- Wind Energy
- Solar Energy
- Geothermal Energy
- Climate Crisis
- Recycling & Waste


9 Pros and Cons of Fossil Fuels
Fossil fuels are the leading energy source today. It is used for various purposes, from electricity generation to heating homes and to power cars and trucks.
Although other alternatives of energy are being developed, such as wind, solar, and nuclear, fossil fuels remain the number one choice for their cost-effectiveness and reliability. Thus, the amount has been increasing each year.
However, fossil fuels are not free of drawbacks. Here, we will discuss fossil fuels along with the pros and cons of fossil fuels. Fossil fuels are natural resources such as coal, oil, gasoline, diesel fuel, and natural gas.
These energy resources have powered over half of the planet for centuries. Still, they have left severe environmental impacts, too, including air and water pollution, environmental degradation, and global warming .
These non-renewable fossil fuels supply about 80 percent of the world’s energy. They provide electricity, heat, and transportation while feeding the processes that make a massive range of products, from steel to plastics.
Fossil fuels such as natural gas, oil, and coal are used as primary energy sources in different parts of the world.
Even if we are aware of the fact that they are one of the primary causes of creating pollution and global warming, people are still relying on this source of energy.
Moreover, in developing countries, coal is considered the best fuel for electricity and heat production. It is used on a large scale because it is an affordable energy source that helps get the facilities and increase the economic level.
However, fossil fuels have several adverse effects on the environment. An in-depth look at fossil fuels’ pros and cons will help us get a clear picture of this form of energy.
Table of Contents
Pros of Fossil Fuels
1. affordable.
Fossil fuels are currently one of the most affordable and cheapest forms of energy in comparison with other sources of energy.
Fossil fuels have been widely used over the last 200 years. A lot of resources, money, and time have been spent on research.
The advanced technological system has made extracting and using them easier in the most cost-effective and efficient ways, like systems that harness natural gas given off during oil extraction.
2. Reliable
Fossil fuels are a natural energy source that does not rely on other natural systems like solar, wind, and water.
Countries like Germany and UK have a large amount of solar infrastructure, but only 60 percent of the days are sunny.
It is a fact that when fossil fuels are burned, it produces harmful gases like carbon dioxide that harm the environment and human health.
Fossil fuels are a reliable energy source that can be used around the clock in any condition. It can provide power even in a disaster or emergency situation.
3. Easy to Transport
Fossil fuels are relatively easier than transporting renewable sources of energy, such as wind, sun, and water, which are pretty impossible as well. It is easier to supply fuels through the help of pipelines.
These pipes are easily laid underground and can transport gas or oil with ease. Although it can be quite expensive at first, once the work is completed, the cost decreases drastically. Therefore, fossil fuels are a relatively cheap, effective, and reliable source of energy.
4. Employment Generation
There is no doubt that fossil fuel industries have created hundreds and thousands of job opportunities for many people. Every year it creates new employment opportunities. So, abandoning the use of fossil fuels will affect the world economy and also leads to high levels of unemployment that would affect the family and country’s income source.
Cons of Fossil Fuels
1. non-renewable.
Fossil fuels are a natural gift from the Earth, which take millions of years to form with the help of natural processes such as the anaerobic decomposition of organic matter. So, it is a non-renewable source of energy, which means there is only a finite amount of fuels available.
Unlike renewable energy sources such as solar and wind, it takes a long time to form, and once it is completely used up, then there will be nothing more left to use it again.
2. Environmental Degradation
The main disadvantage of using fossil fuels is that it creates pollution and increases global warming. Fossil fuels are responsible for causing air pollution, land pollution, and water pollution on the planet.
The burning of fossil fuels produces a high amount of carbon dioxide and causes environmental and health problems. It also leads to climate change and affects biodiversity.
3. Public Health Issues
Another related disadvantage of using fossil fuels is that it has a direct impact on the health of the human being. Potentially, fatal diseases or illnesses such as lung cancer, infection, and asthma have been directly linked to the pollution caused by the burning of fuels. It is neither environment-friendly nor safe to use.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), 7 million premature deaths annually are linked to air pollution. The high levels of air pollution can adversely affect people’s lungs and trigger asthma. Likewise, every year millions of children die due to pollution-related diseases. People who live in areas with a large amount of traffic are at high risk.
4. Rising Costs
About 40 percent of the world’s oil gets produced from the middle-east countries. And, the rest of the world depends on these countries to fulfill the gap. Therefore, as fossil fuels continue depleting, it loses its natural resources to provide the increasing demand each day. As a result, it increases the costs of the resources to fulfill the required demand.
Eventually, renewable energy sources will become cost-effective, and environment-friendly with time as fossil fuels rise in price. Since only a few countries produce fossil fuels, there is an increase in fear of war, lower output, strikes by trade unions that can lead to price fluctuations around the globe.
5. Risk of Oil Spill
Fossil fuels can damage the environment in the form of oil spills. While carrying oil from one place to another, it also takes a high cost and risk. In history, there are many incidents where the oil spill caused the death of animals, birds, fish, and mammals.
It has also resulted in severe harm to aquatic life and the environment. Therefore, oil spills are dangerous to both living and non-living things either on the ground or in the sea.
Despite being cheaper, reliable, more comfortable to transport, creating employment, and many more, it has many cons as well. The major disadvantage of using fossil fuels is that it destroys the environment and creates pollution in the atmosphere. Therefore, it is essential to consider another alternative source of energy, such as solar, wind, hydropower, and nuclear power.
However, some countries have already begun generating substantial portions of electric power from renewable sources. Now, the whole world should switch their choice from non-renewable energy to eco-friendly and renewable energy and make a better place to live for all.
(Last Updated on October 8, 2022 by Sadrish Dabadi)
Nina Howell is a Rewenable Energy researcher and consultant based out of Houston, Texas Area. She earned her Master's Degree in Energy and Earth Resources from Austin Jackson School of Geosciences in 2010, and a Bachelor's Degree in Environmental Science from State University of New York College of Environmental Science and Forestry in 2008. Nina has been working in the energy sector since 2011. She worked as an Energy Supply Analyst from 2011 to 2017 in Bounce Energy and then as a Research and Energy Consultant at GE Renewable Energy from March 2017 to February 2020 . Nina is a mom of 2 beautiful children who are joy to her life. She strongly believes in eco-friendly living and is vocal about renewable energy, environmental issues, water crisis, and sustainable living.
Related Posts
Coals: uses, types, pollution, and solution, 9 pros and cons of nuclear energy, list of natural resources.
Type above and press Enter to search. Press Esc to cancel.
Why are fossil fuels so hard to quit?
We understand today that humanity’s use of fossil fuels is severely damaging our environment. Fossil fuels cause local pollution where they are produced and used, and their ongoing use is causing lasting harm to the climate of our entire planet. Nonetheless, meaningfully changing our ways has been very difficult.
But suddenly, the COVID-19 pandemic brought trade, travel, and consumer spending to a near-standstill. With billions of people recently under stay-at-home orders and economic activity plunging worldwide, the demand for and price of oil have fallen further and faster than ever before. Needless to say, oil markets have been in turmoil and producers around the world are suffering.
Some pundits are now asking if this crisis could be the push the world needs to move away from oil. One asked: “ Could the coronavirus crisis be the beginning of the end for the oil industry? ” Another: “ Will the coronavirus kill the oil industry and help save the climate? ” Meanwhile, 2020 annual greenhouse gas emissions are forecast to decline between 4 – 7% as a result of the virus’ effects, and some of the world’s smoggiest cities are currently enjoying clear skies.
The idea that the pandemic could ultimately help save the planet misses crucial points. First and foremost, damaging the world’s economy is not the way to deal with climate change. And in terms of oil, what will take its place? We haven’t found a good substitute for oil, in terms of its availability and fitness for purpose. Although the supply is finite, oil is plentiful and the technology to extract it continues to improve, making it ever-more economic to produce and use. The same is also largely true for natural gas.
Climate change is real and we see its effects clearly now: In 2019 worldwide, 15 extreme weather events , exacerbated by climate change, caused more than $1 billion in damage each. Four of these events each caused more than $10 billion in damage. The large-scale use of fossil fuels tops the list of factors contributing to climate change. But the concentrated energy that they provide has proven hard to replace. Why?
A reporter raised that very question to me after a press Q&A that I did at a conference a few years ago. “We know that oil contributes to climate change and other environmental problems — why do we still use it? Why don’t we just quit already?,” he asked me.
Until that moment, I hadn’t thought enough about how my experience and background give me a clearer view than many on the promise and challenge of moving to a cleaner energy system. I have gained a wide-angle view of the energy industry as I’ve moved through my career, working in government and in consulting — for both oil and gas and clean energy clients — and then moving into the think tank world.
fossil fuel Generated from the decomposition of ancient plant and animal matter over millions of years. Coal, oil, and natural gas are fossil fuels.
To deal with the challenge of climate change, we must start by understanding the fossil fuel system — namely how energy is produced and used. Although fossil fuel companies are politically powerful, in the United States and around the world, their lobbying prowess is not the key reason that their fuels dominate the global energy system. Likewise, the transition to an all-renewable energy system is not a simple task. But the politics of blame are popular, as we’ve seen during the 2020 election campaign and in light of recent lawsuits against fossil fuel companies. There is plenty of blame to go around, from fossil fuel companies that for years denied the problem to policymakers reluctant to enact the policies needed to force real change. It has been easier for everyone to stick with the status quo.
The world needs technology and strong policy to move in a new direction. Throughout history, humanity’s energy use has moved toward more concentrated, convenient, and flexible forms of energy. Understanding the advantages of today’s energy sources and the history of past transitions can help us understand how to move toward low-carbon energy sources. With greater understanding of the climate challenge, we are making huge strides in developing the technology we need to move toward a low-carbon future. Still, understanding how we got here and why the modern world was built on fossil fuels is crucial to understanding where we go from here.
Our energy comes from the sun, one way or another
In the pre-industrial age, solar energy met all of humanity’s energy needs. Plants convert solar energy into biomass through the process of photosynthesis. People burned this biomass for heat and light. Plants provided food for people and animals, which, in turn, used their muscle power to do work. Even as humans learned to smelt metals and make glass, they fueled the process with charcoal made from wood. Apart from photosynthesis, humans made some use of wind and water power, also ultimately fueled by the sun. Temperature differences in the atmosphere brought about by sunlight drive the wind, and the cycle of rainfall and flowing water also gets its energy from sunlight. But the sun is at the center of this system, and people could only use the energy that the sun provided in real time, mostly from plants.
biomass Plant material, including leaves, stalks, and woody mass. Biomass can be burned directly or processed to create biofuels , like ethanol.
This balance between human energy use and sunlight sounds like utopia, but as the human population grew and became more urban, the bio-based energy system brought problems. In England, wood became scarce in the 1500s and 1600s, since it was not only used for fuel, but also for building material. London, for instance, grew from 60,000 people in 1534 to 530,000 in 1696, and the price of firewood and lumber rose faster than any other commodity. The once lush forests of England were denuded.
In 1900, roughly 50,000 horses pulled cabs and buses around the streets of London, not including carts to transport goods. As you can imagine, this created an enormous amount of waste. As Lee Jackson writes in his book “ Dirty Old London ,” by the 1890s London’s immense horse population generated roughly 1,000 tons of dung per day. All this manure also attracted flies, which spread disease. The transportation system was literally making people sick. The pre-fossil era was not the utopia we envision.
Fossil fuels opened new doors for humanity. They formed from the transformation of ancient plants through pressure, temperature, and tens to hundreds of millions of years, essentially storing the sun’s energy over time. The resulting fuels freed humanity from its reliance on photosynthesis and current biomass production as its primary energy source. Instead, fossil fuels allowed the use of more energy than today’s photosynthesis could provide, since they represent a stored form of solar energy.
First coal, then oil and natural gas allowed rapid growth in industrial processes, agriculture, and transportation. The world today is unrecognizable from that of the early 19th century, before fossil fuels came into wide use. Human health and welfare have improved markedly, and the global population has increased from 1 billion in 1800 to almost 8 billion today. The fossil fuel energy system is the lifeblood of the modern economy. Fossil fuels powered the industrial revolution, pulled millions out of poverty, and shaped the modern world.
How energy density and convenience drove fossil fuel growth
The first big energy transition was from wood and charcoal to coal, beginning in the iron industry in the early 1700s. By 1900, coal was the primary industrial fuel, taking over from biomass to make up half the world’s fuel use. Coal has three times the energy density by weight of dry wood and is widely distributed throughout the world. Coal became the preferred fuel for ships and locomotives, allowing them to dedicate less space to fuel storage.
Oil was the next major energy source to emerge. Americans date the beginning of the oil era to the first commercial U.S. oil well in Pennsylvania in 1859, but oil was used and sold in modern-day Azerbaijan and other areas centuries earlier. Oil entered the market as a replacement for whale oil for lighting, with gasoline produced as a by-product of kerosene production. However, oil found its true calling in the transportation sector. The oil era really took off with the introduction of the Ford Model-T in 1908 and the boom in personal transportation after World War II. Oil overtook coal to become the world’s largest energy source in 1964.
Oil resources are not as extensively distributed worldwide as coal, but oil has crucial advantages. Fuels produced from oil are nearly ideal for transportation. They are energy-dense, averaging twice the energy content of coal, by weight. But more importantly, they are liquid rather than solid, allowing the development of the internal combustion engine that drives transportation today.
Different fuels carry different amounts of energy per unit of weight. Fossil fuels are more energy dense than other sources.
Oil changed the course of history. For example, the British and American navies switched from coal to oil prior to World War I, allowing their ships to go further than coal-fired German ships before refueling. Oil also allowed greater speed at sea and could be moved to boilers by pipe instead of manpower, both clear advantages. During World War II, the United States produced nearly two-thirds of the world’s oil, and its steady supply was crucial to the Allied victory. The German army’s blitzkrieg strategy became impossible when fuel supplies could not keep up, and a lack of fuel took a toll on the Japanese navy.
Natural gas, a fossil fuel that occurs in gaseous form, can be found in underground deposits on its own, but is often present underground with oil. Gas produced with oil was often wasted in the early days of the oil industry, and an old industry saying was that looking for oil and finding gas instead was a quick way to get fired. In more recent times, natural gas has become valued for its clean, even combustion and its usefulness as a feedstock for industrial processes. Nonetheless, because it is in a gaseous form, it requires specific infrastructure to reach customers, and natural gas is still wasted in areas where that infrastructure doesn’t exist.
A final key development in world energy use was the emergence of electricity in the 20th century. Electricity is not an energy source like coal or oil, but a method for delivering and using energy. Electricity is very efficient, flexible, clean, and quiet at the point of use. Like oil, electricity’s first use was in lighting, but the development of the induction motor allowed electricity to be efficiently converted to mechanical energy, powering everything from industrial processes to household appliances and vehicles.
Over the 20th century, the energy system transformed from one in which fossil energy was used directly into one in which an important portion of fossil fuels are used to generate electricity. The proportion used in electricity generation varies by fuel. Because oil — an energy-dense liquid — is so fit-for-purpose in transport, little of it goes to electricity; in contrast, roughly 63% of coal produced worldwide is used to generate electricity. Methods of generating electricity that don’t rely on fossil fuels, like nuclear and hydroelectric generation, are also important parts of the system in many areas. However, fossil fuels are still the backbone of the electricity system, generating 64% of today’s global supply.
Fossil fuels still dominate global electricity generation.
In sum, the story of energy transitions through history has not just been about moving away from current solar flows and toward fossil fuels. It has also been a constant move toward fuels that are more energy-dense and convenient to use than the fuels they replaced. Greater energy density means that a smaller weight or volume of fuel is needed to do the job. Liquid fuels made from oil combine energy density with the ability to flow or be moved by pumps, an advantage that opened up new technologies, especially in transportation. And electricity is a very flexible way of consuming energy, useful for many applications.
Back to the future – the return of the solar era
Fossil fuels allowed us to move away from relying on today’s solar flows, instead using concentrated solar energy stored over millions of years. Before we could make efficient use of solar flows, this seemed like a great idea.
carbon dioxide Carbon dioxide is gas released when carbon-containing fuels (biomass or fossil fuels) are burned. Carbon dioxide is the most important gas contributing to climate change.
However, the advantages of fossil fuels come with a devastating downside. We now understand that the release of carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) from burning fossil fuels is warming our planet faster than anything we have seen in the geological record. One of the greatest challenges facing humanity today is slowing this warming before it changes our world beyond recognition.
Now that there are almost eight billion of us, we clearly see the impact of rising CO 2 concentrations. Going back to the old days of relying mostly on biomass for our energy needs is clearly not a solution. Nonetheless, we need to find a way to get back to reliance on real-time solar flows (and perhaps nuclear energy) to meet our needs. There are so many more of us now, interacting via a vastly larger and more integrated global economy, and using much more energy. But we also have technologies today that are much more efficient than photosynthesis at transforming solar flows to useful energy.
Since 1900, global population and economic activity have skyrocketed, along with fossil fuel consumption.
Unfortunately, the atmospheric concentration of carbon dioxide, the most consequential greenhouse gas, has steadily climbed at the same time, along with global average temperature. .
The earth gets plenty of energy from the sun for all of us, even for our modern energy-intensive lives. The amount of solar energy that reaches habitable land is more than 1,000 times the amount of fossil fuel energy extracted globally per year. The problem is that this energy is diffuse. The sun that warms your face is definitely providing energy, but you need to concentrate that energy to heat your home or move a vehicle.
renewable energy Renewable energy is from a source that is naturally replenished. (Ex: capturing wind using turbines or sunlight using solar cells does not change the amount of wind or sunlight that is available for future use.)
This is where modern technology comes in. Wind turbines and solar photovoltaic (PV) cells convert solar energy flows into electricity, in a process much more efficient than burning biomass, the pre-industrial way of capturing solar energy. Costs for wind and solar PV have been dropping rapidly and they are now mainstream, cost-effective technologies. Some existing forms of generating electricity, mainly nuclear and hydroelectricity, also don’t result in CO 2 emissions. Combining new renewables with these existing sources represents an opportunity to decarbonize — or eliminate CO 2 emissions from — the electricity sector. Electricity generation is an important source of emissions, responsible for 27% of U.S. greenhouse gas emissions in 2018.
However, unlike fossil fuels, wind and solar can only generate electricity when the wind is blowing or the sun is shining. This is an engineering challenge, since the power grid operates in real time: Power is generated and consumed simultaneously, with generation varying to keep the system in balance.
greenhouse gas A gas that traps heat in the earth’s atmosphere, including carbon dioxide, methane, ozone, and nitrous oxides.
Engineering challenges beget engineering solutions, and a number of solutions can help. Power grids that cover a larger area are easier to balance, given that if it isn’t windy or sunny in one location, it may be somewhere else. Demand-response strategies can encourage customers with flexibility in their processes to use more power when renewable power is available and to cut back when it isn’t. Power storage technologies can save excess electricity to be used later. Hydroelectric dams can serve this function now, and declining costs will make batteries more economic for power storage on the grid. Storage solutions work well over a timeframe of hours — storing solar power to use in the evening, for example. But longer-term storage poses a greater challenge. Perhaps excess electricity can be used to create hydrogen or other fuels that can be stored and used at a later time. Finally, fossil fuel generation often fills in the gaps in renewable generation today, especially natural gas generation, which can be efficiently ramped up and down to meet demand.
Transforming solar energy flow into electricity is a clear place to start in creating a decarbonized energy system. A simple formula is to decarbonize the electricity sector and electrify all the energy uses we can. Many important processes can be electrified — especially stationary uses, like in buildings and many industrial processes. To deal with climate change, this formula is the low-hanging fruit.
The two parts of this formula must proceed together. A shiny new electric vehicle in the driveway signals your concern about the environment to your neighbors, but achieving its full potential benefit also requires a greener power system. For today’s power system in the United States, and nearly everywhere in the world, electric vehicles provide emissions benefits , but the extent of those benefits varies greatly by location. Achieving the full potential benefit of electric vehicles would require a grid that supplies all renewable or zero-carbon power, something that no area in the United States consistently achieves today.
Wind and solar power aren’t everything – the remaining challenges
“Electrify everything” is a great plan, so far as it goes, but not everything can be easily electrified. Certain qualities of fossil fuels are difficult to replicate, such as their energy density and their ability to provide very high heat. To decarbonize processes that rely on these qualities, you need low-carbon fuels that mimic the qualities of fossil fuels.
The energy density of fossil fuels is particularly important in the transportation sector. A vehicle needs to carry its fuel around as it travels, so the weight and volume of that fuel are key. Electric vehicles are a much-touted solution for replacing oil, but they are not perfect for all uses. Pound for pound, gasoline or diesel fuel contain about 40 times as much energy as a state-of-the-art battery. On the other hand, electric motors are much more efficient than internal combustion engines and electric vehicles are simpler mechanically, with many fewer moving parts. These advantages make up for some of the battery’s weight penalty, but an electric vehicle will still be heavier than a similar vehicle running on fossil fuel. For vehicles that carry light loads and can refuel often, like passenger cars, this penalty isn’t a big deal. But for aviation, maritime shipping, or long-haul trucking, where the vehicle must carry heavy loads for long distances without refueling, the difference in energy density between fossil fuels and batteries is a huge challenge, and electric vehicles just don’t meet the need.
WEIGHT OF FUEL
Gasoline carries much more energy per unit of weight than a battery. a gas-powered car with a 12.4-gallon tank carries 77.5 pounds of gasoline., a 77.5-pound battery, in contrast, would only carry an electric car 21 miles., an electric car with a range of 360 miles would need a 1,334 pound battery., weight of vehicle, despite the weight of the battery, other components of electric vehicles are lighter and simpler than their counterparts in a gasoline car. thus, the overall weight penalty for electric vehicles isn’t as severe as the weight penalty for the battery alone. .
Industrial processes that need very high heat — such as the production of steel, cement, and glass — pose another challenge. Steel blast furnaces operate at about 1,100° C, and cement kilns operate at about 1,400° C. These very high temperatures are hard to achieve without burning a fuel and are thus difficult to power with electricity.
Renewable electricity can’t solve the emissions problem for processes that can’t run on electricity. For these processes, the world needs zero-carbon fuels that mimic the properties of fossil fuels — energy-dense fuels that can be burned. A number of options exist, but they each have pros and cons and generally need more work to be commercially and environmentally viable.
Biofuels are a possibility, since the carbon released when the biofuel is burned is the same carbon taken up as the plant grew. However, the processing required to turn plants into usable fuels consumes energy, and this results in CO 2 emissions, meaning that biofuels are not zero-carbon unless the entire process runs on renewable or zero-carbon energy. For example, the corn ethanol blended into gasoline in the United States averages only 39% lower CO 2 emissions than the gasoline it replaces, given the emissions that occur from transporting the corn to processing facilities and converting it to fuel. Biofuels also compete for arable land with food production and conservation uses, such as for recreation or fish and wildlife, which gets more challenging as biofuel production increases. Fuels made from crop waste or municipal waste can be better, in terms of land use and carbon emissions, but supply of these wastes is limited and the technology needs improvement to be cost-effective.
Another pathway is to convert renewable electricity into a combustible fuel. Hydrogen can be produced by using renewable electricity to split water atoms into their hydrogen and oxygen components. The hydrogen could then be burned as a zero-carbon fuel, similar to the way natural gas is used today. Electricity, CO 2 , and hydrogen could be also combined to produce liquid fuels to replace diesel and jet fuel. However, when we split water atoms or create liquid fuels from scratch, the laws of thermodynamics are not in our favor. These processes use electricity to, in effect, run the combustion process backwards, and thus use large amounts of energy. Since these processes would use vast amounts of renewable power, they only make sense in applications where electricity cannot be used directly.
Carbon capture and storage or use is a final possibility for stationary applications like heavy industry. Fossil fuels would still be burned and create CO 2 , but it would be captured instead of released into the atmosphere. Processes under development envision removing CO 2 from ambient air. In either case, the CO 2 would then be injected deep underground or used in an industrial process.
The most common use for captured CO 2 today is in enhanced oil recovery, where pressurized CO 2 is injected into an oil reservoir to squeeze out more oil. The idea of capturing CO 2 and using it to produce more fossil fuel seems backwards — does that really reduce emissions overall? But studies show that the captured CO 2 stays in the oil reservoir permanently when it is injected in this way. And if enough CO 2 is injected during oil production, it might make up for the combustion emissions of the produced oil, or even result in overall negative emissions. This won’t be a panacea for all oil use, but could make oil use feasible in those applications, like aviation, where it is very hard to replace.
Carbon capture is today the cheapest way to deal with emissions from heavy industries that require combustion. It has the advantage that it can also capture CO 2 emissions that come from the process itself, rather than from fuel combustion, as occurs in cement production when limestone is heated to produce a component of cement with CO 2 as a by-product.
When considering how carbon capture might contribute to climate change mitigation, we have to remember that fossil fuels are not the ultimate cause of the problem — CO 2 emissions are. If maintaining some fossil fuel use with carbon capture is the easiest way to deal with certain sources of emissions, that’s still solving the fundamental problem.
Our biggest challenges are political
Science clearly tells us that we need to remake our energy system and eliminate CO 2 emissions. However, in addition to the engineering challenges, the nature of climate change makes it politically challenging to deal with as well. Minimizing the impact of climate change requires re-making a multi-trillion-dollar industry that lies at the center of the economy and people’s lives. Reducing humanity’s reliance on fossil fuels requires investments here and now that provide uncertain, long-term benefits. These decisions are particularly difficult for politicians, who tend to focus on policies with immediate, local benefits that voters can see. Last year The New York Times asked , for instance, “whether any climate policy is both big enough to matter and popular enough to happen.” Durable climate policy requires securing buy-in from a range of actors, including politicians from both parties, business leaders, and civil society. Their perspectives inevitably differ, and the lack of consensus — combined with very real efforts to exert pressure on the policymaking process — is a key reason that climate action is so politically difficult. (To try your hand at navigating the policy dilemmas, play our — admittedly simplified! — game below: “A president’s climate quandary.”)
In the United States and other parts of the wealthy world, current efforts focus on reducing the greenhouse gas emissions from our energy-intensive lives. But the second part of today’s energy challenge is providing modern energy to the billion people in the developing world that don’t currently have it. You don’t hear as much about the second goal in the public discourse about climate change, but it’s crucial that developing countries follow a cleaner path than the developed world did. The need to provide both cleaner energy and more energy for developing countries magnifies the challenge, but a solution that leaves out the developing world is no solution at all.
Plentiful and inexpensive fossil fuels make transitioning away from them more difficult. Around 15 years ago, pundits were focused on “peak oil” — the idea that the world was running out of oil, or at least inexpensive oil, and that a reckoning was coming. Events of the past decade have proven that theory wrong. Instead of declining oil production and rising prices, we’ve seen the opposite, nowhere more than here in the United States. Technology has brought about a boom in oil production; geologists long knew the resources were there, but did not know how to make money producing them. There’s no reason to expect this trend to slow down anytime soon. In other words, running out of oil will not save us. The world will need to transition away from oil and other fossil fuels while they are abundant and inexpensive — not an easy task.
To achieve this technically and politically challenging transition, we need to avoid one-dimensional solutions. My own thoughts about how we need to deal with climate change have certainly evolved over time, as we understand the climate system better and as time passes with emissions still increasing. As an example, I used to be skeptical of the idea of carbon capture, either from industrial processes or directly from the air. The engineer in me just couldn’t see using such an energy-hungry process to capture emissions. I’ve changed my mind, with a greater understanding of processes that will be hard to decarbonize any other way.
The accumulation of CO 2 in the atmosphere is like putting air into a balloon. It’s a cumulative system: We’re continually adding to the total concentration of a substance that may last in the atmosphere for up to 200 years. We don’t know when the effects of warming will become overwhelming, but we do know that the system will become stretched and compromised — experiencing more negative effects — as the balloon fills. The cumulative nature of the climate system means that we need more stringent measures the longer that we wait. In other words: Sooner action is better. We need to take action now where it’s easiest, in the electricity and light vehicle sectors, and in making new buildings extremely energy efficient. Other sectors need more technology, like heavy transport and industry, or will take a long time, like improving our existing stock of buildings.
Those pushing to end fossil fuel production now are missing the point that fossil fuels will still be needed for some time in certain sectors. Eliminating unpopular energy sources or technologies, like nuclear or carbon capture, from the conversation is short-sighted. Renewable electricity generation alone won’t get us there — this is an all-technologies-on-deck problem. I fear that magical thinking and purity tests are taking hold in parts of the left end of the American political spectrum, while parts of the political right are guilty of outright denialism around the climate problem. In the face of such stark polarization, the focus on practical solutions can get lost — and practicality and ingenuity are the renewable resources humanity needs to meet the climate challenge.
Correction: An earlier version of a graphic in this piece mistakenly indicated that renewables comprise 0.6% of global electricity generation. It has been corrected to 9.3%.
About the Author
Samantha gross, related content.

Why we still use fossil fuels

How is the COVID-19 pandemic affecting global energy markets?

The United States can take climate change seriously while leading the world in oil and gas production

Brookings experts comment on oil market developments and geopolitical tensions

Will investments in greener energy be yet another victim of the coronavirus?
Acknowledgments.
Editorial: Jeff Ball, Bruce Jones, Anna Newbyu
Research: Historical summaries of energy transitions owe a debt of gratitude to Vaclav Smil, a prolific author on the topic and the grandfather of big-picture thinking on energy transitions.
Graphics and design: Ian McAllister, Rachel Slattery
Web development: Eric Abalahin, Abigail Kaunda, Rachel Slattery
Feature image: Egorov Artem/Shutterstock
- Media Relations
- Terms and Conditions
- Privacy Policy
What Are the Pros and Cons of Fossil Fuels? A Complete Guide
Today, most Americans want to move away from fossil fuels. So why are they still the largest source of energy in the United States?
Green Coast is supported by its readers. We may earn an affiliate commission at no extra cost to you if you buy through a link on this page . Learn more .

Fossil fuels are used every day to create thousands of products and power countless processes essential to daily life. According to the National Academies of Sciences, 81% of the total energy used in the United States comes from coal, oil, and natural gas today.
Despite their prevalence, the use of fossil fuels has become a point of contention for many global citizens, because of the many negative consequences of utilizing them. In fact, 69% of U.S. adults say they prioritize developing alternative energy sources, such as wind and solar, over expanding the production of oil, coal, and natural gas.
You may wonder why we continue to rely on fossil fuels when so many Americans want to develop more sustainable energy sources. The truth is, there are some reasons why it’s still advantageous to use fossil fuels today.
In this guide, we’ll fully examine this debate, looking at the pros and cons of fossil fuels, how they impact our planet, and why they are so difficult to transition away from.
What are fossil fuels?
You are certainly familiar with the most common examples of fossil fuels – coal, oil, and natural gas, but how do these fuels come to be?
Fossil fuels are compound mixtures consisting of decomposing plant and animal material from millions of years ago. This material is trapped in the Earth’s crust and contains carbon and hydrogen, which can be burned for energy.
Fossil fuels are created when this decomposed material undergoes extreme heat and pressure in the Earth’s crust – as the matter is compressed over time, the chemicals begin to break down and transform into natural fuels.
Each fossil fuel is a result of different combinations of carbon, hydrogen, and other compounds. Different organic materials form unique fuels: the most common fossil fuels are the result of unique amounts of pressure and materials.
Coal, oil, and natural gas are a result of these unique processes, according to National Geographic :
- Coal is usually found in sedimentary rock deposits where rock and dead plant and animal matter are piled up in layers. In fact, more than 50% of a piece of coal’s weight is typically from fossilized plants.
- Oil is originally found as a solid material between layers of sedimentary rock, like shale. This material is heated in order to produce the thick oil substance we are familiar with today.
- Natural gas is primarily made of methane and is typically found in pockets above oil deposits. It can also be found in sedimentary rock layers.
Humans extract the stored energy in these materials in a variety of ways. Mining is used to extract solid fossil fuels by digging, scraping, or exposing buried resources. Drilling methods help extract liquid or gaseous fossil fuels that can be pumped up to the surface of the Earth, like oil and natural gas.
Fossil fuels are not renewable, meaning that there is a finite supply of these materials inside the Earth. Over time, as humans have extracted fossil fuels, we have had to drill deeper and deeper into the Earth’s crust to harness these materials.

Today, oil and gas wells can range in depth from a few hundred feet to more than 20,000 feet . In some parts of the world, wells go as deep as 30,000 feet.
Why is it important to extract these fossil fuels?
In short, fossil fuels contain stored energy in the form of carbon and hydrogen, which, when burned, power the mechanical processes we rely on, such as transportation and the electricity we use in our homes every day.
Although there are numerous negative effects of fossil fuel use and extraction, most of the world relies on the energy that fossil fuels produce.
Uses of fossil fuels
Before diving into the specific pros and cons of fossil fuels, it’s important to understand the ways in which fossil fuels are already essential to our daily lives.
While renewable energy sources like solar and wind energy are growing in popularity, the global economy is currently reliant on fossil fuel use. Let’s dive into the numerous ways that fossil fuels are utilized around the world every day.
Transportation
The U.S. spends 29% of its total energy each year to power industrial, farm, rail, and sea transportation with fossil fuels. The main type of fuel used for transportation in the U.S. is petroleum.
These fuels are made from crude oil and natural gas processing, including gasoline, diesel fuel, jet fuel, and propane, according to the U.S. Energy Information Administration ( EIA ). Natural gas and electricity are also widely used for transportation in the U.S.

If you drive a car, truck, or motorcycle, you know that your car’s engine burns fuel that comes from crude oil, or gasoline. Distillate fuels are used mainly by large trucks, buses, trains, and ships. Commercial and private airplanes use jet fuel to power their trips across the country.
In 2021, petroleum products accounted for about 90% of the total energy used in U.S. transportation activities. All in all, the transportation of goods, people, and food uses a large amount of fossil fuel.
Household uses
Fossil fuels are used in our homes as well, but their most prominent use may surprise you.
More than half of the energy use in U.S. homes is used for heating in the winter and air conditioning when it’s warm outside. Of course, the amount of energy used varies by season, geographic region, home size, and the fuels used.
Next on the list of household energy uses is water heating, lighting and refrigeration, processes that occur year-round and power pretty much every home in the U.S. Combined, these activities accounted for 27% of total annual home energy use in 2015.

Many stoves in modern-day homes are powered electrically, but gas-powered stoves utilize propane to cook food. Fossil fuels are present in our households in additional ways – plastic containers, toilet seats, telephones, toys, kitchen utensils, and more. Fossil fuels produce the petrochemicals used in the manufacturing of polyester and plastic products.
Medical and pharmaceutical uses
The transportation and household uses of fossil fuels may not have surprised you, but did you know that fossil fuel extracts also have medical and pharmaceutical uses?
For example, processed plastics made with oil are used in heart valves and other specialized medical equipment. Chemicals derived from crude oil are used in radiological dyes and films, tubing, syringes, and oxygen masks. Even MRI scanners are made from fossil-fuel-derived materials.
Additionally, fossil fuel extracts are used in products many of us use every day. The chemical Benzene , for example, is a natural component of crude oil and gasoline. It’s often used to make some types of lubricants, rubbers, and even drugs.
To better understand why fossil fuels are used in so many products and processes around the world and why detractors want to be rid of these fuels, let’s dive into the pros and cons of fossil fuels.
Advantages of fossil fuels
While there are various cons of utilizing fossil fuels in our households and businesses, there are several reasons why fossil fuel use has become so commonplace over the years.
Let’s examine some of the advantages of fossil fuel use.
1. Efficient energy sources
Fossil fuels are among the most efficient sources of energy, because small amounts of oil or gas, for example, produce a large amount of energy. Different fuels carry different amounts of energy per unit of weight, and fossil fuels are more energy dense than other sources.
The energy density of oil, according to a Drexel University study , is about 35 to 45 gigajoules (10,000 kWh) per cubic meter. Alternatively, solar energy has a density of 1.5 microjoules per cubic meter, over twenty quadrillion times less than oil.
While renewables like solar energy may be more sustainable , it’s difficult to deny that fossil fuels make efficient energy sources.

2. Useful byproducts
Fossil fuels also create byproducts that are widely used throughout homes and businesses. In fact, petrochemicals derived from oil and natural gas make the manufacturing of over 6,000 everyday products and high-tech devices possible.
So, how does oil turn into a plastic item like the toothbrush you use every day?
After crude oil is removed from the ground, it’s sent to a refinery where different parts of the crude oil are separated into usable petroleum products. While most of these groups are used for the production of energy, a few chemicals are used to make various items.
Some of the products made from fossil-fuel-derived materials may surprise you:
- Artificial limbs
- Umbrellas
- Contact lenses
- Swimming pools
These everyday items would not be possible without chemicals derived from fossil fuels.
3. Easy to transport
Transporting fossil fuels is easier when compared to transporting the energy gained from other sources like wind, water, or solar power.
Crude oil moves from the extraction source to refineries using barges and tankers, and over land by trucks and railroads, or underground through pipelines. Natural gas is transported by underground pipelines and liquefied natural gas (LNG) tankers. These materials are housed in metal tankards and containers.

While it is generally considered easy to transport these fossil fuels, it’s important to note that oil spills and natural gas leaks occur frequently. These incidents are a large source of various pollutants leaking into our atmosphere and water sources.
4. Generates thousands of jobs
There are millions of people currently employed by the fossil fuel energy sector – in 2019, nearly 1.7 million people worked in fossil fuel industries, conducting activities such as mining, electricity generation, and transportation.
Many countries rely on the economic activities resulting from fossil fuel extraction and use. Because of this, the adoption of renewable energy must include transitioning these millions of jobs that individuals and families rely on around the world.
5. Readily available and relatively easy to extract
Fossil fuel plants and extraction sites require a relatively small amount of infrastructure. For example, offshore oil rigs and onshore oil derricks pump most of the petroleum that is extracted throughout the world. This process involves drilling a hole into a potential oil patch and then pumping the oil out through a long tube.

Most countries that rely on fossil fuels also already have the infrastructure and knowledge with which to mine and drill for these fuels.
In addition, since fossil fuels have powered our world for over 250 years, there is already infrastructure in place to distribute it and utilize it at a relatively low cost. Most of our infrastructure is, ultimately, already built for fossil fuel use, from cars to gas-powered stoves.
Over the last few centuries, large amounts of fossil fuels have been readily available around the world. Rising population has created more and more demand for these energy sources.
To extract fossil fuel resources at a faster rate, global nations have invested large sums of money into the energy sector. In fact, the International Energy Agency (IEA) predicted that energy sector investment would rise to over 8% in 2022 to reach a total of $2.4 trillion.
Disadvantages of fossil fuels
Now that we understand the various reasons why fossil fuels are considered advantageous around the world let’s dive into the many disadvantages of fossil fuel use.
1. Environmental degradation
Primarily, the burning of fossil fuels causes air pollution , which makes its way into our soil and water sources. The combustion of these fuels releases carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) and other greenhouse gasses, which trap heat in our atmosphere and heat up our planet.
Thus, greenhouse gasses like CO 2 are the primary cause of one of the most existential threats to our planet: climate change. In fact, the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) has found that emissions from fossil fuels are the dominant cause of global warming. In 2018, 89% of global CO 2 emissions came from fossil fuels and industrial activities.

Many places around the world are already experiencing the effects of climate change, such as the ever-rising sea level and extreme natural disasters, and weather patterns. If this persists, the consequences will be disastrous for all living species.
Evidently, the use of fossil fuels contributes to environmental degradation and is worsening climate change by the day.
2. Power stations require lots of reserves of coal
Today, we rely on power stations to produce energy. For power stations to keep working, they require vast amounts of coal : it takes about 1 pound of coal to generate one kWh of electricity.
In addition, large trucks are used to transport coal if power stations are not located near large deposits of coal. This transportation also requires a lot of power which can not only damage the Earth but is also very expensive. In turn, fuel prices will keep rising as a result of high transportation costs.
3. Health complications (from fuel combustion)
Critically, fossil fuel combustion causes air pollution, which can lead to serious health complications that are passed down through generations.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), burning fossil fuels releases pollutants that lead to early death, heart attacks, respiratory disorders, stroke, and asthma. It has also been linked to autism spectrum disorder and Alzheimer’s disease.

Carbon dioxide emissions have also been associated with global warming and the destruction of the ozone layer. The ozone layer protects humans and animals from the powerful rays of the sun, so degrading this layer exposes us to high levels of radiation, which causes skin cancer.
4. High depletion level
Critically, fossil fuels are not renewable energy sources. Unlike water, sun, and wind energy sources, the level of fossil fuels underground is depleting with each passing day.
In the next few centuries, we will run out of fossil fuel reserves. Experts predict we have 139 years left of coal, 54 years left of oil, and 49 years of gas supply. In our lifetime, we must transition to alternative sources of energy to power our everyday lives and critical processes.
5. Oil spills and gas leaks
When transporting oil, there is a high likelihood of the oil spilling onto land and into the sea. In the U.S. alone, there have been over 44 major oil spills since the 1970s, resulting in severe harm to aquatic life.
Ultimately, oil spills are disastrous to all living things and almost impossible to clean up.

The Horizon oil spill that occurred in the Gulf of Mexico released 4.9 million oil barrels into the Gulf of Mexico. The petroleum that had leaked from the well before it was sealed formed a slick extending over more than 57,500 square miles, harming and killing millions of plants and animals in the region.
Natural gas pipelines also leak this harmful fuel into the soil and atmosphere. Leaks are incredibly dangerous because they can kill vegetation and trees, cause explosions and fires, and release greenhouse gasses into the atmosphere.
6. High levels of water usage
Water shortages are a common problem in most parts of the world, especially in developing nations or areas stricken by drought.
In California alone, oil and gas operators used 3 billion gallons of freshwater from municipal sources between 2018 and 2021, an amount equal to what would be used in more than 120 million showers.
Fossil fuel power plants contribute to this problem because they require vast amounts of water for cooling. A study conducted in the U.S. reveals that fossil fuel power plants consume over four times the water that all the water used in homes in the U.S.

The long-term effect of water consumption by fossil fuels is the depletion of finite water resources, and the result is a lack of water. Contaminated water supplies or a lack of water can result in improper sanitation, exposure to chemicals, health issues, and even death.
7. Rising fuel costs
As fossil fuels continue depleting, it is becoming harder and harder to extract them from the Earth. In turn, the cost of extracting fossil fuels has risen. In the U.S., if fossil fuel prices are driven higher, the country could spend more than $30 trillion on fossil fuels between 2010 and 2030.
Also, since only a few countries in the Middle East produce the world’s fossil fuels, there is an increasing fear of war, lower output of fuels, and strikes by trade unions that can lead to fuel fluctuations around the world.
The clean energy transition
While there are clear pros and cons of fossil fuels, it’s clear that the disadvantages of continuing to use fossil fuels far outweighs the benefits. The clean energy transition seeks to make renewable energy sources more reliable and encourage the widespread adoption of renewables over fossil fuels.
Experts agree that switching from more harmful fossil fuels like coal and oil to less emission-intensive fuels like natural gas can result in significant CO 2 and air quality benefits. While it’s not a long-term answer to climate change, switching to natural gas can make a difference in the short term.
However, our supply of fossil fuels will run out soon. Significant investment, private-public partnership, and widespread adoption of renewable energy sources like solar and wind energy must occur before we can successfully phase out the use of the fossil fuels that are harming our planet.
Organizations like the Clean Energy Transition Institute , the United Nations , and the European Commission have identified pathways to decarbonization in the building, industrial, and manufacturing sectors. Like with the domestic use of fossil fuels, these industries must transition away and find alternatives.
Conclusion on the pros and cons of fossil fuels
When we compare the pros and cons of fossil fuels, it is clear that despite their numerous uses, fossil fuels are causing untold damage to our planet, humans, and plant and animal species.
Since human beings have relied upon fossil fuels for a long time, the transition may seem difficult, but it’s necessary for the survival of our planet and species.
However, some countries have begun to generate substantial portions of electric power from renewable sources. Individuals and large organizations and corporations should all join in the clean energy movement, to make the Earth a better home for us all.
Articles you might also like

Electric vs Gas Lawn Mowers: Which is Better?

What is Greywater: A Complete Overview to Everything You Need to Know

8 Solar Panel Developments to Get Excited About

What is a Solar Carport: How They Work And What is the Cost?

Is Water Renewable? 7 Reasons Why Water is Renewable

11 Important Ethanol Pros and Cons You Need to Know

20 Pros and Cons of Petroleum That Everyone Should Know

Are Building Energy Management Systems the Key to Smart Buildings?

The Best Minnesota Energy Rebates and Solar Incentives for Homeowners

Electric Meter Reading Guide: Determine Your Energy Consumption
Pros & Cons of Fossil Fuels: A Future Without Them?
The modern world runs on fossil fuels. but these fuel sources also make us sick and damage the environment. that’s why we need to move toward cleaner energy sources for the future..

Topics covered
What are fossil fuels, the many uses of fossil fuels, high energy content, global availability, on-demand use, thousands of uses, existing infrastructure, basis of the global economy, limited supply, safety risks, water pollution, air pollution, climate change, environmental injustice, rising costs, is there a future for fossil fuels, toward a world without fossil fuels.
How many times do you think you use fossil fuels every day? It’s probably more than you think. If your house is heated with oil or natural gas , you may use these fuels before you even get out of bed. You might use them again to take a shower, cook your breakfast, or drive to work. And you also rely on them in many ways you can’t see. They’re in countless objects you use every day—plastics, cosmetics, and even some medicines.
Fossil fuels are so ubiquitous that it’s hard to imagine a world without them. But in many ways, a world like this would be better than ours. The air and water would be cleaner. The weather would be less extreme. And it’s also quite possible we’d all be spending less on our electric bills .
Fossil fuels are the remains of plants and animals that lived millions of years ago. Coal is formed from plants, while oil and gas come from tiny creatures called plankton. These substances contain all the energy that these living things stored in their bodies while they were alive. Burning them releases all that stored energy at once.
At the same time, it releases large amounts of carbon in the fuel. Most of this enters the atmosphere as carbon dioxide (CO2), the main greenhouse gas responsible for global warming. Burning fossil fuel also releases other greenhouse gases, such as nitrous oxide (N2O). And it produces a variety of other chemicals that can pollute the air and water.

For centuries, the world has relied heavily on fossil fuels. Currently, they account for about 80% of all energy use in the U.S. and the world as a whole . Uses of fossil fuels include:
- Transportation. Oil, or petroleum, provides over 90% of all energy used for transportation in the U.S. It’s the raw material of gasoline used in cars, diesel fuel for trucks, and jet fuel.
- Generating electricity. About 60% of all U.S. power plants run on coal or natural gas. They burn the fuel to heat water and produce steam, which turns the turbines that generate power.
- Industrial processes. Many industries rely on fossil fuels as an energy source. For instance, they’re used in the production of steel , cement , and glass .
- Petroleum products. Oil and gas aren’t only used for energy. They’re also ingredients in many products , including plastics, fertilizers, lubricants, and pharmaceuticals.
- Residential and commercial use. Many homes and businesses use fossil fuels for heating. They’re also used for heating water, cooking, and drying clothes.
Are there any advantages to using fossil fuels?
Obviously, we wouldn’t rely on fossil fuels as much as we do if they didn’t have some benefits. For over 200 years, they have been the most reliable way to power our homes and industries. We’ve built our society around them, and that’s one reason they remain so popular today.
Fossil fuels are a highly efficient source of energy. That means a relatively small amount of oil or gas can produce a large amount of energy. This is especially important in transportation, since a vehicle needs to carry around its own fuel supply. A pound of gasoline holds about 40 times as much energy as a pound of batteries in an electric car . Fossil fuels are also capable of producing the large amounts of heat needed for industrial processes like steel smelting.
Another advantage of fossil fuels is that they’re widely available. Large deposits of coal, oil and gas exist in many parts of the world. And for areas that don’t have them, these fuels are easy to transport. In some parts of the world, fossil fuel use is currently the only alternative to energy poverty .
The electric grid only works if the amount of power produced matches the amount used. But many renewable energy sources, such as wind power and solar power , can’t produce electricity on demand. They only work when the wind is blowing or the sun is shining. Fossil fuels, by contrast, are easy to store until they’re needed.
Fossil fuels go into many of the products we use every day. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, there are over 6,000 products made from oil and natural gas. This includes all kinds of plastic goods, from cell phones to fabrics. Petrochemicals (compounds derived from oil and gas) are also used in fertilizer, lubricants, and pharmaceuticals.
Nowadays, there are alternatives to many fossil fuel uses. For instance, it’s possible to heat homes with electricity and produce power with solar panels. But in many cases, the systems we have now were set up to run on fossil fuels. Switching energy sources means replacing these systems, which takes both time and money.
Fossil fuels play a big role in many countries’ economies. Extracting, transporting, processing, and using them provides nearly 1.7 million jobs in the U.S. alone. Clean energy provides jobs too— more of them worldwide , in fact—but not always in the same places. For countries with a large fossil fuel sector, switching away from fossil fuels is a real blow to the economy.
What are the disadvantages of fossil fuels?
Many of the reasons fossil fuels are so valuable stem from the fact that we built our 20th-century society around them. But in the 21st century, the negatives of fossil fuel use outweigh the positives. These fuels have major environmental and safety risks, and newer alternatives are both greener and cheaper.
Fossil fuels are not a renewable energy source . They take millions of years to form, so we can’t just make more to replace what we use. The current supply of fossil fuels buried in the earth’s crust is all we’ll ever have. As of 2020, the world has enough oil and gas to meet its needs for about 50 years . Coal supplies will last longer—around 140 years. But once they’re gone, they’re gone.
Extracting fossil fuels from the ground is a dangerous process. Underground coal mines can collapse, trapping or killing the miners inside. They also contain trapped pockets of poisonous and explosive gases. And miners who avoid these risks still suffer high rates of lung illness from coal dust exposure. Surface mines are less hazardous for their workers, but they create pollution that threatens the health of nearby communities.
Drilling for oil and gas is also perilous. Without adequate safety measures, oil and gas wells can explode. This happened to the Deepwater Horizon oil rig in 2010, killing 11 workers. A newer method of extracting natural gas, called hydraulic fracturing or fracking, can cause earthquakes .
Besides being dangerous, drilling and fracking are highly water-intensive. In drought-prone California, extracting and refining fossil fuels uses up more than 280 billion gallons of municipal water each year. Coal-burning power plants make this problem worse because they require large amounts of water for cooling.
Fossil fuel use doesn’t just deplete the water supply. It also pollutes it. Fossil fuels contribute to water pollution in multiple ways, including:
- Oil spills and leaks
- Toxic runoff from coal mines
- Air pollutants that end up in rainwater
- Contaminated water injected into the ground for fracking
- Dirty wastewater from oil refineries
All these forms of water pollution are harmful, but oil spills are probably the most destructive. The 2010 Deepwater Horizon explosion released over 4 million barrels of oil into the Gulf of Mexico. The resulting oil slick spread from Texas to Florida and harmed fish, birds, coral, wetlands, and beaches. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is still working on cleaning it up.
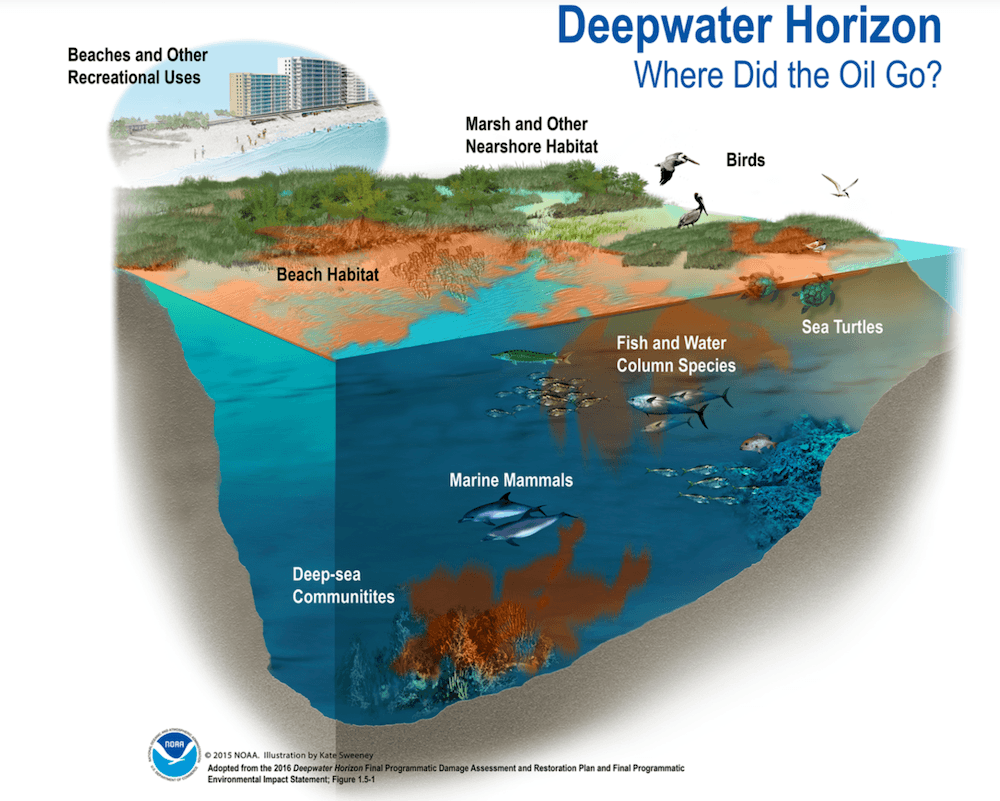
Fossil fuels pollute the air as well as the water. Burning them releases a wide variety of harmful chemicals into the air, including:
- Particulate matter (soot)
- Sulfur dioxide
- Nitrogen oxides, which form ground-level ozone (smog)
These chemicals cause all kinds of health problems , including asthma, bronchitis, heart attacks, strokes, autism, and Alzheimer’s. A 2021 study in Environmental Research concludes fossil fuel air pollution killed over 8 million people in 2018. That’s roughly one out of every five deaths worldwide.
The burning of fossil fuels is the main cause of greenhouse gas emissions responsible for climate change . Global warming is the single biggest threat to our environment. Air and water pollution cause many deaths, but climate change could potentially make the entire planet unlivable. Already, it’s causing increasingly severe weather disasters , including heat waves, storms, droughts, floods, and wildfires. It’s melting polar ice, leading to a rise in sea level . And it’s making the ocean warmer and more acidic , threatening marine life.
The pollution and climate hazards posed by fossil fuels don’t affect everyone equally. Low-income communities and nations are more likely to suffer from polluted air, extreme weather, or sea level rise. Wealthy people and wealthy nations get the most benefit from fossil fuel use, while poorer ones pay the price. This makes fossil fuels a direct threat to environmental justice .
For years, one of the biggest arguments in favor of fossil fuel use was its low cost. But today, most renewable energy sources are cheaper than fossil fuels . And this cost gap will only grow over time. The cost of clean energy solutions is falling across the board, while fossil fuel extraction costs are rising .
Society can’t simply get rid of fossil fuels immediately. There are too many systems built around them, from transportation to manufacturing to agriculture, to change overnight. They will certainly remain an important part of our lives for at least a few years.
But continuing to rely on fossil fuels in the long term is unsustainable. We need to move away from them toward renewable energy, and the faster the better. And this is growing ever easier as we find new approaches to the processes that currently depend on fossil fuels.

Today, there are many alternatives to fossil fuel use. Increasingly, we can rely on electricity to heat our homes, cook our meals, and power our cars. The electricity to support these new technologies can come from wind, solar, hydropower , and nuclear energy . New energy storage methods will help smooth out any gaps in power production.
That doesn’t mean the transition to a clean energy future will be easy. Changing systems people have relied on for decades takes time and money. And it will be difficult to replace fossil fuels for some specific purposes, such as steel smelting, air travel, and petrochemicals. Perhaps in the short term, we will keep using fossil fuels for these jobs, paired with carbon capture to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
But ultimately, our goal must be to eliminate fossil fuels from our lives entirely. Our survival depends on it.

Get matched to a local solar farm and save on your electricity costs.

12 Advantages and Disadvantages of Fossil Fuels
Fossil fuels refer to any fuel that comes from the Earth that is generated by the fossilization process. By definition, this is generally coal, natural gas, and petroleum products. It is the fuel that has helped the world develop into what it is today. Nearly 90% of the energy consumption that we have, even with the rise of renewables and cleaner fuels, comes from fossil fuel.
The combustion of fossil fuels is not without a cost. When fossil fuels burn, they release emissions into our atmosphere. For many in the scientific community, this emission release is at least partially responsible for a global warming effect. It may also contribute to higher pollution levels, which are believed to be responsible for up to 2 million deaths globally each year.
The advantages and disadvantages of fossil fuels show us that the choices we face in the future for fuel consumption are going to be difficult. Here are the key points to consider.
What Are the Advantages of Fossil Fuels?
1. Fossil fuels are a technology that is globally developed. We have numerous technologies available to us because of the presence of fossil fuels. Although this fuel source is often thought of as a way to provide transportation needs, many of the products that we use every day contain items that were manufactured thanks to fossil fuel technologies. That includes the computers and mobile devices that are used to read this content. Even renewable fuels have a foundation built on fossil fuels.
2. Fossil fuels are both cheap and reliable. Because the technologies which surround fossil fuels are well-established, the consumer cost to use them is quite load. The energy that is produced by their refinement and combustion is incredibly consistent. If you pour gasoline into your vehicle, there isn’t a doubt that the fuel will fail to ignite. Fossil fuels give us a strong base load, reliable energy, and it can be created around the clock.
3. Fossil fuels have become safer over time. An example of technology catching up to the emissions problem of fossil fuels comes through clean coal technologies. The emissions can be captured and condensed, reducing the overall amount that escapes into the atmosphere. Some technologies have come close to eliminating the production of greenhouse gases, condensing them into water that can be safely released back into the environment.
4. Fossil fuels still have plenty of availability. New fossil fuel resources are being found annually and often in amounts that are beyond any prediction that could be made. In 2013, up to 233 billion barrels of oil was discovered to be in the Australian Outback. Additional development opportunities exist for tar sands oil, shale oil, and natural gas. It may be a finite resource, but there is still the potential of more than a full century of use available with currently known resources.
5. Fossil fuels contribute to the overall welfare of an economy. We use fossil fuels to transport goods and services to one another. We are productive because of fossil fuels. We can generate renewable energy because of fossil fuels. We drive to the grocery store thanks to fossil fuels. Not only does the purchase of fossil fuels contribute to the national economy, but the use of fossil fuels helps to generate revenues for localized economies. Just about everything we do in life right now is tied, one way or another, to the consumption of a fossil fuel.
What Are the Disadvantages of Fossil Fuels?
1. Fossil fuels are a finite resource. It takes a certain amount of time for the fossilization process to occur on our planet. This means fossil fuels are a finite resource. Once they are harvested, they cannot be replaced in the lifetime of anyone living right now according to our current knowledge. It takes millions of years and specific conditions to replace a fossil fuel. That’s a very different effort compared to the energy released in a daily sunrise.
2. Fossil fuels are often cheap because of subsidies. Many governments tend to subsidize the price of fossil fuels instead of letting the free market govern what they tend to be. Businesses that operate within the fossil fuel industry also receive subsidies so that they can continue providing energy products to consumers at reasonable costs. US Government incentives for fossil fuels are typically $4 billion or more annually. In comparison, renewable energy resources like solar may receive about $1 billion annually.
3. Fossil fuels combust to create an acidic environment. Many of the outcomes which come out of the combustion of fossil fuels without condensing technologies lead to an environment that is more acidic. This acidity can change ocean environments, alter how crops can grow, and may even lead to a higher risk of drought and famine. Many ecosystems on Earth are very sensitive to changing conditions, which means continued fossil fuel use could lead to unpredictable and extremely negative consequences.
4. Fossil fuels can damage the environment through human error. Fossil fuels can also spill during transport, creating environmental damage as the product spills out. This is particularly problematic for petroleum products. From oil pipeline spills to disasters such as the Exxon Valdez spill, human error can cause a lot of unintended environmental damage. Even regular wear and tear, if not properly maintained, can lead to a higher risk of a leak occurring.
5. Fossil fuels aren’t a technology. Although we can make it cheaper to find and access fossil fuels, the fuel itself is not a technology. This means there will always be a baseline price for this product, especially since many of them are traded as commodities. Renewable energy resources, such as wind and solar, are based on technology. The prices for these energy resources has been in a continual decline since the 1970s. In some communities, solar and wind energy is virtually the same price as the energy created through fossil fuel combustion.
6. Fossil fuels may contribute to public health issues. Outside of the risks that pollution causes for premature fatalities, there are ongoing health issues that can be caused by the combustion of fossil fuels. Air pollution that comes from fossil fuel consumption can trigger symptoms that are similar to asthma. It can also create irritation with a person’s air passageways that can trigger chronic coughing, allergy development, lethargy, and other quality of life concerns.
7. Fossil fuels can be dangerous to harvest. Coal miners can develop a condition known as Black Lung Disease, which in severe cases is almost always eventually fatal. Natural gas drillers can be exposed to concentrated chemicals and silica, which can lead to adverse health issues. Oil workers are exposed to toxic chemicals frequently, which can increase their risks of cancer development. This shows that harvesting fossil fuels can be dangerous to personal health.
The advantages and disadvantages of fossil fuels show that life would be very different without them. Life might be very different, however, if we keep using them. That is why these key points deserve careful and frequent attention.
- ENVIRONMENT
Fossil fuels, explained
Much of the world's energy comes from material formed hundreds of millions of years ago, and there are environmental consequences for it.
Decomposing plants and other organisms, buried beneath layers of sediment and rock, have taken millennia to become the carbon-rich deposits we now call fossil fuels. These non-renewable fuels , which include coal, oil, and natural gas, supply about 80 percent of the world’s energy. They provide electricity, heat, and transportation, while also feeding the processes that make a huge range of products, from steel to plastics.
When fossil fuels are burned, they release carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases , which in turn trap heat in our atmosphere, making them the primary contributors to global warming and climate change .
Major types of fossil fuels
There are several main groups of fossil fuels, including:
Coal: Black or brown chunks of sedimentary rock that range from crumbly to relatively hard, coal began to form during the Carboniferous period about 300 to 360 million years ago, when algae and debris from vegetation in swamp forests settled deeper and deeper under layers of mud. Mined via surface or underground methods, coal supplies a third of all energy worldwide, with the top coal consumers and producers in 2018 being China, India, and the United States. Coal is classified into four categories—anthracite, bituminous, sub-bituminous, and lignite–depending on its carbon content.

Carbon dioxide emissions from burning coal account for 44 percent of the world total , and it's the biggest single source of the global temperature increase above pre-industrial levels. The health and environmental consequences of coal use, along with competition from cheap natural gas, have contributed to its decline in the U.S. and elsewhere. But in other places, such as India, demand is expected to rise through 2023.
Oil: Crude oil, a liquid composed mainly of carbon and hydrogen , is often black, but exists in a variety of colors and viscosities depending on its chemical composition. Much of it formed during the Mesozoic period, between 252 and 66 million years ago, as plankton, algae, and other matter sank to the bottom of ancient seas and was eventually buried.
Extracted from onshore and offshore wells, crude oil is refined into a variety of petroleum products , including gasoline, diesel, and heating oil. The top oil-producing countries are the U.S., Saudi Arabia, and Russia, which together account for nearly 40 percent of the world's supply.
Petroleum use accounts for nearly half the carbon emissions in the U.S. and about a third of the global total. In addition to the air pollution released when oil is burned, drilling and transport have led to several major accidents, such as the Exxon Valdez spill in 1989, the Deepwater Horizon disaster in 2010, the devastating Lac Megantic oil train derailment in 2013, and thousands of pipeline incidents . Nonetheless, oil demand continues to rise , driven not only by our thirst for mobility, but for the many products— including plastics —made using petrochemicals, which are generally derived from oil and gas.
Natural gas: An odorless gas composed primarily of methane, natural gas often lies in deposits that, like those for coal and oil, formed millions of years ago from decaying plant matter and organisms. Both natural gas and oil production have surged in the U.S. over the past two decades because of advances in the drilling technique most people know as fracking .
By combining fracking—or hydraulic fracturing—with horizontal drilling and other innovations, the fossil-fuel industry has managed to extract resources that were previously too costly to reach. As a result, natural gas has surpassed coal to become the top fuel for U.S. electricity production, and the U.S. leads the world in natural gas production, followed by Russia and Iran.
Natural gas is cleaner than coal and oil in terms of emissions, but nonetheless accounts for a fifth of the world's total, not counting the so-called fugitive emissions that escape from the industry, which can be significant . Not all of the world’s natural gas sources are being actively mined. Undersea methane hydrates, for example, where gas is trapped in frozen water, are being eyed as a potential gas resource .
Reducing emissions from fossil fuels
Governments around the world are now engaged in efforts to ramp down greenhouse gas emissions from fossil fuels to prevent the worst effects of climate change. At the international level, countries have committed to emissions reduction targets as part of the 2015 Paris Agreement , while other entities—including cities, states, and businesses—have made their own commitments. These efforts generally focus on replacing fossil fuels with renewable energy sources, increasing energy efficiency, and electrifying sectors such as transportation and buildings.
However, many sources of carbon emissions, such as existing power plants that run on natural gas and coal, are already locked in. Considering the world's continuing dependence on fossil fuels, many argue that in addition to efforts aimed at replacing them, we also need to suck carbon from the air with technologies such as carbon capture, in which emissions are diverted to underground storage or recycled before they reach the atmosphere. A handful of commercial-scale projects around the world already capture carbon dioxide from the smokestacks of fossil fuel-fired plants, and while its high costs have prevented wider adoption , advocates hope advances in the technology will eventually make it more affordable.
For Hungry Minds
Related topics.
- FOSSIL FUELS
- AIR POLLUTION
- CLIMATE CHANGE
- GREENHOUSE EFFECT
- CARBON CAPTURE AND STORAGE
- CARBON FOOTPRINT
- RENEWABLE ENERGY
- SUSTAINABILITY
You May Also Like

Another weapon to fight climate change? Put carbon back where we found it

How the historic climate bill will dramatically reduce U.S. emissions

Rest in … compost? These ‘green funerals’ offer an eco-friendly afterlife.

‘It’s now or never’: UN climate report’s 4 urgent takeaways

Mining is a polluting business. Can new tech make it cleaner?
- Environment
- Paid Content
- Photography
- Perpetual Planet
History & Culture
- History & Culture
- History Magazine
- Mind, Body, Wonder
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Your US State Privacy Rights
- Children's Online Privacy Policy
- Interest-Based Ads
- About Nielsen Measurement
- Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information
- Nat Geo Home
- Attend a Live Event
- Book a Trip
- Inspire Your Kids
- Shop Nat Geo
- Visit the D.C. Museum
- Learn About Our Impact
- Support Our Mission
- Advertise With Us
- Customer Service
- Renew Subscription
- Manage Your Subscription
- Work at Nat Geo
- Sign Up for Our Newsletters
- Contribute to Protect the Planet
Copyright © 1996-2015 National Geographic Society Copyright © 2015-2024 National Geographic Partners, LLC. All rights reserved
Pros and Cons of Fossil Fuels
- by Ahsen Soomro

Table of Contents Show
What are fossil fuels, 1. advanced technology, 2. cheap and reliable, 3. highly efficient, 4. easier transportation, 5. job opportunities, 6. easy set-up, 1. major contributors of climate change and global warming, 2. major fuel reserves needed, 3. non-renewable source of energy, 4. unsustainable use of fossil fuels, 5. sweet incentives, 6. accidents can prove to be quite fatal, 7. damage to public health, 8. economic issues, 9. health hazards for coal mine workers, 10. deforestation, conclusion regarding fossil fuels.
Since the dawn of industrialization, the world has been changing rapidly and shaped itself into a modern world that we see today. It all began when we harnessed the power of coal to run large machines and produce resources at a faster rate than human hands making it an everyday phenomenon.
At first, it was just coal, but then oil and natural gas also started being used as a recognized energy source. Together these energy sources could power anything from large factories to cars and provided electricity to the farthest corners. With time, as more and more people shifted to these energy resources, the demand for them increased which caused a surge of fossil fuel mining.
Till today fossil fuels are considered an important energy source. Everything that we touch, see or hear uses energy supplied by these fossil fuels. Although we have alternatives to fossil fuels such as solar, hydropower, wind and even nuclear energy which are in development; we still see an increase in the use of fossil fuels every year. A report by the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) in 2007 claimed that 86.4% of the primary energy used by the world’s population can be traced back to fossil fuel sources.
Fossil fuels and their effects on the environment have been studied extensively. Both pros and cons have been noted and argued on for centuries. Most of the advantages of fossil fuels are used by big refineries and fuel companies as arguments on the world stage, many of which are valid and meticulously researched.
Recently the general public has become aware of the negative effects of fossil fuels on the environment and years of research papers by scientists validate this impact. However, even after a long list of vices we still use fossil fuels because many world systems still rely on it and have provided us with advantages unparalleled by any other resource.
The good and bad effects of fossil fuels still stay as a prominent topic to debate in modern society. Before diving into the debate of whether the fossil fuels are good or bad;let me first tell you what they are and how they are formed.
Fossil fuels can be classified into three major categories which are coal, oil and natural gas.
They are classified based on their natural state, chemical structure, and process of formation. Fossil fuels are formed through years of dead organic materials compressed under immense pressure and temperature in the earth. This matter starts decomposing, releasing the organic matter into the crust and the carbon and hydrogen molecules get converted into fossil fuels.
These molecules form a long chain of hydrocarbons and each type of fossil fuel has a varying length of this chain. This chain takes millions of years to form and is difficult to be created in an artificial setting. Different conditions and resources are required to create each type of fossil fuel. The synthesis of coal requires the decomposition of land-based plant matter and has the longest hydrocarbon chain, which requires more energy to burn but produces the least amount of energy. In comparison to coal, oil has a medium length of the hydrocarbon chain and is made from small plants and ocean animals. The shortest chain is natural gas, which can also be made after burning oil or coal as a byproduct. It releases the highest amount of energy out of the three.
Even though it takes years to synthesize fossil fuels, they are still the most preferred source of energy . To understand their continuing popularity, we need to know the advantages and disadvantages of them and weigh their benefit over risks.
More on Types and Sources of Energy .

Advantages of Fossil Fuels
Fossil fuels have been selected as a major source of energy providing more than 85% of the world’s needs. The following reasons may also answer why we are so dependent on fossil fuels . Let’s see what are the major pros of using fossil fuels in today’s world!
The technology used to obtain fossil fuels has become very well-developed. This is because Fossil fuels have been a sole source of energy for quite a while now and we have been working on the technology to obtain energy from these sources more efficiently.
Fossils fuels are cheap as they are available in huge quantities around the world and as we have spent years and years developing the technologies for it, some believe that it’s better to use fossil fuels so as to reap the efforts. The energy production per gram of fossil fuels is higher than many alternative sources of energy (greater amount of energy released with same amount). They are extremely reliable to be used as primary source of energy, as compared to the other renewable sources of energy which are not reliable.
This means that even small quantities of fossil fuels can generate loads of energy, The best fuels to be used for vehicles is petroleum undoubtedly because no other source of energy comes even close to the rapid generation of energy from petroleum.
Fossil fuels can be transported quite easily. Coals can be transported on trucks and natural gas or petroleum through pipelines. Although initially laying down these pipes costs a fortune, but later on they turn out to be very efficient means of transportation. One can understand that unlike fossil fuels, renewable sources of energy such as Wind and Solar cannot be transported.
Use of Fossil fuels generates thousands of jobs for the workers ranging from mine workers, to truck drivers as well as jobs at petroleum companies. Abandonment of Fossil fuels could result in a very high spike in unemployment, and with the overpopulation issue nowadays, it could lead to an economic crisis.
As we all know, renewable sources of energy are dependent on the availability of the source such as wind or sunlight to generate energy. Fossil fuel plants can however be installed anywhere and made to produce enormous quantities of energy as long as it has a reliable supply of fuel to generate power.
Disadvantages of Fossil Fuels
After using fossil fuels for years on end, we realized that there were some unprecedented cons of using and very well abusing Fossil Fuels. Let’s see what those disadvantages of fossil fuels are.
Fossils fuels are clearly not a green source of energy, they are rather damaging to the environment due to their high carbon content. The carbon di oxide is released from burning fossil fuels which is a greenhouse gas that causes Air Pollution as well as ozone layer depletion. These effects ultimately lead to global warming. Other than that there is also environmental degradation of the earth due to mining practices.
Power stations need a constant supply of fuel to be able to generate the demand of power. This means large quantity of coal needs to be transported everyday which leads to further increase in our carbon footprint. Hence, it is essential to build fossil fuel plants near to fossil fuel reserves to decrease transportation costs and damage to the environment.
Many believe that fossil fuels being non-renewable source of energy mean that they are present in finite amounts in the world and cannot be replenished naturally. However, the truth of the matter is that they are replenished naturally through the process of anaerobic decomposition of organic matter but the process takes millions of years to make reserves sufficient for our use.
Given that the reserves of fossil fuels are plenty but the way we are using fossil fuels is simply unsustainable. It will take a million years for the earth to produce more fossil fuel resources. This has led to people thinking different and shifting to green sources of energy.
Fossil fuels have been quite cheap due to the government providing incentives for use of these sources of energy. Coal, Natural gas and petroleum have received subsidies amounting to $4.22 Billion. Compared to these incentives, Solar, which is a green source of energy only received $1.13 Billion.
Accidents may happen anywhere ranging from nuclear plants to solar panels. Although the accidents happening in fossil fuel mechanisms are not as dangerous as nuclear systems, they are obviously more risky than wind power or solar power. The deep water horizon spill which happened in April of 2010 is still fresh in our minds.
Fossil fuels are extremely opposite to being environment friendly. Burning of these fuels results in all kinds of pollution, the most apparent being air pollution. WHO claims 7 Million premature deaths are because of air pollution . Polluted air can cause various lung diseases and also trigger allergic reactions which could trigger asthma in many people. Humans living In overcrowded cities are more exposed to polluted air and hence carry a higher risk of Asthma.
A few Middle-east countries have been rewarded with surplus amounts of oil reserves and fossil fuels. These countries are behind 40% of the oil production in the world. Majority of the world has to depend on these countries to fulfill their oil demands. Lower production, political instability, economic sanctions and wars have a profound effect on the trade and could lead to high fluctuations in the oil prices.
Mine workers are exposed to highly contagious gasses which have proven to be quite fatal to human health. Hundreds of People working in mines as well as oil-drilling sites die each year.
Trees are cleared out of forests to make way for mining practices. Mining requires quite a large land and hence, can’t be done with trees being present. Other than the mine, many trees need to be cut to make way for roads and infrastructure to make for transports to and from the mine. This leads to severe loss of ecosystems and subsequently habitat destruction.
There are numerous pros and cons of fossil fuels and only a few have been listed here. Perhaps the most important thing to note here is how damaging it is to the environment. Fortunately, quite efficient, green and renewable sources of energy such as solar and wind power have been invented and made available to the population. These alternative sources of energy will lead to less and less people relying on conventional fossil fuels. We need to play our small part in producing a better future.
Ahsen Soomro
My love for nature is not newfound. I have lived on the countryside for over a decade of my life where I realized how human activities impacted the environment. Later during my stint in medical school, I realized that many of our health concerns originate from neglecting our environmental responsibilities and this was just not sustainable in the long run. Raising awareness, not locally but globally, was the mission. This led to the foundation of EnvironmentBuddy!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Pros and Cons of Genetically Modified (GMO) Foods.
11 pros and cons of monoculture farming (monocropping), you may also like, 20 amazing facts about nuclear energy.
- No comments

- 7 minute read
Battery Reconditioning; DIY and Importance

- 3 minute read
Tidal Energy Pros and Cons
Why are fossil fuels a non-renewable energy resource.

- 6 minute read

10 Major Pros and Cons of Fracking!

- 10 minute read
Is Propane Heating Environment-Friendly? Uses, Pros & Risks
- About the Hub
- Announcements
- Faculty Experts Guide
- Subscribe to the newsletter
Explore by Topic
- Arts+Culture
- Politics+Society
- Science+Technology
- Student Life
- University News
- Voices+Opinion
- About Hub at Work
- Gazette Archive
- Benefits+Perks
- Health+Well-Being
- Current Issue
- About the Magazine
- Past Issues
- Support Johns Hopkins Magazine
- Subscribe to the Magazine
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience.
Johns Hopkins forum explores the pros and cons of fossil fuel divestment
Experts offer perspectives on financial, ethical implications of divestment.
By Katie Pearce
The topic of fossil fuel divestment remains a complex one, a Johns Hopkins University forum demonstrated Monday night.
The university invited four experts to share perspectives on the issue as it engages in its own discussions of whether to end private investments in fossil fuel companies. Nearly a third of the university's $3.8 billion endowment is privately invested.
The divestment proposal, first generated by a group of students in 2012 and reissued in 2016, mirrors similar campaigns at universities across the country, said Johns Hopkins Bloomberg Distinguished Professor and discussion moderator Paul Ferraro .
Globally, the divestment movement has gained traction with organizations including city governments, faith groups, and hospitals, but many institutions have also held back from divesting, including Harvard University, Ferraro said.
The panelists Monday reflected the range and nuance of opinions that exist on the topic, with divestment framed on the one hand as a moral imperative, and on the other hand as a financially irresponsible move. Though all of the experts seemed to agree that the combustion of fossil fuels play a role in climate change, they argued for different approaches to the issue.
Students in the audience seemed most receptive to the pro-divestment stances of Ellen Dorsey , executive director of the Wallace Fund, a social progress foundation that is now 100 percent divested from fossil fuels.
Dorsey argued that "no mission-driven organization should hold market positions in industries that undermine its values or pose harms to its constituents," pointing to the health dangers of climate change as contradictory to Johns Hopkins' goals. She added that with the "exploding industry" of sustainable energy, divesting from fossil fuels makes sense financially.
"What began as an ethical call to action quickly became aligned with financial self-interest," Dorsey said, likening fossil fuel companies to outdated technology like landline telephones in the age of cellphones.
David Powell , from the investment management firm Brown Advisory, also attested to the practicality of investing in sustainability. He pointed to successful examples from his firm's own portfolio—including companies that specialize in LED lights and water-saving technologies—and examples of industry leaders such as Nike that are testing sustainable models.
Frank Wolak , an economics professor at Stanford University, presented figures showing that universities can only make a "trivial" dent on global greenhouse gas emissions through their actions. He proposed an alternative, more "cost-effective" approach for Johns Hopkins, encouraging students to create a university-scaled carbon pricing model that governments could replicate.
"In other words, you're building a model for the world," Wolak said, proposing as one idea an app that could monitor each person's carbon footprint on campus.
Rafael Castilla , director of investments at the University of Michigan's Investment Office, provided his own personal perspective on the holes in the divestment argument. He spoke of the hypocrisy he feels in "demonizing" fossil fuels when he and most others consume them every single day.
"I took a plane over here, [which] burned jet fuel," he said. "In the house I live in we burn natural gas."
He added that although there's "no question that there's been a lot of bad actors and irresponsibility in the fossil fuel industry," he believes divestment is an overly simplistic approach to a complicated, deeply embedded problem.
"I don't know that this is a kind of Nancy Reagan-type of approach where all you have to do is 'just say no,'" he said. "Sometimes I feel like the fossil fuel debate has that quality to it."
The Johns Hopkins divestment proposal is under consideration by the Public Interest Investment Advisory Committee , a panel of students, faculty, and staff appointed to advise the university on the social impacts of its investments.
Committee chair Jeffrey Kahn , director of the Berman Institute of Bioethics , wrote in an email that the panel will continue meeting regularly on the topic of divestment "until we've completed our analysis and come to our recommendations" to deliver to Johns Hopkins' board of trustees. Kahn said Monday's forum provided a "helpful discussion about … various ways of approaching such a decision."
Posted in Voices+Opinion , Politics+Society
Tagged sustainability , investing , fossil fuels , emissions
Related Content

Forum explores divesting from fossil fuels
You might also like, news network.
- Johns Hopkins Magazine
- Get Email Updates
- Submit an Announcement
- Submit an Event
- Privacy Statement
- Accessibility
Discover JHU
- About the University
- Schools & Divisions
- Academic Programs
- Plan a Visit
- my.JohnsHopkins.edu
- © 2024 Johns Hopkins University . All rights reserved.
- University Communications
- 3910 Keswick Rd., Suite N2600, Baltimore, MD
- X Facebook LinkedIn YouTube Instagram
- Biology Article
Fossil Fuel
“Fossil fuels are the fuels formed by natural processes such as decomposition of dead and buried organisms. “
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Natural Gas
- Advantages And Disadvantages

What are Fossil Fuels?
Fossil fuels are buried flammable geologic deposits of organic substances such as dead plants and animals that got deposited under several thousand feet of silt. These deposits decayed with the passage of time and got converted to natural gas, coal and petroleum due to the extreme heat and pressure inside the earth’s crust. They are also known as non-renewable sources of energy as it takes a very long time for it to replenish.
Types, Formation and Uses of Fossil Fuels
Fossil fuels are of the following types:
Natural gas
It is a hard, black coloured substance made up of carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen and sulphur.
The major types of coal are- anthracite, bituminous and lignite.
Anthracite has a higher carbon concentration and is the hardest type of coal.
Lignite has a high concentration of oxygen and hydrogen but a low concentration of carbon.
Bituminous is a moderate form of coal.
Coal is processed industrially to obtain derivatives like coke, coal tar and coal gas.
Formation of Coal
The process of formation of coal is known as coalification.
The dense forest present in the low-lying wetland got buried in the earth, millions of years ago.
Soil kept depositing over them and they got compressed.
As they went deeper and deeper, they faced high temperature and pressure.
As a result, the substances slowly got converted into coal.
Uses of Coal
Coal was used to produce steam in the railway engines initially.
It is used to cook food.
It is used to generate electricity in thermal plants.
It is used in industries as fuel.
It is a clear, oily liquid, usually green or black in colour.
It has a very strange smell and is a mixture of petroleum gas, diesel, paraffin wax, petrol, lubricating oil, etc.
It is also termed as “Black Gold” because of its wide range of uses in many industries.
Formation of Petroleum
The sea animals and plants died and their bodies settled at the bottom of the sea.
They got compressed by the layers of sand and clay.
Their encounter with high temperature and pressure converts them into petroleum.
The petroleum is separated from the crude oil by a series of processes in a refinery. This is known as petroleum refining.
Uses of Petroleum
It is used to power internal combustion engines in the form of petrol.
It is used in roofing, road pavements and as a water repellent.
It is used in manufacturing detergents, plastics, fibres, polyethene, etc.
It is a clean and non-toxic fossil fuel.
It is colourless and odourless and can be easily transferred through pipelines.
It is stored as compressed natural gas (CNG) under high pressure.
It is a less polluting and less expensive fossil fuel.
Methane is the most important natural gas.
Formation of Natural Gas
The phytoplankton and zooplankton sink to the bottom of the ocean and mix with organic materials to form an organic-rich mud.
The mud buried under more sediments and lithifies to form an organic shale. This prevents its exposure to oxygen. This is done to protect the organic materials from being decomposed by bacteria.
The increasing pressure and temperature transform the shale into a waxy material known as the kerogen.
At temperatures between 90-160°C kerogen is transformed into natural gas.
Uses of Natural gas
Compressed Natural Gas is used for generating power.
It is used as fuels in automobiles.
It can be used at homes for cooking.
It is used as a starting material in chemicals and fertilizers.

Are Fossil Fuels Renewable?
Fossil fuels are a non-renewable source of energy . Most of the energy used by us is obtained by the burning of fossil fuels. These fossil fuels are used up at a faster rate. They cannot be regrown at a scale compared to their consumption. With the increased demand for the production of various energies, fossil fuel energy is declining. It is difficult to replace them. That is why they are known as a non-renewable source of energy.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Fossil Fuels
Advantages:
Fossil fuels can generate a large amount of electricity at a single location.
They can be found very easily.
They are cost-effective.
Transportation of oil and gas can be done easily through pipelines.
They have become safer over time.
Despite being a finite resource, it is available in plenty.
Disadvantages
Fossil fuels emit carbon dioxide when burnt which is a major greenhouse gas and the primary source of pollution. This has contributed to global warming.
They are a non-renewable resource, i.e., once used they cannot be replaced.
Combustion of fossil fuels makes the environment more acidic. This has led to unpredictable and negative changes in the environment.
Harvesting of fossil fuels also causes fatal diseases among the people. For eg., the coal miners often suffer from Black Lung Disease. The natural gas drillers are constantly exposed to chemicals and silica which is dangerous for their health.
These are the natural sources of energy and have extensive applications in industrial as well as domestic purposes.
For more information on Fossil Fuels or any related topics, please register at BYJU’S Biology .
Related Links

Put your understanding of this concept to test by answering a few MCQs. Click ‘Start Quiz’ to begin!
Select the correct answer and click on the “Finish” button Check your score and answers at the end of the quiz
Visit BYJU’S for all Biology related queries and study materials
Your result is as below
Request OTP on Voice Call
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Post My Comment
This is nice, my child learned lots of this website, he said that he enjoyed it.
It would have been good if assisted with diagrams for better understanding of beginners.
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
- Environmental Science
The Pros and Cons of Fossil Fuels
Format: APA
Academic level: College
Paper type: Essay (Any Type)
Downloads: 0
The First Law of Thermodynamics, also referred to as the Law of Conservation of Energy, states that energy can no longer undergo creation, not destruction. With that, it can only undergo transformation or change from one state to another. The Second Law of Thermodynamics states that the entropy of any system that is isolated always undergoes an increase. At that point, the systems that are isolated undergo evolution toward the thermal equilibrium ( Ciocan, Tazerout, Prisecaru & Durastanti, 2015). The above two scientific laws apply to energy use, energy conversions, and the need for energy efficiency. In specific, the definitions of the laws depict given ambiguities that indicate their applications to disciplines of energy. The laws illustrate the activities of lighting efficiency and thermal conduction as the laws state ( Ciocan et al., 2015) . The use of energy in different disciplines has to fit either of the laws. In its conservation, it is easily converted to another form hence not created nor destroyed. The pros of fossil fuels are that they are well-developed and also, they are reliable and cheap. The energy used in the harnessing of the energy from fossil fuels is developed. The fuels are excellent types of fuel for usage for energy based on load. On the other hand, fossil fuels have got some disadvantages. The energy sources have contributed to global warming ( Ciocan et al., 2015) . It is important to consider the source that will not affect the environment due to the cases of global warming. Also, they are non-renewable, unsustainable, incentivized, and in many cases accidents. The energy source produces low pollution, the operating cost is low, they are reliable, have high proficiency than fossil fuels, and interestingly, renewable. On the other hand, the energy source has an impact on the environment, a problem when it comes to the disposal of radioactive waste, high cases of nuclear accidents, the high cost of production, the presence of uranium which is finite, and high militants target ( Ciocan et al., 2015) . Solar energy is naturally available. It is sustainable, low impact on the environment, and has an energy that is readily independent. On the other hand, it comprises some disadvantages. It is intermittency, hence can only be generated through sunshine. Also, it may take a significant amount of land, and their materials are scarce in supply ( Ciocan et al., 2015) . Wind power is a clean energy and has no fuel to drill, mine, frank, burn, or transport. The source is sustainable and renewable, the costs are low and they decrease with time, they have a domestic supply in abundance, free when the infrastructure is paid for, the low life cycle of the footprint for carbon, and is used for most of the places ( Ciocan et al., 2015) . On the other hand, it is unpredictable as the wind is unsteady and inconsistent, it is not cheap when compared with other sources of energy they pollute the environment as they produce noise, cases of wildlife impact, and localized impact on weather and temperatures at night-time. The energy is renewable, it is green, it is highly reliable, it has a high rate of flexibility, and it is much safe when compared with other sources. On the other hand, it has got consequences for the environment, it is quite expensive, its availability depends on the availability of water, and easily affected by limited reservoirs ( Ciocan et al., 2015) . The characteristics of algae make it be most competitive as a fuel source. It is the most environmentally friendly. The algae are small aquatic organisms that help in the conversion of sunlight into a form of energy and the storage is facilitated in a form of oil. The energy source is so convincing hence attracting more attention. Advantageously, the algae-based biofuels drop in replacement for liquid fuels that are based on petroleum. Also, the fuel is inherently renewable and it stands to be a reliable source. It absorbs the carbon dioxide in its growth, and the waste carbon dioxide and wastewater can be utilized as nutrients. After a clear comparison of the algae source energy with other sources, it is evident that the new source is attentive ( Ciocan et al., 2015) . The source has a higher energy per acre than the bio-fuels. The source is reliable as it can be grown in areas where other types of agriculture are not possible. The production process is recently scaling high and the benefits are evident. Conclusively, when selecting a source of energy, there are things to consider. Reliability, renewability, the power delivered, sustainability, and the effects on the environment should be considered. Recently, it is important to consider the source that will not affect the environment due to the cases of global warming. It is important to consider that to protect the future. Technology advances resonate the best energy source for replicative outcomes. The advantages and disadvantages should be tabled as well so that to come up with the best option.
Reference
Ciocan, A., Tazerout, M., Prisecaru, T., & Durastanti, J. F. (2015, November). Thermodynamic evaluation for a small-scale compressed air energy storage system by integrating renewable energy sources. In Renewable Energy Research and Applications (ICRERA), 2015 International Conference on (pp. 455-460). IEEE.
Delegate your assignment to our experts and they will do the rest.
- New Environmental Paradigm as the Most Prevalent Paradigm in the U.S. Today
- Effect of Food and Temperature Prior to Nucleus Implantation on Cultured Pearl Formation and Quality
Select style:
StudyBounty. (2023, September 16). The Pros and Cons of Fossil Fuels . https://studybounty.com/the-pros-and-cons-of-fossil-fuels-essay
Hire an expert to write you a 100% unique paper aligned to your needs.
Related essays
We post free essay examples for college on a regular basis. Stay in the know!
HACCP: A Systematic Approach to Food Safety
Sampling: the selection of a particular sample or group to represent an entire population, gis uses in national wildlife refuge management, factors that least affect the global environment.
Words: 1188
Restoration of the Chesapeake Bay
Hazard analysis techniques for system safety, running out of time .
Entrust your assignment to proficient writers and receive TOP-quality paper before the deadline is over.
Essay on Fossil Fuels and Renewable Energy | The Pros And Cons Of Fossil Fuels

Essay on Fossil Fuels and Renewable Energy – Fossil fuels are a complex and globalized industry that affects the economy, environment , and social well-being of many people. Let’s dive deeper to understand further about that-
Long Essay on Fossil Fuels and Renewable Energy 1000 Words

It’s no secret that our world is reliant on fossil fuels. For years, we’ve relied on these non-renewable resources to power our homes, our businesses, and our vehicles. But as we become more aware of the environmental impact of fossil fuels, we’re turning to renewable energy sources to provide the power we need. Let’s dive deeper to understand the impacts and future fossil Fuel- In this essay, we’ll explore the pros and cons of both fossil fuels and renewable energy. We’ll take a look at the history of each, their current use, and the potential for each in the future. By the end, you should have a better understanding of where our energy comes from and where it might be headed.
What are Fossil Fuels?
Fossil fuels are natural resources that have been formed over millions of years from the remains of dead plants and animals. Fossil fuels are non-renewable source of energy that are used to generate electricity and power our homes, businesses, and transportation.
There are three main types of fossil fuels: coal, oil, and natural gas.
1. Coal is the most abundant and least expensive fossil fuel, but it is also the dirtiest. 2. Oil is a liquid fossil fuel that is used to power our vehicles and create many of the products we use every day. 3. Natural gas is a clean-burning fossil fuel that is used to heat our homes and generate electricity.
Fossil fuels are a vital part of our economy and our way of life, but they come with some serious environmental concerns. Burning fossil fuels releases harmful emissions into the atmosphere, contributing to climate change and air pollution. Mining and drilling for fossil fuels can also have negative impacts on the environment. Despite these concerns, fossil fuels remain an important part of our world. For now, they are the best option we have for powering our homes, businesses, and transportation.
What are Renewable Energy Sources?

Renewable energy sources are sources of energy that can be replenished or replaced naturally. Means they are renewable and can be reused in one or the other ways. This includes solar, wind, water, biomass, and geothermal energies. Renewables make up a large portion of the world’s energy supply and are crucial to meeting our future energy needs in a sustainable way. Solar energy is by far the most abundant renewable resource on Earth. Every day, the sun emits more energy than we could ever hope to use.
Solar Panels convert sunlight into electricity, which can then be used to power our homes and businesses. Solar energy is also used to heat water and create space heating and cooling systems. Wind Energy is another renewable resource that has seen tremendous growth in recent years. Wind turbines convert the kinetic energy of moving air into electricity. Wind power is one of the fastest-growing sources of renewable electricity in the world. Waterpower is another form of renewable energy that has been used for centuries. Water wheels were once used to grind grain and provide other forms of mechanical power. Biomass is any organic matter that can be used as a fuel source. This includes wood, crops, and even waste products like manure and sewage sludge. Biomass can be burned to produce heat or converted into biofuels like ethanol and biodiesel. Today, hydroelectric dams generate electricity by harnessing the power of moving water. Small-scale hydropower systems can also be used to generate electricity for homes and businesses.
The Pros and Cons of Fossil Fuels
Fossil fuels such as coal and oil have been used to generate electricity for over a century. They are reliable, affordable, and abundant.
Here are some of the key advantages of fossil fuels: –
1. Fossil fuels are a very reliable source of energy. 2. They are much cheaper. 3. They are a very abundant resource. 4. There are huge reserves of coal and oil all over the world. 5. Fossil fuels produce large amounts of energy. Therefore they are used to generate electricity. 6. They can be easily transported and stored.
Fossil fuels have several disadvantages-
1. They are a finite resource, which means that they will eventually run out. 2. They are also non-renewable, meaning that they cannot be replaced once they are used up. 3. Fossil fuels are also responsible for a large percentage of greenhouse gas emissions, which contribute to climate change. 4. Burning fossil fuels releases carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, where they trap heat and cause the Earth to warm. 5. Fossil fuels are also dirty and polluting. Burning them releases harmful chemicals into the air, water, and soil. These pollutants can cause health problems in people and animals and damage the environment.
The Pros and Cons of Renewable Energy Sources
Here, we’ll take a look at the pros and cons of renewable energy sources so you can make an informed decision about which type of energy is right for you.
There are many advantages of renewable energy.
1. First, renewable energy is a clean source of energy. It does not produce emissions that pollute the air or water. 2. Second, renewable energy is a renewable resource. It can be replenished naturally, unlike fossil fuels which are finite resources that will eventually run out. 3. Third, renewable energy is often cheaper than traditional sources of energy. Once the initial investment has been made, the costs of operating a renewable energy system are often lower than the cost of running a fossil fuel-based system. 4.Fourth, renewable energy can help reduce our dependence on foreign oil. By using more domestic sources of energy, we can reduce our reliance on imported oil and gas. 5. Finally, renewable energy is a growing industry with good job prospects. Jobs in the renewable energy sector are often high-paying and stable, making it a good career choice for many people.
There are a few disadvantages of renewable energy to consider as well.
1. First, initial investment costs can be high. 2. Second, renewable energy sources are intermittent, meaning they can’t provide a consistent, 24/7 supply of power. This means that traditional backup power sources, like natural gas or diesel generators, are still needed. 3. Third, the technologies used to generate renewable energy can have negative environmental impacts. For example, large-scale solar farms can take up a lot of land, and wind turbines can kill birds and bats.
Which is Better for the Environment?
There are a lot of factors to consider when trying to determine which is better for the environment. cost, production, and disposal. Here are a few examples:
1. Recycling costs more money and energy than making new products from scratch. 2. Manufacturing products from recycled materials often requires more energy and produces more pollution than making products from virgin materials. 3. Disposing of recycling properly can be difficult and expensive. 4. Some products, like electronics, cannot be recycled at all and must be disposed of in special ways. In general, it is best to avoid disposing of anything in landfills if possible. Recycling should be seen as a last resort when it comes to the environment.
Which is Better for the Economy?
In the context of climate change, the question of which energy source is better for the economy is an important one. On the one hand, fossil fuels are the traditional energy sources and have been used for centuries. They are also relatively cheap and easy to extract. On the other hand, renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power are becoming increasingly popular as they offer a cleaner and more sustainable option. So, which is better for the economy? In general, renewable energy is thought to be better for the economy in the long run. This is because it can help to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, which contribute to climate change. Additionally, renewable energy sources tend to create more jobs than fossil fuel extraction does. This is because renewable energy often relies on technologies that require more manpower to install and maintain.
The world is clearly at a crossroads when it comes to energy. On the one hand, we have traditional fossil fuels like coal and oil, which are dirty, polluting, and slowly running out. On the other hand, we have renewable energy sources like solar and wind power, which are clean, sustainable, and endlessly renewable. The future of energy is clearly moving towards renewables, but the transition will not be easy. We need to invest in renewable energy now if we want to secure a clean and prosperous future for ourselves and our planet.
Related Posts
Suggestions or feedback?
MIT News | Massachusetts Institute of Technology
- Machine learning
- Social justice
- Black holes
- Classes and programs
Departments
- Aeronautics and Astronautics
- Brain and Cognitive Sciences
- Architecture
- Political Science
- Mechanical Engineering
Centers, Labs, & Programs
- Abdul Latif Jameel Poverty Action Lab (J-PAL)
- Picower Institute for Learning and Memory
- Lincoln Laboratory
- School of Architecture + Planning
- School of Engineering
- School of Humanities, Arts, and Social Sciences
- Sloan School of Management
- School of Science
- MIT Schwarzman College of Computing
MIT hosts debate on pros and cons of fossil-fuel divestment
Press contact :, media download.

*Terms of Use:
Images for download on the MIT News office website are made available to non-commercial entities, press and the general public under a Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial No Derivatives license . You may not alter the images provided, other than to crop them to size. A credit line must be used when reproducing images; if one is not provided below, credit the images to "MIT."

Previous image Next image
On Thursday, MIT held an event that Maria Zuber, vice president for research, described in welcoming remarks as likely “a first-of-its-kind occurrence: a serious, campus-wide debate on the pros and cons of fossil-fuel divestment, sponsored by the university senior administration that is being petitioned.”
The debate, held in Kresge Auditorium before hundreds of attendees from MIT and elsewhere, featured two teams of experts, in a classical debate format, who addressed the contentious issue of whether MIT should shed its investments in fossil-fuel companies. It was moderated by Tony Cortese of the Intentional Endowments Network, a group that helps universities align their investments with their values and goals.
“This is not a popularity contest; we’re not counting votes; there’s no applause meter,” Zuber said. “We’re not declaring winners and losers. We are here to learn and to understand both sides of a complex question.”
The two teams — each consisting of an MIT faculty member, a professor from another institution, and an executive from an investment firm — quickly found common ground on several major points. All six participants agreed on the seriousness of climate change, and the need for strong actions to curb greenhouse-gas emissions; they also agreed that one of the most important policy measures to address the issue would be the imposition of a price on the use of fossil fuels, such as a carbon tax. But they differed on whether an MIT divestment from fossil-fuel companies would help address climate change in any meaningful way.
John Sterman, the Jay W. Forrester Professor in Computer Studies at the MIT Sloan School of Management, said in an opening statement for the pro-divestment side that an MIT divestment is “not only right, it is vital to support the policies that are needed to prevent potentially catastrophic climate change. Further, divestment is necessary to preserving the integrity of MIT and our commitment to the scientific method.”
“The stakes are immense,” Sterman said, citing overwhelming evidence that if present trends in the use of fossil fuels continue unabated, “the result would be nothing short of a holocaust.”
MIT “must take a stand,” Sterman said, adding that fossil-fuel companies “continue to fund deniers, undermine the science, confuse the public, and delay action — actions antithetical to the values of MIT. The integrity of the Institute is at stake. … We cannot say that we care about climate change while we invest in an industry that threatens our prosperity, our health, and our lives.”
Responding for the anti-divestment team, Timothy Smith, director of shareholder engagement at the investment firm Walden Asset Management, said that while he agrees with Sterman’s assessment of threat that climate change poses, “I don’t think that automatically leads to only one conclusion — the sale of stock being the approach that you must take.” And Frank Wolak, a professor of economics at Stanford University, added that there’s a reason fossil-fuel companies produce coal and oil: “It’s because we demand them, to heat our homes, to drive our cars, to fly in our airplanes.”
“Divestiture does nothing to address that problem,” Wolak said. “As long as demand is still there for the fossil fuels, the greenhouse-gas emissions will exist, regardless of who owns the assets.”
“We all could agree that divestiture is a symbolic gesture that, sadly, will have no measurable impact on global greenhouse gas emissions, or the behavior of companies that produce fossil fuels,” Wolak added. He pointed out that the global capitalization of the fossil-fuel industry amounts to $60 trillion; MIT’s entire endowment of $12.4 billion represents just 0.02 percent of that, and even the endowments of all U.S. universities combined are less than 1 percent of that figure. The only real effect of divestiture, Wolak said, would be that “different people would be earning the profits.”
Rather than divesting, Wolak argued, MIT “can do much more to actually address the global climate challenge.” Noting the widespread agreement that setting a price on carbon is the most effective approach to reducing greenhouse-gas emissions, he said that actually designing and implementing such a mechanism is a challenge worthy of MIT, and one that could be adopted and tested at a campus level to set an example.
Naomi Oreskes, a professor of the history of science at Harvard University, responded for the pro-divestment team that even if divestment is a symbolic action, “Symbols matter, because they signal our intent, and they invite other people to join in our intent.” She said that while all six panelists agree on the importance of carbon pricing, it’s a false dichotomy to suggest that the two actions are in opposition: Divestment, she said, can be part of a political strategy to build public pressure that could lead to a carbon tax.
Citing figures from the International Energy Agency indicating that construction of fossil-fuel infrastructure should cease by 2017 to avert a climate crisis, Orestes said, “We must stop investing in the industries that are driving us toward crisis.”
Brad Hager, the Cecil and Ida Green Professor in Earth and Planetary Sciences and director of MIT’s Earth Resources Laboratory, arguing against divestment, said that not all fossil fuels are alike, and not all companies in that sector are alike. For example, he said, natural gas is less environmentally damaging than coal, and the shale gas revolution has actually reduced the nation’s carbon footprint. “We need to apply some discrimination, and that’s what’s wrong with this divestment movement: It throws everything out rather than making thoughtful choices about what is good, and what we should keep and what we should get rid of,” Hager said.
Smith, the investment-firm executive who argued against divestment, suggested that stockholder involvement — exercising the rights to make shareholder resolutions and demands for changes from companies — could be more effective than divestment in compelling corporate change. This could be especially effective, he said, if MIT were to combine with other institutional investors to form a bloc to bring pressure on fossil-fuel companies, such as by urging them to invest more in renewable energy alternatives.
Don Gould, president and chief investment officer for Gould Asset Management, arguing in favor of divestment, agreed that shareholder engagement can be a useful mechanism. However, he added: “It’s questionable to expect a coal producer to stop producing coal because of shareholder engagement.”
Gould said that divestment is not really aimed at fossil-fuel companies themselves. “It’s aimed at the policymakers who have to formulate a policy that will provide for a habitable planet,” he said.
Gould is also a trustee of Pitzer College in California, which last year committed itself to — and achieved — full divestment from fossil fuels. Divestment, he said, “aligns an institution’s actions with its values. A university actively committed to engineering a sustainable future for humanity should not be betting its endowment dollars on the opposite outcome. It is a conflict of interest, plain and simple.”
Hager said that as a researcher who has worked with fossil-fuel companies, he has found that “their positions on global warming and the environment span a broad spectrum. Some have an irresponsible cowboy mentality, plundering and laying waste. … Others are much more invested in a sustainable future. For example, Shell leadership is actively promoting a price on carbon, preferring the stable environment that a carbon price would provide.”
Yesterday’s debate was the fourth in a series of open-forum spring events as part of the MIT Climate Change Conversation; next up is a six-date listening tour around campus. The Committee on the MIT Climate Change Conversation will incorporate feedback from these events into a final report to the MIT administration at the end of the academic year. The report will provide a short list of possible actions, in unranked order, with associated pros and cons, and will be released to the MIT community for comment. The report, along with all additional input, will collectively provide a sense of the community’s point of view to MIT’s senior leadership, and will inform its decision-making.
Share this news article on:
Press mentions.
Jennifer Switzer reports for The Tech on MIT’s fossil-fuel divestment debate. “Divestment has been one of the most strongly debated potential actions of academic institutions in recent times,” said Prof. Roman Stocker, head of the MIT Climate Change Committee. “We decided: Why don’t we tackle it head-on?”
MIT hosted a debate between two panels of experts last week to discuss whether the Institute should divest its endowment from fossil-fuel companies, reports Kyle Alspach for BostInno . Each side included “an MIT faculty member, a professor from another institution and an executive from an investment firm.”
Scientific American
Benjamin Hulac reports for Scientific American on a debate held at MIT on whether the Institute should divest its endowment from fossil-fuel companies. The forum included a panel of experts arguing each side of the issue and responding to questions from the audience.
Previous item Next item
Related Links
- Video: "Should MIT Divest? A Debate on Fossil Fuel Investment"
- MIT Conversation on Climate Change
Related Topics
- Climate change
- Special events and guest speakers
- Fossil fuels
- Sustainability
- Environment
Related Articles

To divest, or not to divest?

Communicating climate change: Focus on solutions

How can MIT be a game-changer on climate?
More mit news.

MIT Corporation elects 10 term members, two life members
Read full story →

Diane Hoskins ’79: How going off-track can lead new SA+P graduates to become integrators of ideas

Chancellor Melissa Nobles’ address to MIT’s undergraduate Class of 2024

Noubar Afeyan PhD ’87 gives new MIT graduates a special assignment

Commencement address by Noubar Afeyan PhD ’87

President Sally Kornbluth’s charge to the Class of 2024
- More news on MIT News homepage →
Massachusetts Institute of Technology 77 Massachusetts Avenue, Cambridge, MA, USA
- Map (opens in new window)
- Events (opens in new window)
- People (opens in new window)
- Careers (opens in new window)
- Accessibility
- Social Media Hub
- MIT on Facebook
- MIT on YouTube
- MIT on Instagram
- About Us 👨👩👧
Advantages and Disadvantages of Biofuels
Biofuels have emerged as an alternative to fossil fuels in recent years due to their potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and promote the use of renewable energy. Their main perk is that they are produced from organic materials which replenish seasonally. These materials include plant matter such as corn, soybeans, and sugarcane, as well as animal fats and agricultural waste.
Biofuels are an alternative to fossil fuels (oil, natural gas, and coal). Fossil fuels are non-renewable and release greenhouse gases during their combustion. Compared to fossil fuels, biofuels are considered to be a more environmentally friendly and sustainable energy source due to their renewability and lower emissions of greenhouse gases during burning. But is this energy source such a positive news as it seems at the first glance?
While biofuels certainly have many potential benefits, there are also a number of challenges and trade-offs associated with their production and long-term use at larger scale. Let’s explore the pros and cons of biofuels in order to better understand their future potential as our energy source.
What are biofuels and where are they used the most?
There are several different types of biofuels: liquid biofuels such as bioethanol and biodiesel; solid biofuels like wood pellets, fuelwood, or animals waste; and biogas like landfill gas.
You may think that biofuels are used mainly in transport, but that’s not all. There is a variety of applications, including electricity generation, and heating. In the transport sector, they are often used as a substitute for gasoline and diesel fuel. For example, bioethanol, which is produced from plant matter from corn, sugarcane or rapeseed, can be blended with gasoline to create a fuel called E10, which contains 10 percent of bioethanol and 90 percent of gasoline.
Biodiesel, that is produced from animal fats or vegetable oils, can be used as a replacement for diesel fuel in heavy-duty work vehicles like trucks or buses. Biogas is used predominantly in the electricity sector. This fuel is made from the decomposition of organic matter. Biofuels are also used with success for heating buildings. During their combustion in furnaces and boilers, they produce heat just like fossil fuels do.
Biofuels are a renewable resource, so they can be replenished over time. Fossil fuels , on the other hand, are non-renewable, which means they are finite and will eventually run out. The use of biofuels can therefore help to reduce our reliance on fossil fuels and contribute to a more sustainable energy system.
What are the advantages of biofuels over fossil fuels?
The benefits of biofuels compared to fossil fuels depend on a variety of factors that need to be considered when used on a large scale. These factors are mainly taken into account under the section of disadvantages and will help you understand the complexity of the situation when it comes to finding new energy sources that would replace fossil fuels entirely.
Let’s have a look at the main advantages of biofuels over fossil fuels:
#1 Renewable fuel of biological origin
Biofuels replenish over time, whereas fossil fuels are non-renewable and will eventually run out. By being renewable, they are a type of fuel that could potentially support sustainable development by promoting the use of renewable energy and reducing our impact on the environment.
As an alternative source of energy, they also reduce our reliance on fossil fuels, minimizing or emitting negative effects that come with the use of this polluting and limited source that has been powering our economies since the industrial revolution but has also brought about increased pollution levels and emissions of greenhouse gases. Which brings us to the second advantage…
#2 Lower carbon footprint
The production and use of biofuels generates significantly less greenhouse gas emissions than the production and use of highly polluting fossil fuels.
Biofuels are considered carbon neutral because the carbon dioxide emitted when they are burned is offset by the carbon dioxide that was absorbed by the plants during photosynthesis. What does it mean? The organic material that makes biofuels is made of carbon dioxide absorbed by plants from the atmosphere as they grew. When the plant biomass is burned, it releases this absorbed carbon dioxide back into the atmosphere.
The use of biofuels can help to reduce our reliance on fossil fuels and contribute to a more sustainable energy system. However, it is important to carefully evaluate the environmental impacts of biofuels in order to ensure that they are being used in the most sustainable and responsible way possible.
#3 Improved air quality due to lower emissions
The burning of biofuels generates fewer air pollutants than the burning of fossil fuels, which can improve air quality and public health.
The burning of fossil fuels generates a variety of air pollutants, including carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter. These air pollutants can cause respiratory and cardiovascular problems, as well as damage to crops, forests, and other ecosystems.
Biofuels, on the other hand, are produced from biological materials, which are generally considered to be cleaner-burning than fossil fuels. Just consider: biodiesel is a biodegradable fuel that releases less emissions when burned. Its application in transport industry would cut a big part of the air pollution originating from this growing industry [2] .
According to studies, the levels of carbon dioxide emissions and particulate matter are reduced with biofuels, however, the nitrogen oxides are slightly higher than at fossil fuels [1] .
#4 Reduction of reliance on finite fossil fuels
By using biofuels as an alternative energy source, we can reduce our reliance on fossil fuels, which can help to reduce our impact on the environment and contribute to a more sustainable energy system that is more locally based.
This way biofuels also decrease our dependence on foreign oil, which helps to reduce our trade deficit and improve energy security on a country level.
#5 Locally sourced and good for local economy
In many cases, biofuels can be produced from locally available resources. The production, distribution, and use of biofuels can create jobs in a variety of sectors that will support the production and use of this sustainable alternative. The transition to biofuels will affect especially economic sectors of agriculture, manufacture, reprocessing, recycling, and transportation.
The development of a biofuels industry has great potential to stimulate economic development in rural areas with less job possibilities by creating new markets for crops and other agricultural products. Except providing new livelihood opportunities for local families, they could also represent a sustainable and innovative option that will contribute to rural development.
#6 Sustainable energy source and falls within a circular economy scheme
The development of new biofuels technologies can support innovation and drive economic growth in a sustainable way.
As an alternative source of energy obtained from renewable and biological material, these fuels can be produced using waste materials. This is a great news for sustainable future planning since the use of biofuels is in agreement with the development of a circular economy by closing the loop on resource use.
#7 Improved energy security for individual countries
Biological source of energy can be produced in many cases from locally available resources, which in turn decreases our reliance on imported fossil fuels that are even becoming rarer.
Anything that is local comes with an extra benefit. It has a lower cost for the environment, as it doesn’t have to be brought over a long distance, releasing carbon dioxide emissions. But it is even more economical solution in terms of paying a cost set by international political agreements.
The use of biofuels improves energy security of individual countries by diversifying the energy mix and reducing reliance of countries on a single energy source.
#8 Environmentally friendly energy source
When done right and well-regulated, the production of biofuels has potential to actually support local biodiversity by promoting the growth of crops that are providing support to soils and leave soils less prone to erosion.
An example of such practice could be plantation of diverse prairie grass mixtures. They are perennial. They cover the soil year-round, and support biodiversity of small soil fauna and mammals by providing nutrients. Additionally, the grass mix actually helps to offset carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. The green biomass from these grasses can be harvested regularly for the use as a biofuel.
If biofuels are obtained from sustainable farming of reclaimed lands, their production may be much less polluting in terms of not degrading land or freshwater resources compared to fossil fuels. Restored and gently maintained land will yield enough biomass for biofuel production at lower need for synthetic substances, such as pesticides or fungicides. Higher the diversity of plants, better natural resistance to diseases and pests. This removes the need for application of chemicals and the risk of runoff and water contamination is simply lower.
What are the disadvantages of biofuels?
There are a few potential negative effects of biofuels on the environment and economy that need to be considered when forming an opinion about their use in the future. Let’s start with one of the main arguments against the use of biofuels.
#1 Land use changes and land grabbing
The production of biofuels often leads to land use changes, such as the conversion of natural habitats to cropland. Biofuels are often produced from crops such as corn, sugarcane, and palm oil, which can be grown on a large scale. To meet the increasing demand for biofuels, farmers may convert natural habitats, such as forests and grasslands, into croplands.
Land use change leads to the loss of biodiversity, especially in many places where native ecosystems were previously untouched, as well as increased greenhouse gas emissions from the conversion of carbon-rich ecosystems.
Additionally, biofuel production can also lead to changes in land use patterns, as farmers may shift from growing food crops to biofuel crops in order to take advantage of government incentives or higher prices for biofuel crops. This can lead to food insecurity in local communities and increase in food prices.
#2 Competition for resources with food production
The production of biofuels can in some cases compete with food production in several ways.
One way is through direct competition for land, water, and other resources. For example, if crops grown for biofuels are planted on land that could be used for growing food crops. Unfortunately, in some cases, it is more advantageous for farmers to decide in favor of biofuel crops over food crops, as they sell at higher prices and some monocrops may be easier to cultivate and harvest than diverse food crops.
Additionally, using crops for biofuels can also lead to a decrease in the availability of food, as well as an increase in the cost of food.
Another way in which biofuel production can compete with food production is through the use of food crops, such as corn, as feedstocks for biofuels rather than spending resources on processing corn for human consumption. In the long term, this may lead to a decrease in food availability, nutritional quality of available foods, diversity of food crops, and possibly endanger food security. This is a serious contra argument to consider especially with climate change already shifting our ability to grow crops in certain areas.
The production of biofuels can compete with food production for land and resources, which can lead to higher food prices .
#3 Water consumption
Biofuels can require significant amounts of water for irrigation and processing, which can lead to water depletion and competition with other water uses, including even water for households, or for food production.
The amount of water used to grow biofuels varies depending on the type of biofuel, the location, and the farming practices used. However, some biofuel crops, such as corn and sugarcane, are considered to be water-intensive and their production requires large amounts of irrigation.
For example, it is estimated that growing one hectare of corn for biofuels takes between 3,000 and 5,000 cubic meters of water per year. Other biofuel crops, such as switchgrass and miscanthus, are considered to be more water-efficient and need less water for irrigation.
Additionally, the amount of water used in biofuel production is also affected by the specific farming practices used. If farmers are incentivized to plant crops that are not well suited for the location, they may end up needing more water than any other crops would.
#4 Pesticide pollution
This may sound contradictory to the advantages of biofuels mentioned earlier in this article. But we must realize that nothing in life is straightforward and applicable to all situations. Biofuel production may decrease the pesticide pollution if done sustainably and right, especially if perennial polycultures are involved.
On the other end, if previously untouched natural ecosystem is transformed into a monoculture field than there is a high chance that pesticide pollution will appear and will affect the surrounding environment.
Some biofuel crops, such as corn and sugarcane, are considered to be high-input crops not only when it comes to water demand but even when it comes to the use of pesticides to protect them against insects, weeds, and diseases. However, other biofuel crops, such as switchgrass and miscanthus, are considered to be low-input crops and need less pesticides.
#5 Economic impacts
The development of a biofuels industry can have both positive and negative economic impacts, depending on the specific circumstances. For example, the production of biofuels can create jobs and stimulate economic development, but it can also lead to higher food prices and competition with other industries for resources.
Additionally, biofuel production can also lead to changes in land use patterns, which can displace local communities and increase the cost of land. Furthermore, biofuels can also be more expensive to produce than fossil fuels, which can make them less competitive in the market and discourage investment in the biofuel industry.
It’s worth noting that the negative effects of biofuels can be mitigated by adopting appropriate policies and regulations, such as implementing sustainable land use practices, supporting research and development of advanced biofuels, and promoting the use of biofuels in a way that doesn’t compete with food production.
#6 Higher production costs
The production of biofuels can be more expensive than the production of fossil fuels due to the costs of growing and processing the feedstocks.
The cost of biofuel production can vary depending on the type of biofuel, the location, and the specific technologies used. In general, biofuels are more expensive to produce than fossil fuels on a per-unit energy basis. This is due to the fact that biofuels are derived from renewable resources, such as crops and waste materials, which is more expensive to grow and process than fossil fuels.
However, the cost of biofuel production has been decreasing in recent years due to advancements in technology and economies of scale. Additionally, the cost of biofuels is affected by government policies and subsidies.
It’s also worth noting that the cost of fossil fuels fluctuates greatly depending on the market and political situation. Biofuels’ costs are affected by these fluctuations, so when the price of fossil fuels is high, biofuels can be more cost-competitive.
#7 Limitations in large-scale applications
The character of biofuels when they are only produced from certain feedstocks, such as specific crops, like rapeseed, or certain waste materials, means that they may be in limited supply. This factor could potentially limit the scale of biofuel production when it comes to upscaling their use.
At the same time, biofuels generally have a lower energy density per unit of mass than fossil fuels such as gasoline or diesel. This means that more biofuel is required to produce the same amount of energy as a smaller amount of fossil fuel.
The lower energy density means that transportation and storage of biofuels could be more challenging and may increase the cost of using biofuels as the main fuel source.
#8 Limited compatibility
At the moment, biofuels are not compatible with all types of vehicles and equipment. Compatibility refers to the ability of a fuel to be used in existing infrastructure and equipment without modification or damage. Biofuels are often not compatible with traditional fossil fuel infrastructure because they have different chemical and physical properties.
For example, bioethanol and biodiesel have a higher tendency to absorb moisture than fossil fuels, which can cause corrosion in fuel systems and engines. Additionally, they have a higher viscosity than fossil fuels, which can eventually lead to clogging or damage of fuel filters, injectors, and pumps. The widespread use of biofuels in daily operations requires different storage and handling equipment, engine modifications, and adapted fuel delivery systems.
This lack of compatibility is one of the reasons that biofuels have not been widely adopted as a replacement for fossil fuels. In order for biofuels to become widely used, researchers are working on developing biofuels that are more similar in properties to fossil fuels.
Are biofuels sustainable in a long-term?
Biofuels could be a sustainable energy source over the long term if they are produced and used in a responsible and well-planned manner when all the pros and cons of biofuels versus fossil fuels are considered. In the planning stage, it is important to carefully evaluate the potential impacts of different biofuel production methods and prefer practices that minimize negative environmental and economic impacts.
One of the key challenges in making the use of biofuels more sustainable over the long term is ensuring that they are sourced from feedstocks that have a low carbon footprint and are not in competition with food production . This can be achieved through the use of waste materials and non-food crops for biofuel production, as well as the adoption of sustainable practices such as minimal tillage and the use of cover crops.
It is also important to consider the full life cycle of biofuels, from production to end-use to ensure that they are used in the most sustainable and efficient manner possible. This may involve the use of advanced technologies.
Are biofuels reliable?
The reliability of biofuels as an energy source depends on a variety of factors, such as the feedstocks used, the production methods employed, and the end-use of the biofuels. In general, biofuels can be a reliable energy source if they are produced and used in a responsible and sustainable manner.
One potential challenge to the reliability of biofuels is their limited availability, as they are only produced from certain feedstocks (as mentioned in the disadvantages section). This can limit the scale of biofuel production and make it more vulnerable to disruptions such as droughts, pests, and price fluctuations.
Another challenge is the limited energy density of biofuels. This means they require more space to store the same amount of energy than fossil fuels. This can make them less practical for some applications, such as long-distance transportation.
Overall, the reliability of biofuels as an energy source will depend on the specific circumstances of their production and use.
Was this article helpful?
About greentumble.
Greentumble was founded in the summer of 2015 by us, Sara and Ovi . We are a couple of environmentalists who seek inspiration for life in simple values based on our love for nature. Our goal is to inspire people to change their attitudes and behaviors toward a more sustainable life. Read more about us .
- Agriculture
- Biodiversity
- Deforestation
- Endangered Species
- Green Living
- Solar Energy
Sliding Sidebar

The Pros And Cons Of Solar Energy

Let us explore the advantages and disadvantages of solar energy and find a feasible and logical explanation for whether it is a viable option for use in your area.
We will further investigate any challenges in the installation process or environmental setbacks. In this blog, you will find answers to your questions about the pros and cons of solar energy, setup costs, whether the system is worth the initial cost, and much more!
What Are The Top Pros And Cons Of Solar Energy?
Since the invention of electricity in the late 1870s, fossil fuels have been the primary source of electricity generation. However, fossil fuels are depleting daily.
Today’s technological advancements enable science to discover alternative methods for electricity generation from renewable sources, thereby contributing to preserving fossil fuel reserves for future generations.
Solar energy is one of the most popular renewable energy sources, and its energy-generating capacity has multiplied in the last two to three decades. Solar energy offers many benefits compared to traditional fuel-generated electricity.
When discussing solar panels’ top advantages and disadvantages, we can state that solar energy is a renewable, nonpolluting, and clean source of electricity generation.
However, the biggest drawback of solar energy is its relatively low efficiency, typically ranging from 15-20%. On the other hand, a single solar cell can offer an efficiency of approximately 40%, significantly lower than using fuels as a source of electricity.
Benefits of Solar Energy: Advantages
Electricity is now essential for domestic households, manufacturing, and other industrial sectors. Other fuel sources generate energy at a higher cost than solar, contributing to environmental pollution and degradation.
Here are a few basic but important advantages of solar energy that can help you transform your home by opting for this green energy source:
- Renewability: Solar energy is a renewable energy source because it derives its power from the sun’s rays, which are either eternal or do not deplete with use.
- Environment-Friendly: Solar energy is a green and clean energy source, as no pollutants or harmful chemicals are released when converting solar energy to electrical energy.
- Reduced electricity bills: Solar energy can be used as an alternative to traditional electricity from fossil fuels, significantly reducing and even eliminating electricity bills over time.
- Low Maintenance Cost: Solar power system maintenance is extremely low, and once correctly installed, it can last a long time.
- Generates noise-free energy : Solar power plants generate completely noise-free energy, whereas thermal power plants and even renewable hydropower plants produce a lot of unnecessary noise.
These points can influence people to consider solar power systems as an energy source for their homes or industries.
Cons Of Solar Energy: Disadvantages
Sometimes, looking on the bright side is good but can also have challenges. The cons of solar energy are the other probable aspects you need to look into to determine whether you need solar panels for your home.
Some cons of solar energy are as follows:
- High cost: The initial installation cost for a good solar power system setup is relatively high. For an average household in America, solar power systems can cost about $18,000–$20,000.
- Manufacturing Hazards: While solar energy generates clean and green energy, manufacturing solar panels can be hazardous. Large-scale production of solar panels results in a significant amount of fossil fuels and plastic waste, which is not environmentally friendly.
- Low-efficiency rate: Solar panels’ efficiency rate tends to be below 20%, which could be a better energy conversion efficiency. Although solar cells can achieve an efficiency rate of up to 40%, it’s significantly lower than any other energy conversion method.
- Space Requirement: Solar energy systems also need space for setup, with factors such as a good supply of sunlight throughout the day, easy access for cleaning and maintenance purposes, and a particular type of material in the case of rooftop panel setup.
Here are some things to consider when weighing the pros and cons of solar energy before deciding whether a solar energy system is right for you.
Who Should Use Solar Energy?
People worldwide use solar energy, one of the cleanest and most domesticated sources of electrical energy generation. But when we consider the complete scenario, a question arises: Who exactly is using solar energy, or who should use solar energy?
Well, the answer to this question is quite simple, based on the advantages and disadvantages of solar energy. Before choosing solar energy as an option for energy generation, the right user would consider its positive and negative aspects.
- As solar power setup requires ample space and a high initial cost, only a person with that much land or money would opt to set up a solar power system.
- Furthermore, individuals who care about the environment may consider that solar energy generates zero emissions, making it an environmentally friendly choice. The reduced electricity bills and low maintenance costs can lead to potential customer generation in the solar energy field.
Solar energy’s pros and cons would ultimately help govern and be a deciding factor in answering the question, “Who should use solar energy?”
Is Solar Energy Worth The Cost?
After conducting extensive research and determining that the benefits of solar energy outweigh the cons, you may be wondering about the associated costs and whether the system is worth the investment.
The answers to these questions can depend on many factors. For instance, if you only consider the initial or installation cost of the solar panel, the investment may seem insignificant. However, a reduced electricity bill would appear to be a wise and cost-effective investment in the long run.
The high return on investment is an advantage of solar panels, for which people usually ignore the initial cost.
Also, it’s important to recognize the incredibly positive impact of this energy on the environment. When we consider its renewable nature and its status as one of the most environmentally friendly sources of energy production, the cost becomes less of a concern in decision-making.
Reduced bills, government schemes and incentives for solar setup, and even the possibility of giving the surplus energy to the grid at reverse electricity rates make up for the high initial cost, making solar energy worth every penny you invest.
Are Solar Panels Worth It For Your Home?
The average American household consumes approximately 900 kWh per month or 30 kWh per day of energy. This can lead to a monthly bill of approximately $150–$180 and an annual expense of almost $2000.
Initially, the average cost of setting up a solar power system is approximately $15,000. Still, with government aid and incentives, the investment tax credit allows for a deduction of approximately 30%, bringing the total cost down to about $1000.
Also, you will have a renewable, clean energy source that even saves you an additional $2000 yearly, which you used to pay as your electricity bill. This would lead to recovering your initial cost in about five years and having an infinite free electricity supply for a lifetime, with minimal maintenance cost.
Thus, from a broader perspective, solar panels are worth it for your home or industry, not only in terms of money but also in terms of a cleaner and safer future.
Frequently Asked Questions (Faqs)
- Is solar energy a non-polluting form of energy?
Ans. No toxins are emitted in the conversion process of solar energy to electrical energy, although the manufacturing of solar cells generates large amounts of plastic waste and some toxins.
- Can solar energy completely replace my earlier electricity source?
Ans. Solar can certainly be an excellent alternative for your daily electricity needs. Still, you cannot completely rely on it because it depends on the daily sun hours you get, which can vary easily if your region’s weather is not good.
- What are the five advantages of solar energy?
Ans. Solar energy is a renewable, non-polluting, noise-free, affordable, and low-maintenance technology that is one of the most common electricity generation methods and can even be set up on a very small scale.
- What are the negatives of solar energy?
Ans. Solar energy is a clean form of energy, but its installation costs are pretty high. Also, producing solar cells can produce large quantities of plastic and other degenerate waste. Also, the efficiency rate is relatively low compared to any other traditional method of electricity generation.
- Is solar energy a good choice for my house?
Ans. A solar energy setup requires substantial space and incurs significant installation costs. Furthermore, before installation, you must thoroughly examine certain aspects of the roof’s material and other items.
You can install a solar energy setup if you have checked and verified all these factors.
To set up a solar energy system at home, you must understand its advantages and disadvantages. Before installing a solar energy system at your home or business, learn more about solar energy’s advantages and disadvantages and several other related aspects.
We at Understand Solar provide everything about solar energy, different kinds of solar panel systems, government aid for solar plant setup in the USA, and much more on our website.
You can also submit questions and get answers from our team of experts about anything you need to know about solar energy.
Related Posts
How Many Solar Panels Do I Need For My Home In 2024?
Ground Mount Solar Panels: All You Need To Know
Net Energy Metering (NEM) 3.0: What It Means for Homeowners in California
How to Choose a Solar Installer Near You
- Previous post
How to invest in the solar industry
Advertiser disclosure.
We are an independent, advertising-supported comparison service. Our goal is to help you make smarter financial decisions by providing you with interactive tools and financial calculators, publishing original and objective content, by enabling you to conduct research and compare information for free - so that you can make financial decisions with confidence.
Our articles, interactive tools, and hypothetical examples contain information to help you conduct research but are not intended to serve as investment advice, and we cannot guarantee that this information is applicable or accurate to your personal circumstances. Any estimates based on past performance do not a guarantee future performance, and prior to making any investment you should discuss your specific investment needs or seek advice from a qualified professional.
How We Make Money
The offers that appear on this site are from companies that compensate us. This compensation may impact how and where products appear on this site, including, for example, the order in which they may appear within the listing categories, except where prohibited by law for our mortgage, home equity and other home lending products. But this compensation does not influence the information we publish, or the reviews that you see on this site. We do not include the universe of companies or financial offers that may be available to you.
Editorial disclosure
All reviews are prepared by our staff. Opinions expressed are solely those of the reviewer and have not been reviewed or approved by any advertiser. The information, including any rates, terms and fees associated with financial products, presented in the review is accurate as of the date of publication.
- Share this article on Facebook Facebook
- Share this article on Twitter Twitter
- Share this article on LinkedIn Linkedin
- Share this article via email Email

- • Investing
- • Wealth management
- Connect with Brian Baker, CFA on Twitter Twitter
- Connect with Brian Baker, CFA on LinkedIn Linkedin
- Get in contact with Brian Baker, CFA via Email Email

- Connect with James Royal, Ph.D. on Twitter Twitter
- Connect with James Royal, Ph.D. on LinkedIn Linkedin
- Get in contact with James Royal, Ph.D. via Email Email
The Bankrate promise
At Bankrate we strive to help you make smarter financial decisions. While we adhere to strict editorial integrity , this post may contain references to products from our partners. Here's an explanation for how we make money .
Founded in 1976, Bankrate has a long track record of helping people make smart financial choices. We’ve maintained this reputation for over four decades by demystifying the financial decision-making process and giving people confidence in which actions to take next.
Bankrate follows a strict editorial policy , so you can trust that we’re putting your interests first. All of our content is authored by highly qualified professionals and edited by subject matter experts , who ensure everything we publish is objective, accurate and trustworthy.
Our investing reporters and editors focus on the points consumers care about most — how to get started, the best brokers, types of investment accounts, how to choose investments and more — so you can feel confident when investing your money.
The investment information provided in this table is for informational and general educational purposes only and should not be construed as investment or financial advice. Bankrate does not offer advisory or brokerage services, nor does it provide individualized recommendations or personalized investment advice. Investment decisions should be based on an evaluation of your own personal financial situation, needs, risk tolerance and investment objectives. Investing involves risk including the potential loss of principal.
Editorial integrity
Bankrate follows a strict editorial policy , so you can trust that we’re putting your interests first. Our award-winning editors and reporters create honest and accurate content to help you make the right financial decisions.
Key Principles
We value your trust. Our mission is to provide readers with accurate and unbiased information, and we have editorial standards in place to ensure that happens. Our editors and reporters thoroughly fact-check editorial content to ensure the information you’re reading is accurate. We maintain a firewall between our advertisers and our editorial team. Our editorial team does not receive direct compensation from our advertisers.
Editorial Independence
Bankrate’s editorial team writes on behalf of YOU – the reader. Our goal is to give you the best advice to help you make smart personal finance decisions. We follow strict guidelines to ensure that our editorial content is not influenced by advertisers. Our editorial team receives no direct compensation from advertisers, and our content is thoroughly fact-checked to ensure accuracy. So, whether you’re reading an article or a review, you can trust that you’re getting credible and dependable information.
How we make money
You have money questions. Bankrate has answers. Our experts have been helping you master your money for over four decades. We continually strive to provide consumers with the expert advice and tools needed to succeed throughout life’s financial journey.
Bankrate follows a strict editorial policy , so you can trust that our content is honest and accurate. Our award-winning editors and reporters create honest and accurate content to help you make the right financial decisions. The content created by our editorial staff is objective, factual, and not influenced by our advertisers.
We’re transparent about how we are able to bring quality content, competitive rates, and useful tools to you by explaining how we make money.
Bankrate.com is an independent, advertising-supported publisher and comparison service. We are compensated in exchange for placement of sponsored products and services, or by you clicking on certain links posted on our site. Therefore, this compensation may impact how, where and in what order products appear within listing categories, except where prohibited by law for our mortgage, home equity and other home lending products. Other factors, such as our own proprietary website rules and whether a product is offered in your area or at your self-selected credit score range, can also impact how and where products appear on this site. While we strive to provide a wide range of offers, Bankrate does not include information about every financial or credit product or service.
As more countries seek to move away from fossil fuels such as oil and natural gas, renewable energy sources, such as solar, are poised to benefit from increased investment. Solar energy could provide 45 percent of the electricity in the United States by 2050 if the energy system is fully decarbonized, up from 3 percent in 2020, according to the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL).
This kind of growth holds enormous potential for investors, but there are also risks to be aware of. Here’s what you need to know before investing in solar energy.
The rise of solar power
You might think that solar energy is a relatively new phenomenon, but using the sun as a source of energy actually dates back to the 7th Century B.C. when a magnifying glass was used to concentrate the sun’s rays to make a fire and burn ants. It wasn’t until 1767 that the first solar collector was created thanks to Swiss scientist Horace de Saussure. About 100 years later, French mathematician August Mouchet proposed solar-powered steam engines and worked with his assistant over the next two decades to build them.
Throughout the 1900s, research on solar power increased, leading to new discoveries and advancements. In 1993, Pacific Gas & Electric installed the first grid-supported photovoltaic system in California, which was the first distributed power installation. In 1998, a remote-controlled, solar-powered airplane set an altitude record of 80,000 feet in California.
Going forward, solar energy will be an important component of renewable energy . New buildings will be built using energy-efficient designs and technologies so that they won’t have a need for non-renewable energy. An increasing amount of the electricity needs of the U.S. will also be met using solar energy. Cars and airplanes may also find ways to use solar energy for their power.
Breakdown of the solar industry:
Several different types of companies at various points in the process make up the solar industry, and here’s what the main companies are involved in today:
- Manufacturing components and solar panels – These companies produce solar panels and components that are used to convert the sun’s energy into electricity.
- Installation of solar panels – These companies are involved in the installation of solar panels, often at a commercial scale and may provide financing solutions in addition to their installation offerings.
- Solar facilities – These companies operate facilities that generate solar energy and may also be involved in other renewable energy sources such as wind or hydroelectric plants.
Solar investments to watch
It can be difficult to know how to start investing , but you’ll generally have to choose between individual stocks and funds that hold baskets of companies.
Here are a few of the most popular.
Solar stocks
First Solar (FSLR) – First Solar is a leading manufacturer of advanced solar modules, which it sells to a variety of customers including utility companies, distributors, and commercial and industrial buildings. The company expects to benefit from increased solar panel capacity over the next five years and beyond.
- Market cap: $28.9 billion
- 2023 sales: $3.3 billion
Brookfield Renewable Partners (BEP) – Brookfield Renewable Partners is one of the largest renewable power platforms in the world and operates hydroelectric, wind, solar and storage facilities in North America, South America, Europe and Asia. Brookfield generates strong cash flow and shares that with investors in the form of a dividend , which it hopes to grow by 5 to 9 percent each year.
- Market cap: $18.9 billion
- 2023 sales: $5.0 billion
SolarEdge Technologies (SEDG) – SolarEdge Technologies is a manufacturer of solar components such as inverters and power optimizers. These components convert DC power to AC electricity and help lower the cost of the system. The company’s goal is to become the leading provider of inverter solutions to the solar industry.
- Market cap: $2.8 billion
- 2023 sales: $3.0 billion
Solar-based funds
iShares Global Clean Energy ETF (ICLN) – This iShares fund aims to track the investment performance of an index made up of companies in the clean energy sector. The companies may produce energy from solar, wind or other renewable sources.
- 5-year annualized return: 9.4 percent
- Expense ratio: 0.41 percent
- Assets: $2.4 billion
Invesco Solar ETF (TAN) – The Invesco Solar ETF is based on the MAC Global Solar Energy Index and invests at least 90 percent of its assets in securities that make up the index. Enphase Energy (ENPH), SolarEdge and First Solar are top fund holdings.
- 5-year annualized return: 12.6 percent
- Expense ratio: 0.67 percent
- Assets: $1.1 billion
Fidelity Clean Energy ETF (FRNW) – The Fidelity Clean Energy ETF, launched in 2021, aims to track a Fidelity index of clean energy companies. Companies in the index distribute, produce or provide technology or equipment that supports the production of energy from solar, wind, hydrogen or other renewable sources.
- 1-year return: -24.9 percent
- Expense ratio: 0.39 percent
- Assets: $27.7 million
Pros of investing in solar energy
There are many advantages to investing in solar energy. Here are the major ones:
- Sustainability – Solar energy is classified as renewable because we won’t run out of sunlight, whereas fossil fuels such as oil and natural gas have a limited supply.
- Environmental impact – Relative to fossil fuels, the environmental impact of solar energy is low. It has a much lower carbon impact and doesn’t damage the land the way that fracking and oil drilling can.
- Independence – The U.S. has certain parts where sunlight is abundant (such as the Southwest), which creates the possibility that solar energy could help it become less reliant on and even energy independent from other parts of the world that produce oil. You may even be able to put solar panels on your house and become energy independent as an individual.
- Growth potential – Because we are still in the early stages of solar energy, the potential for future growth is enormous. This is what attracts most investors to the industry, but that growth potential isn’t risk-free.
Cons of investing in solar energy
Despite the potential benefits of investing in solar energy, there are some concerns to be aware of.
- Inconsistent sunlight – One of the challenges of solar energy is the fact that the sun doesn’t shine all the time. The sun is only out during the day and even then, clouds can make solar energy a challenge. Because of this, storage solutions for solar energy hold great opportunities.
- Materials used – Materials used to manufacture the solar panels can be difficult to extract and are in high demand in other areas of technology. With supply chain issues impacting many areas of technology, this could present a challenge to solar manufacturers.
- Land use required – For now, large amounts of land are needed to place solar panels in order to produce meaningful amounts of electricity. Innovation that leads to smaller and more powerful solar panels could help with this challenge over time.
- High valuations – Because of the growth potential of the solar industry, the companies involved may trade at expensive valuations , making it difficult for investors to earn outsized returns. When you pay high prices for assets, you also face the risk that they don’t perform as well as expected and the price falls significantly to correct for that miscalculation.
Bottom line
The solar industry has come a long way since people were using mirrors to start fires. Today, the industry holds great potential as a viable source of renewable energy. Investors have a choice between holding individual stocks and buying funds that invest across the industry and in different renewable energy sources. While the solar energy industry shows potential and has several advantages, don’t forget to pay attention to its risks as well. Remember that any asset can be a bad investment if you pay too high a price.
Editorial Disclaimer: All investors are advised to conduct their own independent research into investment strategies before making an investment decision. In addition, investors are advised that past investment product performance is no guarantee of future price appreciation.

Related Articles

How to invest with CDs

How to invest in commodities

How to invest $100,000

How to invest in electric cars

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
3. Easy to Transport. Fossil fuels are relatively easier than transporting renewable sources of energy, such as wind, sun, and water, which are pretty impossible as well. It is easier to supply fuels through the help of pipelines. These pipes are easily laid underground and can transport gas or oil with ease.
Fossil fuels cause local pollution where they are produced and used, and their ongoing use is causing lasting harm to the climate of our entire planet. Nonetheless, meaningfully changing our ways ...
Now that we understand the various reasons why fossil fuels are considered advantageous around the world let's dive into the many disadvantages of fossil fuel use. 1. Environmental degradation. Primarily, the burning of fossil fuels causes air pollution, which makes its way into our soil and water sources.
Fossil fuels are "[c]oal, crude oil, and natural gas are all considered fossil fuels because they were formed from the fossilized, buried remains of plants and animals that lived millions of years ago. ... The Pros and Cons of Carbon Taxes," iea.org, Nov. 6, 2018 Helen Mountford, "A Carbon Price Can Benefit the Poor while Reducing ...
The current supply of fossil fuels buried in the earth's crust is all we'll ever have. As of 2020, the world has enough oil and gas to meet its needs for about 50 years. Coal supplies will last longer—around 140 years. But once they're gone, they're gone. Safety risks. Extracting fossil fuels from the ground is a dangerous process.
Even renewable fuels have a foundation built on fossil fuels. 2. Fossil fuels are both cheap and reliable. Because the technologies which surround fossil fuels are well-established, the consumer cost to use them is quite load. The energy that is produced by their refinement and combustion is incredibly consistent.
Fossil Fuels: Pros, Cons, and Alternatives. Fossil fuels are widely used in industry and for domestic purposes. They heat our buildings, allow us to travel, and provide us light. Although they have many advantages, these energies are extremely harmful to the planet and to our health. A major source of global warming and 8 million deaths in 2018 ...
Though there are many pros and cons to both sides, alternative energy sources is the better choice than fossil fuels for many reasons. One reason is that fossil fuels isn't a renewable energy source while all alternative energy sources are. Another reason is that fossil fuels is a big contributor to global warming.
Pros And Cons Of Ethanol And Fossil Fuels 907 Words | 4 Pages. This bill has influenced modern environmental bills as well. See also Renewable Fuel Standard policy explained on previous page In 2006, Americans spent over 921 billion dollars on fossil fuels. In 2007, America spent over 360 billion dollars importing fossil fuels.
Decomposing plants and other organisms, buried beneath layers of sediment and rock, have taken millennia to become the carbon-rich deposits we now call fossil fuels. These non-renewable fuels ...
Fossil fuels are the predominant energy source in the modern world, mainly consisting of coal, natural gas and oil. Its extensive use can be attributed to the affordability and reliability of fossil fuels, with these factors preventing renewable energy sources like wind and solar power from surpassing its usage, and in the example of Australia, "around 86% of … electricity is generated ...
1. Advanced Technology. The technology used to obtain fossil fuels has become very well-developed. This is because Fossil fuels have been a sole source of energy for quite a while now and we have been working on the technology to obtain energy from these sources more efficiently. 2.
Katie Pearce. / Apr 18, 2017. The topic of fossil fuel divestment remains a complex one, a Johns Hopkins University forum demonstrated Monday night. The university invited four experts to share perspectives on the issue as it engages in its own discussions of whether to end private investments in fossil fuel companies.
The efficiency of fossil fuel is another factor because it can generate a lot of energy. And carrying it from one place can be done by pipes underground. To put the pipes in place was a very expensive project that's why we should continue to use it. Another positive side is the fact that it creates thousands of jobs every years and that's ...
Disadvantages. Fossil fuels emit carbon dioxide when burnt which is a major greenhouse gas and the primary source of pollution. This has contributed to global warming. They are a non-renewable resource, i.e., once used they cannot be replaced. Combustion of fossil fuels makes the environment more acidic.
Pros And Cons Of Fossil Fuels. Decent Essays. 683 Words; 3 Pages; Open Document. The argument of alternative energy sources vs fossil fuels is a long-lasting argument. Though there are many pros and cons to both sides, alternative energy sources is the better choice than fossil fuels for many reasons. One reason is that fossil fuels isn't a ...
Cons Of Fracking Essay 329 Words | 2 Pages. The main way that oil and natural gas reserves are acquired are through the means of Fracking. Also known as hydrofracking, this method utilizes a drill that drills down thousands of feet underground, which is then flushed with millions of gallons of water along with additive chemicals at high pressures to break the rocks sheltering the reserves.
The pros of fossil fuels are that they are well-developed and also, they are reliable and cheap. The energy used in the harnessing of the energy from fossil fuels is developed. The fuels are excellent types of fuel for usage for energy based on load. On the other hand, fossil fuels have got some disadvantages.
The Pros and Cons of Fossil Fuels. Fossil fuels such as coal and oil have been used to generate electricity for over a century. They are reliable, affordable, and abundant. Here are some of the key advantages of fossil fuels: - 1.Fossil fuels are a very reliable source of energy. 2.They are much cheaper. 3.They are a very abundant resource. 4.
Alternative energies include renewable sources -including solar , tidal , wind , biofuel , hydroelectric, and geothermal -and non-renewable nuclear power. Globally, fossil fuels have been used for energy for much of human history. The Chinese were the first to transition to fossil fuels from wood fire energy.
"As long as demand is still there for the fossil fuels, the greenhouse-gas emissions will exist, regardless of who owns the assets." "We all could agree that divestiture is a symbolic gesture that, sadly, will have no measurable impact on global greenhouse gas emissions, or the behavior of companies that produce fossil fuels," Wolak added.
Biofuels are a renewable and sustainable alternative to fossil fuels. Let's go through the advantages and disadvantages of biofuels to learn more. ... energy source over the long term if they are produced and used in a responsible and well-planned manner when all the pros and cons of biofuels versus fossil fuels are considered. In the planning ...
The Pros And Cons Of Fossil Fueling The Future. Fossil fuels are criticized for contributing to the "global warming" theory, and the "greenhouse effect" blamed on unregulated industry, and transference pollution in our atmosphere. While energy preservation and education are important, it doesn't solve the long-term problem: energy is ...
In this blog, you will find answers to your questions about the pros and cons of solar energy, setup costs, whether the system is worth the initial cost, and much more! What Are The Top Pros And Cons Of Solar Energy? Since the invention of electricity in the late 1870s, fossil fuels have been the primary source of electricity generation.
The solar industry appears poised for growth over the coming decades as more countries move away from fossil fuels and towards renewable energy. ... Pros & cons of financial advising 7 min read ...
Solar panels are a clean and renewable energy source, making them an environmentally friendly way to produce energy. Unlike fossil fuels, which have a definite supply and are harmful to the ...