When you choose to publish with PLOS, your research makes an impact. Make your work accessible to all, without restrictions, and accelerate scientific discovery with options like preprints and published peer review that make your work more Open.
- PLOS Biology
- PLOS Climate
- PLOS Complex Systems
- PLOS Computational Biology
- PLOS Digital Health
- PLOS Genetics
- PLOS Global Public Health
- PLOS Medicine
- PLOS Mental Health
- PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases
- PLOS Pathogens
- PLOS Sustainability and Transformation
- PLOS Collections
- How to Write Discussions and Conclusions

The discussion section contains the results and outcomes of a study. An effective discussion informs readers what can be learned from your experiment and provides context for the results.

What makes an effective discussion?
When you’re ready to write your discussion, you’ve already introduced the purpose of your study and provided an in-depth description of the methodology. The discussion informs readers about the larger implications of your study based on the results. Highlighting these implications while not overstating the findings can be challenging, especially when you’re submitting to a journal that selects articles based on novelty or potential impact. Regardless of what journal you are submitting to, the discussion section always serves the same purpose: concluding what your study results actually mean.
A successful discussion section puts your findings in context. It should include:
- the results of your research,
- a discussion of related research, and
- a comparison between your results and initial hypothesis.
Tip: Not all journals share the same naming conventions.
You can apply the advice in this article to the conclusion, results or discussion sections of your manuscript.
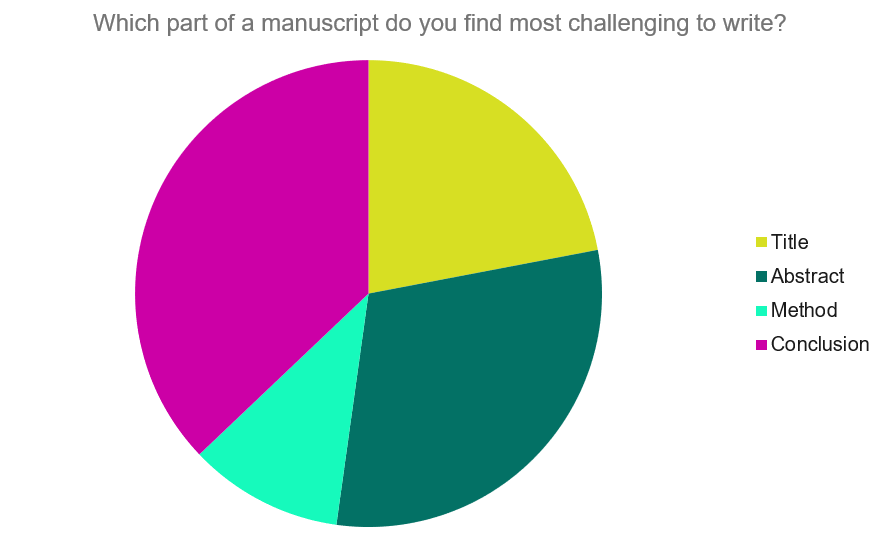
Our Early Career Researcher community tells us that the conclusion is often considered the most difficult aspect of a manuscript to write. To help, this guide provides questions to ask yourself, a basic structure to model your discussion off of and examples from published manuscripts.
Questions to ask yourself:
- Was my hypothesis correct?
- If my hypothesis is partially correct or entirely different, what can be learned from the results?
- How do the conclusions reshape or add onto the existing knowledge in the field? What does previous research say about the topic?
- Why are the results important or relevant to your audience? Do they add further evidence to a scientific consensus or disprove prior studies?
- How can future research build on these observations? What are the key experiments that must be done?
- What is the “take-home” message you want your reader to leave with?
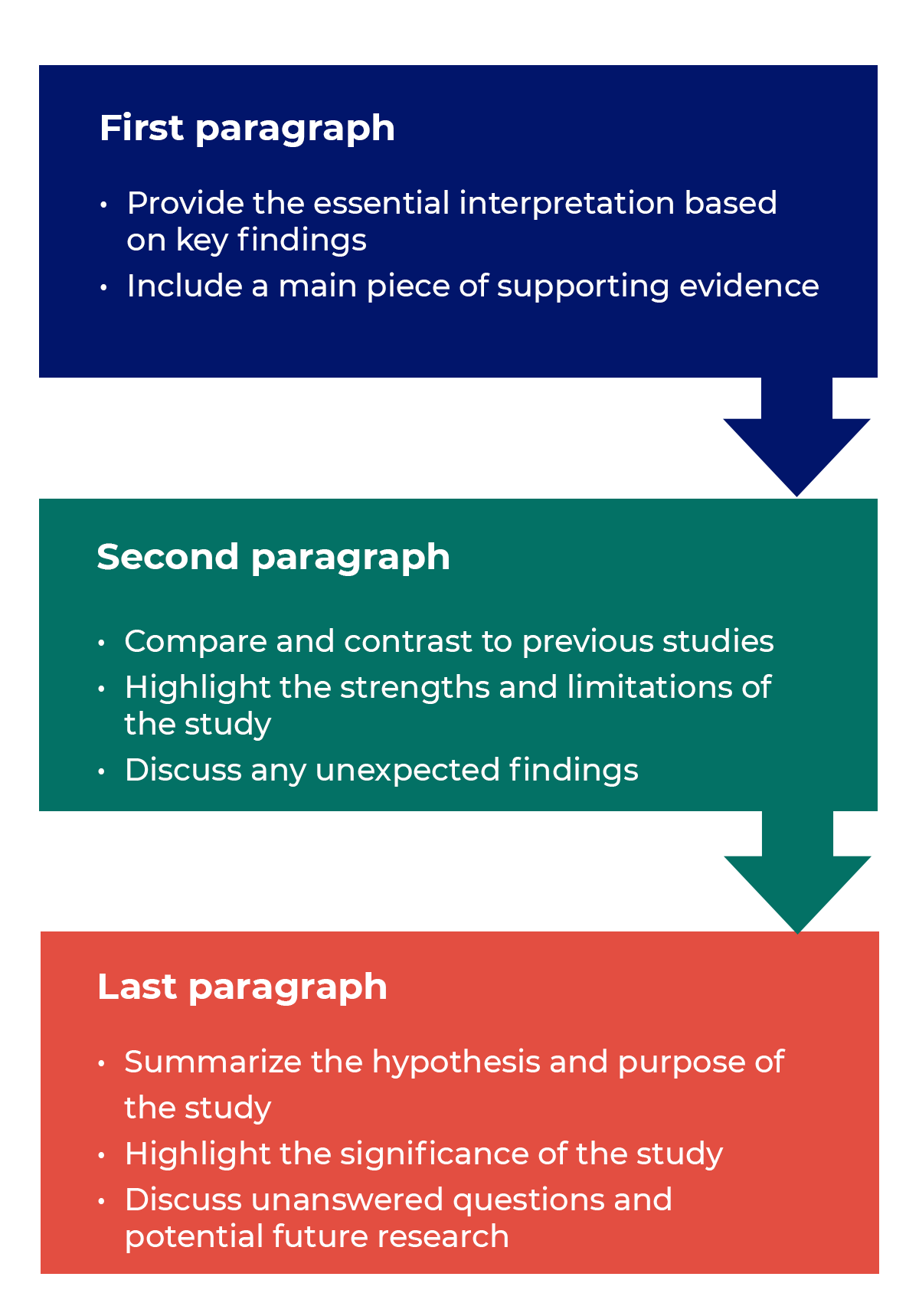
How to structure a discussion
Trying to fit a complete discussion into a single paragraph can add unnecessary stress to the writing process. If possible, you’ll want to give yourself two or three paragraphs to give the reader a comprehensive understanding of your study as a whole. Here’s one way to structure an effective discussion:
Writing Tips
While the above sections can help you brainstorm and structure your discussion, there are many common mistakes that writers revert to when having difficulties with their paper. Writing a discussion can be a delicate balance between summarizing your results, providing proper context for your research and avoiding introducing new information. Remember that your paper should be both confident and honest about the results!

- Read the journal’s guidelines on the discussion and conclusion sections. If possible, learn about the guidelines before writing the discussion to ensure you’re writing to meet their expectations.
- Begin with a clear statement of the principal findings. This will reinforce the main take-away for the reader and set up the rest of the discussion.
- Explain why the outcomes of your study are important to the reader. Discuss the implications of your findings realistically based on previous literature, highlighting both the strengths and limitations of the research.
- State whether the results prove or disprove your hypothesis. If your hypothesis was disproved, what might be the reasons?
- Introduce new or expanded ways to think about the research question. Indicate what next steps can be taken to further pursue any unresolved questions.
- If dealing with a contemporary or ongoing problem, such as climate change, discuss possible consequences if the problem is avoided.
- Be concise. Adding unnecessary detail can distract from the main findings.

Don’t
- Rewrite your abstract. Statements with “we investigated” or “we studied” generally do not belong in the discussion.
- Include new arguments or evidence not previously discussed. Necessary information and evidence should be introduced in the main body of the paper.
- Apologize. Even if your research contains significant limitations, don’t undermine your authority by including statements that doubt your methodology or execution.
- Shy away from speaking on limitations or negative results. Including limitations and negative results will give readers a complete understanding of the presented research. Potential limitations include sources of potential bias, threats to internal or external validity, barriers to implementing an intervention and other issues inherent to the study design.
- Overstate the importance of your findings. Making grand statements about how a study will fully resolve large questions can lead readers to doubt the success of the research.
Snippets of Effective Discussions:
Consumer-based actions to reduce plastic pollution in rivers: A multi-criteria decision analysis approach
Identifying reliable indicators of fitness in polar bears
- How to Write a Great Title
- How to Write an Abstract
- How to Write Your Methods
- How to Report Statistics
- How to Edit Your Work
The contents of the Peer Review Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
The contents of the Writing Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
There’s a lot to consider when deciding where to submit your work. Learn how to choose a journal that will help your study reach its audience, while reflecting your values as a researcher…
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- 9. The Conclusion
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
The conclusion is intended to help the reader understand why your research should matter to them after they have finished reading the paper. A conclusion is not merely a summary of the main topics covered or a re-statement of your research problem, but a synthesis of key points derived from the findings of your study and, if applicable, where you recommend new areas for future research. For most college-level research papers, two or three well-developed paragraphs is sufficient for a conclusion, although in some cases, more paragraphs may be required in describing the key findings and their significance.
Conclusions. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Conclusions. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University.
Importance of a Good Conclusion
A well-written conclusion provides you with important opportunities to demonstrate to the reader your understanding of the research problem. These include:
- Presenting the last word on the issues you raised in your paper . Just as the introduction gives a first impression to your reader, the conclusion offers a chance to leave a lasting impression. Do this, for example, by highlighting key findings in your analysis that advance new understanding about the research problem, that are unusual or unexpected, or that have important implications applied to practice.
- Summarizing your thoughts and conveying the larger significance of your study . The conclusion is an opportunity to succinctly re-emphasize your answer to the "So What?" question by placing the study within the context of how your research advances past research about the topic.
- Identifying how a gap in the literature has been addressed . The conclusion can be where you describe how a previously identified gap in the literature [first identified in your literature review section] has been addressed by your research and why this contribution is significant.
- Demonstrating the importance of your ideas . Don't be shy. The conclusion offers an opportunity to elaborate on the impact and significance of your findings. This is particularly important if your study approached examining the research problem from an unusual or innovative perspective.
- Introducing possible new or expanded ways of thinking about the research problem . This does not refer to introducing new information [which should be avoided], but to offer new insight and creative approaches for framing or contextualizing the research problem based on the results of your study.
Bunton, David. “The Structure of PhD Conclusion Chapters.” Journal of English for Academic Purposes 4 (July 2005): 207–224; Conclusions. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Kretchmer, Paul. Twelve Steps to Writing an Effective Conclusion. San Francisco Edit, 2003-2008; Conclusions. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Assan, Joseph. "Writing the Conclusion Chapter: The Good, the Bad and the Missing." Liverpool: Development Studies Association (2009): 1-8.
Structure and Writing Style
I. General Rules
The general function of your paper's conclusion is to restate the main argument . It reminds the reader of the strengths of your main argument(s) and reiterates the most important evidence supporting those argument(s). Do this by clearly summarizing the context, background, and necessity of pursuing the research problem you investigated in relation to an issue, controversy, or a gap found in the literature. However, make sure that your conclusion is not simply a repetitive summary of the findings. This reduces the impact of the argument(s) you have developed in your paper.
When writing the conclusion to your paper, follow these general rules:
- Present your conclusions in clear, concise language. Re-state the purpose of your study, then describe how your findings differ or support those of other studies and why [i.e., what were the unique, new, or crucial contributions your study made to the overall research about your topic?].
- Do not simply reiterate your findings or the discussion of your results. Provide a synthesis of arguments presented in the paper to show how these converge to address the research problem and the overall objectives of your study.
- Indicate opportunities for future research if you haven't already done so in the discussion section of your paper. Highlighting the need for further research provides the reader with evidence that you have an in-depth awareness of the research problem but that further investigations should take place beyond the scope of your investigation.
Consider the following points to help ensure your conclusion is presented well:
- If the argument or purpose of your paper is complex, you may need to summarize the argument for your reader.
- If, prior to your conclusion, you have not yet explained the significance of your findings or if you are proceeding inductively, use the end of your paper to describe your main points and explain their significance.
- Move from a detailed to a general level of consideration that returns the topic to the context provided by the introduction or within a new context that emerges from the data [this is opposite of the introduction, which begins with general discussion of the context and ends with a detailed description of the research problem].
The conclusion also provides a place for you to persuasively and succinctly restate the research problem, given that the reader has now been presented with all the information about the topic . Depending on the discipline you are writing in, the concluding paragraph may contain your reflections on the evidence presented. However, the nature of being introspective about the research you have conducted will depend on the topic and whether your professor wants you to express your observations in this way. If asked to think introspectively about the topics, do not delve into idle speculation. Being introspective means looking within yourself as an author to try and understand an issue more deeply, not to guess at possible outcomes or make up scenarios not supported by the evidence.
II. Developing a Compelling Conclusion
Although an effective conclusion needs to be clear and succinct, it does not need to be written passively or lack a compelling narrative. Strategies to help you move beyond merely summarizing the key points of your research paper may include any of the following:
- If your essay deals with a critical, contemporary problem, warn readers of the possible consequences of not attending to the problem proactively.
- Recommend a specific course or courses of action that, if adopted, could address a specific problem in practice or in the development of new knowledge leading to positive change.
- Cite a relevant quotation or expert opinion already noted in your paper in order to lend authority and support to the conclusion(s) you have reached [a good source would be from your literature review].
- Explain the consequences of your research in a way that elicits action or demonstrates urgency in seeking change.
- Restate a key statistic, fact, or visual image to emphasize the most important finding of your paper.
- If your discipline encourages personal reflection, illustrate your concluding point by drawing from your own life experiences.
- Return to an anecdote, an example, or a quotation that you presented in your introduction, but add further insight derived from the findings of your study; use your interpretation of results from your study to recast it in new or important ways.
- Provide a "take-home" message in the form of a succinct, declarative statement that you want the reader to remember about your study.
III. Problems to Avoid
Failure to be concise Your conclusion section should be concise and to the point. Conclusions that are too lengthy often have unnecessary information in them. The conclusion is not the place for details about your methodology or results. Although you should give a summary of what was learned from your research, this summary should be relatively brief, since the emphasis in the conclusion is on the implications, evaluations, insights, and other forms of analysis that you make. Strategies for writing concisely can be found here .
Failure to comment on larger, more significant issues In the introduction, your task was to move from the general [the field of study] to the specific [the research problem]. However, in the conclusion, your task is to move from a specific discussion [your research problem] back to a general discussion framed around the implications and significance of your findings [i.e., how your research contributes new understanding or fills an important gap in the literature]. In short, the conclusion is where you should place your research within a larger context [visualize your paper as an hourglass--start with a broad introduction and review of the literature, move to the specific analysis and discussion, conclude with a broad summary of the study's implications and significance].
Failure to reveal problems and negative results Negative aspects of the research process should never be ignored. These are problems, deficiencies, or challenges encountered during your study. They should be summarized as a way of qualifying your overall conclusions. If you encountered negative or unintended results [i.e., findings that are validated outside the research context in which they were generated], you must report them in the results section and discuss their implications in the discussion section of your paper. In the conclusion, use negative results as an opportunity to explain their possible significance and/or how they may form the basis for future research.
Failure to provide a clear summary of what was learned In order to be able to discuss how your research fits within your field of study [and possibly the world at large], you need to summarize briefly and succinctly how it contributes to new knowledge or a new understanding about the research problem. This element of your conclusion may be only a few sentences long.
Failure to match the objectives of your research Often research objectives in the social and behavioral sciences change while the research is being carried out. This is not a problem unless you forget to go back and refine the original objectives in your introduction. As these changes emerge they must be documented so that they accurately reflect what you were trying to accomplish in your research [not what you thought you might accomplish when you began].
Resist the urge to apologize If you've immersed yourself in studying the research problem, you presumably should know a good deal about it [perhaps even more than your professor!]. Nevertheless, by the time you have finished writing, you may be having some doubts about what you have produced. Repress those doubts! Don't undermine your authority as a researcher by saying something like, "This is just one approach to examining this problem; there may be other, much better approaches that...." The overall tone of your conclusion should convey confidence to the reader about the study's validity and realiability.
Assan, Joseph. "Writing the Conclusion Chapter: The Good, the Bad and the Missing." Liverpool: Development Studies Association (2009): 1-8; Concluding Paragraphs. College Writing Center at Meramec. St. Louis Community College; Conclusions. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Conclusions. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Freedman, Leora and Jerry Plotnick. Introductions and Conclusions. The Lab Report. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Leibensperger, Summer. Draft Your Conclusion. Academic Center, the University of Houston-Victoria, 2003; Make Your Last Words Count. The Writer’s Handbook. Writing Center. University of Wisconsin Madison; Miquel, Fuster-Marquez and Carmen Gregori-Signes. “Chapter Six: ‘Last but Not Least:’ Writing the Conclusion of Your Paper.” In Writing an Applied Linguistics Thesis or Dissertation: A Guide to Presenting Empirical Research . John Bitchener, editor. (Basingstoke,UK: Palgrave Macmillan, 2010), pp. 93-105; Tips for Writing a Good Conclusion. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Kretchmer, Paul. Twelve Steps to Writing an Effective Conclusion. San Francisco Edit, 2003-2008; Writing Conclusions. Writing Tutorial Services, Center for Innovative Teaching and Learning. Indiana University; Writing: Considering Structure and Organization. Institute for Writing Rhetoric. Dartmouth College.
Writing Tip
Don't Belabor the Obvious!
Avoid phrases like "in conclusion...," "in summary...," or "in closing...." These phrases can be useful, even welcome, in oral presentations. But readers can see by the tell-tale section heading and number of pages remaining that they are reaching the end of your paper. You'll irritate your readers if you belabor the obvious.
Assan, Joseph. "Writing the Conclusion Chapter: The Good, the Bad and the Missing." Liverpool: Development Studies Association (2009): 1-8.
Another Writing Tip
New Insight, Not New Information!
Don't surprise the reader with new information in your conclusion that was never referenced anywhere else in the paper. This why the conclusion rarely has citations to sources. If you have new information to present, add it to the discussion or other appropriate section of the paper. Note that, although no new information is introduced, the conclusion, along with the discussion section, is where you offer your most "original" contributions in the paper; the conclusion is where you describe the value of your research, demonstrate that you understand the material that you’ve presented, and position your findings within the larger context of scholarship on the topic, including describing how your research contributes new insights to that scholarship.
Assan, Joseph. "Writing the Conclusion Chapter: The Good, the Bad and the Missing." Liverpool: Development Studies Association (2009): 1-8; Conclusions. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina.
- << Previous: Limitations of the Study
- Next: Appendices >>
- Last Updated: May 30, 2024 9:38 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide

Conclusions
What this handout is about.
This handout will explain the functions of conclusions, offer strategies for writing effective ones, help you evaluate conclusions you’ve drafted, and suggest approaches to avoid.
About conclusions
Introductions and conclusions can be difficult to write, but they’re worth investing time in. They can have a significant influence on a reader’s experience of your paper.
Just as your introduction acts as a bridge that transports your readers from their own lives into the “place” of your analysis, your conclusion can provide a bridge to help your readers make the transition back to their daily lives. Such a conclusion will help them see why all your analysis and information should matter to them after they put the paper down.
Your conclusion is your chance to have the last word on the subject. The conclusion allows you to have the final say on the issues you have raised in your paper, to synthesize your thoughts, to demonstrate the importance of your ideas, and to propel your reader to a new view of the subject. It is also your opportunity to make a good final impression and to end on a positive note.
Your conclusion can go beyond the confines of the assignment. The conclusion pushes beyond the boundaries of the prompt and allows you to consider broader issues, make new connections, and elaborate on the significance of your findings.
Your conclusion should make your readers glad they read your paper. Your conclusion gives your reader something to take away that will help them see things differently or appreciate your topic in personally relevant ways. It can suggest broader implications that will not only interest your reader, but also enrich your reader’s life in some way. It is your gift to the reader.
Strategies for writing an effective conclusion
One or more of the following strategies may help you write an effective conclusion:
- Play the “So What” Game. If you’re stuck and feel like your conclusion isn’t saying anything new or interesting, ask a friend to read it with you. Whenever you make a statement from your conclusion, ask the friend to say, “So what?” or “Why should anybody care?” Then ponder that question and answer it. Here’s how it might go: You: Basically, I’m just saying that education was important to Douglass. Friend: So what? You: Well, it was important because it was a key to him feeling like a free and equal citizen. Friend: Why should anybody care? You: That’s important because plantation owners tried to keep slaves from being educated so that they could maintain control. When Douglass obtained an education, he undermined that control personally. You can also use this strategy on your own, asking yourself “So What?” as you develop your ideas or your draft.
- Return to the theme or themes in the introduction. This strategy brings the reader full circle. For example, if you begin by describing a scenario, you can end with the same scenario as proof that your essay is helpful in creating a new understanding. You may also refer to the introductory paragraph by using key words or parallel concepts and images that you also used in the introduction.
- Synthesize, don’t summarize. Include a brief summary of the paper’s main points, but don’t simply repeat things that were in your paper. Instead, show your reader how the points you made and the support and examples you used fit together. Pull it all together.
- Include a provocative insight or quotation from the research or reading you did for your paper.
- Propose a course of action, a solution to an issue, or questions for further study. This can redirect your reader’s thought process and help them to apply your info and ideas to their own life or to see the broader implications.
- Point to broader implications. For example, if your paper examines the Greensboro sit-ins or another event in the Civil Rights Movement, you could point out its impact on the Civil Rights Movement as a whole. A paper about the style of writer Virginia Woolf could point to her influence on other writers or on later feminists.
Strategies to avoid
- Beginning with an unnecessary, overused phrase such as “in conclusion,” “in summary,” or “in closing.” Although these phrases can work in speeches, they come across as wooden and trite in writing.
- Stating the thesis for the very first time in the conclusion.
- Introducing a new idea or subtopic in your conclusion.
- Ending with a rephrased thesis statement without any substantive changes.
- Making sentimental, emotional appeals that are out of character with the rest of an analytical paper.
- Including evidence (quotations, statistics, etc.) that should be in the body of the paper.
Four kinds of ineffective conclusions
- The “That’s My Story and I’m Sticking to It” Conclusion. This conclusion just restates the thesis and is usually painfully short. It does not push the ideas forward. People write this kind of conclusion when they can’t think of anything else to say. Example: In conclusion, Frederick Douglass was, as we have seen, a pioneer in American education, proving that education was a major force for social change with regard to slavery.
- The “Sherlock Holmes” Conclusion. Sometimes writers will state the thesis for the very first time in the conclusion. You might be tempted to use this strategy if you don’t want to give everything away too early in your paper. You may think it would be more dramatic to keep the reader in the dark until the end and then “wow” them with your main idea, as in a Sherlock Holmes mystery. The reader, however, does not expect a mystery, but an analytical discussion of your topic in an academic style, with the main argument (thesis) stated up front. Example: (After a paper that lists numerous incidents from the book but never says what these incidents reveal about Douglass and his views on education): So, as the evidence above demonstrates, Douglass saw education as a way to undermine the slaveholders’ power and also an important step toward freedom.
- The “America the Beautiful”/”I Am Woman”/”We Shall Overcome” Conclusion. This kind of conclusion usually draws on emotion to make its appeal, but while this emotion and even sentimentality may be very heartfelt, it is usually out of character with the rest of an analytical paper. A more sophisticated commentary, rather than emotional praise, would be a more fitting tribute to the topic. Example: Because of the efforts of fine Americans like Frederick Douglass, countless others have seen the shining beacon of light that is education. His example was a torch that lit the way for others. Frederick Douglass was truly an American hero.
- The “Grab Bag” Conclusion. This kind of conclusion includes extra information that the writer found or thought of but couldn’t integrate into the main paper. You may find it hard to leave out details that you discovered after hours of research and thought, but adding random facts and bits of evidence at the end of an otherwise-well-organized essay can just create confusion. Example: In addition to being an educational pioneer, Frederick Douglass provides an interesting case study for masculinity in the American South. He also offers historians an interesting glimpse into slave resistance when he confronts Covey, the overseer. His relationships with female relatives reveal the importance of family in the slave community.
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Douglass, Frederick. 1995. Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass, an American Slave, Written by Himself. New York: Dover.
Hamilton College. n.d. “Conclusions.” Writing Center. Accessed June 14, 2019. https://www.hamilton.edu//academics/centers/writing/writing-resources/conclusions .
Holewa, Randa. 2004. “Strategies for Writing a Conclusion.” LEO: Literacy Education Online. Last updated February 19, 2004. https://leo.stcloudstate.edu/acadwrite/conclude.html.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
How to Write a Conclusion for a Research Paper

3-minute read
- 29th August 2023
If you’re writing a research paper, the conclusion is your opportunity to summarize your findings and leave a lasting impression on your readers. In this post, we’ll take you through how to write an effective conclusion for a research paper and how you can:
· Reword your thesis statement
· Highlight the significance of your research
· Discuss limitations
· Connect to the introduction
· End with a thought-provoking statement
Rewording Your Thesis Statement
Begin your conclusion by restating your thesis statement in a way that is slightly different from the wording used in the introduction. Avoid presenting new information or evidence in your conclusion. Just summarize the main points and arguments of your essay and keep this part as concise as possible. Remember that you’ve already covered the in-depth analyses and investigations in the main body paragraphs of your essay, so it’s not necessary to restate these details in the conclusion.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
Highlighting the Significance of Your Research
The conclusion is a good place to emphasize the implications of your research . Avoid ambiguous or vague language such as “I think” or “maybe,” which could weaken your position. Clearly explain why your research is significant and how it contributes to the broader field of study.
Here’s an example from a (fictional) study on the impact of social media on mental health:
Discussing Limitations
Although it’s important to emphasize the significance of your study, you can also use the conclusion to briefly address any limitations you discovered while conducting your research, such as time constraints or a shortage of resources. Doing this demonstrates a balanced and honest approach to your research.
Connecting to the Introduction
In your conclusion, you can circle back to your introduction , perhaps by referring to a quote or anecdote you discussed earlier. If you end your paper on a similar note to how you began it, you will create a sense of cohesion for the reader and remind them of the meaning and significance of your research.
Ending With a Thought-Provoking Statement
Consider ending your paper with a thought-provoking and memorable statement that relates to the impact of your research questions or hypothesis. This statement can be a call to action, a philosophical question, or a prediction for the future (positive or negative). Here’s an example that uses the same topic as above (social media and mental health):
Expert Proofreading Services
Ensure that your essay ends on a high note by having our experts proofread your research paper. Our team has experience with a wide variety of academic fields and subjects and can help make your paper stand out from the crowd – get started today and see the difference it can make in your work.
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
9-minute read
How to Use Infographics to Boost Your Presentation
Is your content getting noticed? Capturing and maintaining an audience’s attention is a challenge when...
8-minute read
Why Interactive PDFs Are Better for Engagement
Are you looking to enhance engagement and captivate your audience through your professional documents? Interactive...
7-minute read
Seven Key Strategies for Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization is rapidly shaping the digital landscape, requiring content professionals to adapt their...
4-minute read
Five Creative Ways to Showcase Your Digital Portfolio
Are you a creative freelancer looking to make a lasting impression on potential clients or...
How to Ace Slack Messaging for Contractors and Freelancers
Effective professional communication is an important skill for contractors and freelancers navigating remote work environments....
How to Insert a Text Box in a Google Doc
Google Docs is a powerful collaborative tool, and mastering its features can significantly enhance your...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Paper Conclusion – Writing Guide and Examples
Research Paper Conclusion – Writing Guide and Examples
Table of Contents

Research Paper Conclusion
Definition:
A research paper conclusion is the final section of a research paper that summarizes the key findings, significance, and implications of the research. It is the writer’s opportunity to synthesize the information presented in the paper, draw conclusions, and make recommendations for future research or actions.
The conclusion should provide a clear and concise summary of the research paper, reiterating the research question or problem, the main results, and the significance of the findings. It should also discuss the limitations of the study and suggest areas for further research.
Parts of Research Paper Conclusion
The parts of a research paper conclusion typically include:
Restatement of the Thesis
The conclusion should begin by restating the thesis statement from the introduction in a different way. This helps to remind the reader of the main argument or purpose of the research.
Summary of Key Findings
The conclusion should summarize the main findings of the research, highlighting the most important results and conclusions. This section should be brief and to the point.
Implications and Significance
In this section, the researcher should explain the implications and significance of the research findings. This may include discussing the potential impact on the field or industry, highlighting new insights or knowledge gained, or pointing out areas for future research.
Limitations and Recommendations
It is important to acknowledge any limitations or weaknesses of the research and to make recommendations for how these could be addressed in future studies. This shows that the researcher is aware of the potential limitations of their work and is committed to improving the quality of research in their field.
Concluding Statement
The conclusion should end with a strong concluding statement that leaves a lasting impression on the reader. This could be a call to action, a recommendation for further research, or a final thought on the topic.
How to Write Research Paper Conclusion
Here are some steps you can follow to write an effective research paper conclusion:
- Restate the research problem or question: Begin by restating the research problem or question that you aimed to answer in your research. This will remind the reader of the purpose of your study.
- Summarize the main points: Summarize the key findings and results of your research. This can be done by highlighting the most important aspects of your research and the evidence that supports them.
- Discuss the implications: Discuss the implications of your findings for the research area and any potential applications of your research. You should also mention any limitations of your research that may affect the interpretation of your findings.
- Provide a conclusion : Provide a concise conclusion that summarizes the main points of your paper and emphasizes the significance of your research. This should be a strong and clear statement that leaves a lasting impression on the reader.
- Offer suggestions for future research: Lastly, offer suggestions for future research that could build on your findings and contribute to further advancements in the field.
Remember that the conclusion should be brief and to the point, while still effectively summarizing the key findings and implications of your research.
Example of Research Paper Conclusion
Here’s an example of a research paper conclusion:
Conclusion :
In conclusion, our study aimed to investigate the relationship between social media use and mental health among college students. Our findings suggest that there is a significant association between social media use and increased levels of anxiety and depression among college students. This highlights the need for increased awareness and education about the potential negative effects of social media use on mental health, particularly among college students.
Despite the limitations of our study, such as the small sample size and self-reported data, our findings have important implications for future research and practice. Future studies should aim to replicate our findings in larger, more diverse samples, and investigate the potential mechanisms underlying the association between social media use and mental health. In addition, interventions should be developed to promote healthy social media use among college students, such as mindfulness-based approaches and social media detox programs.
Overall, our study contributes to the growing body of research on the impact of social media on mental health, and highlights the importance of addressing this issue in the context of higher education. By raising awareness and promoting healthy social media use among college students, we can help to reduce the negative impact of social media on mental health and improve the well-being of young adults.
Purpose of Research Paper Conclusion
The purpose of a research paper conclusion is to provide a summary and synthesis of the key findings, significance, and implications of the research presented in the paper. The conclusion serves as the final opportunity for the writer to convey their message and leave a lasting impression on the reader.
The conclusion should restate the research problem or question, summarize the main results of the research, and explain their significance. It should also acknowledge the limitations of the study and suggest areas for future research or action.
Overall, the purpose of the conclusion is to provide a sense of closure to the research paper and to emphasize the importance of the research and its potential impact. It should leave the reader with a clear understanding of the main findings and why they matter. The conclusion serves as the writer’s opportunity to showcase their contribution to the field and to inspire further research and action.
When to Write Research Paper Conclusion
The conclusion of a research paper should be written after the body of the paper has been completed. It should not be written until the writer has thoroughly analyzed and interpreted their findings and has written a complete and cohesive discussion of the research.
Before writing the conclusion, the writer should review their research paper and consider the key points that they want to convey to the reader. They should also review the research question, hypotheses, and methodology to ensure that they have addressed all of the necessary components of the research.
Once the writer has a clear understanding of the main findings and their significance, they can begin writing the conclusion. The conclusion should be written in a clear and concise manner, and should reiterate the main points of the research while also providing insights and recommendations for future research or action.
Characteristics of Research Paper Conclusion
The characteristics of a research paper conclusion include:
- Clear and concise: The conclusion should be written in a clear and concise manner, summarizing the key findings and their significance.
- Comprehensive: The conclusion should address all of the main points of the research paper, including the research question or problem, the methodology, the main results, and their implications.
- Future-oriented : The conclusion should provide insights and recommendations for future research or action, based on the findings of the research.
- Impressive : The conclusion should leave a lasting impression on the reader, emphasizing the importance of the research and its potential impact.
- Objective : The conclusion should be based on the evidence presented in the research paper, and should avoid personal biases or opinions.
- Unique : The conclusion should be unique to the research paper and should not simply repeat information from the introduction or body of the paper.
Advantages of Research Paper Conclusion
The advantages of a research paper conclusion include:
- Summarizing the key findings : The conclusion provides a summary of the main findings of the research, making it easier for the reader to understand the key points of the study.
- Emphasizing the significance of the research: The conclusion emphasizes the importance of the research and its potential impact, making it more likely that readers will take the research seriously and consider its implications.
- Providing recommendations for future research or action : The conclusion suggests practical recommendations for future research or action, based on the findings of the study.
- Providing closure to the research paper : The conclusion provides a sense of closure to the research paper, tying together the different sections of the paper and leaving a lasting impression on the reader.
- Demonstrating the writer’s contribution to the field : The conclusion provides the writer with an opportunity to showcase their contribution to the field and to inspire further research and action.
Limitations of Research Paper Conclusion
While the conclusion of a research paper has many advantages, it also has some limitations that should be considered, including:
- I nability to address all aspects of the research: Due to the limited space available in the conclusion, it may not be possible to address all aspects of the research in detail.
- Subjectivity : While the conclusion should be objective, it may be influenced by the writer’s personal biases or opinions.
- Lack of new information: The conclusion should not introduce new information that has not been discussed in the body of the research paper.
- Lack of generalizability: The conclusions drawn from the research may not be applicable to other contexts or populations, limiting the generalizability of the study.
- Misinterpretation by the reader: The reader may misinterpret the conclusions drawn from the research, leading to a misunderstanding of the findings.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

How to Cite Research Paper – All Formats and...

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Paper Format – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

- Walden University
- Faculty Portal
Writing a Paper: Conclusions
Writing a conclusion.
A conclusion is an important part of the paper; it provides closure for the reader while reminding the reader of the contents and importance of the paper. It accomplishes this by stepping back from the specifics in order to view the bigger picture of the document. In other words, it is reminding the reader of the main argument. For most course papers, it is usually one paragraph that simply and succinctly restates the main ideas and arguments, pulling everything together to help clarify the thesis of the paper. A conclusion does not introduce new ideas; instead, it should clarify the intent and importance of the paper. It can also suggest possible future research on the topic.
An Easy Checklist for Writing a Conclusion
It is important to remind the reader of the thesis of the paper so he is reminded of the argument and solutions you proposed.
Think of the main points as puzzle pieces, and the conclusion is where they all fit together to create a bigger picture. The reader should walk away with the bigger picture in mind.
Make sure that the paper places its findings in the context of real social change.
Make sure the reader has a distinct sense that the paper has come to an end. It is important to not leave the reader hanging. (You don’t want her to have flip-the-page syndrome, where the reader turns the page, expecting the paper to continue. The paper should naturally come to an end.)
No new ideas should be introduced in the conclusion. It is simply a review of the material that is already present in the paper. The only new idea would be the suggesting of a direction for future research.
Conclusion Example
As addressed in my analysis of recent research, the advantages of a later starting time for high school students significantly outweigh the disadvantages. A later starting time would allow teens more time to sleep--something that is important for their physical and mental health--and ultimately improve their academic performance and behavior. The added transportation costs that result from this change can be absorbed through energy savings. The beneficial effects on the students’ academic performance and behavior validate this decision, but its effect on student motivation is still unknown. I would encourage an in-depth look at the reactions of students to such a change. This sort of study would help determine the actual effects of a later start time on the time management and sleep habits of students.
Related Webinar
Didn't find what you need? Email us at [email protected] .
- Previous Page: Thesis Statements
- Next Page: Writer's Block
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
- Research Papers
How to Write a Conclusion for a Research Paper
Last Updated: May 8, 2024 Approved
This article was co-authored by Christopher Taylor, PhD . Christopher Taylor is an Adjunct Assistant Professor of English at Austin Community College in Texas. He received his PhD in English Literature and Medieval Studies from the University of Texas at Austin in 2014. wikiHow marks an article as reader-approved once it receives enough positive feedback. This article received 42 testimonials and 83% of readers who voted found it helpful, earning it our reader-approved status. This article has been viewed 2,260,216 times.
The conclusion of a research paper needs to summarize the content and purpose of the paper without seeming too wooden or dry. Every basic conclusion must share several key elements, but there are also several tactics you can play around with to craft a more effective conclusion and several you should avoid to prevent yourself from weakening your paper's conclusion. Here are some writing tips to keep in mind when creating a conclusion for your next research paper.
Sample Conclusions
Writing a basic conclusion.

- Do not spend a great amount of time or space restating your topic.
- A good research paper will make the importance of your topic apparent, so you do not need to write an elaborate defense of your topic in the conclusion.
- Usually a single sentence is all you need to restate your topic.
- An example would be if you were writing a paper on the epidemiology of infectious disease, you might say something like "Tuberculosis is a widespread infectious disease that affects millions of people worldwide every year."
- Yet another example from the humanities would be a paper about the Italian Renaissance: "The Italian Renaissance was an explosion of art and ideas centered around artists, writers, and thinkers in Florence."

- A thesis is a narrowed, focused view on the topic at hand.
- This statement should be rephrased from the thesis you included in your introduction. It should not be identical or too similar to the sentence you originally used.
- Try re-wording your thesis statement in a way that complements your summary of the topic of your paper in your first sentence of your conclusion.
- An example of a good thesis statement, going back to the paper on tuberculosis, would be "Tuberculosis is a widespread disease that affects millions of people worldwide every year. Due to the alarming rate of the spread of tuberculosis, particularly in poor countries, medical professionals are implementing new strategies for the diagnosis, treatment, and containment of this disease ."

- A good way to go about this is to re-read the topic sentence of each major paragraph or section in the body of your paper.
- Find a way to briefly restate each point mentioned in each topic sentence in your conclusion. Do not repeat any of the supporting details used within your body paragraphs.
- Under most circumstances, you should avoid writing new information in your conclusion. This is especially true if the information is vital to the argument or research presented in your paper.
- For example, in the TB paper you could summarize the information. "Tuberculosis is a widespread disease that affects millions of people worldwide. Due to the alarming rate of the spread of tuberculosis, particularly in poor countries, medical professionals are implementing new strategies for the diagnosis, treatment, and containment of this disease. In developing countries, such as those in Africa and Southeast Asia, the rate of TB infections is soaring. Crowded conditions, poor sanitation, and lack of access to medical care are all compounding factors in the spread of the disease. Medical experts, such as those from the World Health Organization are now starting campaigns to go into communities in developing countries and provide diagnostic testing and treatments. However, the treatments for TB are very harsh and have many side effects. This leads to patient non-compliance and spread of multi-drug resistant strains of the disease."

- Note that this is not needed for all research papers.
- If you already fully explained what the points in your paper mean or why they are significant, you do not need to go into them in much detail in your conclusion. Simply restating your thesis or the significance of your topic should suffice.
- It is always best practice to address important issues and fully explain your points in the body of your paper. The point of a conclusion to a research paper is to summarize your argument for the reader and, perhaps, to call the reader to action if needed.

- Note that a call for action is not essential to all conclusions. A research paper on literary criticism, for instance, is less likely to need a call for action than a paper on the effect that television has on toddlers and young children.
- A paper that is more likely to call readers to action is one that addresses a public or scientific need. Let's go back to our example of tuberculosis. This is a very serious disease that is spreading quickly and with antibiotic-resistant forms.
- A call to action in this research paper would be a follow-up statement that might be along the lines of "Despite new efforts to diagnose and contain the disease, more research is needed to develop new antibiotics that will treat the most resistant strains of tuberculosis and ease the side effects of current treatments."

- For example, if you are writing a history paper, then you might discuss how the historical topic you discussed matters today. If you are writing about a foreign country, then you might use the conclusion to discuss how the information you shared may help readers understand their own country.
Making Your Conclusion as Effective as Possible

- Since this sort of conclusion is so basic, you must aim to synthesize the information rather than merely summarizing it.
- Instead of merely repeating things you already said, rephrase your thesis and supporting points in a way that ties them all together.
- By doing so, you make your research paper seem like a "complete thought" rather than a collection of random and vaguely related ideas.

- Ask a question in your introduction. In your conclusion, restate the question and provide a direct answer.
- Write an anecdote or story in your introduction but do not share the ending. Instead, write the conclusion to the anecdote in the conclusion of your paper.
- For example, if you wanted to get more creative and put a more humanistic spin on a paper on tuberculosis, you might start your introduction with a story about a person with the disease, and refer to that story in your conclusion. For example, you could say something like this before you re-state your thesis in your conclusion: "Patient X was unable to complete the treatment for tuberculosis due to severe side effects and unfortunately succumbed to the disease."
- Use the same concepts and images introduced in your introduction in your conclusion. The images may or may not appear at other points throughout the research paper.

- Include enough information about your topic to back the statement up but do not get too carried away with excess detail.
- If your research did not provide you with a clear-cut answer to a question posed in your thesis, do not be afraid to indicate as much.
- Restate your initial hypothesis and indicate whether you still believe it or if the research you performed has begun swaying your opinion.
- Indicate that an answer may still exist and that further research could shed more light on the topic at hand.

- This may not be appropriate for all types of research papers. Most research papers, such as one on effective treatment for diseases, will have the information to make the case for a particular argument already in the paper.
- A good example of a paper that might ask a question of the reader in the ending is one about a social issue, such as poverty or government policy.
- Ask a question that will directly get at the heart or purpose of the paper. This question is often the same question, or some version of it, that you may have started with when you began your research.
- Make sure that the question can be answered by the evidence presented in your paper.
- If desired you can briefly summarize the answer after stating the question. You could also leave the question hanging for the reader to answer, though.

- Even without a call to action, you can still make a recommendation to your reader.
- For instance, if you are writing about a topic like third-world poverty, you can various ways for the reader to assist in the problem without necessarily calling for more research.
- Another example would be, in a paper about treatment for drug-resistant tuberculosis, you could suggest donating to the World Health Organization or research foundations that are developing new treatments for the disease.
Avoiding Common Pitfalls

- These sayings usually sound stiff, unnatural, or trite when used in writing.
- Moreover, using a phrase like "in conclusion" to begin your conclusion is a little too straightforward and tends to lead to a weak conclusion. A strong conclusion can stand on its own without being labeled as such.

- Always state the main argument or thesis in the introduction. A research paper is an analytical discussion of an academic topic, not a mystery novel.
- A good, effective research paper will allow your reader to follow your main argument from start to finish.
- This is why it is best practice to start your paper with an introduction that states your main argument and to end the paper with a conclusion that re-states your thesis for re-iteration.

- All significant information should be introduced in the body of the paper.
- Supporting evidence expands the topic of your paper by making it appear more detailed. A conclusion should narrow the topic to a more general point.
- A conclusion should only summarize what you have already stated in the body of your paper.
- You may suggest further research or a call to action, but you should not bring in any new evidence or facts in the conclusion.

- Most often, a shift in tone occurs when a research paper with an academic tone gives an emotional or sentimental conclusion.
- Even if the topic of the paper is of personal significance for you, you should not indicate as much in your paper.
- If you want to give your paper a more humanistic slant, you could start and end your paper with a story or anecdote that would give your topic more personal meaning to the reader.
- This tone should be consistent throughout the paper, however.

- Apologetic statements include phrases like "I may not be an expert" or "This is only my opinion."
- Statements like this can usually be avoided by refraining from writing in the first-person.
- Avoid any statements in the first-person. First-person is generally considered to be informal and does not fit with the formal tone of a research paper.
Community Q&A
You Might Also Like

- ↑ http://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/724/04/
- ↑ http://www.crlsresearchguide.org/18_Writing_Conclusion.asp
- ↑ http://writing.wisc.edu/Handbook/PlanResearchPaper.html#conclusion
- ↑ http://writingcenter.unc.edu/handouts/conclusions/
- ↑ http://writing2.richmond.edu/writing/wweb/conclude.html
About This Article

To write a conclusion for a research paper, start by restating your thesis statement to remind your readers what your main topic is and bring everything full circle. Then, briefly summarize all of the main points you made throughout your paper, which will help remind your readers of everything they learned. You might also want to include a call to action if you think more research or work needs to be done on your topic by writing something like, "Despite efforts to contain the disease, more research is needed to develop antibiotics." Finally, end your conclusion by explaining the broader context of your topic and why your readers should care about it, which will help them understand why your topic is relevant and important. For tips from our Academic co-author, like how to avoid common pitfalls when writing your conclusion, scroll down! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Ummay Aimen
Sep 30, 2016
Did this article help you?

Oct 22, 2017
Sally Larrin
Mar 17, 2018
Maya Loeven
Jun 4, 2017
Sep 26, 2016

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter
So much is at stake in writing a conclusion. This is, after all, your last chance to persuade your readers to your point of view, to impress yourself upon them as a writer and thinker. And the impression you create in your conclusion will shape the impression that stays with your readers after they've finished the essay.
The end of an essay should therefore convey a sense of completeness and closure as well as a sense of the lingering possibilities of the topic, its larger meaning, its implications: the final paragraph should close the discussion without closing it off.
To establish a sense of closure, you might do one or more of the following:
- Conclude by linking the last paragraph to the first, perhaps by reiterating a word or phrase you used at the beginning.
- Conclude with a sentence composed mainly of one-syllable words. Simple language can help create an effect of understated drama.
- Conclude with a sentence that's compound or parallel in structure; such sentences can establish a sense of balance or order that may feel just right at the end of a complex discussion.
To close the discussion without closing it off, you might do one or more of the following:
- Conclude with a quotation from or reference to a primary or secondary source, one that amplifies your main point or puts it in a different perspective. A quotation from, say, the novel or poem you're writing about can add texture and specificity to your discussion; a critic or scholar can help confirm or complicate your final point. For example, you might conclude an essay on the idea of home in James Joyce's short story collection, Dubliners , with information about Joyce's own complex feelings towards Dublin, his home. Or you might end with a biographer's statement about Joyce's attitude toward Dublin, which could illuminate his characters' responses to the city. Just be cautious, especially about using secondary material: make sure that you get the last word.
- Conclude by setting your discussion into a different, perhaps larger, context. For example, you might end an essay on nineteenth-century muckraking journalism by linking it to a current news magazine program like 60 Minutes .
- Conclude by redefining one of the key terms of your argument. For example, an essay on Marx's treatment of the conflict between wage labor and capital might begin with Marx's claim that the "capitalist economy is . . . a gigantic enterprise of dehumanization "; the essay might end by suggesting that Marxist analysis is itself dehumanizing because it construes everything in economic -- rather than moral or ethical-- terms.
- Conclude by considering the implications of your argument (or analysis or discussion). What does your argument imply, or involve, or suggest? For example, an essay on the novel Ambiguous Adventure , by the Senegalese writer Cheikh Hamidou Kane, might open with the idea that the protagonist's development suggests Kane's belief in the need to integrate Western materialism and Sufi spirituality in modern Senegal. The conclusion might make the new but related point that the novel on the whole suggests that such an integration is (or isn't) possible.
Finally, some advice on how not to end an essay:
- Don't simply summarize your essay. A brief summary of your argument may be useful, especially if your essay is long--more than ten pages or so. But shorter essays tend not to require a restatement of your main ideas.
- Avoid phrases like "in conclusion," "to conclude," "in summary," and "to sum up." These phrases can be useful--even welcome--in oral presentations. But readers can see, by the tell-tale compression of the pages, when an essay is about to end. You'll irritate your audience if you belabor the obvious.
- Resist the urge to apologize. If you've immersed yourself in your subject, you now know a good deal more about it than you can possibly include in a five- or ten- or 20-page essay. As a result, by the time you've finished writing, you may be having some doubts about what you've produced. (And if you haven't immersed yourself in your subject, you may be feeling even more doubtful about your essay as you approach the conclusion.) Repress those doubts. Don't undercut your authority by saying things like, "this is just one approach to the subject; there may be other, better approaches. . ."
Copyright 1998, Pat Bellanca, for the Writing Center at Harvard University
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Conclusions

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Conclusions wrap up what you have been discussing in your paper. After moving from general to specific information in the introduction and body paragraphs, your conclusion should begin pulling back into more general information that restates the main points of your argument. Conclusions may also call for action or overview future possible research. The following outline may help you conclude your paper:
In a general way,
- Restate your topic and why it is important,
- Restate your thesis/claim,
- Address opposing viewpoints and explain why readers should align with your position,
- Call for action or overview future research possibilities.
Remember that once you accomplish these tasks, unless otherwise directed by your instructor, you are finished. Done. Complete. Don't try to bring in new points or end with a whiz bang(!) conclusion or try to solve world hunger in the final sentence of your conclusion. Simplicity is best for a clear, convincing message.
The preacher's maxim is one of the most effective formulas to follow for argument papers:
Tell what you're going to tell them (introduction).
Tell them (body).
Tell them what you told them (conclusion).
How to Write a Conclusion for a Research Paper

When you're wrapping up a research paper, the conclusion is like the grand finale of a fireworks show – it's your chance to leave a lasting impression. In this article, we'll break down the steps to help you write a winning research paper conclusion that not only recaps your main points but also ties everything together. Consider it the "So what?" moment – why should people care about your research? Our professional essay writers will guide you through making your conclusion strong, clear, and something that sticks with your readers long after they've put down your paper. So, let's dive in and ensure your research ends on a high note!
What Is a Conclusion in a Research Paper
In a research paper, the conclusion serves as the final segment, where you summarize the main points and findings of your study. It's not just a repetition of what you've already said but rather a chance to tie everything together and highlight the significance of your research. As you learn how to start a research paper , a good conclusion also often discusses the implications of your findings, suggests potential areas for further research, and leaves the reader with a lasting impression of the importance and relevance of your work in the broader context of the field. Essentially, it's your last opportunity to make a strong impact and leave your readers with a clear understanding of the significance of your research. Here’s a research paper conclusion example:
In conclusion, this research paper has navigated the intricacies of sustainable urban development, shedding light on the pivotal role of community engagement and innovative planning strategies. Through applying qualitative and quantitative research methods, we've uncovered valuable insights into the challenges and opportunities inherent in fostering environmentally friendly urban spaces. The implications of these findings extend beyond the confines of this study, emphasizing the imperative for continued exploration in the realms of urban planning and environmental sustainability. By emphasizing both the practical applications and theoretical contributions, this research underscores the significance of community involvement and forward-thinking strategies in shaping the future of urban landscapes. As cities evolve, incorporating these insights into planning and development practices will create resilient and harmonious urban environments.
Conclusion Outline for Research Paper
This outline for a research paper conclusion provides a structured framework to ensure that your ending effectively summarizes the key elements of your research paper and leaves a lasting impression on your readers. Adjust the content based on the specific requirements and focus of your research.
Restate the Thesis Statement
- Briefly restate the main thesis or research question.
- Emphasize the core objective or purpose of the study.
Summarize Key Findings
- Recap the main points and key findings from each section of the paper.
- Provide a concise overview of the research journey.
Discuss Implications
- Explore the broader implications of the research findings.
- Discuss how the results contribute to the existing body of knowledge in the field.
Address Limitations
- Acknowledge any limitations or constraints encountered during the research process.
- Explain how these limitations may impact the interpretation of the findings.
Suggest Areas for Future Research
- Propose potential directions for future studies related to the topic.
- Identify gaps in the current research that warrant further exploration.
Reaffirm Significance
- Reaffirm the importance and relevance of the research in the broader context.
- Highlight the practical applications or real-world implications of the study.
Concluding Statement
- Craft a strong, memorable closing statement that leaves a lasting impression.
- Sum up the overall impact of the research and its potential contribution to the field.
Study the full guide on how to make a research paper outline here, which will also specify the conclusion writing specifics to improve your general prowess.
Tips on How to Make a Conclusion in Research
Here are key considerations regarding a conclusion for research paper to not only recap the primary ideas in your work but also delve deeper to earn a higher grade:

- Provide a concise recap of your main research outcomes.
- Remind readers of your research goals and their accomplishments.
- Stick to summarizing existing content; refrain from adding new details.
- Emphasize why your research matters and its broader implications.
- Clearly explain the practical or theoretical impact of your findings.
- Prompt readers to reflect on how your research influences their perspective.
- Briefly discuss the robustness of your research methods.
- End with a suggestion for future research or a practical application.
- Transparently address any constraints or biases in your study.
- End on a powerful note, leaving a memorable impression on your readers.
.webp)
For your inspiration, we’ve also prepared this research proposal example APA , which dwells on another important aspect of research writing.
How to Write a Research Paper Conclusion
As you finish your research paper, the conclusion takes center stage. In this section, we've got five practical tips for writing a conclusion for a research paper. We'll guide you through summarizing your key findings, revisiting your research goals, discussing the bigger picture, addressing any limitations, and ending on a powerful note. Think of it as your roadmap to creating a conclusion that not only wraps up your research but also leaves a lasting impact on your readers. Let's dive in and make sure your conclusion stands out for all the right reasons!
.webp)
Synthesize Core Discoveries. Initiate your conclusion by synthesizing the essential discoveries of your research. Offer a succinct recapitulation of the primary points and outcomes you have elucidated in your paper. This aids in reinforcing the gravity of your work and reiterates the pivotal information you have presented.
Revisit Research Objectives. Revisit the research objectives or questions you outlined at the beginning of your paper. Assess whether you have successfully addressed these objectives and if your findings align with the initial goals of your research. This reflection helps tie your conclusion back to the purpose of your study.
Discuss Implications and Contributions. Discuss the broader implications of your research and its potential contributions to the field. Consider how your findings might impact future research, applications, or understanding of the subject matter. This demonstrates the significance of your work and places it within a larger context.
Address Limitations and Future Research. Acknowledge any limitations in your study, such as constraints in data collection or potential biases. Briefly discuss how these limitations might have affected your results. Additionally, suggest areas for future research that could build upon your work, addressing any unanswered questions or unexplored aspects. This demonstrates a thoughtful approach to your research.
End with a Strong Conclusion Statement. Conclude your research paper with a strong and memorable statement that reinforces the key message you want readers to take away. This could be a call to action, a proposal for further investigation, or a reflection on the broader significance of your findings. Leave your readers with a lasting impression that emphasizes the importance of your research. Remember that you can buy a research paper anytime if you lack time or get stuck in writer’s block.
Want to Enjoy the Benefits of Academic Freedom?
With our top-notch writers and 24/7 support, you can relax and focus on what really matters
Stylistic Devices to Use in a Conclusion
Discover distinctive stylistic insights that you can apply when writing a conclusion for a research paper:
- Rhetorical Questions. When using rhetorical questions, strategically place them to engage readers' minds. For instance, you might pose a question that prompts reflection on the broader implications of your findings, leaving your audience with something to ponder.
- Powerful Language. Incorporate strong language to convey a sense of conviction and importance. Choose words that resonate with the overall tone of your research and amplify the significance of your conclusions. This adds weight to your key messages.
- Repetitions. Repetitions can be employed to reinforce essential ideas. Reiterate key phrases or concepts in a way that emphasizes their importance without sounding redundant. This technique serves to drive home your main points.
- Anecdotes. Integrating anecdotes into your conclusion can provide a human touch. Share a brief and relevant story that connects with your research, making the information more relatable and memorable for your audience.
- Vivid Imagery. Lastly, use vivid imagery to paint a picture in the minds of your readers. Appeal to their senses by describing scenarios or outcomes related to your research. This creates a more immersive and lasting impression.
If you have a larger paper to write, for example a thesis, use our custom dissertation writing can help you in no time.
How to Make a Conclusion Logically Appealing
Knowing how to write a conclusion for a research paper that is logically appealing is important for leaving a lasting impression on your readers. Here are some tips to achieve this:
Logical Sequencing
- Present your conclusion in a structured manner, following the natural flow of your paper. Readers should effortlessly follow your thought process, making your conclusion more accessible and persuasive.
Reinforce Main Arguments
- Emphasize the core arguments and findings from your research. By reinforcing key points, you solidify your stance and provide a logical culmination to your paper.
Address Counterarguments
- Acknowledge and address potential counterarguments or limitations in your research. Demonstrate intellectual honesty and strengthen your conclusion by preemptively addressing potential doubts.
Connect with Introduction
- Revisit themes or concepts introduced in your introduction to create a cohesive narrative, allowing readers to trace the logical progression of your research from start to finish.
Propose Actionable Insights
- Suggest practical applications or recommendations based on your findings. This will add a forward-looking dimension, making your conclusion more relevant and compelling.
Highlight Significance
- Clearly articulate the broader implications of your research to convey the importance of your work and its potential impact on the field, making your conclusion logically compelling.
Are you ready to produce an A-grade assignment? If not, opt for a custom research paper from our skilled writers across various disciplines.
Avoid These Things When Writing a Research Paper Conclusion
As you write your conclusion of research paper, there’s a list of things professional writers don’t recommend doing. Consider these issues carefully:

- Repetition of Exact Phrases
- Repetitively using the same phrases or sentences from the main body. Repetition can make your conclusion seem redundant and less engaging.
- Overly Lengthy Summaries
- Providing excessively detailed summaries of each section of your paper. Readers may lose interest if the conclusion becomes too long and detailed.
- Unclear Connection to the Introduction
- Failing to connect the conclusion back to the introduction. A lack of continuity may make the paper feel disjointed.
- Adding New Arguments or Ideas
- Introducing new arguments or ideas that were not addressed in the body. This can confuse the reader and disrupt the coherence of your paper.
- Overuse of Complex Jargon
- Using excessively complex or technical language without clarification. Clear communication is essential in the conclusion, ensuring broad understanding.
- Apologizing or Undermining Confidence
- Apologizing for limitations or expressing doubt about your work. Maintain a confident tone; if limitations exist, present them objectively without undermining your research.
- Sweeping Generalizations
- Making overly broad or unsupported generalizations. Such statements can weaken the credibility of your conclusion.
- Neglecting the Significance
- Failing to emphasize the broader significance of your research. Readers need to understand why your findings matter in a larger context.
- Abrupt Endings
- Concluding abruptly without a strong closing statement. A powerful ending leaves a lasting impression; avoid a sudden or weak conclusion.
Research Paper Conclusion Example
That covers the essential aspects of summarizing a research paper. The only remaining step is to review the conclusion examples for research paper provided by our team.
Like our examples? Order our research proposal writing service to write paper according to your instructions to avoid plagiarizing and to keep your academic integrity strong.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, the knowledge of how to write the conclusion of a research paper is pivotal for presenting your findings and leaving a lasting impression on your readers. By summarizing the key points, reiterating the significance of your research, and offering avenues for future exploration, you can create a conclusion that not only reinforces the value of your study but also encourages further academic discourse. Remember to balance brevity and completeness, ensuring your conclusion is concise yet comprehensive. Emphasizing the practical implications of your research and connecting it to the broader academic landscape will help solidify the impact of your work. Pay someone to write a research paper if you are having a hard time finishing your coursework on time.
Tired of Stressing Over Endless Essays and Deadlines?
Let us take the load off your shoulders! Order your custom research paper today and experience the relief of knowing that your assignment is in expert hands
How To Write A Conclusion For A Research Paper?
What should the conclusion of a research paper contain, how to start a conclusion paragraph for a research paper.

Daniel Parker
is a seasoned educational writer focusing on scholarship guidance, research papers, and various forms of academic essays including reflective and narrative essays. His expertise also extends to detailed case studies. A scholar with a background in English Literature and Education, Daniel’s work on EssayPro blog aims to support students in achieving academic excellence and securing scholarships. His hobbies include reading classic literature and participating in academic forums.

is an expert in nursing and healthcare, with a strong background in history, law, and literature. Holding advanced degrees in nursing and public health, his analytical approach and comprehensive knowledge help students navigate complex topics. On EssayPro blog, Adam provides insightful articles on everything from historical analysis to the intricacies of healthcare policies. In his downtime, he enjoys historical documentaries and volunteering at local clinics.
Related Articles
.webp)
BibGuru Blog
Be more productive in school
- Citation Styles
How to write a conclusion for a research paper

Research paper conclusions provide closure for your paper—but they can be difficult to write. What should you include? In this post, we discuss how to write a conclusion for a research paper.
What is a conclusion?
The conclusion to a research paper sums of your main argument and provides closure for your reader. It will return to your thesis statement and revisit the ways that you proved it.
The content and format of your conclusion will ultimately differ depending on the subject of your paper. Some fields have more specific expectations for what needs to be included.
You should always check your assignment’s guidelines or rubric to ensure that you understand what your instructor expects in a research paper conclusion.
How to write a conclusion
In this section, we break down the main parts of a conclusion and provide tips on how to approach each one.
The opening of a conclusion
The point of a conclusion’s opening statement is to transition from the main body of your paper to the concluding section. Some types of research papers include section headers that label each part of the paper. In these cases, your reader will be able to clearly see that you’re about to conclude.
In most other cases, begin your conclusion with a signal that indicates that you’re moving into the concluding section of your paper. For instance, you might start your conclusion by stating “in conclusion,” “to conclude,” or “in sum.”
What you can include in a conclusion
Although you shouldn’t include any new data or evidence in a conclusion, you can include suggestions for further research, insights about how your research could be applied in different contexts, or a course of action.
The bulk of the conclusion should synthesize—not summarize—the main points of your paper. If your introduction included historical information or an anecdote, return to that information now.
Your conclusion should also answer the “so what” question: why is this research relevant? Who should care about your argument and why?
The ending of a conclusion
Finally, you’ll want to end your conclusion with a closing statement that wraps up your concluding section (and your paper as a whole).
Tips for writing a conclusion
1. don’t include new data or evidence.
Your conclusion should provide closure to your paper, so introducing new information is not appropriate and will likely confuse your reader.

2. Don’t simply restate your thesis
You should never simply copy and paste your thesis statement into your conclusion. Instead, revisit your thesis in light of the evidence and analysis that you put forth in the main body of your paper.
3. Provide closure for your reader
A strong conclusion provides closure for the reader by synthesizing the main points of the paper and putting to rest any questions that the reader may have during the process of reading. The best way to test if your conclusion provides closure is to ask someone to read your paper.
4. Make suggestions for further research
While conclusions should not introduce new data or arguments, they can include suggestions for further research. A single research paper never covers everything—there are always possible new angles and approaches.
Next steps for a successful research paper
Once you’ve written your conclusion, you should review what you’ve written and make revisions, as needed. Then, double-check that you’ve cited all borrowed material and that your paper has a bibliography with accurate citations.
Use BibGuru’s citation generator to quickly create accurate citations for the books, articles, websites, and other sources that you used in your research paper.
Frequently Asked Questions about how to write a conclusion for a research paper
A conclusion contains an opening statement (often a restatement of the thesis), recommendations for further studies or applications, and a closing statement.
Start by signaling to the reader that you are moving into the concluding section.
The length of your conclusion will depend on the length of your paper. Most research paper conclusions will be around 1-2 paragraphs.
End your conclusion with a closing statement that wraps up the paper and provides closure to your reader.

Make your life easier with our productivity and writing resources.
For students and teachers.

Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature
Powerful Academic Phrases to Improve Your Essay Writing

Adopting a formal style of writing is crucial for any type of academic writing, be it scholarly articles, research papers or essays. It requires a deep understanding of the subject matter, the ability to analyze and synthesize complex information, and the skill to communicate ideas effectively. One of the primary challenges of academic writing is the need to balance clarity with accuracy.
There are various factors that should be borne in mind in academic writing. The writing should be clear and precise. It should be well structured with a clear focus while demonstrating the rigor with which the research was conducted. Long winding sentences and emotional language must be completely avoided. While discipline specific language should be used, jargon must be avoided. In other words, academic writing is not easy. However, by using the right words and academic phrases, you can deliver clear, concise writing that can elevate your scholarly papers or essays.
In this article we will look at a few strong academic phrases that can go a long way in improving your academic essay writing.
Table of Contents
Comparing and contrasting, providing examples, elaborating on information, indicating uncertainty, summarising, academic phrases for various situations.
In writing an academic essay, arguments and ideas need to be built and articulated in a compelling manner. These should be supported with appropriate evidence. Furthermore, verifiable facts and examples must be presented in an engaging way and the entire essay should be well structured.
In all these, the usage of right academic phrases becomes helpful. Depending on what you want to convey, different academic phrases can be used in various situations as discussed below.
Very often in essays you may have to engage in the process of comparing and contrasting information, key aspects of two phenomena taken for study, or various sources for your literature review and so on. You will have to bring in to your discussion not just the similarities to your arguments, but also opposing or conflicting perspectives.
Use of appropriate phrases will help organically bring in such similar or contrasting information. For example, some of the phrases that can be used to discuss similarities and differences include: In comparison or by contrast, however, conversely, alternatively, whereas, on the other hand, likewise, in the same way and so on. Example: “The author expresses his opinion based on anecdotal references. By contrast the survey he quotes and tries to argue against is more plausible with the rigorous data it has collected.”
While writing an academic essay, you are required to support and expand your ideas and arguments through the use of examples. Phrases that can be used to provide examples include: for example, for instance, to illustrate, to exemplify, to demonstrate.
Example: “Climate and weather patterns are changing rapidly and its ramifications are staring us in the face. For example, look at what is happening with the incessant rains pouring down during certain summer months.”
As you structure your narrative, you will have to elaborate at various points on the information, ideas, and arguments that you are presenting. This has to be done in a manner that does not adversely affect the smooth flow of the narrative. It is here that the usage of appropriate phrases is crucial to uplift the quality of your essay. Using phrases such as moreover, furthermore, in other words, in addition and so on can aid in providing additional information.
Example: “Rising temperatures are greatly impacting the health of children belonging to vulnerable groups in parts of the Asian sub-continent. Moreover, the lack of adequate government support and dismal welfare measures is making lives harder for such families.”
While writing research papers or essays, researchers often acknowledge the limitations of their studies and the possibilities for conflicting or opposing views. Such recognition is pertinent for the advancement of scientific knowledge. There are various phrases that can be used to indicate uncertainty such as: it could be argued that the data suggest that evidence suggest that, or it is possible due to.
Example: “The evidence suggests that the new teaching methods are beneficial and can be considered as an alternative to existing methods”.
The concluding part of your essay should be a summary of your main ideas and arguments and its significance. To this end, the following phrases can be utilized: to summarise, to conclude, above all, or most significantly.
Example: “To conclude, evidence points to the positive impact of periodic creative workshops on children’s cognitive development.”
While academic writing may be challenging, mastering the use of appropriate academic phrases, avoiding jargon, and delivering clear, concise writing can elevate one’s writing to a higher and contribute to the advancement of knowledge in their respective fields.
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- How to Paraphrase Research Papers Effectively
- How to Use AI to Enhance Your College Essays and Thesis
- 7 Ways to Improve Your Academic Writing Process
- How to Cite Social Media Sources in Academic Writing?
How to Write a High-Quality Conference Paper
How to ace grant writing for research funding with paperpal , you may also like, mla works cited page: format, template & examples, how to ace grant writing for research funding..., how paperpal’s research feature helps you develop and..., how paperpal is enhancing academic productivity and accelerating..., academic editing: how to self-edit academic text with..., 4 ways paperpal encourages responsible writing with ai, what are scholarly sources and where can you..., how to write a hypothesis types and examples , what is academic writing: tips for students.
- Essay Editor
Proposal Essay Examples: Convincing Ideas for Your Research Paper or Essay

Struggling to craft a captivating and well-built proposal essay? Many students find it challenging to compose a proposal-based essay and struggle to generate convincing ideas. If this sounds familiar, read on. In this comprehensive guide, we streamline the process of brainstorming and composing work, offering resources like suggestions on how to write a proposal essay, suggested steps when writing, useful examples, and efficient essay-crafting tips.
Developed through several years of expertise in scholarly writing, our article is meticulously tailored to help you excel in your academic assignments. Join us as we explore crafting an exceptional proposal paper. With the right tools and assistance, you'll move from ambiguity to self-assurance, ready to write an impressive work. Let's master the art of creating an attention-grabbing essay.
What is a Proposal Essay?
A proposal essay succinctly outlines the key content and aim of your intended study, summarizing its primary points and overall intent. Unlike a thesis, which presents the main idea of your academic study, a proposal-focused assignment acts as a detailed plan addressing a specific problem. As a proposal writer, you identify an issue, suggest a possible solution, and then provide persuasive evidence for the audience to have them support your viewpoint. Your goal is to convince them that this view is exceptional and deserves implementation. When writing such an essay, consider it as a chance to immerse in practical issues and showcase analytical and creative thinking skills. These papers serve as strategic tools, allowing an author to present their ideas or beliefs compellingly. Beyond business or economics, they encourage solution-seeking and reasoning skills across a variety of disciplines.
In a nutshell, a proposal-driven assignment allows you to demonstrate your ability to think innovatively and critically, addressing real-life issues with practical solutions. Now that you understand what is a proposal essay, join us in exploring its specifics and revealing your writer’s potential.
How to Write a Proposal Essay
Creating a successful proposal-related paper necessitates thorough preparation and an understanding of your audience's needs. To write such an essay, observe these stages:
- Extensively investigate your assignment’s topic to identify a chosen problem.
- Develop a compelling thesis statement summarizing your suggested solution.
- Make a solid proposal essay outline to logically organize all your ideas and ensure unity and cohesion.
- Present solid proof to support your viewpoints and anticipate any objections.
- Refine your writing carefully to enhance content clarity and logic.
When you are occupied with thoughts on how to write a paper proposal, handy tools like the AI essay generator Aithor have become indispensable helpers. Aithor, our intuitive assistant, empowers writers by utilizing advanced technology to generate ideas, check accuracy, and offer alternative words, improving the piece of writing. Explore the innovative capabilities of our AI tool by visiting https://aithor.com/ai-essay-generator and let it assist you with your assignment.
Check out some additional tips to enhance your overall essay quality:
- Get to know your audience and tailor your planned proposal to its interests.
- Use convincing language to involve your audience to advocate for your notion.
- Incorporate relevant data, instances, and statistics to reinforce your position.
- Address possible counterarguments to demonstrate thorough consideration.
- Use a powerful summary to conclude and inspire to act, urging support for your concepts.
To wrap up, writing a decent proposal-based essay requires in-depth investigation, persuasive argumentation, and attention to detail. By following the mentioned guidelines and additional tips, you can smoothly write a solid solution-focused writing that inspires action.
Prewriting Stage
Setting for a journey of composing a proposal-related assignment can be overwhelming. How to start a proposal essay? To ease this process, academic writers advocate for a systematic approach to craft a captivating piece of writing.
Here's a full guide to guarantee your assignment paper stands out. Know Your Reader
Being sympathetic to your prospective listeners is paramount when writing a persuasive paper. Who will you write for? Identify their key roles, preferences, and concerns to efficiently customize your message. This ensures mutual resonance in your views and addresses their specific needs and expectations.
Research Academic investigation forms the foundation of a robust convincing paper. Even with a prior understanding of the material, delving deeper yields new insights and perspectives. Revising scholarly literature enhances arguments, lending authority and credibility to your message.
Set an Issue
State the topic and challenges precisely and clearly. Use evidence to accentuate its significance and establish your grasp of the matter. That step is pivotal in gaining the audience's sympathy and support.
Define a Solution
Offer a straightforward and practical way out to the identified problem. Ensure its clarity and usefulness, aligning with indicated requirements. Frame your resolution in terms of objectives, delineating primary goals and additional benefits your project will provide.
Write an Essay Proposal Outline
Crafting an outline for your persuasive paper is essential. This helps put your ideas in order and create a logical flow. When structuring your paper, begin with a catchy introduction that describes the problem. Outline your suggested resolution with strong evidence, facts, and illustrations. Finally, summarize the noteworthy aspects and emphasize the relevance of your proposal. This structured approach enhances coherence and persuasiveness.
Ø For executive proposals, add organizational data and budget analysis, maintaining clear and direct language, devoid of unnecessary jargon.
Structure of a Proposal Essay
Generating a credible proposal-focused essay involves several main components, each serving a definite purpose to efficiently convey your key idea. Here's a full breakdown of how to write an essay proposal:
Introduction
- Captivating Intro
Capture the readers' attention with an eye-catching hook. Precisely state your essay’s thesis statement, conveying your message succinctly and convincingly.
- Context and Background
Provide a solid background for your proposed idea, thus setting a stage for the topic matter and its validity.
- Research Relevance
State why your investigation is essential, drawing upon the background info provided.
- Problem Statement
Dive deeper into the presented issue, delineating its relevance and impact to deliver a captivating context for your written work.
- Proposal Statement
State your projected way out to the mentioned challenges. Emphasize its paybacks and mention potential shortcomings to showcase its viability.
- Implementation Plan
Clarify in detail how you wish to put your words into effect, addressing practical considerations and potential obstacles.
- Expected Outcome
Talk about the positive effects that you expect from executing your solution proposal, conveying distinctly its probable impact.
- Evaluation of Feasibility
Consider the proposal’s practicability considering the essential resources and would-be objections.
- Resource Management and Timeline
Indicate the demanded resources and generate a timeline for implementation if applicable.
- Research Queries and Objectives
List the goals of your inquiry and say how will addressing the challenges impact your audience. Utilize credible sources and data to reinforce your arguments.
- Study Design and Methodology
Explain your methodology for addressing the challenge, illustrating the rationale behind your selected approach, and predicting the anticipated outcomes.
- Key Points Summary
Recap the main points from the intro, background, and topic relevance, along with the hypotheses/research questions sections.
- Importance and Potential Impact
Accentuate how your investigation can hypothetically contribute to addressing the mentioned issue and consider potential consequences if the proposal is not implemented.
- Call to Action and Close
Restate the proposal’s relevance, leaving the audience with a convincing call to action. Express gratitude for the committee's consideration and leave readers with a sense of anticipation for the proposed research.
- Bibliography (Optional)
Include a literature list that references the materials used and displays the work’s contents to demonstrate the depth of the investigation. It is usually placed at the end of the whole text as a separate section.
Remember to refine your final draft for clarity and conciseness, testing if the paper proposal format is well-constructed. Consider seeking some feedback from others to enhance the presentation and proposal actuality. Additionally, ensure each paragraph flows smoothly and plausibly and supports your general argument. This ensures content clarity and cohesion throughout your text.
Academic Research Study Proposal Sample 2024
Here is a sample idea for an interesting proposal paper:
- The proposed research study will investigate the risks of sending messages while driving and explore measures to mitigate this hazardous behavior.
- Texting when driving continues to be a widespread issue despite various awareness campaigns and legal restrictions.
- The study will focus on examining the mental and physical distractions caused by this activity. Also, the proposal will delve into the increased likelihood of mishaps and fatalities associated with such behavior.
- Utilizing a mixed-methods approach, the investigation will gather data through surveys, interviews, and driving simulations from a diverse sample of drivers across different age groups and regions.
- Data analysis will include statistical analysis of accident rates, qualitative coding of interview responses, and thematic analysis of driving simulation outcomes.
- The essay's findings aim to raise awareness among policymakers, law enforcement agencies, and the public about the grave dangers of texting when driving.
- Additionally, the investigation will propose recommendations for interventions such as stricter enforcement of existing regulations, educational programs targeting drivers of all ages, and the creation of technological solutions to prevent distraction-related cases.
- Ultimately, this study seeks to add to the lessening of crashes and fatalities caused by texting in a car and encourage safer driving habits in society.
Final Remarks
In composing a robust proposal essay, the journey from beginning to culmination is marked by strategic planning and scrupulous work. If you embrace a methodical approach, a captivating paper will emerge. Such vital details as understanding the audience, conducting in-depth research, describing the challenges, proposing possible way-outs, and structuring your arguments are vital elements of a successfully written work. Each phase of this process contributes to the clarity and persuasiveness of the text, ensuring resonance with readers. Using illustrative examples adds depth and relatability to the proposal.
Ultimately, the proposal paper showcases not only analytical prowess and solution-seeking acumen but also adept communication of intricate concepts. With unwavering dedication and meticulous focus on details, the proposal essay becomes a testament to effective persuasion and insightful discourse.
Related articles
Apa or mla: choosing the right citation style for your paper.
When it comes to academic writing, properly citing your sources is crucial. It not only helps you avoid plagiarism but also adds credibility to your work by showing that you've done your research. However, with various citation styles out there, it can be tricky to know which one to use. Two of the most common styles are APA (American Psychological Association) and MLA (Modern Language Association). In this article, we'll take a closer look at the APA vs MLA format to help you decide which is ri ...
Literary Analysis Essay Example: Discover How to Analyze Literature and Improve Your Writing Skills
Creating a literary analysis essay is one of the most interesting assignments during college and high school studies. It needs both good text interpreting and analytical skills. The number of proper forms is great, including short stories and novels, poems and ballads, comedies and dramas. Any literary work may be analyzed. In brief, when writing this paper a student should give a summary of the text and a detailed review of the language, structure, and other stuff the author used to express hi ...
Will I Get Caught Using Chat GPT?
ChatGPT has been around for a little over a year but already found popularity among all groups of users. School and college students have taken a particular liking to it. However, many students avoid using the chatbot for fear that their teacher might catch them. Read this article to learn more about ChatGPT, its features, and whether your teacher can actually find out if you use it for your homework. What is Chat GPT? ChatGPT was first introduced to the world in November 2022. At the time, ...
How to Write an Evaluation Essay That Engages and Persuades: Helpful Tips and Inspiring Examples
Are you feeling unsure about how to effectively evaluate a subject from your own perspective in an evaluation essay? If you're struggling to understand how to present a balanced assessment, don't worry! We're here to guide you through the process of writing an evaluation that showcases your critical thinking skills. What Is an Evaluation Essay? An evaluation essay is a type of writing in which the writer gives their opinion on a topic. You look at something carefully and think about how good ...
Biographical Essay: Tips and Tricks for Writing a Perfect Biography
Biographical essays are some of the most common texts you can find on the Internet. When you browse a Wiki article about your favorite singer, you are basically reading a biography paper. However, in academia, there are certain rules students need to follow to get perfect marks for their papers. In this article, we will explore what a biographical essay is, why it matters, and how to write an essay about a person. What is a biographical essay? A biographical essay is a paper that focuses on ...
Create a Perfect Essay Structure
Hello Aithors! We're back again with another feature highlight. Today, we want to talk about a tool that can be a game-changer for your essay writing process - our Table of Contents tool. Writing an essay isn't just about getting your ideas down on paper. It's about presenting them in a clear, structured way that makes sense to your reader. However, figuring out the best structure for your essay can sometimes be a tough nut to crack. That's why we developed the Table of Contents feature. The b ...
Ace Your Graduation Speech with Aithor
Hello, Aithors! Can you feel it? That's the buzz of graduation season in the air:) And while we're all about the caps flying and the proud smiles, we also know that being asked to write a graduation speech can feel a bit like being handed a mountain to climb. Crafting a graduation speech is all about capturing the spirit of the journey you've been on, from the triumphs to the trials, and everything in between. It's a reflection of where you've been, and a beacon of light pointing towards where ...
How To Write Reflection Essays
How often do you contemplate how the tapestry of your experiences shapes your thoughts? A reflection paper lets you explore that. It's like deep diving into your life’s precious moments, examining how stories, books, events, or even lectures have influenced your views. This type of academic essay integrates a personal perspective, allowing you to openly express your opinions. In this guide, we will delve into the specifics of reflective writing, share some tips, and show some self-reflection es ...
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Open access
- Published: 31 May 2024
What difference does one course make? Assessing the impact of content-based instruction on students’ sustainability literacy
- Inan Deniz Erguvan ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-8713-2935 1
Humanities and Social Sciences Communications volume 11 , Article number: 708 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
Metrics details
- Language and linguistics
Composition studies, with their cross-disciplinary role in students’ academic lives, can be essential in placing sustainability at the center of students’ learning. This research assessed the impact of content-based instruction on students’ sustainability literacy in a first-year composition course through a mixed-method design. In the quantitative part of this case study, 221 students in different classes of a first-year writing course in a higher education institute in Kuwait during the Fall term of 2022 were first given a pretest to determine their sustainability literacy levels. During a 6-week period, 121 students participated in the content-based instruction emphasizing sustainability, while 100 students comprised the control group, receiving curriculum without any emphasis on sustainability. The allocation of students in these two groups was random, determined solely by the classes they were enrolled in at the beginning of the semester. At the end of the semester, both the experimental and control groups were given a posttest to measure the impact of the instruction on their sustainability literacy levels. For the qualitative component, 60 students from the experimental group and 60 students from the control group were tasked with composing an essay identifying Kuwait’s major sustainability challenges and proposing corresponding solutions. The impact of content-based instruction on students’ literacy levels was measured by conducting a qualitative and quantitative content analysis on their writing. The results showed that the experimental group students made statistically significant improvements in their sustainable literacy levels, scored better on the posttest, used more sustainability terms and concepts, and identified more sustainability-related challenges and solutions in their essays.
Introduction
Our planet faces a critical emergency, evident in ecosystem devastation, species extinction, the depletion and destruction of vital resources, widespread pollution, and extreme poverty affecting billions of people. Scientists attribute these challenges significantly to our ignorance of the limits of Earth’s resources.
With its 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), the United Nations’ 2030 Sustainable Development Agenda is one of the most important attempts to solve the intricate global issues of our day. Reaching the objectives of sustainable development (SD) requires education. According to the UN, sustainability literacy includes the mindsets, abilities, and information people need to genuinely commit to creating a sustainable future and make wise decisions in that direction (Decamps, 2017 ).
The Education for Sustainable Development (ESD) framework, developed by the UN, serves as a roadmap for institutions and educators to revise curricula and teaching pedagogies based on sustainability principles. This framework is employed by hundreds of universities worldwide (Yuan and Zuo, 2013 ). ESD has gained political and institutional acceptability in many parts of the world recognizing the potential of promoting sustainability literacy to foster creative solutions to the world’s problems.
There is consensus that higher education institutions (HEIs) ought to promote sustainable development via research and activism since all students, regardless of their field of study, have the capacity to be social change agents. As a result, pupils need to acquire the skills necessary to contribute to a sustainable future (Buckler and Creech, 2014 ).
HEIs are responsible for teaching sustainability literacy and producing environmentally conscious citizens, given their ability to shape students’ attitudes and perspectives (Stephens et al. 2008 ). This endeavor holds particular significance in creating a new generation keenly aware of the global environmental challenges we are going through (Koehn and Uitto, 2017 ).
Leal Filho ( 2010 ) argues that universities cannot avoid dealing with the biggest problems that humanity is currently experiencing. Additionally, he contends that ESD is especially important in higher education since students will soon be pursuing careers in a variety of fields and will need to understand how their careers can contribute to the solution of sustainability issues. According to Leal Filho ( 2010 ), ESD will inspire students “to take action both during their time as students and, later on, as professionals” (p. 2). Therefore, in order to effectively address the difficulties they will experience in their various disciplines, undergraduates should develop competence-based sustainability awareness and literacy.
Sustainable development is not restricted to a single science. Composition studies, with their inherent cross-disciplinary and distinctive purpose in students’ academic lives, can play an important role in making sustainability a core focus of the curriculum. Composition instructors have the freedom to teach in a variety of contexts and disciplines. While teaching composition is as labor-intensive as any other subject in higher education, writing instructors have more clout to urge students to investigate a wide range of topics than academics who teach in more specialized fields (Owens, 2001 ).
Although certain curricular initiatives have been the subject of research, the impact of curriculum design on improving sustainability understanding has not received as much attention. Because of this, there are currently no guidelines in the literature for developing curriculum that specifically address sustainability learning objectives. Therefore, the goal of this project is to enhance students’ sustainability literacy by supporting the development of a structured curriculum in a first-year writing course. In order to do this, this study examined the benefits of utilizing textual and audiovisual materials in content-based instruction to introduce students to the three dimensions of sustainability as well as the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals.
Content-based instruction (CBI) is a popular approach to language education that combines content and language learning. Content-based education varies from standard language classes in that language comes second to content. This teaching technique is deemed effective because it employs English as a medium to impart content knowledge while providing various opportunities for students to use English in class (Brinton et al. 2003 ). Thus, the use of English stems from meaningful purposes (content learning) and frequent practice (opportunities to use English), resulting in an environment conducive to rich discussions, ultimately improving language fluency while reinforcing the content taught in a variety of academic areas. In other words, content-based language acquisition gives pupils a valid or relevant purpose to use the language they are learning (Kennedy 2006 ).
The CBI is seen as an effective tool for preparing students for higher education studies in a new language and context. Song ( 2006 ) conducted a long-term study to find out how well CBI worked for ESL students at a community college in the United States. According to the study, students enrolled in the content-linked ESL program passed the ESL course with greater marks and pass rates. They also performed better in follow-up ESL and developmental English classes. Overall, compared to their peers, the ESL students who were linked to content demonstrated higher levels of long-term academic performance. Higher GPA overall, graduation and retention rates, and English proficiency exam pass rates were all indicators of this achievement.
According to Stoller ( 2004 ), CBI stands out for its dedication to both language and content-learning objectives. Over the years, the program has garnered support as a result of students’ improved language skills and content-area knowledge at the elementary, middle, and post-secondary education levels, which attests to its perceived successes. According to Kennedy ( 2006 ), kids who study languages in addition to other subjects perform better academically and are able to make links between their studies and the real world. Multiple teaching methodologies are employed in content-based foreign language instruction, which also accounts for the variety of learning styles and intelligences present in the classroom (Kennedy, 2006 ).
However, despite the abundance of interest in using CBI to increase students’ awareness of certain topics and concepts, there is still a lack of research in assessing the impact of CBI on sustainability literacy. There are a few case studies, several reports of individual attempts and class practices to implement CBI in EFL classes to familiarize students with sustainability concepts (Vorholt, 2018 ; Schneider, 2017 ), and the empirical studies tend to focus on assessing teachers’ perspectives on teaching sustainability to their students (Shah et al., 2022 ; Maijala et al., 2023 ). Additionally, studies assessing the impact of CBI on students’ sustainability literacy with an experimental research design are very rare in the literature. Thus, this research is expected to make an important contribution to the field of sustainability education in higher education institutions.
This research employs a case study approach due to its ability to allow in depth, multifaceted explorations of complex issues in a real-world context (Crowe et al., 2011 ). This methodology aligns with the exploratory nature of this research, enabling us to generate a contextualized understanding that contributes to the existing body of knowledge. The selected case institution offers a valuable opportunity to examine a real-world scenario that is both relevant to our research questions and has generated practical implications for decision-makers in the field.
The main research questions that will guide the study are as follows:
Did the content-based instruction have any significant effect on the participants’ sustainability literacy levels?
Are there any differences between the control and experimental groups’ essays in terms of students’ perceptions of sustainability challenges and their solutions in Kuwait?
Sustainability
The idea of sustainability is not so new; it existed before the field of environmental sciences as we know it today. Nonetheless, the need to use resources sustainably has become more widely recognized due to factors including population growth, increased consumption following the Industrial Revolution, and the threat of the depletion of essential resources like coal, oil, and wood. Fears that living standards would not be maintained for current or future generations sparked a style of thinking that led to the creation and acceptance of sustainable development (Du Pisani, 2006 ).
Although there is still no commonly accepted definition of sustainability, its context has eventually widened to include “three pillars”; namely the social, economic, and environmental aspects of sustainability (Purvis et al., 2019 ). Initially, the focus was mainly on the environmental dimension of sustainability and many researchers considered this dimension more important than the other two, however, later, the economic, and social dimensions started to attract similar amounts of attention (Colantonio, 2007 ).
Following the 1972 United Nations Conference on the Human Environment, which was the first UN conference devoted to environmental issues, there have been global efforts to redefine sustainability. There are many definitions of sustainable development, but the one that is most often cited comes from the 1987 Brundtland Report, also known as Our Common Future: “Sustainable development is development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs” (Brundtland, 1987 ).
Solutions to sustainability issues, whether ecological, social, or economic, hinge on decision-making processes at both the organizational and individual levels. It is important to recognize that organizational decisions stem from individual choices (Carley and Behrens, 1999 ). Therefore, the success of sustainability goals largely relies on individual decision-making, particularly in consumer behavior. By opting for sustainable choices, consumers can drive demand for sustainable products and services, articulate their values, reduce their environmental footprint, and contribute to building a culture of sustainability. The positive effect of education on pro-environmental consumption behaviors is evident in the literature (AlNuaimi and AlGhamdi, 2022 ; Adjengdia and Schlegelmilch, 2020 ; Achola et al., 2020 ) and was recognized in the Brundtland Report ( 1987 ).
Furthermore, in 2002, the World Summit on Sustainable Development and the Commission on Sustainable Development emphasized the crucial role of information in informed decision-making. Hence, education emerges as a vital instrument in achieving sustainability goals. It empowers individuals and communities to take meaningful action and make informed choices that safeguard the environment while promoting social and economic development.
Sustainability literacy
Organizations from a variety of sectors have prioritized educational projects aimed at improving people’s understanding of sustainability because they believe that a sustainable future requires a society that is knowledgeable about sustainability. The significance of sustainability education has been emphasized recently by international organizations, private companies, and most significantly, higher education institutions. Renewing interest in creating trustworthy assessments of sustainability literacy and knowledge has coincided with the increased emphasis on sustainability education.
Various approaches have been used to develop a valid assessment tool for sustainability literacy. One noteworthy example is the SULITEST (Sustainability Literacy Test), established after the Rio+20 Conference (Decamps et al., 2017 ). SULITEST is an online standardized set of multiple-choice questions that can be used globally, alongside specialized modules tailored to specific national, regional, and cultural contexts. Décamps et al. ( 2017 ) outlined the structure of this tool and highlighted its potential for measuring sustainability literacy on a global scale, recommending its adoption by educational institutions.
Similarly, Zwickle and Jones ( 2017 ) developed a web-based survey tool to assess the sustainability knowledge of undergraduate students at Ohio State University; this tool involved 1000 participants and comprised 16 multiple-choice questions. In the United States, the American Association for the Advancement of Sustainability in Higher Education (AASHE) introduced the Sustainability Tracking Assessment Rating System (STARS) in 2010, with participation from more than a thousand institutions by 2022. The STARS evaluates the sustainability efforts of colleges and universities in the U.S., rewarding institutions that offer a greater number of sustainability-related courses or even require students to complete at least one sustainability course as part of their general education requirements (Bullock and Wilder, 2016 ). Participating institutions assess the sustainability literacy of their students, focusing on their knowledge of sustainability topics and challenges.
As higher education institutions and society at large increasingly prioritize the importance of individuals’ understanding of sustainability, the need for accurate assessments of sustainability knowledge becomes more significant. The development of improved measures of sustainability knowledge is anticipated to enhance sustainability education and ultimately cultivate a population with higher levels of sustainability literacy (Kuehl et al., 2023 ).
Sustainability in Kuwait
Kuwait is identified as one of the wealthiest countries in the world, owing to its substantial revenues derived from the oil sector. The country enjoys an abundance of wealth from the oil sector which make up more than 90% of Kuwait’s export earnings, a dependence that makes it difficult to diversify the economy and develop other industries that are less reliant on fossil fuels (Eltony, 2002 ). Consequently, Kuwait encounters various sustainability challenges, primarily stemming from its heavy reliance on oil revenues (AlOthman and Palliam, 2018 ). Some of the major environmental challenges faced by Kuwait are air pollution, water scarcity, and waste management. The country has high levels of air pollution due to its petrochemical industry activities and transportation. Water scarcity is a significant issue in Kuwait, where desalination plants are relied upon to meet water needs. Nevertheless, Kuwaitis consume a staggering 520 l of freshwater per capita per day, one of the highest in the world (Kuwait National Development Plan, 2017 ). Waste management poses another significant challenge, as Kuwait generates large amounts of waste due to high mass consumption, necessitating proper disposal and recycling methods (Al Yaqout et al., 2002 ; Koushki et al., 2004 ). Currently, water and energy consumption, along with waste production per capita, rank among the highest globally in Kuwait.
The country has launched several initiatives to promote sustainable development, and the most significant initiative is the Kuwait National Development Plan (KNDP) that serves as a roadmap for sustainable development in Kuwait. The KNDP emphasizes the importance of economic, social, and environmental sustainability and sets targets for reducing carbon emissions, improving waste management, and promoting renewable energy (Kuwait National Development Plan, 2017 ). Kuwait officially embraced the SDGs in September 2015, subsequently integrating them into its Vision 2035 plan.
Despite these efforts, Kuwait currently holds the 101st position out of 163 countries, with an overall score of 64.53 (Sachs et al., 2022 ). Furthermore, there remains a gap in the implementation of sustainable practices by government agencies and a lack of sustainable awareness among the public. Very few studies exist in this domain, with the overarching message emphasizing the need for greater awareness of sustainability in Kuwait. For example, a study by Al Qattan and Gray ( 2021 ) revealed that government policies and practices inadequately address pollution issues, particularly in Kuwaiti water bodies. Similarly, AlSanad ( 2015 ) found that lack of awareness acts as a main barrier to adopting sustainable construction approaches in Kuwait and stresses the need for governmental initiatives such as standards, policies, and incentives to promote sustainability. According to similar research (Koushki et al., 2004 ; AlSulalili et al., 2014 ; Al Beeshi et al., 2020 ), there is a dearth of public knowledge of sustainable waste management techniques and municipal programs for waste prevention, reduction, or recycling.
Kuwait’s overall score of 64.53 places it 101st out of 163 countries, notwithstanding these efforts (Sachs et al., 2022 ). In addition, there is still a lack of public understanding of sustainability issues and a gap in the way government agencies are implementing sustainable practices. There are very few studies in this field, and most of them emphasize how important it is for Kuwaitis to be more conscious of sustainability. Al Qattan and Gray’s study from 2021, for instance, showed that pollution problems are not sufficiently addressed by government policies and practices, especially when it comes to Kuwaiti water bodies. Similar findings were made by AlSanad ( 2015 ), who highlighted the necessity of governmental initiatives such as standards, rules, and incentives and discovered that a major obstacle to Kuwait’s adoption of sustainable construction practices is a lack of awareness.
In conclusion, despite bourgeoning awareness of sustainability among businesses and the government’s initiatives to promote sustainability, Kuwait still requires heightened awareness and implementation of sustainable practices and concerted efforts to address the nation’s oil reliance and propel towards a more sustainable future.
Methodology
This study has a true experimental research design with random assignment of students in control and experimental groups, with a pretest and posttest administered to both groups. A mixed-method sequential explanatory approach was adopted to collect the data, which were first quantitative and then qualitative in two consecutive phases of the study (Creswell, 2012 ; Creswell and Clark, 2011 ). Using mixed methods helps to provide a more comprehensive framework of the phenomenon by enabling rich and informative data and validating and triangulating the data by analyzing the same issue through both quantitative and qualitative methods (Silverman, 2000 ).
Research population
The research population of the study consisted of students at a private university in Kuwait based on an American-style model of higher education that offers instruction in English. A total of 221 first-year composition students participated and were divided into experimental and control groups, with 100 students assigned to the experimental group and 121 to the control group. The allocation of students into these groups was random and determined by their enrollment in specific course sections at the beginning of the semester. The discrepancy in group sizes reflects variations in the number of students per course section, typically ranging from 20 to 25.
In the experimental group, 100 students received specialized content-based instruction focused on sustainability, while the remaining 121 students in the control group completed regular assignments as outlined in the course syllabus, covering various predetermined topics assigned by their writing instructors. Both groups underwent a pretest before the commencement of content-based instruction and a posttest at the conclusion of the semester.
The participants’ demographic information is displayed in Table 1 .
For the qualitative part of the study, the researcher collected essays from students at the end of the Fall semester of 2022. The research population consisted of students in both the experimental and control groups who attended the class and signed the consent form on the day of data collection, week 15 of Fall 2022. There were 65 students who produced an essay in the experimental group and 67 in the control group. Five essays from the experimental group and seven essays from the control group were eliminated because they had a very low word count (less than 100 words), thus, 120 were left for analysis.
Data collection
The quantitative section collected data through an adapted version of the Sustainability Literacy Assessment, prepared by a committee at the University of Wisconsin-Oshkosh to measure the university’s sustainability performance, within the Sustainability Tracking, Assessment & Rating System (STARS) framework ( 2018 ). The assessment form included four sections, testing the knowledge level with five multiple-choice questions, and assessing students’ self-reported skills, attitudes and familiarity with some sustainability topics and concepts on a five-point Likert scale. The Institutional Review Board (IRB) approval (case number 278674) was obtained, and students signed the consent form before the data collection. A total of 221 students completed the questionnaire—121 in the control group and 100 in the experimental group.
Table 2 shows the reliability scores of these sections of the data collection tool. When the scales are examined, it is determined that they have a good level of reliability. A Cronbach’s alpha greater than 0.50 indicates that the scale used is reliable. This also indicates that the internal consistency of the scale used in the study is good.
In the qualitative data collection, students in both the experimental and control groups were asked to write a short essay identifying the major sustainability challenge of Kuwait and offering solutions to this problem. This session was conducted during the scheduled class time of 50 min, on the computer under the instructor’s supervision.
Data analysis
The quantitative data were analyzed using the SPSS Statistics (Statistical Package for Social Sciences) for Windows 25.0 program. Along with descriptive statistical methods (numbers, percentages, minimum-maximum values, median, mean, standard deviation), chi-square analysis was applied to test the homogeneity of the groups. The data were checked for the normal distribution compatibility with Q–Q plot drawing for its skewness and kurtosis values (±3).
For quantitative data comparison in normally distributed data, an independent t test was used for comparisons between two independent groups, and a dependent t test was used for comparisons between two dependent stages. One-way ANOVA was applied for comparisons of more than two independent groups.
Three processes comprise the data analysis process in qualitative research: arranging and prepping the data for analysis, coding and condensing the data to reduce the data into themes and presenting the data in tables and figures (Creswell, 2012 ). The content analysis method was used to assess the data collected for this study. The methodical, impartial, and, if feasible, quantitative examination of the content of different documents is known as content analysis (Bilgin, 2006 ). Content analysis’s primary goal is to find ideas and connections that will contribute to the explanation of the information gathered.
The student essays were imported into the MAXQDA 2022 program, which utilizes visual analysis tools extensively and offers a more structured approach to data analysis than manual analysis (Kuckartz and Rädiker, 2019 ). To identify the most frequent words and word combinations in the essays, a quantitative content analysis was performed using the MaxDictio function of the software. For the qualitative content analysis, a combined approach incorporating both inductive and deductive methods was employed. The researcher thoroughly reviewed the data multiple times, generating initial codes. Codes that were related to each other were then grouped together under relevant themes and assigned appropriate names. Subsequently, the obtained themes were elaborated upon in detail and the findings were interpreted.
Research Question 1
Did the content-based instruction have a significant effect on the participants’ sustainability literacy levels?
The first section of the questionnaire included five questions testing students’ knowledge of sustainability. Table 3 below shows the percentages of correct and incorrect answers in the control and experimental groups according to the pretest and posttest scores.
According to Table 3 , the experimental group of students in the posttest scored the highest percentage in the knowledge questions. The percentage of correct answers produced by the students in the control group did not show a consistent pattern, while it increased in Q1 and Q3, it decreased in Q2, Q4, and Q5.
However, for the experimental group, the students’ correct answers to all the questions increased. To assess whether these differences were statistically significant, an independent t test was conducted between the pretest and posttest scores of the two groups.
Table 4 shows the result of the independent t test conducted to compare the average knowledge of the participants before and after the CBI. There was no statistically significant difference between the control group and experimental group participants’ pretest knowledge averages, but there was a statistically significant difference in posttest averages ( p < 0.05).
The questionnaire also included questions asking students to evaluate their literacy in skills, attitudes, and topics and concepts regarding sustainability. Table 5 shows the results of the independent t test conducted to compare the skills, attitudes, and topic and concept scores of the participants according to their groups. According to these findings, the posttest scores for skills, attitudes, and familiarity with topics and concepts were significantly greater for the experimental group participants than for the control group participants.
Research Question 2
Are there any differences between the control and experimental groups’ essays in terms of their perceptions of sustainability challenges and their solutions in Kuwait?
To analyze this question, students were asked to write an essay identifying the major sustainability challenge of Kuwait and offering some solutions to it. The essays were processed through MAXQDA, and the frequency distributions of the control and experimental group student essays are shown in Table 6 .
According to student perspectives, the major sustainability challenges in Kuwait were dependence on oil, donating money to other countries and unemployment in the economic area. In the environmental realm, pollution and littering were the most frequently mentioned problems, followed by climate change. Loss of biodiversity and scarcity of resources were the other two major environmental sustainability challenges. Social sustainability issues in Kuwait, as per student views, could be listed as health and wellbeing problems, corruption, lack of quality infrastructure, quality of education, gender inequality and discrimination and human rights issues.
Table 6 also shows the number of essays mentioning the coded sustainability problems in each group type. According to these findings, students in the control group identified similar codes for environmental and economic sustainability problems, except for unemployment, with varying frequencies. However, regarding social sustainability problems, no control group student mentioned quality of education, reducing inequality and discrimination, or traffic accidents, and only one student mentioned malnutrition and obesity, corruption and gender equality. These issues were identified by a larger number of students in the experimental group. Overall, in the sustainability problems content analysis, 94 codes were included in the control group, and 137 codes were included in the experimental group.
Table 7 below shows the codes in the student essays for solutions to Kuwait’s major sustainability problems. According to the content analysis of the essays, the control group students did not mention five solutions that were mentioned by the experimental group. These were Kuwaitization and creating jobs in the economic sustainability domain, improving the quality of education, reducing inequality and discrimination, and reducing traffic accidents in the social sustainability domain. Both groups proposed the same solutions in the environmental domain, with control group 84, and experimental 68 codes. However, overall, the control group students had 104 codes, and the experimental group students had 137 codes for sustainability solutions.
A final content analysis was conducted quantitatively, via the MAXDictio function of MAXQDA to test how many sustainability related terms and concepts the students used in their essays. The list prepared by The Association for the Advancement of Sustainability (AASHE)’s Suggested Keywords for Sustainability Course and Research Inventories (The Association for the Advancement of Sustainability in Higher Education, 2023 ) was uploaded to the software and the student essays were analyzed based on these keywords.
According to Table 8 , the word count of the essays in the experimental group reached 27,751, and that of the control group reached 28,303. Despite the higher word count, dictionary-based content analysis revealed that the experimental group used more sustainability related keywords, as listed in the inventory. Students in the experimental group used 122, and the control group used 97 of these suggested sustainability keywords in their essays.
This study aimed to assess the impact of a 6-week course on content-based instruction (CBI) on the sustainability literacy levels of composition students. Our findings indicate that CBI significantly improved the sustainability literacy of the experimental group, as evidenced by their post-test scores and written work.
The first research question was addressed quantitatively, revealing significant improvements in the experimental group’s knowledge levels, skills, attitudes, and familiarity with sustainability concepts compared to those of the control group. This finding suggested that CBI effectively enhanced students’ sustainability literacy.
The second research question was explored qualitatively through the analysis of student essays. The experimental group demonstrated a greater ability to identify sustainability problems facing their country and propose solutions, particularly in the social sustainability domain. Additionally, they used more sustainability-related keywords in their essays, despite the control group having longer essays.
The results of our data analysis for both research questions revealed the positive effect of CBI on student learning. Content-based instruction is indeed widely recognized for its potential to enhance language learning outcomes and our findings are consistent with those of several previous studies in the field. While sustainable development is not frequently included in language education or promoted as part of teacher preparation for language learners (Maijala et al. 2023 ), it can readily succumb to CBI. CBI has begun transforming language-learning environments into places where students utilize language to research urgent global challenges, such as climate change (Turpin, 2022 ). A wide range of curricular approaches are included in CBI, ranging from language-focused programs where content is viewed as a helpful tool for extending the goals of the language curriculum to content-focused programs where content acquisition is prioritized over language learning (Met, 1999 ). As a result, teaching environmental and sustainable education in English as a foreign language (EFL) classes is growing in popularity.
Vorholt ( 2018 ) designed and taught a 6-week CBI course titled, “Environmental Issues” to undergraduate students at Lewis & Clark College, USA. The course focused on ecology versus economy, sustainability, and activism, which involved activities such as service learning and speaking. However, although she published her experiences and guidelines for designing the course, she did not assess the impact of student learning at the end of the course. Another review involved evaluating the opportunities for using an online German class as a vehicle for sustainability education in Ecuador, through content-based instruction (Schneider, 2017 ). This paper proposes adjusting the content of an online class and offering activities that will promote sustainability in a developing economy such as Ecuador.
A similar study was conducted in Switzerland, where SULITEST was administered to first-semester students in an HE institution, both before and after the survey (Zizka and Varga, 2021 ). Although the method used was not content-based instruction, the authors suggested that students from various nationalities and linguistic backgrounds in the Swiss HEI received an introductory course in English and French to sustainable hospitality culture aimed at providing insight into hospitality and tourism challenges and to reflecting on their sustainable solutions. The course did not specifically target the SDGs, but according to the posttest results, students’ knowledge about sustainability in general improved, and even exceeded the worldwide averages overall.
An attempt to incorporate environmental sustainability was made by task-based teaching in a translation course at two universities in Indonesia (Siregar et al., 2022 ). At the end of the course, the posttest demonstrated that the student’s confidence, one of the keys to acquiring a language, increased when using specific terms. The combination of task-based learning with appropriate content that is relevant to personal life, such as environmental sustainability increased the students’ motivation to learn and benefit from the translation activity.
Task-based learning was used in a translation course at two Indonesian institutions in an effort to include environmental sustainability (Siregar et al. 2022 ). The post-test at the end of the course showed that utilizing particular terms boosted the student’s confidence, which is one of the cornerstones to learning a language. Students were more motivated to learn and gain from the translation exercise when task-based learning was combined with relevant, real-world topics, including environmental sustainability.
A closer look at the findings of the second research question highlights the fact that students in both the experimental and control groups produced the highest number of codes for sustainability problems and solutions in the environmental pillar of sustainability. This aligns with the literature which suggests that the environmental pillar of sustainability is most often the one that students are more aware of (Zizka and Varga, 2021 ). For example, Chaplin and Wyton ( 2014 ) found that university students strongly associate recycling and sustainable living, and in many cases, they are believed to be the same thing. According to Drayson et al. ( 2014 ) the environmental dimension is the most prominent dimension in university students’ understanding of sustainable development. Another study conducted in China (Yuan and Zuo, 2013 ) showed that the students’ perceptions of the top priorities for higher education for sustainable development are generally environmentally oriented.
One interesting finding of the content analysis of the essays is that students in the experimental group mentioned more social sustainability problems and solutions than did those in the control group. These essays produced codes such as corruption, gender inequality and (lack of) quality of education, which are indeed some major social sustainability challenges Kuwait is facing, as reported in the Sustainable Development Report by the UN (Sachs et al., 2022 ). Gender inequality in Kuwait has been described as “significant challenges stagnating” by the UN, scoring particularly low in indicators such as the “ratio of female-to-male labor force participation” and ‘seats held by women in the national parliament’. Despite the growing achievements of Kuwaiti women, they still face challenges in social, cultural, and political arenas (Al Zuabi, 2016 ). In his study, Al Zuabi explored the Kuwaiti women’s challenges in attaining participation in the sociopolitical development of Kuwait and found that there are barriers preventing their empowerment and effective participation in national development. The fact that four students in the experimental group presented this problem and offered solutions to ensuring gender equality in the country as opposed to zero students in the control group could be interpreted as a positive influence of the sustainability-focused CBI.
Another major social problem that the country is facing and that emerged in the experimental group essays is corruption. Kuwait’s score in the Corruption Perceptions Index is decreasing (Sachs et al., 2022 ) and is defined as a significant challenge indicator. According to Al Saif ( 2020 ), corruption is a multilayered system in Kuwait that involves more than embezzlement and money laundering, with “wasta” (the Arabic word for the use of connections and influence to gain favors) serving as the cornerstone. Although corruption poses an existential threat to the country, it remains widespread to the extent that it has “become a staple of governance and a feature of everyday life in Kuwait” (Al Saif, 2020 ). Kuwait’s ranking in corruption indices falls every year, and this major social problem was identified solely by experimental group students, rather than by the control group.
The quality of education was another social sustainability problem mentioned by the experimental group students, but not by the control group. Despite some challenges, Quality Education (SDG 4) is a domain in which Kuwait seems to be doing better according to UN standards, with its high literacy and school enrollment rates. However, the Kuwaiti education system falls far below international standards and is quite inefficient, resulting in a higher cost per student. Among 141 countries, Kuwait has been ranked 112th globally in the skillset of graduates and 83rd in the quality of vocational training, according to the Global Competitiveness Report (World Economic Forum, 2019 ). Kuwait University, the only state university in the country, was ranked 9th in the GCC region, 19th in the Arab World, and 83rd in the MENA region (Abualrub, 2016 ). The major underlying reasons include a short school year, a high repetition rate, and low expenditure on school textbooks and teaching materials (Burney et al., 2013 ). The education system would benefit from increased use of technology, improved educational curriculum, and higher recruitment standards for teachers and their teaching skills (Murad and AlAwadhi, 2018 ; AlFelaij, 2016 ; AlHashem and AlHouti, 2021 ).
Foreign language teachers can play a crucial role in promoting sustainability; however, there are certainly some obstacles to implementing sustainability education in foreign language classes. Academics’ attitudes and level of awareness play a key role in shaping the successful implementation of a range of pedagogical techniques for ESD goals (Crosling et al. 2020 ). Currently, the greatest challenge is teachers’ lack of knowledge of sustainability concepts and their limited experience in teaching sustainability (Maijala et al., 2023 ; Shah et al., 2022 ).
In some countries where sustainability issues are on the political and educational agenda, in-service courses aiming to strengthen university teachers’ competence in integrating sustainable development (SD) into their classes are underway. At Uppsala University, Sweden, such a course was open to diverse participants from different faculties and allowed for stimulating exchanges of knowledge and perspectives (Rehn, 2018 ).
Conclusions and recommendations
In conclusion, this study aimed to evaluate the effects of a six-week content-based instruction (CBI) on the sustainability literacy of first-year composition students. The results from the experimental group showed significant enhancements in knowledge, skills, attitudes, and familiarity with sustainability concepts, as evidenced by the independent t test and content analysis findings.
Quantitative analysis revealed a clear increase in students’ sustainability literacy, aligning with CBI’s recognized potential to enhance language learning outcomes. Qualitative examination of the student essays further highlighted a deeper grasp of sustainability issues, particularly in the environmental domain, echoing existing literature regarding heightened environmental awareness among students.
Additionally, the experimental group demonstrated a heightened awareness of pressing social sustainability challenges in Kuwait, such as gender inequality, corruption, and educational quality. These topics were less emphasized or absent in the control group essays, indicating the positive influence of sustainability-focused CBI on students’ understanding of the social dimension of sustainability.
This study contributes to the existing research in two significant ways. First, it highlights the effectiveness of integrating sustainability into language education through CBI within an ESL context. The observed positive impact suggests that targeted interventions can effectively enhance students’ sustainability literacy, even within traditional language-focused curricula.
Second, the study emphasizes the potential of interdisciplinary approaches to bolster sustainability education in higher education. Collaborative efforts, workshops, and training opportunities across departments can equip writing and composition instructors with the pedagogical tools to integrate sustainability into their curriculum, fostering a more sustainable language-teaching culture.
This study is subject to several limitations. These include the relatively short duration of the CBI, and a small research population focusing on a specific group of students. Importantly, this was a case study in which one faculty member designed her own course materials to integrate sustainability into a first-year writing course at a higher education institution. Despite these constraints, the results were positive. Students exposed to CBI with a sustainability theme demonstrated increased sustainability literacy, evident in their improved scores on knowledge tests, incorporation of sustainability concepts, and the identification of sustainability problems and solutions in their essays. While these findings may not be broadly applicable, they suggest the potential impact of dedicated teachers designing courses to enhance student learning. Additionally, the scope of the study was limited because the effects of CBI were measured shortly before the semester ended, precluding assessment of students’ retention levels in subsequent semesters or years. Therefore, further research is necessary to explore this aspect.
Higher education institutions have a powerful opportunity to equip students in all disciplines with the knowledge and skills needed to achieve the UN’s SDGs by 2030 (Briens et al., 2022 ). By integrating sustainability education across all programs, universities can create a generation of graduates prepared to tackle global challenges.
To this end, preparing teachers and faculty to integrate sustainability issues in language teaching is essential. Higher education institutions should create collaborative programs and training for faculty to boost their understanding of sustainability. These initiatives should educate participants on integrating environmental, social, and economic issues into their teaching subjects and encourage them to develop activities that facilitate integrated teaching approaches (Nur et al., 2022 ; Hauschild et al., 2012 ; Çetinkaya et al., 2015 ).
Finally, educators should be encouraged to conduct similar case studies to contribute to a growing body of evidence showing the positive impact of dedicated teaching efforts in promoting sustainability literacy.
Data availability
https://data.mendeley.com/datasets/fhny7btkg7/1 .
Abualrub SY (2016) The problems with Kuwait’s struggling educational system. Kuwait Times. https://kuwaittimes.com/problems-kuwaits-struggling-educational-system/
Achola G, Asamoah-Manu N, Tani YD, Weiss A (2020) Consumer education can lead to behaviour change. Field Actions Sci Rep 22:96–103. http://journals.openedition.org/factsreports/6426
Google Scholar
Adjengdia BB, Schlegelmilch BB (2020) Linking sustainable product attributes and consumer decision-making: Insights from a systematic review, J Clean Prod, 245, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118902
Al Beeshi A, Alsulaili A, Al-Fadhli F (2020) Food waste management in Kuwait: current situation and future needs. 5th Eurasia waste management symposium, 26–28 October 2020. Proceedings, Istanbul, Turkey, https://www.eurasiasymposium.com/EWMS/files/Hall2/Session-6/167_Alsulaili-14.pdf
Al Felaij B (2016) Why integrating technology has been unsuccessful in Kuwait? An exploratory study. E-Learn Digit Media 13(3–4):126–139. https://doi.org/10.1177/2042753016672901
Article Google Scholar
Al Hashem F, Alhouti I (2021) Endless education reform: the case of Kuwait. International perspectives on education and society, 345–367. https://doi.org/10.1108/s1479-367920210000040019
Al Othman S, Palliam R (2018) Environmental degradation: Waste disposal and management in Kuwait. SSRN Electron J https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3272799
AlNuaimi SR, AlGhamdi SG (2022) Sustainable consumption and education for sustainability in higher education. Sustainability 14(12):7255. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14127255
Al Qattan MEA, Gray TS (2021) Marine pollution in Kuwait and its impacts on fish-stock decline in Kuwaiti waters: reviewing the Kuwaiti government’s policies and practices. Front Sustain 2. https://doi.org/10.3389/frsus.2021.667822
Al Saif B (2020) Another Invasion of Kuwait: Corruption may represent an existential threat to the country, but it still remains widespread. Diwan. Malcolm H. Kerr Carnegie Middle East Center. https://carnegie-mec.org/diwan/82453
Al Sanad S (2015) Awareness, drivers, actions, and barriers of sustainable construction in Kuwait. Procedia Eng 118:969–983. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2015.08.538
Al Sulaili A, AlSager B, Albanwan H, Almeer A, AlEssa L (2014) An integrated solid waste management system in Kuwait. Presented at the 5th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology, IPCBEE vol. 69 (2014). IACSIT Press, Singapore, 10.7763/IPCBEE
Al Yaqout AF, Koushki PA, Hamoda MF (2002) Public opinion and siting solid waste landfills in Kuwait. Resour Conserv Recycl 35(4):215–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0921-3449(01)00111-2
Al Zuabi AZ (2016) Sociopolitical participation of Kuwaiti women in the development process: current state and challenges ahead. J Soc Serv Res 42(5):689–702. https://doi.org/10.1080/01488376.2016.1212775
Bilgin N (2006) Sosyal Bilimlerde İçerik Analizi: Teknikler ve Örnek Çalışmalar. Siyasal Kitabevi
Briens EC, Chiu Y, Braun D, Verma P, Fiegel G, Pompeii B, Singh K (2022) Assessing sustainability knowledge for undergraduate students in different academic programs and settings. Int J Sustain High Educ 24(1):69–95. https://doi.org/10.1108/ijshe-10-2021-0455
Brinton D, Snow, MA, Wesche MB (2003) Content-based second language instruction. University of Michigan Press ELT
Brundtland G (1987) Report of the World Commission on Environment and Development: our common future. United Nations General Assembly Document A/42/427
Buckler C, Creech H (2014) Shaping the future we want: UN decade of education for sustainable development; final report. UNESCO. https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/content/documents/1682Shaping%20the%20
Bullock G, Wilder N (2016) The comprehensiveness of competing higher education sustainability assessments. Int J Sustain High Educ 17(3):282–304. https://doi.org/10.1108/ijshe-05-2014-0078
Burney NA, Johnes J, Al-Enezi M, Al-Musallam M (2013) The efficiency of public schools: the case of Kuwait. Educ Econ 21(4):360–379. https://doi.org/10.1080/09645292.2011.595580
Carley KM, Behrens D (1999) Organizational and individual decision-making. In Handbook of systems engineering and management. John Wiley and Sons. http://www.casos.cs.cmu.edu/publications/papers/ORGTHEO25.pdf
Chaplin G, Wyton P (2014) Student engagement with sustainability: understanding the value-action gap. Int J Sustain High Educ 15(4):404–417. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJSHE-04-2012-0029
Colantonio A (2007) Social sustainability: an exploratory analysis of its definition, assessment methods metrics and tools. EIBURS Working Paper Series (2007/01). Oxford Brooks University, Oxford Institute for Sustainable Development (OISD)—International Land Markets Group, Oxford, UK
Creswell JW, Clark VL (2011) Designing and conducting mixed methods research. SAGE
Creswell JW (2012) Educational research: planning, conducting, and evaluating quantitative and qualitative research. Pearson Education
Crosling G, Atherton G, Shuib M, Rahim AA, Azizan SN, & Nasir MI (2020) The teaching of sustainability in higher education: improving environmental resilience in Malaysia. Innovations in Higher Education Teaching and Learning, 17–38. https://doi.org/10.1108/s2055-364120200000022002
Crowe S, Cresswell K, Robertson A, Huby G, Avery A, Sheikh A (2011) The case study approach. BMC Med Res Methodol, 11(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2288-11-100
Çetinkaya G, Ozturk E, Ismail E (2015) Introducing environmental education in teaching foreign language to young learners. Int J Educ Res Rev 3(6):373–378. https://www.internationalscholarsjournals.com/articles/introducing-environmental-education-in-teaching-foreign-language-to-young-learners.pdf
Decamps A (2017) Analysis of determinants of a measure of sustainability literacy (2017/8). UNESCO, https://unesdoc.unesco.org/ark:/48223/pf0000259581
Decamps A, Barbat G, Carteron J-C, Hands V, Parkes C (2017) Sulitest: a collaborative initiative to support and assess sustainability literacy in higher education. Int J Manag Educ 15, 138–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijme.2017.02.006
Drayson R, Bone E, Agombar J, Kemp S (2014) Student attitudes towards and skills for sustainable development. The Higher Education Academy. Retrieved from www.heacademy.ac.uk
Du Pisani JA (2006) Sustainable development—historical roots of the concept. Environ Sci 3(2):83–96. https://doi.org/10.1080/15693430600688831
Eltony MN (2002) Can an oil-based economy be diversified? A case study of Kuwait. J Energy Dev 27(2):197–211. http://www.jstor.org/stable/24808708
Hauschild S, Poltavtchenko E, Stoller FL (2012) Going green: merging environmental education and language instruction. Engl Teach Forum 50(2):2–13. https://americanenglish.state.gov/files/ae/resource_files/50_2_3_hauschild-et-al.pdf
Kennedy TJ (2006) Language learning and its impact on the brain: connecting language learning with the mind through content-based instruction. Foreign Lang Ann 39(3):471–486. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1944-9720.2006.tb02900.x
Koehn PH, Uitto JI (2017) Universities and the sustainable development future: evaluating higher-education contributions to the 2030 agenda. Routledge
Koushki PA, AlHumoud JM, AlDuaij U (2004) Municipal solid waste in Kuwait: trends and attitudes on collection, separation, and willingness to pay. Kuwait J Sci Eng 31(2):173–188
Kuckartz U, Rädiker S (2019) Analyzing qualitative data with MAXQDA: text, audio, and video. Springer, The USA, 10.1007/978-3-030-15671-8
Book Google Scholar
Kuehl C, Sparks AC, Hodges H, Smith ER (2023) Exploring sustainability literacy: developing and assessing a bottom-up measure of what students know about sustainability. Front Sustain 4. https://doi.org/10.3389/frsus.2023.1167041
Kuwait National Development Plan (2017) the Government of Kuwait. https://www.newkuwait.gov.kw/image/NewKuwait_CampaignLaunchEvent.pdf
Leal Filho W (2010) Universities and climate change: Introducing climate change to university programmes. Springer Science & Business Media
Maijala M, Heikkola LM, Kuusalu S-R, Laine P, Mutta M, Mäntylä K (2023) Pre-service language teachers’ perceptions of sustainability and its implementation in language teaching. Lang Teach Res , https://doi.org/10.1177/13621688231170682
Met M (1999) Content-based instruction: defining terms, making decisions. Johns Hopkins University, National Foreign Language Center. https://carla.umn.edu/cobaltt/modules/principles/decisions.html
Murad D, Al Awadhi L (2018) Report: the quality of education in Kuwait. The Cross-Cultural Diwaniya. https://static1.squarespace.com/static/5ae5dab125bf0240808df943/t/5baca382e4966bf0037ab2b0/1538040718718/Report+-+The+Quality+of+Education+in+Kuwait.pdf
Nur S, Anas I, Pilu R (2022) The call for environmentally based language teaching and green pedagogy: climate actions in language education. J Engl Lang Stud 4(1):77–85
Purvis B, Mao Y, Robinson D (2019) Three pillars of sustainability: In search of conceptual origins. Sustain Sci 14(3):681–695. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11625-018-0627-5
Owens D (2001) Composition and sustainability: teaching for a threatened generation. National Council of Teachers of English. https://eric.ed.gov/?id=ED458601
Rehn J (2018) Teaching teachers to teach sustainability—a cross-disciplinary course for integrating ESD in Higher Education. Global University Network for Innovation. https://www.guninetwork.org/articles/teaching-teachers-teach-sustainability-cross-disciplinary-course-integrating-esd-higher
Sachs J, Kroll C, Lafortune G, Fuller G, Woelm F (2022) Sustainable development report 2022. Cambridge University Press. https://doi.org/10.1017/9781009210058
Schneider K (2017) Evaluation of the opportunities for sustainability education through content-based learning in online German classes in Ecuador. Eur J Sustain Dev 6(3):373–382. https://doi.org/10.14207/ejsd.2017.v6n3p373
Shah Z, Kennedy-Clark S, Xie Y, Rahim MS, Mahdavi M, Levula A (2022) Teacher views on teaching sustainability in higher education institutes in Australia. Sustainability 14(14):8431. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148431
Silverman D (2000) Doing qualitative research: a practical handbook. SAGE
Siregar R, Nuraida N, Kalsum EU (2022) Incorporating environment sustainability content in translation teaching through a task-based approach. J Linguist Lit Lang Teach 6(2):251–261. https://doi.org/10.30743/ll.v6i2.5669
Song B (2006) Content-based ESL instruction: long-term effects and outcomes. Engl Specif Purp 25(4):420–437. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.esp.2005.09.002
Stephens JC, Hernandez ME, Román M, Graham AC, Scholz RW (2008) Higher education as a change agent for sustainability in different cultures and contexts. Int J Sustain High Educ 9(3):317–338. https://doi.org/10.1108/14676370810885916
Stoller FL (2004) Content-based instruction: perspectives on curriculum planning. Annu Rev Appl Linguist 24:261–283. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0267190504000108
The Association for the Advancement of Sustainability in Higher Education (2023) AASHE’s suggested keywords for sustainability course and research inventories. Google Docs. https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/1CINYGQ-8nov8qhGx_fQxn-KTSbC4BgpMHLsBgplaQGo/edit#gid=1359647972
The Sustainability Tracking, Assessment & Rating System (2018) University of Wisconsin-Oshkosh|Scorecard|Institutions|STARS reports. https://reports.aashe.org/institutions/university-of-wisconsin-oshkosh-wi/report/2018-01-29/
Turpin KM (2022) Multiliteracies pedagogy: theory to practice for scaffolding sustainability literacies. In Education for sustainable development in foreign language learning: content-based instruction in college-level curricula (pp 34–49). Routledge. https://doi.org/10.4324/9781003080183
Vorholt J (2018) New ways in teaching speaking (2nd ed) TESOL Press
World Economic Forum (2019) The global competitiveness report 2019. https://www3.weforum.org/docs/WEF_TheGlobalCompetitivenessReport2019.pdf
Yuan X, Zuo J (2013) A critical assessment of the higher education for sustainable development from students’ perspectives—a Chinese study. J Clean Prod 48:108–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2012.10.041
Zizka L, Varga P (2021) Teaching sustainability in higher education institutions: assessing hospitality students’ sustainability literacy. J Hosp Tour Educ 33(4):242–257. https://doi.org/10.1080/10963758.2020.1726771
Zwickle A, Jones K (2017) Sustainability knowledge and attitudes—assessing latent constructs. World Sustain Ser, 435–451. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-67122-2_25
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Gulf University for Science and Technology, Mubarak Al-Abdullah, Kuwait
Inan Deniz Erguvan
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Inan Deniz Erguvan as the sole author of this manuscript wrote the literature review, collected and analyzed the data and produced the discussion section of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Inan Deniz Erguvan .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
This study has been funded by Gulf University for Science and Technology, ISG case 4.
Ethical approval
The study used human subjects and the ethics approval from the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of Gulf University for Science and Technology was obtained prior to the application of the survey on students, with the registration number: IRB-278674/2023-24.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all participants. Students signed a consent form before they completed the data collection process.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Erguvan, I.D. What difference does one course make? Assessing the impact of content-based instruction on students’ sustainability literacy. Humanit Soc Sci Commun 11 , 708 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-024-03149-4
Download citation
Received : 07 September 2023
Accepted : 07 May 2024
Published : 31 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-024-03149-4
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies

- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- 3D & Animation
- Game Design & Development
- Graphic Design & Illustration
- UI/UX Design
- Office Productivity
- Video Editing
- Audio & Music
- Free Learning Resources
- Free Online Courses
How to Write a Whitepaper: The Ultimate Guide for Marketers

A whitepaper is an in-depth, persuasive, and informational document that presents a problem and provides a solution. You can use white papers in content marketing to generate interest, establish thought leadership, and influence the decision-making process of potential customers.
Typically ranging from 2,500 to 5,000 words , a well-researched and engaging whitepaper allows you to explore a topic in-depth. It is meant to educate your audience about an issue they are facing and subtly guide them towards your product or service as the ideal solution.
In this comprehensive guide, we will walk you through the methodology and process of planning, researching, writing, formatting, and promoting a white paper that sets you apart as a thought leader in your industry. You will learn how to write a whitepaper by choosing the right topic, crafting a compelling argument, presenting your ideas with clarity, and leveraging your whitepaper to achieve your sales and marketing goals.
Understanding the Purpose and Types of Whitepapers

The primary goal of a whitepaper is to build trust with your audience and provide an in-depth report or guide that demonstrates your company's expertise in the field.
There are several common types of white papers, each serving a unique purpose. Some whitepapers focus on explaining the technical information of a product or service , while others present a business case for adopting a particular solution . Regardless of the specific type, all whitepapers should aim to inform and persuade the reader, rather than serve as a direct sales pitch.
By educating the reader about a specific challenge they face and offering a thoughtful solution to a problem, whitepapers can help establish your company as a trusted authority . This trust is essential for building long-term relationships with your target audience and promote a product or service.
When crafting a whitepaper, it's crucial to keep the purpose of a white paper in mind: to provide value to the reader. While the ultimate goal may be to generate leads or drive sales, the whitepaper itself should focus on delivering helpful, relevant information that addresses the reader's needs and concerns.
Planning and Preparing to Write Your Whitepaper

Writing a whitepaper requires careful planning and preparation to ensure it effectively addresses your potential customers' needs and positions your business as a thought leader. Here's a step-by-step process for writing a whitepaper that resonates with your target audience:
- Define your target audience and their pain points . Understand who will be reading your whitepaper and what challenges they face. Identifying their needs allows you to tailor your content to provide the most relevant and valuable information.
- Choose a specific topic that addresses your audience's needs. Select a whitepaper topic that directly relates to your potential customers' pain points and showcases your unique expertise. A focused, relevant topic will capture your readers' attention and demonstrate how your business can solve their problems.
- Conduct thorough research using credible sources. A compelling whitepaper needs to provide original research, data, and insights. Gather facts and evidence from reputable industry sources, case studies, and your own research findings to support your whitepaper's claims and solutions.
- Create a detailed outline to organize your whitepaper's contents. Structure your whitepaper with a clear introduction, problem statement, background information, proposed solution, and conclusion. A well-organized outline ensures your whitepaper flows logically and keeps readers engaged from start to finish.
What elements should include a Whitepaper?

Here is a summary of the key elements and format that a good whitepaper should include:
- Attention-grabbing title that clearly states the problem or topic the whitepaper covers
- Subtitle providing more context
- Company name and logo
- Publication date
- Name(s) of author(s)
Abstract or Executive Summary
- Concise overview of the whitepaper's contents
- Direct statements of the whitepaper's position or argument to engage the reader
- Enough detail to satisfy an executive while encouraging further reading
Table of Contents
- Organized outline of the whitepaper's sections and subsections
Introduction
- Hook to grab the reader's attention
- Definition of the issue or problem and relevant background information
- Establishes the author's credibility and common ground with the audience
Problem Statement
- Thorough explanation of the specific problem the whitepaper addresses
- Entirely from the perspective of the target audience
- Supported by facts, statistics and examples illustrating the problem's impact
Proposed Solution
- Detailed description of the proposed solution to the stated problem
- Makes a persuasive, evidence-based argument for the solution
- Addresses potential objections and alternative solutions
- Includes supporting visuals like charts, graphs, and infographics
- Summarizes the whitepaper's key points and takeaways
- Reiterates the importance and value of the proposed solution
- Includes a specific call-to-action for readers
- Citations for all research, statistics, and information sources used
Designing Your Whitepaper for Maximum Engagement

The design and layout of your whitepaper play a crucial role in its readability and overall impact. A well-designed whitepaper not only looks professional but also makes the content more accessible and engaging for the reader. You can find different whitepaper examples and templates in websites like Venngage .
Incorporate visual elements like images, charts, and infographics to break up the text and illustrate key points. These elements can help make complex information more digestible and engaging for your audience.
However, avoid turning your whitepaper into a slick sales brochure . While visual elements are important, ensure that each page has more text than visuals to maintain the whitepaper's informative purpose.
Optimize your whitepaper design for multiple devices, as readers may access it on desktops, tablets, or smartphones. Use a responsive layout that adapts to different screen sizes, making it easy to read and navigate.
Remember, a well-designed whitepaper enhances the reading experience, making it more likely that your audience will engage with and share your content.
Promoting Your Whitepaper for Lead Generation

Once you've created a compelling whitepaper, it's time to promote it as part of your content marketing strategy . A well-crafted whitepaper can be a powerful lead magnet, helping you generate interest and capture valuable contact information from potential customers.
To maximize the impact of your whitepaper, create a dedicated landing page to host it. This page should highlight the potential benefits of your whitepaper and include a lead generation form to collect visitor details in exchange for the download.
Leverage your whitepaper across multiple channels to reach a wider audience. Share snippets and links to your whitepaper on social media platforms like LinkedIn, Twitter, and Facebook[16][19]. Incorporate it into your email marketing campaigns, targeting relevant segments of your subscriber list.
Don't let your whitepaper be a one-and-done piece of content. Repurpose the valuable information into various content formats to extend its reach. Transform key sections into blog posts, create engaging videos that summarize the main points, or develop a slide presentation to share on platforms like SlideShare.
A whitepaper is just one type of content in your marketing arsenal. Combine it with other lead generation tactics like eBooks, webinars, and email courses to create a comprehensive content marketing strategy that drives results.
Measuring the Success and ROI of Your Whitepaper

Tracking the performance of your whitepaper is crucial for understanding its impact and optimizing your content marketing strategy. By monitoring key metrics, you can gauge the effectiveness of your whitepaper and make data-driven decisions to improve its ROI.
One essential metric to track is the number of downloads your whitepaper receives. This indicates the level of interest and engagement from your target audience. Additionally, keep a close eye on the leads generated from your whitepaper, as this directly ties to its potential for driving conversions and revenue.
To gain deeper insights into reader engagement, analyze data such as time spent reading, scroll depth, and click-through rates on links within your whitepaper . This information can help you identify areas for improvement and optimize your content to better resonate with your audience.
Gathering feedback from readers is another valuable way to measure the success of your whitepaper. Surveys, comments, and social media mentions can provide qualitative data on how well your content is received and what improvements can be made.
By consistently tracking and analyzing these metrics, you can continually refine your whitepaper marketing strategy to maximize its impact and ROI. Use the insights gained to optimize your content, distribution channels, and promotional efforts, ensuring that your whitepaper remains a valuable asset in your content marketing arsenal.
Conclusion: How to write a Whitepaper
Writing a whitepaper may seem daunting, but by following the key steps and best practices outlined in this guide, you can create a valuable asset for your content marketing strategy. To recap, start by choosing a relevant topic, understanding your audience, and conducting thorough research. Then, craft a compelling outline, write engaging content, and enhance your whitepaper with visuals and a professional design.
Remember, whitepapers are powerful tools for establishing thought leadership, generating leads, and educating your target audience. Investing time and effort into whitepaper writing can differentiate your brand and provide immense value to your readers.
Don't let the process overwhelm you – break it down into manageable steps and leverage the expertise of your team or external resources when needed. With practice and persistence, you'll soon be creating whitepapers that resonate with your audience and drive results for your business.
About Author:
Latest posts:, the 10 best motivational speeches to inspire you and get you in the right mindset, 16 best online jobs for teens in 2024: earn money from home, 100 motivational teamwork quotes to inspire collaboration and success, more from our blog:, the 15 best weekend jobs to grow your earnings, is cider legit honest cider clothing review 2024, 28 of the best sales books of all time to skyrocket your sales skills, how to write a request for proposal (rfp): template and tips, 600+ snazzy name ideas for your hairdressing company in 2024, 500+ clever newspaper name ideas in 2024, 600 best food truck name ideas in 2024, 25 funny out of office messages to make your co-workers rofl, featured reviews, featured posts, information.
Log in using your username and password
- Search More Search for this keyword Advanced search
- Latest content
- Current issue
- BMJ Journals More You are viewing from: Google Indexer
You are here
- Online First
- Pedestrian safety on the road to net zero: cross-sectional study of collisions with electric and hybrid-electric cars in Great Britain
- Article Text
- Article info
- Citation Tools
- Rapid Responses
- Article metrics
- http://orcid.org/0000-0003-4431-8822 Phil J Edwards ,
- Siobhan Moore ,
- Craig Higgins
- London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine , London , UK
- Correspondence to Dr Phil J Edwards, London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine, London WC1E 7HT, UK; phil.edwards{at}LSHTM.ac.uk
Background Plans to phase out fossil fuel-powered internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles and to replace these with electric and hybrid-electric (E-HE) vehicles represent a historic step to reduce air pollution and address the climate emergency. However, there are concerns that E-HE cars are more hazardous to pedestrians, due to being quieter. We investigated and compared injury risks to pedestrians from E-HE and ICE cars in urban and rural environments.
Methods We conducted a cross-sectional study of pedestrians injured by cars or taxis in Great Britain. We estimated casualty rates per 100 million miles of travel by E-HE and ICE vehicles. Numerators (pedestrians) were extracted from STATS19 datasets. Denominators (car travel) were estimated by multiplying average annual mileage (using National Travel Survey datasets) by numbers of vehicles. We used Poisson regression to investigate modifying effects of environments where collisions occurred.
Results During 2013–2017, casualty rates per 100 million miles were 5.16 (95% CI 4.92 to 5.42) for E-HE vehicles and 2.40 (95%CI 2.38 to 2.41) for ICE vehicles, indicating that collisions were twice as likely (RR 2.15; 95% CI 2.05 to 2.26) with E-HE vehicles. Poisson regression found no evidence that E-HE vehicles were more dangerous in rural environments (RR 0.91; 95% CI 0.74 to 1.11); but strong evidence that E-HE vehicles were three times more dangerous than ICE vehicles in urban environments (RR 2.97; 95% CI 2.41 to 3.7). Sensitivity analyses of missing data support main findings.
Conclusion E-HE cars pose greater risk to pedestrians than ICE cars in urban environments. This risk must be mitigated as governments phase out petrol and diesel cars.
- WOUNDS AND INJURIES
- CLIMATE CHANGE
Data availability statement
Data are available in a public, open-access repository. Numerator data (numbers of pedestrians injured in collisions) are publicly available from the Road Safety Data (STATS19) datasets ( https://www.data.gov.uk/dataset/cb7ae6f0-4be6-4935-9277-47e5ce24a11f/road-safety-data ). Denominator data (100 million miles of car travel per year) may be estimated by multiplying average annual mileage by numbers of vehicle registrations (publicly available from Department for Transport, https://www.gov.uk/government/statistical-data-sets/veh02-licensed-cars ). Average annual mileage for E-HE and ICE vehicles may be estimated separately for urban and rural environments using data that may obtained under special licence from the National Travel Survey datasets ( http://doi.org/10.5255/UKDA-Series-2000037 ).
https://doi.org/10.1136/jech-2024-221902
Statistics from Altmetric.com
Request permissions.
If you wish to reuse any or all of this article please use the link below which will take you to the Copyright Clearance Center’s RightsLink service. You will be able to get a quick price and instant permission to reuse the content in many different ways.
WHAT IS ALREADY KNOWN ON THIS TOPIC
Electric cars are quieter than cars with petrol or diesel engines and may pose a greater risk to pedestrians.
The US National Highway Transportation Safety Agency found that during 2000–2007 the odds of an electric or hybrid-electric car causing a pedestrian injury were 35% greater than a car with a petrol or diesel engine.
The UK Transport Research Laboratory found the pedestrian casualty rate per 10 000 registered electric or hybrid-electric vehicles during 2005–2007 in Great Britain was lower than the rate for petrol or diesel vehicles.
WHAT THIS STUDY ADDS
In Great Britain during 2013–2017, pedestrians were twice as likely to be hit by an electric or hybrid-electric car than by a petrol or diesel car; the risks were higher in urban areas.
HOW THIS STUDY MIGHT AFFECT RESEARCH, PRACTICE OR POLICY
The greater risk to pedestrian safety posed by electric or hybrid-electric cars needs to be mitigated as governments proceed to phase out petrol and diesel cars.
Drivers of electric or hybrid-electric cars must be cautious of pedestrians who may not hear them approaching and may step into the road thinking it is safe to do so, particularly in towns and cities.
Introduction
Many governments have set targets to reach net-zero emissions to help mitigate the harms of climate change. Short-term health benefits of reduced emissions are expected from better air quality with longer-term benefits from reduced global temperatures. 1
Transition to electric and hybrid-electric (E-HE) cars
One such target is to phase out sales of new fossil fuel-powered internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles and replace these with E-HE vehicles. 2 3
Pedestrian safety
Road traffic injuries are the leading cause of death for children and young adults. 4 A quarter of all road traffic deaths are of pedestrians. 5 Concerns have been raised that E-HE cars may be more hazardous to pedestrians than ICE cars, due to being quieter. 6 7 It has been hypothesised that E-HE cars pose a greater risk of injury to pedestrians in urban areas where background ambient noise levels are higher. 8 However, there has been relatively little empirical research on possible impacts of E-HE cars on pedestrian road safety. A study commissioned for the US National Highway Transportation Safety Agency based on data from 16 States found that the odds of an E-HE vehicle causing a pedestrian injury were 35% greater than an ICE vehicle. 9 In contrast, a study commissioned by the UK Department for Transport found pedestrian casualty rates from collisions with E-HE vehicles during 2005–2007 were lower than for ICE vehicles. 10 Possible reasons for these conflicting results are that the two studies used different designs and estimated different measures of relative risk—the first used a case–control design and estimated an OR, whereas the second used a cross-sectional study and estimated a rate ratio. ORs will often differ from rate ratios. 11 Other reasons include differences between the USA and the UK in the amount and quality of walking infrastructure. 12
Aim and objectives
We aimed to add to the evidence base on whether E-HE cars pose a greater injury risk to pedestrians than ICE cars by analysing road traffic injury data and travel survey data in Great Britain.
We sought to improve on the previous UK study by using distance travelled instead of number of registered vehicles as the measure of exposure in estimation of collision rates.
The objectives of this study were:
To estimate pedestrian casualty rates for E-HE and ICE vehicles and to compare these by calculating a rate ratio;
To assess whether or not the evidence supports the hypothesis that casualty rate ratios vary according to urban or rural environments. 8
Study design
This study was an analysis of differences in casualty rates of pedestrians per 100 million miles of E-HE car travel and rates per 100 million miles of ICE car travel.
This study was set in Great Britain between 2013 and 2017.
Participants
The study participants were all pedestrians reported to have been injured in a collision with a car or a taxi.
The exposure was the type of propulsion of the colliding vehicle, E-HE or ICE. E-HE vehicles were treated as a single powertrain type, regardless of the mode of operation that a hybrid vehicle was in at the time of collision (hybrid vehicles typically start in electric mode and change from battery to combustion engine at higher speeds). 13
The outcome of interest was a pedestrian casualty.
Effect modification by road environment
We used the urban–rural classification 14 of the roads on which the collisions occurred to investigate whether casualty rate ratios comparing E-HE with ICE vehicles differed between rural and urban environments.
Data sources/measurement
Numerator data (numbers of pedestrians injured in collisions) were extracted from the Road Safety Data (STATS19) datasets. 15
Denominator data (100 million miles of car travel per year) were estimated by multiplying average annual mileage by numbers of vehicle registrations. 16 Average annual mileage for E-HE and ICE vehicles was estimated separately for urban and rural environments using data obtained under special licence from the National Travel Survey (NTS) datasets. 17 We estimated average annual mileage for the years 2013–2017 because the NTS variable for the vehicle fuel type did not include ‘hybrid’ prior to 2013 and data from 2018 had not been uploaded to the UK data service due to problems with the archiving process (Andrew Kelly, Database Manager, NTS, Department for Transport, 23 March 2020, personal communication). Denominators were thus available for the years 2013–2017.
Data preparation
The datasets for collisions, casualties and vehicles from the STATS19 database were merged using a unique identification number for each collision.
Statistical methods
We calculated annual casualty rates for E-HE and ICE vehicles separately and we compared these by calculating a rate ratio. We used Poisson regression models to estimate rate ratios with 95% CIs and to investigate any modifying effects of the road environment in which the collisions occurred. For this analysis, our regression model included explanatory terms for the main effects of the road environment, plus terms for the interaction between type of propulsion and the road environment. The assumptions for Poisson regression were met in our study: we modelled count data (counts of pedestrians injured), traffic collisions were independent of each other, occurring in different places over time, and never occurring simultaneously. Data preparation, management and analyses were carried out using Microsoft Access 2019 and Stata V.16. 18
Sensitivity analysis
We conducted an extreme case analysis where all missing propulsion codes were assumed to be ICE vehicles (there were over a 100 times more ICE vehicles than E-HE vehicles on the roads in Great Britain during our study period, 16 so missing propulsion is more likely to have been ICE).
The sample size for this study included all available recorded road traffic collisions in Great Britain during the study period. We estimated that for our study to have 80% power at the 5% significance level to show a difference in casualty rates of 2 per 100 miles versus 5.5 per 100 miles, we would require 481 million miles of vehicle travel in each group (E-HE and ICE); whereas to have 90% power at the 1% significance level to show this difference, 911 million miles of vehicle travel would be required in each group. Our study includes 32 000 million miles of E-HE vehicle travel and 3 000 000 million miles of ICE vehicle travel and therefore our study was sufficiently powered to detect differences in casualty rates of these magnitudes.
Between 2013 and 2017, there were 916 713 casualties from reported road traffic collisions in Great Britain. 120 197 casualties were pedestrians. Of these pedestrians, 96 285 had been hit by a car or taxi. Most pedestrians—71 666 (74%) were hit by an ICE car or taxi. 1652 (2%) casualties were hit by an E-HE car or taxi. For 22 829 (24%) casualties, the vehicle propulsion code was missing. Most collisions occurred in urban environments and a greater proportion of the collisions with E-HE vehicles occurred in an urban environment (94%) than did collisions with ICE vehicles (88%) ( figure 1 ).
- Download figure
- Open in new tab
- Download powerpoint
Flow chart of pedestrian casualties in collisions with E-HE or ICE cars or taxis from reported road traffic collisions in Great Britain 2013–2017. E-HE, electric and hybrid-electric; ICE, internal combustion engine.
Main results
During the period 2013 to 2017, the average annual casualty rates of pedestrians per 100 million miles were 5.16 (95% CI 4.92 to 5.42) for E-HE vehicles and 2.40 (95% CI 2.38 to 2.41) for ICE vehicles, which indicates that collisions with pedestrians were on average twice as likely (RR 2.15 (95% CI 2.05 to 2.26), p<0.001) with E-HE vehicles as with ICE vehicles ( table 1 ).
- View inline
Pedestrian casualties due to collisions with cars or taxis from reported road traffic collisions in Great Britain 2013–2017—by vehicle propulsion type
In our extreme case analysis, the 22 829 pedestrian casualties where vehicle propulsion was missing were all assumed to have been struck by ICE vehicles. In this case, average casualty rates of pedestrians per 100 million miles were 3.16 (95% CI 3.14 to 3.18) for ICE vehicles, which would indicate that collisions with pedestrians were on average 63% more likely (RR 1.63 (95% CI 1.56 to 1.71), p<0.001) with E-HE vehicles than with ICE vehicles ( table 2 ).
Extreme case sensitivity analysis—pedestrian casualties due to collisions with cars or taxis from reported road traffic collisions in Great Britain 2013–2017 by vehicle propulsion type where 22 829 missing vehicle propulsion codes are assumed to be ICE vehicles
Relative risks according to road environment
Casualty rates were higher in urban than rural environments ( tables 3 and 4 ).
Pedestrian casualties due to collisions with cars or taxis from reported road traffic collisions in Great Britain 2013–2017—by vehicle propulsion type in urban road environments
Pedestrian casualties due to collisions with cars or taxis from reported road traffic collisions in Great Britain 2013–2017—by vehicle propulsion type in rural road environments
Urban environments
Collisions with pedestrians in urban environments were on average over two and a half times as likely (RR 2.69 (95% CI 2.56 to 2.83, p<0.001) with E-HE vehicles as with ICE vehicles ( table 3 ).
The extreme case sensitivity analysis showed collisions with pedestrians in urban environments were more likely with E-HE vehicles (RR 2.05; 95% CI 1.95 to 2.15).
Rural environments
Collisions with pedestrians in rural environments were equally likely (RR 0.91; 95% CI 0.74 to 1.11) with E-HE vehicles as with ICE vehicles ( table 4 ).
The extreme case sensitivity analysis found evidence that collisions with pedestrians in rural environments were less likely with E-HE vehicles (RR 0.68; 95% CI 0.55 to 0.83).
Results of Poisson regression analysis
Our Poisson regression model results ( table 5 ) showed that pedestrian injury rates were on average 9.28 (95% CI 9.07 to 9.49) times greater in urban than in rural environments. There was no evidence that E-HE vehicles were more dangerous than ICE vehicles in rural environments (RR 0.91; 95% CI 0.74 to 1.11), consistent with our finding in table 4 . There was strong evidence that E-HE vehicles were on average three times more dangerous than ICE vehicles in urban environments (RR 2.97; 95% CI 2.41 to 3.67).
Results of Poisson regression analysis of annual casualty rates of pedestrians per 100 million miles by road environment and the interaction between vehicle propulsion type and environment
Statement of principal findings
This study found that in Great Britain between 2013 and 2017, casualty rates of pedestrians due to collisions with E-HE cars and taxis were higher than those due to collisions with ICE cars and taxis. Our best estimate is that such collisions are on average twice as likely, and in urban areas E-HE vehicles are on average three times more dangerous than ICE vehicles, consistent with the theory that E-HE vehicles are less audible to pedestrians in urban areas where background ambient noise levels are higher.
Strengths and weaknesses of the study
There are several limitations to this study which are discussed below.
The data used were not very recent. However, ours is the most current analysis of E-HE vehicle collisions using the STATS19 dataset.
Before we can infer that E-HE vehicles pose a greater risk to pedestrians than ICE vehicles, we must consider whether our study is free from confounding and selection bias. Confounding occurs when the exposure and outcome share a common cause. 19 Confounders in this study would be factors that may both cause a traffic collision and also cause the exposure (use of an E-HE car). Younger, less experienced drivers (ie, ages 16–24) are more likely to be involved in a road traffic collision 20 and are also more likely to own an electric car. 21 Some of the observed increased risk of electric cars may therefore be due to younger drivers preferring electric cars. This would cause positive confounding, meaning that the true relative risk of electric cars is less than we have estimated in our study. Regarding selection bias, it is known that the STATS19 dataset does not include every road traffic casualty in Great Britain, as some non-fatal casualties are not reported to the police. 22 If casualties from collisions are reported to the police differentially according to the type of vehicle propulsion, this may have biased our results; however, there is no reason to suspect that a pedestrian struck by a petrol or diesel car is any more or less likely to report the collision to the police than one struck by an electric car.
We must also address two additional concerns as ours is a cross-sectional study: The accuracy of exposure assignment (including the potential for recall bias) and the adequacy of prevalence as a proxy for incidence. 23 First, the accuracy of exposure assignment and the potential for recall bias are not issues for this study, as the exposure (type of propulsion of the colliding vehicle, E-HE or ICE), is assigned independently of the casualties by the UK Department for Transport who link the vehicle registration number (VRN) of each colliding vehicle to vehicle data held by the UK Driver Vehicle and Licensing Agency (DVLA). 10 Second, we have not used prevalence as a proxy for incidence but have estimated incidence using total distance travelled by cars as the measure of exposure.
We may therefore reasonably infer from our study results that E-HE vehicles pose a greater risk to pedestrians than ICE vehicles in urban environments, and that part of the risk may be due to younger people’s preference for E-HE cars.
A major limitation of the STATS19 road safety dataset used in this study was that it did not contain a vehicle propulsion code for all vehicles in collisions with pedestrians. We excluded these vehicles from our primary analysis (a complete case analysis) and we also conducted an extreme case sensitivity analysis. We will now argue why imputation of missing vehicle propulsion codes would not have added value to this study. Vehicle propulsion data are obtained for the STATS19 dataset by the UK Department for Transport who link the VRN of each colliding vehicle recorded in STATS19 to vehicles data held by the UK DVLA. The STATS19 data on reported collisions and casualties are collected by a Police Officer when an injury road accident is reported to them; Most police officers write details of the casualties and the vehicles involved in their notebooks for transcription onto the STATS19 form later at the Police station. 24 The VRN is one of 18 items recorded on each vehicle involved in a collision. Items may occasionally be missed due to human error during this process. Where a VRN is missing, vehicle propulsion will be missing in the STATS19 dataset. The chance that any vehicle-related item is missing will be independent of any characteristics of the casualties involved and so the vehicle propulsion codes are missing completely at random (MCAR). As the missing propulsion data are very likely MCAR, the set of pedestrians with no missing data is a random sample from the source population and hence our complete case analysis for handling the missing data gives unbiased results. The extreme case sensitivity analysis we performed shows a possible result that could occur, and it demonstrates our conclusions in urban environments are robust to the missing data. Lastly, to impute the missing data would require additional variables which are related to the likelihood of a VRN being missing. Such variables were not available and therefore we do not believe a useful multiple imputation analysis could have been performed.
Strengths and weaknesses in relation to other studies
Our study uses hundreds of millions of miles of car travel as the denominators in our estimates of annual pedestrian casualty rates which is a more accurate measure of exposure to road hazards than the number of registered vehicles, which was used as the denominator in a previous study in the UK. 10 Our results differ to this previous study which found that pedestrian casualty rates from collisions with E-HE vehicles during 2005–2007 were lower than those from ICE vehicles. Our study has updated this previous analysis and shows that casualty rates due to E-HE vehicle collisions exceed those due to ICE vehicle collisions. Similarly, our study uses a more robust measure of risk (casualty rates per miles of car travel) than that used in a US study. 9 Our study results are consistent with this US study that found that the odds of an E-HE vehicle causing a pedestrian injury were 35% greater than an ICE vehicle. Brand et al 8 hypothesised, without any supporting data, that “hybrid and electric low-noise cars cause an increase in traffic collisions involving vulnerable road users in urban areas” and recommended that “further investigations have to be done with the increase of low-noise cars to prove our hypothesis right.” 8 We believe that our study is the first to provide empirical evidence in support of this hypothesis.
Meaning of the study: possible explanations and implications for clinicians and policymakers
More pedestrians are injured in Great Britain by petrol and diesel cars than by electric cars, but compared with petrol and diesel cars, electric cars pose a greater risk to pedestrians and the risk is greater in urban environments. One plausible explanation for our results is that background ambient noise levels differ between urban and rural areas, causing electric vehicles to be less audible to pedestrians in urban areas. Such differences may impact on safety because pedestrians usually hear traffic approaching and take care to avoid any collision, which is more difficult if they do not hear electric vehicles. This is consistent with audio-testing evidence in a small study of vision-impaired participants. 10 From a Public Health perspective, our results should not discourage active forms of transport beneficial to health, such as walking and cycling, rather they can be used to ensure that any potential increased traffic injury risks are understood and safeguarded against. A better transport policy response to the climate emergency might be the provision of safe, affordable, accessible and integrated public transport systems for all. 25
Unanswered questions and future research
It will be of interest to investigate the extent to which younger drivers are involved in collisions of E-HE cars with pedestrians.
If the braking distance of electric cars is longer, 26 and electric cars are heavier than their petrol and diesel counterparts, 27 these factors may increase the risks and the severity of injuries sustained by pedestrians and require investigation.
As car manufacturers continue to develop and equip new electric cars with Collision Avoidance Systems and Autonomous Emergency Braking to ensure automatic braking in cases where pedestrians or cyclists move into the path of an oncoming car, future research can repeat the analyses presented in this study to evaluate whether the risks of E-HE cars to pedestrians in urban areas have been sufficiently mitigated.
Conclusions
E-HE vehicles pose a greater risk to pedestrians than petrol and diesel powered vehicles in urban environments. This risk needs to be mitigated as governments proceed to phase out petrol and diesel cars.
Ethics statements
Patient consent for publication.
Not applicable.
Ethics approval
This study involves human participants and was approved by the LSHTM MSc Research Ethics Committee (reference #16400). The study uses the anonymised records of people injured in road traffic collisions, data which are routinely collected by UK police forces. The participants are unknown to the investigators and could not be contacted.
Acknowledgments
We thank Rebecca Steinbach for her advice on analysis of National Travel Survey data, Jonathan Bartlett for his advice on missing data, and Ben Armstrong for his advice on Poisson regression. We are grateful to the reviewers and to Dr C Mary Schooling, Associate Editor, whose comments helped us improve the manuscript. We are grateful to Jim Edwards and Graham Try for their comments on earlier versions of this manuscript.
- H Baqui A ,
- Benfield T , et al
- Gilchrist J
- ↵ WHO factsheet on road traffic injuries . Available : https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/road-traffic-injuries#:~:text=Approximately%201.19%20million%20people%20die,adults%20aged%205%E2%80%9329%20years [Accessed 14 Apr 2024 ].
- ↵ Reported road casualties great Britain, annual report . 2022 . Available : https://www.gov.uk/government/statistics/reported-road-casualties-great-britain-annual-report-2022 [Accessed 14 Apr 2024 ].
- Maryland General Assembly
- Haas P , et al
- Morgan PA ,
- Muirhead M , et al
- Greenland S
- Buehler R ,
- Alternative Fuels Data Center
- Government-Statistics
- Department for Transport
- Department for Transport. (2023
- Hernán MA ,
- Hernández-Díaz S ,
- Barriers Direct
- Savitz DA ,
- Wellenius GA
- Transport Scotland
Contributors CH and PJE developed the idea for this study and supervised SM in performing the literature search, downloading, managing and analysing the data. SM wrote the first draft of the manuscript, which was the dissertation for her MSc in Public Health. PJE prepared the first draft of the manuscript for the journal. All authors assisted in editing and refining the manuscript. The corresponding author attests that all listed authors meet authorship criteria and that no others meeting the criteria have been omitted. PJE (guarantor) accepts full responsibility for the work and the conduct of the study, had access to the data and controlled the decision to publish.
Funding This study was conducted in part fulfilment of the Masters degree in Public Health at the London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine. The second author was self-funded for her studies for this degree.
Competing interests None declared.
Provenance and peer review Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Read the full text or download the PDF:

COMMENTS
Table of contents. Step 1: Restate the problem. Step 2: Sum up the paper. Step 3: Discuss the implications. Research paper conclusion examples. Frequently asked questions about research paper conclusions.
Write your research paper conclusion 2x faster with Paperpal. Try it now! Remember that a well-crafted research paper conclusion is a reflection of the strength of your research and your ability to communicate its significance effectively. It should leave a lasting impression on your readers and tie together all the threads of your paper.
Begin with a clear statement of the principal findings. This will reinforce the main take-away for the reader and set up the rest of the discussion. Explain why the outcomes of your study are important to the reader. Discuss the implications of your findings realistically based on previous literature, highlighting both the strengths and ...
Highlight the "so what". At the beginning of your paper, you explain to your readers what's at stake—why they should care about the argument you're making. In your conclusion, you can bring readers back to those stakes by reminding them why your argument is important in the first place. You can also draft a few sentences that put ...
The conclusion is intended to help the reader understand why your research should matter to them after they have finished reading the paper. A conclusion is not merely a summary of the main topics covered or a re-statement of your research problem, but a synthesis of key points derived from the findings of your study and, if applicable, where you recommend new areas for future research.
The conclusion allows you to have the final say on the issues you have raised in your paper, to synthesize your thoughts, to demonstrate the importance of your ideas, and to propel your reader to a new view of the subject. It is also your opportunity to make a good final impression and to end on a positive note.
Begin your conclusion by restating your thesis statement in a way that is slightly different from the wording used in the introduction. Avoid presenting new information or evidence in your conclusion. Just summarize the main points and arguments of your essay and keep this part as concise as possible. Remember that you've already covered the ...
Here are some steps you can follow to write an effective research paper conclusion: Restate the research problem or question: Begin by restating the research problem or question that you aimed to answer in your research. This will remind the reader of the purpose of your study. Summarize the main points: Summarize the key findings and results ...
Writing a Conclusion. A conclusion is an important part of the paper; it provides closure for the reader while reminding the reader of the contents and importance of the paper. It accomplishes this by stepping back from the specifics in order to view the bigger picture of the document. In other words, it is reminding the reader of the main ...
of a research paper to write. This handout will focus on the purpose of a conclusion, as well as provide tips about what to do and what to avoid when writing a conclusion. This handout also contains two annotated examples--a short one and a longer one--from published articles.The Purpose of a Conclusion Conclusions aren't simply an overview ...
The point of a conclusion to a research paper is to summarize your argument for the reader and, perhaps, to call the reader to action if needed. 5. Make a call to action when appropriate. If and when needed, you can state to your readers that there is a need for further research on your paper's topic.
Offer a Fresh Perspective: Use the conclusion as an opportunity to provide a fresh perspective or offer insights that go beyond the main body of the paper. This will leave the reader with something new to consider. Leave a Lasting Impression: End your conclusion with a thought-provoking statement or a call to action.
A conclusion is the final paragraph of a research paper and serves to help the reader understand why your research should matter to them. The conclusion of a conclusion should: Restate your topic and why it is important. Restate your thesis/claim. Address opposing viewpoints and explain why readers should align with your position.
The conclusion is where you describe the consequences of your arguments by justifying to your readers why your arguments matter (Hamilton College, 2014). Derntl (2014) also describes conclusion as the counterpart of the introduction. Using the Hourglass Model (Swales, 1993) as a visual reference, Derntl describes conclusion as the part of the ...
Finally, some advice on how not to end an essay: Don't simply summarize your essay. A brief summary of your argument may be useful, especially if your essay is long--more than ten pages or so. But shorter essays tend not to require a restatement of your main ideas. Avoid phrases like "in conclusion," "to conclude," "in summary," and "to sum up ...
Conclusions. Conclusions wrap up what you have been discussing in your paper. After moving from general to specific information in the introduction and body paragraphs, your conclusion should begin pulling back into more general information that restates the main points of your argument. Conclusions may also call for action or overview future ...
To write a conclusion for a research paper, begin by summarizing the main findings or results of your study. Restate your thesis statement or research question and briefly recap the key points discussed in the paper. Reflect on the significance of your findings and discuss their implications for the broader field of study or real-world ...
Research paper conclusion examples. Below, we've created basic templates showing the key parts of a research paper conclusion. Keep in mind that the length of your conclusion will depend on the length of your paper. The order of the parts may vary, too; these templates only demonstrate how to tie them together. 1. Empirical research paper ...
Tips for writing a conclusion. 1. Don't include new data or evidence. Your conclusion should provide closure to your paper, so introducing new information is not appropriate and will likely confuse your reader. 2. Don't simply restate your thesis. You should never simply copy and paste your thesis statement into your conclusion.
Step 5: Start Writing Early . Begin writing early in the research process. Starting with less complex sections like the literature review or methodology can help clarify your thoughts and identify gaps in your research. Early writing reduces the burden as the thesis deadline approaches.
Adopting a formal style of writing is crucial for any type of academic writing, be it scholarly articles, research papers or essays. It requires a deep understanding of the subject matter, the ability to analyze and synthesize complex information, and the skill to communicate ideas effectively.
How to Write a Proposal Essay. Creating a successful proposal-related paper necessitates thorough preparation and an understanding of your audience's needs. To write such an essay, observe these stages: Extensively investigate your assignment's topic to identify a chosen problem.
For the qualitative part of the study, the researcher collected essays from students at the end of the Fall semester of 2022. The research population consisted of students in both the experimental ...
Conclusion: How to write a Whitepaper. Writing a whitepaper may seem daunting, but by following the key steps and best practices outlined in this guide, you can create a valuable asset for your content marketing strategy. To recap, start by choosing a relevant topic, understanding your audience, and conducting thorough research.
Protection from past infection against re-infection from pre-omicron variants was very high and remained high even after 40 weeks. Protection was substantially lower for the omicron BA.1 variant and declined more rapidly over time than protection against previous variants. Protection from severe disease was high for all variants. The immunity conferred by past infection should be weighed ...
Research ares improving the inference for LLMs referenced from the research paper: A Survey on Efficient Inference for Large Language Models. I have read many research papers and identified the following research trends that are improving LLMs in what they do! Research areas: Compression of LLMs; Computational efficiency; Interpretability
Background Plans to phase out fossil fuel-powered internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles and to replace these with electric and hybrid-electric (E-HE) vehicles represent a historic step to reduce air pollution and address the climate emergency. However, there are concerns that E-HE cars are more hazardous to pedestrians, due to being quieter. We investigated and compared injury risks to ...