
Research Topics & Ideas: Education
170+ Research Ideas To Fast-Track Your Project

If you’re just starting out exploring education-related topics for your dissertation, thesis or research project, you’ve come to the right place. In this post, we’ll help kickstart your research topic ideation process by providing a hearty list of research topics and ideas , including examples from actual dissertations and theses..
PS – This is just the start…
We know it’s exciting to run through a list of research topics, but please keep in mind that this list is just a starting point . To develop a suitable education-related research topic, you’ll need to identify a clear and convincing research gap , and a viable plan of action to fill that gap.
If this sounds foreign to you, check out our free research topic webinar that explores how to find and refine a high-quality research topic, from scratch. Alternatively, if you’d like hands-on help, consider our 1-on-1 coaching service .
Overview: Education Research Topics
- How to find a research topic (video)
- List of 50+ education-related research topics/ideas
- List of 120+ level-specific research topics
- Examples of actual dissertation topics in education
- Tips to fast-track your topic ideation (video)
- Free Webinar : Topic Ideation 101
- Where to get extra help
Education-Related Research Topics & Ideas
Below you’ll find a list of education-related research topics and idea kickstarters. These are fairly broad and flexible to various contexts, so keep in mind that you will need to refine them a little. Nevertheless, they should inspire some ideas for your project.
- The impact of school funding on student achievement
- The effects of social and emotional learning on student well-being
- The effects of parental involvement on student behaviour
- The impact of teacher training on student learning
- The impact of classroom design on student learning
- The impact of poverty on education
- The use of student data to inform instruction
- The role of parental involvement in education
- The effects of mindfulness practices in the classroom
- The use of technology in the classroom
- The role of critical thinking in education
- The use of formative and summative assessments in the classroom
- The use of differentiated instruction in the classroom
- The use of gamification in education
- The effects of teacher burnout on student learning
- The impact of school leadership on student achievement
- The effects of teacher diversity on student outcomes
- The role of teacher collaboration in improving student outcomes
- The implementation of blended and online learning
- The effects of teacher accountability on student achievement
- The effects of standardized testing on student learning
- The effects of classroom management on student behaviour
- The effects of school culture on student achievement
- The use of student-centred learning in the classroom
- The impact of teacher-student relationships on student outcomes
- The achievement gap in minority and low-income students
- The use of culturally responsive teaching in the classroom
- The impact of teacher professional development on student learning
- The use of project-based learning in the classroom
- The effects of teacher expectations on student achievement
- The use of adaptive learning technology in the classroom
- The impact of teacher turnover on student learning
- The effects of teacher recruitment and retention on student learning
- The impact of early childhood education on later academic success
- The impact of parental involvement on student engagement
- The use of positive reinforcement in education
- The impact of school climate on student engagement
- The role of STEM education in preparing students for the workforce
- The effects of school choice on student achievement
- The use of technology in the form of online tutoring
Level-Specific Research Topics
Looking for research topics for a specific level of education? We’ve got you covered. Below you can find research topic ideas for primary, secondary and tertiary-level education contexts. Click the relevant level to view the respective list.
Research Topics: Pick An Education Level
Primary education.
- Investigating the effects of peer tutoring on academic achievement in primary school
- Exploring the benefits of mindfulness practices in primary school classrooms
- Examining the effects of different teaching strategies on primary school students’ problem-solving skills
- The use of storytelling as a teaching strategy in primary school literacy instruction
- The role of cultural diversity in promoting tolerance and understanding in primary schools
- The impact of character education programs on moral development in primary school students
- Investigating the use of technology in enhancing primary school mathematics education
- The impact of inclusive curriculum on promoting equity and diversity in primary schools
- The impact of outdoor education programs on environmental awareness in primary school students
- The influence of school climate on student motivation and engagement in primary schools
- Investigating the effects of early literacy interventions on reading comprehension in primary school students
- The impact of parental involvement in school decision-making processes on student achievement in primary schools
- Exploring the benefits of inclusive education for students with special needs in primary schools
- Investigating the effects of teacher-student feedback on academic motivation in primary schools
- The role of technology in developing digital literacy skills in primary school students
- Effective strategies for fostering a growth mindset in primary school students
- Investigating the role of parental support in reducing academic stress in primary school children
- The role of arts education in fostering creativity and self-expression in primary school students
- Examining the effects of early childhood education programs on primary school readiness
- Examining the effects of homework on primary school students’ academic performance
- The role of formative assessment in improving learning outcomes in primary school classrooms
- The impact of teacher-student relationships on academic outcomes in primary school
- Investigating the effects of classroom environment on student behavior and learning outcomes in primary schools
- Investigating the role of creativity and imagination in primary school curriculum
- The impact of nutrition and healthy eating programs on academic performance in primary schools
- The impact of social-emotional learning programs on primary school students’ well-being and academic performance
- The role of parental involvement in academic achievement of primary school children
- Examining the effects of classroom management strategies on student behavior in primary school
- The role of school leadership in creating a positive school climate Exploring the benefits of bilingual education in primary schools
- The effectiveness of project-based learning in developing critical thinking skills in primary school students
- The role of inquiry-based learning in fostering curiosity and critical thinking in primary school students
- The effects of class size on student engagement and achievement in primary schools
- Investigating the effects of recess and physical activity breaks on attention and learning in primary school
- Exploring the benefits of outdoor play in developing gross motor skills in primary school children
- The effects of educational field trips on knowledge retention in primary school students
- Examining the effects of inclusive classroom practices on students’ attitudes towards diversity in primary schools
- The impact of parental involvement in homework on primary school students’ academic achievement
- Investigating the effectiveness of different assessment methods in primary school classrooms
- The influence of physical activity and exercise on cognitive development in primary school children
- Exploring the benefits of cooperative learning in promoting social skills in primary school students
Secondary Education
- Investigating the effects of school discipline policies on student behavior and academic success in secondary education
- The role of social media in enhancing communication and collaboration among secondary school students
- The impact of school leadership on teacher effectiveness and student outcomes in secondary schools
- Investigating the effects of technology integration on teaching and learning in secondary education
- Exploring the benefits of interdisciplinary instruction in promoting critical thinking skills in secondary schools
- The impact of arts education on creativity and self-expression in secondary school students
- The effectiveness of flipped classrooms in promoting student learning in secondary education
- The role of career guidance programs in preparing secondary school students for future employment
- Investigating the effects of student-centered learning approaches on student autonomy and academic success in secondary schools
- The impact of socio-economic factors on educational attainment in secondary education
- Investigating the impact of project-based learning on student engagement and academic achievement in secondary schools
- Investigating the effects of multicultural education on cultural understanding and tolerance in secondary schools
- The influence of standardized testing on teaching practices and student learning in secondary education
- Investigating the effects of classroom management strategies on student behavior and academic engagement in secondary education
- The influence of teacher professional development on instructional practices and student outcomes in secondary schools
- The role of extracurricular activities in promoting holistic development and well-roundedness in secondary school students
- Investigating the effects of blended learning models on student engagement and achievement in secondary education
- The role of physical education in promoting physical health and well-being among secondary school students
- Investigating the effects of gender on academic achievement and career aspirations in secondary education
- Exploring the benefits of multicultural literature in promoting cultural awareness and empathy among secondary school students
- The impact of school counseling services on student mental health and well-being in secondary schools
- Exploring the benefits of vocational education and training in preparing secondary school students for the workforce
- The role of digital literacy in preparing secondary school students for the digital age
- The influence of parental involvement on academic success and well-being of secondary school students
- The impact of social-emotional learning programs on secondary school students’ well-being and academic success
- The role of character education in fostering ethical and responsible behavior in secondary school students
- Examining the effects of digital citizenship education on responsible and ethical technology use among secondary school students
- The impact of parental involvement in school decision-making processes on student outcomes in secondary schools
- The role of educational technology in promoting personalized learning experiences in secondary schools
- The impact of inclusive education on the social and academic outcomes of students with disabilities in secondary schools
- The influence of parental support on academic motivation and achievement in secondary education
- The role of school climate in promoting positive behavior and well-being among secondary school students
- Examining the effects of peer mentoring programs on academic achievement and social-emotional development in secondary schools
- Examining the effects of teacher-student relationships on student motivation and achievement in secondary schools
- Exploring the benefits of service-learning programs in promoting civic engagement among secondary school students
- The impact of educational policies on educational equity and access in secondary education
- Examining the effects of homework on academic achievement and student well-being in secondary education
- Investigating the effects of different assessment methods on student performance in secondary schools
- Examining the effects of single-sex education on academic performance and gender stereotypes in secondary schools
- The role of mentoring programs in supporting the transition from secondary to post-secondary education
Tertiary Education
- The role of student support services in promoting academic success and well-being in higher education
- The impact of internationalization initiatives on students’ intercultural competence and global perspectives in tertiary education
- Investigating the effects of active learning classrooms and learning spaces on student engagement and learning outcomes in tertiary education
- Exploring the benefits of service-learning experiences in fostering civic engagement and social responsibility in higher education
- The influence of learning communities and collaborative learning environments on student academic and social integration in higher education
- Exploring the benefits of undergraduate research experiences in fostering critical thinking and scientific inquiry skills
- Investigating the effects of academic advising and mentoring on student retention and degree completion in higher education
- The role of student engagement and involvement in co-curricular activities on holistic student development in higher education
- The impact of multicultural education on fostering cultural competence and diversity appreciation in higher education
- The role of internships and work-integrated learning experiences in enhancing students’ employability and career outcomes
- Examining the effects of assessment and feedback practices on student learning and academic achievement in tertiary education
- The influence of faculty professional development on instructional practices and student outcomes in tertiary education
- The influence of faculty-student relationships on student success and well-being in tertiary education
- The impact of college transition programs on students’ academic and social adjustment to higher education
- The impact of online learning platforms on student learning outcomes in higher education
- The impact of financial aid and scholarships on access and persistence in higher education
- The influence of student leadership and involvement in extracurricular activities on personal development and campus engagement
- Exploring the benefits of competency-based education in developing job-specific skills in tertiary students
- Examining the effects of flipped classroom models on student learning and retention in higher education
- Exploring the benefits of online collaboration and virtual team projects in developing teamwork skills in tertiary students
- Investigating the effects of diversity and inclusion initiatives on campus climate and student experiences in tertiary education
- The influence of study abroad programs on intercultural competence and global perspectives of college students
- Investigating the effects of peer mentoring and tutoring programs on student retention and academic performance in tertiary education
- Investigating the effectiveness of active learning strategies in promoting student engagement and achievement in tertiary education
- Investigating the effects of blended learning models and hybrid courses on student learning and satisfaction in higher education
- The role of digital literacy and information literacy skills in supporting student success in the digital age
- Investigating the effects of experiential learning opportunities on career readiness and employability of college students
- The impact of e-portfolios on student reflection, self-assessment, and showcasing of learning in higher education
- The role of technology in enhancing collaborative learning experiences in tertiary classrooms
- The impact of research opportunities on undergraduate student engagement and pursuit of advanced degrees
- Examining the effects of competency-based assessment on measuring student learning and achievement in tertiary education
- Examining the effects of interdisciplinary programs and courses on critical thinking and problem-solving skills in college students
- The role of inclusive education and accessibility in promoting equitable learning experiences for diverse student populations
- The role of career counseling and guidance in supporting students’ career decision-making in tertiary education
- The influence of faculty diversity and representation on student success and inclusive learning environments in higher education

Education-Related Dissertations & Theses
While the ideas we’ve presented above are a decent starting point for finding a research topic in education, they are fairly generic and non-specific. So, it helps to look at actual dissertations and theses in the education space to see how this all comes together in practice.
Below, we’ve included a selection of education-related research projects to help refine your thinking. These are actual dissertations and theses, written as part of Master’s and PhD-level programs, so they can provide some useful insight as to what a research topic looks like in practice.
- From Rural to Urban: Education Conditions of Migrant Children in China (Wang, 2019)
- Energy Renovation While Learning English: A Guidebook for Elementary ESL Teachers (Yang, 2019)
- A Reanalyses of Intercorrelational Matrices of Visual and Verbal Learners’ Abilities, Cognitive Styles, and Learning Preferences (Fox, 2020)
- A study of the elementary math program utilized by a mid-Missouri school district (Barabas, 2020)
- Instructor formative assessment practices in virtual learning environments : a posthumanist sociomaterial perspective (Burcks, 2019)
- Higher education students services: a qualitative study of two mid-size universities’ direct exchange programs (Kinde, 2020)
- Exploring editorial leadership : a qualitative study of scholastic journalism advisers teaching leadership in Missouri secondary schools (Lewis, 2020)
- Selling the virtual university: a multimodal discourse analysis of marketing for online learning (Ludwig, 2020)
- Advocacy and accountability in school counselling: assessing the use of data as related to professional self-efficacy (Matthews, 2020)
- The use of an application screening assessment as a predictor of teaching retention at a midwestern, K-12, public school district (Scarbrough, 2020)
- Core values driving sustained elite performance cultures (Beiner, 2020)
- Educative features of upper elementary Eureka math curriculum (Dwiggins, 2020)
- How female principals nurture adult learning opportunities in successful high schools with challenging student demographics (Woodward, 2020)
- The disproportionality of Black Males in Special Education: A Case Study Analysis of Educator Perceptions in a Southeastern Urban High School (McCrae, 2021)
As you can see, these research topics are a lot more focused than the generic topic ideas we presented earlier. So, in order for you to develop a high-quality research topic, you’ll need to get specific and laser-focused on a specific context with specific variables of interest. In the video below, we explore some other important things you’ll need to consider when crafting your research topic.
Get 1-On-1 Help
If you’re still unsure about how to find a quality research topic within education, check out our Research Topic Kickstarter service, which is the perfect starting point for developing a unique, well-justified research topic.

You Might Also Like:

66 Comments
This is an helpful tool 🙏
Special education
Really appreciated by this . It is the best platform for research related items
Research title related to school of students
How are you
I think this platform is actually good enough.
Research title related to students
My field is research measurement and evaluation. Need dissertation topics in the field
Assalam o Alaikum I’m a student Bs educational Resarch and evaluation I’m confused to choose My thesis title please help me in choose the thesis title
Good idea I’m going to teach my colleagues
You can find our list of nursing-related research topic ideas here: https://gradcoach.com/research-topics-nursing/
Write on action research topic, using guidance and counseling to address unwanted teenage pregnancy in school
Thanks a lot
I learned a lot from this site, thank you so much!
Thank you for the information.. I would like to request a topic based on school major in social studies
parental involvement and students academic performance
Science education topics?
plz tell me if you got some good topics, im here for finding research topic for masters degree
How about School management and supervision pls.?
Hi i am an Deputy Principal in a primary school. My wish is to srudy foe Master’s degree in Education.Please advice me on which topic can be relevant for me. Thanks.
Every topic proposed above on primary education is a starting point for me. I appreciate immensely the team that has sat down to make a detail of these selected topics just for beginners like us. Be blessed.
Kindly help me with the research questions on the topic” Effects of workplace conflict on the employees’ job performance”. The effects can be applicable in every institution,enterprise or organisation.
Greetings, I am a student majoring in Sociology and minoring in Public Administration. I’m considering any recommended research topic in the field of Sociology.
I’m a student pursuing Mphil in Basic education and I’m considering any recommended research proposal topic in my field of study
Research Defense for students in senior high
Kindly help me with a research topic in educational psychology. Ph.D level. Thank you.
Project-based learning is a teaching/learning type,if well applied in a classroom setting will yield serious positive impact. What can a teacher do to implement this in a disadvantaged zone like “North West Region of Cameroon ( hinterland) where war has brought about prolonged and untold sufferings on the indegins?
I wish to get help on topics of research on educational administration
I wish to get help on topics of research on educational administration PhD level
I am also looking for such type of title
I am a student of undergraduate, doing research on how to use guidance and counseling to address unwanted teenage pregnancy in school
the topics are very good regarding research & education .
Can i request your suggestion topic for my Thesis about Teachers as an OFW. thanx you
Would like to request for suggestions on a topic in Economics of education,PhD level
Would like to request for suggestions on a topic in Economics of education
Hi 👋 I request that you help me with a written research proposal about education the format
Am offering degree in education senior high School Accounting. I want a topic for my project work
l would like to request suggestions on a topic in managing teaching and learning, PhD level (educational leadership and management)
request suggestions on a topic in managing teaching and learning, PhD level (educational leadership and management)
I would to inquire on research topics on Educational psychology, Masters degree
I am PhD student, I am searching my Research topic, It should be innovative,my area of interest is online education,use of technology in education
request suggestion on topic in masters in medical education .
Look at British Library as they keep a copy of all PhDs in the UK Core.ac.uk to access Open University and 6 other university e-archives, pdf downloads mostly available, all free.
May I also ask for a topic based on mathematics education for college teaching, please?
Please I am a masters student of the department of Teacher Education, Faculty of Education Please I am in need of proposed project topics to help with my final year thesis
Am a PhD student in Educational Foundations would like a sociological topic. Thank
please i need a proposed thesis project regardging computer science
Greetings and Regards I am a doctoral student in the field of philosophy of education. I am looking for a new topic for my thesis. Because of my work in the elementary school, I am looking for a topic that is from the field of elementary education and is related to the philosophy of education.
Masters student in the field of curriculum, any ideas of a research topic on low achiever students
In the field of curriculum any ideas of a research topic on deconalization in contextualization of digital teaching and learning through in higher education
Amazing guidelines
I am a graduate with two masters. 1) Master of arts in religious studies and 2) Master in education in foundations of education. I intend to do a Ph.D. on my second master’s, however, I need to bring both masters together through my Ph.D. research. can I do something like, ” The contribution of Philosophy of education for a quality religion education in Kenya”? kindly, assist and be free to suggest a similar topic that will bring together the two masters. thanks in advance
Hi, I am an Early childhood trainer as well as a researcher, I need more support on this topic: The impact of early childhood education on later academic success.
I’m a student in upper level secondary school and I need your support in this research topics: “Impact of incorporating project -based learning in teaching English language skills in secondary schools”.
Although research activities and topics should stem from reflection on one’s practice, I found this site valuable as it effectively addressed many issues we have been experiencing as practitioners.
Your style is unique in comparison to other folks I’ve read stuff from. Thanks for posting when you have the opportunity, Guess I will just book mark this site.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
- Library databases
- Library website
Education Literature Review: Education Literature Review
What does this guide cover.
Writing the literature review is a long, complex process that requires you to use many different tools, resources, and skills.
This page provides links to the guides, tutorials, and webinars that can help you with all aspects of completing your literature review.
The Basic Process
These resources provide overviews of the entire literature review process. Start here if you are new to the literature review process.
- Literature Reviews Overview : Writing Center
- How to do a Literature Review : Library
- Video: Common Errors Made When Conducting a Lit Review (YouTube)
The Role of the Literature Review
Your literature review gives your readers an understanding of the evolution of scholarly research on your topic.
In your literature review you will:
- survey the scholarly landscape
- provide a synthesis of the issues, trends, and concepts
- possibly provide some historical background
Review the literature in two ways:
- Section 1: reviews the literature for the Problem
- Section 3: reviews the literature for the Project
The literature review is NOT an annotated bibliography. Nor should it simply summarize the articles you've read. Literature reviews are organized thematically and demonstrate synthesis of the literature.
For more information, view the Library's short video on searching by themes:
Short Video: Research for the Literature Review
(4 min 10 sec) Recorded August 2019 Transcript
Search for Literature
The iterative process of research:
- Find an article.
- Read the article and build new searches using keywords and names from the article.
- Mine the bibliography for other works.
- Use “cited by” searches to find more recent works that reference the article.
- Repeat steps 2-4 with the new articles you find.
These are the main skills and resources you will need in order to effectively search for literature on your topic:
- Subject Research: Education by Jon Allinder Last Updated Aug 7, 2023 4168 views this year
- Keyword Searching: Finding Articles on Your Topic by Lynn VanLeer Last Updated Sep 12, 2023 19948 views this year
- Google Scholar by Jon Allinder Last Updated Aug 16, 2023 13609 views this year
- Quick Answer: How do I find books and articles that cite an article I already have?
- Quick Answer: How do I find a measurement, test, survey or instrument?
Video: Education Databases and Doctoral Research Resources
(6 min 04 sec) Recorded April 2019 Transcript
Staying Organized
The literature review requires organizing a variety of information. The following resources will help you develop the organizational systems you'll need to be successful.
- Organize your research
- Citation Management Software
You can make your search log as simple or complex as you would like. It can be a table in a word document or an excel spread sheet. Here are two examples. The word document is a basic table where you can keep track of databases, search terms, limiters, results and comments. The Excel sheet is more complex and has additional sheets for notes, Google Scholar log; Journal Log, and Questions to ask the Librarian.
- Search Log Example Sample search log in Excel
- Search Log Example Sample search log set up as a table in a word document.
- Literature Review Matrix with color coding Sample template for organizing and synthesizing your research
Writing the Literature Review
The following resources created by the Writing Center and the Academic Skills Center support the writing process for the dissertation/project study.
- Critical Reading
- What is Synthesis
- Walden Templates
- Quick Answer: How do I find Walden EdD (Doctor of Education) studies?
- Quick Answer: How do I find Walden PhD dissertations?
Beyond the Literature Review
The literature review isn't the only portion of a dissertation/project study that requires searching. The following resources can help you identify and utilize a theory, methodology, measurement instruments, or statistics.
- Education Theory by Jon Allinder Last Updated May 17, 2024 524 views this year
- Tests & Measures in Education by Kimberly Burton Last Updated Nov 18, 2021 45 views this year
- Education Statistics by Jon Allinder Last Updated Feb 22, 2022 60 views this year
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
Books and Articles about the Lit Review
The following articles and books outline the purpose of the literature review and offer advice for successfully completing one.
- Chen, D. T. V., Wang, Y. M., & Lee, W. C. (2016). Challenges confronting beginning researchers in conducting literature reviews. Studies in Continuing Education, 38(1), 47-60. https://doi.org/10.1080/0158037X.2015.1030335 Proposes a framework to conceptualize four types of challenges students face: linguistic, methodological, conceptual, and ontological.
- Randolph, J.J. (2009). A guide to writing the dissertation literature review. Practical Assessment, Research & Evaluation 14(13), 1-13. Provides advice for writing a quantitative or qualitative literature review, by a Walden faculty member.
- Torraco, R. J. (2016). Writing integrative literature reviews: Using the past and present to explore the future. Human Resource Development Review, 15(4), 404–428. https://doi.org/10.1177/1534484316671606 This article presents the integrative review of literature as a distinctive form of research that uses existing literature to create new knowledge.
- Wee, B. V., & Banister, D. (2016). How to write a literature review paper?. Transport Reviews, 36(2), 278-288. http://doi.org/10.1080/01441647.2015.1065456 Discusses how to write a literature review with a focus on adding value rather and suggests structural and contextual aspects found in outstanding literature reviews.
- Winchester, C. L., & Salji, M. (2016). Writing a literature review. Journal of Clinical Urology, 9(5), 308-312. https://doi.org/10.1177/2051415816650133 Reviews the use of different document types to add structure and enrich your literature review and the skill sets needed in writing the literature review.
- Xiao, Y., & Watson, M. (2017). Guidance on conducting a systematic literature review. Journal of Planning Education and Research. https://doi.org/10.1177/0739456X17723971 Examines different types of literature reviews and the steps necessary to produce a systematic review in educational research.
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.
- Subject List
- Take a Tour
- For Authors
- Subscriber Services
- Publications
- African American Studies
- African Studies
- American Literature
- Anthropology
- Architecture Planning and Preservation
- Art History
- Atlantic History
- Biblical Studies
- British and Irish Literature
- Childhood Studies
- Chinese Studies
- Cinema and Media Studies
- Communication
- Criminology
- Environmental Science
- Evolutionary Biology
- International Law
- International Relations
- Islamic Studies
- Jewish Studies
- Latin American Studies
- Latino Studies
- Linguistics
- Literary and Critical Theory
- Medieval Studies
- Military History
- Political Science
- Public Health
- Renaissance and Reformation
- Social Work
- Urban Studies
- Victorian Literature
- Browse All Subjects
How to Subscribe
- Free Trials
In This Article Expand or collapse the "in this article" section Literature Reviews
Introduction, what is a literature review.
- Literature Reviews for Thesis or Dissertation
- Stand-alone and Systemic Reviews
- Purposes of a Literature Review
- Texts on Conducting a Literature Review
- Identifying the Research Topic
- The Persuasive Argument
- Searching the Literature
- Creating a Synthesis
- Critiquing the Literature
- Building the Case for the Literature Review Document
- Presenting the Literature Review
Related Articles Expand or collapse the "related articles" section about
About related articles close popup.
Lorem Ipsum Sit Dolor Amet
Vestibulum ante ipsum primis in faucibus orci luctus et ultrices posuere cubilia Curae; Aliquam ligula odio, euismod ut aliquam et, vestibulum nec risus. Nulla viverra, arcu et iaculis consequat, justo diam ornare tellus, semper ultrices tellus nunc eu tellus.
- Higher Education Research
- Meta-Analysis and Research Synthesis in Education
- Methodologies for Conducting Education Research
- Mixed Methods Research
- Philosophy of Education
- Politics of Education
- Qualitative Data Analysis Techniques
Other Subject Areas
Forthcoming articles expand or collapse the "forthcoming articles" section.
- Black Women in Academia
- Girls' Education in the Developing World
- History of Education in Europe
- Find more forthcoming articles...
- Export Citations
- Share This Facebook LinkedIn Twitter
Literature Reviews by Lawrence A. Machi , Brenda T. McEvoy LAST REVIEWED: 27 October 2016 LAST MODIFIED: 27 October 2016 DOI: 10.1093/obo/9780199756810-0169
Literature reviews play a foundational role in the development and execution of a research project. They provide access to the academic conversation surrounding the topic of the proposed study. By engaging in this scholarly exercise, the researcher is able to learn and to share knowledge about the topic. The literature review acts as the springboard for new research, in that it lays out a logically argued case, founded on a comprehensive understanding of the current state of knowledge about the topic. The case produced provides the justification for the research question or problem of a proposed study, and the methodological scheme best suited to conduct the research. It can also be a research project in itself, arguing policy or practice implementation, based on a comprehensive analysis of the research in a field. The term literature review can refer to the output or the product of a review. It can also refer to the process of Conducting a Literature Review . Novice researchers, when attempting their first research projects, tend to ask two questions: What is a Literature Review? How do you do one? While this annotated bibliography is neither definitive nor exhaustive in its treatment of the subject, it is designed to provide a beginning researcher, who is pursuing an academic degree, an entry point for answering the two previous questions. The article is divided into two parts. The first four sections of the article provide a general overview of the topic. They address definitions, types, purposes, and processes for doing a literature review. The second part presents the process and procedures for doing a literature review. Arranged in a sequential fashion, the remaining eight sections provide references addressing each step of the literature review process. References included in this article were selected based on their ability to assist the beginning researcher. Additionally, the authors attempted to include texts from various disciplines in social science to present various points of view on the subject.
Novice researchers often have a misguided perception of how to do a literature review and what the document should contain. Literature reviews are not narrative annotated bibliographies nor book reports (see Bruce 1994 ). Their form, function, and outcomes vary, due to how they depend on the research question, the standards and criteria of the academic discipline, and the orthodoxies of the research community charged with the research. The term literature review can refer to the process of doing a review as well as the product resulting from conducting a review. The product resulting from reviewing the literature is the concern of this section. Literature reviews for research studies at the master’s and doctoral levels have various definitions. Machi and McEvoy 2016 presents a general definition of a literature review. Lambert 2012 defines a literature review as a critical analysis of what is known about the study topic, the themes related to it, and the various perspectives expressed regarding the topic. Fink 2010 defines a literature review as a systematic review of existing body of data that identifies, evaluates, and synthesizes for explicit presentation. Jesson, et al. 2011 defines the literature review as a critical description and appraisal of a topic. Hart 1998 sees the literature review as producing two products: the presentation of information, ideas, data, and evidence to express viewpoints on the nature of the topic, as well as how it is to be investigated. When considering literature reviews beyond the novice level, Ridley 2012 defines and differentiates the systematic review from literature reviews associated with primary research conducted in academic degree programs of study, including stand-alone literature reviews. Cooper 1998 states the product of literature review is dependent on the research study’s goal and focus, and defines synthesis reviews as literature reviews that seek to summarize and draw conclusions from past empirical research to determine what issues have yet to be resolved. Theoretical reviews compare and contrast the predictive ability of theories that explain the phenomenon, arguing which theory holds the most validity in describing the nature of that phenomenon. Grant and Booth 2009 identified fourteen types of reviews used in both degree granting and advanced research projects, describing their attributes and methodologies.
Bruce, Christine Susan. 1994. Research students’ early experiences of the dissertation literature review. Studies in Higher Education 19.2: 217–229.
DOI: 10.1080/03075079412331382057
A phenomenological analysis was conducted with forty-one neophyte research scholars. The responses to the questions, “What do you mean when you use the words literature review?” and “What is the meaning of a literature review for your research?” identified six concepts. The results conclude that doing a literature review is a problem area for students.
Cooper, Harris. 1998. Synthesizing research . Vol. 2. 3d ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
The introductory chapter of this text provides a cogent explanation of Cooper’s understanding of literature reviews. Chapter 4 presents a comprehensive discussion of the synthesis review. Chapter 5 discusses meta-analysis and depth.
Fink, Arlene. 2010. Conducting research literature reviews: From the Internet to paper . 3d ed. Los Angeles: SAGE.
The first chapter of this text (pp. 1–16) provides a short but clear discussion of what a literature review is in reference to its application to a broad range of social sciences disciplines and their related professions.
Grant, Maria J., and Andrew Booth. 2009. A typology of reviews: An analysis of 14 review types and associated methodologies. Health Information & Libraries Journal 26.2: 91–108. Print.
DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-1842.2009.00848.x
This article reports a scoping review that was conducted using the “Search, Appraisal, Synthesis, and Analysis” (SALSA) framework. Fourteen literature review types and associated methodology make up the resulting typology. Each type is described by its key characteristics and analyzed for its strengths and weaknesses.
Hart, Chris. 1998. Doing a literature review: Releasing the social science research imagination . London: SAGE.
Chapter 1 of this text explains Hart’s definition of a literature review. Additionally, it describes the roles of the literature review, the skills of a literature reviewer, and the research context for a literature review. Of note is Hart’s discussion of the literature review requirements for master’s degree and doctoral degree work.
Jesson, Jill, Lydia Matheson, and Fiona M. Lacey. 2011. Doing your literature review: Traditional and systematic techniques . Los Angeles: SAGE.
Chapter 1: “Preliminaries” provides definitions of traditional and systematic reviews. It discusses the differences between them. Chapter 5 is dedicated to explaining the traditional review, while Chapter 7 explains the systematic review. Chapter 8 provides a detailed description of meta-analysis.
Lambert, Mike. 2012. A beginner’s guide to doing your education research project . Los Angeles: SAGE.
Chapter 6 (pp. 79–100) presents a thumbnail sketch for doing a literature review.
Machi, Lawrence A., and Brenda T. McEvoy. 2016. The literature review: Six steps to success . 3d ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin.
The introduction of this text differentiates between a simple and an advanced review and concisely defines a literature review.
Ridley, Diana. 2012. The literature review: A step-by-step guide for students . 2d ed. Sage Study Skills. London: SAGE.
In the introductory chapter, Ridley reviews many definitions of the literature review, literature reviews at the master’s and doctoral level, and placement of literature reviews within the thesis or dissertation document. She also defines and differentiates literature reviews produced for degree-affiliated research from the more advanced systematic review projects.
back to top
Users without a subscription are not able to see the full content on this page. Please subscribe or login .
Oxford Bibliographies Online is available by subscription and perpetual access to institutions. For more information or to contact an Oxford Sales Representative click here .
- About Education »
- Meet the Editorial Board »
- Academic Achievement
- Academic Audit for Universities
- Academic Freedom and Tenure in the United States
- Action Research in Education
- Adjuncts in Higher Education in the United States
- Administrator Preparation
- Adolescence
- Advanced Placement and International Baccalaureate Courses
- Advocacy and Activism in Early Childhood
- African American Racial Identity and Learning
- Alaska Native Education
- Alternative Certification Programs for Educators
- Alternative Schools
- American Indian Education
- Animals in Environmental Education
- Art Education
- Artificial Intelligence and Learning
- Assessing School Leader Effectiveness
- Assessment, Behavioral
- Assessment, Educational
- Assessment in Early Childhood Education
- Assistive Technology
- Augmented Reality in Education
- Beginning-Teacher Induction
- Bilingual Education and Bilingualism
- Black Undergraduate Women: Critical Race and Gender Perspe...
- Blended Learning
- Case Study in Education Research
- Changing Professional and Academic Identities
- Character Education
- Children’s and Young Adult Literature
- Children's Beliefs about Intelligence
- Children's Rights in Early Childhood Education
- Citizenship Education
- Civic and Social Engagement of Higher Education
- Classroom Learning Environments: Assessing and Investigati...
- Classroom Management
- Coherent Instructional Systems at the School and School Sy...
- College Admissions in the United States
- College Athletics in the United States
- Community Relations
- Comparative Education
- Computer-Assisted Language Learning
- Computer-Based Testing
- Conceptualizing, Measuring, and Evaluating Improvement Net...
- Continuous Improvement and "High Leverage" Educational Pro...
- Counseling in Schools
- Critical Approaches to Gender in Higher Education
- Critical Perspectives on Educational Innovation and Improv...
- Critical Race Theory
- Crossborder and Transnational Higher Education
- Cross-National Research on Continuous Improvement
- Cross-Sector Research on Continuous Learning and Improveme...
- Cultural Diversity in Early Childhood Education
- Culturally Responsive Leadership
- Culturally Responsive Pedagogies
- Culturally Responsive Teacher Education in the United Stat...
- Curriculum Design
- Data Collection in Educational Research
- Data-driven Decision Making in the United States
- Deaf Education
- Desegregation and Integration
- Design Thinking and the Learning Sciences: Theoretical, Pr...
- Development, Moral
- Dialogic Pedagogy
- Digital Age Teacher, The
- Digital Citizenship
- Digital Divides
- Disabilities
- Distance Learning
- Distributed Leadership
- Doctoral Education and Training
- Early Childhood Education and Care (ECEC) in Denmark
- Early Childhood Education and Development in Mexico
- Early Childhood Education in Aotearoa New Zealand
- Early Childhood Education in Australia
- Early Childhood Education in China
- Early Childhood Education in Europe
- Early Childhood Education in Sub-Saharan Africa
- Early Childhood Education in Sweden
- Early Childhood Education Pedagogy
- Early Childhood Education Policy
- Early Childhood Education, The Arts in
- Early Childhood Mathematics
- Early Childhood Science
- Early Childhood Teacher Education
- Early Childhood Teachers in Aotearoa New Zealand
- Early Years Professionalism and Professionalization Polici...
- Economics of Education
- Education For Children with Autism
- Education for Sustainable Development
- Education Leadership, Empirical Perspectives in
- Education of Native Hawaiian Students
- Education Reform and School Change
- Educational Statistics for Longitudinal Research
- Educator Partnerships with Parents and Families with a Foc...
- Emotional and Affective Issues in Environmental and Sustai...
- Emotional and Behavioral Disorders
- English as an International Language for Academic Publishi...
- Environmental and Science Education: Overlaps and Issues
- Environmental Education
- Environmental Education in Brazil
- Epistemic Beliefs
- Equity and Improvement: Engaging Communities in Educationa...
- Equity, Ethnicity, Diversity, and Excellence in Education
- Ethical Research with Young Children
- Ethics and Education
- Ethics of Teaching
- Ethnic Studies
- Evidence-Based Communication Assessment and Intervention
- Family and Community Partnerships in Education
- Family Day Care
- Federal Government Programs and Issues
- Feminization of Labor in Academia
- Finance, Education
- Financial Aid
- Formative Assessment
- Future-Focused Education
- Gender and Achievement
- Gender and Alternative Education
- Gender, Power and Politics in the Academy
- Gender-Based Violence on University Campuses
- Gifted Education
- Global Mindedness and Global Citizenship Education
- Global University Rankings
- Governance, Education
- Grounded Theory
- Growth of Effective Mental Health Services in Schools in t...
- Higher Education and Globalization
- Higher Education and the Developing World
- Higher Education Faculty Characteristics and Trends in the...
- Higher Education Finance
- Higher Education Governance
- Higher Education Graduate Outcomes and Destinations
- Higher Education in Africa
- Higher Education in China
- Higher Education in Latin America
- Higher Education in the United States, Historical Evolutio...
- Higher Education, International Issues in
- Higher Education Management
- Higher Education Policy
- Higher Education Student Assessment
- High-stakes Testing
- History of Early Childhood Education in the United States
- History of Education in the United States
- History of Technology Integration in Education
- Homeschooling
- Inclusion in Early Childhood: Difference, Disability, and ...
- Inclusive Education
- Indigenous Education in a Global Context
- Indigenous Learning Environments
- Indigenous Students in Higher Education in the United Stat...
- Infant and Toddler Pedagogy
- Inservice Teacher Education
- Integrating Art across the Curriculum
- Intelligence
- Intensive Interventions for Children and Adolescents with ...
- International Perspectives on Academic Freedom
- Intersectionality and Education
- Knowledge Development in Early Childhood
- Leadership Development, Coaching and Feedback for
- Leadership in Early Childhood Education
- Leadership Training with an Emphasis on the United States
- Learning Analytics in Higher Education
- Learning Difficulties
- Learning, Lifelong
- Learning, Multimedia
- Learning Strategies
- Legal Matters and Education Law
- LGBT Youth in Schools
- Linguistic Diversity
- Linguistically Inclusive Pedagogy
- Literacy Development and Language Acquisition
- Literature Reviews
- Mathematics Identity
- Mathematics Instruction and Interventions for Students wit...
- Mathematics Teacher Education
- Measurement for Improvement in Education
- Measurement in Education in the United States
- Methodological Approaches for Impact Evaluation in Educati...
- Mindfulness, Learning, and Education
- Motherscholars
- Multiliteracies in Early Childhood Education
- Multiple Documents Literacy: Theory, Research, and Applica...
- Multivariate Research Methodology
- Museums, Education, and Curriculum
- Music Education
- Narrative Research in Education
- Native American Studies
- Nonformal and Informal Environmental Education
- Note-Taking
- Numeracy Education
- One-to-One Technology in the K-12 Classroom
- Online Education
- Open Education
- Organizing for Continuous Improvement in Education
- Organizing Schools for the Inclusion of Students with Disa...
- Outdoor Play and Learning
- Outdoor Play and Learning in Early Childhood Education
- Pedagogical Leadership
- Pedagogy of Teacher Education, A
- Performance Objectives and Measurement
- Performance-based Research Assessment in Higher Education
- Performance-based Research Funding
- Phenomenology in Educational Research
- Physical Education
- Podcasts in Education
- Policy Context of United States Educational Innovation and...
- Portable Technology Use in Special Education Programs and ...
- Post-humanism and Environmental Education
- Pre-Service Teacher Education
- Problem Solving
- Productivity and Higher Education
- Professional Development
- Professional Learning Communities
- Program Evaluation
- Programs and Services for Students with Emotional or Behav...
- Psychology Learning and Teaching
- Psychometric Issues in the Assessment of English Language ...
- Qualitative, Quantitative, and Mixed Methods Research Samp...
- Qualitative Research Design
- Quantitative Research Designs in Educational Research
- Queering the English Language Arts (ELA) Writing Classroom
- Race and Affirmative Action in Higher Education
- Reading Education
- Refugee and New Immigrant Learners
- Relational and Developmental Trauma and Schools
- Relational Pedagogies in Early Childhood Education
- Reliability in Educational Assessments
- Religion in Elementary and Secondary Education in the Unit...
- Researcher Development and Skills Training within the Cont...
- Research-Practice Partnerships in Education within the Uni...
- Response to Intervention
- Restorative Practices
- Risky Play in Early Childhood Education
- Scale and Sustainability of Education Innovation and Impro...
- Scaling Up Research-based Educational Practices
- School Accreditation
- School Choice
- School Culture
- School District Budgeting and Financial Management in the ...
- School Improvement through Inclusive Education
- School Reform
- Schools, Private and Independent
- School-Wide Positive Behavior Support
- Science Education
- Secondary to Postsecondary Transition Issues
- Self-Regulated Learning
- Self-Study of Teacher Education Practices
- Service-Learning
- Severe Disabilities
- Single Salary Schedule
- Single-sex Education
- Single-Subject Research Design
- Social Context of Education
- Social Justice
- Social Network Analysis
- Social Pedagogy
- Social Science and Education Research
- Social Studies Education
- Sociology of Education
- Standards-Based Education
- Statistical Assumptions
- Student Access, Equity, and Diversity in Higher Education
- Student Assignment Policy
- Student Engagement in Tertiary Education
- Student Learning, Development, Engagement, and Motivation ...
- Student Participation
- Student Voice in Teacher Development
- Sustainability Education in Early Childhood Education
- Sustainability in Early Childhood Education
- Sustainability in Higher Education
- Teacher Beliefs and Epistemologies
- Teacher Collaboration in School Improvement
- Teacher Evaluation and Teacher Effectiveness
- Teacher Preparation
- Teacher Training and Development
- Teacher Unions and Associations
- Teacher-Student Relationships
- Teaching Critical Thinking
- Technologies, Teaching, and Learning in Higher Education
- Technology Education in Early Childhood
- Technology, Educational
- Technology-based Assessment
- The Bologna Process
- The Regulation of Standards in Higher Education
- Theories of Educational Leadership
- Three Conceptions of Literacy: Media, Narrative, and Gamin...
- Tracking and Detracking
- Traditions of Quality Improvement in Education
- Transformative Learning
- Transitions in Early Childhood Education
- Tribally Controlled Colleges and Universities in the Unite...
- Understanding the Psycho-Social Dimensions of Schools and ...
- University Faculty Roles and Responsibilities in the Unite...
- Using Ethnography in Educational Research
- Value of Higher Education for Students and Other Stakehold...
- Virtual Learning Environments
- Vocational and Technical Education
- Wellness and Well-Being in Education
- Women's and Gender Studies
- Young Children and Spirituality
- Young Children's Learning Dispositions
- Young Children's Working Theories
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Legal Notice
- Accessibility
Powered by:
- [66.249.64.20|185.66.15.189]
- 185.66.15.189

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 1: Introduction
Learning objectives.
At the conclusion of this chapter, you will be able to:
- Identify the purpose of the literature review in the research process
- Distinguish between different types of literature reviews
1.1 What is a Literature Review?
Pick up nearly any book on research methods and you will find a description of a literature review. At a basic level, the term implies a survey of factual or nonfiction books, articles, and other documents published on a particular subject. Definitions may be similar across the disciplines, with new types and definitions continuing to emerge. Generally speaking, a literature review is a:
- “comprehensive background of the literature within the interested topic area…” ( O’Gorman & MacIntosh, 2015, p. 31 ).
- “critical component of the research process that provides an in-depth analysis of recently published research findings in specifically identified areas of interest.” ( House, 2018, p. 109 ).
- “written document that presents a logically argued case founded on a comprehensive understanding of the current state of knowledge about a topic of study” ( Machi & McEvoy, 2012, p. 4 ).
As a foundation for knowledge advancement in every discipline, it is an important element of any research project. At the graduate or doctoral level, the literature review is an essential feature of thesis and dissertation, as well as grant proposal writing. That is to say, “A substantive, thorough, sophisticated literature review is a precondition for doing substantive, thorough, sophisticated research…A researcher cannot perform significant research without first understanding the literature in the field.” ( Boote & Beile, 2005, p. 3 ). It is by this means, that a researcher demonstrates familiarity with a body of knowledge and thereby establishes credibility with a reader. An advanced-level literature review shows how prior research is linked to a new project, summarizing and synthesizing what is known while identifying gaps in the knowledge base, facilitating theory development, closing areas where enough research already exists, and uncovering areas where more research is needed. ( Webster & Watson, 2002, p. xiii )
A graduate-level literature review is a compilation of the most significant previously published research on your topic. Unlike an annotated bibliography or a research paper you may have written as an undergraduate, your literature review will outline, evaluate and synthesize relevant research and relate those sources to your own thesis or research question. It is much more than a summary of all the related literature.
It is a type of writing that demonstrate the importance of your research by defining the main ideas and the relationship between them. A good literature review lays the foundation for the importance of your stated problem and research question.
Literature reviews:
- define a concept
- map the research terrain or scope
- systemize relationships between concepts
- identify gaps in the literature ( Rocco & Plathotnik, 2009, p. 128 )
The purpose of a literature review is to demonstrate that your research question is meaningful. Additionally, you may review the literature of different disciplines to find deeper meaning and understanding of your topic. It is especially important to consider other disciplines when you do not find much on your topic in one discipline. You will need to search the cognate literature before claiming there is “little previous research” on your topic.
Well developed literature reviews involve numerous steps and activities. The literature review is an iterative process because you will do at least two of them: a preliminary search to learn what has been published in your area and whether there is sufficient support in the literature for moving ahead with your subject. After this first exploration, you will conduct a deeper dive into the literature to learn everything you can about the topic and its related issues.
Literature Review Tutorial

1.2 Literature Review Basics
An effective literature review must:
- Methodologically analyze and synthesize quality literature on a topic
- Provide a firm foundation to a topic or research area
- Provide a firm foundation for the selection of a research methodology
- Demonstrate that the proposed research contributes something new to the overall body of knowledge of advances the research field’s knowledge base. ( Levy & Ellis, 2006 ).
All literature reviews, whether they are qualitative, quantitative or both, will at some point:
- Introduce the topic and define its key terms
- Establish the importance of the topic
- Provide an overview of the amount of available literature and its types (for example: theoretical, statistical, speculative)
- Identify gaps in the literature
- Point out consistent finding across studies
- Arrive at a synthesis that organizes what is known about a topic
- Discusses possible implications and directions for future research
1.3 Types of Literature Reviews
There are many different types of literature reviews, however there are some shared characteristics or features. Remember a comprehensive literature review is, at its most fundamental level, an original work based on an extensive critical examination and synthesis of the relevant literature on a topic. As a study of the research on a particular topic, it is arranged by key themes or findings, which may lead up to or link to the research question. In some cases, the research question will drive the type of literature review that is undertaken.
The following section includes brief descriptions of the terms used to describe different literature review types with examples of each. The included citations are open access, Creative Commons licensed or copyright-restricted.
1.3.1 Types of Review
1.3.1.1 conceptual.
Guided by an understanding of basic issues rather than a research methodology. You are looking for key factors, concepts or variables and the presumed relationship between them. The goal of the conceptual literature review is to categorize and describe concepts relevant to your study or topic and outline a relationship between them. You will include relevant theory and empirical research.
Examples of a Conceptual Review:
- Education : The formality of learning science in everyday life: A conceptual literature review. ( Dohn, 2010 ).
- Education : Are we asking the right questions? A conceptual review of the educational development literature in higher education. ( Amundsen & Wilson, 2012 ).
1.3.1.2 Empirical
An empirical literature review collects, creates, arranges, and analyzes numeric data reflecting the frequency of themes, topics, authors and/or methods found in existing literature. Empirical literature reviews present their summaries in quantifiable terms using descriptive and inferential statistics.
Examples of an Empirical Review:
- Nursing : False-positive findings in Cochrane meta-analyses with and without application of trial sequential analysis: An empirical review. ( Imberger, Thorlund, Gluud, & Wettersley, 2016 ).
- Education : Impediments of e-learning adoption in higher learning institutions of Tanzania: An empirical review ( Mwakyusa & Mwalyagile, 2016 ).
1.3.1.3 Exploratory
Unlike a synoptic literature review, the purpose here is to provide a broad approach to the topic area. The aim is breadth rather than depth and to get a general feel for the size of the topic area. A graduate student might do an exploratory review of the literature before beginning a synoptic, or more comprehensive one.
Examples of an Exploratory Review:
- Education : University research management: An exploratory literature review. ( Schuetzenmeister, 2010 ).
- Education : An exploratory review of design principles in constructivist gaming learning environments. ( Rosario & Widmeyer, 2009 ).

1.3.1.4 Focused
A type of literature review limited to a single aspect of previous research, such as methodology. A focused literature review generally will describe the implications of choosing a particular element of past research, such as methodology in terms of data collection, analysis and interpretation.
Examples of a Focused Review:
- Nursing : Clinical inertia in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus: A focused literature review. ( Khunti, Davies, & Khunti, 2015 ).
- Education : Language awareness: Genre awareness-a focused review of the literature. ( Stainton, 1992 ).
1.3.1.5 Integrative
Critiques past research and draws overall conclusions from the body of literature at a specified point in time. Reviews, critiques, and synthesizes representative literature on a topic in an integrated way. Most integrative reviews are intended to address mature topics or emerging topics. May require the author to adopt a guiding theory, a set of competing models, or a point of view about a topic. For more description of integrative reviews, see Whittemore & Knafl (2005).
Examples of an Integrative Review:
- Nursing : Interprofessional teamwork and collaboration between community health workers and healthcare teams: An integrative review. ( Franklin, Bernhardt, Lopez, Long-Middleton, & Davis, 2015 ).
- Education : Exploring the gap between teacher certification and permanent employment in Ontario: An integrative literature review. ( Brock & Ryan, 2016 ).
1.3.1.6 Meta-analysis
A subset of a systematic review, that takes findings from several studies on the same subject and analyzes them using standardized statistical procedures to pool together data. Integrates findings from a large body of quantitative findings to enhance understanding, draw conclusions, and detect patterns and relationships. Gather data from many different, independent studies that look at the same research question and assess similar outcome measures. Data is combined and re-analyzed, providing a greater statistical power than any single study alone. It’s important to note that not every systematic review includes a meta-analysis but a meta-analysis can’t exist without a systematic review of the literature.
Examples of a Meta-Analysis:
- Education : Efficacy of the cooperative learning method on mathematics achievement and attitude: A meta-analysis research. ( Capar & Tarim, 2015 ).
- Nursing : A meta-analysis of the effects of non-traditional teaching methods on the critical thinking abilities of nursing students. ( Lee, Lee, Gong, Bae, & Choi, 2016 ).
- Education : Gender differences in student attitudes toward science: A meta-analysis of the literature from 1970 to 1991. ( Weinburgh, 1995 ).
1.3.1.7 Narrative/Traditional
An overview of research on a particular topic that critiques and summarizes a body of literature. Typically broad in focus. Relevant past research is selected and synthesized into a coherent discussion. Methodologies, findings and limits of the existing body of knowledge are discussed in narrative form. Sometimes also referred to as a traditional literature review. Requires a sufficiently focused research question. The process may be subject to bias that supports the researcher’s own work.
Examples of a Narrative/Traditional Review:
- Nursing : Family carers providing support to a person dying in the home setting: A narrative literature review. ( Morris, King, Turner, & Payne, 2015 ).
- Education : Adventure education and Outward Bound: Out-of-class experiences that make a lasting difference. ( Hattie, Marsh, Neill, & Richards, 1997 ).
- Education : Good quality discussion is necessary but not sufficient in asynchronous tuition: A brief narrative review of the literature. ( Fear & Erikson-Brown, 2014 ).
- Nursing : Outcomes of physician job satisfaction: A narrative review, implications, and directions for future research. ( Williams & Skinner, 2003 ).
1.3.1.8 Realist
Aspecific type of literature review that is theory-driven and interpretative and is intended to explain the outcomes of a complex intervention program(s).
Examples of a Realist Review:
- Nursing : Lean thinking in healthcare: A realist review of the literature. ( Mazzacato, Savage, Brommels, 2010 ).
- Education : Unravelling quality culture in higher education: A realist review. ( Bendermacher, Egbrink, Wolfhagen, & Dolmans, 2017 ).
1.3.1.9 Scoping
Tend to be non-systematic and focus on breadth of coverage conducted on a topic rather than depth. Utilize a wide range of materials; may not evaluate the quality of the studies as much as count the number. One means of understanding existing literature. Aims to identify nature and extent of research; preliminary assessment of size and scope of available research on topic. May include research in progress.
Examples of a Scoping Review:
- Nursing : Organizational interventions improving access to community-based primary health care for vulnerable populations: A scoping review. ( Khanassov, Pluye, Descoteaux, Haggerty, Russell, Gunn, & Levesque, 2016 ).
- Education : Interdisciplinary doctoral research supervision: A scoping review. ( Vanstone, Hibbert, Kinsella, McKenzie, Pitman, & Lingard, 2013 ).
- Nursing : A scoping review of the literature on the abolition of user fees in health care services in Africa. ( Ridde, & Morestin, 2011 ).
1.3.1.10 Synoptic
Unlike an exploratory review, the purpose is to provide a concise but accurate overview of all material that appears to be relevant to a chosen topic. Both content and methodological material is included. The review should aim to be both descriptive and evaluative. Summarizes previous studies while also showing how the body of literature could be extended and improved in terms of content and method by identifying gaps.
Examples of a Synoptic Review:
- Education : Theoretical framework for educational assessment: A synoptic review. ( Ghaicha, 2016 ).
- Education : School effects research: A synoptic review of past efforts and some suggestions for the future. ( Cuttance, 1981 ).
1.3.1.11 Systematic Review
A rigorous review that follows a strict methodology designed with a presupposed selection of literature reviewed. Undertaken to clarify the state of existing research, the evidence, and possible implications that can be drawn from that. Using comprehensive and exhaustive searching of the published and unpublished literature, searching various databases, reports, and grey literature. Transparent and reproducible in reporting details of time frame, search and methods to minimize bias. Must include a team of at least 2-3 and includes the critical appraisal of the literature. For more description of systematic reviews, including links to protocols, checklists, workflow processes, and structure see “ A Young Researcher’s Guide to a Systematic Review “.
Examples of a Systematic Review:
- Education : The potentials of using cloud computing in schools: A systematic literature review ( Hartmann, Braae, Pedersen, & Khalid, 2017 )
- Nursing : Is butter back? A systematic review and meta-analysis of butter consumption and risk of cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and total mortality. ( Pimpin, Wu, Haskelberg, Del Gobbo, & Mozaffarian, 2016 ).
- Education : The use of research to improve professional practice: a systematic review of the literature. ( Hemsley-Brown & Sharp, 2003 ).
- Nursing : Using computers to self-manage type 2 diabetes. ( Pal, Eastwood, Michie, Farmer, Barnard, Peacock, Wood, Inniss, & Murray, 2013 ).
1.3.1.12 Umbrella/Overview of Reviews
Compiles evidence from multiple systematic reviews into one document. Focuses on broad condition or problem for which there are competing interventions and highlights reviews that address those interventions and their effects. Often used in recommendations for practice.
Examples of an Umbrella/Overview Review:
- Education : Reflective practice in healthcare education: An umbrella review. ( Fragknos, 2016 ).
- Nursing : Systematic reviews of psychosocial interventions for autism: an umbrella review. ( Seida, Ospina, Karkhaneh, Hartling, Smith, & Clark, 2009 ).
For a brief discussion see “ Not all literature reviews are the same ” (Thomson, 2013).
1.4 Why do a Literature Review?
The purpose of the literature review is the same regardless of the topic or research method. It tests your own research question against what is already known about the subject.
1.4.1 First – It’s part of the whole. Omission of a literature review chapter or section in a graduate-level project represents a serious void or absence of critical element in the research process.
The outcome of your review is expected to demonstrate that you:
- can systematically explore the research in your topic area
- can read and critically analyze the literature in your discipline and then use it appropriately to advance your own work
- have sufficient knowledge in the topic to undertake further investigation
1.4.2 Second – It’s good for you!
- You improve your skills as a researcher
- You become familiar with the discourse of your discipline and learn how to be a scholar in your field
- You learn through writing your ideas and finding your voice in your subject area
- You define, redefine and clarify your research question for yourself in the process
1.4.3 Third – It’s good for your reader. Your reader expects you to have done the hard work of gathering, evaluating and synthesizes the literature. When you do a literature review you:
- Set the context for the topic and present its significance
- Identify what’s important to know about your topic – including individual material, prior research, publications, organizations and authors.
- Demonstrate relationships among prior research
- Establish limitations of existing knowledge
- Analyze trends in the topic’s treatment and gaps in the literature
1.4.4 Why do a literature review?
- To locate gaps in the literature of your discipline
- To avoid reinventing the wheel
- To carry on where others have already been
- To identify other people working in the same field
- To increase your breadth of knowledge in your subject area
- To find the seminal works in your field
- To provide intellectual context for your own work
- To acknowledge opposing viewpoints
- To put your work in perspective
- To demonstrate you can discover and retrieve previous work in the area
1.5 Common Literature Review Errors
Graduate-level literature reviews are more than a summary of the publications you find on a topic. As you have seen in this brief introduction, literature reviews are a very specific type of research, analysis, and writing. We will explore these topics more in the next chapters. Some things to keep in mind as you begin your own research and writing are ways to avoid the most common errors seen in the first attempt at a literature review. For a quick review of some of the pitfalls and challenges a new researcher faces when he/she begins work, see “ Get Ready: Academic Writing, General Pitfalls and (oh yes) Getting Started! ”.
As you begin your own graduate-level literature review, try to avoid these common mistakes:
- Accepts another researcher’s finding as valid without evaluating methodology and data
- Contrary findings and alternative interpretations are not considered or mentioned
- Findings are not clearly related to one’s own study, or findings are too general
- Insufficient time allowed to define best search strategies and writing
- Isolated statistical results are simply reported rather than synthesizing the results
- Problems with selecting and using most relevant keywords, subject headings and descriptors
- Relies too heavily on secondary sources
- Search methods are not recorded or reported for transparency
- Summarizes rather than synthesizes articles
In conclusion, the purpose of a literature review is three-fold:
- to survey the current state of knowledge or evidence in the area of inquiry,
- to identify key authors, articles, theories, and findings in that area, and
- to identify gaps in knowledge in that research area.
A literature review is commonly done today using computerized keyword searches in online databases, often working with a trained librarian or information expert. Keywords can be combined using the Boolean operators, “and”, “or” and sometimes “not” to narrow down or expand the search results. Once a list of articles is generated from the keyword and subject heading search, the researcher must then manually browse through each title and abstract, to determine the suitability of that article before a full-text article is obtained for the research question.
Literature reviews should be reasonably complete, and not restricted to a few journals, a few years, or a specific methodology or research design. Reviewed articles may be summarized in the form of tables, and can be further structured using organizing frameworks such as a concept matrix.
A well-conducted literature review should indicate whether the initial research questions have already been addressed in the literature, whether there are newer or more interesting research questions available, and whether the original research questions should be modified or changed in light of findings of the literature review.
The review can also provide some intuitions or potential answers to the questions of interest and/or help identify theories that have previously been used to address similar questions and may provide evidence to inform policy or decision-making. ( Bhattacherjee, 2012 ).

Read Abstract 1. Refer to Types of Literature Reviews. What type of literature review do you think this study is and why? See the Answer Key for the correct response.
Nursing : To describe evidence of international literature on the safe care of the hospitalised child after the World Alliance for Patient Safety and list contributions of the general theoretical framework of patient safety for paediatric nursing.
An integrative literature review between 2004 and 2015 using the databases PubMed, Cumulative Index of Nursing and Allied Health Literature (CINAHL), Scopus, Web of Science and Wiley Online Library, and the descriptors Safety or Patient safety, Hospitalised child, Paediatric nursing, and Nursing care.
Thirty-two articles were analysed, most of which were from North American, with a descriptive approach. The quality of the recorded information in the medical records, the use of checklists, and the training of health workers contribute to safe care in paediatric nursing and improve the medication process and partnerships with parents.
General information available on patient safety should be incorporated in paediatric nursing care. ( Wegner, Silva, Peres, Bandeira, Frantz, Botene, & Predebon, 2017 ).
Read Abstract 2. Refer to Types of Literature Reviews. What type of lit review do you think this study is and why? See the Answer Key for the correct response.
Education : The focus of this paper centers around timing associated with early childhood education programs and interventions using meta-analytic methods. At any given assessment age, a child’s current age equals starting age, plus duration of program, plus years since program ended. Variability in assessment ages across the studies should enable everyone to identify the separate effects of all three time-related components. The project is a meta-analysis of evaluation studies of early childhood education programs conducted in the United States and its territories between 1960 and 2007. The population of interest is children enrolled in early childhood education programs between the ages of 0 and 5 and their control-group counterparts. Since the data come from a meta-analysis, the population for this study is drawn from many different studies with diverse samples. Given the preliminary nature of their analysis, the authors cannot offer conclusions at this point. ( Duncan, Leak, Li, Magnuson, Schindler, & Yoshikawa, 2011 ).
Test Yourself
See Answer Key for the correct responses.
The purpose of a graduate-level literature review is to summarize in as many words as possible everything that is known about my topic.
A literature review is significant because in the process of doing one, the researcher learns to read and critically assess the literature of a discipline and then uses it appropriately to advance his/her own research.
Read the following abstract and choose the correct type of literature review it represents.
Nursing: E-cigarette use has become increasingly popular, especially among the young. Its long-term influence upon health is unknown. Aim of this review has been to present the current state of knowledge about the impact of e-cigarette use on health, with an emphasis on Central and Eastern Europe. During the preparation of this narrative review, the literature on e-cigarettes available within the network PubMed was retrieved and examined. In the final review, 64 research papers were included. We specifically assessed the construction and operation of the e-cigarette as well as the chemical composition of the e-liquid; the impact that vapor arising from the use of e-cigarette explored in experimental models in vitro; and short-term effects of use of e-cigarettes on users’ health. Among the substances inhaled by the e-smoker, there are several harmful products, such as: formaldehyde, acetaldehyde, acroleine, propanal, nicotine, acetone, o-methyl-benzaldehyde, carcinogenic nitrosamines. Results from experimental animal studies indicate the negative impact of e-cigarette exposure on test models, such as ascytotoxicity, oxidative stress, inflammation, airway hyper reactivity, airway remodeling, mucin production, apoptosis, and emphysematous changes. The short-term impact of e-cigarettes on human health has been studied mostly in experimental setting. Available evidence shows that the use of e-cigarettes may result in acute lung function responses (e.g., increase in impedance, peripheral airway flow resistance) and induce oxidative stress. Based on the current available evidence, e-cigarette use is associated with harmful biologic responses, although it may be less harmful than traditional cigarettes. (J ankowski, Brożek, Lawson, Skoczyński, & Zejda, 2017 ).
- Meta-analysis
- Exploratory
Education: In this review, Mary Vorsino writes that she is interested in keeping the potential influences of women pragmatists of Dewey’s day in mind while presenting modern feminist re readings of Dewey. She wishes to construct a narrowly-focused and succinct literature review of thinkers who have donned a feminist lens to analyze Dewey’s approaches to education, learning, and democracy and to employ Dewey’s works in theorizing on gender and education and on gender in society. This article first explores Dewey as both an ally and a problematic figure in feminist literature and then investigates the broader sphere of feminist pragmatism and two central themes within it: (1) valuing diversity, and diverse experiences; and (2) problematizing fixed truths. ( Vorsino, 2015 ).
Image Attributions
Literature Reviews for Education and Nursing Graduate Students Copyright © by Linda Frederiksen is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

- Research Guides
- CECH Library
Education Basics
Literature review overview.
- Article and Media Sources
- Quick Stats and Reference
- OAE and Praxis Core
- Citation & Annotation
There are eight general steps in conducting an education literature review. Please follow the eight numbered boxes, starting below.
Please note that the general framework for this guide is derived from the work of Joyce P. Gall, M.D. Gall, and Walter R. Borg in Applying Educational Research: a Practical Guide (5th ed., 2005). Also, much of the information on framing the research question comes from Emily Grimm's Selected Reference Sources for Graduate Students in Education and Education Related Areas (1995).
Step 1: Frame Your Research Question(s)
Basic Questions
- What do I want to know? For what purpose? Consider subject terms, synonyms, related concepts and approaches.
- What do I know already?
- Who else might have performed similar research and why? Consider individuals, institutions, governmental agencies and other groups.
- What summarizing or descriptive information is already available? Consider the secondary sources found below.
Time Questions
- For which time span(s) do I need information?
- Would recurrent or temporal events in education affect my research? For example: school terms, budget hearings, conference proceedings, legislative sessions, policy decisions, elections, administrative procedural changes.
Limitation(s) Questions
- Do I have other limitations? For example: language, age group, grade level, type of student, type of school, type of district, geography, curricular area, or style of teaching.
Aspect Questions
- What aspects of education interest me? For example: financial, administrative, teaching, legislative, gender, parental, theoretical, research, developmental, practical or other.
Subjective Aspect Questions
- What are my values, prejudices, biases, and areas of ignorance in regard to my research question(s)?
- Will I let these prejudices limit my research?
- Will I let these prejudices influence my note taking, choice of vocabulary and indexing terms, selection of data, evaluations of the work of other researchers, inclusion of conflicting theories, reporting of data, or my conclusions?
Step 2: Contact Experts to Get Answers or for Guidance to Relevant Publications
Consider consulting other educators, faculty or government officials who may specialize in your research area.
You may also want to consult the American Educational Research Association SIG (Special Interest Group) website for the names of groups and individuals who have expertise in different educational areas. AERA provides the names, addresses, e-mail addresses, and phone numbers of individuals doing research in a variety of areas.
Step 3: Read Secondary Sources to Gain a Broad Overview of the Literature Related to Your Research Area
Use secondary sources to further define your research question and to expand your literature search. Secondary sources include encyclopedias, handbooks, dictionaries, and thesauri. Secondary sources are resources that review research that others have done. They provide a general overview, will give you ideas for key search terms, and often include useful bibliographies for further reading.
Here are some key secondary sources and books on doing educational research:
- Review of Educational Research The Review of Educational Research (RER) publishes critical, integrative reviews of research literature bearing on education, including conceptualizations, interpretations, and syntheses of literature and scholarly work in a field broadly relevant to education and educational research.
- Educational Psychology Review Educational Psychology Review is an international forum for the publication of peer-reviewed integrative review articles, special thematic issues, reflections or comments on previous research or new research directions, interviews, and research-based advice for practitioners.
- Doing educational research : a guide to first-time researchers CECH Prof Ed LB1028 .D65 2004
- Effective action research: developing reflective thinking and practice Electronic (2011)
- Encyclopedia of Education Electronic and Langsam Library Reference, LB 15 .E47 2003
- Encyclopedia of Special Education [electronic resource] : a Reference for the Education of Children, Adolescents, and Adults with Disabilities and other Exceptional Individuals Electronic, 2007.
- Handbook of research on educational communications and technology CECH Library Reference, LB 1028.3 . H355 2008
- Handbook of research on multicultural education CECH Library Reference, LC 1099.3 .H35 2004
- Handbook of research on teaching CECH Library Reference, LB1028 .S39 2001
- How to design and evaluate research in education CECH Reserves LB1028 .F665 2012
- Methods in educational research: from theory to practice Electronic (2010)
- The Phi Delta Kappan [electronic resource] Electronic, Contains many articles that cite research and analyze practical implications.
- The Routledge International Encyclopedia of Education CECH Library Reference, LB 15 .R633 2008
Step 4: Select Preliminary Sources that Index Relevant Research Literature
Preliminary sources index primary research resources such as journal articles, conference proceeding papers, technical reports, government documents, dissertations and more. The CECH Library has created several specialized library guides on topics such as special education, instructional design & technology, and teaching STEM related topics that list which resources are most helpful for doing research in these areas. See below for key databases in education:
Step 5: Identify Subject Terms, or Descriptors, and Use Them to Search Preliminary Sources
Choosing the most appropriate subject search terms, or descriptors, for searching indexes and catalogs can greatly influence your search results. A good place to start is ERIC's thesaurus of descriptors:
Step 6: Read and Evaluate Primary Sources Discovered Through Indexes
For assistance in obtaining copies of primary sources, please consult your liaison librarian .
As you print out copies of articles, review copies of books or reports, remember to look in the sources for bibliographies, names of individuals or groups who have done research on the topic, and for additional subject terms to help you narrow or broaden your research.
Step 7: Classify the Publications You Have Reviewed into Meaningful Categories
As you review the sources you find, classify them into meaningful categories. This will help you prioritize reading them and may indicate useful ways to synthesize what you discover. You may want to create a simple code for the different categories.
Step 8: Prepare Your Literature Review Report
See the following resources for advice on preparing a literature review report:
- << Previous: OAE and Praxis Core
- Next: Citation & Annotation >>
- Last Updated: Apr 30, 2024 11:57 AM
- URL: https://guides.libraries.uc.edu/edbasics
University of Cincinnati Libraries
PO Box 210033 Cincinnati, Ohio 45221-0033
Phone: 513-556-1424
Contact Us | Staff Directory
University of Cincinnati
Alerts | Clery and HEOA Notice | Notice of Non-Discrimination | eAccessibility Concern | Privacy Statement | Copyright Information
© 2021 University of Cincinnati
- Skip to Guides Search
- Skip to breadcrumb
- Skip to main content
- Skip to footer
- Skip to chat link
- Report accessibility issues and get help
- Go to Penn Libraries Home
- Go to Franklin catalog
Education: Literature Reviews
- Handbooks, Encyclopedias, Dictionaries
- Books and Searchable E-Book Collections
- Articles in Education Databases
- Articles in Subject Databases
- Articles in Multidisciplinary Databases
- Full-text Dissertations
- Open Access
- Publications, Reports, Working Papers
- Literature Reviews
- Research Methods
- How to Search Better
- Manage your Citations
- Journal Info / Metrics
- Author Citation Metrics
Getting Started on Literature Reviews
- "Reviewing the Literature" Project Planner SAGE Research Methods. Provides checklists and bullet points for the literature review process, with "Search for reources" links to relevant SAGE Research Methods fulltext books and book chapters.
- "Literature reviews" / Lawrence A. Machi & Brenda T. McEvoy Oxford Bibliographies : Education, 2016. An annotated bibliography identifying and describing books and articles on the theory of literature reviews, their variety, and how to write them.
Selected Books on Writing Literature Reviews
Search Databases for Literature Review Articles and Overview Publications
- ERIC (ProQuest) Filter search results for Document Type = 070 : Information Analyses and 130 : Reference Materials - Bibliographies. ERIC Digests, research syntheses produced by ERIC ceased after ERIC's reform that closed its research-monitoring clearinghouses in the early 2000s. The ERIC database continues to make available the 3,000+ ERIC Digest published in 1980-2003. They may be found in ERIC (ProQuest) using the search filter for Document type = 073
- APA PsycInfo PsycINFO has a Methodology limit, with values of Literature review, Systematic Review, or Meta-analysis.
- Web of Science (WOS) Don't be misled by "science" in the title. WOS also covers the humanities and social sciences. On the left, under Refine Results, Select REVIEWS under Document Types. This is a limit for literature reviews or overview articles. THis may not get all lit reviews. Consider also searching the TS field (Title, Abstract, Author Keyword, Keywords Plus®) with meta-analysis, metaanalysis, synthesis, overview.
- Scopus Do a search in Scopus for a keyword. Then refine the results by selected under "Document type" - review.
- PubMed Perform a search, then under Article Type on the right, see Reviews or Systematic Reviews.
- ProQuest Dissertations & Theses Global: Full Collection Dissertations can sometimes be useful for review-type surveys of the literature on a specific field. Most often authors begin their study with a review of the literature in order to offer context for their contribution.
Selected Journals with Review Articles
- Review of Educational Research (RER) SAGE, for American Educational Research Association (AERA), 1931- . Publishes critical, integrative reviews of research literature bearing on education, including conceptualizations, interpretations, and syntheses of literature and scholarly work in a field broadly relevant to education and educational research.
- Review of Research in Education (RRE) SAGE, for AERA, 1973- . Each RRE annual volume is devoted to a single topic, with research syntheses and literature reviews.
- Educational Research Review Elsevier, for European Association for Research on Learning and Instruction (EARLI), 2006- .
- Campbell Systematic Reviews Wiley, for Campbell Collaboration, 2004- . CSR publishes finalized systematic reviews developed through the Campbell Collaboration. Subjects include education and child welfare.
- Educational Psychology Review An international forum for the publication of peer-reviewed integrative review articles, special thematic issues, reflections or comments on previous research or new research directions, interviews, and research-based advice for practitioners - all pertaining to the field of educational psychology.
- Annual Reviews AnnRev publishes literature-review journals in physical, life and social sciences. Includes anthropology, economics, linguistics, public health, psychology, and sociology. Education topics may be found in many of these discipline-specific journals.
- Annals of the American Academy of Political and Social Science SAGE, for AAPSS, 1890- . Penn's house journal for the social sciences, and one of the oldest US scholarly journals. Each issue presents research syntheses on a specific topic, with one issue per year focusing on education or child welfare.
- Emerging Trends in the Social and Behavioral sciences Wiley, 2015-201?. Review articles on new research fronts. Includes a recurring section on "Educational Institutions" .
Systematic Review Databases
- Systematic Review Data Repository (SRDR) U.S. Department of Health and Human Services - open and searchable archive of systematic reviews and their data.
- Campbell Collaboration - Library of Systematic Reviews Systematic reviews in areas such as education, criminal justice, social policy and social care. (The Campbell Collaboration was formally established at a meeting at the University of Pennsylvania on 24-25 February 2000.)
- EPPI-Centre The Evidence for Policy and Practice Information and Co-ordinating Centre (EPPI-Centre) is part of the Social Science Research Unit at the Institute of Education, University of London. EPPI develops systematic reviews and developing review methods in social science and public policy.
- Cochrane Collaboration Cochrane Reviews are systematic reviews of primary research in human health care and health policy. Since 2011, Cochrane has an official partnership with the WHO.
- What Works Clearinghouse - U.S. Department of Education
- << Previous: Publications, Reports, Working Papers
- Next: Research Methods >>
- Last Updated: Apr 16, 2024 8:23 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.upenn.edu/education

- Library Search
- View Library Account
- The Claremont Colleges Library
- Research Guides
- Conducting a Literature Review
- Getting Started With Research
- Finding Scholarly Articles
- Finding Books & Papers
- Finding Education Data & Testing Resources
What is a Literature Review?
Basics of a literature review, types of literature reviews.
- Citing Your Information (Attribution)
A Literature Review is a systematic and comprehensive analysis of books, scholarly articles and other sources relevant to a specific topic providing a base of knowledge on a topic. Literature reviews are designed to identify and critique the existing literature on a topic to justify your research by exposing gaps in current research . This investigation should provide a description, summary, and critical evaluation of works related to the research problem and should also add to the overall knowledge of the topic as well as demonstrating how your research will fit within a larger field of study. A literature review should offer critical analysis of the current research on a topic and that analysis should direct your research objective. This should not be confused with a book review or an annotated bibliography both research tools but very different in purpose and scope. A Literature Review can be a stand alone element or part of a larger end product, know your assignment. Key to a good Literature Review is to document your process. For more information see:
Planning a Literature Review .
There are many different ways to organize your references in a literature review, but most reviews contain certain basic elements.
- Objective of the literature review - Clearly describe the purpose of the paper and state your objectives in completing the literature review.
- Overview of the subject, issue or theory under consideration – Give an overview of your research topic and what prompted it.
- Categorization of sources – Grouping your research either historic, chronologically or thematically
- Organization of Subtopics – Subtopics should be grouped and presented in a logical order starting with the most prominent or significant and moving to the least significant
- Discussion – Provide analysis of both the uniqueness of each source and its similarities with other source
- Conclusion - Summary of your analysis and evaluation of the reviewed works and how it is related to its parent discipline, scientific endeavor or profession
As Kennedy (2007) notes*, it is important to think of knowledge in a given field as consisting of three layers. First, there are the primary studies that researchers conduct and publish. Second are the reviews of those studies that summarize and offer new interpretations built from and often extending beyond the original studies. Third, there are the perceptions, conclusions, opinion, and interpretations that are shared informally that become part of the lore of field. In composing a literature review, it is important to note that it is often this third layer of knowledge that is cited as "true" even though it often has only a loose relationship to the primary studies and secondary literature reviews.
Given this, while literature reviews are designed to provide an overview and synthesis of pertinent sources you have explored, there are several approaches to how they can be done, depending upon the type of analysis underpinning your study. Listed below are definitions of types of literature reviews:
Argumentative Review This form examines literature selectively in order to support or refute an argument, deeply imbedded assumption, or philosophical problem already established in the literature. The purpose is to develop a body of literature that establishes a contrarian viewpoint. Given the value-laden nature of some social science research [e.g., educational reform; immigration control], argumentative approaches to analyzing the literature can be a legitimate and important form of discourse. However, note that they can also introduce problems of bias when they are used to to make summary claims of the sort found in systematic reviews.
Integrative Review Considered a form of research that reviews, critiques, and synthesizes representative literature on a topic in an integrated way such that new frameworks and perspectives on the topic are generated. The body of literature includes all studies that address related or identical hypotheses. A well-done integrative review meets the same standards as primary research in regard to clarity, rigor, and replication.
Historical Review Few things rest in isolation from historical precedent. Historical reviews are focused on examining research throughout a period of time, often starting with the first time an issue, concept, theory, phenomena emerged in the literature, then tracing its evolution within the scholarship of a discipline. The purpose is to place research in a historical context to show familiarity with state-of-the-art developments and to identify the likely directions for future research.
Methodological Review A review does not always focus on what someone said [content], but how they said it [method of analysis]. This approach provides a framework of understanding at different levels (i.e. those of theory, substantive fields, research approaches and data collection and analysis techniques), enables researchers to draw on a wide variety of knowledge ranging from the conceptual level to practical documents for use in fieldwork in the areas of ontological and epistemological consideration, quantitative and qualitative integration, sampling, interviewing, data collection and data analysis, and helps highlight many ethical issues which we should be aware of and consider as we go through our study.
Systematic Review This form consists of an overview of existing evidence pertinent to a clearly formulated research question, which uses pre-specified and standardized methods to identify and critically appraise relevant research, and to collect, report, and analyse data from the studies that are included in the review. Typically it focuses on a very specific empirical question, often posed in a cause-and-effect form, such as "To what extent does A contribute to B?"
Theoretical Review The purpose of this form is to concretely examine the corpus of theory that has accumulated in regard to an issue, concept, theory, phenomena. The theoretical literature review help establish what theories already exist, the relationships between them, to what degree the existing theories have been investigated, and to develop new hypotheses to be tested. Often this form is used to help establish a lack of appropriate theories or reveal that current theories are inadequate for explaining new or emerging research problems. The unit of analysis can focus on a theoretical concept or a whole theory or framework.
* Kennedy, Mary M. "Defining a Literature." Educational Researcher 36 (April 2007): 139-147.
All content is from The Literature Review created by Dr. Robert Larabee USC
- << Previous: Finding Education Data & Testing Resources
- Next: Citing Your Information (Attribution) >>
- : Aug 31, 2023 2:11 PM
- URL: https://libguides.libraries.claremont.edu/education
LIBRARY HOURS:
See All Hours
One Moment...
See Average Occupancy
- Library Search
- Research & Subject Guides
- Library Databases
- Citation Guide
- Borrowing & Renewing
- Interlibrary Loan
- Library Instruction
- Room Reservations
- Course Reserves
- Library Purchase Request
- Open Educational Resources
- University Archives & Special Collections
- Endeavor: Faculty & Student Publications
- PA History Harvest
- Newspapers & News Sources
- Contact a Librarian
- Meet with a Librarian
- Find My Librarian
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Library Floor Maps
- Library Mission Statement
- Library Directory
- Friends of the Library
- Donate to the Library
- Library Account
Education Research Guide: How to Write a Literature Review
- Journal Articles
- Books for Children / Young Adults
- How to Write a Literature Review
- Library Session Survey
Literature Reviews Explained
Use the articles below to learn about:
- what a literature review is
- how to select and research a topic
- how to write a literature review
- University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill The Writing Center: Literature Reviews
- OWL (Purdue University Online Writing Lab): Using APA to format your Literature Review
Synthesizing Explained
Synthesizing is a method of analyzing the main ideas and important information from your sources as you read and prepare to write a literature review. Review the resources below for sample synthesizing methods. Both examples have tables you can fill out as you read articles to help you organize your thoughts.
- Writing a Literature Review and Using a Synthesis Matrix: NC University Tutorial Center
- Matrix Example from the University of West Florida Libraries
- Synthesizing Cornelsen This article is included in "Writing a Literature Review and Using a Synthesis Matrix" to illustrate synthesizing articles in the sample matrix.
- Synthesizing: Bruley This article is included in "Writing a Literature Review and Using a Synthesis Matrix" to illustrate synthesizing articles in the sample matrix.
Sample Literature Reviews
Make sure you follow any instructions from you professor on how to format your literature review! Use the examples below to get ideas for how you might write about the sources you found in your research.
- Literature Review 1
- Literature Review 2
- Literature Review 3
- << Previous: Websites
- Next: Cite It >>
- Last Updated: May 10, 2024 1:02 PM
- URL: https://library.susqu.edu/education
Blough-Weis Library
514 University Avenue
Selinsgrove, PA 17870
[email protected] | 570.372.4160

LIBRARY COLLECTIONS
- Search the Library


Educational Leadership: Literature Review Strategies
- Literature Review Strategies
- Search Tips
What's a Literature Review?
A Literature Review...
- Provides comprehensive discussion of the scholarly research that has already been done on a topic.
- Includes some summary of important articles on a topic.
- Includes comparison: between how different authors discuss the same topic and how the topic has been handled over time.
- Synthesizes previous ideas on a topic, but also looks for gaps in the literature: what needs to be investigated further?
What Should a Literature Review Do?
A Literature Review should...
- Relate directly and clearly to your thesis or research question.
- Synthesize and contextualize results, not just report them.
- Identify areas of controversy in the literature.
- Formulate questions that need further research.
Adapted from “The Literature Review: A Few Tips on Conducting It”, by Dena Taylor and Margaret Procter, University of Toronto: www.writing.utoronto.ca (file linked below)
- The Literature Review: A Few Tips on Conducting It This two-page PDF handout created by Dena Taylor and Margaret Procter at the University of Toronto has excellent guidance on conducting a literature review.
Literature Review Search Strategies
Strategies for a literature review search...
- Comb through bibliographies of relevant journal articles and books. You'll probably start to see patterns: authors, journals, and themes that show up over and over.
- Find Full Text through the Library : If you find an article in a bibliography that you’d like to access, look for the journal name (not the article name), and follow the steps outlined under the Finding Full-text Material tab in our How to find Full Text Guide .
- Can't get the article you need in full text through PSU? Don't Despair: Try Interlibrary Loan !
- Find out who cited an article , and how many times it was cited, through Google Scholar . This will show you how influential an article was and gives you more articles and authors to investigate.
- Learn How to Gut a Book -- in other words, how to get the most out of a book in the most efficient manner (i.e. it may not be necessary to read an entire book, word for word, taking diligent notes in order to get the gist of the book for use in a literature review).
Journal Ranking, Publication Outlets, Scholarly Communication
What are the top journals in your field? Which journals are the best for your topic?
The following resources can help you answer the following questions, which can be helpful to consider when performing a literature review:
- SCImago Journal & Country Rank Journals and country scientific indicators based on data in the Scopus® database.
- Eigenfactor Free website ranking and mapping academic journals.
- Academic Publishing Information on authors' rights, copyright, open access, and more.
Cited Reference Search
How many times has one of the articles you're using in your literature review been cited?
The answer to that question can tell you not only how influential an article has been, but can lead you to more articles on your topic. Use the following to find out how many times the article you're using has been cited:
Getting Started With Research: Tutorials
Need more help getting started with research? Check out the Library's video tutorials and playlists .
Please also feel free to contact a librarian .
Literature Reviews: An Overview for Graduate Students
This excellent overview of the literature review explains what a literature review and outlines processes and best practices for doing one. It includes input from an NCSU professor on what a literature review is and what it should do. (Shared under a CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 US license, attributed to North Carolina State University Libraries).
Writing the Literature Review: Part 1
Here's another excellent tutorial on what a literature review is and how to write it, in two parts, from David Taylor at the University of Maryland University College's Writing Program. https://youtu.be/2IUZWZX4OGI
Writing the Literature Review: Part 2
Here's part two of David Taylor's "Writing the Literature Review" tutorial, from the University of Maryland University College's Writing Program. https://youtu.be/UoYpyY9n9YQ
Google Scholar
Google Scholar has been customized by the PSU library to find some full-text articles at PSU!
https://stats.lib.pdx.edu/proxy.php?url=http://scholar.google.com
Google Scholar can be extremely helpful in finding out how many times an article has been cited and who cited an article . This can help you determine how important an article is and which other authors you may want to investigate.
Make sure you're checking your discipline's databases as well, for fuller, more complete scholarly coverage of the journal articles on your topic.
PDX Scholar
It can be helpful to look at the work of your peers to get a sense of how certain kinds of writing and research is done, including the literature review.
You can look at the full text of past dissertations, research, and other scholarly work from PSU students and faculty in the library's digital repository, PDXScholar.
- PDXScholar Portland State University's Digital Repository, PDXScholar, preserves the University's research, unique resources, and other scholarly output with the goal of providing persistent, access to that work.
- << Previous: Citation
- Next: Writing >>
- Last Updated: Apr 10, 2024 4:17 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.pdx.edu/edadmin

Research in Education
- Lit Review - Best Sources
- Books and Dissertations
- Interlibrary Loan
- How-To for Google Scholar
- How-To for ERIC (EBSCO)
- How-To for ERIC (Free)
- How-To for APA PsycInfo
- How-To for OneSearch
- Is it Peer Reviewed?
- Finding the DOI
Contact Your Librarian

Top Sources for Literature Reviews in Education
Eric , education full text , and google scholar - best options for education research.
Use these databases to broaden your literature searches.




Additional Sources for Locating Education Research
Multidisciplinary databases for education research.
Use these databases to broaden your literature searches.



Historical education research .

- Next: Books and Dissertations >>
- Last Updated: Aug 22, 2023 3:29 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.uni.edu/education-research
EDUC 760 Literature Review in Education Research
- Course Description
This course provides education practitioners in the doctoral program with research skills and strategies for conducting a literature review. Critical thinking skills, synthesis of information, and application of the literature are emphasized to support the feasibility and relevance of a research study.
For information regarding prerequisites for this course, please refer to the Academic Course Catalog .
Course Guide
View this course’s outcomes, policies, schedule, and more.*
Requires a student login to access.
*The information contained in our Course Guides is provided as a sample. Specific course curriculum and requirements for each course are provided by individual instructors each semester. Students should not use Course Guides to find and complete assignments, class prerequisites, or order books.
A literature review is a comprehensive investigation of previous research and scholarly articles on a topic. Beginning with a theory that serves to frame, or orient, the study, Chapter Two continues with a comprehensive review of the literature that addresses sufficient directly and indirectly related bodies of literature to show the reader that the researcher has a complete understanding of the topic. By conducting a thorough review, the researcher identifies any gaps in the literature and, therefore, a need for a study. Literature reviews are not merely listings or descriptions of the literature but are critiques of the literature that, when synthesized, create a conversation, or dialogue, among the various scholars that comes alive and inspires your reader to be even more interested in the topic and to be ready to consume the study’s findings. Poor literature reviews reflect poorly on the scholar, and, in the case of Christian scholars, reflect poorly on Christianity. As such, the need for Christian scholars to generate exemplary literature reviews is paramount to representing God as the supreme authority and creator of all knowledge.
Course Assignment
Textbook readings and presentations.
The Claxton and Dolan (2021) textbook is used for this course and includes any readings necessary for the candidate to ensure competence with basic literature review development. Additionally, the Galvan and Galvan (2017) text will be used for supplemental material. Finally, the latest APA Style Guide and dissertation templates are required for this course.
Course Requirements Checklist
As the first activity in this course, the candidate will read the Syllabus and Student Expectations and complete the related checklist found in the Course Overview.
Discussions (2)
Discussions are collaborative learning experiences. Therefore, the candidate will complete the discussions in two parts. First, the candidate will post a new thread of 400-500 words in response to the provided discussion prompt. Then, the candidate will reply to at least two classmates, 150-200 words each reply. (CLO: A, E)
Literature Review: Topic Identification Essay Assignment
The candidate will submit a document containing two paragraphs identifying his/her proposed topic for the dissertation. The first paragraph will identify and discuss the topic, including a brief summary of its social and historical contexts, as well as its relationship to education. The second paragraph will give an explanation as why the candidate considers this a worthwhile topic, which may include personal experience and research goals. At least two scholarly, peer-reviewed articles published within the past five years must be cited in the essay with an appropriate reference page attached. (CLO: A, E)
Literature Review: Overview Assignment
The candidate will submit a document containing a one-paragraph overview for the literature review. The overview will follow the template provided, be written in present tense, and be specific to the candidate’s topic from Module 1 (based upon professor feedback). (CLO: E)
Literature Review: Theory Identification Essay Assignment
The candidate will identify 1-2 theories related to the selected topic of study and write a 2-4 paragraph essay. The first paragraph for each theory will explain the theory using the publication(s) of the primary theorist and at least one other work. In the second paragraph, the candidate will justify why the theory was chosen and connect it to the topic. A correctly formatted reference page must be included. (CLO: B, E)
Literature Review Outline Assignment
The candidate will develop a complete literature review outline that will include an improved overview and identify the theory (or theories) of the Theoretical Framework section based on previous professor feedback. The outline must include a title page, the four required level 1 headings (Overview, Theoretical Framework, Related Literature, and Summary), a one-paragraph (improved) Overview, and the name(s) of the theory (or theories) in the Theoretical Framework. The outline must also include the level 2 and 3 APA headings (headings only) identifying the themes and subthemes of the Related Literature section, the Summary section, and the completed reference list., The outline should be 2-3 pages in length, excluding the title page and reference list section. (CLO: A, B, C, E)
Literature Review: Theoretical Framework Section Assignment
The candidate will write the theoretical framework section of the literature review and include it in the working literature review document with the title page, revised Overview, revised Related Literature outline headings (with sources only, no written content), revised Summary, and reference list pages. The assignment should be a total of 2-3 pages, excluding title and reference list pages. (CLO: B, E)
Literature Review: Synthesis Essay Assignment
The candidate will demonstrate an understanding of how to synthesize literature by researching at least 5 sources related to his/her topic, identifying 2 themes evident across those 5 sources, and synthesizing the concepts and source material related to those two themes. Synthesizing and writing concisely are learned skills, and this assignment is an opportunity to practice those skills. This essay must follow APA standards and will include a title page, 2-3 full pages of content, and a reference list. (CLO: D, E)
Literature Review Rough Draft Assignment
The candidate will develop a rough draft of the literature review including the title page, Overview, Theoretical Framework, Related Literature section, Summary, and reference list. All work must be updated and developed based on previous professor feedback. While the Related Literature section may not include content under every level 2 (or level 3) APA heading, all headings must be updated per professor feedback, and the Summary section must be revised. The document must include a minimum of 4 full pages of content (excluding the title and reference list pages). (CLO: C, D, E)
Literature Review Final Assignment
The candidate will develop a final draft of the literature review containing a minimum of 8 full pages of content (excluding the title and reference list pages). The literature review must also use appropriate APA format, incorporate professor feedback. (CLO: E)
Quizzes (4)
Each quiz will cover the Learn section material for the module in which it is assigned. Each quiz will be open-book/open-notes; contain multiple-choice, true/false, or checklist completion questions; and have a 1-hour time limit. (CLO: D, E)

Have questions about this course or a program?
Speak to one of our admissions specialists.
Inner Navigation
- Assignments
Have questions?

Are you ready to change your future?
Apply FREE This Week*
Request Information
*Some restrictions may occur for this promotion to apply. This promotion also excludes active faculty and staff, military, non-degree-seeking, DGIA, Continuing Education, WSB, and certificate students.

Request Information About a Program
Request info about liberty university online, what program are you interested in, choose a program level.
Choose a program level
Bachelor’s
Master’s
Certificate
Select a Field of Study
Select a field of study
Select a Program
Select a program
Next: Contact Info
Legal first name.
Enter legal first name
Legal Last Name
Enter legal last name
Enter an email address
Enter a phone number
Full Address
Enter an address
Apt., P.O. Box, or can’t find your address? Enter it manually instead .
Select a Country
Street Address
Enter Street Address
Enter State
ZIP/Postal Code
Enter Zip Code
Back to automated address search
Start my application now for FREE

- University of La Verne
- Subject Guides
Literature Review Basics
- Tutorials & Samples
- Literature Review Introduction
- Writing Literature Reviews
- Primary & Secondary Sources
Literature Review Tutorials
- Literature Reviews: An Overview for Students What is a literature review? What purpose does it serve in research? What should you expect when writing one? Find out here in this guide from NCSU libraries.
- Write a Lit Review from Virginia Commonwealth University Follow this guide to learn how to write a literature review, beginning with a synthesis matrix.
- Literature Review: The What, Why and How-to Guide This guide will help you understand what is a Literature Review, why it is important and how it is done. Also includes information on Annotated Bibliographies.
- Writing a Literature Review from the University of Toledo Covers what a lit review is, lit review types, writing a lit review and further readings.
- The Literature Review Process A guide from the University of North Texas on selecting a topic, searching the literature, plan before reviewing, reviewing the literature and writing the review.
- The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill Permission granted to use this guide.
Sample Literature Reviews
- Business Literature Review Example One Sharing economy: A comprehensive literature review
- Business Literature Review Example Two Internet marketing: a content analysis of the research
- Education Literature Review Sample One Teachers’ perception of STEM integration and education: a systematic literature review
- Education Literature Review Sample Two Issues and Challenges for Teaching Successful Online Courses in Higher Education: A Literature Review
- Gerontology Literature Review Sample One Attitudes towards caring for older people: literature review and methodology
- Gerontology Literature Review Sample Two Literature review: understanding nursing competence in dementia care
- Psychology Literature Review Sample One Psychological Correlates of University Students’ Academic Performance: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Psychology Literature Review Sample Two Misuse of Prescription Stimulants Among College Students: A Review of the Literature and Implications for Morphological and Cognitive Effects on Brain Functioning
- Public Administration Literature Review Sample One Considering the Environment in Transportation Planning: Review of Emerging Paradigms and Practice in the United States
- Public Administration Literature Review Sample Two Assessing the impact of research on policy: a literature review
- Sociology Literature Review Sample One Employment Among Current and Former Welfare Recipients: A Literature Review
- Sociology Literature Review Sample Two Deployment and family functioning: A literature review of US operations in Afghanistan and Iraq
- Technology Literature Review Sample One Social media and innovation: A systematic literature review and future research directions
- Technology Literature Review Sample Two Blockchain as a disruptive technology for business: A systematic review
- << Previous: Primary & Secondary Sources
- Last Updated: Jun 28, 2023 9:19 AM
- URL: https://laverne.libguides.com/litreviews

Literature Reviews for Education and Nursing Graduate Students
(15 reviews)
Linda Frederiksen, Washington State University Vancouver
Sue F. Phelps, Washington State University Vancouver
Copyright Year: 2017
Publisher: Rebus Community
Language: English
Formats Available
Conditions of use.
Learn more about reviews.
Reviewed by Rebecca Appleton, Professor of Nursing, Marshall University on 5/7/24
It is very through in covering the steps of a well written literature review read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 5 see less
It is very through in covering the steps of a well written literature review
Content Accuracy rating: 5
I have not read the entire book, but what I did read was very good.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 5
It is up to date, but doing a Literature Review is covered in a step-wise manner, includes writing the LR>
Clarity rating: 5
Very clear step-by-step approach
Consistency rating: 5
It is very consistent!
Modularity rating: 5
Chapters are orderly and succinct
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 5
Strait forward order.
Interface rating: 5
I did not notice Interface issues.
Grammatical Errors rating: 5
No grammatical errors were noticed.
Cultural Relevance rating: 5
I did not notice any problems with cultural Insensitivity
I plan to use this in a Nursing Research class for Graduate Students, and I am trying a new approach to finding the best Research Evidence on a Nursing Topic. Can't wait to see if this help my graduate students understand research literature better.
Reviewed by Barbara Schneider, Professor, University of Texas at Arlington on 4/29/24
This textbook covers the range of topics important for a literature review, including formulating a research question, finding scholarly articles, evaluating sources, and synthesizing source content. The videos are great supplements to the text. read more
This textbook covers the range of topics important for a literature review, including formulating a research question, finding scholarly articles, evaluating sources, and synthesizing source content. The videos are great supplements to the text.
Overall, the content is accurate. Consider labeling Nursing as a health profession/discipline.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 4
Much of the content remains relevant. Updated examples would be helpful to today's graduate students.
The textbook is clearly written.
Consistency rating: 4
In general, the text is consistent. There could be more consistency in the formatting of the references.
The modularity is an asset.
There is a logical flow to the topics.
The links to outside materials are helpful.
No grammatical errors were evident.
The examples seemed inclusive.
Those who are new to writing a literature review would find this book useful.
Reviewed by Yolanda Griffiths, Professor of Occupational Therapy, Drake University on 12/15/21
The authors were thorough and very organized in stepping readers through the process of conducting and writing a literature review. Each area is appropriately indexed and examples are provided in a variety of ways. The synthesis section is... read more
The authors were thorough and very organized in stepping readers through the process of conducting and writing a literature review. Each area is appropriately indexed and examples are provided in a variety of ways. The synthesis section is especially useful as students often do not understand what this means. Perhaps some content on plagiarism would benefit this section as well. The flow of the material easily guides users logically through each topic.
The content is accurate and unbiased. The content is presented in an easy to understand way with videos, and examples.
The relevance of the content is classic and the text should be pertinent for many years. The links included in the text are very useful and should be easy for authors to check periodically. Using a digital media is more relevant to today's students than print textbooks. Each section addresses a reasonable chunk of information.
The book is user friendly, written in an easy to understand manner, and graphics or links add to the understanding of the content. Definitions are clearly written. Such as clarifying the types of literature reviews will be useful for students. Providing a test yourself section at the end of sections allows the reader to check if any content was confusing or not clear.
The text is consistently laid out in a logical manner which helps to unpack content which may be new or unfamiliar to the reader/student.
The amount of content allocated to each chapter is appropriate and will be easy to assign readings. The chapter headings are clear and the embedded videos, charts and test questions enlighten each subunit. The hyperlinking in the table of contents helps to navigate the chapters well.
The organization of the content is logical and easy to understand the process of completing a literature review. The book is laid out much like a road map where students can see the big picture as well as the supporting parts to the process. The references by chapter are very useful.
The graphics were clear, and the non-serif font aids in eye fatigue. One recommendation is to lower the brightness of the bold blue text in the table of contents to reduce eye fatigue. There was no problem to play the videos and the audio was clear. All links worked well.
There were no grammatical errors. There were a few typos such as 1.3.1.8 needs a space between "A specific", 2.3 in the phrase "Articles by the type of periodical in which an article it is published" perhaps remove the word "it", in the table on page 41. under Nursing , the word clinical is spelled "Cclinical", remove the capital C.
No evidence of cultural bias or insensitivity.
I am very excited to use this textbook in my doctoral level occupational therapy class. The inclusion of concise explanations of PICO and SPICE will be very useful. This will be a wonderful resource for graduate students and being mindful of costs for textbooks is compassionate.
Reviewed by Susan Bassett, Instructor, Nursing Graduate Program, Eastern New Mexico University on 11/9/21
Each chapter presented a different aspect of doing a literature review. This was organized and orderly. The index/table of contents was very detailed which allowed the reader to easily use this book as a reference while conducting a literature... read more
Each chapter presented a different aspect of doing a literature review. This was organized and orderly. The index/table of contents was very detailed which allowed the reader to easily use this book as a reference while conducting a literature review.
The content appeared to be entirely accurate. It did a good job of combining information for both education and nursing students. The authors addressed pertinent points of research study development as well as the specific methodology of approaching a research-focused literature review.
The text was up-to-date in methodology, which should not change frequently. The many links to websites were very helpful and yet were basic enough that they should be relevant for years. If they do need updating, the are clearly presented and should be easily updated. The breakdown to very small "chunks" of information per section will help in easily updating specific parts of information.
The book presented a rather complex topic in an extremely straight-forward, easy to read, clear manner. Each small "chunk" of information was identified per section numbering which correlated with movement through the content. The writing was professional and yet not overwhelmed with discipline-specific terminology. Where potentially new terminology was presented, it was immediately followed with definitions and examples.
The book was well-organized and moved along the structure set out early in the book. Content was gradually unfolded, as divided per chapter. There was a bit of repetition (probably about three examples) where the authors attempted to tie information together. Although this stood out to a reader, it seemed more useful in organizing than detrimental in repetition.
The book was subdivided into chapters and then into many small modules of discrete information. It could easily be assigned in part. It could also readily be used as a reference for students to go back and easily find processes or pieces of information they might need later.
I found the continual clear and succinct organization of information to be a defining highlight of this book. When presenting early steps of the research process and then linking these steps with how to conduct a literature review and subsequenty organize and write a literature review, this book is presenting numerous procews steps that must work in tandem. This book did that in a clear and easily readable fashion.
The one feature that did distract me was within the bullet points of 1.3.1. "Types of Reviews". There was a mix of complete and incomplete sentences that worked to convey information succinctly, but distracted me as a reader.
Grammatical Errors rating: 4
I did find several spelling and grammaticl errors (1.3.1.8, , 1.3.1.9, 2.1.1, 2.3, 2.3.1.1, , 2.3.1.4, 2.3 Table A., p. 41, p. 53, p. 54). Although small errors (a few letters or spacing) they should be corrected.
I did not find any mistakes in cultural appropriateness The content did repeatedly talk about bias reduction in the process of writing a literature review
I thought this book was very well-written and contained great information for my students. The links provided were very appropriate and helpful. The Table "Guide to searching for literature at various stages of the scholarly communication process” was particularly helpful. I will immediately begin using portions of the content in this book to support my research class. Additionally, I will recommend the entire book as a reference for the dedicated student (or one intending to go forward to a doctoral level of education in nursing). Thank you for collating all this information and helpful links into one clear, easily readable and understandable document.
Reviewed by Leah Nillas, Associate Professor, Illinois Wesleyan University on 9/6/21
This book addresses the basic steps in the process of writing a literature review research. Chapter 2 (What is a Literature Review?) needs to be retitled. I think Chapter 1 (Introduction) clearly defines and characterizes literature review as a... read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 4 see less
This book addresses the basic steps in the process of writing a literature review research. Chapter 2 (What is a Literature Review?) needs to be retitled. I think Chapter 1 (Introduction) clearly defines and characterizes literature review as a research category. Chapter 2 focuses more on the creation of information, information cycle, and selecting appropriate sources. Chapter 7 (Synthesizing Sources) and Chapter 8 (Writing the Lit Review) can still be improved to incorporate specific strategies in synthesizing research literature and examples of writing styles through analysis of a variety of published examples. Writing a synthesis is a challenging skill for most novice researchers.
Information shared is accurate. I did not notice any content error.
Main content is up-to-date. A few citations maybe dated but they are necessary in illustrating different examples of literature reviews. It will be easy to include additional relevant examples of research work that are published recently.
I like how this text is written. Tone is reader friendly and narrative is accessible to novice researchers.
Clearly consistent throughout the chapters.
Clear and purposeful "chunking" of information per chapter.
Readers can easily follow the organization of topics and content.
No obvious interface issues. Appropriate use of multimedia tools.
No grammatical errors.
Text is culturally sensitive. Additional readings, references, or examples can easily be added to incorporate research conducted by diverse authors or literature reviews which focus on diversity and inclusion issues in education and nursing.
This is a good introductory literature review text even for undergraduate education students. Clear discussion of the nature of the research and the writing process. The use of videos and images is helpful in providing multimodal approach in explaining topics or processes. Writing style and tone make the text accessible to novice researchers.
Reviewed by Rebecca Scheckler, Assistant Professor, Radford University on 7/6/20
Two missing topics were inter-library loan and how to avoid plagiarism in writing up the literature review. This second is such an important topic that it deserves its own chapter. read more
Two missing topics were inter-library loan and how to avoid plagiarism in writing up the literature review. This second is such an important topic that it deserves its own chapter.
It is accurate. I found no inaccuracies.
This book is very relevant. Every advanced undergraduate or graduate students requires such a book
I found the book clear. The videos interspersed within the book added much to the clarity. There are lots of good diagrams that add to the clarity. They are not all original but their sources are all cited. The section on boolean searches, usage of asterisks and quotes in searches is very helpful and appropriate although often left out of discussion of searches.
The book is consistent in terminology and framework.
The chapters were cohesive.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 4
I like the links to within the text to the references and other matter. What is needed are back links to the text from the references. I also would have liked links from the exercises to the answers of the exercises.
Interface rating: 4
See navigation links mentioned above. The grey literature link is broken.
I saw no grammatical problems. There are many bulleted lists rather than text which is appropriate to this topic.
There could be more attention to cultural context in the frequent examples.
I wondered why nursing and education were combined. They are similar in nature but not identical. separation them out into two books might be appropriate.
Reviewed by Lisa Shooman, Associate Professor, Worcester State University on 6/29/20
Overall, this book provides a very comprehensive and thorough roadmap for creating a literature review. The videos assist the reader in crystallizing the information presented in the text. There is an effective index and glossary that provide... read more
Overall, this book provides a very comprehensive and thorough roadmap for creating a literature review. The videos assist the reader in crystallizing the information presented in the text. There is an effective index and glossary that provide helpful navigation to the reader.
The content is detailed, clearly explained, error-free, and unbiased. My students would greatly benefit from the lucid information presented in this text to guide them with developing a literature review. I would be eager to adopt this book for my students.
The content is timely and will not be quickly out-of-date. The quiz questions at the end of each chapter are relevant and will aid students with the consolidation of the material. The online format allows for updating, and the version history at the end of the text clearly indicated that the book was updated recently.
The text is clear and not ridden with any excess jargon /technical terminology. Pictures, graphics, and videos further elucidate the text. There are helpful questions that stimulate thought and lists that help to organize information.
The internal consistency in the text is excellent. However, Chapter 1.1 and Chapter 2 have the same title and it would benefit the reader to have different titles that would highlight the differences between these two sections. Chapter 1.1 is an overview and Chapter 2 dives into more depth.
The text is efficiently divided into smaller reading sections that are demarcated by numbers. The subsections in each chapter can be assigned at different points in the course. The text is organized logically and systematically that assists the reader with comprehension and provides a roadmap for creating an effective literature review.
The entire text is presented coherently and concisely. The organization of the text takes the reader through the process of creating an effective literature review. It can be used by multiple health professions, although the length of the text is relatively short it includes a considerable depth of the material. Other disciplines that would benefit from using this test in their courses may include occupational therapy, physical therapy, and speech and language pathology students.
The interface of the text is simple and easy to follow. The cover of the text would benefit from photos, color, and graphic design to appeal to the modern digital reader.
No grammatical or spelling errors are noted.
No cultural biases existed in the text in any way. There are no individuals highlighted in the book, and due to the technical nature of the subject matter, the text is inclusive to a variety of races, ethnicities, and backgrounds. No offensive statements are included in this book.
The authors should consider including other health professionals in the title and provide examples that can relate to other health professionals throughout the text. Other health professionals that can benefit from reading this text include occupational therapy, physical therapy, and speech and language pathology students. Literature reviews are relevant for many health professionals in their master's and doctorate programs and the text could serve a wider audience.
Reviewed by Ellen Rearick, Assistant Professor, Framingham State University on 6/1/20
This text covers all areas and the process of the integrative review appropriately. It is an engaging text for graduate students new to these assignments. read more
This text covers all areas and the process of the integrative review appropriately. It is an engaging text for graduate students new to these assignments.
This text is well done, very accurate
This text is relevant. The updates needed regarding APA format should be relatively easy to implement.
This text is clear and provides users with definitions and examples of the variety of reviews.
Very well written using consistent terminology throughout.
The text's reading sections are easily accessible and users will find them organized. Each chapter and its sections are presented in the sequence of the process of an integrative review.
Very clear and logical order.
The navigation of this text was problem-free.
No grammatical errors noted.
No issues with cultural insensitivity noted.
This was a well-organized text using videos to reinforce content that would benefit any education or nursing graduate student new to the integrative review process.
Reviewed by Ruth Stoltzfus, Professor of Nursing; Dir., Grad Programs in Nursing, Goshen College on 6/1/19
This text provides everything a graduate student needs to write a literature review in a concise manner. If you look at the digital pdf, there are many strategies to help the reader learn the process - videos, diagrams, and also text. read more
This text provides everything a graduate student needs to write a literature review in a concise manner. If you look at the digital pdf, there are many strategies to help the reader learn the process - videos, diagrams, and also text.
I found no evidence of bias and no errors.
This book has long-term relevance. The content will not quickly out-date.
I really liked the way the textbook is structured. The author is concise which makes the textbook easy to read.
I found no inconsistencies in terminology or other aspects related to the content.
I will adopt this text for a research course I use and will likely assign only specific chapters. I plan to recommend the textbook to another faculty who teaches a comprehensive research course with the idea of assigning only specific sections to read..
The textbook begins with an introduction to the subject matter. Subsequent chapters develop specific aspects related to lit reviews. The textbook provides a nice "how to" for each element of a lit review. Chapters are also organized in a smooth, easy to follow format.
I only looked at the digital pdf and print pdf versions. The print pdf indicates that there are videos to watch, but of course since it is a print pdf, there is no linkage. I think this would be obvious to a savvy reader - that a print pdf will be limited in what the reader can access.
I found no grammatical errors in my quick read.
I found no evidence of cultural bias or insensitivity.
This is the first open textbook that I have encountered. I was expecting it to be flat and boring! However, it was neither of those. There were color diagrams, color photos, and even videos embedded in the textbook.
I have adopted this book for the Research Lit Review course that I am teaching soon. I am impressed!
Reviewed by Melissa Wells, Assistant Professor, University of Mary Washington on 5/1/19
This book helps students in education and nursing complete a literature review, which may be the first time these students are tackling such a task. The chapters break down the process into defining the special genre of a literature review;... read more
This book helps students in education and nursing complete a literature review, which may be the first time these students are tackling such a task. The chapters break down the process into defining the special genre of a literature review; providing tips to get started; suggesting where students can find literature to review; explaining how to evaluate sources; detailing the process of documenting sources; giving advice for synthesizing sources; and finally, putting all of these pieces together into a final literature review. Most significantly, the text provides specific examples of ideas presented in the context of both nursing and education, which makes the content directly relatable to the student's course of study. The conclusion recaps the main points of each chapter in bullet form. The text is lacking both an index and a glossary, which would be additions that could strengthen the text.
Content Accuracy rating: 4
The text explains 11 different types of literature reviews that students may encounter or be asked to create. Also, the text is framed to work with multiple methodologies; for example, steps for writing a research question or a hypothesis to frame the literature review are provided. One inconsistency I noted was in diagram 6.2: the APA citation is incorrectly capitalized for the journal title (which should use sentence, not title, capitalization).
The text also includes external links to sources, such as a videos, which provide students with multiple modalities in which to digest the information. An example of a literature review for both education and nursing is provided at the end of the book; instead of embedding these in the text, the hyperlinks refer the reader to the external site. This will be easy to change to a new example in the future, but checks will need to be done to ensure that all such external sources remain actively accessible.
Each chapter opens with learning objectives to help frame the content with which the reader is about to engage. Throughout the text, the language is approachable and reader-friendly. For example, when the text explains more factual components (i.e., what makes a literature review or what the basics of an effective literature review include), this information is presented in bullet points with hyperlinks to the original sources.
Each chapter follows a similar construction, which makes it accessible to the reader. For example, chapters end with a "Practice" and "Check Yourself" section to apply new learning and self-check responses (an answer key is provided in an appendix). Examples in these exercises are either related to nursing or education, continuing with the stated theme of the text.
When I used this text with my own students, I assigned chapters in isolation, since they had already taken a research methods course and were applying that knowledge to create a research proposal in a specific area of study in my course.
The book is organized in such a way that logically walks the reader through the literature review writing process. Clear headings (which are hyperlinked in the table of contents) also allow the reader to jump to specific parts with which they need additional support.
The interface of this document offered a lot of flexibility. Options allowed users to access the text online, or as a download in multiple file types (EPUB, Digital PDF, MOBI, XHTML, Pressbooks XML, Wordpress XML, and Open Document). These formats provide the reader with an opportunity to pick the interface that works best for them.
I did not see any grammatical errors in the text.
Cultural Relevance rating: 4
No culturally insensitive/offensive content was noted. A variety of examples of research topics were included from both nursing and education. Of the images/video thumbnails embedded in the text that involved people, all depicted White people except for 2 images; therefore, more intentional selection of culturally diverse visuals would be helpful in future versions of this text.
I feel this text was helpful to my students as they wrote their own literature reviews. The only weakness in their papers that I noted was their organization of their literature review based on themes/topic, which was addressed in Chapters 7- 8. I now know to focus more on this part of literature review writing with future students. This text is approachable and field-specific, and I will be using it again!
Reviewed by Bernita (Bernie) Missal, Professor, Bethel University on 12/14/18
This book includes all areas that a graduate student needs to begin a literature review. However metasynthesis could have also been included in types of literature review. read more
This book includes all areas that a graduate student needs to begin a literature review. However metasynthesis could have also been included in types of literature review.
This book is accurate although missing qualitative research.
Although content is up to date, some of the article examples need to be updated. (Example: articles published in 1981 and 1992 need to be updated to more recent articles.)
The book is clear and easy to follow. Bullet points were used throughout the book with short paragraphs which helps the student.
Each chapter follows the same format with narrative followed by practice and test questions.
Clear subheadings are used throughout the book.
This book is presented in a logical way and easy for the student to follow.
Images are clear and appropriate for the content.
No specific grammar issues were seen.
It would be helpful for students to include additional examples of cultural studies throughout the book
This book is an excellent resource for graduate students. It has helpful information for the preparation and process for a literature review. Examples of written literature reviews in chapter 8 or in an appendix would be helpful for students.
Reviewed by Nancyruth Leibold, Associate Professor, Southwest Minnesota State University on 6/19/18
The text is overall comprehensive, yet it breaks the information up into manageable parts. See the table of contents for an overview of the topics. The text is very quantitative driven in that the focus is on reviewing quantitative studies. The... read more
The text is overall comprehensive, yet it breaks the information up into manageable parts. See the table of contents for an overview of the topics. The text is very quantitative driven in that the focus is on reviewing quantitative studies. The book included information about PICO statements, but did not include PICO(T) or the time variable, which is not always used in every case. Population was included in the PICO explanation, but a bit more information on the population or aggregate narrowing could improve the PICO section. These items do not hinder use of the book, but these items would need further inclusion by the faculty member using the text as specific to the discipline.
The content in the book is very accurate.
The content in the book is current and should not be obsolete within a short period of time. Any updates would be easy to add.
The text is clear and easy to understand.
The internal organization and terminology of the book is consistent and logical
The text is set up in small reading sessions. The videos and learning activities are well done and break up some of the content, so there is a variety of presentation. The tutorials, figures, practice and self-test areas are also fantastic in that they are quality and sprinkled throughout the text.
The topics in the book are presented in clear and organized fashion. I particularly like the upbeat and personal writing tone of the book. This tone makes it seem like the authors are speaking to me.
The text is free of any significant interface issues. The book is available in many formats. I used the book online and I did have one navigational problem and that is when clicking on a video, it does not open in a new tab and so the book is lost and have to start over going in the start to the book. One easy solution to this is to right click your mouse and then select open in new tab to watch videos. That way, your place in the book is not lost.
No grammar problems present.
The book is not culturally insensitive or offensive in any way.
Overall, this is a well written textbook and I recommend it!
Reviewed by Marjorie Webb, Professor, Metropolitan State University on 6/19/18
From the Introduction to the Conclusion, the text covers the step-by-step process of conducting a literature review. The text includes topics such as, “Where to find the Literature” and “Synthesizing Sources” that will be useful to graduate... read more
From the Introduction to the Conclusion, the text covers the step-by-step process of conducting a literature review. The text includes topics such as, “Where to find the Literature” and “Synthesizing Sources” that will be useful to graduate nursing students.
The content in the text, including texts, links, and diagrams, is accurate and unbiased. Again, it will aid the graduate nursing student in the long process of conducting a literature review.
The text is current and this type of material does not become dated quickly. The authors did use internet links in the text which will need to be monitored periodically to ensure they are still available. Updates to the text will be relatively easy and straightforward. If media styles change, there may be some challenges to updating.
The text is clear and easy to read. Technical terminology is defined and/or explained.
The text is internally consistent.
The text is organized in sections which facilitates assigning readings based on the subject matter for the class time. It would be pretty easy to divide up this text into easily readable units based on headings and subheadings.
This text is structured well. The topics flow in an organized manner and really help the student see the process of a literature review. The authors discuss the both theory and purpose of the review and the day-to-day logistics of actually performing the review. The day-today organization is not always included in other texts.
The interface is well-done with no distractions.
There was no indication of cultural bias.
I think this text is appropriate for graduate nursing students. Some students struggle with the difference between writing about a topic (generally undergraduate writing) and synthesizing literature on a given topic (generally graduate writing). Chapters seven and eight focus on preparing the graduate student to make the jump to graduate-level writing and should really benefit new graduate students.
Reviewed by Susanna Thornhill, Associate Professor , George Fox University on 3/27/18
This book is fairly comprehensive and offers step-by-step instructions for conceptualizing/researching a literature review. The Table of Contents is well-organized to reflect the book's progression, from establishing the basics of why to write a... read more
This book is fairly comprehensive and offers step-by-step instructions for conceptualizing/researching a literature review. The Table of Contents is well-organized to reflect the book's progression, from establishing the basics of why to write a literature review and the various types of literature reviews, to getting started with formulating a research idea/question, finding and evaluating sources, synthesizing sources, and guidelines on writing the literature review, itself. I found this text to be a straightforward guide for my graduate students in education, and while I worried at first that the merging of education and nursing topics would prove distracting to my education students, I don't believe this was the case.
One thing that was not comprehensive in this book was discussion of qualitative research and methodologies as a valid means of conceptualizing research aims. I hoped for a more balanced discussion between methodological branches as it applied to literature reviews; this book overly favored quantitative methodologies and studies in terms of its direction to readers about how to conceptualize/choose a topic and design a research question in relation to it. Variables that cannot be measured are not inherently un-researchable, which is the conclusion put forth in this textbook. This might serve nursing students better than education students in terms of their discipline's requirements, but it still represents an element that could be improved.
Finally, while the background on what a literature review is, how to conceptualize research, and how to search for and synthesize research was all valuable, the chapter on actually writing the literature review was a bit thin, simply offering tips for introduction, body, and conclusion and some questions for self-evaluation. Some of the most difficult work for students writing a literature review is achieving proper focus, organization, hierarchy of themes, balance in treatment of related topics, etc. None of these issues were discussed in the chapter pertaining to the writing of a literature review.
I did not have any concerns about the book's accuracy. Content was accurate, albeit biased to quantitative and positivist views of research. I would have liked to see it include additional prompts to support students in conceptualizing and valuing qualitative research; this is an area where I had to supplement course readings with additional texts.
The only significant error I could discern in the text was a lack of an Answer Key corresponding to the questions posed at the end of each chapter.
Content is up-to-date and seems like it will hold meaning well over the next few years. The only things I anticipate might go out-of-date is technological information on things like citation managers, search guidelines, and database information. This is easily updatable with future versions of the text. In my view, ERIC is not the best database for educational research and I have confirmed this with educational librarians who support my students, yet it is the only one identified in this text as the best subject-specific source of educational research; this could be revised for additional relevance.
I noticed no issues with the book's clarity. The authors write in a clear and straightforward style, making the text easy to read. Overall, they did well writing for students across two disciplines by avoiding nursing or education-specific terms that would have been problematic to readers in the other discipline.
The book is internally consistent and did not have issues with terminology or framework.
No issues with the book's modularity. Chapter headings and sub-headings were appropriately paced and spaced. I assigned this textbook to my graduate students as a whole text that I wanted them to read at the beginning of a course, but it has been easy to refer them back to particular topics as the course has continued.
In future iterations of the book, I suggest hyperlinking the Answer Key to the exercises at the end of each chapter and/or listing the Answer Key in the Table of Contents for easy referral.
I found the book's organization to be straightforward and sensible. The Table of Contents offers a helpful snapshot of the scope of the book and the authors write in a direct and clear style, which contributes to an appropriate flow for the text.
I did not note any navigation problems with any links. All charts/images loaded well in my iBook app. The authors did a nice job of pulling relevant content and links in to support their ideas; it provided an easy way to seek more information if I wanted it, without feeling like the text was loaded down with unnecessary information.
I only found a few small typos in the text, with no grammar issues. The book is obviously written by two very detail-oriented librarians. I appreciated the clarity of the text and lack of errors.
The text was not culturally insensitive; a variety of topics across nursing and education were discussed as examples, which yielded a fairly balanced text regarding cultural considerations.
Reviewed by Alicia Rossiter, Assistant Professor, University of South Florida on 3/27/18
I believe the book gives a comprehensive overview on how to complete a literature view at the graduate level. It begins with an overview of the purpose of a literature review and moves through the steps to completing the review process. read more
I believe the book gives a comprehensive overview on how to complete a literature view at the graduate level. It begins with an overview of the purpose of a literature review and moves through the steps to completing the review process.
I believe the book was accurate and unbiased. It was easy to read but comprehensive.
Content within the text is relevant and supports the literature view process. It did discuss the various databases for searches which may need updating to include new sites, search engines but otherwise relevant and useful information.
The text is easy to read, provides appropriate examples, includes a section on putting the process into practice as well as a "test yourself" section to ensure the content is understood.
The text is consistent throughout in regards to terminology, framework, and set up.
The text is easy to read and content is leveled for the reader but not over simplified. Content is chunked into sections making it easy for the reader to digest the content. The chapters are well laid out and flow from chapter to chapter. Each chapter contains learning objectives, content sections, practice section, and test yourself section. Well organized and great visuals.
Topics are presented in a logical, clear fashion that flow from chapter to chapter and build as the reader moves through the process.
The text is free of interface issues. I could not get the videos to play but other visuals were appropriate and useful to support content.
The text contains no grammatical errors.
The text is not culturally offensive. There was no evidence of bias or cultural insensitivity.
I think this would be a great resource for graduate student learning to navigate the literature review process. It is easy to read, straightforward, and guides the individual through the process from start to finish. I will recommend this text to my graduate students in evidence-based practice and research courses as a recommended reference.
Table of Contents
- Chapter 1: Introduction
- Chapter 2: What is a Literature Review?
- Chapter 3: How to Get Started
- Chapter 4: Where to Find the Literature
- Chapter 5: Evaluating Sources
- Chapter 6: Documenting Sources
- Chapter 7: Synthesizing Sources
- Chapter 8: Writing the Literature Review
Ancillary Material
About the book.
Literature Reviews for Education and Nursing Graduate Students is an open textbook designed for students in graduate-level nursing and education programs. Its intent is to recognize the significant role the literature review plays in the research process and to prepare students for the work that goes into writing one. Developed for new graduate students and novice researchers just entering into the work of a chosen discipline, each of the eight chapters covers a component of the literature review process. Students will learn how to form a research question, search existing literature, synthesize results and write the review. The book contains examples, checklists, supplementary materials, and additional resources. Literature Reviews for Education and Nursing Graduate Students is written by two librarians with expertise guiding students through research and writing assignments, and is openly licensed.
About the Contributors
Linda Frederiksen is the Head of Access Services at Washington State University Vancouver. She has a Master of Library Science degree from Emporia State University in Kansas. Linda is active in local, regional and national organizations, projects and initiatives advancing open educational resources and equitable access to information.
Sue F. Phelps is the Health Sciences and Outreach Services Librarian at Washington State University Vancouver. Her research interests include information literacy, accessibility of learning materials for students who use adaptive technology, diversity and equity in higher education, and evidence based practice in the health sciences
Contribute to this Page
- How we work
Literature Review Education Topics Worthy of In-Depth Research
Get education literature review topics to make yourself stand out.
You already know the scope of your study if you’re writing your literature review in the education field as a separate project or as part of your dissertation or thesis. Unfortunately, literature reviews in the education area take a long time to write. Worst of all, it’s not just reading. You also have to write down what you’ve learned. If you want to be certain that your education literature review will provide excellent outcomes, you should consider writing. It’s extremely relevant if you’re writing your literature review.
The more structured you are while writing a text on literature review education topics, the more likely you’re to succeed. If you have a well-thought-out approach to your education research, it is way easier. As you can see, meticulously planning every aspect of your education topic is essential.
The following will help you select education literature review topics for yourself:
- Make sure you’re clear about the specific things you’ll be researching.
- Consider all the benefits and drawbacks of diverse points of view.
- Make a list of the categories of scholarly papers you want to find.
- You must be sure that there will be plenty of great material.
During this preliminary step of making your literature review, remove any extraneous education sources and examine your future work critically to verify that everything is relevant.
Choose Literature Review Topics in Education in a Well-Structured Way
Because your research on literature review topics in education could take up to two months, selecting an educational subject matter is typically the most challenging task. Consequently, you must spend some time thinking about some good ideas for a literature review in the education field.
Simply jot down the following crucial points:
- Whether you’ve examined the topic’s scope in great detail.
- How interested in the subject of your literature review you are.
- What aspects of your issue will make a significant difference in the field.
- If your chosen education topic is appropriate for your academic setting.
Make sure the chosen ideas for your literature review education topics are relevant to the subject area. Here are several clues for you to solve this literature review issue this without much hassle:
- Choose a wide topic area that interests you.
- Look through the most recent journals on the topic.
- Make a list of the articles that interest you the most.
- Keep track of what gets the most attention.
- Write down the best education topics.
The topic for your educational literature review will be chosen based on how well it meets all three criteria. Knowing where to look for education topics on the internet will help you get started. There’s a good chance you’re familiar with at least some of the themes for your literary reviews.
The following are literature review education topics for you to consider:
- Early childhood education: learning through play.
- Growing classes: do learning outcomes suffer from it?
- What should a proper sex education program look like?
- Reforming the school schedule: the most efficient solution.
- How can career counseling support high school students?
- From homeschooling to successful careers: an overview.
- How to recognize which learning style a student needs?
- The benefits of the flipped classroom approach.
- Boarding schools: advantages & disadvantages.
- Single-sex education vs. mixed-sex education.
Whatever ideas you choose for your literature review, you’ll need to stay current on advances in your field and choose a topic that’s relevant right now in the field.

Entrust Us With the Topic Selection for Your Literature Review
We are experts in providing literature review topics education field relates to. Our extensive literature review knowledge allows us to gain insight into what is currently popular in a variety of sectors, and our specialist authors are well-versed in the process. Our team excels in searching for a wide range of topics.
Our literature review services are based on years of research experience in a variety of research topics on education, as well as topic updates that reflect current trends. You may rest knowing that you’re dealing with experts who are familiar with the subtleties of selecting topics for a literature study.
The ideal topics for literature review in education are possible to find if you use the proper technique. The strategy you take to identify a solid literature review topic differs depending on whether you’re writing your literature review as a separate assignment or performing the entire research.
Here are a couple of suggestions for you to do it excellently:
- In the first scenario, carefully study the instructions and request clarification.
- Examine academic educational publications for current research trends.
- Keep an eye out on professional blogs for trending education topics.
- Attend conferences to keep up with the most recent findings.
- Communicate with experienced students and academics.
Competent people for who you reveal your genuine interest in the topic could assist you in explaining your problem and why it’s important for your literature review. The most significant thing is to pick ideas for your literature review that you enjoy because you’ll be working on it for a long time!
We use cookies to enhance our website for you. Proceed if you agree to this policy or learn more about it.
- Essay Writer Service >
- Topic Collections
120 Fresh and Thought-Provoking Topics for Literature Reviews in Different Disciplines
A literature review is an account of the scholarly works published on a topic. It is different from an annotated bibliography – and far more interesting at that. Instead of being just a list of summaries, a literature review synthesizes the information from all available sources in an overall relationship to your guiding concept. This may be the problem you are discussing, a statement you are arguing, a theory you are verifying, etc.
The goals of a literature review may vary:
- giving a historical overview of the research in the field
- summarizing the existing state of the topic
- finding a problem or a gap in the research field
- developing a new theory, etc.
That is why good literature review topics are often formulated as research questions. This type of paper is not an easy writing. You will need to parse immense volumes of information, synthesize and summarize coherently. You also need to devote plenty of time to reading.
This post contains a list of literature review topics suggested for various subjects. However, when choosing the most fitting one to dig into, ask yourself, what are the passions that you can apply to this research? This assignment will take a while, so you will need more than just a good study discipline to soldier on. A bit of enthusiasm and intrinsic motivation will get you much farther.
Literature Review Topics Examples on English and World Literature
Some of the suggestions in this post are linked to literature review examples in our free database. By clicking on a title, you get to a corresponding sample page, where you can read the entire text. If the topic you like isn't linked, but you would like to read an example, you can order it. We will arrange the most qualified paper writer to prepare it for you exclusively.
Ready? Let's start with topics for literature review papers on English and World Literature.
- Phoenix as a symbol for endurance in a worn path
- The novel Intuition by Allegra Goodman
- Nathaniel Hawthorne's The Birthmark through Girard's Lens
- Ender's Game by an Orson Scott Card
- Depiction of freedom and happiness in Brave New World
- Feminism and Post-Colonialism in Margaret Atwood's Oryx and Crake and Suzanne Collins's The Hunger Games
- Rationality, logic, and mathematics in the novel The Curious Incident Of The Dog In The Night-Time
- Victims of their time as a character type in the World literature
- The last days of Judas Iscariot : a play by Stephen Adly Guirgis
- The use of symbolism in Kafka's prose
- Naturalism in American literature
- Grotesque and Sublime in the prose of Edgar Allan Poe
Lit Review Topic Ideas on Science and Technology
Next are some literature review topic ideas on science and technology.
- Electronic library and effects of its implementation
- Benjamin Franklin: scientist and inventor
- Virtual Reality, science fiction, and society today
- Science, Technology, and Society as a field of knowledge
- Frederick Winslow Taylor and the principles of scientific management
- What is the future of work
- Concepts of science and technology
- The Abolition of Man by C.S. Lewis and influence of technological advancement on man and nature
- Types of machine learning
- Internet of Things and biometrics: implications, benefits, threats
- Emotional intelligence and natural language processing
- SmartCity projects that have already been implemented and their lessons
As the field is vast, we can barely scratch the surface with these suggestions. To help you with brainstorming, here are a few tips on how to choose good topics for a literature review yourself:
- Make sure the topic ties nicely with class requirements as well as your interests
- Do some preliminary research to see if there is enough literature on your topic
- Scale up if the information is scarce or down if there are too many sources to handle
- Use sources recommended for reading in the class materials
- Supplement the list with only trustworthy scholarly sources
Follow these guidelines, and you are on a path to some great ideas!
Psychology Literature Review Topics
When brainstorming topics on psychology, don't forget about the subdisciplines: biopsychology, social, educational, organizational, etc. If the suggestions below won't be enough, try looking for inspiration in Biology, Sociology, Education, or Business. The most exciting topics are often at the intersection of different areas of knowledge!
- Tricyclic antidepressants vs. Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) in treatment of depression
- Stress, its causes, effects, and coping strategies
- The family system and psychology
- Tibetan compassion practices: working with terror, trauma, and transcendence
- Behaviorism psychology
- Culture and psychopathology
- Correlation between diet and cognitive functions in primary school students
- The evolutionary role of phobias and intrusive thoughts
- Popular psychology and its implications
- PTSD in mass disasters survivors: immediate relief and long-term assistance
- Cults and vulnerable populations
- False memories and gaslighting
Nursing Literature Review Topics
Nursing lit review topics are probably the most diverse in scale, as you can see from the examples below. They can describe a larger issue or a concrete solution applied to a narrowly defined problem. Following this principle, you can modify our lit review topics suggestions zooming out or in on the subject material.
- Legalization of medical marijuana and its effects on the youth
- Health effects of fiber: research findings
- Achieving higher levels of education and training for nurses
- Organic foods and cardiovascular disease
- The importance of Central Venous Line (CVL) and Central Venous Access Devices (CVAD)
- What effects do different types of music have on humans and their mental health?
- The use of laboratory-grown organs for transplantation
- The role of xylitol in alleviating dry mouth
- The detection of tar and nicotine content of cigarette smoke extract using HPLC
- Rheumatoid arthritis: etiology, diagnosis, vulnerable populations
- Mobility aids for the elderly and quality of life
- The role of play in the recuperation of hospitalized children
Education Literature Review Topics
To get more ideas from these literature review topic examples, try isolating an issue and put it in another educational context. For instance, student motivation in primary school vs. middle school or sleep deprivation in high school vs. college. This should give you plenty of material for brainstorming.
- Simulation education for crisis prevention program
- A critical consideration of the new pedagogy in its relation to modern science
- Lack of students interest in studying science
- Discovery-based learning and student-centered learning with a focus on mathematics at a high school level
- The adverse effects of sleep deprivation on academic performance: a college student's struggle
- Gender bias in special education programs
- Higher education for senior citizens: challenges and best practices
- Significant challenges of the teaching profession in the US
- Factors contributing to international student mobility
- Student motivation in private vs. state colleges
- Benefits and challenges of homeschooling for students and families
- Correlation between workload, stress levels, and self-esteem in middle-school students
Sociology Literature Review Topics
The best advice on finding current sociology topics is to look at the challenges your community faces. Become the first one to notice and address these issues!
- Are video games affecting our current and future students ?
- Ways to prevent social media bullying
- Spanking of children in the USA
- The relation of poverty and exposure to crime in adolescent men
- Transgender discrimination
- The link between science and Utopia in Utopia and the New Atlantis
- Effectiveness of group therapy in social work
- Peer pressure, depression, and causes of suicide in the adolescents
- Religious separatism social issues connected with it
- Causes and effects of domestic abuse
- Physical appearance and social status
- Race, nationality, ethnicity, and identity
Political Science Literature Review Topics
Political science is one of the more formal disciplines on this list. Being heavy with abstract concepts, it doesn't lend itself easily to casual brainstorming. Well, at least start with these:
- Electoral College, its functions, and role in public life
- Why American and the British IPE are so different
- Contingency planning
- Effects of political gerrymandering
- American political parties
- The present urban regimes in Canada
- International policies and domestic regulations: precedence and clashes
- Tolerance as a political virtue
- Grassroots activism and its impact on state and federal law
- National security and constitutional freedoms
- Historical analysis of anarchism
- The effect of social media on civic engagement
Criminal Justice Literature Review Topics
Criminal justice is a complex field. It's ripe with variance and challenges – which is good for topic ideas at least. And you have state, federal, and international levels to add more variables.
- Juvenile justice and the Missouri model
- Car-related crime in the USA
- An analysis of the impact of sexual harassment/sexual assault in the military
- The process of the arbitration without the involvement of national courts
- Serial killers and profiling
- Policing and criminal justice systems
- Psychological effects of cyberbullying on adolescents
- Sexual human trafficking from the Central America region
- Human sex-trafficking: the Canadian perspective
- Gender and racial bias in criminal investigations
- Possible ethical and legal dilemmas of using sniffer dogs
- Sting operations vs. entrapment: ethics and regulations
Chemistry and Biology Literature Review Topics
Biology is fascinating. It has something for everyone: from biochemistry and genetics to ecosystems and nature preservation. Here are some suggestions to guide your choice:
- Brain size correlation
- Haruko Obokata, ethics of stem cells research, and scientific misconduct
- Genomic and molecular genetics major and its perspectives for students
- DNA use in mass disasters
- DNA detection from dried blood spots
- Captive breeding of marine mammals: pros and cons
- The Dynamics of ER and mitochondria
- Biomarkers in gastric cancer treatment
- The chemistry behind gene splicing
- Carcinogens and hyper-processed foods
- Primates and monkeys as potential sources of novel zoonotic infections
- Natural gases, ecosystems, and the global warming
Business and Marketing Literature Review Topics
Finally, here are some business and marketing topics as well. These disciplines might be relatively new, but they are among the most dynamic and information-rich – which means great fun to explore.
- Effectiveness of neuromarketing in comparison to traditional marketing methods
- Green supply chain management
- Effectiveness of e-marketing to non-profit making organizations
- The value of information
- Shareholder engagement/activism and corporate performance
- The relationship between ethics, stress, and productivity in the workplace
- The role of integrity in business
- Client confidentiality and its role in a prosperous business
- Businesses, their impact on the community, and social responsibility
- Startup fundraising stages
- Innovative marketing in the age of instant feedback: risks and possibilities
- Strategies for staff motivation

Jana Rooheart
Jana Rooheart came to WOWESSAYS™ with a mission to put together and then slice and dice our vast practical experience in crafting all kinds of academic papers. Jana is an aspired blogger with rich expertise in psychology, digital learning tools, and creative writing. In this blog, she willingly shares tricks of pencraft and mind-altering ideas about academic writing any student will find utterly beneficial.
Share with friends using:

275 words = 1 page double-spaced
Looking for essays to inspire you? We have samples of all types on any topic under the sun!
Other pages.
- Teacher Book Reviews
- Coordinator Term Papers
- Bunch Term Papers
- Attendant Term Papers
- Drill Term Papers
- Acre Term Papers
- Deposition Term Papers
- Nexus Term Papers
- Businessman Term Papers
- Abdomen Term Papers
- How Microcredit Help Poor People Term Paper Example
- Online Dating Or Conventional Dating Essay Examples
- Article Review On Also As Would Be Obvious To Any Researcher Of Diplomacy Use Of Force And Diplomacy
- African Slave Trade Essay Examples
- Free Research Paper On Obsessive Compulsive Disorder
- Outliers Analysis Essays Examples
- Free Essay About Definition Of Student
- Project Management Case Study Essay Sample
- Free Smartphone Essay Sample
- Models Of Organizational Change Research Paper Examples
- Free Portraits Of Reconciliation Course Work Sample
- Good Legal Principles Case Study Example
- Good Example Of Essay On The Benefits Of College Education To Students
- Term Paper On Comprehensive Article Review
- Sex In The 21sr Century Media Essay Samples
- Hard Rock Case Studies Example
- Free Critical Thinking On Shared Decision Making
- Great Barrington Essays
- Manuel Zelaya Essays
- Charles Taylor Essays
- Eliza Essays
- You Tube Essays
- Grammy Essays
- National Health Insurance Essays
- Phillips Curve Essays
- Strategic Importance Essays
- Decision Support Systems Essays
- Natalie Essays
- Alessi Essays
- Snow White And The Seven Dwarfs Essays
- Okonkwo Essays
- Impacting Essays
- Pullman Company Essays
Password recovery email has been sent to [email protected]
Use your new password to log in
You are not register!
By clicking Register, you agree to our Terms of Service and that you have read our Privacy Policy .
Now you can download documents directly to your device!
Check your email! An email with your password has already been sent to you! Now you can download documents directly to your device.
or Use the QR code to Save this Paper to Your Phone
The sample is NOT original!
Short on a deadline?
Don't waste time. Get help with 11% off using code - GETWOWED
No, thanks! I'm fine with missing my deadline

Educational Leadership Doctoral Program
- Background Sources & Research Methods
- Identifying Empirical Articles
- Writing a Literature Review
- Citing Sources
Literature Review Tips
- Literature Review and APA Tips
Literature Review Examples
To give you some examples of writing a literature review and an article analysis matrix to keep track of the themes of your articles, I have created a partial literature review and corresponding analysis matrix to demonstrate. My topic is the special education early intervention program called First Step to Success (FSS).
- Synthetic Writing/Literature Example (First Steps to Success)
- Article Analysis Spreadsheet Example (First Step to Success)
- Article Analysis Spreadsheet Example (First Step to Success - PDF Version)
The Process of Writing a Literature Review
Mastering synthetic writing is key to a successful literature review. Use these resources to learn how to analyze the articles you want to use for your literature review, keep track of common themes using an article analysis matrix, and how to convert the notes in the analysis matrix into a piece of synthetic writing.
Think of working on your literature review as a multi-step process:
- Identify a topic.
- Find research articles on that topic.
- Read and analyze each article. (Use the Individual Article Analysis Worksheet )
- Compare all of the themes addressed in the articles. (Use the Article Analysis Matrix )
- Use your notes from the article analysis matrix to decide how to organize your literature review (make an outline).
- Write your literature review by discussing one theme at a time--how is this theme covered in the literature?
- Your literature review will also need an introduction and a conclusion. Some students like to start with the introduction, while others find it is easier to write the introduction after they have written the body of their literature review.
- Don't forget to include References at the end of your paper (and to cite them properly within the text)!
- Individual Article Analysis Worksheet Use this to analyze each of your articles. Focus on questions #4 - #6. These will help you identify the major themes/main ideas in each article you read.
- Article Analysis Matrix After completing the Individual Article Analysis Worksheet for each of your articles, use this Article Analysis Matrix to compile all of the information you have gathered. Use the Example Article Analysis Matrix below as a guide to get started.
Synthetic Writing
A literature review is not the same as a research paper. The point of a literature review is to synthesize the research of others without making a new argument or scholarly contribution. A literature review is also not an annotated bibliography. You should not write about each study you are reviewing in turn, but instead write synthetically to highlight the current state of the literature.
Key Points to Consider:
- The purpose of a literature review is to report the current state of the topic. Literature reviewed should be relatively recent, unless you are delving into the history of the topic.
- Discuss different themes within your literature review rather than individual articles. It will help if you pull information from 2-3 articles for each theme you discuss.
- All works cited should be both in the text of the literature review and the bibliography
- Avoid passive voice (ex: It was found that...); Use active voice ("Smith (2013) reported that...")
- Report what the literature says, not what you think
Writing Your Literature Review
The sites below offer a range of considerations and steps for writing the literature review.
- Learn How to Write a Review of Literature From the University of Wisconsin-Madison Writing Center.
- Literature Reviews From the UNC Chapel Hill Writing Center.
- Literature Review From the University of Houston-Victoria, Texas.
- The Literature Review: A Few Tips on Conducting It From the University of Toronto Health Sciences Writing Centre.
- Writing Literature Reviews From the Temple University Writing Center.
- Getting Started on Your Literature Review From the University of New South Wales Learning Centre.
- << Previous: Journals
- Next: Citing Sources >>
- Last Updated: Apr 18, 2024 1:42 PM
- URL: https://library.ship.edu/eldp
Contact the Ezra Lehman Memorial Library
- Shippensburg on Facebook
- Shippensburg on Twitter
- Shippensburg on YouTube
- Shippensburg on Instagram

A systematic literature review of empirical research on ChatGPT in education
- Open access
- Published: 26 May 2024
- Volume 3 , article number 60 , ( 2024 )
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- Yazid Albadarin ORCID: orcid.org/0009-0005-8068-8902 1 ,
- Mohammed Saqr 1 ,
- Nicolas Pope 1 &
- Markku Tukiainen 1
643 Accesses
Explore all metrics
Over the last four decades, studies have investigated the incorporation of Artificial Intelligence (AI) into education. A recent prominent AI-powered technology that has impacted the education sector is ChatGPT. This article provides a systematic review of 14 empirical studies incorporating ChatGPT into various educational settings, published in 2022 and before the 10th of April 2023—the date of conducting the search process. It carefully followed the essential steps outlined in the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA 2020) guidelines, as well as Okoli’s (Okoli in Commun Assoc Inf Syst, 2015) steps for conducting a rigorous and transparent systematic review. In this review, we aimed to explore how students and teachers have utilized ChatGPT in various educational settings, as well as the primary findings of those studies. By employing Creswell’s (Creswell in Educational research: planning, conducting, and evaluating quantitative and qualitative research [Ebook], Pearson Education, London, 2015) coding techniques for data extraction and interpretation, we sought to gain insight into their initial attempts at ChatGPT incorporation into education. This approach also enabled us to extract insights and considerations that can facilitate its effective and responsible use in future educational contexts. The results of this review show that learners have utilized ChatGPT as a virtual intelligent assistant, where it offered instant feedback, on-demand answers, and explanations of complex topics. Additionally, learners have used it to enhance their writing and language skills by generating ideas, composing essays, summarizing, translating, paraphrasing texts, or checking grammar. Moreover, learners turned to it as an aiding tool to facilitate their directed and personalized learning by assisting in understanding concepts and homework, providing structured learning plans, and clarifying assignments and tasks. However, the results of specific studies (n = 3, 21.4%) show that overuse of ChatGPT may negatively impact innovative capacities and collaborative learning competencies among learners. Educators, on the other hand, have utilized ChatGPT to create lesson plans, generate quizzes, and provide additional resources, which helped them enhance their productivity and efficiency and promote different teaching methodologies. Despite these benefits, the majority of the reviewed studies recommend the importance of conducting structured training, support, and clear guidelines for both learners and educators to mitigate the drawbacks. This includes developing critical evaluation skills to assess the accuracy and relevance of information provided by ChatGPT, as well as strategies for integrating human interaction and collaboration into learning activities that involve AI tools. Furthermore, they also recommend ongoing research and proactive dialogue with policymakers, stakeholders, and educational practitioners to refine and enhance the use of AI in learning environments. This review could serve as an insightful resource for practitioners who seek to integrate ChatGPT into education and stimulate further research in the field.
Similar content being viewed by others
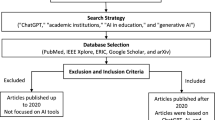
Empowering learners with ChatGPT: insights from a systematic literature exploration
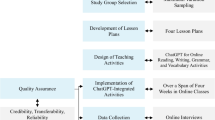
Incorporating AI in foreign language education: An investigation into ChatGPT’s effect on foreign language learners
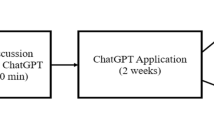
Large language models in education: A focus on the complementary relationship between human teachers and ChatGPT
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction
Educational technology, a rapidly evolving field, plays a crucial role in reshaping the landscape of teaching and learning [ 82 ]. One of the most transformative technological innovations of our era that has influenced the field of education is Artificial Intelligence (AI) [ 50 ]. Over the last four decades, AI in education (AIEd) has gained remarkable attention for its potential to make significant advancements in learning, instructional methods, and administrative tasks within educational settings [ 11 ]. In particular, a large language model (LLM), a type of AI algorithm that applies artificial neural networks (ANNs) and uses massively large data sets to understand, summarize, generate, and predict new content that is almost difficult to differentiate from human creations [ 79 ], has opened up novel possibilities for enhancing various aspects of education, from content creation to personalized instruction [ 35 ]. Chatbots that leverage the capabilities of LLMs to understand and generate human-like responses have also presented the capacity to enhance student learning and educational outcomes by engaging students, offering timely support, and fostering interactive learning experiences [ 46 ].
The ongoing and remarkable technological advancements in chatbots have made their use more convenient, increasingly natural and effortless, and have expanded their potential for deployment across various domains [ 70 ]. One prominent example of chatbot applications is the Chat Generative Pre-Trained Transformer, known as ChatGPT, which was introduced by OpenAI, a leading AI research lab, on November 30th, 2022. ChatGPT employs a variety of deep learning techniques to generate human-like text, with a particular focus on recurrent neural networks (RNNs). Long short-term memory (LSTM) allows it to grasp the context of the text being processed and retain information from previous inputs. Also, the transformer architecture, a neural network architecture based on the self-attention mechanism, allows it to analyze specific parts of the input, thereby enabling it to produce more natural-sounding and coherent output. Additionally, the unsupervised generative pre-training and the fine-tuning methods allow ChatGPT to generate more relevant and accurate text for specific tasks [ 31 , 62 ]. Furthermore, reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF), a machine learning approach that combines reinforcement learning techniques with human-provided feedback, has helped improve ChatGPT’s model by accelerating the learning process and making it significantly more efficient.
This cutting-edge natural language processing (NLP) tool is widely recognized as one of today's most advanced LLMs-based chatbots [ 70 ], allowing users to ask questions and receive detailed, coherent, systematic, personalized, convincing, and informative human-like responses [ 55 ], even within complex and ambiguous contexts [ 63 , 77 ]. ChatGPT is considered the fastest-growing technology in history: in just three months following its public launch, it amassed an estimated 120 million monthly active users [ 16 ] with an estimated 13 million daily queries [ 49 ], surpassing all other applications [ 64 ]. This remarkable growth can be attributed to the unique features and user-friendly interface that ChatGPT offers. Its intuitive design allows users to interact seamlessly with the technology, making it accessible to a diverse range of individuals, regardless of their technical expertise [ 78 ]. Additionally, its exceptional performance results from a combination of advanced algorithms, continuous enhancements, and extensive training on a diverse dataset that includes various text sources such as books, articles, websites, and online forums [ 63 ], have contributed to a more engaging and satisfying user experience [ 62 ]. These factors collectively explain its remarkable global growth and set it apart from predecessors like Bard, Bing Chat, ERNIE, and others.
In this context, several studies have explored the technological advancements of chatbots. One noteworthy recent research effort, conducted by Schöbel et al. [ 70 ], stands out for its comprehensive analysis of more than 5,000 studies on communication agents. This study offered a comprehensive overview of the historical progression and future prospects of communication agents, including ChatGPT. Moreover, other studies have focused on making comparisons, particularly between ChatGPT and alternative chatbots like Bard, Bing Chat, ERNIE, LaMDA, BlenderBot, and various others. For example, O’Leary [ 53 ] compared two chatbots, LaMDA and BlenderBot, with ChatGPT and revealed that ChatGPT outperformed both. This superiority arises from ChatGPT’s capacity to handle a wider range of questions and generate slightly varied perspectives within specific contexts. Similarly, ChatGPT exhibited an impressive ability to formulate interpretable responses that were easily understood when compared with Google's feature snippet [ 34 ]. Additionally, ChatGPT was compared to other LLMs-based chatbots, including Bard and BERT, as well as ERNIE. The findings indicated that ChatGPT exhibited strong performance in the given tasks, often outperforming the other models [ 59 ].
Furthermore, in the education context, a comprehensive study systematically compared a range of the most promising chatbots, including Bard, Bing Chat, ChatGPT, and Ernie across a multidisciplinary test that required higher-order thinking. The study revealed that ChatGPT achieved the highest score, surpassing Bing Chat and Bard [ 64 ]. Similarly, a comparative analysis was conducted to compare ChatGPT with Bard in answering a set of 30 mathematical questions and logic problems, grouped into two question sets. Set (A) is unavailable online, while Set (B) is available online. The results revealed ChatGPT's superiority in Set (A) over Bard. Nevertheless, Bard's advantage emerged in Set (B) due to its capacity to access the internet directly and retrieve answers, a capability that ChatGPT does not possess [ 57 ]. However, through these varied assessments, ChatGPT consistently highlights its exceptional prowess compared to various alternatives in the ever-evolving chatbot technology.
The widespread adoption of chatbots, especially ChatGPT, by millions of students and educators, has sparked extensive discussions regarding its incorporation into the education sector [ 64 ]. Accordingly, many scholars have contributed to the discourse, expressing both optimism and pessimism regarding the incorporation of ChatGPT into education. For example, ChatGPT has been highlighted for its capabilities in enriching the learning and teaching experience through its ability to support different learning approaches, including adaptive learning, personalized learning, and self-directed learning [ 58 , 60 , 91 ]), deliver summative and formative feedback to students and provide real-time responses to questions, increase the accessibility of information [ 22 , 40 , 43 ], foster students’ performance, engagement and motivation [ 14 , 44 , 58 ], and enhance teaching practices [ 17 , 18 , 64 , 74 ].
On the other hand, concerns have been also raised regarding its potential negative effects on learning and teaching. These include the dissemination of false information and references [ 12 , 23 , 61 , 85 ], biased reinforcement [ 47 , 50 ], compromised academic integrity [ 18 , 40 , 66 , 74 ], and the potential decline in students' skills [ 43 , 61 , 64 , 74 ]. As a result, ChatGPT has been banned in multiple countries, including Russia, China, Venezuela, Belarus, and Iran, as well as in various educational institutions in India, Italy, Western Australia, France, and the United States [ 52 , 90 ].
Clearly, the advent of chatbots, especially ChatGPT, has provoked significant controversy due to their potential impact on learning and teaching. This indicates the necessity for further exploration to gain a deeper understanding of this technology and carefully evaluate its potential benefits, limitations, challenges, and threats to education [ 79 ]. Therefore, conducting a systematic literature review will provide valuable insights into the potential prospects and obstacles linked to its incorporation into education. This systematic literature review will primarily focus on ChatGPT, driven by the aforementioned key factors outlined above.
However, the existing literature lacks a systematic literature review of empirical studies. Thus, this systematic literature review aims to address this gap by synthesizing the existing empirical studies conducted on chatbots, particularly ChatGPT, in the field of education, highlighting how ChatGPT has been utilized in educational settings, and identifying any existing gaps. This review may be particularly useful for researchers in the field and educators who are contemplating the integration of ChatGPT or any chatbot into education. The following research questions will guide this study:
What are students' and teachers' initial attempts at utilizing ChatGPT in education?
What are the main findings derived from empirical studies that have incorporated ChatGPT into learning and teaching?
2 Methodology
To conduct this study, the authors followed the essential steps of the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA 2020) and Okoli’s [ 54 ] steps for conducting a systematic review. These included identifying the study’s purpose, drafting a protocol, applying a practical screening process, searching the literature, extracting relevant data, evaluating the quality of the included studies, synthesizing the studies, and ultimately writing the review. The subsequent section provides an extensive explanation of how these steps were carried out in this study.
2.1 Identify the purpose
Given the widespread adoption of ChatGPT by students and teachers for various educational purposes, often without a thorough understanding of responsible and effective use or a clear recognition of its potential impact on learning and teaching, the authors recognized the need for further exploration of ChatGPT's impact on education in this early stage. Therefore, they have chosen to conduct a systematic literature review of existing empirical studies that incorporate ChatGPT into educational settings. Despite the limited number of empirical studies due to the novelty of the topic, their goal is to gain a deeper understanding of this technology and proactively evaluate its potential benefits, limitations, challenges, and threats to education. This effort could help to understand initial reactions and attempts at incorporating ChatGPT into education and bring out insights and considerations that can inform the future development of education.
2.2 Draft the protocol
The next step is formulating the protocol. This protocol serves to outline the study process in a rigorous and transparent manner, mitigating researcher bias in study selection and data extraction [ 88 ]. The protocol will include the following steps: generating the research question, predefining a literature search strategy, identifying search locations, establishing selection criteria, assessing the studies, developing a data extraction strategy, and creating a timeline.
2.3 Apply practical screen
The screening step aims to accurately filter the articles resulting from the searching step and select the empirical studies that have incorporated ChatGPT into educational contexts, which will guide us in answering the research questions and achieving the objectives of this study. To ensure the rigorous execution of this step, our inclusion and exclusion criteria were determined based on the authors' experience and informed by previous successful systematic reviews [ 21 ]. Table 1 summarizes the inclusion and exclusion criteria for study selection.
2.4 Literature search
We conducted a thorough literature search to identify articles that explored, examined, and addressed the use of ChatGPT in Educational contexts. We utilized two research databases: Dimensions.ai, which provides access to a large number of research publications, and lens.org, which offers access to over 300 million articles, patents, and other research outputs from diverse sources. Additionally, we included three databases, Scopus, Web of Knowledge, and ERIC, which contain relevant research on the topic that addresses our research questions. To browse and identify relevant articles, we used the following search formula: ("ChatGPT" AND "Education"), which included the Boolean operator "AND" to get more specific results. The subject area in the Scopus and ERIC databases were narrowed to "ChatGPT" and "Education" keywords, and in the WoS database was limited to the "Education" category. The search was conducted between the 3rd and 10th of April 2023, which resulted in 276 articles from all selected databases (111 articles from Dimensions.ai, 65 from Scopus, 28 from Web of Science, 14 from ERIC, and 58 from Lens.org). These articles were imported into the Rayyan web-based system for analysis. The duplicates were identified automatically by the system. Subsequently, the first author manually reviewed the duplicated articles ensured that they had the same content, and then removed them, leaving us with 135 unique articles. Afterward, the titles, abstracts, and keywords of the first 40 manuscripts were scanned and reviewed by the first author and were discussed with the second and third authors to resolve any disagreements. Subsequently, the first author proceeded with the filtering process for all articles and carefully applied the inclusion and exclusion criteria as presented in Table 1 . Articles that met any one of the exclusion criteria were eliminated, resulting in 26 articles. Afterward, the authors met to carefully scan and discuss them. The authors agreed to eliminate any empirical studies solely focused on checking ChatGPT capabilities, as these studies do not guide us in addressing the research questions and achieving the study's objectives. This resulted in 14 articles eligible for analysis.
2.5 Quality appraisal
The examination and evaluation of the quality of the extracted articles is a vital step [ 9 ]. Therefore, the extracted articles were carefully evaluated for quality using Fink’s [ 24 ] standards, which emphasize the necessity for detailed descriptions of methodology, results, conclusions, strengths, and limitations. The process began with a thorough assessment of each study's design, data collection, and analysis methods to ensure their appropriateness and comprehensive execution. The clarity, consistency, and logical progression from data to results and conclusions were also critically examined. Potential biases and recognized limitations within the studies were also scrutinized. Ultimately, two articles were excluded for failing to meet Fink’s criteria, particularly in providing sufficient detail on methodology, results, conclusions, strengths, or limitations. The review process is illustrated in Fig. 1 .
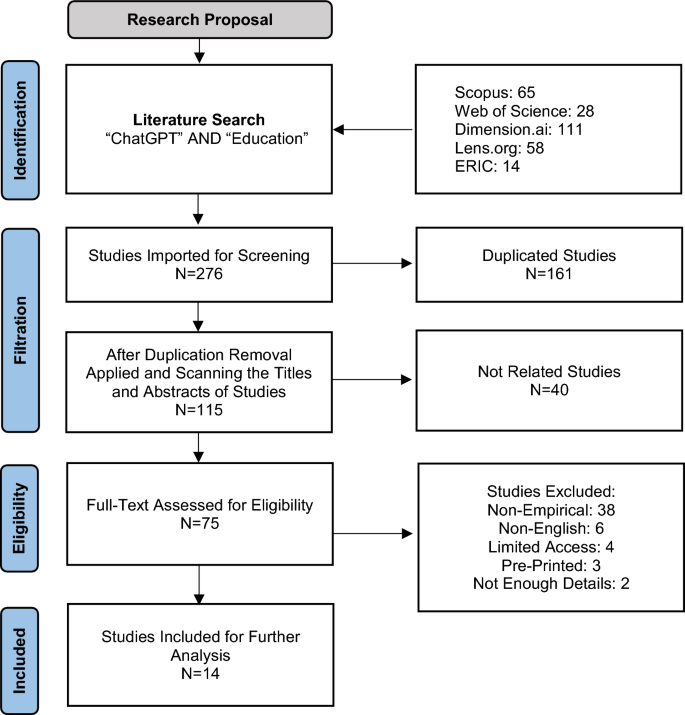
The study selection process
2.6 Data extraction
The next step is data extraction, the process of capturing the key information and categories from the included studies. To improve efficiency, reduce variation among authors, and minimize errors in data analysis, the coding categories were constructed using Creswell's [ 15 ] coding techniques for data extraction and interpretation. The coding process involves three sequential steps. The initial stage encompasses open coding , where the researcher examines the data, generates codes to describe and categorize it, and gains a deeper understanding without preconceived ideas. Following open coding is axial coding , where the interrelationships between codes from open coding are analyzed to establish more comprehensive categories or themes. The process concludes with selective coding , refining and integrating categories or themes to identify core concepts emerging from the data. The first coder performed the coding process, then engaged in discussions with the second and third authors to finalize the coding categories for the first five articles. The first coder then proceeded to code all studies and engaged again in discussions with the other authors to ensure the finalization of the coding process. After a comprehensive analysis and capturing of the key information from the included studies, the data extraction and interpretation process yielded several themes. These themes have been categorized and are presented in Table 2 . It is important to note that open coding results were removed from Table 2 for aesthetic reasons, as it included many generic aspects, such as words, short phrases, or sentences mentioned in the studies.
2.7 Synthesize studies
In this stage, we will gather, discuss, and analyze the key findings that emerged from the selected studies. The synthesis stage is considered a transition from an author-centric to a concept-centric focus, enabling us to map all the provided information to achieve the most effective evaluation of the data [ 87 ]. Initially, the authors extracted data that included general information about the selected studies, including the author(s)' names, study titles, years of publication, educational levels, research methodologies, sample sizes, participants, main aims or objectives, raw data sources, and analysis methods. Following that, all key information and significant results from the selected studies were compiled using Creswell’s [ 15 ] coding techniques for data extraction and interpretation to identify core concepts and themes emerging from the data, focusing on those that directly contributed to our research questions and objectives, such as the initial utilization of ChatGPT in learning and teaching, learners' and educators' familiarity with ChatGPT, and the main findings of each study. Finally, the data related to each selected study were extracted into an Excel spreadsheet for data processing. The Excel spreadsheet was reviewed by the authors, including a series of discussions to ensure the finalization of this process and prepare it for further analysis. Afterward, the final result being analyzed and presented in various types of charts and graphs. Table 4 presents the extracted data from the selected studies, with each study labeled with a capital 'S' followed by a number.
This section consists of two main parts. The first part provides a descriptive analysis of the data compiled from the reviewed studies. The second part presents the answers to the research questions and the main findings of these studies.
3.1 Part 1: descriptive analysis
This section will provide a descriptive analysis of the reviewed studies, including educational levels and fields, participants distribution, country contribution, research methodologies, study sample size, study population, publication year, list of journals, familiarity with ChatGPT, source of data, and the main aims and objectives of the studies. Table 4 presents a comprehensive overview of the extracted data from the selected studies.
3.1.1 The number of the reviewed studies and publication years
The total number of the reviewed studies was 14. All studies were empirical studies and published in different journals focusing on Education and Technology. One study was published in 2022 [S1], while the remaining were published in 2023 [S2]-[S14]. Table 3 illustrates the year of publication, the names of the journals, and the number of reviewed studies published in each journal for the studies reviewed.
3.1.2 Educational levels and fields
The majority of the reviewed studies, 11 studies, were conducted in higher education institutions [S1]-[S10] and [S13]. Two studies did not specify the educational level of the population [S12] and [S14], while one study focused on elementary education [S11]. However, the reviewed studies covered various fields of education. Three studies focused on Arts and Humanities Education [S8], [S11], and [S14], specifically English Education. Two studies focused on Engineering Education, with one in Computer Engineering [S2] and the other in Construction Education [S3]. Two studies focused on Mathematics Education [S5] and [S12]. One study focused on Social Science Education [S13]. One study focused on Early Education [S4]. One study focused on Journalism Education [S9]. Finally, three studies did not specify the field of education [S1], [S6], and [S7]. Figure 2 represents the educational levels in the reviewed studies, while Fig. 3 represents the context of the reviewed studies.

Educational levels in the reviewed studies
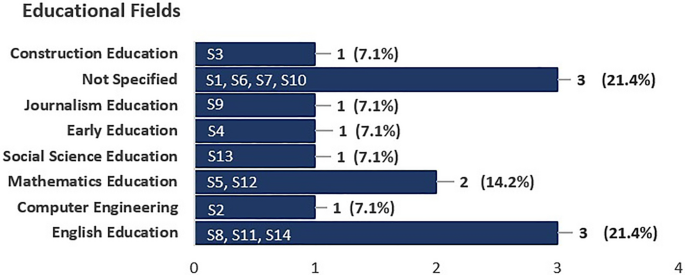
Context of the reviewed studies
3.1.3 Participants distribution and countries contribution
The reviewed studies have been conducted across different geographic regions, providing a diverse representation of the studies. The majority of the studies, 10 in total, [S1]-[S3], [S5]-[S9], [S11], and [S14], primarily focused on participants from single countries such as Pakistan, the United Arab Emirates, China, Indonesia, Poland, Saudi Arabia, South Korea, Spain, Tajikistan, and the United States. In contrast, four studies, [S4], [S10], [S12], and [S13], involved participants from multiple countries, including China and the United States [S4], China, the United Kingdom, and the United States [S10], the United Arab Emirates, Oman, Saudi Arabia, and Jordan [S12], Turkey, Sweden, Canada, and Australia [ 13 ]. Figures 4 and 5 illustrate the distribution of participants, whether from single or multiple countries, and the contribution of each country in the reviewed studies, respectively.
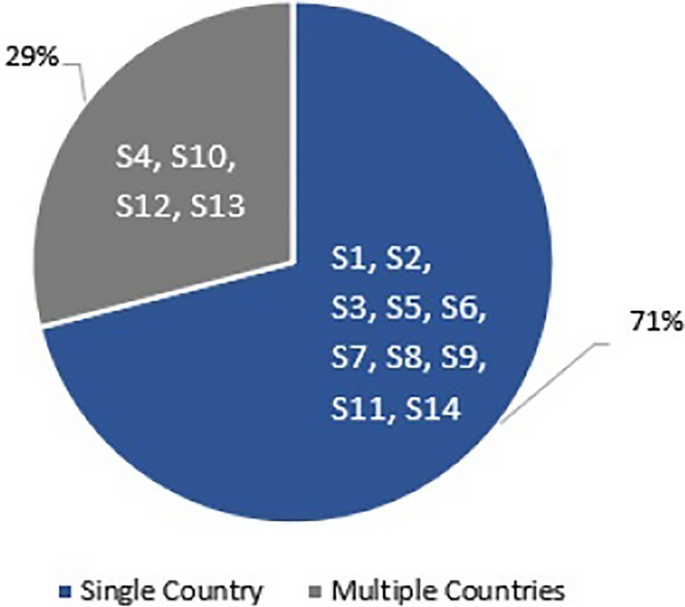
The reviewed studies conducted in single or multiple countries
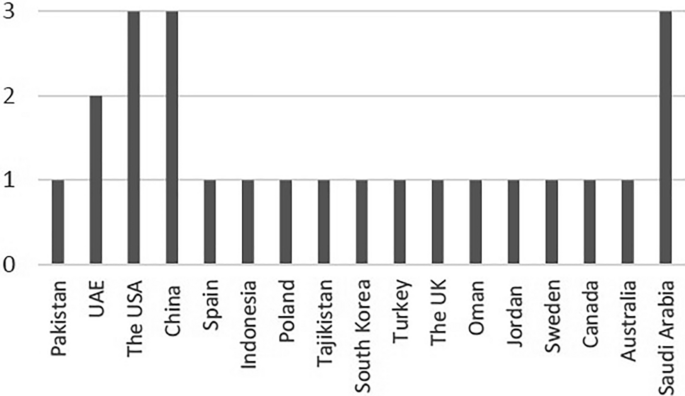
The Contribution of each country in the studies
3.1.4 Study population and sample size
Four study populations were included: university students, university teachers, university teachers and students, and elementary school teachers. Six studies involved university students [S2], [S3], [S5] and [S6]-[S8]. Three studies focused on university teachers [S1], [S4], and [S6], while one study specifically targeted elementary school teachers [S11]. Additionally, four studies included both university teachers and students [S10] and [ 12 , 13 , 14 ], and among them, study [S13] specifically included postgraduate students. In terms of the sample size of the reviewed studies, nine studies included a small sample size of less than 50 participants [S1], [S3], [S6], [S8], and [S10]-[S13]. Three studies had 50–100 participants [S2], [S9], and [S14]. Only one study had more than 100 participants [S7]. It is worth mentioning that study [S4] adopted a mixed methods approach, including 10 participants for qualitative analysis and 110 participants for quantitative analysis.
3.1.5 Participants’ familiarity with using ChatGPT
The reviewed studies recruited a diverse range of participants with varying levels of familiarity with ChatGPT. Five studies [S2], [S4], [S6], [S8], and [S12] involved participants already familiar with ChatGPT, while eight studies [S1], [S3], [S5], [S7], [S9], [S10], [S13] and [S14] included individuals with differing levels of familiarity. Notably, one study [S11] had participants who were entirely unfamiliar with ChatGPT. It is important to note that four studies [S3], [S5], [S9], and [S11] provided training or guidance to their participants before conducting their studies, while ten studies [S1], [S2], [S4], [S6]-[S8], [S10], and [S12]-[S14] did not provide training due to the participants' existing familiarity with ChatGPT.
3.1.6 Research methodology approaches and source(S) of data
The reviewed studies adopted various research methodology approaches. Seven studies adopted qualitative research methodology [S1], [S4], [S6], [S8], [S10], [S11], and [S12], while three studies adopted quantitative research methodology [S3], [S7], and [S14], and four studies employed mixed-methods, which involved a combination of both the strengths of qualitative and quantitative methods [S2], [S5], [S9], and [S13].
In terms of the source(s) of data, the reviewed studies obtained their data from various sources, such as interviews, questionnaires, and pre-and post-tests. Six studies relied on interviews as their primary source of data collection [S1], [S4], [S6], [S10], [S11], and [S12], four studies relied on questionnaires [S2], [S7], [S13], and [S14], two studies combined the use of pre-and post-tests and questionnaires for data collection [S3] and [S9], while two studies combined the use of questionnaires and interviews to obtain the data [S5] and [S8]. It is important to note that six of the reviewed studies were quasi-experimental [S3], [S5], [S8], [S9], [S12], and [S14], while the remaining ones were experimental studies [S1], [S2], [S4], [S6], [S7], [S10], [S11], and [S13]. Figures 6 and 7 illustrate the research methodologies and the source (s) of data used in the reviewed studies, respectively.
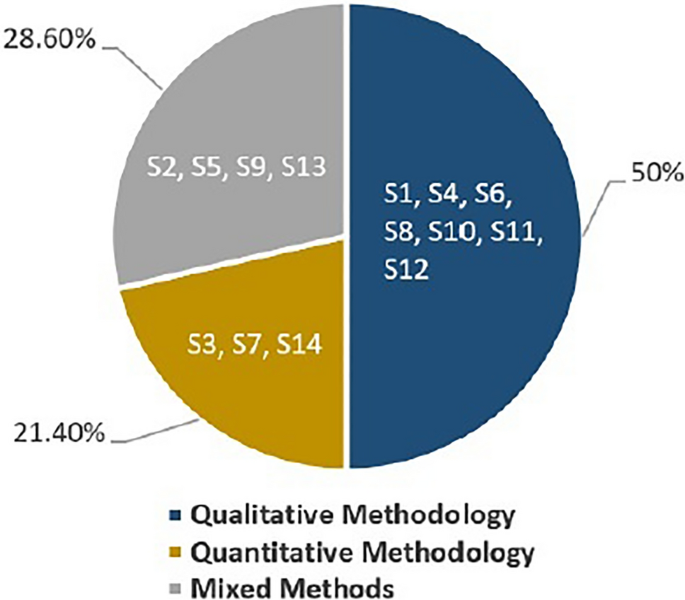
Research methodologies in the reviewed studies
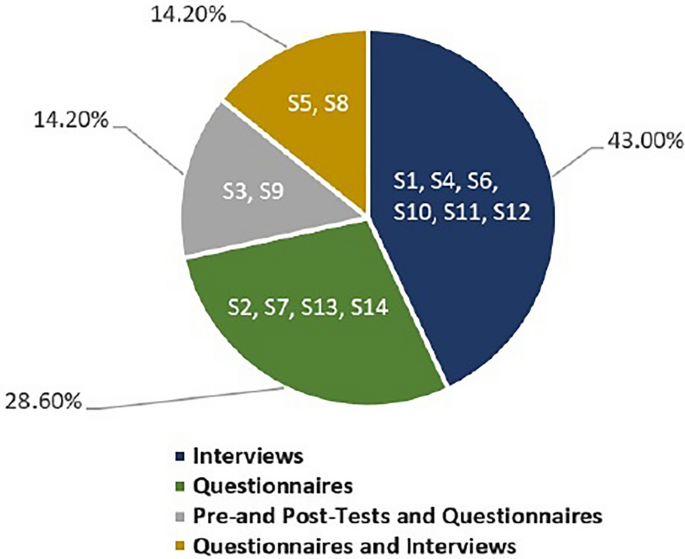
Source of data in the reviewed studies
3.1.7 The aim and objectives of the studies
The reviewed studies encompassed a diverse set of aims, with several of them incorporating multiple primary objectives. Six studies [S3], [S6], [S7], [S8], [S11], and [S12] examined the integration of ChatGPT in educational contexts, and four studies [S4], [S5], [S13], and [S14] investigated the various implications of its use in education, while three studies [S2], [S9], and [S10] aimed to explore both its integration and implications in education. Additionally, seven studies explicitly explored attitudes and perceptions of students [S2] and [S3], educators [S1] and [S6], or both [S10], [S12], and [S13] regarding the utilization of ChatGPT in educational settings.
3.2 Part 2: research questions and main findings of the reviewed studies
This part will present the answers to the research questions and the main findings of the reviewed studies, classified into two main categories (learning and teaching) according to AI Education classification by [ 36 ]. Figure 8 summarizes the main findings of the reviewed studies in a visually informative diagram. Table 4 provides a detailed list of the key information extracted from the selected studies that led to generating these themes.
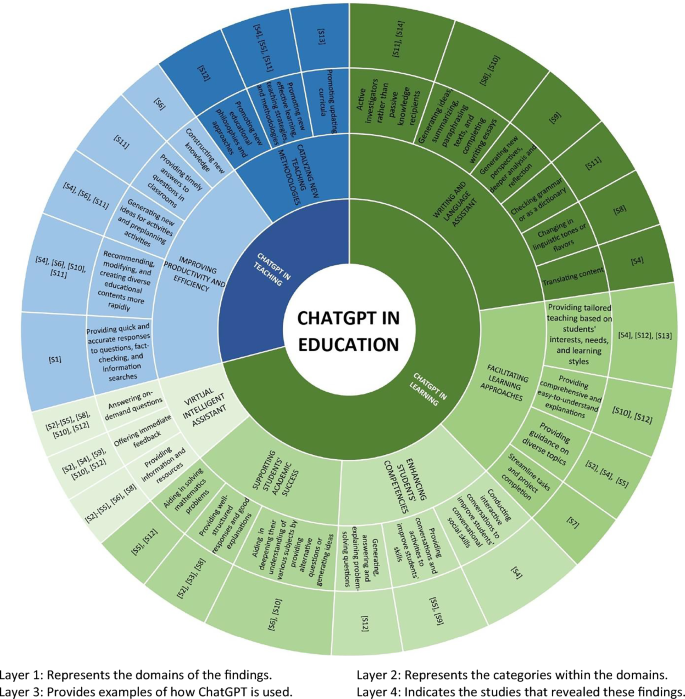
The main findings in the reviewed studies
4 Students' initial attempts at utilizing ChatGPT in learning and main findings from students' perspective
4.1 virtual intelligent assistant.
Nine studies demonstrated that ChatGPT has been utilized by students as an intelligent assistant to enhance and support their learning. Students employed it for various purposes, such as answering on-demand questions [S2]-[S5], [S8], [S10], and [S12], providing valuable information and learning resources [S2]-[S5], [S6], and [S8], as well as receiving immediate feedback [S2], [S4], [S9], [S10], and [S12]. In this regard, students generally were confident in the accuracy of ChatGPT's responses, considering them relevant, reliable, and detailed [S3], [S4], [S5], and [S8]. However, some students indicated the need for improvement, as they found that answers are not always accurate [S2], and that misleading information may have been provided or that it may not always align with their expectations [S6] and [S10]. It was also observed by the students that the accuracy of ChatGPT is dependent on several factors, including the quality and specificity of the user's input, the complexity of the question or topic, and the scope and relevance of its training data [S12]. Many students felt that ChatGPT's answers were not always accurate and most of them believed that it requires good background knowledge to work with.
4.2 Writing and language proficiency assistant
Six of the reviewed studies highlighted that ChatGPT has been utilized by students as a valuable assistant tool to improve their academic writing skills and language proficiency. Among these studies, three mainly focused on English education, demonstrating that students showed sufficient mastery in using ChatGPT for generating ideas, summarizing, paraphrasing texts, and completing writing essays [S8], [S11], and [S14]. Furthermore, ChatGPT helped them in writing by making students active investigators rather than passive knowledge recipients and facilitated the development of their writing skills [S11] and [S14]. Similarly, ChatGPT allowed students to generate unique ideas and perspectives, leading to deeper analysis and reflection on their journalism writing [S9]. In terms of language proficiency, ChatGPT allowed participants to translate content into their home languages, making it more accessible and relevant to their context [S4]. It also enabled them to request changes in linguistic tones or flavors [S8]. Moreover, participants used it to check grammar or as a dictionary [S11].
4.3 Valuable resource for learning approaches
Five studies demonstrated that students used ChatGPT as a valuable complementary resource for self-directed learning. It provided learning resources and guidance on diverse educational topics and created a supportive home learning environment [S2] and [S4]. Moreover, it offered step-by-step guidance to grasp concepts at their own pace and enhance their understanding [S5], streamlined task and project completion carried out independently [S7], provided comprehensive and easy-to-understand explanations on various subjects [S10], and assisted in studying geometry operations, thereby empowering them to explore geometry operations at their own pace [S12]. Three studies showed that students used ChatGPT as a valuable learning resource for personalized learning. It delivered age-appropriate conversations and tailored teaching based on a child's interests [S4], acted as a personalized learning assistant, adapted to their needs and pace, which assisted them in understanding mathematical concepts [S12], and enabled personalized learning experiences in social sciences by adapting to students' needs and learning styles [S13]. On the other hand, it is important to note that, according to one study [S5], students suggested that using ChatGPT may negatively affect collaborative learning competencies between students.
4.4 Enhancing students' competencies
Six of the reviewed studies have shown that ChatGPT is a valuable tool for improving a wide range of skills among students. Two studies have provided evidence that ChatGPT led to improvements in students' critical thinking, reasoning skills, and hazard recognition competencies through engaging them in interactive conversations or activities and providing responses related to their disciplines in journalism [S5] and construction education [S9]. Furthermore, two studies focused on mathematical education have shown the positive impact of ChatGPT on students' problem-solving abilities in unraveling problem-solving questions [S12] and enhancing the students' understanding of the problem-solving process [S5]. Lastly, one study indicated that ChatGPT effectively contributed to the enhancement of conversational social skills [S4].
4.5 Supporting students' academic success
Seven of the reviewed studies highlighted that students found ChatGPT to be beneficial for learning as it enhanced learning efficiency and improved the learning experience. It has been observed to improve students' efficiency in computer engineering studies by providing well-structured responses and good explanations [S2]. Additionally, students found it extremely useful for hazard reporting [S3], and it also enhanced their efficiency in solving mathematics problems and capabilities [S5] and [S12]. Furthermore, by finding information, generating ideas, translating texts, and providing alternative questions, ChatGPT aided students in deepening their understanding of various subjects [S6]. It contributed to an increase in students' overall productivity [S7] and improved efficiency in composing written tasks [S8]. Regarding learning experiences, ChatGPT was instrumental in assisting students in identifying hazards that they might have otherwise overlooked [S3]. It also improved students' learning experiences in solving mathematics problems and developing abilities [S5] and [S12]. Moreover, it increased students' successful completion of important tasks in their studies [S7], particularly those involving average difficulty writing tasks [S8]. Additionally, ChatGPT increased the chances of educational success by providing students with baseline knowledge on various topics [S10].
5 Teachers' initial attempts at utilizing ChatGPT in teaching and main findings from teachers' perspective
5.1 valuable resource for teaching.
The reviewed studies showed that teachers have employed ChatGPT to recommend, modify, and generate diverse, creative, organized, and engaging educational contents, teaching materials, and testing resources more rapidly [S4], [S6], [S10] and [S11]. Additionally, teachers experienced increased productivity as ChatGPT facilitated quick and accurate responses to questions, fact-checking, and information searches [S1]. It also proved valuable in constructing new knowledge [S6] and providing timely answers to students' questions in classrooms [S11]. Moreover, ChatGPT enhanced teachers' efficiency by generating new ideas for activities and preplanning activities for their students [S4] and [S6], including interactive language game partners [S11].
5.2 Improving productivity and efficiency
The reviewed studies showed that participants' productivity and work efficiency have been significantly enhanced by using ChatGPT as it enabled them to allocate more time to other tasks and reduce their overall workloads [S6], [S10], [S11], [S13], and [S14]. However, three studies [S1], [S4], and [S11], indicated a negative perception and attitude among teachers toward using ChatGPT. This negativity stemmed from a lack of necessary skills to use it effectively [S1], a limited familiarity with it [S4], and occasional inaccuracies in the content provided by it [S10].
5.3 Catalyzing new teaching methodologies
Five of the reviewed studies highlighted that educators found the necessity of redefining their teaching profession with the assistance of ChatGPT [S11], developing new effective learning strategies [S4], and adapting teaching strategies and methodologies to ensure the development of essential skills for future engineers [S5]. They also emphasized the importance of adopting new educational philosophies and approaches that can evolve with the introduction of ChatGPT into the classroom [S12]. Furthermore, updating curricula to focus on improving human-specific features, such as emotional intelligence, creativity, and philosophical perspectives [S13], was found to be essential.
5.4 Effective utilization of CHATGPT in teaching
According to the reviewed studies, effective utilization of ChatGPT in education requires providing teachers with well-structured training, support, and adequate background on how to use ChatGPT responsibly [S1], [S3], [S11], and [S12]. Establishing clear rules and regulations regarding its usage is essential to ensure it positively impacts the teaching and learning processes, including students' skills [S1], [S4], [S5], [S8], [S9], and [S11]-[S14]. Moreover, conducting further research and engaging in discussions with policymakers and stakeholders is indeed crucial for the successful integration of ChatGPT in education and to maximize the benefits for both educators and students [S1], [S6]-[S10], and [S12]-[S14].
6 Discussion
The purpose of this review is to conduct a systematic review of empirical studies that have explored the utilization of ChatGPT, one of today’s most advanced LLM-based chatbots, in education. The findings of the reviewed studies showed several ways of ChatGPT utilization in different learning and teaching practices as well as it provided insights and considerations that can facilitate its effective and responsible use in future educational contexts. The results of the reviewed studies came from diverse fields of education, which helped us avoid a biased review that is limited to a specific field. Similarly, the reviewed studies have been conducted across different geographic regions. This kind of variety in geographic representation enriched the findings of this review.
In response to RQ1 , "What are students' and teachers' initial attempts at utilizing ChatGPT in education?", the findings from this review provide comprehensive insights. Chatbots, including ChatGPT, play a crucial role in supporting student learning, enhancing their learning experiences, and facilitating diverse learning approaches [ 42 , 43 ]. This review found that this tool, ChatGPT, has been instrumental in enhancing students' learning experiences by serving as a virtual intelligent assistant, providing immediate feedback, on-demand answers, and engaging in educational conversations. Additionally, students have benefited from ChatGPT’s ability to generate ideas, compose essays, and perform tasks like summarizing, translating, paraphrasing texts, or checking grammar, thereby enhancing their writing and language competencies. Furthermore, students have turned to ChatGPT for assistance in understanding concepts and homework, providing structured learning plans, and clarifying assignments and tasks, which fosters a supportive home learning environment, allowing them to take responsibility for their own learning and cultivate the skills and approaches essential for supportive home learning environment [ 26 , 27 , 28 ]. This finding aligns with the study of Saqr et al. [ 68 , 69 ] who highlighted that, when students actively engage in their own learning process, it yields additional advantages, such as heightened motivation, enhanced achievement, and the cultivation of enthusiasm, turning them into advocates for their own learning.
Moreover, students have utilized ChatGPT for tailored teaching and step-by-step guidance on diverse educational topics, streamlining task and project completion, and generating and recommending educational content. This personalization enhances the learning environment, leading to increased academic success. This finding aligns with other recent studies [ 26 , 27 , 28 , 60 , 66 ] which revealed that ChatGPT has the potential to offer personalized learning experiences and support an effective learning process by providing students with customized feedback and explanations tailored to their needs and abilities. Ultimately, fostering students' performance, engagement, and motivation, leading to increase students' academic success [ 14 , 44 , 58 ]. This ultimate outcome is in line with the findings of Saqr et al. [ 68 , 69 ], which emphasized that learning strategies are important catalysts of students' learning, as students who utilize effective learning strategies are more likely to have better academic achievement.
Teachers, too, have capitalized on ChatGPT's capabilities to enhance productivity and efficiency, using it for creating lesson plans, generating quizzes, providing additional resources, generating and preplanning new ideas for activities, and aiding in answering students’ questions. This adoption of technology introduces new opportunities to support teaching and learning practices, enhancing teacher productivity. This finding aligns with those of Day [ 17 ], De Castro [ 18 ], and Su and Yang [ 74 ] as well as with those of Valtonen et al. [ 82 ], who revealed that emerging technological advancements have opened up novel opportunities and means to support teaching and learning practices, and enhance teachers’ productivity.
In response to RQ2 , "What are the main findings derived from empirical studies that have incorporated ChatGPT into learning and teaching?", the findings from this review provide profound insights and raise significant concerns. Starting with the insights, chatbots, including ChatGPT, have demonstrated the potential to reshape and revolutionize education, creating new, novel opportunities for enhancing the learning process and outcomes [ 83 ], facilitating different learning approaches, and offering a range of pedagogical benefits [ 19 , 43 , 72 ]. In this context, this review found that ChatGPT could open avenues for educators to adopt or develop new effective learning and teaching strategies that can evolve with the introduction of ChatGPT into the classroom. Nonetheless, there is an evident lack of research understanding regarding the potential impact of generative machine learning models within diverse educational settings [ 83 ]. This necessitates teachers to attain a high level of proficiency in incorporating chatbots, such as ChatGPT, into their classrooms to create inventive, well-structured, and captivating learning strategies. In the same vein, the review also found that teachers without the requisite skills to utilize ChatGPT realized that it did not contribute positively to their work and could potentially have adverse effects [ 37 ]. This concern could lead to inequity of access to the benefits of chatbots, including ChatGPT, as individuals who lack the necessary expertise may not be able to harness their full potential, resulting in disparities in educational outcomes and opportunities. Therefore, immediate action is needed to address these potential issues. A potential solution is offering training, support, and competency development for teachers to ensure that all of them can leverage chatbots, including ChatGPT, effectively and equitably in their educational practices [ 5 , 28 , 80 ], which could enhance accessibility and inclusivity, and potentially result in innovative outcomes [ 82 , 83 ].
Additionally, chatbots, including ChatGPT, have the potential to significantly impact students' thinking abilities, including retention, reasoning, analysis skills [ 19 , 45 ], and foster innovation and creativity capabilities [ 83 ]. This review found that ChatGPT could contribute to improving a wide range of skills among students. However, it found that frequent use of ChatGPT may result in a decrease in innovative capacities, collaborative skills and cognitive capacities, and students' motivation to attend classes, as well as could lead to reduced higher-order thinking skills among students [ 22 , 29 ]. Therefore, immediate action is needed to carefully examine the long-term impact of chatbots such as ChatGPT, on learning outcomes as well as to explore its incorporation into educational settings as a supportive tool without compromising students' cognitive development and critical thinking abilities. In the same vein, the review also found that it is challenging to draw a consistent conclusion regarding the potential of ChatGPT to aid self-directed learning approach. This finding aligns with the recent study of Baskara [ 8 ]. Therefore, further research is needed to explore the potential of ChatGPT for self-directed learning. One potential solution involves utilizing learning analytics as a novel approach to examine various aspects of students' learning and support them in their individual endeavors [ 32 ]. This approach can bridge this gap by facilitating an in-depth analysis of how learners engage with ChatGPT, identifying trends in self-directed learning behavior, and assessing its influence on their outcomes.
Turning to the significant concerns, on the other hand, a fundamental challenge with LLM-based chatbots, including ChatGPT, is the accuracy and quality of the provided information and responses, as they provide false information as truth—a phenomenon often referred to as "hallucination" [ 3 , 49 ]. In this context, this review found that the provided information was not entirely satisfactory. Consequently, the utilization of chatbots presents potential concerns, such as generating and providing inaccurate or misleading information, especially for students who utilize it to support their learning. This finding aligns with other findings [ 6 , 30 , 35 , 40 ] which revealed that incorporating chatbots such as ChatGPT, into education presents challenges related to its accuracy and reliability due to its training on a large corpus of data, which may contain inaccuracies and the way users formulate or ask ChatGPT. Therefore, immediate action is needed to address these potential issues. One possible solution is to equip students with the necessary skills and competencies, which include a background understanding of how to use it effectively and the ability to assess and evaluate the information it generates, as the accuracy and the quality of the provided information depend on the input, its complexity, the topic, and the relevance of its training data [ 28 , 49 , 86 ]. However, it's also essential to examine how learners can be educated about how these models operate, the data used in their training, and how to recognize their limitations, challenges, and issues [ 79 ].
Furthermore, chatbots present a substantial challenge concerning maintaining academic integrity [ 20 , 56 ] and copyright violations [ 83 ], which are significant concerns in education. The review found that the potential misuse of ChatGPT might foster cheating, facilitate plagiarism, and threaten academic integrity. This issue is also affirmed by the research conducted by Basic et al. [ 7 ], who presented evidence that students who utilized ChatGPT in their writing assignments had more plagiarism cases than those who did not. These findings align with the conclusions drawn by Cotton et al. [ 13 ], Hisan and Amri [ 33 ] and Sullivan et al. [ 75 ], who revealed that the integration of chatbots such as ChatGPT into education poses a significant challenge to the preservation of academic integrity. Moreover, chatbots, including ChatGPT, have increased the difficulty in identifying plagiarism [ 47 , 67 , 76 ]. The findings from previous studies [ 1 , 84 ] indicate that AI-generated text often went undetected by plagiarism software, such as Turnitin. However, Turnitin and other similar plagiarism detection tools, such as ZeroGPT, GPTZero, and Copyleaks, have since evolved, incorporating enhanced techniques to detect AI-generated text, despite the possibility of false positives, as noted in different studies that have found these tools still not yet fully ready to accurately and reliably identify AI-generated text [ 10 , 51 ], and new novel detection methods may need to be created and implemented for AI-generated text detection [ 4 ]. This potential issue could lead to another concern, which is the difficulty of accurately evaluating student performance when they utilize chatbots such as ChatGPT assistance in their assignments. Consequently, the most LLM-driven chatbots present a substantial challenge to traditional assessments [ 64 ]. The findings from previous studies indicate the importance of rethinking, improving, and redesigning innovative assessment methods in the era of chatbots [ 14 , 20 , 64 , 75 ]. These methods should prioritize the process of evaluating students' ability to apply knowledge to complex cases and demonstrate comprehension, rather than solely focusing on the final product for assessment. Therefore, immediate action is needed to address these potential issues. One possible solution would be the development of clear guidelines, regulatory policies, and pedagogical guidance. These measures would help regulate the proper and ethical utilization of chatbots, such as ChatGPT, and must be established before their introduction to students [ 35 , 38 , 39 , 41 , 89 ].
In summary, our review has delved into the utilization of ChatGPT, a prominent example of chatbots, in education, addressing the question of how ChatGPT has been utilized in education. However, there remain significant gaps, which necessitate further research to shed light on this area.
7 Conclusions
This systematic review has shed light on the varied initial attempts at incorporating ChatGPT into education by both learners and educators, while also offering insights and considerations that can facilitate its effective and responsible use in future educational contexts. From the analysis of 14 selected studies, the review revealed the dual-edged impact of ChatGPT in educational settings. On the positive side, ChatGPT significantly aided the learning process in various ways. Learners have used it as a virtual intelligent assistant, benefiting from its ability to provide immediate feedback, on-demand answers, and easy access to educational resources. Additionally, it was clear that learners have used it to enhance their writing and language skills, engaging in practices such as generating ideas, composing essays, and performing tasks like summarizing, translating, paraphrasing texts, or checking grammar. Importantly, other learners have utilized it in supporting and facilitating their directed and personalized learning on a broad range of educational topics, assisting in understanding concepts and homework, providing structured learning plans, and clarifying assignments and tasks. Educators, on the other hand, found ChatGPT beneficial for enhancing productivity and efficiency. They used it for creating lesson plans, generating quizzes, providing additional resources, and answers learners' questions, which saved time and allowed for more dynamic and engaging teaching strategies and methodologies.
However, the review also pointed out negative impacts. The results revealed that overuse of ChatGPT could decrease innovative capacities and collaborative learning among learners. Specifically, relying too much on ChatGPT for quick answers can inhibit learners' critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Learners might not engage deeply with the material or consider multiple solutions to a problem. This tendency was particularly evident in group projects, where learners preferred consulting ChatGPT individually for solutions over brainstorming and collaborating with peers, which negatively affected their teamwork abilities. On a broader level, integrating ChatGPT into education has also raised several concerns, including the potential for providing inaccurate or misleading information, issues of inequity in access, challenges related to academic integrity, and the possibility of misusing the technology.
Accordingly, this review emphasizes the urgency of developing clear rules, policies, and regulations to ensure ChatGPT's effective and responsible use in educational settings, alongside other chatbots, by both learners and educators. This requires providing well-structured training to educate them on responsible usage and understanding its limitations, along with offering sufficient background information. Moreover, it highlights the importance of rethinking, improving, and redesigning innovative teaching and assessment methods in the era of ChatGPT. Furthermore, conducting further research and engaging in discussions with policymakers and stakeholders are essential steps to maximize the benefits for both educators and learners and ensure academic integrity.
It is important to acknowledge that this review has certain limitations. Firstly, the limited inclusion of reviewed studies can be attributed to several reasons, including the novelty of the technology, as new technologies often face initial skepticism and cautious adoption; the lack of clear guidelines or best practices for leveraging this technology for educational purposes; and institutional or governmental policies affecting the utilization of this technology in educational contexts. These factors, in turn, have affected the number of studies available for review. Secondly, the utilization of the original version of ChatGPT, based on GPT-3 or GPT-3.5, implies that new studies utilizing the updated version, GPT-4 may lead to different findings. Therefore, conducting follow-up systematic reviews is essential once more empirical studies on ChatGPT are published. Additionally, long-term studies are necessary to thoroughly examine and assess the impact of ChatGPT on various educational practices.
Despite these limitations, this systematic review has highlighted the transformative potential of ChatGPT in education, revealing its diverse utilization by learners and educators alike and summarized the benefits of incorporating it into education, as well as the forefront critical concerns and challenges that must be addressed to facilitate its effective and responsible use in future educational contexts. This review could serve as an insightful resource for practitioners who seek to integrate ChatGPT into education and stimulate further research in the field.
Data availability
The data supporting our findings are available upon request.
Abbreviations
- Artificial intelligence
AI in education
Large language model
Artificial neural networks
Chat Generative Pre-Trained Transformer
Recurrent neural networks
Long short-term memory
Reinforcement learning from human feedback
Natural language processing
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses
AlAfnan MA, Dishari S, Jovic M, Lomidze K. ChatGPT as an educational tool: opportunities, challenges, and recommendations for communication, business writing, and composition courses. J Artif Intell Technol. 2023. https://doi.org/10.37965/jait.2023.0184 .
Article Google Scholar
Ali JKM, Shamsan MAA, Hezam TA, Mohammed AAQ. Impact of ChatGPT on learning motivation. J Engl Stud Arabia Felix. 2023;2(1):41–9. https://doi.org/10.56540/jesaf.v2i1.51 .
Alkaissi H, McFarlane SI. Artificial hallucinations in ChatGPT: implications in scientific writing. Cureus. 2023. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.35179 .
Anderson N, Belavý DL, Perle SM, Hendricks S, Hespanhol L, Verhagen E, Memon AR. AI did not write this manuscript, or did it? Can we trick the AI text detector into generated texts? The potential future of ChatGPT and AI in sports & exercise medicine manuscript generation. BMJ Open Sport Exerc Med. 2023;9(1): e001568. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjsem-2023-001568 .
Ausat AMA, Massang B, Efendi M, Nofirman N, Riady Y. Can chat GPT replace the role of the teacher in the classroom: a fundamental analysis. J Educ. 2023;5(4):16100–6.
Google Scholar
Baidoo-Anu D, Ansah L. Education in the Era of generative artificial intelligence (AI): understanding the potential benefits of ChatGPT in promoting teaching and learning. Soc Sci Res Netw. 2023. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.4337484 .
Basic Z, Banovac A, Kruzic I, Jerkovic I. Better by you, better than me, chatgpt3 as writing assistance in students essays. 2023. arXiv preprint arXiv:2302.04536 .
Baskara FR. The promises and pitfalls of using chat GPT for self-determined learning in higher education: an argumentative review. Prosiding Seminar Nasional Fakultas Tarbiyah dan Ilmu Keguruan IAIM Sinjai. 2023;2:95–101. https://doi.org/10.47435/sentikjar.v2i0.1825 .
Behera RK, Bala PK, Dhir A. The emerging role of cognitive computing in healthcare: a systematic literature review. Int J Med Inform. 2019;129:154–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2019.04.024 .
Chaka C. Detecting AI content in responses generated by ChatGPT, YouChat, and Chatsonic: the case of five AI content detection tools. J Appl Learn Teach. 2023. https://doi.org/10.37074/jalt.2023.6.2.12 .
Chiu TKF, Xia Q, Zhou X, Chai CS, Cheng M. Systematic literature review on opportunities, challenges, and future research recommendations of artificial intelligence in education. Comput Educ Artif Intell. 2023;4:100118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.caeai.2022.100118 .
Choi EPH, Lee JJ, Ho M, Kwok JYY, Lok KYW. Chatting or cheating? The impacts of ChatGPT and other artificial intelligence language models on nurse education. Nurse Educ Today. 2023;125:105796. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nedt.2023.105796 .
Cotton D, Cotton PA, Shipway JR. Chatting and cheating: ensuring academic integrity in the era of ChatGPT. Innov Educ Teach Int. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1080/14703297.2023.2190148 .
Crawford J, Cowling M, Allen K. Leadership is needed for ethical ChatGPT: Character, assessment, and learning using artificial intelligence (AI). J Univ Teach Learn Pract. 2023. https://doi.org/10.53761/1.20.3.02 .
Creswell JW. Educational research: planning, conducting, and evaluating quantitative and qualitative research [Ebook]. 4th ed. London: Pearson Education; 2015.
Curry D. ChatGPT Revenue and Usage Statistics (2023)—Business of Apps. 2023. https://www.businessofapps.com/data/chatgpt-statistics/
Day T. A preliminary investigation of fake peer-reviewed citations and references generated by ChatGPT. Prof Geogr. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1080/00330124.2023.2190373 .
De Castro CA. A Discussion about the Impact of ChatGPT in education: benefits and concerns. J Bus Theor Pract. 2023;11(2):p28. https://doi.org/10.22158/jbtp.v11n2p28 .
Deng X, Yu Z. A meta-analysis and systematic review of the effect of Chatbot technology use in sustainable education. Sustainability. 2023;15(4):2940. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15042940 .
Eke DO. ChatGPT and the rise of generative AI: threat to academic integrity? J Responsib Technol. 2023;13:100060. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrt.2023.100060 .
Elmoazen R, Saqr M, Tedre M, Hirsto L. A systematic literature review of empirical research on epistemic network analysis in education. IEEE Access. 2022;10:17330–48. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2022.3149812 .
Farrokhnia M, Banihashem SK, Noroozi O, Wals AEJ. A SWOT analysis of ChatGPT: implications for educational practice and research. Innov Educ Teach Int. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1080/14703297.2023.2195846 .
Fergus S, Botha M, Ostovar M. Evaluating academic answers generated using ChatGPT. J Chem Educ. 2023;100(4):1672–5. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jchemed.3c00087 .
Fink A. Conducting research literature reviews: from the Internet to Paper. Incorporated: SAGE Publications; 2010.
Firaina R, Sulisworo D. Exploring the usage of ChatGPT in higher education: frequency and impact on productivity. Buletin Edukasi Indonesia (BEI). 2023;2(01):39–46. https://doi.org/10.56741/bei.v2i01.310 .
Firat, M. (2023). How chat GPT can transform autodidactic experiences and open education. Department of Distance Education, Open Education Faculty, Anadolu Unive . https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8707-5918
Firat M. What ChatGPT means for universities: perceptions of scholars and students. J Appl Learn Teach. 2023. https://doi.org/10.37074/jalt.2023.6.1.22 .
Fuchs K. Exploring the opportunities and challenges of NLP models in higher education: is Chat GPT a blessing or a curse? Front Educ. 2023. https://doi.org/10.3389/feduc.2023.1166682 .
García-Peñalvo FJ. La percepción de la inteligencia artificial en contextos educativos tras el lanzamiento de ChatGPT: disrupción o pánico. Educ Knowl Soc. 2023;24: e31279. https://doi.org/10.14201/eks.31279 .
Gilson A, Safranek CW, Huang T, Socrates V, Chi L, Taylor A, Chartash D. How does ChatGPT perform on the United States medical Licensing examination? The implications of large language models for medical education and knowledge assessment. JMIR Med Educ. 2023;9: e45312. https://doi.org/10.2196/45312 .
Hashana AJ, Brundha P, Ayoobkhan MUA, Fazila S. Deep Learning in ChatGPT—A Survey. In 2023 7th international conference on trends in electronics and informatics (ICOEI) . 2023. (pp. 1001–1005). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/icoei56765.2023.10125852
Hirsto L, Saqr M, López-Pernas S, Valtonen T. (2022). A systematic narrative review of learning analytics research in K-12 and schools. Proceedings . https://ceur-ws.org/Vol-3383/FLAIEC22_paper_9536.pdf
Hisan UK, Amri MM. ChatGPT and medical education: a double-edged sword. J Pedag Educ Sci. 2023;2(01):71–89. https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.2.31280.23043/1 .
Hopkins AM, Logan JM, Kichenadasse G, Sorich MJ. Artificial intelligence chatbots will revolutionize how cancer patients access information: ChatGPT represents a paradigm-shift. JNCI Cancer Spectr. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1093/jncics/pkad010 .
Househ M, AlSaad R, Alhuwail D, Ahmed A, Healy MG, Latifi S, Sheikh J. Large Language models in medical education: opportunities, challenges, and future directions. JMIR Med Educ. 2023;9: e48291. https://doi.org/10.2196/48291 .
Ilkka T. The impact of artificial intelligence on learning, teaching, and education. Minist de Educ. 2018. https://doi.org/10.2760/12297 .
Iqbal N, Ahmed H, Azhar KA. Exploring teachers’ attitudes towards using CHATGPT. Globa J Manag Adm Sci. 2022;3(4):97–111. https://doi.org/10.46568/gjmas.v3i4.163 .
Irfan M, Murray L, Ali S. Integration of Artificial intelligence in academia: a case study of critical teaching and learning in Higher education. Globa Soc Sci Rev. 2023;8(1):352–64. https://doi.org/10.31703/gssr.2023(viii-i).32 .
Jeon JH, Lee S. Large language models in education: a focus on the complementary relationship between human teachers and ChatGPT. Educ Inf Technol. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-023-11834-1 .
Khan RA, Jawaid M, Khan AR, Sajjad M. ChatGPT—Reshaping medical education and clinical management. Pak J Med Sci. 2023. https://doi.org/10.12669/pjms.39.2.7653 .
King MR. A conversation on artificial intelligence, Chatbots, and plagiarism in higher education. Cell Mol Bioeng. 2023;16(1):1–2. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12195-022-00754-8 .
Kooli C. Chatbots in education and research: a critical examination of ethical implications and solutions. Sustainability. 2023;15(7):5614. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15075614 .
Kuhail MA, Alturki N, Alramlawi S, Alhejori K. Interacting with educational chatbots: a systematic review. Educ Inf Technol. 2022;28(1):973–1018. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-022-11177-3 .
Lee H. The rise of ChatGPT: exploring its potential in medical education. Anat Sci Educ. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1002/ase.2270 .
Li L, Subbareddy R, Raghavendra CG. AI intelligence Chatbot to improve students learning in the higher education platform. J Interconnect Netw. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1142/s0219265921430325 .
Limna P. A Review of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Education during the Digital Era. 2022. https://ssrn.com/abstract=4160798
Lo CK. What is the impact of ChatGPT on education? A rapid review of the literature. Educ Sci. 2023;13(4):410. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci13040410 .
Luo W, He H, Liu J, Berson IR, Berson MJ, Zhou Y, Li H. Aladdin’s genie or pandora’s box For early childhood education? Experts chat on the roles, challenges, and developments of ChatGPT. Early Educ Dev. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1080/10409289.2023.2214181 .
Meyer JG, Urbanowicz RJ, Martin P, O’Connor K, Li R, Peng P, Moore JH. ChatGPT and large language models in academia: opportunities and challenges. Biodata Min. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13040-023-00339-9 .
Mhlanga D. Open AI in education, the responsible and ethical use of ChatGPT towards lifelong learning. Soc Sci Res Netw. 2023. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.4354422 .
Neumann, M., Rauschenberger, M., & Schön, E. M. (2023). “We Need To Talk About ChatGPT”: The Future of AI and Higher Education. https://doi.org/10.1109/seeng59157.2023.00010
Nolan B. Here are the schools and colleges that have banned the use of ChatGPT over plagiarism and misinformation fears. Business Insider . 2023. https://www.businessinsider.com
O’Leary DE. An analysis of three chatbots: BlenderBot, ChatGPT and LaMDA. Int J Intell Syst Account, Financ Manag. 2023;30(1):41–54. https://doi.org/10.1002/isaf.1531 .
Okoli C. A guide to conducting a standalone systematic literature review. Commun Assoc Inf Syst. 2015. https://doi.org/10.17705/1cais.03743 .
OpenAI. (2023). https://openai.com/blog/chatgpt
Perkins M. Academic integrity considerations of AI large language models in the post-pandemic era: ChatGPT and beyond. J Univ Teach Learn Pract. 2023. https://doi.org/10.53761/1.20.02.07 .
Plevris V, Papazafeiropoulos G, Rios AJ. Chatbots put to the test in math and logic problems: A preliminary comparison and assessment of ChatGPT-3.5, ChatGPT-4, and Google Bard. arXiv (Cornell University) . 2023. https://doi.org/10.48550/arxiv.2305.18618
Rahman MM, Watanobe Y (2023) ChatGPT for education and research: opportunities, threats, and strategies. Appl Sci 13(9):5783. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13095783
Ram B, Verma P. Artificial intelligence AI-based Chatbot study of ChatGPT, google AI bard and baidu AI. World J Adv Eng Technol Sci. 2023;8(1):258–61. https://doi.org/10.30574/wjaets.2023.8.1.0045 .
Rasul T, Nair S, Kalendra D, Robin M, de Oliveira Santini F, Ladeira WJ, Heathcote L. The role of ChatGPT in higher education: benefits, challenges, and future research directions. J Appl Learn Teach. 2023. https://doi.org/10.37074/jalt.2023.6.1.29 .
Ratnam M, Sharm B, Tomer A. ChatGPT: educational artificial intelligence. Int J Adv Trends Comput Sci Eng. 2023;12(2):84–91. https://doi.org/10.30534/ijatcse/2023/091222023 .
Ray PP. ChatGPT: a comprehensive review on background, applications, key challenges, bias, ethics, limitations and future scope. Internet Things Cyber-Phys Syst. 2023;3:121–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iotcps.2023.04.003 .
Roumeliotis KI, Tselikas ND. ChatGPT and Open-AI models: a preliminary review. Future Internet. 2023;15(6):192. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi15060192 .
Rudolph J, Tan S, Tan S. War of the chatbots: Bard, Bing Chat, ChatGPT, Ernie and beyond. The new AI gold rush and its impact on higher education. J Appl Learn Teach. 2023. https://doi.org/10.37074/jalt.2023.6.1.23 .
Ruiz LMS, Moll-López S, Nuñez-Pérez A, Moraño J, Vega-Fleitas E. ChatGPT challenges blended learning methodologies in engineering education: a case study in mathematics. Appl Sci. 2023;13(10):6039. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13106039 .
Sallam M, Salim NA, Barakat M, Al-Tammemi AB. ChatGPT applications in medical, dental, pharmacy, and public health education: a descriptive study highlighting the advantages and limitations. Narra J. 2023;3(1): e103. https://doi.org/10.52225/narra.v3i1.103 .
Salvagno M, Taccone FS, Gerli AG. Can artificial intelligence help for scientific writing? Crit Care. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13054-023-04380-2 .
Saqr M, López-Pernas S, Helske S, Hrastinski S. The longitudinal association between engagement and achievement varies by time, students’ profiles, and achievement state: a full program study. Comput Educ. 2023;199:104787. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2023.104787 .
Saqr M, Matcha W, Uzir N, Jovanović J, Gašević D, López-Pernas S. Transferring effective learning strategies across learning contexts matters: a study in problem-based learning. Australas J Educ Technol. 2023;39(3):9.
Schöbel S, Schmitt A, Benner D, Saqr M, Janson A, Leimeister JM. Charting the evolution and future of conversational agents: a research agenda along five waves and new frontiers. Inf Syst Front. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10796-023-10375-9 .
Shoufan A. Exploring students’ perceptions of CHATGPT: thematic analysis and follow-up survey. IEEE Access. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2023.3268224 .
Sonderegger S, Seufert S. Chatbot-mediated learning: conceptual framework for the design of Chatbot use cases in education. Gallen: Institute for Educational Management and Technologies, University of St; 2022. https://doi.org/10.5220/0010999200003182 .
Book Google Scholar
Strzelecki A. To use or not to use ChatGPT in higher education? A study of students’ acceptance and use of technology. Interact Learn Environ. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2023.2209881 .
Su J, Yang W. Unlocking the power of ChatGPT: a framework for applying generative AI in education. ECNU Rev Educ. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1177/20965311231168423 .
Sullivan M, Kelly A, McLaughlan P. ChatGPT in higher education: Considerations for academic integrity and student learning. J ApplLearn Teach. 2023;6(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.37074/jalt.2023.6.1.17 .
Szabo A. ChatGPT is a breakthrough in science and education but fails a test in sports and exercise psychology. Balt J Sport Health Sci. 2023;1(128):25–40. https://doi.org/10.33607/bjshs.v127i4.1233 .
Taecharungroj V. “What can ChatGPT do?” analyzing early reactions to the innovative AI chatbot on Twitter. Big Data Cognit Comput. 2023;7(1):35. https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc7010035 .
Tam S, Said RB. User preferences for ChatGPT-powered conversational interfaces versus traditional methods. Biomed Eng Soc. 2023. https://doi.org/10.58496/mjcsc/2023/004 .
Tedre M, Kahila J, Vartiainen H. (2023). Exploration on how co-designing with AI facilitates critical evaluation of ethics of AI in craft education. In: Langran E, Christensen P, Sanson J (Eds). Proceedings of Society for Information Technology and Teacher Education International Conference . 2023. pp. 2289–2296.
Tlili A, Shehata B, Adarkwah MA, Bozkurt A, Hickey DT, Huang R, Agyemang B. What if the devil is my guardian angel: ChatGPT as a case study of using chatbots in education. Smart Learn Environ. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40561-023-00237-x .
Uddin SMJ, Albert A, Ovid A, Alsharef A. Leveraging CHATGPT to aid construction hazard recognition and support safety education and training. Sustainability. 2023;15(9):7121. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15097121 .
Valtonen T, López-Pernas S, Saqr M, Vartiainen H, Sointu E, Tedre M. The nature and building blocks of educational technology research. Comput Hum Behav. 2022;128:107123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2021.107123 .
Vartiainen H, Tedre M. Using artificial intelligence in craft education: crafting with text-to-image generative models. Digit Creat. 2023;34(1):1–21. https://doi.org/10.1080/14626268.2023.2174557 .
Ventayen RJM. OpenAI ChatGPT generated results: similarity index of artificial intelligence-based contents. Soc Sci Res Netw. 2023. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.4332664 .
Wagner MW, Ertl-Wagner BB. Accuracy of information and references using ChatGPT-3 for retrieval of clinical radiological information. Can Assoc Radiol J. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1177/08465371231171125 .
Wardat Y, Tashtoush MA, AlAli R, Jarrah AM. ChatGPT: a revolutionary tool for teaching and learning mathematics. Eurasia J Math, Sci Technol Educ. 2023;19(7):em2286. https://doi.org/10.29333/ejmste/13272 .
Webster J, Watson RT. Analyzing the past to prepare for the future: writing a literature review. Manag Inf Syst Quart. 2002;26(2):3.
Xiao Y, Watson ME. Guidance on conducting a systematic literature review. J Plan Educ Res. 2017;39(1):93–112. https://doi.org/10.1177/0739456x17723971 .
Yan D. Impact of ChatGPT on learners in a L2 writing practicum: an exploratory investigation. Educ Inf Technol. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-023-11742-4 .
Yu H. Reflection on whether Chat GPT should be banned by academia from the perspective of education and teaching. Front Psychol. 2023;14:1181712. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1181712 .
Zhu C, Sun M, Luo J, Li T, Wang M. How to harness the potential of ChatGPT in education? Knowl Manag ELearn. 2023;15(2):133–52. https://doi.org/10.34105/j.kmel.2023.15.008 .
Download references
The paper is co-funded by the Academy of Finland (Suomen Akatemia) Research Council for Natural Sciences and Engineering for the project Towards precision education: Idiographic learning analytics (TOPEILA), Decision Number 350560.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Computing, University of Eastern Finland, 80100, Joensuu, Finland
Yazid Albadarin, Mohammed Saqr, Nicolas Pope & Markku Tukiainen
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
YA contributed to the literature search, data analysis, discussion, and conclusion. Additionally, YA contributed to the manuscript’s writing, editing, and finalization. MS contributed to the study’s design, conceptualization, acquisition of funding, project administration, allocation of resources, supervision, validation, literature search, and analysis of results. Furthermore, MS contributed to the manuscript's writing, revising, and approving it in its finalized state. NP contributed to the results, and discussions, and provided supervision. NP also contributed to the writing process, revisions, and the final approval of the manuscript in its finalized state. MT contributed to the study's conceptualization, resource management, supervision, writing, revising the manuscript, and approving it.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Yazid Albadarin .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
See Table 4
The process of synthesizing the data presented in Table 4 involved identifying the relevant studies through a search process of databases (ERIC, Scopus, Web of Knowledge, Dimensions.ai, and lens.org) using specific keywords "ChatGPT" and "education". Following this, inclusion/exclusion criteria were applied, and data extraction was performed using Creswell's [ 15 ] coding techniques to capture key information and identify common themes across the included studies.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Albadarin, Y., Saqr, M., Pope, N. et al. A systematic literature review of empirical research on ChatGPT in education. Discov Educ 3 , 60 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s44217-024-00138-2
Download citation
Received : 22 October 2023
Accepted : 10 May 2024
Published : 26 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s44217-024-00138-2
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Large language models
- Educational technology
- Systematic review
Advertisement
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Welcome to the Purdue Online Writing Lab

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The Online Writing Lab at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service of the Writing Lab at Purdue. Students, members of the community, and users worldwide will find information to assist with many writing projects. Teachers and trainers may use this material for in-class and out-of-class instruction.
The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives. The Purdue OWL offers global support through online reference materials and services.
A Message From the Assistant Director of Content Development
The Purdue OWL® is committed to supporting students, instructors, and writers by offering a wide range of resources that are developed and revised with them in mind. To do this, the OWL team is always exploring possibilties for a better design, allowing accessibility and user experience to guide our process. As the OWL undergoes some changes, we welcome your feedback and suggestions by email at any time.
Please don't hesitate to contact us via our contact page if you have any questions or comments.
All the best,
Social Media
Facebook twitter.
INNOVATIONS in pharmacy
Vol. 15 No. 2 (2024)
Copyright (c) 2024 Patrick Gallegos, Salaar, Michael

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License .
Copyright of content published in INNOVATIONS in pharmacy belongs to the author(s).
Leadership and Followership in Health Professions: A Systematic Review
Patrick Gallegos
Cleveland Clinic Akron General
Muhammad Salaar Riaz
Nassau University Medical Center
Michael Peeters
University of Toledo
DOI: https://doi.org/10.24926/iip.v15i2.5987
Keywords: Leadership, Followership, Health Professions
Objective: Leadership discussion, including leadership development programs, is common. However, discussion of followership as a component of leadership seems less frequently discussed. With a focus on leadership and followership, this investigation reviewed the health-professions education literature and characterized leadership-followership within health-professions education.
Methods : Using PubMed, ERIC, and Google Scholar, two investigators independently and systematically searched health-professions education literature for articles related to leadership and followership. Reports were categorized based on the articles by type, application, profession, leadership, and followership qualities.
Results: Eighty-one articles were included. More than half (48/81, 59%) were theoretical, 27% (22/81) empirical, 7% (6/81) commentaries, and 6% (5/81) letters-to-the-editor). Empirical studies did not share outcomes that could be meaningfully combined quantitatively by meta-analysis; however, the vast majority (96%) of theoretical articles discussed a healthcare-related application of leadership and followership (e.g., improving patient care, improving communication, improving organizational efficiency). Thus, a qualitative review was completed. Of the 81 articles, 57% (n=46) involved multiple professions, while 43% (n=35) focused on a specific profession [Nursing (n=16), Medicine (n=7), Others (n=5) Surgery (n=3), Pharmacy (n=2), Veterinary Medicine (n=2)]. While most articles (75%) discussed leadership qualities (with top qualities of effective communication, visionary, and delegating tasks), fewer (57%) discussed followership qualities (with top qualities of being responsible, committed, and supportive). Of note, some qualities overlapped in both leadership and followership (with top qualities of effective communication, being supportive, and providing/receiving feedback).
Conclusions: Leadership-Followership was described in many health-professions’ education literature. However, Pharmacy and Veterinary Medicine had substantially fewer articles published on this topic. Notably, followership did not receive nearly as much attention as leadership. Leadership has a dynamic and complex interaction with followership highlighting that an effective leader must know how to be an effective follower and vice versa. To improve leadership within healthcare teamwork, education should focus on both leadership-followership.
Author Biographies
Muhammad salaar riaz, nassau university medical center.
Internal Medicine Resident
Michael Peeters, University of Toledo
Director of Interprofessional Education

Contact Publishing Services | Acceptable Use of IT Resources
The copyright of these individual works published by the University of Minnesota Libraries Publishing remains with the original creator or editorial team. For uses beyond those covered by law or the Creative Commons license, permission to reuse should be sought directly from the copyright owner listed on each article.
- Open access
- Published: 03 June 2024
Evaluating competency-based medical education: a systematized review of current practices
- Nouf Sulaiman Alharbi 1 , 2 , 3
BMC Medical Education volume 24 , Article number: 612 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
113 Accesses
2 Altmetric
Metrics details
Few published articles provide a comprehensive overview of the available evidence on the topic of evaluating competency-based medical education (CBME) curricula. The purpose of this review is therefore to synthesize the available evidence on the evaluation practices for competency-based curricula employed in schools and programs for undergraduate and postgraduate health professionals.
This systematized review was conducted following the systematic reviews approach with minor modifications to synthesize the findings of published studies that examined the evaluation of CBME undergraduate and postgraduate programs for health professionals.
Thirty-eight articles met the inclusion criteria and reported evaluation practices in CBME curricula from various countries and regions worldwide, such as Canada, China, Turkey, and West Africa. 57% of the evaluated programs were at the postgraduate level, and 71% were in the field of medicine. The results revealed variation in reporting evaluation practices, with numerous studies failing to clarify evaluations’ objectives, approaches, tools, and standards as well as how evaluations were reported and communicated. It was noted that questionnaires were the primary tool employed for evaluating programs, often combined with interviews or focus groups. Furthermore, the utilized evaluation standards considered the well-known competencies framework, specialized association guidelines, and accreditation criteria.
This review calls attention to the importance of ensuring that reports of evaluation experiences include certain essential elements of evaluation to better inform theory and practice.
Peer Review reports
Medical education worldwide is embracing the move toward outcome-based education (OBME) [ 1 , 2 ]. One of the most popular outcome-based approaches being widely adopted by medical schools worldwide is competency-based medical education (CBME) [ 3 ]. CBME considers competencies as the ultimate outcomes that should guide curriculum development at all steps or stages—that is, implementation, assessment, and evaluation [ 3 , 4 , 5 ]. To embrace CBME and prepare medical students for practice, medical educators usually utilize an organized national or international competency framework that describes the abilities that physicians must possess to meet the needs of patients and society. There are numerous global competency frameworks that reflect the characteristics of a competent doctor, for example, CanMEDS, Scottish Doctor, Medical School Projects, ACGME Outcome Project, the Netherlands National Framework, and Saudi Meds [ 1 , 6 , 7 , 8 ].
With the worldwide implementation of CBME and availability of different competency frameworks, educators are expected to evaluate various modifications made to existing medical curricula [ 9 , 10 ]. Such evaluation is intended to explore whether the program is operating as planned and its outcomes are achieved as intended in comparison to predetermined standards as well as to ensure improvement [ 11 , 12 , 13 ]. Furthermore, program evaluation revolves around two main concepts, that is, merit and worth [ 12 , 14 ]. In 1981, Guba and Lincoln explained that the merits of a program are intrinsic, implicit, and independent and do not refer to a specific context or application, while evaluating a program’s worth entails judging the value of any aspect of it in reference to a certain context or precise application [ 12 , 14 ].
To enable educators to determine the merits and worth of an educational program or curriculum, evaluation experts have proposed several models [ 14 , 15 ]. Evaluation models are guiding frameworks that demonstrate what appropriate evaluation looks like and detail how it should be designed and implemented [ 16 ]. Although almost all evaluation models focus on exploring whether a program attains its objectives, they vary in numerous aspects, including their evaluation philosophy, approaches, and the specific areas that they encompass [ 17 ].
It is essential that educators choose a suitable evaluation model when they implement CBME, as the right model will enable them to pinpoint [ 15 , 18 , 19 ]. In other words, a program helps identify areas of success, challenges, and opportunities for improvement in CBME implementation, leading to a deeper comprehension of CBME strategies and their effectiveness. Moreover, implementing CBME demands significant efforts and a wide range of financial, human, time, and infrastructure resources [ 20 ]. Thus, ensuring that these efforts and resources are well utilized to enhance educational and healthcare outcomes is crucial. In addition, evaluation provides valuable evidence for accreditation, quality assurance, policies, and guidelines. Otherwise put, it supports informed decision-making on many levels [ 21 ]. On another front, sharing evaluation results and being transparent about evaluation processes can enhance public trust in available programs, colleges, and universities [ 19 ]. However, deciding which evaluation model to adopt can be challenging [ 9 ].
Not only can it be difficult to select an appropriate model to evaluate a CBME program, but CBME evaluation itself has numerous challenges, particularly given the lack of a common definition or standardized description of what constitutes a CBME program [ 9 , 22 , 23 ]. The complexity of CBME further tangles evaluation efforts, given the multilayered nature of CBME’s activities and outcomes and the need to engage a wide variety of stakeholders [ 11 ]. Moreover, the scarcity and variable quality of reporting in studies focusing on the evaluation of CBME curricula exacerbate these challenges [ 24 ]. Furthermore, few published articles provide a comprehensive overview of available evidence on the topic.
This review is therefore designed to synthesize the findings of published studies that have reported CBME evaluation practices in undergraduate and postgraduate medical schools and programs. Its objective is to explore which CBME program evaluation practices have been reported in the literature by inspecting which evaluation objectives, models, tools, and standards were described in the included studies. In addition, the review inspects the results of evaluations and how they were shared. Thus, the review will serve in supporting educators to make evidence-based decisions when designing a CBME program. In addition, it will provide a useful resource for educators to embrace what was done right, learn from what was done wrong, improve many current evaluation practices, and compare different CBME interventions across various contexts.
Following a preliminary search within relevant journals for publications addressing evaluation practices utilized to assess competency-based curricula in medical education, the researcher used the PEO (participant, educational aspect, and outcomes) model to set and formulate the search question [ 24 ] as follows: participants : healthcare professionals and healthcare profession students; educational aspect : CBME curricula; outcome : program evaluation practices.
Next, the researcher created a clear plan for the review protocol. This review is classified as a systematized review rather than a systematic review [ 25 ]. While it does not meet the criteria for a systematic review because it relies on a single researcher and does not evaluate the quality of the studies included, it adheres to most of the steps outlined in the “Systematic Reviews in Medical Education: A Practical Approach: AMEE guide 94” [ 26 ]. Moreover, the researcher met with a medical educator with a strong background in CBME, an expert in review methods, and a librarian who is an expert in available databases and provided guidance and support for navigating such databases. Feedback was obtained from all three and used to finalize the review protocol. The protocol was followed to ensure that the research progressed in a consistent and systematized manner.
For this review, full-text articles published in peer-reviewed journals in English from 1 January 2000 to 31 December 2022 were searched within the following electronic data bases: PubMed, ERIC, Education Source, and CINHAL. The following terms were utilized to conduct the search: (Competency Based Medical Education OR Outcome Based Medical Education) AND (Evaluation OR assessment) AND (Undergraduate OR Postgraduate) AND (Implementing OR Performance OR Framework OR Program* OR Project OR Curriculum OR Outcome) (Additional file 1 ).
The researcher included articles that were published in English and reported evaluation practices for CBME or OBME curricula whether for undergraduate or postgraduate healthcare professionals. The researcher did not consider research reviews, commentaries, perspective articles, conference proceedings, and graduate theses in this review. In addition, articles that addressed students’ assessments rather than program evaluation were not included. Furthermore, articles that focused on teaching a particular skill (e.g., communication skills) or specific educational strategies (e.g., the effectiveness of Problem Based Learning) were excluded from this review.
To facilitate the screening of articles and ensure the process was properly documented, an online review software that streamlines the production of reviews (Covidence) was utilized, and all the lists of articles retrieved from the specified databases were uploaded to the tool website (available at www.covidence.org ). The tool set the screening to start with the titles and abstracts then to proceed to full texts. During these stages, the reasons for excluding an article were precisely noted. Moreover, the PRISMA diagram (available at http://www.prisma-statement.org/ ) was produced by Covidence to illustrate the process of screening and including articles in this review.
After the decision was made to include an article, a data extraction tool created for the purpose of this review was used (Additional file 2 ). Since the term “program evaluation practices” is general and does not clearly define the method or focus of the analysis involved in critiquing evaluation efforts, the analysis of available evaluation practices in this review was based on the Embedded Evaluation Model (EEM) provided by Giancola (2020) for educators to consider when embedding evaluations into educational program designs and development [ 27 ]. The EEM outlines several steps. In the first step, “Define,” educators are expected to build an understanding of the evaluated program, including its logic and context. In the second step, “Plan,” educators must establish the evaluation-specific objectives and questions and select the model or approach along with the methods or tools that will be utilized to achieve those objectives. The next step, “Implement and Analyze,” requires educators to determine how the data will be collected, analyzed, and managed. In the fourth step, “Interpret the Results,” educators are expected to derive insights from the results in terms of how the evaluation can help with resolving issues and improving the program as well as how the results should be communicated and employed. Finally, in the “Inform and Refine” step, educators should focus on applying the results to realize improvements to the program and promote accountability [ 27 ].
In addition to supporting the aim of the current review, the theoretical insights from Giancola (2020) help to ensure alignment with best practices in curriculum evaluation. Thus, for each article, the extraction tool collected the following information: the author, the publication year, the country and name of the institution that implemented the CBME curriculum, the aim and method of the article, the type of curriculum based on the health profession specialty (e.g., medicine, nursing), the level of the curriculum (postgraduate or undergraduate), the evaluation objective, the approach/model or tool, the evaluation standard, the evaluation results, and the sharing of the evaluation results. The extracted information points are essential to contextualize the evaluation and allow educators to make sense of it and adapt or adjust it to their own situations. Understanding the context of an evaluation is important considering the wide variety of available educational environments, the diversity of evaluators, and the differences in goals, modes, and benchmarks for evaluation, all of which influence how an evaluation is framed and conducted [ 27 ].
The author, publication year , and name and country of the institution that implemented the CBME curriculum provide identifiers for the original article and enable educators to seek further information about a study. The aim and method of the article were highlighted because they clarify the general context in which the evaluation was conducted. For example, this information can help educators understand whether an evaluation was carried out as a single action in response to a certain problem or was a phase or part of a larger project. The type of curriculum based on the health profession specialty (e.g., medicine, nursing) along with the level of the curriculum (postgraduate or undergraduate) have specific implications related to the nature of each specialty and the level of the competencies associated with the advancement of the program. All of the previously mentioned information is vital for educators to define and understand the program they are aiming to evaluate, which is the first step in the EEM. The evaluation objective , approach/model or tool , evaluation standard , evaluation results , and sharing of the evaluation results help to answer the research question of the current review by dissecting various aspects of the evaluation activities. In addition, the reporting of these aspects provides valuable insight into evaluation directives, plans, and execution. For educators, the evaluation objective usually clarifies the focus of the evaluation (e.g., how the program was implemented, the action done to execute education or outcomes of the program, and its effectiveness). The approach/model or tool of an evaluation is a core element of the design and implementation of the evaluation, as it determines the theoretical guidelines that underlie the evaluation and the practical steps for its execution. Based on the evaluation standard, which refers to the target used to compare the evidence or results of the evaluation, educators can judge the relevance of the evaluation to their own practices or activities. This information aligns with steps two and three of the EEM. The evaluation results are the results of the evaluation, which form the cornerstone for emerging solutions or future improvements. Finally, sharing the evaluation results , or communicating the evaluation, is a key part of handling the results and working toward their application. This information is aligned with steps four and five of the EEM.
Search results
Searching the identified databases revealed a total of 640 articles, and 183 total duplicates were removed. A total of 457 articles was considered for screening (371 PubMed, 13 ERIC, 23 Education Source, 50 CINHAL) (Fig. 1 ). Of those articles, 87 were retrieved for full-text screening. Ultimately, 38 studies met the inclusion criteria and were considered eligible to be included in the current review.
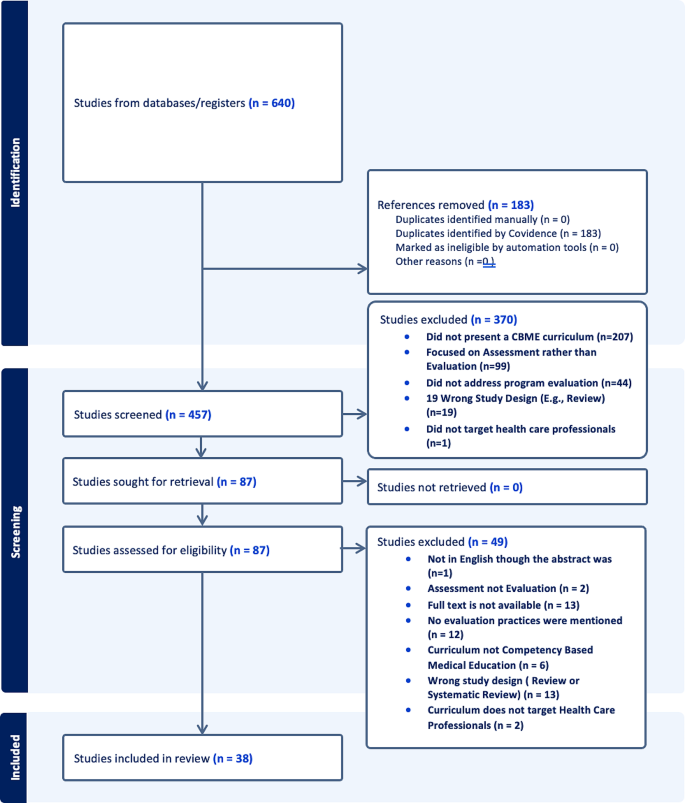
Flowchart illustrating the process of including articles in the review
Findings of the included studies
The 38 studies that met the inclusion criteria were published between 2010 and 2021, and the majority (15%; n = 6) were published in 2019. The studies represented the following countries: Canada (37%, n = 14) [ 10 , 11 , 28 , 29 , 30 , 31 , 32 , 33 , 34 , 35 , 36 , 37 , 38 , 39 ], USA (27.5%, n = 11) [ 40 , 41 , 42 , 43 , 44 , 45 , 46 , 47 , 48 , 49 , 50 ], Australia (5%, n = 2) [ 51 , 52 ], China (5%, n = 2) [ 53 , 54 ], Dutch Caribbean islands (2.5%, n = 1) [ 55 ], Germany (2.5%, n = 1) [ 56 ], Guatemala (2.5%, n = 1) [ 57 ], Korea (2.5%, n = 1) [ 58 ], the Netherlands (2.5%, n = 1) [ 59 ], New Zealand (2.5%, n = 1) [ 60 ], The Republic of Haiti (2.5%, n = 1) [ 61 ], Turkey (2.5%, n = 1) [ 62 ], and the region of West Africa (2.5%, n = 1) [ 63 ].
According to the evidence synthesized from the included studies, most of the evaluation practices were reported in competency-based curricula that targeted the level of postgraduate professionals (57%, n = 22) and were medical in nature (71%, n = 27) (Fig. 2 ).
Curricula specialties in included articles
The findings showed that 37% ( n = 14) of the articles did not report the precise objective of evaluating the curriculum. Moreover, 84% ( n = 32) did not report the evaluation approach or model used to assess the described curricula. The approaches or models reported include Pawson’s model of realist program evaluation [ 37 ], theory-based evaluation approaches [ 10 ], Stufflebeam’s context, inputs, processes, and products (CIPP) model [ 62 ], the concerns-based adoption model, sensemaking and outcome harvesting [ 33 ]the CIPP model [ 48 ], and quality improvement (QI) for program and process improvement [ 50 ]. On the other hand, a wide variety of evaluation tools was reported including observations (3%, n = 1) [ 28 ] surveys or questionnaires (58%, n = 22) [ 10 , 28 , 29 , 31 , 34 , 35 , 36 , 38 , 39 , 41 , 42 , 45 , 49 , 50 , 51 , 52 , 53 , 55 , 56 , 58 , 59 , 63 ] interviews (16%, n = 6) [ 10 , 28 , 37 , 41 , 47 , 62 ], focus groups (13%, n = 5) [ 35 , 37 , 41 , 50 , 59 ], historical document review or analysis (8%, n = 3) [ 10 , 29 , 33 ], educational activity assessment or analysis of the activity by separate reviewers (5%, n = 2) [ 55 , 61 ], stakeholder discussions or reports about their inputs (5%, n = 2) [ 43 , 44 ], curriculum mapping (3%, n = 1) [ 32 ], feedback from external reviews from accrediting bodies (3%, n = 1) [ 32 ], the Dundee Ready Education Environment Measure (DREEM) (3%, n = 1) [ 56 ], and students’ or participants’ assessments (5%, n = 2) [ 38 , 46 ].
Of the studies, 37% ( n = 14) utilized multi methods [ 10 , 28 , 29 , 30 , 32 , 34 , 35 , 37 , 38 , 41 , 48 , 52 , 56 , 59 ]. Furthermore, 7.8% ( n = 3) of the studies reported the nature of the tool, for example, quantitative or qualitative, without specifying the exact tool utilized [ 57 , 60 ]. Moreover, 63% ( n = 24) of the studies included in this review did not report the evaluation standards applied while assessing the competency-based curricula addressed. Yet, those studies that reported their standards were stated in various ways as follows: some publications referred to the standards of specific specialized associations or societies, such as the American Academy of Family Physicians and College of Family Physicians Canada [ 61 ], Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Psychiatrists [ 60 ], and The American Association of Occupational Health Nurses [ 45 ]. Other publications utilized known competency frameworks as their standards, such as CanMED [ 36 , 37 , 59 ], or the competencies of the American Board of Surgery [ 43 ] Association of Canadian Faculties of Dentistry [ 31 ], Royal College of Ophthalmologists [ 52 ], The Florida Consortium for Geriatric Medical Education [ 50 ], or the Dutch Advisory Board for Postgraduate Curriculum Development for Medical Specialists [ 59 ]. Furthermore, many of the publications referred to accreditation standards, such as the Accreditation Standards of the Australian Medical Council [ 51 ], Competencies of Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education [ 43 ], Accreditation Body in the Competency-based Curriculum [ 32 ], and the Commission on Dental Accreditation of Canada [ 31 ]. All the publications included in the review reported the results of their evaluations.
Finally, the results revealed that almost half (52.6%, n = 20) of the authors of the articles mentioned that they were publishing their experience with the intent of sharing lessons learned, yet they did not refer to any other means of sharing the results of their evaluations. In contrast, the other half did not mention any measures taken to communicate and share the evaluation results. Additional file 3 includes the characteristics and details of the data extracted from the studies included addressing evaluation practices in healthcare professionals’ education.
Evaluating a curriculum appropriately is important to ensure that the program is operating as intended [ 13 ]. The present study aimed to review the available literature on the evaluation practices of competency-based undergraduate and postgraduate health professionals’ schools and programs. This review inspected which evaluation objectives, models, tools, and standards were described as well as the results of evaluations and how the results were shared. The synthesized evidence indicates that most of the programs reporting evaluation practices were postgraduate-level medical programs. This focus on CMBE among postgraduate programs can be related to the fact that competency-based education is organized around the most critical competencies useful for health professionals after graduation. Thus, they are better judged at practice [ 64 , 65 , 66 ]. Moreover, although competency-based curricula were introduced to many health professions over 60 years ago, such as pharmacology and chiropractic therapy, within the medical field they have only evolved in the last decade [ 67 ].
Furthermore, the data revealed that there is a discrepancy in how evaluation practices were reported in the literature in terms of evaluation objectives, approaches/models, tools, standards, documenting of results, and communication plans. Each area will be further discussed in the following paragraphs considering the ten-task approach and embedded evaluation model [ 27 , 68 ]. Both guide evaluation as an important step in curriculum development in medical education, detail the evaluation process, and outline many important considerations from design to execution [ 27 , 68 ].
Evaluation is a crucial part of curriculum development, and it can serve many purposes, such as ensuring attaining educational objectives, identifying areas of improvement, improving decision-making, and assuring quality [ 13 , 27 ]. Consequently, when addressing evaluation, it is important for educators to start by explaining the logic of the curriculum by asking, for example, what the program’s outcomes are and whether it is designed for postgraduates or undergraduates [ 27 ]. Moreover, educators must be precise in setting evaluation objectives, which entails answering certain questions: who will use the evaluation data; how will the data be used at both the individual and program level; will the evaluation be summative or formative; and what evaluation questions must be answered [ 27 , 68 , 69 ] However, many of the studies included in this review did not clearly explain the context of the curricula or report the objectives of their evaluation endeavors; rather, they settled for clarifying the objectives of the study or of the publication itself. One reason for this is that evaluation and educational research have many similarities [ 13 ] Nevertheless, the distinction between the two should be clarified, as doing so will enable other medical educators to better understand and benefit from the evaluation experience shared. Moreover, since CBME outcomes are complicated and should be considered on many levels, evaluation plans should include a focus, level, and timeline. The focus of an evaluation can be educational, with outcomes relevant to learners, or clinical, with health outcomes relevant to patients. The level of an evaluation can be micro, meso, or macro, targeting an individual, a program, or a system, respectively. The timeline of an evaluation can investigate outcomes during the program, after the program (i.e., how well learners have put what they learned in a CBME program into practice), and in the long term (i.e., how well learners are doing as practicing physicians) [ 70 ].
Once the evaluation objectives are clearly identified and prioritized, it is logical to start considering the evaluation approach or model that is most appropriate to attain these objectives considering the available resources. In other words, evaluation design should be outlined [ 27 , 68 ]. The choice of an evaluation approach or model affects the accuracy of assessing certain tasks carried out by or to specific subjects in a particular setting [ 68 , 71 , 72 , 73 , 74 , 75 ] This accuracy is referred to as an evaluation’s internal validity. Yet, the external validity of an evaluation entails that the evaluation results are generalizable to other subjects and other settings [ 68 ]. Each model has its own strengths and weaknesses, which require careful examination when planning an evaluation [ 14 , 73 , 74 , 75 ]. Explaining and justifying why a particular evaluation approach was chosen for a specific curriculum can enrich the lessons learned from the evaluation and aid other educators. Furthermore, some of the available models were more utilized within various educational contexts than others [ 17 ] that calls for a continuous documentation of the evaluation approaches or models used to inform theory and practice. Considering the importance of reporting the approaches and models used, it is unfortunate that most of the publications did not indicate the approach/model they used for evaluation, which limits educators’ abilities to utilize the plans and build on their evidence.
Another critical task in the evaluation process is deciding on the measurement tool or instrument to be used. The tool choice will determine what data will be gathered and how they will be collected and analyzed [ 27 , 68 ]. Thus, the choice should consider the evaluation objective as well as the uses, strengths, and limitations of each tool. The evidence in this review indicates that questionnaires or surveys were the most utilized tools in evaluating competency-based curricula. This result can be attributed to the advantages of this method (for example, it is a convenient and economical tool that is easy to administer and analyze and can be utilized with many individuals) [ 27 , 68 ]. Nevertheless, it is important to highlight that questionnaires and surveys usually target attitudes and perceptions, which usually entails only a surface-level evaluation, according to the Kirkpatrick model [ 76 ]. The results also showed that in around 50% of the mixed-methods evaluations, the questionnaires were combined with another tool, such as interviews or focus groups. Understandably, utilizing an additional tool aims to deepen the level of the evaluation focus to include learning, behaviors, or results [ 76 ].
The evaluation evidence must be compared with a standard or target for educators to judge the program and make decisions [ 12 ]. Standards can be implicit or explicit, but they usually provide an understanding of what is ideal [ 12 ]. Worryingly, the results of this review revealed that many of the included studies did not clarify the standards they used to judge different CBME curricula. However, the studies that reported their standards used accreditation criteria or broad competencies frameworks, such as CanMeds, which consider the guides of specialized associations, such as family physicians or nursing. Although deciding what standard to use can be challenging to those designing and evaluating programs, evaluating without an understanding of the level of quality desired can lead to many complications and a waste of resources.
Communicating and reporting evaluation results are crucial to attaining the evaluation objectives [ 27 , 68 , 75 ]. Moreover, effective communication strategies have many important functions, such as providing decision makers with the necessary data to make an informed decision. Informing other stakeholders about the results is also important to achieve their support in implementing program changes and nourish a culture of quality [ 77 , 78 ]. Around half of the authors of studies included in this review indicated that they were publishing to share their own evaluation experiences, while the other half did not. Regardless, none of the studies shared or indicated how their results were reported and communicated, which is an important part of the evaluation cycle that should not be overlooked when sharing evaluation lessons within the scientific community. Reporting the results also ensures quality transformation by closing the evaluation cycle and encourages future engagement in evaluation among different stakeholders [ 78 , 79 , 80 ]. Moreover, the results of the evaluation should be shared publicly to contribute to increasing public trust in educational programs and their outcomes [ 19 , 69 ].
In summary, this review of evaluation practices within competency-based curricula for undergraduate and postgraduate health professional programs provides valuable insight into the current landscape. The results of the review show that most evaluation practices published pertain to postgraduate medical programs. In addition, by examining the objectives, models, tools, standards, and communication of evaluation results, this study exposes a discrepancy between the reported evaluation practices and identified evaluation elements. This discrepancy extends to the data that are reported, which makes it even more difficult to synthesize a holistic picture and definitively fulfill the aim of the review. Moreover, the issue of missing information poses serious challenges for educators who try to leverage existing knowledge to inform their curriculum development and improvement efforts, and it highlights the need for a more systematic and transparent approach to evaluation within CBME.
This review illustrates the importance of agreeing on the main evaluation elements to be reported when publishing a CBME evaluation. Establishing a shared understanding of these fundamental elements will give educators a framework for enhancing the practical utility of evaluation methodologies. In addition, educators and practitioners can ensure that the evaluation process yields more insightful outcomes and is better tailored to meet the needs of the educational context.
Data availability
The datasets used during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
Outcome-Based Medical Education
Competency-Based Medical Education
Embedded Evaluation Model
Zaini R, Bin Abdulrahman K, Alkhotani A, Al-Hayani AA, Al-Alwani A, Jastaniah S. Saudi meds: a competence specification for Saudi medical graduates. Med Teach. 2011;33(7):582–4.
Article Google Scholar
Davis MH, Amin Z, Grande JP, O’Neill AE, Pawlina W, Viggiano TR et al. Case studies in outcome-based education. Med Teach. 2009; 29(7):717–22. https://doi.org/10.1080/01421590701691429
Caccia N, Nakajima A, Kent N. Competency-based medical education: The wave of the future. JOGC. 2015; 37(4):349–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1701-2163(15)30286-3
Danilovich N, Kitto S, Price D, Campbell C, Hodgson A, Hendry P. Implementing competency-based medical education in family medicine: a narrative review of current trends in assessment. Fam Med. 2021;53:9–22.
Hawkins RE, Welcher CM, Holmboe ES, Kirk LM, Norcini JJ, Simons KB et al. Implementation of competency-based medical education: Are we addressing the concerns and challenges? Med Educ. 2015 Oct. 22; 49(11):1086–102. https://doi.org/10.1111/medu.12831
Simpson JG, Furnace J, Crosby J, Cumming AD, Evans PA, David MF, Ben et al. The Scottish doctor-learning outcomes for the medical undergraduate in Scotland: A foundation for competent and reflective practitioners. Med Teach. 2002; 24(2):136–43. https://doi.org/10.1080/01421590220120713
Swing SR. The ACGME outcome project: retrospective and prospective. Med Teach. 2007; 29(7):648–54. https://doi.org/10.1080/01421590701392903
Frank JR, Danoff D. The CanMEDS initiative: Implementing an outcomes-based framework of physician competencies. Med Teach. 2007; 29(7):642–7. https://doi.org/10.1080/01421590701746983
van Melle E, Frank JR, Holmboe ES, Dagnone D, Stockley D, Sherbino J. A core components framework for evaluating implementation of competency-based medical education programs. Acad Med. 2019 Jul 1 [cited 2022 Mar 19]; 94(7):1002–9. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30973365/
Hamza DM, Ross S, Oandasan I. Process and outcome evaluation of a CBME intervention guided by program theory. J Eval Clin Pract. 2020; 26(4):1096–104. https://doi.org/10.1111/jep.13344
Van Melle E, Frank J, Holmboe E, Dagnone D, Stockley D, Sherbino J. A core components framework for evaluating implementation of competency-based medical education programs. Acad Med. 2019;94:1.
Google Scholar
Giancola SP. Program evaluation: Embedding evaluation into program design and development. SAGE Publications; 2020. https://books.google.com.sa/books?id=H-LFDwAAQBAJ
Morrison J, Evaluation. BMJ. 2003; 326(7385):385. http://www.bmj.com/content/326/7385/385.abstract
Glatthorn AA. Curriculum leadership: Strategies for development and implementation. 4th ed. Thousand Oaks, California: SAGE Publications, Inc., 2016. https://search.library.wisc.edu/catalog/9910219273702121
Stufflebeam D. Evaluation models. New Dir Eval. 2001; 2001(89):7–98.
Mertens D, Wilson A. Program evaluation theory and practice. 2nd ed. United States of America: The Guilford; 2019.
Nouraey P, Al-Badi A, Riasati M, Maata RL. Educational program and curriculum evaluation models: a mini systematic review of the recent trends. UJER. 2020;8:4048–55.
Sarah Schiekirka, Markus A, Feufel C, Herrmann-Lingen T, Raupach. Evaluation in medical education: a topical review of target parameters, data collection tools and confounding factors. Ger Med Sci. 2015; 13 (16).
Van Melle E, Hall A, Schumacher D, Kinnear B, Gruppen L, Thoma B, et al. Capturing outcomes of competency-based medical education: the call and the challenge. Med Teach. 2021;43:1–7.
Lomis KD, Mejicano GC, Caverzagie KJ, Monrad SU, Pusic M, Hauer KE. The critical role of infrastructure and organizational culture in implementing competency-based education and individualized pathways in undergraduate medical education. Med Teach. 2021; 43(sup2):S7–16. https://doi.org/10.1080/0142159X.2021.1924364
Taber S, Frank JR, Harris KA, Glasgow NJ, Iobst W, Talbot M. Identifying the policy implications of competency-based education. Med Teach. 2010; 32(8):687–91. https://doi.org/10.3109/0142159X.2010.500706
Zaini RG, bin Abdulrahman KA, Al-Khotani AA, Al-Hayani AMA, Al-Alwan IA, Jastaniah SD. Saudi Meds: A competence specification for Saudi medical graduates. Med Teach. 2011 Jul [cited 2022 Mar 19]; 33(7):582–4. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21696288/
Leung WC. Competency based medical training: review * Commentary: The baby is thrown out with the bathwater. BMJ. 2002 Sept 28; 325(7366):693–6. https://doi.org/10.1136/BMJ.325.7366.693
Hall AK, Schumacher DJ, Thoma B, Caretta-Weyer H, Kinnear B, Gruppen L et al. Outcomes of competency-based medical education: A taxonomy for shared language. Med Teach. 2021;43(7):788–93. https://doi.org/10.1080/0142159X.2021.1925643
Masoomi R. What is the best evidence medical education? Res Dev Med Educ. 2012;1:3–5.
Grant MJ, Booth A. A typology of reviews: An analysis of 14 review types and associated methodologies. Health Info Libr J. 2009; 26(2):91–108. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-1842.2009.00848.x
Sharma R, Gordon M, Dharamsi S, Gibbs T. Systematic reviews in medical education: A practical approach: AMEE Guide 94. Med Teach. 2015; 37(2):108–24. https://doi.org/10.3109/0142159X.2014.970996
Giancola SP. Program evaluation embedding evaluation into program design and development. Thousand Oaks: Sage Publication Ltd.; 2020.
Acai A, Cupido N, Weavers A, Saperson K, Ladhani M, Cameron S et al. Competence committees: The steep climb from concept to implementation. Med Educ. 2021; 55(9):1067–77. https://doi.org/10.1111/medu.14585
Zhang P, Hamza D, Ross S, Oandasan I. Exploring change after implementation of family medicine residency curriculum reform. Fam Med. 2019;51:331–7.
Thoma B, Hall A, Clark K, Meshkat N, Cheung W, Desaulniers P et al. Evaluation of a national competency-based assessment system in emergency medicine: a CanDREAM Study. J Grad Med Educ. 2020;12(4).
Schönwetter D, Law D, Mazurat R, Sileikyte R, Nazarko O. Assessing graduating dental students’ competencies: the impact of classroom, clinic and externships learning experiences. Eur J Dent Educ. 2011;15:142–52.
Nousiainen M, Mironova P, Hynes M, Takahashi S, Reznick R, Kraemer W, et al. Eight-year outcomes of a competency-based residency training program in orthopedic surgery. Med Teach. 2018;40:1–13.
Railer J, Stockley D, Flynn L, Hastings Truelove A, Hussain A. Using outcome harvesting: assessing the efficacy of CBME implementation. J Eval Clin Pract. 2020; 26(4).
Janssen P, Keen L, Soolsma J, Seymour L, Harris S, Klein M, et al. Perinatal nursing education for single-room maternity care: an evaluation of a competency-based model. J Clin Nurs. 2005;14:95–101.
Goudreau J, Pepin J, Dubois S, Boyer L, Larue C, Legault A. A second generation of the competency-based approach to nursing education. Int J Nurs Educ Scholarsh. 2009;6:Article15.
Fahim C, Bhandari M, Yang I, Sonnadara R. Development and early piloting of a CanMEDS competency-based feedback tool for surgical grand rounds. J Surg Educ. 2016;73(3):409–15.
Ellaway R, Mackay M, Lee S, Hofmeister M, Malin G, Archibald D, et al. The impact of a national competency-based medical education initiative in family medicine. Acad Med. 2018;93:1.
D’Souza L, Jaswal J, Chan F, Johnson M, Tay KY, Fung K et al. Evaluating the impact of an integrated multidisciplinary head & neck competency-based anatomy & radiology teaching approach in radiation oncology: a prospective cohort study. BMC Med Educ. 2014; 14(1):124. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6920-14-124
Crawford L, Cofie N, Mcewen L, Dagnone D, Taylor S. Perceptions and barriers to competency-based education in Canadian postgraduate medical education. J Eval Clin Pract. 2020;26(4):1124–31.
Cox K, Smith A, Lichtveld M. A competency-based approach to expanding the cancer care workforce part III—Improving cancer pain and palliative care competency. J Cancer Educ. 2012;27:507–14.
Freedman AM, Simmons S, Lloyd LM, Redd TR, Alperin MM, Salek SS et al. Public health training center evaluation: A framework for using logic models to improve practice and educate the public health workforce. Health Promot Pract. 2014; 15(1 Suppl):80S-8S. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/24578370
Kerfoot B, Baker H, Volkan K, Church P, Federman D, Masser B, et al. Development and initial evaluation of a novel urology curriculum for medical students. J Urol. 2004;172:278–81.
Ketteler E, Auyang E, Beard K, McBride E, McKee R, Russell J, et al. Competency champions in the clinical competency committee: a successful strategy to implement milestone evaluations and competency coaching. J Surg Educ. 2014;71:36–8.
Lipp M. An objectified competency-based course in the management of malocclusion and skeletal problems. J Dent Educ. 2008;72:543–52.
Randolph S, Rogers B, Ostendorf J. Evaluation of an occupational health nursing program through competency achievement on-campus and distance education, 2005 and 2008. AAOHN J. 2011;59:387–99.
Stefanidis D, Acker C, Swiderski D, Heniford BT, Greene F. Challenges during the implementation of a laparoscopic skills curriculum in a busy general surgery residency program. J Surg Educ. 2008;65:4–7.
Stucke R, Sorensen M, Rosser A, Jung S. The surgical consult entrustable professional activity (EPA): defining competence as a basis for evaluation. Am J Surg. 2018;219(2):253–7.
Swider S, Levin P, Ailey S, Breakwell S, Cowell J, Mcnaughton D, et al. Matching a graduate curriculum in public/community health nursing to practice competencies: the Rush University experience. Public Health Nurs. 2006;23:190–5.
Taleghani M, Solomon E, Wathen W. Non-graded clinical evaluation of dental students in a competency‐based education program. J Dent Educ. 2004;68:644–55.
Zuilen M, Mintzer M, Milanez M, Kaiser R, Rodriguez O, Paniagua M, et al. A competency-based medical student curriculum targeting key geriatric syndromes. Gerontol Geriatr Educ. 2008;28:29–45.
Gibson K, Boyle P, Black D, Bennett M, Grimm M, McNeil H. Enhancing evaluation in an undergraduate medical education program. Acad Med. 2008;83:787–93.
Succar T, McCluskey P, Grigg J. Enhancing medical student education by implementing a competency based ophthalmology curriculum. Asia-Pac J Ophthalmol. 2017;6:42–6.
Gruber P, Gomersall C, Joynt G, Shields F, Chu CM, Derrick J. Teaching acute care: a course for undergraduates. Resuscitation. 2007;74:142–9.
Zhang H, Wang B, Zhang L. Reform of the method for evaluating the teaching of medical linguistics to medical students. Chinese Education & Society. 2014; 47(3):60–4. https://doi.org/10.2753/CED1061-1932470305
Koeijers J, Busari J, Duits AJ. A case study of the implementation of a competency-based curriculum in a Caribbean teaching hospital. West Indian Med J. 2012;61:726–32.
Rotthoff T, Ostapczuk MS, de Bruin J, Kröncke KD, Decking U, Schneider M et al. Development and evaluation of a questionnaire to measure the perceived implementation of the mission statement of a competency based curriculum. BMC Med Educ. 2012; 12(1):109. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6920-12-109
Day S, Garcia J, Antillon F, Wilimas J, Mckeon L, Carty R, et al. A sustainable model for pediatric oncology nursing education in low-income countries. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2012;58:163–6.
Lee BH, Chae YM, Hokama T, Kim S. Competency-based learning program in system analysis and design for health professionals. APJPH. 2010; 22(3):299–309. http://www.jstor.org/stable/26723774
Westein M, Vries H, Floor-Schreudering A, Koster A, Buurma H. Development of a postgraduate workplace-based curriculum for specialization of community pharmacists using CanMEDS competencies, entrustable professional activities and programmatic assessment. Am J Pharm Educ. 2018;83:ajpe6863.
de Beer W. Is the RANZCP CPD programme a competency-based educational programme? Australas Psychiatry. 2019; 27(4):404–8. https://doi.org/10.1177/1039856219859279
Battat R, Jhonson M, Wiseblatt L, Renard C, Habib L, Normil M, et al. The Haiti Medical Education Project: Development and analysis of a competency based continuing medical education course in Haiti through distance learning. BMC Med Educ. 2016;16:275.
İlhan E. Evaluation of competency based medical education curriculum. IJPE. 2021;17(3):153–68.
Ekenze SO, Ameh EA. Evaluation of relevance of the components of Pediatric Surgery residency training in West Africa. J Pediatr Surg. 2010; 45(4):801–5. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0022346809008495
Iobst WF, Sherbino J, Cate O, Ten, Richardson DL, Dath D, Swing SR et al. Competency-based medical education in postgraduate medical education. Med Teach. 2010; 32(8):651–6. https://doi.org/10.3109/0142159X.2010.500709
Vakani F, Jafri W, Jafri F, Ahmad A. Towards a competency-based postgraduate medical education. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak; 22(7): 476–7.
Pascual TNB, Ros S, Engel-Hills P, Chhem RK. Medical competency in postgraduate medical training programs. Radiology Education. 2012; pp. 29–45. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-27600-2_4
Frank J, Snell L, Ten Cate O, Holmboe E, Carraccio C, Swing S, et al. Competency-based medical education: theory to practice. Med Teach. 2010;32:638–45.
Lindeman B, Kern D, Lipsett P. Step 6 evaluation and feedback. In: Thomas P, Kern D, Hughes M, Tackett S, Chen B, editors. Curriculum development for medical education: a six-step approach. 4th ed. Johns Hopkins University; 2022. pp. 142–97.
Morrison J. ABC of learning and teaching in medicine: Evaluation. BMJ. 2003; 326(7385):385–7. https://doi.org/10.1136/BMJ.326.7385.385
Wang MC, Ellett CD. Program validation. Topics Early Child Spec Educ. 1982; 1(4):35–49. https://doi.org/10.1177/027112148200100408
McCray E, Lottes JJ. The validation of educational programs. 1976.
Toosi M, Modarres M, Amini M, Geranmayeh M. Evaluation model in medical education: A systematic review. 2016.
Balmer DF, Rama JA, Simpson D. Program evaluation models: Evaluating processes and outcomes in graduate medical education. J Grad Med Educ. 2019; 11(1):99–100. https://doi.org/10.4300/JGME-D-18-01084.1
Vassar M, Wheeler DL, Davison M, Franklin J. Program evaluation in medical education: An overview of the utilization-focused approach. J Educ Eval Health Prof. 2010; 7:1. https://doi.org/10.3352/jeehp.2010.7.1
Kirkpatrick JD, Kirkpatrick WK. Kirkpatrick’s four levels of training evaluation. Association for Talent Development; 2016. (BusinessPro collection). https://books.google.com.sa/books?id=mo--DAAAQBAJ
Moreau KA, Eady K. Program evaluation use in graduate medical education. J Grad Med Educ. 2023; 15(1):15–8. https://doi.org/10.4300/JGME-D-22-00397.1
Durning SJ, Hanson J, Gilliland W, McManigle JM, Waechter D, Pangaro LN. Using qualitative data from a program director’s evaluation form as an outcome measurement for medical school. Mil Med. 2010; 175(6):448–52. https://doi.org/10.7205/MILMED-D-09-00044
Kek M, Hunt L, Sankey M. Closing the loop: A case study of a post-evaluation strategy. 1998.
Wolfhagen HAP, Gijselaers WH, Dolmans D, Essed G, Schmidt HG. Improving clinical education through evaluation. Med Teach. 2009; 19(2):99–103. https://doi.org/10.3109/01421599709019360
Download references
Acknowledgements
The author would like to acknowledge the support that Prof. Ahmad Alrumayyan and Dr. Emad Masuadi gave this research by reviewing its protocol and providing general feedback. In addition, the author would like to acknowledge Dr. Noof Albaz for the discussions about educational program evaluation, which contributed to improving the final version of this manuscript. Thanks, are also due to Mr. Mohammad Alsawadi for reviewing the utilized search terminologies and participating in the selection of appropriate databases and searching them to obtain the needed lists of articles.
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Medical Education, College of Medicine, King Saud bin Abdulaziz University for Health Sciences, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
Nouf Sulaiman Alharbi
King Abdullah International Medical Research Center, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
Ministry of the National Guard - Health Affairs, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
The author takes full responsibility for study conception, design, data collection, analysis, interpretation, and manuscript preparation.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Nouf Sulaiman Alharbi .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Ethical clearance for conducting this review was attained from King Abdullah International Research Center (KAIMRC), King Saud Bin Abdulaziz University for Health Sciences (RYD-22-419812-52334).
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Material 1
Supplementary material 2, supplementary material 3, rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Alharbi, N.S. Evaluating competency-based medical education: a systematized review of current practices. BMC Med Educ 24 , 612 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-024-05609-6
Download citation
Received : 13 November 2023
Accepted : 27 May 2024
Published : 03 June 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-024-05609-6
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Competency-based medical education
- Program evaluation
- Undergraduate medical education
- Postgraduate medical education
- Curriculum development
BMC Medical Education
ISSN: 1472-6920
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
To develop a suitable education-related research topic, you'll need to identify a clear and convincing research gap, and a viable plan of action to fill that gap. If this sounds foreign to you, check out our free research topic webinar that explores how to find and refine a high-quality research topic, from scratch.
In your literature review you will: survey the scholarly landscape. provide a synthesis of the issues, trends, and concepts. possibly provide some historical background. Review the literature in two ways: Section 1: reviews the literature for the Problem. Section 3: reviews the literature for the Project.
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
Lambert 2012 defines a literature review as a critical analysis of what is known about the study topic, the themes related to it, and the various perspectives expressed regarding the topic. Fink 2010 defines a literature review as a systematic review of existing body of data that identifies, evaluates, and synthesizes for explicit presentation.
1.3.1.2 Empirical. An empirical literature review collects, creates, arranges, and analyzes numeric data reflecting the frequency of themes, topics, authors and/or methods found in existing literature. Empirical literature reviews present their summaries in quantifiable terms using descriptive and inferential statistics.
There are eight general steps in conducting an education literature review. Please follow the eight numbered boxes, starting below. Please note that the general framework for this guide is derived from the work of Joyce P. Gall, M.D. Gall, and Walter R. Borg in Applying Educational Research: a Practical Guide (5th ed., 2005). Also, much of the information on framing the research question comes ...
There are eight general steps in conducting an education literature review. Please follow the eight numbered boxes, starting below. Please note that the general framework for this guide is derived from the work of Joyce P. Gall, M.D. Gall, and Walter R. Borg in Applying Educational Research: a Practical Guide (5th ed., 2005). Also, much of the information on framing the research question comes ...
The Literature Review by Lawrence A. Machi; Brenda T. McEvoy From daunting to doable in six steps The process of literature search and composing a formal literature review can be intimidating. But masters and doctoral candidates in Education and related fields have found academic argumentation to be seamlessly intuitive with the six-step process pioneered by this book.
A Literature Review is a systematic and comprehensive analysis of books, scholarly articles and other sources relevant to a specific topic providing a base of knowledge on a topic. Literature reviews are designed to identify and critique the existing literature on a topic to ... Mary M. "Defining a Literature." Educational Researcher 36 (April ...
Synthesizing is a method of analyzing the main ideas and important information from your sources as you read and prepare to write a literature review. Review the resources below for sample synthesizing methods. Both examples have tables you can fill out as you read articles to help you organize your thoughts.
Literature Review Topics. 1. The impact of childhood trauma on adult mental health. This topic will explore the lasting effects of childhood trauma on psychological well-being in adulthood, including the development of disorders such as PTSD, depression, and anxiety. 2.
A literature review is a scholarly paper which provides an overview of current knowledge about a topic. It will typically include substantive findings, as well as theoretical and methodological contributions to a particular topic (Hart 2018, p. xiii).Traditionally in education 'reviewing the literature' and 'doing research' have been viewed as distinct activities.
A Literature Review should... Relate directly and clearly to your thesis or research question. Synthesize and contextualize results, not just report them. Identify areas of controversy in the literature. Formulate questions that need further research. Adapted from "The Literature Review: A Few Tips on Conducting It", by Dena Taylor and ...
This database is a nice compliment to ERIC. Education Full Text generally contains more recently published material than ERIC. Education Full Text is also a good source for articles from professional education magazines. Google Scholar. Use the date range (custom range) to limit your results to more recent research.
Literature Review: Theory Identification Essay Assignment. The candidate will identify 1-2 theories related to the selected topic of study and write a 2-4 paragraph essay. The first paragraph for ...
Review of Education is an official BERA journal publishing educational research from throughout the world, and papers on topics of international interest. Abstract This paper reviews the literature to clarify the image of a student with a high level of well-being (WB) for a future systematic literature review and evidence-based interventions to ...
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays).
A guide from the University of North Texas on selecting a topic, searching the literature, plan before reviewing, reviewing the literature and writing the review. ... Issues and Challenges for Teaching Successful Online Courses in Higher Education: A Literature Review. Gerontology Literature Review Sample One. Attitudes towards caring for older ...
ERIC is an online library of education research and information, sponsored by the Institute of Education Sciences (IES) of the U.S. Department of Education.
Literature Reviews for Education and Nursing Graduate Students is an open textbook designed for students in graduate-level nursing and education programs. Its intent is to recognize the significant role the literature review plays in the research process and to prepare students for the work that goes into writing one. Developed for new graduate students and novice researchers just entering ...
Our extensive literature review knowledge allows us to gain insight into what is currently popular in a variety of sectors, and our specialist authors are well-versed in the process. Our team excels in searching for a wide range of topics. Our literature review services are based on years of research experience in a variety of research topics ...
Education Literature Review Topics. To get more ideas from these literature review topic examples, try isolating an issue and put it in another educational context. For instance, student motivation in primary school vs. middle school or sleep deprivation in high school vs. college. This should give you plenty of material for brainstorming.
50 Best Topics for Literature Review in Education. 1. 5 0 B E S T T O P I C S F O R L I T E R A T U R E R E V I E W I N E D U C A T I O N. 2. 1 Educational process and critical thinking 2 Education evolution throughout history 3 Virtual classrooms 4 Modern education methods 5 Same sex schools 6 Education systems and apprenticeship phenomenon 7 ...
The purpose of a literature review is to report the current state of the topic. Literature reviewed should be relatively recent, unless you are delving into the history of the topic. Discuss different themes within your literature review rather than individual articles. It will help if you pull information from 2-3 articles for each theme you ...
There are many types of literature reviews. The purposes of a literature review will vary, and the sources used in one will depend on the discipline and the review's topic. Literature reviews may have differences that include: Purpose: The reason or objective of the review. One review may be to see how much has been published on a topic (a ...
4. Educational Implications. The literature review provides an opportunity for cooperation between extracurricular exercises (such as testing and dramatization) and can participate in the expansion of their technical teaching method capabilities among science and art instructors.
Over the last four decades, studies have investigated the incorporation of Artificial Intelligence (AI) into education. A recent prominent AI-powered technology that has impacted the education sector is ChatGPT. This article provides a systematic review of 14 empirical studies incorporating ChatGPT into various educational settings, published in 2022 and before the 10th of April 2023—the ...
Mission. The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives.
Abstract. Objective: Leadership discussion, including leadership development programs, is common. However, discussion of followership as a component of leadership seems less frequently discussed. With a focus on leadership and followership, this investigation reviewed the health-professions education literature and characterized leadership-followership within health-professions education.
Few published articles provide a comprehensive overview of the available evidence on the topic of evaluating competency-based medical education (CBME) curricula. The purpose of this review is therefore to synthesize the available evidence on the evaluation practices for competency-based curricula employed in schools and programs for undergraduate and postgraduate health professionals.