- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences

Why Business Models Matter
- Joan Magretta
A good business model begins with an insight into human motivations and ends in a rich stream of profits.
The Idea in Brief
The terms “business model” and “strategy” are among the most sloppily used in business. People use them interchangeably to refer to everything —so they mean nothing.
But no organization can afford fuzzy thinking about these fundamental concepts. A business model and a strategy are two different animals. One explains who your customers are and how you plan to make money by providing them with value; the other, how you’ll beat competitors by being different.
A well-thought-out business model also enables you to test and revise your assumptions about customers, think rigorously about your business, and align employees behind your company’s mission.
Sure, the business-model concept unraveled after flagrant misuse by dot bombs. But when you build a sound model that complements your strategy, you equip your company to beat even your toughest rivals.
The Idea in Practice
Powerful business models pass two tests:
1. The narrative test: The business model tells a logical story explaining who your customers are, what they value, and how you’ll make money providing them that value. The story’s plot may turn on one of two links in the generic business value chain:
- making something that satisfies an unmet need; e.g., American Express traveler’s checks gave travelers new peace of mind
- selling something in innovative ways; e.g., Eastern Exclusives distributes restaurant discount-coupon books in bulk to university housing departments, which distribute them free to dorms
2. The numbers test: A business model’s story holds up only if you tie assumptions about customers to sound economics—your P&L must add up. For example, on-line grocery models failed because customers declined to pay substantially more on-line than in stores. E-grocers couldn’t cover their marketing, technology, and delivery costs. Failing either test can prove fatal. Example:
When EuroDisney opened its Paris theme park, it assumed Europeans were like Americans. But instead of grazing all day at the park’s restaurants, Europeans wanted to eat meals at the same hour. Results? Overloaded restaurants, long lines, frustrated patrons. EuroDisney’s model failed the narrative test because it misunderstood customers’ motivations.
Models passing both tests clarify how your business’s various elements fit together. Example:
On-line auction giant eBay combined a compelling narrative with major profit potential. This on-line business “couldn’t be done offline” and still provide value to collectors, bargain hunters, and small-business people. Its narrow scope of activities creates a highly profitable cost structure. For example, sellers and buyers handle payment and shipping logistics—so eBay incurs no inventory or transportation costs and avoids credit risk.
A Strategy Complement
Having a solid business model isn’t enough. You also need a strategy, to plan how you’ll beat your rivals—by being different. Example:
Wal-Mart used Kmart’s business model—but implemented a unique strategy: Rather than trying to be just like its rivals, it promised different value to customers in different markets. It put big discount stores into “little one-horse towns” that competitors ignored. Founder Sam Walton bet—rightly—that if his stores beat city prices by offering name brands (not second-tier, private-label brands), townspeople would “shop [close to] home.”
“Business model” was one of the great buzzwords of the Internet boom, routinely invoked, as the writer Michael Lewis put it, “to glorify all manner of half-baked plans.” A company didn’t need a strategy, or a special competence, or even any customers—all it needed was a Web-based business model that promised wild profits in some distant, ill-defined future. Many people—investors, entrepreneurs, and executives alike—bought the fantasy and got burned. And as the inevitable counterreaction played out, the concept of the business model fell out of fashion nearly as quickly as the .com appendage itself.
- JM Joan Magretta is a senior associate at the Institute for Strategy and Competitiveness at Harvard Business School. She is the author of Understanding Michael Porter: The Essential Guide to Competition and Strategy .
Partner Center
Why is a business model important?

Learning & Academics
A business model may seem like a straightforward concept. But the term has shifted and changed over time. Today, if a company is incapable of creating an innovative and flexible business model, that could be its downfall.
Today, technology and innovation are the main players in how successful businesses are run and reinvented. With an explosive amount of information available through big data and the resources provided by digital tech, companies can more easily create and continue to capture value for stakeholders.
Businesses that want to start and stay at the cutting edge use design thinking, strategy, and continuous, fearless change in their business models. Some of the most successful businesses today are those that have reinvented the model, disrupting the industry that was and creating the kind of value customers are looking for in the digital era .

What is a business model?
Does a business model have a simple definition? Yes and no. Business models are the logic behind a company, but the concept can be framed in many different ways. And today, the way the idea has been reframed is inspiring the business owners and CEOs of companies from startups to well-established multinationals.
In his book The New, New Thing , Michael Lewis explains that the business model has been thought of as simply the way a business plans to make money. Expanding upon this idea, Peter Drucker talks about the business concept in terms of flexible assumptions about what a company will and will not do: what they get paid for; markets, customers, and competitors; values and behaviors; technology; and a company’s strengths and weaknesses. Joan Magretta adds that a business model is basically a story about how the company will operate, including the activities involved in making and selling a product or service.
Alex Osterwalder offers a simplified format for thinking about these hypotheses adopted by startups and established businesses alike, called the busi n ess model canvas. This business map is a one-page template that includes space for designing, discussing, and reinventing business models. The nine building blocks included are customer segments, value propositions, channels for delivering value, customer relationships, revenue streams, key resources, activities and partners, and cost structure. The idea of having everything mapped out on one page enables forward-thinking leaders to keep things light and flexible in order to invent or innovatively reiterate their business models as situations change and evolve.

Types of business models and tech
Business models have been transformed by technology . Interconnectivity , globalization , and a digital, tech-driven world have all allowed innovative thinkers to rethink traditional models in sectors from travel to retail.
One example of an age-old business model that has been transformed by tech is the platform business model. In the simplest terms, this model brings buyers and sellers together in one space. An in-person marketplace, auction house, or shopping mall are examples of this model that have been around for decades or even centuries. But digital tech has meant these platforms are no longer confined by time and space. Technology has allowed innovative business owners to use this type of model to create enormous digital networks enabling participation and collaboration across the globe. Some of the most successful companies today, including Airbnb , WhatsApp , Facebook , Google , and Alibaba , are examples of reinvented platform business models that use tech to their advantage.

The global business model is another example of one which has been inspired by technology. These models focus on producing and selling globally in a short period of time, relying on the fast pace of globalization and interconnectivity to thrive. The clothing brands Mango and Desigual are good examples of successful models based on selling to small target segments globally in order to achieve economy of scale, in a way that is only possible in a globalized world.
Interconnectivity and the digital world has also led to the availability of big data, allowing businesses to make sure they are offering the goods and services customers are actually looking for. The “seeking-excellence” business model depends on creating innovative products or services that consumers didn’t even know they wanted. The most disruptive thinkers today can use big data to analyze trends and find new value propositions that reinvent the business model—like Apple did with the iPod and iTunes store in the early 2000s.
Inspiring business models that have broken the status quo
Airbnb is one of the most disruptive businesses of the digital era. Founded by a couple of young startupers in 2008, it is the result of a recognized opportunity (when no hotel rooms were available in San Francisco during a conference held in the city), and the technology capable of connecting hosts and renters from around the globe.

As they put it on their About Us page, “ Airbnb uniquely leverages technology to economically empower millions of people around the world to unlock and monetize their spaces, passions, and talents to become hospitality entrepreneurs. ” It is a sharing-economy-based business , eliminating the overhead of owning the rooms that are rented out, like traditional hotels do. And its platform business model—which uses advances in digital tech to create networks that continuously improve—has allowed the business to boom around the world.
Uber is at the top of the list as another example of a business that has taken an existing business model and reinvented the wheel. By looking at how a current business model—taxis—could be improved, Uber was able to take a share of a preexisting market using a disruptive, tech-based model for grabbing a ride.

Now they have expanded and continue to grow through reiterations of their model, including Uber Eats for food delivery; Uber Freight offering shipping services; Uber Health providing rides for patients and healthcare providers; and even technology groups working towards self-driving vehicles and shared air transportation.
In the fast-paced digital world, innovation is a key element of any business model. Executives and CEOs are not responsible for maintaining the status quo defined in one iteration of the business model, but rather for experimenting, learning, and continuously improving to stay ahead of the competition.
Author: IE University
Related posts

The Backstage: Mango’s Global Head of Research dissects the move toward customer-centric mindsets in the fashion industry

Joining IE University’s bachelor’s programs? Your admissions process questions answered

Students step into the consultant role with the Global Consulting Practicum
Popular posts.

Wizer, the app designed by IE Challenge students to help older people find connections in the digital world
Interested in ie university.
- IE Lifelong Learning
- IE Foundation
- Legal Notice
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Ethics Code
- Academics Standards
- Corporate Relations
- IEU Experience
- Innovation & Creativity
- Learning & Academics
- #GOINGTOIEU
Business model innovation: a review and research agenda
New England Journal of Entrepreneurship
ISSN : 2574-8904
Article publication date: 16 October 2019
Issue publication date: 13 November 2019
The aim of this paper is to review and synthesise the recent advancements in the business model literature and explore how firms approach business model innovation.
Design/methodology/approach
A systematic review of business model innovation literature was carried out by analysing 219 papers published between 2010 and 2016.
Evidence reviewed suggests that rather than taking either an evolutionary process of continuous revision, adaptation and fine-tuning of the existing business model or a revolutionary process of replacing the existing business model, firms can explore alternative business models through experimentation, open and disruptive innovations. It was also found that changing business models encompasses modifying a single element, altering multiple elements simultaneously and/or changing the interactions between elements in four areas of innovation: value proposition, operational value, human capital and financial value.
Research limitations/implications
Although this review highlights the different avenues to business model innovation, the mechanisms by which firms can change their business models and the external factors associated with such change remain unexplored.
Practical implications
The business model innovation framework can be used by practitioners as a “navigation map” to determine where and how to change their existing business models.
Originality/value
Because conflicting approaches exist in the literature on how firms change their business models, the review synthesises these approaches and provides a clear guidance as to the ways through which business model innovation can be undertaken.
- Business model
- Value proposition
- Value creation
- Value capture
Ramdani, B. , Binsaif, A. and Boukrami, E. (2019), "Business model innovation: a review and research agenda", New England Journal of Entrepreneurship , Vol. 22 No. 2, pp. 89-108. https://doi.org/10.1108/NEJE-06-2019-0030
Emerald Publishing Limited
Copyright © 2019, Boumediene Ramdani, Ahmed Binsaif and Elias Boukrami
Published in New England Journal of Entrepreneurship . Published by Emerald Publishing Limited. This article is published under the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY 4.0) licence. Anyone may reproduce, distribute, translate and create derivative works of this article (for both commercial and non-commercial purposes), subject to full attribution to the original publication and authors. The full terms of this licence may be seen at http://creativecommons.org/licences/by/4.0/legalcode
1. Introduction
Firms pursue business model innovation by exploring new ways to define value proposition, create and capture value for customers, suppliers and partners ( Gambardella and McGahan, 2010 ; Teece, 2010 ; Bock et al. , 2012 ; Casadesus-Masanell and Zhu, 2013 ). An extensive body of the literature asserts that innovation in business models is of vital importance to firm survival, business performance and as a source of competitive advantage ( Demil and Lecocq, 2010 ; Chesbrough, 2010 ; Amit and Zott, 2012 ; Baden-Fuller and Haefliger, 2013 ; Casadesus-Masanell and Zhu, 2013 ). It is starting to attract a growing attention, given the increasing opportunities for new business models enabled by changing customer expectations, technological advances and deregulation ( Casadesus-Masanell and Llanes, 2011 ; Casadesus-Masanell and Zhu, 2013 ). This is evident from the recent scholarly outputs ( Figure 1 ). Thus, it is essential to comprehend this literature and uncover where alternative business models can be explored.
Conflicting approaches exist in the literature on how firms change their business models. One approach suggests that alternative business models can be explored through an evolutionary process of incremental changes to business model elements (e.g. Demil and Lecocq, 2010 ; Dunford et al. , 2010 ; Amit and Zott, 2012 ; Landau et al. , 2016 ; Velu, 2016 ). The other approach, mainly practice-oriented, advocates that innovative business models can be developed through a revolutionary process by replacing existing business models (e.g. Bock et al. , 2012 ; Iansiti and Lakhani, 2014 ). The fragmentation of prior research is due to the variety of disciplinary and theoretical foundations through which business model innovation is examined. Scholars have drawn on perspectives from entrepreneurship (e.g. George and Bock, 2011 ), information systems (e.g. Al-debei and Avison, 2010 ), innovation management (e.g. Dmitriev et al. , 2014 ), marketing (e.g. Sorescu et al. , 2011 ) and strategy (e.g. Demil and Lecocq, 2010 ). Also, this fragmentation is deepened by focusing on different types of business models in different industries. Studies have explored different types of business models such as digital business models (e.g. Weill and Woerner, 2013 ), service business models (e.g. Kastalli et al. , 2013 ), social business models (e.g. Hlady-Rispal and Servantie, 2016 ) and sustainability-driven business models ( Esslinger, 2011 ). Besides, studies have examined different industries such as airline ( Lange et al. , 2015 ), manufacturing ( Landau et al. , 2016 ), newspaper ( Karimi and Walter, 2016 ), retail ( Brea-Solís et al. , 2015 ) and telemedicine ( Peters et al. , 2015 ).
Since the first comprehensive review of business model literature was carried out by Zott et al. (2011) , several reviews were published recently (as highlighted in Table I ). Our review builds on and extends the extant literature in at least three ways. First, unlike previous reviews that mainly focused on the general construct of “Business Model” ( George and Bock, 2011 ; Zott et al. , 2011 ; Wirtz et al. , 2016 ), our review focuses on uncovering how firms change their existing business model(s) by including terms that reflect business model innovation, namely, value proposition, value creation and value capture. Second, previous reviews do not provide a clear answer as to how firms change their business models. Our review aims to provide a clear guidance on how firms carry out business model innovation by synthesising the different perspectives existing in the literature. Third, compared to recent reviews on business model innovation ( Schneider and Spieth, 2013 ; Spieth et al. , 2014 ), which have touched lightly on some innovation aspects such as streams and motivations of business model innovation research, our review will uncover the innovation areas where alternative business models can be explored. Taking Teece’s (2010) suggestion, “A helpful analytic approach for management is likely to involve systematic deconstruction/unpacking of existing business models, and an evaluation of each element with an idea toward refinement or replacement” (p. 188), this paper aims to develop a theoretical framework of business model innovation.
Our review first explains the scope and the process of the literature review. This is followed by a synthesis of the findings of the review into a theoretical framework of business model innovation. Finally, avenues for future research will be discussed in relation to the approaches, degree and mechanisms of business model innovation.
2. Scope and method of the literature review
Given the diverse body of business models literature, a systematic literature review was carried out to minimise research bias ( Transfield et al. , 2003 ). Compared to the previous business model literature, our review criteria are summarised in Table I . The journal papers considered were published between January 2010 and December 2016. As highlighted in Figure 1 , most contributions in this field have been issued within this period since previous developments in the literature were comprehensively reviewed up to the end of 2009 ( Zott et al. , 2011 ). Using four databases (EBSCO Business Complete, ABI/INFORM, JSTOR and ScienceDirect), we searched peer-reviewed papers with terms such as business model(s), innovation value proposition, value creation and value capture appearing in the title, abstract or subject terms. As a result, 8,642 peer-reviewed papers were obtained.
Studies were included in our review if they specifically address business models and were top-rated according to The UK Association of Business Schools list ( ABS, 2010 ). This rating has been used not only because it takes into account the journal “Impact Factor” as a measure for journal quality, but also uses in conjunction other measures making it one of the most comprehensive journal ratings. By applying these criteria, 1,682 entries were retrieved from 122 journals. By excluding duplications, 831 papers were identified. As Harvard Business Review is not listed among the peer-reviewed journals in any of the chosen databases and was included in the ABS list, we used the earlier criteria and found 112 additional entries. The reviewed papers and their subject fields are highlighted in Table II . Since the focus of this paper is on business model innovation, we selected studies that discuss value proposition, value creation and value capture as sub-themes. This is not only because the definition of business model innovation mentioned earlier spans all three sub-themes, but also because all three sub-themes have been included in recent studies (e.g. Landau et al. , 2016 ; Velu and Jacob, 2014 ). To confirm whether the papers addressed business model innovation, we examined the main body of the papers to ensure they were properly coded and classified. At the end of the process, 219 papers were included in this review. Table III lists the source of our sample.
The authors reviewed the 219 papers using a protocol that included areas of innovation (i.e. components, elements, and activities), theoretical perspectives and key findings. In order to identify the main themes of business model innovation research, all papers were coded in relation to our research focus as to where alternative business models can be explored (i.e. value proposition, value creation and value capture). Coding was cross checked among the authors on a random sample suggesting high accuracy between them. Having compared and discussed the results, the authors were able to identify the main themes.
3. Prior conceptualisations of business model innovation
Some scholars have articulated the need to build the business model innovation on a more solid theoretical ground ( Sosna et al. , 2010 ; George and Bock, 2011 ). Although many studies are not explicitly theory-based, some studies partially used well-established theories such as the resource-based view (e.g. Al-Debei and Avison, 2010 ) and transaction cost economics (e.g. DaSilva and Trkman, 2014 ) to conceptualise business model innovation. Other theories such as activity systems perspective, dynamic capabilities and practice theory have been used to help answer the question of how firms change their existing business models.
Using the activity systems perspective, Zott and Amit (2010) demonstrated how innovative business models can be developed through the design themes that describe the source of value creation (novelty, lock-in, complementarities and efficiency) and design elements that describe the architecture (content, structure and governance). This work, however, overlooks value capture which limits the explanation of the advocated system’s view (holistic). Moreover, Chatterjee (2013) used this perspective to reveal that firms can design innovative business models that translate value capture logic to core objectives, which can be delivered through the activity system.
Dynamic capability perspective frames business model innovation as an initial experiment followed by continuous revision, adaptation and fine-tuning based on trial-and-error learning ( Sosna et al. , 2010 ). Using this perspective, Demil and Lecocq (2010) showed that “dynamic consistency” is a capability that allows firms to sustain their performance while innovating their business models through voluntary and emergent changes. Also, Mezger (2014) conceptualised business model innovation as a distinct dynamic capability. He argued that this capability is the firm’s capacity to sense opportunities, seize them through the development of valuable and unique business models, and accordingly reconfigure the firms’ competences and resources. Using aspects of practice theory, Mason and Spring (2011) looked at business model innovation in the recorded sound industry and found that it can be achieved through various combinations of managerial practices.
Static and transformational approaches have been used to depict business models ( Demil and Lecocq, 2010 ). The former refers to viewing business models as constituting core elements that influence business performance at a particular point in time. This approach offers a snapshot of the business model elements and how they are assembled, which can help in understanding and communicating a business model (e.g. Eyring et al. , 2011 ; Mason and Spring, 2011 ; Yunus et al. , 2010). The latter, however, focuses on innovation and how to address the changes in business models over time (e.g. Sinfield et al. , 2012 ; Girotra and Netessine, 2014 ; Landau et al. , 2016 ). Some researchers have identified the core elements of business models ex ante (e.g. Demil and Lecocq, 2010 ; Wu et al. , 2010 ; Huarng, 2013 ; Dmitriev et al. , 2014 ), while others argued that considering a priori elements can be restrictive (e.g. Casadesus-Masanell and Ricart, 2010 ). Unsurprisingly, some researchers found a middle ground where elements are loosely defined allowing flexibility in depicting business models (e.g. Zott and Amit, 2010 ; Sinfield et al. , 2012 ; Kiron et al. , 2013 ).
Prior to 2010, conceptual frameworks focused on the business model concept in general (e.g. Chesbrough and Rosenbloom, 2002 ; Osterwalder et al. , 2005 ; Shafer et al. , 2005 ) apart from Johnson et al. ’s (2008 ), which is one of the early contributions to business model innovation. To determine whether a change in existing business model is necessary, Johnson et al. (2008) suggested three steps: “Identify an important unmet job a target customer needs done; blueprint a model that can accomplish that job profitably for a price the customer is willing to pay; and carefully implement and evolve the model by testing essential assumptions and adjusting as you learn” ( Eyring et al. , 2011 , p. 90). Although several frameworks have been developed since then, our understanding of business model innovation is still limited due to the static nature of the majority of these frameworks. Some representations ignore the elements and/or activities where alternative business models can be explored (e.g. Sinfield et al. , 2012 ; Chatterjee, 2013 ; Huarng, 2013 ; Morris et al. , 2013 ; Dmitriev et al. , 2014 ; Girotra and Netessine, 2014 ). Other frameworks ignore value proposition (e.g. Zott and Amit, 2010 ), ignore value creation (e.g. Dmitriev et al. , 2014 ; Michel, 2014 ) and/or ignore value capture (e.g. Mason and Spring, 2011 ; Sorescu et al. , 2011 ; Storbacka, 2011 ). Some conceptualisations do not identify who is responsible for the innovation (e.g. Casadesus-Masanell and Ricart, 2010 ; Sinfield et al. , 2012 ; Chatterjee, 2013 ; Kiron et al. , 2013 ). Synthesising the different contributions into a theoretical framework of business model innovation will enable a better understanding of how firms undertake business model innovation.
4. Business model innovation framework
Our framework ( Figure 2 ) integrates all the elements where alternative business models can be explored. This framework does not claim that the listed elements are definitive for high-performing business models, but is an attempt to outline the elements associated with business model innovation. This framework builds on the previous work of Johnson et al. (2008) and Zott and Amit (2010) by signifying the elements associated with business model innovation. Unlike previous frameworks that mainly consider the constituting elements of business models, this framework focuses on areas of innovation where alternative business models can be explored. Moreover, this is not a static view of the constituting elements of a business model, but rather a view enabling firms to explore alternative business models by continually refining these elements. Arrows in the framework indicate the continuous interaction of business model elements. This framework consists of 4 areas of innovation and 16 elements (more details are shown in Table IV ). Each will be discussed below.
4.1 Value proposition
The first area of innovation refers to elements associated with answering the “Why” questions. While most of the previously established models in the literature include at least one of the value proposition elements (e.g. Brea-Solís et al. , 2015 ; Christensen et al. , 2016 ), other frameworks included two elements (e.g. Dahan et al. , 2010 ; Cortimiglia et al. , 2016 ) and three elements (e.g. Eyring et al. , 2011 ; Sinfield et al. , 2012 ). These elements include rethinking what a company sells, exploring new customer needs, acquiring target customers and determining whether the benefits offered are perceived by customers. Modern organisations are highly concerned with innovation relating to value proposition in order to attract and retain a large portion of their customer base ( Al-Debei and Avison, 2010 ). Developing new business models usually starts with articulating a new customer value proposition ( Eyring et al. , 2011 ). According to Sinfield et al. (2012) , firms are encouraged to explore various alternatives of core offering in more depth by examining type of offering (product or service), its features (custom or off-the-shelf), offered benefits (tangible or intangible), brand (generic or branded) and lifetime of the offering (consumable or durable).
In order to exploit the “middle market” in emerging economies, Eyring et al. (2011) suggested that companies need to design new business models that aim to meet unsatisfied needs and evolve these models by continually testing assumptions and making adjustments. To uncover unmet needs, Eyring et al. (2011) suggested answering four questions: what are customers doing with the offering? What alternative offerings consumers buy? What jobs consumers are satisfying poorly? and what consumers are trying to accomplish with existing offerings? Furthermore, Baden-Fuller and Haefliger (2013) made a distinction between customers and users in two-sided platforms, where users search for products online, and customers (firms) place ads to attract users. They also made a distinction between “pre-designed (scale) based offerings” and “project based offerings”. While the former focuses on “one-size-fits-all”, the latter focuses on specific client solving specific problem.
Established firms entering emerging markets should identify unmet needs “the job to be done” rather than extending their geographical base for existing offerings ( Eyring et al. , 2011 ). Because customers in these markets cannot afford the cheapest of the high-end offerings, firms with innovative business models that meet these customers’ needs affordably will have opportunities for growth ( Eyring et al. , 2011 ). Moreover, secondary business model innovation has been advocated by Wu et al. (2010) as a way for latecomer firms to create and capture value from disruptive technologies in emerging markets. This can be achieved through tailoring the original business model to fit price-sensitive mass customers by articulating a value proposition that is attractive for local customers.
4.2 Operational value
The second area of innovation focuses on elements associated with answering the “What” questions. Many of the established frameworks included either one element (e.g. Sinfield et al. , 2012 ; Taran et al. , 2015 ), two elements (e.g. Mason and Spring, 2011 ; Dmitriev et al. , 2014 ). However, very few included three or more elements (e.g. Mehrizi and Lashkarbolouki, 2016 ; Cortimiglia et al. , 2016 ). These elements include configuring key assets and sequencing activities to deliver the value proposition, exposing the various means by which a company reaches out to customers, and establishing links with key partners and suppliers. Focusing on value creation, Zott and Amit (2010) argued that business model innovation can be achieved through reorganising activities to reduce transaction costs. However, Al-Debei and Avison (2010) argued that innovation relating to this dimension can be achieved through resource configuration, which demonstrates a firm’s ability to integrate various assets in a way that delivers its value proposition. Cavalcante et al. (2011) proposed four ways to change business models: business model creation, extension, revision and termination by creating or adding new processes, and changing or terminating existing processes.
Western firms have had difficulty competing in emerging markets due to importing their existing business models with unchanged operating model ( Eyring et al. , 2011 ). Alternative business models can be uncovered when firms explore the different roles they might play in the industry value chain ( Sinfield et al. , 2012 ). Al-Debei and Avison (2010) suggested achieving this through answering questions such as: what is the position of our firm in the value system? and what mode of collaboration (open or close) would we choose to reach out in a business network? Dahan et al. (2010) found cross-sector partnerships as a way to co-create new multi-organisational business models. They argued that multinational enterprises (MNEs) can collaborate with nongovernmental organisations (NGOs) to create products/or services that neither can create on their own. Collaboration allows access to resources that firms would otherwise need to solely develop or purchase ( Yunus et al. , 2010 ). According to Wu et al. (2010) , secondary business model innovation can be achieved when latecomer firms fully utilise strategic partners’ complementary assets to overcome their latecomer disadvantages and build a unique value network specific to emerging economies context.
4.3 Human capital
The third area of innovation refers to elements associated with answering the “Who” questions. Most of the established frameworks in this field tend to focus less on human capital and include one element at most (e.g. Wu et al. , 2010 ; Kohler, 2015 ). However, our framework highlights four elements, which include experimenting with new ways of doing business, tapping into the skills and competencies needed for the new business model through motivating and involving individuals in the innovation process. According to Belenzon and Schankerman (2015) , “the ability to tap into a pool of talent is strongly related to the specific business model chosen by managers” (p. 795). They claimed that managers can strategically influence individuals’ contributions and their impact on project performance.
Organisational learning can be maximised though continuous experimentation and making changes when actions result in failure ( Yunus et al. , 2010 ). Challenging and questioning the existing rules and assumptions and imagining new ways of doing business will help develop new business models. Another essential element of business model design is governance, which refers to who performs the activities ( Zott and Amit, 2010 ). According to Sorescu et al. (2011) , innovation in retail business models can occur as a result of changes in the level of participation by actors engaged in performing the activities. An essential element of retailing governance is the incentive structure or the mechanisms that motivate those involved in carrying out their roles to meet customer demands ( Sorescu et al. , 2011 ). For example, discount retailers tend to establish different compensation and incentive policies ( Brea-Solís et al. , 2015 ). Revising the incentive system can have a major impact on new ventures’ performance by aligning organisational goals at each stage of growth ( Roberge, 2015 ). Zott and Amit (2010) argued that alternative business models can be explored through adopting innovative governance or changing one or more parties that perform any activities. Sinfield et al. (2012) suggested that business model innovation only requires time from a small team over a short period of time to move a company beyond incremental improvements and generate new opportunities for growth. This is supported by Michel’s (2014) finding that cross-functional teams were able to quickly achieve business model innovation in workshops through deriving new ways to capture value.
4.4 Financial value
The final area of innovation focuses on elements associated with answering the “How” questions. Previously developed frameworks tend to prioritise this area of innovation by three elements (e.g. Eyring et al. , 2011 ; Huang et al. , 2013 ), and in one instance four elements (e.g. Yunus et al. , 2010 ). These elements include activities linked with how to capture value through revenue streams, changing the price-setting mechanisms, and assessing the financial viability and profitability of a business. According to Demil and Lecocq (2010) , changes in cost and/or revenue structures are the consequences of both continuous and radical changes. They also argued that costs relate to different activities run by organisations to acquire, integrate, combine or develop resources. Michel (2014) suggested that alternative business models can be explored through: changing the price-setting mechanism, changing the payer, and changing the price carrier. Different innovation forms are associated with each of these categories.
Business model innovation can be achieved through exploring new ways to generate cash flows ( Sorescu et al. , 2011 ), where the organisation has to consider (and potentially change) when the money is collected: prior to the sale, at the point of sale, or after the sale ( Baden-Fuller and Haefliger, 2013 ). Furthermore, Demil and Lecocq (2010) suggested that changes in business models affect margins. This is apparent in the retail business models, which generate more profit through business model innovation compared to other types of innovation ( Sorescu et al. , 2011 ).
5. Ways to change business models
From reviewing the recent developments in the business model literature, alternative business models can be explored through modifying a single business model element, altering multiple elements simultaneously and/or changing the interactions between elements of a business model.
Changing one of the business model elements (i.e. content, structure or governance) is enough to achieve business model innovation ( Amit and Zott, 2012 ). This means that firms can have a new activity system by performing only one new activity. However, Amit and Zott (2012) clearly outlined a systemic view of business models which entails a holistic change. This is evident from Demil and Lecocq’s (2010) work suggesting that the study of business model innovation should not focus on isolated activities since changing a core element will not only impact other elements but also the interactions between these elements.
Another way to change business models is through altering multiple business model elements simultaneously. Kiron et al. (2013) found that companies combining target customers with value chain innovations and changing one or two other elements of their business models tend to profit from their sustainability activities. They also found that firms changing three to four elements of their business models tend to profit more from their sustainability activities compared to those changing only one element. Moreover, Dahan et al. (2010) found that a new business model was developed as a result of MNEs and NGOs collaboration by redefining value proposition, target customers, governance of activities and distribution channels. Companies can explore multiple combinations by listing different business model options they could undertake (desirable, discussable and unthinkable) and evaluate new combinations that would not have been considered otherwise ( Sinfield et al. , 2012 ).
Changing business models is argued to be demanding as it requires a systemic and holistic view ( Amit and Zott, 2012 ) by considering the relationships between core business model elements ( Demil and Lecocq, 2010 ). As mentioned earlier, changing one element will not only impact other elements but also the interactions between these elements. A firm’s resources and competencies, value proposition and organisational system are continuously interacting and this will in turn impact business performance either positively or negatively ( Demil and Lecocq, 2010 ). According to Zott and Amit (2010) , innovative business models can be developed through linking activities in a novel way that generates more value. They argued that alternative business models can be explored by configuring business model design elements (e.g. governance) and connecting them to distinct themes (e.g. novelty). Supporting this, Eyring et al. (2011) suggested that core business model elements need to be integrated in order to create and capture value ( Eyring et al. , 2011 ).
6. Discussion and future research directions
From the above synthesis of the recent development in the literature, several gaps remain unfilled. To advance the literature, possible future research directions will be discussed in relation to approaches, degrees and mechanisms of business model innovation.
6.1 Approaches of business model innovation
Experimentation, open innovation and disruption have been advocated as approaches to business model innovation. Experimentation has been emphasised as a way to exploit opportunities and develop alternative business models before committing additional investments ( McGrath, 2010 ). Several approaches have been developed to assist in business model experimentation including mapping approach, discovery-driven planning and trail-and-error learning ( Chesbrough, 2010 ; McGrath, 2010 ; Sosna et al. , 2010 ; Andries and Debackere, 2013 ). Little is known about the effectiveness of these approaches. It will be worth investigating which elements of the business model innovation framework are more susceptible to experimentation and which elements should be held unchanged. Although business model innovation tends to be characterised with failure ( Christensen et al. , 2016 ), not much has been established on failing business models. It is interesting to explore how firms determine a failing business model and what organisational processes exist (if any) to evaluate and discard these failed business models. Empirical studies could examine which elements of business model innovation framework are associated with failing business models.
Another way to develop alternative business models is through open innovation. Although different categories of open business models have been identified by researchers (e.g. Frankenberger et al. , 2014 ; Taran et al. , 2015 ; Kortmann and Piller, 2016 ), their effectiveness is yet to be established. Further research is needed to examine when can a firm open and/or close element(s) of the business model innovation framework. Future studies could also examine the characteristics of open and/or close business models.
In responding to disruptive business models, how companies extend their existing business model, introduce additional business model(s) and/or replace their existing business model altogether remains underexplored. Future research is needed to unravel the strategies deployed by firms to extend their existing business models as a response to disruptive business models. In introducing additional business models, Markides (2013) suggested that a company will be presented with several options to manage the two businesses at the same time: create a completely separate business unit, integrate the two business models from the beginning or integrate the second business model after a certain period of time. Finding the balance between separation and integration is of vital importance. Further research could identify which of these choices are most common among successful firms introducing additional business models, how is the balance between integration and separation achieved, and which choice(s) prove more profitable. Moreover, very little is known on how firms replace their existing business model. Longitudinal studies could provide insights into how a firm adopts an alternative model and discard the old business model over time. It may also be worth examining the factors associated with the adoption of business model innovation as a response to disruptive business models. Moreover, new developments in digital technologies such as blockchain, Internet of Things and artificial intelligence are disrupting existing business models and providing firms with alternative avenues to create new business models. Thus far, very little is known on digital business models, the nature of their disruption, and how firms create digital business models and make them disruptive. Future research is needed to fill these important gaps in our knowledge.
6.2 Degrees of business model innovation
Business models can be developed through varying degrees of innovation from an evolutionary process of continuous fine-tuning to a revolutionary process of replacing existing business models. Recent research shows that survival of firms is dependent on the degree of their business model innovation ( Velu, 2015, 2016 ). This review classifies these degrees of innovation into modifying a single element, altering multiple elements simultaneously and/or changing the interactions between elements of the business model innovation framework.
In changing a single element, further research is needed to examine which business model element(s) is (are) associated with business model innovation. It is not clear whether firms intentionally make changes to a single element when carrying out business model innovation or stumble at it when experimenting with new ways of doing things. It may also be worth investigating the entry (or starting) points in the innovation process. There is no consensus in the literature on which element do companies start with when carrying out their business model innovation. While some studies suggest starting with the value proposition ( Eyring et al. , 2011 ; Landau et al. , 2016 ), others suggest starting the innovation process with identifying risks in the value chain ( Girotra and Netessine, 2011 ). Dmitriev et al. (2014) suggested two entry points, namely, value proposition and target customers. In commercialising innovations, the former refers to technology-push innovation while the latter refers to market-pull innovation. Also, it is not clear whether the entry point is the same as the single element associated with changing the business model. Further research can explore the different paths to business model innovation by identifying the entry point and subsequent changes needed to achieve business model innovation.
There is little guidance in the literature on how firms change multiple business model elements simultaneously. Landau et al. (2016) claimed that firms entering emerging markets tend to focus on adjusting specific business model components. It is unclear which elements need configuring, combining and/or integrating to achieve a company’s value proposition. Furthermore, the question of which elements can be “bought” on the market or internally “implemented” and their interplay remains unanswered ( DaSilva and Trkman, 2014 ). Casadesus-Masanell and Ricart (2010) argued that “[…] there is (as yet) no agreement as to the distinctive features of superior business models” (p. 196). Further research is needed to explore these distinctive elements of high-performing business models.
In changing the interactions between business model elements, further research is needed to explore how these elements are linked and what interactions’ changes are necessary to achieve business model innovation. Moreover, the question of how firms sequence these elements remains poorly understood. Future research can explore the synergies created over time between these elements. According to Dmitriev et al. (2014) , we need to improve our understanding of the connective mechanisms and dynamics involved in business model development. More work is needed to explore the different modalities of interdependencies among these elements and empirically testing such interdependencies and their effect on business performance ( Sorescu et al. , 2011 ).
It is surprising that the link between business model innovation and organisational performance has rarely been examined. Changing business models has been found to negatively influence business performance even if it is temporary ( McNamara et al. , 2013 ; Visnjic et al. , 2016 ). Contrary to this, evidence show that modifying business models is positively associated with organisational performance ( Cucculelli and Bettinelli, 2015 ). Empirical research is needed to operationalise the various degrees of innovation in business models and examine their link to organisational performance. Longitudinal studies can also be used to explore this association since it may be the case that business model innovation has a negative influence on performance in the short run and that may change subsequently. Moreover, it is not clear whether high-performing firms change their business models or innovation in business models is a result from superior performance ( Sorescu et al. , 2011 ). Further studies are needed to determine the direction of causality. Another link that is worth exploring is business model innovation and social value, which has only been explored in a few studies looking at social business models (e.g. Yunus et al. , 2010 ; Wilson and Post, 2013 ). Further research is needed to examine this link and possibly examine both financial and non-financial business performance.
6.3 Mechanisms of business model innovation
Although we know more about how firms define value proposition, create and capture value ( Landau et al. , 2016 ; Velu and Jacob, 2014 ), what remains as a blind spot is the mechanism of business model innovation. This is due to the fact that much of the literature seems to focus on value creation. To better understand the various mechanisms of business model innovation, future studies must integrate value proposition, value creation and value capture elements. Empirical studies could use the business model innovation framework to examine the various mechanisms of business model innovation. Also, the literature lacks the integration of internal and external perspectives of business model innovation. Very few studies look at the external drivers of business model innovation and the associated internal changes. The external drivers are referred to as “emerging changes”, which are usually beyond manager’s control ( Demil and Lecocq, 2010 ). Inconclusive findings exist as to how firms develop innovative business models in response to changes in the external environment. Future studies could examine the external factors associated with the changes in the business model innovation framework. Active and reactive responses need to be explored not only to understand the external influences, but also what business model changes are necessary for such responses. A better understanding of the mechanisms of business model innovation can be achieved by not only exploring the external drivers, but also linking them to specific internal changes. Although earlier contributions linking studies to established theories such as the resource-based view, transaction cost economics, activity systems perspective, dynamic capabilities and practice theory have proven to be vital in advancing the literature, developing a theory that elaborates on the antecedents, consequences and different facets of business model innovation is still needed ( Sorescu et al. , 2011 ). Theory can be advanced by depicting the mechanisms of business model innovation through the integration of both internal and external perspectives. Also, we call for more empirical work to uncover these mechanisms and provide managers with the necessary insights to carry out business model innovation.
7. Conclusions
The aim of this review was to explore how firms approach business model innovation. The current literature suggests that business model innovation approaches can either be evolutionary or revolutionary. However, the evidence reviewed points to a more complex picture beyond the simple binary approach, in that, firms can explore alternative business models through experimentation, open and disruptive innovations. Moreover, the evidence highlights further complexity to these approaches as we find that they are in fact a spectrum of various degrees of innovation ranging from modifying a single element, altering multiple elements simultaneously, to changing the interactions between elements of the business model innovation framework. This framework was developed as a navigation map for managers and researchers interested in how to change existing business models. It highlights the key areas of innovation, namely, value proposition, operational value, human capital and financial value. Researchers interested in this area can explore and examine the different paths firms can undertake to change their business models. Although this review pinpoints the different avenues for firm to undertake business model innovation, the mechanisms by which firms can change their business models and the external factors associated with such change remain underexplored.
The evolution of business model literature (pre-2000 to 2016)
Business model innovation framework
Previous reviews of business model literature
| (2011) | (2014) | (2016) | Our review | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Term(s) | Business model | Business model | Business model innovation | Business model(s) | Business model | Business model(s); innovation; value proposition; value creation; value capture |
| Period | 1975–2009 | Up to 1 December 2008 | 1981–May 2012 | Up to January/February 2010 | 1965–2013 | 2010–2016 |
| Search | Title; keywords | All-text topics | Keyword | Title; abstract; keywords | Title | Title; abstract; keywords |
| Databases | Business source complete | EBSCO business source premiere | na | na | EBSCO business source complete | EBSCO business complete; ABI/INFORM; JSTOR; ScinceDirect |
| Type | Peer-reviewed papers; books; reports; magazines | Papers; books; websites; unpublished manuscripts | Peer-reviewed journals; recent working papers | Papers; reviews; editorials; books; reviewed publications | Papers in peer-reviewed and non-peer-reviewed journals | Peer-reviewed papers with the exception of ; top-rated papers |
| Sample | 103 | 108 | 35 | 54 | 681 | 219 |
Reviewed papers and their subject fields
| Number of papers/Year | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subject fields | No. of journals | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | Total no. of papers | % of papers |
| Marketing | 14 | 16 | 23 | 34 | 36 | 23 | 26 | 76 | 234 | 24.8 |
| General management | 12 | 18 | 32 | 20 | 33 | 27 | 43 | 47 | 220 | 23.3 |
| Information management | 13 | 8 | 6 | 13 | 14 | 21 | 13 | 20 | 95 | 10.1 |
| Operations, technology and management | 8 | 6 | 9 | 10 | 14 | 14 | 11 | 19 | 83 | 8.8 |
| Strategic management | 2 | 25 | 8 | 3 | 17 | 7 | 3 | 19 | 82 | 8.7 |
| Innovation | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 18 | 5 | 13 | 55 | 5.8 |
| Entrepreneurship and small business management | 6 | 9 | 4 | 3 | 13 | 3 | 14 | 7 | 53 | 5.6 |
| Business ethics and governance | 2 | 11 | 5 | 4 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 6 | 44 | 4.7 |
| Business and area studies | 5 | 5 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 5 | 5 | 26 | 2.8 |
| Operations research and management science | 5 | 4 | 6 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 5 | 25 | 2.7 |
| Organisation studies | 4 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 16 | 1.7 |
| Human resources management and employment studies | 2 | 2 | – | 1 | 3 | – | 1 | 2 | 9 | 1.0 |
| International business and area studies | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 1 | 1 | 0.1 |
| Total | 76 | 111 | 102 | 103 | 151 | 124 | 130 | 222 | 943 | 100.0 |
Source of our sample
| Journals | Number of papers | Weighting (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 42 | 19.2 | |
| 28 | 12.8 | |
| 21 | 9.6 | |
| 16 | 7.3 | |
| 15 | 6.8 | |
| 11 | 5.0 | |
| 10 | 4.6 | |
| 8 | 3.7 | |
| 6 | 2.7 | |
| Others | 62 | 28.3 |
| Total | 219 | 100 |
Business model innovation areas and elements
| Areas of innovation | Elements | Relevant questions | Variables | Studies |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value proposition (Why?) | Core offering | Why our products/services? | Value proposition | |
| Value proposition | (2010) | |||
| Value proposition | ||||
| Value proposition | (2010) | |||
| Value proposition | (2010) | |||
| Type of offering | (2011) | |||
| Offering | (2012) | |||
| Offering | (2012) | |||
| Product/Service offering | (2013) | |||
| Customer value proposition | (2014) | |||
| Change in offering | (2014) | |||
| Product selection | (2015) | |||
| Value propositions | ||||
| Value proposition | (2015) | |||
| Offering | (2016) | |||
| Value proposition | (2016) | |||
| Value proposition | (2016) | |||
| Value proposition/Offering | (2016) | |||
| Value proposition | ||||
| Market offering | (2016) | |||
| Customer needs | Why customers purchase our products/services? | Customer needs | (2011) | |
| Perceived needs | ||||
| Customer need | (2012) | |||
| Customer engagement | ||||
| Target customers | Why target the current segment(s)? | Target customers | (2010) | |
| Target customers | (2012) | |||
| Customer identification | ||||
| Target segments | (2013) | |||
| Target market Segment(s) | (2014) | |||
| Target customers | (2014) | |||
| Customer segments | ||||
| Target customers | (2015) | |||
| Target customers | (2016) | |||
| Value delivery | (2016) | |||
| Market/Customer segment | (2016) | |||
| Customer segment | ||||
| Customers | (2016) | |||
| Customer perceived value | Why customers choose us? | Meeting local needs | (2010) | |
| Affordability | (2011) | |||
| Satisfy perceived needs | ||||
| Operational value (What?) | Key assets | What assets do we need? | Key resources | (2011) |
| Resources | (2012) | |||
| Key assets | (2014) | |||
| Key resources | ||||
| Resources | (2016) | |||
| Value creation | (2016) | |||
| Key resources | (2016) | |||
| Key resources | ||||
| Resources | (2016) | |||
| Key process | What processes do we require? | Key processes | (2011) | |
| Technologies | ||||
| Investment in technology | (2015) | |||
| Processes | (2016) | |||
| Value creation | (2016) | |||
| Partners network | What relationships should we consider? | Value network | ||
| Value network | ||||
| Value network | (2010) | |||
| Network architecture | ||||
| Relationships | (2012) | |||
| Value chain linkages | ||||
| Partners’ network | (2014) | |||
| Partner network | (2014) | |||
| Partner network | (2015) | |||
| Key partners | ||||
| Partner network | (2015) | |||
| Value networking | (2016) | |||
| Supply chain | ||||
| Network | (2016) | |||
| Distribution channels | What channels can deliver our products/services? | Distribution channel | (2010) | |
| Channel | (2011) | |||
| Customer access | (2012) | |||
| Distribution channel | (2014) | |||
| Channels | ||||
| Sales channels | ||||
| Value delivery | (2016) | |||
| Human capital (Who?) | Organisational learning | Who should be engaged in knowledge transfer activities? | Double loop learning | (2010) |
| Experimentation process | (2012) | |||
| Human resource practices | (2015) | |||
| Skills and competencies | Who should execute specific activities? | Resources and competencies | ||
| Core competency | (2010) | |||
| Resources and competencies | ||||
| Core internal competencies | (2013) | |||
| Core competency | (2014) | |||
| Core competences | (2015) | |||
| Domain-specific know-how | (2015) | |||
| Incentives | Who should be reward? | Incentives | (2011) | |
| Human resource practices | (2015) | |||
| Crowd rewards | ||||
| Training | Who requires development to carry out specific activities? | Human resource practices | (2015) | |
| Financial value (How?) | Revenue streams | How do we generate revenue? | Value finance | |
| Volume and structure of revenues | ||||
| Revenue model | (2010) | |||
| Sales revenues | (2010) | |||
| Revenue model | (2011) | |||
| Revenue model | (2012) | |||
| Monetisation | ||||
| Revenue model | (2013) | |||
| Revenue | (2013) | |||
| Revenue drivers | (2013) | |||
| Revenue model | (2014) | |||
| Revenue streams | ||||
| Type of revenue | (2015) | |||
| Value appropriation | (2016) | |||
| Revenue stream | (2016) | |||
| Revenue model | ||||
| Revenue | (2016) | |||
| Revenues | (2016) | |||
| Cost structure | How do we cost our products/services? | Value finance | ||
| Volume and structure of costs | ||||
| Cost structure | (2010) | |||
| Cost structure | (2010) | |||
| Cost structure | (2011) | |||
| Cost | (2013) | |||
| Cost model | (2013) | |||
| Pricing approach | (2013) | |||
| Cost structure | (2014) | |||
| Cost structure | (2014) | |||
| Cost consciousness | (2015) | |||
| Company cost structure | ||||
| Cost drivers | (2015) | |||
| Value appropriation | (2016) | |||
| Cost structure | (2016) | |||
| Costs | (2016) | |||
| Cost structure | ||||
| Finances | (2016) | |||
| Cash flow | How should we manage cash flow? | Capital employed | (2010) | |
| Monetisation | ||||
| Margins | How much surplus can we make? | Margin | ||
| Profit formula | (2010) | |||
| Economic profit equation | (2010) | |||
| Profit formula | (2011) | |||
| Profit model | (2012) | |||
| Profit | (2013) | |||
| Margins | (2013) | |||
| Estimation of profit potential | (2014) | |||
| Profit formula | (2015) | |||
| Profit formula | (2016) |
ABS ( 2010 ), Academic Journal Quality Guide , Version 4 , The Association of Business Schools , London .
Al-Debei , M.M. and Avison , D. ( 2010 ), “ Developing a unified framework of the business model concept ”, European Journal of Information Systems , Vol. 19 No. 3 , pp. 359 - 376 .
Amit , R. and Zott , C. ( 2012 ), “ Creating value through business model innovation ”, MIT Sloan Management Review , Vol. 53 No. 3 , pp. 41 - 49 .
Andries , P. and Debackere , K. ( 2013 ), “ Business model innovation: Propositions on the appropriateness of different learning approaches ”, Creativity and Innovation Management , Vol. 22 No. 4 , pp. 337 - 358 .
Baden-Fuller , C. and Haefliger , S. ( 2013 ), “ Business models and technological innovation ”, Long Range Planning , Vol. 46 No. 6 , pp. 419 - 426 .
Belenzon , S. and Schankerman , M. ( 2015 ), “ Motivation and sorting of human capital in open innovation ”, Strategic Management Journal , Vol. 36 No. 6 , pp. 795 - 820 .
Bock , A.J. , Opsahl , T. , George , G. and Gann , D.M. ( 2012 ), “ The effects of culture and structure on strategic flexibility during business model innovation ”, Journal of Management Studies , Vol. 49 No. 2 , pp. 279 - 305 .
Brea-Solís , H. , Casadesus-Masanell , R. and Grifell-Tatjé , E. ( 2015 ), “ Business model evaluation: quantifying Walmart’s sources of advantage ”, Strategic Entrepreneurship Journal , Vol. 9 No. 1 , pp. 12 - 33 .
Casadesus-Masanell , R. and Llanes , G. ( 2011 ), “ Mixed source ”, Management Science , Vol. 57 No. 7 , pp. 1212 - 1230 .
Casadesus-Masanell , R. and Ricart , J.E. ( 2010 ), “ From strategy to business models and onto tactics ”, Long Range Planning , Vol. 43 Nos 2-3 , pp. 195 - 215 .
Casadesus-Masanell , R. and Zhu , F. ( 2013 ), “ Business model innovation and competitive imitation: the case of sponsor-based business models ”, Strategic Management Journal , Vol. 34 No. 4 , pp. 464 - 482 .
Chatterjee , S. ( 2013 ), “ Simple rules for designing business models ”, California Management Review , Vol. 55 No. 2 , pp. 97 - 124 .
Cavalcante , S. , Kesting , P. and Ulhøi , J. ( 2011 ), “ Business model dynamics and innovation: (re)establishing the missing linkages ”, Management Decision , Vol. 49 No. 8 , pp. 1327 - 1342 .
Chesbrough , H. ( 2010 ), “ Business model innovation: opportunities and barriers ”, Long Range Planning , Vol. 43 Nos. 2-3 , pp. 354 - 363 .
Chesbrough , H. and Rosenbloom , R.S. ( 2002 ), “ The role of the business model in capturing value from innovation: evidence from Xerox corporation’s technology spin off companies ”, Industrial & Corporate Change , Vol. 11 No. 3 , pp. 529 - 555 .
Christensen , C.M. , Bartman , T. and Van Bever , D. ( 2016 ), “ The hard truth about business model innovation ”, MIT Sloan Management Review , Vol. 58 No. 1 , pp. 31 - 40 .
Cortimiglia , M.N. , Ghezzi , A. and Frank , A.G. ( 2016 ), “ Business model innovation and strategy making nexus: evidence from a cross‐industry mixed‐methods study ”, R&D Management , Vol. 46 No. 3 , pp. 414 - 432 .
Cucculelli , M. and Bettinelli , C. ( 2015 ), “ Business models, intangibles and firm performance: evidence on corporate entrepreneurship from Italian manufacturing SMEs ”, Small Business Economics , Vol. 45 No. 2 , pp. 329 - 350 .
Dahan , N.M. , Doh , J.P. , Oetzel , J. and Yaziji , M. ( 2010 ), “ Corporate-NGO collaboration: Co-creating new business models for developing markets ”, Long Range Planning , Vol. 43 Nos 2-3 , pp. 326 - 342 .
DaSilva , C.M. and Trkman , P. ( 2014 ), “ Business model: what it is and what it is not ”, Long Range Planning , Vol. 47 No. 6 , pp. 379 - 389 .
Demil , B. and Lecocq , X. ( 2010 ), “ Business model evolution: in search of dynamic consistency ”, Long Range Planning , Vol. 43 Nos 2-3 , pp. 227 - 246 .
Dmitriev , V. , Simmons , G. , Truong , Y. , Palmer , M. and Schneckenberg , D. ( 2014 ), “ An exploration of business model development in the commercialization of technology innovations ”, R&D Management , Vol. 44 No. 3 , pp. 306 - 321 .
Dunford , R. , Palmer , I. and Benveniste , J. ( 2010 ), “ Business model replication for early and rapid internationalisation: the ING direct experience ”, Long Range Planning , Vol. 43 Nos 5-6 , pp. 655 - 674 .
Esslinger , H. ( 2011 ), “ Sustainable design: beyond the innovation-driven business model ”, The Journal of Product Innovation Management , Vol. 28 No. 3 , pp. 401 - 404 .
Eyring , M.J. , Johnson , M.W. and Nair , H. ( 2011 ), “ New business models in emerging markets ”, Harvard Business Review , Vol. 89 No. 1 , pp. 89 - 95 .
Frankenberger , K. , Weiblen , T. and Gassmann , O. ( 2014 ), “ The antecedents of open business models: an exploratory study of incumbent firms ”, R&D Management , Vol. 44 No. 2 , pp. 173 - 188 .
Gambardella , A. and McGahan , A.M. ( 2010 ), “ Business-model innovation: general purpose technologies and their implications for industry structure ”, Long Range Planning , Vol. 43 Nos 2-3 , pp. 262 - 271 .
George , G. and Bock , A.J. ( 2011 ), “ The business model in practice and its implications for entrepreneurship research ”, Entrepreneurship: Theory & Practice , Vol. 35 No. 1 , pp. 83 - 111 .
Girotra , K. and Netessine , S. ( 2011 ), “ How to build risk into your business model ”, Harvard Business Review , Vol. 89 No. 5 , pp. 100 - 105 .
Girotra , K. and Netessine , S. ( 2014 ), “ Four paths to business model innovation ”, Harvard Business Review , Vol. 92 No. 7 , pp. 96 - 103 .
Hartmann , P.M. , Hartmann , P.M. , Zaki , M. , Zaki , M. , Feldmann , N. and Neely , A. ( 2016 ), “ Capturing value from Big Data – a taxonomy of data-driven business models used by start-up firms ”, International Journal of Operations & Production Management , Vol. 36 No. 10 , pp. 1382 - 1406 .
Hlady-Rispal , M. and Servantie , V. ( 2016 ), “ Business models impacting social change in violent and poverty-stricken neighbourhoods: a case study in Colombia ”, International Small Business Journal , Vol. 35 No. 4 , pp. 1 - 22 .
Huang , H.C. , Lai , M.C. , Lin , L.H. and Chen , C.T. ( 2013 ), “ Overcoming organizational inertia to strengthen business model innovation: an open innovation perspective ”, Journal of Organizational Change Management , Vol. 26 No. 6 , pp. 977 - 1002 .
Huarng , K.-H. ( 2013 ), “ A two-tier business model and its realization for entrepreneurship ”, Journal of Business Research , Vol. 66 No. 10 , pp. 2102 - 2105 .
Iansiti , M. and Lakhani , K.R. ( 2014 ), “ Digital ubiquity: how connections, sensors, and data are revolutionizing business ”, Harvard Business Review , Vol. 92 No. 11 , pp. 91 - 99 .
Johnson , M.W. , Christensen , C.M. and Kagermann , H. ( 2008 ), “ Reinventing your business model ”, Harvard Business Review , Vol. 86 No. 12 , pp. 57 - 68 .
Karimi , J. and Walter , Z. ( 2016 ), “ Corporate entrepreneurship, disruptive business model innovation adoption, and its performance: the case of the newspaper industry ”, Long Range Planning , Vol. 49 No. 3 , pp. 342 - 360 .
Kastalli , I. , Van Looy , B. and Neely , A. ( 2013 ), “ Steering manufacturing firms towards service business model innovation ”, California Management Review , Vol. 56 No. 1 , pp. 100 - 123 .
Kohler , T. ( 2015 ), “ Crowdsourcing-based business models ”, California Management Review , Vol. 57 No. 4 , pp. 63 - 84 .
Kiron , D. , Kruschwitz , N. , Haanaes , K. , Reeves , M. and Goh , E. ( 2013 ), “ The innovation bottom line ”, MIT Sloan Management Review , Vol. 54 No. 2 , pp. 1 - 20 .
Klang , D. , Wallnöfer , M. and Hacklin , F. ( 2014 ), “ The business model paradox: a systematic review and exploration of antecedents ”, International Journal of Management Reviews , Vol. 16 No. 4 , pp. 454 - 478 .
Kortmann , S. and Piller , F. ( 2016 ), “ Open business models and closed-loop value chains ”, California Management Review , Vol. 58 No. 3 , pp. 88 - 108 .
Landau , C. , Karna , A. and Sailer , M. ( 2016 ), “ Business model adaptation for emerging markets: a case study of a German automobile manufacturer in India ”, R&D Management , Vol. 46 No. 3 , pp. 480 - 503 .
Lange , K. , Geppert , M. , Saka-Helmhout , A. and Becker-Ritterspach , F. ( 2015 ), “ Changing business models and employee representation in the airline industry: a comparison of British Airways and Deutsche Lufthansa ”, British Journal of Management , Vol. 26 No. 3 , pp. 388 - 407 .
McGrath , R.G. ( 2010 ), “ Business models: a discovery driven approach ”, Long Range Planning , Vol. 43 Nos. 2-3 , pp. 247 - 261 .
McNamara , P. , Peck , S.I. and Sasson , A. ( 2013 ), “ Competing business models, value creation and appropriation in English football ”, Long Range Planning , Vol. 46 No. 6 , pp. 475 - 487 .
Markides , C.C. ( 2013 ), “ Business model innovation: what can the ambidexterity literature teach us? ”, Academy of Management Perspectives , Vol. 27 No. 3 , pp. 313 - 323 .
Mason , K. and Spring , M. ( 2011 ), “ The sites and practices of business models ”, Industrial Marketing Management , Vol. 40 No. 6 , pp. 1032 - 1041 .
Mehrizi , M.H.R. and Lashkarbolouki , M. ( 2016 ), “ Unlearning troubled business models: from realization to marginalization ”, Long Range Planning , Vol. 49 No. 3 , pp. 298 - 323 .
Mezger , F. ( 2014 ), “ Toward a capability-based conceptualization of business model innovation: insights from an explorative study ”, R&D Management , Vol. 44 No. 5 , pp. 429 - 449 .
Michel , S. ( 2014 ), “ Capture more value ”, Harvard Business Review , Vol. 92 No. 4 , pp. 78 - 85 .
Morris , M.H. , Shirokova , G. and Shatalov , A. ( 2013 ), “ The business model and firm performance: the case of Russian food service ventures ”, Journal of Small Business Management , Vol. 51 No. 1 , pp. 46 - 65 .
Osterwalder , A. , Pigneur , Y. and Tucci , C.L. ( 2005 ), “ Clarifying business models: origins, present, and future of the concept ”, Communications of the Association for Information Systems , Vol. 16 No. 1 , pp. 1 - 25 .
Peters , C. , Blohm , I. and Leimeister , J.M. ( 2015 ), “ Anatomy of successful business models for complex services: insights from the telemedicine field ”, Journal of Management Information Systems , Vol. 32 No. 3 , pp. 75 - 104 .
Rajala , R. , Westerlund , M. and Möller , K. ( 2012 ), “ Strategic flexibility in open innovation – designing business models for open source software ”, European Journal of Marketing , Vol. 46 No. 10 , pp. 1368 - 1388 .
Roberge , M. ( 2015 ), “ The right way to use compensation: to shift strategy, change how you pay your team ”, Harvard Business Review , Vol. 93 No. 4 , pp. 70 - 75 .
Schneider , S. and Spieth , P. ( 2013 ), “ Business model innovation: towards an integrated future research agenda ”, International Journal of Innovation Management , Vol. 17 No. 1 , pp. 134 - 156 .
Shafer , S.M. , Smith , H.J. and Linder , J.C. ( 2005 ), “ The power of business models ”, Business Horizons , Vol. 48 No. 3 , pp. 199 - 207 .
Sinfield , J.V. , Calder , E. , McConnell , B. and Colson , S. ( 2012 ), “ How to identify new business models ”, MIT Sloan Management Review , Vol. 53 No. 2 , pp. 85 - 90 .
Sinkovics , N. , Sinkovics , R.R. and Yamin , M. ( 2014 ), “ The role of social value creation in business model formulation at the bottom of the pyramid – implications for MNEs? ”, International Business Review , Vol. 23 No. 4 , pp. 692 - 707 .
Spieth , P. , Schneckenberg , D. and Ricart , J.E. ( 2014 ), “ Business model innovation – state of the art and future challenges for the field ”, R&D Management , Vol. 44 No. 3 , pp. 237 - 247 .
Sorescu , A. , Frambach , R.T. , Singh , J. , Rangaswamy , A. and Bridges , C. ( 2011 ), “ Innovations in retail business models ”, Journal of Retailing , Vol. 87 No. 1 , pp. S3 - S16 .
Sosna , M. , Trevinyo-Rodríguez , R.N. and Velamuri , S.R. ( 2010 ), “ Business model innovation through trial-and-error learning: the naturhouse case ”, Long Range Planning , Vol. 43 Nos. 2-3 , pp. 383 - 407 .
Storbacka , K. ( 2011 ), “ A solution business model: capabilities and management practices for integrated solutions ”, Industrial Marketing Management , Vol. 40 No. 5 , pp. 699 - 711 .
Taran , Y. , Boer , H. and Lindgren , P. ( 2015 ), “ A business model innovation typology ”, Decision Sciences , Vol. 46 No. 2 , pp. 301 - 331 .
Transfield , D. , Denyer , D. and Smart , P. ( 2003 ), “ Towards a methodology for developing evidence-informed management knowledge by means of systematic review ”, British Journal of Management , Vol. 14 No. 3 , pp. 207 - 222 .
Teece , D.J. ( 2010 ), “ Business models, business strategy and innovation ”, Long Range Planning , Vol. 43 Nos 2-3 , pp. 172 - 194 .
Velu , C. ( 2015 ), “ Business model innovation and third-party alliance on the survival of new firms ”, Technovation , Vol. 35 No. 1 , pp. 1 - 11 .
Velu , C. ( 2016 ), “ Evolutionary or revolutionary business model innovation through coopetition? The role of dominance in network markets ”, Industrial Marketing Management , Vol. 53 No. 1 , pp. 124 - 135 .
Velu , C. and Jacob , A. ( 2014 ), “ Business model innovation and owner–managers: the moderating role of competition ”, R&D Management , Vol. 46 No. 3 , pp. 451 - 463 .
Visnjic , I. , Wiengarten , F. and Neely , A. ( 2016 ), “ Only the brave: product innovation, service business model innovation, and their impact on performance ”, Journal of Product Innovation Management , Vol. 33 No. 1 , pp. 36 - 52 .
Weill , P. and Woerner , S.L. ( 2013 ), “ Optimizing your digital business model ”, MIT Sloan Management Review , Vol. 54 No. 3 , pp. 71 - 78 .
Wilson , F. and Post , J.E. ( 2013 ), “ Business models for people, planet (& profits): exploring the phenomena of social business, a market-based approach to social value creation ”, Small Business Economics , Vol. 40 No. 3 , pp. 715 - 737 .
Wirtz , B.W. , Pistoia , A. , Ullrich , S. and Göttel , V. ( 2016 ), “ Business models: origin, development and future research perspectives ”, Long Range Planning , Vol. 49 No. 1 , pp. 36 - 54 .
Wu , X. , Ma , R. and Shi , Y. ( 2010 ), “ How do latecomer firms capture value from disruptive technologies? A secondary business-model innovation perspective ”, IEEE Transactions on Engineering Management , Vol. 57 No. 1 , pp. 51 - 62 .
Yunus , M. , Moingeon , B. and Lehmann-Ortega , L. ( 2010 ), “ Building social business models: lessons from the grameen experience ”, Long Range Planning , Vol. 43 Nos 2-3 , pp. 308 - 325 .
Zott , C. and Amit , R. ( 2010 ), “ Business model design: an activity system perspective ”, Long Range Planning , Vol. 43 Nos 2-3 , pp. 216 - 226 .
Zott , C. , Amit , R. and Massa , L. ( 2011 ), “ The business model: recent developments and future research ”, Journal of Management , Vol. 37 No. 4 , pp. 1019 - 1042 .
Further reading
Weill , P. , Malone , T.W. and Apel , T.G. ( 2011 ), “ The business models investors prefer ”, MIT Sloan Management Review , Vol. 52 No. 4 , pp. 17 - 19 .
Corresponding author
Related articles, all feedback is valuable.
Please share your general feedback
Report an issue or find answers to frequently asked questions
Contact Customer Support
Business Model Canvas: Explained with Examples
Got a new business idea, but don’t know how to put it to work? Want to improve your existing business model? Overwhelmed by writing your business plan? There is a one-page technique that can provide you the solution you are looking for, and that’s the business model canvas.
In this guide, you’ll have the Business Model Canvas explained, along with steps on how to create one. All business model canvas examples in the post can be edited online.
What is a Business Model Canvas
A business model is simply a plan describing how a business intends to make money. It explains who your customer base is and how you deliver value to them and the related details of financing. And the business model canvas lets you define these different components on a single page.
The Business Model Canvas is a strategic management tool that lets you visualize and assess your business idea or concept. It’s a one-page document containing nine boxes that represent different fundamental elements of a business.
The business model canvas beats the traditional business plan that spans across several pages, by offering a much easier way to understand the different core elements of a business.
The right side of the canvas focuses on the customer or the market (external factors that are not under your control) while the left side of the canvas focuses on the business (internal factors that are mostly under your control). In the middle, you get the value propositions that represent the exchange of value between your business and your customers.
The business model canvas was originally developed by Alex Osterwalder and Yves Pigneur and introduced in their book ‘ Business Model Generation ’ as a visual framework for planning, developing and testing the business model(s) of an organization.
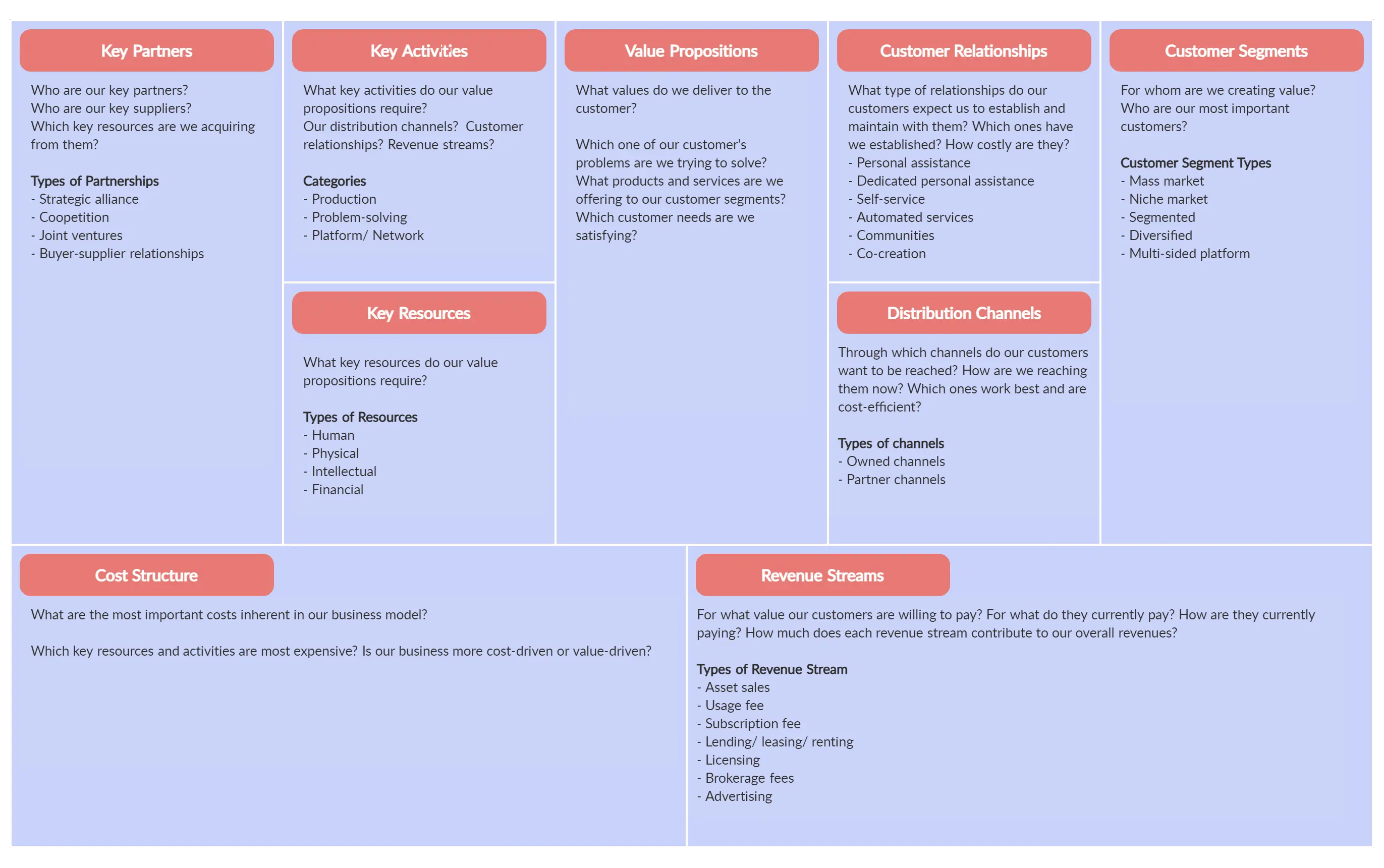
What Are the Benefits of Using a Business Model Canvas
Why do you need a business model canvas? The answer is simple. The business model canvas offers several benefits for businesses and entrepreneurs. It is a valuable tool and provides a visual and structured approach to designing, analyzing, optimizing, and communicating your business model.
- The business model canvas provides a comprehensive overview of a business model’s essential aspects. The BMC provides a quick outline of the business model and is devoid of unnecessary details compared to the traditional business plan.
- The comprehensive overview also ensures that the team considers all required components of their business model and can identify gaps or areas for improvement.
- The BMC allows the team to have a holistic and shared understanding of the business model while enabling them to align and collaborate effectively.
- The visual nature of the business model canvas makes it easier to refer to and understand by anyone. The business model canvas combines all vital business model elements in a single, easy-to-understand canvas.
- The BMC can be considered a strategic analysis tool as it enables you to examine a business model’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and challenges.
- It’s easier to edit and can be easily shared with employees and stakeholders.
- The BMC is a flexible and adaptable tool that can be updated and revised as the business evolves. Keep your business agile and responsive to market changes and customer needs.
- The business model canvas can be used by large corporations and startups with just a few employees.
- The business model canvas effectively facilitates discussions among team members, investors, partners, customers, and other stakeholders. It clarifies how different aspects of the business are related and ensures a shared understanding of the business model.
- You can use a BMC template to facilitate discussions and guide brainstorming brainstorming sessions to generate insights and ideas to refine the business model and make strategic decisions.
- The BMC is action-oriented, encouraging businesses to identify activities and initiatives to improve their business model to drive business growth.
- A business model canvas provides a structured approach for businesses to explore possibilities and experiment with new ideas. This encourages creativity and innovation, which in turn encourages team members to think outside the box.
How to Make a Business Model Canvas
Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to create a business canvas model.
Step 1: Gather your team and the required material Bring a team or a group of people from your company together to collaborate. It is better to bring in a diverse group to cover all aspects.
While you can create a business model canvas with whiteboards, sticky notes, and markers, using an online platform like Creately will ensure that your work can be accessed from anywhere, anytime. Create a workspace in Creately and provide editing/reviewing permission to start.
Step 2: Set the context Clearly define the purpose and the scope of what you want to map out and visualize in the business model canvas. Narrow down the business or idea you want to analyze with the team and its context.
Step 3: Draw the canvas Divide the workspace into nine equal sections to represent the nine building blocks of the business model canvas.
Step 4: Identify the key building blocks Label each section as customer segment, value proposition, channels, customer relationships, revenue streams, key resources, key activities, and cost structure.
Step 5: Fill in the canvas Work with your team to fill in each section of the canvas with relevant information. You can use data, keywords, diagrams, and more to represent ideas and concepts.
Step 6: Analyze and iterate Once your team has filled in the business model canvas, analyze the relationships to identify strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and challenges. Discuss improvements and make adjustments as necessary.
Step 7: Finalize Finalize and use the model as a visual reference to communicate and align your business model with stakeholders. You can also use the model to make informed and strategic decisions and guide your business.
What are the Key Building Blocks of the Business Model Canvas?
There are nine building blocks in the business model canvas and they are:
Customer Segments
Customer relationships, revenue streams, key activities, key resources, key partners, cost structure.
- Value Proposition
When filling out a Business Model Canvas, you will brainstorm and conduct research on each of these elements. The data you collect can be placed in each relevant section of the canvas. So have a business model canvas ready when you start the exercise.
Let’s look into what the 9 components of the BMC are in more detail.
These are the groups of people or companies that you are trying to target and sell your product or service to.
Segmenting your customers based on similarities such as geographical area, gender, age, behaviors, interests, etc. gives you the opportunity to better serve their needs, specifically by customizing the solution you are providing them.
After a thorough analysis of your customer segments, you can determine who you should serve and ignore. Then create customer personas for each of the selected customer segments.
There are different customer segments a business model can target and they are;
- Mass market: A business model that focuses on mass markets doesn’t group its customers into segments. Instead, it focuses on the general population or a large group of people with similar needs. For example, a product like a phone.
- Niche market: Here the focus is centered on a specific group of people with unique needs and traits. Here the value propositions, distribution channels, and customer relationships should be customized to meet their specific requirements. An example would be buyers of sports shoes.
- Segmented: Based on slightly different needs, there could be different groups within the main customer segment. Accordingly, you can create different value propositions, distribution channels, etc. to meet the different needs of these segments.
- Diversified: A diversified market segment includes customers with very different needs.
- Multi-sided markets: this includes interdependent customer segments. For example, a credit card company caters to both their credit card holders as well as merchants who accept those cards.
Use STP Model templates for segmenting your market and developing ideal marketing campaigns
Visualize, assess, and update your business model. Collaborate on brainstorming with your team on your next business model innovation.
In this section, you need to establish the type of relationship you will have with each of your customer segments or how you will interact with them throughout their journey with your company.
There are several types of customer relationships
- Personal assistance: you interact with the customer in person or by email, through phone call or other means.
- Dedicated personal assistance: you assign a dedicated customer representative to an individual customer.
- Self-service: here you maintain no relationship with the customer, but provides what the customer needs to help themselves.
- Automated services: this includes automated processes or machinery that helps customers perform services themselves.
- Communities: these include online communities where customers can help each other solve their own problems with regard to the product or service.
- Co-creation: here the company allows the customer to get involved in the designing or development of the product. For example, YouTube has given its users the opportunity to create content for its audience.
You can understand the kind of relationship your customer has with your company through a customer journey map . It will help you identify the different stages your customers go through when interacting with your company. And it will help you make sense of how to acquire, retain and grow your customers.
This block is to describe how your company will communicate with and reach out to your customers. Channels are the touchpoints that let your customers connect with your company.
Channels play a role in raising awareness of your product or service among customers and delivering your value propositions to them. Channels can also be used to allow customers the avenue to buy products or services and offer post-purchase support.
There are two types of channels
- Owned channels: company website, social media sites, in-house sales, etc.
- Partner channels: partner-owned websites, wholesale distribution, retail, etc.
Revenues streams are the sources from which a company generates money by selling their product or service to the customers. And in this block, you should describe how you will earn revenue from your value propositions.
A revenue stream can belong to one of the following revenue models,
- Transaction-based revenue: made from customers who make a one-time payment
- Recurring revenue: made from ongoing payments for continuing services or post-sale services
There are several ways you can generate revenue from
- Asset sales: by selling the rights of ownership for a product to a buyer
- Usage fee: by charging the customer for the use of its product or service
- Subscription fee: by charging the customer for using its product regularly and consistently
- Lending/ leasing/ renting: the customer pays to get exclusive rights to use an asset for a fixed period of time
- Licensing: customer pays to get permission to use the company’s intellectual property
- Brokerage fees: revenue generated by acting as an intermediary between two or more parties
- Advertising: by charging the customer to advertise a product, service or brand using company platforms
What are the activities/ tasks that need to be completed to fulfill your business purpose? In this section, you should list down all the key activities you need to do to make your business model work.
These key activities should focus on fulfilling its value proposition, reaching customer segments and maintaining customer relationships, and generating revenue.
There are 3 categories of key activities;
- Production: designing, manufacturing and delivering a product in significant quantities and/ or of superior quality.
- Problem-solving: finding new solutions to individual problems faced by customers.
- Platform/ network: Creating and maintaining platforms. For example, Microsoft provides a reliable operating system to support third-party software products.
This is where you list down which key resources or the main inputs you need to carry out your key activities in order to create your value proposition.
There are several types of key resources and they are
- Human (employees)
- Financial (cash, lines of credit, etc.)
- Intellectual (brand, patents, IP, copyright)
- Physical (equipment, inventory, buildings)
Key partners are the external companies or suppliers that will help you carry out your key activities. These partnerships are forged in oder to reduce risks and acquire resources.
Types of partnerships are
- Strategic alliance: partnership between non-competitors
- Coopetition: strategic partnership between partners
- Joint ventures: partners developing a new business
- Buyer-supplier relationships: ensure reliable supplies
In this block, you identify all the costs associated with operating your business model.
You’ll need to focus on evaluating the cost of creating and delivering your value propositions, creating revenue streams, and maintaining customer relationships. And this will be easier to do so once you have defined your key resources, activities, and partners.
Businesses can either be cost-driven (focuses on minimizing costs whenever possible) and value-driven (focuses on providing maximum value to the customer).
Value Propositions
This is the building block that is at the heart of the business model canvas. And it represents your unique solution (product or service) for a problem faced by a customer segment, or that creates value for the customer segment.
A value proposition should be unique or should be different from that of your competitors. If you are offering a new product, it should be innovative and disruptive. And if you are offering a product that already exists in the market, it should stand out with new features and attributes.
Value propositions can be either quantitative (price and speed of service) or qualitative (customer experience or design).
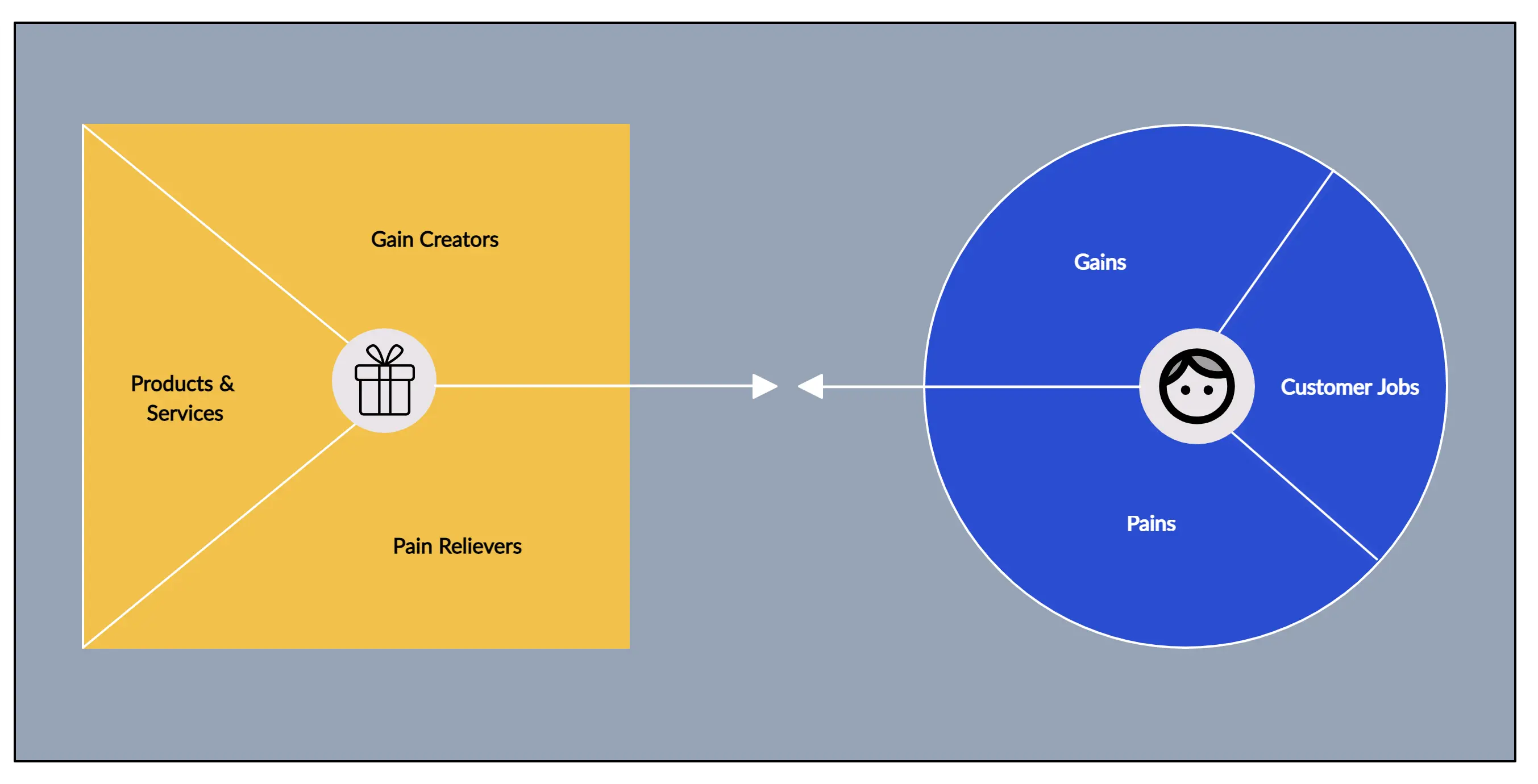
What to Avoid When Creating a Business Model Canvas
One thing to remember when creating a business model canvas is that it is a concise and focused document. It is designed to capture key elements of a business model and, as such, should not include detailed information. Some of the items to avoid include,
- Detailed financial projections such as revenue forecasts, cost breakdowns, and financial ratios. Revenue streams and cost structure should be represented at a high level, providing an overview rather than detailed projections.
- Detailed operational processes such as standard operating procedures of a business. The BMC focuses on the strategic and conceptual aspects.
- Comprehensive marketing or sales strategies. The business model canvas does not provide space for comprehensive marketing or sales strategies. These should be included in marketing or sales plans, which allow you to expand into more details.
- Legal or regulatory details such as intellectual property, licensing agreements, or compliance requirements. As these require more detailed and specialized attention, they are better suited to be addressed in separate legal or regulatory documents.
- Long-term strategic goals or vision statements. While the canvas helps to align the business model with the overall strategy, it should focus on the immediate and tangible aspects.
- Irrelevant or unnecessary information that does not directly relate to the business model. Including extra or unnecessary information can clutter the BMC and make it less effective in communicating the core elements.
What Are Your Thoughts on the Business Model Canvas?
Once you have completed your business model canvas, you can share it with your organization and stakeholders and get their feedback as well. The business model canvas is a living document, therefore after completing it you need to revisit and ensure that it is relevant, updated and accurate.
What best practices do you follow when creating a business model canvas? Do share your tips with us in the comments section below.
Join over thousands of organizations that use Creately to brainstorm, plan, analyze, and execute their projects successfully.
FAQs About the Business Model Canvas
- Use clear and concise language
- Use visual-aids
- Customize for your audience
- Highlight key insights
- Be open to feedback and discussion
More Related Articles

Amanda Athuraliya is the communication specialist/content writer at Creately, online diagramming and collaboration tool. She is an avid reader, a budding writer and a passionate researcher who loves to write about all kinds of topics.
The Importance of Business Models
Chat with Paper: Save time, read 10X faster with AI
Citation Count
Theory of business enterprise
Initiation and implementation of dual business model innovation in the firm, conclusion, conceptual framework, and future research, the promise of entrepreneurship as a field of research, the practice of management, the role of the business model in capturing value from innovation: evidence from xerox corporation's technology spin‐off companies, why business models matter., 管理的实践=the practice of management, related papers (5), trending questions (3).
Business is crucial for society when it operates ethically, socially, and ecologically. Profit-driven enterprises must benefit society and avoid harming nature, emphasizing innovative and sustainable business models for societal well-being.
The paper discusses the importance of business models, including the consideration of ethical, social, and ecological factors.
The paper does not provide information about the advantages and disadvantages of different business models.
- Integrations
- Learning Center
How to Build a Product Roadmap Based on a Business Model Canvas
Could you list all of the key building blocks you need to develop, manage, maintain, market, and sell a product on a single sheet of paper? With the business model canvas, you can! Using the business model canvas approach is a great way to force yourself to focus on the most strategically important elements of your product. As the name suggests, the typical use case for this tool is to outline the fundamental building blocks of a business, but it also can work really well for a product.
Today we’ll show you how the business model canvas works and how you can use it to come up with a high-level product strategy.
What is a Business Model Canvas?
As you can see from the sample example below (thanks, Strategyzer.com), a business model canvas is a one-page summary describing the high-level strategic details needed to get a business (or product) successfully to market.
The categories or buckets contained in a canvas can be customized. But most will look similar to the one here—covering such key areas as:
- The product’s value propositions (what it does and promises)
- Customer segments (who it’s for)
- Key activities (the steps the team must complete to make it successful)
- Key resources (what personnel, tools, and budget the team will have access to)
- Channels (how the organization will market and sell it)
- Customer relationships (how the team will support and work with its customer base)
- Key partners (how third parties will fit into the plan)
- Cost structure (what it costs to build the product as well as how to sell and support it)
- Revenue streams (how the product will make money)
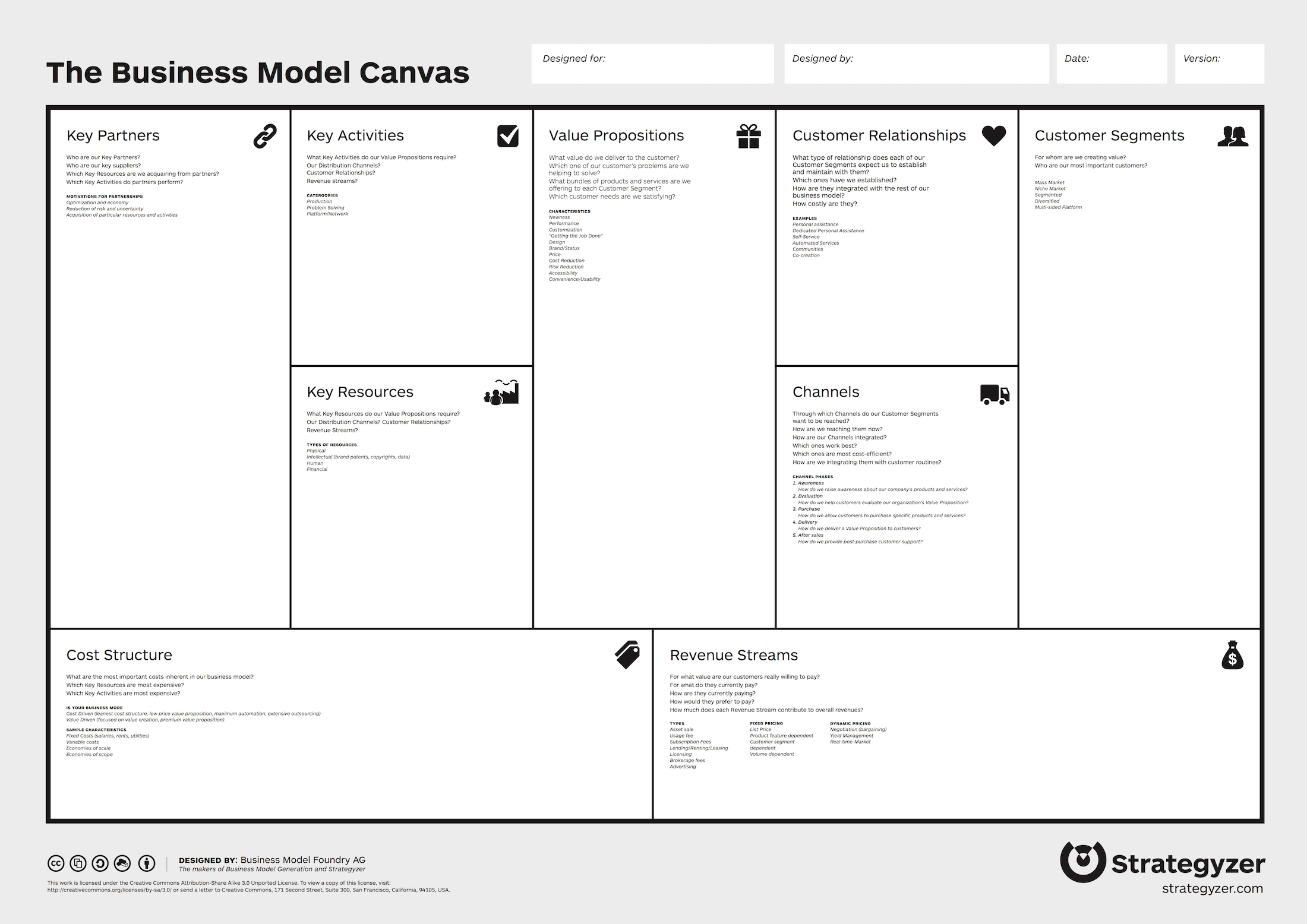
If you think about it, that’s a fairly comprehensive set of building blocks you’ll need to think through for your product before you begin developing it. There will certainly be additional factors that’ll affect your strategy, but if you can fill in these high-level details—which, as you can see, should fit comfortably on a single page—you’ll have a useful strategic guide for developing your product roadmap.
Why Should I Use a Business Model Canvas to Develop a Product Roadmap?
Okay, but why? What’s the benefit of building a business model canvas (or the, even more, stripped-down variation, the lean canvas) to guide my product roadmap ?
There are plenty of reasons. But simply put, you can think of a business model canvas as a mission statement for your product roadmap. It’s a handy reference you can refer to, to make sure your roadmap always reflects all the strategic elements needed for your product’s success.
Tweet This: “Think of a business model canvas as a mission statement for your product roadmap.”
Our co-founder Jim Semick has a couple of great short videos explaining the business model canvas concept, which you can check out in the player below.
As Jim explains, here are a few of the benefits of using a business model canvas to think through product strategies:
1. You can use a business model canvas to roadmap quickly.
You can use this canvas approach in just a few hours (and as Jim says, you can even do it with sticky-notes).
This way, rather than trying to write out every detail about your product plan beforehand, you can just document the highlights—and then you can get rolling translating the canvas into your product roadmap.

2. A business model canvas will be more agile.
One problem with the old structure of documenting a business model—the traditional business plan—was that it was almost always inaccurate as soon as the author finished drafting it.
These meaty plans included detailed cost estimates, revenue projections going years into the future, and long-term plans for growing the staff. How could any of that remain accurate for long?
In product terms, you can think of the business plan as resembling an MRD (Market Requirements Document). It’s long, detailed, and probably mostly untrue by the time it’s done.
But because you can put a canvas together so quickly, it will much more accurately reflect your strategic thinking and your company’s current reality. And if things change, it’ll be easier than a long and detailed plan to adjust. This brings us to Jim’s third benefit…
3. Business model canvas roadmaps allow you to pivot as needed.
If you build a business model canvas to guide your business roadmap , and something happens that forces you to re-prioritize or pivot your product , it will be a lot easier to update this short, high-level document than it would be if you had some monster MRD or business plan to tear apart and edit.
With a one-page business model canvas acting as the strategic undergirding for your roadmap, you’ll always be able to quickly spot any items or plans that need updating whenever priorities change or new realities demand that you adjust your approach.
How Can I Use A Business Model Canvas to Guide My Product Roadmap?
The alexa example.
Let’s talk through a hypothetical example, using Amazon’s Echo device (“Alexa”) as our guide.
Imagine that as they were talking through what belonged in the “Revenue Streams” bucket of the business model canvas, Amazon’s Echo team came up with three sources of revenue to start with:
1) Selling Echo devices.
2) Using the device to sell other stuff as customers ask it to connect to the Amazon marketplace. (“Alexa, please add laundry detergent pods to my shopping cart.”)
3) Licensing Echo’s proprietary speech-recognition technology to other businesses.
Now, if the Echo product team put these on their business model canvas, they’d know that they need to make room for budget, time, and resources on their product roadmap for all of these revenue streams.
Another Hypothetical Example of the Business Model Canvas: Channels
Or think about the Channels bucket in the business model canvas. If your team was building out a canvas, maybe you’d have several ideas for reaching customers:
1) The in-house sales team. 2) Affiliate partners. 3) Word-of-mouth advertising from users.
It’s easy to write. But how are you going to translate that “word-of-mouth” strategy into an actual plan?
Maybe you’ll need to budget time and resources for developing things right into your product that make it easier for users to share their experiences with friends, such as a handy tool to help them tweet about it. Maybe you’ll even want to include an “Invite a friend” feature that lets users easier send a trial license to friends, or a couponing feature that offers some reward to a user who brings in two more users.
The point is, your business model canvas can serve as a great strategic reminder of the things you’ve determined are important enough to make it onto your product roadmap .
So you can always look back and see immediately—it’s just one page, after all—if you’re still working on all of the essential elements of your product, or if you’ve inadvertently strayed from them and gotten lost in the wrong details.
That’s why we’re big proponents of the business model canvas approach to guiding your product roadmap .
Do you have an opinion about using the business model canvas approach for developing and documenting your product’s strategy? Feel free to share them in the comments section.

Product Management Training: 5 Excellent Resources
If you want to become a software developer, one option is to major in computer science or software engineering in...
A Product Manager’s Role in SAFe®
Agile started with software development. Although many organizations have found the principles beneficial. The ability to quickly assess, adjust, and...
5 Roadmap Templates for Product Executives
Product roadmaps shouldn’t be a one-size-fits-all proposition, as different stakeholders care about various elements and require different levels of detail....
Continue exploring
You can search or explore specific categories.
Product Updates
Company news and updates, templates and workbooks, remote product management, product metrics and analytics, product strategy example, product managers, prioritization and backlog, tools and resources, customer-centricity, product leadership, product management, roadmap and roadmap management, product strategy, agile & product development, career and interviews, try productplan free for 14 days, share on mastodon.
Business Essay Examples

13 Business Essay Examples for Students
14 min read
Published on: May 1, 2023
Last updated on: Jan 30, 2024

Share this article
Are you struggling to figure out the structure, research, or data required to make your essay stand out? Or frustrated by the lack of inspiration and ideas for your essay?
But don't give up yet! We have a powerful solution that will make your essay writing a breeze. Our list of business essay examples is here to help!
We have compiled expertly written business essay examples that will illustrate how to write a striking business essay.
With our examples, you'll be able to see how to structure your essay and generate creative ideas for your topic. And our tips will help you make the most of these examples.
So, let's dive in and get ready to learn!
On This Page On This Page -->
What is a Business Essay?
A business essay is a type of academic writing that focuses on business-related topics and issues. These essays can cover a wide range of topics such as marketing, finance, management, entrepreneurship, and more.
The importance of business essay lies in presenting a well-researched and informed analysis. To do this effectively, writers need to conduct extensive research and analysis on the topic at hand.
Referring to examples of business essays can help you gain insight into the structure, tone, and content of a well-written essay.
Business Essay Examples For Students
Here is a list of business writing examples
Business Essay Examples Pdf
Business Essay Example Grade 10
Business Essay Example Grade 11
A Level Business Essay Examples
University Business Essay Examples
International Business Essay Examples
Short Essay About Business
College Essay About Starting A Business
Types of Business Essay with Examples
When it comes to business essay writing, there are several different types that you might encounter.
Here's a brief overview of each type, including their characteristics and an example of each.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
Case Studies
A case study is an in-depth analysis of a specific business situation or problem. It involves extensive research and data analysis to provide recommendations.
Case studies often showcase the application of theory to real-world business scenarios.
In today's highly competitive business environment, it's essential for companies to have effective marketing strategies that can help increase sales and generate revenue. In this case study, we will examine how Company X, a leading retailer, was able to increase their sales through an innovative marketing approach. Company X was facing tough competition from other retailers in the market. They needed to find a way to differentiate themselves and attract more customers. They decided to focus on their customer experience by offering personalized recommendations, exclusive discounts, and rewards programs. They also implemented a multi-channel marketing approach that utilized social media, email marketing, and targeted advertising. Their efforts paid off as they saw a significant increase in customer engagement and sales. Their personalized recommendations and rewards program helped to build customer loyalty, while their multi-channel marketing approach helped them reach a wider audience. Furthermore, Company X also used data analysis and optimization to continuously improve their marketing strategies. They tracked their marketing campaigns and analyzed the results to identify what worked and what didn't. This allowed them to adjust their approach and optimize their marketing spend. In conclusion, Company X was able to increase their sales by implementing effective marketing strategies that focused on the customer experience, utilized a multi-channel approach, and used data analysis for optimization. Their success shows that with the right marketing approach, businesses can achieve their goals and stand out in a highly competitive market. |
Research Papers
Research papers involve a more academic approach to business writing. They typically require an extensive literature review, data analysis, and original research.
Business research papers aim to contribute new knowledge to the field of business. These often involve a hypothesis or research question.
The relationship between employee satisfaction and company profitability has been widely studied and documented in academic literature. A number of studies have consistently shown a positive correlation between employee satisfaction and company profitability (Bockerman & Ilmakunnas, 2012; Saks, 2006). When employees are satisfied, they are more engaged, productive, and committed to the success of the company. This leads to increased profitability and a competitive advantage in the market. Employee satisfaction also has a significant impact on reducing employee turnover and associated costs. Studies have shown that when employees are satisfied, they are less likely to leave their jobs, reducing recruitment and training costs for the company (Harter, Schmidt, & Hayes, 2002). Moreover, employee satisfaction can lead to positive word-of-mouth advertising and increased customer satisfaction. Satisfied employees are more likely to provide excellent customer service, leading to increased customer loyalty and repeat business (Heskett, Sasser, & Schlesinger, 1997). Therefore, it's essential for businesses to prioritize employee satisfaction by providing a positive work environment, opportunities for growth and development, fair compensation, and benefits. Businesses should also regularly assess employee satisfaction levels and address any issues promptly. In conclusion, the evidence shows that employee satisfaction is a crucial factor in the success of a company. By prioritizing employee satisfaction, businesses can increase profitability, reduce turnover costs, and improve customer satisfaction. It's essential for businesses to invest in employee satisfaction and consider it a corporate social responsibility to gain a competitive advantage in the market and achieve long-term success. |
Argumentative Essays
Argumentative business essays aim to persuade the reader to adopt a particular point of view or take a specific action. They present an argument and use evidence and logic to support their claims.
Argumentative essays can address various business topics such as management practices, ethical issues, or market trends.
Benefits of Telecommuting for Companies and Employees Telecommuting, or working from home, has become increasingly popular in the business world in the United States and globally as well. While some employers are still skeptical about the effectiveness of telecommuting, there are many benefits to this work arrangement for both companies and employees. One major benefit of telecommuting is increased productivity. Studies have shown that employees who work from home are often more productive than those who work in traditional office settings. This is likely due to a combination of factors, including fewer distractions, less time spent commuting, and greater flexibility in scheduling. Another benefit of telecommuting is reduced overhead costs for companies. By allowing employees to work from home, companies can save money on office space, utilities, and other expenses. This can be especially beneficial for small businesses or startups that are operating on a tight budget. Telecommuting also has benefits for employees. It can reduce stress and improve work-life balance by allowing employees to spend more time with their families and avoid long commutes. It can also be a valuable perk for attracting and retaining top talent, especially in industries where remote work is becoming increasingly common. Of course, there are some potential downsides to telecommuting as well. For example, it can be more difficult to collaborate with colleagues and build strong relationships with coworkers when working remotely. Additionally, some employees may struggle with self-discipline and motivation when working from home. Overall, however, the benefits of telecommuting for both companies and employees are clear. By embracing this work arrangement, businesses can increase productivity, reduce costs, and improve employee satisfaction and retention. |
White Papers
A white paper is a document that provides a detailed explanation of a particular issue or problem, often with recommendations or solutions.
White papers are typically used to educate stakeholders about a specific topic. These are often used in the business-to-business (B2B) context.
Navigating the Benefits and Challenges of Implementing a New CRM System: Insights for Informed Decision Making. Implementing a new customer relationship management (CRM) system can be a challenging yet highly beneficial undertaking for businesses. In this white paper, we will outline the benefits and challenges of implementing a new CRM system and provide insights to help businesses make informed decisions. Benefits of implementing a new CRM system: Improved customer experience: A CRM system can help businesses gain a better understanding of their customers' needs and preferences, allowing them to tailor their products and services accordingly. This can lead to increased customer satisfaction and loyalty. Increased efficiency: A CRM system can automate many processes, such as customer data management and lead tracking, freeing up valuable time for employees to focus on more strategic tasks. Better data management: A CRM system can provide businesses with a central database for customer information, making it easier to manage and analyze data. This can lead to more informed decision-making and better business outcomes. Challenges of implementing a new CRM system: Cost: Implementing a new CRM system can be expensive, with costs including software licensing, hardware upgrades, and employee training. Implementation time: Implementing a new CRM system can take several months, during which time businesses may experience disruptions to their operations. Resistance to change: Some employees may resist the implementation of a new CRM system, requiring significant effort from management to ensure buy-in and adoption. |
Comparative Essays
Comparative business essays compare and contrast two or more topics or ideas. They typically analyze the similarities and differences between the topics to evaluate their pros and cons.
Comparative essays can focus on various aspects such as products, companies, markets, or strategies.
Coca-Cola and PepsiCo are two of the biggest soft drink companies in the world. Both companies have been in competition for decades, and their marketing strategies have evolved over time. This comparative essay will analyze the marketing strategies of Coca-Cola and PepsiCo. Coca-Cola is known for its classic marketing campaigns that focus on emotions and memories. One of their most famous campaigns is the "Share a Coke" campaign, where the company personalized its products with customers' names. This campaign helped Coca-Cola increase its sales and improve customer loyalty. PepsiCo, on the other hand, is known for its focus on youth culture and celebrity endorsements. The company has collaborated with popular musicians and actors such as Beyoncé and Michael Jackson to promote its products. This marketing strategy has helped PepsiCo attract younger consumers and improve brand recognition. When comparing the marketing strategies of Coca-Cola and PepsiCo, it is important to note that both companies have their strengths and weaknesses. While Coca-Cola's emotional marketing approach has helped it establish a strong brand identity, PepsiCo's focus on youth culture has helped it appeal to a wider audience. In conclusion, the marketing strategies of Coca-Cola and PepsiCo differ significantly, but both companies have been successful in their own right. It is up to each company to determine which marketing approach works best for them and their target audience. Choosing the appropriate essay type can help you in effectively conveying your message to the target audience. |
How to Structure Your Business Essays
As you begin writing your business essay, it's important to structure it in a clear and organized way.
Here's a step-by-step guide with business essay samples to help you do just that:
Executive Summary
The executive summary is a brief overview of your entire essay. It should summarize your main points and highlight your recommendations.
This section should be written after completing the essay, as it gives a clear picture of what the essay covers.
Here is how you start a business essay sample:
| This essay provides an in-depth analysis of the marketing strategies employed by Coca-Cola and PepsiCo. The essay highlights the similarities and differences between the two companies' approaches to product development, distribution, and advertising. Based on the analysis, recommendations are made for how each company can improve their marketing strategies to better meet the needs of their target audience. The implementation plan outlines the steps necessary for each company to execute these recommendations successfully. |
Introduction
The introduction sets the stage for the rest of the essay. It should introduce the topic, provide background information, and explain the purpose of the essay.
Here is a business essay introduction example:
| In recent years, the concept of telecommuting has gained popularity as a means of increasing productivity and reducing costs for companies while providing flexibility for employees. This essay will explore the benefits of telecommuting for both companies and employees, including increased productivity, cost savings, and improved work-life balance. Additionally, the essay will discuss potential challenges associated with telecommuting and provide recommendations for successful implementation of a telecommuting program. |
Industry Analysis
In this section, you'll conduct a thorough analysis of the industry in which the business operates. You should examine factors such as competition, market trends, and customer behavior.
Here is a sample industry analysis
| An analysis of the soft drink industry reveals a highly competitive market dominated by two major players, Coca-Cola and PepsiCo. Both companies have a strong global presence and compete fiercely for market share. Recent trends in the industry show a shift towards healthier beverage options, with consumers becoming increasingly health-conscious. This has led to a rise in demand for low-sugar and low-calorie alternatives, such as sparkling water and fruit-infused drinks. In addition, technological advancements in the industry have allowed for greater customization and personalization of products, with companies using data analytics to better understand consumer preferences and target their marketing efforts. |
Key Issues or Problems
This section should identify the main issues or problems faced by the business. You should provide evidence to support your claims and analyze the impact of these issues.
Here is an example paragraph:
| In recent years, the XYZ Corporation has faced several key issues that have impacted its bottom line. One of the main issues is increasing competition from new entrants in the market. This has led to a decrease in market share and reduced profit margins for the company. Additionally, there has been a shift in consumer preferences towards more environmentally-friendly products, which the company has been slow to adapt to. These issues have caused significant concern for stakeholders and highlight the need for the company to address these challenges in a timely manner. |
Solutions or Recommendation
Here, you'll provide solutions or recommendations to address the issues identified in the previous section. Your solutions should be well-supported and feasible.
For instance:
| To address the issues of low employee morale and high turnover rates, the company should consider implementing an employee engagement program. This could include regular employee feedback sessions, recognition and reward programs, and opportunities for career growth and development. By investing in their employees' well-being and growth, the company can create a more positive work environment and reduce turnover rates. Additionally, the company should consider implementing a mentorship program to provide guidance and support to new employees, which can also contribute to employee retention and overall job satisfaction. |

Implementation Plan
For this part, you'll outline a plan for implementing the solutions or recommendations you've proposed. This is sort of a description of the business model you suggest.
This section should be detailed and include specific action steps.
For example:
| The implementation plan for our proposed solutions will involve several key steps. Firstly, we will need to gather a team of experts to oversee the implementation process. This team will be responsible for coordinating with various departments within the company, such as global marketing and operations, to ensure that the plan is executed smoothly. Secondly, we will need to allocate the necessary resources, such as funding and manpower, to carry out the plan. Finally, we will need to establish a timeline with specific deadlines for each action step, so that we can track our progress and make adjustments as needed. |
Finally, you'll wrap up your essay by summarizing your main points and reiterating your recommendations.
This section should be clear, concise, and impactful.
| In conclusion, this essay has highlighted the importance of customer relationship management (CRM) systems in modern businesses. The analysis of industry trends and key issues facing businesses has shown that effective use of CRM can improve customer satisfaction, increase sales, and ultimately lead to a competitive advantage. Through the proposed solutions and implementation plan outlined in this essay, businesses can overcome the challenges of implementing a new CRM system and reap the benefits. It is recommended that businesses invest in CRM and continuously evaluate their usage to stay ahead of the competition in the ever-changing market. |
By following this structure, your business essay will be well-organized, coherent, and easy to follow for your readers.
Tips for Using Business Essay Examples Effectively
Now that you have quite a few business essay examples at hand, you should know how to use them effectively:
- Use them as a guide, not a template : While it's great to learn from examples, you should never copy them outright. Instead, use them as a starting point for your own research and writing.
- Analyze the strengths and weaknesses of the essay : Take note of what works well in the example essay, as well as any areas that could be improved. This will help you understand how to make your own essay even better.
- Use them to inform your own research and writing : Pay attention to the research methods, sources, and evidence used in the example essay. This can give you ideas for your own research and help you strengthen your arguments.
- Avoid plagiarism and ensure proper citation: Whenever you use ideas or information from an example, make sure to cite your sources. This will help you avoid plagiarism and maintain academic integrity.
You now have a plenty of business essay examples on different topics to help you get started!
By following our tips and studying the sample essays, you can confidently write your own essays that are clear, concise, and impactful.
However, if you still find yourself struggling with your business essays, just reach out to our professional business essay writing service .
We have the best online essay writing service and are ready to provide you a high-quality business. Our writing service has subject specialist writers who can tackle any business essay topic.
So why wait? Contact us today and let our AI essay writer take your business essays to the next level!
Cathy A. (Literature)
For more than five years now, Cathy has been one of our most hardworking authors on the platform. With a Masters degree in mass communication, she knows the ins and outs of professional writing. Clients often leave her glowing reviews for being an amazing writer who takes her work very seriously.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!

Legal & Policies
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Terms of Use
- Refunds & Cancellations
- Our Writers
- Success Stories
- Our Guarantees
- Affiliate Program
- Referral Program
- AI Essay Writer
Disclaimer: All client orders are completed by our team of highly qualified human writers. The essays and papers provided by us are not to be used for submission but rather as learning models only.

ESSAY SAUCE
FOR STUDENTS : ALL THE INGREDIENTS OF A GOOD ESSAY
Essay: Business model
Essay details and download:.
- Subject area(s): Business essays
- Reading time: 9 minutes
- Price: Free download
- Published: 26 June 2012*
- File format: Text
- Words: 2,503 (approx)
- Number of pages: 11 (approx)
Text preview of this essay:
This page of the essay has 2,503 words. Download the full version above.
Business model
Business strategy is an essential component to a firm’s business model and is a vital player in aiding the firm drive itself to achieve its mission. Through a clear business strategy a firm can derive its position in the long term and create a competitive advantage in the market for itself. In this essay we explore the business model of Ryanair and assess their strategy. Ryanair is an Irish low cost airline headquartered in Dublin founded in 1985. It operates 181 aircrafts over 729 routes across Europe and North Africa from 31 bases. Ryanair has seen large success over the recent years due to its low-cost business model and has become the world’s largest airline in terms of international passenger numbers. Taking Porter’s generic business strategies into consideration, Ryanair operates a cost-leadership strategy to drive itself into achieving its mission of being the leading European low-cost carrier (LCC). Throughout this essay the business strategy of Ryanair will be analysed and the sustainability of their model evaluated.
Ryanair’s objective is ‘to firmly establish itself as Europe’s leading low-fares scheduled passenger airline through continued improvements and expanded offerings of its low-fares service’ (Ryanair). Considering their objectives and mission, Ryanair’s decision on their cost-leadership strategy was based on a few main factors which are discussed below.
A major influence was the deregulation of the airline industry in 1978 which removed government intervention within the European continent. Under the new rules, routes and fare decisions were made by individual airlines which meant that they could compete on other factors besides food, cabin crew and frequency. As a result of deregulation, a large number of new airline start-ups emerged within the EU and competition among airlines increased dramatically resulting in downward price pressures. Ryanair was established to take full advantage of these market conditions. By offering low prices, Ryanair entered a huge and virtually unlimited market.
Having seen the major success of the low cost carrier Southwest in the United States, Ryanair decided to follow in their footsteps by establishing a LCC for the European continent that targeted fare conscious leisure travellers and regular low cost business travellers. By doing this Ryanair became the first low-fare airline in Europe. However, they took the Southwest model further by offering no drinks and snacks at all and abolishing the frequent flyer program which Southwest up to this day offers its customers (Boesch 2007).
The evaluation of Porters five forces influenced Ryanair’s choice of a cost-leadership strategy, as the threat presented by new entrants and the threat of substitutes could hinder their success. The threat of new entrants is high within the aviation industry which meant that low fares would help drive away any further competition. The threat of substitutes to Ryanair had to also be carefully examined. Their primary market, Europe, had the availability of high speed trains and car holidays. For Ryanair to be successful, prices had to be low to attract the public, and resist strong competition from substitutes like Eurostar.
As Europe’s largest low fare airline, Ryanair’s competitive advantage remains in their ability to continue as cost leaders; providing the cheapest fares to its customers. This dictates that the company must minimise its own costs to ensure that they are able to offer customers the service at a price below their direct competitors. This leads us to consider some key functional strategies which directly help Ryanair towards their ultimate goal ‘to be Europe’s leading low fares airline’ (Ryanair).
The marketing strategy is perhaps the most obvious and significant functional strategy of Ryanair. Low fares are designed to stimulate demand, attracting fare-conscious travellers, those who may have used alternative forms of transportation or even those who may have not travelled at all. Penetration pricing as it is called helps gain market share and simply, more customers equals more revenue (Wheelen & Hunger 2006). Tickets are almost solely sold on their website ‘www.ryanair.com’ which very importantly keeps sales costs to a minimum since very few phone operators are employed and computers are able to cheaply handle all functions of sales. With ever increasing accessibility of the internet globally anybody with internet access can buy airline tickets from Ryanair, so distribution practically takes care of itself through this medium. Ryan Air relies on low cost promotions and in recent times has concentrated on their ‘One million seats at one pound’ which is usually advertised through their internet site, national press and bulletin boards. It is the simplicity of this promotion which helps keep costs low since expensive advertising agencies can be entirely avoided and advertising can be dealt with in house.
Ryanair’s operations strateg1y determines how the airline will deploy its resources and the policies it will operate by. To keep costs low they operate a ‘no frills’ service onboard aircraft. This means the fare only includes the flight. There are however a number of other measures directly related to a no frills service. These include ticketless boarding, unallocated seats, one class of travel, costs for check-in baggage, no refund policy, basic seats (to increase aircraft capacity) and charging for any additional service. All this significantly reduces costs to Ryanair. The Achilles heel of Ryanair is their greater aircraft utilisation through super quick turnaround times. Essentially this means the aircraft spends very little time on the ground, they achieve this through their human resource policies and by having none or very little cargo in the baggage hold to speed up loading and unloading of the aircraft.
Logistics strategy deals with the flow of products into and out of Ryanair. Again there is heavy emphasis on cost saving and reducing measures. Ryanair fly to secondary airports which are potentially much further from the City centre but accessible enough by other forms of ground transportation. At these airports Ryanair are able to negotiate extremely aggressively and demand the lowest landing and handling fees. Additionally Ryanair is usually able to gain financial assistance with marketing and promotional campaigns at these airports.
As cost leader Ryanair strives to undercut all its rivals but this means very low income per fare and requires maximum utilisation of its resources. Fortunately their financial policy ensures they are able to still profit handsomely from rock bottom fares. The aim is to breakeven on fares but to make their profits out of ancillary charges and commissions from their partners. Ryanair has a number of affiliates such as Hertz car rental, Acumus insurance and booking.com all of whom are advertised readily on the Ryanair website. Since the website has high website traffic its partners are able to reach out to Ryanair’s huge client base and are prepared to pay good commissions to the firm for this privilege (IdeaWorks). Ryanair also generate income from advertising on board the aircraft. Ancillary revenue is generated from many of the services that traditional airlines wouldn’t charge for, such as large baggage into the cargo hold, allocated seating, snacks and drinks.
Ryanair’s strategy when purchasing aircraft is to buy new, uniform aircraft. This is beneficial for a number of reasons all of which directly help cost saving measures. Firstly, by being able to order same aircraft in bulk they are able to negotiate a better price per aircraft. Secondly, uniform aircraft mean that there are potential savings in staff training; air stewards being more familiar with all aircraft and maintenance will be simpler. Finally by buying new, the company has safer, more fuel efficient planes with lower maintenance costs. Safer aircraft also means greater consumer confidence, equating to more fare sales.
Furthermore Ryanair aggressively hedge and fix as many of their costs as possible, such as oil and aircraft prices so they are not subject to future price fluctuations which could adversely affect profitability (Stone 2008).
The human resource policy is again directly related to reducing costs. Employees are expected to pay for their own uniform and equipment. Training given is the required minimum and staff utilisation is among the highest in the airline industry. Many staff are employed on performance contracts and those who do not meet their expectations are readily replaced. Staff are also expected to take on a number of roles, cabin staff will also clean the aircraft prior to the next service, check in staff assist in boarding the aircraft etc.
Ryanair has successfully experienced years of growth both in the number of its aircrafts and passengers since its launch. However, with the global financial system recently suffering its greatest crisis in more than 70 years, existing business models of many aviation firms are coming under great strain. As this economic downturn bankrupts LCCs like XL and Zoom with more expected to follow, the question is whether Ryanair’s cost-leadership strategy is sustainable or not as it continues to offer lower fares in the face of high costs. Although Ryanair has posted losses along with other aviation firms for the latest quarter, it is expected to emerge from this downturn with fewer competitors because its €1.8 billon balance sheet is one of the strongest in the industry. Additionally, as the credit crunch takes its toll, traditional airlines are not in a position to cut fares and the threat of new LCCs is virtually eliminated due to the lack of financing. Although Ryanair faces competition from substitutes like Eurostar, it is at an advantage because of Eurostar’s limited destinations.
Ryanair is sticking to its mantra, when the going gets tough, sell more seats for almost nothing (Symonds 2008). By offering low fares, Ryanair expects passengers to trade down to the low cost airlines rather than stop flying completely. This trend appears accurate so far based on passenger numbers as recession forces millions of passengers to focus on price (Waterman 2009). Additionally, the latest statistics from The European Low Fares Airline Association members show a 15.7% year-on-year growth in the number of passengers for 2008, indicating that the LCC model is robust, even in times of crisis (Latest 2009). Consequently, there is no doubt that Ryanair looks poised for substantial profits and passenger growth in the coming years. However, in order to compete with other LCCs and maintain its continued market share growth in the future, Ryanair needs to improve its poor customer relations.
The sustainability of Ryanair’s cost leadership strategy also depends largely on the price of oil and how effective the firm is in cutting costs in order to continue offering low fares. According to the firm’s latest financial report, ‘Ryanair will enjoy significantly lower oil costs thanks to their recent hedging programme, when most of their competitors are already hedged at much higher prices. These lower prices will drive Ryanair’s traffic growth, maintain high load factors and capture market share from higher cost fuel surcharging competitors’ (3rd Quarter Results 2009). In order to cut costs, Ryanair plans to close all its airport check-in desks by the end of 2009 and have passengers check-in online instead. Other cost saving methods not yet implemented include charging customers for using toilets on airplanes (Lalor 2009). These cost cutting ideas are not very popular among consumers and it means that Ryanair needs to improve its already tarnished brand image in the future which it had attained through negative press reporting and misleading advertisements.
The current strategy at Ryanair is expected to work so well that despite the recession Ryanair’s CEO has underlined the firm’s commitment to expansion. The firm is expected to grow at 20 percent a year because of a 180 aircrafts on order from Boeing. These expansion plans for the future will require the company to increase its landing slots at airports and recruit more employees. Currently Ryanair has limited access to landing slots in major airports and the secondary airports are long distances away from city centres which could make it less attractive in the future. However, a remarkable cut in flights by other European airline carriers due to recession is creating enormous opportunities for Ryanair, as many major airports compete to reduce charges in order to attract Ryanair’s growth (3rd Quarter Results 2009). Availability of skilled personnel shouldn’t be a problem for Ryanair due to recent high unemployment levels. However, Ryanair needs to improve its current low level of empathy for employees if it is to retain them in the future.
Even though Ryanair’s cost leadership strategy is robust and it looks set to serve them well in the future, there are some key areas within the business that can be improved on to enhance the firm’s profitability and brand image.
Ryanair has always been criticised for many aspects of its poor customer relations. According to The Economist, Ryanair’s "cavalier treatment of passengers" had given Ryanair "a deserved reputation for nastiness" and that the airline "has become a byword for appalling customer service… and jeering rudeness towards anyone or anything that gets in its way" (Aviation 2007). If Ryanair is to maintain its large customer base, it needs to ensure that it acknowledges its customers’ concerns and maintains a service focused attitude at all costs. Ryanair needs to invest in servicing customers better by providing a non-premium contact number, improving its non user friendly website, and simplifying the terms and conditions of the flight service. Ryanair should also create a frequent flyer program to establish a fixed customer base and encourage customer loyalty.
Ryanair is notorious for its high staff turnover which negatively affects its reputation as an employer. Over utilization of employees, poor remuneration package, and minimal training are a few other critical items to be considered by Ryanair if it is to retain employees in the future. Ryanair needs to understand that although it is currently possible to replace outgoing employees, but with time Ryanair’s overall image will be tarnished. Resultantly, attracting new employees could become impossible and this will hinder their expansion plans. Ryanair should incorporate a flexible benefits package solely designed to improve employee morale such as flexible working hours and extra holidays. To improve its image amongst employees, training at all employee levels must include exposure to similar techniques and methods that help promote the development of a uniform company identity.
Following huge success in Europe, Ryanair should consider introducing low cost transatlantic flights to support its expansion plans and attain a larger customer base. With a high demand for certain routes like London-New York and room for negotiation in airplane prices and airport slots mainly due to the current financial climate, it is an ideal time to further reap the rewards of the cost leadership strategy that has served Ryanair so well over the years.
Ryanair’s model looks set to survive the current industrial downturn through its lower costs and substantial cash balances. No airline is better placed in Europe than Ryanair to trade through this downturn. It will therefore continue to grow, by lowering fares, taking market share from competitors, and expanding in markets where competitors either withdraw capacity or go bust (Monaghan 2008). By taking the recommended improvements into consideration, it looks like Ryanair’s cost leadership strategy seems ideal for the future.
...(download the rest of the essay above)
About this essay:
If you use part of this page in your own work, you need to provide a citation, as follows:
Essay Sauce, Business model . Available from:<https://www.essaysauce.com/business-essays/business-model/> [Accessed 26-06-24].
These Business essays have been submitted to us by students in order to help you with your studies.
* This essay may have been previously published on Essay.uk.com at an earlier date.
Essay Categories:
- Accounting essays
- Architecture essays
- Business essays
- Computer science essays
- Criminology essays
- Economics essays
- Education essays
- Engineering essays
- English language essays
- Environmental studies essays
- Essay examples
- Finance essays
- Geography essays
- Health essays
- History essays
- Hospitality and tourism essays
- Human rights essays
- Information technology essays
- International relations
- Leadership essays
- Linguistics essays
- Literature essays
- Management essays
- Marketing essays
- Mathematics essays
- Media essays
- Medicine essays
- Military essays
- Miscellaneous essays
- Music Essays
- Nursing essays
- Philosophy essays
- Photography and arts essays
- Politics essays
- Project management essays
- Psychology essays
- Religious studies and theology essays
- Sample essays
- Science essays
- Social work essays
- Sociology essays
- Sports essays
- Types of essay
- Zoology essays
- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →
Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- AI Essentials for Business
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading Change and Organizational Renewal
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
Innovation in Business: What It Is & Why It’s Important

- 08 Mar 2022
Today’s competitive landscape heavily relies on innovation. Business leaders must constantly look for new ways to innovate because you can't solve many problems with old solutions.
Innovation is critical across all industries; however, it's important to avoid using it as a buzzword and instead take time to thoroughly understand the innovation process.
Here's an overview of innovation in business, why it's important, and how you can encourage it in the workplace.
What Is Innovation?
Innovation and creativity are often used synonymously. While similar, they're not the same. Using creativity in business is important because it fosters unique ideas . This novelty is a key component of innovation.
For an idea to be innovative, it must also be useful. Creative ideas don't always lead to innovations because they don't necessarily produce viable solutions to problems.
Simply put: Innovation is a product, service, business model, or strategy that's both novel and useful. Innovations don't have to be major breakthroughs in technology or new business models; they can be as simple as upgrades to a company's customer service or features added to an existing product.
Access your free e-book today.
Types of Innovation
Innovation in business can be grouped into two categories : sustaining and disruptive.
- Sustaining innovation: Sustaining innovation enhances an organization's processes and technologies to improve its product line for an existing customer base. It's typically pursued by incumbent businesses that want to stay atop their market.
- Disruptive innovation: Disruptive innovation occurs when smaller companies challenge larger businesses. It can be classified into groups depending on the markets those businesses compete in. Low-end disruption refers to companies entering and claiming a segment at the bottom of an existing market, while new-market disruption denotes companies creating an additional market segment to serve a customer base the existing market doesn't reach.
The most successful companies incorporate both types of innovation into their business strategies. While maintaining an existing position in the market is important, pursuing growth is essential to being competitive. It also helps protect a business against other companies affecting its standing.
Learn about the differences between sustaining and disruptive innovation in the video below, and subscribe to our YouTube channel for more explainer content!
The Importance of Innovation
Unforeseen challenges are inevitable in business. Innovation can help you stay ahead of the curve and grow your company in the process. Here are three reasons innovation is crucial for your business:
- It allows adaptability: The recent COVID-19 pandemic disrupted business on a monumental scale. Routine operations were rendered obsolete over the course of a few months. Many businesses still sustain negative results from this world shift because they’ve stuck to the status quo. Innovation is often necessary for companies to adapt and overcome the challenges of change.
- It fosters growth: Stagnation can be extremely detrimental to your business. Achieving organizational and economic growth through innovation is key to staying afloat in today’s highly competitive world.
- It separates businesses from their competition: Most industries are populated with multiple competitors offering similar products or services. Innovation can distinguish your business from others.

Innovation & Design Thinking
Several tools encourage innovation in the workplace. For example, when a problem’s cause is difficult to pinpoint, you can turn to approaches like creative problem-solving . One of the best approaches to innovation is adopting a design thinking mentality.
Design thinking is a solutions-based, human-centric mindset. It's a practical way to strategize and design using insights from observations and research.
Four Phases of Innovation
Innovation's requirements for novelty and usefulness call for navigating between concrete and abstract thinking. Introducing structure to innovation can guide this process.
In the online course Design Thinking and Innovation , Harvard Business School Dean Srikant Datar teaches design thinking principles using a four-phase innovation framework : clarify, ideate, develop, and implement.

- Clarify: The first stage of the process is clarifying a problem. This involves conducting research to empathize with your target audience. The goal is to identify their key pain points and frame the problem in a way that allows you to solve it.
- Ideate: The ideation stage involves generating ideas to solve the problem identified during research. Ideation challenges assumptions and overcomes biases to produce innovative ideas.
- Develop: The development stage involves exploring solutions generated during ideation. It emphasizes rapid prototyping to answer questions about a solution's practicality and effectiveness.
- Implement: The final stage of the process is implementation. This stage involves communicating your developed idea to stakeholders to encourage its adoption.
Human-Centered Design
Innovation requires considering user needs. Design thinking promotes empathy by fostering human-centered design , which addresses explicit pain points and latent needs identified during innovation’s clarification stage.
There are three characteristics of human-centered design:
- Desirability: For a product or service to succeed, people must want it. Prosperous innovations are attractive to consumers and meet their needs.
- Feasibility: Innovative ideas won't go anywhere unless you have the resources to pursue them. You must consider whether ideas are possible given technological, economic, or regulatory barriers.
- Viability: Even if a design is desirable and feasible, it also needs to be sustainable. You must consistently produce or deliver designs over extended periods for them to be viable.
Consider these characteristics when problem-solving, as each is necessary for successful innovation.
The Operational and Innovative Worlds
Creativity and idea generation are vital to innovation, but you may encounter situations in which pursuing an idea isn't feasible. Such scenarios represent a conflict between the innovative and operational worlds.
The Operational World
The operational world reflects an organization's routine processes and procedures. Metrics and results are prioritized, and creativity isn't encouraged to the extent required for innovation. Endeavors that disrupt routine—such as risk-taking—are typically discouraged.
The Innovative World
The innovative world encourages creativity and experimentation. This side of business allows for open-endedly exploring ideas but tends to neglect the functional side.
Both worlds are necessary for innovation, as creativity must be grounded in reality. You should strive to balance them to produce human-centered solutions. Design thinking strikes this balance by guiding you between the concrete and abstract.

Learning the Ropes of Innovation
Innovation is easier said than done. It often requires you to collaborate with others, overcome resistance from stakeholders, and invest valuable time and resources into generating solutions. It can also be highly discouraging because many ideas generated during ideation may not go anywhere. But the end result can make the difference between your organization's success or failure.
The good news is that innovation can be learned. If you're interested in more effectively innovating, consider taking an online innovation course. Receiving practical guidance can increase your skills and teach you how to approach problem-solving with a human-centered mentality.
Eager to learn more about innovation? Explore Design Thinking and Innovation ,one of our online entrepreneurship and innovation courses. If you're not sure which course is the right fit, download our free course flowchart to determine which best aligns with your goals.

About the Author
Essays on Business Model
We found 30 free papers on business model, essay examples, costco wholesale corporation: mission, business model, and strategy.
Business Model
Corporation
In 2008, Costco achieved sales of around $71 billion. These sales were spread across its 544 warehouses located in different states, Puerto Rico, Canada, the United Kingdom, Taiwan, Japan, Korea, and Mexico. Among these warehouses, over 50 stores had annual sales exceeding $200 million. Notably, two stores even surpassed $300 million in sales. On average,…
Business Model Canvas Zillow Sample
The internet’s ability to supply entree to information has improved existent estate communications and concern ( Aalberts and Townsend. 2002 ) . Business theoretical accounts represent the concern logic of companies. They are executed by company web sites and are of import to the success of companies. E-business theoretical accounts represent the principle of how…
Cork’D Business Model: Building a Social Network for Wine Lovers
Business Process
Do you like the business model and do you think that Cork’d has a real opportunity that will make them money? Cork’d business model is focused on getting more users to sign in for free. For me this is a weakness for the company because it reduces the sources of revenue. At the same time…
Huckleberry Finn: A Good Role Model
Huckleberry Finn
“The Adventures of Huckleberry Finn” gives a ocular expression at the clip in which the writer Samuel Clemens lived. He explains how he felt about his life through the eyes of a immature male child named Huckleberry Finn. Huckleberry Finn has many escapades that teach him life lessons we can larn from today. Although there…
Kathmandu Sample Assignment
Online Shopping
Founded in 1987 as a small specialist outdoor retailer in Melbourne, Katmandu now operates in Australia, New Zealand and also the UK with a network of about 130 stores and an online shop. The company strives to provide quality, functional, and stylish products with technical attributes. Its products inspire customers to travel, explore the outdoors,…
Dell Operations Strategy
Information Technology
The global and industry issues companies face, combined with the current turbulent financial and economic environment, are challenging even the best companies to remain focused on their core capabilities, customers and markets. To be successful in an uncertain environment, a company must make the right choices that enable it to develop distinctive capabilities and remain…
Strategies to Fight Low-Cost Rivals by Nirmalya Kumar
Consumers desire the advantages that your new offerings would bring and are willing to pay for them. By reducing the cost of the benefits you plan to provide, you can attract more customers. HP’s restructuring has decreased Dell’s cost advantage from 20% to 10%. Customers have shown appreciation for additional benefits such as instant delivery…
Porters 5 forces for Flipkart
Threat of New Entrants : Industry seems to have very high potential but is at its nascent stage. Lots of scope of growth in the future Many small players might enter to explore the market High capital investment is required as it is still in the nascent stage. Would not be much of a deterrent…
Interfaceraise Case Study
Sustainability
1. What is InterfaceRAISE’s value proposition? InterfaceRAISE’s value proposition is that Interface’s firsthand experience in implementing sustainable strategies, practices and culture will accelerate other companies’ leanings and performance in this area. InterfaceRAISE will be a credible peer-to-peer consultancy in this field due to Interface’s reputation as a successful pioneer in sustainable manufacturing. Interface have a…
How to design a winning Business Model? Sample
Value proposition
Because of the economic lag in developed economic systems and the mature markets more and more companies are encouraged to come in in emerging markets. We can detect an increasing force per unit area for MNE to come in in emerging economic systems by aiming in-between and low Base of the Pyramid. The taking companies…
Frequently Asked Questions about Business Model
Don't hesitate to contact us. We are ready to help you 24/7

Hi, my name is Amy 👋
In case you can't find a relevant example, our professional writers are ready to help you write a unique paper. Just talk to our smart assistant Amy and she'll connect you with the best match.
Zara Company’s Business Model Essay
- To find inspiration for your paper and overcome writer’s block
- As a source of information (ensure proper referencing)
- As a template for you assignment
Business Model of Zara
Fashion industry traditional business model, zara business model, disruptive innovation, works cited.
Zara is one of the leading fashion brands that compete with other major fashion retail brands such as H&M, Benetton, etc. It is one of the largest holdings and revenue earners of Inditex. In 1963, Inditex started its operations in La Coruna as garment wholesalers (McAfee, Dessain, & Sjoman, 2007). However, it was not until 1975, when a German customer cancelled a sizable order, that Inditex opened its own retail store and named it Zara (Berfield & Baigorri, 2013).
Initially, the aim of the company was to have a retail outlet for their cancelled shipments but soon they realized the importance of the alliance between retail and manufacturing. This initial experience brought forth the philosophy on which the whole business model of Zara is based on – customer base and manufacturing base should be closely mixed in order to achieve optimal success.
The brand enjoys international presence and is the largest selling brand in Spain. The business model of Zara is different from most of its competitors and its strategic decisions and competitive advantages have been a question of curiosity for academicians. This essay is an exploration of the business model, strategy, and competitive advantages of Zara. Most importantly, the paper strives to answer the question, what is the business model of Zara?
Zara caters to an extensively competitive fashion retail industry where consumer demand and preference fluctuate considerably. The main aim of Zara is to control the tastes and preferences of the customers and change their styles before their taste and preferences change (Hansen, 2012). In order to achieve this, Zara ensures that its stores are up to date in their clothes selection and they have to order at least twice a week to revamp their stock.
The case study on Zara shows that the company has almost no promotion and advertisement cost as opposed to other retail chains like Gap or Benetton who spend heavily on advertising their products and they believe in owning the best retail space (McAfee, Dessain, & Sjoman, 2007). Retail location is an important element of Zara’s business model as it allows the company to reach its target market more easily (McAfee, Dessain, & Sjoman, 2007).
Instead of advertising its products, Zara conducts market research to identify the right locality where they may find the largest pool of their target market in the market segment (Hansen, 2012; McAfee, Dessain, & Sjoman, 2007). This strategy makes opening a store in a new location financially viable.
The business mode followed by Zara is essentially called the disruptive innovation model, which is unlike the traditional business model followed by the traditional retail companies. Therefore, before studying the business mode of Zara, the paper discusses the traditional business model of the fashion industry.
The business mode of the traditional fashion industry is essentially based on designing of clothes and retailing them. However, the time lag that prolongs the designing process and availability of finished products in-store are acute in most of the cases. Fashion brands concentrate more on creating designs for a specific season and making them available in a period of 4 to 5 months. Hence, a fashion brand revamps its design offerings only in 4 months:
The traditional fashion industry calendar introduces two new collections per year. One is the spring/summer collection unveiled in January and February and the other is the fall/winter collection, which unveiled in August and September. The actual design work often takes place a full year before the launch. (Ireland, 2013, para. 4)
The advantages of the traditional model are that it allows considerable time to plan and execute the strategy. It allows companies to book a manufacturing plant in advance at a cheaper cost and help in developing the designs. However, the disadvantages of the traditional model are that the designs have to be perceived in advance and the whole order is locked earlier in advance. Hence, any changes in trend of fashion cannot be incorporated in the fresh seasons’ style.
For instance, after the order has been placed if the company realizes that it has gone ahead with a set of design that are not in fashion then they might have to reduce the prices to clear the stock. Retailers like The Gap have to offer their products at reduced prices as they have a high inventory of products that were not in demand, often face this problem.
Gauging the right trend of the season is also a problem for designers and if they are unable to the products become redundant. Hence, it can be asserted that the traditional business mode of fashion industry often creates supply chain bottlenecks and increases inventory costs (Özlen & Handukic, 2013 ). Further, obsolete style show the fashion brand negatively among the upbeat, fashion conscious customers who easily tire away from older fads.
The main contention of Zara is to sell fashion and not clothes and hence, the company strives to change its product offering as early as possible so that every time a customer enters their store, they are offered something new:
Zara’s strategy requires the generation of a great deal of product variety throughout the year… As part of this fashionably exclusive (yet low cost) image, stores hold very low levels of inventory – typically only a few pieces of each model – and this often means that a store’s entire stock is on display. Because of the low inventory, policy it is not unusual to find empty racks by the end of a day’s trading and therefore stores are completely reliant on regular and rapid replenishment of newly designed products. (Ferdows, Lewis, & Machuca, 2003, p. 63)
The supply chain process of Zara consists of four broad categories – designing and order administration, production, distribution, and retailing. However, the process followed is less generic as it may sound.
Designing is one of the cornerstones of Zara’s success (Ferdows, Lewis, & Machuca, 2003). The process of effective, profitable designing of products that sell within a short time, is possible only if the products are replenished with new designs and fashion to the stores in a short time. The focus of the company is to hire designers who can come up with design ideas in a very short time. Hence, Zara has dedicated teams for designing and product management (Ferdows, Lewis, & Machuca, 2003).
There are focused teams to look into specific areas of their products (Zara’s Secret To Success: The New Science Of Retailing, 2013). For instance, the company has a dedicated team for the women’s sportswear division (Zara’s Secret To Success: The New Science Of Retailing, 2013). The product team is also responsible for collecting trend data on the in-season fashion and fad and accordingly presents it in their product designs. Thus, Zara has a short-term policy of replenishing its fashion line:
Zara is renowned for its ability to deliver new clothes to stores quickly and in small batches. Twice a week, at precise times, store managers order clothes, and twice a week, on schedule, new garments arrive. To achieve this, Zara controls more of it’s manufacturing than do most retailers: About half its clothes are made in Spain or nearby countries. For Zara, its supply chain is its competitive advantage. (Berfield & Baigorri, 2013, para. 2)
The short designing and production cycle provided the strategic competitive advantage for the company to revamp its fashion line very two weeks while the company’s competitors replenishes their line in three or four months.
Zara, unlike its competitors, does not spend on advertising its products. The business model of Zara is solely dependent on logistics and designing. Zara believes in setting up shops in prime locations in large cities where the market segment represents its target customers, thus, making the need to advertise redundant.
The financial model of Zara is also different from its competitors (Ireland, 2013). Usually fashion retailers make payment to the vendors when giving them contract for manufacturing a particular batch of products, thus, restricting their cash. Zara follows similar model for its Asian vendors who supply their steady, basic garments, while the more trendier and short-term designer clothes are delivered by the Spanish, Portuguese, and Turkish vendors. Hence, the level of restricted cash for Zara is much less than its competitors.
The business model of Zara is popularly known as the disruptive business model that allows companies to create a fresh market along with their value network. The model is a self-sustaining mechanism that in future moves ahead to disrupt the market and the new technology simply displaces the older ones.
Usually, the mistake that companies make is to counter competitive forces, upgrade their product offering, and trying to increase their market share. Zara created a niche in the fashion retail market where its competitors were not catering. For instance, Zara catered to the customers that its competitors like H&M, Gap, and Benetton were not supplying. Thus, it whittled a market for itself in the existing market.
The competitive advantages of a company following a disruptive model are selling to customers and just-in-time production. Zara followed these two strategies completely. Direct selling to the customers allows Zara to understand the taste and preference of its customers and the probable changes that it may face and just-in-time production allows the company to replenish its offerings at a very short time, reducing inventory cost considerably (Levine, 2013). Levine therefore points out:
Zara focuses on understanding the items that its customers actually want. This differs from traditional prediction of seasonal trends, and then promoting the line. Inditex does not advertise. Instead, the company invests heavily in the beauty, historical appeal, and location of its shops…The company monitors customer reactions carefully. It notes what they buy and don’t buy. It records their feedback to the staff and is reported to headquarters daily. It is transmitted to a vast team of in-house designers, who quickly develop new designs. (2013, para. 4)
Demand from customers, therefore, is the chief driver for the deliveries to the stores. Usually Zara ships limited pieces to its stores initially, and follows up quickly if the product fetches good response from the customers.
Though most of the fashion retailers rely on vendors from South Asia where labor cost is cheap, Zara relies on making of the trendiest of its fashion attires from costly local vendors as it reduces its response time to just 2 to 3 weeks. This allows great flexibility to the company reducing its inventory cost considerably and enabling faster turnaround (Levine, 2013). Thus, the business model of Zara relies mostly on its logistics and value chain, which helps it to manage and cater to customer preference and demand.
Berfield, S., & Baigorri, M. (2013). Zara’s Fast-Fashion Edge from Bloomberg Businessweek.
Ferdows, K., Lewis, M., & Machuca, J. A. (2003). Zara. Supply Chain Forum , 4 (2), 62-66.
Hansen, S. (2012). How Zara Grew Into the World’s Largest Fashion Retailer from The New York Times.
Ireland, P. (2013). Zara’s Disruptive Growth Strategy from Tycoon Playbook.
Levine, S. R. (2013). How Zara took customer Focus to New Heights from Credit Union Time.
McAfee, A., Dessain, V., & Sjoman, A. (2007). Zara: IT for Fast Fashion. Harvard Busienss Review , 1-23.
Özlen, M. K., & Handukic, I. (2013). Fashion Industry Supply Chain Issues: Zara. European Researcher , 47 (4), 999-1008.
Zara’s Secret To Success: The New Science Of Retailing . (2013) from Forbes.
- Zara apparel fashion Store
- Key Elements of Zara Company’s Business Model
- Astonishing Success of Zara in the Fast Fashion Industry
- Tiffany & Co Strategic Analysis
- Caterpillar Company Analysis
- McDonald’s Company Management Principles
- VIVA Company Lean Management Principles
- Kings County Hospital Center Company Analysis
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2020, April 3). Zara Company's Business Model. https://ivypanda.com/essays/zara-companys-business-model/
"Zara Company's Business Model." IvyPanda , 3 Apr. 2020, ivypanda.com/essays/zara-companys-business-model/.
IvyPanda . (2020) 'Zara Company's Business Model'. 3 April.
IvyPanda . 2020. "Zara Company's Business Model." April 3, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/zara-companys-business-model/.
1. IvyPanda . "Zara Company's Business Model." April 3, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/zara-companys-business-model/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Zara Company's Business Model." April 3, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/zara-companys-business-model/.

- Review of Books
- Agriculture
- Manufacturing
- Energy Policy
New Papers On Analysis Models, Fiscal Response To COVID-19 And Productivity Insights
Press Release – The Treasury
The Treasury has published today three new papers covering policy analysis modelling tools, National Accounts categorisation of COVID-19 funding allocation and expenditure, and key themes from the Treasurys Productivity in a Changing World lecture series.
The Treasury has published today three new papers covering policy analysis modelling tools, National Accounts categorisation of COVID-19 funding allocation and expenditure, and key themes from the Treasury’s Productivity in a Changing World lecture series.
- Murat Özbilgin and Robert Kirkby, Solving Stochastic OLG Models Using Chebyshev Parameterized Expectations (WP 24/03) . There is growing emphasis on understanding how economic policies impact not only economic efficiency but also the distribution of benefits and costs across society. Stochastic overlapping generations (S-OLG) models are key tools for analyzing policies that have repercussions for various generations and groups. However, the primary challenge in using S-OLG models lies in the computational difficulties associated with solving them to reach equilibrium outcomes and conduct policy experiments. This paper demonstrates the application of Chebyshev polynomials in conjunction with the Parameterized Expectations Algorithm (C-PEA) as a solution method for S-OLG models. The findings indicate that C-PEA can be a valuable tool for policy analysts and researchers. It maintains a good balance between accuracy and speed and requires fewer parameters than most alternative methods.
- Andrew Binning, Nairn MacGibbon and Peter Mawson, A National Accounts Categorisation of COVID-19 Funding Allocation and Expenditure (AN 24/05) . This paper presents a National Accounts categorisation of both the funding allocated to the COVID-19 response and the estimated expenditure. This will contribute to a macroeconomic understanding of the fiscal response to the COVID-19 pandemic in New Zealand and the recession that followed. The paper finds that almost 80% of the funding allocated to the COVID-19 response over the first 3 fiscal years has been spent. Estimated COVID-19 expenditure over this period is equivalent to 16% of 2019 GDP. Wage subsidies make up the largest single component of both COVID-19 funding allocations and estimated expenditure. Government consumption makes up the second largest component. This expenditure is more backloaded, spread over a longer time horizon, and allocated across a large number of line items.
- Hilary Devine, Anna Golebicka-Buchanan and Diana Cook, Themes from the Treasury’s Guest Lecture Series: Productivity in a Changing World . This paper provides a summary of the Treasury’s Guest Lecture Series (TGLS) on the theme of Productivity in a Changing World , which ran over 2023-24. Our speakers, and their discussions with audiences, highlighted the wide-ranging and complex interaction between global trends and productivity. Several themes emerged through the series. Most of the speakers recognised the global productivity slowdown, and that New Zealand has not been exempted. Many speakers highlighted the importance of innovation and technological change, and the importance of skills and capabilities which support the diffusion and adoption of new technologies. Several speakers also explored the theme of climate change and productivity, including the compatibility of climate change and productivity goals.
Disclaimer: The views, opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations expressed in these papers are strictly those of the authors. They do not necessarily reflect the views of the New Zealand Treasury or the New Zealand Government. The New Zealand Treasury and the New Zealand Government take no responsibility for any errors or omissions in, or for the correctness of, the information contained in papers and articles.
Content Sourced from scoop.co.nz Original url
Kommentare sind geschlossen.
Latest Business news
- Transpower Restores Second 220 KV Circuit Into Northland
- New Footpaths Boost Equity For Smaller Towns
- Kiwi Employers Face Further Barriers To Fill Lower-skilled Roles
- Cost Pressures On Trucking Firms Continue To Rise
- Warren Bunn – Northland Road Safety Champion
- Mobil Latest To Sponsor Northland Rescue Helicopter Service
- Government Announces $100,000 For Tairāwhiti
- Job Cuts Will Severely Compromise ACC Services
- Three Easy Steps To Entrust Annual Dividend, Two Ways To Be Paid, One Massive Cash Injection For Auckland
- TikTok Campaign Aims To Attract Young People To Retail Careers
- Fabric Of NZ’s Social Security System Unravels As Govt Axes More Than 1400 Roles
- Finding A Car Park In Auckland City Centre Made Easier With New Charges On Sundays And Public Holidays
- Reminder: Metlink Fare Increase From 1 July
- NZ Economy: Slow Grind
- Flick Wins Canstar Blue’s Electricity Award 2024
Recent Comments
- Lan: Unbelievable that a WEST AUSTR...
- jackp: Murray, when Key is involved t...
- Murray Guy: There are no boundaries when i...
- Lan: Canada & EU do it..Bryce ...
- Lan: I read somewhere that they do ...
- Simon Johnson: The former Department of Labou...
- Andrew P Nichols: Long overdue. Nowhere else in ...
- Rafi: I look forward to Mr Lees-Gall...
- Kevin McMahon: Yes, good on Lord Monckton. ...
- Bee: How do you think Kim Jon Key m...
Recently on Scoop
- Business Reports
- China Economic Scan
- Compare house prices
- Deposit Rates
- Direct Broking – NZX & ASX Trading & Prices
- Findata – Market Data
- Good Returns
- Herald Business
- Interest.co.nz – Interest Rates News & Views
- National Business Review
- Property Talk
- Stuff Business
- Value Cruncher – NZX
More From Forbes
7 chatgpt prompts to improve your writing.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
Photo by NICOLAS MAETERLINCK/BELGA MAG/AFP via Getty Images
On writing , author David Sedaris once said, “You need to do the best that you can do, and then you need to take the best that you can do and you need to rewrite it, and rewrite it, and rewrite it.” That’s the dynamic essence of the writing process. Writers refine their drafts, just like they continually refine their craft. I didn’t study writing or literature, so I was intimidated when I began contributing to major publications. But my confidence grew with each byline, and I began to find my voice.
While ChatGPT can be an impressive imitator, it can never generate your unique voice and perspective. It can, however, be a powerful tool for improving your writing, whether you’re penning business articles or important emails. It all starts with the right prompts.
Here are seven that you can use to level up your writing skills.
Automate Your Busywork
There are no shortcuts to becoming a better writer. The prolific author Stephen King once said, “If you want to be a writer, you must do two things above all others: read a lot and write a lot.” That said, you can use AI tools to eliminate some of the tedious tasks involved in writing and leave more time for honing your craft. Here are some prompts to delegate your writing “busywork” to ChatGPT.
1. Generating Ideas And Topics
AI shouldn’t do your writing for you. It lacks the necessary human context and isn’t immune to errors. But it can be a powerful writing partner. As Wharton professor Christian Terwiesch (who challenged ChatGPT to come up with product ideas and compared those ideas to student ideas —ChatGPT won), has said , “Everybody should be using ChatGPT to help them generate ideas.” At worst, you reject all of them. At best, you enrich your pool of ideas.
‘Squad’ Rep. Jamaal Bowman Unseated By Latimer In Pricey New York Primary
Sha’carri richardson, cole hocker, and anna hall dominate u.s. track & field olympic trials, the 11 best mattresses of 2024, according to testing.
Here is a prompt you can use to help get the idea wheels turning:
"I'm an [role/title] writing for [outlet description] targeting [target audience]. Can you suggest some fresh and engaging topics that would appeal to this audience?"
If you’d like ideas related to a certain topic or tailored to a specific style (e.g., a “hot take” versus a personal essay), remember: the more context you provide, the more concise the results.
2. Editing For Grammar And Style
Whether you’re sending an email or publishing an article on a high-traffic website, typos are an embarrassing—and avoidable—faux pas. In today’s world, where internet content exists in perpetuity, anything attached to your name should be error-free. ChatGPT can be a near-instantaneous proofreader. Test out the following prompt:
"Can you proofread this [content] for grammar, punctuation, and style consistency? The intended audience is [audience/recipient]. Please provide a list of any suggested improvements.”
3. Hitting The Right Tone
Spelling and grammar are a crucial part of editing, but they’re relatively objective. Perfecting the tone is more subjective and sometimes more challenging—but just as crucial.
The proper tone can ensure that your text is engaging. It can foster trust and understanding with colleagues and business partners. It can persuade your audience to get on board with your viewpoint. Writing that misses the mark on tone, however, can cause misunderstandings, hurt feelings, damage your credibility, and lose your reader’s interest.
With that in mind, here’s a prompt that can help you achieve the right tone in your writing:
"Can you help me rewrite this [content] for [audience], ensuring it maintains a [describe the desired tone]?
Add context to make ChatGPT’s reply more helpful. For example, if your content should show sensitivity to a certain issue or audience, add it to the prompt.
4. Adding Data And Research
One lesson I’ve learned from contributing to Forbes and other widely-read publications is that my word alone is rarely enough. I can share my personal experiences, but research and data can strengthen any piece of writing.
Instead of researching the traditional way—reviewing your writing and identifying facts that need outside sourcing, then Googling for relevant insight—ChatGPT can speed up the process, leaving you more time to polish those personal anecdotes. Try this prompt:
"I’m writing [describe the content and subject matter] for [target audience] and want to include relevant data and research. Can you review the following text and provide researched-backed statistics and insights on this topic?"
Importantly, always check the sources that ChatGPT generates. It will almost certainly come up with helpful results but they’re not always accurate—that’s where you, human editor, come into play.
Refine Your Craft
To continually improve your writing skills, you can take a page from the habits of professional writers. The following prompts can help you develop practices to become a stronger writer.
5. Daily Writing Prompts
I’ve written before about my morning pages . It’s a great way to clear my head before the day begins and to practice fluidly translating my thoughts into words on paper. If a blank page feels intimidating, writing prompts are a great way to get started. ChatGPT can generate writing prompts in an instant. You can keep it general:
“Can you suggest a couple of writing prompts that I can use to practice the craft of writing?”
Or, if you have a goal in mind, add more context. For example:
“I'm trying to improve engagement with my readers. Can you generate a couple of writing prompts to practice writing engaging content?”
6. Experiment With Different Styles And Voices
If you call your grandmother on the telephone, I’d bet your voice and speaking style sound vastly different from when you’re chatting with your best friend. Writing is the same.
ChatGPT can help you practice toggling between different styles and voices, and in doing so, help you find yours. You can ask ChatGPT for writing prompts to practice a certain style. For example:
“Can you generate three short exercises to help me practice writing in different voices and styles?”
ChatGPT will not only generate exercises, it will also break down the structure and elements of different writing styles and specify the tone.
Or, you can submit text to ChatGPT and ask it to analyze the style and voice. Try this prompt:
“Can you analyze the voice and style of the following text: [insert text].”
I used this prompt to assess the introduction to one of my recent Forbes stories, and ChatGPT said it was “Conversational and Relatable,” “Encouraging and Reassuring,” and “Informative and Practical”—encouraging feedback from my AI editor.
7. Rewrite, Rewrite, Rewrite
In A Moveable Feast , Ernest Hemingway wrote, “The only kind of writing is rewriting.”
If you want to become a writer, you have to embrace rewriting, whether you’re retyping every word or pouring over (and over) a Google Doc draft. Here are a couple of prompts you can use so that ChatGPT can assist in the rewriting process, one excerpt at a time:
“Rewrite this paragraph in the style of [Ernest Hemingway or any other author]."
“Rewrite this introduction so that it sounds like a story in [publication]”
“Rewrite this email so that it will resonate with [audience].”
“Rewrite this paragraph for clarity and concision.”
Importantly, ChatGPT only does part of the work. It falls to the writer to analyze the results, apply those lessons in future drafts, and, of course, to keep writing.

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
Join The Conversation
One Community. Many Voices. Create a free account to share your thoughts.
Forbes Community Guidelines
Our community is about connecting people through open and thoughtful conversations. We want our readers to share their views and exchange ideas and facts in a safe space.
In order to do so, please follow the posting rules in our site's Terms of Service. We've summarized some of those key rules below. Simply put, keep it civil.
Your post will be rejected if we notice that it seems to contain:
- False or intentionally out-of-context or misleading information
- Insults, profanity, incoherent, obscene or inflammatory language or threats of any kind
- Attacks on the identity of other commenters or the article's author
- Content that otherwise violates our site's terms.
User accounts will be blocked if we notice or believe that users are engaged in:
- Continuous attempts to re-post comments that have been previously moderated/rejected
- Racist, sexist, homophobic or other discriminatory comments
- Attempts or tactics that put the site security at risk
- Actions that otherwise violate our site's terms.
So, how can you be a power user?
- Stay on topic and share your insights
- Feel free to be clear and thoughtful to get your point across
- ‘Like’ or ‘Dislike’ to show your point of view.
- Protect your community.
- Use the report tool to alert us when someone breaks the rules.
Thanks for reading our community guidelines. Please read the full list of posting rules found in our site's Terms of Service.
Model Business Corporation Act Resource Center
The Model Business Corporation Act Resource Center provides easy access to the current version of the Model Business Corporation Act (MBCA) and various resource materials related to the MBCA. The MBCA is a Model Act promulgated and periodically amended by the ABA Business Law Section’s Corporate Laws Committee .
MBCA Enactment Map
As of January 1, 2023
- MBCA Enactments by States
MBCA Current Version
- Official Text with Official Comment (.pdf)
- Official Text (Word)
Recommended Books and Other Publications
- Corporate Director's Guidebook, Seventh Edition
- Legal Guidebook for Closely Held Corporations
- Handbook for the Conduct of Shareholders' Meetings, Third Edition
- Model Business Corporation Act Annotated, Fifth Edition
- Model Business Corporation Act (2016 Revision): Official Text with Official Comment & Statutory Cross-References
- Model Nonprofit Corporation Act, 4th Edition
- Annotated Certificate of Designations for Preferred Stock of a Public Company (2013)
MBCA Enactment Toolkit
- “Why Your Jurisdiction Should Adopt the Current Revision of the MBCA”
- Current Version with Official Comment (.pdf)
- Current Version, Blackletter without Official Comment (Word)
Amendments to the MBCA—Proposed and Adopted by the Committee (with Committee Reports)
The Committee accomplishes much of its work through task forces that are assigned to review and offer proposed amendments to the MBCA, including the Official Comment on each section. The amendments may include significant revisions of the MBCA, such as the 2016 Revision. Proposed amendments are presented to the Committee at a first reading. After deliberation by the Committee, which may include referring matters back to the task force, the Committee adopts the proposed amendment at the second reading. After the second reading, the Committee publishes the proposed amendment in The Business Lawyer and invites comments. After expiration of the comment period and the Committee’s consideration of comments received, the Committee considers the amendment on a third reading. If adopted by the Committee on the third and final reading, the amendment is adopted and published in The Business Lawyer . Upon adoption, the amendment becomes part of the MBCA.
View all committee reports on MBCA Amendments.
MBCA Newsletters
- Winter 2023
- Winter 2022
- Summer 2021
- View archived newsletters
Recent State MBCA Enactments and Amendments
- The New and Improved Alabama Business Corporation Law by W. Clark Goodwin (2019).
- 2019 Colorado Business Law Updates--The Colorado Business Corporation Act and the Colorado Corporations and Associations Act, by Avi Lowenstein and Herrick K. Lidstone Jr.
- Proposal to Modify Chapter 607 of the Florida Statutes with Commentary (September 25, 2018) (Florida Business Corporation Act
- Summary of Recently Adopted Changes to the Florida Business Corporation Act and Harmonizing Changes to Other Florida Entity Statutes, Part I by Philip Schwartz and Gary I. Teblum
- Summary of Recently Adopted Changes to the Florida Business Corporation Act (Chapter 607) and Harmonizing Changes to Other Florida Entity Statutes, Part II by Philip Schwartz and Gary I. Teblum
- Iowa Business Corporation Act, the First Comprehensive of Iowa’s Business Corporation Act in Over 30 Years by Willard L. Boyd III and David s. Walker
- Text of House File 844
- Recent Revisions to the North Carolina Business Corporation Act by Heyward Armstrong, Dave Clement and Justin Truesdale
Prior Versions of the MBCA
- 2016 Version
- 2013 Version
- 1984 Revision
- 1969 Revision
- 1950 Version
Upcoming MBCA Programs
Check out the Corporate Laws Committee page for events and programs.
Prior MBCA Workshops and CLE Programs
- The “New” Model Business Corporation Act: Why States Should Adopt It (October 2, 2017)
- Ratifying Defective Corporate Acts (March 29, 2019).
Model Nonprofit Corporation Act
The new fourth edition of the Model Nonprofit Corporation Act (“MNCA”) , adopted by the Committee on Nonprofit Organizations of the Business Law Section, is based in large measure on the MBCA.
The Fourth Edition includes the new and revised provisions of the 2016 Revision of the MBCA and the changes to the MBCA since the 2016 Revision, with some modifications based on the unique nature of nonprofit corporations.
Since its genesis, the MNCA has tracked the MBCA but diverged where appropriate, e.g ., in the realm of shareholders. The Fourth Edition, too, generally tracks the MBCA, including the numbering system and sequence of provisions and a simplified Official Comment.
Many state nonprofit corporation acts are based on earlier editions of the Model Nonprofit Corporation Act. The Fourth Edition provides an up-to-date model statute that accounts for the various types of nonprofit corporations in existence today.
White Papers and Other Resource Materials
View all white papers and other materials .
MBCA State Liaisons
State Liaisons to the Corporate Laws Committee keep the Committee abreast of corporate law developments in their respective states (primarily amendments of corporation laws and other legislation and important judicial decisions relating to corporation laws). The Committee endeavors to keep State Liaisons abreast of amendments of the MBCA and solicits their comments from time to time with respect to proposed amendments and other matters.
Help | Advanced Search
Computer Science > Artificial Intelligence
Title: on layer-wise representation similarity: application for multi-exit models with a single classifier.
Abstract: Analyzing the similarity of internal representations within and across different models has been an important technique for understanding the behavior of deep neural networks. Most existing methods for analyzing the similarity between representations of high dimensions, such as those based on Canonical Correlation Analysis (CCA) and widely used Centered Kernel Alignment (CKA), rely on statistical properties of the representations for a set of data points. In this paper, we focus on transformer models and study the similarity of representations between the hidden layers of individual transformers. In this context, we show that a simple sample-wise cosine similarity metric is capable of capturing the similarity and aligns with the complicated CKA. Our experimental results on common transformers reveal that representations across layers are positively correlated, albeit the similarity decreases when layers are far apart. We then propose an aligned training approach to enhance the similarity between internal representations, with trained models that enjoy the following properties: (1) the last-layer classifier can be directly applied right after any hidden layers, yielding intermediate layer accuracies much higher than those under standard training, (2) the layer-wise accuracies monotonically increase and reveal the minimal depth needed for the given task, (3) when served as multi-exit models, they achieve on-par performance with standard multi-exit architectures which consist of additional classifiers designed for early exiting in shallow layers. To our knowledge, our work is the first to show that one common classifier is sufficient for multi-exit models. We conduct experiments on both vision and NLP tasks to demonstrate the performance of the proposed aligned training.
| Subjects: | Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computation and Language (cs.CL); Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Machine Learning (cs.LG) |
| Cite as: | [cs.AI] |
| (or [cs.AI] for this version) | |
| Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite |
Submission history
Access paper:.
- HTML (experimental)
- Other Formats
References & Citations
- Google Scholar
- Semantic Scholar
BibTeX formatted citation
Bibliographic and Citation Tools
Code, data and media associated with this article, recommenders and search tools.
- Institution
arXivLabs: experimental projects with community collaborators
arXivLabs is a framework that allows collaborators to develop and share new arXiv features directly on our website.
Both individuals and organizations that work with arXivLabs have embraced and accepted our values of openness, community, excellence, and user data privacy. arXiv is committed to these values and only works with partners that adhere to them.
Have an idea for a project that will add value for arXiv's community? Learn more about arXivLabs .
Apple, OpenAI, and Google are involved in the most important deal of the AI era. Who's getting paid?
- Apple's WWDC revealed a partnership with OpenAI, integrating ChatGPT with Siri.
- Apple executive Craig Federighi said there could be a similar deal with Google's Gemini AI model.
- Apple could pit OpenAI and Google against each other in future negotiations over AI distribution.

This week, Apple executive Craig Federighi uttered 12 words that were music to shareholders' ears.
"We're looking forward to doing integrations with other models, including Google Gemini ," he said during Apple's annual WWDC event.
He was talking about Apple's new partnership with OpenAI , which integrates ChatGPT with the Siri digital assistant on iPhones and other Apple devices.
Getting such special treatment on iPhones is the holy grail in tech. Until Monday, it looked like OpenAI had beaten Google to this treasured position. But Federighi went out of his way to say Google might get the same distribution deal for its new Gemini AI model.
Why would he do this? It's all about money, as usual.
The $20 billion deal
There's an existing iPhone distribution deal that looks familiar to anyone who follows the business of technology closely.
Google pays Apple about $20 billion a year to have its search engine be the default on iPhones and other Apple devices. This is incredibly profitable revenue for Apple, and it ensures that Google Search remains dominant in the Western world.
Every few years, this deal comes up for renewal. And the same question always comes up: Will Google keep paying? Why would it cough up so much?
The answer is always that Apple dangles the chance that it may go with Microsoft Bing as its preferred partner instead. This is so unacceptable to Google that the search giant gets out the check book every time.
Without the threat of Microsoft Bing waiting in the wings, Apple would have a lot less leverage in these negotiations.
What's the $20 billion deal for the AI era?
The emergence of generative AI has set the stage for another Apple distribution deal that could have similarly epic proportions and implications.
OpenAI won the first round. Its ChatGPT service now gets the chance to answer millions of queries from Apple users.
Normally, this would entail massive payments from OpenAI to Apple. For now, though, it's unclear who is paying who.
Maybe Apple is paying OpenAI. That would be an incredible upending of the power dynamics that have generated 10s of billions of dollars in revenue for Apple (from those similar Search distribution deals with Google).
However, Apple is behind in the generative AI race. It has no powerful AI models of its own. That's one of the reasons why Siri has been so lame for so many years — and why Apple is now turning to ChatGPT for help.
Or, maybe there are no payments passing between Apple and OpenAI at all. That would also be not great in terms of Apple's ability to squeeze billions out of future AI distribution deals.
A bidding war for AI distribution
All is not lost though. If Apple can set up a similar bidding war for AI distribution, it can probably negotiate large payments again.
This is why Federighi's comments about Google Gemini are so important. If Google is still in the running for similar treatment as OpenAI, then Apple may be able to pit these two AI giants against each other in future negotiations.
It's notable that during WWDC on Monday Apple shares fell about 2%. Then later in the day, Federighi got on stage and mentioned potentially distributing Google Gemini in addition to ChatGPT.
Related stories
On Tuesday, Apple shares surged 7% to a record.
Did Google walk away from a deal?
Let's not get too excited yet, though.
Does Google even want to have its Gemini model distributed on Apple devices, especially if it has to pay up again?
Mark Gurman, the top Apple journalist, reported earlier this year that Google was in talks with Apple. But then, OpenAI got the deal on Monday.
Did Google walk away from this deal? That would be another astounding turn of events.
"What is the gating factor delaying an announcement between Google and Apple?" Morgan Stanley analysts wrote in a research note this week.
Their first answer: "Unit economics obviously matter."
Google must weigh the cost of paying Apple for AI model distribution against the opportunity to get more Gemini users and hopefully generate revenue from their queries in the future.
Data access
The Morgan Stanley analysts also raised another issue that is almost as important.
"Data privacy and access is likely also a key point of negotiation," they wrote.
At WWDC, Apple stressed that user requests and information sent through ChatGPT will not be logged. The Morgan Stanley analysts also think that OpenAI will not be able to train its AI models on this Apple user data.
"Google, which currently has access to data for any queries logged via the web/its mobile app, would likely want this level of access should they be servicing these queries via channels like Siri," the Morgan Stanley analysts wrote.
"Without access to this data, to the extent queries shift to personal assistants over time, Google would be losing access to customer data even if still fulfilling the queries," they added.
So maybe Apple told Google it wouldn't be getting any new user data to train its Gemini models, and that was a deal killer.
The "intelliphone" question
There's another possibility, which should worry Apple shareholders.
Maybe Google doesn't need Apple distribution deals anymore.
Google is a long way ahead of Apple in the generative AI race. Google already has access to oodles of data to train Gemini models. And it still has the Android mobile ecosystem, which is the second most valuable digital distribution channel in tech (after iPhones).
Android boss Sameer Samat recently told me that Google is pushing really hard to bring its AI technology to Android phones, including its own Pixel devices.
Pixels haven't sold that well so far. What if they get AI features that are way better than iPhones? Could consumers switch to Android to get these powerful new tools?
That's unlikely, given all the ways Apple keeps users in the iPhone ecosystem. But there's still a chance.
There's even a new word for these AI-powered smartphones of the future. They're called " intelliphones ."
If Google can lure consumers to its AI-powered Pixel phones, or get them to buy Samsung devices with Google AI built in, then maybe Google doesn't need another expensive Apple distribution deal.
"The way in which AI functionality is built directly into the Android operating system is also enabling Google to improve the utility offered on Pixel phones with new use cases that in some ways may end up being superior to what Apple can offer for now," Morgan Stanley analysts wrote.
"This dynamic could lead to more sales of Android phones over Apple...or simply further increase Google's leverage in negotiations with Apple to offer comparable products on the iPhone," the analysts added.
I asked Google, Apple and OpenAI about all this on Tuesday and I didn't get a response.
Watch: What is ChatGPT, and should we be afraid of AI chatbots?
- Main content

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Why Business Models Matter. by. Joan Magretta. From the Magazine (May 2002) "Business model" was one of the great buzzwords of the Internet boom, routinely invoked, as the writer Michael Lewis ...
This essay considers what a business model is, locates the pursuit of 'ambivalent value' in the strategy literature, and proposes a new strategic role for the business model - as a means of negotiating for a portion of that 'ambivalent value'. We provide a substantive definition of the 'business model', a collection of decisions
Joan Magretta adds that a business model is basically a story about how the company will operate, including the activities involved in making and selling a product or service. Alex Osterwalder offers a simplified format for thinking about these hypotheses adopted by startups and established businesses alike, called the busi n ess model canvas.
The aim of this paper is to review and synthesise the recent advancements in the business model literature and explore how firms approach business model innovation.,A systematic review of business model innovation literature was carried out by analysing 219 papers published between 2010 and 2016.,Evidence reviewed suggests that rather than ...
Here's a step-by-step guide on how to create a business canvas model. Step 1: Gather your team and the required material Bring a team or a group of people from your company together to collaborate. It is better to bring in a diverse group to cover all aspects.
The Importance of the Business Model The ability of a given business model to scale depends significantly on the maturity of the business model itself—that is, its ability to provide socially ...
Why Business Models Matter Essay. Business models became popular as a result of the internet boom that made many companies to begin relying on web-based models. Companies shifted from the traditional methods that were based on strategy and competence in an attempt to embrace the new trend. The new models came with a promise of substantial ...
Third, a. consistent statement is made as to what a business model is and is not, as well as the conditions. in which a business model is an attractive and m eaningful managerial philosophy ...
The business model itself is an important determinant of the firm's revenues to be made from an idea. A well framed business model can outshadow even a weak innovation but a weakly framed business model will hide off a good innovation. 4. Components. Following are the six major elements in business models:
(DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-60918-4_2) This chapter describes the importance of business models. The term "business" usually refers to business organizations or business enterprises that are primarily motivated by profit. However, ethical, social, and ecological considerations can also be part of the functioning of a genuine business enterprise. In fact, business practices can only be ...
As Jim explains, here are a few of the benefits of using a business model canvas to think through product strategies: 1. You can use a business model canvas to roadmap quickly. You can use this canvas approach in just a few hours (and as Jim says, you can even do it with sticky-notes). This way, rather than trying to write out every detail ...
The Business Model Canvas Essay. The Business Model Canvas (BMC) can be defined as a tool that is used in the generation of a business model. "The BMC is made up of nine building blocks forming a chart that describes a firms value proposition, infrastructure, customers, finances, resources, channels, revenue streams and cost structure ...
Get a custom Essay on Importance of business models to the process of project management. 808 writers online . Learn More . But, these mindsets have changed since the current organizations have experienced rapid changes in technology and global competition. This problem is heightened by the continued use of the classical business models with ...
The importance of business essay lies in presenting a well-researched and informed analysis. To do this effectively, writers need to conduct extensive research and analysis on the topic at hand. Referring to examples of business essays can help you gain insight into the structure, tone, and content of a well-written essay. Business Essay ...
1. Introduction. In this essay, we call for research on the impact of business model innovation (BMI) beyond its economic impact on the firm. Although there is growing interest in BMI in the strategic management literature (Foss and Saebi, 2017; Teece, 2018), we believe this corpus of research has been overly focused on firms and how they can be profitable.
According to Staehler [Staehler, 2001], a business model consists of three major. components: t he value proposition, the value architecture, and the revenue model. Alt and Zimmerman increase the ...
In summary, a well-designed business model is essential for entrepreneurs as it defines their value proposition, revenue streams, target market, competitive advantage, and growth potential. It ...
Business strategy is an essential component to a firm's business model and is a vital player in aiding the firm drive itself to achieve its mission. Through a clear business strategy a firm can derive its position in the long term and create a competitive advantage in the market for itself. In this essay we explore the business model of ...
The Importance of Innovation. Unforeseen challenges are inevitable in business. Innovation can help you stay ahead of the curve and grow your company in the process. Here are three reasons innovation is crucial for your business: It allows adaptability: The recent COVID-19 pandemic disrupted business on a monumental scale. Routine operations ...
The value of a business plan is important in the startup of an organization. The value of proper business plan in an organization can determine if the organization will withstand over of time or for years to come for that matter. In implementing a proper business plan, proper planning in it self is important and valuable to the process.
Business Model. Corporation. Words: 1690 (7 pages) In 2008, Costco achieved sales of around $71 billion. These sales were spread across its 544 warehouses located in different states, Puerto Rico, Canada, the United Kingdom, Taiwan, Japan, Korea, and Mexico. Among these warehouses, over 50 stores had annual sales exceeding $200 million.
3. Business Model Canvas (BMC) Business model canvas (BMC) is provides conceptual strategy implementation and the alignment of strategies to business processes [ CITATION Rec09 \l 17417 ]. It is a description of the value a company offers to one or several segments of customers and of the architecture of the firm and its network of partners to generate profitable and sustainable revenue ...
Zara Company's Business Model Essay. Zara is one of the leading fashion brands that compete with other major fashion retail brands such as H&M, Benetton, etc. It is one of the largest holdings and revenue earners of Inditex. In 1963, Inditex started its operations in La Coruna as garment wholesalers (McAfee, Dessain, & Sjoman, 2007).
The Treasury has published today three new papers covering policy analysis modelling tools, National Accounts categorisation of COVID-19 funding allocation and expenditure, and key themes from the Treasurys Productivity in a Changing World lecture series. The Treasury has published today three new ...
The productivity solution market is booming. Businesses invest a lot of money into squeezing every last drop of output from our time, our bodies and our minds. Productivity-focused planners, time ...
New power is needed by the Western mining industry, which is still functioning on a trailing old power business model. This was highlighted at Tuesday's London Indaba, where a spotlight was ...
If you'd like ideas related to a certain topic or tailored to a specific style (e.g., a "hot take" versus a personal essay), remember: the more context you provide, the more concise the results.
Model Nonprofit Corporation Act. The new fourth edition of the Model Nonprofit Corporation Act ("MNCA"), adopted by the Committee on Nonprofit Organizations of the Business Law Section, is based in large measure on the MBCA.. The Fourth Edition includes the new and revised provisions of the 2016 Revision of the MBCA and the changes to the MBCA since the 2016 Revision, with some ...
Analyzing the similarity of internal representations within and across different models has been an important technique for understanding the behavior of deep neural networks. Most existing methods for analyzing the similarity between representations of high dimensions, such as those based on Canonical Correlation Analysis (CCA) and widely used Centered Kernel Alignment (CKA), rely on ...
Google must weigh the cost of paying Apple for AI model distribution against the opportunity to get more Gemini users and hopefully generate revenue from their queries in the future. Data access