

The Story of an Hour
Kate chopin, ask litcharts ai: the answer to your questions.
| Summary & Analysis |
The Story of an Hour Analysis & Summary – Essay Example
This sample will help you write a The Story of an Hour analysis essay! Here you’ll find a The Story of an Hour summary. Essay also contains a plot and character analysis.
Introduction
The story of an hour introduction, the story of an hour main plot, the story of an hour conclusion, the story of an hour analysis.
The Story of an Hour is a short story written by Kate Chopin in 1894. This famous piece of literature was controversial for its time, as the story mentioned a female protagonist who felt relieved after her husband’s death. The conclusion of The Story of an Hour is ironic, which makes the ending memorable.
The following The Story of an Hour literary analysis essay will summarize the plot and present an extensive character analysis of Mrs. Mallard. It will be helpful for those writing a The Story of an Hour critical analysis.
Kate Chopin (born Catherine O’Flaherty) was an American writer. She is best known for her narratives of delicate and brave women’s inner lives. Her novel “The Awakening” and her short stories, among them The Story of an Hour, are being read in countries all over the world today. She is widely recognized as one of the most important authors in America.
In 1984, Kate Chopin wrote The Story of an Hour. It portrays a woman, Louise Mallard, who lost her husband in an accident. However, she later discovers that the husband survived. Mrs. Mallard goes through many emotions and feelings, reevaluating her life. That ultimately kills her when she meets her presumably dead husband at the door. The following The Story of an Hour essay will focus on the plot and the protagonist’s self-development.
The Story of an Hour Summary
Louise Mallard, the main character, had always had a heart problem. It was not a secret for her friends and relatives, so everyone tried to protect her from worries.
One day her husband, Brently Mallard, was mistaken for having died in a horrible railroad accident. Richard, Mr. Mallard’s friend, was the one who learned about this death while in the office. Josephine, Louise’s sister, broke the news to her.
Josephine was very cautious because of Mrs. Mallard’s health issue. She feared such a tragedy would cause a heart attack. Bit by bit, she strategized how to tell everything to her sister, aher plan went perfectly well. Mrs. Mallard wept only once. She did not receive the story like many women would, with a helpless incapacity to acknowledge its meaning. She only cried in her sister’s arms with a feeling of a sudden, wild abandonment (Woodlief 2).
Immediately Mrs. Mallard found herself wondering how she could survive without her husband. She went to a room and locked herself to contemplate the consequences of his death. She was devastated, and this sadness was only natural. This man had been close to her, even though only for a short time. Her sister Josephine and Mr. Richard also mourned the loss (Taibah 1).
Mrs. Mallard was alone in that room, thinking about the future. As she was contemplating her fate, instead of grief, she began realizing that this was the beginning of a better part of her life. Louise saw independence and plenty of possibilities to do what her heart desired. Now, she had only to think about herself.
Later, Josephine comes to Louise’s room, crying with a joyous smile. They descend the house’s stairs, where Mr. Mallard appears at the door. He was not involved in the accident and did not understand why Josephine was crying. At the shock of seeing her husband again, Mrs. Mallard collapses. The doctors declare that she died because of the problems with her heart.
Health issues of the central character play a significant role in the story. The author managed to bring suspense in the way she described telling the bad news to a person with a heart problem. Josephine, Louise’s sister, tries her best to be careful and attentive, expecting a painful response. However, Mrs. Mallard reacts better than anticipated.
The story focuses mostly on femininity and the institution of marriage. The analysis of The Story of an Hour has to speculate on it to reveal the core message.
The author was able to illustrate that men entirely dominate the institution of marriage. Mr. Mallard, for instance, treated his wife the way she wanted only from time to time. For years, Louise has done many things to please her husband without looking after her well-being. So, having received the disturbing news, she is quite happy. It seemed that she had never cared for her husband at all.
Or did she? Mrs. Mallard’s reaction to the death of a spouse is complicated. She cannot escape the loneliness and grief that came with the loss. But the possibility of happiness prevails. Louise knew that marriage had made her a subject for him against her will. She only felt sorrow for the loss of his life but not for living without him. She felt deep inside that she had been freed from the chains of living for another person.
Mr. Mallard’s apparent death saddened Louise at first. She was devastated about his fate but regained strength quickly. Louise was well aware of the fact that she could not bring her husband back. So, she came to terms with it, which wasn’t difficult. Mrs. Mallard saw beyond the painful moment, anticipating freedom for the rest of her life.
The room and environment around Mrs. Mallard symbolize her desire for freedom. For example, Mrs. Mallard could see the tops of trees through the window. They were all aquiver with the new spring life on the open square before her house. There was a delicious breath of rain in the air. A peddler was weeping his wares in the street below. There were spots of blue sky showing up here and there through the clouds in the west facing her window, which had met and piled up one above the other (Woodlief 1).
An open window could be interpreted as a metaphor. It reflects new possibilities and resources that Mrs. Mallard now had in her sights without anybody stopping her. She referred to it as the late spring of life.
The story reveals how women were secretly marginalized. At the time, society expected them to pursue wealth and safety, which came with a husband. Liberty should be neither their worry nor their goal. When Louise felt freedom after Mr. Mallard’s death, she kept it secret for obvious reasons. But then, her sister arrived.
Mrs. Mallard was shocked by the sight of her husband alive. All of her newfound liberty and dreams came crashing down at that moment. This shattering experience even goes to the extreme of destroying her life. Whereas she was to be happy to see her husband alive, Louise died from a heart attack.
Situational irony is presented in the author’s stylistic use of words: “She had died of heart disease…of the joy that kills.” People around anticipated this tragedy from the news about Mr. Mallard’s death, not miraculous survival.
The author explored the character of Mrs. Mallard throughout this story. The reader can’t be surprised by her sudden death or miss its irony. Louise is a woman with a great desire for independence, which a man has deprived her of through marriage. Mr. Mallard represents the absence of her liberty that restores after his death. When Mrs. Mallard sees her husband at the door once again, she collapses and never wakes up.
Based on this The Story of an Hour literary analysis, we can draw several important conclusions. Mrs. Mallard couldn’t control her emotions when they concerned the most vital matters. The lack of liberty and independence may have caused her heart problems in the first place. And they cost her life in the end.
Her husband, Mr. Mallard, took Louise’s freedom when he married her. However, as it became apparent from the story, he never valued her. When she died, he had finally faced the consequences of always taking her existence for granted.
Therefore, the oppressor faced even worse tragedy than the oppressed. The dramatic irony of Mr. Mallard’s unawareness of his wife’s true feelings towards him is a big part of the story. So, in the end, it was Mr. Mallard’s presence that killed his wife.
- Chopin, Kate. The Story of an hour . The Kate Chopin International Society. Web.
- Woodlief, Ann. The Story of an Hour . 2011, Virginia Commonwealth University. Web.
What is the symbolism in The Story of an Hour?
Through The Story of an Hour, the author presents us with the inner feelings and thoughts of a woman using various symbols. Mrs. Mallard’s heart problem symbolizes her dissatisfaction with the marriage, while the open window illustrates her aspirations towards a better, independent life.
What is the meaning behind The Story of an Hour?
Kate Chopin’s The Story of an Hour analysis illustrates that the author wanted to tell us how the society of that time was unfair towards women. It also shows the delicate and complicated inner world of a woman.
What does The Story of an Hour critique?
The Story of an Hour criticizes the typical experience of marriage in the 1890s. For women, such marriage was repressive and meant their loss of personal freedoms. Therefore, the story criticizes the society of that time dominated by men.
How do you start a critical analysis of The Story of an Hour?
Start your analysis of The Story of an Hour with a short introduction. Remember to say a few words about its author and her life. Next, talk about the story and let the reader know what it is about.
What are the two main themes in The Story of an Hour?
Firstly, the theme of a female search for self-identity is featured strongly in the story. The second theme is that of repressive marriage. The reader sees it in the way Mrs. Mallard’s reaction toward her husband’s death shifts.
Cite this paper
- Chicago (N-B)
- Chicago (A-D)
StudyCorgi. (2020, July 9). The Story of an Hour Analysis & Summary – Essay Example. https://studycorgi.com/the-story-of-an-hour-analysis-summary-essay-example/
"The Story of an Hour Analysis & Summary – Essay Example." StudyCorgi , 9 July 2020, studycorgi.com/the-story-of-an-hour-analysis-summary-essay-example/.
StudyCorgi . (2020) 'The Story of an Hour Analysis & Summary – Essay Example'. 9 July.
1. StudyCorgi . "The Story of an Hour Analysis & Summary – Essay Example." July 9, 2020. https://studycorgi.com/the-story-of-an-hour-analysis-summary-essay-example/.
Bibliography
StudyCorgi . "The Story of an Hour Analysis & Summary – Essay Example." July 9, 2020. https://studycorgi.com/the-story-of-an-hour-analysis-summary-essay-example/.
StudyCorgi . 2020. "The Story of an Hour Analysis & Summary – Essay Example." July 9, 2020. https://studycorgi.com/the-story-of-an-hour-analysis-summary-essay-example/.
This paper, “The Story of an Hour Analysis & Summary – Essay Example”, was written and voluntary submitted to our free essay database by a straight-A student. Please ensure you properly reference the paper if you're using it to write your assignment.
Before publication, the StudyCorgi editorial team proofread and checked the paper to make sure it meets the highest standards in terms of grammar, punctuation, style, fact accuracy, copyright issues, and inclusive language. Last updated: January 24, 2024 .
If you are the author of this paper and no longer wish to have it published on StudyCorgi, request the removal . Please use the “ Donate your paper ” form to submit an essay.

A Summary and Analysis of Kate Chopin’s ‘The Story of an Hour’
By Dr Oliver Tearle (Loughborough University)
Some short stories can say all they need to do in just a few pages, and Kate Chopin’s three-page 1894 story ‘The Story of an Hour’ (sometimes known as ‘The Dream of an Hour’) is a classic example. Yet those three pages remain tantalisingly ambiguous, perhaps because so little is said, so much merely hinted at. Yet Chopin’s short story is, upon closer inspection, a subtle, studied analysis of death, marriage, and personal wishes.
Written in April 1894 and originally published in Vogue in December of that year, the story focuses on an hour in the life of a married woman who has just learnt that her husband has apparently died.
‘The Story of an Hour’: plot summary
What happens in that brief hour, that story of an hour? A married woman, Mrs Louise Mallard, who has heart trouble, learns that her husband has died in a railroad accident.
Her sister Josephine breaks the news to her; it was her husband’s friend Richards who first heard about the railroad disaster and saw her husband’s name, Brently Mallard, at the top of the list of fatalities. Her first reaction is to weep at the news that her husband is dead; she then takes herself off to her room to be alone.
She sinks into an armchair and finds herself attuned to a series of sensations: the trees outside the window ‘aquiver with the new spring life’, the ‘breath of rain’ in the air; the sound of a peddler crying his wares in the street below. She finds herself going into a sort of trancelike daze, a ‘suspension of intelligent thought’.
Then, gradually, a feeling begins to form within her: a sense of freedom. Now her husband is dead, it seems, she feels free. She dreads seeing her husband’s face (as she knows she must, when she goes to identify the body), but she knows that beyond that lie years and years of her life yet to be lived, and ‘would all belong to her absolutely’.
She reflects that she had loved her husband – sometimes. Sometimes she hadn’t. But now, that didn’t matter: what matters is the ‘self-assertion’, the declaration of independence, that her life alone represents a new start.
But then, her sister Josephine calls from outside the door for her to come out, worried that Louise is making herself ill. But Louise doesn’t feel ill: she feels on top of the world. She used to dread the prospect of living to a ripe old age, but now she welcomes such a prospect. Eventually she opens the door and she and Josephine go back downstairs.
Richards is still down there, waiting for them. Then, there’s a key in the front door and who should enter but … Mrs Mallard’s husband, Brently Mallard.
It turns out he was nowhere near the scene of the railroad accident, and is unharmed! Mrs Mallard is so shocked at his return that she dies, partly because of her heart disease but also, so ‘they’ said, from the unexpected ‘joy’ of her husband’s return.
‘The Story of an Hour’: analysis
In some ways, ‘The Story of an Hour’ prefigures a later story like D. H. Lawrence’s ‘ Odour of Chrysanthemums ’ (1911), which also features a female protagonist whose partner’s death makes her reassess her life with him and to contemplate the complex responses his death has aroused in her.
However, in Lawrence’s story the husband really has died (in a mining accident), whereas in ‘The Story of an Hour’, we find out at the end of the story that Mr Mallard was not involved in the railroad accident and is alive and well. In a shock twist, it is his wife who dies, upon learning that he is still alive.
What should we make of this ‘dream of an hour’? That alternative title is significant, not least because of the ambiguity surrounding the word ‘dream’. Is Louise so plunged into shock by the news of her husband’s apparent death that she begins to hallucinate that she would be better off without him? Is this her way of coping with traumatic news – to try to look for the silver lining in a very black cloud? Or should we analyse ‘dream’ as a sign that she entertains aspirations and ambitions, now her husband is out of the way?
‘The Dream of an Hour’ perhaps inevitably puts us in mind of Kate Chopin’s most famous story, the short novel The Awakening (1899), whose title reflects its female protagonist Edna Pontellier’s growing awareness that there is more to life than her wifely existence.
But Louisa Mallard’s ‘awakening’ remains a dream; when she awakes from it, upon learning that her husband is still alive and all her fancies about her future life have been in vain, she dies.
‘The Story of an Hour’ and modernism
‘The Story of an Hour’ is an early example of the impressionistic method of storytelling which was also being developed by Anton Chekhov around the same time as Chopin, and which would later be used by modernists such as Katherine Mansfield, James Joyce, and Virginia Woolf.
Although the story uses an omniscient third-person narrator, we are shown things from particular character perspectives in a way that reflects their own confusions and erratic thoughts – chiefly, of course, Louisa Mallard’s own.
But this impressionistic style – which is more interested in patterns of thought, daydreaming, and emotional responses to the world than in tightly structured plots – continues right until the end of the story.
Consider the final sentence of the story: ‘When the doctors came they said she had died of heart disease – of joy that kills.’ The irony, of course, is that Louisa appears to have accepted her husband’s death and to have taken his demise as a chance to liberate herself from an oppressive marriage (note Chopin’s reference to the lines on her face which ‘bespoke repression and even a certain strength’ – what did she need that strength for, we wonder?).
So it was not joy but disappointment, if anything, that brought on the heart attack that killed her. But the (presumably male) doctors who attended her death would not have assumed any such thing: they would have analysed her death as a result of her love for her husband, and the sheer joy she felt at having him back.
Chopin’s story also foreshadows Katherine Mansfield’s ‘The Garden Party’ , and Laura Sheridan’s enigmatic emotional reaction to seeing her first dead body (as with Chopin’s story, a man who has died in an accident). If you enjoyed this analysis of ‘The Story of an Hour’, you might also enjoy Anton Chekhov’s 1900 story ‘At Christmas Time’, to which Chopin’s story has been compared.
Discover more from Interesting Literature
Subscribe to get the latest posts to your email.
Type your email…
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Continue reading

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, the story of an hour: summary and analysis.
General Education

Imagine a world where women are fighting for unprecedented rights, the economic climate is unpredictable, and new developments in technology are made every year. While this world might sound like the present day, it also describes America in the 1890s .
It was in this world that author Kate Chopin wrote and lived, and many of the issues of the period are reflected in her short story, “The Story of an Hour.” Now, over a century later, the story remains one of Kate Chopin’s most well-known works and continues to shed light on the internal struggle of women who have been denied autonomy.
In this guide to Kate Chopin’s “The Story of an Hour,” we’ll discuss:
- A brief history of Kate Chopin and America the 1890s
- “The Story of an Hour” summary
- Analysis of the key story elements in “The Story of an Hour,” including themes, characters, and symbols
By the end of this article, you’ll have an expert grasp on Kate Chopin’s “The Story of an Hour.” So let’s get started!

“The Story of an Hour” Summary
If it’s been a little while since you’ve read Kate Chopin’s “The Story of an Hour,” it can be hard to remember the important details. This section includes a quick recap, but you can find “The Story of an Hour” PDF and full version here . We recommend you read it again before diving into our analyses in the next section!
For those who just need a refresher, here’s “The Story of an Hour” summary:
Mrs. Louise Mallard is at home when her sister, Josephine, and her husband’s friend, Richards, come to tell her that her husband, Brently Mallard, has been killed in a railroad accident . Richards had been at the newspaper office when the news broke, and he takes Josephine with him to break the news to Louise since they’re afraid of aggravating her heart condition. Upon hearing the news of her husband’s death, Louise is grief-stricken, locks herself in her room, and weeps.
From here, the story shifts in tone. As Louise processes the news of her husband’s death, she realizes something wonderful and terrible at the same time: she is free . At first she’s scared to admit it, but Louise quickly finds peace and joy in her admission. She realizes that, although she will be sad about her husband (“she had loved him—sometimes,” Chopin writes), Louise is excited for the opportunity to live for herself. She keeps repeating the word “free” as she comes to terms with what her husband’s death means for her life.
In the meantime, Josephine sits at Louise’s door, coaxing her to come out because she is worried about Louise’s heart condition. After praying that her life is long-lived, Louise agrees to come out. However, as she comes downstairs, the front door opens to reveal her husband, who had not been killed by the accident at all. Although Richards tries to keep Louise’s heart from shock by shielding her husband from view, Louise dies suddenly, which the doctors later attribute to “heart disease—of the joy that kills .”

Kate Chopin, the author of "The Story of an Hour," has become one of the most important American writers of the 19th century.
The History of Kate Chopin and the 1890s
Before we move into “The Story of an Hour” analysis section, it’s helpful to know a little bit about Kate Chopin and the world she lived in.
A Short Biography of Kate Chopin
Born in 1850 to wealthy Catholic parents in St. Louis, Missouri, Kate Chopin (originally Kate O’Flaherty) knew hardship from an early age. In 1855, Chopin lost her father, Thomas, when he passed away in a tragic and unexpected railroad accident. The events of this loss would stay with Kate for the rest of her life, eventually becoming the basis for “The Story of an Hour” nearly forty years later.
Chopin was well-educated throughout her childhood , reading voraciously and becoming fluent in French. Chopin was also very aware of the divide between the powerful and the oppressed in society at the time . She grew up during the U.S. Civil War, so she had first-hand knowledge of violence and slavery in the United States.
Chopin was also exposed to non-traditional roles for women through her familial situation. Her mother, grandmother, and great-grandmother chose to remain widows (rather than remarry) after their husbands died. Consequently, Chopin learned how important women’s independence could be, and that idea would permeate much of her writing later on.
As Chopin grew older, she became known for her beauty and congeniality by society in St. Louis. She was married at the age of nineteen to Oscar Chopin, who came from a wealthy cotton-growing family. The couple moved to New Orleans, where they would start both a general store and a large family. (Chopin would give birth to seven children over the next nine years!)
While Oscar adored his wife, he was less capable of running a business. Financial trouble forced the family to move around rural Louisiana. Unfortunately, Oscar would die of swamp fever in 1882 , leaving Chopin in heavy debt and with the responsibility of managing the family’s struggling businesses.
After trying her hand at managing the property for a year, Chopin conceded to her mother’s requests to return with her children to St. Louis. Chopin’s mother died the year after. In order to support herself and her children, Kate began to write to support her family.
Luckily, Chopin found immediate success as a writer. Many of her short stories and novels—including her most famous novel, The Awakening— dealt with life in Louisiana . She was also known as a fast and prolific writer, and by the end of the 1900s she had written over 100 stories, articles, and essays.
Unfortunately, Chopin would pass away from a suspected cerebral hemorrhage in 1904, at the age of 54 . But Kate Chopin’s “The Story of an Hour” and other writings have withstood the test of time. Her work has lived on, and she’s now recognized as one of the most important American writers of the 19th century.

American life was undergoing significant change in the 19th century. Technology, culture, and even leisure activities were changing.
American Life in the 1890s
“The Story of an Hour” was written and published in 1894, right as the 1800s were coming to a close. As the world moved into the new century, American life was also changing rapidly.
For instance, t he workplace was changing drastically in the 1890s . Gone were the days where most people were expected to work at a trade or on a farm. Factory jobs brought on by industrialization made work more efficient, and many of these factory owners gradually implemented more humane treatment of their workers, giving them more leisure time than ever.
Though the country was in an economic recession at this time, technological changes like electric lighting and the popularization of radios bettered the daily lives of many people and allowed for the creation of new jobs. Notably, however, work was different for women . Working women as a whole were looked down upon by society, no matter why they found themselves in need of a job.
Women who worked while they were married or pregnant were judged even more harshly. Women of Kate Chopin’s social rank were expected to not work at all , sometimes even delegating the responsibility of managing the house or child-rearing to maids or nannies. In the 1890s, working was only for lower class women who could not afford a life of leisure .
In reaction to this, the National American Woman Suffrage Association was created in 1890, which fought for women’s social and political rights. While Kate Chopin was not a formal member of the suffragette movements, she did believe that women should have greater freedoms as individuals and often talked about these ideas in her works, including in “The Story of an Hour.”

Kate Chopin's "The Story of an Hour" a short exploration of marriage and repression in America.
“The Story of an Hour” Analysis
Now that you have some important background information, it’s time to start analyzing “The Story of an Hour.”
This short story is filled with opposing forces . The themes, characters, and even symbols in the story are often equal, but opposite, of one another. Within “The Story of an Hour,” analysis of all of these elements reveals a deeper meaning.
“The Story of an Hour” Themes
A theme is a message explored in a piece of literature. Most stories have multiple themes, which is certainly the case in “The Story of an Hour.” Even though Chopin’s story is short, it discusses the thematic ideas of freedom, repression, and marriage.
Keep reading for a discussion of the importance of each theme!
Freedom and Repression
The most prevalent theme in Chopin’s story is the battle between freedom and “repression.” Simply put , repression happens when a person’s thoughts, feelings, or desires are being subdued. Repression can happen internally and externally. For example, if a person goes through a traumatic accident, they may (consciously or subconsciously) choose to repress the memory of the accident itself. Likewise, if a person has wants or needs that society finds unacceptable, society can work to repress that individual. Women in the 19th century were often victims of repression. They were supposed to be demure, gentle, and passive—which often went against women’s personal desires.
Given this, it becomes apparent that Louise Mallard is the victim of social repression. Until the moment of her husband’s supposed death, Louise does not feel free . In their marriage, Louise is repressed. Readers see this in the fact that Brently is moving around in the outside world, while Louise is confined to her home. Brently uses railroad transportation on his own, walks into his house of his own accord, and has individual possessions in the form of his briefcase and umbrella. Brently is even free from the knowledge of the train wreck upon his return home. Louise, on the other hand, is stuck at home by virtue of her position as a woman and her heart condition.
Here, Chopin draws a strong contrast between what it means to be free for men and women. While freedom is just part of what it means to be a man in America, freedom for women looks markedly different. Louise’s life is shaped by what society believes a woman should be and how a wife should behave. Once Louise’s husband “dies,” however, she sees a way where she can start claiming some of the more “masculine” freedoms for herself. Chopin shows how deeply important freedom is to the life of a woman when, in the end, it’s not the shock of her husband’s return of her husband that kills Louise, but rather the thought of losing her freedom again.
Marriage as a “The Story of an Hour” theme is more than just an idyllic life spent with a significant other. The Mallard’s marriage shows a reality of 1890s life that was familiar to many people. Marriage was a means of social control —that is to say, marriage helped keep women in check and secure men’s social and political power. While husbands were usually free to wander the world on their own, hold jobs, and make important family decisions, wives (at least those of the upper class) were expected to stay at home and be domestic.
Marriage in Louise Mallard’s case has very little love. She sees her marriage as a life-long bond in which she feels trapped, which readers see when she confesses that she loved her husband only “sometimes.” More to the point, she describes her marriage as a “powerful will bending hers in that blind persistence with which men and women believe they have a right to impose a private will upon a fellow-creature.” In other words, Louise Mallard feels injustice in the expectation that her life is dictated by the will of her husband.
Like the story, the marriages Kate witnessed often ended in an early or unexpected death. The women of her family, including Kate herself, all survived their husbands and didn’t remarry. While history tells us that Kate Chopin was happy in her marriage, she was aware that many women weren’t. By showing a marriage that had been built on control and society’s expectations, Chopin’s “The Story of an Hour” highlights the need for a world that respected women as valuable partners in marriage as well as capable individuals.

While this painting by Johann Georg Meyer wasn't specifically of Louise Mallard, "Young Woman Looking Through a Window" is a depiction of what Louise might have looked like as she realized her freedom.
"The Story of an Hour" Characters
The best stories have developed characters, which is the case in “The Story of an Hour,” too. Five characters make up the cast of “The Story of an Hour”:
Louise Mallard
Brently mallard.
- The doctor(s)
By exploring the details of each character, we can better understand their motivations, societal role, and purpose to the story.
From the opening sentence alone, we learn a lot about Louise Mallard. Chopin writes, “Knowing that Mrs. Mallard was afflicted with a heart trouble, great care was taken to break to her as gently as possible the news of her husband’s death.”
From that statement alone, we know that she is married, has a heart condition, and is likely to react strongly to bad news . We also know that the person who is sharing the bad news views Louise as delicate and sensitive. Throughout the next few paragraphs, we also learn that Louise is a housewife, which indicates that she would be part of the middle-to-upper class in the 1890s. Chopin also describes Louise’s appearance as “young,” “fair, calm face,” with lines of “strength.” These characteristics are not purely physical, but also bleed into her character throughout the story.
Louise’s personality is described as different from other women . While many women would be struck with the news in disbelief, Louise cries with “wild abandonment”—which shows how powerful her emotions are. Additionally, while other women would be content to mourn for longer, Louise quickly transitions from grief to joy about her husband’s passing.
Ultimately, Chopin uses Louise’s character to show readers what a woman’s typical experience within marriage was in the 1890s. She uses Louise to criticize the oppressive and repressive nature of marriage, especially when Louise rejoices in her newfound freedom.
Josephine is Louise’s sister . We never hear of Josephine’s last name or whether she is married or not. We do know that she has come with Richards, a friend of Brently’s, to break the news of his death to her sister.
When Josephine tells Louise the bad news, she’s only able to tell Louise of Brently’s death in “veiled hints,” rather than telling her outright. Readers can interpret this as Josephine’s attempt at sparing Louise’s feelings. Josephine is especially worried about her sister’s heart condition, which we see in greater detail later as she warns Louise, “You will make yourself ill.” When Louise locks herself in her room, Josephine is desperate to make sure her sister is okay and begs Louise to let her in.
Josephine is the key supporting character for Louise, helping her mourn, though she never knows that Louise found new freedom from her husband’s supposed death . But from Josephine’s actions and interactions with Louise, readers can accurately surmise that she cares for her sister (even if she’s unaware of how miserable Louise finds her life).
Richards is another supporting character, though he is described as Brently’s friend, not Louise’s friend. It is Richards who finds out about Brently Mallard’s supposed death while at the newspaper office—he sees Brently’s name “leading the list of ‘killed.’” Richards’ main role in “The Story of an Hour” is to kick off the story’s plot.
Additionally, Richard’s presence at the newspaper office suggests he’s a writer, editor, or otherwise employee of the newspaper (although Chopin leaves this to readers’ inferences). Richards takes enough care to double-check the news and to make sure that Brently’s likely dead. He also enlists Josephine’s help to break the news to Louise. He tries to get to Louise before a “less careful, less tender friend” can break the sad news to her, which suggests that he’s a thoughtful person in his own right.
It’s also important to note is that Richards is aware of Louise’s heart condition, meaning that he knows Louise Mallard well enough to know of her health and how she is likely to bear grief. He appears again in the story at the very end, when he tries (and fails) to shield Brently from his wife’s view to prevent her heart from reacting badly. While Richards is a background character in the narrative, he demonstrates a high level of friendship, consideration, and care for Louise.
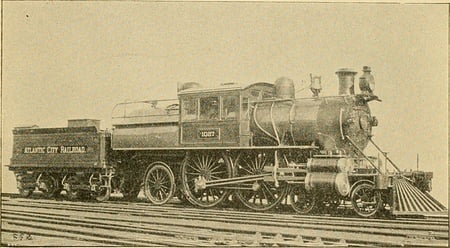
Brently Mallard would have been riding in a train like this one when the accident supposedly occurred.
Mr. Brently Mallard is the husband of the main character, Louise. We get few details about him, though readers do know he’s been on a train that has met with a serious accident. For the majority of the story, readers believe Brently Mallard is dead—though the end of “The Story of an Hour” reveals that he’s been alive all along. In fact, Brently doesn’t even know of the railroad tragedy when he arrives home “travel-stained.”
Immediately after Louise hears the news of his death, she remembers him fondly. She remarks on his “kind, tender hands” and says that Brently “never looked save with love” upon her . It’s not so much Brently as it’s her marriage to him which oppresses Louise. While he apparently always loved Louise, Louise only “sometimes” loved Brently. She constantly felt that he “impose[d] a private will” upon her, as most husbands do their wives. And while she realizes that Brently likely did so without malice, she also realized that “a kind intention or a cruel intention” makes the repression “no less a crime.”
Brently’s absence in the story does two things. First, it contrasts starkly with Louise’s life of illness and confinement. Second, Brently’s absence allows Louise to imagine a life of freedom outside of the confines of marriage , which gives her hope. In fact, when he appears alive and well (and dashes Louise’s hopes of freedom), she passes away.
The Doctor(s)
Though the mention of them is brief, the final sentence of the story is striking. Chopin writes, “When the doctors came they said she had died of heart disease—of the joy that kills.” Just as she had no freedom in life, her liberation from the death of her husband is told as a joy that killed her.
In life as in death, the truth of Louise Mallard is never known. Everything the readers know about her delight in her newfound freedom happens in Louise’s own mind; she never gets the chance to share her secret joy with anyone else.
Consequently, the ending of the story is double-sided. If the doctors are to be believed, Louise Mallard was happy to see her husband, and her heart betrayed her. And outwardly, no one has any reason to suspect otherwise. Her reaction is that of a dutiful, delicate wife who couldn’t bear the shock of her husband returned from the grave.
But readers can infer that Louise Mallard died of the grief of a freedom she never had , then found, then lost once more. Readers can interpret Louise’s death as her experience of true grief in the story—that for her ideal life, briefly realized then snatched away.

In "The Story of an Hour," the appearance of hearts symbolize both repression and hope.
“The Story of an Hour” Symbolism and Motifs
Symbols are any object, word, or other element that appear in the story and have additional meanings beyond. Motifs are elements from a story that gain meaning from being repeated throughout the narrative. The line between symbols and motifs is often hazy, but authors use both to help communicate their ideas and themes.
In “The Story of an Hour,” symbolism is everywhere, but the three major symbols present in the story are:
- The heart
- The house and the outdoors
- Joy and sorrow
Heart disease, referred to as a “heart condition” within the text, opens and closes the text. The disease is the initial cause for everyone’s concern, since Louise’s condition makes her delicate. Later, heart disease causes Louise’s death upon Brently’s safe return. In this case, Louise’s ailing heart has symbolic value because it suggests to readers that her life has left her heartbroken. When she believes she’s finally found freedom, Louise prays for a long life...when just the day before, she’d “had thought with a shudder that life might be long.”
As Louise realizes her freedom, it’s almost as if her heart sparks back to life. Chopin writes, “Now her bosom rose and fell tumultuously...she was striving to beat it back...Her pulses beat fast, and the coursing blood warmed and relaxed every inch of her body.” These words suggest that, with her newfound freedom, the symptoms of her heart disease have lifted. Readers can surmise that Louise’s diseased heart is the result of being repressed, and hope brings her heart back to life.
Unfortunately, when Brently comes back, so does Louise’s heart disease. And, although her death is attributed to joy, the return of her (both symbolic and literal) heart disease kills her in the end.

The House and the Outdoors
The second set of symbols are Louise’s house and the world she can see outside of her window. Chopin contrasts these two symbolic images to help readers better understand how marriage and repression have affected Louise.
First of all, Louise is confined to the home—both within the story and in general. For her, however, her home isn’t a place to relax and feel comfortable. It’s more like a prison cell. All of the descriptions of the house reinforce the idea that it’s closed off and inescapable . For instance, the front door is locked when Mr. Mallard returns home. When Mrs. Mallard is overcome with grief, she goes deeper inside her house and locks herself in her room.
In that room, however, Mrs. Mallard takes note of the outdoors by looking out of her window. Even in her momentary grief, she describes the “open square before her house” and “the new spring life.” The outdoors symbolize freedom in the story, so it’s no surprise that she realizes her newfound freedom as she looks out her window. Everything about the outside is free, beautiful, open, inviting, and pleasant...a stark contrast from the sadness inside the house .
The house and its differences from outdoors serve as one of many symbols for how Louise feels about her marriage: barred from a world of independence.
Joy and Sorrow
Finally, joy and sorrow are motifs that come at unexpected times throughout “The Story of an Hour.” Chopin juxtaposes joy and sorrow to highlight how tragedy releases Louise from her sorrow and gives her a joyous hope for the future.
At first, sorrow appears as Louise mourns the death of her husband. Yet, in just a few paragraphs, she finds joy in the event as she discovers a life of her own. Though Louise is able to see that feeling joy at such an event is “monstrous,” she continues to revel in her happiness.
It is later that, when others expect her to be joyful, Josephine lets out a “piercing cry,” and Louise dies. Doctors interpret this as “the joy that kills,” but more likely it’s a sorrow that kills. The reversal of the “appropriate” feelings at each event reveals how counterintuitive the “self-assertion which she suddenly recognized as the strongest impulse of her being” is to the surrounding culture. This paradox reveals something staggering about Louise’s married life: she is so unhappy with her situation that grief gives her hope...and she dies when that hope is taken away.
Key Takeaways: Kate Chopin's “The Story of an Hour”
Analyzing Chopin’s “The Story of an Hour” takes time and careful thought despite the shortness of the story. The story is open to multiple interpretations and has a lot to reveal about women in the 1890s, and many of the story’s themes, characters, and symbols critique women’s marriage roles during the period .
There’s a lot to dig through when it comes to “The Story of an Hour” analysis. If you’re feeling overwhelmed, just remember a few things :
- Events from Kate Chopin’s life and from social changes in the 1890s provided a strong basis for the story.
- Mrs. Louise Mallard’s heart condition, house, and feelings represent deeper meanings in the narrative.
- Louise goes from a state of repression, to freedom, and then back to repression, and the thought alone is enough to kill her.
Remembering the key plot points, themes, characters, and symbols will help you write any essay or participate in any discussion. Kate Chopin’s “The Story of an Hour” has much more to uncover, so read it again, ask questions, and start exploring the story beyond the page!

What’s Next?
You may have found your way to this article because analyzing literature can be tricky to master. But like any skill, you can improve with practice! First, make sure you have the right tools for the job by learning about literary elements. Start by mastering the 9 elements in every piece of literature , then dig into our element-specific guides (like this one on imagery and this one on personification .)
Another good way to start practicing your analytical skills is to read through additional expert guides like this one. Literary guides can help show you what to look for and explain why certain details are important. You can start with our analysis of Dylan Thomas’ poem, “Do not go gentle into that good night.” We also have longer guides on other words like The Great Gatsby and The Crucible , too.
If you’re preparing to take the AP Literature exam, it’s even more important that you’re able to quickly and accurately analyze a text . Don’t worry, though: we’ve got tons of helpful material for you. First, check out this overview of the AP Literature exam . Once you have a handle on the test, you can start practicing the multiple choice questions , and even take a few full-length practice tests . Oh, and make sure you’re ready for the essay portion of the test by checking out our AP Literature reading list!

Ashley Sufflé Robinson has a Ph.D. in 19th Century English Literature. As a content writer for PrepScholar, Ashley is passionate about giving college-bound students the in-depth information they need to get into the school of their dreams.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!

Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
Literary Theory and Criticism
Home › Literature › Analysis of Kate Chopin’s The Story of an Hour
Analysis of Kate Chopin’s The Story of an Hour
By NASRULLAH MAMBROL on July 28, 2021
Originally entitled “The Dream of an Hour” when it was first published in Vogue (December 1894), “The Story of an Hour” has since become one of Kate Chopin’s most frequently anthologized stories. Among her shortest and most daring works, “Story” examines issues of feminism, namely, a woman’s dissatisfaction in a conventional marriage and her desire for independence. It also features Chopin’s characteristic irony and ambiguity .
The story begins with Louise Mallard’s being told about her husband’s presumed death in a train accident. Louise initially weeps with wild abandon, then retires alone to her upstairs bedroom. As she sits facing the open window, observing the new spring life outside, she realizes with a “clear and exalted perception” that she is now free of her husband’s “powerful will bending hers” (353). She becomes delirious with the prospect that she can now live for herself and prays that her life may be long. Her newfound independence is short-lived, however. In a surprise ending, her husband walks through the front door, and Louise suffers a heart attack and dies. Her death may be considered a tragic defeat or a pyrrhic victory for a woman who would rather die than lose that “possession of self-assertion which she suddenly recognized as the strongest impulse of her being” (353). The doctors ironically attribute her death to the “joy that kills” (354).
BIBLIOGRAPHY Chopin, Kate. The Complete Works of Kate Chopin. Edited by Per Seyersted. Baton Rouge: Louisiana State University Press, 1969. Koloski, Bernard. Kate Chopin: A Study of the Short Fiction. New York: Twayne, 1996. Seyersted, Per. Kate Chopin: A Critical Biography. Baton Rouge: Louisiana State University Press, 1969. Toth, Emily. Kate Chopin. New York: Morrow, 1990

Share this:
Categories: Literature , Short Story
Tags: American Literature , Analysis of Kate Chopin's The Story of an Hour , calicut university materials of Kate Chopin's The Story of an Hour , criticism of Kate Chopin's The Story of an Hour , Kate Chopin , Kate Chopin's The Story of an Hour , Kate Chopin's The Story of an Hour criticism , Kate Chopin's The Story of an Hour essay , Kate Chopin's The Story of an Hour notes , Kate Chopin's The Story of an Hour plot , Literary Criticism , plotKate Chopin's The Story of an Hour , summary of Kate Chopin's The Story of an Hour , The Dream of an Hour , themes of Kate Chopin's The Story of an Hour
Related Articles

You must be logged in to post a comment.
English Studies
This website is dedicated to English Literature, Literary Criticism, Literary Theory, English Language and its teaching and learning.
“The Story of an Hour” by Kate Chopin: A Critical Analysis
“The Story of an Hour” by Kate Chopin, first published in 1894 in the St. Louis Life magazine, was later included in the 1895 collection “Vojageur” and in the 1895 edition of “Bayou Folk”.

Introduction: “The Story of an Hour” by Kate Chopin
“The Story of an Hour” by Kate Chopin, first published in 1894 in the St. Louis Life magazine, was later included in the 1895 collection “Vojageur” and in the 1895 edition of “Bayou Folk”. This iconic short story features a unique narrative structure, where the protagonist, Louise Mallard, experiences a rollercoaster of emotions upon learning of her husband’s death in a railroad accident. The story showcases Chopin’s mastery of exploring themes of freedom, marriage, and the human psyche, all within a concise and gripping narrative that has captivated readers for over a century. Some key features of the story include its use of irony, symbolism, and a focus on the inner experiences of the protagonist, making it a landmark of American literary modernism.
Main Events in “The Story of an Hour” by Kate Chopin
Table of Contents
- Mrs. Mallard Learns of Her Husband’s Death : Mrs. Mallard, afflicted with a heart condition, is gently informed of her husband’s death in a train accident by her sister Josephine and their friend Richards.
- Initial Grief and Solitude : Mrs. Mallard weeps in her sister’s arms and then withdraws to her room alone, overwhelmed by grief.
- Contemplation by the Window : Sitting alone in her room, Mrs. Mallard gazes out the window, observing signs of new life and feeling a sense of physical and emotional exhaustion.
- A Subtle Awakening : Mrs. Mallard begins to feel a subtle and elusive sense of freedom creeping over her, whispering “free, free, free!” as she starts to recognize a new sensation within herself.
- Embracing Freedom : As Mrs. Mallard acknowledges the prospect of freedom from her husband’s will and societal expectations, she feels a rush of joy and welcomes the years ahead for herself.
- Recognition of Self-Assertion : Mrs. Mallard reflects on the strength of her own desires for autonomy and self-assertion, realizing that it surpasses the complexities of love and relationships.
- Resistance and Revelation : Despite her sister’s pleas, Mrs. Mallard resists leaving her newfound sense of liberation, reveling in the elixir of life streaming through her open window.
- Vision of the Future : Mrs. Mallard’s imagination runs wild with possibilities for her future, filled with dreams of spring and summer days that will be entirely her own.
- Triumphant Reveal : Mrs. Mallard emerges from her room, exuding a feverish triumph, and descends the stairs with her sister, unaware of what awaits her.
- Shocking Revelation and Tragic End : The story takes a dramatic turn as Mrs. Mallard’s husband, Brently Mallard, returns home unharmed, unaware of the news of his death. The shock of his appearance leads to Mrs. Mallard’s sudden death, attributed by doctors to “the joy that kills.”
Literary Devices in “The Story of an Hour” by Kate Chopin
| “railroad accident” | Reference to a common and feared event at the time, evoking a sense of tragedy and shock. | |
| “free, free, free” | Repetition of the word “free” at the beginning of successive clauses emphasizes Louise’s longing for freedom and her triumphant feeling. | |
| “She was young, with a fair, calm face, whose lines bespoke repression and even a certain strength.” | Description of Louise’s physical appearance and personality traits, revealing her inner struggles and resilience. | |
| Contrast | “She had loved him—sometimes. Often she had not.” | Juxtaposition of opposing ideas (love and indifference) highlights the complexity of Louise’s feelings and her mixed emotions. |
| “the delicious breath of rain was in the air” | Vivid description of a sensory experience, creating a sense of freshness and new life, symbolizing Louise’s liberation. | |
| “the joy that kills” | Unexpected twist: Louise’s newfound freedom and joy ultimately lead to her death, highlighting the complexity of her emotions. | |
| “a goddess of Victory” | Comparison of Louise to a triumphant deity, emphasizing her sense of empowerment and freedom. | |
| Freedom | Recurring theme of freedom, emphasizing its significance to Louise and her desire for autonomy. | |
| “the patches of blue sky showing here and there” | Attributing human-like qualities to the sky, creating a sense of hope and freedom. | |
| “free” | Emphasis through repeated use of the word “free”, highlighting Louise’s longing and triumphant feeling. | |
| Open window and blue sky | Representation of freedom, hope, and new life, symbolizing Louise’s liberation from her oppressive marriage. | |
| “the kind, tender hands folded in death” | Using a part (hands) to represent the whole (Brently’s deceased body), emphasizing Louise’s emotional response. | |
| Somber, reflective, and triumphant | Author’s attitude, creating a sense of seriousness, introspection, and ultimately, liberation. | |
| “a monstrous joy” | Words conveying a meaning opposite of their literal definition, highlighting the complexity of Louise’s emotions. | |
| Imagery (Visual) | “the tops of trees that were all aquiver with the new spring life” | Description of settings and characters to create vivid mental images, emphasizing the sense of new life and freedom. |
| “What was it? She did not know; it was too subtle and elusive to name.” | Hinting at events that will occur later (Louise’s death), creating tension and suspense. | |
| “She was beginning to recognize this thing that was approaching to possess her, and she was striving to beat it back with her will—” | Unstructured flow of thoughts and feelings, revealing Louise’s inner turmoil and emotional struggle. | |
| Suspense | “There was something coming to her and she was waiting for it, fearfully.” | Tension created by uncertainty, keeping the reader engaged and invested in Louise’s story. |
| Syntax | Short, simple sentences | Unconventional sentence structure, creating a sense of urgency, simplicity, and directness, emphasizing Louise’s emotions and thoughts. |
Characterization in “The Story of an Hour” by Kate Chopin
- Afflicted with a heart condition, which influences her physical and emotional state throughout the story.
- Initially portrayed as experiencing grief and sorrow over her husband’s death but undergoes a transformation as she contemplates the prospect of freedom.
- Symbolizes themes of repression, liberation, and the complexities of marriage and societal expectations.
- Acts as a supportive figure to Mrs. Mallard, informing her of her husband’s death and attempting to comfort her.
- Represents familial bonds and the role of women in supporting each other in times of crisis.
- Present when the news of Brently Mallard’s death is revealed to Mrs. Mallard.
- His actions highlight the societal norms of male friendship and the expectation of delivering difficult news to women.
- Appears briefly at the end of the story, shocking Mrs. Mallard and ultimately leading to her death.
- Serves as a catalyst for Mrs. Mallard’s emotional journey and the revelation of her desire for freedom.
- Represents the constraints of traditional marriage and the loss of individual identity within such relationships.
Major Themes in “The Story of an Hour” by Kate Chopin
- Freedom and Liberation : The story explores the theme of freedom through Mrs. Mallard’s reaction to her husband’s death. Initially grieving, she experiences a profound sense of liberation and anticipates a future free from the constraints of marriage and societal expectations.
- Repression and Identity : Mrs. Mallard’s emotional journey highlights the repression of her true feelings within her marriage and society. Her brief moment of freedom allows her to glimpse her own desires and identity apart from her role as a wife.
- Irony and Unexpected Twists : Chopin employs irony and unexpected twists to challenge conventional narrative expectations. The revelation of Brently Mallard’s survival and Mrs. Mallard’s subsequent death subverts the reader’s assumptions and underscores the complexities of human emotion and experience.
- Death and Joy : The story juxtaposes themes of death and joy, suggesting that liberation and self-realization can emerge from unexpected or even tragic circumstances. Mrs. Mallard’s death, attributed to “the joy that kills,” underscores the paradoxical nature of human emotions and the complexities of inner lives.
Writing Style in “The Story of an Hour” by Kate Chopin
- Descriptive Imagery : Chopin employs vivid and sensory language to create imagery that immerses the reader in the setting and emotions of the story. Descriptions of the springtime scene outside Mrs. Mallard’s window, such as “aquiver with the new spring life,” evoke a sense of renewal and vitality.
- Stream-of-Consciousness : The story delves into Mrs. Mallard’s thoughts and feelings, often in a stream-of-consciousness style. This technique allows readers to experience her internal turmoil and the rapid shifts in her emotions as she grapples with the news of her husband’s death and the prospect of freedom.
- Symbolism : Chopin utilizes symbolism to convey deeper themes and meanings throughout the narrative. For example, the open window symbolizes the possibility of escape and liberation, while Mrs. Mallard’s physical and emotional confinement within her home reflects the constraints of her marriage and societal expectations.
- Irony and Subtext : The story is marked by irony and subtle subtext, particularly in its exploration of Mrs. Mallard’s reaction to her husband’s death. While her initial response appears to be one of grief, it gradually becomes clear that she is experiencing a sense of liberation and joy at the prospect of newfound freedom.
- Economy of Language : Chopin’s writing in “The Story of an Hour” is characterized by its economy of language, with each word carefully chosen to maximize impact. This concise style contributes to the story’s intensity and emotional resonance, allowing readers to experience the protagonist’s inner journey with clarity and immediacy.
Literary Theories and Interpretation of “The Story of an Hour” by Kate Chopin
| Louise’s struggle for autonomy and independence | “There would be no one to live for during those coming years; she would live for herself.” | Louise’s desire for self-assertion and freedom from patriarchal oppression is a central theme. | |
| Louise’s repressed emotions and inner conflict | “She was beginning to recognize this thing that was approaching to possess her, and she was striving to beat it back with her will—” | Louise’s inner turmoil and emotional struggle with her husband’s death reveal her repressed desires and inner conflict. | |
| Symbolic Theory | Symbols of freedom and oppression | “The open window and blue sky” | The open window and blue sky symbolize freedom, hope, and new life, while the closed door and darkness symbolize oppression and confinement. |
Feminist Theory :
- Interpretation: Louise’s struggle for autonomy and independence
- Example: “There would be no one to live for during those coming years; she would live for herself.”
- Explanation: Louise’s desire for self-assertion and freedom from patriarchal oppression is a central theme. She rejects the societal expectations of women and seeks to live for herself, symbolizing her autonomy and independence.
Psychoanalytic Theory:
- Interpretation: Louise’s repressed emotions and inner conflict
- Example: “She was beginning to recognize this thing that was approaching to possess her, and she was striving to beat it back with her will—”
- Explanation: Louise’s inner turmoil and emotional struggle with her husband’s death reveal her repressed desires and inner conflict. Her feelings of freedom and joy are juxtaposed with her guilt and grief, highlighting her complex psyche.
Symbolic Theory:
- Interpretation: Symbols of freedom and oppression
- Example: “The open window and blue sky”
- Explanation: The open window and blue sky symbolize freedom, hope, and new life, while the closed door and darkness symbolize oppression and confinement. The window and sky represent Louise’s desire for escape and freedom, while the door and darkness represent her trapped and oppressive life.
Topics, Questions, and Thesis Statements about “The Story of an Hour” by Kate Chopin
| Gender Roles and Societal Expectations | How does the story challenge traditional gender roles? | In “The Story of an Hour,” Kate Chopin subverts societal expectations by portraying Mrs. Mallard’s reaction to her husband’s death as a complex exploration of liberation and self-assertion. |
| Psychological Realism and Inner Conflict | What psychological insights does the story offer about human emotions and inner conflict? | Through Mrs. Mallard’s internal journey, Chopin provides a nuanced portrayal of human psychology, revealing the complexities of grief, repression, and the pursuit of personal freedom. |
| Irony and Narrative Subversion | How does Chopin use irony to subvert narrative expectations? | Chopin employs irony throughout the story to challenge conventional narrative structures and reveal the unexpected complexities of human experience, particularly in moments of emotional revelation. |
| Symbolism and Subtext | What symbolic elements contribute to the deeper meaning of the story? | The use of symbolism, such as the open window and Mrs. Mallard’s physical confinement, underscores the story’s exploration of liberation, repression, and the struggle for individual identity. |

Short Questions/Answers about/on “The Story of an Hour” by Kate Chopin
- What is the significance of the title “The Story of an Hour” and how does it relate to the story’s themes? The title “The Story of an Hour” refers to the brief period of time during which the protagonist, Louise Mallard, experiences a sense of freedom and liberation after hearing of her husband’s death. This hour represents a turning point in her life, as she momentarily breaks free from the societal expectations and constraints that have defined her marriage. The title highlights the story’s exploration of freedom, individuality, and the oppressive nature of societal norms.
- How does Kate Chopin use symbolism in “The Story of an Hour” to convey the protagonist’s emotional journey and the themes of the story? Kate Chopin employs symbolism throughout the story to convey Louise’s emotional journey and the themes of freedom, individuality, and oppression. The open window, for instance, symbolizes Louise’s newfound freedom and her desire to break free from the constraints of her marriage. The “blue and far” sky represents the limitless possibilities and opportunities that lie ahead. The “new spring of life” and the “delicious breath of rain” symbolize renewal and rejuvenation, reflecting Louise’s growing sense of hope and liberation.
- What role does irony play in “The Story of an Hour,” and how does it contribute to the story’s themes and character development? Irony plays a significant role in “The Story of an Hour,” as it underscores the contradictions and tensions that exist between societal expectations and individual desires. The story’s use of dramatic irony, where the reader is aware of Louise’s inner thoughts and feelings, while the other characters are not, highlights the disconnect between her public and private selves. The situational irony, where Louise’s husband returns alive, subverts the reader’s expectations and underscores the oppressive nature of societal norms, which deny women their individuality and freedom.
- How does “The Story of an Hour” reflect the social and cultural context in which it was written, and what commentary does it offer on the status of women during this time period? “The Story of an Hour” reflects the social and cultural context of the late 19th century, a time when women’s rights and freedoms were severely limited. The story critiques the patriarchal society and the institution of marriage, which often trapped women in loveless and oppressive relationships. Through Louise’s character, Chopin highlights the suffocating nature of societal expectations and the longing for individuality and freedom that many women experienced during this time period. The story’s exploration of these themes offers a commentary on the status of women and the need for greater autonomy and self-expression.
Literary Works Similar to “The Story of an Hour” by Kate Chopin
- “ The Yellow Wallpaper ” by Charlotte Perkins Gilman : This story explores themes of female oppression and mental health as a woman confined to a room by her husband begins to unravel psychologically.
- “ A Jury of Her Peers ” by Susan Glaspell : Based on Glaspell’s play “Trifles,” this story delves into gender roles and justice as women uncover crucial evidence while accompanying their husbands on a murder investigation.
- “The Awakening” by Kate Chopin : Another work by Chopin, this novella examines the constraints of marriage and societal expectations as a woman seeks independence and self-discovery in late 19th-century Louisiana.
- “ The Chrysanthemums ” by John Steinbeck : Set in the Salinas Valley during the Great Depression, this story follows a woman’s encounter with a traveling tinkerer, exploring themes of isolation, longing, and gender roles.
- “The Story of a Dead Man” by Ambrose Bierce : Bierce’s story, similar to “The Story of an Hour,” explores themes of freedom and liberation as a man seemingly returns from the dead, causing his widow to contemplate her newfound independence.
Suggested Readings about/on “The Story of an Hour” by Kate Chopin
Books on kate chopin and “the story of an hour”:.
- Bonner, Thomas Jr. The Kate Chopin Companion . Greenwood, 1988.
- Ewell, Barbara C. Kate Chopin . Ungar, 1986.
- Papke, Mary E. Verging on the Abyss: The Social Fiction of Kate Chopin and Edith Wharton . Greenwood, 1990.
- Seyersted, Per. Kate Chopin: A Critical Biography . Louisiana State UP, 1969.
- Skaggs, Peggy. Kate Chopin . Twayne, 1985.
Articles on “The Story of an Hour”:
- Mitchell, Angelyn. “Feminine Double Consciousness in Kate Chopin’s ‘The Story of an Hour.'” CEAMagazine 5.1 (1992): 59-64.
- Miner, Madonne M. “Veiled Hints: An Affective Stylist’s Reading of Kate Chopin’s ‘Story of an Hour.'” Markham Review 11 (1982): 29-32.
Web Resource:
- The Kate Chopin International Society offers a wealth of information on Chopin and “The Story of an Hour,” including the full text of the story and critical essays: Kate Chopin International Society: https://www.katechopin.org/story-hour/
Representative Quotations from “The Story of an Hour” by Kate Chopin
| “She wept at once, with sudden, wild abandonment, in her sister’s arms.” | Louise’s initial reaction to news of her husband’s death | Feminist Theory: highlights the societal expectation of women’s emotional response to tragedy |
| “There were patches of blue sky showing here and there through the clouds…” | Louise’s gaze out the window, symbolizing freedom and hope | Symbolic Theory: the open window and blue sky represent freedom and new life |
| “She was young, with a fair, calm face, whose lines bespoke repression and even a certain strength.” | Description of Louise’s physical appearance and personality | Psychoanalytic Theory: reveals Louise’s repressed emotions and inner conflict |
| “She said it over and over under her breath: ‘free, free, free!'” | Louise’s whispered word, symbolizing her desire for autonomy | Feminist Theory: highlights the importance of individual freedom and autonomy |
| “There would be no one to live for during those coming years; she would live for herself.” | Louise’s realization of her newfound independence | Existentialist Theory: emphasizes individual responsibility and self-assertion |
| “What could love, the unsolved mystery, count for in the face of this possession of self-assertion…” | Louise’s reflection on the significance of love and self-assertion | Psychoanalytic Theory: reveals the tension between societal expectations and individual desires |
| “She breathed a quick prayer that life might be long.” | Louise’s desire for a long and independent life | Existentialist Theory: emphasizes the individual’s desire for life and autonomy |
Related posts:
- “The Use of Force” by William Carlos Williams
- “An Occurrence at Owl Creek Bridge” by Ambrose Bierce: Analysis
- “The Shawl” by Cynthia Ozick: Analysis
- “The Old Pond” by Matsuo Basho: Analysis
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.


“The Story of an Hour” by Kate Chopin Literary Analysis: Plot, Themes, Characters, Setting, and Symbolism
Kate Chopin’s (1850-1904) short story “ The Story of an Hour” narrates events that happen within an hour.
Louise Mallard is a young, calm, and frail woman who suffers from a heart disease. On this day, Louise learns from her sister Josephine and a family friend, Richards, that her husband, Brently Mallard, has died. She briefly weeps in Josephine’s arms and then heads to her room alone.
While watching the street from her window, she feels an unknown feeling building up and when she gives in to this, Louise realizes that it is the joy of being free from her husband’s constant impositions on her life. The primary character then begins to envision an exciting future and imagines a life where she will live for herself.
However, these feelings of joy and freedom are short-lived. As Louise walks down the stairs from her room, Brently walks into the house and she learns that her husband did not perish in the accident. Mrs. Mallard dies on the spot and the doctor rules that she died of joy. However, with the knowledge of her previous joy, it’s clear that her death is from the disappointment of losing the full free life she had envisioned.
Let’s look at an analysis of the plot, main themes, characters, setting, and other minor literary devices in “ The Story of an Hour” by Kate Chopin
The Story of an Hour Plot Analysis
“The Story of an Hour” by Kate Chopin has a linear or traditional plot structure with an introduction, rising action, climax, falling action, and a resolution at the end.
The very first line serves as an introduction or exposition to the plot. Chopin states that Mrs. Mallard “is afflicted with a heart trouble.” This point sets up the rest of the events to come in the story, while it also introduces Mrs. Mallard’s signature trait. Her heart condition also creates a meek perception of her and explains why the other characters have to take great care when telling her sensitive information. The exposition continues with news of Mr. Mallard’s death. Knowing Mrs. Mallard’s frail heart, Josephine breaks the news with care and “veiled hints that revealed in half concealing”.
A rising action begins in the next part of the story regarding how Mrs. Mallard takes in the news of her husband’s death. It’s expected that a woman learning that her husband just died would take the news with disbelief, loud wailing, or any reaction contrary to Mrs. Mallard. Instead, Chopin explains that Mrs. Mallard “wept at once, with sudden, wild abandonment, in her sister’s arms.” She then goes into her room, supposedly to mourn her husband.
The story comes to a climax when Louise experiences a feeling that’s contrary to the sadness of losing a husband. She realizes and revels in her newfound freedom thinking, “There would be no one to live for during those coming years; she would live for herself. There would be no powerful will bending hers in that blind persistence with which men and women believe they have a right to impose a private will upon a fellow-creature”
“‘Free! Body and soul free!’ she kept whispering.”
After this, a falling action starts with Mrs.Mallard giving in to her sister’s incessant requests and opening her room’s door. Together, they descend the stairs, with Louise feeling victorious and triumphant over her new life. The story finally concludes with a resolution as Brently Mallard enters the room, revealing that he did not die in the railroad accident. Mrs. Mallard dies not because of the joy of her husband’s return, but because of the disappointment as her envisioned life of freedom flashes before her eyes.
Themes in The Story of an Hour by Kate Chopin
Love and marriage as inherent issues is one of the themes this short story presents. The presence of love is not synonymous with a good marriage, as suggested throughout the plot.
Love and Marriage
Mr. and Mrs. Mallard love each other, and Chopin ensures we know this several times. While welcoming the freedom ahead of her, she still feels bad about her husband’s death because nevertheless, he was a kind man who loved her. “She knew that she would weep again when she saw the kind, tender hands folded in death; the face that had never looked save with love upon her, fixed and gray and dead”
Louise also admits that she loves Brently, but not all the time. Most of the time she doesn’t. Despite this, she still perceives her husband’s death as a good thing and a gateway to freedom. It’s almost as if she has just been freed from an oppressive situation.
Note that Mrs. Mallard does not state specifically any specific thing that happens during their marriage to change her feelings towards her husband. She instead rants on how marriage is will-bending, with men and women feeling the need to impose their will on others. In his analysis of the author’s works, Kate Chopin’s Life and Personal Influence , Jasdomin Tolentino affirms that Chopin grew up in an environment where women were always taught “to think independently, but also to be submissive to men.” This is reflected in the story as Mrs. Mallard rejoices in her newfound freedom and independence.
Elaine Fortin in her 2014 essay Early Nineteenth Century Attitudes Toward Women and Their Roles as Represented By Literature Popular in Worcester, Massachusetts adds on this forced submission; “Submissive wives, who followed the, advice not to retort an abusive husband, received praise and were supposedly rewarded with a happy home and a faithful husband.” Chopin describes Mrs. Mallard with a “calm face, whose lines bespoke repression and even a certain strength.” Men, and the patriarchal society at large, repressed a woman’s need for individuality and independence, not even the strong could survive.
Gender Roles and Gender Inequality
Like most feminist literature published around this time (1894), “The Story of an Hour” covers gender roles and gender inequality heavily as themes too.
In the 19th and early 20th centuries, women got the brunt of gender inequality, as society perceived them as inferior to men. They were expected to always depend on their husbands or other male figures in the society like fathers or brothers, as Fortin describes in her literature review above. Domestic roles, including accommodating their husbands through cleaning and cooking, were among a woman’s primary responsibilities. And for those who managed to break these barriers, employment was characterized by lower wages with equal responsibilities, as well as gender discrimination at the workplace. Most women did not seek employment because they lived under their husband’s impositions, including the patriarchal perception that women should stay and tend to the home as men go out and become breadwinners. Fortin also adds that the women had little to no financial independence because everything either belonged to their husbands or fathers.
In The Story of an Hour, Mrs. Mallard is an ideal representation of a woman in the 19 th century who is in search of lost identity and only feels she can achieve this in the absence of her husband. Of interest in the story is that it is only through a husband’s death that a woman during this time would grasp the taste of independence and freedom because then, she’s not living in the shadows of a man. Therefore, despite the sad news and her grief, Mrs. Mallard cannot help but feel happy because life is about to change for the best: she’s finally free. A majority of women did not have the slightest clue about independence and when Louise finally realizes that she is about to live life on her own terms, she’s in utter disbelief.
“She was beginning to recognize this thing that was approaching to possess her, and she was striving to beat it back with her will.”
It is also important to note that Chopin does not refer to Louise by her own name, but that of her husband, until later when we learn of her newfound freedom. In other words, Louise only finds her identity and independence after Brently dies because women in the 19 th century had to identify with a male figure.
From a feminist literature lens , The Story of an Hour falls under the first wave of feminism, when the movement heavily criticized the power of the patriarchal society and the effects it had on women, especially in marriage. An example is married women whose desires and identities were repressed to fit and serve men.
Character Analysis
The story uses both direct and indirect characterization techniques to develop its four characters. Chopin uses a lot of direct characterization of Mrs.Mallard, while she leaves the audience to deduce the traits of the other three characters through indirect characterization.
Mrs. Mallard is the primary character and protagonist . The story begins with details about her heart problem, casting her as fragile and setting the pace for the entire plot. “Knowing that Mrs. Mallard was afflicted with a heart trouble, great care was taken to break to her as gently as possible the news of her husband’s death.” Because of this, Josephine and Richards are careful when breaking the news of Brently’s death. It’s the same reason Josephine worries about Louise’s health when she locks herself in her room.
“Louise, open the door! I beg; open the door–you will make yourself ill. What are you doing, Louise? For heaven’s sake open the door.”
The two worry that the news of her husband’s death would affect her while ironically, it’s the news of his survival that kills her.
Chopin further characterizes Mrs. Mallard as physically weak and mentally exhausted; traits that bolster the issue of repression painted in the story.
“…she was striving to beat it back with her will–as powerless as her two white slender hands would have been.”
It’s also evident in several instances that Mrs. Mallard feels exhausted with life, so much that, “It was only yesterday she had thought with a shudder that life might be long.” This exhaustion seems to stem from her marriage which has made her a repressed, dutiful, and submissive wife.
As she sits to process Brently’s death in her room, there’s “a physical exhaustion that haunted her body and seemed to reach into her soul.” Notice how this perception of her changes when she opens the door and descends the door to welcome and live her new free life. There’s “a feverish triumph in her eyes, and she carried herself unwittingly like a goddess of Victory.”
Although there’s no direct characterization of Brently, we can deduce a few things from Mrs.Mallard’s thoughts and actions. Given her perception of marriage, including hers, her husband shares the same societal and patriarchal expectations of women during that period. She marvels, “There would be no one to live for during those coming years; … that blind persistence with which men and women believe they have a right to impose a private will upon a fellow-creature.”
And yet, Mrs. Mallard knows that her husband loved her. She “ knew that she would weep again when she saw the kind, tender hands folded in death; the face that had never looked save with love upon her.”
The Story of an Hour Setting Analysis
The entire story takes place in Mrs. Mallard’s storied house. Spring season is just starting as the trees come to life and “patches of blue sky showing here and there.”
Spring comes after winter; the cold, lifeless, gloomy, and repressed season. Spring is like a rebirth with its warm weather, as trees grow new life and nature becomes vibrant again. This setting is parallel with what’s happening in Mrs. Mallard’s life. After years of repression in a marriage to someone she doesn’t love, she’s finally free. Life suddenly feels vast and she longs for the life ahead of her, a life she’ll spend living off her own will.
The two rooms where the story’s 60-minutes events take place both represent Louise’s different experiences that all shape the plot. The living room is where she learns about Brently’s death and also where she dies after learning of her husband’s return/survival. It’s a place where cannot be herself and is always under her husband’s will. Even in the end, the doctors conclude that she dies from the happiness of seeing her husband alive, while the true reason is that she has gained and lost her free will in less than an hour.
Mrs. Mallard’s room, on the other hand, is a setting that allows her to be herself, feel her true emotions, and envision a life of freedom.
Symbolism and Motifs in The Story of an Hour by Kate Chopin
Several objects in the story signify the freedom and rebirth Louise experiences, at least for a few minutes. Besides the setting discussed above, Chopin tactfully includes other instances of symbolism to signify Mrs. Mallard’s new life that promises “Spring days, and summer days, and all sorts of days that would be her own.”
The open window with the view before her house has a view of things like trees filled with new spring life, patches of the blue sky amidst clouds, birds chirping, a distant note of someone singing, and so on. All these are signs of something coming to life. She’s embracing and welcoming her new life without Brently, “drinking in a very elixir of life through that open window.” These images and symbols of springtime also double as motifs that reinforce the new great life Mrs.Mallard envisions.
Do you have any literary analysis questions for your essay writing or just loved reading ‘ The Story of an Hour’ by Kate Chopin and wanna start a conversation? Let me know in the comment section below! 🙂
Spread the Love
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Tumblr (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
Published by The Literary Girl
I am most excited when reading and writing about books, stories, and poems. Read some of that excitement here! View all posts by The Literary Girl
5 thoughts on ““The Story of an Hour” by Kate Chopin Literary Analysis: Plot, Themes, Characters, Setting, and Symbolism”
- Pingback: 3 Feminist Short Stories That you will Absolutely Love
- Pingback: “A Jury of her Peers” by Susan Glaspell Feminist Analysis
this was really helpful, thankyou ❤
I am really glad this was helpful!! Thank you for reading 🙂
Leave a Reply

- Already have a WordPress.com account? Log in now.
- Subscribe Subscribed
- Copy shortlink
- Report this content
- View post in Reader
- Manage subscriptions
- Collapse this bar

Analysis of "The Story of an Hour" by Kate Chopin
Self-Determination and Louise Mallard Living for Herself
D Fu Tong Zhao /EyeEm/Getty Images
- Short Stories
- Best Sellers
- Classic Literature
- Plays & Drama
- Shakespeare
- Children's Books
- Ph.D., English, State University of New York at Albany
- B.A., English, Brown University
"The Story of an Hour" by American author Kate Chopin is a mainstay of feminist literary study . Originally published in 1894, the story documents the complicated reaction of Louise Mallard upon learning of her husband's death.
It is difficult to discuss "The Story of an Hour" without addressing the ironic ending. If you haven't read the story yet, you might as well, as it's only about 1,000 words. The Kate Chopin International Society is kind enough to provide a free, accurate version .
At the Beginning, News That Will Devastate Louise
At the beginning of the story, Richards and Josephine believe they must break the news of Brently Mallard's death to Louise Mallard as gently as possible. Josephine informs her "in broken sentences; veiled hints that revealed in half concealing." Their assumption, not an unreasonable one, is that this unthinkable news will be devastating to Louise and will threaten her weak heart.
A Growing Awareness of Freedom
Yet something even more unthinkable lurks in this story: Louise's growing awareness of the freedom she will have without Brently.
At first, she doesn't consciously allow herself to think about this freedom. The knowledge reaches her wordlessly and symbolically, via the "open window" through which she sees the "open square" in front of her house. The repetition of the word "open" emphasizes possibility and a lack of restrictions.
Patches of Blue Sky Amid the Clouds
The scene is full of energy and hope. The trees are "all aquiver with the new spring of life," the "delicious breath of rain" is in the air, sparrows are twittering, and Louise can hear someone singing a song in the distance. She can see "patches of blue sky" amid the clouds.
She observes these patches of blue sky without registering what they might mean. Describing Louise's gaze, Chopin writes, "It was not a glance of reflection, but rather indicated a suspension of intelligent thought." If she had been thinking intelligently, social norms might have prevented her from such a heretical recognition. Instead, the world offers her "veiled hints" that she slowly pieces together without even realizing she is doing so.
A Force Is Too Powerful to Oppose
In fact, Louise resists the impending awareness, regarding it "fearfully." As she begins to realize what it is, she strives "to beat it back with her will." Yet its force is too powerful to oppose.
This story can be uncomfortable to read because, on the surface, Louise seems to be glad that her husband has died. But that isn't quite accurate. She thinks of Brently's "kind, tender hands" and "the face that had never looked save with love upon her," and she recognizes that she has not finished weeping for him.
Her Desire for Self-Determination
But his death has made her see something she hasn't seen before and might likely never have seen if he had lived: her desire for self-determination .
Once she allows herself to recognize her approaching freedom, she utters the word "free" over and over again, relishing it. Her fear and her uncomprehending stare are replaced by acceptance and excitement. She looks forward to "years to come that would belong to her absolutely."
She Would Live for Herself
In one of the most important passages of the story, Chopin describes Louise's vision of self-determination. It's not so much about getting rid of her husband as it is about being entirely in charge of her own life, "body and soul." Chopin writes:
"There would be no one to live for her during those coming years; she would live for herself. There would be no powerful will bending hers in that blind persistence with which men and women believe they have a right to impose a will upon a fellow-creature."
Note the phrase men and women. Louise never catalogs any specific offenses Brently has committed against her; rather, the implication seems to be that marriage can be stifling for both parties.
The Irony of Joy That Kills
When Brently Mallard enters the house alive and well in the final scene, his appearance is utterly ordinary. He is "a little travel-stained, composedly carrying his grip-sack and umbrella." His mundane appearance contrasts greatly with Louise's "feverish triumph" and her walking down the stairs like a "goddess of Victory."
When the doctors determine that Louise "died of heart disease -- of joy that kills," the reader immediately recognizes the irony . It seems clear that her shock was not joy over her husband's survival, but rather distress over losing her cherished, newfound freedom. Louise did briefly experience joy -- the joy of imagining herself in control of her own life. And it was the removal of that intense joy that led to her death.
- 'A Doll's House' Summary
- "The Story of an Hour" Characters
- Quotes From 'The Story of an Hour' by Kate Chopin
- 'The Story of an Hour' Questions for Study and Discussion
- Kate Chopin's 'The Awakening' of Edna Pontellier
- Biography of Kate Chopin, American Author and Protofeminist
- Analysis of 'The Yellow Wallpaper' by C. Perkins Gilman
- 'The Awakening' Quotes
- Kate Chopin's 'The Storm': Quick Summary and Analysis
- 'Their Eyes Were Watching God' Themes, Symbols, and Literary Devices
- Miss Brill's Fragile Fantasy
- "The Woman Destroyed" by Simone de Beauvoir
- "Anna Karenina" Study Guide
- Biography of Harriet Tubman
- 5 Things You Need to Know About "The Glass Castle"
- Jane Eyre Study Guide
Home — Essay Samples — Literature — The Story of An Hour — Analysis of Style, Tone, and Language in The Story of an Hour by Kate Chopin
Analysis of Style, Tone, and Language in The Story of an Hour by Kate Chopin
- Categories: Kate Chopin The Story of An Hour
About this sample

Words: 1203 |
Published: Dec 3, 2020
Words: 1203 | Pages: 2 | 7 min read
The essay analyzes Kate Chopin's short story "The Story of an Hour," focusing on its style, tone, and language. The author highlights how these literary elements contribute to the story's success and its controversial nature.
In terms of style, the essay discusses how Chopin uses imagery to convey the protagonist's transition from oppression to freedom. The symbolism of spring and new life associated with death challenges traditional narratives, suggesting that the death of the husband represents a liberation for the wife. The house itself is portrayed as a symbol of confinement, contrasting with the freedom symbolized by nature.
Regarding tone, the essay points out the optimism and joy felt by the protagonist upon learning of her husband's death, as it signifies her newfound freedom. However, it also highlights the story's melancholic and tragic tones, as the protagonist's liberation is short-lived, leading to her untimely death.
The language analysis delves into Chopin's choice of words and phrases, emphasizing how they reflect the protagonist's feelings of oppression within her marriage. The essay interprets words like "repression" and "feverish triumph" to support the idea that the protagonist felt controlled by her husband. Additionally, the use of vivid language, such as "all aquiver," captures the protagonist's awakening to a new life.
Table of contents
Introduction, style in "the story of an hour”, tone in "the story of an hour”, "the story of an hour” language analysis.

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Prof Ernest (PhD)
Verified writer
- Expert in: Literature

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
1 pages / 557 words
2 pages / 1058 words
1 pages / 802 words
6 pages / 2729 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online

Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on The Story of An Hour
Kate Chopin’s short story “The Story of an Hour” is a captivating and thought-provoking tale that delves into the complexities of human emotions and the impact of societal norms on an individual’s psyche. The story revolves [...]
The "Story of an Hour" by Kate Chopin is a short story that explores the theme of freedom and identity through the character of Mrs. Mallard. In this essay, I will analyze Mrs. Mallard's character in terms of her psychological [...]
Kate Chopin's short story "The Story of an Hour" revolves around the protagonist, Mrs. Mallard, and her emotional journey following the news of her husband's death. Throughout the story, emotions play a crucial role in shaping [...]
First published in 1894, Kate Chopin's "The Story of an Hour" is a short but powerful story that explores the complex emotions of a woman who learns of her husband's death. The narrative delves into the theme of female [...]
Kate Chopin's 'The Story of an Hour' is a psychological exploration of one woman's response to learning that her husband has just been killed in an accident. The story's narrative twist is that it goes against the reader's [...]
Charlotte Perkins Gilman’s “The Yellow Wallpaper,” and Kate Chopin’s “The Story of an Hour” explore ideas of female identity and selfhood, and more importantly, female liberation. These authors present their female characters as [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
Kate Chopin's Short Stories
By kate chopin, kate chopin's short stories summary and analysis of "the story of an hour".
Upon hearing the news of Brently Mallard 's tragic railroad accident death in the newspaper office, his friend Richards rushes to the Mallards' house, where he and Mrs. Mallard's sister Josephine gently inform the weak-hearted Mrs. Mallard of Brently's death. In response, Louise Mallard weeps openly before going to sit alone in her room.
Exhausted, Mrs. Mallard sits motionless in her armchair by the window and looks at all the beauty of the outside world, occasionally sobbing. She is young, with a calm and strong face, but she stares dully into the sky while she waits nervously for a revelation. Finally, she realizes despite her initial opposition that she is now free. Terror leaves her eyes while her pulse beats faster.
Mrs. Mallard knows that she will mourn her loving husband's death, but she also predicts many years of freedom, which she welcomes. She begins planning her future, in which she will live without the burden of other people. She loved her husband, more or less, but love is nothing to her when compared to independence, she decides, as she murmurs, "Free! Body and soul free!"
Josephine asks Mrs. Mallard to let her enter because she is afraid that the grieving widow will make herself ill, but Mrs. Mallard is actually imagining the happiness of the years ahead. In fact, only the day before she had feared living a long life. Triumphantly, she answers the door and goes downstairs with her arm around Josephine's waist, where Richards awaits.
At this moment, Brently Mallard comes in the front door, having been nowhere near the train disaster. Richards moves in front of him to hide him from seeing his wife when she cries out. By the time the doctors arrive, she has died from "heart disease," purportedly from "the joy that kills."
Chopin tackles complex issues involved in the interplay of female independence, love, and marriage through her brief but effective characterization of the supposedly widowed Louise Mallard in her last hour of life. After discovering that her husband has died in a train accident, Mrs. Mallard faces conflicting emotions of grief at her husband's death and exultation at the prospects for freedom in the remainder of her life. The latter emotion eventually takes precedence in her thoughts. As with many successful short stories, however, the story does not end peacefully at this point but instead creates a climactic twist. The reversal--the revelation that her husband did not die after all-- shatters Louise's vision of her new life and ironically creates a tragic ending out of what initially appeared to be a fortuitous turn of events. As a result, it is Mr. Mallard who is free of Mrs. Mallard, although we do not learn whether the same interplay of conflicting emotions occurs for him.
Chopin presents Mrs. Mallard as a sympathetic character with strength and insight. As Louise understands the world, to lose her strongest familial tie is not a great loss so much as an opportunity to move beyond the "blind persistence" of the bondage of personal relationships. In particular, American wives in the late nineteenth century were legally bound to their husbands' power and status, but because widows did not bear the responsibility of finding or following a husband, they gained more legal recognition and often had more control over their lives. Although Chopin does not specifically cite the contemporary second-class situation of women in the text, Mrs. Mallard's exclamations of "Free! Body and soul free!" are highly suggestive of the historical context.
Beyond the question of female independence, Louise seems to suggest that although Brently Mallard has always treated their relationship with the best of intentions, any human connection with such an effect of permanence and intensity, despite its advantages, must also be a limiting factor in some respects. Even Louise's physical description seems to hint at her personality, as Chopin associates her youthful countenance with her potential for the future while mentioning lines that "bespoke repression and even a certain strength." Although neither her sister nor Brently's friend Richards would be likely to understand her point of view, Louise Mallard embraces solitude as the purest prerequisite for free choice.
Mrs. Mallard's characterization is complicated by the fleeting nature of her grief over her husband, as it might indicate excessive egotism or shameless self-absorption. Nevertheless, Chopin does much to divert us from interpreting the story in this manner, and indeed Mrs. Mallard's conversion to temporary euphoria may simply suggest that the human need for independence can exceed even love and marriage. Notably, Louise Mallard reaches her conclusions with the suggestive aid of the environment, the imagery of which symbolically associates Louise's private awakening with the beginning of life in the spring season. Ironically, in one sense, she does not choose her new understanding but instead receives it from her surroundings, "creeping out of the sky." The word "mallard" is a word for a kind of duck, and it may well be that wild birds in the story symbolize freedom.
To unify the story under a central theme, Chopin both begins and ends with a statement about Louise Mallard's heart trouble, which turns out to have both a physical and a mental component. In the first paragraph of "The Story of an Hour," Chopin uses the term "heart trouble" primarily in a medical sense, but over the course of the story, Mrs. Mallard's presumed frailty seems to be largely a result of psychological repression rather than truly physiological factors. The story concludes by attributing Mrs. Mallard's death to heart disease, where heart disease is "the joy that kills." This last phrase is purposefully ironic, as Louise must have felt both joy and extreme disappointment at Brently's return, regaining her husband and all of the loss of freedom her marriage entails. The line establishes that Louise's heart condition is more of a metaphor for her emotional state than a medical reality.

Kate Chopin’s Short Stories Questions and Answers
The Question and Answer section for Kate Chopin’s Short Stories is a great resource to ask questions, find answers, and discuss the novel.
The story of an hour
The first sentence reads,
Knowing that Mrs. Mallard was afflicted with a heart trouble, great care was taken to break to her as gently as possible the news of her husband's death.
The irony is that Mrs. Mallard actually dislikes her husband and...
Which best describes Gouvernail's approach with Mrs. Baroda?
A. Gouvernail is polite but makes no effort to connect with her.
Did you have a question about Chopin's short-story, Caline ?
Study Guide for Kate Chopin’s Short Stories
Kate Chopin's Short Stories study guide contains a biography of Kate Chopin, literature essays, a complete e-text, quiz questions, major themes, characters, and a full summary and analysis.
- About Kate Chopin's Short Stories
- Kate Chopin's Short Stories Summary
- Character List
Essays for Kate Chopin’s Short Stories
Kate Chopin's Short Stories essays are academic essays for citation. These papers were written primarily by students and provide critical analysis of Kate Chopin's Short Stories.
- Kate Chopin's Liberated Women
- Setting in Chopin’s “The Story of an Hour”
- Exploring Feminist Identities: Empowerment Through Duality
- Protagonists’ Responses to Social Constructs of Gender
- Feminism in Kate Chopin’s ‘The Story of An Hour’ – A New Critical Reading
Lesson Plan for Kate Chopin’s Short Stories
- About the Author
- Study Objectives
- Common Core Standards
- Introduction to Kate Chopin's Short Stories
- Relationship to Other Books
- Bringing in Technology
- Notes to the Teacher
- Related Links
- Kate Chopin's Short Stories Bibliography
E-Text of Kate Chopin’s Short Stories
Kate Chopin's Short Stories e-text contains the full text of Kate Chopin's Short Stories.
- Beyond the Bayou
- Ma'ame Pelagie
- Desiree's Baby
- A Respectable Woman
Wikipedia Entries for Kate Chopin’s Short Stories
- Introduction
- Literary themes
- Reception and legacy
- Representation in other media
The Delicate Dance of Sanity and Guilt in Poe’s “The Tell-Tale Heart”
This essay about Edgar Allan Poe’s “The Tell-Tale Heart” explores the psychological themes of guilt and paranoia through the story of an unnamed narrator fixated on an old man’s “vulture-like” eye. The narrative examines the narrator’s descent into madness, highlighting the thin line between sanity and insanity, and uses vivid imagery and first-person perspective to create a tense, claustrophobic atmosphere.
How it works
Edgar Allan Poe’s “The Tell-Tale Heart” is a riveting short story that intricately explores the psychological landscapes of guilt and paranoia. Set in an ambiguous location and told by an unnamed narrator, this tale delves into the mind of a character gripped by obsession and madness. Poe’s work is a prime example of Gothic literature, intertwining themes of insanity, fixation, and the supernatural within a compelling and haunting narrative.
The story begins with the narrator’s insistent declaration of sanity while he recounts his elaborate plan to kill an old man.
The old man’s “vulture-like” eye becomes an object of intense fixation for the narrator, possibly symbolizing a part of himself he wants to eradicate. His cold, calculated description of the murder—from the meticulous preparation to the horrifying execution—reveals a disturbing level of detachment. This clinical narrative contrasts starkly with his repeated claims of sanity, which paradoxically emphasize his descent into madness.
Poe’s choice of first-person narration is particularly effective in this story, allowing readers to immerse themselves in the narrator’s thoughts and feelings. This perspective makes the narrative deeply personal and disturbing, as we experience the protagonist’s spiraling obsession and paranoia firsthand. The narrator’s unreliability is a crucial aspect of the story, creating a sense of ambiguity and tension that keeps readers on edge.
The story reaches its peak with the murder of the old man, followed by the dismemberment and hiding of the body under the floorboards. Poe’s descriptive language becomes especially vivid and gruesome during these scenes, leaving a lasting impression on the reader. However, it is the aftermath of the crime that truly reveals the narrator’s psychological breakdown. The narrator’s perception of the old man’s heartbeat growing louder and more persistent symbolizes his crushing guilt and increasing paranoia. This auditory hallucination drives him to the brink of insanity, culminating in his confession to the police who had come to investigate after neighbors heard a scream.
“The Tell-Tale Heart” is imbued with themes that are central to Poe’s oeuvre. It probes the thin line between sanity and madness, illustrating how guilt can be an all-consuming and destructive force. The narrator’s insistence on his sanity is a futile attempt to hide his deep-seated guilt, and his eventual unraveling underscores the inescapable nature of this emotion. Additionally, the story explores the theme of perception versus reality. The narrator’s distorted view, shaped by his obsession with the old man’s eye, leads to a complete disintegration of his reality.
Furthermore, Poe’s story can be interpreted as a commentary on the nature of evil and the human propensity for violence. The narrator’s actions are driven by an irrational compulsion, suggesting that evil can arise from within and manifest in unexpected ways. This internal conflict is a hallmark of Gothic literature, which often examines the darker facets of the human psyche.
Poe’s writing style in “The Tell-Tale Heart” is marked by its conciseness and its ability to create a tense, claustrophobic atmosphere. The rhythmic, repetitive nature of the prose mimics the beating of the old man’s heart, heightening the story’s sense of urgency and foreboding. Poe’s use of short, staccato sentences and exclamations conveys the narrator’s agitated mental state, while his descriptive passages paint a vivid and unsettling picture of the events.
In sum, “The Tell-Tale Heart” remains one of Edgar Allan Poe’s most compelling and enduring works. Its exploration of guilt, madness, and the supernatural continues to resonate with readers, offering profound insights into the darker aspects of the human condition. Through his masterful use of narration, vivid imagery, and thematic richness, Poe crafts a story that is as thought-provoking as it is chilling. “The Tell-Tale Heart” not only demonstrates Poe’s prowess as a storyteller but also his deep understanding of the complexities of the human mind.
Cite this page
The Delicate Dance of Sanity and Guilt in Poe's "The Tell-Tale Heart". (2024, Jun 28). Retrieved from https://papersowl.com/examples/the-delicate-dance-of-sanity-and-guilt-in-poes-the-tell-tale-heart/
"The Delicate Dance of Sanity and Guilt in Poe's "The Tell-Tale Heart"." PapersOwl.com , 28 Jun 2024, https://papersowl.com/examples/the-delicate-dance-of-sanity-and-guilt-in-poes-the-tell-tale-heart/
PapersOwl.com. (2024). The Delicate Dance of Sanity and Guilt in Poe's "The Tell-Tale Heart" . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/the-delicate-dance-of-sanity-and-guilt-in-poes-the-tell-tale-heart/ [Accessed: 29 Jun. 2024]
"The Delicate Dance of Sanity and Guilt in Poe's "The Tell-Tale Heart"." PapersOwl.com, Jun 28, 2024. Accessed June 29, 2024. https://papersowl.com/examples/the-delicate-dance-of-sanity-and-guilt-in-poes-the-tell-tale-heart/
"The Delicate Dance of Sanity and Guilt in Poe's "The Tell-Tale Heart"," PapersOwl.com , 28-Jun-2024. [Online]. Available: https://papersowl.com/examples/the-delicate-dance-of-sanity-and-guilt-in-poes-the-tell-tale-heart/. [Accessed: 29-Jun-2024]
PapersOwl.com. (2024). The Delicate Dance of Sanity and Guilt in Poe's "The Tell-Tale Heart" . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/the-delicate-dance-of-sanity-and-guilt-in-poes-the-tell-tale-heart/ [Accessed: 29-Jun-2024]
Don't let plagiarism ruin your grade
Hire a writer to get a unique paper crafted to your needs.

Our writers will help you fix any mistakes and get an A+!
Please check your inbox.
You can order an original essay written according to your instructions.
Trusted by over 1 million students worldwide
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers
The Novel “The Story of an Hour” by Kate Chopin Essay
- To find inspiration for your paper and overcome writer’s block
- As a source of information (ensure proper referencing)
- As a template for you assignment
Introduction
Works cited.
The Story of an Hour novel by Kate Chopin, recognized as a masterpiece of short fiction, reflects the complicated self-discovery mechanisms of a woman. Mrs. Mallard, a central character of the story, hears about the death of her husband who was riding on a train. However, the first reaction of grief is replaced by a strange feeling that she initially cannot understand. Unexpectedly, she feels a sense of freedom and happiness in anticipation of a life free from her husband’s despotism. In seeking to understand the author’s idea and the themes presented in the story, this paper will focus on such literary elements as setting, narrator’s point of view, and tone resulting in a concise discussion.
The first literary element under analysis is the setting. The story takes place within one hour, primarily in the Mallards’ house, and nobody enters or leaves the house except Mr. Mallard. This creates a sense of limitation and restraint. Chopin mentions “a comfortable, roomy armchair,” yet the reader has no information concerning the color or size of it (1). Likewise, the setting provides no details about wallpaper or curtains. The lack of precise descriptions makes the atmosphere out-of-body promoting tension and close settlement of the situation.
At the same time, the reader understands that Mrs. Mallard feels quite comfortable in her house, as well as her sister Josephine and friend Richard. This probably means that she is frightened by the outside world.
It is also important to point out that she goes into her room and locks the door after the news is received. The author describes the beautiful landscape outside the window, emphasizing that nature reappears to a new life—to spring. Spring here is the symbol of free life, renovation, and hope. It reflects the main character’s inner world, her emotions, and feelings after she grasps her ideas. Speaking more precisely, the renovation of the soul and the renovation of nature go together in stressing the significance of the change. Chopin uses a circular narrative style to set the integrity of the story. In other words, the author begins and ends the story with Mrs. Mallard’s heart trouble.
I noticed that Josephine, worried about Mrs. Mallard, tries to get her sister out of the room. However, Mrs. Mallard comes out ready for her suddenly changed life. The setting of the story includes two completely different versions of her destiny, namely the free one and the old one, where the loss of freedom becomes the reason for her death. However, it might seem that “the joy that kills” causes her death. In this connection, it seems necessary to provide some background information concerning the characters’ epoch (Chopin 1).
It was a time in American society during the second half of the nineteenth century. In that patriarchal society, wherein women were deprived of a voice, their only opportunity was to express themselves in a non-verbal way. Similarly, it is one of the most important ways to display the state of Mrs. Mallard’s mind. She expresses herself without words. She is not able to say anything but dies under the pressure of the loss of newfound freedom.
The second element that needs to be discussed is the narrator’s point of view. The narrator takes the form of the omniscient third person; that means that he is all-seeing and all-knowing. If the story were written in the first-person narrative, the reader would consider the situation differently. The use of the narrator’s point of view shows Mrs. Mallard in a more sympathetic and kind light, as she remembers her husband’s “tender hands” (Chopin 1). Simultaneously, she thinks about bitter moments in her marriage.
It seems that, in describing such ambiguous feelings, the narrator makes excuses for the main character’s behavior. Again, if it were in the first-person narrative, the reader could think that Mrs. Mallard is selfish and does not love her husband. It is clear from these observations that Mrs. Mallard is a complicated character who discovers her hidden desires. Learning that her husband’s death led to freedom and joy becomes a surprise for her.
As it was stated before, Chopin uses the third-person narrator to explore the complexity of the female character. Moreover, it provides extensive background information in introducing the reader to the secondary characters, namely Josephine and Richard. They confirm the fact that Mrs. Mallard is not alone, and has relatives and friends who also reflect her connection with society and the wish to become a free part of it. In general, the narrator does not condemn or protect this woman. It seems that the author wants to explain how complicated her life is, and offer readers some food for thought.
Finally, the third element contributing to understanding the theme is the tone of the narration. The ambivalent atmosphere created by the dramatic tone is the key to understanding the central character. It goes without saying that other characters are sure that her death is from a sudden double shock. Since the readers know more about the situation, for example, that she experienced “a monstrous joy,” they might guess the actual reason for her death (Chopin 1). Therefore, to evoke a definite emotional response in readers, the author uses dramatic and in some ways ironic tone to show the tragic ending of Mrs. Mallard’s life and the story in general.
The climax of the story is the sudden return of the “deceased” Mr. Mallard, at which time the triumphant and victorious Louise unexpectedly dies. Overall, in the text, there is an ironic tone associated with sympathy, caution, emotion, and anxious triumph at the same time. Obviously, the author does not remove the responsibility of the husband, as his wife was unhappy in the marriage. The last words of the author sound ominously and malignantly like retribution and warning.
Such an ambiguous tone in the story confirms the outlook of Chopin, merging the desire to poeticize the woman’s spiritual independence and the ironic awareness of the initial failure of this attempt. The story ends with the purposefully ironic tone as well, through which the reader perceives that Mrs. Mallards’ heart trouble is much more of a metaphor and emotional state than a physical condition.
In conclusion, one can say that the novel The Story of an Hour by Chopin illustrates the complex inner feelings of Mrs. Mallard. In the end, the woman dies from an intolerable contradiction. Based on such literary elements as setting, narrator’s point of view, and tone, the paper discusses the meaning of the novel. The whole story is a wonderful example of the author’s consistency in the realization of her idea, as the major function of all the elements is the same—to achieve a complicated, dramatic effect. As a result, it was stated that Chopin wants to show the female’s conflicting emotions that reveal her wish for independence from her husband.
Chopin, Kate. The Story of an Hour . n.d. Web.
- Kate Chopin’s “The Story of an Hour”
- The Story of an Hour by Kate Chopin
- Joy That Kills: “The Story of an Hour” by Chopin
- "Babylon Revisited" by Francis Scott Fitzgerald
- American Southern Literature
- "It's Your Ship" by D. Michael Abrashoff
- "The Lady, or the Tiger?" by Frank Stockton
- National Identity in "Song of Solomon" by Morrison
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2020, September 15). The Novel "The Story of an Hour" by Kate Chopin. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-novel-the-story-of-an-hour-by-kate-chopin/
"The Novel "The Story of an Hour" by Kate Chopin." IvyPanda , 15 Sept. 2020, ivypanda.com/essays/the-novel-the-story-of-an-hour-by-kate-chopin/.
IvyPanda . (2020) 'The Novel "The Story of an Hour" by Kate Chopin'. 15 September.
IvyPanda . 2020. "The Novel "The Story of an Hour" by Kate Chopin." September 15, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-novel-the-story-of-an-hour-by-kate-chopin/.
1. IvyPanda . "The Novel "The Story of an Hour" by Kate Chopin." September 15, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-novel-the-story-of-an-hour-by-kate-chopin/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "The Novel "The Story of an Hour" by Kate Chopin." September 15, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-novel-the-story-of-an-hour-by-kate-chopin/.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The Story of an Hour was written by Kate Chopin in 1984. It describes a woman, Mrs. Mallard, who lost her husband in an accident, but later the truth came out, and the husband was alive. This essay will discuss The Story of an Hour with emphasis on the plot and development of the protagonist, Mrs. Mallard, who goes through contrasting emotions ...
After her initial sobs of grief subside, Louise escapes into her bedroom and locks the door. She refuses to let Josephine or Richards follow her. Alone, she falls into a chair placed before an open window. Absolutely drained by her own anguish and haunted by exhaustion, she rests in the chair and looks out the window.
The Story of an Hour is a short story written by Kate Chopin in 1894. This famous piece of literature was controversial for its time, as the story mentioned a female protagonist who felt relieved after her husband's death. The conclusion of The Story of an Hour is ironic, which makes the ending memorable.
Yet Chopin's short story is, upon closer inspection, a subtle, studied analysis of death, marriage, and personal wishes. Written in April 1894 and originally published in Vogue in December of that year, the story focuses on an hour in the life of a married woman who has just learnt that her husband has apparently died.
In this guide to Kate Chopin's "The Story of an Hour," we'll discuss: A brief history of Kate Chopin and America the 1890s. "The Story of an Hour" summary. Analysis of the key story elements in "The Story of an Hour," including themes, characters, and symbols. By the end of this article, you'll have an expert grasp on Kate ...
Analysis of Kate Chopin's The Story of an Hour By NASRULLAH MAMBROL on July 28, 2021. Originally entitled "The Dream of an Hour" when it was first published in Vogue (December 1894), "The Story of an Hour" has since become one of Kate Chopin's most frequently anthologized stories. Among her shortest and most daring works, "Story" examines issues of feminism, namely, a woman's ...
Introduction: "The Story of an Hour" by Kate Chopin. "The Story of an Hour" by Kate Chopin, first published in 1894 in the St. Louis Life magazine, was later included in the 1895 collection "Vojageur" and in the 1895 edition of "Bayou Folk". This iconic short story features a unique narrative structure, where the protagonist ...
Overview. First published in 1894, "The Story of an Hour" by Kate Chopin is a poignant and thought-provoking short story. Set in the late 19th century, the narrative follows Louise Mallard, a woman with a heart condition, who receives the news of her husband's death in a railroad accident. Initially overwhelmed by grief, Louise's ...
The Story of an Hour Analysis. L ouise's newfound hope for the future in the wake of her husband's death encapsulates the oftentimes repressive nature of nineteenth-century marriages.; Chopin uses ...
Summary. Kate Chopin's (1850-1904) short story "The Story of an Hour" narrates events that happen within an hour.. Louise Mallard is a young, calm, and frail woman who suffers from a heart disease. On this day, Louise learns from her sister Josephine and a family friend, Richards, that her husband, Brently Mallard, has died.
Kate Chopin's short story, "The Story of an Hour," is a masterpiece of American literature, recognized for its exploration of complex themes such as freedom, marriage, and societal expectations. In this critical essay, we will delve into the narrative's underlying messages, character development, and the literary devices employed to convey its ...
Updated on May 24, 2019. "The Story of an Hour" by American author Kate Chopin is a mainstay of feminist literary study. Originally published in 1894, the story documents the complicated reaction of Louise Mallard upon learning of her husband's death. It is difficult to discuss "The Story of an Hour" without addressing the ironic ending.
In Kate Chopin's "The Story of an Hour," the author skillfully employs literary devices to explore the theme of female liberation and the constraints of marriage. Through the lens of Mrs. Mallard's experiences, the story reveals the complexities of societal expectations and the potential for personal freedom. This essay will analyze how Chopin ...
This article includes a summary, as well as a look at themes, symbolism and irony. Summary of "The Story of an Hour". Mrs. Mallard, who has heart trouble, is gently given the news that her husband has been killed in a train accident. Her husband's friend Richards found out at the newspaper office, confirmed the name, and went to her sister ...
The essay analyzes Kate Chopin's short story "The Story of an Hour," focusing on its style, tone, and language. The author highlights how these literary elements contribute to the story's success and its controversial nature.
In "The Story of an Hour," there is both internal and external conflict. The essence of the latter is in the opposition of a person to society and its norms. Chopin refers to one of "the numerous paradoxes against which the woman had to survive in the American society in the 19 th century" - imposed roles and stereotypes (Kusi and ...
Kate Chopin's Short Stories Summary and Analysis of "The Story of an Hour". Upon hearing the news of Brently Mallard 's tragic railroad accident death in the newspaper office, his friend Richards rushes to the Mallards' house, where he and Mrs. Mallard's sister Josephine gently inform the weak-hearted Mrs. Mallard of Brently's death.
Introduction. This paper will provide a summary and an analysis of "The Story of an Hour," a short story by Kate Chopin published in 1894. Despite being only several pages long, the passage has become popular among readers. The title refers to the fact that the plot revolves around a woman and what she experiences throughout one hour.
Per Seyersted, in Kate Chopin: A Critical Biography, extols the story's "theme of self-assertion." Burt Bender, in his essay "Kate Chopin's Lyrical Short Stories," argues that the story is a ...
Kate Chopin 's " The Story of an Hour " argues that an individual discover their self-identity only after being freed from confinement. The story also argues that freedom is a very powerful force that affects mental or emotional state of a person. The story finally argues that only through death can one be finally freed.
to deliver a 100% original paper. Learn More. The story title " The story of one hour " is ironic in nature. At first glance, the title implies that the story occurred within an hour, however, Chopin ironically increased the time span and made it occur within several days. The ironic part is that usually, the death of a spouse takes months ...
An Analysis of The Story of an Hour The plot centers around numerous forces in conflict with one another. Throughout the work, concepts and symbols are constantly shown to be equivalent but completely distinct. Examining the wording in Chopin's short narrative reveals that each segment has a deeper importance. The themes and symbolism of the narrative are addressed in this analysis.
Williams 1 De'Quion Williams Professor Tredore ENG-101 15May2023 Literary Analysis of The Story of an Hour Kate Chopin's "The Story of an Hour" is a short story that focuses on the inner thoughts and emotions of a woman in the midst of a personal crisis. The story follows Louise Mallard as she learns of her husband's death and experiences a range of different emotions in the span of an hour.
Once her husband is said to be dead, Josephine, Mrs. Mallard's sister, comes to inform her of this tragic news. Even though Josephine tries to find as gentle words as possible, Mrs. Mallard is still shocked and frustrated. A newly-minted widow locks herself in her room to stay alone with her grief (Chopin, 2014).
Essay Example: Edgar Allan Poe's "The Tell-Tale Heart" is a riveting short story that intricately explores the psychological landscapes of guilt and paranoia. Set in an ambiguous location and told by an unnamed narrator, this tale delves into the mind of a character gripped by obsession and ... Kate Chopin The Picture of Dorian Gray Drama ...
Introduction. The Story of an Hour novel by Kate Chopin, recognized as a masterpiece of short fiction, reflects the complicated self-discovery mechanisms of a woman. Mrs. Mallard, a central character of the story, hears about the death of her husband who was riding on a train. However, the first reaction of grief is replaced by a strange ...