
Research Proposal Example/Sample
Detailed Walkthrough + Free Proposal Template
If you’re getting started crafting your research proposal and are looking for a few examples of research proposals , you’ve come to the right place.
In this video, we walk you through two successful (approved) research proposals , one for a Master’s-level project, and one for a PhD-level dissertation. We also start off by unpacking our free research proposal template and discussing the four core sections of a research proposal, so that you have a clear understanding of the basics before diving into the actual proposals.
- Research proposal example/sample – Master’s-level (PDF/Word)
- Research proposal example/sample – PhD-level (PDF/Word)
- Proposal template (Fully editable)
If you’re working on a research proposal for a dissertation or thesis, you may also find the following useful:
- Research Proposal Bootcamp : Learn how to write a research proposal as efficiently and effectively as possible
- 1:1 Proposal Coaching : Get hands-on help with your research proposal

PS – If you’re working on a dissertation, be sure to also check out our collection of dissertation and thesis examples here .
FAQ: Research Proposal Example
Research proposal example: frequently asked questions, are the sample proposals real.
Yes. The proposals are real and were approved by the respective universities.
Can I copy one of these proposals for my own research?
As we discuss in the video, every research proposal will be slightly different, depending on the university’s unique requirements, as well as the nature of the research itself. Therefore, you’ll need to tailor your research proposal to suit your specific context.
You can learn more about the basics of writing a research proposal here .
How do I get the research proposal template?
You can access our free proposal template here .
Is the proposal template really free?
Yes. There is no cost for the proposal template and you are free to use it as a foundation for your research proposal.
Where can I learn more about proposal writing?
For self-directed learners, our Research Proposal Bootcamp is a great starting point.
For students that want hands-on guidance, our private coaching service is recommended.

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling short course, Research Proposal Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
You Might Also Like:
10 Comments
I am at the stage of writing my thesis proposal for a PhD in Management at Altantic International University. I checked on the coaching services, but it indicates that it’s not available in my area. I am in South Sudan. My proposed topic is: “Leadership Behavior in Local Government Governance Ecosystem and Service Delivery Effectiveness in Post Conflict Districts of Northern Uganda”. I will appreciate your guidance and support
GRADCOCH is very grateful motivated and helpful for all students etc. it is very accorporated and provide easy access way strongly agree from GRADCOCH.
Proposal research departemet management
I am at the stage of writing my thesis proposal for a masters in Analysis of w heat commercialisation by small holders householdrs at Hawassa International University. I will appreciate your guidance and support
please provide a attractive proposal about foreign universities .It would be your highness.
comparative constitutional law
Kindly guide me through writing a good proposal on the thesis topic; Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Financial Inclusion in Nigeria. Thank you
Kindly help me write a research proposal on the topic of impacts of artisanal gold panning on the environment
I am in the process of research proposal for my Master of Art with a topic : “factors influence on first-year students’s academic adjustment”. I am absorbing in GRADCOACH and interested in such proposal sample. However, it is great for me to learn and seeking for more new updated proposal framework from GRADCAOCH.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
- Postgraduate
Research degrees
- Examples of Research proposals
- Apply for 2024
- Find a course
- Accessibility
Examples of research proposals
How to write your research proposal, with examples of good proposals.
Research proposals
Your research proposal is a key part of your application. It tells us about the question you want to answer through your research. It is a chance for you to show your knowledge of the subject area and tell us about the methods you want to use.
We use your research proposal to match you with a supervisor or team of supervisors.
In your proposal, please tell us if you have an interest in the work of a specific academic at York St John. You can get in touch with this academic to discuss your proposal. You can also speak to one of our Research Leads. There is a list of our Research Leads on the Apply page.
When you write your proposal you need to:
- Highlight how it is original or significant
- Explain how it will develop or challenge current knowledge of your subject
- Identify the importance of your research
- Show why you are the right person to do this research
- Research Proposal Example 1 (DOC, 49kB)
- Research Proposal Example 2 (DOC, 0.9MB)
- Research Proposal Example 3 (DOC, 55.5kB)
- Research Proposal Example 4 (DOC, 49.5kB)
Subject specific guidance
- Writing a Humanities PhD Proposal (PDF, 0.1MB)
- Writing a Creative Writing PhD Proposal (PDF, 0.1MB)
- About the University
- Our culture and values
- Academic schools
- Academic dates
- Press office
Our wider work
- Business support
- Work in the community
- Donate or support
Connect with us
York St John University
Lord Mayor’s Walk
01904 624 624
York St John London Campus
6th Floor Export Building
1 Clove Crescent
01904 876 944
- Policies and documents
- Module documents
- Programme specifications
- Quality gateway
- Admissions documents
- Access and Participation Plan
- Freedom of information
- Accessibility statement
- Modern slavery and human trafficking statement
© York St John University 2024
Colour Picker
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Dui id ornare arcu odio.
Felis bibendum ut tristique et egestas quis ipsum. Et netus et malesuada fames ac turpis egestas. Faucibus pulvinar elementum integer enim neque volutpat ac. Hac habitasse platea dictumst vestibulum rhoncus.
Nec ullamcorper sit amet risus nullam eget felis eget. Eget felis eget nunc lobortis mattis aliquam faucibus purus.
How to write a research proposal
What is a research proposal.
A research proposal should present your idea or question and expected outcomes with clarity and definition – the what.
It should also make a case for why your question is significant and what value it will bring to your discipline – the why.
What it shouldn't do is answer the question – that's what your research will do.
Why is it important?
Research proposals are significant because Another reason why it formally outlines your intended research. Which means you need to provide details on how you will go about your research, including:
- your approach and methodology
- timeline and feasibility
- all other considerations needed to progress your research, such as resources.
Think of it as a tool that will help you clarify your idea and make conducting your research easier.
How long should it be?
Usually no more than 2000 words, but check the requirements of your degree, and your supervisor or research coordinator.
Presenting your idea clearly and concisely demonstrates that you can write this way – an attribute of a potential research candidate that is valued by assessors.
What should it include?
Project title.
Your title should clearly indicate what your proposed research is about.
Research supervisor
State the name, department and faculty or school of the academic who has agreed to supervise you. Rest assured, your research supervisor will work with you to refine your research proposal ahead of submission to ensure it meets the needs of your discipline.
Proposed mode of research
Describe your proposed mode of research. Which may be closely linked to your discipline, and is where you will describe the style or format of your research, e.g. data, field research, composition, written work, social performance and mixed media etc.
This is not required for research in the sciences, but your research supervisor will be able to guide you on discipline-specific requirements.
Aims and objectives
What are you trying to achieve with your research? What is the purpose? This section should reference why you're applying for a research degree. Are you addressing a gap in the current research? Do you want to look at a theory more closely and test it out? Is there something you're trying to prove or disprove? To help you clarify this, think about the potential outcome of your research if you were successful – that is your aim. Make sure that this is a focused statement.
Your objectives will be your aim broken down – the steps to achieving the intended outcome. They are the smaller proof points that will underpin your research's purpose. Be logical in the order of how you present these so that each succeeds the previous, i.e. if you need to achieve 'a' before 'b' before 'c', then make sure you order your objectives a, b, c.
A concise summary of what your research is about. It outlines the key aspects of what you will investigate as well as the expected outcomes. It briefly covers the what, why and how of your research.
A good way to evaluate if you have written a strong synopsis, is to get somebody to read it without reading the rest of your research proposal. Would they know what your research is about?
Now that you have your question clarified, it is time to explain the why. Here, you need to demonstrate an understanding of the current research climate in your area of interest.
Providing context around your research topic through a literature review will show the assessor that you understand current dialogue around your research, and what is published.
Demonstrate you have a strong understanding of the key topics, significant studies and notable researchers in your area of research and how these have contributed to the current landscape.
Expected research contribution
In this section, you should consider the following:
- Why is your research question or hypothesis worth asking?
- How is the current research lacking or falling short?
- What impact will your research have on the discipline?
- Will you be extending an area of knowledge, applying it to new contexts, solving a problem, testing a theory, or challenging an existing one?
- Establish why your research is important by convincing your audience there is a gap.
- What will be the outcome of your research contribution?
- Demonstrate both your current level of knowledge and how the pursuit of your question or hypothesis will create a new understanding and generate new information.
- Show how your research is innovative and original.
Draw links between your research and the faculty or school you are applying at, and explain why you have chosen your supervisor, and what research have they or their school done to reinforce and support your own work. Cite these reasons to demonstrate how your research will benefit and contribute to the current body of knowledge.
Proposed methodology
Provide an overview of the methodology and techniques you will use to conduct your research. Cover what materials and equipment you will use, what theoretical frameworks will you draw on, and how will you collect data.
Highlight why you have chosen this particular methodology, but also why others may not have been as suitable. You need to demonstrate that you have put thought into your approach and why it's the most appropriate way to carry out your research.
It should also highlight potential limitations you anticipate, feasibility within time and other constraints, ethical considerations and how you will address these, as well as general resources.
A work plan is a critical component of your research proposal because it indicates the feasibility of completion within the timeframe and supports you in achieving your objectives throughout your degree.
Consider the milestones you aim to achieve at each stage of your research. A PhD or master's degree by research can take two to four years of full-time study to complete. It might be helpful to offer year one in detail and the following years in broader terms. Ultimately you have to show that your research is likely to be both original and finished – and that you understand the time involved.
Provide details of the resources you will need to carry out your research project. Consider equipment, fieldwork expenses, travel and a proposed budget, to indicate how realistic your research proposal is in terms of financial requirements and whether any adjustments are needed.
Bibliography
Provide a list of references that you've made throughout your research proposal.
Apply for postgraduate study
New hdr curriculum, find a supervisor.
Search by keyword, topic, location, or supervisor name
- 1800 SYD UNI ( 1800 793 864 )
- or +61 2 8627 1444
- Open 9am to 5pm, Monday to Friday
- Student Centre Level 3 Jane Foss Russell Building Darlington Campus
Scholarships
Find the right scholarship for you
Research areas
Our research covers the spectrum – from linguistics to nanoscience
Our breadth of expertise across our faculties and schools is supported by deep disciplinary knowledge. We have significant capability in more than 20 major areas of research.
Research facilities
High-impact research through state-of-the-art infrastructure

How do You Write a Project/Research Proposal for Life Science?
Writing a project/research/PhD proposal for life science, which includes biotechnology, microbiology, genetics and allied subjects, is certainly a different task. It often needs exposure to scientific writing and additional skills regarding the subject.
Students’ PhD endeavor starts by preparing the project or research proposal . It actually shows your interest, knowledge and planning for the project. An inadequately written proposal is immediately rejected by the supervisor.
Frankly speaking, students often prepare their project proposals to impress their guide, instead of showing their knowledge and interest. In addition, some students with knowledge fail too. In either scenario, the reason is clear.
Lack of academic writing experience.
Additionally, when we are talking about life science like pure research subjects, things become even more complicated. One has to demonstrate their writing, research and even experimental skills in the proposal.
Thus, it becomes important for students to understand how to write such a piece of academic write-up before doing anything else. I got my doctorate in one of the life science subjects, then moved to the academic writing field to solve our life science students’ problem of academic writing.
If you are searching this phrase, “ How do you write a project/research proposal for life science?” on the Internet and land on this page, you are on the right article and I am perhaps the right person.
So how can we do that? Let’s find out.
How do you write a project/research proposal for life science?
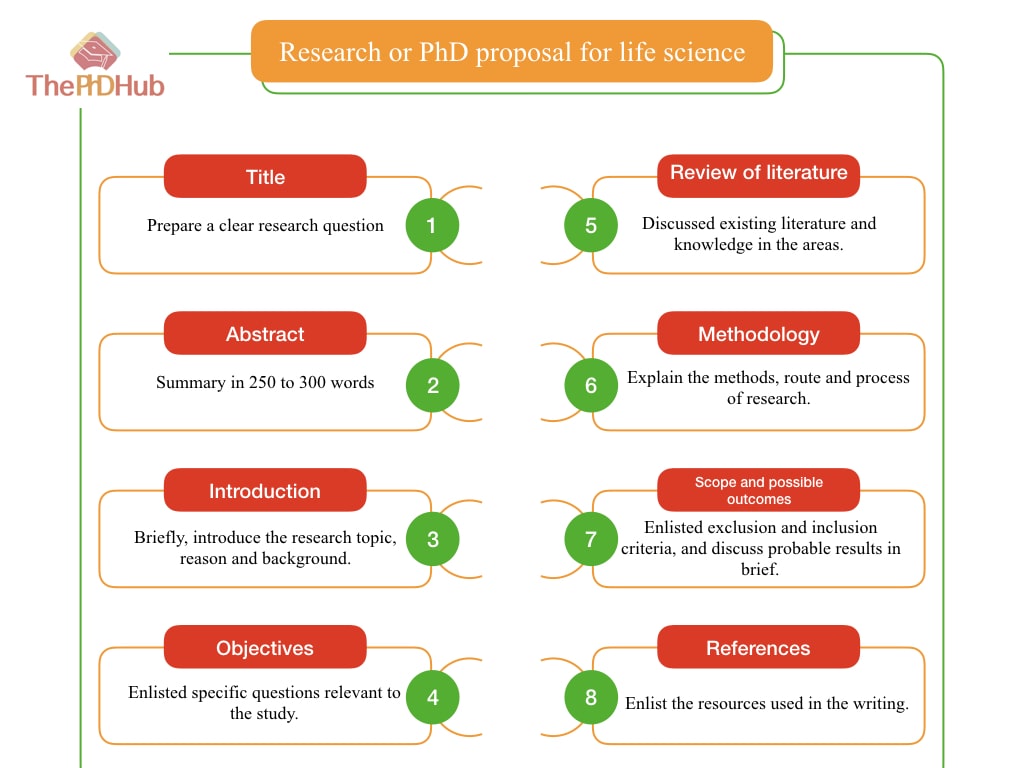
Every research proposal has some common elements, without which it looks incomplete. Oftentimes, a supervisor checks them first. For instance, it should have a background/ introduction, review of literature, methodology, scope and bibliography sections.
When you blankly initiate your life science project proposal writing, it looks easy, but when it gets rejected or you read things on the internet relevant, it becomes difficult. However, by avoiding common mistakes and following a usual guide, the student can write their own.
At this point, you might be willing to do a PhD, first understand that a life science subject research or project proposal is a different venture than a grant proposal and cover letter. So make it clear that you are writing a research proposal that is the same as a PhD or project proposal.
A life science research proposal is certainly a distinct proposal.
- It should have a comprehensive review of the literature section which discusses all of the major points relevant to the research question.
- The research title should be clear, and concise and must show a clear goal, objective, methods and techniques. I have discussed how to prepare a PhD title in our previous article. You can read it there.
- It should elaboratively explain the materials and methodology section. Wet lab experimentation has been significantly involved in life science research/PhD, so beyond doubts, this section must show how the experimental work would go.
- Also, it must demonstrate sampling, analytical and interpretation methods that help to obtain tentative results thereby achieving objectives.
- It should show the scopes of the study and possible outcomes in terms of societal or real-world importance.
- Lastly, Use correct citation and referencing “in-style.”
Moreover, Also keep in mind what should not be included here. Because after all, everything is covered within 10 to 12 pages (including references).
Things to avoid:
- Give a brief background of the topic. Avoid explaining everything here.
- Review associated research, in brief. Keep in mind that it would justify the research question. Do not discuss separate reviews here.
- Avoid including every possible utility that you are going to use, for example, glassware, plasticware, and instruments, etc. Discuss the SOP, route or road map using which the objectives will be achieved.
- Discuss the method which you have selected, not the technique, in the long run you might have to change the technique. For example,
- Avoid giving a clear statement regarding the results. Instead, enlist possible outcomes. For example,
- Do not claim anything in the research proposal. For example,
Research proposal template for life science:
Research work plan: .
I have specifically highlighted the last segment because it is very important and must be included in the research plan, however, students usually avoid it or do not even have an idea about it. Surprisingly, I was not aware of it until I showed it in one of my student’s proposals.
It is amazing, indeed, even I was impressed! It definitely proclaims your interest and preparation for doing research or PhD. It needs a comprehensive explanation to prepare that I think deserves a separate article. Here I am only giving you the template.

Costume PhD writing services:
If you are worried about your research proposal and still lack the concept of how to do it. Leave it to us. I and My team are experienced life science scientists who can do the job for you. Send us an email on [email protected] or [email protected] to get more information.
We can prepare a costume proposal as per your requirements. Remember, we believe in expertise and our’s is in life science. We only accept writing work related to our subject.
Wrapping up:
Life science subjects need attention on so many things. Their focus would be on lab work and hence they face problems in writing such assignments. Sometimes, only bad writing becomes a reason for rejection. This comprehensive guide perhaps benefits you. Still, if you are not sure, contact us, we will help you.
Also, take a tour of our blog, my team has written some amazing articles that certainly help you in your PhD endeavors. If you want to share your PhD experience, please mail us. We will publish your journal to motivate others.

Dr. Tushar Chauhan is a Scientist, Blogger and Scientific-writer. He has completed PhD in Genetics. Dr. Chauhan is a PhD coach and tutor.
Share this:

- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
- Share on Pinterest
- Share on Linkedin
- Share via Email
About The Author

Dr Tushar Chauhan
Related posts.

How to Choose the best Thesis Writing Service in 2022?
1 thought on “how do you write a project/research proposal for life science”.
What’s Going down i’m new to this, I stumbled upon this I’ve found It positively useful and it has aided me out loads. I am hoping to give a contribution & help different users like its helped me. Great job.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
Notify me of new posts by email.
Browser does not support script.
Go to…
- Undergraduate
- Our students
- Postgraduate
- PhD research
- Publications
- Research Centres and Groups
- Our connections
- Student societies
EIS PhD Research Proposal Guidelines
The research proposal is the most important part of your PhD application. We do not expect the proposal to be perfect at this stage, nor do we expect you to stick to it rigidly, as your ideas will almost certainly change once you start to study. However, we do expect it to show convincing evidence of your ability to plan and organise independent research. Please read and follow the guidelines carefully.
Your proposal should be 2,000-3,000 words long , plus bibliography, using the following sections:
- Title – The best titles are simple and descriptive, identifying the topic and approach that will be taken.
- Central research question and objectives – The question your research seeks to answer should be stated simply, then fleshed out to show to show why it is timely and important – both intellectually and politically – for you to be writing a PhD on this topic. After that, you should state, in straightforward terms, how the PhD will answer the research question.
- Literature review – Here you must show how your central research question relates to existing academic studies in your field. This requires a short literature review which will situate your proposed research within the framework of the dominant perspectives on similar issues in the existing literature. Ideally, you should be able to demonstrate how your proposed research fills a gap in the literature and therefore adds substantively and can make a lasting contribution to academic debates. One key criterion for writing a successful PhD is that it is original work, so you must try to avoid setting up your analysis in a way which simply replicates work which can already be found within the literature.
- Theoretical framework – Here, you should detail what theoretical framework(s) will underpin the analysis in your PhD, why that framework has been chosen, and what advantages it gives you for addressing your central research question.
- Case studies and methodology – Here, you should discuss the type of empirical research (statistical work, interviews, surveys etc.) that you will be doing and the case study/case studies that you have chosen. This is essential in all cases except for abstract political theory PhDs. You should show how your theoretical framework informs the methodology that you will use and why that methodology is particularly advantageous for answering the research question.
- Problems – Here, you should reflect on any problems you think you may encounter whilst undertaking your research and indicate how they might be overcome or mitigated. These might include, for example, access to data.
- Bibliography – You should include a complete bibliography for the proposal.
The above draws on the advice issued by the Political and International Studies department at Warwick University.
- Graduate School
Oxford PhD Proposal Sample: The Best Proposal

An Oxford PhD proposal sample, like Oxford personal statement examples , should give you an idea of how to structure and write your own PhD proposal, which is a key element of how to get into grad school . Should you pursue a master's or PhD , you should know that, with few exceptions, all graduate programs require that applicants submit a research proposal. It can vary in length (usually between 1,000 and 3,000 words) and must outline your main research goals and methods and demonstrate your facility with the topic. The almost 35,000 applications Oxford received in a recent year should give you some idea of how competitive getting into a master's or PhD program is.
Writing a stellar proposal is important to make your application stand out, so, to that end, this article will show you an expert-approved Oxford PhD proposal sample based on the actual requirements of an Oxford graduate program.
>> Want us to help you get accepted? Schedule a free strategy call here . <<
Listen to the blog!
Article Contents 11 min read
Oxford phd proposal sample.
PhD Program : DPhil in Migrant Studies
Research Proposal Length: minimum 2000 - maximum 3000 words
To: Matthew J. Gibney, Professor of Politics and Forced Migration
Name: Adrian Toews
Title: Wired and Hungry Masses: Social Media, Migrants and Cultural Bereavement in the Digital Sphere
Proposed Research Topic: Does social media help migrants cross the cultural barriers of their adopted home and succeed in helping them preserve touchstones of their home culture?
Abstract: The ascendance of social media platforms has increased and, strangely, decreased interconnectedness among disparate groups in society. But, while social media has been implicated, rightly, as a catalyst for the rise of disinformation, hate speech, and other anti-social behaviors, I would argue that its ubiquity and prevalence provide those experiencing cultural bereavement with a more-effective coping mechanism, as social media is able to replicate, in a non-physical space, the culturally specific mechanisms they know and which, prior to digital communications, could not be replicated in new, adopted countries and cultures.
Objective: I want to present social media as an informal networking tool, expressive outlet, and cultural road map with which migrants who are experiencing cultural bereavement can engage for two specific reasons: 1) to assuage the grief that accompanies anyone who has left their homeland as a migrant or refugee, and 2) to help them assimilate into their new identity by giving them a window into the cultural norms and practices of their new country or culture.
Wondering if you should go to grad school? Watch this video:
An Oxford PhD proposal sample like this one is only one version of what a proposal can look like, but it should contain at least these basic elements. You should know how to choose a PhD topic at this point in your career, but if you still feel like you need help, then you can hire PhD admission consultants to help you choose your topic and research interests.
Above all, you should know why you want to do a PhD . Answering this question first will be effective in helping you ultimately decide on a program, which can then make it easier for you to write any number of different doctorate-related texts, such as a PhD motivation letter and a statement of intent .
Understanding your true motivations, passions, and research interests is doubly important when pursuing a PhD since you do not want to invest so much time and resources in a subject you are only partially interested in. If you can honestly answer why you want to pursue a PhD, you can then take concrete steps toward defining your research goals and how they can be fulfilled by the program you choose.
Your Oxford PhD proposal should adhere to the requirements set forth by the program you wish to enter. Regardless of your discipline or field, almost all PhD programs at Oxford require that you submit a research proposal of between 2,000 and 3,000 words.
A statement of intent is another type of essay that applicants are often asked to submit to graduate schools. It involves talking about your past academic experiences and achievements, what you intend to do in graduate school, and why you want to go there. A PhD proposal, on the other hand, contains no personal details or experiences.
Instead, a PhD proposal should be a focused, concrete road map built around a specific research question. In your proposal, you list the theoretical approaches that you are going to use, research methods, past scholarship on the same topic, and other investigative tools to answer this question or present evidence from this research to support your argument.
A statement of purpose is another common essay that graduate school applicants must submit. The line between a statement of purpose and a statement of intent is a fine one, but the line between a statement of purpose and a PhD proposal is much more prominent, and there is no mistaking the two. So, you should not read over graduate school statement of purpose examples to learn how to write a PhD proposal.
A statement of purpose can also be research-focused, but in an undefined way. A PhD proposal combines theory and practice and requires that you demonstrate your knowledge of proper scientific research, investigative methods, and the existing literature on your topic.
You should include a title page where you list your name, the program you are applying to, and a title for your research project. You should address it to a specific faculty member, who can perhaps, if they agree, show you how to prepare for a thesis defense . The proposal itself should include an abstract, an overview of the existing scholarship on your topic, research questions, methods, and a bibliography listing all your sources.
The usual length of PhD proposals is between 1,000 and 3,000 words, but your program may have different requirements, which you should always follow.
There are up to 350 different graduate programs at Oxford, all with their own particular requirements, so the university does not set forth a universal set of requirements for all graduate programs. Many of these programs and their affiliated schools offer students advice on how to write a PhD proposal, but there are few, if any, stated requirements other than the implied ones, which are that you have familiarity with how to conduct graduate-level research and are knowledgeable in the field you are researching.
A majority of programs do, yes. There are always exceptions, but a fundamental part of pursuing a PhD involves research and investigation, so it is normal for any PhD program to require that applicants write a PhD proposal.
It is quite possible for your research interests and direction to change during your research, but you should not be discouraged. Graduate programs understand that these things happen, but you should still do your best to reflect the current state of research on your topic and try to anticipate any changes or sudden shifts in direction while you research.
Want more free tips? Subscribe to our channels for more free and useful content!
Apple Podcasts
Like our blog? Write for us ! >>
Have a question ask our admissions experts below and we'll answer your questions, get started now.
Talk to one of our admissions experts
Our site uses cookies. By using our website, you agree with our cookie policy .
FREE Training Webinar:
How to make your grad school application stand out, (and avoid the top 5 mistakes that get most rejected).
Time Sensitive. Limited Spots Available:
We guarantee you'll get into grad school or you don't pay.
Swipe up to see a great offer!
- Skip to Content
- Catalog Home
- Institution Home
- School of Architecture
- College of Arts & Sciences
- School of Business Administration
- School of Communication
- School of Education & Human Development
- College of Engineering
- School of Law
- Rosenstiel School of Marine & Atmospheric Science
- Miller School of Medicine
- Frost School of Music
- School of Nursing & Health Studies
- The Graduate School
- Division of Continuing & International Education
- Search Miami.edu Search
- People Search
- Department Search
- Course Search
- Student Life
Registrar's Office
- Graduate Academic Programs >
- Engineering >
- Biomedical Engineering >
- MS in Medical Physics
- General University Information
- Undergraduate Academic Programs
- Architecture
- Arts and Sciences
- Communication
- Education and Human Development
- BS/MS Five-Year Program in Biomedical Engineering
- BS/MS in Neural Engineering
- Certificate Program in Medical Physics
- MS in Biomedical Engineering
- MS in Neural Engineering
- PhD in Biomedical Engineering
- PhD in Medical Physics
- Chemical, Environmental and Materials Engineering
- Civil and Architectural Engineering
- Electrical and Computer Engineering
- Industrial and Systems Engineering
- Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering
- Ocean Engineering
- Marine, Atmospheric, and Earth Science
- Nursing and Health Studies
- Law Academic Programs
- Graduate Student Handbook for UOnline Students
- Special Programs
- Program Index
- Course Listing
- Previous Bulletin Archives
The medical physics graduate program is accredited by the Commission on Accreditation of Medical Physics Education Programs, Inc. ( CAMPEP ). The program, serving both MS and PhD degrees, ensures that the students receive adequate didactic and clinical training to continue in education and research, enter clinical physics residencies or begin working as medical physicists in radiation therapy and diagnostic radiology departments. MS students are trained with an emphasis on developing skills necessary for clinical medical physicists,
In addition to the requirement of physics minor-equivalent undergraduate coursework, the qualifications and documentation required for admission to the MS program in Medical Physics are the same as for the College of Engineering.
In general, the following four types of students are typically admitted to the MS program in Medical Physics:
- Students with undergraduate degrees in biomedical engineering and other engineering disciplines who seek advanced professional training or specialization in a particular area of medical physics
- Professional engineers with degrees in other engineering disciplines who plan to enter the field of medical physics
- Students with an undergraduate degree in Physics, Mathematics, Computer Science, Chemistry, Biology or other fields of natural or health science who seek to diversify their career opportunities by acquiring a medical physics degree
- Students who are preparing for admission to advanced health-related or other professional programs such as medical school
Students may be given conditional admission and required to take additional undergraduate courses in engineering, physics, and/or mathematics depending on their previous course work, as specified in the admission letter. The requisite courses will be prescribed by the Department Chair or Graduate Program Director during the first advising session.
The objective of the Medical Physics program is to provide advanced knowledge in the field of medical physics with an emphasis on therapeutic medical physics, and to provide the training required for students to become licensed medical physicists. This program is coordinated by the Department of Biomedical Engineering and the Department of Radiation Oncology at the School of Medicine.
The program is opened to students enrolled in the regular MS program, as well as the dual degree (BS/MS) program. Candidates are required to have completed the physics minor equivalent coursework that must include Modern Physics ( PHY 360 or equivalent), before they start their coursework in the Medical Physics program.
Students in the Medical Physics program must complete Human Physiology for Engineers ( BME 602 ) and one of the remaining two courses from the human physiology ( BME 601 or BME 603 ) course series, and 23-credits in the core curriculum in the area of medical physics.
The topic of the non-thesis MS project ( BME 707 / BME 708 ), or MS thesis must be related to medical physics. In general, the project is co-supervised by Faculty from the Department of Biomedical Engineering and the Department of Radiation Oncology
Required Core Courses
All students enrolled in the MS program are required to complete the following core graduate courses:
- Two human physiology courses ( BME 602 , and BME 601 or BME 603 )
- 23 credits in medical physics
The Human Physiology Courses ( BME 601 / BME 602 / BME 603 , 3 credits each) are designed to provide a basic understanding of organ-level physiology and anatomy, neurophysiology, and cellular and molecular biology. Students with an MD from a medical school accredited by the World Health Organization are exempted from taking these courses. Students holding advanced degrees in the life sciences, or equivalent experience in the field, may also be exempt. Each such exception requires the approval of the Department Chairperson and Faculty member responsible for the course of concern. Students who receive an exemption, must replace the exempted course(s) with another 3-credit graduate course(s) that meets the degree requirements.
Curriculum Requirements
Ms in medical physics - nonthesis option.
The MS non-thesis option is intended for students with an undergraduate degree in biomedical engineering or related disciplines who seek advanced training or specialization in a specific area of biomedical engineering; for professional engineers with undergraduate degrees in other disciplines who want to enter the field of biomedical engineering; and for students who want to prepare for admission to advanced health-related or other professional programs.
Non-Thesis MS Project
General description.
All students enrolled in the MS non-thesis program must complete a two-semester 3 credit Master's project ( BME 707 and BME 708 ), under the supervision of a project mentor and departmental project coordinator. The project must demonstrate the candidate’s ability to solve complex scientific or technical problems at the interface of engineering and medical physics.
The MS project can be a research or design project. The project must include a significant research or design component contributed by the M.S. student, including, but not limited to, the design of an experiment or process; the development of a device, instrument, or system; the development of a computer program; the analysis of experimental data. Projects cannot be limited solely to the review of literature, the development of research or design proposals, or the collection of experimental data.
At the completion of their project, students must submit a written project report and complete a public oral defense of their project.
Project Mentor
Students who select the MS non-thesis track must identify a project mentor and select a project before they register for their second semester of full-time study. The project mentor is generally a primary faculty member from the Medical Physics Graduate Program. The role of the project mentor is to help the student identify a suitable project, to monitor the progress of the student, to provide guidance and training in the relevant topics, and to review the final report and presentation.
Students may complete their project under the supervision of a faculty member from another Department at the University of Miami, or from the local biomedical industry, or from a local clinic, under the following conditions:
- The student must receive the approval of the Department Chairman and Graduate Program Director.
- The student must identify a co-mentor who must be a primary faculty member from the Medical Physics Graduate Program. The co-mentor must be familiar with the topic of the proposed project. The role of the co-mentor will be to monitor the student progress and ensure that the Master's project report and presentation satisfy all of the relevant requirements.
Project Coordinator
The project coordinator is a member of the primary faculty of the Department of Biomedical Engineering who is responsible for teaching the BME 707 / BME 708 course. The role of the project coordinator is to:
- Help students identify a project and mentor.
- Ensure that the projects satisfy the program objectives.
- Provide general guidance and graduate scholarship training.
- Ensure that the students are making suitable progress towards the project goals.
Project Abstract
Non-Thesis MS students must submit a one-page project abstract to the Department Chairman or Graduate Program Director and to the MS Project Coordinator at the time when they register for BME 707 / BME 708 . The abstract must include the name of the project mentor (and co-mentor, if any), the title of the proposed project, and a brief description of the goals of the project and proposed methods. The abstract must be approved by the mentor, MS Project Coordinator, and Department Chairman or Graduate Program Director before the student can start work on the project. ( Project Abstract Template )
Project Report
Non-thesis MS students must submit a detailed report describing the work completed during the project. The report must describe the objectives and significance of the work, and summarize the activities completed by the student as part of the MS project. The report must demonstrate that the work performed by the student satisfies the general project criteria. The typical length of non-thesis M.S. project reports is 20 to 30 pages. If the project resulted in the submission of a full-length peer-reviewed scientific article, the article can be submitted in lieu of a report, as long as the following conditions are satisfied:
- The student must be the first author of the article.
- The article must reflect the work performed by the student as part of the project.
- The article must be submitted for publication in a peer-reviewed journal or conference proceedings volume.
- A one to two page introduction must be submitted to summarize the project goals and main outcomes.
The report must be reviewed and approved by the project mentor (and co-mentor, if any). Once the report is approved by the mentor(s), one printed copy and one electronic version in PDF format must be submitted to the Project Coordinator by the specified deadline. The final report must be approved and signed by the Project Mentor(s), Project Coordinator and Graduate Program Director or Department Chairman. ( Signature Page Template )
Project presentation
Non-thesis MS students must give an oral presentation of their project. The oral presentation is generally scheduled during the scheduled final examination time of BME 707 / BME 708 in the semester of graduation.
Project grade
The final grade for the project is given by the Project Coordinator. The final grade is a combination of a grade submitted by the Project Mentor(s) assessing the overall performance of the student on the project, and a grade given by the Project Coordinator assessing the quality of the oral presentation and report.
Curriculum Requirements:
Ms in medical physics - thesis option.
The thesis option is typically selected by students who are oriented towards a career in academic or industrial research and development, or students who want to acquire an initial independent biomedical research experience before seeking admission to doctoral programs.
Thesis Option
General description.
The Master's thesis is a research monograph which describes the significance of the research and summarizes the research activities completed as part of the MS degree requirements. The objective of the thesis is to evaluate the candidate’s competence in the area of the MS research. The thesis must demonstrate that the research is original and that the candidate has the ability to solve complex scientific and/or technical problems at the interface of engineering and medicine or biology.
Thesis Mentor
Students who select the MS thesis track must identify a thesis mentor before they register for their second semester of full-time study. The thesis mentor must hold a primary or secondary faculty appointment in the Department of Biomedical Engineering. Exceptions can be made only with approval of the Graduate Program Director and Department Chairman.
The thesis mentor supervises the research work of the student and provides training and guidance in the relevant research topics, including design of experiments, experimental techniques, and scholarship activities. The mentor helps the student select a thesis topic and develop a plan, and chairs or co-chairs the thesis committee. The mentor works closely with the student to ensure that there is satisfactory progress towards the thesis goals.
Thesis Committee
The thesis must be approved by a thesis committee. The duties of the thesis committee are:
- to consult with and to advise students on their research;
- to meet, at intervals, to review progress and expected results;
- to read and comment upon the draft thesis;
- to meet, when the thesis is completed, to conduct the final oral examination and to satisfy itself that the thesis work is original; that it demonstrates the candidate's ability to solve complex scientific and/or technical problems at the interface of engineering and medicine or biology; that it is written in lucid and correct English; and that it is submitted in approved format.
The thesis committee will consist of not less than three members, with the following requirements:
- The committee chair shall be a Primary Faculty member of the Department of Biomedical Engineering, as well as a regular member of the Graduate Faculty. The Committee Chair is generally also the thesis mentor.
- A thesis mentor who is not a member of the Primary Faculty of the Department of Biomedical Engineering, can serve as Co-Chair of the Thesis Committee, together with a second Co-Chair who shall be a member of the primary faculty of the Department of Biomedical Engineering.
- It is an additional requirement of the Department of Biomedical Engineering that at least two committee members should be primary Faculty members from the Department.
- One committee member must be from outside the Department. Outside members of the thesis committee can include part-time faculty that teach within the Department.
- At least one committee member must be a regular member of the Graduate Faculty of the University of Miami.
The committee is nominated by the Graduate Program Director. Usually, the student consults with his/her research mentor and with the Chairperson or Graduate Program Director to select the Committee members.
Thesis Format and Deadlines
It is the duty of the student to ensure that the thesis defense is scheduled and that a final version of the thesis approved by the Dissertation Editor is submitted to the Dissertation Editor by the required deadlines set by the Graduate School. All information pertaining to the formatting and electronic guidelines for electronic thesis submission can be found on the Graduate School website .
Each thesis must be accompanied by a Certificate of Defense Approval for Master’s Thesis signed by all members of the Committee. Forms can be downloaded from the Graduate School website.
Evaluation Forms
The student is responsible for distributing dissertation evaluation forms to the members of the Thesis Committee for the final oral examination. The evaluation forms are used to assess the overall quality of the graduate program at the Department, College, and University level. The evaluation forms are available on the Graduate School and Department of Biomedical Engineering websites. The completed forms must be collected by the Thesis Mentor and forwarded to the Office Manager at the Department of Biomedical Engineering.
Transfer to MS Non-Thesis Program
Students enrolled in the MS thesis program who do not wish to complete their thesis can transfer to the MS non-thesis program and graduate from the MS program under the following conditions:
- The transfer must be approved by the Department Chair or Graduate Program Director.
- All requirements of the MS non-thesis option must be satisfied, including completion of a two-semester 3 credit Master's project ( BME 707 and BME 708 ), submission of a project report, and oral defense of project. Completed thesis credits may count towards the three credit MS project requirement.
Sample Plan of Study
Ms program in medical physics.
Typical curricula for each option of the MS program in Medical Physics are shown in the following tables. The course sequence and timeline can be adjusted based on individual needs. The minimum residence requirement for the MS degree is two semesters in full-time study or the equivalent in part-time work. Students can also complete the BS/MS program in Medical Physics.
MS without Thesis
Ms with thesis*.
*Students who are not able to complete their thesis during the 3rd semester and have completed all 30 required credits of graduate work, must enroll in 0 credits of Research in Residence ( BME 820 ) to maintain full-time student status.
The goal of the Medical Physics Graduate Program at the University of Miami is to train students to develop the necessary academic framework as well as a thorough practical understanding in medical physics, including areas of diagnostic radiologic physics, health physics, nuclear medicine, and a designated focus on radiation therapy.
Student Learning Outcomes
- Students will be able to apply knowledge of mathematics, science and engineering to formulate and solve relevant medical physics problems.
- Students will be able to communicate scientific and technical research effectively in writing and oral presentations.
- Students will be able to work with physicians and technicians in conducting diagnostic radiology or radiation therapy.

Office of the University Registrar
- 1306 Stanford Drive
- The University Center Room 1230
- Coral Gables, FL 33146
- [email protected]
- Parking & Transportation
Copyright 2024-2025 University of Miami. All Right Reserved. Emergency Information Privacy Statement & Legal Notices
Print Options
Print this page.
The PDF will include all information unique to this page.
PDF of the entire 2022-2023 Academic Catalog.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Indiana University School of Medicine Office of Gift Development 1 1 10 W. Michigan Street LO5 06 Indianapolis, IN 46202. Dear Dean Brater: have reviewed the proposal to offer a PhD degree in Biostatistics at IUPUI. The biostatistics program in the School of Medicine has matured to the point where this is logical.
Therefore, in a good research proposal you will need to demonstrate two main things: 1. that you are capable of independent critical thinking and analysis. 2. that you are capable of communicating your ideas clearly. Applying for a PhD is like applying for a job, you are not applying for a taught programme.
Detailed Walkthrough + Free Proposal Template. If you're getting started crafting your research proposal and are looking for a few examples of research proposals, you've come to the right place. In this video, we walk you through two successful (approved) research proposals, one for a Master's-level project, and one for a PhD-level ...
Research proposals. Your research proposal is a key part of your application. It tells us about the question you want to answer through your research. It is a chance for you to show your knowledge of the subject area and tell us about the methods you want to use. We use your research proposal to match you with a supervisor or team of supervisors.
1.Title. This can change, but make sure to include important 'key words'. 2.Overview of the research. You should provide a short overview of your research and where it fits with. Be as specific as possible in identifying influences or debates you wish to engage with. Be sure to establish a solid and convincing.
required to complete the research project. 6. Budget In half a page give a breakdown of the costs to complete the research project, and provide an explanation of these costs. 7. Funding In half a page highlight any sources of funding that will be used to cover the costs of the research and/or any funding that has already been applied for. 8.
Thesis Proposal Guidelines 1 Thesis Proposal Guidelines Due: Wednesday, July 12 2017 at 3pm (Firm deadline - no extensions!) Prepare a succinct proposal (typically 6-8 double-spaced pages, 1" margins, 12 pt font) concisely describing your proposed project, why it is important, and what you hope to learn from it. Avoid
Guidance for PhD applicants Faculty of Education, University of Cambridge. The 1,500 word research proposal is an important element of your application to doctoral study, whether full-time or part-time. It offers you the opportunity to outline the research you intend to conduct, including how you plan to go about it, and how your research might ...
How to Write a PhD Proposal. 1. Introduction. A PhD proposal is a focused document that int roduces your PhD study idea and seeks to. convince the reader that your idea is interesting, original ...
In general, however, your research proposal should aim to cover the following points: • The overall theme of your research topic, and why it is of interest to you. Why you believe that your research is worth doing, in terms of its contribution to knowledge and/or impact. • The hypothesis(ses) that you intend to test, or the research ...
Research proposal length. The length of a research proposal can vary quite a bit. A bachelor's or master's thesis proposal can be just a few pages, while proposals for PhD dissertations or research funding are usually much longer and more detailed. Your supervisor can help you determine the best length for your work.
Joe Bloggs PhD Research Proposal Page 2 2 Cereal Yield (t/ha) Area (Mha) Production (Mt) Now 2024 Now 2024 Now 2024 Wheat 3.16 3.5 222 226 700 787 Whole grains 3.73 4.1 337 354 1255 1449 Rice 3.04 3.5 162 161 494 564 Table 1. World cereal projections. "Now" is the average 2012-14 and projection for 2024. Source: OECD and
A research proposal should present your idea or question and expected outcomes with clarity and definition - the what. It should also make a case for why your question is significant and what value it will bring to your discipline - the why. What it shouldn't do is answer the question - that's what your research will do.
Postulate a clear, concise and descriptive title. 1. Abstract. A 250 to 300 words small summary of the proposal. Half page. Section 1: Introduction. Introduce your research topic, give a thorough background and reason to choose the present topic. 1.5. Review of literature.
DOCTORAL RESEARCH PROPOSAL Academic Graduate Studies & Research (Ph. D. Programme) Division Birla Institute of Technology and Science, Pilani July 2012 0 . CONTENTS Topic Page No. INTRODUCTION 2 Guidelines for Preparation of Research Proposal 4 ... APPENDIX -6 A Typical Research proposal (Sample Proposals) 17 Checklist for Ph.D. Research ...
Your proposal should be 2,000-3,000 words long, plus bibliography, using the following sections: . Title - The best titles are simple and descriptive, identifying the topic and approach that will be taken.; Central research question and objectives - The question your research seeks to answer should be stated simply, then fleshed out to show to show why it is timely and important - both ...
Abstract and Figures. The present document provides guidelines for writing an excellent and relevant research proposal at MSc as well as at PhD level. Writing a meticulous proposal will help ...
An Oxford PhD proposal sample, like Oxford personal statement examples, should give you an idea of how to structure and write your own PhD proposal, which is a key element of how to get into grad school. Should you pursue a master's or PhD, you should know that, with few exceptions, all graduate programs require that applicants submit a research proposal.
PDF | On Apr 11, 2021, Abhinav Dutta published PhD Research Proposal | Find, read and cite all the research you need on ResearchGate
6. Sample Proposals The proposals in this section are not meant to be replicated to the letter; they are simply examples of what proposals in the social sciences/humanities look like. 6.1 Sample 1 The following is a sample research proposal in the social sciences and has been taken from
Here are real-life research proposal examples of funded research projects in the field of science and technology. Funder. Title. US Geological Survey (USGS) (Mendenhall Postdoctoral Research Fellowship) Using Integrated Population Modelling in Decision-support Tools to Connect Science and Decision Makers.
Sample Research Proposals. You will find here two examples of proposals for postgraduate research from the Department of Social Policy and Criminology. They both give good indication of the sorts of things that need to be included. The first, on fathering after divorce or separation, represents first thoughts on the proposed topic, but sets out ...
Table 7-1 Breakdown of the research proposal per semester 136 Table 7-2 Main assessment criteria 141 Figures Figure 3-1 Link between topic, question and conceptual significance 40 Figure 3-2 Logical sequence of a research proposal based on a research question 53 Figure 3-3 Logical sequence of a research proposal based on a
The medical physics graduate program is accredited by the Commission on Accreditation of Medical Physics Education Programs, Inc. ().The program, serving both MS and PhD degrees, ensures that the students receive adequate didactic and clinical training to continue in education and research, enter clinical physics residencies or begin working as medical physicists in radiation therapy and ...