
- Book Solutions
- State Boards

Case Study Questions Class 10 Science Electricity
Case study questions class 10 science chapter 12 electricity.

At Case Study Questions there will given a Paragraph. In where some Important Questions will made on that respective Case Based Study. There will various types of marks will given 1 marks, 2 marks, 3 marks, 4 marks.
Case study: 1
We can see that, as the applied voltage is increased the current through the wire also increases. It means that, the potential difference across the terminals of the wire is directly proportional to the electric current passing through it at a given temperature.
Thus, V= IR
Where R is the proportionality constant called as resistance of the wire. Thus, we can say that the resistance of the wire is inversely proportional to the electric current. As the resistance increases current through the wire decreases. The resistance of the conductor is directly proportional to length of the conductor, inversely proportional to the area of cross section of the conductor and also depends on the nature of the material from which conductor is made. Thus R= qL/A, where q is the resistivity of the material of conductor. According resistivity of the material they are classified as conductors, insulators and semiconductors. It is observed that the resistance and resistivity of the material varies with temperature. And hence there are vast applications of these materials based on their resistivity.
The SI unit of resistance is ohm while the SI unit of electric current is ampere. The potential difference is measured in volt. Conductors are the materials which are having less resistivity or more conductivity and hence they are used for transmission of electricity. Alloys are having more resistivity than conductors and hence they are used in electric heating devices. While insulators are bad conductors of electricity.
1) What is SI unit of resistivity?
2) What is variable resistance?
3) Why tungsten is used in electric bulbs?
4) 1M ohm = ?
1) The SI unit of resistivity is ohm meter.
2) The electric component which is used to regulate the electric current without changing voltage source is called as variable resistance.
3) Tungsten filament are used in electric bulbs because the resistivity of Tungsten is more and it’s melting point is also high.
4) 1M ohm = 10 6 ohm
Case study: 2
Resistance is the opposition offered by the conductor to the flow of electric current. When two or more resistors are connected in series then electric current through each resistor is same but the electric potential across each resistor will be different. If R1, R2 and R3 are the resistance connected in series then current through each resistor will be I but potential difference across each resistor is V1, V2 and V3 respectively.
Thus, the total potential difference is equal to the sum of potential difference across each resistor. Hence, V= V1 + V2 + V3
Again, IR = IR1 + IR2 + IR3
Thus, R = R1 + R2 + R3
Hence in case of series combination of resistors, the total resistance is the sum of resistance of each resistor in a circuit.
Now, in case of parallel combination of resistors electric current through each resistor is different but the potential difference across each resistor is same. If resistors R1, R2 and R3 are connected in parallel combination then potential difference across each resistor will be V but current through each resistor is I1, I2 and I3 respectively.
Thus, total current through the circuit is the sum of current flowing through each resistor.
I = I1 + I2 + I3
Again, V/R= V/R1 + V/R2 + V/R3
Thus, 1/R = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + 1/R3
Hence, in case of parallel combination of resistors, the reciprocal of total resistance is the sum of reciprocal of each resistance connected in parallel.
Questions:
1) In which case the equivalent resistance is more and why?
2) In our home, which type of combination of electric devices is preferred? Why?
3) If n resistors of resistance R are connected in parallel then what is the equivalent resistance?
1) In case of parallel combination of resistors the equivalent resistance is less than the individual resistance connected in parallel.
Since, 1/R = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + 1/R3 +….
2) At our home, we are connecting electrical devices in parallel combination because in parallel combination equivalent resistance is less and also we can draw an electric current according to the need of electric devices.
3) If n resistors of resistance R are connected in parallel then equivalent resistance is given by,
1/Re = 1/R + 1/R + 1/R +….n times 1/R
Thus, 1/Re = n/R
Hence, Re= R/n is the required equivalent resistance of the given combination.
Case study:3
When electric current flows through the circuit this electrical energy is used in two ways, some part is used for doing work and remaining may be expended in the form of heat. We can see, in mixers after using it for long time it become more hot, fans also become hot after continuous use. This type of effect of electric current is called as heating effect of electric current. If I is the current flowing through the circuit then the amount of heat dissipated in that resistor will be H = VIt
This effect was discovered by Joule, hence it is called as Joule’s law of heating.
Also, we can write, H = I 2 Rt
Thus, heat produced is directly proportional to the square of the electric current, directly proportional to the resistance of the resistor and the time for which electric current flows through the circuit. This heating effect is used in many applications. The heating effect is also used for producing light. In case of electric bulb, the filament produces more heat energy which is emitted in the form of light. And hence filament are made from tungsten which is having high melting point.
In case of electric circuit, this heating effect is used to protect the electric circuit from damage.
The rate of doing work or rate of consumption of energy is called as power. Here, the rate at which electric energy dissipated or consumed in an electric circuit is called as electric power. And it is given by P= VI
The SI unit of electric power is watt.
1) What is the SI unit of electric energy?
2) How heating effect works to protect electric circuit?
3) 1KW h = ?
4) If a bulb is working at a voltage of 200V and the current is 1A then what is the power of the bulb?
1) The SI unit of electric energy is watt hour. And the commercial unit of electric energy is kW h.
2) In case of electric circuit fuse is connected in series with the circuit which protects the electric devices by stopping the extra current flowing through them. When a large amount of current is flowing through the circuit the temperature of the fuse wire increases and because of that fuse wire melts which breaks the circuit.
3) 1kW h = 3.6*10 6 joule
4) Given that,
V = 200V, I = 1A
Then, P = VI = 200*1 = 200 J/s = 200 W
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
We have a strong team of experienced Teachers who are here to solve all your exam preparation doubts
2025 solved specimen paper icse class 10 biology, 2025 solved icse specimen paper class 10 english paper 1, west bengal board class 9 english solution chapter 10 the price of bananas, west bengal board class 9 english solution chapter 9 the north ship.
Sign in to your account
Username or Email Address
Remember Me

Case Study Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity
- Post author: studyrate
- Post published:
- Post category: class 10th
- Post comments: 0 Comments
Case study Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 12 are very important to solve for your exam. Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Case Study Questions have been prepared for the latest exam pattern. You can check your knowledge by solving case study-based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity
Join our Telegram Channel, there you will get various e-books for CBSE 2024 Boards exams for Class 9th, 10th, 11th, and 12th.

In CBSE Class 10 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason . There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage-based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked.
Electricity Case Study Questions With Answers
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity
Case Study/Passage Based Questions
Question 1:
The heating effect of current is obtained by the transformation of electrical energy into heat energy. Just as mechanical energy used to overcome friction is covered into heat, in the same way, electrical energy is converted into heat energy when an electric current flows through a resistance wire. The heat produced in a conductor, when a current flows through it is found to depend directly on (a) strength of current (b) resistance of the conductor (c) time for which the current flows. The mathematical expression is given by H = I 2 Rt. The electrical fuse, electrical heater, electric iron, electric geyser, etc. all are based on the heating effect of current.
(i) What are the properties of heating elements? (a) High resistance, high melting point (b) Low resistance, high melting point (c) Low resistance, high melting point (d) Low resistance, low melting point.
Answer: (b) Low resistance, high melting point
(ii) What are the properties of an electric fuse? (a) Low resistance, low melting point (b) High resistance, high melting point. (c) High resistance, low melting point (d) Low resistance, high melting point
Answer: (c) High resistance, low melting point
(iii) When the current is doubled in a heating device and time is halved, the heat energy produced is
Answer: (a) doubled
(iv) A fuse wire melts at 5 A. It is is desired that the fuse wire of same material melt at 10 A. The new radius of the wire is
Answer: (b) 2 times
(v) When a current of 0.5 A passes through a conductor for 5 min and the resistance of conductor is 10 ohm, the amount of heat produced is
Answer: (c) 750J
Question 2:
The relationship between potential difference and the current was first established by George Simon Ohm. This relationship is known as Ohm’s law. According to this law, the current passed through a conductor is proportional to the potential difference applied between its ends provided the temperature remains constant i.e. I ∝ V or V = IR where R is the constant for the conductor and it is known as the resistance of the conductor. Although Ohm’s law has been found valid over a large class of materials, there are some materials that do not hold Ohm’s law.
2.1) Name the law which is illustrated by the VI graph. (a) Lenz law (b) Faraday’s law (c) Ohm’s law (d) Newton’s law
Answer(c) Ohm’s law
2.2) By increasing the voltage across a conductor, the (a) current will decrease (b) current will increase (c) resistance will increase (d) resistance will decrease
Answer(b) current will increase
2.3) When a battery of 9 V is connected across a conductor and the current flows is 0.1 A, the resistance is (a) 9 Ohm (b) 0.9 Ohm (c) 90 Ohm (d) 900 Ohm
Answer(c) 90 Ohm
2.4) If both the potential difference and resistance in a circuit are doubled then : (a) current remains same (b) current becomes double (c) current becomes zero (d) current becomes half
Answer(a) current remains same
2.5) Keeping the potential difference constant, the resistance of a circuit is doubled. The current will become : (a) double (b) half (c) one fourth (d) 4 time
Answer(b) half
Case Study 3
3.1) The current passing through an electric kettle has been doubled. The heat produced will become : (a) half (b) double (c) four times (d) one fourth
Answer(c) four times
3.2) The heat produced in a wire of resistance ‘a’ when a current ‘b’ flows through it in time ‘c’ is given by : (a) a 2 bc (b) abc 2 (c) ab 2 c (d) abc
Answer(c) ab2c
3.3) What are the properties of heating element ? (a) high resistance, high melting point (b) low resistance, high melting point (c) low resistance, high melting point (d) low resistance, low melting point
Answer (a) high resistance, high melting point
3.4) Calculate the heat produced when 96,000 coulombs of charge is transferred in one hour through a potential difference of 50 volts. (a) 4788 J (b) 4788 kJ (c) 478 kJ (d) 478 J
Answer (b) 4788 kJ
3.5) Which of the following characteristic is not suitable for a fuse wire ? (a) thin and short (b) low melting point (c) thick and short (d) high resistance
Answer (c) thick and short
Case Study 4
Substance through which charges cannot pass is called insulators. Glass, pure water, and all gases are insulators. Insulators are also called dielectrics. In insulators, the electrons are strongly bound to their atoms and cannot get themselves freed. Thus, free electrons are absent in insulators. Insulators can easily be charged by friction. This is due to the reason that when an electric charge is given to an insulator, it is unable to move freely and remains localized. But this does not mean that conductors cannot be charged. A metal rod can be charged by rubbing it with silk if it is held in a handle of glass or amber
4.1) Calculate the current in a wire if a 1500 C charge is passed through it in 5 minutes. (a) 2 A (b) 5 A (c) 3 A (d) 4 A
Answer (b) 5 A
4.2) Electrons and conventional current flows in : (a) The same direction (b) The opposite direction (c) Any direction (d) Can’t say
Answer (b) The opposite direction
4.3) If the current passing through a lamp is 5 A, what charge passes in 10 second ? (a) 0.5 C (b) 3 C (c) 5 C (d) 50 C
Answer (d) 50 C
4.4) One-coulomb charge is equivalent to the charge contained in : (a) 6.2 × 10 19 electrons (b) 2.6 × 10 18 electrons (c) 2.65 × 10 19 electrons (d) 6.25 × 10 18 electrons
Answer (d) 6.25 × 1018 electrons
4.5) When an electric lamp is connected to 12 V battery, it draws a current of 0.5 A. The power of the lamp is : (a) 0.5 W (b) 6 W (c) 12 W (d) 24 W
Answer (b) 6 W
Hope the information shed above regarding Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity with Answers Pdf free download has been useful to an extent. If you have any other queries of CBSE Class 10 Science Electricity Case Study and Passage Based Questions with Answers, feel free to comment below so that we can revert back to us at the earliest possible By Team Study Rate
You Might Also Like
Mcq class 10 social science economics consumer rights quiz with answers, extra questions of class 10 maths chapter 1 real numbers pdf download, extra questions of class 10 maths chapter 7 coordinate geometry pdf download, leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
CBSE Expert
Class 10 Science: Case Study Chapter 12 Electricity PDF Download
In CBSE Class 10 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason . There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage-based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given.

Here we are providing you with Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity Case Study Questions, by practicing these Case Study and Passage Based Questions will help you in your Class 10th Board Exam.
Case Study Chapter 12 Electricity
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity
Case Study/Passage Based Questions
Question 1:
The heating effect of current is obtained by the transformation of electrical energy into heat energy. Just as mechanical energy used to overcome friction is covered into heat, in the same way, electrical energy is converted into heat energy when an electric current flows through a resistance wire. The heat produced in a conductor, when a current flows through it is found to depend directly on (a) strength of current (b) resistance of the conductor (c) time for which the current flows. The mathematical expression is given by H = I 2 Rt. The electrical fuse, electrical heater, electric iron, electric geyser, etc. all are based on the heating effect of current.
(i) What are the properties of heating elements? (a) High resistance, high melting point (b) Low resistance, high melting point (c) Low resistance, high melting point (d) Low resistance, low melting point.
Answer: (b) Low resistance, high melting point
(ii) What are the properties of an electric fuse? (a) Low resistance, low melting point (b) High resistance, high melting point. (c) High resistance, low melting point (d) Low resistance, high melting point
Answer: (c) High resistance, low melting point
(iii) When the current is doubled in a heating device and time is halved, the heat energy produced is
Answer: (a) doubled
(iv) A fuse wire melts at 5 A. It is is desired that the fuse wire of same material melt at 10 A. The new radius of the wire is
Answer: (b) 2 times
(v) When a current of 0.5 A passes through a conductor for 5 min and the resistance of conductor is 10 ohm, the amount of heat produced is
Answer: (c) 750J
Question 2:
The relationship between potential difference and the current was first established by George Simon Ohm. This relationship is known as Ohm’s law. According to this law, the current passed through a conductor is proportional to the potential difference applied between its ends provided the temperature remains constant i.e. I ∝ V or V = IR where R is the constant for the conductor and it is known as the resistance of the conductor. Although Ohm’s law has been found valid over a large class of materials, there are some materials that do not hold Ohm’s law.
2.1) Name the law which is illustrated by the VI graph. (a) Lenz law (b) Faraday’s law (c) Ohm’s law (d) Newton’s law
Answer(c) Ohm’s law
2.2) By increasing the voltage across a conductor, the (a) current will decrease (b) current will increase (c) resistance will increase (d) resistance will decrease
Answer(b) current will increase
2.3) When a battery of 9 V is connected across a conductor and the current flows is 0.1 A, the resistance is (a) 9 Ohm (b) 0.9 Ohm (c) 90 Ohm (d) 900 Ohm
Answer(c) 90 Ohm
2.4) If both the potential difference and resistance in a circuit are doubled then : (a) current remains same (b) current becomes double (c) current becomes zero (d) current becomes half
Answer(a) current remains same
2.5) Keeping the potential difference constant, the resistance of a circuit is doubled. The current will become : (a) double (b) half (c) one fourth (d) 4 time
Answer(b) half
You can also practice Class 10 Science MCQ Questions for Board Exams.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Download India's best Exam Preparation App Now.
Key Features
- Revision Notes
- Important Questions
- Previous Years Questions
- Case-Based Questions
- Assertion and Reason Questions
No thanks, I’m not interested!
CBSE NCERT Solutions
NCERT and CBSE Solutions for free
Case Study Chapter 12 Electricity
Please refer to Chapter 12 Electricity Case Study Questions with answers provided below. We have provided Case Study Questions for Class 10 Science for all chapters as per CBSE, NCERT and KVS examination guidelines. These case based questions are expected to come in your exams this year. Please practise these case study based Class 10 Science Questions and answers to get more marks in examinations.
Case Study Questions Chapter 12 Electricity
Case/Passage – 1
Two tungston lamps with resistances R1 and R2 respectively at full incandescence are connected first in parallel and then in series, in a lighting circuit of negaligible internal resistance. It is given that: R 1 > R 2 .
Question: Which lamp will glow more brightly when they are connected in parallel? (a) Bulb having lower resistance (b) Bulb having higher resistance (c) Both the bulbs (d) None of the two bulbs
Question: Which lamp will glow more brightly when they are connected in series? (a) Bulb having lower resistance (b) Bulb having higher resistance (c) Both the bulbs (d) None of the two bulbs
Question: If the lamp of resistance R 2 now burns out and the lamp of resistance R1 alone is plugged in, will the illumination increase or decrease? (a) Illumination will remain same (b) Illumination will increase (c) Illumination will decrease (d) None
Question: If the lamp of resistance R 1 now burns out, how will the illumination produced change? (a) Net illumination will increase (b) Net illumination will decrease (c) Net illumination will remain same (d) Net illumination will reduced to zero
Question: Would physically bending a supply wire cause any change in the illumination? (a) Illumination will remain same (b) Illumination will increase (c) Illumination will decrease (d) It is not possible to predict from the given datas
Case/Passage – 2
The rate at which electric energy is dissipated or consumed in an electric circuit. This is termed as electric power, P = IV, According to Ohm’s law V = IR We can express the power dissipated in the alternative forms P =I 2 R=V 2 /R
If 100W – 220V is written on the bulb then it means that the bulb will consume 100 joule in one second if used at the potential difference of 220 volts. The value of electricity consumed in houses is decided on the basis of the total electric energy used. Electric power tells us about the electric energy used per second not the total electric energy. The total energy used in a circuit = power of the electric circuit × time.
Question: Which of the following terms does not represent electrical power in a circuit? (a) I 2 R (b) IR 2 (c) VI (d) V 2 /R
Question: Two conducting wires of the same material and of equal lengths and equal diameters are first connected in sereis and then in parallel in an electric circuit. The ratio of heat produced in series and in parallel combinations would be– (a) 1 : 2 (b) 2 : 1 (c) 1 : 4 (d) 4 : 1
Question: In an electrical circuit, two resistors of 2Ω and 4Ω respectively are connected in series to a 6V battery. The heat dissipated by the 4Ω resistor in 5s will be (a) 5 J (b) 10 J (c) 20 J (d) 30 J
Question: In an electrical circuit three incandescent bulbs. A, B and C of rating 40 W, 60 W and 100 W, respectively are connected in parallel to an electric source. Which of the following is likely to happen regarding their brightness? (a) Brightness of all the bulbs will be the same (b) Brightness of bulb A will be the maximum (c) Brightness of bulb B will be more than that of A (d) Brightness of bulb C will be less than that of B
Question: An electric bulb is rated 220V and 100W. When it is operated on 110V, the power consumed will be– (a) 100 W (b) 75 W (c) 50 W (d) 25 W
Case/Passage – 3
Answer the following questions based on the given circuit.
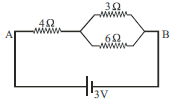
Question: The equivalent resistance between points A and B is (a) 7Ω (b) 6Ω (c) 13Ω (d) 5Ω
Question: The potential drop across the 3Ω resistor is (a) 1 V (b) 1.5 V (c) 2 V (d) 3 V
Question: The current flowing through in the given circuit is (a) 0.5 A (b) 1.5 A (c) 6 A (d) 3 A
Case/Passage – 4
Answer the following questions based on the given circuit.
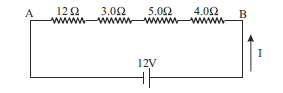
Question: The current through each resistor is (a) 1 A (b) 2.3 A (c) 0.5 A (d) 0.75 A
Question: The equivalent resistance between points A and B, is (a) 12 Ω (b) 36 Ω (c) 32 Ω (d) 24 Ω
Question: The potential drop across the 12Ω resistor is (a) 12 V (b) 6 V (c) 8 V (d) 0.5 V
Case/Passage – 5
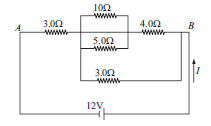
Question: The equivalent resistance between points A and B (a) 6.2 Ω (b) 5.1 Ω (c) 13.33 Ω (d) 1.33 Ω
Question: The current through the 4.0 ohm resistor is (a) 5.6 A (b) 0.98 A (c) 0.35 A (d) 0.68 A
Question: The current through the battery is (a) 2.33 A (b) 3.12 A (c) 4.16 A (d) 5.19 A
Case/Passage – 6
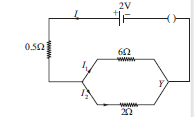
Question: The total resistance of the circuit is (a) 2 Ω (b) 4 Ω (c) 1.5 Ω (d) 0.5 Ω
Question: The current flowing through 6Ω resistor is (a) 0.50 A (b) 0.75 A (c) 0.80 A (d) 0.25
Question: The current flowing through 0.5Ω resistor is (a) 1 A (b) 1.5 A (c) 3 A (d) 2.5 A
Case/Passage – 7
Ohm’s law gives the relationship between current flowing through a conductor with potential difference across it provided the physical conditions and temperature remains constant. The electric current flowing in a circuit can be measured by an ammeter. Potential difference is measured by voltmeter connected in parallel to the battery or cell. Resistances can reduce current in the circuit. A variable resistor or rheostat is used to vary the current in the circuit.
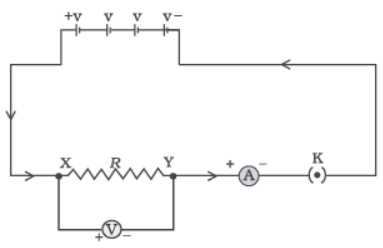
Question. Which type of conductor is represented by the graph given alongside?
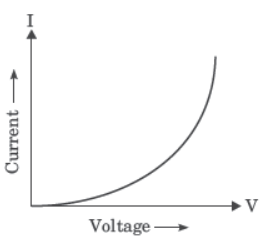
(a) Non-ohmic conductor like thermistor (b) Non-ohmic conductor like metal filament (c) Ohmic conductor like copper (d) None of these
Question. What is the slope of graph in (i) equal to? (a) V (b) I (c) R (d) VI
Question. Which of the following is the factor on which resistance of a conductor does not depend? (a) Length (b) Area (c) Temperature (d) Pressur
Question. What type of conductor is represented by the following graph?
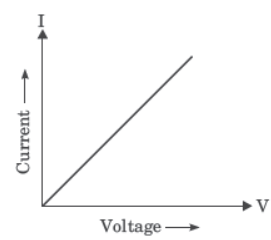
(a) Non-ohmic conductor like thermistor (b) Non-ohmic conductor like metal filament (c) Ohmic conductor like copper (d) None of these
Question. What type of conductors are represented by the following graph?
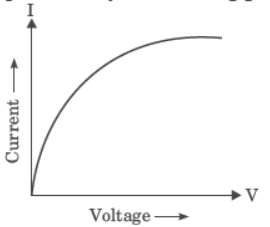
Study this table related to material and their resistivity and answer the questions that follow.
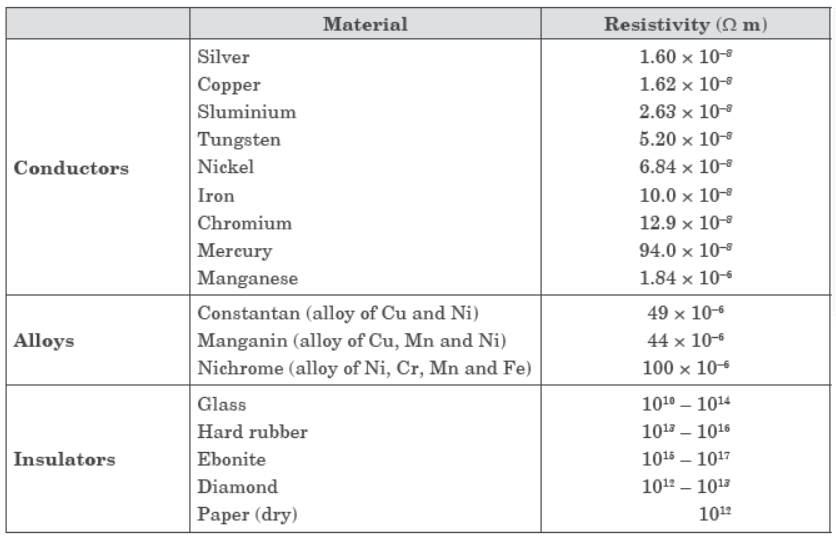
Question. Which of the following is used in transmission wires? (a) Cr (b) Al (c) Zn (d) Fe
Question. Which is the best conducting metal? (a) Cu (b) Ag (c) Au (d) Hg
Question. Which of the following is used as a filament in electric bulbs? (a) Nichrome (b) Tungsten (c) Manganese (d) Silver
Question. What is the range of resistivity in metals, good conductors of electricity? (a) 10–8 to 10–6 Wm (b) 10–6 to 10–4 Wm (c) 1010 to 1014 Wm (d) 1012 to 1014 Wm
Question. Which property of the alloy makes it useful in heating devices like electric iron, toasters, immersion rods, etc.? (a) Higher resistivity (b) Do not oxidise at low temperature (c) Do not reduce at high temperature (d) Oxidise at high temperature

Related Posts

Power Sharing Class 10 Social Science Notes and Questions

CBSE Class 10 English The Book That Saved the Earth Summary

Class 10 Computer Science Notes and Questions

- Andhra Pradesh
- Chhattisgarh
- West Bengal
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Jammu & Kashmir
- NCERT Books 2022-23
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Exemplar Books
- NCERT Exemplar Solution
- States UT Book
- School Kits & Lab Manual
- NCERT Books 2021-22
- NCERT Books 2020-21
- NCERT Book 2019-2020
- NCERT Book 2015-2016
- RD Sharma Solution
- TS Grewal Solution
- TR Jain Solution
- Selina Solution
- Frank Solution
- ML Aggarwal Solution
- Lakhmir Singh and Manjit Kaur Solution
- I.E.Irodov solutions
- ICSE - Goyal Brothers Park
- ICSE - Dorothy M. Noronhe
- Sandeep Garg Textbook Solution
- Micheal Vaz Solution
- S.S. Krotov Solution
- Evergreen Science
- KC Sinha Solution
- ICSE - ISC Jayanti Sengupta, Oxford
- ICSE Focus on History
- ICSE GeoGraphy Voyage
- ICSE Hindi Solution
- ICSE Treasure Trove Solution
- Thomas & Finney Solution
- SL Loney Solution
- SB Mathur Solution
- P Bahadur Solution
- Narendra Awasthi Solution
- MS Chauhan Solution
- LA Sena Solution
- Integral Calculus Amit Agarwal Solution
- IA Maron Solution
- Hall & Knight Solution
- Errorless Solution
- Pradeep's KL Gogia Solution
- OP Tandon Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Previous Year Question Paper
- Value Based Questions
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE MCQs PDF
- Assertion & Reason
- New Revision Notes
- Revision Notes
- HOTS Question
- Marks Wise Question
- Toppers Answer Sheets
- Exam Paper Aalysis
- Concept Map
- CBSE Text Book
- Additional Practice Questions
- Vocational Book
- CBSE - Concept
- KVS NCERT CBSE Worksheets
- Formula Class Wise
- Formula Chapter Wise
- JEE Crash Course
- JEE Previous Year Paper
- Important Info
- JEE Mock Test
- JEE Sample Papers
- SRM-JEEE Mock Test
- VITEEE Mock Test
- BITSAT Mock Test
- Manipal Engineering Mock Test
- AP EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- COMEDK Previous Year Paper
- GUJCET Previous Year Paper
- KCET Previous Year Paper
- KEAM Previous Year Paper
- Manipal Previous Year Paper
- MHT CET Previous Year Paper
- WBJEE Previous Year Paper
- AMU Previous Year Paper
- TS EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- SRM-JEEE Previous Year Paper
- VITEEE Previous Year Paper
- BITSAT Previous Year Paper
- UPSEE Previous Year Paper
- CGPET Previous Year Paper
- CUSAT Previous Year Paper
- AEEE Previous Year Paper
- Crash Course
- Previous Year Paper
- NCERT Based Short Notes
- NCERT Based Tests
- NEET Sample Paper
- Previous Year Papers
- Quantitative Aptitude
- Numerical Aptitude Data Interpretation
- General Knowledge
- Mathematics
- Agriculture
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Political science
- Enviromental Studies
- Mass Media Communication
- Teaching Aptitude
- NAVODAYA VIDYALAYA
- SAINIK SCHOOL (AISSEE)
- Mechanical Engineering
- Electrical Engineering
- Electronics & Communication Engineering
- Civil Engineering
- Computer Science Engineering
- CBSE Board News
- Scholarship Olympiad
- School Admissions
- Entrance Exams
- All Board Updates
- Miscellaneous
- State Wise Books
- Engineering Exam
Electricity Case Study Based Questions Class 10
Students who are studying in CBSE class 10 board, need to get the knowledge about the Electricity Case Study Based Questions. Case based questions are generally based on the seen passages from the chapter Electricity. Through solving the case based questions, students can understand each and every concept.
With the help of Electricity Case Study Based Questions, students don’t need to memorise each answer. As answers for these case studies are already available in the given passage. Questions are asked through MCQs so student’s won’t take time to mark the answers. These multiple choice questions can help students to score the weightage of Electricity.
Electricity Case Study Based Questions with Solutions
Selfstudys provides case studies for the Class 10 Science chapter Electricity with solutions. The Solutions can be helpful for students to refer to if there is a doubt in any of the case studies problems. The solutions from the Selfstudys website are easily accessible and free of cost to download. This accessibility can help students to download case studies from anywhere with the help of the Internet.
Electricity Case Study Based Questions with solutions are in the form of PDF. Portable Document Format (PDF) can be downloaded through any of the devices: smart phone, laptop. Through this accessibility, students don't need to carry those case based questions everywhere.
Features of Electricity Case Study Based Questions
Before solving questions, students should understand the basic details of Electricity. Here are the features of case based questions on Electricity are:
- These case based questions start with short or long passages. In these passages some concepts included in the chapter can be explained.
- After reading the passage, students need to answer the given questions. These questions are asked in the Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ).
- These case based questions are a type of open book test. These case based questions can help students to score well in the particular subject.
- These Electricity Case Study Based Questions can also be asked in the form of CBSE Assertion and Reason .
Benefits of Solving Electricity Case Study Based Questions
According to the CBSE board, some part of the questions are asked in the board exam question papers according to the case studies. As some benefits of solving Electricity Case Study Based Questions can be obtained by the students. Those benefits are:
- Through solving case studies students will be able to understand every concept included in the chapter Electricity
- Passages included in the case study are seen passages, so students don’t need to struggle for getting answers. As these questions and answers can be discussed by their concerned teacher.
- Through these students can develop their observation skills. This skill can help students to study further concepts clearly.
- Case studies covers all the concepts which are included in the Electricity
How to Download Electricity Case Based Questions?
Students studying in CBSE class 10 board, need to solve questions based on case study. It is necessary for students to know the basic idea of Electricity Case Study Based Questions. Students can obtain the basic idea of case based questions through Selfstudys website. Easy steps to download it are:
- Open Selfstudys website.
- Bring the arrow towards CBSE which is visible in the navigation bar.
- A pop-up menu will appear, Select case study from the list.
- New page will appear, select 10 from the list of classes.
- Select Science from the subject list.
- And in the new page, you can access the Electricity Case Study Based Questions.
Tips to solve Electricity Case Study Questions-
Students should follow some basic tips to solve Electricity Case Study Based Questions. These tips can help students to score good marks in CBSE Class 10 Science.
- Generally, the case based questions are in the form of Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs).
- Students should start solving the case based questions through reading the given passage.
- Identify the questions and give the answers according to the case given.
- Read the passage again, so that you can easily answer the complex questions.
- Answer according to the options given below the questions provided in the Electricity Case Study Based Questions.

- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- CBSE Syllabus 2023-24
- Social Media Channels
- Login Customize Your Notification Preferences

One Last Step...

- Second click on the toggle icon

Provide prime members with unlimited access to all study materials in PDF format.
Allow prime members to attempt MCQ tests multiple times to enhance their learning and understanding.
Provide prime users with access to exclusive PDF study materials that are not available to regular users.

If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
Unit 3: Electricity
About this unit.
We can't imagine our lives without electricity. But what exactly is electricity? How does electricity light up our houses? What does a battery do? What is the cost of electricity? We will answer all these questions in this chapter.
Electric current & circuit
- Intro to charge (Opens a modal)
- Unit of charge (Coulombs) (Opens a modal)
- Intro to current (& Amperes) (Opens a modal)
- Finding electric current Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Electric potential & potential difference
- Intro to potential difference (& voltage) (Opens a modal)
- Solved example: Potential difference & work done (Opens a modal)
- Voltage and work Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Circuits, Ohm's law & resistance
- Introduction to circuits and Ohm's law (Opens a modal)
- Solved example: Ohms law (Opens a modal)
- Ohm's law graph (verifying Ohm's law) (Opens a modal)
- Solved example: (Ohm's law graph) (Opens a modal)
- Ohm's law and resistance Get 3 of 3 questions to level up!
Factors on which resistance of a conductor depends on
- Resistivity and conductivity (Opens a modal)
- Resistance and resistivity Get 5 of 7 questions to level up!
Series and parallel resistors
- Series resistors (Opens a modal)
- Parallel resistors (part 1) (Opens a modal)
- Parallel resistors (part 2) (Opens a modal)
- Parallel resistors (part 3) (Opens a modal)
- Finding equivalent resistance Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Identifying types of resistor combinations Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Solving a circuit with series and parallel resistors
- Example: Analyzing a more complex resistor circuit (Opens a modal)
- Solved example: Finding current & voltage in a circuit (Opens a modal)
- Simplifying resistor networks Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Finding currents and voltages (pure circuits) Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Finding currents and voltages (mixed circuits) Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Electric power and heating effect of current
- Electric power & energy (Opens a modal)
- Heating effect of current (Opens a modal)
- Solved example - Calculating power & heat dissipated (Opens a modal)
- Electric power (formula) Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Calculating heat dissipated in circuits Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Electric circuit with Bulbs
- Solved example: Power dissipated in bulbs (Opens a modal)
- Bulbs connected in series or parallel Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Commercial unit of electrical energy
- Commercial unit of electrical energy (Opens a modal)
- Solved example - Cost of operation of electrical device (Opens a modal)
- Finding cost of electrical operation Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Electricity class 10 numerical: CBSE board practice (Opens a modal)
- Electricity class 10: CBSE previous question paper problems (Opens a modal)

Gurukul of Excellence
Classes for Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics by IITians
Category: Case Study Questions for Class 10 Science
Join our Telegram Channel for Free PDF Download
Case Study Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Control and Coordination
Case study questions for class 10 science chapter 15 our environment, case study questions for class 10 science chapter 13 magnetic effect of electric current, case study questions for class 10 science chapter 12 electricity, case study and passage based questions for class 10 science chapter 8 how do organisms reproduce, case study and passage based questions for class 10 science chapter 5 periodic classification of elements, case study and passage based questions for class 10 science chapter 10 light reflection and refraction, case study and passage based questions for class 10 science chapter 3 metals and non metals, case study and passage based questions for class 10 science chapter 6 life processes, case study and passage based questions for class 10 science chapter 11 the human eye and the colourful world, case study and passage based questions for class 10 science chapter 4 carbon and its compounds, case study and passage based questions for class 10 science chapter 9 heredity and evolution, case study and passage based questions for class 10 science chapter 2 acids, bases and salts, case study and passage based questions for class 10 science chapter 1 chemical reactions and equations.
Join our Online Test Series for CBSE, ICSE, JEE, NEET and Other Exams

Editable Study Materials for Your Institute - CBSE, ICSE, State Boards (Maharashtra & Karnataka), JEE, NEET, FOUNDATION, OLYMPIADS, PPTs
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10
- NCERT Class 10 Science
- Chapter 12 Electricity
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity
Ncert solutions for class 10 science electricity – cbse free pdf download.
* According to the CBSE Syllabus 2023-24, this chapter has been renumbered as Chapter 11.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity provides answers and explanations to all the exercise questions provided in the textbook. These NCERT Solutions has questions related to electric cells, electric bulbs, electric circuits, switches, conductors and insulators, and examples of conductors and insulators. It includes a variety of questions like ‘F ill in the Blanks’, ‘True or False’, circuit diagrams, and descriptive answering questions which will help students get acquainted with the concepts.
Download Exclusively Curated Chapter Notes for Class 10 Science Chapter – 12 Electricity
Download most important questions for class 10 science chapter – 12 electricity.
Explore the best resources on the internet for NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science right here at BYJU’S. Our content is the culmination of the knowledge and academic insights from our highly qualified teachers and experts. Besides providing the best answers in NCERT Solutions for Class 10 , we also strive to impart maximum informational value. Of course, this means the content becomes more complex, but we have ensured that the language used is simple and all technical jargon is explained in detail.
- Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations
- Chapter 2 Acids, Bases and Salts
- Chapter 3 Metals and Non-metals
- Chapter 4 Carbon and Its Compounds
- Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of Elements
- Chapter 6 Life Processes
- Chapter 7 Control and Coordination
- Chapter 8 How do Organisms Reproduce?
- Chapter 9 Heredity and Evolution
- Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction
- Chapter 11 The Human Eye and Colourful World
- Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
- Chapter 14 Sources of Energy
- Chapter 15 Our Environment
- Chapter 16 Management of Natural Resources
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12 – Electricity
carouselExampleControls112

Previous Next
Access Answers of Science NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Chapter 12 – Electricity
In text 12.1 Page: 200
1. What does an electric circuit mean?
A continuous closed path made of electric components through which an electric current flows is known as an electric circuit. A simple circuit consists of the following components:
(a) Conductors
2. Define the unit of current.
The unit of current is ampere. Ampere is defined by the flow of one coulomb of charge per second.
3. Calculate the number of electrons constituting one coulomb of charge.
The value of the charge of an electron is 1.6 × 10 -19 C.
According to charge quantization,
Q = nq e , where n is the number of electrons and q e is the charge of an electron.
Substituting the values in the above equation, the number of electrons in a coulomb of charge can be calculated as follows:

Therefore, the number of electrons constituting one coulomb of charge is 6. 25 × 10 18 .
In text 12.2 Page: 202
1. Name a device that helps to maintain a potential difference across a conductor.
A battery consisting of one or more electric cells is one of the devices that help to maintain a potential difference across a conductor.
2. What is meant by saying that the potential difference between two points is 1 V?
When 1 J of work is done to move a charge of 1 C from one point to another, it is said that the potential difference between two points is 1 V.
3. How much energy is given to each coulomb of charge passing through a 6 V battery?
We know that the potential difference between two points is given by the equation,
V = W/Q, where,
W is the work done in moving the charge from one point to another
Q is the charge
From the above equation, we can find the energy given to each coulomb as follows:
Substituting the values in the equation, we get
W = 6V × 1C = 6 J
Hence, 6 J of energy is given to each coulomb of charge passing through a 6 V of battery.
In text 12.5 Page: 209
1. On what factors does the resistance of a conductor depend?
The resistance of the conductor depends on the following factors:
a. Temperature of the conductor
b. Cross-sectional area of the conductor
c. Length of the conductor
d. Nature of the material of the conductor
2. Will current flow more easily through a thick wire or a thin wire of the same material, when connected to the same source? Why?
Resistance is given by the equation,
ρ is the resistivity of the material of the wire,
l is the length of the wire
A is the area of the cross-section of the wire.
From the equation, it is evident that the area of the cross-section of wire is inversely proportional to the resistance. Therefore, the thinner the wire, the more the resistance and vice versa. Hence, current flows more easily through a thick wire than a thin wire.
3. Let the resistance of an electrical component remain constant while the potential difference across the two ends of the component decreases to half of its former value. What change will occur in the current through it?
The change in the current flowing through the electrical component can be determined by Ohm’s Law.
According to Ohm’s Law, the current is given by
Now, the potential difference is reduced to half keeping the resistance constant,
Let the new voltage be V’ = V/2
Let the new resistance be R’ = R and the new amount of current be I’.
The change in the current can be determined using Ohm’s law as follows:

Therefore, the current flowing the electrical component is reduced by half.
4. Why are coils of electric toasters and electric irons made of an alloy rather than a pure metal?
The melting point of an alloy is much higher than a pure metal because of its high resistivity. At high temperatures, alloys do not melt readily. Therefore, alloys are used in heating appliances such as electric toasters and electric irons.
5. Use the data in the table given below and answer the following questions.
a. Which among iron and mercury is a better conductor?
b. Which material is the best conductor?
a. Iron is a better conductor than mercury because the resistivity of mercury is more than the resistivity of iron.
b. Among all the materials listed in the table, silver is the best conductor because the resistivity of silver is lowest among all, i.e., 1.60 × 10 –8 .
In text 12.6 Page: 213
1. Draw a schematic diagram of a circuit consisting of a battery of three cells of 2 V each, a 5 Ω resistor, an 8 Ω resistor, and a 12 Ω resistor, and a plug key, all connected in series.
A battery of three cells of 2 V each equals to battery of potential 6 V. The circuit diagram below shows three resistors of resistance 12 Ω, 8 Ω and 5 Ω connected in series along with a battery of potential 6 V.

2. Redraw the circuit of Question 1, putting in an ammeter to measure the current through the resistors and a voltmeter to measure the potential difference across the 12 Ω resistor. What would be the readings in the ammeter and the voltmeter?
An ammeter should always be connected in series with resistors while the voltmeter should be connected in parallel to the resistor to measure the potential difference as shown in the figure below.

Using Ohm’s Law, we can obtain the reading of the ammeter and the voltmeter.
The total resistance of the circuit is 5 Ω + 8 Ω +12 Ω = 25 Ω.
We know that the potential difference of the circuit is 6 V, hence the current flowing through the circuit or the resistors can be calculated as follows:
I = V/R = 6/25 = 0.24A
Let the potential difference across the 12 Ω resistor be V 1 .
From the obtained current V 1 can be calculated as follows:
V 1 = 0.24A × 12 Ω = 2.88 V
Therefore, the ammeter reading will be 0.24 A and the voltmeter reading be 2.88 V.
In text 12.6.2 Page: 216
1. Judge the equivalent resistance when the following are connected in parallel – (a) 1 Ω and 10 6 Ω, (b) 1 Ω, 10 3 Ω, and 10 6 Ω.
(a) When 1 Ω and 10 6 are connected in parallel, the equivalent resistance is given by

Therefore, the equivalent resistance is 1 Ω.
(b) When 1 Ω, 10 3 Ω, and 10 6 Ω are connected in parallel, the equivalent resistance is given by

Therefore, the equivalent resistance is 0.999 Ω.
2. An electric lamp of 100 Ω, a toaster of resistance 50 Ω, and a water filter of resistance 500 Ω are connected in parallel to a 220 V source. What is the resistance of an electric iron connected to the same source that takes as much current as all three appliances, and what is the current through it?
The electric lamp, the toaster and the water filter connected in parallel to a 220 V source can be shown as using a circuit diagram as follows:

The equivalent resistance of the resistors can be calculated as follows:

The resistance of the electric iron box is 31.25 Ω.
3. What are the advantages of connecting electrical devices in parallel with the battery instead of connecting them in series?
When the electrical devices are connected in parallel there is no division of voltage among the appliances. The potential difference across the devices is equal to supply voltage. Parallel connection of devices also reduces the effective resistance of the circuit.
4. How can three resistors of resistances 2 Ω, 3 Ω, and 6 Ω be connected to give a total resistance of (a) 4 Ω, (b) 1 Ω?
(a) The circuit diagram below shows the connection of three resistors

From the circuit above, it is understood that 3 Ω and 6 Ω are connected in parallel. Hence, their equivalent resistance is given by

The equivalent resistor 2 Ω is in series with the 2 Ω resistor. Now the equivalent resistance can be calculated as follows:
R eq = 2 Ω +2 Ω = 4 Ω
Hence, the total resistance of the circuit is 4 Ω.
(b) The circuit diagram below, shows the connection of three resistors.

From the circuit, it is understood that all the resistors are connected in parallel. Therefore, their equivalent resistance can be calculated as follows:

The total resistance of the circuit is 1 Ω.
5. What is (a) the highest, (b) the lowest total resistance that can be secured by combinations of four coils of resistance 4 Ω, 8 Ω, 12 Ω, 24 Ω?
(a) If the four resistors are connected in series, their total resistance will be the sum of their individual resistances and it will be the highest. The total equivalent resistance of the resistors connected in series will be 4 Ω + 8 Ω + 12 Ω + 24 Ω = 48 Ω.
(b) If the resistors are connected in parallel, then their equivalent resistances will be the lowest.
Their equivalent resistance connected in parallel is

Hence, the lowest total resistance is 2 Ω.
In text 12.7 Page: 218
1. Why does the cord of an electric heater not glow while the heating element does?
The heating element of an electric heater is made of an alloy which has a high resistance. When the current flows through the heating element, the heating element becomes too hot and glows red. The cord is usually made of copper or aluminum which has low resistance. Hence the cord doesn’t glow.
2. Compute the heat generated while transferring 96000 coulomb of charge in one hour through a potential difference of 50 V.
The heat generated can be computed by Joule’s law as follows:
V is the voltage, V = 50 V
I is the current
t is the time in seconds, 1 hour = 3600 seconds
The amount of current can be calculated as follows:

2. An electric iron of resistance 20 Ω takes a current of 5 A. Calculate the heat developed in 30 s.
The amount of heat generated can be calculated using the Joule’s law of heating, which is given by the equation
Substituting the values in the above equation, we get,
H = 100 × 5 × 30 = 1.5 × 10 4 J
The amount of heat developed by the electric iron in 30 s is 1.5 × 10 4 J.
In text 12.8 Page: 220
1. What determines the rate at which energy is delivered by a current?
Electric power is the rate of consumption of electrical energy by electric appliances. Hence, the rate at which energy is delivered by a current is the power of the appliance.
2. An electric motor takes 5 A from a 220 V line. Determine the power of the motor and the energy consumed in 2 h.
The power of the motor can be calculated by the equation,
Substituting the values in the above equation, we get
P = 220 V × 5 A = 1100 W
The energy consumed by the motor can be calculated using the equation,
P = 1100 W × 7200 = 7.92 × 10 6 J
The power of the motor is 1100 W and the energy consumed by the motor in 2 hours is 7.92 × 10 6 J.
Exercises Page: 221
1. A piece of wire of resistance R is cut into five equal parts. These parts are then connected in parallel. If the equivalent resistance of this combination is R′, then the ratio R/R′ is _____.
Answer: d) 25
Explanation:
The resistance is cut into five equal parts, which means that the resistance of each part is R/5.
We know that each part is connected to each other in parallel, hence the equivalent resistance can be calculated as follows:

The ratio of R/R′ is 25.
2. Which of the following does not represent electrical power in a circuit?
Answer : b) IR 2
Electrical power is given by the expression P = VI . (1)
According to Ohm’s law,
Substituting the value of V in (1), we get
P = ( IR ) × I
Similarly, from Ohm’s law,
Substituting the value of I in (1), we get
P = V × V / R = V 2 / R
From this, it is clear that the equation IR 2 does not represent electrical power in a circuit.
3. An electric bulb is rated 220 V and 100 W. When it is operated on 110 V, the power consumed will be _____.
Answer: 25 W
The energy consumed by the appliance is given by the expression
P = VI = V 2 /R
The resistance of the light bulb can be calculated as follows:
Substituting the values, we get
R = (220) 2 /100 = 484 Ω
Even if the supply voltage is reduced, the resistance remains the same. Hence, the power consumed can be calculated as follows:
Substituting the value, we get
P = (110 )2 V/484 Ω = 25 W
Therefore, the power consumed when the electric bulb operates at 110 V is 25 W.
4. Two conducting wires of the same material and of equal lengths and equal diameters are first connected in series and then parallel in a circuit across the same potential difference. The ratio of heat produced in series and parallel combinations would be _____.
Let R s and R p be the equivalent resistance of the wires when connected in series and parallel respectively.
For the same potential difference V, the ratio of the heat produced in the circuit is given by

Hence, the ratio of the heat produced is 1:4.
5. How is a voltmeter connected in the circuit to measure the potential difference between two points?
To measure the voltage between any two points, the voltmeter should be connected in parallel between the two points.

6. A copper wire has diameter 0.5 mm and resistivity of 1.6 × 10 –8 Ω m. What will be the length of this wire to make its resistance 10 Ω? How much does the resistance change if the diameter is doubled?
The resistance of the copper wire of length in meters and area of cross-section m 2 is given by the formula

The length of the wire is 122.72 m and the new resistance is 2.5 Ω.
7. The values of current I flowing in a given resistor for the corresponding values of potential difference V across the resistor are given below –
Plot a graph between V and I and calculate the resistance of that resistor.
The plot between voltage and current is known as IV characteristic. The current is plotted in the y-axis while the voltage is plotted in the x-axis. The different values of current for different values of voltage are given in the table. The I V characteristics for the given resistor is shown below.

The slope of the line gives the value of resistance.
The slope can be calculated as follows:
Slope = 1/ R = BC / AC = 2/6.8
To calculate R ,
R = 6.8/2 = 3.4 Ω
The resistance of the resistor is 3.4 Ω.
8. When a 12 V battery is connected across an unknown resistor, there is a current of 2.5 mA in the circuit. Find the value of the resistance of the resistor
The value of the resistor can be calculated using Ohm’s Law as follows:

9. A battery of 9 V is connected in series with resistors of 0.2 Ω, 0.3 Ω, 0.4 Ω, 0.5 Ω and 12 Ω, respectively. How much current would flow through the 12 Ω resistor?
In series connection, there is no division of current. The current flowing across all the resistors is the same.
To calculate the amount of current flowing across the resistors, we use Ohm’s law.
But first, let us find out the equivalent resistance as follows:
R = 0.2 Ω + 0.3 Ω + 0.4 Ω + 0.5 Ω + 12 Ω = 13.4 Ω
Now, using Ohm’s law,

The current flowing across the 12 Ω is 0.671 A.
10. How many 176 Ω resistors (in parallel) are required to carry 5 A on a 220 V line?
Let us consider the number of resistors required as ‘x.’
The equivalent resistance of the parallel combination of resistor R is given by

The number of resistors required is 4.
11. Show how you would connect three resistors, each of resistance 6 Ω, so that the combination has a resistance of (i) 9 Ω, (ii) 4 Ω.
If we connect all the three resistors in series, their equivalent resistor would 6 Ω + 6 Ω + 6 Ω =18 Ω, which is not the desired value. Similarly, if we connect all the three resistors in parallel, their equivalent resistor would be

which is again not the desired value.
We can obtain the desired value by connecting any two of the resistors in either series or parallel.

If two resistors are connected in parallel, then their equivalent resistance is

The third resistor is in series, hence the equivalent resistance is calculated as follows:
R = 6 Ω + 3 Ω = 9 Ω

When two resistors are connected in series, their equivalent resistance is given by
R = 6 Ω + 6 Ω = 12 Ω
The third resistor is connected in parallel with 12 Ω. Hence the equivalent resistance is calculated as follows:

12. Several electric bulbs designed to be used on a 220 V electric supply line, are rated 10 W. How many lamps can be connected in parallel with each other across the two wires of 220 V line if the maximum allowable current is 5 A?
The resistance of the bulb can be calculated using the expression
P 1 = V 2 /R 1
R 1 = V 2 /P 1

Hence, 110 lamps can be connected in parallel.
13. A hot plate of an electric oven connected to a 220 V line has two resistance coils A and B, each of 24 Ω resistance, which may be used separately, in series, or in parallel. What are the currents in the three cases?
Case (i) When coils are used separately
Using Ohm’s law, we can find the current flowing through each coil as follows:

9.166 A of current flows through each resistor when they are used separately.
Case (ii) When coils connected in series
The total resistance in the series circuit is 24 Ω + 24 Ω = 48 Ω
The current flowing through the series circuit is calculated as follows:

Therefore, a current of 4.58 A flows through the series circuit.
Case (iii) When coils connected in parallel
When the coils are connected in parallel, the equivalent resistance is calculated as follows:

The current in the parallel circuit is 18.33 A.
14. Compare the power used in the 2 Ω resistor in each of the following circuits: (i) a 6 V battery in series with 1 Ω and 2 Ω resistors, and (ii) a 4 V battery in parallel with 12 Ω and 2 Ω resistors.
(i) The potential difference is 6 V and the resistors 1 Ω and 2 Ω are connected in series, hence their equivalent resistance is given by 1 Ω + 2 Ω = 3 Ω. The current in the circuit can be calculated using the Ohm’s law as follows:

Therefore, the power consumed by the 2 Ω is 8 W.
(ii) When 12 Ω and 2 Ω resistors are connected in parallel, the voltage across the resistors remains the same. Knowing that the voltage across 2 Ω resistor is 4 V, we can calculate the power consumed by the resistor as follows:

The power consumed by the 2 Ω resistor is 8 W.
15. Two lamps, one rated 100 W at 220 V, and the other 60 W at 220 V, are connected in parallel to electric mains supply. What current is drawn from the line if the supply voltage is 220 V?
Since both the bulbs are connected in parallel, the voltage across each of them will be the same.
Current drawn by the bulb of rating 100 W can be calculated as follows:
I = 100 W/220 V = 100/220 A
Similarly, the current drawn by the bulb of rating 60 W can be calculated as follows:
I = 60 W/220 V = 60/220 A

16. Which uses more energy, a 250 W TV set in 1 hr, or a 1200 W toaster in 10 minutes?
The energy consumed by electrical appliances is given by the equation
H = Pt , where P is the power of the appliance and t is the time
Using this formula, the energy consumed by a TV of power ration 250 W, can be calculated as follows:
H = 250 W × 3600 seconds = 9 × 10 5 J
Similarly, the energy consumed by a toaster of power rating 1200 W is
H = 1200 W × 600 s = 7.2 × 10 5 J
From the calculations, it can be said that the energy consumed by the TV is greater than the toaster.
17. An electric heater of resistance 8 Ω draws 15 A from the service mains 2 hours. Calculate the rate at which heat is developed in the heater.
The rate at which the heat develops in the heater can be calculated using the following formula
P = (15A) 2 × 8 Ω = 1800 watt
The electric heater produces heat at the rate of 1800 watt
18. Explain the following.
a. Why is the tungsten used almost exclusively for filament of electric lamps?
b. Why are the conductors of electric heating devices, such as bread-toasters and electric irons, made of an alloy rather than a pure metal?
c. Why is the series arrangement not used for domestic circuits?
d. How does the resistance of a wire vary with its area of cross-section?
e. Why copper and aluminium wires are usually employed for electricity transmission?
a. The resistivity and melting point of tungsten is very high. Due to this property, it doesn’t burn readily when heated. Electric lamps operate at high temperature. Hence, tungsten is a choice of metal for the filament of electric lamps.
b. The conductors of electric heating devices are alloys because of their high resistivity. Alloys have higher resistivity than pure metals. Due to its high resistivity, a large amount of heat is produced when current passes through it.
c. The series arrangement is not used for domestic circuits due to the following reasons:
The overall voltage gets distributed in a series circuit. As a result, electric appliances may not get the rated power for their operation.
All the connected appliances cannot be operated independently. If one device is defective, then the entire circuit will not function.
The total resistance becomes large, and as a result, the current is reduced.
d. Resistance is inversely proportional to the area of cross section. When the area of cross section increases the resistance decreases and vice versa.
e. Copper and aluminium are good conductors of electricity and have low resistivity, because of which they are usually employed for electricity transmission. Due to low resistivity, the power losses in the form of heat are also significantly less when electricity is transmitted through them.
Chapter 12 – Electricity is expected to carry at least 8 marks according to the examination trends observed in the previous years. However, the 2018 Class 10 Science exam had questions totalling up to 7 marks for this chapter. Utilize the NCERT Solutions for Class 10 to attain a firm grip on the key concepts present in this chapter of Science.
The topics covered under this chapter’s NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science are:
- Resistivity and Resistance
- Factors that affect the Resistance of a Conductor
- Parallel and Series Combination of Resistors and their applications
- Heating Effect of Electric Current and its Applications
- Electric Power
- The interrelation between P, V, I and R
Electricity is one of the most integral aspects of our society. Electricity has been shaping up to our civilization ever since the dawn of the industrial revolution, powering entire industries and businesses. Today, life without electricity would result in total chaos if we were to lose this important source of energy.
Explore how electricity works at the molecular level, learn important concepts and discover its applications. Find more learning resources at NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science , all designed to help you learn in the most efficient way possible.
Key Features of NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Book Chapter 12 – Electricity
- Content framed in an easy-to-understand language
- Relevant solutions crafted by highly qualified teachers and industry experts
- Additional questions according to the latest prescribed syllabus
- A detailed breakdown of the toughest exam questions
- Access to additional learning resources like sample papers and previous year question papers
At BYJU’S, students can also access NCERT Solutions of other Classes from 1 to 12 for all subjects. These solutions are carefully curated by expert subject tutors according to the latest CBSE syllabus and guidelines.
Frequently Asked Questions on NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12
List out the topics covered in chapter 12 electricity of ncert solutions for class 10 science., why should the students download the ncert solutions for class 10 science chapter 12 pdf, how many exercises are present in chapter 12 of ncert solutions for class 10 science, leave a comment cancel reply.
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

myCBSEguide
- Case Study Questions Class...
Case Study Questions Class 10 Science
Table of Contents
myCBSEguide App
Download the app to get CBSE Sample Papers 2023-24, NCERT Solutions (Revised), Most Important Questions, Previous Year Question Bank, Mock Tests, and Detailed Notes.
Download Case study questions for CBSE class 10 Science in PDF format from the myCBSEguide App . We have the new pattern case study-based questions for free download. Class 10 Science case study questions
This article will guide you through:
What are case study questions?
- Sample Papers with Case Study questions
- Class 10 Science Case Study question examples
- How to get case-based questions for free?
- How to attempt the case-based questions in Science?
Questions based on case studies are some real-life examples. The questions are asked based on a given paragraph i.e. Case Study. Usually, 4-5 questions are asked on the basis of the given passage. In most cases, these are either MCQs or assertion & reason type questions. Let’s take an example to understand. There is one paragraph on how nitrogen is generated in the atmosphere. On the basis of this paragraph, the board asks a few objective-type questions. In other words, it is very similar to the unseen passages given in language papers. But the real cases may be different. So, read this article till the end to understand it thoroughly.
What is CBE?
CBSE stands for competency-based education. The case study questions are part of this CBE. The purpose of CBE is to demonstrate the learning outcomes and attain proficiency in particular competencies.
Questions on Real-life Situations
As discussed the case study questions are based on real-life situations. Especially for grade 10 science, it is very essential to have the practical knowledge to solve such questions. Here on the myCBSEguide app, we have given many such case study paragraphs that are directly related to real-life implications of the knowledge.
Sample Papers with Case Study Questions
Class 10 Science Sample Papers with case study questions are available in the myCBSEguide App . There are 4 such questions (Q.No.17 to 20) in the CBSE model question paper. If you analyze the format, you will find that the MCQs are very easy to answer. So, we suggest you, read the given paragraph carefully and then start answering the questions. In some cases, you will find that the question is not asked directly from the passage but is based on the concept that is discussed there. That’s why it is very much important to understand the background of the case study paragraph.
CBSE Case Study Sample Papers
You can download CBSE case study sample papers from the myCBSEguide App or Student Dashboard. Here is the direct link to access it.
Case Study Question Bank
As we mentioned that case study questions are coming in your exams for the last few years. You can get them in all previous year question papers issued by CBSE for class 1o Science. Here is the direct link to get them too.
Class 10 Science Case Study Question Examples
As you have already gone through the four questions provided in the CBSE model question paper , we are proving you with other examples of the case-based questions in the CBSE class 10 Science. If you wish to get similar questions, you can download the myCBSEguide App and access the Sample question papers with case study-type questions.
Case-based Question -1
Read the following and answer any four questions: Salt of a strong acid and strong base is neutral with a pH value of 7. NaCl common salt is formed by a combination of hydrochloride and sodium hydroxide solution. This is the salt that is used in food. Some salt is called rock salt bed of rack salt was formed when seas of bygone ages dried up. The common salt thus obtained is an important raw material for various materials of daily use, such as sodium hydroxide, baking soda, washing soda, and bleaching powder.
- Phosphoric acid
- Carbonic acid
- Hydrochloric acid
- Sulphuric acid
- Blue vitriol
- Washing soda
- Baking soda
- Bleaching powder
Case-based Question -2
- V 1 + V 2 + V 3
- V 1 – V 2 +V 2
- None of these
- same at every point of the circuit
- different at every point of the circuit
- can not be determined
- 20 3 Ω 203Ω
- 15 2 Ω 152Ω
Case-based Question -3
- pure strips
- impure copper
- refined copper
- none of these
- insoluble impurities
- soluble impurities
- impure metal
- bottom of cathode
- bottom of anode
How to Attempt the Case-Based Questions in Science?
Before answering this question, let’s read the text given in question number 17 of the CBSE Model Question Paper.
All living cells require energy for various activities. This energy is available by the breakdown of simple carbohydrates either using oxygen or without using oxygen.
See, there are only two sentences and CBSE is asking you 5 questions based on these two sentences. Now let’s check the first questions given there.
Energy in the case of higher plants and animals is obtained by a) Breathing b) Tissue respiration c) Organ respiration d) Digestion of food
Now let us know if you can relate the question to the paragraph directly. The two sentences are about energy and how it is obtained. But neither the question nor the options have any similar text in the paragraph.
So the conclusion is, in most cases, you will not get direct answers from the passage. You will get only an idea about the concept. If you know it, you can answer it but reading the paragraph even 100 times is not going to help you.
Test Generator
Create question paper PDF and online tests with your own name & logo in minutes.
Question Bank, Mock Tests, Exam Papers, NCERT Solutions, Sample Papers, Notes
Related Posts
- CBSE Practice Papers 2023
- Class 10 Science Sample Papers 2024
- Competency Based Learning in CBSE Schools
- Class 11 Physical Education Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Sociology Case Study Questions
- Class 12 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Mathematics Case Study Questions
2 thoughts on “Case Study Questions Class 10 Science”
Where is the answer
Class 10 Science MCQ

Leave a Comment
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

- Neet Online Test Pack
12th Standard stateboard question papers & Study material
தமிழ் subjects.

கணினி பயன்பாடுகள்

கணினி அறிவியல்
வணிகக் கணிதம் மற்றும் புள்ளியியல்.

கணினி தொழில்நுட்பம்

கணக்குப்பதிவியல்

English Subjects

Computer Science

Business Maths and Statistics

Accountancy

Computer Applications

Computer Technology

11th Standard stateboard question papers & Study material

9th Standard stateboard question papers & Study material

Social Science

சமூக அறிவியல்
6th standard stateboard question papers & study material.

10th Standard stateboard question papers & Study material

7th Standard stateboard question papers & Study material

8th Standard stateboard question papers & Study material

கணிதம் - old

12th Standard CBSE Subject Question Paper & Study Material

Introductory Micro and Macroeconomics

Business Studies

Indian Society

Physical Education

Bio Technology

Engineering Graphics

Entrepreneurship

Hindi Elective

Home Science

Legal Studies

Political Science

11th Standard CBSE Subject Question Paper & Study Material

Mathematics

Enterprenership

Applied Mathematics
10th standard cbse subject question paper & study material.

9th Standard CBSE Subject Question Paper & Study Material

8th Standard CBSE Subject Question Paper & Study Material

7th Standard CBSE Subject Question Paper & Study Material

6th Standard CBSE Subject Question Paper & Study Material

School Exams

Tamil Nadu State Board Exams

Scholarship Exams

Study Materials , News and Scholarships

Stateboard Tamil Nadu

Free Online Tests

Educational News

Scholarships

Entrance Exams India

Video Materials

10th Standard CBSE
Class 10th Science - Electricity Case Study Questions and Answers 2022 - 2023

Class 10th Science - Electricity Case Study Questions and Answers 2022 - 2023 Study Materials Sep-09 , 2022
QB365 provides a detailed and simple solution for every Possible Case Study Questions in Class 10 Science Subject - Electricity, CBSE. It will help Students to get more practice questions, Students can Practice these question papers in addition to score best marks.

A PHP Error was encountered
Severity: Warning
Message: in_array() expects parameter 2 to be array, null given
Filename: material/details.php
Line Number: 1436
Message: Use of undefined constant EXAM - assumed 'EXAM' (this will throw an Error in a future version of PHP)
Line Number: 1438
QB365 - Question Bank Software
Electricity case study questions with answer key.
Final Semester - June 2015
The rate of flow of charge is called electric current. The SI unit of electric current is Ampere (A). The direction of flow of current is always opposite to the direction of flow of electrons in the current. The electric potential is defined as the amount of work done in bringing a unit positive test charge from infinity to a point in the electric field. The amount of work done in bringing a unit positive test charge from one point to another point in an electric field is defined as potential difference. \(\begin{equation} V_{A B}=V_{B}-V_{A}=\frac{W_{B A}}{q} \end{equation}\) The SI unit of potential and potential difference is volt. (i) The 2 C of charge is flowing through a conductor in 100 rns, the current in the circuit is
(ii) Which of the following is true? (a) Current flows from positive terminal ofthe cell to the negative terminal of the cell outside the cell. (b) The negative charge moves from lower potential to higher potential. (c) The direction of flow of current in same as the direction of flow of positive charge. (d) All of these (iii) The potential difference between the two terminals of a battery, if 100 joules of work is required to transfer 20 coulombs of charge from one terminal of the battery to other is
(iv) The number of electrons flowing per second in a conductor if 1A current is passing through it
(v) The voltage can be written as
The relationship between potential difference and current was first established by George Simon Ohm called Ohm's law. According to this law, the current through a metallic conductor is proportional to the potential difference applied between its ends, provided the temperature remain constant i.e. I \(\begin{equation} \propto \end{equation}\) V or V = IR; where R is constant for the conductor and it is called resistance of the conductor. Although Ohm's law has been found valid over a large class of materials, there do exist materials and devices used in electric circuits where the proportionality of V and I does not hold. (i) If both the potential difference and the resistance in a circuit are doubled, then
(ii) For a conductor, the graph between V and I is there. Which one is the correct?
(iii) The slope of V - I graph (V on x-axis and I on y-axis) gives
(iv) When battery of 9 V is connected across a conductor and the current flows is 0.1 A, the resistance is
(v) By increasing the voltage across a conductor, the
The obstruction offered by a conductor in the path of flow of current is called resistance. The SI unit of resistance is ohm ( \(\begin{equation} \Omega \end{equation}\) ). It has been found that the resistance of a conductor depends on the temperature of the conductor. As the temperature increases the resistance also increases. But the resistance of alloys like mangnin, constantan and nichrome is almost unaffected by temperature. The resistance of a conductor also depends on the length of conductor and the area of cross-section of the conductor. More be the length, more will be the resistance, more be the area of cross-section, lesser will be the resistance. (i) Which of the following is not will desired in material being used for making electrical wires?
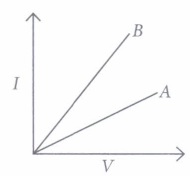
(iii) Two wires of same material one of length L and area of cross-section A, other is of length 2L and area A/2 . Which of the following is correct?
(iv) For the same conducting wire (a) resistance is higher in summer (b) resistance is higher in winter (c) resistance is same is summer or in winter (d) none of these (v) A wire of resistance 20 \(\begin{equation} \Omega \end{equation}\) is cut into 5 equal pieces. The resistance of each part is
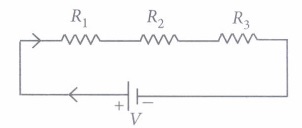
(ii) When the three resistors each of resistance R ohm, connected in series, the equivalent resistance is
(iii) There is a wire oflength 20 cm and having resistance 20 \(\begin{equation} \Omega \end{equation}\) cut into 4 equal pieces and then joined in series. The equivalent resistance is
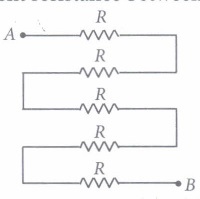
Several resistors may be combined to form a network. The combination should have two end points to connect it with a battery or other circuit elements. When the resistances are connected in series, the current in each resistance is same but the potential difference is different in each resistor. When the resistances are connected in parallel, the voltage drop across each resistance is same but the current is different in each resistor. (i) The household circuits are connected in
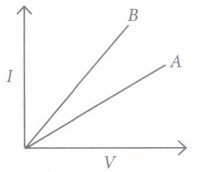
(v) Two resistances 10 \(\begin{equation} \Omega \end{equation}\) and 3 \(\begin{equation} \Omega \end{equation}\) are connected in parallel across a battery. If there is a current of 0.2 A in 10 .Q resistor, the voltage supplied by battery is
The heating effect of current is obtained by transformation of electrical energy in heat energy. Just as mechanical energy used to overcome friction is covered into heat, in the same way, electrical energy is converted into heat energy when an electric current flows through a resistance wire. The heat produced in a conductor, when a current flows through it is found to depend directly on (a) strength of current (b) resistance of the conductor (c) time for which the current flows. The mathematical expression is given by H = I 2 Rt. The electrical fuse, electrical heater, electric iron, electric geyser etc. all are based on the heating effect of current. (i) What are the properties of heating element? (a) High resistance, high melting point (b) Low resistance, high melting point (c) Low resistance, high melting point (d) Low resistance, low melting point. (ii) What are the properties of electric fuse? (a) Low resistance, low melting point (b) High resistance, high melting point. (c) High resistance, low melting point (d) Low resistance, high melting point (iii) When the current is doubled in a heating device and time is halved, the heat energy produced is
(iv) A fuse wire melts at 5 A. It is is desired that the fuse wire of same material melt at 10 A. The new radius of the wire is
(v) When a current of 0.5 A passes through a conductor for 5 min and the resistance of conductor is 10 \(\begin{equation} \Omega \end{equation}\) , the amount of heat produced is
The electrical energy consumed by an electrical appliance is given by the product of its power rating and the time for which it is used. The SI unit of electrical energy is Joule. Actually, Joule represents a very small quantity of energy and therefore it is inconvenient to use where a large quantity of energy is involved. So for commercial purposes we use a bigger unit of electrical energy which is called kilowatt hour. 1 kilowatt-hour is equal to 3.6 x 106 joules of electrical energy. (i) The energy dissipated by the heater is E. When the time of operating the heater is doubled, the energy dissipated is
(ii) The power of a lamp is 60 W The energy consumed in 1 minute is
(iii) The electrical refrigerator rated 400 W operates 8 hours a day. The cost of electrical energy is \(\begin{equation} ₹ \end{equation}\) 5 per kWh. Find the cost of running the refrigerator for one day?
(iv) Calculate the energy transformed by a 5 A current flowing through a resistor of 2 \(\begin{equation} \Omega \end{equation}\) for 30 minutes?
(v) Which of the following is correct? (a) 1 watt hour = 3600 J (b) lkWh = 36x10 6 J (c) Energy (in kWh) = power (in W) x time (in hr) (d) \(\begin{equation} \text { Energy (in kWh) }=\frac{V(\text { volt }) \times I(\text { ampere }) \times t(\text { sec })}{1000} \end{equation}\)
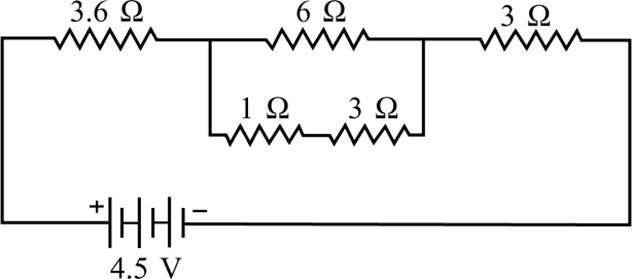
(i) Total resistance of parallel combination is : (a) 2.4 Ω (b) 3 Ω (c) 6 Ω (d) 2 Ω (ii) Equivalent resistance of total circuit is : (a) 5 Ω (b) 9 Ω (c) 11 Ω (d) 13 Ω (iii) Total current in the circuit is : (a) 2 A (b) 4.5 A (c) 0.5 A (d) 10 A (iv) Current in 6 ohm resistance is (a) 0.3 A (b) 0.2 A (c) 4 A (d) 6 A (v) Potential across 3.6 ohm resistance will be : (a) 1.8 V (b) 2.6 V (c) 9 V (d) 4.5 V
*****************************************
- Previous Class 10th Science - Our Environment Case Study Questions and Answers 2022 - 202...
- Next Class 10th Science - Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Case Study Questions a...
10th Standard CBSE Science free Online practice tests
Metals and non-metals - practice test 1.
10 Questions
Acids, Bases and Salts - Practice Test 1
Chemical reactions and equations - practice test 1, reviews & comments about class 10th science - electricity case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023.

Write your Comment

10th Standard CBSE Science Videos
CBSE 10th Science Sample Model Question Paper with Answer Key 2023
10th Standard CBSE Science Usefull Links

- 10th Standard
Other 10th Standard CBSE Subjects

Other 10th Standard CBSE Science Study material
Class 10th science - our environment case ... click to view, class 10th science - magnetic effects of ... click to view, class 10th science - electricity case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023 click to view, class 10th science - human eye and ... click to view, class 10th science - light reflection and ... click to view, class 10th science - heredity and evolution ... click to view, class 10th science - how do organisms ... click to view, class 10th science - life processes case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023 click to view, class 10th science - periodic classification of ... click to view, class 10th science - carbon and its ... click to view, class 10th science - metals and non-metals ... click to view, class 10th science - acids, bases and ... click to view, class 10th science - chemical reactions and ... click to view, 10th standard cbse science board exam model question paper iii 2019-2020 click to view, 10th standard cbse science board exam model question paper ii 2019-2020 click to view, register & get the solution for class 10th science - electricity case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023.
- CBSE- Electricity
- Sample Questions
Electricity-Sample Questions
- STUDY MATERIAL FOR CBSE CLASS 10 PHYSICS
- Chapter 1 - Electricity
- Chapter 2 - Human Eye and the Colourful World
- Chapter 3 - Light- Reflection and Refraction
- Chapter 4 - Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
- Chapter 5 - Sources of Energy
- Bihar Board
CFA Institute
Srm university.
- RBSE 10th Result 2024
- RBSE 12th Result 2024
- Maharashtra HSC Result
- MBSE Result 2024
- TBSE Result 2024
- CBSE Board Result 2024
- Shiv Khera Special
- Education News
- Web Stories
- Current Affairs
- नए भारत का नया उत्तर प्रदेश
- School & Boards
- College Admission
- Govt Jobs Alert & Prep
- GK & Aptitude
- CBSE Class 10 QnA
CBSE Class 10 Physics Electricity Important Questions and Answers for 2023
Cbse class 10 physics electricity important questions and answers: in this article we have covered the chapter electricity from cbse class 10 science. the answers are in the pdf towards the end of the article. .

CBSE Class 10 Physics Electricity Important Questions and Answers: Using the help of these important questions from the chapter Electricity, students appearing in CBSE Class 10 Science board examination can achieve their dream scores. These questions have been specially chosen by subject experts keeping in mind the revised syllabus, latest sample paper and board guidelines.
Electricity is actually the 11th Chapter according to the latest syllabus and updated NCERT Textbook. However, earlier it appeared as Chapter 12. Chapter 11 Electricity is a part of Unit IV. The other chapter in this unit is Magnetic effects of current which is Chapter 12.
The topics covered in this chapter are: Electric current, potential difference and electric current. Ohm’s law; Resistance, Resistivity, Factors on which the resistance of a conductor depends. Series combination of resistors, parallel combination of resistors and its applications in daily life. Heating effect of electric current and its applications in daily life. Electric power, Interrelation between P, V, I and R.
CBSE Class 10 Physics Electricity Important Questions
MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS
Q.1.When electric current is passed, electrons move from:
(a) high potential to low potential.
(b) low potential to high potential.
(c) in the direction of the current.
(d) against the direction of the current.
Q.2. The unit of resistivity is:
(a) V A
(b) V A
(c) V m /A
Q.3. What is the commercial unit of electrical energy?
(a) Joules
(b) Kilojoules
(c) Kilowatt-hour
(d) Watt-hour
Q.4. The instrument used for measuring electric current is :
(a) Ammeter
(b) Galvanometer
(c) Voltmeter
(d) Potentiometer
Q.5. Electrical resistivity of any given metallic wire depends upon
(a) its thickness
(b) its shape
(c) nature of the material
(d) its length
Q.6. In an electrical circuit two resistors of 2 Ω and 4 Ω respectively are connected in series to a 6 V battery. The heat dissipated by the 4 Ω resistor in 5 s will be
(a) 5 J
(b) 10 J
(c) 20 J
Q.7. The heating element of an electric iron is made up of:
(a) copper
(b) nichrome
(c) aluminium
Q.8. Work of 14 J is done to move 2 C charge between two points on a conducting wire. What is the potential difference between the two points?
(a) 28 V
(b) 14 V
(c) 7 V
- mechanical, electrical
- electrical, chemical
- heat, electrical
- chemical, heat
Q.10. The unit of potential difference is :
(a) Volt
(b) Ohm
(c) Ampere
(d) Faraday
- is a good conductor of electricity
- has a low melting point
- has a high melting point
- is not easily available
Q.12. Coulomb is the SI unit of:
(a) Charge
(b) current
(c) potential difference
(d) resistance
ASSERTION-REASON TYPE QUESTIONS
Following questions consist of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions selecting the appropriate option given below:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Q.1.. Assertion (A): When resistances are connected between the same two points they are said to be in series.
Reason(R): When resistors are connected in series the current through each resistor is the same.
Q.2. Assertion (A) : Tungsten metal is used for making filaments of incandescent lamps.
Reason (R) : The melting point of tungsten is very low.
Q.3. Assertion (A): If a graph is plotted between potential difference and current the graph is a straight line passing through the origin.
Reason(R): current is directly proportional to the potential difference.
Q.4. Assertion (A) : Longer wires have greater resistance and the smaller wires have lesser resistance.
Reason (R) : Resistance is inversely proportional to the length of the wire.-
Q.5. Assertion (A) : Alloys are commonly used in electrical heating devices, like electrical iron, toasters etc.
Reason (R) : Alloys do not oxidise (burn) readily at high temperatures.
6. Assertion (A) : Bending a wire does not affect electrical resistance.
Reason (R) : Resistance of a wire is proportional to resistivity of material.
Q.7. Assertion (A): A cell converts chemical energy into electrical energy.
Reason(R): A cell maintains a potential difference across its terminals due to chemical reactions.
CASE STUDY BASED QUESTION
- Which is a better conductor of electric current ?
- Which element will be used for electrical transmission lines ?
- Nichrome is used in the heating elements of electric heating device because:
(A) It has high resistivity
(B) It does not oxidise readily at high temperature
(C) Both of the above
- Series arrangement is not used for domestic circuits because:
(A) Current drawn is less
(B) Current drawn is more
(C) Neither of the above
(D) Both of the above
TWO MARKS QUESTIONS
Q.1.Calculate the number of electrons that would flow per second through the cross- section of a wire when 1 A current flows in it.
Q.2. Define the following terms:
(a) one ampere (b) 1 volt.
Q.3. Keeping the potential difference constant, the resistance of a circuit is doubled. By how much does the current change?
Q.4. How much work is done in moving a charge of magnitude 3 C across two points having a potential difference of 12 V?
Q.5. Define electric power. Write an expression relating electric power, potential difference and resistance.
- Tungsten used almost exclusively for filament of electric lamp.
- Why do we use copper and aluminium wires for transmission of electric current?
Q.7. Distinguish between resistances in series and resistances in parallel.
8. What is the better way of connecting lights and other electrical appliances in domestic wiring? Why?
THREE MARKS QUESTIONS
Q.1. (a) List the factors on which the resistance of a conductor in the shape of a wire depends.
(b) Why are metals good conductors of electricity whereas glass is a bad conductor of electricity? Give reasons..
(c) Why are alloys commonly used in electrical heating devices? Give reason.
2. A nichrome wire has a resistance of 10 Ω. Find the resistance of another nichrome wire, whose length is three times and area of cross-section four times the first wire.
Q.3. State the formula co-relating the electric current flowing in a conductor and the voltage applied across it. Also, show this relationship by drawing a graph. What would be the resistance of a conductor, if the current flowing through it is 0.35 ampere when the potential difference across it is 1.4 volt?
4.Calculate the total cost of running the following electrical devices in April month if the rate of 1 unit of electricity is Rs. 6.00. (i) Electric heater of 1000 W for 5 hours daily. (ii) Electric refrigerator of 400 W for 10 hours daily
5. (i) Consider a conductor of resistance ‘R’, length ‘L’, thickness ‘d’ and resistivity ‘ρ’. Now this conductor is cut into four equal parts. What will be the new resistivity of each of these parts? Why?
(ii) Find the resistance if all of these parts are connected in:
(a) Parallel (b) Series
(iii) Out of the combinations of resistors mentioned above in the previous part, for a given voltage which combination will consume more power and why?
Also Check: CBSE Class 10 Science Sample Paper 2022-23
Electricity has revolutionised the world and our lives. It has an important place in modern society. As an controllable and convenient form of energy, it is utilised for a variety of chores in homes, at schools, hospitals, industries and so on. Thus, students should not just cram the syllabus to score marks in exam but try to actually grasp the content of the chapters as it is a very important topic for academic and personal life as well.
Get here latest School , CBSE and Govt Jobs notification in English and Hindi for Sarkari Naukari and Sarkari Result . Download the Jagran Josh Sarkari Naukri App . Check Board Result 2024 for Class 10 and Class 12 like CBSE Board Result , UP Board Result , Bihar Board Result , MP Board Result , Rajasthan Board Result and Other States Boards.
- Rajasthan Board 12th Result 2024
- rajeduboard.rajasthan.gov.in Result 2024
- Rajasthan Board Class 12th Result 2024
- 12th Result 2024 Rajasthan Board
- rajresults.nic.in Result 2024
- RBSE 12th Toppers List 2024
- Jagran Josh 12th Result 2024 RBSE
- rajresults.nic.in 12th Result 2024
- 12th Result 2024 RBSE Roll Number और Name wise
- CBSE Class 10
Latest Education News
IPL 2024 Full Schedule: आईपीएल 2024 का फुल शेड्यूल,आज किस टीम का है मैच जानें यहां
[चेक करें] rajresults.nic.in 2024 Result: राजस्थान 12वीं रिजल्ट का लिंक, Roll Number से परिणाम देखे और डाउनलोड करें Inter की Marksheet
[कला रिजल्ट] Rajasthan Board 12th Result 2024: 12वीं आर्ट्स में 96.88% छात्र पास, Umang App और Digilocker पर तुरंत देखें रिजल्ट
[रिजल्ट लिंक] JAC 8th Result 2024: 8वीं के नतीजे जल्द, jac.jharkhand.gov.in पर Result Link से डाउनलोड करें Marksheet
IPL 2024 Qualifier 1 KKR vs SRH: संभावित Playing 11,मैच का समय, टीम स्क्वाड और Live स्ट्रीमिंग डिटेल्स यहां देखें
HSC 12th Result 2024 Maharashtra Board LIVE: MSBSHSE Class 12 Result Releasing Today at mahahsscboard.in with Roll Number; Check Latest Updates Here
Vision IQ Test: Only A Person With Night Owl Vision Can Find Three Red Apples In The Bird Box Picture in 9 Seconds. Good Luck!
WhatsApp Rolling Out Locked Chats Feature for Enhanced Security
RBSC 10th Result 2024 Roll Number Link: आज आ सकता है राजस्थान बोर्ड 10वीं रिजल्ट नोटिफिकेशन, rajresults.nic.in से डाउनलोड करें Marksheet
[रिजल्ट लिंक] 12th Result 2024 RBSE Roll Number और Name wise राजस्थान बोर्ड 12वीं आर्ट्स, साइंस और कॉमर्स का रिजल्ट link -rajeduboard.rajasthan.gov.in पर देखें
Class 9 Chemistry Project Ideas 2024-25: Top 5 Easy Topics For Summer Vacations!
UP Board Class 12 General Hindi Syllabus 2024-25: Download Free PDF With Course Structure And Division Of Marks!
Genius IQ Test: Can you solve this maths puzzle in 10 seconds?
MBSE HSSLC Result 2024 LIVE Updates: Check Mizoram Class 12 Science, Commerce and Arts Result Link Online at Official Website - mbse.edu.in
You are a visual ninja if you can find three owls on the rocks in 8 seconds!
Brain Teaser: Only People With Perfect Vision Can Spot the Hidden Number 8 in 19 Seconds
Buddha Purnima Special Rangoli Designs (2024)
20+ Question of the Day for School Assembly with Answers (May 21, 2024)
School Assembly Headlines, May 21: Kerala Rains, RBSE 12th Results, Nancy Tyagi, Iran President, and More Top News in English
RBSE Result 2024: राजस्थान बोर्ड रिजल्ट Link at Jagran Josh, rajeduboard.rajasthan.gov.in, rajresults.nic.in
Question and Answer forum for K12 Students

MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity with Answers
We have compiled the NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity with Answers Pdf free download covering the entire syllabus. Practice MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science with Answers on a daily basis and score well in exams. Refer to the Electricity Class 10 MCQs Questions with Answers here along with a detailed explanation.
Electricity Class 10 MCQs Questions with Answers
1. When electric current is passed, electrons move from: (a) high potential to low potential. (b) low potential to high potential. (c) in the direction of the current. (d) against the direction of the current.

2. The heating element of an electric iron is made up of: (a) copper (b) nichrome (c) aluminium (d) iron

3. The electrical resistance of insulators is (a) high (b) low (c) zero (d) infinitely high
4. Electrical resistivity of any given metallic wire depends upon (a) its thickness (b) its shape (c) nature of the material (d) its length

6. Electric power is inversely proportional to (a) resistance (b) voltage (c) current (d) temperature
MCQ Chapter Electricity Class 10 Question 7. What is the commercial unit of electrical energy? (a) Joules (b) Kilojoules (c) Kilowatt-hour (d) Watt-hour
8. Three resistors of 1 Ω, 2 ft and 3 Ω are connected in parallel. The combined resistance of the three resistors should be (a) greater than 3 Ω (b) less than 1 Ω (c) equal to 2 Ω (d) between 1 Ω and 3 Ω

9. An electric bulb is connected to a 220V generator. The current is 0.50 A. What is the power of the bulb? (a) 440 W (b) 110 W (c) 55 W (d) 0.0023 W
Answer: b Explaination: Here, V = 220 V, I = 0.50 A ∴ Power (P) = VI = 220 x 0.50 = 110 W
10. The resistivity of insulators is of the order of (a) 10 -8 Ω -m (b) 10 1 Ω -m (c) 10 -6 Ω -m (d) 10 6 Ω -m
11. 1 kWh = ……….. J (a) 3.6 × 10 -6 J (b) \(\frac{1}{3.6}\) × 10 6 J (c) 3.6 × 10 6 J (d) \(\frac{1}{3.6}\) × 10 -6 J
12. Which of the following gases are filled in electric bulbs? (a) Helium and Neon (b) Neon and Argon (c) Argon and Hydrogen (d) Argon and Nitrogen
13. 100 J of heat is produced each second in a 4Ω resistor. The potential difference across the resistor will be: (a) 30 V (b) 10 V (c) 20 V (d) 25 V
14. Electric potential is a: (a) scalar quantity (b) vector quantity (c) neither scalar nor vector (d) sometimes scalar and sometimes vector
Electricity Question 15. 1 mV is equal to: (a) 10 volt (b) 1000 volt (c) 10 -3 volt (d) 10 -6 volt
Electricity MCQ Question 16. Coulomb is the SI unit of: (a) charge (b) current (c) potential difference (d) resistance
Fill in the Blanks
1. The SI unit of current is ……… . 2. According to ……… Law, the potential difference across the ends of a resistor is directly proportional to the ……… through it, provided its remains constant. 3. The resistance of a conductor depends directly on its ……… , inversely on its ……… and also on the ……… of the conductor. 4. The SI unit of resistivity is ……… . 5. If the potential difference across the ends of a conductor is doubled, the current flowing through it, gets ……… .
1. ampere 2. Ohm’s, current, temperature 3. length, area of cross-section, material 4. ohm-metre (Ω m) 5. doubled
Hope the information shed above regarding NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity with Answers Pdf free download has been useful to an extent. If you have any other queries of CBSE Class 10 Science Electricity MCQs Multiple Choice Questions with Answers, feel free to reach us so that we can revert back to us at the earliest possible.
2 thoughts on “MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity with Answers”
It was very helpful for me … it helped me to understand the chapter in a better way …the whole chapter was covered in this questions ..Now I think that I am fully prepared for the test …thanks allot
Mastery app thanks
Comments are closed.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
At Case Study Questions there will given a Paragraph. In where some Important Questions will made on that respective Case Based Study. There will various types of marks will given 1 marks, 2 marks, 3 marks, 4 marks. Case study: 1. We can see that, as the applied voltage is increased the current through the wire also increases.
Case Study/Passage Based Questions. Question 1: The heating effect of current is obtained by the transformation of electrical energy into heat energy. Just as mechanical energy used to overcome friction is covered into heat, in the same way, electrical energy is converted into heat energy when an electric current flows through a resistance wire.
Case Study Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity. Question 1: The electrical energy consumed by an electrical appliance is given by the product of its power rating and the time for which it is used. The SI unit of electrical energy is Joule (as shown in figure). Actually, Joule represents a very small quantity of energy and ...
CBSE 10th Standard Science Subject Electricity Case Study Questions With Solution 2021. 10th Standard CBSE. Reg.No. : Science. Time : 00:30:00 Hrs. Total Marks : 16. The rate of flow of charge is called electric current. The SI unit of electric current is Ampere (A). The direction of flow of current is always opposite to the direction of flow ...
The switch if OFF. Q2. A current of 10 A flows through a conductor for two minutes. ( i ) Calculate the amount of charge passed through any area of cross section of the conductor. ( ii ) If the charge of an electron is 1.6 × 10 − 19 C , then calculate the total number of electrons flowing.
CBSE Exam, class 10. About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features NFL Sunday Ticket
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity. Case Study/Passage Based Questions. Question 1: The heating effect of current is obtained by the transformation of electrical energy into heat energy. Just as mechanical energy used to overcome friction is covered into heat, in the same way ...
Case Study Questions Chapter 12 Electricity. Case/Passage - 1. Two tungston lamps with resistances R1 and R2 respectively at full incandescence are connected first in parallel and then in series, in a lighting circuit of negaligible internal resistance. It is given that: R1 > R2.
Electricity Case Study Questions (CSQ's) Practice Tests. Timed Tests. Select the number of questions for the test: Select the number of questions for the test: TopperLearning provides a complete collection of case studies for CBSE Class 10 Physics Electricity chapter. Improve your understanding of biological concepts and develop problem ...
Electricity | Case-Based Questions | CBSE Class 10 Physics | Science Chapter 12 NCERT Solutions | Abhishek Sir | Vedantu Class 9 and 10. In today's video, Ab...
Students should follow some basic tips to solve Electricity Case Study Based Questions. These tips can help students to score good marks in CBSE Class 10 Science. Generally, the case based questions are in the form of Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs). Students should start solving the case based questions through reading the given passage.
Class 10 Physics (India) 4 units · 49 skills. Unit 1. Light - reflection & refraction. ... Electricity class 10 numerical: CBSE board practice ... Electricity class 10: CBSE previous question paper problems (Opens a modal) Up next for you: Unit test. Level up on all the skills in this unit and collect up to 1,300 Mastery points! Start Unit test.
NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 12 - Free PDF Download. NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity are the study materials necessary for you to understand the questions that can be asked from the Class 10 Science Electricity chapter. It is crucial for students to get acquainted with this chapter in order to score excellent marks in their CBSE Class ...
February 25, 2022 March 19, 2023 Physics Gurukul 1 Comment on Case Study Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity Case Study Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity December 19, 2021 March 19, 2023 Physics Gurukul Leave a Comment on Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 How Do Organisms ...
NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity: In this article, we will provide you all the necessary information regarding NCERT solutions for class 10 science physics chapter 12 electricity.Working on CBSE class 10 physics electricity questions and answers will help candidates to score good marks in-class tests as well as in the CBSE Class 10 board exam.
Exercise 12.6 - 3 Questions. Exercise 12.7 - 2 Questions. Exercise 12.8 - 18 Questions. NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity PDF is provided here which can be accessed by the students based on their needs. Clear all your doubts with these NCERT Solutions prepared by subject experts at BYJU'S and ace the CBSE exams.
Class 10 Science Sample Papers with case study questions are available in the myCBSEguide App. There are 4 such questions (Q.No.17 to 20) in the CBSE model question paper. If you analyze the format, you will find that the MCQs are very easy to answer. So, we suggest you, read the given paragraph carefully and then start answering the questions.
The Chapter wise Important case study based questions with their solved answers in CBSE Class 10 Science can be accessed from the table below: CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions ...
10th Standard CBSE. Science. Time : 01:35:00 Hrs. Total Marks : 75. Case Study. The rate of flow of charge is called electric current. The SI unit of electric current is Ampere (A). The direction of flow of current is always opposite to the direction of flow of electrons in the current. The electric potential is defined as the amount of work ...
Calculate the energy consumed (in kWh) in the month of February. 13. A torch bulb is rated at 3V and 600mA. Calculate it's. (a) Power b) Resistance c) Energy consumed if it is lighted for 4 Hrs. 14. State and derive joule's law. An electric iron consumes energy at rate of 420w when heating is at maximum rate and 180 w when heating is at ...
Important Questions of Electricity Class 10 Science Chapter 12. Question 1. A current of 10 A flows through a conductor for two minutes. (i) Calculate the amount of charge passed through any area of cross section of the conductor. (ii) If the charge of an electron is 1.6 × 10 -19 C, then calculate the total number of electrons flowing.
CBSE Class 10 Physics Electricity Important Questions. MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS. Q.1.When electric current is passed, electrons move from: (a) high potential to low potential. (b) low potential ...
Answers. 1. ampere. 2. Ohm's, current, temperature. 3. length, area of cross-section, material. 4. ohm-metre (Ω m) 5. doubled. Hope the information shed above regarding NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity with Answers Pdf free download has been useful to an extent. If you have any other queries of CBSE Class 10 ...