Curriculum / Math / 3rd Grade / Unit 6: Fractions / Lesson 15
Lesson 15 of 24

Criteria for Success
Tips for teachers, anchor tasks.
Problem Set
Target Task
Additional practice.
Explain equivalence by manipulating units and reasoning about their size.
Common Core Standards
Core standards.
The core standards covered in this lesson
Number and Operations—Fractions
3.NF.A.3.A — Understand two fractions as equivalent (equal) if they are the same size, or the same point on a number line.
3.NF.A.3.B — Recognize and generate simple equivalent fractions, e.g., 1/2 = 2/4, 4/6 = 2/3). Explain why the fractions are equivalent, e.g., by using a visual fraction model.
3.NF.A.3.C — Express whole numbers as fractions, and recognize fractions that are equivalent to whole numbers. Example: express 3 in the form 3 = 3/1; recognize that 6/1 = 6. Example: locate 4/4 and 1 at the same point of a number line diagram.
Foundational Standards
The foundational standards covered in this lesson
Measurement and Data
2.MD.A.2 — Measure the length of an object twice, using length units of different lengths for the two measurements; describe how the two measurements relate to the size of the unit chosen.
The essential concepts students need to demonstrate or understand to achieve the lesson objective
- Understand that since equivalent fractions represent the same-sized part of the same-sized whole, the whole that is partitioned into more pieces must have more relevant pieces that constitute its equivalent fraction (MP.7, MP.8). Begin to see this relationship as a multiplicative one (although this explicit understanding is not required until Grade 4).
- Generate simple equivalent fractions in all cases, including those with whole numbers.
- Explain the equivalence of fractions in all cases, including those with whole numbers, using an area model, number line, or other method (MP.3, MP.5).
Suggestions for teachers to help them teach this lesson
This lesson previews the work of Grade 4 of developing an algorithm for finding equivalent fractions, but it also recaps every case of equivalent fractions students have seen thus far in the unit. Therefore, this lesson is optional though highly encouraged since it serves to summarize their work thus far as well as connect to future work on the topic.
Unlock features to optimize your prep time, plan engaging lessons, and monitor student progress.
Tasks designed to teach criteria for success of the lesson, and guidance to help draw out student understanding
a.
Partition the following area model into thirds. Then write a fraction to represent the whole.

Partition the following area model into sixths. Then write a fraction to represent the whole.
Partition the following area model into ninths. Then write a fraction to represent the whole.
b. What do you notice about the number of parts and the size of each part in each model in Part (a)? What do you wonder?
Guiding Questions
- Partition the following number line into wholes. Label each tick mark with a fraction.

- Partition the following number line into halves. Label each tick mark with a fraction.
- Partition the following number line into fourths. Label each tick mark with a fraction.
- Partition the following number line into eighths. Label each tick mark with a fraction.
Unlock the answer keys for this lesson's problem set and extra practice problems to save time and support student learning.
Discussion of Problem Set
- How did you use the patterns we noticed in the Anchor Tasks to solve #1 without needing to draw a model for every fraction?
- What happened to the size of the equal parts in #2a? What happened to the number of equal parts in #2a? How are those related?
- How did you share the chocolate bars equally? What fraction of a chocolate bar did each friend get? What fraction of all the chocolate bars collectively did each friend get? How do these questions demonstrate the importance of specifying the whole?
- Describe the approach you took to solving #5. Is there more than one correct answer?
A task that represents the peak thinking of the lesson - mastery will indicate whether or not objective was achieved
Two fractions have different numerators and denominators. Is it possible for the two fractions to be located at the same point on the number line? Why or why not?
Student Response
An example response to the Target Task at the level of detail expected of the students.
The Extra Practice Problems can be used as additional practice for homework, during an intervention block, etc. Daily Word Problems and Fluency Activities are aligned to the content of the unit but not necessarily to the lesson objective, therefore feel free to use them anytime during your school day.
Extra Practice Problems
Answer keys for Problem Sets and Extra Practice Problems are available with a Fishtank Plus subscription.
Word Problems and Fluency Activities
Help students strengthen their application and fluency skills with daily word problem practice and content-aligned fluency activities.
Topic A: Understanding Unit Fractions and Building Non-Unit Fractions
Partition a whole into equal parts using area models, identifying fractional units.
3.G.A.2 3.NF.A.1
Partition a whole into equal parts using tape diagrams (i.e., fraction strips), identifying and writing unit fractions in fraction notation.
Partition a whole into equal parts using area models and tape diagrams, identifying and writing non-unit fractions in fraction notation.
Identify fractions of a whole that is not partitioned into equal parts.
Draw the whole when given the unit fraction.
Identify a shaded fractional part in different ways, depending on the designation of the whole.
Create a free account to access thousands of lesson plans.
Already have an account? Sign In
Topic B: Fractions on a Number Line
Partition a number line from 0 to 1 into fractional units.
Place any fraction on a number line with endpoints 0 and 1.
Place any fraction on a number line with endpoints 0 and another whole number greater than 1.
Place any fraction on a number line with endpoints greater than 0.
3.NF.A.2 3.NF.A.3.C
Place various fractions on a number line where the given interval is not a whole.
3.NF.A.2 3.NF.A.3.D
Topic C: Equivalent Fractions
Understand two fractions as equivalent if they are the same point on a number line referring to the same whole. Use this understanding to generate simple equivalent fractions.
3.NF.A.3.A 3.NF.A.3.B
Understand two fractions as equivalent if they are the same sized pieces of the same sized wholes, though not necessarily the same shape. Use this understanding to generate simple equivalent fractions.
Express whole numbers as fractions, and recognize fractions that are equivalent to whole numbers.
3.NF.A.3.A 3.NF.A.3.B 3.NF.A.3.C
Topic D: Comparing Fractions
Compare unit fractions (a unique case of fractions with the same numerators) by reasoning about the size of their units. Recognize that comparisons are valid only when the two fractions refer to the same whole. Record the results of comparisons with the symbols >, =, or <.
Compare fractions with the same numerators by reasoning about the size of their units. Record the results of comparisons with the symbols >, =, or <.
Compare fractions with the same denominators by reasoning about their number of units. Record the results of comparisons with the symbols >, =, or <.
Compare and order fractions using various methods.
Understand fractions as numbers.
Topic E: Line Plots
Measure lengths to the nearest half inch.
Measure lengths to the nearest quarter inch.
Generate measurement data and represent it in a line plot.
Create line plots (dot plots).
Request a Demo
See all of the features of Fishtank in action and begin the conversation about adoption.
Learn more about Fishtank Learning School Adoption.
Contact Information
School information, what courses are you interested in, are you interested in onboarding professional learning for your teachers and instructional leaders, any other information you would like to provide about your school.

Effective Instruction Made Easy
Access rigorous, relevant, and adaptable math lesson plans for free
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
Unit 1: Intro to multiplication
Unit 2: 1-digit multiplication, unit 3: addition, subtraction, and estimation, unit 4: intro to division, unit 5: understand fractions, unit 6: equivalent fractions and comparing fractions, unit 7: more with multiplication and division, unit 8: arithmetic patterns and problem solving, unit 9: quadrilaterals, unit 10: area, unit 11: perimeter, unit 12: time, unit 13: measurement, unit 14: represent and interpret data.
Eureka Math Grade 3 Module 3 Lesson 15 Answer Key
Eureka Grade 3 ensures students with the learning targets and success criteria. The Diverse opportunities will develop problem-solving skills among the primary school kids practicing Bigideas Math Grade 3 Solutions. Eureka Textbook Grade 3 answers help Students Master the subject on Consistent practice.

Engage NY Eureka Math 3rd Grade Module 3 Lesson 15 Answer Key
Grade 3 Eureka Math Answer Key is provided by subject experts as per the Common Core curriculum. Grade 3 Eureka Math Solutions provided educates the primary school Kids on all Math concepts of the chapter efficiently. Eureka Math Grade 3 Textbook Answers makes it easy for kids to Grasp the Concepts as well as solve any problem from chapter Tests, Practice Tests, Performance tests, cumulative practice, etc.
Eureka Math Grade 3 Module 3 Lesson 15 Pattern Sheet Answer Key
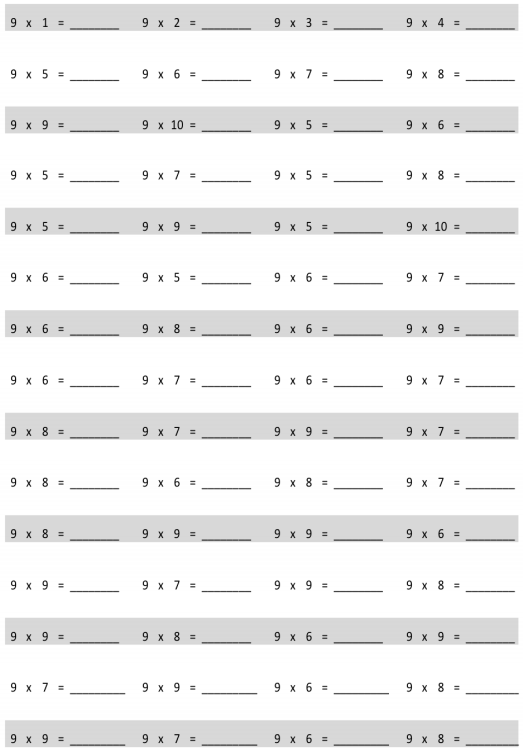
Answer: 9 x 1 = 9, 9 x 2 = 18, 9 x 3 = 27, 9 x 4 = 36, 9 x 5 = 45, 9 x 6 = 54, 9 x 7 = 63, 9 x 8 = 72, 9 x 9 = 81, 9 x 10 = 90, 9 x 5 = 45, 9 x 6 = 54, 9 x 5 = 45, 9 x 7 = 63, 9 x 5 = 45, 9 x 8 = 72, 9 x 5 = 45, 9 x 9 = 81, 9 x 5 = 45, 9 x 10 = 90, 9 x 6 = 54, 9 x 5 = 45, 9 x 6 = 54, 9 x 7 = 63, 9 x 6 = 54, 9 x 8 = 72, 9 x 6 = 54, 9 x 9 = 81, 9 x 6 = 54, 9 x 7 = 63, 9 x 6 = 54, 9 x 7 = 63, 9 x 8 = 72, 9 x 7 = 63, 9 x 9 = 81, 9 x 7 = 63, 9 x 8 = 72, 9 x 6 = 54, 9 x 8 = 72, 9 x 7 = 63, 9 x 8 = 72, 9 x 9 = 81, 9 x 9 = 81, 9 x 6 = 54, 9 x 9 = 81, 9 x 7 = 63, 9 x 9 = 81, 9 x 8 = 72, 9 x 9 = 81, 9 x 8 = 72, 9 x 6 = 54, 9 x 9 = 81, 9 x 7 = 63, 9 x 9 = 81, 9 x 6 = 54, 9 x 8 = 72, 9 x 9 = 81, 9 x 7 = 63, 9 x 6 = 54, 9 x 8 = 72.
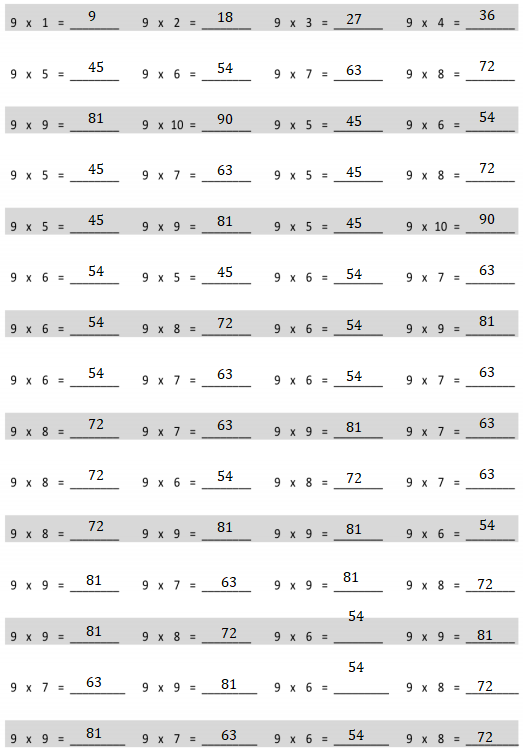
Eureka Math Grade 3 Module 3 Lesson 15 Problem Set Answer Key
Write an equation, and use a letter to represent the unknown for Problems 1 – 6.
Question 1. Mrs. Parson gave each of her grandchildren $9. She gave a total of $36. How many grandchildren does Mrs. Parson have?
Answer: The number of grandchildren = 4.
Explanation: In the above-given question, given that, Mrs. Parson gave each of her grandchildren $9. she gave a total of $36. 9 / c = 36. where c indicates children. c = 36 / 9. c = 4.
Question 2. Shiva pours 27 liters of water equally into 9 containers. How many liters of water are in each container?
Answer: The number of liters of water in each container = 3.
Explanation: In the above-given question, given that, shiva pours 27 liters of water equally into 9 containers. 27 / w = 9. w = 27 / 9. where w indicates water. w = 3.
Question 3. Derek cuts 7 pieces of wire. Each piece is 9 meters long. What is the total length of the 7 pieces?
Answer: The total length of the 7 pieces = 63.
Explanation: In the above-given question, given that, Derek cuts 7 pieces of wire. Each piece is 9 meters long. 7 x l = 9. where l indicates length. l = 7 x 9. l = 63.
Question 4. Aunt Deena and Uncle Chris share the cost of a limousine ride with their 7 friends. The ride cost a total of $63. If everyone shares the cost equally, how much does each person pay?
Answer: The cost each person pays = 9.
Explanation: In the above-given question, given that, Aunt Deena and Uncle Chris share the cost of a limousine ride with their 7 friends. The ride cost a total of $63. 7 / r = 63. where r indicates ride. r = 63 / 7. r = 9.
Question 5. Cara bought 9 packs of beads. There are 10 beads in each pack. She always uses 30 beads to make each necklace. How many necklaces can she make if she uses all the beads?
Answer: The number of necklaces = 3.
Explanation: In the above-given question, given that, Cara bought 9 packs of beads. There are 10 beads in each pack. she always uses 30 beads to make each necklace. 9 / n = 90. where c indicates children. n = 90 / 9. n = 30.
Question 6. There are 8 erasers in a set. Damon buys 9 sets. After giving some erasers away, Damon has 35 erasers left. How many erasers did he give away?
Answer: The number of erasers = 37.
Explanation: In the above-given question, given that, There are 8 erasers in a set. Damon buys 9 sets. After giving some erasers away. Damon has 35 erasers left. where e indicates eraser. e = 72 / 9. e = 8.
Eureka Math Grade 3 Module 3 Lesson 15 Exit Ticket Answer Key
Use a letter to represent the unknown.
Question 1. Mrs. Aquino pours 36 liters of water equally into 9 containers. How much water is in each container?
Answer: The water in each container = 4.
Explanation: In the above-given question, given that, Mrs. Aquino pours 36 liters of water equally into 9 containers. where c indicates container. c = 36 / 9. c = 4.
Question 2. Marlon buys 9 packs of hot dogs. There are 6 hot dogs in each pack. After the barbeque, 35 hot dogs are left over. How many hot dogs were eaten?
Answer: The number of hot dogs were eaten = 19.
Explanation: In the above-given question, given that, Marlon buys 9 packs of hot dogs. There are 6 hot dogs in each pack. 9 x 6 = 54. where n indicates a number of hot dogs. n = 54 – 35. n = 19. Eureka Math Grade 3 Module 3 Lesson 15 Homework Answer Key
Question 1. The store clerk equally divides 36 apples among 9 baskets. Draw a tape diagram, and label the number of apples in each basket as a. Write an equation, and solve for a.
Answer: The number of apples in each basket = 4.
Explanation: In the above-given question, given that, The store clerk equally divides 36 apples among 9 baskets. 9 / n = 36. where n indicates apples. n = 36 / 9. n = 4.
Question 2. Elijah gives each of his friends a pack of 9 almonds. He gives away a total of 45 almonds. How many packs of almonds did he give away? Model using a letter to represent the unknown, and then solve.
Answer: The number of packs of almonds = 5.
Explanation: In the above-given question, given that, Elijah gives each of his friends a pack of 9 almonds. He gives away a total of 45 almonds. 9 / p = 45. where p indicates pack. p = 45 / 9. p = 5.
Question 3. Denice buys 7 movies. Each movie costs $9. What is the total cost of 7 movies? Use a letter to represent the unknown. Solve.
Answer: The total cost of 7 movies = 63.
Explanation: In the above-given question, given that, Denice buys 7 movies. Each movie costs $9. 7 x m= 9. where m indicates total movies. m = 7 x 9. m = 63.
Question 4. Mr. Doyle shares 1 roll of bulletin board paper equally with 8 teachers. The total length of the roll is 72 meters. How much bulletin board paper does each teacher get?
Answer: The bulletin board does each teacher get = 9 meters.
Explanation: In the above-given question, given that, Mr. Doyle shares 1 roll of bulletin board paper equally with 8 teachers. The total length of the roll is 72 meters. 72 / 8 = 9.
Question 5. There are 9 pens in a pack. Ms. Ochoa buys 9 packs. After giving her students some pens, she has 27 pens left. How many pens did she give away?
Answer: The number of pens she give = 54.
Explanation: In the above-given question, given that, There are 9 pens in a pack. Ms. Ochoa buys 9 packs. After giving her students some pens, she has 27 pens left. 9 x 9 = 81. 81 – 27 = 54.
Question 6. Allen buys 9 packs of trading cards. There are 10 cards in each pack. He can trade 30 cards for a comic book. How many comic books can he get if he trades all of his cards?
Answer: The number of comic books can he get if he trades all of his cards = 60.
Explanation: In the above-given question, given that, Allen buys 9 packs of trading cards. There are 10 cards in each pack. He can trade 30 cards for a comic book. 9 x 10 = 90. 90 – 30 = 60.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
This website, about.zearn.org, uses cookies and similar technologies to analyze traffic to the site, and enable us to use social media features. For more information on how we use cookies on this site, including how to change your preferences, please see this cookie policy .
Rising G4 summer series
Content focused on the big ideas.
Our curated series of 3rd grade math lessons is designed for students to complete over any 4-to-6-week summer program.

Multiply & Divide Tricky Numbers
21 Lessons | Grade 3 Mission 3 These 3rd grade math lessons focus on multiplication and division, which is key to success in later grades. Students work deeply with the commutative, distributive and associative properties and they’ll have problem-solving opportunities at the close of each topic.

Find the Area
16 Lessons | Grade 3 Mission 4 These 3rd grade math lessons continue the focus on multiplication and division as students explore area as an attribute of two-dimensional figures and relate it to their prior understandings of multiplication.
approach to Summer Series
Zearn’s targeted summer math content series for rising 4th graders is designed based on:
Big ideas of math that help students build dense connections within and across grades.
Data from billions of math problems completed on our platform, with insights into precisely where students struggle and the most relevant foundational content.
Embedded math learning acceleration throughout digital lessons, including friendly onramps and just-in-time support on all grade-level concepts.

What's included
- Consistent structure of math learning activities, including new concept exploration with on-screen teachers
- Built-in, personalized support right when students need it
- Embedded daily digital diagnostic in every lesson
- Detailed reporting for each student
- Flexibility to share reports with teachers or tutors
- Problem solving activities for teachers or tutors (in Spanish, too!)
- Guidance to facilitate lively math discussions where students explore different ways to solve problems
- Free individual logins for all students and teachers or tutors
- Access to Zearn Help Center with 100+ help topics
Zearn Math’s K-5 materials follow the scope and sequence of Eureka Math/EngageNY. Zearn Math’s grade 6-8 materials align directly with Illustrative Math’s scope and sequence. Zearn digital lessons are designed to maximize learning and engagement through a balance of fluency activities, guided instruction and independent practice. Learn how Zearn Math aligns to your state’s specific standards:
Zearn's Summer Intensive Series is designed to be used flexibly across summer learning models, including in-school summer programming, tutoring, or at home. In addition to digital lessons, we offer instructional materials that educators can use to facilitate rich math discussions around the core ideas of each series.
We’ve created a guide for educators to share with families to orient them to Zearn Math. Download and share our summer math guidance to help families support their child’s learning with Zearn Math this summer:
Each digital lesson in the summer program takes about 30 minutes to complete. Kids work through each component at their own pace. After completing one lesson, they automatically go on to the next lesson in the series.
Students who use Zearn achieve significant gains in math — including those at the lowest levels of math proficiency. Multiple quasi-experimental research studies show students who consistently use Zearn Math experience 2x the learning gains compared to students who do not use Zearn.

Create a free account to get access to all content. For districts and schools interested in targeted Spring/Summer 2023 programs, contact us.
Get started

Create a free account to get access to all content. For districts and schools interested in targeted spring/summer 2024 math programs, contact us.

Reading & Math for K-5
- Kindergarten
- Learning numbers
- Comparing numbers
- Place Value
- Roman numerals
Subtraction
Multiplication
- Order of operations
- Drills & practice
Measurement
- Factoring & prime factors
- Proportions
- Shape & geometry
- Data & graphing
- Word problems
- Children's stories
- Leveled Stories
- Context clues
- Cause & effect
- Compare & contrast
- Fact vs. fiction
- Fact vs. opinion
- Main idea & details
- Story elements
- Conclusions & inferences
- Sounds & phonics
- Words & vocabulary
- Reading comprehension
- Early writing
- Numbers & counting
- Simple math
- Social skills
- Other activities
- Dolch sight words
- Fry sight words
- Multiple meaning words
- Prefixes & suffixes
- Vocabulary cards
- Other parts of speech
- Punctuation
- Capitalization
- Narrative writing
- Opinion writing
- Informative writing
- Cursive alphabet
- Cursive letters
- Cursive letter joins
- Cursive words
- Cursive sentences
- Cursive passages
- Grammar & Writing
Breadcrumbs

Download & Print From only $3.10
Third Grade Math Worksheets
Free grade 3 math worksheets.
Our third grade math worksheets support numeracy development and introduce division, decimals, roman numerals, calendars and concepts in measurement and geometry. Our word problem worksheets review skills in real world scenarios.
Choose your grade 3 topic:
Place Value and Rounding
Order of Operations
Roman Numerals
Fractions and Decimals
Counting Money
Time & Calendar
Data & Graphing
Word Problems

Sample Grade 3 Math Worksheet
What is K5?
K5 Learning offers free worksheets , flashcards and inexpensive workbooks for kids in kindergarten to grade 5. Become a member to access additional content and skip ads.

Our members helped us give away millions of worksheets last year.
We provide free educational materials to parents and teachers in over 100 countries. If you can, please consider purchasing a membership ($24/year) to support our efforts.
Members skip ads and access exclusive features.
Learn about member benefits
This content is available to members only.
Join K5 to save time, skip ads and access more content. Learn More
- Forgot Password?
- Texas Go Math
- Big Ideas Math
- Engageny Math
- McGraw Hill My Math
- enVision Math
- 180 Days of Math
- Math in Focus Answer Key
- Math Expressions Answer Key
- Privacy Policy
Eureka Math Grade 5 Module 5 Lesson 15 Answer Key
Engage ny eureka math 5th grade module 5 lesson 15 answer key, eureka math grade 5 module 5 lesson 15 problem set answer key.
Question 1. The length of a flowerbed is 4 times as long as its width. If the width is “\(\frac{3}{8}\) meter, what is the area? Answer:
The width of the flower bed = 3/8 meters
The length of the flower bed is 4 times as long as its width
Which means, 3/8 x 4 = 12/ 8 = 3/2
Now, Area = length x width
A= 3/2 x 3/8
Therefore, the area of the flowerbed is 9/16 m 2 .
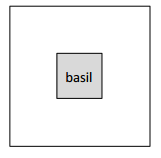
The measurement of basil plot on each side = 5/9 yard
A= 5/8 x 5/8 = 25/64
Therefore, the area of the basil plot = 25/64 yd 2
The measurement of basil plot in each side = 5/9 yard
= 15/8 or 1 7/8 feet
Now, the length of one side
2 feet + 2 feet + 1 7/8 feet
Perimetre = 4 x sides
= 4 x 5 7/8
= 20 + 3 4/8
Therefore, the perimetre of the fence = 23 1/2 feet.
The total area that the fence encloses
= length x width
= 5 7/8 x 5 7/8
= ( 5 x 5 ) + ( 5 x 7/8 ) +( 5 x 7/8 ) + ( 7/8 x 7/8 )
= 25 + 4 3/8 + 4 3/8 + 49/64
= 33 + 48/64 + 49/64
= 33 + 97/64
Therefore, the area that fence encloses = 34 33/64 square feet.
Question 3. Janet bought 5 yards of fabric 2\(\frac{1}{4}\)-feet wide to make curtains. She used \(\frac{1}{3}\) of the fabric to make a long set of curtains and the rest to make 4 short sets. a. Find the area of the fabric she used for the long set of curtains. b. Find the area of the fabric she used for each of the short sets. Answer:
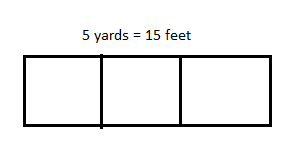
Area = length x width
= 5 x 2 1/4
= 11 1/4 square feet
Therefore, the area of long set is 11 1/4 square feet
15 feet – 5 feet = 10 feet
1/4 of 10 is 2 1/2 feet
Now, the area of each set of shorter curtain
A = 2 1/2 x 2 1/2
( 2 x 2 ) + ( 2 x 1/2 ) + ( 2 x 1/2 ) + ( 1/2 x 1/2 )
= 4 + 1/2 + 1 + 1/8
= 5 + 1/2 +1/8
= 5 5/8 square feet
Therefore, the area of each set of shorter curtain is 5 5/8 square feet.
Question 4. Some wire is used to make 3 rectangles: A, B, and C. Rectangle bs dimensions are \(\frac{3}{5}\) cm larger than Rectangle A’s dimensions, and Rectangle C’s dimensions are \(\frac{3}{5}\) cm larger than Rectangle B’s dimensions. Rectangle A is 2 cm by 3\(\frac{1}{5}\) cm. a. What is the total area of all three rectangles? b. If a 40-cm coil of wire was used to form the rectangles, how much wire is left? Answer:
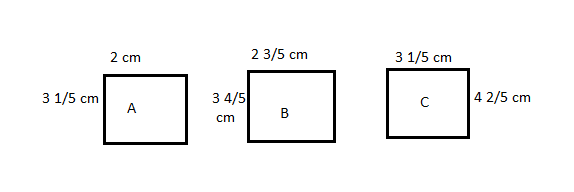
The area of rectangle A =
A = 2 X 3 1/5
= 6 2/5 square centimetres
Area of of rectangle B =
A = 2 3/5 cm x 3 4/5 cm
= 6 + 8/5 + 9/5 + 12/25
= 9 + 21/5 + 12/25
= 9 22/25 square centimetres
Area of rectangle C =
A = 3 1/5 cm x 4 2/5 cm
= 12 + 6/5 + 4/5 + 2/25
= 14 2/25 square centimetres
Total area of three rectangles =
= 6 2/5 + 9 22/25 + 14 2/25
= 29 + 2/5 + 24/25
= 29 +10/25 +24/25
= 30 9/25 square centimetres
Therefore, the area of three rectangles = 30 9/25 square centimetres.
Perimeter of rectangle A =
2 + 2 + 3 1/5 + 3 1/5
= 6 2/5 centimetres
Perimeter of rectangle B =
2 3/5 + 2 3/5 + 3 4/5 + 3 4/5
= 12 4/5 centimetres
Perimeter of rectangle C =
3 1/5 + 3 1/5 + 4 2/5 + 4 2/5
= 15 1/5 centimetres
Total perimeter =
1 2/5 cm + 12 4/5 cm + 15 1/5 cm
= 38 2/5 cm
Now, according to the given condition :
40 cm – 38 2/5 cm
Therefore, the leftover wire length = 1 3/5 cm.
Eureka Math Grade 5 Module 5 Lesson 15 Exit Ticket Answer Key
Wheat grass is grown in planters that are 3\(\frac{1}{2}\) inch by 1\(\frac{3}{4}\) inch. If there is a 6 × 6 array of these planters with no space between them, what is the area covered by the planters? Answer:
The area of planter =
3 1/2 x 1 3/4
( 3 x 1 ) + ( 3 x 3/4 ) + ( 1 x 1/2 ) + ( 1/2 x 3/4 )
= 3 + 9/4 + 1/2 + 3/8
= 24 + 18/8 + 4/8 + 3/8
=49/8 = 6 1/8
According to given condition
= 36 x 6 1/8
= 200 + 1/2
Therefore, the area covered by the planters = 200 1/2 square inches.
Eureka Math Grade 5 Module 5 Lesson 15 Homework Answer Key
Question 1. The width of a picnic table is 3 times its length. If the length is \(\frac{5}{6}\)-yd long, what is the area of the picnic table in square feet? Answer:
1 yard = 3 feet
The area of the picnic table =
5/6 x 3= 15/6 = 5/2 = 2 1/2 feet
Area = 2 1/2 x 7 1/2
A = 5/2 x 15 1/2
= 18 3/4 square feet
Therefore, the area of the table = 2 1/2 square yards.
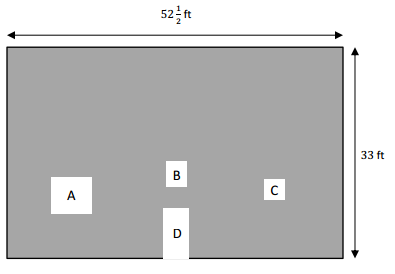
The area of window A =
= 6 1/4 x 5 3/4
= 30 x 1 1/4 + 4 2/4 + 3/16
= 35 + 3/4 + 3/16
= 35 + 15/16
= 35 15/16 square feet
The area of window B =
= 12 1/2 square feet
The area of D =
4 x 8 = 32 square feet
The total area of the wall =
52 1/2 x 33
= 1716 + 33/2
= 1732 1/2 square feet
Now, the total area of A,B,C A and D
= 35 15/16 +12 1/2 + 32 + 9 1/2
= 22 + 35 15/16 +32
Now, the area of the painted wall =
1732 1/2 sq. ft – 89 15/16
= 1642 9/16 square feet
Therefor, the area of the wall painted = 1642 9/16 square feet.
The area of the smallest rectangle =
4 1/2 x 7 3/4
= 24 + 3 + 3 1/2 + 3/8
= 34 7/8 square inches
4 1/2 + 2 1/4
= 4 2/4 + 2 1/4
7 3/4 + 2 1/4 = 10
36 3/4 x 10
= 60 + 7 2/4
= 67 1/2 square inches
6 3/4 + 2 1/4 =9
9 x 12 1/4 =
= 108 + 2 1/4 = 110 1/4 square inches
d. 9 + 2 1/4 = 11 1/4
12 1/4 + 2 1/4 = 14 2/4
11 1/4 x 14 2/4
= 154 + 3 2/4 + 5 1/2 + 1/8
= 163 1/8 square inches.
So, the total area of the figure = 110 + 34 + 67 + 163
= 374 + 1 3/4
= 375 3/4 square inches
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.

COMMENTS
Here is a link to the source for the pages, the "full module" PDF:https://www.engageny.org/resource/grade-3-mathematics-module-3
The source for the homework pages is available here for free. I used the full module PDF:https://www.engageny.org/resource/grade-3-mathematics-module-5
There are 6 hot dogs in each pack. 9 x 6 = 54. where n indicates a number of hot dogs. n = 54 - 35. n = 19. Eureka Math Grade 3 Module 3 Lesson 15 Homework Answer Key. Question 1. The store clerk equally divides 36 apples among 9 baskets. Draw a tape diagram, and label the number of apples in each basket as a.
EngageNY/Eureka Math Grade 3 Module 5 Lesson 15For more videos, answer keys, and other resources, please visit http://EMBARC.onlinePLEASE leave a message if ...
Engage NY Eureka Math 3rd Grade Module 5 Lesson 15 Answer Key Eureka Math Grade 3 Module 5 Lesson 15 Problem Set Answer Key. Question 1. Estimate to label the given fractions on the number line. Be sure to label the fractions at 0 and 1. Write the fractions above the number line. Draw a number bond to match your number line. Answer: Explanation :
Fractions as Numbers on the Number Line. Eureka Essentials: Grade 3. An outline of learning goals, key ideas, pacing suggestions, and more! Fluency Games. Downloadable Resources. Teacher editions, student materials, application problems, sprints, etc. Application Problems.
Curriculum / Math / 3rd Grade / Unit 6: Fractions / Lesson 15. Fractions. Lesson 15 Math. Unit 6. 3rd Grade. Lesson 15 of 24 Download Lesson 15 See All Lessons Jump To. Objective Standards Criteria for Success ... The Extra Practice Problems can be used as additional practice for homework, during an intervention block, etc. Daily Word Problems ...
Grade 3 Module 3 Collapse all Expand all. Multiplication and Division with Units of 0, 1, 6-9, and Multiples of 10 ... Homework Solutions Page. Promethean Flipchart Page. Google Slides Page. ... Lesson 15 Video Page. Lesson PDF Page. Homework Solutions Page. Promethean Flipchart Page. Google ...
style="display:inline-block;width:120px;height:600px" data-ad-client="ca-pub-6375909458048309" data-ad-slot="7271060332">
These worksheets can be used as homework or extra practice. The worksheets match up with the 3rd Grade Ready Math Unit 3 Lesson 15: Multiply to Find Area. There are 4 total worksheets (one for each session). Reported resources will be reviewed by our team. Report this resource to let us know if this resource violates TPT's content guidelines.
10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 Eureka Math™ Grade 3, Module 5 Student File_A Contains copy-ready classwork and homework ... G3-M 5-SE-1.3. 1 -11 .20 15 3. Lesson 1 Homework A STORY OF UNITS Lesson 1: Specify and partition a whole into equal parts, ... Lesson 2 Homework A STORY OF UNITS 3 5 3. Dylan plans to eat 1 fifth of his candy bar.
students above grade level to complete the entire Problem Set with excellence. NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM 3Lesson 15 ... NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM 3Lesson 15 Homework Lesson 15: Place any fraction on a number line with endpoints 0 and 1. Date: 3/28/14 5.D.21
Unit 3: Addition, subtraction, and estimation. 0/1600 Mastery points. Rounding to nearest 10 or 100 Estimate to add multi-digit numbers Strategies for adding two and three-digit numbers Adding with regrouping within 1000. Estimate to subtract multi-digit numbers Strategies for subtracting two and three-digit numbers Subtracting with regrouping ...
The source for the homework pages can be found at the link below. I used the "full module PDF".https://www.engageny.org/resource/grade-3-mathematics-module-7
Engage NY Eureka Math 3rd Grade Module 3 Lesson 15 Answer Key. ... Eureka Math Grade 3 Module 3 Lesson 15 Homework Answer Key. Question 1. The store clerk equally divides 36 apples among 9 baskets. Draw a tape diagram, and label the number of apples in each basket as a. Write an equation, and solve for a.
the area of the desk = 15 sq units. Eureka Math Grade 3 Module 4 Lesson 15 Homework Answer Key. Use a ruler to measure the side lengths of each numbered room in centimeters. Then, find the area. Use the measurements below to match, and label the rooms with the correct areas. Kitchen: 45 square centimeters Living Room: 63 square centimeters
These 3rd grade math lessons focus on multiplication and division, which is key to success in later grades. Students work deeply with the commutative, distributive and associative properties and they'll have problem-solving opportunities at the close of each topic. Log in and access G3M3.
K5 Learning offers free worksheets, flashcards and inexpensive workbooks for kids in kindergarten to grade 5. Become a member to access additional content and skip ads. 3rd grade math worksheets: Addition, subtraction, place value, rounding, multiplication, division, fractions, decimals , time & calander, counting money, roman numerals, order ...
Remainder = _______. Can you show 25 ÷ 4 with one rectangle? ______ Explain how you showed the remainder: Lesson 15 Homework NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM 4. Lesson 15 : Understand and solve division problems with a remainder using the array and area models. Date: 8/28/13. 3.E.26.
Eureka Math Grade 3 Module 7 Lesson 15 Homework Answer Key. Question 1. Miguel glues a ribbon border around the edges of a 5-inch by 8-inch picture to create a frame. What is the total length of ribbon Miguel uses? Answer: The total length of ribbon Miguel uses = 26-inch. Explanation: Length of the rectangular picture = 8-inch
Engage NY // Eureka Math Grade 5 Module 3 Lesson 15 Homework. Engage NY // Eureka Math Grade 5 Module 3 Lesson 15 Homework.
Solve multi step word problems, assess reasonableness of solutions using benchmark numbers, common core, common denominator, tape diagrams, simplify fraction...
Eureka Math Grade 5 Module 5 Lesson 15 Problem Set Answer Key. Question 1. The length of a flowerbed is 4 times as long as its width. If the width is " 38 meter, what is the area? Answer: Given, The width of the flower bed = 3/8 meters. The length of the flower bed is 4 times as long as its width. Which means, 3/8 x 4 = 12/ 8 = 3/2.