An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- HHS Author Manuscripts


Mental Ill-Health Risk Factors in the Construction Industry: Systematic Review
Albert p. c. chan.
1 Professor, Chair Professor and Head, Dept. of Building and Real Estate, Hong Kong Polytechnic Univ., 11 Yuk Choi Rd., Hung Hom, Kowloon, Hong Kong, China
Janet M. Nwaogu
2 Ph.D. Candidate, Dept. of Building and Real Estate, Hong Kong Polytechnic Univ., 11 Yuk Choi Rd., Hung Hom, Kowloon, Hong Kong, China
John A. Naslund
3 Instructor, Dept. of Global Health and Social Medicine, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA 02115
Mental ill health is a significant cause of suicide and disability worldwide. It has particularly affected the construction industry. The construction labor sectors in Australia and the United Kingdom have suicide rates 2 and 3.7 times higher, respectively, than their overall national averages, which has attracted the attention of researchers and the industry. However, few studies have examined the state of construction workers’ mental health. This paper systematically reviews the existing body of knowledge on mental health in the construction industry. In total, 16 journal articles met inclusion criteria, and 32 risk factors (RFs) were deduced. The foremost RFs were related to job demand and job control. A conceptual framework and checklist to aid in better understanding these RFs were developed. In assessing mental health, the primary tool used was the Depression Anxiety Stress Scale. The findings of this study help to deepen the understanding of professional mental health assessment scales and relevant RFs and protective factors as used in the construction industry. The study concludes that stronger methodologies are needed for studies into RFs and protective factors in the construction industry.
Introduction
Workers in the construction industry must endure different weather conditions and engage in repetitive and strenuous jobs ( Boatman et al. 2012 ). Many construction projects are nomadic and cyclical, resulting in high unemployment rates ( European Agency for Safety and Health at Work 2007 ). Other characteristics of the industry include high job demand, long working hours, and unrealistic deadlines ( Beswick et al. 2007 ). These characteristics can have major consequences on the physical and mental health of construction workers.
Considerable research shows that physical and mental health problems can arise from stress related to work and the workplace ( Wang et al. 2017 ). It is essential to monitor the impact of psychosocial risk factors (RFs) on the health of workers, to better understand their effects on mental health and wellbeing, thereby helping to reduce workplace injuries, prevent disabilities, and increase productivity ( Boschman et al. 2013 ). Poor mental health and risk of mental illness have taken a toll on the construction industry in several countries, as reflected by a high risk of depression, anxiety, suicidality, and eventual suicide ( Burki 2018 ; Kamardeen and Loosemore 2016 ; Milner et al. 2015 ). For example, Jacobsen et al. (2013) surveyed workers at a construction site, where 9 of 10 survey respondents reported having mental health challenges and required medical follow-up.
According to the WHO (2001 , p. 1), mental health is “a state of well-being in which the individual realizes his or her abilities, can cope with the normal stresses of life, can work productively and fruitfully, and is able to make a contribution to his or her community.” The definition signifies that good mental health is foundational for well-being and effective functioning ( Herrman and Jané-Llopis 2005 ), while mental ill health (poor mental health) hinders an individual’s ability to realize their potential, work productively, and contribute to their community ( Herrman and Jané-Llopis 2012 ). Common mental health problems in the working population include anxiety and depression ( Battams et al. 2014 ; Grove 2006 ).
Mental ill health has substantial economic costs to nations, organizations, and individuals, which is prevalent in the heavy labor industries. In the United Kingdom (UK), approximately 400,000 workdays per year are reported lost to mental ill health and, specifically among construction workers, there were 1,419 suicides between 2011 and 2015, amounting to 3.7 times the UK national average ( Burki 2018 ). In Australia, death resulting from suicide among construction workers is 2 times the Australian national average ( Mates in Construction 2018 ; Gullestrup et al. 2011 ). Mental ill health or poor mental health is also a risk factor for workplace injuries and fatalities ( Palmer et al. 2014 ; Siu et al. 2004 ). For instance, in the Australian construction industry, for every death lost to fatal workplace accident, six of such cases were intentional suicide (J. Gullestrup, “To study workplace and industry approaches to mental health and suicide prevention globally,” unpublished report, 2019).
Previous studies have revealed that mental ill health and occupational injury have a direct relationship. Park et al. (2001) , through a prospective study, explained that workers with depressive symptoms are at three times the risk of workplace injury and fatalities. Park and colleagues found that, among farmers, depressive symptoms and amount of hours worked were associated with increased workplace injuries. Anxiety, depression, and psychological distress are found to cause sleep problems ( Bowen et al. 2018 ; Taylor et al. 2005 ), which adversely affect well-being and safety. Similarly, in the construction industry, sleep problems are associated with fatigue, which in turn causes workplace injuries and accidents ( Powell and Copping 2016 , 2010 ). Additionally, depression is a significant correlate of fatigue ( Sadeghniiat-Haghighi and Yazdi 2015 ).
Many studies have linked work stress to poor mental health and suicide; however, concerns have been raised about the scarcity of research addressing other factors that can interplay with work-related factors to cause mental health issues and suicide ( Sunindijo and Kamardeen 2017 ). Mental health prevention programs have demonstrated effectiveness and reduction in costs for health management ( Sandler et al. 2014 ; Knapp et al. 2011 ). However, successful prevention of mental health problems and its burden can only be realized after identifying the attributes and exposures, known as risk factors, that can threaten mental health ( Furber et al. 2017 ). Increased insight into risk factors for mental ill health among the construction workforce is necessary to inform the selection of appropriate interventions ( Boschman et al. 2013 ) for achieving a psychologically healthy and safe workplace.
Based on the preceding, the purpose of this study was to systematically review the body of knowledge regarding mental health in the construction industry and, specifically, to evaluate the different risk factors for mental ill health and how mental health has been assessed in the construction industry. Given that few studies to date have used validated scales for assessing mental health in the construction industry ( Love et al. 2010 ), this review addressed the followings questions: (1) what validated mental health diagnosis tools have been used to identify or screen for the state of mental health among construction workers? and (2) what are the risk factors for mental ill health and protective factors for mental health among construction workers?
The overall objective of the study was to provide a guide on how best to evaluate the mental health of construction workers and identify the most appropriate mental health interventions for this population. Further, this review will help researchers focus on specific risk factors for adequate mental illness prevention in the construction industry, which can also inform prevention efforts in other heavy labor industries facing elevated risks of mental ill health and suicide.
Search Strategy
The databases of PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science (WoS) core collection were searched. These databases were selected because PubMed contains the largest concentration of health-related journals ( Harris et al. 2014 ; Fiordelli et al. 2013 ), while Scopus and WoS provide a comprehensive collection of journals in the field of science and are most frequently visited ( Aghaei Chadegani et al. 2013 ). More important, according to Harris et al. (2014) , using one database to retrieve journals during a systematic review is insufficient. For that reason, these various databases were visited.
Several search strings were used; the terms with the highest output related to the domains of “mental health*” “construction industry*”; “psychological health*”; and “construction industry.” Google Scholar was searched with specific studies identified from citations and reference lists of articles retrieved from the initial database searches.
Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
To ensure that studies were eligible for this review, inclusion and exclusion criteria were set. Studies were included if they satisfied all the following criteria:
- Assessed the mental health status of construction workers using a validated scale or at least four questions (items) extracted directly from a validated scale or previous study. In the case of items retrieved from an earlier study, the reference study should have derived the items from a validated mental health scale.
- Studied common mental health problems such as depression, anxiety, and posttraumatic stress disorder. Studies that considered psychological (mental) distress or strain were included if they fulfilled condition (1).
- Considered stressors of mental health, referred to as risk factors for mental ill health;
- Represented a main empirical study and not a pilot study. A pilot study, in this case, was defined as a preliminary study, primarily conducted to test the feasibility of proposed empirical research. According to Fraser et al. (2018) , a pilot study is a precursor to the main research, carried out basically to determine the feasibility of using a designed questionnaire and inform on changes needed to improve on subsequent data collection. Pilot studies were considered only in cases where the pilot was not followed by a main empirical study.
- professionals, supervisors, construction project managers involved in planning, coordinating, and controlling construction projects, and
- frontline workers involved in the manual aspects of construction work.
- Were written in English.
Studies reported in conference presentations, book chapters, reviews, perspective articles, and editorial documents were excluded. Therefore, only empirical studies published in journal articles were included. The reason for this selection criterion is that journal articles undergo peer review, whereas other types of publications, such as conferences papers or grey literature, do not undergo the same rigorous review before publication ( Olawumi and Chan 2018 ). Also, unlike other sources, journal articles generally provide comprehensive and reputable sources of information in a field of study ( Zheng et al. 2016 ; Yi and Chan 2014 ; Ramos-Rodríguez and Ruíz-Navarro 2004 ).
Data Extraction and Synthesis
The data extraction process began with reading the abstracts of identified articles. The following characteristics were noted: target population, methodology, mental health assessment instrument, and research outcome. In cases where the abstracts were not well detailed, the method or data collection section was read to assess eligibility. Only those articles that met eligibility criteria were subjected to further scrutiny. The documents were read thoroughly and the study process and outcomes were recorded. To avoid bias, the reasons for exclusion and findings from the studies were reviewed. After that, the selected studies were independently reviewed and confirmed for correctness of extracted data.
Final Article Selection
The initial database search yielded 107 articles (PubMed = 21; Scopus = 50; and WoS = 36). After removing duplicates, 50 articles were subjected to scrutiny using the inclusion criteria. Thereafter, only 13 articles fell within the inclusion criteria. On reading the 13 articles, additional articles were identified from the citations and reference lists; these articles were viewed in Google Scholar, resulting in three additional journal articles that met the inclusion criteria. Ultimately, 16 articles were included in the review. These articles are deemed adequate based on a similar study of risk factors in male-dominated industries that used 18 articles ( Roche et al. 2015 ). Also, Joyce et al. (2010) selected 10 articles in a well-being-related review after allowing for inclusion and exclusion criteria.
Fig. 1 illustrates the search strategy, exclusion, and inclusion of the final eligible studies. Table 1 provides the details of the included studies and their findings. The following sections summarize the mental health assessment tools employed in the construction industry and the various mental ill-health risk factors and protective factors in the literature, and offer a conceptual framework for mental ill-health risk factors in the construction industry.

Flow chart for the study articles.
Mental health studies and diagnosed mental illnesses
Mental Health Assessment Tools Used in the Included Studies
Eleven mental health assessment tools were identified in the included studies ( Fig. 2 ). These scales were used in 13 studies; in the 3 remaining studies, mental health was probed by using questions extracted from previous studies. Five studies used depression-specific screening tools, particularly the Whooley Depression Screen questions, Center for Epidemiological Studies–Depression (CES–D) Scale, and Hamilton Depression Scale (HAM-D) ( Table 1 ). Thus, these studies screened for depression and its causal factors among construction workers. One study employed an anxiety-specific tool, namely the State-Trait Anxiety Index (STAI-T).

Mental health assessment tools used in the selected studies.
Two studies assessed posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) using two PTSD-specific scales, the Impact of Event Scale (IES) and ICD-10 Classification of Mental and Behavioral Disorder. In one study, the ICD-10 was used to classify construction workers into PTSD and non-PTSD groups, after which the severity of depression was assessed in each category using HAM-D ( Hu et al. 2013 ). Eight studies employed multivariant mental health assessment questionnaires, including the Depression Anxiety Stress Scales (DASS), Hopkins Symptom Checklist (HSCL), General Health Questionnaire (GHQ), and Crown-Crisp Experiential Index (CCEI) ( Table 1 ). All the scales use cut-off points to report the degree of the mental health problem.
DASS was used in five studies ( Kamardeen and Sunindijo 2017 ; Langdon and Sawang 2018 ; Sunindijo and Kamardeen 2017 ; Al-Maskari et al. 2011 ; Haynes and Love 2004 ). This questionnaire measures depression, anxiety, and stress ( Nieuwenhuijsen et al. 2003 ), although the included studies primarily focused on depression and anxiety. The CCEI measures types of anxiety, depression, and hysteria ( Joukamaa 2009 ), and was used in one study to diagnose for depression and anxiety ( Sutherland and Davidson 1993 ). GHQ-28 measures somatic, anxiety, and social dysfunction and severe depression ( Okubo et al. 2011 ), and was used in one of the studies ( Love et al. 2010 ).
One study screened for depression and anxiety using HSCL-25 ( Jacobsen et al. 2013 ). This study revealed that HSCL-25 was employed in the construction industry to determine mental health status following pain and injuries, which are quite typical in the construction workplace ( Jacobsen et al. 2013 ). Generally, the studies revealed a high prevalence of depression and anxiety among construction workers. Fig. 3 shows the scales used for the types of mental ill-health diagnosis and the respective studies.

Mental ill-health and validated assessment scales used in the articles reviewed.
Three studies evaluated the effect of occupational stress on the mental health of construction workers by using four to eight questions extracted from previous studies or scales ( Bowen et al. 2018 , 2014 ; Lingard et al. 2007 ). Two studies ( Jacobsen et al. 2013 ; Al-Maskari et al. 2011 ) reported suicide ideation among construction workers; one of the studies did not employ a professional tool, but the other used the Mini International Psychiatric Interview (MINI). MINI is a multivariant assessment tool for diagnosing depression, anxiety, and suicidality ( Li et al. 2017 ), and was employed in one study for suicide risk assessment ( Jacobsen et al. 2013 ).
Validated Mental Health Assessment Scales Used in the Studies
DASS is a psychometric test that can be administered to determine the severity of depression, anxiety, and stress experienced over a past week ( Ibrahim et al. 2014 ). It is available in variants of DASS 42 or DASS 21, with each having three subscales. The numbers signify the amount of questions in the test. In DASS 21, there are seven questions per subscale, while DASS 42 contains 14 each. DASS has excellent psychometric properties and is adequate for evaluating mental ill health in employees and general populations ( Nieuwenhuijsen et al. 2003 ). DASS is easy to use and effective in detecting change after clinical diagnosis of mental ill health; however, recently, it has been used without a prior diagnosis ( Ng et al. 2007 ). Interestingly, DASS is freely available for use.
GHQ is a widely used psychological health screening tool developed by D. Goldberg ( Montazeri et al. 2003 ; Donath 2001 ). It is used to evaluate emotional distress and psychiatric disorders ( Sterling 2011 ). GHQ assesses somatic symptoms, anxiety, social dysfunction, and depression ( Okubo et al. 2011 ). The tool measures mental health based on the preceding weeks. The tool is available in variants of 60, 30, 28, and 12 item questions as GHQ-60, GHQ-30, GHQ-28, GHQ-12, respectively, and is copyrighted.
HSCL-25 is used to screen for anxiety and depression. HSCL-25 contains 10 items on an anxiety subscale and 15 items on a depression subscale ( Ventevogel et al. 2007 ). Initially, it was designed for use among refugees; in recent times, it is used in screening for mental health among postconflict populations and traumatized refugees. This study revealed that HSCL-25 was used in the construction industry to determine mental health following pain and injuries, which are quite typical in a construction workplace ( Jacobsen et al. 2013 ).
CCEI is a self-rating mental health assessment tool used to screen for anxiety, depression, and hysteria ( Joukamaa 2009 ). CCEI has six subscales containing eight questions each for assessing free-floating anxiety, phobic anxiety, obsessionality, somatic anxiety, depression, and hysteria.
CES–D Scale
CES–D, developed by the National Institute of Mental Health, is ideal for assessing depression symptoms in the general population ( Radloff 1977 ). It contains 20 questions scored from 0 to 3; a higher score is directly proportional to higher severity of depression. However, scores ≥16 indicate the presence of depression ( Dyrbye et al. 2006 ). CES–D is available in variants of 10 and 20 and is not copyrighted.
Whooley Depression Screen
The Whooley Depression Screen is a two-item questionnaire used to assess depression. The questions are designed to elicit a “yes” or “no” answer. For example, one of the questions is, “During the past month, have you often been bothered by little interest or pleasure in doing things?” If the respondents answer “yes” to either of the two questions, they are given another assessment tool called the “help question” ( Suija et al. 2012 ). According to Howard et al. (2018) , the Whooley questions are useful in identifying mental health problems but do not adequately indicate the presence of depression.
HAM-D, developed by A. S. Zigmond and R. P. Snaith, is a 17-item assessment tool used to measure the frequency and state of depression ( Akdemir et al. 2001 ). According to Licht et al. (2005) , HAM-D reliability had been questioned; however, in recent times, it has seen wide application.
STAI-T is a 40-item anxiety assessment tool available in two versions ( Julian 2011 ). According to Balsamo et al. (2013) , the tool assesses state and trait anxiety. To effectively evaluate anxiety, STAI-T has two subscales: state anxiety (S-anxiety) and trait anxiety (T-anxiety) subscales. The S subscale assesses the intensity of feelings and the T subscale evaluates the frequency of anxiety. STAI-T is widely used for assessing anxiety, especially in cases that involve musculoskeletal pain ( White et al. 2002 ). Like other assessment tools, it uses cut-off points, and a higher subtest score indicates greater anxiety.
ICD-10 outlines reliable criteria specifically for conducting research on and classification of mental ill health. It helps to ensure the selection and grouping of individuals with the same symptoms using clearly defined characteristics. It was used in one of the selected studies to identify construction workers with PTSD and those without PTSD. Each group of respondents was assessed for depression using HAM-D ( Hu et al. 2013 ). According to ICD-10, for proper identification of PTSD, the features to look out for include flashbacks, detachment from people, sense of numbness, emotional blunting, hyperarousal, and emotional responses following a traumatic event. A psychiatrist or trained social worker usually administers the ICD-10.
Impact of Event Scale
The Impact of Event Scale (IES) is a good instrument for assessing posttraumatic stress and identifying individuals who require medical attention ( Sundin and Horowitz 2002 ). The IES has two subscales used to measure two types of stress reaction. It has been proven highly valid in detecting PTSD ( Rothbaum et al. 1992 ). The scale elicits information on frequency at which PTSD symptoms were experienced over a preceding week using a scoring system of 0, 1, 3, and 5, respectively. Initially, the IES did not measure the hyperarousal symptom of PTSD as outlined by the Diagnostic Symptom Measure IV (DSM IV). To correct this deficiency, a revised IES with six additional questions and modified response to a 5-point scale with equal intervals 0–4 was developed ( Creamer et al. 2003 ).
MINI is a multivariant assessment tool used to diagnose for depression, anxiety, and suicidality ( Li et al. 2017 ). It can be employed independently or as a second-phase mental ill-health assessment tool. Most often, MINI is used as a second-stage or further diagnostic tool to probe certain concerns raised in a previous assessment ( Li et al. 2017 ), in which case, respondents with severe depression are further examined using MINI module B. MINI module B helps to assess effectively for suicidality. Diagnoses of anxiety and depression, which are the most common mental health problems, can be difficult, and these conditions can be easily overdiagnosed or underdiagnosed.
According to Pettersson et al. (2018) , to mitigate over- or underdiagnoses, a structured interview is deemed important as part of the assessment process. The study further explained that MINI helps to mitigate over- or underdiagnoses by providing a better understanding of a mental ill-health condition and identification of psychiatric and stigmatization disorders. MINI asks for a “yes” or “no” answer.
Risk Factors for Mental Ill Health
A total of 32 stressors of mental health were reported in the included studies ( Table 2 ). The stressors were categorized under eight headings following the studies of Okechukwu et al. (2014) , Love et al. (2010) , Campbell (2006) , Michie (2002) , and Sutherland and Davidson (1993) . As presented in Table 2 , the numbers 1–16 across the column headings correspond, respectively, to the articles listed in Table 1 . The checkmark indicates the frequency of a risk factor identified in the articles. The most-identified risk factors were hours worked per day (excess of 60 h per week), work overload, low opportunity/ability to participate in decision making, and occupational climate (authority, tax autonomy, office politics). However, few studies considered work–life as a stressor.
Risk factors for mental ill-health identified from the literature
Classification of Risk Factors for Mental III Health in the Construction Industry
It was deduced from the selected studies that most (97%) of the identified stressors for mental ill health in the construction industry constitute psychosocial factors. These risk factors can be grouped according to two principles: (1) previous studies that outlined some of these stressors ( Love et al. 2010 ; Sutherland and Davidson 1993 ; Michie 2002 ); and (2) definitions of the stressors. The risk factors were grouped as pertaining to the following: job control, work support, job demand, coping strategy, work hazards, family, workplace injustice, welfare, and socioeconomic factors. Fig. 4 illustrates this as a conceptual framework.

Conceptual framework for mental ill-health risk factors in the construction industry.
From the studies considered, it was determined that construction workers use specific negative coping strategies to help relieve the day’s job stress ( Lingard et al. 2007 ). These coping strategies impact negatively on mental health ( Jacobsen et al. 2013 ). After classification, the mean scores for the risk factors’ variables were determined ( Table 3 ). The mean score was determined by calculating the total number of studies that identified the different measures that form a variable and dividing the total by the number of measures in the variable. For instance, work hazard risk factor was calculated using
Risk factors’ variable ranks
Based on the equation, the mean score of the risk factor was determined and ranked. The result showed that job demand risk factors pose a significant threat to mental health and as such, reforming job design for better quality health and well-being should be enforced.
Protective Factors in the Construction Industry
Although risk factors in the construction industry are about 97% based on psychosocial working conditions, studies on protective factors for mental health in the industry are scarce. Protective factors elicited from the studies can be classified into 10 broad categories: marital status; increased job control; increased job support; reduced job demand; reduced workplace discrimination; family-friendly job opportunities; workplace justice; better welfare; positive socioeconomic measures; and positive (adaptive) coping strategies. A study by Lingard et al. (2007) considered compressed workweek intervention to improve work–family/life balance in the construction industry. The studies revealed some positive coping strategies adopted by construction workers, such as wishful thinking and emotion-focused coping strategies ( Lim et al. 2018 ; Langdon and Sawang 2018 ), which are protective factors. Appropriate mental health promotion and interventions were highlighted by the studies and included adopting a compressed workweek, problem-solving; stress management; workplace feedback mechanism; caring, appreciation, encouraging building teamwork, and communication skills; job security; creating a sense of involvement among employees; improving workplace safety, good quality of environment; encouraging quality relationships among colleagues; and promotion as a reward mechanism. These interventions can enhance protective factors against mental ill health in the construction workplace.
Kamardeen and Sunindijo (2017) considered a combination of personal factors and psychosocial workplace factors. This study deduced that marital status acted as a risk factor and moderator. As a moderator, marital status provided a social support network that could be lacking in the workplace. Kamardeen and Sunindijo (2017) also proposed that interventions should be designed around scheduled casual gatherings such as coffee-break chats and ensuring a more comfortable workplace to cushion the effect of marital status, especially among professionals who are not married.
As illustrated in Fig. 4 , the studies included in this systematic review identified several key risk factors for mental ill health in the construction industry. These risk factors included lack of job control, welfare concerns, workplace hazards, job demand, workplace injustice, family, and lack of support.
Lack of Job Control
Lack of job control emerged as a major risk factor, and reflected, specifically, limited opportunities for decision making, inability to speak about happenings in the workplace, imbalanced work distribution, authoritarian culture, and strict rules for scheduled work routine ( Lim et al. 2018 ; Boschman et al. 2013 ). According to Love et al. (2010) , the impact of lack of job control as a risk factor varied by type of firm and appeared to be present primarily in contracting firms, resulting in higher rates of depression ( Boschman et al. 2013 ). In one study, these factors were described under occupational climate, which includes issues relating to job autonomy, office politics, communication lines, line of authority, and inconsistency in communication flow ( Sutherland and Davidson 1993 ).
Welfare Concerns
Welfare-related risk factors were job insecurity, low income/ financial insecurity, inability to further learning, and low socioeconomic status. Job insecurity was associated with a high level of anxiety among all grade levels (middle and lower levels) of construction sector workers ( Sutherland and Davidson 1993 ). Low income was associated with a high level of depression and suicide ideation ( Al-Maskari et al. 2011 ). Financial insecurity stemmed from family concerns ( Langdon and Sawang 2018 ). Also, job insecurity was found to be higher among married employees ( Lim et al. 2018 ). The burden of financial and job insecurity was related to the ability to care for a family in case of unemployment. Job insecurity is associated with age and project value; Haynes and Love (2004) found that older employees feared job insecurity because of emerging technologies that younger employees are more familiar with.
Project duration and value acted as moderators of the job insecurity risk factor ( Haynes and Love 2004 ). Consequently, concerns about job insecurity were reduced in the case of projects with higher cost and longer schedule durations. Thus, employees working on high-value projects may be more emotionally and psychologically stable because their jobs are likely to be secure for an extended period. Generally, fear of job insecurity was related to length of time of employment. Income appeared to be a moderator among the studies; for instance, higher income was related to improved coping styles, lower anxiety, and lower rates of alcohol abuse.
Fear of failure stemmed from age and overpromotion (i.e., placing employees at a job level greater than their technical ability) ( Haynes and Love 2004 ; Sutherland and Davidson 1993 ). Fear of failure is also related to fear of job insecurity, because underperformance can lead to unemployment. For instance, it was found that age, overpromotion, length of time in employment, and fear of failure appeared to cause construction employees to attempt to prove themselves, which in turn caused increased strain and led to burnout and eventually psychological or mental distress, such as anxiety and depression ( Kamardeen and Sunindijo 2017 ; Bowen et al. 2014 ; Haynes and Love 2004 ).
Work Hazards
Work hazard-related risk factors include physical illness, occupational injury/hazard, posttraumatic stress, and musculoskeletal pain. Occupational injury/hazard contributed to PTSD, which also influenced depression and anxiety ( Hu et al. 2013 ). According to Al-Maskari et al. (2011) , physical illness was associated with depression and suicidal ideation. Similarly, mental distress, which is a warning sign for mental illness, was directly associated with pain in the back and other body sites ( Jacobsen et al. 2013 ). This was consistent with the findings of French (2009) , which attributed psychological distress to musculoskeletal disorders. However, a more recent study revealed that preexisting anxiety and depression raise the risk of developing a musculoskeletal disorder ( Del Campo et al. 2017 ).
Job demand-related risk factors include the nature of work, hours worked per week, work overload, fatigue and need for recovery, and increased work speed. Working for more than 60 h per week was common for contractors and foremen, causing them to feel more stress ( Love et al. 2010 ). Similarly, the risk for mental ill health among construction supervisors and bricklayers increased as a result of fatigue ( Boschman et al. 2013 ). Al-Maskari et al. (2011) reported that depression and suicidal ideation were associated with job demand-related risk factors, especially the nature of work and hours worked.
Workplace Injustice
Workplace injustice-related risk factors were gender discrimination, harassment, bullying, age discrimination, and lack of respect from subordinates. Gender discrimination toward females was reported in the construction industry ( Kamardeen and Sunindijo 2017 ; Bowen et al. 2014 ). Kamardeen and Sunindijo (2017) noted that female professionals were often paid a lower salary than their male counterparts. Also, female professionals suffered several forms of harassment ranging from sexual, verbal, and physical abuse and physical contact. The studies also revealed that, most often, male subordinates would not accept work orders from a female superior; as such, the female professional felt low job control and less support for her role.
Consequently, females suffered more anxiety and depression than their male colleagues. Age discrimination took the form of higher work demand on younger employees accompanied by low job control and less support ( Bowen et al. 2014 ). The age discrimination led to psychological strain. More studies are needed on age discrimination and mental health in the construction industry.
Family-related risk factors included marital status and work-family/life conflict. Work demand was found to impact negatively on family life and the ability to keep up with family responsibility for both male and female professionals; however, it was more commonly found for the latter. Marital status, on the other hand, was reported as an extrinsic risk factor and a moderator ( Kamardeen and Sunindijo 2017 ). Marital status of separated, divorced, widowed, or being single caused personal stress that led to some anxiety and depression. However, when combined with work stress, the severity of the mental health problem in such professionals increased. Marital status among married professionals appeared to act as a moderator to work stress ( Kamardeen and Sunindijo 2017 ).
Lack of Work Support
Love et al. (2010) reported that the absence of work support resulted in construction workers compensating through self-support mechanisms. This points to the need for work support measures to maintain good mental health in the construction industry.
High job demand, low work support, and job control have resulted in construction workers turning to several coping strategies. These coping strategies can broadly be categorized as positive (adaptive) or negative (maladaptive). For instance, alcohol, drug, and substance abuse (ADSA) is used as a diversion for dealing with the effects of strenuous work ( Frone 2006 ). The studies also reported construction workers turning to ADSA ( Sutherland and Davidson 1993 ), with substance abuse found to be associated with anxiety ( Langdon and Sawang 2018 ).
Mushi and Manege (2018) attributed the ADSA coping strategy to the risky or tough nature of each construction trade. Coping through alcohol abuse may also be linked to the strong drinking culture in the construction industry ( Roche et al. 2015 ). However, ADSA as a coping strategy is negative because prolonged ADSA has been linked to increased risk of job safety ( Minchin et al. 2006 ). Additionally, ADSA leads to physical illness, mental illness, and suicidality ( Schulte and Hser 2013 ). For positive coping strategies, Love et al. (2010) revealed that wishful thinking and problemsolving were used by construction workers.
Directions for Further Studies
This systematic review revealed several important risk factors, highlighting many potential pathways to mental ill health among workers in the construction industry. With growing complexity in the workplace and rising daily demands placed on employees, the number of cases of mental ill health is increasing ( Kuhn 2013 ). For instance, psychological distress was related to workplace injuries, and there was a high prevalence of injuries among workers with substantial psychological distress ( Jacobsen et al. 2013 ). To address this serious public health concern, researchers should also examine factors beyond the workplace. For example, the construction industry should consider the effects of a range of psychosocial factors spanning both the workplace and the personal lives of construction workers. The goal is to better understand the interactions among all the risk factors for mental ill health that an employee can experience in his or her daily life, thereby informing the design of intelligent interventions.
The importance of maintaining mental health across all types of construction firms is high. For instance, one study found that employees of contractors are subjected to more mental ill-health risk factors than their counterparts working in consultant firms ( Love et al. 2010 ). Also, many studies have emphasized the mental health of supervisors and people in supervisory positions, whereas fewer studies have mapped out risk factors for construction trades or laborer positions such as bricklaying ( Boschman et al. 2013 ). There is limited research on risk factors and mental ill health by trade. Given the different responsibilities across trades, and the variation in treatment of and working conditions for employees, further investigation of these trends may help provide solutions across the various construction sector trades that can be stressors to mental health. Better understanding of the conditions across trades will inform interventions that will meet the specific needs of each trade.
The construction industry has focused mainly on the impact of work stress on mental health. As such, only psychosocial factors arising from working condition and workplace are considered. Less emphasis has been placed on other psychosocial factors such as marital status, family friction, loneliness, and bereavement. For instance, a study asserted that PTSD is high among construction frontline workers because of workplace hazards ( Stocks et al. 2010 ). Another study demonstrated that other life events among construction workers could also result in PTSD ( Boschman et al. 2013 ). Overall, there is a need for much more research within the industry into specific factors that can increase the risk of mental ill health, which could assist in building more robust interventions in the workplace. For instance, if experiences outside the workplace appear to be the primary source of stress, workplace interventions such as the Employee Assistance Program ( Soeker et al. 2016 ; Nakao et al. 2007 ) could incorporate solutions such as making necessary counseling or therapy resources available to employees in need.
There is a need for intensified research on factors that promote health in addition to research on risk factors only. Research into specific protective factors for mental health in the industry is limited, with protective factors primarily informed by the reversal of risk factors. When protective factors are just a reversal of risk factors, interventions are likely to be shallow and ineffective ( Franklin et al. 2017 ). According to Mrazek and Haggerty (1994) , protective factors can be found within the individual, family, community, and other affiliations. Although the methodologies used in research into protective factors in the industry are weak, protective factors such as optimism, resilience, and self-esteem are given little attention. Studies need to consider a combination of protective factors to better inform on protective factors that best suit different construction workforces.
To effectively identify risk and protective factors, focus group approaches could be used. In conducting the focus group, mental health assessment tools can be used to separate the respondents into the control group (comprising those with no mental ill health) and the target group (those with mental ill health) ( Rodgers 2011 ). Characteristics found more in people without mental ill health but absent in the target group may also constitute protective factors. The results can form the basis for classification of risk factors and protective factors, and for designing follow-up interventions for the construction industry.
Currently, it is unknown whether the rate of mental ill health reported in the construction industry of developed countries, where modern techniques of construction are employed, is consistent with that of lower-income countries. More research into risk factors in emerging and developing economies is essential to determine context and cultural factors that pose a risk for mental ill health. Such research will provide information on the impact of laws and policies for worker protection and safety within construction industries across different regions. This is especially important because expatriate companies execute many construction projects in lower-income countries under different procurement options.
Certainly, assessing risk factors is essential to evaluate the level of risk to health; however, it is important to note that risk factors do not emerge in isolation but, instead, are clustered together. Interventions aimed at promoting mental health should be directed toward clusters of risk factors. The goal is to focus research on protective factors for mental health. For example, to reduce the risk of job demand and fatigue, real-time monitoring technology could be adopted by construction organizations. Alternatively, primary job stress and mental health interventions are needed to ensure improved and sustainable job design policies across the construction sectors of various economies. Following the boom in technology, increased studies into flexible work arrangements ( Rudolph and Baltes 2017 ) within the construction industry are needed. On the secondary intervention aspect, technological interventions to maintain mental fitness through building resilience and stress management should form policy making within the industry.
Furthermore, there is a need for studies on benchmarking job designs, mental health policies, and interventions in the construction workplace. This will help ensure that construction firms uphold psychological health management as a core duty to ensure the well-being of their employees. Studies in the construction industry should assess depression and anxiety at the same time, to determine which mental health problem is most prevalent in the industry and make it possible to identify specific stressors responsible for each.
Last, only two studies assessed suicidality, highlighting the need for more significant examination of the risk of suicide within the construction industry using reliable assessment measures. Greater knowledge of the prevalence of mental illness symptoms is needed, and can inform the selection and implementation of appropriate workplace interventions for mental health promotion and mental ill-health prevention, as well as specific treatment programs. This will, in turn, help to achieve a psychologically healthy and safe workplace.
Limitations
A limitation of this study is the relatively small number of articles selected for review. However, the authors had to ensure that studies reviewed contained information from persons diagnosed as having mental ill health. This was necessary because many studies in the construction industry that related work stress to poor mental health may have equated depression with sadness or anxiety with fear. Another limitation is that the studies included in this review offer fundamental insights regarding the risk factors for mental ill health in the construction industry but, given the small number of studies with limited representation globally, these results cannot generalize across geographic regions or economic contexts.
For instance, most of the studies were carried out in higher-income countries, suggesting the need for more research into the conditions and mental health of construction workers in lower-resource settings. Due to different work settings, variations in the use of sophisticated technology, and differences in cultural and religious beliefs, thorough empirical investigations are needed in different geographical regions and cultures and among different organizational sizes and structures.
There is growing urgency to address the prevalence of mental ill health facing the construction industry. This review contributes a greater understanding of risk factors for mental ill health and protective factors to assist occupational health researchers, construction regulatory bodies, and workforce organizations in developing better-tailored strategies to tackle specific risk factors.
This systematic review revealed that, although several studies have examined the stressors faced by construction workers for many years, only a few have employed reliable mental health assessment tools. Going forward, studies in the industry will need to use a full validated mental health assessment scale to affirm the impact of workplace stress on psychological health.
In total, 32 risk factors were identified from 16 studies spanning eight main categories as detailed in the conceptual framework. This framework and the checklist serve as a coordinated reference guide to risk factors for future use, although future studies are needed to expand on this framework by considering additional risk factors. Other factors could include poor health, lifestyle, poor relationship with family, custody issues, work-family/life balance, and many other psychosocial, contextual, and cultural factors. The workplaces of varied construction trades and professions need mental ill-health and suicidality interventions tailored to the various types of work.
There is a need for intensified research into factors that promote health rather than just those factors that deal with risk. There is a considerable need for the development of more specific, innovative protective factors and emerging intervention frameworks to mitigate the high incidence of mental ill health and suicidality presently plaguing the industry. The findings of this study are useful to policy makers, construction organizations, practitioners, and researchers to develop targeted and sustainable interventions in mitigating mental ill health and resulting impacts among construction personnel and other manual laborers.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Department of Building and Real Estate, Hong Kong Polytechnic University, for funding this study. This work is part of a more extensive Ph.D. study, under which studies sharing a similar background but different scope and content may be published. Dr. Naslund is supported by a grant from the National Institute of Mental Health (5U19MH113211).
Data Availability Statement
Data generated or analyzed during the study are available from the corresponding author on request.
- Aghaei Chadegani A, Salehi H, Yunus MM, Farhadi H, Fooladi M, Farhadi M, and Ale Ebrahim N. 2013. “ A comparison between two main academic literature collections: Web of science and Scopus databases .” Asian Soc. Sci . 9 ( 5 ): 18–26. 10.5539/ass.v9n5p18. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Akdemir A, Türkçapar MH, Örsel SD, Demirergi N, Dag I, and Özbay MH. 2001. “ Reliability and validity of the Turkish version of the Hamilton depression rating scale .” Compr. Psychiatry 42 ( 2 ): 161–165. 10.1053/comp.2001.19756. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Al-Maskari F, Shah SM, Al-Sharhan R, Al-Haj E, Al-Kaabi K, Khonji D, Schneider JD, Nagelkerke NJ, and Bernsen RM. 2011. “ Prevalence of depression and suicidal behaviors among male migrant workers in United Arab Emirates .” J. Immigr. Minor. Health 13 ( 6 ): 1027–1032. 10.1007/s10903-011-9470-9. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Balsamo M, Romanelli R, Innamorati M, Ciccarese G, Carlucci L, and Saggino A. 2013. “ The state-trait anxiety inventory: Shadows and lights on its construct validity .” J. Psychopathology Behav . 35 ( 4 ): 475–486. 10.1007/s10862-013-9354-5. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Battams S, Roche AM, Fischer JA, Lee NK, Cameron J, and Kostadinov V. 2014. “ Workplace risk factors for anxiety and depression in male-dominated industries: A systematic review .” Health Psychol. Behav. Med . 2 ( 1 ): 983–1008. 10.1080/21642850.2014.954579. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Beswick J, Rogers K, Corbett E, Binch S, and Jackson K. 2007. An analysis of the prevalence and distribution of stress in the construction industry . Buxton, UK: Health and Safety Executive. [ Google Scholar ]
- Boatman L, Chaplan D, and Teran S. 2012. Creating the climate for making ergonomic changes . Silver Spring, MD: Center for Construction Research and Training. [ Google Scholar ]
- Boschman JS, van der Molen HF, Sluiter JK, and Frings-Dresen MH. 2013. “ Psychosocial work environment and mental health among construction workers .” Appl. Ergon 44 ( 5 ): 748–755. 10.1016/j.apergo.2013.01.004. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bowen P, Govender R, and Edwards P. 2014. “ Structural equation modeling of occupational stress in the construction industry .” J. Constr. Eng. Manage 140 ( 9 ): 04014042 10.1061/(ASCE)CO.1943-7862.0000877. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bowen P, Govender R, Edwards P, and Cattell K. 2018. “ Work-related contact, work-family conflict, psychological distress, and sleep problems experienced by construction professionals: An integrated explanatory model .” Construct. Manage. Econ 36 ( 3 ): 153–174. 10.1080/01446193.2017.1341638. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Burki T 2018. “ Mental health in the construction industry .” Lancet Psychiatr . 5 ( 4 ): 303 10.1016/S2215-0366(18)30108-1. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Campbell F 2006. Occupational stress in the construction industry . Berkshire, UK: Chartered Institute of Building. [ Google Scholar ]
- Creamer M, Bell R, and Failla S. 2003. “ Psychometric properties of the impact of event scale-revised .” Behav. Res. Ther 41 ( 12 ): 1489–1496. https://doi.org/10.1016Zj.brat.2003.07.010 . [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Del Campo MT, Romo PE, de la Hoz RE, Villamor JM, and Mahíllo-Fernández I. 2017. “ Anxiety and depression predict musculoskeletal disorders in health care workers .” Arch. Environ. Occup. Health 72 ( 1 ): 39–44. 10.1080/19338244.2016.1154002. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Donath S 2001. “ The validity of the 12-item general health questionnaire in Australia: A comparison between three scoring methods .” Aust. N.Z.J. Psychiatry 35 ( 2 ): 231–235. 10.1046/j.1440-1614.2001.00869.x. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Dong XS, Wang X, Largay JA, and Sokas R. 2015. “ Long-term health outcomes of work-related injuries among construction workers—Findings from the National Longitudinal Survey of Youth .” Am. J. Ind. Med 58 ( 3 ): 308–318. 10.1002/ajim.22415. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Dyrbye LN, Thomas MR, and Shanafelt TD. 2006. “ Systematic review of depression, anxiety, and other indicators of psychological distress among US and Canadian medical students .” Acad. Med 81 ( 4 ): 354–373. 10.1097/00001888-200604000-00009. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- European Agency for Safety and Health at Work. 2007. “ Expert forecast on emerging psychosocial risks related to occupational safety and health, Office for Official Publications of the European Communities Luxembourg .” Accessed January 11, 2019 https://osha.europa.eu/en/publications/reports/7807118 .
- Fiordelli M, Diviani N, and Schulz PJ. 2013. “ Mapping mHealth research: A decade of evolution .” J. Med. Internet Res . 15 ( 5 ): e95 10.2196/jmir.2430. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Franklin JC, Ribeiro JD, Fox KR, Bentley KH, Kleiman EM, Huang X, Musacchio KM, Jaroszewski AC, Chang BP, and Nock MK. 2017. “ Risk factors for suicidal thoughts and behaviors: A meta-analysis of 50 years of research .” Psychol. Bull 143 ( 2 ): 187–232. 10.1037/bul0000084. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Fraser J, Fahlman DW, Arscott J, and Guillot I. 2018. “ Pilot testing for feasibility in a study of student retention and attrition in online undergraduate programs .” Int. Rev. Res. Open Distance Learn . 19 ( 1 ): 260–278. 10.19173/irrodl.v19i1.3326. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- French SD 2009. “ The association between musculoskeletal pain and psychological distress among five immigrant groups: Results of a cross-sectional study in Oslo, Norway .” Master thesis, Institute of General Practice and Community Medicine, Univ. of Oslo. [ Google Scholar ]
- Frone MR 2006. “ Prevalence and distribution of alcohol use and impairment in the workplace: A US national survey .” J. Stud. Alcohol 67 ( 1 ): 147–156. 10.15288/jsa.2006.67.147. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Furber G, Leach M, Guy S, and Segal L. 2017. “ Developing a broad categorization scheme to describe risk factors for mental illness, for use in prevention policy and planning .” Aust. N. Z. J. Psychiatry 51 ( 3 ): 230–240. 10.1177/0004867416642844. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Grove B 2006. “ Common mental health problems in the workplace: How can occupational physicians help? ” Occup. Med 56 ( 5 ): 291–293. 10.1093/occmed/kql028. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gullestrup J, Lequertier B, and Martin G. 2011. “ MATES in construction: Impact of a multimodal, community-based program for suicide prevention in the construction industry .” Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 8 ( 11 ): 4180–4196. 10.3390/ijerph8114180. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Harris JD, Quatman CE, Manring MM, Siston RA, and Flanigan DC. 2014. “ How to write a systematic review .” Am. J. Sports Med 42 ( 11 ): 2761–2768. 10.1177/0363546513497567. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Haynes NS, and Love PE. 2004. “ Psychological adjustment and coping among construction project managers .” Construct. Manage. Econ 22 ( 2 ): 129–140. 10.1080/0144619042000201330. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Herrman H, and Jané-Llopis E. 2005. “ Mental health promotion in public health .” Supplement, J. Edu. Health Promot . 12 ( S2 ): 42–47. 10.1177/10253823050120020107. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Herrman H, and Jané-Llopis E. 2012. “ The status of mental health promotion .” Publ. Health Rev . 34 ( 2 ): 6 10.1007/BF03391674. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Howard LM, et al. 2018. “ Accuracy of the Whooley questions and the Edinburgh postnatal depression scale in identifying depression and other mental disorders in early pregnancy .” Br. J. Psych 212 ( 1 ): 50–56. 10.1192/bjp.2017.9. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hu BS, Liang YX, Hu XY, Long YF, and Ge LN. 2013. “ Post-traumatic stress disorder in co-workers following exposure to a fatal construction accident in China .” Int. J. Occup. Environ. Health 6 ( 3 ): 203–207. 10.1179/oeh.2000.63.203. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ibrahim N, Amit N, Suen MWY, and Mazza M. 2014. “ Psychological factors as predictors of suicidal ideation among adolescents in Malaysia .” PLoS One 9 ( 10 ): e110670 10.1371/journal.pone.0110670. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Jacobsen HB, Caban-Martinez A, Onyebeke LC, Sorensen G, Dennerlein JT, and Reme SE. 2013. “ Construction workers struggle with a high prevalence of mental distress, and this is associated with their pain and injuries .” J. Occup. Environ. Med 55 ( 10 ): 1197–1204. 10.1097/JOM.0b013e31829c76b3. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Joukamaa M 2009. “ Crown-Crisp experiential index: A useful tool for measuring neurotic psychopathology .” Nord. J. Psychiat 46 ( 1 ): 49–53. 10.3109/08039489209106182. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Joyce K, Pabayo R, Critchley JA, and Bambra C. 2010. “ Flexible working conditions and their effects on employee health and wellbeing .” Cochrane Database Syst. Rev . 2010 ( 2 ): CD008009 10.1002/14651858.CD008009.pub2. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Julian LJ 2011. “ Measures of anxiety: State-Trait Anxiety Inventory (STAI), Beck Anxiety Inventory (BAI), and Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale-Anxiety (HADS-A) .” Supplement, Arthritis Care Res . 63 ( S11 ): S467–S472. 10.1002/acr.20561. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kamardeen I, and Loosemore M. 2016. “ Suicide in the construction industry: A cross-sectional analysis .” In Proc., RICS COBRA 2016-The Construction, Building and Real Estate Research Conf. of the Royal Institution of Chartered Surveyors London: Royal Institution of Chartered Surveyors. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kamardeen I, and Sunindijo RY. 2017. “ Personal characteristics moderate work stress in construction professionals .” J. Constr. Eng. Manage 143 ( 10 ): 04017072 10.1061/(ASCE)CO.1943-7862.0001386. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Knapp M, McDaid D, and Parsonage M. 2011. Mental health promotion and mental illness prevention: The economic case . London: Dept. of Health. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kuhn K 2013. “ Workplace related mental health problems–risks and prevention .” Die Psychiatr . 10 ( 2 ): 61–70. 10.1055/s-0038-1670857. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Langdon RR, and Sawang S. 2018. “ Construction workers’ well-being: What leads to depression, anxiety, and stress? ” J. Constr. Eng. Manage 144 ( 2 ): 04017100 10.1061/(ASCE)CO.1943-7862.0001406. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Li H, Luo X, Ke X, Dai Q, Zheng W, Zhang C, Cassidy RM, Soares JC, Zhang XY, and Ning Y. 2017. “ Major depressive disorder and suicide risk among adult outpatients at several general hospitals in a Chinese Han population .” PLoS One 12 ( 10 ): e0186143 10.1371/journal.pone.0186143. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Licht RW, Qvitzau S, Allerup P, and Bech P. 2005. “ Validation of the Bech-Rafaelsen Melancholia Scale and the Hamilton Depression Scale in patients with major depression: Is the total score a valid measure of illness severity? ” Acta Psychiatr. Scand 111 ( 2 ): 144–149. 10.1111/j.1600-0447.2004.00440.x. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lim S, Chi S, Lee JD, Lee HJ, and Choi H. 2018. “ Analyzing psychological conditions of field-workers in the construction industry .” Int. J. Occup. Environ. Health 23 ( 4 ): 261–281. 10.1080/10773525.2018.1474419. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lingard H, Brown K, Bradley L, Bailey C, and Townsend K. 2007. “ Improving employees’ work-life balance in the construction industry: Project alliance case study .” J. Constr. Eng. Manage 133 ( 10 ): 807–815. 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9364(2007)133:10(807). [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Love PE, Edwards DJ, and Irani Z. 2010. “ Work stress, support, and mental health in construction .” J. Constr. Eng. Manage 136 ( 6 ): 650–658. 10.1061/(ASCE)CO.1943-7862.0000165. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mates in Construction. 2018. “ Why MATES exists—Are suicide rates high in the construction industry? ” Accessed October 24, 2018 https://matesinconstruction.org.au/about/why-mic-exists/ .
- Michie S 2002. “ Causes and management of stress at work .” Occup. Environ. Med 59 ( 1 ): 67–72. 10.1136/oem.59.F67. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Milner A, Page K, Spencer-Thomas S, and Lamotagne AD. 2015. “ Workplace suicide prevention: A systematic review of published and unpublished activities .” Health Promot. Int . 30 ( 1 ): 29–37. 10.1093/heapro/dau085. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Minchin RE Jr., Glagola CR, Guo K, and Languell JL. 2006. “ Case for drug testing of construction workers .” J. Manage. Eng 22 ( 1 ): 43–50. 10.1061/(ASCE)0742-597X(2006)22:1(43). [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Montazeri A, Harirchi AM, Shariati M, Garmaroudi G, Ebadi M, and Fateh A. 2003. “ The 12-item General Health Questionnaire (GHQ-12): Translation and validation study of the Iranian version .” Health Qual. Life Outcomes 1 ( 1 ): 66 10.1186/1477-7525-1-66. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mrazek PJ, and Haggerty RJ. 1994. Risk and protective factors for the onset of mental disorders . Washington, DC: Institute of Medicine Committee on Prevention of Mental Disorders, National Academies Press. [ Google Scholar ]
- Mushi FV, and Manege SL. 2018. “ Alcohol abuse and illicit drug use at construction sites: Perception of workers at construction sites .” Int. J. Constr. Eng. Manage 7 ( 2 ): 65–72. 10.5923/j.ijcem.20180702.02. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Nakao M, Nishikitani M, Shima S, and Yano E. 2007. “ A 2-year cohort study on the impact of an employee assistance programme (EAP) on depression and suicidal thoughts in male Japanese workers .” Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 81 ( 2 ): 151–157. 10.1007/s00420-007-0196-x. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ng F, Trauer T, Dodd S, Callaly T, Campbell S, and Berk M. 2007. “ The validity of the 21-item version of the depression anxiety stress scales as a routine clinical outcome measure .” Acta Neuropsychiatrica 19 ( 5 ): 304–310. 10.1111/j.1601-5215.2007.00217.x. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Nieuwenhuijsen K, De Boer AGEM, Verbeek JHAM, Blonk RWB, and Van Dijk FJH. 2003. “ The Depression Anxiety Stress Scales (DASS): Detecting anxiety disorder and depression in employees absent from work because of mental health problems .” Supplement, Occup. Environ. Med 60 ( S1 ): 77–82. 10.1136/oem.60.suppl_1.i77. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Okechukwu CA, Souza K, Davis KD, and de Castro AB. 2014. “ Discrimination, harassment, abuse, and bullying in the workplace: Contribution of workplace injustice to occupational health disparities .” Am. J. Ind. Med 57 ( 5 ): 573–586. 10.1002/ajim.22221. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Okubo Y, Natsume S, Usui K, Amaya M, and Tsuboi R. 2011. “ Low-dose, short-term ciclosporin (Neoral®) therapy is effective in improving patients’ quality of life as assessed by Skindex-16 and GHQ-28 in mild to severe psoriasis patients .” J. Dermatol 38 ( 5 ): 465–472. 10.1111/j.1346-8138.2010.01041.x. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Olawumi TO, and Chan DW. 2018. “ A scientometric review of global research on sustainability and sustainable development .” J. Cleaner Prod . 183 ( May ): 231–250. 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.02.162. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Palmer KT, D’Angelo S, Harris EC, Linaker C, and Coggon D. 2014. “ The role of mental health problems and common psychotropic drug treatments in accidental injury at work: A case-control study .” Occup. Environ. Med 71 ( 5 ): 308–312. 10.1136/oemed-2013-101948. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Park H, Sprince NL, Lewis MQ, Burmeister LF, Whitten PS, and Zwerling C. 2001. “ Risk factors for work-related injury among male farmers in Iowa: A prospective cohort study .” J. Occup. Environ. Med 43 ( 6 ): 542–547. 10.1097/00043764-200106000-00007. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pettersson A, Modin S, Wahlström R, af Winklerfelt Hammarberg S, and Krakau I. 2018. “ The mini-international neuropsychiatric interview is useful and well accepted as part of the clinical assessment for depression and anxiety in primary care: A mixed-methods study .” BMC Fam. Pract . 19 ( 1 ): 19 10.1186/s12875-017-0674-5. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Powell R, and Copping A. 2010. “ Sleep deprivation and its consequences in construction workers .” J. Constr. Eng. Manage 136 ( 10 ): 1086–1092. 10.1061/(ASCE)CO.1943-7862.0000211. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Powell RI, and Copping AG. 2016. “ Measuring fatigue-related impairment in the workplace .” J. Eng. Des. Technol 14 ( 3 ): 507–525. 10.1108/JEDT-09-2014-0063. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Radloff LS 1977. “ The CES-D scale: A self-report depression scale for research in the general population .” Appl. Psychol. Meas 1 ( 3 ): 385–401. 10.1177/014662167700100306. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ramos-Rodríguez AR, and Ruíz-Navarro J. 2004. “ Changes in the intellectual structure of strategic management research: A bibliometric study of the Strategic Management Journal, 1980–2000 .” Strategic Manage. J . 25 ( 10 ): 981–1004. 10.1002/smj.397. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Roche AM, Lee NK, Battams S, Fischer JA, Cameron J, and McEntee A. 2015. “ Alcohol use among workers in male-dominated industries: A systematic review of risk factors .” Saf. Sci 78 : 124–141. 10.1016/j.ssci.2015.04.007. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rodgers P 2011. “Understanding risk and protective factors for suicide: A primer for preventing suicide” In Suicide prevention resource center . Waltham, MA: Education Development Center, Inc. [ Google Scholar ]
- Rothbaum BO, Foa EB, Riggs DS, Murdock T, and Walsh W. 1992. “ A prospective examination of post-traumatic stress disorder in rape victims .” J. Traumatic Stress 5 ( 3 ): 455–475. 10.1002/jts.2490050309. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rudolph CW, and Baltes BB. 2017. “ Age and health jointly moderate the influence of flexible work arrangements on work engagement: Evidence from two empirical studies .” J. Occup. Health Psychol . 22 ( 1 ): 40–58. 10.1037/a0040147. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sadeghniiat-Haghighi K, and Yazdi Z. 2015. “ Fatigue management in the workplace .” Ind. Psychiatry J . 24 ( 1 ): 12–17. 10.4103/0972-6748.160915. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sandler I, Wolchik SA, Cruden G, Mahrer NE, Ahn S, Brincks A, and Brown CH. 2014. “ Overview of meta-analyses of the prevention of mental health, substance use, and conduct problems .” Annu. Rev. Clin. Psychol 10 ( 1 ): 243–273. 10.1146/annurev-clinpsy-050212-185524. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Schieman S, and Young MC. 2013. “ Are communications about work outside regular working hours associated with work-to-family conflict, psychological distress and sleep problems? ” Work Stress 27 ( 3 ): 244–261. [ Google Scholar ]
- Schulte MT, and Hser YI. 2013. “ Substance use and associated health conditions throughout the lifespan .” Publ. Health Rev . 35 ( 2 ): 3 10.1007/BF03391702. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Siu OL, Phillips DR, and Leung TW. 2004. “ Safety climate and safety performance among construction workers in Hong Kong: The role of psychological strains as mediators .” Accid. Anal. Prev 36 ( 3 ): 359–366. 10.1016/S0001-4575(03)00016-2. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Soeker S, Matimba T, Msimango H, Moswaane B, and Tom S. 2016. “ The challenges that employees who abuse substances experience when returning to work after completion of Employee Assistance Programme CEAP) .” Work 53 ( 3 ): 569–584. 10.3233/W0R-152230. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sterling M 2011. “ General health questionnaire-28 (GHQ-28) .” J. Physiother 57 ( 4 ): 259 10.1016/S1836-9553(11)70060-1. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Stocks SJ, McNamee R, Carder M, and Agius RM. 2010. “ The incidence of medically reported work-related ill health in the UK construction industry .” Occup. Environ. Med 67 ( 8 ): 574–576. 10.1136/oem.2009.053595. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Suija K, Rajala U, Jokelainen J, Liukkonen T, Härkönen P, Keinanen-Kiukaanniemi S, and Timonen M. 2012. “ Validation of the Whooley questions and the Beck Depression Inventory in older adults .” Scand. J. Prim. Health Care 30 ( 4 ): 259–264. 10.3109/02813432.2012.732473. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sundin EC, and Horowitz MJ. 2002. “ Impact of event scale: Psychometric properties .” Br. J. Psychiatr 180 ( 3 ): 205–209. 10.1192/bjp.180.3.205. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sunindijo RY, and Kamardeen I. 2017. “ Work stress is a threat to gender diversity in the construction industry .” J. Constr. Eng. Manage 143 ( 10 ): 04017073 10.1061/(ASCE)C0.1943-7862.0001387. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sutherland V, and Davidson MJ. 1993. “ Using a stress audit: The construction site manager experience in the UK .” Work Stress 7 ( 3 ): 273–286. 10.1080/02678379308257067. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Taylor DJ, Lichstein KL, Durrence HH, Reidel BW, and Bush AJ. 2005. “ Epidemiology of insomnia, depression, and anxiety .” Sleep 28 ( 11 ): 1457–1464. 10.1093/sleep/28.11.1457. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Tsutsumi A, Kayaba K, Theorell T, and Siegrist J. 2001. “ Association between job stress and depression among Japanese employees threatened by job loss in a comparison between two complementary job-stress models .” Scand. J. Work Environ. Health 27 ( 2 ): 146–153. 10.5271/sjweh.602. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ventevogel P, De Vries G, Scholte WF, Shinwari NR, Faiz H, Nassery R, van den Brink W, and Olff M. 2007. “ Properties of the Hopkins symptom checklist-25 (HSCL-25) and the self-reporting questionnaire (SRQ-20) as screening instruments used in primary care in Afghanistan .” Soc. Psychiatry Psychiatr. Epidemiol . 42 ( 4 ): 328–335. 10.1007/s00127-007-0161-8. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wang C, Mohd-Rahim FA, Chan YY, and Abdul-Rahman H. 2017. “ Fuzzy mapping on psychological disorders in construction management .” J. Constr. Eng. Manage . 143 ( 2 ): 04016094 10.1061/(ASCE)CO.1943-7862.0001217. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- White KP, Nielson WR, Harth M, Ostbye T, and Speechley M. 2002. “ Chronic widespread musculoskeletal pain with or without fibromyalgia: Psychological distress in a representative community adult sample .” J. Rheumatol 29 ( 3 ): 588–594. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- WHO (World Health Organization). 2001. Mental health: Strengthening mental health promotion . Geneva: WHO. [ Google Scholar ]
- Yi W, and Chan APC. 2014. “ Critical review of labor productivity research in construction journals .” J. Manage. Eng 30 ( 2 ): 214–225. 10.1061/(ASCE)ME.1943-5479.0000194. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Zheng X, Le Y, Chan AP, Hu Y, and Li Y. 2016. “ Review of the application of Social Network Analysis (SNA) in construction project management research .” Int. J. Proj. Manage 34 ( 7 ): 1214–1225. 10.1016/j.ijproman.2016.06.005. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
Mental health in the construction industry
- PMID: 29580608
- DOI: 10.1016/S2215-0366(18)30108-1
NAE Perspectives
National Academy of Engineering (NAE)
Sharareh “Sherri” Kermanshachi is associate vice chancellor, associate dean for research, and professor of civil engineering at Penn State University. Apurva Pamidimukkala is assistant professor of research in civil engineering at the University of Texas at Arlington.
Suicide and Mental Health Challenges in the Construction Industry
© National Academy of Sciences. All rights reserved.
Related NAE Perspectives
The Role of Computing and Cognition in Tackling Climate Change
Moving to Evidence-Based Elections
Hidden Curriculum: An Image Holder of Engineering
Increasing Diversity in All Engineering Disciplines
- Load More...
Recent News
Certifying Safety of Ships Carrying Liquefied Gas
Register for June 26 State of the Science Address
Strategies to Govern AI Effectively
Mental Health & Wellbeing in the Construction Workplace
Given the far-reaching effects of COVID-19 throughout the construction industry, it is imperative for business leaders to thoughtfully consider the short- and longterm impact on the mental health and wellbeing of their workforce. There is consensus among mental health providers that the effects of stress, anxiety, worries, and uncertainty spurred by COVID-19 will continue to affect the workforce well beyond the current pandemic.
Mental Health & Wellbeing Are Leadership Imperatives
The construction industry has had a mental health, substance use, and suicide problem well before COVID-19. But until recently, mental health was not openly addressed in the workplace. Beyond COVID-19, discussing and addressing mental health in the workplace will continue to grow in prevalence, helping to make this an easier topic to address. In the absence of concrete research on the impact of mental health in construction, it is appropriate to rely on the mental health and wellbeing practices that have been adopted throughout the industry. Many signs are pointing to the increasing acceptance and importance of addressing mental health in the construction workplace. (See "Addressing Mental Health & Wellbeing in the Construction Workplace".)
Investing in Employees
The mental health and suicide prevention initiative began in the human capital risk management platform in 2014. In 2015, “Leveraging Human Capital Risk Management” was published in CFMA Building Profits and posited that “a contractor’s most important resource, and one of its leading costs, is its employees. By actively investing in employee, supervisory, and leadership development programs, CFMs can expect a positive ROI and other measurable outcomes in both its risk management and human capital investments. This intentional strategy combines organizational development practices to leverage human capital risk management and protect a company’s bottom line.” 1

Caring for Employees
In the post-coronavirus business world, demonstrating a caring culture for employees will be both an expectation and an imperative. MetLife reported in 2015 that 68% of employees believe “employers have a responsibility for the health and wellbeing of their employees,” which grew to 76% in 2019. 2 Moreover, according to PwC’s Health and Well-being Touchstone Survey Results, wellbeing needs to focus beyond physical wellbeing as a “holistic wellness program that target[s] physical, mental, and financial wellbeing and improve[s] morale, enhance[s] culture, and reduce[s] burnout.” 3
Workplace Empathy
While empathy has been seen as a key to making employees feel supported in the workplace, the 2020 State of Workplace Empathy reveals that businesses in the U.S. have more progress to make in this area. There is a pronounced gap between how company executives perceive the performance of their organizations in empathetic practices vs. how employees report the companies’ execution of empathy. Specifically, 86% of CEOs believe that their companies discuss the importance of mental health with their employees; however, only 58% of employees feel the same way. 4
Return on Investment
In recent years, “companies’ mental health expenses have risen more than 10% annually compared with increases of 5% for other medical costs.” 5 Moreover, research by Milliman reported that “if employees have physical illnesses, coupled with a mental health or substance use issue, the costs for treating them is two to three times higher than for those employees with a physical illness alone.” 6
There is growing proof that a business can financially benefit from investments in mental wellbeing. Mental Health America reports in the Mental Health Support Guide that “for every $1 spent on mental health care, a company will receive a $4” ROI. 7
The Centre for Economic Performance conducted a meta-analysis using Gallup data from independent research studies that include observations on the wellbeing of 1,882,131 employees and performance of 82,248 business units, and found that “employee wellbeing is consistently positively correlated with firm performance.” 8 The authors noted that they “focus on the financial, retail, manufacturing, and service sectors because we had fewer than 20 studies for the remaining sectors (materials and construction, personal services, real estate, and transportation and utilities), which we deem insufficient to base inference on.” They concluded that the evidence suggests “a strong, positive relationship between employee wellbeing, employee productivity, and firm performance.” 9
Developing a Construction Industry Wellbeing Model
Concern for addressing mental health in the construction workplace is on the rise, but the reality is that costs and consequences of mental health concerns in construction are understudied.
Before the introduction of a construction-specific wellbeing model, two models existed at the individual worker level.
National Wellness Institute’s Six Dimensions of Wellness
The National Wellness Institute (NWI) created the Six Dimensions of Wellness (Exhibit 1) in 1976. This holistic model integrates various dimensions of personal life to identify the six factors that contribute to wellness and fulfillment: occupational, physical, social, intellectual, spiritual, and emotional. The NWI offers a certification in wellness, various certificate programs in health, resilience, and wellness and is also an authorized continuing education provider for the National Board for Health and Wellness Coaching.
Gallup’s Wellbeing Model
Gallup, a recognized leader in surveys, data analytics, and insights relating to engagement and wellbeing, has researched the direct impact on business outcomes of how employees rate the five interrelated elements of wellbeing – physical, career, social, financial, and community – in their personal lives. Wellbeing and engagement are two related factors identified by Gallup that directly influence business results. 10

Construction Wellbeing Model
The Construction Wellbeing Model (Exhibit 2) was created to provide a framework for developing and implementing a tactical wellbeing strategy in construction companies.
This holistic and integrated model consists of wellbeing tools, strategies, and outcomes.
The construction industry workforce is less uniform or homogeneous when compared to other industries (i.e., financial services, retail, and service sectors). Construction companies have a split between salaried office employees and hourly field employees. For union contractors, labor unions generally provide health and other welfare benefits.
This construction wellbeing model focuses on strategies that address wellbeing initiatives and services for the workplace, workforce, worker, worksites, work tasks, and work groups.

Action Steps to Institute a Strategic Framework that Addresses Mental Health & Wellbeing
Here are some steps to help integrate mental health and wellbeing into your company culture:
- Institute a collective mindset for wellbeing as a part of a respectful workplace committed to equity and social justice. This mindset should also accept mental health as a diversity and inclusion opportunity.
- Recognize the unique challenges to mental health and wellbeing among the construction workforce, which includes U.S. Veterans, National Guard Reservists, workers with frequent shift changes and recurring overtime, and employees with underlying mental health conditions.
- Build a caring culture that embraces wellbeing by incorporating mental health awareness, substance use and addiction recovery, and suicide prevention into safety, health, wellness, employee benefits, and employee/labor relations.
- Promote psychological safety and health by frequently communicating with empathy to employees regarding senior leadership’s concern about mental health in the workplace.
- Verify if your company has an employee assistance program (EAP). If your company does not have an EAP, commit to instituting one to help address the needs of all employees. Consider renaming – or at least promoting – the EAP to an employee and family assistance program (EFAP) to expand awareness that this benefit extends to dependent family members.
- If your company does have an EAP, check your program’s utilization rate and the types of services that are accessed by your employees. This confidential report can help you identify ways to increase the use of your EAP program, such as:
- Communicating the eligibility of work/life balance and behavioral health services available through the EAP.
- Instituting managerial, supervisory, and employee training to educate your entire workforce about the purpose, features, and benefits of the EAP.
- Deploying proactive communication strategies, including sharing various modes of access, to promote use of the EAP.
- Including information about the EAP in your new hire orientation packet, open enrollment packets, and informational sessions about health and other employee benefit programs.
- Union contractors are encouraged to inquire with the unions’ local business managers to understand the behavioral health services and medical health benefits available through the unions’ health and welfare funds. Inquire if the union has an EAP or if they instituted an in-house Member Assistance Program (MAP). Offer to help the unions promote their EAP or MAP to the union employees dispatched to your company.
- Communicate the importance of worker wellbeing with posters, signs, hard hat stickers, wallet cards, and more.
- The Construction Industry Alliance for Suicide Prevention (CIASP) has posters that are effective at letting workers know your company is serious about addressing mental wellbeing at www.preventconstructionsuicide.com.
- For additional ideas on how to weave these topics into your safety, health, and wellness culture, refer to “The Invisible Construction Crisis: Strategies to Address Mental Wellbeing.” 11

Bold leadership is essential to demonstrating a company’s commitment to building awareness and sensitivity to mental health in the workplace.
Addressing mental health and wellbeing is a strategic leadership imperative and is a sound business strategy and practice. Investing in mental health and wellbeing has a positive return on capital investment and an even bigger ROI on your company’s human capital assets – your employees.
- www.cfmabponline.net/cfmabp/20150506?pg=16#pg16.
- www.metlife.com/employee-benefit-trends/ebts-thriving-in-new-work-world-2019.
- www.pwc.com/us/en/services/hr-management/assets/pwc-touchstone- 2019.pdf.
- info.businessolver.com/en-us/empathy-ceo-special-report-ty? submissionGuid=0ad79874-24e5-4f8e-8346-962a6da3c8c8.
- www.cnbc.com/2018/09/26/employers-are-starting-to-think-about-healthy-differently.html.
- milliman-cdn.azureedge.net/-/media/milliman/importedfiles/uploadedfiles/insight/2018/potential-economic-impact-integrated-healthcare.ashx.
- mhanational.org/sites/default/files/Employee Support Guide_FINAL.pdf.
- cep.lse.ac.uk/pubs/download/dp1605.pdf.
- www.gallup.com/workplace/236483/enhances-benefits-employee-engagement.aspx.
- www.csdz.com/the-invisible-construction-crisis-strategies-to-address-mental-wellbeing.
Copyright © 2020 by the Construction Financial Management Association (CFMA). All rights reserved. This article first appeared in September/October 2020 CFMA Building Profits magazine.
About the Author
Cal Beyer, CWP, is Vice President of Risk, Safety & Mental Wellbeing for ethOs, a Holmes Murphy company.
User account menu
- Get in Touch

Understanding Mental Health in the Built Environment
Launched in May 2020, Understanding Mental Health in the Built Environment examines the state of mental health in construction.
Daisie Barnett
Policy Development Manager
Last updated: 11th May 2020
Mental ill-health is a silent crisis within the construction industry, with males three times more likely to commit suicide than those in other sectors.
This reports sheds light on the state of mental health within the industry by asking over 2,000 professionals their thoughts and experiences.
Using evidence from the research, the report outlines recommendations which we believe may help policy makers and the industry address poor mental health and wellbeing within construction.
To read the full report, click the download link below.
Are you a Mates in Mind member?
Log in or register below
Basket adjustments detected!
Your basket has been adjusted. This may be due to an event becoming unavailable or you logging into the site and your active roles changing.
- Mates in Mind
Mental Health in UK Construction: The Statistics

Please note the below contains mentions of suicide.
Article originally posted February 2022, updated November 2023.
Four in five suicides are by men, with suicide the biggest cause of death for men under 35 (source: UK Parliament ). In 2020, workers in construction were at some of the highest risk of suicide in the country, at 3.7 times higher than the national average (source: Office for National Statistics ).
Construction work has a variety of pressures from tight contracts to long hours, time away from loved ones and managing budgets, not to mention the added stresses caused by the pandemic and the rising costs of supplies. Additionally, over half of all UK employees (and notably 57% of Millennials) do not feel comfortable disclosing mental health or psychological conditions (source: Reed ). This results in a culture which prevents many workers from seeking support and help when they may need it, putting further stress on their own mental health and wellbeing.
It is important for employers and individuals to know just how important mental health awareness and support is to workers and the statistics below highlight why change is needed within the construction industry.
Request a Callback to become a Mates in Mind Supporter

https://www.ciob.org/industry/research/Understanding-Mental-Health-Built-Environment
Our Survey Results
In June 2022, we published the findings from our major study of the mental health of self-employed construction workers and those working in small firms. Our results showed that intense workloads, financial problems, poor work-life balance and COVID-19 pressures on the supply of materials combined to significantly raise stress and anxiety levels. This mainly male workforce has long been known to contain workers who are reluctant to talk about their mental health.
Survey findings from over 300 respondents suggest that almost a third are now living with elevated levels of anxiety each day. Construction workers from a range of trades that are often hard to reach, from bricklayers, to groundworkers to plasterers, told researchers from Mates in Mind and the Institute for Employment Studies (IES) that the continuing stigma of mental illness prevents them from discussing it beyond close friends or family members.
Additionally, a report by the Chartered Institute of Building found that 26% of construction industry professionals thought about taking their own lives in 2019 and 56% of construction professionals work for organisations with no policies on mental health in the workplace.
Furthermore, in 2022/23 stress, anxiety, and depression accounted for 49% of work-related ill-health, resulting in 17.1 million working days lost ( HSE ). It is estimated that mental ill-health costs businesses £56bn annually ( Deloitte UK ).
What can be done?
Education and training are key to eliminating the stigma. Mates in Mind has empowered hundreds of organisations across the UK to tackle the silence surrounding mental ill-health and embed a positive culture change within these workplaces. Working alongside our partners , sector leaders and growing community of Supporters , we are able to deliver effective change across the UK by providing the skills, clarity and confidence to employers on how to raise awareness, improve understanding and address the stigma of mental ill-health.
Be part of the change.
Whether you're part of a business, or an organisation looking to bring in more support for its employees, you can find out more about how we can help you by filling out our contact us form and requesting a call back.
As a Mates in Mind Supporter, you will have exclusive access to a range of resources, training and support , designed to help you organisation implement their workplace mental health programme.
- Access an annual assessment of your programme and a tailored recommendations report to help identify any gaps in your approach.
- Free access to our 'Start the Conversation' course , an all-employee general mental health awareness programme.
- Access to a dedicated Support Manager to act as a guide through your organisations mental wellbeing journey and offer any new resources as they become available.
- Counselling through the National Counselling Society at a discounted rate , to help staff members who may need a little extra support.
Request a Callback
Join our Newsletter
Stay up to date with the latest news, training and campaigns by signing up to the Mates in Mind newsletter today.
- Find us British Safety Council Work.Life, Kings House 174 Hammersmith Road London, W6 7JP 020 3510 5018 facebook
Cookies on Mates in Mind

Growing a Mo is like wearing a symbol representing healthier men and a healthier world, all Movember long. It shows everyone you walk past that men’s health matters to you.

Move for Mental Health
Move is how The Order of Mo remembers the 60 men suicide takes globally, every hour. To take part, all you have to do is run or walk 60km over Movember.

Host a Mo-ment
Make having a good time your goal and you won’t go wrong. Get your believers, supporters and followers around. Host an event that raises awareness and funds for men’s health.

Mo your own way
There are many ways to better men’s health. And if you believe doing your own thing is it, we're 100% getting behind you.

Movember fundraisers are a global community of fired up Mo Bros and Mo Sisters – aka rock stars making a difference in mental health and suicide prevention, prostate cancer and testicular cancer.
Your donation could help save a father, a brother, a son, a friend, a partner, a man’s life.

We've funded over 1,320 men's health projects globally

Scaling up mental fitness in the construction industry

Breakthrough in prostate cancer scan imaging techniques

New group counselling programme for London school boys

Boosting the mental health of Scottish teens

Testicular cancer project hits another milestone

Tackling the biggest issue men face after prostate cancer

Supporting GBTQ+ men as they become fathers
Current time by city
For example, New York
Current time by country
For example, Japan
Time difference
For example, London
For example, Dubai
Coordinates
For example, Hong Kong
For example, Delhi
For example, Sydney
Geographic coordinates of Elektrostal, Moscow Oblast, Russia
City coordinates
Coordinates of Elektrostal in decimal degrees
Coordinates of elektrostal in degrees and decimal minutes, utm coordinates of elektrostal, geographic coordinate systems.
WGS 84 coordinate reference system is the latest revision of the World Geodetic System, which is used in mapping and navigation, including GPS satellite navigation system (the Global Positioning System).
Geographic coordinates (latitude and longitude) define a position on the Earth’s surface. Coordinates are angular units. The canonical form of latitude and longitude representation uses degrees (°), minutes (′), and seconds (″). GPS systems widely use coordinates in degrees and decimal minutes, or in decimal degrees.
Latitude varies from −90° to 90°. The latitude of the Equator is 0°; the latitude of the South Pole is −90°; the latitude of the North Pole is 90°. Positive latitude values correspond to the geographic locations north of the Equator (abbrev. N). Negative latitude values correspond to the geographic locations south of the Equator (abbrev. S).
Longitude is counted from the prime meridian ( IERS Reference Meridian for WGS 84) and varies from −180° to 180°. Positive longitude values correspond to the geographic locations east of the prime meridian (abbrev. E). Negative longitude values correspond to the geographic locations west of the prime meridian (abbrev. W).
UTM or Universal Transverse Mercator coordinate system divides the Earth’s surface into 60 longitudinal zones. The coordinates of a location within each zone are defined as a planar coordinate pair related to the intersection of the equator and the zone’s central meridian, and measured in meters.
Elevation above sea level is a measure of a geographic location’s height. We are using the global digital elevation model GTOPO30 .
Elektrostal , Moscow Oblast, Russia
- About company
- GENERAL CONTRACTOR

+7 (495) 526-30-40 +7 (49657) 0-30-99
THE HISTORY OF THE COMPANY CREATION
1993 how the construction company remstroy was created the year 1993 was a period when a lot of construction companies, which had been working successfully during the soviet times and had rich staff capacity, were forced to cease their activity for various reasons. a lot of capable specialists either had to look for another job or change their field. but there were also those who were willing to realise their potential in the field of construction in accordance with the received degree and the experience they had accumulated. thus, in 1993 in elektrostal (moscow oblast) a group of specialists and people sharing each other’s ideas, who had enormous educational background and the highest degree in architecture, organized and registered ooo firm erg which began its rapid development and successful work, offering its service both on the construction market and other areas. 2000 industrial construction is the main area seven years of successful work have shown that combining different types of activities in the same company is not always convenient. and in the year 2000 the founders of ooo firm erg decided to create and register a monoprofile construction company ooo remstroy construction company. industrial construction was chosen as the priority area. it was in this area that the directors of ooo sk remstroy began their working life and grew as specialists. in order to achieve the set goal, they selected a mobile team of professionals in the field of industrial construction, which allows us to cope with the tasks assigned to ooo sk remstroy throughout russia and the near abroad. 2010 manufacturing of metal structures we possess modern equipment that allows us to carry out the entire cycle of works on the manufacture of metal structures of any complexity without assistance. designing – production – installation of metal structures. a staff of professionals and well-coordinated interaction of the departments let us carry out the work as soon as possible and in accordance with all customer’s requirements.” extract from the list of members of self-regulatory organizations, construction.
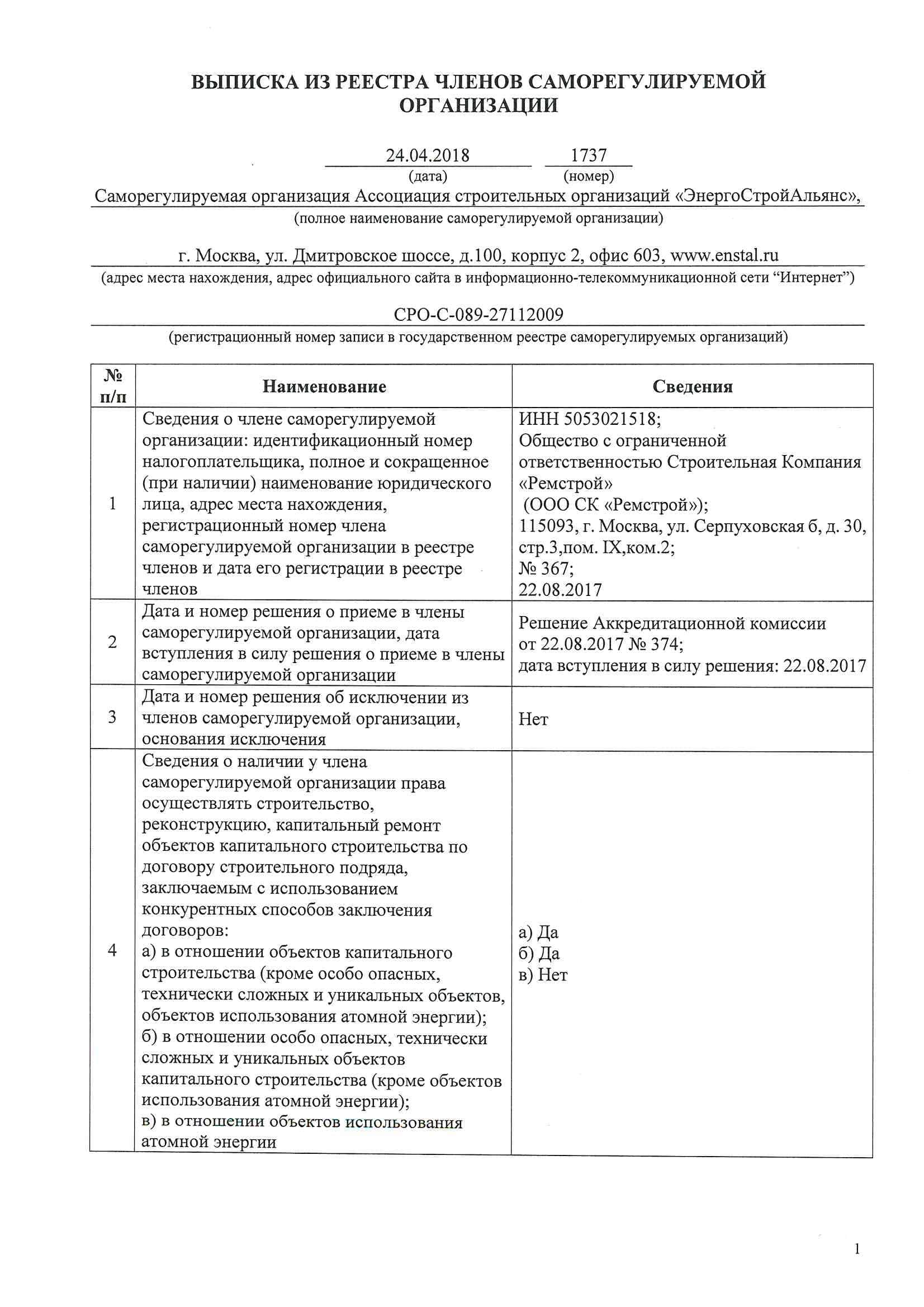
LICENSE OF MINISTRY OF EMERGENCY SITUATIONS
Certificates, system of managing quality.

SYSTEM OF ECOLOGIAL MANAGEMENT

SYSTEM OF OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY AND HEALTH MANAGEMENT

LETTERS OF RECOMMENDATION

THE GEOGRAPHY OF CONSTRUCTION SITES
YOU CAN FIND MORE INFORMATION ON THE CONSTRUCTION SITES OF OOO REMSTROY ON THE PAGE OF THE SITE
OUR CLIENTS

http://remstroi.pro/yandex-promyshlennoe-stroitelstvo

Expedia Rewards is now One Key™
Elektrostal, visit elektrostal, check elektrostal hotel availability, popular places to visit.
- Electrostal History and Art Museum
You can spend time exploring the galleries in Electrostal History and Art Museum in Elektrostal. Take in the museums while you're in the area.
- Cities near Elektrostal

- Places of interest
- Yuri Gagarin Cosmonaut Training Center
- Peter the Great Military Academy
- Central Museum of the Air Forces at Monino
- History of Russian Scarfs and Shawls Museum
- Ramenskii History and Art Museum
- Balashikha Museum of History and Local Lore
- Pekhorka Park
- Balashikha Arena
- Drama Theatre BOOM
- Bykovo Manor
- Malenky Puppet Theater
- Pavlovsky Posad Museum of Art and History
- Saturn Stadium
- Church of Vladimir
- Likino Dulevo Museum of Local Lore
- Orekhovo Zuevsky City Exhibition Hall
- Noginsk Museum and Exhibition Center
- Fairy Tale Children's Model Puppet Theater
- Fifth House Gallery
- Malakhovka Museum of History and Culture

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Mental ill health is a significant cause of suicide and disability worldwide. It has particularly affected the construction industry. The construction labor sectors in Australia and the United Kingdom have suicide rates 2 and 3.7 times higher, respectively, than their overall national averages, which has attracted the attention of researchers and the industry.
Research on mental health in the workplace in general, and in construction in particular, is still in its infancy. But certain statistics stand out. From 2011 to 2015, 1419 individuals working in skilled construction and building trades in England took their own lives. Over the same period, rates of suicide among low-skilled workers in the construction industry were 3·7 times higher than the ...
The construction industry has a lamentable reputation for having a high prevalence of suicides and mental health (MH) problems. Several government and academic reports have identified that construction workers are at a far higher risk of MH disorders than workers in other industrial sectors. While studies on construction workers' MH have significantly increased in recent years, a systematic ...
Despite the growing body of research investigating the factors associated with poor physical and mental health, studies focussing specifically on the mental health of construction workers is ...
UK, the percentage of construction work ers with stress, depression and anxiety was rou ghly. 42.8% ( Kennedy et al., 2012). CPPs are not immune from mental ill-health, as statistics. indicate ...
Workplace Mental Health in the Construction Industry 7 1.0 Introduction Mental health has been defined by several sources with varying definitions. On a fundamental level Oxford dictionary defines it as: mental health; noun. A person's condition with regard to their psychological and emotional well-being. (Oxford Dictionaries, 2018)
A comprehensive review of mental health research in the construction industry utilizing a dual-continuum model of mental health is warranted to understand how the dimensions of mental illness and mental wellbeing have been defined and operationalized given the egregious rates of poor mental health and suicide plaguing the sector.
1. Introduction. The construction industry represents one of the world's largest industrial sectors employing approximately 7% of the global workforce (Sunindijo & Zou, 2012).Mental health issues are reported as a ubiquitous problem in the global construction industry where workers are more at-risk of mental illness than other occupational groups (National Mental Health Commission [NMHC], 2014 ...
Work-related stress, anxiety, and depression are thought to cost the UK construction industry some 400 000 work-days every year. This high rate of suicide among construction workers can largely be attributed to demography. 2·1 million people work in construction in the UK. 89% of the workforce is male. Suicide is the leading cause of death for ...
effective solutions to mental health issues in the construction industry. The aim of this paper is to explore construction industry workers' mental health in the context of individual and immediate project work environment factors within the context of industry structural and behavioural characteristics and to provide a conceptual model
Mental health in the construction industry. Mental health in the construction industry. Mental health in the construction industry Lancet Psychiatry. 2018 Apr;5(4):303. doi: 10.1016/S2215-0366(18)30108-1. Author Talha Burki. PMID: 29580608 DOI: 10.1016 ...
significantly to the mental health issues of construction workers. Employers themselves may be subject to similar issues and risks in their roles, as well as carrying the pr imary liability for the welfare of their workers. Lingard et al. (2017) report that the UK construction industry has higher suicide rates compared with other industries ...
Introduction. Mental health and well-being are high priorities for organizations across industries. This was true before COVID-19, however, is even more so now. Growing mental health concerns exist in the construction industry because it ranks second highest in suicide rates among major industries. 1. Research shows that up to 90% of people who ...
A survey conducted in 2020 revealed that 83% of construction workers had struggled with mental health issues. According to the Center for Disease Control and Prevention, construction occupations have the highest rate of suicide, as well as the highest number of suicides, across all occupational groups. Over 5,000 people working in construction ...
As the pandemic continues to impact the economy and mental health of many workers, construction experiences the second highest rate of suicide among major industries. A new survey of the construction workforce from the American Psychiatric Association (APA) Foundation's Center for Workplace Mental Health, the Construction Financial Management Association, CSDZ and Holmes Murphy, calls ...
The construction industry has had a mental health, substance use, and suicide problem well before COVID-19. But until recently, mental health was not openly addressed in the workplace. Beyond COVID-19, discussing and addressing mental health in the workplace will continue to grow in prevalence, helping to make this an easier topic to address.
Mental ill-health is a silent crisis within the construction industry, with males three times more likely to commit suicide than those in other sectors. This reports sheds light on the state of mental health within the industry by asking over 2,000 professionals their thoughts and experiences. Using evidence from the research, the report ...
This is a report of a mixed-methods research study into enhancing the mental health and well-being of construction workers in the UK. Data collection concerning current practice involved an extensive literature review, interviews with construction and medical professionals and an email survey of 126 workers using 77 questions. The findings indicated that there are major mental health problems ...
Additionally, a report by the Chartered Institute of Building found that 26% of construction industry professionals thought about taking their own lives in 2019 and 56% of construction professionals work for organisations with no policies on mental health in the workplace. Furthermore, in 2022/23 stress, anxiety, and depression accounted for 49 ...
Sports Ambassador Kirsty is taking on a massive challenge. Each day she'll complete either 75 push-ups, 60 sit-ups, 26 pull-ups or 5583m of cardio. Each figure represents a mental health or male suicide statistic. Over the last three days of Movember, she'll then combine all work-outs into one epic, daily final challenge.
Tomlinson (Citation 2015, Citation 2012) situated the growth of the SEN industry within the global "inclusion and education for all" movement following international developments and initiatives, such as the Salamanca statement.According to Tomlinson (Citation 2012), "The more young people are included in mainstream classrooms who cannot perform at ever higher required standards, or ...
Elektrostal, city, Moscow oblast (province), western Russia.It lies 36 miles (58 km) east of Moscow city. The name, meaning "electric steel," derives from the high-quality-steel industry established there soon after the October Revolution in 1917. During World War II, parts of the heavy-machine-building industry were relocated there from Ukraine, and Elektrostal is now a centre for the ...
Geographic coordinates of Elektrostal, Moscow Oblast, Russia in WGS 84 coordinate system which is a standard in cartography, geodesy, and navigation, including Global Positioning System (GPS). Latitude of Elektrostal, longitude of Elektrostal, elevation above sea level of Elektrostal.
2000. Seven years of successful work have shown that combining different types of activities in the same company is not always convenient. And in the year 2000 the founders of OOO Firm ERG decided to create and register a monoprofile construction company OOO Remstroy Construction Company. Industrial construction was chosen as the priority area.
Cities near Elektrostal. Places of interest. Pavlovskiy Posad Noginsk. Travel guide resource for your visit to Elektrostal. Discover the best of Elektrostal so you can plan your trip right.