

Navigating Your PhD Topic Choice
Embarking on an impactful research career, starting with your thesis.
We’ve compiled this guide to share the tools and frameworks we think will be most helpful to you if you’re searching for a meaningful thesis topic for your PhD.
About this guide
If you’re applying for a PhD, this guide can provide comprehensive assistance throughout your journey towards finding the best possible PhD for you. In the first part we focus on how you can decide whether to pursue a PhD, identify the values you want to guide your research and start generating research ideas. In the second half we will introduce a framework you can use to narrow your ideas down to a specific research question and ultimately create a PhD proposal. Finally, we will help you with finding the best possible supportive environment for your project and identifying the next steps of your PhD journey.
If you are not yet very familiar with core concepts like career capital and the ITN framework , we recommend reading the linked articles. We also recommend you read this article to understand why systematic approaches to career decisions are probably more useful than popular advice like “follow your passion”, and why helping others with your career will help you experience your job as more meaningful.
How to use this guide
We recommend completing this guide over multiple sittings, e.g. working through one section per week. However, please adjust the pace to suit your circumstances. We think you will get the most out of this guide if you start from the beginning, but you might want to skip some sections if you’ve already thought deeply about the content.
After reading the articles linked in each step, take some time (5-10 minutes) to answer the prompts we list, or to complete the exercises we recommend. We find that writing your thoughts down on paper is a step that people often want to skip, but it can help tremendously in getting clarity for yourself.
Is a PhD the right next step for you?
Lots of people “stumble” into PhDs. For example, they might see it as a default step in completing their education, or they might have been offered to continue with their previous supervisor. Before committing to a PhD programme, it is good to consider a broad range of alternatives in order to ensure that a PhD is the best path for you at this stage. Make sure you have done enough reflection and updated your plans based on your experiences thus far, instead of going down the “default” academic path.
We also recommend that you take some time to browse through these short descriptions of core concepts , particularly ‘Expected Value’, ‘Opportunity Cost’ and ‘Leverage’. Perhaps note down a few takeaways that apply to your decision.
Reflection prompts
If you’re unsure whether a PhD is right for you, here are some prompts to consider.
- Where do you envision yourself a few years after completing a PhD?
- How does a PhD align with your long-term goals and aspirations?
- Are you genuinely interested and intrinsically motivated by the subject area you intend to pursue with your PhD?
- Have you carefully assessed whether obtaining a PhD is a necessary requirement for your desired career path?
- Are there alternative routes or professional qualifications that may lead you to your desired destination more efficiently, e.g. in less time/ with a better salary?
- Have you talked to people who completed or are currently pursuing the kind of PhD you are considering?
Exercise: exploring career paths
One helpful activity to undertake could be to search for job opportunities that you find exciting. To start, do a job search (2-5 hours) and list the five most attractive options you can find. Now, check which job requirements you’re currently lacking. Do you need a PhD to get the role? Would you get there faster or be better prepared by taking a different route?
Here are some more articles if you are interested in the question ‘Who should do a PhD?’:
- Survival Guide to a PhD – Andrej Karpathy
- Why I’m doing a PhD – Jess Whittlestone
- Pro and Cons of Applying for a PhD – Robert Wiblin
Reflect on your values and moral beliefs
Understanding your values and moral beliefs is an ongoing endeavour and you don’t need to have it figured out before choosing your topic. However, we do encourage reflection on this, as doing so might significantly shift your motivation to work on some problems over others. If that happens, the earlier you make this shift the better. What do we mean when we say doing good ? Most people agree that they want to “do good” with their lives. However, it is worth reflecting on what this actually means to you. We recommend reading the article linked above to learn more about some concepts we think are particularly relevant when reflecting on this question, such as impartiality, the moral circle, and uncertainty. This will help you to get a better understanding of what sort of thesis topics would align with your values and what kind of problems you want to contribute to solving with your research.
- How much do you value animal lives vs human lives ?
- How important do you think is it to reduce existential risks for humanity?
- How much do you value future generations ? How do you feel about improving existing lives vs lives that exist in the future?
This flowchart from the Global Priorities Project can help you navigate through this cause prioritisation process.
Here are two further resources that could help you with this reflection:
How to compare global problems for yourself – 80,000 Hours
World’s Biggest Problems Quiz | ClearerThinking.org
Getting inspired
Now it’s time to get inspired! You can read more about how research can change the world , and how academic research can be highly impactful . Finally, have a look at our thesis topic profiles for inspiration or, if you have no time constraints, sign up to our Topic Discovery Digest to receive biweekly inspirational emails. These emails cover a range of particularly impactful research areas, along with example research questions that are recommended by our experts and relevant to many different disciplines of study. We recommend you read the 3-5 profiles that interest you the most in depth.
- Which of the topic profiles that sparked your interest are new to you? How could you quickly get a better understanding of what it is like to work on these topics?
- How would disregarding your current skill set change your top choices? Would you consider taking some time out to “upskill” to switch to a new area of research, if possible?
- What are the uncertainties that, if you could find an answer to them, would help you decide between your top choices?
See here if you want to learn more about how we go about writing our thesis topic profiles and why we prioritise these topics.
Side note: Because we try to feature problems that are particularly important, tractable, and neglected, you might see some problems listed on our site that it’s uncommon to see described as global problems, while others are not featured. As an example, in our “human health and wellbeing” category, we list anti-aging research but not cancer research. We think research on widely recognised problems such as cancer is highly important. However, because so many more researchers are already working on these problems, we think that – all else equal – you will probably have a bigger impact working on problems that are relatively neglected.
Generating ideas
After reading a few of our topic profiles , we recommend that you start a brainstorming document as an ongoing way of collecting research questions you’re interested in. This will help you keep track of and develop your ideas during your idea generation phase, and make it easier for others to give you feedback later on.
In addition to exploring our topic profiles, you could also identify questions through a literature review and reach out to your supervisor or other researchers in the field(s) you’re interested in and ask what they think some of the most important and neglected open questions are. Moreover, you could contact some of the organisations listed on our topic profiles and ask if there are research projects you could undertake that would be decision-relevant for them. Reaching out to others at this stage can also help to discard unfeasible ideas early on, before you invest too much time in them.
Some tools that might be useful during the idea generation phase:
- Connected papers – explore connections between research papers in a visual graph.
- Elicit – an AI research assistant to help you automate research workflows, like parts of literature review.
- Find more resources and tools for research here .
We recommend collecting at least 20 research questions, grouped into overarching topics or research fields, and then adding some context, e.g. relevant papers and researchers, why you think this question is worth addressing, what relevant expertise you already have, and how qualified you are to work on this compared to other options.
NB : We think that many people feel too limited by their past work, so we think you should probably lean towards considering questions and topics that are slightly outside your comfort zone.
Exercise: create a brainstorming document
Use this template to create a brainstorming document.
Comparing options
Once you feel you have collected enough research questions in your brainstorming document, you can start comparing how these research questions score on the factors that are most important to you. We recommend you take 15-20 minutes to think about which factors are key to your decision of pursuing a PhD and write them down. Here are some factors (adapted from this post ) that you could consider:
- Importance – How large in scale and/or severity is the problem your question would address?
- Tractability – How realistic is it that you would make progress? Is your research question concrete and manageable, and do you have a clear strategy to tackle it?
- Neglectedness – Will others work on this question if you don’t?
- Actionability – Would your research have a clear audience and could it inform positive actions? Will this project generate genuinely new and useful findings/data? Will it help to translate/ communicate important ideas that need more attention/ awareness?
- Learning value – Will you learn useful things from working on the project? Will it help you build valuable research skills, build your model of how something important works, and/ or help you refine a vaguely defined concept into a crisp, important question?
- Exploration value – Will this project help you decide what to do next?
- Personal fit & situational fit – Does your personal background make you a good fit for working on this question? Do you currently have or can you find support for working on it, e.g. excellent mentorship?
- Credentials and career capital – Will the output demonstrate your research competence? For example, if you could get a reference from a particularly prestigious researcher by working on one of the projects you’re interested in, this might be an important consideration. Will the project reflect well on you, and is it shareable with others (or could it be developed into something shareable/ a publication)? Will the project allow you to build relationships with people whom it will be helpful to know going forward?
- Intrinsic motivation – Are you excited about working on this project?
- Method efficacy – How well can a particular approach help solve the problem that you are trying to address?
Exercise: sketch theories of change for your research questions
Once you’ve considered which of these factors matter to you, take a few minutes to sketch a theory of change for each research question you’re considering.
A theory of change is a step by step plan of how you hope to achieve a positive impact with your research, starting with the context you’d be working in, the research outputs you would plan to produce, and the short- and long-term impacts you would hope to achieve with your research. Sketching some theories of change will help you outline how your research ideas could have a positive impact, giving you something to get feedback on in the next step below.
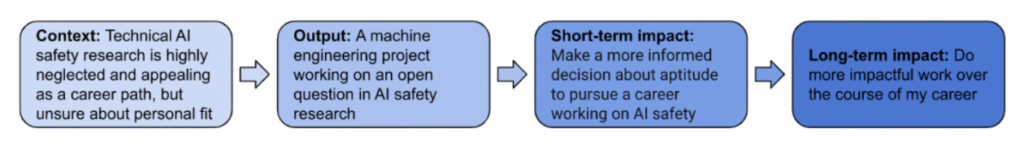
Consider whether your research could have negative outcomes too
When you’re considering the value of working on a particular research problem, it may also be important to remember that research isn’t a monolithic force for good. Research has done a lot of good, but there are many examples of it doing a lot of harm as well. There is a long history of research being biased by the discriminatory beliefs and blindspots of its time, as well as being used to justify cruelty and oppression . Research has made warfare more deadly and has facilitated the development of intensive factory farming . Dual-use biotechnology research is intended to help humanity, but could, for example, cause a catastrophic pandemic in the event of a lab accident or if the technology was misused. While some researchers are trying to increase the chance that future artificial intelligence is safe for humanity , many more researchers are focused on making AI more powerful.
While it isn’t realistic for researchers to foresee every way their research could be (mis)used, many researchers are trying to create frameworks for thinking about how research can do harm and how to avoid this. For example, if you’re interested in working on biosecurity or AI safety, you could explore concepts such as differential progress and information hazards . If you’re working on global health questions, it may be important to educate yourself about the concept of parachute science .
Reach out to others for feedback
At this point, we think it could be helpful to identify some experts who might be interested in talking about your collection of potential research questions, and reach out to them for feedback. Getting feedback might then help you to prioritise between questions, develop your methodology further or discard projects before investing too much effort in them. You could seek feedback via two strategies – firstly, by sending your brainstorming document to people asking for general comments, and secondly, by seeking out people who have specialist knowledge on specific questions you’re considering and asking for their feedback on those ideas.
Here are some ways of connecting with other researchers:
- Reach out to your existing connections
- Attend research conferences related to your field of interest and speak to relevant people there, e.g. 1-1s at EAGs could be a great place to reach out to people for feedback on research ideas on directions that we recommend
- Are there any local student and/ or reading groups in your area that focus on a research area that you are planning to work on?
- Public Slack channels on your research area, e.g. List of EA Slack workspaces
When preparing to reach out to experts, keep these key points in mind:
- Give the expert relevant information about yourself (e.g. What is your background? What is the scope of the project you’re planning to work on?).
- Prepare a short agenda if they’ve agreed to call you and share it with them beforehand (although they might not have time to read it, many people appreciate having the option to consider topics of discussion in advance).
- Think about what your key uncertainties actually are and what kind of feedback you want from the expert. Would you like their overall reaction? Detailed comments? Feedback on the strengths and weaknesses of your research ideas? Specific suggestions to improve your ideas? Feedback on how you plan to use the outputs of your research project?
- Consider having a brainstorming document ready to share with them.
- You might want to have a look at this and this for more information about how to prepare.
Exercise: creating a weighted-factor model
Choosing which factors you want to base your thesis decision on will help you to reflect on what is important to you. Once you’ve done the exercise above and gathered some feedback from other people about your ideas, think about how much weight you want to give each factor. Lastly, try to evaluate how the research questions you’re considering score on each factor. The outcome of this ranking can serve as guidance for deciding on a question and can help clarify your intuitions about which questions would be the best fit for your dissertation. Here is an example of a ranking of potential thesis questions using a weighted-factor model (WFM).
Refining your research question
Once you have settled on a research question, it is time to develop a well-scoped and viable research proposal. The purpose of the proposal is to identify a relevant research topic, explain the context of the research, define concrete goals, and propose a realistic work plan to achieve them. If you’ve already built a Theory of Change for your research question, we recommend adding detail at this stage to help you create a proposal. We also think it’s important to reach out to your supervisor or other relevant people in the field of your research interests to ask for feedback, as this will help you develop an appropriate methodology.
Here are a few more tips that could help you with narrowing the scope of your research project or refining your research question:
- First, make sure you have a detailed model of the problem you are planning to address in your research. Who are the different actors involved? How can research help fill gaps in our current knowledge? What are the particularly neglected approaches and interventions for this problem?
- You will only be able to make a valuable research contribution if your project is focused. Break down goals into discrete tasks and summarise what you are actually going to do. We suggest you create a detailed plan for the first few months of your project, a less detailed but fully coherent plan for the first year, describe a direction you might take in the second year, and generate some ideas for the following years. This will help you understand how much work is involved in every step and evaluate what is feasible in the available time frame.
- Consider practical questions. What kind of facilities do you have? Do you meet the university requirements?
- Try to develop the smallest possible question that can be answered and that data can be collected on, then have conditional upgrades/sub-questions based on that. This can be ambitious, but each stage should be developed enough to not be overwhelming or too vague.
- Start with a research question that’s as simple as possible and that you’re confident will be successful. From there, you can slowly and incrementally work towards pursuing more complex research questions.
Find the best possible supportive environment
There are many different types of PhD programmes available – from 3-year PhDs to which you apply with a very specific project idea, to 6-year PhD programmes in which the first years are dedicated to coursework. It is important to find the best environment for your studies, with crucial considerations including the university and its community, the supportiveness of the supervisor/lab and the availability of funding. This section has advice on these three points and aims to facilitate you reflecting on them.
How much does the reputation of the university where you study your PhD matter for an academic career?
This is a commonly asked question among students, and we have compiled a set of key insights based on conversations with 30 of our experts.
- The general advice is that you should pick the most prestigious university or research hub that you can get into.
- The importance of your university’s reputation varies across regions, with the US and the UK placing more significance on it compared to Europe or Australia. For the US especially, you will likely get a much better education and teaching quality, as well as access to resources, from a more prestigious university.
- It is worth noting that high-quality research labs (and supervisors) can be found outside of big-name universities, as specific research hubs may exist elsewhere.
- It is important to note that even researchers in the most prestigious universities can be poor supervisors.
- Ideally, you’ll find a great supervisor at a highly reputable institution. However, if you have to decide, finding an excellent supervisor seems to be the superior consideration – see below.
- The significance of the university’s reputation increases if your career aspirations involve influencing government, e.g. in policy roles.
- Outstanding research, impactful contributions to the field, and a strong professional network could potentially outweigh the importance of a university’s reputation.
Find a standout advisor
We think it is very important to find someone who genuinely cares about your research question and who will make a lot of time to supervise you well. Further, your supervisor will influence how effective you are in your work and how much you enjoy the research, as they will be the primary person guiding you throughout your whole research process. Especially at the PhD level, your advisor’s network matters tremendously for how well- connected you are and what sorts of opportunities will be open to you. So, here are some green flags to look out for in a supervisor:
- They care about your research question (pitch your ideas to the supervisor and see how enthusiastic they are about the potential project).
- They have the skills to supervise your project (check if they have experience in the methodologies you want to use).
- They truly care about mentoring you well (ask questions about their mentoring style, get a feel for how you match as a person).
- Their previous and current students are satisfied with them as a supervisor (ideally the person has a good track record of supervising other students – arrange a meeting with at least one current or past student).
- They are successful (e.g. based on their citation count and general prestige).
Sign up for access to our database of potential supervisors who work on the research directions we recommend. Here are more tips on finding the right person to supervise you.
Financing your studies
Even if you get accepted to a programme, it does not automatically mean that you get funding as well. Here are some tips if you need to apply for funding independently:
Consider a wide range of funding sources, e.g. national scholarships, university scholarships, grants and foundations dedicated to specific causes, and excellence scholarships (e.g. Gates or Rhodes Scholarships). Here is our funding database which includes funding opportunities relevant to the research directions we recommend.
- Consider the university environment – Would you be happy to live in the city of the programme you are applying to for 3-6 years? Do some university environments offer a more stimulating environment than others? Are there other researchers with similar values or motivations to you in this research hub?
- Do you have any hard criteria for choosing the location for your PhD? For example, would you consider moving abroad for an exciting opportunity?
- What do you already know about the application process? What uncertainties do you have and how can you go about resolving them?
We recommend that you make a list of the programmes that best fit your research interests and other factors that are important to you. Then, check the requirements and deadlines for each of them and write down the next steps you need to take to apply. We also recommend reaching out to people who have gone through the PhD programme(s) you are applying to to hear about their experiences.
Set out your next steps
Take a few minutes now to write down your next steps for applying to the programs you’re interested in.
It could be helpful to sign up for some accountability buddy schemes, ask friends to check on your progress, or to set yourself a hard deadline on some important next steps that you want to take. You could schedule some time in your calendar right now, or make a note in your to-do list about a task that you want to complete soon.
Reflection prompts:
- What information do you need to get right now?
- What are you uncertain about?
- What is keeping you from advancing with your project and how could you concretely resolve this?
Examples for concrete next steps could be:
- Reach out to people for feedback on your brainstorming document
- Reach out to potential supervisors
- Apply to an EAG or other academic conference and make a list of people you want to speak to
- Reach out to people who have gone through the program you are applying to
- Reach out to current PhD students about proposal examples
Here are some further resources that could be helpful for you:
- Tips on impactful research
- Resources and tools for research
- Looking after your mental health
- Our Effective Thesis Community
- Research internships and other opportunities
For more general career advice, there are some other organisations that could help you with 1:1 advising. We recommend the following:
- 80,000 hours offers one-time 1:1 advising calls about using your career to help solve one of the world’s most pressing problems. They can help you choose your focus, make connections, and find a fulfilling job to tackle important problems.
- Magnify Mentoring pairs mentees who are interested in pursuing high-impact careers with more experienced mentors for a series of one-on-one meetings.
- Probably Good is running 1:1 advising calls to brainstorm career paths, evaluate options, plan next steps, and to connect you with relevant people and opportunities.
- Lastly, please leave us some feedback . Thank you!
Subscribe to the Topic Discovery Digest
Subscribe to our Topic Discovery Digest to find thesis topics, tools and resources that can help you significantly improve the world.

Apply for coaching
Want to work on one of our recommended research directions? Apply for coaching to receive personalised guidance.

Funding database
Find funding for your PhD on one of our recommended research directions.

Opportunities newsletter
Sign up to receive our fortnightly newsletter of personalised, research-related opportunities.

Sign up to access our database of potential supervisors
Sign up for access to our database of potential supervisors who work on the research directions we recommend.
Effective Thesis
Privacy policy
Stay in touch
Are you interested in applying for coaching or to our other services in future? Stay in touch and get our quarterly updates by signing up to our newsletter!
Educational resources and simple solutions for your research journey
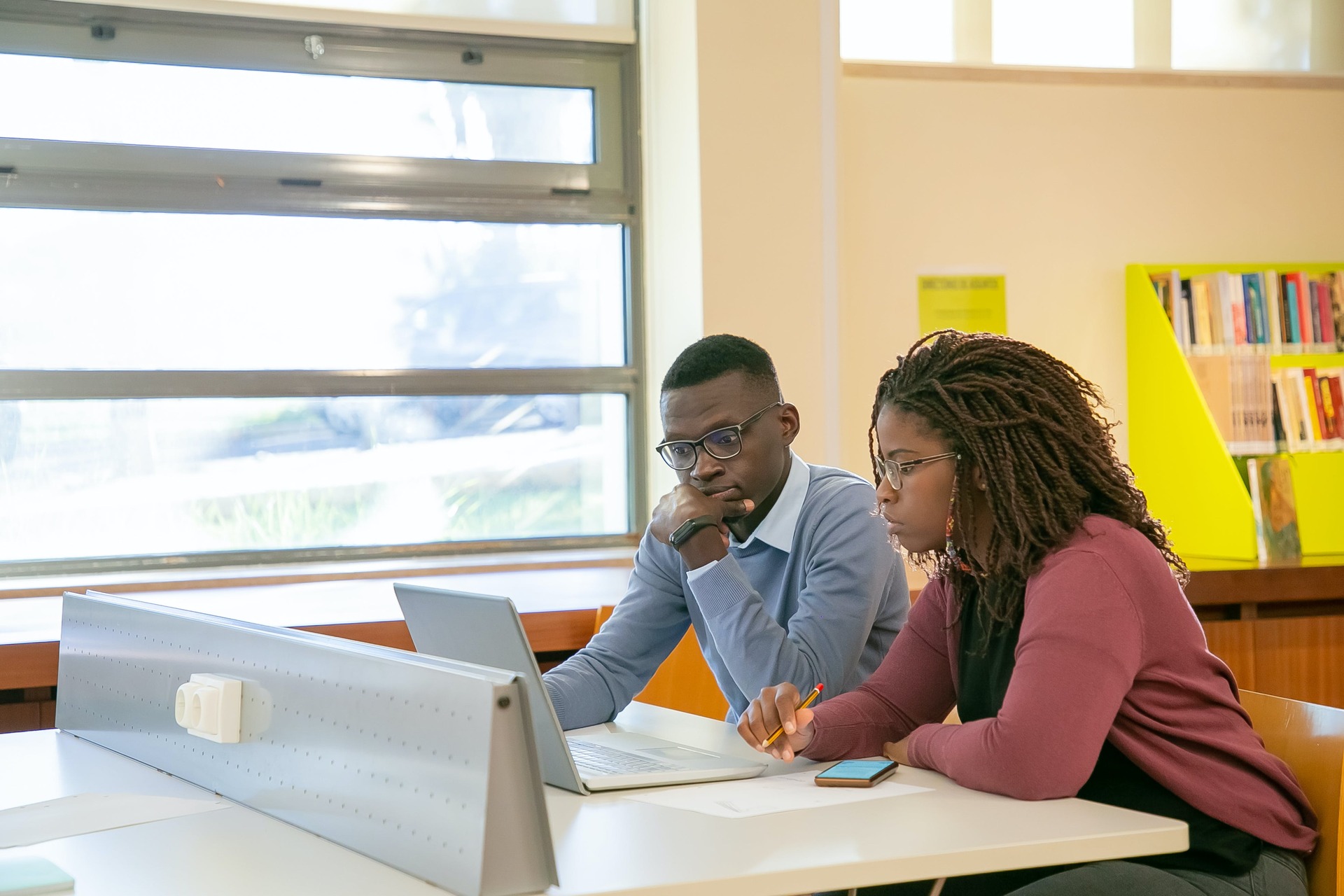

How to Choose a PhD Research Topic

For most doctoral aspirants, starting on their PhD journey can be both exciting and challenging at the same time. It often begins with having to make a critical decision – choosing a research topic. A well-considered and relevant PhD research topic is crucial because it significantly impacts the overall success and quality of your Ph.D. research. While it may be perfectly normal for your topic to evolve as you progress in your research and make discoveries, the significance of the right PhD thesis topic cannot be overstated.
The path to earning a PhD often lasts several years. To maintain the motivation and unwavering commitment throughout this journey, you must have a genuine interest in the subject matter you choose to explore. Your enthusiasm can be a driving force, leading you to overcome obstacles and persist in your academic pursuits.
Let’s explore some methods to help you navigate the process of PhD topic selection, from brainstorming to finalizing your proposal.¹²³
- Focus on your field of study – It is always a good idea to consider your past research experiences and what questions or problems intrigue you. Remember, while the subject of your PhD should definitely interest you, it should also contribute to the existing body of knowledge in your field. Deeply engaging with subjects that genuinely captivate you can lead to both academic excellence and personal fulfillment. Therefore, take time to evaluate trending PhD topics carefully – this can also help you make your choice.
- Review relevant academic literature – Immerse yourself in the literature of your field. Conduct thorough research to identify gaps, controversies, or unexplored avenues in current research. The existing body of knowledge can provide invaluable insights into potential research areas.
- Assess available resources – It is critical to assess the feasibility of your chosen topic. Consider the resources, data, and tools required to conduct your research. Ensure that you have access to the necessary resources and that your chosen PhD thesis topic aligns with your academic and financial capabilities.
- Seek guidance from trusted advisors – Consulting with experienced mentors and advisors is essential. They can provide guidance, suggest refinements to your topic, and help you avoid potential pitfalls. Their insights can be invaluable in shaping your research direction.
Table of Contents
Formulating a Focused Research Question
After PhD topic selection, the next step is to refine it into a straightforward research question. Your research question should be specific, relevant, and well-defined. It should be detailed enough to guide your research and provide clear direction while also leaving room for exploration and analysis. Consider the significance of your question – why is it important, and what contributions can your research make to the field?
Creating a Research Proposal
Once you have a well-defined research question, you will need to create a research proposal. This document is a blueprint for your entire research efforts. In the research proposal, you will outline the precise scope of your study, the objectives you aim to achieve, the methodology you intend to employ, and the anticipated outcomes of your research.
Your research proposal typically goes through a thorough review and approval process involving critical evaluation and feedback from your academic advisors. This scrutiny ensures that your research is not only academically sound but also aligns with the standards and expectations of your academic institution.
The approval of your research proposal marks the culmination of your efforts to refine your PhD research topic. This process finalizes your research topic and sets the stage for the beginning of your PhD journey.
Evolution of Your PhD Research Topic
It’s important to remember that choosing a PhD thesis topic can be daunting, and it’s okay for your topic to evolve as you progress through your doctoral studies. New findings and interesting discoveries may lead you in unexpected directions. This adaptability is a natural part of the PhD journey. 4
Your Ph.D. dissertation serves a dual purpose: enhancing your understanding of your field and making valuable contributions to it. While it doesn’t need to be groundbreaking, it must demonstrate originality and your research and argumentation skills. In essence, a Ph.D. program aims to identify scholars capable of making noteworthy contributions to their fields. Thus, your dissertation is a critical milestone in your academic career, and it all begins with the careful selection of your PhD research topic.5
References:
- How to Choose a Dissertation Topic For Your Doctoral Degree. Walden University website. https://www.waldenu.edu/online-doctoral-programs/resource/how-to-choose-a-dissertation-topic-for-your-doctoral-degree
- How to Choose a PhD Topic. Doctoral Journey, Grand Canyon University website; August 2020. https://www.gcu.edu/blog/doctoral-journey/how-choose-phd-topic
- How do you select a research topic for your dissertation or thesis? LinkedIn Higher Education article, November 2023. https://www.linkedin.com/advice/1/how-do-you-select-research-topic-your-dissertation
- How to decide on a PhD topic. The University of Queensland website, April 2022. https://study.uq.edu.au/stories/how-to-decide-phd-topic
- John Komlos, John Goldsmith. How does one choose a dissertation topic? IIT Delhi. https://web.iitd.ac.in/~mamidala/HTMLobj-155/How_to_choose_a_PhD_topic.htm
R Discovery is a literature search and research reading platform that accelerates your research discovery journey by keeping you updated on the latest, most relevant scholarly content. With 250M+ research articles sourced from trusted aggregators like CrossRef, Unpaywall, PubMed, PubMed Central, Open Alex and top publishing houses like Springer Nature, JAMA, IOP, Taylor & Francis, NEJM, BMJ, Karger, SAGE, Emerald Publishing and more, R Discovery puts a world of research at your fingertips.
Try R Discovery Prime FREE for 1 week or upgrade at just US$72 a year to access premium features that let you listen to research on the go, read in your language, collaborate with peers, auto sync with reference managers, and much more. Choose a simpler, smarter way to find and read research – Download the app and start your free 7-day trial today !
Related Posts

How Publishers Can Enhance Reader Engagement with R Discovery’s Article Recommendation System

What is Research? Definition, Types, Methods, and Examples

How to Choose a Good Research Topic for Your PhD
Choosing the right research topic is quite often a daunting task, especially for PhD students. However, developing a good research question has a positive impact on students’ research careers. Thesis advisors offer help during this initial stage. Later on, PhD students are expected to choose their own research topic for subsequent studies.
When navigating through several interesting research topics, it becomes necessary to strike the right balance between curiosity and societal needs. Moreover, funding agencies fund compelling research proposals based on meaningful and highly relevant research topics. Selecting a good research topic can, therefore, increase the odds of academic success.
PhD Research Topic and Your Career
Performing a meticulous literature survey helps researchers identify existing research gaps and devise novel strategies for addressing them. Once the research gap is identified, it becomes imperative to choose a meaningful research question. A well-chosen research question can lead to a compelling research proposal. In fact, doctoral researchers can positively shape their entire career by finalizing a good research proposal. Researchers are expected to choose topics that can potentially lead to impactful publications. Good publications fetch good citations. Well-published and well-cited researchers can easily find satisfying jobs in academia or industry. Choosing the right research topic, thus, can open doors to satisfying job opportunities worldwide.
Pathway to Success
There are several ways to ensure success in research. When in graduate school, students need to undertake several measures to identify a compelling research topic. Although conducting a thorough literature survey certainly facilitates this process, it is virtually impossible to choose the right research topic solely based on literature surveys. Students and early-stage researchers, therefore, need to brainstorm thoroughly with their advisor, talk to experts, and attend research seminars/conferences to listen to (and network with) established researchers. Quite often, taking up the relevant coursework (especially for interdisciplinary research areas) simplifies the process of research topic selection.
Choosing the right research question helps researchers stay focused and motivated throughout their career. Meaningful research questions eventually lead to meaningful discoveries and inventions. Robert Smith presented in Graduate Research: A Guide for Students in the Sciences (ISI Press, 1984) a list of 11 research questions to consider:
- Can you enthusiastically pursue it?
- Can you sustain your interest while pursuing it?
- Is the problem solvable?
- Is it worth pursuing?
- Will it lead to other research problems?
- Is it manageable in size?
- What is the potential for making an original contribution to the literature in the field?
- Will the scholars in your field receive the results well if you solve the problem?
- Are you (or will you become) competent to solve it?
- By solving it, will you have demonstrated independent skills in your discipline?
- Will the necessary research prepare you in an area of demand or promise for the future?
Keeping these questions in mind while developing a research question can set the stage for a productive and fulfilling career.
Common Mistakes
There are several mistakes that students and early-stage researchers commit during the process of research topic selection. Some of the most common mistakes include:
- Extending thesis work even after graduate school : If researchers choose topics that are direct extensions or clear derivatives of their thesis work, then they do not make significant value addition to the respective field of study. Choosing a radically new research topic, while still embarking on the broad area of specialization is indeed the key to success.
- Choosing an obscure, irrelevant, or non-compelling research topic : This can adversely affect the researcher’s motivation levels and can drastically decrease their odds of attaining success.
- Letting PhD advisors choose research topics for you : Although researchers often pursue work within the same field even after earning their PhD, they are less likely to conduct research on the same exact topic. For this reason, letting your advisor tell you what to study rather than you developing a question based on your own reading and experiences in the laboratory is another common mistake that can have lifelong consequences.
Finally, scientists should work in an environment that nurtures the natural chaos of developing a research direction. PhD advisors should also make it a point to thoroughly groom and mentor their PhD students. A good thesis advisor enables his/her students to choose good research topics.
Did your thesis advisor choose a research topic for you? Did he/she train and mentor you well? Were you able to choose your own research topic? Are you happy with your chosen research topic? Please share your thoughts with us in the comments section below!
Research topics for science or literature: Deep knowledge and a keen interest in any subject with a scholarly attitude are the prerequisites for any research work.
I am allowed to choose my research topic.
i want research topic for p.hd

Thank you for posting your query. Selecting a good research topic is the first step towards carrying out a successful and impactful research study. A good research topic can help you attract funding and also help you to successfully publish in a prestigious journal. Unfortunately we are not aware of your field of research and hence will not be able to suggest you research topics. However, we can share few tips that might be helpful in selecting an appropriate research topic for your PhD. While choosing a research topic, you must carry out a thorough literature survey in your field or genre of research and look for a research gap. Identifying the research gap makes it easy to select a research topic and an appropriate research question. Once you have selected a research topic, you can check through our checklist available here .
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Reporting Research
Academic Essay Writing Made Simple: 4 types and tips
The pen is mightier than the sword, they say, and nowhere is this more evident…
![proposed phd research topics What is Academic Integrity and How to Uphold it [FREE CHECKLIST]](https://www.enago.com/academy/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/FeatureImages-59-210x136.png)
Ensuring Academic Integrity and Transparency in Academic Research: A comprehensive checklist for researchers
Academic integrity is the foundation upon which the credibility and value of scientific findings are…

- AI in Academia
AI vs. AI: How to detect image manipulation and avoid academic misconduct
The scientific community is facing a new frontier of controversy as artificial intelligence (AI) is…

- Diversity and Inclusion
Need for Diversifying Academic Curricula: Embracing missing voices and marginalized perspectives
In classrooms worldwide, a single narrative often dominates, leaving many students feeling lost. These stories,…

- Career Corner
- Trending Now
Recognizing the Signs: A guide to overcoming academic burnout
As the sun set over the campus, casting long shadows through the library windows, Alex…
7 Steps of Writing an Excellent Academic Book Chapter
When Your Thesis Advisor Asks You to Quit
Virtual Defense: Top 5 Online Thesis Defense Tips

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.

How to Write a PhD Research Proposal
- Applying to a PhD
- A research proposal summarises your intended research.
- Your research proposal is used to confirm you understand the topic, and that the university has the expertise to support your study.
- The length of a research proposal varies. It is usually specified by either the programme requirements or the supervisor upon request. 1500 to 3500 words is common.
- The typical research proposal structure consists of: Title, Abstract, Background and Rationale, Research Aims and Objectives, Research Design and Methodology, Timetable, and a Bibliography.
What is a Research Proposal?
A research proposal is a supporting document that may be required when applying to a research degree. It summarises your intended research by outlining what your research questions are, why they’re important to your field and what knowledge gaps surround your topic. It also outlines your research in terms of your aims, methods and proposed timetable .
What Is It Used for and Why Is It Important?
A research proposal will be used to:
- Confirm whether you understand the topic and can communicate complex ideas.
- Confirm whether the university has adequate expertise to support you in your research topic.
- Apply for funding or research grants to external bodies.
How Long Should a PhD Research Proposal Be?
Some universities will specify a word count all students will need to adhere to. You will typically find these in the description of the PhD listing. If they haven’t stated a word count limit, you should contact the potential supervisor to clarify whether there are any requirements. If not, aim for 1500 to 3500 words (3 to 7 pages).
Your title should indicate clearly what your research question is. It needs to be simple and to the point; if the reader needs to read further into your proposal to understand your question, your working title isn’t clear enough.
Directly below your title, state the topic your research question relates to. Whether you include this information at the top of your proposal or insert a dedicated title page is your choice and will come down to personal preference.
2. Abstract
If your research proposal is over 2000 words, consider providing an abstract. Your abstract should summarise your question, why it’s important to your field and how you intend to answer it; in other words, explain your research context.
Only include crucial information in this section – 250 words should be sufficient to get across your main points.
3. Background & Rationale
First, specify which subject area your research problem falls in. This will help set the context of your study and will help the reader anticipate the direction of your proposed research.
Following this, include a literature review . A literature review summarises the existing knowledge which surrounds your research topic. This should include a discussion of the theories, models and bodies of text which directly relate to your research problem. As well as discussing the information available, discuss those which aren’t. In other words, identify what the current gaps in knowledge are and discuss how this will influence your research. Your aim here is to convince the potential supervisor and funding providers of why your intended research is worth investing time and money into.
Last, discuss the key debates and developments currently at the centre of your research area.
4. Research Aims & Objectives
Identify the aims and objectives of your research. The aims are the problems your project intends to solve; the objectives are the measurable steps and outcomes required to achieve the aim.
In outlining your aims and objectives, you will need to explain why your proposed research is worth exploring. Consider these aspects:
- Will your research solve a problem?
- Will your research address a current gap in knowledge?
- Will your research have any social or practical benefits?
If you fail to address the above questions, it’s unlikely they will accept your proposal – all PhD research projects must show originality and value to be considered.
5. Research Design and Methodology
The following structure is recommended when discussing your research design:
- Sample/Population – Discuss your sample size, target populations, specimen types etc.
- Methods – What research methods have you considered, how did you evaluate them and how did you decide on your chosen one?
- Data Collection – How are you going to collect and validate your data? Are there any limitations?
- Data Analysis – How are you going to interpret your results and obtain a meaningful conclusion from them?
- Ethical Considerations – Are there any potential implications associated with your research approach? This could either be to research participants or to your field as a whole on the outcome of your findings (i.e. if you’re researching a particularly controversial area). How are you going to monitor for these implications and what types of preventive steps will you need to put into place?
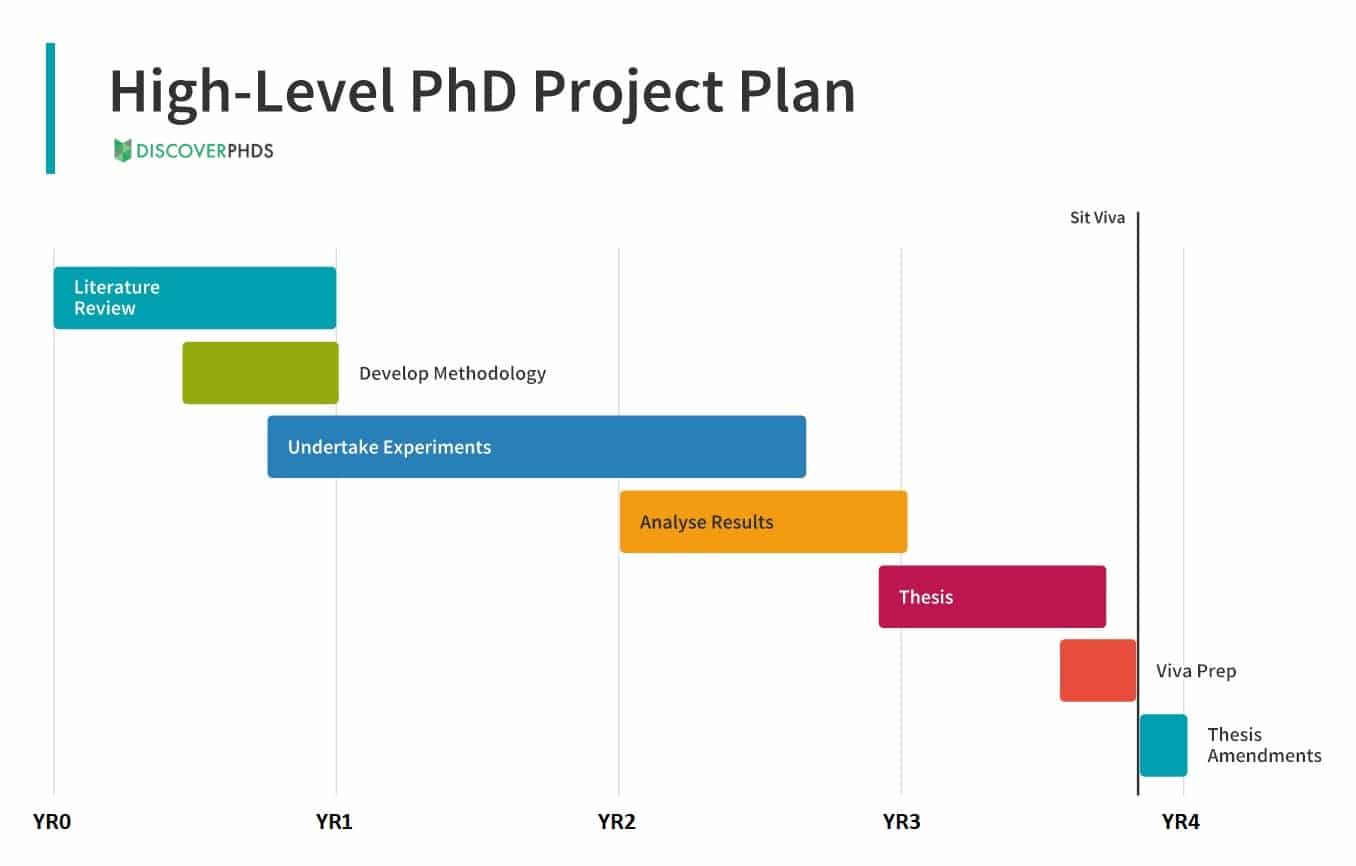
6. Timetable
We’ve outlined the various stages of a PhD and the approximate duration of a PhD programme which you can refer to when designing your own research study.
7. Bibliography
Plagiarism is taken seriously across all academic levels, but even more so for doctorates. Therefore, ensure you reference the existing literature you have used in writing your PhD proposal. Besides this, try to adopt the same referencing style as the University you’re applying to uses. You can easily find this information in the PhD Thesis formatting guidelines published on the University’s website.
Finding a PhD has never been this easy – search for a PhD by keyword, location or academic area of interest.
Questions & Answers
Here are answers to some of the most common questions we’re asked about the Research Proposal:
Can You Change a Research Proposal?
Yes, your PhD research proposal outlines the start of your project only. It’s well accepted that the direction of your research will develop with time, therefore, you can revise it at later dates.
Can the Potential Supervisor Review My Draft Proposal?
Whether the potential supervisor will review your draft will depend on the individual. However, it is highly advisable that you at least attempt to discuss your draft with them. Even if they can’t review it, they may provide you with useful information regarding their department’s expertise which could help shape your PhD proposal. For example, you may amend your methodology should you come to learn that their laboratory is better equipped for an alternative method.
How Should I Structure and Format My Proposal?
Ensure you follow the same order as the headings given above. This is the most logical structure and will be the order your proposed supervisor will expect.
Most universities don’t provide formatting requirements for research proposals on the basis that they are a supporting document only, however, we recommend that you follow the same format they require for their PhD thesis submissions. This will give your reader familiarity and their guidelines should be readily available on their website.
Last, try to have someone within the same academic field or discipline area to review your proposal. The key is to confirm that they understand the importance of your work and how you intend to execute it. If they don’t, it’s likely a sign you need to rewrite some of your sections to be more coherent.
Browse PhDs Now
Join thousands of students.
Join thousands of other students and stay up to date with the latest PhD programmes, funding opportunities and advice.
Unraveling the Mysteries of PhD Project Topics Selection
Blog Summary
A PhD requires distinct skill sets from a master’s and a bachelor’s. The biggest obstacle for PhD candidates is choosing a project subject or problem statement. This blog article aims to inform readers about how to select and complete their PhD projects. Your inner motivation and areas of interest should be the top considerations while selecting your specialization. Never start a PhD program without getting clarification on the research labs you should choose. For application alerts, while enrolled in your master’s program, register with PhD Portals. Select an interest-provoking subject, then read everything there is to know about it. A successful thesis requires adhering to the “Write, Rewrite, and Write” cycle.
How Do I Choose a PhD Project?
What makes a good phd project, tips to apply for a phd project, tips to write your phd thesis, why tsl-ucn, start your journey to obtaining a phd.
Pursuing a PhD, unlike your master’s or bachelor’s program, demands altogether different skill sets. You have a fixed set of subjects with some open elective and core-elective to study in those programs. But in a PhD program , you are aware of your stream of study like computer science, management, finance, humanities, etc.
But the PhD project topics on which you carry out research are wide open. You are supposed to narrow down to a particular thesis topic idea or field of study. Selecting a PhD project topic or problem statement is the biggest challenge for PhD students. This blog post attempts to educate scholars on selecting a PhD project of their choice and completing it.
Choosing a PhD project topic is the primary work in pursuing a PhD program. It is not like choosing an undergraduate or postgraduate program. It demands patience. So, take your time.
Next, you should be in a position to decide what type of PhD project you want to pursue. Broadly there are three types of PhD projects:
- Advertised PhD projects
- Self-proposed PhD projects
- Professional Doctorates
The Advertised Projects are common in Science, Technology, Engineering, and Medicine (STEM) . Research groups and Well-established laboratories offer these programs.
The Self-proposed projects are common in the Humanities and Arts arena. Here, you are free to choose a thesis topic as long as it falls in the purview of a research topic.
Professional Doctorates in vocational subjects like Business and Management awarded to practitioners are not academic qualifications.
A PhD project should, first of all, have a clear goal. So, it starts with a proposal. A PhD proposal is a clear and concise document illustrating the problem statement and the goals of your work. It should also highlight why it is worth pursuing?
A typical PhD project involves Five steps:
- Identifying a problem statement
- Carrying out a comprehensive literature review
- Conducting Original Research and finding out results
- Producing a Thesis that documents your results
- Writing the thesis and taking up Viva-Voce
Tips for choosing a PhD project and topics
Here you have two sets of Tips:
- Tips to Apply for a PhD project and choosing a PhD project topic
1. Be Aware of Your Niche
Just because you are a computer science postgraduate and AI or Data Science is the trend; You needn’t select these areas. What matters is your interest and inner drive that should be the priority in choosing your niche.
2. Your Comfort Level to Relocate to Another City
Once you have identified your niche and the University/Research Labs, you may have to relocate to a new city. Make up your mind to relocate and also be decisive in making your choice.
3. Identify the Departments and Research Labs Succinctly
You are supposed to conduct a lot of research before boiling it down to a particular Department or University. This is a necessity as it is crucial to identify your core interests and ideas.
4. Obtain Clarity from Your Research Supervisor
Never dive into a PhD program without seeking clarity about the Research labs you are supposed to join. If it is a funded project, get clarification about all facts that are not obvious. Have one to one discussion with your Research Supervisor over Skype or any messenger to seek clarity regarding questions like,
- How many people work in the lab?
- What are their designations?
- Are you supposed to collaborate with any of them?
5. Register with PhD Portals to Get Application Alerts
During your Master’s Program, register with online portals that provide information on PhD programs offered by various Labs and Universities. This helps you to be informed about itineraries of multiple institutes.
6. Seek Seniors and Teachers Help
Ignorance is the biggest culprit that sinks your career ship. Regardless of how small your doubt is, get it clarified from your professors and seniors. Discuss issues like how to formulate an email, cover letter, resume, and other application procedures.
7. Understand the Team Well
It is not only the project that should create enthusiasm; it is also the team you will be working with. The team is vital to complete a project. Before diving into a project, try to understand whether you can get along with your teammates.
8. Different Types of Funding Exists
When you apply for funded projects, you often come across various types. Some are not funded, while some are competition-funded also. Your enthusiasm for getting into the project plays a vital role in the supervisors picking you in competitive funding. So, Love your work to the core.
9. Always Apply for More than One University/Institute
Prepare as many applications as possible and shoot them to different institutes. This process provides a wide array of experience in how to draft an application and approach the institutes. Such skills will help you in the long term.
10. Failure is the Stepping Stone to Success
You might fail once or twice in getting shortlisted or fail to perform in the interview. The number of interviews you have faced will help nurture your interpersonal skills.
Below are the general tips any PhD scholar should follow to be successful.
- While choosing a PhD project topic most crucial parameter is to rely on a topic that is interesting for you.
- Thoroughly read everything about the topic.
- Find a theoretical basis to support your idea.
- Be prepared to shift gears as the research progresses and your presumptions about the outcomes change.
- Be open to taking inputs from others to fine-tune your views.
- Formulate a committee of researchers,
- Be diligent in gathering data.
- The Panache for Effective Thesis Writing is Follow ing the “Write, Rewrite, and Write” Cycle. It doesn’t matter if your writing is good or bad; take tips from professional writers online. Most importantly, Good writing is all about Editing again and again. So, never feel daunted by Thesis writing; enjoy every bit of it.
- Sit with your Research Supervisor and prepare well-structured content with a Table of Content adequately defined. Regardless of being an expert writer or novice, your first draft always needs tweaking. Never be disheartened by re-editing work patience is key here.
- Thesis Writing needn’t be boring and monotony work. Bring in flair to your writing by inserting adjectives, says, expert writers.
- A chronologically written thesis is a misconception. As soon as you complete a piece of experiment or research, document it neatly when it is fresh in your mind. Later it can be integrated into the Final Thesis as per the Table of Contents.
- Once you research and write a chapter, take a break and come back with a critical perspective to discover possible mistakes. This always helps. Do not write in a marathon-style take breaks.
- Plagiarism is the biggest enemy of any research document. Whenever you quote an existing work, paraphrase properly and provide references and citations.
- All universities have their Templates and Preferred Style of References . Religiously stick to the guidelines given by your university.
- Follow the same house style of spellings does not club “-ize” with “-ise” styles. If you prefer to use “improvize,” use it in all places, do not mix up with “improvise.”
- While quoting from other sources, ensure that you do not make spelling mistakes. Copy the quotes exactly.
- Your thesis is the window to showcase both your professionalism and research abilities to the outer world. Work with diligence and give it a professional appeal.
Taksha Smartlabz in association with the University of Central Nicaragua (TSL-UCN) provides various PhD programs with an advanced blended learning system that is designed with working professionals in mind. It provides the opportunity to study from anywhere and at any time.
Taking up a PhD project involves various steps. Initially, you have to identify the domain of your interest and apply for a university or research lab. On getting selected, get involved in the meticulous work of carrying out research, documenting your findings, publishing papers, coming up with thesis work, and defending your work in research gathering.
The process of selecting your PhD project is the most crucial step in the entire process. Understanding whether you are looking out for Advertised/Self Proposed PhD projects or Professional Doctorates is vital in the initial stages.
Enroll now, to reap the benefits of this program, and obtain a PhD in your niche.
Subscribe For Newsletter
Select Category School of Public Health and Social Work School of Business Management and Public Administration School of Research School of Nursing
Select Program Ph.D in Public Health Master of Public Health Doctor of Public Health Administration
Ph.D in Management Doctor of Business Administration
Ph.D in Clinical Research
Ph.D in Nursing
From Zambia to the World: Toddy Sinkamba’s Journey to a PhD in Nursing
Is an executive master of business administartion right for you find out, social workers who earn the most: top specializations, the ultimate career advancement: value of an online emba, a testimonial of texila’s phd in social work experience, related posts, how can a school principal perform effectively with a doctorate in education, the pros and cons of a part-time phd, everything you need to become a counseling psychologist, mental health matters: a clinical approach, counseling psychology and its role in managing stress in older adults, is an online phd program worth it find out now.
- More Networks
How to write a research proposal
What is a research proposal.
A research proposal should present your idea or question and expected outcomes with clarity and definition – the what.
It should also make a case for why your question is significant and what value it will bring to your discipline – the why.
What it shouldn't do is answer the question – that's what your research will do.
Why is it important?
Research proposals are significant because Another reason why it formally outlines your intended research. Which means you need to provide details on how you will go about your research, including:
- your approach and methodology
- timeline and feasibility
- all other considerations needed to progress your research, such as resources.
Think of it as a tool that will help you clarify your idea and make conducting your research easier.
How long should it be?
Usually no more than 2000 words, but check the requirements of your degree, and your supervisor or research coordinator.
Presenting your idea clearly and concisely demonstrates that you can write this way – an attribute of a potential research candidate that is valued by assessors.
What should it include?
Project title.
Your title should clearly indicate what your proposed research is about.
Research supervisor
State the name, department and faculty or school of the academic who has agreed to supervise you. Rest assured, your research supervisor will work with you to refine your research proposal ahead of submission to ensure it meets the needs of your discipline.
Proposed mode of research
Describe your proposed mode of research. Which may be closely linked to your discipline, and is where you will describe the style or format of your research, e.g. data, field research, composition, written work, social performance and mixed media etc.
This is not required for research in the sciences, but your research supervisor will be able to guide you on discipline-specific requirements.
Aims and objectives
What are you trying to achieve with your research? What is the purpose? This section should reference why you're applying for a research degree. Are you addressing a gap in the current research? Do you want to look at a theory more closely and test it out? Is there something you're trying to prove or disprove? To help you clarify this, think about the potential outcome of your research if you were successful – that is your aim. Make sure that this is a focused statement.
Your objectives will be your aim broken down – the steps to achieving the intended outcome. They are the smaller proof points that will underpin your research's purpose. Be logical in the order of how you present these so that each succeeds the previous, i.e. if you need to achieve 'a' before 'b' before 'c', then make sure you order your objectives a, b, c.
A concise summary of what your research is about. It outlines the key aspects of what you will investigate as well as the expected outcomes. It briefly covers the what, why and how of your research.
A good way to evaluate if you have written a strong synopsis, is to get somebody to read it without reading the rest of your research proposal. Would they know what your research is about?
Now that you have your question clarified, it is time to explain the why. Here, you need to demonstrate an understanding of the current research climate in your area of interest.
Providing context around your research topic through a literature review will show the assessor that you understand current dialogue around your research, and what is published.
Demonstrate you have a strong understanding of the key topics, significant studies and notable researchers in your area of research and how these have contributed to the current landscape.
Expected research contribution
In this section, you should consider the following:
- Why is your research question or hypothesis worth asking?
- How is the current research lacking or falling short?
- What impact will your research have on the discipline?
- Will you be extending an area of knowledge, applying it to new contexts, solving a problem, testing a theory, or challenging an existing one?
- Establish why your research is important by convincing your audience there is a gap.
- What will be the outcome of your research contribution?
- Demonstrate both your current level of knowledge and how the pursuit of your question or hypothesis will create a new understanding and generate new information.
- Show how your research is innovative and original.
Draw links between your research and the faculty or school you are applying at, and explain why you have chosen your supervisor, and what research have they or their school done to reinforce and support your own work. Cite these reasons to demonstrate how your research will benefit and contribute to the current body of knowledge.
Proposed methodology
Provide an overview of the methodology and techniques you will use to conduct your research. Cover what materials and equipment you will use, what theoretical frameworks will you draw on, and how will you collect data.
Highlight why you have chosen this particular methodology, but also why others may not have been as suitable. You need to demonstrate that you have put thought into your approach and why it's the most appropriate way to carry out your research.
It should also highlight potential limitations you anticipate, feasibility within time and other constraints, ethical considerations and how you will address these, as well as general resources.
A work plan is a critical component of your research proposal because it indicates the feasibility of completion within the timeframe and supports you in achieving your objectives throughout your degree.
Consider the milestones you aim to achieve at each stage of your research. A PhD or master's degree by research can take two to four years of full-time study to complete. It might be helpful to offer year one in detail and the following years in broader terms. Ultimately you have to show that your research is likely to be both original and finished – and that you understand the time involved.
Provide details of the resources you will need to carry out your research project. Consider equipment, fieldwork expenses, travel and a proposed budget, to indicate how realistic your research proposal is in terms of financial requirements and whether any adjustments are needed.
Bibliography
Provide a list of references that you've made throughout your research proposal.
Apply for postgraduate study
New hdr curriculum, find a supervisor.
Search by keyword, topic, location, or supervisor name
- 1800 SYD UNI ( 1800 793 864 )
- or +61 2 8627 1444
- Open 9am to 5pm, Monday to Friday
- Student Centre Level 3 Jane Foss Russell Building Darlington Campus
Scholarships
Find the right scholarship for you
Research areas
Our research covers the spectrum – from linguistics to nanoscience
Our breadth of expertise across our faculties and schools is supported by deep disciplinary knowledge. We have significant capability in more than 20 major areas of research.
Research facilities
High-impact research through state-of-the-art infrastructure
Stack Exchange Network
Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
How to find a good topic for a PhD research proposal?
In many countries an application for a PhD position includes a written research proposal, so my questions is what are some advises/strategies to come up with a good topic/idea for a PhD research proposal and how can one assess the quality/fruitfulness of an idea ? As an undergraduate student one just doesn't have the experience to foresee which ideas might have promising research results and which probably won't have. (And I doubt that potential supervisors have the time to comment on every idea of every potential applicant in cases where it is possible to establish some kind of contact before the actual application.)
- graduate-admissions
- application
- research-topic
- It seems unwise to undertake a PhD without at least a general topic already in mind. In my (very limited) experience students already have research experience and have established research relationships with faculty. For example, the fourth year of my undergrad ("Honours" in Australia), was a year supervised research. This is how I developed my research interests and found a supervisor. – Stephen Tierney Commented Apr 23, 2013 at 11:07
- 1 This is an extremely popular paper on the subject: weizmann.ac.il/mcb/UriAlon/nurturing/HowToChooseGoodProblem.pdf – Bitwise Commented Apr 23, 2013 at 17:57
5 Answers 5
- Jot down your interests.
- Future goals (long term and short term). Doesn't have to be accurate but just to give you the "big picture".
- Speak with your PhD advisor (if you already have one).
- Align his/her interests with yours and see if you have common ground (you may need to lean towards his interests or find another advisor)
- Once you have a list of topics that you could explore, do a literature review and figure out for what topics you'd have a taste.
Each person has his own formula on what to choose as their PhD proposal. This was the way I went about it.
PhD (Mechanical Engineering Expected Fall 2012)
- 3 I would stress that you should speak to your potential advisor (even if you don't have one yet!). You certainly shouldn't submit something that no potential supervisor has ever seen. This is not necessarily because the proposal would be better with their help, but there might be nobody who would be able to advise you. – Lars Kotthoff Commented Feb 15, 2012 at 19:21
- Thanks for the answer! The problem in many european countries is, that you don't apply for graduate school and then find a topic and supervisor at the university which accepted you (i believe this is how it works in the U.S.?), but you are supposed to come up with something in before (when you apply in the first place). See e.g. in this example what the applicants and their proposals will be judged on. – tobigue Commented Feb 15, 2012 at 19:34
- Regardless of what it says officially, it's always a good idea to at least establish contact with your potential advisor. If anything, it will show them that you're motivated. I think most people will be happy to give you at least some feedback on your proposal. – Lars Kotthoff Commented Feb 15, 2012 at 20:13
- 4 In most cases I know (Europe, Physics) the research proposal was written together between the PhD advisor and the candidate, or by the PhD advisor. You could in theory start without an advisor, but in practice almost everyone finds one before starting. – finitud Commented Jul 7, 2014 at 10:18
In your case, I would find scientific publications aimed at the student/general population in your field, and read the articles written for the public. Both Science and Nature will have numerous articles in each issue that can be read and understood by the general public. Some subfields have publications directed specifically at the student/enthusiast population (such as IEEE Spectrum for Engineering).
By reading through these publications, you will get a sense for what the current major research focus is in a wide variety of fields, and you'll get a feel for what's interesting to you.
Talk to professors in fields that interest you! You'd be surprised at how many professors (admittedly, not all of them) would be willing to spend 15 minutes talking to you about their research, and their field in general. I'm not going to say "showing initiative is key to making progress", because it's not, but it can help, and you'll learn a tremendous amount this way.
Find a subject that you really really are passionately interested in, and care about finding out more about it. This subject is going to become almost your entire life for a few years, and you will need huge dedication to it, in order to complete.
Talk, ideally over a coffee, but by phone or (worst-case) email if you can't meet in person, with people who recently completed their PhDs and are now actively researching in this field; discuss your ideas and recent developments in the field.
Find an area that your intended supervisor is up-to-date in.
If you do it right, your PhD will lead you to knowing more than anyone else in the world about this very very specific subject: so it will really help if you're going to be keen to pursue it as a career after completing your PhD, even after writing several papers and making plenty of conference presentations on it.
One aspect of a PhD is pursuing original research in your given field. I believe it is hard for an undergraduate to know what research has / hasn't been in covered in all of the topics they may be interested in.
Therefore, I would advise that you consider the topics you are interested in, and find out which Researchers / Professors are working in those fields, in the universities that you are considering. Then, you should ask them what they are working on at the moment, and what potential projects they would have in mind for a new PhD student joining them. This will give you a feel for the kind of research that you could be doing.
There are already very good answers above; I would only like to add that you should also take into account whether you can get a scholarship/funding for your research topic. Your personal interests may not necessarily align with those of your potential funders. Consider how much you would be willing to compromise your own interests to be able to receive a scholarship. Most people cannot support themselves financially through the course of a PhD programme, so this point is not to be underestimated.
If you apply for a government scholarship for example, they will likely want you to study a topic that is of high policy relevance to them and you need to think about whether you can offer that or modify your original ideas in such a way that they will meet the policy priorities of the government at the point of application. Governments tend to publish their strategic priorities in various documents online, so it will not be difficult to make the connections between your research and their needs.
University departments giving scholarships tend to be more flexible with regard to research topics as long as the quality and originality of the proposed research is high, but again, it would be best to get an opinion from a member of the department on the chances of your proposal attracting sufficient interest that it will get funding.
Without funding, it will be close to impossible to do a PhD.
You must log in to answer this question.
Not the answer you're looking for browse other questions tagged phd graduate-admissions application research-topic ..
- Featured on Meta
- Upcoming sign-up experiments related to tags
Hot Network Questions
- Am I wasting my time self-studying program pre-requisites?
- How to draw a number of circles inscribed in a square so that the sum of the radii of the circle is greatest?
- Bibliographic references: “[19,31-33]”, “[33,19,31,32]” or “[33], [19], [31], [32]”?
- Would killing 444 billion humans leave any physical impact on Earth that's measurable?
- Could alien species with blood based on different elements eat the same food?
- How to use "given" in expository writing.
- Could an Alien decipher human languages using only comms traffic?
- Why focus on T gates and not some other single qubit rotation R making Clifford + R universal?
- Is parallel motion between the melody and one " inner voice" within the accompaniment considered bad voice leading?
- I have an active multiple-entry C1 US visa. I also have a Canadian citizenship certificate. Need to travel (not transit) US in 20 days. My options?
- Story featuring an alien with an exotic sensorium (sonar?) that helps solve a murder
- How to modify overlay specifications in a new command in LaTeX Beamer?
- How did the `long` and `short` integer types originate?
- Is there any reason to keep old checks?
- Does it matter to deselect faces before going back to Object Mode?
- Where did Borobudur's stones come from?
- KiCad footprint pad clearance not applied
- BIOS support for 286 Protected Mode
- If "Good luck finding a new job" is sarcastic, how do I change the sentence to make it sound well-intentioned?
- Why was the SNES color gamut RGB?
- English translation of a quatrain from the "Rubaiyat" of Omar Khayyam
- Tool Storage Corrosion Risk
- How are secret encodings not a violation of amateur radio regulations?
- Is intrinsic spin a quantum or/and a relativistic phenomenon?
Griffith University
Popular sites
Home > Research study > Choose your research topic
- Choose your research topic
- Find a supervisor
- Scholarship application tips
- Griffith Graduate Research School
Develop a research proposal
Once you have established that you meet entry requirements for your preferred program, you need to clarify your chosen area of study and identify a research area and/or research question, clarify its importance and prepare a research proposal. Your research question will provide the key research focus for the full duration of your degree so it is important that you consult a wide variety of resources and select a topic you feel highly motivated to investigate. Depending on your area of study and research, you may be starting at the very beginning or you may already have a research topic or area of focus from an already established research team.
How to choose your research topic
Choosing a research topic and writing your research proposal can be difficult when you're faced with a lot of choice. Current Griffith PhD candidates and supervisors give some advice to help you create a winning research proposal.
How to develop a research proposal
Think carefully about your motivation to complete an HDR program—what are you passionate about, what topic or question or problem do you want to tackle? Remember you will be spending a lot of time on this topic so a keen interest is a must.
Find a connection with a Griffith school, department, research centre or institute to find a match for your research area and/or research question. Some research centres and institutes have proposed research projects and hot topics for prospective candidates.
Find out more
Narrow your focus to a single research topic. Once you have connected with your prospective supervisor, it is important that you seek their input and advice on your research proposal. Developing a research proposal is an iterative process, so expect to work on a number of drafts before you finalise your research proposal. You need to allow time to prepare multiple drafts and seek feedback along the way. Your potential supervisor is the best person to contact, so make sure you reach out to find one as soon as possible. Where applicable, this may also be an appropriate time to seek a connection with an industry partner or external organisation who could collaborate on your research. They will also provide input to your research proposal.
Your draft research proposal should include the following:
- Student name
- Dissertation/thesis title
- Summary of project (maximum 100 words)
- Rationale—brief review of relevant research in the field
- Statement of the principal focus of intended research
- Significance of the study
- Intended methodology and project feasibility
- (Where applicable) details of an industry partner or external organisation’s involvement in project
- Anticipated project costs (if required by your enrolling school or research centre)
- Any requirements for specialist equipment or resources.
Your proposal should be no longer than 2–3 pages.

Professors' advice
What you’re doing is something that nobody else has ever done before, so you’re going to come across problems that nobody has solved before.
Professor Robert Sang
In preparing a research proposal for your application, keep in mind the objective, which is to demonstrate that you have thought about the topic deeply, have some interesting ideas about the topic, and have considered possible methodologies of research and the project’s feasibility. It is advantageous to show why you think that your chosen topic is significant or interesting.
Professor Gerry Docherty

Choosing Topics for PhD Applications: Your Ultimate Guide
Are you considering applying for a PhD program? Congratulations on taking the first step towards advancing your academic career! However, with this exciting opportunity comes the daunting task of deciding which topic to pursue in your application. As an applicant, you want to choose a topic that not only aligns with your interests and strengths but also stands out among other applicants. With so many options available, it can be overwhelming and intimidating to make this decision. But fear not, because in this blog post we will provide you with the ultimate guide on choosing topics for PhD applications that will help set you apart and increase your chances of being accepted into a program. So buckle up and get ready to discover how to leave a lasting impression through an impressive choice of topic.
Navigating PhD Application Topics: US vs UK Perspectives
In both the US and UK, the potential topic of your PhD application plays a critical role in the admission process; however, there are key differences to consider. In the US, your research proposal is less emphasized in the initial application. Students often spend their first couple of years on coursework before defining their research topic alongside their chosen advisor. Conversely, in the UK, students are expected to present a detailed research proposal right from the application stage. The proposal should outline the research question, methodology, and proposed timeline, demonstrating the applicant’s capability to conduct independent research. This divergence stems from the different philosophies of doctoral studies between the two countries, with the US favoring a more holistic approach and the UK favoring a more specialized and targeted one.
When preparing your statement of purpose for a PhD application, it’s crucial to tailor your approach to the requirements and expectations of either the US or UK education system, as they differ significantly.
If you are applying to a US institution, your statement should reflect a wide-ranging understanding of your chosen field, highlighting your academic achievements and intellectual curiosity. You aren’t expected to fully commit to a particular research question at this stage.
On the other hand, having a specific research topic in your statement of purpose can stand you in good stead, even when applying to US institutions. A well-defined research question demonstrates your ability to think critically, your understanding of the field, and your aptitude for independent study. This can leave a lasting impression on the admissions committee and distinguish your application from others. While it’s not mandatory to stick to this topic throughout your PhD, it serves as an indicator of your research interests and potential.
Conversely, if you are applying in the UK , your statement should demonstrate a focused and informed understanding of your proposed research topic. You should provide details of your research question, proposed methodology, and tentative timeline. This shows your ability to conduct specialized, independent research. Capture your awareness of the research landscape and show how your work would contribute to the existing body of knowledge.
In either case, remember to emphasize your passion for your chosen field, your preparedness to undertake rigorous academic work, and your potential to contribute meaningfully to the academic community.

Trust the adventure
Embarking on a PhD journey often feels like stepping into the unknown; it’s a venture filled with opportunities for personal and professional growth. Embracing the mantra ‘Trust the adventure’ when choosing potential topics for PhD applications translates into maintaining an open mind towards unexplored research areas that spark your curiosity. It’s about daring to venture beyond your comfort zone and delving into fields that might initially seem daunting or tangential to your primary area of interest. Often, the most groundbreaking discoveries occur at the intersection of disparate disciplines. By allowing your curiosity to guide you, you may find yourself at the forefront of innovative research, breaking new ground and contributing novel insights to your field of study.
Start brainstorming early
As you embark on your PhD journey, the importance of starting your brainstorming early cannot be overstated. It isn’t a process that should be hurried; rather, it is a thoughtful exploration of potential research topics that may serve as the cornerstone for your academic pursuits. The sooner you engage in this intellectual exploration, the more time you will have to thoroughly investigate. This early onset not only allows you to refine your interests but also provides ample time to assess the feasibility and scope of your research. Remember, a PhD is a commitment of several years; hence, the topic you choose should not only intrigue you, but it should also have the potential to contribute significant insights to your chosen field. Nurturing your ideas from the embryonic stage can lead to a robust research proposal that is both innovative and achievable.

Follow your interests
When considering potential topics for your PhD applications , it’s crucial to align your research interests with these topics. The essence of a PhD journey is the passion, curiosity, and intellectual excitement that a research question can inspire within you. This is not just about finding a suitable topic; it is about identifying an area or question in your chosen field that truly resonates with you. Choosing to explore an issue that you are genuinely interested in can make the process of researching and writing significantly more engaging, and it often results in higher-quality work. This is mainly because passion fuels perseverance, a trait indispensable when facing inevitable research hurdles. It’s important to remember that a PhD is not a sprint; it’s a marathon that requires sustained interest and dedication over several years. Hence, following your interests can serve as a guiding compass in the vast sea of research possibilities, leading you towards a topic that could potentially sustain your motivation throughout your PhD journey.
Look for gaps in existing research
When examining potential topics for PhD applications, identifying gaps in existing research is a crucial step. This process involves critically analyzing current literature in your field of interest and determining what questions have been left unanswered. These gaps may represent areas of study that have been overlooked, underdeveloped, or yet to be explored in depth. By focusing on these gaps, your research could answer lingering questions or clarify ambiguities in your field. This approach requires a fine balance of critical thinking, creativity and intellectual curiosity as you seek to identify not only what is known but, more importantly, what remains to be discovered. Ultimately, pursuing these areas of uncharted knowledge allows you to expand on existing research in a meaningful and impactful way.

Consider broader trends and themes
When exploring potential topics for PhD applications, it’s essential to consider broader trends and themes within your field. These often reflect the evolving dynamics and directions in which your discipline is headed. Engaging with these emerging themes can position your research at the forefront of academic thought and debate. Consider how your unique perspectives or insights could contribute to these conversations. Maybe you’ve observed a trend that others haven’t, or perhaps you can apply a new theoretical framework that could shed light on these emerging themes. By aligning your research with these broader trends, you not only increase its relevance and potential impact, but also demonstrate your ability to contribute meaningfully to your field. Remember, a PhD isn’t just an academic endeavour, but a conversation with the broader academic community.
Talk to professors and professionals
Engaging in detailed conversations with professors and professionals in your field can provide invaluable insights when it comes to identifying potential PhD research topics. These individuals possess a wealth of knowledge and experience, have a deep understanding of the current landscape of the field, and are usually up-to-date with the latest research trends and emerging topics. Conversing with them can help broaden your perspective, provide new angles for your research, and even challenge preconceived notions you may have. They may highlight certain areas of study that you might not have otherwise considered or share their own experiences and challenges they faced during their research journey. Furthermore, they can guide you towards resources and literature that could be instrumental in shaping the direction of your PhD research . Therefore, it is crucial to leverage their expertise and experiences as you navigate the terrain of potential PhD research topics.
Review conference programs and journals
Reviewing conference programs and academic journals in your field is another strategic way to discover potential PhD research topics. These platforms often spotlight novel theories, groundbreaking methodologies, and recurring themes in the discipline, giving you a sense of the most pressing issues and the direction the field is moving in. Conferences and journals disseminate cutting-edge research and are the venues where scholars introduce innovative ideas and paradigms, and discuss and challenge current thinking. By studying these resources, you can identify patterns, trends, and gaps in the existing literature, which could lead to a unique and relevant PhD research topic. For instance, a particular theme may repeatedly appear but lacks comprehensive exploration, or there might be contradictory findings that require further investigation. Additionally, you may uncover a novel approach to an issue that has never been applied before, presenting an opportunity to extend its application and contribute a new perspective to your field. Hence, staying informed about these platforms can help you find a research topic that is both of interest to you and of value to your field.

Connect topics to your skills and background
Connecting potential topics to your skills and background is critical when exploring potential topics to write about in your statement of purpose for PhD applications. This exercise not only allows you to capitalize on your unique strengths, experiences, and knowledge but also enables you to showcase your ability to contribute significantly to the field of study. For instance, if you have extensive experience in data analysis, you might consider focusing on a research topic that would benefit from this expertise. Similarly, if your background is in a unique area, perhaps you could integrate this into your research by investigating a topic that intersects your field of study and your unique background. By relating your research topic to your skills and background, you convey to the admissions committee that you are not just academically capable but also bring a unique perspective to the table, thus elevating your candidacy. Therefore, reflecting upon and articulating your unique skills, experiences, and background in relation to your potential research topic can make your statement of purpose more compelling and increase your chances of acceptance.
Experiment with different angles
Experimenting with different angles or giving fresh twists to topics can be a valuable tactic when selecting a PhD research topic. This approach involves looking at common or established topics from a new perspective or applying novel methodologies or theories. For instance, you might study a well-known issue but through the lens of a lesser-explored theoretical framework, or apply an established method to a new population or context. Such innovative twists can yield unique insights, thereby adding value to the field and setting your application apart. By demonstrating your ability to think creatively and critically, you showcase your potential to make original contributions to your discipline. Moreover, this approach can also demonstrate your adaptability and resilience, traits that are highly valued in research environments. However, it’s essential to balance this originality with feasibility. Ensure that your ‘twist’ is not so out-of-the-box that it becomes impossible to manage within the scope of a PhD program , or doesn’t resonate with potential advisors or funding bodies. So, while you dare to think differently, also ensure your topic is grounded in academic rigour and practical viability. This delicate balance between originality and pragmatism can truly give you a competitive edge in your PhD applications .

Don’t be afraid to rework your ideas
Embracing flexibility in refining your research ideas is not just beneficial but often necessary for a robust research plan to discover topics for PhD applications. When scouting potential topics for your statement of purpose, don’t feel constrained by your initial ideas. As you delve deeper into the literature and engage in academic discussions, you may find angles or aspects that necessitate a rethinking or reshaping of your original concept. Perhaps new findings emerge that challenge your initial assumptions or the practicality of your methods, or perhaps feedback from a trusted mentor or peer points towards a more fruitful direction. In such instances, don’t hesitate to rework your ideas. This process is not indicative of failure, but of growth and refinement. It demonstrates your capacity to understand, adapt and improve, which are critical skills for any successful researcher. In fact, a proposal that has been iteratively refined may likely be more compelling and robust than one that hasn’t been questioned or challenged. Remember, the ultimate goal is not to stick to your first idea, but to arrive at a research question that is meaningful, manageable and has the potential to contribute significantly to your field. Hence, see this process of reworking and refining as a journey towards a stronger, more compelling research proposal

Trust your instincts
Trust in your instincts is a key guiding principle when choosing potential topics for PhD applications. This is not to say that you should ignore practical considerations or informed advice, but it means that at the core of your decision-making process, your innate curiosity and intellectual passion should have a significant role. It is this curiosity that will sustain your motivation during the challenging journey of in-depth research. When you stumble upon a topic or a research question that sparks your interest and makes you want to delve deeper, pay close attention. If it keeps drawing you back, it might just be the right path for you. This innate draw towards a topic often signifies a personal connection, a vested interest, and a level of commitment necessary for rigorous scholarly research. It’s like a compass pointing you towards the areas where you can make significant contributions. So, as you navigate the complex landscape of research topics, remember to trust your instincts and let your innate curiosity guide you towards the right path.
In conclusion, applying for a PhD program is an exciting but challenging journey. Choosing the right topics for PhD application can be intimidating, but with our guide, you now have the tools to make a well-informed decision. Remember to align your interests and strengths while also standing out from the competition with your topic choice. And if you feel like you need an extra boost for your application, don’t forget to check out our statement of purpose services specifically tailored for PhD applicants. This could be just the edge you need to secure your spot in a prestigious program. So don’t let fear hold you back, take the leap and start crafting your impressive application today. Trust us when we say that all of your hard work and dedication will be worth it in the end when you are accepted into the PhD program of your dreams. Congratulations once again on taking this courageous step towards advancing your academic career. We wish you the best of luck in all of your future endeavors!
With a Master’s from McGill University and a Ph.D. from New York University, Dr. Philippe Barr is the founder of The Admit Lab . As a tenure-track professor, Dr. Barr spent a decade teaching and serving on several graduate admission committees at UNC-Chapel Hill before turning to full-time consulting. With more than seven years of experience as a graduate school admissions consultant, Dr. Barr has stewarded the candidate journey across multiple master’s programs and helped hundreds of students get admitted to top-tier graduate programs all over the world .
Subscribe to our YouTube c hannel for weekly tutorials on navigating the graduate application process and making the most of your graduate school journey.
Share this:
Join the conversation.
- Pingback: Statement of Purpose: A Complete No BS Guide - The Admit Lab
- Pingback: Economics PhD Statement of Purpose Tips - The Admit Lab
- Pingback: Tips For A Winning PhD Research Statement - The Admit Lab
- Pingback: Average Age of PhD Student: How Old Is Too Old? -
- Pingback: How to Write About Your Research Interests 101 -
- Pingback: PhD Interview: How to Kill It -
Leave a comment
Leave a reply cancel reply, discover more from admit lab.
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
- Interesting for you
- My settings

How to Write a Successful PhD Research Proposal
What is a research proposal.
A research proposal is a document of around 3,000-4,000 words outlining the research you are going to undertake. The majority of universities require PhD applicants to submit a research proposal when applying for a PhD position.
Find PhD programmes abroad
Why a research proposal?
Apart from being an essential requirement for PhD entry, a research proposal helps your future supervisors to better understand your line of thinking, experience in doing research and how you are planning to go about writing your thesis. In addition to this, a research proposal is a great tool that can help you to structure your thinking and outline the path you would like to follow during your PhD studies.
What should I include in a research proposal?
Before you start writing a research proposal, carefully check the website of the university you are applying for. Many universities provide guidelines on writing research proposals that will help you both to structure your thinking and meet the requirements of a specific university.
Regardless of university specific requirements, most of the research proposals usually include:
- Title and abstract: In case of predefined PhD projects, a title is usually provided by the university. In other cases, an applicant is expected to provide a preliminary title which will be further elaborated in the process of thesis writing. An abstract should usually be no longer than a page, and provide a brief summary of what you are going to cover in your research proposal.
- Literature review: The literature review demonstrates the applicant’s knowledge of the main research achievements in the area of study. You should pay attention to providing some of the key references in your area of research which requires doing extensive research on your part.
- Research problem, aim and objectives: As a result of your literature review, you should identify the main gap in your research area on which you are going to focus in your PhD project. Once the research problem is identified, you will be able to pose the main aim and objectives of your project.
- You should dedicate some space to Research methodology , or, in other words, explaining how you are going to go about doing your research. This section also demonstrates your knowledge of the existing research methodologies in your area of study.
- Ethical considerations: You should check some literature on ethics of conducting research in your area and outline some key ethical aspects related to the proposed project.
- Increasingly applicants are asked to outline the impact of their research studies . This can include both the impact on your research area and society in general. It is important to dedicate some time to this section since it will add more value to your proposal.
- References: Do not forget to specify all the references at the end of the proposal.
An obvious but very important point is the format of your research proposal. Make sure that the formatting of the document is consistent throughout and that the structure is clear. If possible, it can be a good idea to give the document to your academic tutor or colleague for revision.
It is important to remember that a research proposal is a provisional rather than a definitive document. It will most likely change extensively during the first several months of your PhD programme. Nevertheless, at the stage of application it is an essential document that helps evaluators make their decision in relation to your application. Therefore, it is worth investing time and effort in it! Good luck!
Interesting programmes for you
Explore more than 10000 Ph.D. Degrees from all around the world with Studyportals.
Go to your profile page to get personalised recommendations!
School of Sociology, Politics and International Studies
How to write a phd research proposal.
In order to help you with your application, the information below aims to give some guidance on how a typical research proposal might look.
Your research proposal is a concise statement (up to 3,000 words) of the rationale for your research proposal, the research questions to be answered and how you propose to address them. We know that during the early stages of your PhD you are likely to refine your thinking and methodology in discussion with your supervisors.
However, we want to see that you can construct a fairly rigorous, high quality research proposal.
We use your research proposal to help us decide whether you would be a suitable candidate to study at PhD level. We therefore assess your proposal on its quality, originality, and coherence. It also helps us to decide if your research interests match those of academics in the School of Sociology, Politics and International Studies (SPAIS) and whether they would be able to provide suitably qualified supervision for your proposed research.
Format of the research proposal
Your proposal should include the following:
Title. A short, indicative title is best.
Abstract. This is a succinct summary of your research proposal (approximately 200-300 words) that will present a condensed outline, enabling the reader to get a very quick overview of your proposed project, lines of inquiry and possible outcomes. An abstract is often written last, after you have written the proposal and are able to summarise it effectively.
Rationale for the research project. This might include a description of the question/debate/phenomenon of interest; an explanation of why the topic is of interest to you; and an outline of the reasons why the topic should be of interest to research and/ or practice (the 'so what?' question).
Aims and initial research question. What are the aims and objectives of the research? State clearly the puzzle you are addressing, and the research question that you intend to pursue. It is acceptable to have multiple research questions, but it is a good idea to clarify which is the main research question. If you have hypotheses, discuss them here. A research proposal can and should make a positive and persuasive first impression and demonstrate your potential to become a good researcher. In particular, you need to demonstrate that you can think critically and analytically as well as communicate your ideas clearly.
Research context for your proposed project. Provide a short introduction to your area of interest with a succinct, selective and critical review of the relevant literature. Demonstrate that you understand the theoretical underpinnings and main debates and issues in your research area and how your proposed research will make an original and necessary contribution to this. You need to demonstrate how your proposed research will fill a gap in existing knowledge.
Intended methodology. Outline how you plan to conduct the research and the data sources that you will use. We do not expect you to have planned a very detailed methodology at this stage, but you need to provide an overview of how you will conduct your research (qualitative and/or quantitative methods) and why this methodology is suited for your proposed study. You need to be convincing about the appropriateness and feasibility of the approaches you are suggesting, and reflective about problems you might encounter (including ethical and data protection issues) in collecting and analysing your data.
Expected outcomes and impact. How do you think the research might add to existing knowledge; what might it enable organisations or interested parties to do differently? Increasingly in academia (and this is particularly so for ESRC-funded studentships), PhD students are being asked to consider how their research might contribute to both academic impact and/or economic and societal impact. (This is well explained on the ESRC website if you would like to find out more.) Please consider broader collaborations and partnerships (academic and non-academic) that will support your research. Collaborative activity can lead to a better understanding of the ways in which academic research can translate into practice and it can help to inform and improve the quality of your research and its impact.
Timetable. What is your initial estimation of the timetable of the dissertation? When will each of the key stages start and finish (refining proposal; literature review; developing research methods; fieldwork; analysis; writing the draft; final submission). There are likely to overlaps between the stages.
Why Bristol? Why – specifically – do you want to study for your PhD at Bristol ? How would you fit into the School's research themes and research culture . You do not need to identify supervisors at the application stage although it can be helpful if you do.
Bibliography. Do make sure that you cite what you see as the key readings in the field. This does not have to be comprehensive but you are illustrating the range of sources you might use in your research.
We expect your research proposal to be clear, concise and grammatically correct. Prior to submitting your research proposal, please make sure that you have addressed the following issues:
- Have you included a clear summary of what the proposed research is about and why it is significant?
- Have you clearly identified what your proposed research will add to our understanding of theory, knowledge or research design?
- Does it state what contributions it will make to policy and/or practice?
- Does the proposal clearly explain how you will do the research?
- Is the language clear and easy to understand by someone who is not an expert in the field?
- Is the grammar and spelling correct?
Research Proposal Example/Sample
Detailed Walkthrough + Free Proposal Template
If you’re getting started crafting your research proposal and are looking for a few examples of research proposals , you’ve come to the right place.
In this video, we walk you through two successful (approved) research proposals , one for a Master’s-level project, and one for a PhD-level dissertation. We also start off by unpacking our free research proposal template and discussing the four core sections of a research proposal, so that you have a clear understanding of the basics before diving into the actual proposals.
- Research proposal example/sample – Master’s-level (PDF/Word)
- Research proposal example/sample – PhD-level (PDF/Word)
- Proposal template (Fully editable)
If you’re working on a research proposal for a dissertation or thesis, you may also find the following useful:
- Research Proposal Bootcamp : Learn how to write a research proposal as efficiently and effectively as possible
- 1:1 Proposal Coaching : Get hands-on help with your research proposal

PS – If you’re working on a dissertation, be sure to also check out our collection of dissertation and thesis examples here .
FAQ: Research Proposal Example
Research proposal example: frequently asked questions, are the sample proposals real.
Yes. The proposals are real and were approved by the respective universities.
Can I copy one of these proposals for my own research?
As we discuss in the video, every research proposal will be slightly different, depending on the university’s unique requirements, as well as the nature of the research itself. Therefore, you’ll need to tailor your research proposal to suit your specific context.
You can learn more about the basics of writing a research proposal here .
How do I get the research proposal template?
You can access our free proposal template here .
Is the proposal template really free?
Yes. There is no cost for the proposal template and you are free to use it as a foundation for your research proposal.
Where can I learn more about proposal writing?
For self-directed learners, our Research Proposal Bootcamp is a great starting point.
For students that want hands-on guidance, our private coaching service is recommended.

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling short course, Research Proposal Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
You Might Also Like:
10 Comments
I am at the stage of writing my thesis proposal for a PhD in Management at Altantic International University. I checked on the coaching services, but it indicates that it’s not available in my area. I am in South Sudan. My proposed topic is: “Leadership Behavior in Local Government Governance Ecosystem and Service Delivery Effectiveness in Post Conflict Districts of Northern Uganda”. I will appreciate your guidance and support
GRADCOCH is very grateful motivated and helpful for all students etc. it is very accorporated and provide easy access way strongly agree from GRADCOCH.
Proposal research departemet management
I am at the stage of writing my thesis proposal for a masters in Analysis of w heat commercialisation by small holders householdrs at Hawassa International University. I will appreciate your guidance and support
please provide a attractive proposal about foreign universities .It would be your highness.
comparative constitutional law
Kindly guide me through writing a good proposal on the thesis topic; Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Financial Inclusion in Nigeria. Thank you
Kindly help me write a research proposal on the topic of impacts of artisanal gold panning on the environment
I am in the process of research proposal for my Master of Art with a topic : “factors influence on first-year students’s academic adjustment”. I am absorbing in GRADCOACH and interested in such proposal sample. However, it is great for me to learn and seeking for more new updated proposal framework from GRADCAOCH.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly

Book a free consultation
+91-6364827406
+91-9360923317

Get Professional Expert guidance to finish your PhD at ease
- Aug 4, 2021
A Simple Beginner's Guide to PhD Research Topic Formulation
Greetings!!
Are you puzzled as to how you need to formulate a topic for your PhD research work? Feeling obscured under a lot of articles or books that you’ve read which only led to confusion? If it’s been more than a weeks’ time since you started, and one idea after another is running through your mind without any hint like how to mold one idea into a proper research project – you’re certainly feeling the burden!
We are here to help you in bringing up an appropriate approach for a workable research project. In addition, we have a provided a comprehensive 6-step-guideline for “Finding out a good and original PhD research topic”.
What is a ‘PhD research topic’?
There are some misinterpretations and uncertainty around the word ‘topic’, and many PhD scholars thinks that they require a general topic to get started with their research. However, it is not right. Normally, a PhD research topic is the heart of your research project which simply exposes the complete idea of your research work and further by using it, the dissertation/thesis needs to be framed out. In practice, deciding on a research topic and working out your research questions goes hand-in-hand.
Below six steps will guide you in formulating a good research topic for your PhD

Step 1. Research the state-of-art in your interested research domain
Initially find atleast 5-8 appropriate keywords for a literature search.
Further postulate your search regarding literature survey databases which you search, its publishing dates, topographical areas, or applied methods and techniques.
Summarize all the articles which you read and keep reference number for the same, so you can always revisit articles.
Step 2. Breakthrough your project ideas
Identify and write down all the project ideas which comes to your mind. Just gather your thoughts, without critically assessing them.
Find a quiet spot and write out all project ideas that come to your mind. Just collect all your thoughts, without critically evaluating them.
After few days, revisit your ideas and start reviewing and crossing out research ideas which are not worthwhile.
Continue adding new ideas and refine your list, as you go on with the reading process.
Step 3. Slender down your research ideas
After working on this, go through your formulated list and gradually narrow it down to 2-3 best research ideas.
Further to it, start in brainstorming each promising research idea, may be atleast one per day.
Pen down all possible and clear research questions, problem gaps, ideas for experiments/analysis, how to gather pragmatic evidence, hypothesis you’re having etc.
Step 4. Develop a “project work sheet”
Create and maintain a page “project work sheet” that surface out the specifically more about your research project in terms of approach, methods, techniques to be used of and expected outcomes of the research work taken.
The purpose of maintaining this project work sheet is to test how do you feel about the research topic-either positively or indifferent? You have time to work on the research topic for the approaching years. Preferably, you’re passionate about it.
Step 5. Discussing with your research guide/supervisor
Present all the formulated research topic to your supervisor would be always the best choice as they will help you in knowing whether the topics suggested is good to move ahead or need to work upon.
Now, based on their opinion (regarding time, funds, facilities & methods available) move further with any one of the research topics.
Integrate all their feedback on your “project-work sheet” to further polish them.
Step 6. Decide and develop statement of objectives
During this process, you might have decided one topic which is better and stands out with more potential. Go for that and start to further analyze the pro’s and con’s of it. But finally make a decision and move forward.
For the finalized research topic, create atleast 3-6 objectives which briefly gives the research project’s goal. Include research questions to answer or the hypothesis you’ll work with.
Conclusion:
If you’re one among those PhD candidates, it is most important to find your goal for doing PhD, now identifying the goal is your goal! We know that finding a research topic is a harder part, however the above mentioned six steps will definitely guide you in cracking and bringing about a good research topic.
Hope this article will be helpful for all the readers who are in the beginning stage of your PhD research work. In case of any queries related to this post, feel free to reach us through your comments or visit our website.
Recent Posts
What's the difference between a research article and a review article-The hidden secrets?
How to conduct literature survey for PhD-Wanted to know the secrets
Step by step process of PhD journey: UnknoWN Secrets
Cookies on our website
We use some essential cookies to make this website work.
We'd like to set additional cookies to understand how you use our site. And we'd like to serve you some cookies set by other services to show you relevant content.

- Schools and departments
International Development
- Postgraduate study
PhD research
- Undergraduate study
- Postgraduate prospectus
- Why International Development at Sussex?
- People and contacts

As a doctoral researcher at Sussex, you will be a valued part of our academic community and encouraged to participate in seminars, research activities and teaching. You will be supported by two supervisors with expertise on your topic and we encourage you to reach out to faculty members to discuss your research ideas before applying. Explore some of the projects our doctoral researchers are leading below.
Current and recent research topics in international development, include:
- A development challenge in a crisis state. HIV/AIDS prevention programmes and behavioural change in Zimbabwe. A case of Harare residents
- Biodiversity conservation in South India: understanding the environmental practices and politics of indigenous communities in Nilgiri biosphere
- Conservation, participation, and development: the rhetoric and reality of medicinal plant policies in Nepal
- Dollar Bananas vs. Fair Trade Bananas: A study of a neo-colonial relationship
- Groundwater Apathy: An Optic to Explain Groundwater (Non)Governance: A Case Study of the Indus Basin of Pakistan
- Integrated conservation in Mexico: reconciling conservation and sustainable development within protected nature areas
- Knowledge sharing on child labour and its prevention: the involvement of child migrant workers in Samut Sakhon, Thailand
- Networks, malandros and social control: exploring the connections between inequality and violence in Venezuela
- Perceptions and realities of the poor in Nigeria: poverty, livehihoods and risks
- Queering Cuba: How have women engaging in non-normative sexualities and gender identities participated in political, economic and social life?
- When disaster strikes: why people in Bangladesh make certain decisions on their livelihoods when faced with environmental stress and climate change impacts.
Information for PhD students
- PhD degrees
- Find out how to apply for a PhD
- Explore our scholarships
- UB Directory
- School of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences >
- Information for Students >
- Policy Library: SPPS Graduate Programs >
Research Proposal
After successful completion of the departmental Preliminary Examination, all PhD and PharmD/PhD students must submit and orally defend a written Research proposal outlining their proposed dissertation research.
Students should register for PHC 511 Research Proposal in the Spring semester following completion of the Preliminary Examination. If the preliminary examination is written in January, they should use time in Spring semester following the completion of the Preliminary Examination to develop their research ideas and to write the proposal. If the preliminary examination is written in June, they should use time in the Fall semester following the completion of the Preliminary Examination to develop their research ideas and to write the proposal.
The deadline for submission of the Research Proposal to the Dissertation Committee write-up is June/January 15. The deadline for the oral defense of the Research Proposal is August/March 1st.
Written approval from the Director of Graduate Studies is required if the dates have to be altered because of scheduling conflicts for the committee members.
Failure to meet the submission and defense deadlines will result in a grade of “F” for the proposal.
The research proposal should be written in the format of a National Institutes of Health R01 grant. The most current formatting guidelines should be used. The page limits, line spacing, font size, headings of the different sections should be similar to those currently recommended for National Institutes of Health R01 grants. The instructions and forms can be obtained from the National Institutes of Health site. At this time the link is http://grants.nih.gov/grants/funding/phs398/phs398.html
The proposal should be submitted to the student’s PhD Dissertation Committee members along with copies of the three most pertinent articles cited in the proposal. The student will defend the proposal orally before the Dissertation Committee. Normally, the defense will consist of a 10-15 minute presentation by the student followed by questions by the Dissertation Committee members.
The advisor’s role in the preparation of the written document is limited to an examination of the Specific Aims proposed by the student. Students should not have access to any written grant proposal of the advisor relevant to the subject matter. The evaluation of the proposed Specific Aims should assess feasibility of the proposed aims, which should occur prior to the actual writing by the student. The advisor should not edit, review or make suggestions for document revision prior to document distribution to all committee members. Additionally, the advisor should give the thesis committee an indication of any other contribution the advisor has made to the thesis proposal.
The Research Proposal will be graded by letter grade by the Dissertation Committee, based on the content and scientific merit of the written proposal and the student’s ability to orally defend any criticisms and answer the questions posed concerning the proposal and related areas. Each member of the thesis committee is encouraged to prepare a written evaluation of the student’s document and oral defense and distribute it to the student. If the committee requires certain revisions or additions, a written notice shall be transmitted by the Chair of the Dissertation Committee to the student detailing the revisions/additions and the timeframe for submission.
A letter grade will be given by the Dissertation Committee, with the passing grade set at B-, although certain revisions/additions may be required, as specified earlier.
A student who fails the proposal (i.e., with a grade of C+ or below) is required to re-submit the entire proposal within 60 days, and to schedule an oral defense within 30 days thereafter. The Director of Graduate Studies/designate, in consultation with the student, will appoint two additional Department faculty members to serve on the committee. These two additional committee members shall not participate in questioning the student in the defense, but shall participate in the grading process. The grade for this examination must be either a “Pass” or a “Fail” (i.e., no conditional passes). Failure in this second proposal defense automatically terminates the student in the PhD program, and removal of assistantship.
Computational Research PhD Fellowships Info Session - Graduate Education - College of Engineering - Purdue University

Computational Research PhD Fellowships Info Session
| Event Date: | June 19, 2024 |
|---|---|
| Time: | 10:00AM - 11:00AM |
| Location: | Virtual |
| Contact Name: | Office of Graduate Professional Development |
| Contact Email: | [email protected] |
| Open To: | PhD Students |
| Priority: | No |
| School or Program: | Graduate Program |
| College Calendar: | Show |
Sign up for workshops from our professional development series at gspd.gosignmeup.com

Related Link: gspd.gosignmeup.com
Ph.D. student is lead author on paper published on cover of 'Optica Quantum'
Interdisciplinary research from the center for detectors focuses on entanglement in quantum information systems.
Ph.D. student Evan Manfreda-Schulz’s first published paper was featured on the cover of Optica Quantum.
Microsystems engineering Ph.D. student Evan Manfreda-Schulz ’20 ( physics ) accomplished something many academic researchers aim for when his first paper was published on the cover of Optica Quantum .
The paper, “Generating high-dimensional entanglement using a foundry-fabricated photonic integrated circuit,” is a culmination of years of study in the realm of quantum information systems. The work was co-authored by J. Dulany Elliot ’23 (physics and computer science ); Matthew can Niekerk ’23 Ph.D. (microsystems engineering); Daniel Proctor ’23 (physics), Mario Ciminelli , engineer in the Department of Electrical and Microelectronic Engineering ; Tom Palone , reliability and packaging engineer in the Department of Manufacturing and Mechanical Engineering Technology ; Christopher C. Tison, Air Force Research Laboratory; Michael L. Fanto '20 Ph.D. (microsystems engineering) Air Force Research Laboratory; Stefan F. Preble , professor in the Department of Electrical and Microelectronic Engineering; and Gregory A. Howland , assistant professor in the School of Physics and Astronomy . The work was supported, in part, by the Air Force Research Laboratory and the RIT-L3Harris Quantum Information Science and Technology Collaboration.
RIT has emerged as a leader in quantum technology, which leverages the behavior of quantum systems at the single particle level. Quantum resources such as entanglement, which is observed via correlations in the measurement statistics of disparate particles, are key to unlocking new possibilities and capabilities in computing, communication, imaging, and sensing.
“Entanglement is a resource for all sorts of things that we might want to use quantum information systems for,” explained Manfreda-Schulz. “Generating it is one part of the challenge, and figuring out how much of it you have is another.”
The team used a silicon photonic integrated circuit to generate 1.45 ebits of high-dimensional quantum entanglement. They documented how the system was designed, packaged, and calibrated using an array of four tunable photon pair sources. Then they described how they used an entanglement witness to quantify the resource they generated. The research represents an advancement towards the efficient deployment of quantum information systems built on the platform of silicon integrated photonics.
This research comes under the direction of RIT’s Center for Detectors , an interdisciplinary center that designs, develops, and implements photon devices for a wide range of scientific areas, and the Integrated Photonics Lab .
“I’m really grateful for everyone in the group,” added Manfreda-Schulz. “It’s not just something that I did, it’s our whole team. I’m appreciative of all the help I received along the way.”
Recommended News
June 18, 2024
Amid War, Ukrainian Teenagers Travel to U.S. for Academic Competition
MSNBC talks to a Ukrainian scholar who traveled to RIT last week as part of the international Genius Olympiad competition about her life among the wartime activities in her home country.

Comic Charlie Berens and Marvel Cinematic Universe actress Alaqua Cox scheduled for RIT’s Brick City Homecoming and Family Weekend
A stand-up comedian who enjoys poking fun at his Midwestern background and a Marvel Cinematic Universe actress are the headliners expected at this year’s RIT Brick City Homecoming and Family Weekend.
June 17, 2024

RIT Formula Racing zooms to big win at SAE Michigan this past weekend
RIT Racing held a mere three-point lead at the top of the leaderboard for the Michigan SAE Formula electric competition June 14-16, but it was enough to give the team one of its biggest wins since it began racing more than 30 years ago.

The asymmetric response of firms to demand and cost changes: a puzzle
Long Island Business News talks to Amit Batabyal, the Arthur J. Gosnell Professor of Economics and interim head of the Department of Sustainability, about how national firms respond differently to local demand and cost changes.
- What is a PhD?
Written by Mark Bennett
A PhD is a doctoral research degree and the highest level of academic qualification you can achieve. The degree normally takes between three and four years of full-time work towards a thesis offering an original contribution to your subject.
This page explains what a PhD is, what it involves and what you need to know if you’re considering applying for a PhD research project , or enrolling on a doctoral programme .
The meaning of a PhD
The PhD can take on something of a mythic status. Are they only for geniuses? Do you have to discover something incredible? Does the qualification make you an academic? And are higher research degrees just for people who want to be academics?
Even the full title, ‘Doctor of Philosophy’, has a somewhat mysterious ring to it. Do you become a doctor? Yes, but not that kind of doctor. Do you have to study Philosophy? No (not unless you want to) .
So, before going any further, let's explain what the term 'PhD' actually means and what defines a doctorate.
What does PhD stand for?
PhD stands for Doctor of Philosophy. This is one of the highest level academic degrees that can be awarded. PhD is an abbreviation of the Latin term (Ph)ilosophiae (D)octor. Traditionally the term ‘philosophy’ does not refer to the subject but its original Greek meaning which roughly translates to ‘lover of wisdom’.
What is a doctorate?
A doctorate is any qualification that awards a doctoral degree. In order to qualify for one you need to produce advanced work that makes a significant new contribution to knowledge in your field. Doing so earns you the title 'Doctor' – hence the name.
So, is a PhD different to a doctorate? No. A PhD is a type of doctorate .
The PhD is the most common type of doctorate and is awarded in almost all subjects at universities around the world. Other doctorates tend to be more specialised or for more practical and professional projects.
Essentially, all PhDs are doctorates, but not all doctorates are PhDs.
Do you need a Masters to get a PhD?
Not necessarily. It's common for students in Arts and the Humanities to complete an MA (Master of Arts) before starting a PhD in order to acquire research experience and techniques. Students in Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (STEM) don't always need an MS/MSc (Master of Science) to do a PhD as you'll gain training in lab techniques and other skills during your undergraduate degree.
Whether a Masters is a requirement for a PhD also varies by country. Australian PhDs may require a Masters as the equivalent of their own 'honours year' (where students work on research). US PhD programmes often include a Masters.
We have a whole guide dedicated to helping you decide whether a PhD without a Masters is the right route for you.
The origin of the PhD
Despite its name, the PhD isn't actually an Ancient Greek degree. Instead it's a much more recent development. The PhD as we know it was developed in nineteenth-century Germany, alongside the modern research university.
Higher education had traditionally focussed on mastery of an existing body of scholarship and the highest academic rank available was, appropriately enough, a Masters degree.
As the focus shifted more onto the production of new knowledge and ideas, the PhD degree was brought in to recognise those who demonstrated the necessary skills and expertise.
The PhD process – what's required to get a PhD?
The typical length of a PhD is three to four years full-time, or five to six years part-time.
Unlike most Masters courses (or all undergraduate programmes), a PhD is a pure research degree. But that doesn’t mean you’ll just spend years locked away in a library or laboratory. In fact, the modern PhD is a diverse and varied qualification with many different components.
Whereas the second or third year of a taught degree look quite a lot like the first (with more modules and coursework at a higher level) a PhD moves through a series of stages.
A typical PhD normally involves:
- Carrying out a literature review (a survey of current scholarship in your field).
- Conducting original research and collecting your results .
- Producing a thesis that presents your conclusions.
- Writing up your thesis and submitting it as a dissertation .
- Defending your thesis in an oral viva voce exam.
These stages vary a little between subjects and universities, but they tend to fall into the same sequence over the three years of a typical full-time PhD.
The first year of a PhD
The beginning of a PhD is all about finding your feet as a researcher and getting a solid grounding in the current scholarship that relates to your topic.
You’ll have initial meetings with your supervisor and discuss a plan of action based on your research proposal.
The first step in this will almost certainly be carrying out your literature review . With the guidance of your supervisor you’ll begin surveying and evaluating existing scholarship. This will help situate your research and ensure your work is original.
Your literature review will provide a logical jumping off point for the beginning of your own research and the gathering of results . This could involve designing and implementing experiments, or getting stuck into a pile of primary sources.
The year may end with an MPhil upgrade . This occurs when PhD students are initially registered for an MPhil degree and then ‘upgraded’ to PhD candidates upon making sufficient progress. You’ll submit material from your literature review, or a draft of your research findings and discuss these with members of your department in an upgrade exam . All being well, you’ll then continue with your research as a PhD student.
PhDs in other countries
The information on the page is based on the UK. Most countries follow a similar format, but there are some differences. In the USA , for example, PhD students complete reading assignments and examinations before beginning their research. You can find out more in our guides to PhD study around the world .
The second year of a PhD
Your second year will probably be when you do most of your core research. The process for this will vary depending on your field, but your main focus will be on gathering results from experiments, archival research, surveys or other means.
As your research develops, so will the thesis (or argument) you base upon it. You may even begin writing up chapters or other pieces that will eventually form part of your dissertation .
You’ll still be having regular meetings with your supervisor. They’ll check your progress, provide feedback on your ideas and probably read any drafts your produce.
The second year is also an important stage for your development as a scholar. You’ll be well versed in current research and have begun to collect some important data or develop insights of your own. But you won’t yet be faced with the demanding and time-intensive task of finalising your dissertation.
So, this part of your PhD is a perfect time to think about presenting your work at academic conferences , gaining teaching experience or perhaps even selecting some material for publication in an academic journal. You can read more about these kinds of activities below.
The third year of a PhD
The third year of a PhD is sometimes referred to as the writing up phase.
Traditionally, this is the final part of your doctorate, during which your main task will be pulling together your results and honing your thesis into a dissertation .
In reality, it’s not always as simple as that.
It’s not uncommon for final year PhD students to still be fine-tuning experiments, collecting results or chasing up a few extra sources. This is particularly likely if you spend part of your second year focussing on professional development.
In fact, some students actually take all or part of a fourth year to finalise their dissertation. Whether you are able to do this will depend on the terms of your enrolment – and perhaps your PhD funding .
Eventually though, you are going to be faced with writing up your thesis and submitting your dissertation.
Your supervisor will be very involved in this process. They’ll read through your final draft and let you know when they think your PhD is ready for submission.
All that’s left then is your final viva voce oral exam. This is a formal discussion and defence of your thesis involving at least one internal and external examiner. It’s normally the only assessment procedure for a PhD. Once you’ve passed, you’ve done it!
Looking for more information about the stages of a PhD?
How do you go about completing a literature review? What's it like to do PhD research? And what actually happens at an MPhil upgrade? You can find out more in our detailed guide to the PhD journey .
Doing a PhD – what's it actually like?
You can think of the ‘stages’ outlined above as the basic ‘roadmap’ for a PhD, but the actual ‘journey’ you’ll take as a research student involves a lot of other sights, a few optional destinations and at least one very important fellow passenger.
Carrying out research
Unsurprisingly, you’ll spend most of your time as a PhD researcher… researching your PhD. But this can involve a surprisingly wide range of activities.
The classic image of a student working away in the lab, or sitting with a pile of books in the library is true some of the time – particularly when you’re monitoring experiments or conducting your literature review.
Your PhD can take you much further afield though. You may find yourself visiting archives or facilities to examine their data or look at rare source materials. You could even have the opportunity to spend an extended period ‘in residence’ at a research centre or other institution beyond your university.
Research is also far from being a solitary activity. You’ll have regular discussions with your supervisor (see below) but you may also work with other students from time to time.
This is particularly likely if you’re part of a larger laboratory or workshop group studying the same broad area. But it’s also common to collaborate with students whose projects are more individual. You might work on shorter projects of joint interest, or be part of teams organising events and presentations.
Many universities also run regular internal presentation and discussion groups – a perfect way to get to know other PhD students in your department and offer feedback on each other’s work in progress.
Working with your supervisor
All PhD projects are completed with the guidance of at least one academic supervisor . They will be your main point of contact and support throughout the PhD.
Your supervisor will be an expert in your general area of research, but they won’t have researched on your exact topic before (if they had, your project wouldn’t be original enough for a PhD).
As such, it’s better to think of your supervisor as a mentor, rather than a teacher.
As a PhD student you’re now an independent and original scholar, pushing the boundaries of your field beyond what is currently known (and taught) about it. You’re doing all of this for the first time, of course. But your supervisor isn’t.
They’ll know what’s involved in managing an advanced research project over three years (or more). They’ll know how best to succeed, but they’ll also know what can go wrong and how to spot the warning signs before it does.
Perhaps most importantly, they’ll be someone with the time and expertise to listen to your ideas and help provide feedback and encouragement as you develop your thesis.
Exact supervision arrangements vary between universities and between projects:
- In Science and Technology projects it’s common for a supervisor to be the lead investigator on a wider research project, with responsibility for a laboratory or workshop that includes several PhD students and other researchers.
- In Arts and Humanities subjects, a supervisor’s research is more separate from their students’. They may supervise more than one PhD at a time, but each project is essentially separate.
It’s also becoming increasingly common for PhD students to have two (or more) supervisors. The first is usually responsible for guiding your academic research whilst the second is more concerned with the administration of your PhD – ensuring you complete any necessary training and stay on track with your project’s timetable.
However you’re supervised, you’ll have regular meetings to discuss work and check your progress. Your supervisor will also provide feedback on work during your PhD and will play an important role as you near completion: reading your final dissertation draft, helping you select an external examiner and (hopefully) taking you out for a celebratory drink afterwards!
Professional development, networking and communication
Traditionally, the PhD has been viewed as a training process, preparing students for careers in academic research.
As such, it often includes opportunities to pick up additional skills and experiences that are an important part of a scholarly CV. Academics don’t just do research after all. They also teach students, administrate departments – and supervise PhDs.
The modern PhD is also viewed as a more flexible qualification. Not all doctoral graduates end up working in higher education. Many follow alternative careers that are either related to their subject of specialism or draw upon the advanced research skills their PhD has developed.
PhD programmes have begun to reflect this. Many now emphasise transferrable skills or include specific training units designed to help students communicate and apply their research beyond the university.
What all of this means is that very few PhD experiences are just about researching and writing up a thesis.
The likelihood is that you’ll also do some (or all) of the following during your PhD:
The work is usually paid and is increasingly accompanied by formal training and evaluation.
Conference presentation
As a PhD student you’ll be at the cutting edge of your field, doing original research and producing new results. This means that your work will be interest to other scholars and that your results could be worth presenting at academic conferences .
Doing this is very worthwhile, whatever your career plans. You’ll develop transferrable skills in public speaking and presenting, gain feedback on your results and begin to be recognised as an expert in your area.
Conferences are also great places to network with other students and academics.
Publication
As well as presenting your research, you may also have the opportunity to publish work in academic journals, books, or other media. This can be a challenging process.
Your work will be judged according to the same high standards as any other scholar’s and will normally go through extensive peer review processes. But it’s also highly rewarding. Seeing your work ‘in print’ is an incredible validation of your PhD research and a definite boost to your academic CV.
Public engagement and communication
Academic work may be associated with the myth of the ‘ivory tower’ – an insular community of experts focussing on obscure topics of little interest outside the university. But this is far from the case. More and more emphasis is being placed on the ‘impact’ of research and its wider benefits to the public – with funding decisions being made accordingly.
Thankfully, there are plenty of opportunities to try your hand at public engagement as a PhD student. Universities are often involved in local events and initiatives to communicate the benefits of their research, ranging from workshops in local schools to public lectures and presentations.
Some PhD programmes include structured training in order to help students with activities such as the above. Your supervisor may also be able to help by identifying suitable conferences and public engagement opportunities, or by involving you in appropriate university events and public engagement initiatives.
These experiences will be an important part of your development as a researchers - and will enhance the value of your PhD regardless of your career plans.
What is a PhD for – and who should study one?
So, you know what a PhD actually is, what’s involved in completing one and what you might get up to whilst you do. That just leaves one final question: should you do a PhD?
Unfortunately, it’s not a question we can answer for you.
A PhD is difficult and uniquely challenging. It requires at least three years of hard work and dedication after you’ve already completed an undergraduate degree (and probably a Masters degree too).
You’ll need to support yourself during those years and, whilst you will be building up an impressive set of skills, you won’t be directly progressing in a career.
But a PhD is also immensely rewarding. It’s your chance to make a genuine contribution to the sum of human knowledge and produce work that other researchers can (and will) build on in future. However obscure your topic feels, there’s really no such thing as a useless PhD.
A PhD is also something to be incredibly proud of. A proportionately tiny number of people go on to do academic work at this level. Whatever you end up doing after your doctorate you’ll have an impressive qualification – and a title to match. What’s more, non-academic careers and professions are increasingly recognising the unique skills and experience a PhD brings.
Other PhDs - do degree titles matter?
The PhD is the oldest and most common form of higher research degree, but a few alternatives are available. Some, such as the DPhil are essentially identical to a PhD. Others, such as the Professional Doctorate or DBA are slightly different. You can find out more in our guide to types of PhD .
Is a PhD for me?
There’s more advice on the value of a PhD – and good reasons for studying one – elsewhere in this section. But the following are some quick tips if you’re just beginning to consider a PhD.
Speak to your lecturers / tutors
The best people to ask about PhD study are people who’ve earned one. Ask staff at your current or previous university about their experience of doctoral research – what they enjoyed, what they didn’t and what their tips might be.
If you’re considering a PhD for an academic career, ask about that too. Are job prospects good in your field? And what’s it really like to work at a university?
Speak to current PhD students
Want to know what it’s like studying a PhD right now? Or what it’s like doing research at a particular university? Ask someone who knows.
Current PhD students were just like you a year or two ago and most will be happy to answer questions.
If you can’t get in touch with any students ‘face to face’, pop over to the Postgraduate Forum – you’ll find plenty of students there who are happy to chat about postgraduate research.
Take a look at advertised projects and programmes
This may seem like a strange suggestion. After all, you’re only going to study one PhD, so what’s the point of reading about lots of others?
Well, looking at the details of different PhD projects is a great way to get a general sense of what PhD research is like. You’ll see what different PhDs tend to have in common and what kinds of unique opportunity might be available to you.
And, with thousands of PhDs in our database , you’re already in a great place to start.
Read our other advice articles
Finally, you can also check out some of the other advice on the FindAPhD website. We’ve looked at some good (and bad) reasons for studying a PhD as well as the value of a doctorate to different career paths.
More generally, you can read our in-depth look at a typical PhD journey , or find out more about specific aspects of doctoral study such as working with a supervisor or writing your dissertation .
We add new articles all the time – the best way to stay up to date is by signing up for our free PhD opportunity newsletter .
Ready to find your PhD?
Head on over to our PhD search listings to learn what opportunities are on offer within your discipline.
Our postgrad newsletter shares courses, funding news, stories and advice
You may also like....

What happens during a typical PhD, and when? We've summarised the main milestones of a doctoral research journey.

The PhD thesis is the most important part of a doctoral degree. This page will introduce you to what you need to know about the PhD dissertation.

This page will give you an idea of what to expect from your routine as a PhD student, explaining how your daily life will look at you progress through a doctoral degree.

Our guide tells you everything about the application process for studying a PhD in the USA.
FindAPhD. Copyright 2005-2024 All rights reserved.
Unknown ( change )
Have you got time to answer some quick questions about PhD study?
Select your nearest city
You haven’t completed your profile yet. To get the most out of FindAPhD, finish your profile and receive these benefits:
- Monthly chance to win one of ten £10 Amazon vouchers ; winners will be notified every month.*
- The latest PhD projects delivered straight to your inbox
- Access to our £6,000 scholarship competition
- Weekly newsletter with funding opportunities, research proposal tips and much more
- Early access to our physical and virtual postgraduate study fairs
Or begin browsing FindAPhD.com
or begin browsing FindAPhD.com
*Offer only available for the duration of your active subscription, and subject to change. You MUST claim your prize within 72 hours, if not we will redraw.

Do you want hassle-free information and advice?
Create your FindAPhD account and sign up to our newsletter:
- Find out about funding opportunities and application tips
- Receive weekly advice, student stories and the latest PhD news
- Hear about our upcoming study fairs
- Save your favourite projects, track enquiries and get personalised subject updates

Create your account
Looking to list your PhD opportunities? Log in here .
$2.6 million in grant funding to support research on genetic causes of blindness
IU School of Medicine Jun 17, 2024

stock.adobe.com
INDIANAPOLIS – Indiana University School of Medicine’s Yoshikazu Imanishi, PhD , was recently awarded a four-year, $2.1 million grant from the National Eye Institute and a three-year, $500,000 grant from the Foundation Fighting Blindness to study genetic causes of blindness.
Some of the most devastating vision impairments and causes of blindness occur in people who have inherited mutated genes from their parents. These conditions are called retinitis pigmentosa, afflicting 1 in 4,000 people in the United States.
Through the National Eye Institute grant, Imanishi aims to understand why proteins in photoreceptor neurons — specialized cells found in the retina that convert light energy into electrical signals that ultimately reach the brain — get misplaced and cause blindness. He’ll also study how different parts of these cells are organized and supported by cytoskeletal elements, which are like the bones of cells.

“My goal is to better understand what causes blindness,” said Imanishi, associate professor of ophthalmology at the IU School of Medicine and director of ocular neurobiology at the school’s Stark Neurosciences Research Institute . “This grant aims to help us develop treatments and possibly find a cure for people who have retinitis pigmentosa, a condition caused by specific genetic mutations.”
The Foundation Fighting Blindness grant will fund Imanishi’s research project to discover small molecules that mitigate vision loss associated with PRPH2 gene mutations. The project will use an innovative method that allows scientists to quickly test thousands of potential drugs to find effective treatments.
This research is supported by the IU School of Medicine’s Eugene and Marilyn Glick Eye Institute .
About the IU School of Medicine
The IU School of Medicine is the largest medical school in the U.S. and is annually ranked among the top medical schools in the nation by U.S. News & World Report. The school offers high-quality medical education, access to leading medical research and rich campus life in nine Indiana cities, including rural and urban locations consistently recognized for livability. According to the Blue Ridge Institute for Medical Research, the IU School of Medicine ranks No. 13 in 2023 National Institutes of Health funding among all public medical schools in the country.
SEARCH THE NEWSROOM
Subscribe to the news.
We've added you to our mailing list!
Sorry, there was a problem
Media Contacts
Related news.
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- 13 June 2024
Cyberattacks are hitting research institutions — with devastating effects
- Diana Kwon 0
Diana Kwon is a freelance science journalist based in Berlin.
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
You have full access to this article via your institution.

Ransomware attacks lock users out of their systems until a payment is made. Credit: solarseven/Getty
Last October, a cyberattack hit the Berlin Natural History Museum and brought research to a standstill. Scientists were left without access to the data and programs required for their work, putting projects on hold and leaving students in limbo. Months later, systems have only just begun to crawl back online.
The museum is not alone. In the past year, cyberattacks have struck several research institutions in Germany and beyond. Most involve ransomware, in which data or systems are locked until a payment is made. The attacks are part of a growing trend at academic institutions worldwide, where they can have devastating effects — delaying research projects, disrupting student enrolment and affecting researchers’ mental health.

So … you’ve been hacked
“In the 13 years I’ve been here, this is by far the most painful thing I have experienced,” says Johannes Vogel, director-general of the Berlin Natural History Museum, which conducts research in a wide range of fields including palaeontology, geology and genetics. “The attack is an ongoing challenge.”
In the past few years, cyberattacks have hit institutions including the British Library in London, the University of Manchester, UK, Carnegie Mellon University in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, and Stanford University in California.
Cleaning up after such an attack can be arduous. To contain the damage from the ransomware attack, which, according to a criminal investigation by German authorities, came from a group of Russian hackers, the Berlin museum took its entire system offline. As a result, the museum’s roughly 450 employees lost access to e-mail and other digital services. For researchers, this meant being unable to access data and specialized programs required for their work. In addition, data — including some personal information from visitors — were stolen by the attackers. Although the museum was able to stay open by outsourcing parts of visitor services and administration, most of its research was put on hold. In the months since the attack, the museum has been working with cybersecurity experts to clean up and rebuild the digital infrastructure. Information-technology services might not be completely restored until the end of the year, says Vogel.
Severed connection
It was a February morning at the Berlin University of Applied Sciences and Technology (BHT) when staff received red alerts informing them that digital services were shutting down. The university had been hit with a ransomware attack from Akira — a well-known hacker group that has, as of this January, claimed roughly US$42 million from attacks on more than 250 organizations. In response, the university shut down all its servers and severed its connection to the Internet.
The shutdown meant that professors and students were completely locked out of digital services — and those who could continue their work remotely did so off-site, according to Peter Tröger, head of the computer and information-systems laboratory at BHT. The loss of e-mail was especially difficult, because making appointments, scheduling PhD defences and accessing journals all require a university e-mail address, Tröger says.
The attack also affected student enrolment. Because it occurred in between terms, an estimated 100 or so students couldn’t enroll, and ended up at other universities instead.
Internet connectivity is being re-established in steps, prioritizing services such as payroll and student enrolment. E-mail was restored after a few weeks, but many labs — mostly those heavily reliant on IT — remain partly offline as a team goes into each lab’s digital infrastructure to investigate how it was affected by the attack, and whether its security measures are up to date. “There’s a long waiting line,” Tröger says. Without digital services, “people need to find different ways to spend their time in a reasonable and useful manner”.
The Helmholtz Centre for Materials and Energy in Berlin, a materials-research institute, experienced a cyberattack last June. This delayed many projects by anything from weeks to months, says Ina Helms, the head of communication at the centre. “Inability to access research software was one of the factors that caused many projects to experience delays,” she says.

Berlin Natural History Museum was struck by a ransomware attack last October. Credit: Imago/Alamy
For students, losing the ability to work is especially disruptive. The cyberattack has affected projects at the Berlin Natural History Museum to varying degrees — some researchers were able to focus on literature reviews or work on external computers. Others were unable to work at all. Because master’s and doctoral students have a limited time frame in which to conduct work, the disruption meant that many needed to request for extensions from universities, funding bodies and collaborators, according to a group representing early-career researchers at the museum. “Many of the early career scientists were very stressed about the situation,” the representatives said in an e-mail. “It also affected their mental health.”
‘Easy targets’
For hackers, academic institutions are desirable targets for two reasons: some have deep pockets from which to pay a ransom, and they contain valuable data that can be sold such as employee records and intellectual property linked to cutting-edge research, says Harjinder Singh Lallie, a cybersecurity expert at the University of Warwick, UK. “This is why ransomware is such a good attack, because you’ve got two lines of potential monetization.”
Educational institutions are also more likely to have outdated security systems, says Lallie, and their digital infrastructure is more diverse than that of, say, financial institutions, which often use a single operating system and have highly secured computers. At universities, for instance, in addition to the computers in labs and offices, students and staff have personal devices — each of which hackers can use to infiltrate the institution. And the diversity of collaborators and suppliers from outside the university add layers of vulnerability. “The number of possible entry points we have is quite remarkable,” Lallie says. “All an attacker needs is for one student to have a lousy phone.”
Lallie notes that there are several things institutions can do to protect themselves from an attack. This includes introducing multi-factor authentication for log-ins, securely backing up data and teaching its students and staff about cyberawareness.
For academic institutions, the question now might not be whether they will be attacked — but when. “You’ve got to assume now that your systems are going to be hit with a ransomware attack,” Lallie says. “If you make that assumption, you can prepare to a certain degree to ensure minimal disruption.”
Nature 630 , 535-536 (2024)
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-024-01711-3
Reprints and permissions
Related Articles

- Research data
- Research management

Not all ‘open source’ AI models are actually open: here’s a ranking
News 19 JUN 24

Open access is working — but researchers in lower-income countries enjoy fewer benefits
Nature Index 11 JUN 24

How a few days in space can disrupt a person’s biology
News 11 JUN 24

What’s the state of hiring researchers in science? Share your insights with Nature
Career News 19 JUN 24

How researchers and their managers can build an actionable career-development plan
Career Column 17 JUN 24

Three ways to recognize hidden labour in research
Nature Index 13 JUN 24
Senior Research Associate (m/f/d) - permanent position - Institute of Neuropathology
Main topics of scientific projects are: Kallikrein-8 as an early biomarker and therapeutic Target for Alzheimer’s Disease Epigenetic effects of e...
Essen, Nordrhein-Westfalen (DE)
Universitätsklinikum (AöR)
Department of Health and Human Services (DHHS), is seeking exceptional candidates for the position of Director
Bethesda, Maryland (US)
National Institutes of Health
Principal Investigator Positions at the Institute for Regenerative Biology and Medicine, CIMR
Regenerative Biology and Medicine, including but not limited to disease immunology, ageing, biochemistry of extracellular matrix...
Beijing, China
The Chinese Institutes for Medical Research (CIMR), Beijing
Principal Investigator Positions at the Institute for Molecular and Cellular Therapy, CIMR, Beijing
We're looking for outstanding scientists at all ranks interested in developing novel therapeutics in all disease areas.
Post-Doctoral Fellowship in Regenerative Biology and Medicine (Lab of. Dr. Yuval Rinkevich)
Discovery of cellular and molecular mechanisms of tissue repair and regeneration.
Institute for Regenerative Biology and Medicine, Chinese Institutes for Medical Research (CIMR)
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
As part of the PhD application process, you may be asked to summarise your proposed research topic in a research proposal. This is a document which summarises your intended research and will include the title of your proposed project, an Abstract, Background and Rationale, Research Aims and Objectives, Research Methodology, Timetable, and a ...
The purpose of the proposal is to identify a relevant research topic, explain the context of the research, define concrete goals, and propose a realistic work plan to achieve them. If you've already built a Theory of Change for your research question, we recommend adding detail at this stage to help you create a proposal.
Written by Mark Bennett. You'll need to write a research proposal if you're submitting your own project plan as part of a PhD application. A good PhD proposal outlines the scope and significance of your topic and explains how you plan to research it. It's helpful to think about the proposal like this: if the rest of your application explains ...
Formulating a Focused Research Question. After PhD topic selection, the next step is to refine it into a straightforward research question. Your research question should be specific, relevant, and well-defined. It should be detailed enough to guide your research and provide clear direction while also leaving room for exploration and analysis.
Choosing a PhD topic can seem like a pretty daunting prospect. You'll need to decide on a subject that's substantial and original enough to occupy your time for at least three years - and one that you won't find yourself losing interest in. Focusing on the Arts, Humanities and Social Sciences, this page features a selection of tips for ...
So, you're finally nearing the end of your degree and it's now time to find a suitable topic for your dissertation or thesis. Or perhaps you're just starting out on your PhD research proposal and need to find a suitable area of research for your application proposal.. In this post, we'll provide a straightforward 6-step process that you can follow to ensure you arrive at a high-quality ...
Formal proposal: In many programs, you will need to submit a formal proposal that outlines your research question, methodology, and relevance to the field. Ethical considerations: If your research involves human subjects, ensure that you comply with all ethical guidelines and obtain necessary approvals. What Makes a Good PhD Dissertation Topic?
Therefore, in a good research proposal you will need to demonstrate two main things: 1. that you are capable of independent critical thinking and analysis. 2. that you are capable of communicating your ideas clearly. Applying for a PhD is like applying for a job, you are not applying for a taught programme.
Choosing a radically new research topic, while still embarking on the broad area of specialization is indeed the key to success. Choosing an obscure, irrelevant, or non-compelling research topic: This can adversely affect the researcher's motivation levels and can drastically decrease their odds of attaining success.
1. Title. Your title should indicate clearly what your research question is. It needs to be simple and to the point; if the reader needs to read further into your proposal to understand your question, your working title isn't clear enough. Directly below your title, state the topic your research question relates to.
Tips for choosing a PhD project and topics. Here you have two sets of Tips: Tips to Apply for a PhD project and choosing a PhD project topic; Tips to Write your PhD Thesis; Tips to Apply for a PhD project. 1. Be Aware of Your Niche. Just because you are a computer science postgraduate and AI or Data Science is the trend; You needn't select ...
A research proposal should present your idea or question and expected outcomes with clarity and definition - the what. It should also make a case for why your question is significant and what value it will bring to your discipline - the why. What it shouldn't do is answer the question - that's what your research will do.
In many countries an application for a PhD position includes a written research proposal, so my questions is what are some advises/strategies to come up with a good topic/idea for a PhD research proposal and how can one assess the quality/fruitfulness of an idea?As an undergraduate student one just doesn't have the experience to foresee which ideas might have promising research results and ...
When writing your PhD proposal you need to show that your PhD is worth it, achievable, and that you have the ability to do it at your chosen university. With all of that in mind, let's take a closer look at each section of a standard PhD research proposal and the overall structure. 1. Front matter.
3. Narrow your focus to a single research topic. Once you have connected with your prospective supervisor, it is important that you seek their input and advice on your research proposal. Developing a research proposal is an iterative process, so expect to work on a number of drafts before you finalise your research proposal.
Manchester Metropolitan University Faculty of Science and Engineering. This is a full-time, self-funded PhD opportunity in the Faculty of Science and Engineering. It is open to both home and overseas students. Read more. Supervisor: Dr G Wood. 15 July 2024 PhD Research Project Self-Funded PhD Students Only. More Details.
The impact of poverty on education. The use of student data to inform instruction. The role of parental involvement in education. The effects of mindfulness practices in the classroom. The use of technology in the classroom. The role of critical thinking in education.
When examining potential topics for PhD applications, identifying gaps in existing research is a crucial step. This process involves critically analyzing current literature in your field of interest and determining what questions have been left unanswered. These gaps may represent areas of study that have been overlooked, underdeveloped, or yet ...
References: Do not forget to specify all the references at the end of the proposal. An obvious but very important point is the format of your research proposal. Make sure that the formatting of the document is consistent throughout and that the structure is clear. If possible, it can be a good idea to give the document to your academic tutor or ...
Your research proposal is a concise statement (up to 3,000 words) of the rationale for your research proposal, the research questions to be answered and how you propose to address them. We know that during the early stages of your PhD you are likely to refine your thinking and methodology in discussion with your supervisors.
Detailed Walkthrough + Free Proposal Template. If you're getting started crafting your research proposal and are looking for a few examples of research proposals, you've come to the right place. In this video, we walk you through two successful (approved) research proposals, one for a Master's-level project, and one for a PhD-level ...
In practice, deciding on a research topic and working out your research questions goes hand-in-hand. Below six steps will guide you in formulating a good research topic for your PhD. Step 1. Research the state-of-art in your interested research domain. Initially find atleast 5-8 appropriate keywords for a literature search.
PhD research. As a doctoral researcher at Sussex, you will be a valued part of our academic community and encouraged to participate in seminars, research activities and teaching. You will be supported by two supervisors with expertise on your topic and we encourage you to reach out to faculty members to discuss your research ideas before applying.
After successful completion of the departmental Preliminary Examination, all PhD and PharmD/PhD students must submit and orally defend a written Research proposal outlining their proposed dissertation research. Students should register for PHC 511 Research Proposal in the Spring semester following completion of the Preliminary Examination.
In this session for PhD students, several fellowship opportunities for doctoral computational researchers will be discussed along with key insights to the deadlines, proposal components, and application procedures. Many of these fellowships are open to international and domestic students from computer science, various fields of engineering, statistics, mathematics, and other computational ...
Microsystems engineering Ph.D. student Evan Manfreda-Schulz '20 accomplished something many academic researchers aim for when his first paper was published on the cover of Optica Quantum. The paper, "Generating high-dimensional entanglement using a foundry-fabricated photonic integrated circuit," is a culmination of years of study in the realm of quantum information systems.
Researchers from Johns Hopkins Medicine have proposed a novel approach to address the kidney donor shortage by using kidneys from deceased donors who were on dialysis. ... New Research Supports Expansion of Kidney Donation to Include Organs from Deceased Patients Who Once Had Dialysis ... PhD; Nitya Srialluri, MD, MS, MHS, and Heather Thiessen ...
The second year of a PhD. Your second year will probably be when you do most of your core research. The process for this will vary depending on your field, but your main focus will be on gathering results from experiments, archival research, surveys or other means.. As your research develops, so will the thesis (or argument) you base upon it. You may even begin writing up chapters or other ...
INDIANAPOLIS - Indiana University School of Medicine's Yoshikazu Imanishi, PhD, was recently awarded a four-year, $2.1 million grant from the National Eye Institute and a three-year, $500,000 grant from the Foundation Fighting Blindness to study genetic causes of blindness.. Some of the most devastating vision impairments and causes of blindness occur in people who have inherited mutated ...
The loss of e-mail was especially difficult, because making appointments, scheduling PhD defences and accessing journals all require a university e-mail address, Tröger says.