McKinsey Solve
- Fundamentals
- How it works
- Skills tested
- How to prepare
- A guide to the McKinsey Problem Solving Game

MCC is here to help
McKinsey’s Solve assessment has been making candidates sweat ever since it was initially trialled at the firm’s London office back in 2017 - and things have gotten even more difficult since a new version launched in Spring 2023, adding the Redrock case study.
More recently, in Summer 2023, we have seen a new iteration of that Redrock case, as we continue to interview test takers to keep you updated. This replaces the case study about optimising wolf pack populations across Redrock Island with one about boosting the overall plant biodiversity on the same island.
Since its initial roll-out, the Solve assessment has definitely been the most idiosyncratic, but also the most advanced, of the screening tests used by the MBB firms.
It can be hard to understand how an ecology-themed video game can tell McKinsey whether you’ll make a good management consultant, let alone know how to prepare yourself to do well in that game. When you consider that McKinsey are potentially cutting 70%+ of the applicant pool based on this single test, you can hardly blame applicants for being worried.
Matters are definitely not helped by the dearth of reliable, up-to-date information about what could very well be - with a top-tier consulting job on the line - the most important test you will take over your entire career. This was already true with the version of Solve that had been around for a few years, let alone the new iterations.
What information is available online is then often contradictory. For a long time, there was huge disagreement as to whether it is actually possible to meaningfully prepare for the Solve assessment - before you’ve even considered how to go about that preparation. There is also a lot of confusion and inaccuracy around the new Redrock case - largely as it is such a recent addition, and individual test takers tend to misremember details.
Luckily, we at MCC have been interviewing test takers both before and after the Redrock case rollout and have been following up to see which strategies and approaches actually work to push individuals through to interview.
Here, we’ll explain that it is indeed possible to prepare effectively for both versions of Solve and give you some ideas for how you can get started. Understanding how the Solve assessment works, what it tests you for and how is critical for all but the most hurried preparations.
This article makes for a great introduction to the Solve assessment. However, if you are going to be facing this aptitude test yourself and want full information and advice for preparation, then you should ideally get our full PDF guide:
Master the Solve Assessment
What is the mckinsey solve assessment.
In simple terms, the McKinsey Solve assessment is a set of ecology-themed video games. In these games, you must do things like build food chains, protect endangered species, manage predator and prey populations, boost biodiversity and potentially diagnose diseases within animal populations or identify natural disasters.
Usually, you will be given around 70 minutes to complete two separate games, spending about the same amount of time on each.
Until recently, these games had uniformly been Ecosystem Building and Plant Defence. However, since Spring 2023, McKinsey has been rolling out a new version across certain geographies. This replaces the Plant Defence game with the new Redrock case study. Some other games have also been run as tests.
We’ll run through a little more on all these games below to give you an idea of what you’ll be up against for both versions and possible new iterations.
An important aspect that we'll cover in more detail here is that the Solve games don't only score you on your answers (your "product score"), but also on the method you use to arrive at them (your "process score") - considerably impacting optimal strategy.
In the past, candidates had to show up to a McKinsey office and take what was then the Digital Assessment or PSG on a company computer. However, candidates are now able to take the re-branded Solve assessment at home on their own computers.
Test takers are allowed to leverage any assistance they like (you aren’t spied on through your webcam as you would be with some other online tests), and it is common to have a calculator or even another computer there to make use of.
Certainly, we strongly advise every candidate to have at least a pen, paper and calculator on their desk when they take the Solve assessment.
Common Question: Is the Solve assessment the same thing as the PSG?
In short, yes - “Solve” is just the newer name for the McKinsey Problem Solving Game.
We want to clear up any potential confusion right at the beginning. You will hear this same screening test called a few different things in different places. The Solve moniker itself is a relatively recent re-branding by McKinsey. Previously, the same test was known as either the Problem Solving Game (usually abbreviated to PSG) or the Digital Assessment. You will also often see that same test referred to as the Imbellus test or game, after the firm that created the first version.
You will still see all these names used across various sites and forums - and even within some older articles and blog posts here on MyConsultingCoach. McKinsey has also been a little inconsistent on what they call their own assessment internally. Candidates can often become confused when trying to do their research, but you can rest assured that all these names refer to the same screening test - though, of course, folk might be referring to either the legacy or Redrock versions.
How and why does McKinsey use the Solve assessment?
It’s useful to understand where the Solve assessment fits into McKinsey’s overall selection process and why they have felt the need to include it.
Let’s dive right in…
How is the Solve Assessment used by McKinsey?
McKinsey's own account of how the Solve assessment is used in selection can be seen in the following video:
Whilst some offices initially stuck with the old PST, the legacy Solve assessment was soon rolled out globally and given universally to candidates for roles at pretty well every level of the hierarchy. Certainly, if you are a recent grad from a Bachelor’s, MBA, PhD or similar, or a standard experienced hired, you can expect to be asked to complete the Solve assessment.
Likewise, the new Redrock case study versions seem to be in the process of being rolled out globally - though at this point it seems you might be given either (especially as McKinsey has been having significant technical problems with this new online case study) and so should be ready for both.
At present, it seems that only those applying for very senior positions, or perhaps those with particularly strong referrals and/or connections, are allowed to skip the test. Even this will be office-dependent.
As noted above, one of the advantages of the Solve assessment is that it can be given to all of McKinsey’s hires. Thus, you can expect to be run into the same games whether you are applying as a generalist consultant or to a specialist consulting role - with McKinsey Digital , for example.
The takeaway here is that, if you are applying to McKinsey for any kind of consulting role, you should be fully prepared to sit the Solve Assessment!
Where does the Solve assessment fit into the recruitment process?
You can expect to receive an invitation to take the Solve assessment shortly after submitting your resume.
It seems that an initial screen of resumes is made, but that most individuals who apply are invited to take the Solve assessment.
Any initial screen is not used to make a significant cut of the candidate pool, but likely serves mostly to weed out fraudulent applications from fake individuals (such as those wishing to access the Solve assessment more than once so they can practice...) and perhaps to eliminate a few individuals who are clearly far from having the required academic or professional background, or have made a total mess of their resumes.
Your email invitation will generally give you either one or two weeks to complete the test, though our clients have seen some variation here - with one individual being given as little as three days.
Certainly, you should plan to be ready to sit the Solve assessment within one week of submitting your resume!
Once you have completed the test, McKinsey explain on their site that they look at both your test scores and resume (in more detail this time) to determine who will be invited to live case interviews. This will only be around 30% of the candidates who applied - possibly even fewer.
One thing to note here is that you shouldn’t expect a good resume to make up for bad test scores and vice versa. We have spoken to excellent candidates whose academic and professional achievements were not enough to make up for poor Solve performance. Similarly, we don’t know of anyone invited to interview who hadn’t put together an excellent resume.
Blunty, you need great Solve scores and a great resume to be advanced to interview.
Your first port of call to craft the best possible resume and land your invitation to interview is our excellent free consulting resume guide .
Why does this test exist?

As with Bain, BCG and other major management consulting firms, McKinsey receives far far more applications for each position than they can ever hope to interview. Compounding this issue is that case interviews are expensive and inconvenient for firms like McKinsey to conduct. Having a consultant spend a day interviewing just a few candidates means disrupting a whole engagement and potentially having to fly that consultant back to their home office from wherever their current project was located. This problem is even worse for second-round interviews given by partners.
Thus, McKinsey need to cut down their applicant pool as far as possible, so as to shrink the number of case interviews they need to give without losing the candidates they actually want to hire. Of course, they want to accomplish this as cheaply and conveniently as possible.
The Problem Solving Test (invariably shortened to PST) had been used by McKinsey for many years. However, it had a number of problems that were becoming more pronounced over time, and it was fundamentally in need of replacement. Some of these were deficiencies with the test itself, though many were more concerned with how the test fitted with the changing nature of the consulting industry.
The Solve assessment was originally developed and iterated by the specialist firm Imbellus ( now owned by gaming giant Roblox ) to replace the long-standing PST in this screening role and offers solutions to those problems with its predecessor.
We could easily write a whole article on what McKinsey aimed to gain from the change, but the following few points cover most of the main ideas:
- New Challenges: Previously, candidates were largely coming out of MBAs or similar business-focussed backgrounds and the PST’s quickfire business questions were thus perfectly sufficient to select for non-technical generalist consulting roles. However, as consulting projects increasingly call for a greater diversity and depth of expertise, McKinsey cannot assume the most useful talent – especially for technical roles – is going to come with pre-existing business expertise. A non-business aptitude test was therefore required.
- Fairness and the Modern Context: The covid pandemic necessitated at-home aptitude testing. However, even aside from this, online testing dramatically reduces the amount of travel required of candidates. This allows McKinsey to cast a wider net, providing more opportunities to those living away from hub cities, whilst also hugely reducing the carbon footprint associated with the McKinsey selection process.
- Gaming the System: More pragmatically, the Solve assessment is a much harder test to “game” than was the PST, where highly effective prep resources were available and readily allowed a bad candidate with good preparation to do better than a good candidate. The fact that game parameters change for every individual test taker further cuts down the risk of candidates benefitting from shared information. The recent move towards the Redrock version then also helps McKinsey stay ahead of those developing prep resources for the legacy Solve assessment.
- Cost Cutting: A major advantage of scrapping the old pen-and-paper PST is that the formidable task of thinning down McKinsey’s applicant pool can be largely automated. No test rooms and invigilation staff need to be organised and no human effort is required to devise, transport, catalogue and mark papers.
Impress your interviewer

There has been a bit of variation in the games included in the Solve assessment/PSG over the years and what specific form those games take. Imbellus and McKinsey had experimented with whole new configurations as well as making smaller, iterative tweaks over time. That being said, the new 2023 Redrock case studies (seemingly added by McKinsey themselves without Imbellus) are by far the largest change to Solve since that assessment's genesis back in 2017.
Given that innovation seems to continue (especially with the lengthy feedback forms some candidates are being asked to fill in after sitting the newest iteration), there is always the chance you might be the first to receive something new.
However, our surveys of, and interviews with, those taking the Solve assessment - both before and after recent changes - mean we can give you a good idea of what to expect if you are presented with either the legacy or one of the Redrock versions of Solve.
We provide much more detailed explanation of each of the games in our Solve Assessment PDF Guide - including guidance on optimal scenarios to maximise your performance. Here, though, we can give a quick overview of each scenario:
Ecosystem Building
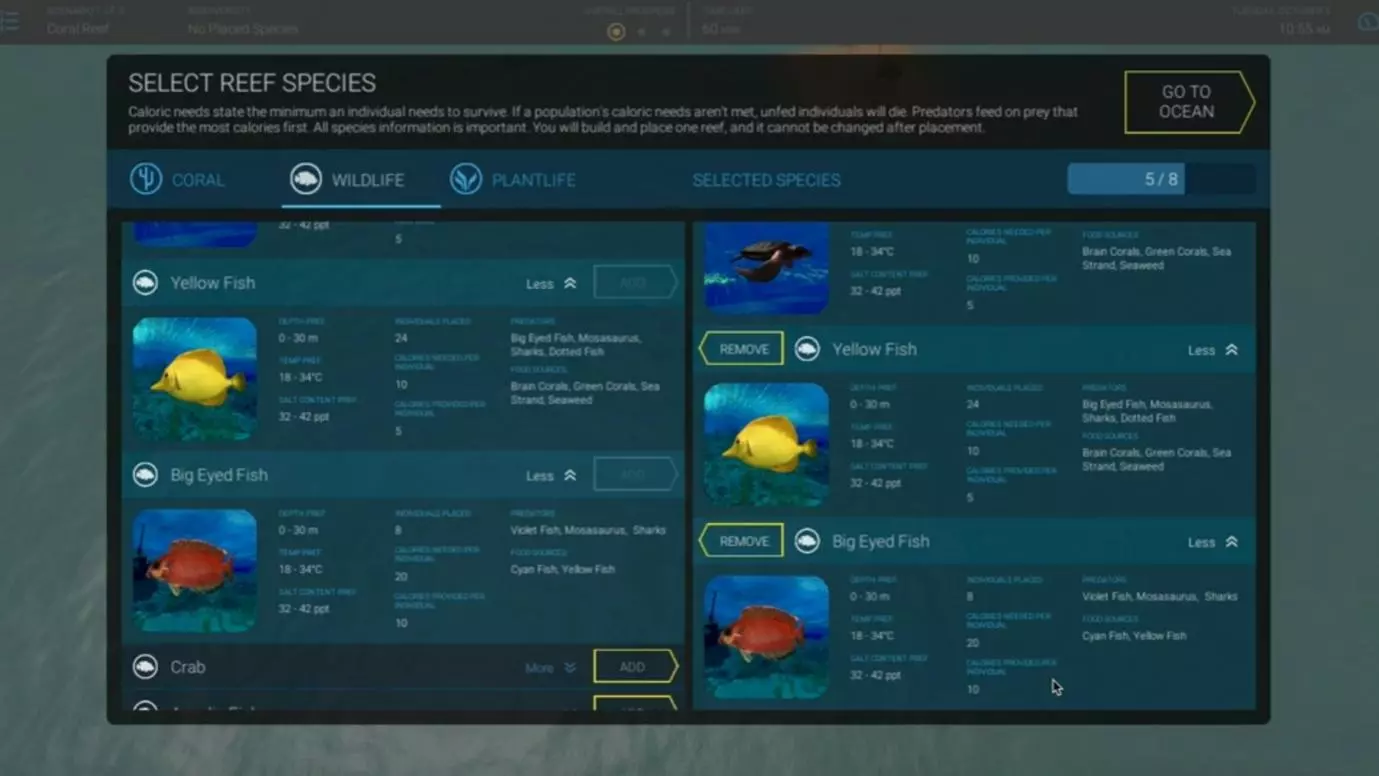
In this scenario, you are asked to assemble a self-sustaining ecosystem in either an aquatic, alpine or jungle environment (though do not be surprised if environments are added, as this should be relatively easy to do without changing the underlying mechanics).
The game requires you to select a location for your ecosystem. Several different options are given, all with different prevailing conditions. You then have to select a number of different plant and animal species to populate a functioning food chain within that location.
In previous versions of the game, you would have had to fit as many different species as possible into a functioning food chain. However, newer iterations of the Solve assessment require a fixed number of eight or, more recently, seven species to be selected.
Species selection isn’t a free-for-all. You must ensure that all the species you select are compatible with one another - that the predator species you select are able to eat the prey you have selected for them etc. All the species must also be able to survive in the conditions prevailing at the location you have selected.
So far, this sounds pretty easy. However, the complexity arises from the strict rules around the manner and order in which the different species eat one another. We run through these in detail in our guide, with tips for getting your food chain right. However, the upshot is that you are going to have to spend some significant time checking your initial food chain - and then likely iterating it and replacing one or more species when it turns out that the food chain does not adhere to the eating rules.
Once you have decided on your food chain, you simply submit it and are moved on to the next game. In the past, test takers were apparently shown whether their solution was correct or not, but this is no longer the case.
Test takers generally report that this game is the easier of the two, whether it is paired with the Plant Defence game in the legacy Solve or the Redrock case study in the new version. Candidates will not usually struggle to assemble a functioning ecosystem and do not find themselves under enormous time pressure. Thus, we can assume that process scores will be the main differentiator between individuals for this component of the Solve assessment.
For ideas on how to optimise your process score for this game, you can see our PDF Solve guide .
Plant Defence
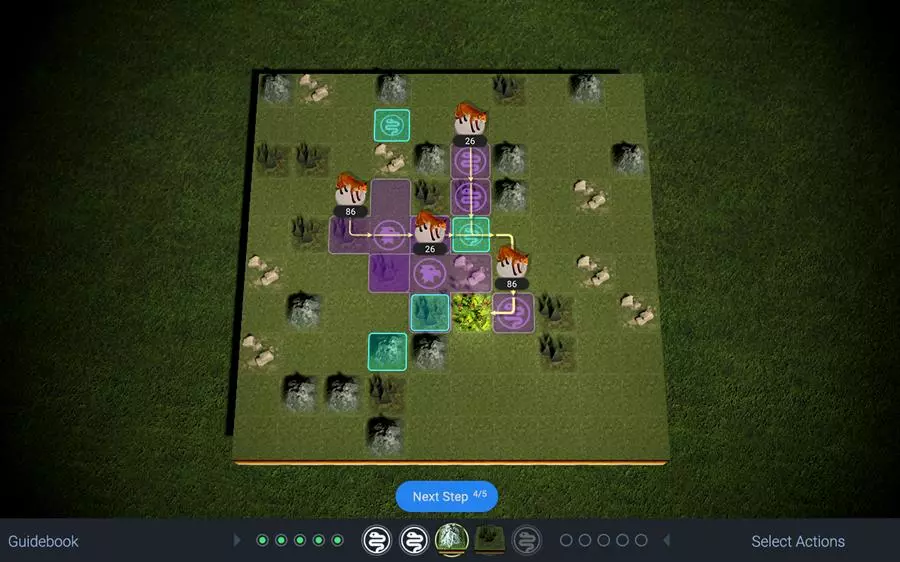
As mentioned, this game has been replaced with the Redrock case study in the new newer version of the Solve assessment, rolled out from Spring 2023 and further iterated in Summer 2023. However, you might still be asked to sit the legacy version, with this game, when applying to certain offices - so you should be ready for it!
This scenario tasks you with protecting an endangered plant species from invasive species trying to destroy it.
The game set-up is much like a traditional board game, with play taking place over a square area of terrain divided into a grid of the order of 10x10 squares.
Your plant is located in a square near the middle of the grid and groups of invaders - shown as rats, foxes or similar - enter from the edges of the grid before making a beeline towards your plant.
Your job then is to eliminate the invaders before they get to your plant. You do this by placing defences along their path. These can be terrain features, such as mountains or forests, that either force the invaders to slow down their advance or change their path to move around an obstacle. To actually destroy the invaders though, you use animal defenders, like snakes or eagles, that are able to deplete the groups of invaders as they pass by their area of influence.
Complication here comes from a few features of the game. In particular:
- You are restricted in terms of both the numbers of different kinds of defenders you can use and where you are allowed to place them. Thus, you might only have a couple of mountains to place and only be allowed to place these in squares adjacent to existing mountains.
- The main complication is the fact that gameplay is not dynamic but rather proceeds in quite a restricted turnwise manner. By this, we mean that you cannot place or move around your defences continuously as the invaders advance inwards. Rather, turns alternate between you and invaders and you are expected to plan your use of defences in blocks of five turns at once, with only minimal allowance for you to make changes on the fly as the game develops.
The plant defence game is split into three mini-games. Each mini-game is further split into three blocks of five turns. On the final turn, the game does not stop, but continues to run, with the invaders in effect taking more and more turns whilst you are not able to place any more defences or change anything about your set-up.
More and more groups of invaders pour in, and your plant will eventually be destroyed. The test with this “endgame” is simply how many turns your defences can stand up to the surge of invaders before they are overwhelmed.
As opposed to the Ecosystem Building scenario, there are stark differences in immediate candidate performance - and thus product score - in this game. Some test takers’ defences will barely make it to the end of the standard 15 turns, whilst others will survive 50+ turns of endgame before they are overwhelmed.
In this context, as opposed to the Ecosystem Building game typically preceding it, it seems likely that product score will be the primary differentiator between candidates.
We have a full discussion of strategies to optimise your defence placement - and thus boost your product score - in our Solve guide .
Redrock Case Study

This is the replacement for the Plant Defence game in the newest iteration of Solve.
One important point to note is that, where the Solve assessment contains this case study, you have a strict, separate time limit of 35 minutes for each half of the assessment. You cannot finish one game early and use the extra time in the other, as you could in the legacy Solve assessment.
McKinsey has had significant issues with this case study, with test takers noting several major problems. In particular:
- Glitches/crashes - Whilst the newest, Summer 2023 version seems to have done a lot to address this issue, many test takers have had the Redrock case crash on them. Usually, this is just momentary and the assessment returns to where it was in a second or two. If this happens to you, try to just keep calm and carry on. However, there are reports online of some candidates having the whole Solve assessment crash and being locked out as a result. If this happens, contact HR.
- Poor interface - Even where there are no explicit glitches, users note that several aspects of the interface are difficult to use and/or finicky, and that they generally seem poorly designed compared to the older Ecosystem Building game preceding it. For example, test takers have noted that navigation is difficult or unclear and the drag and drop feature for data points is temperamental - all of this costing precious time.
- Confusing language - Related to the above is that the English used is often rather convoluted and sometimes poorly phrased. This can be challenging even for native English speakers but is even worse for those sitting Solve in their second language. It can make the initial instructions difficult to understand - compounding the previous interface problem. It can also make questions difficult, requiring a few readings to comprehend.
- Insufficient time - Clearly, McKinsey intended for Redrock to be time pressured. Whilst the newest, Summer 2023 iteration of the Redrock case seems slightly more forgiving in this regard, time is still so scarce that many candidates don't get through all the questions. This is plainly sub-optimal for McKinsey - as well as being stressful and disheartening for candidates. We would expect further changes to be made to address this issue in future.
McKinsey are clearly aware of these issues, as even those sitting the new version of Redrock have been asked to complete substantial feedback surveys. Do note, then, that this raises the likelihood of further changes to the Redrock case study in the near term - meaning you should always be ready to tackle something new.
For the time being, though, we can take you through the fundamentals of the current version of the Redrock case study. For more detail, see our freshly updated PDF Guide .
The Scenario
Whilst changes to the details are likely in future, the current Redrock case study is set on the Island of Redrock. This island is a nature reserve with populations of various species, including wolves, elk and several varieties of plant.
In the original Redrock case, it is explained that the island's wolves are split into four packs, associated with four geographical locales. These packs predate the elk and depend upon them for food, such that there is a dynamic relationship between the population numbers of both species. Your job is to ensure ecological balance by optimising the numbers of wolves in the four packs, such that both wolves and elk can sustainably coexist.
In the newer iteration of the case, first observed in Summer 2023, you are asked to assess which, if any, of three possible strategies can successfully boost the island's plant biodiversity by a certain specified percentage. Plants here are segmented into grasses, trees and shrubs.
The Questions
The Redrock case study's questions were initially split into three sections, but a fourth was added later. These sections break down as follows:
- Investigation - Here, you have access to the full description of the case, with all the data on the various animal populations. Your task is to efficiently extract all the most salient data points and drag-and-drop them to your "Research Journal" workspace area. This is important, as you subsequently lose access to all the information you don't save at this stage.
- Analysis - You must answer three numerical questions using information you saved in the Investigation section. This can include you dragging and dropping values to and from an in-game calculator.
- Report - Formerly the final section, you must complete a pre-written report on the wolf populations or plant biodiversity levels, including calculating numerical values to fill in gaps and using an in-game interface to make a chart to illustrate your findings. You will leverage information saved in the Investigation section, as well as answers calculated in the Analysis section.
- Case Questions - This section adds a further ten individual case questions. These are wolf-themed, so are thematically similar to the original Redrock case, but are slightly incongruous with the newer, plant-themed version of Redrock. In both instances, though, these questions are entirely separable from the main case preceding them, not relying on any information from the previous sections. The ten questions are highly quantitative and extremely time pressured. Few test takers finish them before being timed out.
This is a very brief summary - more detail is available in our PDF Guide .
Other Games - Disease and Disaster Identification

There have been accounts of some test takers being given a third game as part of their Solve assessment. At time of writing, these third games have always been clearly introduced as non-scored beta tests for Imbellus to try out potential new additions to the assessment. However, the fact that these have been tested means that there is presumably a good chance we’ll see them as scored additions in future.
Notably, these alternative scenarios are generally variations on a fairly consistent theme and tend to share a good deal of the character of the Ecosystem Building game. Usually, candidates will be given a whole slew of information on how an animal population has changed over time. They will then have to wade through that information to figure out either which kind of natural disaster or which disease has been damaging that population - the commonality with the Ecosystem Building game being in the challenge of dealing with large volumes of information and figuring out which small fraction of it is actually relevant.
Join thousands of other candidates cracking cases like pros
What does the solve assessment test for.
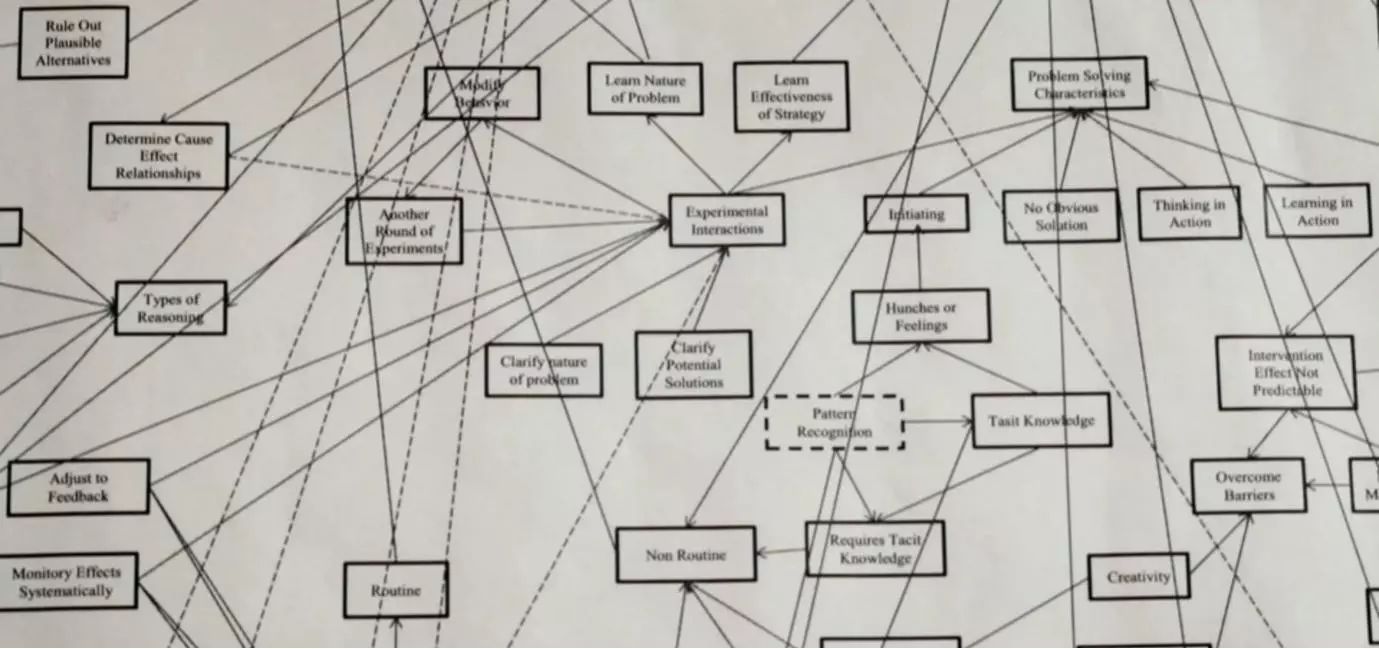
Whilst information on the Solve assessment can be hard to come by, Imbellus and McKinsey have at least been explicit on what traits the test was designed to look for. These are:
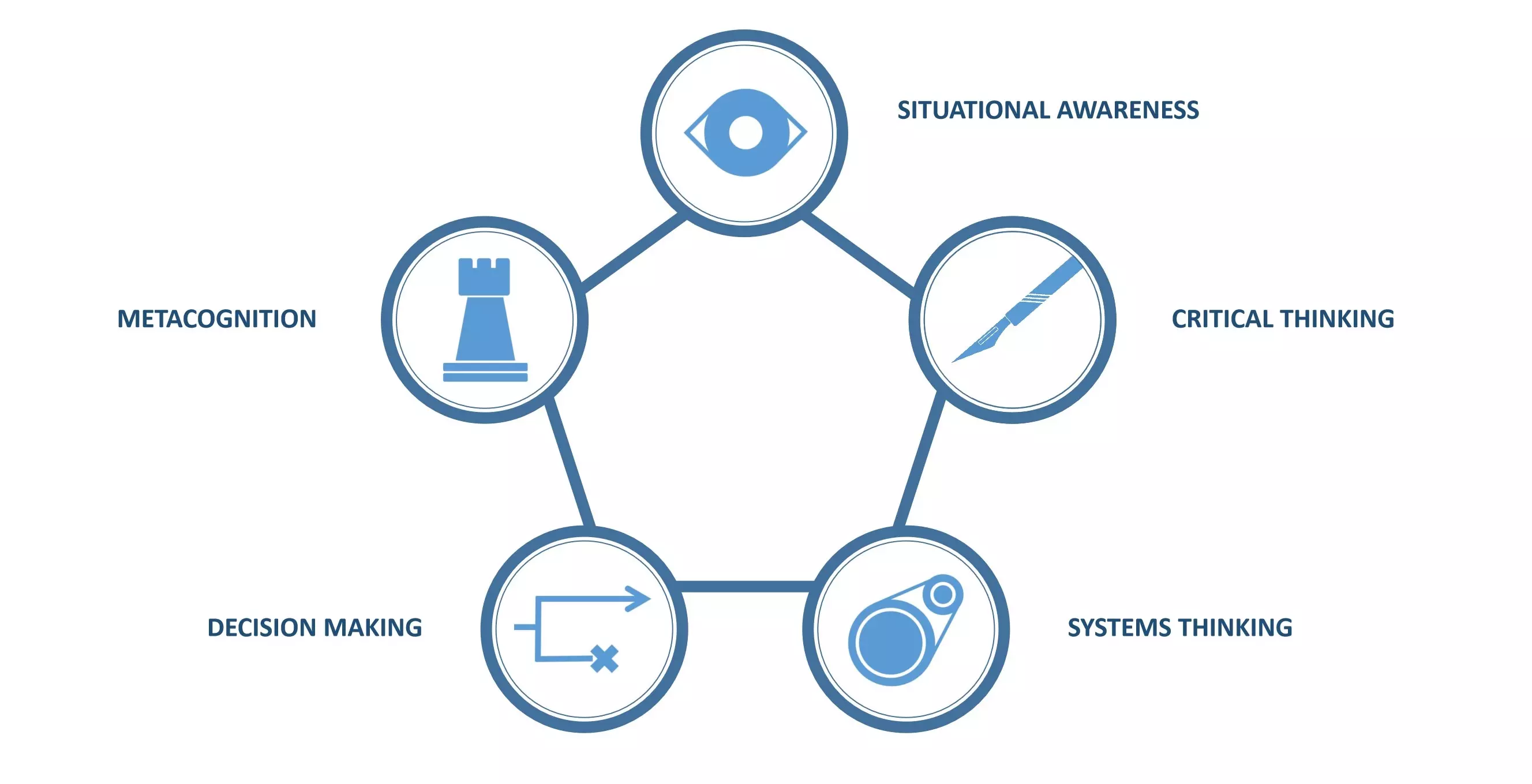
- Critical Thinking : making judgements based on the objective analysis of information
- Decision Making : choosing the best course of action, especially under time pressure or with incomplete information
- Metacognition : deploying appropriate strategies to tackle problems efficiently
- Situational Awareness : the ability to interpret and subsequently predict an environment
- Systems Thinking : understanding the complex causal relationships between the elements of a system
Equally important to understanding the raw facts of the particular skillset being sought out, though, is understanding the very idiosyncratic ways in which the Solve assessment tests for these traits.
Let's dive deeper:
Process Scores
Perhaps the key difference between the Solve assessment and any other test you’ve taken before is Imbellus’s innovation around “process scores”.
To explain, when you work through each of the games, the software examines the solutions you generate to the various problems you are faced with. How well you do here is measured by your “product score”.
However, scoring does not end there. Rather, Solve's software also constantly monitors and assesses the method you used to arrive at that solution. The quality of the method you used is then captured in your “process score”.
To make things more concrete here, if you are playing the Ecosystem Building game, you will not only be judged on whether the ecosystem you put together is self-sustaining. You will also be judged on the way you have worked in figuring out that ecosystem - presumably, on how efficient and organised you were. The program tracks all your mouse clicks and other actions and will thus be able to capture things like how you navigate around the various groups of species, how you place the different options you select, whether you change your mind before you submit the solution and so on.
You can find more detail on these advanced aspects of the Solve assessment and the innovative work behind it in the presentation by Imbellus founder Rebecca Kantar in the first section of the following video:
Compared to other tests, this is far more like the level of assessment you face from an essay-based exam, where the full progression of your argument towards a conclusion is marked - or a maths exam, where you are scored on your working as well as the final answer (with, of course, the major advantage that there is no highly qualified person required to mark papers).
Clearly, the upshot of all this is that you will want to be very careful how you approach the Solve assessment. You should generally try to think before you act and to show yourself in a very rational, rigorous, ordered light.
We have some advice to help look after your process scores in our PDF Guide to the McKinsey Solve Assessment .
A Different Test for Every Candidate
Another remarkable and seriously innovative aspect of the Solve assessment is that no two candidates receive exactly the same test.
Imbellus automatically varies the parameters of their games to be different for each individual test taker, so that each will be given a meaningfully different game to everyone else’s.
Within a game, this might mean a different terrain setting, having a different number of species or different types of species to work with or more or fewer restrictions on which species will eat which others.
Consequently, even if your buddy takes the assessment for the same level role at the same office just the day before you do, whatever specific strategy they used in their games might very well not work for you.
This is an intentional feature designed to prevent test takers from sharing information with one another and thus advantaging some over others. At the extreme, this feature would also be a robust obstacle to any kind of serious cheating.
To manage to give every candidate a different test and still be able to generate a reliable ranking of those candidates across a fundamental skillset, without that test being very lengthy, is a considerable achievement from Imbellus. At high level, this would seem to be approximately equivalent to reliably extracting a faint signal from a very noisy background on the first attempt almost every time.
(Note that we are yet to confirm to what extent and how this also happens with the new Redrock case studies, but it seems to be set up to allow for easy changes to be made to the numerical values describing the case, so we assume there will be similar, widespread of variation.)
Preparation for the McKinsey Solve assessment
Understanding what the Solve assessment tests for immediately begs the question as to whether it is possible to usefully prepare and, if so, what that preparation should look like.
Is it Really Possible to Prepare for the McKinsey Solve Assessment?

In short, yes you can - and you should!
As noted previously, there has been a lot of disagreement over whether it is really possible to prep for the Solve assessment in a way that actually makes a difference.
Especially for the legacy version, there has been a widespread idea that the Solve assessment functions as something like an IQ test, so that preparation beyond very basic familiarisation to ensure you don’t panic on test day will not do anything to reliably boost your scores (nobody is going to build up to scoring an IQ of 200 just by doing practice tests, for example).
This rationale says that the best you can do is familiarise yourself with what you are up against to calm your nerves and avoid misunderstanding instructions on test day. However, this school of thought says there will be minimal benefit from practice and/or skill building.
The utility of preparation has become a clearer with the addition of the Redrock case study to the new version of Solve. Its heavily quantitative nature, strong time pressure and structure closely resembling a traditional business case make for a clearer route to improvement.
However, as we explain in more detail in our PDF guide to the Solve assessment, the idea that any aspect of either version of Solve can't be prepared for has been based on some fundamental misunderstandings about what kind of cognitive traits are being tested. Briefly put, the five key skills the Solve assessment explicitly examines are what are known as higher-order thinking skills.
Crucially, these are abilities that can be meaningfully built over time.
McKinsey and Imbellus have generally advised that you shouldn’t prepare. However, this is not the same as saying that there is no benefit in doing so. McKinsey benefits from ensuring as even a playing field as possible. To have the Solve test rank candidates based purely on their pre-existing ability, they would ideally wish for a completely unprepared population.
How to prep

We discuss how to prep for the Solve assessment in full detail in our PDF guide . Here, though, we can give you a few initial pointers to get you started. In particular, there are some great ways to simulate different games as well as build up the skills the Solve assessment tests for.
Playing video games is great prep for the legacy Solve assessment in particular, but remains highly relevant to the new Redrock version.
Contrary to what McKinsey and Imbellus have said - and pretty unfortunately for those of us with other hobbies - test takers have consistently said that they reckoned the Problem Solving Game, and now the Solve assessment, favours those with strong video gaming experience.
If you listened when your parents told you video games were a waste of time and really don’t have any experience, then putting in some hours on pretty much anything will be useful. However, the closer the games you play are to the Solve scenarios, the better. We give some great recommendations on specific games and what to look for more generally in our Solve guide - including one free-to-play game that our clients have found hugely useful as prep for the plant defence game!
PST-Style Questions
The inclusion of the Redrock case studies in the new version of Solve really represents a return to something like a modernised PST. Along with the similar new BCG Casey assessment, this seems to be the direction of travel for consulting recruitment in general.
Luckily, this means that you can leverage the wealth of existing PST-style resources to your advantage in preparation.
Our PST article - which links to some free PST questions and our full PST prep resources - is a great place to start. However, better than old-fashioned PDF question sets are the digital PST-style questions embedded in our Case Academy course . Conducted online with a strict timer running, these are a much closer approximation of the Solve assessment itself. These questions are indeed a subset of our Case Academy course, but are also available separately in our Course Exercises package .
Quick Mathematics With a Calculator and/or Excel
Again, specifically for the Redrock assessment, you will be expected to solve math problems very quickly. The conceptual level of mathematics required is not particularly high, but you need to know what you are doing and get through it fast using a calculator nand/or Excel, if you are already comfortable with that program.
Our article on consulting math is a great place to start to understand what is expected of you throughout the recruiting process, with our consulting math package (a subset of our Case Academy course) providing more in-depth lessons and practice material.
Learn to Solve Case Studies
With the Redrock case studies clearly being ecology-themed analogues to standard business case studies, it's pretty obvious that getting good at case studies will be useful.
However, the Solve assessment as a whole is developed and calibrated to be predictive of case interview performance, so you can expect that improving your case solving ability will indirectly bring up your performance across the board.
Of course, this overlaps with your prep for McKinsey's case interviews. For more on how to get started there, see the final section of this article.
Learning About Optimal Strategies for the Games
The first thing to do is to familiarise yourself with the common game scenarios from the Solve assessment and how you can best approach them to help boost your chances of success.
Now, one thing to understand is that, since the parameters for the games change for each test taker, there might not be a single definitive optimal strategy for every single possible iteration of a particular game. As such, you shouldn’t rely on just memorising one approach and hoping it matches up to what you get on test day.
Instead, it is far better to understand why a strategy is sensible in some circumstances and when it might be better to do something else instead if the version of the game you personally receive necessitates a different approach.
In this article, we have given you a useful overview of the games currently included in the Solve assessment. However, a full discussion with suggested strategies is provided in our comprehensive Solve guide .
With the limited space available here, this is only a very brief sketch of a subset of the ways you can prep.
As noted, what will help with all of these and more is reading the extensive prep guidance in our full PDF guide to the Solve assessment...
The MCC Solve Assessment Guide
Preparing for the Solve assessment doesn’t have to be a matter of stumbling around on your own. This article is a good introduction. From here, though our new, updated PDF guide to the McKinsey Solve assessment is your first stop to optimise your Solve preparation.
This guide is based on our own survey work and interviews with real test takers, as well as iterative follow-ups on how the advice in previous editions worked out in reality.
Does it make sense to invest in a guide?
Short answer: yes. If you just think about the financials, a job at McKinsey is worth millions in the long run. If you factor in experience, personal growth and exit opportunities, the investment is a no-brainer.
How our guide can help you ace the test
Don't expect some magic tricks to game the system (because you can't), but rather an in-depth analysis of key areas crucial to boost your scores. This helps you to:
As noted, the guide is based on interviews with real recent test takers and covers the current games in detail. Being familiar with the game rules, mechanics and potential strategies in advance will massively reduce the amount of new information you have to assimilate from scratch on test day, allowing you to focus on the actual problems at hand.
Despite the innovative environment, the Solve assessment tests candidates for the same skills evaluated in case interviews, albeit on a more abstract level. Our guide breaks these skills down and provides a clear route to develop them. You also benefit from the cumulative experience of our clients, as we have followed up to see which prep methods and game strategies were genuinely helpful.
A clear plan of how to prepare is instrumental for success. Our guide includes a detailed, flexible preparation strategy, leveraging a whole host of diverse prep activities to help you practice and build your skills as effectively as possible. Importantly, our guide helps you prioritise the most effective aspects of preparation to optimise for whatever timeframe you have to work in.
Overall, the MyConsultingCoach Solve guide is designed to be no-nonsense and straight to the point. It tells you what you need to know up front and - for those of you in a hurry - crucial sections are clearly marked to read first to help you prep ASAP.
For those of you starting early with more time to spare, there is also a fully detailed, more nuanced discussion of what the test is looking for and how you can design a more long-term prep to build up the skills you need - and how this can fit into your wider case interview prep.
Importantly, there is no fluff to bulk out the page count. The market is awash with guides at huge page counts, stuffed full of irrelevant material to boost overall document length. By contrast, we realise your time is better spent actually preparing than ploughing through a novel.
If this sounds right for you, you can purchase our PDF Solve guide here:
McKinsey Solve Assessment Guide
- Full guide to both the legacy version of the Solve assessment and the newer Redrock Case Study versions
- In-depth description of the different games and strategies to beat them
- Preparation strategies for the short, medium and long-term prep
- No fluff - straight to the point, with specific tips for those without much time
- Straight to your inbox
- 30 days money-back guarantee, no questions asked. Simply email us and we will refund the full amount.
The Next Step - Case Interviews

So, you pour in the hours to generate an amazing resume and cover letter. You prepare diligently for the Solve assessment, going through our PDF guide and implementing all the suggestions. On test day, you sit down and ace Solve. The result is an invitation to a live McKinsey case interview.
Now the real work begins…
Arduous as application writing and Solve prep might have seemed, preparing for McKinsey case interviews will easily be an order of magnitude more difficult.
Remember that McKinsey tells candidates not to prepare for Solve - but McKinsey explicitly expects applicants to have rigorously prepared for case interviews .
The volume of specific business knowledge and case-solving principles, as well as the sheer complexity of the cases you will be given, mean that there is no way around knuckling down, learning what you need to know and practicing on repeat.
If you want to get through your interviews and actually land that McKinsey offer, you are going to need to take things seriously, put in the time and learn how to properly solve case studies.
Unfortunately, the framework-based approach taught by many older resources is unlikely to cut it for you. These tend to falter when applied to difficult, idiosyncratic cases - precisely the kind of case you can expect from McKinsey!
The method MCC teaches is based specifically on the way McKinsey train incoming consultants. We throw out generic frameworks altogether and show you how to solve cases like a real management consultant on a real engagement.
You can start reading about the MCC method for case cracking here . To step your learning up a notch, you can move on to our Case Academy course .
To put things into practice in some mock interviews with real McKinsey consultants, take a look at our coaching packages .
And, if all this (rightfully) seems pretty daunting and you’d like to have an experienced consultant guide you through your whole prep from start to finish, you can apply for our comprehensive mentoring programme here .
Looking for an all-inclusive, peace of mind program?
Our comprehensive packages.
Get our Solve guide for free if you purchase any of the following packages. Just email us with your order number and we will send the guide straight to your inbox.
Access to our Case Academy and to coaching will help you prepare for Solve and for the following rounds!
The MCC bundle
- All Case Interview Course Videos
- All Case Interview Course Exercises
- All Fit Interview Course Videos
- All case interview self-assessment modules
- Available on all devices
- Premium support for questions
- Lifetime access
Bridge to Consulting
- 5 one-hour sessions with ex-MBB (McKinsey/Bain/BCG) coach of your choice
- Session personalisation (skill level and preparation stage)
- Choice of interview format (Fit, Case or Both)
- AI-powered performance benchmarking, skill-gap assessment and actionable feedback through your Dashboard
- Full Access to Case Academy (Course, Exercises, Self-Assessments, Fit and Math)
- McKinsey Digital Assessment Guide
- All our PST material
Case Interview Course
- 16+ hours of lectures covering all aspects of the case interview
- Introduction to the consulting interview
- Case Interview foundations section
- Problem Driven Approach
- Building blocks
- Efficiency tools
- Problem driven structure in action
- Roadmap for preparation planning
Account not confirmed

Romulus’s Substack
The mckinsey problem solving approach to consulting: a comprehensive guide, by: jason branin.

In the realm of management consulting, McKinsey & Company stands out as a beacon of excellence and innovation. Since its founding in 1926 by James O. McKinsey, the firm has grown to become one of the most prestigious and influential consulting firms in the world. Central to McKinsey's success is its unique problem-solving approach, which has not only shaped the firm’s own practices but has also significantly influenced the broader consulting industry. This article delves into the intricacies of the McKinsey Problem Solving Approach, exploring its methodologies, tools, and the impact it has on delivering high-value solutions to clients.
The Essence of the McKinsey Problem Solving Approach
Thanks for reading Romulus’s Substack! Subscribe for free to receive new posts and support my work.
At its core, the McKinsey Problem Solving Approach is a structured methodology designed to tackle complex business challenges through a combination of rigorous analysis, strategic thinking, and practical recommendations. This approach is characterized by its systematic nature, emphasizing clarity, precision, and thoroughness in every step of the problem-solving process. The primary objective is to deliver actionable insights and sustainable solutions that drive tangible results for clients.
Key Components of the McKinsey Problem Solving Approach
1. Defining the Problem
The first and most crucial step in the McKinsey Problem Solving Approach is defining the problem. This involves clearly articulating the issue at hand, setting the boundaries for the analysis, and establishing the objectives of the engagement. McKinsey consultants use a structured framework known as the “problem statement” to capture the essence of the challenge. A well-defined problem statement typically includes:
- Context: The background information and relevant facts about the client and the issue.
- Objective: The desired outcome or goal of the analysis.
- Scope: The boundaries and constraints of the problem.
- Hypotheses: Initial assumptions or potential solutions that will be tested during the analysis.
By investing time and effort in defining the problem accurately, McKinsey ensures that the subsequent analysis is focused, relevant, and aligned with the client’s needs.
2. Disaggregating the Problem
Once the problem is defined, the next step is to break it down into smaller, manageable components. This process, known as disaggregation, allows consultants to tackle each part of the problem systematically. McKinsey employs the MECE (Mutually Exclusive, Collectively Exhaustive) principle to ensure that all aspects of the problem are covered without any overlap or gaps. The MECE framework helps in organizing information logically and ensures that the analysis is comprehensive.
For example, if the problem involves improving a company's profitability, McKinsey might disaggregate it into components such as revenue enhancement, cost reduction, and operational efficiency. Each of these components is then further broken down into sub-components, allowing for a detailed and focused analysis.
3. Conducting the Analysis
The analysis phase is where McKinsey's analytical rigor comes to the fore. This phase involves gathering data, testing hypotheses, and developing insights. McKinsey consultants use a variety of tools and techniques to conduct their analysis, including:
- Benchmarking: Comparing the client’s performance against industry standards or best practices.
- Financial Modeling: Building detailed models to simulate different scenarios and their financial impact.
-Root Cause Analysis: Identifying the underlying causes of the problem rather than just addressing the symptoms.
-Scenario Planning: Exploring different future scenarios to anticipate potential challenges and opportunities.
Data-driven decision-making is a hallmark of McKinsey’s approach. The firm places a strong emphasis on using quantitative data to support its findings and recommendations. This ensures that the solutions proposed are not only theoretically sound but also practically viable.
4. Synthesizing Insights
After conducting the analysis, the next step is to synthesize the insights and draw conclusions. This involves distilling the vast amount of data and information into clear, actionable insights that address the client’s problem. McKinsey consultants use the “Pyramid Principle,” a communication technique developed by Barbara Minto, a former McKinsey consultant, to present their findings. The Pyramid Principle advocates starting with the main conclusion or recommendation and then supporting it with key arguments and data.
This top-down approach ensures that the most important insights are communicated upfront, making it easier for clients to understand and act upon the recommendations. It also helps in structuring complex information in a logical and coherent manner.
5. Developing Recommendations
Based on the synthesized insights, McKinsey consultants develop specific recommendations for the client. These recommendations are not just theoretical ideas but practical, actionable steps that the client can implement to address the problem. McKinsey places a strong emphasis on creating “value-driven” recommendations that deliver measurable impact.
To ensure the recommendations are actionable, McKinsey follows a few guiding principles:
- Feasibility: Ensuring that the recommendations are realistic and can be implemented within the client’s constraints.
- Sustainability: Focusing on long-term solutions that deliver sustained benefits rather than short-term fixes.
- Client Buy-in: Engaging the client throughout the process to ensure they understand and are committed to the recommendations.
6. Implementing Solutions
The final step in the McKinsey Problem Solving Approach is implementing the solutions. McKinsey often works closely with clients to support the implementation phase, ensuring that the recommendations are executed effectively. This involves developing detailed implementation plans, setting up monitoring mechanisms, and providing ongoing support and guidance.
McKinsey’s commitment to implementation reflects its philosophy of “seeing it through.” The firm recognizes that the true value of its consulting services lies not just in developing insightful recommendations but in helping clients achieve tangible results.
Tools and Techniques in the McKinsey Problem Solving Approach
McKinsey employs a wide range of tools and techniques to support its problem-solving approach. Some of the most commonly used tools include:
1. The Issue Tree
The Issue Tree is a visual representation of the problem and its sub-components. It helps in organizing the problem into a hierarchical structure, making it easier to identify the key issues and areas of focus. The Issue Tree is typically used during the disaggregation phase to break down the problem into smaller, manageable parts.
2. The Decision Tree
The Decision Tree is a tool used to map out different decision paths and their potential outcomes. It helps in evaluating the implications of different choices and identifying the most optimal decision. The Decision Tree is particularly useful in scenarios where there are multiple possible solutions or courses of action.
3. The Hypothesis Pyramid
The Hypothesis Pyramid is a tool used to structure hypotheses in a logical manner. It helps in organizing hypotheses into a hierarchy, with the main hypothesis at the top and supporting hypotheses underneath. This tool is used to guide the analysis and ensure that all relevant hypotheses are tested systematically.
4. The MECE Framework
The MECE (Mutually Exclusive, Collectively Exhaustive) framework is a key principle in the McKinsey Problem Solving Approach. It ensures that all aspects of the problem are covered without any overlap or gaps. The MECE framework is used during the disaggregation phase to organize information logically and comprehensively.
5. The Pyramid Principle
The Pyramid Principle is a communication technique used to present findings and recommendations in a clear and structured manner. It advocates starting with the main conclusion or recommendation and then supporting it with key arguments and data. This top-down approach ensures that the most important insights are communicated upfront.
The Impact of the McKinsey Problem Solving Approach
The McKinsey Problem Solving Approach has had a profound impact on the field of management consulting and beyond. Some of the key impacts include:
1. Driving Business Success
McKinsey’s structured and rigorous approach to problem-solving has helped countless organizations achieve significant improvements in performance and profitability. By providing data-driven insights and practical recommendations, McKinsey has enabled clients to address complex challenges and capitalize on new opportunities.
2. Setting Industry Standards
McKinsey’s methodologies and best practices have set industry standards for consulting. Many of the tools and techniques developed by McKinsey, such as the MECE framework and the Pyramid Principle, have become widely adopted across the consulting industry. McKinsey’s emphasis on analytical rigor and strategic thinking has influenced the way consulting firms approach problem-solving.
3. Fostering Innovation
McKinsey’s approach to problem-solving fosters innovation by encouraging consultants to think creatively and challenge conventional wisdom. The firm’s focus on developing hypotheses and testing them systematically promotes a culture of experimentation and continuous improvement. This has led to the development of innovative solutions that drive business success.
4. Building Client Capabilities
McKinsey’s commitment to implementation and client engagement helps build the capabilities of client organizations. By working closely with clients throughout the problem-solving process, McKinsey ensures that clients not only achieve immediate results but also develop the skills and knowledge to sustain improvements over the long term.
The McKinsey Problem Solving Approach is a testament to the firm’s commitment to excellence and innovation. Its structured methodology, emphasis on analytical rigor, and focus on delivering actionable insights have made McKinsey a trusted advisor to some of the world’s most successful organizations. By continually refining its approach and embracing new tools and techniques, McKinsey remains at the forefront of the consulting industry, helping clients navigate complex challenges and achieve sustainable growth.
As businesses continue to face an ever-changing landscape, the principles and practices of the McKinsey Problem Solving Approach will remain highly relevant. Its focus on defining the problem accurately, conducting rigorous analysis, and developing practical recommendations provides a robust framework for tackling the most pressing business issues. For organizations seeking to drive performance and innovation, embracing the McKinsey Problem Solving Approach can be a powerful catalyst for success.
If you are looking to continue this conversation or are looking for some advice, please, feel free to reach out to me at [email protected].
Ready for more?

McKinsey Problem Solving: Six steps to solve any problem and tell a persuasive story
The McKinsey problem solving process is a series of mindset shifts and structured approaches to thinking about and solving challenging problems. It is a useful approach for anyone working in the knowledge and information economy and needs to communicate ideas to other people.
Over the past several years of creating StrategyU, advising an undergraduates consulting group and running workshops for clients, I have found over and over again that the principles taught on this site and in this guide are a powerful way to improve the type of work and communication you do in a business setting.
When I first set out to teach these skills to the undergraduate consulting group at my alma mater, I was still working at BCG. I was spending my day building compelling presentations, yet was at a loss for how to teach these principles to the students I would talk with at night.
Through many rounds of iteration, I was able to land on a structured process and way of framing some of these principles such that people could immediately apply them to their work.
While the “official” McKinsey problem solving process is seven steps, I have outline my own spin on things – from experience at McKinsey and Boston Consulting Group. Here are six steps that will help you solve problems like a McKinsey Consultant:
Step #1: School is over, stop worrying about “what” to make and worry about the process, or the “how”
When I reflect back on my first role at McKinsey, I realize that my biggest challenge was unlearning everything I had learned over the previous 23 years. Throughout school you are asked to do specific things. For example, you are asked to write a 5 page paper on Benjamin Franklin — double spaced, 12 font and answering two or three specific questions.
In school, to be successful you follow these rules as close as you can. However, in consulting there are no rules on the “what.” Typically the problem you are asked to solve is ambiguous and complex — exactly why they hire you. In consulting, you are taught the rules around the “how” and have to then fill in the what.
The “how” can be taught and this entire site is founded on that belief. Here are some principles to get started:
Step #2: Thinking like a consultant requires a mindset shift
There are two pre-requisites to thinking like a consultant. Without these two traits you will struggle:
- A healthy obsession looking for a “better way” to do things
- Being open minded to shifting ideas and other approaches
In business school, I was sitting in one class when I noticed that all my classmates were doing the same thing — everyone was coming up with reasons why something should should not be done.
As I’ve spent more time working, I’ve realized this is a common phenomenon. The more you learn, the easier it becomes to come up with reasons to support the current state of affairs — likely driven by the status quo bias — an emotional state that favors not changing things. Even the best consultants will experience this emotion, but they are good at identifying it and pushing forward.
Key point : Creating an effective and persuasive consulting like presentation requires a comfort with uncertainty combined with a slightly delusional belief that you can figure anything out.
Step #3: Define the problem and make sure you are not solving a symptom
Before doing the work, time should be spent on defining the actual problem. Too often, people are solutions focused when they think about fixing something. Let’s say a company is struggling with profitability. Someone might define the problem as “we do not have enough growth.” This is jumping ahead to solutions — the goal may be to drive more growth, but this is not the actual issue. It is a symptom of a deeper problem.
Consider the following information:
- Costs have remained relatively constant and are actually below industry average so revenue must be the issue
- Revenue has been increasing, but at a slowing rate
- This company sells widgets and have had no slowdown on the number of units it has sold over the last five years
- However, the price per widget is actually below where it was five years ago
- There have been new entrants in the market in the last three years that have been backed by Venture Capital money and are aggressively pricing their products below costs
In a real-life project there will definitely be much more information and a team may take a full week coming up with a problem statement . Given the information above, we may come up with the following problem statement:
Problem Statement : The company is struggling to increase profitability due to decreasing prices driven by new entrants in the market. The company does not have a clear strategy to respond to the price pressure from competitors and lacks an overall product strategy to compete in this market.
Step 4: Dive in, make hypotheses and try to figure out how to “solve” the problem
Now the fun starts!
There are generally two approaches to thinking about information in a structured way and going back and forth between the two modes is what the consulting process is founded on.
First is top-down . This is what you should start with, especially for a newer “consultant.” This involves taking the problem statement and structuring an approach. This means developing multiple hypotheses — key questions you can either prove or disprove.
Given our problem statement, you may develop the following three hypotheses:
- Company X has room to improve its pricing strategy to increase profitability
- Company X can explore new market opportunities unlocked by new entrants
- Company X can explore new business models or operating models due to advances in technology
As you can see, these three statements identify different areas you can research and either prove or disprove. In a consulting team, you may have a “workstream leader” for each statement.
Once you establish the structure you you may shift to the second type of analysis: a bottom-up approach . This involves doing deep research around your problem statement, testing your hypotheses, running different analysis and continuing to ask more questions. As you do the analysis, you will begin to see different patterns that may unlock new questions, change your thinking or even confirm your existing hypotheses. You may need to tweak your hypotheses and structure as you learn new information.
A project vacillates many times between these two approaches. Here is a hypothetical timeline of a project:

Step 5: Make a slides like a consultant
The next step is taking the structure and research and turning it into a slide. When people see slides from McKinsey and BCG, they see something that is compelling and unique, but don’t really understand all the work that goes into those slides. Both companies have a healthy obsession (maybe not to some people!) with how things look, how things are structured and how they are presented.
They also don’t understand how much work is spent on telling a compelling “story.” The biggest mistake people make in the business world is mistaking showing a lot of information versus telling a compelling story. This is an easy mistake to make — especially if you are the one that did hours of analysis. It may seem important, but when it comes down to making a slide and a presentation, you end up deleting more information rather than adding. You really need to remember the following:
Data matters, but stories change hearts and minds
Here are four quick ways to improve your presentations:
Tip #1 — Format, format, format
Both McKinsey and BCG had style templates that were obsessively followed. Some key rules I like to follow:
- Make sure all text within your slide body is the same font size (harder than you would think)
- Do not go outside of the margins into the white space on the side
- All titles throughout the presentation should be 2 lines or less and stay the same font size
- Each slide should typically only make one strong point
Tip #2 — Titles are the takeaway
The title of the slide should be the key insight or takeaway and the slide area should prove the point. The below slide is an oversimplification of this:

Even in consulting, I found that people struggled with simplifying a message to one key theme per slide. If something is going to be presented live, the simpler the better. In reality, you are often giving someone presentations that they will read in depth and more information may make sense.
To go deeper, check out these 20 presentation and powerpoint tips .
Tip #3 — Have “MECE” Ideas for max persuasion
“MECE” means mutually exclusive, collectively exhaustive — meaning all points listed cover the entire range of ideas while also being unique and differentiated from each other.
An extreme example would be this:
- Slide title: There are seven continents
- Slide content: The seven continents are North America, South America, Europe, Africa Asia, Antarctica, Australia
The list of continents provides seven distinct points that when taken together are mutually exclusive and collectively exhaustive . The MECE principle is not perfect — it is more of an ideal to push your logic in the right direction. Use it to continually improve and refine your story.
Applying this to a profitability problem at the highest level would look like this:
Goal: Increase profitability
2nd level: We can increase revenue or decrease costs
3rd level: We can increase revenue by selling more or increasing prices
Each level is MECE. It is almost impossible to argue against any of this (unless you are willing to commit accounting fraud!).
Tip #4 — Leveraging the Pyramid Principle
The pyramid principle is an approach popularized by Barbara Minto and essential to the structured problem solving approach I learned at McKinsey. Learning this approach has changed the way I look at any presentation since.
Here is a rough outline of how you can think about the pyramid principle as a way to structure a presentation:

As you build a presentation, you may have three sections for each hypothesis. As you think about the overall story, the three hypothesis (and the supporting evidence) will build on each other as a “story” to answer the defined problem. There are two ways to think about doing this — using inductive or deductive reasoning:

If we go back to our profitability example from above, you would say that increasing profitability was the core issue we developed. Lets assume that through research we found that our three hypotheses were true. Given this, you may start to build a high level presentation around the following three points:

These three ideas not only are distinct but they also build on each other. Combined, they tell a story of what the company should do and how they should react. Each of these three “points” may be a separate section in the presentation followed by several pages of detailed analysis. There may also be a shorter executive summary version of 5–10 pages that gives the high level story without as much data and analysis.
Step 6: The only way to improve is to get feedback and continue to practice
Ultimately, this process is not something you will master overnight. I’ve been consulting, either working for a firm or on my own for more than 10 years and am still looking for ways to make better presentations, become more persuasive and get feedback on individual slides.
The process never ends.
The best way to improve fast is to be working on a great team . Look for people around you that do this well and ask them for feedback. The more feedback, the more iterations and more presentations you make, the better you will become. Good luck!
If you enjoyed this post, you’ll get a kick out of all the free lessons I’ve shared that go a bit deeper. Check them out here .
Do you have a toolkit for business problem solving? I created Think Like a Strategy Consultant as an online course to make the tools of strategy consultants accessible to driven professionals, executives, and consultants. This course teaches you how to synthesize information into compelling insights, structure your information in ways that help you solve problems, and develop presentations that resonate at the C-Level. Click here to learn more or if you are interested in getting started now, enroll in the self-paced version ($497) or hands-on coaching version ($997). Both versions include lifetime access and all future updates.
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pocket (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
Resources >
Mckinsey approach to problem solving, a guide to the 7-step mckinsey problem solving process.
McKinsey and Company is recognized for its rigorous approach to problem solving. They train their consultants on their seven-step process that anyone can learn.
This resource guides you through that process, largely informed by the McKinsey Staff Paper 66. It also includes a PowerPoint Toolkit with slide templates of each step of the process that you can download and customize for your own use.
In this guide you'll learn:
Overview of the mckinsey approach to problem solving, problem solving process, problem definition.
- Problem Statement
Stakeholder Analysis Worksheet
Structure the problem, hypothesis trees, issue trees, analyses and workplan, synthesize findings, craft recommendations, communicate, distinctiveness practices, harness the power of collaboration, sources and additional reading, request the mckinsey approach to problem solving.
Problem solving — finding the optimal solution to a given business opportunity or challenge — is the very heart of how consultants create client impact, and considered the most important skill for success at McKinsey.
The characteristic “McKinsey method” of problem solving is a structured, inductive approach that can be used to solve any problem. Using this standardized process saves us from reinventing the problem-solving wheel, and allows for greater focus on distinctiveness in the solution. Every new McKinsey associate must learn this method on his or her first day with the firm.
There are four fundamental disciplines of the McKinsey method:
1. Problem definition
A thorough understanding and crisp definition of the problem.
2. The problem-solving process
Structuring the problem, prioritizing the issues, planning analyses, conducting analyses, synthesizing findings, and developing recommendations.
3. Distinctiveness practices
Constructing alternative perspectives; identifying relationships; distilling the essence of an issue, analysis, or recommendation; and staying ahead of others in the problem-solving process.
4. Collaboratio n
Actively seeking out client, customer, and supplier perspectives, as well as internal and external expert insight and knowledge.
Once the problem has been defined, the problem-solving process proceeds with a series of steps:
- Structure the problem
- Prioritize the issues
- Plan analyses
- Conduct analyses
- Synthesize findings
- Develop recommendations
Not all problems require strict adherence to the process. Some steps may be truncated, such as when specific knowledge or analogies from other industries make it possible to construct hypotheses and associated workplans earlier than their formal place in the process. Nonetheless, it remains important to be capable of executing every step in the basic process.
When confronted with a new and complex problem, this process establishes a path to defining and disaggregating the problem in a way that will allow the team to move to a solution. The process also ensures nothing is missed and concentrates efforts on the highest-impact areas. Adhering to the process gives the client clear steps to follow, building confidence, credibility, and long-term capability.
The most important step in your entire project is to first carefully define the problem. The problem definition will serve the guide all of the team’s work, so it is critical to ensure that all key stakeholders agree that it is the right problem to be solving.
The problem definition will serve the guide all of the team’s work, so it is critical to ensure that all key stakeholders agree that it is the right problem to be solving.
There are often dozens of issues that a team could focus on, and it is often not obvious how to define the problem.
In any real-life situation, there are many possible problem statements. Your choice of problem statement will serve to constrain the range of possible solutions.
Constraints can be a good thing (e.g., limit solutions to actions within the available budget.) And constraints can be a bad thing (e.g., eliminating the possibility of creative ideas.) So choose wisely.
The problem statement may ignore many issues to focus on the priority that should be addressed. The problem statement should be phrased as a question, such that the answer will be the solution.
Example scenario – A family on Friday evening :
A mother, a father, and their two teenage children have all arrived home on a Friday at 6 p.m. The family has not prepared dinner for Friday evening. The daughter has lacrosse practice on Saturday and an essay to write for English class due on Monday. The son has theatre rehearsal on both Saturday and Sunday and will need one parent to drive him to the high school both days, though he can get a ride home with a friend.
The family dog, a poodle, must be taken to the groomer on Saturday morning. The mother will need to spend time this weekend working on assignments for her finance class she is taking as part of her Executive MBA. The father plans to go on a 100-mile bike ride, which he can do either Saturday or Sunday. The family has two cars, but one is at the body shop. They are trying to save money to pay for an addition to their house.
Potential problem definitions – A family on Friday evening :
The problem definition should not be vague, without clear measures of success. Rather, it should be a SMART definition:
- Action-oriented
Given one set of facts, it is possible to come up with many possible problem statements. The choice of problem statement constrains the range of possible solutions.
Before starting to solve the problem, the family first needs to agree on what problem they want to solve.
- What should the family do for dinner on Friday night?
- How can the family schedule their activities this weekend to accomplish everything planned given that they only have one vehicle available?
- How can the family increase income or reduce expenses to allow them to save $75K over the next 12 months to pay for the planned addition to their house?
Problem Statement Worksheet
This is a helpful tool to use to clearly define the problem. There are often dozens of issues that a team could focus on, and it is often not obvious how to define the problem. In any real-life situation, there are many possible problem statements. Your choice of problem statement will serve to constrain the range of possible solutions.
- Use a question . The problem statement should be phrased as a question, such that the answer will be the solution. Make the question SMART: specific, measurable, action-oriented, relevant, and time-bound. Example: “How can XYZ Bank close the $100 million profitability gap in two years?”
- Context . What are the internal and external situations and complications facing the client, such as industry trends, relative position within the industry, capability gaps, financial flexibility, and so on?
- Success criteria . Understand how the client and the team define success and failure. In addition to any quantitative measures identified in the basic question, identify other important quantitative or qualitative measures of success, including timing of impact, visibility of improvement, client capability building required, necessary mindset shifts, and so on.
- Scope and constraints . Scope most commonly covers the markets or segments of interest, whereas constraints govern restrictions on the nature of solutions within those markets or segments.
- Stakeholders . Explore who really makes the decisions — who decides, who can help, and who can block.
- Key sources of insight . What best-practice expertise, knowledge, and engagement approaches already exist? What knowledge from the client, suppliers, and customers needs to be accessed? Be as specific as possible: who, what, when, how, and why.
In completing the Problem Statement Worksheet, you are prompted to define the key stakeholders.
As you become involved in the problem-solving process, you should expand the question of key stakeholders to include what the team wants from them and what they want from the team, their values and motivations (helpful and unhelpful), and the communications mechanisms that will be most effective for each of them.
Using the Stakeholder Analysis Worksheet allows you to comprehensively identify:
- Stakeholders
- What you need from them
- Where they are
- What they need from you
The two most helpful techniques for rigorously structuring any problem are hypothesis trees and issue trees. Each of these techniques disaggregates the primary question into a cascade of issues or hypotheses that, when addressed, will together answer the primary question.
A hypothesis tree might break down the same question into two or more hypotheses.
The aim at this stage is to structure the problem into discrete, mutually exclusive pieces that are small enough to yield to analysis and that, taken together, are collectively exhaustive.
Articulating the problem as hypotheses, rather than issues, is the preferred approach because it leads to a more focused analysis of the problem. Questions to ask include:
- Is it testable – can you prove or disprove it?
- It is open to debate? If it cannot be wrong, it is simply a statement of fact and unlikely to produce keen insight.
- If you reversed your hypothesis – literally, hypothesized that the exact opposite were true – would you care about the difference it would make to your overall logic?
- If you shared your hypothesis with the CEO, would it sound naive or obvious?
- Does it point directly to an action or actions that the client might take?
Quickly developing a powerful hypothesis tree enables us to develop solutions more rapidly that will have real impact. This can sometimes seem premature to clients, who might find the “solution” reached too quickly and want to see the analysis behind it.
Take care to explain the approach (most important, that a hypothesis is not an answer) and its benefits (that a good hypothesis is the basis of a proven means of successful problem solving and avoids “boiling the ocean”).
Example: Alpha Manufacturing, Inc.
Problem Statement: How can Alpha increase EBITDA by $13M (to $50M) by 2025?
The hypotheses might be:
- Alpha can add $125M revenues by expanding to new customers, adding $8M of EBITDA
- Alpha can reduce costs to improve EBITDA by $5M
These hypotheses will be further disaggregated into subsidiary hypotheses at the next level of the tree.
Often, the team has insufficient knowledge to build a complete hypothesis tree at the start of an engagement. In these cases, it is best to begin by structuring the problem using an issue tree.
An issue tree is best set out as a series of open questions in sentence form. For example, “How can the client minimize its tax burden?” is more useful than “Tax.” Open questions – those that begin with what, how, or why– produce deeper insights than closed ones. In some cases, an issue tree can be sharpened by toggling between issue and hypothesis – working forward from an issue to identify the hypothesis, and back from the hypothesis to sharpen the relevant open question.
Once the problem has been structured, the next step is to prioritize the issues or hypotheses on which the team will focus its work. When prioritizing, it is common to use a two-by-two matrix – e.g., a matrix featuring “impact” and “ease of impact” as the two axes.
Applying some of these prioritization criteria will knock out portions of the issue tree altogether. Consider testing the issues against them all, albeit quickly, to help drive the prioritization process.
Once the criteria are defined, prioritizing should be straightforward: Simply map the issues to the framework and focus on those that score highest against the criteria.
As the team conducts analysis and learns more about the problem and the potential solution, make sure to revisit the prioritization matrix so as to remain focused on the highest-priority issues.
The issues might be:
- How can Alpha increase revenue?
- How can Alpha reduce cost?
Each of these issues is then further broken down into deeper insights to solutions.
If the prioritization has been carried out effectively, the team will have clarified the key issues or hypotheses that must be subjected to analysis. The aim of these analyses is to prove the hypotheses true or false, or to develop useful perspectives on each key issue. Now the task is to design an effective and efficient workplan for conducting the analyses.
Transforming the prioritized problem structure into a workplan involves two main tasks:
- Define the blocks of work that need to be undertaken. Articulate as clearly as possible the desired end products and the analysis necessary to produce them, and estimate the resources and time required.
- Sequence the work blocks in a way that matches the available resources to the need to deliver against key engagement milestones (e.g., important meetings, progress reviews), as well as to the overall pacing of the engagement (i.e., weekly or twice-weekly meetings, and so on).
A good workplan will detail the following for each issue or hypothesis: analyses, end products, sources, and timing and responsibility. Developing the workplan takes time; doing it well requires working through the definition of each element of the workplan in a rigorous and methodical fashion.
It’s useful to match the workplan to three horizons:
- What is expected at the end of the engagement
- What is expected at key progress reviews
- What is due at daily and/or weekly team meetings
The detail in the workplan will typically be greater for the near term (the next week) than for the long term (the study horizon), especially early in a new engagement when considerable ambiguity about the end state remains.
Here are three different templates for a workplan:
This is the most difficult element of the problem-solving process. After a period of being immersed in the details, it is crucial to step back and distinguish the important from the merely interesting. Distinctive problem solvers seek the essence of the story that will underpin a crisp recommendation for action.
Although synthesis appears, formally speaking, as the penultimate step in the process, it should happen throughout. Ideally, after you have made almost any analytical progress, you should attempt to articulate the “Day 1” or “Week 1” answer. Continue to synthesize as you go along. This will remind the team of the question you are trying to answer, assist prioritization, highlight the logical links of the emerging solution, and ensure that you have a story ready to articulate at all times during the study.
McKinsey’s primary tool for synthesizing is the pyramid principle. Essentially, this principle asserts that every synthesis should explain a single concept, per the “governing thought.” The supporting ideas in the synthesis form a thought hierarchy proceeding in a logical structure from the most detailed facts to the governing thought, ruthlessly excluding the interesting but irrelevant.
While this hierarchy can be laid out as a tree (like with issue and hypothesis trees), the best problem solvers capture it by creating dot-dash storylines — the Pyramid Structure for Grouping Arguments.
Pyramid Structure for Grouping Arguments
- Focus on action. Articulate the thoughts at each level of the pyramid as declarative sentences, not as topics. For example, “expansion” is a topic; “We need to expand into the European market” is a declarative sentence.
- Use storylines. PowerPoint is poor at highlighting logical connections, therefore is not a good tool for synthesis. A storyline will clarify elements that may be ambiguous in the PowerPoint presentation.
- Keep the emerging storyline visible. Many teams find that posting the storyline or story- board on the team-room wall helps keep the thinking focused. It also helps in bringing the client along.
- Use the situation-complication-resolution structure. The situation is the reason there is action to be taken. The com- plication is why the situation needs thinking through – typically an industry or client challenge. The resolution is the answer.
- Down the pyramid: does each governing thought pose a single question that is answered completely by the group of boxes below it?
- Across: is each level within the pyramid MECE?
- Up: does each group of boxes, taken together, provide one answer – one “so what?” – that is essentially the governing thought above it?
- Test the solution. What would it mean if your hypotheses all came true?
It is at this point that we address the client’s questions: “What do I do, and how do I do it?” This means not offering actionable recommendations, along with a plan and client commitment for implementation.
The essence of this step is to translate the overall solution into the actions required to deliver sustained impact. A pragmatic action plan should include:
- Relevant initiatives, along with a clear sequence, timing, and mapping of activities required
- Clear owners for each initiative
- Key success factors and the challenges involved in delivering on the initiatives
Crucial questions to ask as you build recommendations for organizational change are:
- Does each person who needs to change (from the CEO to the front line) understand what he or she needs to change and why, and is he or she committed to it?
- Are key leaders and role models throughout the organization personally committed to behaving differently?
- Has the client set in place the necessary formal mechanisms to reinforce the desired change?
- Does the client have the skills and confidence to behave in the desired new way?
Once the recommendations have been crafted in the problem-solving process, it’s vital to effectively communicate those findings and recommendations.
An executive summary is a great slide to use for this. See more on executive summary slides, including 30 templates, at our Ultimate Guide to Executive Summary Slides .
Great problem solvers identify unique disruptions and discontinuities, novel insights, and step-out opportunities that lead to truly distinctive impact. This is done by applying a number of practices throughout the problem-solving process to help develop these insights.
Expand: Construct multiple perspectives
Identifying alternative ways of looking at the problem expands the range of possibilities, opens you up to innovative ideas, and allows you to formulate more powerful hypotheses. Questions that help here include:
- What changes if I think from the perspective of a customer, or a supplier, or a frontline employee, or a competitor?
- How have other industries viewed and addressed this same problem?
- What would it mean if the client sought to run the company like a low-cost airline or a cosmetics manufacturer?
Link: Identify relationships
Strong problem solvers discern connections and recognize patterns in two different ways:
- They seek out the ways in which different problem elements – issues, hypotheses, analyses, work elements, findings, answers, and recommendations – relate to one another.
- They use these relationships throughout the basic problem-solving process to identify efficient problem-solving approaches, novel solutions, and more powerful syntheses.
Distill: Find the essence
Cutting through complexity to identify the heart of the problem and its solution is a critical skill.
- Identify the critical problem elements. Are there some issues, approaches, or options that can be eliminated completely because they won’t make a significant difference to the solution?
- Consider how complex the different elements are and how long it will take to complete them. Wherever possible, quickly advance simpler parts of the problem that can inform more complex or time-consuming elements.
Lead: Stay ahead/step back
Without getting ahead of the client, you cannot be distinctive. Paradoxically, to get ahead – and stay ahead – it is often necessary to step back from the problem to validate or revalidate the approach and the solution.
- Spend time thinking one or more steps ahead of the client and team.
- Constantly check and challenge the rigor of the underlying data and analysis.
- Stress-test the whole emerging recommendation
- Challenge the solution against a set of hurdles. Does it satisfy the criteria for success as set out on the Problem Statement Worksheet?
No matter how skilled, knowledgeable, or experienced you are, you will never create the most distinctive solution on your own. The best problem solvers know how to leverage the power of their team, clients, the Firm, and outside parties. Seeking the right expertise at the right time, and leveraging it in the right way, are ultimately how we bring distinctiveness to our work, how we maximize efficiency, and how we learn.
When solving a problem, it is important to ask, “Have I accessed all the sources of insight that are available?” Here are the sources you should consider:
- Your core team
- The client’s suppliers and customers
- Internal experts and knowledge
- External sources of knowledge
- Communications specialists
The key here is to think open, not closed. Opening up to varied sources of data and perspectives furthers our mission to develop truly innovative and distinctive solutions for our clients.
- McKinsey Staff Paper 66 — not published by McKinsey but possibly found through an internet search
- The McKinsey Way , 1999, by Ethan M. Rasiel
For consultants
© Copyright 2024 by Umbrex
Designed by our friends at Filez
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Service
Bridging the labor mismatch in US construction
The US construction sector seems set for a jobs boom. The US Bipartisan Infrastructure Law projects $550 billion of new infrastructure investment over the next decade, which our modeling suggests could create 3.2 million new jobs across the nonresidential construction value chain. That’s approximately a 30 percent increase in the overall US nonresidential construction workforce, which would mean 300,000 to 600,000 new workers entering the sector—every year.
This is a big ask for an industry that is already struggling to find the people it needs. In October 2021, 402,000 construction positions 1 Included both nonresidential and residential construction openings. Further granularity is not available from the US Bureau of Labor Statistics. remained unfilled at the end of the month, the second-highest level recorded since data collection began in December 2000.
In this environment, wages have already increased significantly since the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, reflecting intense competition for employees, with employers offering higher pay or other nonwage benefits. Between December 2019 and 2021, construction wages grew by 7.9 percent. 2 Quarterly Census of Employment and Wages, US Bureau of Labor Statistics. Competition from other sectors for the same pool of labor is heating up, too. For example, over the same period, transportation and warehousing wages grew by 12.6 percent. The prospect of higher pay and better working conditions is already tempting experienced workers away from construction and into these and other sectors.
No end in sight
Today’s mismatches are likely to persist because of structural shifts in the labor market. The relationship between job openings and unemployment has departed from historical trends. In January 2022—two years from the start of the pandemic—the US unemployment rate stood at 4.0 percent, close to its prepandemic level of 3.5 percent. Job openings remained exceptionally high, however, with 10.9 million unfilled positions as of the end of December 2021, compared with 5.9 million in December 2019.
This labor supply imbalance has multiple root causes, some shorter term and cyclical while others are more structural in nature. For example, the pandemic brought forward the retirements of many in the baby-boomer generation, with an estimated 3.2 million leaving the workforce in 2020—over a million more than in any year before 2016. According to the American Opportunity Survey , among those who are unemployed, concerns about physical health, mental health, and lack of childcare remain the dominant impediments preventing reentry into the workforce. Research on the “Great Attrition/Great Attraction” also highlights the importance of nonwage components of the employee value proposition. Record job openings and quit rates highlight employees’ growing emphasis on feeling valued by their organization, supportive management, and flexibility and autonomy at work.
Additionally, the pipeline of new construction workers is not flowing as freely as it once did. Training programs have been slow to restart operations after pandemic-driven safety concerns led to their suspension the spring of 2020. The industry is finding it more difficult to attract the international workforce that has been an important source of talent for engineering, design, and contracting activities. Net migration has been falling since 2016, a trend accelerated by COVID-19 travel restrictions. 3 Population estimates, US Census Bureau. Between 2016 and 2021, net migration declined steadily from 1.06 million to 244,000.
Would you like to learn more about Capital Excellence ?
Impact on projects.
The interconnected nature of the construction value chain means that the labor mismatch generates knock-on effects across the project life cycle and supply chain. By late 2021, project owners were reporting that up to 25 percent of material deliveries to sites were either late or incomplete. In project execution, the combination of higher hourly rates, premiums and incentives, and overtime payments was resulting in overall labor costs as much as double prepandemic levels. Meanwhile, difficulty accessing skilled and experienced people was leading some owners to report project delays related to issues around the quality and productivity of on-site work.
In some US cities and their suburbs, wage growth has surpassed the level seen in core Gulf Coast counties at the height of the shale oil boom. Labor shortages in the shale sector drove wages up by 5 to 10 percent and were correlated with steep drops in productivity. The productivity of some tasks fell by 40 percent or more during shale construction peaks (exhibit), and overall productivity declined by about 40 percent per year when labor was in short supply. This forced owners to extend project timelines by 20 to 25 percent. The impact of a long-term, nationwide labor mismatch might be even more severe than the shale industry’s experience, given that oil companies were able to attract new workers from around the country.
Getting back into balance
The labor mismatch in the construction sector is bad today, and set to get worse. To avoid a decade or more of rising costs, falling productivity, and ever-increasing project delays, companies in the industry should consider thoughtful actions now.
Those actions could address three components of the challenge. First, companies could do everything possible to maximize productivity through measures aimed at improving efficiency across the value chain. Second, they could expand the pool of available labor by doubling down on accessing diverse talent and working harder to retain the employees already in their organization. Finally, they could consider making labor a strategic priority, with senior leadership attention within companies.
Improving construction productivity
Companies could access a range of levers to reduce the labor content required per job and drive to improve productivity in project development and delivery. Those levers involve changes to project designs and fresh thinking about when, where, and how work is done.
Improvements in productivity occur long before work starts on the ground. They include rigorous control of project scope, design simplification, and standardization. Increasing the use of off-site and modular construction , for example, could allow projects to capture multiple benefits, including accelerated design cycles; the greater productivity associated with industrialized, factory floor manufacturing techniques; automation; and less time spent on site.
Smarter execution management, enabled by digital technologies and analytics techniques could drive better, faster decision making during project delivery. Real-time data collection, for example, gives project managers earlier, more detailed insights about progress, allowing them to intervene more effectively to maintain productivity and keep projects on track. Intelligent simulation software allows teams to evaluate hundreds of thousands of possible critical paths, identifying approaches that could be more efficient or less risky than the conventional wisdom.
Lean construction is another proven way to drive significant and sustainable productivity improvements. Establishing a centralized, continuous improvement engine could enhance on-site execution through integrated planning, performance management, and waste elimination. Key stakeholders across the project work with a common, agreed set of key performance indicators. That allows them to address issues in real time and facilitates collaboration to reduce waste and variability work. Capability building across the planning and construction teams could help team members understand and adopt lean construction practices.


Here comes the 21st century’s first big investment wave. Is your capital strategy ready?
Reimagining talent.
To ensure access to the skills they need, construction sector companies can accelerate the onboarding of recruits, boost retention by revisiting what employees want beyond wages, and invest more in developing their pipelines of future workers.
In the near term, employers could prioritize review of job applications and reduce the number of steps in both the interview and onboarding process. In the medium term, both the public and private sectors could look to reduce hiring timelines and shift to a skills-based approach when hiring.
In the medium term, retaining current staff and attracting new talent will both turn on understanding of what employees value beyond wages. Competitive wages are now table stakes, so employees are thinking about a broader set of benefits and workplace characteristics when making decisions about where to work. Research on attrition in the postpandemic workplace has shown that they are placing more emphasis on autonomy, flexibility, support, and upward mobility.
In the longer term, the construction industry can consider a new approach to talent attraction, development, and retention. Talent acquisition could begin early, through partnerships with educational institutions including universities, colleges, and high schools. These partnerships could boost awareness of the possibilities of a career in the sector and ensure future employees have appropriate skills prior to onboarding.
Companies could also look more widely for potential recruits, considering individuals who have taken alternative educational paths, such as technical degrees or hands-on experience. The Rework America Alliance , a Markle-led coalition in which McKinsey is a partner, illustrates the importance of skills-based, rather than credential-based, hiring. A skills-based perspective is key to tapping into the talents of the 106 million workers who have built capabilities through experience but whose talents are often unrecognized because they don’t have a four-year college degree. A skills-based approach could be complemented by reimagining apprenticeships to bring younger students and vocational talent into the industry at an earlier stage in their careers.
Employers could consider working with a range of nontraditional sources of talent, including veteran-transition programs, formerly incarcerated individuals, and others. Homeboy Industries provides an example of the local impact, effectiveness, and potential of working with often overlooked population segments. Moreover, identifying and attracting talent from outside the traditional paths used by the construction industry could also help it to increase the diversity of its workforce. Today, 88 percent of the sector’s workforce is White and 89 percent is male. 4 Labor Force Statistics from the Current Population Survey Database, US Bureau of Labor Statistics, accessed March 10, 2022.
Looking at labor through a strategic lens
Labor and skills shortages have the potential to slow growth and erode profitability across the construction value chain. For C-suites, there’s no other single issue that could protect against significant cost erosion. Companies could consider establishing a systematic talent acquisition and retention program, led by a C-level executive and a core part of the CEO agenda. That program could first be tasked with building a robust fact base on current and emerging labor needs and availability gaps. It could then identify a bold set of initiatives that address labor-related issues across the value chain. This exercise starts in the boardroom, but it doesn’t stop there. Leadership will likely need to be increasingly present in the field and on the job site too, celebrating and recognizing top talent throughout the organization.
The labor challenge extends well beyond corporate boundaries. Since the successful delivery of a project could be jeopardized by labor shortages in a single value-chain participant, project owners and contractors may want to adapt the structure of project relationships and contracts. Moving away from traditional contracting methods to collaborative contracts , for example, allows participants to share market risks and opportunities as a project evolves, rather than baking in worst-case estimates at the outset of negotiations.
The US construction sector is poised to revitalize, replace, and expand the country’s infrastructure. Done right, that will power inclusive growth and set up the economy for success in the 21st century. To do so, the sector will need to address its labor challenges. That calls for the application of a diverse set of tools and approaches to create better jobs, get the most out of its people, and optimize agility and collaboration across the value chain.
Garo Hovnanian is a partner in McKinsey’s Philadelphia office, Ryan Luby is a senior knowledge expert in the New York office, and Shannon Peloquin is a partner in the Bay Area office.
The authors wish to thank Tim Bacon, Luis Campos, Roberto Charron, Justin Dahl, Rebecca de Sa, Bonnie Dowling, Bryan Hancock, Rawad Hasrouni, Adi Kumar, Jonathan Law, Michael Neary, Nikhil Patel, Gaby Pierre, Jose Maria Quiros, Kurt Schoeffler, Shubham Singhal, Stephanie Stefanski, Jennifer Volz, and Jonathan Ward for their contributions to this article.
Explore a career with us
Related articles.

America 2022 in charts: An economic opportunity snapshot

‘Great Attrition’ or ‘Great Attraction’? The choice is yours
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

PROBLEM SOLVING WITH THE MCKINSEY METHOD

Related Papers
Erma Hollingsworth
Falconer Mitchell
Abijeet Amatya
Pang Kitotko
The Journal of Economic Education
Dennis Weisman
Antonio Scontrino
Lerato Kekana
Songyos Pongrojphaw
Emanuel Onoszko
Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
RELATED PAPERS
Cracked it!
Corey Phelps
Bruce Harreld
Juan A. Marin-Garcia
Randy Machemehl
Bhupender Pandey
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
McKinsey PST: Question Types, Study Plan & Mock Tests
The McKinsey Problem Solving Test (McKinsey PST) is a very crucial part of the McKinsey recruitment process. It is where most of the applicant pool is eliminated, and yet there are so few resources to help you prepare for it. Fortunately, you’ve found the ultimate guide to nail the test with an unbelievable level of detail!
Table of Contents
McKinsey PST overview
What is the mckinsey pst.
The McKinsey Problem Solving Test (or PST) is a paper-based test used at McKinsey & Company to select candidates for the case interviews. The PST is conducted after resume screening; it has 6 types of question, testing the candidate on 3 crucial problem-solving skills – data interpretation, mental calculations and logical reasoning.
McKinsey PST passing score / Acceptance rate
McKinsey has never officially stated the passing score or acceptance rate for the PST. However, these numbers can be estimated using reports from test-takers, with passing score being around 70%, and acceptance rate at roughly 30-35% (1 in every 3 candidates will pass).
Does McKinsey still use the PST?
Currently, the McKinsey PST is being replaced by the new Problem-Solving Game. However, the transition is not complete globally. In addition, the new Problem-Solving Game still retains the core principles from the old test, so preparing for the PST is still relevant.

Why do they need PST?
It’s very similar to what we have here! McKinsey believes that the gap between CV screening and in-person case interviews is too big. The firm may miss many good candidates with bad resumes or may interview too many candidates who don’t live up to their resumes.
At the end of the day, in-person interviews are expensive, and the Problem Solving Test provides a cost-effective solution.
Who has to take the McKinsey PST?
Every candidate who passes the resume screening round has to take the McKinsey PST – if they apply for the management consulting track. Some report indicates that MBA applicants might be waived from the test – however, this is rare and you should confirm with the target office HR.
What does PST look like?
26 questions, 1 hour, paper-based, and no calculator! The test has 26 multiple choice questions set within the context of 3 business cases. A candidate has exactly 60 minutes to finish the test. He will be provided with a watch, pencils, scratch paper, and the test is in a paper-based format. No calculator is allowed. No personal assistant is allowed. Just you and the test!
As the business landscape is changing, candidate recruitment has become increasingly complex. This requires another way of presenting PST content for McKinsey. They have changed the format into gamification and planned to implement this method to all McKinsey offices within 2020. Visit the mock game designed exclusively for MConsultingPrep followers!
PST vs. GMAT vs. SAT?
If you are new to PST, you may hear the myth that PST is similar to the Math section in GMAT or SAT. In fact, being excellent in SAT Math does help with quantitative calculation in PST, however, the context is different. The SAT Math section includes only simple calculations in simple context; meanwhile, logic in business problems is highly emphasized in PST.
Why is this test so challenging?
- You will not have enough time to properly think through each question.
If you are going to read every single word in the case background and do every calculation “asked”, you will not be able to finish the test. You will need to know how to work through stress and pressure, how to give out “high-probability” answers instead of “exactly-right” ones, and how to painlessly skip questions.
- You will be judged by a machine (or if by a person, they will try to be like a machine).
I myself feel much more comfortable in an in-person case interview, where I will be fine as long as I have the right tactics. The interviewers generally allow candidates to make a few mistakes here and there, to slow down the process if needed, and to ask for help when necessary. In the PST, the result is all that matters. There will be no mercy granted. If you don’t get enough correct answers, you are out.
- On top of those, the questions themselves are hard!
A huge amount of logical and analytical reasoning is required. You will need to really grasp the logical fundamentals of how management consultants solve problems, e.g: the difference between a conclusion vs a hypothesis; etc.
How to prepare for the McKinsey PST?
Step 1 : Seek confirmation from the target office if you must take the PST
Step 2: Get familiar with official sample tests from McKinsey
Step 3 : Learn the logic of each question type, common mistakes, and how to answer correctly
Step 4: Practice mental math to improve calculation speed and accuracy
Step 5 : Practice speed reading and data selection
Step 6 : Practice answering individual question type under time pressure
Step 7 : Do one mock test with simulated test conditions
Step 8 : Review the test and your performance
Step 9 : Return to step 3, 4, 5, 6 to for further practice on weakness
Step 10 : Do mock test again, repeat until you can confidently hit 90% or more
McKinsey PST question types
Some emailed me and asked what they should do if there were 3 days left until the PST. I would still suggest you follow our spirit of learning. When you have little time, choose which question you want to prioritize, tackle it carefully and decide how deep you will go into it. If I were in your shoes, I would use this prioritization table
In addition to the above, I would suggest you practice your math in these last days. The learning curve at the beginning is usually high for anything, including Mental Math . Doing better math can significantly improve your test score. It reduces simple mistakes (which can still cost you points) and allows you to have more time for other questions.
McKinsey PST study plan
These are the same steps I took to pass the PST years ago, and the basis for my product – the PST Comprehensive Package which has helped countless candidates pass this notoriously difficult consulting test.
Step 1. Answer the questions correctly
You are recommended to first answer all the test questions correctly without time pressure. Before, you need to break down all the questions into 6 question types as below. Besides, it is necessary to understand how these questions are constructed, what are their logical foundation, and even how the wrong choices are made.
Step 2. Answer the questions quickly
There will be no turning point that indicates you it is about time to move to the second step, but you should gradually try to answer the questions both correctly and quickly. Once getting all the correct answers without clocking, you should put yourself under time constraint. If you don’t know how to increase your speed, you have better to start with 3 tips below:
#1. Increase your reading speed.
The PST contains 3 business cases with various number and case context, which requires you to read as fast as possible (of course correctly). Many candidates cannot finish their PST because of being overwhelmed in text. The Princeton intensive program is helpfulto increase your speed by 2 times faster without difficulties.
#2. Increase your calculator speed.
Half of the test involves math, which have no way to improve but practice rigorously. The more you practice, the better you gain. If you haven’t found any efficient tips, try our method to score well with Mental Math!
#3. Embrace test-hacking tips.
After years of coaching students to MBB, I have collected wonderful tips and tricks to nail your test with less effort! Find out some of those tricks as below or check out the McKinsey PST Comprehensive for more detail!
Reading facts
Reading-facts is the most common question type in the McKinsey PST (38%) and the BCG Potential Test (up to 100%). These questions test your ability to understand the facts/data itself. There will be no inferring, logic, hypothesizing, or creativity needed. Instead, proficiency in chart reading and calculations will be handy here. See the picture below for an illustration.

QUESTION FORMAT
The following are a few examples of typical question formats:
- Which of the following values is the best estimate of…?
- Which of the following statements is valid based on the data…?
- Which of the following can be concluded from Exhibit…?
Sometimes even though the word “conclude” is used, questions don’t require any logical reasoning, just your ability to read facts and perform basic calculations. In these cases, I still classify these questions into the reading-facts category.
SAMPLE QUESTION
This question is written based on an official McKinsey practice PST.
Which of the following statements is valid based on the data in Table 1?
A) Soccer revenue was more than $325 thousand five years ago
B) Tennis revenue grew by no less than 1.2% in each of the last five years
C) The total revenue of Saigon League did not grow at all in the last five years
D) If the growth rate in the last 5 years is maintained, Soccer revenue will be more than $420K 5 years from now.
You will see that no tricky logical reasoning is needed here. All you need in order to answer these questions is the ability to read the table and perform calculations correctly.
COMMON MISTAKES
A good way to determine the correct option is to investigate if the other three are wrong. Now there are two ways you can be wrong in this type of PST question: (1) Incorrect calculation and (2) Misread the facts/ data
Type #2 is harder to understand, so I will dive deeper into that here. Let’s look at the sample question above. Hope you got D, the correct choice.
Example 1: How you can misread the data – Why A is wrong
If you overlook the phrase “Average annual” on column 3′s title, then Soccer revenue 5 years ago would be: $342.8 k / (100% + 4.5%) = $328 k, which is more than $325 thousand. Revenue grew at an average rate of 4.5% in EACH of the last 5 years. It is NOT 4.5% over the whole period of 5 years.
Example 2: How you can misread the data – Why B is wrong
If you overlook the phrase “Average” in column 3′s title, then it seems like the growth rate for each of the last 5 years is exactly 1.2%, no more, no less. B, therefore, seems correct. However, as indicated in the table, 1.2% is just an average figure, which means there are years with a lower or higher growth rate.
Example 3: How you can misread the data – Why C is wrong
If you overlook the second column of the table (Revenue this year column), then it seems like the average overall growth rate for Saigon League is 0% (4.5% + 3.3% + 1.2% – 9% = 0%), which makes C correct. However, different lines have different sizes. Even though Golf had negative growth of 9%, it is a relatively small line so its impact on the overall rate is small as well.
Hope that you will not make this mistake in your real PST. Again, PST is a simple test… when you have enough time!
PREPARATION GUIDE
Skill #1: Calculation
We have a detailed article on Consulting Math and how to strengthen your quantitative proficiency.
Skill #2: Chart/exhibit/table reading
Always take a moment to read and understand every single chart or graph you encounter in your everyday life.After all, practice makes perfect.
You can also improve your reading speed through an amazing speed reading program by Princeton University .
Skill #3: Attention to details
The devil is in the details. It’s the little things that can make or break a project, and no true consultants would let themselves be caught unaware.
Develop a habit in daily life. Have the mindset that I am not going to miss any stupid details.
For every practice question you get in this type, make sure you understand not only why an answer is right, but also why an answer is wrong, exactly like what I did above.
PRACTICE QUESTIONS

Which of the following statements is valid based on the data provided on Graph 3 above?
A) The Service-to-Agriculture ratio increased by more than 3 times between 1995 and 2007
B) Service GDP in 1995 is more than Industry GDP in 2007
C) Agriculture is where GDP value dropped the most between 1995 and 2007
D) In 2007, Service GDP is no less than 6 times Agriculture GDP
Correct answer: D
If you want to practice more, check out my PST Comprehensive Package for questions and answers!
Fact-based conclusion
Once you get into consulting, you will probably hear the term “fact-based” a million times a day. Consulting is the business of making conclusions based on facts. Consultants face tons of different problems throughout the course of any project: from the top to the granular level, from function to function, from industry to industry, etc. Fact-based conclusion is such a fundamental aspect of consulting that it weighs in heavily on the PST.
Fact-based conclusion questions test your ability to draw and recognize sound and logical conclusions based on a set of data/facts provided. See the picture below for an illustration.

- Which of the following statements is a valid conclusion based on …?
- Which of the following statements can be concluded from …?
The McKinsey team has an interview with the Chief Operating Officer of the New Bingham Mine, Salt Lake City. During the interview, the following facts have been gathered:
- The factory must have at least one safety inspector 24 hours a day, seven days a week, in accordance with Federal and State labor regulations.
- To maximize operational efficiency, there must be exactly 10 line workers operating the mine.
- The mine operates from 8 am until 5 pm, Monday to Sunday.
- The mine employs 4 safety inspectors and 16 line workers to make 20 workers in total.
- The total weekly labor cost for the Bingham Mine is $16,000.
Which of the following statements is a valid conclusion?
A. One-fifth of the total labor cost for the mine is for safety inspectors.
B. At least one safety inspector must work more than 40 hours per week.
C. Line workers do not work more than 40 hours per week.
D. The majority of the mine’s labor cost is for line workers.
A – Fit-well but not fact-based
There are 4 inspectors out of 20 employees so it seems like the cost of the inspectors can very well be 1/5 of total labor cost. But a missing piece of data to conclude that is: does each person get a similar total income?
C – Fit well but not fact-based
The mine opens for 9 hours per day, 7 days per week, and there must be 10 line workers at a time, so it is 630 man-hours per week at the line positions. There are 16 line workers, so on average each of them only needs to work 39 hours per week. This seems to fit very well with the proposed conclusion: line workers do not work more than 40 hours per week. However, a missing piece of data to conclude is: does every line worker work the same amount of time (if not, there can be some who work over 40 hours while others work less)?
D – Fit well but not fact-based
Similar to A, there are more line workers, so it seems like the total cost for line workers is more than the total cost for safety inspectors. But a missing piece of data needed to conclude is: does each worker get paid the same amount?
=> Only B is proven true by the provided facts
There are 24 * 7 = 168 inspector hours needed in a week, equaling 42 hours per week per inspector. So there must be one who works more than 40 hours.
Identifying proven true conclusions is an important foundation to master all conclusion-related questions. However, most conclusion-related questions in the McKinsey Problem Solving Test will be given in other formats. In this section, we will learn about the two types of twists: (1) False conclusions and (2) Conclusions reversed . Let’s start with the first one.
TWIST TYPE 1: FALSE CONCLUSION
Any proposed conclusion must fall into one of the following three groups: Proven True, Proven False, and Unproven. This twist is when a question asks you to identify the False Conclusion instead of the True Conclusion.
- Which of the following statements is FALSE based on …?
- Which of the following statements is FALSE based on … ?
METHODOLOGY
A proposed conclusion is proven false when you can point out at least one instance where the conclusion is wrong. Similarly, with true conclusion questions, unproven conclusions should also not be selected.
Notice that proven FALSE conclusions are NOT conclusions not proven TRUE. A conclusion will stay unproven until it is proved to be TRUE or FALSE.
Which of the following statements is FALSE based on Table 1?
A. A, Inc. had lower average economic growth in the last five years than D, LTD.
B. A, Inc. had higher average economic growth in the last five years than D, LTD.
C. Investment risk rating is based on the difference between maximum and minimum revenue growth in the past five years.
D. Potential rating is based on the maximum recent revenue.
Of A and B, A seems to be false and B seems to be true. However, both of them are unproven. The maximum and minimum figures are not enough to conclude the average.
We don’t know if C is right or not, but we know that it is not proven false. In the provided data, there is no instance where the larger difference between maximum and minimum recent revenue growth indicates smaller risk (and vice versa).
With D, we know for sure that it is proven false because we can point out an instance where the assertion conflicts with the data (B Corp. vs. D, LTD.).
TWIST TYPE 2: CONCLUSIONS REVERSED
Very often, conclusion questions in the McKinsey Problem Solving Test are given in a reversed format. You will be given the conclusion first and asked to pick what facts/ data would be enough to come up with that conclusion.
The key to answering this type of question is to recognize which proposed fact makes the stated conclusion proven or unproven.
This question is written based on an official McKinsey practice PST:
FOCUS Travel is a premium Russian tourism company, offering tours to South East Asian countries. Facing the economic downturn, FOCUS revenue has been hurt badly. While the CFO (Chief Finance Officer) proposed an overall price cut to stay competitive, the CMO (Chief Marketing Officer) is concerned that a price reduction would negatively impact the premium perception of the brand, which drives a lot of sales.
Which of the following statements, if TRUE, would best support the CMO’s assertion?
A. In a recent survey, FOCUS’s customers quoted “price” as the most important indicator in choosing travel agencies in a list of ten factors.
B. In a recent survey, FOCUS’s customers quoted “price” as the most important indicator of quality in a list of ten factors.
C. In a recent survey, there were customers who said they would not buy FOCUS’s services if there was a 10% price increase.
D. In a recent survey, there were customers who said they would not buy FOCUS’s services if there was a 10% price decrease.
In this question, the “conclusion” has been given to us: Price reduction will negatively impact the premium perception, which will in turn negatively impact sales.
Of the four proposed answers, which facts are enough to prove the provided “conclusion” above?
A: This fact is only enough to conclude that price will impact sales. Not enough to prove that price reduction will negatively impact sales.
C: This fact is irrelevant.
D: This fact is not enough to conclude that price reduction will negatively impact sales because not all customers say so. The word “there were” can be understood as either a minority or a majority. It is only enough to conclude the proposed conclusions when “there were” is replaced with “the majority of” or “all“ .
With B, we can logically infer that price reduction will negatively impact the quality perception, which in turn will hurt to sales.
3.3. Root-cause reason
This question gives you a particular set of facts/data and asks you to identify what could be the cause for them. When doing a real consulting project, we consultants have to find out the root-cause reason. There may be various reasons that can cause the current situation, but the root-cause reason will help us tackle and solve it more efficiently. You can see the picture below for an illustration.

The following are a few examples of typical root-cause reason question format:
- Which of the following reasons, if TRUE, will help explain the Facts …?
- Which of the following does NOT explain the Facts …?
- Which of the following points is NOT a valid reason for the Facts …?
Only B is proven true by the provided facts
Facts provided: Visits to the website MConsultingPrep were relatively low last month.
Root-cause Reason Question: What reasons, if TRUE, would help explain the low traffic to MConsultingPrep last month?
The correct answers can be any of the following:
1. The quality of contents has been bad
2. Because of technical issues, some visitors could not access the website
3. Last month was December when the overall demand for job prep materials is lowest in the year
4. Other new consulting prep blogs opened recently
Fact-based Conclusion Question: What can be concluded from the data provided?
All of the statements above can be the reason for the stated fact, but NONE of them can be concluded from it.
An example of a statement that can be concluded: Because the conversion rate stayed constant over the years, revenue last month was relatively low.
What makes a statement NOT a potential reason for a particular fact?
There are two ways a statement cannot be the potential reason: (1) Wrong Subject and (2) Wrong Trend.
- A statement is (1) Wrong on Subject when the subject is irrelevant, which means the statement has zero effect on the phenomenon mentioned in the stated fact.
- A statement is (2) Wrong on Trend when the direction is reversed, which usually means the statement has a reversed effect on the phenomenon mentioned in the stated fact
Illustrative example Let’s continue with the simple example above. The Stated Fact: Visits to the MConsultingPrep blog were relatively low last month. (1) Example of a “Wrong Subject” statement: “Some new Investment Banking Prep blogs opened recently” Here the subject “Investment Banking Prep blogs” is irrelevant to the stated fact. The statement (1) will have zero effect on the stated fact. (2) Example of a “Wrong Trend” statement: “Some other existing Consulting Prep blogs closed recently” Here, even though the subject “Consulting Prep blogs” is relevant, the trend is reversed. The exit of Consulting Blogs will increase visits to MConsultingPrep. Therefore, statement (2) will have an opposite effect on the stated fact.
PRACTICE QUESTION
Fletcher is a major Steel producer in the Pacific continent. It has markets in New Zealand, Australia and other South East Asia countries. Of many types of steels, re-bar (reinforced bar) is typically used in high-rises and big construction projects.
There are three main groups of steel consumers in New Zealand:
- Homeowners purchase steel at retail sizes for purposes of self-constructing and self-renovating their homes
- Scaled private construction companies, who often contracts large construction projects and steel orders
- State-owned Enterprises (SOE), who build government’s projects such as roads, bridges, schools, hospitals, etc. (SOEs usually have bargaining power since steel providers need governments’ permissions in order to be legally used in particular countries.)
Table 1 below shows the size of re-bar steel market (in billions of $US)
Which of the following statements, if TRUE, best explains why future trends for South East Asia sales differ from sales in the other two markets?
A) South East Asia population is expected to grow strongest, which lead to high steel demand from individual homeowners.
B) South East Asia economy will be heavily based on SOE, so will the construction market.
C) South East Asia economy will shift toward privatization, so will the construction market.
D) Developed markets of New Zealand and Australia will have the most advanced steel production technology and facilities.
Correct answer: C
Word Problem
Word Problem is a quantitative question where the answer cannot be calculated directly from the data provided. Usually, we have to set up one or more equations in order to solve this kind of question. Word Problem questions in the McKinsey PST and Case Interviews are just the word problems we usually see in schools, GMAT… but put into business contexts. The method to solve them, therefore, is the same.
Table 1: Data on the Washing Room of Jean Valjean Restaurant
Suppose the restaurant opens 350 days a year. There are 3 meal shifts per day, 1 shift lasts 3 hours, 1 customer uses an average of 5 dishes per visit, and currently the restaurant hosts 530 customers on average daily.
What percentage of increase in the number of daily visits would be required in order to make purchasing the machines financially beneficial?
Step 1 . Convert data/facts into manageable and standardized format and units (only needed for complex questions).
Step 2 . Set up an equation with one (or more) unknown variables, i.e. X, Y, Z, etc.
Tips: Don’t worry about having to make the variable as the question asked. Just set up the equation in a way that makes the most sense to you as long as the variables can be easily converted to the asked variable. It will save much more time and helps you avoid silly mistakes.
Step 3 . Solve the equation and get the answer.
METHODOLOGY ILLUSTRATION
Let’s solve the sample question above together.
Step 1: This is a very complex question with many non-standardized and not ready-to-use data. If I am going to tackle this question on my PST, I would convert the provided figures and write them out on a table as follows.
Notice that I have converted all the necessary data points into the same unit of “Franc per day”.
The only data point not fully converted is the Labor cost in Manual Process (measured by the “per dish” variable), yet I want to make sure that I go as far as I can.
See how simple the problem is now!
Step 2: Now that we have very manageable data, let’s go ahead and set up an equation that will help us find the answer. The asked variable here is: what percent increase in current daily visits does Jean Valjean need?
As mentioned above, it is NOT necessary to put the variable question is looking for in the equation. In this case, doing so will result in a very awkward and complicated equation.
Instead, I set up the equation that makes the most sense to me (do note that there is more than one way to set up equations). Let Y be the “break-even size” (measured by people). I can easily calculate the percentage asked for after getting the break-even size.
Cost per day of Manual Process = Cost per day of Machine Process
Washing cost + Set up cost = Washing cost + Set up cost + other cost
Y x 5 dishes x 0.1 Franc + 30 Franc = 270 Franc + 90 Franc + 200 Franc
After executing step 1 and step 2, the problem becomes a lot easier. Now we have:
0.5 Y = 530
Y = 2 x 530
Once we have Y (the new “break-even” visit volume) of 2 * 530, we can quickly convert Y into the asked variable: What percent increase of 530 customers/day does Jean Valjean need?
The final answer is C.
Client Interpretation
In every consulting project, communication with the clients’ top-level (usually the Chairman or CEO) is always important. During my time with McKinsey, we usually hear an update every one or two weeks from our Project Director (usually a partner) on his meeting with the clients’ top level. Messages from those meetings are important on-going steers for the project. No surprise it makes up an entire question category in the Problem Solving Test.
Client Interpretation questions test your ability to read, understand, and interpret the messages the client is trying to convey in the case question or description. To some extent, this is very similar to GMAT verbal questions.
- Which of the following best summarizes the CEO’s concerns?
- Which of the following statements best describes the thoughts of the CEO regarding…?
- Based on the opinion of the head of the Department, which of the following statements is valid?
- Which of the following statements best describes the CEO’s aims for the McKinsey research?
Case context:
Mommy said she saw some dirty clothes on the dining table. She is also quite shocked to see Kevin’s toys in every room throughout the house. She even complains about how much time it takes her every night to clean up Kevin’s mess. “I will have to have a very straightforward conversation with Kevin tonight!”, said mom
Which of the following statements best describes the Mom’s concern?
A. Mom is not happy about too many of Kevin’s toys sitting on the dining table
B. Mom does not expect to see that many of Kevin’s toys in the house
C. Mom does not like to be responsible for anyone’s mess
D. Mom is too busy these days
E. Mom wants to talk to Kevin
F. Mom wants Kevin to be tidier
In this example, we continuously get small data points, all leading to one bottom-line, not explicitly mentioned but can be reasonably interpreted:
Kevin is too messy and mom doesn’t like that!
Notice that, the bottom-line here is not explicitly stated but it IS the bottom-line. All 4 sentences in the case context are small pieces of data leading to that final “so-what”. Having this “so-what” in mind, you can just skim through the answer and quickly pick F without concern about other choices.
In case you are curious about how other choices are “wrong-choice” …
Choices B and E are in fact right according to the case context, but not the bottom-line.
Choices A is simple wrong according to the case context (Tip #2)
Choices C and D are neither right or wrong according to the case context. There are not enough “evidence” to be reasonably interpreted using common sense.
TIPS AND TRICKS
Tip #1: Read the case description before going to multiple choices!
Normally the strategy of scanning through the answers first before going back to the case description works when you have a very long case description and don’t know where to look for the right information. Scanning through the answers helps you get a more focused read on the case description. However, the client’s assertion is typically found in a very short and specific part of the case description. So once you realize it’s a Client Interpretation question, go back to the case description and find that very specific part of the client’s assertion. Make sure you understand it very well. Then the rest of the work is just determining which of the four choices has the same meaning as the original assertion.
Tip #2: Cross out some obviously wrong choices …
… by recognizing a few words or short phrases that make a choice incorrectly reflect the client’s assertion. Sometimes, you can do this very quickly and effectively. If not, please see tips #3.
Tip #3: Catch the bottom-line, the “so-what” of client’s assertion
Client’s expression as quoted in the case context is always a bit blur and confusing. That is very realistic of what you may encounter in the real consulting work. It also makes these question types challenging. But in almost every situation, there is always one “so-what”, stated explicitly or implicitly. The trick here is to catch that so-what, ignore the noise, and go straight for the answer choice. Most of the time, the wrong choices DO contain a part of the client’s assertion, but either not the whole idea or the main, the bottom-line, the most important one!
Using this method, you can fly and land straight to the correct choice, not having to care too much about how wrong choices are made of. But if you are curious, some of the most common wrong-choice types:
- Choice that is simply wrong according to the client’s assertion (Tip #2 above).
- Choice that is in fact right, but is a minor point, NOT the bottom-line of the client’s assertion.
- Choice that seems to be right, but cannot be reasonably interpreted by common sense (not by scientifically supporting logic like in other question types).
Gangnam Market is a convenience-stores chain mainly in the Gangnam district, Seoul, Korea. Though it has been losing money almost every year since 2000, Gangnam Market secures a good deal of strategic locations in the highly populated Gangnam district. Recently, Gangnam Market was acquired by Lotte Mart in its aspiration to expand to the mini-market market. Lotte right away sets up a transformation project to get Gangnam Market back on track. The CEO of Gangnam Market states that aggressive transformation targets are fine for newly acquired stores with a similar operation model with Lotte’s big stores, but he hopes that the parent company is realistic about the convenience-stores model Gangnam has been operating with.
Which of the following statements best reflect the concerns of Gangnam Market’s CEO?
A) He is concerned that Gangnam Market will never be able to transform itself into Lotte system because Gangnam Market only presents in a specific geographic location
B) He is concerned that Lotte Mart sets transformation milestones that are too aggressive and not realistic for newly acquired companies like Gangnam Market
C) He is concerned that Lotte Mart’s transformation milestones are not realistic for companies with different operational model from Lotte Mart like Gangnam Market
D) He is concerned that Lotte Mart’s transformation targets are too high for Gangnam Market because it has been losing money for a while
Formulae questions are generally like word problems in PST where you don’t have to provide the actual numerical results, just the formulae containing letters representing input variables. Normally, the question will provide input variables in letter format and you will be asked to provide the right formulae in letter format (e.g. it takes the process center T hours to process each file. If the speed is doubled, it takes T/2 hours to process each file). This is one of the easiest PST question types on the McKinsey PST. Let’s make sure you don’t lose points on any question of this type in your exam!
Table 3.6.1: Labor Cost and Processing Data – Holcim Missouri plant
Which of the following formulae accurately calculates the annual cement output per worker?
A. (c x p) / (b + w)
B. (c x p) / [(b + w) x 12]
C. 144 x (c x p) / (b + w)
D. 12 x (c x p) / (b + w)
FORMULAE FOR SUCCESS IN FORMULAE QUESTIONS
Formula 1: Calculate first before looking at the given option
A popular technique for multiple-choice questions is to read the answers first before coming back to the facts. However, that technique would not help you with Formulae Questions. The reason for this is that, often, the end-result formula has already been simplified (e.g. canceling out the same variable on both numerator and denominator) as much as possible. It gives you neither the path to get there nor any hints on how to solve the problem. For instance, when you look at the four options in the example above, does any of them give you a sense of what it represents or how to get there? What does (c x p) represent? What do you get by multiplying Cement output by Monthly labor income?
Formula 2: Divide the problem into smaller pieces (take one step at a time)
This is the universal tip for everybody in the consulting industry, and it also works great here! Often, the result cannot be directly calculated from the provided variables. However, if you take an extra step in-between, the problem becomes a lot easier. Let’s solve the sample question above together to illustrate this point. I broke the problem into smaller steps as below:
- Step 1: Annual cement output per worker = Total annual cement output / Total number of workers
- Step 2: Since we already have Total annual cement output of (c), the next step is to calculate the total number of workers. Total number of workers = Total labor cost / Salary of 1 worker Both Total labor cost and salary are provided. Bingo!
- Step 3: Simplify the final formulae
Formula 3: Get the reading-facts tools right
In some aspects, the formulae question is also a tweaked version of reading-facts questions. You still need to read some facts and perform some calculations (with letters instead of real numbers). Therefore, it is important to master those reading-facts tools and apply them here.
Illustration of a usual mistake: Now come back to Step 2 above and explicitly solve it.
Step 2: Total number of workers = Total labor cost / Salary of 1 worker = (b + w) / p
Step 3: Annual cement output per worker = c / [(b + w) / p] = (c x p) / (b + w)]
Chosen choice: A
Unfortunately, A is NOT the correct answer, because the above calculation doesn’t take into account the difference in units – the salary is on a monthly basis whereas the total labor cost is on an annual basis. If you convert the unit, the final choice should be D.
No matter how beautifully you have tackled the problem, you will not get any credit if small mistakes like this slip through the crack. Make sure you don’t get blindsided by this kind of pitfall!
VICEM is a leading cement company in South East Asia. The following data regarding its business and production has been gathered.
Table 3.6.2: VICEM Business and Production data
Clinker factor is defined as the amount of clinker needed to produce 100 units of cement.
Which of the following formulas calculates the amount of clinker (in tons) needed to purchase in a year?
A) [(s x f) / 100] – c
B) [(p – s) / 100] – c
C) (p x f) – c
D) [(p x f) / 100] – c
ANSWER KEY
McKinsey PST sample test
Download McKinsey PST practice test (PDF): TOYO case .
More free materials like this can be found in our Prospective Candidate Starter Pack – a collection of beginner’s materials to consulting resume, screening tests and case interviews.
Scoring in the McKinsey PSG/Digital Assessment
The scoring mechanism in the McKinsey Digital Assessment
Related product
/filters:quality(75)//case_thumb/public/1714968238487_solve_aio.png)
McKinsey Solve Simulation (All-in-One)
The one and only existing platform to practice three mini-games of McKinsey Solve in a simulated setting
This article will give a detailed explanation of failing the test and practical advice to minimize the chance of poor performance in the McKinsey game.
The McKinsey Solve (other names: PSG, Problem Solving Game, Digital Assessment, Imbellus) is a two-piece gamified test designed by Imbellus for McKinsey.
There are 2 techniques to boost your reading speed. Learn how to practice them effectively & overcome 3 common loopholes that limit your reading performance.
The effectiveness of the Adiwiyata audiovisual media based on examples non-examples cooperative in improving students' problem-solving skills, creative thinking skills, and environmental literacy
- Al-Muhdhar, Mimien Henie Irawati
- Abdillah, Racy Rizky
- Suhadi, Suhadi
- Wardhani, Yayang Setya
- Astuti, Lia
- Wulandari, Intan Ayu Idha
- Wulandari, Feni Eka
- Achmad, Ruchimah
Education plays a role in creating a young generation with character and life skills. Based on the problem, problem-solving skills, creative thinking skills, and character to the environment in the form of students' environmental literacy need to be improved. Efforts that must be made to train students to have a sense of caring for the environment to produce problem-solving solutions and creative ideas in the context of sustainable development are through the Adiwiyata Program. This study aims to test the effectiveness of Adiwiyata audiovisual media based on Examples Non-Examples Cooperative in improving the problem-solving skills, creative thinking skills, and environmental literacy of 10th-grade students at SMAN 2 Malang. The research design used was pre-experiment one group pretest-posttest. The research population is all 10th at SMAN 2 Malang. The research sample was students of 10th MIPA 4 at SMAN 2 Malang, which was determined by purposive sampling. This research was conducted in November 2021. The data analysis technique used a normalised gain score. The results of the N-gain test of problem-solving skills are 0.81 in the high effectiveness category, creative thinking skills are 0.73 in the high effectiveness category, and environmental literacy is 0.59 in the moderate effectiveness category, so it can be said that there is an increase between pretest and post-test results. This can happen because all indicators of problem-solving skills, creative thinking skills, and environmental literacy are trained for students at each step of the Examples Non-Examples Cooperative model. Adiwiyata audiovisual media is packaged in the form of a website with many features to help students improve problem-solving, creative thinking, and environmental literacy. The adiwiyata audiovisual media is based on Examples Non-Examples Cooperative, which can increase the effectiveness of problem-solving skills, creative thinking skills, and environmental literacy of 10th-grade students at SMAN 2 Malang.
- SCIENCE EDUCATION AND TECHNOLOGY
Watch CBS News
Google, IBM make strides toward quantum computers that may revolutionize problem solving
By Scott Pelley
December 3, 2023 / 7:17 PM EST / CBS News
Artificial intelligence is the magic of the moment but this is a story about what's next, something incomprehensible. Tomorrow, IBM will announce an advance in an entirely new kind of computing--one that may solve problems in minutes that would take today's supercomputers millions of years. That's the difference in quantum computing, a technology being developed at IBM, Google and others. It's named for quantum physics, which describes the forces of the subatomic realm. The science is deep and we can't scratch the surface, but we hope to explain enough so that you won't be blindsided by a breakthrough that could transform civilization.
The quantum computer pushes the limits of knowledge--new science, new engineering-- all leading to this processor that computes with the atomic forces that created the universe.
Dario Gil: I think this moment, it feels to us like the pioneers of the 1940s and 50s that were building the first digital computers.
Dario Gil is something of a quantum crusader. Spanish-born with a Ph.D. in electrical engineering, Gil is head of research at IBM.
Scott Pelley: How much faster is this than say, the world's best supercomputer today?
Dario Gil: We are now in a stage where we can do certain calculations with these systems that would take the biggest supercomputers in the world to be able to do some similar calculation. But the beauty of it, is that we see that we're gonna continue to expand that capability, such that not even a million or a billion of those supercomputers connected together could do the calculations of these future machines. So, we've come a long way. And the most exciting part is that we have a road map and a journey right now, where that is going to continue to increase at a rate that is gonna be shocking.

Scott Pelley: I'm not sure the world is prepared for this change.
Dario Gil: Definitely not.
To understand the change, go back to 1947 and the invention of a switch called a transistor.
Computers have processed information on transistors ever since, getting faster as more transistors were squeezed onto a chip--billions of them today.
But it takes that many because each transistor holds information in only two states. It's either on or it's off-- like a coin-- heads or tails. Quantum abandons transistors and encodes information on electrons that behave like this coin we created with animation. Electrons behave in a way so that they are heads and tails and everything in between. You've gone from handling one bit of information at a time on a transistor to exponentially more data.
Michio Kaku: You can see that there's a fantastic amount of information stored, when you can look at all possible angles, not just up or down.
Physicist Michio Kaku of the City University of New York, already calls today's computers "classical." He uses a maze to explain quantum's difference.
Michio Kaku: Let's look at a classical computer calculating how a mouse navigates a maze. It is painful. One by one, it has to map every single left turn, right turn, left turn, right turn before it finds the goal. Now a quantum computer scans all possible routes simultaneously. This is amazing. How many turns are there? Hundreds of possible turns, right? Quantum computers do it all at once.
Kaku's book, titled "Quantum Supremacy," explains the stakes.
Michio Kaku: We're looking at a race, a race between China, between IBM, Google, Microsoft, Honeywell, all the big boys are in this race to create a workable, operationally efficient quantum computer. Because the nation or company that does this, will rule the world economy.

But a reliable, general purpose, quantum computer is a tough climb yet. Maybe that's why this wall is in the lobby of Google's quantum lab in California.
Here, we got an inside look, starting with a microscope's view of what replaces the transistor.
Google employee: This right here is one qubit and this is another qubit, this is a five qubit chain.
Those crosses, at the bottom, are qubits, short for quantum bits. They hold the electrons and act like artificial atoms. Unlike transistors, each additional qubit doubles the computer's power. It's exponential. so, while 20 transistors are 20 times more powerful than one. Twenty qubits are a million times more powerful than one.
Charina Chou: So this gets positioned right here on the fridge.
Charina Chou, chief operating officer of Google's lab, showed us the processor that holds the qubits. Much of that above chills the qubits to what physicists call near absolute zero.
Scott Pelley: Near absolute zero I understand is about 460 degrees below zero Fahrenheit. So that's about as cold as anything can get.
Charina Chou: Yes, almost as cold as possible.
That temperature, inside a sealed computer, is one of the coldest places in the universe. The deep freeze eliminates electrical resistance and isolates the qubits from outside vibrations so they can be controlled with an electro-magnetic field. The qubits must vibrate in unison. But that's a tough trick called coherence.
Scott Pelley: Once you have achieved coherence of the qubits, how easy is that to maintain?
Charina Chou: It's really hard. Coherence is very challenging.
Coherence is fleeting. In all similar machines, coherence breaks down constantly--creating errors.
Charina Chou: We're making about one error in every hundred or so steps. Ultimately, we think we're gonna need about one error in every million or so steps. That would probably be identified as one of the biggest barriers.

Mitigating those errors and extending coherence time while scaling up to larger machines are the challenges facing German-American scientist Hartmut Neven, who founded Google's lab, and its casual style, in 2012.
Scott Pelley: Can the problems that are in the way of quantum computing be solved?
Hartmut Neven: I should confess, my subtitle here is chief optimist. After having said this, I would say at this point, we don't need any more fundamental breakthroughs. We need little improvements here and there. If we have all the pieces together, we just need to integrate them well to build larger and larger systems.
Scott Pelley: And you think that all of this will be integrated into a system in what period of time?
Hartmut Neven: Yeah. We often say we wanna do it by the end of the decade so that we can use this Kennedy quote, "Get it done by the end of the decade."
Scott Pelley: The end of this decade?
Hartmut Neven: Yes.
Scott Pelley: Five or six years?
That's about the timeline Dario Dil predicts. And the IBM research director told us something surprising.
Scott Pelley: There are problems that classical computers can never solve.
Dario Gil: Can never solve. And I think this is an important point because we're accustomed to say, "ah computers get better." Actually, there are many, many problems that are so complex that we can make that statement that, "Actually, classical computers will never be able to solve that problem." Not now, not 100 years from now, not 1,000 years from now." You actually require a different way to represent information and process information. That's what quantum gives you.
Quantum could give us answers to impossible problems in physics, chemistry, engineering and medicine. Which is why IBM and Cleveland Clinic have installed one of the first quantum computers to leave the lab for the real world.
Serpil Erzurum: It takes way too much time to find the solutions we need.

We sat down with Dario Gil and Dr. Serpil Erzurum, chief research officer at Cleveland Clinic. She told us health care would be transformed if quantum computers can model the behavior of proteins- the molecules that regulate all life. Proteins change shape to change function in ways too complex to follow. and when they get it wrong that causes disease.
Serpil Erzurum: It takes on many shapes, many, many shapes, depending upon what it's doing, and where it is, and which other protein it's with. I need to understand the shape it's in when it's doing an interaction or a function that I don't want it to do for that patient. Cancer, autoimmunity. It's a problem. We are limited completely by the computational ability to look at the structure in real time for any, even one, molecule.
Cleveland Clinic is so proud of its quantum computer they set it up in a lobby. Behind the glass, that shiny silver cylinder encloses the kind of cooling system and processor you saw earlier. Quantum is not solving the protein problem yet. This is more of a trial run to introduce researchers to quantum's potential.
Scott Pelley: The people using this machine, are they having to learn an entirely different way to communicate with a computer?
Dario Gil: I think that's what's really nice, that you actually just use a regular laptop, and you write a program very much like you would write a traditional program. But when you, you know, click, you know, "go" and "run," it just happens to run on a very different kind of computer.
There are a half dozen competing designs in the race. China named quantum a top national priority and the U.S. government is spending nearly a billion dollars a year on research. The first change comes next year when the U.S. publishes new standards for encryption because quantum is expected one day to break the codes that lock everything from national secrets to credit cards. Tomorrow, IBM will unveil its Quantum System Two with three times the qubits as the machine you saw in Cleveland. This past August, we saw System Two under construction.
Dario Gil: It's a machine unlike anything we have ever built.
Scott Pelley: And this is it.
Dario Gil: And this is it.
IBM's Dario Gil told us System Two has the room to expand to thousands of qubits.
Scott Pelley: What are the chances that this is one of those things that's gonna be ready in five years and always will be?
Dario Gil: We don't see an obstacle right now that would prevent us from building systems that will have tens of thousands and even a 100 thousand qubits working with each other. So we are highly confident that we will get there.
Of all the amazing things we heard, it was physicist Michio Kaku who led us down the path to the biggest idea of all. He said we were walking through a quantum computer. Processing information with subatomic particles is how the universe works.
Michio Kaku: You know when I look at the night sky, I see stars, I look at the flowers, the trees I realize that it's all quantum, the splendor of the universe itself. The language of the universe is the language of the quantum.
Learning that language may bring more than inconceivable speed. Reverse engineering nature's computer could be a window on creation itself.
Produced by Denise Schrier Cetta and Katie Brennan. Broadcast associates, Michelle Karim and Eliza Costas. Edited by Warren Lustig

Scott Pelley, one of the most experienced and awarded journalists today, has been reporting stories for 60 Minutes since 2004. The 2023-24 season is his 20th on the broadcast. Scott has won half of all major awards earned by 60 Minutes during his tenure at the venerable CBS newsmagazine.
More from CBS News

Apple is set for a big AI announcement. Here's what to expect.

How much would a $60,000 home equity loan cost per month?

Why you should get a debt consolidation loan this June

Sullivan says "there could be a cease-fire tomorrow" if "Hamas would say yes to the deal"
share this!
April 29, 2024
This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies . Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
Intervention based on science of reading and math boosts comprehension and word problem-solving skills
by University of Kansas
New research from the University of Kansas has found that an intervention based on the science of reading and math effectively helped English learners boost their comprehension, visualize and synthesize information, and make connections that significantly improved their math performance.
The intervention , performed for 30 minutes twice a week for 10 weeks with 66 third-grade English language learners who displayed math learning difficulties, improved students' performance when compared to students who received general instruction. This indicates that emphasizing cognitive concepts involved in the science of reading and math are key to helping students improve, according to researchers.
"Word problem-solving is influenced by both the science of reading and the science of math. Key components include number sense, decoding, language comprehension and working memory. Utilizing direct and explicit teaching methods enhances understanding and enables students to effectively connect these skills to solve math problems . This integrated approach ensures that students are equipped with necessary tools to navigate both the linguistic and numerical demands of word problems," said Michael Orosco, professor of educational psychology at KU and lead author of the study.
The intervention incorporates comprehension strategy instruction in both reading and math, focusing and decoding, phonological awareness, vocabulary development, inferential thinking, contextualized learning and numeracy.
"It is proving to be one of the most effective evidence-based practices available for this growing population," Orosco said.
The study, co-written with Deborah Reed of the University of Tennessee, was published in the journal Learning Disabilities Research and Practice .
For the research, trained tutors implemented the intervention, developed by Orosco and colleagues based on cognitive and culturally responsive research conducted over a span of 20 years. One example of an intervention session tested in the study included a script in which a tutor examined a word problem explaining that a person made a quesadilla for his friend Mario and gave him one-fourth of it, then asked students to determine how much remained.
The tutor first asked students if they remembered a class session in which they made quesadillas and what shape they were, and demonstrated concepts by drawing a circle on the board, dividing it into four equal pieces, having students repeat terms like numerator and denominator. The tutor explains that when a question asks how much is left, subtraction is required. The students also collaborated with peers to practice using important vocabulary in sentences. The approach both helps students learn and understand mathematical concepts while being culturally responsive.
"Word problems are complex because they require translating words into mathematical equations, and this involves integrating the science of reading and math through language concepts and differentiated instruction," Orosco said. "We have not extensively tested these approaches with this group of children. However, we are establishing an evidence-based framework that aids them in developing background knowledge and connecting it to their cultural contexts."
Orosco, director of KU's Center for Culturally Responsive Educational Neuroscience, emphasized the critical role of language in word problems, highlighting the importance of using culturally familiar terms. For instance, substituting "pastry" for "quesadilla" could significantly affect comprehension for students from diverse backgrounds. Failure to grasp the initial scenario could impede subsequent problem-solving efforts.
The study proved effective in improving students' problem-solving abilities, despite covariates including an individual's basic calculation skills, fluid intelligence and reading comprehension scores. That finding is key, as while ideally all students would begin on equal footing and there would be few variations in a classroom, in reality, covariates exist and are commonplace.
The study had trained tutors deliver the intervention, and its effectiveness should be further tested with working teachers, the authors wrote. Orosco said professional development to help teachers gain the skills is necessary, and it is vital for teacher preparation programs to train future teachers with such skills as well. And helping students at the elementary level is necessary to help ensure success in future higher-level math classes such as algebra.
The research builds on Orosco and colleagues' work in understanding and improving math instruction for English learners. Future work will continue to examine the role of cognitive functions such as working memory and brain science, as well as potential integration of artificial intelligence in teaching math.
"Comprehension strategy instruction helps students make connections, ask questions, visualize, synthesize and monitor their thinking about word problems," Orosco and Reed wrote. "Finally, applying comprehension strategy instruction supports ELs in integrating their reading, language and math cognition…. Focusing on relevant language in word problems and providing collaborative support significantly improved students' solution accuracy."
Provided by University of Kansas
Explore further
Feedback to editors

Study reveals complex dynamics of philanthropic funding for US science
9 minutes ago

'Quantum optical antennas' provide more powerful measurements on the atomic level
13 minutes ago

Researchers use 3D visualization to predict, prevent hurricane damage
21 minutes ago
Nanoparticles reprogram mouse immune systems to cope with allergens
42 minutes ago

New imaging device combines education and microbial research
47 minutes ago

Study finds natural climate variability impacts Arctic and global warming
58 minutes ago

Researchers identify potential microbes and genes that impact forever chemicals

Webb Telescope reveals asteroid collision in neighboring star system

Galactic bloodlines: Many nearby star clusters originate from only three 'families'

Interventions against misinformation also increase skepticism toward reliable sources, finds study
Relevant physicsforums posts, how is physics taught without calculus.
2 hours ago
Is "College Algebra" really just high school "Algebra II"?
4 hours ago
UK School Physics Exam from 1967
May 27, 2024
Physics education is 60 years out of date
May 16, 2024
Plagiarism & ChatGPT: Is Cheating with AI the New Normal?
May 13, 2024
Physics Instructor Minimum Education to Teach Community College
May 11, 2024
More from STEM Educators and Teaching
Related Stories
Study shows program improves teaching skills, students' word problem–solving
Jun 14, 2022
Study shows approach can help English learners improve at math word problems
Jun 19, 2018

Study examines role of working memory, cognitive functions in English learners learning to write
Oct 17, 2023

Cognitive study shows lack of bilingual education adversely affects English language learners' writing skills
Oct 14, 2021

How vocabulary breadth and depth influence bilingual reading comprehension
Aug 21, 2023

Study validates the simple view of reading for enhancing second and foreign language learners' experience
Aug 17, 2023
Recommended for you

First-generation medical students face unique challenges and need more targeted support, say researchers

Investigation reveals varied impact of preschool programs on long-term school success
May 2, 2024

Training of brain processes makes reading more efficient
Apr 18, 2024

Researchers find lower grades given to students with surnames that come later in alphabetical order
Apr 17, 2024

Earth, the sun and a bike wheel: Why your high-school textbook was wrong about the shape of Earth's orbit
Apr 8, 2024

Touchibo, a robot that fosters inclusion in education through touch
Apr 5, 2024
Let us know if there is a problem with our content
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form . For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines ).
Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request
Thank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.
E-mail the story
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Phys.org in any form.
Newsletter sign up
Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox. You can unsubscribe at any time and we'll never share your details to third parties.
More information Privacy policy
Donate and enjoy an ad-free experience
We keep our content available to everyone. Consider supporting Science X's mission by getting a premium account.
E-mail newsletter

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The McKinsey guide to problem solving. Become a better problem solver with insights and advice from leaders around the world on topics including developing a problem-solving mindset, solving problems in uncertain times, problem solving with AI, and much more.
That's what we've found after decades of problem solving with leaders across business, nonprofit, and policy sectors. These leaders learn to adopt a particularly open and curious mindset, and adhere to a systematic process for cracking even the most inscrutable problems. They're terrific problem solvers under any conditions.
In this episode of the Inside the Strategy Room podcast, McKinsey senior partner Chris Bradley interviews Rob McLean, McKinsey director emeritus, about applying a disciplined, comprehensive approach to problem solving. You can listen to the episode on Apple Podcasts, Spotify, or Google Podcasts.. Sean Brown: From McKinsey's Strategy and Corporate Finance Practice, I'm Sean Brown.
The rest of us can look for insights by methodically and systematically scrutinizing three areas: a valuable problem to solve, a technology that enables a solution, and a business model that generates money from it. You could argue that nearly every successful innovation occurs at the intersection of these three elements.
Drawing on consulting practitioner approaches, this article presents a translation of the McKinsey approach as a six-stage structured problem-solving methodology that can be used to guide students on how to develop solutions in a systematic, logical, and evidence-based way.
In simple terms, the McKinsey Solve assessment is a set of ecology-themed video games. In these games, you must do things like build food chains, protect endangered species, manage predator and prey populations, boost biodiversity and potentially diagnose diseases within animal populations or identify natural disasters.
The McKinsey Problem Solving Approach is a testament to the firm's commitment to excellence and innovation. Its structured methodology, emphasis on analytical rigor, and focus on delivering actionable insights have made McKinsey a trusted advisor to some of the world's most successful organizations. By continually refining its approach and ...
8 Steps to Problem-Solving from McKinsey. Solve at the first meeting with a hypothesis. Intuition is as important as facts. Do your research but don't reinvent the wheel. Tell the story behind ...
McKinsey consultants apply two methodologies to problem-solving: top-down and bottom-up. Most professionals intuitively opt for a bottom-up approach. Consultants often bias towards top-down.
The McKinsey problem solving process is a series of mindset shifts and structured approaches to thinking about and solving challenging problems. It is a useful approach for anyone working in the knowledge and information economy and needs to communicate ideas to other people. ... This involves doing deep research around your problem statement ...
Drawing on consulting practitioner approaches, this article presents a translation of the McKinsey approach as a six-stage structured problem-solving methodology that can be used to guide students ...
Problem solving — finding the optimal solution to a given business opportunity or challenge — is the very heart of how consultants create client impact, and considered the most important skill for success at McKinsey. The characteristic "McKinsey method" of problem solving is a structured, inductive approach that can be used to solve ...
Techniques for prioritization problem : a. Pareto rule (80/20) — It is a tool to identify the important issues that can be solved that would provide the most impact in the problem statement ...
Between December 2019 and 2021, construction wages grew by 7.9 percent. 2Quarterly Census of Employment and Wages, US Bureau of Labor Statistics. Competition from other sectors for the same pool of labor is heating up, too. For example, over the same period, transportation and warehousing wages grew by 12.6 percent.
2017 •. Emanuel Onoszko. Download Free PDF. View PDF. PROBLEM SOLVING WITH THE MCKINSEY METHOD fMCKINSEY PROBLEM SOLVING APPROACH Focus of today's discussion Managing • Team Leadership • Vision • Client • Self Business Need • Competitive • Organizational • Financial • Operational Problem Intuition • Inspiration ...
The McKinsey Problem Solving Test (or PST) is a paper-based test used at McKinsey & Company to select candidates for the case interviews. The PST is conducted after resume screening; it has 6 types of question, testing the candidate on 3 crucial problem-solving skills - data interpretation, mental calculations and logical reasoning.
The research sample was students of 10th MIPA 4 at SMAN 2 Malang, which was determined by purposive sampling. This research was conducted in November 2021. The data analysis technique used a normalised gain score. The results of the N-gain test of problem-solving skills are 0.81 in the high effectiveness category, creative thinking skills are 0 ...
Google, IBM make strides toward quantum computers that may revolutionize problem solving. December 3, 2023 / 7:17 PM EST / CBS News. Artificial intelligence is the magic of the moment but this is ...
More information: Michael J. Orosco et al, Supplemental intervention for third-grade English learners with significant problem-solving challenges, Learning Disabilities Research & Practice (2024 ...