Essay Papers Writing Online
Ultimate guide on writing an effective evaluation essay – tips, examples, and guidelines.

Are you puzzled when it comes to writing an evaluation essay? In this guide, we will provide you with all the essential information you need to master the art of crafting a compelling appraisal composition. Whether you are new to this type of writing or just looking to refine your skills, this comprehensive manual will equip you with the necessary tools and techniques to excel. From understanding the purpose and structure of an evaluation essay to exploring various tips and examples, this guide has got you covered.
An evaluation essay is a piece of writing that aims to assess the value or quality of a particular subject or phenomenon. It involves analyzing a topic, presenting your judgment or opinion on it, and providing evidence or examples to support your claims. This type of essay requires critical thinking, research, and effective communication skills to present a well-balanced evaluation.
Throughout this guide, we will delve into the nitty-gritty of writing an evaluation essay. We will start by discussing the key elements that make up a successful evaluation essay, such as establishing clear criteria, conducting thorough research, and adopting a structured approach. Additionally, we will explore practical tips and strategies to help you gather relevant information, organize your thoughts, and present a persuasive argument. To illustrate these concepts, we will provide you with a range of examples covering various topics and subjects.

Tips for Writing a Top-Notch Evaluation Essay
When it comes to crafting a high-quality evaluation essay, there are several key tips to keep in mind. By following these guidelines, you can ensure that your essay stands out and effectively evaluates the subject matter at hand.
1. Be objective and unbiased: A top-notch evaluation essay should approach the topic with an unbiased and objective perspective. Avoid personal bias or overly emotional language, and instead focus on presenting an honest and well-balanced evaluation of the subject.
2. Provide clear criteria: To effectively evaluate something, it’s important to establish clear criteria or standards by which to assess it. Clearly define the criteria you will be using and explain why these specific factors are essential in evaluating the subject. This will help provide structure to your essay and ensure that your evaluation is thorough and comprehensive.
3. Support your evaluation with evidence: In order to make a convincing argument, it’s crucial to support your evaluation with solid evidence. This can include examples, statistics, expert opinions, or any other relevant information that strengthens your claims. By providing strong evidence, you can enhance the credibility of your evaluation and make it more persuasive.
4. Consider multiple perspectives: A well-rounded evaluation takes into account multiple perspectives on the subject matter. Acknowledge and address counterarguments or differing opinions, and provide thoughtful analysis and reasoning for your stance. This demonstrates critical thinking and a comprehensive evaluation of the topic.
5. Use clear and concise language: Clarity is vital in an evaluation essay. Use clear and concise language to express your thoughts and ideas, avoiding unnecessary jargon or complex vocabulary. Your essay should be accessible to a wide audience and easy to understand, allowing your evaluation to be conveyed effectively.
6. Revise and edit: Don’t neglect the importance of revising and editing your essay. Take the time to review your work and ensure that your evaluation is well-structured, coherent, and error-free. Pay attention to grammar, spelling, and punctuation, as these details can greatly impact the overall quality of your essay.
7. Conclude with a strong summary: For a top-notch evaluation essay, it’s important to conclude with a strong and concise summary of your evaluation. Restate your main points and findings, providing a clear and memorable conclusion that leaves a lasting impression on the reader.
By following these tips, you can enhance your writing skills and create a top-notch evaluation essay that effectively assesses and evaluates the subject matter at hand.
Choose a Relevant and Engaging Topic
When it comes to writing an evaluation essay, one of the most important aspects is selecting a topic that is both relevant and engaging. The topic you choose will determine the focus of your essay and greatly impact the overall quality of your writing. It is crucial to choose a topic that not only interests you but also captivates your audience.
When selecting a topic, consider the subject matter that you are knowledgeable or passionate about. This will enable you to provide a well-informed evaluation and maintain your readers’ interest throughout your essay. Additionally, choose a topic that is relevant in today’s society or has a direct impact on your target audience. This will ensure that your evaluation essay has a practical and meaningful purpose.
Furthermore, it is essential to select a topic that is controversial or debatable. This will allow you to present different perspectives and arguments to support your evaluation. By choosing a topic that sparks discussions and debates, you can engage your readers and encourage them to think critically about the subject matter.
In conclusion, choosing a relevant and engaging topic is crucial for writing an effective evaluation essay. By selecting a topic that interests you, appeals to your readers, and is relevant to society, you can ensure that your essay is engaging and impactful. Remember to choose a topic that is controversial or debatable to provide a comprehensive evaluation and encourage critical thinking among your audience.
Develop a Strong Thesis Statement

Crafting an impactful thesis statement is an essential aspect of writing an evaluation essay. The thesis statement serves as the main argument or claim that you will be supporting throughout your essay. It encapsulates the central idea and sets the tone for the rest of the paper.
When developing your thesis statement, it is crucial to be clear, concise, and specific. It should provide a clear indication of your stance on the subject matter being evaluated while also highlighting the main criteria and evidence that will be discussed in the body paragraphs. A strong thesis statement should be thought-provoking and hook the reader’s attention, compelling them to continue reading.
To build a strong thesis statement, you need to engage in a careful analysis of the topic or subject being evaluated. Consider the various aspects that you will be assessing and select the most significant ones to include in your argument. Your thesis statement should be focused and arguable, allowing for a clear position on the matter.
Additionally, it is crucial to avoid vague or general statements in your thesis. Instead, aim for specificity and clarity. By clearly stating your evaluation criteria, you provide a roadmap for the reader to understand what aspects you will be analyzing and what conclusions you intend to make.
Furthermore, a strong thesis statement should be supported by evidence and examples. You should be able to provide concrete support for your evaluation through relevant facts, statistics, or expert opinions. This strengthens the credibility and persuasiveness of your argument, making your thesis statement more compelling.
In summary, developing a strong thesis statement is a critical step in writing an evaluation essay. It sets the foundation for your argument, guiding your analysis and providing a clear direction for the reader. By being clear, concise, specific, and well-supported, your thesis statement helps you create a persuasive and impactful evaluation essay.
Provide Clear and Concise Criteria for Evaluation
One of the most important aspects of writing an evaluation essay is providing clear and concise criteria for evaluation. In order to effectively evaluate a subject or topic, it is essential to establish specific standards or benchmarks that will be used to assess its performance or quality.
When establishing criteria for evaluation, it is crucial to be thorough yet succinct. Clear criteria enable the reader to understand the basis upon which the evaluation is made, while concise criteria ensure that the evaluation remains focused and impactful.
There are several strategies you can employ to provide clear and concise criteria for evaluation. One approach is to define specific attributes or characteristics that are relevant to the subject being evaluated. For example, if you are evaluating a restaurant, you might establish criteria such as the quality of the food, the level of service, and the ambience of the establishment.
Another strategy is to utilize a scoring system or rating scale to assess the subject. This can help provide a more quantitative evaluation by assigning numerical values to different aspects of the subject. For instance, a movie review might use a rating scale of 1 to 5 to evaluate the acting, plot, and cinematography of the film.
In addition to defining specific attributes or using a scoring system, it is important to provide examples or evidence to support your evaluation. This can help make your criteria more concrete and relatable to the reader. For instance, if you are evaluating a car, you could provide examples of its fuel efficiency, handling performance, and safety features.
By providing clear and concise criteria for evaluation, you can effectively communicate your assessment to the reader and support your conclusions. This will help ensure that your evaluation essay is well-structured, informative, and persuasive.
Support Your Evaluation with Solid Evidence

When writing an evaluation essay, it is crucial to support your evaluations with solid evidence. Without proper evidence, your evaluation may appear weak and unsubstantiated. By providing strong evidence, you can convince your readers of the validity of your evaluation and make a compelling argument.
One effective way to support your evaluation is by using concrete examples. These examples can be specific instances or cases that illustrate the strengths or weaknesses of the subject being evaluated. By presenting real-life examples, you can provide tangible evidence and make your evaluation more persuasive.
Another way to support your evaluation is by referring to expert opinions or research studies. These external sources can add credibility to your evaluation and demonstrate that your assessment is based on sound knowledge and expertise. Citing respected experts or referencing reputable studies can enhance the validity of your evaluation and make it more convincing.
In addition to concrete examples and expert opinions, statistical data can also be a powerful tool for supporting your evaluation. Numbers and statistics can provide objective evidence and strengthen your evaluation by adding a quantitative dimension to your argument. By citing relevant statistics, you can add weight to your evaluations and demonstrate the magnitude of the subject’s strengths or weaknesses.
Furthermore, it is important to consider counterarguments and address them in your evaluation. By acknowledging opposing viewpoints and addressing them effectively, you can strengthen your own evaluation and demonstrate a thorough understanding of the subject. This approach shows that you have considered different perspectives and have arrived at a well-rounded evaluation.
In conclusion, supporting your evaluation with solid evidence is essential to writing a persuasive evaluation essay. By using concrete examples, expert opinions, statistical data, and addressing counterarguments, you can bolster the validity and strength of your evaluation. Remember to present your evidence clearly and logically, making your evaluation more compelling and convincing to your readers.
Use a Structured Format to Organize Your Essay
When writing an evaluation essay, it is important to use a structured format to organize your thoughts and arguments. This will help you present your ideas in a clear and logical manner, making it easier for your reader to follow along and understand your points. By using a structured format, you can ensure that your essay flows smoothly and effectively communicates your evaluation.
One effective way to structure your evaluation essay is to use a table format. This allows you to present your evaluation criteria and supporting evidence in a concise and organized manner. By using a table, you can easily compare and contrast different aspects of the subject being evaluated, making it easier for your reader to grasp the overall evaluation.
In addition to using a table format, you should also follow a logical structure within each section of your essay. Start with a clear introduction, where you introduce the subject you are evaluating and provide some background information. Then, present your evaluation criteria and explain why these criteria are important for assessing the subject. Next, provide specific examples and evidence to support your evaluation, using the table format as a guide. Finally, end your essay with a strong conclusion that summarizes your evaluation and reinforces your main points.
By using a structured format, you can effectively organize your evaluation essay and present your ideas in a clear and concise manner. This will make your essay more engaging and persuasive, and help your reader understand and appreciate your evaluation.
Related Post
How to master the art of writing expository essays and captivate your audience, convenient and reliable source to purchase college essays online, step-by-step guide to crafting a powerful literary analysis essay, tips and techniques for crafting compelling narrative essays.
7 Steps for How to Write an Evaluation Essay (Example & Template)
In this ultimate guide, I will explain to you exactly how to write an evaluation essay.
1. What is an Evaluation Essay?
An evaluation essay should provide a critical analysis of something.
You’re literally ‘evaluating’ the thing you’re looking up.
Here’s a couple of quick definitions of what we mean by ‘evaluate’:
- Merriam-Webster defines evaluation as: “to determine the significance, worth, or condition of usually by careful appraisal and study”
- Collins Dictionary says: “If you evaluate something or someone, you consider them in order to make a judgment about them, for example about how good or bad they are.”
Here’s some synonyms for ‘evaluate’:
So, we could say that an evaluation essay should carefully examine the ‘thing’ and provide an overall judgement of it.
Here’s some common things you may be asked to write an evaluation essay on:
This is by no means an exhaustive list. Really, you can evaluate just about anything!
Get a Pdf of this article for class
Enjoy subscriber-only access to this article’s pdf
2. How to write an Evaluation Essay
There are two secrets to writing a strong evaluation essay. The first is to aim for objective analysis before forming an opinion. The second is to use an evaluation criteria.
Aim to Appear Objective before giving an Evaluation Argument
Your evaluation will eventually need an argument.
The evaluation argument will show your reader what you have decided is the final value of the ‘thing’ you’re evaluating.
But in order to convince your reader that your evaluative argument is sound, you need to do some leg work.
The aim will be to show that you have provided a balanced and fair assessment before coming to your conclusion.
In order to appear balanced you should:
- Discuss both the pros and cons of the thing
- Discuss both the strengths and weaknesses of the thing
- Look at the thing from multiple different perspectives
- Be both positive and critical. Don’t make it look like you’re biased towards one perspective.
In other words, give every perspective a fair hearing.
You don’t want to sound like a propagandist. You want to be seen as a fair and balanced adjudicator.
Use an Evaluation Criteria
One way to appear balanced is to use an evaluation criteria.
An evaluation criteria helps to show that you have assessed the ‘thing’ based on an objective measure.
Here’s some examples of evaluation criteria:
- Strength under pressure
- Longevity (ability to survive for a long time)
- Ease of use
- Ability to get the job done
- Friendliness
- Punctuality
- Ability to predict my needs
- Calmness under pressure
- Attentiveness
A Bed and Breakfast
- Breakfast options
- Taste of food
- Comfort of bed
- Local attractions
- Service from owner
- Cleanliness
We can use evaluation criteria to frame out ability to conduct the analysis fairly.
This is especially true for if you have to evaluate multiple different ‘things’. For example, if you’re evaluating three novels, you want to be able to show that you applied the same ‘test’ on all three books!
This will show that you gave each ‘thing’ a fair chance and looked at the same elements for each.
3. How to come up with an Evaluation Argument
After you have:
- Looked at both good and bad elements of the ‘thing’, and
- Used an evaluation criteria
You’ll then need to develop an evaluative argument. This argument shows your own overall perspective on the ‘thing’.
Remember, you will need to show your final evaluative argument is backed by objective analysis. You need to do it in order!
Analyze first. Evaluate second.
Here’s an example.
Let’s say you’re evaluating the quality of a meal.
You might say:
- A strength of the meal was its presentation. It was well presented and looked enticing to eat.
- A weakness of the meal was that it was overcooked. This decreased its flavor.
- The meal was given a low rating on ‘cost’ because it was more expensive than the other comparative meals on the menu.
- The meal was given a high rating on ‘creativity’. It was a meal that involved a thoughtful and inventive mix of ingredients.
Now that you’ve looked at some pros and cons and measured the meal based on a few criteria points (like cost and creativity), you’ll be able to come up with a final argument:
- Overall, the meal was good enough for a middle-tier restaurant but would not be considered a high-class meal. There is a lot of room for improvement if the chef wants to win any local cooking awards.
Evaluative terms that you might want to use for this final evaluation argument might include:
- All things considered
- With all key points in mind
4. Evaluation Essay Outline (with Examples)
Okay, so now you know what to do, let’s have a go at creating an outline for your evaluation essay!
Here’s what I recommend:
4.1 How to Write your Introduction
In the introduction, feel free to use my 5-Step INTRO method . It’ll be an introduction just like any other essay introduction .
And yes, feel free to explain what the final evaluation will be.
So, here it is laid out nice and simple.
Write one sentence for each point to make a 5-sentence introduction:
- Interest: Make a statement about the ‘thing’ you’re evaluating that you think will be of interest to the reader. Make it a catchy, engaging point that draws the reader in!
- Notify: Notify the reader of any background info on the thing you’re evaluating. This is your chance to show your depth of knowledge. What is a historical fact about the ‘thing’?
- Translate: Re-state the essay question. For an evaluative essay, you can re-state it something like: “This essay evaluates the book/ product/ article/ etc. by looking at its strengths and weaknesses and compares it against a marking criteria”.
- Report: Say what your final evaluation will be. For example you can say “While there are some weaknesses in this book, overall this evaluative essay will show that it helps progress knowledge about Dinosaurs.”
- Outline: Simply give a clear overview of what will be discussed. For example, you can say: “Firstly, the essay will evaluate the product based on an objective criteria. This criteria will include its value for money, fit for purpose and ease of use. Next, the essay will show the main strengths and weaknesses of the product. Lastly, the essay will provide a final evaluative statement about the product’s overall value and worth.”
If you want more depth on how to use the INTRO method, you’ll need to go and check out our blog post on writing quality introductions.
4.2 Example Introduction
This example introduction is for the essay question: Write an Evaluation Essay on Facebook’s Impact on Society.
“Facebook is the third most visited website in the world. It was founded in 2004 by Mark Zuckerberg in his college dorm. This essay evaluates the impact of Facebook on society and makes an objective judgement on its value. The essay will argue that Facebook has changed the world both for the better and worse. Firstly, it will give an overview of what Facebook is and its history. Then, it will examine Facebook on the criteria of: impact on social interactions, impact on the media landscape, and impact on politics.”
You’ll notice that each sentence in this introduction follows my 5-Step INTRO formula to create a clear, coherent 5-Step introduction.
4.3 How to Write your Body Paragraphs
The first body paragraph should give an overview of the ‘thing’ being evaluated.
Then, you should evaluate the pros and cons of the ‘thing’ being evaluated based upon the criteria you have developed for evaluating it.
Let’s take a look below.
4.4 First Body Paragraph: Overview of your Subject
This first paragraph should provide objective overview of your subject’s properties and history. You should not be doing any evaluating just yet.
The goal for this first paragraph is to ensure your reader knows what it is you’re evaluating. Secondarily, it should show your marker that you have developed some good knowledge about it.
If you need to use more than one paragraph to give an overview of the subject, that’s fine.
Similarly, if your essay word length needs to be quite long, feel free to spend several paragraphs exploring the subject’s background and objective details to show off your depth of knowledge for the marker.
4.5 First Body Paragraph Example
Sticking with the essay question: Write an Evaluation Essay on Facebook’s Impact on Society , this might be your paragraph:
“Facebook has been one of the most successful websites of all time. It is the website that dominated the ‘Web 2.0’ revolution, which was characterized by user two-way interaction with the web. Facebook allowed users to create their own personal profiles and invite their friends to follow along. Since 2004, Facebook has attracted more than one billion people to create profiles in order to share their opinions and keep in touch with their friends.”
Notice here that I haven’t yet made any evaluations of Facebook’s merits?
This first paragraph (or, if need be, several of them) should be all about showing the reader exactly what your subject is – no more, no less.
4.6 Evaluation Paragraphs: Second, Third, Forth and Fifth Body Paragraphs
Once you’re confident your reader will know what the subject that you’re evaluating is, you’ll need to move on to the actual evaluation.
For this step, you’ll need to dig up that evaluation criteria we talked about in Point 2.
For example, let’s say you’re evaluating a President of the United States.
Your evaluation criteria might be:
- Impact on world history
- Ability to pass legislation
- Popularity with voters
- Morals and ethics
- Ability to change lives for the better
Really, you could make up any evaluation criteria you want!
Once you’ve made up the evaluation criteria, you’ve got your evaluation paragraph ideas!
Simply turn each point in your evaluation criteria into a full paragraph.
How do you do this?
Well, start with a topic sentence.
For the criteria point ‘Impact on world history’ you can say something like: “Barack Obama’s impact on world history is mixed.”
This topic sentence will show that you’ll evaluate both pros and cons of Obama’s impact on world history in the paragraph.
Then, follow it up with explanations.
“While Obama campaigned to withdraw troops from Iraq and Afghanistan, he was unable to completely achieve this objective. This is an obvious negative for his impact on the world. However, as the first black man to lead the most powerful nation on earth, he will forever be remembered as a living milestone for civil rights and progress.”
Keep going, turning each evaluation criteria into a full paragraph.
4.7 Evaluation Paragraph Example
Let’s go back to our essay question: Write an Evaluation Essay on Facebook’s Impact on Society .
I’ve decided to use the evaluation criteria below:
- impact on social interactions;
- impact on the media landscape;
- impact on politics
Naturally, I’m going to write one paragraph for each point.
If you’re expected to write a longer piece, you could write two paragraphs on each point (one for pros and one for cons).
Here’s what my first evaluation paragraph might look like:
“Facebook has had a profound impact on social interactions. It has helped people to stay in touch with one another from long distances and after they have left school and college. This is obviously a great positive. However, it can also be seen as having a negative impact. For example, people may be less likely to interact face-to-face because they are ‘hanging out’ online instead. This can have negative impact on genuine one-to-one relationships.”
You might notice that this paragraph has a topic sentence, explanations and examples. It follows my perfect paragraph formula which you’re more than welcome to check out!
4.8 How to write your Conclusion
To conclude, you’ll need to come up with one final evaluative argument.
This evaluation argument provides an overall assessment. You can start with “Overall, Facebook has been…” and continue by saying that (all things considered) he was a good or bad president!
Remember, you can only come up with an overall evaluation after you’ve looked at the subject’s pros and cons based upon your evaluation criteria.
In the example below, I’m going to use my 5 C’s conclusion paragraph method . This will make sure my conclusion covers all the things a good conclusion should cover!
Like the INTRO method, the 5 C’s conclusion method should have one sentence for each point to create a 5 sentence conclusion paragraph.
The 5 C’s conclusion method is:
- Close the loop: Return to a statement you made in the introduction.
- Conclude: Show what your final position is.
- Clarify: Clarify how your final position is relevant to the Essay Question.
- Concern: Explain who should be concerned by your findings.
- Consequences: End by noting in one final, engaging sentence why this topic is of such importance. The ‘concern’ and ‘consequences’ sentences can be combined
4.9 Concluding Argument Example Paragraph
Here’s a possible concluding argument for our essay question: Write an Evaluation Essay on Facebook’s Impact on Society .
“The introduction of this essay highlighted that Facebook has had a profound impact on society. This evaluation essay has shown that this impact has been both positive and negative. Thus, it is too soon to say whether Facebook has been an overall positive or negative for society. However, people should pay close attention to this issue because it is possible that Facebook is contributing to the undermining of truth in media and positive interpersonal relationships.”
Note here that I’ve followed the 5 C’s conclusion method for my concluding evaluative argument paragraph.
5. Evaluation Essay Example Template
Below is a template you can use for your evaluation essay , based upon the advice I gave in Section 4:
6. 23+ Good Evaluation Essay Topics
Okay now that you know how to write an evaluation essay, let’s look at a few examples.
For each example I’m going to give you an evaluation essay title idea, plus a list of criteria you might want to use in your evaluation essay.
6.1 Evaluation of Impact
- Evaluate the impact of global warming on the great barrier reef. Recommended evaluation criteria: Level of bleaching; Impact on tourism; Economic impact; Impact on lifestyles; Impact on sealife
- Evaluate the impact of the Global Financial Crisis on poverty. Recommended evaluation criteria: Impact on jobs; Impact on childhood poverty; Impact on mental health rates; Impact on economic growth; Impact on the wealthy; Global impact
- Evaluate the impact of having children on your lifestyle. Recommended evaluation criteria: Impact on spare time; Impact on finances; Impact on happiness; Impact on sense of wellbeing
- Evaluate the impact of the internet on the world. Recommended evaluation criteria: Impact on connectedness; Impact on dating; Impact on business integration; Impact on globalization; Impact on media
- Evaluate the impact of public transportation on cities. Recommended evaluation criteria: Impact on cost of living; Impact on congestion; Impact on quality of life; Impact on health; Impact on economy
- Evaluate the impact of universal healthcare on quality of life. Recommended evaluation criteria: Impact on reducing disease rates; Impact on the poorest in society; Impact on life expectancy; Impact on happiness
- Evaluate the impact of getting a college degree on a person’s life. Recommended evaluation criteria: Impact on debt levels; Impact on career prospects; Impact on life perspectives; Impact on relationships
6.2 Evaluation of a Scholarly Text or Theory
- Evaluate a Textbook. Recommended evaluation criteria: clarity of explanations; relevance to a course; value for money; practical advice; depth and detail; breadth of information
- Evaluate a Lecture Series, Podcast or Guest Lecture. Recommended evaluation criteria: clarity of speaker; engagement of attendees; appropriateness of content; value for monet
- Evaluate a journal article. Recommended evaluation criteria: length; clarity; quality of methodology; quality of literature review ; relevance of findings for real life
- Evaluate a Famous Scientists. Recommended evaluation criteria: contribution to scientific knowledge; impact on health and prosperity of humankind; controversies and disagreements with other scientists.
- Evaluate a Theory. Recommended evaluation criteria: contribution to knowledge; reliability or accuracy; impact on the lives of ordinary people; controversies and contradictions with other theories.
6.3 Evaluation of Art and Literature
- Evaluate a Novel. Recommended evaluation criteria: plot complexity; moral or social value of the message; character development; relevance to modern life
- Evaluate a Play. Recommended evaluation criteria: plot complexity; quality of acting; moral or social value of the message; character development; relevance to modern life
- Evaluate a Film. Recommended evaluation criteria: plot complexity; quality of acting; moral or social value of the message; character development; relevance to modern life
- Evaluate an Artwork. Recommended evaluation criteria: impact on art theory; moral or social message; complexity or quality of composition
6.4 Evaluation of a Product or Service
- Evaluate a Hotel or Bed and Breakfast. Recommended evaluation criteria: quality of service; flexibility of check-in and check-out times; cleanliness; location; value for money; wi-fi strength; noise levels at night; quality of meals; value for money
- Evaluate a Restaurant. Recommended evaluation criteria: quality of service; menu choices; cleanliness; atmosphere; taste; value for money.
- Evaluate a Car. Recommended evaluation criteria: fuel efficiency; value for money; build quality; likelihood to break down; comfort.
- Evaluate a House. Recommended evaluation criteria: value for money; build quality; roominess; location; access to public transport; quality of neighbourhood
- Evaluate a Doctor. Recommended evaluation criteria: Quality of service; knowledge; quality of equipment; reputation; value for money.
- Evaluate a Course. Recommended evaluation criteria: value for money; practical advice; quality of teaching; quality of resources provided.
7. Concluding Advice

Evaluation essays are common in high school, college and university.
The trick for getting good marks in an evaluation essay is to show you have looked at both the pros and cons before making a final evaluation analysis statement.
You don’t want to look biased.
That’s why it’s a good idea to use an objective evaluation criteria, and to be generous in looking at both positives and negatives of your subject.
Read Also: 39 Better Ways to Write ‘In Conclusion’ in an Essay
I recommend you use the evaluation template provided in this post to write your evaluation essay. However, if your teacher has given you a template, of course use theirs instead! You always want to follow your teacher’s advice because they’re the person who will be marking your work.
Good luck with your evaluation essay!

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ Social-Emotional Learning (Definition, Examples, Pros & Cons)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ What is Educational Psychology?
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ What is IQ? (Intelligence Quotient)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 5 Top Tips for Succeeding at University
2 thoughts on “7 Steps for How to Write an Evaluation Essay (Example & Template)”
What an amazing article. I am returning to studying after several years and was struggling with how to present an evaluative essay. This article has simplified the process and provided me with the confidence to tackle my subject (theoretical approaches to development and management of teams).
I just wanted to ask whether the evaluation criteria has to be supported by evidence or can it just be a list of criteria that you think of yourself to objectively measure?
Many many thanks for writing this!

Usually we would want to see evidence, but ask your teacher for what they’re looking for as they may allow you, depending on the situation.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

sukanya sitthikongsak / Getty Images
By Colin Baker Leaders Staff
Colin Baker
Leadership and Business Writer
Colin Baker is a business writer for Leaders Media. He has a background in as a television journalism, working as...
Learn about our editorial policy
Updated Aug 30, 2022
What Is a Job Evaluation, and How Do You Conduct One?
What is a job evaluation, why job evaluations matter, methods of job evaluation, the job evaluation process, job evaluation maintenance, the ongoing process of job evaluations.
How much should a company pay its employees? If businesses want to retain their best talent, they need to compensate team members with a satisfying wage that makes them feel valued and appreciated. Employees agree as well and consider what they earn to be a critical component of their jobs. An SHRM report found that 60 percent of employees say that the level of compensation at their job was “very important.” It’s no wonder that job satisfaction often goes hand in hand with how much a worker earns. Companies need a fair way to determine wages, and that means conducting a job evaluation.
The job evaluation process compares roles within an organization and industry to determine fair pay. It also helps define employees’ responsibilities at work. Normally, human resources, executive leadership teams, and outside partners such as labor unions participate in the job evaluation process, providing insight into what constitutes fair pay.
It’s more important than ever for companies to perform job evaluations. Paying someone too little means they’re more likely to look for work elsewhere. Additionally, job roles can quickly become outdated, and any business using out-of-date standards risks falling behind. Russian companies suffered for years from outdated evaluation standards. The reason? They kept using the same framework established by the Soviet Union, even after the USSR dissolved. Because of this, some of their most talented workers had little choice but to come to America to earn good money. For example, Jan Koum , the founder of WhatsApp, was one of them. As a teenager, he struggled in the U.S., too, but found opportunities to showcase his talents and make a name for himself.
Needless to say, businesses should avoid those risks and undertake the job evaluation process. Many companies choose to hire an outside firm or neutral consultants to perform a job evaluation. Senior employees may take part since they have the expertise on what it takes to fulfill a job role, but they will usually try to take a more hands-off approach to guarantee impartiality.
Besides determining the proper pay structure for a job or career, they can also help companies define the role’s job description and specifications. They also outline the expected performance standards and can help workers understand what it takes to succeed in their jobs.
Companies have a variety of job evaluation methods they can use when they’re ready to begin the process. These methods fall under several different categories. Knowing the different types helps leaders and their human resources team pick the option that works best for the business.
Quantitative
The quantitative approach looks at hard numbers. People who love data and use it to make important business decisions will likely prefer to work with job evaluation methods centered around quantitative strategies. Others may favor quantitative analysis since it generally means a more objective view of job roles.
Qualitative
A job review sometimes falls under the qualitative approach. This method means companies or consultancies use their own observations and descriptions to define a job. Qualitative strategies tend to be faster, but they can also be more subjective than quantitative approaches.
An internal job evaluation strategy sticks to a comparison of jobs inside the same organization. This strategy tends to focus solely on the company itself and not on outside forces. Small businesses may use this approach since the comparison usually takes less time.
External job evaluations approach the topic a bit differently. They look at the market as a whole and not just the organization. This can be helpful when a business is small or where shortages of skills may exist.
With these different strategies in mind, let’s take a look at the most common job evaluation methods and where they fall under the aforementioned categories.
Point Factor Method: Quantitative/Internal
The point factor method is perhaps the most common structure companies use for their job evaluations. With the point method of job evaluation, organizations look at a job and determine the compensable factors involved. For example, how much experience is needed to perform the job well? What type of knowledge does the employee need? To whom does the employee report?
Organizations assign each of these factors a point score. They then add up the total amount of points and compare that total to the points from other jobs within the organization. From there, companies can choose a fair pay grade for the position based on the overall value it brings to the business.
Job Ranking: Qualitative/Internal
When a company pursues the job ranking method, they usually do it because it’s the easiest method to follow. Due to its simplicity, it’s a favorite of many small businesses. Organizations simply take all the jobs they have and rank them by order of importance and value. The jobs at the top of the list will have the highest compensation. The jobs on the lower end will receive lower pay.
Essentially, this places every job in a hierarchy based on the opinions of each business leader and manager. While small businesses may appreciate how easy it is to follow the job ranking system, companies with more than a hundred employees might want to steer clear of it.
Factor Comparison: Quantitative/Internal
When combining the job ranking method with the point factor method, the factor comparison method emerges. First, businesses rank jobs in the organization based on several different factors. Those factors include what each job role manages, the knowledge and skills used, how much freedom they have, benefits, and more. Once this is complete, the factors receive a point value. Based on that, jobs can be rearranged and reranked. This new ranking serves as the basis for compensation.
Job Classification: Qualitative/Internal
The job classification method starts with businesses writing a job description for each position in their organization. They then assign each description a grade level. Grade levels may be based on the level of skill needed to do the job. So a classification such as CEO may receive a high grade level.
Businesses may also create grades within the same family of jobs. For example, the sales division may receive its own grade, while the marketing department may have a separate grading scale. Organizations set compensation levels for each job based on these grades.
Custom Factor Comparison: Quantitative/Internal
The custom factor comparison method is perhaps the least common strategy because of the resources and time needed to complete it. Businesses must also constantly maintain it as they monitor market rates. The method follows many of the same steps as the factor comparison method, only this one is more tailored to an individual company. It also goes into much more detail than other strategies.
Market Pricing: Quantitative/External
The market pricing method is the most common external strategy for the job evaluation process. This method involves looking at market data to determine the average pay structure or salary for a particular job position. Compensation surveys from third parties are one way organizations access this information.
However, the market pricing method has a few problems, especially when the data is incomplete or provides an oversimplified view. For example, someone with a job title in one company may have vastly different responsibilities from someone with the same title at another business. Since this method only looks at external factors, it doesn’t take into account internal value and may lead to inequalities.
With these job evaluation methods in mind, it’s time to look at the steps that go into the job evaluation system.
1. Planning
The first step involves the development of a plan. Businesses must determine how much time and how many resources they have available for this goal. They also must identify what tools they want to use and if they need outside help.
This part of the process also determines what method, as outlined above, they’ll pursue. Will they try for the common point factor method? Is the job ranking method more in line with their needs? They also need to choose the level of customization they’ll use for the job analysis. A proprietary scheme, for example, usually comes from a consultancy and is designed for use in many organizations. More customized schemes, however, may better serve a specific organization, but they require more resources and fine-tuning.
The second step is designing the job review. This requires collecting important data, often through workshops focused on pay management and how different roles affect businesses. These provide insight into the value of various jobs within a company. This step also identifies what aspects of the job evaluation should serve as the main benchmarks for the organization to follow.
3. Validation
In the validation step, organizations test their designs. That means analyzing the data collected in the previous step. In addition, this is where they implement the job evaluation method they want to follow. Changes come with the testing, as each leader or manager tweaks the model and streamlines it. A natural consequence of this is that some jobs may fall outside the defined job position. Organizations need to look at each of these outlier jobs and find a good spot for them within the model.
4. Roll Out
Once the model has been finalized, it’s time to roll it out for the whole organization to see. For this step, businesses need to communicate to their employees two major items. First, they need to explain how the compensation model has changed, and second, why the changes occurred. Workers are protective of their pay, so they’ll likely be defensive about any adjustments management makes, even if the adjustments are only minor. Open communication about such policy changes helps address questions before they arise. Every level of the organization should know about new compensation policies as they can affect everything from performance reviews to the hiring process .
Once a company has completed the job evaluation system, that doesn’t mean the work is over. Job analysis is an ongoing procedure, one that requires reviews at regular intervals. As a result, organizations should conduct audits often to ensure the model is performing well and accurately reflects fair compensation rates. Jobs change all the time, and companies create new jobs with frequency as the times and technologies change. Because of this, evaluating jobs should be a top priority for organizations.
So how often should businesses audit their compensation methods? That depends on the company. Small businesses may not see the same sort of drastic changes large corporations do, so their reevaluations might take place years apart. Larger companies may perform audits more frequently, especially if they have the resources to do so. No matter how often such major reevaluations occur, small changes may be necessary from time to time.
As always, organizations must consider legal ramifications. In terms of compensation, companies must make sure all get paid equally for the same work. If there are any inequalities discovered, they must investigate right away.
As explained above, job evaluations should be a constant in companies. They take consistent refinement and use of job evaluation methods to ensure everyone receives what they deserve as they provide value to an organization. They are especially important when it comes to new hires. For more advice on the hiring process and building a team, check out these articles:
- Hiring Employees: 3 Hires You Need To Create Growth & Freedom
- Job Interview Questions: How To Hire The Right Person For The Job
- The Ideal Team Player: How to Grow an Effective Team
Search Leaders.com

📕 Studying HQ
The ultimate guide to writing an evaluation essay, carla johnson.
- June 14, 2023
- Essay Topics and Ideas , How to Guides
Evaluation essays are a common type of writing assignment in school. They ask students to evaluate and analyze the quality or value of something like a book, movie, product, or service. In this article, we’ll give you the most complete guide to writing an evaluation essay. We’ll talk about everything from an evaluation essay’s purpose and importance to the steps you need to take to write a good one.
An evaluation essay is a type of writing that tries to give an unbiased opinion about a topic based on a set of criteria. It’s not just a summary of the topic; it’s a critical analysis of what’s good and bad about it . The writer should give a fair assessment of the topic by pointing out both its strengths and weaknesses.
The point of an evaluation essay is to give a critical analysis of a topic so that the reader can form a well-informed opinion about it. For this kind of essay , the writer needs to know a lot about the subject, including its background, history, and effects. It is a good activity for students to do because it helps them learn how to think critically , do research, and write well.
Evaluation essays are also important in academic writing because they help students show that they can think critically and explain their ideas clearly. Because of this, evaluation essays are often given in many different classes, such as literature, film studies, business, and marketing. By learning how to write an evaluation essay, students can do better in school and improve their chances of getting jobs in their chosen fields.
An evaluation essay is a type of academic writing that asks students to give a critical analysis of a certain topic based on a set of criteria. The point of writing an evaluation essay is to give the reader an unbiased look at the topic so that they can form an opinion about it.
Lastly, evaluation essays are an important part of academic writing because they help students improve their critical thinking, research, and writing skills, all of which are important for academic success and moving up in a career. In the sections that follow, we’ll talk more about the steps you need to take to write a good evaluation essay.
What You'll Learn
Choosing a Topic for an Evaluation Essay
Choosing the right topic is crucial when it comes to writing an effective evaluation essay. A well-chosen topic will not only make the writing process easier but will also ensure that the essay is engaging and relevant to the reader. Here are some tips for selecting an evaluation essay topic:
– Choose a topic that you are interested in: It is essential to choose a topic that you are passionate about and have some knowledge of. This will make the writing process more enjoyable and will also result in a more engaging and informative essay .
– Select a topic that is relevant: Choose a subject that is current and relevant to the reader. This will ensure that your essay is informative and interesting to read.
– Narrow down your topic: It is important to select a topic that is specific and narrow. This will enable you to focus on a particular aspect of the subject and provide a more detailed evaluation.
– Consider both sides of the argument: Choose a topic that allows you to evaluate both the strengths and weaknesses of the subject. This will ensure that your essay is balanced and provides a fair evaluation .
– Use credible sources: Ensure that your topic is backed by credible sources, such as academic journals, books, and reputable websites.
Here is a list of 50 evaluation essay topics:
1. The impact of social media on modern relationships
2. The effectiveness of online learning compared to traditional classroom learning
3. The portrayal of mental health in popular media4. The impact of technology on our daily lives
5. The effectiveness of government policies on climate change
6. The quality of customer service in the hospitality industry
7. The effectiveness of performance-enhancing drugs in sports
8. The portrayal of women in the media
9. The impact of smartphones on communication skills
10. The effectiveness of gun control laws in reducing gun violence
11. The quality of healthcare services in rural areas
12. The impact of video games on children’s behavior
13. The effectiveness of alternative medicine in treating chronic illnesses
14. The portrayal of minorities in the media
15. The impact of social media on body image and self-esteem
16. The effectiveness of online dating in finding a partner
17. The quality of fast food restaurants
18. The impact of globalization on cultural diversity
19. The effectiveness of police body cameras in reducing police brutality
20. The portrayal of mental illness in popular media
21. The impact of artificial intelligence on job opportunities
22. The effectiveness of vaccination programs in preventing diseases
23. The quality of public transportation in urban areas
24. The impact of social media on political campaigns
25. The effectiveness of rehabilitation programs for prisoners
26. The portrayal of LGBTQ+ individuals in the media
27. The impact of technology on education
28. The effectiveness of animal testing in developing new drugs
29. The quality of public schools in low-income areas
30. The impact of social media onteenagers’ mental health
31. The effectiveness of renewable energy sources in reducing carbon emissions
32. The portrayal of disability in the media
33. The impact of celebrity culture on society
34. The effectiveness of anti-bullying programs in schools
35. The quality of public parks and recreation areas
36. The impact of social media on political polarization
37. The effectiveness of online therapy in treating mental illness
38. The portrayal of aging in the media
39. The impact of automation on job security
40. The effectiveness of recycling programs in reducing waste
41. The quality of public libraries
42. The impact of social media on privacy
43. The effectiveness of parenting classes in improving child behavior
44. The portrayal of mental health in the workplace
45. The impact of technology on the music industry
46. The effectiveness of drug rehabilitation programs
47. The quality of public restrooms
48. The impact of social media on activism
49. The effectiveness of sex education programs in schools
50. The portrayal of race in the media.
Understanding the Structure of an Evaluation Essay
A basic structure for an evaluation essay is an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion. The purpose of the introduction is to give background information about the subject and explain how it will be judged. Based on the criteria set out in the introduction, the body paragraphs should give a detailed analysis of the topic. In the end, the conclusion should summarize the main points of the essay and give a final opinion on the subject.
Here is a breakdown of each section of an evaluation essay:
1. Introduction: The introduction should begin with an attention-grabbing hook that draws the reader in and provides some background information on the subject. This should be followed by a clear thesis statement that outlines the criteria that will be used to evaluate the subject.
2. Body Paragraphs: Each of the body paragraphs should look at a different part of the topic and judge it based on the criteria set out in the introduction. Every paragraph should start with a topic sentence that makes it clear what is being evaluated and how. The evaluation should then be backed up with evidence , such as examples, statistics, and quotes from reliable sources.
3. Conclusion: The conclusion should provide a summary of the main points made in the essay and restate the thesis statement . The writer should then provide a final evaluation of the subject based on the evidence presented in the body paragraphs. This evaluation should be balanced and fair, taking into account both the strengths and weaknesses of the subject.
An evaluation essay outline can be helpful in organizing and structuring the essay. Here is an example of an evaluation essay outline:
I. Introduction
– Hook
– Background information
– Thesis statement
II. Body Paragraphs
– Aspect 1
– Criteria
– Evidence
– Aspect 2
– Aspect 3
-Criteria
III. Conclusion
– Summary of main points
– Restate thesis statement
– Final evaluation
Understanding the structure of an evaluation essay and choosing the right topic are both critical to writing an effective evaluation essay. By following the tips provided for selecting a topic and using an evaluation essay outline, you can create a well-organized and engaging essay that provides a fair assessment of the subject.
Writing an Effective Evaluation Essay
Writing an effective evaluation essay requires careful planning and execution. Here are some tips to help you write a powerful evaluation essay:
1. Developing a thesis statement for an evaluation essay: A strong thesis statement should clearly state the criteria that will be used to evaluate the subject. It should also provide a clear indication of the writer’s stance on the subject, whether it is positive, negative, or neutral.
2. Tips for writing a powerful evaluation essay:
– Use specific criteria: Provide clear and specific criteria for evaluating the subject, and use evidence to support your evaluation.
– Use credible sources: Use credible sources to support your evaluation, such as academic journals, books, and reputable websites.
– Be objective: Provide a balanced evaluation of the subject, highlighting both its strengths and weaknesses.
– Use clear and concise language: Use clear and concise language to make your evaluation easy to understand and engaging to read.
– Use transitions: Use transitions to connect your ideas and ensure that the essay flows smoothly.
3. Common mistakes to avoid when writing an evaluation essay:
– Being too subjective: Avoid being too subjective and provide a balanced evaluation of the subject.
– Failing to provide evidence: Use evidence to support your evaluation, and avoid making unsupported claims.
– Focusing too much on summary: Avoid simply summarizing the subject and focus on providing a critical analysis of its merits and demerits.
– Failing to use credible sources: Use credible sources to support your evaluation andavoid relying solely on personal opinions or unsupported claims.
Examples of Evaluation Essays
To help you get a better understanding of how to write an effective evaluation essay, here are 10 inspiring evaluation essay examples from different fields:
1. Evaluation of the effectiveness of the COVID-19 vaccine rollout strategy in the United States
2. Evaluation of the impact of the #MeToo movement on workplace culture
3. Evaluation of the nutritional value of plant-based diets compared to meat-based diets
4. Evaluation of the effectiveness of the Paris Climate Agreement in reducing global carbon emissions
5. Evaluation of the impact of social media influencers on consumer behavior
6. Evaluation of the effectiveness of mindfulness meditation in reducing stress and anxiety
7. Evaluation of the quality of customer service provided by leading airlines
8. Evaluation of the portrayal of mental illness in popular TV shows
9. Evaluation of the effectiveness of online therapy in treating depression and anxiety
10. Evaluation of the impact of video games on children’s cognitive development
Writing an effective evaluation essay involves selecting the right topic, understanding the structure of the essay, and following the tips provided to develop a powerful evaluation essay. By avoiding common mistakes and using credible sources, you can create an engaging and informative evaluation essay that provides a balanced assessment of the subject. The examples provided can also serve as a guide to help you craft a compelling evaluation essay in any field.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. what is an evaluation essay.
An evaluation essay is a type of academic writing that asks students to evaluate and analyze the quality or value of something like a book, movie, product, or service. The writer should give a fair assessment of the topic by pointing out both its strengths and weaknesses.
2. What are the elements of an evaluation essay?
An evaluation essay has three parts: an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion. In the introduction, you should give some background information about the topic and explain how it will be judged. Based on the criteria set out in the introduction, the body paragraphs should give a detailed analysis of the topic. In the end, the conclusion should summarize the main points of the essay and give a final opinion on the topic .
3. How do I choose a topic for an evaluation essay?
To pick a topic for an evaluation essay, think about something you are interested in and know a little bit about. It’s also important to choose a topic that is relevant and specific. Think about both sides of the argument and back up your opinion with information from reliable sources.
4. What is the difference between an evaluation essay and a review?
The main difference between an evaluation essay and a review is that an evaluation essay has a different focus and goal. An evaluation essay tries to give a critical analysis of the subject based on a set of criteria, while a review gives a summary of the subject and often includes personal opinions.
In conclusion, writing an effective evaluation essay is an essential skill for students to master, as it helps to develop critical thinking , research, and writing abilities. To write an effective evaluation essay, it is important to choose the right topic, understand the structure of the essay, and follow the tips provided in this guide. It is also important to avoid common mistakes and use credible sources to support your evaluation.
Start by filling this short order form order.studyinghq.com
And then follow the progressive flow.
Having an issue, chat with us here
Cathy, CS.
New Concept ? Let a subject expert write your paper for You
Have a subject expert write for you now, have a subject expert finish your paper for you, edit my paper for me, have an expert write your dissertation's chapter, popular topics.
Business StudyingHq Essay Topics and Ideas How to Guides Samples
- Nursing Solutions
- Study Guides
- Free College Essay Examples
- Privacy Policy
- Writing Service
- Discounts / Offers
Study Hub:
- Studying Blog
- Topic Ideas
- How to Guides
- Business Studying
- Nursing Studying
- Literature and English Studying
Writing Tools
- Citation Generator
- Topic Generator
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Conclusion Maker
- Research Title Generator
- Thesis Statement Generator
- Summarizing Tool
- Terms and Conditions
- Confidentiality Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Refund and Revision Policy
Our samples and other types of content are meant for research and reference purposes only. We are strongly against plagiarism and academic dishonesty.
Contact Us:
📞 +15512677917
2012-2024 © studyinghq.com. All rights reserved
Job Evaluation Essays
Importance and methods of job evaluation for organizational effectiveness, popular essay topics.
- American Dream
- Artificial Intelligence
- Black Lives Matter
- Bullying Essay
- Career Goals Essay
- Causes of the Civil War
- Child Abusing
- Civil Rights Movement
- Community Service
- Cultural Identity
- Cyber Bullying
- Death Penalty
- Depression Essay
- Domestic Violence
- Freedom of Speech
- Global Warming
- Gun Control
- Human Trafficking
- I Believe Essay
- Immigration
- Importance of Education
- Israel and Palestine Conflict
- Leadership Essay
- Legalizing Marijuanas
- Mental Health
- National Honor Society
- Police Brutality
- Pollution Essay
- Racism Essay
- Romeo and Juliet
- Same Sex Marriages
- Social Media
- The Great Gatsby
- The Yellow Wallpaper
- Time Management
- To Kill a Mockingbird
- Violent Video Games
- What Makes You Unique
- Why I Want to Be a Nurse
- Send us an e-mail
Benchmarking on Job Evaluation Essay
Introduction, recommended job evaluation system.
Job evaluation and its analysis is a process that entails the creation of structures that establish the worth of every job in an organization. It is based on job itself, the required skills, the specific duties, as well as the working conditions. Job evaluation aims at providing a fair, systematic and consistent mode of measuring the value of jobs in an organization (Otis & Leukart, 2004).
Job titles can be misleading; in big enterprises, it might be difficult to remember various job titles existing, which calls for a detailed job description that will form a basis for the job evaluation. This paper will look at job evaluation in general, and identify various job evaluation plans that have been used by organizations.
Point factor evaluation system
The first thing that has to be taken into consideration is the identification of factors that can be compensated, and that are shared by the group being evaluated. In this system of evaluation, jobs are not evaluated at once, but instead they are broken down into various factors and sub factors.
Their values are then measured separately, and those that have been grouped into factors are put together. The result of summing up individual values becomes the job’s value. The factors that are used in this evaluation process are responsibility, education and working conditions. The skill factor is further subdivided into sub factors that include complexity, knowledge and communication. Effort is further subdivided into physical and mental sub factors. Responsibility is further sub divided into decisions and resources (Kaufman, 2006).
The point factor evaluation system starts as a point of information statement that acts as the main document to be used for the job evaluation. It is also used for other practices in the human resource sector, such as compensation, recruitment, performance appraisal and restructuring. This evaluation technique is unbiased, hence, more effective as compared to others (Heartfied, 2010).
Ranking is another job evaluation process which is very easy and fast. It is also not expensive and quite efficient for small organizations that have few classifications of jobs. Jobs are placed in hierarchy from the top to the lowest ones. Its main advantage consists in the fact that it is simple, and it is easy to communicate the obtained results to employees (Heartfied, 2010).
Classification
In this process of evaluation, the various job groupings are described, after which a detailed report of the jobs within each grouping illustrates the various job’s characteristics. The various groupings are further grouped, based on the similarity between tasks. This system is mostly utilized by organizations that have limited resources. This evaluation method is simple and allows new jobs as well as those whose roles have changed to be included into the system.
Aim of job evaluation
There are various reasons why organizations carry out job evaluations. One of them is a change in an organization, which in turn requires new job places. This can also be carried out in case of reported dissatisfaction among employees on how the various jobs are graded. Such issues as those related to pay, may arise and compel an organization to carry out job evaluations.
Benefits of job evaluation
Job evaluation enables an organization to determine the duties and responsibilities of each employee. It also helps in the determination of training methods required for particular jobs, as well as making improvements in job designs. Job evaluation is a tool that is powerful when it comes to the compensation of employees (Milkovich, 2010).
In case employees feel that the job evaluation criteria that an organization uses are unfair, they are entitled to make appeals against the decisions. An effective job evaluation provides an organization with the information that can be used in the development of job descriptions, which meet the needs of the organization (Kaufman, 2006).
From the research that has been conducted, it must be stressed out that different organizations apply different job evaluation techniques, depending on a number of factors within the organization. Such factors are size and the available resources set aside to carry out the evaluation process.
From the reviews made and from the information gathered from my peers, I would recommend the use of a point factor system of evaluation for the organization. Although it has been used for a long time, it is more efficient as compared to modern systems. I propose this system to Tech Plaza, since it is a relatively large organization with various job positions and responsibilities. The organizations need a job evaluation system that will cover all these positions.
The point factor system is, therefore, appropriate since it will classify the jobs into factors. It is appropriate because it will ensure that the evaluation process is conducted thoroughly. It is also efficient as it is not biased since the person, carrying out the evaluation process assigns the total points that can be awarded even before the compensable factors get into the equation. The system is also easy to apply, hence, it is the most appropriate system to choose.
Heartfied, S. (2010). Conduct a job evaluation . Web.
Kaufman, L. (2006). Job evaluation systems: concepts and issues . Kingston, Ont.: Industrial Relations Centre, Queen’s University at Kingston.
Milkovich, T. (2010). Compensation . Georgia: South University.
Otis, J. & Leukart, R. (2004). Job evaluation, a basis for sound wage administration . New York: Prentice-Hall.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2023, December 9). Benchmarking on Job Evaluation. https://ivypanda.com/essays/benchmarking-on-job-evaluation/
"Benchmarking on Job Evaluation." IvyPanda , 9 Dec. 2023, ivypanda.com/essays/benchmarking-on-job-evaluation/.
IvyPanda . (2023) 'Benchmarking on Job Evaluation'. 9 December.
IvyPanda . 2023. "Benchmarking on Job Evaluation." December 9, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/benchmarking-on-job-evaluation/.
1. IvyPanda . "Benchmarking on Job Evaluation." December 9, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/benchmarking-on-job-evaluation/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Benchmarking on Job Evaluation." December 9, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/benchmarking-on-job-evaluation/.
- Explanation of the Benchmarking Key Concept
- Strategy: The Benchmarking Program
- Key effectiveness measures of implementing benchmarking process in oil and gas industry
- Comparing and Contrasting Models of Change Management
- HR Department Selection and Recruitment Functions
- Managing Globalisation: A Case of Indesit
- The Five Most Important Questions by Peter Drucker
- Both, Derek. “What is Change Management”.
Evaluation Essay
Evaluation Essay - Definition, Examples, and Writing Tips
13 min read

People also read
Learn How to Write an Editorial on Any Topic
Best Tips on How to Avoid Plagiarism
How to Write a Movie Review - Guide & Examples
A Complete Guide on How to Write a Summary for Students
Write Opinion Essay Like a Pro: A Detailed Guide
How to Write a Thematic Statement - Tips & Examples
How to Write a Bio - Quick Tips, Structure & Examples
How to Write a Synopsis – A Simple Format & Guide
How to Write a Comparative Essay – A Complete Guide
Visual Analysis Essay - A Writing Guide with Format & Sample
List of Common Social Issues Around the World
Writing Character Analysis - Outline, Steps, and Examples
11 Common Types of Plagiarism Explained Through Examples
Article Review Writing: A Complete Step-by-Step Guide with Examples
A Detailed Guide on How to Write a Poem Step by Step
Detailed Guide on Appendix Writing: With Tips and Examples
Are you unsure about what it takes to evaluate things from your perspective in an evaluation essay?
If you’re having a hard time understanding how to present a balanced assessment of the subject, worry not! We are here to help you get through the evaluation essay writing process.
In this blog, you will learn all about evaluation essays. From the definition, writing process, topics, tips, and a lot more, you’ll learn how to write an evaluation essay effortlessly!
Continue reading to get a better idea.
- 1. What is an Evaluation Essay?
- 2. Evaluation Essay Structure
- 3. How to Start an Evaluation Essay?
- 4. How to Write an Evaluation Essay?
- 5. How to Format Your Evaluation Essay?
- 6. Evaluation Essay Examples
- 7. Evaluation Essay Topics For College Students
- 8. Evaluation Essay vs. Review
What is an Evaluation Essay?
Let’s first understand the evaluation essay meaning, here is the standard definition:
An evaluation essay offers a value judgment or an opinion of something. It presents an overall view of a particular subject’s quality. Moreover, it provides a critical analysis and a complete evaluation of something.
What is the Purpose of an Evaluation Essay?
The main purpose of an evaluation essay is to present an opinion and evaluate a topic critically. This type of writing determines the condition, worth, or significance by careful appraisal and study.
This essay features the writer’s opinion, but when done correctly, it does not sound opinionated. Instead, it provides the facts and evidence to justify the opinions about the essay’s subject.
To write a good evaluation essay, you need to master critical evaluation and present the evaluation in an unbiased manner. You may also discuss both the pros and cons of the subject.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job
Evaluation Essay Structure
The four different ways to format and organize the evaluation essay are as follows.
1. Chronological Structure
It is a sequential organization that could be used for evaluating historical or current events. It tells how something works and assesses the effectiveness of a mechanism, procedure, or process.
2. Spatial Structure
The spatial organization structure is used for evaluating or describing art or architecture. Here, you will define one element of the artifact and spatially move to the next.
3. Compare and Contrast Structure
The compare and contrast structure is used to evaluate or review the culinary or music genre. Here the writer evaluates a subject by comprising and contrasting it with the known subject.
4. Point-by-Point Structure
The point-by-point structure is also used for culinary and music reviews. But, in this structure, you describe one element and then evaluate it, describe the second element and evaluate it, and so on.
After setting the criteria and collecting evidence for strengthening your judgment, you’ll start your evaluation essay. Let’s see what are the steps involved in starting an evaluation essay.
How to Start an Evaluation Essay?
When you start writing an evaluation essay, grabbing the reader’s attention is essential. For this, hook the reader from the beginning until the end to ensure that your essay’s opening follows an engaging tone.
Step 1. Choose an Interesting Topic
Deciding the topic and evaluation essay criteria is important. Make sure it's not just compelling and interesting, but also informative so that you can find enough material for a detailed evaluation.
Step 2. Set the Evaluation Essay Criteria
For an evaluation essay, you have to set the criteria for evaluation first. Criteria are the standards or measures by which someone assesses the quality or value of the subject.
Some key points to establish the criteria are:
- Identifying relevant aspects that relate to the subject
- Defining the criteria clearly so that it is specific and understandable for readers
- Your criteria should be directly relevant to the nature of the subject
- Always consider the audience’s expectations and standards while setting the criteria
- Your thesis statement should always align with your evaluation criteria
Step 3. Collect Evidence for Your Judgment
The author’s judgment of the subject states whether the subject is good or bad. It is an overall assessment or the opinion supported by the evidence. The judgment corresponds to the benchmarks set by the author in the essay criteria.
The evidence is a combination of supporting data and facts. Using the evidence, the author demonstrates how well the subject meets the judgment. The evidence serves as the foundation of your evaluation.
Without providing strong and accurate evidence, you will not be able to convince the readers of your judgment.
Step 4. Decide the Essay Structure
After that, decide on the structure that you want to follow. It can be a chronological or point-by-point structure
Step 5. Craft the Essay Outline
When you create an essay outline , evaluate what should be added and removed. If you skip this step before writing, you may lose track of what to include in your essay while you write.
So, writing an outline for your evaluation essay is a critical step that eases your writing journey.
Here is a sample evaluation essay outline:

Step 6. Declare Your Thesis Statement
For an evaluation essay that keeps the reader hooked from the start, opt for a catchy thesis statement . The thesis should state the main point of the evaluation.
In the thesis statement, you should always express your stance on the subject clearly. In doing so, the readers will have a clear idea about the purpose and direction of your essay.
Now, understand how to write an evaluation essay by following the detailed procedure mentioned below.
Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers!
How to Write an Evaluation Essay?
Here is a step-by-step guide for you to write an evaluation essay.
Step 1. Write the Introduction
The introduction is the first impression your readers will have of you, so it's crucial to make a good one. It should capture attention and excite readers, drawing them into what you have to say about this topic.
The following are the elements that you should consider while writing the introduction:
- Start with an interesting hook statement so that you can get the reader’s attention.
- Provide background information about the topic for the reader to understand the subject
- Establish the evaluation essay thesis statement. It sets out the overall purpose of the evaluation, so make sure it is apparent and to the point
Read this evaluation essay introduction example, and you’ll understand exactly what to pen down in yours:
Step 2. Draft the Body Section
The body of the essay consists of three paragraphs. Each paragraph holds different ideas related to one another and flows smoothly from start to finish, just like how a good story should be told.
Here are the important points that must be included in the body paragraphs.
- Start with the topic sentence that presents your judgment about the topic
- Present the supporting evidence to back up the topic sentence and your viewpoint.
- Present a balanced evaluative argument to show impartiality
- Compare and contrast the subject to another subject to show the strengths and weaknesses
- Present the evaluation from multiple perspectives, while being both positive and critical
- Always use transition words between your paragraphs to ensure a smooth and coherent flow for the reader.
Step 3. Write the Conclusion
It is the final chance to convince your reader to agree with your point of view. You’re supposed to summarize and conclude the essay. In the conclusion , you present your final evaluation of the essay.
Keep in mind the following aspects while writing a closing paragraph of an evaluation essay.
- Summarize the points and evaluative arguments that you made in the body section.
- Justify your thesis statement.
- Provide a concrete and secure conclusion to your argument by ultimately leaving the reader convinced by your evaluation.
Step 4. Proofread, Revise, and Edit
The final step is proofreading and editing. Always spend enough time reading your essay carefully. It will help you catch the unintentional mistakes you have made and recover them. If needed, you can also revise your essay 2–3 times.
How to Format Your Evaluation Essay?
For formatting your evaluation essay, follow the standard academic writing guidelines. You can opt for different formatting styles like APA, MLA, or Chicago.
In general, you should stick to the below formatting guidelines:
Font and Size:
- Use a legible font such as Times New Roman or Arial.
- Choose a standard font size, often 12-point.
- Set one-inch margins on all sides of the paper.
- Double-space the entire essay, including the title, headings, and body paragraphs.
- Create a title for your essay that reflects the subject and purpose of the evaluation.
- Center the title on the page.
- Use title case (capitalize the first letter of each major word).
- Include a header with your last name and page number in the top right corner.
- Follow the format “Last Name Page Number” (e.g., “Smith 1”).
Citations (if applicable):
- Include citations for any sources used in your evaluation.
- Follow the citation style specified by your instructor or the required style guide (APA, MLA, Chicago).
Counterargument (if included):
- Clearly label and present any counterargument.
- Provide a well-reasoned response to the counterargument.
References or Works Cited Page (if applicable):
- Include a separate page for references or a works cited page if your essay includes citations.
- List all sources in the appropriate citation style.
Well, the time has come to look at some great evaluation essay examples. Getting help from sample essays is always a great way to perfect your evaluation papers.
Evaluation Essay Examples
Evaluation can be written on any topic, i.e., book, movie, music, etc. Below, we have given some evaluation essay examples for students:
Evaluation Essay Sample PDF
Movie Evaluation Essay Example
Critical evaluation Essay Example PDF
Product Evaluation Essay PDF
Source Evaluation Essay Example PDF
Employee Self-Evaluation Essay Example
How to Start A Self-Evaluation Essay Example PDF
Evaluation Essay Topics For College Students
For writing an amazing evaluation essay, the first thing that you require is an essay topic. Here are some incredible topic ideas for college students. You can use or mold them according to your preference.
- Artificial intelligence's impact on society: A double-edged sword?
- Evaluate the online teaching and on-campus teaching styles
- Analyze and evaluate the Real Madrid football team and their performance
- Is media a threat to cultural cohesion or a source of enrichment?
- Compare and evaluate recorded music and live performance
- Evaluate how a university's football team impacts students' personalities
- Critically evaluate a remake of an original movie you have watched recently
- Analyze how the roles of females and males changed in recent romantic movies
- Evaluate your favorite restaurant, its food, aroma, and everything
- Critically evaluate gender disparities in college majors and career choices.
Evaluation Essay vs. Review
At first glance, an evaluation essay might look like a review. But, there are some notable differences between them. See this table to see how both pieces of writing differ from each other.
To conclude,
After reading the step-by-step guide and examples, you must have learned the art of writing a good evaluation essay. We’re confident that you’re now able to provide a balanced and effective evaluation of the topics you choose for your essay.
But writing a perfect essay is not that simple; you require a lot of practice and experience to become a good writer. That is why we are here to help you write any type of academic essay.
MyPerfectWords.com is a writing service that offers help for all academic writing assignments. We have a team of professional writers who are experts in writing all types of essays and evaluation papers.
So what are you waiting for? Buy custom essay online and have a sigh of relief!
Frequently Asked Questions
1. what are the four components of an evaluation essay.
The four components of an evaluation essay are:
- Introduction
- Background information
2. What are the 4 types of evaluation?
The four types of evaluation are:

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Dr. Barbara is a highly experienced writer and author who holds a Ph.D. degree in public health from an Ivy League school. She has worked in the medical field for many years, conducting extensive research on various health topics. Her writing has been featured in several top-tier publications.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading
Job evaluation as a mechanism for achieving the fairness of a wage structure in the administrative system: theoretical perspectives
Journal of Humanities and Applied Social Sciences
ISSN : 2632-279X
Article publication date: 16 August 2021
Issue publication date: 31 January 2023
This paper aims to present a theoretical framework which reveals the relationship between job evaluation (JE) and the development of fair wage structure from the organizational justice (OJ) perspective. It focuses on analyzing the dimensions of job-based pay structure and the use of multifaceted construct of OJ (procedures, distribution and interaction) to determine how the perceived justice of JE's multi-levels construct contributes to achieve the fairness of wage structure.
Design/methodology/approach
This paper adopts an analytical descriptive approach in terms of explaining the perspectives and viewpoints related to the analysis. This paper is based on examining a theoretical framework provided by the authors based on a theoretical review of literature and a set of empirical evidences.
The design of a hierarchical wage structure counts on the multidimensional approach of JE which consists of three dimensions (processes, outcomes and social system). In addition, the determination of wage structure fairness is dependent on the assessment of the perceived justice of: JE's procedures, wages distribution and management's treatment with its employees.
Originality/value
This study provides a new theoretical contribution in studying the relationship between JE and the design of fair wage structure. This contribution can be regarded as a theoretical foundation for conducting some empirical and comparative studies in the future. The study affords directive mechanisms to policymakers in order to enhance the fairness of the wage structure across the state.
- Job evaluation
- Wage structure
- Administrative system
- Theoretical perspectives
El Balshy, S.A.E.M. and Ismael, M. (2023), "Job evaluation as a mechanism for achieving the fairness of a wage structure in the administrative system: theoretical perspectives", Journal of Humanities and Applied Social Sciences , Vol. 5 No. 1, pp. 3-19. https://doi.org/10.1108/JHASS-02-2021-0038
Emerald Publishing Limited
Copyright © 2021, Suzan Abd El Moneim El Balshy and Mamdouh Ismael
Published in Journal of Humanities and Applied Social Sciences . Published by Emerald Publishing Limited. This article is published under the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY 4.0) licence. Anyone may reproduce, distribute, translate and create derivative works of this article (for both commercial and non-commercial purposes), subject to full attribution to the original publication and authors. The full terms of this licence may be seen at http://creativecommons.org/licences/by/4.0/legalcode
1. Introduction
JE is a systematic and consistent approach, which its main objective is to develop fair wage grades corresponding to consistent job levels. This objective is achieved by a set of sequent processes, fair distribution of monetary values between the similar jobs and employees' acceptance of the wage adjustment decisions. This multidimensional approach of developing a hierarchical wage structure requires enhancing “justice” across its different stages to achieve the fair wage based on the relative value of jobs among the employees performing the same job.
Although “justice” is important in developing a hierarchical wage structure, there is a scarcity of studies on employing OJ construct with its three main dimensions (distribution, procedures and interaction) in explaining the relationship between JE and the development of a fair wage structure. Most studies have discussed this relationship from some restricted theoretical perspectives. For example, a number of JE scholars (e.g. Dep, 2006 ; O'Riordan, 2008 ; Choudhary, 2016 ) have examined job-based pay from the “rationality” perspective. Their analyses have revealed that the logical foundations of JE have given legitimacy for taking consistent decisions and judgments toward the determination of a fair wage. While El- Hajji's (2011) study findings have suggested the possibility of achieving the wage fairness in the context of JE scheme through both the internal and external “consistency” of wages. As for the field study of Jones et al. (1999) , although they have indicated that pay increase is associated with the fairness of JE procedures, their analytical perspective was strictly limited as they have discussed JE as well as other practices related-pay (e.g. performance). Moreover, their study has lacked the theoretical conceptualization of JE in the context of procedural justice.
We, the authors, have argued that this is a worthy subject of research because it provides a conceptualization of multidimensional approach of job-based pay in the context of the three dimensions of OJ (procedural, distributive, interactional justice), which helps to determine the mechanisms required for designing a fair job and wage structure. Since it represents a new theoretical contribution for both JE and OJ literature, it will add value to JE literature (e.g. Armstrong and Baron, 1995 ; Armstrong and Murlis, 2007 ). Because it underpins the arguments advocating job-based pay, on one hand, and acts as an extension to the very small number of OJ literature, such as Jones et al. study (1999) , on the other hand. This theoretical framework may be criticized or improved by scholars and by pursuing new avenues of inquiry. Besides, they may employ the suggested theoretical structure as a foundation for conducting further empirical and comparative studies in the future. Therefore, this contribution will fill in the theoretical gap in the public administration literature.
Accordingly, the purpose of this paper is to investigate the extent to which the OJ theory is used to explain the relationship between JE and the development of a fair wage structure. We have structured this paper in a way that achieves this objective as follows: we begin with the theoretical framework of the study followed by a section on examining the dilemma of developing a hierarchical wage structure. Thereafter, we have discussed the rational link between JE and the design of a consistent grading, on one hand, and fair wage structure in the view of multifaceted construct of OJ, on the other hand. Finally, it concludes with results, implications of the study and a future research agenda in light of the research points of the study.
The current study introduces a theoretical structure ( Figure 1 ) reflecting the relationship between the two study variables in light of the analysis of the three dimensions of the OJ. We have built up our analysis based on the overviews of both JE's and OJ's scholars, results of justice studies and the justice theories relevant to the study objective.
2. Research methodology
Identify the structured processes of designing a hierarchical wage structure.
Discuss the two opposing sides of scholars' debate against the traditional system of job-based pay in order to identify the extent to which this paper contributes to develop the arguments advocating JE technique.
Examine the logical link between JE and the development of fair wage structure through the analysis of dimensionality of job-based pay in view of its rational framework and associated organizational implications, and the development of conceptualization of job-based pay through the use of multifaceted construct of OJ (procedures, distribution and interaction).
3. Theoretical framework of the study
It addresses the definitions, systematic approach of JE and the administration of a hierarchical wage structure as follow:
3.1 Concepts and definitions
3.1.1 definition of job evaluation.
Some scholars have defined JE as the determination of job importance, or its relative weight, compared to other jobs. This could be attained by analyzing and describing jobs that clarify duties and responsibilities of a specific task or conditions, which should be met by a jobholder ( Hashem, 1989 , p. 314).
Furthermore, Omran (1997 , p. 210) has focused on evaluating the quality of a job, or its relative worth, compared to other jobs in the organization through job analysis. This analysis has revealed the nature of the duties and responsibilities of the job and the conditions expected from those who are performing it.
Bose (2012 , p. 245) has described JE as a methodological procedure for identifying the relative size of jobs within an organization and for establishing a consistent wage structure.
It can also be defined as “a process of identifying and measuring the factors (competencies), in each job, for which compensation is paid” ( Eargle, 2013 , p. 16). Another definition adopted by ILO (1982 , p. 60) has made a similar assertion; whereas it is “a method of studying and grading jobs in order to provide a basis for a fair wage structure.”
From our perspective, JE can be defined as a systematic process aims at determining the relative value of a job compared to others. This process depends on the results of the job analysis that produce both the job description and specification. As such, the difference in job values is counterbalanced by differences in wage levels.
3.1.2 Definition of a fair wage structure based on the relative value of jobs
We have attempted to develop the definition of a fair wage structure based on the relative worth of jobs by examining the following definitions:
3.1.2.1 Definition of a fair wage
According to Merriam-Webster Dictionary (2019) , a fair wage is defined as “a wage that is reasonable for the type of work done.” In the economics field, researchers consider wage rates to be fair in two aspects: the first takes the narrower perspective and when similar employees in the same industry receive wages equal to the current rate. Pigou (1985 , p. 436) has embraced another aspect, which was related to the broader perspective and considered the wage rate to be fair when it is equal to the prevalent rate for similar work throughout the country and in the generality of trades.
In the administration field, researchers address the concept from the relative value perspective of the job compared to other jobs in order to achieve the internal justice. This assumes that the increase of wage rate from one grade to a higher one, in the wage scale, will be commensurated with the increase level in responsibilities and burdens added to the employee as a result of their transfer to a higher grade in the organizational structure ( Al-Shehri, 2016 , pp. 29–30).
Hence, a fair wage based on the relative value can be defined as the compensation an employee gets in exchange to the provisions of physical effort and mental power commensurately with the level of work difficulty, responsibilities and the skills required for performing the job expressed in monetary value; it includes two aspects, which are direct wages and other material on one hand and in-kind benefits on the other hand. Moreover, it is similar to the wage paid to the same work within and outside the organization.
3.1.2.2 Definition of wage structure
Researchers have agreed that wage structure represents the next step in job evaluation. This is because pay categories are identified according to the job hierarchy. Accordingly, it is defined as the sequence of jobs, in an orderly manner, based on the value of each job in relation to other jobs with specific pay rates, whereas, in the organization, jobs are arranged from the top to the bottom according to their relative importance. Consequently, wage rate is determined, separately, for each job ( Hussnein, 2014 , p. 89).
The different levels of pay for jobs or groups of jobs by referencing to their relative internal value as determined by job evaluation and to external relativities as established by market rate surveys. Sometimes to negotiate rates for jobs, they provide scope for pay progression in accordance with performance, competence, contribution or service.
Al-Khair and Al-Mikhlafi (2006) have pointed out that wage structure is related to the job pricing through identifying wage grades according to job levels in order to identify the monetary value representing the numerical value of the job.
From an analytical study of the above definitions, we may conclude a comprehensive definition of a fair wage structure based on the relative value as a determination of fair wage grades in relation to consistent job levels that are identified by its internal relative values based on JE. Thus, the incumbents of similar jobs receive similar wages-including direct wage and in-kind benefit-throughout the State.
3.2 Systematic approach of JE: processes and implementation steps
The systematic approach of JE will be discussed, in terms of highlighting its processes and implementation steps, as follows:
3.2.1 Job evaluation processes
Job analysis : It identifies the duties, responsibilities, working conditions and roles of a job. Such information produce both job description and job specifications.
Job rating: This includes assigning the relative score of each job in relation to other jobs and ranking their values.
Money allocation : It is concerned with determining the money rate of wages to each job according to its relative size.
Job classification : It involves grading different jobs into certain categories of scale of pay.
3.2.2 Implementation steps of job evaluation
Preparation: This stage involves the drafting of implementation program, selection of adequate methods and training of all the involved parties.
Analysis and evaluation : This stage aims to announce the objective of JE and collect information before producing job descriptions.
Developing wage structure : The design of the final wage structure is formulated based on the evolution and pricing of grades.
Implementation and control : The management seeks to achieve a final agreement with the employees' representatives on the procedures required for implementing the suggested wage structure.
3.3 Administration of a hierarchical wage structure: guiding principles and steps
The design of a suggested/new wage structure, according to JE's systematic methodology, is based on two aspects:
3.3.1 Guiding principles of a hierarchical wage structure
Simplify managing job and pay relativities.
Enhance fairness, consistency and transparency in identifying the pay rates and managing both the job and wage structure.
Allow jobs to be properly graded and not subjected to grade drift.
Define the pay levels and the scope as required for pay progression.
Enable the organizations to control the implementation of wage policies and budgets.
3.3.2 Steps of designing a hierarchical wage structure
First: clustering jobs to set pay ranges.
Second: calculating range spreads.
Third: determining range progressions.
Fourth: identifying the grades number and pointing difference between the grades.
Fifth: costing the salary structure.
Generally, it is clear that designing a hierarchical wage structure depends on an objective, rational and standardized methodology of JE that acts as a reasonable mechanism underpinning the fairness of wage structure through taking consistent decisions regarding the development of internally consistent job hierarchy and, accordingly, the determination of related wage grades.
4. Dilemma of developing a wage structure based on the relative value of jobs
Through the literature review, we have found much controversial debate, between both opponents and proponents against job-based pay. Their arguments have centered on four aspects as follows (as shown in Table 1 ).
Focus is the first point of difference, where performance-based pay rewards employee for the skills they possesses rather than the responsibilities of the job as a case in the traditional system, where the emphasis is on the employee's job title or grade ( Baldwin, 2003 , pp. 49, 77; Eargle, 2013 , p. 128).
Arguably, the most fundamental reason for applying JE is to design an equitable and defensible wage structure. The proponent scholars (e.g. Armstrong and Baron, 1995 ; Armstrong and Murlis, 2007 ; El-Hajji, 2011 ) have settled on the advantages of JE as a rational and objective tool seeking to produce order out of chaos and establish the internal relativities of jobs based on consistent judgments. Moreover, it assists organizations to meet their legal and ethical obligations against the principle of “equal pay for work of equal value” by using the analytical schemes that facilitate frameworks to be designed in a way that underpins judgments on grading jobs and, therefore, pay rates.
However, the opponent scholars ( Baldwin, 2003 ; Ledford, 1995 ) have advocated the new-pay system as it intends to reinforce the organization's strategic goals and encourage the development of employees' skills and learning opportunities. Thus, base pay is identified according to the number of jobs individuals can perform.
Third, perhaps it is the most significant difference, it is the disadvantages of both systems; the advocating views of new pay model (e.g. Baldwin, 2003 ; Lawler, 1995 ; Eargle, 2013 ) have criticized JE to restrict individuals' duties and responsibilities to the job description; consequently, it limits individuals' creativity. They have argued that JE focuses on internal pay relations and works against strategic and competitive pay. In addition, JE can create undesirable power relationships in the organization. Furthermore, they have believed that the notion of paying, according to the job content, is an outmoded idea to pay in the context of market-oriented approach. Similarly, an empirical study ( Maycock, 2009 ) has revealed that the new pay system also has disadvantages as it may reduce pay equity and include unfairness in the evaluation process due to the inaccurate measurements and managers' subjectivity. This indicates that employees are also being controlled via reward system.
Finally, compared to job-based pay, the new model is more adequate to the flatter organizations with fewer promotional levels while the traditional model promotes a bureaucratic approach that adheres to the organizational rigidity and hierarchy (as cited in Armstrong and Baron, 1995 , p. 44).
Despite the preceding criticisms against job-based pay mode, it is still the most attractive mechanism for some governments that attempt to reform both their job and wage structures. For example, Egypt has recently taken a set of arrangements to reform the traditional approach of job-based pay model, which has been implemented by virtue of decision No. 134 of 1978 ( Amin, 2019 ). Additionally, the head of Central Agency for Organization and Administration (hereinafter referred as CAOA, 2019b ) has issued a decision No 35 of 2019. This decision aims at reviewing job description cards, evaluating jobs and job budget forms (Form No. 5) and studying the proposals introduced by the administrative units, whether to establish and re-evaluate jobs or to examine self-financing proposals for jobs at different levels ( CAOA, 2019a ). The traditional model of the Egyptian case focuses on the job titles (e.g. “floor supervisor,” “clerk-typist,” “machine operator”) and assigns a pay scale to these jobs. Additionally, the wages of supervisory jobs, for example, may also take into account the number of employees being supervised. As for pay progression, it is based on the time spent on the job (Decision No. 35 of 2019). These characteristics are completely different from performance-based pay model, where pay levels are established on the basis of skills and knowledge required to perform the task and are higher compared to job-based pay ( Baldwin, 2003 ).
With respect to the discussions mentioned earlier, we have observed that most scholars' discussions focused on JE's rationality and its main function on grading jobs within a grade structure and developing a consistent wage structure. Hitherto, no research has examined how the multidimensional construct of OJ contributes to underpin the “fairness” of a hierarchical wage structure. Accordingly, we hope our theoretical structure, which will be discussed in the following section, adds a value in this regard.
5. Relationship between JE and the development of a fair wage structure in the context of OJ construct
In this section, we provide a theoretical structure ( Figure 1 ) that addresses the link between JE and the development of a fair wage structure from OJ perspective. This framework will be discussed through the analysis of the following aspects:
5.1 Dimensionality of job-based pay
We believe that the analysis of JE dimensionality structure will aid in determining whether the process of developing a hierarchical wage structure is a uni- or multi-dimensional. This examination will act as a basis for developing a conceptualization of the perceived justice toward a hierarchical wage structure. The items for this dimensionality will be generated by analyzing the seminal work in the JE literature relevant to both the rational framework of JE and its associated organizational implications.
5.1.1 Rational framework of job-based pay
Most of the management scholars view JE as a systematic and consistent approach underpinning the principle of “equal pay for work of equal value.” For example, Dep (2006 , p. 285) has indicated that JE is a systematic approach of ordering jobs with regard to their relative size to the organization. In addition, it is a technique for obtaining job facts, analyzing jobs, preparing job description cards and conducting assessments and comparisons. Hence, it provides a reasonable basis for comparing the relative size of jobs; therefore, it defines their internal relativities of jobs and taking consistent decisions of grading jobs within a grade structure. In this context, Choudhary (2016 , p. 92) have emphasized that these structured procedures aimed at studying the requirements of jobs and establishing a specific scope for their measurement to create a hierarchy of jobs.
Moreover, Quaid (1993 , p. 223) has viewed JE as a rational process which is processed by rational people, who have developed rational and acceptable standards that allow rational results to be achieved. Therefore, this rational part of JE helps laying the rationale for addressing the wage's issues. In this framework, Armstrong and Baron (1995 , pp. 16-17) have observed that organizations have taken initiatives to apply a JE technique in order to improve rational judgments rather than the political ones in assigning wages.
5.1.2 Associated organizational implications of developing a hierarchical wage structure
The implementation of JE technique has deep implications on the organization, such as the management's decision to objectively update or re-evaluate the job description, if it is inaccurate ( Picardi, 2019 , p. 110). Furthermore, Joffe (1989 , p. 289) has demonstrated that JE's application has also a notable impact on changing the organizational structures relevant to grading structure and correcting relations among various jobs. He believed that a grade structure with defined point ranges represents a means for grading both new and changing jobs.
Within this framework, the organizations may take a decision either to develop a new grading structure, if the current one is discredited or out-of-date, or redesign the existing grading structure, if the existing one is formally established; sometimes as what takes place in the public sector ( Armstrong and Baron, 1995 , pp. 344-345).
Other scholars ( O'Riordan, 2008 ; Joffe, 1989 ) have indicated that such consistent decisions, on grading jobs in the structure and setting pay rates, may influence the relationship between the management and employees if they do not accept and support these decisions as fair and equitable.
Thus, the management decisions regarding wage grades modification may raise employees' concerns of perceived inequity in the new order. In this case, the organization should establish an agreed procedure to limit employees' grievances ( Joffe, 1989 , p. 285). Hence, the organization should determine, before the announcement of any initial results, how to deal with the employees' appeal ( Dep, 2006 , p. 287).
Sequent processes and steps : It refers to the implementation of JE.
In conjunction with a group of administrative activities, such as collecting information, analyzing jobs, preparing job description cards and selecting JE's criteria. The veracity of every process is dependent on the accuracy of the preceding step.
Logical outcomes : It indicates that the application of JE's processes and steps lead to some organizational consequences regarding establishing the internal relativities, grading jobs, identifying the range of job weight.
The social system : It provides the context of human interaction between the management and employees that generates either the acceptance or objection of the management's decisions.
Preparation level : At this level, the management may take a decision to review or update an inaccurate job description.
Outcomes level : The most notable changes that are correlated with JE implementation are correcting the complex relation between jobs and pricing jobs according to the new job levels.
Relations level : It reflects the degree by which the management takes a set of arrangements to deal with the employees' appeal, such as providing them with opportunities to participate in the decision making process or establishing an approved mechanism for dealing with their complains.
5.2 Conceptualization of job-based pay in the context of OJ construct
The main objective of examining the OJ is to determine how the perceived justice of JE procedures, distribution of wages based on the relative value and the organizational communication between managers and employees, is formed. It also attempts to identify how the fairness of new wage structure, is assessed.
5.2.1 Content and multidimensionality of OJ
OJ concept has received a great attention from the management scholars. According to Baldwin (2006 , p. 1), OJ is “the extent to which employee perceives workplace procedure, interactions and outcomes to be fair in nature.” Scholars have studied two, three and even four dimensions of OJ in the literature. However, the current study depends on Greenberg's (1990) three-dimensional model, as follows:
5.2.1.1 Procedural justice
It refers to the perceived fairness of the allocation process ( Cropanzano and Bagger, 2006 , p. 590). Additionally, it focuses on the fairness of the decision process leading to a particular outcome, such as fair pay. The individuals' perception of procedural justice are likely to be promoted if they are given the chance to present evidence and voice their concerns before decisions are made ( Baldwin, 2006 , p. 2).
A significant body of studies (e.g. Greenberg, 1996 ; Thibaut and Walker, 1975 ; Leventhal, 1980 ) have indicated that providing control over the process and decision making by allowing the employees to participate in the design of reward system can produce a feeling of process justice even when the outcomes are not to their advantage. It focuses on an individual's cognitive map of events that precedes the distribution of rewards. In this setting, some empirical evidences have found a positive impact of procedural justice on determining fair pay (e.g. Cloutier and Vihuber, 2008 ; Jones et al. , 1999 ; Folger and Konovsky, 1989 ).
Consistency rule : An individual's assessment to procedural fairness may be based on the consistent application of allocation procedures across individuals and over time.
Bias-suppression rule : It is related to the degree in which decisions are based on facts not subjective feelings.
Accuracy rule : It indicates the degree in which gathering information is accurate and up to date.
Representativeness rule : It allows individuals to have opportunities to express their views before the decision is made.
Correctability rule : It is related to the opportunity to revise and modify decisions.
Ethicality rule : It indicates the decisions are not based on gender, age, etc., but on the ethical values.
Thus, based on the framework of job-based pay, the perceived justice of JE's procedures is concerned with one's perception of the JE's processes fairness regarding gathering information, analyzing and classifying jobs, selecting JE's criteria and rating jobs. Moreover, individuals may use the six criteria of Leventhal (1980) , whether to make accurate, consistent and neutral decisions and represent all basic concerns of the affected parties or to assess if the JE's processes and practices are fair or unfair.
Additionally, according to the voice criteria, the perceived fairness toward JE's practices is likely to be also enhanced by providing employees the opportunities to express their views and voice their concerns before making decisions related to reviewing job description, redesigning jobs and modifying wage grades.
5.2.1.2 Distributive justice
It refers to the individual's perception that the rewards or resources are fair when distributed in accordance with certain criteria. These criteria may require sharing rewards equally or determining the rewards according to the contributions ( Leventhal, 1980 , p. 30). Scholars have identified several distributive rules of a social nature, such as equity ( Adams, 1965 ), equality and need ( Deutsch, 1975 ) or of a historical nature (As cited in Rutte and Messick, 1995 , p. 245). In this study, we focus on the equity rule, which serves the study objective.
As it can be difficult for determining the level of reward for a particular degree of input, people tend to make this judgment in relative terms, looking for a contribution–outcome ratio that is similar to that of their peers.
Additionally, Till and Karren (2011 , p. 43) have indicated that two types of equity (internal and external) comparisons are associated with individuals occupying the same job. Internal equity focuses on comparisons among individuals doing the same job inside the organization while external equity reflects comparisons among employees in an organization with those outside the same organization.
As far as we know, the effect of distributive justice perceptions regarding job-based pay is rarely been investigated. Hence, we depend on Greenberg's (1996) study findings, which revealed the possibility of applying equity theory to a range of elements. Based on this, the individuals' perception toward the distributive justice of the wages they receive, according to the relative size of their jobs, counts on the ratio of their relative value of jobs content (input)/wages (output) is equal to the ratios of their peers. In this case, the comparison criteria will be extended to involve the employees occupying the similar jobs inside and outside the organization as indicated by Till and Karren (2011) . This comparison criterion is more adequate to the incumbents of similar jobs in the administrative systems, where some of these systems are still suffering from wage differential among employees occupying the same jobs, such as the Egyptian case – as discussed earlier.
Based on this, the perceived justice toward the distribution of job-based pay is dependent on the social comparison that represents an important source of information in which individuals rely on to decide the extent to which the distribution of wages among incumbents of similar jobs is fair.
5.2.1.3 Interactional justice
Bies and Moag (1986) have introduced interactional justice as an independent dimension. It included the provision of information that explained the reasons beyond the outcomes as well as focusing on the human interaction between the presenter and receiver of justice. Moreover, it referred to the perceived fairness of interpersonal treatment that one receives. There are two correlated forms of this justice; first, the informational justice, which refers to the accuracy and clarity by which decision-makers justify events and explain decisions in details. Second, the interpersonal justice, which refers to the dignity and respect by which the individual is treated ( Cropanzano and Bagger, 2006 , p. 590). Both of these types were introduced as sub-parts of interactional justice. The fairness rules of the first type of justice are represented in justification and truthfulness, whereas the rules of the second type of justice are represented in respect and propriety ( Colquitt, 2001 ; Greenberg, 1990 ).
Although there are few studies that have examined the impact of interactional justice on pay fairness, some empirical evidences have demonstrated that the confidence between the management and employees acts as a strong factor in achieving pay plans and systems ( Léné, 2014 ; Ismail and Zakaria, 2009 ). Additionally, providing employees with adequate explanations and justifications has a positive influence on their behaviors ( Ismail and Zakaria, 2009 ; Greenberg, 1993 ).
Generally, we agree with justice scholars' views that employees' approval of justice-based evaluations often meet their psychological needs, such as respect, self-esteem and belonging ( Barclay and Kiefer, 2014 ; Rupp, 2011 ). Hence, employees' acceptance of the final wage structure depends on how far the individuals are treated respectfully, and whether they receive adequate explanations or justifications for decisions taken by their management, particularly, those related to wage grades modification. Additionally, this insight is aligned with JE scholars' viewpoints (e.g. Joffe, 1989 ; Dep, 2006 ), which clarifies that the absence of communication between the management and employees may raise the concerns regarding perceived inequity. Accordingly, the interactional justice, with its both types (informational and interpersonal), is considered as a requirement for applying a final wage structure.
5.2.2 Overall justice
Some empirical studies have addressed the relationship between each type of justice and a broad range of individuals' attitudes. For example, Colquitt et al. (2001) have clarified that work performance is mainly related to perceived procedural justice.
Whereas other justice scholars (e.g. Goldman and Cropanzano, 2014 ; Ambrose and Schminke, 2009 ; Greenberg, 2001 ; Shapiro, 2001 ) have criticized the exclusive focus on specific types of justice.
They believed that the focus on specific dimensions of the construct does not reflect the depth of an individual's experience of justice. As a result, they have called for the overall justice which is defined as “A global evaluation of the fairness of an entity based on personal experiences as well as on the experiences of others” ( Holtz and Harold, 2009 , p. 1185). They have demonstrated that overall justice provides an accurate and complete picture of how individuals make fair judgments.
Following this aspect, Eib (2015 , p. 10) has indicated that overall justice is preferred over justice dimensions when the goal is to appraise broad outcomes (e.g. health, job satisfaction). He has postulated, “General impressions of justice are relatively stable and may only change when justice-relevant information is drastically inconsistent with the general impression.” The findings of some empirical researches ( Ambrose and Schminke, 2009 ; Beugre and Baron, 2001 ) have supported this ideology; they found that the combination of two or three dimensions of OJ are strong predictors of overall justice perception.
Furthermore, a group of justice scholars ( Ambrose and Schminke's, 2009 ; Shapiro, 2001 ) have discussed an overall justice influence on organizational phenomenon. They have demonstrated that overall justice has a positive impact on outcomes and plays a mediating role between justice dimensions and outcomes including organizational commitment and job performance.
Concerning the evaluative perceptions of overall justice, some scholars ( Van den Bos, 2001 ; Lind, 2001 ) have used the “Fairness Heuristic Theory” to introduce an explanation to how employees form their perception toward overall justice. According to their analysis, the amount of information, available to employees, enable them to make conscious assessment of fairness. Even in the case of insufficient or less relevant information, individuals use other information, whether related to procedural or outcomes, to assess what is fair. In other words, people use available justice information to form their fair impression of outcomes.
According to the preceding analysis, we believe that the concentration on a particular dimension of determining the wage structure fairness based on the relative worth or size of jobs – as a different independent practice – may lead to embarrassing outcomes. As for the overall justice assessment the general assessment (e.g. Eib, 2015 ; Beugre and Baron, 2001 ; Shapiro, 2001 ), according to the information availability ( Van den bos, 2001 ; Lind, 2001 ), regarding JE's procedures and wage distribution among similar jobs, it will produce a holistic and accurate judgments toward the hierarchical wage structure fairness. These general justice experiences may act as a mediating role ( Ambrose and Schminke, 2009 ; Shapiro, 2001 ) between the perceived justice of JE's procedures, the distribution of job-based pay and the human interaction between the managers and employees on one hand, and the acceptance of a new wage structure as a fair organizational outcome on the other hand (see Figure 1 ).
6. Findings, recommendations and future research agenda
6.1 conclusion.
The current research has examined the relationship between JE and the development of a fair wage structure by developing a comprehensive definition of fair wage structure based on the relative worth of jobs. Moreover, it has discussed the methodological foundations for identifying the internal relativities of jobs, establishing consistent job levels and designing a hierarchical wage structure. In this paper, we have examined the insights and discussions raised by management scholars toward both traditional and new pay systems to determine to what extent the study findings contribute to the current debate. Finally, we have used OJ theory and other related intellectual perspectives of both JE's and OJ's scholars to develop an understanding of how the JE multidimensional approach underpins the “fairness” in designing a wage structure.
6.2 Findings
Results demonstrate that JE, as a management technique, seeks to manage the internal relativities of jobs and identify pay rates based on rational judgments. It is not a “one and done” activity. As it correlates with a set of administrative schemes (e.g. collecting information, job description, rating the jobs), which by turn, represents the input of JE.
Moreover, results indicate that the proponents of job-based pay model have adopted, basically, the “rationality” rather than the “fairness” perspective in their advocate. They view JE as a an effective mechanism for, rationally, fixing wages by using a logical method, which relies on a set of reasonable rules leading to make consistent decisions on grading jobs, accordingly, set pay rates.
Additionally, results emphasize that although the traditional system of job-based pay is still an area of confusion among management scholars, some governments (e.g. Egypt) has, recently, intended to re-evaluate its existing traditional approach of JE as a valuable tool dealing with the issues of wage disparity among employees in the similar jobs.
Results point out that the significant stands of the scholars' arguments, against both the traditional and new pay systems, have focused on four main elements related to focus, advantages, disadvantages and organizational shape. Accordingly, the present study adds a new aspect of discussion among the scholars. This aspect is related to the use of OJ construct in developing a fair wage structure.
Dimensionality of job-based pay : It refers to multi-levels construct of JE that consists of three main dimensions, namely, sequent processes, logical outcomes and social system. These three dimensions represent the pivotal foundations for whether developing a new grading structure or redesigning an existing one. Each dimension is affiliated with a set of organizational implications. This means that there are three levels of changes (preparation, outcome and relation), which are parallel to JE's dimensions, as shown in Figure 1 .
– Consistency: It refers to the need for determining the relative and monetary values and pay ranges of similar jobs in a similar way.
– Bias suppression : It requires the raters objectivity and the application of JE technique, which should be based on facts not gender nor any subjective preferences, such as evaluating jobs according to gender occupying these jobs (direct bias) or making JE's judgments according to the discriminatory of current wages (indirect bias).
– Accuracy : It is related to the accuracy of information relevant to JE's policies and practices, such as those related to job analysis and description. It should reflect the reality and be up to date to take decisions correctly.
– Representativeness : It refers to the capacity of the organization to represent employees' concerns of wage adjustment, for instance, within the executive committees and JE units.
– Correctability : The organization's tendency to revise and evaluate the employees' complaints and grievances to make equitable decisions about re-assigning job-linked scores, redesigning jobs and modifying wage grades.
– Ethicality : The compatibility of decisions, which are related to the assignment of jobs' numerical and monetary values on one side and moral and ethical values, on the other side, regardless the age, gender, etc.
Distributive justice of job-based pay: It seeks to employ the equity rule ( Adams, 1965 ) to form the individuals' perception against job-based pay. This will be through providing them with information related to their peers' wages in order to compare their wage (outcome)/relative value of job content (input) ratio with other employees' ratio (referents), who occupy the same jobs with the same skills inside and outside the organization.
Interactional justice of job-based pay : It reveals that the management can administer employees' grievances and objections toward its decisions relevant to wage grade modification, particularly the downgrades case, through employees' participation in decision making, treating them with respect and providing them with adequate justifications as well as sufficient information.
Overall justice toward the hierarchical wage structure: It indicates that evaluative perceptions against the final wage structure draws on the inclusive assessment of JE's procedural, money values' distributive and human interaction mechanism. This means that the available justice information, of two or three preceding dimensions, will provide more accurate and complete overview than the focus on a particular dimension.
Hence, the study suggests that a formulation of general justice experiences will act as mediation for determining whether the new wage structure is fair or unfair.
Based on aforementioned results, we believe that promoting “fairness” of job-based pay has the potential to address the different wage issues in the administrative systems. The success of achieving this objective depends on the degree of adherence to normal standards or fairness rules of job-based pay relating to procedures, distribution and organizational interaction.
6.3 Recommendations
We believe that a development of a fair wage structure at government entities, may achieve a set of advantages, such as the achievement of wage fairness between similar jobs, the governments' ability to control the wage costs and the public satisfaction and confidence toward the government policies. Therefore, we provide some recommendations as a valuable input to the Policy-makers, executive managers and HR practitioners, who are involved in job and wage structure reforms, as follows:
Policymakers have to formulate the guiding and legal frameworks of applying JE in a way that enhances the fairness, transparency and objectivity of the practices related to collecting information, conducting interviews, preparing job description cards, identifying job-related scores, redesigning jobs and dealing with upgraded and downgraded jobs, employees' complaints and transferring to equivalent grades. In addition, building an institutional and human capacity will provide both public bodies and employees with skills and tools that enable them to share information about JE's processes and its outcomes.
Additionally, they have to face the challenges concerning confidential policies of wage and take further arrangements in order to promote the policy of information disclosure in this regard. Furthermore, practitioners should pay specific attention to develop the interactive communication tools between the different stakeholders and knowledge sharing with employees on a regular basis.
Moreover, the establishment of a department for following and monitoring is a vital mechanism for ensuring the compliance of ministries, government agencies and JE units, with guiding and fairness rules. Furthermore, it ensures the conformity to the normative standards across all stages of developing a hierarchical wage structure.
Finally, our results suggest the use of the fairness standards in a way that underpins implementing consistent, accurate, objective policies and practices of job-based pay, on one hand, and reinforce both the employees' access to the information and participation in the decision making, on the other hand. This, in its turn, will assist the practitioners to assess their practices and conduct benchmarking practices.
Accordingly, taking such arrangements will reflect positively on employees' attitudes and satisfaction level; they will understand the logic behind conducting some organizational changes and taking the decisions of adjusting wage grades. Therefore, they will be able to formulate their comprehensive assessment toward the fair wage they receive.
6.4 Future research agenda
Conclusively, we, the authors, recommend some further researches related to the topic researched, such as the use of the proposed theoretical structure to make comparative studies between the traditional and the new pay systems. In addition, further researches, about assessing the fairness of a hierarchical wage structure of the single international practices between the developing and developed countries can be done.
Relationship between JE and the development of a fair wage structure in the context of OJ construct
Traditional wage structure versus new wage structure
Source(s): Prepared by the researchers
Adams , J.S. ( 1965 ), “ Inequity in social exchange ”, in Berkowitz , L. (Ed.), Advances in Experimental Social Psychology , Vol. 2 , Academic Press , New York , pp. 267 - 299 .
Al-Khair , A.T. and Al-Mikhlafi , A.W. ( 2006 ), “ The scientific foundations for achieving justice in job wage structures ”, Tishreen University Journal for Scientific Research and Studies , Vol. 28 No. 2 , pp. 3 - 20 .
Al-Shehri , M.E. ( 2016 ), Salaries and Wages Administration , Institute of Public Administration , Riyadh .
Ambrose , L.M. and Schminke , M. ( 2009 ), “ The role of overall justice judgments in organizational justice research: a test of mediation ”, Journal of Applied Psychology , Vol. 94 No. 2 , pp. 491 - 500 .
Amin , E. ( 2019 ), “ An international perspective of job grading in the Egyptian administrative system ”, Review of Economics and Political Science .
Armstrong , M. ( 2007 ), A Handbook of Employee Reward Management and Practice , 2nd ed. , Kogan Page , London .
Armstrong , M. and Baron , A. ( 1995 ), The Job Evaluation Handbook , 1st ed. , CIPD Publishing , London .
Armstrong , M. and Murlis , H. ( 2007 ), Reward Management: A Handbook of Remuneration Strategy and Practice , 5th ed. , Kogan Page , London .
Armstrong , M. and Taylor , S. ( 2017 ), Armstrong's Handbook of Human Resource Management Practice , 14th ed. , Kogan Page Publishers , New York .
Baldwin , D.A. ( 2003 ), The Library Compensation Handbook: A Guide for Administrators , Librarian and Staff, Libraries Unlimited , Westport .
Baldwin , S. ( 2006 ), “ Organizational justice, institute of employment ”, available at: https://www.employment-studies.co.uk/system/files/resources/files/mp73.pdf ( accessed 22 August 2020 ).
Barclay , J.L. and Kiefer , T. ( 2014 ), “ Approach or avoid? Exploring overall justice and the differential effects of positive and negative emotions ”, Journal of Management , available at: file:///C:/Users/nour/AppData/Local/Temp/barclayandkieferJoMinpress.pdf ( accessed 7 May 2020 ).
Beugre , C.D. and Baron , R.A. ( 2001 ), “ Perceptions of systemic justice: the effects of distributive, procedural, and interactional justice ”, Journal of Applied Social Psychology , Vol. 31 No. 2 , pp. 324 - 339 .
Bies , R.J. and Moag , J.F. ( 1986 ), “ Interactional justice: communication criteria of fairness ”, in Lewicki , R.J. , Sheppard , B.H. and Bazerman , M.H. (Eds), Research on Negotiation in Organizations , JAI Press , Greenwich, CT , Vol. 1 , pp. 43 - 55 .
Bose , D.C. ( 2012 ), Principles of Management and Administration , 2nd ed. , PHI Private Learning , New Delhi .
CAOA ( 2019a ), “ Job grading ”, available at: http://www.caoa.gov.eg/WebForms/ContentPages.aspx?Vu2z2OiuNisTYC61MG92SjlY/s5/mQYEBBJlmQbeF5Q ( accessed 6 June 2019 ).
CAOA ( 2019b ), “ Decision No35 of 2019 ”, available at: http://www.caoa.gov.eg/App_Files/Uploads/Attachments/1558519941.pdf ( accessed 28 April 2021 ).
Chaneta , I. ( 2014 ), “ Effects of job evaluation on decisions involving pay equity ”, Asian Social Science , Vol. 10 No. 4 , pp. 145 - 152 .
Choudhary , S. ( 2016 ), “ Job evaluation: a strategy for compensation consistency ”, International Journal of Advanced Research in Management and Social Sciences , Vol. 5 No. 5 , pp. 90 - 100 .
Cloutier , J. and Vihuber , L. ( 2008 ), “ Procedural justice criteria in salary determination ”, Journal of Managerial Psychology , Vol. 23 No. 6 , pp. 713 - 740 .
Colquitt , J.A. ( 2001 ), “ On the dimensionality of organizational justice: a construct validation of a measure ”, Journal of Applied Psychology , Vol. 86 No. 3 , pp. 386 - 400 .
Colquitt , J.A. , Conlon , D.E. , Wesson , M.J. , Porter , C.O.L.H. and Ng , K.Y. ( 2001 ), “ Justice at the millennium: a meta-analytic review of 25 years of organizational justice research ”, Journal of Applied Psychology , Vol. 86 No. 3 , pp. 425 - 445 .
Cropanzano , R. and Bagger , J. ( 2006 ), “ Organizational justice ”, in Greenhaus , J.H. and Callanan , G.A. (Eds), Encyclopedia of Career Development , Sage Publication , Thousand Oaks, CA , Vol. 1 , pp. 590 - 591 .
Dep , T. ( 2006 ), Strategic Approach to Human Resource Management: Concept, Tools, and Application , Atlantic Publishers and Distributers , New Delhi .
Deutsch , M. ( 1975 ), “ Equity, equality, and need: what determines which value will be used as the basis of distributive justice? ”, Journal of Social Issues , Vol. 31 No. 3 , pp. 137 - 149 .
Eargle , F.L. ( 2013 ), Job Evaluation: Traditional Approaches and Emerging Technology , 1st ed ., Lulu.Com , Abu Dhabi .
Eib , C. ( 2015 ), “ Process of organizational justice: insights into the perception and enactment of justice ”, Stockholm University , available at: http://www.diva-portal.org/smash/get/diva2:789976/FULLTEXT01.pdf ( accessed 27 September 2020 ).
El-Hajji , M.A. ( 2011 ), “ Wage consistency in the context of job evaluation: an analytical view ”, International Journal of Business and Social Science , Vol. 2 No. 10 , pp. 31 - 37 .
Folger , R. and Konovsky , M.A. ( 1989 ), “ Effects of procedural and distributive justice on reactions to pay raise decisions ”, Academy of Management Journal , Vol. 32 No. 1 , pp. 115 - 131 .
Goldman , B. and Cropanzano , R. ( 2014 ), “ 'Justice' and 'fairness' are not the same thing ”, Journal of Organizational Behavior , Vol. 36 No. 2 , pp. 313 - 318 .
Greenberg , J. ( 1990 ), “ Organizational justice: yesterday, today, and tomorrow ”, Journal of Management , Vol. 16 , pp. 399 - 432 .
Greenberg , J. ( 1993 ), “ The social side of fairness: interpersonal and informational classes of organizational justice ”, in Cropanzano , R. (Ed.), Justice in the Workplace: Approaching Fairness in Human Resource Management , Lawrence Erlbaum Associates , Hillsdale, NJ , pp. 79 - 103 .
Greenberg , J. ( 1996 ), The Quest for Job Justice on the Job , Sage , Thousand Oaks, CA .
Greenberg , J. ( 2001 ), “ Setting the justice agenda: seven unanswered questions about ‘what, why, and how' ”, Journal of Vocational Behavior , Vol. 58 , pp. 210 - 219 .
Hashem , Z.M. ( 1989 ), Human Resources Management , That Al Salasil for Printing, Publishing and Distribution , Al-Kuwait .
Holtz , B.C. and Harold , C.M. ( 2009 ), “ Fair today, fair tomorrow? A longitudinal investigation of overall justice perception ”, Journal of Applied Psychology , Vol. 94 No. 5 , pp. 1185 - 1199 .
Hussnein , A.Gh. ( 2014 ), Administrative Frustration (Causes - Treatment) , Arab Group for Training and Publishing , Cairo .
ILO ( 1982 ), Wages, A Workers Education Manual , 3rd ed. , ILO , Geneva .
Ismail , A. and Zakaria , N. ( 2009 ), “ Relationship between interactional justice and pay for performance as an antecedent of job satisfaction: an empirical study in Malaysia ”, International Journal of Business and Management , Vol. 4 No. 3 , pp. 190 - 199 .
Joffe , B. ( 1989 ), The Impact of Job Evaluation in Large Local Authorities, Master of Arts in Sociology , University of Cape Town , Cape Town .
Jones , F.F. , Scarpello , V. and Bergmann , T. ( 1999 ), “ Pay procedures-what makes them fair? ”, Journal of Occupational and Organizational Psychology , Vol. 72 No. 2 , pp. 129 - 145 .
Lawler , E. ( 1995 ), “ The new pay: a strategic approach ”, Compensation and Benefits Review , July-August , pp. 14 - 22 .
Léné , A. ( 2014 ), “ Skill-based pay in practice: an interactional justice perspective ”, European Journal of Training and Development , Vol. 38 No. 7 , pp. 628 - 641 .
Ledford , G.E. Jr ( 1995 ), “ Paying for the skills, knowledge, and competencies of knowledge workers ”, Compensation and Benefits Review , Vol. 27 , pp. 55 - 62 .
Leventhal , G.S. ( 1980 ), “ What should Be done with equity theory ”, in Gergen , K.J. , Greenberg , M.S. and Willis , R.H. (Eds), Social Exchange: Advances in Theory and Research , Plenium , New-York , Vol. 2012 , pp. 1 - 55 .
Lind , E.A. ( 2001 ), “ Fairness heuristics theory: justice judgments as pivotal cognitions in organizational relations ”, in Greenberg , J. and Cropanzano , R. (Eds), Advances in Organizational Justice , Stanford University Press , Stanford, CA , pp. 56 - 88 .
Maykock , E. ( 2009 ), “ An investigation into performance based pay in Nigerian Financial Institutions ”, Ph.D Thesis of Philosophy , University of Bedfordshire , Bedfordshire .
Merriam-Webster Dictionary ( 2019 ), “ Fair wage ”, available at: https://www.merriam.com/dictionary/fair%20wag ( accessed 5 April 2019 ).
Omran , K.M. ( 1997 ), Human Resources Management , Dar Kareem for Printing , Cairo .
O'Riordan , J. ( 2008 ), “ A review of the civil service grading and pay system ”, Institute of Public Administration , available at: https://www.ipa.ie/_fileUpload/Documents/CPMR_DP_38_Review_ofthe_Civil_Service_Grading_Pay_System.pdf ( accessed 20 September 2019 ).
Picardi , C.A. ( 2019 ), Recruitment and Selection: Strategies to Workforce Planning and Assessment , Sage Publications , London .
Pigou , A.C. ( 1985 ), “ Fair wage ”, in Ghodke , N.B. (Ed.), Encyclopedic Dictionary of Economics , Miltal Publications , New Delhi , p. 436 , 1 .
Quaid , M. ( 1993 ), “ Job evaluation as institutional myth ”, Journal of Management Studies , Vol. 30 No. 2 , pp. 239 - 260 .
Rupp , D.E. ( 2011 ), “ An employee-centered model of organizational justice and social responsibility ”, Organizational Psychology Review , Vol. 1 , pp. 72 - 94 .
Rutte , C.G. and Messick , D.M. ( 1995 ), “ An integrated model of perceived unfairness in organizations ”, Social Justice Research , Vol. 8 No. 3 , pp. 239 - 261 .
Shapiro , D. ( 2001 ), “ The death of justice theory is likely if theorists neglect the wheels already invented and the voices of injustice victims ”, Journal of Vocational Behavior , Vol. 58 No. 2 , pp. 235 - 242 .
Sharma , R.C. ( 2016 ), Industrial Relations and Labour Legislation , PHI Learning Private , New Delhi .
Singer , P.M. and Francisco , L.L. ( 2009 ), Developing a Compensation Plan for Your Library , 2nd ed. , American Library Association , Chicago .
Thibaut and Walker , L. ( 1975 ), Procedural Justice: A Psychological Analysis , Erlbaum , Hillsdale, NJ .
Till , E. and Karren , R. ( 2011 ), “ Organizational justice perceptions and pay level satisfaction ”, Journal of Managerial Psychology , Vol. 25 No. 1 , pp. 42 - 57 .
Van den Bos , K. ( 2001 ), “ Fairness heuristic theory: assessing the information to which people are reacting has a positive role in understanding organizational justice ”, in Gilliland , S. , Steiner , D. and Sharlicki , D. (Eds), Theoretical and Cultural Perspectives on Organizational Justice, A Volume in Research in Social Issues in Management , Information Age Publishing , Greenwich , pp. 63 - 84 .
Corresponding author
Related articles, we’re listening — tell us what you think, something didn’t work….
Report bugs here
All feedback is valuable
Please share your general feedback
Join us on our journey
Platform update page.
Visit emeraldpublishing.com/platformupdate to discover the latest news and updates
Questions & More Information
Answers to the most commonly asked questions here

ESSAY SAUCE
FOR STUDENTS : ALL THE INGREDIENTS OF A GOOD ESSAY
Essay: Job evaluation
Essay details and download:.
- Subject area(s): Business essays
- Reading time: 6 minutes
- Price: Free download
- Published: 11 November 2015*
- File format: Text
- Words: 1,731 (approx)
- Number of pages: 7 (approx)
Text preview of this essay:
This page of the essay has 1,731 words. Download the full version above.
Job evaluation is defined as a method for determining the worth of a job in comparison to the different jobs in the organization. To establish a justified pay structure for all the employees of the organization, job evaluation gives a means to compare the quality of the work in a particular job, in other words, the worth of a job. It is different from job analysis; rather job evaluation is done after the stage of job analysis in order to obtain some information about the concerned jobs. Job analysis is defined as a process of determining the skills, duties and responsibilities, in a systematic way, required for a particular job. Thus job evaluation is a method which commences from job evaluation from job analysis but it ends at a point where the worth of the job is determined by ensuring internal as well as external pay equity. In this competitive business environment, it is essential to maintain pay equity otherwise the organization may lose its crucial talent. Equity: Overpayment Inequity (Positive Equity): Underpayment Inequity (Negative equity): Where, Input: Any value that person brings to a job. Outcome: any sort of benefit that an employee is awarded from his/her job. Objectives of job evaluation ‘ To build a systematic, reasonable, deliberate structure of jobs based on their worth to the organization. ‘ To support a current pay rate structure or to build up one that accommodates internal equity. ‘ To support in setting pay rates that are tantamount to those of in comparable jobs in different organizations to contend in market place for best talent. ‘ To give a balanced premise to arranging pay rates when bargaining collectively with a recognized union. ‘ To guarantee the reasonable and fair remuneration of workers in connection to their obligations. ‘ To guarantee equity in pay for jobs of comparable efforts, responsibility, efforts and working conditions by utilizing a framework that reliably and precisely surveys contrasts in relative quality among jobs. ‘ To create a system of techniques to determine the grade levels and the resulting pay range for new jobs or the jobs which have advanced and changed. ‘ To distinguish a ladder of progression for future development to all workers who are interested in enhancing their remuneration. ‘ To comply with equal pay legislation and regulations deciding pay contrasts as indicated by job content. ‘ To add to a base for merit or performance-related pay. Characteristics of job evaluation The essential goal of job evaluation is to figure out the value of work; however this is a quality which differs occasionally and from spot to place affected by certain economic pressure. The principle features of job evaluation are: ‘ To supply bases for compensation arrangement established on realities as opposed to on dubious moderate thoughts. ‘ It endeavors to assess jobs, not individuals. ‘ Job evaluation is the yield given by job analysis. ‘ Job evaluation does not plan pay structure, it helps in supporting the framework by decreasing number of separate and diverse rates. ‘ Job evaluation is not made by people rather it is carried out by gathering of specialists. ‘ Job evaluation decides the estimation of job. Further the estimation of each of the perspectives, for example, aptitude and obligation levels are additionally related and concentrated on regarding the job. ‘ Job evaluation helps the administration to keep up abnormal amounts of representative gainfulness and worker fulfillment. Process of job evaluation Job analysis describes the skills, duties and responsibilities required for a job. Job evaluation adds to an arrangement for contrasting jobs regarding those things the association considers vital determinants of job worth. This procedure includes various steps that will be quickly expressed here and afterward talked about all the more completely. 1. Job Analysis: The primary step is an investigation of the jobs in the association. Through job analysis, data on job substance is acquired, together with a valuation for worker prerequisites for effective execution of the job. This data is recorded in the exact, steady dialect of a job description. 2. Compensable Factors: The following step is choosing what the association “is paying for” – that is, the thing that variable or elements put one job at a more elevated amount in the job chain of importance than an alternate. These compensable elements are the measuring sticks used to focus the relative position of jobs. As it were, picking compensable components is the heart of job evaluation. Not just do these variables spot jobs in the association’s job progressive system, yet they additionally serve to advise job officeholders which commitments are remunerated. 3. Building up the Method: The third venture in job evaluation is to choose a technique for evaluating the association’s jobs as indicated by the factor(s) picked. The technique ought to allow reliable situation of the association’s jobs containing a greater amount of the elements higher in the job progression, than those jobs lower in the progressive system. 4. Job Structure: The fourth step is contrasting jobs with build up a job structure. This includes picking and relegating chiefs, arriving at and recording choices, and setting up the job progression. 5. Pay Structure: The last step is evaluating the job structure to land at a compensation structure. Merits of job evaluation Job evaluation is a procedure of deciding the relative worth of a job. It is a procedure which is useful actually for encircling remuneration arranges by the personnel manager. Job evaluation as a methodology is worthwhile to an organization from multiple points of view: ‘ Decrease in disparities in pay structure – It is discovered that individuals and their inspiration is needy upon how well they are being paid. Accordingly the primary target of job evaluation is to have outer and interior consistency in compensation structure so that imbalances in pay rates are lessened. ‘ Specialization – Because of division of work and subsequently specialization, an expansive number of endeavors have landed hundred positions and numerous representatives to perform them. Hence, an endeavor ought to be made to characterize a job and accordingly settle pay rates for it. This is conceivable just through job evaluation. ‘ Aides in choice of representatives – The job evaluation data can be useful at the time of determination of applicants. The elements that are resolved for job evaluation can be considered while selecting the workers. ‘ Amicable relationship in the middle of workers and administrator – Through job evaluation, agreeable and harmonious relations can be kept up in the middle of representatives and administration, so that a wide range of pay rates debates can be minimized. ‘ Institutionalization – The procedure of deciding the pay differentials for distinctive jobs get to be institutionalized through job evaluation. This aide in bringing consistency into compensation structure. ‘ Pertinence of new jobs – Through job evaluation, one can comprehend the relative estimation of new jobs in a worry. Demerits of job evaluation ‘ In spite of the fact that there are numerous methods for applying job evaluation in an adaptable way, fast changes in innovation and in the supply of and interest for specific aptitudes, make issues of change that may need further study. ‘ At the point when job evaluation brings about considerable changes in the current pay structure, the likelihood of executing these progressions in a generally brief time may be limited by the money related breaking points inside which the firm needs to work. ‘ At the point when there is an extensive extent of motivating force workers, it might be hard to keep up a sensible and worthy structure of relative profit. ‘ The methodology of job rating is, to some degree, vague on the grounds that a portion of the components and degrees can be measured with precision. ‘ Job evaluation takes quite a while to finish, requires specific specialized staff and quite expensive. Methods of job evaluation Job Ranking: As indicated by this technique, jobs are arranged from highest to lowest, in place of their worth or legitimacy to the organization. Jobs can likewise be organized by relative trouble in performing them. The jobs are analyzed in general instead of on the premise of essential considers the job; the job at the highest priority on the rundown has the most astounding quality and clearly the job at the base of the rundown will have the least esteem. Jobs are typically positioned in every division and afterward the office rankings are joined to build up an authoritative positioning. The variety in installment of compensations relies on upon the variety of the way of the job performed by the workers. The positioning technique is easy to comprehend and practice and it is ideally equipped for a little association. Its straightforwardness however attempts to its inconvenience in huge associations on the grounds that rankings are hard to grow in an extensive, complex organization. Besides, this sort of positioning is very subjective in nature and may outrage numerous workers. In this way, a more investigative and productive method for job evaluation is called for. Job Classification: As per this system, a predetermined number of job groups or job classes are built and jobs are allotted to these characterizations. This technique spots gatherings of jobs into job classes or job grades. Separate classes may incorporate office, administrative, administrative, work force, and so on. Class I – Executives: Further order under this classification may be Office Manager, Deputy Office administrator, Office director, Departmental chief, and so forth. Class II – Skilled workers: Under this classification may come the Purchasing partner, Cashier, Receipts assistant, and so forth. Class III – Semiskilled workers: Under this classification may come Stenotypists, Machine-administrators, Switchboard administrator and so on. Class IV – Unskilled workers: This classification may involve peons, delivery people, housekeeping staff, File agents, Office young men, and so forth. The job reviewing system is less subjective when contrasted with the prior positioning strategy. The framework is straightforward and adequate to pretty much all representatives without a second thought. One in number point for the system is that it considers all the elements that a job involves. This framework can be viably utilized for a mixed bag of jobs. The shortcomings of the Grading technique are: ‘ Actually when the prerequisites of distinctive jobs contrast, they may be joined into a solitary class, contingent upon the status a job conveys. ‘ It is hard to compose all inclusive descriptions of a grade. ‘ The system distorts sharp contrasts between diverse jobs and distinctive evaluations. ‘ At the point when individual job depictions and grade portrayals don’t match well, the evaluators tend to characterize the job utilizing their subjective judgments.
...(download the rest of the essay above)
About this essay:
If you use part of this page in your own work, you need to provide a citation, as follows:
Essay Sauce, Job evaluation . Available from:<https://www.essaysauce.com/business-essays/essay-job-evaluation/> [Accessed 10-05-24].
These Business essays have been submitted to us by students in order to help you with your studies.
* This essay may have been previously published on Essay.uk.com at an earlier date.
Essay Categories:
- Accounting essays
- Architecture essays
- Business essays
- Computer science essays
- Criminology essays
- Economics essays
- Education essays
- Engineering essays
- English language essays
- Environmental studies essays
- Essay examples
- Finance essays
- Geography essays
- Health essays
- History essays
- Hospitality and tourism essays
- Human rights essays
- Information technology essays
- International relations
- Leadership essays
- Linguistics essays
- Literature essays
- Management essays
- Marketing essays
- Mathematics essays
- Media essays
- Medicine essays
- Military essays
- Miscellaneous essays
- Music Essays
- Nursing essays
- Philosophy essays
- Photography and arts essays
- Politics essays
- Project management essays
- Psychology essays
- Religious studies and theology essays
- Sample essays
- Science essays
- Social work essays
- Sociology essays
- Sports essays
- Types of essay
- Zoology essays
Job Evaluation Practical Technique
Job evaluation is a practical technique, designed to enable trained and experienced staff to judge the size of one job relative to others. It does not directly determine pay levels, but will establish the basis for an internal ranking of jobs. An approach designed to enable a job to be compared to all other jobs in an Institution in a systematic and transparent way in order to create a fair rank order of jobs, usually as the basis for a grading and pay structure, to ensure equal pay for work of equal value Some Principles of Job Evaluation Clearly defined and identifiable jobs must exist.
These jobs will be accurately described in an agreed job description. All jobs in an organisation will be evaluated using an agreed job evaluation scheme. Job evaluators will need to gain a thorough understanding of the job Job evaluation is concerned with jobs, not people. It is not the person that is being evaluated. The job is assessed as if it were being carried out in a fully competent and acceptable manner.
Job evaluation is based on judgement and is not scientific.However if applied correctly it can enable objective judgements to be made. It is possible to make a judgement about a job’s contribution relative to other jobs in an organisation. The real test of the evaluation results is their acceptability to all participants. Job evaluation can aid organisational problem solving as it highlights duplication of tasks and gaps between jobs and functions. Job Evaluation – The Future As organisations constantly evolve and new organisations emerge there will be challenges to existing principles of job evaluation.

Proficient in: Work
“ Amazing as always, gave her a week to finish a big assignment and came through way ahead of time. ”
Whether existing job evaluation techniques and accompanying schemes remain relevant in a faster moving and constantly changing world, where new jobs and roles are invented on a regular basis, remains to be seen. The formal points systems, used by so many organisations is often already seen to be inflexible. Sticking rigidly to an existing scheme may impose barriers to change. Constantly updating and writing new jobs together with the time that has to be spent administering the job evaluation schemes may become too cumbersome and time consuming for the benefits that are derived.
Does this mean that we will see existing schemes abandoned or left to fall into disrepute ? Will providers of job evaluation schemes examine and, where necessary, modify them to ensure they are up to date and relevant ? Simply sticking rigidly to what is already in place may not be enough to ensure their survival. Job Evaluation – More Job evaluation is essentially one part of a tripartite subject, which is collectively referred to as Job Study (other names exist). The three parts are Job Analysis, Job Evaluation – the information collected is evaluated using a numerical scale or ranking and rating methodology: and Merit Rating – BSI definition (32542). BSI definition – 32529 – “Any method ranking the relative worth of jobs which can then be used as a basis for a remuneration system” It is essentially a comparative process. Job evaluation evaluates selected job factors, which are regarded as important for the effective performance of the job, according to one of several alternative methods.
The resulting numerical gradings can form the basis of an equitable structure of job gradings. The job grades may or may not be used for status or payment purposes. Explanation: Job Evaluation is concerned with measuring the demands the job places on its holder. Most factors that contribute to this job pressure, e. g. physical strength required, knowledge of mathematics required, are assessed and the result is a numerical estimate of the total job pressure. When evaluations are carried out on all hourly paid personnel the technique’s uses include establishing relative wage rates for different tasks.
It is possible to use it for all grades of personnel, even senior management. Illustration:The Time Span of Discretion is an interesting and unusual method of job evaluation developed by Elliot Jaques for the Glacier Metal Company. In this method the job pressure is assessed according to the length of time over which managers decisions commit the company. A machine operative, for example, is at any moment committing the company only for the period needed to make one product unit or component. The manager who buys the machine is committing the company for ten years. Job evaluation is the process of determining the appropriate Career Group and Role to which a position is assigned.
The job evaluation process has four steps: Selecting the Occupational Family: The first step is to determine the appropriate Occupational Family by reviewing the vocational characteristics (the nature and type of work performed) outlined in the Employee Work Profile. Comparing and Selecting the Career Group: The second step is to compare the Concept of Work capsule that describes the array of work performed in the various Career Group Descriptions to the Employee Work Profile in order to determine the appropriate Career Group.Comparing and Selecting a Role within a Career Group: The third step is to evaluate and compare the Work Description (position objective, purpose of position, knowledge, skills, abilities and competencies; education, experience, certification and licensure, core responsibilities and special assignments) outlined in the Employee Work Profile to the various Role Descriptions and the factor matrices to determine the appropriate Role.
Comparing to other positions within a Role to ensure consistency: The final step is to confirm the assignment of the position to the Role by checking to make sure that it is consistent with other positions assigned to the same Role Job Evaluation: Methods: The two most common methods of job evaluation that have been used are first, whole job ranking, where jobs are taken as a whole and ranked against each other. The second method is one of awarding points for various aspects of the job.In the points system various aspects or parts of the job such as education and experience required to perform the job are assessed and a points value awarded – the higher the educational requirements of the job the higher the points scored.
The most well known points scheme was introduced by Hay management consultants in 1951. This scheme evaluates job responsibilities in the light of three major factors – know how, problem solving and accountability Ranking Ranking This method is one of the simplest to administer. Jobs are compared to each other based on the overall worth of the job to the organization. The ‘worth’ of a job is usually based on judgements of skill, effort (physical and mental), responsibility (supervisory and fiscal), and working conditions. Advantages Simple. Very effective when there are relatively few jobs to be evaluated (less than 30).
Disadvantages Difficult to administer as the number of jobs increases. Rank judgements are subjective. Since there is no standard used for comparison, new jobs would have to be compared with the existing jobs to determine its appropriate rank. In essence, the ranking process would have to be repeated each time a new job is added to the organization. Ranking Methods Ordering Simply place job titles on 3×5 inch index cards then order the titles by relative importance to the organization. Weighting Paired Comparison Job Evaluation: Methods: Classification Classification Jobs are classified into an existing grade/category structure or hierarchy. Each level in the grade/category structure has a description and associated job titles. Each job is assigned to the grade/category providing the closest match to the job. The classification of a position is decided by comparing the whole job with the appropriate job grading standard.
To ensure equity in job grading and wage rates, a common set of job grading standards and instructions are used. Because of differences in duties, skills and knowledge, and other aspects of trades and labor jobs, job grading standards are developed mainly along occupational lines. The standards do not attempt to describe every work assignment of each position in the occupation covered. The standards identify and describe those key characteristics of occupations which are significant for distinguishing different levels of work.They define these key characteristics in such a way as to provide a basis for assigning the appropriate grade level to all positions in the occupation to which the standards apply.
Advantages Simple. The grade/category structure exists independent of the jobs. Therefore, new jobs can be classified more easily than the Ranking Method. Disadvantages Classification judgments are subjective. The standard used for comparison (the grade/category structure) may have built in biases that would affect certain groups of employees (females or minorities). Some jobs may appear to fit within more than one grade/category.Job Evaluation: Methods: Factor Comparison Factor Comparison A set of compensable factors are identified as determining the worth of jobs.
Typically the number of compensable factors is small (4 or 5). Examples of compensable factors are: Skill Responsibilities Effort Working Conditions Next, benchmark jobs are identified. Benchmark jobs should be selected as having certain characteristics. equitable pay (not overpaid or underpaid) range of the factors (for each factor, some jobs would be at the low end of the factor while others would be at the high end of the factor).
The jobs are then priced and the total pay for each job is divided into pay for each factor. See example matrix below: Job Evaluation: Factor Comparison The hourly rate is divided into pay for each of the following factors: Job Hourly Rate . Pay for Skill Pay for Effort Pay for Responsibility Pay for Working Conditions This process establishes the rate of pay for each factor for each benchmark job. Slight adjustments may need o be made to the matrix to ensure equitable dollar weighting of the factors. The other jobs in the organization are then compared with the benchmark jobs and rates of pay for each factor are summed to determine the rates of pay for each of the other jobs. Advantages The value of the job is expressed in monetary terms. Can be applied to a wide range of jobs. Can be applied to newly created jobs. Disadvantages The pay for each factor is based on judgements that are subjective.
The standard used for determining the pay for each factor may have build in biases that would affect certain groups of employees (females or minorities). Job Evaluation: Methods: Point MethodPoint Method A set of compensable factors are identified as determining the worth of jobs. Typically the compensable factors include the major categories of: Skill Responsibilities Effort Working Conditions These factors can then be further defined. Skill Experience Education Ability Responsibilities Fiscal Supervisory Effort Mental Physical Working Conditions Location Hazards Extremes in Environment The point method is an extension of the factor comparison method. Each factor is then divided into levels or degrees which are then assigned points. Each job is rated using the job evaluation instrument.
The points for each factor are summed to form a total point score for the job. Jobs are then grouped by total point score and assigned to wage/salary grades so that similarly rated jobs would be placed in the same wage/salary grade. Advantages The value of the job is expressed in monetary terms. Can be applied to a wide range of jobs. Can be applied to newly created jobs. Disadvantages The pay for each factor is based on judgments that are subjective. The standard used for determining the pay for each factor may have built-in biases that would affect certain groups of employees (females or minorities).
Performance appraisal, also known as employee appraisal, is a method by which the performance of an employee is evaluated (generally in terms of quality, quantity, cost and time). The roots of performance appraisal can be found in Frederick Winslow Taylor’s time and motion study[citation needed]. Performance appraisal is a part of career development. Performance appraisals are a regular review of employee performance within organizations. Generally, the aims of a scheme are: Give feedback on performance to employees. Identify employee training needs.
Document criteria used to allocate organizational rewards.Form a basis for personnel decisions-salary (merit) increases,promotions, disciplinary actions, etc. Provide the opportunity for organizational diagnosis and development. Facilitate communication between employee and administrator. Validate selection techniques and human resource policies to meet federal Equal Employment Opportunity requirements. A common approach to assessing performance is to use a numerical or scalar rating system whereby managers are asked to score an individual against a number of objectives/attributes. Employees are also allowed the opportunity to assess the person (manager) at the same time.This is known as 360° appraisal.
The most popular methods that are being used as performance appraisal process are: Management by objectives (MBO) 360 degree appraisal Thus performance appraisal is important for effective human resource management. Performance appraisal is a process of evaluating employee performance in order to guide and develop the employee’s potential. In many extension organizations which are government departments, the performance appraisal is nothing more than a confidential judgement of work done and a character report used to facilitate disciplinary action or promotion.
The employees do not get feedback about their performance. Extension organizations need to have an open appraisal system to provide feedback and opportunities for open discussion with employees on their performance, because they have immense potential to grow and develop. This system can create a healthy working climate and employee motivation. The performance appraisal which aims at facilitating employee development has the following major purposes:
- to provide feedback and guidance,
- to set performance goals,
- to identify training needs,
- to provide inputs for management of pay administration,
The steps involved in effective performance appraisal are identification of key performance areas and setting yearly objectives under each KPA, identification of critical attributes for effective performance, periodic review of performance, discussion of performance with employees and identification of training and developmental needs (Pareek ; Rao, 1992).
The potential appraisal is a future-oriented appraisal by which the potential of an employee to occupy higher positions and to assume higher responsibilities is evaluated.The potential appraisal can help the extension staff to know their strengths and weaknesses and can motivate them to further develop their skills. Thus the potential appraisal helps in planning overall career development of employees. Some of the techniques used for the appraisal are self-appraisals, peer rating, the management by objectives (MBO) approach, psychological test and simulated work exercises, case analyses, and leadership exercises.
Cite this page
Job Evaluation Practical Technique. (2019, Jun 20). Retrieved from https://paperap.com/paper-on-essay-job-evaluation-2/
"Job Evaluation Practical Technique." PaperAp.com , 20 Jun 2019, https://paperap.com/paper-on-essay-job-evaluation-2/
PaperAp.com. (2019). Job Evaluation Practical Technique . [Online]. Available at: https://paperap.com/paper-on-essay-job-evaluation-2/ [Accessed: 10 May. 2024]
"Job Evaluation Practical Technique." PaperAp.com, Jun 20, 2019. Accessed May 10, 2024. https://paperap.com/paper-on-essay-job-evaluation-2/
"Job Evaluation Practical Technique," PaperAp.com , 20-Jun-2019. [Online]. Available: https://paperap.com/paper-on-essay-job-evaluation-2/. [Accessed: 10-May-2024]
PaperAp.com. (2019). Job Evaluation Practical Technique . [Online]. Available at: https://paperap.com/paper-on-essay-job-evaluation-2/ [Accessed: 10-May-2024]
- 13 Principles of Aseptic Technique in Operating Room Pages: 6 (1711 words)
- Narrative Technique In Sons And Lovers Pages: 3 (616 words)
- Citizen Kane Experimented With Technique Pages: 4 (946 words)
- A Study of the Stylistic Technique of Nathaniel Hawthorne Pages: 2 (475 words)
- Tim Burton’s Cinema Technique Essay Pages: 2 (523 words)
- Is Symbolism a Narrative Technique Pages: 4 (1067 words)
- Worm And Wheel Drive Practical Discussion Pages: 2 (497 words)
- Nursing Practical Skill Development Pages: 4 (1099 words)
- An Ethical Dilemma Is a Practical Conflict Pages: 4 (935 words)
- How the History of Practical Nurse’s Influence Healthcare Today Pages: 3 (813 words)

- How It Works
- Book Report
- Research Proposal
- Poster Service
- Book Review
- Capstone Project
- Discussion Post
- Article Review
- Blog Article
- Business Plan
- Business Report
- Interview Essay
- Literature Analysis
- Marketing Plan
- Prewritten Essay
- Questions Answers
- White Paper
- Dissertation
- Editing Service
- Formatting Service
- Revision Service
- Excel Homework
- Film Critique
- Synopsis Writing
- IB Extended Essay
- Letter Writing
- Movie Review
- Literature Review
- Poem Writing
- Article Critique
- Grant Proposal
- Scholarship Essay
- Speech Writing
- Questionnaire
- Thesis Proposal
- Essay Writing UK
- Cyber Bullying Essay
This website uses cookies in order to provide you the most relevant information. Please accept cookies for better performance Read more »
Job Analysis and Job Evaluation Essay
Job analysis refers to the process of collecting relevant information relating to a job position. The primary goal of job analysis is to come up with a job description. The process involves the collection of data that is relevant in establishing the mental and physical abilities of the individual to fill the job position. It establishes the skills, experience and educational capacity of the job’s candidate. It also involves the definition of the nature of the job, amount of work required of the job position. The process involves the description of the occupant’s responsibilities and duties.
Job evaluation refers to the process of determining the comparative job worth of an organization’s work in order to create the organization’s job structure. The process involves determination of the content of the job, the skills needed to perform the job, the value of the job to the organization. The process also involves the evaluation of the company culture and external market. The process determines how well the job fit into these two forces. A human resource manager achieves job evaluation by using such methods as job ranking, job classification/grading or point method, which involves assigning values to the different job components of a job from which the sum total is used for evaluation.
Job analysis is done prior to job evaluation
The two processes are essential in ensuring internal consistency. Organizations perform these processes to comply with legal regulations of equal pay and to ensure internal consistency in the job structure. Internal job consistency is achieved by determining the relative worth of each job to the organization based on the job’s complexity and value to the organization. Describe the challenges in developing compensations that are both internally consistent and market competitive.
Compensation plans exist in organizations for such reasons as to retain the existing workforce or for the purpose of attracting a competitive workforce. The plans exist in both formal and informal modes depending on the intended purpose of the compensation plan. Compensation irrespective of the size of the organization can be identified due to its features that should be considered in designing compensation plans. Designing an effective compensation plan ought to undergo the following processes. Definition of the different jobs, the analysis of the organization’s compensation composition and patterns of other compensation plans in the industry and determination of a fair reward range. The process also involves the provision of all elements that constitute the compensation plan, revising the existing plans and finally the implementation and regular evaluation of the plan.
Challenges that arise in the construction of compensation plans may affect the internal consistency of the organization as well as the market competitiveness of the compensation plan. A HRM’s key challenge is maintenance of equity as regards internal, external equity and individual equity. The development of a fair pay structure is crucial but posses a great challenge to the managers. Human resource managers face challenges in ensuring that the goal of formulating the compensation plan is consistent with organizational overall objectives. Decisions in the formation of the plan should also be made while considering the decision making process practiced in the organization. Decisions in establishing rates that are market competitive while taking consideration of the financial position and strategic plan of the organization may prove challenging. This relates to the ability of the organization in maintaining its market position in paying wages at or above the market rate. Challenge may also arise in the implementation and change over process to the new plan. The implementation process should not be seen to alter the organization functions and should match the overall organizational goals. An overall challenge for human resource managers would be in establishing a balance between internal consistency and market competitiveness in the formulation of the compensation plan.
Two employees perform the same job and each received exemplary performance ratings. Employees performing similar jobs which result to them being awarded a similar performance rating which in the case is exemplary deserve similar reward. The reward, salary increment, should be equal irrespective of the pay quartile in which the two employees fall. This would serve to ensure that the organization uphold the standards of equity and fairness in its compensation structure. It would be unfair for an employee to receive more pay for the same kind of work. The organization should come up with pay structures that reward performance in other forms such as bonuses and benefits. Salary increment could be awarded but at similar percentage for both employees in order for the organization to uphold equity.
Discuss the basic concept of insurance and how it applies to health care.
Insurance is a risk transfer mechanism used by individuals. The insurance involves the transfer of risk to an insurer at a fee known as premiums. The procedure involves two major parties the insured and the insurer who is the insurance company. Premiums are determined based on the value of loss at stake and the likelihood of the risk actually occurring. The premiums are calculated using various actuarial and statistical techniques. There are many forms of insurance covers among them health insurance, property insurance and life assurance. A health insurance also known as healthcare insurance applies the same concept as any other insurance policy. It is thus a contract between the insured who is the policy holder and another individual (company) or government for the reimbursement of medical costs incurred by the policy holder for the treatment or preventive care of any ailment provided by medical institutions and their personnel. Except for the Family and Medical Leave Act, the remaining legally required benefits were conceived decades ago.
Describe the changes in the business environment and society that might affect the relevance or perhaps the viability of any of these benefits.
Employee benefit plans such as the family and medical leave provided by various Acts of parliament face the risk of being seen as irrelevant in the changing business environment. The legal environment is in constant change where laws are amended. Changes occur relating to taxes and legal compliance is likely to cause inconsistencies with employee benefits established in the past years. Changes in financial environment resulting from varying growth rates may interfere with the viability of employee benefits. An organization facing financial difficulty may be forced to cut down on the payment of employee benefits. Organizations facing financial success may also have an ability to pay for more benefits than are provided for by the law. The employee benefits are not consistent to the financial variations in the country.
Mergers are a common scenario in today’s business world. The mergers often involve organizations from different fields, which results to variations in the employee benefits paid to the employee from different organizations. The implementation of old policies may result to unfair remedies to individuals taking into consideration current structural changes in organizations. Employee demographics were not considered in the formulation of various employee benefits in the Acts of parliament. Employee demographics involve the changing composition of a company’s employees where an organization may consist of many parents. Such an organization may need to come up with day care benefits that have not been considered in the family and medical leave Act in order to retain its employees. The changing business environment as a result may make the benefit plans redundant.
New customer 15% off
Sample categories
- Consideration
- Observation
- The biggest writers database
- Only certified BA, MA or PhD writers
- Only up-to-date sources
- 96% of returning clients
- 24/7 customer support
- Free revision within 48 hours
- Free plagiarism report (upon request)
- 300 words per page
- Any formatting style
- Additional editing and proofreading service
Everyone Benefits from our Affiliate Program!
Flexible and Easy Way to Earn! It Is Your Chance To Earn 10% From All Orders That Your Referees Place With Our Company.
New offer: Become our VIP client
Because VIP clients enjoy these exclusive benefits:
- Extended revision period
- Paper delivery before the deadline
- Free 1-page draft to each order
- Free plagiarism check
- TOP editors and TOP writers
- VIP support service
- SMS notification of the order status
* You deserve a special treatment because you are special! *
Essays on Job evaluation
We found 3 free papers on job evaluation, essay examples, compensation: termination of employment and merit pay programs.
Job evaluation
Strategic Compensations is a major component of the human resources system. There are many aspects within strategic compensation. The current literature in business strategy and human resource management has focused increasing attention on the need for a stronger link between management compensation and business strategy (Hufnagel). There are strategic and contextual factors within strategic compensation….
FastCat: Phase 1 “High-Five” Compensation Package
Compensation
In Phase 1 of the FastCat Compensation Case, our team has included our recommendations regarding strategies, objectives, the formation of an internal structure, and an implementation plan that will allow a seamless transition from FastCat’s previous compensation structure, which was nearly non-existent, to the proposed structure our team of compensation specialists is proposing. INDEX Executive…
Job Evaluation: Compare & Contrast, The Best Method and Which Is Not
Introduction The perspective on choosing the correct job evaluation method mainly depends on the advantages to the specific job position and duties performed. The ability to define and correlate the overall aspects to each method provides an understanding towards the fundamentals on job evaluation. The four methods available are ranking, classification, factor comparison, and point…
Frequently Asked Questions about Job evaluation
Don't hesitate to contact us. We are ready to help you 24/7

Hi, my name is Amy 👋
In case you can't find a relevant example, our professional writers are ready to help you write a unique paper. Just talk to our smart assistant Amy and she'll connect you with the best match.
Essay on Job Evaluation | India | Workers | Industrial Management
Here is a compilation of essays on ‘Job Evaluation’ for class 11 and 12. Find paragraphs, long and short essays on ‘Job Evaluation’ especially written for school and college students.
Essay on Job Evaluation
Essay Contents:
- Essay on the Comments on Job Evaluation
Essay # 1. Definition of Job Evaluation:
Job evaluation may be defined as a method of studying and grading jobs in order to provide a basis for a fair wage structure. It is concerned with the ranking of jobs and not directly with the men who do them.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Within each grade some workers will be more efficient than others; their wage rates under job evaluation systems will be the same. Job evaluation must be regarded as only one of the factors in determining wage structures, especially where wage rates and scales are fixed by, collective bargaining.
According to Kimball and Kimball, “Job evaluation represents an effort to determine the relative value of every job in a plant and to determine what the fair basic wage for such a job should be.”
Essay # 2. Objectives of Job Evaluation:
It attempts to provide a fair method of setting up a wage structure by indicating that jobs requiring similar efforts, skill and responsibility should be equally remunerated, and that jobs calling for higher qualities should be paid more. Its object is to ensure equal pay for equal or equivalent work.
Changes in the classification or grading of jobs must be made when processes and methods of work are altered. Some jobs may become more difficult and should be upgraded.
Frequently, jobs have been graded and wages fixed independently by the manager or foreman in each department, and are unfair in relation to the grades and wages in other departments of the same undertaking; and this causes discontent among those workers who consider themselves underpaid.
A carefully devised wage structure for the whole undertaking may do much to remove these grievances. Managements hold similar views, and if job evaluation is done intelligently and fairly and representatives of the workers take part with management in the work, a basis for agreement between them may not be difficult to find.
Job evaluation has been more effective for manual and clerical workers than for the higher ranks of management and senior technicians, although it has been used to devise salary structures for them also. Its application has been widest in individual undertakings, particularly in the metal industry.
As undertakings grow in size and employ large numbers of workers on many different kinds of work, the management increasingly feels the need for a sort of yardstick to measure the relative qualities of the various occupations, and accordingly to establish wage and salary structures that give proper recognition to each grade.
The principles and methods of job evaluation have been extended to cover an industry or even more widely for the establishment of grading between industries on a national basis. These wider developments are, however, still in an early state, though job evaluation was tried on a nation-wide scale in the Netherlands after the Second World War.
Essay # 3. Practical Application of Job Evaluation:
It is new necessary to consider the use of the results of job evaluation for wage fixing. In arty undertaking the wage rates of different grades should be such that the workers accept them as fair. If several jobs are grouped together within a grade, the wage differences between them should be such as are considered reasonable because of the higher or lower qualities required in each case.
In other words, when, after job evaluation changes are made in wage differentials (that is in the wage structure) these should be considered equitable by a considerable majority of the workers. One of the main difficulties encountered, when a new wage structure based on job evaluation is introduced is that the wages previously paid for some jobs may be out of line with the new scale.
However, it must not be overlooked that, as time goes on, the scale determined by a job evaluation is likely to require modification. For example, if tools, machines or processes are introduced that make a job easier, its rating may be changed.
A wage structure based on job evaluation is liable to be disturbed by conditions of demand and supply affecting different grades of workers. For example, if there is a shortage of skilled electrical engineers with specialised experience, it will no doubt be necessary during the shortage to pay them higher wages than their job evaluation grade would justify in relation to the qualities of other skilled, experienced workers.
Problems arise also in fixing the wages of piece-workers. These can be solved fairly easily if the work is standardised and not frequently changed. Job evaluation has been introduced on an increasing scale in industrialised countries since the Second World War.
By the mid-1960s some 50 million employees in the United States, or two-thirds of the employed labour force, were graded under job evaluation schemes of various kinds. They are in operation mainly at the level of the plant or undertaking, although a few industry-wide plans (e.g. for the steel industry) are in existence.
Larger organisations (200 or more employees) are found to be more likely to use job evaluation than smaller ones. In the United Kingdom, according to a survey by the National Board for Prices and Incomes in 1968, job evaluation covered 23 per cent, or over 6 million employees, of the employed labour force.
As in the United States, job evaluation tends to be applied at the level of the plant or undertaking and is more widely adopted in large organisations (according to the 1968 survey, 54 per cent of organisations with over 5,000 employees used job evaluation).
Unlike their counterparts in the United States, however, managerial and white-collar employees in the United Kingdom are more likely to work under job evaluation schemes than blue-collar workers.
Since 1968 the use of job evaluation appears to have been extended considerably, in part under the influence of the legislation requiring equal pay between men and women. In Sweden there are a number of industry-wide job evaluation plans covering at least 20 per cent of blue-collar workers, with the object of maintaining skill differentials that had been narrowed because of the upgrading of lower-paid jobs.
In the Federal Republic of Germany both industry-wide and regional job evaluation schemes are in existence. In the Netherlands a national job evaluation scheme for blue-collar workers was introduced after 1948 to implement a national wage policy, but since then a number of variants of this scheme have been developed and applied.
In countries with centrally planned economies job evaluation has been extensively applied. Occupations in each industry are classified into grades according to skill. In the early periods, because of shortages of skilled workers, wide differences in basic rates were fixed between the wages paid to workers in the lowest and to those in the highest grades in order to encourage workers to become skilled.
Later, when the number of skilled workers increased as a result of training and experience, the differences were narrowed considerably.
The number of grades is small in comparison with other industrial countries, and the tendency in recent years has been to reduce it somewhat in order to simplify the wage system. In most industries there are new only six or seven grades, whereas formerly in some industries there were 10 or 12.
The steps or differences from one grade to another differ somewhat within industries and between industries in recognition of differences in the time it takes for workers to acquire the training and experience they needed to qualify them to move from a lower to a higher grade.
Essay # 4. Practice of Job Evaluation in India:
The Background and Scope
In India, job evaluation as a method of rationalizing wage structure has been attempted, by and large, in public sector. Some bigger private sector industries have also taken recourse to job evaluation with cooperation of trade unions.
The following discussion is meant for providing a brief background and scope of job evaluation in India. The evolution of job evaluation has synchronized with the recommendations of the Third Pay Commission, Administrative Staff College sample evaluation, and Staff Inspection Unit of the Ministry of Finance.
In 1956, a collective agreement between Tata Iron and Steel Company (TISCO) and Tata Worker’s Union (INTUC) provided a framework of job evaluation acceptable to both. But generally speaking, trade unions in India do not find favour with job analysis as a system, because of the defective procedure of job analysis, job description and failure to evaluate conditions and hazards of job by managements.
Trade unions seem to be apprehensive of job displacement and reduction of wage rates on account of job evaluation upsetting traditional wage structure.
Wage Boards in our country have also not recommended nor have they adopted job evaluation for standardizing wage structure and wage differentials in different industries. Both unions and managements are more in favour of collective bargaining than job evaluation for fulfilling the professed objectives of job evaluation.
In Faridabad of North India and in Tamil Nadu, wage and salary surveys were made in 1976 to ascertain how jobs in cycle industries are rated in comparable industries. In this respect, various Chambers of Commerce may collect and supply data relating to job contents, qualities of personnel, and job description as between different industries and regions.
After getting full information regarding different types of jobs, job analysis is undertaken under Indian conditions, observation and interviews are generally preferred for this purpose rather than questionnaire and written description.
In most of the Indian industries, job description in personnel department covers
(i) Job title
(ii) Job summary
(iii) Duties
(iv) Tools, machines, materials records etc.
(v) Supervision
(vi) Working conditions
(vii) Job qualities and job relations.
Essay # 5. Methods of Job Evaluation:
i . Grading System:
Various methods of job evaluation are in use. Under one of the simplest systems a number of labour grades are introduced. It may, for example, be found that in an engineering works there are 60 different manual occupations; a decision is taken to simplify the system and classify the occupations into four, five, eight or other suitable number of grades.
A simple four-grade system could be: highly skilled, skilled, semi-skilled, and unskilled. The 60 occupations would then be discussed in detail by supervisors and others with special knowledge of the characteristics required for each occupation.
Among the principal characteristics are skill, intelligence and mental effort, physical effort, training and experience required, and working conditions whether in high temperatures, dust, high humidity, dirt, noise and fumes or in normal atmospheric and pleasant conditions.
Many of the occupations may fall easily into one or other of the grades but others may be so near the border-line that their grading is rather doubtful; workers doing somewhat difficult but light work may fairly be put in the same grade as workers doing simple but very heavy work.
Executive and administrative salaried grades in private industry and government service can similarly be classified and descriptions given of the qualifications required for each class or grade.
In a low grade the occupational requirement may be an ability to do simple routine office work under close supervision and with little or no need for the worker to exercise independent judgment. Higher grades could require, in varying degree, educational qualifications, administrative ability, leadership, responsibility and powers of independent judgment.
ii . Point Rating System:
Other systems are based on similar general principles but differ in detail. The one most widely used is point rating. This involves a systematic analysis of the factors or qualities required for each job.
These are broadly similar to those mentioned above in describing the grading or classification method: for example, skill, divided into education for training, experience and initiative; effort, both physical and mental; responsibility for equipment, material, safety of others, and the work of others; and job conditions, including good or poor conditions and risks involved.
Then each of these factors is considered according to the degree required; for example, effort required may be very little, little, average, great, or very great. Points are given to each degree of each factor. Descriptions of the work required by each job are examined and broken down into factors and degrees.
Points are given to each degree, the number of points increasing with the importance of the degree. Thus 5 points may be given where very little effort is required and the number raised progressively up to 25 points for very great effort.
Similarly, points varying according to degree are given for each of the other factors or qualities required by the job. The points are then totaled and these give the rating of each job in relation to other jobs. Many variations of this method have been applied indifferent undertakings.
One variation is to use it first for a number of carefully selected jobs which can readily be recognised, described and analysed into their various elements and degrees. These jobs should include some in the most highly skilled occupations, some in the middle range and others requiring relatively little skill.
These are systematically rated by the point’s method. The ratings are then examined; if the results seem unsatisfactory, the factors chosen and the points given to the different degrees are revised so as to give good results, and the system is then applied to all the occupations.
Essay # 6. Job Ranking and Grading System—Job Evaluation:
These two methods are called “non-analytical” as they do not require the analysis of job content. The job ranking system is generally applied in small plants on organisations with a limited number of jobs, such as in small scale industries in West Bengal.
This is the most simple and inexpensive method of job evaluation which is based on accurate job description and organisation charts. The small sized factories find this method easier to adopt and implement.
Each job is ranked by all other jobs, outlining a hierarchy of jobs or job groups. Then standard wage rates are assigned to each level or groups of jobs, which are closely related in terms of rates and contents and treated on a par for purposes of promotion and transfer.
Job grading method is generally adopted in India for salaried people particularly in public sector and government services. In this method the lumber of grades on classifications and their functions are determined. This system takes into account difference in degrees of responsibility, skill, training, etc.
Different Pay Commissions as appointed by the Government of India and the Administrative Reforms Commission have strongly advocated and adopted reduction in number of grades for rationalizing pay scale or grades. In the U.K. also after nationalizing Coal Industry, this method was adopted. In India recently the latest Central Pay Commission has recommended narrowing down of different pay scales.
However, the Pay Commissions of Government of India were of opinion, that in large undertakings, this method might not yield desired results, though it is simple to apply. The main problem is to classify the dissimilar jobs accurately in relation to a limited number of grades.
Essay # 7. Factor-Comparison and Profit Rating System of Job Evaluation:
These two methods are called analytical methods as they require analysis of job content for determining each value. In India the first is seldom favoured by unions and workers. For managements, this method also appears to be clumsy and expensive.
For instance, it can only be applied by experts or committees. This factor comparison method locates within an organisation a small number of widely diversified “Key Jobs” which are, by and large, well remunerate.
Then four or five important job factors are taken on the basis of job analysis, and are located as important in greater or lesser degree in all jobs. Generally, the following factors are considered: mental requirement, skill requirements, physical requirements, responsibility and working conditions etc.
Then key jobs are ranked in respect of each of the factors, and each key job’s current rate of pay is analysed to decide the percentage of the total rate attributable to each job element.
In India, this method has been applied generally to manual, clerical and supervisory jobs as the factors, i.e., skills, have been broadly well defined. Under this system the existing wage and salary practices are reflected in weight-age given to factors without any external comparisons.
Under the point rating system, which is considered the most scientific and systematic method, the following steps are adopted:
First, a group of important factors are defined and selected for the determination of wages, some such factors as education, training, mental, physical effort, responsibility, work environment.
Second, for each factor, a number of degrees are distinguished, i.e., average, small, very small etc.
Third, point values are assigned to each degree of each factor.
Fourth, by taking each individual job and comparing the job description with the degree in respect of all factors, jobs are evaluated.
The following two tables will give an idea of a job evaluation scheme based on point rating system as reported to the I.L.O. which was applied to some Indian Plants.
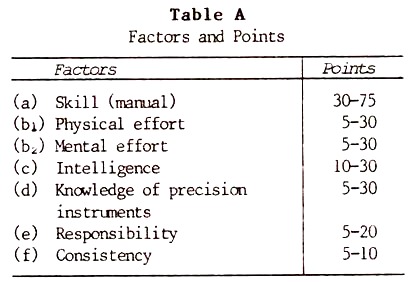
In some Indian firms, the problem of adjustment of existing wage rates to the new rates based on above type of job evaluation has been experienced at the time of collective bargaining.
The accommodation process is given in the following chart:
It will be evident from the above chart that balance dots represent the existing wage rates, the lowest rate in the above company being Rs. 10/- per day and the highest rate is Rs. 29/- per day. The line—indicates the trend of these wage rates; and the line—indicates the proposed new rates of wages.
The introduction of scientific wage structure is possible on the basis of the point rating system. But in many Indian Companies, the objectivity for which this system is noted, has been impaired by some arbitrary Values and definitions assigned by persons who are not experts in the subject.
Essay # 8. Merit Rating as Supplementary to Job Evaluation:
Some Indian Companies prefer to combine merit rating with job evaluation. While job evaluation system evaluates job and not the worker, the merit rating system evaluates the worker along with the job. The initial step of merit rating is evaluation of employee performance by immediate supervisors, which is actually performance appraisal.
The supervisor records the results of his analysis on a standard merit rating inventory forms by comparing actual performance against job assignments and work standard. The final step in this process is the use of the knowledge from such evaluation in making pay change recommendation.
The following may be mentioned as some specific types of merit rating inventories as developed in some companies to assist managers:
(i) Graphic rating scales,
(ii) Check lists,
(iii) Grouping and ranking,
(iv) Direct appraisal,
(v) Standards of performance,
(vi) Critical incident method.
Essay # 9. Maturity Curves – Technique of Managerial Job Evaluation :
But managerial and supervisory jobs which are generally unsupervised may sometimes be required to be evaluated. This is not our subject matter of discussion. So a brief reference may be made to the technique of maturity curves.
In examining this technique the following steps are necessary:
(a) The basic yard-stick is the seniority or length of service.
(b) Annual or monthly salary.
(c) Maturity or career curves create a salary structure for each occupation group i.e., graduate engineers, junior managers etc.
(d) For each year, individual curves mark the highest and the lowest rates and selected percentiles.
(e) The appropriate rate for an individual manager is based on his comparative rating in his occupation and year.
Curves are developed on the basis of survey of occupations and years of experience, i.e., seniority or maturity indicator and current salaries. Salary rates are plotted for each specific job classification on the vertical axis and experience is plotted on the horizontal axis. This is shown in the following diagram.
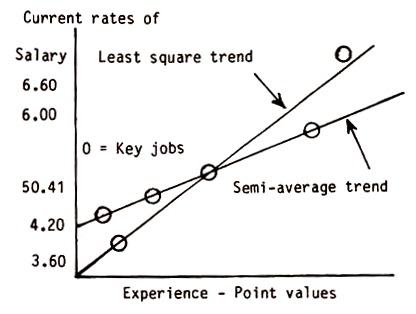
An individual firm may use only the central half or only the upper half of the distribution for its own structure, and within the range the individual is assigned an appropriate salary.
Essay # 10. Comments on Job Evaluation:
Job evaluation as internal alignment system should be based on the principle of equity and fair wage differentials as between different occupations requiring different skills.
The prevailing methods should also take into consideration the following aspects:
External alignment or job pricing based cm comparison of the company wage rates with other comparable external rates.
The relative wages of an employee is no less important than absolute wages. The main purpose of job evaluation is to determine the relative worth of the job and to remove unfair wage differentials. If this objective is not achieved in an enterprise by specific job evaluation method, then the scheme will be self-defeating.
The prevailing job evaluation methods in Indian industries should be such as to remove the discrepancies of a wage payment system which allows high wages and salaries to persons not requiring high skills and responsibilities.
Also the job evaluation system should ensure cordial industrial relations, collective bargaining as well as uniformity in wage structure.
The procedures to be followed in implementing job evaluation system may be suggested as follows:
(a) The job evaluation programme should be so planned and procedures so adopted as to be acceptable to unions.
(b) Selection of jobs to be evaluated.
(c) Procedures for the preparation of job descriptions and job specifications should be formal and specific.
(d) Committees should be appointed to perform job evaluation after selection of a job evaluation method.
(e) Periodic review should be made to keep supervision of job evaluation.
In India, as in other countries, the contemporary job evaluation methods are not applicable to managerial and executive jobs requiring a good deal of decision-making, planning and supervision. It is much more difficult to apply to engineers and scientists. It is, therefore, advisable for Indian enterprises to exclude these types of jobs from the purview of evaluation system.
Application of “career curve” approach, adoption of professional degrees and seniority may be considered as some methods of job evaluation rather than any standard system to executive and managerial jobs for evaluation.
In the USA a sophisticated system known as “Hay System” is adopted for managerial job evaluation under which all such types of jobs are standardised into three basic factors, i.e.,
(i) Know-how,
(ii) Problem-solving and
(iii) Accountability.
Under each of these main factors job description may be prepared on the basis of breadth and depth and evaluated accordingly.
In India, another problem of job evaluation is external alignment or job pricing in respect of a particular wage rate of a specific job of a company as compared with other similar companies. This is necessary for retaining or attracting qualified and efficient employees. But this is not an easy task for employers as job contents with same designations may differ considerably among employers.
The wage payment methods may also differ with varying cost of living in different geographical regions. Nevertheless, external alignment tends to follow equalisation of wage rates as between different jobs in different labour markets on the basis of perfect competition of supply and demand.
Closely related to job pricing, problems of individual pay determination may also crop up in course of job evaluation. In Indian enterprises, this problem may be dealt with by adopting single rates, informal approach, legislated or administered rules and merit rating approach.
The last one may be adopted in managerial job evaluation method as a special form of job performance appraisal. Without going into details, four important merit rating inventories may be mentioned for the consideration of management, i.e., graphic rating scales, check lists, grouping and ranking, direct appraisal, standards of performance and critical incident method.
Finally, some necessary conditions should be fulfilled for the success of job evaluation at plant level.
Some of these conditions may be as follows:
(i) Recognised unions should participate in the preparation and implementation of job evaluation.
(ii) The job evaluation scheme should be simple and clear to rank and file workers, and management must be able to communicate it to workers.
(iii) The method should be implemented jointly with management and union.
(iv) Wage rates and job classifications on the basis of job evaluation should be negotiable under collective bargaining even after job evaluation system is introduced.
(v) Prevailing wage rates should not-be reduced while job evaluation scheme is being prepared.
(vi) Wage and salary surveys and job descriptions must precede job evaluation analysis in a company.
Related Articles:
- Essay on Wage Differentials in India | Workers | Industrial Management
- Wage Structure of Workers in India | Essay | Industrial Management
- Essay on Wage Policy in India | Workers | Industrial Management
- Estimation of Industrial Wages in India | Workers | Industrial Management
We use cookies
Privacy overview.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
An evaluation essay is a piece of writing that aims to assess the value or quality of a particular subject or phenomenon. It involves analyzing a topic, presenting your judgment or opinion on it, and providing evidence or examples to support your claims. This type of essay requires critical thinking, research, and effective communication skills ...
How to write an Evaluation Essay. There are two secrets to writing a strong evaluation essay. The first is to aim for objective analysis before forming an opinion. The second is to use an evaluation criteria. Aim to Appear Objective before giving an Evaluation Argument. Your evaluation will eventually need an argument.
Conclusion. Job evaluation encompasses ranking jobs in an organization. This management tool refuses to go out of fashion for various reasons. This is because job evaluation greatly helps in reducing employee turnover in organizations. Job evaluation helps organizations to reduce grievances that are wage-related.
Job Evaluation Schemes Essay example. Factors/Explanation of a Job Evaluation Scheme: A job evaluation scheme is "a method to determine the value of each job in relation to all jobs within the organization." A job evaluation process is useful because sometimes job titles can be misleading- either unclear or unspecific- and in large ...
Download. Job evaluation system is an imperative part of any organization to evaluate importance of a job prevailing in any organization. Job evaluation highlights value addition by an employee in an organization. This system facilitates skilled and professional staff to review importance of one job in comparison with others.
The job evaluation process compares roles within an organization and industry to determine fair pay. It also helps define employees' responsibilities at work. Normally, human resources, executive leadership teams, and outside partners such as labor unions participate in the job evaluation process, providing insight into what constitutes fair pay.
Job evaluations are a step-by-step process to determine how much money a position should earn. There are different methods of job evaluation, but the point of each method is determining the value the position brings to the company. This ensures the salary is equal to the work. The HR department performs job evaluations based on the role rather ...
Job evaluation and pay structure Essay. Table of Contents. Job evaluation is the process of establishing a structure for jobs in an organisation. The concern for job evaluation is not for people, but the job itself. A pay structure is the procedure of administering its pay philosophy. We will write a custom essay on your topic. 809 writers online.
Writing an effective evaluation essay requires careful planning and execution. Here are some tips to help you write a powerful evaluation essay: 1. Developing a thesis statement for an evaluation essay: A strong thesis statement should clearly state the criteria that will be used to evaluate the subject.
Job Evaluation Essays. Importance and Methods of Job Evaluation for Organizational Effectiveness. Job evaluation involves determining the value of different jobs within an organization through comparison analysis. Human resource management, often in conjunction with workers' unions, is responsible for developing the appropriate job evaluation ...
Job Evaluation There are three major job evaluation methods. These are the time span of discretion, the decision band method and the problem-solving method. The time span of discretion method requires the inputs of whether it is a single- or multiple-task job, the standards used, and the normal length of time between when a subordinate starts a task and when the supervisor checks his or her ...
Essay # 4. Scope of Job Evaluation: Evaluation of clerical, technical, professional and supervisory jobs handled more or less on the principles that are used in evaluating manual or factory jobs. The chief differences that are found to exist revolve round a different approach to the collection of information about the job and a different method ...
Job evaluation and its analysis is a process that entails the creation of structures that establish the worth of every job in an organization. It is based on job itself, the required skills, the specific duties, as well as the working conditions. Job evaluation aims at providing a fair, systematic and consistent mode of measuring the value of ...
There are different ways for job evaluation. Here is a brief discussion of the main approaches ( Adamus, 2009) 1-Ranking job posts: this method is based on the ranking of jobs from the hardest to ...
Here is a step-by-step guide for you to write an evaluation essay. Step 1. Write the Introduction. The introduction is the first impression your readers will have of you, so it's crucial to make a good one. It should capture attention and excite readers, drawing them into what you have to say about this topic.
Job Evaluation. job evaluation |Job analysis is a systematic approach to defining the job role, description, requirements, responsibilities, evaluation, etc. | |It helps in finding out required level of education, skills, knowledge, training, etc for the job position. It also depicts the| |job worth i.e. measurable effectiveness of the job and ...
This paper aims to present a theoretical framework which reveals the relationship between job evaluation (JE) and the development of fair wage structure from the organizational justice (OJ) perspective. It focuses on analyzing the dimensions of job-based pay structure and the use of multifaceted construct of OJ (procedures, distribution and ...
1. Job Analysis: The primary step is an investigation of the jobs in the association. Through job analysis, data on job substance is acquired, together with a valuation for worker prerequisites for effective execution of the job. This data is recorded in the exact, steady dialect of a job description. 2.
Essay On Job Evaluation. 1090 Words5 Pages. Job Evaluation The value or worth of a job is calculated by doing job evaluation. It is a systematic process by which we will calculate the comparative worth of each job in our company. This job evaluation will help us in determining the basis of the wages and salaries offered for each job.
Download. Essay, Pages 11 (2559 words) Views. 132. Job evaluation is a practical technique, designed to enable trained and experienced staff to judge the size of one job relative to others. It does not directly determine pay levels, but will establish the basis for an internal ranking of jobs. An approach designed to enable a job to be compared ...
Job evaluation refers to the process of determining the comparative job worth of an organization's work in order to create the organization's job structure. The process involves determination of the content of the job, the skills needed to perform the job, the value of the job to the organization. The process also involves the evaluation of ...
Job evaluation. Words: 2853 (12 pages) Introduction The perspective on choosing the correct job evaluation method mainly depends on the advantages to the specific job position and duties performed. The ability to define and correlate the overall aspects to each method provides an understanding towards the fundamentals on job evaluation.
Essay # 4. Practice of Job Evaluation in India: The Background and Scope. In India, job evaluation as a method of rationalizing wage structure has been attempted, by and large, in public sector. Some bigger private sector industries have also taken recourse to job evaluation with cooperation of trade unions.