
- Walden University
- Faculty Portal

Common Assignments: Executive Summaries
Basics of executive summaries.
Executive summaries are common in the Walden MBA program, but they are also found as part of some government and business documents. As a student, you should complete an executive summary when specifically requested to do so. An executive summary is a comprehensive review of a larger document. For example, a 35-page report may begin with a single-page executive summary all of the main information in the longer report. Any findings, conclusions, recommendations, or other details that appear in the larger document must be touched on in the executive summary. Readers should be able to read the executive summary alone and have a complete understanding of the larger document in its entirety.
How to Write an Executive Summary
It is important to meet all length and content expectations, so be sure to review the specific directions for your assignment. Also remember that the executive summary can only be written after the full-length document is complete.
Tips for completing the executive summary from Walden University (2013) include:
- List all of the main points in the same order in which they occur in the paper that you are summarizing.
- Take each point and turn it into a sentence.
- Add additional sentences to clarify or explain each point.
- Add a short introduction and a short conclusion. Include the name of the article, report, etc. and the author(s) in the introduction.
- Check grammar, spelling, and punctuation.
- Check for plagiarism.
- Read the summary slowly and carefully to make sure it covers all of the main points clearly, yet concisely. Also, check to be sure it is interesting. You want to catch your reader’s attention.
- Set it aside. Let some time pass and read it again. Often, you will catch items that you did not see the first time.
For academic writing, be sure to include appropriate citations and a reference. This is typically not part of a business executive summary but should be included for purposes of this program.
Executive Summary Versus Abstract
Like an executive summary, an abstract is a short summary of a larger text. Both executive summaries and abstracts are meant to capture the main ideas, findings, and conclusions of a longer document. Executive summaries, however, tend to include more details than abstracts. An abstract includes enough information for readers to decide if they want to read the full-length document. Executive summaries must include enough information for readers to understand the full-length document without reading it.
Another difference between executive summaries and abstracts are the fields where they are used. Generally, executive summaries are common in business and government, while abstracts are more common in academia and at Walden, especially when seeking publication in a professional journal.
Didn't find what you need? Email us at [email protected] .
- Previous Page: Content and Structure of KAM-Based PDPs
- Next Page: Theses
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.
How To Write A High-Impact Executive Summary
By Derek Jansen | January 2018

In this post, I’ll deconstruct the often-misunderstood executive summary and show you how to develop a high-impact executive summary for your assignment, research report or even your dissertation or thesis.
So, what is an executive summary?
An executive summary (sometimes called an abstract ) is quite simply a summary of summaries. In other words, an executive summary provides a concise summary of each of your assignment or report chapters/sections . More specifically, it should communicate the key points/insights/findings/suggestions from the following chapters:
- Introduction
- Recommendations
- Implementation (if applicable)
- Reflection (if applicable)
I’ll discuss which key points from each section need to be addressed a bit later. On a separate note – if you’re writing an executive summary for a dissertation or thesis, all of the concepts described in this post will still apply to you, however, you’ll include an additional paragraph about your methodology, and you’ll likely spend more word count discussing your analysis findings.
The 4 Important Attributes Of An Exec Summary
Before I discuss what goes into the executive summary, let’s quickly look at 4 attributes that make for a strong executive summary:
#1 – It should be able to stand alone.
The executive summary should be able to stand independently as an informative document . In other words, the reader should be able to grasp your broad argument without having to read the full document. Further reading should be purely for attaining more detail. Simply put, the executive summary should be a “Mini-Me” of the assignment.
This independence means that anything you write in the executive summary will need to be re-stated in the body of your assignment. A common mistake that students make is to introduce key points in the executive summary and then not discuss them again in the document – accordingly, the marker must view the main document as missing these key points. Simply put – make sure you discuss key points in both the executive summary and the main body . It will feel repetitive at times – this is normal.

#2 – It should be written for the intelligent layman.
When crafting your executive summary, its useful to keep the intelligent layman front of mind. What I mean by this is that you should write your summary assuming that your reader (i.e. the marker) will be intelligent but won’t be familiar with your topic and/or industry. This means that you should explain any technical concepts, avoid jargon and explain acronyms before using them.
#3 – It should be concise.
Typically, your executive summary should be a one-pager (one and a half pages at worst). To summarise a 3000 – 5000-word document into one page is no easy task, so you’ll need to:
- Present only the most important information (key insights, recommendations, etc).
- Write concisely – i.e. with brevity and completeness.
To the first point, I’ll explain what the “most important” information is for each chapter shortly. To the second point (writing concisely), there are various ways to do this, including:
- Using simple, straightforward language.
- Using the active voice.
- Removing bloaty adverbs and adjectives.
- Reducing prepositional phrases.
- Avoiding noun strings.
Does this sound like gibberish to you? Don’t worry! The Writing Center at the University of Wisconson-Madison provides a practical guide to writing more concisely, which you can download here.
On a related note, you typically would not include headings, citations or bulleted/numbered lists in your executive summary. These visual components tend to use a lot of space, which comes at a premium, as you know.
#4 – It should be written last.
Given that your executive summary is a summary of summaries, it needs to be written last , only once you’ve identified all your key insights, recommendations and so on. This probably sounds obvious, but many students start writing the summary first (potentially because of its position in the document) and then end up re-writing it multiple times, or they don’t rewrite it and consequently end up with an executive summary which is misaligned with the main document.
Simply put, you should leave this section until everything else is completed. Once your core body content is completed, you should read through the entire document again and create a bullet-point list of all the key points . From this list, you should then craft your executive summary . The approach will also help you identify gaps, contradictions and misalignments in your main document.

So, what goes into an executive summary?
Right, let’s get into the meat of it and consider what exactly should go into your executive summary. As I’ve mentioned, you need to present only the absolutely key point points from each of your chapters, but what does this mean exactly?
Each chapter will typically take the form of 1 paragraph (with no headings) in your executive summary. So, 5 chapters means 5 paragraphs. Naturally, some will be longer than others (let this be informed by the mark allocation), but assuming one page contains 500 words, you’re aiming for roughly 100 words per paragraph (assuming a 5-paragraph structure). See why conciseness is key!
Now, let’s look at what the key points are for each chapter in the case of a typical MBA assignment or report. In the case of a dissertation or thesis, the paragraph structure would still mimic the chapter structure – you’d just have more chapters, and therefore, more paragraphs.
Paragraph 1: Introduction
This paragraph should cover the following points:
- A very brief explanation of the business (what does it do, for whom and where?).
- Clear identification and explanation of the problem or opportunity that will be the focus of the assignment/report.
- A clear statement of the purpose of the assignment (i.e. what research questions will you seek to answer?).
- Brief mention of what data sources were utilised (i.e. secondary research) and any fieldwork undertaken (i.e. primary research ).
In other words, your first paragraph should introduce the business, the problem/opportunity to be addressed, why it’s important, and how you approached your analysis. This paragraph should make it clear to the reader what the assignment is all about at a broad level. Here’s a practical example:
This assignment focuses on ABC Ltd, a XXX business based in XXX, which provides XXX to XXX customers. To date, the firm has relied almost exclusively on XXX marketing channel. Consequently, ABC Ltd has little understanding of consumer segments, wants, and needs. This marketing channel is now under regulatory threat due to XXX. The core challenge, therefore, is that whilst ABC Ltd seeks to grow its market share, it has little understanding of its market characteristics or competitive set, and its sole marketing channel under regulatory threat. Accordingly, the objective of this assignment is XXX. The assignment draws on survey, interview, and industry data.
Paragraph 2: Analysis and findings
In this paragraph, you should discuss the following:
- What exactly did you analyse? For example, you might have analysed the macro context (i.e. PESTLE analysis), followed by the meso (i.e. competitor or industry analysis) and then the micro (i.e. internal organisational analysis).
- What were your key findings in relation to the purpose of the assignment? For example, you may have identified 4 potential causes of a problem and would then state them.
In other words, your second paragraph should concisely explain what you analysed and what your main findings were . An example of this:
Segmentation analysis, consisting of macro, industry and firm-level analyses, revealed a strong segmentation variable in the form of XXX, with distinct needs in each segment. Macro analysis revealed XXX, while industry and firm-level analyses suggested XXX. Subsequently, three potential target segments were established, namely XXX, XXX and XXX. These were then evaluated using the Directional Policy Matrix, and the results indicated XXX.
From a presentation perspective, you might structure this section as:
- Analysis 1, findings from analysis 1.
- Analysis 2, findings from analysis 2.
- Analysis 3, findings from analysis 3.
Importantly, you should only discuss the findings that are directly linked to the research questions (i.e. the purpose of the assignment) – don’t digress into interesting but less relevant findings. Given that the analysis chapter typically counts for a large proportion of marks, you could viably write 2-3 paragraphs for this. Be guided by the mark allocation.
Lastly, you should ensure that the findings you present here align well with the recommendations you’ll make in the next paragraph. Think about what your recommendations are, and, if necessary, reverse engineer this paragraph to create a strong link and logical flow from analysis to recommendations.

Paragraph 3: Recommendations
With the key findings from your analysis presented in the preceding paragraph, you should now discuss the following:
- What are your key recommendations?
- How do these solve the problems you found in your analysis?
- Were there any further conclusions?
Simply put, this paragraph (or two) should present the main recommendations and justify their use (i.e. explain how they resolve the key issue). As mentioned before, it’s critically important that your recommendations tightly align with (and resolve) the key issues that you identified in the analysis. An example:
Based on the Directional Policy Matrix analysis, it is recommended that the firm target XXX segment, because of XXX. On this basis, a positioning of XXX is proposed, as this aligns with the segment’s key needs. Furthermore, a provisional high-level marketing mix is proposed. The key aspects of the marketing mix include XXX, XXX and XXX, as these align with the firm’s positioning of XXX. By adopting these recommendations, the key issue of XXX will be resolved.
Also, note that (typically) the tone changes from past to present tense when you get to the recommendations section.
Paragraph 4: Implementation
If your assignment brief requires an implementation/project plan-type section, this paragraph will typically include the following points:
- Time requirements (how long will it take?)
- People requirements (what skills are needed and where do you find them?)
- Money requirements (what budget is required?)
- How will the project or change be managed? (i.e. project management plan)
- What risks exist and how will these be managed?
Depending on what level of detail is required by your assignment brief, you may need to present more, less or other details in this section. As always, be guided by the assignment brief.
A practical example:
A high-level implementation plan is proposed, including a stakeholder analysis, project plan and business case. Resource requirements are presented, detailing XXX, XXX and XXX requirements. A risk analysis is presented, revealing key risks including XXX, XXX and XXX. Risk management solutions are proposed, including XXX and XXX.

Paragraph 5: Reflection
As with the implementation chapter, the need for a reflection chapter/section will vary between assignments and universities. If your assignment has this requirement, it’s typically good to cover the following points:
- What were your key learnings? What were your ah-ha moments?
- What has changed in the real world as a consequence of these learnings? I.e. how has your actual behaviour and approach to “X” changed, if any?
- What are the benefits and/or disadvantages of this change, if any?
This section is very personal, and so each person’s reflections will be different. Don’t take the above points as gospel.
Time to test it out.
Once you’ve written up your executive summary and feel confident that it’s in good shape, it’s time to test it out on an unsuspecting intelligent layman. This is a critically important step, since you, as the writer, are simply too close to the work to judge whether it all makes sense to a first-time reader. In fact, you are the least suitable person on the planet!
So, find someone who is not familiar with your assignment topic (and ideally, not familiar with your industry), and ask them to have a read through your executive summary. Friends and family will usually tell you its great, regardless of the quality, so you need to test them on their understanding. Do this by asking them to give the details back to you in their own words. Poke and prod – can they tell you what the key issues and recommendations were (in their own words!). You’ll quickly spot the gaps this way, and be able to flesh out any weak areas.
Wrapping up.
In this post, I’ve discussed how to write the all too often undercooked executive summary. I’ve discussed some important attributes of a strong executive summary, as well as the contents that typically go into it. To recap on the key points:
The key attributes of a high-impact executive summary:
- It should be able to stand alone.
- It should be written for the intelligent layman.
- It should be concise.
- It should be written last.
The key contents of a high-impact executive summary:
Each paragraph should cover a chapter from the document. For example, In the case of a typical assignment, it would be something like:
- Summary of the introduction chapter.
- Summary of the analysis chapter.
- Summary of the recommendations and/or conclusions chapter.
- Depending – summary of the implementation and reflection.
Lastly, don’t forget to test out your executive summary on an unsuspecting layman or two. This is probably the most important step of them all!
If you have any questions or suggestions, we’d love to hear from you. Please get in touch here or leave a comment below.
You Might Also Like:

Thanks so much for your methodical process and explanation of Executive Summary. It is exactly what I was researching for.
Regards Saane
It’s a pleasure!
This was really helpful with how to structure my assignment.
Thank you so much for the step by step process. It’s so helpful for beginners like me.
Great! This post is very informative and gives clear guidance on to write an executive summary. Thanks very much for sharing this information, it’s very helpful.
Thanks for the feedback, Anna. Best of luck with your writing 🙂
Thank you for the great article, really helped explain what was needed.
Great insight and tips . Thanks
Thank you so much for sharing this. It was exactly what I was looking for.
Thank you for your help
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- Executive Summary
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
An executive summary is a thorough overview of a research report or other type of document that synthesizes key points for its readers, saving them time and preparing them to understand the study's overall content. It is a separate, stand-alone document of sufficient detail and clarity to ensure that the reader can completely understand the contents of the main research study. An executive summary can be anywhere from 1-10 pages long depending on the length of the report, or it can be the summary of more than one document [e.g., papers submitted for a group project].
Bailey, Edward, P. The Plain English Approach to Business Writing . (New York: Oxford University Press, 1997), p. 73-80 Todorovic, Zelimir William and Marietta Wolczacka Frye. “Writing Effective Executive Summaries: An Interdisciplinary Examination.” In United States Association for Small Business and Entrepreneurship. Conference Proceedings . (Decatur, IL: United States Association for Small Business and Entrepreneurship, 2009): pp. 662-691.
Importance of a Good Executive Summary
Although an executive summary is similar to an abstract in that they both summarize the contents of a research study, there are several key differences. With research abstracts, the author's recommendations are rarely included, or if they are, they are implicit rather than explicit. Recommendations are generally not stated in academic abstracts because scholars operate in a discursive environment, where debates, discussions, and dialogs are meant to precede the implementation of any new research findings. The conceptual nature of much academic writing also means that recommendations arising from the findings are distributed widely and not easily or usefully encapsulated. Executive summaries are used mainly when a research study has been developed for an organizational partner, funding entity, or other external group that participated in the research . In such cases, the research report and executive summary are often written for policy makers outside of academe, while abstracts are written for the academic community. Professors, therefore, assign the writing of executive summaries so students can practice synthesizing and writing about the contents of comprehensive research studies for external stakeholder groups.
When preparing to write, keep in mind that:
- An executive summary is not an abstract.
- An executive summary is not an introduction.
- An executive summary is not a preface.
- An executive summary is not a random collection of highlights.
Christensen, Jay. Executive Summaries Complete The Report. California State University Northridge; Clayton, John. "Writing an Executive Summary that Means Business." Harvard Management Communication Letter (July 2003): 2-4; Keller, Chuck. "Stay Healthy with a Winning Executive Summary." Technical Communication 41 (1994): 511-517; Murphy, Herta A., Herbert W. Hildebrandt, and Jane P. Thomas. Effective Business Communications . New York: McGraw-Hill, 1997; Vassallo, Philip. "Executive Summaries: Where Less Really is More." ETC.: A Review of General Semantics 60 (Spring 2003): 83-90 .
Structure and Writing Style
Writing an Executive Summary
Read the Entire Document This may go without saying, but it is critically important that you read the entire research study thoroughly from start to finish before you begin to write the executive summary. Take notes as you go along, highlighting important statements of fact, key findings, and recommended courses of action. This will better prepare you for how to organize and summarize the study. Remember this is not a brief abstract of 300 words or less but, essentially, a mini-paper of your paper, with a focus on recommendations.
Isolate the Major Points Within the Original Document Choose which parts of the document are the most important to those who will read it. These points must be included within the executive summary in order to provide a thorough and complete explanation of what the document is trying to convey.
Separate the Main Sections Closely examine each section of the original document and discern the main differences in each. After you have a firm understanding about what each section offers in respect to the other sections, write a few sentences for each section describing the main ideas. Although the format may vary, the main sections of an executive summary likely will include the following:
- An opening statement, with brief background information,
- The purpose of research study,
- Method of data gathering and analysis,
- Overview of findings, and,
- A description of each recommendation, accompanied by a justification. Note that the recommendations are sometimes quoted verbatim from the research study.
Combine the Information Use the information gathered to combine them into an executive summary that is no longer than 10% of the original document. Be concise! The purpose is to provide a brief explanation of the entire document with a focus on the recommendations that have emerged from your research. How you word this will likely differ depending on your audience and what they care about most. If necessary, selectively incorporate bullet points for emphasis and brevity. Re-read your Executive Summary After you've completed your executive summary, let it sit for a while before coming back to re-read it. Check to make sure that the summary will make sense as a separate document from the full research study. By taking some time before re-reading it, you allow yourself to see the summary with fresh, unbiased eyes.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Length of the Executive Summary As a general rule, the correct length of an executive summary is that it meets the criteria of no more pages than 10% of the number of pages in the original document, with an upper limit of no more than ten pages [i.e., ten pages for a 100 page document]. This requirement keeps the document short enough to be read by your audience, but long enough to allow it to be a complete, stand-alone synopsis. Cutting and Pasting With the exception of specific recommendations made in the study, do not simply cut and paste whole sections of the original document into the executive summary. You should paraphrase information from the longer document. Avoid taking up space with excessive subtitles and lists, unless they are absolutely necessary for the reader to have a complete understanding of the original document. Consider the Audience Although unlikely to be required by your professor, there is the possibility that more than one executive summary will have to be written for a given document [e.g., one for policy-makers, one for private industry, one for philanthropists]. This may only necessitate the rewriting of the introduction and conclusion, but it could require rewriting the entire summary in order to fit the needs of the reader. If necessary, be sure to consider the types of audiences who may benefit from your study and make adjustments accordingly. Clarity in Writing One of the biggest mistakes you can make is related to the clarity of your executive summary. Always note that your audience [or audiences] are likely seeing your research study for the first time. The best way to avoid a disorganized or cluttered executive summary is to write it after the study is completed. Always follow the same strategies for proofreading that you would for any research paper. Use Strong and Positive Language Don’t weaken your executive summary with passive, imprecise language. The executive summary is a stand-alone document intended to convince the reader to make a decision concerning whether to implement the recommendations you make. Once convinced, it is assumed that the full document will provide the details needed to implement the recommendations. Although you should resist the temptation to pad your summary with pleas or biased statements, do pay particular attention to ensuring that a sense of urgency is created in the implications, recommendations, and conclusions presented in the executive summary. Be sure to target readers who are likely to implement the recommendations.
Bailey, Edward, P. The Plain English Approach to Business Writing . (New York: Oxford University Press, 1997), p. 73-80; Christensen, Jay. Executive Summaries Complete The Report. California State University Northridge; Executive Summaries. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Clayton, John. "Writing an Executive Summary That Means Business." Harvard Management Communication Letter , 2003; Executive Summary. University Writing Center. Texas A&M University; Green, Duncan. Writing an Executive Summary. Oxfam’s Research Guidelines series ; Guidelines for Writing an Executive Summary. Astia.org; Markowitz, Eric. How to Write an Executive Summary. Inc. Magazine, September, 15, 2010; Kawaski, Guy. The Art of the Executive Summary. "How to Change the World" blog; Keller, Chuck. "Stay Healthy with a Winning Executive Summary." Technical Communication 41 (1994): 511-517; The Report Abstract and Executive Summary. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Writing Executive Summaries. Effective Writing Center. University of Maryland; Kolin, Philip. Successful Writing at Work . 10th edition. (Boston, MA: Cengage Learning, 2013), p. 435-437; Moral, Mary. "Writing Recommendations and Executive Summaries." Keeping Good Companies 64 (June 2012): 274-278; Todorovic, Zelimir William and Marietta Wolczacka Frye. “Writing Effective Executive Summaries: An Interdisciplinary Examination.” In United States Association for Small Business and Entrepreneurship. Conference Proceedings . (Decatur, IL: United States Association for Small Business and Entrepreneurship, 2009): pp. 662-691.
- << Previous: 3. The Abstract
- Next: 4. The Introduction >>
- Last Updated: Jun 18, 2024 10:45 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide

How to Write an Executive Summary for an Assignment Right and Neat
Table of Contents
What is an executive summary?
Contents of an executive summary, what is the purpose of an executive summary, how to write an executive summary for an assignment in 6 steps.
- Overview of the Management Team
- The Products/Services
- Your Customers
- Marketing/Sales
- Sales Forecast/Requirements
Executive Summary Tips!
Executive summary example.

We all know the importance of first impressions and an executive summary provides exactly this to your reader. It’s essential to learn how to write an executive summary for an assignment well!
An executive summary (or management summary/abstract) is basically a succinct summary for an assignment or report that provides an overview of the assignment’s sections.
When writing an executive summary for an assignment, you generally need to include 3-5 parts:
- An introduction
- An analysis
- Your recommendations
- The implementation (if applicable)
- Your reflection (if applicable)
An executive summary/management summary/abstract is primarily produced for government or business purposes and plans. The summary gives the reader the opportunity to understand an assignment or report quickly and easily without reading the full contents.
Firstly, explain the purpose of the business assignment by providing the company name, location, legal structure, type of service/products, founding date, financial information, and the business’s key milestones that can be used to measure success.
2. Overview of the Management Team
Next, give the reader a brief insight into the management team’s experience/expertise and their individual contributions to the company.
3. The Products/Services
Now, describe the company’s products/services, its competitors and how your product or service is different to its competitors (why it is unique).
4. Your Customers
This section is where you must aim to show that you have carried out extensive market research /analysis and explain your customers’ behaviors. Incorporate statistics to demonstrate your understanding of what the findings have shown customers want.
5. Marketing/Sales
Summarize your marketing plan for key customers and explain why this method is going to work.
6. Sales Forecast/Requirements
Find the writer according to your requirements
- AssignmentBro is a team of experienced writers in any field of academic research
- We thoroughly choose writers with advanced multistep selection process
- Our writers work according to the highest academic standards
To write a good executive summary, follow these top tips!
- Pay attention to the required length, content, and citation style required by your educational establishment. Different establishments can have very different requirements.
- If you do not understand the assignment brief, be sure to get assignment help from your instructor and ask them plenty of questions. It will waste valuable time and energy if you are unclear on the assignment and start in the wrong direction.
- Write the executive summary only after the rest of the assignment is complete.
- Ask your instructor for a good assignment example if you are unsure of how to write any aspects of an assignment or you can simply key in online ‘ example of introduction for assignmen t’ or ‘example of conclusion for assignment’, to obtain useful examples. Reading an example text is often more valuable than written instructions of how to write things.
- Your conclusion can help you write an executive summary for assignment as essentially the executive summary is a summary of the conclusion. To write a conclusion for an assignment, remember that it is written in the opposite order to an introduction so, it begins with the thesis, moves on to the main points relating to the thesis, and it ends with statements about the general topic.
- Do not claim that your product/service has no competitors. This is almost impossible, and investors may not trust you have carried out sufficient research.
- Aim to show an in-depth understanding (to reassure investors) and remember that great interest from investors can be gained via a tight budget (if possible).
- Provide a logical order for the reader by stating the main points in the order they are covered in the assignment.
- Remember how important your assignment heading is. This will be read even before the executive summary. It needs to be clear, professional, and interesting.
- Have a rest before proofreading. As an executive summary provides the first impression, it needs to be completely free of spelling, punctuation, and grammatical errors. Also, see if you can take out any unnecessary words to keep it straight to the point.
In order to gain a deeper understanding, see below for an example of an executive summary for assignment.
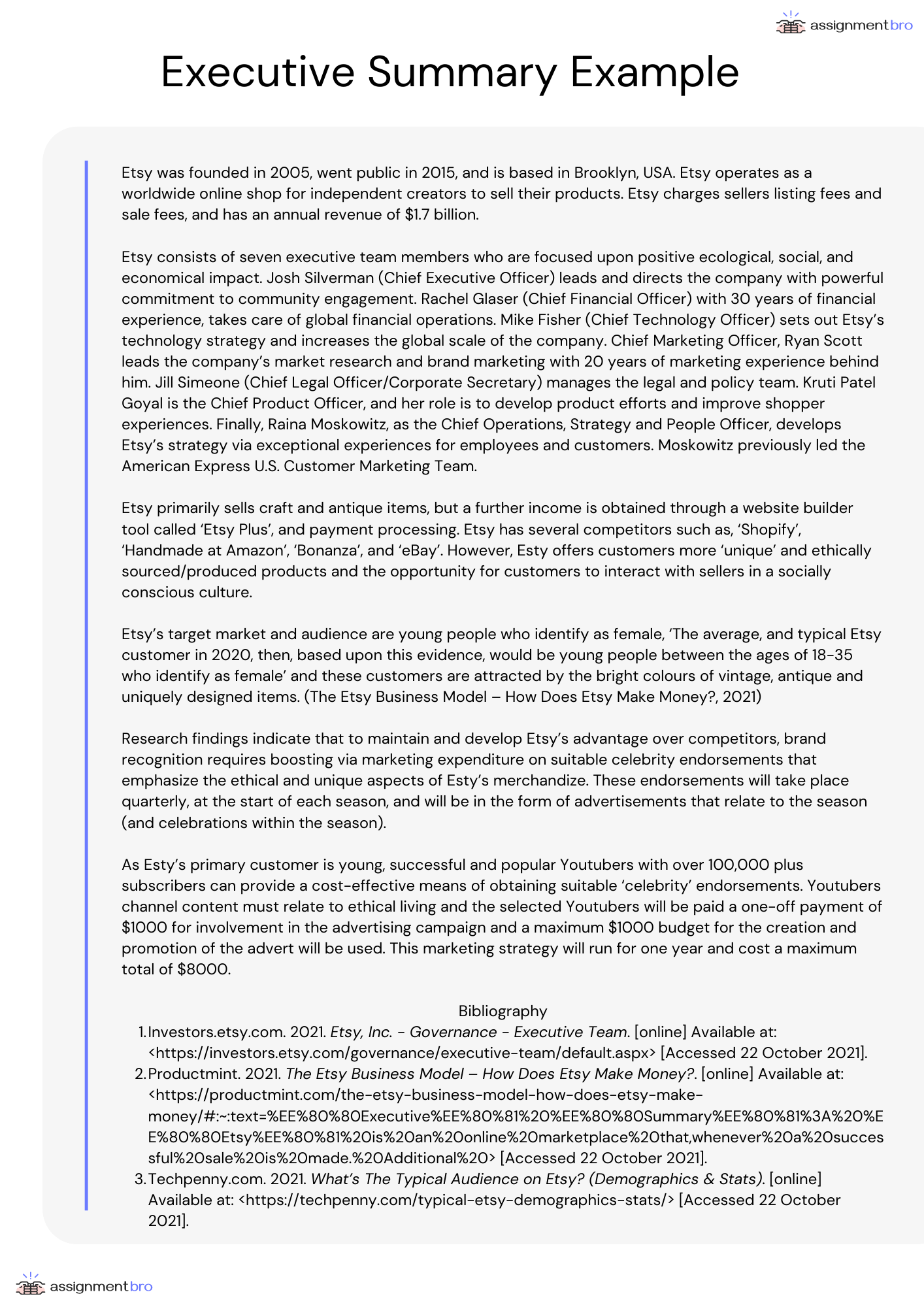
Overall, to write an executive summary for a report or assignment is not easy. It requires the ability to mindfully focus on the key information only and write it in an extremely minimalist way. Hopefully, the steps and tips provided in this article can help you on your way to success!

Bibliographies are generally not the easiest or most fun writing tasks, but they are necessary, so it’s important to get them right! Read on, to find out ‘how to make bibliography’...
Bibliographies are generally not the easiest or most fun writing...
What Is an Abstract? An abstract is a short (generally under 250 words) summary of a larger piece of work, such as a dissertation or research paper. Whether it’s an abstract for a...
What Is an Abstract? An abstract is a short (generally under 250...
What Is A Report For An Assignment? Contrary to a popular belief, a report for an assignment is not a simple outline. It is a deep analytical work that must be done. It is often approached...
What Is A Report For An Assignment? Contrary to a popular belief, a...
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Product overview
- All features
- App integrations
CAPABILITIES
- project icon Project management
- Project views
- Custom fields
- Status updates
- goal icon Goals and reporting
- Reporting dashboards
- workflow icon Workflows and automation
- portfolio icon Resource management
- Time tracking
- my-task icon Admin and security
- Admin console
- asana-intelligence icon Asana AI
- list icon Personal
- premium icon Starter
- briefcase icon Advanced
- Goal management
- Organizational planning
- Campaign management
- Creative production
- Content calendars
- Marketing strategic planning
- Resource planning
- Project intake
- Product launches
- Employee onboarding
- View all uses arrow-right icon
Project plans
- Team goals & objectives
- Team continuity
- Meeting agenda
- View all templates arrow-right icon
- Work management resources Discover best practices, watch webinars, get insights
- What's new Learn about the latest and greatest from Asana
- Customer stories See how the world's best organizations drive work innovation with Asana
- Help Center Get lots of tips, tricks, and advice to get the most from Asana
- Asana Academy Sign up for interactive courses and webinars to learn Asana
- Developers Learn more about building apps on the Asana platform
- Community programs Connect with and learn from Asana customers around the world
- Events Find out about upcoming events near you
- Partners Learn more about our partner programs
- Support Need help? Contact the Asana support team
- Asana for nonprofits Get more information on our nonprofit discount program, and apply.
Featured Reads

- Project planning |
- How to write an executive summary, with ...
How to write an executive summary, with examples

The best way to do that is with an executive summary. If you’ve never written an executive summary, this article has all you need to know to plan, write, and share them with your team.
What is an executive summary?
An executive summary is an overview of a document. The length and scope of your executive summary will differ depending on the document it’s summarizing, but in general an executive summary can be anywhere from one to two pages long. In the document, you’ll want to share all of the information your readers and important stakeholders need to know.
Imagine it this way: if your high-level stakeholders were to only read your executive summary, would they have all of the information they need to succeed? If so, your summary has done its job.
You’ll often find executive summaries of:
Business cases
Project proposals
Research documents
Environmental studies
Market surveys
In general, there are four parts to any executive summary:
Start with the problem or need the document is solving.
Outline the recommended solution.
Explain the solution’s value.
Wrap up with a conclusion about the importance of the work.
What is an executive summary in project management?
In project management, an executive summary is a way to bring clarity to cross-functional collaborators, team leadership, and project stakeholders . Think of it like a project’s “ elevator pitch ” for team members who don’t have the time or the need to dive into all of the project’s details.
The main difference between an executive summary in project management and a more traditional executive summary in a business plan is that the former should be created at the beginning of your project—whereas the latter should be created after you’ve written your business plan. For example, to write an executive summary of an environmental study, you would compile a report on the results and findings once your study was over. But for an executive summary in project management, you want to cover what the project is aiming to achieve and why those goals matter.
The same four parts apply to an executive summary in project management:
Start with the problem or need the project is solving. Why is this project happening? What insight, customer feedback, product plan, or other need caused it to come to life?
Outline the recommended solution, or the project’s objectives. How is the project going to solve the problem you established in the first part? What are the project goals and objectives?
Explain the solution’s value. Once you’ve finished your project, what will happen? How will this improve and solve the problem you established in the first part?
Wrap up with a conclusion about the importance of the work. This is another opportunity to reiterate why the problem is important, and why the project matters. It can also be helpful to reference your audience and how your solution will solve their problem. Finally, include any relevant next steps.
If you’ve never written an executive summary before, you might be curious about where it fits into other project management elements. Here’s how executive summaries stack up:
Executive summary vs. project plan
A project plan is a blueprint of the key elements your project will accomplish in order to hit your project goals and objectives. Project plans will include your goals, success metrics, stakeholders and roles, budget, milestones and deliverables, timeline and schedule, and communication plan .
An executive summary is a summary of the most important information in your project plan. Think of the absolutely crucial things your management team needs to know when they land in your project, before they even have a chance to look at the project plan—that’s your executive summary.
Executive summary vs. project overview
Project overviews and executive summaries often have similar elements—they both contain a summary of important project information. However, your project overview should be directly attached to your project. There should be a direct line of sight between your project and your project overview.
While you can include your executive summary in your project depending on what type of project management tool you use, it may also be a stand-alone document.
Executive summary vs. project objectives
Your executive summary should contain and expand upon your project objectives in the second part ( Outline the recommended solution, or the project’s objectives ). In addition to including your project objectives, your executive summary should also include why achieving your project objectives will add value, as well as provide details about how you’re going to get there.
The benefits of an executive summary
You may be asking: why should I write an executive summary for my project? Isn’t the project plan enough?
Well, like we mentioned earlier, not everyone has the time or need to dive into your project and see, from a glance, what the goals are and why they matter. Work management tools like Asana help you capture a lot of crucial information about a project, so you and your team have clarity on who’s doing what by when. Your executive summary is designed less for team members who are actively working on the project and more for stakeholders outside of the project who want quick insight and answers about why your project matters.
An effective executive summary gives stakeholders a big-picture view of the entire project and its important points—without requiring them to dive into all the details. Then, if they want more information, they can access the project plan or navigate through tasks in your work management tool.
How to write a great executive summary, with examples
Every executive summary has four parts. In order to write a great executive summary, follow this template. Then once you’ve written your executive summary, read it again to make sure it includes all of the key information your stakeholders need to know.
1. Start with the problem or need the project is solving
At the beginning of your executive summary, start by explaining why this document (and the project it represents) matter. Take some time to outline what the problem is, including any research or customer feedback you’ve gotten . Clarify how this problem is important and relevant to your customers, and why solving it matters.
For example, let’s imagine you work for a watch manufacturing company. Your project is to devise a simpler, cheaper watch that still appeals to luxury buyers while also targeting a new bracket of customers.
Example executive summary:
In recent customer feedback sessions, 52% of customers have expressed a need for a simpler and cheaper version of our product. In surveys of customers who have chosen competitor watches, price is mentioned 87% of the time. To best serve our existing customers, and to branch into new markets, we need to develop a series of watches that we can sell at an appropriate price point for this market.
2. Outline the recommended solution, or the project’s objectives
Now that you’ve outlined the problem, explain what your solution is. Unlike an abstract or outline, you should be prescriptive in your solution—that is to say, you should work to convince your readers that your solution is the right one. This is less of a brainstorming section and more of a place to support your recommended solution.
Because you’re creating your executive summary at the beginning of your project, it’s ok if you don’t have all of your deliverables and milestones mapped out. But this is your chance to describe, in broad strokes, what will happen during the project. If you need help formulating a high-level overview of your project’s main deliverables and timeline, consider creating a project roadmap before diving into your executive summary.
Continuing our example executive summary:
Our new watch series will begin at 20% cheaper than our current cheapest option, with the potential for 40%+ cheaper options depending on material and movement. In order to offer these prices, we will do the following:
Offer watches in new materials, including potentially silicone or wood
Use high-quality quartz movement instead of in-house automatic movement
Introduce customizable band options, with a focus on choice and flexibility over traditional luxury
Note that every watch will still be rigorously quality controlled in order to maintain the same world-class speed and precision of our current offerings.
3. Explain the solution’s value
At this point, you begin to get into more details about how your solution will impact and improve upon the problem you outlined in the beginning. What, if any, results do you expect? This is the section to include any relevant financial information, project risks, or potential benefits. You should also relate this project back to your company goals or OKRs . How does this work map to your company objectives?
With new offerings that are between 20% and 40% cheaper than our current cheapest option, we expect to be able to break into the casual watch market, while still supporting our luxury brand. That will help us hit FY22’s Objective 3: Expanding the brand. These new offerings have the potential to bring in upwards of three million dollars in profits annually, which will help us hit FY22’s Objective 1: 7 million dollars in annual profit.
Early customer feedback sessions indicate that cheaper options will not impact the value or prestige of the luxury brand, though this is a risk that should be factored in during design. In order to mitigate that risk, the product marketing team will begin working on their go-to-market strategy six months before the launch.
4. Wrap up with a conclusion about the importance of the work
Now that you’ve shared all of this important information with executive stakeholders, this final section is your chance to guide their understanding of the impact and importance of this work on the organization. What, if anything, should they take away from your executive summary?
To round out our example executive summary:
Cheaper and varied offerings not only allow us to break into a new market—it will also expand our brand in a positive way. With the attention from these new offerings, plus the anticipated demand for cheaper watches, we expect to increase market share by 2% annually. For more information, read our go-to-market strategy and customer feedback documentation .
Example of an executive summary
When you put it all together, this is what your executive summary might look like:
![student executive summary sample for assignment [Product UI] Example executive summary in Asana (Project Overview)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/8aa7d41f-aed9-4f82-bb7a-4305cea4404d/inline-project-planning-executive-summary-examples-1-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
Common mistakes people make when writing executive summaries
You’re not going to become an executive summary-writing pro overnight, and that’s ok. As you get started, use the four-part template provided in this article as a guide. Then, as you continue to hone your executive summary writing skills, here are a few common pitfalls to avoid:
Avoid using jargon
Your executive summary is a document that anyone, from project contributors to executive stakeholders, should be able to read and understand. Remember that you’re much closer to the daily work and individual tasks than your stakeholders will be, so read your executive summary once over to make sure there’s no unnecessary jargon. Where you can, explain the jargon, or skip it all together.
Remember: this isn’t a full report
Your executive summary is just that—a summary. If you find yourself getting into the details of specific tasks, due dates, and attachments, try taking a step back and asking yourself if that information really belongs in your executive summary. Some details are important—you want your summary to be actionable and engaging. But keep in mind that the wealth of information in your project will be captured in your work management tool , not your executive summary.
Make sure the summary can stand alone
You know this project inside and out, but your stakeholders won’t. Once you’ve written your executive summary, take a second look to make sure the summary can stand on its own. Is there any context your stakeholders need in order to understand the summary? If so, weave it into your executive summary, or consider linking out to it as additional information.
Always proofread
Your executive summary is a living document, and if you miss a typo you can always go back in and fix it. But it never hurts to proofread or send to a colleague for a fresh set of eyes.
In summary: an executive summary is a must-have
Executive summaries are a great way to get everyone up to date and on the same page about your project. If you have a lot of project stakeholders who need quick insight into what the project is solving and why it matters, an executive summary is the perfect way to give them the information they need.
For more tips about how to connect high-level strategy and plans to daily execution, read our article about strategic planning .
Related resources
4 ways to establish roles and responsibilities for team success
Cost control: How to monitor project spending to increase profitability
How to use a feasibility study in project management
How to track utilization rate and drive team profitability
Student Academic Success Center
Executive summaries, download pdf handout: executive summaries, watch video: writing your engineering executive summary, compare example executive summaries (pdf).
When readers want you to communicate your findings in a clear, no-nonsense way, the executive summary is the first place they look. However, most executive summary readers are busy and do not always have a nuanced understanding of your research field. This can be a problem! Luckily, we can teach you strategies to help solve this problem, including:
- How to tailor your message to your audience
- How to compact complex content into a one-page summary
Need personalized advice?
Schedule an Appointment
Related Resources
- BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
- Making the Case for Your Research
- Document Design
Quick Links
- Academic Calendar
- Academic Integrity
- Bias Reporting and Response
- Statement of Assurance
- Documents, Forms, and News [Internal Staff Only]
Other Helpful Departments
- Disability Resources
- Center for Student Diversity & Inclusion
- Graduate Education
- Office of International Education
- University Health Services
How it works
Transform your enterprise with the scalable mindsets, skills, & behavior change that drive performance.
Explore how BetterUp connects to your core business systems.
We pair AI with the latest in human-centered coaching to drive powerful, lasting learning and behavior change.
Build leaders that accelerate team performance and engagement.
Unlock performance potential at scale with AI-powered curated growth journeys.
Build resilience, well-being and agility to drive performance across your entire enterprise.
Transform your business, starting with your sales leaders.
Unlock business impact from the top with executive coaching.
Foster a culture of inclusion and belonging.
Accelerate the performance and potential of your agencies and employees.
See how innovative organizations use BetterUp to build a thriving workforce.
Discover how BetterUp measurably impacts key business outcomes for organizations like yours.
A demo is the first step to transforming your business. Meet with us to develop a plan for attaining your goals.

- What is coaching?
Learn how 1:1 coaching works, who its for, and if it's right for you.
Accelerate your personal and professional growth with the expert guidance of a BetterUp Coach.
Types of Coaching
Navigate career transitions, accelerate your professional growth, and achieve your career goals with expert coaching.
Enhance your communication skills for better personal and professional relationships, with tailored coaching that focuses on your needs.
Find balance, resilience, and well-being in all areas of your life with holistic coaching designed to empower you.
Discover your perfect match : Take our 5-minute assessment and let us pair you with one of our top Coaches tailored just for you.

Research, expert insights, and resources to develop courageous leaders within your organization.
Best practices, research, and tools to fuel individual and business growth.
View on-demand BetterUp events and learn about upcoming live discussions.
The latest insights and ideas for building a high-performing workplace.
- BetterUp Briefing
The online magazine that helps you understand tomorrow's workforce trends, today.
Innovative research featured in peer-reviewed journals, press, and more.
Founded in 2022 to deepen the understanding of the intersection of well-being, purpose, and performance
We're on a mission to help everyone live with clarity, purpose, and passion.
Join us and create impactful change.
Read the buzz about BetterUp.
Meet the leadership that's passionate about empowering your workforce.
For Business
For Individuals
How to write an executive summary in 10 steps

Whether presenting a business plan, sharing project updates with stakeholders, or submitting a project proposal, an executive summary helps you grab attention and convey key insights.
Think of it as a condensed version of a document, report, or proposal that highlights the most important information clearly and concisely. It's like a "cheat sheet" that gives you a snapshot of the main points without reading the entire thing.
Throughout the article, we'll explore some examples of executive summaries to give you a better understanding of how they can be applied. Plus, we'll provide you with ready-to-use templates and best practices for writing compelling executive summaries.
What is an executive summary?
An executive summary is a concise overview of a longer document or report. It is typically written for busy executives or decision-makers who may not have the time to read the entire document but still need to grasp its key points and recommendations.
An effective executive summary should capture the essence of the document, highlighting the most important information in a brief and easily understandable way. It should provide a snapshot of the document's purpose, methodology, major findings, and key recommendations. The summary should be written in a way that allows the reader to quickly grasp the main ideas and make informed decisions based on the information presented.
Why do you need to write one?
For a business owner , an executive summary is one of the most important documents you will have. Like a business plan , they help you lay out the potential value of your business and your potential for success.
Unlike a business proposal, however, an executive summary is designed to be read in a brief amount of time. That makes them ideal for a variety of uses, like project proposals and research summaries. Sending your strategic plan to a prospective investor or stakeholder likely won’t get you far. But a brief report that clearly states your key findings and what’s in it for them might help you — and your proposal — stand out. It isn't all the details. It's what gets you the meeting to share more.
An executive summary is also a business document that can travel without you. It may be presented to other leaders and potential investors. If it’s written well, it will take on a life of its own. You may find that you get support and resources from places you never imagined.
What should be included in an executive summary?
Your executive summary should include brief descriptions of who your product, service, or proposal is for and your competitive advantage. Be sure to introduce your report concisely yet clearly . Note the most important points and its overall purpose––what do you hope to achieve with this report?
Also, include any necessary background information and statistics about the industry, high-level information about your business model, necessary financial information, or other insights you discuss in the report. Depending on your proposal, you may want to consider summarizing a market analysis of your target market.
Typically, an executive summary follows a structured format, including sections such as:
- Introduction: Provides a brief background and context for the document.
- Objective or purpose: Clearly states the goal of the document and what it aims to achieve.
- Methodology: Briefly describes the approach, data sources, and methods used to conduct the research or analysis.
- Findings: Summarizes the main findings, conclusions, or results derived from the document.
- Recommendations: Outlines the key recommendations or proposed actions based on the findings.
- Conclusion: Provides a concise wrap-up of the main points and emphasizes the significance of the document.

How do you write an executive summary?
When tackling an executive summary, it's all about following a structured approach to ensure you effectively communicate those crucial points, findings, and recommendations. Let’s walk through some steps and best practices to make it a breeze:
Step 1: Get to know the document
Take the time to dive into the full document or report that your executive summary will be based on. Read it thoroughly and identify the main objectives, key findings, conclusions, and recommendations.
Step 2: Know your audience
Think about who you're writing the executive summary for. Consider their knowledge level, interests, and priorities. This helps you tailor the summary to their needs and make it relevant and impactful.
Step 3: Outline the structure
Create an outline for your executive summary with sections like introduction, objective, methodology, findings, recommendations, and conclusion. This way, you'll have a logical flow that's easy to follow.
Step 4: Start strong
Kick off your executive summary with a captivating opening statement. Make it concise, engaging, and impactful to hook the reader and make them want to keep reading.
Step 5: Summarize objectives and methodology
Give a brief overview of the document's objectives and the methodology used to achieve them. This sets the context and helps the reader understand the approach taken.
Step 6: Highlight key findings
Summarize the main findings, conclusions, or results. Focus on the juiciest and most relevant points that support the document's purpose. Keep it clear and concise to get the message across effectively.
Step 7: Present key recommendations
Outline the important recommendations or proposed actions based on the findings. Clearly state what needs to be done, why it matters, and how it aligns with the document's objectives. Make those recommendations actionable and realistic.
Step 8: Keep it snappy
Remember, an executive summary should be short and sweet. Skip unnecessary details, jargon, or technical language . Use straightforward language that hits the mark.
Step 9: Review and polish
Once you've written the executive summary, give it a careful review for clarity, coherence, and accuracy. Make sure it captures the essence of the full document and represents its content faithfully. Take the extra step to edit out any fluff or repetition.
Step 10: Dress to impress
Consider formatting and presentation. Use headings, bullet points, and formatting styles to make it visually appealing and easy to skim. If it makes sense, include some graphs, charts, or visuals to highlight key points.

Tips for writing an effective executive summary
- Adapt your language and tone to suit your audience.
- Keep things concise and crystal clear—say no to jargon.
- Focus on the most important info that packs a punch.
- Give enough context without overwhelming your reader.
- Use strong and persuasive language to make your recommendations shine.
- Make sure your executive summary makes sense even if the full document isn't read.
- Proofread like a pro to catch any pesky grammar, spelling, or punctuation errors.
Executive summary template for business plans
Here's a general template for creating an executive summary specifically for business plans:
[Your Company Name]
[Business Plan Title]
Business overview
Provide a brief introduction to your company, including its name, location, industry, and mission statement . Describe your unique value proposition and what sets your business apart from competitors.
Market analysis
Summarize the key findings of your market research. Provide an overview of the target market, its size, growth potential, and relevant trends. Highlight your understanding of customer needs, preferences, and behaviors.
Product or service offering
Outline your core products or services, including their key features and benefits. Emphasize how your offerings address customer pain points and provide value. Highlight any unique selling points or competitive advantages.
Business model
Explain your business model and revenue generation strategy. Describe how you will generate revenue, the pricing structure, and any distribution channels or partnerships that contribute to your business's success.
Marketing and sales strategy
Summarize your marketing and sales approach. Highlight the key tactics and channels you will use to reach and attract customers. Discuss your promotional strategies, pricing strategies, and customer acquisition plans.
Management team
Introduce the key members of your management team and their relevant experience. Highlight their expertise and how it positions the team to execute the business plan successfully. Include any notable advisors or board members.
Financial projections
Summarize your financial projections, including revenue forecasts, expected expenses, and projected profitability. Highlight any key financial metrics or milestones. Briefly mention your funding needs, if applicable.
Funding requirements
If seeking funding, outline your funding requirements, including the amount needed, its purpose, and the potential sources of funding you are considering. Summarize the expected return on investment for potential investors.
Reiterate the vision and potential of your business. Summarize the key points of your business plan, emphasizing its viability, market potential, and the expertise of your team. Convey confidence in the success of your venture.
Note: Keep the executive summary concise and focused, typically within one to two pages. Use clear and compelling language, emphasizing the unique aspects of your business. Tailor the template to suit your specific business plan, adjusting sections and details accordingly.
Remember, the executive summary serves as an introduction to your business plan and should pique the reader's interest, conveying the value and potential of your business in a concise and persuasive manner.
Executive summary examples
Every executive summary will be unique to the organization's goals, vision, and brand identity. We put together two general examples of executive summaries to spark your creativity and offer some inspiration.
These are not intended to be used as-is but more to offer ideas for how you may want to put your own executive summary together. Be sure to personalize your own summary with specific statistics and relevant data points to make the most impact.
Example 1: executive summary for a communications business plan
Introduction:
We're thrilled to present our innovative [insert product] that aims to revolutionize the way people connect and engage. Our vision is to empower individuals and businesses with seamless communication solutions that break barriers and foster meaningful connections.
Market opportunity:
The communications industry is evolving rapidly, and we've identified a significant opportunity in the market. With the proliferation of remote work, the need for reliable and efficient communication tools has skyrocketed. Our extensive market research indicates a demand for solutions that prioritize user experience, security, and flexibility.
Product offering:
At [Company Name], we've developed a suite of cutting-edge communication tools designed to meet the diverse needs of our customers. Our flagship product is a unified communication platform that integrates voice, video, messaging, and collaboration features into a seamless user experience. We also offer customizable solutions for businesses of all sizes, catering to their unique communication requirements.
Unique value proposition:
What sets us apart from the competition? Our user-centric approach and commitment to innovation. We prioritize user experience by creating intuitive interfaces and seamless interactions. Our solutions are scalable, adaptable, and designed to keep up with evolving technological trends. By combining ease of use with advanced features, we deliver unparalleled value to our customers.
Target market:
Our primary focus is on small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) that require efficient and cost-effective communication tools. We also cater to individuals, remote teams, and larger enterprises seeking reliable and secure communication solutions. Our target market encompasses industries such as technology, finance, healthcare, and professional services.
Business model:
To generate revenue, we employ a subscription-based business model. Customers can choose from different plans tailored to their specific needs, paying a monthly or annual fee. We also offer additional services such as customization, integration, and customer support, creating additional revenue streams and fostering long-term customer relationships.
Marketing and sales strategy:
Our marketing strategy centers around building brand awareness through targeted digital campaigns, content marketing, and strategic partnerships. We'll leverage social media, industry influencers, and online communities to reach our target audience. Additionally, our sales team will engage in proactive outreach, nurturing leads and providing personalized consultations to convert prospects into loyal customers.
Team and expertise:
Our team is composed of experienced professionals with a deep understanding of the communications industry. Led by our visionary founder and supported by a skilled and diverse team, we have the expertise to drive innovation, develop robust products, and deliver exceptional customer service. We're passionate about our mission and dedicated to making a lasting impact in the market.
Financial projections:
Based on extensive market research and financial analysis, we anticipate strong growth and profitability. Our financial projections indicate steady revenue streams, with increasing customer adoption and market share. We're committed to managing costs effectively, optimizing our resources, and continuously reinvesting in research and development.
Funding requirements:
To fuel our ambitious growth plans and accelerate product development, we're seeking [funding amount] in funding. These funds will be allocated towards expanding our team, scaling our infrastructure, marketing efforts, and ongoing product innovation. We believe this investment will position us for success and solidify our market presence.
Conclusion:
In summary, [Company Name] is poised to disrupt the communications industry with our innovative solutions and customer-centric approach. We're ready to make a positive impact by empowering individuals and businesses to communicate effectively and effortlessly. Join us on this exciting journey as we redefine the future of communication. Together, we'll shape a connected world like never before.
Example 2: executive summary for a project proposal
[Project Name]
[Project Proposal Date]
Hello! We're thrilled to present our project proposal for [Project Name]. This executive summary will provide you with a high-level overview of the project, its objectives, and the value it brings.
Project overview:
Our project aims to [describe the project's purpose and scope]. It's a response to [identify the problem or opportunity] and has the potential to bring significant benefits to [stakeholders or target audience]. Through meticulous planning and execution, we're confident in our ability to achieve the desired outcomes.
Objectives:
The primary goal of our project is to [state the overarching objective]. In addition, we have specific objectives such as [list specific objectives]. By accomplishing these goals, we'll create a positive impact and drive meaningful change.
Our proposed approach for this project is based on a thorough analysis of the situation and best practices. We'll adopt a structured methodology that includes [describe the key project phases or activities]. This approach ensures efficient utilization of resources and maximizes project outcomes.
The benefits of this project are truly exciting. Through its implementation, we anticipate [describe the anticipated benefits or outcomes]. These benefits include [list specific benefits], which will have a lasting and positive effect on [stakeholders or target audience].
Implementation timeline:
We've devised a comprehensive timeline to guide the project from initiation to completion. The project is divided into distinct phases, with well-defined milestones and deliverables. Our timeline ensures that tasks are executed in a timely manner, allowing us to stay on track and deliver results.
Resource requirements:
To successfully execute this project, we've identified the key resources needed. This includes [list the resources required, such as human resources, technology, equipment, and funding]. We're confident in our ability to secure the necessary resources and allocate them effectively to ensure project success.
A project of this nature requires a well-planned budget. Based on our analysis, we've estimated the required funding to be [state the budget amount]. This budget encompasses all project-related costs and aligns with the anticipated benefits and outcomes.
Our project proposal is an exciting opportunity to address [the problem or opportunity] and create tangible value for [stakeholders or target audience]. With a clear vision, defined objectives, and a robust implementation plan, we're ready to embark on this journey. Join us as we bring this project to life and make a lasting impact.

Is an executive summary the same as a project plan?
While both are important components of project management and documentation , they serve different purposes and contain distinct information.
An executive summary, as discussed earlier, is a concise overview of a longer document or report. It provides a snapshot of the key points, findings, and recommendations. It focuses on high-level information and aims to provide an overview of the document's purpose, methodology, findings, and recommendations.
On the other hand, a project plan is a detailed document that outlines the specific activities, tasks, timelines, resources, and milestones associated with a project. It serves as a roadmap for project execution, providing a comprehensive understanding of how the project will be carried out.
A project plan typically includes objectives, scope, deliverables, schedule, budget, resource allocation, risk management, and communication strategies. It is intended for project team members, stakeholders, and those directly involved in the execution.
In summary, an executive summary offers a condensed overview of a document's key points, while a project plan provides a comprehensive and detailed roadmap for executing a project.
Executive summaries vs. abstracts
An executive summary is not the same as an abstract. Executive summaries focus on the main points of a proposal. They highlight when and why a reader should invest in the company or project.
An abstract, on the other hand, concentrates on what the business does and its marketing plan. It typically doesn’t include detailed information about finances.
While it is usually compelling, it’s less of an elevator pitch and more of a summary. The goal of an abstract is to inform, not to persuade. On the other hand, the goal of an executive summary is to give readers who are pressed for time just enough information that they’ll want to look further into your proposition.
When do you use an executive summary?
An executive summary is used in various situations where there is a need to present a condensed overview of a longer document or report. Here are some common instances when an executive summary is used:
- Business proposals: When submitting a business proposal to potential investors, partners, or stakeholders, an executive summary is often included. It provides a concise overview of the proposal, highlighting the key aspects such as the business idea, market analysis, competitive advantage, financial projections, and recommended actions.
- Reports and research studies: Lengthy reports or research studies often include an executive summary at the beginning. This allows decision-makers, executives, or other stakeholders to quickly understand the purpose, methodology, findings, and recommendations of the report without going through the entire document.
- Project updates: During the course of a project, project managers may prepare executive summaries to provide updates to stakeholders or higher-level management. These summaries give a brief overview of the project's progress, achievements, challenges, and upcoming milestones.
- Strategic plans: When developing strategic plans for an organization, an executive summary is often included to provide an overview of the plan's goals, objectives, strategies, and key initiatives. It allows executives and stakeholders to grasp the essence of the strategic plan and its implications without reading the entire document.
- Funding requests: When seeking funding for a project or venture, an executive summary is commonly used as part of the funding proposal. It provides a succinct summary of the project, highlighting its significance, potential impact, financial requirements, and expected outcomes.
In general, an executive summary is used whenever there is a need to communicate the main points, findings, and recommendations of a document concisely and efficiently to individuals who may not have the time or inclination to read the entire content. It serves as a valuable tool for understanding and facilitates quick decision-making.
5 ways project managers can use executive summaries
Project managers can use executive summaries in various ways to effectively communicate project updates, status reports, or proposals to stakeholders and higher-level management. Here are some ways project managers can use executive summaries:
- Project status updates: Project managers can provide regular executive summaries to stakeholders and management to communicate the current status of the project. The summary should include key achievements, milestones reached, challenges encountered, and any adjustments to the project plan. It allows stakeholders to quickly grasp the project's progress and make informed decisions or provide guidance as needed.
- Project proposals: When pitching a project idea or seeking approval for a new project, project managers can prepare an executive summary to present the essential aspects of the project. The summary should outline the project's objectives, scope, anticipated benefits, resource requirements, estimated timeline, and potential risks. It helps decision-makers understand the project's value and make an informed choice about its initiation.
- Project closure reports: At the end of a project, project managers can prepare an executive summary as part of the project closure report. The summary should highlight the project's overall success, key deliverables achieved, lessons learned, and recommendations for future projects. It provides a concise overview of the project's outcomes and acts as a valuable reference for future initiatives.
- Steering committee meetings: When project managers present updates or seek guidance from a steering committee or governance board, an executive summary can be an effective tool. The summary should cover the important aspects of the project, such as progress, issues, risks, and upcoming milestones. It ensures that decision-makers are well-informed about the project's status and can provide relevant guidance or support.
- Change requests: When submitting a change request for a project, project managers can include an executive summary to summarize the proposed change, its impact on the project, potential risks, and benefits. It helps stakeholders and decision-makers quickly assess the change request and make informed decisions about its implementation.
Using executive summaries, project managers can efficiently communicate project-related information to stakeholders, executives, and decision-makers. The summaries provide a concise overview of the project's status, proposals, or closure reports, allowing stakeholders to quickly understand the key points and take appropriate action.
When should you not use an executive summary?
While executive summaries are widely used in many situations, there are some cases where they may not be necessary or suitable. Here are a few scenarios where an executive summary may not be appropriate, along with alternative approaches:
- Highly technical documents: If the document contains highly technical or specialized information that requires a detailed understanding, an executive summary alone may not be sufficient. In such cases, it is better to provide the complete document and supplement it with explanatory materials, presentations , or meetings where experts can explain and discuss the technical details.
- Personal or creative writing: Executive summaries are typically used for informational or analytical documents. If the content is more personal in nature, such as a memoir, novel, or creative piece, an executive summary may not be relevant. Instead, focus on providing an engaging introduction or book blurb that entices readers and conveys the essence of the work.
- Short documents: If the document itself is already concise and can be easily read in its entirety, an executive summary may be redundant. In these cases, it is more effective to present the complete document without an additional summary.
- Interactive presentations: In situations where you can present information interactively, such as in meetings, workshops, or conferences, it may be more effective to engage the audience directly rather than relying solely on an executive summary. Use visual aids, demonstrations, discussions, and Q&A sessions to convey the necessary information and capture the audience's attention.
Final thoughts on writing a compelling executive summary
An executive summary isn’t the kitchen sink — it’s the bells and whistles. Geared toward busy decision-makers, these one-pagers communicate your case for action and proposed solutions. When it’s written well, your audience will walk away with an understanding of what needs to be done, why it needs to happen, and why they should help it move forward.
But writing it well doesn’t just mean spell-checking. It means tailoring your communication to an influential, yet busy and distracted audience. To be effective, you’ll need to write your proposal with empathy and an understanding of what matters to them .
Elevate your executive skills
Discover coaching that sharpens your leadership and enhances decision-making. Start today.
Allaya Cooks-Campbell
With over 15 years of content experience, Allaya Cooks Campbell has written for outlets such as ScaryMommy, HRzone, and HuffPost. She holds a B.A. in Psychology and is a certified yoga instructor as well as a certified Integrative Wellness & Life Coach. Allaya is passionate about whole-person wellness, yoga, and mental health.
Tips for how to write a LinkedIn summary and examples
12 resume career objective examples and tips for writing one, writing a resignation letter that’s effective and professional, executive development is personalized to leaders everywhere, how executive functioning governs daily life activities, what is a career statement, and should you write one, 10 personal brand statements to put all eyes on you, what is executive coaching: benefits for the 2024 workforce, how stanford executive education embraces vulnerability as a form of resilience, similar articles, how to create a scope of work in 8 steps, how to write a speech that your audience remembers, 3 problem statement examples and steps to write your own, what’s a project scope, and how do you write one, how the minto pyramid principle can enhance your communication skills, how to make decisions like a multi-billion dollar corporation, cv versus resume demystify the differences once and for all, how to write a memo: 8 steps with examples, stay connected with betterup, get our newsletter, event invites, plus product insights and research..
3100 E 5th Street, Suite 350 Austin, TX 78702
- Platform Overview
- Integrations
- Powered by AI
- BetterUp Lead™
- BetterUp Manage™
- BetterUp Care®
- Sales Performance
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Case Studies
- Why BetterUp?
- About Coaching
- Find your Coach
- Career Coaching
- Communication Coaching
- Life Coaching
- News and Press
- Leadership Team
- Become a BetterUp Coach
- BetterUp Labs
- Center for Purpose & Performance
- Leadership Training
- Business Coaching
- Contact Support
- Contact Sales
- Privacy Policy
- Acceptable Use Policy
- Trust & Security
- Cookie Preferences

- WRITING SKILLS
- Business Writing
How to Write an Executive Summary
Search SkillsYouNeed:
Writing Skills:
- A - Z List of Writing Skills
The Essentials of Writing
- Common Mistakes in Writing
- Improving Your Grammar
- Active and Passive Voice
- Using Plain English
- Writing in UK and US English
- Clarity in Writing
- Writing Concisely
- Coherence in Writing
- The Importance of Structure
- Know Your Audience
- Know Your Medium
- Business Writing Tips
- How to Write a Report
- How to Write a To-Do List
- How to Write a Business Case
- How to Write a Press Release
- Writing a Marketing Strategy
- Writing Marketing Copy
- Copywriting
- Taking Minutes and the Role of the Secretary
- How to Write a Letter
- Writing Effective Emails
- Good Email Etiquette
- Write Emails that Convince, Influence and Persuade
- Storytelling in Business
- Using LinkedIn Effectively
Subscribe to our FREE newsletter and start improving your life in just 5 minutes a day.
You'll get our 5 free 'One Minute Life Skills' and our weekly newsletter.
We'll never share your email address and you can unsubscribe at any time.
Being asked to write an executive summary, whether for a policy paper, pamphlet, briefing paper or report, may be a daunting prospect if you’ve never done it before.
However, ask a few questions, and keep a few simple rules in your mind and it becomes much more straightforward. This page sets out the questions to ask, whether of yourself or someone else, and a few warnings and conventions to bear in mind.
Executive Summary Content
Two key questions you need to ask before you start
- Who is the intended audience of my executive summary?
- Which of the contents of the paper that I am summarising do they really need to know?
These questions are important because they tell you what you need to include in the executive summary, so let’s unpack them a little:
The Intended Audience
As with all writing projects it is important to know your audience . The intended audience for an executive summary may be quite different from the intended audience for the longer document, whether it’s a policy paper, report, or something else.
The executive summary serves several possible purposes.
People may read the executive summary to find out if they need to read the full report. This group may include people within the organisation and outside, but the report is likely to touch on what they do every day. They will often be subject experts; they just need to know if there is anything new that they should read. This group will be looking for a broad summary of the contents of the wider paper.
People may want to find out if they’d find the full report interesting and relevant , even if not strictly essential. Again, this group is likely to be subject experts, but may also include analysts searching for a particular ‘angle’ on the subject. This group will also welcome a straightforward summary of the contents.
They may read the executive summary instead of the full report . It’s this group that you really need to worry about, because they’re likely to include the Board or executive team of your organisation, as well as journalists. What goes into the executive summary, therefore, is the message that they’re going to take away, that may well be spread more widely. For these people, the executive summary is their window onto the subject and it needs to be transparent, not opaque, if they are to understand it.
Think about your intended audience: who do you want to read your executive summary and why?
Don’t worry about other people who might read it; this is your intended audience , the people to whom you or your immediate line manager are going to send the summary. If the summary is for publication, which groups do you most want to read it?
What Does Your Intended Audience Need to Know?
Once you have identified your intended audience, you can then think about what they need to know or do as a result of reading your paper. This can be split into two parts:
First categorise the document by whether it needs action or is for information only. This will determine the language that you use.
Next, you need to identify what, when they have finished reading, are the key messages that you want your audience to have in their heads. Information and concepts that they did not have before.
Top Tip A good way to think about the key content is to imagine meeting your boss or CEO in the car park or at the coffee machine. What three key points about your document would you want to tell them?
Work on reducing your key messages down to three, or at the most, five bullet points of one or two sentences. Working on them before you start writing will mean that they are absolutely clear in your head as you write.
Writing your Executive Summary
Some organisations have very clear structures that are used for documents like executive summaries and others are more open.
Before you start, check whether you need to work within a specific structure or not. For example, if you are writing a summary of an academic report for submission, you may have a word count restriction, or need to remain within one side of paper.
When you are writing your executive summary, you should keep your intended audience in mind at all times and write it for them.
If your audience includes your boss or Chief Executive think: how much do they already know, and how much do you need to explain?
If your audience includes journalists, you probably need to explain everything. If it’s simply as a summary of a paper because you have to publish one, then you simply need to summarise the paper.
If you find yourself getting bogged down in the detail at this stage, it’s a good idea to talk to someone else about what to include.
The language you use needs to be fairly formal, whether or not the summary is intended for publication. If in doubt, check out our page: Formal and Informal Writing .
Broadly, an executive summary, as you might expect, summarises the main points of the underlying paper, and draws out the key points. It usually has three sections: introduction, main body and conclusion.
The introduction sets the scene, and explains what the paper is about, including what action needs to be taken as a result. It doesn’t need to be more than one or two sentences. For an internal paper, you might write:
This paper explains the findings of the research about [subject] and its relevance to the organisation. It notes five key findings, and makes three recommendations for action within the organisation. You are asked to take note of these, and decide whether the recommendations should be implemented.
For an executive summary of a published paper, it is not unusual for the first paragraph to be more attention-grabbing.
For example, from a recently-published report about green energy and the internet:
For the estimated 2.5 billion people around the world who are connected to the internet, it is impossible to imagine life without it. The internet has rewoven the fabric of our daily lives – how we communicate with each other, work and entertain ourselves – and become a foundation of the global economy.
[Source: Greenpeace, Clicking Clean ].
This example still sets the scene: the importance of the internet, but the idea here is to keep people reading, not just provide information. Again, it’s all about your audience and what they need or want.
The main body of the text outlines the key findings and/or recommendations from the report or paper to which this is the summary. The main section needs to focus on the interesting and most relevant bits of the report.
Most importantly, the main section of the executive summary needs to stand alone without the reader having to refer to the main body of the report or policy paper. This is worth checking by getting someone who doesn’t know much about the subject to read it over for you.
Finally, you need a conclusion , which outlines the take-home messages or action needed from the person reading the report. Bullet points are a useful form to highlight the key points, and this is where your three to five messages come in.
Once you’ve finished, check it against our checklist to make sure that you’ve covered everything.
Checklist for writing an executive summary
- Have you kept in mind the audience at all times?
- Have you addressed it to them?
- Have you met any word count or structural requirements?
- Have you clearly outlined the key messages and any action needed as a result?
- Does the executive summary make sense by itself, without the report attached?
Final Words of Warning
An executive summary cannot be all things to all people. You only have a few hundred words. You need to focus firmly on your intended audience and their needs. Other people may find it useful; your intended audience relies on it.
Continue to: How to Write a Report How to Write a Business Case
See also: Commercial Awareness Employability Skills Note-Taking

How do I write and properly format an executive summary?
An executive summary is a concise version of a lengthier document, proposal, or multiple related reports. It is one of the first things (and sometimes the only thing) recipients of your document will read; therefore, it should be short and (often) persuasive. Executive summaries are commonly used in business plans, marketing plans, proposals, and other longer documents in order summarize and highlight main points. Remember that readers often do not have much time, so you have to capture their attention quickly, and convince them to keep reading.
Read this overview to build your understanding of executive summaries.
Considerations Before Getting Started:
- Though the executive summary is typically at the beginning of a document, many writers benefit from writing it last. This allows the writer to thoroughly develop all conclusions and arguments during other stages of the writing process, and simply focus on summarizing and persuading in the executive summary (rather than developing new arguments).
- Assuming you are writing the executive summary last, do not add anything new to it; anything included in the executive summary should be in the larger document.
- Be mindful of tone, and consider your readers when developing your executive summary. Are they experts on the topic, or generalists? If they are experts, you can likely use professional jargon, but if generalists, use terminology easily understood by all.
- Executive summary lengths vary according to the length of the larger document, and are usually anywhere from 1-4 pages. As a rule of thumb, executive summaries are 10% of the entire document or less.
Writing the Executive Summary:
- Place the executive summary on its own page(s).
- The first paragraph should immediately capture the reader's attention, whether it's a story, surprising fact, or insightful quote.
- Experts recommend using bullet-points (when possible) to present your ideas and keep it concise.
- Align the order of your executive summary with the order of the main document.
- Be confident. Believe in yourself and what you are presenting. If you do not write with confidence, your reader will sense this, and will follow suit.
- Avoid cliches and claims you can't support with evidence.
An executive summary is not:
- An abstract
- An introduction
- A conclusion
- A simple copy & paste from various sections of the larger document. Information from the larger document should instead be synthesized and presented via (short) paraphrases.
Review the articles below for examples and more information about writing executive summaries:
- The Executive Summary
- Writing Recommendations and Executive Summaries
- Building a Business Plan - Executive Summary
- Sample Executive Summary from a Business Plan (See pg 4 of the document)
- How to Write an Executive Summary (from Inc.com)
Note: In regards to APA formatting , remember to use an APA-approved font, double spacing, one inch margins, etc. as required by APA formatting standards. There is no official APA format for executive summaries. Check with your instructor or review your assignment instructions if you have questions about page length or other expectations.
- Business and Accounting
- Reading and Writing
- Last Updated Jul 17, 2020
- Views 124236
- Answered By Kate Anderson, Librarian
FAQ Actions
- Share on Facebook
Comments (0)
Hello! We're here to help! Please log in to ask your question.
Need an answer now? Search our FAQs !
How can I find my course textbook?
You can expect a prompt response, Monday through Friday, 8:00 AM-4:00 PM Central Time (by the next business day on weekends and holidays).
Questions may be answered by a Librarian, Learning Services Coordinator, Instructor, or Tutor.
- U.S. Locations
- UMGC Europe
- Learn Online
- Find Answers
- 855-655-8682
- Current Students
UMGC Effective Writing Center Writing an Executive Summary
Explore more of umgc.
- Writing Resources
An executive summary is a brief document typically directed at top-level managers who sometimes make decisions based upon a reading of this summary alone. As a result, the executive summary must be concise but comprehensive, meaning that it must present in summary form all major sections of the main report:
- methods of analyzing the problem
- results of analysis
- recommendations
To repeat, because of the critical role it plays, the executive summary is often the first and only part read by key decision makers. Therefore, it must be designed so that it can be read independently of the main document. Typically, figures and tables are not referenced in the executive summary. Uncommon terminology, symbols, and acronyms are avoided. If the executive summary is sufficiently persuasive, the entire proposal will then be read in full.
Therefore, your summary is key to the success of your proposal and should reflect these characteristics:
- Perfect Miniaturization . The executive summary should contain the same sections in the same order as the full report.
- Major Findings Only . Because it is a distilled version of the full report, the summary should include only the proposal's principal points and major evidence. Most charts, tables, and deep-level analysis are reserved for full proposal.
- Proportional . The executive summary should typically be only 10% the length of the full proposal it distills. Therefore, the executive summary for a 10-page proposal would be 1 page or less.
- Stand Alone . The summary should be written in a way that it can be read as a stand-alone document. Before submitting it, allow a test subject to read the summary. The subject should be able to give to you the basics of the full proposal from one reading of the summary.
- Flawless . Like a job resume, even the most minor error of proofreading or grammar can spell rejection.
Sample Executive Summary:

Parts of this Sample Executive Summary:
Subheadings : The summary's subheadings should reflect the report's main divisions. Subheadings of the executive summary should not be the same as those of the main report.
Purpose : The summary provides a purpose of the report in concise format using present tense.
Results : Findings and conclusions are reported in condensed form without reference to tables or appendices. Lists are used when possible.
Recommendations : These should be in list form whenever possible.
Our helpful admissions advisors can help you choose an academic program to fit your career goals, estimate your transfer credits, and develop a plan for your education costs that fits your budget. If you’re a current UMGC student, please visit the Help Center .
Personal Information
Contact information, additional information.
By submitting this form, you acknowledge that you intend to sign this form electronically and that your electronic signature is the equivalent of a handwritten signature, with all the same legal and binding effect. You are giving your express written consent without obligation for UMGC to contact you regarding our educational programs and services using e-mail, phone, or text, including automated technology for calls and/or texts to the mobile number(s) provided. For more details, including how to opt out, read our privacy policy or contact an admissions advisor .
Please wait, your form is being submitted.
By using our website you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more about how we use cookies by reading our Privacy Policy .
- How It Works
- Prices & Discounts
How to Write an Executive Summary for an Essay
Table of contents
An executive summary is a short, stand-alone summary of a long essay. It briefly describes the content and purpose of the essay as well as its main conclusions and recommendations.
An executive summary for an essay often summarizes the main points of the essay in a condensed form that’s easy to digest. A good executive summary is typically no more than 10% of the original document and can be written before or after the main essay is completed.
As a college student, writing executive summaries will be part of your coursework from time to time. Since it's often a challenge for many students, this article will help you learn the most effective way to write the best executive summary for an essay.
What’s the Purpose of an Executive Summary
The purpose of an executive summary is to give your audience a quick and easy way to understand the main points of your essay without having to read the entire essay.
It’s often written for an audience that is unfamiliar with the topic and is meant to provide a quick overview of the main points.
An executive summary simply gives the reader a condensed version of the essay. When written before the main essay, it can help to give the author the context for the rest of the essay and keep them focused when writing.
How Long Should an Executive Summary be
An executive summary should be no more than 10% of the length of the essay it is summarizing. This means that it should be concise, clear, and objective. The language you use should also be simple and easy to understand, even if your reader is not familiar with the subject matter.
You want to keep it as short as possible without leaving out the critical components.
Therefore, when writing your executive summary, it’s important to keep your target audience in mind— keep in mind who will be reading your executive summary and what their needs are.
Your goal is to give them all the information they need without overwhelming them or bogging them down with too much detail.
What Are the 5 Parts of An Executive Summary
When writing an executive summary for an essay, there are various components you should never leave out.
The five critical parts of an executive essay include:
1. The background information
The first part of your executive summary should provide some background information on the topic of your essay. This will help to orient your reader and provide context for the rest of the summary.
Be sure to include important details like:
- What the essay is about;
- Who is involved in the essay;
- When the incident happens;
- Where the incidence happens;
- Why they happen.
2. A statement of purpose
The second part of your executive summary should state the purpose of your essay. You can do this in one or two sentences.
Be sure to make your statement of purpose clear and concise so that your reader knows what to expect from the rest of the summary.
3. An overview of the main points
The third part of your executive summary should give an overview of the main points in your essay.
If you’re writing the summary before the essay, this is where you will list the main arguments or ideas that you will be discussing in your essay. If your summary is coming after the essay is complete, you’ll simply state the points that have been discussed in the essay.
Be sure to include support for each point so that your reader knows what evidence to expect in the main essay.
4. Conclusion
The fourth part of your executive summary should provide a brief conclusion that ties together all of the main points from your essay.
The conclusion should briefly restate your thesis and leave your reader with a sense of closure about the topic.
5. Main recommendations
Finally, recommend the actions that could be taken from reading your essay. This section is optional but can be helpful if you want to propose specific changes or solutions based on the findings of the essay.
What to Do Before Writing an Executive Summary
Before writing your executive summary, start by reading the essay thoroughly to understand the concept. As you read, take note of the main points and arguments made in the essay.
Once you have a good understanding of the essay, then you can begin drafting the executive summary.
How Do You Write an Executive Summary for An Essay
Writing an executive summary is simple. You only need to have the five major parts in mind and follow a simple procedure. Here’s a step-by-step guide to writing the best executive summary.
1. Write the introduction
When writing an essay, you always start with the introduction. Similarly, you’ll need to start with the introduction when writing your executive summary. Start by writing a short introduction that highlights the title of the essay, the author(s), and the background of the essay.
Include a clear and concise statement that summarizes the purpose of the essay. When writing the introduction, be sure to include your thesis statement or the main argument of the essay.
2. List the main points
After the introduction, list all the main points in the order they appear in the body of the essay. Summarize the main arguments made in the body of the essay. Remember, your goal is only to provide a concise overview, so don't go into too much detail here.
3. Support the main points
After listing the main points, add one to two sentences to support each point explained in the essay. Be sure to include any supporting evidence or examples in brief.
4. Add a short conclusion
Once you’ve finished writing the main points, write a short statement that summarizes the essay’s conclusion. In other words, what is the author's overall argument or main point at the end of the essay? This forms the conclusion of your executive summary.
5. Proofread and edit
The final step in writing your executive summary is to proofread it to check for grammar, spelling, and punctuation errors.
As you proofread, identify the errors, then edit and revise the summary as needed to ensure that it is clear and concise. Remove fluffy words that don’t add meaning to the essay and re-read to ensure every sentence makes sense.
You can also make your work easier by using editing software like Grammarly to help you identify and fix grammatical errors in your summary.
6 tips for writing an executive summary
As you can see, writing an executive summary is not rocket science. Once you follow the steps outlined above, you’re on the right track.
Here are more tips to keep in mind that will help you write the best executive summary for an essay:
1. Keep it clear and concise : Skip the jargon and use simple language that’s easy to understand.
2. Keep it short : An executive summary should be no more than one page long. When it gets longer than that, it ceases to be a summary.
3. Avoid fluff : Include only the most important information in your summary. The executive summary should only include a brief overview of the main points. It’s not necessary to include every single detail in summary.
4. Edit carefully : Make sure there are no grammar or spelling errors in the executive summary before submitting it, as these may make you lose points.
5. Check for clarity : Read the summary out loud or in your head to make sure it’s easy to understand and that every statement makes sense. Delete any sentence that sounds weird or doesn’t make any sense.
6. Make it easy to read : Your assay summary should be simple for anyone to read, regardless of their academic level. Therefore, be sure to use short sentences and clear language to make your summary easy to read.
Key takeaways
An executive summary is a great way to provide your target audience with a quick overview of your essay without them having to read the entire thing.
As a student, writing an executive summary for an essay can also be very helpful when writing your essays. It gives you context for the rest of the essay and prevents you from hitting writer’s block when you start writing. Always strive to keep your executive essay summary brief, use clear and concise language, and edit carefully after writing.
These tips will help you write the best executive summary for an essay that accurately reflects the contents of the main essay, but if you’re still stuck, you can reach out to Writers Per Hour.
Our writers can help you write a top-notch executive summary from scratch which is sure to serve as the cherry on the cake!
Share this article
Achieve Academic Success with Expert Assistance!
Crafted from Scratch for You.
Ensuring Your Work’s Originality.
Transform Your Draft into Excellence.
Perfecting Your Paper’s Grammar, Style, and Format (APA, MLA, etc.).
Calculate the cost of your paper
Get ideas for your essay

- Coursework Help
- Thesis Help
- Case Study Help
- Referencing Style Help
- Proofreading Services
- Rewrite Services
- Assessment Help
- Submenu item 1
- Submenu item 2
- Referencing Style Help
- Nursing Assignment Helper
- Management Assignment Helper
- Marketing Assignment Helper
- Programming Assignment Helper
- Finance Assignment Helper
- Accounting Assignment Helper
- Law Assignment Helper
- Computer Science Assignment
- Statistics Assignment Helper
- Engineering Assignment Helper
- Science Assignment Helper
- TAFE Assignment Helper
- Economics Assignment Helper
- Dissertation Proposal
- Dissertation Writing
- Dissertation Experts
- Research Writing
- Dissertation Proofreding
- Thesis Writing
- Law Dissertation
- Nursing Dissertation
- Accounting Dissertation
- Finance Dissertation
- Economics Dissertation
- Statistics Dissertation
- Chemistry Dissertation
- Accounting Exam Quiz
- Finance Exam Quiz
- Statisics Exam Quiz
- Economics Exam Quiz
- Biology Exam Quiz
- History Exam Quiz
- Maths Exam Quiz
- Reviews 4.95/5

Importance And Procedure Of Best Executive Summary For Assignment
- The Student Helpline
- Academic Blog

Know The Importance And Procedure To Write The Best Assignment Executive Summary
Every student must produce a variety of assignments in today's world of advanced educational systems. These assignments include case studies and reports in a format and structure that is quite specific. To write a flawless assignment, you must be aware of each necessary step, and the executive summary is the critical component of those assignments. When talking about the assignment executive summary is an important part of any management assignment , which provides an overview of your research work, information, and data. This is the first impression you will make on the reader while delivering the assignment.
A well-written executive summary consists of a comprehensive summary of your document, concise background, research work, and major critical points of your topic. Therefore it is very crucial to write the executive summary in a very concise and comprehensive way. Hence, in this blog, we are going to learn to write an executive summary and its importance for business management assignment writing .
What Is The Importance Of Writing An Executive Summary For An Assignment?
An executive summary is an essential part of any management assignment, which provides an overview of the significant key points of your information. It is written to provide information related to your topic so that readers can quickly identify the data and how you have exemplified it further in your assignment. Since students must know the right way and procedure to write the executive summary for an assignment that provides a report and highlight the significant information and data in your assignment, it must deliver all the vital information regarding your introduction, methodology, results, and conclusion. It is the initial paragraph in the body of a report proposal, and it should be able to stand alone from the bigger document. A well-written executive summary will help you to analyze the problems and recommend a course of action in a brief synopsis. Also, keep in mind the importance of an executive summary, so the reader can easily understand your working model and research work. You can also define your solutions, expected outcomes, and how you have defined the topic in the right way.
How To Write An Executive Summary For An Assignment With Step-By-Step Guidance?
As we all know, the executive summary is written for the management assignment, depending on the document you are writing for. You can write the executive summary for a business plan, business case study, research document, business proposal, and other report writing. Here are some steps to write a qualitative and perfect executive summary for an assignment.
- Length Of The Executive Summary: students must be aware of the length of the executive summary since you don't have to write a long paragraph on it. Authentically, an executive summary should be under 300 words. But sometimes, it might fluctuate if you are writing a dissertation. If you don't know the right word count for the executive summary, then you just have to write the 10% of the whole report.
- Suitable Language: The language used should be suitable for the intended audience. Understanding your audience is one of the most crucial things to know before writing professionally. Therefore, always use concise language that the reader or audience can easily comprehend, and they can easily get the right information and conclusion from your paperwork.
- Concise Introduction: The first paragraph should grab the reader's interest right away. A powerful introduction paragraph can draw a reader in and encourage them to continue reading, just as a speech frequently begins with a joke to break the ice and put listeners at ease to better hear what is going to be said. This does not imply that you begin with a joke. Stick to your areas of expertise, but keep in mind that most readers will only give you a few phrases to capture their attention before they move on.
- Most Relevant Information: The executive summary shouldn't deviate from what comes after it. It's not the place to make fresh points; it's a summation. Doing so would be perplexing and put your entire proposition in danger. Simply said, you are not required to write about every issue raised in your assignment. The main keywords, outcomes, and solution to the assignment must be known to you to properly elaborate it. Determine the issue or need, and persuade your audience that it has to be fixed.
Read About: How To Frame A Management Assignment Professionally
Here Is The Right Template For Writing A Perfect Executive Summary Assignment.
Before you start writing the executive summary, a student must know its template. Also, you must know the right format for an executive summary sample. Here we have mentioned some major points for the template of the executive summary assignment.
- Focus on the Introduction
- Always include the appropriate Table of Contents in the form of a bulleted list. Describe the function of the company and list its advantages.
- Offer a suggestion and describe its benefits.
- Justify the proposed solution by outlining how it fits the company.
- A strong conclusion that emphasizes the significance of the project once more
If you are still facing any kind of issue in dealing with the executive summary then you can go through the most authentic examples of executive summary for assignment. You just have to collaborate with the assignment help services, and then you can easily be able to get the best examples for your executive summary.
This is merely a simple executive summary example that you can use as a guide. If there is still a problem when writing the executive summary, you may seek the help of an assignment writer who will assist you how in completing your executive summary in the best way possible. They are highly skilled professionals that will help you write the executive summary with the most accurate and concise information possible, which will strictly increase the quality of your work.
Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- Mathematics
- Engineering
- Programming
- Agriculture
- Dissertation
- Writing Skills
Recent Posts

You may also like

Harvard Supplemental Essays

Explanatory Essay

5 Paragraph Essay

Diversity Essay

Informative Essay Topics

- Assignments
- Dissertations
- Research Proposal
- Report Writing
- Literature Review
- CDR Writing
- Resume Writing
- Engineering
- IT & Computer Science
- Value Added Services
- Plagiarism Check
- Proofreading & Editing
- Expert Consultation
- Live Session 1-On-1
- Quality Check
- By University
- By Subject Codes
- Free Samples
- Reviews 4.5/5
- Help & Support
- Certified Experts
- Our Policies
- Ask your Question
- Request Callback
- Get $50 Off
- Get 500 Words Free
- Premium Membership
Quick Searches
- Samples - e.g. Management Assignment Samples
- Services - e.g. MATLAB Assignment Help
- Support : FAQs , Policies, Ordering Support
How to Write an Executive Summary (See Our Sample)
Author : Celina
Table of Content
Executive Summary vs Abstract: Know the Basic Differences
Steps for writing an executive summary for a report, executive summary sample, we deliver 100% authentic executive summary.
University professors generally want to know from the students what an Executive Summary is all about. Its definition is simple but writing a precise summary of a report can be a challenging task. An Executive summary is a critical section of your report or assignment, which is produced for the purpose of displaying an entire document in a clear-cut and condensed manner. This is done so that when professors read it, they get all the important information about your document, without having to go through it all. Thus, the main motive of this blog is to provide you with a successful Executive summary format, which can guide, and enable you to write a flawless and to-the-point briefing of academic documents. It will not only help you get high scores but also, you will save time and effort that can be utilized for other important tasks as well.

Students often get confused between an Executive summary and an abstract. That is okay, and we will help you to know a few basic differences between them. But, let us first understand how they are similar in nature. The purpose of both, the summary and abstract are the same, i.e., to provide a precise understanding of your entire document in a short statement. Also, they are placed at the beginning of a write-up, which means that they are independent elements and do not form a part of their main body. An abstract is usually short in length, which could be only up to ten lines long. It is generally used to provide an overview of a medium-length academic document for a reader. This enables him to quickly ascertain the document’s purpose. An Executive Summary, on the other hand, is comparatively longer than an abstract and covers a little more than one page. It is a highly condensed form of your entire work and is used in full-length documents.
Interesting Read: Writing A Winning Executive Summary
Learn how to acknowledge any source of information using the APA 7th style .
Download Now

- Start With the Subject Matter and Define : for what purpose you are writing this report. You can also write what it provides a reader with apart from its purpose. An essential way to start a summary is to briefly about the background of the problem.
- Methods of Analysis : In this part, you will talk about the most appropriate methods that have been used in the analysis of your report. There can be more than one method, but they all must aim towards a report’s goals.
- Findings : Next, you will show a few key findings from your analysis. Try not to copy them straight from its main body. Simply paraphrase them in a condensed form. You will understand this better after reading the Executive summary template provided below.
- Problem Solution : In the previous section, you must have found out various challenges and problems to your topic. So, to address them, you will define a few appropriate measures and solutions to counter those concerns.
- Recommendations and Conclusions : The second last part of your summary shall include a writer’s point of view of his recommendations apart from the problem solution. You are free to write anything, provided that they are relevant to the problem.
- Limitations : You can end an executive summary with recommendations and conclusions. But some students also prefer to add a few limitations to their report at the end of their summary. Just three to five lines will prove sufficient for this section.
You Might Like: Guide to Product Planning Summary Report Writing
To help you better understand the above steps, My Assignment Services brings you a sample of an executive summary. It will give you a clear vision of what a summary should look like. Moreover, you can also follow these steps, even if you have already written it, and still want to improve its effectiveness. With the help of this sample, we are sure that you will be able to produce an excellent grade level of work that should easily fetch you better grades and improve your academic performance. This summary is written to find a connection between work design and employee innovation. Studies show that there is a positive relationship between employee innovation and task performance. It is written exactly as per the guidelines of the student’s university. Once you read it, you will understand that it follows all the steps mentioned above in a clear and concise manner.
Executive Summary Work design is referred to as the process of defining the way work will be performed and the tasks that will be required in a given job. The purpose of this report is to find a relationship between work design and employee innovation. An array of studies has shown a positive relationship between employee innovation and task performance. However, the traditional view of task performance focuses mainly on what is within an employee’s work description, without taking into account an employee’s non-explicit contribution to an organization. This report follows the understanding that CERA is looking to free the potential of their employees and allow innovative employee thinking within and beyond their work descriptions. There is therefore a need to redefine the work design in the various departments within CERA so as to foster innovative thinking. This is a work redesign. This report will take a look at the work redesign options available to CERA, particularly focusing on Rachael Amaro’s drafting department. This report finds that the mechanistic approach is best suited for Rachael’s drafting department, because it is the most relevant approach, making it the best suited for ensuring employee innovation in Rachael’s drafting department.

Related Study Materials
- ENT203 Venture marketing proposal
- MAN7057 Digital Marketing Strategies Assignment Sample
- MKT101A Culture Bean Cafe Analysis Assignment Sample
- HC2022 Business Planning Resources Assignment Sample
- Bickford’s Premium Juice Products Analysis Assignment Sample
- The Quantitative Strategic Planning Matrix Assignment Sample
- Using Data Sciences in Marketing Assignment Sample
- Blending Traditional and Digital Marketing Assignment Sample
- Macro-Social Marketing Assignment Sample
- Business-To-Business Marketing Assignment Sample
Our Experts can answer your Assignment questions instantly.
Loved reading this Blog? Share your valuable thoughts in the comment section.
About the Author
Hello, everyone! I’m Celina, an educationist and academic consultant. I enjoy reading, learning, and implementing the same in the assignments. I also take a lot of pride in guiding students with their assignments. I have 6 years of experience in writing assignments for students and when not doing that I follow my passion for blogging. I spent my spare time often researching new trends of writing.
How Our Project Management Assignment Samples Will Help You?
Finance accounting assignment help (gaap - assb), related posts.

Major's Courses In Melbourne University (Part 3/3)
June 26, 2018.

Assignments Are a Threat to Creativity
March 31, 2018.

Longest Day is Here - Welcome June Solstice!
June 21, 2018, get quote in 5 minutes*.
- Algeria (+213)
- Antigua and barbuda (+1268)
- Australia (+61)
- Austria (+43)
- Azerbaijan (+994)
- Bahrain (+973)
- Bangladesh (+880)
- Canada (+1)
- China (+86)
- Congo (+243)
- Cyprus (+357)
- Europe (+3)
- France (+33)
- Germany (+49)
- Ghana (+233)
- Greece (+30)
- Hong kong (+8)
- Hungary (+36)
- India (+91)
- Indonesia (+62)
- Iran (islamic republic of) (+98)
- Ireland (+353)
- Jamaica (+1)
- Japan (+82)
- Jordan (+962)
- Kazakhstan (+7)
- Kenya (+254)
- Kuwait (+965)
- Latvia (+371)
- Lesotho (+266)
- Malaysia (+60)
- Maldives (+960)
- Malta (+356)
- Mauritius (+230)
- Myanmar (+95)
- Namibia (+264)
- Nepal (+977)
- Netherlands (+31)
- New zealand (+64)
- Nigeria (+234)
- Norway (+47)
- Oman (+968)
- Pakistan (+92)
- Papua new guinea (+675)
- Philippines (+63)
- Poland (+48)
- Qatar (+974)
- Saudi arabia (+966)
- Singapore (+65)
- Somalia (+252)
- South africa (+27)
- South korea (+82)
- Spain (+34)
- Sri lanka (+94)
- Sweden (+46)
- Switzerland (+41)
- Taiwan (+886)
- Thailand (+66)
- Turkey (+90)
- Uganda (+256)
- Ukraine (+380)
- United arab emirates (+971)
- United kingdom (+44)
- United states america (+1)
- Uzbekistan (+998)
- Vietnam (+84)
- Yemen (+967)
- Zambia (+260)
- Zimbabwe (+263)
1,212,718 Orders
4.9/5 Rating
5,063 Experts

Bonanza Offer Get 40% Off * on your assignment today
Trending now
How to Write a Reflection Paragraph in an Assignment?
Project management assignment sample online, project proposal assignment sample online, how to solve cubic equation ax^3+ bx^2+ cx+d = 0, impact of western systems and structures on aboriginal and torres strait islander cultures, best digital marketing assignment sample online, marketing assignment sample online, how to write gibbs reflective cycle, why are ethics important in research, business management assignment sample online, advantages & disadvantages of conceptual framework (cf) in accounting.
The Student Corner
Subscribe to get updates, offers and assignment tips right in your inbox.
Popular Posts
- Assignment Help How to Write a Reflection Paragraph in an Assignment? Mike Carey June 16, 2018
- Management Project Management Assignment Sample Online Charles Hill October 04, 2017
- Assignment Help Project Proposal Assignment Sample Online Andy Johnson October 25, 2017
- Engineering How To Solve Cubic Equation Ax^3+ Bx^2+ Cx+D = 0 Chloe Kirner March 22, 2019
- General Impact of Western Systems and Structures on Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Cultures Celina January 15, 2020
- Marketing How to Write an Executive Summary (See Our Sample) Celina May 11, 2018
Download Guide Book
- Australia(+61)
- Germany(+49)
- Hong kong(+8)
- Ireland(+353)
- Jordan(+962)
- Kenya(+254)
- Malaysia(+60)
- New zealand(+64)
- Nigeria(+234)
- Pakistan(+92)
- Saudi arabia(+966)
- Singapore(+65)
- South africa(+27)
- Sweden(+46)
- United arab emirates(+971)
- United kingdom(+44)
- United states america(+1)
Searching across 1 Million Samples...
Doing your Assignment with our samples is simple, take Expert assistance to ensure HD Grades. Here you Go....
Today's Special Get Upto 50% OFF *

Select Coupon

Get Quote In 5 Minutes*

Popular Searches
- Order An Assignment
- Ask Prices?
- Amazing Offers
- Why Prefer us?
- Exclusive Offer Buy One Get One Free! Claim Now
- Other Services
Executive Summary Help Australia
Don't Let Deadlines Scare You! Receive Complete Assistance from start to end for High Grades.
- Affordable & Budget-Friendly Rates.
- Expert Assistance with Assignments, Dissertations, Reports, Exams, and more.
- FREE Turnitin Report.
- Trusted by 250k+ Students .
- Rated 4.9/5 across Australia, US, and UK.
Get Quote In 2 Minutes*
Stay Calm, Achieve Success & Secure Your Path without Stress!
- (+213)" > Algeria (+213)
- (+268)" > Antigua And Barbuda (+268)
- (+61)" > Australia (+61)
- (+43)" > Austria (+43)
- (+994)" > Azerbaijan (+994)
- (+973)" > Bahrain (+973)
- (+880)" > Bangladesh (+880)
- (+55)" > Brazil (+55)
- (+1)" > Canada (+1)
- (+86)" > China (+86)
- (+243)" > Congo (+243)
- (+357)" > Cyprus (+357)
- (+45)" > Denmark (+45)
- (+849)" > Dominican Republic (+849)
- (+20)" > Egypt (+20)
- (+3)" > Europe (+3)
- (+679)" > Fiji (+679)
- (+358)" > Finland (+358)
- (+33)" > France (+33)
- (+220)" > Gambia (+220)
- (+49)" > Germany (+49)
- (+233)" > Ghana (+233)
- (+30)" > Greece (+30)
- (+592)" > Guyana (+592)
- (+852)" > Hong Kong (+852)
- (+36)" > Hungary (+36)
- (+91)" > India (+91)
- (+62)" > Indonesia (+62)
- (+98)" > Iran (islamic Republic Of) (+98)
- (+964)" > Iraq (+964)
- (+353)" > Ireland (+353)
- (+1)" > Jamaica (+1)
- (+81)" > Japan (+81)
- (+962)" > Jordan (+962)
- (+7)" > Kazakhstan (+7)
- (+254)" > Kenya (+254)
- (+965)" > Kuwait (+965)
- (+371)" > Latvia (+371)
- (+961)" > Lebanon (+961)
- (+266)" > Lesotho (+266)
- (+60)" > Malaysia (+60)
- (+960)" > Maldives (+960)
- (+356)" > Malta (+356)
- (+230)" > Mauritius (+230)
- (+976)" > Mongolia (+976)
- (+95)" > Myanmar (+95)
- (+264)" > Namibia (+264)
- (+977)" > Nepal (+977)
- (+31)" > Netherlands (+31)
- (+64)" > New Zealand (+64)
- (+234)" > Nigeria (+234)
- (+47)" > Norway (+47)
- (+968)" > Oman (+968)
- ()" > Other ()
- (+92)" > Pakistan (+92)
- (+675)" > Papua New Guinea (+675)
- (+63)" > Philippines (+63)
- (+48)" > Poland (+48)
- (+974)" > Qatar (+974)
- (+7)" > Russian Federation (+7)
- (+966)" > Saudi Arabia (+966)
- (+65)" > Singapore (+65)
- (+252)" > Somalia (+252)
- (+27)" > South Africa (+27)
- (+82)" > South Korea (+82)
- (+34)" > Spain (+34)
- (+94)" > Sri Lanka (+94)
- (+211)" > Sudan (+211)
- (+46)" > Sweden (+46)
- (+41)" > Switzerland (+41)
- (+886)" > Taiwan (+886)
- (+66)" > Thailand (+66)
- (+90)" > Turkey (+90)
- (+256)" > Uganda (+256)
- (+971)" > United Arab Emirates (+971)
- (+44)" > United Kingdom (+44)
- (+1)" > United States America (+1)
- (+998)" > Uzbekistan (+998)
- (+84)" > Vietnam (+84)
- (+967)" > Yemen (+967)
- (+260)" > Zambia (+260)
- (+263)" > Zimbabwe (+263)
Bring Perfection To Your Executive Summary With Our Experts!
What makes us the best help for executive summary assignment in australia.
Are you stuck with writing your executive summary or do not know how to further proceed with that? Or you do not know what an executive summary is all about? Don't worry!! You are at the right place for finding your solution!!
An executive summary is a piece of short document that is related to a particular business or field per se. The whole intention to write an executive summary is to summarize the facts of a lengthy document to give the reader an idea of what is written in that lengthy file.
So is your best friend scoring more than you and showing off? Don't get stressed as the services provided by our experts of writing executive summary assignment in Australia will help you score the best in your class. Does that give you a sense of relief?

When it comes to writing an executive summary for assignment, students often find it difficult as they are anyways short of time to read such lengthy articles, journals, and files to summarise it and even though when they even try, they tend to miss some important parts from the document which leads them to a bad result for their scorecard. But students do not need to worry about writing your executive summary or executive summary report as an impeccable online executive summary assignment is just a click away to take over their entire load related to your academic writing.
We understand the frustration you go through just with the thought of reading lengthy documents. Our services have the potential to provide you with an excellent solution. So why to look for some other online platform? The best is there to serve you. As we believe in providing the original quality content and even minor plagiarism comes under the zero-tolerance policy of our organisation. And along with this, the experts will strictly abide by your instructions while preparing assignment so that any of your requirements are not missed.
Don't worry if it is your first time here!! You will not leave getting disappointed!! That's our promise to you!!
The experts know how to write an executive summary for an assignment. They are very dedicated and extremely talented when it comes to crafting an executive summary. We have the experts who hail from the prestigious universities from all around the globe and who are native English speakers and holds an extremely good command over the language. This is done to ensure that the experts are capable enough to go through the entire document with ease and does not find any difficulty in understanding the subject per se. With us, you can also avail an executive summary sample for assignment through which you can easily gauge the executive summary writing skills of our experts.
We have a robust team of well-versed experts for writing online executive summary assignments who keenly scan a document so that any important information is not missed. The experts include all the relevant facts, problems along with the solutions, measures or the steps to be taken, and at last the analysis and the conclusion over the topic to assure the readers or students that the documents have been carefully scanned by the person who wrote the executive summary of the document. Thereby, various examples of executive summary for an assignment can be found by a student.
An executive summary sample for the assignment has been provided on our portal of Sample Assignment . So that the students can see the piece of various executive summaries written by our extremely talented experts to get an idea as to what an incredible piece of an executive summary they will receive, once the student provides us with a chance to serve them with executive summary assignment in Australia.
The scholars who avail help for executive summary assignments in Australia are enrolled in various programs such a graduation, post-graduation and even PhD holders are there to diligently craft your assignment.

Our executive summary assignment services believe in providing the students with their respective assignments before the given deadline to ensure that the student has ample time to figure out any irregularity in their assignment so that the revised assignment can reach them within the deadline and it will not affect their grades in a long run.
This is a major reason why our services for providing help with online executive summary assignment offer aid to numerous students all across Australia. To assure that they won't receive fewer marks despite putting so many efforts in their assignments.
The executive summary sample will include a summary of the report, which will target the audience mindset; the expert will pay emphasis on maintaining order for writing an executive summary and will not include any extra information which is not required. Justifications and recommendations will be made by the experts in your executive summary. The expert will use the bullet points along with the sub-headings to make the reader more aware as to what is written in the lengthy document.
Our services for writing an executive summary report are extremely affordable keeping in mind the money crunch of the students. Our motto is to make sure that all the students can avail of our best assignment writing services without any fail especially all our students should be able to afford them.
We offer students with round the clock customer care services to solve every query for our online executive summary assignment writing to maximize the student's satisfaction.
Confidentiality is the biggest criteria considered by us. Any personal information cannot be shared with any third party.
You can avail our services in three easy steps:
- Upload your assignment questions on our portal with additional requirements such as subject, topics, word count, and referencing style, etc.
- Choose your deadline, you can also avail the express assignment help in which the assignment will be delivered within 6 hours.
- Click on pay now and you can avail some exciting discounts, you can also place your order in a group and enjoy group discounts with us.
So what are you waiting for? Come and avail our services of writing an executive summary for assignments and enjoy the best grades in class.
Related Links:
- OSH Assignment Help Australia
- CELTA Assignment Help Australia
- NCFE Assignment Help Australia
- Essay Writing Service Australia
- Ocaml Assignment Help Australia
- Treat Assignment Help Australia
- Erlang Assignment Help Australia
- Fashion Assignment Help
- Safety Assignment Help Australia
- Tourism Assignment Help Australia
Clients Speaks

Get Flat 50% Off on your Assignment Now!

Request Callback
- Algeria (+213)
- Australia (+61)
- Bahrain (+973)
- Bangladesh (+880)
- Canada (+1)
- China (+86)
- Europe (+3)
- Germany (+49)
- Hong kong (+8)
- India (+91)
- Iran (islamic republic of) (+98)
- Ireland (+353)
- Jordan (+962)
- Kenya (+254)
- Malaysia (+60)
- Myanmar (+95)
- New zealand (+64)
- Nigeria (+234)
- Pakistan (+92)
- Qatar (+974)
- Saudi arabia (+966)
- Singapore (+65)
- Somalia (+252)
- South africa (+27)
- Sri lanka (+94)
- Sweden (+46)
- United arab emirates (+971)
- United kingdom (+44)
- United states america (+1)

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Executive summaries are common in the Walden MBA program, but they are also found as part of some government and business documents. As a student, you should complete an executive summary when specifically requested to do so. An executive summary is a comprehensive review of a larger document. For example, a 35-page report may begin with a ...
Typically, your executive summary should be a one-pager (one and a half pages at worst). To summarise a 3000 - 5000-word document into one page is no easy task, so you'll need to: Present only the most important information (key insights, recommendations, etc). Write concisely - i.e. with brevity and completeness.
1000 words - a stand-alone document. Usually, 1-2 pages in. PAEs. Writing: concise sentences, active voice, jargon-free (define terms). Key components: Problem statement (1-2 paragraphs, not all factors) Problem statements answers "what's wrong" and will possibly quantify the scope of the problem with 1-2 data points.
How to Write an Executive Summary . An executive summary is a concise document, demonstrating the problem, findings and recommendation of a longer policy report. Writing an executive summary will help your audience quickly understand the policy problem and proposed solution of your report. It is intended for a busy reader; and is a
An executive summary is a thorough overview of a research report or other type of document that synthesizes key points for its readers, saving them time and preparing them to understand the study's overall content. ... of academe, while abstracts are written for the academic community. Professors, therefore, assign the writing of executive ...
An executive summary is a brief overview of a document's purpose, results, and conclusions condensed for the quick reading of an executive or manager. It is placed at the beginning of a longer report or proposal and summarizes specific aspects of its content. The reader of the summary is usually not interested in the technical details of a ...
Provide a logical order for the reader by stating the main points in the order they are covered in the assignment. Remember how important your assignment heading is. This will be read even before the executive summary. It needs to be clear, professional, and interesting. Have a rest before proofreading.
In general, there are four parts to any executive summary: Start with the problem or need the document is solving. Outline the recommended solution. Explain the solution's value. Wrap up with a conclusion about the importance of the work. Free cross-functional project template.
Compare Example Executive Summaries (PDF) When readers want you to communicate your findings in a clear, no-nonsense way, the executive summary is the first place they look. However, most executive summary readers are busy and do not always have a nuanced understanding of your research field. This can be a problem! Luckily, we can teach you ...
The executive summary is not an abstract for your assignment. An extract is neither stand-alone nor a comprehensive synopsis of the assignment An executive summary should be focused. It needs to be written clearly and concisely ... - A Research Guide for Students, 'Tips How to Write an Executive Summary Properly', Available at: https://www ...
Here are several general steps to consider when writing an executive summary: 1. Research effective executive summaries. Before you write your own executive summary, it may be helpful to review summaries written by others. This is especially true for those writing an executive summary for the first time.
An executive summary should summarize the key points of the report. It should restate the purpose of the report, highlight the major points of the report, and describe any results, conclusions, or recommendations from the report. It should include enough information so the reader can understand what is discussed in the full report, without ...
Step 3: Outline the structure. Create an outline for your executive summary with sections like introduction, objective, methodology, findings, recommendations, and conclusion. This way, you'll have a logical flow that's easy to follow.
It usually has three sections: introduction, main body and conclusion. The introduction sets the scene, and explains what the paper is about, including what action needs to be taken as a result. It doesn't need to be more than one or two sentences. For an internal paper, you might write: This paper explains the findings of the research about ...
The format of an executive summary is comprised of the following: The subject is mainly the introduction of the assignment. Analysis and Methods represent to the methods you have used and your analysis. Findings include data results. Conclusion - solutions to the problems discussed in the assignment. Recommendations - proposed ...
As a rule of thumb, executive summaries are 10% of the entire document or less. Writing the Executive Summary: Place the executive summary on its own page (s). The first paragraph should immediately capture the reader's attention, whether it's a story, surprising fact, or insightful quote. Experts recommend using bullet-points (when possible ...
The executive summary should typically be only 10% the length of the full proposal it distills. Therefore, the executive summary for a 10-page proposal would be 1 page or less. Stand Alone. The summary should be written in a way that it can be read as a stand-alone document. Before submitting it, allow a test subject to read the summary.
2. A statement of purpose. The second part of your executive summary should state the purpose of your essay. You can do this in one or two sentences. Be sure to make your statement of purpose clear and concise so that your reader knows what to expect from the rest of the summary. 3.
Here Is The Right Template For Writing A Perfect Executive Summary Assignment. Before you start writing the executive summary, a student must know its template. Also, you must know the right format for an executive summary sample. Here we have mentioned some major points for the template of the executive summary assignment. Focus on the ...
Learning Development p: 4921 5350 e: [email protected]. An executive summary provides the essential information of the report as a whole. There are many types of report, so the following table describes the main features of the beginning, middle and end that would be included in an executive summary. You need to be aware of the type and ...
Executive Summary Sample. To help you better understand the above steps, My Assignment Services brings you a sample of an executive summary. It will give you a clear vision of what a summary should look like. Moreover, you can also follow these steps, even if you have already written it, and still want to improve its effectiveness.
Thereby, various examples of executive summary for an assignment can be found by a student. An executive summary sample for the assignment has been provided on our portal of Sample Assignment. So that the students can see the piece of various executive summaries written by our extremely talented experts to get an idea as to what an incredible ...