- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources

How to Write a Rhetorical Analysis Essay–Examples & Template
What is a Rhetorical Analysis Essay?
A rhetorical analysis essay is, as the name suggests, an analysis of someone else’s writing (or speech, or advert, or even cartoon) and how they use not only words but also rhetorical techniques to influence their audience in a certain way. A rhetorical analysis is less interested in what the author is saying and more in how they present it, what effect this has on their readers, whether they achieve their goals, and what approach they use to get there.
Its structure is similar to that of most essays: An Introduction presents your thesis, a Body analyzes the text you have chosen, breaks it down into sections and explains how arguments have been constructed and how each part persuades, informs, or entertains the reader, and a Conclusion section sums up your evaluation.
Note that your personal opinion on the matter is not relevant for your analysis and that you don’t state anywhere in your essay whether you agree or disagree with the stance the author takes.
In the following, we will define the key rhetorical concepts you need to write a good rhetorical analysis and give you some practical tips on where to start.
Key Rhetorical Concepts
Your goal when writing a rhetorical analysis is to think about and then carefully describe how the author has designed their text so that it has the intended effect on their audience. To do that, you need to consider a number of key rhetorical strategies: Rhetorical appeals (“Ethos”, “Logos”, and “Pathos”), context, as well as claims, supports, and warrants.
Ethos, Logos, and Pathos were introduced by Aristotle, way back in the 4th century BC, as the main ways in which language can be used to persuade an audience. They still represent the basis of any rhetorical analysis and are often referred to as the “rhetorical triangle”.
These and other rhetorical techniques can all be combined to create the intended effect, and your job as the one analyzing a text is to break the writer’s arguments down and identify the concepts they are based on.
Rhetorical Appeals
Rhetorical appeal #1: ethos.
Ethos refers to the reputation or authority of the writer regarding the topic of their essay or speech and to how they use this to appeal to their audience. Just like we are more likely to buy a product from a brand or vendor we have confidence in than one we don’t know or have reason to distrust, Ethos-driven texts or speeches rely on the reputation of the author to persuade the reader or listener. When you analyze an essay, you should therefore look at how the writer establishes Ethos through rhetorical devices.
Does the author present themselves as an authority on their subject? If so, how?
Do they highlight how impeccable their own behavior is to make a moral argument?
Do they present themselves as an expert by listing their qualifications or experience to convince the reader of their opinion on something?
Rhetorical appeal #2: Pathos
The purpose of Pathos-driven rhetoric is to appeal to the reader’s emotions. A common example of pathos as a rhetorical means is adverts by charities that try to make you donate money to a “good cause”. To evoke the intended emotions in the reader, an author may use passionate language, tell personal stories, and employ vivid imagery so that the reader can imagine themselves in a certain situation and feel empathy with or anger towards others.
Rhetorical appeal #3: Logos
Logos, the “logical” appeal, uses reason to persuade. Reason and logic, supported by data, evidence, clearly defined methodology, and well-constructed arguments, are what most academic writing is based on. Emotions, those of the researcher/writer as well as those of the reader, should stay out of such academic texts, as should anyone’s reputation, beliefs, or personal opinions.
Text and Context
To analyze a piece of writing, a speech, an advertisement, or even a satirical drawing, you need to look beyond the piece of communication and take the context in which it was created and/or published into account.
Who is the person who wrote the text/drew the cartoon/designed the ad..? What audience are they trying to reach? Where was the piece published and what was happening there around that time?
A political speech, for example, can be powerful even when read decades later, but the historical context surrounding it is an important aspect of the effect it was intended to have.
Claims, Supports, and Warrants
To make any kind of argument, a writer needs to put forward specific claims, support them with data or evidence or even a moral or emotional appeal, and connect the dots logically so that the reader can follow along and agree with the points made.
The connections between statements, so-called “warrants”, follow logical reasoning but are not always clearly stated—the author simply assumes the reader understands the underlying logic, whether they present it “explicitly” or “implicitly”. Implicit warrants are commonly used in advertisements where seemingly happy people use certain products, wear certain clothes, accessories, or perfumes, or live certain lifestyles – with the connotation that, first, the product/perfume/lifestyle is what makes that person happy and, second, the reader wants to be as happy as the person in the ad. Some warrants are never clearly stated, and your job when writing a rhetorical analysis essay is therefore to identify them and bring them to light, to evaluate their validity, their effect on the reader, and the use of such means by the writer/creator.

What are the Five Rhetorical Situations?
A “rhetorical situation” refers to the circumstance behind a text or other piece of communication that arises from a given context. It explains why a rhetorical piece was created, what its purpose is, and how it was constructed to achieve its aims.
Rhetorical situations can be classified into the following five categories:
Asking such questions when you analyze a text will help you identify all the aspects that play a role in the effect it has on its audience, and will allow you to evaluate whether it achieved its aims or where it may have failed to do so.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Outline
Analyzing someone else’s work can seem like a big task, but as with every assignment or writing endeavor, you can break it down into smaller, well-defined steps that give you a practical structure to follow.
To give you an example of how the different parts of your text may look when it’s finished, we will provide you with some excerpts from this rhetorical analysis essay example (which even includes helpful comments) published on the Online Writing Lab website of Excelsior University in Albany, NY. The text that this essay analyzes is this article on why one should or shouldn’t buy an Ipad. If you want more examples so that you can build your own rhetorical analysis template, have a look at this essay on Nabokov’s Lolita and the one provided here about the “Shitty First Drafts” chapter of Anne Lamott’s writing instruction book “Bird by Bird”.
Analyzing the Text
When writing a rhetorical analysis, you don’t choose the concepts or key points you think are relevant or want to address. Rather, you carefully read the text several times asking yourself questions like those listed in the last section on rhetorical situations to identify how the text “works” and how it was written to achieve that effect.
Start with focusing on the author : What do you think was their purpose for writing the text? Do they make one principal claim and then elaborate on that? Or do they discuss different topics?
Then look at what audience they are talking to: Do they want to make a group of people take some action? Vote for someone? Donate money to a good cause? Who are these people? Is the text reaching this specific audience? Why or why not?
What tone is the author using to address their audience? Are they trying to evoke sympathy? Stir up anger? Are they writing from a personal perspective? Are they painting themselves as an authority on the topic? Are they using academic or informal language?
How does the author support their claims ? What kind of evidence are they presenting? Are they providing explicit or implicit warrants? Are these warrants valid or problematic? Is the provided evidence convincing?
Asking yourself such questions will help you identify what rhetorical devices a text uses and how well they are put together to achieve a certain aim. Remember, your own opinion and whether you agree with the author are not the point of a rhetorical analysis essay – your task is simply to take the text apart and evaluate it.
If you are still confused about how to write a rhetorical analysis essay, just follow the steps outlined below to write the different parts of your rhetorical analysis: As every other essay, it consists of an Introduction , a Body (the actual analysis), and a Conclusion .
Rhetorical Analysis Introduction
The Introduction section briefly presents the topic of the essay you are analyzing, the author, their main claims, a short summary of the work by you, and your thesis statement .
Tell the reader what the text you are going to analyze represents (e.g., historically) or why it is relevant (e.g., because it has become some kind of reference for how something is done). Describe what the author claims, asserts, or implies and what techniques they use to make their argument and persuade their audience. Finish off with your thesis statement that prepares the reader for what you are going to present in the next section – do you think that the author’s assumptions/claims/arguments were presented in a logical/appealing/powerful way and reached their audience as intended?
Have a look at an excerpt from the sample essay linked above to see what a rhetorical analysis introduction can look like. See how it introduces the author and article , the context in which it originally appeared , the main claims the author makes , and how this first paragraph ends in a clear thesis statement that the essay will then elaborate on in the following Body section:
Cory Doctorow ’s article on BoingBoing is an older review of the iPad , one of Apple’s most famous products. At the time of this article, however, the iPad was simply the latest Apple product to hit the market and was not yet so popular. Doctorow’s entire career has been entrenched in and around technology. He got his start as a CD-ROM programmer and is now a successful blogger and author. He is currently the co-editor of the BoingBoing blog on which this article was posted. One of his main points in this article comes from Doctorow’s passionate advocacy of free digital media sharing. He argues that the iPad is just another way for established technology companies to control our technological freedom and creativity . In “ Why I Won’t Buy an iPad (and Think You Shouldn’t, Either) ” published on Boing Boing in April of 2010, Cory Doctorow successfully uses his experience with technology, facts about the company Apple, and appeals to consumer needs to convince potential iPad buyers that Apple and its products, specifically the iPad, limit the digital rights of those who use them by controlling and mainstreaming the content that can be used and created on the device .
Doing the Rhetorical Analysis
The main part of your analysis is the Body , where you dissect the text in detail. Explain what methods the author uses to inform, entertain, and/or persuade the audience. Use Aristotle’s rhetorical triangle and the other key concepts we introduced above. Use quotations from the essay to demonstrate what you mean. Work out why the writer used a certain approach and evaluate (and again, demonstrate using the text itself) how successful they were. Evaluate the effect of each rhetorical technique you identify on the audience and judge whether the effect is in line with the author’s intentions.
To make it easy for the reader to follow your thought process, divide this part of your essay into paragraphs that each focus on one strategy or one concept , and make sure they are all necessary and contribute to the development of your argument(s).
One paragraph of this section of your essay could, for example, look like this:
One example of Doctorow’s position is his comparison of Apple’s iStore to Wal-Mart. This is an appeal to the consumer’s logic—or an appeal to logos. Doctorow wants the reader to take his comparison and consider how an all-powerful corporation like the iStore will affect them. An iPad will only allow for apps and programs purchased through the iStore to be run on it; therefore, a customer must not only purchase an iPad but also any programs he or she wishes to use. Customers cannot create their own programs or modify the hardware in any way.
As you can see, the author of this sample essay identifies and then explains to the reader how Doctorow uses the concept of Logos to appeal to his readers – not just by pointing out that he does it but by dissecting how it is done.
Rhetorical Analysis Conclusion
The conclusion section of your analysis should restate your main arguments and emphasize once more whether you think the author achieved their goal. Note that this is not the place to introduce new information—only rely on the points you have discussed in the body of your essay. End with a statement that sums up the impact the text has on its audience and maybe society as a whole:
Overall, Doctorow makes a good argument about why there are potentially many better things to drop a great deal of money on instead of the iPad. He gives some valuable information and facts that consumers should take into consideration before going out to purchase the new device. He clearly uses rhetorical tools to help make his case, and, overall, he is effective as a writer, even if, ultimately, he was ineffective in convincing the world not to buy an iPad .
Frequently Asked Questions about Rhetorical Analysis Essays
What is a rhetorical analysis essay.
A rhetorical analysis dissects a text or another piece of communication to work out and explain how it impacts its audience, how successfully it achieves its aims, and what rhetorical devices it uses to do that.
While argumentative essays usually take a stance on a certain topic and argue for it, a rhetorical analysis identifies how someone else constructs their arguments and supports their claims.
What is the correct rhetorical analysis essay format?
Like most other essays, a rhetorical analysis contains an Introduction that presents the thesis statement, a Body that analyzes the piece of communication, explains how arguments have been constructed, and illustrates how each part persuades, informs, or entertains the reader, and a Conclusion section that summarizes the results of the analysis.
What is the “rhetorical triangle”?
The rhetorical triangle was introduced by Aristotle as the main ways in which language can be used to persuade an audience: Logos appeals to the audience’s reason, Ethos to the writer’s status or authority, and Pathos to the reader’s emotions. Logos, Ethos, and Pathos can all be combined to create the intended effect, and your job as the one analyzing a text is to break the writer’s arguments down and identify what specific concepts each is based on.
Let Wordvice help you write a flawless rhetorical analysis essay!
Whether you have to write a rhetorical analysis essay as an assignment or whether it is part of an application, our professional proofreading services feature professional editors are trained subject experts that make sure your text is in line with the required format, as well as help you improve the flow and expression of your writing. Let them be your second pair of eyes so that after receiving paper editing services or essay editing services from Wordvice, you can submit your manuscript or apply to the school of your dreams with confidence.
And check out our editing services for writers (including blog editing , script editing , and book editing ) to correct your important personal or business-related work.
- Features for Creative Writers
- Features for Work
- Features for Higher Education
- Features for Teachers
- Features for Non-Native Speakers
- Learn Blog Grammar Guide Community Events FAQ
- Grammar Guide
What Is a Rhetorical Analysis and How to Write a Great One

Helly Douglas

Do you have to write a rhetorical analysis essay? Fear not! We’re here to explain exactly what rhetorical analysis means, how you should structure your essay, and give you some essential “dos and don’ts.”
What is a Rhetorical Analysis Essay?
How do you write a rhetorical analysis, what are the three rhetorical strategies, what are the five rhetorical situations, how to plan a rhetorical analysis essay, creating a rhetorical analysis essay, examples of great rhetorical analysis essays, final thoughts.
A rhetorical analysis essay studies how writers and speakers have used words to influence their audience. Think less about the words the author has used and more about the techniques they employ, their goals, and the effect this has on the audience.

In your analysis essay, you break a piece of text (including cartoons, adverts, and speeches) into sections and explain how each part works to persuade, inform, or entertain. You’ll explore the effectiveness of the techniques used, how the argument has been constructed, and give examples from the text.
A strong rhetorical analysis evaluates a text rather than just describes the techniques used. You don’t include whether you personally agree or disagree with the argument.
Structure a rhetorical analysis in the same way as most other types of academic essays . You’ll have an introduction to present your thesis, a main body where you analyze the text, which then leads to a conclusion.
Think about how the writer (also known as a rhetor) considers the situation that frames their communication:
- Topic: the overall purpose of the rhetoric
- Audience: this includes primary, secondary, and tertiary audiences
- Purpose: there are often more than one to consider
- Context and culture: the wider situation within which the rhetoric is placed
Back in the 4th century BC, Aristotle was talking about how language can be used as a means of persuasion. He described three principal forms —Ethos, Logos, and Pathos—often referred to as the Rhetorical Triangle . These persuasive techniques are still used today.
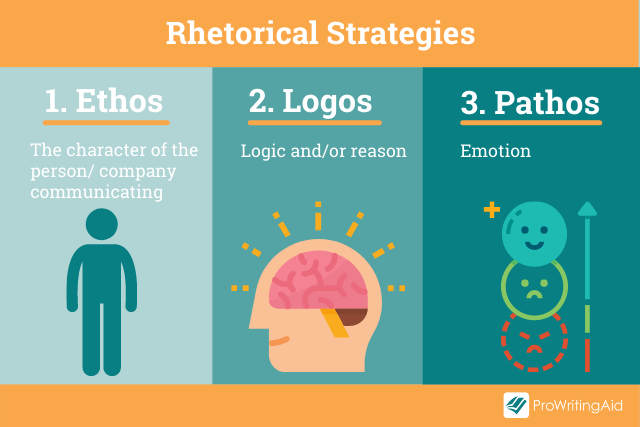
Rhetorical Strategy 1: Ethos
Are you more likely to buy a car from an established company that’s been an important part of your community for 50 years, or someone new who just started their business?
Reputation matters. Ethos explores how the character, disposition, and fundamental values of the author create appeal, along with their expertise and knowledge in the subject area.
Aristotle breaks ethos down into three further categories:
- Phronesis: skills and practical wisdom
- Arete: virtue
- Eunoia: goodwill towards the audience
Ethos-driven speeches and text rely on the reputation of the author. In your analysis, you can look at how the writer establishes ethos through both direct and indirect means.
Rhetorical Strategy 2: Pathos
Pathos-driven rhetoric hooks into our emotions. You’ll often see it used in advertisements, particularly by charities wanting you to donate money towards an appeal.
Common use of pathos includes:
- Vivid description so the reader can imagine themselves in the situation
- Personal stories to create feelings of empathy
- Emotional vocabulary that evokes a response
By using pathos to make the audience feel a particular emotion, the author can persuade them that the argument they’re making is compelling.
Rhetorical Strategy 3: Logos
Logos uses logic or reason. It’s commonly used in academic writing when arguments are created using evidence and reasoning rather than an emotional response. It’s constructed in a step-by-step approach that builds methodically to create a powerful effect upon the reader.
Rhetoric can use any one of these three techniques, but effective arguments often appeal to all three elements.
The rhetorical situation explains the circumstances behind and around a piece of rhetoric. It helps you think about why a text exists, its purpose, and how it’s carried out.
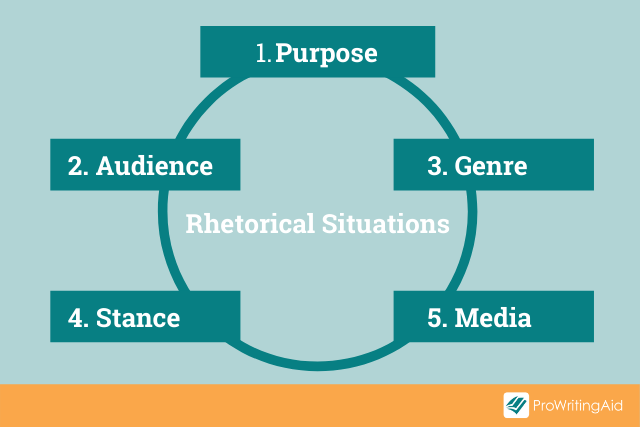
The rhetorical situations are:
- 1) Purpose: Why is this being written? (It could be trying to inform, persuade, instruct, or entertain.)
- 2) Audience: Which groups or individuals will read and take action (or have done so in the past)?
- 3) Genre: What type of writing is this?
- 4) Stance: What is the tone of the text? What position are they taking?
- 5) Media/Visuals: What means of communication are used?
Understanding and analyzing the rhetorical situation is essential for building a strong essay. Also think about any rhetoric restraints on the text, such as beliefs, attitudes, and traditions that could affect the author's decisions.
Before leaping into your essay, it’s worth taking time to explore the text at a deeper level and considering the rhetorical situations we looked at before. Throw away your assumptions and use these simple questions to help you unpick how and why the text is having an effect on the audience.

1: What is the Rhetorical Situation?
- Why is there a need or opportunity for persuasion?
- How do words and references help you identify the time and location?
- What are the rhetoric restraints?
- What historical occasions would lead to this text being created?
2: Who is the Author?
- How do they position themselves as an expert worth listening to?
- What is their ethos?
- Do they have a reputation that gives them authority?
- What is their intention?
- What values or customs do they have?
3: Who is it Written For?
- Who is the intended audience?
- How is this appealing to this particular audience?
- Who are the possible secondary and tertiary audiences?
4: What is the Central Idea?
- Can you summarize the key point of this rhetoric?
- What arguments are used?
- How has it developed a line of reasoning?
5: How is it Structured?
- What structure is used?
- How is the content arranged within the structure?
6: What Form is Used?
- Does this follow a specific literary genre?
- What type of style and tone is used, and why is this?
- Does the form used complement the content?
- What effect could this form have on the audience?
7: Is the Rhetoric Effective?
- Does the content fulfil the author’s intentions?
- Does the message effectively fit the audience, location, and time period?
Once you’ve fully explored the text, you’ll have a better understanding of the impact it’s having on the audience and feel more confident about writing your essay outline.
A great essay starts with an interesting topic. Choose carefully so you’re personally invested in the subject and familiar with it rather than just following trending topics. There are lots of great ideas on this blog post by My Perfect Words if you need some inspiration. Take some time to do background research to ensure your topic offers good analysis opportunities.

Remember to check the information given to you by your professor so you follow their preferred style guidelines. This outline example gives you a general idea of a format to follow, but there will likely be specific requests about layout and content in your course handbook. It’s always worth asking your institution if you’re unsure.
Make notes for each section of your essay before you write. This makes it easy for you to write a well-structured text that flows naturally to a conclusion. You will develop each note into a paragraph. Look at this example by College Essay for useful ideas about the structure.
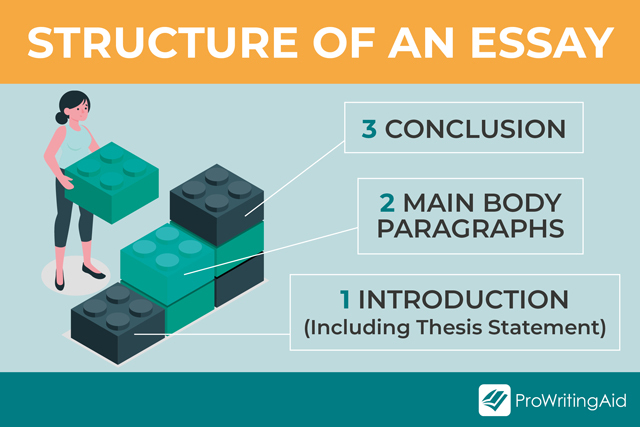
1: Introduction
This is a short, informative section that shows you understand the purpose of the text. It tempts the reader to find out more by mentioning what will come in the main body of your essay.
- Name the author of the text and the title of their work followed by the date in parentheses
- Use a verb to describe what the author does, e.g. “implies,” “asserts,” or “claims”
- Briefly summarize the text in your own words
- Mention the persuasive techniques used by the rhetor and its effect
Create a thesis statement to come at the end of your introduction.
After your introduction, move on to your critical analysis. This is the principal part of your essay.
- Explain the methods used by the author to inform, entertain, and/or persuade the audience using Aristotle's rhetorical triangle
- Use quotations to prove the statements you make
- Explain why the writer used this approach and how successful it is
- Consider how it makes the audience feel and react
Make each strategy a new paragraph rather than cramming them together, and always use proper citations. Check back to your course handbook if you’re unsure which citation style is preferred.
3: Conclusion
Your conclusion should summarize the points you’ve made in the main body of your essay. While you will draw the points together, this is not the place to introduce new information you’ve not previously mentioned.
Use your last sentence to share a powerful concluding statement that talks about the impact the text has on the audience(s) and wider society. How have its strategies helped to shape history?
Before You Submit
Poor spelling and grammatical errors ruin a great essay. Use ProWritingAid to check through your finished essay before you submit. It will pick up all the minor errors you’ve missed and help you give your essay a final polish. Look at this useful ProWritingAid webinar for further ideas to help you significantly improve your essays. Sign up for a free trial today and start editing your essays!
You’ll find countless examples of rhetorical analysis online, but they range widely in quality. Your institution may have example essays they can share with you to show you exactly what they’re looking for.
The following links should give you a good starting point if you’re looking for ideas:
Pearson Canada has a range of good examples. Look at how embedded quotations are used to prove the points being made. The end questions help you unpick how successful each essay is.
Excelsior College has an excellent sample essay complete with useful comments highlighting the techniques used.
Brighton Online has a selection of interesting essays to look at. In this specific example, consider how wider reading has deepened the exploration of the text.

Writing a rhetorical analysis essay can seem daunting, but spending significant time deeply analyzing the text before you write will make it far more achievable and result in a better-quality essay overall.
It can take some time to write a good essay. Aim to complete it well before the deadline so you don’t feel rushed. Use ProWritingAid’s comprehensive checks to find any errors and make changes to improve readability. Then you’ll be ready to submit your finished essay, knowing it’s as good as you can possibly make it.
Try ProWritingAid's Editor for Yourself
Be confident about grammar
Check every email, essay, or story for grammar mistakes. Fix them before you press send.
Helly Douglas is a UK writer and teacher, specialising in education, children, and parenting. She loves making the complex seem simple through blogs, articles, and curriculum content. You can check out her work at hellydouglas.com or connect on Twitter @hellydouglas. When she’s not writing, you will find her in a classroom, being a mum or battling against the wilderness of her garden—the garden is winning!
Get started with ProWritingAid
Drop us a line or let's stay in touch via :
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
How to Write a Rhetorical Analysis Essay

3-minute read
- 22nd August 2023
A rhetorical analysis essay is a type of academic writing that analyzes how authors use language, persuasion techniques , and other rhetorical strategies to communicate with their audience. In this post, we’ll review how to write a rhetorical analysis essay, including:
- Understanding the assignment guidelines
- Introducing your essay topic
- Examining the rhetorical strategies
- Summarizing your main points
Keep reading for a step-by-step guide to rhetorical analysis.
What Is a Rhetorical Strategy?
A rhetorical strategy is a deliberate approach or technique a writer uses to convey a message and/or persuade the audience. A rhetorical strategy typically involves using language, sentence structure, and tone/style to influence the audience to think a certain way or understand a specific point of view. Rhetorical strategies are especially common in advertisements, speeches, and political writing, but you can also find them in many other types of literature.
1. Understanding the Assignment Guidelines
Before you begin your rhetorical analysis essay, make sure you understand the assignment and guidelines. Typically, when writing a rhetorical analysis, you should approach the text objectively, focusing on the techniques the author uses rather than expressing your own opinions about the topic or summarizing the content. Thus, it’s essential to discuss the rhetorical methods used and then back up your analysis with evidence and quotations from the text.
2. Introducing Your Essay Topic
Introduce your essay by providing some context about the text you’re analyzing. Give a brief overview of the author, intended audience, and purpose of the writing. You should also clearly state your thesis , which is your main point or argument about how and why the author uses rhetorical strategies. Try to avoid going into detail on any points or diving into specific examples – the introduction should be concise, and you’ll be providing a much more in-depth analysis later in the text.
3. Examining the Rhetorical Strategies
In the body paragraphs, analyze the rhetorical strategies the author uses. Here are some common rhetorical strategies to include in your discussion:
● Ethos : Establishing trust between the writer and the audience by appealing to credibility and ethics
● Pathos : Appealing to the audience’s emotions and values
● Logos : Employing logic, reason, and evidence to appeal to the reader
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
● Diction : Deliberately choosing specific language and vocabulary
● Syntax : Structuring and arranging sentences in certain ways
● Tone : Conveying attitude or mood in certain ways
● Literary Devices : Using metaphors, similes, analogies , repetition, etc.
Keep in mind that for a rhetorical analysis essay, you’re not usually required to find examples of all of the above rhetorical strategies. But for each one you do analyze, consider how it contributes to the author’s purpose, how it influences the audience, and what emotions or thoughts it could evoke in the reader.
4. Summarizing Your Main Points
In your conclusion , sum up the main points of your analysis and restate your thesis. Without introducing any new points (such as topics or ideas you haven’t already covered in the main body of your essay), summarize the overall impact that the author’s rhetorical strategies likely had on their intended audience.
Expert Proofreading Services
Ensure that your rhetorical analysis essay stands out by having our expert team proofread it. Send in your free sample of 500 words or less and see for yourself the difference in your work!
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
9-minute read
How to Use Infographics to Boost Your Presentation
Is your content getting noticed? Capturing and maintaining an audience’s attention is a challenge when...
8-minute read
Why Interactive PDFs Are Better for Engagement
Are you looking to enhance engagement and captivate your audience through your professional documents? Interactive...
7-minute read
Seven Key Strategies for Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization is rapidly shaping the digital landscape, requiring content professionals to adapt their...
4-minute read
Five Creative Ways to Showcase Your Digital Portfolio
Are you a creative freelancer looking to make a lasting impression on potential clients or...
How to Ace Slack Messaging for Contractors and Freelancers
Effective professional communication is an important skill for contractors and freelancers navigating remote work environments....
How to Insert a Text Box in a Google Doc
Google Docs is a powerful collaborative tool, and mastering its features can significantly enhance your...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
Are you seeking one-on-one college counseling and/or essay support? Limited spots are now available. Click here to learn more.
How to Write the AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay (With Example)
November 27, 2023

Feeling intimidated by the AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay? We’re here to help demystify. Whether you’re cramming for the AP Lang exam right now or planning to take the test down the road, we’ve got crucial rubric information, helpful tips, and an essay example to prepare you for the big day. This post will cover 1) What is the AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay? 2) AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Rubric 3) AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis: Sample Prompt 4) AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example 5)AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example: Why It Works
What is the AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay?
The AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay is one of three essays included in the written portion of the AP English Exam. The full AP English Exam is 3 hours and 15 minutes long, with the first 60 minutes dedicated to multiple-choice questions. Once you complete the multiple-choice section, you move on to three equally weighted essays that ask you to synthesize, analyze, and interpret texts and develop well-reasoned arguments. The three essays include:
Synthesis essay: You’ll review various pieces of evidence and then write an essay that synthesizes (aka combines and interprets) the evidence and presents a clear argument. Read our write up on How to Write the AP Lang Synthesis Essay here.
Argumentative essay: You’ll take a stance on a specific topic and argue your case.
Rhetorical essay: You’ll read a provided passage, then analyze the author’s rhetorical choices and develop an argument that explains why the author made those rhetorical choices.
AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Rubric
The AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay is graded on just 3 rubric categories: Thesis, Evidence and Commentary, and Sophistication . At a glance, the rubric categories may seem vague, but AP exam graders are actually looking for very particular things in each category. We’ll break it down with dos and don’ts for each rubric category:
Thesis (0-1 point)
There’s nothing nebulous when it comes to grading AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay thesis. You either have one or you don’t. Including a thesis gets you one point closer to a high score and leaving it out means you miss out on one crucial point. So, what makes a thesis that counts?
- Make sure your thesis argues something about the author’s rhetorical choices. Making an argument means taking a risk and offering your own interpretation of the provided text. This is an argument that someone else might disagree with.
- A good test to see if you have a thesis that makes an argument. In your head, add the phrase “I think that…” to the beginning of your thesis. If what follows doesn’t logically flow after that phrase (aka if what follows isn’t something you and only you think), it’s likely you’re not making an argument.
- Avoid a thesis that merely restates the prompt.
- Avoid a thesis that summarizes the text but does not make an argument.
Evidence and Commentary (0-4 points)
This rubric category is graded on a scale of 0-4 where 4 is the highest grade. Per the AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis rubric, to get a 4, you’ll want to:
- Include lots of specific evidence from the text. There is no set golden number of quotes to include, but you’ll want to make sure you’re incorporating more than a couple pieces of evidence that support your argument about the author’s rhetorical choices.
- Make sure you include more than one type of evidence, too. Let’s say you’re working on your essay and have gathered examples of alliteration to include as supporting evidence. That’s just one type of rhetorical choice, and it’s hard to make a credible argument if you’re only looking at one type of evidence. To fix that issue, reread the text again looking for patterns in word choice and syntax, meaningful figurative language and imagery, literary devices, and other rhetorical choices, looking for additional types of evidence to support your argument.
- After you include evidence, offer your own interpretation and explain how this evidence proves the point you make in your thesis.
- Don’t summarize or speak generally about the author and the text. Everything you write must be backed up with evidence.
- Don’t let quotes speak for themselves. After every piece of evidence you include, make sure to explain your interpretation. Also, connect the evidence to your overarching argument.
Sophistication (0-1 point)
In this case, sophistication isn’t about how many fancy vocabulary words or how many semicolons you use. According to College Board , one point can be awarded to AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis essays that “demonstrate sophistication of thought and/or a complex understanding of the rhetorical situation” in any of these three ways:
- Explaining the significance or relevance of the writer’s rhetorical choices.
- Explaining the purpose or function of the passage’s complexities or tensions.
- Employing a style that is consistently vivid and persuasive.
Note that you don’t have to achieve all three to earn your sophistication point. A good way to think of this rubric category is to consider it a bonus point that you can earn for going above and beyond in depth of analysis or by writing an especially persuasive, clear, and well-structured essay. In order to earn this point, you’ll need to first do a good job with your thesis, evidence, and commentary.
- Focus on nailing an argumentative thesis and multiple types of evidence. Getting these fundamentals of your essay right will set you up for achieving depth of analysis.
- Explain how each piece of evidence connects to your thesis.
- Spend a minute outlining your essay before you begin to ensure your essay flows in a clear and cohesive way.
- Steer clear of generalizations about the author or text.
- Don’t include arguments you can’t prove with evidence from the text.
- Avoid complex sentences and fancy vocabulary words unless you use them often. Long, clunky sentences with imprecisely used words are hard to follow.
AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis: Sample Prompt
The sample prompt below is published online by College Board and is a real example from the 2021 AP Exam. The prompt provides background context, essay instructions, and the text you need to analyze. For sake of space, we’ve included the text as an image you can click to read. After the prompt, we provide a sample high scoring essay and then explain why this AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis essay example works.
Suggested time—40 minutes.
(This question counts as one-third of the total essay section score.)
On February 27, 2013, while in office, former president Barack Obama delivered the following address dedicating the Rosa Parks statue in the National Statuary Hall of the United States Capitol building. Rosa Parks was an African American civil rights activist who was arrested in 1955 for refusing to give up her seat on a segregated bus in Montgomery, Alabama. Read the passage carefully. Write an essay that analyzes the rhetorical choices Obama makes to convey his message.
In your response you should do the following:
- Respond to the prompt with a thesis that analyzes the writer’s rhetorical choices.
- Select and use evidence to support your line of reasoning.
- Explain how the evidence supports your line of reasoning.
- Demonstrate an understanding of the rhetorical situation.
- Use appropriate grammar and punctuation in communicating your argument.
AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example
In his speech delivered in 2013 at the dedication of Rosa Park’s statue, President Barack Obama acknowledges everything that Parks’ activism made possible in the United States. Telling the story of Parks’ life and achievements, Obama highlights the fact that Parks was a regular person whose actions accomplished enormous change during the civil rights era. Through the use of diction that portrays Parks as quiet and demure, long lists that emphasize the extent of her impacts, and Biblical references, Obama suggests that all of us are capable of achieving greater good, just as Parks did.
Although it might be a surprising way to start to his dedication, Obama begins his speech by telling us who Parks was not: “Rosa Parks held no elected office. She possessed no fortune” he explains in lines 1-2. Later, when he tells the story of the bus driver who threatened to have Parks arrested when she refused to get off the bus, he explains that Parks “simply replied, ‘You may do that’” (lines 22-23). Right away, he establishes that Parks was a regular person who did not hold a seat of power. Her protest on the bus was not part of a larger plan, it was a simple response. By emphasizing that Parks was not powerful, wealthy, or loud spoken, he implies that Parks’ style of activism is an everyday practice that all of us can aspire to.
AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example (Continued)
Even though Obama portrays Parks as a demure person whose protest came “simply” and naturally, he shows the importance of her activism through long lists of ripple effects. When Parks challenged her arrest, Obama explains, Martin Luther King, Jr. stood with her and “so did thousands of Montgomery, Alabama commuters” (lines 27-28). They began a boycott that included “teachers and laborers, clergy and domestics, through rain and cold and sweltering heat, day after day, week after week, month after month, walking miles if they had to…” (lines 28-31). In this section of the speech, Obama’s sentences grow longer and he uses lists to show that Parks’ small action impacted and inspired many others to fight for change. Further, listing out how many days, weeks, and months the boycott lasted shows how Parks’ single act of protest sparked a much longer push for change.
To further illustrate Parks’ impact, Obama incorporates Biblical references that emphasize the importance of “that single moment on the bus” (lines 57-58). In lines 33-35, Obama explains that Parks and the other protestors are “driven by a solemn determination to affirm their God-given dignity” and he also compares their victory to the fall the “ancient walls of Jericho” (line 43). By of including these Biblical references, Obama suggests that Parks’ action on the bus did more than correct personal or political wrongs; it also corrected moral and spiritual wrongs. Although Parks had no political power or fortune, she was able to restore a moral balance in our world.
Toward the end of the speech, Obama states that change happens “not mainly through the exploits of the famous and the powerful, but through the countless acts of often anonymous courage and kindness” (lines 78-81). Through carefully chosen diction that portrays her as a quiet, regular person and through lists and Biblical references that highlight the huge impacts of her action, Obama illustrates exactly this point. He wants us to see that, just like Parks, the small and meek can change the world for the better.
AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example: Why It Works
We would give the AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis essay above a score of 6 out of 6 because it fully satisfies the essay’s 3 rubric categories: Thesis, Evidence and Commentary, and Sophistication . Let’s break down what this student did:
The thesis of this essay appears in the last line of the first paragraph:
“ Through the use of diction that portrays Parks as quiet and demure, long lists that emphasize the extent of her impacts, and Biblical references, Obama suggests that all of us are capable of achieving greater good, just as Parks did .”
This student’s thesis works because they make a clear argument about Obama’s rhetorical choices. They 1) list the rhetorical choices that will be analyzed in the rest of the essay (the italicized text above) and 2) include an argument someone else might disagree with (the bolded text above).
Evidence and Commentary:
This student includes substantial evidence and commentary. Things they do right, per the AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis rubric:
- They include lots of specific evidence from the text in the form of quotes.
- They incorporate 3 different types of evidence (diction, long lists, Biblical references).
- After including evidence, they offer an interpretation of what the evidence means and explain how the evidence contributes to their overarching argument (aka their thesis).
Sophistication
This essay achieves sophistication according to the AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis essay rubric in a few key ways:
- This student provides an introduction that flows naturally into the topic their essay will discuss. Before they get to their thesis, they tell us that Obama portrays Parks as a “regular person” setting up their main argument: Obama wants all regular people to aspire to do good in the world just as Rosa Parks did.
- They organize evidence and commentary in a clear and cohesive way. Each body paragraph focuses on just one type of evidence.
- They explain how their evidence is significant. In the final sentence of each body paragraph, they draw a connection back to the overarching argument presented in the thesis.
- All their evidence supports the argument presented in their thesis. There is no extraneous evidence or misleading detail.
- They consider nuances in the text. Rather than taking the text at face value, they consider what Obama’s rhetorical choices imply and offer their own unique interpretation of those implications.
- In their final paragraph, they come full circle, reiterate their thesis, and explain what Obama’s rhetorical choices communicate to readers.
- Their sentences are clear and easy to read. There are no grammar errors or misused words.
AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay—More Resources
Looking for more tips to help your master your AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay? Brush up on 20 Rhetorical Devices High School Students Should Know and read our Tips for Improving Reading Comprehension . If you’re ready to start studying for another part of the AP English Exam, find more expert tips in our How to Write the AP Lang Synthesis blog post.
Considering what other AP classes to take? Read up on the Hardest AP Classes .
- High School Success

Christina Wood
Christina Wood holds a BA in Literature & Writing from UC San Diego, an MFA in Creative Writing from Washington University in St. Louis, and is currently a Doctoral Candidate in English at the University of Georgia, where she teaches creative writing and first-year composition courses. Christina has published fiction and nonfiction in numerous publications, including The Paris Review , McSweeney’s , Granta , Virginia Quarterly Review , The Sewanee Review , Mississippi Review , and Puerto del Sol , among others. Her story “The Astronaut” won the 2018 Shirley Jackson Award for short fiction and received a “Distinguished Stories” mention in the 2019 Best American Short Stories anthology.
- 2-Year Colleges
- Application Strategies
- Best Colleges by Major
- Best Colleges by State
- Big Picture
- Career & Personality Assessment
- College Essay
- College Search/Knowledge
- College Success
- Costs & Financial Aid
- Data Visualizations
- Dental School Admissions
- Extracurricular Activities
- Graduate School Admissions
- High Schools
- Homeschool Resources
- Law School Admissions
- Medical School Admissions
- Navigating the Admissions Process
- Online Learning
- Private High School Spotlight
- Summer Program Spotlight
- Summer Programs
- Teacher Tools
- Test Prep Provider Spotlight

“Innovative and invaluable…use this book as your college lifeline.”
— Lynn O'Shaughnessy
Nationally Recognized College Expert
College Planning in Your Inbox
Join our information-packed monthly newsletter.
I am a... Student Student Parent Counselor Educator Other First Name Last Name Email Address Zip Code Area of Interest Business Computer Science Engineering Fine/Performing Arts Humanities Mathematics STEM Pre-Med Psychology Social Studies/Sciences Submit
Calculate for all schools
Your chance of acceptance, your chancing factors, extracurriculars, tips for writing a rhetorical analysis essay.
In my English class, we have to write a rhetorical analysis essay and I've never done one before. Can anyone give me some advice on how to break down the text and write a solid essay? I'd really appreciate any help you guys can provide!
First and foremost, it's essential to understand the basic structure of a rhetorical analysis essay and what the purpose is. Rhetorical analysis essays focus on examining how authors use rhetorical strategies (such as ethos, pathos, and logos) to create an argument or persuade the audience. Here is a step-by-step guide to help you write an effective rhetorical analysis essay:
1. Carefully read the text: Begin by reading the text multiple times to ensure that you thoroughly understand the arguments presented. Note down significant points, arguments, and claims made by the author.
2. Identify rhetorical strategies: After understanding the text, identify the rhetorical strategies the author uses, such as ethos (credibility), pathos (emotional appeal), and logos (logical appeal). Keep in mind that authors may also utilize rhetorical devices like analogy, juxtaposition, or irony to enrich their arguments.
3. Analyze the effectiveness of rhetorical strategies: Examine how the rhetorical strategies contribute to the author's purpose and message. Assess the effectiveness of each strategy and how they work in tandem to persuade the audience.
4. Develop a thesis statement: Craft a concise and clear thesis statement that outlines your essay's focus. The thesis should articulate the author's purpose, the rhetorical strategies used, and your analysis of their effectiveness.
5. Outline your essay: Create an outline that includes the introduction, main points supporting your thesis, and a conclusion. This will help you organize your thoughts and ensure a coherent flow throughout the essay.
6. Write the introduction: In the introduction, provide some background on the text and author, as well as a brief summary of the main arguments. Your thesis statement should be placed at the end of the introduction.
7. Develop body paragraphs: Each body paragraph should focus on one rhetorical strategy, starting with a topic sentence that connects to your thesis statement. Then, provide evidence from the text to illustrate the strategy's use and effectiveness. Finally, analyze how the strategy contributes to the author's overall message and purpose.
8. Write the conclusion: Summarize your analysis, restate your thesis, and discuss the implications or significance of your findings. Avoid introducing new ideas in this section.
9. Revise and edit: Make sure to proofread your essay and revise any errors in grammar, syntax, or punctuation. Also, check for clarity, coherence, and cohesion throughout the essay.
By following these steps and maintaining a clear focus on the author's rhetorical strategies, you'll be well on your way to crafting a strong rhetorical analysis essay. Good luck!
About CollegeVine’s Expert FAQ
CollegeVine’s Q&A seeks to offer informed perspectives on commonly asked admissions questions. Every answer is refined and validated by our team of admissions experts to ensure it resonates with trusted knowledge in the field.
TeacherHabits.com Becomes a Part of BetterWritingServices.com
TeacherHabits.com, a popular site for teachers with lots of great tips and ideas for educators, is now teaming up with BetterWritingServices.com, a site dedicated to helping students write awesome essays. This is a big deal for both sites and for everyone who uses them!
What’s Happening?
If you’ve been a fan of TeacherHabits.com, you know it’s a great place to find help for teaching, especially writing. Now that it’s joining forces with BetterWritingServices.com, you’ll get even more useful information!
The writing team at TeacherHabits.com will continue writing articles that focus on how to teach academic writing, especially essays and research papers, as well as share useful teaching tips to help other educators make their work lives easier.
Students, you’re not left out! This will help you better understand teachers and give you insight into what educators expect from you in writing assignments. Teachers, in turn, will be able to read about and understand students’ challenges.
What to Look Forward to
- More New Content: There will be more articles, reviews, videos, and tools that help both teachers and students.
- Personalized Help: If you’re really stuck on an essay, you can get one-on-one help from people who know their job.
As these two sites come together, watch for new content ideas coming your way. Whether you’re a teacher wanting to spice up your lessons or a student looking to ace your next college paper, the new combined site has got your back.
Apart from writing informational articles, BetterWritingServices.com can also help you find the best essay writing service for your specific needs, whether you’re looking for someone to proofread your work, assist with research, or even write an essay from scratch.
We have a separate team that is focused on writing reviews and helping students find the most effective tools to improve their studying process, from software and apps to textbooks and online courses.
P.S. We’ve also recently launched our forum, where you can discuss any topics related to education. This forum is a great place to share experiences, ask questions, and connect with others who have similar interests and challenges.
Students and teachers can create topics and join conversations like this one that discusses top research paper writing services , you can virtually discuss anything as long as it falls into the categories of education and academic development.
We’re really excited about what this partnership will bring. It’s a chance to make a big difference in the way we teach and learn. Stay tuned for more updates, and let’s make learning awesome together.
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Write a Rhetorical Analysis
Last Updated: April 2, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Megan Morgan, PhD . Megan Morgan is a Graduate Program Academic Advisor in the School of Public & International Affairs at the University of Georgia. She earned her PhD in English from the University of Georgia in 2015. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 1,378,492 times.
A rhetorical analysis can be written about other texts, television shows, films, collections of artwork, or a variety of other communicative mediums that attempt to make a statement to an intended audience. In order to write a rhetorical analysis, you need to be able to determine how the creator of the original work attempts to make his or her argument. You can also include information about whether or not that argument is successful. To learn more about the right way to write a rhetorical analysis, continue reading.
Gathering Information

- The speaker refers to the first and last name of the writer. If the writer has any credentials that lend to his or her authority on the matter at hand, you should also briefly consider those. Note that if the narrator is different from the writer, though, it could also refer to the narrator.
- The occasion mostly refers to the type of text and the context under which the text was written. For instance, there is a big difference between an essay written for a scholarly conference and a letter written to an associate in the field.
- The audience is who the text was written for. This is related to the occasion, since the occasion can include details about the audience. In the example above, the audience would be a conference of scholars versus an associate in the field.
- The purpose refers to what the writer wants to accomplish in the text. It usually includes selling a product or point of view.
- The subject is simply the topic the writer discusses in the text.

- Ethos, or ethical appeals, rely on the writer's credibility and character in the garnering of approval. Mentions of a writer's character or qualifications usually qualify as ethos. For instance, if a family therapist with 20 years of practice writes an article on improving familial relations, mention of that experience would be using ethos. Despite their name, these appeals don't have anything to do with "ethics" as we usually think of them.
- Logos, or logical appeals, use reason to make an argument. Most academic discourse should make heavy use of logos. A writer who supports an argument with evidence, data, and undeniable facts uses logos.
- Pathos, or pathetic appeals, seek to evoke emotion in order to gain approval. These emotions can include anything from sympathy and anger to the desire for love. If an article about violent crime provides personal, human details about victims of violent crime, the writer is likely using pathos.

- Analogies and figurative language, including metaphors and similes, demonstrate an idea through comparison.
- Repetition of a certain point or idea is used to make that point seem more memorable.
- Imagery often affects pathos. The image of a starving child in a low income country can be a powerful way of evoking compassion or anger.
- Diction refers to word choice. Emotionally-charged words have greater impact, and rhythmic word patterns can establish a theme more effectively.
- Tone essentially means mood or attitude. A sarcastic essay is vastly different from a scientific one, but depending on the situation, either tone could be effective.
- Addressing the opposition demonstrates that the writer is not afraid of the opposing viewpoint. It also allows the writer to strengthen his or her own argument by cutting down the opposing one. This is especially powerful when the author contrasts a strong viewpoint he or she holds with a weak viewpoint on the opposing side.

- Ask yourself how the rhetorical strategies of appeals and style help the author achieve his or her purpose. Determine if any of these strategies fail and hurt the author instead of helping.
- Speculate on why the author may have chosen those rhetorical strategies for that audience and that occasion. Determine if the choice of strategies may have differed for a different audience or occasion.
- Remember that in a rhetorical analysis, you do not need to agree with the argument being presented. Your task is to analyze how well the author uses the appeals to present her or his argument.
Writing the Introduction

- By letting the reader know that your paper is a rhetorical analysis, you let him or her know exactly what to expect. If you do not let the reader know this information beforehand, he or she may expect to read an evaluative argument instead.
- Do not simply state, "This paper is a rhetorical analysis." Weave the information into the introduction as naturally as possible.
- Note that this may not be necessary if you are writing a rhetorical analysis for an assignment that specifically calls for a rhetorical analysis.

- The introduction is a good place to give a quick summary of the document. Keep it quick, though. Save the majority of the details for your body paragraphs, since most of the details will be used in defending your analysis.

- You do not necessarily need to mention these details in this order. Include the details in a matter that makes sense and flows naturally within your introductory paragraph.

- Try stating which rhetorical techniques the writer uses in order to move people toward his or her desired purpose. Analyze how well these techniques accomplish this goal.
- Consider narrowing the focus of your essay. Choose one or two design aspects that are complex enough to spend an entire essay analyzing.
- Think about making an original argument. If your analysis leads you to make a certain argument about the text, focus your thesis and essay around that argument and provide support for it throughout the body of your paper.
- Try to focus on using words such as "effective" or "ineffective" when composing your thesis, rather than "good" or "bad." You want to avoid seeming like you are passing value judgments.
Writing the Body

- The order of logos, ethos, and pathos is not necessarily set in stone. If you intend to focus on one more than the other two, you could briefly cover the two lesser appeals in the first two sections before elaborating on the third in greater detail toward the middle and end of the paper.
- For logos, identify at least one major claim and evaluate the document's use of objective evidence.
- For ethos, analyze how the writer or speaker uses his or her status as an "expert" to enhance credibility.
- For pathos, analyze any details that alter the way that the viewer or reader may feel about the subject at hand. Also analyze any imagery used to appeal to aesthetic senses, and determine how effective these elements are.
- Wrap things up by discussing the consequences and overall impact of these three appeals.

- Start from the beginning of the document and work your way through to the end. Present details about the document and your analysis of those details in the order the original document presents them in.
- The writer of the original document likely organized the information carefully and purposefully. By addressing the document in this order, your analysis is more likely to make more coherent sense by the end of your paper.

- Evidence often include a great deal of direct quotation and paraphrasing.
- Point to spots in which the author mentioned his or her credentials to explain ethos. Identify emotional images or words with strong emotional connotations as ways of supporting claims to pathos. Mention specific data and facts used in analysis involving logos.

- Avoid use of the first-person words "I" and "we." Stick to the more objective third-person.
Writing the Conclusion

- When restating your thesis, you should be able to quickly analyze how the original author's purpose comes together.
- When restating your thesis, try to bring more sophistication or depth to it than you had in the beginning. What can the audience now understand about your thesis that they would not have without reading your analysis?

- Keep this information brief. You spent an entire essay supporting your thesis, so these restatements of your main ideas should only serve as summaries of your support.

- Indicate what that research must entail and how it would help.
- Also state why the subject matter is important enough to continue researching and how it has significance to the real world.
Writing Help

Community Q&A
- Avoid the use of "In conclusion..." While many writers may be taught to end conclusion paragraphs with this phrase as they first learn to write essays, you should never include this phrase in an essay written at a higher academic level. This phrase and the information that usually follows it is empty information that only serves to clutter up your final paragraph. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- Do not introduce any new information in your conclusion. Summarize the important details of the essay. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- Do not argue in an analysis. Focus on the "how" they made their point, not if it's good or not. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/academic_writing/establishing_arguments/rhetorical_strategies.html
- ↑ https://writingcenter.tamu.edu/Students/Writing-Speaking-Guides/Alphabetical-List-of-Guides/Academic-Writing/Analysis/Rhetorical-Analysis
- ↑ https://courses.lumenlearning.com/englishcomp1/chapter/text-an-overview-of-the-rhetorical-modes/
- ↑ https://oer.pressbooks.pub/informedarguments/chapter/rhetorical-modes-of-writing/
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/visual_rhetoric/analyzing_visual_documents/organizing_your_analysis.html
- ↑ https://www.pfw.edu/offices/learning-support/documents/WriteARhetoricalAnalysis.pdf
About This Article

To write a rhetorical analysis, start by determining what the author of the work you're analyzing is trying to argue. Then, ask yourself if they succeeded in making their argument. Whether you think they did or didn't, include quotes and specific examples in your analysis to back up your opinion. When you're writing your analysis, use the third-person to appear objective as opposed to using "I" or "we." Also, make sure you include the author's name, profession, and purpose for writing the text at the beginning of your analysis to give reader's some context. To learn different ways to structure your rhetorical analysis from our English Ph.D. co-author, keep reading! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Dec 15, 2016
Did this article help you?
Theophilus Ndubisi Chukwu
Aug 13, 2016
Pamela Austin
Sep 28, 2017
John Cornelius
Jul 13, 2016
McKenzie Jameson
Oct 18, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles


Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Develop the tech skills you need for work and life

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

6.2: Rhetorical Analysis
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 250454
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
This chapter builds on the rhetorical concepts introduced in the section, Reading and Writing Rhetorically.
What Is “Rhetorical Analysis”?
Rhetoric : The art of persuasion
Analysis : Breaking down the whole into pieces for the purpose of examination
Unlike a straightforward summary, a rhetorical analysis does not only require a restatement of ideas; instead, you must recognize rhetorical moves that an author is making in an attempt to persuade his or her audience to do or to think something. In the 21st century’s abundance of information, it can sometimes be difficult to discern what is a rhetorical strategy and what is simple manipulation; however, an understanding of rhetoric and rhetorical moves will help you become more savvy with the information surrounding you on a day-to-day basis. In other words, rhetorical moves can be a form of manipulation, but if one can recognize those moves, then one can be a more critical consumer of information rather than blindly accepting whatever one reads, sees, hears, etc.
The goal of a rhetorical analysis is to explain what is happening in the text, why the author might have chosen to use a particular move or set of rhetorical moves, and how those choices might affect the audience. The text you analyze might be explanatory, although there will be aspects of argument because you must negotiate with what the author is trying to do and what you think the author is doing. As Edward P.J. Corbett observes, rhetorical analysis “is more interested in a literary work for what it does than for what it is” (qtd. in Nordqvist).
One of the elements of doing a rhetorical analysis is looking at a text’s rhetorical situation. The rhetorical situation is the context out of a which a text is created.
Another element of rhetorical analysis is simply reading and summarizing the text. You have to be able to describe the basics of the author’s thesis and main points before you can begin to analyze it.
To do rhetorical analysis, you will connect the rhetorical situation to the text. You will go beyond summarizing and instead look at how the author shapes his or her text based on its context. In developing your reading and analytical skills, allow yourself to think about what you’re reading, to question the text and your responses to it, as you read. Use the following questions to help you to take the text apart—dissecting it to see how it works:
- Does the author successfully support the thesis or claim? Is the point held consistently throughout the text, or does it wander at any point?
- Is the evidence the author used effective for the intended audience? How might the intended audience respond to the types of evidence that the author used to support the thesis/claim?
- What rhetorical moves do you see the author making to help achieve his or her purpose? Are there word choices or content choices that seem to you to be clearly related to the author’s agenda for the text?
- Describe the style and tone in the piece. Is it friendly? Authoritative? Does it lecture? Is it biting or sarcastic? Does the author use simple language, or is it full of jargon? Does the language feel positive or negative? Point to aspects of the text that create the tone; spend some time examining these and considering how and why they work.
- Is the author objective, or does he or she try to convince you to have a certain opinion? Why does the author try to persuade you to adopt this viewpoint? If the author is biased, does this interfere with the way you read and understand the refer to the written word: “Proofread your text before submitting the paper.”
- A text refers to any form of communication, primarily written or oral, that forms a coherent unit, often as an object of study. A book can be a text, and a speech can be a text, but television commercials, magazine ads, website, and emails can also be texts: “Dieting advertisements formed one of the texts we studied in my Sociology class.”“?
- Do you feel like the author knows who you are? Does the text seem to be aimed at readers like you or at a different audience? What assumptions does the author make about their audience? Would most people find these reasonable, acceptable, or accurate?
- Does the text’s flow make sense? Is the line of reasoning logical? Are there any gaps? Are there any spots where you feel the reasoning is flawed in some way?
- Does the author try to appeal to your emotions? Does the author use any controversial words in the headline or the article? Do these affect your reading or your interest?
- Do you believe the author? Do you accept their thoughts and ideas? Why or why not?
Once you have done this basic, rhetorical, critical reading of your text, you are ready to think about how the rhetorical situation–the context out of which the text arises–influences certain rhetorical appeals (logos, pathos, ethos) that appear in it.
A Guide to Rhetoric, Genre, and Success in First-Year Writing by Melanie Gagich & Emilie Zickel is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Linked in this textbook is Laura Bolin Carroll’s essay. Click here to read Caroll’s essay: Backpacks vs. Briefcases: Steps Toward Rhetorical Analysis
Professional Examples of Rhetorical Analysis
Hooks, Bell. Cultural Criticism & Transformation . video. LCSC Library
Kilbourne, Jean. 20 Oct 2015. “ Jesus is a Brand of Jeans .” The Humanist .
Kilbourne, Jean. Killing Us Softly video series. LCSC Library.
Kilbourne, Jean. Deadly Persuasion video series. LCSC Library.
Meslin, Dave. 2010. Antidote to Apathy . TED Talk.
- Essay Guides
- Main Academic Essays
Rhetorical Analysis Essay: Learn How to Write It With Our Guide
- Speech Topics
- Basics of Essay Writing
- Essay Topics
- Other Essays
- Research Paper Topics
- Basics of Research Paper Writing
- Miscellaneous
- Chicago/ Turabian
- Data & Statistics
- Methodology
- Admission Writing Tips
- Admission Advice
- Other Guides
- Student Life
- Studying Tips
- Understanding Plagiarism
- Academic Writing Tips
- Basics of Dissertation & Thesis Writing
- Research Paper Guides
- Formatting Guides
- Basics of Research Process
- Admission Guides
- Dissertation & Thesis Guides

Table of contents
Use our free Readability checker
A rhetorical analysis is an essay where you break down a text into its components to examine how these parts work together to create an effect. You will look at elements like the author's use of logos, ethos, and pathos. The goal of a rhetorical analysis essay is not to say if the text is good or bad. Instead, it's about understanding how the author communicates and persuades their audience. You should explain why the author might have chosen specific strategies and whether they are powerful.
Many students reading this article may have never heard about rhetorical essays. It makes sense because usually, only AP English or college students receive such assignments. Still, knowing how to complete one is beneficial. With this guide from StudyCrumb , you will learn what rhetorical analysis is and which appeals authors can use. You will find out how to write a rhetorical analysis essay . Cheer yourself up, as after going through our recommendations, you will meet your professor's highest expectations!
What Is a Rhetorical Analysis
Let's begin with a rhetorical analysis essay definition. It is crucial to understand the differences between various types of papers. As for rhetorical analysis – it is an essay that focuses on the publication author's main ideas . In contrast to literary analysis essay , we should be less concerned with what they say and notice how they sound instead. While reading a suggested or assigned piece, students should keep an eye on:
- What goals did the author pursue by writing their work?
- What rhetorical devices did they use?
- How do they appeal to the reader?
The primary task is breaking a non-fiction work (speech, advertisement, article) into parts. Then, one should define how they perform together to convince, educate or entertain an audience . You shouldn't write about whether you agree or disagree with the author. Alternatively, you aim at discussing how their argument is made and what tone they use. Evaluate their approach in terms of being successful.
Rhetorical Appeals
Writing a rhetorical analysis essay requires you to understand and distinguish rhetorical appeals. These persuasive techniques are used to convince readers and get their approval by calling to emotions, experience, and other characteristics of human nature. There are three main kinds of appeals: ethos, pathos, and logos . In his book " Rhetoric ," Aristotle brought these concepts to life. Now, these rhetorical techniques are excellent strategies that authors use to persuade their audience. But what exactly do these terms mean? Let's make it clear:
- Ethos As an ethical appeal, this approach focuses on proving that your expertise in subject matter is superior. The primary goal of using this technique is to make readers believe you. Provide evidence of your qualification and achieve stunning impact.
- Pathos This approach suggests you call upon audience's emotions. In this context, pathetic doesn't mean something negative. Effective use of this concept can conjure various feelings in one's mind. Sympathy, anger, compassion, sadness – all of these can be used to make your audience accept your argument and acquire endorsement.
- Logos It is a logical appeal that uses interpretation and evidence to prove an issue. One can notice this type of technique in academic writing as well. Most academic audiences appreciate logos-driven methods because they help provide undeniable facts and data.
Summing it up, a good persuasive argument can include all of these appeals. So if you want to make a massive impact on your public in your writing, consider using all of them.

How to Write a Rhetorical Analysis Essay?
By now, you might be wondering: "How to start a rhetorical analysis essay?" The answer is clear – start with text evaluation. In context of rhetorical analysis, it's not necessarily a written piece you should review. It could also be a commercial, debate, or illustration. In such cases, you should also mind imagery and sound aspects. While analyzing your text, consider applying the SOAPS action plan. Here, the first S stands for speaker, O – occasion, A – audience, P – purpose, and the last S is for subject. To put it into practice when you read the text, ask yourself these questions:
- Who is the author?
- Why did they decide to write the article?
- Who are the readers, and why is the author appealing to them?
- What were the author's intentions while writing the piece?
- What is the author's main argument?
Lastly, you should closely examine the text's main point. Find an explicitly stated claim, define presented evidence that supports it. After that, find the warrant – reasoning that connects supporting evidence with a claim. Also, look at rhetorical appeals the writer uses and outline them in your paper.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Introduction
Once you complete your analysis part, get ready to write a rhetorical essay introduction. It should give your readers a message of what your paper will be about. An appropriately crafted opening paragraph should include:
- Hook Start your paper with a catchy sentence to grab your readers' attention. This way, you will stir up their interest to know what comes next in your written piece.
- Background on the context Add some relevant information about your subject to let readers know what exactly you are analyzing. Some exclusive details that might expand the context can also be helpful for such purposes. Refer to the author and their publication title in this part.
- Thesis statement Your thesis should be the fundamental argument you make regarding author's rhetorical techniques used throughout the text. It should be a clear statement that defines your approach to analyzing the publication. Also, you can create a statement by Rhetorical Analysis Thesis Statement Generator .

Rhetorical Paper: Body Paragraphs
The main body of a rhetorical analysis paper is where you directly describe your findings of a text. It usually consists of 3 paragraphs. Sometimes you can focus on a single appeal in each section. Dedicate one for showing how pathos works, the other one for ethos, and the last one for logos. However, it's not always necessary to follow this structure. If the text's part you are analyzing includes specifics of two concepts at once, you can outline this in a single paragraph. Start each section with a topic sentence that gives an overview of what this paragraph will be about. Include quotations from your text as evidence and cite them correctly to avoid plagiarism. Next, express your argument by analyzing how this piece of text functions in rhetoric using ethos, pathos, or logos concepts. End each body paragraph with a brief concluding statement that shows the core of your analysis . And remember: your main body sections should directly relate to the thesis statement you have developed before.

Rhetorical Analysis: Essay Conclusion
Last but not least, let's find out how to conclude a rhetorical analysis essay. This paragraph should draw the final line in your paper. There are a couple of simple recommendations that will help to answer the question, " How to write a good conclusion for an easy ?"
- Begin with a brief synopsis of the claims you made in your essay.
- Extend background by emphasizing relevance of analysis.
- Conclude your investigation with a powerful, noteworthy statement leaving food for thought for your readers.

After you've completed your essay, all that's left is editing and proofreading. Don't skip this process, and never overestimate your abilities. It's always better to double-check what you've done and ensure that your work is impeccable. You may need rhetorical analysis topics for your essay. Check them out in our blog.
Bottom Line
A rhetorical analysis essay can be a tricky task. Nevertheless, writing one following our tips will help you breeze through this assignment and get a high grade. As you've got all necessary tools, completing this task won't be a headache anymore.
If you still have questions or require writing help, feel free to contact us 24/7. Our team of professional writers will be delighted to assist you. If you need a rhetorical analysis paper, coursework, or any other type of work, we will do it for you. Expect a timely delivery and top-notch quality!
Frequently Asked Questions
1. how many sources do i need in a rhetorical analysis essay.
As for the primary source – it will be the one you are analyzing. Secondary sources will help you find good evidence and data, as well as some relevant background information. So stick to 3-5 sources for first-rate outcome unless rubric given by your professor states otherwise.
2. How to write a visual rhetorical analysis?
The main idea is to choose good visuals – a photo, film scene, or youtube video. Then analyze it paying attention to selected visual choices, controversies, or elements that may seem irrelevant. After that, review popular media to see what other people think about your piece. Perhaps, you will determine that some of them feel exactly like you do. In the analysis part, mention your findings. Try to answer such questions:
- Who cares about all this visual stuff?
- What emotions does it bring?
- How do chosen visual elements invoke these feelings?
- Is there any allegory behind the visuals?

Daniel Howard is an Essay Writing guru. He helps students create essays that will strike a chord with the readers.
You may also like

What are your chances of acceptance?
Calculate for all schools, your chance of acceptance.
Your chancing factors
Extracurriculars.
How to Write the AP Lang Rhetorical Essay
Do you know how to improve your profile for college applications.
See how your profile ranks among thousands of other students using CollegeVine. Calculate your chances at your dream schools and learn what areas you need to improve right now — it only takes 3 minutes and it's 100% free.
Show me what areas I need to improve
What’s Covered:
What is the ap lang rhetorical essay, tips for writing the ap lang rhetorical essay.
- AP Lang Rhetorical Essay Example
How Will AP Scores Affect College Chances?
The AP English Language Exam is one of the most common AP exams you can take. However, the average score on the exam in 2020 was a 2.96 out of 5. While this may seem a bit low, it is important to note that over 550,000 students take the exam annually. With some preparation and knowing how to study, it is totally possible to do well on this AP exam.
The AP Lang Rhetorical Essay is one section of the AP English Language Exam. The exam itself is 3 hours and 15 minutes long, and is broken into two sections. The first part of the exam is a 60 minute, 45-question multiple-choice section. The questions on this part of the exam will test your ability to read a passage and then interpret its meaning, style, and overall themes. After the multiple-choice section, there is a section lasting 2 hours and 15 minutes with three “free response” essays. This includes the synthesis essay, the rhetorical analysis essay, and the argument essay.
- In the synthesis essay , you will have to develop an argument using pieces of evidence provided to you.
- The argumentative essay will have you pick a side in a debate and argue for or against it.
- The rhetorical essay requires that you discuss how an author’s written passage contributes to a greater meaning or theme.
The rhetorical essay is perhaps the most unique of all AP Lang exam essays because it requires the test taker to analyze and interpret the deeper meanings of the passage and connect them to the author’s writing style and writing syntax in only 40 minutes. This essay can be the trickiest because it requires you to have knowledge of rhetorical strategies and then apply them to a passage you’ve never seen before.
1. Outline Your Essay Before Writing
One of the most important parts of the AP Lang essays is structuring your essay so that it makes sense to the reader. This is just as important as having good content. For this essay in particular, you’ll want to read the passage first and write a brief outline of your points before you begin the essay. This is because you will want to write the essay using the passage chronologically, which will be discussed in detail below.
2. Understand Rhetorical Strategies
If you feel like you don’t know where to start as you prepare to study for the rhetorical essay portion of the exam, you aren’t alone. It is imperative that you have a grasp on what rhetorical strategies are and how you can use them in your essay. One definition of rhetoric is “language carefully chosen and arranged for maximum effect.” This can include types of figurative language (metaphor, simile, personification, pun, irony, etc.) elements of syntax (parallelism, juxtaposition, anthesis, anaphora, etc), logical fallacies, or persuasive appeals. Overall, there are many elements that you can analyze in an essay and having a good grasp on them through practice and memorization is important.
3. Keep the Essay Well Structured
Even if you understand the various rhetorical strategies you can use, where do you begin? First of all, you’ll want to write a strong introduction that outlines the purpose of the piece. At the end of this introduction, you will write a thesis statement that encapsulates all the rhetorical strategies you discuss. Perhaps these are style elements, tone, or syntax. Be sure to be specific as you list these.
Next, you will create your body paragraphs. As you discuss the rhetorical elements in the piece and tie them back to the work’s meanings, be sure to discuss the points in chronological order. You don’t have to discuss every single strategy, but just pick the ones that are most important. Be sure to cite the line where you found the example. At the end of the essay, write a short conclusion that summarizes the major points above.
4. Be Sure to Explain Your Examples
As you write the essay, don’t just list out your examples and say something like “this is an example of ethos, logos, pathos.” Instead, analyze how the example shows that rhetoric device and how it helps the author further their argument. As you write the rhetorical essay, you’ll want to be as specific and detail-focused as possible.

Discover your chances at hundreds of schools
Our free chancing engine takes into account your history, background, test scores, and extracurricular activities to show you your real chances of admission—and how to improve them.
AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example
Below is a prompt and example for a rhetorical essay, along with its score and what the writer did well and could have improved:
The passage below is an excerpt from “On the Want of Money,” an essay written by nineteenth-century author William Hazlitt. Read the passage carefully. Then write an essay in which you analyze the rhetorical strategies Hazlitt uses to develop his position about money.

Student essay example:
In his essay, Hazlitt develops his position on money through careful use of adjectives and verbs, hypothetical situations, and images. His examples serve to impress upon the reader the highly negative consequences of being in “want of money.”
Hazlitt’s word choice in his opening phrase provides an example of his technique in the rest of the essay. It is not necessary to follow “literally” with “truly” yet his repetition of the same ideas emphasizes his point. In his next sentence, one that lasts forty-six lines, Hazlitt condignly repeats similar ideas, beating into his audience the necessity of having money in this world. The parallelism throughout that one long sentence, “it is not to be sent for to court, or asked out to dinner…it is not to have your own opinion consulted or sees rejected with contempt..” ties the many different situations Haziltt gives together. What could have become a tedious spiel instead becomes a melodious recitation, each example reminding you of one before it, either because of the similarities in structure or content. Hazlitt addresses many different negative effects of not having money but manages to tie them together with his rhetorical strategies.
The diction of the passage fully relays Hazlitt’s position about money. In every example he gives a negative situation but in most emphasizes the terrible circumstance with strong negative adjectives or verbs. “Rejected,” “contempt,” “disparaged,” “scrutinized,” “irksome,” “deprived,” “assailed” “chagrin;” the endless repetition of such discouragement shows how empathetically Hazlitt believes money is a requisite for a happy life. Even the irony of the last sentences is negative, conveying the utter hopelessness of one without money. Through one may have none in life, pitiless men will proceed to mock one’s circumstances, “at a considerable expense” after death!
In having as the body of his essay one long sentence, Hazlitt creates a flow that speeds the passage along, hardly giving the reader time to absorb one idea before another is thrown at him. The unceasing flow is synonymous with Hazlitt’s view of the life of a person without money: he will be “jostled” through life, unable to stop and appreciate the beauty around him or to take time for his own leisure.
The score on this essay was a 6 out of 6. This essay started out very strong as the student had a concrete thesis statement explaining the strategies that Hazlitt used to develop his position on money as well as Hazlitt’s belief on the topic. In the thesis statement, the student points out that adjectives, verbs, hypothetical situations, and images help prove Hazlitt’s point that wanting money can be problematic.
Next, the student broke down their points into three main subsections related to their thesis. More specifically, the student first discusses word choice of repetition and parallelism. When the student discusses these strategies, they list evidence in the paragraph that can be found chronologically in Hazlitt’s essay. The next paragraph is about diction, and the student used specific adjectives and verbs that support this idea. In the last paragraph, the student emphasized how the speed and flow of the essay helped describe Hazlitt’s viewpoint on life. This last concluding sentence is particularly thoughtful, as it goes beyond the explicit points made in the essay and discusses the style and tone of the writing.
It is important to remember that in some ways, the rhetorical essay is also an argumentative essay, as the student must prove how certain rhetorical strategies are used and their significance in the essay. The student even discussed the irony of the paragraph, which is not explicit in the passage.
Overall, this student did an excellent job organizing and structuring the essay and did a nice job using evidence to prove their points.
Now that you’ve learned about the AP Lang rhetorical essay, you may be wondering how your AP scores impact your chances of admission. In fact, your AP scores have relatively little impact on your admissions decision , and your course rigor has much more weight in the application process.
If you’d like to know your chances of admission, be sure to check out our chancing calculator! This tool takes into account your classes, extracurriculars, demographic information, and test scores to understand your chances at admission at over 600 schools. Best of all, it is completely free!
Related CollegeVine Blog Posts

210 Rhetorical Analysis Essay Topics
Table of contents
- 1 What is a Rhetorical Analysis Essay?
- 2 How to Choose a Rhetorical Analysis Essay Topic?
- 3 Comparative Rhetorical Analysis Topics
- 4 Rhetorical Analysis Ideas For High School Students
- 5 Rhetorical Analysis Topics for College Students
- 6 Rhetorical Analysis Essay Topics on Education
- 7 Rhetorical Analysis Essay Topics on Literature
- 8 Rhetorical Analysis Topics List on Speeches
- 9 Visual Rhetorical Essay Topics
- 10 Topics for a Rhetorical Analysis Essay on Society
- 11 Topics for Rhetorical Analysis Essay on a Person
- 12 Rhetorical Analysis Essay Topics on Philosophy
- 13 Rhetorical Analysis Essay Topics on History
- 14 Rhetorical Analysis Essay Topics on Business
- 15 Rhetorical Analysis Essay Topics on Government
- 16 Rhetorical Analysis Essay Topics on Culture
- 17 Conclusion
With any rhetorical analysis essay writing, effective communication is everything. If you’re a student or want to elevate your persuasive skills, learning how to engage your readers is the first step.
When it comes to selecting thought-provoking rhetorical analysis topics, where do you begin? This is where a wise companion in PapersOwl comes in handy. With this seasoned guide, you can easily navigate the complex world of rhetorical analysis. Until then, take a look at our extensive collection of topics that’ll get your creative juices flowing.
We have created a list of 210 essays that will inspire you to craft a powerful academic essay. These rhetorical analysis paper topics cater to all skill levels too.
What is a Rhetorical Analysis Essay?
This type of analysis essay identifies the rhetorical devices and strategies used by an author, all while highlighting how they have used words to sway their audience.
For example, a rhetorical paper looks at an influential political speech through purpose, key claims, and tone. In an essay, students cover by following a structured approach.
- Introduction. Students present the text, author, and thesis statement. These outline the main argument or points of the analysis.
- Main body paragraphs. These delve into specific strategies, appeals, and devices to support the analysis. Make your essay authentic by keeping it true to the facts.
- Conclusion. The end wraps up the essay by summarizing the main points. It will also discuss the effectiveness of the persuasive techniques.
How to Choose a Rhetorical Analysis Essay Topic?
Finding the right topic comes down to writing about something you’re familiar with. This is because you’ll need to showcase insightful analysis to write a rhetorical analysis essay successfully. The best way to do this is to make sure the rhetorical topics you pick are something you’re interested in.
Tip 1. Start by identifying the rhetorical situation essay topics that interest you. This will make background research and thematic analysis that much more enjoyable. Then ask yourself:
- What subjects or themes are intriguing for you to rhetorically analyze?
- Are there specific rhetorical analysis example topics in your field of study that you excel in or are passionate about?
- Have you studied similar subjects or texts in the past that might help your rhetorical analysis assignment ideas come to life?
Tip 2. Choose from rhetorical analysis ideas that match your interests and expertise. Select rhetoric research paper topics relevant to your course or subject area. And make sure there is enough information to write a defined argument. It needs to be complex enough to allow a thorough literary analysis of the themes and the most valuable rhetorical strategies.
Tip 3. Make sure the rhetorical analysis paper topic is suitable. It will need to meet the expectations of rhetorical analysis topics. This means highlighting the importance symbolism plays in the author’s message.
- Is there enough emotional depth and background research for you to work with?
- Can you cover the rhetorical situation within the word limit?
- Is it interesting enough to engage your reader?
Need help with essay writing? Get your paper written by a professional writer Get Help Reviews.io 4.9/5
Comparative Rhetorical Analysis Topics
Here, you’ll rhetorically analyze two texts by similarities, differences, and effectiveness. Sometimes, though, a critical eye is needed. This is when students seek a reputable analytical essay writing service like PapersOwl for help. Here you’ll find expert advice on the most effective academic writing so that you can study with peace of mind.
- The Persuasive Techniques Used By Martin Luther King Jr. And Malcolm X In Their Speeches.
- Does Innovation Outweigh Invention?
- Washington Vs. Lincoln.
- What Is Better For The Economy: Traditional Postal Service Or Email?
- The Persuasive Techniques Of Apple And Samsung In Advertisements.
- The Persuasive Devices Of President Biden’s Speech Vs. President Obama’s Speech.
- Classical Conditioning Or Operant Conditioning. Which Is More Practical?
- The Art Of The Greeks And The Romans.
- What Drives Business Growth In 2023. E-Commerce Or Traditional?
- Education Or Life Without It?
- The Use Of Persuasion In Barack Obama’s And Donald Trump’s Presidential Speeches.
- Command Economy Or The Free Market.
- Philosophy Vs. Religion.
- Ethos, Pathos, And Logos In Op-Ed Articles By Conservative And Liberal Columnists.
- Persuasive Techniques Used In Public Service Announcements On Smoking And Drug Abuse.
Rhetorical Analysis Ideas For High School Students
These easy rhetorical analysis topics encourage students to examine all forms of communication. A rhetorical analysis essay requires looking at written texts, acceptance speeches, or visuals.
It will also help you develop critical thinking skills by understanding how language is used to achieve a particular goal.
- A Rhetorical Analysis On The Meaning Of Mona Lisa’s Smile.
- How William Shakespeare Became Known As The Greatest Writer In The World.
- The Final Speech Of Martin Luther King Jr.
- The Reasons For WW2.
- Novels And Movies About “Frankenstein”: Similarities And Differences.
- The Impact Of Electronic Media On Culture.
- Why Do Films And TV Fail to Capture The Full Essence Of The Books They Are Based On?
- Heroism As Defined By J. K. Rowling And J. R. R. Tolkien.
- A Detailed Analysis Of TV And Online Advertisement.
- The Power Of Social Media: A Rhetoric Paper
- How Sherlock Holmes Is Perceived On TV And Why Not Everyone Likes Him.
- Why Do People Write Fan Fiction?
- My School Principal’s Speech.
- William Shakespeare’s “Romeo And Juliet”: An Analysis.
- Why Are Dogs Known As “Man’s Best Friend”?
Rhetorical Analysis Topics for College Students
These detailed rhetorical analysis topics cover complex primary themes and issues. Through rhetorical analysis, college students learn how language sends a message.
You’ll also improve your own persuasive writing skills by looking at the different types of rhetorical analysis.
- The Use Of Parallelism, Repetition, And Allusion In Martin Luther King Jr.’s “I Have A Dream” Speech.
- Do Women Or Men React Better To Media Advertisement Messages?
- How Does Online Content Manipulate Persuasive Devices?
- What Effect Does Music Have On Film And TV?
- The Persuasive Devices Of The American National Anthem.
- Symbolism In Maya Angelou’s “I Know Why The Caged Bird Sings”.
- How Syrian Politics Sparked War.
- The Persuasive Techniques Used In A Popular Advertisement Or Commercial.
- Why Are Ted Talks So Popular?
- How Does An Influential Newspaper Editorial Manipulate Rhetoric Devices To Benefit Its Argument?
- My Favorite Poem By William Shakespeare.
- The Impact Of A Popular Social Media Influencer’s Posts Or Videos.
- Rhetorical Devices In Famous Song Lyrics
- The Use Of Metaphor In A Speech From Your School Director On Graduation Day.
- The Effectiveness Of Rhetoric Devices In A Well-Known Op-Ed Or Opinion Piece.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Topics on Education
An essay topic on education looks at different forms of communication. You’ll analyze the author’s purpose, as well as their emotional appeal.
All while understanding the nuances of educational discussions and elevating your analytical skills.
- Education System And Educational Technologies .
- Importance Of Time Management Skills .
- Integration Of America’s Public Schools .
- Standardized Testing In Measuring Students’ Academic Performance.
- A Detailed Analysis Essay On The “No Child Left Behind” Policy.
- The Persuasive Techniques Used In Debates Surrounding Homeschooling Versus Traditional Schooling.
- An Analysis Essay On The Proponents And Opponents Of School Vouchers.
- The Language And Persuasive Strategies Used In Promoting Stem Education In Schools.
- An Analysis Essay On Inclusive Education And Its Impact On Special Needs.
- The Arguments For And Against Implementing Technology In The Classroom.
- The Role Of Standardized Curricula In Fostering Critical Thinking And Creativity In Students.
- Promoting Social-Emotional Learning In Schools.
- The Role Of Teachers’ Unions In Shaping Educational Policies And Outcomes.
- Examining Peer Research Papers On The Arguments For And Against Implementing School Uniforms.
- How Policymakers Use Rhetorical Devices To Debate How Teachers’ Unions Shape Education.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Topics on Literature
Authors, poets, and playwrights use a variety of forms of communication in their literary works. Through them, you’ll learn how authors create meaningful literary pieces and gain an appreciation of novels rhetorical strategies.
- Symbolism And Literary Devices In “The Lord Of The Rings” Trilogy.
- The Significance Of Stream-Of-Consciousness Narrative Style In Virginia Woolf’s “Mrs. Dalloway”.
- The Literary Texts Of William Shakespeare.
- Examine The Use Of Rhetorical Devices In A Famous Poem, Such As Maya Angelou’s “Still I Rise”.
- What Does Solitude Symbolize In 21st-Century Literary Texts Compared To The 20th Century?
- Analyzing The Persuasive Strategies Used By Simone De Beauvoir In “The Second Sex”.
- A Detailed Analysis Essay On The Primary Themes Present In Shakespeare’s “Hamlet”.
- Different Rhetorical Devices In “The Bible”.
- The Rhetoric Devices And Symbolism Of Stephen King.
- The Power Of Symbolism And Metaphor In F. Scott Fitzgerald’s “The Great Gatsby”.
- The Literary Devices Of “Pride And Prejudice” And How They’re Still Relevant Today.
- Gender And Power In Jane Austen’s “Pride And Prejudice”.
- Romanticism In William Wordsworth’s Poem “Tintern Abbey”.
- How Harper Lee’s “To Kill A Mockingbird” Confronts Issues Of Racial Injustice
- The Influence Of Gothic Elements In Edgar Allan Poe’s “The Tell-Tale Heart” And “The Fall Of The House Of Usher”.
Rhetorical Analysis Topics List on Speeches
The speech topics for an analysis essay focus on analyzing the elements of a speech. You’ll go deep into the speaker’s choice of words, tone, delivery style, use of rhetorical devices, and the structure of the speech.
By evaluating these components, a detailed rhetorical analysis reveals the speaker’s underlying strategies. Then you can explain how the techniques engage, persuade, and inspire their target audience.
- Rhetorical Analysis Of Barack Obama’s Victory Speech .
- A Rhetorical Analysis Essay On Speeches By Greta Thunberg And David Attenborough.
- The 1588 Speech By Queen Elizabeth on The Spanish Armada.
- A Rhetorical Analysis Essay On Susan B. Anthony’s “On Women’s Right To Vote” Speech.
- Commencement Speeches By Influential Figures Like Steve Jobs And Oprah Winfrey.
- The Role Of Emotional Appeal In Abraham Lincoln’s Gettysburg Address.
- A Rhetorical Analysis Essay On Winston Churchill In His “We Shall Fight On The Beaches” Speech.
- An Examination Of Logos In John F. Kennedy’s Inaugural Address.
- The Persuasive Power Of Repetition In The Famous “Yes We Can” Speech By Barack Obama.
- How Rhetorical Devices Vary In Nelson Mandela’s “Long Walk To Freedom” Speech.
- The Effectiveness Of Analogy And Anecdote In Steve Jobs’ Stanford Commencement Address.
- The Impact Of Tone And Pacing In George Washington’s Resignation Speech.
- The Use Of Persuasive Strategies In Malcolm X’s “The Ballot Or The Bullet” Speech
- The Effect Of Formal Or Informal Language In Speech Delivery.
- The Impact Of Persuasive Techniques In Greta Thunberg’s “How Dare You” Speech At The United Nations Climate Action Summit.
Visual Rhetorical Essay Topics
Visual essays explore how the things we see persuade a target audience and evoke emotional responses. The things you’ll look at with visual analysis essay writing include color, layout, and concrete or abstract images. By doing so, you’ll learn how visual communication impacts our media-rich society.
- A Rhetorical Analysis Essay On The Use Of Color Symbolism In Political Campaign Posters.
- The Impact Of Visual Metaphors In Advertising On Consumer Behavior.
- The Role Of Typography And Font Choice In Conveying A Message In Graphic Design.
- Examining The Use Of Pathos In Public Service Announcements Related To Climate Change.
- The Persuasive Power Of Visual Storytelling In Documentary Films.
- How Social Media Platforms Use Visuals To Shape User Behaviors And Opinions.
- The Influence Of Iconic Photographs On Public Perception Of Historical Events.
- A Visual Rhetorical Analysis Essay On Memes And Their Role In Shaping Online Discourse.
- Developing A Brand Identity Through Visual Symbols And Logos.
- The Role Of Visual Composition In Enhancing The Persuasiveness Of Infographics.
- A Rhetorical Analysis Essay On The Impact Of Editorial Cartoons On Shaping Public Opinion.
- How Visual Metaphors In Music Videos Influence Viewers’ Interpretations Of The Song.
- The Visual Rhetorical Analysis Essay On Visual Arts In The Streets.
- How Visual Rhetorical Composition Is Used In Propaganda Posters To Evoke Nationalistic Emotions.
- Visual Aesthetics in Aligning Branding With A Target Audience.
Topics for a Rhetorical Analysis Essay on Society
A rhetorical essay on society examines how language influences or critiques societal concerns. Through all types of media, you learn how certain strategies persuade or inform an audience about social issues.
- Unconscious Racism And How It Affects People Of Color .
- Racism And Shootings .
- Why The Color Of Your Skin Does Not Matter .
- The Biggest Problem In The United States Of America Is Illegal Immigrants .
- The Problem Of Mass Shootings
- Gun Violence .
- The Role Of Persuasion In Environmental Activism And Climate Change Debates.’
- A Rhetorical Analysis Paper On The Persuasive Techniques In Advertisements Targeting Societal Issues.
- The Influence Of Celebrity Endorsements On Public Opinion And Social Issues.
- The Language And Symbols Used In Anti-Bullying Campaigns.
- A Rhetorical Analysis Paper On The LGBTQ+ Community.
- Public Health Campaigns Addressing Mental Health Stigma.
- A Detailed Rhetorical Analysis Essay On The Discourse Surrounding The Legalization Of Marijuana.
- The Power Of Language In Promoting Or Challenging Racial Stereotypes.
- The Influence Of Rhetorical Devices In Attitudes Toward Wealth Inequality And Social Mobility.
Topics for Rhetorical Analysis Essay on a Person
An outstanding rhetorical analysis paper looks at persuasive strategies to understand the writer’s intention. These essays examine how someone uses language to shape public opinion or inspire change.
- Nikola Tesla – The Inventor Behind It All .
- Changes By Tupac .
- President Donald Trump And His Politics .
- About Fidel Castro .
- How Steve Jobs Used Persuasive Strategies To Reinvent Apple And Inspire Consumer Loyalty.
- The Distinct Rhetoric Of Greta Thunberg In Her Climate Change Activism.
- Analyzing The Persuasive Techniques Of Elon Musk’s Public Presentations And Interviews.
- The Rhetorical Analysis Essay On Susan B. Anthony’s Fight For Women’s Suffrage.
- Do Abstract Images Matter? What Does Boo Radley Represent In “To Kill A Mockingbird”?
- The Rhetorical Composition Of Malala Yousafzai In Her Advocacy For Girls’ Education.
- Nelson Mandela’s Fight Against Apartheid.
- Dissecting The Persuasive Strategies Of Adolf Hitler In His Propaganda Campaigns.
- The Persuasive Techniques Employed By Mahatma Gandhi In His Fight For Indian Independence.
- How Winston Churchill Inspired A Nation During World War 2.
- Maya Angelou In Her Poems And Speeches: A Rhetorical Analysis Essay.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Topics on Philosophy
Philosophers use persuasive techniques, arguments, and linguistic choices in their rhetorical analysis essays to convey their ideas. It will be your job to define their impact by looking at how they engage and convince their readers.
You’ll learn how philosophical concepts are presented and articulated, and you’ll develop your analytical abilities.
- The Calvinistic Doctrine Of Predestination .
- The Use Of Persuasive Devices In Plato’s “Allegory Of The Cave”.
- A Rhetorical Analysis Essay On Descartes’ “Cogito, Ergo Sum” Argument.
- Persuasive Techniques Used By Immanuel Kant In His “Critique Of Pure Reason”.
- A Linguistic Examination Of John Locke’s “A Rhetorical Essay Concerning Human Understanding”.
- The Role Of Ethos, Logos, And Pathos In Jean-Jacques Rousseau’s “The Social Contract”.
- The Persuasive Strategies Of Friedrich Nietzsche In “Thus Spoke Zarathustra”.
- Analysis Of The Socratic Method In “Dialogues” By Plato.
- Persuasive Language In John Stuart Mill’s “On Liberty”.
- Rhetorical Devices In “Leviathan” By Thomas Hobbes.
- Metaphor And Symbolism In Søren Kierkegaard’s “Fear And Trembling”.
- Linguistic Examination Of Martin Heidegger’s “Being And Time”.
- The Persuasive Power Of Bertrand Russell’s “Why I Am Not A Christian”.
- Analyze Main Rhetorical Devices In Ludwig Wittgenstein’s “Philosophical Investigations”.
- A Rhetorical Analysis Essay On The Language Of Metaphysics In George Berkeley’s “A Treatise Concerning The Principles Of Human Knowledge”.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Topics on History
History essays examine and check historical speeches, texts, and events through the lens of expression.
These rhetorical analysis topics will have you studying the words of influential figures throughout history. And how their messages shaped public opinion through the power of language and persuasion.
- The Civil War .
- A Rhetorical Analysis Essay On The “Zimmermann Telegram” And Its Impact On World War I
- The Debates Surrounding The U.S. Constitution.
- American Revolution And The Declaration Of Independence.
- Persuasive Techniques In The Abolitionist Movement
- The Persuasive Power Of Queen Elizabeth I’s Speech To The Troops At Tilbury.
- Thomas Paine’s “Common Sense” Pamphlet.
- The Speeches Of Marcus Tullius Cicero And Their Impact On Roman Society.
- Emancipation Proclamation. Analyzing Abraham Lincoln’s Use Of Diction.
- Techniques Employed In The Women’s Suffrage Movement.
- The Use Of Persuasive Expression In The Civil Rights Movement.
- Wartime Propaganda Posters.
- European Union Formation Through Written And Spoken Persuasive Techniques.
- The Cuban Missile Crisis.
- 1979 Iranian Revolution.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Topics on Business
The business rhetorical analysis examines how communication achieves specific goals. These rhetoric topics look at how marketing campaigns or business proposals affect society.
- Disney Is Destroying Lives
- Completely Legal For Walmart To Hire Many Part Time Workers
- Brexit Bad For Business Ain’t It
- Insights Into The Power Of Storytelling In Business Presentations.
- Campaigns Promoting Corporate Social Responsibility Have Great Power
- Rhetorical Strategies Used In Customer Testimonials And Reviews To Persuade Potential Clients.
- The Persuasive Techniques Used By Businesses To Promote Environmentally-Friendly Practices.
- How Spoken And Written Techniques Reinforce Or Challenge Traditional Gender Roles In The Workplace.
- A Rhetorical Analysis Essay On How Businesses Respond To Public Relations Disasters.
- Exploring The Language That Conveys Corporate Values And Mission Statements.
- The Impact Of Social Media Influencers On Business Promotion.
- The Persuasive Techniques Used In “Shark Tank” Pitches And Startup Competitions.
- Exploring The Strategies Used By Businesses To Regain Trust After Controversies Or Scandals.
- From Commercials To Viral Ad Campaigns: How Advertising Works In 2023.
- How Companies Persuade Other Organizations To Collaborate Or Form Partnerships.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Topics on Government
These rhetorical analysis topics cover political speeches to propaganda in policy documents.
You’ll learn how language and tone rally support for specific initiatives. As well as develop a deeper appreciation for this topic’s influence on political discourse.
- What Does Change Mean In Us History?
- United States Key Role In Support Of Human Rights .
- Essay About Brown V. Board Of Education .
- Police Brutality And Abuse Towards Blacks .
- The Language And Communication Strategies Used In International Diplomacy.
- A Rhetorical Analysis Essay On Political Party Platforms And How They Attract Voters.
- Shaping Public Opinion On Controversial Legislation.
- A Global Village Rhetorical Analysis Essay On The Success Or Failure Of Social Movements.
- A Rhetoric Analysis Of The Impact Of Language In The Framing Of National Security Issues.
- The Role Of Persuasion In The Portrayal Of Political Figures In The Media.
- Examining The Language And Communication Strategies Used In Political Crisis Management.
- Shaping Public Discourse On Controversial Topics Through Rhetorical Analysis.
- Promoting Specific Government Policies Through Written And Spoken Strategy.
- The Rhetorical Richness Of Visual Arts In Media.
- The Use Of Emotional Appeals In Government Public Service Announcements.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Topics on Culture
Culture-specific rhetorical strategies contribute to the unique characteristics of different societies. And studying them encourages the development of critical thinking and analytical skills.
Through language, you will learn how cultural norms, values, and traditions are conveyed and reinforced.
- Women And Men Pay Gap
- Thinking Queerly: Race, Sex, Gender
- Abortion Illegal
- The Society Acceptance Of LGBT
- A Rhetorical Analysis Essay On The Relationship Between Popular Culture And Consumer Behavior.
- Cultural Festivals And Their Impact On Societal Values.
- The Influence Of Social Media On The Evolution Of Cultural Trends.
- Persuasive Language In Cultural Documentaries.
- Literary Persuasion In The Promotion And Preservation Of Cultural Heritage.
- Popular Art Criticism.
- Cultural Stereotypes: Perceptions and Acceptances.
- Language And Communication Strategies Used In Cultural Diplomacy.
- Mainstream Media’s Representation Of Minority Cultures.
- Language And Symbolism In Traditional Cultural Rituals.
- Cultural And Artistic Movements Throughout History
Rhetorical analysis is a fascinating way to explore the power of language and persuasion. Understanding methods used to persuade and improve analytical skills is essential for students.
Luckily, there are 210 essay topics to select from here, so there is no shortage of good rhetorical analysis topics to explore.
From the speeches of world leaders to advertisements, you’ll develop a deeper appreciation for the art of persuasion. Furthermore, you learn how to use rhetorical devices to captivate audiences by analyzing popular media.
Readers also enjoyed

WHY WAIT? PLACE AN ORDER RIGHT NOW!
Just fill out the form, press the button, and have no worries!
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Topics
320+ Best Rhetorical Analysis Essay Topics
20 min read

People also read
Rhetorical Analysis Essay - A Complete Guide With Examples
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example - Free Samples
Crafting an Effective Rhetorical Analysis Essay Outline - Free Samples!
Ethos, Pathos, and Logos - Structure, Usage & Examples
Looking for the right rhetorical analysis essay topic can be a tough challenge for some people!
It’s a well-established fact that for such essays, you need to have an excellent grip on the topic you choose.
For that purpose, we have created a comprehensive list of rhetorical analysis essay topics, so you can pick the topic that matches your interest perfectly. Before coming to the topic ideas, let’s briefly discuss what is a rhetorical analysis essay.
- 1. Introduction to Rhetorical Analysis Essay Writing
- 2. Good Rhetorical Analysis Essay Topics
- 3. Controversial Topics For Rhetorical Analysis
- 4. Hot Rhetorical Analysis Essay Topics In 2024
- 5. Rhetorical Analysis Essay Ideas for Different Academic Levels
- 6. Fictional Rhetorical Analysis Topics For Essay
- 7. Non-Fictional Topics for Rhetorical Analysis Essay
- 8. Rhetorical Analysis Essay Topics About Speeches
- 9. Unique Literature Rhetorical Analysis Essay Topics
- 10. Current Rhetorical Analysis Topics
- 11. Rhetorical Essay Topics About Advertisements
- 12. Visual Rhetorical Analysis Essay Topics
- 13. Funny Rhetorical Analysis Essay Topics
- 14. Comparative Rhetorical Analysis Essay Topics
- 15. Argumentative Rhetorical Analysis Essay Topics
- 16. Interesting Rhetorical Analysis Topics
- 17. How to Choose a Rhetorical Analysis Essay Topic?
Introduction to Rhetorical Analysis Essay Writing
In a rhetorical analysis essay , a writer deeply analyzes a work of literature, art, or film, takes a stance, and thoroughly evaluates the purpose of the original content.
The goal is to ensure effective delivery to the audience.
Having said that, a rhetorical analysis essay finds out how effective the message of the original content was. And how the author or speaker uses rhetorical advice and strategies to convey their message.
Now, let’s move on to the handpicked list of topics!
Good Rhetorical Analysis Essay Topics
- Rhetorical Devices in Barack Obama's Presidential Inauguration
- A Rhetorical Analysis of Donald Trump's Twitter Communication.
- Exploring the Language of Feminism in Contemporary Media.
- Unpacking the Rhetorical Appeals in Climate Change Advocacy Campaigns.
- Examining Persuasive Techniques in Civil Rights Movement Literature.
- Analyzing Rhetorical Strategies in Advertising to Children.
- The Rhetoric of Fear in Post-9/11 Political Speeches.
- Investigating the Rhetorical Appeals in Superhero Movie Trailers.
- A Rhetorical Analysis of Visual Elements in Graphic Design Campaigns.
- Exploring Rhetorical Strategies in Online Activism Movements such as #BlackLivesMatter.
Easy Rhetorical Analysis Essay Topics
- “Pride and Prejudice” by Jane Austen.
- “The Revenant” by Michael Punke.
- “Witches' Loaves” by O. Henry.
- “Adventures of Huckleberry Finn” by Mark Twain.
- “Unbroken” by Laura Hillenbrand.
- “The Lottery” by Shirley Jackson.
- “Yes Please” by Amy Poehler.
- “To Kill a Mockingbird” by Harper Lee.
- “Fight Club” by Chuck Palahniuk.
- “A White Heron” by Sarah Orne Jewett.
Controversial Topics For Rhetorical Analysis
- Analyzing Rhetoric in Gun Control Debates.
- The Power of Persuasion in Abortion Rights Advocacy.
- Deconstructing Rhetorical Strategies in Immigration Reform Discussions.
- Exploring Ethical Dilemmas in Euthanasia Debates.
- Framing Climate Change Discourse in Political Campaigns.
- Unveiling Persuasive Techniques in Vaccination Controversies.
- Analyzing Rhetoric in LGBTQ+ Rights Movements.
- The Rhetoric of Police Brutality Protests.
- Deconstructing Persuasion in Capital Punishment Arguments.
- Exploring the Rhetoric of Cultural Appropriation Discussions.
Hot Rhetorical Analysis Essay Topics In 2024
- Unveiling Rhetoric in Virtual Reality Marketing.
- Analyzing Persuasion in Climate Change Debates.
- The Power of Social Media Influencers' Discourse.
- Deconstructing Persuasive Techniques in Cryptocurrency Promotion.
- Exploring Rhetorical Strategies in Gen Z Activism.
- Framing Mental Health Discourse in Online Communities.
- Analyzing Ethical Dilemmas in AI Ethics Debates.
- Unveiling Persuasive Techniques in Space Tourism Advertising.
- Deconstructing Rhetoric in Genetic Engineering Debates.
- Exploring the Rhetoric of Universal Basic Income Advocacy.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Ideas for Different Academic Levels
We know some students struggle with finding good topics for rhetorical analysis essays. This list has some interesting ideas for different academic levels to get you started!
Just pick a topic and write a great essay.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Topics for College Students
- “Antigone” by Sophocles.
- “The Birthmark” by Nathaniel Hawthorne.
- “The Crucible” by Arthur Miller.
- “Dubliners” by James Joyce.
- “East of Eden” by John Steinbeck.
- “Fahrenheit 451” by Ray Bradbury.
- “A Yellow Raft in Blue Water” by Michael Dorris.
- “Where the Red Fern Grows” by Wilson Rawls.
- “The Tempest” by William Shakespeare.
- “Song of Solomon” by Toni Morrison.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Topics for High School
- “And Then There Were None” by Agatha Christie.
- “Beloved” by Toni Morrison.
- “The Canterbury Tales” by Geoffrey Chaucer.
- “Death of a Salesman” by Arthur Miller.
- “An Enemy of the People” by Henrik Ibsen.
- “Frankenstein” by Mary Shelley.
- “Young Goodman Brown” by Nathaniel Hawthorne.
- “The Waves” by Virginia Woolf.
- “Their Eyes Were Watching God” by Zora Neale Hurston.
- “The Story of an Hour” by Kate Chopin.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Topics for Middle School
- "Yes, Please" By Amy Poehler
- "The Revenant" By Michael Punke
- The Primary Themes In "Alice's Adventures In Wonderland"
- "Huckleberry Finn" Rhetorical Analysis
- "Witches Loaves" By O'Henry
- Discuss My Philosophy for a Happy Life by Sam Berns.
- The Painted Veil.
- Analyze Romeo and Juliet.
- Analyze the “The Power of Introverts” by Susan Cain.
- Amy Poehler. “Yes, Please.”

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
Fictional Rhetorical Analysis Topics For Essay
- Analyzing Persuasive Techniques in "Game of Thrones".
- A Study of Propaganda in Suzanne Collins' "The Hunger Games" Trilogy.
- Analyzing Rhetorical Strategies in Arthur Conan Doyle's Detective Stories.
- Analyzing Persuasive Techniques in "The Bachelor" Franchise.
- Examining Persuasive Techniques in J.K. Rowling's "Harry Potter" Series.
- Analyzing Persuasion in George Orwell's "Animal Farm".
- Deconstructing the Rhetorical Devices of Edgar Allan Poe's "The Raven".
- The Rhetorical Manipulation in George R.R. Martin's "A Song of Ice and Fire" Series.
- Unveiling the Rhetoric of Hope in Suzanne Collins' "Mockingjay".
- Analyzing Rhetorical Techniques in Shakespeare's "Julius Caesar".
Non-Fictional Topics for Rhetorical Analysis Essay
- “Mini Habits: Smaller Habits, Bigger Results” by Stephen Guise.
- “The Ethics of Belief” by William Kingdon Clifford.
- “Easter Island's End” by Jared Diamond.
- “Sinners in the Hands of an Angry God” by Jonathan Edwards.
- “Traveling Mercies” by Anne Lamott.
- “A nation among nations” by Thomas H. Bender.
- “Guns, Germs, and Steel” by Jared Diamond.
- “The Price of Inequality” by Joseph Stiglitz.
- “The Spirit Level” by Kate Pickett and Richard G. Wilkinson.
- “The Status Syndrome” Michael Marmot.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Topics About Speeches
- “I Have a Dream” by Martin Luther King, Jr.
- “Letter from Birmingham Jail” by Martin Luther King, Jr.
- Inaugural Address of President John F. Kennedy.
- Emma Goldman’s Address to the Jury.
- League of Nations Final Address by Thomas Woodrow Wilson.
- “Every Man a King” by Huey Pierce Long.
- “The Evil Empire” by Ronald Reagan.
- “Mercy for Leopold and Loeb” by Clarence Seward Darrow.
- “A Time for Choosing” by Ronald Reagan.
- “The Struggle for Human Rights” by Anna Eleanor Roosevelt.
Unique Literature Rhetorical Analysis Essay Topics
- Rhetorical Devices in "Americanah" by Chimamanda Ngozi Adichie
- Persuasive Techniques in "The Tell-Tale Heart" by Edgar Allan Poe
- Rhetorical Analysis of "Beloved" by Toni Morrison
- Rhetorical Strategies in "One Hundred Years of Solitude" by Gabriel Garcia Marquez
- Silence in "The Catcher in the Rye" by J.D. Salinger
- Rhetorical Analysis of "The Handmaid's Tale" by Margaret Atwood
- Rhetorical Devices in "Never Let Me Go" by Kazuo Ishiguro
- Persuasive Techniques in "Norwegian Wood" by Haruki Murakami
- Rhetorical Analysis of "American Gods" by Neil Gaiman
- Rhetorical Strategies in "One Flew Over the Cuckoo's Nest" by Ken Kesey
Current Rhetorical Analysis Topics
- Social Media Influencers' Rhetoric on TikTok
- COVID-19 Conspiracy Theories: Rhetorical Analysis
- Environmental Justice Advocacy in Indigenous Speeches
- Analyzing the "Cancel Culture" Debate Rhetoric
- The Rhetorical Impact of Deepfake Technology
- Mental Health Advocacy in Contemporary Novels
- Veganism Rhetoric: Animal Rights Activism
- Cybersecurity Rhetoric: Phishing Scam Persuasion
- LGBTQ+ Rights Advocacy on College Campuses
- Persuasive Techniques in Elon Musk's SpaceX Presentations
Rhetorical Essay Topics About Advertisements
- Rhetorical Appeals in Nike's "Dream Crazy" Ad Campaign featuring Colin Kaepernick.
- Analyzing Persuasive Techniques in Coca-Cola's "Share a Coke" Marketing Strategy.
- Examining Dove's "Real Beauty" Advertising Campaign.
- Deconstructing the Rhetorical Devices in Apple's "1984" Commercial.
- Revealing Persuasive Techniques in Burger King's "Moldy Whopper" Campaign.
- Rhetorical Strategies in Always' "Like a Girl" Advertising Campaign.
- Analyzing the Rhetoric of Fear in Anti-Smoking Public Service Announcements.
- Examining Budweiser's "Puppy Love" Super Bowl Commercial.
- Rhetorical Mastery in Guinness' "Surfer" Ad
- Unpacking the Rhetoric of Inclusivity in Target's "Take Pride" Advertising Campaign.
Visual Rhetorical Analysis Essay Topics
- Analyze Poe's Poetry, “The Raven.”
- A favorite poem written by William Shakespeare.
- Analysis of James Joyce’s Ulysses.
- Martin Luther King Jr.’s last speech.
- Sinners in the Hands of an Angry God.
- Clifford's “The Ethics Of Belief” Summary And Analysis
- “Easter Islands' End” By Jared Diamond
- “Success Strategies” Analysis
- Jonathan Edwards’ Sermons
- “Guns, Germs, And Steel” By Jared Diamond
Funny Rhetorical Analysis Essay Topics
- Maximus’ Speech to Commodus from Gladiator
- “Inside the Mind of a Master Procrastinator” by Tim UrbanHealthcare
- Harvard Graduation Speech by Donovan Livington
- Obama’s Final Farewell Speech
- Pink’s VMA acceptance speech
- Do you love your family members or not?
- Do all people grow old?
- A rhetoric analysis of Coca-Cola’s logo colours
- What is your opinion of prequels and remakes?
- Payment of college athletes
Comparative Rhetorical Analysis Essay Topics
- The lottery vs. the hunger games
- Non-fictional novels and fictional novels
- President Obama’s speech on inauguration compared to that of President Trump
- Religious texts and their rhetorical composition.
- Medicines vs. natural remedies
- Social sciences vs. humanities
- Economic upliftment vs. better standard of living
- Compare movies based on Stephen King’s works versus his novels
- Hurricanes vs. tornadoes
- Football vs. basketball
Argumentative Rhetorical Analysis Essay Topics
- Political Speeches and Rhetoric
- Advertising Influence on Consumer Behavior
- Climate Change Communication
- Social Media Persuasion
- Rhetoric in Gun Control Debates
- Fake News and Rhetorical Techniques
- Environmental Activism and Rhetoric
- Healthcare Debates and Persuasion
- Rhetoric in Civil Rights Movements
- Rhetorical Strategies in Literature
Interesting Rhetorical Analysis Topics
Here are some more interesting rhetoric project ideas for you. Check out to find the topic for your next assignment:
Rhetorical Essay Topics About Songs
- Deciphering Rhetorical Devices in Bob Dylan's "Blowin' in the Wind".
- Analyzing Persuasive Techniques in Beyoncé's "Formation".
- The Rhetoric of Protest: Examining Kendrick Lamar's "Alright".
- Unraveling the Rhetoric of Love in Adele's "Someone Like You".
- Deconstructing Persuasive Techniques in Eminem's "Lose Yourself".
- The Power of Pathos in Billie Eilish's "When the Party's Over".
- Rhetorical Strategies in Michael Jackson's "Man in the Mirror".
- Unveiling the Rhetoric of Rebellion in Rage Against the Machine's "Killing in the Name".
- Analyzing Ethos and Logos in Queen's "Bohemian Rhapsody".
- The Rhetoric of Hope in John Lennon's "Imagine".
Rhetorical Essay Topics About Books
- Identity Rhetoric in "The Namesake" by Jhumpa Lahiri
- Persuasive Techniques in "The Remains of the Day"
- Rhetorical Strategies in "White Teeth" by Zadie Smith
- Unpacking Memory Rhetoric in "The Book Thief" by Markus Zusak
- Persuasion in "The God of Small Things" by Arundhati Roy
- Rhetorical Mastery in "One Hundred Years of Solitude"
- Analyzing Appeals in "Midnight's Children" by Salman Rushdie
- Survival Rhetoric in "Life of Pi" by Yann Martel
- Persuasive Techniques in "The Unbearable Lightness of Being"
- Love Rhetoric in "Wuthering Heights" by Emily Brontë
Rhetorical Essay Topics About Films
- The Rhetorical Impact of Color in "The Grand Budapest Hotel".
- Analyzing Persuasive Techniques in Quentin Tarantino's "Pulp Fiction".
- Unveiling the Rhetoric of Identity in "Moonlight".
- Deconstructing the Rhetoric of Power in "The Dark Knight".
- The Rhetoric of Redemption in "The Shawshank Redemption".
- Exploring Rhetorical Devices in Christopher Nolan's "Inception".
- The Power of Symbolism in Guillermo del Toro's "Pan's Labyrinth".
- Rhetorical Strategies in Denis Villeneuve's "Arrival".
- Unraveling the Rhetoric of Society in Bong Joon-ho's "Parasite".
- Analyzing Ethos and Logos in Martin Scorsese's "The Wolf of Wall Street".
Rhetorical Essay Topics About Television Shows
- The Rhetoric of Morality in "Breaking Bad".
- Analyzing Persuasive Techniques in "The Crown".
- Unveiling the Rhetoric of Surveillance in "Black Mirror".
- Deconstructing the Rhetoric of Identity in "Orphan Black".
- The Rhetoric of Family Dynamics in "This Is Us".
- Exploring Rhetorical Devices in "The Handmaid's Tale".
- The Power of Satire in "Veep".
- Rhetorical Strategies in "The Marvelous Mrs. Maisel".
- Unraveling the Rhetoric of Power in "House of Cards".
- Analyzing Ethos and Logos in "The Good Place".
Rhetorical Essay Topics About News Stories
- Crisis Rhetoric in Natural Disasters News.
- Fear Tactics in Cybersecurity Reporting.
- Refugee Crisis Media Persuasion.
- Political Division in News Framing.
- Health Rhetoric in Pandemic Coverage.
- Climate Change News Analysis.
- Framing Social Justice Movements in Media.
- Technology Rhetoric in AI News.
- Economic Inequality Reporting Strategies.
- Justice Rhetoric in Crime News.
Rhetorical Essay Topics About Historical Events
- Persuasion in Civil Rights Movement Rhetoric.
- Propaganda in World War II Media.
- Rhetoric of Revolution: Analyzing the French Revolution Speeches.
- Unveiling Colonialism Rhetoric in Historical Accounts.
- The Power of Speeches in the Suffragette Movement.
- Analyzing Persuasive Techniques in the Vietnam War Protests.
- Deconstructing Propaganda in Soviet Union Era Media.
- The Rhetoric of Independence: Exploring Revolutionary War Documents.
- Media Persuasion in the Cold War Era.
- Rhetorical Analysis of Holocaust Testimonies.
Rhetorical Essay Topics About Websites
- Unpacking Persuasive Techniques on E-commerce Sites.
- Analyzing Rhetoric in Social Media Platforms.
- The Rhetoric of Health Advice Websites.
- Deconstructing Persuasion in Online Dating Platforms.
- Exploring Environmental Advocacy Websites' Rhetoric.
- Persuasive Techniques in Financial Advice Blogs.
- The Rhetoric of Conspiracy Theory Websites.
- Analyzing Persuasion in Travel Booking Websites.
- Unveiling Rhetorical Strategies in Recipe Sharing Platforms.
- Framing in News Aggregator Websites.
Rhetorical Essay Topics About Dictators
- Analyzing Persuasion in Hitler's Speeches.
- Propaganda Tactics of Mussolini's Regime.
- Deconstructing Kim Jong-un's Rhetoric.
- The Rhetoric of Stalin's Five-Year Plans.
- Unveiling Mao Zedong's Cult of Personality.
- The Power of Persuasion in Franco's Spain.
- Analyzing Idi Amin's Authoritarian Rhetoric.
- Propaganda Techniques of Saddam Hussein's Regime.
- The Rhetoric of Pol Pot's Khmer Rouge.
- Deconstructing Gaddafi's Revolutionary Speeches.
Rhetorical Essay Topics About Heroism
- Examining Persuasive Techniques in Heroic Legends.
- The Rhetoric of Courage in Everyday Heroes.
- Deconstructing Superhero Mythos.
- Unveiling the Rhetoric of Sacrifice in War Heroes.
- Analyzing Persuasion in Historical Figures' Biographies.
- The Power of Inspirational Speeches in Heroic Acts.
- Rhetorical Strategies of Humanitarian Campaigns.
- Exploring Persuasive Techniques in Folklore Heroes.
- The Rhetoric of Bravery in Sports Legends.
- Deconstructing Heroic Narratives in Literature.
Rhetorical Essay Topics About Racism
- Analyzing Rhetoric in Anti-Racism Movements.
- Deconstructing Racial Stereotypes in Media.
- The Rhetoric of White Supremacy Groups.
- Unveiling Implicit Bias in Everyday Language.
- Exploring Rhetorical Strategies in Black Lives Matter Protests.
- Persuasion in Political Discourse on Systemic Racism.
- The Power of Narrative in Civil Rights Speeches.
- Rhetorical Devices in Anti-Asian Hate Crime Reporting.
- Framing Racism in Educational Curriculum Debates.
- Analyzing Persuasive Techniques in Diversity Training Materials.
Rhetorical Essay Topics About Religion
- Analyzing Rhetoric in Evangelical Preaching.
- Deconstructing Persuasion in Islamic Sermons.
- The Rhetoric of Conversion in Religious Texts.
- Unveiling the Power of Testimonials in Faith Journeys.
- Exploring Rhetorical Strategies in Buddhist Teachings.
- Persuasive Techniques in New Age Spirituality Movements.
- The Power of Rituals: A Rhetorical Analysis.
- Rhetoric of Salvation in Christian Apologetics.
- Framing Morality in Religious Political Speeches.
- Analyzing Persuasive Techniques in Atheist Manifestos.
Rhetorical Essay Topics About Technology
- The Rhetoric of Artificial Intelligence in Sci-Fi Films.
- Deconstructing Persuasion in Tech Company Keynote Speeches.
- Analyzing Rhetoric in Social Media Algorithms.
- Unveiling Ethical Dilemmas in Biometric Data Collection.
- Exploring Persuasive Techniques in Tech Product Reviews.
- The Power of Digital Activism in Online Movements.
- Rhetorical Strategies in Cybersecurity Awareness Campaigns.
- Framing Privacy Issues in Smart Home Device Advertising.
- Analyzing Persuasion in Virtual Reality Gaming Promotions.
- Deconstructing Tech Start-up Pitch Presentations.
Rhetorical Essay Topics About Sports
- Analyzing Persuasion in Sports Apparel Advertising.
- Deconstructing Athlete Endorsement Speeches.
- The Rhetoric of Team Spirit in Fan Chants.
- Unveiling the Power of Sports Commentary.
- Exploring Rhetorical Strategies in Olympic Opening Ceremonies.
- Persuasive Techniques in Sports Betting Commercials.
- The Rhetoric of Victory Speeches in Championship Moments.
- Framing Athlete Activism in Sports News Coverage.
- Analyzing Persuasion in Sports Nutrition Marketing.
- Deconstructing Coach Pep Talks.
Rhetorical Essay Topics About Celebrities
- Unveiling the Rhetoric of Influence in Celebrity TED Talks.
- Analyzing Persuasive Techniques in George Washington Biographies.
- Deconstructing Literary References in Celebrity Autobiographies.
- Exploring Rhetorical Strategies in Winston Churchill's Speeches.
- Framing Celebrity Activism in Social Media Campaigns.
- Persuasive Techniques in Celebrity Endorsements.
- The Rhetoric of Fame: Celebrity Interviews Analysis.
- Analyzing Ethos and Logos in George Washington Quotes.
- Unveiling the Power of Persuasion in Celebrity Political Speeches.
- Deconstructing Celebrity Apology Speeches.
Poetry Topics for Rhetorical Analysis
- The Rhetorical Devices in Sylvia Plath's "Daddy".
- Analyzing Persuasive Techniques in Langston Hughes' "Harlem".
- Deconstructing Rhetoric in Maya Angelou's "Still I Rise".
- Exploring Ethos and Pathos in T.S. Eliot's "The Waste Land".
- The Power of Symbolism in Emily Dickinson's "Because I could not stop for Death".
- Unveiling the Rhetoric of Nature in Robert Frost's "The Road Not Taken".
- Framing Racial Discourse in Claude McKay's "If We Must Die".
- Analyzing Persuasion in Allen Ginsberg's "Howl".
- The Rhetoric of Nature in Wordsworth's Romantic Poetry.
- Exploring the Rhetoric of Love in Pablo Neruda's "Sonnet XVII".
How to Choose a Rhetorical Analysis Essay Topic?
The following are some tips to consider while selecting the topics for your rhetorical analysis paper.
- Pick Your Interest: Choose something you find intriguing! This will make researching and writing more enjoyable.
- Consider the Text: Can it be analyzed rhetorically? Speeches, ads, poems, even movies can work!
- Think Audience: Who is the text aimed at? How does it try to influence them?
- Research Potential: Is there enough information available to analyze the text thoroughly?
- Go Specific: Don't just analyze a whole speech - focus on a specific technique used.
To conclude, writing a rhetoric paper can be challenging. It is suggested to take a professional’s help for your academic writing assignments and not risk your grades.
To get professional assistance, get help from the expert analytical essay writing service at MyPerfectWords.com . Our qualified writers draft 100% original content for the students and guarantee better grades.
Visit our legit essay writing service now and push your essay writing game to new heights.
So why wait? Connect with us now to shine in your essay writing assignments!
Frequently Asked Questions
What makes an author's rhetoric effective.
An author's rhetoric is effective when it persuades or influences the audience by employing persuasive techniques such as ethos (credibility) , pathos (emotion) , and logos (logic) . Effective rhetoric often involves clarity, coherence, compelling argumentation, and a deep understanding of the audience's values and beliefs.
What is a famous example of a rhetorical question?
A famous example of a rhetorical question is Martin Luther King Jr.'s question in his "I Have a Dream" speech: " And so even though we face the difficulties of today and tomorrow, I still have a dream." This question is not meant to be answered but rather to provoke thought and reflection, emphasizing the persistence of King's dream despite challenges.
What are the 3 main parts of a rhetorical analysis?
The three main parts of a rhetorical analysis typically include:
- Introduction: Providing context for the text or discourse being analyzed, including information about the author, the audience, the purpose, and the rhetorical situation.
- Analysis: Examining the rhetorical strategies used by the author, such as appeals to ethos, pathos, and logos, as well as other rhetorical devices like imagery, tone, and structure.
- Conclusion: Summarizing the key findings of the analysis and discussing the overall effectiveness of the author's rhetoric in achieving their purpose and influencing their audience.

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Nova Allison is a Digital Content Strategist with over eight years of experience. Nova has also worked as a technical and scientific writer. She is majorly involved in developing and reviewing online content plans that engage and resonate with audiences. Nova has a passion for writing that engages and informs her readers.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A rhetorical analysis is a type of essay that looks at a text in terms of rhetoric. This means it is less concerned with what the author is saying than with how they say it: their goals, techniques, and appeals to the audience. A rhetorical analysis is structured similarly to other essays: an introduction presenting the thesis, a body analyzing ...
Rhetorical appeal #2: Pathos. The purpose of Pathos-driven rhetoric is to appeal to the reader's emotions. A common example of pathos as a rhetorical means is adverts by charities that try to make you donate money to a "good cause". To evoke the intended emotions in the reader, an author may use passionate language, tell personal stories ...
Name the author of the text and the title of their work followed by the date in parentheses. Use a verb to describe what the author does, e.g. "implies," "asserts," or "claims". Briefly summarize the text in your own words. Mention the persuasive techniques used by the rhetor and its effect.
1. Choose and study a text. Review the work you're analyzing more than once to become as familiar as possible with the author's argument and writing style. Make sure you have read the text thoroughly, and that you fully understand each point that the author is making as well as the context. Consider choosing a text that covers a topic that ...
5. State your thesis. Now that you've completed your analysis of the material, try to summarize it into one clear, concise thesis statement that will form the foundation of your essay. Your thesis statement should summarize: 1) the argument or purpose of the speaker; 2) the methods the speaker uses; and 3) the effectiveness of those methods ...
2. Introducing Your Essay Topic. Introduce your essay by providing some context about the text you're analyzing. Give a brief overview of the author, intended audience, and purpose of the writing. You should also clearly state your thesis, which is your main point or argument about how and why the author uses rhetorical strategies.
The AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay is one of three essays included in the written portion of the AP English Exam. The full AP English Exam is 3 hours and 15 minutes long, with the first 60 minutes dedicated to multiple-choice questions. Once you complete the multiple-choice section, you move on to three equally weighted essays that ask you ...
Rhetorical Analysis. Rhetoric is the study of how writers and speakers use words to influence an audience. A rhetorical analysis is an essay that breaks a work of non-fiction into parts and then explains how the parts work together to create a certain effect—whether to persuade, entertain or inform. You can also conduct a rhetorical analysis ...
Here is a step-by-step guide to help you write an effective rhetorical analysis essay: 1. Carefully read the text: Begin by reading the text multiple times to ensure that you thoroughly understand the arguments presented. Note down significant points, arguments, and claims made by the author. 2.
Learn what a rhetorical analysis essay is. Learn how to write a rhetorical analysis essay and get an example of a rhetorical analysis essay outline.
Follow these steps when writing your rhetorical analysis essay: 1. Gather information. Use the SOAPSTone technique to identify the components of the work and plan your analysis. SOAPSTone is an acronym commonly used in literary analysis that stands for Speaker, Occasion, Audience, Purpose, Subject, Tone. 2.
Creating engaging content for your rhetorical analysis essay involves the following steps: Use proper citations to support your analysis. Proofread your work to ensure clarity and coherence. Analyze the text by considering the author's argument, the evidence used, and the overall effectiveness of the argument.
3.What is the name of the author? 4.What is the work about (the topic)? Briefly summarize the text in no more than two or three sentences. 5.What do you know about the writer? (social, racial, or historical position in relation to the audience, professional title, etc.) 6.What is the writer's purpose or intention?
The purpose refers to what the writer wants to accomplish in the text. It usually includes selling a product or point of view. The subject is simply the topic the writer discusses in the text. 2. Examine the appeals. Appeals are the first classification of rhetorical strategy and involve the ethos, logos, and pathos.
Rhetoric: The art of persuasion. Analysis: Breaking down the whole into pieces for the purpose of examination. Unlike a straightforward summary, a rhetorical analysis does not only require a restatement of ideas; instead, you must recognize rhetorical moves that an author is making in an attempt to persuade his or her audience to do or to think ...
rhetorical analysis, both by your insights into your topic and by the way you write your essay. As with all academic writing, your ultimate goal is to persuade your readers that your claims about rhetoric and the text are valid and provable. We have several examples to use as models for how to write your essay: Selzer's analysis of
Check out the UPDATED version here: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oU1_rGvAElg&t=109sApologies in advance that this video is SUPER quick. I explain these co...
A rhetorical analysis is an essay where you break down a text into its components to examine how these parts work together to create an effect. You will look at elements like the author's use of logos, ethos, and pathos. The goal of a rhetorical analysis essay is not to say if the text is good or bad. Instead, it's about understanding how the ...
Good Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example. The step-by-step writing process of a rhetorical analysis essay is far more complicated than ordinary academic essays. This essay type critically analyzes the rhetorical means used to persuade the audience and their efficiency. The example provided below is the best rhetorical analysis essay example:
Tips for Writing the AP Lang Rhetorical Essay. 1. Outline Your Essay Before Writing. One of the most important parts of the AP Lang essays is structuring your essay so that it makes sense to the reader. This is just as important as having good content. For this essay in particular, you'll want to read the passage first and write a brief ...
A Rhetorical Analysis Essay On Susan B. Anthony's "On Women's Right To Vote" Speech. Commencement Speeches By Influential Figures Like Steve Jobs And Oprah Winfrey. The Role Of Emotional Appeal In Abraham Lincoln's Gettysburg Address. A Rhetorical Analysis Essay On Winston Churchill In His "We Shall Fight On The Beaches" Speech.
Describe what the author says, then try to have 2 analysis sentences for each description of what the author says. i.e. 2 evidence sentences from the text for each rhetorical strategy, 4 analysis sentences = for each body paragraph. Conclusion: Have a good thesis, body paragraphs follow thesis, and write quickly lol. Your introduction is easy.
Introduction to Rhetorical Analysis Essay Writing. In a rhetorical analysis essay, a writer deeply analyzes a work of literature, art, or film, takes a stance, and thoroughly evaluates the purpose of the original content.. The goal is to ensure effective delivery to the audience. Having said that, a rhetorical analysis essay finds out how effective the message of the original content was. And ...