- Search by keyword
- Search by citation
Page 1 of 507

Spatiotemporal epidemiology of substance-related accidental acute toxicity deaths in Canada from 2016 to 2017
In Canada, substance-related accidental acute toxicity deaths (AATDs) continue to rise at the national and sub-national levels. However, it is unknown if, where, when, and to what degree AATDs cluster in space...
- View Full Text
The effect of educational intervention based on health belief model on colorectal cancer screening behaviors
Colorectal cancer is the second most prevalent cause of death from malignancies globally. The present study was conducted targeting the influence of an educational intervention based on the health belief model...
Burden of drug use disorders in the United States from 1990 to 2021 and its projection until 2035: results from the GBD study
Drug use disorders (DUDs) have emerged as one of the most significant public health crises, exerting a substantial influence on both community health and socio-economic progress. The United States (US) also su...
Community led health promotion to counter stigma and increase trust amongst priority populations: lessons from the 2022–2023 UK mpox outbreak
Stigma, lack of trust in authorities, and poor knowledge can prevent health-seeking behaviour, worsen physical and mental health, and undermine efforts to control transmission during disease outbreaks. These f...
Association of the American Heart Association’s new “Life’s Essential 8” with all-cause mortality in patients with chronic kidney disease: a cohort study from the NHANES 2009–2016
People with chronic kidney disease (CKD) are more likely to die prematurely, and this increased risk of death is primarily attributable to deaths from cardiovascular disease (CVD). We aim to investigate the re...
Maternal depressive symptom trajectories and associations with child feeding
Responsive feeding, when caregivers attend to children’s signals of hunger and satiation and respond in an emotionally supportive and developmentally appropriate way, is associated with the development of heal...
Neonatal mortality and associated factors among newborns in Mogadishu, Somalia: a multicenter hospital-based cross-sectional study
Neonatal mortality is a significant public health problem in Sub-Saharan Africa, particularly in Somalia, where limited data exists about this. Mogadishu, the densely populated capital, faces a high rate of ne...
Thriving from work questionnaire: German translation and validation
The Thriving from Work questionnaire is a comprehensive indicator of positive well-being for employees, applicable in both research and practical contexts. Current discussions underline the crucial impact that...
Working mechanisms of the use and acceptability of ecological momentary interventions: a realist evaluation of a guided self-help ecological momentary intervention targeting self-esteem
Technology improves accessibility of psychological interventions for youth. An ecological momentary intervention (EMI) is a digital intervention geared toward intervening in daily life to enhance the generaliz...
The impact of temperature, humidity and closing school on the mumps epidemic: a case study in the mainland of China
To control resurging infectious diseases like mumps, it is necessary to resort to effective control and preventive measures. These measures include increasing vaccine coverage, providing the community with adv...
Only 9% of mothers have eight and more ANC visit in 14 sub-saharan African countries; evidence from the most recent DHS 2018–2023: a multilevel analysis
The world health organization’s global health observatory defines maternal mortality as annual number of female deaths, regardless of the period or location of the pregnancy, from any cause related to or cause...
Parental reports of hospital- and community-based follow-up services, self-efficacy, and symptoms of depression a few months after discharge of a prematurely born child
Many parents report the transition from hospital to home as challenging after the birth of a preterm-born child. This study investigates parental perceptions of community-based follow-up services after hospita...
Modifiable factors influencing attention performance in healthy children: insights from a comprehensive school nutrition study
There is inconclusive evidence for the effects of various leisure activities on attention performance in children. The literature reports inconsistent associations between activities such as physical activiti...
Psychometric assessment of the Runyankole-translated Marlowe-Crowne Social Desirability Scale among persons with HIV in Uganda
Social desirability can negatively affect the validity of self-reported measures, including underreporting of stigmatized behaviors like alcohol consumption. The Marlowe-Crowne Social Desirability Scale (SDS) ...
An international perspective on young stroke incidence and risk factors: a scoping review
Stroke among younger age groups is increasing globally. While there is a focus on research conducted on people under 65 years who have had a stroke, there is a paucity of data on the incidence and risk factors...
Effect of sexual health education on sexual function and satisfaction of menopausal migrant women: an application of the theory of planned behavior
This study investigated the effect of an intervention based on the theory of planned behavior on sexual function and satisfaction of migrant women during menopause in Iran.
The association between screen time exposure and myopia in children and adolescents: a meta-analysis
This study aimed to systematically review epidemiological evidence on associations between screen time exposure and myopia in children and adolescents, and to quantitatively evaluate summary effect estimates f...
U-shaped relationship between non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and cognitive impairment in Chinese middle-aged and elderly: a cross-sectional study
The relationship between blood lipids and cognitive function has long been a subject of interest, and the association between serum non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (non-HDL-C) levels and cognitive imp...
The impact of telecom industry employees’ stress perception on job burnout: moderated mediation model
The rapid development of the telecommunications industry in the post-COVID-19 era has brought tremendous pressure to employees making them a high-risk group for job burnout. However, prior research paid less a...
Do health literacy, physical health and past rehabilitation utilization explain educational differences in the subjective need for medical rehabilitation? Results of the lidA cohort study
Medical rehabilitation can be helpful for maintaining workers’ health and work ability. Its contribution to longer working lives is of high economic relevance in aging populations. In Germany, individuals must...
How predictive of future healthcare utilisation and mortality is data-driven population segmentation based on healthcare utilisation and chronic condition comorbidity?
In recent years data-driven population segmentation using cluster analyses of mainly health care utilisation data has been used as a proxy of future health care need. Chronic conditions patterns tended to be e...
Factors associated with hookworm and Schistosoma mansoni infections among school-aged children in Mayuge district, Uganda
Hookworm infection and schistosomiasis are two of sub-Saharan Africa's most common neglected tropical diseases. An annual mass drug administration (MDA) program against schistosomiasis and soil-transmitted hel...
Translation and adaptation of the person-centered maternity care scale to a Persian-speaking population: a confirmatory factor analysis
Recognized as the most exhaustive multidimensional evaluation of women's person-centered experiences during childbirth, the Person-Centered Maternity Care (PCMC) Scale offers domain-specific insights into face...
Web-based occupational stress prevention in German micro- and small-sized enterprises – process evaluation results of an implementation study
Structural and behavioral interventions to manage work-related stress are effective in employees. Nonetheless, they have been implemented insufficiently, particularly in micro- and small-sized enterprises (MSE...
Barriers and facilitators to uptake and persistence on prep among key populations in Southern Province, Zambia: a thematic analysis
Especially in high HIV prevalence contexts, such as Zambia, effective biomedical prevention tools are needed for priority populations (PPs), including key populations (KPs), who are at higher risk. HIV pre-exp...
The association of female reproductive factors with history of cardiovascular disease: a large cross-sectional study
This study aimed to explore the association of female reproductive factors (age at first birth (AFB), age at last birth (ALB), number of pregnancies, and live births) with history of cardiovascular disease (CVD).
Vaping cessation support recommendations from adolescents who vape: a qualitative study
Youth vaping is a serious public health concern, being more prevalent than any other tobacco use. To inform cessation interventions, we explored what adolescents perceive as their reasons for quitting and stra...
New Orleans school meal programs during the COVID-19 pandemic: challenges and innovations identified through qualitative interviews
School meal programs are critical to reducing childhood food insecurity. This study identified challenges and innovations in school meal service in a disaggregated charter school system during COVID-19 in New ...
The Childbearing sense of coherence scale (CSOC-scale): development and validation
the salutogenic theory is essential to explain an individual’s ability to maintain health during the perinatal period. While previous studies mainly focused on the perspectives from a family-level orientation ...
Social support as perceived, provided and needed by family-members of migrants with type 2 diabetes – a qualitative study
Social support provided by a family member has been found to have a buffering effect on distress and is associated with better diabetes self-care. This study explores the meaning of social support, as describe...
Correction to: Examining psychosocial pathways to explain the link between breastfeeding practices and child behaviour in a longitudinal cohort
The original article was published in BMC Public Health 2024 24 :675
Attitudes toward an HPV vaccine for condyloma acuminata and willingness to undergo vaccination among STD clinic attendees in China: Focus on STI prevention with HPV vaccine
Condyloma acuminata (CA) is a common, and recurrent sexually transmitted disease (STD) that greatly contributes to direct health care costs and has a substantial psychosocial impact. Human papillomavirus (HPV)...
Identifying emerging hot spots of road traffic injury severity using spatiotemporal methods: longitudinal analyses on major roads in Ghana from 2005 to 2020
Although road traffic injuries and deaths have decreased globally, there is substantial national and sub-national heterogeneity, particularly in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs). Ghana is one of few co...
Childcare needs as a barrier to healthcare among women in a safety-net health system
Childcare needs are an understudied social determinant of health. The effect of childcare needs on access to healthcare must be understood to inform health system interventions and policy reform. This study so...
Creating a healthy and sustainable food environment to promote plant-based food consumption: clear barriers and a gradual transition
A shift away from diets high in animal-based foods towards diets high in plant-based foods is desirable considering human health, environmental sustainability, and animal welfare. As the food environment plays...
Impact of health literacy, social support, and socioeconomic position on the serum uric acid level in asymptomatic hyperuricaemia patients in China: a structural equation model
Hyperuricaemia (HUA) poses a significant public health challenge on a global scale. It is mostly asymptomatic hyperuricemia (AHU) with unsatisfactory recognition and control rates. The role of health literacy ...
Wealth and education-related inequalities in the utilisation of reproductive, maternal, newborn, and child health interventions within scheduled tribes in India: an analysis of Odisha and Jharkhand
The utilisation of Reproductive, Maternal, Newborn and Child Health (RMNCH) services remains lower among the Scheduled Tribes (ST) in India than among the rest of the country’s population. The tribal populatio...
Roles of caregiver-child interaction on the association of socioeconomic status with early childhood development: a population-based study in rural China
Socioeconomic status (SES) has been previously associated with children’s early development, health, and nutrition; however, evidence about the potential role of caregiver-child interaction in such association...
Taking emic and etic to the family level: interlinking parents’ and children’s COVID-19 views and experiences in Germany
COVID-19 impacted families globally, restricting movement, and changing daily routines and family dynamics. In order to explore and contrast children’s and parents’ experiences and perceptions of life during C...
A Spanish version of the Three-Dimensional Work Fatigue Inventory (3D-WFI): factor structure, internal consistency, and criterion validity
In the working population, there are risks of overload due to physical, mental, and emotional demands. No instrument is available in Spanish to measure these three types of work fatigue (WF) separately. This p...
Associations between allostatic load and hepatic steatosis and liver fibrosis: evidence from NHANES 2017–2020
Allostatic load, the cumulative strain resulting from chronic stress responses, has been linked to disease occurrence and progression, yet research quantifying this relationship is limited. This study aimed to...
Effects of confounding and effect-modifying lifestyle, environmental and medical factors on risk of radiation-associated cardiovascular disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of death worldwide. It has been known for some considerable time that radiation is associated with excess risk of CVD. A recent systematic review of radiation ...
The relationship between sleep disturbance and aggressive behaviour among community-dwelling schizophrenia patients: a moderated mesomeric effect model
Sleep disturbance is the most common concern of patients with schizophrenia and can lead to a poor prognosis, a low survival rate and aggressive behaviour, posing a significant threat to social security and st...
Patient activation in adults with visual impairment: a study of related factors
This study aims to analyze variables related to patient activation in 78 individuals with visual impairment. The Patient Activation Measure (PAM) scores of participants showed no differences between males and ...
The impact of social cohesion and risk communication on excess mortality due to COVID-19 in 213 countries: a retrospective analysis
Tools for assessing a country’s capacity in the face of public health emergencies must be reviewed, as they were not predictive of the COVID-19 pandemic. Social cohesion and risk communication, which are relat...
Characteristics of drug overdose suicide attempts presenting to the psychiatric emergency department of Beijing Anding Hospital
Overdose-related suicide attempts represent a significant portion of self-harm presentations in the psychiatric emergency department (ED). Identifying specific patient characteristics associated with these att...
Co-occurrence of obesogenic behaviors and their implications for mental health during the COVID-19 pandemic: a study with university students
The university years are a critical period for young adults, as they are more exposed to obesogenic behaviors and experience stressful situations that compromise their mental health. This study aims to estimat...
YouTube/ Bilibili/ TikTok videos as sources of medical information on laryngeal carcinoma: cross-sectional content analysis study
YouTube, a widely recognized global video platform, is inaccessible in China, whereas Bilibili and TikTok are popular platforms for long and short videos, respectively. There are many videos related to larynge...
Uncovering multi-level mental healthcare barriers for migrants: a qualitative analysis across China, Germany, Netherlands, Romania, and South Africa
Forced displacement is a significant issue globally, and it affected 112 million people in 2022. Many of these people have found refuge in low- and middle-income countries. Migrants and refugees face complex a...
Work environment adversity and non-communicable Disease risk among drivers working for application-based-cab-aggregators in an Indian metropolis
Bengaluru, a metropolis in Southern India, is one of the largest markets for cab aggregator companies. Drivers working for these companies play a vital role in urban transportation but unlike other drivers, th...
Important information
Editorial board
For authors
For editorial board members
For reviewers
- Manuscript editing services
Annual Journal Metrics
2022 Citation Impact 4.5 - 2-year Impact Factor 4.7 - 5-year Impact Factor 1.661 - SNIP (Source Normalized Impact per Paper) 1.307 - SJR (SCImago Journal Rank)
2023 Speed 32 days submission to first editorial decision for all manuscripts (Median) 173 days submission to accept (Median)
2023 Usage 24,332,405 downloads 24,308 Altmetric mentions
- More about our metrics
Peer-review Terminology
The following summary describes the peer review process for this journal:
Identity transparency: Single anonymized
Reviewer interacts with: Editor
Review information published: Review reports. Reviewer Identities reviewer opt in. Author/reviewer communication
More information is available here
- Follow us on Twitter
BMC Public Health
ISSN: 1471-2458
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Skip to Content
Google Health research publications
Publishing our work allows us to share ideas and work collaboratively to advance healthcare. This is a comprehensive view of our publications and associated blog posts.
Blog Posts [more at Google Keyword Blog & Google Research Blog ]
by Karen DeSalvo
Google Keyword Blog | 19-Mar-2024
by Ronit Levavi Morad & Preeti Singh
Google Keyword Blog | 8-Mar-2024
Google Keyword Blog | 6-Feb-2024
by Aashima Gupta
Google Keyword Blog | 9-Jan-2024
by Jeff Dean, James Manyika, & Demis Hassabis
Google Research Blog | 22-Dec-2023
by Molly McHugh-Johnson
Google Keyword Blog | 20-Dec-2023
by Ivor Horn
Google Keyword Blog | 2-Nov-2023
by Yossi Mattia Shravya Shetty
Google Keyword Blog | 31-Oct-2023
by Yossi Mattias
Google Keyword Blog | 23-Oct-2023
by Nira Goren
Google Keyword Blog | 18-Oct-2023
by Michaell Howell
Google Keyword Blog | 9-Oct-2023
Google Keyword Blog | 3-Oct-2023
Google Keyword Blog | 18-Jul-2023
Blog Posts [more at Google Keyword Blog & Google AI Blog ]
by Susan Thomas
Google Keyword Blog | 5-Jul-2023
Google Keyword Blog | 13-Jun-2023
Google Keyword Blog | 23-May-2023
Google Keyword Blog | 22-May-2023
by Megan Jones Bell
Google Keyword Blog | 15-May-2023
Google Keyword Blog | 13-Apr-2023
Google Keyword Blog | 14-Mar-2023
by Greg Corrado & Yossi Matias
Google Research Blog | 23-Feb-2023
Google Keyword Blog | 26-Jan-2023
by Katie Malczyk
Google Keyword Blog | 17-Jan-2023
Google Keyword Blog | 5-Jan-2023
by Iz Conroy
Google Keyword Blog | 21-Dec-2022
by Hema Budaraju
Google Keyword Blog | 14-Dec-2022
Google Keyword Blog | 15-Nov-2022
Google Cloud Blog | 14-Nov-2022
by Jeff Dean
Google Keyword Blog | 2-Nov-2022
Google Keyword Blog | 27-Oct-2022
by Riva Sciuto
Google Keyword Blog | 19-Oct-2022
Google Keyword Blog | 12-Sep-2022
by Lauren Winer
Google Keyword Blog | 25-Aug-2022
by Anne Merritt
Google Keyword Blog | 20-Jul-2022
Google Keyword Blog | 17-May-2022
by Megan Jones Bell & Garth Graham
Google Keyword Blog | 10-May-2022
Google Keyword Blog | 24-Mar-2022
by Greg Corrado
Google Research Blog | 24-Mar-2022
by Paul Muret
Google Keyword Blog | 15-Mar-2022
Google Keyword Blog | 8-Mar-2022
Google Research Blog | 11-Jan-2022
Google Keyword Blog | 2-Dec-2021
Google Keyword Blog | 17-Oct-2021
by Alicia Cormie
Google Keyword Blog | 6-May-2021
Google Keyword Blog | 16-Apr-2021
Google Keyword Blog | 23- Feb-2021
Google Research Blog | 12-Jan-2021
by David Feinberg
LinkedIn Blog | 8-Dec-2020
by Dave Greenwood
Google Keyword Blog | 2-Dec-2020
by Anna Lurchenko
Google Design Blog | 29-Jul-2020
by Daniel Gillison, Jr
Google Keyword Blog | 28-May-2020
Google Research Blog | 9-Jan-2020
by Yun Liu & Po-Hsuan Cameron Chen
Google Research Blog | 10-Dec-2019
Google Keyword Blog | 20-Nov-2019
by Ruth Porat
Google Keyword Blog | 21-Oct-2019
by Dominic King
Google Keyword Blog | 18-Sep-2019
Google Research Blog | 15-Jan-2019
Google Keyword Blog | 17-Jun-2019
by Kent Walter
Google Keyword Blog | 13-Dec-2018
Google Research Blog | 12-Jan-2018
by Paula Schnurr & Teri Brister
Google Keyword Blog | 5-Dec-2017
by Mary Giliberti
Google Keyword Blog | 23-Aug-2017
by Katherine Chou
Google Research Blog | 17-May-2017
Google Research Blog | 12-Jan-2017
COVID-19 Blog Posts
Google Keyword Blog | 16-Jun-2022
COVID-19 Blog Posts [more at Google Keyword Blog ]
by Lauren Gallagher
Google Keyword Blog | 11-Feb-2022
Google Keyword Blog | 8-Dec-2021
by Tomer Shekel
Google Keyword Blog | 9-Jun-2021
by the COVID Response team, Google India
Google India Blog | 10-May-2021
Google Keyword Blog | 15-Apr-2021 [Spanish version]
by Stephen Ratcliffe
Google Keyword Blog | 24-Feb-2021
by Sundar Pichai
Google Keyword Blog | 25-Jan-2021
by Steph Hannon
Google Keyword Blog | 11-Dec-2020
by Karen DeSalvo & Kristie Canegallo
Google Keyword Blog | 10-Dec-2020
Google Keyword Blog | 24-Nov-2020 [Spanish version]
Google Keyword Blog
10-Nov-2020
Google Keyword Blog | 27-Oct-2020
Google Keyword Blog | 17-Sept-2020
by Mollie Javerbaum & Meghan Houghton
Google Keyword Blog | 10-Sep-2020
by Evgeniy Gabrilovich
Google Keyword Blog | 2-Sep-2020
by Dave Burke
Google Keyword Blog | 31-Jul-2020
by Apple & Google
Google Keyword Blog | 20-May-2020
by Megan Washam
Google Keyword Blog | 13-May-2020
Google Keyword Blog | 8-May-2020
Google Africa Blog
Google Africa Blog | 23-Apr-2020
Google Keyword Blog | 10-Apr-2020
by Julie Black
Google Keyword Blog | 6-Apr-2020
by Jen Fitzpatrick & Karen DeSalvo
Google Keyword Blog | 3-Apr-2020
by Emily Moxley
Google Keyword Blog | 21-Mar-2020
Google Keyword Blog | 15-Mar-2020
Google Keyword Blog | 6-Mar-2020
Lawrence, H. R., Schneider, R. A., Rubin, S. B., Mataric, M. J., McDuff, D. J. & Bell, M. J.
arXiv [cs.CL] (2024).
Graham, G., Goren, N., Sounderajah, V. & DeSalvo, K.
Nat. Med. (2024). [readcube]
Weng, W.-H., Sellergen, A., Kiraly, A. P., D’Amour, A., Park, J., Pilgrim, R., Pfohl, S., Lau, C., Natarajan, V., Azizi, S., Karthikesalingam, A., Cole-Lewis, H., Matias, Y., Corrado, G. S., Webster, D. R., Shetty, S., Prabhakara, S., Eswaran, K., Celi, L. A. G. & Liu, Y.
The Lancet Digital Health 6, e126–e130 (2024).
Howell M., Corrado G., DeSalvo K.
JAMA. 331(3):242–244 (2024).
Lehmann, L. S., Natarajan, V. & Peng, L. Chapter 39
(ed. Krittanawong, C.) Artificial Intelligence in Clinical Practice. 341–344 (Academic Press, 2024).
Lang, O., Traynis, I. & Liu, Y.
Nat Biomed Eng (2023). [readcube]
Deng, C.-Y., Mitani, A., Chen, C. W., Peng, L. H., Hammel, N. & Liu, Y
(eds. Yogesan, K., Goldschmidt, L., Cuadros, J. & Ricur, G.) 199–218. Springer International Publishing, 2023. [readcube]
Serghiou, S. & Rough, K.
Am. J. Epidemiol. (2023).
DeSalvo Karen B. & Howell Michael D.
NEJM Catalyst non-issue commentary (2023).
DeSalvo, K. B., Kadakia, K. T. & Chokshi, D. A.
JAMA Health Forum 2, e214051–e214051 (2021).
Kadakia, K. T., Howell, M. D. & DeSalvo, K. B.
JAMA 326, 385–386 (2021).
DeSalvo, K. B. & Kadakia, K. T.
Am. J. Public Health 111, S179–S181 (2021).
Sounderajah, V., Ashrafian, H., Rose, S., Shah, N. H., Ghassemi, M., Golub, R., Kahn, C. E., Jr, Esteva, A., Karthikesalingam, A., Mateen, B., Webster, D., Milea, D., Ting, D., Treanor, D., Cushnan, D., King, D., McPherson, D., Glocker, B., Greaves, F., Harling, L., Ordish, J., Cohen, J. F., Deeks, J., Leeflang, M., Diamond, M., McInnes, M. D. F., McCradden, M., Abràmoff, M. D., Normahani, P., Markar, S. R., Chang, S., Liu, X., Mallett, S., Shetty, S., Denniston, A., Collins, G. S., Moher, D., Whiting, P., Bossuyt, P. M. & Darzi, A.
Nat. Med. (2021).
Chen, P.-H. C., Mermel, C. H. & Liu, Y.
The Lancet Digital Health (2021). doi:10.1016/S2589-7500(21)00216-8
Kelly, C. J., Brown, A. P. Y. & Taylor, J. A.
(eds. Lidströmer, N. & Ashrafian, H.) 1–18 (Springer International Publishing, 2021).
Poplin, R., Zook, J. M. & DePristo, M.
JAMA 326, 268–269 (2021).
Mitani, A., Hammel, N. & Liu, Y.
Nature Biomedical Engineering 1–3 (2021). [readcube]
Esteva, A., Chou, K., Yeung, S., Naik, N., Madani, A., Mottaghi, A., Liu, Y., Topol, E., Dean, J. & Socher, R.
npj Digital Medicine 4, 5 (2021).
Steiner, D. F., Chen, P.-H. C. & Mermel, C. H.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 1875, 188452 (2021).
Liu, Y., Yang, L., Phene, S. & Peng, L.
Artificial Intelligence in Medicine 247–264 (2021).
Warnert, E. A. H., Kasper, L., Meltzer, C. C., Lightfoote, J. B., Bucknor, M. D., Haroon, H., Duggan, G., Gowland, P., Wald, L., Miller, K. L., Morris, E. A. & Anazodo, U. C.
J. Magn. Reson. Imaging (2020). doi:10.1002/jmri.27476 [readcube]
Rakha, E. A., Toss, M., Shiino, S., Gamble, P., Jaroensri, R., Mermel, C. H. & Chen, P.-H. C.
J. Clin. Pathol. (2020). doi:10.1136/jclinpath-2020-206908
Sayres, R., Hammel, N. & Liu, Y.
Annals of Eye Science 5, 18–18 (2020).
Ibrahim, A., Gamble, P., Jaroensri, R., Abdelsamea, M. M., Mermel, C. H., Chen, P.-H. C. & Rakha, E. A.
Breast 49, 267–273 (2020).
Liu, Y., Chen, P.-H. C., Krause, J. & Peng, L.
JAMA 322, 1806–1816 (2019). [readcube]
Kelly, C. J., Karthikesalingam, A., Suleyman, M., Corrado, G., & King, D.
BMC Med. 17, 195 (2019).
Rajkomar, A., Hardt, M., Howell, M. D., Corrado, G., & Chin, M. H.
Ann. Intern. Med. 169(12):866-872 (2018).
Curiel-Lewandrowski, C., Novoa, R. A., Berry, E., Celebi, M. E., Codella, N., Giuste, F., Gutman, D., Halpern, A., Leachman, S., Liu, Y., Liu, Y., Reiter, O. & Tschandl, P.
599–628. Springer New York (2019).
Chen, C. P.-H., Liu, Y., & Peng, L.
Nat. Mater. 18, 410–414 (2019). [readcube]
Rajkomar, A., Dean, J., & Kohane I.
N. Engl. J. Med. 380:1347-1358 (2019).
Esteva, A., Robicquet, A., Ramsundar, B., Kuleshov, V., DePristo, M., Chou, K., Cui, C., Corrado, G., Thrun, S. & Dean, J.
Nat. Med. 25, 24–29 (2019). [readcube]
Rough K, Thompson J.
Ophthalmology. 125(8):1136-1138 (2018).
Wachter, R. M., Howell, M. D.
JAMA 320(1):25-26 (2018).
Cross-Specialty Applied AI
by Krishnamurthy (Dj) Dvijotham & Taylan Cemgil
Google Deepmind | 17-Jul-2023
by Shekoofeh Azizi & Laura Culp
Google Research Blog | 26-Apr-2023
by Alex D’Amour & Katherine Heller
Google Research Blog | 18-Oct-2021
by Shekoofeh Azizi
Google Research Blog | 13-Oct-2021
Publications
Reinke, A., Tizabi, M. D., Baumgartner, M., Eisenmann, M., Heckmann-Nötzel, D., Kavur, A. E., Rädsch, T., Sudre, C. H., Acion, L., Antonelli, M., Arbel, T., Bakas, S., Benis, A., Buettner, F., Cardoso, M. J., Cheplygina, V., Chen, J., Christodoulou, E., Cimini, B. A., Farahani, K., Ferrer, L., Galdran, A., van Ginneken, B., Glocker, B., Godau, P., Hashimoto, D. A., Hoffman, M. M., Huisman, M., Isensee, F., Jannin, P., Kahn, C. E., Kainmueller, D., Kainz, B., Karargyris, A., Kleesiek, J., Kofler, F., Kooi, T., Kopp-Schneider, A., Kozubek, M., Kreshuk, A., Kurc, T., Landman, B. A., Litjens, G., Madani, A., Maier-Hein, K., Martel, A. L., Meijering, E., Menze, B., Moons, K. G. M., Müller, H., Nichyporuk, B., Nickel, F., Petersen, J., Rafelski, S. M., Rajpoot, N., Reyes, M., Riegler, M. A., Rieke, N., Saez-Rodriguez, J., Sánchez, C. I., Shetty, S., Summers, R. M., Taha, A. A., Tiulpin, A., Tsaftaris, S. A., Van Calster, B., Varoquaux, G., Yaniv, Z. R., Jäger, P. F. & Maier-Hein, L.
Nat. Methods 21, 182–194 (2024). [readcube]
Brown, A., Tomasev, N., Freyberg, J., Liu, Y., Karthikesalingam, A. & Schrouff, J.
Nat. Commun. 14, 4314 (2023).
Dvijotham, K., Winkens, J., Barsbey, M., Ghaisas, S., Stanforth, R., Pawlowski, N., Strachan, P., Ahmed, Z., Azizi, S., Bachrach, Y., Culp, L., Daswani, M., Freyberg, J., Kelly, C., Kiraly, A., Kohlberger, T., McKinney, S., Mustafa, B., Natarajan, V., Geras, K., Witowski, J., Qin, Z. Z., Creswell, J., Shetty, S., Sieniek, M., Spitz, T., Corrado, G., Kohli, P., Cemgil, T. & Karthikesalingam, A.
Nat. Med. 1–7 (2023).
Azizi, S., Culp, L., Freyberg, J., Mustafa, B., Baur, S., Kornblith, S., Chen, T., Tomasev, N., Mitrović, J., Strachan, P., Mahdavi, S. S., Wulczyn, E., Babenko, B., Walker, M., Loh, A., Chen, P.-H. C., Liu, Y., Bavishi, P., McKinney, S. M., Winkens, J., Roy, A. G., Beaver, Z., Ryan, F., Krogue, J., Etemadi, M., Telang, U., Liu, Y., Peng, L., Corrado, G. S., Webster, D. R., Fleet, D., Hinton, G., Houlsby, N., Karthikesalingam, A., Norouzi, M. & Natarajan, V.
Nature Biomedical Engineering 1–24 (2023). [readcube]
Schrouff, J., Harris, N., Koyejo, O. O., Alabdulmohsin, I., Schnider, E., Opsahl-Ong, K., Brown, A., Roy, S., Mincu, D., Chen, C., Dieng, A., Liu, Y., Natarajan, V., Karthikesalingam, A., Heller, K. A., Chiappa, S. & D’Amour, A.
NeurIPS (2022).
McKinney, S. M.
medRxiv (2022).
Freeman, B., Hammel, N., Phene, S., Huang, A., Ackermann, R., Kanzheleva, O., Hutson, M., Taggart, C., Duong, Q. & Sayres, R.
HCOMP 9, 60–71 (2021).
Azizi, S., Mustafa, B., Ryan, F., Beaver, Z., Freyberg, J., Deaton, J., Loh, A., Karthikesalingam, A., Kornblith, S., Chen, T., Natarajan, V. & Norouzi, M.
Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV) 3478–3488 (2021).
Sadilek, A., Liu, L., Nguyen, D., Kamruzzaman, M., Serghiou, S., Rader, B., Ingerman, A., Mellem, S., Kairouz, P., Nsoesie, E. O., MacFarlane, J., Vullikanti, A., Marathe, M., Eastham, P., Brownstein, J. S., Arcas, B. A. Y., Howell, M. D. & Hernandez, J.
NPJ Digit Med 4, 132 (2021).
Mustafa, B., Loh, A., Freyberg, J., MacWilliams, P., Karthikesalingam, A., Houlsby, N. & Natarajan, V.
arXiv [cs.CV] (2021).
arXiv [eess.IV] (2021).
D’Amour, A., Heller, K., Moldovan, D., Adlam, B., Alipanahi, B., Beutel, A., Chen, C., Deaton, J., Eisenstein, J., Hoffman, M. D., Hormozdiari, F., Houlsby, N., Hou, S., Jerfel, G., Karthikesalingam, A., Lucic, M., Ma, Y., McLean, C., Mincu, D., Mitani, A., Montanari, A., Nado, Z., Natarajan, V., Nielson, C., Osborne, T. F., Raman, R., Ramasamy, K., Sayres, R., Schrouff, J., Seneviratne, M., Sequeira, S., Suresh, H., Veitch, V., Vladymyrov, M., Wang, X., Webster, K., Yadlowsky, S., Yun, T., Zhai, X. & Sculley, D.
arXiv [cs.LG] (2020).
Winkens, J., Bunel, R., Roy, A. G., Stanforth, R., Natarajan, V., Ledsam, J. R., MacWilliams, P., Kohli, P., Karthikesalingam, A., Kohl, S., Cemgil, T., Ali Eslami, S. M. & Ronneberger, O.
Hartman, T., Howell, M., Dean, J., Hoory, S., Slyper, R., Laish, I., Gilon, O, Vainstein, D., Corrado, G., Chou, K., Po, M., Williams, J., Ellis, S., Bee, G., Hassidim, A., Amira, R., Beryozkin, G., Szpektor, I., & Matias, Y.
BMC (2020).
Dermatology
by Pooja Rao
Google Research Blog | 19-Mar-2024
by Mike Schaekermann & Ivor Horn
Google Research Blog | 15-Mar-2024
by Dave Steiner & Rory Pilgrim
Google Research Blog | 8-Mar-2024
by Lou Wang
Google Keyword Blog | 14-Jun-2023
Google Keyword Blog | 08-Feb-2022
by Abhijit Guha Roy & Jie Ren
Google Research Blog | 27-Jan-2022
by Miles Hutson & Aaron Loh
TensorFlow Blog | 11-Oct-2021
by Peggy Bui & Yuan Liu
Google Keyword Blog | 18-May-2021
by Ayush Jain & Peggy Bui
Google Keyword Blog | 28-Apr-2021
by Timo Kohlberger & Yuan Liu
Google Research Blog | 19-Feb-2020
by Yuan Liu & Peggy Bui
Google Research Blog | 12-Sep-2019
Schaekermann, M., Spitz, T., Pyles, M., Cole-Lewis, H., Wulczyn, E., Pfohl, S. R., Martin, D., Jr, Jaroensri, R., Keeling, G., Liu, Y., Farquhar, S., Xue, Q., Lester, J., Hughes, C., Strachan, P., Tan, F., Bui, P., Mermel, C. H., Peng, L. H., Matias, Y., Corrado, G. S., Webster, D. R., Virmani, S., Semturs, C., Liu, Y., Horn, I. & Cameron Chen, P.-H.
eClinicalMedicine (2024).
Rikhye, R. V., Hong, G. E., Singh, P., Smith, M. A., Loh, A., Muralidharan, V., Wong, D., Sayres, R., Phung, M., Betancourt, N., Fong, B., Sahasrabudhe, R., Nasim, K., Eschholz, A., Matias, Y., Corrado, G. S., Chou, K., Webster, D. R., Bui, P., Liu, Y., Liu, Y., Ko, J. & Lin, S.
Mayo Clinic Proceedings: Digital Health (2024).
Alabdulmohsin, I.M., Schrouff, J., Koyejo, S.
35. NeurIPS (2022).
Vemulapalli, R., Morningstar, W. R., Mansfield, P. A., Eichner, H., Singhal, K., Afkanpour, A. & Green, B.
arXiv [cs.LG] (2022).
Huang, S. J., Liu, Y., Kanada, K., Corrado, G. S., Webster, D. R., Peng, L., Bui, P. & Liu, Y.
Skin Health and Disease (2021).
Guha Roy, A., Ren, J., Azizi, S., Loh, A., Natarajan, V., Mustafa, B., Pawlowski, N., Freyberg, J., Liu, Y., Beaver, Z., Vo, N., Bui, P., Winter, S., MacWilliams, P., Corrado, G. S., Telang, U., Liu, Y., Cemgil, T., Karthikesalingam, A., Lakshminarayanan, B. & Winkens, J.
Med. Image Analysis. 75, 102274 (2021). [ reading link ]
Weng, W.-H., Deaton, J., Natarajan, V., Elsayed, G. F. & Liu, Y.
JAMA Netw Open 4, e217249–e217249 (2021).
Machine Learning for Health NeurIPS Workshop (ML4H), PMLR 136:415-429 (2020).
Singh, N., Lee, K., Coz, D., Angermueller, C., Huang, S., Loh, A. & Liu, Y.
in 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW) 3172–3181 (2020).
Liu, Y., Jain, A., Eng, C., Way, D. H., Lee, K., Bui, P., Kanada, K., de Oliveira Marinho, G., Gallegos, J., Gabriele, S., Gupta, V., Singh, N., Natarajan, V., Hofmann-Wellenhof, R., Corrado, G. S., Peng, L. H., Webster, D. R., Ai, D., Huang, S., Liu, Y., Carter Dunn, R. & Coz, D.
Nat. Med. (2020). [readcube]
Ghorbani, A., Natarajan, V., Coz, D. & Liu, Y.
Machine Learning for Health NeurIPS Workshop (ML4H), PMLR 116:155-170 (2020).
Eng, C., Liu, Y. & Bhatnagar, R.
Br. J. Dermatol. (2019). readcube
by Yossi Matias & Ehud Rivlin
Google Research Blog | 5-Aug-2021
by Robin Suchan
Verily Press | 5-Aug-2021
by Daniel Freedman & Ehud Rivlin
Google Research Blog | 28-Aug-2020
Golany, T., Aides, A., Freedman, D., Rabani, N., Liu, Y., Rivlin, E., Corrado, G. S., Matias, Y., Khoury, W., Kashtan, H. & Reissman, P.
Surg. Endosc. (2022).
Livovsky, D. M., Veikherman, D., Golany, T., Aides, A., Dashinsky, V., Rabani, N., Ben Shimol, D., Blau, Y., Katzir, L., Shimshoni, I., Liu, Y., Segol, O., Goldin, E., Corrado, G., Lachter, J., Matias, Y., Rivlin, E. & Freedman, D.
Gastrointest. Endosc. (2021).
Freedman, D., Blau, Y., Katzir, L., Aides, A., Shimshoni, I., Veikherman, D., Golany, T., Gordon, A., Corrado, G., Matias, Y. & Rivlin, E.
IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 1–1 (2020).
Epidemiological Forecasting
by Joel Shor & Sercan Arik
by Tomas Pfister
Google Cloud Blog | 15-Nov-2020
by Dario Sava
Google Cloud Blog | 3-Aug-2020
Tsai, T. C., Arik, S., Jacobson, B. H., Yoon, J., Yoder, N., Sava, D., Mitchell, M., Graham, G. & Pfister, T.
NPJ Digit Med 5, 59 (2022).
Cramer, E. Y., Ray, E. L., Lopez, V. K., Bracher, J., Brennen, A., Castro Rivadeneira, A. J., Gerding, A., Gneiting, T., House, K. H., Huang, Y., Jayawardena, D., Kanji, A. H., Khandelwal, A., Le, K., Mühlemann, A., Niemi, J., Shah, A., Stark, A., Wang, Y., Wattanachit, N., Zorn, M. W., Gu, Y., Jain, S., Bannur, N., Deva, A., Kulkarni, M., Merugu, S., Raval, A., Shingi, S., Tiwari, A., White, J., Abernethy, N. F., Woody, S., Dahan, M., Fox, S., Gaither, K., Lachmann, M., Meyers, L. A., Scott, J. G., Tec, M., Srivastava, A., George, G. E., Cegan, J. C., Dettwiller, I. D., England, W. P., Farthing, M. W., Hunter, R. H., Lafferty, B., Linkov, I., Mayo, M. L., Parno, M. D., Rowland, M. A., Trump, B. D., Zhang-James, Y., Chen, S., Faraone, S. V., Hess, J., Morley, C. P., Salekin, A., Wang, D., Corsetti, S. M., Baer, T. M., Eisenberg, M. C., Falb, K., Huang, Y., Martin, E. T., McCauley, E., Myers, R. L., Schwarz, T., Sheldon, D., Gibson, G. C., Yu, R., Gao, L., Ma, Y., Wu, D., Yan, X., Jin, X., Wang, Y.-X., Chen, Y., Guo, L., Zhao, Y., Gu, Q., Chen, J., Wang, L., Xu, P., Zhang, W., Zou, D., Biegel, H., Lega, J., McConnell, S., Nagraj, V. P., Guertin, S. L., Hulme-Lowe, C., Turner, S. D., Shi, Y., Ban, X., Walraven, R., Hong, Q.-J., Kong, S., van de Walle, A., Turtle, J. A., Ben-Nun, M., Riley, S., Riley, P., Koyluoglu, U., DesRoches, D., Forli, P., Hamory, B., Kyriakides, C., Leis, H., Milliken, J., Moloney, M., Morgan, J., Nirgudkar, N., Ozcan, G., Piwonka, N., Ravi, M., Schrader, C., Shakhnovich, E., Siegel, D., Spatz, R., Stiefeling, C., Wilkinson, B., Wong, A., Cavany, S., España, G., Moore, S., Oidtman, R., Perkins, A., Kraus, D., Kraus, A., Gao, Z., Bian, J., Cao, W., Lavista Ferres, J., Li, C., Liu, T.-Y., Xie, X., Zhang, S., Zheng, S., Vespignani, A., Chinazzi, M., Davis, J. T., Mu, K., Pastore Y Piontti, A., Xiong, X., Zheng, A., Baek, J., Farias, V., Georgescu, A., Levi, R., Sinha, D., Wilde, J., Perakis, G., Bennouna, M. A., Nze-Ndong, D., Singhvi, D., Spantidakis, I., Thayaparan, L., Tsiourvas, A., Sarker, A., Jadbabaie, A., Shah, D., Della Penna, N., Celi, L. A., Sundar, S., Wolfinger, R., Osthus, D., Castro, L., Fairchild, G., Michaud, I., Karlen, D., Kinsey, M., Mullany, L. C., Rainwater-Lovett, K., Shin, L., Tallaksen, K., Wilson, S., Lee, E. C., Dent, J., Grantz, K. H., Hill, A. L., Kaminsky, J., Kaminsky, K., Keegan, L. T., Lauer, S. A., Lemaitre, J. C., Lessler, J., Meredith, H. R., Perez-Saez, J., Shah, S., Smith, C. P., Truelove, S. A., Wills, J., Marshall, M., Gardner, L., Nixon, K., Burant, J. C., Wang, L., Gao, L., Gu, Z., Kim, M., Li, X., Wang, G., Wang, Y., Yu, S., Reiner, R. C., Barber, R., Gakidou, E., Hay, S. I., Lim, S., Murray, C., Pigott, D., Gurung, H. L., Baccam, P., Stage, S. A., Suchoski, B. T., Prakash, B. A., Adhikari, B., Cui, J., Rodríguez, A., Tabassum, A., Xie, J., Keskinocak, P., Asplund, J., Baxter, A., Oruc, B. E., Serban, N., Arik, S. O., Dusenberry, M., Epshteyn, A., Kanal, E., Le, L. T., Li, C.-L., Pfister, T., Sava, D., Sinha, R., Tsai, T., Yoder, N., Yoon, J., Zhang, L., Abbott, S., Bosse, N. I., Funk, S., Hellewell, J., Meakin, S. R., Sherratt, K., Zhou, M., Kalantari, R., Yamana, T. K., Pei, S., Shaman, J., Li, M. L., Bertsimas, D., Skali Lami, O., Soni, S., Tazi Bouardi, H., Ayer, T., Adee, M., Chhatwal, J., Dalgic, O. O., Ladd, M. A., Linas, B. P., Mueller, P., Xiao, J., Wang, Y., Wang, Q., Xie, S., Zeng, D., Green, A., Bien, J., Brooks, L., Hu, A. J., Jahja, M., McDonald, D., Narasimhan, B., Politsch, C., Rajanala, S., Rumack, A., Simon, N., Tibshirani, R. J., Tibshirani, R., Ventura, V., Wasserman, L., O’Dea, E. B., Drake, J. M., Pagano, R., Tran, Q. T., Ho, L. S. T., Huynh, H., Walker, J. W., Slayton, R. B., Johansson, M. A., Biggerstaff, M. & Reich, N. G.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 119, e2113561119 (2022).
Arık, S. Ö., Shor, J., Sinha, R., Yoon, J., Ledsam, J. R., Le, L. T., Dusenberry, M. W., Yoder, N. C., Popendorf, K., Epshteyn, A., Euphrosine, J., Kanal, E., Jones, I., Li, C.-L., Luan, B., Mckenna, J., Menon, V., Singh, S., Sun, M., Ravi, A. S., Zhang, L., Sava, D., Cunningham, K., Kayama, H., Tsai, T., Yoneoka, D., Nomura, S., Miyata, H. & Pfister, T.
NPJ Digit Med 4, 146 (2021).
Kapoor, A., Ben, X., Liu, L., Perozzi, B., Barnes, M., Blais, M. & O’Banion, S.
Arik, Li, Yoon, Sinha, Epshteyn, Le, Menon, Singh, Zhang, Nikoltchev, Sonthalia, Nakhost, Kanal & Pfister.
Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020.
Eye Diseases
by Michelle Budzyna & Molly McHugh-Johnson
Google Keyword Blog | 27-Sep-2023
by Kasumi Widner
Google Keyword Blog | 30-May-2023
by Angus Turner
Google Australia Blog | 7-Mar-2023
by Emma Beede
Google Keyword Blog | 25-Apr-2020
by Kasumi Widner & Sunny Virmani
Google Keyword Blog | 25-Feb-2019
Verily Blog | 25-Feb-2019
by Rory Sayres & Jonathan Krause
Google Research Blog | 13-Dec-2018
by Mustafa Suleyman
DeepMind Blog | 13-Aug-2018
by Lily Peng
Google Keyword Blog | 29-Nov-2016
by Lily Peng & Varun Gulshan
Google Research Blog | 29-Nov-2016
Bora, A., Tiwari, R., Bavishi, P., Virmani, S., Huang, R., Traynis, I., Corrado, G. S., Peng, L., Webster, D. R., Varadarajan, A. V., Pattanapongpaiboon, W., Chopra, R. & Ruamviboonsuk, P.
Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 12, 11 (2023).
Widner, K., Virmani, S., Krause, J., Nayar, J., Tiwari, R., Pedersen, E. R., Jeji, D., Hammel, N., Matias, Y., Corrado, G. S., Liu, Y., Peng, L. & Webster, D. R.
Nat. Med. 1–3 (2023). [readcube]
Srisubat, A., Kittrongsiri, K., Sangroongruangsri, S., Khemvaranan, C., Shreibati, J. B., Ching, J., Hernandez, J., Tiwari, R., Hersch, F., Liu, Y., Hanutsaha, P., Ruamviboonsuk, V., Turongkaravee, S., Raman, R. & Ruamviboonsuk, P.
Ophthalmol Ther (2023).
Chia, M. A., Hersch, F., Sayres, R., Bavishi, P., Tiwari, R., Keane, P. A. & Turner, A. W.
Br. J. Ophthalmol. (2023).
Ruamviboonsuk, P., Tiwari, R., Sayres, R., Nganthavee, V., Hemarat, K., Kongprayoon, A., Raman, R., Levinstein, B., Liu, Y., Schaekermann, M., Lee, R., Virmani, S., Widner, K., Chambers, J., Hersch, F., Peng, L. & Webster, D. R.
The Lancet Digital Health (2022).
Pedersen Elin Rønby, Cuadros Jorge, Khan Mahbuba, Fleischmann Sybille, Wolff Gregory, Hammel Naama, Liu Yun & Leung Geoffrey.
NEJM Catalyst (2021).
Wilson, M., Chopra, R., Wilson, M. Z., Cooper, C., MacWilliams, P., Liu, Y., Wulczyn, E., Florea, D., Hughes, C. O., Karthikesalingam, A., Khalid, H., Vermeirsch, S., Nicholson, L., Keane, P. A., Balaskas, K. & Kelly, C. J.
JAMA Ophthalmol. (2021).
Limwattanayingyong, J., Nganthavee, V., Seresirikachorn, K., Singalavanija, T., Soonthornworasiri, N., Ruamviboonsuk, V., Rao, C., Raman, R., Grzybowski, A., Schaekermann, M., Peng, L. H., Webster, D. R., Semturs, C., Krause, J., Sayres, R., Hersch, F., Tiwari, R., Liu, Y. & Ruamviboonsuk, P.
Journal of Diabetes Research, 1–8 (2020).
Hsu J, Phene S, Mitani A, Luo J, Hammel N, Krause J, Sayres R.
in ACM-CHIL [arXiv] (2020)
Bresnick, G., Cuadros, J. A., Khan, M., Fleischmann, S., Wolff, G., Limon, A., Chang, J., Jiang, L., Cuadros, P. & Pedersen, E. R.
BMJ Open Diabetes Research and Care 8, e001154 (2020).
Beede, E., Baylor, E., Hersch, F., Iurchenko, A., Wilcox, L., Ruamviboonsuk, P. & Vardoulakis, L. M.
Proceedings of the 2020 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems 1–12. Association for Computing Machinery (2020).
Schaekermann, M., Cai, C. J., Huang, A. E. & Sayres, R.
Proceedings of the 2020 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems 1–13. Association for Computing Machinery (2020).
Phene, S., Dunn, R. C., Hammel, N., Liu, Y., Krause, J., Kitade, N., Schaekermann, M., Sayres, R., Wu, D. J., Bora, A., Semturs, C., Misra, A., Huang, A. E., Spitze, A., Medeiros, F. A., Maa, A. Y., Gandhi, M., Corrado, G. S., Peng, L. & Webster, D. R.
Ophthalmology 126, 1627–1639 (2019).
Schaekermann, M., Hammel, N., Terry, M., Ali, T. K., Liu, Y., Basham, B., Campana, B., Chen, W., Ji, X., Krause, J., Corrado, G. S., Peng, L., Webster, D. R., Law, E. & Sayres, R.
Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 8, 40 (2019).
Gulshan, V., Rajan, R. P., Widner, K., Wu, D., Wubbels, P., Rhodes, T., Whitehouse, K., Coram, M., Corrado, G., Ramasamy, K., Raman, R., Peng, L. & Webster, D. R.
JAMA Ophthalmol. (2019).
Ruamviboonsuk, P., Krause, J., Chotcomwongse, P., Sayres, R., Raman, R., Widner, K., Campana, B. J. L., Phene, S., Hemarat, K., Tadarati, M., Silpa-Archa, S., Limwattanayingyong, J., Rao, C., Kuruvilla, O., Jung, J., Tan, J., Orprayoon, S., Kangwanwongpaisan, C., Sukumalpaiboon, R., Luengchaichawang, C., Fuangkaew, J., Kongsap, P., Chualinpha, L., Saree, S., Kawinpanitan, S., Mitvongsa, K., Lawanasakol, S., Thepchatri, C., Wongpichedchai, L., Corrado, G. S., Peng, L. & Webster, D. R.
npj Digit Med 2, 25 (2019).
Sayres, R., Taly, A., Rahimy, E., Blumer, K., Coz, D., Hammel, N., Krause, J., Narayanaswamy, A., Rastegar, Z., Wu, D., Xu, S., Barb, S., Joseph, A., Shumski, M., Smith, J., Sood, A. B., Corrado, G. S., Peng, L. & Webster, D. R.
Ophthalmology 126, 552–564 (2019).
Fauw, J., Ledsam, J.R., Romera-Paredes, B., Nikolov, S., Tomasev, N., Blackwell, S., Askham, H., Glorot, X., O’Donoghue, B., Visentin, D., van den Driessche, G., Lakshminarayanan, B., Meyer, C., Mackinder, F., Bouton, S., Ayoub, K., Chopra, R., King, D., Karthikesalingam, A., Hughes, C.O., Raine, R., Hughes, J., Sim, D. A., Egan, C., Tufail, A., Montgomery, H., Hassabis, D., Rees, G., Back, T., Khaw, P.T., Suleyman, M., Cornebise, J., Keane, P.A., & Ronneberger, O.
Nat. Med. 24, 1342–1350 (2018). [readcube]
Krause, J., Gulshan, V., Rahimy, E., Karth, P., Widner, K., Corrado, G. S., Peng, L., & Webster, D.R.
Ophthalmology 125, 1264–1272 (2018). [arXiv]
Bouskill, K., Smith-Morris, C., Bresnick, G., Cuadros, J. & Pedersen, E. R.
BMC Health Services Research 18, (2018).
Smith-Morris, C., Bresnick, G. H., Cuadros, J., Bouskill, K. E. & Pedersen, E. R.
Med. Anthropol. 39, 109–122 (2018).
Guan, M., Gulshan, V., Dai, A, Hinton, G.
AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (2018).
Gulshan, V., Peng, L., Coram, M., Stumpe, M. C., Wu, D., Narayanaswamy, A., Venugopalan, S., Widner, K., Madams, T., Cuadros, J., Ramasamy, K., Nelson, P., Mega, J., & Webster, D.
JAMA 316, 2402–2410 (2016).
Blog Posts [more at Fitbit Blog ]
Google Keyword Blog | 6-Mar-2024
by Mike Darling
Google Keyword Blog | 24-Jan-2024
by Javier L. Prieto
Google Keyword Blog | 17-Jan-2024
by Amy McDonough
Google Keyword Blog | 26-Oct-2023
Google Keyword Blog | 19-Oct-2023
by Sandeep Waraich
Google Keyword Blog | 4-Oct-2023
by TJ Varghese
Google Keyword Blog | 28-Sep-2023
by Maggie Stanphill & Bhanu Narasimhan
Google Keyword Blog | 1-Aug-2023
by Elena Perez & Samy Abdel-Ghaffer
Google Keyword Blog | 2-Jun-2023
by Elena Perez
Google Keyword Blog | 4-May-2023
Google Keyword Blog | 16-Mar-2023
by Zahra Barnes
Google Keyword Blog | 20-Dec-2022
Google Keyword Blog | 6-Oct-2022
Google Keyword Blog | 29-Sep-2022
Google Keyword Blog | 24-Aug-2022
by The Fitbit Team
Google Keyword Blog | 22-Jun-2022
Google Keyword Blog | 11-Apr-2022
Speed, C., Arneil, T., Harle, R., Wilson, A., Karthikesalingam, A., McConnell, M. & Phillips, J.
PLOS Digit Health 2, e0000236 (2023).
Lubitz, S. A., Faranesh, A. Z., Selvaggi, C., Atlas, S. J., McManus, D. D., Singer, D. E., Pagoto, S., McConnell, M. V., Pantelopoulos, A. & Foulkes, A. S.
Circulation (2022).
Natarajan, A., Su, H.-W. & Heneghan, C.
Front. Physiol. 13, 898251 (2022).
Natarajan, A., Su, H.-W., Heneghan, C., Blunt, L., O’Connor, C. & Niehaus, L.
NPJ Digit Med 4, 136 (2021).
Blog Posts [more at DeepVariant Blog ]
by Andrew Carroll
Google Keyword Blog | 10-May-2023
by Andrew Carroll & Kishwar Shafin
Google Research Blog | 10-May-2023
Babak Behsaz & Andrew Carroll
Google Research Blog | 27-Apr-2023
by Sara Ahadi & Andrew Carroll
Google Research Blog | 11-Apr-2023
Google Keyword Blog | 26-Oct-2022
by Andrew Carroll & Pi-Chuan Chang
Google Keyword Blog | 13-Jan-2022
by Farhad Hormozdiari & Andrew Carroll
Google Open Source Blog | 11-Jan-2022
by Andrew Carroll & Cory McLean
Google Research Blog | 23-Jun-2021
Google Research Blog | 18-Sep-2020
by Pi-Chuan Chang & Lizzie Dorfman
Google Research Blog | 19-Apr-2018
by Mark DePristo & Ryan Poplin
Google Research Blog | 4-Dec-2017
by Phing Lee
Google Keyword Blog | 17-Nov-2017
Kolmogorov, M., Billingsley, K. J., Mastoras, M., Meredith, M., Monlong, J., Lorig-Roach, R., Asri, M., Alvarez Jerez, P., Malik, L., Dewan, R., Reed, X., Genner, R. M., Daida, K., Behera, S., Shafin, K., Pesout, T., Prabakaran, J., Carnevali, P., Yang, J., Rhie, A., Scholz, S. W., Traynor, B. J., Miga, K. H., Jain, M., Timp, W., Phillippy, A. M., Chaisson, M., Sedlazeck, F. J., Blauwendraat, C. & Paten, B.
Nat. Methods 20, 1483–1492 (2023).
Rhie, A., Nurk, S., Cechova, M., Hoyt, S. J., Taylor, D. J., Altemose, N., Hook, P. W., Koren, S., Rautiainen, M., Alexandrov, I. A., Allen, J., Asri, M., Bzikadze, A. V., Chen, N.-C., Chin, C.-S., Diekhans, M., Flicek, P., Formenti, G., Fungtammasan, A., Garcia Giron, C., Garrison, E., Gershman, A., Gerton, J. L., Grady, P. G. S., Guarracino, A., Haggerty, L., Halabian, R., Hansen, N. F., Harris, R., Hartley, G. A., Harvey, W. T., Haukness, M., Heinz, J., Hourlier, T., Hubley, R. M., Hunt, S. E., Hwang, S., Jain, M., Kesharwani, R. K., Lewis, A. P., Li, H., Logsdon, G. A., Lucas, J. K., Makalowski, W., Markovic, C., Martin, F. J., Mc Cartney, A. M., McCoy, R. C., McDaniel, J., McNulty, B. M., Medvedev, P., Mikheenko, A., Munson, K. M., Murphy, T. D., Olsen, H. E., Olson, N. D., Paulin, L. F., Porubsky, D., Potapova, T., Ryabov, F., Salzberg, S. L., Sauria, M. E. G., Sedlazeck, F. J., Shafin, K., Shepelev, V. A., Shumate, A., Storer, J. M., Surapaneni, L., Taravella Oill, A. M., Thibaud-Nissen, F., Timp, W., Tomaszkiewicz, M., Vollger, M. R., Walenz, B. P., Watwood, A. C., Weissensteiner, M. H., Wenger, A. M., Wilson, M. A., Zarate, S., Zhu, Y., Zook, J. M., Eichler, E. E., O’Neill, R. J., Schatz, M. C., Miga, K. H., Makova, K. D. & Phillippy, A. M.
Nature (2023).
Liao, W.-W., Asri, M., Ebler, J., Doerr, D., Haukness, M., Hickey, G., Lu, S., Lucas, J. K., Monlong, J., Abel, H. J., Buonaiuto, S., Chang, X. H., Cheng, H., Chu, J., Colonna, V., Eizenga, J. M., Feng, X., Fischer, C., Fulton, R. S., Garg, S., Groza, C., Guarracino, A., Harvey, W. T., Heumos, S., Howe, K., Jain, M., Lu, T.-Y., Markello, C., Martin, F. J., Mitchell, M. W., Munson, K. M., Mwaniki, M. N., Novak, A. M., Olsen, H. E., Pesout, T., Porubsky, D., Prins, P., Sibbesen, J. A., Sirén, J., Tomlinson, C., Villani, F., Vollger, M. R., Antonacci-Fulton, L. L., Baid, G., Baker, C. A., Belyaeva, A., Billis, K., Carroll, A., Chang, P.-C., Cody, S., Cook, D. E., Cook-Deegan, R. M., Cornejo, O. E., Diekhans, M., Ebert, P., Fairley, S., Fedrigo, O., Felsenfeld, A. L., Formenti, G., Frankish, A., Gao, Y., Garrison, N. A., Giron, C. G., Green, R. E., Haggerty, L., Hoekzema, K., Hourlier, T., Ji, H. P., Kenny, E. E., Koenig, B. A., Kolesnikov, A., Korbel, J. O., Kordosky, J., Koren, S., Lee, H., Lewis, A. P., Magalhães, H., Marco-Sola, S., Marijon, P., McCartney, A., McDaniel, J., Mountcastle, J., Nattestad, M., Nurk, S., Olson, N. D., Popejoy, A. B., Puiu, D., Rautiainen, M., Regier, A. A., Rhie, A., Sacco, S., Sanders, A. D., Schneider, V. A., Schultz, B. I., Shafin, K., Smith, M. W., Sofia, H. J., Abou Tayoun, A. N., Thibaud-Nissen, F., Tricomi, F. F., Wagner, J., Walenz, B., Wood, J. M. D., Zimin, A. V., Bourque, G., Chaisson, M. J. P., Flicek, P., Phillippy, A. M., Zook, J. M., Eichler, E. E., Haussler, D., Wang, T., Jarvis, E. D., Miga, K. H., Garrison, E., Marschall, T., Hall, I. M., Li, H. & Paten, B.
Nature 617, 312–324 (2023).
Cosentino, J., Behsaz, B., Alipanahi, B., McCaw, Z. R., Hill, D., Schwantes-An, T.-H., Lai, D., Carroll, A., Hobbs, B. D., Cho, M. H., McLean, C. Y. & Hormozdiari, F.
Nat. Genet. (2023).
Liu, D., Belyaeva, A., Shafin, K., Chang, P.-C., Carroll, A. & Cook, D. E.
bioRxiv (2022).
Belyaeva, A., Shor, J., Cook, D. E., Shafin, K., Liu, D., Töpfer, A., Wenger, A. M., Rowell, W. J., Yang, H., Kolesnikov, A., McLean, C. Y., Nattestad, M., Carroll, A. & Chang, P.-C.
Yuan, B., McLean, C. Y., Hormozdiari, F. I. & Cosentino, J.
Baid, G., Cook, D. E., Shafin, K., Yun, T., Llinares-López, F., Berthet, Q., Belyaeva, A., Töpfer, A., Wenger, A. M., Rowell, W. J., Yang, H., Kolesnikov, A., Ammar, W., Vert, J.-P., Vaswani, A., McLean, C. Y., Nattestad, M., Chang, P.-C. & Carroll, A.
Nat. Biotechnol. (2022).
Wagner, J., Olson, N. D., Harris, L., Khan, Z., Farek, J., Mahmoud, M., Stankovic, A., Kovacevic, V., Yoo, B., Miller, N., Rosenfeld, J. A., Ni, B., Zarate, S., Kirsche, M., Aganezov, S., Schatz, M. C., Narzisi, G., Byrska-Bishop, M., Clarke, W., Evani, U. S., Markello, C., Shafin, K., Zhou, X., Sidow, A., Bansal, V., Ebert, P., Marschall, T., Lansdorp, P., Hanlon, V., Mattsson, C.-A., Barrio, A. M., Fiddes, I. T., Xiao, C., Fungtammasan, A., Chin, C.-S., Wenger, A. M., Rowell, W. J., Sedlazeck, F. J., Carroll, A., Salit, M. & Zook, J. M.
Cell Genom 2, (2022).
Markello, C., Huang, C., Rodriguez, A., Carroll, A., Chang, P.-C., Eizenga, J., Markello, T., Haussler, D. & Paten, B.
Genome Res. 32, 893–903 (2022).
Goenka, S. D., Gorzynski, J. E., Shafin, K., Fisk, D. G., Pesout, T., Jensen, T. D., Monlong, J., Chang, P.-C., Baid, G., Bernstein, J. A., Christle, J. W., Dalton, K. P., Garalde, D. R., Grove, M. E., Guillory, J., Kolesnikov, A., Nattestad, M., Ruzhnikov, M. R. Z., Samadi, M., Sethia, A., Spiteri, E., Wright, C. J., Xiong, K., Zhu, T., Jain, M., Sedlazeck, F. J., Carroll, A., Paten, B. & Ashley, E. A.
Gorzynski, J. E., Goenka, S. D., Shafin, K., Jensen, T. D., Fisk, D. G., Grove, M. E., Spiteri, E., Pesout, T., Monlong, J., Baid, G., Bernstein, J. A., Ceresnak, S., Chang, P.-C., Christle, J. W., Chubb, H., Dalton, K. P., Dunn, K., Garalde, D. R., Guillory, J., Knowles, J. W., Kolesnikov, A., Ma, M., Moscarello, T., Nattestad, M., Perez, M., Ruzhnikov, M. R. Z., Samadi, M., Setia, A., Wright, C., Wusthoff, C. J., Xiong, K., Zhu, T., Jain, M., Sedlazeck, F. J., Carroll, A., Paten, B. & Ashley, E. A.
N. Engl. J. Med. (2022).
Gorzynski, J. E., Goenka, S. D., Shafin, K., Jensen, T. D., Fisk, D. G., Grove, M. E., Spiteri, E., Pesout, T., Monlong, J., Bernstein, J. A., Ceresnak, S., Chang, P.-C., Christle, J. W., Chubb, H., Dunn, K., Garalde, D. R., Guillory, J., Ruzhnikov, M. R. Z., Wright, C., Wusthoff, C. J., Xiong, K., Hollander, S. A., Berry, G. J., Jain, M., Sedlazeck, F. J., Carroll, A., Paten, B. & Ashley, E. A.
Circ Genom Precis Med 15, e003591 (2022).
Sirén, J., Monlong, J., Chang, X., Novak, A. M., Eizenga, J. M., Markello, C., Sibbesen, J. A., Hickey, G., Chang, P.-C., Carroll, A., Gupta, N., Gabriel, S., Blackwell, T. W., Ratan, A., Taylor, K. D., Rich, S. S., Rotter, J. I., Haussler, D., Garrison, E. & Paten, B.
Science 374 (2021).
McCaw, Z. R., Colthurst, T., Yun, T., Furlotte, N. A., Carroll, A., Alipanahi, B., McLean, C. Y. & Hormozdiari, F.
Nat. Commun. 13, 241 (2022).
O’Connell, J., Yun, T., Moreno, M., Li, H., Litterman, N., Kolesnikov, A., Noblin, E., Chang, P.-C.,Shastri, A., Dorfman, E. H., Shringarpure, S., Auton, A., Carroll, A. & McLean, C. Y.
Communications Biology 4, 1–9 (2021).
Shafin, K., Pesout, T., Chang, P.-C., Nattestad, M., Kolesnikov, A., Goel, S., Baid, G., Kolmogorov, M., Eizenga, J. M., Miga, K. H., Carnevali, P., Jain, M., Carroll, A. & Paten, B.
Nat. Methods 18, 1322–1332 (2021). [readcube]
Baid, G., Cook, D. E., Shafin, K., Yun, T., Llinares-López, F., Berthet, Q., Wenger, A. M., Rowell, W. J., Nattestad, M., Yang, H., Kolesnikov, A., Töpfer, A., Ammar, W., Vert, J.-P., Vaswani, A., McLean, C. Y., Chang, P.-C. & Carroll, A.
bioRxiv 2021.08.31.458403 (2021).
Alipanahi, B., Hormozdiari, F., Behsaz, B., Cosentino, J., McCaw, Z. R., Schorsch, E., Sculley, D., Dorfman, E. H., Foster, P. J., Peng, L. H., Phene, S., Hammel, N., Carroll, A., Khawaja, A. P. & McLean, C. Y.
Am. J. Hum. Genet. (2021).
Yun, T., Li, H., Chang, P-C., Lin, M., Carroll, A., & McLean, C. Y.
Bioinformatics 36, 5582-5589 (2021).
Yadlowsky, S., Yun, T., McLean, C. & D’Amour, A.
arXiv [stat.ML] (2021).
Alipanahi, B., Hormozdiari, F., Behsaz, B., Cosentino, J., McCaw, Z. R., Schorsch, E., Sculley, D., Dorfman, E. H., Phene, S., Hammel, N., Carroll, A., Khawaja, A. P. & McLean, C. Y.
arXiv [q-bio.GN] (2020).
McLean, C. Y., Hwang, Y., Poplin, R. & DePristo, M. A.
Bioinformatics 35, 4389–4391 (2019).
Wenger, A. M., Peluso, P., Rowell, W. J., Chang, P.-C., Hall, R. J., Concepcion, G. T., Ebler, J., Fungtammasan, A., Kolesnikov, A., Olson, N. D., Töpfer, A., Alonge, M., Mahmoud, M., Qian, Y., Chin, C.-S., Phillippy, A. M., Schatz, M. C., Myers, G., DePristo, M. A., Ruan, J., Marschall, T., Sedlazeck, F. J., Zook, J. M., Li, H., Koren, S., Carroll, A., Rank, D. R. & Hunkapiller, M. W.
Nat. Biotechnol. 37, 1155–1162 (2019). [readcube]
Poplin, R., Chang, P.-C., Alexander, D., Schwartz, S., Colthurst, T., Ku, A., Newburger, D., Dijamco, J., Nguyen, N., Afshar, P. T., Gross, S. S., Dorfman, L., McLean, C. Y. & DePristo, M. A.
Nat. Biotechnol. 36, 983–987 (2018). [readcube]
Telenti, A., Lippert, C., Chang, P.-C. & DePristo, M.
Hum. Mol. Genet. 27, R63–R71 (2018).
Kelley, D. R., Reshef, Y. A., Bileschi, M., Belanger, D., McLean, C. Y. & Snoek, J.
Genome Res. 28, 739–750 (2018).
Google Health Studies
by Nicholas Allen
Google Keyword Blog | 23-May-2022
by Jon Morgan & Paul Eastham
Google Keyword Blog | 9-Dec-2020
Health Sensors and Signals
Google Keyword Blog | 25-Jan-2024
by Stephanie Scott
by Xiaoran "Van" Fan & Trausti Thormundsson
Google Research Blog | 27-Oct-2023
by Michael Dixon & Reena Singhal Lee
Google Research Blog | 9-Nov-2021
by Ashton Udall
Google Keyword Blog | 16-Mar-2021
Google Research Blog | 16-Mar-2021
by Shwetak Patel
Google Keyword Blog | 4-Feb-2021
Fan, X., Pearl, D., Howard, R., Shangguan, L. & Thormundsson, T. APG.
Proceedings of the 29th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking 1–15. Association for Computing Machinery (2023).
Yang, Y., Liu, X., Wu, J., Borac, S., Katabi, D., Poh, M.-Z. & McDuff, D.
arXiv [cs.LG] (ICLR 2023).
Bae, S., Borac, S., Emre, Y., Wang, J., Wu, J., Kashyap, M., Kang, S.-H., Chen, L., Moran, M., Cannon, J., Teasley, E. S., Chai, A., Liu, Y., Wadhwa, N., Krainin, M., Rubinstein, M., Maciel, A., McConnell, M. V., Patel, S., Corrado, G. S., Taylor, J. A., Zhan, J. & Po, M. J.
bioRxiv (2021).
Dixon, M., Schneider, L. D., Yu, J., Hsu, J., Pathak, A., Shin, D., Lee, R. S., Malhotra, M., Mixter, K., McConnell, M. V., Taylor, J. A., Patel, S. N.,
Google Whitepaper (2021).
Large Language Models
Blog Posts [more at Med-PaLM site ]
by Yossi Matias
by Dr. Ivor Horn
by Alan Karthikesalingam & Vivek Natarajan
Google Research Blog | 12-Jan-2024
by Yossi Matias & Aashima Gupta
Google Cloud Blog | 13-Dec-2023
by Michael Howell
by Aashima Gupta & Greg Corrado
Google Cloud Blog | 29-Aug-2023
by Greg Corrado and Yossi Matias
Google Research Blog | 3-Aug-2023
by James Manyika & Jeff Dean
Google Keyword Blog | 25-May-2023
by Aashima Gupta & Amy Waldron
Google Cloud Blog | 13-April-2023
Pfohl, S. R., Cole-Lewis, H., Sayres, R., Neal, D., Asiedu, M., Dieng, A., Tomasev, N., Rashid, Q. M., Azizi, S., Rostamzadeh, N., McCoy, L. G., Celi, L. A., Liu, Y., Schaekermann, M., Walton, A., Parrish, A., Nagpal, C., Singh, P., Dewitt, A., Mansfield, P., Prakash, S., Heller, K., Karthikesalingam, A., Semturs, C., Barral, J., Corrado, G., Matias, Y., Smith-Loud, J., Horn, I. & Singhal, K.
arXiv [cs.CY] (2024).
Tu, T., Azizi, S., Driess, D., Schaekermann, M., Amin, M., Chang, P.-C., Carroll, A., Lau, C., Tanno, R., Ktena, I., Mustafa, B., Chowdhery, A., Liu, Y., Kornblith, S., Fleet, D., Mansfield, P., Prakash, S., Wong, R., Virmani, S., Semturs, C., Sara Mahdavi, S., Green, B., Dominowska, E., Aguera y Arcas, B., Barral, J., Webster, D., Corrado, G. S., Matias, Y., Singhal, K., Florence, P., Karthikesalingam, A. & Natarajan, V.
NEJM AI (2024).
Tu, T., Palepu, A., Schaekermann, M., Saab, K., Freyberg, J., Tanno, R., Wang, A., Li, B., Amin, M., Tomasev, N., Azizi, S., Singhal, K., Cheng, Y., Hou, L., Webson, A., Kulkarni, K., Sara Mahdavi, S., Semturs, C., Gottweis, J., Barral, J., Chou, K., Corrado, G. S., Matias, Y., Karthikesalingam, A. & Natarajan, V.
arXiv [cs.AI] (2024).
Goel, A., Gueta, A., Gilon, O., Liu, C., Erell, S., Nguyen, L. H., Hao, X., Jaber, B., Reddy, S., Kartha, R., Steiner, J., Laish, I. & Feder, A.
arXiv [cs.CL] (2023).
McDuff, D., Schaekermann, M., Tu, T., Palepu, A., Wang, A., Garrison, J., Singhal, K., Sharma, Y., Azizi, S., Kulkarni, K., Hou, L., Cheng, Y., Liu, Y., Sara Mahdavi, S., Prakash, S., Pathak, A., Semturs, C., Patel, S., Webster, D. R., Dominowska, E., Gottweis, J., Barral, J., Chou, K., Corrado, G. S., Matias, Y., Sunshine, J., Karthikesalingam, A. & Natarajan, V.
arXiv [cs.CY] (2023)
Tanno, R., Barrett, D. G. T., Sellergren, A., Ghaisas, S., Dathathri, S., See, A., Welbl, J., Singhal, K., Azizi, S., Tu, T., Schaekermann, M., May, R., Lee, R., Man, S., Ahmed, Z., Mahdavi, S., Belgrave, D., Natarajan, V., Shetty, S., Kohli, P., Huang, P.-S., Karthikesalingam, A. & Ktena, I.
arXiv [eess.IV] (2023).
Galatzer-Levy, I. R., McDuff, D., Natarajan, V., Karthikesalingam, A. & Malgaroli, M.
Xu, S., Yang, L., Kelly, C., Sieniek, M., Kohlberger, T., Ma, M., Weng, W.-H., Kiraly, A., Kazemzadeh, S., Melamed, Z., Park, J., Strachan, P., Liu, Y., Lau, C., Singh, P., Chen, C., Etemadi, M., Kalidindi, S. R., Matias, Y., Chou, K., Corrado, G. S., Shetty, S., Tse, D., Prabhakara, S., Golden, D., Pilgrim, R., Eswaran, K. & Sellergren, A.
arXiv [cs.CV] (2023).
Belyaeva, A., Cosentino, J., Hormozdiari, F., Eswaran, K., Shetty, S., Corrado, G., Carroll, A., McLean, C. Y. & Furlotte, N. A.
arXiv [q-bio.QM] (2023).
Liu, X., McDuff, D., Kovacs, G., Galatzer-Levy, I., Sunshine, J., Zhan, J., Poh, M.-Z., Liao, S., Di Achille, P. & Patel, S.
Singhal, K., Tu, T., Gottweis, J., Sayres, R., Wulczyn, E., Hou, L., Clark, K., Pfohl, S., Cole-Lewis, H., Neal, D., Schaekermann, M., Wang, A., Amin, M., Lachgar, S., Mansfield, P., Prakash, S., Green, B., Dominowska, E., Aguera y Arcas, B., Tomasev, N., Liu, Y., Wong, R., Semturs, C., Sara Mahdavi, S., Barral, J., Webster, D., Corrado, G. S., Matias, Y., Azizi, S., Karthikesalingam, A. & Natarajan, V.
Singhal, K., Azizi, S., Tu, T., Sara Mahdavi, S., Wei, J., Chung, H. W., Scales, N., Tanwani, A., Cole-Lewis, H., Pfohl, S., Payne, P., Seneviratne, M., Gamble, P., Kelly, C., Scharli, N., Chowdhery, A., Mansfield, P., Aguera y Arcas, B., Webster, D., Corrado, G. S., Matias, Y., Chou, K., Gottweis, J., Tomasev, N., Liu, Y., Rajkomar, A., Barral, J., Semturs, C., Karthikesalingam, A. & Natarajan, V.
Medical Audio
by Laurent El Shafey and Izhak Shafran
16-Aug-2019
by Julie Cattiau
Google Keyword Blog | 7-May-2019
by Katherine Chou and Chung-Cheng Chiu
Google Research Blog | 21-Nov-2017
Blankemeier, L., Baur, S., Weng, W.-H., Garrison, J., Matias, Y., Prabhakara, S., Ardila, D. & Nabulsi, Z.
arXiv [cs.LG] (2023).
Shafran, I., Du, N., Tran, L., Perry, A., Keyes, L., Knichel, M., Domin, A., Huang, L., Chen, Y., Li, G., Wang, M., El Shafey, L., Soltau, H. & Paul, J. S.
Proceedings of the Language Resources and Evaluation Conference. arXiv [cs.CL] (2020).
Du, N., Chen, K., Kannan, A., Tran, L., Chen, Y. & Shafran, I.
Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of the Association of Computational Linguistics. arXiv [cs.LG] (2019).
Rajkomar, A., Kannan, A., Chen, K., Vardoulakis, L., Chou, K., Cui, C., & Dean, J.
JAMA Intern. Med. 179, 836–838 (2019).
El Shafey, L., Soltau, H. & Shafran, I.
Proceedings of Interspeech. arXiv [cs.CL] (2019).
Du, N., Wang, M., Tran, L., Li, G. & Shafran, I.
Proc. Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. arXiv [cs.CL] (2019).
Chiu, C.-C., Tripathi, A., Chou, K., Co, C., Jaitly, N., Jaunzeikare, D., Kannan, A., Nguyen, P., Sak, H., Sankar, A., Tansuwan, J., Wan, N., Wu, Y., & Zhang X.
arXiv [cs.CL] (2017).
Medical Records
by Alvin Rajkoma and Eric Loreaux
Google Research Blog | 24-Jan-2023
by Jinsung Yoon and Sercan O. Arik
Google Research Blog | 21-Dec-2022
by Subhrajit Roy & Diana Mincu
Google Research Blog | 22-Jul-2021
by Kathryn Rough & Alvin Rajkomar
Google Research Blog | 2-Apr-2020
by Alvin Rajkomar & Eyal Oren
Google Research Blog | 22-Jan-2019
by Demis Hassabis & Mustafa Suleyman & Dominic King
DeepMind Blog | 13-Nov-2018
Google Research Blog | 8-May-2018
by Patrik Sundberg & Eyal Oren
Google Research Blog | 2-Mar-2018
Seneviratne, M. G., Li, R. C., Schreier, M., Lopez-Martinez, D., Patel, B. S., Yakubovich, A., Kemp, J. B., Loreaux, E., Gamble, P., El-Khoury, K., Vardoulakis, L., Wong, D., Desai, J., Chen, J. H., Morse, K. E., Downing, N. L., Finger, L. T., Chen, M.-J. & Shah, N.
BMJ Health Care Inform 29, (2022).
Loreaux, E., Yu, K., Kemp, J., Seneviratne, M., Chen, C., Roy, S., Protsyuk, I., Harris, N., D’Amour, A., Yadlowsky, S. & Chen, M.-J.
Rajkomar, A., Loreaux, E., Liu, Y., Kemp, J., Li, B., Chen, M.-J., Zhang, Y., Mohiuddin, A. & Gottweis, J.
Nat. Commun. 13, 7456 (2022).
Stupp, D., Barequet, R., Lee, I.-C., Oren, E., Feder, A., Benjamini, A., Hassidim, A., Matias, Y., Ofek, E. & Rajkomar, A.
Roy, S., Mincu, D., Loreaux, E., Mottram, A., Protsyuk, I., Harris, N., Xue, Y., Schrouff, J., Montgomery, H., Connell, A., Tomasev, N., Karthikesalingam, A. & Seneviratne, M.
J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. (2021).
Tomašev, N., Harris, N., Baur, S., Mottram, A., Glorot, X., Rae, J. W., Zielinski, M., Askham, H., Saraiva, A., Magliulo, V., Meyer, C., Ravuri, S., Protsyuk, I., Connell, A., Hughes, C. O., Karthikesalingam, A., Cornebise, J., Montgomery, H., Rees, G., Laing, C., Baker, C. R., Osborne, T. F., Reeves, R., Hassabis, D., King, D., Suleyman, M., Back, T., Nielson, C., Seneviratne, M. G., Ledsam, J. R. & Mohamed, S.
Nat. Protoc. 1–23 (2021). [readcube]
Xue Y, Du N, Mottram A, Seneviratne A, Dai AM.
NeurIPS (2020).
Xue Y, Zhou D, Du N, Dai A, Xu Z, Zhang K, Cui C.
KDD (2020).
Choi E, Xu Z, Li Y, Dusenberry MW, Flores G, Xue Y, Dai AM.
AAAI (2020).
Dusenberry MW, Tran D, Choi E, Kemp J, Nixon J, Jerfel G, Heller K, & Dai AM.
ACM CHIL (2020).
Hardt M, Rajkomar A, Flores G, Dai A, Howell M, Corrado G, Cui C, & Hardt M.
Rough, K., Dai, A. M., Zhang, K., Xue, Y., Vardoulakis, L. M., Cui, C., Butte, A. J., Howell, M. D. & Rajkomar, A.
Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 108, 145–154 (2020).
Tomašev, N., Glorot, X., Rae, J. W., Zielinski, M., Askham, H., Saraiva, A., Mottram, A., Meyer, C., Ravuri, S., Protsyuk, I., Connell, A., Hughes, C. O., Karthikesalingam, A., Cornebise, J., Montgomery, H., Rees, G., Laing, C., Baker, C. R., Peterson, K., Reeves, R., Hassabis, D., King, D., Suleyman, M., Back, T., Nielson, C., Ledsam, J. R. & Mohamed, S.
Nature 572, 116–119 (2019). [readcube]
Connell, A., Montgomery, H., Martin, P., Nightingale, C., Sadeghi-Alavijeh, O., King, D., Karthikesalingam, A., Hughes, C., Back, T., Ayoub, K., Suleyman, M., Jones, G., Cross, J., Stanley, S., Emerson, M., Merrick, C., Rees, G., Laing, C. & Raine, R.
npj Digit Med 2, 67 (2019).
Connell A., Raine R., Martin P., Barbosa E.C., Morris S., Nightingale C., Sadeghi-Alavijeh O., King D., Karthikesalingam A., Hughes C., Back T., Ayoub K., Suleyman M., Jones G., Cross J., Stanley S., Emerson M., Merrick C., Rees G., Montgomery H., & Laing C.
J Med Internet Res 21(7):e13147 (2019).
Connell A, Black G, Montgomery H, Martin P, Nightingale C, King D, Karthikesalingam A, Hughes C, Back T, Ayoub K, Suleyman M, Jones G, Cross J, Stanley S, Emerson M, Merrick C, Rees G, Laing C, & Raine R.
J Med Internet Res 21(7):e13143 (2019).
Kemp J, Rajkomar A, & Dai AM.
arXiv [cs.LG] (2019).
Pfohl SR, Dai AM, & Heller K.
Xue Y, Zhou D, Du N, Dai AM, Xu Z, Zhang K,& Cui C.
Zhang K, Xue Y, Flores G, Rajkomar A, Cui C, & Dai AM.
Rajkomar A, Oren E, Chen K, Dai AM, Hajaj N, Hardt M, Liu PJ, Liu X, Marcus J, Sun M, Sundberg P, Yee H, Zhang K, Zhang Y, Flores G, Duggan GE, Irvine J, Le Q, Litsch K, Mossin A, Tansuwan J, Wang, Wexler J, Wilson J, Ludwig D, Volchenboum SL, Chou K, Pearson M, Madabushi S, Shah NH, Butte AJ, Howell MD, Cui C, Corrado GS, Dean J.
npj Digital Med 1, 18 (2018).
Novel Biomarkers
by Boris Babenko & Akib Uddin
Google Research Blog | 24-Mar-2023
by Boris Babenko & Naama Hammel
by Terry Spitz & Jim Winkens
Google Keyword Blog | 18-May-2020
by Jason Yim, Reena Chopra, Jeffrey De Fauw & Joseph Ledsam
DeepMind Blog | 18-May-2020
by Akinori Mitani
Google Keyword Blog | 28-Jan-2020
Google Research Blog | 2-Feb-2018
Lang, O., Yaya-Stupp, D., Traynis, I., Cole-Lewis, H., Bennett, C. R., Lyles, C. R., Lau, C., Irani, M., Semturs, C., Webster, D. R., Corrado, G. S., Hassidim, A., Matias, Y., Liu, Y., Hammel, N. & Babenko, B.
EBioMedicine 102, 105075 (2024).
Ahadi, S., Wilson, K. A., Jr, Babenko, B., McLean, C. Y., Bryant, D., Pritchard, O., Kumar, A., Carrera, E. M., Lamy, R., Stewart, J. M., Varadarajan, A., Berndl, M., Kapahi, P. & Bashir, A.
Elife 12, (2023).
Babenko, B., Traynis, I., Chen, C., Singh, P., Uddin, A., Cuadros, J., Daskivich, L. P., Maa, A. Y., Kim, R., Kang, E. Y.-C., Matias, Y., Corrado, G. S., Peng, L., Webster, D. R., Semturs, C., Krause, J., Varadarajan, A. V., Hammel, N. & Liu, Y.
The Lancet Digital Health (2023).
Babenko, B., Mitani, A., Traynis, I., Kitade, N., Singh, P., Maa, A. Y., Cuadros, J., Corrado, G. S., Peng, L., Webster, D. R., Varadarajan, A., Hammel, N. & Liu, Y.
Nat Biomed Eng (2022).
Liu, X., Ali, T. K., Singh, P., Shah, A., McKinney, S. M., Ruamviboonsuk, P., Turner, A. W., Keane, P. A., Chotcomwongse, P., Nganthavee, V., Chia, M., Huemer, J., Cuadros, J., Raman, R., Corrado, G. S., Peng, L., Webster, D. R., Hammel, N., Varadarajan, A. V., Liu, Y., Chopra, R. & Bavishi, P.
Ophthalmol Retina (2022).
Mitani, A., Traynis, I., Singh, P., Corrado, G. S., Webster, D. R., Peng, L. H., Varadarajan, A. V., Liu, Y. & Hammel, N.
doi:10.1101/2021.12.30.21268488
Bora, A., Balasubramanian, S., Babenko, B., Virmani, S., Venugopalan, S., Mitani, A., de Oliveira Marinho, G., Cuadros, J., Ruamviboonsuk, P., Corrado, G. S., Peng, L., Webster, D. R., Varadarajan, A. V., Hammel, N., Liu, Y. & Bavishi, P.
The Lancet Digital Health (2020). doi:10.1016/S2589-7500(20)30250-8
Moraes, G., Fu, D. J., Wilson, M., Khalid, H., Wagner, S. K., Korot, E., Ferraz, D., Faes, L., Kelly, C. J., Spitz, T., Patel, P. J., Balaskas, K., Keenan, T. D. L., Keane, P. A. & Chopra, R.
Ophthalmology (2020). doi:10.1016/j.ophtha.2020.09.025
Narayanaswamy, A., Venugopalan, S., Webster, D. R., Peng, L., Corrado, G. S., Ruamviboonsuk, P., Bavishi, P., Brenner, M., Nelson, P. C. & Varadarajan, A. V.
Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2020 273–283 (2020). doi:10.1007/978-3-030-59710-8_27 arXiv
Yim, J., Chopra, R., Spitz, T., Winkens, J., Obika, A., Kelly, C., Askham, H., Lukic, M., Huemer, J., Fasler, K., Moraes, G., Meyer, C., Wilson, M., Dixon, J., Hughes, C., Rees, G., Khaw, P. T., Karthikesalingam, A., King, D., Hassabis, D., Suleyman, M., Back, T., Ledsam, J. R., Keane, P. A. & De Fauw, J.
Varadarajan, A. V., Bavishi, P., Ruamviboonsuk, P., Chotcomwongse, P., Venugopalan, S., Narayanaswamy, A., Cuadros, J., Kanai, K., Bresnick, G., Tadarati, M., Silpa-Archa, S., Limwattanayingyong, J., Nganthavee, V., Ledsam, J. R., Keane, P. A., Corrado, G. S., Peng, L. & Webster, D. R.
Nat. Commun. 11, 130 (2020).
Mitani, A., Huang, A., Venugopalan, S., Corrado, G. S., Peng, L., Webster, D. R., Hammel, N., Liu, Y. & Varadarajan, A. V.
Nat Biomed Eng (2019). [readcube]
Babenko, B., Balasubramanian, S., Blumer, K. E., Corrado, G. S., Peng, L., Webster, D. R., Hammel, N. & Varadarajan, A. V.
arXiv [cs.CV] (2019).
aradarajan, A.V., Poplin, R., Blumer, K., Angermueller, C., Lesdam, J., Chopra, R., Keane, P.A., Corrado, G. S., Peng, L., Webster, D. R.
Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 59, 2861–2868 (2018).
Poplin, R., Varadarajan, A. V., Blumer, K., Liu, Y., McConnell, M. V., Corrado, G. S., Peng, L., & Webster, D. R.
Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2, 158–164 (2018). [readcube]
Open Health Stack
Blog Posts [more at OHS Blog ]
by Yossi Mattia & Shravya Shetty
by Richa Tiwari
Open Health Stack Blog | 10-Oct-2023.
Open Health Stack Blog | 2-Sep-2023.
by Abirami Sukumaran & Omar Ismail
Google Cloud Blog | 17-Aug-2023.
by Fred Hersch
Google Keyword Blog | 14-Mar-2023.
by Katherine Chou & Sudhi Herle
Android Developers Blog | 24-Mar-2022
by Fred Hersch & Jing Tang
Mehl, G. L., Seneviratne, M. G., Berg, M. L., Bidani, S., Distler, R. L., Gorgens, M., Kallander, K. E., Labrique, A. B., Landry, M. S., Leitner, C., Lubell-Doughtie, P. B., Marcelo, A. D., Matias, Y., Nelson, J., Nguyen, V., Nsengimana, J. P., Orton, M., Otzoy Garcia, D. R., Oyaole, D. R., Ratanaprayul, N., Roth, S., Schaefer, M. P., Settle, D., Tang, J., Tien-Wahser, B., Wanyee, S. & Hersch, F.
Oxf Open Digit Health, (2023).
Digital Public Goods Alliance - Promoting digital public goods to create a more equitable world (2023). 14-Dec-2023.
Google Open Source Blog | 17-May-2023
by Justin Krogue, Yun Liu, Po-Hsuan Cameron Chen & Ellery A
Nature Portfolio Health Community Blog | 10-May-2023
by Ellery Wulczyn and Yun Liu
Google Research Blog | 14-Mar-2023
Google Cloud Blog | 12-Dec-2022
Verily Blog | 16-Mar-2022
by Po-Hsuan Cameron Chen & Maggie Demkin
Google Research Blog | 11-Feb-2022
by Po-Hsuan Cameron Chen & Yun Liu
Google Keyword Blog | 23-Sept-2021
by People + AI Research
People + AI Research Blog | 14-May-2021
by Dave Steiner, Yun Liu, Craig Mermel, Kurt Zatloukal, Heimo Muller, Markus Plass
npj Digital Medicine Blog | 19-Apr-2021
Google Cloud Blog | 2-Sep-2020
by Kunal Nagpal & Craig Mermel
Google Keyword Blog | 23-Jul-2020
by Narayan Hedge & Carrie Cai
Google Research Blog | 19-July-2019
by Martin Stumpe & Craig Mermel
Google Research Blog | 16-Nov-2018
Google Research Blog | 12-Oct-2018
Google Research Blog | 16-Apr-2018
by Martin Stumpe & Lily Peng
Google Research Blog | 3-Mar-2017
McNeil, C., Wong, P. F., Sridhar, N., Wang, Y., Santori, C., Wu, C.-H., Homyk, A., Gutierrez, M., Behrooz, A., Tiniakos, D., Burt, A. D., Pai, R. K., Tekiela, K., Cameron Chen, P.-H., Fischer, L., Martins, E. B., Seyedkazemi, S., Freedman, D., Kim, C. C. & Cimermancic, P.
Mod. Pathol. 37, 100377 (2023).
Lai, J., Ahmed, F., Vijay, S., Jaroensri, T., Loo, J., Vyawahare, S., Agarwal, S., Jamil, F., Matias, Y., Corrado, G. S., Webster, D. R., Krause, J., Liu, Y., Chen, P.-H. C., Wulczyn, E. & Steiner, D. F.
Krogue, J. D., Azizi, S., Tan, F., Flament-Auvigne, I., Brown, T., Plass, M., Reihs, R., Müller, H., Zatloukal, K., Richeson, P., Corrado, G. S., Peng, L. H., Mermel, C. H., Liu, Y., Chen, P.-H. C., Gombar, S., Montine, T., Shen, J., Steiner, D. F. & Wulczyn, E.
Commun. Med. 3, 59 (2023).
L’Imperio, V., Wulczyn, E., Plass, M., Müller, H., Tamini, N., Gianotti, L., Zucchini, N., Reihs, R., Corrado, G. S., Webster, D. R., Peng, L. H., Chen, P.-H. C., Lavitrano, M., Liu, Y., Steiner, D. F., Zatloukal, K. & Pagni, F.
JAMA Netw Open 6, e2254891 (2023).
Jaroensri, R., Wulczyn, E., Hegde, N., Brown, T., Flament-Auvigne, I., Tan, F., Cai, Y., Nagpal, K., Rakha, E. A., Dabbs, D. J., Olson, N., Wren, J. H., Thompson, E. E., Seetao, E., Robinson, C., Miao, M., Beckers, F., Corrado, G. S., Peng, L. H., Mermel, C. H., Liu, Y., Steiner, D. F. & Chen, P.-H. C.
npj Breast Cancer 8, 1–12 (2022).
Bulten, W., Kartasalo, K., Chen, P.-H. C., Ström, P., Pinckaers, H., Nagpal, K., Cai, Y., Steiner, D. F., van Boven, H., Vink, R., Hulsbergen-van de Kaa, C., van der Laak, J., Amin, M. B., Evans, A. J., van der Kwast, T., Allan, R., Humphrey, P. A., Grönberg, H., Samaratunga, H., Delahunt, B., Tsuzuki, T., Häkkinen, T., Egevad, L., Demkin, M., Dane, S., Tan, F., Valkonen, M., Corrado, G. S., Peng, L., Mermel, C. H., Ruusuvuori, P., Litjens, G. & Eklund, M.
Nat. Med. 1–10 (2022).
Sadhwani, A., Chang, H.-W., Behrooz, A., Brown, T., Auvigne-Flament, I., Patel, H., Findlater, R., Velez, V., Tan, F., Tekiela, K., Wulczyn, E., Yi, E. S., Mermel, C. H., Hanks, D., Chen, P.-H. C., Kulig, K., Batenchuk, C., Steiner, D. F. & Cimermancic, P.
Sci. Rep. 11, 1–11 (2021).
Gamble, P., Jaroensri, R., Wang, H., Tan, F., Moran, M., Brown, T., Flament-Auvigne, I., Rakha, E. A., Toss, M., Dabbs, D. J., Regitnig, P., Olson, N., Wren, J. H., Robinson, C., Corrado, G. S., Peng, L. H., Liu, Y., Mermel, C. H., Steiner, D. F. & Chen, P.-H. C.
Communications Medicine 1, 1–12 (2021).
Wulczyn, E., Nagpal, K., Symonds, M., Moran, M., Plass, M., Reihs, R., Nader, F., Tan, F., Cai, Y., Brown, T., Flament-Auvigne, I., Amin, M. B., Stumpe, M. C., Müller, H., Regitnig, P., Holzinger, A., Corrado, G. S., Peng, L. H., Chen, P.-H. C., Steiner, D. F., Zatloukal, K., Liu, Y. & Mermel, C. H.
Communications Medicine 1, 1–8 (2021).
Cai, C.J., Steiner, D., Wilcox, L., Terry, M. and Winter, S.
Proceedings of the ACM SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, ACM (2021).
Wulczyn, E., Steiner, D. F., Moran, M., Plass, M., Reihs, R., Tan, F., Flament-Auvigne, I., Brown, T., Regitnig, P., Chen, P.-H. C., Hegde, N., Sadhwani, A., MacDonald, R., Ayalew, B., Corrado, G. S., Peng, L. H., Tse, D., Müller, H., Xu, Z., Liu, Y., Stumpe, M. C., Zatloukal, K. & Mermel, C. H.
npj Digital Medicine 4, 1–13 (2021).
Steiner, D. F., Nagpal, K., Sayres, R., Foote, D. J., Wedin, B. D., Pearce, A., Cai, C. J., Winter, S. R., Symonds, M., Yatziv, L., Kapishnikov, A., Brown, T., Flament-Auvigne, I., Tan, F., Stumpe, M. C., Jiang, P.-P., Liu, Y., Chen, P.-H. C., Corrado, G. S., Terry, M. & Mermel, C. H.
JAMA Netw Open 3, e2023267–e2023267 (2020).
Nagpal, K., Foote, D., Tan, F., Liu, Y., Chen, P.-H. C., Steiner, D. F., Manoj, N., Olson, N., Smith, J. L., Mohtashamian, A., Peterson, B., Amin, M. B., Evans, A. J., Sweet, J. W., Cheung, C., van der Kwast, T., Sangoi, A. R., Zhou, M., Allan, R., Humphrey, P. A., Hipp, J. D., Gadepalli, K., Corrado, G. S., Peng, L. H., Stumpe, M. C. & Mermel, C. H.
JAMA Oncol (2020).
Wulczyn, E., Steiner, D. F., Xu, Z., Sadhwani, A., Wang, H., Flament-Auvigne, I., Mermel, C. H., Chen, P.-H. C., Liu, Y. & Stumpe, M. C.
PLOS ONE 15, e0233678 (2020).
Kohlberger, T., Liu, Y., Moran, M., Chen, P.-H. C., Brown, T., Hipp, J. D., Mermel, C. H. & Stumpe, M. C.
J. Pathol. Inform. 10, 39 (2019).
Chen, P.C., Gadepalli, K., MacDonald, R., Liu, Y., Kadowaki, S., Nagpal, K., Kohlberger, T., Dean, J., Corrado, G.S., Hipp, J.D., Mermel, C.H., Stumpe, M. C.
Nat Med 25, 1453–1457 (2019). [readcube]
Liu, Y., Kohlberger, T., Norouzi, M., Dahl, G. E., Smith, J. L., Mohtashamian, A., Olson, N., Peng, L.H., Hipp, J.D., Stumpe, M.C. (2019).
Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 143, 859–868 (2019).
Hegde, N., Hipp, J. D., Liu, Y., Emmert-Buck, M., Reif, E., Smilkov, D., Terry, M., Cai, C. J., Amin, M. B., Mermel, C. H., Nelson, P. Q., Peng, L. H., Corrado, G. S. & Stumpe, M. C.
npj Digit Med 2, 56 (2019).
Cai, C.J., Winter, S., Steiner, D., Wilcox, L. and Terry, M.
Proceedings of the ACM on Human-computer Interaction, 3(CSCW), pp.1-24 (2019)
Cai, C.J., Reif, E., Hegde, N., Hipp, J., Kim, B., Smilkov, D., Wattenberg, M., Viegas, F., Corrado, G.S., Stumpe, M.C. and Terry, M.
In Proceedings of the 2019 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (pp. 1-14) (2019).
Nagpal, K., Foote, D., Liu, Y., Chen, P.H.C., Wulczyn, E., Tan, F., Olson, N., Smith, J.L., Mohtashamian, A., Wren, J.H., Corrado, G.S., MacDonald, R., Peng, L. H., Amin, M.B., Evans, A.J., Sanjoi, A.R., Mermel, C. H., Hipp, J. D., Stumpe, M. C.
npj Digit. Med. 2, 48 (2019).
Steiner, D. F., MacDonald, R., Liu, Y., Truszkowski, P., Hipp, J. D., Gammage, C., Thng, F., Peng, L., Stumpe, M.C.
Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 42, 1636–1646 (2018).
Liu, Y., Gadepalli, K., Norouzi, M., Dahl, G.E., Kohlberger, T., Boyko, A., Venugopalan, S., Timofeev, A., Nelson, P.Q., Corrado, G.S. and Hipp, J.D., Peng, L., Stumpe, M. C.
arXiv preprint arXiv:1703.02442 (2017).
Public & Environmental Health
by Kristina Gligoric
Nature Portfolio Health Community Blog | 22-Nov-2023
Google Keyword | 10-Oct-2023
by Charlotte Stanton
Google Africa Blog | 9-May-2023
by Kate Brandt
Google Keyword Blog | 29-Mar-2023
by Adam Sadilek & Xerxes Dotiwalla
Google Research Blog | 12-Nov-2019
Wong, K. L. M., Banke-Thomas, A., Olubodun, T., Macharia, P. M., Stanton, C., Sundararajan, N., Shah, Y., Prasad, G., Kansal, M., Vispute, S., Shekel, T., Ogunyemi, O., Gwacham-Anisiobi, U., Wang, J., Abejirinde, I.-O. O., Makanga, P. T., Afolabi, B. B. & Beňová, L.
Commun. Med. 4, 34 (2024).
Gligorić, K., Kamath, C., Weiss, D. J., Bavadekar, S., Liu, Y., Shekel, T., Schulman, K. & Gabrilovich, E.
Communications Medicine 3, 1–11 (2023).
Macharia, P. M., Wong, K. L. M., Olubodun, T., Beňová, L., Stanton, C., Sundararajan, N., Shah, Y., Prasad, G., Kansal, M., Vispute, S., Shekel, T., Gwacham-Anisiobi, U., Ogunyemi, O., Wang, J., Abejirinde, I.-O. O., Makanga, P. T., Afolabi, B. B. & Banke-Thomas, A.
Sci Data 10, 736 (2023).
Veneri, P., Kaufmann, T., Vispute, S., Shekel, T., Gabrilovich, E., Wellenius, G. A., Dijkstra, L. & Kansal, M.
(Organisation for Economic Co-Operation and Development (OECD), 2023).
Weintraub, R. L., Miller, K., Rader, B., Rosenberg, J., Srinath, S., Woodbury, S. R., Schultheiss, M. D., Kansal, M., Vispute, S., Serghiou, S., Flores, G., Kumok, A., Shekel, T., Gabrilovich, E., Ahmad, I., Chiang, M. E. & Brownstein, J. S.
Am. J. Public Health e1–e5 (2023).
Gupta, J., Tay, Y., Kamath, C., Tran, V., Metzler, D., Bavadekar, S., Sun, M. & Gabrilovich, E.
Proceedings of the 2022 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. 521–530 (2022).
Vaidyanathan, U., Sun, Y., Shekel, T., Chou, K., Galea, S., Gabrilovich, E. & Wellenius, G. A.
Sci. Rep. 12, 8946 (2022). [readcube]
Wahltinez, O., Cheung, A., Alcantara, R., Cheung, D., Daswani, M., Erlinger, A., Lee, M., Yawalkar, P., Lê, P., Navarro, O. P., Brenner, M. P. & Murphy, K.
Sci Data 9, 162 (2022).
Malahy, S., Sun, M., Spangler, K., Leibler, J., Lane, K., Bavadekar, S., Kamath, C., Kumok, A., Sun, Y., Gupta, J., Griffith, T., Boulanger, A., Young, M., Stanton, C., Mayer, Y., Smith, K., Shekel, T., Chou, K., Corrado, G., Levy, J., Szpiro, A., Gabrilovich, E. & Wellenius, G. A.
arXiv [cs.SI] (2021).
Bavadekar, S., Boulanger, A., Davis, J., Desfontaines, D., Gabrilovich, E., Gadepalli, K., Ghazi, B., Griffith, T., Gupta, J., Kamath, C., Kraft, D., Kumar, R., Kumok, A., Mayer, Y., Manurangsi, P., Patankar, A., Perera, I. M., Scott, C., Shekel, T., Miller, B., Smith, K., Stanton, C., Sun, M., Young, M. & Wellenius, G.
arXiv [cs.CR] (2021).
Woskie, L. R., Hennessy, J., Espinosa, V., Tsai, T. C., Vispute, S., Jacobson, B. H., Cattuto, C., Gauvin, L., Tizzoni, M., Fabrikant, A., Gadepalli, K., Boulanger, A., Pearce, A., Kamath, C., Schlosberg, A., Stanton, C., Bavadekar, S., Abueg, M., Hogue, M., Oplinger, A., Chou, K., Corrado, G., Shekel, T., Jha, A. K., Wellenius, G. A. & Gabrilovich, E.
PLoS One 16, e0253071 (2021).
Wellenius, G. A., Vispute, S., Espinosa, V., Fabrikant, A., Tsai, T. C., Hennessy, J., Dai, A., Williams, B., Gadepalli, K., Boulanger, A., Pearce, A., Kamath, C., Schlosberg, A., Bendebury, C., Mandayam, C., Stanton, C., Bavadekar, S., Pluntke, C., Desfontaines, D., Jacobson, B. H., Armstrong, Z., Gipson, B., Wilson, R., Widdowson, A., Chou, K., Oplinger, A., Shekel, T., Jha, A. K. & Gabrilovich, E.
Nat. Commun. 12, 3118 (2021).
Venkatramanan, S., Sadilek, A., Fadikar, A., Barrett, C. L., Biggerstaff, M., Chen, J., Dotiwalla, X., Eastham, P., Gipson, B., Higdon, D., Kucuktunc, O., Lieber, A., Lewis, B. L., Reynolds, Z., Vullikanti, A. K., Wang, L. & Marathe, M.
Nat. Commun. 12, 726 (2021).
Weiss, D. J., Nelson, A., Vargas-Ruiz, C. A., Gligorić, K., Bavadekar, S., Gabrilovich, E., Bertozzi-Villa, A., Rozier, J., Gibson, H. S., Shekel, T., Kamath, C., Lieber, A., Schulman, K., Shao, Y., Qarkaxhija, V., Nandi, A. K., Keddie, S. H., Rumisha, S., Amratia, P., Arambepola, R., Chestnutt, E. G., Millar, J. J., Symons, T. L., Cameron, E., Battle, K. E., Bhatt, S. & Gething, P. W.
Nat. Med. (2020).
Abueg, M., Hinch, R., Wu, N., Liu, L., Probert, W. J. M., Wu, A., Eastham, P., Shafi, Y., Rosencrantz, M., Dikovsky, M., Cheng, Z., Nurtay, A., Abeler-Dörner, L., Bonsall, D. G., McConnell, M. V., O’Banion, S. & Fraser, C.
medRxiv (2020). doi:10.1101/2020.08.29.20184135
Bavadekar, S., Dai, A., Davis, J., Desfontaines, D., Eckstein, I., Everett, K., Fabrikant, A., Flores, G., Gabrilovich, E., Gadepalli, K., Glass, S., Huang, R., Kamath, C., Kraft, D., Kumok, A., Marfatia, H., Mayer, Y., Miller, B., Pearce, A., Perera, I. M., Ramachandran, V., Raman, K., Roessler, T., Shafran, I., Shekel, T., Stanton, C., Stimes, J., Sun, M., Wellenius, G. & Zoghi, M.
arXiv [cs.CR] (2020).
Wellenius, G. A., Vispute, S., Espinosa, V., Fabrikant, A., Tsai, T. C., Hennessy, J., Williams, B., Gadepalli, K., Boulanger, A., Pearce, A., Kamath, C., Schlosberg, A., Bendebury, C., Stanton, C., Bavadekar, S., Pluntke, C., Desfontaines, D., Jacobson, B., Armstrong, Z., Gipson, B., Wilson, R., Widdowson, A., Chou, K., Oplinger, A., Shekel, T., Jha, A. K. & Gabrilovich, E.
arXiv [q-bio.PE] (2020).
Aktay, A., Bavadekar, S., Cossoul, G., Davis, J., Desfontaines, D., Fabrikant, A., Gabrilovich, E., Gadepalli, K., Gipson, B., Guevara, M., Kamath, C., Kansal, M., Lange, A., Mandayam, C., Oplinger, A., Pluntke, C., Roessler, T., Schlosberg, A., Shekel, T., Vispute, S., Vu, M., Wellenius, G., Williams, B. & Wilson, R. J.
Ruktanonchai, N. W., Floyd, J. R., Lai, S., Ruktanonchai, C. W., Sadilek, A., Rente-Lourenco, P., Ben, X., Carioli, A., Gwinn, J., Steele, J. E., Prosper, O., Schneider, A., Oplinger, A., Eastham, P. & Tatem, A. J.
Science 369, 1465–1470 (2020).
Sadilek, A., Hswen, Y., Bavadekar, S., Shekel, T., Brownstein, J. S. & Gabrilovich, E.
npj Digital Medicine 3, 1–12 (2020).
Bassolas, A., Barbosa-Filho, H., Dickinson, B., Dotiwalla, X., Eastham, P., Gallotti, R., Ghoshal, G., Gipson, B., Hazarie, S. A., Kautz, H., Kucuktunc, O., Lieber, A., Sadilek, A., & Ramasco, J. J.
Nat. Commun. 10, 4817 (2019).
Sadilek, A., Caty, S., DiPrete, L., Mansour, R., Schenk Jr., T., Bergtholdt, M., Jha, A., Ramaswami P., & Gabrilovich E.
npj Digital Med 1, 36 (2018).
by Atilla Kiraly & Rory Pilgrim
Google Research Blog | 20-Mar-2024
by Shravya Shetty
by Yossi Matias & Shravya Shetty
Google Africa Blog | 31-Oct-2023
by Angelica Willis & Akib Uddin
TensorFlow Blog | 20-Jun-2023
by Perry Nelson & Aisha Walcott-Bryant
Google Africa Blog | 1-Jun-2023
Google Keyword Blog | 28-Nov-2022
by Nicole Linton
Google Keyword Blog | 21-Oct-2022
by Akib Uddin & Andrew Sellergren
Google Research Blog | 19-Jul-2022
Google Japan Blog | 25-Nov-2021
by Zaid Nabulsi & Po-Hsuan Cameron Chen
Google Research Blog | 1-Sep-2021
by Rory Pilgrim & Shruthi Prabhakara
by Sunny Jansen & Krish Eswaran
Google Keyword Blog | 25-Feb-2021
by Cian Hughes
Google Keyword Blog | 29-Oct-2020
by Shravya Shetty & Daniel Tse
Google Keyword Blog | 1-Jan-2020
by Dave Steiner & Shravya Shetty
Google Research Blog | 3-Dec-2019
Google Keyword Blog | 20-May-2019
Kiraly, A. P., Cunningham, C. A., Najafi, R., Nabulsi, Z., Yang, J., Lau, C., Ledsam, J. R., Ye, W., Ardila, D., McKinney, S. M., Pilgrim, R., Liu, Y., Saito, H., Shimamura, Y., Etemadi, M., Melnick, D., Jansen, S., Corrado, G. S., Peng, L., Tse, D., Shetty, S., Prabhakara, S., Naidich, D. P., Beladia, N. & Eswaran, K.
Radiol Artif Intell e230079 (2024).
Lucido, J. J., DeWees, T. A., Leavitt, T. R., Anand, A., Beltran, C. J., Brooke, M. D., Buroker, J. R., Foote, R. L., Foss, O. R., Gleason, A. M., Hodge, T. L., Hughes, C. O., Hunzeker, A. E., Laack, N. N., Lenz, T. K., Livne, M., Morigami, M., Moseley, D. J., Undahl, L. M., Patel, Y., Tryggestad, E. J., Walker, M. Z., Zverovitch, A. & Patel, S. H.
Front. Oncol. 13, (2023).
Lee, C., Willis, A., Chen, C., Sieniek, M., Watters, A., Stetson, B., Uddin, A., Wong, J., Pilgrim, R., Chou, K., Tse, D., Shetty, S. & Gomes, R. G.
JAMA Netw Open 6, e2248685 (2023).
Gomes, R. G., Vwalika, B., Lee, C., Willis, A., Sieniek, M., Price, J. T., Chen, C., Kasaro, M. P., Taylor, J. A., Stringer, E. M., McKinney, S. M., Sindano, N., Dahl, G. E., Goodnight, W., Gilmer, J., Chi, B. H., Lau, C., Spitz, T., Saensuksopa, T., Liu, K., Tiyasirichokchai, T., Wong, J., Pilgrim, R., Uddin, A., Corrado, G., Peng, L., Chou, K., Tse, D., Stringer, J. S. A. & Shetty, S.
Communications Medicine 2, 1–9 (2022).
Kazemzadeh, S., Yu, J., Jamshy, S., Pilgrim, R., Nabulsi, Z., Chen, C., Beladia, N., Lau, C., McKinney, S. M., Hughes, T., Kiraly, A. P., Kalidindi, S. R., Muyoyeta, M., Malemela, J., Shih, T., Corrado, G. S., Peng, L., Chou, K., Chen, P.-H. C., Liu, Y., Eswaran, K., Tse, D., Shetty, S. & Prabhakara, S.
Radiology 212213 (2022).
Sellergren, A. B., Chen, C., Nabulsi, Z., Li, Y., Maschinot, A., Sarna, A., Huang, J., Lau, C., Kalidindi, S. R., Etemadi, M., Garcia-Vicente, F., Melnick, D., Liu, Y., Eswaran, K., Tse, D., Beladia, N., Krishnan, D. & Shetty, S.
Radiology 212482 (2022).
Anand, A., Beltran, C. J., Brooke, M. D., Buroker, J. R., DeWees, T. A., Foote, R. L., Foss, O. R., Hughes, C. O., Hunzeker, A. E., John Lucido, J., Morigami, M., Moseley, D. J., Pafundi, D. H., Patel, S. H., Patel, Y., Ridgway, A. K., Tryggestad, E. J., Wilson, M. Z., Xi, L. & Zverovitch, A.
medRxiv 2021.12.07.21266421 (2021).
Nabulsi, Z., Sellergren, A., Jamshy, S., Lau, C., Santos, E., Kiraly, A. P., Ye, W., Yang, J., Pilgrim, R., Kazemzadeh, S., Yu, J., Kalidindi, S. R., Etemadi, M., Garcia-Vicente, F., Melnick, D., Corrado, G. S., Peng, L., Eswaran, K., Tse, D., Beladia, N., Liu, Y., Chen, P.-H. C. & Shetty, S.
Sci. Rep. 11, 1–15 (2021).
Nikolov, S., Blackwell, S., Zverovitch, A., Mendes, R., Livne, M., De Fauw, J., Patel, Y., Meyer, C., Askham, H., Romera-Paredes, B., Kelly, C., Karthikesalingam, A., Chu, C., Carnell, D., Boon, C., D’Souza, D., Moinuddin, S. A., Garie, B., McQuinlan, Y., Ireland, S., Hampton, K., Fuller, K., Montgomery, H., Rees, G., Suleyman, M., Back, T., Hughes, C. O., Ledsam, J. R. & Ronneberger, O.
J. Med. Internet Res. 23, e26151 (2021).
Duggan, G. E., Reicher, J. J., Liu, Y., Tse, D. & Shetty, S.
Br J Radiol. 94, 20210435 (2021).
McKinney, S. M., Sieniek, M., Godbole, V., Godwin, J., Antropova, N., Ashrafian, H., Back, T., Chesus, M., Corrado, G. S., Darzi, A., Etemadi, M., Garcia-Vicente, F., Gilbert, F. J., Halling-Brown, M., Hassabis, D., Jansen, S., Karthikesalingam, A., Kelly, C. J., King, D., Ledsam, J. R., Melnick, D., Mostofi, H., Peng, L., Reicher, J. J., Romera-Paredes, B., Sidebottom, R., Suleyman, M., Tse, D., Young, K. C., De Fauw, J. & Shetty, S.
Nature 577, 89–94 (2020). [readcube]
Majkowska, A., Mittal, S., Steiner, D. F., Reicher, J. J., McKinney, S. M., Duggan, G. E., Eswaran, K., Cameron Chen, P.-H., Liu, Y., Kalidindi, S. R., Ding, A., Corrado, G. S., Tse, D. & Shetty, S.
Radiology 191293 (2019).
Ardila, D., Kiraly, A. P., Bharadwaj, S., Choi, B., Reciher, J. J., Peng, L., Tse, D., Etemadi, M., Ye, W., Corrado, G., Naidich, D. P., Shetty, S.
Nat. Med. 25, 954–961 (2019). [readcube]
Blog Posts [more at Youtube Official Blog ]
by The YouTube Team
Youtube Official Blog | 6-Feb-2024
by Garth Graham
Youtube Official Blog | 10-Jan-2024
Youtube Official Blog | 14-Dec-2023
by James Beser
Youtube Official Blog | 2-Nov-2023
Youtube Official Blog | 7-Sep-2023
Youtube Official Blog
15-Aug-2023
12-Jun-2023
15-May-2023
Youtube Official Blog | 18-Apr-2023
by Jessica DiVento Dzuban
Youtube Official Blog | 7-Oct-2022
Youtube Official Blog | 1-Mar-2023
Youtube Official Blog | 27-Oct-2022
Youtube Official Blog | 28–Sep-2022
Youtube Official Blog | 12–Sep-2022
Youtube Official Blog | 15-Jun-2022
Youtube Official Blog | 24-Mar-2022
Youtube Official Blog | 26-Jan-2022
Youtube Official Blog | 13-Oct-2021
Youtube Official Blog | 19-Jul-2021
Research articles
Nab-paclitaxel, cisplatin, and capecitabine versus cisplatin and gemcitabine as first line chemotherapy in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma, lateral episiotomy or no episiotomy in vacuum assisted delivery in nulliparous women, global burden of type 1 diabetes in adults aged 65 years and older, antiplatelet therapy after coronary artery bypass surgery, mailed feedback to primary care physicians on antibiotic prescribing, tislelizumab plus chemotherapy versus placebo plus chemotherapy as first line treatment for advanced gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction adenocarcinoma, epidural analgesia during labour and severe maternal morbidity, exposure to antibiotics during pregnancy or early infancy and risk of neurodevelopmental disorders, clinical and healthcare use outcomes after cessation of long term opioid treatment due to prescriber workforce exit, effect of the hpv vaccination programme on incidence of cervical cancer by socioeconomic deprivation in england, long acting progestogens vs combined oral contraceptive pill for preventing recurrence of endometriosis related pain, ultra-processed food consumption and all cause and cause specific mortality, comparative effectiveness of second line oral antidiabetic treatments among people with type 2 diabetes mellitus, efficacy of psilocybin for treating symptoms of depression, reverse total shoulder replacement versus anatomical total shoulder replacement for osteoarthritis, effect of combination treatment with glp-1 receptor agonists and sglt-2 inhibitors on incidence of cardiovascular and serious renal events, prenatal opioid exposure and risk of neuropsychiatric disorders in children, temporal trends in lifetime risks of atrial fibrillation and its complications, antipsychotic use in people with dementia, predicting the risks of kidney failure and death in adults with moderate to severe chronic kidney disease, impact of large scale, multicomponent intervention to reduce proton pump inhibitor overuse, esketamine after childbirth for mothers with prenatal depression, glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist use and risk of thyroid cancer, use of progestogens and the risk of intracranial meningioma, delirium and incident dementia in hospital patients, derivation and external validation of a simple risk score for predicting severe acute kidney injury after intravenous cisplatin, quality and safety of artificial intelligence generated health information, large language models and the generation of health disinformation, 25 year trends in cancer incidence and mortality among adults in the uk, cervical pessary versus vaginal progesterone in women with a singleton pregnancy, comparison of prior authorization across insurers, diagnostic accuracy of magnetically guided capsule endoscopy with a detachable string for detecting oesophagogastric varices in adults with cirrhosis, ultra-processed food exposure and adverse health outcomes, added benefit and revenues of oncology drugs approved by the ema, exposure to air pollution and hospital admission for cardiovascular diseases, short term exposure to low level ambient fine particulate matter and natural cause, cardiovascular, and respiratory morbidity, optimal timing of influenza vaccination in young children, effect of exercise for depression, association of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease with cardiovascular disease and all cause death in patients with type 2 diabetes, duration of cpr and outcomes for adults with in-hospital cardiac arrest, clinical effectiveness of an online physical and mental health rehabilitation programme for post-covid-19 condition, atypia detected during breast screening and subsequent development of cancer, publishers’ and journals’ instructions to authors on use of generative ai in academic and scientific publishing, effectiveness of glp-1 receptor agonists on glycaemic control, body weight, and lipid profile for type 2 diabetes, neurological development in children born moderately or late preterm, invasive breast cancer and breast cancer death after non-screen detected ductal carcinoma in situ, all cause and cause specific mortality in obsessive-compulsive disorder, acute rehabilitation following traumatic anterior shoulder dislocation, perinatal depression and risk of mortality, undisclosed financial conflicts of interest in dsm-5-tr, effect of risk mitigation guidance opioid and stimulant dispensations on mortality and acute care visits, update to living systematic review on sars-cov-2 positivity in offspring and timing of mother-to-child transmission, perinatal depression and its health impact, christmas 2023: common healthcare related instruments subjected to magnetic attraction study, using autoregressive integrated moving average models for time series analysis of observational data, demand for morning after pill following new year holiday, christmas 2023: christmas recipes from the great british bake off, effect of a doctor working during the festive period on population health: experiment using doctor who episodes, christmas 2023: analysis of barbie medical and science career dolls, christmas 2023: effect of chair placement on physicians’ behavior and patients’ satisfaction, management of chronic pain secondary to temporomandibular disorders, christmas 2023: projecting complete redaction of clinical trial protocols, christmas 2023: a drug target for erectile dysfunction to help improve fertility, sexual activity, and wellbeing, christmas 2023: efficacy of cola ingestion for oesophageal food bolus impaction, conservative management versus laparoscopic cholecystectomy in adults with gallstone disease, social media use and health risk behaviours in young people, untreated cervical intraepithelial neoplasia grade 2 and cervical cancer, air pollution deaths attributable to fossil fuels, implementation of a high sensitivity cardiac troponin i assay and risk of myocardial infarction or death at five years, covid-19 vaccine effectiveness against post-covid-19 condition, association between patient-surgeon gender concordance and mortality after surgery, intravascular imaging guided versus coronary angiography guided percutaneous coronary intervention, treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms in men in primary care using a conservative intervention, autism intervention meta-analysis of early childhood studies, effectiveness of the live zoster vaccine during the 10 years following vaccination, effects of a multimodal intervention in primary care to reduce second line antibiotic prescriptions for urinary tract infections in women, pyrotinib versus placebo in combination with trastuzumab and docetaxel in patients with her2 positive metastatic breast cancer, association of dcis size and margin status with risk of developing breast cancer post-treatment, racial differences in low value care among older patients in the us, pharmaceutical industry payments and delivery of low value cancer drugs, rosuvastatin versus atorvastatin in adults with coronary artery disease, clinical effectiveness of septoplasty versus medical management for nasal airways obstruction, ultrasound guided lavage with corticosteroid injection versus sham lavage with and without corticosteroid injection for calcific tendinopathy of shoulder, early versus delayed antihypertensive treatment in patients with acute ischaemic stroke, mortality risks associated with floods in 761 communities worldwide, interactive effects of ambient fine particulate matter and ozone on daily mortality in 372 cities, association between changes in carbohydrate intake and long term weight changes, future-case control crossover analysis for adjusting bias in case crossover studies, association between recently raised anticholinergic burden and risk of acute cardiovascular events, suboptimal gestational weight gain and neonatal outcomes in low and middle income countries: individual participant data meta-analysis, efficacy and safety of an inactivated virus-particle vaccine for sars-cov-2, effect of invitation letter in language of origin on screening attendance: randomised controlled trial in breastscreen norway, visits by nurse practitioners and physician assistants in the usa, non-erosive gastro-oesophageal reflux disease and oesophageal adenocarcinoma, venous thromboembolism with use of hormonal contraception and nsaids, food additive emulsifiers and risk of cardiovascular disease, balancing risks and benefits of cannabis use, promoting activity, independence, and stability in early dementia and mild cognitive impairment, effect of home cook interventions for salt reduction in china, follow us on, content links.
- Collections
- Health in South Asia
- Women’s, children’s & adolescents’ health
- News and views
- BMJ Opinion
- Rapid responses
- Editorial staff
- BMJ in the USA
- BMJ in South Asia
- Submit your paper
- BMA members
- Subscribers
- Advertisers and sponsors
Explore BMJ
- Our company
- BMJ Careers
- BMJ Learning
- BMJ Masterclasses
- BMJ Journals
- BMJ Student
- Academic edition of The BMJ
- BMJ Best Practice
- The BMJ Awards
- Email alerts
- Activate subscription
Information
- Search Menu
- Sign in through your institution
- Browse content in Arts and Humanities
- Browse content in Archaeology
- Prehistoric Archaeology
- Browse content in Art
- History of Art
- Browse content in Classical Studies
- Classical History
- Classical Literature
- Classical Reception
- Greek and Roman Archaeology
- Digital Humanities
- Browse content in History
- Diplomatic History
- Environmental History
- Genocide and Ethnic Cleansing
- History by Period
- Legal and Constitutional History
- Regional and National History
- Social and Cultural History
- Theory, Methods, and Historiography
- World History
- Browse content in Language Teaching and Learning
- Language Teaching Theory and Methods
- Browse content in Linguistics
- Applied Linguistics
- Language Families
- Language Evolution
- Lexicography
- Browse content in Literature
- Bibliography
- Literary Studies (American)
- Literary Studies (20th Century onwards)
- Literary Studies (British and Irish)
- Literary Studies (Women's Writing)
- Literary Theory and Cultural Studies
- Shakespeare Studies and Criticism
- Browse content in Media Studies
- Browse content in Music
- Applied Music
- Medicine and Music
- Music Theory and Analysis
- Musical Structures, Styles, and Techniques
- Musicology and Music History
- Browse content in Philosophy
- Aesthetics and Philosophy of Art
- Epistemology
- History of Western Philosophy
- Metaphysics
- Moral Philosophy
- Philosophy of Science
- Philosophy of Mind
- Philosophy of Mathematics and Logic
- Practical Ethics
- Browse content in Religion
- Christianity
- Judaism and Jewish Studies
- Religion and Science
- Religion and Law
- Religion and Art, Literature, and Music
- Religious Studies
- Browse content in Society and Culture
- Ethical Issues and Debates
- Browse content in Law
- Arbitration
- Company and Commercial Law
- Comparative Law
- Competition Law
- Browse content in Constitutional and Administrative Law
- Parliamentary and Legislative Practice
- Employment and Labour Law
- Environment and Energy Law
- Financial Law
- History of Law
- Human Rights and Immigration
- Intellectual Property Law
- Browse content in International Law
- Private International Law and Conflict of Laws
- Public International Law
- IT and Communications Law
- Jurisprudence and Philosophy of Law
- Law and Society
- Legal System and Practice
- Medical and Healthcare Law
- Browse content in Medicine and Health
- Browse content in Allied Health Professions
- Dietetics and Nutrition
- Physiotherapy
- Radiography
- Anaesthetics
- Browse content in Clinical Medicine
- Acute Medicine
- Cardiovascular Medicine
- Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics
- Dermatology
- Endocrinology and Diabetes
- Gastroenterology
- Geriatric Medicine
- Infectious Diseases
- Medical Oncology
- Medical Toxicology
- Rheumatology
- Sleep Medicine
- Clinical Neuroscience
- Community Medical Services
- Critical Care
- Forensic Medicine
- History of Medicine
- Browse content in Medical Dentistry
- Restorative Dentistry and Orthodontics
- Medical Ethics
- Medical Skills
- Medical Statistics and Methodology
- Browse content in Neurology
- Neuropathology
- Nursing Studies
- Browse content in Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Gynaecology
Occupational Medicine
- Paediatrics
- Browse content in Pathology
- Clinical Cytogenetics and Molecular Genetics
- Medical Microbiology and Virology
- Patient Education and Information
- Browse content in Pharmacology
- Psychopharmacology
- Browse content in Preclinical Medicine
- Molecular Biology and Genetics
- Reproduction, Growth and Development
- Primary Care
- Professional Development in Medicine
- Browse content in Psychiatry
- Child and Adolescent Psychiatry
- Forensic Psychiatry
- Browse content in Public Health and Epidemiology
- Epidemiology
- Public Health
- Browse content in Radiology
- Clinical Radiology
- Interventional Radiology
- Radiation Oncology
- Reproductive Medicine
- Browse content in Surgery
- Cardiothoracic Surgery
- Gastro-intestinal and Colorectal Surgery
- Neurosurgery
- Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
- Trauma and Orthopaedic Surgery
- Browse content in Science and Mathematics
- Browse content in Biological Sciences
- Aquatic Biology
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics and Computational Biology
- Developmental Biology
- Ecology and Conservation
- Evolutionary Biology
- Genetics and Genomics
- Microbiology
- Molecular and Cell Biology
- Plant Sciences and Forestry
- Research Methods in Life Sciences
- Structural Biology
- Systems Biology
- Zoology and Animal Sciences
- Browse content in Chemistry
- Medicinal Chemistry
- Mineralogy and Gems
- Physical Chemistry
- Browse content in Computer Science
- Artificial Intelligence
- Computer Architecture and Logic Design
- Human-Computer Interaction
- Mathematical Theory of Computation
- Browse content in Computing
- Computer Security
- Computer Networking and Communications
- Browse content in Earth Sciences and Geography
- Atmospheric Sciences
- Environmental Geography
- Geology and the Lithosphere
- Meteorology and Climatology
- Browse content in Engineering and Technology
- Agriculture and Farming
- Biological Engineering
- Civil Engineering, Surveying, and Building
- Energy Technology
- Engineering (General)
- Environmental Science, Engineering, and Technology
- Transport Technology and Trades
- Browse content in Environmental Science
- Environmental Sustainability
- Management of Land and Natural Resources (Environmental Science)
- Browse content in Materials Science
- Ceramics and Glasses
- Composite Materials
- Nanotechnology
- Browse content in Mathematics
- Applied Mathematics
- Biomathematics and Statistics
- Mathematical Education
- Mathematical Analysis
- Probability and Statistics
- Pure Mathematics
- Browse content in Neuroscience
- Cognition and Behavioural Neuroscience
- Neuroscientific Techniques
- Browse content in Physics
- Astronomy and Astrophysics
- Classical Mechanics
- Relativity and Gravitation
- Browse content in Psychology
- Clinical Psychology
- Cognitive Neuroscience
- Cognitive Psychology
- Health Psychology
- Music Psychology
- Neuropsychology
- Organizational Psychology
- Browse content in Social Sciences
- Browse content in Anthropology
- Human Evolution
- Browse content in Business and Management
- Human Resource Management
- Industrial and Employment Relations
- Industry Studies
- Information and Communication Technologies
- Organizational Theory and Behaviour
- Public and Nonprofit Management
- Browse content in Criminology and Criminal Justice
- Criminology
- Browse content in Economics
- Agricultural, Environmental, and Natural Resource Economics
- Behavioural Economics and Neuroeconomics
- Econometrics and Mathematical Economics
- Economic History
- Economic Development and Growth
- Financial Markets
- Financial Institutions and Services
- Health, Education, and Welfare
- Labour and Demographic Economics
- Law and Economics
- Public Economics
- Urban, Rural, and Regional Economics
- Browse content in Education
- Schools Studies
- Teaching of Specific Groups and Special Educational Needs
- Environment
- Browse content in Human Geography
- Economic Geography
- Browse content in Interdisciplinary Studies
- Communication Studies
- Museums, Libraries, and Information Sciences
- Browse content in Politics
- Foreign Policy
- Gender and Politics
- International Relations
- International Organization (Politics)
- Political Sociology
- Political Theory
- Political Behaviour
- Political Economy
- Political Institutions
- Public Administration
- Public Policy
- Quantitative Political Methodology
- Regional Political Studies
- Security Studies
- Browse content in Regional and Area Studies
- African Studies
- Japanese Studies
- Research and Information
- Browse content in Social Work
- Addictions and Substance Misuse
- Browse content in Sociology
- Economic Sociology
- Gender and Sexuality
- Gerontology and Ageing
- Health, Illness, and Medicine
- Migration Studies
- Race and Ethnicity
- Social Movements and Social Change
- Social Research and Statistics
- Social Stratification, Inequality, and Mobility
- Sociology of Religion
- Urban and Rural Studies
- Journals A to Z
- Books on Oxford Academic
What are the trending topics in Public Health and related disciplines?
You can identify some of the most discussed and influential topics with the help of Altmetric attention scores, which take into account several outlets including social media, news articles, and policy documents.
Drawing from a selection of Public Health and Medicine journals, we have compiled a list of the articles that have been mentioned the most over the past few months.
Discover the articles that are trending right now, and catch up on current topics in Public Health and related disciplines. We will update our collection every few weeks; come back to this page to be on top of the latest conversations in Public Health and Medicine. Previously featured articles are listed here .
You can also sign up for e-alerts to make sure you never miss the latest research from our journals.
*Last updated October 2021*
Age and Ageing
Alcohol and alcoholism, american journal of epidemiology, annals of work exposures and health, epidemiologic reviews, european journal of public health, family practice, health education research, health policy and planning, health promotion international, international health, international journal of epidemiology, international journal for quality in health care, journal of public health, journal of travel medicine, journal of tropical pediatrics, nicotine & tobacco research, transactions of the royal society of tropical medicine & hygiene, behaviour change interventions to increase physical activity in hospitalised patients: a systematic review, meta-analysis and meta-regression.
There is moderate-certainty evidence that behaviour change interventions are associated with increased physical activity levels among older hospitalised patients.
Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder and Alcohol and Other Substance Use Disorders in Young Adulthood: Findings from a Canadian Nationally Representative Survey
This study from Canada found that one in three young adults with ADHD had a lifetime alcohol use disorder, and that young adults with ADHD were also three times more likely to develop a substance use disorder. Targeted outreach and interventions for this extremely vulnerable population are warranted.
Expiring Eviction Moratoriums and COVID-19 Incidence and Mortality
According to this study, resuming evictions in summer 2020 was associated with increased COVID-19 incidence and mortality in US states, with an estimated 433,700 excess cases and 10,700 excess deaths. Explore more research on COVID-19 in a curated collection from the AJE: https://academic.oup.com/aje/pages/covid-19
The Development of a Covid-19 Control Measures Risk Matrix for Occupational Hygiene Protective Measures
The British Occupational Hygiene Society (BOHS) developed a control banding matrix for employers and others to help assess the risks of COVID-19 infection, and calls for further work to validate the reliability of the tool. Browse the Annals' collection on occupational hygiene for virus protection: https://academic.oup.com/annweh/pages/covid-19
Immunization to Protect the US Armed Forces: Heritage, Current Practice, and Prospects
In 1777, George Washington ordered a mandatory inoculation program for his troops, in what would become the first mass immunization mandate in the US. This archival article discussess and contextualizes immunization practices for US Armed Forces.
Does face mask use elicit risk-compensation? Quasi-experimental evidence from Denmark during the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic
Responding to concerns that that face mask use could elicit a false sense of security and lead to riskier behaviours, this study from Denmark found that mask use overall correlated positively with protective behaviours.
Evidence reversals in primary care research: a study of randomized controlled trials
While medical practice is often undermined by subsequent investigation, randomized trials relevant to primary care generally hold up over time.
Social media influencers can be used to deliver positive information about the flu vaccine: findings from a multi-year study
This study shows the potential for using social media influencers to inspire positive engagements on pro-vaccine health messaging. For more content on accurate information's importance for public health, browse the latest article collection from HER: https://academic.oup.com/her/pages/covid-19
COVID-19 Preparedness and Response Plans from 106 countries: a review from a health systems resilience perspective
Current emergency response planning does not have adequate coverage to maintain health systems functionality for essential health service delivery alongside emergency-specific interventions and healthcare. The findings from this study can help align health emergency planning with broader population health needs.
Rise and demise: a case study of public health nutrition in Queensland, Australia, over three decades
This case study shows that that ongoing efforts are needed to improve sustainability of nutrition policy and programmes to address all diet-related diseases.
Institutional and behaviour-change interventions to support COVID-19 public health measures: a review by the Lancet Commission Task Force on public health measures to suppress the pandemic
This review article outlines evidence for a range of institutional measures and behaviour-change measures, and highlights research and knowledge gaps.
Quantifying impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic through life-expectancy losses: a population-level study of 29 countries
The COVID-19 pandemic triggered significant mortality increases in 2020 of a magnitude not witnessed since World War II in Western Europe or the breakup of the Soviet Union in Eastern Europe.
Gender in the Consolidated Criteria for Reporting Qualitative Research (COREQ) Checklist
The authors propose an update to the Equator’s Consolidated criteria for reporting qualitative research (COREQ) checklist, with the aim of enhancing inclusivity.
Rate of reinfections after SARS-CoV-2 primary infection in the population of an Italian province: a cohort study
This study confirms previous findings on a low risk of SARS-CoV-2 reinfection. If confirmed, these findings suggest that more targeted restriction policies can be applied to the subjects that recovered after a first infection. Read highly cited papers on COVID-19 from the Journal of Public Health: https://academic.oup.com/jpubhealth/pages/covid-19
The reproductive number of the Delta variant of SARS-CoV-2 is far higher compared to the ancestral SARS-CoV-2 virus
Given the Delta variant's high reproductive number associated with higher transmissibility, in a context of globally still low vaccine coverage rates and lower vaccine effectiveness, public health and social measures will need to be substantially strengthened. A high reproductive number also means that much higher vaccine coverage rates need to be achieved compared to the originally assumed.
Neurological Complications of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Neurological complications are rare in children suffering from COVID-19. Still, these children are at risk of developing seizures and encephalopathy, more in those suffering from severe illness.
Reactions to Sales Restrictions on Flavored Vape Products or All Vape Products Among Young Adults in the United States
The researchers examined support for and perceived impact of e-cigarette sales restrictions. Findings suggest that bans on flavored vape products could have a positive impact on lower-risk users, but that other young adult user subgroups may not experience benefit.
Covid-19 and Health at Work
An editorial from the earlier stages of the pandemic highlights the importance of properly fitted respirators for worker safety and outlines occupational hygiene measures.
Lessons from the field: delivering trachoma mass drug administration safely in a COVID-19 context
Guidelines for safe mass drug administration for neglected tropical diseases were developed in a COVID-19 context; training and implementation were assessed through an observation checklist.
For more research on the impact of COVID-19 on NTDs, explore the March 2021 special issue: https://academic.oup.com/trstmh/issue/115/3
Previously featured
Age and frailty are independently associated with increased COVID-19 mortality and increased care needs in survivors: results of an international multi-centre study
Trajectories of Alcohol Use and Related Harms for Managed Alcohol Program Participants over 12 Months Compared with Local Controls: A Quasi-Experimental Study
Estimating the Effect of Social Distancing Interventions on COVID-19 in the United States
Selecting Controls for Minimizing SARS-CoV-2 Aerosol Transmission in Workplaces and Conserving Respiratory Protective Equipment Supplies
What Do We Know About the Association Between Firearm Legislation and Firearm-Related Injuries?
Denialism: what is it and how should scientists respond?
Acute cooling of the feet and the onset of common cold symptoms
The effect of falsely balanced reporting of the autism–vaccine controversy on vaccine safety perceptions and behavioral intentions
Climate change: an urgent priority for health policy and systems research
Power, control, communities and health inequalities I: theories, concepts and analytical frameworks
Research ethics in context: understanding the vulnerabilities, agency and resourcefulness of research participants living along the Thai–Myanmar border
Tobacco smoking and mortality among Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander adults in Australia
Quality and safety in the time of Coronavirus: design better, learn faster
Years of life lost associated with COVID-19 deaths in the United States
In-flight transmission of SARS-CoV-2: a review of the attack rates and available data on the efficacy of face masks
Stability of the Initial Diagnosis of Autism Spectrum Disorder by DSM-5 in Children: A Short-Term Follow-Up Study
Impact of Tobacco Smoking on the Risk of COVID-19: A Large Scale Retrospective Cohort Study
Mental health of staff working in intensive care during COVID-19
The benefits and costs of social distancing in high- and low-income countries
A classification tree to assist with routine scoring of the Clinical Frailty Scale
Recent Advances in the Potential of Positive Allosteric Modulators of the GABAB Receptor to Treat Alcohol Use Disorder
The recent oubreak of smallpox in Meschede, West Germany
Your Hair or Your Service: An Issue of Faith for Sikh Healthcare Professionals During the COVID-19 Pandemic
Emerging Infections: Pandemic Influenza
Identifying the views of adolescents in five European countries on the drivers of obesity using group model building
Novel multi-virus rapid respiratory microbiological point-of-care testing in primary care: a mixed-methods feasibility evaluation
Public health crisis in the refugee community: little change in social determinants of health preserve health disparities
In search of ‘community’: a critical review of community mental health services for women in African settings
COVID-19, a tale of two pandemics: novel coronavirus and fake news messaging
Disrupting vaccine logistics
Use of directed acyclic graphs (DAGs) to identify confounders in applied health research: review and recommendations
Measurement and monitoring patient safety in prehospital care: a systematic review
Black Lives Matter protests and COVID-19 cases: relationship in two databases
The positive impact of lockdown in Wuhan on containing the COVID-19 outbreak in China
Severe Malnutrition and Anemia Are Associated with Severe COVID in Infants
A Single-Arm, Open-Label, Pilot, and Feasibility Study of a High Nicotine Strength E-Cigarette Intervention for Smoking Cessation or Reduction for People With Schizophrenia Spectrum Disorders Who Smoke Cigarettes
Healthcare workers and protection against inhalable SARS-CoV-2 aerosols
Affiliations
- Copyright © 2024
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Institutional account management
- Rights and permissions
- Get help with access
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.
Research Topics & Ideas: Healthcare
100+ Healthcare Research Topic Ideas To Fast-Track Your Project

Finding and choosing a strong research topic is the critical first step when it comes to crafting a high-quality dissertation, thesis or research project. If you’ve landed on this post, chances are you’re looking for a healthcare-related research topic , but aren’t sure where to start. Here, we’ll explore a variety of healthcare-related research ideas and topic thought-starters across a range of healthcare fields, including allopathic and alternative medicine, dentistry, physical therapy, optometry, pharmacology and public health.
NB – This is just the start…
The topic ideation and evaluation process has multiple steps . In this post, we’ll kickstart the process by sharing some research topic ideas within the healthcare domain. This is the starting point, but to develop a well-defined research topic, you’ll need to identify a clear and convincing research gap , along with a well-justified plan of action to fill that gap.
If you’re new to the oftentimes perplexing world of research, or if this is your first time undertaking a formal academic research project, be sure to check out our free dissertation mini-course. In it, we cover the process of writing a dissertation or thesis from start to end. Be sure to also sign up for our free webinar that explores how to find a high-quality research topic.
Overview: Healthcare Research Topics
- Allopathic medicine
- Alternative /complementary medicine
- Veterinary medicine
- Physical therapy/ rehab
- Optometry and ophthalmology
- Pharmacy and pharmacology
- Public health
- Examples of healthcare-related dissertations
Allopathic (Conventional) Medicine
- The effectiveness of telemedicine in remote elderly patient care
- The impact of stress on the immune system of cancer patients
- The effects of a plant-based diet on chronic diseases such as diabetes
- The use of AI in early cancer diagnosis and treatment
- The role of the gut microbiome in mental health conditions such as depression and anxiety
- The efficacy of mindfulness meditation in reducing chronic pain: A systematic review
- The benefits and drawbacks of electronic health records in a developing country
- The effects of environmental pollution on breast milk quality
- The use of personalized medicine in treating genetic disorders
- The impact of social determinants of health on chronic diseases in Asia
- The role of high-intensity interval training in improving cardiovascular health
- The efficacy of using probiotics for gut health in pregnant women
- The impact of poor sleep on the treatment of chronic illnesses
- The role of inflammation in the development of chronic diseases such as lupus
- The effectiveness of physiotherapy in pain control post-surgery

Topics & Ideas: Alternative Medicine
- The benefits of herbal medicine in treating young asthma patients
- The use of acupuncture in treating infertility in women over 40 years of age
- The effectiveness of homoeopathy in treating mental health disorders: A systematic review
- The role of aromatherapy in reducing stress and anxiety post-surgery
- The impact of mindfulness meditation on reducing high blood pressure
- The use of chiropractic therapy in treating back pain of pregnant women
- The efficacy of traditional Chinese medicine such as Shun-Qi-Tong-Xie (SQTX) in treating digestive disorders in China
- The impact of yoga on physical and mental health in adolescents
- The benefits of hydrotherapy in treating musculoskeletal disorders such as tendinitis
- The role of Reiki in promoting healing and relaxation post birth
- The effectiveness of naturopathy in treating skin conditions such as eczema
- The use of deep tissue massage therapy in reducing chronic pain in amputees
- The impact of tai chi on the treatment of anxiety and depression
- The benefits of reflexology in treating stress, anxiety and chronic fatigue
- The role of acupuncture in the prophylactic management of headaches and migraines

Topics & Ideas: Dentistry
- The impact of sugar consumption on the oral health of infants
- The use of digital dentistry in improving patient care: A systematic review
- The efficacy of orthodontic treatments in correcting bite problems in adults
- The role of dental hygiene in preventing gum disease in patients with dental bridges
- The impact of smoking on oral health and tobacco cessation support from UK dentists
- The benefits of dental implants in restoring missing teeth in adolescents
- The use of lasers in dental procedures such as root canals
- The efficacy of root canal treatment using high-frequency electric pulses in saving infected teeth
- The role of fluoride in promoting remineralization and slowing down demineralization
- The impact of stress-induced reflux on oral health
- The benefits of dental crowns in restoring damaged teeth in elderly patients
- The use of sedation dentistry in managing dental anxiety in children
- The efficacy of teeth whitening treatments in improving dental aesthetics in patients with braces
- The role of orthodontic appliances in improving well-being
- The impact of periodontal disease on overall health and chronic illnesses

Tops & Ideas: Veterinary Medicine
- The impact of nutrition on broiler chicken production
- The role of vaccines in disease prevention in horses
- The importance of parasite control in animal health in piggeries
- The impact of animal behaviour on welfare in the dairy industry
- The effects of environmental pollution on the health of cattle
- The role of veterinary technology such as MRI in animal care
- The importance of pain management in post-surgery health outcomes
- The impact of genetics on animal health and disease in layer chickens
- The effectiveness of alternative therapies in veterinary medicine: A systematic review
- The role of veterinary medicine in public health: A case study of the COVID-19 pandemic
- The impact of climate change on animal health and infectious diseases in animals
- The importance of animal welfare in veterinary medicine and sustainable agriculture
- The effects of the human-animal bond on canine health
- The role of veterinary medicine in conservation efforts: A case study of Rhinoceros poaching in Africa
- The impact of veterinary research of new vaccines on animal health
Topics & Ideas: Physical Therapy/Rehab
- The efficacy of aquatic therapy in improving joint mobility and strength in polio patients
- The impact of telerehabilitation on patient outcomes in Germany
- The effect of kinesiotaping on reducing knee pain and improving function in individuals with chronic pain
- A comparison of manual therapy and yoga exercise therapy in the management of low back pain
- The use of wearable technology in physical rehabilitation and the impact on patient adherence to a rehabilitation plan
- The impact of mindfulness-based interventions in physical therapy in adolescents
- The effects of resistance training on individuals with Parkinson’s disease
- The role of hydrotherapy in the management of fibromyalgia
- The impact of cognitive-behavioural therapy in physical rehabilitation for individuals with chronic pain
- The use of virtual reality in physical rehabilitation of sports injuries
- The effects of electrical stimulation on muscle function and strength in athletes
- The role of physical therapy in the management of stroke recovery: A systematic review
- The impact of pilates on mental health in individuals with depression
- The use of thermal modalities in physical therapy and its effectiveness in reducing pain and inflammation
- The effect of strength training on balance and gait in elderly patients
Topics & Ideas: Optometry & Opthalmology
- The impact of screen time on the vision and ocular health of children under the age of 5
- The effects of blue light exposure from digital devices on ocular health
- The role of dietary interventions, such as the intake of whole grains, in the management of age-related macular degeneration
- The use of telemedicine in optometry and ophthalmology in the UK
- The impact of myopia control interventions on African American children’s vision
- The use of contact lenses in the management of dry eye syndrome: different treatment options
- The effects of visual rehabilitation in individuals with traumatic brain injury
- The role of low vision rehabilitation in individuals with age-related vision loss: challenges and solutions
- The impact of environmental air pollution on ocular health
- The effectiveness of orthokeratology in myopia control compared to contact lenses
- The role of dietary supplements, such as omega-3 fatty acids, in ocular health
- The effects of ultraviolet radiation exposure from tanning beds on ocular health
- The impact of computer vision syndrome on long-term visual function
- The use of novel diagnostic tools in optometry and ophthalmology in developing countries
- The effects of virtual reality on visual perception and ocular health: an examination of dry eye syndrome and neurologic symptoms
Topics & Ideas: Pharmacy & Pharmacology
- The impact of medication adherence on patient outcomes in cystic fibrosis
- The use of personalized medicine in the management of chronic diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease
- The effects of pharmacogenomics on drug response and toxicity in cancer patients
- The role of pharmacists in the management of chronic pain in primary care
- The impact of drug-drug interactions on patient mental health outcomes
- The use of telepharmacy in healthcare: Present status and future potential
- The effects of herbal and dietary supplements on drug efficacy and toxicity
- The role of pharmacists in the management of type 1 diabetes
- The impact of medication errors on patient outcomes and satisfaction
- The use of technology in medication management in the USA
- The effects of smoking on drug metabolism and pharmacokinetics: A case study of clozapine
- Leveraging the role of pharmacists in preventing and managing opioid use disorder
- The impact of the opioid epidemic on public health in a developing country
- The use of biosimilars in the management of the skin condition psoriasis
- The effects of the Affordable Care Act on medication utilization and patient outcomes in African Americans
Topics & Ideas: Public Health
- The impact of the built environment and urbanisation on physical activity and obesity
- The effects of food insecurity on health outcomes in Zimbabwe
- The role of community-based participatory research in addressing health disparities
- The impact of social determinants of health, such as racism, on population health
- The effects of heat waves on public health
- The role of telehealth in addressing healthcare access and equity in South America
- The impact of gun violence on public health in South Africa
- The effects of chlorofluorocarbons air pollution on respiratory health
- The role of public health interventions in reducing health disparities in the USA
- The impact of the United States Affordable Care Act on access to healthcare and health outcomes
- The effects of water insecurity on health outcomes in the Middle East
- The role of community health workers in addressing healthcare access and equity in low-income countries
- The impact of mass incarceration on public health and behavioural health of a community
- The effects of floods on public health and healthcare systems
- The role of social media in public health communication and behaviour change in adolescents
Examples: Healthcare Dissertation & Theses
While the ideas we’ve presented above are a decent starting point for finding a healthcare-related research topic, they are fairly generic and non-specific. So, it helps to look at actual dissertations and theses to see how this all comes together.
Below, we’ve included a selection of research projects from various healthcare-related degree programs to help refine your thinking. These are actual dissertations and theses, written as part of Master’s and PhD-level programs, so they can provide some useful insight as to what a research topic looks like in practice.
- Improving Follow-Up Care for Homeless Populations in North County San Diego (Sanchez, 2021)
- On the Incentives of Medicare’s Hospital Reimbursement and an Examination of Exchangeability (Elzinga, 2016)
- Managing the healthcare crisis: the career narratives of nurses (Krueger, 2021)
- Methods for preventing central line-associated bloodstream infection in pediatric haematology-oncology patients: A systematic literature review (Balkan, 2020)
- Farms in Healthcare: Enhancing Knowledge, Sharing, and Collaboration (Garramone, 2019)
- When machine learning meets healthcare: towards knowledge incorporation in multimodal healthcare analytics (Yuan, 2020)
- Integrated behavioural healthcare: The future of rural mental health (Fox, 2019)
- Healthcare service use patterns among autistic adults: A systematic review with narrative synthesis (Gilmore, 2021)
- Mindfulness-Based Interventions: Combatting Burnout and Compassionate Fatigue among Mental Health Caregivers (Lundquist, 2022)
- Transgender and gender-diverse people’s perceptions of gender-inclusive healthcare access and associated hope for the future (Wille, 2021)
- Efficient Neural Network Synthesis and Its Application in Smart Healthcare (Hassantabar, 2022)
- The Experience of Female Veterans and Health-Seeking Behaviors (Switzer, 2022)
- Machine learning applications towards risk prediction and cost forecasting in healthcare (Singh, 2022)
- Does Variation in the Nursing Home Inspection Process Explain Disparity in Regulatory Outcomes? (Fox, 2020)
Looking at these titles, you can probably pick up that the research topics here are quite specific and narrowly-focused , compared to the generic ones presented earlier. This is an important thing to keep in mind as you develop your own research topic. That is to say, to create a top-notch research topic, you must be precise and target a specific context with specific variables of interest . In other words, you need to identify a clear, well-justified research gap.
Need more help?
If you’re still feeling a bit unsure about how to find a research topic for your healthcare dissertation or thesis, check out Topic Kickstarter service below.

You Might Also Like:

16 Comments
I need topics that will match the Msc program am running in healthcare research please
Hello Mabel,
I can help you with a good topic, kindly provide your email let’s have a good discussion on this.
Can you provide some research topics and ideas on Immunology?
Thank you to create new knowledge on research problem verse research topic
Help on problem statement on teen pregnancy
This post might be useful: https://gradcoach.com/research-problem-statement/
can you provide me with a research topic on healthcare related topics to a qqi level 5 student
Please can someone help me with research topics in public health ?
Hello I have requirement of Health related latest research issue/topics for my social media speeches. If possible pls share health issues , diagnosis, treatment.
I would like a topic thought around first-line support for Gender-Based Violence for survivors or one related to prevention of Gender-Based Violence
Please can I be helped with a master’s research topic in either chemical pathology or hematology or immunology? thanks
Can u please provide me with a research topic on occupational health and safety at the health sector
Good day kindly help provide me with Ph.D. Public health topics on Reproductive and Maternal Health, interventional studies on Health Education
may you assist me with a good easy healthcare administration study topic
May you assist me in finding a research topic on nutrition,physical activity and obesity. On the impact on children
I have been racking my brain for a while on what topic will be suitable for my PhD in health informatics. I want a qualitative topic as this is my strong area.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Sports (Basel)

Physical Activity and Sports—Real Health Benefits: A Review with Insight into the Public Health of Sweden
Christer malm.
1 Sports Medicine Unit, Department of Community Medicine and Rehabilitation, Umeå University, 901 87 Umeå, Sweden; [email protected]
Johan Jakobsson
Andreas isaksson.
2 Department of Molecular Medicine and Surgery, Karolinska Institutet, 171 77 Solna, Sweden; [email protected]
Positive effects from sports are achieved primarily through physical activity, but secondary effects bring health benefits such as psychosocial and personal development and less alcohol consumption. Negative effects, such as the risk of failure, injuries, eating disorders, and burnout, are also apparent. Because physical activity is increasingly conducted in an organized manner, sport’s role in society has become increasingly important over the years, not only for the individual but also for public health. In this paper, we intend to describe sport’s physiological and psychosocial health benefits, stemming both from physical activity and from sport participation per se. This narrative review summarizes research and presents health-related data from Swedish authorities. It is discussed that our daily lives are becoming less physically active, while organized exercise and training increases. Average energy intake is increasing, creating an energy surplus, and thus, we are seeing an increasing number of people who are overweight, which is a strong contributor to health problems. Physical activity and exercise have significant positive effects in preventing or alleviating mental illness, including depressive symptoms and anxiety- or stress-related disease. In conclusion, sports can be evolving, if personal capacities, social situation, and biological and psychological maturation are taken into account. Evidence suggests a dose–response relationship such that being active, even to a modest level, is superior to being inactive or sedentary. Recommendations for healthy sports are summarized.
1. Introduction
Sport is a double-edged sword regarding effects on health. Positive effects are achieved primarily through physical activity, which is the main part of most sports. Many secondary effects of sport also bring health benefits, such as psychosocial development of both young [ 1 ] and old [ 2 ], personal development [ 3 ], later onset, and less consumption of alcohol [ 4 , 5 ]. Finally, those who play sports have a higher level of physical activity later in life [ 6 ], and through sport, knowledge of nutrition, exercise, and health can be developed [ 7 ]. Negative effects include the risk of failure leading to poor mental health [ 8 , 9 ], risk of injury [ 10 , 11 ], eating disorders [ 12 ], burnout [ 13 ], and exercise-induced gastrointestinal tract discomfort [ 14 ]. In sport, there are unfortunately also reports of physical and psychological abuse [ 15 ]. Negative aspects are more common in elite-level sports, where there is a fine balance between maximum performance and negative health. A somewhat unexpected effect of sport participation is that people submitting to planned training in some cases perform less physical activity compared to those who are exercising without a set schedule. One explanation can be a reduced spontaneous physical activity in the latter group [ 16 ]. Because physical activity is increasingly executed in an organized manner [ 17 , 18 , 19 ], sport’s role in society has become increasingly important over the years, not only for the individual but also for public health.
In this paper, we describe the health effects of sport from a physiological and psychological perspective, related both to physical activity and added values of sport per se. Initially, brief definitions of various concepts related to physical activity and health are given. This is then followed by: (1) A brief description of how physical activity and training affect our body from a physiological perspective; (2) a report on the health effects of physical activity and training; and (3) sport’s specific influences on the various dimensions of health. We chose to discuss the subject from an age-related perspective, separating children/adolescents, adults, and the elderly, as well as separating for sex in each age group.
2. Definitions of Physical Activity, Exercise, Training, Sport, and Health
Definitions and terms are based on “Physical activity in the prevention and treatment of disease” (FYSS, www.fyss.se [Swedish] [ 20 ]), World Health Organization (WHO) [ 21 ] and the US Department of Human Services [ 22 ]. The definition of physical activity in FYSS is: “Physical activity is defined purely physiologically, as all body movement that increases energy use beyond resting levels”. Health is defined according to the World Health Organization (WHO) as: “[…] a state of complete physical, mental and social wellbeing and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity” [ 21 ].
Physical activity can occur spontaneously (leisure/work/transport) or organized and be divided according to purpose: Physical exercise is aimed primarily at improving health and physical capacity. Physical training is aimed primarily at increasing the individual’s maximum physical capacity and performance [ 23 ]. Physical inactivity is described as the absence of body movement, when energy consumption approximates resting levels. People who do not meet recommendations for physical activity are considered physically inactive and are sometimes called “sedentary”. Sport can be organized by age, sex, level of ambition, weight or other groupings [ 24 ]. Sport can also be spontaneous [ 7 , 17 ] and defined as a subset of exercises undertaken individually or as a part of a team, where participants have a defined goal [ 7 ]. General recommendations for physical activity are found in Table 1 , not considering everyday activities. One can meet the daily recommendations for physical activity by brief, high-intensity exercise, and remaining physically inactive for the rest of the day, thereby creating a “polarization” of physical activity: Having a high dose of conscious physical training, despite having a low energy expenditure in normal life due to high volumes of sedentary time. Polarization of physical activity may lead to increased risk of poor health despite meeting the recommendations for physical activity [ 25 , 26 , 27 ]. During most of our lives, energy expenditure is greater in normal daily life than in sport, physical training, and exercise, with the exceptions of children and the elderly, where planned physical activity is more important [ 28 ].
Recommendations regarding physical activity for different target groups. Note that additional health effects can be achieved if, in addition to these recommendations, the amount of physical activity increases, either by increasing the intensity or duration or a combination of both.
| Target Group | Recommendations | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| | All children and adolescents are recommended at least 60 minutes daily physical activity. Longer is better. The physical activity should be primarily of aerobic nature and the intensity moderate (easy/medium pulse increase) to high (marked pulse increase). Aerobic physical activity at high intensity at least 3 times a week. Muscle-strengthening physical activity 3 times a week. Weight-bearing activity, such as running and jumping, is positive for bone mineral density. The physical activity level will gradually be adapted to the individual’s biological and psychosocial maturation. | Development of muscles and skeletal and nervous system. Maintain a healthy weight and a good mental health. Social development, integration, good self-esteem, and self-confidence. Enhanced learning ability. Recommendations are universal, but for individuals with illness, there may be special recommendations. |
| | All adults from 18 years of age and above are recommended to be aerobically physically active at least 150 minutes a week at a moderate intensity (medium pulse increase), or at least 75 minutes per week at vigorous intensity (marked pulse increase). The activities should be distributed over at least three separate days. Muscle-strengthening physical activity at least twice a week should be performed. | Improvements in aerobic work capacity and muscle strength. Recommendations are universal, but for individuals with illness, there may be special recommendations. Profits from carrying out the activity are lower risk of disease, such as disturbed metabolism and certain cancers and bone fractures. |
| | Same recommendations as adults. Muscle strengthening exercises should be performed at a high velocity, if possible. Balance training should be incorporated prior to aerobic and muscle strengthening training. Individuals with impaired ability should perform as much exercise as possible. | Improvements in aerobic work capacity, muscle strength, and balance. Recommendations are universal, but for individuals with illness, there may be special recommendations. Medical advice may be required before exercise commences. Benefits of carrying out the activity are the same as for adults, and better functional health and independence. |
Compiled from FYSS 2017 ( www.fyss.se ) and WHO 2017 ( www.who.int ).
3. Aerobic and Muscle-Strengthening Physical Activity
Physical activity is categorized according to FYSS as: (1) Aerobic physical activity and (2) muscle-strengthening physical activity. Physical activity in everyday life and exercise training is mainly an aerobic activity, where a majority of energy production occurs via oxygen-dependent pathways. Aerobic physical activity is the type of activity typically associated with stamina, fitness, and the biggest health benefits [ 29 , 30 , 31 ]. Muscle-strengthening physical activity is referred to in everyday language as “strength training” or “resistance training” and is a form of physical exercise/training that is primarily intended to maintain or improve various forms of muscle strength and increase or maintain muscle mass [ 32 ]. Sometimes, another category is defined: Muscle-enhancing physical activity, important for maintenance or improvement of coordination and balance, especially in the elderly [ 33 ]. According to these definitions, muscle-strengthening activities primarily involve the body’s anaerobic (without oxygen) energy systems, proportionally more as intensity increases.
Exercise intensity can be expressed in absolute or relative terms. Absolute intensity means the physical work (for example; Watts [W], kg, or metabolic equivalent [MET]), while relative intensity is measured against the person’s maximum capacity or physiology (for example; percentage of maximum heart rate (%HR), rate of perceived exhaustion (RPE), W·kg −1 or relative oxygen uptake in L·min −1 ·kg −1 (VO 2 )). In terms of recommendations to the public, as in Table 1 , the intensity is often described in subjective terms (“makes you breathe harder” for moderate intensity, and “makes you puff and pant” for vigorous intensity) [ 27 ]. While objective criteria such as heart rate and accelerometry will capture the intensity of activity, they may not distinguish between different types of physical activity behaviors [ 34 ]. FYSS defines low intensity as 20%–39% of VO 2 max, <40 %HR, 1.5–2.9 METs; moderate intensity as 40%–59% of VO 2 max, 60–74 %HR, 3.0–5.9 METs, and vigorous intensity as 60%–89% of VO 2 max, 75–94 %HR, 6.0–8.9 METs. Absolute intensity, however, can vary greatly between individuals where a patient with heart disease may have a maximal capacity of <3 MET, and an elite athlete >20 MET [ 35 ].
4. How does the Body Adapt to Physical Activity and Training?
Adaption to physical activity and training is a complex physiological process, but may, in the context of this paper, be simplified by a fundamental basic principle:” The general adaptation syndrome (GAS)” [ 36 , 37 , 38 ]. This principle assumes that physical activity disturbs the body’s physiological balance, which the body then seeks to restore, all in a dose-related response relationship. The overload principle states that if exercise intensity is too low, overload is not reached to induce desired physiological adaptations, whereas an intensity too high will result in fatigue and possibly overtraining. Thus, for adaptation to occur, greater than normal stress must be induced, interspersed with sufficient recovery periods for restoration of physiological balance [ 39 ]. During and immediately after physical exercise/training, functions of affected tissues and systems are impaired, manifested as temporarily decreased performance. You feel tired. In order to gradually improve performance capacity, repeated cycles of adequate overload and recovery are required [ 40 ]. In practice, positive effects can be seen after a relatively short period of a few weeks, but more substantial improvements if the training is maintained for a longer period.
As a rule of thumb, it is assumed that all people can adapt to physical activity and exercise, but the degree of adaptation depends on many factors, including age, heredity, the environment, and diet [ 41 , 42 , 43 , 44 ]. The hereditary factor (genetics) may be the most critical for adaptation [ 45 ]. The degree of adaptation also depends on how the person in question trained previously; a well-trained athlete usually does not have the same relative improvement as an untrained one. Even if training is thought to be specific to mode, intensity, and duration, there are some overlaps. For example, it has been found that strength training in some individuals contributes to a relatively large positive impact on health and endurance, effects previously associated primarily with aerobic exercise [ 46 , 47 ]. The overload principle may, if applied too vigorously in relation to a person’s individual adaptation ability, have detrimental effects, including reduced performance, injury, overtraining, and disease [ 10 ]. Training is a commodity that must be renewed; otherwise, you gradually lose achieved performance improvements [ 48 ], although some capacities, such as muscle memory, seem to persist for life [ 49 ].
General recommendations for health may be stated, but individual predispositions make general training schedules for specific performance effects unpredictable. All exercise training should be adjusted to individual purposes, goals, and circumstances.
5. Health Effects of Physical Activity and Training
Human biology requires a certain amount of physical activity to maintain good health and wellbeing. Biological adaption to life with less physical activity would take many generations. People living today have, more or less, the same requirements for physical activity as 40,000 years ago [ 50 , 51 ]. For an average man with a body weight of 70 kg, this corresponds to about 19 km daily walking in addition to everyday physical activity [ 52 ]. For most people, daily physical activity decreases, while planned, conscious exercise and training increases [ 19 , 53 ]. Unfortunately, average daily energy intake is increasing more than daily energy output, creating an energy surplus. This is one reason for the increasing number of overweight people, and a strong contributor to many health problems [ 54 ]. More sedentary living (not reaching recommended level of physical activity), combined with increased energy intake, impairs both physical and mental capabilities and increases the risk of disease. Despite this, Swedes (as an example) seemed to be as physically active and stressed but had better general health in 2015, compared to 2004 ( Figure 1 ). Compared to 2004–2007, the Swedish population in 2012–2015 reported better overall health (more county-dots are blue) and less fatigue (smaller county-dots) with similar level of physical activity (~65% indicated at least 30 min daily physical activity) and stress (~13% were stressed).

Selected physical and mental health indicators of a Sweden cohort, in relation to the degree of physical activity for the period of years 2004–2007 ( N = 29,254) and years 2012–2015 ( N = 38,553). Surveyed subjects are age 16 to 84 years old, with data representing median scores of four years, not normalized for age. Y-axis: Percentage of subjects reporting “stressed”; X-axis: Percentage of subjects indicating physical active at least 30 minutes each day. Each dot represents one County (Län), dot-size indicates self-reported fatigue, and color self-reported healthiness of the County. If 70% of the population states they are having “Good/Very good” health, the dot is blue. If less than 70% states they are having good/very good health, the dot is red. The circle indicated with a black arrow corresponds to nation median. The black line connected to the nation circle represents the movement in the X–Y plane from the year 2004 to 2007, and from 2012 to 2015, respectively. Data retrieved from the Public Health Agency of Sweden 2019-04-22 ( www.folkhalsomyndigheten.se ).
Results in Figure 1 may in part be explained by a polarization of who is physically active: Some individuals are extremely active, others very inactive, giving a similar central tendency (mean/median). As physical activity and mental stress are not changed, but health is, the figure indicates that other factors must be more important to our overall health and fatigue. Recently, a national study of Swedish 11- to 15-year-olds concluded that this age group is inactive for most of their time awake, that is, sitting, standing or moving very little [ 55 ]. Time as inactive increased with age, from 67 percent for 11-year-olds to 75 percent for 15-year-olds. The study states that in all age groups, the inactive time is evenly distributed over the week, with school time, leisure time, and weekend. Further, those who feel school-related stress have more inactive time, both overall and during school hours, than those who have less school-related stress.
People active in sports have, in general, better health than those who do not participate in sports, because they are physically and mentally prepared for the challenges of sports, abilities that in many cases can be transferred to other parts of life [ 56 ].
However, there is a certain bias in this statement. Sport practitioners are already positively selected, because sickness and injury may prevent participation. As many health benefits of sport are related to the level of physical activity, separation of sport and physical exercise may be problematic. Regardless, societal benefits of these health effects can be seen in lower morbidity, healthier elderly, and lower medical costs [ 7 , 57 , 58 ].
Health effects of physical activity in many cases follow a dose–response relationship; dose of physical activity is in proportion to the effect on health [ 59 , 60 ]. Figure 2 depicts the relationship between risk of death and level of physical activity, in a Finnish twin cohort, adjusted for smoking, occupational group, and alcohol consumption [ 59 ]. Odds ratio (OR) for the risk of all-cause mortality in a larger sample in the same study was 0.80 for occasional exercisers ( p = 0.002, 95% CI = 0.69–0.91). This dose–response relationship between risk of all-cause mortality and physical activity is evident in several extensive studies [ 60 , 61 , 62 ]. The total dose is determined by the intensity (how strenuous), duration (duration), and frequency (how often). While Figure 2 shows sex differences in death rates, it is likely that sedentary behavior is equally hazardous for men and women, but inconsistent results sometime occur due to inadequate assessment measures, or low statistical power [ 59 , 63 ]. To obtain the best possible development due to physical exercise/training, both for prevention and treatment purposes, a basic understanding of how these variables affect the dose of activity is required, as well as understanding how they can be modified to suit individual requirements. A physically active population is important for the health of both the individual and society, with sport participation being one, increasingly important, motivator for exercise.

Relative risk (odds ratio; OR) of premature death in relationship to level of physical activity, in 286 male and 148 female twin pairs, adjusted for smoking, occupational group, and use of alcohol [ 59 ].
There is strong scientific evidence supporting an association between physical exercise/training and good physical and mental health. For example: A reduction in musculoskeletal disorders and reduced disability due to chronic disease [ 27 , 64 ], better mental health with reduced anxiety [ 65 , 66 ], insomnia [ 67 ], depression [ 31 ], stress [ 68 ], and other psychological disorders [ 69 ]. Physical and mental health problems are related to an increased risk of developing a number of our major public health diseases and may contribute to premature death ( Table 2 ).
Health-related physiological effects of aerobic and muscle strengthening physical activity. Green circle indicates that the activity contributes with an effect, whereas a red circle indicates that the activity has no proven effect. Orange circle indicates that the activity may in some cases be effective.
| Effects on the Body | Health Effects | Aerobic | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Larger proportion slow-twitch fibers [ , ] | Lower risk for metabolic syndrome with increased exchange of gases and nutrition [ , ] | ||
| Larger proportion slow-twitch [ ] | Increased strength, coordination and balance in elderly [ ] and in sickness [ ], lower risk for fall [ ] | ||
| Formation of new capillaries [ ] | Increased aerobic capacity [ ] | ||
| Improved endothelial function [ ] | Lower risk for cardiovascular disease [ ], improved function in heart disease [ ] | ||
| Increased mitochondrial volume [ ] | Increased aerobic capacity [ ] | ||
| Improved glucose transport [ ] | Lower risk or metabolic syndrome/Type-2 diabetes [ ] | ||
| Improved insulin sensitivity [ ] | Improved health in people with Type-2 diabetes [ ], prevention of Typ-2 diabetes [ ] | ||
| Increased heart capacity [ ] | Lower risk for cardiovascular disease [ ], fewer depressions [ , ], also in children [ ] | ||
| Increased skeletal volume and mineral content [ ] | Improved skeletal health [ , ] | ||
| Improved body composition [ ] | Lower risk for metabolic syndrome [ ] | ||
| Improved blood pressure regulation [ , ] | Lower risk for cardiopulmonary disease [ ] | ||
| Improved blood lipid profile [ ] | Lower risk for cardiopulmonary disease in elderly [ , ] and Alzheimer’s [ ] No effect on blood lipid profiles in children and adolescents [ ] | ||
| Improved peripheral nerve function [ ] | Better coordination, balance and reaction [ , ], especially in children and elderly [ ] | ||
| Enhanced release of signaling substances [ , ] | Better sleep [ ], less anxiety [ ], treatment of depression [ ] | ||
| Improved hippocampus function [ ] | Improved cognition and memory [ ], less medication [ ] | ||
| Positive effects on mental capacity [ ] | Counteract brain degeneration by diseases [ ] and age [ ] | ||
| Improved immune function [ ] | Decreased overall risk for disease [ , ], anti-inflammatory effects [ , ] | ||
| Strengthening the connection between brain, metabolism and immune function [ ] | Decreased risk for disease [ ], improved metabolism [ ], decreased risk for depression [ ] | ||
| Improved intestinal function [ , ] | Improved health [ ], mitigated metabolic syndrome, obesity, liver disease, and some cancers [ ] |
5.1. Effects on Physical Health
The effects of physical activity and exercise are both acute (during and immediately after) and long-lasting. Effects remaining after a long period of regular physical activity have far-reaching consequences for health and are described below. For example, some muscle enzymes’ activity can be quickly increased by physical exercise/training but just as quickly be lost when idle [ 118 ]. Other changes remain for months or years even if training ends—for instance, increased number and size of muscle fibers and blood vessels [ 49 , 119 , 120 ]. Good health, therefore, requires physical activity to be performed with both progression and continuity. Most of the conducted physical exercise/training is a combination of both aerobic and muscle strengthening exercise, and it can be difficult to distinguish between their health effects ( Table 2 ).
To describe ill-health, indicators of life expectancy, disease incidence (number), and prevalence (how often) are used [ 121 ]. In describing the relationship between physical activity and falling ill with certain diseases, the dose–response relationship, the effect size (the risk reduction that is shown in studies), and the recommended type and dose of physical activity are considered [ 122 ]. Table 3 shows the relative effects of regular physical activity ton the risk of various diseases (US Department of Human Services, 2009). The greatest health gains are for people who move from completely sedentary to moderately active lifestyles, with health effects seen before measurable improvements in physical performance. Previously, most scientific studies collected data only on aerobic physical activity. However, resistance exercise also shows promising health (mental and physical) and disease-prevention effects [ 123 , 124 , 125 , 126 , 127 ].
Disease prevention effects of regular physical activity.
| Health Condition | Risk Reduction or Health Improvement | Recommendations for Physical Activity | Dose-Response Relationship | Differences between Sex, Age, Ethnicity etc. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30% (44% elderly) | General recommendations | Yes | No | |
| 20%–35% | General recommendations | Yes | Insufficient evidence | |
| 30%–40% | General recommendations | Yes | No | |
| 25%–42% | General recommendations, data primarily on aerobic PA | Yes | Insufficient evidence | |
| Brain cancer: Limited evidence ; Breast cancer: 20%; Bladder cancer: 13%–15%; Colon cancer: 30%; Endometrial cancer: 17%–35%; Esophageal cancer : 6%–21%; Gastric cancer: 19%; Head & neck cancers: 15%–22%, limited evidence; Hematological cancers: No-low effect, limited evidence ; Lung cancer: 13%–26%; Ovarian cancer: Limited/conflicting evidence; Pancreatic & prostate cancer: Limited evidence; Renal cancer: 11%–23%; Rectal cancer: No risk reduction, limited evidence; Thyroid cancer: No risk reduction | General recommendations, data primarily on aerobic PA | Renal & thyroid cancer: No. Lung, hematological, head and neck cancers: Limited evidence. Other; Yes. | Breast cancer: Weaker evidence for Hispanic and Black women. Gastric cancer: Weaker evidence for women Renal cancer: Weaker evidence for Asians Lung cancer: Greater effect for women Other: Limited evidence/No known difference | |
| PA alone, without diet intervention only has an effect at large volume | General recommendations, combined with diet interventions | Yes | No | |
| PA supports weight maintenance | General recommendations, stronger evidence for aerobic PA | Limited evidence | Insufficient evidence | |
| 36%–68% for hip fracture 1%–2% increased bone density | General recommendations including muscle- strengthening physical activity | Yes | Hip fracture: Largest effect in elderly women Bone density: Largest effect in women | |
| Magnitude is highly variable and mode-dependent | Weight bearing activity | Yes | Decreased effect with age | |
| 30% increased chance to counteract or postpone a decrease in functional strength/capacity 30% lower risk of falls | General recommendations including muscle- and skeletal-strengthening physical activity | Functional health: Yes Falls: No/unclear | Increased functional capacity mostly seen in older adults ages 65 or more. | |
| 20%–30% lower | General recommendations | Yes | No | |
| Improved quality, sleep onset latency and total sleep time | General recommendations | No | No | |
| 20%–30% lower | General recommendations | No | No | |
| 20%–30% lower | General recommendations | No | No | |
| Improved for preadolescent children and adults aged 50 years or older | General recommendations | Conflicting findings | Insufficient evidence for adolescents and adults. Ethnicity: No. |
Compiled from US Department of Health and Human Service, https://health.gov/paguidelines/report/ [ 62 , 146 ] 1 : Risk reduction refers to the relative risk in physically active samples in comparison to a non-active sample, i.e., a risk reduction of 20% means that the physically active sample has a relative risk of 0.8, compared to the non-active sample, which has 1.0. 2 : In general, general recommendations for PA that are described and referred to herein apply to most conditions. However, in some cases, more specific recommendations exist, more in depth described by the US Department of Health and Human Service, amongst others [ 62 ]. 3 : Evidence is dependent on cancer subtype; refer to US Department of Health and Human Service [ 62 ] for in-depth guidance. PA = Physical.
Aerobic physical activity has been shown to benefit weight maintenance after prior weight loss, reduce the risk of metabolic syndrome, normalize blood lipids, and help with cancer/cancer-related side effects ( Table 2 and Table 3 ), while effects on chronic pain are not as clear [ 29 ].
Muscle-strengthening physical activity has, in contrast to aerobic exercise, been shown to reduce muscle atrophy [ 128 ], risk of falling [ 75 ], and osteoporosis [ 74 ] in the elderly. Among the elderly, both men and women adapt positively to strength training [ 129 ]. Strength training also prevents obesity [ 130 ], enhances cognitive performance if done alongside aerobic exercise [ 131 ], counteracts the development of neurodegenerative diseases [ 132 , 133 , 134 ], reduces the risk of metabolic syndrome [ 135 ], counteracts cancer/cancer-related side effects [ 135 , 136 ], reduces pain and disability in joint diseases [ 137 ], and enhances bone density [ 137 , 138 ]. The risk of falling increases markedly with age and is partly a result of reduced muscle mass, and reduced coordination and balance [ 76 , 139 , 140 ]. A strong correlation between physical performance, reduced risk of falls, and enhanced quality of life is therefore, not surprisingly, found in older people [ 141 ]. Deterioration in muscle strength, but not muscle mass, increases the risk of premature death [ 142 ] but can be counteracted by exercise as a dose–response relationship describes the strength improvement in the elderly [ 122 , 143 ]. Recommendations state high-intensity strength training (6–8 repetitions at 80% of 1-repetition maximum) as most effective [ 144 ]. Muscle strengthening physical activity for better health is recommended as a complement to aerobic physical activity [ 29 ]. Amongst the elderly, vibration training can be an alternative to increase strength [ 145 ].
5.2. Effects on Mental Health
Mental illness is a global problem affecting millions of people worldwide [ 147 ]. Headache, stress, insomnia, fatigue, and anxiety are all measures of mental ill health. The term “ ill health ” constitutes a collection of several mental health problems and symptoms with various levels of seriousness. Studies have compared expected health benefits from regular physical activity for improvement of mental health with other treatments, for example, medication. Most recent studies show that physical activity and exercise used as a primary, or secondary, processing method have significant positive effects in preventing or alleviating depressive symptoms [ 31 , 148 , 149 , 150 , 151 ] and have an antidepressant effect in people with neurological diseases [ 152 ]. Training and exercise improve the quality of life and coping with stress and strengthen self-esteem and social skills [ 69 , 153 ]. Training and exercise also lessen anxiety in people who are diagnosed with an anxiety- or stress-related disease [ 68 ], improve vocabulary learning [ 154 ], memory [ 155 , 156 ], and creative thinking [ 157 ].
The same Swedish data as used in Figure 1 show that between the years 2004–2007 and 2012–2015 anxiety, worry, and insomnia decreased but were not obviously correlated to the slightly increased level of physical activity in the population during the same period. Thus, in a multifactorial context, the importance of physical exercise alone cannot be demonstrated in this dataset.
Some of the suggested physiological explanations for improved mental health with physical activity and exercise are greater perfusion and increased brain volume [ 107 , 158 ], increased volume of the hippocampus [ 106 ], and the anti-inflammatory effects of physical activity, reducing brain inflammation in neurological diseases [ 159 ]. Physical exercise may also mediate resilience to stress-induced depression via skeletal muscle peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha (PGC-1α), enhancing kynurenine conversion to kynurenine acid, which in turn protects the brain and reduces the risk for stress-induced depression [ 153 ]. Further, increased release of growth factors, endorphins, and signaling molecules are other exercise-induced enhancers of mental health [ 69 ].
6. How Sport Affects Health
Sport’s main purposes are to promote physical activity and improve motor skills for health and performance and psychosocial development [ 56 ]. Participants also gain a chance to be part of a community, develop new social circles, and create social norms and attitudes. In healthy individuals, and patients with mental illness, sport participation has been shown to provide individuals with a sense of meaning, identity, and belonging [ 160 , 161 ]. Whether the sport movement exists or not, training and competition including physical activity will happen. Sport’s added values, in addition to the health benefits of physical activity, are therefore of interest. Some argue that it is doubtful, or at least not confirmed, that health development can come from sport, while others believe that healthy sport is something other than health, reviewed in depth by Coakley [ 162 ]. In a sporting context, health is defined as subjective (e.g., one feels good), biological (e.g., not being sick), functional (e.g., to perform), and social (e.g., to collaborate) [ 163 ]. Holt [ 56 ] argued that the environment for positive development in young people is distinctly different from an environment for performance, as the latter is based on being measured and assessed. That said, certain skills (goal setting, leadership, etc.) can be transferred from a sporting environment to other areas of life. The best way to transfer these abilities is, at the moment, unclear.
Having the goal to win at all costs can be detrimental to health. This is especially true for children and adolescents, as early engagement in elite sports increases the risk of injury, promotes one-dimensional functional development, leads to overtraining, creates distorted social norms, risks psychosocial disorders, and has the risk of physical and psychological abuse [ 15 , 164 ]. Of great importance, therefore, is sport’s goal of healthy performance development, starting at an early age. For older people, a strong motivating factor to conduct physical activity is sports club membership [ 165 ]. One can summarize these findings by stating sport’s utility at the transition between different stages of the life; from youth to adulthood and from adulthood to old age. There, sports can be a resource for good physical and mental health [ 166 ].
Today, a higher proportion of the population, compared to 50 years ago, is engaged in organized sports, and to a lesser extent performs spontaneous sports ( Figure 3 ), something that Engström showed in 2004 [ 17 ] and is confirmed by data from The Swedish Sports Confederation ( www.rf.se ). Of the surveyed individuals in 2001, 50%–60% of children and young people said they were active in a sports club. The trend has continued showing similar progression to 2011, with up to 70% of school students playing sports in a club. Furthermore, the study shows that those active in sport clubs also spontaneously do more sports [ 167 ]. Similar data from the years 2007–2018, compiled from open sources at The Swedish Sports Confederation, confirm the trend with an even higher share of youths participating in organized sports, compared to 1968 and 2001 ( Figure 4 ).

Spontaneous sport has decreased over the last decades, to the advantage of organized sport. Data compiled from Engström, 2004, The Swedish Research Council for Sport Science.

Data compiled from open sources report Sport Statistics (Idrotten i siffror) at The Swedish Sports Confederation for the year 2011 ( www.rf.se ).
Taking part in sports can be an important motivator for physical activity for older people [ 165 , 166 ]. With aging, both participation in sports ( Figure 4 ) and physical activity in everyday life [ 168 ] decreases. At the same time, the number of people who are physically active both in leisure and in organized sports increases (The Public Health Agency of Sweden 2017; www.folkhalsomyndigheten.se ). Consequently, among elderly people, a greater proportion of the physical activity occurs within the context of sport [ 8 , 28 ]. Together, research shows that organized sports, in clubs or companies, are more important for people’s overall physical activity than ever before. Groups that are usually less physically active can be motivated through sport—for example, elderly men in sport supporters’ clubs [ 169 ], people in rural areas [ 170 ], migrants [ 171 ], and people with alternative physical and mental functions [ 172 ]. No matter how you get your sporting interest, it is important to establish a physical foundation at an early age to live in good health when you get older ( Figure 5 ). As seen in Figure 5 , a greater sport habitus at age 15 results in higher physical activity at 53 years of age. Early training and exposure to various forms of sports are therefore of great importance. Participation creates an identity, setting the stage for a high degree of physical activity later in life [ 173 ].

Odds ratio (OR) of physical activity at age 53 in relation to Sport habitus at age 15. Sport habitus (“the total physical capital"), including cultural capital, athletic diversity, and grades in physical education and health are, according to Engström [ 173 ], the factors most important for being physically active in later life. For a further discussion on sport habitus, the readers are referred to Engström, 2008 [ 173 ]. Numbers above bar show the 95% confidence interval. ** = significant difference from “Very low”, p < 0.01. *** = p < 0.001.
7. Sport’s Effects on the Health of Children and Young People
The effects of participation in organized sports for children and young people are directly linked to physical activity, with long term secondary effects; an active lifestyle at a young age fosters a more active lifestyle as an adult. As many diseases that are positively affected by physical activity/exercise appear later in life, continued participation in sport as an adult will reduce morbidity and mortality.
It must be emphasized that good physical and mental health of children and young people participating in sport requires knowledge and organization based on everyone’s participation. Early specialization counteracts, in all regards, both health and performance development [ 174 , 175 ].
7.1. Positive Aspects
According to several reviews, there is a correlation between high daily physical activity in children and a low risk for obesity, improved development of motor and cognitive skills, as well as a stronger skeleton [ 176 , 177 ]. Positive effects on lipidemia, blood pressure, oxygen consumption, body composition, metabolic syndrome, bone density and depression, increased muscle strength, and reduced damage to the skeleton and muscles are also described [ 178 , 179 ]. If many aspects are merged in a multidimensional analysis [ 8 , 173 ], the factors important for future good health are shown to be training in sports, broad exposure to different sports, high school grades, cultural capital, and that one takes part in sport throughout childhood ( Table 4 ).
Compiled health profiles for men and women at the age of 20 years, depending on participation in organized sports at the age of 5, 7, 8, 10, 14, and 17 years.
| Physical Activity at Age 20 Years | Girls | Boys | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sport Participation as Young | ||||||
| Participate | Quit | Never | Participate | Quit | Began late | |
| ⮉ | ⮉ | ⮋ | ⮉ | ⮉ | ⮋ | |
| ⇔ | ⇔ | ⇔ | ⮉ | ⮉ | ⮋ | |
| ⇔ | ⇔ | ⇔ | ⇔ | ⇔ | ⇔ | |
| ⇔ | ⇔ | ⇔ | ⇔ | ⇔ | ⇔ | |
| ⇔ | ⇔ | ⇔ | ⮋ | ⮉ | ⮉ | |
| ⮉ | ⮉ | ⮋ | ⮉ | ⮋ | ⮉ | |
| ) | ⮉ | ⮉ | ⮋ | ⮉ | ⮋ | ⮉ |
| ⮉ | ⮉ | ⮋ | ⇔ | ⇔ | ⇔ | |
| ⇔ | ⇔ | ⇔ | ⇔ | ⇔ | ⇔ | |
| ⇔ | ⇔ | ⇔ | ⇔ | ⮉ | ⇔ | |
| ⇔ | ⇔ | ⇔ | ⇔ | ⇔ | ⇔ | |
| ⇔ | ⇔ | ⇔ | ⇔ | ⇔ | ⇔ | |
Classification with repeated latent class analysis creates three groups for girls and boys, respectively: Children who never participated (girls only), participated, quit prematurely, or began late (only boys) in sports. Arrows indicate whether participation in sports at young age has an effect on health at 20 years of age. Green up arrow is positive, red down arrow negative, and a horizontal black double arrow shows that sport had no significant effect. Modified from Howie et. al., 2016 [ 8 ].
Psychological benefits of sports participation of young people were compiled by Eime et al. [ 1 ], where the conclusion was that sporting children have better self-esteem, less depression, and better overall psychosocial health. One problem with most of these studies, though, is that they are cross-sectional studies, which means that no cause–effect relationship can be determined. As there is a bias for participating children towards coming from socially secure environments, the results may be somewhat skewed.
7.2. Negative Aspects
As Table 4 and Table 5 show, there are both positive and negative aspects of sports. Within children’s and youth sports, early specialization to a specific sport is a common phenomenon [ 175 ]. There is no scientific evidence that early specialization would have positive impact, neither for health nor for performance later in life [ 175 ]. No model or method including performance at a young age can predict elite performance as an adult. By contrast, specialization and competitiveness can lead to injury, overtraining, increased psychological stress, and reduced training motivation, just to mention a few amongst many negative aspects [ 174 , 175 ]. Another important aspect is that those who are excluded from sports feel mentally worse [ 8 ]. As there is a relationship between depressive episodes in adolescence, and depression as adults [ 116 ], early exclusion has far-reaching consequences. Therefore, sports for children and young people have future health benefits by reducing the risk of developing depression and depressive symptoms, as well as improved wellbeing throughout life.
Positive and negative aspects with sport (at young age).
| Aspect | Positive | Negative |
|---|---|---|
| Better self-esteem Better academic results That endurance and hard work pay off Independence and responsibility Making wise decisions Keep a positive attitude Manage stress Set clear goals Higher assessment of skills Higher working standards Better discipline Late alcohol store Lower alcohol consumption (in most sports) Less drugs Greater social capital Better relationships with adults Uses TV/PC less Lower risk of school dropout | Emotional fatigue One-dimensional identity Risk of abuse Increased stress Injuries Temptation for doping Fear of punishment Fear of failure Feeling pressure from the surroundings Fear of disappointing surroundings Risk of burnout Risk of overtraining Poor sleep Decrepit Repeated infections Risk of self-sacrifice Risk of self-injury Increased risk of destructive decisions (doping, cheating etc.) Risk of depression in case of rejection | |
| The usefulness of teamwork Good communication Larger contributions to society later in life Larger contributions to the family later in life Lower crime Opportunity in developing countries Increased chance of being active in sports clubs as older Easier to reach with education | Less integrated with the family Social isolation from other society | |
| Greater physical literacy Abilities to live a healthy life as adult and elderly Less smoking Less drugs Lower body fat Larger muscle mass Beneficial metabolism Higher aerobic and anaerobic capacity Lower risk for fractures as older Reduced general disease risk | Physical fatigue Increased injury risk Risk of eating disorders Overtraining Temptation for doping Risk of abuse (physical and mental) Unilateral training and development For Para athletes, injury can be a double handicap Worse oral health |
While some degree of sport specialization is necessary to develop elite-level athletes, research shows clear adverse health effects of early specialization and talent selection [ 180 ]. More children born during the fall and winter (September–December) are excluded [ 181 ], and as a group, they are less physically active than spring (January–April) children, both in sports and leisure ( Figure 6 ). In most sports and in most countries, there is a skewed distribution of participants when sorted by birth-date, and there are more spring children than fall children among those who are involved in sport [ 182 , 183 , 184 , 185 , 186 ]. Because a large part of the physical activity takes place in an organized form, this leads to lower levels of physical activity for late-born persons (Malm, Jakobsson, and Julin, unpublished data). Early orientation and training in physical activity and exercise will determine how active you are later in life. Greater attention must be given to stimulating as many children and young people as possible to participate in sport as long as possible, both in school and on their leisure time. According to statistics from the Swedish Sports Confederation in 2016, this relative-age effect persists throughout life, despite more starting than ending with sport each year [ 18 ].

The figure shows the distribution of 7597 children aged 10 years and younger who in 2014 were registered as active in one particular, individual sport in Sweden (data compiled from the Swedish Sport Confederation, www.rf.se ). Spring, Summer, and Fall represent January–April, May–August, and September–December, respectively.
When summarize, the positive and negative aspects of sport at a young age can be divided into three categories: (1) Personal identification, (2) social competence, and (3) physiological capacity, briefly summarized in Table 5 . A comprehensive analysis of what is now popularly known as “physical literacy” has recently been published [ 187 ].
7.3. Relevance of Sports
Sports can make children and young people develop both physically and mentally and contribute with health benefits if planned and executed exercise/training considers the person’s own capacities, social situation, and biological as well as psychological maturation. In children and adolescents, it is especially important to prevent sports-related injuries and health problems, as a number of these problems are likely to remain long into adulthood, sometimes for life. Comprehensive training is recommended, which does not necessarily mean that you have to participate in various sports. What is required is diverse training within every sport and club. Research shows that participation in various sports simultaneously during childhood and adolescence is most favorable for healthy and lifelong participation [ 8 , 173 , 188 , 189 ].
8. Sport’s Effects on the Health of Adults and the Elderly
Adults who stop participating in sports reduce their physical activity and have health risks equal to people who have neither done sports nor been physical [ 190 , 191 ]. Lack of adherence to exercise programs is a significant hindrance in achieving health goals and general physical activity recommendations in adults and the elderly [ 192 ]. While several socioeconomic factors are related to exercise adherence, it is imperative that trainers and health care providers are informed about factors that can be modulated, such as intervention intensity (not to high), duration (not too long), and supervision, important for higher adherence, addressed more in depth by Rivera-Torres, Fahey and Rivera [ 192 ].
Healthy aging is dependent on many factors, such as the absence of disease, good physical and mental health, and social commitment (especially through team sports or group activities) [ 193 ]. Increased morbidity with age may be partly linked to decreased physical activity. Thus, remaining or becoming active later in life is strongly associated with healthy aging [ 194 ]. With increased age, there is less involvement in training and competition ( Figure 4 ), and only 20% of adults in Sweden are active, at least to some extent, in sports clubs, and the largest proportion of adults who exercise do it on their own. The following sections describes effects beyond what is already provided for children and youths.
8.1. Positive Aspects
Participation in sports, with or without competition, promotes healthy behavior and a better quality of life [ 166 ]. Exclusion from sports at a young age appears to have long-term consequences, as the previously described relative age effect ( Figure 6 ) remains even for master athletes (Malm, Jakobsson, and Julin, unpublished data). Because master athletes show better health than their peers [ 95 ], actions should be taken to include adults and elderly individuals who earlier in life were excluded from, or never started with sport [ 195 ]. As we age, physical activity at a health-enhancing intensity is not enough to maintain all functions. Higher intensity is required, best comprising competition-oriented training [ 196 , 197 ]. One should not assume that high-intensity exercise cannot be initiated by the elderly [ 198 ]. Competitive sports, or training like a competitive athlete as an adult, can be one important factor to counter the loss of physical ability with aging [ 199 ]. In this context, golf can be one example of a safe form of exercise with high adherence for older adults and the elderly, resulting in increased aerobic performance, metabolic function, and trunk strength [ 200 , 201 ].
8.2. Negative Aspects
Increased morbidity (e.g., cardiovascular disease) with aging is seen also among older athletes [ 202 ] and is associated with the same risk factors as in the general population [ 203 ]. An increased risk of cardiovascular disease among adults (master) compared to other populations has been found [ 204 ]. Unfortunately, the designs and interpretations of these studies have been criticized, and the incidence of cardiac arrest in older athletes is unclear [ 205 ]. In this context, the difference between competitive sports aiming to optimize performance and recreational sports has to be taken into account, where the former is more likely to induce negative effects due to high training loads and/or impacts during training and games. Although high-intensity training even for older athletes is positive for aerobic performance, it does not prevent the loss of motor units [ 206 ].
Quality of life is higher in sporting adults compared to those who do not play sports, but so is the risk of injury. When hit by injury, adults and young alike may suffer from psychological disorders such as depression [ 207 ], but with a longer recovery time in older individuals [ 208 ]. As with young athletes, secession of training at age 50 years and above reduces blood flow in the brain, including the hippocampus, possibly related to long-term decline in mental capacity [ 209 ].
8.3. Relevance of Sport
As for children and young people, many positive health aspects come through sport also for adults and the elderly [ 210 ]. Sport builds bridges between generations, a potential but not elucidated drive for adults’ motivation for physical activity. The percentage of adults participating in competitive sports has increased in Sweden since 2010, from about 20 percent to 30 percent of all of those who are physically active [ 18 ], a trend that most likely provides better health for the group in the 30–40 age group and generations to come.
9. Recommendations for Healthy Sport
- 1. Plan exercise, rest, and social life. For health-promoting and healthy-aging physical activity, refer to general guidelines summarized in this paper: Aerobic exercise three times a week, muscle-strengthening exercise 2–3 times a week.
- 2. Set long-term goals.
- 3. Adopt a holistic performance development including physiological, medical, mental, and psychosocial aspects.
- ○ a. Exercise load (time, intensity, volume);
- ○ b. Recovery (sleep, resting heart rate, appetite, estimated fatigue, etc.);
- ○ c. Sickness (when–where–how, type of infections, how long one is ill, etc.);
- ○ d. Repeat type- and age-specific physical tests with relevant evaluation and feedback;
- ○ e. Frequency of injuries and causes.
- ○ a. Motivation for training, competition, and socializing;
- ○ b. Personal perception of stress, anxiety, depression, alienation, and self-belief;
- ○ c. Repeat type- and age-specific psychological tests with relevant evaluation and feedback.
- 6. Register and interpret signs of overtraining, such as reduced performance over time, while maintaining or increasing exercise load.
Author Contributions
C.M. and A.J. conceived and designed the review. C.M., A.J., J.J. and interpreted the data and drafted the manuscript. J.J. edited the manuscript, tables, and figures. All authors approved the final version.
This work was supported by the Swedish Sports Confederation.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
- Fact sheets
- Facts in pictures
Publications
- Questions and answers
- Tools and toolkits
- HIV and AIDS
- Hypertension
- Mental disorders
- Top 10 causes of death
- All countries
- Eastern Mediterranean
- South-East Asia
- Western Pacific
- Data by country
- Country presence
- Country strengthening
- Country cooperation strategies
- News releases
- Feature stories
- Press conferences
- Commentaries
- Photo library
- Afghanistan
- Cholera
- Coronavirus disease (COVID-19)
- Greater Horn of Africa
- Israel and occupied Palestinian territory
- Disease Outbreak News
- Situation reports
- Weekly Epidemiological Record
- Surveillance
- Health emergency appeal
- International Health Regulations
- Independent Oversight and Advisory Committee
- Classifications
- Data collections
- Global Health Estimates
- Mortality Database
- Sustainable Development Goals
- Health Inequality Monitor
- Global Progress
- Data collection tools
- Global Health Observatory
- Insights and visualizations
- COVID excess deaths
- World Health Statistics
- Partnerships
- Committees and advisory groups
- Collaborating centres
- Technical teams
- Organizational structure
- Initiatives
- General Programme of Work
- WHO Academy
- Investment case
- WHO Foundation
- External audit
- Financial statements
- Internal audit and investigations
- Programme Budget
- Results reports
- Governing bodies
- World Health Assembly
- Executive Board
- Member States Portal
- Science Division /
- Research for health
Research for Health
WHO’s goal: Forward looking and prioritized global health research
Research for health is a global endeavour, and WHO has a unique role to play in ensuring that these efforts can help improve health for all.
WHO provides leadership, calling on the wider scientific community to engage behind global health concerns. This is based on a deep understanding of the needs of countries, and rigorous assessment by international experts.
WHO has three key objectives to promote forward-looking and prioritized global health research:

Anticipating scientific, technological, and epidemiological shifts
To stay on top of scientific and technological advancements and epidemiological trends, WHO must anticipate new trends, technologies, research, and discoveries in medical and public health.
Through continuous, rigorous, and systematic horizon scanning, the Science Division assesses and identifies emerging issues, for early identification of potential health benefits or threats. It actively prospects for scientific and technological innovations that could change the equation on advancing health.
Science in action: the WHO Advisory Committee on Developing Global Standards for Governance and Oversight of Human Genome Editing
This committee examines the scientific, ethical, social, and legal challenges associated with human genome editing, and makes recommendations on the ethical framework for research and application of this technology.

Setting a global research agenda to address gaps, emerging areas, and country priorities
Truly useful innovations are not simply new; they are designed explicitly with the needs of the user in mind. By analyzing gaps, inequities, emerging areas and country priorities, the WHO research agenda anticipates the complex issues affecting people’s health and supports the discovery of innovative solutions to address them.
Science in action: R&D Blueprint for dementia research.
In 2017, the World Health Assembly adopted a Global Action Plan on the Public Health Response to Dementia. A key component of this plan was a call to action for research and innovation. To move this forward, the Science Division is developing an R&D Blueprint for dementia research.

Strengthening confidence in science
The Science Division supports countries in developing their scientific expertise and research capacities and facilitating the development of new and innovative research methodologies. This will improve understanding of the determinants of health, health systems, and the transformative potential of innovations in health.
Science in action: WHO Science Council
At WHO, Research for Health covers five key functions , which are integrated to apply research and innovation and achieve impact for people’s health around the world.

Foresight and emerging technologies
We try to get ahead of the curve by understanding what is needed to improve health for all in the future, and where the best new ideas are emerging.
Advances in science and technology hold great promise for new ways to address global health and support healthier populations worldwide. WHO engages in horizon scanning across the science and technology landscape. It also supports countries in doing their own futures and foresight exercises to understand their future needs. The aim of foresight is to identify and connect known, new, or emerging issues that could significantly impact global health within the next two decades.
Emerging technologies offer great health opportunities but also pose potentially significant challenges. The WHO Foresight function provides ongoing monitoring of emerging technologies to spot potential risks and come up with strategies for prevention and mitigation.

Research prioritization and support, R&D optimization
We identify gaps in current research priorities, and promote and support research that can best address unmet needs.
WHO has a unique role in supporting research for health , because we can help ensure health research is directed towards the biggest unmet needs in global health. We do this by sharing upstream research information from clinical trials , and research and development pipelines , and by providing guidance for research priority setting exercises.
WHO can determine strategic public health areas and identify key research and development needs. It then produces a clear target product profile to promote research and development that will be of most benefit. By mapping existing target product profiles in the Target Product Profile Directory and developing new ones based on identified public health needs, WHO steers innovation in support of improved health for all.
Product developers seek advice from WHO on whether or not their product likely has value for public health. In this way, WHO, expedites development of health related products, including novel therapeutics, diagnostics, and repurposing existing products.
Research for Health works with researchers and innovators to ensure they are aligned with the Prequalification Team and WHO’s technical departments on the package of evidence that will be needed to secure prequalification or a WHO policy recommendation. This process informs clinical trials on life-saving medical products, technologies and processes. A coordinated scientific advice process is currently in pilot phase.

Health ethics and governance
By putting ethics at the heart of decision-making and providing guidance on governance, WHO promotes this ethos within WHO and throughout the global health community.
In addition to supporting projects conducted by WHO, we are often called upon by development partners at country level for our expertise in global health ethics. Our Health Ethics and Governance unit produces guidance and tools for Member States on ethics in research and public health. Inside and outside WHO, it also helps researchers and public health specialists navigate ethical challenges posed by their projects.

Research policy for access
The best ideas are not just the brightest, but the one that actually get implemented and make an impact. WHO provides leadership on policies in research to ensure access and scale-up.
Having the right research policy is a key step towards ensuring health research has actual impact. This means that research priorities match real-world problems. At WHO, Research for Health works to ensure that the needs of countries are clearly articulated, and then communicated to the research community.
At WHO we promote an end-to-end approach in research policy. Working with local health systems and communities is needed to better understand the delivery and uptake of new products and to achieve widespread and equitable access. WHO can help broker multinational studies, foster regulatory harmonization, and promote dialogue among all stakeholders.

Taking knowledge from evidence to impact
Through a global network for evidence-informed health policy-making and tailored country support, WHO brings together researchers, policy-makers and implementers to translate evidence into improved health policies and programmes.
Public health problems are often complex and require nuanced, context-specific solutions and tailored implementation strategies. To make a difference for patients, communities and medical professionals, reliable evidence on how to tackle a health issue needs to be synthesized, reflected in a local context, and effectively communicated between researchers and decision-makers.
Through a set of field-tested and user-friendly tools, the Evidence to Policy and Impact Unit supports countries in bridging the gap between public health research, policy, and programme. Evidence briefs for policy and rapid response mechanisms put key research findings into context and place them at the fingertips of decision-makers. Policy dialogues provide researchers, policy-makers, and partner organizations with a forum to rally behind evidence-informed policy options and effective health interventions, discuss the findings, and share their own experiences and values. Citizen engagement strategies give voice to the beliefs and perspectives of individuals and communities, upholding accountability and democratic deliberation as core principles of equitable health care.
WHO’s global Evidence-informed Policy Network (EVIPNet) is a key initiative building sustainable and resilient capacity for evidence-informed decision-making and knowledge translation with Member States and in WHO offices at country, regional and international level. With over 15 years of experience and active teams in close to 50 countries, EVIPNet has successfully strengthened national health systems and emergency response capacity around the globe. The network also forms a vivid community of practice, facilitating decentralized peer-support among members and offering a treasure trove of successful strategies in evidence-informed health policy-making.
Research for Health within WHO
WHO’s Research for Health Department supports teams and units across the entire organization to establish their own research priorities . It helps people working in different parts of our global network connect the dots and create a better coordinated research response. This in turns helps keep WHO on track, ensuring that the research done within WHO is aligned with the health-related Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and our own Triple Billion Targets of 1 billion more people benefitting from universal health coverage, 1 billion more people better protected from health emergencies, and 1 billion more people enjoying better health and well-being.
Research for Health: our role in the global public health research community
WHO’s technical units are just one part of a global web of research for health, encompassing academia, national and regional research bodies, product development partnerships and the private sector. WHO helps to provide global guidance for research priority setting. Our global, regional and country-level reach means we can help to clearly articulate the needs of the countries, and we are uniquely well-placed to broker multinational research efforts.
Pan American Health Organization regional meeting on human genomic research for health held
WHO advisory group convenes its first meeting on responsible use of the life sciences in Geneva
Stakeholders convene in Uganda on responsible use of the life sciences
Public consultation
CLOSED - Call for Experts – Technical Advisory Group on the responsible use of the life sciences and dual-use research
Public consultation on WHO guidance for best practices for clinical trials

Protocol: using data to drive governance
This document introduces a collaboratively developed study protocol to identify what data and information is currently being collected by governments and...

Evidence generation for development of health products: a practical guide for WHO staff
This document describes the main elements that World Health Organization (WHO) technical departments should elaborate on when providing guidance on evidence...

Report of the fifth meeting of the WHO Diagnostic Technical Advisory Group for Neglected Tropical Diseases:...
The WHO Department of Control of Neglected Tropical Diseases (WHO/NTD) manages a diverse portfolio of 20 diseases and disease groups, each with its own...

Performing a landscape analysis: understanding health product research and development
A landscape analysis related to health products aims to identify and characterize all the products that exist or are being developed in a specific topic...
Reference management. Clean and simple.
The top list of research databases for medicine and healthcare

3. Cochrane Library
4. pubmed central (pmc), 5. uptodate, frequently asked questions about research databases for medicine and healthcare, related articles.
Web of Science and Scopus are interdisciplinary research databases and have a broad scope. For biomedical research, medicine, and healthcare there are a couple of outstanding academic databases that provide true value in your daily research.
Scholarly databases can help you find scientific articles, research papers , conference proceedings, reviews and much more. We have compiled a list of the top 5 research databases with a special focus on healthcare and medicine.
PubMed is the number one source for medical and healthcare research. It is hosted by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and provides bibliographic information including abstracts and links to the full text publisher websites for more than 28 million articles.
- Coverage: around 35 million items
- Abstracts: ✔
- Related articles: ✔
- References: ✘
- Cited by: ✘
- Links to full text: ✔
- Export formats: XML, NBIB
Pro tip: Use a reference manager like Paperpile to keep track of all your sources. Paperpile integrates with PubMed and many popular databases. You can save references and PDFs directly to your library using the Paperpile buttons and later cite them in thousands of citation styles:
EMBASE (Excerpta Medica Database) is a proprietary research database that also includes PubMed. It can also be accessed by other database providers such as Ovid .
- Coverage: 38 million articles
- References: ✔
- Cited by: ✔
- Full text: ✔ (requires institutional subscription to EMBASE and individual publishers)
- Export formats: RIS
The Cochrane Library is best know for its systematic reviews. There are 53 review groups around the world that ensure that the published reviews are of high-quality and evidence based. Articles are updated over time to reflect new research.
- Coverage: several thousand high quality reviews
- Full text: ✔
- Export formats: RIS, BibTeX
PubMed Central is the free, open access branch of PubMed. It includes full-text versions for all indexed papers. You might also want to check out its sister site Europe PMC .
- Coverage: more than 8 million articles
- Export formats: APA, MLA, AMA, RIS, NBIB
Like the Cochrane Library, UpToDate provides detailed reviews for clinical topics. Reviews are constantly updated to provide an up-to-date view.
- Coverage: several thousand articles from over 420 peer-reviewed journals
- Related articles: ✘
- Full text: ✔ (requires institutional subscription)
- Export formats: ✘
PubMed is the number one source for medical and healthcare research. It is hosted at the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and provides bibliographic information including abstracts and links to the full text publisher websites for more than 35 million items.
EMBASE (Excerpta Medica Database) is a proprietary research database that also includes in its corpus PubMed. It can also be accessed by other database providers such as Ovid.
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
Health sciences articles from across Nature Portfolio
The health sciences study all aspects of health, disease and healthcare. This field of study aims to develop knowledge, interventions and technology for use in healthcare to improve the treatment of patients.

Food fortification programmes and zinc deficiency
The complex realities of most countries grappling with zinc deficiency pose challenges to the implementation of highly compliant, mandatory, large-scale food fortification programmes.
- Nicola M. Lowe
- Swarnim Gupta
First encounter with SARS-CoV-2: immune portraits of COVID susceptibility
Controlled infection with SARS-CoV-2 of people who hadn’t previously been exposed to the virus reveals how molecular and cellular signatures of the immune response portend effective defence against COVID-19.
- Benjamin Israelow
- Akiko Iwasaki
Sex organs sense vibrations through specialized touch neurons
A little-studied sensory structure called the Krause corpuscle is responsible for detecting light touch and is essential for normal sexual behaviour in mice. The findings have interesting implications for human sexual intimacy.
- Anastasia-Maria Zavitsanou
- Ishmail Abdus-Saboor
Related Subjects
- Endocrinology
- Gastroenterology
- Health care
- Health occupations
- Medical research
- Molecular medicine
- Pathogenesis
- Rheumatology
- Risk factors
- Signs and symptoms
Latest Research and Reviews
Construction of a digital twin of chronic graft vs. host disease patients with standard of care
- Yi-Bin Chen
- Jonathan Peachey
Hard-Flaccid syndrome: a survey of sexual medicine practitioners’ knowledge and experience
- Gustavo Gryzinski
- Muhammed Moukhtar Hammad
- Faysal Yafi
LRG1 and SDR16C5 protein expressions differ according to HPV status in oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma
- Reija Randén-Brady
- Timo Carpén
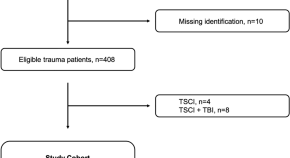
Admission levels of serum biomarkers have additive and cumulative prognostic value in traumatic brain injury
- Ida A. Kaaber
- Claus V. B. Hviid
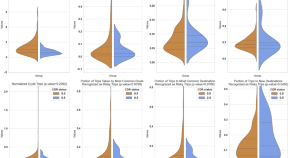
Impact of cognitive impairment on driving behaviour and route choices of older drivers: a real-world driving study
- Reihaneh Derafshi
- Ganesh M. Babulal
- Sayeh Bayat
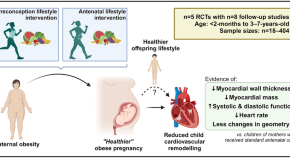
Maternal obesity and offspring cardiovascular remodelling — the effect of preconception and antenatal lifestyle interventions: a systematic review
- Samuel J. Burden
- Rahaf Alshehri
- Paul D. Taylor
News and Comment

Could rats and dogs detect disease better than the finest lab equipment?
The animals’ keen sense of smell could improve the detection of illnesses such as cancer and tuberculosis.
- Sarah DeWeerdt
The whole picture in digital pathology
- Ananya Rastogi
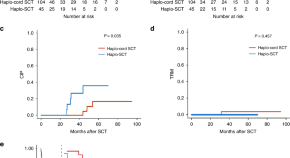
Haploidentical-cord blood stem cell transplantation versus haploidentical stem cell transplantation for non-CR acute leukemia patients: a multicenter study

Put people at the heart of schizophrenia research
Scientists, health-care professionals, carers and individuals affected by the condition must work more closely with one another to improve people’s lives.
- Constanza Morén
Debunking the myths of intermittent fasting
Despite the mounting evidence supporting the use of intermittent fasting as a safe and effective weight loss intervention, many myths about fasting persist in popular culture. Here, we review some common beliefs about intermittent fasting that are not supported by scientific evidence.
- Krista A. Varady
- Sofia Cienfuegos
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
77 interesting medical research topics for 2024
Last updated
25 November 2023
Reviewed by
Brittany Ferri, PhD, OTR/L
Short on time? Get an AI generated summary of this article instead
Medical research is the gateway to improved patient care and expanding our available treatment options. However, finding a relevant and compelling research topic can be challenging.
Use this article as a jumping-off point to select an interesting medical research topic for your next paper or clinical study.
- How to choose a medical research topic
When choosing a research topic , it’s essential to consider a couple of things. What topics interest you? What unanswered questions do you want to address?
During the decision-making and brainstorming process, here are a few helpful tips to help you pick the right medical research topic:
Focus on a particular field of study
The best medical research is specific to a particular area. Generalized studies are often too broad to produce meaningful results, so we advise picking a specific niche early in the process.
Maybe a certain topic interests you, or your industry knowledge reveals areas of need.
Look into commonly researched topics
Once you’ve chosen your research field, do some preliminary research. What have other academics done in their papers and projects?
From this list, you can focus on specific topics that interest you without accidentally creating a copycat project. This groundwork will also help you uncover any literature gaps—those may be beneficial areas for research.
Get curious and ask questions
Now you can get curious. Ask questions that start with why, how, or what. These questions are the starting point of your project design and will act as your guiding light throughout the process.
For example:
What impact does pollution have on children’s lung function in inner-city neighborhoods?
Why is pollution-based asthma on the rise?
How can we address pollution-induced asthma in young children?
- 77 medical research topics worth exploring in 2023
Need some research inspiration for your upcoming paper or clinical study? We’ve compiled a list of 77 topical and in-demand medical research ideas. Let’s take a look.
- Exciting new medical research topics
If you want to study cutting-edge topics, here are some exciting options:
COVID-19 and long COVID symptoms
Since 2020, COVID-19 has been a hot-button topic in medicine, along with the long-term symptoms in those with a history of COVID-19.
Examples of COVID-19-related research topics worth exploring include:
The long-term impact of COVID-19 on cardiac and respiratory health
COVID-19 vaccination rates
The evolution of COVID-19 symptoms over time
New variants and strains of the COVID-19 virus
Changes in social behavior and public health regulations amid COVID-19
Vaccinations
Finding ways to cure or reduce the disease burden of chronic infectious diseases is a crucial research area. Vaccination is a powerful option and a great topic to research.
Examples of vaccination-related research topics include:
mRNA vaccines for viral infections
Biomaterial vaccination capabilities
Vaccination rates based on location, ethnicity, or age
Public opinion about vaccination safety
Artificial tissues fabrication
With the need for donor organs increasing, finding ways to fabricate artificial bioactive tissues (and possibly organs) is a popular research area.
Examples of artificial tissue-related research topics you can study include:
The viability of artificially printed tissues
Tissue substrate and building block material studies
The ethics and efficacy of artificial tissue creation
- Medical research topics for medical students
For many medical students, research is a big driver for entering healthcare. If you’re a medical student looking for a research topic, here are some great ideas to work from:
Sleep disorders
Poor sleep quality is a growing problem, and it can significantly impact a person’s overall health.
Examples of sleep disorder-related research topics include:
How stress affects sleep quality
The prevalence and impact of insomnia on patients with mental health conditions
Possible triggers for sleep disorder development
The impact of poor sleep quality on psychological and physical health
How melatonin supplements impact sleep quality
Alzheimer’s and dementia
Cognitive conditions like dementia and Alzheimer’s disease are on the rise worldwide. They currently have no cure. As a result, research about these topics is in high demand.
Examples of dementia-related research topics you could explore include:
The prevalence of Alzheimer’s disease in a chosen population
Early onset symptoms of dementia
Possible triggers or causes of cognitive decline with age
Treatment options for dementia-like conditions
The mental and physical burden of caregiving for patients with dementia
- Lifestyle habits and public health
Modern lifestyles have profoundly impacted the average person’s daily habits, and plenty of interesting topics explore its effects.
Examples of lifestyle and public health-related research topics include:
The nutritional intake of college students
The impact of chronic work stress on overall health
The rise of upper back and neck pain from laptop use
Prevalence and cause of repetitive strain injuries (RSI)
- Controversial medical research paper topics
Medical research is a hotbed of controversial topics, content, and areas of study.
If you want to explore a more niche (and attention-grabbing) concept, here are some controversial medical research topics worth looking into:
The benefits and risks of medical cannabis
Depending on where you live, the legalization and use of cannabis for medical conditions is controversial for the general public and healthcare providers.
Examples of medical cannabis-related research topics that might grab your attention include:
The legalization process of medical cannabis
The impact of cannabis use on developmental milestones in youth users
Cannabis and mental health diagnoses
CBD’s impact on chronic pain
Prevalence of cannabis use in young people
The impact of maternal cannabis use on fetal development
Understanding how THC impacts cognitive function
Human genetics
The Human Genome Project identified, mapped, and sequenced all human DNA genes. Its completion in 2003 opened up a world of exciting and controversial studies in human genetics.
Examples of human genetics-related research topics worth delving into include:
Medical genetics and the incidence of genetic-based health disorders
Behavioral genetics differences between identical twins
Genetic risk factors for neurodegenerative disorders
Machine learning technologies for genetic research
Sexual health studies
Human sexuality and sexual health are important (yet often stigmatized) medical topics that need new research and analysis.
As a diverse field ranging from sexual orientation studies to sexual pathophysiology, examples of sexual health-related research topics include:
The incidence of sexually transmitted infections within a chosen population
Mental health conditions within the LGBTQIA+ community
The impact of untreated sexually transmitted infections
Access to safe sex resources (condoms, dental dams, etc.) in rural areas
- Health and wellness research topics
Human wellness and health are trendy topics in modern medicine as more people are interested in finding natural ways to live healthier lifestyles.
If this field of study interests you, here are some big topics in the wellness space:
Gluten sensitivity
Gluten allergies and intolerances have risen over the past few decades. If you’re interested in exploring this topic, your options range in severity from mild gastrointestinal symptoms to full-blown anaphylaxis.
Some examples of gluten sensitivity-related research topics include:
The pathophysiology and incidence of Celiac disease
Early onset symptoms of gluten intolerance
The prevalence of gluten allergies within a set population
Gluten allergies and the incidence of other gastrointestinal health conditions
Pollution and lung health
Living in large urban cities means regular exposure to high levels of pollutants.
As more people become interested in protecting their lung health, examples of impactful lung health and pollution-related research topics include:
The extent of pollution in densely packed urban areas
The prevalence of pollution-based asthma in a set population
Lung capacity and function in young people
The benefits and risks of steroid therapy for asthma
Pollution risks based on geographical location
Plant-based diets
Plant-based diets like vegan and paleo diets are emerging trends in healthcare due to their limited supporting research.
If you’re interested in learning more about the potential benefits or risks of holistic, diet-based medicine, examples of plant-based diet research topics to explore include:
Vegan and plant-based diets as part of disease management
Potential risks and benefits of specific plant-based diets
Plant-based diets and their impact on body mass index
The effect of diet and lifestyle on chronic disease management
Health supplements
Supplements are a multi-billion dollar industry. Many health-conscious people take supplements, including vitamins, minerals, herbal medicine, and more.
Examples of health supplement-related research topics worth investigating include:
Omega-3 fish oil safety and efficacy for cardiac patients
The benefits and risks of regular vitamin D supplementation
Health supplementation regulation and product quality
The impact of social influencer marketing on consumer supplement practices
Analyzing added ingredients in protein powders
- Healthcare research topics
Working within the healthcare industry means you have insider knowledge and opportunity. Maybe you’d like to research the overall system, administration, and inherent biases that disrupt access to quality care.
While these topics are essential to explore, it is important to note that these studies usually require approval and oversight from an Institutional Review Board (IRB). This ensures the study is ethical and does not harm any subjects.
For this reason, the IRB sets protocols that require additional planning, so consider this when mapping out your study’s timeline.
Here are some examples of trending healthcare research areas worth pursuing:
The pros and cons of electronic health records
The rise of electronic healthcare charting and records has forever changed how medical professionals and patients interact with their health data.
Examples of electronic health record-related research topics include:
The number of medication errors reported during a software switch
Nurse sentiment analysis of electronic charting practices
Ethical and legal studies into encrypting and storing personal health data
Inequities within healthcare access
Many barriers inhibit people from accessing the quality medical care they need. These issues result in health disparities and injustices.
Examples of research topics about health inequities include:
The impact of social determinants of health in a set population
Early and late-stage cancer stage diagnosis in urban vs. rural populations
Affordability of life-saving medications
Health insurance limitations and their impact on overall health
Diagnostic and treatment rates across ethnicities
People who belong to an ethnic minority are more likely to experience barriers and restrictions when trying to receive quality medical care. This is due to systemic healthcare racism and bias.
As a result, diagnostic and treatment rates in minority populations are a hot-button field of research. Examples of ethnicity-based research topics include:
Cancer biopsy rates in BIPOC women
The prevalence of diabetes in Indigenous communities
Access inequalities in women’s health preventative screenings
The prevalence of undiagnosed hypertension in Black populations
- Pharmaceutical research topics
Large pharmaceutical companies are incredibly interested in investing in research to learn more about potential cures and treatments for diseases.
If you’re interested in building a career in pharmaceutical research, here are a few examples of in-demand research topics:
Cancer treatment options
Clinical research is in high demand as pharmaceutical companies explore novel cancer treatment options outside of chemotherapy and radiation.
Examples of cancer treatment-related research topics include:
Stem cell therapy for cancer
Oncogenic gene dysregulation and its impact on disease
Cancer-causing viral agents and their risks
Treatment efficacy based on early vs. late-stage cancer diagnosis
Cancer vaccines and targeted therapies
Immunotherapy for cancer
Pain medication alternatives
Historically, opioid medications were the primary treatment for short- and long-term pain. But, with the opioid epidemic getting worse, the need for alternative pain medications has never been more urgent.
Examples of pain medication-related research topics include:
Opioid withdrawal symptoms and risks
Early signs of pain medication misuse
Anti-inflammatory medications for pain control
- Identify trends in your medical research with Dovetail
Are you interested in contributing life-changing research? Today’s medical research is part of the future of clinical patient care.
As your go-to resource for speedy and accurate data analysis , we are proud to partner with healthcare researchers to innovate and improve the future of healthcare.
Should you be using a customer insights hub?
Do you want to discover previous research faster?
Do you share your research findings with others?
Do you analyze research data?
Start for free today, add your research, and get to key insights faster
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 18 April 2023
Last updated: 27 February 2023
Last updated: 6 February 2023
Last updated: 15 January 2024
Last updated: 6 October 2023
Last updated: 5 February 2023
Last updated: 16 April 2023
Last updated: 7 March 2023
Last updated: 9 March 2023
Last updated: 12 December 2023
Last updated: 11 March 2024
Last updated: 13 May 2024
Latest articles
Related topics, .css-je19u9{-webkit-align-items:flex-end;-webkit-box-align:flex-end;-ms-flex-align:flex-end;align-items:flex-end;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-flex-direction:row;-ms-flex-direction:row;flex-direction:row;-webkit-box-flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-box-pack:center;-ms-flex-pack:center;-webkit-justify-content:center;justify-content:center;row-gap:0;text-align:center;max-width:671px;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}}@media (max-width: 799px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}} decide what to .css-1kiodld{max-height:56px;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-1kiodld{display:none;}} build next, decide what to build next.

Users report unexpectedly high data usage, especially during streaming sessions.

Users find it hard to navigate from the home page to relevant playlists in the app.

It would be great to have a sleep timer feature, especially for bedtime listening.

I need better filters to find the songs or artists I’m looking for.
Log in or sign up
Get started for free
300+ Health Related Research Topics For Medical Students(2023)

In the world of academia and healthcare, finding the right health-related research topics is essential. Whether you are a medical student, a college student, or a seasoned researcher, the choice of your research topic greatly impacts the quality and relevance of your work. This blog, health related research topics, is your guide to selecting the perfect subject for your research.
In this post, we will share 5 invaluable tips to help you pick suitable health-related research topics. Additionally, we will outline the crucial elements that every health-related research paper should incorporate.
Furthermore, we’ve compiled a comprehensive list of 300+ health-related research topics for medical students in 2023. These include categories like mental health, public health, nutrition, chronic diseases, healthcare policy, and more. We also offer guidance on selecting the right topic to ensure your research is engaging and meaningful.
So, whether you are delving into mental health, investigating environmental factors, or exploring global health concerns, health-related research topics will assist you in making informed and impactful choices for your research journey, even within the hardest medical specialties .
What Is Health Research?
Table of Contents
Health research is like detective work to understand how our bodies work and how to keep them healthy. It’s like asking questions and finding answers about things like sickness, medicine, and how to live better. Scientists and doctors do health research to learn new ways to treat illnesses, like finding better medicines or discovering new ways to prevent diseases.
Health research is a puzzle, where scientists collect information, do experiments, and study many people to find out what makes us healthy or sick. They want to find clues and put them together to help us stay well and live longer. So, health research is like a quest to learn more about our bodies and find ways to make them work their best, keeping us happy and strong.
5 Useful Tips For Choosing Health Related Research Topics
Here are some useful tips for choosing health related research topics:
Tip 1: Follow Your Interests
When picking a health research topic, it’s a good idea to choose something you’re curious and excited about. If you’re interested in a subject, you’ll enjoy learning more about it, and you’ll be motivated to do your best. So, think about what aspects of health catch your attention and explore those areas for your research.
Tip 2: Consider Relevance
Your research topic should be meaningful and have real-world importance. Think about how your research can contribute to solving health problems or improving people’s well-being. Topics that are relevant and can make a positive impact on health and healthcare are usually more valuable.
Tip 3: Check Available Resources
Before deciding on a research topic, make sure you have access to the necessary resources, like books, articles, or equipment. It’s important that you can find the information and tools you need to conduct your research effectively.
Tip 4: Keep It Manageable
Select a research topic that you can handle within the available time and resources. It’s better to choose a more focused and manageable topic rather than something too broad or complex. This way, you can delve deep into the subject and produce meaningful results.
Tip 5: Seek Guidance
Don’t hesitate to ask for guidance from teachers, professors, or experts in the field. They can help you refine your research topic, provide valuable insights, and suggest improvements. Seeking advice can make your research journey smoother and more successful.
Important Elements That Must Be Present In A Health Related Research Paper
Here are some important elements that must be present in a health related research paper:
1. Clear Title and Introduction
A good health research paper needs a clear title that tells people what it’s about. The introduction should explain why the research is important and what the paper will discuss. It’s like the map that shows the way.
2. Methods and Data
You should describe how you did your research and the data you collected. This helps others understand how you found your information. It’s like showing your work in math so that others can check it.
3. Results and Conclusions
After doing your research, you need to show what you discovered. Share the results and what they mean. Conclusions tell people what you found out and why it’s important. It’s like the “So what?” part of your paper.
4. Citations and References
When you use other people’s ideas or words, you need to give them credit. Citations and references show where you got your information. It’s like saying, “I learned this from here.”
5. Clear Language and Organization
Make sure your paper is easy to read and well-organized. Use clear and simple language so that everyone can understand. Organize your paper logically, with a beginning, middle, and end, like a good story. This makes your research paper more effective and useful.
In this section, we will discuss 300+ health related research topics for medical students(2023):
Health Related Research Topics
- How living choices affect health and how long people live.
- Ways to make it easier for people in underserved areas to get medical care.
- The role of DNA in determining susceptibility to different diseases.
- There are differences in health between race and ethnic groups and between socioeconomic groups.
- Checking how well health education programs encourage people to behave in a healthy way.
- The effects that stress has on the body and mind.
- Looking at the pros and cons of different vaccine plans.
- The link between how well you sleep and your general health.
- The use of technology to make health care better.
- How cultural beliefs and habits affect how people seek health care.
Mental Health Related Research Topics
- Identifying the factors contributing to the rise in mental health disorders among adolescents.
- Examining the effectiveness of different therapeutic approaches for treating depression and anxiety.
- How social media can hurt your mental health and self-esteem.
- We are looking into the link between traumatic events in youth and mental health problems later in life.
- Stigma and racism in mental health care, and how they make people less healthy.
- Ways to lower the suicide rate among people who are at high risk.
- Exercise and other forms of physical action can help your mental health.
- The link between using drugs and having mental health problems.
- Mental health support for frontline healthcare workers during and after the COVID-19 pandemic.
- Exploring the potential of digital mental health interventions and apps.
Health Related Research Topics For College Students
- The impact of college stress on physical and mental health.
- Assessing the effectiveness of college mental health services.
- The role of peer influence on college students’ health behaviors.
- Nutrition and dietary habits among college students.
- Substance use and abuse on college campuses.
- Investigating the prevalence of sleep disorders among college students.
- Exploring sexual health awareness and behaviors among college students.
- Evaluating the relationship between academic performance and overall health.
- The influence of social media on college students’ health perceptions and behaviors.
- Ideas for getting people on college grounds to be more active and eat better.
Public Health Related Research Topics
- Evaluating the impact of public health campaigns on smoking cessation .
- The effectiveness of vaccination mandates in preventing disease outbreaks.
- Looking into the link between the health of the people in cities and the quality of the air.
- Strategies for addressing the opioid epidemic through public health initiatives.
- The role of public health surveillance in early disease detection and response.
- Assessing the impact of food labeling on consumer choices and nutrition.
- Looking at how well public health measures work to lower the number of overweight and obese kids.
- The importance of water quality in maintaining public health.
- This paper examines various strategies aimed at enhancing mother and child health outcomes in emerging nations.
- Addressing the mental health crisis through public health interventions.
Mental Disorder Research Topics
- The mental health effects of social isolation, with a particular focus on the COVID-19 pandemic.
- Exploring the relationship between mental health and creative expression.
- Cultural differences influence the way in which mental health disorders are perceived and treated.
- The use of mindfulness and meditation techniques in managing mental health.
- Investigating the mental health challenges faced by LGBTQ+ individuals.
- Examining the role of nutrition and dietary habits in mood disorders.
- The influence of childhood experiences on adult mental health.
- Innovative approaches to reducing the stigma surrounding mental health.
- Mental health support for veterans and active-duty military personnel.
- The relation between sleep disorders and mental health.
Nutrition and Diet-Related Research Topics
- The impact of dietary patterns (e.g., Mediterranean, ketogenic) on health outcomes.
- Investigating the role of gut microbiota in digestion and overall health.
- The effects of food labeling and nutritional education on dietary choices.
- The correlation between chronic disease prevention and nutrition.
- Assessing the nutritional needs of different age groups (children, adults, elderly).
- Exploring the benefits and drawbacks of various diet fads (e.g., intermittent fasting, veganism).
- The role of nutrition in managing obesity and weight-related health issues.
- Studying nutrition and mental wellness.
- Impact of food insecure areas on population health and diet.
- Strategies for promoting healthy eating in schools and workplaces.
Chronic Disease Research Topics
- The contribution of inflammation to the progression and development of chronic diseases.
- Evaluating the effectiveness of lifestyle modifications in managing chronic conditions.
- The impact of chronic stress on various health conditions.
- Investigating disparities in the management and treatment of chronic diseases among different populations.
- Exploring the genetics of chronic diseases and potential gene therapies.
- The impact that environmental factors, including pollution, have on the prevalence of chronic diseases.
- Assessing the long-term health consequences of childhood obesity.
- Strategies for improving the quality of life for individuals living with chronic diseases.
- The importance of maintaining a healthy level of physical activity and exercise for both the prevention and treatment of chronic illnesses.
- Investigating innovative treatments and therapies for chronic diseases, such as gene editing and personalized medicine.
Healthcare Policy and Access Research Topics
- Assessing how the Affordable Care Act affects healthcare access and outcomes.
- Telehealth’s impact on rural healthcare access.
- Investigating the cost-effectiveness of various healthcare payment models (e.g., single-payer, private insurance).
- Assessing healthcare disparities among different racial and socioeconomic groups.
- The influence of political ideologies on healthcare policy and access.
- Healthcare professional shortage solutions, including nurses and doctors.
- The impact of malpractice reform on healthcare quality and access.
- Examining the role of pharmaceutical pricing and regulation in healthcare access.
- The use of technology in streamlining healthcare administration and improving access.
- Exploring the intersection of healthcare policy, ethics, and patient rights.
Environmental Health Research Topics
- The impact of climate change on public health, including increased heat-related illnesses and vector-borne diseases.
- Studying air pollution’s effects on the cardiovascular and respiratory systems.
- Assessing the health consequences of exposure to environmental toxins and pollutants.
- Exploring the role of green spaces and urban planning in promoting public health.
- The impact of water quality and sanitation on community health.
- Strategies for minimizing the health risks linked with natural catastrophes and extreme weather events.
- Investigating the health implications of food and water security in vulnerable populations.
- The influence of environmental justice on health disparities.
- Evaluating the benefits of renewable energy sources in reducing air pollution and promoting health.
- The role of public policy in addressing environmental health concerns.
Infectious Disease Research Topics
- Tracking the evolution and spread of infectious diseases, including COVID-19.
- Investigating the effectiveness of vaccination campaigns in preventing outbreaks.
- Antimicrobial resistance and strategies to combat it.
- Assessing the role of vector-borne diseases in global health, such as malaria and Zika virus.
- The impact of travel and globalization on the spread of infectious diseases.
- Strategies for early detection and containment of emerging infectious diseases.
- The role of hygiene and sanitation in reducing infectious disease transmission.
- Investigating the cultural factors that influence infectious disease prevention and treatment.
- The use of technology in disease surveillance and response.
- Examining the ethical and legal considerations in managing infectious disease outbreaks.
Women’s Health Research Topics
- Exploring the gender-specific health issues faced by women, such as reproductive health and menopause.
- Investigating the impact of hormonal contraception on women’s health.
- Assessing the barriers to accessing quality maternal healthcare in low-income countries.
- The role of gender-based violence in women’s mental and physical health.
- Strategies for promoting women’s sexual health and reproductive rights.
- Exploring the relationship between breast cancer and genetics.
- The influence of body image and societal pressures on women’s mental health.
- Investigating healthcare disparities among different groups of women, including racial and ethnic disparities.
- Strategies for improving access to women’s healthcare services, including family planning and prenatal care.
- The use of telemedicine and technology to address women’s health needs, especially in remote areas.
Children’s Health Research Topics
- The impact of early childhood nutrition on long-term health and development.
- Environmental toxin exposure and child health.
- Assessing the role of parenting styles in children’s mental and emotional well-being.
- Strategies for preventing and managing childhood obesity.
- The influence of media and technology on children’s physical and mental health.
- Exploring the challenges faced by children with chronic illnesses and disabilities.
- The relevance of early child mental wellness and developmental condition intervention.
- Investigating the role of schools in promoting children’s health and well-being.
- Strategies for addressing child healthcare disparities, including access to vaccines and preventive care.
- Adverse childhood experiences and adult health.
Aging and Gerontology Research Topics
- Investigating the factors contributing to healthy aging and longevity.
- Assessing the impact of dementia and Alzheimer’s disease on elderly individuals and their families.
- Strategies for improving elder care services and addressing the aging population’s healthcare needs.
- Exploring the social isolation and mental health challenges faced by the elderly.
- The importance of nutrition and exercise in old age.
- Investigating the impact of age-related chronic diseases, such as arthritis and osteoporosis.
- Assessing the financial and ethical aspects of end-of-life care for the elderly.
- Strategies for promoting intergenerational relationships and support networks.
- The influence of cultural differences on aging and health outcomes.
- Exploring technology and innovation in elder care, including assistive devices and telemedicine.
Health Technology and Innovation Research Topics
- The impact of telemedicine and virtual health platforms on patient care and outcomes.
- Investigating the use of wearable health technology in monitoring and managing chronic conditions.
- Assessing the ethical and privacy considerations of health data collection through technology.
- Investigating medical diagnoses and treatment with AI and ML.
- The role of robotics in healthcare, including surgical procedures and elder care.
- Investigating the use of 3D printing in healthcare, such as prosthetics and medical devices.
- The influence of mobile health apps on patient engagement and self-care.
- Strategies for implementing electronic health records (EHRs) and interoperability.
- The impact of precision medicine and genomics on personalized healthcare.
- Exploring the future of healthcare delivery through telehealth, remote monitoring, and AI-driven diagnostics.
Global Health Research Topics
- Investigating the challenges of global health equity and healthcare access in low- and middle-income countries.
- Assessing the effectiveness of international health organizations in addressing global health crises.
- Resource-limited mother and child health strategies.
- Exploring the impact of infectious diseases in global health, including tuberculosis and HIV/AIDS.
- The role of clean water and sanitation in improving global health outcomes.
- Investigating the social determinants of health in different global regions.
- Assessing the impact of humanitarian aid and disaster relief efforts on public health.
- Strategies for combating malnutrition and food insecurity in developing countries.
- The influence of climate change on global health, including the spread of vector-borne diseases.
- Exploring innovative approaches to global health, such as community health workers and telemedicine initiatives.
- Exploring the artificial intelligence and machine learning in medical treatment.
Health Disparities and Equity Research Topics
- The impact of socioeconomic status on healthcare access and health outcomes.
- Strategies to decrease racial and ethnic disparities in maternal and child health.
- LGBTQ+ healthcare disparities and interventions for equitable care.
- Health disparities among rural and urban populations in developed and developing countries.
- Cultural competence in healthcare and its role in reducing disparities.
- The intersection of gender, race, and socioeconomic status in health disparities.
- Addressing health disparities in the elderly population.
- The role of discrimination in perpetuating health inequities.
- Strategies to improve healthcare access for individuals with disabilities.
- The impact of COVID-19 on health disparities and lessons learned for future pandemics.
Cancer Research Topics
- Advancements in precision medicine for personalized cancer treatment.
- Immunotherapy breakthroughs in cancer treatment.
- Environmental factors and cancer risk: A comprehensive review.
- The role of genomics in understanding cancer susceptibility.
- Cancer treatment and survivorship, as well as quality of life following cancer therapy.
- The economics of cancer treatment and its impact on patients.
- Cancer prevention and early detection strategies in underserved communities.
- Palliative care and end-of-life decisions in cancer patients.
- Emerging trends in cancer epidemiology and global burden.
- Ethical considerations in cancer clinical trials and research.
Pharmaceutical Research Topics
- Repurposing existing medications in order to address uncommon illnesses.
- The impact of nanotechnology in drug delivery and targeting.
- Pharmacogenomics and personalized medicine: Current status and future prospects.
- Challenges and opportunities in developing vaccines for emerging infectious diseases.
- Quality control and safety in the pharmaceutical manufacturing process.
- Drug pricing and access: A global perspective.
- Green chemistry approaches in sustainable pharmaceutical development.
- The part that artificial intelligence plays in the search for new drugs and their development.
- Biopharmaceuticals and the future of protein-based therapies.
- Regulatory challenges in ensuring drug safety and efficacy.
Epidemiology Research Topics
- Emerging infectious diseases and global preparedness.
- The COVID-19 pandemic will have long-term effect on the health of the general population.
- Social determinants of health and their impact on disease prevalence.
- Environmental epidemiology and the study of health effects of pollution.
- Big data and its role in modern epidemiological research.
- Spatial epidemiology and the study of disease clusters.
- Epidemiological aspects of non-communicable diseases (NCDs) like diabetes and obesity.
- Genetic epidemiology and the study of hereditary diseases.
- Epidemiological methods for studying mental health disorders.
- Epidemiology of zoonotic diseases and their prevention.
Alternative and Complementary Medicine Research Topics
- Efficacy and safety of herbal remedies in complementary medicine.
- Mind-body interventions and their role in managing chronic pain.
- Acupuncture and its potential in the treatment of various conditions.
- Integrating traditional and complementary medicine into mainstream healthcare.
- Yoga and meditation for stress reduction and mental health.
- Biofield therapies and their impact on well-being.
- Ayurvedic medicine and its modern applications in health and wellness.
- Chiropractic care and its use in musculoskeletal health.
- Ethical considerations in the practice and regulation of alternative medicine.
- Integrating traditional Chinese medicine into Western healthcare systems.
Occupational Health and Safety Research Topics
- Occupational hazards in healthcare settings and strategies for prevention.
- The impact of remote work on occupational health and well-being.
- Ergonomics and its role in preventing workplace injuries.
- Occupational exposure to hazardous chemicals and long-term health effects.
- Mental health in the office: Stress, burnout, and interventions.
- Occupational safety in the construction industry: Recent developments.
- Role of technology in enhancing workplace safety.
- Occupational health disparities among different industries and occupations.
- The economics of workplace safety and the cost-benefit analysis.
- Business impacts of OSHA regulations.
Addiction and Substance Abuse Research Topics
- The opioid epidemic: Current status and future strategies.
- Dual diagnosis: Co-occurring mental health disorders and substance abuse.
- Harm reduction approaches in addiction treatment.
- The role of family and social support in addiction recovery.
- Behavioral addictions: Understanding and treating non-substance-related addictions.
- Novel pharmacotherapies for addiction treatment.
- The impact of COVID-19 on substance abuse and addiction.
- Substance abuse prevention programs in schools and communities.
- Stigmatization of addiction and its impact on treatment-seeking behavior.
- Substance abuse in the elderly population: Unique challenges and solutions.
Biomedical Research Topics
- Recent advancements in gene editing technologies (e.g., CRISPR-Cas9).
- Regenerative medicine and tissue engineering for organ replacement.
- Bioinformatics and its role in analyzing large-scale biological data.
- Stem cell research and its important applications in regenerative medicine.
- Biomarker discovery for early disease detection and monitoring.
- Precision medicine and its potential to transform healthcare.
- The microbiome and its impacts on human health and disease.
- Aging-related research and interventions for healthy aging.
- Neurodegenerative diseases and potential therapeutic approaches.
- Biomedical ethics in the age of cutting-edge research.
Maternal and Child Health Research Topics
- The influence of the mother’s nutrition on the development and health of the fetus.
- Maternal mental health and its positive effects on child development.
- Preterm birth prevention and interventions for at-risk pregnancies.
- Neonatal screening and early diagnosis of congenital diseases.
- Breastfeeding promotion and support for new mothers.
- Pediatric immunization programs and vaccine hesitancy.
- Child obesity prevention and intervention strategies.
- Maternal and child health in low-resource and conflict-affected areas.
- Maternal mortality reduction and improving access to obstetric care.
- Adverse childhood experiences (ACEs) and their long-term health consequences.
Mental Health Stigma Research Topics
- Understanding the origins and perpetuation of mental health stigma.
- Media and pop culture’s impact on mental disease views.
- Reducing stigma in the workplace and promoting mental health support.
- Stigma associated with specific mental health conditions (e.g., schizophrenia, bipolar disorder).
- Intersectionality and how it influences mental health stigma.
- Anti-stigma campaigns and their effectiveness in changing public attitudes.
- Stigma in online communities and the role of social media in shaping opinions.
- Cultural and cross-cultural perspectives on mental health stigma.
- The impact of self-stigma on individuals seeking mental health treatment.
- Legislative and policy efforts to combat mental health stigma.
Health Education and Promotion Research Topics
- Health literacy and its impact on informed decision-making.
- Promoting healthy behaviors in schools and educational settings.
- Social marketing campaigns for health behavior change.
- Community-based health promotion programs in underserved areas.
- The role of technology and social media in health education.
- Tailoring health messages to diverse populations and cultural sensitivity.
- The use of behavioral economics in health promotion strategies.
- Investigating the effectiveness of school-based sex education programs.
- Health education for the elderly population: Challenges and solutions.
- Promoting mental health awareness and resilience through education.
Healthcare Quality and Patient Safety Research Topics
- Patient-centered care and its impact on healthcare quality.
- Reducing medical errors and negative events in healthcare settings.
- Continuous quality improvement in healthcare organizations.
- The role of healthcare accreditation in ensuring quality and safety.
- Patient engagement and shared decision-making in healthcare.
- Electronic health records and patient safety.
- The ethics of telling patients and families about medical blunders.
- Medication safety and preventing adverse drug events.
- Cultural competence in healthcare and its effect on patient safety.
- Disaster preparedness and response in healthcare settings.
Health Informatics and Data Analytics Research Topics
- Big data analytics in healthcare for predictive modeling.
- Artificial intelligence in medical image analysis and diagnostics.
- Health information exchange and interoperability challenges.
- Electronic health record (EHR) usability and user satisfaction.
- Patient data privacy and security in health informatics.
- Telemedicine and its impact on healthcare delivery and data management.
- Real-time monitoring and data analytics for disease outbreaks.
- Health informatics applications in personalized medicine.
- Natural language processing for clinical notes and text analysis.
- The role of data analyticsin enhancing healthcare quality and outcomes.
Neurological Disorders Research Topics
- Neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative diseases (e.g., Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s).
- Stroke prevention and rehabilitation strategies.
- Advances in brain imaging techniques for diagnosing neurological disorders.
- Pediatric neurological disorders: Diagnosis and intervention.
- Neurogenetics and the role of genetics in neurological conditions.
- Traumatic brain injury: Long-term effects and rehabilitation.
- Neurorehabilitation and quality of life improvement in patients with neurological disorders.
- Neurological consequences of long COVID and post-viral syndromes.
- The gut-brain connection and its implications for neurological health.
- Ethical considerations in neurological research and treatment.
Bioethics in Health Research Topics
- Informed consent and its challenges in clinical trials and research.
- Ethical considerations in human genome editing and gene therapy.
- Allocation of healthcare resources and the principles of distributive justice.
- The ethics of organ transplantation and organ trafficking.
- End-of-life decision-making, including physician-assisted suicide.
- Ethical issues in the use of Artficial intelligence in healthcare decision-making.
- Research involving vulnerable populations: Balancing benefits and risks.
- Ethical considerations in global health research and disparities.
- Ethical implications of emerging biotechnologies, such as CRISPR-Cas9.
- Autonomy and decision-making capacity in healthcare ethics.
Read More
- Biology Research Topics
- Neuroscience Research Topics
Points To Be Remembered While Selecting Health Related Research Topics
When selecting a health-related research topic, there are several important considerations to keep in mind to ensure your research is meaningful and effective. Here are 7 key points to remember:
- Interest and Passion: Choose a topic that is according to your interests you, as your enthusiasm will fuel your research.
- Relevance: Ensure your topic addresses a real health issue or concern that can make a positive impact.
- Resources Availability: Confirm that you have access to the necessary materials and information for your research.
- Manageability: Pick a topic that is not too broad, ensuring it’s something you can investigate thoroughly.
- Guidance: Seek advice from experts or mentors to refine your topic and receive valuable insights.
- Ethical Considerations : Always consider the ethical implications of your research and ensure it complies with ethical guidelines.
- Feasibility: Ensure that the research can be completed within the available time and resources.
In the ever-evolving landscape of health research, selecting the right topic is the foundation for meaningful contributions. This blog has provided a roadmap for choosing health-related research topics, emphasizing the importance of personal interest, relevance, available resources, manageability, and expert guidance. Additionally, it has offered 300+ research topics across various domains, including mental health, public health, nutrition, chronic diseases, healthcare policy, and more.
In addition, with these insights, researchers, students, and healthcare professionals can embark on journeys that not only align with their passions but also address critical healthcare challenges. By making informed choices, we can collectively advance the frontiers of health and well-being.
Related Posts

Step by Step Guide on The Best Way to Finance Car

The Best Way on How to Get Fund For Business to Grow it Efficiently
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
Research Articles and Papers
Browse our library of telehealth research studies.
Trends and Disparities in Pandemic Telehealth Use among People with Disabilities
This research examines telehealth use among people with disabilities during the COVID-19 pandemic, highlighting increased reliance on audio-only telehealth to maintain access to care. Despite higher telehealth usage, overall care rates declined, especially for people with disabilities, with mobility disabilities showing the highest usage and hearing disabilities the lowest, indicating a need for tailored telehealth policies.
- Office of the Assistant Secretary for Planning and Evaluation
- Madjid Karimi, Lok Wong Samson, Sara J Couture, Trinidad Beleche, Helen Lamont, William Marton, Scott R Smith, Nancy De Lew, and Tom Buchmueller
- Health equity
- Medicare and Medicaid
- Telehealth experience
Telehealth and delivery of alcohol use disorder treatment in the Veterans Health Administration
This study investigates telehealth utilization among Veterans Health Administration patients receiving treatment for alcohol use disorder (AUD) during the COVID-19 pandemic. Findings indicate that while telehealth, particularly video visits, is associated with increased psychotherapy visits and medication coverage days for AUD treatment, certain patient groups, such as older individuals and those with specific substance use disorders or mental health conditions, are less likely to utilize video telehealth, highlighting the importance of maintaining multiple treatment modalities to ensure equitable access to care.
- National Institutes of Health
- Ponni V Perumalswami, Megan A Adams, Madeline C Frost, Rob Holleman, Hyungjin Myra Kim, Lan Zhang, Lewei Allison Lin
- Behavioral health
Telemedicine and In-Person Visit Modality Mix and Electronic Health Record Use in Primary Care
This study examined how telehealth use affects the amount of time providers spend documenting information in the electronic health record (EHR). The research found no evidence that telehealth increases EHR-based work on days when all visits are conducted using telehealth. However, on days that the provider delivered care both virtually and in-person, there was a small increase in the provider's EHR-based work.
- Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality
- Nate C. Apathy, Garrett Zabala, Kylie Gomes, Patti Spaar, Seth A. Krevat, Raj M. Ratwani
Listening to Black Pregnant and Postpartum People: Using Technology to Enhance Equity in Screening and Treatment of Perinatal Mental Health and Substance Use Disorders
This study explored the experiences of Black pregnant and postpartum individuals using a text/phone-based screening and referral program for perinatal mood and anxiety disorders, perinatal substance use disorders, and intimate partner violence. Findings highlighted the program's ease of use, convenience, and reduction in perceived judgment, contributing to increased comfort in discussing mental health and substance use concerns, ultimately addressing racial disparities in screening and treatment attendance.
- Health Resources and Services Administration
- Sara M Witcraft, Emily Johnson, Anna E Eitel, Angela D Moreland, Courtney King, Mishka Terplan, Constance Guille
- Maternal health
Changes in telemedicine use and ambulatory visit volumes at a multispecialty cardiovascular center during the COVID-19 pandemic
This study investigates the adoption of telemedicine in cardiology clinics during the COVID-19 pandemic, revealing a substantial increase in usage. With variations across subspecialties, higher telemedicine utilization correlated with larger increases in new patient visits, highlighting its potential to increase access to cardiovascular care.
- Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality; National Institutes of Health
- Neil M Kalwani, Esli Osmanlliu, Vijaya Parameswaran, Lubna Qureshi, Rajesh Dash, Paul A Heidenreich, David Scheinker, Fatima Rodriguez
Text And Telephone Screening And Referral Improved Detection And Treatment Of Maternal Mental Health Conditions
In a randomized controlled trial comparing a text- and telephone-based screening program with usual in-person screening and referral care, participants in the program were three times more likely to be screened. Among those screened, program participants were more likely to screen positive, be referred to treatment, and attend treatment compared to those receiving usual care.
- Constance Guille, Courtney King, Kathryn King, Ryan Kruis, Dee Ford, Lizmarie Maldonado, Paul J Nietert, Kathleen T Brady, Roger B Newman
Telehealth Use and Health Equity for Mental Health and Substance Use Disorder During the COVID-19 Pandemic: An Updated Systematic Review
This brief is an updated systematic review on health equity and the use of telehealth for patients with mental health conditions and substance use disorders (SUD). Findings continue to reveal lower telehealth utilization among disadvantaged groups. This update included more studies looking at short-term clinical secondary outcomes and telehealth for alcohol-use disorder and SUD treatment.
- Health Resources and Services Administration; Health Resources and Services Administration's Telehealth Research Center
- J Priyanka Vakkalanka, Khyathi Gadag, Lauren Lavin, Sara Ternes, Heather S Healy, Kimberly A S Merchant, Wakina Scott, Whitney Wiggins, Marcia M Ward, Nicholas M Mohr
- Rural health
Large-Scale Telemedicine Implementation for Outpatient Clinicians
This study introduces a learning collaborative designed to facilitate telemedicine implementation among outpatient clinicians in the early stages of the COVID-19 pandemic. The collaborative involved a diverse group, with participants from primary care (71%), rural settings (51%), and community health centers (28%). This collaborative demonstrated a model to rapidly disseminate knowledge during emergencies.
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services
- Wong, David; Cross, Israel H; Ramers, Christian B; Imtiaz, Farah; Scott, John D; Dezan, Amanda M; Armistad, Amy J; Manteuffel, Marie E; Wagner, Dennis M; Hunt, Richard C; England, William L; Kwong, Mei Wa; Dizon, Raynald A; Lamers, Vanessa; Plotkin, Ilya; Jolly, B Tilman; Jones, Walter; Daly, Darin D; Yeager, Megan; Riley, Jinean A; Krupinski, Elizabeth A; Solomon, Andrew P; Wibberly, Katharine H; Struminger, Bruce B
Antibiotic Receipt for Pediatric Telemedicine Visits With Primary Care vs Direct-to-Consumer Vendors
This study compared antibiotic prescribing practices for pediatric acute respiratory tract infection visits between telehealth with primary care practitioners and commercial direct-to-consumer telemedicine companies. Results showed that telemedicine integrated within primary care had lower rates of antibiotic prescribing and follow-up care compared to direct-to-consumer telemedicine companies.
- Samuel R Wittman, Alejandro Hoberman, Ateev Mehrotra, Lindsay M Sabik, Jonathan G Yabes, Kristin N Ray
- Pediatric care
The Role of Human-Centered Design in Healthcare Innovation: A Digital Health Equity Case Study
Amidst the complexities of health care delivery, human-centered design (HCD) offers innovative solutions. During the COVID-19 pandemic, HCD was used to address disparities in virtual service utilization among specific patient populations. This research study explored lessons learned from using HCD in clinical care settings.
- Ximena A Levander, Hans VanDerSchaaf, Vanessa Guerrero Barragán, Hetal Choxi, Amber Hoffman, Emily Morgan, Eva Wong, Raghav Wusirika, Anthony Cheng
Telephone-Based Rehabilitation Intervention to Optimize Activity Participation After Breast Cancer: A Randomized Clinical Trial
This study aimed to determine if a telephone-based coaching rehabilitation intervention could improve activity participation in breast cancer survivors post-treatment. While the intervention didn't show significant differences in overall participation measures compared to a control group, participants reported greater improvements in self-selected activity satisfaction and performance.
- Kathleen Doyle Lyons, Stephen B Wechsler, Deborah B Ejem, Courtney J Stevens, Andres Azuero, Sarah Khalidi, Mark T Hegel, Sarah M Dos Anjos, Megan E Codini, Mary D Chamberlin, Jamme L Morency, Jazmine Coffee-Dunning, Karen E Thorp, Danielle Z Cloyd, Susan Goedeken, Robin Newman, Colleen Muse, Gabrielle Rocque, Kimberly Keene, Maria Pisu, Jennifer Echols, Marie A Bakitas
- Chronic conditions
Adapting telehealth to address health equity: Perspectives of primary care providers across the United States
This research investigates how Federally Qualified Health Centers (FQHCs) utilized telehealth during the COVID-19 pandemic to address the health care needs of underserved populations, including those experiencing homelessness, individuals with disabilities, and non-English speakers. Through clinician interviews, the study reveals innovative strategies such as deploying telehealth in shelters, distributing mobile devices, and adapting group therapy sessions. The study emphasizes the crucial role of telehealth in promoting health equity.
- Rachel Azar, Rachel Chan, Miriam Sarkisian, Robert D Burns, James P Marcin, Christine Gotthardt, Keshia R De Guzman, Jennifer L Rosenthal, Sarah C Haynes
Racial and Ethnic Differences in Telemedicine Use
This study investigated telehealth use among traditional Medicare enrollees from March 2020 to February 2022. While initially, Black, Hispanic, and other racial groups had more telemedicine visits than White individuals, after adjusting for various factors such as geographic region, they received fewer telemedicine visits, indicating persistent disparities in access to telemedicine among racial and ethnic minorities.
- Felippe O Marcondes, Sharon-Lise T Normand, Benjamin Le Cook, Haiden A Huskamp, Jorge A Rodriguez, Michael L Barnett, Lori Uscher-Pines, Alisa B Busch, Ateev Mehrotra
Telehealth Treatment for Opioid Use Disorder During Pregnancy
This study investigated pregnant patients receiving opioid use disorder (OUD) treatment via a telehealth program. The study found that most patients received continuous care throughout pregnancy, with high retention rates and medication adherence.
- M Justin Coffey, Maxwell Weng, Cynthia Jimes, Shannon Brigham, Marlene C Lira
Telemedicine vs Telephone Consultations and Medication Prescribing Errors Among Referring Physicians: A Cluster Randomized Crossover Trial
This research study compared rates of emergency department (ED) physician-related medication errors among critically ill children receiving either video telemedicine or telephone consultations. The results indicated no statistically significant differences in medication errors between the two consultation methods.
- James P Marcin, Monica K Lieng, Jamie Mouzoon, Hadley S Sauers-Ford, Daniel Tancredi, Annie Cabri, Vaibhavi A Pandya, Alex S Park, Nathan Kuppermann
- February 2024
- Emergency health
Best Practices for Telehealth in Nurse-Led Care Settings-A Qualitative Study
This study explores the adoption of telehealth in nurse-led care sites in response to the COVID-19 pandemic. Through interviews with providers and patients, it identifies key best practices for implementing telehealth to enhance health equity, emphasizing the flexibility and potential of telehealth within nurse-led care models to deliver equitable care.
- Charlotte R Weiss, Mia Roberts, Melissa Florell, Rachel Wood, Rachel Johnson-Koenke, Claudia R Amura, Katherine Kissler, Amy J Barton, Jacqueline Jones
The association between rurality, dual Medicare/Medicaid eligibility and chronic conditions with telehealth utilization: An analysis of 2019-2020 national Medicare claims
This study reveals widening disparities in telehealth utilization among Medicare beneficiaries from 2019 to 2020, particularly among minority groups, rural residents, and dual Medicare/Medicaid eligible beneficiaries, with differences increasing as the number of chronic conditions rises. These findings underscore the challenge of ensuring equitable access to telehealth services, as those with the greatest health care needs may face barriers to utilization.
- Cari A Bogulski, George Pro, Mahip Acharya, Mir M Ali, Clare C Brown, Corey J Hayes, Hari Eswaran
Care Partner Engagement in Secure Messaging Between Patients With Diabetes and Their Clinicians: Cohort Study
Patient engagement through secure messaging in digital patient portals is linked to improved diabetes outcomes, yet disparities in use exist among older patients and racial and ethnic underserved groups. This study explored whether involving care partners could address disparities. The study found that those with care partners tend to use secure messaging more frequently and initiate messaging earlier.
- Wagahta Semere, Andrew J Karter, Courtney R Lyles, Mary E Reed, Leah Karliner, Celia Kaplan, Jennifer Y Liu, Jennifer Livaudais-Toman, Dean Schillinger
Availability of Mental Telehealth Services in the US
This study examined the availability and characteristics of telehealth for major depressive disorder, general anxiety disorder, and schizophrenia across mental health treatment facilities in the US. The findings reveal that while telehealth availability did not differ by clinical condition or patient demographics, variations were observed at the facility, county, and state levels.
- Jonathan Cantor, Megan S Schuler, Samantha Matthews, Aaron Kofner, Joshua Breslau, Ryan K McBain
Perinatal Telehealth: Meeting Patients Where They Are
This qualitative study examines perinatal patients' and providers' experiences with telehealth during and after the COVID-19 pandemic, aiming to inform future utilization of telehealth in delivering equitable perinatal care. Through interviews with patients and providers, numerous themes emerged, including unexpected advantages of telehealth, patient empowerment, providers' concerns about adverse outcomes and equitable care, strategies to improve telehealth experience and address access. This research highlights the potential for telehealth to enhance perinatal care while addressing access disparities.
- Katherine Kissler, E Brie Thumm, Denise C Smith, Jessica L Anderson, Rachel E Wood, Rachel Johnson, Mia Roberts, Alex Carmitchel-Fifer, Nicole Patterson, Claudia R Amura, Amy J Barton, Jacqueline Jones
Primary Care Providers' Experiences Treating Opioid Use Disorder Using Telehealth in the Height of the COVID-19 Pandemic
This study explores the use of telehealth for opioid use disorder (OUD) treatment during the COVID-19 pandemic, particularly in rural areas. Findings show that telehealth facilitated behavioral health counseling and maintained patient relationships, but in-person visits remained crucial for certain tasks such as urine drug screenings.
- Sarah Alexandra Marshall, Lachan E Siebenmorgen, Katherine Youngen, Tyrone Borders, Nickolas Zaller
- January 2024
Telehealth Use and Health Equity for Mental Health and Substance Use Disorder During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Systematic Review
This research study explored clinical effectiveness and telehealth utilization for mental health and substance use disorder management, particularly for underrepresented groups. Findings reveal disparities in telehealth utilization, notably among rural residents, older individuals, and Black/African American minorities.
Patient Characteristics Associated With Phone and Video Visits at a Tele-Urgent Care Center During the Initial COVID-19 Response: Cross-Sectional Study
This study examines the utilization of telemedicine modalities, particularly phone and video visits, in an urgent care setting during the COVID-19 pandemic. Findings suggest significant differences in utilization based on patient demographics.
- Saif Khairat, Roshan John, Malvika Pillai, Philip McDaniel, Barbara Edson
Exploring telemental health practice before, during, and after the COVID-19 pandemic
This study examined the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the utilization of telemedicine among mental health providers. Findings reveal a significant increase in daily telemedicine use during the pandemic, with more than half of providers' caseloads being served remotely. The study highlights a general increase in comfort with telemedicine and provider expectation for continued use post-pandemic.
- Demi Zhu, Samantha R Paige, Henry Slone, Arianna Gutierrez, Caroline Lutzky, Hannah Hedriana, Janelle F Barrera, Triton Ong, Brian E Bunnell
Use of in-network insurance benefits is critical for improving retention in telehealth-based buprenorphine treatment
This study examined the relationship between insurance status and 6-month retention among patients with opioid use disorder receiving care through a telehealth. Findings indicate that patients with in-network insurance coverage were more likely to be retained compared to cash-pay patients, suggesting that insurance status plays a significant role in treatment retention.
- Arthur Robin Williams, Christopher Rowe, Lexie Minarik, Zack Gray, Sean M Murphy, Harold A Pincus
Assessment of Pregnancy-Related Telehealth Interventions in the United States: A 10-Year Scoping Review
This scoping review examines pregnancy-related telehealth interventions, indicating a growing body of literature on the subject since 2011. While most studies focused on synchronous interaction between providers and patients, outcomes primarily assessed maternal/infant health, patient satisfaction, and attendance/compliance. The study highlighted the need for further research on telehealth's impact on patient satisfaction, health disparities, and cost-benefit in pregnancy-related care.
- Hannah C McCoy, Mary Kathryn Allison, Michelle Hernandez, Mir M Ali, Melony Stokes, Cari A Bogulski, Hari Eswaran
Chronic Disease Management through Clinical Video Telehealth on Health Care Utilization, and Mortality in the Veterans Health Administration: A Retrospective Cohort Study
This study investigated the impact of clinical video telehealth on health care utilization and mortality among older Veterans with chronic conditions like congestive heart failure (CHF), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and diabetes mellitus (DM). Clinical video telehealth was associated with increased emergency department visits across all conditions but its association with inpatient admissions and mortality varied.
- J Priyanka Vakkalanka, Andrea Holcombe, Marcia M Ward, Knute D Carter, Kimberly D McCoy, Heidi M Clark, Jeydith T Gutierrez, Kimberly A S Merchant, Nicholas M Mohr
An mHealth Design to Promote Medication Safety in Children with Medical Complexity
This study worked to identify medication safety challenges for children with medical complexity and to develop requirements for a mobile health app to address the challenges. Future steps include piloting the tools to evaluate usability and effectiveness in reducing medication errors.
- Anna Jolliff, Ryan J Coller, Hannah Kearney, Gemma Warner, James A Feinstein, Michelle A Chui, Steve O'Brien, Misty Willey, Barbara Katz, Theodore D Bach, and Nicole E Werner
- Remote patient monitoring
Gaps in internet use narrowed among older adults with Medicare during the COVID-19 pandemic but persist
This research explores internet usage among older adults with Medicare. The study reveals disparities in internet access, with higher rates among White individuals, younger age groups, those with higher education levels and better health and lower usage among minority groups, older individuals, and those with limited income and assets.
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services
- Megan K Beckett, Ann Haas, Debra Saliba, Steven C Martino, Nate Orr, Lauren Fuentes, Joy Binion, Sarah Gaillot, Jennifer Gildner, Marc N Elliott
Telemedicine use and decrements to type 2 diabetes and hypertension care during the COVID-19 pandemic
This research study investigates the impact of telemedicine use on the quality of care for adults with type 2 diabetes and/or hypertension. Telemedicine use was associated with lower odds of hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) monitoring for adults with type 2 diabetes and lower odds of blood pressure testing for those with type 2 diabetes and/or hypertension. The study suggests that additional measures may be necessary to ensure high-quality care.
- Hector P Rodriguez, Elizabeth Ciemins, Karl Rubio, Cori Rattelman, John K Cuddeback, Jeff T Mohl, Salma Bibi & Stephen M Shortell
Development of a Novel Telemedicine Tool to Reduce Disparities Related to the Identification of Preschool Children with Autism
This research focuses on a telemedicine-based assessment tool to address care disparities for children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD). Findings include higher clinician diagnostic accuracy and certainty when confirming existing ASD diagnoses than ruling out ASD.
- Liliana Wagner, Alison Vehorn, Amy S Weitlauf, Ambar Munoz Lavanderos, Joshua Wade, Laura Corona, Zachary Warren
- December 2023
Enhancing access and impact of the Medicare Diabetes Prevention Program using telehealth: a narrative review
This review looked at telehealth in diabetes prevention programs for older adults. The study found that diabetes prevention programs using telehealth are beneficial for increasing program reach, program impact, and social support, including for underserved populations.
- Natalie D Ritchie, Melanie T Turk
Exploring Telehealth to Improve Discharge Outcomes in Children
This research study aims to address the inpatient to outpatient transition by proposing a telehealth follow-up visit after hospital discharge and evaluating beliefs of this approach. Through interviews with pediatric hospitalists, senior residents, and caregivers, the study identified three primary themes: the potential benefits of telehealth follow-up visit after hospital discharge, the need for it to enhance current practices rather than replace them, and concerns about workflow challenges and resource limitations.
- Bhargavi Ram, Jennifer Lynn Rosenthal, Emily Stieren, Michelle Hamline
Telehealth Delivery in Part C Early Intervention: Provider and Caregiver Perspectives
The study investigates the impact of the shift to telehealth for Part C early intervention EI services at the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic. All surveyed providers reported changes in service aspects and approximately half of surveyed caregivers reported that satisfaction with services remained the same.
- Alice Bravo, Lisa V Ibañez, Sabine Scott, Catherine Dick, Pascale Carpentier, Wendy L Stone
Temporal Trends in Telehealth Availability in Mental Health Treatment Settings: Differences in Growth by State Rurality, 2015-2020
This research investigates the growth of telehealth availability in outpatient mental health treatment facilities across the US from 2015 to 2020, examining differences by state urbanicity and rurality. The study found that telehealth adoption increased rapidly during this period, with more significant growth in urban areas compared to rural. There were substantial variations among states, suggesting a need for tailored approaches to address the unique challenges faced by different populations and regions.
- George Pro, Brian Fairman, Jure Baloh, Don Willis, Broome E E Montgomery
Implementation Considerations for Family-Based Telehealth Interventions for Youth in Foster Care: Focus Group Study With Child Welfare System Professionals
This study investigated child welfare professionals' perspectives on providing family-based interventions through telehealth to foster youth in out-of-county placements. The professionals identified various factors influencing intervention delivery including environmental, predisposing, enabling, and need.
- Hannah P Leo, Johanna B Folk, Christopher Rodriguez, Marina Tolou-Shams
Adaptation of the Tele-Harm Reduction intervention to promote initiation and retention in buprenorphine treatment among people who inject drugs: a retrospective cohort study
This study examined buprenorphine initiation and retention among people who inject drugs with opioid use disorder who received a telehealth intervention in a harm reduction setting. There was a 58.7% three-month retention rate for buprenorphine among participants. This study found that harm reduction settings may be a suitable venue for telehealth interventions.
- Edward Suarez, Jr, Tyler S Bartholomew, Marina Plesons, Katrina Ciraldo, Lily Ostrer, David P Serota, Teresa A Chueng, Morgan Frederick, Jason Onugha, Hansel E Tookes
Use of a Mobile-Assisted Telehealth Regimen to Increase Exercise in Transplant Candidates: A Home-Based Prehabilitation Pilot and Feasibility Trial
This study used a home-based exercise intervention, including telehealth sessions and personal activity trackers, to enhance physical fitness for liver transplant candidates. Results showed significant improvements in the Liver Frailty Index and the 6-minute walk test, demonstrating the potential benefits of telehealth for liver transplant candidates.
- Andres Duarte-Rojo, Pamela M Bloomer, Rachel K Grubbs, Jonathan G Stine, Daniela Ladner, Christopher B Hughes, Michael A Dunn, John M Jakicic
- November 2023
Clinician Perceptions of Barriers and Facilitators for Delivering Early Integrated Palliative Care via Telehealth
This study explores telehealth for delivering early integrated palliative care (EIPC) to patients with advanced lung cancer. A survey of palliative care clinicians highlights positive perceptions of telehealth, with many agreeing that telehealth enhances access. Clinicians noted some barriers to telehealth use at the patient, organization, and system level.
- Katrina Grace Sadang, Joely A Centracchio, Yael Turk, Elyse Park, Josephine L Feliciano, Isaac S Chua, Leslie Blackhall, Maria J Silveira, Stacy M Fischer, Michael Rabow, Finly Zachariah, Carl Grey, Toby C Campbell, Jacob Strand, Jennifer S Temel, Joseph A Greer
Understanding rural-urban differences in veterans' internet access, use and patient preferences for telemedicine
This study examines telemedicine utilization among rural and urban veterans receiving care from the Veterans Health Administration (VA), finding that while most patients have internet access, rural patients are less likely to have had a telemedicine visit. Both rural and urban patients recommend technology training to improve telemedicine access.
- United States Department of Veterans Affairs
- Amy M J O'Shea, Mikayla Gibson, James Merchant, Kelby Rewerts, Kelly Miell, Peter J Kaboli, Stephanie L Shimada
A Community-Based Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis Telehealth Program Focused on Latinx Sexual Minority Men
This research describes the development and implementation of a community-based organization pre-exposure prophylaxis (CBO-PrEP) telehealth program to address barriers faced by Latinx sexual minority men. The program established protocols for referrals, insurance coverage, and appointments. The results indicate that CBO-PrEP successfully engaged the target population, with a high percentage undergoing laboratory testing and receiving PrEP prescriptions, showcasing the potential impact of collaborative approaches.
- Elí A Andrade, Gabriela Betancourt, Gustavo Morales, Omar Zapata, Lissette Marrero, Sage Rivera, Eric Nieves, Carolina Miranda, Chanelle Diaz, Robert Beil, Viraj V Patel, Jonathan Ross
Socioeconomic Determinants of Remote Patient Monitoring Implementation Among Rural and Urban Hospitals
This study investigated the relationship between social determinants of health and the adoption of remote patient monitoring (RPM) for chronic disease management. The study found that both rural and urban hospitals near households with lower middle socioeconomic status are less likely to have adopted RPM when compared with their counterparts near households with the highest socioeconomic status. The findings underscore the importance of addressing disparities in access to RPM services.
- Matthew Najarian, Anthony Goudie, Jonathan P Bona, Mandana Rezaeiahari, Sean G Young, Cari A Bogulski, Corey J Hayes
Completion of Recommended Tests and Referrals in Telehealth vs In-Person Visits
This retrospective cohort study conducted at a large urban hospital-based primary care practice and an affiliated community health center aimed to assess the association of diagnostic loop closure (completion of recommended tests and specialty referrals) for telehealth visits compared to in-person visits. The findings revealed that rates of diagnostic loop closure were low across all visit modalities with patients with telehealth visits less likely to close the loop compared to those with in-person visits.
- Anthony Zhong, Maelys J Amat, Timothy S Anderson, Umber Shafiq, Scot B Sternberg, Talya Salant, Leonor Fernandez, Gordon D Schiff, Mark D Aronson, James C Benneyan, Sara J Singer, Russell S Phillips
Association of Remote Patient Monitoring with Mortality and Healthcare Utilization in Hypertensive Patients: a Medicare Claims-Based Study
This study evaluated the association between remote patient monitoring (RPM) use and patient outcomes among Medicare beneficiaries aged 65 years and older with hypertension. RPM use was associated with reduced hazards of mortality and hospitalizations. However, there was an increase in cardiovascular-related outpatient visits, suggesting potential benefits and trade-offs of RPM implementation in managing hypertension in older adults.
- Mahip Acharya, Mir M Ali, Cari A Bogulski, Ambrish A Pandit, Ruchira V Mahashabde, Hari Eswaran, Corey J Hayes
Adapting Connect for Health pediatric weight management program for telehealth in response to the COVID-19 pandemic
This study focused on telehealth experiences for a primary care, pediatric weight management intervention. The results highlight the importance of a combination of in-person and virtual visits to align with patient and provider preferences, with specific considerations for those with limited English proficiency.
- Meg Simione, Kelly Aschbrenner, Haley Farrar-Muir, Man Luo, Jazmin Granadeno, Ariadne Caballero-Gonzalez, Sarah N Price, Carlos Torres, Alexy Arauz Boudreau, Lauren Fiechtner, Simon J Hambidge, Kerry Sease, Elsie M Taveras

Telehealth utilization in gynecologic oncology clinical trials
This study assesses the safety and feasibility of implementing telehealth and remote clinical trial operations in gynecologic oncology during the COVID-19 pandemic. The study found virtual provider visits and off-site laboratory testing increased during the telehealth period. While minor protocol deviations increased, major deviations and adverse events remained of low incidence and did not differ.
- Leslie Andriani, Jinhee Oh, Erin McMinn, Emily Gleason, Nathanael C Koelper, Jesse Chittams, Fiona Simpkins, Emily M Ko
- October 2023
Use of Telemedicine and Quality of Care Among Medicare Enrollees With Serious Mental Illness
This cohort study investigates the impact of telemedicine use during the COVID-19 pandemic on mental health care for Medicare beneficiaries with serious mental illnesses. The study categorizes practices based on telemedicine use and compares changes in care patterns and quality metrics. The findings indicate that practices with higher telemedicine use saw an increase in mental health visits per year compared with prepandemic levels, with no significant changes observed in other quality metrics.
- Andrew D Wilcock, Haiden A Huskamp, Alisa B Busch, Sharon-Lise T Normand, Lori Uscher-Pines, Pushpa V Raja, Jose R Zubizarreta, Michael L Barnett, Ateev Mehrotra
Evaluating the association between expanded coverage of direct-to-consumer telemedicine and downstream utilization and quality of care for urinary tract infections and sinusitis
This study compares direct-to-consumer (DTC) telemedicine and in-person visits for urinary tract infections (UTIs) and sinusitis, analyzing rates of testing, follow-up care, and quality. The study finds that DTC telemedicine coverage is associated with reductions in antibiotics for sinusitis and laboratory tests for UTI, without changes in overall office and outpatient visits or emergency department visits.
- Jiani Yu, Peter J Huckfeldt, Pamela J Mink, Ateev Mehrotra, Jean M Abraham
Persistence of Telemedicine Usage for Breast and Prostate Cancer after the Peak of the COVID-19 Pandemic
This study investigates utilization of telemedicine for breast and prostate cancer patients. The findings underscore specific contexts where providers and patients use telehealth.
- Susan Chimonas, Allison Lipitz-Snyderman, Zoe Spiegelhoff, Nirjhar Chakraborty, Kenneth Seier, Charlie White, Gilad Kuperman
Telemedicine Buprenorphine Initiation and Retention in Opioid Use Disorder Treatment for Medicaid Enrollees
This retrospective cohort study examined the outcomes of telemedicine versus in-person care for initiating transmucosal buprenorphine treatment of opioid use disorder (OUD) during the COVID-19 pandemic. The study found that telemedicine initiation was associated with better 90-day retention in buprenorphine treatment and was not associated with an increased risk of opioid-related nonfatal overdose.
- Lindsey R Hammerslag, PhD Aimee Mack, MPH Redonna K Chandler, PhD Laura C Fanucchi, MD, MPH Daniel J Feaster, PhD Marc R LaRochelle, MD, MPH Michelle R Lofwall, MD Michael Nau, PhD Jennifer Villani, PhD, MPH Sharon L Walsh, PhD Philip M Westgate, PhD Svetla Slavova, PhD Jeffery C Talbert, PhD
Remote Monitoring Compared With In-Office Surveillance of Blood Pressure in Patients With Pregnancy-Related Hypertension: A Randomized Controlled Trial
This study looked at individuals with hypertensive disorders or pregnancy and compared blood pressure ascertainment within 10 days of postpartum discharge using in-office blood pressure assessment versus remote patient monitoring. The study found that those using remote monitoring showed significantly higher rates of blood pressure ascertainment compared to the in-office group. Remote monitoring had no significant differences in readmission rates or initiation of antihypertensive medications post-discharge, suggesting that remote monitoring has the potential to enhance postpartum care.
- Brittany J Arkerson, Matthew M Finneran, Solita R Harris, Jessica Schnorr, Eliza R McElwee, Lauren Demosthenes, Renata Sawyer
Financial performance of rural hospitals persistently lacking or having telehealth technology
This study analyzed the adoption of telehealth by rural hospitals and its impact on their financial performance from 2009 to 2019. Findings suggest that telehealth adoption was influenced by hospital and community characteristics, with factors such as hospital ownership, patient demographics, and insurance status playing significant roles. The study found that rural hospitals adopting telehealth exhibited better financial performance over the 11-year period compared to non-adopters, indicating potential benefits for sustainability and service provision in rural health care settings.
- Saleema A Karim, J Mick Tilford, Cari A Bogulski, Maysam Rabbani, Corey J Hayes, Hari Eswaran
- September 2023
A New Frontier in Telehealth Research: A National Telehealth Data Warehouse
The National Telehealth Data Warehouse will analyze telehealth encounters comprehensively, aiming to assess its utility, cost-impact, and effects on clinical outcomes, particularly in response to the COVID-19 pandemic. This initiative aims to facilitate robust research studies and develop quality measures specific to telehealth, ultimately contributing to reducing disparities in healthcare and expanding access to care for all.
- Jason C Goldwater, Yunxi Zhang, Yael Harris, Chandra Saurabh, Richard L Summers
- Workforce development
Sociodemographic disparities in the use of cardiovascular ambulatory care and telemedicine during the COVID-19 pandemic
This research study investigated the association of patient and visit characteristics with telehealth modality in cardiology clinics during the COVID-19 pandemic. The study found disparities in video-based telehealth for older patients, Black patients, those with limited English proficiency, and Medicaid recipients. Further research is needed to understand barriers and outcomes related to telehealth among diverse populations.
- Esli Osmanlliu, Neil M Kalwani, Vijaya Parameswaran, Lubna Qureshi, Rajesh Dash, David Scheinker, Fatima Rodriguez
Mobile Health Intervention in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized Clinical Trial
The study investigated the impact of clinical pharmacists and health coaches utilizing telehealth on hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) levels for African American and Latinx patients with type 2 diabetes. The study found that, among participating patients, HbA1c levels improved, suggesting that this telehealth intervention can improve blood glucose levels in the studied populations.
- Ben S Gerber, Alana Biggers, Jessica J Tilton, Daphne E Smith Marsh, Rachel Lane, Dan Mihailescu, JungAe Lee, Lisa K Sharp
Older Veterans' Experiences of a Multicomponent Telehealth Program: Qualitative Program Evaluation Study
This study focuses on addressing the multifaceted needs of older veterans with multiple health conditions through a telehealth program. Qualitative interviews with program participants identified areas for improvement and adaptation.
- Michelle R Rauzi, Meredith L Mealer, Lauren M Abbate, Jennifer E Stevens-Lapsley, Kathryn A Nearing
Researcher Experience and Comfort With Telemedicine and Remote Patient Monitoring in Cancer Treatment Trials
This research focused on the integration of telemedicine and remote patient monitoring (RPM) in oncology practices since the onset of COVID-19, particularly in treatment trials. A survey was conducted to assess experience and comfort levels with telemedicine and RPM. The findings suggest that while telemedicine and RPM has been increasingly used in cancer treatment trials, there is a higher level of researcher comfort compared to real-world experience.
- Morgan R L Lichtenstein, Laura A Levit, Caroline Schenkel, Kelsey Kirkwood, Lola A Fashoyin-Aje, Suanna S Bruinooge, Michael J Kelley, Josh A Mailman, Allison Magnuson, Daniel P Mirda, Divya Natesan, Dawn L Hershman
Telemedicine Critical Care-Mediated Mortality Reductions in Lower-Performing Patient Diagnosis Groups: A Prospective, Before and After Study
This study evaluated the impact of implementing telemedicine critical care on risk-adjusted mortality in adult intensive care units at academic medical centers. The study found that, overall, there was a slight decrease in risk-adjusted mortality after telemedicine critical care implementation, although not statistically significant. However, a subgroup of patients with a history of lower performance in ICU care experienced a significant reduction in standardized mortality ratio and risk-adjusted mortality, while the higher-performing patient group showed no significant changes.
- Walter A Boyle, Christopher M Palmer, Lisa Konzen, Bradley A Fritz, Jason White, Michelle Simkins, Brian Dieffenderfer, Ayesha Iqbal, Jill Bertrand, Shelley Meyer, Paul Kerby, Sara Buckman, Vladimir Despotovic, Jim Kozlowski, Patricia Crimmins Reda, Igor Zwir, C Charles Gu, Uchenna R Ofoma
Telemedicine Visits in US Skilled Nursing Facilities
This cohort study investigated the telehealth use in skilled nursing facilities (SNFs) during the COVID-19 pandemic. The study revealed that telehealth adoption in SNFs significantly increased in early 2020 and gradually stabilized at a higher rate than before the pandemic. Importantly, higher telemedicine use in SNFs was linked to improved access to psychiatry visits.
- Agne Ulyte, Ateev Mehrotra, Andrew D Wilcock, Gillian K SteelFisher, David C Grabowski, Michael L Barnett
- August 2023
An Integrated Teledermatology Model: Attacking Access to Skin Care in a Rural State
This review highlights the significance of teledermatology in modern health care, particularly focusing on the integrated teledermatology model. Emphasizing the value of both live synchronous and store-and-forward modalities, the program demonstrates cost-effectiveness and reliability, providing essential access to dermatological care in rural areas where in-person consultations are limited.
- Maggie Holmes, Ioachim Preda-Naumescu, Ana Preda-Naumescu, Thy Huynh
Telehealth and In-Person Mental Health Service Utilization and Spending, 2019 to 2022
This study examines trends in mental health service utilization and spending before and during the COVID-19 pandemic. During the acute phase of the pandemic, in-person visits decreased and telehealth visits increased. In the post-acute phase, telehealth visits stabilized and in-person visits increased, resulting in overall mental health service utilization being higher than before the pandemic by August 2022.
- Jonathan H Cantor, Ryan K McBain, Pen-Che Ho, Dena M Bravata, Christopher Whaley
Telehealth use and perceptions among prostate cancer survivors
This study investigated telehealth disparities among prostate cancer survivors. One-third of survivors had used telehealth, with 10% considering it comparable to in-person visits. Those with lower education were less likely to use telehealth and less likely to feel inclined to use it, highlighting the importance of addressing these disparities.
- Luke W Chen, Deborah S Usinger, Aaron J Katz
Comparing the Discussion of Telehealth in Two Social Media Platforms: Social Listening Analysis
This study compared telehealth-related discussions on social media before and during the COVID-19 pandemic. Both of the platforms reviewed exhibited a surge in discussions related to telehealth during the pandemic, with one focusing more on news and services and one involving more user discussions and inquiries about using telehealth for therapy or counseling. The findings highlight the evolving discourse on telehealth in social media and suggest platform-specific differences in how telehealth is perceived and discussed by users.
- Catherine C Shoults, Leah Dawson, Corey Hayes, Hari Eswaran
Telemedicine in Primary Care: Lessons Learned About Implementing Health Care Innovations During the COVID-19 Pandemic
This research study examines the experiences of primary care clinicians with telemedicine during the first two years of the COVID-19 pandemic. Respondents noted initial telehealth implementation challenges due to infrastructure and reimbursement issues. Over time, clinicians' attitudes toward telemedicine improved, with many considering it an important tool alongside in-person care.
- Rebecca S Etz, Craig A Solid, Martha M Gonzalez, Erin Britton, Kurt C Stange, Sarah R Reves
Why U.S. Patients Declined Hospital-at-Home during the COVID-19 Public Health Emergency: An Exploratory Mixed Methods Study
This study aimed to understand patient refusals of hospital-at-home during the COVID-19 Public Health Emergency. The study highlights the need to improve education about hospital-at-home and to address domestic barriers and diagnostic challenges.
- Nels Paulson, Margaret P Paulson, Michael J Maniaci, Rachel A Rutledge, Shealeigh Inselman, Stephanie J Zawada
Use of Medication for Opioid Use Disorder Among Adults With Past-Year Opioid Use Disorder in the US, 2021
This study examines the prevalence of medication for opioid use disorder (MOUD) receipt among US adults with past-year opioid use disorder (OUD). The study found that despite guidelines recommending MOUD, around 1 in 5 adults with past-year OUD received any form of MOUD. Disparities were identified, particularly among Black adults, women, the unemployed, and those in nonmetropolitan areas, who were less likely to receive MOUD. Those who used telehealth for substance use treatment were more likely to have received MOUD.
- National Institutes of Health; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
- Christopher M Jones, Beth Han, Grant T Baldwin, Emily B Einstein, Wilson M Compton
Towards a conceptual framework for addressing state-level barriers to decentralized clinical trials in the U.S.
This article proposes a framework to identify barriers to decentralized clinical trials, including those related to policies and regulations governing virtual care.
- Stephanie J Zawada, Kevin C Ruff, Tara Sklar, Bart M Demaerschalk
- Telehealth policy
Telehealth Lifestyle Redesign Occupational Therapy for Diabetes: Preliminary Effectiveness, Satisfaction, and Engagement
This research evaluates telehealth delivery in an occupational therapy intervention for young adults with diabetes. Preliminary results suggest that telehealth clients experienced significant improvements in occupational performance, satisfaction, and health management, with high levels of satisfaction.
- Seth Mitchell, John Sideris, Jeanine Blanchard, Gabrielle Granados, Jesús Díaz, Elizabeth Pyatak
State Medicaid Telehealth Coverage Policy Decisions Since the COVID-19 Public Health Emergency
This report analyzes state Medicaid telehealth policy changes during the COVID-19 pandemic through May 2022. The study reviews both temporary and permanent state Medicaid telehealth policies to provide insight into the evolving landscape of telehealth regulation.
- Peggy G Chen, Sara E Heins, Stephanie Dellva
Changes in Telehealth Experienced by Advanced Practice RNs During COVID-19
This research study investigates advanced practice RNs' experiences with telehealth before and during the COVID-19 pandemic. A survey found that while a majority of respondents did not use telehealth before the pandemic, half of them began using it daily during the pandemic. The study highlights the challenges and benefits of telehealth adoption and suggests that telehealth is likely to remain an integral part of health care, emphasizing the need for recommendations for advanced practice RN.
- Mavis N Schorn, Carole R Myers, Julie Barroso, Karen Hande, Tamika Hudson, Jennifer Kim, and Ruth Kleinpell
Factors Associated with Remote Patient Monitoring Services Provision by Hospitals and Health Care Systems in the United States
This research study investigates factors influencing the provision of remote patient monitoring (RPM), finding that 40% of hospitals reviewed offered RPM. Positive associations were observed with hospital participation in clinically integrated networks and private, non-profit ownership, while negative associations were noted with critical access hospital designation, for-profit ownership, and location in the South.
- Ambrish A Pandit, Hari Eswaran, Cari A Bogulski, Maysam Rabbani, Mary 'Katy' Allison, Leah Dawson, Corey J Hayes
Variations in Physician Telemedicine Provision
This research study examines the variation in telemedicine adoption among primary care physicians. While overall telemedicine use declined over time, about 32.5% of physicians continued to provide relatively high rates of telemedicine services. Physician preferences had an impact on telemedicine adoption, with individual physicians explaining 7.7% of the variation in telemedicine use, highlighting the role of physician behavior in patient access to telehealth services.
- Nate C Apathy, Ram A Dixit, Christian L Boxley, Katharine T Adams, Ethan Booker, Raj M Ratwani
Assessment Fidelity of Parents Implementing a Standardized Telehealth Infant Autism Screener
The research demonstrates that telehealth is effective for pediatric occupational therapy and that remote parent coaching provides benefits for parents and infants. The study evaluated telehealth-delivered observational autism screening tool for infants, with parents achieving an 82% adherence rate to the fidelity checklist. This study suggests that a parent coaching telehealth approach may be valid for pediatric telehealth assessments.
- Allison Q Phillips, Emily Campi, Meagan R Talbott, Grace T Baranek
Federal telehealth policy changes during the COVID-19 public health emergency: Associations with telemental health use among rural and urban Medicare beneficiaries
Medicare beneficiaries faced increased mental health concerns with limited access to mental health services during the COVID-19 pandemic. This study compared rural and urban Medicare fee-for-service beneficiary use of telemental health from 2019 to 2020. The analysis found a significant rise in telemental health use for both groups, with urban residents benefiting disproportionately. Among rural beneficiaries, older age was linked to lower telemental health use, indicating a need to address barriers.
- Health Resources and Services Administration's Telehealth Research Center; Health Resources and Services Administration
- Jean A Talbot PhD,MPH, Amanda R Burgess MPH,MPPM, Yvonne C Jonk PhD, Heidi O'Connor MS
Rural-Urban Disparities in Video Telehealth Use During Rapid Mental Health Care Virtualization Among American Indian/Alaska Native Veterans
This research focuses on the differences in utilization of video telehealth for mental health care among American Indian/Alaska Native veterans and non-American Indian/Alaska Native veterans. The study reveals increased telehealth use across all veteran groups but noted a significant difference in telehealth use among rural and urban populations, especially among American Indian/Alaska Native veterans.
- Isabelle S Kusters, Amber B Amspoker, Kristen Frosio, Stephanie C Day, Giselle Day, Anthony Ecker, Julianna Hogan, Jan A Lindsay, Jay Shore
Telehealth Utilization Among Occupational Therapists in Oncology: Results From a National Survey
This study aimed to explore the prevalence and perceptions of telehealth services among occupational therapy practitioners (OTPs) in oncology. The findings indicate that despite limited access prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, a majority of OTPs in oncology settings support telehealth use, with the highest endorsement relating to accessibility. Telehealth-delivered occupational therapy treatments in oncology were considered well-suited for areas such as education, quality of life, and psychosocial interventions.
- Alix G Sleight, Caroline M Klein, Alexandra E Feldman, Leah I Stein Duker
Prevalence and appropriateness of in-person versus not-in-person ambulatory antibiotic prescribing in an integrated academic health system: A cohort study
This study examines ambulatory antibiotic prescribing in an integrated health delivery system from 2016 to 2019. The study reveals the need for ambulatory stewardship interventions focused on all antibiotic prescribing.
- Tiffany Brown, Ji Young Lee, Adriana Guzman, Michael A Fischer, Mark W Friedberg, Kao-Ping Chua, Jeffrey A Linder
Changes in Telehealth Experienced by Advanced Practice RNs During COVID-19: US Survey Results
The article examines the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on advanced practice registered nurses (APRNs) and their use of telehealth. While a majority of APRNs did not utilize telehealth before the pandemic, its use significantly increased during the pandemic, with half of the respondents incorporating telehealth into their daily practice. The findings highlight both the barriers faced, such as limited access to technology for certain populations, and the benefits observed, including improved patient access to care. The study emphasizes the need for enhanced APRN education, policy, and practice to ensure expanded health care access.
- Mavis N Schorn, Carole R Myers, Julie Barroso, Karen Hande, Tamika Hudson, Jennifer Kim, Ruth Kleinpell
Telehealth Services for Primary Care and Urgent Care to Support Rural Schools and Students
This study looked at students receiving primary care or urgent care services from school-based telehealth programs. Of the students seeking primary care telehealth services, 67.7% did not have a primary care provider outside of the school. The availability of both primary care and urgent care telehealth services in the school allowed most students to return to the classroom without the need for further follow-up.
- Marcia M Ward, Kimberly A S Merchant, Fred Ullrich, Divya Bhagianadh, Knute D Carter, Kristin Smith, Theresa L Gillette, Sheila Freed, Luke J Mack
- School-based health
Updated Medicare FFS Telehealth Trends by Beneficiary Characteristics, Visit Specialty, and State, 2019-2021
This research examines Medicare fee-for-service (FFS) use of telehealth from 2019 to 2021 by beneficiary characteristic, visit specialty, and geography. This report found telehealth use among Medicare FFS beneficiaries in 2021 continued to be far above pre-pandemic levels, but lower than at the peak of 2020. Telehealth use in 2021 remained highest for behavioral health compared to non-behavioral health among Medicare FFS beneficiaries. The analysis found audio-only eligible telehealth comprised about one quarter of Medicare FFS telehealth in both 2020 and 2021. This report notes a wide variation across states in use of telehealth for Medicare FFS beneficiaries.
- Lok Wong Samson, Sara J Couture, Tim B Creedon, Laura Jacobus-Kantor, Steven Sheingold
Expansion of Telehealth Availability for Mental Health Care After State-Level Policy Changes From 2019 to 2022
This study aimed to investigate the associations between state policies and the availability of telehealth services at outpatient mental health treatment facilities. The state policies studied, payment parity, reimbursement for audio-only, participation in the Interstate Medical Licensure Compact, and participation in the Psychology Interjurisdictional Compact, were associated with expansion of telehealth availability for mental health care at mental health treatment facilities.
- Ryan K McBain, Megan S Schuler, Nabeel Qureshi, Samantha Matthews, Aaron Kofner, Joshua Breslau, Jonathan H Cantor
Postpartum Care up to 1 Year After Pregnancy: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
This systematic review evaluates postpartum care within the first year after pregnancy, focusing on alternative health care delivery strategies and extension of health insurance coverage. Findings suggest that certain factors, such as where health care was provided (by telephone or in clinic), may not impact depression or anxiety symptoms. More research is needed to improve postpartum care, especially for individuals at higher risk of complications.
- Ian J Saldanha, Gaelen P Adam, Ghid Kanaan, Michael L Zahradnik, Dale W Steele, Valery A Danilack, Alex Friedman Peahl, Kenneth K Chen, Alison M Stuebe, Ethan M Balk
The use of telehealth-supported stewardship activities in acute-care and long-term care settings: An implementation effectiveness trial
This study assessed the implementation of telehealth-supported stewardship activities in Veterans' Administration medical centers acute-care and long-term care units. The program resulted in reductions in antibiotic use in long-term care units but not in smaller acute-care units.
- Daniel J Livorsi, Stacey Hockett Sherlock, Cassie Cunningham Goedken, Sandra Pratt, David A Goodman, Kim C Clarke, Hyunkeun Cho, Heather Schacht Reisinger, Eli N Perencevich
Telepsychiatry Use Before and During the COVID-19 Pandemic Among Children Enrolled in Medicaid
This study investigated the utilization of telepsychiatry among children enrolled in Medicaid before and during the COVID-19 pandemic. Findings revealed a significant increase in telehealth usage, while overall mental health service utilization declined.
- Mir M Ali, Kristina D West, Erin Bagalman, Tisamarie B Sherry
Management of Postpartum Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy
This research study examines management strategies for postpartum hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, emphasizing home blood pressure (BP) monitoring, pharmacological treatment, and magnesium sulfate regimens. Results show that home blood pressure monitoring likely improves BP measurement adherence and decreases disparities between non-Black and Black patients in adherence to recommended BP surveillance.
- Dale W Steele, Gaelen P Adam, Ian J Saldanha, Ghid Kanaan, Michael L Zahradnik, Valery A Danilack-Fekete, Alison M Stuebe, Alex F Peahl, Kenneth K Chen, Ethan M Balk
Medical Assistants’ Telehealth Roles and Skills in Primary Care During the COVID-19 Pandemic
This publication investigates the involvement of medical assistants (MAs) in delivering primary care via telehealth during the COVID-19 pandemic. It highlights the evolving roles and responsibilities of MAs in telehealth delivery, emphasizing the importance of training and education to support their effectiveness in both in-person and virtual healthcare settings. Additionally, this research underscores the need for addressing challenges such as staffing shortages and turnover to ensure the sustained expansion of telehealth in primary care.
- Samantha W Pollack, Susan M Skillman, Tracy M Mroz, Bianca K Frogner
The Impact of Pandemic Concerns on Consumers' Teledentistry Use During the First Months of the COVID-19 Pandemic
This study examines factors associated with teledentistry use among adults during the COVID-19 pandemic, utilizing data from a nationally representative survey. Results show that a significant proportion of respondents used teledentistry for the first time due to the pandemic, with higher utilization among those with greater pandemic concerns, younger age groups, higher income levels, and urban residents. The study underscores the need for expanded regulatory changes to teledentistry to address broader patient needs beyond the pandemic, particularly targeting populations originally underserved by teledental programs.
- Ellen O'Malley, Simona Surdu, Margaret Langelier
Primary Care Telemedicine Use among Assisted Living Residents with Dementia during COVID-19: Race and Dual Enrollment Status
Telehealth services expanded to help primary care providers connect to assisted living facility residents with dementia during the COVID-19 pandemic. This study found that while Black and Hispanic assisted living facility residents and those in assisted living facilities with a higher proportion of duals were less likely to use telehealth early in the pandemic these racial and ethnic or socioeconomic differences did not persist.
- National Institutes of Health; Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality
- Yechu Hua, MA, Helena Temkin-Greener, PhD, Shubing Cai, PhD
Postdischarge Noninvasive Telemonitoring and Nurse Telephone Coaching Improve Outcomes in Heart Failure Patients With High Burden of Comorbidity
The purpose of this research is to investigate the effectiveness of noninvasive telemonitoring and nurse telephone coaching as a post-discharge strategy for heart failure patients, with a focus on how comorbidity burden influences its impact. The study reveals that noninvasive telemonitoring and nurse telephone coaching improved survival among heart failure patients with a high comorbidity burden.
- Asher Kimchi, Harriet U Aronow, Yu-Ming Ni, Michael K Ong, James Mirocha, Jeanne T Black, Andrew D Auerbach, Theodore G Ganiats, Sheldon Greenfield, Patrick S Romano, Ilan Kedan; BEAT-HF Research Group
Telehealth Use to Address Cardiovascular Disease and Hypertension in the United States: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, 2011-2021
This review explored the utilization of telehealth for hypertension and cardiovascular disease management, with a specific emphasis on social determinants of health and health disparities. The findings suggest that telehealth is comparable to in-person care for blood pressure and cardiovascular disease management.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
- Tiara N Jackson, Meera Sreedhara, Myles Bostic, Michelle Spafford, Shena Popat, Kincaid Lowe Beasley, Julia Jordan, Roy Ahn
Digital health and telehealth in cancer care: a scoping review of reviews
This research conducted a scoping review of reviews on digital health and telehealth interventions in cancer care. The results showed that while many reviews summarized interventions for cancer patients, there were notable gaps in addressing older adults, bereavement, and sustainability, as well as limited comparisons between telehealth and in-person care.
- Kelly M Shaffer, Kea L Turner, Chelsea Siwik, Brian D Gonzalez, Rujula Upasani, Jillian V Glazer, Robert J Ferguson, Catherine Joshua, Carissa A Low
Effect of Chronic Disease Home Telehealth Monitoring in the Veterans Health Administration on Healthcare Utilization and Mortality
This study investigates the impact of home telehealth monitoring on hospitalizations, emergency department (ED) visits, and mortality in veterans aged 65 and older with congestive heart failure (CHF), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), or diabetes mellitus (DM). The results show that the initiation of home telehealth monitoring was associated with increased ED visits but no change in hospitalizations. Those with CHF or DM had lower all-cause mortality while those with COPD had higher health care utilization and all-cause mortality.
- Nicholas M Mohr, J Priyanka Vakkalanka, Andrea Holcombe, Knute D Carter, Kimberly D McCoy, Heidi M Clark, Jeydith Gutierrez, Kimberly A S Merchant, George J Bailey, Marcia M Ward
Care coordination between rural primary care and telemedicine to expand medication treatment for opioid use disorder: Results from a single-arm, multisite feasibility study
This study focuses on the feasibility of implementing a care coordination model involving telemedicine for medication treatment of opioid use disorder (MOUD) in rural settings. The intervention involved establishing referral and coordination between rural clinics and a telemedicine provider. Results indicated that implementing the care coordination model led to an increase in patient-days on MOUD, particularly in clinics with limited MOUD capacity. This suggests that the model is most effective in expanding access to MOUD in rural areas where resources for MOUD are limited.
- Yih-Ing Hser PhD, Larissa J Mooney MD, Laura-Mae Baldwin MD, MPH, Allison Ober MSW, PhD, Lisa A Marsch PhD, Seth Sherman PhD, Abigail Matthews PhD, Sarah Clingan PhD, Zhe Fei PhD, Yuhui Zhu PhD, Alex Dopp PhD, Megan E Curtis PhD, Katie P Osterhage MMS, Emily G Hichborn BS, Chunqing Lin PhD, Megan Black MPH, Stacy Calhoun PhD, Caleb C Holtzer MD, MPH, Noah Nesin MD, Denise Bouchard DNP-C, Maja Ledgerwood DSW, LCSW, Margaret A. Gehring FNP, DNP, Yanping Liu MD, PhD, Neul Ah Ha BS, Sean M Murphy PhD, Maria Hanano BA, Andrew J Saxon MD
Telehealth Use, Care Continuity, and Quality: Diabetes and Hypertension Care in Community Health Centers Before and During the COVID-19 Pandemic
This research study explores the relationship between care continuity and the quality of diabetes and hypertension care in community health centers (CHCs) both before and during the COVID-19 pandemic, with a focus on the mediating effect of telehealth. The study found that higher care continuity is associated with telehealth use and A1c testing.
- Aaron A Tierney, Denise D Payán, Timothy T Brown, Adrian Aguilera, Stephen M Shortell, Hector P Rodriguez
Updated National Survey Trends in Telehealth Utilization and Modality (2021-2022)
This report includes trends in national telehealth utilization from 2021 to 2022. Results show that while overall telehealth use remains steady, disparities in video telehealth use exist among different populations and insurance types.
- Euny C Lee, Violanda Grigorescu, Idia Enogieru, Scott R Smith, Lok Wong Samson, Ann B Conmy, and Nancy De Lew
Telemental health in emergency care settings: A qualitative analysis of considerations for sustainability and spread
The study examines the barriers and facilitators for the sustainability and expansion of a model of telehealth care, telemental health video. The findings showed overall satisfaction, with increased comfort for patients in discussing difficult topics, and benefits for clinicians in terms of cross-coverage and safety. Adequate infrastructure and workforce capacity are crucial to ensure successful uptake of this model.
- McKenzie K Roddy, Patricia Chen, Alvin D Jeffery, Jeydith Gutierrez, Melissa Rubenstein, Corey Campbell, Eric Blake, Michael J Ward
Telehealth for management of chronic non-cancer pain and opioid use disorder in safety net primary care
This study qualitatively assesses the benefits and challenges of telehealth for managing chronic non-cancer pain, opioid use disorder, and multi-morbidity in urban safety net primary care patients. Factors such as patient burden, communication and technology challenges, pain control, opioid misuse, and medical complexity should be considered when making decisions about continuing or expanding telehealth services.
- Alexis Cooke, Stacy Castellanos, Celeste Enriquez, Pamela Olsen, Christine Miaskowski, Margot Kushel, Kelly Ray Knight
Trends in Telehealth Visits During Pregnancy, 2018 to 2021
This study analyzed trends in prenatal telehealth visits during pregnancy and identified patient characteristics associated with the number of prenatal telehealth visits. The findings showed prenatal telehealth utilization increased significantly during the COVID-19 pandemic.
- Mahip Acharya, Mir M Ali, Corey J Hayes, Cari A Bogulski, Everett F Magann, Hari Eswaran
Association between broadband capacity and telehealth utilization among Medicare Fee-for-service beneficiaries during the COVID-19 pandemic
This study used county-level data to assess the association between broadband access and telehealth utilization in the United States during the COVID-19 pandemic. The findings show decreased telehealth utilization in rural areas and indicates the importance of broadband access for health care access.
- Ambrish A Pandit, Ruchira V Mahashabde, Clare C Brown, Mahip Acharya, Catherine C Shoults, Hari Eswaran, Corey J Hayes
Comparison of Telehealth and In-person Behavioral Health Services and Payment in a Large Rural Multisite Usual Care Study
This study compared behavioral health services for in-person and telehealth cohorts and examined relative value units (RVU) and payment. Behavioral health services provided by telehealth used services with lower RVUs than behavioral health services provided in-person, on average, even after adjusting for patient demographics and diagnosis.
- Marcia M Ward, Knute D Carter, Divya Bhagianadh, Fred Ullrich, Kimberly A S Merchant, James P Marcin, Kari Beth Law, Carly McCord, Jonathan Neufeld, Eve-Lynn Nelson, Dan M Shane
Remote Cardiovascular Hypertension Program Enhanced Blood Pressure Control During the COVID-19 Pandemic
The study assessed the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on a remote hypertension management program. The study found that the remote clinical management program delivered significant improvements in blood pressure control and increased home blood pressure monitoring despite disruptions in traditional care.
- Simin Gharib Lee, Alexander J Blood, Christopher P Cannon, William J Gordon, Hunter Nichols, David Zelle, Benjamin M Scirica, Naomi D L Fisher
Telehealth and In-Person Behavioral Health Services in Rural Communities Before and During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Multisite Prospective Cohort Study
This research study examines the changes in patient and treatment characteristics in telehealth and in-person behavioral health services. The study found health care providers adjusted both telehealth and in-person service delivery during the COVID-19 pandemic.
- Marcia M Ward, Fred Ullrich, Divya Bhagianadh, Eve-Lynn Nelson, James P Marcin, Knute D Carter, Kari Beth Law, Carly McCord, Jonathan Neufeld, Kimberly A S Merchant
Whole Health coaching to rural Veterans through telehealth: Advantages, gaps, and opportunities
This study examines how Whole Health coaches adapted to using telehealth to engage rural Veterans during the COVID-19 pandemic, identifying advantages and gaps. Findings emphasize the need for a blended approach that integrates virtual, in-person, and lower-tech options.
- Kelsea LeBeau, Deepthi S Varma, Consuelo M Kreider, Gail Castañeda, Cheri Knecht, Diane Cowper Ripley, Huanguang Jia, and J Hale-Gallardo
Utilization of Remote Patient Monitoring Within the United States Health Care System: A Scoping Review
This scoping review examines remote patient monitoring (RPM) studies and reimbursement policies in the United States. Findings show a significant increase in RPM-related literature from 2015 to 2021, with cardiovascular diseases among the most studied. Future research on RPM should focus on outcomes and trends in reimbursement policies.
- Corey J Hayes, Leah Dawson, Hannah McCoy, Michelle Hernandez, Jennifer Andersen, Mir M Ali, Cari A Bogulski, Hari Eswaran
Implementation of a women's reproductive behavioral health telemedicine program: a qualitative study of barriers and facilitators in obstetric and pediatric clinics
This study focuses on the implementation of a telemedicine program for perinatal mood and anxiety disorders and substance use disorders in community obstetric and pediatric clinics. Barriers to implementation included practical challenges such as staffing, space, and technology support, while facilitators included the high demand for mental health and substance use disorder services and the commitment of clinics to address these health concerns. The study highlights the importance of addressing resource and technology needs, while leveraging clinics' commitment to women's health, to ensure successful implementation of telemedicine programs.
- Katherine R Sterba, Emily E Johnson, Edie Douglas, Rubin Aujla, Lisa Boyars, Ryan Kruis, Rebecca Verdin, Rachel Grater, Kathryn King, Dee Ford, Constance Guille
Association of Receipt of Opioid Use Disorder-Related Telehealth Services and Medications for Opioid Use Disorder With Fatal Drug Overdoses Among Medicare Beneficiaries Before and During the COVID-19 Pandemic
This study examined the association between receipt of telehealth services and medications for opioid use disorder (OUD) and fatal drug overdoses before and during the COVID-19 pandemic among Medicare beneficiaries. The study found that the receipt of OUD-related telehealth services, receipt of medications for OUD from opioid treatment programs, and receipt of buprenorphine in office-base settings were all associated with reduced risk for fatal drug overdose.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; National Institutes of Health; Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services
- Christopher M Jones, Carla Shoff, Carlos Blanco, Jan L Losby, Shari M Ling, Wilson M Compton
Patient Characteristics Associated With Being Offered or Choosing Telephone vs Video Virtual Visits Among Medicare Beneficiaries
This goal of this study was to understand the characteristics of Medicare beneficiaries who received telephone-only telehealth visits when both telephone and video options were available. Results show Medicare beneficiaries often reported being offered or choosing telephone-only visits even when video visits were available.
- Ishani Ganguli, E John Orav, Ruth Hailu, Joyce Lii, Meredith B Rosenthal, Christine S Ritchie, Ateev Mehrotra
Use of Telemedicine among Office-Based Physicians, 2021
Telemedicine adoption gradually rose prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, but the field saw a significant increase during the pandemic as a way for physicians to provide health services while limiting patient exposure to the virus. The widespread use of telemedicine could impact the quality, cost, and accessibility of health care, so it's important to understand its usage. This data brief documents rates of telemedicine use by office-based physicians, the types of tools used, physician characteristics, satisfaction levels, and plans to continue using telemedicine beyond the pandemic.
- Yuriy Pylypchuk, Wesley Barker
Telehealth Use and Access to Care for Underserved Populations Before and During the COVID-19 Pandemic
This research study investigates the relationship between access to care and telehealth utilization before and during the COVID-19 pandemic. It finds a significant increase in telehealth use during the pandemic, with disparities in usage among different demographic groups. During the pandemic, telehealth appeared to substitute for in-person visits.
- Clese Erikson, Yoon Hong Park, Natalie Felida, Michael Dill
- February 2023
Parent-Reported Use of Pediatric Primary Care Telemedicine: Survey Study
The COVID-19 pandemic resulted in the widespread availability of telemedicine services for children from primary care practices. This study is specifically focused on children who typically receive medical services in person while identifying factors that are linked to the usage of telemedicine services provided by primary care providers. Research outcomes reveal that promoting access to primary care, ensuring payment for primary care telemedicine, and removing obstacles in non-metropolitan areas can all contribute to the equitable use of primary telemedicine care for children.
- Kristin N Ray, Samuel R Wittman, Sarah Burns, Tran T Doan, Kelsey A Schweiberger, Jonathan G Yabes, Janel Hanmer, Tamar Krishnamurti
Considerations for TelePrEP Programs
This study examines the development and implementation of a telePrEP program aimed at increasing access to pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) for HIV prevention, particularly in regions with high HIV incidence rates. The program involves strong partnerships with local health departments, electronic evaluation tools, and efforts to address barriers and limitations to enrollment and retention, ultimately emphasizing the potential of telehealth in expanding PrEP uptake among vulnerable populations.
- Nicole A Cooper, Marty S Player, Vanessa A Diaz
- January 2023
Racial and Ethnic Disparity in 4Ms among Older Adults Among Telehealth Users as Primary Care
This study investigates the quality of primary care delivered via telehealth in relation to equity among older adults across race and ethnicity in provider-shortage urban areas. The study examines the documentation of 4M (what matters, mobility, medication, and mentation) and self-reported racial and ethnic backgrounds in Southern Nevada. The findings indicate disparities, such as reduced documentation for what matters among Asian/Hawaiian/Pacific Islanders and mobility among Black individuals.
- Ji Won Yoo, Hee-Taik Kang, Ian Choe, Laurie Kim, Dong-Hun Han, Jay J Shen, Yonsu Kim, Peter S Reed, Iulia Ioanitoaia-Chaudhry, Maria Teresa Chong, Mingon Kang, Jerry Reeves, Maryam Tabrizi
Inequitable access to general and behavioral healthcare in the US during the COVID-19 pandemic: A role for telehealth?
The COVID-19 pandemic had extensive consequences, including increased psychological distress and alcohol consumption, which created heightened challenges particularly for disadvantaged communities. To mitigate the impact of lockdowns, medical office closures, and fear of transmission, telehealth services were expanded early in the pandemic to provide continued access to health care. This study investigates the accessibility of general and behavioral health care services and disparities during the first year of the pandemic.
- Nina Mulia, Yu Ye, Thomas K Greenfield, Priscilla Martinez, Deidre Patterson, William C Kerr, Katherine J Karriker-Jaffe
Telemedicine along the cascade of care for substance use disorders during the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States
The way healthcare services are provided has transformed because of the COVID-19 pandemic, which created an opportunity to advance telemedicine by formalizing clinical guidance. In this study, researchers aim to outline the delivery of substance use disorder (SUD) treatments and services through telemedicine along the continuum of care in the United States since the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic. This review summarizes telemedicine-based delivery, including screening/assessment, prescription, monitoring, recovery support and other related services.
- National Institutes of Health; United States Department of Veterans Affairs
- Chunqing Lin, Huyen Pham, Yuhui Zhu, Sarah E Clingan, Lewei Allison Lin, Sean M Murphy, Cynthia I Campbell, Tanya R Sorrell, Yanping Liu, Larissa J Mooney, Yih-Ing Hser
Telemedicine Use and Quality of Opioid Use Disorder Treatment in the US During the COVID-19 Pandemic
There is limited understanding and knowledge about the potential consequences of the rapid shift to telehealth for opioid use disorder (OUD) treatment during the COVID-19 pandemic. The purpose of this study is to investigate the correlation between telemedicine utilization during the COVID-19 pandemic and indicators of OUD treatment quality. The results of this study indicate that patients who were treated by clinicians with both high and low levels of telemedicine usage had comparable clinical outcomes during the COVID-19 pandemic, which suggests that telemedicine is a viable substitute for in-person OUD care.
- Ruth Hailu, Ateev Mehrotra, Haiden A Huskamp, Alisa B Busch, Michael L Barnett
Use of Telehealth During the COVID-19 Era
This study focuses on the use of telehealth during the peak of the COVID-19 pandemic, highlighting the clinical outcomes and characteristics of patients who utilized digital health services. Patients utilizing telehealth and telemedicine services are more likely to be young to middle-aged, female, White, of higher socioeconomic status, and living in urban settings.
- Elham Hatef, Renee F Wilson, Susan M Hannum, Allen Zhang, Hadi Kharrazi, Jonathan P Weiner, Stacey A Davis, Karen A Robinson
Federally Qualified Health Centers Use of Telehealth to Deliver Integrated Behavioral Health Care During COVID-19
During the COVID-19 pandemic, Federally Qualified Health Centers (FQHCs) providing integrated behavioral health (IBH) services shifted to deliver care via telehealth. FQHC administrators reported that telehealth was essential and addressed workforce issues but noted concerns around payment parity and reimbursement and the impact on core components of IBH.
- Brianna M Lombardi, Lisa de Saxe Zerden, Catherine Greeno
- December 2022
A mixed-methods analysis of telehealth implementation in nursing homes amidst the COVID-19 pandemic
Nursing homes implemented telehealth services to adapt to the COVID-19 pandemic. This study found an increase in telehealth adoption. Training, integrated equipment, and staff presence during visits was identified as telehealth facilitators. Barriers included smartphone usage, billing issues, interoperability, and staffing challenges.
- Kimberly R Powell, Amy E Winkler, Jianfang Liu, Gregory L Alexander
Comparison of in-person vs. telebehavioral health outcomes from rural populations across America
The goal of this research is to examine the outcomes in patient symptoms of anxiety and depression. Results show no clinical or statistical difference in depression or anxiety symptoms between patients treated via telehealth and in-person.
- Carly McCord, Fred Ullrich, Kimberly A S Merchant, Divya Bhagianadh, Knute D Carter, EveLynn Nelson, James P Marcin, Kari Beth Law, Jonathan Neufeld, Annaleis Giovanetti, Marcia M Ward
Evaluation of Telehealth Visit Attendance After Implementation of a Patient Navigator Program
With the expansion and increase of telehealth during the COVID-19 pandemic, clinicians and patients faced the challenge of acclimating to virtual care through video visits. The study investigates the visit attendance for patients, comparing outcomes of those who received navigator outreach to those who did not. The results show visit attendance improvement for video visits after telehealth navigator outreach.
- Oren J Mechanic, Emma M Lee, Heidi M Sheehan, Tenzin Dechen, Ashley L O'Donoghue, Timothy S Anderson, Catherine Annas, Leanne B Harvey, Allison A Perkins, Michael A Severo, Jennifer P Stevens, Alexa B Kimball
Telehealth-guided provider-to-provider communication to improve rural health: A systematic review
Rural health care is an ongoing research focal point as remote care, remote patient monitoring, and telehealth services continue to expand nationwide. This study assesses health care disparities, benefits, and the utilization of telehealth-supported provider-to-provider communication in rural populations through a systemic review of observational studies. Researchers assessed trials and observational studies from several medical databases to determine barriers for rural provider-to-provider collaboration, evidence gaps, and the key takeaways from their findings.
- Annette M Totten, Dana M Womack, Jessica C Griffin, Marian S McDonagh, Cynthia Davis-O'Reilly, Ian Blazina, Sara Grusing, Nancy Elder
State Medicaid Telehealth Policies Before and During the COVID-19 Public Health Emergency: 2022 Update
This research highlights that state Medicaid programs have significant discretion in services delivered via telehealth. During the COVID-19 pandemic, all states and the District of Columbia utilized telehealth flexibilities provided by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Some states made telehealth flexibilities permanent, while others let them expire. Additional research is needed to assess the impact of increased telehealth utilization in Medicaid on access to care, utilization rates, and quality of care.
- Jacquelyn Rudich, Ann B Conmy, Rose C Chu, Christie Peters, Nancy De Lew, Benjamin D Sommers
- November 2022
Racial/Ethnic Differences in Children’s Mental Health Services Use Before and During the COVID-19 Pandemic Issue Brief
This research brief provides a comprehensive analysis of the disparities in children's mental health services utilization across racial and ethnic groups. The report finds an increase in telehealth for mental health care during the COVID-19 pandemic. This increase was not large enough to combat the overall decrease in mental health care, which disproportionately affected minority children.
- Mir M Ali, Kristina D West, Timothy B Creedon
Digital Health Technologies in Pediatric Trials
This research study explores the potential of using miniaturized sensors and other technologies to collect physiological and functional data directly from pediatric patients participating in clinical trials. The review discusses the advantages and disadvantages of these technologies in various pediatric diseases, highlighting the need for more reports on their use in this population. While the objective and frequent measurements provided by digital health technology offer opportunities to enhance drug evaluation in infants and young children, challenges remain in selecting the appropriate design, metrics, and sensors for each disease.
- Leonard Sacks, Elizabeth Kunkoski, Marianne Noone
Low-Volume Emergency Departments are More Likely to Use Telehealth for Sepsis Care in a National Rural Telehealth Network
Low-volume emergency departments (EDs) have higher rates of mortality as compared to higher volume EDs. This multicenter, retrospective study evaluated the prevalence of tele-ED use for sepsis care to understand variations across rural EDs and identify factors that predict the need for sepsis consultation using telemedicine.
- Nicholas M Mohr, Tracy Young, Allison R Schuette, Fred Ullrich, Luke J Mack, Katie DeJong, Amanda Bell, Mark Pals, Carlos A Camargo Jr, Kori S Zachrison, Krislyn M Boggs, Adam Skibbe, Dan M Shane, Knute D Carter, Kimberly A.S. Merchant, Marcia M Ward
Pre-Pandemic Telehealth Use among Children in Medicaid Managed Care and Fee-for-Service Programs
This study assessed the use of telehealth by Medicaid MCOs to provide pediatric care. The researchers analyzed variations in telehealth use based on geography, race, and ethnicity and identified the health conditions and services that accounted for the greatest percentage of telehealth visits for children enrolled in Medicaid MCOs.
- Yvonne Jonk, Heidi O’Connor, Jean A Talbot
Telehealth and Public Health Practice in the United States- Before, During and After the COVID-19 Pandemic
In 2020, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) established a telehealth unit as part of its COVID-19 emergency response and a CDC telehealth workgroup. The workgroups identified ways that telehealth can benefit public health including increasing access to reduce health disparities, enhancing disease management and preventative care, and triaging care to ensure appropriate use of health services.
- Antonio J Neri, Geoffrey P Whitfield, Erica T Umeakunne, Jeffrey E Hall, Carol J DeFrances, Ami B Shah, Paramjit K Sandhu, Hanna B Demeke, Amy R Board, Naureen J Iqbal, Katia Martinez, Aaron M Harris, Frank V Strona
Teledentistry Trends in the United States During the COVID-19 Pandemic
This qualitative study examines the implementation and challenges of teledentistry in response to the COVID-19 pandemic across four states. Through interviews with key stakeholders and analysis of state policies and regulations, this study highlights the rapid adoption of teledentistry during the pandemic, common challenges faced by dental practitioners, and the potential for telehealth to address disparities in access to dental care, particularly in rural and low-income populations.
- Miranda Werts, Prashanta Patel, and Elizabeth Mertz
- October 2022
Association Between In-Person vs Telehealth Follow-up and Rates of Repeated Hospital Visits Among Patients Seen in the Emergency Department
Improved patient mortality is associated with the promptness of follow-up visits from the emergency department (ED). Although in-person follow up visits after ED discharges are known to be effective, the success of telehealth as a follow-up option is unspecified. This cohort study examines the difference in the rates of patients who were discharged from the ED and have an in-person follow-up in comparison to those patients who have telehealth follow-up appointments.
- Vivek V Shah, Chad W Villaflores, Linh H Chuong, Richard K Leuchter, Austin S Kilaru, Sitaram Vangala, Catherine A Sarkisian
Association of Adequacy of Broadband Internet Service with Access to Primary Care in the Veterans Health Administration Before and During the COVID-19 Pandemic
While the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) offered several telehealth services before the pandemic, the use of telehealth by veterans significantly increased during the COVID-19 pandemic. An analysis of data from VHA found that veterans who lived in communities with limited or no access to broadband were less likely to access primary care via telehealth during the pandemic. Reduced access to broadband was associated with neighborhood-level social disadvantage, worsening access disparities.
- Amy MJ O’Shea, Aaron Baum, Bjarni Haraldsson, Ariana Shahnazi, Matthew R Augustine, Kailey Mulligan, Peter J Kaboli
Quality of Telehealth-Delivered Inpatient Palliative Care During the Early COVID-19 Pandemic
This study focused on the use of palliative primary care using telehealth and hybrid models during the pandemic. The research findings suggest that the use of telehealth may expand the availability of palliative care for individuals and their families who are not conveniently located near a health center that offers this important service. The authors note that telehealth may be more appropriate for some palliative care services than for others.
- Ann A Soliman, Kathleen M Akgun, Jane Coffee, Jennifer Kapo, Laura J Morrison, Elizabeth Hopkinson, Dena Schulman-Green, Shelli L Feder
Receipt of Telehealth Services, Receipt and Retention of Medications for Opioid Use Disorder, and Medically Treated Overdose Among Medicare Beneficiaries Before and During the COVID-19 Pandemic
To ensure access to substance use disorder services during the pandemic, the government authorized the use of telehealth to prescribe and manage medications for opioid use disorder (MOUD). This study looked at over 150,000 Medicare beneficiaries living with OUD during the pandemic and found that MOUD prescribing via telehealth improved retention in an OUD-treatment program using prescribed medication and reduced the likelihood of medically treated overdose.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services; National Institutes of Health
- Christopher M Jones, Carla Shoff, Kevin Hodges, Carlos Blanco, Jan L Losby, Shari M Ling, Wilson M Compton
Targeted Telehealth Education Increases Interest in Using Telehealth among a Diverse Group of Low-Income Older Adults
Telehealth has the potential to empower older adults to have more autonomy over their health, but they are less likely to use telehealth. This research study focuses on an education program targeting vulnerable, low-income, minority older adults. Results show that the program increased their confidence in accessing and using telehealth, resulting in improved health promotion and achieving the aim of promoting telehealth use among this population.
- Emily Jezewski, Abigale Miller, MaryAnn Eusebio, Jane Potter
Transitioning to telehealth? A guide to evaluating outcomes
This research study addresses the need for comprehensive evaluation of telehealth outcomes and performance, considering access to care, cost, experience, and effectiveness. The study emphasizes the understudied aspects of telehealth accessibility and accommodations and highlights the importance of establishing an evaluation system for telehealth outcomes.
- Melinda M Li, Kristin L Rising, Elizabeth M Goldberg
- September 2022
The Vital Role of CHWs During the COVID-19 Pandemic within the South Texas Communities
This publication discusses the crucial role of Community Health Workers (CHWs) during the COVID-19 pandemic, particularly in rural communities which faced heightened vulnerability. It highlights the psychological distress experienced by frontline healthcare workers, including CHWs, and proposes the development of tailored mental health support programs. In response, the South Texas Area Health Education Center initiated a COVID-19 Project Extension for Community Healthcare Outcomes (ECHO) program, utilizing community-based participatory research principles to train and support CHWs in providing essential services and resources to their communities.
- Pamela Recto, Jose Zapata Jr, Eduardo Gandara, Andrea Moreno-Vasquez, Annette Zavala Idar, Martha Castilla, Ludivina Hernandez, Melissa Flores, Juana Escareno, Cynthia Castillo, Vicky Morales, Janna Lesser
Certain Medicare Beneficiaries, Such as Urban and Hispanic Beneficiaries, Were More Likely Than Others to Use Telehealth During the First Year of the COVID-19 Pandemic
This data brief examines the characteristics of Medicare beneficiaries who used telehealth during the first year of the pandemic. This report discusses how the temporary expansion of telehealth impacted various beneficiary groups. In addition, the learnings can help to inform future work in increasing beneficiary access to telehealth.
- HHS Office of Inspector General (OIG)
Effect of a Comprehensive Telehealth Intervention vs Telemonitoring and Care Coordination in Patients With Persistently Poor Type 2 Diabetes Control
This study addresses poorly controlled type 2 diabetes by comparing simple and comprehensive telehealth interventions. The trial shows that comprehensive telehealth is more effective than telemonitoring and care coordination, improving outcomes for patients at a reasonable cost. These findings suggest that implementing comprehensive telehealth could enhance diabetes care.
- Matthew J Crowley, Phillip E Tarkington, Hayden B Bosworth, Amy S Jeffreys, Cynthia J Coffman, Matthew L Maciejewski, Karen Steinhauser, Valerie A Smith, Moahad S Dar, Sonja K Fredrickson, Amy C Mundy, Elizabeth M Strawbridge, Teresa J Marcano, Donna L Overby, Nadya T Majette Elliott, Susanne Danus, David Edelman
Transgender Individuals and Digital Health
The use of digital health technologies including telehealth and mhealth expands access to health care as well as education and the ability to access resources to improve overall health such as housing and employment. This study discusses how digital health technologies can reduce disparities in quality of care for transgender individuals.
- Asa E. Radix, Keosha Bond, Pedro B. Carneiro, Arjee Restar
Age and Racial Disparities in Telehealth Use Among People with HIV During the COVID-19 Pandemic
This research study analyzed HIV care appointments at an urban tertiary hospital to assess the uptake of telehealth and sociodemographic variations in utilization among people with HIV. The findings indicated age and racial differences in terms of in-person versus telehealth appointments.
- Eleanor E Friedman, Samantha A Devlin, Sarah F Gilson, Jessica P Ridgway
- August 2022
Adoption of telemedicine in a rural United States cancer center amidst the COVID-19 pandemic: A qualitative study
Oncology, the branch of medicine that deals with the diagnosis and treatment of cancer, has been slower than other fields of medicine to utilize telemedicine. This study aims to better understand the different factors that affect provider and patient hesitancy for telemedicine uptake and sustained use in oncology. Overall, providers favored telemedicine utilization for lower-acuity cancer care visits that were less dependent on physical exams, and more focused on patient education. The results give researchers important data that can aid in the improvement of virtual cancer care, giving the opportunity for increased access to rural and underserved communities.
- Matthew Brian Mackwood, Rebecca L Butcher, Danielle Vaclavik, Jennifer A Alford-Teaster, Kevin M Curtis, Mary L Lowry, Tor D Tosteson, Wenyan Zhao, Anna N A Tosteson
Assessing Technical Feasibility and Acceptability of Telehealth Palliative Care in Nursing Homes
The goal of this study is to assess the technical feasibility and acceptability of using telehealth for palliative care consultations in nursing homes. The findings demonstrated that palliative care video visits were well-received, with participants expressing comfort, improved communication, and potential future use, highlighting the value of telehealth as a cost-effective means to enhance access to palliative care services in nursing homes.
- Caroline E Stephens, Theresa A Allison, Lynn A Flint, Daniel David, Victoria Wertz, Elizabeth Halifax, Pamela Barrientos, Christine S Ritchie
Mindfulness-Based Smoking Cessation Delivered Through Telehealth and Text Messaging for Low-Income Smokers: Protocol for a Randomized Controlled Trial
Telehealth has the potential to widely expand patient access to the intervention and treatment for tobacco usage. Low-income minority groups often struggle with quitting due to a lack of healthcare infrastructure around smoking cessation interventions, and therefore experience tobacco-related health problems at a greater rate. This study uses telehealth sessions and SMS text messaging to deliver mindfulness-based smoking cessation treatment, with the hope of reaching population groups that normally do not have access to in-person treatment centers. Data will continue to be collected until the spring of 2024.
- Claire A Spears, Josephine Mhende, China Hawkins, Vuong Van Do, Matthew J Hayat, Michael P Eriksen, Donald Hedeker, Lorien C Abroms, David W Wetter
Telehealth for the Longitudinal Management of Chronic Conditions: Systematic Review
This systematic review looked for studies that compare use and outcomes of in-person and telehealth care for chronic care management of congestive heart failure, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and type 2 diabetes mellitus.
- Allison A Lewinski, Conor Walsh, Sharron Rushton, Diana Soliman, Scott M Carlson, Matthew W Luedke, David J Halpern, Matthew J Crowley, Ryan J Shaw, Jason A Sharpe, Anastasia-Stefania Alexopoulos, Amir Alishahi Tabriz, Jessica R Dietch, Diya M Uthappa, Soohyun Hwang, Katharine A Ball Ricks, Sarah Cantrell, Andrzej S Kosinski, Belinda Ear, Adelaide M Gordon, Jennifer M Gierisch, John W Williams Jr, Karen M Goldstein
Variation in Virtual and Non- virtual Behavioral Health Visits Among Michigan Medicaid Enrollees
The study used Michigan Medicaid data to investigate the utilization patterns of telebehavioral health services before and during the COVID-19 pandemic. The study aimed to determine if there was an increase in telebehavioral health use among Michigan Medicaid enrollees during the pandemic, analyzing data from 2018 to 2021 by demographic factors such as age, race/ethnicity, sex, and rurality.
- Victoria Schoebel, Isabella Ginsberg, Sarah Clark, Kyle Grazier
The future of telehealth in type 1 diabetes
Telehealth services have been utilized in type 1 diabetes (T1D) clinical care for years, but the COVID-19 pandemic accelerated adoption and sparked interest in long-term integration into routine care. This review examines the existing literature on telemedicine in T1D care, highlighting its benefits and barriers. The findings indicate that telehealth can effectively contribute to improved glycemic control and long-term outcomes in T1D and it is anticipated that future care models will adopt a hybrid approach combining both in-person and telehealth visits.
- Erin C Cobry, R Paul Wadwa
"I was Unsure at First": A Qualitative Evaluation of Patient Perceptions of VA Clinical Video Telehealth Visits in the V-IMPACT Program
Many veterans have skepticism about telehealth. This study examines how veteran’s opinions of telehealth change once they experience a virtual appointment. Findings show a wide variety of patient responses to telehealth appointments, and these experiences offer an opportunity for future telehealth providers to better understand the needs of their patients to make virtual care as effective and supportive as possible.
- Ashley C Mog, Megan Moldestad, Rachael Kenney, Lauren Stevenson, Marcie Lee, P Michael Ho, George G Sayre
Adapting PCIT-Health for Telehealth Delivery: A Case Study
Parent-Child Interaction Therapy-Health (PCIT-Health) is a form of behavior parent training that focuses on helping parents learn skills for better managing a child’s behavior, including obesity-related behaviors. This study examines the experience of one family using telehealth to receive PCIT. The results show that the family had a positive experience with telehealth-delivered PCIT, and that the parent’s skillset of positive parenting practices increased. This study gave researchers more information on patient experience with telehealth-delivered PCIT so that in the future there can be a wider implementation of this practice for improving child behavioral problems.
- Sarah E Domoff, Mikaela M Overton, Aubrey L Borgen, Larissa N Niec
Association between state payment parity policies and telehealth usage at community health centers during COVID-19
Parity policies are the combined amount of reimbursement that a health benefit plan allows for the compensation to the distant site and the originating site which are required to not be less than the total amount allowed for healthcare services provided in-person. This study highlights the association between payment parity policies and the use of telehealth at community health centers, particularly during COVID-19.
- Clese Erikson, Jordan Herring, Yoon Hong Park, Qian Luo, Guenevere Burke
Broadband access and telemedicine adoption for opioid use disorder treatment in the United States
Buprenorphine is a medication used for patients who struggle with opioid use disorder, but only about 1 in 5 patients receive treatment. The COVID-19 pandemic increased telehealth utilization for addiction treatment with studies supporting telemedicine as an effective way to deliver treatment for opioid use disorder. This study aims to identify the percentage of the US population that experience challenges with treatment accessibility. Barriers to treatment that are examined in this study include limited internet access and the number of buprenorphine-waivered providers near a patient’s residence.
- Mir M Ali, Robin Ghertner
COVID-19 Telemedicine and Vaccination at an Urban Safety Net HIV Medicine Clinic
The Owen Clinic at UC San Diego Health developed a telemedicine clinic in response to the COVID-19 pandemic to ensure the continuity of care for patients with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), and other high-risk populations. This study gives an in-depth review of the Owen Clinic and various virtual-medical services it provided throughout the pandemic that ultimately were effective in treating and monitoring high-risk patients.
- Ryan Anson, Aaron Willcott, Will Toperoff, Afsana Karim, Michael Tang, Darcy Wooten, J Tyler Lonergan, Laura Bamford
Expanding access to substance use services and mental health care for people with HIV in Alabama, a technology readiness assessment using a mixed methods approach
Due to Alabama's vast amount of rural area, there are many obstacles that patients can face while trying to receive treatment for HIV. Specifically, HIV patients often experience challenges with access to treatment for mental health and substance use disorders (SUD) due to a lack of public health infrastructure and limited amounts of health care providers near their residence. This study examines if adopting telehealth screenings for mental health and SUDs can improve rural patients access to healthcare services.
- Ellen F Eaton, Kaylee Burgan, Greer McCollum, Sera Levy, James Willig, Michael J Mugavero, Sushanth Reddy, Eric Wallace, Tom Creger, Stefan Baral, Susanne Fogger, Karen Cropsey
Improving heart failure care and guideline-directed medical therapy through proactive remote patient monitoring-home telehealth and pharmacy integration
This study evaluates the use of remote patient monitoring (RPM) home-telehealth and pharmacist consultations on high-risk cardiovascular patients, with the overall goal being a reduction in hospital admissions due to heart failure. A registered nurse, cardiovascular physician, and pharmacist all play a crucial role in care delivery during this study, working together to improve guideline-directed medical therapy (GDMT) prescription. Results from this study show that the number of patients who maximized GDMT care increased, which may have assisted in the reduction of hospital admissions due to heart failure during the study.
- Kimberly A Lynch, David A Ganz, Debra Saliba, Donald S Chang, Shelly S de Peralta
Managing innovation: a qualitative study on the implementation of telehealth services in rural emergency departments
This study focuses on the integration of telehealth services for emergency departments in rural areas and highlights gaps in the implementation and long-term utilization. Researchers administered semi-structured interviews from six U.S. health care systems that provided emergency telehealth services. Results include necessary implementation factors in strategies, capability, relationships, financials, protocols, environment, service characteristics, and accountability.
- Mochamad Muska Nataliansyah, Kimberly AS Merchant, James A Croker, Xi Zhu, Nicholas M Mohr, James P Marcin, Hicham Rahmouni, Marcia M Ward
The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on people who inject drugs accessing harm reduction services in an rural American state
Harm reduction services, such as syringe service programs (SSPs), shelters, peer support groups, and low barrier buprenorphine treatment are services for people who inject drugs (PWID) and their recovery process. Prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, PWID faced many challenges with access to these services, but the pandemic exacerbated these barriers even further. This study examines the impact that COVID-19 had on access to harm-reduction services, specifically for Maine residents.
- Kinna Thakarar, Michael Kohut, Rebecca Hutchinson, Rebecca Bell, Hannah E Loeb, Debra Burris, Kathleen M Fairfield
Emergency Departments' Uptake of Telehealth for Stroke Versus Pediatric Care: Observational Study
The study aimed to investigate the discrepancy in the adoption of telestroke and pediatric telehealth services in emergency departments. The researchers hypothesized that differences in financial incentives, prehospital routing policy, and certification requirements could have contributed to the uneven adoption. The study shows the most frequently indicated reason for adoption of telehealth services was related to clinical care.
- Kori S Zachrison, Emily M Hayden, Krislyn M Boggs, Tehnaz P Boyle, Jingya Gao, Margaret E Samuels-Kalow, James P Marcin, Carlos A Camargo Jr
Association Between Telemedicine Use in Nonmetropolitan Counties and Quality of Care Received by Medicare Beneficiaries With Serious Mental Illness
For people diagnosed with serious mental illnesses such as schizophrenia, bipolar I disorder, and other related psychotic disorders, accessibility to specialty mental health care services is an ongoing barrier. This cohort study explores the association between greater telemental health service use in a nonmetropolitan county and quality measures including 118,670 patients diagnosed with schizophrenia, bipolar I disorder, and/or related psychotic disorders. This includes the use of specialty mental health care and medical adherence of patients with schizophrenia or related psychotic disorders. Results from the study reveal slight increases in encounters with outpatient specialty mental health professionals and increased possibility of follow-up after being hospitalized.
- Bill Wang, Haiden A Huskamp, Sherri Rose, Alisa B Busch, Lori Uscher-Pines, Pushpa Raja, Ateev Mehrotra
Behavioral healthcare organizations' experiences related to use of telehealth as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic: an exploratory study
The COVID-19 pandemic resulted in many behavioral health services having to transition to deliver care virtually via telehealth. This study analyzes the experiences of behavioral health organizations that used telehealth during the pandemic to determine any common themes. Results show that organizations viewed convenience, increased access to disadvantaged populations, and lack of commute as advantages of telehealth; common disadvantages included limited access to technology and possible ineffective treatments.
- Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration
- Abby Kisicki, Sara Becker, Michael Chaple, David H Gustafson, Bryan J Hartzler, Nora Jacobson, Ann A Murphy, Stephanie Tapscott, Todd Molfenter
Clinical Appropriateness of Telehealth: A Qualitative Study of Endocrinologists' Perspectives
Since the use of telehealth in outpatient endocrinology is likely to remain common after the COVID-19 pandemic, this study examines how endocrinologists determine clinical appropriateness for telehealth and identifies their strategies to navigate barriers to safe and effective use. This research is crucial due to the absence of guidelines on telehealth use in this field, and the findings show the need for expert guidance to anchor future evidence-based guidelines for determining clinical appropriateness of telehealth in endocrinology.
- Kailyn E Sitter, Denise H Wong, Rendelle E Bolton, Varsha G Vimalananda
Evaluation of an experiential clinical learning option during pandemic teaching suspensions
Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, many educational environments had to transition to virtual learning, including teaching hospitals for medical students. This study evaluates one hospital’s transition to using telehealth for a new learning program that allows students to become familiar with clinician and patient perspectives of different care models. The curriculum specifically focuses on using virtual care in the multidisciplinary field of addiction medicine.
- Jules Canfield, Ve Truong, Agata Bereznicka, Karsten Lunze
Factors influencing uptake of telemental health via videoconferencing at high and low adoption sites within the Department of Veterans Affairs during COVID-19: a qualitative study
The purpose of this study is to determine factors that influence site-level uptake of telemental health via videoconferencing (TMH-V) by examining both a low adoption site and a high adoption site within the US Department of Veterans Affairs. Findings show that while there are many positive and negative influencers of TMH-V uptake, the biggest influencer was site complexity. User-friendly sites that are accessible to patients with a limited technology skill set positively affect site uptake. Unfortunately, a majority of the sites examined were not user-friendly, so complexity had an overall negative influence. Understanding the various influencers of site-level uptake allows for improvement on future implementation, overall increasing patient access to virtual mental health care.
- Samantha L Connolly, Jennifer L Sullivan, Jan A Lindsay, Stephanie L Shimada, Leonie Heyworth, Kendra R Weaver, Christopher J Miller
Long-term Effects of Remote Patient Monitoring in Patients Living with Diabetes: A Retrospective Look at Participants of the Mississippi Diabetes Telehealth Network Study
This study examines the effectiveness of long-term remote patient monitoring (RPM) for patients with diabetes in the state of Mississippi. While RPM has been proven to be an effective tool for monitoring patient’s hemoglobin A1C levels, the ability of RPM to support patients in maintaining treatment is unclear. Many participants experienced reductions in hemoglobin levels after 12 months of nurse coaching and diabetes self-management education that were provided via telehealth, indicating that RPM could be an important tool in managing chronic diseases, specifically diabetes.
- Tearsanee Carlisle Davis, Ashley S. Allen, and Yunxi Zhang
Parent satisfaction with the parent-provider partnership and therapy service delivery for children with disabilities during COVID-19: Associations with sociodemographic variables
Parents of children with disabilities played a huge role in facilitating the continuity of care for their children throughout the COVID-19 pandemic, especially through managing and delivering therapies remotely. This study aims to examine the relationship between sociodemographic factors and parent satisfaction with the delivery of therapy services for children with disabilities during the pandemic. Factors impacting parents' satisfaction with therapy services included access to telehealth services, number of household essential workers, number of children, parent education, and more.
- Ashley N Murphy, Ellie Bruckner, Linzy M Pinkerton, Heather J Risser
Perception of Telehealth During the COVID-19 Pandemic Among Survivors of Gynecologic Cancer
This study aimed to understand the preferences of gynecologic cancer survivors for telehealth cancer care. Over half preferred in-person visits. Many noted concerns about missing out on physical examination during telehealth visits. The study highlights the need for careful evaluation of patient concerns and education to develop future care models that include telehealth elements for gynecologic cancer survivors.
- Nicholas Quam, Ashley E Stenzel, Katherine Brown, Patricia Jewett, Helen M Parsons, Jane Hui, Rahel G Ghebre, Anne Blaes, Deanna Teoh, Rachel I Vogel
Perceptions and Use of Telehealth Among Mental Health, Primary, and Specialty Care Clinicians During the COVID-19 Pandemic
The purpose of this study was to capture healthcare providers attitudes towards telehealth utilization during the COVID-19 pandemic, since physician’s attitudes may impact utilization rates of telehealth by patients. Findings show differences in video, phone, and in-person care utilization across specialties, as well as clinicians attitudes towards telehealth having an impact on patient utilization.
- Samantha L Connolly, Christopher J Miller, Allen L Gifford, Michael E Charness
Predictors of telemedicine use during the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States-an analysis of a national electronic medical record database
Although telehealth utilization has rapidly increased within the past years, disadvantaged groups still face barriers to access. This is a retrospective study that analyzes outpatient medical encounters for patients using a national electronic medical record database from March 1 to December 31, 2020. Findings show that older and non-Hispanic Black patients had significantly lower levels of telehealth utilization than other patient groups.
- Sameed Ahmed M Khatana , Lin Yang, Lauren A Eberly, Howard M Julien, Srinath Adusumalli, Peter W Groeneveld
Public health implications of adapting HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis programs for virtual service delivery in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic: a systematic review
Based on a systematic review, the authors suggest a virtual service delivery model for PrEP that can be leveraged for the COVID-19 public health emergency using the internet and social media for demand creation, community-based self-testing, telehealth platforms for risk assessment and follow-up, applications for support groups and adherence/appointment reminders, and applications and internet for monitoring.
- Pragna Patel, Michael Kerzner, Jason B Reed, Patrick Sullivan, Wafaa M El-Sadr
Schedule of Visits and Televisits for Routine Antenatal Care
This is a systematic review that examines the role that telehealth can play in the future of antenatal care. Various factors that could facilitate or create a barrier in the implementation of telehealth for antenatal care were also reviewed. Studies reviewed show that there were no differences in the amount of preterm births or neonatal intensive care unit admissions when comparing telehealth and in-person visits, and that both patients and providers are open to telehealth utilization in this field, but more research is needed.
- Ethan M. Balk, Kristin J. Konnyu, Wangnan Cao, Monika Reddy Bhuma, Valery A. Danilack, Gaelen P. Adam, Kristen A. Matteson, Alex Friedman Peahl
Strategies to Ensure Continuity of Care Using Telemedicine with Older Adults during COVID-19: A Qualitative Study of Physicians in Primary Care and Geriatrics
This study examines the utilization of telehealth by patients aged 65 and older during the COVID-19 pandemic, as well as explore the experiences of primary care physicians and geriatricians by conducting interviews. Examining various strategies used to maintain the care of patients aged 65 and older throughout the pandemic allows for future improvement of telehealth utilization for geriatricians. Findings indicate the importance of evaluating a patient's technological readiness in advance, making accommodations for disabilities, and involving caregivers throughout the telehealth experience.
- Kevin Chen, Natalie M Davoodi, Daniel H Strauss, Melinda Li, Frances N Jimenez, Kate M Guthrie, Elizabeth M Goldberg
Telehealth for Women's Preventative Services
This study evaluated the effectiveness, use, and implementation of telehealth for women's preventative services for reproductive healthcare and interpersonal violence (IPV), and to evaluate patient preferences and engagement for telehealth, particularly in the context of COVID-19. Three of the 16 studies indicated that telehealth utilization increased during COVID-19 public health emergency.
- Cantor A, Nelson HD, Pappas M, Atchison C, Hatch B, Huguet N, Flynn B, McDonagh M.
The Lack of a Physical Exam During New Patient Telehealth Visits Does Not Impact Plans for Office and Operating Room Procedures
This study examines if surgical plans made during a telehealth visit remain unchanged after a pre-operative examination immediately before surgery. Data for this study was gathered during the COVID-19 pandemic on urology patients. Results show that majority of surgical planning made during new patient visits stayed the same after in-person examinations, signaling that telehealth can be a useful tool in the future for virtual surgical planning.
- Nicholas W Eyrich, Juan J Andino, Roberta E Ukavwe, Mark W Farha, Akshar K Patel, Daniel Triner, Chad Ellimoottil
The Role of Telehealth and Clinical Informatics in Data Driven Primary Care Redesign
Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, telehealth has experienced many updates in the past 3 years. These innovations have presented a new opportunity in the health care field for utilization of new ways to remotely monitor medically complex patients This study uses clinical informatics linked to inpatient and emergency department use to evaluate telehealth utilization of various population segments. Results show that there is potential to improve patient outcomes using telehealth in the primary care and acute care settings, as well as decrease emergency department and inpatient utilization.
- Jodie L Brown, Sharon Hewner
Using Implementation Science to Understand Teledermatology Implementation Early in the COVID-19 Pandemic: Cross-sectional Study
Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, the use of telehealth in dermatology practices (teledermatology) has experienced rapid expansion. Implementation science uses evidence-based practices to improve the quality and effectiveness of healthcare services, and this study aims to understand more about how implementation science can be used in dermatologic care, as well as in teledermatology. Results from this study give health care providers insight on how to successfully continue the use teledermatology after the pandemic.
- Shanelle Mariah Briggs, Jules Benjamin Lipoff, Sigrid Marie Collier
Addressing Hypertension Outcomes Using Telehealth and Population Health Managers: Adaptations and Implementation Considerations
This study examines various population health approaches to help with hypertension management. Telehealth is one approach that this study focuses on, with it being a cost-effective strategy that addresses multiple barriers to hypertension utilization and care delivery. Results show that telehealth is an effective strategy for advancing hypertension care within a population health paradigm by addressing multiple drivers of high blood pressure.
- National Institutes of Health; United States Department of Veterans Affairs; Health Resources and Services Administration
- Connor Drake, Allison A. Lewinski, Abigail Rader, Julie Schexnayder, Hayden B. Bosworth, Karen M. Goldstein, Jennifer Gierisch, Courtney White-Clark, Felicia McCant, and Leah L. Zullig
An Economic and Health Outcome Evaluation of Telehealth in Rural Sepsis Care: A Comparative Effectiveness Study
Sepsis is one of the top reasons for hospital mortality and healthcare costs. Telehealth has been shown to improve short-term sepsis care; however, the effect on costs and long-term outcomes is unclear. This study compares costs and outcomes for sepsis treated in rural emergency departments.
- Nicholas M Mohr, Allison R Schuette, Fred Ullrich, Luke J Mack, Katie De Jong, Carlos A Camargo, Kori S Zachrison, Krislyn M Boggs, Adam Skibbe, Amanda Bell, Mark Pals, Dan M Shane, Knute D Carter, Kimberly A S Merchant, Marcia M Ward
Describing Changes in Telebehavioral Health Utilization and Services Delivery in Rural School Settings in Pre- and Early Stages of the COVID-19 Public Health Emergency
Due to significant provider shortages, challenges exist for patients attempting to receive behavioral health services especially in light of the COVID-19 pandemic. In this study, researchers collected data from students in fifteen school-based telehealth programs in rural areas nationwide. Results of the study show increased utilization and implementation of telebehavioral services in school-based programs as a direct response to the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic.
- Marcia M Ward, Fred Ullrich, Kimberly AS Merchant, Knute D Carter, Divya Bhagianadh, Meghan Lacks, Erika Taylor, Jennifer Gordon
Evaluation of Mental Health Mobile Applications
This is a technical brief that examines the potential of mobile application (app) utilization for mental health and wellness services. Although there are many mobile apps available for mental health services, there is little guidance that consumers and patients can use when trying to determine what application to use. This brief also provides a framework to assess apps based on different strengths and limitations.
- Smisha Agarwal, Madhu Jalan, Holly C. Wilcox, Ritu Sharma, Rachel Hill, Emily Pantalone, Johannes Thrul, Jacob C. Rainey, Karen A. Robinson, Ph.D.
Postpartum during a pandemic: Challenges of low-income individuals with healthcare interactions during COVID-19
The COVID-19 pandemic resulted in many changes in women’s healthcare delivery for childbirth and the postpartum period, but these changes particularly affected low-income patients. This study examines various challenges that low-income patients experienced during the pandemic.
- Maria V Gomez-Roas, Ka'Derricka M Davis, Karolina Leziak, Jenise Jackson, Brittney R Williams, Joe M Feinglass, William A Grobman, Lynn M Yee
Telehealth: Current Definitions and Future Trends
This report defines common telehealth terms across a variety of contexts (clinicians, academia, federal stakeholders) and explains why it is important to use terminology that is contextually appropriate. Most patients will not distinguish between the terms “telehealth” and “telemedicine” in their use. Academic researchers may need to distinguish the terms to accurately describe and frame their research. Among federal stakeholders, telehealth is currently the most used term and would have the most recognition.
- Hari Eswaran, Leah Dawson
Telemedicine versus in-Person Primary Care: Impact on Visit Completion Rate in a Rural Appalachian Population
The purpose of this study is to understand the affects that telehealth has on patient access and visit completion rates for primary care in a rural community. While the COVID-19 pandemic increased telehealth utilization and availability, little research has been done to determine if the increased availability of virtual care has actually improved access to healthcare in rural and underserved areas. Findings from this study show that the introduction of telehealth in these rural communities created an increase in appointment completion by 20%, indicating that there was an overall increase in patient access.
- Treah Haggerty, Heather M Stephens, Shaylee A Peckens, Erika Bodkins, Michael Cary, Geri A Dino, Cara L Sedney
The Potential of Telecommunication Technology to Address Racial/Ethnic Disparities in HIV PrEP Awareness, Uptake, Adherence, and Persistence in Care: A Review
The purpose of this review was to understand how studies have used electronic telecommunication technology to increase awareness, uptake, adherence, and persistence in PrEP care among Black and Hispanic/Latino persons and how it can reduce social and structural barriers that contribute to disparities in HIV infection.
- Kimberly N Evans, Rashida Hassan, Ashley Townes, Kate Buchacz, Dawn K Smith
Defining Telehealth for Research, Implementation, and Equity
The COVID-19 pandemic made telehealth an essential service for health care access which led to the development of temporary policies with varying definitions and regulations by state and organization. Currently, more permanent guidelines are being established which has provided an opportunity to re-evaluate how telehealth is integrated into regular health care delivery. By defining a clear understanding of telehealth and its components, the clinical care can improve and more precise control and expectations for researchers, patients and providers can be implemented.
- Joy Roy, Deborah R Levy, Yalini Senathirajah
Primary care telemedicine during the COVID-19 pandemic: patient’s choice of video versus telephone visit
This study investigates how patient characteristics influenced the choice between video and audio-only telehealth appointments. The analysis of almost one million patient-scheduled primary care telehealth visits found that 39% were video visits. Patients who were Black or Hispanic, living in lower socioeconomic status or areas with limited internet access, were less likely to opt for video visits. Patients aged 65 or older, those with previous video visit experience or mobile portal access, or those seeing their own provider were more inclined to choose video visits. The research highlights a digital divide and underscores the importance of maintaining telephone telemedicine options.
- Jie Huang, Ilana Graetz, Andrea Millman, Anjali Gopalan, Catherine Lee, Emilie Muelly, and Mary E Reed
Temporary telehealth policies were developed by various organizations and states during the COVID-19 emergency, with varying definitions, regulations, and coverage. As these policies are being replaced with more permanent guidelines, there is an opportunity to form a consensus in definitions to set a standard of care.
In the early stages of the COVID-19 pandemic, states and the federal government quickly implemented policy changes to expand access to health care. As a result, the definition of telehealth and the services included varied across entities. The researchers discuss the implications of this variance which will impact policy and research and hinder efforts to address health disparities. As a result, efforts must be made to establish a single definition for telehealth that is consistently used.
Direct and indirect effects of a Project ECHO longitudinal clinical tele-mentoring program on viral suppression for persons with HIV: a population-based analysis
Project ECHO tele-mentoring for community providers was associated with improvement in viral suppression for people with HIV whose providers participate or work in the same clinic system as a provider who participates.
- Health Resources and Services Administration; National Institutes of Health
- Brian R Wood, Karin Bauer, Richard Lechtenberg, Susan E Bushkin, Lea Bush, Jeff Capizzi, Beth Crutsinger-Perry, Steven J Erly, Timothy W Menza, Jennifer R Reuer, Matthew R Golden, James P Hughes
Tele-urgent Care for Low-Acuity Conditions: A Systematic Review
The pandemic increased the use of tele-urgent care to improve timely access to health care while preventing unnecessary, in-person contact. This research study reviewed the literature to determine whether tele-urgent care might be an effective substitute for in-person care for low-acuity conditions in the future. While there was no evidence of costs savings, the research suggests that tele-urgent care may increase access by triaging patients to the right level of care.
- Nathan Boucher, Elizabeth Van Voorhees, Anita Vashi, Olivia Dong, Perri Morgan, Janeen E. Smith, Soheir Adam, Amir Alishahi Tabriz, Michael J. Mulholland, Jessica R. Dietch, John D. Whited, Joel C. Boggan, Jessica J. Fulton, C. Blake Cameron, Adelaide Gordon, Karen M. Goldstein, Belinda Ear, John W. Williams, Sarah Cantrell, Sarah W. Dickerson, Jennifer M. Gierisch
Telemedicine Use in Disasters: A Scoping Review
Disasters of all scales are a recurring issue and challenge for the health care systems, especially for providers and hospitals nationwide. The utilization of telemedicine is a direct response to improve access to health care during disasters, which is referred to as disaster telemedicine. This study focuses on literature that provides insight and response recommendations into the current use of disaster telemedicine for the most common barriers in regional disaster health.
- National Institutes of Health; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services
- Mark Litvak, Katherine Miller, Tehnaz Boyle, Rachel Bedenbaugh, Christina Smith, David Meguerdichian, David Reisman, Paul Biddinger, Adam Licurse, Eric Goralnick
Telestroke Infrastructure, Processes and Support Needs: A Survey of Hospitals in Five States
Telehealth and the use of telehealth for stroke treatment and services is considered be cost-effective, specifically for its use and ability to provide timely treatments. This study reviews multiple telestroke programs to identify how other and existing programs can implement and sustain their telestroke services and programs.
- Christopher M Shea, Kea Turner, Josh Weinstein, Amir Alishahi Tabriz, Nimmy Babu, Jessica Link Reeve, Steve North
Social Work Answers the (Video) Call: Tele-Behavioral Health Use During COVID-19
This research study investigates the utilization of tele-behavioral health among social work professionals before and during the COVID-19 pandemic, along with perceived barriers and supports to technology use. The study, conducted through an electronic survey distributed to practicing social work professionals, reveals a significant increase in tele-behavioral health usage since the pandemic's onset. While barriers exist, particularly concerning client access, social workers express a strong desire for tele-behavioral health to continue post-pandemic. The study recommends measures to ensure parity and reimbursement, enhance training for practitioners, and provide support for clients in accessing tele-behavioral health services.
- Brianna M Lombardi, Lisa de Saxe Zerden, Christopher Thyberg
Increasing Telehealth Access to Care for Older Adults During the COVID-19 Pandemic at an Academic Medical Center: Video Visits for Elders Project (VVEP)
This research publication outlines the Video Visits for Elders Project, which aimed to improve access to virtual care for older adults amidst the COVID-19 pandemic. Through outreach efforts and technical assistance, the project successfully facilitated video visits for a significant portion of elderly patients, highlighting the importance of addressing technological barriers to ensure equitable access to telemedicine. The findings underscore the ongoing need for health systems to prioritize technological support to enhance access to care for vulnerable populations, especially in the post-pandemic era where telemedicine remains crucial.
- Janet N Chu, Celia Kaplan, Jonathan S Lee, Jennifer Livaudais-Toman, Leah Karliner
Child Health, Vulnerability, and Complexity: Use of Telehealth to Enhance Care for Children and Youth With Special Health Care Needs
Telehealth has the potential to improve the quality of care, particularly deficiencies related to access and patient experience of care for children and youth with special health care needs and reduce disparities related to accessing in-person care.
- Jeanne Van Cleave, Christopher Stille, David E Hall
Deploying a telemedicine collaborative care intervention for posttraumatic stress disorder in the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs: A stepped wedge evaluation of an adaptive implementation strategy
This study uses two strategies, standard implementation and enhanced implementation, to determine the best way to incorporate telehealth utilization in trauma-focused psychotherapy for veterans with post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Results show that although telehealth is an effective means for engaging veterans in treatment, neither of these strategies were successful at incorporating telehealth into routine care treatment of PTSD.
- John C Fortney, Suparna Rajan, Heather S Reisinger, Jane Moeckli, John P Nolan, Edwin S Wong, Peter Rise, Valentina V Petrova, George G Sayre, Jeffrey M Pyne, Anouk Grubaugh, Fatma Simsek-Duran, Kathleen M Grubbs, Leslie A Morland, Bradford Felker, Paula P Schnurr
mHealth Interventions for Self-management of Hypertension: Framework and Systematic Review on Engagement, Interactivity, and Tailoring
The prevention or management of hypertension is an area of interest for researchers. This systematic review explores user engagement for hypertension-focused mobile health (mHealth) interventions as well as tailoring and interactivity for mHealth users. Digital behavior change interventions require engagement to be effective for users.
- Weidan Cao, M Wesley Milks, Xiaofu Liu, Megan E Gregory, Daniel Addison, Ping Zhang, Lang Li
Telehealth During COVID-19: Suicide Prevention and American Indian Communities in Montana
The risk of suicide among American Indian and Alaskan Native Communities during the COVID-19 pandemic significantly exceeded that of other racial and ethnic groups. Telehealth is an effective way to deliver behavioral health services in these communities. This study assessed Montana-based provider perceptions of the potential for telehealth to reduce suicides and the implications for future research.
- Zachary Pruitt, Kate P Chapin, Haley Eakin, Annie L Glover
Telehealth Use Among Older Adults During COVID-19: Associations with Sociodemographic and Health Characteristics, Technology Device Ownership, and Technology Learning
While the number of older adults using telehealth increased significantly during the COVID-19 pandemic, adoption and use of this care modality lagged that of younger adults. In this study, the authors investigate the factors that contribute to this discrepancy and discuss the implications.
- Namkee G Choi, Diana M DiNitto, C Nathan Marti, Bryan Y Choi
Telemedicine and visit completion among people with HIV during the COVID-19 pandemic compared to pre-pandemic
During the COVID-19 public health emergency, telemedicine visit completion among people with HIV increased significantly, especially among populations with lower pre-pandemic engagement.
- Walid G El-Nahal, Nicola M Shen, Jeanne C Keruly, Joyce L Jones, Anthony T Fojo, Bryan Lau, Yukari C Manabe, Richard D Moore, Kelly A Gebo, Catherine R Lesko, Geetanjali Chander
Empowerment through technology: A systematic evaluation of the content and quality of mobile applications to empower individuals with cancer
Mobile health application availability has increased for cancer patients due to a focus on patient empowerment. This systematic review evaluates and summarizes the evidence of mobile health apps and their characteristics and qualities. The evaluation found that cancer patient apps should be designed for usability and usefulness for a diverse group.
- Teresa Hagan Thomas, Kailey Go, Kelsey Go, Natalie Jane McKinley, Kayla R Dougherty, Kai-Lin You, Young Ji Lee
- February 2022
Evaluation of Online Patient Portal vs Text-Based Blood Pressure Monitoring Among Black Patients With Medicaid and Medicare Insurance Who Have Hypertension and Cardiovascular Disease
There is a considerable issue of unmonitored hypertension and cardiovascular disease among Black patients. Twenty Black patients with Medicaid and Medicare insurance who have hypertension and cardiovascular disease (CVD) or CVD risk factors were enrolled in this randomized pilot clinical trial. Researchers assessed the increased use and acceptability of a text-based model for home blood pressure (BP) monitoring compared with online portal use. When combined with telemonitoring, self measured BP is associated with improved BP control, although disparities in telemedicine access may limit the beneficial outcomes of home BP monitoring for Black patients.
- Lauren A Eberly, Monika Sanghavi, Howard M Julien, Laura Burger, Neel Chokshi, Jennifer Lewey
National Survey Trends in Telehealth Use in 2021: Disparities in Utilization and Audio vs. Video Services
This report analyzes national trends in telehealth utilization and how use of video-enabled vs. audio-only telehealth services differ across patient populations. The study finds notable disparities by race, ethnicity, income, age, and insurance status in access to video-enabled telehealth.
- Madjid Karimi, Euny C. Lee, Sara J. Couture, Aldren Gonzales, Violanda Grigorescu, Scott R. Smith, Nancy De Lew, Benjamin D. Sommers
Telehealth Exercise Intervention in Older Adults With HIV: Protocol of a Multisite Randomized Trial
This study aims to successfully develop a synchronous telehealth exercise intervention program for people with HIV to improve cardiorespiratory fitness.
- Krisann K. Oursler, Vincent C. Marconi, Brandon C. Briggs, John D. Sorkin, Alice S. Ryan
Telehealth Utilization During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Preliminary Selective Review
During the COVID-19 pandemic, in-person health care visits dramatically decreased, and the utilization of telehealth services increased. The purpose of this study is to examine various patterns in telehealth utilization based off certain factors, including geographical location, type of health care service, and a patient’s age, race, and income.
- Amelia Harju, Jonathan Neufeld
Understanding Caregiver Satisfaction with a Telediagnosis Assessment of Autism Spectrum Disorder
Access to providers who are qualified to diagnose autism-spectrum disorder (ASD) is challenging for parents of children who show signs of ASD. Telehealth has increasingly been used as a resource to decrease the wait time for early diagnosis and increase timely access to services. Overall, caregivers were satisfied with telediagnostic assessment, but the researchers identified variation including experience and accuracy of the diagnosis.
- Maranda K Jones, Matthew A Zellner, Amanda N Hobson, Amy Levin, Megan Y Roberts
A Pilot Study Examining Access to and Satisfaction with Maternal Mental Health and Substance Use Disorder Treatment via Telemedicine
It is common for women to experience mental health problems and substance use disorders (SUDs) while pregnant and during the postpartum year. Unfortunately, many women are not able to receive proper treatment for these problems due to barriers to care, but using telehealth as a tool to increase access is one way to combat this. This study was conducted to evaluate patient satisfaction with their accessibility to proper treatment for these disorders, as well as their experiences with this care being delivered via telehealth. Results show that women receiving mental health and SUD treatment via telemedicine within their obstetrician's office had high levels of satisfaction, and that it significantly increased access to care.
- National Institutes of Health; Health Resources and Services Administration
- Constance Guille, Emily Johnson, Edie Douglas, Rubin Aujla, Lisa Boyars, Ryan Kruis, Rebecca Beeks, Kathryn King, Dee Ford, Katherine Sterba
- January 2022
Evaluation of a telemedicine pilot program for the provision of HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis in the Southeastern United States
In this telePrEP feasibility study, adherence to PrEP remained high and most participants preferred telemedicine or a combination of telemedicine and in-person office visits to only in-person office visits. Without this program, many participants were unlikely to have received PrEP.
- Marty S Player, Nicole A Cooper, Suzanne Perkins, Vanessa A Diaz
Experiences with Telemedicine for HIV Care During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Mixed-Methods Study
People with HIV and clinical staff perceive telemedicine visits as useful, with benefits including the ability to engage and re-engage patients in care, perceived patient-centeredness and flexibility, the opportunity to engage family and multidisciplinary care team members, and the opportunity to enhance telemedicine use proficiency through practice and support.
- Dini Harsono, Yanhong Deng, Sangyun Chung, Lydia A Barakat, Gerald Friedland, Jaimie P Meyer, Elizabeth Porter, Merceditas Villanueva, Michael S Wolf, Jessica E Yager, E Jennifer Edelman
Patient Experience with In-Person and Telehealth Visits Before and During the COVID-19 Pandemic at a Large Integrated Health System in the United States
The positive experiences with telehealth reported in this study, especially video based telehealth, may be due to patient appreciation of efforts made to maintain access during the COVID-19 public health emergency, the focused nature of telehealth visits, and help by staff for navigation technical issues.
- Ron D Hays, Samuel A Skootsky
Rapid Implementation of a Telemedicine Program in a Ryan White–Funded HIV Clinic During a Global Pandemic
With the introduction of telemedicine in an HIV clinic, the average monthly number of patient encounters increased, the mean no-show rate decreased, and viral suppression increased. Patient satisfaction also increased during this period.
- Peter T Ender, Rebecca H Markson, Ambuj Suri, Katey Ruppert, Nichole Padron, Jill C Stoltzfus, Victoria Berges, Rajika Reed
Tele-Audiology: Current State and Future Directions
Tele-audiology can reduce barriers to hearing care by increasing access to care and reducing barriers such as time and travel. This study reviewed existing literature that found audiology services like hearing screenings, diagnostic tests, and rehabilitation can be safely delivered via telehealth and increase access to individuals who may otherwise have limited access to a hearing specialist.
- Kristin L D’Onofrio, Fan-Gang Zeng
The Changing Nature of Telehealth Use by Primary Care Physicians in the United States
The use of telehealth by primary care providers has evolved over the past several years. Using survey data, this study examined changes in the use of telehealth by primary care physicians. The study delineated physician characteristics associated with primary care providers that plan to continue using telehealth versus those who indicated that they are likely to discontinue the use of telehealth.
- Timothy Callaghan, Carly McCord, David Washburn, Kirby Goidel, Cason Schmit, Tasmiah Nuzhath, Abigail Spiegelman, Julia Scobee
Use of Telehealth Services for Prenatal Care in Mississippi: Comparison of Pre-COVID-19 Pandemic and Pandemic Obstetric Management
There has been little research to examine the use of telehealth during the COVID-19 public health emergency and its impact on the delivery of care during pregnancy and outcomes associated with pregnancy. This study examines prenatal care practices during the height of the first wave of the COVID-19 public health emergency, compared to the immediate pre-pandemic time period, and explores maternal and birth outcomes during these time periods.
- Jennifer C Reneker, Yunxi Zhang, Dorthy K Young, Xiaojian Liu, Elizabeth A Lutz
Brief Report: Supporting Access to HIV Care for Children and Youth During the COVID-19 Pandemic With Telemedicine and Rideshare
Telemedicine has the potential to bridge pediatric health care gaps. Telemedicine combined with rideshare support ensured uninterrupted access to HIV care among pediatric and adolescent patients.
- Wei Li A Koay, Supriya Prabhakar, Anne Neilan, Joanna Meyers, Nara Lee, Natella Rakhmanina
- December 2021
Medicare Beneficiaries’ Use of Telehealth in 2020: Trends by Beneficiary Characteristics and Location
This research report examines changes in Medicare fee-for-service Part B visits and the use of telehealth in 2020 during the COVID-19 public health emergency by beneficiary characteristics, provider specialty, and location.
- Lok Wong Samson, Wafa Tarazi, Gina Turrini, Steven Sheingold
Patient and Provider Perspectives on Pediatric Telemedicine During the COVID-19 Pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic led to rapid expansion of telemedicine services, and the purpose of this study is to better understand perceptions of telemedicine and compare parent/guardian satisfaction between in-person and telemedicine encounters.
- Sophie E Katz, Preston Spencer, Christine Stroebel, Lora Harnack, Jason Kastner, Ritu Banerjee
Technology Support Challenges and Recommendations for Adapting an Evidence-Based Exercise Program for Remote Delivery to Older Adults: Exploratory Mixed Methods Study
During the pandemic, a growing number of older adults with chronic conditions accessed exercise classes through videoconferencing technology to help meet their clinician’s recommendations for fitness. While users of a tele-exercise program found it helpful, technology barriers such as access to a webcam, experience using videoconferencing, and ability to troubleshoot technology were identified as barriers to participation.
- Nancy Gell, Elise Hoffman , Kushang Patel
Telehealth for HIV Care Services in South Carolina: Utilization, Barriers, and Promotion Strategies During the COVID-19 Pandemic
Telehealth was used to provide a wide array of medical and supportive HIV services, including case management, support groups, housing, food, and transportation services. Staff education, cell phone distribution, client empowerment and technology use guidance, bureaucracy and process adjustments, and reimbursement changes are all strategies that could further facilitate telehealth use to deliver care and treatment to people with HIV.
- Valerie Yelverton, Shan Qiao, Sharon Weissman, Bankole Olatosi, Xiaoming Li
Bringing Iowa TelePrEP to Scale: A Qualitative Evaluation
Regional partnerships between public health organizations and telehealth programs have the potential to expand access to HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis in rural and small urban areas, but the best practices on how to successfully conduct these partnerships are unknown. Iowa TelePrEP is a regional public health‒partnered telehealth model created by the Iowa Department of Public Health and the University of Iowa to assess barriers and facilitators to statewide expansion and the lessons learned in the process. The facilitators of expansion included early public health partner engagement, model acceptability and inclusion of a navigator, and adaptability to local public health partner settings.
- Emily E Chasco, Cody Shafer, Dena M B Dillon, Seth Owens, Michael E Ohl, Angela B Hoth
- November 2021
Development and Preliminary Feasibility of iByte4Health: A Mobile Health (mHealth) Pediatric Obesity Prevention Intervention to Engage Parents with Low-Income of Children 2-9 Years
Pediatric obesity continues to be a major public health concern with minority, low-income youth most at risk. This study assesses the use of mobile health (mHealth) programs such as iByte4Health, a text-messaging based obesity prevention program. The goal of iByte4Health is to deliver patent and child-focused content which encourages conversations towards key health behaviors, goals, and behavioral changes.
- Gina L Tripicchio, Melissa Kay, Sharon Herring, Travis Cos, Carolyn Bresnahan, Danielle Gartner, Laura Stout Sosinsky, Sarah B Bass
Georgia Leverages Telehealth to Expand HIV Care Management in Underserved Areas
In Georgia, HIV telehealth has been successful at bridging gaps in patient care and in training local providers to offer comprehensive HIV care. A total of 60 telemedicine solutions were deployed in Georgia to expand HIV care access in 12 Georgia health districts. Among Ryan White HIV/AIDS Program clients who had a telehealth visit, 99.4% were prescribed antiretroviral therapy and 91.4% were virally suppressed.
- Suleima Salgado, Gregory Felzien, Jared Brumbeloe
Implementation of Telehealth Services in Rural Schools: A Qualitative Assessment
Many rural areas have a shortage of health care professional to meet the needs of the community. Several schools located in rural areas have implemented telehealth solutions to address the unmet health needs of students. This study captures insights from telehealth programs funded through the School-Based Telehealth Network Grant Program to identify facilitators and barriers to inform implementation of telehealth programs in rural schools.
- Kimberly Fox, Amanda Burgess, Martha Elbaum Williamson, John Massey, George Shaler, Karen Pearson, Jennifer MacKenzie, Kimberly Merchant, Xi Zhu, Marcia Ward
Telehealth Competencies for Nursing Education and Practice
Telehealth has seen significant growth as a health care delivery method, specifically among advanced practice nurses. With lack of standardized telehealth training, advanced practice nurses are not equipped to maximize use of telehealth to provide care for patients. In this research, the Four P’s of Telehealth framework (planning, preparing, providing, and performance evaluation) was used to identify, develop, and evaluate telehealth competencies. Effective use of these competencies to guide training development will provide the necessary education and tools needed to assume leadership roles in all phases of telehealth implementation and delivery.
- Carolyn M Rutledge, Jennifer O’Rourke, Anne M Mason, Katherine Chike-Harris, Lyn Behnke, Lolita Melhado, Loureen Downes, Tina Gustin
- October 2021
Trends in Outpatient Telemedicine Utilization Among Rural Medicare Beneficiaries, 2010-2019
In a study of 10.4 million rural Medicare beneficiaries, researchers discovered continuous growth in telemedicine use among Medicare beneficiaries with a disproportionate share of all telemedicine visits for serious mental illness (e.g., bipolar disorder) between 2010 and 2019 – especially for care provided by nurse practitioners and other non-physician clinicians.
- Michael L. Barnett, Haiden A. Huskamp, Alisa B. Busch, Lori Uscher-Pines, Krisda H. Chaiyachati, Ateev Mehrotra
Employing telehealth within HIV care: advantages, challenges, and recommendations
While the COVID-19 pandemic added new challenges within the medical field, it also presented new opportunities, such as catalyzing the implementation of telehealth within spaces that offer care for people living with HIV, substance use disorders, and various behavioral health problems.
- Melissa Grove, L. Lauren Brown, Hannan K. Knudsen, Erika G. Martin, Bryan R. Garner
State Medicaid Telehealth Policies Before and During the COVID-19 Public Health Emergency
The pandemic led to an expansion of telehealth access for individuals receiving Medicaid across the United States. Based on Medicaid claims data, the authors discuss the growth in telehealth use by Medicaid and Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP) recipients. The report also analyzes state policies for telehealth reimbursement under Medicaid and discusses how these changes are likely to impact access and health equity.
- Rose C Chu, Christie Peters, Nancy De Lew, Benjamin D Sommers
Keeping Pace With 21st Century Healthcare: A Framework for Telehealth Research, Practice, and Program Evaluation in Occupational Therapy
The use of telehealth in occupational therapy is steadily increasing, but there is little framework around the evaluation of these services. This study introduces the PACE Framework, which aims to support researchers and practitioners in systematically evaluating components of telehealth service delivery in occupational therapy through population and health outcomes, access for all clients, costs and cost-effectiveness, and the experiences of clients and occupational therapy practitioners.
- Lauren M. Little, Kristen A. Pickett, Rachel Proffitt, Jana Cason
This study examines telehealth utilization for HIV services in South Carolina, identifies barriers to telehealth during the COVID-19 public health emergency, and investigates strategies to facilitate remote HIV care delivery.
Telehealth for the Treatment of Serious Mental Illness and Substance Use Disorders
This guide reviews the research on the effectiveness of using telehealth for serious mental illness and substance abuse disorders. It makes recommendations for practice and provides examples of how practitioners use these practices in their programs.
Seeing the Value of Video: A Qualitative Study on Patient Preference for Using Video in a Veteran Affairs Telemental Health Program Evaluation
A web-based treatment program for veterans utilizes video visits with mental health experts to conduct online cognitive behavioral therapy that targets treating clinically significant symptoms of depression and post-traumatic stress disorder. This program evaluated whether or not veterans thought that using video during these sessions is important, and why it may or may not be important. Results show that being able to visually see a provider has distinct benefits for care and the patient-provider relationship, which gives important information for future telehealth use when debating whether to use video or phone for remote care.
- Patricia V Chen, Ashley Helm, Terri Fletcher, Miryam Wassef, Julianna Hogan, Amy Amspoker, Marylene Cloitre, Jan Lindsay
Comparative effects of telephone versus in-office behavioral counseling to improve HIV treatment outcomes among people living with HIV in a rural setting
People with HIV at risk for discontinuing HIV care and treatment failure living in rural areas expressed a preference for telephone-delivered behavioral counseling and those who received telephone counseling completed a greater number of sessions.
- Seth C Kalichman, Harold Katner, Lisa A Eaton, Ellen Banas, Marnie Hill, Moira O Kalichman
Evaluation of an Intrahospital Telemedicine Program for Patients Admitted With COVID-19: Mixed Methods Study
In this study, virtual care was associated with reductions in personal protective equipment use, reductions in COVID-19 exposure risk, and patient and provider satisfaction.
- Sean Legler, Matthew Diehl, Brian Hilliard, Andrew Olson, Rebecca Markowitz, Christopher Tignanelli, Genevieve B Melton, Alain Broccard, Jonathan Kirsch, Michael Usher
Use of Telehealth in Substance Use Disorder Services During and After COVID-19: Online Survey Study
This study investigated the widespread adoption of telephone and video technologies for delivering treatment for substance use disorders (SUDs) during the COVID-19 pandemic. The study looked at the acceptance and intent to use telehealth among service providers beyond the pandemic. Findings revealed high utilization rates of telehealth services across different SUD treatment modalities, with organizations expressing intent to continue using telehealth post-pandemic. The study highlighted the influence of perceived usefulness and ease of use on the acceptance of telehealth, emphasizing their potential for sustained application in SUD care.
- Todd Molfenter, Nancy Roget, Michael Chaple, Stephanie Behlman, Olivia Cody, Bryan Hartzler, Edward Johnson, Maureen Nichols, Patricia Stilen, Sara Becker
- February 2021
Evaluation of Pragmatic Telehealth Physical Therapy Implementation During the COVID-19 Pandemic
The goal of this study is to evaluate the implementation of telehealth physical therapy in response to COVID-19 and identify strategies to maintain and scale up its use in a large urban academic medical center. The results indicate that telehealth physical therapy was utilized and accessible during the COVID-19 pandemic, providing guidance for future initiatives to expand its use and study in physical therapy through health policy, quality improvement, and implementation science efforts.
- Matthew J Miller, Sang S Pak, Daniel R Keller, Deborah E Barnes
- January 2021
HRSA's Evidence-Based Tele-Emergency Network Grant Program: Multi-site Prospective Cohort Analysis Across Six Rural Emergency Department Telemedicine Networks
Six rural hospital systems received grants from HRSA to study how their emergency telehealth departments affect outcomes for patients. Telehealth was often the patient’s first point of contact and usually resulted in a transfer to a distant hospital or local inpatient facility. Findings suggest that emergency telehealth plays an important role in improving access for rural emergency patients.
- Sarah Heppner, Nicholas Mohr, Knute Carter, Fred Ullrich, Kimberly Merchant, Marcia Ward
The Future of Telehealth in School-Based Health Centers: Lessons from COVID-19
A qualitative analysis of nationally-led "Listening and Learning" sessions by the School-Based Health Alliance revealed substantial innovation and expansion of telehealth services due to COVID-10. School-based health programs were shown to reduce barriers to health care access, protect the most vulnerable, and decrease the spread of disease. Telehealth implementations in schools may also help keep youth from emergency departments and provide needed mental health care.
- Anna Goddard, Erin Sullivan, Paula Fields, Suzanne Mackey
The Provision of Counseling to Patients Receiving Medications for Opioid Use Disorder: Telehealth Innovations and Challenges in the Age of COVID-19
Medications for opioid use disorders (MOUD) combined with behavioral health therapy is an effective approach for the treatment of patients with a substance use disorder (SUD). During the COVID-19 pandemic, the government enacted waivers that allowed behavioral health care for SUD, including prescribing and refilling MOUD to be delivered virtually. This article reviews how these changes have impacted access and describes the need to identify models for hybrid care of patients with SUD in the future.
- Jaclyn MW Hughto, Lisa Peterson, Nicholas S Perry, Alex Donoyan, Matthew J Mimiaga, Kimberly M Nelson, David W Pantalone
Patient Characteristics Associated With Telemedicine Access for Primary and Specialty Ambulatory Care During the COVID-19 Pandemic
Telemedicine use has expanded since the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, and the purpose of this study was to evaluate what inequities may exist in its design. Among patients scheduled for primary care and ambulatory telemedicine visits, differences were seen in rates of telemedicine and video use.
- Lauren A Eberly, Michael J Kallan, Howard M Julien, Norrisa Haynes, Sameed Ahmed M Khatana, Ashwin S Nathan, Christopher Snider, Neel P Chokshi, Nwamaka D Eneanya, Samuel U Takvorian, Rebecca Anastos-Wallen, Krisda Chaiyachati, Marietta Ambrose, Rupal O'Quinn, Matthew Seigerman, Lee R Goldberg, Damien Leri, Katherine Choi, Yevginiy Gitelman, Daniel M Kolansky, Thomas P Cappola, Victor A Ferrari, C William Hanson, Mary Elizabeth Deleener, Srinath Adusumalli
- December 2020
Maternal Telehealth Access Project (MTAP) Report on Community Grant Program
The Maternal Telehealth Access Project (MTAP) was launched to ensure that quality telehealth prenatal and postpartum services are accessible and available in underserved communities during the COVID-19 public health emergency. Increased access to perinatal services and support via telehealth, including clinical care, care coordination, support, and doulas/community health workers leads to improved clinical outcomes for moms and babies.
- Leslie deRosset, Sarah Verbiest, Dorothy Cilenti, Dawn Godbolt, Kelli Sheppard
- November 2020
Telebehavioral Health Use Among Rural Medicaid Beneficiaries: Relationships with Telehealth Policies
This study examines Medicaid telehealth policies and telebehavioral health use among rural fee-for-service (FFS) patients. It finds that rural Medicaid FFS beneficiaries may have better access to telebehavioral health services when they give informed consent in a provider setting.
- Jean Talbot, Yvonne Jonk, Amanda Burgess, Deborah Thayer, Erika Ziller, Nathan Paluso, Andrew Coburn
- October 2020
Telehealth Use in a Rural State: A Mixed Methods Study Using Maine's All-Payer Claims Database
The expansion of telehealth in Maine is partly driven by Medicare patients. This research suggests telehealth is improving access to behavioral health and speech-language pathology. Telehealth is limited, however, by access problems including provider shortages, lack of broadband, and other insurance coverage like Medicare and commercial policies.
- Yvonne Jonk, Martha Williamson, Deborah Thayer, Jennifer MacKenzie, Catherine McGuire, Kimberley Fox, Andrew Coburn
Opioid Use Disorder ECHO: A Program Evaluation of a Project That Provides Knowledge and Builds Capacity for Community Health Workers in Medically Underserved Areas of South Texas
This research publication addresses the rising concern of opioid use disorder by implementing the Opioid Addiction Treatment ECHO for CHWs program. This program trained CHWs in rural and medically underserved areas via teleconferencing technology. The program focused on behavioral health integration, specifically targeting opioid prescription misuse, and resulted in increased knowledge attainment among CHWs. The study concludes that the ECHO model effectively connected subject matter experts with CHWs in local communities, highlighting its potential in addressing public health challenges.
- Joseph Zapata Jr, Angela Colistra, Janna Lesser, Belinda Flores, Annette Zavala-Idar, Andrea Moreno-Vasquez
- September 2020
Environmental Scan on Telehealth in the Context of Alternative Payment Models (APMs) and Physician-Focused Payment Models (PFPMs)
This publication explores the integration of telehealth within Medicare's alternative payment models (APMs) and physician-focused payment models (PFPMs). The study examines the evolution of telehealth coverage and reimbursement policies under Medicare and Medicaid, discusses the effectiveness of telehealth interventions across various clinical settings, and identifies key issues and opportunities for optimizing telehealth integration within APMs and PFPMs, including challenges related to billing, interoperability, and patient-centered care.
Leveraging Digital Platforms to Scale Health Care Workforce Development: The Career 911 Massive Open Online Course
A massive open online course (MOOC) called Career 911 was created to encourage students from diverse backgrounds to explore health-related professions.
- Melissa A Simon, Shaneah Taylor, Laura S Tom
Telepsychiatric Consultation as a Training and Workforce Development Strategy for Rural Primary Care
There is a shortage of rural primary care personnel with expertise in team care for patients with common mental disorders. This research investigated the feasibility of regular systematic case reviews through telepsychiatric consultation, within collaborative care for depression, as a continuous training and workforce development strategy in rural clinics.
- Morhaf Al Achkar, Ian M. Bennett, Lydia Chwastiak, Theresa Hoeft, Tre Normoyle, Melinda Vredevoogd, Davis G. Patterson
Averted Transfers in Rural Emergency Departments Using Telemedicine: Rates and Costs Across Six TeleED Networks
Using telemedicine in rural emergency departments saved an average of $2,673 per patient by avoiding transport costs. The majority of the cost savings went to public insurance.
- Marcia Ward, Knute Carter, Fred Ullrich, Kimberly Merchant, Nabil Natafgi, Xi Zhu, Paula Weigel, Sarah Heppner, Nicholas Mohr
- August 2020
Outcomes of a Rapid Adolescent Telehealth Scale-Up During the COVID-19 Pandemic
In response to the COVID-19 public health emergency, health systems needed to quickly transition from in-person visits to telehealth. This study examines the unique challenges within adolescent medicine during this transition, such as patient confidentiality during digital communication and multidisciplinary care teams learning to use video formats.
- Sarah M. Wood, Krishna White, Rebecka Peebles, Julia Pickel, Maryam Alausa, Jamie Mehringer, Nadia Dowshen
A telehealth lifestyle intervention to reduce excess gestational weight gain in pregnant women with overweight or obesity (GLOW): a randomised, parallel-group, controlled trial
Significant weight gain in pregnancy among overweight or obese women increases their already elevated risk of having gestational diabetes, a cesarean delivery, and post-partum weight retention. It also increases the chances of a larger infant and the child's risk of obesity. This research investigated whether a telehealth lifestyle intervention reduced excess weight gain in participants.
- Assiamira Ferrara, Monique M Hedderson, Susan D Brown, Samantha F Ehrlich, Ai-Lin Tsai, Juanran Feng, Maren Galarce, Santica Marcovina, Patrick Catalano, Charles P Quesenberry
Process of Identifying Measures and Data Elements for the HRSA School-Based Telehealth Network Grant Program
An analysis of the School-Based Telehealth Network Grant Program’s initiatives to measure the effect that telehealth has on the quality of healthcare services offered in schools. The project also aimed to identify a common set of measures that could assess school-based telehealth services, utilization, processes, and outcomes.
- Marcia Ward, Kimberley Fox, Kimberly Merchant, Amanda Burgess, Fred Ullrich, Karen Pearson, George Shaler, Christopher Shea, Steve North, Carlos Mena
Project Moxie: Results of a Feasibility Study of a Telehealth Intervention to Increase HIV Testing Among Binary and Nonbinary Transgender Youth
Because transgender youth have low rates of engagement in HIV prevention, Project Moxie tested the feasibility of an intervention that provides home-based HIV self-testing combined with video-chat counseling.
- Rob Stephenson, Kieran Todd, Erin Kahle, Stephen Sullivan, Michael Miller-Perusse, Akshay Sharma, Keith Horvath
Telehealth with remote blood pressure monitoring compared with standard care for postpartum hypertension
Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy (HDP) affect 10% of the pregnancies in the United States and are the most common reason for postpartum hospital readmissions. This study considers whether postpartum home telehealth with remote blood pressure monitoring could reduce the readmission rates during the first 6 weeks postpartum in women with HDP.
- Kara Kjersten Hoppe, Nicole Thomas, Melissa Zernick, Julia B Zella, Thomas Havighurst, KyungMann Kim, Makeba Williams, Brenda Niu, Ali Lohr, Heather M Johnson
Emergency Department Telemedicine Consults are Associated with Faster Time-to-ECG and Time-to-Fibrinolysis for Myocardial Infarction Patients
Heart attack is a common and deadly event that requires treatment as soon as possible. Telemedicine can improve how quickly heart attacks are diagnosed and treated in rural hospitals.
- Aspen Miller, Marcia Ward, Fred Ullrich, Kimberly Merchant, Morgan Swanson, Nicholas Mohr
- February 2020
PrEPTECH: a telehealth-based initiation program for human immunodeficiency virus pre-exposure prophylaxis in young men of color who have sex with men. A pilot study of feasibility.
This pilot study uses a telehealth-based approach to pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) initiation as a solution to barriers such as stigma, cost, adherence concerns, and medical distrust.
- Oliver N. Refugio, Mabel M. Kimble, Cara L. Silva, James E. Lykens, Christian Bannister, Jeffrey D. Klausner
- January 2020
Provider-to-Provider Telemedicine Improves Adherence to Sepsis Bundle Care in Community Emergency Departments
Sepsis occurs when an infection reaches the bloodstream and getting care quickly improves the chances of survival. In this study, telemedicine in the emergency department improved the rates of adhering to the sepsis treatment protocol. The timely replacement of fluids and the administration of antibiotics greatly improved sepsis care at rural community hospitals.
- Nicholas Mohr, Kaylyn Campbell, Morgan Swanson, Fred Ullrich, Kimberly Merchant, Marcia Ward
Treatment of Opioid Use Disorder in Pregnant Women via Telemedicine: A Nonrandomized Controlled Trial
Increased rates of maternal and infant morbidity and mortality are associated with opioid use disorder (OUD). The use of telehealth for maternal care practices for pregnant and postpartum individuals can improve access to care and telehealth services, while reducing the effects of OUD. However, additional evaluation is required before expanding this health care delivery method.
- Constance Guille, Annie N Simpson, Edie Douglas, Lisa Boyars, Kathryn Cristaldi, James McElligott, Donna Johnson, Kathleen Brady
Emergency Department Telemedicine Consults Decrease Time to Interpret Computed Tomography of the Head in a Multi-Network Cohort
A study of emergency telemedicine (tele-ED) for stroke care in four tele-ED networks. Tele-ED was associated with decreased time to diagnostic imaging interpretation and time to thrombolytic medication.
- Morgan Swanson, Aspen Miller, Marcia Ward, Fred Ullrich, Kimberly Merchant, Nicholas Mohr
- November 2019
Tele-Emergency Behavioral Health in Rural and Underserved Areas
Severe shortages of behavioral health specialists in rural and underserved areas make placing patients in appropriate facilities difficult. This paper describes two different emergency departments in the Midwest using telemedicine to address behavioral health access and placement for patients in rural and underserved areas. Findings suggest that transfer to in-patient facilities was much higher in both models when using telemedicine.
- Paula Weigel, Divya Bhagianadh, Kimberly Merchant, Amy Wittrock, Hicham Rahmouni, Amanda Bell, Stephanie Laws, Marcia Ward
A Postpartum Remote Hypertension Monitoring Protocol Implemented at the Hospital Level
This study evaluated using remote blood pressure monitoring on postpartum women with hypertension when they leave the hospital. It found that remote monitoring of this type showed high patient compliance, retention, and satisfaction.
- Alisse Hauspurg, Lara S Lemon, Beth A Quinn, Anna Binstock, Jacob Larkin, Richard H Beigi, Andrew R Watson, Hyagriv N Simhan
- October 2019
The Use of Telehealth in School-Based Health Centers
School-based telehealth programs can expand health care access to rural and underserved youth by eliminating barriers to access, such as transportation. This article describes characteristics of School-Based Telehealth Centers using technology to add to the access of care beyond onsite providers for underserved communities.
- Hayley Love, Nirmita Panchal, John Schlitt, Caroline Behr, Samira Soleimanpour
Development of a tailored, telehealth intervention to address chronic pain and heavy drinking among people with HIV infection: integrating perspectives of patients in HIV care
Chronic pain and heavy drinking commonly co-occur and can influence the course of HIV, but there have been no interventions designed to address both conditions among people living with HIV. This study aims to better understand pain symptoms, patterns of alcohol use, treatment experiences, and technology use in order to tailor a telehealth intervention that will address all these conditions.
- Tibor P. Palfai, Jessica L. Taylor, Richard Saitz, Maya P. L. Kratzer, John D. Otis, Judith A. Bernstein
- August 2019
The Use of and Experiences With Telelactation Among Rural Breastfeeding Mothers: Secondary Analysis of a Randomized Controlled Trial
Telelactation services connecting breastfeeding mothers to lactation consultants increase access to professional breastfeeding support in rural areas. This research shows both high demand for and positive experiences with these telehealth services in an underserved population.
- Kandice Kapinos, Virginia Kotzias, Debra Bogen, Kristin Ray, Jill Demirci, Mary Ann Rigas, Lori Uscher-Pines
Telehealth and texting intervention to improve HIV care engagement, mental health and substance use outcomes in youth living with HIV: a pilot feasibility and acceptability study protocol
This study aims to evaluate the feasibility, acceptability, and preliminary clinical outcomes of a 12-session telehealth counseling series provided to young adults living with HIV that will include education, motivational enhancement and problem-solving around HIV care, mental health, substance use, and other challenges.
- Angie R Wootton, Dominique A Legnitto, Valerie A Gruber, Carol Dawson-Rose, Torsten B Neilands, Mallory O Johnson, Parya Saberi
Cell Phone Counseling Improves Retention of Mothers With HIV Infection in Care and Infant HIV Testing in Kisumu, Kenya: A Randomized Controlled Study
This study shows the effectiveness of cell phone counseling to keep pregnant women with HIV in care in Kisumu, Kenya. Phone counseling helps reach and retain pregnant women with HIV infection and postpartum mothers in care. It also improved infant HIV testing and antenatal and postnatal care services.
- United States Agency for International Development
- Avina Sarna, Lopamudra Ray Saraswati, Jerry Okal, James Matheka, Danmark Owuor, Roopal J Singh, Nancy Reynolds, Sam Kalibala
Randomized Controlled Trial of a Mobile Health Intervention to Promote Retention and Adherence to Preexposure Prophylaxis Among Young People at Risk for Human Immunodeficiency Virus: The EPIC Study
Young people are the least likely to use protection against sexually transmitting HIV. An interactive text-messaging intervention significantly increased the odds of using protection among young individuals at risk for getting HIV.
- Albert Y Liu, Eric Vittinghoff, Patricia von Felten, K Rivet Amico, Peter L Anderson, Richard Lester, Erin Andrew, Ixchell Estes, Pedro Serrano, Jennifer Brothers, Susan Buchbinder, Sybil Hosek, Jonathan D Fuchs
Text Messages Can Encourage Patients to Discuss and Receive HIV Testing in Primary Care
Regular HIV testing does not often happen in primary care visits. Providers want patients to ask for the test, as opposed to suggesting it themselves. This study finds that using a patient-centered text message campaign may prompt patients to discuss HIV testing with their physicians, thereby increasing HIV testing.
- Renata Wettermann, Haley Marek, Thomas P. Giordano, Monisha Arya
Pediatric tele-emergency care: A study of two delivery models
The study evaluates two tele-emergency department programs for pediatric patients with different designs, one general and one specialized. The study shows design choices affect how programs are evaluated and highlights the challenge of creating standard metrics.
- Paula A Weigel, Kimberly A S Merchant, Amy Wittrock, Jamie Kissee, Fred Ullrich, Amanda L Bell, James P Marcin, Marcia M Ward
The Third National Telemedicine & Telehealth Service Provider Showcase Conference: Advancing Telehealth Partnerships
The “Telemedicine & Telehealth Service Provider Showcase” (SPS) Conference, a national conference established in 2014, is a space for discussion on telehealth and relevant components of the telehealth services industry. Key topics shared in the SPS 2017 Conference include the following and more: development of effective partnerships; using telehealth services as a strategic asset; important reimbursement; direct-to-consumer initiatives; legislative and regulatory issues, and overall takeaways.
- Dale C Alverson, Elizabeth A Krupinski, Kristine A Erps, Nancy S Rowe, Ronald S Weinstein
Feasibility and acceptability of an online positive affect intervention for those living with comorbid HIV depression
This article presents pilot data of using an online intervention to improve the outlook of people living with both HIV and depression. The intervention was rated well by patients and was shown to be both acceptable and feasible to use.
- S. M. Bassett, M. Cohn, P. Cotten, I. Kwok, J. T. Moskowitz
Implementation Strategies for Telestroke: A Qualitative Study of Telestroke Networks in North Carolina
This study examines the adoption decision process and strategies employed during telestroke network development, implementation, and sustainability.
- Christopher Shea, Kea Turner, Amir Alishahi Tabriz, Steve North
- September 2018
Telestroke Adoption Among Community Hospitals in North Carolina: A Cross-Sectional Study
Telestroke is the use of telemedicine in stroke care. This study identifies community and hospital characteristics associated with adoption of telestroke among acute care hospitals in North Carolina.
- Christopher Shea, Amir Tabriz, Kea Turner, Steve North, Kristin Reiter
Telemedicine Use Decreases Rural Emergency Department Length of Stay for Transferred North Dakota Trauma Patients
Emergency department telemedicine consults for trauma patients were associated with faster hospital transfers and the increased use of radiography.
- Nicholas M. Mohr, J. Priyanka Vakkalanka, Karisa K. Harland, Amanda Bell, Brian Skow, Dan M. Shane, Marcia M. Ward
A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
A lock ( ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- 10 Essential Public Health Services
- Cooperative Agreements, Grants & Partnerships
- Public Health Professional: Programs
- Health Assessment: Index
- Research Summary
- COVID-19 Health Disparities Grant Success Stories Resources
- Communication Resources
- Show All Home
Research Summary: Social Determinants of Health
- Social determinants of health are the non-medical factors that influence health outcomes.
- This pages provides an overview of CDC research on social determinants of health.
- This searchable list of peer-reviewed articles is categorized according to the Healthy People 2030 framework.

What CDC is doing
CDC conducts and publishes research on the social determinants of health (SDOH). This page offers a searchable list of recent peer-reviewed articles written by CDC researchers on various SDOH topics. These are organized according to the Healthy People 2030 place-based framework:
- Economic stability explores the link between people's financial resources (like income, cost of living, and socioeconomic status) and their health. Key issues include poverty, employment, food security, and housing stability.
- Education examines the relationship between education and health and well-being. Important areas include graduation rates, higher education, educational attainment, language and literacy, and early childhood education and development.
- Social and community context focuses on how the characteristics of environments where people live, learn, work, and play affect their health and well-being. It covers topics like community cohesion, civic participation, discrimination, racism, xenophobia, cultural norms, interpersonal violence, workplace conditions, and incarceration. Another contextual factor is immigration status, especially for people who migrated from less-developed countries.
- Health and healthcare looks at how people's access to and understanding of health services impact their health. Issues include healthcare access, health insurance coverage, English language proficiency, health literacy, and the health implications for people who migrate to or within the United States, even temporarily.
- Neighborhood and built environment explores the relationship between where people live (like housing, neighborhoods, and overall environment) and their health and well-being. Topics include housing quality, access to transportation, availability of healthy foods, water and air quality, and community violence and crime.
- General SDOH topics and methods cover broader SDOH or SDOH-related topics that don't fit neatly under the Healthy People 2030 SDOH domains. It encompasses methodologies, strategies, measurements, and policies related to SDOH.
Explore the research
To reach the database, please click on this link . Filter articles by the categories outlined above and use the search box to further sort articles by keyword or author name.
For more information about article selection, visit Frequently Asked Questions .
If you know about CDC-published research that was not included here and meets the inclusion criteria, please contact us at [email protected] .
Public Health Gateway
CDC's National Center for State, Tribal, Local, and Territorial Public Health Infrastructure and Workforce helps drive public health forward and helps HDs deliver services to communities.
- Introduction
- Conclusions
- Article Information
NCA4 indicates Fourth National Climate Assessment.
Incidence rate ratio of emergency department visits with increasing temperature compared with optimal temperature. Main model adjusted for relative humidity and day of the week. Shading represents the 95% CI. The optimal temperature is the first percentile of the county-specific temperature distribution, at which minimum morbidity occurs. The additional temperatures shown on the x-axis represent the 25th, 50th, 75th, and 100th percentiles of the county-specific temperature distribution, converted to the equivalent actual temperature across all counties in the study area.
Incidence rate ratio of emergency department visits with increasing temperature compared with optimal temperature. Main model adjusted for relative humidity and day of the week. Shading indicates the 95% CI. The optimal temperature is the first percentile of the county-specific temperature distribution, at which minimum morbidity occurs. The additional temperatures shown on the x-axis represent the 25th, 50th, 75th, and 100th percentiles of the county-specific temperature distribution, converted to the equivalent actual temperature across all counties in the study area.
eTable. CCS Codes and Corresponding ICD-9/ICD-10 Codes.
eFigure 1. Time Course for Extreme Heat Exposure Response Curve.
eFigure 2. Sensitivity Analysis Results and Time Course for Composite Mental Health End Point.
eFigure 3. Time Course for Cause-Specific Mental Health Emergency Department Visits.
eFigure 4. Incidence Rate Ratio of Emergency Department Visits for 95th Percentile of Temperature vs Optimal Temperature Among Subgroups, and Heterogeneity Tests.
eAppendix. Sample R Code for Analysis.
- Association Between the 2021 Heat Wave in the Pacific Northwest and Emergency Department Visits JAMA Research Letter December 20, 2022 This study used a health care claims data set of enrollees in commercial and Medicare Advantage insurance plans to assess the association between the June 2021 heat wave and the rates of emergency department visits in Portland, Oregon, and Seattle, Washington. Amruta Nori-Sarma, PhD; Chad Milando, PhD; Kate R. Weinberger, PhD; Jeremy J. Hess, MD; Nicole A. Errett, PhD; Gregory A. Wellenius, ScD
- Identifying and Preparing for the Mental Health Burden of Climate Change JAMA Psychiatry Editorial April 1, 2022 Nick Obradovich, PhD; Kelton Minor, MS
See More About
Select your interests.
Customize your JAMA Network experience by selecting one or more topics from the list below.
- Academic Medicine
- Acid Base, Electrolytes, Fluids
- Allergy and Clinical Immunology
- American Indian or Alaska Natives
- Anesthesiology
- Anticoagulation
- Art and Images in Psychiatry
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assisted Reproduction
- Bleeding and Transfusion
- Caring for the Critically Ill Patient
- Challenges in Clinical Electrocardiography
- Climate and Health
- Climate Change
- Clinical Challenge
- Clinical Decision Support
- Clinical Implications of Basic Neuroscience
- Clinical Pharmacy and Pharmacology
- Complementary and Alternative Medicine
- Consensus Statements
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Critical Care Medicine
- Cultural Competency
- Dental Medicine
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- Diagnostic Test Interpretation
- Drug Development
- Electronic Health Records
- Emergency Medicine
- End of Life, Hospice, Palliative Care
- Environmental Health
- Equity, Diversity, and Inclusion
- Facial Plastic Surgery
- Gastroenterology and Hepatology
- Genetics and Genomics
- Genomics and Precision Health
- Global Health
- Guide to Statistics and Methods
- Hair Disorders
- Health Care Delivery Models
- Health Care Economics, Insurance, Payment
- Health Care Quality
- Health Care Reform
- Health Care Safety
- Health Care Workforce
- Health Disparities
- Health Inequities
- Health Policy
- Health Systems Science
- History of Medicine
- Hypertension
- Images in Neurology
- Implementation Science
- Infectious Diseases
- Innovations in Health Care Delivery
- JAMA Infographic
- Law and Medicine
- Leading Change
- Less is More
- LGBTQIA Medicine
- Lifestyle Behaviors
- Medical Coding
- Medical Devices and Equipment
- Medical Education
- Medical Education and Training
- Medical Journals and Publishing
- Mobile Health and Telemedicine
- Narrative Medicine
- Neuroscience and Psychiatry
- Notable Notes
- Nutrition, Obesity, Exercise
- Obstetrics and Gynecology
- Occupational Health
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopedics
- Otolaryngology
- Pain Medicine
- Palliative Care
- Pathology and Laboratory Medicine
- Patient Care
- Patient Information
- Performance Improvement
- Performance Measures
- Perioperative Care and Consultation
- Pharmacoeconomics
- Pharmacoepidemiology
- Pharmacogenetics
- Pharmacy and Clinical Pharmacology
- Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation
- Physical Therapy
- Physician Leadership
- Population Health
- Primary Care
- Professional Well-being
- Professionalism
- Psychiatry and Behavioral Health
- Public Health
- Pulmonary Medicine
- Regulatory Agencies
- Reproductive Health
- Research, Methods, Statistics
- Resuscitation
- Rheumatology
- Risk Management
- Scientific Discovery and the Future of Medicine
- Shared Decision Making and Communication
- Sleep Medicine
- Sports Medicine
- Stem Cell Transplantation
- Substance Use and Addiction Medicine
- Surgical Innovation
- Surgical Pearls
- Teachable Moment
- Technology and Finance
- The Art of JAMA
- The Arts and Medicine
- The Rational Clinical Examination
- Tobacco and e-Cigarettes
- Translational Medicine
- Trauma and Injury
- Treatment Adherence
- Ultrasonography
- Users' Guide to the Medical Literature
- Vaccination
- Venous Thromboembolism
- Veterans Health
- Women's Health
- Workflow and Process
- Wound Care, Infection, Healing
Others Also Liked
- Download PDF
- X Facebook More LinkedIn
Nori-Sarma A , Sun S , Sun Y, et al. Association Between Ambient Heat and Risk of Emergency Department Visits for Mental Health Among US Adults, 2010 to 2019. JAMA Psychiatry. 2022;79(4):341–349. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2021.4369
Manage citations:
© 2024
- Permissions
Association Between Ambient Heat and Risk of Emergency Department Visits for Mental Health Among US Adults, 2010 to 2019
- 1 Department of Environmental Health, Boston University School of Public Health, Boston, Massachusetts
- 2 OptumLabs Visiting Scholar, Eden Prairie, Minnesota
- 3 Department of Psychiatry, Boston Medical Center, Boston, Massachusetts
- 4 Boston University School of Public Health, Boston, Massachusetts
- 5 Department of Epidemiology, Boston University School of Public Health, Boston, Massachusetts
- Editorial Identifying and Preparing for the Mental Health Burden of Climate Change Nick Obradovich, PhD; Kelton Minor, MS JAMA Psychiatry
- Research Letter Association Between the 2021 Heat Wave in the Pacific Northwest and Emergency Department Visits Amruta Nori-Sarma, PhD; Chad Milando, PhD; Kate R. Weinberger, PhD; Jeremy J. Hess, MD; Nicole A. Errett, PhD; Gregory A. Wellenius, ScD JAMA
Question Are periods of higher ambient temperature associated with an increase in emergency department (ED) visits for mental health conditions among US adults with health insurance?
Findings In this case-crossover study of 3 496 762 ED visits among 2 243 395 unique individuals, higher warm-season temperatures were associated with an increased risk of ED visits for any mental health condition and for specific mental health conditions.
Meaning This information could aid clinicians providing services for mental health in preparing for increased stress on individuals and the health care system during times when extreme heat is anticipated.
Importance The implications of extreme heat for physical health outcomes have been well documented. However, the association between elevated ambient temperature and specific mental health conditions remains poorly understood.
Objective To investigate the association between ambient heat and mental health–related emergency department (ED) visits in the contiguous US among adults overall and among potentially sensitive subgroups.
Design, Setting, and Participants This case-crossover study used medical claims data obtained from OptumLabs Data Warehouse (OLDW) to identify claims for ED visits with a primary or secondary discharge psychiatric diagnosis during warm-season months (May to September) from 2010 through 2019. Claims for adults aged 18 years or older with commercial or Medicare Advantage health insurance who were living in 2775 US counties were included in the analysis. Emergency department visits were excluded if the Clinical Classifications Software code indicated that the visits were for screening for mental health outcomes and impulse control disorders.
Exposures County-specific daily maximum ambient temperature on a continuous scale was estimated using the Parameter-Elevation Relationships on Independent Slopes model. Extreme heat was defined as the 95th percentile of the county-specific warm-season temperature distribution.
Main Outcomes and Measures The daily incidence rate of cause-specific mental health diagnoses and a composite end point of any mental health diagnosis were assessed by identifying ED visit claims using primary and secondary discharge diagnosis International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision and International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, Tenth Revision codes. Conditional logistic regression models were used to estimate the incidence rate ratio (IRR) and 95% CIs for the association between daily temperature and incidence rates of ED visits.
Results Data from 3 496 762 ED visits among 2 243 395 unique individuals were identified (56.8% [1 274 456] women; mean [SD] age, 51.0 [18.8] years); of these individuals, 14.3% were aged 18 to 26 years, 25.6% were aged 27 to 44 years, 33.3% were aged 45 to 64 years, and 26.8% were aged 65 years or older. Days of extreme heat were associated with an IRR of 1.08 (95% CI, 1.07-1.09) for ED visits for any mental health condition. Associations between extreme heat and ED visits were found for specific mental health conditions, including substance use disorders (IRR, 1.08; 95% CI, 1.07-1.10); anxiety, stress-related, and somatoform disorders (IRR, 1.07; 95% CI, 1.05-1.09); mood disorders (IRR, 1.07; 95% CI, 1.05-1.09); schizophrenia, schizotypal, and delusional disorders (IRR, 1.05; 95% CI, 1.03-1.07); self-harm (IRR, 1.06; 95% CI, 1.01-1.12); and childhood-onset behavioral disorders (IRR, 1.11; 95% CI, 1.05-1.18). In addition, associations were higher among men (IRR, 1.10; 95% CI, 1.08-1.12) and in the US Northeast (IRR, 1.10; 95% CI, 1.07-1.13), Midwest (IRR, 1.11; 95% CI, 1.09-1.13), and Northwest (IRR, 1.12; 95% CI, 1.03-1.21) regions.
Conclusions and Relevance In this case-crossover study of a large population of US adults with health insurance, days of extreme heat were associated with higher rates of mental health–related ED visits. This finding may be informative for clinicians providing mental health services during periods of extreme heat to prepare for increases in health service needs when times of extreme heat are anticipated.
Exposure to high ambient temperatures (ie, heat) is a recognized threat to public health and has been documented to be associated with excess morbidity 1 and mortality. 2 - 4 Seven of the warmest years on record for the contiguous US have occurred since 2014, with 2016 reaching the greatest temperatures and 2020 now ranked as the second warmest year in the available 141-year record. 5 As climate change leads to more days with extreme temperatures, and particularly, higher summertime temperatures, the burden of disease associated with ambient heat is expected to increase. Heat stress is known to trigger adverse physiological responses in the human body, ranging from heat rash and muscle cramps or fatigue to broad consequences for a range of human organ systems and heat stroke, which can be fatal. 6
In addition to the association between extreme heat and physical health, a growing number of studies have reported on the potential adverse effects of heat on mental health. Ambient temperature has been previously associated with exacerbation of symptoms for many mental and behavioral disorders, including self-reported adverse mental health outcomes, 7 - 9 and elevated risk of emergency department (ED) visits for any mental health cause, 9 mood-anxiety disorders, substance use, and schizophrenia 10 , 11 as well as higher suicide risk. 9 , 12 , 13 However, existing studies have been limited by small sample sizes, specific populations or geographic areas, or reliance on self-reported mental health symptoms. Thus, the association between heat and mental health remains incompletely quantified, and little is known about whether certain population subgroups have increased risk factors for visiting the ED for mental health diagnoses because of exposure to higher ambient temperature.
Mental health consequences of elevated ambient temperature can arise during both warm- and cool-temperature seasons. However, the underlying processes that lead to elevated adverse mental health outcomes may be different by season. For example, cold temperatures may affect health on a different time scale, with substantially longer lag effects during cold periods compared with hot periods. 14 - 16 In addition, virtually all extreme heat events in the US occur during the warm season. Therefore, although it is important to assess the association between temperature and mental health across the entire year, the proposed statistical method in the current analysis is better suited to a warm-season-only model. The aim of this study was to investigate the association between warm-season (May through September) temperatures between 2010 and 2019 and rates of ED visits for a broad range of mental health outcomes among adults with commercial and Medicare Advantage health insurance living in the contiguous US. We focus on ED visits, which represent the most severe presentations of mental health exacerbations both from a clinical perspective and in terms of stress on health systems to provide care. We further investigated whether observed associations differed across strata defined by age, sex, and geographic region and explored the time course of the observed association.
In this case-crossover study, we obtained medical claims between January 1, 2010, and December 31, 2019, from the OptumLabs Data Warehouse (OLDW), which contains deidentified, longitudinal health information on enrollees and patients, representing a diverse mixture of ages, ethnicities, and geographies throughout the contiguous US. 17 We identified claims for ED visits related to mental health ( Figure 1 A) based on the International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision (ICD-9) or International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, Tenth Revision (ICD-10) code, revenue code, Current Procedural Terminology code, and place of service code. For each claim, we then extracted information on the age, sex, and county of residence of the individual as well as the admission date and principal diagnosis code (based on ICD-9 until 2015 or ICD-10 after 2015) for each ED visit. Information on race and ethnicity was unavailable in these data sets. We limited our analysis to ED visits occurring among individuals aged 18 years or older. The institutional review board of Boston University deemed the study exempt from review and waived the requirement for informed consent because the study involved analysis of deidentified data. This study followed the Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology ( STROBE ) reporting guideline.
We applied the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality’s Clinical Classifications Software scheme 18 to ICD-9 and ICD-10 principal diagnosis codes at discharge, including primary discharge diagnosis and secondary diagnoses, to classify ED visits into clinically meaningful and mutually exclusive disease groups. The Clinical Classifications Software scheme is a comprehensive classification tool for clustering diagnoses into a manageable number of categories based on disease characteristics and treatment protocol and is widely used to analyze disease-specific conditions. We identified the disease groups for relevant mental health outcomes 19 as specified in Table 1 . We excluded the Clinical Classifications Software codes for screening for mental health outcomes because the data-generation process is different than for a diagnosis and may lead to inaccuracies in the data. We further excluded ED visits for impulse control disorders, which are uncommon in this data set.
We obtained daily maximum ambient temperature data from the Parameter-Elevation Regressions on Independent Slopes (PRISM) model from the PRISM Climate Group, 20 which is a validated spatiotemporal model with approximately 4-km horizontal grid spacing. 21 To represent population exposure to temperature, we calculated a population-weighted mean daily maximum temperature provided by the PRISM model for each day in each county, as described previously in the literature. 22 We limited the study period to the warm-season months (May through September; henceforth referred to as the warm season for simplicity) to represent heat exposure. We estimated extreme temperature as days with a daily maximum ambient temperature greater than or equal to the 95th percentile of county-specific temperature ( Figure 1 B). For sensitivity analyses, we also estimated a population-weighted mean daily ambient temperature based on PRISM data.
We used a case-crossover study 23 , 24 to estimate the association between daily maximum temperature and the incidence rate per county-day of ED visits with a diagnosis for a composite end point of any mental health condition and ED visits for specific mental health conditions. In this study design, participants serve as their own control, and the inference is based on the comparison of exposures over time within the same individual. This design has the advantage of controlling for all known and unknown potential confounders that are time invariant or vary relatively slowly over long periods of time (eg, socioeconomic status, age, and sex). We used a time-stratified approach to select control periods such that ambient temperature during the case period was compared with ambient temperature on other days of the same year, month, and day of the week as the case day. 25 , 26 This approach to selecting control periods serves to minimize confounding by seasonal and long-term time patterns as well as day of the week. 25 In addition, we adjusted for relative humidity (natural spline with 3 df ) and federal holidays.
In the primary analysis, we applied a well-established distributed lag nonlinear modeling framework to allow for both nonlinear exposure-response functions and nonlinear lag-response functions. 27 , 28 We modeled exposure-response functions using a quadratic B-spline, with 1 internal knot placed at the 50th percentile of county-specific warm-season months’ temperature distribution. For the lag-response function, we used a natural cubic B-spline with 2 knots placed at equal intervals on the log scale of lags up to 5 days. We used conditional logistic regression models to estimate the incidence rate ratio (IRR) and 95% CIs for the association between daily temperature and incidence rates of ED visits, comparing ED visits associated with ambient temperature with ED visits associated with the optimal temperature. The optimal temperature was estimated as the temperature percentile with minimum ED visits across the county-specific temperature distribution. Extreme heat was defined as ambient temperature at the 95th percentile of the county-specific temperature distribution. We first considered the association between temperature and the IRR of ED visits associated with a composite end point of any mental health condition. We subsequently considered the association between temperature and the IRR of ED visits for specific mental health conditions.
We performed a series of sensitivity analyses using the composite mental health end point to assess the robustness of our findings. First, we varied the key modeling parameters to estimate the association between ambient heat and ED visits for the composite mental health end point. This sensitivity analysis included exposure-response functions using a quadratic B-spline with 2 and 3 internal knots. We modeled the lag-response function using a natural cubic B-spline with 3 knots placed at equal intervals on the log scale of lags up to 5 days. Second, because there is no consensus on which exposure metrics should be used to examine the impact of heat, we used daily mean temperature in the sensitivity analysis.
To examine differences in the rate of ED visits for population subgroups, we evaluated whether the association between warm-season heat and incidence of ED visits varied across strata defined by age, sex, and region in the US (defined using the Fourth National Climate Assessment 29 regions). We used the Wald test to assess whether the associations were homogeneous across strata. 30
We conducted all analyses in R software, version 3.6.3 (R Foundation for Statistical Computing), with the survival package, version 3.2-7, for the conditional logistic regression and the dlnm package, version 2.4.2, for the distributed lag nonlinear model.
Between 2010 and 2019, we identified 3 496 762 claims for ED visits occurring among 2 243 395 unique individuals (56.8% [1 274 456] women and 43.2% [968 939] men; mean [SD] age, 51.0 [18.8] years); of these individuals, 14.3% were aged 18 to 26 years, 25.6% were aged 27 to 44 years, 33.3% were aged 45 to 64 years, and 26.8% were aged 65 years or older. This sample represented claims for mental health conditions among 21 048 502 individuals (approximately 6.8% of the 2015 US population) enrolled in commercial or Medicare Advantage health insurance plans. Emergency department visits for substance use disorders were most common, followed by ED visits for anxiety, stress-related, and somatoform disorders and for mood disorders ( Table 1 ). The individuals included in this analysis resided in 1 of 2775 US counties; these counties are the most populated areas within the contiguous US, accounting for locations where approximately 97.6% of the 2020 US population (331 449 281 people) resided.
Overall, higher warm-season temperatures were associated with monotonically higher rates of ED visits for any mental health condition ( Figure 2 ). Specifically, days of extreme heat had an IRR of 1.08 (95% CI, 1.07-1.09) for ED visits for any mental health condition compared with days of optimal temperature. The increase in IRR was highest on the same day (lag 0), with some evidence of continued higher IRR 2 to 4 days later (eFigure 1 and eAppendix in the Supplement ). This result was robust to sensitivity analysis incorporating various modeling parameters (eFigure 2 in the Supplement ). Days of extreme heat were also associated with higher rates of ED visits for specific mental health conditions, including substance use disorders (IRR, 1.08; 95% CI, 1.07-1.10); anxiety, stress-related, and somatoform disorders (IRR, 1.07; 95% CI, 1.05-1.09); mood disorders (IRR, 1.07; 95% CI, 1.05-1.09); schizophrenia, schizotypal, and delusional disorders (IRR, 1.05; 95% CI, 1.03-1.07); self-harm (IRR, 1.06; 95% CI, 1.01-1.12); and childhood-onset behavioral disorders (IRR, 1.11; 95% CI, 1.05-1.18) ( Table 2 ). The association between higher temperatures and mental health was less evident for other specific mental health conditions, including adult personality and behavior disorders and other miscellaneous disorders that are not otherwise classified ( Figure 3 ). There was no evidence of lag effects of temperature for specific causes (eFigure 3 in the Supplement ). We evaluated how the observed associations between higher temperature and ED visits for any mental health condition varied by age, sex, and geographic region within the US (eFigure 4 in the Supplement ). We found no evidence of heterogeneity across age groups but found elevated rates of ED visits for mental health among men (IRR, 1.10; 95% CI, 1.08-1.12) compared with women (IRR, 1.06; 95% CI, 1.05-1.08). We also found that IRRs were higher in the Northeast (IRR, 1.10; 95% CI, 1.07-1.13), Midwest (IRR, 1.11; 95% CI, 1.09-1.13), and Northwest (IRR, 1.12; 95% CI, 1.03-1.21) US.
In this nationwide study of ED visits among adults with commercial and Medicare Advantage health insurance in the contiguous US, we found that days of extreme heat were associated with higher rates of ED visits for a composite measure of mental health diagnoses and ED visits associated with specific mental health conditions, including substance use disorders; anxiety, stress-related, and somatoform disorders; mood disorders; schizophrenia, schizotypal, and delusional disorders; self-harm; and childhood-onset behavioral disorders.
Relatively few studies have examined the association between heat and ED visits for mental health. Regional studies conducted in many cities and countries, including in California, 9 , 31 Southern California, 32 and New York 10 in the US; Adelaide, Australia 10 ; Paris, France 33 ; Tel Aviv, Israel 34 ; the Baix Camp and Tarragona region of Spain 35 ; and Canada, 36 have found an increasing number of ED visits for a variety of mental health conditions associated with increasing temperatures. Another study based in Barcelona, Spain, found no association between heat and ED visits in the general population but did find elevated risk factors among patients with psychiatric histories, as well as more alcohol and drug misuse, during an extreme heat wave in 2003. 37 However, these studies often rely on data from local hospitals or regional health care utilization data, potentially limiting the generalizability of results. By comparison, our findings extend the previous work by examining the implications of temperature for ED utilization for mental health conditions among adults with health insurance across the entire contiguous US.
In addition, we examined the potential for elevated rates of ED visits associated with any mental health diagnosis among different age groups as well as among men vs women and within different US regions. We found no evidence of differential associations between temperature and mental health stratified by age groups, which stands in contrast to previous findings. 10 We also found that the rate of ED visits on days of extreme heat was higher among men vs women, a different result from past work. 31 We also found higher rates of ED visits in the US Northwest, Northeast, and Midwest, a regional analysis that has not been previously conducted for mental health outcomes in the US. This finding may suggest that there is an increased risk of adverse mental health outcomes in regions of the US that are less well adapted to heat (ie, where adaptive measures such as air conditioning may be less prevalent compared with areas, such as the Southeastern and Southwestern US, that have historically experienced higher temperatures 38 ).
There are several potential pathways by which heat may exacerbate mental health conditions. Exogenous stressors are well known to exacerbate existing mental health conditions. Our finding that heat was associated with a similar increase in the rate of ED visits for a variety of different mental health conditions is consistent with the hypothesis that heat is an external stressor that is not specific to any given mental health condition. One etiological mechanism may be disrupted sleep during periods of high ambient temperature, which may be associated with adverse mental health outcomes. 39 Daytime discomfort or irritation owing to elevated temperature may be a stressor that exacerbates preexisting conditions. Another biological pathway may be the increase in hopelessness, maladaptive anxiety, and stress attributable to the anticipation of climate change and associated extreme events. 40 - 43 In addition, on warmer days, patients may visit the ED to seek relief from high temperatures. Heat could also affect opening hours of other health care facilities, which could be associated with an increase in ED visits. These and other social and health care system factors might explain elevated ED visits on days of extreme temperature.
This study has strengths. To our knowledge, it is the largest and most comprehensive analysis of daily ambient temperature associated with ED visits for mental health diagnoses among adults aged 18 years or older across the contiguous US. Because we focused on ED visits, which represent clinically meaningful exacerbations of mental health conditions, we were able to assess the costliest interactions between temperature and mental health both at the individual level and from the perspective of the health care system. With such a large data set, we were able to explore the consequences of temperature on a wide range of illnesses associated with adverse mental health outcomes, filling an important gap in the existing literature. The current analysis focused on the warm season; future work is needed to further characterize the implications of temperature for mental health outcomes during cold seasons. We were also able to identify some strata of the population that may have more risk factors for adverse mental health outcomes owing to extreme heat. Additional studies are needed to identify other populations that may be at greater risk for adverse outcomes and to gain insights into the pathophysiologic mechanisms underlying the observed associations in an effort to identify effective strategies to prevent adverse mental health outcomes.
The association between elevated ambient temperature and an increased rate of ED visits for specific mental health conditions, such as substance use disorders, may be of particular relevance to mental health practitioners and public health officials during periods of extreme heat. It is possible that the association between extreme heat and exacerbation of symptoms for many mental and behavioral disorders is not limited to ED visits but may also include a broader group of people with mental health conditions that may not require emergency care. During and following periods of high temperature, mental health and emergency care practitioners may consider increasing capacity to provide necessary mental health services. This consideration is particularly important given the potential for climate change to increase both the frequency and severity of extreme temperatures, 29 which may further increase demand for clinical services related to mental health and may also lead to increased direct emotional responses such as anxiety. 40
This study also has limitations. First, although our use of the case-crossover study presented some advantages, there are some limitations to causal interpretation of the effect size estimates. This study design is appropriate when exposure is intermittent, the implications for the risk of outcome are immediate, and the outcome itself is abrupt—a series of general criteria that suit our study. 23 , 24 We estimate that potential causes of bias within our study design would bias the results toward the null. For example, we used the population-weighted mean daily maximum temperature as a proxy for personal heat exposure, potentially leading to some exposure misclassification. However, we expect that this exposure misclassification would be nondifferential and on average tend to bias our results toward the null. In addition, there may be unmeasured time-varying confounders, including time spent outdoors and activity levels, which we anticipate would be nondifferential and on average bias our results toward the null.
Second, we did not consider other meteorological characteristics, such as precipitation or cloud cover, either of which may alter mental health. 44 , 45 However, given that warm-season days with precipitation or substantial cloud cover are generally cooler than what would be observed under equivalent clear-sky conditions, we expect that any confounding by these elements (if present) would have biased our estimates toward the null hypothesis of no association between extreme heat and an increase in ED visits for mental health conditions.
Third, our study is based on health care utilization data, and given that it specifically focused on ED visits, we anticipate that the mental health diagnoses included in this study likely represent the most severe presentations. The less severe outcomes associated with increasing temperature are an area for future research.
Fourth, use of deidentified medical claims data limits the information available on individual-level characteristics; data on race and ethnicity, individual markers of socioeconomic means, occupation, and time-activity patterns were not available. Although these factors cannot confound the results because of the use of the study’s design, we were not able to comprehensively assess individual-level risk factors.
Fifth, our data are limited to individuals with commercial health insurance or Medicare Advantage (ie, data do not include recipients of Medicaid health coverage for individuals with a low income or Medicare without supplemental plans, hence likely skewing of the sample toward wealthier socioeconomic status), potentially limiting the generalizability of our results.
Results of this case-crossover study suggest that there was an association between elevated ambient temperature and ED visits for any mental health condition and for specific mental health diagnoses. This finding could aid clinicians who provide mental health services in preparing for increases in health service needs when high ambient temperature is anticipated. Further research could investigate the implications of sustained periods of extreme heat (heat waves) for health outcomes and continue to investigate the association among different populations. In addition, future work could characterize the implications of elevated temperatures during cold periods for mental health outcomes and the consequences of additional meteorological characteristics and multiple extreme weather events that may occur with elevated ambient temperature or may be triggered by periods of extreme heat.
Accepted for Publication: November 30, 2021.
Published Online: February 23, 2022. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2021.4369
Open Access: This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the CC-BY License . © 2022 Nori-Sarma A et al. JAMA Psychiatry .
Corresponding Authors: Amruta Nori-Sarma, PhD, MPH ( [email protected] ), and Shengzhi Sun, PhD ( [email protected] ), Department of Environmental Health, Boston University School of Public Health, 715 Albany St, Talbot 4W, Boston, MA 02118.
Author Contributions: Drs Nori-Sarma and S. Sun had full access to all of the data in the study and take responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis.
Concept and design: Nori-Sarma, S. Sun, Galea, Wellenius.
Acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data: Nori-Sarma, S. Sun, Y. Sun, Spangler, Oblath, Gradus, Wellenius.
Drafting of the manuscript: Nori-Sarma, Y. Sun, Gradus.
Critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content: Nori-Sarma, S. Sun, Spangler, Oblath, Galea, Gradus, Wellenius.
Statistical analysis: Nori-Sarma, S. Sun, Y. Sun.
Obtained funding: Wellenius.
Administrative, technical, or material support: Spangler, Oblath, Galea.
Supervision: Gradus, Wellenius.
Conflict of Interest Disclosures: Dr Galea reported receiving personal fees from Sharecare outside the submitted work. Dr Wellenius reported receiving grants from the National Institutes of Health’s National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences and the Wellcome Trust during the conduct of the study and serving as a consultant for the Health Effects Institute and Google. No other disclosures were reported.
Funding/Support: This study was supported by grant R01-ES029950 from the National Institutes of Health’s National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (Drs Nori-Sarma, S. Sun, Spangler, and Wellenius and Mr Y. Sun) and grant 216033-Z-19-Z from the Wellcome Trust (Drs Nori-Sarma, S. Sun, Spangler, and Wellenius and Mr Y. Sun).
Role of the Funder/Sponsor: The National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences and the Wellcome Trust had no role in the design and conduct of the study; collection, management, analysis, and interpretation of the data; preparation, review, or approval of the manuscript; and decision to submit the manuscript for publication.
- Register for email alerts with links to free full-text articles
- Access PDFs of free articles
- Manage your interests
- Save searches and receive search alerts
Market Design in Regulated Health Insurance Markets: Risk Adjustment vs. Subsidies
Health insurance is increasingly provided through managed competition, in which subsidies for consumers and risk adjustment for insurers are key market design instruments. We illustrate that subsidies offer two advantages over risk adjustment in markets with adverse selection. They provide greater flexibility in tailoring premiums to heterogeneous buyers, and they produce equilibria with lower markups and greater enrollment. We assess these effects using demand and cost estimates from the California Affordable Care Act marketplace. Holding government spending fixed, we estimate that subsidies can increase enrollment by 16 percentage points (76%) over risk adjustment, while all consumers are weakly better off.
Einav and Finkelstein gratefully acknowledge support from the Sloan Foundation and from the Laura and John Arnold Foundation. Tebaldi acknowledges support from the Becker Friedman Institute. We thank Ben Handel, Mike Whinston, and many seminar participants for helpful comments. The views expressed herein are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Bureau of Economic Research.
I would like to disclose that I am an adviser to Nuna Health, a data analytics startup company, which specializes in analytics of health insurance claims. I am not being paid by them, but have received equity (nominal value is less than $1,000 the market value is hard to assess).
MARC RIS BibTeΧ
Download Citation Data
Working Groups
More from nber.
In addition to working papers , the NBER disseminates affiliates’ latest findings through a range of free periodicals — the NBER Reporter , the NBER Digest , the Bulletin on Retirement and Disability , the Bulletin on Health , and the Bulletin on Entrepreneurship — as well as online conference reports , video lectures , and interviews .

Comparing the Health Impacts of Diet Soda and Regular Soda
This essay is about comparing the health impacts of diet soda and regular soda. Regular soda, high in sugar and calories, is linked to obesity, diabetes, and dental issues. Diet soda, sweetened with artificial substitutes, offers fewer calories but raises concerns about long-term health effects and metabolic disorders. The essay discusses how both beverages can affect weight management and dental health. It emphasizes that while diet soda might seem like a better choice for reducing calorie intake, moderation and healthier alternatives like water and herbal teas are recommended for better overall health. Both types of soda have drawbacks, and balanced dietary habits are crucial for well-being.
How it works
The ongoing discourse surrounding the comparative virtues of diet soda versus its regular counterpart has persisted for an extended duration. Advocates and critics exist on both sides of the spectrum, with the ultimate decision often hinging upon individual inclinations and health considerations. To ascertain which option may hold superiority, it becomes imperative to delve into the constituent ingredients, potential health ramifications, and the contextual framework of their consumption.
Conventional soda typically derives its sweetness from high-fructose corn syrup or sucrose, thereby contributing a notable calorific quotient to one’s dietary intake.
A solitary serving of conventional soda can harbor upwards of 140 calories, entirely attributable to sugar content. This elevated sugar concentration can precipitate a rapid surge in blood glucose levels, subsequently followed by a plummet that may exacerbate cravings for additional sugary fare. Over prolonged periods, excessive indulgence in sugary beverages has been implicated in an array of health maladies, encompassing but not limited to obesity, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular afflictions.
Conversely, diet soda assumes the guise of a reduced-calorie alternative, harnessing artificial sweeteners such as aspartame, sucralose, or stevia to confer sweetness sans the caloric burden. For individuals seeking to curtail their caloric intake, diet soda may present itself as an appealing prospect. Nonetheless, the protracted health repercussions of artificial sweeteners constitute a subject of ongoing scientific inquiry and contention. While certain studies posit the innocuous nature of these sweetening agents for the majority of the populace, others sound alarm bells regarding potential correlations with metabolic irregularities, perturbations in gut microbiota, and heightened appetitive propensities.
One argument buttressing the merit of diet soda revolves around its innocuousness vis-à-vis dental degradation, as compared to its conventional counterpart. The sucrose inherent in conventional soda catalyzes an interaction with oral bacteria, engendering the formation of acids that erode tooth enamel, thereby precipitating cavitation. Conversely, diet sodas, albeit retaining an acidic profile, eschew the inclusion of sucrose, thereby mitigating the likelihood of dental detriments. However, it merits acknowledgment that the acidic nature of both varieties of soda may still confer dental peril if habitually consumed.
Furthermore, consideration must be accorded to the potential ramifications of both beverages upon weight management endeavors. The exorbitant sugar and calorie content characterizing conventional soda may incite weight accrual if ingested to excess. In contrast, diet soda, with its calorie-deficient constitution, might ostensibly emerge as a preferable option for individuals endeavoring to shed or sustain weight. Nevertheless, certain empirical inquiries hint at the possibility that diet soda consumption may not invariably precipitate weight reduction and might even be causatively linked to weight amplification in select individuals. This paradoxical phenomenon could be ascribed to psychoemotional dynamics such as compensatory dietary behaviors or physiological facets encompassing the organism’s reaction to artificial sweeteners.
Beyond the prism of individual health repercussions, it behooves one to contemplate the broader lifestyle and dietary proclivities concomitant with soda imbibition. Individuals habituated to regular soda consumption, irrespective of its dietary guise, may exhibit heightened propensities toward other deleterious dietary patterns, typified by augmented consumption of processed comestibles and diminished intake of fruits and vegetables. These overarching dietary predilections can exert a profound influence upon overall health status and susceptibility to chronic morbidities.
In adjudging whether diet soda eclipses its conventional counterpart in terms of merit, it proves indispensable to acknowledge the inherent deficiencies prevalent within both iterations. The conspicuous sugar concentration characterizing conventional soda engenders manifest peril vis-à-vis obesity, diabetes, and dental integrity. Diet soda, notwithstanding its calorie abstinence, assumes an aura of uncertainty concerning the protracted ramifications of artificial sweeteners and may not represent the panacea for weight management as purportedly construed.
In summation, moderation emerges as the cardinal tenet. For adherents of soda, moderation and exploration of healthier alternatives, such as pure water, herbal infusions, or naturally imbued sparkling water, may constitute the superlative stratagem. These alternatives proffer hydration devoid of the deleterious health sequelae attendant upon both conventional and diet sodas. For individuals espousing weight management objectives or health optimization imperatives, directing focus toward a balanced dietary regimen underscored by the preponderance of unadulterated comestibles and minimal processed sugar content is likely to be more efficacious than the mere transposition from conventional to diet soda.
Cite this page
Comparing the Health Impacts of Diet Soda and Regular Soda. (2024, Jun 17). Retrieved from https://papersowl.com/examples/comparing-the-health-impacts-of-diet-soda-and-regular-soda/
"Comparing the Health Impacts of Diet Soda and Regular Soda." PapersOwl.com , 17 Jun 2024, https://papersowl.com/examples/comparing-the-health-impacts-of-diet-soda-and-regular-soda/
PapersOwl.com. (2024). Comparing the Health Impacts of Diet Soda and Regular Soda . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/comparing-the-health-impacts-of-diet-soda-and-regular-soda/ [Accessed: 20 Jun. 2024]
"Comparing the Health Impacts of Diet Soda and Regular Soda." PapersOwl.com, Jun 17, 2024. Accessed June 20, 2024. https://papersowl.com/examples/comparing-the-health-impacts-of-diet-soda-and-regular-soda/
"Comparing the Health Impacts of Diet Soda and Regular Soda," PapersOwl.com , 17-Jun-2024. [Online]. Available: https://papersowl.com/examples/comparing-the-health-impacts-of-diet-soda-and-regular-soda/. [Accessed: 20-Jun-2024]
PapersOwl.com. (2024). Comparing the Health Impacts of Diet Soda and Regular Soda . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/comparing-the-health-impacts-of-diet-soda-and-regular-soda/ [Accessed: 20-Jun-2024]
Don't let plagiarism ruin your grade
Hire a writer to get a unique paper crafted to your needs.

Our writers will help you fix any mistakes and get an A+!
Please check your inbox.
You can order an original essay written according to your instructions.
Trusted by over 1 million students worldwide
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers
- Alzheimer's disease & dementia
- Arthritis & Rheumatism
- Attention deficit disorders
- Autism spectrum disorders
- Biomedical technology
- Diseases, Conditions, Syndromes
- Endocrinology & Metabolism
- Gastroenterology
- Gerontology & Geriatrics
- Health informatics
- Inflammatory disorders
- Medical economics
- Medical research
- Medications
- Neuroscience
- Obstetrics & gynaecology
- Oncology & Cancer
- Ophthalmology
- Overweight & Obesity
- Parkinson's & Movement disorders
- Psychology & Psychiatry
- Radiology & Imaging
- Sleep disorders
- Sports medicine & Kinesiology
- Vaccination
- Breast cancer
- Cardiovascular disease
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Colon cancer
- Coronary artery disease
- Heart attack
- Heart disease
- High blood pressure
- Kidney disease
- Lung cancer
- Multiple sclerosis
- Myocardial infarction
- Ovarian cancer
- Post traumatic stress disorder
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Schizophrenia
- Skin cancer
- Type 2 diabetes
- Full List »
share this!
June 18, 2024
This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies . Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
Cost may not keep many people from filling opioid addiction treatment prescriptions
by University of Michigan
When people get a prescription for the opioid addiction medication called buprenorphine, they almost always fill it—even if they have to pay more out of their own pocket, a new study shows. The paper is published in the Journal of General Internal Medicine .
Whether it's their first prescription for the medication, or they've been taking it for months, nearly all patients pick up the order from the pharmacy, according to the new findings from a University of Michigan team. Even among those just starting on buprenorphine , higher costs aren't a deterrent.
The researchers say this suggests that removing barriers that prevent clinicians from prescribing buprenorphine should be the main focus of efforts to increase the number of people with opioid addiction who get treated with buprenorphine.
"Our findings suggest that cost-sharing may not be a particularly strong barrier to buprenorphine dispensing," said Kao-Ping Chua, M.D., Ph.D., a member of the U-M Opioid Research Institute who is an assistant professor in the U-M Medical School and School of Public Health. "This may be because patients understand how effective buprenorphine is and are willing to pay for it."
In the study, the researchers report findings from an analysis of more than 2.3 million pharmacy records for buprenorphine prescriptions in 2022 for 286,000 people with private insurance , and more than 1.2 million similar records for nearly 145,000 people with Medicare.
Just over 1 in every 100 buprenorphine prescriptions sent to pharmacies were abandoned by the patients—that is, they were not picked up in the 14 days after the pharmacy received the prescription.
Moreover, the research shows that for every $10 increase in cost-sharing, there was only a minimal increase in abandonment of prescriptions—just one-tenth of one percentage point.
This contrasts with another recent paper the team published , on cost-sharing for naloxone, a medication that can save a person from dying if they overdose on any opioid.
In that paper, every $10 increase in cost-sharing was associated with an increase in abandonment of 2 to 3 percentage points.
Costs and behaviors
Even when the monthly cost of buprenorphine was $150 or more, which it was for 3% of people with commercial insurance, less than 6% of the prescriptions were abandoned. Less than 1% of people with Medicare coverage had cost-sharing over $100, but even among them, abandonment was rare, ranging from just under 2% to just over 3%.
The researchers looked at data for five different forms of immediate-release buprenorphine products, both generic and name-brand formulations, prescribed to patients of all ages. About half of the prescriptions were for a generic form of a film containing both buprenorphine and naloxone that patients put under their tongue or on the inside of their cheek to dissolve.
Long-acting injections for opioid use disorder and patches used for pain relief were not included.
The average cost for a month's supply of their prescribed product was $28 for people with commercial insurance and $8 for those with Medicare.
But 44% of people with commercial insurance paid $10 or less for a month's supply, as did 84% of those with Medicare coverage. And the cost was less than $20 a month for 66% of commercially insured and 92% of Medicare participants.
Trends in people new to addiction medication
People who hadn't been on buprenorphine before were more likely to abandon prescriptions, and the chance of abandonment was highest for those who would pay the most for their first prescription.
The researchers suggest that this was likely due in part to the fact that patients new to the drug hadn't yet experienced its impacts on their cravings for opioids.
Still, less than 5% of new-to-buprenorphine patients abandoned their first prescription even at monthly costs of up to $70.
This is lower than the overall rate of prescription abandonment among people new to any drug, as reported by the health care analytics company, IQVIA, whose data the U-M team used.
Additional study information
The researchers didn't study prescriptions for people covered by Medicaid, because that program for people with very low incomes has minimal to no cost-sharing for medications. They also couldn't tell what kind of cost-sharing individuals had, whether it was co-pays, deductibles or co-insurance, though they did know what the final cost would be after any coupons from manufacturers.
Just over 8% of people with commercial insurance and nearly 15% of those with Medicare coverage received a prescription for brand name, as opposed to generic, buprenorphine products. Manufacturers of brand name medications may offer coupons to those with high costs ; the new study is based on the cost to a patient after any such coupon is applied.
Other research on buprenorphine use has shown people falling off their treatment, including for those with private insurance that involves cost-sharing. The new study suggests that this may have much more to do with a gap in continuous prescriptions, or the cost of seeing a provider to get a prescription renewed, rather than patients not filling a prescription when they get one.
Chua is co-director of the Research and Data Domain at the U-M Opioid Research Institute (ORI), as well as a faculty member in the Susan B. Meister Child Health Evaluation and Research Center (CHEAR) and the Institute for Healthcare Policy and Innovation (IHPI).
Co-authors include Thuy Nguyen, Ph.D., a health economist at the U-M School of Public Health and member of ORI and IHPI; ORI co-director Amy Bohnert, Ph.D., ORI/IHPI member Pooja Lagisetty, M.D., M.S., CHEAR member Usha Nuliyalu, M.S., and Rena Conti, Ph.D., from Boston University.
Explore further
Feedback to editors

Walking brings huge benefits for low back pain, study finds
3 hours ago
Combination targeted treatment produces lasting remissions in people with resistant aggressive B-cell lymphoma
4 hours ago

Study finds one copy of protective genetic variant helps stave off early-onset Alzheimer's disease

Drugs for enlarged prostate may also protect against dementia with Lewy bodies
5 hours ago

New study establishes best practices for supervised psilocybin
6 hours ago

During a heat wave, high indoor temperatures can also prove dangerous

Scientists reveal how an unstructured protein traps cancer-promoting molecules

Addressing maternal prenatal depression can lead to longer gestation, researchers say
8 hours ago
Researchers develop portable serological test for rapid COVID-19 immunity monitoring

In sync: The biological underpinnings of romantic attraction and bonding
Related stories.
High out-of-pocket costs may be barrier to filling naloxone prescriptions, study shows
Jun 14, 2024

It's easier now to treat opioid addiction with medication—but use has changed little, study finds
Apr 24, 2024

More doctors can prescribe a leading addiction treatment. Why aren't more people getting help?
Apr 28, 2024

Buprenorphine prescription fills for OUD plateau during pandemic
Dec 22, 2020
New study identifies gaps in treatment for opioid use disorder as overdose emergencies soar
Nov 30, 2021

Disparities in filled buprenorphine prescriptions worse during pandemic
Jun 3, 2022
Recommended for you

Study uses powerful new 'digital cohort' method to understand vaping epidemic
21 hours ago

Why mental health care providers decide to practice in rural communities
Jun 18, 2024

Study indicates rates of problem marijuana use are rising among seniors

Study finds medication treatment for opioid use disorder offered at only a third of outpatient mental health facilities

Identifying connections between adverse childhood events and substance use disorders
Jun 17, 2024

Feeling unsafe in your neighborhood makes you more likely to smoke, study shows
Let us know if there is a problem with our content.
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form . For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines ).
Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request
Thank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.
E-mail the story
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Medical Xpress in any form.
Newsletter sign up
Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox. You can unsubscribe at any time and we'll never share your details to third parties.
More information Privacy policy
Donate and enjoy an ad-free experience
We keep our content available to everyone. Consider supporting Science X's mission by getting a premium account.
E-mail newsletter

Research Clusters
- Geographic Clusters
- Sectoral Clusters
Research Support
- Funding Opportunities + Grants
- Working Papers
- Career Opportunities
- Undergraduate Study Abroad Programs
- Request a Brochure
- Find a Program

The clusters are built around a simple principle: we can produce more and better research by creating a common infrastructure, whether geographic or sectoral, upon which to then engage in research and policy work. At inception, we absorbed and expanded several existing clusters, and are proactively building new ones.
Geographic Research Clusters
Geographic research clusters collect long-term panel data. They seek to remedy a major constraint in understanding development in low-income countries: the absence of detailed, multi-level, long-term scientific data that follows individuals over time and describes both the natural and built environment in which they reside.
The clusters involve a long-term commitment to research collaboration with local institutions, policy engagement and the opportunity for Northwestern students to participate. Explore our geographic research clusters using the links below.
- The Philippines
View our current research projects .
Sectoral Research Clusters
Our sectoral clusters are a group of related projects tackling a narrow sector within development. The goal here is to create a core operation that engages with potential partners for project development, supports the research community in order to enhance the quality of work conducted, and develops appropriate communications and policy strategies given the evidence. At inception, we include Innovations for Poverty Action’s (IPA) Financial Inclusion Program, Social Protection Program, and Small/Medium Enterprises (SME) Program as sectoral clusters. We plan to expand and develop clusters on other sectors like corruption, early childhood development, agricultural extension and technology, etc., as funding and campus support come to fruition.
Specific activities within a sectoral cluster include:
- Core support to develop projects for a research network
- Researcher gatherings to present both early stage and completed work
- Funding to be granted competitively within a researcher network on a tightly defined set of research and policy questions
- Communications work to engage appropriate stakeholders after research is completed
Research Methods Cluster
Not all clusters are identical, but its role is generally the same in that we started by collecting long-term panel data. Alongside these data, we conduct experiments to measure the impact of interventions of interest in economics, political science, psychology and public health, as well as test theories of interest for policy-relevant academic research. Clusters fill the following key niches:
- Collection of long-term data to gather in-depth information about individuals, families and their communities. These data can support the design and implementation of new interventions for testing and are sufficiently flexible to accommodate new graduate student research questions.
- Economies of scope in research : Currently, the infrastructure for conducting field research is wasteful, with large surveys frequently being rolled out for the purpose of single projects. Many research questions could be answered by starting with a large, representative dataset and then finding implementing parties willing to overlap their operations over the sample frame, rather than the other way around. This is particularly true on theory-led experimentation, in which the researcher is designing a field activity deliberately to test specific theories of development.
- Multi-faceted interventions , which enable observation of the interactions of different programs. This facilitates research on interactions between different dimensions of behavior. Simultaneous testing to compare program effectiveness is critical for policymakers and donors tasked with making decisions on the allocation of scarce resources.
Participate
- Training sites: Student-training sites continuously host students, both undergraduate and graduate, to learn about and contribute to the research process. The partnership will support summer, semester-long or yearlong internships for Northwestern undergraduates working in one of the clusters. Students in research clusters engage directly in the research process.
- Development research: Northwestern faculty and graduate students are invited to contribute to ongoing development research in China , Ghana and The Philippines .
- Research assistantships: There will also be a post-baccalaureate program of research assistants working for one to two years on cluster research, as well as direct engagement of PhD or MBA students in cluster-supported research.
Contact us about the Global Poverty Research Lab
847.467.3714