Argumentative Essay Guide
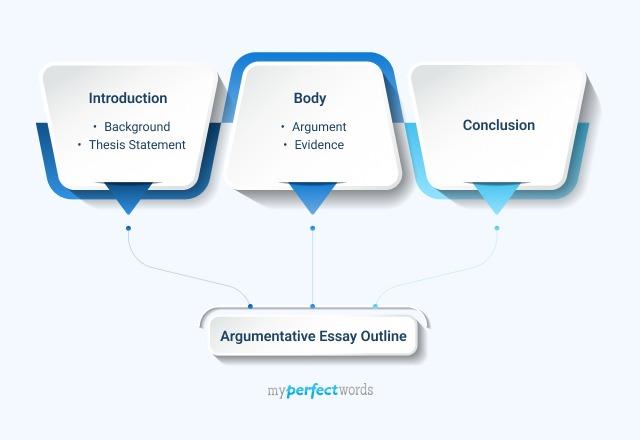
Argumentative Essay Outline

Argumentative Essay Outline: How to Structure Your Argumentative Essay
11 min read
People also read
The Ultimate Guide to Argumentative Essay Writing
250+ Argumentative Essay Topic Ideas To Help You Out
Argumentative Essay Examples: Samples & Tips
Learn the 3 Different Types of Argument and Multiple Argument Claims
Preparing to write an argumentative essay but don’t know where to start?
Making an outline is an important step in prewriting. Having a defined outline makes the essay writing process much simpler. It helps you logically present your ideas and saves you from getting stuck with writer’s block.
In this blog, we are going to teach you about how to write an outline for your essay. You’ll also get examples and templates to help you out.
So continue reading!
- 1. How To Write An Argumentative Essay Outline?
- 2. Types of Arguments and Argumentative Essay Outlines
- 3. Argumentative Essay Outline Examples
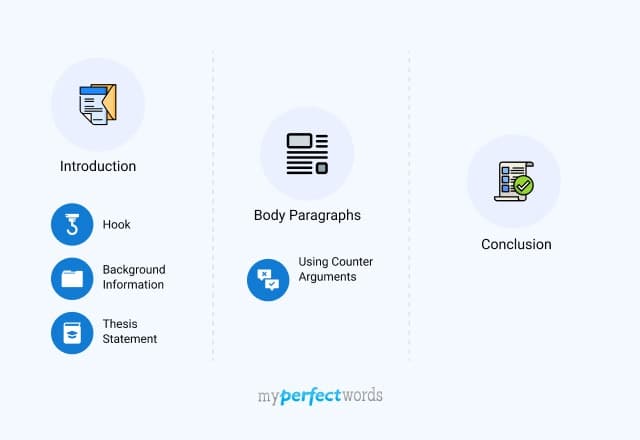
How To Write An Argumentative Essay Outline?
A simple argumentative essay outline follows the same structure as any other type of essay. The difference lies in the content of the body paragraphs. Unlike a persuasive essay, where the focus is on convincing the reader through emotional appeals, the argumentative essay presents the argument.
Some paragraphs introduce your own argument, while others state the opposing arguments and their refutations.
Here is an argumentative essay outline template you could follow for writing your essay:
The most common structure to craft an argumentative essay is as follows:
1. Argumentative Essay Introduction
The introductory paragraph introduces the main argument and provides a brief background of the argumentative essay topic you chose. Essay introductions act as a roadmap for the entire essay. For an argumentative essay, this is where you lay the foundation for your argument. An introduction comprises the following essential components:
- Hook Statement
A hook statement is written to grab the attention of your reader immediately. It should intrigue the reader and make them read the complete essay. For example, if you are writing an argumentative essay on animal testing, your hook statement could be:
- Background Information
Provide brief background information about your argument and the main claim of your essay. It will make it easier for the reader to understand the argument you will make in your essay. For example:
- Thesis Statement
An argumentative essay thesis statement should highlight your perspective, stance, and reason for your position. A thesis statement must be clearly defined, arguable, and defendable. It should express the importance of your argument and a reason why the reader should read your essay. For Example:
In case you're looking for some inspiration for your topic, check out our argumentative essay topics blog!
2. Argumentative Essay Supporting Paragraphs
In the body paragraph, you present your point of view and provide evidence that supports your argument. The goal here is to explain how valid your claim is by providing evidence that strengthens your argument.
For Example:
Here are four basic things that a body paragraph should state.
a. The purpose: Why are you making an argument about a particular issue?
b. Topic sentence: This is a fact or an example that helps the reader better understand your argument. The topic sentence of a paragraph should focus on just one point.
c. Provide evidence: State facts with examples and statistics that support your thesis statement and the topic sentence. Make sure that you have collected authentic evidence from credible sources.
d. Concluding sentence: The concluding sentence should reassert how the topic sentence helps the reader better understand the claim.
3. Argumentative Essay Counter Arguments Paragraph
The counter-argument is the other side of the issue that you will prove wrong by stating the specific reasons. In this paragraph, you mention the opposing views that the reader might pose against your argument and refute them. Conclude this paragraph by reasserting the thought provoking central idea of your essay.
4. Argumentative Essay Conclusion
A good argumentative essay conclusion summarizes the entire discussion of the essay and provides a call to action. It holds the same significance as the introduction paragraph. Here, you restate your thesis statement to remind the reader of your essay’s overall argument. Tell the reader that you have critically analyzed both sides of the argument. And based on the evidence, you have proved your side of the argument right. Explain the importance of your argument and bring your discussion to a logical end. You can propose a solution if your claim has specified a problem or make future predictions about the claim. Tell your reader the consequences if your argument is not believed and what good will happen if it's believed.
Here is an example:
Use the following argumentative essay outline graphic organizer to structure your essay efficiently.
Argumentative Essay Outline Graphic Organizer
Here’s a video demonstrating how you can prepare an argumentative essay outline:

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
Types of Arguments and Argumentative Essay Outlines
Your argumentative essay structure is affected by the type of argument you are using. There are three argumentative writing models: Classical, Rogerian, and Toulmin.
Let's take a look at each one:
Classical Argument
The classical argument is the oldest and most used argument model. It is based on the principles of rhetoric, which is the art of persuasion. This type of argument has a clear structure with distinct steps, making it an ideal choice for an essay or paper.
Here is the classical argumentative writing structure.
Classical Argumentative Essay Outline Template
Rogerian argument.
The Rogerian model allows both sides of an issue to be discussed to reach a common ground.
Unlike the classical approach, the Rogerian argument seeks to understand both sides of an issue before moving forward. This style of argumentation does not look for a single ‘right’ answer but seeks to create a dialogue between all parties.
Rhetorical Rogerian Argumentative Essay Outline Template
Toulmin argument.
The Toulmin argument is a model that breaks down an issue into its component parts to analyze it more thoroughly. The Toulmin argument is composed of six parts: a claim, grounds, warrant, backing, qualifier, and rebuttal.
The first part lays out the main point being argued (the “claim”) . This is followed by the evidence that supports it (the “grounds”) . It is then connected to an underlying assumption or principle (the “warrant”) .
The warrant is then supported by additional evidence (the “backing”) , which may be followed by qualifications (the “qualifier”) . Finally, the argument may anticipate and address possible counterarguments (the “rebuttal”) .
Toulmin Argumentative Essay Outline Template
Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers!
Argumentative Essay Outline Examples
Argumentative Essay Outline Example PDF
Argumentative Essay Outline Worksheet
5 Paragraph Argumentative Essay Outline
MLA Argumentative Essay Outline
Conclusion Argumentative Essay Outline
Argumentative Essay Outline AP Lang
Vaccine Argumentative Essay Outline
Social Media Argumentative Essay Outline
Abortion Argumentative Essay Outline
Gun Control Argumentative Essay Outline
Need more sample essays to get a better idea? Give our argumentative essay examples a read!
The Bottom Line! We've covered all the essential elements of structuring your argumentative essay. With this guide, you're now well-prepared to craft a compelling essay that effectively presents your viewpoint and supports your argument with evidence.
Remember the key components: the introduction that hooks your reader, a clear thesis statement, well-organized body paragraphs, counterarguments, and a strong conclusion. Don't forget to cite your sources properly to give credibility to your work.
If you are unable to craft a perfect outline, you can always seek the help of an expert and professional essay writer at MyPerfectWords.com.
Our affordable argumentative essay writing service can help you write a top-notch argumentative paper. Our skilled writers conduct research to find facts and evidence to support your claim and write an original essay according to your needs.
So buy custom essay online from our expertts today!

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Nova Allison is a Digital Content Strategist with over eight years of experience. Nova has also worked as a technical and scientific writer. She is majorly involved in developing and reviewing online content plans that engage and resonate with audiences. Nova has a passion for writing that engages and informs her readers.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
Praxis Core Writing
Course: praxis core writing > unit 1, argumentative essay | quick guide.
- Source-based essay | Quick guide
- Revision in context | Quick guide
- Within-sentence punctuation | Quick guide
- Subordination and coordination | Quick guide
- Independent and dependent Clauses | Video lesson
- Parallel structure | Quick guide
- Modifier placement | Quick guide
- Shifts in verb tense | Quick guide
- Pronoun clarity | Quick guide
- Pronoun agreement | Quick guide
- Subject-verb agreement | Quick guide
- Noun agreement | Quick guide
- Frequently confused words | Quick guide
- Conventional expressions | Quick guide
- Logical comparison | Quick guide
- Concision | Quick guide
- Adjective/adverb confusion | Quick guide
- Negation | Quick guide
- Capitalization | Quick guide
- Apostrophe use | Quick guide
- Research skills | Quick guide
Argumentative essay (30 minutes)
- states or clearly implies the writer’s position or thesis
- organizes and develops ideas logically, making insightful connections between them
- clearly explains key ideas, supporting them with well-chosen reasons, examples, or details
- displays effective sentence variety
- clearly displays facility in the use of language
- is generally free from errors in grammar, usage, and mechanics
- organizes and develops ideas clearly, making connections between them
- explains key ideas, supporting them with relevant reasons, examples, or details
- displays some sentence variety
- displays facility in the use of language
- states or implies the writer’s position or thesis
- shows control in the organization and development of ideas
- explains some key ideas, supporting them with adequate reasons, examples, or details
- displays adequate use of language
- shows control of grammar, usage, and mechanics, but may display errors
- limited in stating or implying a position or thesis
- limited control in the organization and development of ideas
- inadequate reasons, examples, or details to explain key ideas
- an accumulation of errors in the use of language
- an accumulation of errors in grammar, usage, and mechanics
- no clear position or thesis
- weak organization or very little development
- few or no relevant reasons, examples, or details
- frequent serious errors in the use of language
- frequent serious errors in grammar, usage, and mechanics
- contains serious and persistent writing errors or
- is incoherent or
- is undeveloped or
- is off-topic
How should I build a thesis?
- (Choice A) Kids should find role models that are worthier than celebrities because celebrities may be famous for reasons that aren't admirable. A Kids should find role models that are worthier than celebrities because celebrities may be famous for reasons that aren't admirable.
- (Choice B) Because they profit from the admiration of youths, celebrities have a moral responsibility for the reactions their behaviors provoke in fans. B Because they profit from the admiration of youths, celebrities have a moral responsibility for the reactions their behaviors provoke in fans.
- (Choice C) Celebrities may have more imitators than most people, but they hold no more responsibility over the example they set than the average person. C Celebrities may have more imitators than most people, but they hold no more responsibility over the example they set than the average person.
- (Choice D) Notoriety is not always a choice, and some celebrities may not want to be role models. D Notoriety is not always a choice, and some celebrities may not want to be role models.
- (Choice E) Parents have a moral responsibility to serve as immediate role models for their children. E Parents have a moral responsibility to serve as immediate role models for their children.
How should I support my thesis?
- (Choice A) As basketball star Charles Barkley stated in a famous advertising campaign for Nike, he was paid to dominate on the basketball court, not to raise your kids. A As basketball star Charles Barkley stated in a famous advertising campaign for Nike, he was paid to dominate on the basketball court, not to raise your kids.
- (Choice B) Many celebrities do consider themselves responsible for setting a good example and create non-profit organizations through which they can benefit youths. B Many celebrities do consider themselves responsible for setting a good example and create non-profit organizations through which they can benefit youths.
- (Choice C) Many celebrities, like Kylie Jenner with her billion-dollar cosmetics company, profit directly from being imitated by fans who purchase sponsored products. C Many celebrities, like Kylie Jenner with her billion-dollar cosmetics company, profit directly from being imitated by fans who purchase sponsored products.
- (Choice D) My ten-year-old nephew may love Drake's music, but his behaviors are more similar to those of the adults he interacts with on a daily basis, like his parents and teachers. D My ten-year-old nephew may love Drake's music, but his behaviors are more similar to those of the adults he interacts with on a daily basis, like his parents and teachers.
- (Choice E) It's very common for young people to wear fashions similar to those of their favorite celebrities. E It's very common for young people to wear fashions similar to those of their favorite celebrities.
Want to join the conversation?
- Upvote Button navigates to signup page
- Downvote Button navigates to signup page
- Flag Button navigates to signup page
Argumentative Essay Examples to Inspire You (+ Free Formula)
.webp)
Table of contents

Meredith Sell
Have you ever been asked to explain your opinion on a controversial issue?
- Maybe your family got into a discussion about chemical pesticides
- Someone at work argues against investing resources into your project
- Your partner thinks intermittent fasting is the best way to lose weight and you disagree
Proving your point in an argumentative essay can be challenging, unless you are using a proven formula.
Argumentative essay formula & example
In the image below, you can see a recommended structure for argumentative essays. It starts with the topic sentence, which establishes the main idea of the essay. Next, this hypothesis is developed in the development stage. Then, the rebuttal, or the refutal of the main counter argument or arguments. Then, again, development of the rebuttal. This is followed by an example, and ends with a summary. This is a very basic structure, but it gives you a bird-eye-view of how a proper argumentative essay can be built.

Writing an argumentative essay (for a class, a news outlet, or just for fun) can help you improve your understanding of an issue and sharpen your thinking on the matter. Using researched facts and data, you can explain why you or others think the way you do, even while other reasonable people disagree.
Free AI argumentative essay generator > Free AI argumentative essay generator >
What Is an Argumentative Essay?
An argumentative essay is an explanatory essay that takes a side.
Instead of appealing to emotion and personal experience to change the reader’s mind, an argumentative essay uses logic and well-researched factual information to explain why the thesis in question is the most reasonable opinion on the matter.
Over several paragraphs or pages, the author systematically walks through:
- The opposition (and supporting evidence)
- The chosen thesis (and its supporting evidence)
At the end, the author leaves the decision up to the reader, trusting that the case they’ve made will do the work of changing the reader’s mind. Even if the reader’s opinion doesn’t change, they come away from the essay with a greater understanding of the perspective presented — and perhaps a better understanding of their original opinion.
All of that might make it seem like writing an argumentative essay is way harder than an emotionally-driven persuasive essay — but if you’re like me and much more comfortable spouting facts and figures than making impassioned pleas, you may find that an argumentative essay is easier to write.
Plus, the process of researching an argumentative essay means you can check your assumptions and develop an opinion that’s more based in reality than what you originally thought. I know for sure that my opinions need to be fact checked — don’t yours?
So how exactly do we write the argumentative essay?
How do you start an argumentative essay
First, gain a clear understanding of what exactly an argumentative essay is. To formulate a proper topic sentence, you have to be clear on your topic, and to explore it through research.
Students have difficulty starting an essay because the whole task seems intimidating, and they are afraid of spending too much time on the topic sentence. Experienced writers, however, know that there is no set time to spend on figuring out your topic. It's a real exploration that is based to a large extent on intuition.
6 Steps to Write an Argumentative Essay (Persuasion Formula)
Use this checklist to tackle your essay one step at a time:

1. Research an issue with an arguable question
To start, you need to identify an issue that well-informed people have varying opinions on. Here, it’s helpful to think of one core topic and how it intersects with another (or several other) issues. That intersection is where hot takes and reasonable (or unreasonable) opinions abound.
I find it helpful to stage the issue as a question.
For example:
Is it better to legislate the minimum size of chicken enclosures or to outlaw the sale of eggs from chickens who don’t have enough space?
Should snow removal policies focus more on effectively keeping roads clear for traffic or the environmental impacts of snow removal methods?
Once you have your arguable question ready, start researching the basic facts and specific opinions and arguments on the issue. Do your best to stay focused on gathering information that is directly relevant to your topic. Depending on what your essay is for, you may reference academic studies, government reports, or newspaper articles.
Research your opposition and the facts that support their viewpoint as much as you research your own position . You’ll need to address your opposition in your essay, so you’ll want to know their argument from the inside out.
2. Choose a side based on your research
You likely started with an inclination toward one side or the other, but your research should ultimately shape your perspective. So once you’ve completed the research, nail down your opinion and start articulating the what and why of your take.
What: I think it’s better to outlaw selling eggs from chickens whose enclosures are too small.
Why: Because if you regulate the enclosure size directly, egg producers outside of the government’s jurisdiction could ship eggs into your territory and put nearby egg producers out of business by offering better prices because they don’t have the added cost of larger enclosures.
This is an early form of your thesis and the basic logic of your argument. You’ll want to iterate on this a few times and develop a one-sentence statement that sums up the thesis of your essay.
Thesis: Outlawing the sale of eggs from chickens with cramped living spaces is better for business than regulating the size of chicken enclosures.
Now that you’ve articulated your thesis , spell out the counterargument(s) as well. Putting your opposition’s take into words will help you throughout the rest of the essay-writing process. (You can start by choosing the counter argument option with Wordtune Spices .)

Counterargument: Outlawing the sale of eggs from chickens with too small enclosures will immediately drive up egg prices for consumers, making the low-cost protein source harder to afford — especially for low-income consumers.
There may be one main counterargument to articulate, or several. Write them all out and start thinking about how you’ll use evidence to address each of them or show why your argument is still the best option.
3. Organize the evidence — for your side and the opposition
You did all of that research for a reason. Now’s the time to use it.
Hopefully, you kept detailed notes in a document, complete with links and titles of all your source material. Go through your research document and copy the evidence for your argument and your opposition’s into another document.
List the main points of your argument. Then, below each point, paste the evidence that backs them up.
If you’re writing about chicken enclosures, maybe you found evidence that shows the spread of disease among birds kept in close quarters is worse than among birds who have more space. Or maybe you found information that says eggs from free-range chickens are more flavorful or nutritious. Put that information next to the appropriate part of your argument.
Repeat the process with your opposition’s argument: What information did you find that supports your opposition? Paste it beside your opposition’s argument.
You could also put information here that refutes your opposition, but organize it in a way that clearly tells you — at a glance — that the information disproves their point.
Counterargument: Outlawing the sale of eggs from chickens with too small enclosures will immediately drive up egg prices for consumers.
BUT: Sicknesses like avian flu spread more easily through small enclosures and could cause a shortage that would drive up egg prices naturally, so ensuring larger enclosures is still a better policy for consumers over the long term.
As you organize your research and see the evidence all together, start thinking through the best way to order your points.
Will it be better to present your argument all at once or to break it up with opposition claims you can quickly refute? Would some points set up other points well? Does a more complicated point require that the reader understands a simpler point first?
Play around and rearrange your notes to see how your essay might flow one way or another.
4. Freewrite or outline to think through your argument
Is your brain buzzing yet? At this point in the process, it can be helpful to take out a notebook or open a fresh document and dump whatever you’re thinking on the page.
Where should your essay start? What ground-level information do you need to provide your readers before you can dive into the issue?
Use your organized evidence document from step 3 to think through your argument from beginning to end, and determine the structure of your essay.
There are three typical structures for argumentative essays:
- Make your argument and tackle opposition claims one by one, as they come up in relation to the points of your argument - In this approach, the whole essay — from beginning to end — focuses on your argument, but as you make each point, you address the relevant opposition claims individually. This approach works well if your opposition’s views can be quickly explained and refuted and if they directly relate to specific points in your argument.
- Make the bulk of your argument, and then address the opposition all at once in a paragraph (or a few) - This approach puts the opposition in its own section, separate from your main argument. After you’ve made your case, with ample evidence to convince your readers, you write about the opposition, explaining their viewpoint and supporting evidence — and showing readers why the opposition’s argument is unconvincing. Once you’ve addressed the opposition, you write a conclusion that sums up why your argument is the better one.
- Open your essay by talking about the opposition and where it falls short. Build your entire argument to show how it is superior to that opposition - With this structure, you’re showing your readers “a better way” to address the issue. After opening your piece by showing how your opposition’s approaches fail, you launch into your argument, providing readers with ample evidence that backs you up.
As you think through your argument and examine your evidence document, consider which structure will serve your argument best. Sketch out an outline to give yourself a map to follow in the writing process. You could also rearrange your evidence document again to match your outline, so it will be easy to find what you need when you start writing.
5. Write your first draft
You have an outline and an organized document with all your points and evidence lined up and ready. Now you just have to write your essay.
In your first draft, focus on getting your ideas on the page. Your wording may not be perfect (whose is?), but you know what you’re trying to say — so even if you’re overly wordy and taking too much space to say what you need to say, put those words on the page.
Follow your outline, and draw from that evidence document to flesh out each point of your argument. Explain what the evidence means for your argument and your opposition. Connect the dots for your readers so they can follow you, point by point, and understand what you’re trying to say.
As you write, be sure to include:
1. Any background information your reader needs in order to understand the issue in question.
2. Evidence for both your argument and the counterargument(s). This shows that you’ve done your homework and builds trust with your reader, while also setting you up to make a more convincing argument. (If you find gaps in your research while you’re writing, Wordtune Spices can source statistics or historical facts on the fly!)

Get Wordtune for free > Get Wordtune for free >
3. A conclusion that sums up your overall argument and evidence — and leaves the reader with an understanding of the issue and its significance. This sort of conclusion brings your essay to a strong ending that doesn’t waste readers’ time, but actually adds value to your case.
6. Revise (with Wordtune)
The hard work is done: you have a first draft. Now, let’s fine tune your writing.
I like to step away from what I’ve written for a day (or at least a night of sleep) before attempting to revise. It helps me approach clunky phrases and rough transitions with fresh eyes. If you don’t have that luxury, just get away from your computer for a few minutes — use the bathroom, do some jumping jacks, eat an apple — and then come back and read through your piece.
As you revise, make sure you …
- Get the facts right. An argument with false evidence falls apart pretty quickly, so check your facts to make yours rock solid.
- Don’t misrepresent the opposition or their evidence. If someone who holds the opposing view reads your essay, they should affirm how you explain their side — even if they disagree with your rebuttal.
- Present a case that builds over the course of your essay, makes sense, and ends on a strong note. One point should naturally lead to the next. Your readers shouldn’t feel like you’re constantly changing subjects. You’re making a variety of points, but your argument should feel like a cohesive whole.
- Paraphrase sources and cite them appropriately. Did you skip citations when writing your first draft? No worries — you can add them now. And check that you don’t overly rely on quotations. (Need help paraphrasing? Wordtune can help. Simply highlight the sentence or phrase you want to adjust and sort through Wordtune’s suggestions.)
- Tighten up overly wordy explanations and sharpen any convoluted ideas. Wordtune makes a great sidekick for this too 😉

Words to start an argumentative essay
The best way to introduce a convincing argument is to provide a strong thesis statement . These are the words I usually use to start an argumentative essay:
- It is indisputable that the world today is facing a multitude of issues
- With the rise of ____, the potential to make a positive difference has never been more accessible
- It is essential that we take action now and tackle these issues head-on
- it is critical to understand the underlying causes of the problems standing before us
- Opponents of this idea claim
- Those who are against these ideas may say
- Some people may disagree with this idea
- Some people may say that ____, however
When refuting an opposing concept, use:
- These researchers have a point in thinking
- To a certain extent they are right
- After seeing this evidence, there is no way one can agree with this idea
- This argument is irrelevant to the topic
Are you convinced by your own argument yet? Ready to brave the next get-together where everyone’s talking like they know something about intermittent fasting , chicken enclosures , or snow removal policies?
Now if someone asks you to explain your evidence-based but controversial opinion, you can hand them your essay and ask them to report back after they’ve read it.
Share This Article:

How To Prepare For Studying Abroad (From Someone Who’s Done It)


Strategic Negotiation: How to Ask For A Raise Over Email
.webp)
Metaphor vs. Simile: What’s the Difference? (+ Examples)
Looking for fresh content, thank you your submission has been received.
- Writing Worksheets and Other Writing Resources
- Thesis, Analysis, & Structure
Suggestions for Developing Argumentative Essays
About the slc.
- Our Mission and Core Values

1. Select an arguable topic, preferably one which interests, puzzles, or appeals to you.
Make sure your topic is neither too broad--something which warrants a dissertation--nor too limited. Decide what your goals are for the paper. What is your purpose? What opinion, view, or idea do you want to prove? Try to articulate your purpose clearly before you begin writing. If you cannot state your purpose clearly, try to freewrite about your topic.
2. Take a position on your topic, and form a thesis statement.
Your thesis must be arguable; it must assert or deny something about your topic. To be arguable, a thesis must have some probability of being true. It should not, however, be generally accepted as true; it must be a statement with which people may disagree. Keep in mind that a thesis contains both an observation and an opinion:
A good way to test the strength of your thesis is to see if it yields a strong antithesis.
Common thesis pitfalls:
- A thesis expressed as a fragment.
- A thesis which is too broad.
- A thesis worded as a question. (Usually the answer to the question yields the thesis)
- A thesis which includes extraneous information.
- A thesis which begins with I think or in my opinion.
- A thesis which deals with a stale or trite issue.
- A thesis which contains words which lead to faulty generalizations (all, none, always, only, everyone, etc.)
Thesis writing tips:
- A thesis evolves as you work with your topic. Brainstorm, research, talk, and think about your topic before settling on a thesis. If you are having trouble formulating a thesis, begin freewriting about your topic. Your freewrite may suggest a workable thesis.
- During the writing process, consider your thesis a working thesis and be willing to modify and re-focus it as you draft and revise your paper.
- Copy your working thesis on an index card and keep it in front of you as you research and write. Having your thesis in plain view may help focus your writing.
3. Consider your audience.
Plan your paper with a specific audience in mind. Who are your readers? Are they a definable group--disinterested observers, opponents of your point of view, etc.? Perhaps you are writing to your classmates. Ask your professor or GSI who you should consider your target audience. If you are not certain of your audience, direct your argument to a general audience.
4. Present clear and convincing evidence.
Strong essays consist of reasons supported by evidence . Reasons can be thought of as the main points supporting your claim or thesis. Often they are the answers to the question, "Why do you make that claim?" An easy way to think of reasons is to see them as "because phrases." In order to validate your reasons and make your argument successful, support your reasons with ample evidence.
The St. Martin's Guide to Writing (Axelrod & Cooper, 2nd ed., New York: St. Martin's Press, 1988) lists the following forms of evidence:
- authorities
- textual evidence
For most college papers, you will include evidence you have gathered from various sources and texts. Make sure you document your evidence properly. When using evidence, make sure you (1) introduce it properly, and (2) explain its significance. Do not assume that your evidence will speak for itself--that your readers will glean from your evidence that which you want them to glean. Explain the importance of each piece of evidence-- how it elucidates or supports your point, why it is significant. Build evidence into your text, and use it strategically to prove your points.
In addition to using evidence, thoughtful writers anticipate their readers' counterarguments Counterarguments include objections, alternatives, challenges, or questions to your argument. Imagine readers responding to your argument as it unfolds. How might they react? A savvy writer will anticipate and address counterarguments. A writer can address counterarguments by acknowledging , accommodating , and/or refuting them.
5. Draft your essay.
As is the case with any piece of writing, you should take your argumentative essay through multiple drafts. When writing and revising your drafts, make sure you:
- provide ample evidence , presented logically and fairly
- deal with the opposing point of view
- pay particular attention to the organization of your essay. Make sure its structure suits your topic and audience
- address and correct any fallacies of logic
- include proper transitions to allow your reader to follow your argument
6. Edit your draft.
After you have written a developed draft, take off your writer's hat and put on your reader's hat. Evaluate your essay carefully and critically. Exchange a draft of your essay with classmates to get their feedback. Carefully revise your draft based on your assessment of it and suggestions from your peers. For self-assessment and peer response to your draft, you may want to use a peer editing sheet. A peer editing sheet will guide you and your peers by asking specific questions about your text (i.e., What is the thesis of this essay? Is it arguable? Does the writer include ample evidence? Is the structure suitable for the topic and the audience?).
You may also want to avail yourself of the Writing Drop-In Tutoring or By-Appointment Tutoring at the Student Learning Center .
Luisa Giulianetti Student Learning Center, University of California, Berkeley ©1996 UC Regents
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported License.
- Chess (Gr. 1-4)
- TV (Gr. 1-4)
- Metal Detectors (Gr. 2-6)
- Tetris (Gr. 2-6)
- Seat Belts (Gr. 2-6)
- The Coliseum (Gr. 2-6)
- The Pony Express (Gr. 2-6)
- Wintertime (Gr. 2-6)
- Reading (Gr. 3-7)
- Black Friday (Gr. 3-7)
- Hummingbirds (Gr. 3-7)
- Worst Game Ever? (Gr. 4-8)
- Carnivorous Plants (Gr. 4-8)
- Google (Gr. 4-8)
- Honey Badgers (Gr. 4-8)
- Hyperinflation (Gr. 4-8)
- Koko (Gr. 4-8)
- Mongooses (Gr. 5-9)
- Trampolines (Gr. 5-9)
- Garbage (Gr. 5-9)
- Maginot Line (Gr. 5-9)
- Asian Carp (Gr. 5-9)
- Tale of Two Countries (Gr. 6-10)
- Kevlar (Gr. 7-10)
- Tigers (Gr. 7-11)
- Statue of Liberty (Gr. 8-10)
- Submarines (Gr. 8-12)
- Castles (Gr. 9-13)
- Gutenberg (Gr. 9-13)
- Author's Purpose Practice 1
- Author's Purpose Practice 2
- Author's Purpose Practice 3
- Fact and Opinion Practice 1
- Fact and Opinion Practice 2
- Fact and Opinion Practice 3
- Idioms Practice Test 1
- Idioms Practice Test 2
- Figurative Language Practice 1
- Figurative Language Practice 2
- Figurative Language Practice 3
- Figurative Language Practice 4
- Figurative Language Practice 5
- Figurative Language Practice 6
- Figurative Language Practice 7
- Figurative Language Practice 8
- Figurative Language Practice 9
- Figurative Language of Edgar Allan Poe
- Figurative Language of O. Henry
- Figurative Language of Shakespeare
- Genre Practice 1
- Genre Practice 2
- Genre Practice 3
- Genre Practice 4
- Genre Practice 5
- Genre Practice 6
- Genre Practice 7
- Genre Practice 8
- Genre Practice 9
- Genre Practice 10
- Irony Practice 1
- Irony Practice 2
- Irony Practice 3
- Making Inferences Practice 1
- Making Inferences Practice 2
- Making Inferences Practice 3
- Making Inferences Practice 4
- Making Inferences Practice 5
- Main Idea Practice 1
- Main Idea Practice 2
- Point of View Practice 1
- Point of View Practice 2
- Text Structure Practice 1
- Text Structure Practice 2
- Text Structure Practice 3
- Text Structure Practice 4
- Text Structure Practice 5
- Story Structure Practice 1
- Story Structure Practice 2
- Story Structure Practice 3
- Author's Purpose
- Characterizations
- Context Clues
- Fact and Opinion
- Figurative Language
- Grammar and Language Arts
- Poetic Devices
- Point of View
- Predictions
- Reading Comprehension
- Story Structure
- Summarizing
- Text Structure
- Character Traits
- Common Core Aligned Unit Plans
- Teacher Point of View
- Teaching Theme
- Patterns of Organization
- Project Ideas
- Reading Activities
- How to Write Narrative Essays
- How to Write Persuasive Essays
- Narrative Essay Assignments
- Narrative Essay Topics
- Persuasive Essay Topics
- Research Paper Topics
- Rubrics for Writing Assignments
- Learn About Sentence Structure
- Grammar Worksheets
- Noun Worksheets
- Parts of Speech Worksheets
- Punctuation Worksheets
- Sentence Structure Worksheets
- Verbs and Gerunds
- Examples of Allitertion
- Examples of Hyperbole
- Examples of Onomatopoeia
- Examples of Metaphor
- Examples of Personification
- Examples of Simile
- Figurative Language Activities
- Figurative Language Examples
- Figurative Language Poems
- Figurative Language Worksheets
- Learn About Figurative Language
- Learn About Poetic Devices
- Idiom Worksheets
- Online Figurative Language Tests
- Onomatopoeia Worksheets
- Personification Worksheets
- Poetic Devices Activities
- Poetic Devices Worksheets
- About This Site
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Use
- Understanding CCSS Standards
- What's New?
Ereading Worksheets
Free reading worksheets, activities, and lesson plans., site navigation.
- Learn About Author’s Purpose
- Author’s Purpose Quizzes
- Character Types Worksheets and Lessons
- List of Character Traits
- Differentiated Reading Instruction Worksheets and Activities
- Fact and Opinion Worksheets
- Irony Worksheets
- Animal Farm Worksheets
- Literary Conflicts Lesson and Review
- New Home Page Test
- Lord of the Flies Chapter 2 Worksheet
- Lord of the Flies Chapter 5 Worksheet
- Lord of the Flies Chapter 6 Worksheet
- Lord of the Flies Chapter 10 Worksheet
- Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass
- Sister Carrie
- The Count of Monte Cristo
- The Odyssey
- The War of the Worlds
- The Wizard of Oz
- Mood Worksheets
- Context Clues Worksheets
- Inferences Worksheets
- Main Idea Worksheets
- Making Predictions Worksheets
- Nonfiction Passages and Functional Texts
- Setting Worksheets
- Summarizing Worksheets and Activities
- Short Stories with Questions
- Story Structure Activities
- Story Structure Worksheets
- Tone Worksheets
- Types of Conflict Worksheets
- Reading Games
- Figurative Language Poems with Questions
- Hyperbole and Understatement Worksheets
- Simile and Metaphor Worksheets
- Simile Worksheets
- Hyperbole Examples
- Metaphor Examples
- Personification Examples
- Simile Examples
- Understatement Examples
- Idiom Worksheets and Tests
- Poetic Devices Worksheets & Activities
- Alliteration Examples
- Allusion Examples
- Onomatopoeia Examples
- Onomatopoeia Worksheets and Activities
- Genre Worksheets
- Genre Activities
- Capitalization Worksheets, Lessons, and Tests
- Contractions Worksheets and Activities
- Double Negative Worksheets
- Homophones & Word Choice Worksheets
- ‘Was’ or ‘Were’
- Simple Subjects & Predicates Worksheets
- Subjects, Predicates, and Objects
- Clauses and Phrases
- Type of Sentences Worksheets
- Sentence Structure Activities
- Comma Worksheets and Activities
- Semicolon Worksheets
- End Mark Worksheets
- Noun Worksheets, Lessons, and Tests
- Verb Worksheets and Activities
- Pronoun Worksheets, Lessons, and Tests
- Adverbs & Adjectives Worksheets, Lessons, & Tests
- Preposition Worksheets and Activities
- Conjunctions Worksheets and Activities
- Interjections Worksheets
- Parts of Speech Activities
- Verb Tense Activities
- Past Tense Worksheets
- Present Tense Worksheets
- Future Tense Worksheets
- Point of View Activities
- Point of View Worksheets
- Teaching Point of View
- Cause and Effect Example Paragraphs
- Chronological Order
- Compare and Contrast
- Order of Importance
- Problem and Solution
- Text Structure Worksheets
- Text Structure Activities
- Essay Writing Rubrics
- Narrative Essay Topics and Story Ideas
- Narrative Essay Worksheets & Writing Assignments
- Persuasive Essay and Speech Topics
Persuasive Essay Worksheets & Activities
- Writing Narrative Essays and Short Stories
- Writing Persuasive Essays
- All Reading Worksheets
- Understanding Common Core State Standards
- Remote Learning Resources for Covid-19 School Closures
- What’s New?
- Ereading Worksheets | Legacy Versions
- Online Figurative Language Practice
- Online Genre Practice Tests
- Online Point of View Practice Tests
- 62 School Project Ideas
- 2nd Grade Reading Worksheets
- 3rd Grade Reading Worksheets
- 4th Grade Reading Worksheets
- 5th Grade Reading Worksheets
- 6th Grade Reading Worksheets
- 7th Grade Reading Worksheets
- 8th Grade Reading Worksheets
- 9th Grade Reading Worksheets
- 10th Grade Reading Worksheets
- Membership Billing
- Membership Cancel
- Membership Checkout
- Membership Confirmation
- Membership Invoice
- Membership Levels
- Your Profile
Want Updates?
84 comments.
Thank you so much. This has truly helped me in my exams and throughout the beneficial journey of my school year.
Ellen Davis
How will I be able to check my work, when I print it out to work on them? Where are the answers?
I guess it depends on what you are working on. On what are you working?
Kareema Coles
Ummm the pdf version is not working…is the link still valid?
Which link?
This is an amazing website with fabulous ideas and printable ready to go lessons!!! Thank you so much! I wish I could meet you!!!
Thank you very much for this amazing resource and great ideas. They are extremely comprehensive and well designed. Thank you very much for your kind consideration and not adding a Price-tag to your valuable resources. Highly appreciated.
Sandra Conner
Thank you so much for sharing your knowledge and your work with us. As teachers, we are always in need of fresh material. I teach college level creative writing classes, and your worksheets help my students. Sometimes I change the essay topics to fit their particular age group or interest, but having these examples laid out for us and made available for use in our classrooms is wonderful.
Lifesaver! Thank you for the great ideas and guidance. I am a new teacher, and finding this site has made a true turn around in my instruction. Thank you, thank you, thank you!!!
Thank you for these great step by step resources
Macca Malbrán
Despite all the negative comments above, you should keep up for the ones (like me) who are absolutely grateful for these material.
Thanks for sharing! Best.
I give this website 3stares only for the info but in general 1star
I give your comment 0 stars because your position lacks support or evidence of any kind. Complete some of these worksheets and begin your argument again.
that’s stupid from where do u get the worksheets
I wrote them.
I did not see any activities that required the student to write an entire essay.
https://www.ereadingworksheets.com/writing/persuasive-essay-topics/
Lamar Mohamed
Thank you for this information! They helped me in my exam so much!
These are fantastic resources! Thank you so much for sharing them. I only wish I had found them earlier in the school year!
There’s always next year…
Thank you so much for all you do for teachers. I love an use practically everything on your Website!
That’s awesome. Thanks for visiting my website.
I really like this website
Shenard McDougal
How can a teacher get the answers to the worksheets?
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Subscribe Now
Popular content.
- Author's Purpose Worksheets
- Characterization Worksheets
- Common Core Lesson and Unit Plans
- Online Reading Practice Tests
- Plot Worksheets
- Reading Comprehension Worksheets
- Summary Worksheets
- Theme Worksheets
New and Updated Pages
- Capitalization Worksheets
- Contractions Worksheets
- Double Negatives Worksheets
- Homophones & Word Choice Worksheets
BECOME A MEMBER!
- Grade Levels
- Search Site
- Language Arts Topics
Argumentative Writing Worksheets
The we choose to take a stand on an issue of any sorts, there is a requirement to validate your position if we are intent on finding the truth. When we work to substantiate our stance in a written form the piece we will create is viewed as augmentative writing. It can be viewed as the written form of a debate. In order to prepare for such a work, you will need to do a bit of detective work. Outside of a full-fledged research paper, this is one of the lengthiest investigations that you will need to do in order to write a well-prepared piece. The best arguments are prepared by fully understanding the stance of both sides of the issue. I have found from over a decade of working on this form of writing with students that at first it is difficult for them. This is because students have been conditioned to only find one correct answer. In an argumentative essay you will need to explore all of the things that support your side of the argument. I also find that after students get some experience with writing these pieces, they enjoy it and get stronger with every successive project. These worksheets with help students learn to approach these types of works and the process that is required to prepare great works.
Argumentative Writing Worksheets To Print:
Essay Outline - Use the graphic organizer to write an argumentative essay on the assigned topic.
Argument Writing Organizer - What would you say to the person who disagreed with you to change their mind? Present the counterargument. What would someone say if they disagreed with you?
Writing Prompt - Should the government offer free Internet access to everyone in the country?
Counterarguments - A counterargument is an argument someone makes in order to disagree with your claim. When writing an argumentative essay, it is important to anticipate the main counterarguments against your claim and to rebut (argue against, disprove) them. Doing so will make your essay more persuasive. It will also demonstrate that you have taken the time to consider different viewpoints.
Structuring Your Essays - We provide you with a handy outline to keep by your side as you write your essays.
Make a Claim - Should everyone be required to go to school?
What Do You Think? - Should schools be held legally responsible for the consequences of bullying?
My Outline - A great exercise to get yourself ready to create a masterpiece.
The MEAT Technique - This acronym stands for the order in which you create a hook, add background information, and finish it off with a thesis.
Transitions for Making Arguments - Transitional words and phrases are important in this type of writing because they allow you to move between paragraphs, ideas, and source information in a clear way that your reader can easily follow.
The Essay - Take a pro or con position on one of the topics. Use the outline below to organize your thoughts.
Restrooms - In Europe public restrooms are gender neutral. Should the U.S. have gender neutral public restrooms?
Have At It! - A series of ideas to get you working away on your own thoughts.
Convince Them! - This can be used as a tool to assess your work and see if you achieved your goal.
Analyze an Argument - What facts/reasons/evidence does the author use to support the claim? Does the author convince you to believe/agree with the claim? Why or why not?
Argumentative Essay Outline Worksheets - The focus in this series is to plan.
How to Write a Solid Argumentative Essay
There is a common format that is often followed here that is called the five-paragraph format. It begins with an introductory paragraph that states the issue and your stance on it. That is followed by three evidentiary body paragraphs that support your position and it ends with a conclusion paragraph. I am personally not a fan of carrying this into all forms of essay writing. I find that it several handcuffs students into thinking that this method fits all situations. There will be circumstances where you have endless evidence that must be explored and other times you may just have a single body of evidence. Complex issues require complex solutions. There also must be room for authors to flesh out their thoughts and create a sense of context for their readers.
Here are some clear principles that I encourage you reflect on as you write these types of works. In the introductory section we do need to give a brief overview of how we intent to substantiate our claims. We want to make sure our language flows well from paragraph to paragraph. As we transition into exploring the evidence make sure you cover all aspects of why your point is to be believed by the audience that is reading this. The body of your work should contain the evidence and that can be communicated any number of ways facts, data, even charts. It is important to make sure that the evidence is fully explained. When preparing a conclusion make sure that you reflect back on the introduction for your original thesis and all the evidence that backs up your position on the issue.
Teachers: Upgrade Now
- Print all 25,000+ worksheets
- All grade levels and topics
- Save endless hours of your time...
- Answers to everything too!
Get FREE English Worksheets In Your Email
- How We Are Aligned To The Common Core
- Educator Resources
- Privacy Policy
- Newsletters
© English Worksheets Land . All rights reserved.
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
current events conversation
What Students Are Saying About Tech in the Classroom
Does technology help students be more organized, efficient and prepared for the future? Or is it just a distraction?

By The Learning Network
Is there a problem with screens in schools?
We invited students to weigh in on that question in our Picture Prompt Tech in the Classroom , which was based on an Opinion essay arguing that we should “get tech out of the classroom before it’s too late.”
Is there too much tech in your school day? — we asked students. Would you prefer more screen-free time while you are learning, or even during lunch or free periods?
Below, they share the good, the bad and the ugly about technology use in school.
Thank you to everyone who participated in the conversation on our writing prompts this week!
Please note: Student comments have been lightly edited for length.
Some students saw the value of technology in schools, including its ability to prepare students for the future.
I believe that technology in the classroom is a good thing when it is properly moderated. I think completely taking away screens from a student will not help them develop computer skills which they will most likely need in a world like ours, where most of everything is online. Sometimes phones cannot get the job done, and computers will be needed. If schools completely remove devices from the curriculum, then students will be completely clueless when they take classes involving a computer. Too much screen time can be bad for the student, but if it is well moderated, then screen time won’t be an issue.
— Saheed, GMS
I personally do not mind the amount of technology in the classroom. I personally find typing to be a lot easier instead of writing. On top of that, this amount of technology is used in adults’ day to day lives, too. Writing has become less and less relevant for everyone, because most jobs require a computer nowadays. So I think it’s actually better to have the amount of technology we do in the classroom.
— Timothy, Greenbelt Middle
They said, even though there might be down sides, the good outweighs the bad.
Screens in the classroom allows students to complete work in a more organized manner and use online resources to help them learn. It helps teachers to be able to make sure students turn work in before a certain time. However, having screens in the classroom raises students overall screen time which is bad for their eye health and sleep.
— Emily, Greenbelt Middle
I believe that computers should definitely be used at school because it has more pros than cons. They help with everything. The only problem with them is the people using them. The people using them are often misusing them and not charging them.
— Deegan, California
And they argued that tech is so entrenched in the student experience that taking it away would cause a lot of disruption.
There are no problems with screens in school. I believe without screens, school would be much less productive, produce so much waste of paper, and assignments would be lost a lot. Also when I have paper homework, which is almost never, almost every time I get it I forget because everything is on the iPad. This is important because if there is any change in the iPads we use, it’ll affect everyone drastically. Also it would just be really annoying to get used to a whole new thing.
— August, GBW
But another contingent of students said, “There is definitely a problem with screens in school.” They called them a distraction.
There is definitely a problem with screens in school. While regular technology use in school is highly efficient and much more convenient than using textbooks and paper, I still feel like using technology as the main method for learning is detrimental. There are plenty of students in my classes who are hiding behind their iPads to play games or go on their phones rather than utilizing their technology to enhance their learning experience. So in turn, I think we need to minimize (but not completely take away) the prominence of tech in our classrooms. This matters because it’s so important for students to learn how to completely pay attention and focus in on one task so that they are prepared for the moments in life where they don’t get the opportunity to look at their phone if they’re bored or to text their friends. Trust me, this may seem like I’m one hundred percent anti-phones but the truth is I love my phone and am somewhat addicted to it, so I realize that it’s a major distraction for myself in the classroom. Moreover, staring at an iPad screen for 7 hours a day puts significant strain on our eyes, so for the sake of our health and our attention spans, we need to minimize tech use in school.
— Mary, Glenbard West High School
Tech inside classrooms has had many positive effects and many negative effects. Without technology, it would take forever to find sources/information and it would also take ages to do complex things. With technology, people can easily find information and they can easily do many things but the big downside is that they can easily just search up games and get distracted. On one side, it has provided many different changes to students so they can learn in a fun and entertaining way but in another, people are mostly on their phones scrolling through YouTube or Instagram. Many people don’t have control over their body and have a big urge to go on their cellphones.
— Srikanth, Greenbelt Middle School
In my opinion, yes there is a problem with screens in schools. It distracts kids from focusing on their work. Many students are always on their phone during class, and it is disrespectful as well as sad for them. They will not be able to learn the material that is being taught. Personally, I think that screens should be reduced in class, but I do not think that is possible. Whenever a teacher takes away someone’s phone, they get very mad and say that it is their right to have their phone. In these cases it is very confusing on how to act for the teacher!
— Kadambari, gms
Some reported that their peers use technology to cheat.
It might be a problem depending on what people are doing. If it is used for school, like typing an essay, working on homework, or checking your grades it’s okay, but I know people who abuse this privilege. They go onto YouTube and watch things, listen to music when they aren’t supposed to, and play games. Many people cheat to the point where it takes forever to start a test because people don’t close out their tabs. It helps to be able to do these ‘Quick Writes’ as we call them in my ELA class because I can write faster (I know it’s called typing). It’s harder to access things because of the restriction because people mess around so they block so many useful websites and words from our computer. I like to type on the computer, but I feel people abuse this privilege too much.
— Nina, California
When the teachers assign tests on computers, sometimes teachers have to lock students’ screens to make sure they’re not cheating. Sometimes they do it on paper and they try to cheat while hiding their phones in their laps. And then if another student sees them doing that, they will tell and the student who would have the phone out could start a big argument.
— Taylor, Huntington Beach
Several lamented the sheer number of hours teenagers spend in front of screens.
I feel that we have become too comfortable with using screens for nearly every lesson in school, because it has gotten to the point where we are spending upwards of 4 hours on our laptops in school alone. I understand that it would be hard to switch back to using journals and worksheets, but it would be very beneficial for kids if we did.
— Chase, school
I think we should reduce the tech a little just because most students are going straight to screens when they get home, after a full day of screens … Although I know this would be very difficult to do because everything in the world now seems to go online.
— Jaydin, California
And they even worried about their handwriting in a world full of typing.
I think technology in a class is very helpful, but I think that we should incorporate more writing. Since the pandemic, most of the work has been online and it never gave students the opportunity to write as much. When we came back from lockdown, I almost forgot how to write with a pencil. My handwriting was very different. And now we don’t get much time to write with our hands so I think we should have fewer screens.
— Eric, Greenbelt
Some students said that less time spent on screens in school would give them a break from the always-on digital culture they live in.
Although typing is useful and using the internet is very useful, I think we should go back to how it was about 20-40 years ago when all people used the computer for was to type an essay. Drama didn’t get spread in a millisecond, we didn’t have to worry as much about stereotypes. Now all kids want to do is text each other and watch videos. I’m well aware that I have fallen into this trap and I want out, but our lives revolve around technology. You can’t get away from it. I know this is about schools not using technology, which the world without it would be impossible now, but life would be so much simpler again.
— Ivy, Huntington Beach, CA
I will say that my phone is usually always with me during school hours, but I don’t use it all the time. I may check the time or play a short game as a brain break. But I do see some people absolutely glued to their phones during class time, and it’s honestly embarrassing. You really can’t go without your phone for an hour?? It’s almost like an addiction at this point. I understand using your phone to quickly distract yourself; I do it too. And I also think it’s okay to have your phone/electronic during lunch time or free periods. But using it to the point that you can’t properly pay attention in class is just embarrassing. So, in summary, I do think that schools are having a problem with screens.
— Allison, Greenbelt Middle School
And they named classes in which they think screens do and do not have a place.
I feel like for classes for younger kids, technology is definitely not good. Kids should be playing, using their hands, and actually experiencing things instead of being on tablets in kindergarten. I think using computers in school is good though. It’s a lot more efficient, and we live in a society where fast and efficient things are the trend.
— sarah, maryland
I think screens have their place, and will always have their place, in schools and education. The capabilities of computers will always surpass anything else, and they should not be banned from school environments. Still, I have one exception: English class. Other than final drafts of essays, everything in English should be on paper. You can formulate ideas better and minimize outside influence on your thinking.
— Addie, The Potomac School
Learn more about Current Events Conversation here and find all of our posts in this column .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Matthew Barbee, 2015 1 Name_____ Class_____ In an argumentative essay, your job is make the reader agree with your opinion about a controversial topic. You have to (1) state your opinion, (2) give reasons to support your opinion, and (3) argue against the opposite opinion. Overall, you must convince the audience that your side of the
The most common structure to craft an argumentative essay is as follows: 1. Argumentative Essay Introduction. The introductory paragraph introduces the main argument and provides a brief background of the argumentative essay topic you chose. Essay introductions act as a roadmap for the entire essay.
A. As basketball star Charles Barkley stated in a famous advertising campaign for Nike, he was paid to dominate on the basketball court, not to raise your kids. Many celebrities do consider themselves responsible for setting a good example and create non-profit organizations through which they can benefit youths. B.
Procedure: introduce focus of the lesson: Writing Task 2 - developing an argument. give each student a copy of Worksheet 1 and one minute to read the Task 2 question. elicit possible next steps before writing i.e. brainstorming ideas. draw attention to the True / False task and clarify the importance of spending time with the question before ...
Introduce the issue: Briefly explain the issue and the controversy surrounding the argument. Give background information. State your claim: This is the thesis statement. It is a promise to the reader that the essay will address the argument and prove the claim. Use one of these key words to form the thesis: Ex.
Argumentative essay formula & example. In the image below, you can see a recommended structure for argumentative essays. It starts with the topic sentence, which establishes the main idea of the essay. Next, this hypothesis is developed in the development stage. Then, the rebuttal, or the refutal of the main counter argument or arguments.
Make a claim. Provide the grounds (evidence) for the claim. Explain the warrant (how the grounds support the claim) Discuss possible rebuttals to the claim, identifying the limits of the argument and showing that you have considered alternative perspectives. The Toulmin model is a common approach in academic essays.
5. Draft your essay. As is the case with any piece of writing, you should take your argumentative essay through multiple drafts. When writing and revising your drafts, make sure you: provide ample evidence, presented logically and fairly; deal with the opposing point of view; pay particular attention to the organization of your essay.
Argumentative Essay Planning Sheet My Topic and my side Reason 1 and three facts and/or stats that support that reason Reason: 1. 2. 3. Sources: Reason 2 and three facts and/or stats that support that reason Reason: 1. 2. 3. Sources: Reason 3 and three facts and/or stats that support that reason Reason: 1. 2. 3. Sources: Counterclaim 1 and
Introductory Paragraphs. The introductory paragraph is the first-paragraph in the persuasive essay. I teach my students that their introductory paragraphs should have three parts: an attention-catcher, a thesis, and a preview.The introductory paragraph is perhaps the most important paragraph in the essay because it is the first and possibly last chance to make an impact on the reader.
Beyond that, there are a few more tricks that one can use to enhance one's skills quickly. These persuasive essay worksheets and activities will help students master these tricks. Creating Persuasive Attention Catchers Activity - Students practice creating persuasive leads that immediately push the reader toward their side of the argument.
Argumentative Writing Worksheets. The we choose to take a stand on an issue of any sorts, there is a requirement to validate your position if we are intent on finding the truth. When we work to substantiate our stance in a written form the piece we will create is viewed as augmentative writing. It can be viewed as the written form of a debate.
Worksheet. 1. Jared believes that the minimum wage should be higher. In his argumentative essay he addresses the view of opponents who claim that a higher wage will cause companies to hire fewer ...
List any emotionally charged words that the writer might want to change. List two facts that are particularly relevant and credible for making the reader want to consider the writer's viewpoint. 1. 2. List one idea that might need some work to accomplish the goal of making the reader consider the writer's viewpoint. Do ideas seem connected?
Explorer's Argument Advertisement and Essay 59-62 Cues, Sequences, and Transition Words 63-64 Ideas for Opinion/Argument Writing: Sample Prompts that Appeal to Students 65 Opinion/Argument Reading and Writing Vocabulary 66-67 Writing Checklist: Opinion/Argument Writing 3-6 68 Writing Conference Strategies; One-on-One Conferences; and ...
Downloads: 9. Argumentative essay topics and argument tables. Level: advanced. Age: 14-17. Downloads: 10. A collection of downloadable worksheets, exercises and activities to teach Argumentative essay, shared by English language teachers.
17/05/2020. Country code: EG. Country: Egypt. School subject: English as a Second Language (ESL) (1061958) Main content: Argumentative Writing (2030018) From worksheet author: STUDENTS READ AND HIGHLIGHT THE FEATURES OF ARGUMENTATIVE WRITING. Other contents: Academic Writing.
ARGUMENTATIVE RESEARCH PAPER. Knowing how to create an argumentative research paper is essential to your achievement in university because you will be assigned to make persuasive resear... 69 uses. A selection of English ESL argumentative essay printables.
Serious essays require a valid argument, and our argument writing worksheets give children the tools to succeed. Our entertaining printables allow your child to argue which food is best, what type of vacation they prefer, and whether spending or saving money is a better practice.
28/09/2021. Country code: AR. Country: Argentina. School subject: Grammar (1061914) Main content: Argumentative Essays (1547075) From worksheet author: Exercises to practice writing. Other contents:
Read further to find. 649 uses. A selection of English ESL argumentative printables.
To practice argument writing, match the evidence in this fun memory game. Fourth- and fifth-grade students working on essay writing will find pieces of evidence to support different claims. This worksheet is a great way to start teaching kids about the structure of an opinion/persuasive essay that is backed up by facts. Download Free Worksheet.
Argumentative Essay. Loading ad... Ahlam Lahmar. Member for 5 years 1 month Age: 17-18. Level: 12. Language: English (en) ID: 945334. 26/04/2021. Country code: AE ... Interactive Worksheets For Students & Teachers of all Languages and Subjects. Worksheets. Worksheets; Make Interactive Worksheets; Browse Worksheets; Wookbooks. Workbooks; Learn.
Moreover, staring at an iPad screen for 7 hours a day puts significant strain on our eyes, so for the sake of our health and our attention spans, we need to minimize tech use in school. — Mary ...