What Is Critical Thinking in Social Work?
- Career Advice
- Frustrations at Work
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Pinterest" aria-label="Share on Pinterest">
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Reddit" aria-label="Share on Reddit">
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Flipboard" aria-label="Share on Flipboard">

Effective Communication Skills for Social Workers
Top 5 values in being a social worker, legal & ethical issues facing social workers.
- Clinical Model Vs. Developmental Model in Social Work Practice
- Emotional Stresses of Being a Clinical Psychologist
Social workers offer many valuable services to people in need. They provide mental health services, such as diagnosis and counseling, advocate for clients who are unable to do so themselves, provide direct care services, such as housing assistance and help clients obtain social services benefits. The ability to remain open-minded and unbiased while gathering and interpreting data, otherwise known as critical thinking, is crucial for helping clients to the fullest extent possible. Critical thinking is one of the top skills required to be a successful social worker.
Meaning of Critical Thinking
The Foundation for Critical Thinking describes critical thinking as the ability to analyze, synthesize, evaluate and apply new information. Critical thinking in social work practice involves looking at a person or situation from an objective and neutral standpoint, without jumping to conclusions or making assumptions. Social workers spend their days observing, experiencing and reflecting on all that is happening around them.
In your role as a social worker, you obtain as much data as possible from interviews, case notes, observations, research, supervision and other means. Social workers must be self-aware of their feelings and beliefs. Stereotypical biases or prejudices must be recognized and not allowed to influence thinking when assembling a plan of action to help your clients to the highest level possible.
Importance of Critical Thinking
Critical thinking is important for the development of social work skills in direct practice. Social workers help people from all walks of life and come across people or populations with experiences, ideas and opinions that often vary from their own culture and background. Clients may be misunderstood and misjudged if thinking critically does not take place in a social context.
Applying critical thinking and analysis in social work helps social workers formulate a treatment plan or intervention for working with a client. First, you need to consider the beliefs, thoughts or experiences that underlie your client's actions without making a snap decision. What seems crazy or irrational to you at first may in fact be better understood in the context of cultural and biopsychosocial factors that play a role in your client's life. Critical thinking helps you objectively examine these factors, consider their importance and impact on your course of action, while simultaneously maintaining professional detachment and a non-biased attitude.
Interrelated Critical Thinking Skills
To develop critical thinking skills as a social worker, you need to have the ability to self-reflect and observe your own behaviors and thoughts about a particular client or situation. Self-awareness, observation and critical thinking are closely intertwined and impact your ability to be an effective social worker. For example, observing your gut reactions and initial responses to a client without immediately taking action can help you identify transference and counter-transference reactions, which can have a negative or harmful impact on your client.
Self-reflection is particularly important when working with clients who have very different or very similar backgrounds and beliefs to your own. You don't want your abilities to be clouded by your own preconceived notions or biases. Likewise, you don't want to merge with a client with whom you over-identify because you come from very similar situations or have had similar experiences.
Purpose of Clinical Supervision
Social workers engage in clinical practice under professional supervision to hone their critical thinking abilities. According to the Administration for Children and Families , clinical supervision not only encourages critical thinking but also helps social workers develop other core social work skills. Clinical experiences focus on maintaining positive social work ethics, self-reflection and the ability to intervene in crises.
Many, if not most, social work settings require or, at least offer, the opportunity to participate in peer, individual or group supervision. Discussing your cases or clients with a supervisor or with colleagues can help you sort out your own opinions and judgments and prevent these issues from impacting your work.
- The Center for Critical Thinking: Defining Critical Thinking
- Administration for Children and Families: Clinical Supervision
Related Articles
Why acceptance is important as a social worker, how not to impose your values on clients, what are some assumptions for working as a social worker, skills needed to be a clinical social worker, distinguishing characteristics of social work, what qualities make a good developmental psychologist, social work interviewing skills, social counselor pay scale & education required, differences between psychologists & clinical social workers, most popular.
- 1 Why Acceptance Is Important as a Social Worker
- 2 How Not to Impose Your Values on Clients
- 3 What Are Some Assumptions for Working as a Social Worker?
- 4 Skills Needed to Be a Clinical Social Worker
- Search Menu
- Sign in through your institution
- Advance articles
- Editor's Choice
- Author Guidelines
- Submission Site
- Open Access
- About The British Journal of Social Work
- About the British Association of Social Workers
- Editorial Board
- Advertising and Corporate Services
- Journals Career Network
- Self-Archiving Policy
- Dispatch Dates
- Journals on Oxford Academic
- Books on Oxford Academic

Article Contents
- < Previous
Critical Thinking and Professional Judgement in Social Work, Lynne Rutter and Keith Brown
- Article contents
- Figures & tables
- Supplementary Data
Lee Quinney, Critical Thinking and Professional Judgement in Social Work, Lynne Rutter and Keith Brown, The British Journal of Social Work , Volume 48, Issue 4, June 2018, Pages 1128–1131, https://doi.org/10.1093/bjsw/bcx056
- Permissions Icon Permissions
As a book that will probably be attractive to both final-year and PQ students considering ways of improving and invigorating their practice, this text provides an effective introduction to critical thinking and judgement because it offers a balanced proportionate oversight of literature and key issues: it does what it says it does—I love that! It refers to a raft of well-known age-old writers on critical reflection (e.g. Brookfield, 1987 ; Schὂn, 1997 ) and more contemporary ones referring to aspects of risk assessment, judgement and decision making (e.g. Taylor, 2013 ), capturing the need for much more focused post-qualifying training in the wake of the Laming Report (2009) and move towards more specific education and training for newly qualified social workers and then those in their Assessed First Year in Practice (ASYE). Unfortunately, ASYE is not discussed because the book appears more focused on cognate understanding of critical thinking and judgement in an introductory manner rather than policy and practice capabilities or knowledge and skills statements. This means potentially good chapters analysing critical thinking and reflection at the ASYE stage of a career are lost in this edition. For example, the Professional Capabilities Framework for ASYE refers to showing creativity in tackling and solving problems, and using critically reflective techniques to evaluate information and test hypothesis (see BASW, 2017 ).
The academic depth and analysis of chapters are limited, but it is a small book and it does not neglect to reference key historical publications, so I imagine this enables many readers to go away and undertake further focused reading whilst not being overwhelmed by too much theory within chapters. As a consequence, they will however be informed and able to develop the depth of their own knowledge and skills at the next stage of their professional development. I appreciate not all readers will be so sure of this or necessarily agree; however, if there is any doubt in their confidence or the knowledge and perceived level of their own critical thinking and decision making, then this book has the potential to help facilitate self-appraisal.
It supports the notion that critical thinking and professional judgement are central facets of modern professionalised social work. On reflection, though, were they not central facets of social work practice going back 100 years, with its early origins in social theory linked to social reform and housing support led by Octavia Hill and follower Henrietta Barnett ( Barnett and Barnett, 1909 )? So what’s changed? Well, this book helps the reader to consider aspects of critical thinking in a pragmatic manner and with some exacting historical reference to well-known writers such as Brookfield (1987) or Balin et al. (1999) . It also tells readers of the importance of understanding different types of bias, logical arguments, and the difference between deductive and indicative process. Thus, it has the potential to provide a necessary companion to the practitioner in need of an introduction to concepts and thinking processes that underlay evidence-informed practice. Perhaps more crucially, it could aid insight into the social and cognitive processes that enable us to process and analyse information derived from experience and improve how social workers might communicate their understandings and recommendations in practice. Ultimately, critical thinking is often short, self-directed, self-monitored and thus can help practitioners to challenge their own thinking about issues. This can help to modify perspectives, improve communication and manage egocentricity ( Paul and Elder, 2008 ).
In general, the book introduces chapters on principles of critical thinking and professional judgement, using knowledge in practice, critical reflection, writing reflective assignments and developing critical practice. It does not adopt a radical or in-depth critical social scientific position. In some ways, it is refreshing that it does not, as it more clearly gets to the point of meeting its own aims and objectives. The lack of in-depth theoretical discourse might frustrate some of the hungry theorists amongst us. Social theorists disinterested in evidence-informed practice will still, however, have helpful references to lead them into further reading given that this small book is fit for purpose: there should be no surprises.
It is fair to assume that many readers know critical thinking and judgement are not new arrivals in the competency matrix of social work, but the increased focus on these cognate areas of practice are closely tied to the dominance and growth of managerialism within social care and growing concern with practitioners and their ability to competently utilise evidence and reflect-in-action in response to uncertainty and complexity. The focus is not on organisational systems and resources that can influence the well-being of practitioners and the quality of decision making informed by judgements; or on how, in recent years, structural and virtuous influences on decision making have been neglected in literature. For instance, inequality and transforming lives have been accused of being side-lined within the profession in deference to both resource-allocation control and more effective risk assessment able to better predict risk of fatalities (see Butler and Drakeford, 2005 ; Munro, 2011 ; Pease, 2013 ).
I have used earlier editions of this book to revisit reflexivity and judgement during my own post-qualifying practice over the years: if you know the literature, it is a kindly reminder of important issues—for example, habits of mind, professional knowledge, reflexivity and judgement. So there is a brief but purposeful lens upon academic domains, but also chapters on practical skills such as writing and critical analysis.
So what are its main limitations? Well, for a book on critical thinking, one would assume critical analysis is essential, but at times the self-imposed limitations set by the book due to the page numbers and variety of chapters mean discussion and analysis can seem very brief and descriptive in places, such as the deductive arguments on p. 13 and embedded critical thinking on p. 58. The authors appear to know the book has its limitations so at least they have given some focal points for further reading where other books would not do so well. On balance, the book is therefore both reassuring and teasing for those who are curious and with a thirst for more knowledge. Whilst the book says it is aimed at post-qualifying practitioners, I think it will act as a more directive and focused companion for ASYE study candidates—for example, how to digest experience and decide what is or is not important. It should be an essential ASYE course text and, where resources allow, a compulsory text purchased for all newly qualified practitioners with resources to fund PQ development. In fact, there seems to be potential for further books on ASYE and post-ASYE professional decision making and judgement in social work to address this current gap in the literature.
If you are a newly qualified practitioner, one returning back to practice or study, or an academic revisiting this area of training after a break, it is a start. Equally, it is potentially useful for health and social care students and workers. Attention to detail and good choice of structure and writers represent the strength of this book. In future editions, more research and evidence-based discussion might be more appealing given that the changing nature of social work demands this more and more. Will practitioners be better decision makers after reading this book alone? No, I very much doubt so, but it will act as a useful guide to help them appraise their practice, and in some cases begin a journey towards improvement in their critical thinking as a qualified social worker. In this sense, the book is a must-have early text for qualified social workers.
Balin S. , Case R. , Coombs J. R. , Daniels L. B. ( 1999 ) ‘ Conceptualising critical thinking’, Journal of Curriculum Studies , 31 , pp. 285 – 302 .
Google Scholar
Barnett A. , Barnett H. ( 1909 ) Towards Social Reform , New York , Macmillan Co .
Google Preview
BASW ( 2017 ) Professional Capabilities Framework , available online at https://www.basw.co.uk/pcf/ (accessed 1 April 2017).
Brookfield S. ( 1987 ) Developing Critical Thinkers , Milton Keynes , Open University Press .
Butler I. , Drakeford M. ( 2005 ) Scandal, Social Policy and Social Welfare , Basingstoke , Palgrave Macmillan .
Laming Report ( 2009 ) ‘The protection of children in England: A progress report’, DoCSF, available online at https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/the-protection-of-children-in-england-a-progress-report (accessed 7 April 2017).
Munro E. ( 2011 ) The Munro Review of Child Protection: Final Report—A Child Centred System , Cm 8062, London, HM Department for Education : The Stationery Office .
Paul R. , Elder L. ( 2008 ) The Miniature Guide to Critical Thinking Concepts and Tools , Tomales, CA , Foundation for Critical Thinking Press .
Pease B. ( 2013 ) ‘A history of critical and radical social work’, in Grey M. , Webb S. (eds), The New Politics of Social Work , Basingstoke , Palgrave Macmillan .
Schὂn D. ( 1997 ) Educating the Reflective Practitioner , London , Temple Smith .
Taylor B. ( 2013 ) Professional Decision Making and Risk in Social Work , London , SAGE .
Email alerts
Citing articles via.
- Recommend to your Library
Affiliations
- Online ISSN 1468-263X
- Print ISSN 0045-3102
- Copyright © 2024 British Association of Social Workers
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Institutional account management
- Rights and permissions
- Get help with access
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.
Open Access is an initiative that aims to make scientific research freely available to all. To date our community has made over 100 million downloads. It’s based on principles of collaboration, unobstructed discovery, and, most importantly, scientific progression. As PhD students, we found it difficult to access the research we needed, so we decided to create a new Open Access publisher that levels the playing field for scientists across the world. How? By making research easy to access, and puts the academic needs of the researchers before the business interests of publishers.
We are a community of more than 103,000 authors and editors from 3,291 institutions spanning 160 countries, including Nobel Prize winners and some of the world’s most-cited researchers. Publishing on IntechOpen allows authors to earn citations and find new collaborators, meaning more people see your work not only from your own field of study, but from other related fields too.
Brief introduction to this section that descibes Open Access especially from an IntechOpen perspective
Want to get in touch? Contact our London head office or media team here
Our team is growing all the time, so we’re always on the lookout for smart people who want to help us reshape the world of scientific publishing.
Home > Books > Empathy Study
Critical Thinking in Social Work Training
Submitted: 14 July 2019 Reviewed: 04 September 2019 Published: 15 November 2019
DOI: 10.5772/intechopen.89538
Cite this chapter
There are two ways to cite this chapter:
From the Edited Volume
Empathy Study
Edited by Makiko Kondo and Bala Nikku
To purchase hard copies of this book, please contact the representative in India: CBS Publishers & Distributors Pvt. Ltd. www.cbspd.com | [email protected]
Chapter metrics overview
1,281 Chapter Downloads
Impact of this chapter
Total Chapter Downloads on intechopen.com
Total Chapter Views on intechopen.com
It is the look at the that leads us to questioning and the answers guide us to updating and the production of knowledge. There is always, in the debates of social work professionals, the question of the search for an intervention project that gives a new meaning to the profession in order to respond, not only theoretically coherent but also efficiently, to the demands placed upon them. The purpose of this chapter is to highlight the importance of critical thinking in the training of social workers. The research is based on an exploratory study carried out with recently graduated university students, whose results point to the benefits of this soft skill in the ability to analyze, understand interactions, detect inconsistencies, systematic problem-solving, reflect on beliefs and values, and reintegrate information as a whole.
- critical thinking
- social work
- soft skills
Author Information
Helena belchior-rocha *.
- Centre for Research and Studies in Sociology (CIES-IUL), Instituto Universitário de Lisboa (ISCTE-IUL), Lisbon, Portugal
Inês Casquilho-Martins
*Address all correspondence to: [email protected]
1. Introduction
The development of skills in critical thinking by students of higher education is nowadays, faced by the challenges of society and the job market place, essential for professional and personal success. This theme has been the subject of increasing reflection and encouragement by different national and international bodies and entities, such as A3ES, 1 the European Commission, OECD, the World Economic Forum, etc. However, despite the interest expressed, there is still a long way for critical thinking to be a generalized priority in the pedagogical practices of teachers, promoted in an intentional, systematic, and transversal way to any area of knowledge.
Thinking about it, in 2009, the Soft Skills Lab (SSL) with the intention of giving students the possibility of complementing their curriculum with soft skills, among which is critical thinking, was created in our university. 2 Being both teachers in social work and critical thinking at the LCT, we decided to carry out this exploratory study to understand the impact of this curricular unit on newly graduated students.
A partial and non-critical view can compromise the performance of any professional, and it is no different with social workers. Common sense concepts are so embedded in our society that even social work students, most of the time, at the beginning of the graduation have a completely wrong idea about what the profession is. The knowledge provided by common sense lead people to believe that the social worker is a kind of a good Samaritan, and this is only one of the challenges students are going to face.
Over time, reality is altered and new conceptions are incorporated into the way of living, learning, acting, interacting, and thinking. The new resources that are constantly added to the already existing ones have or should have the purpose of better serving the individual and society in general. Dealing with the new and complex situations of the contemporary world requires more and more expertise in ways of thinking and acting and relating. Faced with this reality of constant transformations, how can we find autonomy to decide on what is relevant, important, pertinent, and ethical? Critical thinking fits into this question, when it serves as a filter to select what should be harnessed or discarded in this actual avalanche of instantaneous information.
Reflective analysis on the theoretical foundations and intervention models allows social workers to re-equate the directionality of professional action in the context of critical thinking that frames objectivity and questions the reality where it is intervened, as well as the meaning of this intervention in its micro, meso, and macro levels from local to global and from global to local, an exercise that social works constantly need.
As Granja says:
Knowing in Social Work means understanding the social problems as total social phenomena that arise from the operation of the structures and social relations, without denying the particularity of the individual processes and act with a mission to prevent and repair the structural inefficiencies that prevent the poorest from accessing indispensable resources for building themselves as full citizens [ 1 ].
Knowledge about the transformation of social reality requires an investment that results from a reflexive activity involving professionals, in a link between theoretical knowledge and practice, through an interdisciplinary approach that requires a theoretical synthesis built with other areas of social sciences, namely psychology, sociology, anthropology and economics, law, public and social policies, among others, which aims to “change the systems of opportunities, promote social relations dynamics and overcoming the deficit of civic participation” [ 1 ].
Social work practice focuses on social problems, that is, lack of income, unemployment, isolation and breakdown of social ties, domestic violence, children and young people at risk, school drop-out and failure, and migrants and refugees, among many others which by their complexity require a multidimensional combination of vulnerability and the articulation with structural phenomena and current social policies.
It is better evident for all the importance that critical thinking has in the education of future professionals, although it is nothing new, given the fact that is always in the debates of social work professionals the question of the search for an intervention project that gives a new meaning to the profession in order to respond, not only theoretically coherent but also efficiently, to the demands placed.
Social work as a profession has always demanded critical abilities and qualities from its practitioners because decisions have to be made “on the spot” and under pressure. With practice situations being so complex, the consequences of any decisions and action are extremely important [ 2 ].
A reflexive practice leads to thinking through the mediation of concepts and allows to reconstruct the problems and to construct new ways of solving problems. The ability to select data and identify patterns in the professional activity in order to be recognized and transmissible to become sources of knowledge and to be prepare for lifelong learning. For the development of this reflection, it is necessary to have a structured thought about the phenomena that allow analyzing and constructing operational representations.
This requirement goes beyond “competent practice” and demands “critical practice” [ 3 ], and the development of “critical being,” that is, a person who not only reflects critically on knowledge but also develops their powers of critical self-reflection and critical action [ 4 ].
In the research that Ford et al. [ 5 , 6 ] made on criticality with students in social work education, these ideas have been explored and they conclude that the intellectual resources for critical thinking are: (1) background knowledge; (2) critical concepts; (3) critical thinking standards; (4) strategies; and (5) habits of mind. This allows us to realize that this process has to be permanent and rooted as a mindset.
The more we know about a situation and the circumstances that caused it, the better we can articulate with a structural question, be it social, economic, cultural, or political, including beliefs, values in order to clarify the range of available options and solutions, so that the professional can make an informed decision about the problems that are dealing with.
Beginning to deal with this type of “how to” knowledge is where a practitioner’s ignorance becomes obvious and can cause anxiety. It may well be the reason why many new qualified workers take a very prescriptive, rule-based approach to try to ensure they do not do anything wrong. In many ways such a focus on detail and correctness ensures that practitioners can be more critically aware of what they are doing than experienced workers who have established routines [ 2 ].
Gray et al. add that “Social workers need to examine closely the strengths and limitations of research evidence. Regardless of how strong the evidence for a particular intervention might be, social workers are in a position where they must critically reflect on their work in the political, social, organizational, and interpersonal contexts, make professional judgements, engage in debate with decision-makers about resource allocation, negotiate appropriate practices and, when necessary, argue convincingly for the effectiveness of the work that is done. This requires skills in formulating and presenting well-supported arguments and the interpersonal and written communication skills to convey a position convincingly” [ 7 ].
Based on these assumptions, we did a review of the literature and developed an exploratory study with the aim of understanding the perception of recent students in social work about the importance of critical thinking.
2. The importance of critical thinking in education
According to the literature, the importance of critical thinking skills is recognized in the academic and professional contexts, in which the need to implement measures that facilitate their development and awareness of their usefulness is mentioned.
We find several approaches to critical thinking, some more vague, others more objective, but we cannot easily find a consensus between them, either in terms of definition, in terms of the terminology used, or in the type of methodology designed to develop it [ 8 , 9 ].
The scientific areas in which we can find greater literary production and investigation around critical thinking are philosophy, psychology, and education [ 10 , 11 , 12 ].
We find different contributions from the disciplinary areas mentioned above in an attempt to define critical thinking, and there are no definitions that fit exclusively in one or another area, since many of these authors cross the areas in terms of the research they develop. It is not our goal to find the best definition of critical thinking, or even the most complete one. The various theories focus on different aspects, put the focus on different circumstances, conceptualized in a way that is not always consensual and sometimes even antagonistic. Despite the differences, we find, in these definitions, points of convergence that we think allow us to have a perception about what critical thinking might actually be [ 10 , 13 ].
An argument goes from the premises to the conclusion and is one in which there are good reasons for the assumptions to be true, and in addition, the premises have good reasons to support or support the conclusion.
It is focused initially on the holistic assessment of a situation, not explicit reasoning and analysis. In other words, they establish the inductive or deductive links necessary to bring the different parts of a situation into a meaningful whole, to allow it to make sense. Every situation one experiences and faces may be different, but it is imperative to know enough of the parties to make general sense of the whole in order to start dealing with it.
The foundation for critical thinking defines critical thinking as:
the type of thinking—about any subject, content, or problem—in which the thinker improves the quality of his thinking by competently analyzing, evaluating and reconstructing it. Critical thinking is self-directed, self-disciplined, self-monitored, and self-corrective. It presupposes consent to rigorous standards of excellence and a conscious control of its use. It implies effective communication and problem-solving skills, as well as a commitment to surpass our natural egocentrism and sociocentrism [ 14 ].
According to the Delphi Report, referenced by Facione, in addition to the skills associated with critical thinking, there are still a set of aptitudes, divided into two approaches: one related to life skills in general, and another related to specific issues, doubts, and problems. Regarding the first, the Delphi Report describes the following as critical thinker’s skills: (1) curiosity over a wide variety of issues; (2) concern about becoming and staying well informed; (3) alert to opportunities to use critical thinking; (4) trust in the rational research process; (5) confidence in your own reasoning abilities; (6) open mind regarding divergent views about the world; (7) flexibility when considering alternatives and opinions; (8) understanding of the opinions of others; (9) honesty in the evaluation of reasoning; (10) honesty when confronted by our own egocentric and sociocentric prejudices, stereotypes, and tendencies; (11) caution in the suspension, elaboration or alteration of judgments; and (12) predisposition to reconsider and revise viewpoints, where honest reflection suggests change is necessary [ 15 , 16 ].
Regarding the approach related to specific issues, the Delphi Report refers the following as aptitudes: (1) clarity in affirming an issue or concern; (2) method in dealing with complexity; (3) diligence in searching for relevant information; (4) reasonability in the selection and application of criteria; (5) concern to focus attention on the subject; (6) persistence despite any difficulties that may arise; and (7) accuracy to the level allowed by subject and circumstance.
Critical thinking is multidimensional, encompassing the intellectual (logic, rationality), psychological (self-consciousness, empathy), sociological (in terms of socio-historical context), ethics (norms and moral evaluation), and philosophical (meaning of nature and human life) [ 17 ].
It is also due to its characteristics of transversatility and multidimensionality that the authors argue that critical thinking has for centuries been the basis for the creation and maintenance of a democratic and democratically participative society, qualified by an active, pluralistic, and autonomous citizenship [ 18 , 19 , 20 , 21 , 22 ].
In education, we highlight pioneering authors who have emphasized critical thinking (although with other terminologies), from the Greek philosopher Socrates and the concepts of “knowledge” and “maièutica,” to the American philosopher, psychologist, and educator John Dewey, and reflection on “thinking” and “reflecting” [ 23 , 24 ].
Dewey is even considered the “father” of the modern tradition of critical thinking [ 25 ] when, in the early twentieth century, he advocated the need for education to prepare students for the complex demands of citizenship and the world of work [ 26 ].
The debate about the operationalization of critical thinking, the development and teaching of critical thinking, the skills of critical thinking, and the evaluation of critical thinking, are thus essential topics in education from the last decades of the twentieth century until now, specifically for social work, a recent study in this area recommends a future research agenda for critical thinking [ 27 ]. As competence, or set of competencies, critical thinking can be developed and evaluated. In this sense, the exploratory study presented here intends to contribute to the evaluation of the importance that students attribute to critical thinking, as well as to the evaluation of critical thinking as competence.
2.1 Social work education and critical thinking
The twentieth century imposes on contemporary social work the challenge of establishing theoretical categories and methodologies that broaden its interdisciplinary horizon and stimulate the conception of the human being as a builder of its own reality [ 28 ]. The increasing complexity leads us to the search for alternatives, skills, and a competence to manage the theoretical-practical process, related to the attempt to understand the reality in constant movement, the tendencies and the possibilities that are put to our daily lives.
Social work education in Portugal according to Branco [ 29 ] “focuses on the dynamics of break and continuity between its pivotal socio-political periods and international influences” the same author in its latest article marks these periods saying that:
The social work education itinerary in Portugal during the period between the Republican Regime foundations (1910), the constitution of Estado Novo (1933–1945), the succession of Salazar (1968), the revolutionary crises associated with the Carnation Revolution of 1974 and the academisation period (1989 to the present) [ 29 ].
Questions related to the production of knowledge and the dissemination of this same knowledge arise later (also for socio-historical reasons), with the affirmation of the profession as a specific area of knowledge. In Portugal, with the development of the academic career in the area of social work, (undergraduate, master, and doctorate), the theoretical and practical dimensions, namely training, intervention, and research, have been developing and, consequently, we have assisted to a greater theoretical production (in the form of theses, dissertations, articles, and books) and an intensification of the research effort and its dissemination, which has given to Portuguese social work a greater visibility among the scientific community [ 30 ].
Consequently, the construction of knowledge was imposed as a means of awareness of the subjects involved in the teaching-learning process, in a critical perspective of knowledge as a tool for the realization of the political-professional ethical project and for the transformation of the socio-institutional and political- cultural reality. This awareness has undoubtedly been one of the means for advancing professional maturity.
The experience of this critical thinking course comes from the university, where the study was done through the creation in 2009 of a Cross Skills Laboratory to give students extra skills with the aim of developing a reflexive practice that, rather than aiming at the constitution of a stabilized knowledge, intends to develop the capacities of reflexivity and action; understand the importance of critical thinking in academic and professional context; identify the elements and analyze simple and complex arguments; recognize errors on daily speech; assess the quality of arguments and argumentative texts; and create simple and complex arguments in oral debates and written texts. The students that successfully complete this curriculum unit will be able to analyze arguments regarding their structure and content; argue on an issue; identify the deductive validity on propositions; and question arguments, identifying its weaknesses.
According to Jones “Critical thinking can lead us to open up self-doubt and this is a good thing because it lead us to really examine why we think and act as we do” [ 31 ] and “Developing an ability to understand why you react and think as you do is part of a recognition of you own inner resources” [ 31 ] this author also argues that:
To be able to think about how we, and others, think—thinking about thinking. In doing this you will be thinking about the reasoning, motives and arguments of others. You will have the ability to see all sides of the question and analyze its strengths and weak-in these [ 31 ].
And is corroborated by other authors that alert us by saying that
The technical rationality model also fails to recognize how understanding is developed from the integration of theory and practice (…) Reflective learning incorporates both theoretical and practical themes and issues and seeks to integrate these—to open a dialogue between theory and practice [ 32 ].
It is a continuous process of reflection and allows the interveners to develop their theory directly from their experience. In addition, it allows you to “tailor” your intervention to each specific context using a range of non-defined skills and perspectives.
3. Methodology
The present study is exploratory and quantitative and aims to understand the perception of recent graduate students in social work on the importance of learning critical thinking in higher education and its impact on the labor market.
It aims to identify the potential of learning critical thinking during its formation, including future usefulness in the professional field. Although we do not intend to prove hypotheses, we seek to explore the results based not only on the perception of the respondents, but also to categorize the critical-thinking skills acquired as potentialities in teaching in social work and as knowledge of support to the professional exercise.
In a universe of 154 newly graduated students between 2015 and 2017, whose training integrated the curricular unit of critical thinking in their curriculum, we used an intentional sample of 79 individuals recently graduated in social work.
A bibliographical review was made on the subject and we used as a data collection technician, a questionnaire in which we used a Likert scale of level 5. The Likert scales [ 33 ] are widely used to measure postures and opinions with a higher level of a question of “yes” or “no,” in this questionnaire was composed of a set of sentences (items) in relation to each one of which the respondents were asked to express the degree of agreement from the non-positive (level 1), until very positive (level 5). We also added two questions to understand the degree of satisfaction with the critical thinking training with a scale from 0 to 10, in which 0 was totally dissatisfied and 10 totally satisfied and an open question to perceive the benefits and disadvantages of learning critical thinking.
The questionnaire was divided into two parts: socio-demographic characterization and the identification of the importance of critical thinking contribution as training in its learning.
The age of the participants is between 21 and 45 years, with an average of 24.5 years, mostly females, 87.3, 91.1% Portuguese and 78.5% is inserted in the job market (as social workers) and 94.4% attended this curricular unit in the first year of the degree.
Ability to analyze
Systematic problem solving
Understand interactions and detect inconsistencies
Reflection on beliefs and values
The reintegration of information as a whole
We are aware that one of the limitations of this study is that there is no credit for its generalization [ 34 ] given the fact that it has a small sample (although representative in terms of results for our university) and is exploratory.
Another limitation is that the respondents themselves may have given skewed responses because they know the purpose of the study, they may want to appreciate the university that formed them and give answers that they consider “correct.” It was attempted to overcome this limitation by saying that both the institution and the participants would be anonymous.
We intend to continue this study in a first phase at national level with partnerships with other universities and later extend to a study in the Iberian Peninsula (Portugal-Spain).
The results show that the majority of respondents considered that the contents seized in their critical thinking training were positive or very positive with Likert scores (1–5) between 4.53 and 3.89. The average of responses in the different categories considered the impact of the contents acquired positive 50.55% and very positive 35.27%, understanding this competence as an active element of learning as students, stimulating a clear, logical, and organized thinking, helping to develop the necessary skills during the frequency of higher education and currently in the labor market ( Figure 1 ).

Distribution of respondents’ answers on the current impacts of content acquired during their training.
According to the results, the greatest impact of learning was reflected in the development of strategies for decision-making and in the capacity to train a rigorous analytical view, both with a mean score in the answers of 4.53 (Likert scale-Ls). These figures translate into the impacts of these two categories, which were considered positive by 36.71% of the respondents and very positive by 58.23%. It is also noted that 5.06% of the respondents consider neither positive nor negative.
The identification of the barriers to critical thinking obtained the highest percentage of answers with the classification of positives (67.09%) along with the diagnosis in problem solving (63.29%). In the categories of preparation for problem solving and articulation of daily information, there was a balanced preference for responses, mainly considering positive or very positive.
Respondents answered that the impact on the preparation for problem solving was both very positive (44.30%) and positive (44.30%), considering neither positive or negative 10.13% nor negative 1.27%. In the articulation of information with the everyday situations, 46.84% was very positive, 44.30 positive, and 8.86 neither positive nor negative.
Regarding the ability to identify argumentation errors, 25.32% of the respondents answered that the impacts were neither positive nor negative. This is the category in which neutrality assumes greater expression, although it continues to be less than the responses that consider the very positive (37.97%) and positive (36.71%).
As for the less-valued aspects, but still with an average that considers these competences as positive, are the dimensions of acquisition of learning strategies through reading (3.89 Ls) and acquisition of learning strategies through listening (3.99 Ls). The responses in these two categories vary in their distribution, and the acquisition of learning strategies through reading 32.91% of the respondents considered that the impact of this competence was neither positive nor negative, while 45.57% considered that it was positive and 21.52% which was very positive.
Regarding the acquisition of learning strategies through listening 20.25% considered that was very positive, 59.49% positive, 18.99% that was neither positive nor negative, and 1.27 responded that the impact was negative.
In the acquisition of research techniques and information systematization, most of the answers were positive 55.23%, positive for 22.78% of the respondents, and 16.46% neither positive nor negative. This competence was the one with a residual value, presented the highest percentage of responses that considered the negative impact (2.53%).
The comprehension of the structure of an argumentative text and the acquisition of competences for an argumentative discourse were both considered 55 by 0.70% of the respondents as having a positive impact. The understanding of the structure of an argumentative text also registered 34.18% of responses that indicate a very positive impact and 10.13% that consider that the impact was neither positive nor negative.
In the acquisition of competences for a care argumentative discourse 33.91% considered to have had a very positive impact and 11.39% did not have a positive or negative impact. The ability to develop abstract reasoning was for 26.58% of the respondents considered very positive, 53.16% positive, and 20.25% neither negative nor positive. The break with common sense was perceived as a competence with a very positive impact by 53.16% of the respondents, 37.97% answered that the impact on this competence was very positive, and the remaining ones were neither positive nor negative, 8.86%.
Finally, the acquisition of skills for clear and objective writing had 48.10% considering that the impact of the contents acquired was positive, followed by 26.71% of the responses as very positive and 15.19% which was neither positive nor negative. Other aspects analyzed were the satisfaction with the curricular unit of critical thinking and professional satisfaction, as well as the aspects that were considered as advantages or disadvantages in their training.
Using a satisfaction scale of 0–10 in which 0 is totally unsatisfied and 10 is fully satisfied, the highest number of equal answers with the classification 8 regarding satisfaction with the program they had in their training of critical thinking was 32.91% of the respondents and 34.18% with the same classification relative to the importance in the labor market. The answers ranged from 4 to 10 in both questions, with the average rating being 7.57 and 7.67, respectively.
In addition to the satisfaction with critical thinking learning in both academic and professional spheres, among the main advantages, respondents identified the improvement of their attention and observation abilities of the real world, as well as the contribution in the decision-making supported by an exercise of rational discernment. It was also mentioned the improvement of the capacities to identify key ideas avoiding irrelevant elements, the facilitation in the process of transmitting ideas and perspectives, and the development of this competence to various situations and contexts. There were no disadvantages to register except for the reference to the difficulty in interpreting texts and access to scientific sources of information.
About the importance of critical thinking associated with the issue of values and beliefs and of a more comprehensive thinking, respondents considered the knowledge acquired with critical thinking as extremely important because it allows them to question universal opinions, general judgments, and mind-beliefs, in order to be able to perform quality work in their intervention with people.
5. Discussion
This exploratory study gives us the perception that the recent graduate students in social work who attended the critical thinking curricular unit valued this learning in their training, but also in the usefulness and articulation with the job market.
Participants’ responses show that the majority of respondents considered that the competences learned in their training in critical thinking were positive or very positive, with critical thinking being an active element in their higher education, stimulating reflection and acting capacities in the service domain of a clear, logical and systematized form, helping to develop the skills needed during higher education attendance and currently in the labor market.
5.1 Ability to analyze
Among the dimensions analyzed stand the development of strategies to support decision-making and analytical capacity through rigorous and systematized procedures. The development of strategies for decision-making includes efficient, quick, and objective forms of planning in the analysis of situations. Here, it includes the ways of acting in complex situations that aim for more efficient and effective responses through thought patterns that can increase the confidence and assertiveness of the responses when implementing them.
The training capacity of a rigorous analytical vision leads to a cognitive reflection, free of opinions and value judgments, focusing on a critical action of analysis of information, facts and events, and managing to select and systematize what is significant in an idea developed or presented. It also promotes a process of evaluation of evidence and facts at the expense of opinions, as well as a reflection on the issues in a structured, logical, and informed way.
The acquisition of research techniques and systematization of information refers to the training of valid and reliable bibliographic research and the careful use of information sources. It is necessary to establish critical thinking in premises based on evidence, supported by theoretical or empirical data.
Although with a less significant expression, the competences of acquiring learning strategies through reading and listening are also present in the development of this competence. It is important to apply research and information selection processes in written texts, the analysis of written narratives, and documentary information to support the development of critical thinking, as well as the listening of oral, synchronous, or asynchronous narratives that allow the acquisition of information to support the construction of logical and consistent reasoning.
5.2 Systematic problem solving
It is also highlighted the importance of critical thinking as support for diagnosis and problem solving, focusing on the ability to analyze and evaluate situations, looking at them by different prisms, particularly in relation to issues associated with ideologies, religion, ethics, or human behavior.
The preparation of these professionals for the resolution of problems and for the articulation of daily information promotes competences for an accuracy in the way they reflected and act when facing questions that imply the analysis of a complex situation, dilemmas or unforeseen situations, developing the training for think and anticipate problems critically, generating solutions that are useful in solving problems, in project management or in the way different parts of an activity or task is developed.
In this field, the capacity to observe reality and current analysis through the collection and application of information in plural and multidimensional contexts is highlighted and allows the development of forms of analysis and adaptation in different areas and groups in the face of a diversified reality of constant transformations.
5.3 Understand interactions and detect inconsistencies
The understanding of the structure of an argumentative text and the acquisition of competences for the construction of a discourse are developed competences that allow the identification of reasons and conclusions, together with the evaluation of the premises that support the presented conclusions.
It encompasses the ability to identify points of view in a clear, systematic, and objective way, identifying simple and complex lines of reasoning. It also contributes to a better communication and interaction with others, achieving through a clearer discourse to present convincing quality arguments and reinforcing points of view in a structured way.
This relates to a process that involves conscious choices, supported by evidence that gives strength to our discourse, be it oral or written, allowing cumulatively to be able to interpret and deconstruct our ideas and others ideas. It also allows for an evolution in the capacities of relationship and communication, making possible the selection about what is more or less relevant.
The ability to detect inconsistencies in performance, through the identification of fallacies, refers to the development of the ability to recognize the most common argumentations failures and to be attentive to failures in the arguments of others.
It makes possible to identify errors of argumentation with a competence that contributes to finding weaknesses and strengths in the discourses of others and be able to counteract them, as well as to formulate its own arguments. It also highlights the ability to recognize information manipulation techniques and fallacies and present a well-grounded, clear, and organized perspective in order to convince others. It also promotes a correct grammatical and conceptual use, avoiding abstract, vague or general terms that compromise attention-getting to what is central to the argument, through precise, specific, and concrete language.
5.4 Reflection on beliefs and values
The importance of overcoming the barriers to critical thinking are recognized as a relevant aspect that refers to the pertinence of the approach of this theme, resulting in the development of skills of conceptualization of criticism and overcoming inhibition to criticism and in the ability to be free of emotional influences or affective, avoiding that they affect the clarity of the reasoning and must be analyzed by the evidences.
Also, it is recognized that common sense is capable of creating absolutisms all the time and the tendency of the great mass of our society is to absorb them easily; creating a vision of the world capable of guiding our whole existence. We are hardly willing to question what is going on around us and seek a second opinion of the facts. Instead, we prefer the convenience of thinking like others, following the vast majority, prefer superficiality. Because it is hard work creating critical thinking, these students create added value in both professional and personal life and it’s a lifelong tool.
5.5 The reintegration of information as a whole
The capacity for development of abstract reasoning aims to identify the positioning of others, arguments, and conclusions, leading to innovation processes. It develops concepts and ideas analysis skills from a more systemic and global perspective. Rupture with common sense contributes to the use of facts as support for action to the detriment of individual knowledge supported by lack of evidence, aiding in the foundation of arguments, and ideas that are proven theoretically or empirically.
Some research [ 35 ] refers that as they are in control of their thoughts, that is, they are aware, understand, self-direct, and self-evaluate; have “tacit knowledge” groups that form “patterns” and represent the learning and generalization of previous experiences, research, and theory; recognize other significant patterns and principles and irrelevant aspects in a situation and bind to these existing known patterns and thus assess in depth (patterns or contours formed in the mind) that when adapted to the problem suggest solution procedures and periodically checks us for review, progress, and evaluate results.
6. Conclusions
Teaching is a privileged context for the development of critical thinking in individuals, and the teacher plays a fundamental role in the conduct of this complex process with theoretical, practical, and motivational components of active learning [ 10 ].
Experts in the area of critical thinking collaborated in the definition of strategies and methodologies of approach for the operationalization of the development of these competences in educational contexts, as in the case of the Delphi Report already mentioned, that resulted from the meeting of a group of experts with the objective, through the Delphi Method, to constitute a set of propositions and recommendations that would act as guiding lines for education agents and other professionals related to this area, regarding teaching, and evaluation of critical thinking.
In pedagogical terms, there are different ways of teaching and exercising critical thinking among students. The two most common approaches are: the creation of a course or program specifically dedicated to the development of critical thinking; and the incorporation of the development of critical thinking in curricular subjects.
Based on the literature, we cannot say that one approach is more effective than the other, but we can say that the perception of the key benefits that our graduated students report in conducting our critical thinking programs refers to ensuring good practice that is already being realized through discussions with others and the link between theory and practice to rethink their practices, allowing them to perceive when they fall into the bureaucratic routine and adopt more appropriate methods and approaches.
An awareness and acceptance of uncertainty in the practice of any professional is an important way to lessen stress. There are no perfect solutions out there to find, so we cannot be called on to work perfectly. If we accept the fact that the things we do or decide on are still dependent on something uncertain or on future happenings, and work in a way that takes account of that (i.e. constantly reviewing the things we deal with, decide on, or do), then this is really what “thinking critically” is all about [ 2 ].
The key is to strike a balance between the need for certainty and the need to be aware of other ways of doing or thinking about practice. This is where critical reflection (especially involving others) can play a key role in building trust by analyzing practice based on strengths, but also allows consideration of alternative options, points of view, etc., within a space safe, and where uncritical rigidity is not established.
These characteristics should be present not only in the students but also in the teachers. They must know how to model the learning they want to pass. Is it possible to give classes that do not develop these skills but reach other academic goals? Of course yes. But, it is also possible to achieve academic goals, curricular goals, and programmatic content by developing these skills at the same time.
Not least, we find the evaluation. In order to gauge how the process is going, we must evaluate. It is a great challenge to evaluate these skills, it is true. It will be easier to evaluate if you have memorized dates and locations. But as it is a challenge to know how much a student contributed in a group work and not fail to do so, we cannot give up to train our students in skills that will be valid for the rest of their lives because of the difficulty we encounter in the evaluation and the technology resources that allow new forms of formative and summative evaluation.
It cannot be forgotten that the surprises with which every social worker is confronted in everyday contacts and relationships need to be analyzed not only with common sense look but also with critical thinking and the autonomy of a thought based on solid concepts should be a factor of considerable importance. This will mean that in each complex situation, the values that underpin knowledge are at the service of conscious decision-making.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful and want to thank all the participants for their availability and collaboration, so that this study was possible.
The publication of this paper was supported by Portuguese national funds through Foundation for Science and Technology in the scope of the UID / SOC / 03126/2019 project. We appreciate the support given by the CIES-IUL and the funding of the Foundation for Science and Technology.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
- 1. Granja B, Queirós MC. Problemas e desafios da investigação em serviço social. Intervenção Social. 2011; 38 :233-251. ISSN: 0874-1611 (Portuguese)
- 2. Brown K, Rutter L. Critical Thinking for Social Work. 2nd ed. Southernhay East: Learning Matters Ltd.; 2008. 3, 42, 47 p. ISBN: 978 1 84445 157 9
- 3. Adams R, Dominelli L, Payne M, editors. Critical Practice in Social Work. Basingstoke: Palgrave; 2002
- 4. Barnett R. Higher Education: A Critical Business. Buckingham: Society for Research in Higher Education and Open University Press; 1997. ISBN: 0 335 19703 5
- 5. Ford P, Johnston B, Mitchell R, Myles F. Social work education and criticality: Some thoughts from research. Social Work Education. 2004; 23 (2):185-198. DOI: 10.1080/0261547042000209198
- 6. Ford P, Johnston B, Mitchell R, Myles F. Practice learning and the development of students as critical practitioners: Some findings from research. Social Work Education. 2005; 24 (4):391-407. DOI: 10.1080/02615470500096910
- 7. Gray M, Plath D, Webb SA. Evidence-Based Social Work: A Critical Stance. London and New York: Routledge Taylor & Francis Group; 2009. ISBN 0-203-87662-89
- 8. Bailin S, Case R, Coombs JR, Daniels LB. Conceptualizing critical thinking. Journal of Curriculum Studies. 1999; 31 (3):285-302. DOI: 10.1080/002202799183133
- 9. Washburn P. The Vocabulary of Critical Thinking. New York: Oxford University Press; 2010. ISBN: 0195324803
- 10. Almeida LS, Franco AHR. Critical thinking: Its relevance for education in a shifting society. Revista de Psicología. 2011; 29 (1):176-195. ISSN 0254-9247
- 11. Baker M, Rudd R. Relationships between critical and creative thinking. Journal of Southern Agricultural Education Research. 2001; 51 :173-188. http://www.jsaer.org/pdf/vol51Whole.pdf
- 12. Lai ER. Critical Thinking: A Literature Review—Research Report [Online]. Pearson Education; 2011. Available from: http://images.pearsonassessments.com/images/tmrs/CriticalThinkingReviewFINAL.pdf [Accessed: 23 May 2019]
- 13. Halpern D. Teaching for critical thinking: Helping college students develop the skills and dispositions of a critical thinker. New Directions for Teaching and Learning. 1999; 80 :69-74. DOI: 10.1002/tl.8005
- 14. Foundation for Critical Thinking. Our Concept and Definition of Critical Thinking [Internet]. 2007. Available from: https://www.criticalthinking.org/pages/our-conception-of-critical-thinking/411 [Accessed: 02 June 2019]
- 15. Facione PA. Critical Thinking: A Statement of Expert Consensus for purposes of Educational Assessment and Instruction—Executive Summary “The Delphi Report” [Internet]. 1990a. Available from: http://assessment.aas.duke.edu/documents/Delphi_Report.pdf [Accessed: 02 June 2019]
- 16. Facione PA. Critical Thinking: A Statement of Expert Consensus for Purposes of Educational Assessment and Instruction—Research Findings and recommendations (ERIC Report No. ED315423) [Internet]. 1990b. Available from: http://www.eric.ed.gov/PDFS/ED315423.pdf [Accessed: 23 May 2019]
- 17. Paul R, Elder L, Bartell T. California Teacher Preparation for Instruction in Critical Thinking (ERIC Report No. ED437379) [Internet]. 1997. Available from: http://www.eric.ed.gov/PDFS/ED437379.pdf [Accessed: 23 May 2019]
- 18. Angeli C, Valanides N. Instructional effects on critical thinking: performance on ill-defined issues. Learning and Instruction. 2009; 19 :322-324. DOI: 10.1016/j.learninstruc.2008.06.010
- 19. Brookfield SD. Developing Critical Thinkers: Challenging Adults to Explore Alternative Ways of Thinking and Acting. Buckingham: Open University Press; 1991. ISBN: 978-1-555-42356-8
- 20. Dewey J. Democracy and Education [Internet]. Penn State Electronic Classics Series Publication; 2001. Available from: https://nsee.memberclicks.net/assets/docs/KnowledgeCenter/BuildingExpEduc/BooksReports/10.%20democracy%20and%20education%20by%20dewey.pdf [Accessed: 24 May 2019]
- 21. Freire P. Educação Como Prática da Liberdade. Rio de Janeiro: Editora Paz e Terra; 1967 (Brasilian)
- 22. Kuhn D. A developmental model of critical thinking. Educational Research. 1999; 28 (2):16-46. DOI: 10.3102/0013189x028002016
- 23. Riddell T. Critical assumptions: Thinking critically about critical thinking. The Journal of Nursing Education. 2007; 46 (3):121-126. https://www.healio.com/journals/jne/2007-3-46-3/%7Bfd7bf35f-0615-4e21-9291-56bf66297a8f%7D/critical-assumptions-thinking-critically-about-critical-thinking#
- 24. Wang S-Y, Tsai J-C, Chiang H-C, Lai C-S, Lin H-J. Socrates, problem-based learning and critical thinking—A philosophic point of view. The Kaohsiung Journal of Medical Sciences. 2008; 24 (3 Supplement):S6-S13. DOI: 10.1016/s1607-551x(08)70088-3
- 25. Fisher A. Critical Thinking: An intrOduction. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 2001
- 26. Halpern D, Nummendal SG. Closing thoughts about helping students improve how they think. Teaching of Psychology. 1995; 22 (1):82-83. DOI: 10.1207/s15328023top2201_24
- 27. Verburgh A. Effectiveness of approaches to stimulate critical thinking in social work curricula. Studies in Higher Education. 2019; 44 (5):880-889. DOI: 10.1080/03075079.2019.1586336
- 28. Belchior Rocha H, Marques Ferreira P, Silva TP, Braz Ramalho V. Serviço social crítico: da modernidade à contemporaneidade. Alternativas: Cuadernos de Trabajo Social. 2013; 20 :79-90. DOI: 10.14198/ALTERN2013.20.05
- 29. Branco F. Social work education: The Portuguese story in a local and global perspective. Practice. 2018; 30 (4):271-291. DOI: 10.1080/09503153.2018.1485144
- 30. Leitão Ferreira J. Serviço social: Profissão e ciência. Contributos para o debate científico nas ciências sociais. Cuadernos de Trabajo Social. 2014; 27 (2):329-341. DOI: 10.5209/rev_CUTS.2014.v27.n2.44782
- 31. Jones S. Critical Learning for Social Work Students. Exeter: Learning Matters Ltd; 2009. 93, 109 p. ISBN-13: 978-1844452019
- 32. Thompson N, Pascal J. Developing critically reflective practice. Reflective Practice. 2012; 13 (2):311-325. DOI: 10.1080/14623943.2012.657795
- 33. Lima L. Atitudes: Estrutura e mudança. In: Vala J, Monteiro MB, editors. Psicologia Social. Lisboa: Fundação Calouste Gulbenkian; 2000 (Portuguese)
- 34. Kates S. A qualitative exploration into voters’ ethical perceptions of political advertising: Discourse, disinformation, and moral boundaries. Journal of Business Ethics. 1998; 17 (16):1871-1885. DOI: 10.1023/a:1005796113389
- 35. Macaulay C. Transfer of learning. In: Cree VE, Macaulay C, editors. Transfer of Learning in Professional and Vocational Learning. London: Routledge; 2000. pp. 1-26. ISBN: 0415204194
- A3ES is our National Accreditation Agency for higher education courses.
- It is a public University with 15 graduations, 49 masters, 22 PhDs, and around 8868 students.
© 2019 The Author(s). Licensee IntechOpen. This chapter is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Continue reading from the same book
Edited by Makiko Kondo
Published: 09 September 2020
By Makiko Kondo, Sachie Okanishi, Etsuko Arai, Kumiko...
780 downloads
By Noriko Okabe
1792 downloads
By José de Almeida Brites, Américo Baptista, Catarina...
1257 downloads
- Write For Us

- The Role of Omega-3 Fatty Acids In Men’s Sexual Health May 23, 2024
- London ADHD Specialists: Get Expert Help May 16, 2024
- The Evolution of Diamonds: Unveiling the Marvels of 4Cs Lab Grown Diamonds May 15, 2024
- Mastering the Art of Timing: When Is the Best Time to Sell Bitcoin? May 11, 2024
- Is web.de/ Home Improvement a Thing? May 10, 2024
- Family Therapy and Counselling in Johannesburg May 7, 2024
Why Critical Thinking Is Important In Social Work And How It Is Used
Critical thinking is universal, promotes creativity, it makes you happier, improves relationships, it is an activity for the mind, how critical thinking is used in social work.

Tips for Online Students , Tips for Students
Why Is Critical Thinking Important? A Survival Guide
Updated: December 7, 2023
Published: April 2, 2020

Why is critical thinking important? The decisions that you make affect your quality of life. And if you want to ensure that you live your best, most successful and happy life, you’re going to want to make conscious choices. That can be done with a simple thing known as critical thinking. Here’s how to improve your critical thinking skills and make decisions that you won’t regret.
What Is Critical Thinking?
You’ve surely heard of critical thinking, but you might not be entirely sure what it really means, and that’s because there are many definitions. For the most part, however, we think of critical thinking as the process of analyzing facts in order to form a judgment. Basically, it’s thinking about thinking.
How Has The Definition Evolved Over Time?
The first time critical thinking was documented is believed to be in the teachings of Socrates , recorded by Plato. But throughout history, the definition has changed.
Today it is best understood by philosophers and psychologists and it’s believed to be a highly complex concept. Some insightful modern-day critical thinking definitions include :
- “Reasonable, reflective thinking that is focused on deciding what to believe or do.”
- “Deciding what’s true and what you should do.”
The Importance Of Critical Thinking
Why is critical thinking important? Good question! Here are a few undeniable reasons why it’s crucial to have these skills.
1. Critical Thinking Is Universal
Critical thinking is a domain-general thinking skill. What does this mean? It means that no matter what path or profession you pursue, these skills will always be relevant and will always be beneficial to your success. They are not specific to any field.
2. Crucial For The Economy
Our future depends on technology, information, and innovation. Critical thinking is needed for our fast-growing economies, to solve problems as quickly and as effectively as possible.
3. Improves Language & Presentation Skills
In order to best express ourselves, we need to know how to think clearly and systematically — meaning practice critical thinking! Critical thinking also means knowing how to break down texts, and in turn, improve our ability to comprehend.
4. Promotes Creativity
By practicing critical thinking, we are allowing ourselves not only to solve problems but also to come up with new and creative ideas to do so. Critical thinking allows us to analyze these ideas and adjust them accordingly.
5. Important For Self-Reflection
Without critical thinking, how can we really live a meaningful life? We need this skill to self-reflect and justify our ways of life and opinions. Critical thinking provides us with the tools to evaluate ourselves in the way that we need to.

6. The Basis Of Science & Democracy
In order to have a democracy and to prove scientific facts, we need critical thinking in the world. Theories must be backed up with knowledge. In order for a society to effectively function, its citizens need to establish opinions about what’s right and wrong (by using critical thinking!).
Benefits Of Critical Thinking
We know that critical thinking is good for society as a whole, but what are some benefits of critical thinking on an individual level? Why is critical thinking important for us?
1. Key For Career Success
Critical thinking is crucial for many career paths. Not just for scientists, but lawyers , doctors, reporters, engineers , accountants, and analysts (among many others) all have to use critical thinking in their positions. In fact, according to the World Economic Forum, critical thinking is one of the most desirable skills to have in the workforce, as it helps analyze information, think outside the box, solve problems with innovative solutions, and plan systematically.
2. Better Decision Making
There’s no doubt about it — critical thinkers make the best choices. Critical thinking helps us deal with everyday problems as they come our way, and very often this thought process is even done subconsciously. It helps us think independently and trust our gut feeling.
3. Can Make You Happier!
While this often goes unnoticed, being in touch with yourself and having a deep understanding of why you think the way you think can really make you happier. Critical thinking can help you better understand yourself, and in turn, help you avoid any kind of negative or limiting beliefs, and focus more on your strengths. Being able to share your thoughts can increase your quality of life.
4. Form Well-Informed Opinions
There is no shortage of information coming at us from all angles. And that’s exactly why we need to use our critical thinking skills and decide for ourselves what to believe. Critical thinking allows us to ensure that our opinions are based on the facts, and help us sort through all that extra noise.

5. Better Citizens
One of the most inspiring critical thinking quotes is by former US president Thomas Jefferson: “An educated citizenry is a vital requisite for our survival as a free people.” What Jefferson is stressing to us here is that critical thinkers make better citizens, as they are able to see the entire picture without getting sucked into biases and propaganda.
6. Improves Relationships
While you may be convinced that being a critical thinker is bound to cause you problems in relationships, this really couldn’t be less true! Being a critical thinker can allow you to better understand the perspective of others, and can help you become more open-minded towards different views.
7. Promotes Curiosity
Critical thinkers are constantly curious about all kinds of things in life, and tend to have a wide range of interests. Critical thinking means constantly asking questions and wanting to know more, about why, what, who, where, when, and everything else that can help them make sense of a situation or concept, never taking anything at face value.
8. Allows For Creativity
Critical thinkers are also highly creative thinkers, and see themselves as limitless when it comes to possibilities. They are constantly looking to take things further, which is crucial in the workforce.
9. Enhances Problem Solving Skills
Those with critical thinking skills tend to solve problems as part of their natural instinct. Critical thinkers are patient and committed to solving the problem, similar to Albert Einstein, one of the best critical thinking examples, who said “It’s not that I’m so smart; it’s just that I stay with problems longer.” Critical thinkers’ enhanced problem-solving skills makes them better at their jobs and better at solving the world’s biggest problems. Like Einstein, they have the potential to literally change the world.
10. An Activity For The Mind
Just like our muscles, in order for them to be strong, our mind also needs to be exercised and challenged. It’s safe to say that critical thinking is almost like an activity for the mind — and it needs to be practiced. Critical thinking encourages the development of many crucial skills such as logical thinking, decision making, and open-mindness.
11. Creates Independence
When we think critically, we think on our own as we trust ourselves more. Critical thinking is key to creating independence, and encouraging students to make their own decisions and form their own opinions.
12. Crucial Life Skill
Critical thinking is crucial not just for learning, but for life overall! Education isn’t just a way to prepare ourselves for life, but it’s pretty much life itself. Learning is a lifelong process that we go through each and every day.
How to Think Critically
Now that you know the benefits of thinking critically, how do you actually do it?
How To Improve Your Critical Thinking
- Define Your Question: When it comes to critical thinking, it’s important to always keep your goal in mind. Know what you’re trying to achieve, and then figure out how to best get there.
- Gather Reliable Information: Make sure that you’re using sources you can trust — biases aside. That’s how a real critical thinker operates!
- Ask The Right Questions: We all know the importance of questions, but be sure that you’re asking the right questions that are going to get you to your answer.
- Look Short & Long Term: When coming up with solutions, think about both the short- and long-term consequences. Both of them are significant in the equation.
- Explore All Sides: There is never just one simple answer, and nothing is black or white. Explore all options and think outside of the box before you come to any conclusions.
How Is Critical Thinking Developed At School?
Critical thinking is developed in nearly everything we do. However, much of this important skill is encouraged to be practiced at school, and rightfully so! Critical thinking goes beyond just thinking clearly — it’s also about thinking for yourself.
When a teacher asks a question in class, students are given the chance to answer for themselves and think critically about what they learned and what they believe to be accurate. When students work in groups and are forced to engage in discussion, this is also a great chance to expand their thinking and use their critical thinking skills.
How Does Critical Thinking Apply To Your Career?
Once you’ve finished school and entered the workforce, your critical thinking journey only expands and grows from here!
Impress Your Employer
Employers value employees who are critical thinkers, ask questions, offer creative ideas, and are always ready to offer innovation against the competition. No matter what your position or role in a company may be, critical thinking will always give you the power to stand out and make a difference.
Careers That Require Critical Thinking
Some of many examples of careers that require critical thinking include:
- Human resources specialist
- Marketing associate
- Business analyst
Truth be told however, it’s probably harder to come up with a professional field that doesn’t require any critical thinking!
Photo by Oladimeji Ajegbile from Pexels
What is someone with critical thinking skills capable of doing.
Someone with critical thinking skills is able to think rationally and clearly about what they should or not believe. They are capable of engaging in their own thoughts, and doing some reflection in order to come to a well-informed conclusion.
A critical thinker understands the connections between ideas, and is able to construct arguments based on facts, as well as find mistakes in reasoning.
The Process Of Critical Thinking
The process of critical thinking is highly systematic.
What Are Your Goals?
Critical thinking starts by defining your goals, and knowing what you are ultimately trying to achieve.
Once you know what you are trying to conclude, you can foresee your solution to the problem and play it out in your head from all perspectives.
What Does The Future Of Critical Thinking Hold?
The future of critical thinking is the equivalent of the future of jobs. In 2020, critical thinking was ranked as the 2nd top skill (following complex problem solving) by the World Economic Forum .
We are dealing with constant unprecedented changes, and what success is today, might not be considered success tomorrow — making critical thinking a key skill for the future workforce.
Why Is Critical Thinking So Important?
Why is critical thinking important? Critical thinking is more than just important! It’s one of the most crucial cognitive skills one can develop.
By practicing well-thought-out thinking, both your thoughts and decisions can make a positive change in your life, on both a professional and personal level. You can hugely improve your life by working on your critical thinking skills as often as you can.
Related Articles
Why Critical Thinking Is Important (& How to Improve It)
Last updated May 1, 2023. Edited and medically reviewed by Patrick Alban, DC . Written by Deane Alban .
By improving the quality of your thoughts and your decisions, better critical thinking skills can bring about a big positive change in your life. Learn how.
The quality of your life largely depends on the quality of the decisions you make.
Amazingly, the average person makes roughly 35,000 conscious decisions every day!
Imagine how much better your life would be if there were a way to make better decisions, day in and day out?
Well, there is and you do it by boosting a skill called critical thinking .
Learning to master critical thinking can have a profoundly positive impact on nearly every aspect of your life.
What Exactly Is Critical Thinking?
The first documented account of critical thinking is the teachings of Socrates as recorded by Plato.
Over time, the definition of critical thinking has evolved.
Most definitions of critical thinking are fairly complex and best understood by philosophy majors or psychologists.
For example, the Foundation for Critical Thinking , a nonprofit think tank, offers this definition:
“Critical thinking is the intellectually disciplined process of actively and skillfully conceptualizing, applying, analyzing, synthesizing, and/or evaluating information gathered from, or generated by, observation, experience, reflection, reasoning, or communication, as a guide to belief and action.”
If that makes your head spin, here are some definitions that you may relate to more easily.
Critical thinking is “reasonable, reflective thinking that is focused on deciding what to believe or do.”
WHAT'S THE BEST BRAIN SUPPLEMENT?
I hear this question often. Here's my answer:
#1 Live a brain-healthy lifestyle first (Be Brain Fit tells you how).
#2 Give Mind Lab Pro a try.
This brain supplement meets all 12 of my requirements for a high-quality brain supplement, including effectiveness, safety, purity, and value. So it's easier for you to be mentally sharper, positive, and more productive.
Choosing the right brain supplement is all about quality. And, when you buy a 3-month supply, you get 1 extra month free . See why I recommend Mind Lab Pro.
Or, a catchy way of defining critical thinking is “deciding what’s true and what you should do.”
But my favorite uber-simple definition is that critical thinking is simply “thinking about thinking.”
6 Major Benefits of Good Critical Thinking Skills
Whether or not you think critically can make the difference between success and failure in just about every area of your life.
Our human brains are imperfect and prone to irrationality, distortions, prejudices, and cognitive biases .
Cognitive biases are systematic patterns of irrational thinking.
While the number of cognitive biases varies depending on the source, Wikipedia, for example, lists nearly 200 of them !
Some of the most well-known cognitive biases include:
- catastrophic thinking
- confirmation bias
- fear of missing out (FOMO)
Critical thinking will help you move past the limitations of irrational thinking.
Here are some of the most important ways critical thinking can impact your life.
1. Critical Thinking Is a Key to Career Success
There are many professions where critical thinking is an absolute must.
Lawyers, analysts, accountants, doctors, engineers, reporters, and scientists of all kinds must apply critical thinking frequently.
But critical thinking is a skill set that is becoming increasingly valuable in a growing number of professions.

Critical thinking can help you in any profession where you must:
- analyze information
- systematically solve problems
- generate innovative solutions
- plan strategically
- think creatively
- present your work or ideas to others in a way that can be readily understood
And, as we enter the fourth industrial revolution , critical thinking has become one of the most sought-after skills.

According to the World Economic Forum , critical thinking and complex problem-solving are the two top in-demand skills that employers look for.
Critical thinking is considered a soft or enterprise skill — a core attribute required to succeed in the workplace .
NUTRITION FOR THE MIND/BODY CONNECTION
It’s almost impossible to live a lifestyle that provides all the nutrients needed for good brain health and performance. The reason? All of us confront multiple nutrient thieves — stress, poor diet, insomnia, pharmaceuticals, pollution, and more — that steal nutrients that the brain needs to thrive.
- Provides the building blocks to create new brain cells and brain chemicals
- Helps increase resilience to stress to avoid mental burnout
- Supplies the brain with the fuel it needs for mental energy
A foundational principle of mental health and cognitive performance is to supply the body with the best nutrition possible. And, when you buy a 3-month supply of any Performance Lab supplement, you get 1 extra month free . See why I recommend Performance Lab.
According to The University of Arizona, other soft skills include :
- interpersonal skills
- communication skills
- digital literacy
Critical thinking can help you develop the rest of these soft skills.
Developing your critical thinking can help you land a job since many employers will ask you interview questions or even give you a test to determine how well you can think critically.
It can also help you continually succeed in your career, since being a critical thinker is a powerful predictor of long-term success.
2. Critical Thinkers Make Better Decisions
Every day you make thousands of decisions.
Most of them are made by your subconscious , are not very important, and don’t require much thought, such as what to wear or what to have for lunch.
But the most important decisions you make can be hard and require a lot of thought, such as when or if you should change jobs, relocate to a new city, buy a house, get married, or have kids.
At work, you may have to make decisions that can alter the course of your career or the lives of others.
Critical thinking helps you cope with everyday problems as they arise.
It promotes independent thinking and strengthens your inner “BS detector.”
It helps you make sense of the glut of data and information available, making you a smarter consumer who is less likely to fall for advertising hype, peer pressure, or scams.

3. Critical Thinking Can Make You Happier
Knowing and understanding yourself is an underappreciated path to happiness.
We’ve already shown how your quality of life largely depends on the quality of your decisions, but equally as important is the quality of your thoughts.
Critical thinking is an excellent tool to help you better understand yourself and to learn to master your thoughts.
You can use critical thinking to free yourself from cognitive biases, negative thinking , and limiting beliefs that are holding you back in any area of your life.
Critical thinking can help you assess your strengths and weaknesses so that you know what you have to offer others and where you could use improvement.
Critical thinking will enable you to better express your thoughts, ideas, and beliefs.
Better communication helps others to understand you better, resulting in less frustration for both of you.
Critical thinking fosters creativity and out-of-the-box thinking that can be applied to any area of your life.
It gives you a process you can rely on, making decisions less stressful.
4. Critical Thinking Ensures That Your Opinions Are Well-Informed
We have access to more information than ever before .
Astoundingly, more data has been created in the past two years than in the entire previous history of mankind.
Critical thinking can help you sort through the noise.
American politician, sociologist, and diplomat Daniel Patrick Moynihan once remarked , “You are entitled to your opinion. But you are not entitled to your own facts.”
Critical thinking ensures your opinions are well-informed and based on the best available facts.
You’ll get a boost in confidence when you see that those around you trust your well-considered opinions.
5. Critical Thinking Improves Relationships
You might be concerned that critical thinking will turn you into a Spock-like character who is not very good at relationships.
But, in fact, the opposite is true.
Employing critical thinking makes you more open-minded and better able to understand others’ points of view.
Critical thinkers are more empathetic and in a better position to get along with different kinds of people.
Critical thinking keeps you from jumping to conclusions.
You can be counted on to be the voice of reason when arguments get heated.
You’ll be better able to detect when others:
- are being disingenuous
- don’t have your best interests at heart
- try to take advantage of or manipulate you
6. Critical Thinking Makes You a Better, More Informed Citizen
“An educated citizenry is a vital requisite for our survival as a free people.”
This quote has been incorrectly attributed to Thomas Jefferson , but regardless of the source, these words of wisdom are more relevant than ever.
Critical thinkers are able to see both sides of any issue and are more likely to generate bipartisan solutions.
They are less likely to be swayed by propaganda or get swept up in mass hysteria.
They are in a better position to spot fake news when they see it.
5 Steps to Improve Your Critical Thinking Skills
Some people already have well-developed critical thinking skills.
These people are analytical, inquisitive, and open to new ideas.
And, even though they are confident in their own opinions, they seek the truth, even if it proves their existing ideas to be wrong.
They are able to connect the dots between ideas and detect inconsistencies in others’ thinking.
But regardless of the state of your critical thinking skills today, it’s a skill set you can develop.
While there are many techniques for thinking rationally, here’s a classic 5-step critical thinking process .
How to Improve Your Critical Thinking Skills
Clearly define your question or problem.
This step is so important that Albert Einstein famously quipped:
“If I had an hour to solve a problem, I’d spend 55 minutes thinking about the problem and 5 minutes thinking about solutions.”
Gather Information to Help You Weigh the Options
Consider only the most useful and reliable information from the most reputable sources.
Disregard the rest.
Apply the Information and Ask Critical Questions
Scrutinize all information carefully with a skeptic’s eye.
Not sure what questions to ask?
You can’t go wrong starting with the “5 Ws” that any good investigator asks: Who? What? Where? When? Why?
Then finish by asking “How?”
You’ll find more thought-provoking questions on this Critical Thinking Skills Cheatsheet .
Consider the Implications
Look for potential unintended consequences.
Do a thought experiment about how your solution could play out in both the short term and the long run.
Explore the Full Spectrum of Viewpoints
Examine why others are drawn to differing points of view.
This will help you objectively evaluate your own viewpoint.
You may find critical thinkers who take an opposing view and this can help you find gaps in your own logic.
Watch the Video
This TED-Ed video on YouTube elaborates on the five steps to improve your critical thinking.
Recommended: Upgrading brain health is key to making your brain work better.
- Improve your mental clarity and focus.
- Boost your memory and your ability to learn.
- Increase your capacity to think critically, solve problems, and make decisions.
P.S. Like what you've read on this page? Get more like this -- Sign up for our emails .
- Grades 6-12
- School Leaders
Enter Today's Teacher Appreciation Giveaway!
What Is Critical Thinking and Why Do We Need To Teach It?
Question the world and sort out fact from opinion.
The world is full of information (and misinformation) from books, TV, magazines, newspapers, online articles, social media, and more. Everyone has their own opinions, and these opinions are frequently presented as facts. Making informed choices is more important than ever, and that takes strong critical thinking skills. But what exactly is critical thinking? Why should we teach it to our students? Read on to find out.
What is critical thinking?
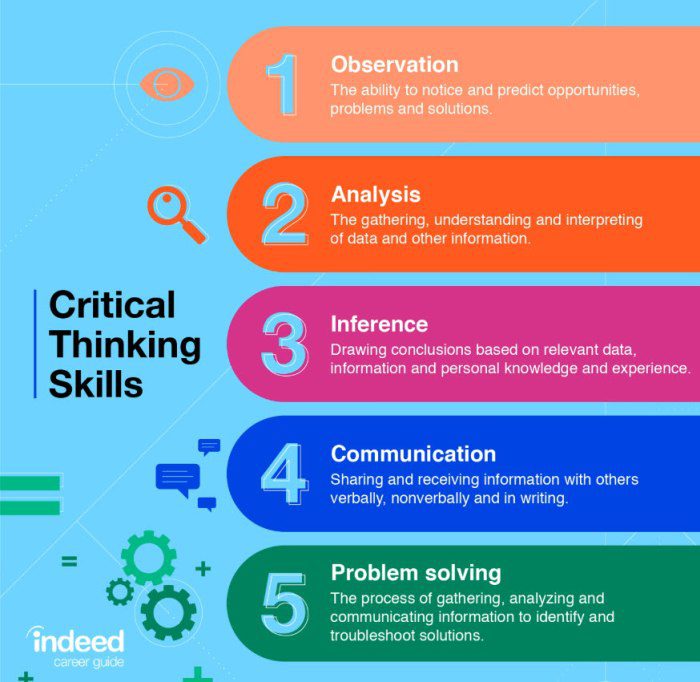
Source: Indeed
Critical thinking is the ability to examine a subject and develop an informed opinion about it. It’s about asking questions, then looking closely at the answers to form conclusions that are backed by provable facts, not just “gut feelings” and opinion. These skills allow us to confidently navigate a world full of persuasive advertisements, opinions presented as facts, and confusing and contradictory information.
The Foundation for Critical Thinking says, “Critical thinking can be seen as having two components: 1) a set of information and belief-generating and processing skills, and 2) the habit, based on intellectual commitment, of using those skills to guide behavior.”
In other words, good critical thinkers know how to analyze and evaluate information, breaking it down to separate fact from opinion. After a thorough analysis, they feel confident forming their own opinions on a subject. And what’s more, critical thinkers use these skills regularly in their daily lives. Rather than jumping to conclusions or being guided by initial reactions, they’ve formed the habit of applying their critical thinking skills to all new information and topics.
Why is critical thinking so important?
Imagine you’re shopping for a new car. It’s a big purchase, so you want to do your research thoroughly. There’s a lot of information out there, and it’s up to you to sort through it all.
- You’ve seen TV commercials for a couple of car models that look really cool and have features you like, such as good gas mileage. Plus, your favorite celebrity drives that car!
- The manufacturer’s website has a lot of information, like cost, MPG, and other details. It also mentions that this car has been ranked “best in its class.”
- Your neighbor down the street used to have this kind of car, but he tells you that he eventually got rid of it because he didn’t think it was comfortable to drive. Plus, he heard that brand of car isn’t as good as it used to be.
- Three independent organizations have done test-drives and published their findings online. They all agree that the car has good gas mileage and a sleek design. But they each have their own concerns or complaints about the car, including one that found it might not be safe in high winds.
So much information! It’s tempting to just go with your gut and buy the car that looks the coolest (or is the cheapest, or says it has the best gas mileage). Ultimately, though, you know you need to slow down and take your time, or you could wind up making a mistake that costs you thousands of dollars. You need to think critically to make an informed choice.
What does critical thinking look like?

Source: TeachThought
Let’s continue with the car analogy, and apply some critical thinking to the situation.
- Critical thinkers know they can’t trust TV commercials to help them make smart choices, since every single one wants you to think their car is the best option.
- The manufacturer’s website will have some details that are proven facts, but other statements that are hard to prove or clearly just opinions. Which information is factual, and even more important, relevant to your choice?
- A neighbor’s stories are anecdotal, so they may or may not be useful. They’re the opinions and experiences of just one person and might not be representative of a whole. Can you find other people with similar experiences that point to a pattern?
- The independent studies could be trustworthy, although it depends on who conducted them and why. Closer analysis might show that the most positive study was conducted by a company hired by the car manufacturer itself. Who conducted each study, and why?
Did you notice all the questions that started to pop up? That’s what critical thinking is about: asking the right questions, and knowing how to find and evaluate the answers to those questions.
Good critical thinkers do this sort of analysis every day, on all sorts of subjects. They seek out proven facts and trusted sources, weigh the options, and then make a choice and form their own opinions. It’s a process that becomes automatic over time; experienced critical thinkers question everything thoughtfully, with purpose. This helps them feel confident that their informed opinions and choices are the right ones for them.
Key Critical Thinking Skills
There’s no official list, but many people use Bloom’s Taxonomy to help lay out the skills kids should develop as they grow up.
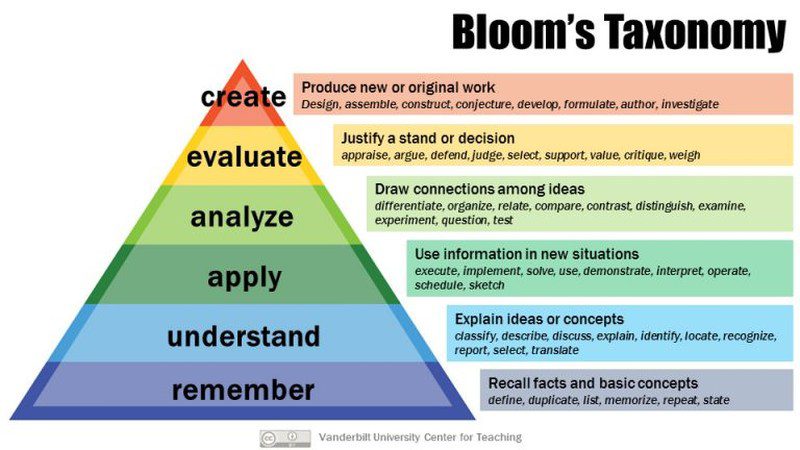
Source: Vanderbilt University
Bloom’s Taxonomy is laid out as a pyramid, with foundational skills at the bottom providing a base for more advanced skills higher up. The lowest phase, “Remember,” doesn’t require much critical thinking. These are skills like memorizing math facts, defining vocabulary words, or knowing the main characters and basic plot points of a story.
Higher skills on Bloom’s list incorporate more critical thinking.
True understanding is more than memorization or reciting facts. It’s the difference between a child reciting by rote “one times four is four, two times four is eight, three times four is twelve,” versus recognizing that multiplication is the same as adding a number to itself a certain number of times. When you understand a concept, you can explain how it works to someone else.
When you apply your knowledge, you take a concept you’ve already mastered and apply it to new situations. For instance, a student learning to read doesn’t need to memorize every word. Instead, they use their skills in sounding out letters to tackle each new word as they come across it.
When we analyze something, we don’t take it at face value. Analysis requires us to find facts that stand up to inquiry. We put aside personal feelings or beliefs, and instead identify and scrutinize primary sources for information. This is a complex skill, one we hone throughout our entire lives.
Evaluating means reflecting on analyzed information, selecting the most relevant and reliable facts to help us make choices or form opinions. True evaluation requires us to put aside our own biases and accept that there may be other valid points of view, even if we don’t necessarily agree with them.
Finally, critical thinkers are ready to create their own result. They can make a choice, form an opinion, cast a vote, write a thesis, debate a topic, and more. And they can do it with the confidence that comes from approaching the topic critically.
How do you teach critical thinking skills?
The best way to create a future generation of critical thinkers is to encourage them to ask lots of questions. Then, show them how to find the answers by choosing reliable primary sources. Require them to justify their opinions with provable facts, and help them identify bias in themselves and others. Try some of these resources to get started.
5 Critical Thinking Skills Every Kid Needs To Learn (And How To Teach Them)
- 100+ Critical Thinking Questions for Students To Ask About Anything
- 10 Tips for Teaching Kids To Be Awesome Critical Thinkers
- Free Critical Thinking Poster, Rubric, and Assessment Ideas
More Critical Thinking Resources
The answer to “What is critical thinking?” is a complex one. These resources can help you dig more deeply into the concept and hone your own skills.
- The Foundation for Critical Thinking
- Cultivating a Critical Thinking Mindset (PDF)
- Asking the Right Questions: A Guide to Critical Thinking (Browne/Keeley, 2014)
Have more questions about what critical thinking is or how to teach it in your classroom? Join the WeAreTeachers HELPLINE group on Facebook to ask for advice and share ideas!
Plus, 12 skills students can work on now to help them in careers later ..

You Might Also Like

Teach them to thoughtfully question the world around them. Continue Reading
Copyright © 2024. All rights reserved. 5335 Gate Parkway, Jacksonville, FL 32256

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
I applaud the authors' powerfully argued case for claiming that to ignore the use of critical thinking and analysis through poor critical habit, managerial pressures, culture or organisational stress is to fail yourself, the profession and most importantly of all the people whose lives are touched by you through your social work practice.
critical thinking further. We do not intend to cover the full range of critical thinking 'skills' (indeed, this would consider them to be something like a checklist, which is inappropriate for practice) but instead highlight a few basic principles to underpin the process of enhancing the critical aspects of your own learning and development.
Critical reflection is a fundamental component of critical practice in social work (Fook, 2016; Testa and Egan, 2016).Yet while an extensive body of literature addresses critical reflection methods and processes (Chiu, 2006; Fook and Gardner, 2007; Morley, 2014a), the examination of the process that links critical reflection and critical practice in the professional field remains ...
Critical thinking is important for the development of social work skills in direct practice. Social workers help people from all walks of life and come across people or populations with experiences, ideas and opinions that often vary from their own culture and background. Clients may be misunderstood and misjudged if thinking critically does ...
Well, for a book on critical thinking, one would assume critical analysis is essential, but at times the self-imposed limitations set by the book due to the page numbers and variety of chapters mean discussion and analysis can seem very brief and descriptive in places, such as the deductive arguments on p. 13 and embedded critical thinking on p.
BOOK REVIEWS. Applying critical thinking and analysis in. social work. Michaela Rogers and Dan Allen, 2019. Sage Publications, London, UK. ISBN 978-1-5264-3658-0, pp. 195, paperback, NZD35.32. B ...
Educational Policy 2.1.3- Apply critical thinking to inform and communicate professional judgments. Social workers are knowledgeable about the principles of logic, scientific inquiry, and reasoned discernment. They use critical thinking augmented by creativity and curiosity. Critical thinking also requires the synthesis and communication of ...
This critical review mines the literature on critical thinking for insight into the kinds of thinking social work scholars consider important. Analysis indicates that critical thinking in social work is generally treated as a form of practical reasoning. Further, epistemological disagreements divide 2 distinct proposals for how practical ...
This article describes how logic models are used to teach critical. thinking in social work courses. By breaking down the helping. process into parts, logic modeling enables students to think about. the clinical experience as a whole and to understand the causal relationships between these parts. Students are exposed to the.
The critical thinking program in the social work curriculum has been supported by a ... The synthesis suggests that we need to anticipate the relatively fluid and fuzzy features of social contexts ...
Critical thinking is a key construct in social work education; however, a universally accepted definition of the construct remains elusive. To determine collective agreement in meaning and viable methods of assessment for critical thinking in social work education, researchers administered an online survey to a national sample of social work ...
The paper examines the role of critical thinking in an experience-based model of social work education. Within this model, the development of a critical approach to our own understanding of, as well as to existing knowledge about, the world is fundamental for students and educators alike. ... As well as describing the critical thinking ...
Dr Joanna Rawles. presentation and discussion for anyone who has a role in supporting and enabling social work students and practitioners to embed critical thinking into their reflection. Based on the following book chapter Rawles, J. (2023) 'Critical thinking and reflective practice' in Parker, J (ed) (2nd Ed) (2023) Introducing Social Work:
Ann Marie Mumm and Robert C. Kerstinc. Social workers in direct practice rely on critical thinking to apply. theories, make informed decisions, and explain their assessments and decisions. This article describes methods for teaching critical thinking to graduate and undergraduate social work students in practice courses.
The foundation for critical thinking defines critical thinking as: the type of thinking—about any subject, content, or problem—in which the thinker improves the quality of his thinking by competently analyzing, evaluating and reconstructing it. Critical thinking is self-directed, self-disciplined, self-monitored, and self-corrective.
The book is divided into three parts - An Introduction to Critical Thinking and Analysis; An Introduction to Critical Reading and Writing; Critical Thinking and Analysis in Practice. Within this framework there are a total of nine chapters and each of these chapters have the following components: Theoretical Background; Relevance to Social ...
Successful social workers understand the need to think outside the box. This trick helps them maneuver everyday challenges and increase trust among clients. Should you have difficulty imbibing this skill, speak to a professional for guidance. Critical thinking is the ability to analyze, synthesize, evaluate and apply new information.
4. Seek feedback and collaboration. 5. Experiment and reflect. Be the first to add your personal experience. 6. Here's what else to consider. Critical thinking skills are essential for social ...
It makes you a well-rounded individual, one who has looked at all of their options and possible solutions before making a choice. According to the University of the People in California, having critical thinking skills is important because they are [ 1 ]: Universal. Crucial for the economy. Essential for improving language and presentation skills.
Critical thinking can help you better understand yourself, and in turn, help you avoid any kind of negative or limiting beliefs, and focus more on your strengths. Being able to share your thoughts can increase your quality of life. 4. Form Well-Informed Opinions.
Decision-making improves. Applying critical thinking helps you make decisions that require a lot of thought. Big, life-changing decisions, like whether or not to make a career move, are aided by critical thinking, which encourages you to research and favor objective logic over your initial emotional response.
Critical thinking will enable you to better express your thoughts, ideas, and beliefs. Better communication helps others to understand you better, resulting in less frustration for both of you. Critical thinking fosters creativity and out-of-the-box thinking that can be applied to any area of your life.
The Foundation for Critical Thinking says, "Critical thinking can be seen as having two components: 1) a set of information and belief-generating and processing skills, and 2) the habit, based on intellectual commitment, of using those skills to guide behavior.". In other words, good critical thinkers know how to analyze and evaluate ...