I was sleeping because I was tired. As and since are so casual as to imply merely circumstances attendant on the main statement: As (or since ) I was tired, I was sleeping. The reason, proof, or justification introduced by for is like an afterthought or a parenthetical statement: I was famished, for I had not eaten all day. The more formal inasmuch as implies concession; the main statement is true in view of the circumstances introduced by this conjunction: Inasmuch as I was tired, it seemed best to sleep.
On this page you'll find 61 synonyms, antonyms, and words related to because, such as: as, as a result of, as long as, as things go, being, and by cause of.
From Roget's 21st Century Thesaurus, Third Edition Copyright © 2013 by the Philip Lief Group.
Related Words and Phrases
Bottom_desktop desktop:[300x250].
Synonyms of because
- as in since
- More from M-W
- To save this word, you'll need to log in. Log In
conjunction
Thesaurus definition of because.
Synonyms & Similar Words
- considering
- inasmuch as
Phrases Containing because
Articles related to because.

We Added 455 New Words to the...
We Added 455 New Words to the Dictionary for October 2021
An update of 455 new words, from 'dad bod' to 'deplatform'

'The Reason Is Because': Redundant But...
'The Reason Is Because': Redundant But Acceptable
If 'because' can mean 'that,' why not say "the reason is because"?

'Since' vs. 'As' vs. 'Because'
Which conjunction should you use to show cause?
Thesaurus Entries Near because
Cite this entry.
“Because.” Merriam-Webster.com Thesaurus , Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/thesaurus/because. Accessed 20 May. 2024.
More from Merriam-Webster on because
Nglish: Translation of because for Spanish Speakers
Britannica English: Translation of because for Arabic Speakers
Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free!

Can you solve 4 words at once?
Word of the day.
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Popular in Grammar & Usage
More commonly misspelled words, your vs. you're: how to use them correctly, every letter is silent, sometimes: a-z list of examples, more commonly mispronounced words, how to use em dashes (—), en dashes (–) , and hyphens (-), popular in wordplay, the words of the week - may 17, birds say the darndest things, a great big list of bread words, 10 scrabble words without any vowels, 12 more bird names that sound like insults (and sometimes are), games & quizzes.

Places on our 2024 summer school are filling fast. Don’t miss out. Enrol now to avoid disappointment
- 40 Useful Words and Phrases for Top-Notch Essays

To be truly brilliant, an essay needs to utilise the right language. You could make a great point, but if it’s not intelligently articulated, you almost needn’t have bothered.
Developing the language skills to build an argument and to write persuasively is crucial if you’re to write outstanding essays every time. In this article, we’re going to equip you with the words and phrases you need to write a top-notch essay, along with examples of how to utilise them.
It’s by no means an exhaustive list, and there will often be other ways of using the words and phrases we describe that we won’t have room to include, but there should be more than enough below to help you make an instant improvement to your essay-writing skills.
If you’re interested in developing your language and persuasive skills, Oxford Royale offers summer courses at its Oxford Summer School , Cambridge Summer School , London Summer School , San Francisco Summer School and Yale Summer School . You can study courses to learn english , prepare for careers in law , medicine , business , engineering and leadership.
General explaining
Let’s start by looking at language for general explanations of complex points.
1. In order to
Usage: “In order to” can be used to introduce an explanation for the purpose of an argument. Example: “In order to understand X, we need first to understand Y.”
2. In other words
Usage: Use “in other words” when you want to express something in a different way (more simply), to make it easier to understand, or to emphasise or expand on a point. Example: “Frogs are amphibians. In other words, they live on the land and in the water.”
3. To put it another way
Usage: This phrase is another way of saying “in other words”, and can be used in particularly complex points, when you feel that an alternative way of wording a problem may help the reader achieve a better understanding of its significance. Example: “Plants rely on photosynthesis. To put it another way, they will die without the sun.”
4. That is to say
Usage: “That is” and “that is to say” can be used to add further detail to your explanation, or to be more precise. Example: “Whales are mammals. That is to say, they must breathe air.”
5. To that end
Usage: Use “to that end” or “to this end” in a similar way to “in order to” or “so”. Example: “Zoologists have long sought to understand how animals communicate with each other. To that end, a new study has been launched that looks at elephant sounds and their possible meanings.”
Adding additional information to support a point
Students often make the mistake of using synonyms of “and” each time they want to add further information in support of a point they’re making, or to build an argument . Here are some cleverer ways of doing this.
6. Moreover
Usage: Employ “moreover” at the start of a sentence to add extra information in support of a point you’re making. Example: “Moreover, the results of a recent piece of research provide compelling evidence in support of…”
7. Furthermore
Usage:This is also generally used at the start of a sentence, to add extra information. Example: “Furthermore, there is evidence to suggest that…”
8. What’s more
Usage: This is used in the same way as “moreover” and “furthermore”. Example: “What’s more, this isn’t the only evidence that supports this hypothesis.”
9. Likewise
Usage: Use “likewise” when you want to talk about something that agrees with what you’ve just mentioned. Example: “Scholar A believes X. Likewise, Scholar B argues compellingly in favour of this point of view.”
10. Similarly
Usage: Use “similarly” in the same way as “likewise”. Example: “Audiences at the time reacted with shock to Beethoven’s new work, because it was very different to what they were used to. Similarly, we have a tendency to react with surprise to the unfamiliar.”
11. Another key thing to remember
Usage: Use the phrase “another key point to remember” or “another key fact to remember” to introduce additional facts without using the word “also”. Example: “As a Romantic, Blake was a proponent of a closer relationship between humans and nature. Another key point to remember is that Blake was writing during the Industrial Revolution, which had a major impact on the world around him.”
12. As well as
Usage: Use “as well as” instead of “also” or “and”. Example: “Scholar A argued that this was due to X, as well as Y.”

13. Not only… but also
Usage: This wording is used to add an extra piece of information, often something that’s in some way more surprising or unexpected than the first piece of information. Example: “Not only did Edmund Hillary have the honour of being the first to reach the summit of Everest, but he was also appointed Knight Commander of the Order of the British Empire.”
14. Coupled with
Usage: Used when considering two or more arguments at a time. Example: “Coupled with the literary evidence, the statistics paint a compelling view of…”
15. Firstly, secondly, thirdly…
Usage: This can be used to structure an argument, presenting facts clearly one after the other. Example: “There are many points in support of this view. Firstly, X. Secondly, Y. And thirdly, Z.
16. Not to mention/to say nothing of
Usage: “Not to mention” and “to say nothing of” can be used to add extra information with a bit of emphasis. Example: “The war caused unprecedented suffering to millions of people, not to mention its impact on the country’s economy.”
Words and phrases for demonstrating contrast
When you’re developing an argument, you will often need to present contrasting or opposing opinions or evidence – “it could show this, but it could also show this”, or “X says this, but Y disagrees”. This section covers words you can use instead of the “but” in these examples, to make your writing sound more intelligent and interesting.
17. However
Usage: Use “however” to introduce a point that disagrees with what you’ve just said. Example: “Scholar A thinks this. However, Scholar B reached a different conclusion.”
18. On the other hand
Usage: Usage of this phrase includes introducing a contrasting interpretation of the same piece of evidence, a different piece of evidence that suggests something else, or an opposing opinion. Example: “The historical evidence appears to suggest a clear-cut situation. On the other hand, the archaeological evidence presents a somewhat less straightforward picture of what happened that day.”
19. Having said that
Usage: Used in a similar manner to “on the other hand” or “but”. Example: “The historians are unanimous in telling us X, an agreement that suggests that this version of events must be an accurate account. Having said that, the archaeology tells a different story.”
20. By contrast/in comparison
Usage: Use “by contrast” or “in comparison” when you’re comparing and contrasting pieces of evidence. Example: “Scholar A’s opinion, then, is based on insufficient evidence. By contrast, Scholar B’s opinion seems more plausible.”
21. Then again
Usage: Use this to cast doubt on an assertion. Example: “Writer A asserts that this was the reason for what happened. Then again, it’s possible that he was being paid to say this.”
22. That said
Usage: This is used in the same way as “then again”. Example: “The evidence ostensibly appears to point to this conclusion. That said, much of the evidence is unreliable at best.”
Usage: Use this when you want to introduce a contrasting idea. Example: “Much of scholarship has focused on this evidence. Yet not everyone agrees that this is the most important aspect of the situation.”
Adding a proviso or acknowledging reservations
Sometimes, you may need to acknowledge a shortfalling in a piece of evidence, or add a proviso. Here are some ways of doing so.
24. Despite this
Usage: Use “despite this” or “in spite of this” when you want to outline a point that stands regardless of a shortfalling in the evidence. Example: “The sample size was small, but the results were important despite this.”
25. With this in mind
Usage: Use this when you want your reader to consider a point in the knowledge of something else. Example: “We’ve seen that the methods used in the 19th century study did not always live up to the rigorous standards expected in scientific research today, which makes it difficult to draw definite conclusions. With this in mind, let’s look at a more recent study to see how the results compare.”
26. Provided that
Usage: This means “on condition that”. You can also say “providing that” or just “providing” to mean the same thing. Example: “We may use this as evidence to support our argument, provided that we bear in mind the limitations of the methods used to obtain it.”
27. In view of/in light of
Usage: These phrases are used when something has shed light on something else. Example: “In light of the evidence from the 2013 study, we have a better understanding of…”
28. Nonetheless
Usage: This is similar to “despite this”. Example: “The study had its limitations, but it was nonetheless groundbreaking for its day.”
29. Nevertheless
Usage: This is the same as “nonetheless”. Example: “The study was flawed, but it was important nevertheless.”
30. Notwithstanding
Usage: This is another way of saying “nonetheless”. Example: “Notwithstanding the limitations of the methodology used, it was an important study in the development of how we view the workings of the human mind.”
Giving examples
Good essays always back up points with examples, but it’s going to get boring if you use the expression “for example” every time. Here are a couple of other ways of saying the same thing.
31. For instance
Example: “Some birds migrate to avoid harsher winter climates. Swallows, for instance, leave the UK in early winter and fly south…”
32. To give an illustration
Example: “To give an illustration of what I mean, let’s look at the case of…”
Signifying importance
When you want to demonstrate that a point is particularly important, there are several ways of highlighting it as such.
33. Significantly
Usage: Used to introduce a point that is loaded with meaning that might not be immediately apparent. Example: “Significantly, Tacitus omits to tell us the kind of gossip prevalent in Suetonius’ accounts of the same period.”
34. Notably
Usage: This can be used to mean “significantly” (as above), and it can also be used interchangeably with “in particular” (the example below demonstrates the first of these ways of using it). Example: “Actual figures are notably absent from Scholar A’s analysis.”
35. Importantly
Usage: Use “importantly” interchangeably with “significantly”. Example: “Importantly, Scholar A was being employed by X when he wrote this work, and was presumably therefore under pressure to portray the situation more favourably than he perhaps might otherwise have done.”
Summarising
You’ve almost made it to the end of the essay, but your work isn’t over yet. You need to end by wrapping up everything you’ve talked about, showing that you’ve considered the arguments on both sides and reached the most likely conclusion. Here are some words and phrases to help you.
36. In conclusion
Usage: Typically used to introduce the concluding paragraph or sentence of an essay, summarising what you’ve discussed in a broad overview. Example: “In conclusion, the evidence points almost exclusively to Argument A.”
37. Above all
Usage: Used to signify what you believe to be the most significant point, and the main takeaway from the essay. Example: “Above all, it seems pertinent to remember that…”
38. Persuasive
Usage: This is a useful word to use when summarising which argument you find most convincing. Example: “Scholar A’s point – that Constanze Mozart was motivated by financial gain – seems to me to be the most persuasive argument for her actions following Mozart’s death.”
39. Compelling
Usage: Use in the same way as “persuasive” above. Example: “The most compelling argument is presented by Scholar A.”
40. All things considered
Usage: This means “taking everything into account”. Example: “All things considered, it seems reasonable to assume that…”
How many of these words and phrases will you get into your next essay? And are any of your favourite essay terms missing from our list? Let us know in the comments below, or get in touch here to find out more about courses that can help you with your essays.
At Oxford Royale Academy, we offer a number of summer school courses for young people who are keen to improve their essay writing skills. Click here to apply for one of our courses today, including law , business , medicine and engineering .
Comments are closed.
- Features for Creative Writers
- Features for Work
- Features for Higher Education
- Features for Teachers
- Features for Non-Native Speakers
- Learn Blog Grammar Guide Community Events FAQ
- Grammar Guide
Words to Use in an Essay: 300 Essay Words

Hannah Yang

Table of Contents
Words to use in the essay introduction, words to use in the body of the essay, words to use in your essay conclusion, how to improve your essay writing vocabulary.
It’s not easy to write an academic essay .
Many students struggle to word their arguments in a logical and concise way.
To make matters worse, academic essays need to adhere to a certain level of formality, so we can’t always use the same word choices in essay writing that we would use in daily life.
If you’re struggling to choose the right words for your essay, don’t worry—you’ve come to the right place!
In this article, we’ve compiled a list of over 300 words and phrases to use in the introduction, body, and conclusion of your essay.
The introduction is one of the hardest parts of an essay to write.
You have only one chance to make a first impression, and you want to hook your reader. If the introduction isn’t effective, the reader might not even bother to read the rest of the essay.
That’s why it’s important to be thoughtful and deliberate with the words you choose at the beginning of your essay.
Many students use a quote in the introductory paragraph to establish credibility and set the tone for the rest of the essay.
When you’re referencing another author or speaker, try using some of these phrases:
To use the words of X
According to X
As X states
Example: To use the words of Hillary Clinton, “You cannot have maternal health without reproductive health.”
Near the end of the introduction, you should state the thesis to explain the central point of your paper.
If you’re not sure how to introduce your thesis, try using some of these phrases:
In this essay, I will…
The purpose of this essay…
This essay discusses…
In this paper, I put forward the claim that…
There are three main arguments for…

Example: In this essay, I will explain why dress codes in public schools are detrimental to students.
After you’ve stated your thesis, it’s time to start presenting the arguments you’ll use to back up that central idea.
When you’re introducing the first of a series of arguments, you can use the following words:
First and foremost
First of all
To begin with
Example: First , consider the effects that this new social security policy would have on low-income taxpayers.
All these words and phrases will help you create a more successful introduction and convince your audience to read on.
The body of your essay is where you’ll explain your core arguments and present your evidence.
It’s important to choose words and phrases for the body of your essay that will help the reader understand your position and convince them you’ve done your research.
Let’s look at some different types of words and phrases that you can use in the body of your essay, as well as some examples of what these words look like in a sentence.
Transition Words and Phrases
Transitioning from one argument to another is crucial for a good essay.
It’s important to guide your reader from one idea to the next so they don’t get lost or feel like you’re jumping around at random.
Transition phrases and linking words show your reader you’re about to move from one argument to the next, smoothing out their reading experience. They also make your writing look more professional.
The simplest transition involves moving from one idea to a separate one that supports the same overall argument. Try using these phrases when you want to introduce a second correlating idea:
Additionally
In addition
Furthermore
Another key thing to remember
In the same way
Correspondingly
Example: Additionally , public parks increase property value because home buyers prefer houses that are located close to green, open spaces.
Another type of transition involves restating. It’s often useful to restate complex ideas in simpler terms to help the reader digest them. When you’re restating an idea, you can use the following words:
In other words
To put it another way
That is to say
To put it more simply
Example: “The research showed that 53% of students surveyed expressed a mild or strong preference for more on-campus housing. In other words , over half the students wanted more dormitory options.”
Often, you’ll need to provide examples to illustrate your point more clearly for the reader. When you’re about to give an example of something you just said, you can use the following words:
For instance
To give an illustration of
To exemplify
To demonstrate
As evidence
Example: Humans have long tried to exert control over our natural environment. For instance , engineers reversed the Chicago River in 1900, causing it to permanently flow backward.
Sometimes, you’ll need to explain the impact or consequence of something you’ve just said.
When you’re drawing a conclusion from evidence you’ve presented, try using the following words:
As a result
Accordingly
As you can see
This suggests that
It follows that
It can be seen that
For this reason
For all of those reasons
Consequently
Example: “There wasn’t enough government funding to support the rest of the physics experiment. Thus , the team was forced to shut down their experiment in 1996.”

When introducing an idea that bolsters one you’ve already stated, or adds another important aspect to that same argument, you can use the following words:
What’s more
Not only…but also
Not to mention
To say nothing of
Another key point
Example: The volcanic eruption disrupted hundreds of thousands of people. Moreover , it impacted the local flora and fauna as well, causing nearly a hundred species to go extinct.
Often, you'll want to present two sides of the same argument. When you need to compare and contrast ideas, you can use the following words:
On the one hand / on the other hand
Alternatively
In contrast to
On the contrary
By contrast
In comparison
Example: On the one hand , the Black Death was undoubtedly a tragedy because it killed millions of Europeans. On the other hand , it created better living conditions for the peasants who survived.
Finally, when you’re introducing a new angle that contradicts your previous idea, you can use the following phrases:
Having said that
Differing from
In spite of
With this in mind
Provided that
Nevertheless
Nonetheless
Notwithstanding
Example: Shakespearean plays are classic works of literature that have stood the test of time. Having said that , I would argue that Shakespeare isn’t the most accessible form of literature to teach students in the twenty-first century.
Good essays include multiple types of logic. You can use a combination of the transitions above to create a strong, clear structure throughout the body of your essay.
Strong Verbs for Academic Writing
Verbs are especially important for writing clear essays. Often, you can convey a nuanced meaning simply by choosing the right verb.
You should use strong verbs that are precise and dynamic. Whenever possible, you should use an unambiguous verb, rather than a generic verb.
For example, alter and fluctuate are stronger verbs than change , because they give the reader more descriptive detail.
Here are some useful verbs that will help make your essay shine.
Verbs that show change:
Accommodate
Verbs that relate to causing or impacting something:
Verbs that show increase:
Verbs that show decrease:
Deteriorate
Verbs that relate to parts of a whole:
Comprises of
Is composed of
Constitutes
Encompasses
Incorporates
Verbs that show a negative stance:
Misconstrue

Verbs that show a positive stance:
Substantiate
Verbs that relate to drawing conclusions from evidence:
Corroborate
Demonstrate
Verbs that relate to thinking and analysis:
Contemplate
Hypothesize
Investigate
Verbs that relate to showing information in a visual format:
Useful Adjectives and Adverbs for Academic Essays
You should use adjectives and adverbs more sparingly than verbs when writing essays, since they sometimes add unnecessary fluff to sentences.
However, choosing the right adjectives and adverbs can help add detail and sophistication to your essay.
Sometimes you'll need to use an adjective to show that a finding or argument is useful and should be taken seriously. Here are some adjectives that create positive emphasis:
Significant
Other times, you'll need to use an adjective to show that a finding or argument is harmful or ineffective. Here are some adjectives that create a negative emphasis:
Controversial
Insignificant
Questionable
Unnecessary
Unrealistic
Finally, you might need to use an adverb to lend nuance to a sentence, or to express a specific degree of certainty. Here are some examples of adverbs that are often used in essays:
Comprehensively
Exhaustively
Extensively
Respectively
Surprisingly
Using these words will help you successfully convey the key points you want to express. Once you’ve nailed the body of your essay, it’s time to move on to the conclusion.
The conclusion of your paper is important for synthesizing the arguments you’ve laid out and restating your thesis.
In your concluding paragraph, try using some of these essay words:
In conclusion
To summarize
In a nutshell
Given the above
As described
All things considered
Example: In conclusion , it’s imperative that we take action to address climate change before we lose our coral reefs forever.
In addition to simply summarizing the key points from the body of your essay, you should also add some final takeaways. Give the reader your final opinion and a bit of a food for thought.
To place emphasis on a certain point or a key fact, use these essay words:
Unquestionably
Undoubtedly
Particularly
Importantly
Conclusively
It should be noted
On the whole
Example: Ada Lovelace is unquestionably a powerful role model for young girls around the world, and more of our public school curricula should include her as a historical figure.
These concluding phrases will help you finish writing your essay in a strong, confident way.
There are many useful essay words out there that we didn't include in this article, because they are specific to certain topics.
If you're writing about biology, for example, you will need to use different terminology than if you're writing about literature.
So how do you improve your vocabulary skills?
The vocabulary you use in your academic writing is a toolkit you can build up over time, as long as you take the time to learn new words.
One way to increase your vocabulary is by looking up words you don’t know when you’re reading.
Try reading more books and academic articles in the field you’re writing about and jotting down all the new words you find. You can use these words to bolster your own essays.
You can also consult a dictionary or a thesaurus. When you’re using a word you’re not confident about, researching its meaning and common synonyms can help you make sure it belongs in your essay.
Don't be afraid of using simpler words. Good essay writing boils down to choosing the best word to convey what you need to say, not the fanciest word possible.
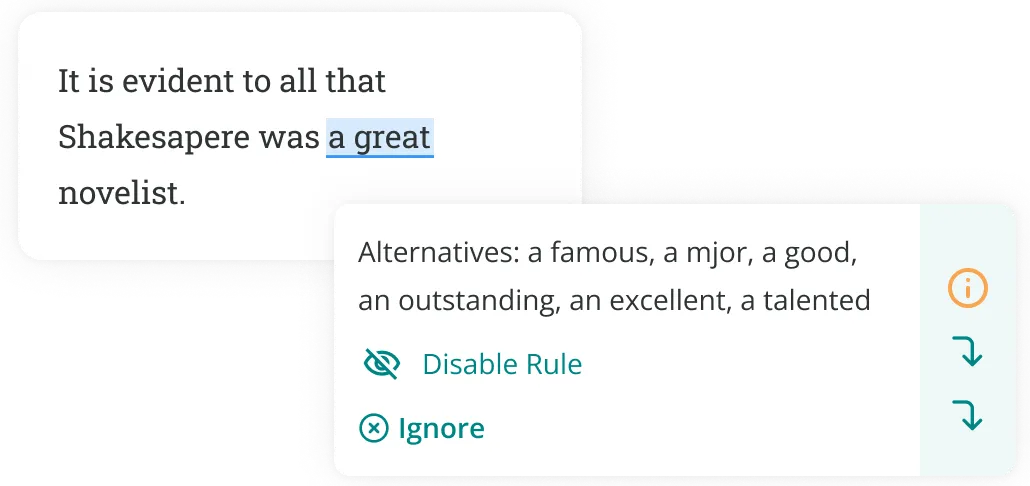
Finally, you can use ProWritingAid’s synonym tool or essay checker to find more precise and sophisticated vocabulary. Click on weak words in your essay to find stronger alternatives.
There you have it: our compilation of the best words and phrases to use in your next essay . Good luck!

Good writing = better grades
ProWritingAid will help you improve the style, strength, and clarity of all your assignments.
Hannah Yang is a speculative fiction writer who writes about all things strange and surreal. Her work has appeared in Analog Science Fiction, Apex Magazine, The Dark, and elsewhere, and two of her stories have been finalists for the Locus Award. Her favorite hobbies include watercolor painting, playing guitar, and rock climbing. You can follow her work on hannahyang.com, or subscribe to her newsletter for publication updates.
Get started with ProWritingAid
Drop us a line or let's stay in touch via :

Word Choice
What this handout is about.
This handout can help you revise your papers for word-level clarity, eliminate wordiness and avoid clichés, find the words that best express your ideas, and choose words that suit an academic audience.
Introduction
Writing is a series of choices. As you work on a paper, you choose your topic, your approach, your sources, and your thesis; when it’s time to write, you have to choose the words you will use to express your ideas and decide how you will arrange those words into sentences and paragraphs. As you revise your draft, you make more choices. You might ask yourself, “Is this really what I mean?” or “Will readers understand this?” or “Does this sound good?” Finding words that capture your meaning and convey that meaning to your readers is challenging. When your instructors write things like “awkward,” “vague,” or “wordy” on your draft, they are letting you know that they want you to work on word choice. This handout will explain some common issues related to word choice and give you strategies for choosing the best words as you revise your drafts.
As you read further into the handout, keep in mind that it can sometimes take more time to “save” words from your original sentence than to write a brand new sentence to convey the same meaning or idea. Don’t be too attached to what you’ve already written; if you are willing to start a sentence fresh, you may be able to choose words with greater clarity.
For tips on making more substantial revisions, take a look at our handouts on reorganizing drafts and revising drafts .
“Awkward,” “vague,” and “unclear” word choice
So: you write a paper that makes perfect sense to you, but it comes back with “awkward” scribbled throughout the margins. Why, you wonder, are instructors so fond of terms like “awkward”? Most instructors use terms like this to draw your attention to sentences they had trouble understanding and to encourage you to rewrite those sentences more clearly.
Difficulties with word choice aren’t the only cause of awkwardness, vagueness, or other problems with clarity. Sometimes a sentence is hard to follow because there is a grammatical problem with it or because of the syntax (the way the words and phrases are put together). Here’s an example: “Having finished with studying, the pizza was quickly eaten.” This sentence isn’t hard to understand because of the words I chose—everybody knows what studying, pizza, and eating are. The problem here is that readers will naturally assume that first bit of the sentence “(Having finished with studying”) goes with the next noun that follows it—which, in this case, is “the pizza”! It doesn’t make a lot of sense to imply that the pizza was studying. What I was actually trying to express was something more like this: “Having finished with studying, the students quickly ate the pizza.” If you have a sentence that has been marked “awkward,” “vague,” or “unclear,” try to think about it from a reader’s point of view—see if you can tell where it changes direction or leaves out important information.
Sometimes, though, problems with clarity are a matter of word choice. See if you recognize any of these issues:
- Misused words —the word doesn’t actually mean what the writer thinks it does. Example : Cree Indians were a monotonous culture until French and British settlers arrived. Revision: Cree Indians were a homogenous culture.
- Words with unwanted connotations or meanings. Example : I sprayed the ants in their private places. Revision: I sprayed the ants in their hiding places.
- Using a pronoun when readers can’t tell whom/what it refers to. Example : My cousin Jake hugged my brother Trey, even though he didn’t like him very much. Revision: My cousin Jake hugged my brother Trey, even though Jake doesn’t like Trey very much.
- Jargon or technical terms that make readers work unnecessarily hard. Maybe you need to use some of these words because they are important terms in your field, but don’t throw them in just to “sound smart.” Example : The dialectical interface between neo-Platonists and anti-disestablishment Catholics offers an algorithm for deontological thought. Revision : The dialogue between neo-Platonists and certain Catholic thinkers is a model for deontological thought.
- Loaded language. Sometimes we as writers know what we mean by a certain word, but we haven’t ever spelled that out for readers. We rely too heavily on that word, perhaps repeating it often, without clarifying what we are talking about. Example : Society teaches young girls that beauty is their most important quality. In order to prevent eating disorders and other health problems, we must change society. Revision : Contemporary American popular media, like magazines and movies, teach young girls that beauty is their most important quality. In order to prevent eating disorders and other health problems, we must change the images and role models girls are offered.
Sometimes the problem isn’t choosing exactly the right word to express an idea—it’s being “wordy,” or using words that your reader may regard as “extra” or inefficient. Take a look at the following list for some examples. On the left are some phrases that use three, four, or more words where fewer will do; on the right are some shorter substitutes:
Keep an eye out for wordy constructions in your writing and see if you can replace them with more concise words or phrases.
In academic writing, it’s a good idea to limit your use of clichés. Clichés are catchy little phrases so frequently used that they have become trite, corny, or annoying. They are problematic because their overuse has diminished their impact and because they require several words where just one would do.
The main way to avoid clichés is first to recognize them and then to create shorter, fresher equivalents. Ask yourself if there is one word that means the same thing as the cliché. If there isn’t, can you use two or three words to state the idea your own way? Below you will see five common clichés, with some alternatives to their right. As a challenge, see how many alternatives you can create for the final two examples.
Try these yourself:
Writing for an academic audience
When you choose words to express your ideas, you have to think not only about what makes sense and sounds best to you, but what will make sense and sound best to your readers. Thinking about your audience and their expectations will help you make decisions about word choice.
Some writers think that academic audiences expect them to “sound smart” by using big or technical words. But the most important goal of academic writing is not to sound smart—it is to communicate an argument or information clearly and convincingly. It is true that academic writing has a certain style of its own and that you, as a student, are beginning to learn to read and write in that style. You may find yourself using words and grammatical constructions that you didn’t use in your high school writing. The danger is that if you consciously set out to “sound smart” and use words or structures that are very unfamiliar to you, you may produce sentences that your readers can’t understand.
When writing for your professors, think simplicity. Using simple words does not indicate simple thoughts. In an academic argument paper, what makes the thesis and argument sophisticated are the connections presented in simple, clear language.
Keep in mind, though, that simple and clear doesn’t necessarily mean casual. Most instructors will not be pleased if your paper looks like an instant message or an email to a friend. It’s usually best to avoid slang and colloquialisms. Take a look at this example and ask yourself how a professor would probably respond to it if it were the thesis statement of a paper: “Moulin Rouge really bit because the singing sucked and the costume colors were nasty, KWIM?”
Selecting and using key terms
When writing academic papers, it is often helpful to find key terms and use them within your paper as well as in your thesis. This section comments on the crucial difference between repetition and redundancy of terms and works through an example of using key terms in a thesis statement.
Repetition vs. redundancy
These two phenomena are not necessarily the same. Repetition can be a good thing. Sometimes we have to use our key terms several times within a paper, especially in topic sentences. Sometimes there is simply no substitute for the key terms, and selecting a weaker term as a synonym can do more harm than good. Repeating key terms emphasizes important points and signals to the reader that the argument is still being supported. This kind of repetition can give your paper cohesion and is done by conscious choice.
In contrast, if you find yourself frustrated, tiredly repeating the same nouns, verbs, or adjectives, or making the same point over and over, you are probably being redundant. In this case, you are swimming aimlessly around the same points because you have not decided what your argument really is or because you are truly fatigued and clarity escapes you. Refer to the “Strategies” section below for ideas on revising for redundancy.
Building clear thesis statements
Writing clear sentences is important throughout your writing. For the purposes of this handout, let’s focus on the thesis statement—one of the most important sentences in academic argument papers. You can apply these ideas to other sentences in your papers.
A common problem with writing good thesis statements is finding the words that best capture both the important elements and the significance of the essay’s argument. It is not always easy to condense several paragraphs or several pages into concise key terms that, when combined in one sentence, can effectively describe the argument.
However, taking the time to find the right words offers writers a significant edge. Concise and appropriate terms will help both the writer and the reader keep track of what the essay will show and how it will show it. Graders, in particular, like to see clearly stated thesis statements. (For more on thesis statements in general, please refer to our handout .)
Example : You’ve been assigned to write an essay that contrasts the river and shore scenes in Mark Twain’s Huckleberry Finn. You work on it for several days, producing three versions of your thesis:
Version 1 : There are many important river and shore scenes in Huckleberry Finn.
Version 2 : The contrasting river and shore scenes in Huckleberry Finn suggest a return to nature.
Version 3 : Through its contrasting river and shore scenes, Twain’s Huckleberry Finn suggests that to find the true expression of American democratic ideals, one must leave “civilized” society and go back to nature.
Let’s consider the word choice issues in these statements. In Version 1, the word “important”—like “interesting”—is both overused and vague; it suggests that the author has an opinion but gives very little indication about the framework of that opinion. As a result, your reader knows only that you’re going to talk about river and shore scenes, but not what you’re going to say. Version 2 is an improvement: the words “return to nature” give your reader a better idea where the paper is headed. On the other hand, they still do not know how this return to nature is crucial to your understanding of the novel.
Finally, you come up with Version 3, which is a stronger thesis because it offers a sophisticated argument and the key terms used to make this argument are clear. At least three key terms or concepts are evident: the contrast between river and shore scenes, a return to nature, and American democratic ideals.
By itself, a key term is merely a topic—an element of the argument but not the argument itself. The argument, then, becomes clear to the reader through the way in which you combine key terms.
Strategies for successful word choice
- Be careful when using words you are unfamiliar with. Look at how they are used in context and check their dictionary definitions.
- Be careful when using the thesaurus. Each word listed as a synonym for the word you’re looking up may have its own unique connotations or shades of meaning. Use a dictionary to be sure the synonym you are considering really fits what you are trying to say.
- Under the present conditions of our society, marriage practices generally demonstrate a high degree of homogeneity.
- In our culture, people tend to marry others who are like themselves. (Longman, p. 452)
- Before you revise for accurate and strong adjectives, make sure you are first using accurate and strong nouns and verbs. For example, if you were revising the sentence “This is a good book that tells about the Revolutionary War,” think about whether “book” and “tells” are as strong as they could be before you worry about “good.” (A stronger sentence might read “The novel describes the experiences of a soldier during the Revolutionary War.” “Novel” tells us what kind of book it is, and “describes” tells us more about how the book communicates information.)
- Try the slash/option technique, which is like brainstorming as you write. When you get stuck, write out two or more choices for a questionable word or a confusing sentence, e.g., “questionable/inaccurate/vague/inappropriate.” Pick the word that best indicates your meaning or combine different terms to say what you mean.
- Look for repetition. When you find it, decide if it is “good” repetition (using key terms that are crucial and helpful to meaning) or “bad” repetition (redundancy or laziness in reusing words).
- Write your thesis in five different ways. Make five different versions of your thesis sentence. Compose five sentences that express your argument. Try to come up with four alternatives to the thesis sentence you’ve already written. Find five possible ways to communicate your argument in one sentence to your reader. (We’ve just used this technique—which of the last five sentences do you prefer?)Whenever we write a sentence we make choices. Some are less obvious than others, so that it can often feel like we’ve written the sentence the only way we know how. By writing out five different versions of your thesis, you can begin to see your range of choices. The final version may be a combination of phrasings and words from all five versions, or the one version that says it best. By literally spelling out some possibilities for yourself, you will be able to make better decisions.
- Read your paper out loud and at… a… slow… pace. You can do this alone or with a friend, roommate, TA, etc. When read out loud, your written words should make sense to both you and other listeners. If a sentence seems confusing, rewrite it to make the meaning clear.
- Instead of reading the paper itself, put it down and just talk through your argument as concisely as you can. If your listener quickly and easily comprehends your essay’s main point and significance, you should then make sure that your written words are as clear as your oral presentation was. If, on the other hand, your listener keeps asking for clarification, you will need to work on finding the right terms for your essay. If you do this in exchange with a friend or classmate, rest assured that whether you are the talker or the listener, your articulation skills will develop.
- Have someone not familiar with the issue read the paper and point out words or sentences they find confusing. Do not brush off this reader’s confusion by assuming they simply doesn’t know enough about the topic. Instead, rewrite the sentences so that your “outsider” reader can follow along at all times.
- Check out the Writing Center’s handouts on style , passive voice , and proofreading for more tips.
Questions to ask yourself
- Am I sure what each word I use really means? Am I positive, or should I look it up?
- Have I found the best word or just settled for the most obvious, or the easiest, one?
- Am I trying too hard to impress my reader?
- What’s the easiest way to write this sentence? (Sometimes it helps to answer this question by trying it out loud. How would you say it to someone?)
- What are the key terms of my argument?
- Can I outline out my argument using only these key terms? What others do I need? Which do I not need?
- Have I created my own terms, or have I simply borrowed what looked like key ones from the assignment? If I’ve borrowed the terms, can I find better ones in my own vocabulary, the texts, my notes, the dictionary, or the thesaurus to make myself clearer?
- Are my key terms too specific? (Do they cover the entire range of my argument?) Can I think of specific examples from my sources that fall under the key term?
- Are my key terms too vague? (Do they cover more than the range of my argument?)
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Anson, Chris M., and Robert A. Schwegler. 2010. The Longman Handbook for Writers and Readers , 6th ed. New York: Longman.
Cook, Claire Kehrwald. 1985. Line by Line: How to Improve Your Own Writing . Boston: Houghton Mifflin.
Grossman, Ellie. 1997. The Grammatically Correct Handbook: A Lively and Unorthodox Review of Common English for the Linguistically Challenged . New York: Hyperion.
Houghton Mifflin. 1996. The American Heritage Book of English Usage: A Practical and Authoritative Guide to Contemporary English . Boston: Houghton Mifflin.
O’Conner, Patricia. 2010. Woe Is I: The Grammarphobe’s Guide to Better English in Plain English , 3rd ed. New York: Penguin Publishing Group.
Tarshis, Barry. 1998. How to Be Your Own Best Editor: The Toolkit for Everyone Who Writes . New York: Three Rivers Press.
Williams, Joseph, and Joseph Bizup. 2017. Style: Lessons in Clarity and Grace , 12th ed. Boston: Pearson.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift

19 Other Ways to Say “I Believe” in an Essay

If you’re wondering how to say “I believe” in an essay without using first-person phrasing, you’ve come to the right place!
In this article, we’ve compiled a list of synonyms that you can use instead of saying “I believe” in an essay. We’ll also discuss whether you should use the original phrase at all.
Other Ways to Say “I Believe”
- One might argue
- It would seem
- This suggests
- It is my belief
- As I see it
- From my perspective
- It could be argued
- I would argue
- This illustrates
- This evidences
- In my opinion
- This proves
- In the author’s opinion
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- It’s okay to use “I believe” in an essay if the person grading your paper permits you to use personal pronouns.
- You can say “one might argue” if you want to use a more formal alternative in the third person.
- “It appears” is another good option that removes the personal pronoun “I.”
Don’t go anywhere! In the next section, we’ll discuss two great alternatives for the phrase “I believe” that you can use in your academic writing.
Moreover, we’ll provide some helpful examples and discuss whether it’s a bad idea to use “I believe” in your essay.
One Might Argue
If you’re wondering what to say instead of “I believe” in an essay, a great choice is “one might argue.”
Some academics may view this alternative as superior to the original phrase. After all, it is written in the third person. Therefore, you can get the same point across without using “I.” In some formal academic essays , it is expected by markers that personal pronouns should be avoided.
Additionally, this alternative makes it clear that your statement isn’t certain, just like the original. The word “might” implies that you are expressing an opinion or making just a potential argument.
Finally, let’s see how one might use this phrase in a few examples:
One might argue that the individual responsibility of consumers to buy sustainable products is far less than the responsibility that should be placed on large industries.
Although our findings show that fewer children are taking an interest in mathematics, one might argue that this has more to do with the teaching style of educators rather than the content of the subject itself.
Another way to say “I believe” without using the first person is “it appears.”
Like the original phrase, this one indicates that the statement following it is not certain. In fact, it is simply an observation .
Although this phrase is not necessarily superior to “I believe,” it does remove the personal pronoun “I,” which is often seen as preferable by teachers and professors.
It also has the benefit of using the same number of words as “I believe.” Therefore, it won’t increase your word count , unlike some of the other synonyms on our list.
To see this phrase in action, have a look at the examples below:
It appears that several of the mice in our experiment exhibited empathy when faced with one of their fellows trapped in a cage.
Although Otis Blackwell was a clear stylistic inspiration to Elvis, in addition to being the writer of many of his popular songs, it appears that only a small minority of the public is privy to this truth.
Can I Use “I Believe” in an Essay?
Whether it is okay to use “I believe” in an essay greatly depends on context .
There are some academics and writers out there who think using phrases like “I believe” is bad writing . Firstly, they argue that it is redundant . Obviously, you believe the statement you’re making, or you wouldn’t be making it in the first place!
Secondly, some academics think that personal pronouns should be avoided in academic writing . Therefore, it’s no good to start your statements with “I.”
On the other hand, in recent times, many academics have argued that all forms of education and information should be accessible. This means that everyone should be able to follow and understand them – not just people who were privileged enough to get a university education!
People who hold this opinion say that a phrase like “I believe” is perfectly effective. After all, it lets the reader know that you are expressing an opinion and not a fact. Additionally, it is straightforward and easy for any reader to follow.
Therefore, as a rule of thumb, we would always recommend speaking to the person who is going to grade your essay before you start . If they are a traditionalist and would prefer very formal writing, use one of our alternatives.
If they are happy to read a paper with personal pronouns and straightforward writing in it, go ahead and use “I believe.”
In conclusion, it’s okay to use “I believe” if the person marking your essay is okay with it!
We hope you found this article helpful. If you did, why not bookmark this page so you can come back whenever you like?
- 19 Gender-Neutral Alternatives to “Dear Sir or Madam”
- 16 Other Ways to Say “Looking Forward to Working With You”
- 14 Other Ways to Say “Looking Forward to Meeting You”
- 25 Other Ways to Say “Looking Forward to Being Part of the Team”
We are a team of experienced communication specialists.
Our mission is to help you choose the right phrase or word for your emails and texts.
Choosing the right words shouldn't be your limitation!
© WordSelector

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Exercises to Test Your Because-Cognition. Remove most instances of because by substitution or rewording.. Exercise 1. Millie knew she'd never pass the biology test, because she hadn't studied enough. But the lack of studying wasn't because of anything she had done. It was because she was exhausted. Every night for two weeks, her sleep had been disturbed because Mr. Clarke's dogs barked.
Other Options. Another way to get round the use of 'because' is to rearrange the sentence: The way the moles kept digging up Marjorie's garden made her very angry. Here, we have reversed the elements of the sentence and used the word 'made' to indicate the relationship between Marjorie's anger and the moles in her garden.
1. As: As is a direct synonym for because (for example, "He opted not to go see the movie, as it had gotten poor reviews"), but it's inferior. 2. As a result of: This phrase is a substitute for "because of," not because, as in "As a result of his intervention, the case was reopened and they were ultimately exonerated.". 3.
3. For. You can find for as an alternative to because in poetic writing. It is not commonly found in either casual or professional writing. Let's eat because I am hungry. Let's eat, for I am hungry. 4. Inasmuch as. This alternative is as formal as they come, but can be used exactly as because.
Synonyms for "Because". The word "because" is used to join two ideas and express cause and effect: The lemonade fizzed because we shook the bottle. However, if you find yourself overusing the word "because," there are alternatives available. We're going to look at some here.
She went to bed early because she was tired. he went to bed early for better rest. Because vs. Due to "Because" is used to introduce a reason and is followed by a subject and a verb. "Due to" is used to modify a noun and is often followed by a noun or noun phrase. I went to the store because I needed to buy some groceries.
And since 'because' is a common term in academic writing, we recommend learning a few alternatives. Synonyms for 'Because' There are plenty of words and phrases you can use in place of 'because' when introducing an explanation or justification in an essay. To demonstrate, we'll work with this example sentence:
Subscribe. There are two main ways to use 'because'. One is as a conjunction, where 'because' is followed by a subject and a verb: A qualitative approach was chosen because it enables collection of in-depth data. In these cases, alternatives include 'since' and 'as', both of which are also conjunctions: A qualitative approach ...
Another way to say Because? Synonyms for Because (other words and phrases for Because).
Find 51 different ways to say BECAUSE, along with antonyms, related words, and example sentences at Thesaurus.com.
Beginning a sentence with "because" is acceptable so long as the because-clause is followed by another clause that completes the sentence. In other words, the trick with "because," as with any other subordinating conjunction (e.g. although, since, when, etc.), is to remember that "because" always implies a two-part sentence: a ...
owing to the fact that. seeing that. 'cause. for the reason that. whereas. as long as. forasmuch as. insofar as. insomuch as.
Synonyms for BECAUSE: since, now, seeing, for, whereas, considering, as, being (as or as how or that), inasmuch as, 'cause
This is because, there was no reason to. Writers do get confused with the comma placement of "this is because." It is not an introductory clause. Therefore, it does not need a comma after it. You should avoid placing one. Feel free to bookmark this page to remind yourself of the best synonyms for "this is because."
As you can see, "because" can frequently be eliminated without a replacement word. Even when a replacement is necessary, there are a plethora of words that can effectively take the place of "because" without changing the meaning of the sentence or damaging a paragraph's natural rhythm. The word "because" is a valid word and is ...
4. That is to say. Usage: "That is" and "that is to say" can be used to add further detail to your explanation, or to be more precise. Example: "Whales are mammals. That is to say, they must breathe air.". 5. To that end. Usage: Use "to that end" or "to this end" in a similar way to "in order to" or "so".
If you're struggling to choose the right words for your essay, don't worry—you've come to the right place! In this article, we've compiled a list of over 300 words and phrases to use in the introduction, body, and conclusion of your essay. Contents: Words to Use in the Essay Introduction. Words to Use in the Body of the Essay.
Synonyms for BECAUSE: being, so, for, that, since, therefore, thus, since, on-account-of, in consequence of, in-view-of, by reason of, for the reason that, for-the-sake-of, in-behalf-of, on the grounds that. ... 45 Math Puns That Are Better Than Pi Itself Circular Reasoning Fallacy Examples Begging the Question Fallacy Examples Because Is Also ...
Writing is a series of choices. As you work on a paper, you choose your topic, your approach, your sources, and your thesis; when it's time to write, you have to choose the words you will use to express your ideas and decide how you will arrange those words into sentences and paragraphs. As you revise your draft, you make more choices.
QuillBot's AI-powered paraphrasing tool will enhance your writing. Your words matter, and our paraphrasing tool is designed to ensure you use the right ones. With unlimited Custom modes and 9 predefined modes, Paraphraser lets you rephrase text countless ways. Our product will improve your fluency while also ensuring you have the appropriate ...
It Appears. Another way to say "I believe" without using the first person is "it appears.". Like the original phrase, this one indicates that the statement following it is not certain. In fact, it is simply an observation. Although this phrase is not necessarily superior to "I believe," it does remove the personal pronoun "I ...