
- Case Studies
- Free Coaching Session

Production Plan in Business Plan: A Comprehensive Guide to Success
Last Updated:
May 20, 2024

In any business venture, a solid production plan is crucial for success. A production plan serves as a roadmap that outlines the steps, resources, and strategies required to manufacture products or deliver services efficiently. By carefully crafting a production plan within a business plan, entrepreneurs can ensure optimal utilisation of resources, timely delivery, cost efficiency, and customer satisfaction. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of creating an effective production plan in a business plan , exploring its key components, strategies, and the importance of aligning it with overall business objectives .
Key Takeaways on Production Plans in Business Planning
- A production plan : a detailed outline that guides efficient product manufacturing or service delivery.
- Importance of a production plan : provides a roadmap for operations, optimises resource utilisation, and aligns with customer demand.
- Key components : demand forecasting, capacity planning, inventory management, resource allocation, and quality assurance.
- Strategies : lean manufacturing, JIT inventory, automation and technology integration, supplier relationship management, and continuous improvement.
- Benefits of a well-executed production plan : improved efficiency, reduced costs, enhanced product quality, and increased profitability.

What is a Production Plan?
A production Seamless Searches plan is a detailed outline that specifies the processes, resources, timelines, and strategies required to convert raw materials into finished goods or deliver services. It serves as a blueprint for the entire production cycle, guiding decision-making and resource allocation. The production plan considers factors such as demand forecasting, capacity planning, inventory management, and quality assurance to ensure efficient operations and optimal customer satisfaction.
Why is a Production Plan Important in a Business Plan?
The inclusion of a production plan in a business plan is vital for several reasons. First and foremost, it provides a clear roadmap for business operations, helping entrepreneurs and managers make informed decisions related to production processes. A well-developed production plan ensures that resources are utilised efficiently, minimising wastage and optimising productivity.
Additionally, a production plan allows businesses to align their production capabilities with customer demand. By forecasting market trends and analysing customer needs, businesses can develop a production plan that caters to current and future demands, thus avoiding overstocking or understocking situations.
Furthermore, a production plan helps businesses enhance their competitive advantage. By implementing strategies such as lean manufacturing and invoice automation , companies can streamline their production processes, reduce costs, improve product quality, and ultimately outperform competitors.
Key Components of a Production Plan
To create an effective production plan, it is crucial to consider several key components. These components work together to ensure efficient operations and successful fulfilment of customer demands. Let's explore each component in detail.
Demand Forecasting
Demand forecasting is a critical aspect of production planning. By analysing historical data, market trends, and customer behaviour, businesses can predict future demand for their products or services. Accurate demand forecasting allows companies to optimise inventory levels, plan production capacity, and ensure timely delivery to customers.
One approach to demand forecasting is quantitative analysis, which involves analysing historical sales data to identify patterns and make predictions. Another approach is qualitative analysis, which incorporates market research, customer surveys, and expert opinions to gauge demand fluctuations. By combining both methods, businesses can develop a robust demand forecast, minimising the risk of underproduction or overproduction. Utilising a free notion template for demand forecasting can further streamline this process, allowing businesses to organise and analyse both quantitative and qualitative data efficiently in one centralised location.
Capacity Planning
Capacity planning involves determining the optimal production capacity required to meet projected demand. This includes assessing the production capabilities of existing resources, such as machinery, equipment, and labour, and identifying any gaps that need to be addressed. By conducting a thorough capacity analysis, businesses can ensure that their production capacity aligns with customer demand, avoiding bottlenecks or excess capacity.
An effective capacity plan takes into account factors such as production cycle times, labour availability, equipment maintenance, and production lead times. It helps businesses allocate resources efficiently, minimise production delays, and maintain a consistent level of output to meet customer expectations.
Inventory Management
Efficient inventory management is crucial for a successful production plan. It involves balancing the cost of holding inventory with the risk of stockouts. By maintaining optimal inventory levels, businesses can reduce carrying costs while ensuring that sufficient stock is available to fulfil customer orders.
Inventory management techniques, such as the Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) model and Just-in-Time (JIT) inventory system, help businesses strike the right balance between inventory investment and customer demand. These methods consider factors such as order frequency, lead time, and carrying costs to optimise inventory levels and minimise the risk of excess or insufficient stock.
Resource Allocation
Resource allocation plays a pivotal role in a production plan. It involves assigning available resources, such as labour, materials, and equipment, to specific production tasks or projects. Effective resource allocation ensures that resources are utilised optimally, avoiding underutilisation or overutilisation.
To allocate resources efficiently, businesses must consider factors such as skill requirements, resource availability, project timelines, and cost constraints. By conducting a thorough resource analysis and implementing resource allocation strategies, businesses can streamline production processes, minimise bottlenecks, and maximise productivity.
Quality Assurance
Maintaining high-quality standards is essential for any production plan. Quality assurance involves implementing measures to monitor and control the quality of products or services throughout the production process. By adhering to quality standards and conducting regular inspections, businesses can minimise defects, ensure customer satisfaction, and build a positive brand reputation.
Quality assurance techniques, such as Total Quality Management (TQM) and Six Sigma , help businesses identify and rectify any quality-related issues. These methodologies involve continuous monitoring, process improvement, and employee training to enhance product quality and overall operational efficiency.
In addition to the core components of a production plan, it's also important for businesses to consider the broader aspects of their business strategy, including marketing and advertising. Understanding the costs and returns of different marketing approaches is crucial for comprehensive business planning. For instance, direct response advertising costs can vary significantly, but they offer the advantage of measurable responses from potential customers. This type of advertising can be a valuable strategy for businesses looking to directly engage with their target audience and track the effectiveness of their marketing efforts.
Strategies for Developing an Effective Production Plan
Developing an effective production plan requires implementing various strategies and best practices. By incorporating these strategies into the production planning process, businesses can optimise operations and drive success. Let's explore some key strategies in detail.
Lean Manufacturing
Lean manufacturing is a systematic Seamless Searches approach aimed at eliminating waste and improving efficiency in production processes. It emphasises the concept of continuous improvement and focuses on creating value for the customer while minimising non-value-added activities.
By adopting lean manufacturing principles, such as just-in-time production, standardised work processes, and visual management, businesses can streamline operations, reduce lead times, and eliminate unnecessary costs. Lean manufacturing not only improves productivity but also enhances product quality and customer satisfaction.
Just-in-Time (JIT) Inventory
Just-in-Time (JIT) inventory is a strategy that aims to minimise inventory levels by receiving goods or materials just when they are needed for production. This strategy eliminates the need for excess inventory storage, reducing carrying costs and the risk of obsolete inventory.
By implementing a JIT inventory system, businesses can optimise cash flow, reduce storage space requirements, and improve overall supply chain efficiency. However, it requires robust coordination with suppliers, accurate demand forecasting, and efficient logistics management to ensure timely delivery of materials.
Automation and Technology Integration
Automation and technology integration play a crucial role in modern production planning, as well as mobile app development . By leveraging technology, businesses can streamline processes, enhance productivity, and reduce human error. Automation can be implemented in various aspects of production, including material handling, assembly, testing, and quality control.
Continuous Improvement
Continuous improvement is a fundamental principle of effective production planning. It involves regularly evaluating production processes, identifying areas for improvement, and implementing changes to enhance efficiency and quality.
By fostering a culture of continuous improvement, businesses can drive innovation, optimise resource utilisation, and stay ahead of competitors. Techniques such as Kaizen, Six Sigma, and value stream mapping can help businesses identify inefficiencies, eliminate waste, and streamline production workflows.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the role of a production plan in business planning.
A1: A production plan plays a crucial role in business planning by providing a roadmap for efficient production processes. It helps align production capabilities with customer demand, optimise resource utilisation, and ensure timely delivery of products or services.
How does a production plan affect overall business profitability?
A2: A well-developed production plan can significantly impact business profitability. By optimising production processes, reducing costs, and enhancing product quality, businesses can improve their profit margins and gain a competitive edge in the market.
What are the common challenges faced in production planning?
A3: Production planning can present various challenges, such as inaccurate demand forecasting, capacity constraints, supply chain disruptions, and quality control issues. Overcoming these challenges requires robust planning, effective communication, and the implementation of appropriate strategies and technologies.
What is the difference between short-term and long-term production planning?
A4: Short-term production planning focuses on immediate production requirements, such as daily or weekly schedules. Long-term production planning, on the other hand, involves strategic decisions related to capacity expansion, technology investments, and market expansion, spanning months or even years.
How can a production plan be adjusted to accommodate changes in demand?
A5: To accommodate changes in demand, businesses can adopt flexible production strategies such as agile manufacturing or dynamic scheduling. These approaches allow for quick adjustments to production levels, resource allocation, and inventory management based on fluctuating customer demand.
In conclusion, a well-crafted production plan is essential for business success. By incorporating a production plan into a comprehensive business plan, entrepreneurs can optimise resource utilisation, meet customer demands, enhance product quality, and drive profitability. Through effective demand forecasting, capacity planning, inventory management, resource allocation, and quality assurance, businesses can streamline production processes and gain a competitive edge in the market.
People Also Like to Read...

Are You Ready For Your Expansion Plans?

How To Build Your Digital Marketing Plan
© 2016 - 2024 Robin Waite. All rights reserved.
What Is Production Planning & Why Is It Important?

Business success often hinges on making the products that customers want in a timely and cost-effective way. Production planning helps companies achieve those goals. It maps out all the processes, resources and steps involved in production, from forecasting demand to determining the raw materials, labor and equipment needed. Production planning helps companies build realistic production schedules, ensure production processes run smoothly and efficiently, and adjust operations when problems occur.
What Is a Production Plan?
A production plan describes in detail how a company’s products and services will be manufactured. It spells out the production targets, required resources, processes and overall schedule. The plan also maps all of the operational steps involved and their dependencies. The goal is to design the most efficient way to make and deliver the company’s products at the desired level of quality. A well-designed production plan can help companies increase output and save money by developing a smoother workflow and reducing waste.
What Is Production Planning?
Production planning involves developing a comprehensive strategy for making the company’s products and services. Initially adopted by large manufacturers, production planning has since become more popular among small and midsize businesses in multiple industries — largely because technology has made it easier to plan and track production processes with less effort. Production planning covers many different aspects of production, from forecasting demand to determining the raw materials, workforce, equipment and steps needed to make the company’s products.
Production Planning vs. Production Scheduling
While production planning provides an overview of what the company plans to do, production scheduling creates a more detailed view of exactly how the company will do it. The production schedule describes when each step in the production plan will occur, as well as the workers, machinery and other specific resources assigned to the job. Production scheduling can be extremely complex, especially when there are many interdependent production steps and the company is making multiple products simultaneously. Production scheduling software (opens in new tab) can help businesses create complex schedules, monitor progress in real time and quickly make adjustments when necessary.
Key Takeaways
- Production planning describes in detail how a company’s products and services will be manufactured.
- A production plan defines the production targets, required resources and overall schedule, together with all the steps involved in production and their dependencies.
- A well-designed production plan helps companies deliver products on time, reduce costs and respond to problems.
- Technology has made it easier for small and midsize companies in multiple industries to use production planning to optimize operations.
Product Planning Explained
Production planning is a broad discipline that involves much more than a focus on manufacturing process efficiency. It is intertwined with nearly every other aspect of the business, including finance, sales, inventory and human resources. Production planning activities include demand forecasting to determine the right mix of products to meet customer needs, as well as selecting the optimal approach to building those products. Production planning also assesses the resources needed to meet production goals and lays out in detail all the operations in the production process. Production plans must include the flexibility to make operational adjustments when problems occur — such as machine breakdowns, staffing shortages and supply-chain problems.
Why Is Production Planning Important?
A well-constructed production plan can help to boost revenue, profit and customer satisfaction, while a poorly designed plan can cause production problems and perhaps even sink the company. Specific benefits of production planning include:
- Knowledge. A production plan provides a framework for understanding the resources and production steps required to meet customer needs. It also helps companies understand the potential problems that may occur during production and how to mitigate them.
- Efficiency. Detailed production planning reduces bottlenecks and helps minimize costs. It also helps ensure the high quality of a product, and it keeps expenses on budget.
- Customer satisfaction. Production planning helps ensure that the company can make and deliver products to customers on time, leading to higher customer satisfaction and a greater likelihood of repeat business.
Types of Production Planning
The design of a product plan depends on the production method that the company uses, as well as other factors, such as product type, equipment capabilities and order size. Here are three of the main types of production planning:
Batch production planning.
Refers to manufacturing identical items in groups rather than one at a time or in a continuous process. For some businesses, batch production can greatly increase efficiency. A bakery creating items for sale the next day might first make a batch of chocolate chip cookies, then move on to oatmeal raisin cookies followed by loaves of semolina bread. A clothing manufacturer making goods for the summer might first set up its cutting and sewing machines to make 500 navy-blue T-shirts, then switch to red fabric and thread to make 400 tank tops. A good production plan for batch processing should look out for potential bottlenecks or delays when switching between batches.
Job- or project-based planning.
Used by many small- and medium-sized businesses, job production planning focuses on the creation of a single item by one person or team. Job-based planning is typically used where the specificity of each client’s requirements means it is difficult to make products in bulk. Many construction businesses use this method. Makers of custom jewelry and dresses are other examples of businesses that may use job production planning.
Flow production planning.
In flow production, also known as continuous production, standardized items are continuously mass-produced on an assembly line. Large manufacturers use this method to create a constant stream of finished goods. During production, each item should move seamlessly from one step along the assembly line to the next. Flow production is most effective at reducing costs and delays when there’s steady demand for the company’s products. Manufacturers can then readily determine their needs for equipment, materials and labor at each stage along the assembly line to help streamline production and avoid delays. The automotive industry and makers of canned foods and drinks are among the companies that use this method.

5 Steps to Make a Production Plan
Production planning is a robust undertaking that starts with forecasting and includes process design and monitoring. Here are five typical production planning steps:
Forecast product demand.
Estimate how much of each product you’ll need to produce over a designated period. Historical data can help with forecasting, but you’ll also need to pay attention to other factors that can affect demand, such as market trends and the economic situation for your customer base. Demand planning software can help companies make more informed decisions about the right amount of product needed to meet demand.
Map out production steps and options.
This step determines the processes, steps and resources needed to produce the required output. At this stage, the company may also examine different options for achieving its production goals, such as outsourcing some stages. The production mapping identifies which steps are interdependent and which can be performed simultaneously. Let’s say the job is to produce 1,000 children’s bicycles. Manufacturing the bicycle frames consists of a series of steps that must happen in sequence — cutting metal tubes, welding and painting — while other activities like assembling wheels can occur in parallel. Do you have all the right equipment? What happens if a machine breaks down? Are your suppliers able to meet your demand?
Choose a plan and schedule production.
Select a production plan after comparing the cost, time required and risks for each option. Sharing the selected plan with all necessary stakeholders typically helps assure a smoother production process since all the stakeholders are aware of what’s needed. Create a detailed production schedule that lays out in detail how the company will execute the plan, including the resources and timing for each step.
Monitor and control.
Once production has begun, you’ll need to track performance and continually compare it against the targets described in the production plan. Careful monitoring helps the company to detect any issues as soon as they pop up, so they can be quickly addressed.
Adjust accordingly.
It’s almost inevitable that production will be affected by events that you can’t plan for or predict. Those events can include changes to client specifications, supply chain lags, equipment failures and worker illness. You may also see ways to improve the production plan after seeing it in action for a while. So it’s vital to keep production plans flexible enough to allow for adjustment when needed. Football coaches often make adjustments to their game strategy at halftime — and the same holds true for production planning.
3 Common Product Planning Mistakes
Being aware of potential pitfalls ahead of time can help companies avoid or mitigate problems once production has started. Here are three of the most common production planning mistakes.
Not anticipating hiccups along the way.
In any complex production process, plans can go awry. Production planning should therefore include risk management strategies, including backup plans companies can rely on in the event of problems. Failing to do so can result in serious problems. For example, if a machine breaks on the line and you didn’t budget for repairs and workforce overtime, the issue may strain the company’s financial resources.
Keeping your distance.
Though production management software can provide real-time visibility into a company’s production status, it’s a good idea to supplement that information with in-person visits to the production line. Those visits can provide valuable insights into how production works in practice — insights that you might not gain if you’re stuck behind a desk.
Failing to maintain equipment.
There’s a tradition in football that the quarterback buys presents for his offensive linemen at the end of each season. Why? Because they protect him and enable him to do his job. Your manufacturing equipment is your company’s offensive line, so don’t neglect it. Tracking usage and paying for regular preventive maintenance helps ensure that your machines can keep your business functioning.
Production Planning KPIs
Key performance indicators (KPIs) are important metrics that help companies track the health of their production processes. By monitoring KPIs and comparing them to target values defined in production plans, businesses can determine whether production is on track and pinpoint problems that need to be addressed. Typical production KPIs include:
This key efficiency metric tracks the percentage of time that production is not occurring during scheduled operating hours. Causes include machine breakdowns, tool adjustments and accidents. Some downtime may be necessary for functions such as machine maintenance, but generally, the less downtime the better.
Setup time.
Also referred to as changeover time, this is the amount of time it takes to switch between jobs. Setup time impacts overall productivity because production is halted during these periods. Production schedules should consider how much time and effort it takes to reconfigure production for each job, including changes to the equipment, raw materials and workforce. Designing production schedules to minimize changeover time can increase efficiency.
Production rate.
In a manufacturing environment, this is typically measured as the number of units produced during a specific period. Comparing the actual production rate for each process with the planned rate can help businesses identify strengths and weaknesses and begin to address problems.
Overall equipment effectiveness (OEE).
This is a measure of overall manufacturing productivity that accounts for quality, performance and availability. The formula for OEE is:
OEE = Quality x performance x availability
Quality is typically measured as the percentage of parts that meet quality standards. Performance is how fast a process is running compared to its maximum speed, which is expressed as a percentage. Availability is the percentage of uptime during a company’s scheduled operating hours. Increasing OEE can be achieved by lowering downtime, reducing waste and maintaining a high production rate.
Rejection rate.
This is the number or percentage of products that failed to pass quality checks. Depending on the nature of the product and the problem, it may be possible to salvage some rejected items by reworking them, while others may need to be scrapped.
On-time orders.
Production delays can be costly both in terms of money and reputation. Generating products on schedule means you’re less likely to need costly expedited shipping or other emergency measures to meet deadlines. And delivering orders on time helps keep customers happy, which means they’re more likely to keep doing business with your company.
Production Planning Tools
Businesses rely on a variety of tools to build production plans and track progress, ranging from visualization tools to sophisticated software that automates many of the steps involved. Typical tools include:
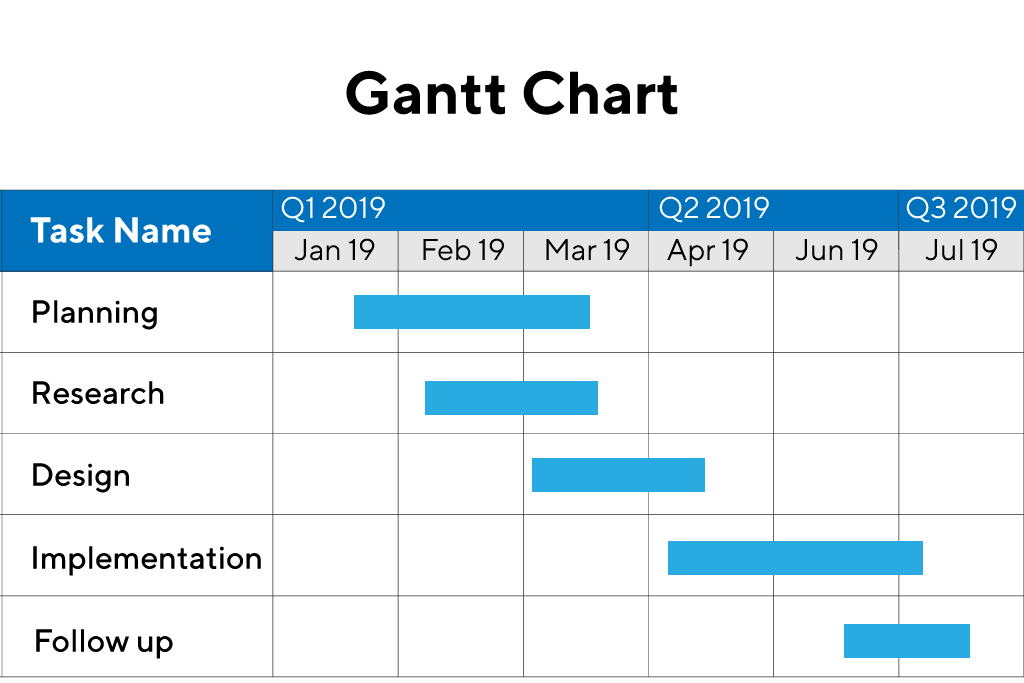
Gantt charts.
A Gantt chart is a detailed visual timeline of all the tasks scheduled for a particular job. More than 100 years since its invention by mechanical engineer Henry Laurence Gantt, this chart remains integral to manufacturing and many other industries. Production planning involves coordinating and scheduling many tasks , and the Gantt chart visually represents when each task will take place and how long it will last. Manually creating and updating Gantt charts to reflect complex, ever-changing production schedules can be a time-consuming and error-prone job, however.
Spreadsheets.
Small companies sometimes start out by tracking simple production plans using spreadsheets. However, for most companies, the inherent complexity of production planning quickly outstrips the capabilities of spreadsheet software.
Production planning software.
Production planning involves a wide range of activities, including forecasting, managing the supply chain, tracking inventory and scheduling jobs. Those activities require information from across the company and beyond. Production planning information is integral to business operations and is used by other groups within the company, including finance. That’s a key reason many companies use enterprise resource planning (ERP) application suites that include production planning software and provide a single solution for managing the entire business.
Manage and Optimize Production With NetSuite
NetSuite cloud-based production management software helps companies maximize manufacturing productivity and minimize cost. NetSuite provides real-time visibility into each aspect of the production process, from inventory tracking and monitoring the production floor to fulfilling orders. Production scheduling capabilities let businesses create and update complex real-time production schedules with minimal effort. Because NetSuite production management software is part of an integrated suite of ERP applications , businesses can share production progress with the entire organization and link production processes to financial reports, inventory management and order management.
Production planning is an important function that can boost profitability and customer satisfaction as well as efficiency. It helps companies match output to demand, optimize production processes and determine how to overcome production problems.
Award Winning Cloud Inventory
Production Planning FAQs
What are the 5 steps in production planning.
Here are five typical steps in the production planning process:
- Forecast the short- and long-term demand for your product.
- Map out the various options and processes for manufacturing these goods
- Choose the option that checks as many boxes as possible, and develop a production schedule.
- Monitor production against the plan.
- Adjust the plan where needed. In other words, if it’s broken, fix it.
What are the 3 activities of production planning?
Production planning activities can be divided into three main areas: Develop a production process and strategy; gather the resources needed, from raw materials to machinery and personnel; and select and train the necessary people.
What are the types of production planning?
Three of the main types of production planning are batch planning, job planning and flow or continuous planning . The choice depends on your resources as well as the nature of the product. Batch planning makes the same item in bulk before moving on to another item. Job planning, also called project-based planning, focuses more on custom design and single-item production. Flow production involves a steady stream of mass-produced items moving along the line.
What is the role of production planning?
Production planning is critical to ensure the production process runs smoothly and efficiently and delivers products on time. Planning allows a business to make certain that all necessary preparation is completed before starting production.
Inventory Management

What Is Perishable Inventory? Strategies, Tracking & Free Template
Inventory management is a challenge faced by any business selling a product, but the challenge is particularly acute for businesses dealing in products that expire or quickly lose value over time. By giving special attention…

Trending Articles

Learn How NetSuite Can Streamline Your Business
NetSuite has packaged the experience gained from tens of thousands of worldwide deployments over two decades into a set of leading practices that pave a clear path to success and are proven to deliver rapid business value. With NetSuite, you go live in a predictable timeframe — smart, stepped implementations begin with sales and span the entire customer lifecycle, so there’s continuity from sales to services to support.
Before you go...
Discover the products that 37,000+ customers depend on to fuel their growth.
Before you go. Talk with our team or check out these resources.
Want to set up a chat later? Let us do the lifting.
NetSuite ERP
Explore what NetSuite ERP can do for you.
Business Guide
Complete Guide to Cloud ERP Implementation
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
What Is a Business Plan?
A business plan is a document that details a company's goals and how it intends to achieve them. Business plans can be of benefit to both startups and well-established companies. For startups, a business plan can be essential for winning over potential lenders and investors. Established businesses can find one useful for staying on track and not losing sight of their goals. This article explains what an effective business plan needs to include and how to write one.
Key Takeaways
- A business plan is a document describing a company's business activities and how it plans to achieve its goals.
- Startup companies use business plans to get off the ground and attract outside investors.
- For established companies, a business plan can help keep the executive team focused on and working toward the company's short- and long-term objectives.
- There is no single format that a business plan must follow, but there are certain key elements that most companies will want to include.
Investopedia / Ryan Oakley
Understanding Business Plans
Any new business should have a business plan in place prior to beginning operations. In fact, banks and venture capital firms often want to see a business plan before they'll consider making a loan or providing capital to new businesses.
Even if a business isn't looking to raise additional money, a business plan can help it focus on its goals. A 2017 Harvard Business Review article reported that, "Entrepreneurs who write formal plans are 16% more likely to achieve viability than the otherwise identical nonplanning entrepreneurs."
Ideally, a business plan should be reviewed and updated periodically to reflect any goals that have been achieved or that may have changed. An established business that has decided to move in a new direction might create an entirely new business plan for itself.
There are numerous benefits to creating (and sticking to) a well-conceived business plan. These include being able to think through ideas before investing too much money in them and highlighting any potential obstacles to success. A company might also share its business plan with trusted outsiders to get their objective feedback. In addition, a business plan can help keep a company's executive team on the same page about strategic action items and priorities.
Business plans, even among competitors in the same industry, are rarely identical. However, they often have some of the same basic elements, as we describe below.
While it's a good idea to provide as much detail as necessary, it's also important that a business plan be concise enough to hold a reader's attention to the end.
How to Write a Business Plan
While there are any number of templates that you can use to write a business plan, it's best to try to avoid producing a generic-looking one. Let your plan reflect the unique personality of your business.
Many business plans use some combination of the sections below, with varying levels of detail, depending on the company.
Common Elements of a Business Plan
The length of a business plan can vary greatly from business to business. Regardless, it's best to fit the basic information into a 15- to 25-page document. Other crucial elements that take up a lot of space—such as applications for patents—can be referenced in the main document and attached as appendices.
These are some of the most common elements in many business plans:
- Executive summary: This section introduces the company and includes its mission statement along with relevant information about the company's leadership, employees, operations, and locations.
- Products and services: Here, the company should describe the products and services it offers or plans to introduce. That might include details on pricing, product lifespan, and unique benefits to the consumer. Other factors that could go into this section include production and manufacturing processes, any relevant patents the company may have, as well as proprietary technology . Information about research and development (R&D) can also be included here.
- Market analysis: A company needs to have a good handle on the current state of its industry and the existing competition. This section should explain where the company fits in, what types of customers it plans to target, and how easy or difficult it may be to take market share from incumbents.
- Marketing strategy: This section can describe how the company plans to attract and keep customers, including any anticipated advertising and marketing campaigns. It should also describe the distribution channel or channels it will use to get its products or services to consumers.
- Financial plans and projections: Established businesses can include financial statements, balance sheets, and other relevant financial information. New businesses can provide financial targets and estimates for the first few years. Your plan might also include any funding requests you're making.
The best business plans aren't generic ones created from easily accessed templates. A company should aim to entice readers with a plan that demonstrates its uniqueness and potential for success.
2 Types of Business Plans
Business plans can take many forms, but they are sometimes divided into two basic categories: traditional and lean startup. According to the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) , the traditional business plan is the more common of the two.
- Traditional business plans : These plans tend to be much longer than lean startup plans and contain considerably more detail. As a result they require more work on the part of the business, but they can also be more persuasive (and reassuring) to potential investors.
- Lean startup business plans : These use an abbreviated structure that highlights key elements. These business plans are short—as short as one page—and provide only the most basic detail. If a company wants to use this kind of plan, it should be prepared to provide more detail if an investor or a lender requests it.
Why Do Business Plans Fail?
A business plan is not a surefire recipe for success. The plan may have been unrealistic in its assumptions and projections to begin with. Markets and the overall economy might change in ways that couldn't have been foreseen. A competitor might introduce a revolutionary new product or service. All of this calls for building some flexibility into your plan, so you can pivot to a new course if needed.
How Often Should a Business Plan Be Updated?
How frequently a business plan needs to be revised will depend on the nature of the business. A well-established business might want to review its plan once a year and make changes if necessary. A new or fast-growing business in a fiercely competitive market might want to revise it more often, such as quarterly.
What Does a Lean Startup Business Plan Include?
The lean startup business plan is an option when a company prefers to give a quick explanation of its business. For example, a brand-new company may feel that it doesn't have a lot of information to provide yet.
Sections can include: a value proposition ; the company's major activities and advantages; resources such as staff, intellectual property, and capital; a list of partnerships; customer segments; and revenue sources.
The Bottom Line
A business plan can be useful to companies of all kinds. But as a company grows and the world around it changes, so too should its business plan. So don't think of your business plan as carved in granite but as a living document designed to evolve with your business.
Harvard Business Review. " Research: Writing a Business Plan Makes Your Startup More Likely to Succeed ."
U.S. Small Business Administration. " Write Your Business Plan ."
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps 1 of 25
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example 2 of 25
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, and How to Create One 3 of 25
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained 4 of 25
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One 5 of 25
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills 6 of 25
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One 7 of 25
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact 8 of 25
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan 9 of 25
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details 10 of 25
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks 11 of 25
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons 12 of 25
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites 13 of 25
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin 14 of 25
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit 15 of 25
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons 16 of 25
- Best Startup Business Loans for May 2024 17 of 25
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros and Cons, and Differences From an LLC 18 of 25
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types 19 of 25
- What Is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined 20 of 25
- Corporation: What It Is and How To Form One 21 of 25
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide 22 of 25
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide 23 of 25
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips 24 of 25
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide 25 of 25
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-1456193345-2cc8ef3d583f42d8a80c8e631c0b0556.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
What is production planning and how to do it? A comprehensive guide.
Production planning is crucial for efficient production. Let’s explore all about it and see how to handle it in ERP software.

Production planning is vital to fulfil orders on time. If you don’t know your stock levels, workstation availability, or job schedules, you won’t be keeping your customers happy.
Whether you’re a new manufacturer oiling your machinery for the first time or a seasoned manufacturer shipping thousands of items, production planning is a must. Similar to how scrums and monthly plans run operations smoothly, production plans ensure optimal usage of resources.
In this blog, let’s understand the basic terms around production planning, see how it’s done, look at common pitfalls to be aware of, see the types of production planning, some topics around production planning, and finally an example of handling production planning in ERPs.
1. Production planning basics
1.1 what is production planning.
Production planning is the planning and allocation of raw materials, workers, and workstations to fulfill manufacturing orders on time. In a make to order environment, manufacturing orders or work orders themselves are created after receiving customer orders. A company that follows make to stock style of manufacturing will create work orders on a timely basis depending on demands. Production plans are usually set by the production managers who supervise the shop floor. A good production plan makes the best use of available resources to deliver orders on time.
1.2 Why should you do production planning
Handling a few production orders in spreadsheets works but for large manufacturing shops, the complexity increases a lot. Production planning helps to plan the procurement of raw materials based on the quantity of finished products to be manufactured. It also affects inventory, cash flow, sales, and distribution.
2. How to do production planning
2.1 five tips to improve production planning.
These tips to keep your production plan on track and improve its efficiency
2.1.1 Forecasting demand
Before production planning, the first action to take is forecasting demands for your products. While this may not be accurate to the last digit, getting rough estimates rolling is important to allocate resources. Forecasting can be done based on factors like historical order data and market trends/demands. Drawing out proper forecasts helps planning the type and quantity of materials to be produced and also the planning of raw material procurement.
2.1.2 Control inventory
Both, inventory shortage and inventory surplus are undesirable states. You can’t proceed with production when there’s a shortage and you waste space and money when there’s a surplus. Efficiently controlling inventory involves reordering when current inventory dips below a certain level, calculating the lead times to order items with long lead times earlier, and factoring in storage conditions. A well-controlled raw material inventory helps run a smooth production line and outputs finished goods inventory on time.
2.1.3 Plan for everything and everyone
Often, when making production plans, some machine or some person is unaccounted for. The problem here is that that machine may go down or the worker may be on leave, or worse, working on something else. Hence, plan for every machine, raw material, workstation, warehouse, and employee.
2.1.4 Monitor
Once the production plan is final and work orders are handed out, the manufacturing process begins. At this point, things may go wrong, machines pause, or items may get misplaced. Constantly monitoring the factory floor with supervisors or with IoT devices ensures that all the pieces are moving as planned.
2.1.5 Adapt
Despite your best planning, things go wrong on the factory floor. Anything can happen from suppliers making late deliveries to workers falling sick to machines failing. It’s important to be flexible and adapt to these changes quickly so that the planned quantities can be delivered on time. Ideally, you should also plan for any such risks beforehand.
2.2 KPIs for production planning
A few key performance indicators to track in production planning are:
- Production cost : This is essentially the monetary cost involved in producing the item. Costs include raw materials, electricity, fuel, worker salaries, rent, etc.
- Capacity utilization rate : It’s the percentage of actual manufacturing output against the total possible manufacturing output. If many machines and workers are sitting idle, your capacity utilization is low. Ideally, you want it high but never full.
- Projected versus actual hours : When planning, you may allocate a certain number of hours for completion of the production plan. But, it may take longer due to delays from workers or unexpected tasks. This KPI gives you a picture of how much time it was supposed to take and how much it did.
- Employee utilization (productivity) : You want workers to be working properly during the punch in and punch out. Nobody wants to be a machine by working to the dot but working 4 hours out of 8 is also not reasonable.
- Takt time : Takt time is a lean manufacturing concept. It is the time taken to produce a single unit of item.
3. Production planning pitfalls and avoiding them
First, let us understand the pitfalls or things that could go wrong during production planning. These occur in areas from idle inventory storage to active workers.
3.1 Stockouts
What is it?
It’s the shortage of raw materials that can happen after fulfilling large orders or due to negligence.
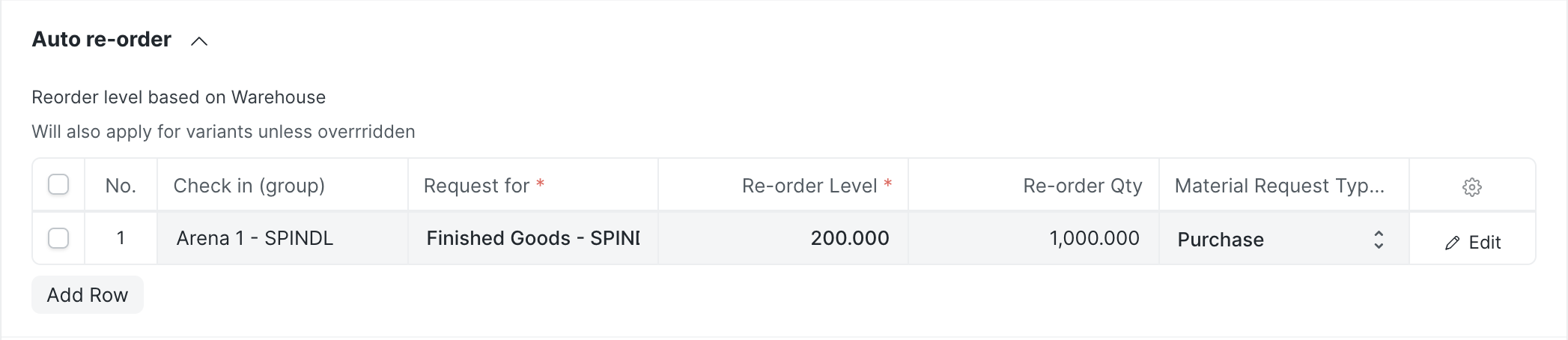
How to avoid it?
By checking inventory reports regularly or better yet, setting up automatic reordering.
How to do it?
By setting automatic reordering like this:
3.2 Assigning work to workstation on downtime
Assigning operations to a workstation that was supposed to be on downtime. This causes confusion and the work doesn’t get done because there’s no machine available.
Get a view of which workstations are on downtime and assign only to available machines. (version 13)
By analyzing the downtime of different machines and assigning work appropriately:
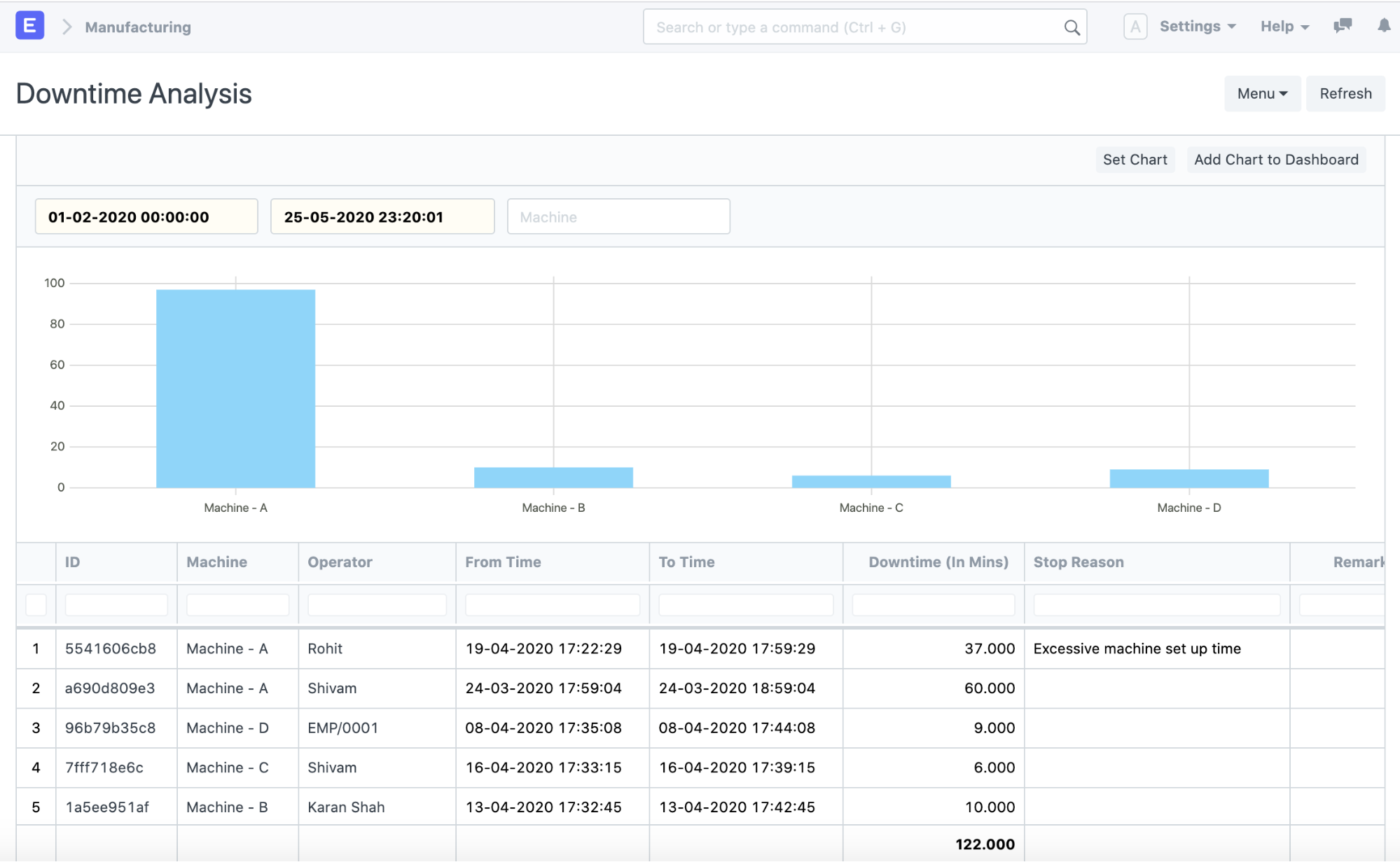
3.3 Bottlenecks
These are roadblocks in the production line that halt the processing of materials midway. For example, if items are waiting at the painting stations to get painted, the painting station is a bottleneck since it’s stopping the items from going ahead.
Bottlenecks can happen anywhere in the production line. Scan all the machines and even check if there are enough workers to carry out tasks. Through planning and ensuring the availability of machines and resources is a good way to avoid bottlenecks.
Setting up regular maintenance activities helps by keeping machines running. Eliminating bottlenecks in the production depends a lot on having sufficient machinery, manpower, and a regular supply of raw materials.
3.4 Insufficient worker training
Some specialized machines need trained workers for operation. Hiring rookies running specialized machines result in work not getting done.
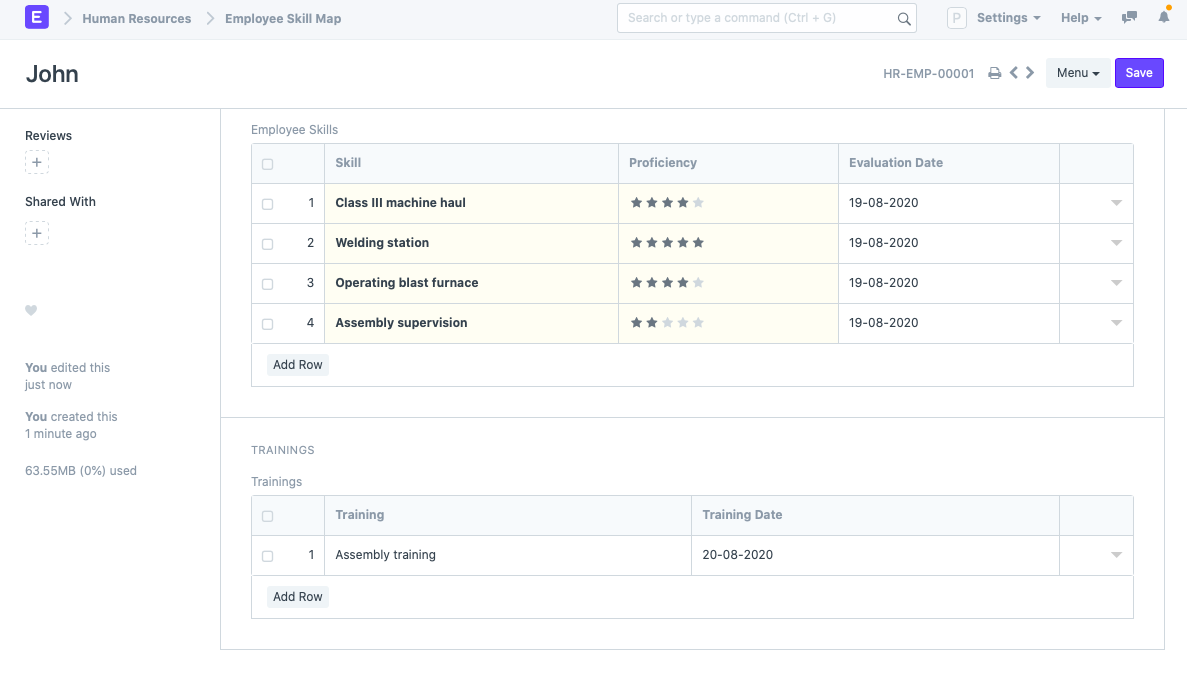
Interview candidates for skills and experience in operating similar machinery. Even after interviews, thorough training should be done to ensure that the worker is ready to use the machines in production.
From the human resources module, first, test the employee’s skill proficiency. Then, set training events to enhance their skills. Updated employee skill maps help supervisors better allocate work to the right people and help the ones that are lagging.
4. Types of production planning
The different types of production planning are based on the manufacturing process followed in the factory. A single organization can deal with different types of manufacturing depending on the goods produced.
When items are manufactured in batches with unique batch numbers allotted to each batch. Production planning in batches helps run machinery in a well-planned manner as the next step is planned and the machines are allocated accordingly.
This type of production planning is common in job shops where custom material processing requirements are carried out. Each production plan will most likely be different from the last with the use of different materials, machinery, and operations on the materials.
In flow method, materials are processed smoothly from one machine to the next with very little human intervention. Any waiting time or bottlenecks are removed so that the materials ‘flow’ continuously till they become finished goods. Standardized work and quality control are essential to ensure consistent quality when producing items with the flow method.
5. Topics around production planning
5.1 production planning and control.
Production planning is about planning resources for delivering products and production control is about controlling the production system to achieve targets optimally. Production control has more to do with monitoring the production line and taking corrective action where things are not moving as planned.
‘Production planning and control’ is simply applying both these concepts to get an efficient production line.
Let’s understand the benefits of using both these methods together:
- Better organization for on-time delivery to customers
- Optimum resource utilization
- Less investment in inventory
- Avoid resource wastage
- Increased efficiency, hence reduced costs
- Improved quality by catching and reducing defects
Now let’s look at these topics individually to further distinguish between them.
5.1.1 Production planning
The steps involved in production planning are:
- Planning : This involves planning shop floor resources to deliver finished goods on time.
- Routing : The exact route/path or set of operations the materials go through is known as a routing. Finding optimum routes that reduce wastage and promote continuous flow is a part of production planning. Finding better routings is about using workstations, machines, and workers in different orders without affecting the product to deliver the items faster.
- Scheduling : The machines, activities, and workers are scheduled to do tasks that are a part of the production plan. Scheduling well helps in delivering the finished products on time.
- Loading : Loading here refers to overloading the production line to see how much it can handle. By loading each point, the last bits of efficiency can be squeezed to get the maximum value.
5.1.2 Production control
The steps involved in production control are:
- Dispatching : After the production plan is ready it’s time to implement it by dispatching items in and out of the production line. Different operations and the corresponding workstations are managed to dispatch items to them. The time to complete each activity or ‘job’ is recorded.
- Followup : After issuing a plan, bottlenecks and other problems may arise. Follow-ups are done by supervisors to eliminate any bottlenecks and ensure that things are going according to plan.
- Inspection : Routine inspections are done during production to verify that the materials are being processed correctly. Note that this is different from quality inspections which are done after the product is finished.
- Correction : The results from other steps in production control are reviewed and corrections are made where necessary. This includes the routings, scheduling work, and even conversations with workers who are taking those long breaks.
5.2 Production planning and inventory control
An indispensable part of manufacturing is managing your inventory. Controlling inventory is an essential part of production planning. Proper inventory control involves ensuring an adequate supply of raw materials which results in the timely delivery of products. It also minimizes the overstocking of finished products. Maintaining both—proper inventory levels and accurate data—helps in good production planning.
5.3 Production planning vs production scheduling
Production planning is about planning the number of resources needed to finish multiple manufacturing orders. Production scheduling is about timing the activities, machines, and workers right to run the production process. The work and workloads are optimized in production scheduling. There are two ways production scheduling is performed:
- Forward scheduling : Say, if resources are available today, plan from today till the order due date.
- Backward scheduling : If the availability date of resources is not certain, plan from the due date backward to a number of days.
Production scheduling levels the inventory, labor, and helps in estimating delivery dates accurately.
6. Production planning in ERP software
A production plan can be created and managed easily by using ERP software. You’d need the items, bill of materials, routings, customer orders, and material requests ready before creating a production plan.
6.1 Creating the production plan
Once you have the prerequisite records ready, it’s time to create the production plan. Let’s follow through step by step.
If the items to produce have been requested via a customer order or material requisitions, they can be fetched into the production plan.
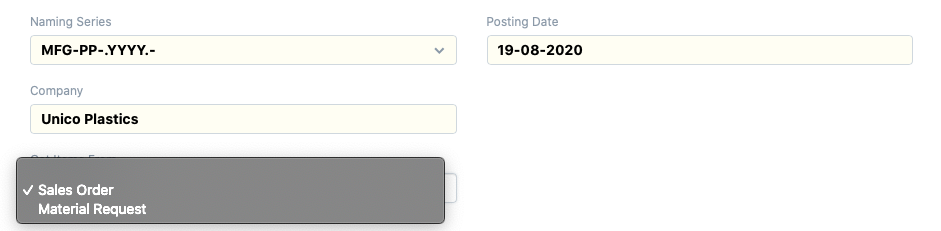
By clicking on ‘Get Sales Orders’, either multiple orders or multiple requests can be fetched here, like this:
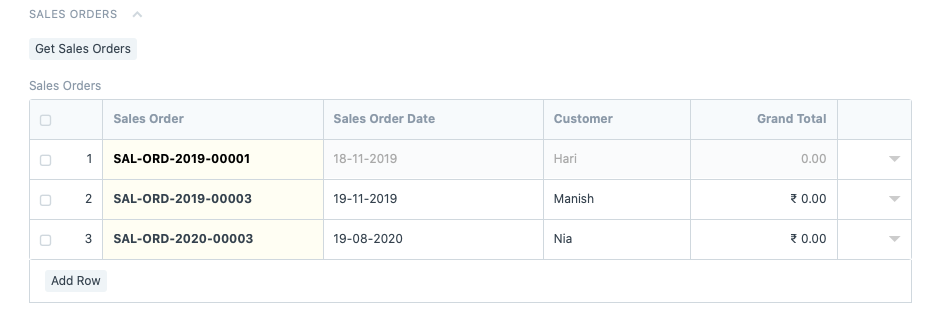
If you have a ton of orders or requests, set filters to narrow down your search like this:
Now, by clicking on ‘Get Items for Work Order’, the items to be manufactured using the current production plan will be fetched. The quantities can be increased in case you want to account for SKUs. It’s a good idea to keep extra inventory for items that take a very long time to manufacture but have predictable, fast demands.

Now that you know what items to manufacture since the bill of materials has been fetched, it’s time to plan for the raw materials. Clicking on ‘Get Raw Materials for Production’ will fetch all the raw materials and sub-assemblies required for manufacturing. If the inventory levels are present in the warehouses, they’ll not be fetched here. Click on ‘Download Required Materials’ to download the raw material list as a spreadsheet, send it to others or print it.
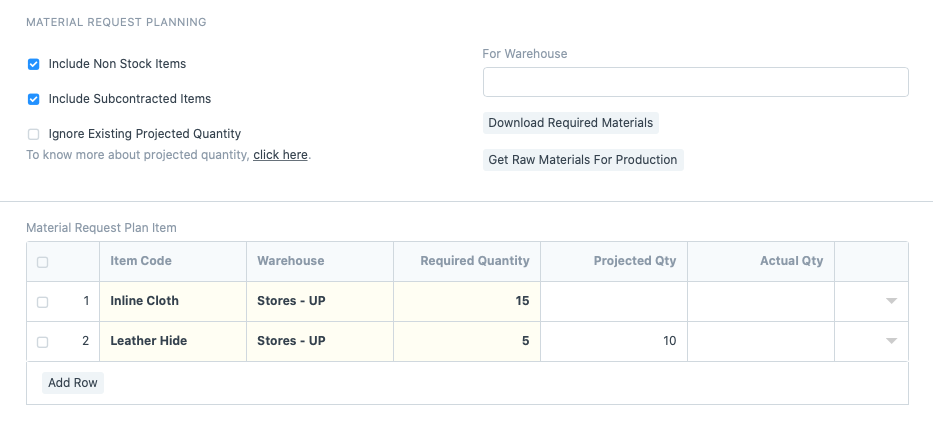
Some options to note here are:
- Including non-stock items in case you want to account for some external items that you don’t store in your inventory but will be used in production.
- Some subassemblies may be subcontracted, you can choose to include or exclude them in your plan. The choice here depends on whether the subcontracting is for operations or assembly among other factors.
- Projected quantity will show the inventory levels that should be produced based on demands and requests. If you want to ignore this number and produce quantities that you see fit, go ahead and tick the ‘Ignore Existing Projected Quantity’ checkbox.
- Finally, you submit and start with the production plan. Then, from the production plan work orders can be created. One work order for each BOM will be created if you click on ‘Create > Work Order’.
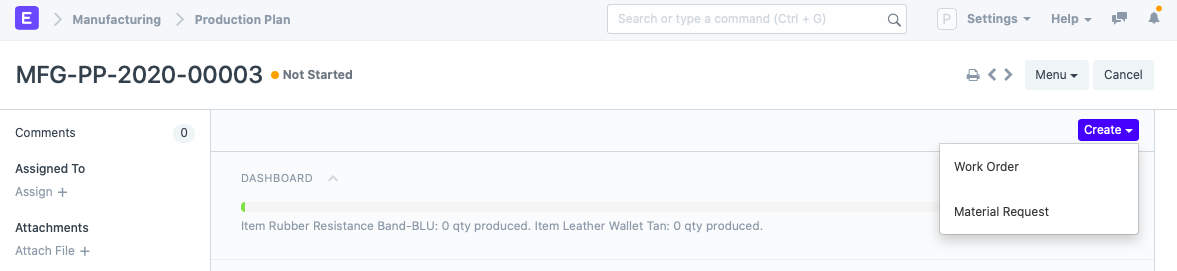
In the work order, the quantity to be produced can be changed depending on whether you want to produce some quantities later. Work orders are used by shop floor supervisors.
From the work orders, job cards are created to record the operations on raw materials. The jobs/operations are done at different workstations/machines.
Once the ‘jobs’ are done on the materials and items are processed, the work order is complete.
Now, depending on the quantity of items produced, the following details can be seen in the last section of the production plan:
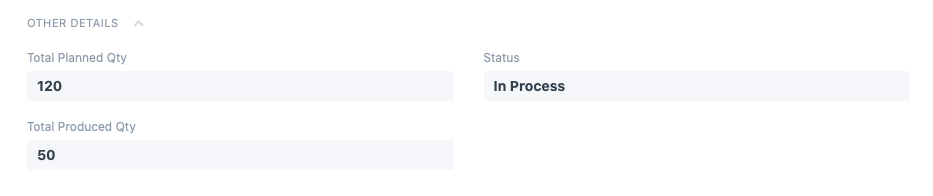
6.2 Scheduling the plan
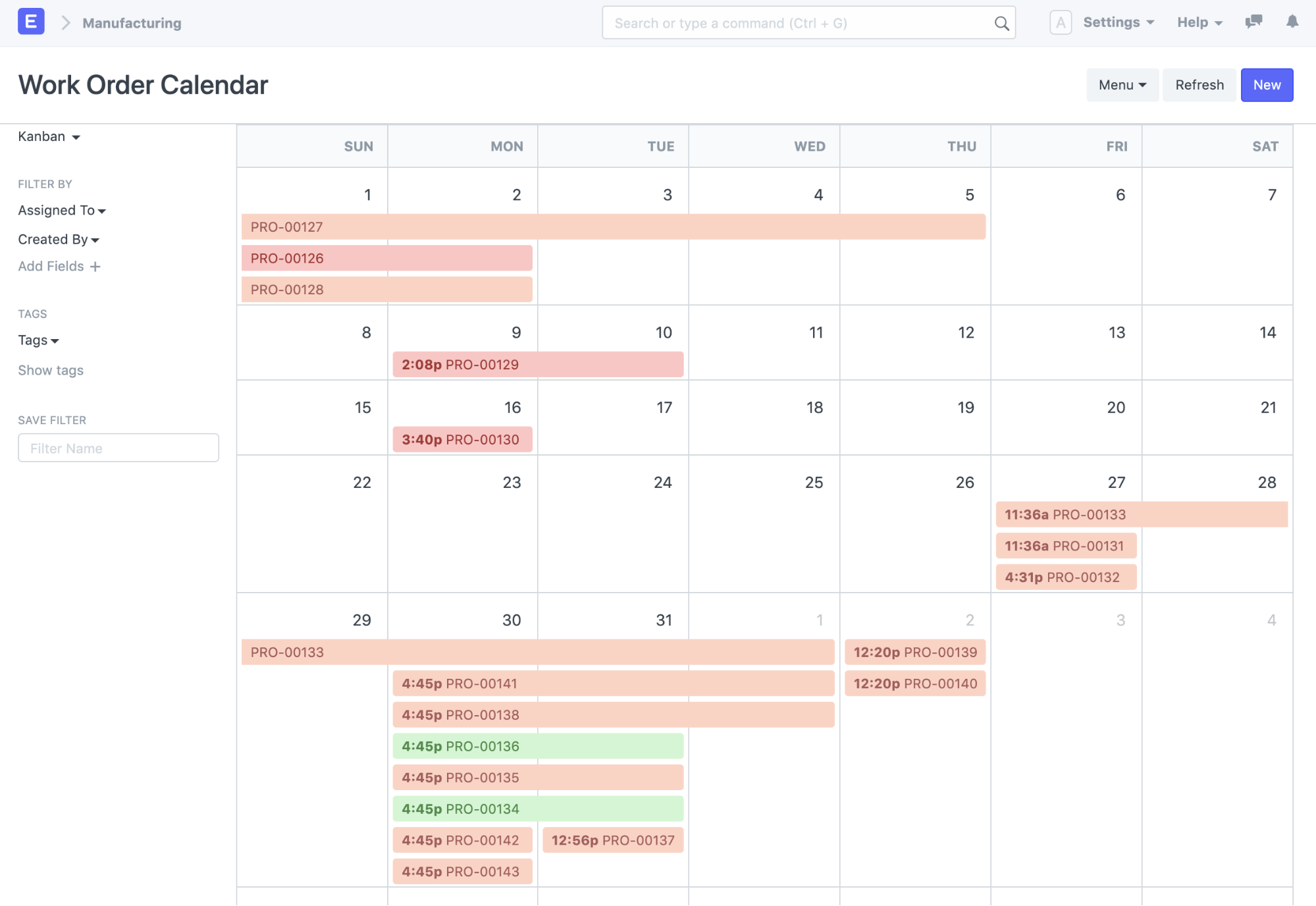
Creating a production plan is one part of the planning process, the other is scheduling different resources to the production plan. Factors like machine downtime, workstation capacity, and availability of raw materials are taken into consideration when scheduling.
In ERPNext, capacity planning is enabled by default. If you go to the calendar from the work order list, you can see the workstations for which materials are transferred and work has started (orange), neither materials are transferred nor work has started (red), and the ones that have been completed (green).
6.3 Role of project management in production planning
In larger organizations with multiple orders or when you get a large project from a client to produce hundreds of different items, project management comes handy. By using a project in ERPNext, you can create multiple work orders against it to track them all from one place.
That's it. Production planning is done easily with the right tools. By allocating resources carefully, planning for inventory, and avoiding mistakes, you can deliver you orders on time.
First, we introduced what a production plan is and discussed its importance. Then, we talked about the important things to note before creating a production plan and talked about the common mistakes to avoid when planning. Further, we talked about the types of production plans and the role of software in production planning.
For a monthly digest of such blogs and more updates, subscribe to our newsletter .
- Production planning
- Methods of production
- Scheduling (production processes)
ERPNext documentation
- Production Plan
- Capacity Planning
- Operations: Methods of Production (Overview) | Business | tutor2u
- Production plan: Top tips for improving your operations
- Grace college production planning
Prasad Ramesh
Marketing at Frappe.
Thank you very much for your informative info on production planning as I really need to use as guidance for my job as production planner
We are extremely impressed with this article because it contains a lot of great information. We, at MGH Distributors, are a part of the Import and distribution business. Our food products include Candies, cakes, cooking oil, beverages, jelly products, cookies and many more. The FMCG range brings to you world-class razors, blades, bar soaps. Visit our website to know more
Thank you for this very good overview on production in ERPNext.
How to Write a Business Plan: Step-by-Step Guide + Examples

Noah Parsons
24 min. read
Updated May 7, 2024
Writing a business plan doesn’t have to be complicated.
In this step-by-step guide, you’ll learn how to write a business plan that’s detailed enough to impress bankers and potential investors, while giving you the tools to start, run, and grow a successful business.
- The basics of business planning
If you’re reading this guide, then you already know why you need a business plan .
You understand that planning helps you:
- Raise money
- Grow strategically
- Keep your business on the right track
As you start to write your plan, it’s useful to zoom out and remember what a business plan is .
At its core, a business plan is an overview of the products and services you sell, and the customers that you sell to. It explains your business strategy: how you’re going to build and grow your business, what your marketing strategy is, and who your competitors are.
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow.
A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It’s also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals.
After completing your plan, you can use it as a management tool to track your progress toward your goals. Updating and adjusting your forecasts and budgets as you go is one of the most important steps you can take to run a healthier, smarter business.
We’ll dive into how to use your plan later in this article.
There are many different types of plans , but we’ll go over the most common type here, which includes everything you need for an investor-ready plan. However, if you’re just starting out and are looking for something simpler—I recommend starting with a one-page business plan . It’s faster and easier to create.
It’s also the perfect place to start if you’re just figuring out your idea, or need a simple strategic plan to use inside your business.
Dig deeper : How to write a one-page business plan
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
- What to include in your business plan
Executive summary
The executive summary is an overview of your business and your plans. It comes first in your plan and is ideally just one to two pages. Most people write it last because it’s a summary of the complete business plan.
Ideally, the executive summary can act as a stand-alone document that covers the highlights of your detailed plan.
In fact, it’s common for investors to ask only for the executive summary when evaluating your business. If they like what they see in the executive summary, they’ll often follow up with a request for a complete plan, a pitch presentation , or more in-depth financial forecasts .
Your executive summary should include:
- A summary of the problem you are solving
- A description of your product or service
- An overview of your target market
- A brief description of your team
- A summary of your financials
- Your funding requirements (if you are raising money)
Dig Deeper: How to write an effective executive summary
Products and services description
This is where you describe exactly what you’re selling, and how it solves a problem for your target market. The best way to organize this part of your plan is to start by describing the problem that exists for your customers. After that, you can describe how you plan to solve that problem with your product or service.
This is usually called a problem and solution statement .
To truly showcase the value of your products and services, you need to craft a compelling narrative around your offerings. How will your product or service transform your customers’ lives or jobs? A strong narrative will draw in your readers.
This is also the part of the business plan to discuss any competitive advantages you may have, like specific intellectual property or patents that protect your product. If you have any initial sales, contracts, or other evidence that your product or service is likely to sell, include that information as well. It will show that your idea has traction , which can help convince readers that your plan has a high chance of success.
Market analysis
Your target market is a description of the type of people that you plan to sell to. You might even have multiple target markets, depending on your business.
A market analysis is the part of your plan where you bring together all of the information you know about your target market. Basically, it’s a thorough description of who your customers are and why they need what you’re selling. You’ll also include information about the growth of your market and your industry .
Try to be as specific as possible when you describe your market.
Include information such as age, income level, and location—these are what’s called “demographics.” If you can, also describe your market’s interests and habits as they relate to your business—these are “psychographics.”
Related: Target market examples
Essentially, you want to include any knowledge you have about your customers that is relevant to how your product or service is right for them. With a solid target market, it will be easier to create a sales and marketing plan that will reach your customers. That’s because you know who they are, what they like to do, and the best ways to reach them.
Next, provide any additional information you have about your market.
What is the size of your market ? Is the market growing or shrinking? Ideally, you’ll want to demonstrate that your market is growing over time, and also explain how your business is positioned to take advantage of any expected changes in your industry.
Dig Deeper: Learn how to write a market analysis
Competitive analysis
Part of defining your business opportunity is determining what your competitive advantage is. To do this effectively, you need to know as much about your competitors as your target customers.
Every business has some form of competition. If you don’t think you have competitors, then explore what alternatives there are in the market for your product or service.
For example: In the early years of cars, their main competition was horses. For social media, the early competition was reading books, watching TV, and talking on the phone.
A good competitive analysis fully lays out the competitive landscape and then explains how your business is different. Maybe your products are better made, or cheaper, or your customer service is superior. Maybe your competitive advantage is your location – a wide variety of factors can ultimately give you an advantage.
Dig Deeper: How to write a competitive analysis for your business plan
Marketing and sales plan
The marketing and sales plan covers how you will position your product or service in the market, the marketing channels and messaging you will use, and your sales tactics.
The best place to start with a marketing plan is with a positioning statement .
This explains how your business fits into the overall market, and how you will explain the advantages of your product or service to customers. You’ll use the information from your competitive analysis to help you with your positioning.
For example: You might position your company as the premium, most expensive but the highest quality option in the market. Or your positioning might focus on being locally owned and that shoppers support the local economy by buying your products.
Once you understand your positioning, you’ll bring this together with the information about your target market to create your marketing strategy .
This is how you plan to communicate your message to potential customers. Depending on who your customers are and how they purchase products like yours, you might use many different strategies, from social media advertising to creating a podcast. Your marketing plan is all about how your customers discover who you are and why they should consider your products and services.
While your marketing plan is about reaching your customers—your sales plan will describe the actual sales process once a customer has decided that they’re interested in what you have to offer.
If your business requires salespeople and a long sales process, describe that in this section. If your customers can “self-serve” and just make purchases quickly on your website, describe that process.
A good sales plan picks up where your marketing plan leaves off. The marketing plan brings customers in the door and the sales plan is how you close the deal.
Together, these specific plans paint a picture of how you will connect with your target audience, and how you will turn them into paying customers.
Dig deeper: What to include in your sales and marketing plan
Business operations
The operations section describes the necessary requirements for your business to run smoothly. It’s where you talk about how your business works and what day-to-day operations look like.
Depending on how your business is structured, your operations plan may include elements of the business like:
- Supply chain management
- Manufacturing processes
- Equipment and technology
- Distribution
Some businesses distribute their products and reach their customers through large retailers like Amazon.com, Walmart, Target, and grocery store chains.
These businesses should review how this part of their business works. The plan should discuss the logistics and costs of getting products onto store shelves and any potential hurdles the business may have to overcome.
If your business is much simpler than this, that’s OK. This section of your business plan can be either extremely short or more detailed, depending on the type of business you are building.
For businesses selling services, such as physical therapy or online software, you can use this section to describe the technology you’ll leverage, what goes into your service, and who you will partner with to deliver your services.
Dig Deeper: Learn how to write the operations chapter of your plan
Key milestones and metrics
Although it’s not required to complete your business plan, mapping out key business milestones and the metrics can be incredibly useful for measuring your success.
Good milestones clearly lay out the parameters of the task and set expectations for their execution. You’ll want to include:
- A description of each task
- The proposed due date
- Who is responsible for each task
If you have a budget, you can include projected costs to hit each milestone. You don’t need extensive project planning in this section—just list key milestones you want to hit and when you plan to hit them. This is your overall business roadmap.
Possible milestones might be:
- Website launch date
- Store or office opening date
- First significant sales
- Break even date
- Business licenses and approvals
You should also discuss the key numbers you will track to determine your success. Some common metrics worth tracking include:
- Conversion rates
- Customer acquisition costs
- Profit per customer
- Repeat purchases
It’s perfectly fine to start with just a few metrics and grow the number you are tracking over time. You also may find that some metrics simply aren’t relevant to your business and can narrow down what you’re tracking.
Dig Deeper: How to use milestones in your business plan
Organization and management team
Investors don’t just look for great ideas—they want to find great teams. Use this chapter to describe your current team and who you need to hire . You should also provide a quick overview of your location and history if you’re already up and running.
Briefly highlight the relevant experiences of each key team member in the company. It’s important to make the case for why yours is the right team to turn an idea into a reality.
Do they have the right industry experience and background? Have members of the team had entrepreneurial successes before?
If you still need to hire key team members, that’s OK. Just note those gaps in this section.
Your company overview should also include a summary of your company’s current business structure . The most common business structures include:
- Sole proprietor
- Partnership
Be sure to provide an overview of how the business is owned as well. Does each business partner own an equal portion of the business? How is ownership divided?
Potential lenders and investors will want to know the structure of the business before they will consider a loan or investment.
Dig Deeper: How to write about your company structure and team
Financial plan
Last, but certainly not least, is your financial plan chapter.
Entrepreneurs often find this section the most daunting. But, business financials for most startups are less complicated than you think, and a business degree is certainly not required to build a solid financial forecast.
A typical financial forecast in a business plan includes the following:
- Sales forecast : An estimate of the sales expected over a given period. You’ll break down your forecast into the key revenue streams that you expect to have.
- Expense budget : Your planned spending such as personnel costs , marketing expenses, and taxes.
- Profit & Loss : Brings together your sales and expenses and helps you calculate planned profits.
- Cash Flow : Shows how cash moves into and out of your business. It can predict how much cash you’ll have on hand at any given point in the future.
- Balance Sheet : A list of the assets, liabilities, and equity in your company. In short, it provides an overview of the financial health of your business.
A strong business plan will include a description of assumptions about the future, and potential risks that could impact the financial plan. Including those will be especially important if you’re writing a business plan to pursue a loan or other investment.
Dig Deeper: How to create financial forecasts and budgets
This is the place for additional data, charts, or other information that supports your plan.
Including an appendix can significantly enhance the credibility of your plan by showing readers that you’ve thoroughly considered the details of your business idea, and are backing your ideas up with solid data.
Just remember that the information in the appendix is meant to be supplementary. Your business plan should stand on its own, even if the reader skips this section.
Dig Deeper : What to include in your business plan appendix
Optional: Business plan cover page
Adding a business plan cover page can make your plan, and by extension your business, seem more professional in the eyes of potential investors, lenders, and partners. It serves as the introduction to your document and provides necessary contact information for stakeholders to reference.
Your cover page should be simple and include:
- Company logo
- Business name
- Value proposition (optional)
- Business plan title
- Completion and/or update date
- Address and contact information
- Confidentiality statement
Just remember, the cover page is optional. If you decide to include it, keep it very simple and only spend a short amount of time putting it together.
Dig Deeper: How to create a business plan cover page
How to use AI to help write your business plan
Generative AI tools such as ChatGPT can speed up the business plan writing process and help you think through concepts like market segmentation and competition. These tools are especially useful for taking ideas that you provide and converting them into polished text for your business plan.
The best way to use AI for your business plan is to leverage it as a collaborator , not a replacement for human creative thinking and ingenuity.
AI can come up with lots of ideas and act as a brainstorming partner. It’s up to you to filter through those ideas and figure out which ones are realistic enough to resonate with your customers.
There are pros and cons of using AI to help with your business plan . So, spend some time understanding how it can be most helpful before just outsourcing the job to AI.
Learn more: 10 AI prompts you need to write a business plan
- Writing tips and strategies
To help streamline the business plan writing process, here are a few tips and key questions to answer to make sure you get the most out of your plan and avoid common mistakes .
Determine why you are writing a business plan
Knowing why you are writing a business plan will determine your approach to your planning project.
For example: If you are writing a business plan for yourself, or just to use inside your own business , you can probably skip the section about your team and organizational structure.
If you’re raising money, you’ll want to spend more time explaining why you’re looking to raise the funds and exactly how you will use them.
Regardless of how you intend to use your business plan , think about why you are writing and what you’re trying to get out of the process before you begin.
Keep things concise
Probably the most important tip is to keep your business plan short and simple. There are no prizes for long business plans . The longer your plan is, the less likely people are to read it.
So focus on trimming things down to the essentials your readers need to know. Skip the extended, wordy descriptions and instead focus on creating a plan that is easy to read —using bullets and short sentences whenever possible.
Have someone review your business plan
Writing a business plan in a vacuum is never a good idea. Sometimes it’s helpful to zoom out and check if your plan makes sense to someone else. You also want to make sure that it’s easy to read and understand.
Don’t wait until your plan is “done” to get a second look. Start sharing your plan early, and find out from readers what questions your plan leaves unanswered. This early review cycle will help you spot shortcomings in your plan and address them quickly, rather than finding out about them right before you present your plan to a lender or investor.
If you need a more detailed review, you may want to explore hiring a professional plan writer to thoroughly examine it.
Use a free business plan template and business plan examples to get started
Knowing what information to include in a business plan is sometimes not quite enough. If you’re struggling to get started or need additional guidance, it may be worth using a business plan template.
There are plenty of great options available (we’ve rounded up our 8 favorites to streamline your search).
But, if you’re looking for a free downloadable business plan template , you can get one right now; download the template used by more than 1 million businesses.
Or, if you just want to see what a completed business plan looks like, check out our library of over 550 free business plan examples .
We even have a growing list of industry business planning guides with tips for what to focus on depending on your business type.
Common pitfalls and how to avoid them
It’s easy to make mistakes when you’re writing your business plan. Some entrepreneurs get sucked into the writing and research process, and don’t focus enough on actually getting their business started.
Here are a few common mistakes and how to avoid them:
Not talking to your customers : This is one of the most common mistakes. It’s easy to assume that your product or service is something that people want. Before you invest too much in your business and too much in the planning process, make sure you talk to your prospective customers and have a good understanding of their needs.
- Overly optimistic sales and profit forecasts: By nature, entrepreneurs are optimistic about the future. But it’s good to temper that optimism a little when you’re planning, and make sure your forecasts are grounded in reality.
- Spending too much time planning: Yes, planning is crucial. But you also need to get out and talk to customers, build prototypes of your product and figure out if there’s a market for your idea. Make sure to balance planning with building.
- Not revising the plan: Planning is useful, but nothing ever goes exactly as planned. As you learn more about what’s working and what’s not—revise your plan, your budgets, and your revenue forecast. Doing so will provide a more realistic picture of where your business is going, and what your financial needs will be moving forward.
- Not using the plan to manage your business: A good business plan is a management tool. Don’t just write it and put it on the shelf to collect dust – use it to track your progress and help you reach your goals.
- Presenting your business plan
The planning process forces you to think through every aspect of your business and answer questions that you may not have thought of. That’s the real benefit of writing a business plan – the knowledge you gain about your business that you may not have been able to discover otherwise.
With all of this knowledge, you’re well prepared to convert your business plan into a pitch presentation to present your ideas.
A pitch presentation is a summary of your plan, just hitting the highlights and key points. It’s the best way to present your business plan to investors and team members.
Dig Deeper: Learn what key slides should be included in your pitch deck
Use your business plan to manage your business
One of the biggest benefits of planning is that it gives you a tool to manage your business better. With a revenue forecast, expense budget, and projected cash flow, you know your targets and where you are headed.
And yet, nothing ever goes exactly as planned – it’s the nature of business.
That’s where using your plan as a management tool comes in. The key to leveraging it for your business is to review it periodically and compare your forecasts and projections to your actual results.
Start by setting up a regular time to review the plan – a monthly review is a good starting point. During this review, answer questions like:
- Did you meet your sales goals?
- Is spending following your budget?
- Has anything gone differently than what you expected?
Now that you see whether you’re meeting your goals or are off track, you can make adjustments and set new targets.
Maybe you’re exceeding your sales goals and should set new, more aggressive goals. In that case, maybe you should also explore more spending or hiring more employees.
Or maybe expenses are rising faster than you projected. If that’s the case, you would need to look at where you can cut costs.
A plan, and a method for comparing your plan to your actual results , is the tool you need to steer your business toward success.
Learn More: How to run a regular plan review
Free business plan templates and examples
Kickstart your business plan writing with one of our free business plan templates or recommended tools.

Free business plan template
Download a free SBA-approved business plan template built for small businesses and startups.
Download Template

One-page plan template
Download a free one-page plan template to write a useful business plan in as little as 30-minutes.

Sample business plan library
Explore over 500 real-world business plan examples from a wide variety of industries.
View Sample Plans
How to write a business plan FAQ
What is a business plan?
A document that describes your business , the products and services you sell, and the customers that you sell to. It explains your business strategy, how you’re going to build and grow your business, what your marketing strategy is, and who your competitors are.
What are the benefits of a business plan?
A business plan helps you understand where you want to go with your business and what it will take to get there. It reduces your overall risk, helps you uncover your business’s potential, attracts investors, and identifies areas for growth.
Having a business plan ultimately makes you more confident as a business owner and more likely to succeed for a longer period of time.
What are the 7 steps of a business plan?
The seven steps to writing a business plan include:
- Write a brief executive summary
- Describe your products and services.
- Conduct market research and compile data into a cohesive market analysis.
- Describe your marketing and sales strategy.
- Outline your organizational structure and management team.
- Develop financial projections for sales, revenue, and cash flow.
- Add any additional documents to your appendix.
What are the 5 most common business plan mistakes?
There are plenty of mistakes that can be made when writing a business plan. However, these are the 5 most common that you should do your best to avoid:
- 1. Not taking the planning process seriously.
- Having unrealistic financial projections or incomplete financial information.
- Inconsistent information or simple mistakes.
- Failing to establish a sound business model.
- Not having a defined purpose for your business plan.
What questions should be answered in a business plan?
Writing a business plan is all about asking yourself questions about your business and being able to answer them through the planning process. You’ll likely be asking dozens and dozens of questions for each section of your plan.
However, these are the key questions you should ask and answer with your business plan:
- How will your business make money?
- Is there a need for your product or service?
- Who are your customers?
- How are you different from the competition?
- How will you reach your customers?
- How will you measure success?
How long should a business plan be?
The length of your business plan fully depends on what you intend to do with it. From the SBA and traditional lender point of view, a business plan needs to be whatever length necessary to fully explain your business. This means that you prove the viability of your business, show that you understand the market, and have a detailed strategy in place.
If you intend to use your business plan for internal management purposes, you don’t necessarily need a full 25-50 page business plan. Instead, you can start with a one-page plan to get all of the necessary information in place.
What are the different types of business plans?
While all business plans cover similar categories, the style and function fully depend on how you intend to use your plan. Here are a few common business plan types worth considering.
Traditional business plan: The tried-and-true traditional business plan is a formal document meant to be used when applying for funding or pitching to investors. This type of business plan follows the outline above and can be anywhere from 10-50 pages depending on the amount of detail included, the complexity of your business, and what you include in your appendix.
Business model canvas: The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea.
One-page business plan: This format is a simplified version of the traditional plan that focuses on the core aspects of your business. You’ll typically stick with bullet points and single sentences. It’s most useful for those exploring ideas, needing to validate their business model, or who need an internal plan to help them run and manage their business.
Lean Plan: The Lean Plan is less of a specific document type and more of a methodology. It takes the simplicity and styling of the one-page business plan and turns it into a process for you to continuously plan, test, review, refine, and take action based on performance. It’s faster, keeps your plan concise, and ensures that your plan is always up-to-date.
What’s the difference between a business plan and a strategic plan?
A business plan covers the “who” and “what” of your business. It explains what your business is doing right now and how it functions. The strategic plan explores long-term goals and explains “how” the business will get there. It encourages you to look more intently toward the future and how you will achieve your vision.
However, when approached correctly, your business plan can actually function as a strategic plan as well. If kept lean, you can define your business, outline strategic steps, and track ongoing operations all with a single plan.
Noah is the COO at Palo Alto Software, makers of the online business plan app LivePlan. He started his career at Yahoo! and then helped start the user review site Epinions.com. From there he started a software distribution business in the UK before coming to Palo Alto Software to run the marketing and product teams.

Table of Contents
- Use AI to help write your plan
- Common planning mistakes
- Manage with your business plan
- Templates and examples
Related Articles

5 Min. Read
How To Write a Business Plan for a Life Coaching Business + Free Example

7 Min. Read
How to Write a Bakery Business Plan + Sample

3 Min. Read
What to Include in Your Business Plan Appendix

1 Min. Read
How to Calculate Return on Investment (ROI)
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
- Digital Marketing
- Apps & Website

The Ultimate Guide to Efficient Production Planning and Scheduling

- Key Takeaways
According to Statista, 85% of manufacturers consider production planning and scheduling software crucial for their operations in 2024.
Gartner’s latest report reveals that by 2024, AI-driven production planning solutions will reduce manufacturing downtime by 30% globally.
SEMrush data from 2024 shows that companies integrating advanced scheduling technologies experience a 25% increase in production efficiency.
Effective production planning and scheduling are vital for maximizing productivity, minimizing costs, and meeting customer demands efficiently.
Monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs) and leveraging data-driven insights drive continuous optimization and enhance competitiveness in the manufacturing landscape.
Have you ever wondered how products magically appear on store shelves exactly when you need them? Behind this seemingly effortless process lies the intricate art of production planning and scheduling. Picture a symphony where each note is meticulously orchestrated to create a harmonious melody. Similarly, production planning harmonizes demand forecasts, resource allocation, and scheduling to ensure products are available when and where they are needed. But what does it truly entail, and how does it shape the world of manufacturing?
Overview of Production Planning
- Definition and purpose of production planning
Production planning is the strategic process used in manufacturing to determine the what, when, and how of production. It involves forecasting demand, scheduling production activities, and allocating resources efficiently to meet market demands. The main goal is to optimize the use of resources, minimize production costs, and ensure timely delivery of products.
- Importance in the manufacturing process
- Central to the manufacturing process, production planning ensures resources are used efficiently, reducing waste and maximizing output.
- It helps in scheduling the production runs, maintaining inventory at optimal levels, and improving the overall productivity of the manufacturing unit.
- Proper planning can lead to increased production capacity, improved product quality, and higher customer satisfaction.
- Relationship between production planning and business strategy
- Production planning is tightly interwoven with business strategy, impacting a company’s ability to meet market demands and achieve financial targets.
- Strategic planning in production helps in aligning manufacturing goals with the business objectives, enhancing the ability to respond to competitive pressures and market opportunities.
- It supports long-term business success by ensuring that the manufacturing process is efficient, cost-effective, and aligned with the broader business goals.
The Production Planning Process
- Steps involved in production planning
- Identify Objectives: Establish clear goals for production, including quantity, quality, and timeline requirements.
- Demand Forecasting: Analyze market trends, historical data, and sales forecasts to predict future product demand.
- Resource Assessment: Evaluate the availability of resources such as materials, labor, and machinery needed for production.
- Capacity Planning: Determine the production capacity to meet forecasted demand, considering constraints like machine availability and labor skills.
- Process Design: Define the production process, including the sequence of operations, required equipment, and labor needs.
- Scheduling: Develop a detailed production schedule that outlines when and where each product will be manufactured.
- Execution: Implement the production plan, coordinating resources and monitoring the production process.
- Monitoring and Control: Track production progress, compare actual performance against the plan, and make adjustments as needed.
- Key phases from demand forecasting to final execution
- Demand Forecasting Phase: Involves analyzing past sales data, market trends, and economic indicators to predict future product demand.
- Planning Phase: Translates the forecasted demand into a viable production plan, determining the quantity of products to be produced and the required resources.
- Scheduling Phase: Involves creating a timeline for when each task in the production process should be completed.
- Execution Phase: The actual production takes place based on the planning and scheduling phases, with a focus on efficiency and adherence to the plan.
- Monitoring and Control Phase: Ongoing assessment of the production process to ensure it aligns with the plan, with adjustments made as necessary to address any issues.
- Role of technology in modern production planning
- Automation of Tasks: Technology automates repetitive tasks in the production planning process, increasing efficiency and reducing errors.
- Data Analysis and Forecasting: Advanced data analytics tools help in accurately forecasting demand and optimizing resource allocation.
- Real-time Monitoring: Modern systems provide real-time visibility into the production process, enabling quick decision-making and adjustments.
- Integration of Systems: Technology integrates various aspects of production planning, such as inventory management, procurement, and scheduling, for streamlined operations.
- Machine Learning and AI: These technologies are increasingly used to predict trends, automate scheduling, and optimize production processes for better outcomes.
Types of Production Planning
- Flow Production Planning and its Characteristics
- Definition : Flow production planning involves continuous movement of materials through the production process. This method is often used in large-scale manufacturing where products go through a series of steps and processes in a fixed sequence.
- Standardization : Products are usually standardized, allowing for a streamlined and efficient production process.
- Automation : High levels of automation are common, reducing manual labor and increasing consistency.
- Continuous Operation : Production runs continuously over long periods, optimizing machinery use and reducing setup times.
- High Volume : Suitable for high-volume production where demand is consistent and predictable.
- Cost Efficiency : Economies of scale can be achieved, lowering the per-unit cost of production.
- Mass Production Planning and its Efficiency
- Definition : Mass production planning is focused on producing large quantities of standardized products. It is characterized by the assembly line system where each worker or machine performs a specific task repetitively.
- Economies of Scale : Significant reduction in cost per unit as production volume increases.
- Standardized Products : Uniformity in products helps in streamlining the manufacturing process and reducing variability.
- Specialized Labor and Machinery : Workers and machines specialize in specific tasks, increasing speed and efficiency.
- Inventory Management : Often involves maintaining large inventories to ensure a continuous production flow.
- Time-Saving : The assembly line reduces the time taken from start to finish, enhancing overall productivity.
- Process Production Planning and its Application
- Definition : Process production planning is used in industries where production is continuous and the output is in the form of a product flow, such as chemicals, oil, and gas.
- Continuous Flow : Production occurs in a continuous, unbroken flow through a series of processes or operations.
- Chemical Processes : Commonly used in chemical manufacturing where raw materials undergo chemical reactions to form new products.
- Customization and Flexibility : Allows for some level of customization, depending on the complexity of the process and the end-product requirements.
- Quality Control : Rigorous quality control is essential to ensure that the output remains consistent and meets the required standards.
- Integration with Other Systems : Often integrated with other production and business planning systems to ensure smooth operations and efficient resource use.
Demand Forecasting and Product Demand Planning
- Techniques for predicting market demand
- Historical Sales Analysis: Examining past sales data to identify trends and patterns that can predict future demand.
- Market Research: Conducting surveys, interviews, and focus groups to gather information on consumer preferences and buying behaviors.
- Delphi Method: Using a panel of experts to forecast demand through iterative rounds of questioning and consensus building.
- Time Series Analysis: Employing statistical techniques to model and forecast future demand based on historical time series data.
- Econometric Modeling: Utilizing advanced statistical methods to forecast demand by considering various economic factors like GDP, unemployment rates, and consumer spending.
- Impact of demand forecasting on production planning
- Resource Allocation: Accurate demand forecasting helps in determining the required quantity of resources, including labor, materials, and machinery, ensuring they are adequately allocated to meet production needs.
- Inventory Management: Facilitates optimal inventory levels, preventing overstocking or stockouts, and reducing holding costs.
- Capacity Planning: Assists in planning the production capacity needed to meet future demand, helping in the decision-making process for expansion or downsizing.
- Lead Time Reduction: Enables better planning of the production schedule, reducing lead times and improving customer satisfaction.
- Risk Management: Provides a basis for identifying potential risks in the supply chain and developing strategies to mitigate them.
- Tools and software used in demand planning
- SAP Integrated Business Planning (SAP IBP): Offers advanced analytics for demand planning, helping businesses to make accurate forecasts and optimize inventory levels.
- Oracle Demand Management Cloud: Provides capabilities for demand sensing, shaping, and forecasting, helping to improve the accuracy of demand predictions.
- IBM Planning Analytics: Uses AI and machine learning to provide insights into demand trends, helping businesses to forecast demand more accurately.
- Microsoft Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management: Includes demand forecasting features that allow for the creation of demand forecasts based on historical data.
- Anaplan: A cloud-based platform that provides tools for demand planning, allowing businesses to model different scenarios and their potential impacts on demand.
Material Requirement Planning (MRP)
- Understanding the MRP System
- What It Is: Material Requirement Planning (MRP) is a system used to manage manufacturing processes. It helps in planning and controlling inventory levels, production, and delivery schedules.
- Functionality: MRP calculates the materials needed for production and the timing to procure them. It uses data from production schedules, inventory records, and bill of materials (BOM) to ensure that materials are available for production and products are ready for delivery.
- Integration with ERP: MRP is often integrated within larger Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems like SAP ERP or Oracle NetSuite. This integration allows for a more comprehensive view of the company’s operations and resources.
- How MRP Integrates with Production Planning
- Seamless Coordination: MRP ensures that the manufacturing process has the necessary materials at the right time and place. It aligns the production schedule with material availability, reducing downtime and increasing efficiency.
- Data-Driven Planning: Through integration with production planning, MRP systems like Microsoft Dynamics 365, Infor CloudSuite Industrial, or Epicor ERP use real-time data to adjust plans based on actual performance, inventory levels, and demand forecasts.
- Streamlined Processes: MRP integrates with other aspects of production planning to provide a streamlined process, from order intake to final delivery. This integration helps in coordinating production cycles, reducing lead times, and improving customer satisfaction.
- Benefits of MRP in Inventory Management and Cost Reduction
- Inventory Optimization: MRP helps in maintaining optimal inventory levels, reducing excess stock, and minimizing shortages. Tools like Fishbowl Inventory or MRPeasy are designed to automate inventory control, helping businesses avoid overproduction and underproduction.
- Cost Savings: By ensuring materials are purchased only as needed and reducing waste, MRP systems contribute to significant cost savings. It reduces carrying costs of inventory and minimizes the risk of obsolescence.
- Efficiency Improvement: MRP enables more efficient use of resources by scheduling production runs at the optimal time, based on material availability. This leads to smoother operations and reduced production costs.
- Analytical Insights: With advanced MRP software like SAP ERP or Oracle NetSuite, companies gain insights into their operations, helping them make informed decisions about procurement, production scheduling, and inventory management.
Scheduling in Production Planning
- Different Types of Scheduling Methods
- Forward Scheduling : This method schedules tasks as soon as the resources are available, moving forward from the current date. It’s useful for meeting customer demand promptly but can lead to increased inventory costs if production outpaces demand.
- Backward Scheduling : Begins with the end date (due date) and schedules tasks in reverse order to meet this deadline. It’s effective for ensuring on-time delivery but can put pressure on the production process to meet tight deadlines.
- Resource Leveling Scheduling : Aims to minimize fluctuations in resource usage. This method smooths out the demand for resources, reducing peaks and troughs in resource allocation and ensuring a more consistent workload.
- Critical Path Method (CPM) : Identifies the longest stretch of dependent tasks and measures the time required to complete them. This method focuses on critical tasks that impact the project timeline, helping to prioritize activities to prevent delays.
- Importance of Scheduling in Production Efficiency
- Optimizes Resource Use: Good scheduling makes sure resources are used well, cutting down on wasted time and getting the most out of what’s available.
- Reduces Production Time: Planning carefully what needs to be done and when helps speed up how quickly things get made.
- Improves On-time Delivery: Making sure production matches delivery deadlines means products are ready when they’re supposed to be, making customers happier.
- Enhances Flexibility: Having a solid schedule helps companies handle unexpected changes better, keeping things running smoothly even when things don’t go as planned.
- Tools and Techniques for Effective Scheduling
- Microsoft Project: Microsoft Project helps you plan your projects. It has tools like Gantt charts to schedule tasks and manage resources.
- Asana: Asana helps teams keep track of their projects. You can set deadlines and see how tasks are progressing in real-time.
- Trello: Trello is a simple way to manage tasks. It uses cards to organize your work and visualize your workflow, great for small projects.
- Primavera P6: Primavera P6 is for big projects. It helps plan, schedule, and control large-scale projects, especially in fields like construction and engineering.
- Monday.com: Monday.com is a flexible tool for planning and tracking work. It supports scheduling, time tracking, and setting up workflows, perfect for teams of any size.
Challenges in Production Planning and Scheduling
- Common Obstacles in Production Planning and Scheduling:
- Lack of accurate demand forecasting tools like SAP Integrated Business Planning (IBP) or Oracle Demand Management.
- Inadequate communication between departments, which can be addressed with tools like Slack or Microsoft Teams.
- Insufficient data analytics capabilities, highlighting the need for solutions like Tableau or Power BI for data visualization and analysis.
- Impact of Supply Chain Disruptions on Production Planning:
- Delays in raw material procurement due to supply chain disruptions like those caused by global events (e.g., COVID-19).
- Shortages of critical components affecting production schedules, which can be mitigated with tools such as Kinaxis RapidResponse for supply chain management.
- Transportation and logistics challenges leading to delays in receiving materials or delivering finished products, requiring solutions like Descartes or MercuryGate for supply chain optimization.
- Strategies for Flexible and Responsive Planning:
- Implementing agile manufacturing principles using methodologies like Kanban or Lean Production.
- Utilizing advanced planning and scheduling (APS) software such as Preactor or PlanetTogether to optimize production schedules and adapt to changes quickly.
- Developing contingency plans and alternative sourcing strategies to address supply chain disruptions effectively.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and Metrics
- Essential KPIs for Evaluating Production Planning Effectiveness:
- Production Efficiency Ratio (PER): Measures the ratio of actual production output to the maximum potential output, indicating how efficiently resources are utilized.
- On-time Delivery Performance: Tracks the percentage of orders delivered on time, reflecting the reliability and effectiveness of production planning.
- Inventory Turnover: Calculates how many times inventory is sold and replaced within a specific period, indicating production and sales alignment.
- Resource Utilization Rate: Measures the utilization of resources like machinery, labor, and raw materials, indicating efficiency in resource allocation .
- Production Cost Variance: Compares actual production costs to budgeted costs, highlighting cost control and efficiency in production processes.
- How to Measure and Improve Production Planning Performance:
- Businesses use software like SAP or Oracle to plan production, check progress, and find ways to improve.
- Companies use lean methods like JIT and TQM to reduce waste, improve processes, and get better results.
- Monitoring key numbers, listening to production teams, and regularly checking progress help find problems and improve operations.
- Training programs help employees learn planning tools and improve decision-making, making them better at their jobs.
- The Role of Analytics in Production Planning and Improvement:
- Predictive Analytics: Using tools like Tableau or Power BI to guess what might happen, like how many products will be needed, how much stock should be kept, and how to plan production better.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Using data and charts to make smart decisions, spot patterns, and plan production better.
- Real-time Monitoring: Using smart sensors and machines to watch production as it happens, catch problems early, and fix them quickly to make production smoother and better.
- Collaborative Planning Platforms: Using tools like Asana or Trello to help teams work together, talk, and plan production in a way that’s easy and efficient.
Good production planning and scheduling are very important for factories to work well. They help in delivering things on time, using resources wisely, saving money, and working better. By guessing how much people will want, planning what to use wisely, making good schedules, and checking things regularly, companies can deal with problems, change plans, and keep working smoothly. Trying new tools and watching how well things go helps businesses make good decisions, get better all the time, and stay ahead in manufacturing.
- Q. What is production planning, and why is it important?
Production planning is the process of organizing resources to ensure efficient manufacturing. It’s crucial for optimizing productivity, minimizing costs, and meeting customer demand effectively.
- Q. How does technology impact production planning?
Technology such as AI and automation enhances accuracy, efficiency, and decision-making in production planning. It enables real-time data analysis, predictive modeling, and streamlines communication for better coordination.
- Q. What are the common challenges in production scheduling?
Challenges in scheduling include managing complex workflows, handling unforeseen disruptions, and balancing resource allocation. Effective planning, flexibility, and proactive problem-solving are key to overcoming these challenges.
- Q. What are the benefits of integrating production planning and scheduling?
Integration leads to improved operational efficiency, reduced lead times, optimized resource utilization, and better coordination between departments. It ensures timely production and enhances overall business performance.
- Q. How can companies measure the success of production planning?
Key performance indicators (KPIs) such as production cycle time, resource utilization, on-time delivery, and cost per unit are used to measure the effectiveness of production planning. Regular performance evaluations and data analysis drive continuous improvement.

Related Post
Understanding forward chaining and how it can revolutionize your project management, ai business solutions: a game-changer for modern enterprises, building a robust churn prediction model for business success, explore top marketing automation workflows to achieve exceptional outcomes, sms marketing strategies: boost engagement and conversions, boosting productivity: how network optimization drives business success, table of contents.
Expand My Business is Asia's largest marketplace platform which helps you find various IT Services like Web and App Development, Digital Marketing Services and all others.
- IT Staff Augmentation
- Data & AI
- E-commerce Development
Article Categories
- Technology 678
- Business 321
- Digital Marketing 283
- Social Media Marketing 129
- E-Commerce 127
- Website Development 108
- Software 102
Sitemap / Glossary
Copyright © 2024 Mantarav Private Limited. All Rights Reserved.

- Privacy Overview
- Strictly Necessary Cookies
This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
Strictly Necessary Cookie should be enabled at all times so that we can save your preferences for cookie settings.
If you disable this cookie, we will not be able to save your preferences. This means that every time you visit this website you will need to enable or disable cookies again.
How to make a business plan
Table of Contents
How to make a good business plan: step-by-step guide.
A business plan is a strategic roadmap used to navigate the challenging journey of entrepreneurship. It's the foundation upon which you build a successful business.
A well-crafted business plan can help you define your vision, clarify your goals, and identify potential problems before they arise.
But where do you start? How do you create a business plan that sets you up for success?
This article will explore the step-by-step process of creating a comprehensive business plan.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a formal document that outlines a business's objectives, strategies, and operational procedures. It typically includes the following information about a company:
Products or services
Target market
Competitors
Marketing and sales strategies
Financial plan
Management team
A business plan serves as a roadmap for a company's success and provides a blueprint for its growth and development. It helps entrepreneurs and business owners organize their ideas, evaluate the feasibility, and identify potential challenges and opportunities.
As well as serving as a guide for business owners, a business plan can attract investors and secure funding. It demonstrates the company's understanding of the market, its ability to generate revenue and profits, and its strategy for managing risks and achieving success.
Business plan vs. business model canvas
A business plan may seem similar to a business model canvas, but each document serves a different purpose.
A business model canvas is a high-level overview that helps entrepreneurs and business owners quickly test and iterate their ideas. It is often a one-page document that briefly outlines the following:
Key partnerships
Key activities
Key propositions
Customer relationships
Customer segments
Key resources
Cost structure
Revenue streams
On the other hand, a Business Plan Template provides a more in-depth analysis of a company's strategy and operations. It is typically a lengthy document and requires significant time and effort to develop.
A business model shouldn’t replace a business plan, and vice versa. Business owners should lay the foundations and visually capture the most important information with a Business Model Canvas Template . Because this is a fast and efficient way to communicate a business idea, a business model canvas is a good starting point before developing a more comprehensive business plan.
A business plan can aim to secure funding from investors or lenders, while a business model canvas communicates a business idea to potential customers or partners.
Why is a business plan important?
A business plan is crucial for any entrepreneur or business owner wanting to increase their chances of success.
Here are some of the many benefits of having a thorough business plan.
Helps to define the business goals and objectives
A business plan encourages you to think critically about your goals and objectives. Doing so lets you clearly understand what you want to achieve and how you plan to get there.
A well-defined set of goals, objectives, and key results also provides a sense of direction and purpose, which helps keep business owners focused and motivated.
Guides decision-making
A business plan requires you to consider different scenarios and potential problems that may arise in your business. This awareness allows you to devise strategies to deal with these issues and avoid pitfalls.
With a clear plan, entrepreneurs can make informed decisions aligning with their overall business goals and objectives. This helps reduce the risk of making costly mistakes and ensures they make decisions with long-term success in mind.
Attracts investors and secures funding
Investors and lenders often require a business plan before considering investing in your business. A document that outlines the company's goals, objectives, and financial forecasts can help instill confidence in potential investors and lenders.
A well-written business plan demonstrates that you have thoroughly thought through your business idea and have a solid plan for success.
Identifies potential challenges and risks
A business plan requires entrepreneurs to consider potential challenges and risks that could impact their business. For example:
Is there enough demand for my product or service?
Will I have enough capital to start my business?
Is the market oversaturated with too many competitors?
What will happen if my marketing strategy is ineffective?
By identifying these potential challenges, entrepreneurs can develop strategies to mitigate risks and overcome challenges. This can reduce the likelihood of costly mistakes and ensure the business is well-positioned to take on any challenges.
Provides a basis for measuring success
A business plan serves as a framework for measuring success by providing clear goals and financial projections . Entrepreneurs can regularly refer to the original business plan as a benchmark to measure progress. By comparing the current business position to initial forecasts, business owners can answer questions such as:
Are we where we want to be at this point?
Did we achieve our goals?
If not, why not, and what do we need to do?
After assessing whether the business is meeting its objectives or falling short, business owners can adjust their strategies as needed.
How to make a business plan step by step
The steps below will guide you through the process of creating a business plan and what key components you need to include.
1. Create an executive summary
Start with a brief overview of your entire plan. The executive summary should cover your business plan's main points and key takeaways.
Keep your executive summary concise and clear with the Executive Summary Template . The simple design helps readers understand the crux of your business plan without reading the entire document.
2. Write your company description
Provide a detailed explanation of your company. Include information on what your company does, the mission statement, and your vision for the future.
Provide additional background information on the history of your company, the founders, and any notable achievements or milestones.
3. Conduct a market analysis
Conduct an in-depth analysis of your industry, competitors, and target market. This is best done with a SWOT analysis to identify your strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Next, identify your target market's needs, demographics, and behaviors.
Use the Competitive Analysis Template to brainstorm answers to simple questions like:
What does the current market look like?
Who are your competitors?
What are they offering?
What will give you a competitive advantage?
Who is your target market?
What are they looking for and why?
How will your product or service satisfy a need?
These questions should give you valuable insights into the current market and where your business stands.
4. Describe your products and services
Provide detailed information about your products and services. This includes pricing information, product features, and any unique selling points.
Use the Product/Market Fit Template to explain how your products meet the needs of your target market. Describe what sets them apart from the competition.
5. Design a marketing and sales strategy
Outline how you plan to promote and sell your products. Your marketing strategy and sales strategy should include information about your:
Pricing strategy
Advertising and promotional tactics
Sales channels
The Go to Market Strategy Template is a great way to visually map how you plan to launch your product or service in a new or existing market.
6. Determine budget and financial projections
Document detailed information on your business’ finances. Describe the current financial position of the company and how you expect the finances to play out.
Some details to include in this section are:
Startup costs
Revenue projections
Profit and loss statement
Funding you have received or plan to receive
Strategy for raising funds
7. Set the organization and management structure
Define how your company is structured and who will be responsible for each aspect of the business. Use the Business Organizational Chart Template to visually map the company’s teams, roles, and hierarchy.
As well as the organization and management structure, discuss the legal structure of your business. Clarify whether your business is a corporation, partnership, sole proprietorship, or LLC.
8. Make an action plan
At this point in your business plan, you’ve described what you’re aiming for. But how are you going to get there? The Action Plan Template describes the following steps to move your business plan forward. Outline the next steps you plan to take to bring your business plan to fruition.
Types of business plans
Several types of business plans cater to different purposes and stages of a company's lifecycle. Here are some of the most common types of business plans.
Startup business plan
A startup business plan is typically an entrepreneur's first business plan. This document helps entrepreneurs articulate their business idea when starting a new business.
Not sure how to make a business plan for a startup? It’s pretty similar to a regular business plan, except the primary purpose of a startup business plan is to convince investors to provide funding for the business. A startup business plan also outlines the potential target market, product/service offering, marketing plan, and financial projections.
Strategic business plan
A strategic business plan is a long-term plan that outlines a company's overall strategy, objectives, and tactics. This type of strategic plan focuses on the big picture and helps business owners set goals and priorities and measure progress.
The primary purpose of a strategic business plan is to provide direction and guidance to the company's management team and stakeholders. The plan typically covers a period of three to five years.
Operational business plan
An operational business plan is a detailed document that outlines the day-to-day operations of a business. It focuses on the specific activities and processes required to run the business, such as:
Organizational structure
Staffing plan
Production plan
Quality control
Inventory management
Supply chain
The primary purpose of an operational business plan is to ensure that the business runs efficiently and effectively. It helps business owners manage their resources, track their performance, and identify areas for improvement.
Growth-business plan
A growth-business plan is a strategic plan that outlines how a company plans to expand its business. It helps business owners identify new market opportunities and increase revenue and profitability. The primary purpose of a growth-business plan is to provide a roadmap for the company's expansion and growth.
The 3 Horizons of Growth Template is a great tool to identify new areas of growth. This framework categorizes growth opportunities into three categories: Horizon 1 (core business), Horizon 2 (emerging business), and Horizon 3 (potential business).
One-page business plan
A one-page business plan is a condensed version of a full business plan that focuses on the most critical aspects of a business. It’s a great tool for entrepreneurs who want to quickly communicate their business idea to potential investors, partners, or employees.
A one-page business plan typically includes sections such as business concept, value proposition, revenue streams, and cost structure.
Best practices for how to make a good business plan
Here are some additional tips for creating a business plan:
Use a template
A template can help you organize your thoughts and effectively communicate your business ideas and strategies. Starting with a template can also save you time and effort when formatting your plan.
Miro’s extensive library of customizable templates includes all the necessary sections for a comprehensive business plan. With our templates, you can confidently present your business plans to stakeholders and investors.
Be practical
Avoid overestimating revenue projections or underestimating expenses. Your business plan should be grounded in practical realities like your budget, resources, and capabilities.
Be specific
Provide as much detail as possible in your business plan. A specific plan is easier to execute because it provides clear guidance on what needs to be done and how. Without specific details, your plan may be too broad or vague, making it difficult to know where to start or how to measure success.
Be thorough with your research
Conduct thorough research to fully understand the market, your competitors, and your target audience . By conducting thorough research, you can identify potential risks and challenges your business may face and develop strategies to mitigate them.
Get input from others
It can be easy to become overly focused on your vision and ideas, leading to tunnel vision and a lack of objectivity. By seeking input from others, you can identify potential opportunities you may have overlooked.
Review and revise regularly
A business plan is a living document. You should update it regularly to reflect market, industry, and business changes. Set aside time for regular reviews and revisions to ensure your plan remains relevant and effective.
Create a winning business plan to chart your path to success
Starting or growing a business can be challenging, but it doesn't have to be. Whether you're a seasoned entrepreneur or just starting, a well-written business plan can make or break your business’ success.
The purpose of a business plan is more than just to secure funding and attract investors. It also serves as a roadmap for achieving your business goals and realizing your vision. With the right mindset, tools, and strategies, you can develop a visually appealing, persuasive business plan.
Ready to make an effective business plan that works for you? Check out our library of ready-made strategy and planning templates and chart your path to success.
Get on board in seconds
Join thousands of teams using Miro to do their best work yet.
- Credit cards
- View all credit cards
- Banking guide
- Loans guide
- Insurance guide
- Personal finance
- View all personal finance
- Small business
- Small business guide
- View all taxes
You’re our first priority. Every time.
We believe everyone should be able to make financial decisions with confidence. And while our site doesn’t feature every company or financial product available on the market, we’re proud that the guidance we offer, the information we provide and the tools we create are objective, independent, straightforward — and free.
So how do we make money? Our partners compensate us. This may influence which products we review and write about (and where those products appear on the site), but it in no way affects our recommendations or advice, which are grounded in thousands of hours of research. Our partners cannot pay us to guarantee favorable reviews of their products or services. Here is a list of our partners .
How to Write a Business Plan, Step by Step

Many or all of the products featured here are from our partners who compensate us. This influences which products we write about and where and how the product appears on a page. However, this does not influence our evaluations. Our opinions are our own. Here is a list of our partners and here's how we make money .
What is a business plan?
1. write an executive summary, 2. describe your company, 3. state your business goals, 4. describe your products and services, 5. do your market research, 6. outline your marketing and sales plan, 7. perform a business financial analysis, 8. make financial projections, 9. summarize how your company operates, 10. add any additional information to an appendix, business plan tips and resources.
A business plan outlines your business’s financial goals and explains how you’ll achieve them over the next three to five years. Here’s a step-by-step guide to writing a business plan that will offer a strong, detailed road map for your business.

ZenBusiness
A business plan is a document that explains what your business does, how it makes money and who its customers are. Internally, writing a business plan should help you clarify your vision and organize your operations. Externally, you can share it with potential lenders and investors to show them you’re on the right track.
Business plans are living documents; it’s OK for them to change over time. Startups may update their business plans often as they figure out who their customers are and what products and services fit them best. Mature companies might only revisit their business plan every few years. Regardless of your business’s age, brush up this document before you apply for a business loan .
» Need help writing? Learn about the best business plan software .
This is your elevator pitch. It should include a mission statement, a brief description of the products or services your business offers and a broad summary of your financial growth plans.
Though the executive summary is the first thing your investors will read, it can be easier to write it last. That way, you can highlight information you’ve identified while writing other sections that go into more detail.
» MORE: How to write an executive summary in 6 steps
Next up is your company description. This should contain basic information like:
Your business’s registered name.
Address of your business location .
Names of key people in the business. Make sure to highlight unique skills or technical expertise among members of your team.
Your company description should also define your business structure — such as a sole proprietorship, partnership or corporation — and include the percent ownership that each owner has and the extent of each owner’s involvement in the company.
Lastly, write a little about the history of your company and the nature of your business now. This prepares the reader to learn about your goals in the next section.
» MORE: How to write a company overview for a business plan

The third part of a business plan is an objective statement. This section spells out what you’d like to accomplish, both in the near term and over the coming years.
If you’re looking for a business loan or outside investment, you can use this section to explain how the financing will help your business grow and how you plan to achieve those growth targets. The key is to provide a clear explanation of the opportunity your business presents to the lender.
For example, if your business is launching a second product line, you might explain how the loan will help your company launch that new product and how much you think sales will increase over the next three years as a result.
» MORE: How to write a successful business plan for a loan
In this section, go into detail about the products or services you offer or plan to offer.
You should include the following:
An explanation of how your product or service works.
The pricing model for your product or service.
The typical customers you serve.
Your supply chain and order fulfillment strategy.
You can also discuss current or pending trademarks and patents associated with your product or service.
Lenders and investors will want to know what sets your product apart from your competition. In your market analysis section , explain who your competitors are. Discuss what they do well, and point out what you can do better. If you’re serving a different or underserved market, explain that.
Here, you can address how you plan to persuade customers to buy your products or services, or how you will develop customer loyalty that will lead to repeat business.
Include details about your sales and distribution strategies, including the costs involved in selling each product .
» MORE: R e a d our complete guide to small business marketing
If you’re a startup, you may not have much information on your business financials yet. However, if you’re an existing business, you’ll want to include income or profit-and-loss statements, a balance sheet that lists your assets and debts, and a cash flow statement that shows how cash comes into and goes out of the company.
Accounting software may be able to generate these reports for you. It may also help you calculate metrics such as:
Net profit margin: the percentage of revenue you keep as net income.
Current ratio: the measurement of your liquidity and ability to repay debts.
Accounts receivable turnover ratio: a measurement of how frequently you collect on receivables per year.
This is a great place to include charts and graphs that make it easy for those reading your plan to understand the financial health of your business.
This is a critical part of your business plan if you’re seeking financing or investors. It outlines how your business will generate enough profit to repay the loan or how you will earn a decent return for investors.
Here, you’ll provide your business’s monthly or quarterly sales, expenses and profit estimates over at least a three-year period — with the future numbers assuming you’ve obtained a new loan.
Accuracy is key, so carefully analyze your past financial statements before giving projections. Your goals may be aggressive, but they should also be realistic.
NerdWallet’s picks for setting up your business finances:
The best business checking accounts .
The best business credit cards .
The best accounting software .
Before the end of your business plan, summarize how your business is structured and outline each team’s responsibilities. This will help your readers understand who performs each of the functions you’ve described above — making and selling your products or services — and how much each of those functions cost.
If any of your employees have exceptional skills, you may want to include their resumes to help explain the competitive advantage they give you.
Finally, attach any supporting information or additional materials that you couldn’t fit in elsewhere. That might include:
Licenses and permits.
Equipment leases.
Bank statements.
Details of your personal and business credit history, if you’re seeking financing.
If the appendix is long, you may want to consider adding a table of contents at the beginning of this section.
How much do you need?
with Fundera by NerdWallet
We’ll start with a brief questionnaire to better understand the unique needs of your business.
Once we uncover your personalized matches, our team will consult you on the process moving forward.
Here are some tips to write a detailed, convincing business plan:
Avoid over-optimism: If you’re applying for a business bank loan or professional investment, someone will be reading your business plan closely. Providing unreasonable sales estimates can hurt your chances of approval.
Proofread: Spelling, punctuation and grammatical errors can jump off the page and turn off lenders and prospective investors. If writing and editing aren't your strong suit, you may want to hire a professional business plan writer, copy editor or proofreader.
Use free resources: SCORE is a nonprofit association that offers a large network of volunteer business mentors and experts who can help you write or edit your business plan. The U.S. Small Business Administration’s Small Business Development Centers , which provide free business consulting and help with business plan development, can also be a resource.
On a similar note...
Find small-business financing
Compare multiple lenders that fit your business

- Entrepreneurship

How to Write a Production Plan for a Business?
A production plan is a critical component of any business that involves manufacturing, construction, or other forms of production. It outlines how a company will produce its goods or services, and it provides a roadmap for success. In this article, we’ll take a look at how to write a production plan for your business.
1. Understand Your Product
The first step in creating a production plan is to understand your product. What are you producing? What are its components? How is it made? Answering these questions will help you determine what resources you need, how long it will take to produce, and how you will produce it.
Before creating a production plan, make sure you have a clear understanding of what you are producing. This will help you make informed decisions about the production process and ensure that you are using the right resources.
2. Determine Your Production Capacity
Once you understand your product, you need to determine your production capacity. How much of your product can you produce in a given period? This will depend on the resources you have available, such as equipment, personnel, and materials.
To determine your production capacity, you should consider the following factors:
– The capacity of your equipment – The availability of raw materials – The number of personnel available – The amount of time required to produce each unit
By understanding your production capacity, you can create a production plan that is realistic and achievable.
3. Create a Production Schedule
With a clear understanding of your product and production capacity, you can create a production schedule. This schedule should outline when you will produce each unit of your product, as well as the resources required to produce it.
When creating a production schedule, you should consider the following factors:
– The production capacity of your equipment – The availability of raw materials – The number of personnel available – The amount of time required to produce each unit – The demand for your product
By creating a production schedule, you can ensure that you are using your resources effectively and efficiently.
4. Determine Your Material Requirements
To produce your product, you will need to determine your material requirements. This includes the raw materials needed to produce each unit, as well as any additional materials required for packaging or shipping.
When determining your material requirements, you should consider the following factors:
– The number of units you plan to produce – The amount of raw materials required for each unit – The cost of the raw materials – The availability of the raw materials
By understanding your material requirements, you can ensure that you have the resources you need to produce your product.
5. Develop a Quality Control Plan
Quality control is an essential component of any production plan. It ensures that your product meets the standards set by your company and your customers.
When developing a quality control plan, you should consider the following factors:
– The standards set by your company and your customers – The methods you will use to ensure quality – The personnel responsible for quality control – The equipment required for quality control
By developing a quality control plan, you can ensure that your product meets the highest standards of quality.
6. Determine Your Personnel Needs
To produce your product, you will need personnel with the right skills and experience. When determining your personnel needs, you should consider the following factors:
– The number of personnel required – The skills and experience required – The cost of personnel – The availability of personnel
By understanding your personnel needs, you can ensure that you have the right people in place to produce your product.
7. Develop a Maintenance Plan
Equipment maintenance is an essential component of any production plan. It ensures that your equipment is in good working order and reduces the risk of breakdowns.
When developing a maintenance plan, you should consider the following factors:
– The frequency of maintenance – The personnel responsible for maintenance – The cost of maintenance – The equipment required for maintenance
By developing a maintenance plan, you can ensure that your equipment is always in good working order.
8. Determine Your Cost of Production
To determine the profitability of your product, you need to determine your cost of production. This includes the cost of raw materials, personnel, equipment, and any other expenses associated with production.
When determining your cost of production, you should consider the following factors:
– The cost of raw materials – The cost of personnel – The cost of equipment – The cost of maintenance – The cost of overhead
By understanding your cost of production, you can ensure that your product is profitable.
9. Monitor and Adjust Your Production Plan
Once you have created your production plan, you need to monitor its effectiveness. This involves tracking your production output, monitoring your costs, and making adjustments as needed.
When monitoring and adjusting your production plan, you should consider the following factors:
– Production output – Cost of production – Quality control results – Equipment maintenance issues
By monitoring and adjusting your production plan, you can ensure that your product is produced efficiently and effectively.
10. Benefits of a Production Plan
A production plan offers several benefits to your business, including:
– Increased efficiency – Improved quality control – Reduced costs – Increased profitability – Better resource management
By creating a production plan, you can ensure that your business is producing its products or services in the most efficient and effective way possible.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions and answers about writing a production plan for a business:
What is a production plan?
A production plan is a document that outlines the steps a business will take to manufacture or produce a product. It includes details about the materials needed, the timeline for production, and the resources required to complete the project. A production plan is essential for ensuring that a business can efficiently and effectively produce goods.
When writing a production plan, it’s important to consider factors like the demand for your product, the availability of resources, and the complexity of the manufacturing process. By taking these factors into account, you can create a plan that will help your business succeed.
What should be included in a production plan?
A production plan should include a detailed timeline for production, a list of the materials needed for manufacturing, and information about the resources required to complete the project. It should also outline the steps involved in the manufacturing process and any quality control measures that will be used to ensure that the final product meets the necessary standards.
Additionally, a production plan should include information about the expected demand for the product, as well as any potential challenges that may arise during production. By including these details in your plan, you can ensure that your business is prepared to meet the needs of your customers and overcome any obstacles that may arise.
What are the benefits of a production plan?
Having a production plan in place can provide several benefits for a business. For one, it can help ensure that the manufacturing process is efficient and cost-effective, as it allows you to identify any potential issues and address them before they become major problems. Additionally, a production plan can help you manage your resources more effectively, as it provides a clear timeline for production and ensures that you have the necessary materials and personnel in place to complete the project.
Finally, a production plan can help you stay on track and meet your deadlines, which is essential for maintaining a positive reputation with your customers and stakeholders. By creating a detailed plan and sticking to it, you can ensure that your business is able to deliver high-quality products on time and within budget.
How can I create a production plan?
To create a production plan, start by identifying the materials and resources you will need to manufacture your product. Then, create a detailed timeline for production that includes key milestones and deadlines. Be sure to consider factors like the complexity of the manufacturing process, the availability of resources, and the expected demand for your product.
Once you have a basic plan in place, review it carefully to identify any potential issues or challenges. Make adjustments as needed to ensure that your plan is realistic and achievable. Finally, communicate your plan clearly to your team and stakeholders to ensure that everyone is on the same page and working towards the same goals.
How often should I update my production plan?
It’s important to review and update your production plan regularly to ensure that it remains relevant and effective. Depending on the nature of your business and the products you produce, you may need to update your plan on a monthly, quarterly, or annual basis.
When updating your plan, be sure to consider any changes in demand, resources, or production processes that may have occurred since the last update. This will help you ensure that your plan remains accurate and effective, and that your business is able to meet the needs of your customers and stakeholders.
Production Plan
To create a successful production plan, start by identifying your goals and objectives. Consider factors such as customer demand, production capacity, and available resources. From there, break down your plan into manageable steps, and set realistic timelines for each stage of production.
Lastly, remember that your production plan is not set in stone. As your business grows and evolves, your production plan will need to evolve with it. Be prepared to make changes and adjustments to your plan as needed, and don’t be afraid to seek out help and advice from experts in the field. With the right approach and a solid plan in place, you can take your business to the next level and achieve lasting success.
RELATED ARTICLES
What is sampling in marketing research, how much does it cost to do market research, how important is marketing for small business, how to create a budget for a multimillion dollar business, how to file for domestic partnership in massachusetts, how to name a partnership, what is a quasi partnership, 10 benefits of investing in money market instruments for businesses, 10 common business goals and how to set them, 10 common financial risks faced by businesses and how to manage them, 10 common types of bonds for business financing and investments, 10 customer retention techniques to foster long-term loyalty, how can trust be gained between the business and development, software startup ideas, the dummies guide to starting your own business, how to find new businesses before they open, what must an entrepreneur assume when starting a business, editor’s choice, how to minimize the budget in snow removal business, is boses product development process customer centered, how to dissolution of partnership firm, does a partnership file a tax return, how to open a corporate bank account in the philippines, stay in touch.
To be updated with all the latest news, offers and special announcements.
Copyright © 2023. All rights reserved.
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Use
10.1 Production and Operations Management—An Overview
- Why is production and operations management important in both manufacturing and service firms?
Production , the creation of products and services, is an essential function in every firm. Production turns inputs, such as natural resources, raw materials, human resources, and capital, into outputs, which are products and services. This process is shown in Exhibit 10.3 . Managing this conversion process is the role of operations management .
The goal of customer satisfaction is an important part of effective production and operations. In the past, the manufacturing function in most companies was inwardly focused. Manufacturing had little contact with customers and didn’t always understand their needs and desires. In the 1980s, many U.S. industries, such as automotive, steel, and electronics, lost customers to foreign competitors because their production systems could not provide the quality customers demanded. As a result, today most American companies, both large and small, consider a focus on quality to be a central component of effective operations management.
Stronger links between marketing and manufacturing also encourage production managers to be more outwardly focused and to consider decisions in light of their effect on customer satisfaction. Service companies find that making operating decisions with customer satisfaction in mind can be a competitive advantage.
Operations managers, the people charged with managing and supervising the conversion process, play a vital role in today’s firm. They control about three-fourths of a firm’s assets, including inventories, wages, and benefits. They also work closely with other major divisions of the firm, such as marketing, finance, accounting, and human resources, to ensure that the firm produces its goods profitably and satisfies its customers. Marketing personnel help them decide which products to make or which services to offer. Accounting and human resources help them face the challenge of combining people and resources to produce high-quality goods on time and at reasonable cost. They are involved in the development and design of goods and determine what production processes will be most effective.
Production and operations management involve three main types of decisions, typically made at three different stages:
- Production planning. The first decisions facing operations managers come at the planning stage. At this stage, managers decide where, when, and how production will occur. They determine site locations and obtain the necessary resources.
- Production control. At this stage, the decision-making process focuses on controlling quality and costs, scheduling, and the actual day-to-day operations of running a factory or service facility.
- Improving production and operations . The final stage of operations management focuses on developing more efficient methods of producing the firm’s goods or services.
All three decisions are ongoing and may occur simultaneously. In the following sections, we will take a closer look at the decisions and considerations firms face in each stage of production and operations management.
Gearing Up: Production Planning
An important part of operations management is production planning . Production planning allows the firm to consider the competitive environment and its own strategic goals to find the best production methods. Good production planning has to balance goals that may conflict, such as providing high-quality service while keeping operating costs low, or keeping profits high while maintaining adequate inventories of finished products. Sometimes accomplishing all these goals is difficult.
Production planning involves three phases. Long-term planning has a time frame of three to five years. It focuses on which goods to produce, how many to produce, and where they should be produced. Medium-term planning decisions cover about two years. They concern the layout of factory or service facilities, where and how to obtain the resources needed for production, and labor issues. Short-term planning, within a one-year time frame, converts these broader goals into specific production plans and materials management strategies.
Four important decisions must be made in production planning. They involve the type of production process that will be used, site selection, facility layout, and resource planning.
Concept Check
- What are the three types of decisions that must be made in production planning?
- What are the three phases of production planning?
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/introduction-business/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Lawrence J. Gitman, Carl McDaniel, Amit Shah, Monique Reece, Linda Koffel, Bethann Talsma, James C. Hyatt
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Introduction to Business
- Publication date: Sep 19, 2018
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/introduction-business/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/introduction-business/pages/10-1-production-and-operations-management-an-overview
© Apr 5, 2023 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Building Your Business
- Becoming an Owner
- Business Plans
How To Write the Operations Plan Section of the Business Plan
Susan Ward wrote about small businesses for The Balance for 18 years. She has run an IT consulting firm and designed and presented courses on how to promote small businesses.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/SusanWardLaptop2crop1-57aa62eb5f9b58974a12bac9.jpg)
Stage of Development Section
Production process section, the bottom line, frequently asked questions (faqs).
The operations plan is the section of your business plan that gives an overview of your workflow, supply chains, and similar aspects of your business. Any key details of how your business physically produces goods or services will be included in this section.
You need an operations plan to help others understand how you'll deliver on your promise to turn a profit. Keep reading to learn what to include in your operations plan.
Key Takeaways
- The operations plan section should include general operational details that help investors understand the physical details of your vision.
- Details in the operations plan include information about any physical plants, equipment, assets, and more.
- The operations plan can also serve as a checklist for startups; it includes a list of everything that must be done to start turning a profit.
In your business plan , the operations plan section describes the physical necessities of your business's operation, such as your physical location, facilities, and equipment. Depending on what kind of business you'll be operating, it may also include information about inventory requirements, suppliers, and a description of the manufacturing process.
Keeping focused on the bottom line will help you organize this part of the business plan.
Think of the operating plan as an outline of the capital and expense requirements your business will need to operate from day to day.
You need to do two things for the reader of your business plan in the operations section: show what you've done so far to get your business off the ground and demonstrate that you understand the manufacturing or delivery process of producing your product or service.
When you're writing this section of the operations plan, start by explaining what you've done to date to get the business operational, then follow up with an explanation of what still needs to be done. The following should be included:
Production Workflow
A high-level, step-by-step description of how your product or service will be made, identifying the problems that may occur in the production process. Follow this with a subsection titled "Risks," which outlines the potential problems that may interfere with the production process and what you're going to do to negate these risks. If any part of the production process can expose employees to hazards, describe how employees will be trained in dealing with safety issues. If hazardous materials will be used, describe how these will be safely stored, handled, and disposed.
Industry Association Memberships
Show your awareness of your industry's local, regional, or national standards and regulations by telling which industry organizations you are already a member of and which ones you plan to join. This is also an opportunity to outline what steps you've taken to comply with the laws and regulations that apply to your industry.
Supply Chains
An explanation of who your suppliers are and their prices, terms, and conditions. Describe what alternative arrangements you have made or will make if these suppliers let you down.
Quality Control
An explanation of the quality control measures that you've set up or are going to establish. For example, if you intend to pursue some form of quality control certification such as ISO 9000, describe how you will accomplish this.
While you can think of the stage of the development part of the operations plan as an overview, the production process section lays out the details of your business's day-to-day operations. Remember, your goal for writing this business plan section is to demonstrate your understanding of your product or service's manufacturing or delivery process.
When writing this section, you can use the headings below as subheadings and then provide the details in paragraph format. Leave out any topic that does not apply to your particular business.
Do an outline of your business's day-to-day operations, including your hours of operation and the days the business will be open. If the business is seasonal, be sure to say so.

The Physical Plant
Describe the type, site, and location of premises for your business. If applicable, include drawings of the building, copies of lease agreements, and recent real estate appraisals. You need to show how much the land or buildings required for your business operations are worth and tell why they're important to your proposed business.
The same goes for equipment. Besides describing the equipment necessary and how much of it you need, you also need to include its worth and cost and explain any financing arrangements.
Make a list of your assets , such as land, buildings, inventory, furniture, equipment, and vehicles. Include legal descriptions and the worth of each asset.
Special Requirements
If your business has any special requirements, such as water or power needs, ventilation, drainage, etc., provide the details in your operating plan, as well as what you've done to secure the necessary permissions.
State where you're going to get the materials you need to produce your product or service and explain what terms you've negotiated with suppliers.
Explain how long it takes to produce a unit and when you'll be able to start producing your product or service. Include factors that may affect the time frame of production and describe how you'll deal with potential challenges such as rush orders.
Explain how you'll keep track of inventory .
Feasibility
Describe any product testing, price testing, or prototype testing that you've done on your product or service.
Give details of product cost estimates.
Once you've worked through this business plan section, you'll not only have a detailed operations plan to show your readers, but you'll also have a convenient list of what needs to be done next to make your business a reality. Writing this document gives you a chance to crystalize your business ideas into a clear checklist that you can reference. As you check items off the list, use it to explain your vision to investors, partners, and others within your organization.
What is an operations plan?
An operations plan is one section of a company's business plan. This section conveys the physical requirements for your business's operations, including supply chains, workflow , and quality control processes.
What is the main difference between the operations plan and the financial plan?
The operations plan and financial plan tackle similar issues, in that they seek to explain how the business will turn a profit. The operations plan approaches this issue from a physical perspective, such as property, routes, and locations. The financial plan explains how revenue and expenses will ultimately lead to the business's success.
Want to read more content like this? Sign up for The Balance's newsletter for daily insights, analysis, and financial tips, all delivered straight to your inbox every morning!

Business Planning

Written by True Tamplin, BSc, CEPF®
Reviewed by subject matter experts.
Updated on June 08, 2023
Get Any Financial Question Answered
Table of contents, what is business planning.
Business planning is a crucial process that involves creating a roadmap for an organization to achieve its long-term objectives. It is the foundation of every successful business and provides a framework for decision-making, resource allocation, and measuring progress towards goals.
Business planning involves identifying the current state of the organization, determining where it wants to go, and developing a strategy to get there.
It includes analyzing the market, identifying target customers, determining a competitive advantage, setting financial goals, and establishing operational plans.
The business plan serves as a reference point for all stakeholders , including investors, employees, and partners, and helps to ensure that everyone is aligned and working towards the same objectives.
Importance of Business Planning
Business planning plays a critical role in the success of any organization, as it helps to establish a clear direction and purpose for the business. It allows the organization to identify its goals and objectives, develop strategies and tactics to achieve them, and establish a framework of necessary resources and operational procedures to ensure success.
Additionally, a well-crafted business plan can serve as a reference point for decision-making, ensuring that all actions taken by the organization are aligned with its long-term objectives.
It can also facilitate communication and collaboration among team members, ensuring that everyone is working towards a common goal.
Furthermore, a business plan is often required when seeking funding or investment from external sources, as it demonstrates the organization's potential for growth and profitability. Overall, business planning is essential for any organization looking to succeed and thrive in a competitive market.
Business Planning Process
Step 1: defining your business purpose and goals.
Begin by clarifying your business's purpose, mission, and long-term goals. These elements should align with the organization's core values and guide every aspect of the planning process.
Step 2: Conducting Market Research and Analysis
Thorough market research and analysis are crucial to understanding the industry landscape, identifying target customers, and gauging the competition. This information will inform your business strategy and help you find your niche in the market.
Step 3: Creating a Business Model and Strategy
Based on the insights from your market research, develop a business model that outlines how your organization will create, deliver, and capture value. This will inform the overall business strategy, including identifying target markets, value propositions, and competitive advantages.
Step 4: Developing a Marketing Plan
A marketing plan details how your organization will promote its products or services to target customers. This includes defining marketing objectives, tactics, channels, budgets, and performance metrics to measure success.
Step 5: Establishing Operational and Financial Plans
The operational plan outlines the day-to-day activities, resources, and processes required to run your business. The financial plan projects revenue, expenses, and cash flow, providing a basis for assessing the organization's financial health and long-term viability.
Step 6: Reviewing and Revising the Business Plan
Regularly review and update your business plan to ensure it remains relevant and reflects the organization's current situation and goals. This iterative process enables proactive adjustments to strategies and tactics in response to changing market conditions and business realities.

Components of a Business Plan
Executive summary.
The executive summary provides a high-level overview of your business plan, touching on the company's mission, objectives, strategies, and key financial projections.
It is critical to make this section concise and engaging, as it is often the first section that potential investors or partners will read.
Company Description
The company description offers a detailed overview of your organization, including its history, mission, values, and legal structure. It also outlines the company's goals and objectives and explains how the business addresses a market need or problem.
Products or Services
Describe the products or services your company offers, emphasizing their unique features, benefits, and competitive advantages. Detail the development process, lifecycle, and intellectual property rights, if applicable.
Market Analysis
The market analysis section delves into the industry, target market, and competition. It should demonstrate a thorough understanding of market trends, growth potential, customer demographics, and competitive landscape.
Marketing and Sales Strategy
Outline your organization's approach to promoting and selling its products or services. This includes marketing channels, sales tactics, pricing strategies, and customer relationship management .
Management and Organization
This section provides an overview of your company's management team, including their backgrounds, roles, and responsibilities. It also outlines the organizational structure and any advisory or support services employed by the company.
Operational Plan
The operational plan describes the day-to-day operations of your business, including facilities, equipment, technology, and personnel requirements. It also covers supply chain management, production processes, and quality control measures.
Financial Plan
The financial plan is a crucial component of your business plan, providing a comprehensive view of your organization's financial health and projections.
This section should include income statements , balance sheets , cash flow statements , and break-even analysis for at least three to five years. Be sure to provide clear assumptions and justifications for your projections.
Appendices and Supporting Documents
The appendices and supporting documents section contains any additional materials that support or complement the information provided in the main body of the business plan. This may include resumes of key team members, patents , licenses, contracts, or market research data.

Benefits of Business Planning
Helps secure funding and investment.
A well-crafted business plan demonstrates to potential investors and lenders that your organization is well-organized, has a clear vision, and is financially viable. It increases your chances of securing the funding needed for growth and expansion.
Provides a Roadmap for Growth and Success
A business plan serves as a roadmap that guides your organization's growth and development. It helps you set realistic goals, identify opportunities, and anticipate challenges, enabling you to make informed decisions and allocate resources effectively.
Enables Effective Decision-Making
Having a comprehensive business plan enables you and your management team to make well-informed decisions, based on a clear understanding of the organization's goals, strategies, and financial situation.
Facilitates Communication and Collaboration
A business plan serves as a communication tool that fosters collaboration and alignment among team members, ensuring that everyone is working towards the same objectives and understands the organization's strategic direction.

Business planning should not be a one-time activity; instead, it should be an ongoing process that is continually reviewed and updated to reflect changing market conditions, business realities, and organizational goals.
This dynamic approach to planning ensures that your organization remains agile, responsive, and primed for success.
As the business landscape continues to evolve, organizations must embrace new technologies, methodologies, and tools to stay competitive.
The future of business planning will involve leveraging data-driven insights, artificial intelligence, and predictive analytics to create more accurate and adaptive plans that can quickly respond to a rapidly changing environment.
By staying ahead of the curve, businesses can not only survive but thrive in the coming years.
Business Planning FAQs
What is business planning, and why is it important.
Business planning is the process of setting goals, outlining strategies, and creating a roadmap for your company's future. It's important because it helps you identify opportunities and risks, allocate resources effectively, and stay on track to achieve your goals.
What are the key components of a business plan?
A business plan typically includes an executive summary, company description, market analysis, organization and management structure, product or service line, marketing and sales strategies, and financial projections.
How often should I update my business plan?
It is a good idea to review and update your business plan annually, or whenever there's a significant change in your industry or market conditions.
What are the benefits of business planning?
Effective business planning can help you anticipate challenges, identify opportunities for growth, improve decision-making, secure financing, and stay ahead of competitors.
Do I need a business plan if I am not seeking funding?
Yes, even if you're not seeking funding, a business plan can be a valuable tool for setting goals, developing strategies, and keeping your team aligned and focused on achieving your objectives.

About the Author
True Tamplin, BSc, CEPF®
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide , a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University , where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon , Nasdaq and Forbes .
Related Topics
- Business Continuity Planning (BCP)
- Business Exit Strategies
- Buy-Sell Agreements
- Capital Planning
- Change-In-Control Agreements
- Cross-Purchase Agreements
- Decision Analysis (DA)
- Employee Retention and Compensation Planning
- Endorsement & Sponsorship Management
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
- Entity-Purchase Agreements
- Family Business Continuity
- Family Business Governance
- Family Limited Partnerships (FLPs) and Buy-Sell Agreements
- Human Resource Planning (HRP)
- Manufacturing Resource Planning (MRP II)
- Plan Restatement
Ask a Financial Professional Any Question
Find advisor near you, our recommended advisors.

Taylor Kovar, CFP®
WHY WE RECOMMEND:
Fee-Only Financial Advisor Show explanation
Certified financial planner™, 3x investopedia top 100 advisor, author of the 5 money personalities & keynote speaker.
IDEAL CLIENTS:
Business Owners, Executives & Medical Professionals
Strategic Planning, Alternative Investments, Stock Options & Wealth Preservation

Claudia Valladares
Bilingual in english / spanish, founder of wisedollarmom.com, quoted in gobanking rates, yahoo finance & forbes.
Retirees, Immigrants & Sudden Wealth / Inheritance
Retirement Planning, Personal finance, Goals-based Planning & Community Impact
We use cookies to ensure that we give you the best experience on our website. If you continue to use this site we will assume that you are happy with it.
Fact Checked
At Finance Strategists, we partner with financial experts to ensure the accuracy of our financial content.
Our team of reviewers are established professionals with decades of experience in areas of personal finance and hold many advanced degrees and certifications.
They regularly contribute to top tier financial publications, such as The Wall Street Journal, U.S. News & World Report, Reuters, Morning Star, Yahoo Finance, Bloomberg, Marketwatch, Investopedia, TheStreet.com, Motley Fool, CNBC, and many others.
This team of experts helps Finance Strategists maintain the highest level of accuracy and professionalism possible.
Why You Can Trust Finance Strategists
Finance Strategists is a leading financial education organization that connects people with financial professionals, priding itself on providing accurate and reliable financial information to millions of readers each year.
We follow strict ethical journalism practices, which includes presenting unbiased information and citing reliable, attributed resources.
Our goal is to deliver the most understandable and comprehensive explanations of financial topics using simple writing complemented by helpful graphics and animation videos.
Our writing and editorial staff are a team of experts holding advanced financial designations and have written for most major financial media publications. Our work has been directly cited by organizations including Entrepreneur, Business Insider, Investopedia, Forbes, CNBC, and many others.
Our mission is to empower readers with the most factual and reliable financial information possible to help them make informed decisions for their individual needs.
How It Works
Step 1 of 3, ask any financial question.
Ask a question about your financial situation providing as much detail as possible. Your information is kept secure and not shared unless you specify.

Step 2 of 3
Our team will connect you with a vetted, trusted professional.
Someone on our team will connect you with a financial professional in our network holding the correct designation and expertise.

Step 3 of 3
Get your questions answered and book a free call if necessary.
A financial professional will offer guidance based on the information provided and offer a no-obligation call to better understand your situation.

Where Should We Send Your Answer?

Just a Few More Details
We need just a bit more info from you to direct your question to the right person.
Tell Us More About Yourself
Is there any other context you can provide.
Pro tip: Professionals are more likely to answer questions when background and context is given. The more details you provide, the faster and more thorough reply you'll receive.
What is your age?
Are you married, do you own your home.
- Owned outright
- Owned with a mortgage
Do you have any children under 18?
- Yes, 3 or more
What is the approximate value of your cash savings and other investments?
- $50k - $250k
- $250k - $1m
Pro tip: A portfolio often becomes more complicated when it has more investable assets. Please answer this question to help us connect you with the right professional.
Would you prefer to work with a financial professional remotely or in-person?
- I would prefer remote (video call, etc.)
- I would prefer in-person
- I don't mind, either are fine
What's your zip code?
- I'm not in the U.S.
Submit to get your question answered.
A financial professional will be in touch to help you shortly.

Part 1: Tell Us More About Yourself
Do you own a business, which activity is most important to you during retirement.
- Giving back / charity
- Spending time with family and friends
- Pursuing hobbies
Part 2: Your Current Nest Egg
Part 3: confidence going into retirement, how comfortable are you with investing.
- Very comfortable
- Somewhat comfortable
- Not comfortable at all
How confident are you in your long term financial plan?
- Very confident
- Somewhat confident
- Not confident / I don't have a plan
What is your risk tolerance?
How much are you saving for retirement each month.
- None currently
- Minimal: $50 - $200
- Steady Saver: $200 - $500
- Serious Planner: $500 - $1,000
- Aggressive Saver: $1,000+
How much will you need each month during retirement?
- Bare Necessities: $1,500 - $2,500
- Moderate Comfort: $2,500 - $3,500
- Comfortable Lifestyle: $3,500 - $5,500
- Affluent Living: $5,500 - $8,000
- Luxury Lifestyle: $8,000+
Part 4: Getting Your Retirement Ready
What is your current financial priority.
- Getting out of debt
- Growing my wealth
- Protecting my wealth
Do you already work with a financial advisor?
Which of these is most important for your financial advisor to have.
- Tax planning expertise
- Investment management expertise
- Estate planning expertise
- None of the above
Where should we send your answer?
Submit to get your retirement-readiness report., get in touch with, great the financial professional will get back to you soon., where should we send the downloadable file, great hit “submit” and an advisor will send you the guide shortly., create a free account and ask any financial question, learn at your own pace with our free courses.
Take self-paced courses to master the fundamentals of finance and connect with like-minded individuals.
Get Started
Hey, did we answer your financial question.
We want to make sure that all of our readers get their questions answered.
Great, Want to Test Your Knowledge of This Lesson?
Create an Account to Test Your Knowledge of This Topic and Thousands of Others.
Get Your Question Answered by a Financial Professional
Create a free account and submit your question. We'll make sure a financial professional gets back to you shortly.
To Ensure One Vote Per Person, Please Include the Following Info
Great thank you for voting..
- Contact sales
Start free trial
The Production Process: Steps & Types

Getting a product from an idea to the marketplace is a long journey that’s mapped in the production process. Another way to look at the production process is as a series of detailed steps that take you from one point to the next until you’ve completed the process.
There are many production methods and types of production, but before explaining those steps, it’s important to understand the term. Then let’s look at various types of product methods and offer a few examples of the production process to make it clear.
What Is a Production Process?
The production process takes resources, such as raw materials, labor, capital and equipment, and turns them into finished goods or services for consumers. The goal of the production process isn’t only to produce but to do so efficiently. The goods or services should be delivered to customers as quickly as possible.
Capital, labor and whatever other resources are required to produce goods and services are called the factors of production. Capital is the amount of money invested in assets, such as machinery, raw materials, etc. Labor is the people who are involved in the time and effort required to put into the process.
A production process must be effective as it impacts a company’s business performance. Therefore, project management software is used to streamline the process and deliver quality without overspending or extending the production time.
ProjectManager is award-winning project management software that helps to plan, manage and track the production process. Our kanban boards are customizable to capture every step of your production process with kanban cards where important files can be attached, subtasks added, priority set, tags made to make them easy to find in a global search and much more. Managers can visualize their workflow to respond quickly to client inquiries and accurately estimate delivery. Get started with ProjectManager today for free.
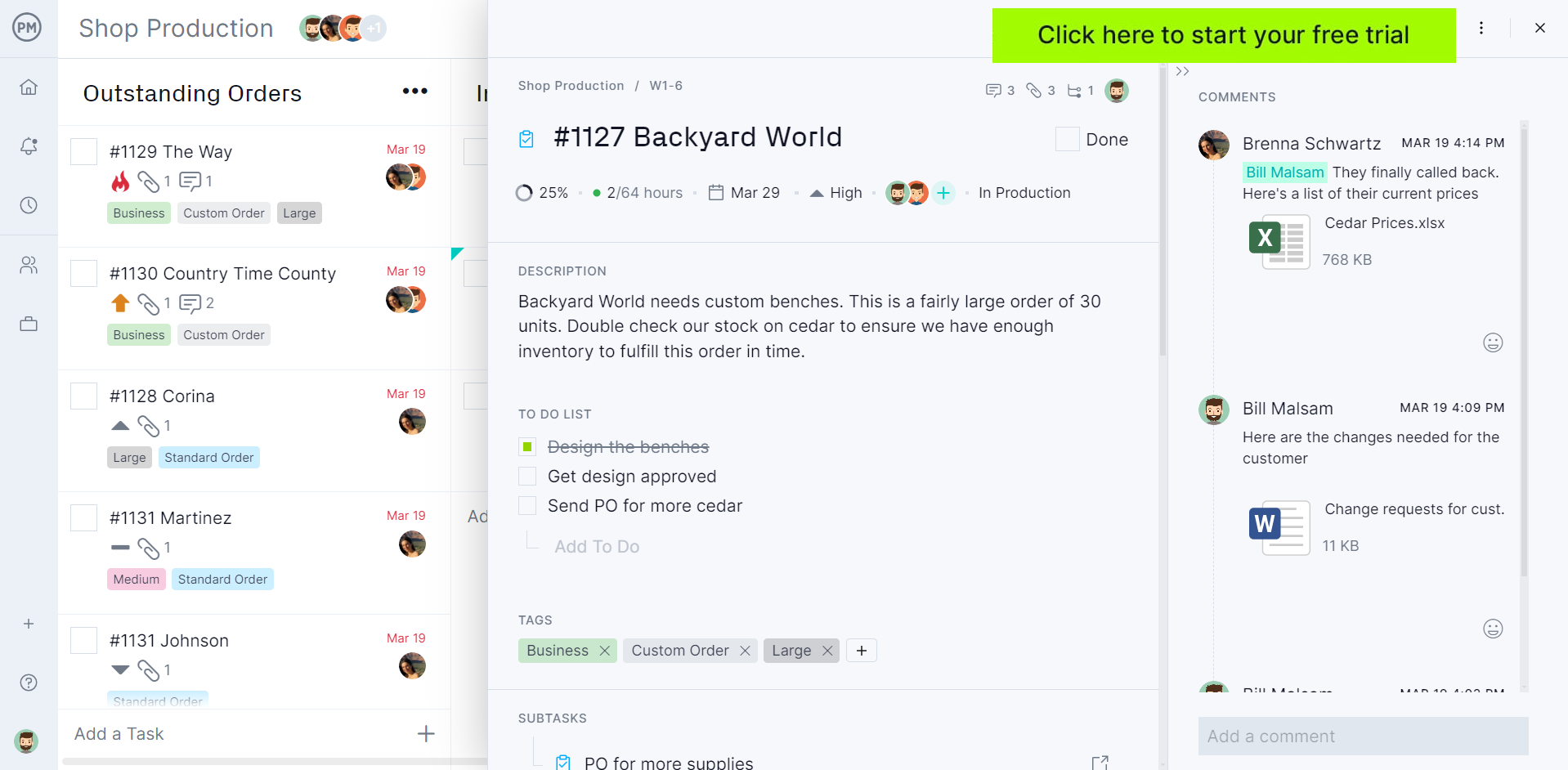
Steps of the Production Process
There are various stages that a typical production process goes through. These steps, of course, can vary from one manufacturer to another and across industries, but in general, the steps defined below are part of any production management process.
Production Planning
Before you can go into production, you’ll need to do some planning . At this point, you’re going to define the purpose and the goals of the production as well as figure out how you’re going to achieve them.
Production Routing
Once the plan is in place, the procurement of the necessary resources such as raw materials, begins. The raw materials might need processing, finishing and to be checked for quality and distribution. These activities are also part of the routing step. At this point, decisions are made to determine the quantity and quality of the goods and services and their place in production. All steps are important in the production process, but this might be the most important.
Production Scheduling
A schedule in the production process is where you determine the timing of the job. Each stage of the production process should have a start date and an end date. Everyone working on the production line will have a scheduled workflow.
Get your free
Capacity Planning Template
Use this free Capacity Planning Template for Excel to manage your projects better.
Production Dispatching
This stage marks the start of production. There are many different activities that can take place over the course of dispatching, from the provision of items, maintenance of records to the monitoring of planned workflows and the times a machine is working or idle to ensure the production process is moving forward as expected.
Production Control
Production control is the stage when the actual production process is compared to the planned production process. This identifies issues that took the production off track and helps managers come up with plans to remedy those issues for the next production cycle.
6 Types of Production Methods
Generally speaking, there are six types of production methods: mass, craft, catch, job and service production as well as mass customization. While there are different types of production methods, some have a fairly similar journey with set stages and parameters and others are different, allowing for customization. Let’s take a look at each to better understand them.
1. Mass Production
Mass production is a continuous process in which everyone is working continuously to produce the same item at the same time. The forms and sizes of the products remain the same. All resources are directed to produce the same range. Multiple tasks will be done simultaneously to improve efficiency .
2. Craft Production
Craft production is when a product is made one by one, whether with tools or without, though it usually occurs in a job shop setting. This was the most common method of production prior to the Industrial Revolution, for example, making pottery by hand.
Related: 10 Free Manufacturing Templates for Excel
3. Batch Production
Similar to mass production, batch production differs in that it’s produced in batches. That allows production to be divided on the size of the product, its color, form and so forth. An example of this would be the silk screening of T-shirts, which are produced in different sizes, colors, etc.
4. Job Production
A job production is one done in limited quantities. It can also be done in accordance with a customer’s specific preference. This type of production method is small-scale with the production of the job being completed before taking up other jobs.
5. Service Production
Service production is usually done by an automatic process that’s triggered by the customer. This is becoming more common with the dominance of online establishments such as Amazon that are streamlining the process of ordering to delivering products.
6. Mass Customization
Mass customization is similar to craft production, only it’s produced in mass quantity. There can be customization on the shape, color, pattern, etc., but the production will make many similar items.
Free Capacity Planning Template
Regardless of your production methods, you need to carefully manage your resources to stay efficient and maintain profitability. Download our free capacity planning template for Excel to schedule your resources, track costs and meet customer demand.
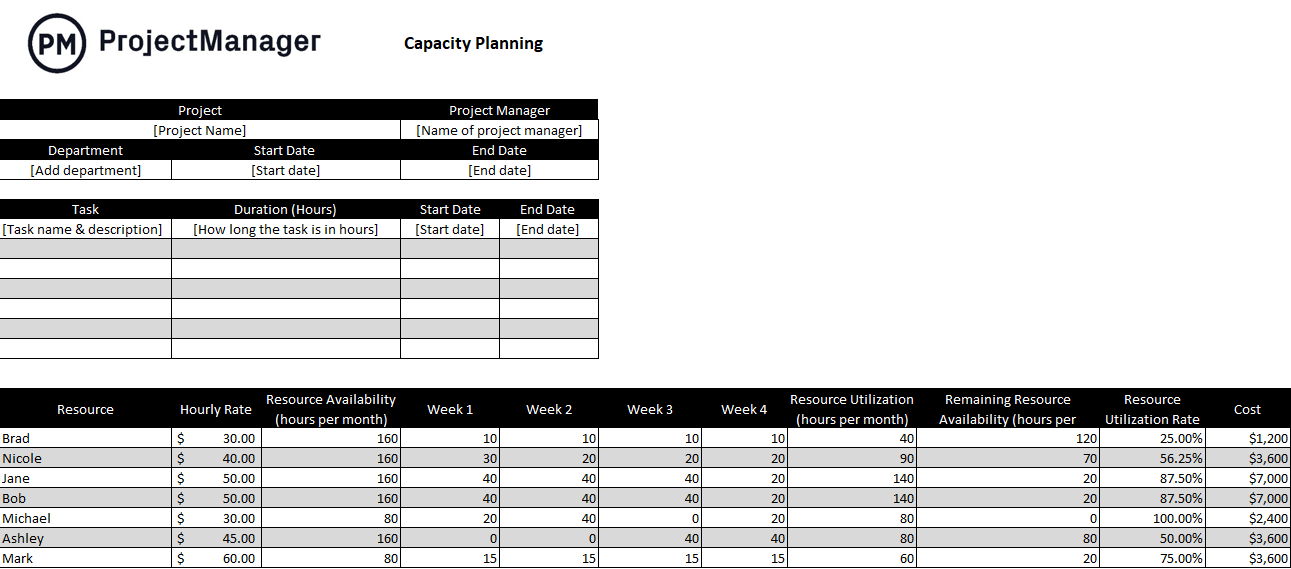
Production Process Examples
To make these various production methods more understandable, let’s explore some examples of each in the production process.
Mass Production Example
Mass production examples are myriad across industries. Two examples of this type of production method can be found in the automobile industry and electronics industries. Both of these types of production are known for their constantly working assembly lines and production that usually works around the clock to produce products efficiently.
Craft Production Example
While craft production was the prominent method of production before the Industrial Revolution, it’s still used today. You’ll find it in the production of designer clothes, which are made for the runway or privileged customers who are looking for one-of-a-kind designs. These items are made by hand and often specifically for special events.
Batch Production Example
We’ve mentioned above that T-shirts are an example of a batch production process, but there are more. For example, baking is batch production as is craft brewing, both popular and widespread illustrations of the vitality of the batch production process.
Job Production Example
In terms of job production, you can find it in industries as diverse as shipbuilding and customer furniture production. More examples include making specific pieces for a house, such as railing for buildings and repairing computers or making flower arrangements for a wedding.
Service Production Example
While delivery from online stores such as Amazon might be how most of us interact with the service product process, it’s not the only example of this production method. If you use a consultant or have a lawyer on retainer, then you’re using service production. These aren’t products but services, but their production is the same.
Mass Customization Example
There are companies that mass produce products, such as sneakers, that still allow customers to customize their products. Nike is one such manufacturer that allows its customers to personalize their own Nike products, whether that’s clothing or footwear. These customization options range from color to design. It’s a powerful marketing tool that creates brand loyalty from its customers, which is worth the added complexities in mass customization production.

How ProjectManager Helps Manage the Production Process
Whichever type of production process your company employs, project management software can help you run your jobs more efficiently. ProjectManager is award-winning project management software that helps manufacturers track jobs, resources and invoices to save money and deliver their products to market on time, within budget and meeting quality expectations.
Use Multiple Tools for Planning
Our kanban boards are essential for tracking production and always knowing where your work is in terms of completion. But that’s only one of the multiple product views available on our software, all of which share the same updated real-time data. Schedules can be created on robust Gantt charts that also can set a baseline to monitor variance to stay on track. The calendar view is a great tool to see if you’ll have the materials in stock when you need them to better plan your production. You can upload invoices and other documentation to tasks on every view so you have a centralized hub collecting important information with our unlimited file storage.
Track Costs and More With a Real-Time Dashboard
Our software gives manufacturers live budget tracking. Add your budget to the project and, once you’ve set a baseline to capture the planned costs, you can monitor your planned costs against your actual costs in real time. Our live dashboard captures this metric and many more, converting the data into easy-to-read graphs and charts that make it easy to digest this information at a glance. Unlike lightweight software tools, there’s no time-consuming configuration necessary to get our dashboard up and running. It’s plug-and-play.
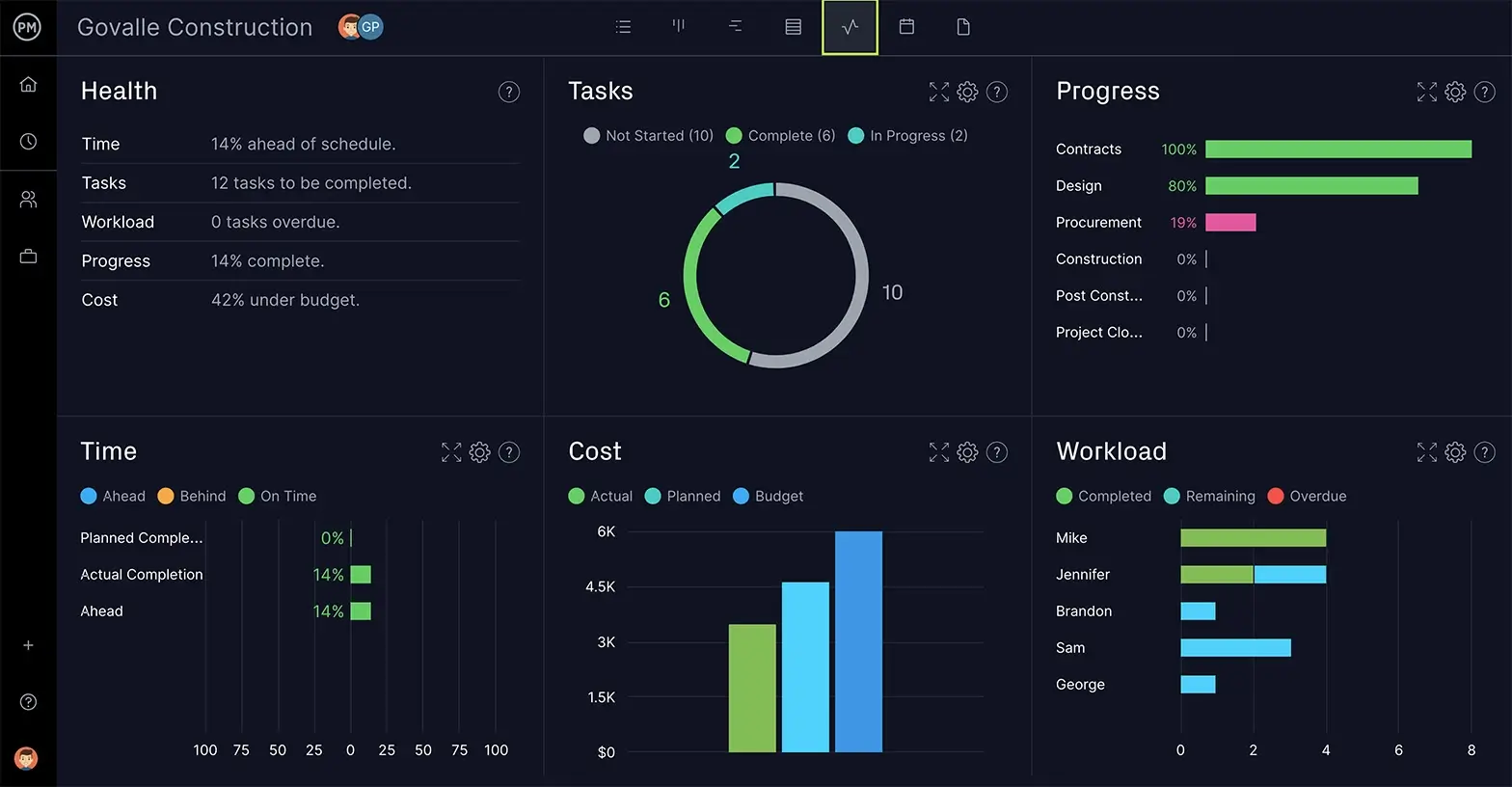
For more detailed information, toggle to our reporting features and generate a status report, portfolio report, reports on variance, timesheets and more in seconds. All reports can be customized to show only the data you want to see and then easily shared with stakeholders to keep them updated. Use risk management, task management and resource management features to keep your production processes running smoothly.
ProjectManager is online project management software that connects everyone on the production line from those in the office to workers on the floor. Share files, comment on the task level and much more. Get the features manufacturers need to empower teams to plan, manage and track their work in real time. Get started with ProjectManager today for free.

Deliver your projects on time and on budget
Start planning your projects.

Production Company Business Plan Template
Written by Dave Lavinsky

Production Company Business Plan
Over the past 20+ years, we have helped over 500 entrepreneurs and business owners create business plans to start and grow their production companies.
If you’re unfamiliar with creating a production company business plan, you may think creating one will be a time-consuming and frustrating process. For most entrepreneurs it is, but for you, it won’t be since we’re here to help. We have the experience, resources, and knowledge to help you create a great business plan.
In this article, you will learn some background information on why business planning is important. Then, you will learn how to write a production company business plan step-by-step so you can create your plan today.
Download our Ultimate Business Plan Template here >
What is a Production Company Business Plan?
A business plan provides a snapshot of your production company as it stands today, and lays out your growth plan for the next five years. It explains your business goals and your strategies for reaching them. It also includes market research to support your plans.
Why You Need a Business Plan for a Production Company
If you’re looking to start a production company or grow your existing production company, you need a business plan. A business plan will help you raise funding, if needed, and plan out the growth of your production company to improve your chances of success. Your production company business plan is a living document that should be updated annually as your company grows and changes.
Sources of Funding for Production Companies
With regards to funding, the main sources of funding for a production company are personal savings, credit cards, bank loans, and angel investors. When it comes to bank loans, banks will want to review your business plan and gain confidence that you will be able to repay your loan and interest. To acquire this confidence, the loan officer will not only want to ensure that your financials are reasonable, but they will also want to see a professional plan. Such a plan will give them the confidence that you can successfully and professionally operate a business. Personal savings and bank loans are the most common funding paths for production companies.
Finish Your Business Plan Today!
How to write a business plan for a production company.
If you want to start a production company or expand your current one, you need a business plan. The guide below details the necessary information for how to write each essential component of your production company business plan.
Executive Summary
Your executive summary provides an introduction to your business plan, but it is normally the last section you write because it provides a summary of each key section of your plan.
The goal of your executive summary is to quickly engage the reader. Explain to them the kind of production company you are running and the status. For example, are you a startup, do you have a production company that you would like to grow, or are you operating a chain of production companies?
Next, provide an overview of each of the subsequent sections of your plan.
- Give a brief overview of the production industry.
- Discuss the type of production company you are operating.
- Detail your direct competitors. Give an overview of your target customers.
- Provide a snapshot of your marketing strategy. Identify the key members of your team.
- Offer an overview of your financial plan.
Company Overview
In your company overview, you will detail the type of production company you are operating.
For example, your production company might specialize in one of the following types of production companies:
- Feature Film Production Company : this type of production company handles all of the necessities that go with producing a major film – hiring on-screen and off-screen talent, writers, musicians, location scouts, a team for pre-production, post-production, legal, etc.
- Commercial Production Company: this type of production company can produce stock footage, short corporate videos, training videos, and creative projects such as music videos and short films
- Post Production Company: this type of production company handles video editing, special effects, color correction, sound mixing, and editing to eventually produce the final video.
- Niche Production Company: this type of production company focuses on one specific niche that it has perfected. They often combine the best of animation, commercial, and post-production companies.
In addition to explaining the type of production company you will operate, the company overview needs to provide background on the business.
Include answers to questions such as:
- When and why did you start the business?
- What milestones have you achieved to date? Milestones could include the number of clients served, the number of films with positive reviews, reaching X number of clients served, etc.
- Your legal business structure. Are you incorporated as an S-Corp? An LLC? A sole proprietorship? Explain your legal structure here.
Industry Analysis
In your industry or market analysis, you need to provide an overview of the production industry.
While this may seem unnecessary, it serves multiple purposes.
First, researching the production industry educates you. It helps you understand the market in which you are operating.
Secondly, market research can improve your marketing strategy, particularly if your analysis identifies market trends.
The third reason is to prove to readers that you are an expert in your industry. By conducting the research and presenting it in your plan, you achieve just that.
The following questions should be answered in the industry analysis section of your production company business plan:
- How big is the production industry (in dollars)?
- Is the market declining or increasing?
- Who are the key competitors in the market?
- Who are the key suppliers in the market?
- What trends are affecting the industry?
- What is the industry’s growth forecast over the next 5 – 10 years?
- What is the relevant market size? That is, how big is the potential target market for your production company? You can extrapolate such a figure by assessing the size of the market in the entire country and then applying that figure to your local population.
Customer Analysis
The customer analysis section of your production company business plan must detail the customers you serve and/or expect to serve.
The following are examples of customer segments: individuals, companies, filmmakers, studios.
As you can imagine, the customer segment(s) you choose will have a great impact on the type of production company you operate. Clearly, small businesses would respond to different marketing promotions than filmmakers, for example.
Try to break out your target customers in terms of their demographic and psychographic profiles. With regards to demographics, including a discussion of the ages, genders, locations, and income levels of the potential customers you seek to serve.
Psychographic profiles explain the wants and needs of your target customers. The more you can recognize and define these needs, the better you will do in attracting and retaining your customers.
Finish Your Production Company Business Plan in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your business plan?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!
Competitive Analysis
Your competitive analysis should identify the indirect and direct competitors your business faces and then focus on the latter.
Direct competitors are other production companies.
Indirect competitors are other options that customers have to purchase from that aren’t directly competing with your product or service. This includes social media platforms, web developers, apps and even college or university students. You need to mention such competition as well.
For each such competitor, provide an overview of their business and document their strengths and weaknesses. Unless you once worked at your competitors’ businesses, it will be impossible to know everything about them. But you should be able to find out key things about them such as
- What types of clients do they serve?
- What type of production company are they?
- What is their pricing (premium, low, etc.)?
- What are they good at?
- What are their weaknesses?
With regards to the last two questions, think about your answers from the customers’ perspective. And don’t be afraid to ask your competitors’ customers what they like most and least about them.
The final part of your competitive analysis section is to document your areas of competitive advantage. For example:
- Will you provide concierge services or customized packages for your clients?
- Will you offer products or services that your competition doesn’t?
- Will you provide better customer service?
- Will you offer better pricing?
Think about ways you will outperform your competition and document them in this section of your plan.
Marketing Plan
Traditionally, a marketing plan includes the four P’s: Product, Price, Place, and Promotion. For a production company business plan, your marketing strategy should include the following:
Product : In the product section, you should reiterate the type o f production company that you documented in your company overview. Then, detail the specific products or services you will be offering. For example, will you provide video editing, music editing, pre-production, or post-production services?
Price : Document the prices you will offer and how they compare to your competitors. Essentially in the product and price sub-sections of yo ur plan, yo u are presenting the products and/or services you offer and their prices.
Place : Place refers to the site of your production company. Document where your company is situated and mention how the site will impact your success. For example, is your production company located in New York or Los Angeles, a business district, a standalone office, or purely online? Discuss how your site might be the ideal location for your customers.
Promotions : The final part of your production company marketing plan is where you will document how you will drive potential customers to your location(s). The following are some promotional methods you might consider:
- Be part of filmmaker associations and networks
- Reach out to websites
- Distribute flyers
- Engage in email marketing
- Advertise on social media platforms
- Improve the SEO (search engine optimization) on your website for targeted keywords
Operations Plan
While the earlier sections of your business plan explained your goals, your operations plan describes how you will meet them. Your operations plan should have two distinct sections as follows.
Everyday short-term processes include all of the tasks involved in running your production company , including client communication and interaction, planning and producing production services, billing clients, etc.
Long-term goals are the milestones you hope to achieve. These could include the dates when you expect to book your Xth client, or when you hope to reach $X in revenue. It could also be when you expect to expand your production company to a new city.
Management Team
To demonstrate your production company’s potential to succeed, a strong management team is essential. Highlight your key players’ backgrounds, emphasizing those skills and experiences that prove their ability to grow a company.
Ideally, you and/or your team members have direct experience in managing production companies. If so, highlight this experience and expertise. But also highlight any experience that you think will help your business succeed.
If your team is lacking, consider assembling an advisory board. An advisory board would include 2 to 8 individuals who would act as mentors to your business. They would help answer questions and provide strategic guidance. If needed, look for advisory board members with experience in managing a production company or successfully running a small filmmaking company.
Financial Plan
Your financial plan should include your 5-year financial statement broken out both monthly or quarterly for the first year and then annually. Your financial statements include your income statement, balance s heet, and cash flow statements.
Income Statement
An income statement is more commonly called a Profit and Loss statement or P&L. It shows your revenue and then subtracts your costs to show whether you turned a profit or not.
In developing your income statement, you need to devise assumptions. For example, will you book 5 films or videos per day, and/or offer production packages ? And will sales grow by 2% or 10% per year? As you can imagine, your choice of assumptions will greatly impact the financial forecasts for your business. As much as possible, conduct research to try to root your assumptions in reality.
Balance Sheets
Balance sheets show your assets and liabilities. While balance sheets can include much information, try to simplify them to the key items you need to know about. For instance, if you spend $50,000 on building out your production company, this will not give you immediate profits. Rather it is an asset that will hopefully help you generate profits for years to come. Likewise, if a lender writes you a check for $50,000, you don’t need to pay it back immediately. Rather, that is a liability you will pay back over time.
Cash Flow Statement
Your cash flow statement will help determine how much money you need to start or grow your business, and ensure you never run out of money. What most entrepreneurs and business owners don’t realize is that you can turn a profit but run out of money and go bankrupt.
When creating your Income Statement and Balance Sheets be sure to include several of the key costs needed in starting or growing a production company:
- Cost of equipment and production studio supplies
- Payroll or salaries paid to staff
- Business insurance
- Other start-up expenses (if you’re a new business) like legal expenses, permits, computer software, and equipment
Attach your full financial projections in the appendix of your plan along with any supporting documents that make your plan more compelling. For example, you might include your studio location lease or a list of production services you plan to offer.
Writing a business plan for your production company is a worthwhile endeavor. If you follow the template above, by the time you are done, you will truly be an expert. You will understand the production industry, your competition, and your customers. You will develop a marketing strategy and will understand what it takes to launch and grow a successful production company.
Production Company Business Plan FAQs
What is the easiest way to complete my production company business plan.
Growthink's Ultimate Business Plan Template allows you to quickly and easily write your production company business plan.
How Do You Start a Production Company Business?
Starting a production company business is easy with these 14 steps:
- Choose the Name for Your Production Company Business
- Create Your Production Company Business Plan
- Choose the Legal Structure for Your Production Company Business
- Secure Startup Funding for Your Production Company Business (If Needed)
- Secure a Location for Your Business
- Register Your Production Company Business with the IRS
- Open a Business Bank Account
- Get a Business Credit Card
- Get the Required Business Licenses and Permits
- Get Business Insurance for Your Production Company Business
- Buy or Lease the Right Production Company Business Equipment
- Develop Your Production Company Business Marketing Materials
- Purchase and Setup the Software Needed to Run Your Production Company Business
- Open for Business
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your Production Company business plan?
OR, Let Us Develop Your Plan For You
Since 1999, Growthink has developed business plans for thousands of companies who have gone on to achieve tremendous success. Click here to hire someone to write a business plan for you from Growthink’s team.
Other Helpful Business Plan Articles & Templates

This browser is no longer supported.
Upgrade to Microsoft Edge to take advantage of the latest features, security updates, and technical support.
Help organizations manage and optimize their plan to produce processes
- 2 contributors
Applies to: Dynamics 365 Finance, Dynamics 365 Guides, Dynamics 365 Human Resources, Dynamics 365 Project Operations, Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management, Dynamics 365 Business Central, Power Apps, Power BI, Power Automate
This article introduces the plan to produce end-to-end business process. It outlines how Microsoft Business Applications can help organizations manage and optimize their plan to produce processes.
Plan to produce overview
The term plan to produce is used to describe a collection of business processes that an organization implements to support the planning and execution of the production process. Planning refers to the definition of production strategies, reviewing the long term production plan, and building a production schedule. The production business process incorporates the activities before, during, and after the execution of the procedures that result from taking raw materials and creating sub-assemblies or finished goods.
The plan to produce process covers several different approaches to manufacturing. For example, discrete manufacturing, process or batch manufacturing, lean manufacturing, and job-shop manufacturing. These are all considered different modes of manufacturing, but the core concepts in the business process are largely the same.
The plan to produce process is highly interconnected to the other end to end business processes, such as forecast to plan , procure to pay, inventory to deliver, record to report, order to cash, and acquire to dispose . The upstream or downstream relationship of plan to produce to the other processes is highly dependent on the operational strategies of each organization. For example, plan to produce could be an upstream process of order to cash in a make-to-stock scenario, but would be a downstream process instead in a make to order scenario. Organizations also often use multiple different operational strategies when they offer different types of products. This choice is fully supported by Dynamics 365.
It is important to note that the inventory management processes related to plan to produce are not included in this process definition. They are located in the inventory to deliver process. Learn more at Inventory to deliver - introduction to the end-to-end business process .
It is important to note that the supply and demand planning process is part of the forecast to plan business process, and the planning in the plan to produce process begins with scheduling production. Learn more at Forecast to plan introduction .
The high-level strategy for plan to produce processes should be planned at the early phases of a larger business solution. The design and decisions made about this process have an impact on downstream processes including integrations, data that must be migrated, and so on. The production process is often considered business-critical scope for implementing a technology solution, but may sometimes be slated for later phases when a finance-first implementation strategy is chosen.
Every organization has variations to the plan to produce process. Here, we define the basic outline for any organization looking to implement a Microsoft technology solution to support the plan to produce process.
The plan to produce business process is key to any company that produces the product that they sell. A strong plan to produce process ensures that production runs efficiently within the capacity of materials and production resources to deliver products on time and at a minimized cost. Getting the plan to produce process right allows all other areas of the business to run smoothly and ultimately results in high customer satisfaction and brand loyalty.
Dynamics 365 includes many tools to support the execution and control of the plan to produce process. The core Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management tool tracks production data like bills of materials and routings, supports production scheduling and capacity planning, and aligns the production process with other areas of the business. Power Apps can be used to make custom, quick, low-code solutions to support some of the more unique needs in your production process. Power BI and Azure Data Lake together can provide real-time visibility into shopfloor data and metrics to ensure that operations are receiving valuable feedback to control the quality and process of production.
Stakeholders
The key stakeholders required to define the plan to produce business processes include:
Inventory stakeholders – examples: Warehouse manager, Transportation planner
Customer service stakeholders – examples: VP of Customer Service, Customer service director, Customer satisfaction manager, Call center manager
Planning stakeholders – examples: COO, VP of Operations, Operations manager, Planning manager
Procurement stakeholders – examples: Director of procurement, Buyer, Purchasing agent, Purchasing manager
Sales stakeholders – examples: VP of Sales, Sales director, General manager
Production stakeholders – examples: Production manager, Production scheduler
Engineering stakeholders - examples: Product owner, Engineering manager
Costing stakeholders - examples: Cost accountant, controller
Plan to produce benefits
When your organization plans to implement Microsoft Business Applications to assist with the plan to produce process, there are several benefits the solution can help provide. These key benefits should be used to determine if the solution is a good fit for your business and to drive the specific business requirements for implementing the solution. As a side effect, these benefits can be used to create a baseline for your goals and objectives for the project so that you can measure the success of implementing solutions to meet those business requirements.
Increase delivery date accuracy
Using Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management to track and control the plan to produce process allows the business to accurately estimate customer delivery dates. The sales order entry process can reference current production operations and material and resource capacity to systemically calculate a realistic date when a customer order can be shipped, which ultimately increases customer satisfaction and improves the order on time and in full (OTIF) percentage.
Improve insight into current production operations
Providing accurate status updates is as important as providing realistic estimates to customers. With the full operations traceability provided in Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management, production supervisors and customer service representatives can quickly view the current status of shop floor operations to advise customers and internal stakeholders of order progress. Visibility into the procurement and planning operations can also provide production managers the tools they need to adjust the schedule based on supply chain disruptions or other variations.
Quickly and efficiently scale operations
The organized and controlled approach to production data management in Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management allows organizations to efficiently roll out new products and locations by using the engineering change control tools and product templates to streamline processes. The system also supports capturing standard sets of production instructions and sharing with operators either via a printed job sheet or through the shop floor interface.
Enhance control of production costs and decrease cost variances
Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management supports tracking production cost estimates and actuals for materials, labor, and overhead costs. Knowing the true cost of conversion in your production process helps ensure that you're properly setting product prices, and insights into cost variance can help identify opportunities for improving the production process.
Optimize production schedule
By modeling your production process in Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management, you can use tools like sequencing rules, substitution planning, and resource load allocation to create a production schedule that is optimized to reduce changeovers, meet operational requirements, and still supports on time order delivery.
Improve quality control
Dynamics 365 enables manufacturers to track quality metrics throughout the production process, from raw materials to finished goods, ensuring consistent quality and reducing the risk of defects. It provides support for standardization of testing process and automating pass/fail assessments. It also ties in to the inventory management of quarantined materials and handling non-conformances and corrective actions.
If you want to implement Dynamics 365 solutions to assist with your plan to produce business processes, you can use the following resources and steps to learn more.
Define the goals and objectives of implementing a plan to produce technology solution. Learn more at Implementation strategy .
Define the business process scope of your project. Learn more at Process-focused solution .
Request a demo or get a free trial of Dynamics 365 solutions for the plan to produce business process. Learn more at Request a demo .
Learn more about the Power Platform products at Business Application Platform
Get an overview of the plan to produce process. Learn more at Plan to produce overview .
If you want to implement Dynamics 365 solutions to help with your track production costs business processes, use the following resources and steps to learn more.
Define product costing overview
Define production strategies
Plan production operations
Run production operations overview
Outsource production operations
Control production quality
Track production costs
Return to the overview of business process areas at Plan to produce business process areas .
Related resources
You can use the following resources to learn more about the plan to produce process in Dynamics 365.
TechTalk series on the plan to produce process: Production control in Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management
TechTalk on Manufacturing Accounting: Part 4: Manufacturing Accounting in Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management
TechTalk on Production Variance Analysis: Part 7: Production Variance Analysis in Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management
Product documentation: Production process overview - Supply Chain Management
Product training: Get started with production control in Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management
Related product certification: Exam MB-335: Microsoft Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management Functional Consultant Expert (beta)
Dynamics 365 Community Forum: Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management Forum - Production Control
Find definitions of terminology used in content for plan to produce in the Glossary: Dynamics 365 business processes article
Was this page helpful?
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback .
Submit and view feedback for
Additional resources
- Starting a Business
- Growing a Business
- Small Business Guide
- Business News
- Science & Technology
- Money & Finance
- For Subscribers
- Write for Entrepreneur
- Entrepreneur Store
- United States
- Asia Pacific
- Middle East
- South Africa
Copyright © 2024 Entrepreneur Media, LLC All rights reserved. Entrepreneur® and its related marks are registered trademarks of Entrepreneur Media LLC
An Introduction to Business Plans Why is a business plan so vital to the health of your business? Read the first section of our tutorial on How to Build a Business Plan to find out.
A business plan is a written description of your business's future. That's all there is to it--a document that desribes what you plan to do and how you plan to do it. If you jot down a paragraph on the back of an envelope describing your business strategy, you've written a plan, or at least the germ of a plan.
Business plans can help perform a number of tasks for those who write and read them. They're used by investment-seeking entrepreneurs to convey their vision to potential investors. They may also be used by firms that are trying to attract key employees, prospect for new business, deal with suppliers or simply to understand how to manage their companies better.
So what's included in a business plan, and how do you put one together? Simply stated, a business plan conveys your business goals, the strategies you'll use to meet them, potential problems that may confront your business and ways to solve them, the organizational structure of your business (including titles and responsibilities), and finally, the amount of capital required to finance your venture and keep it going until it breaks even.
Sound impressive? It can be, if put together properly. A good business plan follows generally accepted guidelines for both form and content. There are three primary parts to a business plan:
- The first is the business concept , where you discuss the industry, your business structure, your particular product or service, and how you plan to make your business a success.
- The second is the marketplace section , in which you describe and analyze potential customers: who and where they are, what makes them buy and so on. Here, you also describe the competition and how you'll position yourself to beat it.
- Finally, the financial section contains your income and cash flow statement, balance sheet and other financial ratios, such as break-even analyses. This part may require help from your accountant and a good spreadsheet software program.
Breaking these three major sections down even further, a business plan consists of seven key components:
- Executive summary
- Business description
- Market strategies
- Competitive analysis
- Design and development plan
- Operations and management plan
- Financial factors
In addition to these sections, a business plan should also have a cover, title page and table of contents.
How Long Should Your Business Plan Be? Depending on what you're using it for, a useful business plan can be any length, from a scrawl on the back of an envelope to, in the case of an especially detailed plan describing a complex enterprise, more than 100 pages. A typical business plan runs 15 to 20 pages, but there's room for wide variation from that norm. Much will depend on the nature of your business. If you have a simple concept, you may be able to express it in very few words. On the other hand, if you're proposing a new kind of business or even a new industry, it may require quite a bit of explanation to get the message across.
The purpose of your plan also determines its length. If you want to use your plan to seek millions of dollars in seed capital to start a risky venture, you may have to do a lot of explaining and convincing. If you're just going to use your plan for internal purposes to manage an ongoing business, a much more abbreviated version should be fine.
Who Needs a Business Plan?
About the only person who doesn't need a business plan is one who's not going into business. You don't need a plan to start a hobby or to moonlight from your regular job. But anybody beginning or extending a venture that will consume significant resources of money, energy or time, and that is expected to return a profit, should take the time to draft some kind of plan.
Startups. The classic business plan writer is an entrepreneur seeking funds to help start a new venture. Many, many great companies had their starts on paper, in the form of a plan that was used to convince investors to put up the capital necessary to get them under way.
Most books on business planning seem to be aimed at these startup business owners. There's one good reason for that: As the least experienced of the potential plan writers, they're probably most appreciative of the guidance. However, it's a mistake to think that only cash-starved startups need business plans. Business owners find plans useful at all stages of their companies' existence, whether they're seeking financing or trying to figure out how to invest a surplus.
Established firms seeking help. Not all business plans are written by starry-eyed entrepreneurs. Many are written by and for companies that are long past the startup stage. WalkerGroup/Designs, for instance, was already well-established as a designer of stores for major retailers when founder Ken Walker got the idea of trademarking and licensing to apparel makers and others the symbols 01-01-00 as a sort of numeric shorthand for the approaching millennium. Before beginning the arduous and costly task of trademarking it worldwide, Walker used a business plan complete with sales forecasts to convince big retailers it would be a good idea to promise to carry the 01-01-00 goods. It helped make the new venture a winner long before the big day arrived. "As a result of the retail support up front," Walker says, "we had over 45 licensees running the gamut of product lines almost from the beginning."
These middle-stage enterprises may draft plans to help them find funding for growth just as the startups do, although the amounts they seek may be larger and the investors more willing. They may feel the need for a written plan to help manage an already rapidly growing business. Or a plan may be seen as a valuable tool to be used to convey the mission and prospects of the business to customers, suppliers or others.
Plan an Updating Checklist Here are seven reasons to think about updating your business plan. If even just one applies to you, it's time for an update.
- A new financial period is about to begin. You may update your plan annually, quarterly or even monthly if your industry is a fast-changing one.
- You need financing , or additional financing. Lenders and other financiers need an updated plan to help them make financing decisions.
- There's been a significant market change . Shifting client tastes, consolidation trends among customers and altered regulatory climates can trigger a need for plan updates.
- Your firm develops or is about to develop a new product , technology , service or skill. If your business has changed a lot since you wrote your plan the first time around, it's time for an update.
- You have had a change in management . New managers should get fresh information about your business and your goals.
- Your company has crossed a threshold, such as moving out of your home office, crossing the $1 million sales mark or employing your 100th employee .
- Your old plan doesn't seem to reflect reality any more. Maybe you did a poor job last time; maybe things have just changed faster than you expected. But if your plan seems irrelevant, redo it.
Finding the Right Plan for You
Business plans tend to have a lot of elements in common, like cash flow projections and marketing plans. And many of them share certain objectives as well, such as raising money or persuading a partner to join the firm. But business plans are not all the same any more than all businesses are.
Depending on your business and what you intend to use your plan for, you may need a very different type of business plan from another entrepreneur. Plans differ widely in their length, their appearance, the detail of their contents, and the varying emphases they place on different aspects of the business.
The reason that plan selection is so important is that it has a powerful effect on the overall impact of your plan. You want your plan to present you and your business in the best, most accurate light. That's true no matter what you intend to use your plan for, whether it's destined for presentation at a venture capital conference, or will never leave your own office or be seen outside internal strategy sessions.
When you select clothing for an important occasion, odds are you try to pick items that will play up your best features. Think about your plan the same way. You want to reveal any positives that your business may have and make sure they receive due consideration.
Types of Plans Business plans can be divided roughly into four separate types. There are very short plans, or miniplans. There are working plans, presentation plans and even electronic plans. They require very different amounts of labor and not always with proportionately different results. That is to say, a more elaborate plan is not guaranteed to be superior to an abbreviated one, depending on what you want to use it for.
- The Miniplan. A miniplan may consist of one to 10 pages and should include at least cursory attention to such key matters as business concept, financing needs, marketing plan and financial statements, especially cash flow, income projection and balance sheet. It's a great way to quickly test a business concept or measure the interest of a potential partner or minor investor. It can also serve as a valuable prelude to a full-length plan later on.
Be careful about misusing a miniplan. It's not intended to substitute for a full-length plan. If you send a miniplan to an investor who's looking for a comprehensive one, you're only going to look foolish.
- The Working Plan. A working plan is a tool to be used to operate your business. It has to be long on detail but may be short on presentation. As with a miniplan, you can probably afford a somewhat higher degree of candor and informality when preparing a working plan.
A plan intended strictly for internal use may also omit some elements that would be important in one aimed at someone outside the firm. You probably don't need to include an appendix with resumes of key executives, for example. Nor would a working plan especially benefit from, say, product photos.
Fit and finish are liable to be quite different in a working plan. It's not essential that a working plan be printed on high-quality paper and enclosed in a fancy binder. An old three-ring binder with "Plan" scrawled across it with a felt-tip marker will serve quite well.
Internal consistency of facts and figures is just as crucial with a working plan as with one aimed at outsiders. You don't have to be as careful, however, about such things as typos in the text, perfectly conforming to business style, being consistent with date formats and so on. This document is like an old pair of khakis you wear into the office on Saturdays or that one ancient delivery truck that never seems to break down. It's there to be used, not admired.
- The Presentation Plan. If you take a working plan, with its low stress on cosmetics and impression, and twist the knob to boost the amount of attention paid to its looks, you'll wind up with a presentation plan. This plan is suitable for showing to bankers, investors and others outside the company.
Almost all the information in a presentation plan is going to be the same as your working plan, although it may be styled somewhat differently. For instance, you should use standard business vocabulary, omitting the informal jargon, slang and shorthand that's so useful in the workplace and is appropriate in a working plan. Remember, these readers won't be familiar with your operation. Unlike the working plan, this plan isn't being used as a reminder but as an introduction.
You'll also have to include some added elements. Among investors' requirements for due diligence is information on all competitive threats and risks. Even if you consider some of only peripheral significance, you need to address these concerns by providing the information.
The big difference between the presentation and working plans is in the details of appearance and polish. A working plan may be run off on the office printer and stapled together at one corner. A presentation plan should be printed by a high-quality printer, probably using color. It must be bound expertly into a booklet that is durable and easy to read. It should include graphics such as charts, graphs, tables and illustrations.
It's essential that a presentation plan be accurate and internally consistent. A mistake here could be construed as a misrepresentation by an unsympathetic outsider. At best, it will make you look less than careful. If the plan's summary describes a need for $40,000 in financing, but the cash flow projection shows $50,000 in financing coming in during the first year, you might think, "Oops! Forgot to update that summary to show the new numbers." The investor you're asking to pony up the cash, however, is unlikely to be so charitable.
- The Electronic Plan. The majority of business plans are composed on a computer of some kind, then printed out and presented in hard copy. But more and more business information that once was transferred between parties only on paper is now sent electronically. So you may find it appropriate to have an electronic version of your plan available. An electronic plan can be handy for presentations to a group using a computer-driven overhead projector, for example, or for satisfying the demands of a discriminating investor who wants to be able to delve deeply into the underpinnings of complex spreadsheets.
Source: The Small Business Encyclopedia , Business Plans Made Easy , Start Your Own Business and Entrepreneur magazine .
Continue on to the next section of our Business Plan How-To >> Plan Your Plan
Want to be an Entrepreneur Leadership Network contributor? Apply now to join.
Editor's Pick Red Arrow
- Lock Want to Start a Simple Business That Helps the Planet? After 'One Night's Worth of Research,' He Started an Eco-Friendly Gig and Now Makes $200,000 a Year
- I've Negotiated High-Pressure, Multi-Million-Dollar Deals for Artists Like Bruno Mars and Enrique Iglesias — Here's the Strategy That Always Helps Me Win
- Lock This Toxic Money Habit Is Becoming More Common — If You've Picked It Up, Your Finances Are at Serious Risk , Expert Warns
- 'This Year Almost Broke Me': Tom Schwartz Reveals 'Scandoval' Almost Shut Down His Restaurant After Losing 80% of His Business
- 'Not What Anybody Signed Up For': A Legal Expert Weighs in on the Labor Rule That Could Destroy Franchising
- Lock Anyone Can Try the Simple Strategy That One Billionaire Investor Used to Make His First Million Dollars Tax-Free
Most Popular Red Arrow
These coworkers-turned-friends started a side hustle on amazon — now it's a 'full hustle' earning over $20 million a year: 'jump in with both feet'.
Achal Patel and Russell Gong met at a large consulting firm and "bonded over a shared vision to create a mission-led company."
These Are the 10 Most Profitable Cities for Airbnb Hosts, According to a New Report
Here's where Airbnb property owners and hosts are making the most money.
An Iconic Las Vegas Casino Is Shuttering This Summer After 34 Years
The Mirage will close on July 17.
How to Turn Your Hobby Into a Successful Business
A hobby, interest or charity project can turn into a money-making business if you know the right steps to take.
Want to Be More Productive? Here's How Google Executives Structure Their Schedules
These five tactics from inside Google will help you focus and protect your time.
This Couple Turned Their Startup Into a $150 Million Food Delivery Company. Here's What They Did Early On to Make It Happen.
Selling only online to your customers has many perks. But the founders of Little Spoon want you to know four things if you want to see accelerated growth.
Successfully copied link
How to describe your product and service in a business plan like a pro
It’s deceiving.
You’d think that this part of a business plan does exactly what it says on the tin–describe your product & service offering– right ?
And yes, you are partially right.
But there’s a very specific way in which this description should be written to make sure that your business has the best chance of succeeding – in real life and under the eagle eye of a potential backer (if you’re preparing a business plan for external financing purposes).
Keep reading to find out the secret sauce to writing a winning product and service description:
WHAT is the Product and Service Description in a Business Plan?
This business plan section is also known as:
- Product and/or Service Overview
HOW Do You Write a Product and Service Description in a Business Plan?
So, what should a good product/service overview contain?
Here are some items to consider including into this section:
1. Portfolio:
The range of products and/or services that a business offers to potential and current customers.
2. Features and benefits (value proposition):
Explain what the product/service does and how it works.
3. Problem and solution (value proposition cont.):
The problem(s) the product or service solves. Every business needs to solve a problem that its customers face. Explain what the problem is and how the product or service solves it.
4. Innovation:
If the company is doing something new and different, explain why the world needs the innovation.
5. Proprietary advantages:
Any proprietary features that contribute to a competitive advantage. This could include: intellectual property (e.g., copyright, trademark, patent filings, trade secret), exclusive agreements with suppliers or vendors, exclusive licenses (e.g., for a product, service or technology), company’s own research and development activities.
6. Development stage:
Current stage of development of the product / service (e.g., idea, development, testing, prototype, already on the market).
7. Product life-cycle:
Estimate the life span of the product or service.
Specify whether the product or service under consideration is a short-lived fad or has a long-term potential.
8. Future:
Mention plans for changes and new additions to the current portfolio of products / services.
Describe any plans to move into new markets in the future (e.g., serving different types or sizes of customers, industries, geographic areas).
Make your best guess at when the business will be ready to address these markets and what it needs to do first to be ready.
9. Limitations:
If applicable, explain any risks or limitations associated with the product (e.g., liability issues like guarantees or returns), along with any legal advice received regarding these issues.
10. Visual aids:
Use photos, images, diagrams and other graphics to help the reader visualize and learn about the products / services.
If the business is tackling several distinct problems through different products / services, describe the solutions individually .
However, for a large line of products / services, there is no need to list each one, just identifying the general categories will suffice.
How LONG Is the Product and Service Chapter of a Business Plan?
This part of a business plan can be very short, just a couple of paragraphs, or it can spread over multiple pages, depending on how many products/services you offer and how much explanation they require.
If your products or services are particularly complex , technical , innovative , or proprietary , you will want to provide more information and spend considerable time describing them.
This is especially true if you are seeking funding for a new product or service, particularly one that is not immediately understandable to the business plan readers, and if potential funders are likely to be motivated by the specifics.
In any case, when describing a product or service, provide just enough information to paint a clear picture of what it is and does . A brief explanation of what you will be making, selling or doing is appropriate here.
Excessive detail makes this section cumbersome for a reader to wade through. Reserve detailed descriptions (e.g., production processes) for the Appendix.
In any case, it is a good idea to first summarize the value proposition of each product or service into a one short sentence, and only then continue with a more detailed description of the product or service.
If any images or graphics are available that would contribute to the understanding of the product or service, the writers of a business plan should use them.
Otherwise, include any product or service details , such as technical specifications, drawings, photos, patent documents and other support information, in the Appendix section of the business plan document.
TOP 4 TIPS for Writing a Product and Service Overview
Tip #1: features v. benefits.
Don’t just list the features of the product / service.
Instead, describe the specific benefits it will offer to customers – from their perspective.
Make it clear what your customers will gain through buying your product or service. Include information about the specific benefits of your product or service – from your customers’ perspective.
Features are not the same thing as benefits. And you need to understand both.
Confused? Let’s clarify:
What Is the Difference Between Features and Benefits?
Tip #2: problem v. solution.
If at all possible, present the information in the Problem >> Solution format.
Start by describing the key problem that your customers have, immediately followed by the solution with which you will address this need for your target market.
Tip #3: Competitive Advantage
You should also comment on your ability to meet consumers’ key problems or unmet needs in a way that brings your product or service advantages over the competition.
For example:
- If you have a common business, such as a restaurant:
Explain why your customers need your particular restaurant. Do you offer lower prices? More convenient hours? A better location? A different concept, such as a vegan ice-cream pop up store? A specialty that is not otherwise available in your area, such as a Peruvian ceviche or Hungarian goulash?
- If your company is doing something new and innovative :
What is it about the existing solutions that is subpar? Maybe you are improving on a mediocre product category, such as creating better medical uniforms for healthcare workers (e.g., more flattering cut, trendy designs, sustainable materials). Or perhaps your new blockchain solution has the potential to entirely eliminate the middle-men in an entire industry.
Although the subject of competitive advantage regarding the business as a whole will be fully explored in the Market and Competitor Analysis part of a business plan, it is advisable to touch on it here also – in the context of the company’s products and service.
Tip #4: Validating the Problem and Solution
Speaking of which, when you are doing market research and analysis for your business plan, remember to validate the problem and solution your product or service is addressing.
There is a plethora of minor issues out there that people are perfectly fine with just tolerating. To build a solid business, though, you need a problem that a sufficient number of people are motivated to solve. That is, that they recognize it as a problem that’s worth paying you to solve. Even if they didn’t realize it was solvable until they were presented with your solution.
So, how do you get evidence that prospects are willing to pay for your solution?
Validation of Problem
Describe what you’ve done so far to confirm that the problem you are focused on is a real problem for your customers.
- Existing Business:
For an established business, this is probably just a matter of recapping your success in the marketplace. Your customers have already voted with their wallets.
- New Business:
For a startup, it is important to survey and have conversations with as many potential customers as possible about where they are having problems, how they solve them today, and validate that they are interested enough in addressing those problems to pay for a good solution.
Validation of Solution
Describe how you have tested your ideas with existing or potential customers to confirm that there is a good market for the products or services you plan to offer. Summarize the positive customer feedback or market traction that you have achieved with your solution so far.
For an established business, the answers probably lie in your paying customer base – their existence itself, combined with their repeat business, word-of-mouth referrals, follow-up customer surveys, and other indicators of customer satisfaction.
For a new business, you can start validating your solution immediately by trying it out with potential customers, even informally or at no charge, to get their opinion. If your product or service does not exist yet, talk to prospects about what you plan to offer and measure their feedback.
In summary, this section should answer the million dollar question:
What makes you think that people will buy, be satisfied with, and recommend your products or services?
Related Questions
What are products and services.
Products and services are items that businesses offer for sale to a market. While services are intangible, meaning that they do not exist in a physical form, products are of tangible nature, in other words – you can touch them.
What is a Product Line?
Product line is a group of related products that are all produced or sold by one entity and typically marketed under one brand name.
What is a Service Line?
Service line is a group of related services that are all produced or sold by one entity and typically marketed under one brand name.
Sign up for our Newsletter
Get more articles just like this straight into your mailbox.
Related Posts
Recent Posts
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
4 Common Types of Team Conflict — and How to Resolve Them
- Randall S. Peterson,
- Priti Pradhan Shah,
- Amanda J. Ferguson,
- Stephen L. Jones

Advice backed by three decades of research into thousands of team conflicts around the world.
Managers spend 20% of their time on average managing team conflict. Over the past three decades, the authors have studied thousands of team conflicts around the world and have identified four common patterns of team conflict. The first occurs when conflict revolves around a single member of a team (20-25% of team conflicts). The second is when two members of a team disagree (the most common team conflict at 35%). The third is when two subgroups in a team are at odds (20-25%). The fourth is when all members of a team are disagreeing in a whole-team conflict (less than 15%). The authors suggest strategies to tailor a conflict resolution approach for each type, so that managers can address conflict as close to its origin as possible.
If you have ever managed a team or worked on one, you know that conflict within a team is as inevitable as it is distracting. Many managers avoid dealing with conflict in their team where possible, hoping reasonable people can work it out. Despite this, research shows that managers spend upwards of 20% of their time on average managing conflict.
- Randall S. Peterson is the academic director of the Leadership Institute and a professor of organizational behavior at London Business School. He teaches leadership on the School’s Senior Executive and Accelerated Development Program.
- PS Priti Pradhan Shah is a professor in the Department of Work and Organization at the Carlson School of Management at the University of Minnesota. She teaches negotiation in the School’s Executive Education and MBA Programs.
- AF Amanda J. Ferguson is an associate professor of Management at Northern Illinois University. She teaches Organizational Behavior and Leading Teams in the School’s MBA programs.
- SJ Stephen L. Jones is an associate professor of Management at the University of Washington Bothell. He teaches Organizational and Strategic Management at the MBA level.
Partner Center
Japan and ASEAN plan joint strategy on auto production, Nikkei reports
- Medium Text

- Company BYD Co Ltd Follow
- Company Honda Motor Co Ltd Follow
Sign up here.
Reporting by Ayushman Ojha; Editing by Leslie Adler
Our Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. New Tab , opens new tab

Business Chevron

Dollar steady; ether fuels crypto rally
The dollar was firm on Tuesday while the yen struggled on the weaker side of the 156 level, though trade was mostly rangebound as investors generally stuck to their views of the expected timing and extent of Federal Reserve rate cuts this year.


Cost of living help and a future made in Australia
Investing in a future made in australia.
Investing in a Future Made in Australia and the skills to make it a reality
Print or save page
On this page
Attracting investment in key industries
Making Australians the beneficiaries of change
A Future Made in Australia is about creating new jobs and opportunities for every part of our country by maximising the economic and industrial benefits of the move to net zero and securing Australia’s place in a changing global economic and strategic landscape.
The Government’s $22.7 billion Future Made in Australia package will help facilitate the private sector investment required for Australia to be an indispensable part of the global economy.
For more information refer to the Future Made in Australia fact sheet [PDF 438KB]
Better deploying capital in priority areas
The Future Made in Australia package will realise Australia’s potential to become a renewable energy superpower, value‑add to our resources and strengthen economic security by better attracting and enabling investment in priority areas. The Government will create a Future Made in Australia Act and establish a National Interest Framework that identifies priority industries and ensures investments associated with them are responsible and targeted.
The Framework will have a focus on industries that contribute to the net zero transformation where Australia has a comparative advantage, and where Australia has national interest imperatives related to economic resilience and security.
Strengthening and streamlining approvals
This Budget provides a faster pathway to better decisions on environmental, energy, planning, cultural heritage and foreign investment approvals.
This includes:
- $134.2 million to better prioritise approvals for renewable energy projects of national significance, and support faster decisions on environment, cultural heritage and planning approvals.
- Working with the states and territories through the Energy and Climate Change Ministerial Council to accelerate electricity grid connections.
- $20.7 million to improve engagement with communities impacted by the energy transition and accelerate the delivery of key energy projects.
- $15.7 million to strengthen scrutiny of high‑risk foreign investment proposals, enhance monitoring and enforcement activities and support faster decisions.
The Government will also encourage foreign investment by providing refunds of 75 per cent of application fees for unsuccessful competitive bids.
Promoting sustainable finance
The Government is committing $17.3 million to mobilise private sector investment in sustainable activities. This includes extending Australia’s sustainable finance taxonomy to the agriculture sector and developing a labelling regime for financial products marketed as sustainable.
The Government will also examine opportunities to improve data quality and provide $1.3 million to develop and issue guidance for best practice transition plans.
Making Australia a renewable energy superpower
Powering australia with cheaper, cleaner, more reliable energy.
Australia’s potential to produce abundant renewable energy is a powerful source of comparative advantage. To realise this, the Government is unlocking more than $65 billion of investment in renewable capacity through the Capacity Investment Scheme by 2030.
This Budget helps Australians benefit from cheaper, cleaner energy sooner by investing $27.7 million to integrate consumer energy resources like batteries and solar into the grid.
The New Vehicle Efficiency Standard will save Australians around $95 billion at the bowser by 2050 and reduce transport emissions.
Unlocking investment in net zero industries and jobs
This Budget accelerates growth of new industries by establishing the $1.7 billion Future Made in Australia Innovation Fund and delivering a 10‑year extension of funding to the Australian Renewable Energy Agency. It also delivers the $44.4 million Energy Industry Jobs Plan and $134.2 million for skills and employment support in key regions.
The Future Made in Australia package establishes time‑limited incentives to invest in new industries. The Hydrogen Production Tax Incentive will make Australia’s pipeline of hydrogen projects commercial sooner, at an estimated cost of $6.7 billion over the decade. This Budget also expands the Hydrogen Headstart program by $1.3 billion.
Boosting demand for Australia’s green exports
The Government is making it easier for businesses and trading partners to source low‑emissions products by building better markets and product standards for green products.
This Budget provides $32.2 million to fast‑track the initial phase of the Guarantee of Origin scheme, focused on renewable hydrogen, and bring forward the expansion of the scheme to accredit the emissions content of green metals and low‑carbon liquid fuels. The Government is also working closely with trading partners to identify opportunities to drive greater supply chain transparency and better market recognition of high environmental, social and governance standards in the critical minerals sector.
Realising the opportunities of the net zero transformation
Australia is committed to reaching net zero greenhouse gas emissions by 2050 and is developing six sector plans covering:
- electricity and energy
- agriculture and land
- the built environment.
This Budget continues investment in effective emissions abatement, including through $63.8 million to support emissions reduction efforts in the agriculture and land sector.
The Government is also investing $399 million to establish the Net Zero Economy Authority and support the economy‑wide net zero transformation. This Budget also invests an additional $48 million in reforms to the Australian Carbon Credit Unit scheme and $20.7 million to improve community engagement.
Strengthening resources and economic security
Backing a strong resources sector.
The Government is investing $8.8 billion over the decade to add more value to our resources and strengthen critical minerals supply chains. This Budget establishes a production tax incentive for processing and refining critical minerals at an estimated cost of $7 billion over the decade. It commits up to $1.2 billion in strategic critical minerals projects through the Critical Minerals Facility and the Northern Australia Infrastructure Facility, and pre‑feasibility studies for common user precincts.
This is in addition to $566.1 million to support Geoscience Australia to map all of Australia’s critical minerals, strategic materials, groundwater and other resources essential for the transition to net zero.
Manufacturing clean energy technologies
The Government is committing $1.5 billion to manufacturing clean energy technologies, including the $1 billion Solar Sunshot and $523.2 million Battery Breakthrough Initiative. These investments will be delivered by ARENA.
Strengthening supply chains
To support the delivery of the 82 per cent renewable energy target, the Government has formed the National Renewable Energy Supply Chain Action Plan with states and territories. The Government will invest an additional $14.3 million working with trade partners to support global rules on unfair trade practices and to negotiate benchmarks for trade in high quality critical minerals.
Digital, science and innovation
Investing in new technologies and capabilities.
The Government is investing $466.4 million to partner with PsiQuantum and the Queensland Government to build the world’s first commercial‑scale quantum computer in Brisbane.
The Government will undertake a strategic examination of Australia’s research and development (R&D) system with $38.2 million invested in a range of science, technology, engineering, and maths programs.
The Government is providing $448.7 million to partner with the United States in the Landsat Next satellite program to provide access to critical data to monitor the earth’s climate, agricultural production, and natural disasters.
Modernising and digitising industries
This Budget commits $288.1 million to support Australia’s Digital ID System. A National Robotics Strategy will also be released to promote the responsible production and adoption of robotics and automation technologies for advanced manufacturing in Australia.
Reforming tertiary education
The Government is committing $1.6 billion over 5 years, and an additional $2.7 billion from 2028–29 to 2034–35 to reform the tertiary education system and deliver Australia's future workforce.
This includes $1.1 billion for reforms to university funding and tertiary system governance.
Over $500 million will be provided for skills and training in priority industries and to support women’s participation in these sectors.
The Government will set a tertiary attainment target of 80 per cent of the working‑age population by 2050.
Supporting students on placements
The Government will establish Commonwealth Prac Payments (CPP) for students undertaking mandatory placements. From 1 July 2025, the payment will provide more than 73,000 eligible students, including teachers, nurses, midwives and social workers with $319.50 per week during their placements.
Felicity is a full‑time student receiving Youth Allowance, living by herself. She is studying a Bachelor of Nursing and must stop paid work during her mandatory prac placement. During her prac, Felicity receives $712.05 per week from the Government including: $319.50 of CPP, $285.55 of Youth Allowance (YA), $103.50 of Commonwealth Rent Assistance (CRA) and $3.50 of Energy Supplement.
Felicity receives $351.55 a week more than she would have in 2023 before indexation and the changes to YA, CRA and CPP in the current and 2023–24 Budget

Broadening access to university
From January 2026, needs‑based funding will provide per student funding contributions for under‑represented students. The Government will also provide $350.3 million to fully fund university enabling courses and increase pathways for prospective students to university.
Skills pipeline for priority industries
Skills and training for Future Made in Australia industries
The Government will expand eligibility to the New Energy Apprenticeships Program to include work in the clean energy sector, including in construction and advanced manufacturing. This will provide access to $10,000 incentive payments and support our target of 10,000 new energy apprentices.
The Government will commit $30 million to turbocharge the VET teaching workforce for clean energy courses and $50 million to upgrade and expand clean energy training facilities.
The Government will invest $55.6 million to establish the Building Women’s Careers program to support women’s participation in key industries including clean energy and advanced manufacturing.
Supporting apprentices and building the construction workforce
The $5,000 support payments to apprentices in priority occupations will be maintained for another 12 months to 1 July 2025, up from $3,000 in the absence of any changes. Employers of these apprentices will receive a $5,000 hiring incentive, up from $4,000 in the absence of changes. This will provide certainty to apprentices while the Strategic Review of the Apprenticeship Incentive System is underway.
The Government will also invest $88.8 million to deliver 20,000 new fee‑free TAFE places including pre‑apprenticeships in courses relevant to the construction sector. The Government will provide $1.8 million to deliver streamlined skills assessments for around 1,900 migrants from comparable countries to work in Australia’s housing construction industry.
Strengthening our defence industry capability
An integrated and focused approach to defending Australia
The Government is investing an additional $50.3 billion over ten years to implement the 2024 National Defence Strategy to meet Australia’s strategic needs.
Overall funding for Defence will reach $765 billion over the decade. Defence’s Integrated Investment Program has been rebuilt to create a focused Australian Defence Force, accelerate delivery of priority capabilities, and provide certainty to grow Australia’s defence industry. This includes funding for the Royal Australian Navy’s surface combatant fleet and establishing a guided weapons and explosive ordnance manufacturing capability earlier.
The Government is reforming Defence’s budget to support the National Defence Strategy and delivery of priority capabilities.
Developing defence industry and skills
Industry development grants funding of $165.7 million will also help businesses to scale up and deliver the Sovereign Defence Industrial Priorities, which include continuous naval shipbuilding and sustainment, and development and integration of autonomous systems.
The Government is providing $101.8 million to attract and retain the skilled industrial workforce to support Australian shipbuilding and delivery of conventionally armed, nuclear powered submarines. This includes a pilot apprenticeship program in shipbuilding trades and technologies.
Investing in civil maritime capabilities
The Government is providing $123.8 million to maintain and enhance civil maritime security capabilities. This includes $71.2 million to increase the Australian Border Force’s on‑water response and aerial surveillance capabilities.
Securing Australia’s place in the world
Strengthening relationships and simplifying trade
A stable, prosperous and resilient Pacific region
The Government is delivering over $2 billion in development assistance to the Pacific in 2024–25. This includes the Australia‑Tuvalu Falepili Union.
Investing in our relationship with Southeast Asia
Following the launch of Australia’s Southeast Asia Economic Strategy to 2040, the Government is committing $505.9 million to deepen ties with the region.
Australia recently celebrated 50 years of partnership with the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN). At the ASEAN‑Australia Special Summit, the Government announced a range of new and expanded initiatives, including a $2 billion Southeast Asia Investment Financing Facility to boost Australian trade and investment.
Simplifying trade
The Government will abolish 457 nuisance tariffs from 1 July 2024, streamlining $8.5 billion in annual trade and eliminating tariffs on goods such as toothbrushes, fridges, dishwashers, clothing and sanitary products.
The Government will provide $29.9 million to coordinate trade simplification and deliver the Digital Trade Accelerator program, and $10.9 million to enhance the Go Global Toolkit to support exporters.
The Government is expanding the Australia‑India Business Exchange, diversifying trade and helping more Australian businesses build commercial ties with India and across South Asia. There will be $2 million to support Australian agricultural exporters entering the Chinese markets.
Support for small businesses
Helping small businesses
This Budget’s Small Business Statement reaffirms the Government’s commitment to deliver a better deal for small businesses, with $641.4 million in targeted support.
For more information refer to the small business fact sheet [PDF 0.98MB]
Improving cash flow
The Government is providing $290 million to extend the $20,000 instant asset write‑off for 12 months. There will be $25.3 million to improve payment times to small businesses and $23.3 million to increase eInvoicing adoption.
Easing cost pressures and reducing the administrative burden
This Budget provides $3.5 billion of energy bill relief, including rebates of $325 to around one million small businesses.
The Government is reducing the administrative burden for small business by abolishing 457 nuisance tariffs and delivering $10 million to provide additional support for small business employers administering the Paid Parental Leave scheme.
Supporting confidence and resilience in the small business sector
This Budget invests a further $10.8 million in tailored, free and confidential financial and mental wellbeing supports for small business owners.
The Government is providing $20.5 million to the Fair Work Ombudsman to help small businesses understand and comply with recent workplace relations changes.
There will be $3 million to implement the Government’s response to the Review of the Franchising Code of Conduct, including remaking and enhancing the Code, and an additional $2.6 million to support more small businesses through alternative dispute resolution.
A more resilient Australia
Preparing for the future
The Government is preparing Australia for future droughts and heightened risk of natural disasters.
Disaster resilience and preparedness
The Government will provide $138.7 million to improve Australia’s response and resilience to natural hazards and disasters. Support includes: funding for the National Emergency Management Agency to supply communities with vital goods, equipment, and temporary accommodation during an emergency, aerial firefighting capability, and mental health support. This is in addition to the $11.4 billion previously committed for Disaster Recovery Funding Arrangements for the states and territories.
The Government is establishing a pilot program for Australia’s Strategic Fleet. These vessels will improve Australia’s capacity to respond and support communities and supply chains during crises.
Preparing for drought and climate change
This Budget provides $174.6 million from the National Water Grid Fund to deliver new water infrastructure projects that will enhance water security, boost agricultural production and help drought proof regional communities.
The Government will provide $519.1 million from its Future Drought Fund to help farmers and rural communities manage the impacts of climate change and prepare for future droughts.

This investment will build the drought resilience of more farmers like Victorian cropper Ed Rickard.
The Fund supported Ed in developing a better farm business plan, which identified his need for weather stations and soil moisture probes. It also helped him implement a succession plan that ensured his farm’s long-term viability.
Back to top
China is kicking America's ass in the EV battery race and it's going to define the 21st century
In recent years, the relationship between the US and China — the world's economic superpowers — has devolved into an unwieldy tug-of-war between economic interdependence and deep-seated distrust. On one hand, diplomats are trying furiously to maintain a stable world and keep money flowing between the two countries. But at the same time, one of the relationship's most salient features is that it is a contest for control over the technology that will define the 21st century.
In the latter battle there is one area where the US has fallen woefully behind: batteries. China's state-supported enterprises — let's call them China Inc. — dominate in every aspect of the development of batteries for electric vehicles, from the mining and refining of raw materials to the manufacture of the batteries themselves.
"The danger is that we won't have a domestic battery sector and we will totally in perpetuity rely on China to build cells for us," Tu Le, the founder of the consultancy Sino Auto Insights, told me. And without cheap batteries to power fleets of cheap electric vehicles, he argued, companies like GM and Ford "run the risk of becoming regional players and losing their international status."
Until US automakers can source batteries domestically, or from friendly nations, they will depend on maintaining good relations with Beijing. It is an increasingly fraught partnership, even setting geopolitics aside. For the past 40 years China needed foreign automakers to help develop its own car industry through joint ventures. But as China's domestic electric-vehicle market takes off, the tables have turned. Beijing is boosting its homegrown products, and foreign automakers — which already need China Inc.'s batteries to build more EVs — are losing market share.
The winner of the battery war will not only control the electric-vehicle market but also produce thousands of jobs, control the future of mobility, and dictate the West's ability to transition to greener forms of energy.
Beijing's battery plan
China has been working to dominate the battery space since at least 2015, when the leadership of the Chinese Communist Party crafted the National Key Research and Development Program New Energy Vehicle Key Special Implementation Plan. Despite its long, formal-sounding name, the document sets out a clear goal: to corner the market for key materials like lithium, cobalt, and nickel; invest in their extraction; and build factories for battery manufacturing.
The plan starts at the most basic level of battery production: raw materials like cobalt, lithium, manganese, and nickel. Most of these minerals lie outside China — in countries such as Chile, Australia, Bolivia, and the Democratic Republic of Congo. But China Inc. has negotiated ownership stakes and partnerships with mines all over the world. From 2018 to the first half of 2021, China Inc. invested about $4.3 billion in lithium mines internationally, according to the research firm S&P Capital IQ. And once these minerals are pulled out of the ground, they are shipped to Chinese-owned refineries that transform the metals for use in the final product. By 2019, Chinese companies made up 80% of the world's output for battery materials. This would not have been possible without Beijing's willingness to pay whatever price and withstand whatever losses it took to build the industry.
"At the end of the day even if DC or Brussels or Tokyo manages to support competing suppliers of minerals and companies that can turn minerals and metals into components, the mineral commodity markets are hard to predict," Jane Nakano, a senior fellow in the Energy Security and Climate Change Program at the Center for Strategic and International Studies, told me. "It's very difficult for private-sector non-state-supported entities to plan ahead."
In the past, this is where the Chinese value chain would end. The refined materials would get shipped out to the US or Europe where they would then be transformed into batteries. Not anymore: Beijing is trying to do that work in-house.
"In the 1970s and '80s China was exporting minerals to us to make higher-value goods," Nakano explained. "That's precisely the situation the Chinese wanted to get out of. That's why they came up with their tech strategy."
Nowadays when Beijing wants to develop technology, it sprays money at any companies that want to give it a shot and watches them duke it out until a few come out on top. Once the dominant parties have revealed themselves, everyone else is cut off and left to wither.
The undisputed champion of the Chinese battery-manufacturing battle is Contemporary Amperex Technology Co. Limited. The company, first called Amperex Technology Limited, was founded in Hong Kong in 1999. Using patented technology licensed from the US's Bell Labs it became a battery supplier for companies including Apple and Samsung. But by 2008 it wanted to manufacture in China for easier access to its market and to take advantage of government incentives. To do that, though, it had to move its headquarters from Hong Kong, which was (and technically still is) politically separate from Beijing. Eventually the company set up shop in a county in northeastern China that was once governed by a young Communist Party secretary named Xi Jinping. And so ATL became CATL. By 2022 it controlled about 32% of the world's market share for electric-vehicle batteries, and about half of China's domestic market. As of now, CATL has 13 factories worldwide that supply batteries for Tesla, Toyota, and Daimler. Earlier this month, Ford announced plans to build a $3.5 billion battery plant in Michigan with technology licensed from CATL.
Coming in a not-so-close second is China's BYD. Within China, it's a top-selling car company that makes its own batteries. Thanks to that inherent demand, it has taken just over 13% of global market share for EV batteries. And thanks to its ownership of its battery supply chain, it's able to make cars cheaply. Its BYD Song Plus — the best-selling car in China in the first quarter of this year — comes in both electric and combustion-engine versions and sells for under $30,000.
Role reversal
As Chinese companies have started to dominate the battery space, the US is trying to avoid a role reversal of past decades in which it would depend on China for higher-value batteries.
To prevent this outcome, the US needs to start investing in every part of the value chain for batteries. And it starts with the country's vast resources of " white gold ," the name for lithium used among those who believe its large deposits can be exploited to create the country's next great source of energy. As of now, the US has only one open lithium mine in Nevada. Lithium extraction and refining are messy, and environmental concerns have kept US output limited to about 1% of the world's supply.
"We really haven't gotten our heads in the game in terms of resource extraction," Nakano said.
To boost this output, companies are rushing to extract lithium deposits from California's Salton Sea, a dry region east of San Diego. Geologists estimate that the region could supply enough lithium to support the manufacturing of 7.5 million car batteries a year. US companies like BHE Renewables, backed by Warren Buffett's conglomerate Berkshire Hathaway, and EnergySource Minerals are looking to advance technology that will extract lithium using clean energy and while doing as little environmental damage as possible. President Joe Biden's 2022 Inflation Reduction Act legislation set aside $200 million, through the Department of Defense, to establish an end-to-end American supply chain of rare-earth metals, lithium, and nickel that can be used in domestic battery efforts.
America is also lacking capacity further down the manufacturing chain. The US is home to only two processing plants that produce lithium hydroxide , a more lightweight, concentrated version of the metal used for batteries. This month, Tesla broke ground on a third facility in Texas. The Inflation Reduction Act set a goal of refining enough lithium domestically to supply 2 million electric vehicles annually. The Biden administration hopes to accomplish this in two ways — one carrot and one stick. To try to lure companies, the law provides subsidies for companies that invest in that refining process, but it also sets stringent requirements for how much of an EV battery's components must be sourced in the US — or from countries with which we have free-trade agreements — to be considered domestically produced and avoid tariffs. But all of this planning and incentivizing this will take time to kick into gear. For example, EnergySource Minerals has said its mine could be operational by 2025.
A time to squeeze
While the US has a long way to go to catch up to China, there are some analysts who see Beijing's hand in the market as more clumsy than capitalist, and who say the CCP's ambitions will actually make it easier for American firms to catch up. Anne Stevenson-Yang, the research director of J Capital Research, predicted in a recent note to clients that Beijing's push to increase the supply of materials required for battery manufacturing will ultimately make it dramatically cheaper to enter the battery market over the next few years. Yang's research indicates the price of lithium carbonate — another critical chemical for batteries — has been sliced in half since November and will drop by another two-thirds this year.
"That is because of massive new Chinese capacity," she wrote. "If all goes as planned, lithium will be in global surplus as 2024 rolls around."
We've seen this dynamic when China enters a market before. Beijing throws a staggering amount of cash at an industrial product or late-stage technology until there's so much domestic supply that a capacity glut ensues. China then dumps that excess capacity into foreign markets, depressing prices globally. Stevenson-Yang sees parts of China's battery supply chain as the next glut it will need to dump.
"There are certain issues around security and having a manufacturing base in the US that makes sense, but we don't have to worry about the tech war," she said by phone. "China is like the Russian army in the 18th century. Everyone feared the 'Great Bear to the North,' but they eventually found out that size doesn't mean quality — size means size."
But the potential of a battery supply glut tomorrow doesn't help carmakers meet their needs today. Until the US and its friends can offer them another supply of electric batteries, auto manufacturers all need China Inc., especially as they ramp up their EV ambitions.
"We don't have a major player in the battery cell space, full stop. US battery makers will not likely be able to make a profitable battery until at least 2030," Sino Auto Insights' Le said. "The reality is GM and Ford can't build a $40,000 EV that will help their bottom line for the foreseeable future without BYD and CATL batteries."
And then there's Tesla. Elon Musk has said the company's goal is to manufacture 20 million cars annually by 2030 . To put that in perspective, Toyota — the world's biggest carmaker — sold just over 10 million cars last year, while Tesla sold just over 1 million. If Musk wants to reach his goal, Tesla not only needs Chinese consumers to keep buying his cars, but he also needs China's cheap batteries and manufacturing infrastructure to make a car cheap enough to sell to markets like Latin America, Southeast Asia and India.
"Musk can continue to be very effusive of the Chinese government and their support of the EV sector in China," Le said. "But if the US-China relationship continues to deteriorate, it's inevitable that it's going to be much tougher for any US company to do business in China."
And of course, Le pointed out, wherever Tesla goes in the world BYD will be there to compete on price.
"The IRA will create opportunities in the mobility space," Le said of the Inflation Reduction Act. "But if we're looking at evolutionary improvements, China Battery Inc. will still dominate. If we're looking at revolutionary developments over the next five to seven years, though, they'll be over here in the US. Of course, this is in the backdrop of BYD and CATL continuing to lower prices on current tech making transitioning to new technology a tougher decision for OEMs."
It's a complicated race, one of sometimes conflicting incentives and allegiances. The Inflation Reduction Act has upset the US's European allies while at the same time establishing protocols for cooperation to wrest the battery supply chain from China. US car manufacturers can't make cheap electric vehicles for the US market without China Inc., while at the same time the US government is creating policy to push back against China's ambition to dominate the EV market entirely, not just domestically. We cannot make clean energy without making a mess environmentally and geopolitically. For now China is winning the battery contest, but that doesn't mean the US or its allies should give in. There's always time to catch up in a race with no end.
Linette Lopez is a senior correspondent at Insider.
About Discourse Stories
Through our Discourse journalism, Business Insider seeks to explore and illuminate the day’s most fascinating issues and ideas. Our writers provide thought-provoking perspectives, informed by analysis, reporting, and expertise. Read more Discourse stories here .

Related stories
More from Economy
Most popular
- Main content
China Film Pavilion Returns to Cannes to Showcase Excellence of Country’s Movie Business
For its third year, China Film Co-Production Corporation brought together the Chinese film community and international industry leaders through events and conversations
By Partner Content
Partner Content
- China Film Pavilion Returns to Cannes to Showcase Excellence of Country’s Movie Business 4 days ago
- Winners of 14th Annual Beijing International Film Festival Announced, ‘Gold or S— ’ Takes Top Prize 3 weeks ago
- New York Film Academy Expands Miami Campus in Brand New Renovation 2 months ago

Under the guidance and support of the China Film Administration, China Film Pavilion, which is organized by China Film Co-Production Corporation (CFCC), once again promoted exchanges and cooperation between the Chinese film community and their international counterparts at the 77th Cannes International Film Festival, which opened May 14 and runs through May 25.
Popular on Variety
“Since 2022, when China Film Pavilion was first set up, the number of foreign visitors interested in Chinese films has been increasing by year,” said a China Film Pavilion staff member. “New released blockbusters, actions and comedies as well as animations all attracted attention.”
Among the films presented at the booth were “Legends of the Condor Heroes: The Gallants,” “Chang An” and “Creation of the Gods Ⅰ: Kingdom of Storms” — all of which exemplify the allure of traditional Chinese culture.
“We hope to promote exchanges and cooperation between Chinese and foreign film industries through China Film Pavilion and help Chinese films go global,” a CFCC spokesperson said. “Through the pavilion, and film as a medium, mutual understanding between Chinese and foreign filmmakers can be deepened to further foster communication and cooperation for mutual development. China Film Pavilion will continue to explore a broader platform for Chinese and foreign film exchanges.”
In 2023, a total of 971 films were produced nationwide in China, including 792 feature films, and China’s mainland hit box office of RMB 55 billion (approximately $7.6 billion) with admissions of 1.3 billion, making China the world’s second-largest film market. In 2024, the Chinese film market has shown consistently strong momentum. Influenced by various factors such as quality content, continuous market expansion and robust audience support, the box office for the New Year, Spring Festival and Qingming Festival have all hit new heights. As of May 5, China’s 2024 box office was approximately $2.8 billion, accounting for 35% of the global box office, temporarily ranking first in the world. The flourishing Chinese market has also sparked the interest of international filmmakers.
On May 15, the “Roundtable: How China’s Film Industry Cooperates with International Community” event, about envisioning new directions and futures for international film cooperation, took place at the China Pavilion in the international village. Filmmakers from China and abroad discussed fostering international film cooperation and envisioned the future with an international perspective. Mao Yu, executive deputy director general of China Film Administration, attended the event, shared China’s film practices and achievements in recent years and engaged in discussions with guests. Actor Huang Bo, vice chairman of the China Film Association, and actor Fei Xiang also attended the event.
Later during the festival, the pavilion will host several special events such as film promotion activities for the documentary “Kangxi and Louis XIV,” a Chinese French co-production, and “Fade Away Pastoral,” a film about the migration of pastoralists in Xinjiang, China. In addition, this year’s “Blue Book of Film: Global Film Industry Development Report” will be unveiled.
The pavilion will also host China Film Foundation’s “China’s New Talents Going Global Program” series events, including “Dialogue: Infinite Possibilities of Films,” “Roundtable: The Pathway from Short Film to Feature Film” and “Panel Discussion: The Voice and Perseverance of Female Filmmakers,” etc.
“We were eager to share all these wonderful films with audiences worldwide,” an exhibitor said. “At the booth, we fully experienced the expectations of foreign buyers for Chinese films and felt their eagerness to cooperate with Chinese filmmakers. The pavilion also bridged us with our overseas counterparts and enables us to embrace more business and cooperation opportunities.”
More From Our Brands
How to watch the 2024 nba playoffs: livestream without cable, former washington commanders owner donates $35 million maryland estate to charity, big ten reclaims revenue lead after earning $880m in fy23, the best loofahs and body scrubbers, according to dermatologists, ratings: csi: vegas draws biggest audience ever with unplanned series finale, verify it's you, please log in.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A production plan serves as a roadmap that outlines the steps, resources, and strategies required to manufacture products or deliver services efficiently. By carefully crafting a production plan within a business plan, entrepreneurs can ensure optimal utilisation of resources, timely delivery, cost efficiency, and customer satisfaction.
A production plan defines the production targets, required resources and overall schedule, together with all the steps involved in production and their dependencies. A well-designed production plan helps companies deliver products on time, reduce costs and respond to problems. Technology has made it easier for small and midsize companies in ...
Business Plan: A business plan is a written document that describes in detail how a business, usually a new one, is going to achieve its goals. A business plan lays out a written plan from a ...
Here are 10 key steps you should follow when planning your production process. 1. Use Production Forecasting Methods for Estimating Customer Demand. The first step of the production planning process is to forecast the customer demand for your product for a future period like a year or a quarter.
Production planning is the act of developing a guide for the design and production of a given product or service. Production planning helps organizations make the production process as efficient as possible. Production planning originated to optimize the manufacturing process, and today, its general logic is applied in various forms to design ...
Production planning is the planning and allocation of raw materials, workers, and workstations to fulfill manufacturing orders on time. In a make to order environment, manufacturing orders or work orders themselves are created after receiving customer orders. A company that follows make to stock style of manufacturing will create work orders on ...
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow. A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It's also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals. After completing your plan, you can ...
Production planning is the strategic process used in manufacturing to determine the what, when, and how of production. It involves forecasting demand, scheduling production activities, and allocating resources efficiently to meet market demands. The main goal is to optimize the use of resources, minimize production costs, and ensure timely ...
The steps below will guide you through the process of creating a business plan and what key components you need to include. 1. Create an executive summary. Start with a brief overview of your entire plan. The executive summary should cover your business plan's main points and key takeaways.
Learn about the best business plan software. 1. Write an executive summary. This is your elevator pitch. It should include a mission statement, a brief description of the products or services your ...
To write a production plan for a business, follow these steps: Define the business's goals and objectives. Determine the production process, including materials, labor, and equipment needed. Set production targets and timelines. Allocate resources and determine a budget. Create contingency plans for potential issues.
Production and operations management involve three main types of decisions, typically made at three different stages: Production planning. The first decisions facing operations managers come at the planning stage. At this stage, managers decide where, when, and how production will occur. They determine site locations and obtain the necessary ...
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
By. Susan Ward. Updated on September 13, 2022. Fact checked by David Rubin. In This Article. How To Write the Operations Plan Section of the Business Plan. Stage of Development Section. Production Process Section. The Bottom Line.
A business plan is a document that contains the operational and financial plan of a business, and details how its objectives will be achieved. It serves as a road map for the business and can be used when pitching investors or financial institutions for debt or equity financing. A business plan should follow a standard format and contain all ...
Business planning is a crucial process that involves creating a roadmap for an organization to achieve its long-term objectives. It is the foundation of every successful business and provides a framework for decision-making, resource allocation, and measuring progress towards goals. Business planning involves identifying the current state of ...
Production Planning. Before you can go into production, you'll need to do some planning. At this point, you're going to define the purpose and the goals of the production as well as figure out how you're going to achieve them. Production Routing. Once the plan is in place, the procurement of the necessary resources such as raw materials ...
The Better Business Planning Process. The business plan process includes 6 steps as follows: Do Your Research. Strategize. Calculate Your Financial Forecast. Draft Your Plan. Revise & Proofread. Nail the Business Plan Presentation. We've provided more detail for each of these key business plan steps below.
Traditionally, a marketing plan includes the four P's: Product, Price, Place, and Promotion. For a production company business plan, your marketing strategy should include the following: Product: In the product section, you should reiterate the type of production company that you documented in your company overview.
Planning refers to the definition of production strategies, reviewing the long term production plan, and building a production schedule. The production business process incorporates the activities before, during, and after the execution of the procedures that result from taking raw materials and creating sub-assemblies or finished goods.
There are three primary parts to a business plan: The first is the business concept, where you discuss the industry, your business structure, your particular product or service, and how you plan ...
The right production process for each organization typically depends on the technology available, how many products the company needs to produce and organizational structure. In this article, we review what a production process is, the elements of choosing the right production process and the types of processes available.
1. Portfolio: The range of products and/or services that a business offers to potential and current customers. 2. Features and benefits (value proposition): Explain what the product/service does and how it works. 3. Problem and solution (value proposition cont.): The problem (s) the product or service solves.
Item 1 of 2 Robotic arms assemble cars in the production line for Leapmotor's electric vehicles at a factory in Jinhua, Zhejiang province, China, April 26, 2023.
Summary. Managers spend 20% of their time on average managing team conflict. Over the past three decades, the authors have studied thousands of team conflicts around the world and have identified ...
Japan and the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) plan to create their first joint strategy on automobile production and sales within the Southeast Asian bloc to counter China's ...
By definition, DINKs aren't necessarily rich, but they do have a reputation for living a life of freedom and excess cash. This story is available exclusively to Business Insider subscribers.
The Hydrogen Production Tax Incentive will make Australia's pipeline of hydrogen projects commercial sooner, at an estimated cost of $6.7 billion over the decade. ... The Fund supported Ed in developing a better farm business plan, which identified his need for weather stations and soil moisture probes. It also helped him implement a ...
The plan starts at the most basic level of battery production: raw materials like cobalt, lithium, manganese, and nickel. Most of these minerals lie outside China — in countries such as Chile ...
Partner Content China Film Pavilion Returns to Cannes to Showcase Excellence of Country's Movie Business For its third year, China Film Co-Production Corporation brought together the Chinese ...