- Deutschland
- Asia, Australia & New Zealand
- Europe, Middle East & Africa
- United States & Canada
- Latinoamérica

Brand Marketing Case Studies
This collection features brands and content creators that used video and other digital tactics to drive innovation, connect with their consumers, and drive brand and business metrics. Learn about best practices, creative executions, and how brands achieved success through digital.
Share this page
Comedy central’s innovative search/youtube strategy sends fans on an internet-wide easter egg hunt, fiat's 500x crossover ad drives audience engagement on youtube, how orkin's youtube content strategy exterminated the 'ew'-factor and boosted brand awareness, gillette wins with a digital-first approach for gillette body, how maybelline new york's eye-catching youtube campaign dared consumers to 'go nude', driving sales for retailers with youtube's trueview for shopping, l'oréal canada finds beauty in programmatic buying, rosetta stone embraces mobile video to generate 10x increase in site traffic, new balance races past pre-order goal with youtube trueview and google lightbox ads, how budweiser won the big game with "puppy love", jcpenney optical boosts in-store traffic and brand exposure with google advertising, how activision reached over 2m subscribers on youtube, aéropostale partners with youtube star bethany mota to drive leads, sales and fans, mondelēz international improves campaign effectiveness with google’s brand lift solution, visit california lifts intent to travel to california with a unique experience on youtube, toyota drives engagement with first +post ads campaign, brand usa boosts travel intent 22% with 'discover america' campaign, kraft serves up a fresh take on food with a side of google, hyatt brings its brand experience to life with google solutions, ehealth boosts brand awareness with google display ads, sunrun uses google's brand lift solution to measure campaign recall, topshop reinvents its london fashion week show on google+ and engagement triples, chevrolet drives brand awareness for its new traverse, unilever's 'project sunlight' shines with 77 million youtube views, mercedes-benz france's immersive youtube experience fuels shift in brand perception, youtube and broadway: a cinderella story, chef jamie oliver's food tube: a recipe for youtube success, the record breaking love affair between evian® and youtube, nextiva attracts new customers with youtube trueview ads, vice's youtube success: growing sustained viewership through breakout videos, land rover finds success with engagement ads.
Coca-Cola Marketing Strategy: A 2024 Comprehensive Case Study
Introduced over a century ago, Coca-Cola remains the world’s most consumed soda, illustrating its unparalleled ability to engage and captivate consumers globally. This case study explores the marketing strategy of Coca-Cola that continues to make it the leading manufacturer and licensor of nonalcoholic beverages, offering a staggering 3,500 varieties across more than 200 countries.

From Pharmacist's Elixir to Global Refreshment Drink
On May 8, 1886, Dr. John Pemberton created what is now known as Coca-Cola. Originally sold at a pharmacy in Atlanta as a medicinal elixir, Coca-Cola has transformed into a global refreshment enjoyed daily by millions.
What is Coca-Cola's Marketing Strategy?
The strategic marketing decisions made by Coca-Cola are largely responsible for its success. The company's approach includes comprehensive branding , widespread distribution, creative advertising, and innovative customer engagement tactics. Coca-Cola’s overarching vision continues to drive its global agenda, remaining focused on refreshing the world in mind, body, and spirit and making a difference to the people and communities it serves. This vision has enabled the company to maintain direction and momentum through periods of uncertainty.
Coca-Cola Target Audience
- Age : Targets youths (10–35 years) with celebrity endorsements and vibrant campaigns, while also catering to health-conscious older adults with products like Diet Coke and Coke Zero.
- Income and Family Size: Offers various packaging options across different price points to ensure affordability for students, middle-class families, and low-income groups.
- Geographical Segmentation: Tailors its formulas to suit regional tastes, such as sweeter versions in Asia, to resonate with local preferences.
- Gender: Differentiates offerings like Coca-Cola Light for women and Coke Zero for men, focusing on taste preferences linked to gender.
Advertising

From early advertisements in newspapers to groundbreaking campaigns like "I’d Like to Buy the World a Coke," Coca-Cola has always known the power of effective advertising. Each campaign not only promoted their product but also cemented Coca-Cola’s place in the cultural landscape. Coca-Cola’s advertising campaigns are designed to resonate on a global scale while maintaining local relevance. These strategies include:
- Creative Campaigns: Engaging and visually appealing ads that capture the essence of joy and refreshment.
- Emotional Branding : Utilizing regional languages and culturally relevant content to connect emotionally with consumers.
- Celebrity Partnerships: Collaborating with local and international celebrities to widen reach.
- Wide Coverage: Utilizing multiple channels, from traditional media to digital platforms.
- Engagement : Interactive campaigns and social media strategies to engage with a younger audience.
- Sponsorships : Long-standing partnerships with major events like the Olympics, FIFA World Cup, American Idol and popular TV shows enhancing brand visibility and consumer connection globally.
Coca-Cola has also embraced personalization in its past campaigns, from names on bottles to personalized marketing emails, enhancing consumer loyalty and personal connection with the brand.
1. "Share a Coke" Campaign
Launched initially in Australia in 2011, the "Share a Coke" campaign is one of the most celebrated and successful marketing strategies in Coca-Cola's history. The campaign was groundbreaking in its approach—replacing the iconic Coca-Cola logo on bottles with common first names. The idea was simple yet powerful: personalize the Coke experience to encourage sharing and create a personal connection with the product. Consumers could find bottles with their names or the names of friends and family, making it not just a purchase but a personalized social experience. The campaign heavily leveraged social media, encouraging people to share their Coca-Cola moments online with the hashtag #ShareaCoke, which amplified the campaign's reach exponentially. After its initial success in Australia, the campaign rolled out in over 80 countries with country-specific names and designs, each resonating with local audiences and cultural nuances.
2. "I'd Like to Buy the World a Coke" (Hilltop)
Originally aired in 1971, the "Hilltop" commercial for Coca-Cola, also known as "I'd Like to Buy the World a Coke," remains one of the most iconic advertisements in the history of television. Conceived by Bill Backer of McCann Erickson, the commercial featured a diverse group of young people from all over the world singing on a hilltop in Italy. The ad's simple yet profound message of hope and unity, expressed through the lyrics "I'd like to buy the world a home and furnish it with love," struck a chord during a time of political unrest and social change. The commercial became more than just an ad; it became a cultural icon, evoking feelings of peace and camaraderie at a global scale. The ad's popularity led to several remakes and re-releases over the decades, including a famous 1990 version featuring the original singers and their children, and a Super Bowl version in 2011.
3. "The Happiness Machine"
As part of its "Open Happiness" campaign, Coca-Cola launched "The Happiness Machine" video in 2010. The campaign featured a specially designed Coke vending machine placed in a college campus that dispensed not just bottles of Coke but surprising acts of "happiness" – from pizza and flowers to balloon animals. The video quickly went viral, thanks to its genuine, unscripted reactions and feel-good vibe. It amassed millions of views on YouTube, bringing widespread attention and goodwill toward the brand. This campaign emphasized Coca-Cola's focus on selling experiences and emotions associated with the brand, not just the product. It highlighted the brand’s commitment to spreading joy and happiness. The success of the "Happiness Machine" led to the creation of similar campaigns globally, harnessing the power of viral marketing and showing the brand's innovative approach to engaging with younger audiences.
Social Media and Digital Marketing

Coca-Cola has evolved its marketing strateg y from traditional mediums to a more integrated, multi-channel approach. The focus is now on building personal connections with consumers and leveraging digital platforms for targeted and engaging marketing campaigns. This shift has allowed Coca-Cola to maintain its relevance. Coca-Cola has embraced the digital age with robust online presence across platforms like Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, YouTube, and Snapchat. The brand leverages SEO , email marketing , content marketing , and video marketing to engage a broader audience effectively.
Coca-Cola Marketing Strategy
Coca-Cola employs a dual-channel marketing strategy :
- Personal Channels: Direct interaction with consumers to build personal connections.
- Non-Personal Channels: A mix of traditional and digital media, including newspapers, TV, social media, email, and outdoor advertising, to ensure widespread reach.
Coca-Cola’s Marketing Mix: The 4 Ps
- Product Strategy: Coca-Cola boasts an extensive portfolio of 500 products, positioned strategically within the market to maximize reach and profitability. Coca-Cola’s commitment to maintaining its original formula and ensuring product quality has fostered deep brand loyalty . Even when new recipes were introduced, such as New Coke, the public’s attachment to the original formula brought it swiftly back. To cater to diverse consumer tastes, Coca-Cola has expanded its product portfolio to include juices, teas, coffees, and other beverages. This diversification strategy helps the company penetrate different market segments.
- Pricing Strategy: Initially maintained a constant price for decades, it now employs a flexible pricing strategy to remain competitive without compromising perceived quality. Coca-Cola's pricing strategy is carefully crafted to remain competitive while ensuring profitability.
- Place Strategy: Operates a vast distribution network across six global regions, supported by an extensive supply chain involving bottling partners and distributors, ensuring global product availability.
- Promotion Strategy: Invests heavily in diverse advertising strategies to maintain brand visibility and consumer engagement across various platforms.

Coca-Cola's Growth Strategy
- Winning More Consumers : Expanding the consumer base through effective marketing and innovative product offerings.
- Gaining Market Share: Outperforming competitors by understanding consumer needs better and responding quickly.
- Maintaining Strong System Economics: Ensuring profitability and sustainability across the supply chain.
- Strengthening Impact Across Stakeholders: Building a positive influence on consumers, communities, and environments.
- Equipping for Future Success: Preparing the organization to meet future challenges through continuous learning and adaptation.
Additionally, sustainability is integral to Coca-Cola's growth strategy. The company has focused on reducing its environmental footprint, using resources more efficiently, and promoting recycling. These efforts are aligned with its mission to make a difference, ensuring that growth is sustainable over the long term.
These objectives serve as the north stars for Coca-Cola, guiding all strategic decisions and initiatives.
Brand Portfolio Optimization
The iconic Coca-Cola logo and the classic bottle design are instantly recognizable worldwide, making branding a cornerstone of their strategy. This section examines how consistent branding across various platforms plays a critical role in Coca-Cola's marketing . Keeping a uniform visual identity and engaging in significant sponsorships have allowed Coca-Cola to remain relevant and beloved by generations. In a significant move to optimize its brand portfolio , Coca-Cola reduced its brand count from 400 to 200 master brands. This strategic decision was aimed at focusing on those brands that align with and support the company's growth objectives. By doing so, Coca-Cola has ensured that it invests in brands with the highest potential for growth and profitability, balancing global, regional, and local brands to cover all drinking occasions.

Managing Missteps With Grace
Coca-Cola’s ability to handle marketing and business errors gracefully, such as the New Coke debacle, shows a brand well-versed in crisis management and responsive public relations.
Lessons for Marketers
- Brand Identity is Essential: A strong, consistent brand identity is vital for long-term success.
- Prioritize Product Quality : High product quality should always be a priority, supporting marketing efforts and building consumer trust.
- Strategic Pricing is Key: Effective pricing strategies can significantly impact brand perception and customer loyalty.
- Explore New Markets: Expanding into new markets can drive growth and help maintain relevance.
- Responsive PR Matters: Managing public relations actively and effectively can mitigate potential damages and boost brand image.
What Makes Coca-Cola’s Marketing Strategy So Successful?
Coca-Cola’s enduring success is attributed to its ability to adapt to consumer needs, maintain a strong emotional connection with customers, and continuously innovate its marketing strategies .
Coca-Cola's success story is a playbook for marketers aiming to build a lasting brand that not only survives but thrives through changing times. By understanding and implementing these strategies, other brands can aim to replicate Coca-Cola's enduring appeal.
Please fill out the form below if you have any advertising and partnership inquiries.

Consultation & Audit

28 Case Study Examples Every Marketer Should See
Published: March 08, 2023
Putting together a compelling case study is one of the most powerful strategies for showcasing your product and attracting future customers. But it's not easy to create case studies that your audience can’t wait to read.

In this post, we’ll go over the definition of a case study and the best examples to inspire you.

What is a case study?
A case study is a detailed story of something your company did. It includes a beginning — often discussing a conflict, an explanation of what happened next, and a resolution that explains how the company solved or improved on something.
A case study proves how your product has helped other companies by demonstrating real-life results. Not only that, but marketing case studies with solutions typically contain quotes from the customer. This means that they’re not just ads where you praise your own product. Rather, other companies are praising your company — and there’s no stronger marketing material than a verbal recommendation or testimonial. A great case study is also filled with research and stats to back up points made about a project's results.
There are myriad ways to use case studies in your marketing strategy . From featuring them on your website to including them in a sales presentation, a case study is a strong, persuasive tool that shows customers why they should work with you — straight from another customer. Writing one from scratch is hard, though, which is why we’ve created a collection of case study templates for you to get started.
Fill out the form below to access the free case study templates.

Free Case Study Templates
Showcase your company's success using these three free case study templates.
- Data-Driven Case Study Template
- Product-Specific Case Study Template
- General Case Study Template
Download Free
All fields are required.
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
There’s no better way to generate more leads than by writing case studies . But without case study examples to draw inspiration from, it can be difficult to write impactful studies that convince visitors to submit a form.
Marketing Case Study Examples
To help you create an attractive and high-converting case study, we've put together a list of some of our favorites. This list includes famous case studies in marketing, technology, and business.
These studies can show you how to frame your company offers in a way that is both meaningful and useful to your audience. So, take a look, and let these examples inspire your next brilliant case study design.
These marketing case studies with solutions show the value proposition of each product. They also show how each company benefited in both the short and long term using quantitative data. In other words, you don’t get just nice statements, like "This company helped us a lot." You see actual change within the firm through numbers and figures.
You can put your learnings into action with HubSpot's Free Case Study Templates . Available as custom designs and text-based documents, you can upload these templates to your CMS or send them to prospects as you see fit.

1. " How Handled Scaled from Zero to 121 Locations with the Help of HubSpot ," by HubSpot

What's interesting about this case study is the way it leads with the customer. That reflects a major HubSpot cornerstone, which is to always solve for the customer first. The copy leads with a brief description of why the CEO of Handled founded the company and why he thought Handled could benefit from adopting a CRM. The case study also opens up with one key data point about Handled’s success using HubSpot, namely that it grew to 121 locations.
Notice that this case study uses mixed media. Yes, there is a short video, but it's elaborated upon in the other text on the page. So while your case studies can use one or the other, don't be afraid to combine written copy with visuals to emphasize the project's success.
Key Learnings from the HubSpot Case Study Example
- Give the case study a personal touch by focusing on the CEO rather than the company itself.
- Use multimedia to engage website visitors as they read the case study.
2. " The Whole Package ," by IDEO

Here's a design company that knows how to lead with simplicity in its case studies. As soon as the visitor arrives at the page, they’re greeted with a big, bold photo and the title of the case study — which just so happens to summarize how IDEO helped its client. It summarizes the case study in three snippets: The challenge, the impact, and the outcome.
Immediately, IDEO communicates its impact — the company partnered with H&M to remove plastic from its packaging — but it doesn't stop there. As the user scrolls down, the challenge, impact, and progress are elaborated upon with comprehensive (but not overwhelming) copy that outlines what that process looked like, replete with quotes and intriguing visuals.
Key Learnings from the IDEO Case Study Example
- Split up the takeaways of your case studies into bite-sized sections.
- Always use visuals and images to enrich the case study experience, especially if it’s a comprehensive case study.
3. " Rozum Robotics intensifies its PR game with Awario ," by Awario
In this case study, Awario greets the user with a summary straight away — so if you’re feeling up to reading the entire case study, you can scan the snapshot and understand how the company serves its customers. The case study then includes jump links to several sections, such as "Company Profile," "Rozum Robotics' Pains," "Challenge," "Solution," and "Results and Improvements."
The sparse copy and prominent headings show that you don’t need a lot of elaborate information to show the value of your products and services. Like the other case study examples on this list, it includes visuals and quotes to demonstrate the effectiveness of the company’s efforts. The case study ends with a bulleted list that shows the results.
Key Learnings from the Awario Robotics Case Study Example
- Create a table of contents to make your case study easier to navigate.
- Include a bulleted list of the results you achieved for your client.
4. " Chevrolet DTU ," by Carol H. Williams

If you’ve worked with a company that’s well-known, use only the name in the title — like Carol H. Williams, one of the nation’s top advertising agencies, does here. The "DTU," stands for "Discover the Unexpected." It generates interest because you want to find out what the initials mean.
They keep your interest in this case study by using a mixture of headings, images, and videos to describe the challenges, objectives, and solutions of the project. The case study closes with a summary of the key achievements that Chevrolet’s DTU Journalism Fellows reached during the project.
Key Learnings from the Carol H. Williams Case Study Example
- If you’ve worked with a big brand before, consider only using the name in the title — just enough to pique interest.
- Use a mixture of headings and subheadings to guide users through the case study.
5. " How Fractl Earned Links from 931 Unique Domains for Porch.com in a Single Year ," by Fractl

Fractl uses both text and graphic design in their Porch.com case study to immerse the viewer in a more interesting user experience. For instance, as you scroll, you'll see the results are illustrated in an infographic-design form as well as the text itself.
Further down the page, they use icons like a heart and a circle to illustrate their pitch angles, and graphs to showcase their results. Rather than writing which publications have mentioned Porch.com during Fractl’s campaign, they incorporated the media outlets’ icons for further visual diversity.
Key Learnings from the Fractl Case Study Example
- Let pictures speak for you by incorporating graphs, logos, and icons all throughout the case study.
- Start the case study by right away stating the key results, like Fractl does, instead of putting the results all the way at the bottom.
6. " The Met ," by Fantasy
What's the best way to showcase the responsiveness and user interface of a website? Probably by diving right into it with a series of simple showcases— which is exactly what Fantasy does on their case study page for the Metropolitan Museum of Art. They keep the page simple and clean, inviting you to review their redesign of the Met’s website feature-by-feature.
Each section is simple, showing a single piece of the new website's interface so that users aren’t overwhelmed with information and can focus on what matters most.
If you're more interested in text, you can read the objective for each feature. Fantasy understands that, as a potential customer, this is all you need to know. Scrolling further, you're greeted with a simple "Contact Us" CTA.
Key Learnings from the Fantasy Case Study Example
- You don’t have to write a ton of text to create a great case study. Focus on the solution you delivered itself.
- Include a CTA at the bottom inviting visitors to contact you.
7. " Rovio: How Rovio Grew Into a Gaming Superpower ," by App Annie
If your client had a lot of positive things to say about you, take a note from App Annie’s Rovio case study and open up with a quote from your client. The case study also closes with a quote, so that the case study doesn’t seem like a promotion written by your marketing team but a story that’s taken straight from your client’s mouth. It includes a photo of a Rovio employee, too.
Another thing this example does well? It immediately includes a link to the product that Rovio used (namely, App Annie Intelligence) at the top of the case study. The case study closes with a call-to-action button prompting users to book a demo.
Key Learnings from the App Annie Case Study Example
- Feature quotes from your client at the beginning and end of the case study.
- Include a mention of the product right at the beginning and prompt users to learn more about the product.
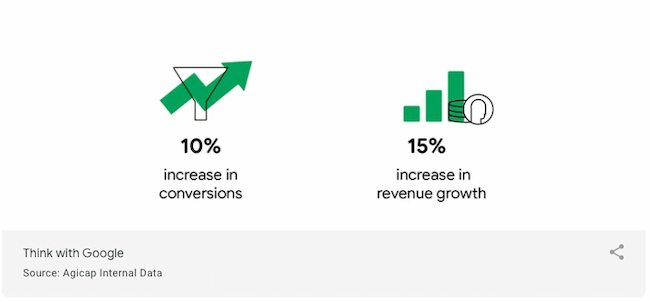
8. " Embracing first-party data: 3 success stories from HubSpot ," by Think with Google

Google takes a different approach to text-focused case studies by choosing three different companies to highlight.
The case study is clean and easily scannable. It has sections for each company, with quotes and headers that clarify the way these three distinct stories connect. The simple format also uses colors and text that align with the Google brand.
Another differentiator is the focus on data. This case study is less than a thousand words, but it's packed with useful data points. Data-driven insights quickly and clearly show how the value of leveraging first-party data while prioritizing consumer privacy.
Key Learnings from the Think with Google Case Study Example
- A case study doesn’t need to be long or complex to be powerful.
- Clear data points are a quick and effective way to prove value.
9. " In-Depth Performance Marketing Case Study ," by Switch

Switch is an international marketing agency based in Malta that knocks it out of the park with this case study. Its biggest challenge is effectively communicating what it did for its client without ever revealing the client’s name. It also effectively keeps non-marketers in the loop by including a glossary of terms on page 4.
The PDF case study reads like a compelling research article, including titles like "In-Depth Performance Marketing Case Study," "Scenario," and "Approach," so that readers get a high-level overview of what the client needed and why they approached Switch. It also includes a different page for each strategy. For instance, if you’d only be interested in hiring Switch for optimizing your Facebook ads, you can skip to page 10 to see how they did it.
The PDF is fourteen pages long but features big fonts and plenty of white space, so viewers can easily skim it in only a few minutes.
Key Learnings from the Switch Case Study Example
- If you want to go into specialized information, include a glossary of terms so that non-specialists can easily understand.
- Close with a CTA page in your case study PDF and include contact information for prospective clients.
10. " Gila River ," by OH Partners

Let pictures speak for you, like OH Partners did in this case study. While you’ll quickly come across a heading and some text when you land on this case study page, you’ll get the bulk of the case study through examples of actual work OH Partners did for its client. You will see OH Partners’ work in a billboard, magazine, and video. This communicates to website visitors that if they work with OH Partners, their business will be visible everywhere.
And like the other case studies here, it closes with a summary of what the firm achieved for its client in an eye-catching way.
Key Learnings from the OH Partners Case Study Example
- Let the visuals speak by including examples of the actual work you did for your client — which is especially useful for branding and marketing agencies.
- Always close out with your achievements and how they impacted your client.
11. " Facing a Hater ," by Digitas
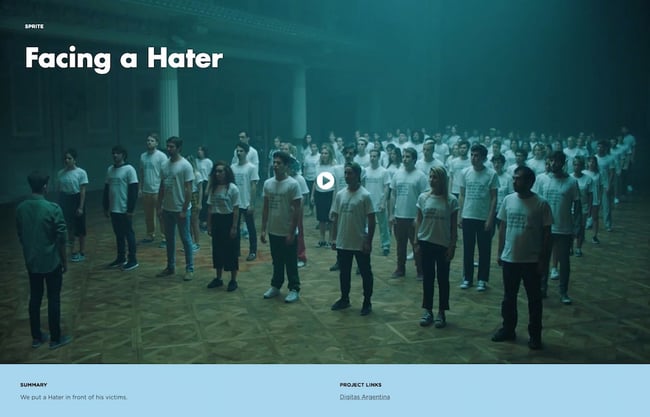
Digitas' case study page for Sprite’s #ILOVEYOUHATER campaign keeps it brief while communicating the key facts of Digitas’ work for the popular soda brand. The page opens with an impactful image of a hundred people facing a single man. It turns out, that man is the biggest "bully" in Argentina, and the people facing him are those whom he’s bullied before.
Scrolling down, it's obvious that Digitas kept Sprite at the forefront of their strategy, but more than that, they used real people as their focal point. They leveraged the Twitter API to pull data from Tweets that people had actually tweeted to find the identity of the biggest "hater" in the country. That turned out to be @AguanteElCofler, a Twitter user who has since been suspended.
Key Learnings from the Digitas Case Study Example
- If a video was part of your work for your client, be sure to include the most impactful screenshot as the heading.
- Don’t be afraid to provide details on how you helped your client achieve their goals, including the tools you leveraged.
12. " Better Experiences for All ," by HermanMiller

HermanMiller sells sleek, utilitarian furniture with no frills and extreme functionality, and that ethos extends to its case study page for a hospital in Dubai.
What first attracted me to this case study was the beautiful video at the top and the clean user experience. User experience matters a lot in a case study. It determines whether users will keep reading or leave. Another notable aspect of this case study is that the video includes closed-captioning for greater accessibility, and users have the option of expanding the CC and searching through the text.
HermanMiller’s case study also offers an impressive amount of information packed in just a few short paragraphs for those wanting to understand the nuances of their strategy. It closes out with a quote from their client and, most importantly, the list of furniture products that the hospital purchased from the brand.
Key Learnings from the HermanMiller Case Study Example
- Close out with a list of products that users can buy after reading the case study.
- Include accessibility features such as closed captioning and night mode to make your case study more user-friendly.
13. " Capital One on AWS ," by Amazon
Do you work continuously with your clients? Consider structuring your case study page like Amazon did in this stellar case study example. Instead of just featuring one article about Capital One and how it benefited from using AWS, Amazon features a series of articles that you can then access if you’re interested in reading more. It goes all the way back to 2016, all with different stories that feature Capital One’s achievements using AWS.
This may look unattainable for a small firm, but you don’t have to go to extreme measures and do it for every single one of your clients. You could choose the one you most wish to focus on and establish a contact both on your side and your client’s for coming up with the content. Check in every year and write a new piece. These don’t have to be long, either — five hundred to eight hundred words will do.
Key Learnings from the Amazon AWS Case Study Example
- Write a new article each year featuring one of your clients, then include links to those articles in one big case study page.
- Consider including external articles as well that emphasize your client’s success in their industry.
14. " HackReactor teaches the world to code #withAsana ," by Asana

While Asana's case study design looks text-heavy, there's a good reason. It reads like a creative story, told entirely from the customer's perspective.
For instance, Asana knows you won't trust its word alone on why this product is useful. So, they let Tony Phillips, HackReactor CEO, tell you instead: "We take in a lot of information. Our brains are awful at storage but very good at thinking; you really start to want some third party to store your information so you can do something with it."
Asana features frequent quotes from Phillips to break up the wall of text and humanize the case study. It reads like an in-depth interview and captivates the reader through creative storytelling. Even more, Asana includes in-depth detail about how HackReactor uses Asana. This includes how they build templates and workflows:
"There's a huge differentiator between Asana and other tools, and that’s the very easy API access. Even if Asana isn’t the perfect fit for a workflow, someone like me— a relatively mediocre software engineer—can add functionality via the API to build a custom solution that helps a team get more done."
Key Learnings from the Asana Example
- Include quotes from your client throughout the case study.
- Provide extensive detail on how your client worked with you or used your product.
15. " Rips Sewed, Brand Love Reaped ," by Amp Agency

Amp Agency's Patagonia marketing strategy aimed to appeal to a new audience through guerrilla marketing efforts and a coast-to-coast road trip. Their case study page effectively conveys a voyager theme, complete with real photos of Patagonia customers from across the U.S., and a map of the expedition. I liked Amp Agency's storytelling approach best. It captures viewers' attention from start to finish simply because it's an intriguing and unique approach to marketing.
Key Learnings from the Amp Agency Example
- Open up with a summary that communicates who your client is and why they reached out to you.
- Like in the other case study examples, you’ll want to close out with a quantitative list of your achievements.
16. " NetApp ," by Evisort
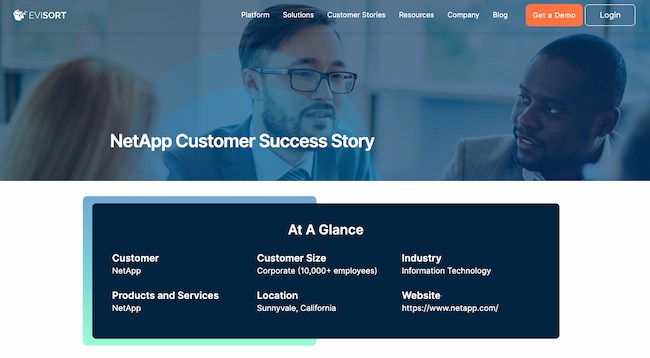
Evisort opens up its NetApp case study with an at-a-glance overview of the client. It’s imperative to always focus on the client in your case study — not on your amazing product and equally amazing team. By opening up with a snapshot of the client’s company, Evisort places the focus on the client.
This case study example checks all the boxes for a great case study that’s informative, thorough, and compelling. It includes quotes from the client and details about the challenges NetApp faced during the COVID pandemic. It closes out with a quote from the client and with a link to download the case study in PDF format, which is incredibly important if you want your case study to be accessible in a wider variety of formats.
Key Learnings from the Evisort Example
- Place the focus immediately on your client by including a snapshot of their company.
- Mention challenging eras, such as a pandemic or recession, to show how your company can help your client succeed even during difficult times.
17. " Copernicus Land Monitoring – CLC+ Core ," by Cloudflight
Including highly specialized information in your case study is an effective way to show prospects that you’re not just trying to get their business. You’re deep within their industry, too, and willing to learn everything you need to learn to create a solution that works specifically for them.
Cloudflight does a splendid job at that in its Copernicus Land Monitoring case study. While the information may be difficult to read at first glance, it will capture the interest of prospects who are in the environmental industry. It thus shows Cloudflight’s value as a partner much more effectively than a general case study would.
The page is comprehensive and ends with a compelling call-to-action — "Looking for a solution that automates, and enhances your Big Data system? Are you struggling with large datasets and accessibility? We would be happy to advise and support you!" The clean, whitespace-heavy page is an effective example of using a case study to capture future leads.
Key Learnings from the Cloudflight Case Study Example
- Don’t be afraid to get technical in your explanation of what you did for your client.
- Include a snapshot of the sales representative prospects should contact, especially if you have different sales reps for different industries, like Cloudflight does.
18. " Valvoline Increases Coupon Send Rate by 76% with Textel’s MMS Picture Texting ," by Textel

If you’re targeting large enterprises with a long purchasing cycle, you’ll want to include a wealth of information in an easily transferable format. That’s what Textel does here in its PDF case study for Valvoline. It greets the user with an eye-catching headline that shows the value of using Textel. Valvoline saw a significant return on investment from using the platform.
Another smart decision in this case study is highlighting the client’s quote by putting it in green font and doing the same thing for the client’s results because it helps the reader quickly connect the two pieces of information. If you’re in a hurry, you can also take a look at the "At a Glance" column to get the key facts of the case study, starting with information about Valvoline.
Key Learnings from the Textel Case Study Example
- Include your client’s ROI right in the title of the case study.
- Add an "At a Glance" column to your case study PDF to make it easy to get insights without needing to read all the text.
19. " Hunt Club and Happeo — a tech-enabled love story ," by Happeo

In this blog-post-like case study, Happeo opens with a quote from the client, then dives into a compelling heading: "Technology at the forefront of Hunt Club's strategy." Say you’re investigating Happeo as a solution and consider your firm to be technology-driven. This approach would spark your curiosity about why the client chose to work with Happeo. It also effectively communicates the software’s value proposition without sounding like it’s coming from an in-house marketing team.
Every paragraph is a quote written from the customer’s perspective. Later down the page, the case study also dives into "the features that changed the game for Hunt Club," giving Happeo a chance to highlight some of the platform’s most salient features.
Key Learnings from the Happeo Case Study Example
- Consider writing the entirety of the case study from the perspective of the customer.
- Include a list of the features that convinced your client to go with you.
20. " Red Sox Season Campaign ," by CTP Boston
What's great about CTP's case study page for their Red Sox Season Campaign is their combination of video, images, and text. A video automatically begins playing when you visit the page, and as you scroll, you'll see more embedded videos of Red Sox players, a compilation of print ads, and social media images you can click to enlarge.
At the bottom, it says "Find out how we can do something similar for your brand." The page is clean, cohesive, and aesthetically pleasing. It invites viewers to appreciate the well-roundedness of CTP's campaign for Boston's beloved baseball team.
Key Learnings from the CTP Case Study Example
- Include a video in the heading of the case study.
- Close with a call-to-action that makes leads want to turn into prospects.
21. " Acoustic ," by Genuine

Sometimes, simple is key. Genuine's case study for Acoustic is straightforward and minimal, with just a few short paragraphs, including "Reimagining the B2B website experience," "Speaking to marketers 1:1," and "Inventing Together." After the core of the case study, we then see a quote from Acoustic’s CMO and the results Genuine achieved for the company.
The simplicity of the page allows the reader to focus on both the visual aspects and the copy. The page displays Genuine's brand personality while offering the viewer all the necessary information they need.
- You don’t need to write a lot to create a great case study. Keep it simple.
- Always include quantifiable data to illustrate the results you achieved for your client.
22. " Using Apptio Targetprocess Automated Rules in Wargaming ," by Apptio
Apptio’s case study for Wargaming summarizes three key pieces of information right at the beginning: The goals, the obstacles, and the results.
Readers then have the opportunity to continue reading — or they can walk away right then with the information they need. This case study also excels in keeping the human interest factor by formatting the information like an interview.
The piece is well-organized and uses compelling headers to keep the reader engaged. Despite its length, Apptio's case study is appealing enough to keep the viewer's attention. Every Apptio case study ends with a "recommendation for other companies" section, where the client can give advice for other companies that are looking for a similar solution but aren’t sure how to get started.
Key Learnings from the Apptio Case Study Example
- Put your client in an advisory role by giving them the opportunity to give recommendations to other companies that are reading the case study.
- Include the takeaways from the case study right at the beginning so prospects quickly get what they need.
23. " Airbnb + Zendesk: building a powerful solution together ," by Zendesk
Zendesk's Airbnb case study reads like a blog post, and focuses equally on Zendesk and Airbnb, highlighting a true partnership between the companies. To captivate readers, it begins like this: "Halfway around the globe is a place to stay with your name on it. At least for a weekend."
The piece focuses on telling a good story and provides photographs of beautiful Airbnb locations. In a case study meant to highlight Zendesk's helpfulness, nothing could be more authentic than their decision to focus on Airbnb's service in such great detail.
Key Learnings from the Zendesk Case Study Example
- Include images of your client’s offerings — not necessarily of the service or product you provided. Notice how Zendesk doesn’t include screenshots of its product.
- Include a call-to-action right at the beginning of the case study. Zendesk gives you two options: to find a solution or start a trial.
24. " Biobot Customer Success Story: Rollins College, Winter Park, Florida ," by Biobot
Like some of the other top examples in this list, Biobot opens its case study with a quote from its client, which captures the value proposition of working with Biobot. It mentions the COVID pandemic and goes into detail about the challenges the client faced during this time.
This case study is structured more like a news article than a traditional case study. This format can work in more formal industries where decision-makers need to see in-depth information about the case. Be sure to test different methods and measure engagement .
Key Learnings from the Biobot Case Study Example
- Mention environmental, public health, or economic emergencies and how you helped your client get past such difficult times.
- Feel free to write the case study like a normal blog post, but be sure to test different methods to find the one that best works for you.
25. " Discovering Cost Savings With Efficient Decision Making ," by Gartner

You don't always need a ton of text or a video to convey your message — sometimes, you just need a few paragraphs and bullet points. Gartner does a fantastic job of quickly providing the fundamental statistics a potential customer would need to know, without boggling down their readers with dense paragraphs. The case study closes with a shaded box that summarizes the impact that Gartner had on its client. It includes a quote and a call-to-action to "Learn More."
Key Learnings from the Gartner Case Study Example
- Feel free to keep the case study short.
- Include a call-to-action at the bottom that takes the reader to a page that most relates to them.
26. " Bringing an Operator to the Game ," by Redapt

This case study example by Redapt is another great demonstration of the power of summarizing your case study’s takeaways right at the start of the study. Redapt includes three easy-to-scan columns: "The problem," "the solution," and "the outcome." But its most notable feature is a section titled "Moment of clarity," which shows why this particular project was difficult or challenging.
The section is shaded in green, making it impossible to miss. Redapt does the same thing for each case study. In the same way, you should highlight the "turning point" for both you and your client when you were working toward a solution.
Key Learnings from the Redapt Case Study Example
- Highlight the turning point for both you and your client during the solution-seeking process.
- Use the same structure (including the same headings) for your case studies to make them easy to scan and read.
27. " Virtual Call Center Sees 300% Boost In Contact Rate ," by Convoso

Convoso’s PDF case study for Digital Market Media immediately mentions the results that the client achieved and takes advantage of white space. On the second page, the case study presents more influential results. It’s colorful and engaging and closes with a spread that prompts readers to request a demo.
Key Learnings from the Convoso Case Study Example
- List the results of your work right at the beginning of the case study.
- Use color to differentiate your case study from others. Convoso’s example is one of the most colorful ones on this list.
28. " Ensuring quality of service during a pandemic ," by Ericsson
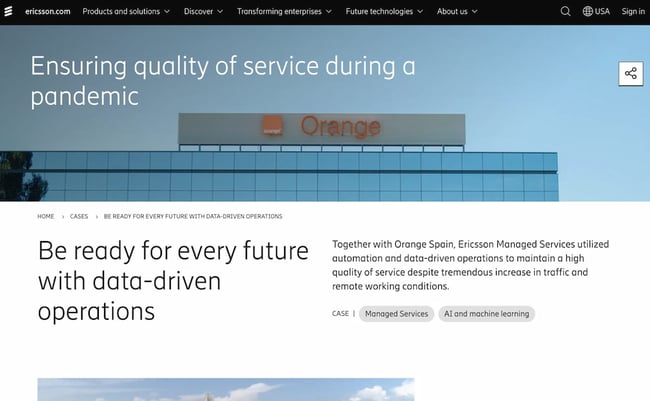
Ericsson’s case study page for Orange Spain is an excellent example of using diverse written and visual media — such as videos, graphs, and quotes — to showcase the success a client experienced. Throughout the case study, Ericsson provides links to product and service pages users might find relevant as they’re reading the study.
For instance, under the heading "Preloaded with the power of automation," Ericsson mentions its Ericsson Operations Engine product, then links to that product page. It closes the case study with a link to another product page.
Key Learnings from the Ericsson Case Study Example
- Link to product pages throughout the case study so that readers can learn more about the solution you offer.
- Use multimedia to engage users as they read the case study.
Start creating your case study.
Now that you've got a great list of examples of case studies, think about a topic you'd like to write about that highlights your company or work you did with a customer.
A customer’s success story is the most persuasive marketing material you could ever create. With a strong portfolio of case studies, you can ensure prospects know why they should give you their business.
Editor's note: This post was originally published in August 2018 and has been updated for comprehensiveness.

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.
![marketing mix brand case study 7 Pieces of Content Your Audience Really Wants to See [New Data]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/contenttypes.webp)
7 Pieces of Content Your Audience Really Wants to See [New Data]

How to Write a Case Study: Bookmarkable Guide & Template

How to Market an Ebook: 21 Ways to Promote Your Content Offers
![marketing mix brand case study How to Write a Listicle [+ Examples and Ideas]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/listicle-1.jpg)
How to Write a Listicle [+ Examples and Ideas]
![marketing mix brand case study What Is a White Paper? [FAQs]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/business%20whitepaper.jpg)
What Is a White Paper? [FAQs]

What is an Advertorial? 8 Examples to Help You Write One

How to Create Marketing Offers That Don't Fall Flat

20 Creative Ways To Repurpose Content

16 Important Ways to Use Case Studies in Your Marketing

11 Ways to Make Your Blog Post Interactive
Showcase your company's success using these free case study templates.
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform
Marketing Research
40 case studies in branding.
[Apple: Innovation and Design as Brand Identity]
[Nike: Building a Global Brand Through Storytelling and Innovation]
[Tesla: Revolutionizing the Automotive Industry Through Innovation and Sustainability]
[Amazon: Transforming Retail and Beyond]
[Zoom: Connecting the World Through Video Communications]
[Beyond Meat: A Plant-Based Revolution]
[TikTok: A Dance with Global Success]
[Coca-Cola: Quenching the World’s Thirst for Over a Century]
[Netflix: Redefining the Future of Entertainment]
[Airbnb: Disrupting the Hospitality Industry]
[Starbucks: Brewing Success Through Innovation and Responsibility]
[The Walt Disney Company: A Kingdom of Creativity and Innovation]
[McDonald’s: Serving Success with a Side of Innovation]
[Dove (Unilever): Crafting Beauty and Confidence]
[IKEA: A Symphony of Design, Affordability, and Sustainability]
[LEGO: Building Blocks of Innovation and Success]
[Slack: Revolutionizing Workplace Communication]
[Patagonia: A Case Study in Sustainable Business Practices]
[Spotify: Transitioning from music sales to subscription streaming]
[Warby Parker: Disrupting the traditional eyewear market with an online-first approach]
[Allbirds: A Case Study in Sustainable Footwear Innovation]
40.1 Apple : Innovation and Design as Brand Identity
- Introduction:
Apple Inc., known for its revolutionary technology and design, has built its brand on innovation and a unique user experience. What began as a garage startup in 1976 has become one of the world’s most valuable companies. Let’s explore how Apple achieved this success.
- Background:
Founding and Early Years: Founded by Steve Jobs, Steve Wozniak, and Ronald Wayne, Apple started as a computer manufacturer. The launch of the Apple I computer in 1976 marked the company’s debut, and the subsequent Apple II became a significant success.
Rise to Prominence: With the introduction of the Macintosh in 1984, Apple emphasized graphical user interface, leading the way in user-friendly computing. The iPod, iPhone, iPad, and MacBook line have since become iconic products.
- Product Development: Regularly updating products to include the latest technology.
- Software Ecosystem: Creating a seamless software environment that ties different Apple products together.
- Aesthetic Appeal: Sleek and modern design across all products.
- User Experience: Emphasizing intuitive interfaces.
- Apple Ecosystem: The interoperability of products encourages customers to stay within the Apple brand.
- Customer Service: Apple’s customer support, including the Genius Bar in Apple Stores, provides personalized service.
- Store Design: Apple Stores are known for their minimalist design and layout.
- In-Store Experience: Offering hands-on experience with products and one-on-one customer service.
- High Pricing Strategy: Apple’s premium pricing limits accessibility for many consumers.
- Dependence on Key Products: A significant reliance on the iPhone, which generates a large portion of revenue.
- Manufacturing Practices: Criticisms regarding working conditions in factories.
- Environmental Concerns: Issues related to recycling and waste management.
- Cultural Impact and Legacy:
Apple’s marketing has not only sold products but also shaped culture.
Think Different Campaign: This campaign emphasized Apple’s image as a company for creative and unconventional thinkers.
Influence on Music Industry: With the iPod and iTunes, Apple changed how people buy and listen to music.
Smartphone Revolution: The iPhone transformed mobile communication.
- Conclusion:
Apple’s brand is more than just a logo; it’s a symbol of innovation, quality, and a unique customer experience. By consistently focusing on design and innovation, Apple has maintained a strong brand identity that resonates with consumers globally. Its success offers essential insights into how a focus on innovation, design, and customer experience can build a powerful and enduring brand. The company’s challenges and criticisms also provide a nuanced understanding of the complexities of operating at the forefront of technology.
- Further Exploration:
Apple’s Advertising: Analyzing various Apple advertising campaigns over the years.
Competitor Analysis: Understanding how Apple’s branding strategies compare with competitors like Samsung, Google, and Microsoft.
Future Outlook: Speculating on Apple’s future in an ever-changing technology landscape.
This extended case study provides a comprehensive view of Apple’s branding, suitable for students who want to delve deeply into branding’s multifaceted nature. It includes various aspects of branding, marketing, challenges, and impact, allowing for a rich understanding of how a brand can shape not only a company’s success but also influence broader culture and industry trends.
40.2 Nike: Building a Global Brand Through Storytelling and Innovation
Nike, Inc. is a household name synonymous with athleticism, performance, and innovation. Through its creative marketing strategies and commitment to design, Nike has become a leader in the sports apparel industry. This case study will explore Nike’s rise to prominence and the branding strategies that have kept it at the forefront of the sports industry.
- Founding and Early Years: Founded as Blue Ribbon Sports in 1964 by Bill Bowerman and Phil Knight, the company changed its name to Nike, Inc. in 1971. The famous swoosh logo and the “Just Do It” slogan became integral parts of the brand’s identity.
- Growth and Expansion: With an initial focus on running shoes, Nike expanded into various sports, including basketball, soccer, and golf, becoming a multi-sport brand.
- Historical Partnerships: Nike’s collaboration with athletes like Michael Jordan led to the creation of the Air Jordan line.
- Global Ambassadors: Associating with top athletes like Serena Williams, Cristiano Ronaldo, and LeBron James.
- Emotional Connection: Creating ads that resonate emotionally with consumers, such as the “Find Your Greatness” campaign.
- Social Commentary: Engaging in cultural conversations, like the Colin Kaepernick campaign.
- Technological Advancements: Such as Nike Air cushioning technology and Flyknit fabric.
- Customization: Allowing consumers to personalize products through the NIKEiD platform.
- Nike Run Clubs: Building a community around the brand through running clubs and apps.
- Sustainability Initiatives: Such as the “Move to Zero” campaign focusing on reducing environmental impact.
- Market Competition: Competition from brands like Adidas and Under Armour.
- Pricing Strategies: Balancing premium pricing with accessibility for a broader audience.
- Labor Practices: Historical criticisms regarding factory working conditions.
- Sustainability Challenges: Managing environmental impacts across the supply chain.
Nike’s influence goes beyond sports apparel.
Influence on Streetwear: Collaborations with designers like Virgil Abloh have made Nike relevant in fashion circles.
Promotion of Women’s Sports: Marketing campaigns focusing on female athletes.
Global Reach: Establishing a presence in various global markets and sports.
Nike’s brand success lies in its ability to intertwine sports, culture, and personal aspiration. Its collaborations with athletes, investment in storytelling, and commitment to innovation have made it a leader in the sports apparel industry. The challenges and criticisms it has faced provide insight into the complexities of maintaining a global brand. Understanding Nike’s branding strategies offers an exciting exploration into how a brand can connect with consumers on multiple levels and across diverse markets.
Analyzing Advertising Campaigns: Students may explore various campaigns to understand how Nike connects with different demographics.
Competitor Analysis: Comparing Nike’s strategies with competitors to understand market dynamics.
Future of Sports Branding: Speculating on the future of branding in the sports industry and how Nike may continue to innovate.
This comprehensive case study provides a deep understanding of Nike’s branding strategies and allows students to appreciate the multifaceted nature of branding in the modern market. The connections between sports, culture, innovation, and marketing weave together to create a compelling story that offers valuable insights for anyone interested in branding, marketing, or the sports industry.
40.3 Tesla: Revolutionizing the Automotive Industry Through Innovation and Sustainability
Tesla, Inc. is not just a car manufacturer; it’s a technology company with a mission to accelerate the world’s transition to sustainable energy. Founded by a group of engineers, including Elon Musk, who became the public face of the company, Tesla has become a symbol of innovation and environmental responsibility. This case study explores how Tesla achieved this status.
- Founding and Early Years: Founded in 2003 by Martin Eberhard and Marc Tarpenning, and later joined by Elon Musk, JB Straubel, and Ian Wright, Tesla started with a vision to create electric cars that didn’t compromise on performance.
- Road to Success: The launch of the Tesla Roadster in 2008 proved that electric cars could be both stylish and powerful. Subsequent models, including the Model S, Model X, Model 3, and Model Y, diversified the product line.
- Autopilot: Developing self-driving technology.
- Battery Technology: Pioneering advancements in battery efficiency and lifespan.
- Clean Energy Products: Including solar panels and the Powerwall for energy storage.
- Sustainable Manufacturing: Efforts to minimize environmental impact in production.
- Online Sales: Bypassing traditional dealerships, selling directly to consumers online.
- Customer Experience: Creating unique showrooms and offering test drives.
- Elon Musk’s Twitter Presence: Utilizing social media to promote and defend the brand.
- Product Launches: Hosting grand events to unveil new products.
- Production Challenges: Meeting demand and managing quality control.
- Market Competition: Growing competition from traditional automakers entering the EV market.
- Labor Practices: Controversies related to factory conditions.
- Autopilot Safety Concerns: Debates over the safety of Tesla’s self-driving technology.
Changing Automotive Industry: Pushing the entire automotive industry towards electric vehicles.
Energy Conversation: Shaping dialogues about renewable energy and climate change.
Stock Market Phenomenon: Tesla’s unique position in the stock market as a technology/automotive company.
Tesla’s brand represents a fusion of technology, sustainability, and luxury. Through innovative products, a focus on environmental responsibility, and disruptive sales models, Tesla has not only built a successful brand but has also changed the landscape of the automotive industry. Analyzing Tesla’s strategies, challenges, and impacts provides valuable insights into how a brand can be a catalyst for industry-wide change.
Comparative Analysis: Understanding how Tesla’s branding strategies differ from traditional automotive brands.
Future of Mobility: Speculating on the future of electric vehicles, autonomous driving, and Tesla’s role in shaping that future.
Global Expansion: Exploring Tesla’s efforts to expand into various global markets, such as China and Europe.
40.4 Amazon: Transforming Retail and Beyond
Amazon, founded by Jeff Bezos in 1994, started as an online bookstore and quickly expanded into a vast e-commerce platform that sells virtually everything. Beyond retail, Amazon has also entered cloud computing, entertainment, and even healthcare. This case study will explore Amazon’s diverse business activities and how they’ve contributed to its colossal success.
- Early Years: Started in a garage, focusing on books, before expanding into other categories.
- Global Expansion: Rapid growth into international markets and diversified product offerings.
- Customer Experience: One-click ordering, personalized recommendations, and fast shipping.
- Amazon Prime: Subscription model offering free shipping, video streaming, and more.
- Amazon Marketplace: Allowing third-party sellers to reach Amazon’s vast customer base.
- Amazon Web Services (AWS): A leading provider of cloud computing services.
- Voice Technology: Introduction of Alexa and Echo smart speakers.
- Amazon Studios: Producing and distributing original content.
- Twitch Acquisition: Engaging the gaming community.
- Whole Foods Acquisition: Entering the brick-and-mortar retail space.
- Amazon Pharmacy: Expanding into the healthcare sector.
- Market Power: Criticisms related to monopolistic practices.
- Tax Practices: Scrutiny over tax strategies and contributions.
- Working Conditions: Concerns over conditions in warehouses and treatment of employees.
- Environmental Impact: Criticisms related to packaging and carbon footprint.
- Changing Retail Landscape: Influencing consumer expectations and competitors’ strategies.
- Innovation Leader: Setting standards in technology, logistics, and customer service.
Amazon’s success story is a testament to innovation, diversification, and relentless focus on customer experience. By continuously expanding into new areas, Amazon has not only transformed retail but also various other industries. Examining Amazon’s strategies, challenges, and cultural impact provides a deep understanding of modern business dynamics and the role of branding in shaping industry landscapes.
Competitive Analysis: Understanding Amazon’s position among global tech giants.
Future Projections: Exploring potential new markets and technologies for Amazon.
Regulatory Landscape: Analyzing potential legal and regulatory challenges.
This extensive case study offers students a multifaceted exploration of one of the world’s most impactful brands. From e-commerce to entertainment, Amazon’s influence is felt across multiple sectors. Understanding its success and challenges provides insights into innovation, strategy, ethics, and the complex dynamics of modern business environments.
40.5 Zoom: Connecting the World Through Video Communications
Zoom Video Communications, known simply as Zoom, played a pivotal role in connecting people during a time of global upheaval. Founded by Eric Yuan in 2011, Zoom quickly rose to prominence as a leading platform for video conferencing, webinars, and collaboration. This case study explores Zoom’s exponential growth, the strategies that propelled it, and the challenges it faced along the way.
- Founding Vision: Eric Yuan, a former Cisco executive, founded Zoom with a mission to make video communication frictionless and reliable.
- Early Growth: Despite entering a competitive market, Zoom differentiated itself through ease of use and robust performance.
- Ease of Use: Simple interface, quick setup, and no user account required for joining meetings.
- Quality and Reliability: Consistent video and audio quality across various devices and internet connections.
- Business and Enterprise Solutions: Offering scalable solutions for organizations of all sizes.
- Education Sector: Customized features for virtual classrooms and administrative meetings.
- Healthcare Integration: Compliance with healthcare regulations for telemedicine use.
- Localization: Tailoring offerings to different regions and languages.
- Strategic Partnerships: Collaborating with hardware vendors and integrators for seamless user experience.
- Free Access for Schools: Providing free access to educational institutions during lockdowns.
- Scaling Infrastructure: Rapidly expanding server capacity to handle surging demand.
- Security Enhancements: Addressing early security concerns with significant updates and transparency.
- “Zoombombing” Incidents: Unwanted intrusions into meetings raised questions about security.
- Data Privacy Concerns: Scrutiny over encryption and data handling practices.
- Competing Platforms: Navigating competition from established players like Microsoft and new entrants like Google.
- Sustaining Growth: Challenges in maintaining growth rates as restrictions lift and in-person meetings resume.
- Changing Work Culture: Enabling remote work, hybrid models, and global collaboration.
- Social Connections: Facilitating social interactions, virtual family gatherings, and online events.
- Redefining Communication: Setting new standards for video communication and online engagement.
Zoom’s journey is a compelling study in understanding customer needs, agile adaptation, and effective scaling. From a startup competing against tech giants to becoming a household name, Zoom’s story offers valuable lessons in innovation, strategic planning, crisis management, and ethical considerations. Analyzing Zoom’s branding, growth strategies, challenges, and cultural impact provides rich insights into the dynamics of technology-driven market disruption and the responsibilities that come with rapid success.
Competitive Landscape Analysis: Understanding Zoom’s position in a fast-evolving market.
Ethical and Regulatory Considerations: Analyzing Zoom’s response to security and privacy concerns.
Long-term Strategy and Sustainability: Evaluating Zoom’s plans to sustain growth and diversify offerings.
40.6 Beyond Meat: A Plant-Based Revolution
Beyond Meat has become a synonym for the plant-based food movement, leading the way in creating meat alternatives that cater to a growing global demand for sustainable and ethical eating. This case study explores the company’s journey, its innovative products, market strategies, and the broader impact on the food industry.
- Founding Vision: Established by Ethan Brown in 2009, Beyond Meat aimed to address environmental, health, and ethical concerns related to animal agriculture.
- Product Innovation: The development of plant-based meat substitutes that mimic the taste, texture, and appearance of traditional meat.
- Not Just for Vegetarians: Positioning products to appeal to meat-eaters looking to reduce meat consumption.
- Retail and Food Service Partnerships: Collaborations with supermarkets, fast-food chains, and restaurants.
- Celebrity Endorsements: Engaging well-known advocates of plant-based diets, such as Bill Gates and Leonardo DiCaprio.
- Sustainability Messaging: Emphasizing the environmental and health benefits of plant-based foods.
- Adaptation to Local Tastes: Developing products tailored to various global markets and cuisines.
- Regulatory Compliance: Navigating complex food regulations in different countries.
- Rising Competitors: Facing competition from both traditional food companies and new entrants in the plant-based sector.
- Product Differentiation: Striving to stand out in an increasingly crowded market.
- Taste and Texture Expectations: Meeting consumer expectations for flavors and textures similar to traditional meat.
- Price Barriers: Addressing price competitiveness with animal-based products.
- Transparency in Ingredients: Providing clear information about ingredients and processing methods.
- Life Cycle Analysis: Assessing the full environmental impact of products, from production to consumption.
- Changing Consumer Habits: Influencing a shift in dietary preferences towards plant-based options.
- Industry Collaboration: Collaborations with traditional meat producers and food service providers.
- Impact on Animal Agriculture: Contributing to debates about the sustainability and ethics of conventional meat production.
Beyond Meat’s story represents a transformative moment in the food industry, reflecting a broader cultural shift towards sustainability and conscious consumption. By analyzing Beyond Meat’s product innovation, market strategies, challenges, and cultural impact, students can gain insights into how a company can both lead and adapt to changing consumer values and industry dynamics. This case encourages critical thinking about innovation, branding, competition, ethics, and the interplay between business and societal needs.
Comparative Analysis with Competitors: Examining strategies and approaches of other players in the plant-based food market.
Consumer Behavior Study: Investigating consumer attitudes towards plant-based alternatives.
Sustainability Assessment: Conducting a comprehensive analysis of the sustainability aspects of plant-based foods.
40.7 TikTok: A Dance with Global Success
TikTok, a social media app developed by Chinese tech company ByteDance, has quickly become a sensation, particularly among younger users. This case study examines TikTok’s rapid growth, innovative content delivery, competition, and the complex regulatory landscape it navigates.
- Launch and Growth: TikTok was launched in 2016 and merged with Musical.ly in 2018 to expand its reach in the U.S. market.
- Algorithm Magic: TikTok’s unique algorithm offers personalized content, leading to higher engagement and user retention.
- Short Video Format: Users create engaging 15-second videos with a wide array of editing tools.
- Personalized Feed: The “For You Page” algorithm provides a customized content feed, enhancing user experience.
- Hashtag Challenges: Promoting user-generated content through viral challenges.
- Collaborations and Duets: Enabling collaboration between users to foster community.
- Music and Dance Focus: Strong emphasis on music and dance-related content.
- Influencer Partnerships: Collaborating with youth influencers to drive adoption.
- Local Content Adaptation: Encouraging content that resonates with local cultures and trends.
- Strategic Advertising: Utilizing in-app advertising and partnerships with brands.
- Data Security Issues: Ongoing debates over data privacy and national security.
- Regulatory Scrutiny: Challenges related to compliance with international regulations.
- Competing for Attention: A battle with platforms like Instagram, Snapchat, and YouTube.
- Intellectual Property Concerns: Issues related to copyright and content ownership.
- Democratizing Content Creation: Empowering individuals to become content creators.
- Cultural Influence: Fostering global cultural exchange and trends.
TikTok’s story is a fascinating example of how a social media platform can become a global phenomenon through innovative technology, strategic targeting, community engagement, and adaptability to local cultures. This case allows students to explore various aspects of social media business, including algorithms, user engagement, competition, regulation, and cultural impact.
Algorithm Analysis: Delve into how TikTok’s algorithm works and compare it with other platforms.
Regulatory Compliance Study: Investigate TikTok’s compliance with different countries’ regulatory frameworks.
Cultural Impact Research: Explore how TikTok influences and reflects cultural trends across the globe.
40.8 Coca-Cola: Quenching the World’s Thirst for Over a Century
Coca-Cola, founded in 1886, has grown to become one of the world’s leading beverage companies. This case study explores Coca-Cola’s brand legacy, marketing innovations, product diversity, sustainability initiatives, and the challenges and opportunities in an ever-changing global beverage market.
- Founding and Early Years: From a pharmacy concoction to a global brand.
- Iconic Advertising Campaigns: A look at some of Coca-Cola’s most memorable marketing efforts.
- Logo and Packaging: The evolution of Coca-Cola’s iconic logo and bottle design.
- Sponsorships and Partnerships: Coca-Cola’s association with sports events, entertainment, and charities.
- Local Market Adaptation: Customizing products and campaigns to fit regional tastes and cultures.
- Digital Engagement: Leveraging social media and technology for customer engagement.
- Beverage Portfolio: Introduction to Coca-Cola’s diverse product line, including soft drinks, water, and juices.
- Health-Conscious Offerings: Response to changing consumer preferences towards healthier options.
- Water Stewardship: Initiatives to reduce water usage and support community water projects.
- Recycling and Packaging: Commitment to reducing plastic waste through recycling and innovative packaging.
- Market Competition: An overview of competitors like PepsiCo and changing consumer tastes.
- Health and Regulatory Scrutiny: Challenges related to sugar content and obesity concerns.
- Emerging Markets: Strategies and challenges in entering and thriving in new markets.
- Economic Sensitivities: How global economic fluctuations affect sales and operations.
Coca-Cola’s story offers an inspiring journey into the world of branding, marketing, innovation, and corporate responsibility. The brand’s ability to adapt, innovate, and remain socially responsible provides valuable insights for anyone interested in business, marketing, and sustainability.
Marketing Analysis: Investigate how Coca-Cola has maintained its brand appeal over time.
Sustainability Evaluation: Examine Coca-Cola’s efforts in promoting environmental stewardship.
Global Business Study: Analyze Coca-Cola’s strategies in adapting to different cultures and markets.
This student version of the Coca-Cola case study serves as an engaging educational resource for courses related to business, marketing, branding, sustainability, and global commerce. Through exploration, discussion, and critical analysis, students can uncover the multifaceted dynamics that have shaped Coca-Cola’s success and its continued relevance in today’s competitive and evolving marketplace. It invites learners to reflect on the power of branding, the importance of innovation, the challenges of global expansion, and the growing significance of corporate social responsibility in modern business.
40.9 Netflix: Redefining the Future of Entertainment
Netflix, founded in 1997, has transformed from a DVD rental service to a global streaming giant. With over 200 million subscribers worldwide, Netflix has redefined the way people consume entertainment. This case study explores Netflix’s growth, innovation, content strategy, and the challenges it faces in a competitive market.
- Founding and Early Growth: From a mail-order DVD service to streaming pioneer.
- Subscription Model: Introduction of the subscription model that revolutionized content consumption.
- Streaming Technology: Development of cutting-edge streaming technology to deliver content seamlessly.
- Personalized Recommendations: Utilization of algorithms to tailor content suggestions to individual viewers.
- Original Content Creation: Investment in exclusive shows and movies to differentiate from competitors.
- Content Licensing: Acquiring rights to popular shows and movies to broaden the content library.
- Localization Strategy: Adapting content to suit diverse cultural tastes and regulatory requirements.
- Emerging Markets Growth: Expanding into developing regions with unique pricing and content strategies.
- Streaming Wars: Competition with other streaming platforms like Amazon Prime, Disney+, and HBO Max.
- Regulatory and Legal Hurdles: Navigating complex international laws and content regulations.
- Content Piracy Concerns: Efforts to combat unauthorized sharing and illegal streaming of content.
Netflix’s story is a testament to innovation, adaptability, and the power of a customer-centric approach. The lessons drawn from Netflix’s success and ongoing challenges provide valuable insights for those interested in technology, media, marketing, and global business strategy.
Technology Analysis: Investigate how Netflix’s technological advancements have shaped its success.
Content Strategy Evaluation: Examine how Netflix’s original content creation has redefined the entertainment industry.
Global Business Study: Analyze Netflix’s strategies for entering and thriving in diverse global markets.
40.10 Airbnb: Disrupting the Hospitality Industry
Airbnb, established in 2008, has emerged as a disruptive force in the global hospitality industry. This platform connects hosts and travelers, providing unique accommodations and experiences. This case study examines Airbnb’s innovation, growth, and the challenges it faces, providing comprehensive insights for students interested in entrepreneurship, technology, law, and global business.
- Founding Story: How an idea to rent air mattresses turned into a revolutionary business concept.
- Peer-to-Peer Model: Airbnb’s model of connecting hosts with travelers and its impact on traditional lodging.
- Platform Design: Exploration of the user-friendly design, including search functionality, booking process, and communication between hosts and guests.
- Trust and Community Building: Methods of establishing trust through reviews, verification processes, host education, community guidelines, and conflict resolution.
- Revenue Model: Understanding Airbnb’s commission-based revenue model, pricing strategies, and value proposition for hosts and guests.
- Global Growth Strategy: Airbnb’s rapid expansion into various cities and countries, including marketing strategies, partnerships, and local engagement.
- Experiences and Diversification: Introduction of Airbnb Experiences, business travel accommodations, and other extensions of the platform.
- Challenges in Scaling: Examination of the obstacles faced during rapid growth, including maintaining quality, customer support, and local adaptation.
- Local Regulations and Compliance: Encounters with legal issues, zoning laws, city ordinances, and ongoing battles with regulators and the traditional hotel industry.
- Impact on Housing Markets: Exploration of criticisms and studies on Airbnb’s effect on local housing prices, availability, gentrification, and neighborhood dynamics.
- Safety and Liability Concerns: Analysis of safety measures, insurance policies, host responsibilities, and incidents that have raised concerns.
- Sustainable Travel Initiatives: Airbnb’s efforts to promote eco-friendly travel practices, partnerships with local communities, and support for responsible hosting.
- Community Outreach and Disaster Response: Airbnb’s involvement in community development and providing emergency accommodations during natural disasters or crises.
- Brand Identity and Positioning: Examination of Airbnb’s brand evolution, advertising campaigns, social media presence, and efforts to differentiate itself from competitors.
- Customer Segmentation and Personalization: Strategies for targeting different customer segments and personalizing the user experience through algorithms and data analysis.
Airbnb’s transformation of the hospitality industry offers an in-depth look into technology-driven disruption, entrepreneurial innovation, community engagement, legal complexities, and social impact. The multifaceted nature of Airbnb’s journey provides a rich context for exploring diverse business concepts.
- Further Exploration and Assignments:
Platform Analysis Project: Students analyze Airbnb’s platform functionality, user experience, and technological innovations.
Regulatory Environment Study: Research and debates on the legal and ethical aspects of Airbnb’s operations in different regions.
Global Strategy Simulation: Group exercise to plan Airbnb’s entry into a new market, considering cultural, legal, and market dynamics.
Social Impact Assessment: Critical evaluation of Airbnb’s social responsibility efforts, community impact, and sustainability initiatives.
40.11 Starbucks: Brewing Success Through Innovation and Responsibility
Starbucks, founded in 1971 in Seattle, Washington, has become a global coffee icon, known for its premium quality coffee, unique store ambiance, and commitment to social responsibility. This case study examines Starbucks’ journey from a single store to an international chain, focusing on its strategic decisions, marketing practices, innovations, and challenges.
- Founding and Early Years: How Starbucks transformed from a single store selling quality coffee beans into a global coffeehouse chain.
- Mission and Vision: An examination of Starbucks’ commitment to inspiring and nurturing the human spirit, one cup at a time.
- Retail Innovation: An exploration of Starbucks’ unique store designs, customer experience, and the introduction of the “third place” concept.
- Product Diversification: Starbucks’ expansion into various products, including specialty beverages, food, packaged products, and even non-coffee items.
- Global Expansion: Strategies and challenges in entering new markets across different continents.
- Brand Building and Positioning: How Starbucks built a strong brand that emphasizes quality, community, and ethical sourcing.
- Loyalty Programs: The impact and success of Starbucks’ rewards program in enhancing customer loyalty and retention.
- Digital Engagement: Utilizing mobile apps, social media, and digital marketing to engage customers.
- Ethical Sourcing: Commitment to sourcing ethically produced coffee through fair trade practices and farmer support.
- Environmental Initiatives: Efforts in reducing waste, conserving energy, and promoting reusable products.
- Community Engagement: Investing in local communities through education, volunteerism, and support for local causes.
- Market Saturation: The challenge of maintaining growth amid increasing competition and market saturation.
- Cultural Sensitivity: Navigating cultural differences in global markets and occasional backlashes.
- Economic Factors: Responding to economic downturns and changes in consumer spending habits.
- Mobile Ordering: Implementing mobile ordering and payment systems to enhance convenience.
- Data Analytics: Leveraging data to personalize marketing and enhance customer experiences.
- Partnerships with Technology Companies: Collaborations to expand reach and offer new products.
Starbucks’ story offers valuable insights into brand building, global expansion, innovation, social responsibility, and resilience in the face of challenges. Its journey from a single store to a global chain showcases the importance of strategic decision-making, adaptability, and commitment to core values.
Supply Chain Analysis: Investigate Starbucks’ complex supply chain and its approach to ensuring quality and ethical practices.
Competitive Landscape Study: Analyze Starbucks’ competitive positioning and the dynamics of the coffeehouse industry.
Crisis Management Review: Examine Starbucks’ response to various challenges and crises over the years.
40.12 The Walt Disney Company: A Kingdom of Creativity and Innovation
The Walt Disney Company, founded in 1923 by Walt and Roy O. Disney, has grown from a small animation studio to a global entertainment conglomerate. This case study delves into Disney’s storied history, business diversification, technological leadership, and strategies that have made it a symbol of creativity and imagination.
- Founding and Early Success: The birth of Mickey Mouse, the creation of the first synchronized sound and full-color cartoons, and the groundbreaking “Snow White and the Seven Dwarfs.”
- Expanding the Magic Kingdom: Disney’s foray into theme parks, beginning with Disneyland in 1955 and followed by a global expansion.
- Diversification: Exploration of Disney’s diversification into various entertainment sectors, including movies, television, theme parks, merchandise, and media networks.
- Content Creation and Distribution: Examination of Disney’s strategies in producing and distributing content through various channels, including streaming services like Disney+.
- Global Expansion: Analysis of Disney’s strategies to enter and thrive in international markets, including China and Europe.
- Brand Building: How Disney built a universally loved brand based on storytelling, characters, and immersive experiences.
- Synergy: Understanding how Disney leverages its characters and stories across multiple business segments.
- Digital Engagement: Exploration of Disney’s digital marketing efforts, social media presence, and engagement with younger audiences.
- Revolutionizing Animation: Disney’s pioneering role in animation technology, including the introduction of CGI.
- Immersive Experiences: The integration of technology in theme parks for personalized and interactive experiences.
- Strategic Acquisitions: Insight into Disney’s acquisitions, including Pixar, Marvel, Lucasfilm, and 21st Century Fox.
- Collaborations and Partnerships: Exploration of Disney’s collaborations with other companies to enhance its product offerings and reach.
- Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR): Disney’s efforts in environmental conservation, community support, and ethical sourcing.
- Content and Cultural Sensitivity: Balancing storytelling with cultural respect and inclusiveness.
- Market Saturation and Competition: Navigating an increasingly competitive media and entertainment landscape.
- Regulatory and Legal Challenges: Adhering to varying regulations across global markets.
- Pandemic Response: Adaptation and response to the COVID-19 pandemic’s impact on various business segments.
The Walt Disney Company’s journey offers a captivating exploration of creativity, innovation, strategic thinking, and adaptability. From pioneering animation to building global theme parks, launching streaming services, and acquiring leading entertainment brands, Disney’s story is a rich lesson in entrepreneurship, marketing, technology, and global business strategies.
Leadership Analysis: Investigate Disney’s leadership strategies and the role of key leaders in shaping the company.
Competitive Landscape Study: Analyze Disney’s competitive positioning and the dynamics of the entertainment industry.
Crisis Management Review: Examine Disney’s response to various challenges, including economic downturns and unexpected crises.
40.13 McDonald’s: Serving Success with a Side of Innovation
McDonald’s is more than just a fast-food chain; it’s a global phenomenon that has shaped the way people eat around the world. Founded in 1940 by Richard and Maurice McDonald, the company has since evolved into a multi-billion-dollar giant with thousands of locations worldwide. This case study examines the key ingredients behind McDonald’s success.
- Founding and Early Growth: A look at McDonald’s beginnings, from a single drive-in to the creation of the Speedee Service System, a precursor to the modern fast-food restaurant.
- Global Expansion: How McDonald’s turned the Golden Arches into an international symbol, adapting to various cultures and tastes.
- Franchising: Exploration of McDonald’s franchising model and how it fueled the company’s rapid growth.
- Menu Innovation: How McDonald’s constantly innovates its menu to meet consumer demands and local preferences.
- Supply Chain Management: Examination of McDonald’s logistical prowess in sourcing and distributing ingredients across the globe.
- Sustainability Efforts: An insight into McDonald’s initiatives to reduce environmental impact and promote sustainable practices.
- Iconic Branding: Understanding how the Golden Arches and characters like Ronald McDonald became global icons.
- Advertising and Promotions: A review of memorable ad campaigns and marketing strategies that resonate with various demographics.
- Customer Experience: How McDonald’s focuses on customer satisfaction through services like McDelivery and the recent digital transformation.
- Digital Ordering and Mobile Apps: Exploration of McDonald’s embrace of technology to enhance customer convenience.
- Smart Restaurants: How technology is changing the in-store experience, from kiosks to AI-powered drive-thrus.
- Health Concerns: Analysis of criticisms regarding the nutritional content of McDonald’s food and the company’s response.
- Labor Practices: Discussion of challenges related to employee wages, benefits, and working conditions.
- Competitive Landscape: Examination of the fast-food market competition and how McDonald’s maintains its edge.
- Adaptation to Changing Consumer Preferences: The shift towards healthier options and how McDonald’s is responding.
- Investments in Technology: Future technological innovations that may shape the McDonald’s experience.
- Sustainability Goals: Long-term objectives in minimizing environmental impact and promoting social responsibility.
McDonald’s journey offers a multifaceted case study in entrepreneurship, innovation, marketing, global expansion, and adaptability. From flipping burgers in a single location to flipping the script on fast food worldwide, the company continues to evolve, facing new challenges and seizing opportunities.
40.14 Dove (Unilever): Crafting Beauty and Confidence
Dove, a personal care brand owned by Unilever, has become synonymous with beauty and self-esteem through its innovative products and socially conscious campaigns. This case study invites you to explore Dove’s journey and its commitment to promoting a more inclusive and positive depiction of beauty.
- Dove’s Inception: A look at the brand’s origins in 1957 with the launch of the Dove Beauty Bar.
- Product Portfolio: Overview of Dove’s wide range of personal care products, including body wash, hair care, and skincare.
- The “Real Beauty” Campaign: Examination of Dove’s groundbreaking campaign that challenged conventional beauty standards.
- Customer Engagement: Insights into Dove’s interaction with customers through social media, events, and community outreach.
- Global Expansion: Strategies behind Dove’s growth into various international markets and adaptation to different cultures.
- Research and Development: A look at how Dove constantly innovates its product line through scientific research and consumer insights.
- Sustainability Initiatives: Understanding Dove’s efforts in reducing environmental impact and promoting ethical sourcing.
- Promoting Self-Esteem: Analysis of Dove’s initiatives to enhance self-esteem, particularly among young women, through education and advertising.
- Partnerships and Collaborations: How Dove collaborates with NGOs, influencers, and other stakeholders to amplify social messages.
- Market Competition: Assessment of the competitive landscape and how Dove differentiates itself.
- Advertising Backlash: Discussion of certain advertising missteps and how the brand managed the fallout.
- Trend Adaptation: Exploration of how Dove aligns with emerging beauty and wellness trends.
- Technology Integration: How Dove leverages technology, including AI and data analytics, for product development and personalized experiences.
- Sustainability Goals: Examination of Dove’s long-term commitment to environmental sustainability and ethical practices.
Dove’s journey presents an engaging case study that goes beyond products and marketing to encompass social values, consumer connection, innovation, and global reach. The brand’s commitment to challenging beauty norms and promoting self-esteem has set it apart in a crowded market.
40.15 IKEA: A Symphony of Design, Affordability, and Sustainability
- Founding and Mission: Founded in Sweden in 1943 by Ingvar Kamprad, IKEA’s mission is to “create a better everyday life for many people.” It emphasizes affordability, design, and functionality.
- Overview of Offerings: IKEA offers a wide range of home furnishings, including furniture, kitchen appliances, decor, and accessories.
- Global Presence: With over 400 stores in 50 countries, IKEA has become a global leader in the home furnishing industry.
- Product Design and Development: IKEA’s products are known for minimalist design, functionality, and ease of assembly. Collaboration with designers worldwide keeps its offerings fresh and innovative.
- Supply Chain and Manufacturing: A well-integrated supply chain with close relationships to over 1,000 suppliers allows IKEA to maintain low costs while ensuring quality and sustainability.
- Retail Experience: The IKEA in-store experience is distinctive with showrooms, self-service warehouses, and in-store restaurants offering Swedish cuisine.
- Pricing Strategy: IKEA’s cost-conscious approach means designing products from the price tag up, ensuring affordability without compromising on quality.
- Digitalization and E-commerce: With a strong online presence, IKEA provides customers with online shopping options, planning tools, and virtual product previews.
- Advertising Campaigns: IKEA uses creative and often humorous advertising to appeal to a broad customer base, focusing on life improvement and solutions.
- Online Engagement: Digital catalogs, apps, and social media keep IKEA’s audience engaged and provide valuable customer insights.
- In-store Promotions: Seasonal displays and in-store events promote new products and encourage customer interaction.
- Brand Identity and Values: IKEA’s brand emphasizes sustainability, inclusiveness, and accessibility.
- Environmental Practices: Commitment to sustainable sourcing, waste reduction, and energy efficiency are core to IKEA’s operations.
- Renewable Energy Projects: IKEA invests in wind and solar energy, aiming to produce as much renewable energy as it consumes in its operations by 2030.
- Social Responsibility: The IKEA Foundation supports initiatives related to children’s education, refugee support, and climate change.
- Sustainable Product Lines: IKEA offers products that promote sustainable living, from energy-efficient appliances to recycled materials.
- Cultural Adaptation: IKEA adapts its product lines and marketing to reflect local tastes, customs, and living conditions.
- Market Entry Strategies: IKEA studies each market carefully, adapting its store format and product selection to local needs.
- Challenges in Different Markets: Navigating regulations, cultural differences, and local competition has posed challenges in some markets.
- Competition and Market Pressures: IKEA faces competition from both traditional furniture stores and online platforms.
- Cultural Missteps: Some global marketing campaigns have been criticized for insensitivity to local cultures.
- Quality Concerns: IKEA’s emphasis on low cost has sometimes led to perceived quality issues.
- Emerging Markets: Expansion into new markets like India and South America presents opportunities and challenges.
- Technological Innovations: IKEA is exploring augmented reality, artificial intelligence, and smart home technologies.
- Sustainability Goals: Commitment to further sustainability through its entire value chain.
- Collaborations and Partnerships: IKEA’s collaboration with designers, tech companies, and even other retailers fuels innovation.
IKEA’s unique blend of design, affordability, sustainability, and global reach has made it a standout brand in the home furnishing industry. The company’s multifaceted approach offers a rich study of modern retail, branding, international business, and corporate responsibility. The complexities and successes of IKEA’s model provide invaluable insights and inspiration for students across various disciplines.
40.16 LEGO: Building Blocks of Innovation and Success
- Founding and History: LEGO was founded in 1932 by Ole Kirk Christiansen in Billund, Denmark. The LEGO brick, as we know it today, was launched in 1958.
- Product Portfolio: Beyond the iconic bricks, LEGO’s products include themed sets, video games, movies, and educational tools.
- Mission and Values: LEGO’s mission is to “Inspire and develop the builders of tomorrow” through creative play and learning.
- Innovation in Design: LEGO constantly innovates its product line, incorporating new themes and licensed partnerships (e.g., Star Wars, Marvel).
- Quality and Precision: The manufacturing process emphasizes precision and quality, ensuring compatibility across generations of LEGO bricks.
- Digital Expansion: LEGO has embraced digital gaming and augmented reality experiences, extending the brand into the digital realm.
- Brand Building: LEGO’s brand revolves around creativity, imagination, learning, and fun.
- Advertising and Promotion: Utilizing various channels, LEGO engages customers through inventive advertising campaigns and social media.
- Community Engagement: LEGO Ideas invites fans to submit and vote on new product ideas. The LEGO community is actively engaged in product development, events, and online forums.
- Retail Experience: LEGO stores offer hands-on experiences with play areas, workshops, and exclusive products.
- Online Shopping: The online store provides an extensive product selection, customization options, and exclusive membership benefits.
- Global Distribution: LEGO products are available in more than 140 countries through various retail channels.
- LEGO Education: Through LEGO Education, the company offers learning solutions that encourage hands-on, playful learning in schools.
- Charitable Activities: The LEGO Foundation supports children’s development and learning through various global initiatives.
- Environmental Sustainability: LEGO is committed to reducing its environmental impact, including the goal to produce all products and packaging with sustainable materials by 2030.
- Market Pressures: Facing competition from both traditional toys and digital games, LEGO has had to continuously innovate and adapt.
- Intellectual Property Issues: LEGO has faced legal challenges around patents and copyrights, particularly concerning the design of its bricks.
- Economic Fluctuations: Economic downturns and shifts in consumer behavior have influenced LEGO’s sales and growth strategies.
- Adaptation to Local Markets: LEGO tailors its marketing and product strategies to different cultures and consumer preferences.
- Challenges in Emerging Markets: Entering new markets such as China has presented both opportunities and challenges, including issues related to counterfeiting.
- Technological Innovation: LEGO continues to explore new technologies, such as 3D printing and artificial intelligence.
- Collaborations and Licensing: Partnerships with entertainment franchises and designers fuel creativity and market reach.
- Focus on Adult Fans: LEGO has been expanding its appeal to adult fans through complex sets and themes that cater to various interests.
LEGO’s journey from a small carpentry shop to a global brand is a study in innovation, adaptability, community engagement, and brand stewardship. Its commitment to quality, creativity, and social responsibility offers a multifaceted case study with insights into product development, marketing, sustainability, global business strategy, and more. The story of LEGO inspires aspiring entrepreneurs, marketers, designers, and leaders to think creatively and act with purpose and integrity.
40.17 Slack: Revolutionizing Workplace Communication
- Founding and Background: Launched in 2013 by Stewart Butterfield, Eric Costello, Cal Henderson, and Serguei Mourachov, Slack has quickly become one of the leading tools for team communication.
- Business Model: Slack offers a freemium model where basic features are free, with paid plans for more functionality.
- Key Features: Slack provides channels, direct messaging, file sharing, integrations with other tools, and more to enhance team communication.
- Innovation and Updates: Continual updates and feature enhancements have kept Slack at the forefront of workplace communication tools.
- User-Centric Design: Slack’s interface is designed for ease of use and collaboration, reducing email overload.
- Target Audience: Primarily targeting businesses, both small and large, Slack has also found usage in communities and other groups.
- Growth Strategies: Referral programs, partnerships, and effective content marketing have contributed to Slack’s rapid adoption.
- Customer Engagement: Slack has utilized community engagement, feedback, and customer support to foster loyalty and improve its product.
- Competitors: Major competitors include Microsoft Teams, Zoom, and others offering communication and collaboration tools.
- Differentiation: Slack’s integrations, customization, and user experience have been key differentiators.
- Security Concerns: As with many digital platforms, security and privacy have been challenges, and Slack has implemented measures to ensure data protection.
- Freemium to Premium: The free version attracts users, while additional features and support drive customers to paid plans.
- Enterprise Solutions: Slack’s Enterprise Grid offers solutions tailored to large organizations, including advanced security and administrative features.
- Localization and Cultural Adaptation: Slack has localized its product for various markets and cultures to drive global adoption.
- Challenges in Emerging Markets: Issues such as local compliance, competition, and connectivity can present challenges in various regions.
- Pandemic Response: The shift to remote work during the COVID-19 pandemic led to a surge in Slack usage, adapting to new work patterns.
- Long-term Trends: Remote and hybrid work trends may shape Slack’s future development and market positioning.
- Strategic Acquisitions: Acquiring companies like Rimeto added capabilities to Slack’s portfolio.
- Partnerships: Collaborations with companies like Google, Salesforce, and others have extended Slack’s functionality.
- Salesforce Acquisition: The pending acquisition by Salesforce as of the cut-off knowledge date may significantly shape Slack’s future direction.
- Continued Innovation: Slack continues to explore new features, integrations, and market opportunities.
Slack’s story offers insights into the fast-paced world of technology startups, product development, global expansion, and market competition. Its response to changing work patterns and its strategic acquisitions and partnerships make it a rich subject for study. The lessons from Slack’s journey are relevant to aspiring entrepreneurs, product managers, marketers, and others interested in technology, innovation, and the future of work.
40.18 Patagonia: A Case Study in Sustainable Business Practices
- Background: Patagonia, founded in 1973 by Yvon Chouinard, is an outdoor clothing and gear retailer known for its commitment to environmental sustainability.
- Mission: “Build the best product, cause no unnecessary harm, use business to inspire and implement solutions to the environmental crisis.”
- Innovation: Patagonia has been a leader in developing sustainable fabrics and materials.
- Quality & Durability: Emphasizing long-lasting products to reduce consumerism.
- Recycling & Repairing: Offering repair services and encouraging recycling of products through programs like “Worn Wear.”
- Transparency: Publicly sharing supply chain information and environmental impacts.
- Activism Marketing: Taking strong stances on environmental and social issues.
- Community Engagement: Collaborating with NGOs and community organizations.
- Supply Chain: Focusing on ethical production, fair labor practices, and organic materials.
- Environmental Activism: Regularly donating to environmental causes and supporting conservation efforts.
- B Corp Certification: Patagonia is a certified B Corporation, aligning profit with purpose.
- Profit vs. Purpose: Balancing strong financial growth with a commitment to environmental and social responsibility.
- Investing in Sustainability: Reinvesting profits in sustainable initiatives and environmental causes.
- Market Competition: Navigating a competitive market while maintaining ethical standards.
- Scale and Growth: Balancing growth and scalability with sustainability commitments.
- Greenwashing Accusations: Managing perceptions and criticisms related to authenticity and impact.
- International Expansion: Adapting sustainable practices across diverse markets and cultures.
- Global Partnerships: Collaborating with global organizations to expand environmental initiatives.
- Employee Engagement: Fostering a workplace culture that aligns with company values.
- Leadership and Governance: Maintaining leadership that embodies the brand’s ethos.
- Influencing Other Brands: Patagonia’s practices have influenced other companies to consider sustainability.
- Industry Collaboration: Working with competitors on common goals such as responsible sourcing.
- Adaptation to Climate Change: Developing strategies to mitigate and adapt to the impacts of climate change.
- New Market Opportunities: Exploring new product lines and markets while adhering to core values.
Patagonia serves as a compelling example of a company that has successfully integrated sustainability, ethical considerations, and environmental activism into every aspect of its business. From innovative product development to bold marketing strategies and influential industry leadership, Patagonia’s case study offers valuable insights for those interested in business ethics, environmental stewardship, social entrepreneurship, and innovative brand management. The brand’s ongoing challenges and successes provide rich material for analysis and reflection on the future of sustainable business practices.
40.19 Spotify: Transitioning from music sales to subscription streaming
- Background: Spotify, founded in 2006 by Daniel Ek and Martin Lorentzon, transformed the way people access and enjoy music.
- Mission: “To unlock the potential of human creativity—by giving a million creative artists the opportunity to live off their art and billions of fans the opportunity to enjoy and be inspired by it.”
- Streaming Model: Spotify’s on-demand streaming model allows users to access millions of songs and podcasts.
- Algorithm & Personalization: The use of algorithms to create personalized playlists and recommendations.
- Freemium Model: Free, ad-supported tier alongside premium subscriptions.
- Revenue Streams: Subscriptions, advertising, and partnerships.
- User Engagement: Innovative playlists like “Discover Weekly” engage users.
- Collaborations: Partnerships with artists, labels, and other brands.
- International Reach: Spotify has expanded to numerous countries, adapting to various markets and regulations.
- Localized Content: Offering content that resonates with local cultures and tastes.
- Market Competitors: Facing competitors like Apple Music, Amazon Music, and YouTube Music.
- Royalty Disputes: Navigating complex relationships with labels, artists, and rights holders.
- Environmental Footprint: Efforts to reduce carbon footprint and promote sustainable practices.
- Supporting Artists: Initiatives to support emerging artists and creatives.
- New Features: Continual innovation in features and user experience.
- Podcasts and Original Content: Investing in podcasts and original content to diversify offerings.
- Technology Investments: Exploring technologies like AI to enhance user experience.
- Changing Consumer Behavior: Transforming the way people consume and interact with music.
- Influence on the Music Industry: Affecting record labels, artists, and music distribution.
Spotify’s rise as a leading music streaming platform offers a multifaceted case study encompassing technology innovation, marketing strategies, global expansion, and industry impact. From navigating complex licensing agreements to crafting personalized user experiences, Spotify’s journey provides valuable insights into digital transformation, competitive strategy, customer engagement, and the future of entertainment. It serves as a valuable example for understanding modern business dynamics in the digital age, including the ongoing challenges and opportunities of operating in a rapidly evolving industry.
40.20 Warby Parker: Disrupting the traditional eyewear market with an online-first approach
- Background: Founded in 2010, Warby Parker aimed to offer designer eyewear at a fraction of the price through a direct-to-consumer model.
- Mission: “To offer designer eyewear at a revolutionary price, while leading the way for socially conscious businesses.”
- Design: In-house design leading to unique and affordable eyewear.
- Home Try-On: A free program allowing customers to try on glasses at home before purchasing.
- Direct-to-Consumer: Selling directly to customers through e-commerce and physical stores, cutting out intermediaries.
- Social Responsibility: “Buy a Pair, Give a Pair” program donates glasses to those in need.
- Digital Marketing: Effective use of social media and content marketing.
- Community Engagement: Building brand loyalty through community events and collaborations.
- Physical Stores: Combining e-commerce with brick-and-mortar stores for an omnichannel experience.
- International Growth: Expanding to Canada and other markets, adapting to local regulations and preferences.
- Traditional Competitors: Competition with traditional eyewear brands and retailers.
- Copycat Brands: Managing competition from similar direct-to-consumer eyewear startups.
- Environmentally Conscious Manufacturing: Commitment to using sustainable materials.
- Carbon Neutrality: Efforts to reduce and offset carbon emissions.
- Virtual Try-On: Use of augmented reality for virtual try-ons via mobile app.
- Telehealth Services: Offering eye exams and prescriptions through telehealth technology.
- Disrupting Traditional Retail: Changing the way people shop for glasses.
- Promoting Social Responsibility: Encouraging other brands to adopt socially responsible practices.
Warby Parker’s innovative approach to eyewear retail has not only disrupted traditional industry practices but also set new standards in customer experience, social responsibility, and sustainability. Through its unique business model, commitment to social causes, and use of technology, Warby Parker has carved out a unique position in the market. The case study of Warby Parker offers valuable insights into how innovative thinking, customer-centric approaches, and ethical business practices can create a strong brand identity and successful business in today’s competitive retail landscape. It’s an exemplary story for understanding modern entrepreneurship, retail strategies, marketing, and social entrepreneurship.
40.21 Allbirds: A Case Study in Sustainable Footwear Innovation
- Background: Allbirds, founded in 2016 by Tim Brown and Joey Zwillinger, aimed to create comfortable and sustainable footwear.
- Mission: “To tread lighter on the planet while making better things people love to wear.”
- Sustainable Materials: Allbirds uses renewable materials like merino wool and eucalyptus fiber.
- Comfort and Design: Combining sustainable materials with comfortable and aesthetically appealing design.
- Direct-to-Consumer: Selling directly to customers to reduce costs and improve accessibility.
- Ethical Sourcing: Ensuring the ethical treatment of animals and workers in the supply chain.
- Storytelling: Emphasizing the brand’s commitment to sustainability and innovative materials.
- Word-of-Mouth: Leveraging satisfied customers as brand advocates.
- International Presence: Expanding into international markets while staying true to the brand’s values.
- Localized Initiatives: Tailoring products and marketing to suit local preferences.
- Market Competitors: Competing with established footwear brands and other sustainable startups.
- Scale and Sustainability: Balancing growth with maintaining eco-friendly practices.
- Carbon Footprint: Measuring and reducing the brand’s carbon footprint.
- Circular Economy: Exploring ways to make footwear more recyclable and sustainable.
- Transparency: Sharing information about the supply chain and material sources.
- Community Engagement: Partnering with organizations for social and environmental causes.
- Research and Development: Continuing to innovate with new materials and product lines.
- Market Expansion: Exploring new markets and consumer segments.
- Changing Consumer Behavior: Influencing the way consumers think about sustainable products.
- Inspiring Competitors: Encouraging other brands to prioritize sustainability.
Allbirds’ unique approach to footwear production, blending innovation, comfort, and sustainability, has positioned it as a leader in the sustainable fashion movement. The Allbirds case study provides a valuable window into the world of sustainable business, marketing, and product innovation. By exploring Allbirds’ strategies and challenges, students can gain insights into how a commitment to ethical practices, environmental consciousness, and customer satisfaction can drive success in today’s competitive market. The case offers lessons for those interested in entrepreneurship, sustainable business practices, and ethical consumerism.
10 Marketing Case Study Examples: Learn How to Master Them in Your Campaigns
There are millions of blog posts, articles, and videos across the internet that try to give you advice about marketing. According to Google, at least 7,050,000 unique content pieces include the phrase “marketing tips.”
But with plenty of outdated and filler content creation to just build out a website, it’s hard to find applicable advice that actually works online.
In this article, you’ll learn from marketing case study examples that demonstrate what it takes to master channels like social media, email marketing , and PPC, as well as how to use case studies in your own campaigns.
Don’t rely on empty words. Learn powerful marketing best practices that are backed up with examples and data.
What is a marketing case study?
In marketing, a case study is an in-depth study of the effectiveness of a certain tool, tactic, or strategy. It focuses on measurable outcomes, like an increase in sales, visitors, or production hours.
Typically, it includes a few key elements:
- Introduction to the customer/client
- The problem the client needed to solve (should align with problems prospective clients also need to solve)
- The solution (and context of why your company/software was the right fit)
- Data from before and after implementing the solution

In a sense, a case study documents the journey of working with your company. And it gives potential future customers a reason to trust your company.
What are the different types of case studies in marketing?
In marketing, there are three main types of case studies that are commonly used:
1. Third-person or client case studies: These highlight the experience of a specific client working with your company or using your product.
2. Explanatory case studies: These case studies explore the impact of a phenomenon or tactic, such as the company’s marketing strategy, and how it impacted their growth. In this case, it’s not based on first-hand experience, but rather observation and inference.
3. Implementation case studies: An implementation case study takes the average client case study a bit further, focusing on the actual implementation and covering it in detail.
You can also divide the case studies further by the type of medium they use — video or text.
And in 2021, video case studies are becoming more and more popular. Many companies even use them as remarketing ads to address potential objections.
Why should you use case studies?
Case studies are a powerful way to prove that your products or services work, showcase your expertise, and build trust with potential customers.
It’s a way to transition away from just “telling” your customer and instead start “showing” them through examples. There’s a reason the old copywriting maxim goes, “Show, don’t tell.”
Consumers’ trust in companies to tell the truth in advertising materials is lower than ever. In 2020, only 14% of consumers said they trust advertising to be honest about a product or service.
But that doesn’t mean you can’t generate trust with your company’s website.
Consumers trust third-party reviews, testimonials, and data. In fact, 91% of 18–34-year-olds trust online reviews as much as personal recommendations.
So you need social proof. And client case studies — especially those that interview the current clients — are the best of both worlds. You get to highlight data while getting powerful social proof that shows that your product works.
When just adding a simple customer testimonial to your website can increase conversion rates by up to 34% , imagine what a detailed, compelling case study can do.
1. Email marketing case study: Your Therapy Source
If you think that email is a medium of the past, think again. At ActiveCampaign, we have hundreds of recent case studies that prove the opposite.
For example, Your Therapy Source receives a 2000% return on investment (ROI) from our campaigns simply by taking advantage of basic marketing automation .

In particular, a basic abandoned cart email represents around 30% of all revenue generated by automations.
With ActiveCampaign, that’s incredibly easy to set up. You can take advantage of our integrations with key e-commerce platforms like WooCommerce , Shopify , and more.

Because the case study goes into detail about exactly how the company achieved the results, it’s a combination of an implementation case study and a regular third-person case study.
2. Instagram marketing case study: Converse
If you look at all the top Instagram accounts in clothing, Converse has a much higher engagement rate than its competitors.
At 1.79%, their social media posts have an organic engagement rate over 15 times higher than Nike.

Why is that?
Let’s take a closer look at how they achieve these numbers:
When looking at Converse’s top Instagram posts, you quickly notice a trend. Collaborations with influential creators and artists — lately Tyler, the Creator — get a different level of engagement.

The post promoting their new collaboration shoe got over 183,000 likes in a few weeks. Converse even took it a step further and produced a short film with Tyler.
If you want to reach a wider number of people, combining audiences is a great strategy.

This is an example of an explanatory case study.
First, we worked backward from Converse’s powerful Instagram results. Then, we identified tactics that contribute to their high levels of engagement.
Because we didn’t work directly with Converse, and we’re only observing as an outsider, this is an explanatory case study.
3. Content marketing case study: porch.com
Fractl is a content marketing agency that worked with porch.com for over a year to earn 931 unique domain links, 23,000 monthly organic visits, and more.

The case study focuses on results over method — that means it’s a typical third-person case study.
They’re showcasing the results the company generated for a specific outside client without getting into the how-to.
These types of case studies are most useful for persuading hesitant potential customers to get on board. Showing that you’ve generated results for similar companies or people in the past is the best way to prove your skill set.
Depending on your target audience, going into detail with an implementation case study may be a better option.
4. SEO case study: Zapier study by Ryan Berg
This in-depth case study by Ryan Berg is a perfect example of how you can use explanatory case studies in your marketing.
It breaks down Zapier’s SEO strategy and how they created over 25,000 unique landing pages to improve their search rankings for different search terms.

Zapier’s main strategy revolves around targeting relevant long-tail keywords like “app A + app B integration.” That’s the key they used to generate serious organic traffic over the long term.
By breaking down industry leaders and how they rose to success, you can borrow some of their brand power and credibility.
You can use these kinds of case studies if your current clients don’t allow you to go into detail about the tactics you use to grow their online presence.
These case studies demonstrate to potential clients that you know what you’re talking about and have the expertise needed to help them succeed in their industry.
5. PPC case study: Google Ads and Saraf Furniture
When it comes to pay-per-click (PPC) advertising, Google was one of the earliest innovators. And in 2021, it’s still the largest digital advertiser globally, with $146.92 billion in ad revenue in 2020.
You might not think they need any more credibility, but Google still uses case studies, especially in emerging markets like India.
This case study shows how Google Ads helped Saraf Furniture generate 10 times more inbound leads each month and hire 1,500 new carpenters as a result.

Without going into details about the methods, it’s another typical third-person case study designed to build trust.
6. Video marketing case study: L’Oréal and YouTube
In this case study, various members of L’Oréal’s global marketing team break down exactly how they used YouTube ads to launch a new product.
As a result of the campaign, they were able to establish their new product as the No. 2 in its category and earn 34% of all mass sales across a network of online retailers.
The case study breaks down how they used YouTube for different stages — from awareness to loyalty. It’s another example of a third-person implementation case study.
7. Remarketing case study: AdRoll and Yoga Democracy
AdRoll is a remarketing platform that tracks your visitors and lets you show them targeted ads across the internet.
Their case study with Yoga Democracy perfectly showcases the power of the platform.

Look at these highlights:
- 200% increase in conversions
- 50% reduction in CPA
- 19% of total revenue attributed to AdRoll
These are metrics you’d love to show any potential customer. The case study goes into detail about how they built an effective remarketing campaign, including cart recovery emails and ads.
Because of the detail, you can classify this as an implementation case study.
8. Influencer marketing case study: Trend and WarbyParker
This influencer marketing case study from Warby Parker and Trend showcases how you can use influencer marketing even with a limited budget.

The “Wearing Warby” campaign was centered around showcasing influencers wearing Warby Parker glasses in their everyday life.
From mundane tasks like eating breakfast to artists creating a new masterpiece — it showcased Warby Parker’s products in use and made the brand more approachable for influencers’ followers.
This is another third-person case study, as it doesn’t go into much detail beyond the results.
9. Customer experience case study: App Annie and Coca-Cola
In this case study, Greg Chambers, the director of innovation for Coca-Cola, explains what App Annie brings to the table.
Instead of specific numbers and metrics, it focuses on the big-picture benefits that App Annie has on Coca-Cola’s customer experience.
The video interview format is also perfect for driving trust with potential customers.
Again, this is a typical third-person case study that you see a lot in the marketing world.
10. SaaS case study: Asana and Carta
Of course, it’s not just agencies and advertising platforms that need to master the use of case studies in digital marketing.
Let’s explore an example of a case study outside the marketing industry, in this case specifically for B2B marketers.
Asana is a project management platform that helps companies make their workflows more efficient.

It’s a good example of a case study that focuses more on the lived experience and less on the metrics.
This is a third-person case study that is closer to a client interview or testimonial, which is a good option if it’s hard to quantify improvements with metrics.
Best practices: How to use case studies in your own marketing campaigns

In this section, you’ll learn best practices to help you maximize the value of case studies in your own marketing campaigns.
Let’s look at four steps you can take to effectively use case studies.
Include a dedicated case study/customer stories page on your website
Most companies with a successful online presence have one of these pages. Emulate the top competitors in your industry by creating an improved version of their pages.
You can also add a case studies section to your resources page or blog.
Build CTAs into your case study pages
The chances are low that a random Googler will make it to your case studies. Most likely, it’s someone who thinks they might need your product.
So don’t be afraid to include calls to action throughout your case study pages.
Share case studies as part of your email marketing campaigns
Email marketing is hands-down the best channel for nurturing potential needs . That means you should always use case studies and customer success stories in your campaigns.
But it’s important that it doesn’t feel too promotional. Instead, share the unique steps they took to ensure success to deliver value, not just pitch.
Use case study video ads to overcome objections
When you’re thinking about buying a product, it’s easy to talk yourself out of it.
“It’s too expensive.” “It won’t work for me.” There are a lot of excuses and objections out there.
A case study video can be a powerful tool to overcome these objections in potential buyers.
Don’t overlook case studies when you’re planning your next marketing campaign. Towards the bottom end of the funnel, in stages like decision and action, they’re a powerful marketing tool.
When used right, case studies will help you fill your sales pipeline and provide your sales team with qualified leads.
Hopefully, the examples in this article taught you how you can use case studies in social media, email, and content marketing strategy to further your business goals.
You should also have learned how to use case studies to sell your company’s expertise.
If you want to grow your business, it’s crucial to learn from the people who have gone before you. In marketing, trying to learn all principles from scratch through trial and error would be a costly mistake.
If you’re ready to take advantage of marketing automation and email marketing tools that help similar businesses generate ROIs of 20x or higher, start your ActiveCampaign trial today .
No credit card required. Instant set-up.
Please enter a valid email address to continue.
Related Posts

ClickFunnels is a popular sales funnel builder that offers a range of features and capabilities for creating effective marketing funnels....

As startups and brands move upmarket and seek to target higher-value enterprise clients, they come to a crucial realization: The...

How do you know what they want, what they really, really want? 90’s music references aside, how do you know...
Try it now, for free

- About / Contact
- Privacy Policy
- Alphabetical List of Companies
- Business Analysis Topics
Aldi’s Marketing Mix (4P) Analysis

Aldi’s marketing mix (4Ps) focuses on low prices and a mixture of promotional tactics for competitive products that draw buyers into the company’s retail locations. The decisions, strategies, and tactics in this 4P (Product, Price, Place, and Promotion) aim for optimizing the company’s effectiveness in reaching its target market and growing its sales revenues. The effectiveness of this marketing mix and related strategies ensures business success despite the competitive obstacles and issues explained in the Five Forces analysis of Aldi . The discount supermarket chain’s marketing mix is known for low prices and a no-frills approach to providing efficient retail service.
Aldi’s marketing strategy involves using low selling prices to effectively compete with Lidl, Walmart , Whole Foods , Costco Wholesale , Amazon ’s e-commerce and brick-and-mortar stores, and other retail businesses. The marketing mix of Home Depot , which is not a direct competitor, also influences Aldi’s marketing mix and marketing strategy implementation.
Products in Aldi’s 4Ps
The products sold at Aldi’s stores and website target consumer demand, especially for basic commodities, like food and household essentials. The company’s product mix involves merchandise and service for this 4P. Aldi’s marketing mix includes the following products:
- Retail service
- Consumer goods
Aldi provides retail service, which is an organizational product (or output) that involves managing the movement and sale of merchandise to shoppers. In addition, the company has private-label branding for various consumer goods. Although other companies manufacture these goods, Aldi owns merchandise through its brands. In this marketing mix, retail service and consumer goods are what buyers pay for when they shop at the company’s stores. The selection of products and private labels used in this marketing mix implements the cost and product objectives of Aldi’s competitive strategy and growth strategies . For example, the company’s competitive strategy aims for low costs that affect the kinds of products that are available at the company’s stores. Also, the company’s marketing strategy involves a product mix that accounts for current trends in the retail market. For instance, the external factors explained in the PESTEL/PESTLE analysis of Aldi inform decisions about the types of merchandise included in this marketing mix.
Aldi’s Price & Pricing Strategy
This 4P includes price points and price ranges that capitalize on strategic objectives for low costs and low prices. Aldi’s marketing mix applies the following pricing strategies:
- Everyday low price (EDLP) strategy
- Market-oriented pricing strategy
- Loss leader strategy
Aldi is known for low prices, which are a consequence of the Everyday Low Price (EDLP) strategy. However, the company’s marketing mix also applies market-oriented pricing, which is a strategy that adjusts prices according to market factors, including supply and demand, as well as trends in consumption and consumer preferences. Moreover, Aldi’s marketing strategy involves loss leader pricing for a different set of products every week or season. Through these pricing strategies, the company’s 4Ps attract customers for more sales revenues. These pricing strategies are based on the goals of affordability and savings stated in Aldi’s mission and vision . These strategies are especially effective on price-sensitive shoppers. High efficiency and productivity combined with low costs achieved in Aldi’s operations management enable the low prices used in this marketing mix.
Place in Aldi’s Marketing Mix
The locations or places complement each other in this 4P to grow the company’s retail market reach. The following places are included in this marketing mix of Aldi:
- Aldi stores
- Aldi grocery website
Aldi’s stores are the primary places for sales transactions. These store locations are based on accessibility and proximity to consumer populations. This marketing mix also includes online shopping services for customers’ convenience. The company’s website reinforces the market presence established through the stores. The divisions of Aldi’s business structure (corporate structure) represent some of the managerial requirements of the location or place decisions in the distribution strategy for this element of the marketing mix.
Aldi’s Promotion
Aldi’s marketing communications mix promotes the discount supermarket chain and its private-label brands. Marketing campaigns and promotional tactics in the company’s 4Ps enhance corporate and brand image and persuade customers to shop at the company’s stores. For promotion, Aldi’s marketing mix applies the following:
- Sales promotion (weekly or seasonal)
- Advertising
- Public relations
Sales promotion is regularly used through weekly discounts and special offers at Aldi stores. This marketing mix also includes advertising to promote the company, its retail service, and its brands. On the other hand, the company’s public relations focus on developing a positive business image that encourages people to buy from the company’s stores and website. The public relations component of this 4P reflects Aldi’s corporate social responsibility (CSR) and ESG goals for sustainability and other stakeholder interests . The promotional tactics in the company’s marketing strategy rely on retail business strengths and competencies to successfully communicate with target customers. For example, strong brands, strong control on product selection, and the other competitive advantages detailed in the SWOT analysis of Aldi contribute to the effectiveness of sales promotion and advertising used in this marketing mix.
- Aldi Finds .
- Aldi – Online Grocery Shopping for Pickup and Delivery .
- Aldi Products .
- Pimentel, P. C., Bassi-Suter, M., & Didonet, S. R. (2024). Brand activism as a marketing strategy: An integrative framework and research agenda. Journal of Brand Management, 31 (2), 212-234.
- Reddy, T. N., Ghouse, S. M., & JS, R. K. (2023). Marketing Mix – Review of P. Research Journal of Humanities and Social Sciences, 14 (1), 55-58.
- Spanjaard, D., & Freeman, L. (2023). Supermarket tribes and the temple of Aldi: A comparison between the UK and Australia. Journal of Consumer Culture, 23 (1), 3-26.
- Copyright by Panmore Institute - All rights reserved.
- This article may not be reproduced, distributed, or mirrored without written permission from Panmore Institute and its author/s.
- Educators, Researchers, and Students: You are permitted to quote or paraphrase parts of this article (not the entire article) for educational or research purposes, as long as the article is properly cited and referenced together with its URL/link.
Marketing Results
22 Marketing Case Study Examples (With Template)
February 17, 2016 by Will Swayne

Prospects who aren’t ready to buy – or who are “sitting on the fence” – tend to be resistant to even well-crafted marketing messages. But a bunch of well aimed marketing case studies can often tip the scales in your favour.
“Sell benefits, not features” is good advice, but benefit-rich copy can actually deter prospects who haven’t reached the decision stage yet.
And too many benefits in the absence of marketing proof elements can ring hollow in today’s increasingly sceptical marketplace.
We published our first marketing case study back in 2005 and I quickly realised the power of case studies as a versatile and effective marketing tactic.
Why are marketing case studies so effective?
Here are three reasons:
- Case studies show, they don’t tell. Telling you I can get you more qualified leads is one thing. Showing you how a similar company to yours got 145% more leads with 24% lower marketing costs is another.
- Prospects are typically curious to understand how others have achieved the results they desire. They will eagerly devour a well-constructed case study.
- Case studies are also a great tool for closing fence-sitting prospects. For many years I’ve asked prospects why they chose to work with us, and the most common response seems to be, “I was impressed by your case studies” , or “I saw you helped someone in my industry so I figure you can help us too” .
Now let’s look at how to structure and effectively promote a case study, and then some marketing case study examples for you to replicate.
Our Recommended Case Study Template
Here’s the case study structure we’ve adopted which has proven effective:
- Start with a major headline that summarises the key result achieved: e.g. “Investment Property Strategist Triples Leads In 6 Months” . This gets the prospect excited about reading on.
- Then introduce the background . In other words, the “Before” scenario.Don’t bore the reader with too many details about the history of the client. But DO provide an insight into the “trigger” that led to them seeking your assistance. e.g. “The client noticed smaller competitors starting to appear ahead of them on Google”. And, DO talk about the negative effects of the “Before” state. E.g. “New customer acquisition that had previously been growing by 10% every quarter had flatlined for the last 12 months.”
- Now talk about the solution . Here’s where you explain what you did to achieve the outcomes. I like to list different services or solutions in the form of bullet points. Also, include significant details and facts and figures to add “richness” to the story. Where possible, demonstrate with images, screenshots or other proof elements. Emphasise anything you did differently to the standard approach, or anything that highlights your point-of-difference benefits.
- Now talk about your results . Results are the crux of any good case study.I like to go with a number of punchy bullet points, populated with specific numbers. E.g . “Lead volume up 75%… New customer volume from online sources up 145%… 1,540 more organic search engine visitors per month.”
- Include a testimonial from the client. What was their reaction to your work? The “Before-During-After” approach is a good structure for testimonials. A strong testimonial adds texture and credibility to the data in your core case study.
- End with a call-to-action . This can be relatively low-key. For example, “Contact us to explore how you can enjoy similar breakthrough results.”
You can see more examples of different implementations of this concept on our online marketing case studies page.
How To Promote Your Case Study
A case study that never gets read won’t help you.
Here are some of our favourite promotional methods:
- Optimise each case study for search engines . A good start is using a <title> tag on your case study pages in the format: “<INDUSTRY> <SERVICE> case study”. For example, “Accountant online marketing case study” or “Car sales lead generation case study” . This will tend to rank you well for anyone searching for case studies about your industry.
- Send case studies to your email subscribers . These emails achieve high engagement both as broadcasts, and as “drip emails” within an automation sequence .
- Create a print booklet of case studies to send to prospects and clients via snail mail or distribute at trade shows.
- Case studies make great social media updates and can be recycled every few months using different headlines.
22 Marketing Case Study Examples
1. fuji xerox australia business equipment, tripled leads for 60% less marketing spend.
In 90 days, we doubled web lead flow with lower marketing costs.
Read the full case study here.
Paul Strahl , National e-Business Manager

2. Surf Live Saving Foundation
Surf lottery grows online revenue 47%.
Marketing Results delivered tangible business improvements, including 47% higher revenue from digital, year-on-year.
Yin Tang , Surf Live Saving Foundation

3. ABC Reading Eggs
Integrated search and conversion management for abc reading eggs.
Marketing Results have been instrumental in profitably expanding our ad spend, while removing waste.
Matthew Sandblom , Managing Director ABC Reading Eggs

4. MAP Home Loans
From 70 hour weeks to 40 hour weeks with 100% annual growth.
I now make twice as much money, have less stress and fewer hours.
Craig Vaunghan , Principal MAP Home Loans

5. Inkjet Wholesale
Online advertising roi doubles – in just three months.
We couldn’t be happier – conversion rates are up, costs are down, ROI has doubled.
Glenn Taylor , National Marketing Manager Inkjet Wholesale

6. Breaking Into Wall Street
Info-marketing business achieves 300% revenue growth with 7-figure profits.
Marketing Results provided the marketing support to grow my annual revenue 300%+. They don’t just advise – they implement.
Brian DeChesare , Founder Breaking Into Wall Street

7. LatestBuy
Brw fast 100 online retailer latestbuy.com.au boosts sales by 45.3%.
Revenue had flatlined… Now it is up by 45%, with over 80% of that due to conversion rate optimisation.
Shaun Campbell , Co-Owner LatestBuy.com.au

8. directSMS
More traffic, less cost, lead volume doubles.
More than doubled the number of qualified enquiries via our website for the same ad spend.
Ramez Zaki , Co-Founder directSMS

9. Business Coach and Author, Pure Bookkeeping
Successful marketing automation and 100.95% year on year growth.
50%+ of business comes directly through online channels and none of this would have happened without Marketing Results.
Peter Cook , Business Coach & Author Pure Bookkeeping

10. Positive Training Solutions
Higher rankings plus more, higher-quality leads.
Marketing Results excels in strategic and online marketing.
James Grima , Managing Director Positive Training Solutions

11. Geelong’s Gym
From 5-6 leads a month to 60-70. 10x increase.
We’ve gone from 5 – 6 leads per month to 60 – 70!
Gerard Spriet , Owner Geelong’s Gym

12. Super Finance – SMSF Property
A new pipeline delivering a steady flow of web leads.
Outstanding quality of web generated leads!
Yannick Ieko , Director Super Finance

13. College For Adult Learning – Training Organisation
300%+ more sales with 60% lower cost per sale.
I expect at least another 60% more leads and 80-90% more revenue by continuing to work with Marketing Results.
Rob Golding , Director College For Adult Learning

14. The Gourmet Guardian – Food Safety Programs
4 times more leads and a 269% revenue increase.
Your AdWords strategies have quadrupled leads, almost tripled revenue and reduced my dependence on contract work to zero.
Gavin Buckett , Managing Director The Gourmet Guardian

15. Quick Coach – Life Coaching Courses
More qualified sales plus a facebook roi of 1285%.
The results have been fantastic… I have had over 500 potential students opt in via Google wanting to change their lives and those of their clients.
Glen Murdoch , Founder & CEO Quick Coach

16. Investment House – Property Development
Clients lined up for everything we can find.
We have clients lined up for everything we can find.
Colin Ferguson , Managing Director Investment House

17. Cosmetic Surgery Lead Generation
257% increase in qualified lead volume.
In less than a year, our enquiry volume increased by over 257% while increasing the quality and conversion rate of those leads.
Dee Tozer , Managing Director Medici Clinics


18. All Suburbs Catering
61% roi gain in less than 5 months….
20% more enquiries for 34% less cost – a compounded gain of 61% in only 5 months.
Jeff Veale , Managing Director All Suburbs Catering

19. Trilogy Funding
549 qualified sales leads in 3 months.
549 qualified sales leads in 3 months.
Ed Nixon , Principal Trilogy Funding

20. Customized Stickers
Online revenue rockets by 800%.
With Marketing Result on our side, our website revenue has increased by over 800% in only 18 months.
Anthony Khoury , Managing Director Customized Stickers

21. Technoledge
Engaging ceos of ideal target companies.
We’re routinely seeing CEOs of Australian hi techs with turnover of $5 million to $50 million (our target audience) opting in and proceeding to self-qualify before they contact us for a meeting. This is what digital marketing is supposed to do.
Tracey James , Director Technoledge

22. First Aid Training
Specialist first aid training company doubles revenue in 6 months.
We’ve streamlined customer acquisition, increased customer lifetime value, and doubled our revenue in 6 months!
Dave Hundt , Director Kids First Aid

I encourage you to put these tips into action and see how they work for you.
What other ways have you used case studies effectively in your business?

Almost there: please complete this form to get instant access to the video series…
“Double Your Leads In 30 Days”
Your privacy is 100% guaranteed.
Almost there: please tell us where to send your free report, plus valuable lead generation tips and case studies…

“FREE DOWNLOAD: The Financial Services Lead Generation Guide”
Oops! We could not locate your form.
We guarantee 100% privacy. You can unsubscribe with one click, any time you like.

“FREE DOWNLOAD: The Property Services Lead Generation Guide”

“FREE DOWNLOAD: The Education & Training Lead Generation Guide”

“How To Craft A Killer Unique Value Proposition That Attracts More Ideal Clients”
“name of the free upgrade goes here”.
Please tell us where to send your bonus content:
- Marketing Mix Modelling
- Marketing Analysis
- Freelance Partnerships
- Testimonials
- Get in touch
- Marketing mix modelling: 3 case studies from 2020
Introduction
My last blog was a review of my year with my business owner hat on, but what of the work that keeps that business ticking over?
The work that I have undertaken in 2020 has all turned out to be marketing mix modelling, by chance and circumstance rather than by design. But it has provided a useful opportunity to showcase the different ways that a consultant with my skills can help. It is also a good illustration of the variety of ways that the same approach is used for different end goals. Businesses remain anonymous for obvious reasons.
1. Tiny cog, big machine
The whole engagement is vast, and the ultimate output is a tool that the client uses to make a first pass at global marketing spend allocation by country, brand, and channel. The aim of these marketing mix models is to produce the response curves that fuel the allocation tool’s engine. I have written more about how that works here.
There are two main implications of this type of engagement. First, the number of models that needs to be produced runs to several hundred. Second, because countries, brands and channels are compared it is important that the models are structured similarly. Simplicity and consistency win out over complexity and uniqueness.
All the time in my book.
Thankfully, these days the heavy lifting in terms of data processing can be largely automated and initial models are built quickly to a template. But there are some countries where the data is not so good or complete. And others where the marketing has such a small relative impact that some judgement calls needed to be made.
It was those models that I worked on and other than to understand how it was put together I was not involved in the data processing nor the steps after the model was built. It freed up some senior time in the wider team to enable oversight rather than them stepping down into the nuts and bolts too often and losing that widescreen vision.
Global consumer packaged goods brand
My contribution: 13 countries, 25 brands
3-month attachment to team
2. Specialist subject
Another large project. In addition to marketing response curves the client delivery also involved presentations to marketing and consumer teams. With the purpose of explaining sales movements, diving into more detail about campaigns and providing recommendations on how to improve the efficiency of activities.
Like in the first case study, data had already been processed. But lockdown in the UK scattered the core team, so they sought out experienced hands who could take on chunks of the delivery and see it through right from exploratory analysis through to presenting to the client. I took a set of brands that sit in the same product category.
All of the models were ‘refreshes’ of existing models rather than new builds. One of the skills that experience gifts analysts is the ability to judge how much change should be expected versus previous results. With both the analytical and client teams all working remotely, clear communication was also needed.
The models were based on data pre-Covid and results were delivered while most countries were still in some sort of lockdown. Part of the discussion with clients was then naturally about whether recommendations still held. If not, what factors need to be considered for immediate decisions.
Global beverages brand
My contribution: 3 countries, 3 brands
3. The Full Monty
A smaller business, but still multiple countries – a theme than runs through my career. Me operating independently to provide B2B consultancy. The client had never commissioned marketing mix modelling before, and the primary questions were about measuring the return on investment of the two main paid marketing channels.
Every stage of the engagement was undertaken by me with the cooperation of the client and data owners within the business. The process took 10 weeks following these steps:
- Initial briefing à Proposed solution
- Data request issued à Data collation and processing
- Feasibility study including go/no-go recommendation
- Exploratory data analysis à Initial model builds
- Interim results à Feedback à Model refinement
- Final model builds à Final results & recommendations
- Delivery of assets: Models, Dataset, Forecasting tool
The model period included Covid-19 first waves and so the scale and speed of sales erosion and recovery due only to the pandemic was measured. The trough was driven largely by lockdowns with “uncertainty” (proxied by death rates) playing a smaller role. There was a sales bounce due to pent up demand, that settles at a slightly lower level.
There was no evidence that marketing worked differently during the lockdown and so it became a significant driver of the low sales during that period. The importance of connecting to customers was also highlighted with a peak in incremental sales driven by the website chat function during lockdown.
Both main paid marketing channels were working to drive sales but over different timeframes, which led to recommending that both should be continued. The channel where most money is spent experiences diminishing returns at higher spend levels, which led to recommending the most efficient spend ranges for each country.
The effect of paid marketing is not visible by looking at sales over time. Only by using a modelling approach to strip out other impacts was the marketing impact identified. These other impacts included: industry trends, underlying seasonality, changes to the businesses’ service offer and non-controllable factors like search algorithm changes.
2 countries, 1 brand
2-month consultancy
About the only threads loosely tying these three engagements together is that the same analytical approach was used and that two ran headlong into Covid-19. The scale and the scope of each engagement were very different and show how versatile an approach marketing mix modelling can be.
‘Models’ were not the goal, just a means to get to business recommendations. To get those models and to translate the outputs needed as much attention and skill directed to data analysis (structured ‘looking’) and communication (effective ‘talking’) as to statistics.
And careful thought around the mechanics and implications of an unprecedented event.
If you would like my experienced eye on your marketing effectiveness, get in touch.
Please ask before reproducing my material partially or wholly for commercial use. © Jo Gordon Consulting Ltd 2020
- +44 (0)7757 086033 - Jo Gordon
- [email protected]
- Advertising
- Marketing Mix
- SWOT Analysis
- Privacy Policy
Power of Versace’s Marketing Mix – A Case Study
- May 29, 2023

The Marketing Mix of Versace tells the 4ps (Product, Price, Place, and Promotion) of the best Italian luxury fashion company – Versace!
Versace is founded by Gianni Versace in 1978. The brand is known for its bold and flashy designs, often featuring bright colors and bold prints. Versace’s clothing, accessories, and home furnishings are a favorite among celebrities and have been worn by many famous individuals, including Madonna, Elton John, and Jennifer Lopez.
The brand also operates several retail stores worldwide and sells its products through high-end department stores. Versace is currently owned by Michael Kors Holdings Limited.
Versace’s aesthetic is heavily influenced by Greek and Roman mythology, and many of the brand’s designs feature references to these ancient cultures.
Let’s start with the Versace Marketing Mix to learn more about their product, price, promotion, and distribution approaches.
Product In The Marketing Mix Of Versace
Versace is a luxury fashion brand that has always believed in offering modern and fashionable products since its beginning. After his first collection for Callaghan, Genny and Complice were met with great appreciation.

This marked the inception of the brand under the name ‘Gianni Versace Donna’. Initially, the brand began by launching clothing for both men and women, but over time it has expanded to include a wide range of products such as jewelry, accessories, and home furnishings.
Following the untimely death of Gianni Versace, his sister Donatella Versace took over the ownership of the brand and introduced ‘Young Versace’ and ‘Versus’ in 1993.
These new lines helped to further solidify the brand’s global success and reach new heights in the fashion industry. Versace’s designs are highly sought after, particularly by celebrities such as the Prince of Wales and Hollywood stars like Jennifer Lopez.
The brand is known for its unique and trendy designs that set a new style statement in the world of fashion. Versace’s products are always on the cutting edge, pushing boundaries and creating new trends. The brand’s aesthetic is heavily influenced by Greek and Roman mythology, which is reflected in many of its designs.
Versace’s iconic Medusa logo is also a recognizable symbol of the brand and is prominently featured on many of its products.
Price In The Marketing Mix Of Versace
Versace has quickly made a name for itself with its modern and fashionable designs. Known for its high-end couture, glamour, and perfect designs, Versace targets the elite class with a taste for innovative and luxurious items.
The company has positioned itself as a superior brand in the fashion industry and has been able to maintain its reputation through its premium pricing strategy.
The brand’s customers are more conscious of brand value than monetary matters, making it possible for Versace to maintain its high pricing policy.
Wearing a Versace garment is seen as an honor in the fashion industry, making customers eager to buy and wear items from the brand’s collections.
Versace also offers customized apparel that is unique and breathtaking. Due to their exclusive nature, these items come at a higher premium price. However, the brand’s customers are willing to pay the extra cost for these one-of-a-kind designs.
This, in turn, has helped Versace maintain its reputation in the consumer market with great success. The brand has also expanded into other areas such as jewelry, accessories, and home furnishings, further cementing its position as a luxury lifestyle brand.
Place In The Marketing Mix Of Versace
Versace is a well-known brand with a presence in multiple countries around the world. Its headquarters are located in Milan, Italy. Over time, Versace has expanded its operations to other countries and opened its first boutique outside of Italy in 1991 in Glasgow, Scotland.
In 2011, Versace entered into a partnership with H&M to launch a new line of clothing and home items that were sold in H&M outlets. In 2015, the brand collaborated with Lil Buck to launch a line of exclusive sneakers. That same year, Versace entered into a deal with Chinese firm Mind Group to design luxury residential towers in China, which would be known as Versace Residencies.
To maintain its commercial success, Versace manages its sales activities through its retail, distribution, and sales departments. The company has several partnerships that help it sell and market its products through its outlets.
Versace also has an official website that offers distribution and purchasing facilities in several countries, even where the brand does not have an outlet. This has greatly impacted its sales figures as it has grown significantly with the opening of its online store.
The brand’s online store has enabled it to reach a wider audience and expand its customer base.
Versace has been able to establish itself as a premium brand that offers innovative and luxurious products. The brand’s high-end couture, glamour, style, and perfect designs appeal to its sophisticated customers.
With a reputation for offering unique and trendy designs, Versace sets a new style statement in the world of fashion, which has helped it to maintain its success in the consumer market.
Promotions In The Marketing Mix Of Versace
Versace is a luxury brand that is well-known for its high-end couture, glamour, and perfect designs. The brand has positioned itself as a superior brand that caters to the elite class with a very high taste for innovative and luxurious items.
Though the brand does not require any media to promote itself, as its name is only sufficient, it still pays a lot of attention to making it a synonym for luxury. The logo of Versace, a Greek mythological figure, Medusa is equally catchy as well as lavish to make an impact on people.

Versace being the brand for celebrities has directly or indirectly been promoted by these celebrities throughout its journey. The collection ‘Young Versace’ and ‘Versus’ introduced by Donatella Versace in 1993 enjoyed widespread international coverage for its ‘Black Versace dress of Elizabeth Hurley’.
To promote more, Versace started with sponsorship and partnership. It made a partnership with Lamborghini in 2006 to produce the Lamborghini Murciélago LP640 VERSACE. The interior of the car was designed by Versace with car seats embroidered with the Versace logo. To keep the exclusivity, only 10 units of the car were produced.
In 2008, Versace teamed up with AgustaWestland to create the AgustaWestland AW109 Grand Versace VIP luxury helicopter.
The helicopter had a Versace leather interior and a design on the outside. It also came up with Versace Residences to promote the luxurious brand name. The brand also started with luxurious hotel chains to keep their visibility high for the premier segment of society.
Versace also conducts and sponsors various fashion shows to show their unique and bold designs. The company is also utilizing social media to promote via its official YouTube channel, official Facebook page, etc.
I hope you have gathered all the essential information about the Marketing Mix of Versace and the 4 P’s of Versace. Stay tuned for more Marketing Mix Articles.
- Sign into My Research
- Create My Research Account
- Company Website
- Our Products
- About Dissertations
- Español (España)
- Support Center
Select language
- Bahasa Indonesia
- Português (Brasil)
- Português (Portugal)
Welcome to My Research!
You may have access to the free features available through My Research. You can save searches, save documents, create alerts and more. Please log in through your library or institution to check if you have access.

Translate this article into 20 different languages!
If you log in through your library or institution you might have access to this article in multiple languages.

Get access to 20+ different citations styles
Styles include MLA, APA, Chicago and many more. This feature may be available for free if you log in through your library or institution.

Looking for a PDF of this document?
You may have access to it for free by logging in through your library or institution.

Want to save this document?
You may have access to different export options including Google Drive and Microsoft OneDrive and citation management tools like RefWorks and EasyBib. Try logging in through your library or institution to get access to these tools.

- Document 1 of 1
- More like this
- Scholarly Journal
The impact of marketing mix elements on brand loyalty: A case study of mobile phone industry
No items selected.
Please select one or more items.
[[missing key: loading-pdf-error]] [[missing key: loading-pdf-link]]
In today's highly competitive markets, keeping customers and retaining their loyalty is considered crucial in maintaining business. Companies and retailers also need to look for various marketing strategies in order to improve their customers’ loyalty. Having knowledge and skills about marketing is one of the capabilities which is required for success in the competition. In consumable markets, brands are the main points of differentiation between the competitive presentations, thus, they are crucial for the success of the companies. The purpose of this study was to analyze the impact of marketing mix elements on brand loyalty. The present study is applicable in terms of objective and descriptive survey in terms of data collection. To evaluate the model and hypotheses, data collection was carried out through surveying 384 mobile phone users. For data analysis and verification of the model, structural equation modeling approach (SEM) and confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) were used and based on the results of the path analysis, the relationship between the variables in the model is investigated. Results indicated the positive impact of products elements, distribution channels, and promotional activities on brand loyalty. Also, the findings showed that indexes of satisfaction and trust which are considered as mediating variables between marketing mix and brand loyalty had positive and significant impact on brand loyalty in the mobile phone industry.
You have requested "on-the-fly" machine translation of selected content from our databases. This functionality is provided solely for your convenience and is in no way intended to replace human translation. Show full disclaimer
Neither ProQuest nor its licensors make any representations or warranties with respect to the translations. The translations are automatically generated "AS IS" and "AS AVAILABLE" and are not retained in our systems. PROQUEST AND ITS LICENSORS SPECIFICALLY DISCLAIM ANY AND ALL EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION, ANY WARRANTIES FOR AVAILABILITY, ACCURACY, TIMELINESS, COMPLETENESS, NON-INFRINGMENT, MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. Your use of the translations is subject to all use restrictions contained in your Electronic Products License Agreement and by using the translation functionality you agree to forgo any and all claims against ProQuest or its licensors for your use of the translation functionality and any output derived there from. Hide full disclaimer
Suggested sources
- About ProQuest
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Browse All Articles
- Newsletter Sign-Up
Marketing →

- 07 May 2024
- Cold Call Podcast
Lessons in Business Innovation from Legendary Restaurant elBulli
Ferran Adrià, chef at legendary Barcelona-based restaurant elBulli, was facing two related decisions. First, he and his team must continue to develop new and different dishes for elBulli to guarantee a continuous stream of innovation, the cornerstone of the restaurant's success. But they also need to focus on growing the restaurant’s business. Can the team balance both objectives? Professor Michael I. Norton discusses the connections between creativity, emotions, rituals, and innovation – and how they can be applied to other domains – in the case, “elBulli: The Taste of Innovation,” and his new book, The Ritual Effect.

- 29 Feb 2024
Beyond Goals: David Beckham's Playbook for Mobilizing Star Talent
Reach soccer's pinnacle. Become a global brand. Buy a team. Sign Lionel Messi. David Beckham makes success look as easy as his epic free kicks. But leveraging world-class talent takes discipline and deft decision-making, as case studies by Anita Elberse reveal. What could other businesses learn from his ascent?

- 17 Jan 2024
Psychological Pricing Tactics to Fight the Inflation Blues
Inflation has slowed from the epic rates of 2021 and 2022, but many consumers still feel pinched. What will it take to encourage them to spend? Thoughtful pricing strategies that empower customers as they make purchasing decisions, says research by Elie Ofek.

- 05 Dec 2023
What Founders Get Wrong about Sales and Marketing
Which sales candidate is a startup’s ideal first hire? What marketing channels are best to invest in? How aggressively should an executive team align sales with customer success? Senior Lecturer Mark Roberge discusses how early-stage founders, sales leaders, and marketing executives can address these challenges as they grow their ventures in the case, “Entrepreneurial Sales and Marketing Vignettes.”

Tommy Hilfiger’s Adaptive Clothing Line: Making Fashion Inclusive
In 2017, Tommy Hilfiger launched its adaptive fashion line to provide fashion apparel that aims to make dressing easier. By 2020, it was still a relatively unknown line in the U.S. and the Tommy Hilfiger team was continuing to learn more about how to serve these new customers. Should the team make adaptive clothing available beyond the U.S., or is a global expansion premature? Assistant Professor Elizabeth Keenan discusses the opportunities and challenges that accompanied the introduction of a new product line that effectively serves an entirely new customer while simultaneously starting a movement to provide fashion for all in the case, “Tommy Hilfiger Adaptive: Fashion for All.”

- Research & Ideas
Are Virtual Tours Still Worth It in Real Estate? Evidence from 75,000 Home Sales
Many real estate listings still feature videos and interactive tools that simulate the experience of walking through properties. But do they help homes sell faster? Research by Isamar Troncoso probes the post-pandemic value of virtual home tours.

- 17 Oct 2023
With Subscription Fatigue Setting In, Companies Need to Think Hard About Fees
Subscriptions are available for everything from dental floss to dog toys, but are consumers tiring of monthly fees? Elie Ofek says that subscription revenue can provide stability, but companies need to tread carefully or risk alienating customers.

- 29 Aug 2023
As Social Networks Get More Competitive, Which Ones Will Survive?
In early 2023, TikTok reached close to 1 billion users globally, placing it fourth behind the leading social networks: Facebook, YouTube, and Instagram. Meanwhile, competition in the market for videos had intensified. Can all four networks continue to attract audiences and creators? Felix Oberholzer-Gee discusses competition and imitation among social networks in his case “Hey, Insta & YouTube, Are You Watching TikTok?”

- 26 Jun 2023
Want to Leave a Lasting Impression on Customers? Don't Forget the (Proverbial) Fireworks
Some of the most successful customer experiences end with a bang. Julian De Freitas provides three tips to help businesses invest in the kind of memorable moments that will keep customers coming back.

- 31 May 2023
With Predictive Analytics, Companies Can Tap the Ultimate Opportunity: Customers’ Routines
Armed with more data than ever, many companies know what key customers need. But how many know exactly when they need it? An analysis of 2,000 ridesharing commuters by Eva Ascarza and colleagues shows what's possible for companies that can anticipate a customer's routine.

- 30 May 2023
Can AI Predict Whether Shoppers Would Pick Crest Over Colgate?
Is it the end of customer surveys? Definitely not, but research by Ayelet Israeli sheds light on the potential for generative AI to improve market research. But first, businesses will need to learn to harness the technology.

- 24 Apr 2023
What Does It Take to Build as Much Buzz as Booze? Inside the Epic Challenge of Cannabis-Infused Drinks
The market for cannabis products has exploded as more states legalize marijuana. But the path to success is rife with complexity as a case study about the beverage company Cann by Ayelet Israeli illustrates.

- 07 Apr 2023
When Celebrity ‘Crypto-Influencers’ Rake in Cash, Investors Lose Big
Kim Kardashian, Lindsay Lohan, and other entertainers have been accused of promoting crypto products on social media without disclosing conflicts. Research by Joseph Pacelli shows what can happen to eager investors who follow them.

- 10 Feb 2023
COVID-19 Lessons: Social Media Can Nudge More People to Get Vaccinated
Social networks have been criticized for spreading COVID-19 misinformation, but the platforms have also helped public health agencies spread the word on vaccines, says research by Michael Luca and colleagues. What does this mean for the next pandemic?

- 02 Feb 2023
Why We Still Need Twitter: How Social Media Holds Companies Accountable
Remember the viral video of the United passenger being removed from a plane? An analysis of Twitter activity and corporate misconduct by Jonas Heese and Joseph Pacelli reveals the power of social media to uncover questionable situations at companies.

- 06 Dec 2022
Latest Isn’t Always Greatest: Why Product Updates Capture Consumers
Consumers can't pass up a product update—even if there's no improvement. Research by Leslie John, Michael Norton, and Ximena Garcia-Rada illustrates the powerful allure of change. Are we really that naïve?

- 29 Nov 2022
How Much More Would Holiday Shoppers Pay to Wear Something Rare?
Economic worries will make pricing strategy even more critical this holiday season. Research by Chiara Farronato reveals the value that hip consumers see in hard-to-find products. Are companies simply making too many goods?

- 26 Oct 2022
How Paid Promos Take the Shine Off YouTube Stars (and Tips for Better Influencer Marketing)
Influencers aspire to turn "likes" into dollars through brand sponsorships, but these deals can erode their reputations, says research by Shunyuan Zhang. Marketers should seek out authentic voices on YouTube, not necessarily those with the most followers.

- 25 Oct 2022
Is Baseball Ready to Compete for the Next Generation of Fans?
With its slower pace and limited on-field action, major league baseball trails football in the US, basketball, and European soccer in revenue and popularity. Stephen Greyser discusses the state of "America's pastime."

- 18 Oct 2022
When Bias Creeps into AI, Managers Can Stop It by Asking the Right Questions
Even when companies actively try to prevent it, bias can sway algorithms and skew decision-making. Ayelet Israeli and Eva Ascarza offer a new approach to make artificial intelligence more accurate.
How to Create a Social Media Marketing Strategy in 9 Easy Steps [Free Template]
Creating your social media marketing strategy doesn’t need to be painful. Create an effective plan for your business in 9 simple steps.

A social media marketing strategy is a summary of everything you plan to do and hope to achieve on social media. It guides your actions and lets you know whether you’re succeeding or failing.
The more specific your plan is, the more effective it will be. Keep it concise. Don’t make it so lofty and broad that it’s unattainable or impossible to measure.
In this post, we’ll walk you through a nine-step plan to create a winning social media strategy of your own. We’ve even got expert insights from Amanda Wood, Hootsuite’s Senior Manager of Social Marketing.
How to create a social media strategy:
Bonus: Get a free social media strategy template to quickly and easily plan your own strategy. Also use it to track results and present the plan to your boss, teammates, and clients.
What is a social media marketing strategy?
A social media strategy is a document outlining your social media goals, the tactics you will use to achieve them and the metrics you will track to measure your progress.
Your social media marketing strategy should also list all of your existing and planned social media accounts along with goals specific to each platform you’re active on. These goals should align with your business’s larger digital marketing strategy.
Finally, a good social media plan should define the roles and responsibilities within your team and outline your reporting cadence.
Create. Schedule. Publish. Engage. Measure. Win.
Creating your own social media marketing strategy (video guide)
No time to read the whole article? Let Amanda, Hootsuite’s own Senior Manager of Social Media Marketing, guide you through our free social media marketing strategy template in less than 10 minutes:
How to create a social media marketing strategy in 9 steps
Step 1. choose goals that align to business objectives, set s.m.a.r.t. goals.
The first step to creating a winning social media strategy is to establish clear objectives and goals. Without goals, you have no way to measure success and return on investment (ROI) .
Each of your social media marketing goals should be SMART : s pecific, m easurable, a ttainable, r elevant and t ime-bound.
Psst: Need help getting started? We’ve got social strategy guides for small businesses , financial services , government , higher education , healthcare , real estate , law firms , and non-profits .
Oh, and if you need examples of smart social media goals , we’ve got you covered there too.
Once you’ve decided on your goals, track them in a social media strategy doc — grab our free template if you don’t have one already.
Track meaningful metrics
Vanity metrics like number of followers and likes are easy to track, but it’s hard to prove their real value. Instead, focus on things like engagement, click-through, and conversion rates.
For inspiration, take a look at these 19 essential social media metrics .
You may want to track different goals for different social media networks, or even different uses for each network.
For example, if you use LinkedIn to drive traffic to your website, you would measure click-throughs. If Instagram is for brand awareness, you might track the number of Instagram Story views. And if you advertise on Facebook, cost-per-click (CPC) is a common success metric.
Social media goals should align with your overall marketing objectives. This makes it easier to show the value of your work and secure buy-in from your boss.
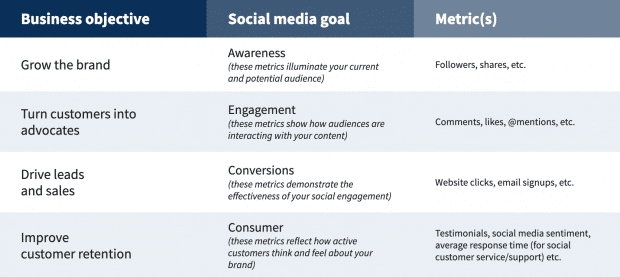
Start developing a successful social media marketing plan by writing down at least three goals for social media.
“ It’s easy to get overwhelmed by deciding what to post and which metrics to track, but you need to focus on what you want to get out of social media to begin with,” says Amanda Wood, Hootsuite’s Senior Manager of Social Marketing. “Don’t just start posting and tracking everything: match your goals to your business, and your metrics to your goals.”
Step 2. Learn everything you can about your audience
Get to know your fans, followers, and customers as real people with real wants and needs, and you will know how to target and engage them on social media.
When it comes to your ideal customer, you should know things like:
- Average income
- Typical job title or industry
Here’s a simple guide and template for creating audience/buyer personas .
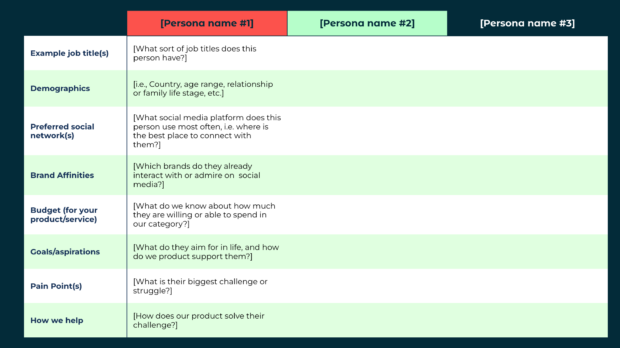
Don’t forget to document this information in your strategy doc!
Social media analytics can also provide a ton of valuable information about who your followers are, where they live, and how they interact with your brand on social media. These insights allow you to refine your strategy and better target your audience.
Jugnoo, an Uber-like service for auto-rickshaws in India, used Facebook Analytics to learn that 90% of their users who referred other customers were between 18- and 34-years-old, and 65% of that group was using Android. They used that information to target their ads, resulting in a 40% lower cost per referral.
Check out our guide to using social media analytics and the tools you need to track them .
Step 3. Get to know your competition
Odds are your competitors are already using social media, and that means you can learn from what they’re doing.
Conduct a competitive analysis
A competitive analysis allows you to understand who the competition is and what they’re doing well (and not so well). You’ll get a good sense of what’s expected in your industry, which will help you set social media targets of your own.
It will also help you spot opportunities and weaknesses you can document in your social strategy doc.
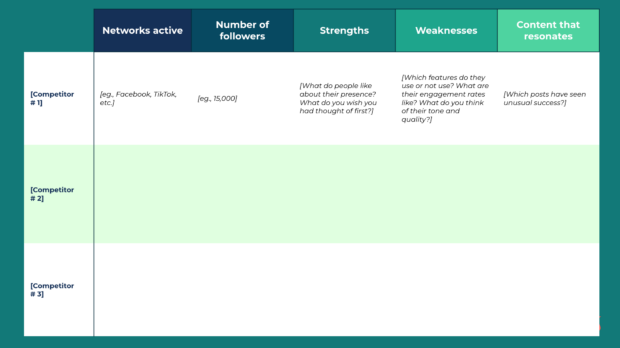
Maybe one of your competitors is dominant on Facebook, for example, but has put little effort into X (Twitter) or Instagram. You might want to focus on the social media platforms where your audience is underserved, rather than trying to win fans away from a dominant player.
Use social media listening
Social listening is another way to keep an eye on your competitors.
Do searches of the competition’s company name, account handles, and other relevant keywords on social media. Find out what they’re sharing and what other people are saying about them. If they’re using influencer marketing, how much engagement do those campaigns earn them?
Pro tip : Use Hootsuite Streams to monitor relevant keywords, hashtags and accounts in real-time.
Try Hootsuite for free. You can cancel anytime.
As you track, you may notice shifts in how your competitors and industry leaders are using social media. You may come across new, exciting trends. You might even spot specific social content or a campaign that really hits the mark—or totally bombs.
Use this kind of intel to optimize and inform your own social media marketing strategy.
Just don’t go overboard on the spy tactics, Amanda advises. “ Make sure you aren’t ALWAYS comparing yourself to the competition — it can be a distraction. I’d say checking in on a monthly basis is healthy. Otherwise, focus on your own strategy and results.”
Step 4. Do a social media audit
If you’re already using social media, take stock of your efforts so far. Ask yourself the following questions:
- What’s working, and what’s not?
- Who is engaging with you?
- What are your most valuable partnerships?
- Which networks does your target audience use?
- How does your social media presence compare to the competition?
Once you collect that information, you’ll be ready to start thinking about ways to improve.
We’ve created an easy-to-follow social media audit guide and template to walk you through each step of this process.
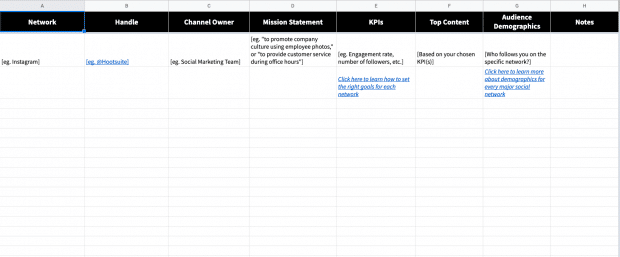
Your audit should give you a clear picture of what purpose each of your social accounts serves. If the purpose of an account isn’t clear, think about whether it’s worth keeping.
To help you decide, ask yourself the following questions:
- Is my audience here?
- If so, how are they using this platform?
- Can I use this account to help achieve my goals?
Asking these tough questions will keep your social media strategy focused.
Look for impostor accounts
During the audit, you may discover fake accounts using your business name or the names of your products.
These imposters can be harmful to your brand—never mind that they’re capturing followers that should be yours.
You may want to get your accounts verified too to ensure your fans know they are dealing with the real you.
Here’s how to get verified on:
- X (Twitter)
Step 5. Set up accounts and improve profiles
Decide which networks to use.
As you decide which social networks to use, you will also need to define your strategy for each.
Benefit Cosmetics’ social media manager, Angela Purcaro, told eMarketer : “For our makeup tutorials … we’re all about Snapchat and Instagram Stories. [X], on the other hand, is designated for customer service.”
Hootsuite’s own social team even designates different purposes for formats within networks. On Instagram, for example, they use the feed to post high-quality educational infographics and product announcements and Stories to cover live events or quick social media updates.
View this post on Instagram A post shared by Hootsuite 🦉 (@hootsuite)
Pro tip : Write out a mission statement for each network. A one-sentence declaration to keep you focused on a specific goal.
Example: “We will use X for customer support to keep email and call volumes down.”
Or: “We will use LinkedIn for promoting and sharing our company culture to help with recruitment and employee advocacy.”
One more: “We will use Instagram to highlight new products and repost quality content from influencers.”
If you can’t create a solid mission statement for a particular social media channel, you may want to ask yourself if it’s worth it.
Note : While larger businesses can and do tackle every platform, small businesses may not be able to — and that’s ok! Prioritize social platforms that will have the most impact on your business and make sure your marketing team has the resources to handle content for those networks. If you need help focusing your efforts, check out our 18-minute social media plan .
Set up your profiles
Once you’ve decided which networks to focus on, it’s time to create your profiles. Or improve existing ones so they align with your strategy.
- Make sure you fill out all profile fields
- Include keywords people would use to search for your business
- Use consistent branding (logos, images, etc.) across networks so your profiles are easily recognizable
Pro tip : Use high-quality images that follow the recommended dimensions for each network. Check out our always-up-to-date social media image size cheat sheet for quick reference.
We’ve also got step-by-step guides for each network to walk you through the process:
- Create a Facebook business page
- Create an Instagram business account
- Create a TikTok account
- Create a X (Twitter) business account
- Create a Snapchat account
- Create a LinkedIn Company Page
- Create a Pinterest business account
- Create a YouTube channel
Don’t let this list overwhelm you. Remember, it’s better to use fewer channels well than to stretch yourself thin trying to maintain a presence on every network.
Optimize your profiles (and content) for search
Never heard of social SEO ? It’s time to learn.
44% of Gen Z consumers use social platforms to research their purchase decisions, which means it’s extra critical that your channels are optimized for social search.
That means making sure your profile names are clear and descriptive, you’re including relevant hashtags and keywords in your bio and on every post, and you’re using features like alt text and captions to include your target keywords as naturally as possible.
Step 6. Find inspiration
While it’s important that your brand be unique, you can still draw inspiration from other businesses that are great on social.
“ I consider it my job to stay active on social: to know what’s trending, which campaigns are winning, what’s new with the platforms, who’s going above and beyond,” says Amanda. “This might be the most fun step for you, or the hardest one, but it’s just as crucial as the rest of them.”
Social media success stories
You can usually find these on the business section of the social network’s website. ( Here’s Facebook’s , for example.)
Case studies can offer valuable insights that you can apply to your own social media plan.
Award-winning accounts and campaigns
You could also check out the winners of The Facebook Awards or The Shorty Awards for examples of brands that are at the top of their social media game.
For learning and a laugh, check out Fridge-Worthy, Hootsuite’s bi-weekly awards show highlighting brands doing smart and clever things on social media.
Your favorite brands on social media
Who do you enjoy following on social media? What do they do that compels people to engage and share their content?
National Geographic, for example, is one of the best on Instagram, combining stunning visuals with compelling captions.
View this post on Instagram A post shared by National Geographic (@natgeo)
Then there’s Shopify. The ecommerce brand uses Facebook to sell themselves by showcasing customer stories and case studies.
And Lush Cosmetics is a great example of superior customer service on X. They use their 280 characters to answer questions and solve problems in an extremely charming and on-brand way.
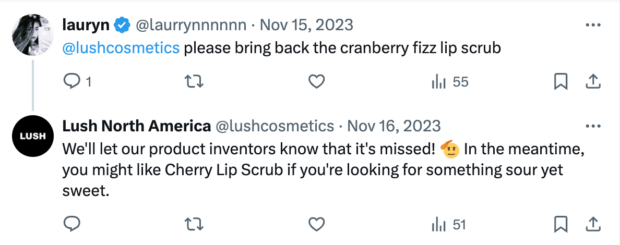
Source: lushcosmetics on X
Notice that each of these accounts has a consistent voice, tone, and style. That’s key to letting people know what to expect from your feed. That is, why should they follow you? What’s in it for them?
Consistency also helps keep your content on-brand even if you have multiple people on your social media team.
For more on this, read our guide on establishing a compelling brand voice on social media .
Ask your followers
Consumers can also offer social media inspiration.
What are your target customers talking about online? What can you learn about their wants and needs?
If you have existing social channels, you could also ask your followers what they want from you. Just make sure that you follow through and deliver what they ask for.
Step 7. Create a social media content calendar
Sharing great content is essential, of course, but it’s equally important to have a plan in place for when you’ll share content to get the maximum impact.
Your social media content calendar also needs to account for the time you spend interacting with the audience (although you need to allow for some spontaneous engagement as well).
Set your posting schedule
Your social media content calendar lists the dates and times at which you will publish types of content on each channel. It’s the perfect place to plan all of your social media activities—from images, link sharing, and re-shares of user-generated content to blog posts and videos. It includes both your day-to-day posting and content for social media campaigns.
Your calendar also ensures your posts are spaced out appropriately and published at the best times to post .
Pro tip: You can plan your whole content calendar and get recommended best times to post on every network based on your past engagement rate, impressions, or link click data in Hootsuite.
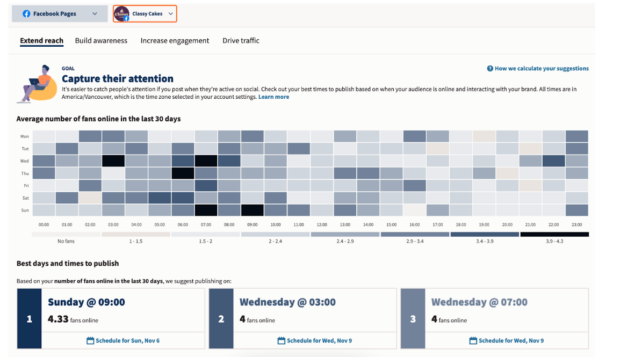
Hootsuite’s Best Time to Publish feature
Determine the right content mix
Make sure your content strategy and calendar reflect the mission statement you’ve assigned to each social profile, so that everything you post is working to support your business goals.
(We know, it’s tempting to jump on every meme, but there should always be a strategy behind your social media marketing efforts!)
You might decide that:
- 50% of content will drive traffic back to your website
- 25% of content will be curated from other sources
- 20% of content will support lead-generation goals (newsletter sign-ups, ebook downloads, etc.)
- 5% of content will be about your company culture
Placing these different post types in your content calendar will ensure you maintain the right mix.
If you’re starting from scratch and you’re not sure what types of content to post, try the 80-20 rule :
- 80% of your posts should inform, educate, or entertain your audience
- 20% can directly promote your brand.

You could also try the social media content marketing rule of thirds :
- One-third of your content promotes your business, converts readers, and generates profit.
- One-third of your content shares ideas and stories from thought leaders in your industry or like-minded businesses.
- One-third of your content is personal interactions with your audience

Whatever you decide on, be sure to document it in your strategy doc.
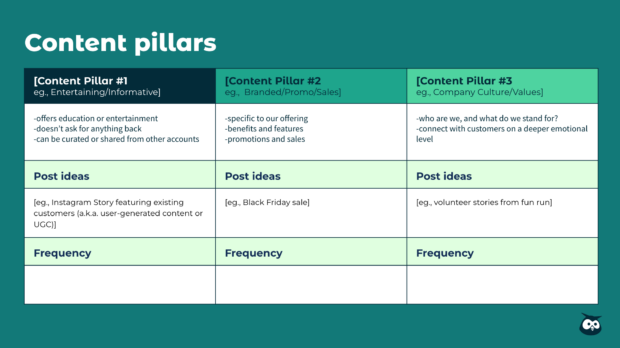
Don’t post too much or too little
If you’re starting a social media marketing strategy from scratch, you may not have figured out how often to post to each network for maximum engagement yet.
Post too frequently and you risk annoying your audience. But, if you post too little, you risk looking like you’re not worth following.
Start with these posting frequency recommendations:
- Instagram (feed): 3-7 times per week
- TikTok: 3-5 times per week
- Facebook: 1-2 times per day
- X (Twitter): 1-5 times per day
- LinkedIn: 1-5 times per day

Pro tip : Once you have your social media content calendar planned out, use a scheduling tool to prepare messages in advance rather than updating constantly throughout the day.
We might be biased, but we think Hootsuite is the best social media management tool. You can schedule social media posts to every network and the intuitive calendar view gives you a full picture of all your social activity each week.
Try It Free
Step 8. Create compelling content
Remember those mission statements you created for each channel in Step 5? Well, it’s time to go a bit deeper, a.k.a. provide some examples of the type of content you’ll post to fulfill your mission on each network.
If you’re not sure what to post, here’s a long list of social media content ideas to get you started. Or (to make it even easier) you can use an AI tool like OwlyWriter to generate on-brand content in a flash.
The idea here is to:
- Keep your content aligned with the purpose of each network;
- Show other stakeholders (if applicable) what kind of content they can expect to see on each network.
This last point especially will help you avoid any tension when your colleagues want to know why you haven’t posted their case study/whitepaper/blog post to TikTok yet. It’s not in the strategy, Linda!
Ideally, you will generate content types that are both suited to the network and the purpose you’ve set out for that network.
For example, you wouldn’t want to waste time posting brand awareness tweets if you’ve designated X/Twitter for primarily customer support. And you wouldn’t want to post super polished corporate video ads to TikTok, as users expect to see short, unpolished videos on that platform.
It might take some testing over time to figure out which type of content works best on which type of network, so prepare to update this section frequently.
We won’t lie: content creation isn’t as easy as everyone not on the social team seems to think. But if you’re struggling, Amanda suggests going back to basics.
The first question to ask is: is there cohesion between your content types? Is your content providing value? Do you have a good mix of entertaining, or educational content? What does it offer that makes a person stop and spend time? Creating a few different content pillars or categories that encompass different aspects of storytelling for your brand, and what you can offer your audience is a good start.
This brings us to Step 9.
Step 9. Track performance and make adjustments
Your social media marketing strategy is a hugely important document for your business, and you can’t assume you’ll get it exactly right on the first try.
As you start to implement your plan and track your results, you may find that some strategies don’t work as well as you’d anticipated, while others are working even better than expected.
That’s why it’s important to document your progress along the way.
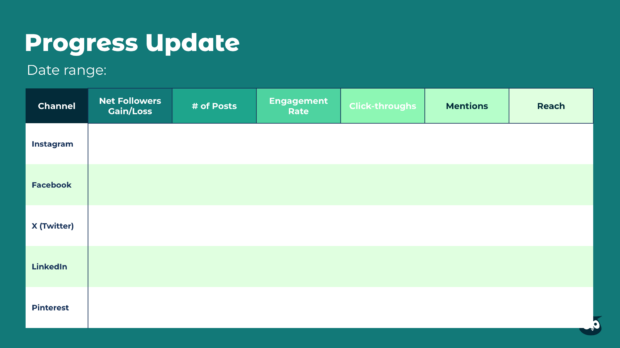
Look at performance metrics
In addition to the analytics within each social network (see Step 2), you can use UTM parameters to track social visitors as they move through your website, so you can see exactly which social posts drive the most traffic to your website.
Benchmark your results
You’ve got your numbers, but how do they stack up to the competition in your industry? Industry benchmarks are a great way to evaluate your performance against other businesses in your category.
If you’ve got Hootsuite Analytics , you can use our built-in social media benchmarking tool to compare the performance of your social accounts against the average of brands in your industry with just a couple of clicks.
You can set up custom timeframes, switch between networks — Instagram, Facebook, X (Twitter), LinkedIn, and TikTok — and look up benchmarks for metrics like followers, audience growth rate, engagement rate, clicks, shares, and much more.
You’ll also find resources to improve your performance right in the summary section:
Re-evaluate, test, and do it all again
Once this data starts coming in, use it to re-evaluate your strategy regularly. You can also use this information to test different posts, social marketing campaigns, and strategies against one another. Constant testing allows you to understand what works and what doesn’t, so you can refine your social media marketing strategy in real time.
You’ll want to check the performance of all your channels at least once a week and get to know the basics of social media reporting so you can track your growth over time.
Pro tip: If you use Hootsuite, you can review the performance of all your posts on every network in one place. Once you get the hang of checking your analytics, you may even want to customize different reports to show specific metrics over a variety of different time periods.
Surveys can also be a great way to find out how well your social media strategy is working. Ask your followers, email list, and website visitors whether you’re meeting their needs and expectations, and what they’d like to see more of. Then make sure to deliver on what they tell you.
Finalizing your social media strategy
Spoiler alert: nothing is final.
Social media moves fast. New networks emerge, others go through demographic shifts.
Your business will go through periods of change as well.
All of this means that your social media marketing strategy should be a living document that you review and adjust as needed. Refer to it often to stay on track, but don’t be afraid to make changes so that it better reflects new goals, tools, or plans.
When you update your social strategy, make sure to watch our 5-step video on how to updating your social media strategy for 2024:
Social media strategy template
Ready to start documenting? Grab your free social media strategy template below!

What’s next? When you’re ready to put your plan into action, we’re here to help…
Save time managing your social media marketing strategy with Hootsuite. From a single dashboard you can easily:
- Plan, create, and schedule posts to every network
- Track relevant keywords, topics, and accounts
- Stay on top of engagement with a universal inbox
- Get easy-to-understand performance reports and improve your strategy as needed
Try Hootsuite for Free
With files from Shannon Tien .
Do it better with Hootsuite , the all-in-one social media tool. Stay on top of things, grow, and beat the competition.
Become a better social marketer.
Get expert social media advice delivered straight to your inbox.
Christina Newberry is an award-winning writer and editor whose greatest passions include food, travel, urban gardening, and the Oxford comma—not necessarily in that order.
Amanda Wood is a senior social marketing professional who combines analytical and creative thinking to build brands.
As head of social at Hootsuite, Amanda oversees the global social strategy encompassing organic and paid social on Instagram, Facebook, Twitter, TikTok, and LinkedIn, a social engagement and listening strategy, and an employee advocacy program.
As the leader of a high-performing social team, she has extensive experience collaborating with creatives to bring campaigns to life on social and drive business results.
Related Articles

How To Set and Exceed Social Media Goals [9 Examples]
Struggling to structure your efforts on social? Set yourself up for success with our guide to setting and exceeding smart social media goals.

How To Run the Easiest Social Media Audit [FREE TEMPLATES]
A social media audit is the best way to review and improve any social marketing strategy. Our free checklist and template make it easy.

How to Create a Social Media Calendar and Stay Organized
Social media content calendars are the best way to plan and organize your content. Build one in 4 easy steps or use our free templates.

Social Media Marketing Tools: The Complete Guide
Automate your work, save time, and build better relationships with your audience by using the right social media marketing tools.
Elaborative Marketing Mix of Apple Inc. – With Deep Dive in 4 Ps
By Aditya Shastri
Apple is a well-known technology brand with a worldwide reputation for its focus on technological innovation, high-quality product lines, and outstanding marketing. The company is involved in developing and designing hardware products such as iPhones, iPods, Mac, as w ell as the development of software and online services. Since 2010, Apple has been rated as the most valuable brand by Forbes every year.
In this blog, we shall discuss the Marketing Mix of Apple inc. in detail, covering all the 4ps strategies. Let us start by getting to know a bit more about Apple.
ABOUT APPLE

Apple is considered to be a multinational technology company, based in California that designs, develops, and sells consumer electronics, computer software, and online services. It is considered as one of the great technology companies on par with Amazon , Google, Microsoft , and Facebook.
Steve Jobs’ vision helped Apple establish itself as the market’s leading technology brand. Now under the leadership of Tim Cook, Apple has grown faster in recent years. Apple is also the first brand with a market value of more than 2 trillion US dollars to have its own operating system intact. Since we have a brief knowledge of the company, let’s dive deep into Apple’s marketing mix.
MARKETING MIX OF APPLE
A company’s marketing mix includes the strategies and tactics involved in implementing a marketing plan. Marketing mix focuses on specific 4Ps variables of product, price, place, and promotion.
In developing its marketing mix, Apple uses a strategy that promotes premium branding. This approach aims to focus on the premium brand and ensure that all 4Ps of Apple support the maintenance of a strong brand image.
Marketing mix thus holistically covers the marketing and business strategies that surround a business. Let us learn more about the marketing mix of Apple.
1. Apple Product Mix

The company is known to have introduced new innovative products over the past few years. Apple products line over time to meet the needs of global customers. The Apple product mix includes both goods and services. The product element of the marketing mix indicates that Apple is in the consumer electronics business.
Here is a list of Apple product mix :
- Apple watch
Services offered by apple
- Apple Music
- Apple news
- Apple books
- Apple arcade
- Apple podcasts
- Apple fitness+
The product mix of Apple focuses on quality rather than quantity. It focuses on the chosen products and continues to enhance them rather than branching bent designs to other products within the same category. Apple’s product strategy shows that it has diversified its business from computer technology business to information technology.
2. Apple Pricing Strategy

Apple has built the image of itself as a premium brand. Its product range includes only higher-end products and they only target people with high affordability. The company follows a premium pricing policy. Apple products are expensive and are considered a status symbol. Apple never prices lower than its competitors to maintain the image of a premium brand. Lowering the sale price will dilute the brand image.
One of the reasons Apple follows a premium pricing strategy is its high-end technology and superior-quality products. Apple does not offer its product on sale and the price of the products is generally standard. Naturally, with such a huge fan following and brand image, the company charging higher prices for its products is justified.
3. Apple Place Strategy

Apple products are available almost everywhere across the globe. The company uses various distribution channels to serve the demands of global customers. They use both online and offline channels for distribution purposes. Apple stores: Apple has set up outlets in different locations where customers can purchase products directly from the company.
E-commerce platforms: Customers can purchase products directly through Apple’s official website and other online portals such as Amazon, Flipkart , etc. These portals are one of the biggest points of sale for Apple products.
Corporate resellers: Apple also has tie-ups with various corporate resellers who are authorized to sell Apple products. Due to the premium image, these stores are handpicked based on the size of the store, monthly sales, etc. The global availability of Apple products allows the company to target a larger customer base and also helps in creating brand awareness on a global scale.
4. Apple Promotion Strategy
The Apple marketing mix focuses on aggressive advertising using various channels like medium, TV, billboards, online ads, etc. It makes use of both conventional and non-conventional techniques to promote its product. The products are also promoted from its website and also from other online channels including social media.
In 1997, Steve Jobs launched the “Think Different” advertising campaign. He wanted to explain the value of apples in the fast-paced world. He said, “Apple’s core values is that [ we believe ] people with passion can change the world for the better.” The campaign inspired people to be confident about themselves and not only “think different” but be different and be proud of themselves.
As we all know that Apple targets a selected segment of society, the most focus of its promotional activities is on its products and therefore the differentiating factors which make it unique and better than its competitors. The promotion & marketing mix of Apple also uses public relations as a means to attract more customers.
The ads are simple and to the point with no irrelevant information. Commercial ads are run when a product is first launched and print ads run throughout the lifetime of the merchandise. The use of ads can help brands get alot of exposure online.
The primary goal of its promotional activities of Apple is to make the customer aware of the superior user experience of Apple products.

One effective way to promote a product is through the use of a short film or ad, as demonstrated by Apple’s recent release, “The Greatest.” This film, created by Apple’s in-house team and directed by Kim Gehrig through production company Somesuch, features disabled individuals using Apple’s accessibility technologies in their daily lives.
By showcasing how these technologies can assist individuals with disabilities in various aspects of their lives, the film effectively promotes the value and benefits of Apple’s products. Additionally, the film’s focus on innovation and transformative solutions aligns with the theme of the International Day of Persons With Disabilities. With its use of a powerful song by the Marliya Choir, “The Greatest” not only promotes Apple’s products but also resonates with viewers on an emotional level.
Watch the film here –
Apple is known for its effective use of billboard advertisements to make a statement. With their recent billboard in Canada, placed strategically outside a company owned by Google’s parent company, Alphabet, they are able to take a direct jab at their competitor and highlight their commitment to privacy.
Apple’s approach to billboard advertisements is to use short and impactful messages that align with its brand values. By placing billboards in highly visible and strategic locations, such as outside a competitor’s office, they are able to generate buzz and attention to their message. This approach has proven to be successful for Apple in the past, and its recent billboard in Canada is yet another example of its efficient use of billboard advertisements. Therefore, Apple’s marketing mix incorporates a blend of online and offline strategies to effectively reach its target audiences.

(Source: GSM Arena)
Conclusion
The marketing mix of Apple focuses on simplicity and innovation and tries to connect to the hearts of its customers thereby making the brand the most valuable in the world.
We hope this case study about the 4Ps of Apple provided you with some useful information on Apple’s marketing mix.
If you find it interesting share it with your friends and relatives along with that check out this institute to learn more about advertising strategy and marketing strategy visit our website for further details and don’t miss out on checking out our knowledge portal to read about such interesting case studies.
If you want to gain a comprehensive understanding of digital marketing, we highly recommend that you take our Online Digital Marketing Courses . This course will provide you with all the essential digital marketing skills and knowledge you need to succeed in the field. In addition, you will learn about various tools and techniques to maximize the potential of digital marketing.
Aditya Shastri
Lead Trainer & Head of Learning & Development at IIDE
Leads the Learning & Development segment at IIDE. He is a Content Marketing Expert and has trained 6000+ students and working professionals on various topics of Digital Marketing. He has been a guest speaker at prominent colleges in India including IIMs...... [Read full bio]
Great content great explanation on apple mix.
It’s always great to learn about Apple & its marketing strategies must say truly an informative case study on the marketing mix of Apple.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Submit Comment
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Related Posts

Marketing Mix Of Uniqlo with Updated Company Overview and Explanations
by Aditya Shastri | May 15, 2024
Uniqlo is a Japanese clothing brand known for its high-quality essential pieces formed from the...

In-depth Marketing Strategy of Bata India – India’s Largest Footwear Company
In this article, we will learn about the marketing strategy of Bata India, the largest footwear...

Airtel: Case Study on its Business Model and Marketing Strategy
Bharti Airtel is one of the three telecom giants of India, known for its distinct and engaging...
" * " indicates required fields
I’m Interested in This Masterclass
By providing your contact details, you agree to our Terms of Use & Privacy Policy
How to Get Food Influencers to Promote Your Restaurant
Learn strategies to collaborate with food influencers and boost your restaurant's visibility, sales, and brand awareness on social media.

Whether you're an experienced marketer or new to digital marketing, this article will help you navigate the complex world of influencer marketing and maximize its benefits for your restaurant.
For further reading, our Food Influencer Marketing Guide for Restaurants outlines detailed strategies on how to work with influencers so you can leverage their reach on platforms like Instagram, TikTok, and YouTube.
What is food influencer marketing?
Food influencer marketing taps into the credibility and influence of social media personalities to enhance your brand's visibility and convert their followers into new customers. Influencer marketing taps into the credibility and influence of social media personalities to enhance your brand's visibility and convert their followers into new customers. Influencers can be powerful allies in increasing brand recognition and driving sales. By partnering with the right influencers, your restaurant can reach a broader audience beyond traditional advertising channels.
Benefits of influencer marketing for restaurants
Influencer marketing offers several benefits for restaurants:
Trust and authenticity : Followers often trust influencers' recommendations as much as advice from friends.
High ROI : Influencer campaigns typically yield a high return on investment , significantly outperforming traditional digital advertising.
Brand awareness : Influencers help spread the word about your restaurant, fostering a virtuous cycle of social media engagement.
Surveys show that social media influencers significantly impact Gen Z and millennial dining choices. For example, 24% of Gen Z and 17% of millennials try new restaurants based on influencer recommendations. Over half of millennial TikTok users have ordered from a restaurant they discovered on the platform.
Overall, the influencer marketing industry as a whole has grown 70% since 2020 , and is expected to be worth some $24 billion by the end of 2024 .
Influencer example: The Keith Lee effect
When influencer Keith Lee awards a restaurant a positive rating on TikTok, it can cause the famous "Keith Lee effect" — a sudden and dramatic spike in business due to the fact that his reviews reach an audience of over 16 million followers. This surge in visibility can lead to increased foot traffic, online orders, and greater brand awareness.
A brief overview of food influencer marketing
Begin by identifying potential influencers who align with your brand's values and goals. Consider their audience, engagement rates, and content style, as well as the potential cost of engaging in a partnership with them. Establish clear communication upfront to ensure a positive and collaborative relationship.
Influencer types
Restaurant influencers don't conform to a single category — they include professional critics, hobbyist foodies, culinary creatives, and lifestyle or travel vloggers. For restaurants, finding and partnering with the right influencer as part of a broader marketing strategy can help boost the business' visibility. There is a wide variety of influencers out there, and our downloadable guide breaks down each tier of influencer, including estimated costs and reach.
Nano-influencers are cost-effective and great for personalized engagement.
Micro-influencers are ideal for growing brand awareness, with authority in specific niches.
Mid-tier influencers are known for professional-quality content across multiple channels.
Macro-influencers can be expensive, but are guaranteed to reach an enormous audience.
Mega-influencers are considered "celebrities" from a social media perspective.
Influencer channels
Just as influencers have distinct content topics, audiences, and follower counts, they're also active across a diverse set of social media platforms. Here's a rundown of the top channels in the influencer marketing space from the State of Influencer Marketing 2024 benchmark report :
TikTok is great for generating engagement and excitement, and is famous for challenges that go viral. It's the channel of choice for 69% of brands that use influencer marketing.
Instagram is a popular platform for not only showcasing menu items, but the entire restaurant experience — 47% of brands that use influencer marketing utilize Instagram.
YouTube is a go-to platform for more substantial content such as behind-the-scenes tours, in-depth reviews, and interviews. This is the influencer marketing platform of choice for 33% of brands.
Facebook attracts a large and diverse audience, especially among demographics who may not be as active on the newer social channels, and 28% of brands use it for influencer marketing.
How to create Instagrammable dishes
Focus on the quality of your ingredients, garnishes, and composition to ensure your dishes translate well on camera. Thoughtful lighting and location can make your food look even more appealing. Familiar, hearty dishes often resonate more with audiences than overly stylized food.
View this post on Instagram
Influencer examples: Hispanic Heritage Month
During Hispanic Heritage Month, DoorDash sponsored campaigns with influencers visiting restaurants such as wezzarepas in Los Angeles, Puerto Viejo in New York City, La Victoria in San Jose, Bogota Bistro in Brooklyn, and Sergio's in Miami. These collaborations highlighted the unique offerings of these establishments, enhancing their visibility and customer engagement.
Popular questions about working with food influencers
What data and analytics should i be aware of.
Understanding customer insights and other analytics is important. This data can help you select influencers whose followers match your target audience, ensuring that your campaign reaches the right people. Analytics like customer location, order history, item preferences, and reviews can help you determine which menu items to promote, and when.
What do I need to know about the influencer and their audience?
Research the influencer’s engagement rates, audience demographics, and content style. Ensure they align with your brand values and that their audience matches your target market.
What are the different types of influencer partnerships?
Influencer partnerships can vary from one-off posts to long-term collaborations. Here are some innovative marketing ideas for working with influencers:
Exclusive events: Host tasting events or menu launches.
Discount codes: Share special codes that influencers can distribute to their followers.
Giveaways and contests: Engage potential customers through exciting social media contests.
Custom collaborations: Co-create menu items or showcase behind-the-scenes activities.
How do I evaluate influencer engagement rates?
Engagement rates indicate how actively an influencer's followers interact with their content. High engagement rates often mean a more loyal and engaged audience, making the influencer a valuable partner.
How do I measure campaign performance?
Track metrics such as likes, comments, shares, and clicks to evaluate the success of your influencer campaign. Sales data and redemption of discount codes can also provide insights into the campaign's effectiveness.
Influencer marketing case study: Coyo Taco
Coyo Taco , a Miami-based taqueria, integrates influencer collaborations into their regular marketing strategy. They host micro and macro-influencers weekly and have larger campaigns involving multiple influencers to promote events and partnerships. For instance, their collaboration with DoorDash involved influencers of varying calibers, resulting in a successful promotion tracked through unique discount codes.
"Each week, we have at least three influencers coming in to dine at one of our five locations across South Florida, whether it's a micro-influencer or a macro-influencer. And then we'll have larger campaigns or events, with 10 to 15 influencers posting throughout the week to promote it."

Download the Food Influencer Marketing Guide for Restaurants
By creating social media conversations around your restaurant, an influencer marketing campaign can be the catalyst for more engagement, where your customers feel inspired to share their experience. This is a powerful strategy for restaurants looking to grow their audience and increase brand visibility.
P artnering with the right influencers and leveraging their reach across various platforms can help restaurants achieve significant business growth. For more insights and detailed strategies, download our complete guide to food influencer marketing.

Subscribe for insights to help you run a great business, delivered weekly to your inbox.
Recent Posts

What are the Most Popular Drinks for College Students?

How to Build an Authentic Restaurant Brand on Social Media

Top 10 Most Popular Holidays for Alcohol Delivery

How Technology Marketers Lead the Way in AI Experimentation [New Research]

- by Robert Rose
- | Published: February 21, 2024
- | Trends and Research
In a 20-minute demo, the sales engineer deftly clicked through the interface, configured a new image set, assigned the metadata, and set the rights-management properties. He logged in as different users to demonstrate a sophisticated workflow. Then, he published an asset and showed how the system presented it in channel-specific formats.
No fewer than five times, he mentioned how “easy” it was for the business user to do what once only experts could do.
I interrupted him. “Here’s the thing,” I said, “That isn’t easy for someone who doesn’t understand what you’re doing.”
As technology marketers, what you offer to the world seems simple from the outside. You provide a new tool to help your customers do something they couldn’t before acquiring it. But the more amazing the thing they can now do, the more skilled they usually need to be at using it.
Said another way, a chainsaw in the hands of a lumberjack is a simple tool. But in my hands? It’s an ER trip waiting to happen.
Today, businesses work with some of the most sophisticated digital technology and interfaces in any industry. But that doesn’t make technology easier to market. It still involves a complex and difficult journey made more challenging by how quickly things change.
We looked at the answers of 272 technology marketers who responded to CMI’s July 2023 survey to find out. (For more information about the full study of 1,084 marketers, see B2B Content Marketing Benchmarks, Budgets, and Trends .)
One not-too-surprising finding: Tech content marketers outpace their marketing peers in AI use. More than two-thirds (79%) of tech marketers say they use AI compared with 72% of B2B marketers as a whole and only 58% of enterprise marketers.
What else to expect this year? Technology marketers say they’ll focus on these things in 2024:
- Increasing traffic, leads, and sales
- Nurturing existing clients
- Leveraging AI for content creation while ensuring authentic, quality content
- Enhancing content creation processes and systems
- Focusing on thought leadership
- Measuring content performance and value.
The most common trends mentioned center around:
- AI proliferation in content creation — with concerns about authenticity and oversaturation.
- Authenticity and uniqueness — valuing human-created content that stands out from AI-generated noise, prioritizing quality over quantity.
- AI’s impact on SEO and content ranking — changes in SEO strategies to accommodate AI algorithms, emphasizing FAQ-oriented and thought leadership content.
- Increased personalization — hyper-personalized content delivery using AI-driven tools to cater to individual personas or niche segments.
Let’s look deeper into the research sponsored by Foundry , an IDG, Inc. company .
Table of contents
Team structure
Content marketing challenges
Use of content types, distribution channels, and paid channels
Social media use
Content management and operations
Measurement and goals
Success factors
Budgets and spending
Action steps
Methodology
Ai use: 79% of technology marketers use generative tools.
Many respondents predicted a rise in the use of AI to generate content . In fact, 79% say they already use AI for content-related tasks. How?
More than half (53%) use generative AI to brainstorm new topics. Around half use the tools to write drafts (48%) and research headlines and keywords (43%). Fewer said they use AI to outline assignments (29%), proofread (19%), generate graphics/images (10%), and create videos (7%) and audio (7%).

Most don’t pay for generative AI tools (yet)
Of those using generative AI tools, 88% use free tools (e.g., ChatGPT ). Thirty-seven percent use tools embedded in their content creation/management systems, and 30% pay for tools like Writer and Jasper .
AI in content remains mostly ungoverned
When asked if their organizations have guidelines for using generative AI tools, 26% said yes, 63% said no, and 11% were unsure.

“Change, especially rapid change, is not something most organizations adapt to quickly,” says Yadin Porter de León , global content marketing executive. “The capabilities of generative AI tools currently represent a form of rapid change that very few people can even grasp. So, it’s no surprise that very few companies have created or communicated guidelines for its use … because they don’t know how.”
Yadin says marketers should:
- Educate your team members so that they can be, at the very least, AI-literate.
- Establish an AI council to organize activities across the organization.
- Establish clear policies and guidelines for using AI.
- Identify use cases for the business and run pilot projects guided by those principles.
How AI is changing SEO
In the open-ended responses, several respondents predicted AI’s significant impact on SEO. How will AI’s integration in search engines shift technology marketers’ SEO strategy? Here’s what we found:
Twenty-seven percent say they’re not doing any of those things, while 29% say they’re unsure, suggesting that many may be doing little to nothing.
Now is the time to act.
Ryan Brock , chief solution officer at DemandJump, says, “The days of building a keyword list based on metrics like search volume are over … at least for now. Until the dust settles and we collectively figure out what kinds of answers we trust Bard (now known as Gemini) with and which ones will always require a more thoughtful comparison of sources to find, we’ve got to use topical authority as the North Star for our tactical content decisions.”
Ryan thinks of it this way: “I’m still going to be working to answer basic questions as part of my pillar content strategy, but I also acknowledge that answering them works more to build a foundation of topical authority than to drive immediate, convertible traffic.
“Those traffic and conversion-driving queries will become harder to come by than they’ve ever been, so when I find one I need to rank well for, I should be able to do so quickly and efficiently. Competing on a query-by-query level just doesn’t work when every business in a sector sees the same dwindling number of targets.
“Building interconnected, ‘choose-your-own-adventure’ style networks of pillar content is the best way to lay the proper topical authority foundation so you can rank fast when you find a term that’s ripe for true thought leadership.”
Team structure: How does the work get done?
Generative AI isn’t the only issue affecting content marketing these days. We also asked marketers about how they organize their teams .
Among larger technology companies (100-plus employees), more than half (54%) say content requests go through a centralized content team. Others say each department/brand produces its own content (22%), and the departments/brand/products share responsibility (20%). Three percent indicate other, while 1% say they outsource it.

Content strategies integrate with marketing, comms, and sales
Seventy percent say their organizations integrate content strategy into the overall marketing sales/communication/strategy, and 2% say it’s integrated into another strategy. Fourteen percent say content in marketing is a stand-alone strategy, and 4% say it’s a stand-alone strategy for all content produced by the company. Eight percent say they don’t have a content strategy. The remaining 2% say other or are unsure.
Employee churn means new teammates; content teams experience enlightened leadership
Thirty-three percent of technology marketers say team members resigned in the last year, 28% say team members were laid off, and about half (51%) say they had new team members acclimating to their ways of working.
While team members come and go, the understanding of content doesn’t. Fifty percent strongly agree, and 30% somewhat agree that the leader to whom their content team reports understands the work they do. Only 14% disagree. The remaining 6% neither agree nor disagree.
And remote work seems well-tolerated: Only 21% say collaboration is challenging due to remote or hybrid work.
Content marketing challenges: The right content, lack of resources
Most technology marketers (61%) cite creating the right content for their audience as a challenge.
Other content creation challenges include differentiating content (58%), creating content consistently (49%), creating quality content (43%), optimizing for SEO (43%), creating enough content to keep up with internal demand (40%), and creating content that requires technical skills (36%). One in four (25%) say they are challenged to create enough content to keep up with external demand.

Other hurdles
The most frequently cited non-creation challenge, by far, is a lack of resources (66%), followed by aligning content efforts across sales and marketing (52%) and aligning content with the buyer’s journey (52%). Forty-five percent say they have difficulty accessing subject matter experts, and 44% say they are challenged with workflow issues/content approval processes. Only 28% cite keeping up with new technologies as a challenge, 27% pick a lack of strategy, 12% say keeping up with privacy rules, and 13% point to tech integration issues.

Use of content types, distribution channels, and paid channels: Staying at the top
We asked technology marketers about the types of content they produce, their distribution channels , and paid content promotion. We also asked which formats and channels produce the best results.
Popular content types and formats
As in the previous year, the three most popular content types are short articles/posts (96%), case studies/customer stories (93%), and videos (90%). Eighty-two percent use thought leadership e-books/white papers, 81% use long articles/posts, 63% use data visualizations/visual content, 62% use product/technical data sheets, and 56% use research reports. Less than half of technology marketers use brochures (45%), interactive content (35%), livestreaming content (34%), and audio content (31%).

Effective content types and formats
Which formats are most effective?
Fifty-nine percent say case studies/customer stories deliver some of the best results. Almost as many (57%) name thought leadership e-books/white papers. Slightly more than half say research reports (53%) and videos (51%).

Popular content distribution channels
Regarding the channels used to distribute content, 90% use blogs and social media platforms (organic), followed by webinars (79%), email newsletters (78%), and email (74%). Sixty-four percent use in-person events, and 58% use digital events.
Less frequently used channels include:
- Microsites (40%)
- Podcasts (30%)
- Hybrid events (24%)
- Branded online communities (23%)
- Digital magazines (21%)
- Direct mail (19%)
- Online learning platform (18%)
- Print magazines (12%)
- Mobile apps (7%)
- Separate content brands (3%).

Effective content distribution channels
Which channels perform the best? Most surveyed tech marketers point to webinars (56%) and in-person events (53%). Forty-four percent say blogs, 43% pick email, and 37% say social media platforms (organic).

Popular paid content channels
When technology marketers pay to promote content , which channels do they invest in? Ninety-three percent use paid content distribution channels.
Of those, 77% use social media advertising/promoted posts, 71% use sponsorships, 70% use search engine marketing/pay-per-click, and 66% use digital display advertising. Around one in three use native advertising (38%) and partner emails (33%). Far fewer invest in print display advertising (11%).

Effective paid content channels
Search engine marketing and pay-per-click produce good results, according to 61% of tech marketers. Fifty-three percent say sponsorships deliver good results, followed by social media advertising/promoted posts (43%) and partner emails (34%).

Social media use: One platform rises way above
When asked which organic social media platforms deliver the best value for their organization, technology marketers (92%) pick LinkedIn. Twenty-seven percent cite YouTube as a top performer, 18% say Facebook, and 10% pick Instagram and Twitter. Only 1% cite TikTok.

It makes sense that 73% say they increased their use of LinkedIn over the last 12 months, while only 36% boosted their YouTube presence, 19% increased Instagram use, 15% grew their Facebook presence, 12% increased X use, and 9% increased TikTok use.
Which platforms are marketers giving up? Did you guess X? You’re right — 34% of marketers say they decreased their X use. Twenty-four percent reduced their use of Facebook, with 14% decreasing on Instagram and YouTube, 3% pulling back on TikTok, and only 2% decreasing their use of LinkedIn.
Interestingly, we saw a significant rise in technology marketers who use TikTok: 17% say they use the platform, which is triple from last year (5%).

Content management and operations: The right tech isn’t a guarantee
To explore how teams manage content, we asked tech marketers about their technology use and investments and the challenges they face scaling their content .
Content management technology
Among the technologies used to manage content, technology marketers point to:
- Analytics tools (82%)
- Social media publishing/analytics (73%)
- Email marketing software (71%)
- Content creation/calendaring/collaboration/workflow (66%)
- Content management system (58%)
- Customer relationship management system (57%)
- Marketing automation system (38%)
- Sales enablement platform (30%)
- Digital asset management (DAM) system (24%)
But having technology doesn’t mean it’s the right technology (or its capabilities are used). Only 29% say they have the right tech to manage content across the organization. Thirty-two percent say they have the technology but aren’t using its potential, and 28% say they haven’t acquired the right technology. Eleven percent are unsure.

Even so, 40% of technology marketers say their organization is likely to invest in new technology in 2024; however, another 39% say it’s unlikely. Twenty-one percent say their organization is neither likely nor unlikely to invest.

Scaling content production
This year, we introduced a new question to understand what challenges technology marketers face while scaling content production .
Almost half (49%) say it’s a lack of communication across silos, and the same number say it’s not enough content repurposing. Thirty-one percent say they have no structured content production process, and 29% say they lack an editorial calendar with clear deadlines. Six percent say scaling is not a current focus.
Among the other hurdles are difficulty locating digital content assets (19%), translation/localization issues (17%), technology issues (15%), and no style guide (13%).

Measurement and goals: Generating sales and revenue rises
Almost half (43%) of technology marketers agree their organization measures content performance effectively — but the same amount (43%) disagree. Thirteen percent neither agree nor disagree. Only 1% say they don’t measure content performance.
The four most frequently used metrics to assess content performance are conversions (77%), website traffic (73%), email engagement (72%), and website engagement (70%). Sixty percent say they rely on quality of leads, 58% use social media analytics, 55% rely on search ratings, and 52% say quantity of leads. Less than half use tracking the cost to acquire a lead, subscriber, and/or customer (32%) and email subscribers (31%).

The most common challenge measuring content performance experienced by technology marketers is integrating/correlating data across multiple platforms (88%), followed by extracting insights from data (82%), tying performance data to goals (81%), organizational goal setting (73%), and lack of training (71%).

Among the goals assisted by content marketing, 82% of technology marketers say it created brand awareness in the last 12 months. Eighty percent say it helped generate demands/leads, 71% say it helped nurture subscribers/audiences/leads, and 61% say it helped generate sales revenue (up from 48% the previous year).
Less than half say it helped grow loyalty with existing clients/customers (46%), grow a subscribed audience (42%), and reduce customer support costs (14%).

Success factors: Know your audience
To separate top performers from the pack, we asked technology marketers to assess the success of their content marketing.
Twenty-seven percent rate the organization’s success as extremely or very successful. Another 58% report moderate success, and 15% feel minimally or not at all successful.
The most common factor for successful technology marketers is knowing their audience (81%).
That success factor makes sense because “creating the right content for our audience” is the top challenge. Top-performing content marketers prioritize knowing their audiences to create the right content for those audiences.
Top performers also set goals that align with their organization’s objectives (74%), have a documented strategy (67%), and collaborate with other teams (64%). Thought leadership (62%) and effectively measuring and demonstrating content performance (59%) also help top technology performers reach content marketing success.

Several other dimensions identify the differentiators of top technology performers:
- 75% of the most successful say they’re backed by leaders who understand their work. In contrast, just 50% of all tech respondents feel their leaders understand.
- They’re less likely to report a lack of resources (57% of top performers say they lack resources vs. 66% of all tech content marketers).
- They’re more likely to have the right content management technologies. About half (49%) of the top performers say they have the technology they need, compared with 29% of all tech marketers.
- Nearly three-fourths (74%) of top performers say they measure content performance effectively, compared with 43% of the whole set of tech marketers.
- They are more likely to use content marketing successfully to create brand awareness (96% vs. 82%), nurture subscribers/audiences/leads (82% vs. 71%), generate sales/revenue (81% vs. 61%), grow loyalty with existing customers/clients (64% vs. 46%), and grow a subscribed audience (57% vs. 42%).
Little difference exists between top performers and all respondents when it comes to the adoption of generative AI tools and related guidelines.

Budgets and spending: Holding steady
To explore budget plans for 2024, we asked technology marketers about their knowledge of their organization’s budget/budgeting process for content marketing. Of the 53% who have knowledge of their budgets, we followed up to assess the specifics.
Content marketing as a percentage of total marketing spend
Here’s what they say about the total marketing budget (excluding salaries):
- 18% say content marketing consumes at least one-fourth of the total marketing budget.
- More than one in three (37%) indicate that 10% to 24% of the marketing budget goes to content marketing.
- Just under half (45%) say less than 10% of the marketing budget goes to content marketing.
Content marketing budget outlook for 2024
Forty-eight percent think their content marketing budget will increase this year compared with 2023, whereas 39% think it will stay the same. Only 7% think it will decrease, and 6% are unsure.

Where will the budget go?
Next, we asked where respondents plan to increase their spending.
Sixty-nine percent of technology marketers say they would increase their investment in video, followed by in-person events (60%), thought leadership content (54%), webinars (41%), paid advertising (40%), online community building (27%), audio content (22%), digital events (21%), and hybrid events (11%).

Of course, content doesn’t exist in a vacuum.
Kami Buckner , HPC solutions marketing manager at Dell Technologies, notes that content must be integrated into a larger plan and support the customer journey by driving them to other content.
“Videos, in-person events, and thought leadership content may rank similarly in this survey because they are often developed to complement each other,” she says. “Thought leadership content is an important component of any event plan, and videos are an effective peripheral asset that can engage an audience to generate interest in downloading long-form thought leadership pieces, generate excitement before and after events, and be displayed at the event.”
For example, Dell developed a 15-second video to use on social media to drive viewers to a landing page, which hosted the 60-second sizzle reel to promote an upcoming event. We also:
- Launched thought leadership content around the video and event.
- Created and displayed another video at the event highlighting key points in the new thought leadership content that could be shared post-event.
- Developed a virtual reality experience for the event that built credibility for Dell Technologies, both hosting and serving thought leadership content.
Action steps: What tech marketers should do
These results from tech marketers reflect what we find across other B2B organizations. You should know your audience, lean into brand awareness, integrate data across the buyer’s journey, and invest more in thought leadership, events, and video.
But what should you prioritize as a technology marketer? Given where you are in 2024 and your relationship with modern technology, put these three things at the top of your list:
- Lean into the brand and develop relationships early and often . Marketing pundits laugh at the idea of technology companies developing “relationships” with audiences and buyers. They cynically surmise, “Nobody wants a relationship with their hydraulic actuator provider.” That may be true, but it doesn’t relieve you from trying. Today’s world makes it more imperative that technology companies differentiate, not just by providing the fastest, cheapest, easiest, or most scalable product on the market. You must also differentiate by helping customers be the best versions of themselves. As I used to say to my marketing team, “Our competitive advantage isn’t that we help people become better digital asset managers; it’s that we help digital asset managers become better people.” That leads to the second action.
- Grow owned media’s importance in your products and services. A differentiating strategy provides a reason for people to engage with you outside the small portion of their lives that goes into their buying journey. Owned media experiences create an ecosystem of value for your customers in the pre- and post-buying journey, foster a competitive advantage, and celebrate the complexity your products inherently induce. Yes, your tools are complex and sophisticated and do amazing things. Let you be the source of how to do those things better than anyone else.
- Connect first-party data. How you connect your buyers’ digital interactions will be the fabric that develops better relationships with your customers. If you understand their true intentions, needs, and wants, and more importantly, how they evolve, you can optimize every experience that leads and follows a sale. Of course, you likely must make big changes to implement any one or all three of these action steps. An audit, where you examine all your customers’ content-driven experiences along their journey, can help you develop a plan for which ones to keep, which should change, and which should be sunset for good. Creating this ecosystem gives you the power to transform what is seen as overly complex and hard into a worthwhile evolution and innovation. Your technology is not there to make the customer’s journey “easy” — it’s there to make it “worth it!”
For the 14 th annual content marketing survey, CMI and MarketingProfs surveyed 1,080 recipients around the globe in July 2023, representing a range of industries, functional areas, and company sizes. The survey was emailed to a sample of marketers using lists from CMI and MarketingProfs.
This article presents the findings from the 272 respondents, mostly from North America, who indicated their organization is a technology company and that they are either content marketers or work in marketing, communications, or other roles involving content.
Of this group, 84% represent B2B companies, while 13% work for B2B+B2C brands, and 3% say they work for a tech company of a different nature. Thirty-six percent work at businesses with more than 1,000 employees, 36% work at places with between 100 and 999 employees, 23% work for brands with 10 to 99 employees, and 5% work at tech companies with between one and nine employees.
Thanks to the survey participants who made this research possible and everyone who helped disseminate these findings throughout the content marketing industry.

Interested in sharing the key takeaways from this report with your team or associates? You can download a summary here (registration required).
Get the latest Content Marketing Institute research reports while they're hot – subscribe to the daily or weekly newsletter.
Cover image by Joseph Kalinowski/Content Marketing Institute
About Content Marketing Institute

Content Marketing Institute (CMI) exists to do one thing: advance the practice of content marketing through online education and in-person and digital events. We create and curate content experiences that teach marketers and creators from enterprise brands, small businesses, and agencies how to attract and retain customers through compelling, multichannel storytelling. Global brands turn to CMI for strategic consultation, training, and research. Organizations from around the world send teams to Content Marketing World, the largest content marketing-focused event, the Marketing Analytics & Data Science (MADS) conference, and CMI virtual events, including ContentTECH Summit. Our community of 215,000+ content marketers shares camaraderie and conversation. CMI is organized by Informa Connect. To learn more, visit www.contentmarketinginstitute.com .
About Foundry, an IDG Inc. company

Foundry helps companies bring their visions to reality through a combination of media, marketing technologies and proprietary data on a global scale. Our intent data and martech platforms are powered by data from an owned and operated ecosystem of global editorial brands, awards, and events, all engineered and integrated to drive marketing campaigns for technology companies. Foundry is dedicated to generating and innovating with data, driving demand for technology marketers with 38 offices in markets around the globe. Foundry is a wholly owned subsidiary of International Data Group, Inc. ( IDG ), the world’s leading tech media, data, research and marketing services company. To learn more about Foundry, visit www.foundryco.com .
Robert Rose
You are here: Influencer Marketing Hub » Influencer Marketing » TikTok Creator Marketplace: The Ultimate Guide for 2024
TikTok Creator Marketplace: The Ultimate Guide for 2024
If you want to break through the noise in today’s competitive market, one way is by being fresh and creative. You need to think outside the box and use new platforms to build your business brand. The TikTok Creator Marketplace, a global community of creators, artists, and influencers who create videos on TikTok, is one example.
In this guide, we’ll show you how to join the TikTok Creator Marketplace and what benefits it can offer your business in 2024.
TikTok Creator Marketplace: The Ultimate Guide for 2024:
What is tiktok, what is tiktok creator marketplace, how does tiktok creator marketplace work, how can brands join tiktok creator marketplace, what are the benefits of tiktok creator marketplace, how to work with tiktok creators, what to keep in mind when using tiktok creator marketplace.
TikTok is a social media platform released by the Chinese company ByteDance. It is known for its short videos, typically around 15 seconds long, and its users are primarily Gen Z and young millennials. In contrast to other social media platforms like Facebook and Instagram, TikTok is more focused on entertainment and creativity, which has made it extremely popular with its target demographic.
Launched in 2019, the TikTok Creator Marketplace is a place for creators to sell their content and collaborate with brands. It’s also a great opportunity for businesses to connect with talented creators and get their videos seen by millions of people.
With social media platforms such as TikTok that have extreme popularity with Gen-Z users, brands are shifting away from traditional methods like TV commercials and investing in digital marketing strategies. Flocking to the TikTok Creator Marketplace to create videos that will resonate with this audience is a great way to do this.
By joining the TikTok Creator Marketplace platform, brands access a wide range of TikTok creators who can produce videos for their products or services.
Once your account is all set up, you can take a look at the TikTok Creator Marketplace homepage and can browse through creators by location and category, and even the number of views, followers or reach.
- How to Do Text-to-Speech on TikTok (+ 10 World-Class Examples)
- What Are TikTok Stories? (+Why Should You Care)
- Why Your Brands Needs User-Generated Content on TikTok
If you already have a TikTok Ads Manager account, you can use that to log in to the Creator Marketplace platform. If you don't, signing up to the TikTok Creator Marketplace is easy and only takes a few minutes.
You will need to create an account and complete all the required information such as your name, business email address, and phone number. Afterward, you will need to verify your account by clicking on the link in the verification email TikTok sends you.
When you're done creating your account, you can now customize your profile. You can add your company logo as your profile picture, link it to your brands' social media accounts, and even add a description of your company.
Once your profile is complete, you can start browsing through the TikTok Creator Marketplace, find creators that fit your target audience and contact them about working together.
When you find a TikTok creator you would like to work with, send them a message through the TikTok Creator Marketplace platform. You can also follow them on TikTok and leave comments on their videos.
As TikTok grows in popularity, the TikTok Creator Marketplace is becoming an increasingly attractive option for businesses looking to reach a new audience. If you’re thinking about joining the TikTok Creator Marketplace in 2024, be sure to keep these benefits in mind.

1) TikTok is a global influencer platform next to Facebook and Instagram.
TikTok has grown to be an international phenomenon as a social media platform. With over one billion active users , it’s second only to Facebook in terms of social media platforms. This means that if you want to reach a large audience with your videos through influencer marketing, joining the TikTok Creator Marketplace is a great place to do it.
2) You have access to a global community of creators to engage your target audience.
Signing up to the Creator Marketplace can give you access to a global community of TikTok creators. With over 8 million active creators, there is a perfect creator for your brand, regardless of your target audience.
Creators on TikTok are creative and passionate about their work, so working with them can help create high-quality, engaging, and entertaining videos that will resonate with viewers. You can reach out to creators directly through the platform with their ready-made template messages and initiate conversations about collaboration.
3) It's a great way to build brand awareness across the globe.
TikTok Creator Marketplace is a great way to build brand awareness. By working with creators who have large followings on TikTok, you can reach a new audience that might not be aware of your brand.
Moreover, if you have plans of widening your brand exposure to other parts of the world, TikTok is the perfect platform for that. TikTok is popular in countries like Japan, South Korea, and India, so collaborating with creators from these regions can help you tap into new markets.
4) TikTok Creator Marketplace is easy to use as 1-2-3.
Using the TikTok Creator Marketplace platform for creating brand campaigns is a straightforward process. Once you have decided on the intent of your campaign , you can then filter through the creator list based on their location, audience reach, and average content views, to name a few.
5) Data is king in the TikTok Creator Marketplace.
Collaborating with creators on TikTok to build your brand takes a lot of preparation and consideration. With the TikTok Creator Marketplace, you can get a detailed overview of each creator’s statistics, from the core metrics page to audience demographics and video performance trends.
In addition, you can also get details on the past performance of creators and see how they have performed with similar brands. This information is extremely valuable for making data-driven decisions about your collaborations. With these, you can make an educated decision on who you want to work with and what kind of content would be the most effective for your campaign.
6) You get access to first-party data through the TikTok Creator Marketplace API.
In September 2021, TikTok launched an API for its Creator Marketplace , which provides brands with access to TikTok’s first-party data. This data includes information on creator stats, video performance, and audience insights.
The TikTok Creator Marketplace API gives you the ability to track your campaign’s performance in real-time and make changes accordingly. You can also use it to create custom reports and dashboards for your team. With that said, you get the most out of your campaigns and maximize your ROI by using this data to make informed decisions about your collaborations.
7) Getting on TikTok is a fun way to build your brand.
The brand of TikTok is about fun and creativity, so it makes sense that using the TikTok Creator Marketplace is a fun way to build your brand. By working with creators who have creative and engaging content, you can create videos that are both entertaining and informative for viewers.
Moreover, TikTok is a great platform to experiment with new ideas and trends in video marketing. If you find creators who are doing something new and interesting, you can collaborate with them and explore the trend further. Who knows, you might just come up with the next big thing in TikTok influencer marketing.
Creators Tool Tip
There are several tools like Beacons that creators can use to monetize content and start selling virtually anything. With the help of tools like these, creators get access to valuable insights into target audiences helping them to make data-driven decisions.
TikTok creators can be a great asset for your brand, but it’s important to understand how to work with them effectively. Here are some tips on how to get the most out of collaborations with TikTok creators.

- Have a clear goal in mind : Always have a clear goal in mind when collaborating with TikTok creators. Whether you want to increase brand awareness, drive traffic to your website, or increase sales, make sure that the goals of the collaboration are clear from the beginning.
- Give clear instructions and guidelines : When working with TikTok creators, it’s important to give them clear instructions and guidelines about what you want them to create. This will help ensure that the final product is aligned with your brand’s goals and vision.
- Don’t be afraid to give feedback : As the client, it’s important to provide constructive feedback throughout the collaboration process. This will help creators improve their content and achieve the results you desire for the campaign.
- Be prepared to invest : Even if you can propose the talent fees based on your own budget, TikTok creators may not come cheap, especially if you want to tap into larger audiences. However, the payoff can be worth it if you achieve your desired results.
- Keep track of your goals : It’s important to keep track of your goals for each collaboration and measure how successful they are in achieving them. This will help you better understand what works well with TikTok creators and what doesn’t, so you can adjust your strategy accordingly.
- Build your relationship with your influencer : TikTok creators aren't just after the one-time payment, they want to build a relationship with your brand. By maintaining open communication and being responsive to their needs, you can create a long-term partnership that will be beneficial for both parties.
When it comes to TikTok, the sky's the limit. As a platform that continues to grow in popularity, more and more users are looking for ways to create content and share it with the world.
TikTok Creator Marketplace offers an easy way for creators of all levels of experience to sell their videos and gain exposure. However, there are a few things to keep in mind before using TikTok Creator Marketplace. Here are some tips:

- Be sure to read the Terms and Conditions : Before you start using TikTok Creator Marketplace, be sure to read the Terms and Conditions. This will ensure that you are aware of the rules and regulations of the marketplace.
- Make your own internal vetting process for your Creators : Partnering with TikTok creators is crucial to the success of your campaign, but you don’t have to partner with just anyone. Make sure to have an internal vetting process to ensure that you are working with creators who align with your brand and goals.
- Ensure the videos follow the content guidelines : TikTok has a set of content guidelines and policies. If you just started a collaboration with a TikTok Creator, it may be prudent for you to have a preview of the videos to make sure they follow TikTok’s guidelines.
- Keep an eye on the metrics : As with any marketing campaign, it’s important to keep track of the metrics and measure how successful the collaboration is in achieving your desired results. This will help you understand what works well on TikTok and what doesn’t, and help you decide on future content.
- Be prepared for the unexpected : As with any marketing campaign, there is always a chance for something unplanned to happen. It could be a sudden change in the content guidelines or the possibility of your video being posted beyond your target date. Whatever it is, be prepared to have a backup plan in place.
By following these tips, you can maximize your chances of success when using TikTok Creator Marketplace. TikTok offers a great opportunity for brands to reach new audiences and achieve their marketing goals. With the right approach, you can find the TikTok creators that are a perfect fit for your brand and launch a successful campaign.
Final Thoughts
2022 had TikTok written all over it. The app will continue to be a powerful marketing tool for anyone looking to reach new audiences and achieve their desired results. As TikTok grows in popularity, more and more businesses are starting to see the value in working with creators on the platform.
Joining the TikTok Creator Marketplace is a great way to connect and work with some of the best creators to get your brand in front of TikTok's massive audience. The platform is easy to use and provides access to valuable data that can help you make informed decisions about your collaborations.
If you’re looking for a fun and creative way to build your brand, TikTok Creator Marketplace is the way to go. If you’re not already on TikTok, now is the time to join the fun.

13 Best Marketing Campaigns on Facebook
When you’re marketing on a platform like Facebook, where there’s an abundance of...

6 Examples of Viral Social Media Campaigns and What Makes Them...
Here’s an open secret: virality isn’t guaranteed. It may not happen, even if you’ve...

Valuable Insights from Social Media Platform Case Studies Based...
For brands, it can be a struggle to understand how each social media platform works and...

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Brand Marketing Case Studies. This collection features brands and content creators that used video and other digital tactics to drive innovation, connect with their consumers, and drive brand and business metrics. Learn about best practices, creative executions, and how brands achieved success through digital. Case Study.
1. "Share a Coke" Campaign. Launched initially in Australia in 2011, the "Share a Coke" campaign is one of the most celebrated and successful marketing strategies in Coca-Cola's history. The campaign was groundbreaking in its approach—replacing the iconic Coca-Cola logo on bottles with common first names.
Diet Coke- In several markets, Diet Coke is referred to as Coca-Cola Light. A calorie and sugar-free soft drink. It was first introduced in 1982. Coca-Cola Zero: Introduced in 2005, this sugar-free beverage became a million-dollar brand in 2007. The product mix of Coca Cola includes: Carbonated Soft Drinks.
This has helped the company to be one of the leading sportswear brands in the world in order to generate higher sales. 4. Marketing Mix of Adidas: Promotion Strategy. This one is the most important part of the Adidas marketing mix strategy. It is a well-known fact that the TV ads of Adidas are Adrenaline pumping.
McDonald's marketing mix (4Ps) involves approaches that meet business objectives in different markets around the world. The marketing mix defines the strategies and tactics that the fast-food restaurant company uses to reach target customers, in terms of products, place, promotion, and price (the 4P). In this business analysis case, McDonald ...
Open up with a summary that communicates who your client is and why they reached out to you. Like in the other case study examples, you'll want to close out with a quantitative list of your achievements. 16. " NetApp ," by Evisort. Evisort opens up its NetApp case study with an at-a-glance overview of the client.
That's why in this case study, we'll dig deeper into McDonald's Marketing Strategy in India and globally from a marketing perspective by going through its marketing strategies, marketing mix, marketing campaigns, and SWOT analysis. So let us start by first learning more about the business model and brand history of McDonald's.
BMW's marketing mix involves the variables of product, price, place, and promotion (4Ps) used for the automotive and motorcycle business. The company's marketing strategy sets the premium branding used in this marketing mix for the automotive and motorcycle markets. BMW's 4P tactics ensure the premium status of the company's brands ...
40.2 Nike: Building a Global Brand Through Storytelling and Innovation. Introduction: Nike, Inc. is a household name synonymous with athleticism, performance, and innovation. Through its creative marketing strategies and commitment to design, Nike has become a leader in the sports apparel industry. This case study will explore Nike's rise to ...
Without going into details about the methods, it's another typical third-person case study designed to build trust. 6. Video marketing case study: L'Oréal and YouTube. In this case study, various members of L'Oréal's global marketing team break down exactly how they used YouTube ads to launch a new product.
From one juggernaut to another, now we will describe Apple's marketing mix according to product, price, promotion, and place. Product Apple's product mix is mostly confined to consumer electronics and online services. As is the case with Amazon, however, Apple is expanding into other industries. The current product mix consists of: Most of these products […]
Received: 15/12/2020 Online Published: 22/04/2021. Accepted: 21/ 03/2021. Abstract. This investigation explores the role of Price, place, promotion, and product (4Ps) in creation of br and equity ...
Aldi's marketing mix (4Ps) focuses on low prices and a mixture of promotional tactics for competitive products that draw buyers into the company's retail locations. The decisions, strategies, and tactics in this 4P (Product, Price, Place, and Promotion) aim for optimizing the company's effectiveness in reaching its target market and ...
We're routinely seeing CEOs of Australian hi techs with turnover of $5 million to $50 million (our target audience) opting in and proceeding to self-qualify before they contact us for a meeting. This is what digital marketing is supposed to do. Read the full case study here. Tracey James, Director. Technoledge. 22.
1. Tiny cog, big machine. The whole engagement is vast, and the ultimate output is a tool that the client uses to make a first pass at global marketing spend allocation by country, brand, and channel. The aim of these marketing mix models is to produce the response curves that fuel the allocation tool's engine.
Power of Versace's Marketing Mix - A Case Study. Nachiket Shelke. May 29, 2023. Marketing Mix. The Marketing Mix of Versace tells the 4ps (Product, Price, Place, and Promotion) of the best Italian luxury fashion company - Versace! Versace is founded by Gianni Versace in 1978. The brand is known for its bold and flashy designs, often ...
McDonald's employs the four pillars of marketing mix, which are as follows: Product: A product is a tangible item or service that a firm provides to its customers. Packaging, guarantee, and appearance are all characteristics of a product. It is also the physical and non-physical part of the product, consumers have the right to spend their ...
Let us view each of the 7Ps of IKEA's Marketing Mix: 1. Product Strategy of IKEA. IKEA has always come up with unique ways to cope up with the dynamic business environment. The product line of IKEA includes the following items in its product portfolio: Furniture (outdoor, indoor, storage) Baby & children's products.
the most important elements to increase the customer satisfaction (95.4%) and (93%) respectively. The promotion of product has a very good level to increase sells in the company (80.6% - 85%). The ...
Abstract. The case discusses home grown dairy brand Amul's foray into the carbonated drinks space in India with the launch of a fizzy fruit based dairy drink 'Tru Seltzer' in October 2020. Said to be India's first seltzer, Amul Tru Seltzer was available in two flavors — lemon and orange - and was affordably priced at just Rs 15 for ...
In consumable markets, brands are the main points of differentiation between the competitive presentations, thus, they are crucial for the success of the companies. The purpose of this study was to analyze the impact of marketing mix elements on brand loyalty. The present study is applicable in terms of objective and descriptive survey in terms ...
Reach soccer's pinnacle. Become a global brand. Buy a team. Sign Lionel Messi. David Beckham makes success look as easy as his epic free kicks. But leveraging world-class talent takes discipline and deft decision-making, as case studies by Anita Elberse reveal. What could other businesses learn from his ascent?
With over 15 years in content marketing, Werner founded Influencer Marketing Hub in 2016. He successfully grew the platform to attract 5 million monthly visitors, making it a key site for brand marketers globally. His efforts led to the company's acquisition in 2020.
mainly this research focuses on the marketing mix role in creating brand equity. An empirical research of Yoo et al. (2000) have examined that there is a correlation between marketing mix and brand equity. The same study also critically evaluates the brand equity being affected negatively by various factors (Yoo et al. 2000).
The ecommerce brand uses Facebook to sell themselves by showcasing customer stories and case studies. And Lush Cosmetics is a great example of superior customer service on X. They use their 280 characters to answer questions and solve problems in an extremely charming and on-brand way.
New research into B2B content marketing trends for 2024 reveals specifics of AI implementation, social media use, and budget forecasts, plus content success factors. ... Fifty-three percent say case studies/customer stories and videos deliver some of their best results. Almost as many (51%) names thought leadership e-books or white papers, 47% ...
Marketing mix focuses on specific 4Ps variables of product, price, place, and promotion. In developing its marketing mix, Apple uses a strategy that promotes premium branding. This approach aims to focus on the premium brand and ensure that all 4Ps of Apple support the maintenance of a strong brand image.
Influencer marketing case study: Coyo Taco Coyo Taco, a Miami-based taqueria, integrates influencer collaborations into their regular marketing strategy. They host micro and macro-influencers weekly and have larger campaigns involving multiple influencers to promote events and partnerships.
As in the previous year, the three most popular content types are short articles/posts (96%), case studies/customer stories (93%), and videos (90%). Eighty-two percent use thought leadership e-books/white papers, 81% use long articles/posts, 63% use data visualizations/visual content, 62% use product/technical data sheets, and 56% use research ...
7) Getting on TikTok is a fun way to build your brand. The brand of TikTok is about fun and creativity, so it makes sense that using the TikTok Creator Marketplace is a fun way to build your brand. By working with creators who have creative and engaging content, you can create videos that are both entertaining and informative for viewers.