- Thesis Action Plan New
- Academic Project Planner

Literature Navigator
Thesis dialogue blueprint, writing wizard's template, research proposal compass.
- Why students love us
- Why professors love us
- Rebels Blog (Free)
- Why we are different
- All Products
- Coming Soon
How to Write a Thesis in a Month: A Step-by-Step Guide

Writing a thesis in a month might seem like an impossible task, but with a well-structured plan and disciplined approach, it is achievable. This guide provides a step-by-step approach to help you navigate through the process efficiently, from planning and research to writing and final submission.
Key Takeaways
- Establish a clear and structured thesis plan with achievable milestones.
- Conduct efficient research using academic databases and organize your materials effectively.
- Write a compelling introduction and literature review by synthesizing relevant sources.
- Choose appropriate research methods and ensure ethical compliance during data collection.
- Revise and edit your thesis thoroughly, incorporating feedback and proofreading for consistency.
Developing a Structured Thesis Plan
Creating a structured thesis plan is essential for successfully completing your thesis within a month. A well-organized plan will help you stay on track and manage your time effectively throughout the thesis journey .
Identifying Key Milestones
Start by identifying the key milestones in your thesis journey. These milestones could include completing your research proposal, finishing data collection, and drafting each chapter. By breaking down the process into smaller, manageable steps , you can make steady progress and avoid feeling overwhelmed.
Creating a Timeline
Once you have identified the key milestones, create a timeline that outlines when you plan to achieve each one. This timeline should be realistic and take into account any other commitments you may have. Use tools like Gantt charts or project management software to visualize your timeline and track your progress.
Allocating Time for Each Section
Allocate specific time blocks for each section of your thesis. For example, you might dedicate one week to writing the introduction and literature review, two weeks to data collection, and another week to data analysis. By allocating time for each section, you ensure that you have enough time to complete each part of your thesis without rushing.
Remember, developing a structured thesis plan is not just about setting deadlines; it's about creating a roadmap that guides you through the entire thesis journey. With a clear plan in place, you can approach your thesis with confidence and precision.
Conducting Efficient Research
Conducting efficient research is crucial for creating an effective master thesis outline with thesis action plan . This step-by-step guide will help you organize and focus on completing your thesis journey.
Writing the Introduction and Literature Review
The introduction and literature review are crucial components of your thesis. They set the stage for your research by providing context and background information. This section should outline the topic, present your research question, and give an overview of the methodology used in your study. A strong literature review will provide a comprehensive summary of prior work while also identifying gaps in knowledge that your research aims to fill.
Methodology and Data Collection
Choosing appropriate research methods.
Selecting the right research methods is crucial for the success of your thesis. Assess your data collection methods critically to ensure the reliability and validity of your research findings. Consider whether qualitative, quantitative, or mixed methods best suit your research questions and objectives.
Designing Data Collection Instruments
Your data collection instruments, such as surveys, interviews, or observation protocols, should be designed to gather comprehensive and relevant data. By organizing your data into categories and subgroups, you create typologies and taxonomies that help in identifying patterns and behaviors. This structured approach aids in drawing meaningful conclusions and verifying them through continuous comparison and validation.
Ensuring Ethical Compliance
Ethical considerations are paramount in any research involving human participants. Ensure that your study complies with ethical guidelines, including obtaining informed consent and ensuring confidentiality. This not only protects your participants but also enhances the credibility of your research.
Analyzing Data and Presenting Results
Once you have gathered your data, the next critical step is to analyze it in a way that supports your research objectives . Focus on quantitative data analysis using statistical methods to uncover patterns, trends, and relationships. For qualitative data, employ diverse analytical methods to interpret the underlying meanings and implications.
Organize your findings into clear, concise formats. Tables are particularly useful for presenting quantitative data. For example:
| Variable | Description | Results |
|---|---|---|
| Var1 | Description | Result |
| Var2 | Description | Result |
Data Analysis Techniques
Ensure that your analysis aligns with your study design and underlying assumptions. This congruence is vital for the integrity of your research findings. Organize your data into categories and subgroups to create typologies and taxonomies that help in identifying patterns and behaviors. This structured approach aids in drawing meaningful conclusions and verifying them through continuous comparison and validation.
Interpreting Findings
Results and discussion provide a platform to present the findings of a research study. They are essential components of any research paper as they provide an opportunity to analyze and interpret the data collected during the study. Results typically include descriptive statistics, tables, figures, or graphs that display the main outcomes of the research.
Visualizing Data Effectively
Employ graphical methods like matrices and networks to summarize and compare data effectively. This not only makes your data more accessible but also highlights key insights that might be overlooked in textual descriptions. By visualizing your data, you can communicate complex information clearly and efficiently, making it easier for your audience to grasp the significance of your findings.
Revising and Editing Your Thesis
Revising and editing your thesis is a crucial step in ensuring that your work is polished and coherent. Don't edit too soon ; wait until you feel confident in your paper's focus and organization. This will allow you to approach the editing process with a clear mind and a fresh perspective. To keep your revisions organized, consider saving each iteration of your dissertation as a new file and labeling each file clearly with a revision number or date. This disciplined approach will help you effectively structure and refine your dissertation.
Self-Editing Techniques
When you receive feedback on your work, be prepared to make revisions. Receiving constructive criticism can be challenging, but it’s an essential part of the writing process. Remember, your preliminary work will not be graded, and only the final product will be evaluated. As you continue to work on your thesis, you’ll gain experience and improve your writing skills.
Incorporating Feedback
Once you've completed these steps, seek feedback from peers or mentors who can provide a fresh perspective. Their insights can be invaluable in identifying areas that may need further refinement. After incorporating their suggestions, your thesis will be ready for the final approval from your committee.
Proofreading for Consistency
To ensure a comprehensive review, consider the following checklist:
- Review and refine your thesis statement
- Check the organization of chapters and sections
- Verify the accuracy of data and citations
- Confirm that all research questions have been addressed
- Perform a thorough spell-check and grammar review
Preparing for the Final Submission
As you approach the final stages of your thesis journey, it's crucial to ensure that every detail is meticulously attended to. This phase involves not only the finalization of your document but also adhering to institutional guidelines and preparing for any necessary presentations or defenses.
Preparing for the final submission of your thesis can be a daunting task, but it doesn't have to be. At Research Rebels, we offer a step-by-step Thesis Action Plan designed to help you overcome the common obstacles students face. Don't let anxiety and sleepless nights hold you back. Visit our website to claim your special offer now and take the first step towards a stress-free thesis submission.
Writing a thesis in a month is an ambitious yet achievable goal, provided one approaches it with a structured plan and disciplined mindset. This guide has outlined the essential steps, from initial topic selection to the final stages of revision, offering practical advice and strategies to streamline the process. By adhering to a clear timeline, leveraging available resources, and maintaining a focused and methodical approach, students can navigate the complexities of thesis writing with confidence. Remember, the key to success lies in consistent effort, effective time management, and a proactive attitude towards overcoming challenges. With determination and the right tools, completing a thesis within a month is not only possible but can also be a rewarding academic accomplishment.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is it really possible to write a thesis in a month.
Yes, it is possible to write a thesis in a month with a clear plan, disciplined approach, and efficient time management.
How should I structure my thesis plan?
Your thesis plan should include identifying key milestones, creating a timeline, and allocating time for each section of your thesis.
What are some tips for conducting efficient research?
Utilize academic databases, organize your research materials, and employ effective note-taking strategies to streamline your research process.
How can I ensure ethical compliance in my research?
Choose appropriate research methods, design data collection instruments carefully, and follow ethical guidelines set by your institution.
What techniques can I use for data analysis?
Use statistical software, qualitative analysis methods, and data visualization tools to analyze and present your findings effectively.
What should I do to prepare for the final submission of my thesis?
Follow formatting guidelines, compile appendices and references, and conduct a final review checklist to ensure your thesis is ready for submission.

How Many References Should You Include in a Master Thesis?

Dissertation How to Write: A Step-by-Step Guide

Crafting Effective Literature Review Research Questions: Tips and Strategies

From Research Question to Thesis Statement: A Step-by-Step Guide

Managing Anxiety While Writing Your Thesis: Tips and Techniques

From Discussion to Distinction: The Key Aspects of Theoretical Contributions

Celebrating Milestones: Balancing Achievements in Your Bachelor Thesis and Special Occasions

Presentation Perfection: How to Deliver with Confidence

The Role of Sports and Recreation in Thesis Work

Students' Guide to Lucrative Side Gigs: Earning Money While Studying

Thesis Action Plan

- Rebels Blog
- Blog Articles
- Terms and Conditions
- Payment and Shipping Terms
- Privacy Policy
- Return Policy
© 2024 Research Rebels, All rights reserved.
Your cart is currently empty.
Think of yourself as a member of a jury, listening to a lawyer who is presenting an opening argument. You'll want to know very soon whether the lawyer believes the accused to be guilty or not guilty, and how the lawyer plans to convince you. Readers of academic essays are like jury members: before they have read too far, they want to know what the essay argues as well as how the writer plans to make the argument. After reading your thesis statement, the reader should think, "This essay is going to try to convince me of something. I'm not convinced yet, but I'm interested to see how I might be."
An effective thesis cannot be answered with a simple "yes" or "no." A thesis is not a topic; nor is it a fact; nor is it an opinion. "Reasons for the fall of communism" is a topic. "Communism collapsed in Eastern Europe" is a fact known by educated people. "The fall of communism is the best thing that ever happened in Europe" is an opinion. (Superlatives like "the best" almost always lead to trouble. It's impossible to weigh every "thing" that ever happened in Europe. And what about the fall of Hitler? Couldn't that be "the best thing"?)
A good thesis has two parts. It should tell what you plan to argue, and it should "telegraph" how you plan to argue—that is, what particular support for your claim is going where in your essay.
Steps in Constructing a Thesis
First, analyze your primary sources. Look for tension, interest, ambiguity, controversy, and/or complication. Does the author contradict himself or herself? Is a point made and later reversed? What are the deeper implications of the author's argument? Figuring out the why to one or more of these questions, or to related questions, will put you on the path to developing a working thesis. (Without the why, you probably have only come up with an observation—that there are, for instance, many different metaphors in such-and-such a poem—which is not a thesis.)
Once you have a working thesis, write it down. There is nothing as frustrating as hitting on a great idea for a thesis, then forgetting it when you lose concentration. And by writing down your thesis you will be forced to think of it clearly, logically, and concisely. You probably will not be able to write out a final-draft version of your thesis the first time you try, but you'll get yourself on the right track by writing down what you have.
Keep your thesis prominent in your introduction. A good, standard place for your thesis statement is at the end of an introductory paragraph, especially in shorter (5-15 page) essays. Readers are used to finding theses there, so they automatically pay more attention when they read the last sentence of your introduction. Although this is not required in all academic essays, it is a good rule of thumb.
Anticipate the counterarguments. Once you have a working thesis, you should think about what might be said against it. This will help you to refine your thesis, and it will also make you think of the arguments that you'll need to refute later on in your essay. (Every argument has a counterargument. If yours doesn't, then it's not an argument—it may be a fact, or an opinion, but it is not an argument.)
This statement is on its way to being a thesis. However, it is too easy to imagine possible counterarguments. For example, a political observer might believe that Dukakis lost because he suffered from a "soft-on-crime" image. If you complicate your thesis by anticipating the counterargument, you'll strengthen your argument, as shown in the sentence below.
Some Caveats and Some Examples
A thesis is never a question. Readers of academic essays expect to have questions discussed, explored, or even answered. A question ("Why did communism collapse in Eastern Europe?") is not an argument, and without an argument, a thesis is dead in the water.
A thesis is never a list. "For political, economic, social and cultural reasons, communism collapsed in Eastern Europe" does a good job of "telegraphing" the reader what to expect in the essay—a section about political reasons, a section about economic reasons, a section about social reasons, and a section about cultural reasons. However, political, economic, social and cultural reasons are pretty much the only possible reasons why communism could collapse. This sentence lacks tension and doesn't advance an argument. Everyone knows that politics, economics, and culture are important.
A thesis should never be vague, combative or confrontational. An ineffective thesis would be, "Communism collapsed in Eastern Europe because communism is evil." This is hard to argue (evil from whose perspective? what does evil mean?) and it is likely to mark you as moralistic and judgmental rather than rational and thorough. It also may spark a defensive reaction from readers sympathetic to communism. If readers strongly disagree with you right off the bat, they may stop reading.
An effective thesis has a definable, arguable claim. "While cultural forces contributed to the collapse of communism in Eastern Europe, the disintegration of economies played the key role in driving its decline" is an effective thesis sentence that "telegraphs," so that the reader expects the essay to have a section about cultural forces and another about the disintegration of economies. This thesis makes a definite, arguable claim: that the disintegration of economies played a more important role than cultural forces in defeating communism in Eastern Europe. The reader would react to this statement by thinking, "Perhaps what the author says is true, but I am not convinced. I want to read further to see how the author argues this claim."
A thesis should be as clear and specific as possible. Avoid overused, general terms and abstractions. For example, "Communism collapsed in Eastern Europe because of the ruling elite's inability to address the economic concerns of the people" is more powerful than "Communism collapsed due to societal discontent."
Copyright 1999, Maxine Rodburg and The Tutors of the Writing Center at Harvard University

How to write a PhD thesis: a step-by-step guide
A draft isn’t a perfect, finished product; it is your opportunity to start getting words down on paper, writes Kelly Louise Preece
Kelly Louise Preece

Created in partnership with

You may also like

Popular resources
.css-1txxx8u{overflow:hidden;max-height:81px;text-indent:0px;} The secrets to success as a provost
Using non verbal cues to build rapport with students, emotionally challenging research and researcher well-being, augmenting the doctoral thesis in preparation for a viva, how hard can it be testing ai detection tools.
Congratulations; you’ve finished your research! Time to write your PhD thesis. This resource will take you through an eight-step plan for drafting your chapters and your thesis as a whole.

Organise your material
Before you start, it’s important to get organised. Take a step back and look at the data you have, then reorganise your research. Which parts of it are central to your thesis and which bits need putting to one side? Label and organise everything using logical folders – make it easy for yourself! Academic and blogger Pat Thomson calls this “Clean up to get clearer” . Thomson suggests these questions to ask yourself before you start writing:
- What data do you have? You might find it useful to write out a list of types of data (your supervisor will find this list useful too.) This list is also an audit document that can go in your thesis. Do you have any for the “cutting room floor”? Take a deep breath and put it in a separate non-thesis file. You can easily retrieve it if it turns out you need it.
- What do you have already written? What chunks of material have you written so far that could form the basis of pieces of the thesis text? They will most likely need to be revised but they are useful starting points. Do you have any holding text? That is material you already know has to be rewritten but contains information that will be the basis of a new piece of text.
- What have you read and what do you still need to read? Are there new texts that you need to consult now after your analysis? What readings can you now put to one side, knowing that they aren’t useful for this thesis – although they might be useful at another time?
- What goes with what? Can you create chunks or themes of materials that are going to form the basis of some chunks of your text, perhaps even chapters?
Once you have assessed and sorted what you have collected and generated you will be in much better shape to approach the big task of composing the dissertation.
Decide on a key message
A key message is a summary of new information communicated in your thesis. You should have started to map this out already in the section on argument and contribution – an overarching argument with building blocks that you will flesh out in individual chapters.
You have already mapped your argument visually, now you need to begin writing it in prose. Following another of Pat Thomson’s exercises, write a “tiny text” thesis abstract. This doesn’t have to be elegant, or indeed the finished product, but it will help you articulate the argument you want your thesis to make. You create a tiny text using a five-paragraph structure:
- The first sentence addresses the broad context. This locates the study in a policy, practice or research field.
- The second sentence establishes a problem related to the broad context you have set out. It often starts with “But”, “Yet” or “However”.
- The third sentence says what specific research has been done. This often starts with “This research” or “I report…”
- The fourth sentence reports the results. Don’t try to be too tricky here, just start with something like: “This study shows,” or “Analysis of the data suggests that…”
- The fifth and final sentence addresses the “So What?” question and makes clear the claim to contribution.
Here’s an example that Thomson provides:
Secondary school arts are in trouble, as the fall in enrolments in arts subjects dramatically attests. However, there is patchy evidence about the benefits of studying arts subjects at school and this makes it hard to argue why the drop in arts enrolments matters. This thesis reports on research which attempts to provide some answers to this problem – a longitudinal study which followed two groups of senior secondary students, one group enrolled in arts subjects and the other not, for three years. The results of the study demonstrate the benefits of young people’s engagement in arts activities, both in and out of school, as well as the connections between the two. The study not only adds to what is known about the benefits of both formal and informal arts education but also provides robust evidence for policymakers and practitioners arguing for the benefits of the arts. You can find out more about tiny texts and thesis abstracts on Thomson’s blog.
- Writing tips for higher education professionals
- Resource collection on academic writing
- What is your academic writing temperament?
Write a plan
You might not be a planner when it comes to writing. You might prefer to sit, type and think through ideas as you go. That’s OK. Everybody works differently. But one of the benefits of planning your writing is that your plan can help you when you get stuck. It can help with writer’s block (more on this shortly!) but also maintain clarity of intention and purpose in your writing.
You can do this by creating a thesis skeleton or storyboard , planning the order of your chapters, thinking of potential titles (which may change at a later stage), noting down what each chapter/section will cover and considering how many words you will dedicate to each chapter (make sure the total doesn’t exceed the maximum word limit allowed).
Use your plan to help prompt your writing when you get stuck and to develop clarity in your writing.
Some starting points include:
- This chapter will argue that…
- This section illustrates that…
- This paragraph provides evidence that…
Of course, we wish it werethat easy. But you need to approach your first draft as exactly that: a draft. It isn’t a perfect, finished product; it is your opportunity to start getting words down on paper. Start with whichever chapter you feel you want to write first; you don’t necessarily have to write the introduction first. Depending on your research, you may find it easier to begin with your empirical/data chapters.
Vitae advocates for the “three draft approach” to help with this and to stop you from focusing on finding exactly the right word or transition as part of your first draft.

This resource originally appeared on Researcher Development .
Kelly Louse Preece is head of educator development at the University of Exeter.
If you would like advice and insight from academics and university staff delivered direct to your inbox each week, sign up for the Campus newsletter .
The secrets to success as a provost
Emotions and learning: what role do emotions play in how and why students learn, the podcast: bringing an outsider’s eye to primary sources, a diy guide to starting your own journal, formative, summative or diagnostic assessment a guide, harnessing the power of data to drive student success.
Register for free
and unlock a host of features on the THE site
The Grad Student Way
Your One Stop Grad School and PhD Resource
- Second Income Ebook
- Twitter GradStudentWay
- LinkedIn GradStudentWay
- Facebook Page
- RSS Feed GradStudentWay
- Networking Guide
- Write Your PhD Thesis In One Month Or Less
Thesis/dissertation writing need not be a multi-month ordeal that makes you pull your hair out and roll up into a fetal position. The trick is to get a head start , set goals and deadlines, and work steadily—not feverishly—toward that ultimate satisfaction of handing your magnum opus to the graduate school. The first three sections of this article are devoted to ways that you can get way ahead of the curve from the very beginning of your graduate program—BEFORE push comes to shove.
1.) GET STARTED RIGHT AWAY— YES, REALLY .
NEWS FLASH: you can start working on your thesis or dissertation almost from the moment you decide on a lab/advisor .
In the beginning, there were papers …
The starting point for any newbie graduate student is to read boatloads of relevant papers so that you can learn your advisor’s repertoire of experimental techniques or areas of interest, what has been done so far in the field, what questions remain to be answered, and where your research will contribute.
Keep in mind that these seminal papers will be heavily integrated into your thesis or dissertation:
a) The introduction, in which you give all the pertinent background to set the stage for your research and make everyone on your committee (and beyond!) understand why it’s important
b) Data chapters, where previously published data lend validity to your findings, or are at least taken into consideration as you interpret your data
Let’s back up. How do you find these papers? Hopefully, your advisor will provide you with a few of the original papers that got the ball rolling. Find out what papers cite them . You can perform Boolean searches in Pubmed and Google Scholar (great tips explaining how to do this can be found at Boolean.pdf ).
Note that in Pubmed, you will need to go to “Advanced Search,” where the builder constructs the Boolean search for you (Figure 1). Pubmed offers another great strategy: you can set up citation alerts that notify you via e-mail every time one of these pivotal articles is cited. Pubmed has a tutorial on how to do this here: myncbi.html . You can control how often you receive these alerts, or adjust later based on how inundated your inbox becomes.
FIGURE 1. PubMed’s Boolean Search builder.
Google scholar offers a similar citation alert service. Go to Google Scholar, http://scholar.google.com/ , and click on “Alerts” (see Figure 2). From the next screen, click “Create Alert” (Figure 3). You can set up alerts based on Boolean searches (Figure 4), or by author . Also, since many principal authors have varied interests, you can customize by using a combination Boolean/search-by-author approach (Figure 5). Enter your e-mail address, and you’re good to go.
FIGURE 2. Setting up alerts in Google Scholar. First, click “Alerts.”
FIGURE 3. Setting up alerts in Google Scholar, part 2. Next, click “Create Alert.”
FIGURE 4. Setting up alerts in Google Scholar, part 3. Setting up your search criteria using Boolean operators.
FIGURE 5. Setting up alerts in Google Scholar, part 4. The combined Author/Boolean operator search in Google Scholar.
ORGANIZING your boatloads of papers…
Let’s back up again. Realize that unless you are a genius, you will probably have to revisit these nuggets of wisdom several times during your graduate career, particularly when you have a better grasp on the research. Also, unless you are a genius, you will find yourself wondering, “What was that paper that explained________?” This is where being organized will save you TONS of time.
I am a big fan of saving paper and not printing out reams of articles to be read and then stuffed into filing cabinets . I highly recommend a citation management program, such as Endnote . Find out which program your advisor uses (see if he or she will let you install the program on your computer). Some departments even offer this software free of charge. Not only are all of the citations in your library searchable, but you can also file them into folders based on the subject matter (Figure 6).
FIGURE 6. Filing papers in EndNote–beats a filing cabinet!
As you do your literature search, you download the citations into your citation manager. Most e-journals have a “download to citation manager” link. Google Scholar also recently added a very nice “Cite” function that lets you import citations directly into your citation manager (Figure 7).
FIGURE 7. Google Scholar’s Cite function.
You can also search PubMed from within Endnote, which saves you several steps (Figure 8). In addition, the program has a lovely feature called Cite-While-You-Write that links with Microsoft Word. No more the parenthetical “ need citation !” statements in your text. With the CWYW feature, you can pull up all of the papers in your Endnote library that pertain to your text, and with the click of one button in Word—voilà! Citations inserted (Figure 9)! You can format the bibliography later, when your behemoth is completely written—yet another convenient, automatic feature.
FIGURE 8. Searching for papers from within EndNote.
FIGURE 8. EndNote’s Cite While You Write function.
2) Intermediate documents: the thesis/dissertation proposal and grant applications
Think of your thesis or dissertation proposal and any grant applications as being a big first step toward the first chapter of your final document: the introduction. Preparation of these documents entails a thorough review of pertinent literature to set the stage and explain the rationale for the research you are proposing. So by this logic, you should have taken a very large bite out of the first chapter of your thesis or dissertation by the time you take your preliminary exams.
3) Methods: you do them every day, why not take the time to write them up?
In the STEM fields, theses and dissertations require a chapter devoted to methods. You have your own set of experimental and/or statistical techniques that you presumably learn from your advisor, then troubleshoot and tweak based on your specific needs. You know how you write detailed notes on the conditions of each experiment every time you do them in your lab notebook? (RIGHT?!) This is all information that you can take even an hour per week to write up in your thesis document. Check out the previous papers from your advisor to get ideas on wording, and then re-work it so it’s your own (citing relevant papers, of course). By the time you actually for-real start writing your thesis or dissertation, your methods chapter can be practically done already!
4) After the greenlight…careful planning and sticking to a schedule!
You’ve received the greenlight to “start” writing your thesis or dissertation from your committee. Now what? Well, you have a good chunk of the intro done already, right? Your chapter 2 is practically done as well! Be sure to check out the deadlines not only for getting your document to your committee, but also for depositing it with the graduate school. Wouldn’t it stink to defend your thesis in April, but not graduate until December because you missed the deadline?
Now, I will tell you a huge time-saving tip . Before you start (well, continue) writing, find a colleague who has recently turned in their thesis or dissertation and still has their final word document kicking around . Ask your colleague for permission to use their document in the following way: you are not going to copy anything in that document… EXCEPT THE FORMATTING.
You know the part where the clerk at the grad school pulls out the ruler and measures your margins, page number position and other random stuff while you hold your breath? All of that will already be in your colleague’s word document. Why re-invent the wheel? Just use the document as a template—delete ALL of the text and leave the margins and other formatting alone. (Of course, check over everything carefully before you deposit your document!) Anything you’ve written up to this point can easily be pasted into the template.
Next, agree upon deadlines : “I’ll have chapter 1 to you by________.” If you have been working ahead on your document and your reference library as described above, it should take you about a week to finish up chapter 1 (your introduction) and chapter 2 (methods). Can you do a chapter per week for each of the remaining chapters? Put the deadline in your calendar, and stick to it. Then, based on how much time you are still expected to spend in the lab, decide a set number of hours per day that you will spend on nothing but writing.
I would suggest asking your advisor for blocks of time to hole up at the library, or wherever it is that you do your best work . Then do it. You will be working weekends, no doubt, but try to work steadily and avoid all-nighters. Adjust as necessary—you may need to have an additional meeting with your advisor to request more time away from lab.
Do have a colleague read your document installments before you give them to your advisor . Run spell check and do all the basics before you offer up your baby to the red pen of death. If you really struggle with writing, or if you are not a native English speaker, there are services out there that will clean up your document on a by-the-hour basis. Spare your advisor the frustration of correcting simple errors.
Now, a caveat.
Just because you have a deadline that you are sticking to like an embedded tick does not mean that your advisor will adhere to similar deadlines in getting you edits and feedback . Many advisors, bless their hearts, are procrastinators (erm…busy with grant deadlines, writing their own papers, editing, and other important stuff that advisors do). Don’t sweat it… the ball is now in your advisor’s court, and you will now move steadily on to the next installment.
Which is due by __________in your calendar.
3) BACKUP, BACKUP, BACKUP!
And this time I do mean “backup”—as in your document. There is NO excuse for losing your thesis or dissertation . You should have MULTIPLE copies saved: on your computer, in Dropbox, on an external hard drive, etc. These copies should be clearly marked with dates in case you have to revert back to a prior version. They should also be marked after being edited by your advisor or others.
4) The final weeks
This will be a stressful time unless you are extremely lucky. It usually goes something like this: “Move this section to page 89.” Then two days later: “Put it back where it was.” Your advisor is stressed too—so try to take everything in stride.
If at all possible, try to get your thesis printed off for your committee a day or two in advance . This allows a cushion for the inevitable printer meltdown or copier jam. In my case, I got my final edits at 11 pm the night before my dissertation was due. Luckily, there weren’t a lot of changes to make, and there were no printer fiascos. I finished the edits by midnight and had the whole thing printed off by about 2 in the morning. Although I won’t say that I wasn’t completely stressed out and about to melt down myself…
You want your dissertation to look nice for your committee and to be easy for them to handle and write in . I’m a fan of bindings—I used three ring binders with pockets so that I could also include a CD with a copy of the document. But that’s not for everybody. Spiral bindings are just as good, but again, require planning because you’ll have to take your stack of documents somewhere like FedEx Kinkos. Even though it can be like herding cats to track down all the members of your committee, try to personally deliver your documents to them—not only for security’s sake, but to remind them of who you are.
I kid. Sort of.
5) After the defense
You may have loads of changes to make to your thesis or dissertation based on your committee members’ comments . You feel elated and relieved to have your defense over with. After the effects of the all-night post-defense bender have worn off, try to work diligently on the edits so that you don’t run up against the grad school’s deposit deadline. Make an appointment for a pre-check of your document to catch any formatting errors well in advance of the deadline.
Once you have deposited your thesis or dissertation with the graduate school (congratulations!), investigate how many bound copies you need. Most departments require a bound copy, as will your advisor. Then you need one, of course, and then there’s your parents…
University towns usually have at least one book bindery in addition to services on campus. There are online services as well—but be careful to check their ratings. You generally have to figure up the number of color-copy and high-resolution pages you have versus regular black and white. You send this estimate along with a digital copy of your dissertation and your selections for binding color, lettering, etc. There is something deeply satisfying about finally holding that beautifully bound book—that YOU wrote—in your hands at last.
In summary, it is possible to write your thesis or dissertation in under a month with good preparation, organization, and planning . The end result makes it all worthwhile. Keep in mind that if you move on to a postdoc or any other position that requires writing papers and grants, these same strategies apply.
Further Reading
About the Author:
Search The Grad Student Way
Most recent posts.
- PhD Career Series: Finding and Developing Your Inner Leader
- Top 11 Alternative Entry Level PhD Science Careers To Skip the PostDoc
- PhD Myth Busters: Making the Transition From Academia to Industry
- How A Rock Band Helped Save My PhD
- Is A PhD Really Worth It? Or A Waste of Time?
- Dealing With PhD Stress The Right Way: Advice From 3 PhD Graduates
- PhD Career Series: Product Management
- 5 Ways to Gain Valuable Skills Outside of Your Academic Training
- A PhD Student’s Race Against Time – How To Win/Graduate Faster
- Going Freelance Out of Graduate School
- 10 Ways To Successfully Defend Your PhD
- Considering Grad School? Important Things You Should Know Before, During, and After Applying
- Short and Sweet: Five Job Hunting Mistakes PhD Graduates Should Avoid
- Welcome To The ‘Academic Fight Club’
Second Income
- Career Development
- Cool Research
- Entrepreneurship
- Grad School Finance
- Grad School Hardships
- Grad School Humor
- Grad School Insights
- Grad School Poetry
- Grad Student Advice Series
- Grad Student Way Background
- Guest Posts
- PhD Careers In-Depth
- Popular Posts
- Post-Doctoral Related
- Professional Development
- Scientific Discoveries
- Transition From Academia Into Industry
- What's The Worst That Can Happen?
| M | T | W | T | F | S | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | |||||
| 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
| 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 |
| 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 |
| 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |
Recent Comments
- Andrew Martin on Top 11 Alternative Entry Level PhD Science Careers To Skip the PostDoc
- Ryan Raver on Is A PhD Really Worth It? Or A Waste of Time?
- Ya-Huei Huang on 10 Ways To Successfully Defend Your PhD
- Krutika I on 10 Ways To Successfully Defend Your PhD
- HABIB ULLAH SIDDIQUI on Grad Student Advice Series: 10 Ways To Be A Successful PhD Student
- sgo on 10 Ways To Successfully Defend Your PhD
- Tuscon Peter on 7 Easy Ways For Graduate Or College Students To Earn Alternative Income Or Make Money Online
- Jim on 7 Easy Ways For Graduate Or College Students To Earn Alternative Income Or Make Money Online
Recent Posts
- October 2018
- November 2015
- January 2015
- December 2014
- November 2013
- September 2013
- August 2013
- February 2013
- January 2013
- December 2012
- October 2012
- September 2012
- August 2012
- Entries feed
- Comments feed
- WordPress.org
Grad School Networking
Featured Posts
Grad Student Advice Series: What to do with your PhD: Post Doc or Real Job?
6 Ways To Survive Grad School and Achieve Work-Life Balance
7 Easy Ways For Graduate Or College Students To Earn Alternative Income Or Make Money Online
Return to top of page
Copyright © 2024 · eleven40 Child Theme on Genesis Framework · WordPress · Log in
- +44 (0) 207 391 9032
Recent Posts
- Everything You Should Know About Academic Writing: Types, Importance, and Structure
- Concise Writing: Tips, Importance, and Exercises for a Clear Writing Style
How to Write a PhD Thesis: A Step-by-Step Guide for Success
- How to Use AI in Essay Writing: Tips, Tools, and FAQs
- Copy Editing Vs Proofreading: What’s The Difference?
How Much Does It Cost To Write A Thesis? Get Complete Process & Tips
- How Much Do Proofreading Services Cost in 2024? Per Word and Hourly Rates With Charts
- Academic Editing: What It Is and Why It Matters
- How to Identify Research Gaps
- How to Use AI to Prepare for Exams
- Academic News
- Custom Essays
- Dissertation Writing
- Essay Marking
- Essay Writing
- Essay Writing Companies
- Model Essays
- Model Exam Answers
- Oxbridge Essays Updates
- PhD Writing
- Significant Academics
- Student News
- Study Skills
- University Applications
- University Essays
- University Life
- Writing Tips

Since 2006, Oxbridge Essays has been the UK’s leading paid essay-writing and dissertation service
We have helped 10,000s of undergraduate, Masters and PhD students to maximise their grades in essays, dissertations, model-exam answers, applications and other materials. If you would like a free chat about your project with one of our UK staff, then please just reach out on one of the methods below.
Writing a PhD thesis is a complicated and demanding process that involves rigorous research, detailed analysis, and structured writing. This guide provides an extensive overview of each step required to craft a successful PhD thesis, offering essential insights and strategies that benefit novice and seasoned researchers.
Step 1: Understand the Requirements
The initial step in crafting your PhD thesis is to thoroughly understand its specific requirements, which can vary widely between disciplines and institutions. A thesis must contribute new knowledge to its field, necessitating a deep familiarity with the expected structure, depth of analysis, and submission formalities. Your university guidelines should state how many words in a PhD thesis are needed within your discipline—usually ranging from 60,000 to 80,000 words.
Step 2: Choose Your Topic Wisely
Selecting a suitable topic is crucial and should be approached with great care. Your subject should interest you, fill a research gap, and be feasible within your available time and resources. Extensive preliminary reading and discussions with advisors are crucial at this stage to refine your topic and formulate precise research questions.
Step 3: Develop a Detailed Proposal
A detailed proposal acts as your thesis roadmap, outlining your research questions, the study's significance, methodologies, and a preliminary literature review. This document guides your research trajectory and is a reference point throughout your project.
Step 4: Conduct Rigorous Research
The research phase forms the backbone of your thesis. It involves systematic data collection, comprehensive literature review, and meticulous analysis. Effective research methods are crucial, and keeping organised, detailed records during this phase will facilitate a smoother writing process later on.
Step 5: Start Writing Early
Begin writing early in the research process. Starting with less complex sections like the literature review or methodology can help clarify your thoughts and identify gaps in your research. Early writing reduces the burden as the thesis deadline approaches.
Step 6: Structure Your Thesis
A PhD thesis usually has an introduction, a literature review, a methodology, findings, a discussion, a conclusion, and a list of references. Each section serves a distinct purpose: the introduction presents your research question and its significance, while the conclusion synthesises your findings and highlights their importance. But, how long is a PhD thesis typically? It usually ranges from 100 to 300 pages, varying by field and the nature of the research conducted.
Step 7: Seek Feedback Regularly
Regular feedback from your supervisor and peers is invaluable. Sharing drafts of chapters as you complete them ensures you remain on the correct path and integrates diverse perspectives that can enhance your work.
Step 8: Revise Thoroughly
Revision is a critical phase in which good writing is refined into excellent writing. Use feedback to enhance your arguments, clarify points, and refine your prose. Expect multiple rounds of revisions and be prepared to rework sections as needed.
Step 9: Proofread and Edit
Comprehensive proofreading and editing are crucial to ensure your thesis is error-free. Consider employing PhD thesis help from a PhD thesis writing service if needed. These professionals can provide detailed feedback and help polish your document to perfection.
Step 10: Prepare for the Viva
The final step is the viva, where you'll present your research to a panel of experts in your field. Thorough preparation, including a deep understanding of your research and readiness for potential questions, is essential. This presentation is your opportunity to highlight the significance and rigour of your work.
The Importance of a High-Quality PhD Thesis
A high-quality PhD thesis is not just a requirement for completing your doctorate; it significantly contributes to your field of study. Furthermore, it highlights your ability to conduct independent research, contribute original insights, and communicate complex ideas clearly and effectively. The calibre of your thesis can influence your academic and professional future, impacting job opportunities, postdoctoral positions, and the ability to publish your work in reputable journals.
Seeking Professional Help: Sources and Providers
When crafting your PhD thesis, seeking professional help can be a wise decision. Support can come from various sources:
University Resources : Most universities offer writing centres and libraries with professionals skilled in research methodologies, writing, and editing. PhD Thesis Writing Services : Specialised services can provide comprehensive help throughout the writing process. These services employ experienced PhD thesis writers familiar with the nuances of doctoral writing across various disciplines. Independent Consultants : Expert consultants or freelance PhD thesis writers can offer personalised guidance and feedback, focusing on specific areas of your thesis where you need extra help.
The Advantages of Professional PhD Thesis Help
Opting for professional PhD thesis help offers several advantages:
- Expert Guidance : Professional writers and editors bring expertise that can help you improve your thesis. They understand the academic standards and can help ensure your thesis meets them.
- Time Management : With the help of a PhD thesis writing service, you can manage your time more effectively. Professionals can speed up the research, writing, and revision processes, allowing you to focus on other important academic or personal commitments.
- Reduced Stress : The process of writing a PhD thesis can be stressful. Having a professional by your side can alleviate much of this stress by ensuring you are on the right track and providing reassurance through expert feedback.
Key Takeaways
A high-quality PhD thesis is the masterpiece of your academic career, thus requiring meticulous attention to detail and a deep understanding of your research topic. When asking, "How many words are in a PhD thesis?" it's important to note that quality and depth of research often matter more than the word count.
Utilising professional help, whether through university resources, dedicated PhD thesis writing services, or independent consultants, can provide invaluable support. These professionals enhance the quality of your work and help streamline the entire thesis process, allowing you to present a polished, scholarly work that stands out in your field. By investing in professional help, you invest in your academic success and future career prospects.

How to Tell if a Source is Reliable

The Difference Between Reference and Bibliography
Writing services.
- Essay Plans
- Critical Reviews
- Literature Reviews
- Presentations
- Dissertation Title Creation
- Dissertation Proposals
- Dissertation Chapters
- PhD Proposals
- CV Writing Service
- Business Proofreading Services
Editing Services
- Proofreading Service
- Editing Service
- Academic Editing Service
Additional Services
- Marking Services
- Consultation Calls
- Personal Statements
- Tutoring Services
Our Company
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Become a Writer
Terms & Policies
- Fair Use Policy
- Policy for Students in England
- Privacy Policy
- Terms & Conditions
- [email protected]
- More contact options
Payment Methods
Cryptocurrency payments.
- Interesting
- Scholarships
- UGC-CARE Journals
How to Write a Research Paper in a Month?
How to write a research paper in a month: a step-by-step guide with timeline.
Writing a research paper is one of the challenging tasks in research, but with proper planning and organization, it can be accomplished within a month. While the timeline may seem tight, this article will guide you through a step-by-step procedure to efficiently write a research paper in just 30 days. By following this timeline strictly, one can successfully navigate the research process and produce a high-quality paper .
Learn how to write a research paper in just one month with our comprehensive step-by-step guide. This timeline-based approach will help you manage your time effectively and achieve efficient results. Discover research tips, writing techniques, and valuable strategies to stay organized throughout the process. Enhance your research productivity and successfully complete your paper within the given deadline.
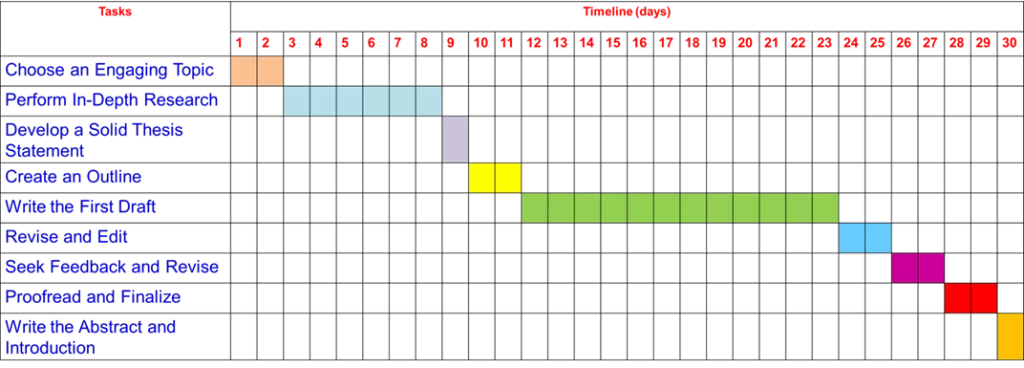

Step 1: Choose an Engaging Topic (Days 1-2):
- Selecting an intriguing and research-worthy topic is the first crucial step.
- Spend some time brainstorming ideas, exploring academic journals, and consulting your professor or advisor.
- Ensure your topic is specific, manageable, and aligns with your field of study.
Also Read: How to Choose the Right Title for a PhD thesis and Research Paper?
Step 2: Perform In-Depth Research (Days 3-8):
- Dedicate a significant portion of time to conducting thorough research.
- Utilize academic databases, online libraries, and reputable sources to gather relevant information.
- Take detailed notes and organize your sources using a citation management tool such as EndNote or Zotero.
Also Read: Top 5 Free Reference Management Software for Research
Step 3: Develop a Solid Thesis Statement (Day 9):
- Based on your research, craft a clear and concise thesis statement that summarizes your paper’s main argument or focus.
- Your thesis statement should be specific and supportable with evidence from your research.
Also Read: What is a Thesis Statement -Example
Step 4: Create an Outline (Days 10-11):
- Construct a well-organized outline that serves as a roadmap for your paper .
- Divide your research into sections and sub-sections, ensuring a logical flow of ideas.
- This step will help you maintain coherence throughout the writing process.
Also Read: A Simple Thesis Outline for Your Research
Step 5: Write the First Draft (Days 12-23):
- Begin writing your paper based on the outline you created.
- Aim to complete a specific number of pages or sections each day, keeping in mind the deadline.
- Focus on expressing your ideas and arguments clearly, avoiding perfectionism during this initial draft.
Also Read: 12 Steps to plan, draft, write, and finish a PhD thesis or dissertation?
Step 6: Revise and Edit (Days 24-25):
- Once the first draft is complete, take a break for a day to gain a fresh perspective.
- Return to your paper and start revising it critically.
- Pay attention to sentence structure, grammar , and clarity.
- Eliminate any unnecessary information and ensure that your arguments are supported by evidence.
Also Read: Editor for Thesis Images – Online Free Photo
Step 7: Seek Feedback and Revise Again (Days 26-27):
- Share your paper with peers , professors, and experts to obtain valuable feedback.
- Consider their suggestions and incorporate necessary changes into your paper.
- This step helps improve the overall quality of your work and ensures it meets the required standards.
Also Read: Eight Effective Tips to Overcome Writer’s Block in PhD Thesis Writing
Step 8: Proofread and Finalize (Days 28-29):
- Proofread your paper meticulously, checking for spelling errors, typos, and formatting inconsistencies.
- Ensure that your paper adheres to the specified citation style (APA, MLA, etc.).
- Verify that your references are accurately cited and cross-checked with your citation management tool.
Also Read: 9 Free Proofreaders and Grammar Checkers for Thesis
Step 9: Write the Abstract and Introduction (Day 30):
- Craft a concise abstract that summarizes the key points of your paper.
- Then, write an engaging introduction that introduces the topic, provides background information, and presents your thesis statement.
- These sections should capture the reader’s attention and provide a clear context for your research.
- Finally, submit the paper to a reputed journal.
Also Read: Example of Abstract for Research Paper – Tips and Dos and Donts
10 Tips to Write a Research Paper in a Month

1. Plan your time
Create a realistic timeline that outlines the tasks you need to complete at each stage of the research paper writing process.
2. Select a focused topic
Choose a research topic that is manageable and aligns with your interests and available resources.
3. Conduct efficient research
Utilize online databases, academic journals, and credible sources to gather relevant information quickly. Take organized notes to streamline your writing process.
4. Develop a strong thesis statement
Formulate a clear and concise thesis statement that outlines the main argument or objective of your research paper.
5. Create an outline
Structure your research paper by creating a detailed outline that includes the introduction, main body paragraphs, and conclusion. This will help you maintain a logical flow throughout your writing.
6. Break it down into smaller tasks
Divide your research paper into smaller, manageable tasks such as literature review, data analysis, and drafting different sections. This approach will make the writing process less overwhelming.
7. Stay focused and organized
Maintain a distraction-free work environment, organize your research materials, and keep track of your sources to save time when citing references.
8. Write regularly
Set aside dedicated time each day for writing. Even if it’s just a small portion of your paper, consistent progress will help you stay on track.
9. Edit and revise
Allocate time for editing and proofreading your research paper. Check for clarity, coherence, grammar, and spelling errors to ensure a polished final product.
10. Seek feedback
Share your draft with peers, professors, or writing centers for valuable feedback. Incorporate suggestions and refine your paper further for a well-rounded research outcome.
By following these tips, you can effectively write a research paper within a month while maintaining a high standard of quality and academic integrity.
Conclusion:
Writing a research paper within a month is an achievable goal if you follow a systematic approach. By allocating time to each stage of the process, from topic selection to final proofreading, you can efficiently complete a well-researched and well-written paper. Always stay focused, organize your thoughts, seek feedback, and revise your work. With determination and proper planning, you can produce a high-quality research paper that contributes to your field of study. Happy researching!

Check the Web Story: 10-tips-to-write-a-research-paper-in-a-month
- accelerated academic writing
- deadline-driven writing
- effective research
- efficient writing
- fast research paper
- quick research paper
- Research Methodology
- research organization
- Research Paper Writing
- research planning
- research process
- research productivity
- research strategies
- research tips and tricks
- Scopus Journals
- time management tips
- time-bound research paper
- writing hacks
- writing process
- writing techniques
How to Check Scopus Indexed Journals 2024
List of open access sci journals in computer science, 24 best online plagiarism checker free – 2024, most popular, india – sri lanka joint research funding opportunity, apply for the dst-jsps indo-japan call 2024, india-eu partner up for explainable and robust ai research, scopus indexed journals list 2024, 5 free data analysis and graph plotting software for thesis, the hrd scheme india 2024-25, 6 best online chemical drawing software 2024, best for you, what is phd, popular posts, how to write a research paper a complete guide, popular category.
- POSTDOC 317
- Interesting 258
- Journals 234
- Fellowship 130
- Research Methodology 102
- All Scopus Indexed Journals 92
Mail Subscription

iLovePhD is a research education website to know updated research-related information. It helps researchers to find top journals for publishing research articles and get an easy manual for research tools. The main aim of this website is to help Ph.D. scholars who are working in various domains to get more valuable ideas to carry out their research. Learn the current groundbreaking research activities around the world, love the process of getting a Ph.D.
Contact us: [email protected]
Google News
Copyright © 2024 iLovePhD. All rights reserved
- Artificial intelligence

ORGANIZING CREATIVITY
How to generate, capture, and collect ideas to realize creative projects., how to write a dissertation thesis in a month: outlines, outlines, outlines.
2010-05-23 Daniel Circus Ponies Notebook , Doing Science , Learning to do Science , Science , Scrivener , Tools , Writing 41
“Writing a book is an adventure: to begin with it is a toy and amusement; then it becomes a master, and than it becomes a tyrant; and the last phase is just as you are about to be reconciled to your servitude – you kill the monster and fling him to the public.” Winston Churchill
Last year I took a vacation for a month to write my dissertation thesis. And it took me that one month to come up with the first draft, which made it into the final version with only minor alterations (but a lot of error checking ). While the lack of major alterations might be in part due to my academic advisers (and my) wish to finish the work as soon as possible, I think the major part of this is due to the way it was written, or rather structured.
Doing a dissertation thesis is a major project, the writing itself is a different but not less complicated animal. I think it is a mistake to start writing in sentences unless you know the structure and the content. Once you write sentences, they stick together and are hard to change. And I think it is nearly impossible to write a 200+ pages work if you do not structure it beforehand, and there is a great way to do so: Outlines.
Most people know outlines from school. Many teachers try to give this valuable hint for exams. Plan what you write before you start writing. An outline for a dissertation is similar, but not quite the same. For one thing, it is much more detailed .
How detailed? Well, everything you want to write later should be included in it, without the actual sentences. Metaphorically it should contain the bones of the text, the whole skeleton, and hints for everything else. This means
- the order you want to write the different pieces of information that make your theory
- the notes you made about your studies, the design, the participants, the instruments, the procedure
- the results of any statistical analysis you made
- the ideas for and the issues you want to raise in the discussion
It also includes any notes you do not want to forget and any ideas, e.g., for further studies even if you cannot realize them (a valuable hint from my informal academic adviser: you will have ideas of things you want to realize but you cannot realize everything, so make notes and raise these points in “future work”).
Given that the outline only contains the information, but not the sentences, it is easily changeable. And once you get in the flow of adding flesh to the bones, you can write really fast. An additional benefit of using outlines: I used the same outline as a basis for the articles I wrote about my dissertation. The outline also allows you to focus only on the relevant part by using the hierarchical structure: You can arrange the information similar to the structure you use for your PhD thesis and simply fold in the parts you do not need at the moment. This way, thousands of lines of text become easily manageable. For example, you can fold the parts between the introduction and the discussion to write parts of the discussion while simulateneously seeing parts of the introduction. Sure, you could do something similar with Word’s “split view”, but not as easy and with this focus on the parts you want to see.
Personally, my outline for my dissertation was a 66.5 MB Circus Ponies Notebook file, containing 333,215 words (> 2.2 million characters, equivalent of about 1305 pages). I made sure to write down everything I did, the results of any analysis, etc. It was more or less structured in the way I wanted to write my dissertation. With this outline next to my writing program ( Scrivener ), it was possible to come up with a good first draft within a month. Why? Because I first read the whole outline, taking care to move the information that did not fit where it was to the correct place, then sorted each sub-point (e.g,, theory, results of Study 1) in the correct order, and then used this sorted outline that contained all the information I needed to write it as a guideline to write that chapter. Given that the sources were marked in the outline (see Academic Workflow ) I did not have to check other sources for the actual writing. I didn’t even have to re-check statistical printouts — it was all in that one huge outline (and then in a smaller one that dealt only with the chapter).
I created the outline before I started to write, during the last year of my PhD. But thinking back, it would have been much easier to create the outline during the whole PhD thesis time, as soon as the topic and the first experiments were decided. Noting the decisions (and the reasons for doing so), the results, etc. while planning and doing the studies would have made it much easier in the end, but it also worked this way.
So, I can only highly recommend creating a detailed outline prior to writing and using it for the writing process. It makes an insanely complex work manageable. 🙂
- Circus_Ponies_Notebook
- conveying_ideas
- infrastructure
15 Comments
I received a question regarding the transfer of notes from other programs to Circus Ponies Notebook:
Hi Daniel! My name is Chris and I´m working on my dissertation manuscript for my MD at the moment. I´m using Scrivener for writing, Bookends as BibRef tool for Scrivener and Papers for getting and sorting my papers. Yet, I´ve done a lot of work, writing on my self and using associated project scripts of my Institute. My question is, how can I import the manuscript´s status quo of Outline, BibRef and Content into CPN for not losing so much time by starting again from the beginning… Thx a lot, Chris
Hmmm, if I understand the question correctly you are currently using three different programs for writing your dissertation (Bookends, Scrivener and Papers) and now you want to create an outline in CPN … good question … hmm, first, do you really want to take a step back? An outline makes sense to organize the material you have in a red thread and collect all information in one place that you can use (with Scrivener) to write you dissertation in one go. At the moment, you already have written text … hmmm …
Okay, it’s difficult to say (will be influenced by a lot of factors I don’t know, like the rules of your field for dissertations, the time you have left, your goals, your working habits, etc. pp.) and I wouldn’t bet my dissertation on it, but I would probably go alone the lines of this:
1. What is the problem? Do I have problems making a coherent package out of my material? In this case, going back to an outline might be one way to solve it. If, however, I’m just not motivated to write, I don’t want to finish it or I’m looking for some other thing to do, I’d grind my teeth and punch through writing the way I did before.
2. If it’s the first case and now I have to put my material in one CPN file, I’d create one outlining page, start with the sections of the dissertation (title page, abstract, introduction …), highlight them, and then manually copy the text I have already written into this outline. The reason is that if the structure is a problem (it usually is), you need little cells of text (one argument per cell) that you can organize hierarchically and move really easily. You can try to automate it by copying your whole text first (depending on the fonts you have used, e.g., for formulas or the importance of formatting you have already used by compiling a draft from Scrivener and using this as a starting point), then paste it into a pure text editor (like TextWrangler) and then copy it onto the notebook page with “Edit – Paste – Paste Text as Outline” to avoid switching between two applications, but the division into cells you’ll have to do yourself.
3. While pasting I would use the situation to make notes (using a cell on its own with text in another color). You might have some ideas what to do and what you still need to check, use that moment.
x. optional: If I need the references as keywords (only if you want to write what they have said as text and keep the reference in the margin) I’d copy all references (only author and year or however they are cited in the text in your discipline, mind the Miller 1999a, Miller 1999b, etc. if one author has published multiple papers in one year) at the end of the outline, and then — for each reference — highlight it in the text (not the cell) and make a keyword out of it (assign as keyword). This way CPN already knows the keywords and I can assign them to the margins easily (you have to leave at least one occurrence of the keyword in the file, so give the references a top cell like “refs” and fold this in and keep it at the end of the outline where it doesn’t bug you. But this is a large step backwards in the process, as I would tag cells with only one reference. This means splitting up/copying sentences if you refer to multiple sources.
4. Then I’d resort the cells in a fitting order. I’d make sure that the whole structure has a hierarchical order and let’s me easily see the gist of the different sections (summaries in the higher cells). I’d make sure that the whole picture is coherent and invest work in the parts that aren’t. Perhaps changing the structure, perhaps hitting literature again.
5. Once I’m sure I have a coherent work that is “enough” to get me the grad I need (for me: “magna cum laude” to stay in research, which luckily worked out) and after checking with my supervisor, I’d write the whole text (I can recommend taking a month off and copying the text sectionwise into a new CPN file and then checking the order again. If you stumble during writing it’s often the order/structure that’s a problem. Try to catch this first.)
6. While writing I’d put the text citations into the text (or use the Reference Manager that you have assigned to Scrivener). After writing the text, if I did the references manually, I’d put in the references at the end of the document.
But like said, I’d only do this if structure really is a problem. CPN is great for making an outline that really deserves the name — that contains all the information in one huge structure you need to write. A good outline (yup, like said, this means manual work) allows you to see the structure on the higher levels, allowing you to fold in the sublevels and concentrate on whether your arguments make sense. This is often lost in the text.
One important aspect: Keep your papers (with notes regarding the papers) sorted the way you did it (if it works for you). The dissertation is a project that will be finished. The outline you create for writing it can be used as a starting point for articles and future work, but one day you’ll have to go back to the place you have sorted your papers in. I have tried using CPN for organizing papers I read and while some aspects worked really well (like tagging each cell with the reference) it got slow fast. I switched to a Wiki (and highly automated some functions with Javascript/PHP, i.e., Ferret) to make it usable. Currently I have over 1000 papers/books/whatever in my literature section — DokuWiki can handle it, CPN would probably have been slow as hell. So, whatever you do, use CPN’s outline function to get the structure in order and get all your material for this project in one place if you need to, but keep your literature in a separate collection.
I hope this answers your question.
Best regards
This is the third often read posting I have in my blog. I think (and am pretty certain) that outlines, especially using Circus Ponies Notebook, helped me — or rather enabled me — to finish not only my diploma thesis but also my dissertation thesis, not only in a month but ever . I’m curious, what are your experiences? Did it work for you? If now, why? If you found another solution, what worked for you? It would be nice to hear a comment from you if you have read this posting. 🙂
Very useful. Concerning your most recent comment: I think it’s the third most read article in your blog because it’s the number 1 google search result for : how to write a dissertation thesis in 1 month –> which brought me here.. Add millions of other lazy bastards who work at the last minute and voila!
thank you for the comment — I didn’t know that Google liked this posting that much, cool 🙂
Best regards (and good luck for your thesis)
PS: The writing took one month, the preparation for the writing phase took a little longer. 😉
I commend your spirit and your nice expressions. I do really enjoy every single word you wrote. I’m working right now on my thesis and I’m totally frustrated, bored, don’t know how to finish it and how to manage my time. What you wrote made me think that writing a thesis is not so hard but it needs time, outlining and most important optimism!
Thanks for sharing this with us.
Thank you for the positive feedback 🙂
I think it’s quite normal to feel this way when doing a dissertation thesis — there are many crises (e.g., Dissertation Crises , or Dissertation Crisis — Past the Mountain ) and while a dissertation is (supposed to be) difficult, it’s good to keep it in perspective. For example:
“A PhD is a stepping stone into a research career. All you need to do is to demonstrate your capacity for independent, critical thinking. That’s all you need to do. A PhD is three years of solid work, not a Nobel Prize” Maths–Eng/Female/18, in Mullins & Kiley, 2002
“Das Kapital wasn’t Marx’s thesis: and my PhD thesis doesn’t have to be my life’s work. It’s a training ground.” catspyjamas on phinished.org
“The only good dissertation is a DONE dissertation.” Capella faculty quote
So, if you are stuck, perhaps creating an outline will help. And like Churchill said, “If you’re going through hell, keep going.” I wish you the best 🙂
Hi Daniel. I read your story about your thesis writing and understood you write about 333000 words in just one month,how did you do that?I am a PhD student in engineering really struggling with my writing up, I almost have not written anything because of my depression problems. I have about a month and half to submit, I have no limit but want to write at least 100 pages except the bibliography and appendices. I appreciate if you advice me how to do it.many thanks Hannah
Mai I mention here that I do have outlines and kind of know the structure of thesis writing.
Hoi Hannah,
nope, writing 333k words in a month would be a feat beyond me. 😉 I created the outline during my dissertation prior to sitting down to write the thesis. What I did write in that month was the dissertation thesis itself which was 250 pages long and had about 71000 words. I did not use all the material I had in my outline and the hierarchical structure made it possible (and fairly easy) to select among the material I wanted to use.
Regarding your case — difficult. If you have a depression (in the clinical term, not in the colloquial meaning), then this should probably be a priority (and not my field of expertise, that’s something for the local health service). Regarding the writing — personally it helped me a lot to use the outliner to create a content outline . This goes beyond the structure — it externalizes all what you want to write and allows you to resort the content in the structure that fits best, without starting to write sentences that stick together. Then you can focus on the criteria on scientific writing (e.g., Alley’s criteria, see here or the other postings in that series ). However, there is a huge risk here if you have a deadline looming: It stays pre-text for a long time. For me writing the thesis from the content outline was quick (I can type with 10 fingers and am reasonably fast), but it was easy for me to sort the material and I had no looming deadline. So, using the same strategy might be a way that might work, but nobody can guarantee success.
All the best
Well i completed my thesis in few weeks, but i adopted a unique method, I had the draft out sourced and when i got it back i made my own changes to it and it was ready. I used [URL REMOVED] They were right on money and topic
Normally such a comment would be sorted into the spam folder, but after removing the I’ve approved it to make a point. Outsourcing is not a unique method — it’s unfortunately common with some people who think they can buy an academic degree. Well, some are paying for college and some will pay for others to do their work later, so why not for the thesis too? Well, because it’s plagiarism. Unless you stated that you used a ghostwriting service in your thesis — which I doubt that you did, because any university worth the name would not accept that work as yours — you lied about who did the work. And the academic work should be your own. Not only did you not learn the necessary skills — nope, seeing the result is easy, doing it on your own is something completely different — you betrayed yourself of the chance to do a difficult high-level piece of work. Something like this is frequently a once-in-a-lifetime opportunity and you blew it. The funny thing, I am willing to bet that in the future — give it 5 to 10 years — some hackers or whistleblowers will make the customers of these ‘services’ public. Or Google/Plagiarism software will improve so much that it will detect these kinds of plagiarisms. And then a lot of people who thought they could buy their title, or a huge chunk of the work necessary will lose it. So, congratulations, you not only blew an academic adventure that you could have had with the right mindset, you also put a time bomb in your CV. Tick-tock-tick-tock … have fun.
Love, love, love your comment to Jenni. Writing my dissertation is proving to be extremely hard but mainly because I want it to be the best possible representation of my body of knowledge. The idea of outsourcing a dissertation is ridiculous. Sooner or later the truth will come out. If Jenni had her “own details” to begin with, she should have used them to produce her own work!
Thank you, I doubt that it will change anything given that “she” seems to be the companies ad/spam person (received another spam message disguised as “PhD student testimonial”), but perhaps other readers will think twice on “outsourcing” the work. 🙂
Thank you, very useful, informative articles. I only have one question is how to write an essay on a topic that you do not know and do not lose face? How to write a good informative article in a short period of time and not to make mistakes? In internet many articles which give different advice, such as, this article https://thesiswhisperer.com/2011/03/24/how-to-write-1000-words-a-day-and-not-go-bat-shit-crazy/ , but they can not really help me and answer my questions. I study at the Institute and I need in a short time write a good dissertation. Now I do not know what to do … looking for a different article in internet about thesis writing. There I found this article http://phdify.com/blog/how-many-chapters-in-a-dissertation on how to write a dissertation, but it do not tell me how to write a dissertation 2 months. Can you give me some good advice?
Hoi Jenifer,
the only (honest) advice I can give you is to talk to your advisor. They (and the committee) are the ones determining what is necessary for your dissertation. I am recommending this because it seems to me that the problem is not how to write a certain amount of words, or how to write a thesis in a certain amount of time, but because I think there is some confusion about what the dissertation is about. And I might be wrong here! I think for most writing tips to work you have to be clear about what your contribution in your thesis is — and for that you need discussions with your supervisor. Once that is determined, you can do an outline (as I would recommend) or use Mewburn’s tips.
(And as for outlines — yup, I think there are great, but they will not work for everyone. They are an option you should know about. And while I did write my thesis in a month — the first and nearly final draft that is — I did it with an outline I had created during nearly three years of studying.)
26 Trackbacks / Pingbacks
- The mobile Scientist » Blog Archive » Apple iBooks 2 and Apple iBooks Author - Psychology & Technology in Mobile Media
- Organizing Creativity & Crisis of the Dissertation « The Returning Researcher
- How to Write a Dissertation Thesis in a Month: Outlines, Outlines, Outlines | ORGANIZING CREATIVITY | Hùng Trang @ Thailand
- Workshop: Scientific Work — Reading & Using Literature | ORGANIZING CREATIVITY
- Workshop: Scientific Work — Possible Academic Literature Workflow | ORGANIZING CREATIVITY
- Scrivener — A perfect program for dissertation writing | ORGANIZING CREATIVITY
- Circus Ponies Notebook: The Best Tool for Structuring Creative Writing Projects (esp. Research Projects) | ORGANIZING CREATIVITY
- Curio | ORGANIZING CREATIVITY
- Writing Articles with a Mind Map | ORGANIZING CREATIVITY
- How to create a content outline in Circus Ponies Notebook | ORGANIZING CREATIVITY
- Visually developing ideas in Keynote | ORGANIZING CREATIVITY
- Another academic workflow visualization | ORGANIZING CREATIVITY
- Non-Destructive Graffiti | ORGANIZING CREATIVITY
- Dealing With the Plagiarism Plague Among Students | ORGANIZING CREATIVITY
- Writing | ORGANIZING CREATIVITY
- Workshop: Scientific Work — Writing #2 Knowing What To Write | ORGANIZING CREATIVITY
- Perhaps I need a question section … | ORGANIZING CREATIVITY
- Workshop: Scientific Work — Topic Notebooks | ORGANIZING CREATIVITY
- Master’s Projects & Theses: Tips & Tools for Your Winter Break! | Journalism Library Blog
- Outsourcing a Thesis | ORGANIZING CREATIVITY
- A Critical Look at Scientific Writing Courses | ORGANIZING CREATIVITY
- Beware of a (wo)man of one book | ORGANIZING CREATIVITY
- Circus Ponies Notebook 4 | ORGANIZING CREATIVITY
- How to Write a Dissertation in One Month
- Configuring Scrivener (Make Scrivener grey — and get that icon back) | ORGANIZING CREATIVITY
- Winter Break: Some Project and Thesis Tips! – Libraries Spotlight BLOG
Comments are closed.
Timeline for Writing a Research Paper in a Month
Writing a research paper is a time-consuming task that requires careful planning, thorough research, and effective organization of ideas. While it’s ideal to have ample time to complete a research paper, there may be instances where you find yourself with a tight deadline, such as completing the paper in a month.
Table of Contents
A Step-by-Step Guide and Timeline for Writing a Research Paper in a Month

Step 1: Set Goals (Day 1)
Identify the research topic, specific guidelines, formatting style, and submission deadline.
Step 2: Choose a Research Topic (Days 2-3)
Brainstorm ideas, conduct preliminary research, and choose a topic that is manageable within the given timeframe.
Step 3: Conduct In-Depth Research (Days 4-8)
With a limited timeframe, efficient research is key. Use academic databases, libraries, and reputable online sources to gather relevant information.
Step 4: Develop a Strong Thesis Statement (Day 9)
A well-defined thesis statement forms the foundation of a research paper. Analyze your research findings and develop a clear, concise, and arguable thesis statement that encapsulates the main argument of your paper.
Step 5: Create an Outline (Days 10-11)
Divide your paper into sections such as introduction, literature review, methodology, results, discussion, and conclusion.
Step 6: Write the Introduction and Literature Review (Days 12-14 )
Begin writing your research paper by crafting a compelling introduction that provides background information, presents the research question, and outlines the significance of the study.
Step 7: Work on the Methodology, Results, and Discussion Sections (Days 15-21)
Read More: Design A Questionnaire for Research: 6 Steps to Get You Started
Be concise, objective, and critical in your analysis.
Step 8: Write the Conclusion and Abstract (Days 22-23)
Read More: Abstract for Research Paper
Step 9: Revise, Edit, and Proofread (Days 24-28):
Consider seeking feedback from peers or professors to gain different perspectives and improve the overall quality of your paper.
Step 10: Format and Finalize (Days 29-30)
Pay attention to margins, font size, line spacing, and citation formatting.
Finally, submit the paper to a reputed journal.
10 Tips for Writing a Research Paper in a Month
3. Carry out Effective Research: Use online databases, scholarly publications, and reliable sources to quickly obtain pertinent information. To make writing easier, take well-organized notes.
Read More: How to build Research Questions on the basis of Theoretical Model?
8. Writing Regul arly: Set aside time each day specifically for writing. Consistently making progress on your paper, even if it’s just a little amount, will help you stay on track.
You can successfully complete a research paper within a month by using the advice provided here while upholding a high level of academic integrity and quality.
Remember to break down the tasks, conduct thorough research, and maintain a clear and focused approach throughout the writing process.
Other articles
Citation Styles
Related Posts
Clinical research design: elements and importance, dependent variable in research: examples, what is an independent variable, how to write a high-quality conference paper, what are scholarly sources and where can you find them, how to write a conclusion for research paper | examples, how to write effective grants for research funding, how to paraphrase research papers effectively, tips to self edit your research paper: why is self editing important, six useful tips for finding research gap, leave a reply cancel reply.

How to write a masters thesis in 2 months [Easy steps to start writing]
Writing a master’s thesis is completely possible to write a thesis within two months as long as you stay completely focused on your writing and you do a little bit every single day. I was able to write my thesis (master’s and PhD) in approximately two months – but I did have some of the sections already prepared.
To complete your master’s thesis in two months you should start by creating an outline of the sections and headings of your thesis. Then, worked diligently to fill in the gaps with data and analysis.
It would help if you create a schedule of how many sections you need to complete a day to write up in two months.
Also, it is important that you get your supervisor on board from the earliest opportunity so that they understand the urgency and their responsibility of getting any drafts back to you in a timely fashion.
How long does it take to write a master’s or graduate thesis?
Writing a graduate thesis can be a long and arduous process that can take anywhere from one month to many years.
It is essential to start writing your thesis early in your final year of graduate school, as it requires extensive research, data collection and analysis, in addition to the actual writing.
It is important that you go into the thesis writing portion of your degree with as much of the data analysis done as possible.
When you are writing you want to focus 100% on the production of words on a page.
Depending on the topic and depth of study, it can take anywhere from six weeks to two or three months just to complete the first draft.
This is followed by further revisions and edits before finalizing the dissertation.
| Week | Actions |
|---|---|
| Week 1 | Collect all of the data into one place and create a structure with all of the chapters and sections you want to write. Finish up any experiments quickly and make your data as presentable and “thesis ready” as possible. Start putting bullet points under each section so you understand what you want to write in each. |
| Week 2 | Write the introduction using your literature review from earlier in your studies and add more recent updated papers. When is ready send it off to your supervisor. |
| Week 3 | Write your methodology section by including all of the methods you have used throughout your thesis and send it off to your supervisor as soon as you have a draft. |
| Week 4 | Write your results and discussion by laying in your tables, figures and schematics and then filling out explanations of each underneath. Do this for each of the main results from your thesis. When this is ready send it to your supervisor for review. |
| Week 5 | Edit your introduction and your methodology section return from your supervisor. Start writing your conclusion section and give it to your supervisor as soon as possible. |
| Week 6 | Address all of the comments from your supervisor about your results and discussion and then start working on your abstract to go at the front of your thesis. |
| Week 7 | Bring together all of the sections and read your thesis from beginning to end making sure that it makes sense and that there are logical connections between each chapter and section. |
| Week 8 | Work through each chapter with your supervisor and make corrections as you go. Get the red pen out and refine all of your words and sentences. At the end of this week, your masters thesis should be in a position to submit. |
My 8 tips on how to write a thesis or dissertation in two months
Writing a thesis or dissertation in two months can be a daunting task, but it is certainly possible. This assumes that you have all of the data analysis done and you are literally just writing up what you have found.
Here are eight tips that can help you finish writing your thesis in 30 days:
- Start by breaking up the task into manageable chunks and set deadlines for each stage of the process. This will make it easier to stay on track and not become overwhelmed by the whole project.
- Make sure to give yourself enough time to do a thorough literature review, as this is an important part of any thesis or dissertation. Many people have already completed the literature review in the early stages of their graduate degree. Revisit and use as much of this literature review is possible and add the research from recent years.
- Write your first draft as quickly as possible; don’t worry too much about grammar and spelling right now, that comes later. It is all about getting the words out onto the page as quickly as possible.
- Set aside some time every day for writing your thesis; even if it’s only an hour or two, this will help you stay focused and motivated throughout the entire writing process. I used to work in two hour blocks. I was able to squeeze three of these in a day which meant I got a lot of writing done.
- Don’t forget to use helpful tools like Grammarly to ensure the quality of your work is at its highest level before submitting it for review.
- Take regular breaks during your writing sessions; this will help you stay fresh and focused on what needs to be done next. I used to take a break every two hours away from my screen and ensure that I refuelled with good food and caffeine.
- Seek feedback from other PhD students or experts in your field; getting constructive criticism can help you improve the quality of your thesis significantly before submitting. However, do not allow people to sit on the draft for ages. We need a quick turnaround if we are going to complete your thesis in two months.
- Finally, plan ahead and stick to deadlines; this will help keep you on track with completing your thesis in a month’s time!
If you want to know more about how to finish a masters thesis in two months check out my other video where I show you the unglamorous trues about writing a thesis.
Understanding what you are going into and what is likely to happen is half the battle.
If you want to know more about how long a Masters’s thesis and PhD dissertation is you can check out my other articles:
- How Long is a Masters Thesis? [Your writing guide]
- How long is a PhD dissertation? [Data by field]
- Is writing a masters thesis hard? Tips on how to write a thesis
What are the common structures of a Masters’s thesis?
The common structure of a thesis or dissertation usually includes:
- the main text,
- literature review,
- methodology,
- results and discussions
- conclusions
Depending on the school and field of study, there may be additional elements such as appendices.
Generally speaking, the first step in writing a thesis or dissertation is to create a literature review that assesses relevant academic sources related to the topic at hand. This is typically done in the early stages of your research project so you can reuse many parts of your literature review in your thesis. Just make sure you update it with new information.
Then, the methodology section outlines how research was conducted and what methods were used.
The main text presents your findings and conclusions based on your research and the final part of the thesis is to summarise everything you have just written in an abstract.
Each section must be written with clarity and accuracy in order to be accepted by graduate school. However, initially you only have to worry about getting your ideas out onto the page – you can refine them for clarity and accuracy in the editing stage.
Here are all of the sections of a typical master’s thesis and how to write them quickly.
Introduction/literature review
The introduction and literature review are an important part of any academic paper. It outlines the topic, provides background information, and introduces the research question.
The introduction is typically the first section of a paper and should explain the general context and importance of the research being undertaken.
The literature review follows the introduction and provides an overview of relevant previous studies, theories, or debates related to the paper’s research question.
This section may include summaries of key articles or books that have been published on the topic, as well as alternative perspectives and arguments.
A strong literature review will provide a comprehensive summary of prior work while also identifying gaps in knowledge that can be addressed by the current study.
Reuse your literature review from the early stages of your project and update it with more recent publications.
Methodology in a thesis
this is the part of the thesis which details the methods used in researching and writing the paper.
The methodology should include information on how data was collected, analyzed, and interpreted.
I quite often like to start with the methodology because it feels like I am making a lot of progress whilst it being a relatively easy to write.
Feel free to look at other people’s theses that have used the same techniques and follow a similar format that they used. It is common for research groups to share their methodology sections with each other including any schematics required to describe your research process.
You can republish these as long as you reference the appropriate studies and people.
It can also explain why certain methods were chosen over others and provide justification for any assumptions made during the research process.
Results and discussion
Results and discussion provide a platform to present the findings of a research study.
They are essential components of any research paper as they provide an opportunity to analyze and interpret the data collected during the study.
Results typically include descriptive statistics, tables, figures, or graphs that display the main outcomes of the research.
These are what you should place under the headings first.
Create a story with the figures and tables you have already created throughout your research. If you haven’t done them already, create the figures and tables that display your data before writing.
The discussion section should explain how these results relate to prior studies and answer the original research question posed in the introduction.
It should also discuss any limitations or unexpected findings that emerged from the study, as well as potential implications for future research.
Conclusions in a thesis
Conclusions in a thesis are important because they provide readers with a final summary of the main points and themes discussed throughout the thesis.
The conclusion should not introduce any new information, but rather draw on existing evidence to summarize the overall argument presented in the thesis.
It should also reiterate the main points of the paper and include implications for further study or action that could be taken based on the findings.
Conclusions should be written in clear language, using strong arguments and evidence to support their claims.
It is really important to avoid making broad generalizations or unsubstantiated statements in one’s conclusions as this could weaken an otherwise sound argument.
The abstract of a thesis
The abstract of a thesis is a concise summary of the contents of the entire thesis.
And it should be written as one of the last parts of your thesis.
It should give an overview of all the major aspects discussed in the thesis, such as the research question, methodology, findings and conclusions.
The aim of an abstract is to give potential readers a clear idea of what the full dissertation contains without having to read it word for word.
An effective abstract should be concise and self-contained; it should be able to stand alone without needing any explanation or clarification from outside sources.
It should provide enough detail so that readers can determine whether they have an interest in reading the full dissertation.
Writing motivation
If you want to know more about how to increase your writing motivation check out my other video below.
Wrapping up
this article has been through everything you need to know about if you can write a Masters thesis in two months.
It is completely doable as long as you have all of the appropriate data and figures ready and you are committed to writing consistently throughout the two months.
Another really important part of completing your master’s thesis on time is getting buy in from your supervisors so that they return any drafts as quickly as possible.
Work diligently and consistently and in no doubt that you will be able to finish your master’s thesis in two months.

Dr Andrew Stapleton has a Masters and PhD in Chemistry from the UK and Australia. He has many years of research experience and has worked as a Postdoctoral Fellow and Associate at a number of Universities. Although having secured funding for his own research, he left academia to help others with his YouTube channel all about the inner workings of academia and how to make it work for you.
Thank you for visiting Academia Insider.
We are here to help you navigate Academia as painlessly as possible. We are supported by our readers and by visiting you are helping us earn a small amount through ads and affiliate revenue - Thank you!

2024 © Academia Insider

More From Forbes
We need to acknowledge non-binary people in the workplace.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
Cubes form gender neutral pronouns they and them.
There are plenty of non-binary and gender nonconforming people in the United States. And yet so much of the discussion surrounding queerness revolves around gay and bisexual people. But what about people who identify as asexual or intersex? And what about pansexual people like me? A lot of popular articles about the LGBTQ+ community mention bisexual erasure, but I have never seen an article about asexual, intersex, two-spirit, or pansexual erasure.
The same goes for non-binary representation. It is more socially acceptable to be queer when you aren’t non-binary and/or trans. This is something I’ve seen first hand as a pansexual non-binary woman (she/they). I identify as a woman and a person. It tends to confuse people and so they just call me she. Going by she is just part of me, not all of me.
My pronouns change, which tends to make people uncomfortable and confused. People usually ask me “is being non-binary the same as being trans?” They are entirely separate identities for some people, while others identify as both. I only identify as non-binary. I have dealt with so much ignorance because of my desire to be myself and go by she/they. I was fortunate enough to have very supportive friends when I changed my pronouns.
Being A Non-Binary Woman
Despite receiving support from friends not everyone responded well when I started going by she/they. One time someone close to me said “I don’t do that stuff” when I told them my pronouns are she/they. Another time a previous employer only referred to me as they but only during Pride Month. And a former romantic interest told me my pronouns were “ridiculous and silly” and that he “didn’t want to spend time with some woke millennial.” At times it feels like I am erased, ignored, and silenced due to being non-binary. My existence as someone who goes by she/they has been treated like a problem— at previous jobs, in my dating life, at professional events, and in my culture.
Being non-binary can be really tough, especially when it comes to the workplace. It can be exhausting to navigate trying to hide or not mention your pronouns. There are several questions I have to consider now that I openly going by she/they. Should I put my pronouns next to my name on a Zoom call? Should my pronouns be in my email signature? Should I speak up when someone at work dismisses non-binary people while discussing LGBTQ+ colleagues or clients?
India Pakistan T20 Clash In New York Today Here s What To Know About The Biggest Cricket Game Of The Year
‘hit man’ mows down ‘godzilla minus one’ as film trends big on netflix, a very big opportunity crypto suddenly braced for a tremendous china earthquake after bitcoin ethereum and xrp price boom.
These are questions I have asked myself over and over. It’s important to note that some people aren’t prejudiced— they just don’t understand non-binary identity or the terminology surrounding it. They might be afraid to ask or don’t know how to ask. Rather than avoiding non-binary identity altogether, do a little research on how to be a better ally to non-binary people. One of the best things you can do to be a better ally to non-binary people is to adhere to their preferred pronouns.
Using Preferred Pronouns
Being an ally for non-binary people starts with asking about and using preferred pronouns. Most people don’t realize that pronoun use is a form of suicide prevention. Many non-binary and/or trans people have had to hide their identity and their pronouns. Being able to live a life where you can truly be yourself prevents some queer people from taking their own lives. I know there were times I questioned whether life was worth living because I was hiding who I was— a neurodivergent , Black, and non-binary woman.
Way too many queer people don’t feel supported. Across the world there is a growing collective sense of queerphobia based on fear, misunderstanding, and some religious beliefs. Queerphobia can lead to people experiencing physical, emotional, and verbal abuse from family members, classmates, and colleagues. That’s why it’s important to make a conscious effort to use someone’s preferred pronouns.
If you fear you will accidentally use the wrong pronouns with someone who is non-binary, give yourself a reminder before you speak with them. It could be a sticky note, reminder on your phone, or even a rhyme in your head. Figure out some sort of system to adhere to someone’s preferred pronouns until you’ve got them down. Respecting preferred pronouns may make more of a difference than you think.
Challenging Queerphobia At Work
Employers should set an example by discouraging queerphobia in the workplace. If an employee is non-binary they shouldn’t feel like they can’t say their pronouns or list them on calls or documents. Sadly, many people accept misgendering in professional settings to keep their jobs and maintain their professional network. Some professionals will test non-binary people by misgendering them and seeing how they respond. Speaking up for yourself about queerphobia does not make you any less of a team player. Intentionally misgendering someone is not okay even if you’re in a corporate setting.
Historically most of corporate America has been known to be predominantly white, male, and heterosexual. The boys club mentality displayed in films like The Wolf of Wall Street needs to be challenged and dismantled in order for non-binary people to feel safe at work. Someone who goes by they/them is not a man or a woman, they are a person. If you are an employer and plan on following inclusive hiring practices, have gender neutral restrooms in your office.
You can also encourage people to put their pronouns in their email signature and next to their name on Zoom meetings. Refusing to erase people’s queerness is a way to challenge queerphobia in the workplace. Companies and employees alike can show support for queer people by recognizing our identities and culture all year. So, I’ll leave you with this. What are you doing for queer people when it isn’t Pride Month?

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
Join The Conversation
One Community. Many Voices. Create a free account to share your thoughts.
Forbes Community Guidelines
Our community is about connecting people through open and thoughtful conversations. We want our readers to share their views and exchange ideas and facts in a safe space.
In order to do so, please follow the posting rules in our site's Terms of Service. We've summarized some of those key rules below. Simply put, keep it civil.
Your post will be rejected if we notice that it seems to contain:
- False or intentionally out-of-context or misleading information
- Insults, profanity, incoherent, obscene or inflammatory language or threats of any kind
- Attacks on the identity of other commenters or the article's author
- Content that otherwise violates our site's terms.
User accounts will be blocked if we notice or believe that users are engaged in:
- Continuous attempts to re-post comments that have been previously moderated/rejected
- Racist, sexist, homophobic or other discriminatory comments
- Attempts or tactics that put the site security at risk
- Actions that otherwise violate our site's terms.
So, how can you be a power user?
- Stay on topic and share your insights
- Feel free to be clear and thoughtful to get your point across
- ‘Like’ or ‘Dislike’ to show your point of view.
- Protect your community.
- Use the report tool to alert us when someone breaks the rules.
Thanks for reading our community guidelines. Please read the full list of posting rules found in our site's Terms of Service.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
MLA General Format

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
MLA Style specifies guidelines for formatting manuscripts and citing research in writing. MLA Style also provides writers with a system for referencing their sources through parenthetical citation in their essays and Works Cited pages.
Writers who properly use MLA also build their credibility by demonstrating accountability to their source material. Most importantly, the use of MLA style can protect writers from accusations of plagiarism, which is the purposeful or accidental uncredited use of source material produced by other writers.
If you are asked to use MLA format, be sure to consult the MLA Handbook (9th edition). Publishing scholars and graduate students should also consult the MLA Style Manual and Guide to Scholarly Publishing (3rd edition). The MLA Handbook is available in most writing centers and reference libraries. It is also widely available in bookstores, libraries, and at the MLA web site. See the Additional Resources section of this page for a list of helpful books and sites about using MLA Style.
Paper Format
The preparation of papers and manuscripts in MLA Style is covered in part four of the MLA Style Manual . Below are some basic guidelines for formatting a paper in MLA Style :
General Guidelines
- Type your paper on a computer and print it out on standard, white 8.5 x 11-inch paper.
- Double-space the text of your paper and use a legible font (e.g. Times New Roman). Whatever font you choose, MLA recommends that the regular and italics type styles contrast enough that they are each distinct from one another. The font size should be 12 pt.
- Leave only one space after periods or other punctuation marks (unless otherwise prompted by your instructor).
- Set the margins of your document to 1 inch on all sides.
- Indent the first line of each paragraph one half-inch from the left margin. MLA recommends that you use the “Tab” key as opposed to pushing the space bar five times.
- Create a header that numbers all pages consecutively in the upper right-hand corner, one-half inch from the top and flush with the right margin. (Note: Your instructor may ask that you omit the number on your first page. Always follow your instructor's guidelines.)
- Use italics throughout your essay to indicate the titles of longer works and, only when absolutely necessary, provide emphasis.
- If you have any endnotes, include them on a separate page before your Works Cited page. Entitle the section Notes (centered, unformatted).
Formatting the First Page of Your Paper
- Do not make a title page for your paper unless specifically requested or the paper is assigned as a group project. In the case of a group project, list all names of the contributors, giving each name its own line in the header, followed by the remaining MLA header requirements as described below. Format the remainder of the page as requested by the instructor.
- In the upper left-hand corner of the first page, list your name, your instructor's name, the course, and the date. Again, be sure to use double-spaced text.
- Double space again and center the title. Do not underline, italicize, or place your title in quotation marks. Write the title in Title Case (standard capitalization), not in all capital letters.
- Use quotation marks and/or italics when referring to other works in your title, just as you would in your text. For example: Fear and Loathing in Las Vegas as Morality Play; Human Weariness in "After Apple Picking"
- Double space between the title and the first line of the text.
- Create a header in the upper right-hand corner that includes your last name, followed by a space with a page number. Number all pages consecutively with Arabic numerals (1, 2, 3, 4, etc.), one-half inch from the top and flush with the right margin. (Note: Your instructor or other readers may ask that you omit the last name/page number header on your first page. Always follow instructor guidelines.)
Here is a sample of the first page of a paper in MLA style:

The First Page of an MLA Paper
Section Headings
Writers sometimes use section headings to improve a document’s readability. These sections may include individual chapters or other named parts of a book or essay.
MLA recommends that when dividing an essay into sections you number those sections with an Arabic number and a period followed by a space and the section name.
MLA does not have a prescribed system of headings for books (for more information on headings, please see page 146 in the MLA Style Manual and Guide to Scholarly Publishing , 3rd edition). If you are only using one level of headings, meaning that all of the sections are distinct and parallel and have no additional sections that fit within them, MLA recommends that these sections resemble one another grammatically. For instance, if your headings are typically short phrases, make all of the headings short phrases (and not, for example, full sentences). Otherwise, the formatting is up to you. It should, however, be consistent throughout the document.
If you employ multiple levels of headings (some of your sections have sections within sections), you may want to provide a key of your chosen level headings and their formatting to your instructor or editor.
Sample Section Headings
The following sample headings are meant to be used only as a reference. You may employ whatever system of formatting that works best for you so long as it remains consistent throughout the document.
Formatted, unnumbered:
Level 1 Heading: bold, flush left
Level 2 Heading: italics, flush left
Level 3 Heading: centered, bold
Level 4 Heading: centered, italics
Level 5 Heading: underlined, flush left
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Working with sources
- How to Quote | Citing Quotes in APA, MLA & Chicago
How to Quote | Citing Quotes in APA, MLA & Chicago
Published on April 15, 2022 by Shona McCombes and Jack Caulfield. Revised on May 31, 2023.
Quoting means copying a passage of someone else’s words and crediting the source. To quote a source, you must ensure:
- The quoted text is enclosed in quotation marks or formatted as a block quote
- The original author is correctly cited
- The text is identical to the original
The exact format of a quote depends on its length and on which citation style you are using. Quoting and citing correctly is essential to avoid plagiarism which is easy to detect with a good plagiarism checker .

Table of contents
How to cite a quote in apa, mla and chicago, introducing quotes, quotes within quotes, shortening or altering a quote, block quotes, when should i use quotes, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about quoting sources.
Every time you quote, you must cite the source correctly . This looks slightly different depending on the citation style you’re using. Three of the most common styles are APA , MLA , and Chicago .
Citing a quote in APA Style
To cite a direct quote in APA , you must include the author’s last name, the year, and a page number, all separated by commas . If the quote appears on a single page, use “p.”; if it spans a page range, use “pp.”
An APA in-text citation can be parenthetical or narrative. In a parenthetical citation , you place all the information in parentheses after the quote. In a narrative citation , you name the author in your sentence (followed by the year), and place the page number after the quote.
Punctuation marks such as periods and commas are placed after the citation, not within the quotation marks .
- Evolution is a gradual process that “can act only by very short and slow steps” (Darwin, 1859, p. 510) .
- Darwin (1859) explains that evolution “can act only by very short and slow steps” (p. 510) .
Complete guide to APA
Citing a quote in mla style.
An MLA in-text citation includes only the author’s last name and a page number. As in APA, it can be parenthetical or narrative, and a period (or other punctuation mark) appears after the citation.
- Evolution is a gradual process that “can act only by very short and slow steps” (Darwin 510) .
- Darwin explains that evolution “can act only by very short and slow steps” (510) .
Complete guide to MLA
Citing a quote in chicago style.
Chicago style uses Chicago footnotes to cite sources. A note, indicated by a superscript number placed directly after the quote, specifies the author, title, and page number—or sometimes fuller information .
Unlike with parenthetical citations, in this style, the period or other punctuation mark should appear within the quotation marks, followed by the footnote number.
| , 510. |
Complete guide to Chicago style
Don't submit your assignments before you do this
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students. Free citation check included.

Try for free
Make sure you integrate quotes properly into your text by introducing them in your own words, showing the reader why you’re including the quote and providing any context necessary to understand it. Don’t present quotations as stand-alone sentences.
There are three main strategies you can use to introduce quotes in a grammatically correct way:
- Add an introductory sentence
- Use an introductory signal phrase
- Integrate the quote into your own sentence
The following examples use APA Style citations, but these strategies can be used in all styles.
Introductory sentence
Introduce the quote with a full sentence ending in a colon . Don’t use a colon if the text before the quote isn’t a full sentence.
If you name the author in your sentence, you may use present-tense verbs , such as “states,” “argues,” “explains,” “writes,” or “reports,” to describe the content of the quote.
- In Denmark, a recent poll shows that: “A membership referendum held today would be backed by 55 percent of Danish voters” (Levring, 2018, p. 3).
- In Denmark, a recent poll shows that support for the EU has grown since the Brexit vote: “A membership referendum held today would be backed by 55 percent of Danish voters” (Levring, 2018, p. 3).
- Levring (2018) reports that support for the EU has grown since the Brexit vote: “A membership referendum held today would be backed by 55 percent of Danish voters” (p. 3).
Introductory signal phrase
You can also use a signal phrase that mentions the author or source, but doesn’t form a full sentence. In this case, you follow the phrase with a comma instead of a colon.
- According to a recent poll, “A membership referendum held today would be backed by 55 percent of Danish voters” (Levring, 2018, p. 3).
- As Levring (2018) explains, “A membership referendum held today would be backed by 55 percent of Danish voters” (p. 3).
Integrated into your own sentence
To quote a phrase that doesn’t form a full sentence, you can also integrate it as part of your sentence, without any extra punctuation .
- A recent poll suggests that EU membership “would be backed by 55 percent of Danish voters” in a referendum (Levring, 2018, p. 3).
- Levring (2018) reports that EU membership “would be backed by 55 percent of Danish voters” in a referendum (p. 3).
When you quote text that itself contains another quote, this is called a nested quotation or a quote within a quote. It may occur, for example, when quoting dialogue from a novel.
To distinguish this quote from the surrounding quote, you enclose it in single (instead of double) quotation marks (even if this involves changing the punctuation from the original text). Make sure to close both sets of quotation marks at the appropriate moments.
Note that if you only quote the nested quotation itself, and not the surrounding text, you can just use double quotation marks.
- Carraway introduces his narrative by quoting his father: “ “ Whenever you feel like criticizing anyone, ” he told me, “ just remember that all the people in this world haven’t had the advantages that you’ve had ” ” (Fitzgerald 1).
- Carraway introduces his narrative by quoting his father: “‘Whenever you feel like criticizing anyone,’ he told me, ‘just remember that all the people in this world haven’t had the advantages that you’ve had ” (Fitzgerald 1).
- Carraway introduces his narrative by quoting his father: “‘Whenever you feel like criticizing anyone,’ he told me, ‘just remember that all the people in this world haven’t had the advantages that you’ve had’” (Fitzgerald 1).
- Carraway begins by quoting his father’s invocation to “remember that all the people in this world haven’t had the advantages that you’ve had” (Fitzgerald 1).
Note: When the quoted text in the source comes from another source, it’s best to just find that original source in order to quote it directly. If you can’t find the original source, you can instead cite it indirectly .
Often, incorporating a quote smoothly into your text requires you to make some changes to the original text. It’s fine to do this, as long as you clearly mark the changes you’ve made to the quote.
Shortening a quote
If some parts of a passage are redundant or irrelevant, you can shorten the quote by removing words, phrases, or sentences and replacing them with an ellipsis (…). Put a space before and after the ellipsis.
Be careful that removing the words doesn’t change the meaning. The ellipsis indicates that some text has been removed, but the shortened quote should still accurately represent the author’s point.
Altering a quote
You can add or replace words in a quote when necessary. This might be because the original text doesn’t fit grammatically with your sentence (e.g., it’s in a different verb tense), or because extra information is needed to clarify the quote’s meaning.
Use brackets to distinguish words that you have added from words that were present in the original text.
The Latin term “ sic ” is used to indicate a (factual or grammatical) mistake in a quotation. It shows the reader that the mistake is from the quoted material, not a typo of your own.
In some cases, it can be useful to italicize part of a quotation to add emphasis, showing the reader that this is the key part to pay attention to. Use the phrase “emphasis added” to show that the italics were not part of the original text.
You usually don’t need to use brackets to indicate minor changes to punctuation or capitalization made to ensure the quote fits the style of your text.
Scribbr Citation Checker New
The AI-powered Citation Checker helps you avoid common mistakes such as:
- Missing commas and periods
- Incorrect usage of “et al.”
- Ampersands (&) in narrative citations
- Missing reference entries

If you quote more than a few lines from a source, you must format it as a block quote . Instead of using quotation marks, you set the quote on a new line and indent it so that it forms a separate block of text.
Block quotes are cited just like regular quotes, except that if the quote ends with a period, the citation appears after the period.
To the end of his days Bilbo could never remember how he found himself outside, without a hat, a walking-stick or any money, or anything that he usually took when he went out; leaving his second breakfast half-finished and quite unwashed-up, pushing his keys into Gandalf’s hands, and running as fast as his furry feet could carry him down the lane, past the great Mill, across The Water, and then on for a mile or more. (16)
Avoid relying too heavily on quotes in academic writing . To integrate a source , it’s often best to paraphrase , which means putting the passage in your own words. This helps you integrate information smoothly and keeps your own voice dominant.
However, there are some situations in which quoting is more appropriate.
When focusing on language
If you want to comment on how the author uses language (for example, in literary analysis ), it’s necessary to quote so that the reader can see the exact passage you are referring to.
When giving evidence
To convince the reader of your argument, interpretation or position on a topic, it’s often helpful to include quotes that support your point. Quotes from primary sources (for example, interview transcripts or historical documents) are especially credible as evidence.
When presenting an author’s position or definition
When you’re referring to secondary sources such as scholarly books and journal articles, try to put others’ ideas in your own words when possible.
But if a passage does a great job at expressing, explaining, or defining something, and it would be very difficult to paraphrase without changing the meaning or losing the weakening the idea’s impact, it’s worth quoting directly.
If you want to know more about ChatGPT, AI tools , citation , and plagiarism , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- ChatGPT vs human editor
- ChatGPT citations
- Is ChatGPT trustworthy?
- Using ChatGPT for your studies
- What is ChatGPT?
- Chicago style
- Paraphrasing
- Critical thinking
Plagiarism
- Types of plagiarism
- Self-plagiarism
- Avoiding plagiarism
- Academic integrity
- Consequences of plagiarism
- Common knowledge
A quote is an exact copy of someone else’s words, usually enclosed in quotation marks and credited to the original author or speaker.
In academic writing , there are three main situations where quoting is the best choice:
- To analyze the author’s language (e.g., in a literary analysis essay )
- To give evidence from primary sources
- To accurately present a precise definition or argument
Don’t overuse quotes; your own voice should be dominant. If you just want to provide information from a source, it’s usually better to paraphrase or summarize .
Every time you quote a source , you must include a correctly formatted in-text citation . This looks slightly different depending on the citation style .
For example, a direct quote in APA is cited like this: “This is a quote” (Streefkerk, 2020, p. 5).
Every in-text citation should also correspond to a full reference at the end of your paper.
A block quote is a long quote formatted as a separate “block” of text. Instead of using quotation marks , you place the quote on a new line, and indent the entire quote to mark it apart from your own words.
The rules for when to apply block quote formatting depend on the citation style:
- APA block quotes are 40 words or longer.
- MLA block quotes are more than 4 lines of prose or 3 lines of poetry.
- Chicago block quotes are longer than 100 words.
If you’re quoting from a text that paraphrases or summarizes other sources and cites them in parentheses , APA and Chicago both recommend retaining the citations as part of the quote. However, MLA recommends omitting citations within a quote:
- APA: Smith states that “the literature on this topic (Jones, 2015; Sill, 2019; Paulson, 2020) shows no clear consensus” (Smith, 2019, p. 4).
- MLA: Smith states that “the literature on this topic shows no clear consensus” (Smith, 2019, p. 4).
Footnote or endnote numbers that appear within quoted text should be omitted in all styles.
If you want to cite an indirect source (one you’ve only seen quoted in another source), either locate the original source or use the phrase “as cited in” in your citation.
In scientific subjects, the information itself is more important than how it was expressed, so quoting should generally be kept to a minimum. In the arts and humanities, however, well-chosen quotes are often essential to a good paper.
In social sciences, it varies. If your research is mainly quantitative , you won’t include many quotes, but if it’s more qualitative , you may need to quote from the data you collected .
As a general guideline, quotes should take up no more than 5–10% of your paper. If in doubt, check with your instructor or supervisor how much quoting is appropriate in your field.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. & Caulfield, J. (2023, May 31). How to Quote | Citing Quotes in APA, MLA & Chicago. Scribbr. Retrieved June 9, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/working-with-sources/how-to-quote/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to block quote | length, format and examples, how to paraphrase | step-by-step guide & examples, how to avoid plagiarism | tips on citing sources, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
Get the Reddit app
Discussion forum for current, past, and future students of any discipline completing post-graduate studies - taught or research.
Can you write your master’s thesis in 1 week?
I have 2 days to send the fist draft and I just have 30 pages out of 80. I wrote those 30 pages today haha but I’m not sure if I’ll be able to finish the 50 next in 2 days. Even if I’m not sure I have to do it so I just want to hear some miracle stories to get more energy.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Writing a thesis in a month is an ambitious yet achievable goal, provided one approaches it with a structured plan and disciplined mindset. This guide has outlined the essential steps, from initial topic selection to the final stages of revision, offering practical advice and strategies to streamline the process.
Instead of inserting "work on thesis" into your calendar, insert measurable goals like "finish Figure 1" or "write two pages of Chapter 2.". 7. Write In Very Short Bursts. Writing in several short bursts is more efficient than writing in a few, long extended periods of time. If you ever tried to write for several hours in a row, you ...
Here are two ways that I managed to do it. Write. Even when you have zero motivation. This applies especially to those who are in the situation I was in. Since the aim is to fill your content ...
A good thesis has two parts. It should tell what you plan to argue, and it should "telegraph" how you plan to argue—that is, what particular support for your claim is going where in your essay. Steps in Constructing a Thesis. First, analyze your primary sources. Look for tension, interest, ambiguity, controversy, and/or complication.
Step 2: Write your initial answer. After some initial research, you can formulate a tentative answer to this question. At this stage it can be simple, and it should guide the research process and writing process. The internet has had more of a positive than a negative effect on education.
You create a tiny text using a five-paragraph structure: The first sentence addresses the broad context. This locates the study in a policy, practice or research field. The second sentence establishes a problem related to the broad context you have set out. It often starts with "But", "Yet" or "However".
FIGURE 8. EndNote's Cite While You Write function. 2) Intermediate documents: the thesis/dissertation proposal and grant applications. Think of your thesis or dissertation proposal and any grant applications as being a big first step toward the first chapter of your final document: the introduction.
Step #1 - Apply to Write a Thesis: An initial application and project description, due one month before the end of the semester prior to that in which the students intends to register for thesis ... 590 (if the student is taking two semesters to write the thesis) or Week 4 (if the student is taking one semester to write the thesis). Upon ...
Welcome to the Purdue OWL. This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Step 1: Understand the Requirements. The initial step in crafting your PhD thesis is to thoroughly understand its specific requirements, which can vary widely between disciplines and institutions. A thesis must contribute new knowledge to its field, necessitating a deep familiarity with the expected structure, depth of analysis, and submission ...
10 Tips to Write a Research Paper in a Month. 1. Plan your time. Create a realistic timeline that outlines the tasks you need to complete at each stage of the research paper writing process. 2. Select a focused topic. Choose a research topic that is manageable and aligns with your interests and available resources. 3.
the order you want to write the different pieces of information that make your theory. the notes you made about your studies, the design, the participants, the instruments, the procedure. the results of any statistical analysis you made. the ideas for and the issues you want to raise in the discussion. It also includes any notes you do not want ...
You can't write a master's thesis in one day. You simply can't. Well, I had to. The place the 1-day master thesis plan belongs to. Spoiler alert: it's a garbage bin.
4. Create a compelling thesis statement: Write a thesis statement that summarises your research paper's major argument or goal in a clear, succinct manner. 5. Making an outline: Make a thorough outline of your research paper that contains the introduction, primary body paragraphs, and conclusion. This will assist you in keeping your writing ...
I procrastinated 3 months away and did 90% of the research and writing in about one month for my 40 page minimum master's thesis. You can see a flurry of activity on my github in the 1-1.5 weeks of writing. I'm now doing a PhD straight out of my master's. You'll be okay.
I handed in my PhD thesis just over a month ago - around 200 pages and 60,000 words representing three and a half years of research work. I also wrote the entire first draft in a single weekend - and this is how I did it. The Australian National University Thesis Bootcamp (#ANUTBC) is a unique program run by Dr Inger Mewburn ( @thesiswhisperer ...
Week. Actions. Week 1. Collect all of the data into one place and create a structure with all of the chapters and sections you want to write. Finish up any experiments quickly and make your data as presentable and "thesis ready" as possible. Start putting bullet points under each section so you understand what you want to write in each. Week 2.
2. Finding the Right Thesis Topic. It is a subject that you have to determine the boundaries of in a boundless universe. The subject of the thesis must be about a specific topic, not a general one ...
CNN —. A "planet parade" during which six planets will appear to align in the sky near dawn is on the way, but only three planets will be visible with the naked eye — and the phenomenon is ...
ADMIN MOD. [Advice] I need to write an undergraduate thesis in one month. It needs to be about 40 pages long, dealing with literary representations of people with disabilities. Since I started the project, I've fallen out of love with the whole premise. I have about 8 or 9 pages written so far.
That's why it's important to make a conscious effort to use someone's preferred pronouns. If you fear you will accidentally use the wrong pronouns with someone who is non-binary, give ...
Significant_Owl8974. •. So if your thesis is paper based 15 days is a tight amount of time to write an intro/background chapter and staple all your publications together. If that is the case invest in caffeine and prepare not to sleep. If you need to do any more than that you need an extension.
Learn how to format and cite your paper in APA style with Purdue OWL's comprehensive guide on general guidelines, major sections, and resources.
An abstract is a 150- to 250-word paragraph that provides readers with a quick overview of your essay or report and its organization. It should express your thesis (or central idea) and your key points; it should also suggest any implications or applications of the research you discuss in the paper. According to Carole Slade, an abstract is ...
In the case of a group project, list all names of the contributors, giving each name its own line in the header, followed by the remaining MLA header requirements as described below. Format the remainder of the page as requested by the instructor. In the upper left-hand corner of the first page, list your name, your instructor's name, the ...
Citing a quote in APA Style. To cite a direct quote in APA, you must include the author's last name, the year, and a page number, all separated by commas. If the quote appears on a single page, use "p."; if it spans a page range, use "pp.". An APA in-text citation can be parenthetical or narrative.
Reply reply. canttouchthisJC. •. You can probably do two revisions in one week but any masters advisor would have wanted a copy of your thesis a while back. I had 19 revisions of my thesis and it took me two and a half months from my initial revision till what was actually written, submitted, and published.