Places on our 2024 summer school are filling fast. Don’t miss out. Enrol now to avoid disappointment
- How to Write an EPQ Essay

Writing an EPQ essay can seem like a daunting task, which is why we’ve written this nine-step guide to help make the whole process easier.
In addition to the A-Levels you’re already doing, you can choose to take an EPQ (Extended Project Qualification). An EPQ is an independent research project, and it’s extremely beneficial as it counts towards UCAS tariff points.
Consisting of around 5,000 words, an EPQ essay is an in-depth assignment which takes about 120 hours to complete.
That may seem like a lot of extra work to take on alongside your existing studies, however it can be hugely beneficial when applying to get into university.
Choosing to undertake independent research and reading can prove to future educators that you’re willing to take on extra work to really show what you can do academically, as well as demonstrating that you have interests that go beyond the curriculum. An EPQ sits nicely with a summer school course such as a law summer school , business summer school , engineering summer school and medicine summer school . During your course you have the chance to explore and understand your subject further, demonstrating your commitment to your studies, and develop ideas for your EPQ.

How do you write an EPQ essay?
To write an EPQ essay, you need to: come up with a compelling idea that you’re interested in, write down everything you know about the subject to generate further ideas, find the best essay question to use, reference your sources properly, write a sharp introduction and conclusion, get feedback on your essay, and make sure you double-check your work before submitting it.
The key to writing any extended document is planning, which is why we’ve written this nine-step guide to help you write the best EPQ essay.
Read on for our top tips on how to write an extended project essay.
9 steps to write your EPQ essay
1. come up with an idea.
One of the main reasons students fail their EPQ is because they’ve chosen the wrong subject matter. It’s vital that you choose a topic you’re genuinely interested in, otherwise you won’t have any motivation to work on it. Because of the extra workload, many students choose to start their EPQ over the summer holidays, and with all the distractions that summer brings (trips to the beach, sunbathing in the garden or hanging out with friends in the park) there’s even more reason to pick a subject you don’t find boring, or you’ll just look for any excuse to avoid doing it. Before finalising your topic, you might want to discuss your ideas with your supervisor so they can check you’re on the right track.
2. Write down everything you know about the subject.
Before doing any extra reading, it’s really helpful to write down everything you already know about your chosen subject. This can help to get your thoughts and ideas – which are often jumbled up – out of your head and down onto a piece of paper or computer screen so that you can begin to organise and make sense of them. This is also useful for identifying any gaps in your knowledge. However, if the gaps in your knowledge are vast and your chosen topic isn’t giving you enough inspiration, don’t be afraid to abandon your original idea entirely and come up with something new. It’s better to start again from scratch at this stage, rather than 2,000 words in.
3. Think of a question
Whatever your chosen topic, you’ll need to think of a question to answer. This is an extremely important part of your EPQ and will form the basis of your essay, so it really is worth thinking long and hard about. The way in which you phrase your question or hypothesis will affect the structure and flow of the whole essay. For example, some typical essay question formats include ‘Compare and contrast’, ‘Critically evaluate’ and ‘Analyse and conclude’. The type of question you want to answer will affect whether you need to highlight and critique a number of theories or evaluate how useful a particular concept is. And remember that your extended project essay needs to be approximately 5,000 words long, so you should choose a question that allows for extended research and arguments. It’s also worth bearing in mind that questions without definitive answers are better as there will generally be much more to write about.
4. Research the topic
Next, you should start thinking about the main body of the essay and how you’re going to go about fleshing out your ideas. Ideally, this step should take up half the amount of total time you spend working on your EPQ essay. You should spend a good deal of time reading books, papers and online journals that have been written about your chosen subject. The Internet is an excellent source of information, but anyone can write anything and publish it online, so make sure your sources are credible and recognised by the examining body. Wikipedia, for example, should be avoided as a reliable source of information as anyone can edit the text that’s been written there. While doing your research, you’re going to come across many different opinions and arguments and it’s all going to come from a variety of sources. So now is also a good time to think about how you’re going to organise it all.
5. Remember to reference your sources
As with any piece of academic work, referencing your sources is vital so the examiners can check you’re not plagiarising. It’s also good to demonstrate that your information has come from a range of places so the person marking your essay can see that you’ve researched your topic widely and have considered several different viewpoints. You’ll need to provide a bibliography at the end of your EPQ essay and if you can’t say where your information has come from, you’ll be unable to use it, so it’s a good idea to get into the habit of doing this as you go along. Whether you choose to create a spreadsheet on your computer or annotate photocopies and clippings with a pen, it doesn’t matter how you go about doing this as long as you remember to do it. It’ll make your life so much easier in the long-run!
6. Create subsections
Splitting your essay up into sections can help to make sure you’re writing enough and exploring the topic in as much depth as possible. Keep your word count in mind when dividing up your essay and try to split each section equally. But while mini topics are good for breaking the 5,000 words down into more manageable chunks, you have to make sure each one relates back to your original question, otherwise you could risk wasting some of those words on irrelevant information. Don’t sacrifice the important stuff by shoehorning facts and figures into your chosen subsections. It’s worth thinking about the order of these sections too. It’s usually best to write in a ‘news story’ format, with the most important subtitles at the top and the less relevant stuff filtering down to the bottom, however you could consider working chronologically if that works better for your chosen topic.
7. Write an introduction and a conclusion
As strange as it sounds, it can be helpful to write your introduction and conclusion paragraphs once you’ve completed the main body of the essay. This is because your thoughts on the subject matter are more likely to be more organised, therefore it will be easier to summarise the main points clearly and concisely. Your first paragraph should introduce the subject matter, briefly expanding upon your question and how you’re going to go about answering it, while your conclusion should refer back to the title and answer the question you asked at the beginning of your essay. Ensure that both paragraphs are as direct and succinct as possible, in order to show that you have a clear understanding of your topic.
8. Ask for feedback
Whether it’s a friend, a relative or – even better – your course tutor, it’s a good idea to have your work checked over by someone else. Because you’ve spent hour upon hour absorbed in your subject matter, you can lose sight of certain things, so it makes sense to have your EPQ essay looked at from a different viewpoint. A second opinion can ensure that everything you’ve written is concise and accurate and the person checking your work can give you advice on what to leave out or add in; especially if they already have some knowledge on the subject matter.
9. Double-check everything before submitting your work
It’s a good idea to leave it a day or so before coming back to your essay to proofread it so that you’re viewing it with a fresh pair of eyes. We recommend going over it a couple of times – once to check that you’ve covered everything in terms of the subject matter and another for housekeeping. You want to ensure that you don’t lose any marks for basic things like spelling, punctuation and grammar. You should also take this time to make sure footnotes are accurate, as well as checking over any graphs, charts, diagrams and images.
We hope you’ve enjoyed reading this step-by-step guide and we’re confident that you now have everything you need to go on to successfully write an EPQ essay. Good luck!
How To Write An EPQ Essay (Step-by-Step Guide)
In A-Level by Think Student Editor March 29, 2019 8 Comments
Whatever the reasons were for you choosing to write an EPQ, the grade you get is most definitely important to you. That is why I have written this (hopefully) detailed guide on how to write an EPQ.
1. Think Of An EPQ Topic That Genuinely Interests You

It’s important to choose an EPQ you’re interested in, or you may run into some problems . Many students take EPQs each year, and many students fail because they make this mistake.
If you don’t take an EPQ you’re interested in, you’ll have no motivation to work on it . This will be because you start to want to do other things, anything instead of your EPQ.
Think about revision, for example. Is it interesting? Nope. Would you rather be playing videogames, watching Netflix, or literally anything else? Yeah, me too.
If you’re not motivated to write your EPQ essay, then you’ll either not do it or do it badly. If you don’t work hard for it, you won’t get good marks – and therefore there’s less point in even taking it in the first place .
If you find an EPQ topic to write your essay on that genuinely peaks your interest, you’ll find it much easier to get better grades in it.
A more interesting EPQ essay topic will mean that your focus is better . This will result in a better EPQ, meaning more marks when you hand it in.
You’ll also enjoy the EPQ a lot more if you find it interesting . You’ll find the whole experience a lot more fun, and therefore a lot easier too.
To find an EPQ topic that genuinely interests you, you just have to think about what you like. There are lots of different things you can do, but you only get to choose once – so choose carefully.
And if you’re really stuck on ideas, take a look at this list of 600+ EPQ ideas that guarantee an A* . Any of these ideas will be great for your EPQ, so just choose one that interests you and that you’ll actually enjoy.
2. Create A Mind Map Surrounding Your EPQ Topic

A mind map is where you write down everything you know about a topic . In this case, you’d be writing down all the ideas and concepts surrounding your EPQ topic.
That way you can see everything you need to write about in your EPQ essay. You’re essentially making a mood board for whatever EPQ idea you’ve chosen, and it will help you get in the right mindset for the task ahead.
Mind maps are most commonly used to identify gaps in your knowledge . Students tend to use them when revising to work out what they don’t know, whilst also helping them consolidate what they do know.
In terms of your EPQ essay, a mind map will provide a loose structure for you to follow . You’ll come up with lots of different things you can write about, and that will make the essay a lot easier.
In addition to this, whilst creating your mind map you may even decide to change your topic entirely. You might find that the topic you’ve chosen isn’t giving you any idea inspiration, and so you move on to a different topic.
To make sure you get your mind maps right, you might want to follow this helpful guideline . It’s mainly about studying, but the same things can be said for planning your EPQ essay.
Don’t try rushing in to your EPQ essay without first creating a mind map . Mind maps are more useful than most students think…
Mind maps will help you avoid getting lost in what you’ve written, what you’ve missed, and what you’re planning on doing. You can use your EPQ topic mind maps as a sort of checklist as you write your EPQ essay.
3. Use Your Mind Map To Think Of A Question Related To Your Main EPQ Topic

Many students forget to think about this, but it’s probably the most important part of your EPQ . If you get this bit wrong, you can say goodbye to a good grade in your EPQ.
The question relating to your EPQ topic of choice is what you’ll spend your time working on . The 5000 words you write will be about this question, and so it really needs to be a good one.
If you don’t make it a question that interests you, then you’ll find it harder to write as much about it. Find a question that genuinely peaks your interest (relating to your EPQ of course) and the rest will come naturally.
It’s also important, however, that you choose a question where there’s a lot to write about . If you choose a question with lots to write about, you can use that to your advantage when trying to reach those 5000 words.
However, if you don’t choose a question where there’s a lot to write about, you’ll find that your EPQ is slow and drains you. Not only that, but it’ll probably be worse in terms of grade too.
I’d suggest doing a little background research into your question before you start writing your EPQ essay . Just check that there’s lots to write about and then you can avoid starting something you can’t finish.
As a general rule, you’ll want questions that don’t have definitive answers. If you can find a question that is inconclusive, you’re onto a winner.
If you can’t be bothered to look up EPQ questions, then there’s an alternative . Take a look at this list of 600+ EPQ ideas that guarantee an A* .
4. Write Down Subtitles That Relate To Your Main EPQ Question

Writing down subtitles for your EPQ question means that you’ll have a better idea of what’s actually going into your EPQ essay .
When you create your subtitles for your EPQ essay, you’re essentially writing down all the mini-topics you’ll write about. You split up the massive 5000 word count into smaller, more manageable parts.
I’d suggest making as many subtitles as you can that relate to your main EPQ question. Just go for a massive brainstorm ( potentially using your mind map ) to try and come up with lots of subtitles.
That way you maximize the chances of you making some actually good subtitles. You’ll have lots of options to choose from, and your EPQ will benefit from having such a varied range of points.
You also put yourself in the right mindset for your EPQ essay . You’ll be much more open to different ideas and approaches whilst actually writing the EPQ, and examiners will see this and give you extra credit.
However, you need to make sure that the subtitles you’re writing actually relate to your EPQ question . If they don’t, you could run into some serious problems.
If you choose to work on a subtitle that doesn’t wholly relate to your EPQ question, you risk filling up your word count with irrelevant information. That means less room for the important stuff, and less marks for you.
Make sure you check all your subtitles before you start writing . Work out what the plan is before you start writing, so that you don’t have to rewrite a large portion of your EPQ essay.
So grab a pen and paper, sit down, put on some nice music, and get to writing those subtitles.
5. Triple Check That Every Subtitle Question Actually Relates To The Main EPQ Topic

By this point, you should have around 16 subtitles that you want to include in your EPQ essay . 16 subtitles will give you a nice 300 word per subtitle guide, give or take a few.
Any more subtitles, and you run the risk of overcomplicating your EPQ. Any fewer, and you’ll struggle to reach that gargantuan 5000 word count.
It’s essential that you break down your EPQ essay into smaller modules like this, to make it easier for you in the long term. 16 subtitles will mean the best productivity for you when you actually come to write your EPQ essay .
The next step is to order your subtitles, for easier reading. You’ll want to make the layout of your subtitles as sensible and as easy to follow as possible for your examiner .
If you please your examiner like this, they’ll be more inclined to give you more marks. They mark you on your written communication, and therefore you’ll want to make sure you’re communicating the most effective way.
Try ordering your subtitles by the order of most important to least important . Laying out your subtitles this way will show your examiner that you’ve really thought about your EPQ and understand what they want to see.
Alternatively, you could lay out your subtitles chronologically . What I mean by this is that you start with your question, move onto research, then explanations, and finally a conclusion.
This is probably the best way to lay out your EPQ essay subtitles . It’s the easiest way to follow the process you went through, and examiners like to see EPQ essays that are laid out like this.
It’s how I laid my EPQ essay subtitles out, and I got an A* – so I’d suggest doing the same.
6. Allocate A Word Count To Each Element Of Your EPQ Structure

You’ll want an introductory paragraph to start with, and that should only take about 200-300 words . Don’t go overboard with your introduction, as you should aim to make the bulk of your essay about your EPQ question.
I’ve already mentioned it, but you want to write about 300 words per subtitle . This is the perfect amount of words to write if you want the EPQ essay to go as smoothly as possible.
16 subtitles at 300 words each will put you at just under 5000 words – 4800, to be exact. That will leave you just enough room to add a short introduction too.
You can go for less subtitles, but that means a higher word count for each individual subtitle . If you make your word count per subtitle too high, then you’ll struggle when it comes to actually writing your EPQ essay.
You could also try more subtitles if you want, but that then means you’d write less per subtitle . That means there’s less room for all your explanation, and less marks when you hand it in.
I’d recommend keeping your subtitle count between 14 and 18 . That way you give yourself the best chances of your EPQ being easier to write.
You also make it easier for you to enjoy, too. Making your EPQ essay subtitles this long means you’ll find it easier and less monotonous, and therefore you’ll enjoy it more.
The word count of each element in your EPQ essay has an impact on your productivity and focus, too . Generally, the shorter the piece of writing you have to do, the more productive you’ll be.
Setting yourself short-term goals like this will help you stay focused and make your EPQ that little bit better. It’s worth setting effective word counts for your EPQ essay elements for those extra marks .
7. Research, Research ( And A Little Bit More Research )

Research should make up about 40%-50% of your total EPQ essay . That’s a lot of research, and you can see from this figure that quality research is crucial to your success.
The reason research takes up so much space is because you need to explore all opportunities within your question. Research will help you develop ideas and improve your knowledge of the subject, helping you to better answer your EPQ essay question.
And besides, who doesn’t want help reaching the massive 5000 word count?
There are many ways to research, with the most common being the internet, and books . Both ways of researching are valid and useful, but you still need to be careful.
Especially with the internet, you may come across facts and information that isn’t entirely accurate. This is because anybody can access anything, and usually the information you see online is edited by people who aren’t professionals.
Try to stay away from websites like Wikipedia, where anybody can change the information you see . There are much better alternatives out there, like Google Scholar for example.
Whereas with books, they have to go through a long-winded process to ensure they’re accurate . Books tend to be slightly more reliable than the internet, especially if they have an ‘exam-board approved’ label on them.
I’d also recommend keeping track of all the sources of your information, as you’ll have to write a bibliography at the end of your EPQ .
What that basically means is that you have to reference each individual source of information after you’ve written your EPQ essay. That’s just so examiners can check to see if you’re plagiarising any content, in case you were wondering.
8. Check That Your EPQ Structure Still Makes Sense

You should have around 16 subtitles ready to go, in chronological order or order of importance . I’d suggest chronological order, but that’s up to you.
You should also have space to add an introduction and conclusion paragraphs . They shouldn’t take up too much space, but still leave some room for you to add them in.
You’ll actually want to wait until the end of your EPQ essay to write either of these paragraphs, so it might help to add placeholders until you get to writing them.
Around 7 of your subtitles should be based on research . You’ll want to leave yourself a nice amount of in-depth research, whilst also allowing room for all that explanation.
If you don’t give the right proportions for your research and explanation subtitles, your EPQ can become lopsided. Examiners will easily spot this and take away precious marks.
You’ll want your conclusion to be longer than your introduction, as you’re essentially summing up all that you’ve written . Your conclusion should be about the same size as your subtitles, but maybe just a little bit bigger.
If all else fails, just read through your structure and think about it from an examiners’ point of view. Does it all make sense? Are the subtitles in a sensible order? Have you left space for your introduction and conclusion paragraphs?
If you reckon you’ve got all these elements in the right order and the right sizes, you should be good to go. Just keep a clear focus on your EPQ essay question, and you can’t go wrong.
9 . Write Down The Answers To Each Of Your Subtitles

Start with your subtitles to get the main bulk of your EPQ essay underway . The quicker you get your subtitles done, the sooner you can finish your EPQ.
Starting your subtitles first is a good idea, as they make up most of your EPQ. You’ll want to get them done first, and then you have time after that to work on the finer details.
As I’ve said, your subtitles should be around 300 words long . This will allow you just enough space to answer the subtitle, without repeating yourself or going overboard.
If you go too far over 300 words, you risk either repeating yourself or just extending your points so much that your words become empty. Empty words = no marks, which is what you definitely don’t want.
If you don’t write 300 words, the points you make are likely to be underdeveloped. This means you can’t get into the top band of marks no matter how good what you’re saying is – there’s just simply not enough of it.
Of course, if you think you can express yourself in more or less than 300 words, go for it . Everybody’s different, and some people have better writing skills than others.
The amount of words you write per subtitle can also depend on how many subtitles you have . If you have less subtitles, you write more words per subtitle, and vice versa – simple maths.
Try to explore every possibility within your subtitle. The more routes you go down and the further the detail you go into, the more marks you’ll get from the examiner.
10 . Write The Introduction And Conclusion Paragraphs

Your introduction paragraph needs to be slightly shorter than your average subtitle paragraph . Usually about 200-300 words, the introduction will basically talk about what’s to come in your EPQ essay.
If you make your introduction too long, you waste space that you might need for your research/explanations. You also take up space that could be used for your conclusion, which is very important.
It’s a good idea to write your introduction paragraph after you’ve written all of your subtitles . It may sound odd, but there’s method to the madness.
If you write your introductory paragraph last, it’ll be a lot more accurate than if you’d have done it at the start. You’ll know exactly what’s in your EPQ, and therefore your introduction can accurately ‘introduce’ your essay .
Your conclusion paragraph should be slightly longer than your average subtitle, and definitely longer than your introduction . I’d say about 400 words, your conclusion should sum up everything you’ve talked about in your EPQ essay.
Your conclusion should essentially answer the question you asked at the start of your EPQ essay. You should aim to include everything you talked about in your other subtitles (that’s why it’s a little bit longer).
You’ll obviously want to write your conclusion paragraph after everything else, or you’ll have nothing to conclude. Once you get on to your conclusion, you’re on the home stretch.
11. Get Someone To Proof Read It To Make Sure There Are No Errors

Proof reading your EPQ essay is so, so, SO important to your success . If you don’t proof read your EPQ essay, you may miss some pretty crucial mistakes…
I’m not just talking about the spelling mistakes you may have made (although you might want to fix those too). I mean the mistakes where you contradict yourself, go off topic, or even just get your facts wrong.
I’m sure I don’t need to explain it, but these mistakes will cost you dearly when your EPQ gets examined . Sometimes just a few marks can be the difference between an A and an A*, so you need to maximize your chances of success.
A good way to ensure your EPQ essay is perfect is to get someone else to look through it. Having a second opinion ensures that everything you’ve written is accurate and concise, and it’s better than just checking through it yourself.
If you rely on your own methods of checking through your work, you’re more likely to miss mistakes . Having a fresh perspective on your work broadens the chances of catching every mistake you make.
It doesn’t matter who you get to check your work . You can ask friends, family, or even your teachers/tutor – just get it proof read before you send it off to be marked .
If you need to check through it for spelling mistakes or wording issues, there’s a handy little trick I used for my EPQ essay. Paste your entire essay into google translate, and have it read out to you .
That way you can listen and check for anything that’s not quite right, and sort it out in time for your EPQ essay to be examined.
Thanks so much for the help !
This is so, so helpful, thanks so much!
How many resources should I have for my EPQ?
20-25 should be the right number
Hi, thanks for the cool tips! I will definitely keep it for myself
Hello, thanks for the cool advice, but the most difficult thing for me is 1 point – to think through the topic itself. Therefore, already at the first stage, I give up and turn to the college essay writing service. This service helped me more than once or twice. My friends also use it. Also, it is difficult for me to create a mental map, which is in point 2. Therefore, I would rather spend my writing time on purposes that are useful to me.
This is so useful! I have been working on my EPQ over the past few weeks and have had a few big quandries about how I should go about forming an answer to my question and this has made it much clearer. Thank you!
Would you like to explore a topic?
- LEARNING OUTSIDE OF SCHOOL
Or read some of our popular articles?
Free downloadable english gcse past papers with mark scheme.
- 19 May 2022
How Will GCSE Grade Boundaries Affect My Child’s Results?
- Akshat Biyani
- 13 December 2021
The Best Free Homeschooling Resources UK Parents Need to Start Using Today
- Joseph McCrossan
- 18 February 2022
Everything You Need to Know About the EPQ: Full FAQ
- August 18, 2022

What is the A-level extended project?
Does the extended project count as an a-level , is it hard to get an a in epq .
- Is A-level 3 extended project an AS-level?
Do Unis care about EPQ?
Does oxbridge care about epq .
- Does the EPQ give UCAS points? And can you get an A* in EPQ?
Can you get into uni with 2 A-levels and an EPQ? And does EPQ lower entry requirements?
Can you fail an epq , is an epq harder than an as-level , is an epq really worth it or is epq a waste of time .
- How many UCAS points is A* A*A *?
What are good topics for EPQ?
What are the benefits of epq .
- How many hours a week is EPQ?
Can you do EPQ in Year 13?
How many hours a week should i spend on my epq .
- Do you have to write 5000 words for the EPQ?
Can you write a book for EPQ?
Can you use first person in epq .
.jpg?width=848&name=student-house-apartment-university-decoration-moving%20(1).jpg)
The A-level extended project qualification (also known as the EPQ) is an A-level standard standalone qualification designed to develop a person’s abilities beyond what is offered by the A-levels syllabus . The EPQ aims to demonstrate skills which will help the candidate’s application for university or a job.
The EPQ is worth up to 28 UCAS points (which is equivalent to half of an A-Level).
The EPQ is an independent student-led project. This means that students get to plan and conduct their research however they like. The only condition is that the topic they choose can not be covered by their other qualifications. They need to think outside the box!
Students will have to write an essay of 5,000 words or present an object, artefact or performance with a shorter report.
According to the AQA website (AQA is one of the exam boards which offers the EPQ), the EPQ gives a student the chance to take responsibility for the choice, design and decision making of an individual project (or an individual role in a group project). Students:
- develop critical thinking and independent learning skills
- demonstrate their creative and self-starter qualities
- grow planning, research, and presentation skills
- practice decision-making and problem-solving
- advance technology expertise
Undertaking an EPQ can also deliver other benefits for students, such as:
- improved A-level performance for students taking EPQ
- increasing student motivation by allowing them to study topics of personal interest
- enabling students to apply their new skills to other areas of study.
The OCR website provides an example EPQ project which might be useful to look at.
The EPQ counts as half of an A-level. This means that you get EPQ UCAS points. Doing an EPQ boosts your UCAS credits which means that you can apply for university even if your A-level grades are slightly below the university’s entry requirements. Don’t forget that sometimes retaking A-levels can be a winning solution .
Instead of viewing the EPQ as an A-level, try and look at it like an A-level booster pack! If you get straight A*s then the EPQ can make you stand out against someone who hasn’t.
This question really depends on each student. Some people find it easy to get top marks in the EPQ and others find it more of a challenge.
Take a look at the specifications of the EPQ very carefully. If you follow the marking scheme, it is much easier to know what to do to get top marks. This way you can also see if the EPQ is a good fit for you in terms of learning style.
Remember that each exam board has different specifications for the EPQ. These are all the different exam boards’ EPQ specification guidelines in one place. 😇
- AQA EPQ specification
- Edexcel EPQ specification
- OCR EPQ specification
- WJEC EPQ specification
- ASDAN EPQ specification
Our GoStudent Tutors can help you prepare for your EPQ by giving you some one-to-one tutoring to target your topic and subject!
Is a level 3 extended project an AS-level?
If you want to make this a points system, technically an EPQ outranks an AS qualification. An A* in your EPQ will count as up to 28 UCAS points while an A* in an AS-level subject will only count for 20 UCAS points.
An AS-level is the qualification you get below a full A-level. A full A-level counts for 56 UCAS points!
If you want a full breakdown of what different qualifications are worth in terms of UCAS points, have a look at the UCAS points breakdown which includes the IB, BTEC, Scottish Highers, and Welsh Baccalaureate.
One of the big questions people often have about anything extra-curricular is: do universities care? The answer is: yes, they do!
Universities want good candidates. They want students who can think outside of the box, take the initiative, and people who have the motivation to work hard. The EPQ is designed to showcase all of these things and universities rate them very highly.
It is important to say that some universities don’t value them as much as others. But, at the end of the day, having an extra qualification won’t ever work against you!
As with all things, you have to balance what you gain against what it costs. There are many people who argue that the time and energy dedicated to doing an EPQ can be better spent elsewhere. But that is down to the individual and what they think they are capable of.
If you’re thinking about which university to choose, have a look through our guide for choosing the right university for you.
Both the University of Cambridge and the University of Oxford recognise the EPQ for undergraduate applications. The University of Oxford says:
“Where applicants have undertaken the EPQ, this will not be a condition of any offer but the University recognises that the EPQ will provide an applicant with the opportunity to develop research and academic skills relevant for study at Oxford. Candidates are encouraged to draw upon relevant EPQ experience when writing their personal statement.”
This means that your EPQ will not be ‘make or break’ for your university application, but it will benefit your application overall and you should definitely mention it in your personal statement .
So Oxford is a kind of ‘yes’, but how does Cambridge (some argue the better uni) 😉 look at EPQ? The University of Cambridge says,
“We welcome the EPQ and would encourage applicants to take one as it will help to develop independent study and research skills valuable for higher education.”
So both Oxbridge universities recognise and appreciate the EPQ. 🥳
If you are considering applying to Oxbridge, then we suggest you read our handy article on how to apply to Oxford and Cambridge .
Does the EPQ give UCAS points? And can you get an A* in EPQ?
Yes, you get EPQ UCAS points. Your EPQ will be graded between A* - E. The higher the grade you get the more UCAS points your EPQ will be worth (which is the same for your A-level qualifications).
Here is a breakdown of what EPQ grade is worth how many UCAS points:
You can theoretically get into university with two A-levels and an EPQ, but it’s not advised. We suggest that you do all 3 A-levels and then do an EPQ on top of it. If you replace an A-level with an EPQ, then your number of UCAS points is impacted.
Remember, universities don’t just look at UCAS points. There are ways to get into uni without A-levels !
If you didn’t quite meet your university’s entry requirements with A-levels alone, but you have some EPQ UCAS points, then that university may well take that into consideration.
If you need a bit of help with your A-levels studies, remember that it is never too late to sign up for some one-to-one tutoring with one of our specially selected GoStudent Tutors .
Sadly, as with most qualifications, you can indeed fail the EPQ.
If you do not meet the necessary criteria to get an E grade, you will be awarded a U, which stands for unclassified. This indicates the student has failed the EPQ.
Follow our advice above and research the EPQ specification and mark scheme for your examination body. You will have a better understanding of what is required for success with an EPQ.
This depends on each student and where their academic strengths and motivations lie. Students that benefit from a structured learning approach may find the EPQ harder than an AS-level.
On the other hand, students who prefer to set their own learning goals and are comfortable with time management are more likely to find success with an EPQ.
As with all qualifications, the EPQ is what you make of it. If you don’t work hard and you get a low score, then it may well feel like a waste of time. If you don’t choose to study something meaningful to you, it will be a long and arduous process.
The idea behind the EPQ is that you get to choose something that you are passionate about, and you use that to showcase your ability to excel independently.
According to an article in London Local, the long-term benefit of an EPQ is that it shows “future employers that you’re a self-motivated character with useful skills”.
This suggests that the value of the EPQ is not only in applying for university, but also in giving you experiences which will help you after uni.
How many UCAS points is A* A* A*?
An A* is worth 56 UCAS points, so if you manage to get an impressive three A*s at A-level, you have racked up a grand total of 168 UCAS points.
If you got three A*s at A-level and also an A* in your EPQ you will have 196 UCAS points. That is a UCAS score universities can’t ignore. 😏
There is a wide range of topics that are suitable for an EPQ. However, it all boils down to finding a topic that you are interested in, won’t get tired of, and you can delve into significant detail with.
AQA advises that you ‘focus on a topic that's interesting and may not be available through other qualifications’.
It is also a good idea to consider a topic which bears some relation to what you want to study at university.
Once you have chosen a general area that interests you, you need to focus even deeper on a specific part of that topic. The idea is that your EPQ should be unique and there shouldn’t be too many people writing about it. You will need to become an expert!
There are many benefits to doing an EPQ. As well as gaining UCAS points, and having something to put on your personal statement , the EPQ gives you important transferable skills such as independent research and critical thinking.
Ignoring UCAS and university applications, if you throw yourself into your EPQ, it can be an amazing experience.
You have around six months to complete your EPQ (that is around 130 week days). The AQA website suggests that students should spend 120 hours on their EPQ – this includes brainstorming, planning, researching, and writing.
This means that, if you spend around an hour every working day on your EPQ, you’ll have more than enough time. Undertaking an EPQ is a big commitment. You will have a supervisor who you will probably meet with on a regular basis.
It is very important that you plan ahead and don’t leave it all to the last minute.
In theory, you can do your EPQ at any stage of your education. Usually, people begin thinking about it in year 12, and spend the summer before year 13 doing their preliminary research.
If you want to do an EPQ in year 13, you should talk with your school beforehand to make sure they’re happy to support you with it.
Do you have to write 5000 words for EPQ?
Usually, people write 5,000 words for their EPQ. If you present an artefact, then your report should be a minimum of 1,000 words.
Many people think that using an artefact is easier, but it can be just as challenging. If you have an artefact, you need to have a very clear and cohesive report which justifies your project.
Yes! You can write a book for your EPQ. The only thing that we advise before you embark on this mammoth task, is to acknowledge the scope of the project. You will need to be realistic about time requirements. Your book will count as your artefact and will still need a report to accompany it.
Academia has become more inclusive of different writing styles. Most universities (including Cambridge), say that it is perfectly acceptable to write academic essays in the first person. So if it’s good enough for the University of Cambridge it is probably good enough for your EPQ.
We hope that our article has given you some useful information on the EPQ and how you should approach it. Remember, our website is full of useful articles about A-levels published by our wonderful GoStudent experts. Check out the exams section of our blog for more A-level content.

Popular posts

- By Guy Doza

- By Akshat Biyani

- By Joseph McCrossan
- In LEARNING TRENDS

4 Surprising Disadvantages of Homeschooling
- By Andrea Butler

What are the Hardest GCSEs? Should You Avoid or Embrace Them?
- By Clarissa Joshua
More great reads:

Parent Mental Health Day: Tips to Protect Your Own Mental Health
- By Sharlene Matharu
- January 26, 2023
- 16 min read

Help Your Kids Pack Their School Bags: Top Tips and PDF Checklist
- By Amelia Johansson
- September 6, 2022

18 Ways to Make their First Day of School Perfect
- August 26, 2022
Book a free trial session
Sign up for your free tutoring lesson..

EPQ Guide: Expressing your ideas
- The Inquiry Process
- Developing a line of inquiry
- Finding and selecting sources
- Working with ideas
Expressing your ideas

This is the stage you have been building towards - writing your report. Although that is largely the focus of this page , it is not all there is to the EPQ.
Your EPQ will be assessed on:
- Your completed Production Log
- if your project is a research based written report of any kind (e.g. a science investigation or an essay) it should be approximately 5,000 words long
- If your project is an artefact, it must be accomapanied by a research based written report of a minimum of 1,000 words. For artefacts, you may include photos showing various stages of the production process as well as the final product. You do not need to submit a large artefact as evidence - photographs or other media are fine.
- If your product was itself a presentation then you still need to produce a presentation about the process of producing it!
- Your presentation must be delivered live to a non-specialist audience and might use flipcharts or posters, presentation tools such as PowerPoint or Prezi or short video clips. The evidence for your presentation will include a record in your Production Log of questions your supervisor asked and how you responded.
Am I ready?
Am I ready to start writing my essay?
Before you start writing, think:
- Is my investigation largely complete? As you write you may find that you need a few additional resources or information to support your argument, but you should not sta rt to write until you are largely sure where your argument is going.
- Have I filled in a Research Organiser (which you will find on the Working with Ideas tab)? This will help you to organise your thoughts and make sure you understand the argument you intend to make and have the evidence to support it. While not compulsory, it makes writing your final essay significantly easier.
- Do I understand how to write in an appropriate academic style? Guidance is given in the Academic Writing box below.
- Do I know how to import my sources from my Investigative Journal? Don't waste time putting all your citation data in again! Import all your sources as you set up your document. There are helpsheets in the Resources for PC / Mac users boxes to the right.
You should use the Oakham APAv3 Academic Writing Template (below) rather than a generic Word template to set up your essay.
(The image below is taken from the EE LibGuide, but the template is just as useful for EPQs)

Citing and referencing
There are many different ways to acknowledge the sources you use. These are called referencing styles . You are free to use any recognised referencing style you wish for your EPQ, but Oakham's 'house style' is APA. We suggest you use this because we already have a lot of support in place for it. APA is an 'Author-date' system, meaning that you show which source you have used by putting the author and date in brackets after it in your text, and then put the full reference in an alphabetical list at the end of the essay. The Library does not support 'footnote referencing', where you put all the information in a footnote at the bottom of the page. If you want help with this then please talk to the member of staff who suggested that you use it.
For detailed information and guidance on how to use sources in your writing and how to cite and reference them accurately using the tools in Microsoft Word, consult the Citing and Referencing LibGuide . This site includes information about how to reference all sorts of different kinds of sources, including videos and works of art, and what to do if you are using a source written in a language that is not the language of your essay. It also gives some examples of how to use in-text citations , whether quoting, paraphrasing or just referring to a source more generally, and how to use the automatic citing and referencing tools in Word .

Academic writing
Stages in an academic essay

Your thesis is the point you want to make. It emerges from your research and your task is to use the evidence you have found to establish it as the most reasonable response to that research.
In both approaches, you must state the research question in your introduction, and make sure you return to it in your conclusion .
Sections required in your essay
Have a look at the Formal Presentation guide in the sidebar for a guide to laying out your essay.
Paragraph Structure
Paragraphs themselves have a structure - the most common you will have come across is likely to be PEEL. The letters often stand for slightly different things in different subjects, but the idea is largely the same - introduce your main idea for the paragraph ( Point ), justify it with Evidence and/or Examples , and Evaluate this evidence. Finally, Link back to the Research Question and/or Link forward to the next paragraph.
This is not the only way to write a paragraph and, with experience, you will soon find that your argument develops a flow of its own that does not require a formula - indeed, your essay would be very dull if every paragraph followed exactly the same structure. However, this structure can be a useful scaffold to get you started and make sure you don't miss anything important.

The structure of academic writing
Note that the following graphic was originally produced for the IB Extended Essay, but is equally applicable to the EPQ.

Planning your essay
It is vital to plan your essay before you start writing. An essay plan provides an outline of your argument and how it develops.
What sections and subsections do you need?
Although this might change as you write your essay, you should not start writing until you have your overall structure. Then think about roughly how you are going to divide your 5000 words between the different sections. 5000 words seems like a lot before you start writing, but it is much easier to write to the limit, section by section, than to try to cut your essay down once it is written.
What will the reader will expect to see and where?
Look back at your checklist and think about where in your essay you are planning to include the required information. Make sure the flow of your essay makes sense to a reader who may be a subject expert but knows little about your topic. Have you included background information? Details of experimental methods? Arguments and counter arguments?
Now get writing!
You've read all the guidance. You've made your plan. Now you have a blank screen in front of you and you just need to get started! Start with the section you think you will find easiest to write and work outwards from there, or follow the steps below to get started. Don't forget to write with the word limit in mind though.

What if you are writing lots of paragraphs but your essay just doesn't seem to be coming together?
1. Condense each paragraph into a short statement or bullet point. This is the skeleton structure of your essay.
2. Look at the order of the statements.
- Is the order logical?
- Does each point follow another in a sensible order?
- Do you need to change the order?
- Do you need to add paragraphs?
- Do you need to remove paragraphs?
3. Add, subtract and rearrange the paragraphs until your structure makes sense.
4. Redraft using your new paragraph order.
Image by OpenClipart-Vectors from Pixabay
Willard, D. (2003) My journey to and b eyond tenure in a secular university . Retrieved from: www.dwillard.org/articles/individual/my-journey-to-and-beyond-tenure-in-a-secular-university . Accessed: 9th May 2020
Oh no! It's too long!!
If you haven't managed to write to the word limit and are suddenly faced with cutting down an essay that is over the word limit, try these tips on concise writing from Purdue Online Writing Lab.

Use the menu on the left of this page from Purdue OWL to browse the four very practical pages on writing concisely and one on the Paramedic Method for reducing your word count.
AQA Guide to completing the Production Log: Expressing your ideas

AQA copyright notice
The presentation above contains slides from the AQA presentation Teaching slides: how to complete the production log (available from the AQA EPQ Teaching and Learning Resources website ). These slides are Copyright © 2020 AQA and its licensors. All rights reserved.
A downloadable copy of the Production Log can be found here , on the Home tab of this guide.
Formal presentation

Guides for PC users
- Citing and Referencing in Word 2016 for Windows
- Managing Sources in Word 2016 for Windows
- Creating a Table of Contents in Word 2016 for Windows
Guides for Mac users
- Managing Sources in Word 2016 for Mac
- Citing and Referencing in Word 2016 for Mac
- << Previous: Working with ideas
- Next: Reflecting >>
- Last Updated: Feb 27, 2023 2:28 PM
- URL: https://oakham-rutland.libguides.com/EPQ
Smallbone Library homepage
Search the Library Catalogue
Access our Subscription Databases
Normal term-time Library opening hours: Mon-Fri: 08:30-21:15 Sat: 08:00-16:00 Sun: 14:00-18:00 (Summer Term only)

How To Write An EPQ Essay & Dissertation (9 Steps)
Writing an EPQ essay involves several steps to ensure a well-structured and compelling piece.
Here is a 9-step guide to help you write an effective EPQ essay:
- Brainstorm EPQ topic ideas : Choose an engaging topic that interests you and is relevant to your academic or career goals.
- Conduct research : Gather information from various sources to support your arguments and provide evidence.
- Create a structure : Organise your essay with a clear introduction, main body, and conclusion. Outline the main points and arguments you will cover in each section.
- Write an introduction : Begin your essay with an introductory paragraph that introduces the topic, outlines the scope of the essay, and provides an overview of the structure 4 .
- Develop the main body : Write the main body of the essay, focusing on presenting your arguments, evidence, and analysis. Ensure each paragraph has a clear topic sentence and flows logically from one point to the next.
- Use proper referencing : Cite your sources correctly to avoid plagiarism and demonstrate your research skills.
- Write a conclusion : Summarise your main points and answer the question you posed at the beginning of the essay.
- Review and revise : Proofread your essay for grammar, spelling, and punctuation errors. Ensure your arguments are clear, coherent, and well-supported 1 .
- Seek feedback : Ask a teacher, tutor, or peer to review your essay and provide constructive feedback to help you improve your work
The article below is designed to help you develop a strong foundation for writing your EPQ essay by providing practical tips and guidance from an expert in the field.
You’ll learn about key elements such as structure, formatting, research methods, argumentation techniques and more so that you can craft a compelling paper that stands out from the crowd.
By following these steps, you’ll have all the tools necessary to make sure your EPQ essay stands out and meets its desired goals.
- 1 Understanding The EPQ Essay Requirements
- 2.1 Organizing Ideas
- 2.2 Outlining Content
- 3 Formatting Your Essay
- 4 Researching For Your Essay
- 5 Developing Your Argument
- 6 Crafting A Compelling Conclusion
- 7 Writing a good EPQ essay
Understanding The EPQ Essay Requirements
Navigating the world of EPQ essay writing can be intimidating, and even overwhelming at times! But never fear – with a little bit of knowledge and preparation you’ll find yourself soaring towards success.
At its core, crafting an effective EPQ essay comes down to analyzing expectations and exploring options. It’s important to take into account the specific requirements for your topic or course; many professors will have different standards that need to be met.
Once you’re clear on what needs to be accomplished, it’s time to get creative – start brainstorming ideas and looking for relevant sources that support them. Be sure to record everything as you go along so you don’t forget any key details later on in the process.
Research is essential here, but make sure not to lose sight of the bigger picture: Your paper should still reflect your unique perspective and originality. With this approach, you can create an engaging work that will stand out from the crowd — one which takes readers on a journey of exploration through freedom-filled imagination!
Structuring Your EPQ Essay
Organizing your ideas is an important part of writing an EPQ essay.
Start by making a list of the main points you want to make and then organize them into groups that fit with your argument.
Once you have your ideas organized, you can start outlining the content. This will help you create a logical flow of information and ensure that your essay is structured in a clear and concise way.
It’ll also make it easier to write the actual essay, and make sure that you haven’t skipped any important points.
Organizing Ideas
Organizing your ideas is an important part of writing a successful EPQ essay. Before you start jotting down notes or typing away on your computer, identify the sources that will be most useful in completing your project.
Ask yourself questions like “what do I already know?” and “where can I find more information?” By identifying these sources early on, you’ll ensure that all the research needed to write a quality paper has been done ahead of time.
Once you’ve identified the best source material for your project, it’s time to develop a structure for your essay. Think about how each point should flow logically from one to another and what order would make the most sense when reading through your work.
As with any type of academic writing, having an outline helps keep everything organized and makes it easier to create well-structured argument points throughout your paper.
Additionally, if there are sections where multiple topics require further discussion, consider breaking them up into separate paragraphs so readers can easily digest each idea independently.
Writing an EPQ essay doesn’t have to be overwhelming; by taking proactive steps to organize ideas before starting the actual writing process, you’re sure to craft an impressive piece of work!
Outlining Content
Once you’ve identified the sources and outlined your structure, it’s time to start brainstorming techniques for what content should be included in your essay.
This is an important step to ensure that all the key points are covered in a logical order. Brainstorming can include anything from writing down ideas as they come to mind or even mapping out each section with bullet points.
Additionally, if there are any specific topics you’d like to discuss further, consider breaking them up into separate paragraphs so readers can easily digest each idea independently.
No matter which strategy works best for you, it’s essential to make sure that each point has been thoroughly researched beforehand—this will guarantee that only quality information is presented throughout your paper.
Writing an EPQ essay doesn’t have to be daunting; by taking proactive steps such as outlining the content of your project ahead of time, you’re sure to craft an impressive piece!
Formatting Your Essay
The formatting of your essay is as important as the structure. When structuring, you made sure all the pieces were in place and ready to go; now it’s time to make them look nice.
You should consider several stylistic choices when formatting:
- Word choice – Use precise language that adds power and meaning to each sentence without detracting from its original intent
- Font size – Choose a font size that looks professional yet comfortable for reading
- Headers/subheaders – Create visual breaks between sections using headers or subheaders with interesting titles that capture readers’ attention
- Margins – Establish margins so your reader can easily find where one section ends and another begins
By implementing these subtle but powerful formatting techniques, you will improve the overall quality of your EPQ essay and ensure a successful submission!
Researching For Your Essay
The research phase of an EPQ essay is one of the most important steps to ensure you can write a quality paper. Defining your objectives clearly and citing sources accurately are essential for success. As such, it’s important to take your time during this step, as any mistakes here will be difficult to recover from later on in the writing process.
When researching for your essay, begin by getting organized. Gather all pertinent information related to your topic and compile them into separate folders or files so they’re easy to access when needed.
Once that’s completed, start reading up on relevant materials and taking notes along the way – summarize each source and make sure you properly cite authors at the end of each note taken. Doing so will help you save valuable time looking back through books or articles once you move onto actually putting pen to paper (or fingers to keys).
Ultimately, if done correctly, research should provide a solid foundation which allows you to create an innovative and unique piece of work without having to worry about accuracy or plagiarism issues!
Developing Your Argument
Having completed your research, it’s time to develop your argument.
To do this, start by brainstorming ideas about the topic and evaluating sources for their relevance and suitability. Consider which evidence is best placed to support your position on a particular issue or idea.
After gathering all of your information from various sources, try to identify the common themes that emerge in relation to the topic you are researching. In order to form an effective argument, you will need to assess how each piece of evidence fits together in order to demonstrate its relevance and importance.
This could include looking at different perspectives on an issue or comparing multiple results of research studies into a specific field. Additionally, make sure that when forming your argument you take note of any counter arguments which may be presented as these can help strengthen your overall conclusion.
Once you have identified all relevant points related to your argument, consider how they work together and analyse them more deeply – this will allow you to draw meaningful conclusions from the data available.
Crafting A Compelling Conclusion
The conclusion of your EPQ essay is essential to summarizing all the points you have made and discussing their implications. It’s important to remember that this section should be both succinct and clear, so as not to confuse or distract from the main message of your paper.
When writing a compelling conclusion, start by restating your thesis statement in a different way than you did at the beginning of your paper.
Take some time to review each point discussed throughout the body paragraphs and summarize them briefly. This will help remind readers what they just read and why it matters.
Additionally, make sure to tie up loose ends, such as unanswered questions, by either providing an answer or referring back to prior sections.
Finally, conclude with a strong sentence that drives home the importance of your topic while offering insight into future research possibilities or other relevant discussions.
Writing a good EPQ essay
In conclusion, writing an EPQ essay is a unique challenge that requires serious attention and hard work.
With the right structure, research, argumentation, and conclusion in place however, you can put together a compelling piece of writing that will impress even the most discerning master’s student.
One interesting statistic to consider when crafting your essay is that only 50% of students who submit an EPQ are successful in achieving their desired grade.
This serves as a reminder to emphasise quality over quantity in your work: focus on making sure each element of your essay is thoroughly researched and well-written before submitting it for review.
What Is The 11 Plus Exam?
The Ultimate Guide to A-Levels for Psychology
Leave a comment Cancel reply
Reach out to us for career and sponsorship opportunities.
© 2024 Acrosophy Excellence in Application
A Medical MBA Company The Medical MBA Ltd Company number: 13561401 86-90 Paul Street, London, England, United Kingdom, EC2A 4NE
All about the sixth form EPQ – Extended Project Qualification
Summary: Taking the sixth form EPQ (Extended Project Qualification) can add significant interest to your studies, and EPQ will add considerable value to your university application. This article explains what an EPQ involves.
What is an EPQ?
EPQ is short for Extended Project Qualification. An EPQ is an independent research project which involves writing an essay of 5000 words (that's around 10 typed pages), or creating a product, which might be anything from an art object to an iPhone app. As the project evolves, you must complete a production log to record specific stages of the project and this also contributes to your project result. The third component of the project is an oral presentation.
Generally, the whole process from start to finish takes about 120 hours. There's no set time limit for doing an EPQ, but most students use the summer vacation at the end of Year 12 to do the preliminary research and then complete the project in the early part of Year 13. It is a formal 'level 3' qualification that attracts slightly higher UCAS Tariff points than a new AS-Level. All three exam boards offer EPQ - my college uses the EPQ structure provided by AQA .
You receive teaching and guidance to get you started, to help with planning and researching and presentation skills, and to keep you on track as you work through your chosen project. There's no formal restriction on what you do the project on: that's negotiated between you and your project adviser, who will help you choose a topic you will enjoy and cope with.
The three assessments which decide your result are done by your teachers, though the exam board 'moderates' their marks to check they're grading correctly.
What is the benefit of completing an EPQ?
The Extended Project Qualification teaches you some key high-level skills that individual A-level courses don't have time to include, and many students say it adds considerable interest to their sixth-form programme.
However, there are also several major benefits to completing an EPQ when it comes to applying to university . At its simplest EPQ helps you with UCAS points - EPQ is valued at 50% of a full A level in the UCAS tariff. But perhaps the greatest advantage of an EPQ is in helping convince top universities to make you an offer.
EPQ provides very clear evidence of that you have interests and ability which go beyond the A-Level curriculum. It demonstrates clearly that you are capable of undertaking the kind of independent reading, research, and essay writing that is the mainstay of most undergraduate degrees.
This is hugely important in the UCAS application process where universities often have little to distinguish between students with similar predicted grades.
Additionally, an EPQ provides highly relevant material for your UCAS Personal Statement and for you to talk about in university interviews. Most top schools in the UK have made the completion of an EPQ (or an internal equivalent) compulsory for all Year 12 students.
What skills do I need to complete a successful EPQ?
An EPQ is the longest and most extensive project that you will do during your school years, so it stretches your normal skills . The EPQ requires:
- a great interest in the research topic: interest and curiosity in a subject are the fuel of motivation to keep you going deeper in order to answer a research question – an Extended Project Qualification is not a ‘lukewarm’ enterprise!
- organizational skills: planning the project over a 20-week period and making sure that each stage is completed in time is essential to creating a high-quality end-product and attracting the highest assessment marks in the process.
- good time-management skills because it is not part of the normal school curriculum. Making sure you spend enough time on the project each week, while juggling the demands of your A-Levels, is key to a successful project.
To decide if EPQ is right for you needs good advice from teachers who know you well. If you are a top-grade student, you should enjoy and cope well with EPQ and it could make all the difference getting you into a top university. If your academic potential is more modest you may well benefit from EPQ, but it could also make demands on you which affect your main A level work.
Success Stories from my college
Anastasia completed her EPQ on the use of light in architecture, looking at its development through European architectural history and examining contemporary technical developments. The completion of the project developed her existing knowledge of architecture in a way that not only enhanced her A-Level subjects, particularly History of Art, but added an extra dimension to her UCAS application, and helped in the interviews which got her a place at one of the UK’s best schools of architecture. Furthermore, her EPQ gave her a considerable advantage over her competitors when she came to apply for work placements in her first year at university.
Anna completed an EPQ on the use of satire in the work of the Italian author Dante. The project provided strong evidence in her UCAS Personal Statement to support her application to study English Literature. Her EPQ was the main topic of discussion in her interview for a place at Cambridge University, which she was duly offered. When asked what she thought was the main reason that her Cambridge interview had been so successful, Anna answered simply: “I just talked about my EPQ!”.
Article written by William Stockland, Head of Faculty of Culture & Society at Ashbourne College

Related articles on this site
Choosing the right A-level subjects
FAQs about A-level choice
Further advice articles
- FAQs about A-level retakes and options for resitting
- Exam remarks - what to do, and when - updated for 2023
- Appealing against your A-level or GCSE results in 2023
- One year A-levels courses at CIFE colleges
- Sixth-form advice articles about university entrance...
- Sixth-form advice articles about study skills...
- Advice articles about sixth-form choices...
Need any help?
Name (required): Please leave this field empty. Email (required): Phone number: Tell us how we can help: Confirm acceptance of Privacy Policy
The data entered on this form will be used only for the purpose of responding to your enquiry. It will not be used for sales/marketing, nor shared with any third party unless required to respond to your query (i.e. with one of our partner colleges).

Courses at cife colleges
GCSE courses Two-year A level courses Final-year A level courses One-year A level courses A level retake courses University Foundation courses Easter A level & GCSE revision courses
Advice articles
FAQs about retakes Revision UCAS personal statement Tips for a top UCAS application For international students Choosing the right A levels Oxbridge and medicine interviews All advice articles
More about cife FAQ about colleges News Why colleges join cife Useful links Fees at cife colleges Contact us

What is an EPQ? A Comprehensive Guide
EPQ (Extended Project Qualification) is an independent research project allowing students to delve deeper into a topic of interest.
It is equivalent to half an A-level qualification and is highly recommended for students who want to develop their research skills and gain additional UCAS points.
Table of Contents
A-Level Qualification
EPQ is an A-level qualification that allows students to conduct independent research, which can be an essay, report, artefact, presentation, or thesis.
The research project is completed under the supervision of a tutor who provides guidance and support throughout the project.
EPQ Structure
The EPQ project comprises several stages: topic selection, research, planning, development, and evaluation. The project should be completed within a year, and the final product should be around 5,000 words or equivalent.
EPQ topics can be on any subject, but they are recommended to be relevant to the degree course or career path the student wishes to pursue. Some popular EPQ topics include art, English literature, music, short films, novels, and invention.
EPQ is an excellent opportunity for students to develop their research skills and gain additional UCAS points. It allows students to explore a topic of interest in depth and develop their critical thinking and analytical skills.
The Value of EPQ
University applications.
EPQ is a valuable asset for university applications. It demonstrates that the student has the skills and commitment to work independently on a project.
EPQ also shows that the student is passionate about a particular subject and willing to go above and beyond the standard curriculum to explore it further.
The EPQ is valued at a maximum of 28 UCAS points, equivalent to half of an A-level. This renders it a beneficial qualification for students to acquire.
Universities also consider EPQ when making offers; some even lower their entry requirements for students who have completed an EPQ.
EPQ can also be used to strengthen a student’s statement. It provides evidence of the student’s initiative, communication, and self-motivated attitude. It shows that the student is willing to take on challenges and can manage their time effectively.
Job Applications
EPQ is also valuable for job applications. It demonstrates that the student has the skills and commitment to work independently on a project.
It shows that the student is passionate about a particular subject and willing to go above and beyond the standard requirements to explore it further.
🌟 Hey Students! 🚀 Ready for the ultimate experience? Join us on Studentsinside.com's Facebook , YouTube , WhatsApp , and LinkedIn . Click now for tips, fun, and success vibes! 🌈✨ #StudentLife #JoinUs
EPQ can be used to strengthen a student’s CV. It provides evidence of the student’s initiative, communication, and self-motivated attitude. It shows that the student is willing to take on challenges and can manage their time effectively.
Having an EPQ can distinguish a student in a competitive job market, as employers value the qualities it represents.
Conducting an EPQ
When conducting an EPQ, there are several vital steps to remember. These include planning and research, writing the EPQ, and presenting the EPQ. By following these steps, students can ensure that they can complete their project successfully and earn their qualifications.
Planning and Research
The first step in conducting an EPQ is to plan and conduct research. This involves developing a research question and conducting independent research to gather information and data. It is crucial to develop strong research skills during this stage, including evaluating sources and critically analyzing data.
Writing the EPQ
Once the research is complete, the next step is to write the EPQ. This involves organizing the information and data gathered during research into a well-structured essay or dissertation. It is essential to write in an academic style, using appropriate language and citing sources correctly.
Presenting the EPQ
Finally, students must present their EPQ clearly and engagingly. This may involve creating a presentation or delivering a speech, and it is crucial to effectively communicate the essential findings and conclusions of the project. Strong communication skills are necessary during this stage, as students must be able to convey their ideas and research to others.
Grading and Evaluation
Grade requirements.
EPQs are graded from A* to E, with A* being the highest grade. The grade boundaries differ from year to year and from exam board to exam board. For example, in 2019, the grade boundaries for the AQA EPQ were 45 for an A*, 40 for an A, 35 for a B, and so on.
To earn the top grades, students must show proficiency in the four evaluation criteria listed:
- AO1: Manage
- AO2: Use resources
- AO3: Develop and realise
- AO4: Review
Students must produce a production log, a written report, supplementary evidence, and a presentation. The production log should document the student’s progress throughout the project, and the written report should be around 5,000 words long.
Feedback and Revision
EPQ supervisors provide feedback on students’ work throughout the project. Students can use this feedback to revise their work and improve their grades.
The revision process is an essential part of the EPQ cycle, and students should take advantage of the feedback they receive to make their work as strong as possible.
Challenges and Tips
Dealing with anxiety.
Undertaking an EPQ can be a daunting task, and it is common for students to experience anxiety and stress during the process.
It’s normal to feel anxious. Just break your project into smaller, doable tasks to make things easier. This can make everything feel less overwhelming and more manageable.
Another way to manage anxiety is to set realistic goals and deadlines. This helps prevent procrastination and ensures that progress is being made. It is also essential to take breaks and practice self-care to avoid burnout.
When undertaking an EPQ, it is crucial to approach it with a clear plan and strategy. One helpful tip is to choose a topic of personal interest, as this can help maintain motivation and engagement throughout the project.
It is also essential to conduct thorough and independent research, using various sources to ensure a well-rounded understanding of the topic. Critical thinking skills are crucial when evaluating sources and forming arguments, so developing these skills throughout the project is vital.
It’s crucial to stay organized and monitor your progress during the project. You can achieve this by using calendars, to-do lists, and note-taking software to keep tabs on deadlines, tasks, and research.
Covid-19 Impact
The current COVID-19 pandemic has presented unique challenges for EPQ students, including limited access to resources and difficulty conducting primary research.
However, it has also created opportunities to explore emerging issues related to the pandemic, such as the impact on mental health or the effectiveness of government responses.
When conducting research during the pandemic, it is essential to be flexible and adaptable. This may include using online resources and conducting virtual interviews or surveys.
It is also crucial to consider the limitations of the pandemic when setting goals and expectations and to communicate with supervisors and teachers to ensure that the project remains feasible and achievable.

Mohammed Debon is an SEO Expert, Webmaster, and a proud parent of three. Mohammed created this website to help fellow parents find comprehensive information about various educational programs and make well-informed decisions for their children's future. With expertise in the digital landscape, Mohammed aims to streamline the process of selecting the right education system and provide valuable resources for parents worldwide.
Similar Posts

IGCSE vs. IB: Making the Right Choice for Your Child’s Future
When choosing the right curriculum for their children, parents often need clarification on IGCSE and IB. Both programs are designed to offer students a high-quality education but differ in their approaches and curriculum. This article briefly overviews the two curricula and highlights their differences to help parents make an informed decision. The IB program is…

IGCSE Grading System Revealed: How to Secure Your Path to Top Universities!
Let’s explore the IGCSE grading system! We’ll learn how it works, what changes are coming, and why it’s essential for getting into college or finding a job. Plus, get some handy tips and tricks on how to get better grades. So, if you’re curious about how the IGCSE grading system can affect your future, keep…

ICSE vs IGCSE: Breaking Down Subjects, Skills, and Syllab
ICSE and IGCSE are two worldwide education boards. ICSE is the Indian Certificate of Secondary Education, and IGCSE is the International General Certificate of Secondary Education. ICSE was established in 1986 by the Government of India to provide a uniform education system nationwide. It is a general board conducted under the Council for the Indian…

Is IGCSE Chemistry Hard? A Comprehensive Analysis
IGCSE Chemistry is a subject that many students dread. It is often considered one of the hardest subjects to study for. The question is, is IGCSE Chemistry hard? The perception of its difficulty can differ from person to person, but certain factors make this subject challenging for students. One of the reasons why IGCSE Chemistry is considered…

Do US Universities Accept IGCSE? A Comprehensive Guide
US universities are known for their rigorous admissions process, often requiring students to meet specific academic criteria. This can be incredibly challenging for international students, as their educational backgrounds may differ significantly from those of US students. One common question international students ask is whether US universities accept IGCSE (International General Certificate of Secondary Education)…

What IGCSE Subjects Are Needed For Business?
Various academic and career opportunities are available for students interested in pursuing a business career. Navigating these opportunities’ paths can be complex, but grasping the options is essential. IGCSE subjects lay a strong foundation for specialized business studies. Take the Cambridge IGCSE Business Studies syllabus as an example. It enhances learners’ grasp of business operations…
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

- Plagiarism Checker
- About Premier Essays
- Terms and Conditons
- Write a Review

- Premier Essay
Essay Planner Template | The Only How-to Guide You Will Ever Need

A Discussion Essay | How to Write, Structure & Samples

How to Write a Psychology Essay | Everything You Need to Know

How to Write an Analytical Essay | An Ultimate Guide

How to Write a Law Essay | The Only How-to Guide You Will Ever Need


What Is a Rebuttal in an Argumentative Essay | Importance and Examples

Essay Planner Example | Useful Tips and Benefits

Tips for Writing an Essay | Everything You Need to Know

How to Write An Evaluation Essay | The Only How-to Guide You Will Ever Need
How to write epq essay: a step by step guide with examples, get an experienced writer start working, review our examples before placing an order, learn how to draft academic papers.

How to Write a Student Reflective Essay: Structure With Example And Tips

How To Propose Effective Essay Questions? Practical Examples

EPQ essay stands for Extended Project Qualification essay. It is an independent research project undertaken by students, allowing them to explore a topic of their choice in-depth and produce an extended essay enhancing critical thinking and research skills.
As students begin their college assignments, they have to complete an independent research project that is long, intensive, and takes more time to complete.
So by completing EPQ essays, students uncover the ability to develop creative thinking and analytical problem-solving skills that will help them to get into their desired colleges.
Review Our Quality Student Assignment Help Guide
This comprehensive guide aims to provide valuable insights into EPQ essay examples, guiding toward crafting outstanding EPQ essay papers that demonstrate their academic prowess.
Free Premier Essay Writing Topics
Essay Writing is an essential part of academics which presents the ideas, arguments, opinions, or positions of the writer regarding the topic. The writer supports his claims using facts, evidence, or survey studies.
- Clear presentation or understanding of the type of essay
- An appealing introduction with an unambiguous thesis statement
- A well-defined structure of body paragraphs supporting the thesis
A prospective conclusion with an optimistic tone
Pay For Now 9.98$
What is EPQ Essay?
EPQ essays serve as a source of inspiration and guidance for individuals working on their EPQ projects. This write-up showcases the structure, content, and quality of essays that have achieved excellence.
By examining successful EPQ essays, you gain a deeper understanding of effective research methodologies , critical analysis , and compelling presentation techniques.
How to Crafting an Outstanding EPQ Essay?
To create an EPQ essay that stands out, you should consider the following key elements to writing your own EPQ essay:
1. Choosing an Engaging Topic
Select a topic that aligns with your interests, which will keep you motivated throughout the research process . Additionally, ensure that your chosen subject has sufficient academic resources to support your analysis and arguments.
2. Effective Research Methodology
Devise a well-structured research plan encompassing primary and secondary research methods . This will enable you to gather a diverse range of information and perspectives, enhancing the credibility and depth of your essay.
3. Structuring the Essay
Organize your essay into logical sections, including an introduction, methodology, analysis, findings , and conclusion. This coherent structure allows readers to navigate through your work seamlessly, following your arguments and insights effortlessly.
4. Compelling Introduction
Begin your essay with a captivating introduction that clearly states your research question or objective. Engage your readers by providing context, significance, and a glimpse of what they can expect from your essay.
5. Thorough Analysis and Critical Thinking
Demonstrate your analytical skills by critically evaluating your research findings and existing literature. Incorporate different perspectives and theories to enrich your arguments and provide a well-rounded analysis of your topic.
6. Well-Supported Arguments
Back up your claims with credible evidence, such as academic research , case studies , or expert opinions. Ensure that your sources are reliable and properly cited, adhering to academic integrity standards.
7. Coherent Writing Style
Maintain a clear and concise writing style throughout your essay. Use appropriate academic language and terminology to convey your ideas effectively. Avoid excessive jargon and strive for clarity without sacrificing depth.
8. Effective Conclusion
Summarize your key findings and arguments in a concise and impactful conclusion. Emphasize the significance of your research and its potential implications. Leave your readers with a thought-provoking ending that encourages further exploration of the topic.
By incorporating these essential elements, you can create an outstanding EPQ essay that showcases your research skills and academic excellence.

Premier Essays Plagiarism Services
The opinion of a writer based on his knowledge
Writer's stance based on facts Backing claims with statistical data Comparative analysis based on results And many more!
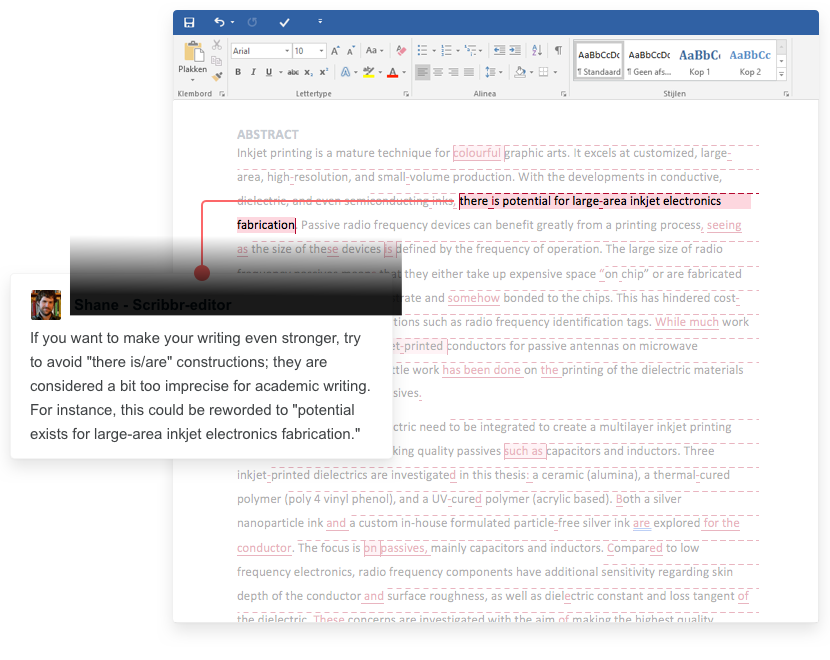
Example EPQ Essay: An Insightful Guide
When it comes to EPQ example essays, one aspect that captures attention is the word count. Many students wonder how to effectively manage an EPQ 5000-word essay example. Fear not, for we have carefully curated a diverse selection of EPQ essay examples to shed light on this matter.
- Abstract: This essay examines the various consequences of climate change on coastal ecosystems, focusing on the ecological disruptions caused by rising sea levels, ocean acidification, and extreme weather events.
- Methodology: The author employs a multidisciplinary approach, combining scientific research, statistical analysis, and case studies to provide a comprehensive evaluation of the subject matter.
- Findings: The essay highlights the vulnerability of coastal ecosystems, emphasizing the urgent need for sustainable practices and environmental conservation measures.
- Conclusion: The author concludes by emphasizing the importance of collective action in mitigating the adverse effects of climate change on coastal ecosystems.
Final Thought
In the pursuit of academic excellence, EPQ essay examples offer a guiding light, enabling individuals to navigate the complexities of research, analysis, and presentation. By harnessing the power of these examples, you can unlock their full potential and produce outstanding work that contributes to the scholarly discourse.
So, let the rich and diverse world of EPQ essay examples inspire and guide you on your academic journey. Harness the power of these examples to unlock your own academic excellence and make a meaningful impact in your chosen field of study.
Related Topics
Generic nouns
Specific nouns
Group nouns
Individual pronouns
- Mass and discrete nouns
Examples
other .
Mass and discrete nouns
Get an Immediate Response
Discuss your requirments with our writers
WhatsApp Us Email Us Chat with Us
Related posts
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- How It Works
- Prices & Discounts
How to Write an A+ Extended Project Qualification Essay
Table of contents
As you start your college assignments, you will come across an independent research project that is lengthy, intensive, and takes around 120 hours to complete the assignment entirely – this is the Extended Project Qualification Essay (EPQ).
An EPQ assignment helps in developing and broadening creative thinking and analytical problem-solving skills, as well as being beneficial for getting students into their desired colleges for other further education.
Well, everything has its first time, and if you’re wondering how to approach the EPQ essay, this article will help you get started.
9-Step Guide to Write a Perfect EPQ Essay
The EPQ essay plays a significant role in building academic confidence, enhancing creative writing skills , and demonstrating your passion for a particular subject or topic.
<<Check EPQ Sample>>
While working on this EPQ essay, students learn how to manage their time, meet deadlines, work on constructive feedback, learn independently, and conduct thorough research.
Here’s how you can write an A+ extended project qualification essay in 9 steps.
1. Brainstorm topic ideas
The first thing to do before you start writing your EPQ essay is to find an engaging topic that interests you. Look for ideas and brainstorm subject matter essay topics that are significant to you and intrigue your mind.
Many students make the mistake of choosing boring topics they are not interested in. This eventually leads them to draft up an average, low-quality assignment.
Choosing an appropriate topic that genuinely interests you will help you stay focused and motivate you to work hard and efficiently on your EPQ assignment.
You would also understand your subject matter better and learn more – which would result in making this assignment a high-scoring, fun, and engaging experience.
2. Jot down your ideas
Before you start researching your topic and learning brand new information, use your prior knowledge and write down everything – thoughts, ideas, facts, statistics – you know about your topic and subject matter.
This will help you understand the pieces of information you already have and can thus assist in organizing them for easier understanding and reference. You will also be able to identify if there are any fixable gaps in your knowledge, as this will be held as the foundation of how you will proceed to the next steps for researching your topic.
If you find that you aren’t inspired, you do not have a lot of information on your topic or there are massive gaps in your knowledge, it is better to eradicate the entire idea and start afresh than to submit a half-measured, uninteresting essay.
3. Create mind maps to define the subject matter
Whether your EPQ question is from a Maths, Physics, Biology, Psychology, etc. background, you are required to create a question or a prompt through which you can write your essay.
An Extended Project Qualification essay is mostly a 5000-word essay – and drafting an interesting, engaging, and inspiring essay without a question or a prompt is almost impossible.
Many students fail to do well and get a good grade on this particular essay assignment because they give the topic and content of the essay more important than the essay prompt .
Create a mind map and fill in any idea or thought that comes to you related to your topic. Through this mind map, you can remove ideas that don't pertain to the subject and segregate interesting points to craft your essay question that genuinely piques your interest.
However, it is also a best practice to choose a prompt that has a variety of information, references, statistics, and arguments to it.
This will make it easier to do your research on this topic. Make sure to choose a question that doesn't have a conclusive answer so that you can do extra added research on it and learn more about this subject.
Here’s a video by Justin Sung on using mind maps correctly.
4. Research the topic
Now is the time to focus on the body of the EPQ essay. Try to flesh out all the information you can find about your topic, thus filling the gaps you found in your prior knowledge.
At this time, make it a point to adhere to your chosen title for the essay, the essay question, and the structure you’ve used to lay down your arguments. Check for reliable sources of information such as books, articles, online journals, and more through the internet.
Keep a note of all the references and sources you’ve used to scourge up quality information for your essay assignment. Eventually, this list of sources would be a good way to organize your reference page or bibliography.
5. Structure and organize your essay
As you’ve gathered all the relevant information about your EPQ essay topic, it is time to organize your essay to have better readability, flow, and transitions through different arguments and paragraphs.
The structure needs to provide a robust framework for your essay content and exactly express what and how you want your essay to be delivered. It also helps you stay focused on the essay prompt and the kind of research you need to do to answer it.
Keep in mind to include some essential portions in your essay structure, such as the chronological list of subtitles for subsections and a placeholder to add in the introduction and conclusion paragraphs.
6. Create subtitles for your subsections
Split your essay body into subsections to make it easier to follow a structure and keep space for adding in any new related information. Creating subsections will also help you identify any missing facts and if you’ve explored the topic in detail.
Divide the 5000-word essay into equal and manageable portions with subtitles, and make sure to keep each subsection 100% related to your essay question. These subtitles are mini-topics that will help you get a better idea of what you want to say in your essay.
To create these subsections, you could choose to divide them chronologically or even in a most-important-subsection to least-important-subsection format.
7. Allocate a word count for each subsection
It's not an easy feat to write a 5000-word essay, which is why allocating a specific word count limit to each subsection would help complete the entire essay in a much smoother way.
You must divide your subsections into 16 subtitles, with about 300 words for each subtitle. This will help you reach 4800 words, leaving 200 words for any added paragraphs, points, or arguments. You can choose to keep the number of subtitles between 14 to 18 and allocate the word count to each of them accordingly.
Writing short, manageable portions for your EPQ essay makes the experience more productive, focused, effective, and less monotonous.
8. Write the introduction and conclusion paragraphs
Once you’ve completed writing down the answers to your subtitles, the next step is to write your introduction and conclusion paragraphs.
Your introduction paragraph needs to be shorter than your subtitled subsection. It should encapsulate what your readers should expect out of your essay and a summary of what you want to express, including your main thesis statement.
Whereas your conclusion paragraph should be longer than the subtitled subsections as well as the introduction paragraph. The conclusion should essentially be able to answer the essay prompt which was asked at the beginning of the essay, and aim to include essential points from each subtitled subsection for clarity of understanding.
As a best practice, it is recommended to build your introduction and conclusion paragraphs once you’ve completed writing your main body, as you will have all your arguments and points in place and have a better grasp of how you answered your EPQ essay question.
9. Review and ask for feedback
Lastly, whether it's a friend, parent, or peer, you should get your EPQ essay reviewed and proofread by someone else to receive a fresh perspective and a different opinion on your content and framework before submitting your final draft.
Neglecting to proofread your work would invite unnecessary errors, grammatical issues, and spelling mistakes. Reviewing and proofreading your essay could help identify and fix wrong academic vocabulary , vague arguments, incomplete sentence structures, accuracy, contradictions, incorrect facts, and more.
For students aiming at standout grades, an A+ Extended Project Qualification Essay can be the game-changer. While it requires a high degree of knowledge-sourcing, meticulous application, and strong conviction to write an impressive piece, the above suggestions will go a long way in easing the path.
From the time you zero down on a riveting topic to the final moment you press the submit button, this should be your handy to-do reckoner for surefire success.
We at Writers Per Hour can help you write a stellar EPQ essay. Our professional essay writers are subject matter experts in their respective fields and hail from leading universities across the US, UK, and Australia.
All you have to do is fill out the order form, give us your requirements, and we’ll assign the best writer for the task. With our safe payment methods and transparent policies, we’re an essay writing service you can truly trust.
Share this article
Achieve Academic Success with Expert Assistance!
Crafted from Scratch for You.
Ensuring Your Work’s Originality.
Transform Your Draft into Excellence.
Perfecting Your Paper’s Grammar, Style, and Format (APA, MLA, etc.).
Calculate the cost of your paper
Get ideas for your essay

Chris Rand Writes
Cambridge, England.

How to get a 100%, A* EPQ mark – some tips
My son did his Extended Project Qualification (EPQ) in 2018, at Hills Road Sixth Form College, Cambridge, and it was really interesting to watch. For something worth just half an A-level (and in reality when it comes to university applications, worth nothing), it required an astonishing amount of work. For busy sixth-formers to find the time or the motivation requires some dedication. That said, the EPQ is a good introduction to doing a properly planned and structured research project, so I encouraged my son to take the trouble. He did so, and his project was eventually marked 100% (A*) in 2019.
My best advice is to reverse-engineer the whole exercise. Remember, the EPQ is not about your project itself, but about the process of planning and executing it. So get the detailed marking scheme from the exam board’s website, and painstakingly go through every single item, noting what needs to be done to get full marks. Keep this in mind throughout the project.
Show how you’ve developed a range of skills by creating as much supporting material around the project as you can. For example, the core product from my son’s project was always going to be a dissertation. But along the way he also created a blog (to use as the project diary), a video and a podcast. He interviewed real people for comments, created an illustration in Adobe Illustrator and found out how to use Microsoft Excel for a Gantt Chart. All of these gave him new things to learn, and more importantly to write about.
There’s no way around it: if you want to get a really top mark in your EPQ, you’re going to have to devote all the time they suggest, and possibly more. But it can be an interesting experience.
My son’s project was eventually picked up by a campaigning group which I belong to, and published on their website . However, the best place to see the project in full is at the website he created to showcase the work here .
3 thoughts on “ How to get a 100%, A* EPQ mark – some tips ”
Hi, great tips. I will definitely use these.
I don’t know how I got here, but this was a really interesting read with good insight and advice. Congratulations to your son. My daughter did an EPQ in engineering materials and biomimicry and was very proud of it. Unlike you, I didn’t get to see it! She was a shy worker. So much work and dedication can go into such a project (including travel to attend a conferences, writing to researchers, waiting for replies, etc). She messed up a bit in her A level results, but her EPQ helped get accepted on her course. So in her case it did count. She ended up being a top mark student in her university course.
Really interesting that the EPQ counted for something, Mari. And so pleased your daughter’s hard work paid off!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Most Commented Posts
- O2 Arena Parking Tips 284 Comments
- The odd tale of Alphascript Publishing and Betascript Publishing 78 Comments
- Broooooce at the Emirates 47 Comments
- A workaround for the Google Docs "cannot transfer ownership" problem 42 Comments
- A list of brothers who have played football in the First Division (or Premier League) 30 Comments
- Bryant Victoria Kitchen Extension - Roll the Credits 26 Comments
- Virgin Media TV Anywhere iPad app: hands-on user review 22 Comments
- ABC at the Royal Albert Hall review 20 Comments
- Scandinavia and Russia Cruise - a Port Guide and Tips 18 Comments
- Our Experience of Moving House in Cambridge 17 Comments

What is an EPQ - Complete EPQ Guide
Dr Rahil Sachak-Patwa
The EPQ, introduced in 2006, has quickly become one of the most popular additional options for A-level students to take. Worth half an A-level , the EPQ is a fantastic way of increasing the total UCAS points a student applies to university with. What’s more, EPQ can be a valuable experience as it allows individuals to explore an interest that may not be directly related to their studies. But, what is an EPQ?
This qualification is still fairly new for most students and parents. Without understanding what it is, students might decide not to take the EPQ, even if they would have enjoyed it. In this article, we’ll give you all the information you need about the EPQ. Our complete guide will cover absolutely everything you need to know, touching on the most frequently asked questions.
By the end of this article, you’ll be an EPQ whiz. Let’s get right into it.
What is EPQ?
EPQ is an acronym that stands for Extended Project Qualification. What that actually means is that students will have to embark on their own research journey. At the end of this research, they’ll have to produce a 5,000-word essay or create a product alongside a 1,500-word essay.
EPQ can be about absolutely anything. No matter what you’re interested in, if you can find an academic way of exploring it, then you’re good to go. EPQ is an exercise in independent research, allowing students to learn more about their favourite topics.
While most students focus their EPQ on a part of their A Level subjects that they enjoy, it could be on something totally unrelated. So, what is the EPQ? Well, the EPQ is whatever you’d like it to be!
What Qualification is an EPQ?
According to AQA , the EPQ is an A-level standard qualification. This means that most students will get their EPQ results with all of their other examination results in August. However, students must remember that the extended project qualification is worth only half of an A-level. At maximum, this qualification is worth 28 UCAS points if the student were to get an A* in EPQ.
As a qualification, the EPQ is recognized by employers and universities, making it an excellent option for those looking to expand their education while still at school. Most of the time, it is taken as a fourth option for those currently sitting three A-level options.
Which Universities like EPQ?
The vast majority of UK universities now accept the EPQ as a valuable addition to a student’s A-level subjects. While it cannot be used as part of a grade offer, some universities will lower the grade offer they make to students. This means that a student that needs AAA to get into a university might receive an AAB offer due to having a great EPQ result.
All 24 of the Russell Group universities currently accept the EPQ and look upon it favourably. While not all universities will lower your grade offerings due to the EPQ, they will take it into account. The EPQ demonstrates independent research skills, which are vital for success in university and further education.
How to Write an EPQ Introduction
The introduction paragraph to your EPQ is one of the most important parts of your entire essay. As this is the first thing that your teachers and examiners will read, it’s important to make a good impression.
Most of the time, your introduction will be around 300 to 400 words. This section will introduce your project, discuss what you’re going to write about, and summarize the project. We recommend that you write your EPQ introduction last, as you need to know what you’ve covered in the project.
Your EPQ conclusion is much more important than the introduction, so make sure you save enough words to cover the conclusion.
How to Get an A* in EPQ
The EPQ is more about the process than the final product. With that in mind, you should work backwards. Start by looking through the mark scheme and see what you need to do to get full marks. From there, you can reverse engineer a topic that you think is interesting and has lots of potential for research.
Planning is vital if you want to do well in EPQ, meaning you should outline your whole project as early on as possible.
While there is no set formula to get an A* in EPQ, there are a few different tips you can include to distinguish yourself from the crowd. We recommend that A* EPQ students do the following:
- Pick a topic area that has lots of academic research around it.
- Think ahead; planning will get you far in the EPQ.
- Don’t forget your log; fill it in as you go.
- Balance breadth and depth, you should have a concise argument that covers a select topic in lots of detail.
- Take your time to write; try not to wait till the last minute to write your EPQ essay.
By following these tips, you’ll be well on your way to getting an A* in EPQ.

Source - AQA Grade A* Description
EPQ Results - How Many People Get an A* or A?
Every year, AQA, which is the largest exam board which hosts the EPQ, releases information on the overall results. On August 18th, 2022, AQA released results statistics for their June 2022 exams.
In 2022, 22.6% of students got an A* in the EPQ. 26.5% of students got an A in the EPQ, which was the largest segment. 21% of students got a B in the EPQ, with this being the third largest segment.
As you can see below, the lower grades of C, D, E, and U, all had a lower percentage of students. In 2022, only 2% of students got a U in the EPQ.
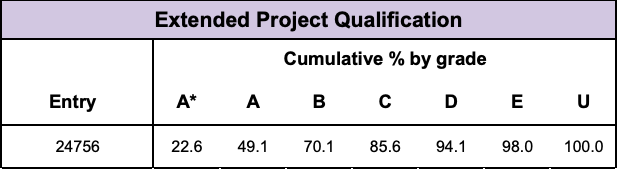
Source - EPQ Exam Results Table
What to Include in EPQ Presentation
The EPQ presentation is an important part of the process, involving public speaking skills. To create a good presentation, you should outline the process, your aims, what you’ve achieved, and what you’ve learnt. There are many different ways you can structure your EPQ presentation, but we suggest that you cover a few core areas.
You should talk about the following points in your EPQ presentation:
1. Topic - What is your topic; what did you study? Create a concise description of what you did.
2. Logic - How did you get to your topic? What is the logic you followed behind choosing your topic? Perhaps you’re going to study that subject at university, or you just had an interest that you wanted to explore further.
3. Objectives - Clearly state the purpose of your investigation and outline the academic reasoning behind the direction you took. What was the point of your EPQ; What did you want to find out or prove?
4. Research Pathway - Next, you should outline the research that you moved through when conducting your extended project qualification. Examiners love setbacks and changes, so be sure to chart any developments you had throughout the project.
5. Conclusions - Where did your EPQ end up? Discuss what your main conclusions were and what you discovered from all of your research.
6. Self-Improvement - What have you personally learnt from your EPQ? Is there anything you’ve discovered that will help you in the future? Perhaps you’ve learnt that you love independent research, or maybe you’ve discovered the importance of time management.
7. Review - At the end of your EPQ presentation, give an overview of the project again. Talk about your main discoveries, if your hypothesis was correct, and what you’ve learnt along the way. Most importantly, how will you use this knowledge going forward?
Across these 7 steps, you’ll have everything you need to score well in the EPQ presentation.
To give you absolutely all the information you need on the EPQ, we’ve collected all of the most asked questions that students have.
We’ll cover all of the following questions:
- What does EPQ stand for?
- Is EPQ worth it?
- What skills does the EPQ test?
- How many words is EPQ?
- When are EPQ results released?
- How long does the EPQ take?
- What exam board runs EPQ?
- Who marks EPQ?
- How is the EPQ marked?
- How many UCAS points is EPQ?
- How hard is it to get an A in EPQ?
- Does Oxbridge care about EPQ?
- How many people take the EPQ each year?
- What are the best EPQ Ideas?
- Can you fail an EPQ?
What Does EPQ Stand for?
EPQ stands for Extended Project Qualification. It is worth the same as half of an A Level, and is typically taken by students studying three A Levels.
Is EPQ Worth it?
The EPQ is worth it for students that want to strengthen their university application. Scoring well in the EPQ can give a student more UCAS points. Additionally, some universities will lower a student’s offer by one grade if they have an EPQ. That means that if a student needed AAB to get into their chosen course, a university could offer ABB.
The difference of one grade might not seem like much, but it actually gives students a huge advantage. The EPQ is well worth taking for anyone that’s looking to go to university. Over recent years, more and more higher education institutions have sung the praises of the EPQ, using it as a good measure of which students excel in independent learning.
In many UK universities, courses are almost exclusively independent learning. Especially in BA subjects, students could have under ten contact hours a week, leaving them to study by themselves for much of the time. EPQ gives students a jump start in these skills and helps them thrive at university.
Here is what one A-Level tutor has to say about the EPQ:
"I found the EPQ to be a valuable experience that allowed me to delve deeper into a topic that truly interested me. It was a chance to explore a subject that wasn't covered in my other classes and to develop critical thinking and research skills that have been useful in my university studies. It was also the most enjoyable A-level that I took, as I had control of what I wanted to work on, which you don't get with other subjects which are assessed my exams and have a fixed syllabus"
What Skills Does the EPQ Test?
The EPQ is an independent qualification, meaning a student has to do all the research, planning, and writing by themselves. Due to this, there are a range of skills tested. An EPQ tests the following skills:
- Problem-solving
- Organization
- Creative thinking
- Independent learning
- Time management
- Essay writing
- Communication
Get expert help with the EPQ
The world's leading online EPQ tutoring provider trusted by students, parents, and schools globally.
4.92 /5 based on 480 reviews
How Many Words Is EPQ?
Standing for Extended Project Qualification, the EPQ really took the ‘E’ seriously. This extended project comes in at a total of 5,000 words, which is the longest piece of work a student will create in their final two years at school.
That said, many students have stated that they wrote over this amount and still scored an A or an A*. Depending on the project’s nature, that 5,000-word limit could only be a guideline. As always, it’s best to discuss with your teacher if you’re planning on exceeding a 5,000-word EPQ.
Alternatively, you could create something for your EPQ. If you create something, you still have to write an extended essay. Often, these will be longer than 1,500 words and will explain the process you went through to create your EPQ.
When are EPQ Results Released?
You will get your EPQ grade in either November, February, or August, depending on which EPQ cohort you are in. For most students, you will receive your EPQ results in August, with all of your other A Level exam results.
That said, due to the fact that your teacher marks your EPQ, they will likely know your mark beforehand. If you have a discussion with your EPQ teacher, you might be able to find out your grade early. However, beware of this, as your result could be moderated down or up by a few marks, changing your overall grade.
How Long Does the EPQ take?
The EPQ takes around 120 hours of work. Students will begin their EPQ in October and aim to finish by April, giving them plenty of time to slowly work through the project.
Over this six-month period, a student will need to put in one hour of independent work for every hour lesson they have each week. In total, these 120 hours will fly by, with the long period of time that students have making this a very low-stress course option.
Remember, as you’re navigating your own research, it’s important to effectively manage your own time. Planning ahead can be a lifesaver and will help you pace your EPQ better.
What Exam Board Runs EPQ?
UCAS states that all of the major UK exam boards run the EPQ. That means that AQA, ASDAN, City & Guilds, OCR, VTCT, WJEX, and Pearson all run the EPQ.
However, out of the 30,000 people that take the EPQ each year, around 25,000 of them do it through AQA. This means that AQA is the exam board that runs the EPQ for the vast majority of students.
Who Marks EPQ?
The EPQ is initially marked by your subject teacher. They will give you a raw mark out of 50. While grade boundaries will change every year and will depend on which exam board you are working through, you typically need around 45 points for an A* and 40 for an A in the EPQ.
In 2020, the AQA grade boundaries for the EPQ were are follows:
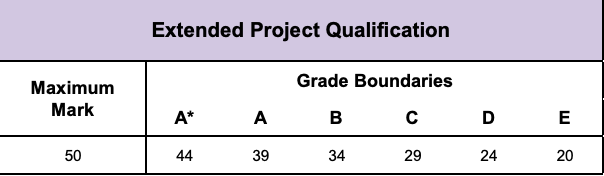
Source . - EPQ Grade Boundaries
After all of the EPQs from your year are marked, they will be sent off for moderation. Your moderator will be from the exam board and will double-check that your teachers are marking correctly. If they are marking too high or too low, the exam board will lower or increase all of the marks across your entire year.
How is the EPQ Marked?
Across each AO (Assessment Area), the EPQ varies in how many marks they afford students. The specific breakdown is as follows:
- AO1 - 15-25%
- AO2 - 15-25%
- AO3 - 35-45%
- AO4 - 15-25%
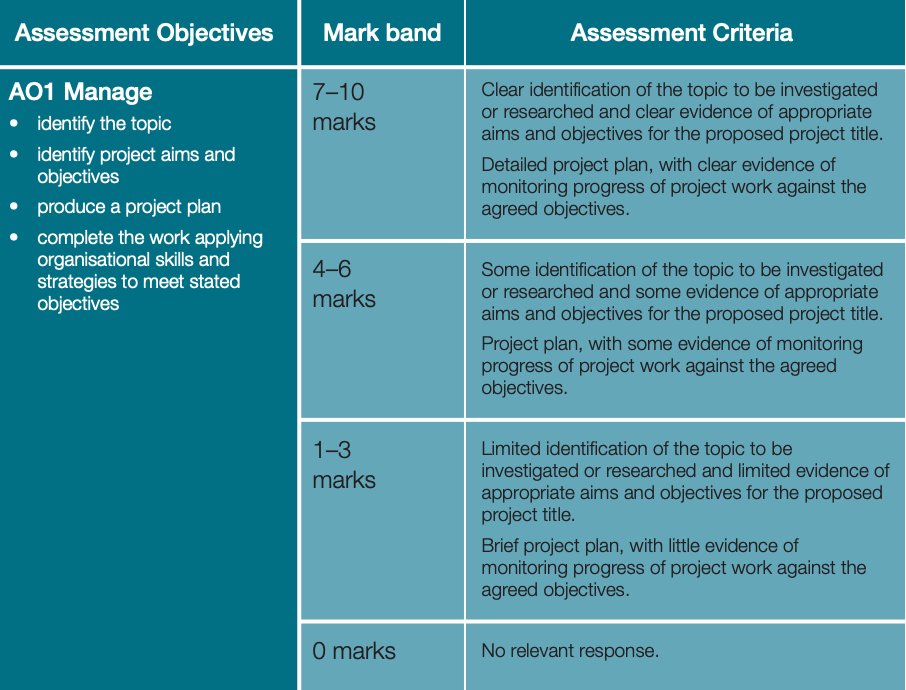
Source - EPQ Mark Scheme
How Many UCAS Points is EPQ?
The EPQ is often taken by students that want to strengthen their university application. Most of the time, students that take three A levels will extend what they’re offering by including the EPQ. Once they successfully complete the EPQ, they can use it as an additional qualification.
The EPQ gives UCAS points . Depending on which mark the student got, they will receive a different amount of EPQ UCAS points:
- EPQ A* - 28 Points
- EPQ A - 24 Points
- EPQ B - 20 Points
- EPQ C - 16 Points
- EPQ D - 12 Points
- EPQ E - 8 Points
As you can see, the EPQ grades move from E-A*. A student that receives an A* in the EPQ will receive 28 UCAS points, while a student that receives an E in the EPQ will receive only 8 UCAS points.
Is it Hard to Get an A in EPQ?
The EPQ is a reflection of a student’s ability to independently research and pull their findings together into a coherent project. Most of the time, if students are good at researching, writing, and clearly presenting their knowledge, they will not have much of a problem with the EPQ.
While getting an A in any subject is difficult, getting an A in the EPQ is easier than getting an A in an A-level. Due to the independent nature of the EPQ, a student that works hard in this area will be able to explore a topic they love while also getting a great additional qualification.
Around 50% of students will get an A* or an A in the EPQ, based on the 2022 EPQ results released by AQA.
Does Oxbridge Care About EPQ?
Both the University of Oxford and the University of Cambridge have issued statements that show they are both interested in the EPQ. Oxford says that the EPQ won’t impact an offer, but it will show that a student has the academic research skills that are needed to thrive in their environment.
Equally, Cambridge has stated that EPQ is a welcome addition to any application as it shows great “Independent study and research skills”, both of which are “valuable to higher education”. That means that Oxbridge does care about EPQ, seeing it as a valuable addition to a student’s application.
While it won’t make or break an application, any solid qualification like the EPQ is a welcome addition.
Can You Fail an EPQ?
Yes, you can fail the EPQ. If you’re in a position where you expect a very low grade in your EPQ, you could talk to your school about dropping the qualification. Many students who are struggling enlist the help of an EPQ tutor to help them achieve a passing grade. We recommend that you try and complete your EPQ, even if it gets a low grade, as you’ll still gain UCAS points from an EPQ with a low grade.
How Many People Take the EPQ Each Year?
Taking the EPQ is actually incredibly common, with many students across the UK and beyond taking this qualification every single year. Based on statistics by UCAS, around 30,000 students take the EPQ every year.
These numbers were once slightly skewed as the EPQ was a mandatory segment of the Progression and Level 3 Advanced Diplomas, which have now been dissolved.
What Are the Best EPQ Ideas?
The vert best EPQ Ideas are the ones that you naturally connect with. Take a look at what A-Levels you’re currently studying. If you’re taking A Level Maths, A Level Physics, and A Level Biology, then something about science would be a great choice. As you’re passionate about those subjects, an EPQ in that area will be much easier for you.
That said, if you’re studying A Level English, A Level History, and A Level History, then something from those areas will be much more appropriate. Be sure to match your EPQ ideas with the subjects that you have a passion for. If you’d like a helping hand, then be sure to check out our list of 400+ EPQ ideas and examples , covering all subjects.
In that list, we break down the best EPQ ideas for different subjects, helping you find inspiration for your extended project qualification.
Need help from an expert?
The world’s top online tutoring provider trusted by students, parents, and schools globally.
Study and Practice for Free
Trusted by 100,000+ Students Worldwide
Achieve Top Grades in Your Exams with our Free Resources:
STUDY NOTES
Expert-crafted notes designed to make learning the material engaging and clear.
PRACTICE QUESTIONS
Comprehensive questions to boost your revision and exam preparedness.
PAST EXAM PAPERS
Extensive collection of previous exam papers for effective revision.
Need Expert Help?
If you’re looking for assistance with your EPQ, then get in touch with our team. We’ll put you in contact with one of our world-class tutors to help you plan, research, and write your EPQ .

Professional tutor and Cambridge University researcher

Written by: Dr Rahil Sachak-Patwa
Rahil spent ten years working as private tutor, teaching students for GCSEs, A-Levels, and university admissions. During his PhD he published papers on modelling infectious disease epidemics and was a tutor to undergraduate and masters students for mathematics courses.
Related Posts

400+ EPQ Ideas and Examples for All Subjects (2024)

Should you take an EPQ to study medicine?

Choosing Your A-Levels - A Complete Guide

Hire a tutor
Please fill out the form and we'll find a tutor for you
- Select your country
- Afghanistan
- Åland Islands
- American Samoa
- Antigua and Barbuda
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Bouvet Island
- British Indian Ocean Territory
- Brunei Darussalam
- Burkina Faso
- Cayman Islands
- Central African Republic
- Christmas Island
- Cocos (Keeling) Islands
- Congo, The Democratic Republic of the
- Cook Islands
- Cote D'Ivoire
- Czech Republic
- Dominican Republic
- El Salvador
- Equatorial Guinea
- Falkland Islands (Malvinas)
- Faroe Islands
- French Guiana
- French Polynesia
- French Southern Territories
- Guinea-Bissau
- Heard Island and Mcdonald Islands
- Holy See (Vatican City State)
- Iran, Islamic Republic Of
- Isle of Man
- Korea, Democratic People'S Republic of
- Korea, Republic of
- Lao People'S Democratic Republic
- Libyan Arab Jamahiriya
- Liechtenstein
- Macedonia, The Former Yugoslav Republic of
- Marshall Islands
- Micronesia, Federated States of
- Moldova, Republic of
- Netherlands
- Netherlands Antilles
- New Caledonia
- New Zealand
- Norfolk Island
- Northern Mariana Islands
- Palestinian Territory, Occupied
- Papua New Guinea
- Philippines
- Puerto Rico
- Russian Federation
- Saint Helena
- Saint Kitts and Nevis
- Saint Lucia
- Saint Pierre and Miquelon
- Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
- Sao Tome and Principe
- Saudi Arabia
- Serbia and Montenegro
- Sierra Leone
- Solomon Islands
- South Africa
- South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands
- Svalbard and Jan Mayen
- Switzerland
- Syrian Arab Republic
- Taiwan, Province of China
- Tanzania, United Republic of
- Timor-Leste
- Trinidad and Tobago
- Turkmenistan
- Turks and Caicos Islands
- United Arab Emirates
- United Kingdom
- United States
- United States Minor Outlying Islands
- Virgin Islands, British
- Virgin Islands, U.S.
- Wallis and Futuna
- Western Sahara

Still have questions? Let’s get in touch.
- The Open University
- Guest user / Sign out
- Study with The Open University
My OpenLearn Profile
Personalise your OpenLearn profile, save your favourite content and get recognition for your learning
EPQs: writing up your dissertation
The Extended Project Qualification (EPQ) is an opportunity for you to work independently on a topic that really interests you or that you think is important. It is equivalent to an A-level qualification. These articles are designed to help you if you are enrolled on an EPQ.
See previous article in series: Finding and using evidence
Writing up your dissertation.
Being able to communicate well is an essential skill for both university and working life. One of the aims of the EPQ is to help you develop your skills in using different communication tools, so you can communicate what you have found clearly and appropriately for different audiences.
Communication is also a vital part of the research cycle. The progress of research thrives on the exchange, review and discussion of ideas. Writing is one of the ways in which we communicate what we have found out and share it with others.
Sharing the results of your research by writing well and effectively gives your readers the opportunity to learn from the work you have done.
This article offers suggestions and support for developing your skills in writing in the academic style that is needed for your EPQ dissertation.
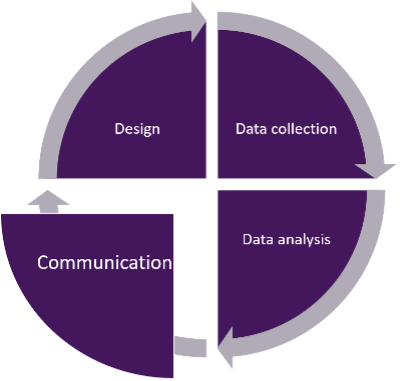
Getting organised .
It’s worth considering a few practical points first. The start of writing is a good time to gather your material together and get yourself organised.
- Don’t lose your work
- Timings & deadlines
- Organise your records
- Laying out the document
- Tables, graphs and charts
You don’t want to find yourself a few days – or hours – from the submission deadline when a computer breakdown or accident means you lose everything you’ve done.
It has happened before, and you don’t want it to happen to you!
Build a routine for backups into your work pattern. For example, when you sit down to write, save a copy (named, for example, Version 1, Version 2 ... Version 25 ...) of the existing document before you make any changes.
And back up your backup. Once a week, make a backup copy of your files (your dissertation, your notes and the resources you have collected) to an external hard drive, memory stick or cloud storage.
Work out how much time you have to write your dissertation, and how much time you want to allocate to each section. (There’ll be more on this shortly under ‘Structuring the dissertation – Start with the structure’.)
Make sure you know – and have written down! – the deadlines for submitting your dissertation, including deadlines for any draft versions your teacher might want to see. Use these to help plan your writing time.
There are many tools to choose from to keep yourself on track. For example, you could create a table with a list of tasks.
Or you could make a simple Gantt chart, using a spreadsheet. If you use Microsoft Excel, it has some Gantt chart templates. The advantage of a Gantt chart is that it makes it easier to see how you can overlap some tasks, and you can mark important milestones such as submission deadlines .
As you have gone through the process of collecting and analysing the evidence you need to answer your research question, you will have gathered records of:
- what you looked for (the search terms you used in your searches)
- where you looked (search engines, websites, etc.)
- what you read / watched / listened to (academic papers, articles, videos, podcasts, etc.)
- the notes you made on your reading, listening and watching
- the data you have gathered.
All these sources contribute to the content of your written dissertation. Hopefully you have good records, but if you got a bit behind, now is the time to sort them out and remind yourself what you did and what you found out.
If you need a reminder of what information you need to keep, look back at Article 2 – Finding and using evidence .
Organising your records and keeping a note of the sources you mention in the text as you write helps you build a comprehensive reference list.
There is more information on how to set out your reference list later in this article (see ‘Structuring the dissertation – Referencing styles’ ).
Laying out your document in a clear and neat style helps make your readers’ life easier.
For the text , use a classic font such as Arial, Helvetica or Times New Roman. It’s best to avoid quirky fonts such as Comic Sans, or difficult to read fonts such as Lucida handwriting.
For easy reading, the font shouldn’t be too small. 11 or 12 point is a popular choice for the main (or body) text, which is usually black in colour. You can use larger fonts for headings and sub-headings, and perhaps make them bold or a different colour.
Generous margins also make the document easier to read. As a guide, around half the area of the page should be white space; on an A4 page, that means margins of about 2cm all round.
Use the paragraph styling tool . It’s well worth investing some time learning to use paragraph styling in Microsoft Word and Mac Pages ; it can really speed up the creation of long documents and help you produce good-looking work.
This tool gives you control over the appearance of the text in your document. For example, you can use it to include automatic numbering for your headings ( Word or Pages ). This means you don’t have to manually change all the numbering if you insert a new heading or delete one that is no longer useful. You can also use automatic numbering for figure and table captions. Or, if you decide you don’t like the font you have used, you can change it in the paragraph style and it will be changed throughout the document.
Some kinds of evidence – such as numeric data – work well when displayed as graphs, charts and tables.
Readers should be able to make sense of the graph, chart or table without explanation.
Look at Table 2. Is it clear what information the creator wanted to share?
A better example can be seen below in Table 3:
Graphs and charts need titles too. They should also have axis titles (naming what is plotted on each axis, with the relevant units) and axis labels (the values plotted).
When it comes to plotting graphs, using different shapes or line styles can help readers distinguish different data points or collections of data on a single graph. You can use contrasting colours, but keep in mind that too many colours can be distracting for the reader. And some readers – for example, people who are colour-blind or have vision problems – might not be able to distinguish between certain colours, so choose carefully.
Look at Figure 3. Does it have all the elements of a good graph? Could anything be improved?
This has many of the requirements of a good graph. The title explains what the graph is about, the axes are labelled and the four search terms are each given their own colour, with a key to show which is which.
It could be made better by:
- making the graph larger, so that the four lines are more separate
- choosing different colours – the orange for ‘Perseverance’ and the yellow for ‘astrobiology’ are difficult to distinguish from each other.
Evidently, something interesting must have happened in mid-February to cause this spike in searches – you might remember that on 18 February 2021, the NASA Mars Perseverance Rover mission landed on Mars!
Structuring the dissertation .
Facing a blank page and the prospect of writing 5000 or so words can feel daunting. But you can structure the way you write to help make the task easier.
- Start with the structure
- Facing the blank page
- The narrative arc
- Finishing things off
- Referencing styles
Starting with the structure will help you consider how you want the dissertation to flow, and how to allocate your time and effort.
This example, taken from the Edexcel documentation, gives a suggested word count for the different sections of a ‘research review’ dissertation. All the exam boards publish their requirements, so you should check the requirements for your board and the type of EPQ you are doing .
A ‘research review’ dissertation would probably follow something like the structure above. For other kinds of project, check with your teacher or look at the exam board’s requirements. Knowing what structure the exam board is expecting helps you to know where to focus your effort.
In Table 4, you can see that the biggest section of the dissertation is the discussion/development/analysis of the argument, so it would make sense to spend the largest part of your writing time on this section. Look back at the Gantt chart under ‘Getting organised – Tables, graphs and charts’ for an example of time allocated in this way.
You’ve opened a new document. You know the sections you need to include.
How do you get started on the sentences that will fill the gaps in between? Two researchers offered suggestions from their experience.

Robert, a space scientist, says he usually works out the first paragraph in his head before sitting down to write.
- Ann’s summary
This is how Charlotte described her approach. First step, open a Word document!
Second step, write titles and sub-headings on the page. These can be working titles that you can come back to and polish once you have developed the document. But getting that structure down on the page is a key step for Charlotte in building the document and working out how the manuscript is going to flow. Once she’s broken the document up into sections, it feels much less daunting for her. Instead of starting at word one of six thousand, she’s working on smaller, more manageable chunks – word one of a hundred, or two hundred.
Step three is to write down the aims, objectives and scope of the document. And then she goes on to write the conclusions. And she says yes, that’s not a typo – if you’ve done a good job of researching the topic, developing the aims and objectives and making your notes, then writing the conclusion first should be relatively easy. The benefit of writing the end of your manuscript before the beginning is that you’re less likely to go off on tangents when you’re writing the rest of the manuscript, because you know where you’re heading.
If you feel you’ve thoroughly researched your topic and you’re still finding it hard to work out what your conclusions are, then it may be a good idea to turn your research notes into a presentation, during which you can ask yourself ‘what key message do I want the audience to walk away with?’, and that will be your conclusion.
Step five: write the remaining sections of the dissertation, justifying and building your arguments for each conclusion.
Charlotte’s main points

Charlotte’s steps are:
- Open a Word document!
- Write titles and sub-headings on the page.
- Write down the aims, objectives and scope of the document.
- Write the conclusion – ask yourself ‘what key message do I want the audience to walk away with?’
- Write the remaining sections, justifying and building your arguments for each conclusion.
Headings and sub-headings
Charlotte described how she likes to set up the headings and sub-headings that structure her writing, even though she knows they might change as the document develops.
Using descriptive headings, such as ‘The history of ...’ tells the reader what to expect in that section or chapter. This is sometimes called ‘signposting’, because the headings and sub-headings guide the reader around your work.
As well as descriptive headings, you can number your headings and sub-headings:
- Section 1: An introduction to…
- Section 1.1 : The history of ...
This means you can refer the reader back and forth (e.g. ‘see Section 1.2’), which cuts down repetition and wasted words.
Both approaches have the merit of getting something on to the blank page, which makes it look much less scary.
Whether you start with an opening paragraph, a set of headings, or another method that works for you, getting those first few words on the page is one of the biggest hurdles to clear.
Narrative – the story thread that runs through any piece of work we create – is important in any piece of writing. Stories keep people’s attention, as storytellers have known for hundreds of years. Writers, broadcasters and podcasters continue to make use of this fact today.
One way to think about how you shape your story is to consider its narrative arc. Yes, even the most ‘science-y’ of dissertations has a story.
Click on the crosses on Figure 6 to find out more about the components of the narrative arc.
Figure 6 The narrative arc
Points on the narrative arc
Description : A parabolic curve representing the narrative arc of a story. The first half of the curve rises to a peak, showing the points that build interest in the story. The second half falls back to the baseline, showing how we reflect on the details of the story and bring it to a close.
– In the Introduction , attract the reader’s attention at the start, perhaps by telling them what got you interested in the question; a personal interest, an ambition or a desire to know more about a topic.
– In the Introduction , describe the journey to your research question. Make sure you do actually tell your reader what your question is (you’d be surprised how often people forget that!)
Information
– In the Research Review section, you show the reader how you found your evidence; tell them about the keywords you used, the mindmaps, flowcharts, tables you made; what information was important and what was not; what stayed in and what didn’t.
– This is your analysis of the material you found, showing how you pulled together the information you uncovered in your review and what it meant for your question. However, this isn’t an absolute rule; where you put the analysis depends on the kind of dissertation you are writing.
– Tell the reader what you found out and how it relates to what is already known.
– Use the Conclusion to round off your story. What’s the answer to your research question? What did you discover? What’s still not known?
There are a couple of sections of the dissertation that are best dealt with towards the end of the writing process: abstract and bibliography.
The abstract
At the beginning of the dissertation, you should provide a short summary or abstract.
An abstract is like a trailer for a film or television programme. It gives the reader a sense of what’s in the dissertation. However, unlike a trailer, it’s OK to give away the ending! Someone who only reads the abstract, and never looks at the dissertation, should still understand the scope of your work.
For this reason, it’s easier to write the abstract towards the end of your writing time, when you have a complete picture of your work in your mind.
The abstract is usually quite short (perhaps only 200 words) and is written in one paragraph. That’s not much space, so what should you include?
A typical abstract would tell the reader:
- why you did this research – the question you set out to answer
- how you did the research – the methods you used to collect the data and where you looked for it
- what you found out – a summary of your main findings
- the key message – the answer to your question; if your readers could remember just one thing from your dissertation, this would be it.
One way to approach writing the abstract is to read through your dissertation section by section. For each section, write one or two sentences that summarise the main point. Click on ‘example’ to see what we mean.
The use of complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) is growing rapidly among young people, but the usefulness and safety of some therapies is controversial. Therefore, I investigated the question: what are the best places to reach young people with information about CAM?
Using Google Scholar, I searched for articles using different combinations of these search terms: ‘alternative medicine’, ‘complementary medicine’, understanding, knowledge, motivation, CAM. I filtered the results to keep only articles that related to the use of CAM by young people. I defined ‘young’ as people under the age of 25. I downloaded twenty complete papers, articles and other resources from open access sources and the Open University research repository.
Use of CAM by young people has increased since 2000. Young women use CAM more than young men. The most common sources for getting information about CAM are friends and family and social media.
Key message
The best way to provide information for young people about CAM is through social media.
Take away the headings and polish the sentences and you have an abstract:
The use of complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) is growing rapidly among young people, but the usefulness and safety of some therapies is controversial. Therefore, I investigated the question: what are the best places to reach young people with information about CAM? Using Google Scholar, I searched for articles using different combinations of these search terms: ‘alternative medicine’, ‘complementary medicine’, understanding, knowledge, motivation, CAM. I filtered the results to keep only articles that related to the use of CAM by young people. I defined ‘young’ as people under the age of 25. My search found twenty relevant papers, articles and other resources, which I downloaded from open access sources and the Open University research repository. My results show that young people’s most common sources for information about CAM are friends and family and social media. Therefore, I believe that using social media is the best way to provide information about CAM for young people.
The bibliography or reference list
The last thing to include in your dissertation is the bibliography or reference list * .
Your reference list shows the people who read (and mark!) your dissertation how well you have researched your subject and how your arguments are supported by evidence from other people’s research.
It is also evidence of how you have been open and honest in your work. Readers can use it to find the sources that you used and check that you have read and used them correctly.
Using your reference list, a reader should be able to find that source for themselves if they want to follow up an idea or check something you have written. Including a reference list helps you avoid plagiarism (passing off someone else’s work as your own), because readers can check the original source if they have any doubts.
If you need a reminder of what information you should keep, look back at ‘Finding and using evidence – Keeping track’ .
* A reference list is a list of all references to other people’s work that you have mentioned in your dissertation. A bibliography is a list of references, plus the background readings or other material that you have read but not actually mentioned.
The Open University Library Services’ Referencing and plagiarism page has lots of help and pointers to further information about references and referencing styles.
If you go on to study at university, and have to write essays, assignments and reports, you will be asked to set out – or ‘style’ – reference lists in a specific way. There are many different referencing styles; which one you are asked to use will depend on the subject you are studying and the university’s requirements.
For the EPQ, check the requirements of your exam board or ask your teacher what these are.
Even if you aren’t asked to use a specific style, you should aim to include as much information about the sources as possible. The minimum information would be:
- the authors’ (or creators’) names
- the year the source was published
- the title of the article or book chapter, or the name of the artwork, film or video
- the title of the journal or the book in which the article/chapter appeared
- for books – the name of the publisher
- for online sources – the name of the website and the page on which the article appeared, the URL of the website, and the date on which you read the article*.
*The date you found the article is important for online sources, as websites sometimes disappear or are changed. If the reader can’t find the same article but knows when you found it, that suggests they can trust the source.
These examples are laid out in the Harvard referencing style, which is a style used in many university subjects.
Books and ebooks
Surname, Initial. (Year of publication) Title . Edition if later than first. Place of publication: publisher. Series and volume number if relevant.
Mukherjee, S. (2011) The Emperor of all Maladies . London: Fourth Estate.
Article from an academic journal
Surname, Initial. (Year of publication) ‘Title of article’, Title of Journal , volume number (issue number), page reference. Doi: doi number if available OR Available at: URL (Accessed date)
Ungar, S. (2008) ‘Global bird flu communication: hot crisis and media reassurance’, Science Communication , 29(4), 472-497. DOI: 10.1177/1075547008316219
Article from a newspaper or magazine
Surname, Initial. (Year of publication) ‘Title of article’, Title of Newspaper , Day and month, Page reference if available. Available at: URL (Accessed: date).
Rice-Oxley, M. (2021) ‘Do good things come to those who wait?’, The Guardian , 26 February. Available at https://www.theguardian.com/world/2021/feb/26/do-good-things-come-to-those-who-wait (Accessed 26 February 2021).
Organisation (Year that the page was last updated) Title of web page . Available at: URL (Accessed: date).
BBC Online (2020) How New Zealand relied on science and empathy . Available at: bbc.co.uk/news/world-asia-52344299 (Accessed 17 September 2020).
Writing clearly .
Good writing takes time, effort and energy. Being able to produce clear, readable, logical and well-argued pieces of writing is important in both university and in your working life.
- Precise & concise
- Keep it simple
- A word about style
- Quoting others

Blaise Pascal was a seventeenth-century mathematician, physicist, inventor, philosopher and writer. He once wrote:
‘ Je n’ai fait celle-ci plus longue que parce que je n’ai pas eu le loisir de la faire plus courte ’ .
–Blaise Pascal, Provincial Letters, Letter XVI, December 1656.
Translation: ‘I wrote this very long [letter] because I didn’t have the time to make it shorter’.
What do you think Pascal meant by this?

Claire, whose research looks for evidence of how we might ‘ sniff’ for life , produced a mind map of what she thinks Pascal meant (Figure 9). The audio below describes her process.
Claire’s mind map takes us on quite a journey. Starting from Pascal’s premise that it’s better to write short than long, slower than quicker, makes her think about the need for concision, to look for concise words, words that are specific and measured, not being confusing, the need to choose the right word. Not always easy in English, where one word can have a variety of meanings.
She suggest perhaps using a thesaurus, but that could lead down the pathway of having too many words to choose from and not being able to decide which one to pick. Thinking about the dissertation, she introduces a word we all dread – waffling! No one wants to be a waffler, and giving too much information might make your readers’ heads explode.
And yet we must explain our concepts, because we want our writing to be understood by everyone but that means a balance with explaining too much. We need to give enough detail to make our point understood, and scientific, if it’s that kind of research question, without being too complicated. All in all, it comes down to the need to simplify.
More tips from Ann
As Pascal – and Claire – suggest, taking out what isn’t needed is as important as putting in what is.
Writing clearly and to the point takes time, effort and energy. Allow yourself plenty of time to draft, review, get feedback, edit ... draft again, review again, get more feedback, edit again … … check, proof-read, finish.
As we established earlier, your dissertation will have a word allowance. EdExcel, for example, suggests a research review dissertation should be around 6000 words. That sounds like a lot, but then, you’ve done a lot of work that needs to be included.
The exact figure will depend on the exam board’s requirements and the kind of EPQ you have carried out, so check before you start writing, or ask your teacher.
The best writers keep things as simple as possible. It’s a way of being kind to your readers and making the task of reading easier.
However, keeping things simple isn’t simple. As Steve Jobs, the designer and co-founder of Apple said: ‘Simple can be harder than complex: you have to work hard to get your thinking clean to make it simple’. The same applies to writing.
When you’ve done a complex piece of work, it’s tempting to think you can only describe it in complex language. But you should try to avoid the pitfall of using over-complicated language. You don’t want to run the risk of sounding pompous or making your text too difficult to understand.
You’ve almost certainly come across simple questions with unnecessarily complicated answers before. Here’s an example. Which is the best answer to this question?
The Up Goer Five challenge
To practise writing in simple language, you can take the Up Goer Five challenge. This is a project by the artist Randall Monroe, creator of XKCD .
The challenge is to explain a hard idea using only the ‘ten hundred’ most common words in the English language. As an example, how might we explain ‘astrobiology’?:
We think about where we might find living things. We take stuff from places – dry places, cold places, hot places – and we put it in stuff that we think has what living things need to grow. We wait, then we use a seeing-small-things tool to look for the living things. At the moment, we look at stuff from here but one day, we want to look at stuff from other stars.

Have a go at using the Up Goer Five text editor (which has a link to the ten hundred most common words ) to explain an idea related to your research topic. If you find it tricky to think of an idea, here are a few to get you started:
- global warming and its consequences
- what causes earthquakes
- the problems caused by the misuse of antibiotics.
You wouldn’t write your dissertation in this style, but experimenting with writing like this helps develop skills in keeping things simple, avoiding jargon and complicated language and writing in short sentences and paragraphs.
We all write in different ways every day, depending on who we’re writing for. The style of a textbook is different from the style of a WhatsApp message; we write an email to a family member in a different style from the way we would write a personal statement for a university application.
When we write anything, we start by thinking about our readers and the kind of writing they are expecting to see.
For the EPQ dissertation, start by checking the requirements of the exam board you are studying with. It is very likely that the exam board will want the dissertation to be written in a formal style; the kind of style you will have seen in the academic articles and books you drew on in your research.
Plagiarism is presenting someone else’s work as your own. It is, essentially, theft of someone else’s work.
Learning alongside a friend, discussing ideas or sharing your thoughts can be helpful and valuable. We have also encouraged you to take notes on everything that you find. So, it is likely that you have ideas you want to present in your report that are not entirely your own.
Plagiarism can occur in a variety of ways. It can mean copying someone else’s text and passing it off as your own, or copying and pasting text/images from a web page and pretending they are your own work. It can also overlap with what is called ‘collusion’, which means collaborating with someone to share work on a task that you are expected to complete by yourself.
Try this interactive resource from OpenLearn to understand some of the challenges and ways to avoid plagiarism. This is aimed at university students, but it will be relevant for the EPQ.

All my own work
Plagiarism comes in all shapes and forms. Step into the shoes of a university student to learn the challenges and temptations facing her during her assignment, and help make it all her own work.
Level: 1 Introductory
There will be points in your dissertation when you want to present ideas that have come from someone else’s work. How can you do this while avoiding plagiarism?
Identify your sources
If you have used an image, graph or chart created by someone else, identify where the image has come from and who made it.

You might remember this image from Article 1 , in the section on dealing with feedback.
This image comes from an online picture library, creazilla.com. They have placed it in the ‘public domain’, which means it can be re-used freely. Show this information in the image caption within your work.
If you create a graph, chart or table yourself, identify the source of the data, as you saw earlier in ‘ Getting organised – Tables, graphs and charts ’.
If you find a phrase or a sentence in a source that helpfully illustrates a point you are trying to make, you can quote that in your work. You must quote it exactly as the authors wrote it. After the quote, you give the name of the author, the date of publication and the page where the quote is from. Then give the full reference in your reference list (see ‘ Structuring the dissertation – Referencing styles ’). For example:
This shows that the format of an infographic can influence people’s responses to the evidence. For example, ‘ graphs commonly used to show descriptive statistics, such as line or area graphs, may also appear “scientific” and create a pseudo sense of trustworthiness ’ (Li et al., 2018, p. 4).
The quote marks (‘…’) show which words are the quote.
We use the Latin phrase ‘et al.’ (meaning ‘and others’) when an article has more than three authors, so that the reader doesn’t have to read through a long list of names. In the reference list, you would see the full list of authors along with the other source details:
Li, N., Brossard, D., Scheufele, D., Wilson, P. and Rose, K. (2018) ‘Communicating data: interactive infographics, scientific data and credibility’, Journal of Science Communication, 17(2), A06. DOI: 10.22323/2.17020206
When you paraphrase, you express an idea that has come from someone else in your own words. You might do this to re-state the idea in simpler language, or to bring together the ideas of several writers on the same topic. Paraphrasing can also help you show that any new ideas you’ve put together from your research are supported by earlier research.
You should show where the ideas you have paraphrased came from, but because you are not directly quoting, you need only give the authors’ names and the date of publication. For example:
My survey of fifty young people aged 16 to 18 showed that their social media posts were most often connected with current events. This is supported by earlier research, which shows that the most common topics for young people’s posts are current events, health and fitness, and celebrity and entertainment news, closely followed by science and technology (Hargittai, Füchslin & Schäfer, 2018) .
In the reference list, you would see:
Hargittai, E., Füchslin, T. and Schäfer, M. (2018) ‘How do young adults engage with science and research on social media?’, Social Media + Society, July-September 2018, 1-10, DOI: 10.1177/205630511879772
Although your dissertation must be all your own work, you can ask for help to review what you have written.
How do you ask for help, then, while keeping the dissertation all your own work and avoiding plagiarism?
Reviews – who and when?
Before you ask someone to review your work, you can check some things for yourself.
Check the spelling and grammar . Microsoft Word has built-in tools, or you can use online ones such as Grammarly . The more technically correct your writing is, the more your reviewers will be able to focus their energy on the content.
Then read it all through yourself . Some people like to read through silently, line by line, others prefer to read the text out loud. You can record yourself and listen back later, or use the Read Aloud function in Word, if you’re using that software. This has the advantage of using a different part of your brain – when you listen, you hear mistakes that you just don’t see in writing.
After you have reviewed it yourself, ask others to do the same. Getting someone else’s feedback on your work is immensely valuable. This is where you can collaborate with friends or classmates – if you ask them to review your work, you can offer to review theirs. And families can help too; even if they don’t know anything about your topic, the questions they ask will help you review your work.
- Michael asks for help
- Who could you ask for help?

Listen to the audio in the next tab about how Michael, who is a microbiologist, asks for help. When does he do this, and who does he ask?
Michael turns to his colleagues, his family and his senior colleagues at work. He asks for help at different stages: perhaps when he’s struggling a little, when he’s written the first draft and later on at the final stages, when he’s finished editing.
For Michael, feedback is incredibly important, not only for the actual content of the work, but for assessing how easy it is to understand. And he felt it’s always important to consider reviews of our writing from the viewpoint that the reviewer wants to help us improve our work, not criticise it. In terms of who he asks, first he calls on his peers; when he was at school, friends in his class and year, and now his colleagues, who can comment on the content of the work and how easy it is for them to follow. When he was at school, he also turned to his parents. During high school, his parents helped with input on grammar, spelling and how easy it was to understand. Now, his wife performs that role. As he says, by having someone from outside the field review your work, you can gain valuable insights. He also thinks about his seniors – in his current job, his senior colleagues will read multiple drafts of a manuscript before it’s complete. This is always an advantage – it allows him to get input from someone more experienced and means the work is improved.
In terms of when, he asks for help when he’s struggling, perhaps to find the right direction for a piece of work. Discussing the work with a friend or a teacher can start him developing insights on where it should start. Certainly after completing and spell-checking a first draft, he’ll ask for help.
And of course it’s always important to go back and review after editing, because when you change a piece of work, it’s easy to introduce errors, as well as fix them.
Conclusion.

Other articles in this series...

EPQs: designing your research question
You’ve already decided to do an EPQ, so it might seem a little odd to start this resource by asking you to consider why you want to do a research project. People do an EPQ for all sorts of reasons. Why do you want to do an EPQ?

EPQs: finding and using evidence
Finding the evidence that will help you understand a topic or answer a question is an important stage in the research process. And once you have found it, you will need to examine it closely and carefully, to judge how reliable it is and whether it is useful to help you answer your question.

EPQs: why give a presentation?
What are the guidelines for the presentation?
Become an OU student
Ratings & comments, share this free course, copyright information, publication details.
- Originally published: Friday, 3 March 2023
- Body text - Creative Commons BY-NC-SA 4.0 : The Open University
- Image 'Graph of the EPQ cycle' - Copyright: Ann Grand
- Image 'Comparison of four search terms used in Google in the UK from Jan to May 2021.' - Copyright: Ann Grand
- Image 'Robert, a space scientist.' - Copyright: Robert from AstrobiologyOU
- Image 'Sketch of Blaise Pascal' - Copyright: Wikimedia Commons
- Image 'Photo of Claire' - Copyright: Claire Batty
- Image 'Claire's mind map' - Copyright: Claire Batty
- Image 'Screenshot from the UpGoer project' - Copyright: XKCD
- Image 'Responses to feedback ' - Copyright: creazilla.com Public Domain boy crying angry woman happy man
- Image 'Photo of Michael' - Copyright: Michael Macey
- Image 'Extended Project Qualification banner' - Copyright: © Betta0147 | Dreamstime.com
- Image 'All my own work' - The Open University under Creative Commons BY-NC-SA 4.0 license
- Image 'EPQs: why give a presentation?' - Alphabet Yellow © Betta0147 | Dreamstime.com under Creative Commons BY-NC-SA 4.0 license
- Image 'EPQs: writing up your dissertation' - © Betta0147 | Dreamstime.com under Creative Commons BY-NC-SA 4.0 license
- Image 'EPQs: finding and using evidence' - Alphabet Yellow © Betta0147 | Dreamstime.com under Creative Commons BY-NC-SA 4.0 license
- Image 'EPQs: designing your research question' - © Betta0147 | Dreamstime.com under Creative Commons BY-NC-SA 4.0 license
Rate and Review
Rate this article, review this article.
Log into OpenLearn to leave reviews and join in the conversation.
Article reviews
For further information, take a look at our frequently asked questions which may give you the support you need.
- Help Us Out
Login with your site account:
Create a site account:
0 words 0 characters
- Sentence case
- Text as .pdf
- Text as .txt
- Text as .doc
What is WordCounter?
Apart from counting words and characters, our online editor can help you to improve word choice and writing style, and, optionally, help you to detect grammar mistakes and plagiarism. To check word count, simply place your cursor into the text box above and start typing. You'll see the number of characters and words increase or decrease as you type, delete, and edit them. You can also copy and paste text from another program over into the online editor above. The Auto-Save feature will make sure you won't lose any changes while editing, even if you leave the site and come back later. Tip: Bookmark this page now.
Knowing the word count of a text can be important. For example, if an author has to write a minimum or maximum amount of words for an article, essay, report, story, book, paper, you name it. WordCounter will help to make sure its word count reaches a specific requirement or stays within a certain limit.
In addition, WordCounter shows you the top 10 keywords and keyword density of the article you're writing. This allows you to know which keywords you use how often and at what percentages. This can prevent you from over-using certain words or word combinations and check for best distribution of keywords in your writing.
In the Details overview you can see the average speaking and reading time for your text, while Reading Level is an indicator of the education level a person would need in order to understand the words you’re using.
Disclaimer: We strive to make our tools as accurate as possible but we cannot guarantee it will always be so.
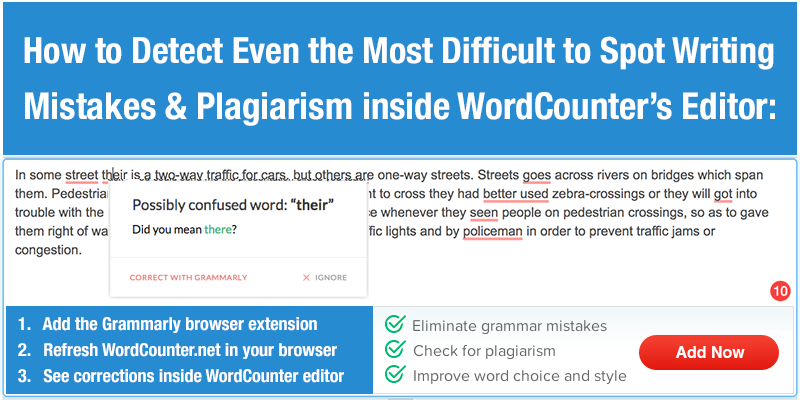
- 0 Unique Words
- 0 Characters
- 0 Characters (no spaces)
- 0 Sentences
- 0 Longest Sentence (words)
- 0 Shortest Sentence (words)
- 0 Avg. Sentence (words)
- 0 Avg. Sentence (chars)
- 0 Avg. Word Length
- 0 Paragraphs
- 0 Syllables
- 0 Words (Publisher)
- N/A Reading Level
- N/A Reading Time
- N/A Speaking Time
- N/A Hand Writing Time
- More ( 0 ) Share
Keyword Density x1 x2 x3
Keep track of the number of words you write each day using the activity button. ACTIVITY
This button helps you clean up your document by removing funky characters, unneeded new lines, etc.
- Email Fix (Remove word wrapping)
- Microsoft Word Document Fix (Remove invalid characters)
- Remove multiple new lines
My Writing Details
- N/A Reading Level
- N/A Reading Time
- N/A Speaking Time
- N/A Hand Writing Time
Step 1. What do you want to share?
- Unique Words
- Characters (no spaces)
- Longest Sentence (words)
- Shortest Sentence (words)
- Avg. Sentence (words)
- Avg. Sentence (chars)
- Avg. Word Length
- Words (Publisher)
- Reading Level
- Reading Time
- Speaking Time
- Hand Writing Time
Step 2. What do you want to say?
Step 3. Where do you want to share it?
- Keyword Density
Step 1. What do you want to say?
Step 2. Where do you want to share it?
Upload File
Click the upload button below to select a text document. Supported formats are PDF, TXT, DOC, DOCX, ODT.
Save To Drive
Use this button to save your current writing to Google Drive
You can turn on or off different counting options here.
- Hand Writing Time Letters Per Minute Slow Normal Fast
- Reading Time Words Per Minute Slow Normal Fast
- Speaking Time Words Per Minute Slow Normal Fast
You can turn on or off different buttons provided for different functionalities.
- ACTIVITY Keeps track of your word and character count.
- AUTO-SAVE When turned on, WordCounter will automatically save your document every 30 seconds. You can then switch back to previous versions of your document at any time.
- CASE Gives different case options. Applies to your entire document or only the text you select.
- CLEAN TEXT After pasting a document into WordCounter, this will clean it up by removing invalid characters, word wrapping issues and unneeded new lines.
- CLEAR Delete all of the text in your document.
- DOWNLOAD Download your written text (PDF, TXT, DOC) to your device.
- FIND AND REPLACE Find and replace any words or sentences you want.
- GOAL Set writing goals (such as 500 words) and WordCounter will let you know when you've reached them. You can also share and embed your goals.
- PRINT Print your document quickly and easily.
- PROOF READ WordCounter reads your document back to you. Make sure to turn up your volume! Rate Valid values are 0.1 to 10 Pitch Valid values are 0 to 2 Voices
- REDO Redo your last changes. Click multiple times to redo multiple changes.
- SAVE Saves your text for later retrieval. Be sure and click the SAVE button each time you want to save.
- SAVE TO DRIVE Saves your document to Google Drive. Great for backup purposes.
- SPEED Use a timer to see how fast you're typing.
- SPELL A powerful spelling and grammar checker for your document.
- TALK TO TYPE Speak into your microphone and WordCounter will type for you. Language Country
- THESAURUS Select (with your mouse) a word in your document and click the thesaurus button to get a list of synonyms.
- UNDO Undo your last changes. Click multiple times to undo multiple changes.
- UPLOAD Upload your existing document (PDF, TXT, DOC, DOCX, ODT) into WordCounter.
Enter the number of characters, words, sentences or paragraphs you want to set for a goal.
Existing Goals
You can set, delete and edit your goals.
Embed Your Goal into your Web Page
Record your count of words and characters.
New Activity
Previous activities.
You can edit and delete your records.
New Document
Previous documents.
You can load, edit and delete your documents.
Find and Replace
- Help WordCounter
- Embed WordCounter
- Report a Bug
- Privacy Policy
Found a Bug

COMMENTS
In addition to the A-Levels you're already doing, you can choose to take an EPQ (Extended Project Qualification). An EPQ is an independent research project, and it's extremely beneficial as it counts towards UCAS tariff points. Consisting of around 5,000 words, an EPQ essay is an in-depth assignment which takes about 120 hours to complete.
Whether your chosen EPQ topic is Maths, English, Science, or anything else - you'll need a question to write about. Without a question, you won't have anything to write about, and 5000 words will be a lot harder to reach…. Many students forget to think about this, but it's probably the most important part of your EPQ.
Students will have to write an essay of 5,000 words or present an object, ... Do you have to write 5000 words for EPQ? ... If you present an artefact, then your report should be a minimum of 1,000 words. Many people think that using an artefact is easier, but it can be just as challenging. If you have an artefact, you need to have a very clear ...
Your EPQ will be assessed on: Your completed Production Log; A written report (sometimes referred to in this guide as an essay) if your project is a research based written report of any kind (e.g. a science investigation or an essay) it should be approximately 5,000 words long
7. Allocate a word count to each section of your structure. You know your essay has to be 5,000 words long and you know which sections you want to put into it because you've planned your structure. To make life easy for yourself you should now allocate a word count to each section.
A project which consists solely of written work should be approximately 5000 words; for example an investigation, exploration of a hypothesis or extended essay or academic report. Projects where the majority of the evidence is provided in other formats should include a report or record of work undertaken which is at least 1000 words.
An EPQ, or Extended Project Qualification, is a project that can be taken on by A-level students, and it's worth 50% of an A-level. Your EPQ could be a: Dissertation of around 5,000 words. Project, report or artefact backed up by paper work.
Write an introduction: Begin your essay with an introductory paragraph that introduces the topic, outlines the scope of the essay, and provides an overview of the structure 4. Develop the main body: Write the main body of the essay, focusing on presenting your arguments, evidence, and analysis. Ensure each paragraph has a clear topic sentence ...
colours, words and images to 'mind map' your idea visually. » Use Who, What, Why, Where, When and How (WWWWWH) questions to help you. » Once you have an idea of what you are interested in, you can decide what kind of project your EPQ will be: Artefact? Experiment? Essay? » Think carefully how to title your project (i.e. how to write the ...
Each EPQ Essays Item Has Its Word Count. We believe that 5000 words for one essay is a lot, and as our experience shows, it is challenging to create content for several such words. Therefore, to simplify the task, it is essential to divide the text into parts and select the required number of words.
EPQ is short for Extended Project Qualification. An EPQ is an independent research project which involves writing an essay of 5000 words (that's around 10 typed pages), or creating a product, which might be anything from an art object to an iPhone app. As the project evolves, you must complete a production log to record specific stages of the ...
amount of work required to write a good essay, which results in two things: (1) late nights near the submission deadline, and (2) a disappointing grade. If you want to achieve a good mark, you should start planning your essay as soon as you have agreed your essay question with your supervisor. The following table may be a useful aid.
How to write an EPQ introduction. The first thing to do is to establish the purpose of the essay - in doing this, we want to break down the question that is being answered and examine the components of it. This sounds like it is just an exercise in definitions, and to an extent it is, but it's more complicated than it may appear because it ...
EPQ is an A-level qualification that allows students to conduct independent research, which can be an essay, report, artefact, presentation, or thesis. ... and the written report should be around 5,000 words long. Feedback and Revision. EPQ supervisors provide feedback on students' work throughout the project. Students can use this feedback ...
Example EPQ Essay: An Insightful Guide. When it comes to EPQ example essays, one aspect that captures attention is the word count. Many students wonder how to effectively manage an EPQ 5000-word essay example. Fear not, for we have carefully curated a diverse selection of EPQ essay examples to shed light on this matter.
Here's how you can write an A+ extended project qualification essay in 9 steps. 1. Brainstorm topic ideas. The first thing to do before you start writing your EPQ essay is to find an engaging topic that interests you. Look for ideas and brainstorm subject matter essay topics that are significant to you and intrigue your mind.
He did so, and his project was eventually marked 100% (A*) in 2019. My best advice is to reverse-engineer the whole exercise. Remember, the EPQ is not about your project itself, but about the process of planning and executing it. So get the detailed marking scheme from the exam board's website, and painstakingly go through every single item ...
EPQ is an acronym that stands for Extended Project Qualification. What that actually means is that students will have to embark on their own research journey. At the end of this research, they'll have to produce a 5,000-word essay or create a product alongside a 1,500-word essay. EPQ can be about absolutely anything.
9) EPQ series: Charlotte on facing the blank page. Writing clearly. Good writing takes time, effort and energy. Being able to produce clear, readable, logical and well-argued pieces of writing is important in both university and in your working life. Precise & concise. Keep it simple. A word about style. Plagiarism.
The Extended Project Qualification (EPQ) will require the teaching of relevant planning, organisational, project management, study and presentation skills and a piece of independent work undertaken by the student. This work will be guided and overseen by the student's Supervisor, monitored by the Centre Coordinator and
Knowing the word count of a text can be important. For example, if an author has to write a minimum or maximum amount of words for an article, essay, report, story, book, paper, you name it. WordCounter will help to make sure its word count reaches a specific requirement or stays within a certain limit.
A. tlmurphy. Original post by Jas2007. With this EPQ thing do you have to create your own question to write an essay on. You do have to choose your own subject/question but it doesn't have to be a 5,000-word essay. You can do different things depending on what subject you choose.