Essay on Diabetes for Students and Children
500+ words essay on diabetes.
Diabetes is a very common disease in the world. But people may never realize, how did they get diabetes and what will happen to them and what will they go through. It may not be your problem but you have to show respect and care for the one who has diabetes. It can help them and also benefited you to know more about it and have a better understanding of it. Diabetes is a metabolic disorder which is identified by the high blood sugar level. Increased blood glucose level damages the vital organs as well as other organs of the human’s body causing other potential health ailments.


Types of Diabetes
Diabetes Mellitus can be described in two types:
Description of two types of Diabetes Mellitus are as follows
1) Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus is classified by a deficiency of insulin in the blood. The deficiency is caused by the loss of insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. This type of diabetes is found more commonly in children. An abnormally high or low blood sugar level is a characteristic of this type of Diabetes.
Most patients of type 1 diabetes require regular administration of insulin. Type 1 diabetes is also hereditary from your parents. You are most likely to have type 1 diabetes if any of your parents had it. Frequent urination, thirst, weight loss, and constant hunger are common symptoms of this.
2) Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus is characterized by the inefficiency of body tissues to effectively respond to insulin because of this it may be combined by insulin deficiency. Type 2 diabetes mellitus is the most common type of diabetes in people.
People with type 2 diabetes mellitus take medicines to improve the body’s responsiveness to insulin or to reduce the glucose produced by the liver. This type of diabetes mellitus is generally attributed to lifestyle factors like – obesity, low physical activity, irregular and unhealthy diet, excess consumption of sugar in the form of sweets, drinks, etc.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Causes of Diabetes
By the process of digestion, food that we eat is broken down into useful compounds. One of these compounds is glucose, usually referred to as blood sugar. The blood performs the job of carrying glucose to the cells of the body. But mere carrying the glucose to the cells by blood isn’t enough for the cells to absorb glucose.
This is the job of the Insulin hormone. Pancreas supply insulin in the human body. Insulin acts as a bridge for glucose to transit from blood to the body cells. The problem arises when the pancreas fails to produce enough insulin or the body cells for some reason do not receive the glucose. Both the cases result in the excess of glucose in the blood, which is referred to as Diabetes or Diabetes Mellitus.
Symptoms of Diabetes
Most common symptoms of diabetes are fatigue, irritation, stress, tiredness, frequent urination and headache including loss of strength and stamina, weight loss, increase in appetite, etc.
Levels of Diabetes
There are two types of blood sugar levels – fasting blood sugar level and postprandial blood sugar level. The fasting sugar level is the sugar level that we measure after fasting for at least eight hours generally after an overnight fast. Blood sugar level below 100 mg/dL before eating food is considered normal. Postprandial glucose level or PP level is the sugar level which we measure after two hours of eating.
The PP blood sugar level should be below 140 mg/dL, two hours after the meals. Though the maximum limit in both the cases is defined, the permissible levels may vary among individuals. The range of the sugar level varies with people. Different people have different sugar level such as some people may have normal fasting sugar level of 60 mg/dL while some may have a normal value of 90 mg/dL.
Effects of Diabetes
Diabetes causes severe health consequences and it also affects vital body organs. Excessive glucose in blood damages kidneys, blood vessels, skin resulting in various cardiovascular and skin diseases and other ailments. Diabetes damages the kidneys, resulting in the accumulation of impurities in the body.
It also damages the heart’s blood vessels increasing the possibility of a heart attack. Apart from damaging vital organs, diabetes may also cause various skin infections and the infection in other parts of the body. The prime cause of all type of infections is the decreased immunity of body cells due to their inability to absorb glucose.
Diabetes is a serious life-threatening disease and must be constantly monitored and effectively subdued with proper medication and by adapting to a healthy lifestyle. By following a healthy lifestyle, regular checkups, and proper medication we can observe a healthy and long life.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App


Essay on Diabetes
Students are often asked to write an essay on Diabetes in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Diabetes
What is diabetes.
Diabetes is a chronic disease where the body can’t control blood sugar levels. This happens because the body either doesn’t make enough insulin or can’t use it properly.
Types of Diabetes
There are two main types: Type 1 and Type 2. Type 1 is when the body doesn’t produce insulin. Type 2 is when the body doesn’t use insulin well.
Managing Diabetes
Diabetes can be managed through a healthy diet, regular exercise, and medication. Regular check-ups are also important to monitor blood sugar levels.
The Impact of Diabetes
If not managed, diabetes can lead to serious health problems like heart disease, kidney disease, and vision loss.
250 Words Essay on Diabetes
Introduction.
Diabetes, a chronic metabolic disorder, is characterized by an increased level of glucose in the blood. It arises due to the body’s inability to produce or effectively utilize insulin, a hormone responsible for glucose regulation.
Etiology of Diabetes
Diabetes is classified into two major types: Type 1 and Type 2. Type 1 diabetes, an autoimmune disorder, is a result of the body’s immune system attacking insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. On the other hand, Type 2 diabetes, the more prevalent form, is primarily associated with insulin resistance and often linked to obesity and sedentary lifestyle.
Impact and Management
Diabetes can lead to severe complications like heart disease, kidney failure, and blindness if left unmanaged. Management involves lifestyle modifications, including a healthy diet, regular physical activity, and medication or insulin therapy as needed.
Prevention and Future Research
Prevention strategies for Type 2 diabetes involve promoting healthier lifestyles and early detection. For Type 1 diabetes, research is still ongoing to understand its triggers. Advances in technology and medicine, such as artificial pancreas systems and islet cell transplantation, show promise for future diabetes management.
Diabetes, a global health crisis, requires comprehensive understanding and management strategies. With ongoing research and advancements, the future holds potential for improved diabetes care and prevention.
500 Words Essay on Diabetes
Introduction to diabetes.
There are primarily two types of diabetes: Type 1 and Type 2. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system attacks the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. This type is less common and usually develops early in life. Type 2 diabetes, on the other hand, is more prevalent and typically develops in adulthood. It occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn’t produce enough to maintain a normal glucose level.
Risk Factors and Symptoms
Several factors increase the risk of developing diabetes, including genetics, obesity, lack of physical activity, and poor diet. Additionally, certain ethnic groups are at a higher risk.
Management and Treatment
While there is currently no cure for diabetes, it can be effectively managed with a combination of lifestyle changes and medication. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and maintaining a healthy weight are crucial for managing both types of diabetes.
For Type 1 diabetes, insulin injections or use of an insulin pump are necessary. Type 2 diabetes can often be managed with lifestyle changes and oral medication, but insulin may be required as the disease progresses.
Complications and Prevention
Prevention strategies for Type 2 diabetes include regular physical activity, a healthy diet, maintaining a normal body weight, and avoiding tobacco use. Early detection through regular health screenings is also critical, as early treatment can prevent or delay the onset of complications.
Diabetes is a significant global health concern that requires concerted efforts for effective management and prevention. Understanding the disease, its risk factors, and the importance of early detection can go a long way in reducing the impact of this chronic condition. Through lifestyle changes and medical intervention, individuals with diabetes can lead healthy and fulfilling lives.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *


Essay on Diabetes in English for Children and Students

Table of Contents
Essay on Diabetes: Diabetes is a metabolic disease, in which the human body fails to utilize the sugar (glucose) content in blood, thus resulting in high blood sugar levels over a prolonged period of time. Sugar present in our blood is a carried by a hormone called Insulin, to the cells and stored or used as a source of energy. Diabetes occurs when the body doesn’t produce enough insulin or the insulin is unable to effectively transfer the produced glucose to the body tissues.
Diabetes is a serious health concern and requires regular medical care. Most common symptoms of diabetes include – frequent urination, unusual weight loss, increased appetite and a desire to consume sweets.
Fill Out the Form for Expert Academic Guidance!
Please indicate your interest Live Classes Books Test Series Self Learning
Verify OTP Code (required)
I agree to the terms and conditions and privacy policy .
Fill complete details
Target Exam ---
Long and Short Essay on Diabetes in English
Below we have provided long and short essay on diabetes of varying length on various aspects of diabetes. After going through the essay you will be able to speak or write on various issues like – causes, symptoms, types, levels and effects of diabetes.
It will also focus on diet that should be taken by a diabetic person and its effects on other vital organs of human body.
Also, you will know about the global spread of diabetes and its preventive measures as well as the significance of the World Diabetes Day.
You can choose any Diabetes essay of your choice from the essays given below and use the information in competitions, debates, class tests etc.
Short Essay on Diabetes –200 words
A Silent Threat to Humanity
Diabetes is a metabolic disease which is caused due to the excess of sugar (glucose) in human blood. It is also called as Diabetes Mellitus (DM). Our body produces a hormone – Insulin, which is primarily responsible for carrying glucose present in our blood to the cells to be stored and used as energy source. Problem occurs when either the pancreas doesn’t produce enough insulin, or the insulin produced is somehow unable to effectively transfer the glucose from blood to the cells.
A persistent increased blood sugar level is a potential threat to the vital organs and other parts of human body. Initial symptoms of diabetes are frequent urination, dizziness, weight loss, increased hunger etc. Diabetes may cause severe complications like – consciousness loss, kidney failure, brain stroke, foot ulcers and damage to the eyes.
Diabetes Mellitus has become the most common disease and around 425 million people globally are suffering from diabetes; out of which 82 million belong to the south-east Asian region. India, which is also a part of south-east Asia, has over seven crores cases of diabetes recorded annually.
With lifestyle changes and less physical exercise, more and more people are getting affected by diabetes. It is estimated that given to the present state of affairs, total number of diabetes patients in south-east Asia alone, will rise to 151 million.
Essay on Diabetes – 300 Words
Effects of Diabetes and Diabetes Day
Diabetes or Diabetes Mellitus is a metabolic disease caused due to the excess of blood sugar level in human body. An excessive quantity of sugar in blood, damages other vital organs like – kidney, heart and brain. Though, it is caused by the under production of insulin hormone by the pancreas, it is also a life style disease, caused due to unhealthy dietary habits and lack of physical exercise.
Effects of Diabetes on Health
Diabetes has wide range of effects on human body and health. It is the condition in which the glucose present in the human blood is somehow fails to be utilized as the source of energy. It could be either due to under production of insulin hormone, which carries sugar from blood to the cells, or it could be due to the unresponsiveness of cells to receive the sugar.
Whatever the reason may be, it results in excess blood sugar (glucose) content. Diabetes may potentially affect the vital organs like heart, kidney, brain and eyes. It may cause cardiovascular diseases, heart attack, kidney failure, hearing loss, bacterial and fungal skin infections and brain stroke.
World Diabetes Day and its Significance
Globally, around 425 million people are suffering from diabetes and the number is about to increase significantly in coming years if the preventive measures are not taken. Therefore, to raise awareness of people about diabetes, International Diabetes Federation (IDF) observes World Diabetes Day every year on 14 th November.
World Diabetes Day was first launched in 1991, as a counter measure to the increasing number of diabetes patients around the world.
Diabetes Mellitus is a global threat, with billions affected globally by it, it becomes imperative to raise public awareness about the causes, symptoms and effects of diabetes in order to effectively reduce the number of patients globally. Global events like World Diabetes Day play a significant role in freeing the world from Diabetes Mellitus.

Essay on Diabetes – 400 Words
Diabetes Mellitus and Kidney Problems
Diabetes Mellitus is a condition when human body is unable to effectively utilize the sugar (glucose) present in its blood ultimately leading to high blood glucose level. Blood is a vital body fluid that reaches all the body parts, and an abnormally high glucose level in blood could potentially damage the vital body organs and other body parts.
Causes and Symptoms of Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes is identified by high sugar (glucose) content in human blood. Glucose is a source of energy for the body and is normally present in blood which supplies glucose to other parts of body. The body parts that receive glucose do so with help of a hormone called Insulin. As long as the pancreas normally produces insulin, the blood glucose level is maintained. But, an abnormality in insulin production or its inefficiency to effectively transfer the glucose to the body tissues, leads to excess of glucose in blood. This metabolic condition is identified as Diabetes or Diabetes Mellitus.
Common symptoms of diabetes mellitus include tiredness, loss of stamina, sweating, persistent hunger, loss of weight and frequent urination. Any such symptoms must not be neglected and proper medical advice must be sought.
How Diabetes is Related to the Health of Kidney
Diabetes is one of the most common causes of kidney failure. Kidneys are the vital body organ which cleans the blood. A high content of glucose in blood damages the blood vessels of kidney, resulting in a medical condition called Diabetic Nephropathy.
With damaged blood vessels, your kidneys will not be able to effectively clean the blood, resulting in waste accumulation in your blood and body as well. This cycle continues, further damaging the kidneys and also other body parts. If the damage continues, it might result in serious complications including kidney failure.
The damage to the kidneys begins long before the other symptoms of diabetes actually appear. Patients suffering from diabetes should get their kidneys examined from time to time. Retention of urine in the bladder caused due to diabetes might also result in pressure on kidneys, further damaging them.
It is recorded that around 30 to 40% of diabetes patients will eventually face kidney failure. The number is disturbing given the billions of diabetes patients worldwide. Apart from raising people’s awareness on diabetes, there is also a need to make the tests of kidneys affordable for a common man. Diabetes patients must be regularly tested for the health of their kidneys and other vital organs.
Essay on Diabetes – 500 Words
Diabetes Mellitus and Heart Attack
Diabetes is a metabolic condition in which the blood retains more glucose, than it should under normal conditions. A high blood glucose level may damage the vital organs of human body like kidney, eyes, ear, heart and brain. Diabetes is caused due to under production of insulin hormone by the pancreas, which acts as a bridge for blood sugar (glucose), to move from blood to the other cells of the body.
Signs of Diabetes Mellitus
Some of the typical symptoms of Diabetes include anxiety, tiredness, blurred vision, headache, irritation, weakness, loss of stamina and faster heartbeat. These are only initial symptoms of diabetes and indicate the forthcoming severe consequences. Every sign of diabetes speaks volumes about the effects of the disease. For example, tiredness, dizziness is caused due to the inability of one’s body cells to successfully convert blood glucose into energy. Increased blood sugar levels in the blood damages the vital organs including heart.
Person suffering from diabetes is more likely to have cardiovascular complications including heart attack. Diabetes leads to high blood pressure and high cholesterol levels, escalating the possibility of a heart attack.
High glucose content in the blood damages the blood vessels of heart. Damaged blood vessels are unable to pump the required blood at the required rate, ultimately causing heart attack and other heart diseases. People suffering from diabetes are more likely to have cardiovascular disorders from a very early age, than the people who are not suffering from diabetes.
There are also certain factors which might increase one’s chance of heart attack, like smoking, drinking liquor, obesity, high cholesterol level and unhealthy lifestyle. The given factors, if present with diabetes, substantially increase the chances of a heart attack.
Prevention is Better than Cure
The best way for a diabetic person to stop a heart attack from occurring is by keeping a check on his/her blood sugar level. A diabetic person should always take necessary precautions to keep his/her blood sugar level under control. The precautions include – routine checkup of sugar level and heart, avoiding unhealthy and oily food, quit smoking, adapting to healthy lifestyle, regular exercise, and early morning walks etc.
The blood vessels of a diabetic patient are already weaker as compared to that of a normal human being. If a diabetic patient consumes unhealthy or junk food, he/she increases his/her cholesterol level, which together with the damaged blood vessels makes a heart attack most likely possibility. Activities like exercising and walking keep one’s cholesterol level under control, hence decreasing the chances of a heart attack.
A diabetic person must also take precautionary measures to keep his/her high blood pressure under control. Such patients are more likely to get a heart attack when compared to any normal patient of high blood pressure.
Diabetes is a silent killer; when unchecked, it slowly damages the vital organs resulting in their malfunction and severe health complications. Necessary precautionary measures should be taken, especially by a diabetic person to keep his/her heart and other vital organs in a healthy condition. Diabetes damages the heart’s blood vessels increasing the possibility of a heart attack.
Long Essay on Diabetes – 600 Words
This one is a complete essay providing information about “Meaning, Types, Causes, Symptoms, Effects and Levels of Diabetes.”
Diabetes is a metabolic disorder which is identified by the high blood sugar (glucose) level. An increased blood glucose level damages the vital organs as well as other organs of the human’s body causing other potential health ailments.
Types of Diabetes
Diabetes Mellitus could be further classified into the following two types –
1) Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus is classified by deficiency of insulin in blood. The deficiency is caused by the loss of insulin producing beta cells in pancreas. This type of diabetes is found more common in children. It is characterized by an abnormally high or low blood sugar levels.
The patients of type 1 diabetes require regular administration of insulin. The type 1 diabetes is hereditary i.e. you are most likely to have type 1 diabetes if any of your parents had it. Symptoms of Type 1 diabetes include frequent urination, thirst, weight loss and constant hunger.
2) Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus is characterized by the inefficiency of body tissues to effectively respond to insulin, which may be combined by insulin deficiency. Type 2 diabetes mellitus is the most common type of diabetes.
People with type 2 diabetes mellitus take medicines to improve the body’s responsiveness to insulin or to reduce the glucose produced by the liver. This type of diabetes mellitus is generally attributed to lifestyle factors like – obesity, low physical activity, irregular and unhealthy diet, excess consumption of sugar in form of sweets, drinks etc.
Causes of Diabetes
The food that we eat is broken down into useful compounds through the process of digestion. One of these compounds is glucose, usually referred to as blood sugar. Glucose is food for the cells of human body i.e. body cells rely on the availability of glucose for further using it as a source of energy. The job of carrying glucose to the cells of the body is done by the blood.
But mere carrying the glucose to the cells by blood isn’t enough for the cells to absorb glucose, a job which is done by hormone insulin, supplied by the pancreas. Insulin acts as a bridge for glucose to transit from blood to the body cells. Problem arises when the pancreas fails to produce enough insulin or the body cells for some reason doesn’t respond to receive the glucose; both the cases result in the excess of glucose in blood, which is referred as Diabetes or Diabetes Mellitus.
Symptoms of Diabetes
Most common symptoms of diabetes are fatigue, irritation, stress, tiredness, frequent urination and headache including loss of strength and stamina, weight loss, increase in appetite etc.
Levels of Diabetes
There are two types of blood sugar levels – fasting blood sugar level (blood sugar test before food) and postprandial blood sugar level (blood sugar test two hours after having meal). Sugar level measured after fasting for at least eight hours generally after an overnight fast is called fasting sugar level. Blood sugar level below 100 mg/dL (milligrams per deciliter) before eating food is considered normal.
Sugar level measured after two hours of eating is called postprandial glucose level or PP level. The PP blood sugar level should be below 140 mg/dL, two hours after the meals.
Though, the maximum limit in both the cases is defined, the permissible levels may vary among individuals. Some people may have normal fasting sugar level of 60 mg/dL while some may have the normal value of 90 mg/dL.
Effects of Diabetes
Diabetes may have severe health consequences and it affects vital body organs. Excessive glucose in blood damages kidneys, blood vessels, skin resulting in various cardiovascular and skin diseases and other ailments. Diabetes damages the kidneys, resulting in accumulation of impurities in body. It also damages the heart’s blood vessels increasing the possibility of a heart attack.
Apart from damaging vital organs, diabetes may cause various skin infections and the infection in other parts of the body. The prime cause of all type of infections is the decreased immunity of body cells due to their inability to absorb glucose.
Diabetes is a serious life threatening disease and must be constantly monitored and effectively subdued with proper medication and by adapting to a healthy life style. By following a healthy lifestyle, regular checkups and proper medication one can observe a healthy and long life.
| Also Check | |
|---|---|

Essay on Diabetes FAQs
Can eating too much sugar cause diabetes.
No, eating too much sugar doesn't directly cause diabetes, but it can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes over time.
What are the 3 main symptoms of diabetes?
The 3 main symptoms of diabetes are frequent urination, excessive thirst, and unexplained weight loss.
Who gets diabetes and why?
Anyone can get diabetes, but it's more common in those with a family history, poor diet, or lack of physical activity.
How can I prevent diabetes naturally?
You can prevent diabetes naturally by maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet, and staying physically active.
What is the main prevention of diabetes?
The main prevention of diabetes involves lifestyle changes, like eating well and exercising regularly.
Related content
Talk to our academic expert!
Language --- English Hindi Marathi Tamil Telugu Malayalam
Get access to free Mock Test and Master Class
Register to Get Free Mock Test and Study Material
Offer Ends in 5:00
Please select class
- Skip to main content
- Skip to secondary menu
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
A Plus Topper
Improve your Grades
Diabetes Essay | Essay on Diabetes for Students and Children in English
February 12, 2024 by Prasanna
Diabetes Essay: Diabetes is a metabolic disorder that primarily causes high blood glucose. The most common types of Diabetes are Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes. Type 1 diabetes is caused due to genetic disorder, whereas Type 2 diabetes is primarily a lifestyle disorder. The other types of Diabetes are prediabetes and gestational diabetes. Prediabetes is a borderline phase preceding Diabetes when the blood glucose levels are higher than usual but not as high as Diabetes itself.
Prediabetes gets cured once the glucose levels return to normal. Gestational Diabetes is caused in pregnant women, and it occurs mainly during the gestational phase, thus the name. This condition usually gets reversed once the fetus is delivered. Both prediabetes and Gestational Diabetes are reversible conditions, while Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes are chronic conditions and usually last a lifetime after its onset.
You can also find more Essay Writing articles on events, persons, sports, technology and many more.
Long and Short Essays on Diabetes for Students and Kids in English
We are providing students with essay samples on a long essay of 500 words and a short essay of 150 words on the topic of Diabetes for reference.
Long Essay on Diabetes 500 Words in English
Long Essay on Diabetes is usually given to classes 7, 8, 9, and 10.
Diabetes is a severe metabolic disorder that causes high blood glucose. Diabetes can be both reversible as well as chronic. Chronic Diabetes includes Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes, in which Type 1 is caused due to genetic reasons, whereas Type 2 is caused due to an irregular lifestyle. Reversible Diabetes includes prediabetes and gestational diabetes. Prediabetes usually precedes the onset of type 2 diabetes but can be corrected with proper diet and exercise.
Gestational Diabetes occurs only during pregnancy, and once the baby is born, the condition gets better in the mother’s body. However, women with gestational Diabetes stand a risk of suffering from Type 2 diabetes later on in their lives. Chronic Diabetes is caused by a lack of insulin hormone production or the body’s resistance to the insulin produced. Insulin produced by the beta cells of Islets of Langerhans of the pancreas is responsible for regulating glucose levels in the blood.
Usually, when the blood glucose levels increase, it sends a signal to the pancreas to produce insulin, helping the cells absorb the glucose. After that, the level of blood glucose comes down to normal, and insulin secretion drops. In Type 1 diabetes, the body’s immunity system fuelled by a genetic reason leads the immune response to attack the beta cells and destroy them, thereby diminishing or almost inhibiting insulin production. In this condition, the patient needs a steady influx of insulin in regular insulin injections to maintain normal blood glucose levels. Obesity or lifestyle habits barely play any role in this form of Diabetes.
On the other hand, Type 2 diabetes is caused due to unhealthy lifestyle habits such as prolonged lack of proper sleep, excessive alcohol and tobacco consumption, excessive consumption of junk food, and obesity, to name a few. This condition is caused due to the body’s resistance to the insulin present in the bloodstream and the pancreas’ consequent inability to produce enough insulin to overcome this.
As a result, the cells fail to absorb the glucose, and blood glucose levels increase abnormally. Type 2 diabetes is usually kept in check with medications that constitute insulin sensitizers. People with a sedentary lifestyle, lack of physical exercise, polycystic ovarian syndrome, high cholesterol, hypertension, and obesity are at a high risk of developing Type 2 diabetes. The risk of getting affected with diabetes increases with age. Some of the common symptoms of diabetes include frequent urination, increase in thirst, and appetite.
Apart from medications, Diabetes can be kept in check by maintaining a healthy diet, proper exercise, optimum sleep and water consumption, and abstaining from tobacco, alcohol, and junk food consumption. Prolonged chronic Diabetes can trigger a host of other life-threatening diseases. Some of them being chronic kidney failure (nephropathy), neurological damage (neuropathy), coronary artery disease, stroke, atherosclerosis, retina damage (retinopathy), Alzheimer’s disease, microbial skin infections, foot damage, and hearing impairment. In a few cases, it can even cause depression.
Short Essay on Diabetes 150 Words in English
Short Essay on Diabetes is usually given to classes 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6.
Diabetes is a metabolic disorder that causes an increase in blood glucose levels. It can be both chronic as well as reversible. Chronic diabetes types are more commonly found as compared to reversible ones.
Chronic types are Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes. Type 1 diabetes is caused due to genetic reasons and leads to an autoimmune attack on the body’s insulin-producing cells. Thus, insulin production is inhibited. Type 2 diabetes is caused due to an unhealthy lifestyle and obesity. While Type 1 diabetes is treated with insulin injections, Type 2 diabetes requires a combination of insulin sensitizer medication as-well-as a healthy diet and proper exercise.
Chronic Diabetes can give rise to other diseases like heart failure, kidney failure, loss of eyesight, nerve damage, and depression. People with high cholesterol, hypertension, obesity, a sedentary lifestyle, and high alcohol consumption are at a high risk of developing diabetes later on.
10 Lines on Diabetes Essay in English

FAQ’s on Diabetes Essay
Question 1. What is Diabetes?
Answer: Diabetes is a metabolic disorder characterized by high blood glucose and a decrease in insulin levels in the blood.
Question 2. How is insulin produced?
Answer: The insulin hormone is produced by beta cells in the Islets of Langerhans in the pancreas.
Question 3. Can Diabetes cause heart failure?
Answer: Diabetes can trigger coronary artery disease resulting in heart failure.
Question 4. Can diabetes cause kidney failure?
Answer: Prolonged Diabetes can cause chronic kidney failure in many patients.
- Picture Dictionary
- English Speech
- English Slogans
- English Letter Writing
- English Essay Writing
- English Textbook Answers
- Types of Certificates
- ICSE Solutions
- Selina ICSE Solutions
- ML Aggarwal Solutions
- HSSLive Plus One
- HSSLive Plus Two
- Kerala SSLC
- Distance Education
From Research to Reflection: A Step-by-Step Guide to Writing an Essay on Diabetes

Diabetes is a chronic disease that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by high blood glucose levels, which can lead to various complications if left untreated. One of the most significant complications of diabetes is its impact on cardiovascular health.
The link between diabetes and cardiovascular disease is well-established. People with diabetes are two to four times more likely to develop cardiovascular disease than those without the disease.
The reasons for this are complex, but they include that diabetes can damage blood vessels and nerves throughout the body, including those that supply the heart and brain. This can lead to a range of cardiovascular problems, such as heart attacks, strokes, and peripheral artery disease .
We can guarantee you that most people are not even aware of this much information on diabetes. This is why writing an essay on diabetes makes sense.
What’s more, while writing an essay on diabetes, you make yourself aware of this disease and work towards reflecting on it.
Influence Of Diabetes On The Society
Diabetes can have a significant impact on society in a number of ways.
Here are some examples:
- Healthcare costs: Diabetes is a chronic disease that requires ongoing medical care, including regular check-ups, medications, and in some cases, hospitalization. The cost of treating diabetes can be substantial, both for individuals and for society as a whole. In 2017, the total cost of diabetes in the US was estimated to be $327 billion, including direct medical costs and lost productivity.
- Public health: Diabetes is a major public health issue , with an estimated 463 million adults worldwide living with the disease. Diabetes can lead to various health complications, including heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and blindness. As a result, diabetes is a leading cause of death and disability worldwide.
- Lifestyle changes: Diabetes is closely linked to lifestyle factors such as diet and physical activity. As a result, efforts to prevent or manage diabetes often involve promoting healthy lifestyle habits such as regular exercise and a balanced diet. These lifestyle changes can have a broader impact on society by promoting overall health and well-being.
- Stigma: Diabetes can be stigmatized, with some people blaming individuals with diabetes for their disease. This can lead to discrimination and social isolation, which can have a negative impact on mental health and well-being.
- Education and awareness: Diabetes education and awareness campaigns can play an important role in reducing the impact of diabetes on society. By promoting an understanding of the disease and its risk factors and encouraging early diagnosis and treatment, these campaigns can help to improve health outcomes and reduce healthcare costs.
Diabetes can significantly impact society, both in terms of healthcare costs and public health outcomes. By promoting education and awareness and encouraging healthy lifestyle habits, we can work to reduce the impact of diabetes on individuals and society as a whole.
Why Such A Subject?
While there are many subjects to write essays on, why write an essay on such a difficult subject? Well, when an educational institution asks you to write an essay, they look at your writing skills and try to figure out your personality along with it.
If you are writing about something that can bring change in society, it can impress them. Writing an essay on diabetes will allow you to stand out from all the other students who have submitted essays on almost the same topic.
Below are a few reasons why writing an essay on diabetes is a good idea.
- To Raise Awareness: Diabetes is a chronic disease that affects millions of people worldwide, yet many people are still unaware of its causes, symptoms, and complications. Writing an essay on diabetes can help raise awareness about the disease, its impact on individuals and communities, and the importance of prevention and management.
- To Educate: Diabetes is a complex disease that requires careful management and monitoring. Writing an essay on diabetes can help educate individuals about the different types of diabetes, risk factors, signs and symptoms, and treatment options.
- To Promote Research: There is ongoing research on diabetes, including new treatments and management strategies. Writing an essay on diabetes can help promote research by highlighting the importance of funding and supporting research efforts.
- To Advocate For Change: Writing an essay on diabetes can help advocate for policy changes that improve access to diabetes care, support for those with diabetes, and prevention efforts.
- To Demonstrate Understanding: Writing an essay on diabetes can be an opportunity to demonstrate an understanding of the disease and its impact on individuals and communities. It can also showcase critical thinking skills and research abilities.
Writing an essay on diabetes can help raise awareness, educate, promote research, advocate for change, and demonstrate an understanding of the disease. It can be an important way to promote public health and improve the lives of individuals with diabetes.
A Step-by-Step Guide To Writing An Essay On Diabetes
Writing an essay on diabetes requires thorough research and reflection. You can’t just proceed with a diabetes essay like any normal essay topic. When writing an essay on diabetes, you can’t get wrong with your facts and information. One mistake in your information can affect your whole efforts.
When you are doing research for your essay, ensure that you are picking information from credible resources.
Follow the steps below to write a high-quality essay.
Step 1: Choose A Specific Topic
The topic of diabetes is vast, so it is essential to narrow it down to a specific area you can thoroughly explore in your essay. Consider the audience, the essay’s purpose, and the assignment’s scope. For instance, you could focus on the causes of diabetes, the different types of diabetes, the impact of diabetes on a particular population, or the latest treatment options for diabetes.
Step 2: Conduct Research
Once you have a specific topic, conduct thorough research to gather relevant information from credible sources such as academic journals, government publications, and reputable websites. Take notes on key points, statistics, and quotes that you can use to support your arguments.
Step 3: Develop A Thesis Statement
Based on your research, develop a clear and concise thesis statement that summarizes the main argument of your essay. Your thesis statement should be debatable and provide a roadmap for the rest of your essay.
Step 4: Create An Outline
Use your research and thesis statement to create an outline for your essay. Organize your ideas into logical sections and subsections, and ensure each point supports your thesis statement.
Step 5: Write The Essay
Using your outline as a guide, write your essay. Start with an introduction that provides background information and a clear thesis statement. Use the body paragraphs to present your arguments and support them with evidence from your research. End with a conclusion that restates your thesis and summarizes your main points.
Step 6: Edit And Proofread
After you have written your essay, edit and proofread it carefully to ensure it is clear, concise, and error-free. Check for spelling and grammatical errors, and ensure your ideas flow logically.
Step 7: Reflect On Your Essay
Finally, take some time to reflect on your essay. Consider the strengths and weaknesses of your argument, and think about what you could have done differently. This reflection can help you improve your writing skills and prepare for future assignments.
By following this step-by-step guide, you can write a well-researched and thoughtful essay on diabetes. Remember to choose a specific topic, conduct thorough research, develop a clear thesis statement, create an outline, write the essay, edit and proofread, and reflect on your work.
However, if you find it difficult to write an essay on diabetes, but the opportunity is too good to miss, ask a professional to ‘ write my essay for me ’.
Things To Consider!
Define your purpose.
Before you start writing, it’s important to clarify why you’re writing about diabetes.
Are you trying to educate readers about the disease? Discuss a specific aspect of diabetes research or treatment. Argue for a particular approach to diabetes prevention or management.
Defining your purpose can help guide your writing and ensure that you stay focused on your main goals.
Know Your Audience
Who will be reading your essay? Are they experts in diabetes, or are they general readers who may not be familiar with the disease? Understanding your audience can help you tailor your writing style and language to make your essay as accessible and engaging as possible.
Research Thoroughly
Diabetes is a complex and multi-faceted disease, so it’s important to do your research to ensure you comprehensively understand the topic. Find reputable sources, such as peer-reviewed journals, government websites, or expert organizations like the American Diabetes Association.
Consider Multiple Perspectives
There are many different viewpoints on diabetes, from healthcare providers to patients to public health advocates. When writing your essay, consider different perspectives and present a balanced view of the topic.
Use Clear, Concise Language
Diabetes is a technical topic with many medical terms and concepts that may be unfamiliar to some readers. To make your essay as accessible as possible, try to use clear, concise language that is easy to understand. Use layman’s terms when appropriate, and define any technical terms you use.
Use Examples And Anecdotes
Diabetes can be a dry and technical topic, so using examples and anecdotes can help to bring your writing to life and make it more engaging for readers. Consider including real-life stories of people with diabetes or describing specific research studies or medical interventions in detail.
Edit And Proofread Carefully
Finally, edit and proofread your essay carefully before submitting it. Look for spelling and grammar errors and any unclear or confusing language. Consider having someone else read your essay to get a fresh perspective and catch any mistakes you may have missed.
Related posts

Essay on Diabetes
Introduction
Diabetes is a healthcare condition that has continued to affect so many people, both young and old. Understanding more about Diabetes will help people live a healthy lifestyle by avoiding all the possible things that might cause it. In this assignment, I will assess why Diabetes is a significant health issue to individuals and the world. I will discuss the background of Diabetes, its definitions, and the types of Diabetes. Besides, I will discuss what is needed to promote individual and group health for people who have Diabetes. By the end of the assignment, one will have better knowledge about Diabetes since I will also discuss the causes and preventive measures that can be undertaken to prevent the disease. Towards the end of the assignment, I will describe three achievable health promotion goals, hence helping fight against Diabetes. I will also describe some of the interventions and roles that different people, groups, and organizations play to reduce the high cases of Diabetes in the world.
During the medieval ages, being diagnosed with Diabetes was like a death sentence. The pioneers of diabetes treatment were Thomas Willis, Sushruta, and Arataeus (Mandal, 2021). The three were Greek physicians who encouraged people to exercise on horsebacks to prevent excess urination. They also described other therapies like overfeeding and taking wine to reduce starvation and excessive loss of fluids (Mandal, 2021). On the other hand, the ancient Indians would test for Diabetes by taking ants near a person’s urine. If the human urine attracted the ants, then the person would be diagnosed with urine (Mandal, 2021). Diabetes is a disease that is the leading cause of high blood sugar levels. People who have Diabetes have bodies that cannot make enough insulin, or their bodies cannot use the insulin they have effectively (Healthline, 2021). Insulin is the hormone that moves sugars from the blood to the body cells. There are several types of Diabetes, including type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, gestational diabetes, prediabetes, and Diabetes insipidus (Healthine, 2021). All these types affect our bodies differently, and they all have different effects, hence different coping strategies.
The rationale for Choosing Diabetes
Diabetes is among the most severe health issues in the world. This is the reason why I chose to discuss it to create awareness about it. The bad thing with Diabetes is that one can get it and not know that they have it. By the time they realize that they have Diabetes, the condition is worse, and the person is highly affected. According to Genesis Medical Associates (2015), one out of three adults have higher blood sugar levels; a condition referred to as prediabetes. If the persons do not change their lifestyles, the sugar levels increase, leading to other types of Diabetes (Genesis Medical Associates, 2015). Learning about Diabetes will allow people to support each other in the fight against Diabetes. This includes eating healthy meals and maintaining a healthy lifestyle through exercising (Dowshen, 2021). Another reason why I chose to discuss Diabetes is to learn more about the causes and how to manage the disease. Since most people do not know about the condition, it is crucial to educate them so that in case they feel any symptoms, and they can get the treatment as early as possible (Dowshen, 2021). It is easy to deal with Diabetes as long as the signs are detected early enough and the patient follows the given guidelines on healthy living.
Epidemiology
Diabetes is a significant health concern since it affects so many people in the world. Diabetes can affect any person. However, some ethnic groups are affected more than others. The Alaska Natives and the American Indians are more affected by Diabetes as compared to all other ethnic groups. In terms of age, more than sixty-five years are more prone to getting diabetes than young people. According to Shaikh (2021), % of the people who are more than 65 years have diabetes. However, the young people are also affected but at a meager percentage compared to the older people.
The risk factors for Type 1 diabetes are hereditary, hence easily transferred from parents to children. Type 1 diabetes primarily affects young children and teenagers. Also, white Americans are at a higher risk of getting the disease than African Americans and Latino Americans (Shaikh, 2021). Type 2 diabetes affects middle and old age persons. Also, other risk factors for type 2 diabetes include genes, being overweight, a history of gestational pregnancy, and giving birth to a baby that is more than 9lbs (Shaikh, 2021).
It is important to note that diabetes is more prone in rural areas where people do not have access to health services and education. In the United Kingdom, 28% of the people with diabetes have issues obtaining medication due to a lack of health services and knowledge on how to go about diabetes treatment (Whicher et al., 2019 p.243). Besides, most of the people who are in the rural do not go for annual health checkups; hence their conditions get worse daily.
Assessment and assessment tools for Diabetes
Different tools are used during the assessment of diabetes. Assessing diabetes is very important as it helps differentiate between different types of diabetes and the extent of the condition. The Diabetes Prevention Screening Tool helps identify the persons at risk of getting diabetes (Diabetes Education Services, 2021). Such people are encouraged to join the CDC prevention program. There is also the Risk Test for Pre Diabetes patients to understand the risks they face as pre-diabetics (Diabetes Education Services, 2021).
The Diabetes Risk calculator is a tool that is used to detect undiagnosed diabetes and prediabetes. The social Support Assessment Tool helps diabetic patients to have a support system (Diabetes Initiative, 2020). Patients who have Diabetes need a lot of support from family and friends. The support shown will help them adhere to the doctor’s instructions, hence improving the chances of being better. Another assessment is the Mental Health Progress Report. The report is filled up during the patient’s follow-up visits. The assessment involves questions determining if the patient is affected by the condition mentally (Diabetes Initiative, 2020). It helps the doctors to guide the patient on how they can cope mentally with Diabetes.
Health Promotion Goals that you will like to Achieve
One of the goals that I would like to achieve is to reduce the high number of people diagnosed with Diabetes. I will encourage people to ensure they exercise at least thirty minutes a day to become physically fit. To make this goal achievable, I will create small groups that will act as support systems. This will help push people towards healthy living, preventing them from being diagnosed with the condition (Cecelia Health, 2021). My goal is realistic since it is easy to adopt a good eating habit and exercise at least thirty minutes daily. Still, it becomes easier when these activities are done in groups so that members feel motivated. To ensure that the goal is achieved, I will set a time frame of three months. Each member must have dropped at least 10 pounds within three months and managed to exercise at least 30 minutes daily, consistently.
The second goal is to enhance a better diabetes management program. Most people who have diabetes do not know what they should avoid, while others ignore the advice given to them by the doctors. In this case, I will form a group of people of different ages who are diabetic. The group formed will be a support system that will help each other cope with Diabetes. I will encourage the group members to remain healthy by eating the right food and exercising daily (McDermott, 2020). For those that are older, they can do simple exercises like jogging and walking a few kilometers daily. After five months, I will assess each patient’s changes in sugar levels and the general healthcare status (McDermott, 2020). I expect the sugar levels to be expected or close to normal for most patients within this period. Besides, the patients will have adapted to the new lifestyle since they got used to it.
Interventions for your health promotion goals
As indicated above, the first goal is to reduce the high numbers of people diagnosed with diabetes. The first health intervention is by ensuring that people are engaging in vigorous activities and exercises. Before one retires to bed, they must ensure that they have done a bit of practice to increase the metabolic activities of their bodies (Harvard T.H CHAN, 2021). Exercising helps maintain a moderate weight; hence, the high obesity and overweight people will reduce significantly. Besides, exercise helps increase insulin sensitivity in the body. As a result, the body cells can consume the sugars that are in the bloodstream.
For this intervention to work, both individuals and groups work together. A person must know that they have a personal responsibility to ensure that they maintain healthy body weight. Besides, organizations can play a significant role by ensuring that they create team-building activities (Harvard T.H CHAN, 2021). Organizations can set a day or two per month whereby all the employees and employers are involved in various team-building activities. This will help to ensure that at least all members keep fit, even if some of the members might not be keeping fit at a personal level. Since young people are also at a very high risk of getting diabetes, schools should develop a schedule to see all the students engage in exercise activities (John Muir Health, 2021). For example, the school can decide to have a physical exercise lesson after every two days.
Another intervention that will see few people being diagnosed with diabetes is maintaining a healthy eating lifestyle. Most people, especially teenagers, eat food that is full of calories. First, one should ensure they increase the fiber intake (Science Daily, 2018). Fiber is essential as it helps to slow down the digestion of carbs and sugars. Foods that contain more fibers include legumes, vegetables, and whole grains. Too many carbs place a person at a very high risk of getting diabetes. Another healthy eating habit is taking plenty of water to stay hydrated at all times (John Muir Health, 2021). When one takes a lot of water, it also helps the kidney eliminate excess sugars through the urine (Science Daily, 2018). A well-hydrated person is at a lower risk of getting diabetes. However, one should avoid sugar-sweetened drinks as they raise the level of glucose in the blood.
Both individuals and organizations have a role to play when it comes to maintaining a healthy eating lifestyle. Families should ensure that they prepare meals that are balanced diet. As an individual, one has a choice to eat whatever they want. Following this, one should avoid taking foods with high carb content instead of increasing the intake of high fiber meals. Organizations should also participate in this intervention by preparing healthy meals for their employees (Science Daily, 2018). Communities should be encouraged to grow more fibers and take the origin foods rather than rely on ready-made foods with high calories. Also, schools can be involved by ensuring that they have a reasonable timetable for all the meals, and the fiber intake for each student should be higher than the carb intake.
The second goal is enhancing better management for people who are living with diabetes. Individuals have a tremendous responsibility to ensure that they follow the given guidelines to stabilize sugar levels efficiently. As a diabetic patient, one should know the type of diabetes they are suffering from and the measures they are supposed to take to become better (NIH, 2021). The first step that a diabetic person should take is to ensure that they are not stressed. Stress triggers sugar levels, hence raising them. To reduce stress triggers, one can listen to their favorite music, take a walk, breathing in and out, or doing their favorite activities (Diabetes UK, 2021). Also, a person needs to have a support system to reach out in case they feel stressed.
The second step that one can take to deal with diabetes is ensuring that they eat well. After being assessed by the doctor, a health care team should help the sick person come up with a meal plan (Diabetes UK, 2021). The meal plan should contain fewer calories, fewer sugars and salt, and high saturated fats. Also, a diabetic person should eat foods that have high fiber, like rice and bread. Instead of drinking sweetened juices, a diabetic person should ensure that they take plenty of clean drinking water. This helps to keep the body hydrated at all times.
Both individuals and groups have a significant role in ensuring that diabetic persons are taken care of. They have the necessary things needed for them to reduce sugar levels. Health facilities should make sure that they do follow-ups so that if a patient has forgotten to go for checkups, they can go upon being reminded. Besides, other organizations like NGOs should develop fiber for needy people who might not afford such things.
Evaluation of your Health Promotion Care
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle through exercise is not hard to achieve as long as the people involved know the benefits of exercising. Exercising is an effective strategy that will help prevent diabetes and prevent other diseases like heart attack and stroke (Diabetes UK, 2021). However, people should be allowed to choose the kind of exercise that they want to do. Instead of going for a run, one can engage in other activities like playing football, netball, or swimming (Harvard T.H CHAN, 2021). Since people are not the same, one should not be forced to go for a morning jog, yet they like swimming. If this is done, the exercises will be more effective since people will be doing them willingly. I would recommend that the government makes it paramount for organizations to have different days from engaging in other activities like swimming, running, jogging, etc. Also, schools should ensure that there are various exercises for all the students to have one or two activities that they can engage in easily.
The second promotion of care was encouraging people to eat healthy meals. From the above discussion, it is evident that people need to engage in healthy lifestyles. Whether a person has diabetes or not, engaging in a healthy lifestyle is very important (Science Daily, 2018. Following this, one should ensure that they avoid high calories and have high fibers. This healthcare plan can be effective only if the government and other non-governmental organizations are willing to provide the proper meals for the people in need. Some diabetic people do not have access to medical care; hence they cannot do follow-ups about their conditions. As a result, the health care plan will become hard to achieve if the doctors and health care workers do not follow up on their patients to ensure they have taken the right medicines and that the sugar levels are not increasing (John Muir Health, 2021. For this, I would recommend that treatment of diabetes becomes free of charge in all public healthcare institutions. This will make it easy for the poor diabetic people to go for checkups since they know they will not be asked for any money to get the services they need. During the Diabetes Awareness week in the country, the government led by the health care sector should ensure that people are educated about diabetes. This will help people learn more about it and engage in activities that will help reduce diseases.
Tannahill Health Promotion Model
The Tannahill Health Promotion Model helps in the prevention of diabetes and protection of people who have diabetes. As discussed above, diabetes can be prevented through eating the right foods and ensuring that one is physically fit. The Tannahill Health promotion strategy also suggests a good communication flow between the patient and the health care providers (Queens University Belfast, 2021). In this case, the healthcare providers should do the follow up’s for their patients. The third aspect of the Tannahill Health promotion program is that the citizens should be given health protection through the legislature, social measures, and financial measures (Queens University Belfast, 2021). This includes helping needy people eat healthy meals and ensuring that organizations and companies give their employees the proper meals. Besides, Companies, organizations, and schools should set aside specific days where each person is engaged in other activities like swimming, ring, and playing their favorite games.
Diabetes is indeed one of the most severe diseases in the world. Diabetes affects both the young and the old and people of all ages. Although people at the age of 65 and older are more prone to being diagnosed with diabetes, other factors also determine if a person is prone to getting diabetes (Healthline, 2021). For example, a child can get diabetes from their parents; hence they get hereditary diabetes. Women who have experienced gestational diabetes are also at a very high risk of contracting the disease again (Shaikh, 2021). People who are not physically fit are also prone to getting diabetes. Following this, it is evident that although some people are more prone to getting diabetes, several other factors play a significant role.
Although diabetes is a severe condition worldwide, it can be controlled and the high rates reduced. This can be achieved through two maintaining it; exercising and eating suitable meals. Since some people cannot afford the healthy diet recommended for diabetic people, the government and other non-governmental organizations can provide such meals to the people (Whicher et al., 2019 p.243. Also, ensuring that the medication services are accessible at the public hospitals will encourage most people to go for follow-ups. Exercising is easy since there are so many activities that help burn calories (Shaikh, 2021). That is why it is essential to let the person choose activities they are good at and concentrate on them. Generally, although diabetes is a serious condition, it is easy to prevent and manage it if all resources are available.
Cecelia Health, 2021. How to Set and Achieve SMART Goals — in Life and Diabetes – Cecelia Health . [online] Cecelia Health. Available at: <https://www.ceceliahealth.com/how-to-set-and-achieve-smart-goals-in-life-and-diabetes/> [Accessed 1 June 2021].
Diabetes Education Services, 2021. Screening Tools for Diabetes – Diabetes Education Services . [online] Diabetes Education Services. Available at: <https://diabetesed.net/screening-tools-for-diabetes/> [Accessed 1 June 2021].
Diabetes Initiative, 2020. Tools: Assessment Instruments . [online] Diabetesinitiative.org. Available at: <http://www.diabetesinitiative.org/resources/type/assessmentInstruments.html> [Accessed 1 June 2021].
Diabetes UK, 2021. 10 Tips for Healthy Eating with Diabetes . [online] Diabetes UK. Available at: <https://www.diabetes.org.uk/guide-to-diabetes/enjoy-food/eating-with-diabetes/10-ways-to-eat-well-with-diabetes> [Accessed 1 June 2021].
Dowshen, S., 2021. Diabetes Control: Why It’s Important (for Teens) – Nemours KidsHealth . [online] Kidshealth.org. Available at: <https://kidshealth.org/en/teens/diabetes-control.html> [Accessed 1 June 2021].
Genesis Medical Associates, 2015. The Importance Of Understanding And Preventing Diabetes – Genesis Medical Associates, Inc . [online] Genesismedical.org. Available at: <https://www.genesismedical.org/blog/the-importance-of-understanding-and-preventing-diabetes> [Accessed 1 June 2021].
Harvard T.H CHAN, 2021. Simple Steps to Preventing Diabetes . [online] The Nutrition Source. Available at: <https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/disease-prevention/diabetes-prevention/preventing-diabetes-full-story/> [Accessed 1 June 2021].
Healthline, 2021. Everything You Need to Know About Diabetes . [online] Healthline. Available at: <https://www.healthline.com/health/diabetes#:~:text=Diabetes%20mellitus%2C%20commonly% 20known%20as,the%20insulin%20it%20does%20make.> [Accessed 1 June 2021].
John Muir Health, 2021. Preventing Diabetes . [online] Johnmuirhealth.com. Available at: <https://www.johnmuirhealth.com/health-education/conditions-treatments/diabetes-articles/preventing-diabetes.html> [Accessed 1 June 2021].
Mandal, A., 2021. History of Diabetes . [online] News Medical. Available at: <https://www.news-medical.net/health/History-of-Diabetes.aspx#:~:text=The%20term%20diabetes%20was%20probably,sweet%20taste%20of%20the%20urine.> [Accessed 1 June 2021].
McDermott, A., 2020. 7 Long-Term Goals for Better Diabetes Management . [online] Healthline. Available at: <https://www.healthline.com/health/type-2-diabetes/living-better-with-type-2-diabetes/long-term-goals-everyone-with-type-2-diabetes-should-make> [Accessed 1 June 2021].
NIH, 2021. 4 Steps to Manage Your Diabetes for Life | NIDDK . [online] National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Available at: <https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/diabetes/overview/managing-diabetes/4-steps> [Accessed 1 June 2021].
Queens University Belfast, 2021. Health Promotion. [online] Queens University Belfast. Available at https://www.qub.ac.uk/elearning/public/HealthyEating/HealthPromotion/ [Accessed 1 June 2021]
Science Daily, 2018. Physical exercise reduces the risk of developing diabetes, study shows . [online] ScienceDaily. Available at: <https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2018/02/180220102420.htm> [Accessed 1 June 2021].
Shaikh, J., 2021. What Population Is Most Affected by Diabetes? . [online] MedicineNet. Available at: <https://www.medicinenet.com/what_population_is_most_affected_by_diabetes/article.htm> [Accessed 1 June 2021].
Whicher, C., O’Neill, S., and Holt, R., 2019. Diabetes in the UK: 2019. Diabetic Medicine , [online] 37(2), pp.242-247. Available at: <https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.1111/dme.14225> [Accessed 1 June 2021].
Cite this page
Similar essay samples.
- Essay on Toxicology
- Essay on Toyota Business Operations Follow Up
- Essay on Careers in Finance
- Essay on History and Philosophy of Science
- Reflective Assignment on Teaching Practice
- Essay on Trump and Populism on Twitter
Home — Essay Samples — Nursing & Health — Other Diseases & Conditions — Diabetes
Essays About Diabetes
The factors and impact of type 2 diabetes, the burden of diabetes, made-to-order essay as fast as you need it.
Each essay is customized to cater to your unique preferences
+ experts online
The Dangers of Diabetes and The Proper Management of The Disease
Diabetes: type 1 and type 2, overview of diabetes mellitus, research on diabetes and its effects on people, let us write you an essay from scratch.
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
A Research on The Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Types, causes and treatment of diabetes, diabetes mellitus: definition, types, effects and causes, results of diabetes mellitus type 2 progressing, get a personalized essay in under 3 hours.
Expert-written essays crafted with your exact needs in mind
The Types of Diabetes
The type 1 and type 2 diabetes, overview of diabetes mellitus: symptoms, types and treatment, what is gestational diabetes, critically analyse the effect of physical activity on type 2 diabetes, home remedies for diabetes, a study on diabetes, the risks of amputation, and life after amputation, the need for special diabetes program in america, insulin therapy in type 2 diabetes mellitus, medications for blood glucose and pressure control during diabetes, diabetes in children: definition of diabetes burnout and how peer pressure contributes to diabetes, recommendations to delay the onset of diabetes and control of diabetes, the np influence and diabetes, the types of diabetes mellitus, review of the consequences of diabetes mellitus, current methods of treating diabetic foot ulcer, the role and responsibilities of a registered nurse when treating diabetic patients, methods of improvement in the awareness & treatment of insulin abuse, diabetes: how to eat healthy and maintain good levels, behavioral interventions to improve glycemic control in african americans with t2dm.
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level (hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time.
Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased appetite.
There are three main types of diabetes mellitus: Type 1 diabetes, Type 2 diabetes, and Gestational diabetes.
Family history, obesity, lack of exercise, genetics, air pollution, etc.
More than 37 million people in the United States have diabetes, and 1 in 5 of them don’t know they have it. Diabetes is the 7th leading cause of death in the United States. In the last 20 years, the number of adults diagnosed with diabetes has more than doubled as the American population has aged and become more overweight or obese.
Relevant topics
- Eating Disorders
- Medical Marijuana
- Childhood Obesity
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock Locked padlock icon ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- Entire Site
- Research & Funding
- Health Information
- About NIDDK
- Diabetes Overview
What Is Diabetes?
- Español
Diabetes is a disease that occurs when your blood glucose, also called blood sugar, is too high. Glucose is your body’s main source of energy. Your body can make glucose, but glucose also comes from the food you eat.
Insulin is a hormone made by the pancreas that helps glucose get into your cells to be used for energy. If you have diabetes, your body doesn’t make enough—or any—insulin, or doesn’t use insulin properly. Glucose then stays in your blood and doesn’t reach your cells.
Diabetes raises the risk for damage to the eyes, kidneys, nerves, and heart. Diabetes is also linked to some types of cancer. Taking steps to prevent or manage diabetes may lower your risk of developing diabetes health problems.

What are the different types of diabetes?
The most common types of diabetes are type 1, type 2, and gestational diabetes.
Type 1 diabetes
If you have type 1 diabetes , your body makes little or no insulin. Your immune system attacks and destroys the cells in your pancreas that make insulin. Type 1 diabetes is usually diagnosed in children and young adults, although it can appear at any age. People with type 1 diabetes need to take insulin every day to stay alive.
Type 2 diabetes
If you have type 2 diabetes , the cells in your body don’t use insulin properly. The pancreas may be making insulin but is not making enough insulin to keep your blood glucose level in the normal range. Type 2 diabetes is the most common type of diabetes. You are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes if you have risk factors , such as overweight or obesity , and a family history of the disease. You can develop type 2 diabetes at any age, even during childhood.
You can help delay or prevent type 2 diabetes by knowing the risk factors and taking steps toward a healthier lifestyle, such as losing weight or preventing weight gain.
Gestational diabetes
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy. Most of the time, this type of diabetes goes away after the baby is born. However, if you’ve had gestational diabetes, you have a higher chance of developing type 2 diabetes later in life. Sometimes diabetes diagnosed during pregnancy is type 2 diabetes.
Prediabetes
People with prediabetes have blood glucose levels that are higher than normal but not high enough to be diagnosed with type 2 diabetes. If you have prediabetes, you have a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes in the future. You also have a higher risk for heart disease than people with normal glucose levels.
Other types of diabetes
A less common type of diabetes, called monogenic diabetes , is caused by a change in a single gene . Diabetes can also come from having surgery to remove the pancreas, or from damage to the pancreas due to conditions such as cystic fibrosis or pancreatitis .
How common are diabetes and prediabetes?
More than 133 million Americans have diabetes or prediabetes. 1
As of 2019, 37.3 million people—or 11.3% of the U.S. population—had diabetes. 1 More than 1 in 4 people over the age of 65 had diabetes. Nearly 1 in 4 adults with diabetes didn’t know they had the disease. 2
About 90% to 95% of diabetes cases are type 2 diabetes. 3
In 2019, 96 million adults—38% of U.S. adults—had prediabetes. 4
What other health problems can people with diabetes develop?
Over time, high blood glucose can damage your heart , kidneys , feet , and eyes . If you have diabetes, you can take steps to lower your chances of developing diabetes health problems by taking steps to improve your health and learning how to manage the disease . Managing your blood glucose, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels can help prevent future health problems.

This content is provided as a service of the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK), part of the National Institutes of Health. NIDDK translates and disseminates research findings to increase knowledge and understanding about health and disease among patients, health professionals, and the public. Content produced by NIDDK is carefully reviewed by NIDDK scientists and other experts.
NIDDK would like to thank: Daniel Bessesen, M.D., University of Colorado; Domenico Accili, M.D., Columbia University
An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock Locked padlock icon ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.

- Health Topics
- Drugs & Supplements
- Medical Tests
- Medical Encyclopedia
- About MedlinePlus
- Customer Support
How to Prevent Diabetes
What is type 2 diabetes.
If you have diabetes, your blood sugar levels are too high. With type 2 diabetes , this happens because your body does not make enough insulin, or it does not use insulin well (this is called insulin resistance). If you are at risk for type 2 diabetes, you might be able to prevent or delay developing it.
Who is at risk for type 2 diabetes?
Many Americans are at risk for type 2 diabetes. Your chances of getting it depend on a combination of risk factors such as your genes and lifestyle. The risk factors include:
- Having prediabetes , which means you have blood sugar levels that are higher than normal but not high enough to be called diabetes
- Being overweight or having obesity
- Being age 45 or older
- A family history of diabetes
- Being African American, Alaska Native, American Indian, Asian American, Hispanic/Latino, Native Hawaiian, or Pacific Islander
- Having high blood pressure
- Having a low level of HDL (good) cholesterol or a high level of triglycerides
- A history of diabetes in pregnancy
- Having given birth to a baby weighing 9 pounds or more
- An inactive lifestyle
- A history of heart disease or stroke
- Having depression
- Having polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- Having acanthosis nigricans, a skin condition in which your skin becomes dark and thick, especially around your neck or armpits
How can I prevent or delay getting type 2 diabetes?
If you are at risk for diabetes, you may be able to prevent or delay getting it. Most of the things that you need to do involve having a healthier lifestyle. So if you make these changes, you will get other health benefits as well. You may lower your risk of other diseases, and you will probably feel better and have more energy. The changes are:
- Losing weight and keeping it off. Weight control is an important part of diabetes prevention. You may be able to prevent or delay diabetes by losing 5 to 10% of your current weight. For example, if you weigh 200 pounds, your goal would be to lose between 10 to 20 pounds. And once you lose the weight, it is important that you don't gain it back.
- Following a healthy eating plan. It is important to reduce the amount of calories you eat and drink each day, so you can lose weight and keep it off. To do that, your diet should include smaller portions and less fat and sugar. You should also eat a variety of foods from each food group, including plenty of whole grains, fruits, and vegetables. It's also a good idea to limit red meat, and avoid processed meats.
- Get regular exercise. Exercise has many health benefits , including helping you to lose weight and lower your blood sugar levels. These both lower your risk of type 2 diabetes. Try to get at least 30 minutes of physical activity 5 days a week. If you have not been active, talk with your health care professional to figure out which types of exercise are best for you. You can start slowly and work up to your goal.
- Don't smoke. Smoking can contribute to insulin resistance, which can lead to type 2 diabetes. If you already smoke, try to quit .
- Talk to your health care provider to see whether there is anything else you can do to delay or to prevent type 2 diabetes. If you are at high risk, your provider may suggest that you take one of a few types of diabetes medicines .
NIH: National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases
- Diabetes Prevention: 5 Tips for Taking Control (Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research) Also in Spanish
- Diabetes Risk Factors (American Heart Association)
- Prevent Type 2 Diabetes in Kids (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention)
- Simple Steps to Preventing Diabetes (Harvard School of Public Health)
Clinical Trials
Journal articles references and abstracts from medline/pubmed (national library of medicine).
- Article: Reach and Weight Loss Among Comparison Group Participants Who Enrolled in...
- Article: Using the Translating Research into Practice framework to develop a diabetes...
- Article: Higher habitual intakes of flavonoids and flavonoid-rich foods are associated with...
- How to Prevent Diabetes -- see more articles
The information on this site should not be used as a substitute for professional medical care or advice. Contact a health care provider if you have questions about your health.
A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
A lock ( ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- Risk Factors
- Providing Care
- Living with Diabetes
- Clinical Guidance
- DSMES for Health Care Providers
- Prevent Type 2 Diabetes: Talking to Your Patients About Lifestyle Change
- Employers and Insurers
- Community-based Organizations (CBOs)
- Toolkits for Diabetes Educators and Community Health Workers
- National Diabetes Statistics Report
- Reports and Publications
- Data and Statistics
- Current Research Projects
Related Topics:
- Show All Home
- National Diabetes Prevention Program
- State, Local, and National Partner Diabetes Programs for Public Health
- Diabetes Self-Management Education and Support (DSMES) Toolkit
What to know
The lifestyle change program that is part of the CDC-led National Diabetes Prevention Program is proven to help prevent or delay type 2 diabetes.
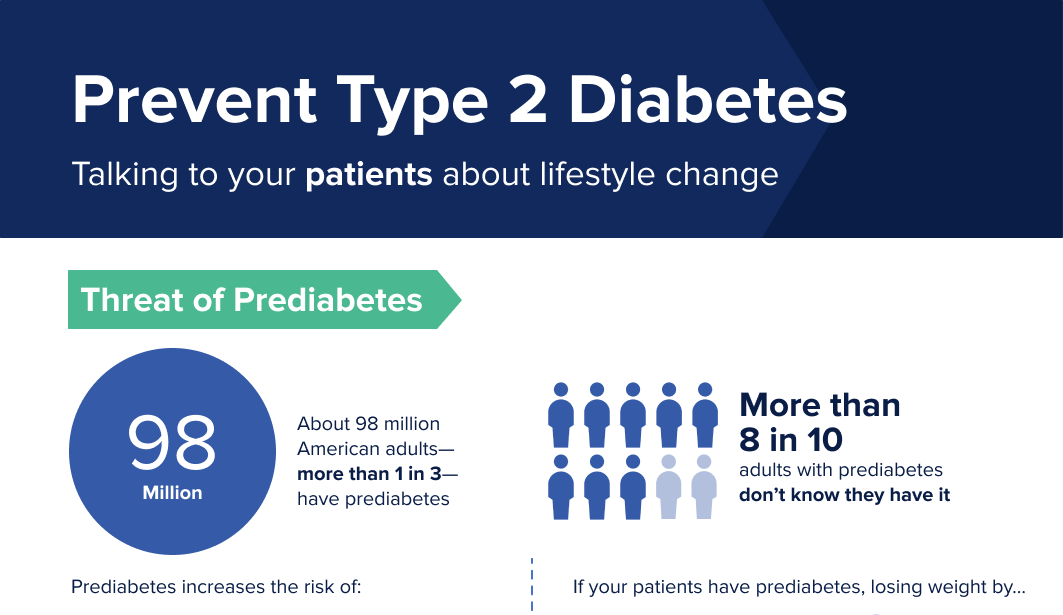
Additional formats
- Print Ready [PDF – 159 KB]
- Larger version [JPG]
Graphic text
Prevent type 2 diabetes.
Talking to your patients about lifestyle change.
Threat of Prediabetes
About 98 million American adults— more than 1 in 3 —have prediabetes.
More than 8 in 10 adults with prediabetes don't know they have it.
Prediabetes increases the risk of:
- Type 2 Diabetes
- Heart Disease
If your patients have prediabetes, losing weight by eating healthy and being more active can cut their risk of getting type 2 diabetes in half.
Lifestyle Change Program
The lifestyle change program that is part of the CDC-led National Diabetes Prevention Program is proven to help prevent or delay type 2 diabetes . It is based on research that showed:
- 58% lower incidence of type 2 diabetes after weight loss of 5 to 7% of body weight achieved by reducing calories and increasing physical activity to at least 150 minutes per week.
- 71% reduced incidence of type 2 diabetes for people 60 and older.
- 27% lower incidence of type 2 diabetes in lifestyle change program participants after 15 years.
The lifestyle change program provides:
- A trained lifestyle coach
- CDC-approved curriculum
- Group support over the course of a year
- A full year of in-person or online meetings
Your patients will learn to make achievable and realistic life changes
- Eat healthy
- Manage stress
- Incorporate physical activity into their daily routine
- Solve problems that get in the way of healthy changes
Patient Eligibility
- 18 years or older, and
- Overweight, and
- Diagnosed with prediabetes or previously diagnosed with gestational diabetes
How you can help your patients
- Test your at-risk patients for prediabetes.
- Refer your patients with prediabetes to a CDC-approved lifestyle change program.
Learn more from CDC and find an approved lifestyle change program at: www.cdc.gov/diabetes-prevention
Diabetes is a chronic disease that affects how your body turns food into energy. About 1 in 10 Americans has diabetes.
For Everyone
Health care providers, public health.

Body Paragraph
Ai generator.
Whether you’re crafting an essay , report , or any other form of written communication, the body paragraphs serve as the heart of your composition. They provide the substantive content that supports your main ideas, arguments, or points. Understanding how to construct compelling body paragraphs is essential for conveying your message effectively and persuasively. In this guide, we’ll delve into the definition of body paragraphs, explore the step-by-step process to create them, address common FAQs, and highlight their significance in written communication.
What is a Body Paragraph?
A body paragraph is a section of an essay that develops a single main idea, supported by evidence, examples, and explanations. Each body paragraph typically starts with a topic sentence, followed by supporting details, and concludes with a sentence that reinforces the paragraph’s main point or transitions to the next idea. Effective body paragraphs help to structure and advance the essay’s argument.
Body Paragraph Format
Body paragraphs form the core of an essay, providing the details and evidence that support the thesis statement . A well-structured body paragraph enhances clarity, flow, and persuasiveness in writing . Here’s a guide to constructing effective body paragraphs:
1. Topic Sentence
The topic sentence introduces the main idea of the paragraph. It should be clear, concise, and directly related to the thesis statement.
- Example : “Regular exercise significantly improves mental health.”

2. Explanation
Expand on the topic sentence by providing a brief explanation or elaboration. This helps to clarify the main idea and set up the evidence.
- Example : “Engaging in physical activities releases endorphins, which are natural mood lifters.”
3. Evidence
Present specific evidence to support the main idea. This can include quotes, statistics, examples, or research findings.
- Example : “A study by the Mayo Clinic found that participants who exercised regularly reported a 30% decrease in symptoms of depression and anxiety.”
4. Analysis
Analyze the evidence to show how it supports the topic sentence. Explain the significance and implications of the evidence.
- Example : “This decrease in mental health symptoms highlights the profound impact of physical activity on psychological well-being, suggesting that regular exercise can be an effective non-pharmaceutical treatment for mental health issues.”
5. Transition
Conclude the paragraph by linking back to the thesis or transitioning smoothly to the next paragraph. This helps maintain coherence and flow in the essay.
- Example : “Therefore, incorporating regular exercise into one’s routine can be a crucial step towards improving mental health. Next, we will explore the benefits of exercise on cognitive function.”
Examples of Body Paragraph for Essay
1. the benefits of reading.
Reading regularly enhances cognitive functions. When individuals read, they engage multiple areas of the brain, improving neural connectivity. A study by the University of California found that regular readers exhibit higher levels of brain activity, particularly in areas related to language comprehension and analytical thinking. This increased brain activity suggests that reading not only improves comprehension skills but also enhances critical thinking and problem-solving abilities. Moreover, reading has been linked to a reduced risk of cognitive decline in older adults, further highlighting its long-term benefits. Therefore, incorporating reading into daily routines can significantly boost cognitive health and preserve mental sharpness over time.
2. The Impact of Technology on Education
Technology has revolutionized education by providing greater access to information and resources. With the advent of the internet and digital tools, students can access a vast array of educational materials from anywhere in the world. According to a report by the Pew Research Center, 92% of teachers reported that the internet has a major impact on their ability to access content, resources, and materials for their teaching. This accessibility not only enhances the learning experience but also enables personalized learning, where students can learn at their own pace and according to their interests. Furthermore, educational technologies such as online courses and virtual classrooms have made education more inclusive, reaching students in remote and underserved areas. Consequently, the integration of technology in education has democratized learning, making it more accessible and tailored to individual needs.
3. The Importance of Environmental Conservation
Environmental conservation is crucial for sustaining biodiversity and ensuring the health of our planet. Ecosystems are interdependent, and the loss of one species can have a ripple effect on others. For instance, the decline of bee populations, which are vital pollinators, has significant implications for plant reproduction and agricultural productivity. According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), 75% of the world’s food crops depend, at least in part, on pollination by bees and other insects. This interdependence underscores the importance of protecting species to maintain ecological balance and food security. Additionally, conserving natural habitats helps mitigate climate change by preserving forests that act as carbon sinks. Therefore, concerted efforts in environmental conservation are essential for the well-being of all life forms on Earth and the stability of our ecosystems.
4. The Advantages of Learning a Second Language
Learning a second language enhances cognitive abilities and cultural understanding. Bilingual individuals often exhibit improved memory, problem-solving skills, and multitasking abilities. Research from Pennsylvania State University indicates that bilingualism can delay the onset of Alzheimer’s disease by up to five years. This cognitive boost is attributed to the mental exercise of switching between languages and processing complex linguistic structures. Moreover, learning a new language fosters cultural empathy and global awareness. It allows individuals to better understand and appreciate cultural differences, promoting tolerance and reducing prejudice. In an increasingly interconnected world, these skills are invaluable, making bilingualism a significant asset both personally and professionally.
5. The Role of Physical Exercise in Health
Physical exercise plays a pivotal role in maintaining overall health and well-being. Regular physical activity helps control weight, reduce the risk of chronic diseases, and improve mental health. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) states that adults who engage in moderate-intensity exercise for at least 150 minutes per week lower their risk of heart disease, stroke, and diabetes. Additionally, exercise promotes the release of endorphins, which are natural mood lifters, reducing symptoms of depression and anxiety. Engaging in physical activities also enhances sleep quality, boosts energy levels, and improves muscle and bone strength. Consequently, incorporating regular exercise into one’s lifestyle is essential for physical and mental health, leading to a better quality of life.
Examples of Body Paragraph for Argumentative Essay
1. the case for universal healthcare.
Universal healthcare is essential for ensuring that all citizens have access to necessary medical services. In countries with universal healthcare, individuals do not have to worry about the financial burden of medical expenses, which can lead to better overall public health outcomes. For instance, a study conducted by the Commonwealth Fund found that countries with universal healthcare systems, such as Canada and the United Kingdom, have higher life expectancy and lower infant mortality rates compared to the United States. This data suggests that when people have access to healthcare without financial barriers, they are more likely to seek preventive care and treatment for illnesses, leading to healthier populations. Moreover, universal healthcare can reduce economic inequality by alleviating the financial strain on low-income families who might otherwise be unable to afford medical care. Therefore, implementing a universal healthcare system is a necessary step towards a healthier, more equitable society.
2. The Need for Renewable Energy
Investing in renewable energy sources is crucial for combating climate change and ensuring sustainable development. Fossil fuels, such as coal and oil, contribute significantly to greenhouse gas emissions, which are the primary drivers of global warming. According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), renewable energy sources like wind, solar, and hydropower produce little to no greenhouse gases during operation. This makes them a much cleaner alternative to traditional energy sources. Additionally, the renewable energy sector has the potential to create millions of jobs worldwide. The International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) reports that the renewable energy industry employed over 11 million people globally in 2018, a number that is expected to grow as investment in this sector increases. By transitioning to renewable energy, we can significantly reduce our carbon footprint while also fostering economic growth and job creation. Therefore, prioritizing renewable energy investments is imperative for a sustainable future.
3. The Benefits of Online Education
Online education provides greater accessibility and flexibility for students, making it an invaluable tool in modern education. Traditional classroom settings can be restrictive for individuals who have other commitments such as work or family. A report by the National Center for Education Statistics (NCES) shows that the number of students enrolled in at least one online course has steadily increased over the past decade, reaching over 6 million in the United States alone. This rise in online education enrollment demonstrates its growing popularity and effectiveness. Furthermore, online education allows for a personalized learning experience where students can learn at their own pace and revisit material as needed. Studies from the U.S. Department of Education suggest that students in online learning conditions performed modestly better, on average, than those receiving face-to-face instruction. Therefore, embracing online education can enhance learning opportunities and outcomes for a diverse range of students.
4. The Importance of Animal Testing in Medical Research
Animal testing remains a necessary practice for advancing medical research and ensuring the safety of new treatments. Many medical breakthroughs, including vaccines and life-saving treatments, have been developed through research conducted on animals. For instance, the polio vaccine, which has nearly eradicated the disease globally, was developed through extensive animal testing. Without such testing, it would have been impossible to ensure the vaccine’s effectiveness and safety. Moreover, regulatory agencies like the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) require animal testing to evaluate the safety of new drugs before they can be approved for human trials. This process helps protect human participants from potential adverse effects. While it is crucial to continue seeking alternative methods, current scientific capabilities still rely on animal testing to a significant extent. Therefore, until reliable and effective alternatives are found, animal testing remains an essential component of medical research.
5. The Impact of Social Media on Society
Social media has a profound impact on society, influencing everything from communication to mental health. Platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram have revolutionized the way people interact, share information, and stay connected. However, research indicates that excessive use of social media can lead to negative mental health outcomes. A study published in the Journal of Social and Clinical Psychology found that individuals who limited their social media use to 30 minutes per day reported significant reductions in feelings of loneliness and depression. This suggests that while social media can facilitate connection, overuse can exacerbate feelings of isolation and anxiety. Additionally, the spread of misinformation on social media platforms poses a significant threat to public discourse and democratic processes. Therefore, it is essential to promote responsible use of social media and implement measures to combat misinformation to mitigate its negative impacts on society.
Examples of Body Paragraph for Informative Essay
1. the history of the internet.
The internet has a rich history that dates back to the early days of computer networking. The concept of a global network began in the 1960s with the creation of ARPANET, funded by the United States Department of Defense. ARPANET, which stands for Advanced Research Projects Agency Network, was the first network to implement the TCP/IP protocol suite, which became the foundation of the modern internet. In the 1980s, the development of personal computers and the World Wide Web, invented by Tim Berners-Lee in 1989, revolutionized how information was shared and accessed. The introduction of web browsers, like Mosaic and Netscape, in the early 1990s made the internet more user-friendly and accessible to the general public. This period marked the beginning of the internet’s rapid expansion and integration into everyday life, leading to the interconnected digital world we experience today.
2. The Benefits of a Balanced Diet
A balanced diet is essential for maintaining good health and well-being. Consuming a variety of foods ensures that the body receives the necessary nutrients it needs to function properly. For example, fruits and vegetables are rich in vitamins and minerals, which support immune function and reduce the risk of chronic diseases. Protein-rich foods, such as lean meats, beans, and nuts, are crucial for muscle repair and growth, while whole grains provide sustained energy and help regulate blood sugar levels. According to the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, a balanced diet that includes a wide range of nutrients can improve overall health and reduce the risk of conditions like heart disease, diabetes, and obesity. Furthermore, staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water is also a key component of a balanced diet, as it aids digestion and helps maintain body temperature. Therefore, incorporating a variety of nutrient-rich foods into one’s diet is fundamental to achieving and maintaining optimal health.
3. The Role of Technology in Modern Education
Technology plays a pivotal role in modern education, transforming the way students learn and teachers instruct. With the advent of digital tools and online resources, educational opportunities have expanded significantly. For instance, interactive software and applications make learning more engaging and personalized, catering to individual student needs. According to a report by the National Education Association (NEA), technology in the classroom has been shown to improve student motivation and academic performance. Moreover, online learning platforms, such as Coursera and Khan Academy, provide access to a vast array of courses and educational materials, enabling lifelong learning beyond the traditional classroom setting. These resources allow students to learn at their own pace and revisit difficult concepts as needed. Consequently, the integration of technology in education not only enhances learning experiences but also prepares students for a digital future.
4. The Importance of Environmental Conservation
Environmental conservation is crucial for preserving the planet’s biodiversity and natural resources. Human activities, such as deforestation, pollution, and overfishing, have led to significant environmental degradation. For example, the destruction of rainforests not only results in the loss of countless species but also contributes to climate change by reducing the Earth’s capacity to absorb carbon dioxide. The World Wildlife Fund (WWF) reports that approximately 27% of the Amazon rainforest has been destroyed in the past 50 years, posing a severe threat to global biodiversity. Conservation efforts, such as protecting natural habitats, promoting sustainable practices, and reducing carbon emissions, are essential to mitigate these impacts. By implementing and supporting conservation initiatives, we can help ensure that natural ecosystems remain intact for future generations. Therefore, environmental conservation is a responsibility that must be shared by individuals, communities, and governments worldwide.
5. The Advantages of Learning a Second Language
Learning a second language offers numerous cognitive, social, and professional benefits. Research indicates that bilingual individuals often have better cognitive flexibility, which is the ability to switch between tasks and think about multiple concepts simultaneously. A study published in the journal Psychological Science found that bilingualism can enhance executive function, which includes skills such as problem-solving, memory, and attention control. In addition to cognitive advantages, knowing a second language can improve cultural awareness and communication skills. This is particularly valuable in today’s globalized world, where cross-cultural interactions are common. Professionally, bilingualism can open up job opportunities and enhance career prospects in various fields, such as international business, translation, and diplomacy. Therefore, investing time and effort in learning a second language can yield significant personal and professional rewards.
Examples of Body Paragraph for Research Paper
1. the effects of climate change on polar bear populations.
Climate change has significantly impacted polar bear populations, primarily through the loss of their sea ice habitat. Polar bears rely on sea ice as a platform for hunting seals, their primary food source. According to a study by the National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC), the Arctic sea ice extent has declined by approximately 13% per decade since the late 1970s. This reduction in sea ice forces polar bears to travel greater distances and expend more energy to find food, leading to malnutrition and decreased survival rates, especially among cubs. Moreover, a report by the World Wildlife Fund (WWF) indicates that the shrinking ice habitat also increases the likelihood of human-polar bear conflicts as bears venture closer to human settlements in search of food. These findings underscore the urgent need for comprehensive climate policies to mitigate the effects of global warming and protect polar bear populations.
2. The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare
Artificial intelligence (AI) has revolutionized healthcare by enhancing diagnostic accuracy and improving patient outcomes. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of medical data, identifying patterns that may not be evident to human clinicians. For instance, a study published in Nature Medicine demonstrated that an AI system could diagnose skin cancer with greater accuracy than dermatologists, achieving a sensitivity rate of 95% compared to 86.6% for human experts. This capability allows for earlier detection and treatment of diseases, potentially saving lives. Additionally, AI-driven predictive analytics can help in managing chronic conditions by forecasting disease progression and suggesting personalized treatment plans. According to a report by Accenture, AI applications in healthcare could save the U.S. healthcare economy up to $150 billion annually by 2026 through efficiencies and improved outcomes. These advancements highlight the transformative potential of AI in making healthcare more efficient, accurate, and accessible.
3. The Impact of Social Media on Political Polarization
Social media has played a significant role in exacerbating political polarization by creating echo chambers and facilitating the spread of misinformation. Algorithms on platforms like Facebook and Twitter often promote content that aligns with users’ existing beliefs, reinforcing their viewpoints and isolating them from opposing perspectives. A study by the Pew Research Center found that 62% of Americans get their news from social media, where they are more likely to encounter sensationalized and biased information. This selective exposure can deepen ideological divides and reduce the likelihood of constructive political discourse. Moreover, research published in Science revealed that false news stories on social media spread six times faster than true stories, further fueling division and mistrust. These findings indicate that social media not only mirrors but also amplifies societal divisions, necessitating interventions to promote media literacy and responsible content sharing.
4. The Benefits of Bilingual Education Programs
Bilingual education programs offer significant cognitive and academic benefits to students. Studies have shown that bilingual individuals possess enhanced executive function, which includes skills such as problem-solving, multitasking, and memory. For example, research conducted by the American Psychological Association (APA) indicates that bilingual children outperform monolingual peers in tasks that require switching attention and inhibiting distractions. These cognitive advantages translate into academic success, with bilingual students often achieving higher scores in standardized tests. Additionally, a longitudinal study by the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) found that students enrolled in dual-language programs were more likely to graduate high school and attend college compared to their monolingual counterparts. These outcomes suggest that bilingual education not only supports cognitive development but also enhances long-term educational achievement. Therefore, expanding access to bilingual programs can provide substantial benefits to students and society as a whole.
5. The Economic Impact of Renewable Energy Adoption
Adopting renewable energy sources has significant positive impacts on the economy, including job creation and energy security. The transition to renewable energy requires a substantial workforce to manufacture, install, and maintain technologies such as solar panels and wind turbines. According to the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), the renewable energy sector employed over 11 million people globally in 2018, with job numbers expected to rise as investment in this sector increases. This job creation can stimulate economic growth, particularly in regions struggling with unemployment. Furthermore, renewable energy reduces dependence on imported fuels, enhancing national energy security and price stability. A report by the U.S. Department of Energy highlights that increased use of domestic renewable energy sources can protect the economy from fluctuations in global fossil fuel markets. Thus, the economic benefits of renewable energy adoption extend beyond environmental considerations, offering substantial advantages for employment and national security.
Examples of Body Paragraph for Students
1. the importance of time management for students.
Effective time management is crucial for students to achieve academic success and maintain a healthy work-life balance. Properly managing time allows students to prioritize tasks, ensuring that important assignments and study sessions are completed efficiently. For instance, a study by the University of California, Berkeley found that students who practiced time management techniques, such as using planners and setting specific goals, achieved higher grades and reported lower stress levels. By breaking down larger tasks into smaller, manageable steps, students can avoid last-minute cramming and reduce anxiety. Moreover, time management skills are not only beneficial for academic purposes but also for extracurricular activities and personal life. Students who balance their schedules effectively can participate in sports, hobbies, and social events, contributing to their overall well-being and personal development. Therefore, mastering time management is essential for students to succeed academically and enjoy a balanced lifestyle.
2. The Benefits of Extracurricular Activities
Participating in extracurricular activities offers numerous benefits that enhance students’ educational experiences and personal growth. Engaging in activities such as sports, clubs, and arts programs helps students develop essential skills that are not typically taught in the classroom. For example, involvement in team sports teaches valuable lessons in teamwork, leadership, and perseverance. According to a report by the National Center for Education Statistics (NCES), students who participate in extracurricular activities are more likely to have higher academic achievement and better attendance records. These activities also provide opportunities for students to explore their interests and talents, which can influence their future career choices and aspirations. Additionally, extracurricular involvement fosters a sense of belonging and community, helping students build friendships and support networks. Thus, engaging in extracurricular activities is instrumental in promoting well-rounded development and enriching the overall educational experience for students.
3. The Impact of Nutrition on Academic Performance
Proper nutrition plays a vital role in students’ academic performance and overall health. Consuming a balanced diet that includes a variety of nutrients helps maintain energy levels, improve concentration, and enhance cognitive function. A study published in the Journal of School Health found that students who ate a nutritious breakfast performed better on standardized tests and had higher attendance rates compared to those who skipped breakfast. Healthy eating habits also contribute to better mood regulation and reduced stress, which are important for academic success. For instance, foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as fish and flaxseeds, have been shown to support brain health and improve memory. Schools that implement nutrition education programs and provide healthy meal options can significantly impact students’ learning outcomes. Therefore, promoting proper nutrition is essential for students to achieve their full academic potential and maintain overall well-being.
4. The Advantages of Using Technology in the Classroom
Integrating technology into the classroom offers numerous advantages that enhance the learning experience for students. Digital tools and resources make learning more interactive and engaging, catering to different learning styles and needs. For instance, educational apps and online platforms allow students to practice skills at their own pace and receive immediate feedback. According to a report by the U.S. Department of Education, schools that utilize technology effectively see improvements in student motivation and achievement. Technology also facilitates access to a wealth of information and educational materials, enabling students to conduct research and expand their knowledge beyond the textbook. Furthermore, incorporating technology prepares students for the digital world, equipping them with essential skills for future careers. Thus, the use of technology in education not only enhances academic performance but also prepares students for success in a technologically advanced society.
5. The Importance of Reading for Pleasure
Reading for pleasure is an important habit that benefits students academically and personally. Engaging in recreational reading improves literacy skills, vocabulary, and comprehension. A study by the National Literacy Trust found that students who read for enjoyment are more likely to perform better academically, particularly in language and literacy subjects. Additionally, reading for pleasure enhances creativity and imagination, allowing students to explore new ideas and perspectives. For example, reading fiction can increase empathy by helping students understand and relate to characters’ experiences and emotions. Beyond academic benefits, reading provides a relaxing escape from the pressures of school and daily life, promoting mental well-being. Therefore, encouraging students to read for pleasure is essential for their overall development and success.
More Examples & Samples of Body Paragraph in PDF
1. developing body paragraphs example.
2. Strong Body Paragraphs Example

3. Body Paragraph Structure and Development

4. Basic Body Paragraphs Example

5. How to Write Body Paragraphs Example

6. Purpose of a Body Paragraph Example

Parts of a Body Paragraph
A well-constructed body paragraph is essential for a coherent and persuasive essay. Each body paragraph should support the main thesis of the essay and contribute to the overall argument or analysis. Here are the key parts of a body paragraph:
The topic sentence introduces the main idea of the paragraph. It should be clear, concise, and directly related to the thesis statement of the essay.
- Example : “Effective time management is crucial for students to achieve academic success.”
The explanation elaborates on the topic sentence, providing context or a brief overview of the main idea. It sets up the evidence and analysis that will follow.
- Example : “Properly managing time allows students to prioritize tasks, ensuring that important assignments and study sessions are completed efficiently.”
Evidence provides specific support for the main idea. This can include quotes, statistics, examples, or research findings. Evidence makes the argument more credible and persuasive.
- Example : “A study by the University of California, Berkeley found that students who practiced time management techniques, such as using planners and setting specific goals, achieved higher grades and reported lower stress levels.”
The analysis explains how the evidence supports the topic sentence. It connects the evidence to the main idea and shows the significance or implications of the evidence.
- Example : “By breaking down larger tasks into smaller, manageable steps, students can avoid last-minute cramming and reduce anxiety, leading to better academic performance.”
5. Transition or Concluding Sentence
The transition or concluding sentence links back to the thesis or sets up the next paragraph. It ensures coherence and flow in the essay.
- Example : “Therefore, mastering time management is essential for students to succeed academically and enjoy a balanced lifestyle.”
How to Start a Body Paragraph
Starting a body paragraph effectively is essential for maintaining coherence and ensuring that each paragraph contributes meaningfully to the essay. Here are key steps and tips for starting a body paragraph:
1. Craft a Strong Topic Sentence
The topic sentence is the most important part of the body paragraph. It introduces the main idea of the paragraph and ties it to the thesis statement.
- Example : “Implementing renewable energy sources is essential for reducing greenhouse gas emissions.”
2. Connect to the Thesis Statement
Ensure that the topic sentence clearly relates to and supports the essay’s thesis statement. This connection helps maintain the overall coherence of the essay.
- Example : “Given the urgent need to address climate change, implementing renewable energy sources is essential for reducing greenhouse gas emissions.”
3. Use Transition Words or Phrases
If the paragraph follows another body paragraph, use transition words or phrases to create a smooth flow of ideas. This helps guide the reader through the argument or analysis.
- Example : “Moreover, implementing renewable energy sources is essential for reducing greenhouse gas emissions.”
4. Introduce the Main Idea Clearly
State the main idea in a way that is easy to understand and sets up the explanation and evidence that will follow.
- Example : “Implementing renewable energy sources is essential for reducing greenhouse gas emissions, as it offers a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels.”
How to End a Body Paragraph
Ending a body paragraph effectively is crucial for maintaining the flow and coherence of your essay. A strong concluding sentence can reinforce your main point, connect to the thesis, and provide a smooth transition to the next paragraph. Here are key steps and tips for ending a body paragraph:
1. Summarize the Main Point
Briefly restate the main idea of the paragraph without repeating it verbatim. This reinforces the point you’ve made.
- Example : “Therefore, renewable energy sources are essential for reducing greenhouse gas emissions.”
2. Connect to the Thesis
Ensure that the concluding sentence links back to the thesis statement, reinforcing how the paragraph supports the overall argument.
- Example : “This reduction in emissions is a critical step in combating climate change, aligning with the global effort to create a more sustainable future.”
3. Provide a Transition
Use a transitional phrase or sentence to smoothly lead into the next paragraph. This helps maintain coherence and guides the reader through your essay.
- Example : “As we explore further, the economic benefits of renewable energy adoption also become apparent.”
4. Avoid Introducing New Information
Do not introduce new arguments or evidence in the concluding sentence. The focus should be on wrapping up the current paragraph and preparing for the next one.
How to Write a Body Paragraph

1. Start with a Topic Sentence
- Purpose : Introduce the main idea of the paragraph.
- Example : “One of the most significant advantages of renewable energy is its positive impact on the environment.”
2. Provide an Explanation
- Purpose : Clarify the topic sentence and provide context.
- Example : “Renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, produce little to no greenhouse gas emissions during their operation.”
3. Present Evidence
- Purpose : Support the main idea with relevant data, quotes, or examples.
- Example : “According to a 2020 report by the International Energy Agency, solar power capacity grew by 22% worldwide, reducing CO2 emissions by approximately 1.2 billion tons annually.”
4. Include Analysis
- Purpose : Explain how the evidence supports the main idea.
- Example : “This significant reduction in emissions highlights how transitioning to renewable energy sources can mitigate climate change, a pressing global issue.”
5. Conclude with a Closing Sentence
- Purpose : Summarize the paragraph’s main point and transition to the next paragraph.
- Example : “Therefore, the shift to renewable energy is not only beneficial for reducing environmental harm but also essential for sustainable development.”
How long should a body paragraph be?
A body paragraph typically ranges from 5-8 sentences or 150-200 words, balancing detail and clarity without overwhelming the reader.
What is the purpose of a topic sentence?
A topic sentence introduces the main idea of the paragraph and sets the tone for the content that follows.
How can I ensure coherence in my body paragraph?
Use transitional words and phrases, maintain a logical flow of ideas, and ensure all sentences relate to the main idea.
What types of evidence can I use?
Use facts, statistics, quotes, examples, and anecdotes from credible sources to support your main idea effectively.
Why is analysis important in a body paragraph?
Analysis explains how your evidence supports your main idea, demonstrating critical thinking and deepening the reader’s understanding.
How do I transition between body paragraphs?
Use transitional sentences or phrases that connect the ideas of consecutive paragraphs, maintaining a smooth flow throughout your essay.
What should a closing sentence do?
A closing sentence should summarize the paragraph’s main point and provide a transition to the next paragraph.
Can I use personal experiences as evidence?
Yes, personal anecdotes can be powerful evidence, especially in narrative or persuasive essays, if they are relevant and support your point.
How many body paragraphs should an essay have?
The number of body paragraphs depends on the essay’s length and complexity, but typically ranges from 3-5 for standard essays.
What common mistakes should I avoid in body paragraphs?
Avoid vague topic sentences, lack of evidence, poor transitions, and irrelevant details that do not support the main idea.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
How To Write Better Essays: 5 Outside-the-Box Techniques + Writing Tips

Table of contents

Brinda Gulati
Stuck on a B, chasing that A+? We've all been there.
I have two degrees in Creative Writing from the University of Warwick with First Class Honors. From 2013 to 2014, I also studied English Literature at the National University of Singapore.
Translation: I’ve written a lot of academic essays.
Some good. Some inspired. And others, plain lousy.
After a few Bs and the occasional C, I cracked the code on writing good essays. An average academic essay answers a question; but an essay that gets an A+ solves a problem — whether through discussion, analysis, definition, comparison, or evaluation.
In this blog post, I’ll walk you through how to write better essays. You’ll learn how to construct bullet-proof arguments with five unique thinking techniques, cut the fluff, and discover F.O.C.U.S. to improve your essay writing skills.
Because essays don’t have to be boring. And writing them doesn’t have to either.
What Makes A Good Essay?
What is “good” writing? The answer is subjective. For example, I loved reading My Year of Rest and Relaxation by Ottessa Moshfegh, but to some, it might be drivel.
Nonetheless, many examples of good writing share some core qualities.
There are five overarching qualities of good essay writing : flow, organization, clarity, unity, and specificity.
I’ve made a fun little acronym to help you remember them better: F.O.C.U.S.™️
F low: Does the writing flow smoothly from one point to the next?
O rganization: Have you structured your essay with a clear beginning, middle, and end?
C larity: Is the writing clear, error-free, and unambiguous?
U nity: Are all the elements of your writing supporting the central thesis?
S pecificity: Have you provided specific details, examples, and evidence to justify your main points?
A Fellow at The European Graduate School, and my most cherished mentor, Dr. Jeremy Fernando , has perhaps read, written, and graded thousands of academic essays over the years.
His advice?
“You’re asking the reader to go on an explorative journey with you; the least you should do is ensure the trip you’re taking them on is the same as the advertised one.”
5 Creative Thinking Techniques For Writing Better Essays
The thing is, good essay writing doesn’t start at — or even as — writing .
There’s reading, re-reading, pre-writing, revising, then actually writing, editing, and then writing some more.
As with most persuasive arguments , you need frameworks: points of reference, mental models, and structured approaches to guide your decision making.
That's exactly what we have here.
1. Try Reverse Outlining
A reverse outline is just what it sounds like: a process that distills a paper down to its bare essentials, leaving only the key points and topic sentences. The result? A clear, bullet-point blueprint of the paper's structure, whether it's your own work or someone else's.
Key Benefits:
✅Creates an X-ray of a paper's structure to identify its central arguments and assess its logical flow.
✅Helps you actively engage with someone else’s work to deepen your understanding of the material.
✅Reveals structural issues in your own essay, such as missing or misplaced points, redundancies, or weak arguments.
How To Create A Reverse Outline:
This is a two-step, and perhaps infinitely repeatable process.
Take a blank page and draw a line straight down the middle.
- In the left-hand margin, write down the keywords for each paragraph in your essay. Stick to the main points. Be brief.
- In the right-hand margin, write down how the keyword or topic supports the main argument. Again, don't sit down to write Bonfire of the Vanities . Make it concise . The goal is to persuasively explain your arguments in a few words.
2. Practice The Lotus Blossom Technique
In this structured brainstorming exercise, you plant your main problem in the center box of a 3x3 grid. Then, you’ll fill the surrounding boxes with related themes to expand your thinking. The method was developed by Yasuo Matsumura at Clover Management Research in Japan.
Key Benefits:
✅ A fun, novel alternative to traditional mind-mapping and spider-diagramming.
✅Helps you visualize your essay slowly unfolding from its core. (Like a lotus, basically.)
✅I like how it's creative and thorough at the same time. An equal combination of freedom and structure.

How To Practice The Lotus Blossom Technique:
- Put your problem/essay question in the center square.
- Fill in the surrounding eight boxes with ideas related to the problem. At this point, you don’t need to elaborate.
- Now, flesh out each of your eight ideas. Or, as with the lotus flower image — add another row of petals.

When all your boxes are filled in, you'll have 64 ideas for one essay argument. As far as starting-off points go, this one’s hard to beat.
Pro Tip : Did you know that dim light is a creative stimulant? Go dark. Light some candles.
3. Build A Toulmin Argument Model
According to philosopher Stephen E. Toulmin, arguments are broken down into six key components: claim, grounds, warrant, qualifier, rebuttal, and backing.
There are three essential parts to every argument: the claim, the grounds, and the warrant.
- The claim is the main argument you want to prove to your audience.
- The grounds of an argument are the evidence and facts that support it.
- The warrant is the assumption which links a claim to its grounds, whether implied or explicitly stated.
✅Craft persuasive arguments through an in-depth analysis that closely examines each part of your essay.
✅Analyzing an argument from its components can help clarify its logic.
✅The rebuttal component encourages you to anticipate and address counterarguments. The more perspectives you consider, the more well-rounded your argument will be.
How To Build A Toulmin Argument Model:
Let’s take a published paper — “ Coffee and Health: A Review of Recent Human Research ” by Jane V. Higdon and Balz Frei — and break it down using the Toulmin model.
Get Wordtune for free > Get Wordtune for free >
- Claim: Consuming moderate amounts of coffee (3-4 cups a day with 300-400 mg of caffeine) has few health risks and some health benefits. Nevertheless, caffeine may be more harmful to pregnant women, children, adolescents, and the elderly.
- Grounds: According to epidemiological studies, coffee may prevent diabetes type 2, Parkinson's disease, and liver disease.
- Warrant: Studies suggest that coffee consumption in moderation may have some health benefits and poses minimal health risks.
- Backing : A number of well-designed prospective cohort studies with large sample sizes are cited as supporting evidence.
- Qualifier: This study applies specifically to healthy adults who consume moderate amounts of filtered coffee. Optimal intake hasn’t been defined.
- Rebuttal: Some may be more sensitive to negative effects. Further research is needed.
I don’t know about you, but I often get convinced of my own arguments when writing essays, and then it’s hard for me to consider other perspectives.
So, if you want a sparring buddy, here’s how Wordtune can help you with counterarguments:
First, I’ve copy-pasted our claim from above 👇🏼

Next, click on the little purple sparkle icon and choose “Counterargument” from the drop-down menu.

Lo and behold! Not only does Wordtune provide accurate contextual suggestions for a convincing opposing opinion, it goes one step further and cites a clickable source for the research .
Nothing short of time-saving magic , if you ask me.
4. Ask The Five Whys
You need to ask “why” five times to get to the root of any problem. That’s what the inventor of the method, and founder of Toyota Industries, Sakichi Toyoda, believed.
✅The approach identifies the real problem, not just its surface symptoms.
✅It’s an easy-to-do and straightforward process that gets to the heart of your essay question.
✅Use this approach in combination with the Toulmin Model to build a killer essay argument.
Asking The Five Whys:
Let’s look at a sample essay question and drill down to its core.

When you have the core of the problem in your palm, you can then start thinking of solutions. Perhaps finding more cost-effective ways to train and support teachers. Or exploring alternative funding options, such as grants and partnerships with local businesses.
5. Experiment With The Ben Franklin Exercise
Franklin wasn’t always a prodigious scholar. While working at a print shop, he reverse engineered the prose from the British magazine, The Spectator , to learn how to write better without a tutor.
He took detailed notes at a sentence level, contemplated them for some time, and then re-created the sentences without looking at the originals.
In fact, research from MIT shows that it's “not just the study of tiny details that accelerates learning; the act of assembling those details yourself is what makes the difference.” This is called constructionist learning.
✅Improve your essay writing by studying works of skilled authors through practiced imitation.
✅Organizing your notes from memory will help you construct a solid structure for your essay, and evaluate any gaps in logic and flow.
✅Actively deconstructing and constructing the material allows you to engage deeply with it, and therefore, write better essays.
How I Use The Ben Franklin Exercise:
One of my favorite passages in Literature — as clichéd as may it be — is from Chuck Palahniuk’s Fight Club .

- Note how “strongest” and “smartest” are alliterative words, creating a sense of rhythm right in the first sentence.
- The imagery of banality — pumping gas, waiting tables, etc. is at once, vivid and relatable, moving and unmoving.
- The phrase “midddle children of the history man” places the narrative in a broader, more relevant context.
- Notice how the “g” is capitalized for the first mention of war and depression, but then it switches to a small “g” for the same words in the next sentence.
- The repetition of “very very pissed off” is much more effective than simply saving “livid.”
Similarly, start by taking a paragraph from an essay you like. Make sentence-level notes and rewrite its essence without looking at it.
My Top Tips To Write A Good Essay
1. write lousy first drafts.
You heard me. Write as if your keyboard doesn’t have keys for punctuation. Write as if no one is ever going to read your essay. The goal is to eliminate self-censorship . When you first start writing down your main points, don’t assume the role of a self-editor.
TRY THIS : Open a blank page, set a timer for two and a half minutes, and type until the bell goes off. Take a break. Repeat. Don’t re-read what you’ve typed.
Forget proper spelling. Forget good grammar. Those polishes are all for later, when you have something to polish.
This is freewriting.
And it’s wildly effective in getting you to stop thinking about deadlines, blinking cursors, and that A+. My highest-scoring essays have all begun with messy, unstructured, poorly-worded first drafts.
2. Read Other Essays Like A Writer
Think of your favorite book. What makes you call it your favorite? Or a series you’ve watched recently. ( Behind Her Eyes is especially good.) What compels you to see it all the way through? The same principle applies to good essay writing. Have you read an essay in your research that hooked you? Or a friend’s work you wish you could put your name to?
Read like a writer — become a proactive participant in examining why the writing works. Instead of passively drawing stars next to important observations, ask yourself, “ Why do I like these passages? What are they doing? And how are they doing it?” (Use the Ben Franklin Exercise here.)
Take apart the essay you’re reading like a forensic pathologist doing an autopsy.
3. Start With An Outline
Speaking of autopsies, a good essay has good bones. Once you’ve disgorged your ideas on the page, start arranging them under headers.

This blog too, was born in the Notes app on my phone. But if you’re taking the reader with you somewhere, you should know where you’re headed too.
Pro Tip : Keep two working documents for your essay. One where you dump all the links, sources, and keywords. The other is where you work on your final draft for submission.
4. Cut The Fluff
The deadline’s in a few hours and you’re scrambling to hit minimum word count . Long, winding sentences with gratuitous adjectives you’ve just looked up in the thesaurus to sound more cerebral, erudite, scholarly.
I get it. I’ve done it. And those essays have bellyflopped. Professors know when you’re trying to game them.
Here’s an actual sentence from one of my essays I wrote in 2017:
“Ibsen’s realist drama, and in particular, A Doll’s House , is replete with the problems that chapter and verse modern life – the patriarchal model of the family, money and debt, and the performance of gender.”
And much to my embarrassment, this is the scathing comment from my then-professor:
“This makes no sense.”

Let’s rework this sentence to make sense using Wordtune (a clever AI helper I wish I had during my university days):
“The patriarchal family model, money and debt, and gendered performance are all apparent in Ibsen's realist drama, especially A Doll's House .”

Much more sensible.
5. Get Feedback, Edit, And Revise
I can’t emphasize this enough — don’t submit your first draft! Have someone else read it, perhaps a friend in the same class or even from a different major. Look at their eyebrows to see which sections make them frown in confusion.
Ask them to red-pen sentences and logical gaps. And then —- edit, edit edit!
Sleep on it. Let the essay stew in the back of your mind for a full night, and come back to it with fresh eyes.
Start (Pre-)Writing Better Essays
The ability to write persuasively will serve you well no matter what stage of your life you are in: high school, university scholar, or a professional trying to get ahead. After all, the human mind is hardwired for storytelling.
Remember, the key is to F.O.C.U.S.
Whether you’re crawling or speeding towards a deadline, bag that A+ with a smart AI assistant like Wordtune !
Share This Article:

The Dos and Don’ts of Using AI to Study
.webp)
How to Use Modal Verbs for Clear Communication

A Friendly Guide to Apostrophes vs Quotation Marks
Looking for fresh content, thank you your submission has been received.
357 Diabetes Essay Topics & Examples
When you write about the science behind nutrition, heart diseases, and alternative medicine, checking titles for diabetes research papers can be quite beneficial. Below, our experts have gathered original ideas and examples for the task.
🏆 Best Diabetes Essay Examples & Topics
⭐ most interesting diabetes research paper topics, ✅ simple & easy diabetes essay topics, 🎓 good research topics about diabetes, 💡 interesting topics to write about diabetes, 👍 good essay topics on diabetes, ❓ diabetes research question examples.
- Adult-Onset Type 2 Diabetes: Patient’s Profile Any immediate care as well as post-discharge treatment should be explained in the best manner possible that is accessible and understandable to the patient.
- Diabetes Mellitus: Symptoms, Types, Effects Insulin is the hormone that controls the levels of glucose in the blood, and when the pancreas releases it, immediately the high levels are controlled, like after a meal.
- Living With a Chronic Disease: Diabetes and Asthma This paper will look at the main effects of chronic diseases in the lifestyle of the individuals and analyze the causes and the preventive measures of diabetes as a chronic disease.
- Diabetes Mellitus Management in the Elderly Diabetes mellitus is a health complication involving an increase in the concentration in the concentration of blood sugar either due to a failure by cells to effectively respond to the production of insulin in the […]
- Intervention Methods for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus An individual should maintain a regulated glycemic control using the tenets of self-management to reduce the possibility of complications related to diabetes.
- Nursing Care Development Plan for Diabetes and Hypertension In addressing the first nursing diagnosis, the main aim of the nursing interventions will be to prevent the development of secondary hypoglycemia by increasing blood glucose levels.
- Health Promotion: Diabetes Mellitus and Comorbidities This offers a unique challenge in the management of diabetes and other chronic diseases; the fragmented healthcare system that is geared towards management of short-term medical emergencies often is not well prepared for the patient […]
- Relation Between Diabetes And Nutrition Any efforts to lessen and eliminate the risk of developing diabetes must involve the dietary habit of limiting the consumption of carbohydrates, sugar, and fats. According to Belfort-DeAguiar and Dongju, the three factors of obesity, […]
- Diabetes Impact on Cardiovascular and Nervous Systems Diabetes is one of the commonest conditions affecting many people in different parts of the world. The first type is also called “juvenile diabetes” and it occurs when the body of an individual is incapable […]
- Diabetes in Adults in Oxfordshire On a national level, Diabetes Research and Wellness Foundation aims to prevent the spread of the decease through research of the causes and effective treatment of diabetes 2 type.
- Case Study of Patient with DKA and Diabetes Mellitus It is manifested by a sharp increase in glucose levels and the concentration of ketone bodies in the blood, their appearance in the urine, regardless of the degree of violation of the patient’s consciousness.
- Qualitative Research in Diabetes Management in Elderly Patient To achieve the research aim, which is to find out the causes of diabetes among elderly people, the researcher will have to organize the research team.
- Type 2 Diabetes as a Public Health Issue In recent years, a steady increase in the incidence and prevalence of diabetes is observed in almost all countries of the world.
- Diabetes Management Plan: Diagnosis and Development The purpose of this paper is to analyze the provided subjective and objective information to diagnose and develop a management plan for the patient in the case study.
- Gestational Diabetes in a 38-Year-Old Woman The concept map, created to meet B.’s needs, considers her educational requirements and cultural and racial hurdles to recognize her risk factors and interventions to increase her adherence to the recommended course of treatment.B.said in […]
- Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Its Implications You call an ambulance and she is taken in to the ED. Background: Jean is still very active and works on the farm 3 days a week.
- Development of Comprehensive Inpatient and Outpatient Programs for Diabetes Overcoming the fiscal and resource utilization issues in the development of a comprehensive diabetes program is essential for the improvement of health and the reduction of treatment costs.
- Healthcare Cost Depending on Chronic Disease Management of Diabetes and Hypertension A sufficient level of process optimization and the presence of a professional treating staff in the necessary number will be able to help improve the indicators.
- Improving Glycemic Control in Black Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Information in them is critical for answering the question and supporting them with the data that might help to acquire an enhanced understanding of the issue under research. Finally, answering the PICOT question, it is […]
- Shared Decision-Making That Affects the Management of Diabetes The article by Peek et al.is a qualitative study investigating the phenomenon of shared decision-making that affects the management of diabetes. The researchers demonstrate the racial disparity that can arise in the choice of approaches […]
- Managing Obesity as a Strategy for Addressing Type 2 Diabetes When a patient, as in the case of Amanda, requires a quick solution to the existing problem, it is necessary to effectively evaluate all options in the shortest possible time.
- Tests and Screenings: Diabetes and Chronic Kidney Disease The test is offered to patients regardless of gender, while the age category is usually above 45 years. CDC1 recommends doing the test regardless of gender and is conducted once or twice to check the […]
- Obesity Management for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes American Diabetes Association states that for overweight and obese individuals with type 2 diabetes who are ready to lose weight, a 5% weight reduction diet, physical exercise, and behavioral counseling should be provided.
- COVID-19 and Diabetes Mellitus Lim et al, in their article, “COVID-19 and diabetes mellitus: from pathophysiology to clinical management”, explored how COVID-19 can worsen the symptoms of diabetes mellitus.
- The Importance of Physical Exercise in Diabetes II Patients The various activities help to improve blood sugar levels, reduce cardiovascular cases and promote the overall immunity of the patient. Subsequently, the aerobic part will help to promote muscle development and strengthen the bones.
- Diabetes Education Workflow Process Mapping DSN also introduces the patient to the roles of specialists involved in managing the condition, describes the patient’s actions, and offers the necessary educational materials.
- Diabetes: Treatment Complications and Adjustments One of the doctor’s main priorities is to check the compatibility of a patient’s medications. The prescriptions of other doctors need to be thoroughly checked and, if necessary, replaced with more appropriate medication.
- The Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus PICOT (Evidence-Based) Project Blood glucose levels, A1C, weight, and stress management are the parameters to indicate the adequacy of physical exercise in managing T2DM.
- Chronic Disease Cost Calculator (Diabetes) This paper aims at a thorough, detailed, and exhaustive explanation of such a chronic disease as diabetes in terms of the prevalence and cost of treatment in the United States and Maryland.
- Diabetes Mellitus Epidemiology Statistics This study entails a standard established observation order from the established starting time to an endpoint, in this case, the onset of disease, death, or the study’s end. It is crucial to state this value […]
- Epidemiology: Type II Diabetes in Hispanic Americans The prevalence of type II diabetes in Hispanic Americans is well-established, and the search for inexpensive prevention methods is in the limelight.
- Diabetes: Risk Factors and Effects Trends in improved medical care and the development of technology and medicine are certainly contributing to the reduction of the problem. All of the above indicates the seriousness of the problem of diabetes and insufficient […]
- Barriers to Engagement in Collaborative Care Treatment of Uncontrolled Diabetes The primary role of physicians, nurses, and other healthcare team members is to provide patients with medical treatment and coordinate that care while also working to keep costs down and expand access.
- Hereditary Diabetes Prevention With Lifestyle Modification Yeast infections between the fingers and toes, beneath the breast, and in or around the genital organs are the common symptoms of type 2 diabetes.
- Health Equity Regarding Type 2 Diabetes According to Tajkarimi, the number of research reports focusing on T2D’s prevalence and characteristics in underserved minorities in the U. Adapting the program’s toolkits to rural Americans’ eating and self-management habits could also be instrumental […]
- Diabetes Mellitus: Treatment Methods Moreover, according to the multiple findings conducted by Park et al, Billeter et al, and Tsilingiris et al, bariatric surgeries have a positive rate of sending diabetes into remission.
- Diagnosing Patient with Insulin-Dependent Diabetes The possible outcomes of the issues that can be achieved are discussing the violations with the patient’s family and convincing them to follow the medical regulations; convincing the girl’s family to leave her at the […]
- Human Service for Diabetes in Late Adulthood The mission of the Georgia Diabetic Foot Care Program is to make a positive difference in the health of persons living with diabetes.
- Diabetes: Symptoms and Risk Factors In terms of the problem, according to estimates, 415 million individuals worldwide had diabetes mellitus in 2015, and it is expected to rise to 642 million by the year 2040.
- Diabetes: Types and Management Diabetes is one of the most prevalent diseases in the United States caused when the body fails to optimally metabolize food into energy.
- Epidemiology of Diabetes and Forecasted Trends The authors note that urbanization and the rapid development of economies of different countries are the main causes of diabetes. The authors warn that current diabetes strategies are not effective since the rate of the […]
- The Aboriginal Diabetes Initiative in Canada The ADI’s goal in the CDS was to raise type 2 diabetes awareness and lower the incidence of associated consequences among Aboriginal people.
- Communicating the Issue of Diabetes The example with a CGM sensor is meant to show that doctors should focus on educating people with diabetes on how to manage their condition and what to do in extreme situations.
- Obesity and Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 The goal is to define the features of patient information to provide data on the general course of the illness and its manifestations following the criteria of age, sex, BMI, and experimental data.
- The Prevention of Diabetes and Its Consequences on the Population At the same time, these findings can also be included in educational programs for people living with diabetes to warn them of the risks of fractures and prevent them.
- Uncontrolled Type 2 Diabetes and Depression Treatment The data synthesis demonstrates that carefully chosen depression and anxiety treatment is likely to result in better A1C outcomes for the patient on the condition that the treatment is regular and convenient for the patients.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Prevention and Education Schillinger et al.came to the same conclusion; thus, their findings on the study of the Bigger Picture campaign effectiveness among youth of color are necessary to explore diabetes prevention.
- A Diabetes Quantitative Article Analysis The article “Correlates of accelerometer-assessed physical activity and sedentary time among adults with type 2 diabetes” by Mathe et al.refers to the global issue of the prevention of diabetes and its complications.
- A Type 2 Diabetes Quantitative Article Critique Therefore, the main issue is the prevention of type 2 diabetes and its consequences, and this paper will examine one of the scientific studies that will be used for its exploration.
- The Diabetes Prevention Articles by Ford and Mathe The main goal of the researchers was to measure the baseline MVPA of participants and increase their activity to the recommended 150 minutes per week through their participation in the Diabetes Community Lifestyle Improvement Program.
- Type 2 Diabetes in Hispanic Americans The HP2020 objectives and the “who, where, and when” of the problem highlight the significance of developing new, focused, culturally sensitive T2D prevention programs for Hispanic Americans.
- Diabetes Mellitus as Problem in US Healthcare Simultaneously, insurance companies are interested in decreasing the incidence of diabetes to reduce the costs of testing, treatment, and provision of medicines.
- Diabetes Prevention as a Change Project All of these queries are relevant and demonstrate the importance of including people at high risk of acquiring diabetes in the intervention.
- Evidence Synthesis Assignment: Prevention of Diabetes and Its Complications The purpose of this research is to analyze and synthesize evidence of good quality from three quantitative research and three non-research sources to present the problem of diabetes and justify the intervention to address it.
- Diabetes Mellitus: Causes and Health Challenges Second, the nature of this problem is a clear indication of other medical concerns in this country, such as poor health objectives and strategies and absence of resources.
- Diabetes Mellitus (DM) Disorder Case Study Analysis Thus, informing the patient about the importance of regular medication intake, physical activity, and adherence to diet in maintaining diabetes can solve the problem.
- Diabetes Mellitus in Young Adults Thus, programs for young adults should predominantly focus on the features of the transition from adolescence to adulthood. As a consequence, educational programs on diabetes improve the physical and psychological health of young adults.
- A Healthcare Issue of Diabetes Mellitus Diabetes mellitus is seen as a primary healthcare issue that affects populations across the globe and necessitates the combination of a healthy lifestyle and medication to improve the quality of life of people who suffer […]
- Control of LDL Cholesterol Levels in Patients, Gestational Diabetes Mellitus In addition, some patients with hypercholesterolemia may have statin intolerance, which reduces adherence to therapy, limits treatment efficacy, and increases the risk of CVD.
- Exploring Glucose Tolerance and Gestational Diabetes Mellitus In the case of a glucose tolerance test for the purpose of diagnosing GDM type, the interpretation of the test results is carried out according to the norms for the overall population.
- Type 2 Diabetes Health Issue and Exercise This approach will motivate the patient to engage in exercise and achieve better results while reducing the risk of diabetes-related complications.
- Diabetes Interventions in Children The study aims to answer the PICOT Question: In children with obesity, how does the use of m-Health applications for controlling their dieting choices compare to the supervision of their parents affect children’s understanding of […]
- Diabetes Tracker Device and Its Advantages The proposed diabetes tracker is a device that combines the functionality of an electronic BGL tester and a personal assistant to help patients stick to their diet plan.
- Disease Management for Diabetes Mellitus The selection of the appropriate philosophical and theoretical basis for the lesson is essential as it allows for the use of an evidence-based method for learning about a particular disease.
- Latino People and Type 2 Diabetes The primary aim of the study is to determine the facilitators and barriers to investigating the decision-making process in the Latin population and their values associated with type 2 diabetes.
- Diabetes Self-Management Education and Support Program The choice of this topic and question is based on the fact that despite the high prevalence of diabetes among adolescents in the United States, the use of DSMES among DM patients is relatively low, […]
- Diabetes Mellitus Care Coordination The aim is to establish what medical technologies, care coordination and community resources, and standards of nursing practice contribute to the quality of care and safety of patients with diabetes.
- Healthy Lifestyle Interventions in Comorbid Asthma and Diabetes In most research, the weight loss in cases of comorbid asthma and obesity is reached through a combination of dietary interventions and physical exercise programs.
- PDSA in Diabetes Prevention The second step in the “Do” phase would be to isolate a few members of the community who are affected by diabetes voluntarily.
- Diabetes: Statistics, Disparities, Therapies The inability to produce adequate insulin or the body’s resistance to the hormone is the primary cause of diabetes. Diabetes is a serious health condition in the U.S.and the world.
- Type 2 Diabetes Prescriptions and Interventions The disadvantage is the difficulty of obtaining a universal model due to the complexity of many factors that can affect the implementation of recommendations: from the variety of demographic data to the patient’s medical history.
- Health Education for Female African Americans With Diabetes In order to address and inform the public about the challenges, nurses are required to intervene by educating the population on the issues to enhance their understanding of the risks associated with the conditions they […]
- Diabetes Risk Assessment and Prevention It is one of the factors predisposing patients suffering from diabetes to various cardiovascular diseases. With diabetes, it is important to learn how to determine the presence of carbohydrates in foods.
- Diabetes Mellitus: Preventive Measures In addition to addressing the medical specialists who will be of service in disease prevention, it will emphasize the intervention programs required to help control the spread of the illness.
- “The Diabetes Online Community” by Litchman et al. The researchers applied the method of telephone interviews to determine the results and effectiveness of the program. The study described the value of DOC in providing support and knowledge to older diabetes patients.
- Mobile App for Improved Self-Management of Type 2 Diabetes The central focus of the study was to assess the effectiveness of the BlueStar app in controlling glucose levels among the participants.
- Type 2 Diabetes in Minorities from Cultural Perspective The purpose of this paper is to examine the ethical and cultural perspectives on the issue of T2DM in minorities. Level 2: What are the ethical obstacles to treating T2DM in ethnic and cultural minorities?
- Ethics of Type 2 Diabetes Prevalence in Minorities The purpose of this article analysis is to dwell on scholarly evidence that raises the question of ethical and cultural aspects of T2DM prevalence in minorities.
- Type 2 Diabetes in Minorities: Research Questions The Level 2 research questions are: What are the pathophysiological implications of T2DM in minorities? What are the statistical implications of T2DM in minorities?
- Improving Adherence to Diabetes Treatment in Primary Care Settings Additionally, the patients from the intervention group will receive a detailed explanation of the negative consequences of low adherence to diabetes treatment.
- An Advocacy Tool for Diabetes Care in the US To ensure the implementation and consideration of my plea, I sent a copy of the letter to the government officials so it could reach the president.
- Diabetes and Allergies: A Statistical Check The current dataset allowed us to test the OR for the relationship between family history of diabetes and the presence of diabetes in a particular patient: all variables were dichotomous and discrete and could take […]
- Type 2 Diabetes in Adolescents According to a National Diabetes Statistics Report released by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the estimated prevalence of the disease was 25 cases per 10,000 adolescents in 2017. A proper understanding of T2D […]
- Analysis of Diabetes and Its Huge Effects In the US, diabetes is costly to treat and has caused much physical, emotional and mental harm to the people and the families of those who have been affected by the disease.
- Nursing: Self-Management of Type II Diabetes Sandra Fernandes and Shobha Naidu’s journal illustrates the authors’ understanding of a significant topic in the nursing profession.”Promoting Participation in self-care management among patients with diabetes mellitus” article exposes readers to Peplau’s theory to understand […]
- The Impact of Vegan and Vegetarian Diets on Diabetes Vegetarian diets are popular for a variety of reasons; according to the National Health Interview Survey in the United States, about 2% of the population reported following a vegetarian dietary pattern for health reasons in […]
- “Diabetes Prevention in U.S. Hispanic Adults” by McCurley et al. This information allows for supposing that face-to-face interventions can be suitable to my practicum project that considers measures to improve access to care among African Americans with heart failure diseases. Finally, it is possible to […]
- Diabetes Disease of the First and Second Types It is a decrease in the biological response of cells to one or more effects of insulin at its average concentration in the blood. During the first type of diabetes, insulin Degludec is required together […]
- Person-Centered Strategy of Diabetes and Dementia Care The population of focus for this study will be Afro-American women aged between sixty and ninety who have diabetes of the second type and dementia or are likely to develop dementia in the future.
- Video Consultations Between Patients and Clinicians in Diabetes, Cancer, and Heart Failure Services For example, during one of my interactions with the patient, I was asked whether the hospital had the policy to avoid face-to-face interaction during the pandemic with the help of video examinations.
- Diets to Prevent Heart Disease, Cancer, and Diabetes In order to prevent heart disease, cancer, and diabetes, people are required to adhere to strict routines, including in terms of diet. Additionally, people wanting to prevent heart disease, cancer, and diabetes also need to […]
- The Centers for Diabetes’ Risks Assessment In general, the business case for the Centers for Diabetes appears to be positive since the project is closely aligned with the needs of the community and the targets set by the Affordable Care Act.
- Diabetes Management: Case Study Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes contrast based on their definitions, the causes, and the management of the conditions. Since the CDC promotes the avoidance of saturated fat and the increase of fiber intake for […]
- Diabetes Mellitus as Leading Cause of Disability The researchers used data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, where more than 12% of older people in the US live with the condition.
- Depression in Diabetes Patients The presence of depression concomitant to diabetes mellitus prevents the adaptation of the patient and negatively affects the course of the underlying disease.
- The Relationship Between Diabetes and COVID-19 After completing the research and analyzing the articles, it is possible to suggest a best practice that may be helpful and effective in defining the relationship between diabetes and COVID-19 and providing a way to […]
- Pre-diabetes and Urinary Incontinence Most recent reports indicate that a physiotherapy procedure gives a positive result in up to 80% of patients with stage I or SUI and mixed form and 50% of patients with stage II SUI.
- Type 1 Diabetes: Recommendations for Alternative Drug Treatments Then, they have to assess the existing levels of literacy and numeracy a patient has. Tailoring educational initiatives to a person’s unique ethnic and cultural background is the basis of cultural competence in patient education.
- Type 2 Diabetes: A Pharmacologic Update Diabetes presents one of the most common diagnoses in causes of ED visits among adults and one of the leading causes of death in the United States.
- Diabetes: Vulnerability, Resilience, and Care In nursing care, resilience is a critical concept that shows the possibility of a person to continue functioning and meeting objectives despite the existing challenges.
- Diabetes Prevention in the United States The analysis of these policies and the other strategies provides the opportunity to understand what role they might play in the improvement of human health. NDPP policy, on the other hand, emphasizes the role of […]
- Teaching Experience: Diabetes Prevention The primary objective of the seminar is to reduce the annual number of diabetes cases and familiarize the audience with the very first signs of this disease.
- Summary of Type 2 Diabetes: A Pharmacologic Update The authors first emphasize that T2D is one of the most widespread diseases in the United States and the seventh leading cause of death.
- Insulin Effects in a Diabetes Person I will use this source to support my research because the perception of diabetes patients on insulin therapy is essential for understanding the impact they cause on the person.
- Diabetes and Medical Intervention In the research conducted by Moin et al, the authors attempted to define the scope of efficiency of such a tool as an online diabetes prevention program in the prevention of diabetes among obese/overweight population […]
- Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 and a Healthy Lifestyle Relationship The advantage of this study over the first is that the method uses a medical approach to determining the level of fasting glucose, while the dependences in the study of Ugandans were found using a […]
- Diabetes and Its Economic Effect on Healthcare For many years, there has been an active increase in the number of cases of diabetes of all types among the global population, which further aggravates the situation.
- Pathogenesis and Prevention of Diabetes Mellitus and Hypertension The hormone is produced by the cells of the islets of Langerhans found in the pancreas. It is attributed to the variation in the lifestyle of these individuals in these two geographical zones.
- Parental Intervention on Self-Management of an Adolescent With Diabetes Diabetes development and exposure are strongly tied to lifestyle, and the increasing incidents rate emphasizes the severity of the population’s health problem.
- Addressing the Needs of Hispanic Patients With Diabetes Similarly, in the program at hand, the needs of Hispanic patients with diabetes will be considered through the prism of the key specifics of the community, as well as the cultural background of the patients.
- Diabetes Issues: Insulin Price and Unaffordability According to the forecast of researchers from Stanford University, the number of people with type 2 diabetes who need insulin-containing drugs in the world will increase by about 79 million people by 2030, which will […]
- Diabetes: Epidemiologic Study Design For instance, the range of their parents’ involvement in the self-management practices can be a crucial factor in treatment and control.
- What to Know About Diabetes? Type 1 diabetes is caused by autoimmune reaction that prevent realization of insulin in a body. Estimated 5-10% of people who have diabetes have type 1.
- Diabetes in Saudi Arabia It is expected that should this underlying factor be discovered, whether it is cultural, societal, or genetic in nature, this should help policymakers within Saudi Arabia create new governmental initiatives to address the problem of […]
- “Medical Nutrition Therapy: A Key to Diabetes Management and Prevention” Article Analysis In the process of MNT application, the dietitian keeps a record of the changes in the main components of food and other components of the blood such as blood sugars to determine the trend to […]
- Global and Societal Implications of the Diabetes Epidemic The main aim of the authors of this article seems to be alerting the reader on the consequences of diabetes to the society and to the whole world.
- Diabetes and Hypertension Avoiding Recommendations Thus, the promotion of a healthy lifestyle should entail the encouragement of the population to cease smoking and monitor for cholesterol levels.
- Pregnant Women With Type I Diabetes: COVID-19 Disease Management The grounded theory was selected for the given topic, and there are benefits and drawbacks of utilizing it to study the experiences of pregnant women with type I diabetes and COVID-19.
- Current Recommendations for the Glycemic Control in Diabetes Management of blood glucose is one of the critical issues in the care of people with diabetes. Therefore, the interval of the A1C testing should also depend on the condition of the patient, the physician’s […]
- Diabetes Mellitus: Types, Causes, Presentation, Treatment, and Examination Diabetes mellitus is a chronic endocrinologic disease, which is characterized by increased blood glucose concentration.
- Diabetes Problem at Country Walk Community: Intervention and Evaluation This presentation develops a community health nursing intervention and evaluation tool for the diabetes problem affecting Country Walk community.
- The Minority Diabetes Initiative Act’s Analysis The bill provides the right to the Department of Health and Human Services to generate grants to public and nonprofit private health care institutions with the aim of providing treatment for diabetes in minority communities.
- Communication Challenges Between Nurses and Patients With Type 2 Diabetes According to Pung and Goh, one of the limitations of communication in a multicultural environment is the language barrier that manifests itself in the direct interaction of nurses with patients and in the engagement work […]
- Diabetes Type 2 from Management Viewpoint Demonstrate the effects of type 2 diabetes and provide background information on the disease; Discuss the management plans of diabetes centers and critically analyze the frameworks implemented in the hospitals; Examine the existing methodology models […]
- Nursing Plan for the Patient with Diabetes Type 2, HTN, and CAD The health of the population is the most valuable achievement of society, so the preservation and strengthening of it is an essential task in which everyone should participate without exception.
- Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus Diabetes is a serious public health concern that introduces a group of metabolic disorders caused by changes in the sugar blood level.
- Diabetes Mellitus Type II: A Case of a Female Adult Patient In this presentation, we are going to develop a care plan for a 47-year-old woman with a 3-year-old history of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 (also known as Type II DM).
- Diabetes Insipidus: Disease Process With Implications for Healthcare Professionals This presentation will consider the topic of Diabetes Insipidus (DI) with a focus on its etiology and progress.
- The Nature of Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Type 1 diabetes mellitus is a chronic autoimmune disease that has an active genetic component, which is identified by increased blood glucose levels, also known as hyperglycemia.
- A Study of Juvenile Type 1 Diabetes in the Northwest of England The total number of children under seventeen years living with type 1 diabetes in North West England by 2009 was 2,630.
- Imperial Diabetes Center Field Study The purpose is to examine the leadership’s practices used to maintain and improve the quality and safety standards of the facility and, using the observations and scholarly research, offer recommendations for improvement.
- Diabetes Risk Assessment After completing the questionnaire, I learned that my risk for the development of diabetes is above average. Modern risk assessment tools allow identifying the current state of health and possibilities of developing the disease.
- The Role of Telenursing in the Management of Diabetes Type 1 Telemedicine is the solution that could potentially increase the coverage and improve the situation for many t1DM patients in the world.
- Health Issues of Heart Failure and Pediatric Diabetes As for the population, which is intended to participate in the research, I am convinced that there is the need to specify the patients who should be examined and monitored.
- Juvenile Diabetes: Demographics, Statistics and Risk Factors Juvenile diabetes, also referred to as Type 2 diabetes or insulin-dependent diabetes, describes a health condition associated with the pancreas’s limited insulin production. The condition is characterized by the destruction of the cells that make […]
- Diabetes Mellitus: Pathophysiologic Processes The main function of insulin produced by cells within the pancreas in response to food intake is to lower blood sugar levels by the facilitation of glucose uptake in the cells of the liver, fat, […]
- Type 2 Diabetes Management in Gulf Countries One such study is the systematic review on the quality of type 2 diabetes management in the countries of the cooperation council for the Arab states of the Gulf, prepared by Alhyas, McKay, Balasanthiran, and […]
- Patient with Ataxia and Diabetes Mellitus Therefore, the therapist prioritizes using the cushion to the client and persuades the patient to accept the product by discussing the merits of the infinity cushion with a low profile in enabling the customer to […]
- Diabetes Evidence-Based Project: Disseminating Results In this presentation, the involvement of mentors and collaboration with administration and other stakeholders are the preferred steps, and the idea to use social networking and web pages has to be removed.
- Leadership in Diabetes Management Nurses can collaborate and apply evidence-based strategies to empower their diabetic patients. The involvement of all key stakeholders is also necessary.
- The Problem of Diabetes Among African Americans Taking into consideration the results of the research and the information found in the articles, the problem of diabetes among African Americans has to be identified and discussed at different levels.
- Childhood Obesity, Diabetes and Heart Problems Based on the data given in the introduction it can be seen that childhood obesity is a real problem within the country and as such it is believed that through proper education children will be […]
- Hypertension and Antihypertensive Therapy and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus In particular, Acebutolol impairs the functions of epinephrine and norepinephrine, which are neurotransmitters that mediate the functioning of the heart and the sympathetic nervous system.
- Diabetes: Diagnosis and Treatment The disease is characterized by the pancreas almost not producing its own insulin, which leads to an increase in glucose levels in the blood.
- How to Manage Type 2 Diabetes The article is significant to the current research problem as the researchers concluded that the assessment of metabolic processes in diabetic patients was imperative for adjusting in the management of the condition.
- Clinical Trial of Diabetes Mellitus On the other hand, type II diabetes mellitus is caused by the failure of the liver and muscle cells to recognize the insulin produced by the pancreatic cells.
- Diabetes: Diagnosis and Related Prevention & Treatment Measures The information presented on the articles offers an insight in the diagnosis of diabetes among various groups of persons and the related preventive and treatment measures. The study identified 3666 cases of initial stages of […]
- Reinforcing Nutrition in Schools to Reduce Diabetes and Childhood Obesity For example, the 2010 report says that the rates of childhood obesity have peaked greatly compared to the previous decades: “Obesity has doubled in Maryland over the past 20 years, and nearly one-third of youth […]
- The Connection Between Diabetes and Consuming Red Meat In light of reporting the findings of this research, the Times Healthland gave a detailed report on the various aspects of this research.
- Synthesizing the Data From Relative Risk Factors of Type 2 Diabetes Speaking of such demographic factors as race, the white population suffers from it in the majority of cases, unlike the rest of the races, the remaining 0.
- Using Exenatide as Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Adults Kendal et al.analyzed the effects of exenatide as an adjunct to a combination of metformin and sulfonylurea against the combination of the same drugs without the adjunct.
- Enhancing Health Literacy for People With Type 2 Diabetes Two professionals, Andrew Long, a professor in the school of heath care in the University of Leeds, and Tina Gambling, senior lecturer in the school of health care studies from the University of Cardiff, conducted […]
- The Scientific Method of Understanding if Coffee Can Impact Diabetes The hypothesis of the experiment ought to be straightforward and understandable. The control group and the experiment group for the test are then identified.
- Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: Review This is because of the current patterns that show an increase in the prevalence of diabetes in offspring born to mothers with GDM.
- Health Service Management of Diabetes During the task, Fay makes a countless number of short calls and often takes water irrespective of the time of the day or the prevailing weather conditions.
- Necrotizing Fasciitis: Pathophysiology, Role of Diabetes In the event of such an infection, the body becomes desperate to get rid of the intruders. For WBC, zero is given if the count is below 15cells/mm3, one is given if the count lies […]
- The Benefits of Sharing Knowledge About Diabetes With Physicians In this research, 3600 diabetic patients were surveyed from twelve hospitals, but due to exclusion criterion, only 1,200 were considered for this particular research. The system allocated numbers to the participants out of which 100 […]
- Gestational Diabetes Mellitus – NSW, Australia We had a deeper evaluation of the implications of GDM and we cited the inadequacy of resources and technology as the contributors of GDM.
- Health and Wellness: Stress, Diabetes and Tobacco Related Problems Emotional health and well being refers to our ability to deal with our emotions as well as the emotions of those around us.
- 52-Year-Old Female Patient With Type II Diabetes
- Healthy People Project: Personal Review About Diabetes
- Nursing Diagnosis: Type 1 Diabetes & Hypertension
- Nursing Care For the Patient With Diabetes
- Coronary Heart Disease Aggravated by Type 2 Diabetes and Age
- Diabetes as the Scourge of the 21st Century: Locating the Solution
- Psychosocial Implications of Diabetes Management
- Gestational Diabetes in a Pregnant Woman
- Diabetes Mellitus: Prominent Metabolic Disorder
- Holistic Approach to Man’s Health: Diabetes Prevention
- Holistic Image in Prevention of Diabetes
- Educational Strategies for Diabetes to Patients
- Diabetes and Obesity in the United Arab Emirates
- Epidemiological Problem: Diabetes in Illinois
- Diabetes as a Chronic Condition
- Managing Diabetes Through Genetic Engineering
- Diabetes, Functions of Insulin, and Preventive Practices
- Treating of Diabetes in Adults
- Counseling and Education Session in Type II Diabetes
- Diabetes II: Reduction in the Incidence
- Community Health Advocacy Project: Diabetes Among Hispanics
- Community Health Advocacy Project: Hispanics With Diabetes
- Hispanics Are More Susceptible to Diabetes That Non-Hispanics
- Rates Diabetes Between Hispanics Males and Females
- Diabetes Mellitus and HFSON Conceptual Framework
- Prince Georges County Community Health Concern: Diabetes
- Fats and Proteins in Relation to Type 2 Diabetes
- Alcohol Interaction With Medication: Type 2 Diabetes
- Diabetes Management and Evidence-Based Practice
- Critical Analysis of Policy for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Australia
- The Treatment and Management of Diabetes
- Obesity and Diabetes: The Enemies Within
- Impact of Diabetes on the United Arab Emirates’ Economy
- Childhood Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes
- Health Nursing and Managing Diabetes
- Diabetes Management: How Lifestyle, Daily Routine Affect Blood Sugar
- Diabetes Management: Diagnostics and Treatment
- Diabetes Mellitus Type 2: The Family Genetic History
- Diabetes Type II: Hormonal Mechanism and Intracellular Effects of Insulin
- Social, Behavioral, and Psychosocial Causes of Diseases: Type 2 Diabetes
- Supportive Intervention in the Control of Diabetes Mellitus
- Enhancing Foot Care Practices in Patients With Diabetes
- Community Health Promotion: The Fight Against Diabetes in a Community Setting
- Diabetes in Australia and Saudi Arabia
- Diabetes: The Advantages and Disadvantages of Point of Care Testing
- Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 or Non-Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus
- Diabetes Prevention Measures in the Republic of the Marshall Islands
- Impact of Diabetes on Healthcare
- Gestational Diabetes: American Diabetes Association Publishers
- Gestational Diabetes: Child Bearing Experience
- Diabetes Mellitus Effects on Periodontal Disease
- Diabetes Type II Disease in the Community
- The Relationship of Type 2 Diabetes and Depression
- Glycemic Control in Individuals With Type 2 Diabetes
- The Diagnosis of Diabetes in Older Adults and Adolescents
- Physical Activity in Managing Type-2 Diabetes
- High Risk of Developing Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Children With Type 1 Diabetes in Clinical Practice
- Type 2 Diabetes Treatment Analysis
- Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Revealing the Diagnosis
- The Type 2 Diabetes Prevention: Lifestyle Choices
- Indigenous and Torres Strait Population and Diabetes
- Interpretation of the Diabetes Interview Transcript
- Type 1 Diabetes: Using Glucose Monitoring in Treatment
- Managing Type 2 Diabetes Patients’ Blood Sugar Prior to and After Surgical Procedures
- Diabetes Prevention: The Sanofi-Aventis Leaflet Review
- Canagliflozin and Cardiovascular and Renal Events in Type 2 Diabetes: Medical Terminology Definition
- Modern Diabetes Treatment Tools
- Diabetes: Encapsulation to Treat a Disease
- Current Dietary for the Treatment of Diabetes
- Diabetes: Discussion of the Disease
- Stranahan on Diabetes Impairs Hippocampal Function
- A Clinical-Based Study of Young Adults Who Have Diabetes
- Panax Ginseng for Diabetes Treatment
- Depression and Diabetes Association in Adults
- Is There Anu Cure For Diabetes?
- Diabetes Self-Management: Evidence-Based Nursing
- Diabetes Type 2 in Children: Causes and Effects
- Health, Culture, and Identity as Diabetes Treatment Factors
- Diabetes Prevention in Chinese Elderly in Hunan
- “Experiences of Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Starting Insulin Therapy” by Phillips
- Type 2 Diabetes: Nursing Change Project
- Diabetes and Health Promotion Concepts
- Type 2 Diabetes in Geriatric Patients
- Cultural Empowerment. Diabetes in Afro-Americans
- Diabetes Self-Management: Relationships & Expectations
- Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus
- Improving Comprehensive Care for Patients With Diabetes
- Side Effects of Metformin in Diabetes Treatment
- Type 2 Diabetes and Drug Treatments
- Diabetes Mellitus and Health Determinants
- Nursing Leadership in Diabetes Management
- Diabetes Education for African American Women
- Latent Autoimmune Adult Diabetes
- Obesity: Epidemiology and Health Consequences
- Diabetes in Urban Cities of United States
- Diabetes in Australia: Analysis
- Type 2 Diabetes in the Afro-American Bronx Community
- Type 2 Diabetes From Cultural and Genetic Aspects
- Type 2 Diabetes in Bronx: Evidence-Based Practice
- Type 2 Diabetes in Bronx Project for Social Change
- Ambition Diabetes and Diet on Macbeths’ Example
- Diabetes as Community Health Issue in the Bronx
- Diabetes Treatment and Care
- Transition from Pediatric to Adult Diabetes Care
- Diabetes Awareness Program and Strategic Planning
- Diabetes: Disease Control and Investigation
- Diabetes Pain Questionnaire and Patient Feedback
- Perception of Diabetes in the Hispanic Population
- Clinical Studies of Diabetes Mellitus
- Diabetes Mellitus and Problems at Work
- Diabetes in the US: Cost Effectiveness Analysis
- Diabetes Investigation in Space Flight Research
- Diabetes Care Advice by Food and Drug Administration
- Artificial Intelligence for Diabetes: Project Experiences
- Diabetes Patients’ Long-Term Care and Life Quality
- Chronic Care Model for Diabetes Patients in the UAE
- Diabetes Among British Adults and Children
- Endocrine Disorders: Diabetes and Fibromyalgia
- Future Technologies: Diabetes Treatment and Care
- Epidemiology of Type 1 Diabetes
- Diabetes: Treatment Technology and Billing
- Pathophysiology of Mellitus and Insipidus Diabetes
- Cure for Diabetes: The Impossible Takes a Little Longer
- Stem Cell Therapy as a Potential Cure for Diabetes
- Stem Cell Therapy and Diabetes Medical Research
- Type II Diabetes Susceptibility and Socioeconomic Status
- Diabetes Mellitus Type 2: Pathophysiology and Treatment
- Obesity and Hypertension in Type 2 Diabetes Patients
- Strongyloides Stercoralis Infection and Type 2 Diabetes
- Socioeconomic Status and Susceptibility to Type II Diabetes
- Diabetes Mellitus: Differential Diagnosis
- Diabetes Disease in the USA Adults
- Education for African Americans With Type 2 Diabetes
- Diabetes Treatment and Funding in Fulton County
- Diabetes Care: Leadership and Strategy Plan
- Diabetes Mellitus’ New Treatment: Principles and Process
- Diet and Nutrition: European Diabetes
- Preventing the Proliferation Diabetes
- Diabetes: Symptoms, Treatment, and Prevention
- Diabetes and Cardiovascular Diseases in Medicine
- Ecological Models to Deal with Diabetes in Medicine
- Different Types of Diabetes Found in Different Countries
- Analysis of Program “Prevent Diabetes Live Life Well”
- The Effect of Physical, Social, and Health Variables on Diabetes
- Micro and Macro-Cosmos in Medicine and Care Models for Prevention of Diabetes
- Why Qualitative Method Was Chosen for Diabetes Program Evaluation
- Humanistic Image of Managing Diabetes
- Diabetes mellitus Education and hemoglobin A1C level
- Obesity, Diabetes and Heart Disease
- Illuminate Diabetes Event Design
- Cause and Diagnosis of Type 2 diabetes
- Patient Voices: Type 2 Diabetes. Podcast Review
- Type I Diabetes: Pathogenesis and Treatment
- Human Body Organ Systems Disorders: Diabetes
- Age Influence on Physical Activity: Exercise and Diabetes
- Hemoglobin A1C Test for Diabetes
- Why Injury and Diabetes Have Been Identified as National Health Priority?
- What Factors Are Involved in the Increasing Prevalence of Type II Diabetes in Adolescents?
- Does the Socioeconomic Position Determine the Incidence of Diabetes?
- What Are the Four Types of Diabetes?
- How Fat and Obesity Cause Diabetes?
- How Exercise Affects Type 2 Diabetes?
- How Does the Treatment With Insulin Affect Type 2 Diabetes?
- How Diabetes Does Cause Depression?
- Does Diabetes Prevention Pay For Itself?
- How Does Snap Participation Affect Rates of Diabetes?
- Does Overeating Sugar Cause Diabetes, Cavities, Acne, Hyperactivity and Make You Fat?
- Why Diabetes Mellitus and How It Affects the United States?
- Does Alcohol Decrease the Risk of Diabetes?
- How Does a Person With Diabetes Feel?
- Does Periodontal Inflammation Affect Type 1 Diabetes in Childhood and Adolescence?
- How Can the Paleolithic Diet Control Type 2 Diabetes?
- How Does Insulin Help Diabetes Be Controlled?
- Does Economic Status Matter for the Regional Variation of Malnutrition-Related Diabetes?
- How Can Artificial Intelligence Technology Be Used to Treat Diabetes?
- What Are the Main Causes and Treatments of Diabetes?
- What Evidence Exists for Treatments Depression With Comorbid Diabetes Using Traditional Chinese Medicine and Natural Products?
- Why Was Qualitative Method Chosen for Diabetes Program Evaluation?
- What Are the Three Types of Diabetes?
- How Does Poverty Affect Diabetes?
- What Is the Leading Cause of Diabetes?
- How Is Diabetes Diagnosed?
- What Are the Main Symptoms of Diabetes?
- How Diabetes Adversely Affects Your Body?
- What Are the Most Common Symptoms of Undiagnosed Diabetes?
- Epigenetics Essay Titles
- Alcohol Abuse Paper Topics
- Pathogenesis Research Ideas
- Therapeutics Research Ideas
- Hypertension Topics
- Osteoarthritis Ideas
- Cardiomyopathy Titles
- Malnutrition Titles
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, February 25). 357 Diabetes Essay Topics & Examples. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/diabetes-essay-examples/
"357 Diabetes Essay Topics & Examples." IvyPanda , 25 Feb. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/diabetes-essay-examples/.
IvyPanda . (2024) '357 Diabetes Essay Topics & Examples'. 25 February.
IvyPanda . 2024. "357 Diabetes Essay Topics & Examples." February 25, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/diabetes-essay-examples/.
1. IvyPanda . "357 Diabetes Essay Topics & Examples." February 25, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/diabetes-essay-examples/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "357 Diabetes Essay Topics & Examples." February 25, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/diabetes-essay-examples/.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Diabetes Mellitus can be described in two types: 1) Type 1. 2) Type 2. Description of two types of Diabetes Mellitus are as follows. 1) Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus is classified by a deficiency of insulin in the blood. The deficiency is caused by the loss of insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. This type of diabetes is found more commonly ...
Eating Healthy Food. The first step is to eat healthy food. This means lots of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Try to avoid foods with a lot of sugar, like candy and soda. These foods can cause your blood sugar to spike, which can lead to diabetes. Eating a balanced diet can help keep your blood sugar levels steady.
Diabetes: Types and Management Essay. Diabetes is a chronic disease that undermines the body's metabolizing of food into energy. Upon consumption, food eaten is mostly digested into glucose that is then released into the blood. This raises the level of glucose in the blood, which stimulates insulin release from the pancreas.
Doctor: The first step in the treatment of type 2 diabetes is consumption of healthy diet. This involves avoiding excessive consumption of foods that contain sugar and fats as they are likely to increase the levels of sugar in the blood. In addition, getting involved in physical activity and losing excessive weight are also important.
Students are often asked to write an essay on Diabetes in their schools and colleges. And if you're also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic. ... With ongoing research and advancements, the future holds potential for improved diabetes care and prevention. 500 Words Essay on Diabetes
Essay on Diabetes: Diabetes is a metabolic disease, in which the human body fails to utilize the sugar (glucose) content in blood, thus resulting in high blood sugar levels over a prolonged period of time. Sugar present in our blood is a carried by a hormone called Insulin, to the cells and stored or used as a source of energy. Diabetes occurs when the body doesn't produce enough insulin or ...
1. Diabetes is a severe metabolic disorder mainly caused due to obesity. 2. Type 2 diabetes is a lifestyle disorder, while Type 1 diabetes is genetic. 3. 1 out of every five people above the age of 65 has Diabetes. 4. 79% of adults living with Diabetes belong to developing nations and third world countries. 5.
Diabetes has increased from 108 million in 1980 to 422 million today (Forouhi 22). Diabetes is one of the leading causes of blindness, kidney failure, heart attacks, strokes, and lower limb amputations (Saeedi). Diabetes mortality increased by 3% by age group between 2000 and 2019 (Cole 378). Diabetes and diabetes-related kidney disease killed ...
Writing an essay on diabetes can help promote research by highlighting the importance of funding and supporting research efforts. To Advocate For Change: Writing an essay on diabetes can help advocate for policy changes that improve access to diabetes care, support for those with diabetes, and prevention efforts.
Conclusion. The DCCT, the DPP, and the Look AHEAD are three interventions, which have proved that nutrition and physical activity are central in the treatment and management of diabetes among the population. The DCCT intervention aims at aiding a diabetic patient to understand how to manage body weight and blood glucose levels.
Diabetes is a disease that is the leading cause of high blood sugar levels. People who have Diabetes have bodies that cannot make enough insulin, or their bodies cannot use the insulin they have effectively (Healthline, 2021). Insulin is the hormone that moves sugars from the blood to the body cells.
Sometimes, you just need to see good essay samples on diabetes to kickstart the process of writing your paper. With a good example, you would know how to create a better outline and elements to include in the introduction and conclusion sections. Ensure that you have used original content to avoid plagiarism.
Good Essays. 997 Words. 4 Pages. Open Document. Diabetes. Diabetes is a lifelong disease that can affect both children and adults. This disease is the sixth leading cause of death in the United States. It claims about 178,000 lives each year. Type one diabetes, also known as insulin dependent diabetes mellitus, usually occurs in people less ...
With aggressive care, there are strict guidelines to keep diabetes in check. The goal of the intensive treatment is to lower the blood glucose level by administering glucose checks by pricking fingers multiple times a day. Get Access. Free Essay: Public health emphasizes the importance of prevention and proactively taking care of one's body.
Diabetes is a disease that occurs when your blood glucose, also called blood sugar, is too high. Glucose is your body's main source of energy. Your body can make glucose, but glucose also comes from the food you eat. Insulin is a hormone made by the pancreas that helps glucose get into your cells to be used for energy.
High mortality rates are caused by the disease complications that gradually progress, significantly reducing the quality and duration of one's life. This paper aims to examine type 2 diabetes, including the related problems, potential solutions, and recommendations. Get a custom Essay on Type 2 Diabetes as a Public Health Issue.
This assignment will address the public health issue of the increasing prevalence of diabetes mellitus (diabetes) and explore links with health inequalities both nationally and locally. It will discuss the frameworks available which give guidance for standards of care for diabetes patients and their influence on diabetes care.
As of January 2011, 25.8 million children and adults have been diagnosed with Type II diabetes (American Diabetes Association). Type II diabetes is a disease that causes high blood sugar levels due to a malfunction within the body to properly use insulin. The role of insulin is to lower and control blood sugar levels so they do not get too high.
The changes are: Losing weight and keeping it off. Weight control is an important part of diabetes prevention. You may be able to prevent or delay diabetes by losing 5 to 10% of your current weight. For example, if you weigh 200 pounds, your goal would be to lose between 10 to 20 pounds. And once you lose the weight, it is important that you ...
Harvard College Writing Center 2 Tips for Reading an Assignment Prompt When you receive a paper assignment, your first step should be to read the assignment prompt carefully to make sure you understand what you are being asked to do. Sometimes your assignment will be open-ended ("write a paper about anything in the course that interests you").
Type 2 Diabetes; Heart Disease; Stroke; If your patients have prediabetes, losing weight by eating healthy and being more active can cut their risk of getting type 2 diabetes in half. Lifestyle Change Program. The lifestyle change program that is part of the CDC-led National Diabetes Prevention Program is proven to help prevent or delay type 2 ...
diabetes essay in english| diabitic disease essay| diabetes essayhow to prevent diabetes essay, diabetes risk factors, diabetes essay, diabetic disease, diab...
HOW TO PREVENT DIABETES ESSAY WRITING IN ENGLISH#howtopreventdiabetesessaywriting#diabetesawarenessessaywriting#essayondiabetes📌 Your Queries Solved :essay ...
According to Ekoé, Rewers, Williams and Zimmet (2008), the major effects of diabetes include long term damage, dysfunction, and failure of various body organs. Get a custom Research Paper on Diabetes: Symptoms, Treatment, and Prevention. Other chronic diseases include cancer, arthritis, asthma, and obesity. In a definition by the World Health ...
Effective body paragraphs help to structure and advance the essay's argument. Body Paragraph Format. Body paragraphs form the core of an essay, providing the details and evidence that support the thesis statement. A well-structured body paragraph enhances clarity, flow, and persuasiveness in writing. Here's a guide to constructing effective ...
Similarly, start by taking a paragraph from an essay you like. Make sentence-level notes and rewrite its essence without looking at it. My Top Tips To Write A Good Essay 1. Write Lousy First Drafts. You heard me. Write as if your keyboard doesn't have keys for punctuation. Write as if no one is ever going to read your essay.
357 Diabetes Essay Topics & Examples. Updated: Feb 25th, 2024. 25 min. When you write about the science behind nutrition, heart diseases, and alternative medicine, checking titles for diabetes research papers can be quite beneficial. Below, our experts have gathered original ideas and examples for the task.