Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Referencing
- Harvard Style Bibliography | Format & Examples

Harvard Style Bibliography | Format & Examples
Published on 1 May 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on 7 November 2022.
In Harvard style , the bibliography or reference list provides full references for the sources you used in your writing.
- A reference list consists of entries corresponding to your in-text citations .
- A bibliography sometimes also lists sources that you consulted for background research, but did not cite in your text.
The two terms are sometimes used interchangeably. If in doubt about which to include, check with your instructor or department.
The information you include in a reference varies depending on the type of source, but it usually includes the author, date, and title of the work, followed by details of where it was published. You can automatically generate accurate references using our free reference generator:
Harvard Reference Generator
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Formatting a harvard style bibliography, harvard reference examples, referencing sources with multiple authors, referencing sources with missing information, frequently asked questions about harvard bibliographies.
Sources are alphabetised by author last name. The heading ‘Reference list’ or ‘Bibliography’ appears at the top.
Each new source appears on a new line, and when an entry for a single source extends onto a second line, a hanging indent is used:

Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Reference list or bibliography entries always start with the author’s last name and initial, the publication date and the title of the source. The other information required varies depending on the source type. Formats and examples for the most common source types are given below.
- Entire book
- Book chapter
- Translated book
- Edition of a book
| Format | Author surname, initial. (Year) . City: Publisher. |
| Example | Coetzee, J. M. (2000) . London: Vintage. |
| Notes |
| Format | Author surname, initial. (Year) ‘Chapter title’, in Editor name (ed(s).) . City: Publisher, pp. page range. |
| Example | Greenblatt, S. (2010) ‘The traces of Shakespeare’s life’, in De Grazia, M. and Wells, S. (eds.) . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, pp. 1–14. |
| Notes |
| Format | Author surname, initial. (Year) . Translated from the [language] by ranslator name. City: Publisher. |
| Example | Saramago, J. (1997) . Translated from the Portuguese by G. Gontiero. London: Vintage. |
| Notes |
| Format | Author surname, initial. (Year) . Edition. City: Publisher. |
| Example | Danielson, D. (ed.) (1999) . 2nd edn. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. |
| Notes |
Journal articles
- Print journal
- Online-only journal with DOI
- Online-only journal without DOI
| Format | Author surname, initial. (Year) ‘Article title’, , Volume(Issue), pp. page range. |
| Example | Maceachen, D. B. (1950) ‘Wilkie Collins and British law’, , 5(2), pp. 121–139. |
| Notes |
| Format | Author surname, initial. (Year) ‘Article title’, , Volume(Issue), page range. DOI. |
| Example | Adamson, P. (2019) ‘American history at the foreign office: Exporting the silent epic Western’, , 31(2), pp. 32–59. doi:10.2979/filmhistory.31.2.02. |
| Notes |
| Format | Author surname, initial. (Year) ‘Article title’, , Volume(Issue), pagerange. Available at: URL (Accessed: Day Month Year). |
| Example | Theroux, A. (1990) ‘Henry James’s Boston’, , 20(2), pp. 158–165. Available at: https://www.jstor.org/stable/20153016 (Accessed: 13 February 2020). |
| Notes |
- General web page
- Online article or blog
- Social media post
| Format | Author surname, initial. (Year) . Available at: URL (Accessed: Day Month Year). |
| Example | Google (2019) . Available at: https://policies.google.com/terms?hl=en-US (Accessed: 29 April 2020). |
| Notes |
| Format | Author surname, initial. (Year) ‘Article title’, , Date. Available at: URL (Accessed: Day Month Year). |
| Example | Rakich, N. (2020) ‘How does Biden stack up to past Democratic nominees?’, , 28 April. Available at: https://fivethirtyeight.com/features/how-does-biden-stack-up-to-past-democratic-nominees/ (Accessed: 29 April 2020). |
| Notes |
| Format | Author surname, initial. [username] (Year) or text [Website name] Date. Available at: URL (Accessed: Day Month Year). |
| Example | Dorsey, J. [@jack] (2018) We’re committing Twitter to help increase the collective health, openness, and civility of public conversation … [Twitter] 1 March. Available at: https://twitter.com/jack/status/969234275420655616 (Accessed: 29 April 2020). |
| Notes |
| Format | Author surname, initial. (Year) [Medium]. Institution, City or Available at: URL (Accessed: Day Month Year). |
| Example | Bosch, H. (1482) [Triptych]. Groeningemuseum, Bruges. |
| Notes |
| Format | Author surname, initial. (Year) . Date. Available at: URL (Accessed: Day Month Year). |
| Example | Vox (2020) . 10 April. Available at: https://youtu.be/BE-cA4UK07c (Accessed: 29 April 2020). |
| Notes |
Newspapers and magazines
- Newspaper article
- Magazine article
| Format | Author surname, initial. (Year) ‘Article title’, , date, p. page number. Available at: URL (Accessed: Day Month Year). |
| Example | Butler, S. (2020) ‘Women’s fashion manufacturer to make reusable gowns for NHS’, , 28 April. Available at: https://www.theguardian.com/society/2020/apr/28/womens-fashion-manufacturer-to-make-reusable-gowns-for-nhs (Accessed: 29 April 2020). |
| Notes |
| Format | Author surname, initial. (Year) ‘Article title’, , Volume(Issue) or (Month) or (Season), pp. page range. Available at: URL (Accessed: Day Month Year). |
| Example | Newman, J. (2020) ‘For autistic youths entering adulthood, a new world of challenges awaits’, , (May), pp. 20–24. |
| Notes |
When a source has up to three authors, list all of them in the order their names appear on the source. If there are four or more, give only the first name followed by ‘ et al. ’:
| Number of authors | Reference example |
|---|---|
| 1 author | Davis, V. (2019) … |
| 2 authors | Davis, V. and Barrett, M. (2019) … |
| 3 authors | Davis, V., Barrett, M. and McLachlan, F. (2019) … |
| 4+ authors | Davis, V. (2019) … |
Sometimes a source won’t list all the information you need for your reference. Here’s what to do when you don’t know the publication date or author of a source.
Some online sources, as well as historical documents, may lack a clear publication date. In these cases, you can replace the date in the reference list entry with the words ‘no date’. With online sources, you still include an access date at the end:
When a source doesn’t list an author, you can often list a corporate source as an author instead, as with ‘Scribbr’ in the above example. When that’s not possible, begin the entry with the title instead of the author:
Though the terms are sometimes used interchangeably, there is a difference in meaning:
- A reference list only includes sources cited in the text – every entry corresponds to an in-text citation .
- A bibliography also includes other sources which were consulted during the research but not cited.
In Harvard referencing, up to three author names are included in an in-text citation or reference list entry. When there are four or more authors, include only the first, followed by ‘ et al. ’
| In-text citation | Reference list | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 author | (Smith, 2014) | Smith, T. (2014) … |
| 2 authors | (Smith and Jones, 2014) | Smith, T. and Jones, F. (2014) … |
| 3 authors | (Smith, Jones and Davies, 2014) | Smith, T., Jones, F. and Davies, S. (2014) … |
| 4+ authors | (Smith , 2014) | Smith, T. (2014) … |
In Harvard style referencing , to distinguish between two sources by the same author that were published in the same year, you add a different letter after the year for each source:
- (Smith, 2019a)
- (Smith, 2019b)
Add ‘a’ to the first one you cite, ‘b’ to the second, and so on. Do the same in your bibliography or reference list .
To create a hanging indent for your bibliography or reference list :
- Highlight all the entries
- Click on the arrow in the bottom-right corner of the ‘Paragraph’ tab in the top menu.
- In the pop-up window, under ‘Special’ in the ‘Indentation’ section, use the drop-down menu to select ‘Hanging’.
- Then close the window with ‘OK’.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2022, November 07). Harvard Style Bibliography | Format & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 7 June 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/referencing/harvard-bibliography/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, a quick guide to harvard referencing | citation examples, harvard in-text citation | a complete guide & examples, referencing books in harvard style | templates & examples, scribbr apa citation checker.
An innovative new tool that checks your APA citations with AI software. Say goodbye to inaccurate citations!

How to Write a Bibliography for a Research Paper

Do not try to “wow” your instructor with a long bibliography when your instructor requests only a works cited page. It is tempting, after doing a lot of work to research a paper, to try to include summaries on each source as you write your paper so that your instructor appreciates how much work you did. That is a trap you want to avoid. MLA style, the one that is most commonly followed in high schools and university writing courses, dictates that you include only the works you actually cited in your paper—not all those that you used.
Academic Writing, Editing, Proofreading, And Problem Solving Services
Get 10% off with 24start discount code, assembling bibliographies and works cited.
- If your assignment calls for a bibliography, list all the sources you consulted in your research.
- If your assignment calls for a works cited or references page, include only the sources you quote, summarize, paraphrase, or mention in your paper.
- If your works cited page includes a source that you did not cite in your paper, delete it.
- All in-text citations that you used at the end of quotations, summaries, and paraphrases to credit others for their ideas,words, and work must be accompanied by a cited reference in the bibliography or works cited. These references must include specific information about the source so that your readers can identify precisely where the information came from.The citation entries on a works cited page typically include the author’s name, the name of the article, the name of the publication, the name of the publisher (for books), where it was published (for books), and when it was published.
The good news is that you do not have to memorize all the many ways the works cited entries should be written. Numerous helpful style guides are available to show you the information that should be included, in what order it should appear, and how to format it. The format often differs according to the style guide you are using. The Modern Language Association (MLA) follows a particular style that is a bit different from APA (American Psychological Association) style, and both are somewhat different from the Chicago Manual of Style (CMS). Always ask your teacher which style you should use.
A bibliography usually appears at the end of a paper on its own separate page. All bibliography entries—books, periodicals, Web sites, and nontext sources such radio broadcasts—are listed together in alphabetical order. Books and articles are alphabetized by the author’s last name.
Most teachers suggest that you follow a standard style for listing different types of sources. If your teacher asks you to use a different form, however, follow his or her instructions. Take pride in your bibliography. It represents some of the most important work you’ve done for your research paper—and using proper form shows that you are a serious and careful researcher.
Bibliography Entry for a Book
A bibliography entry for a book begins with the author’s name, which is written in this order: last name, comma, first name, period. After the author’s name comes the title of the book. If you are handwriting your bibliography, underline each title. If you are working on a computer, put the book title in italicized type. Be sure to capitalize the words in the title correctly, exactly as they are written in the book itself. Following the title is the city where the book was published, followed by a colon, the name of the publisher, a comma, the date published, and a period. Here is an example:
Format : Author’s last name, first name. Book Title. Place of publication: publisher, date of publication.
- A book with one author : Hartz, Paula. Abortion: A Doctor’s Perspective, a Woman’s Dilemma . New York: Donald I. Fine, Inc., 1992.
- A book with two or more authors : Landis, Jean M. and Rita J. Simon. Intelligence: Nature or Nurture? New York: HarperCollins, 1998.
Bibliography Entry for a Periodical
A bibliography entry for a periodical differs slightly in form from a bibliography entry for a book. For a magazine article, start with the author’s last name first, followed by a comma, then the first name and a period. Next, write the title of the article in quotation marks, and include a period (or other closing punctuation) inside the closing quotation mark. The title of the magazine is next, underlined or in italic type, depending on whether you are handwriting or using a computer, followed by a period. The date and year, followed by a colon and the pages on which the article appeared, come last. Here is an example:
Format: Author’s last name, first name. “Title of the Article.” Magazine. Month and year of publication: page numbers.
- Article in a monthly magazine : Crowley, J.E.,T.E. Levitan and R.P. Quinn.“Seven Deadly Half-Truths About Women.” Psychology Today March 1978: 94–106.
- Article in a weekly magazine : Schwartz, Felice N.“Management,Women, and the New Facts of Life.” Newsweek 20 July 2006: 21–22.
- Signed newspaper article : Ferraro, Susan. “In-law and Order: Finding Relative Calm.” The Daily News 30 June 1998: 73.
- Unsigned newspaper article : “Beanie Babies May Be a Rotten Nest Egg.” Chicago Tribune 21 June 2004: 12.
Bibliography Entry for a Web Site
For sources such as Web sites include the information a reader needs to find the source or to know where and when you found it. Always begin with the last name of the author, broadcaster, person you interviewed, and so on. Here is an example of a bibliography for a Web site:
Format : Author.“Document Title.” Publication or Web site title. Date of publication. Date of access.
Example : Dodman, Dr. Nicholas. “Dog-Human Communication.” Pet Place . 10 November 2006. 23 January 2014 < http://www.petplace.com/dogs/dog-human-communication-2/page1.aspx >
After completing the bibliography you can breathe a huge sigh of relief and pat yourself on the back. You probably plan to turn in your work in printed or handwritten form, but you also may be making an oral presentation. However you plan to present your paper, do your best to show it in its best light. You’ve put a great deal of work and thought into this assignment, so you want your paper to look and sound its best. You’ve completed your research paper!
Back to How To Write A Research Paper .
ORDER HIGH QUALITY CUSTOM PAPER

- Grades 6-12
- School Leaders
NEW: Classroom Clean-Up/Set-Up Email Course! 🧽
How To Write a Bibliography (Plus Printable Guide With Examples)
Give credit where credit is due.

Writing a research paper involves a lot of work. Students need to consult a variety of sources to gather reliable information and ensure their points are well supported. Research papers include a bibliography, which can be a little tricky for students. Learn how to write a bibliography in multiple styles and find basic examples below.
Plus grab our printable Bibliography Guide for Students with examples from all three major style guides: APA (American Psychological Association), MLA (Modern Language Association), or The Chicago Manual of Style . Just fill out the form on this page to get the free guide.
IMPORTANT: Each style guide has its own very specific rules, and they often conflict with one another. Additionally, each type of reference material has many possible formats, depending on a variety of factors. The overviews shown here are meant to guide students in writing basic bibliographies, but this information is by no means complete. Students should always refer directly to the preferred style guide to ensure they’re using the most up-to-date formats and styles.
What is a bibliography?
When you’re researching a paper, you’ll likely consult a wide variety of sources. You may quote some of these directly in your work, summarize some of the points they make, or simply use them to further the knowledge you need to write your paper. Since these ideas are not your own, it’s vital to give credit to the authors who originally wrote them. This list of sources, organized alphabetically, is called a bibliography.
A bibliography should include all the materials you consulted in your research, even if you don’t quote directly from them in your paper. These resources could include (but aren’t limited to):
- Books and e-books
- Periodicals like magazines or newspapers
- Online articles or websites
- Primary source documents like letters or official records
Bibliography vs. References
These two terms are sometimes used interchangeably, but they actually have different meanings. As noted above, a bibliography includes all the materials you used while researching your paper, whether or not you quote from them or refer to them directly in your writing.
A list of references only includes the materials you cite throughout your work. You might use direct quotes or summarize the information for the reader. Either way, you must ensure you give credit to the original author or document. This section can be titled “List of Works Cited” or simply “References.”
Your teacher may specify whether you should include a bibliography or a reference list. If they don’t, consider choosing a bibliography to show all the works you used in researching your paper. This can help the reader see that your points are well supported and allow them to do further reading on their own if they’re interested.
Bibliography vs. Citations
Citations refer to direct quotations from a text that are woven into your own writing. There are a variety of ways to write citations, including footnotes and endnotes. These are generally shorter than the entries in a reference list or bibliography. Learn more about writing citations here.
What does a bibliography entry include?
Depending on the reference material, bibliography entries include a variety of information intended to help a reader locate the material if they want to refer to it themselves. These entries are listed in alphabetical order and may include:
- Author/s or creator/s
- Publication date
- Volume and issue numbers
- Publisher and publication city
- Website URL
These entries don’t generally need to include specific page numbers or locations within the work (except for print magazine or journal articles). That type of information is usually only needed in a footnote or endnote citation.
What are the different bibliography styles?
In most cases, writers use one of three major style guides: APA (American Psychological Association), MLA (Modern Language Association), or The Chicago Manual of Style . There are many others as well, but these three are the most common choices for K–12 students.
Many teachers will state their preference for one style guide over another. If they don’t, you can choose your own preferred style. However, you should also use that guide for your entire paper, following their recommendations for punctuation, grammar, and more. This will ensure you are consistent throughout.
Below, you’ll learn how to write a simple bibliography using each of the three major style guides. We’ve included details for books and e-books, periodicals, and electronic sources like websites and videos. If the reference material type you need to include isn’t shown here, refer directly to the style guide you’re using.
APA Style Bibliography and Examples

Technically, APA style calls for a list of references instead of a bibliography. If your teacher requires you to use the APA style guide , you can limit your reference list to only items you cite throughout your work.
How To Write a Bibliography (References) Using APA Style
Here are some general notes on writing an APA reference list:
- Title your bibliography section “References” and center the title on the top line of the page.
- Do not center your references; they should be left-aligned. For longer items, subsequent lines should use a hanging indent of 1/2 inch.
- Include all types of resources in the same list.
- Alphabetize your list by author or creator, last name first.
- Do not spell out the author/creator’s first or middle name—only use their initials.
- If there are multiple authors/creators, use an ampersand (&) before the final author/creator.
- Place the date in parentheses.
- Capitalize only the first word of the title and subtitle, unless the word would otherwise be capitalized (proper names, etc.).
- Italicize the titles of books, periodicals, and videos.
- For websites, include the full site information, including the http:// or https:// at the beginning.
Books and E-Books APA Bibliography Examples
For books, APA reference list entries use this format (only include the publisher’s website for e-books):
Last Name, First Initial. Middle Initial. (Publication date). Title with only first word capitalized (unless there’s a proper name/noun) . Publisher. Publisher’s website
- Wynn, S. (2020). City of London at war 1939–45 . Pen & Sword Military. https://www.pen-and-sword.co.uk/City-of-London-at-War-193945-Paperback/p/17299
Periodical APA Bibliography Examples
For journal or magazine articles, use the following format. If you viewed the article online, include the URL at the end of the citation.
Last Name, First Initial. Middle Initial. (Publication date). Title of article. Magazine or Journal Title (Volume number) Issue number, page numbers. URL
- Bell, A. (2009). Landscapes of fear: Wartime London, 1939–1945. Journal of British Studies (48) 1, 153–175. https://www.jstor.org/stable/25482966
Here’s the format for newspapers. For print editions, include the page number/s. For online articles, include the full URL:
Last Name, First Initial. Middle Initial. (Year, Month Date) Title of article. Newspaper title. Page number/s. URL
- Blakemore, E. (2022, November 12) Researchers track down two copies of fossil destroyed by the Nazis. The Washington Post. https://www.washingtonpost.com/science/2022/11/12/ichthyosaur-fossil-images-discovered/
Electronic APA Bibliography Examples
For articles with a specific author on a website, use this format:
Last Name, First Initial. Middle Initial. (Year, Month Date). Title . Site name. URL
- Wukovits, J. (2023, January 30). A World War II survivor recalls the London Blitz . British Heritage . https://britishheritage.com/history/world-war-ii-survivor-london-blitz
When an online article doesn’t include a specific author or date, list it like this:
Title . (Year, Month Date). Site name. Retrieved Month Date, Year, from URL
- Growing up in the Second World War . (n.d.). Imperial War Museums. Retrieved May 12, 2023, from https://www.iwm.org.uk/history/growing-up-in-the-second-world-war
When you need to list a YouTube video, use the name of the account that uploaded the video, and format it like this:
Name of Account. (Upload year, month day). Title [Video]. YouTube. URL
- War Stories. (2023, January 15). How did London survive the Blitz during WW2? Cities at war: London [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/uwY6JlCvbxc
For more information on writing APA bibliographies, see the APA Style Guide website.
APA Bibliography (Reference List) Example Pages

MLA Style Bibliography Examples

MLA style calls for a Works Cited section, which includes all materials quoted or referred to in your paper. You may also include a Works Consulted section, including other reference sources you reviewed but didn’t directly cite. Together, these constitute a bibliography. If your teacher requests an MLA Style Guide bibliography, ask if you should include Works Consulted as well as Works Cited.
How To Write a Bibliography (Works Cited and Works Consulted) in MLA Style
For both MLA Works Cited and Works Consulted sections, use these general guidelines:
- Start your Works Cited list on a new page. If you include a Works Consulted list, start that on its own new page after the Works Cited section.
- Center the title (Works Cited or Works Consulted) in the middle of the line at the top of the page.
- Align the start of each source to the left margin, and use a hanging indent (1/2 inch) for the following lines of each source.
- Alphabetize your sources using the first word of the citation, usually the author’s last name.
- Include the author’s full name as listed, last name first.
- Capitalize titles using the standard MLA format.
- Leave off the http:// or https:// at the beginning of a URL.
Books and E-Books MLA Bibliography Examples
For books, MLA reference list entries use the following format. Add the URL at the end for e-books.
Last Name, First Name Middle Name. Title . Publisher, Date. URL
- Wynn, Stephen. City of London at War 1939–45 . Pen & Sword Military, 2020. www.pen-and-sword.co.uk/City-of-London-at-War-193945-Paperback/p/17299
Periodical MLA Bibliography Examples
Here’s the MLA-style format for magazines, journals, and newspapers. For online articles, add the URL at the end of the listing:
For magazines and journals:
Last Name, First Name. “Title: Subtitle.” Name of Journal , volume number, issue number, Date of Publication, First Page Number–Last Page Number.
- Bell, Amy. “Landscapes of Fear: Wartime London, 1939–1945.” Journal of British Studies , vol. 48, no. 1, January 2009, pp. 153–175. www.jstor.org/stable/25482966
When citing newspapers, include the page number/s for print editions or the URL for online articles:
Last Name, First Name. “Title of article.” Newspaper title. Page number/s. Year, month day. Page number or URL
- Blakemore, Erin. “Researchers Track Down Two Copies of Fossil Destroyed by the Nazis.” The Washington Post. 2022, Nov. 12. www.washingtonpost.com/science/2022/11/12/ichthyosaur-fossil-images-discovered/
Electronic MLA Bibliography Examples
Last Name, First Name. Year. “Title.” Month Day, Year published. URL
- Wukovits, John. 2023. “A World War II Survivor Recalls the London Blitz.” January 30, 2023. https://britishheritage.com/history/world-war-ii-survivor-london-blitz
Website. n.d. “Title.” Accessed Day Month Year. URL.
- Imperial War Museum. n.d. “Growing Up in the Second World War.” Accessed May 9, 2023. www.iwm.org.uk/history/growing-up-in-the-second-world-war.
Here’s how to list YouTube and other online videos:
Creator, if available. “Title of Video.” Website. Uploaded by Username, Day Month Year. URL.
- “How did London survive the Blitz during WW2?” Cities at war: London | War stories.” YouTube . Uploaded by War Stories, 15 Jan. 2023. youtu.be/uwY6JlCvbxc.
For more information on writing MLA-style bibliographies, see the MLA Style website.
MLA Bibliography (Works Cited) Example Pages

Chicago Manual of Style Bibliography Examples
The Chicago Manual of Style (sometimes called “Turabian”) actually has two options for citing reference material: Notes and Bibliography and Author-Date. Regardless of which you use, you’ll need a complete detailed list of reference items at the end of your paper. The examples below demonstrate how to write that list.
How To Write a Bibliography Using The Chicago Manual of Style

Here are some general notes on writing a Chicago -style bibliography:
- You may title it “Bibliography” or “References.” Center this title at the top of the page and add two blank lines before the first entry.
- Left-align each entry, with a hanging half-inch indent for subsequent lines of each entry.
- Single-space each entry, with a blank line between entries.
- Include the “http://” or “https://” at the beginning of URLs.
Books and E-Books Chicago Manual of Style Bibliography Examples
For books, Chicago -style reference list entries use the following format. (For print books, leave off the information about how the book was accessed.)
Last Name, First Name Middle Name. Title . City of Publication: Publisher, Date. How e-book was accessed.
- Wynn, Stephen. City of London at War 1939–45 . Yorkshire: Pen & Sword Military, 2020. Kindle edition.
Periodical Chicago Manual of Style Bibliography Examples
Here’s the style format for magazines, journals, and newspapers. For online articles, add the URL at the end of the listing.
For journal and magazine articles, use this format:
Last Name, First Name. Year of Publication. “Title: Subtitle.” Name of Journal , Volume Number, issue number, First Page Number–Last Page Number. URL.
- Bell, Amy. 2009. “Landscapes of Fear: Wartime London, 1939–1945.” Journal of British Studies, 48 no. 1, 153–175. https://www.jstor.org/stable/25482966.
When citing newspapers, include the URL for online articles:
Last Name, First Name. Year of Publication. “Title: Subtitle.” Name of Newspaper , Month day, year. URL.
- Blakemore, Erin. 2022. “Researchers Track Down Two Copies of Fossil Destroyed by the Nazis.” The Washington Post , November 12, 2022. https://www.washingtonpost.com/science/2022/11/12/ichthyosaur-fossil-images-discovered/.
Electronic Chicago Manual of Style Bibliography Examples
Last Name, First Name Middle Name. “Title.” Site Name . Year, Month Day. URL.
- Wukovits, John. “A World War II Survivor Recalls the London Blitz.” British Heritage. 2023, Jan. 30. britishheritage.com/history/world-war-ii-survivor-london-blitz.
“Title.” Site Name . URL. Accessed Month Day, Year.
- “Growing Up in the Second World War.” Imperial War Museums . www.iwm.org.uk/history/growing-up-in-the-second-world-war. Accessed May 9, 2023.
Creator or Username. “Title of Video.” Website video, length. Month Day, Year. URL.
- War Stories. “How Did London Survive the Blitz During WW2? | Cities at War: London | War Stories.” YouTube video, 51:25. January 15, 2023. https://youtu.be/uwY6JlCvbxc.
For more information on writing Chicago -style bibliographies, see the Chicago Manual of Style website.
Chicago Manual of Style Bibliography Example Pages

Get Your Free Printable Bibliography Style Guide

Just fill out the form on this page to grab our printable Bibliography Guide for Students with examples from all three major style guides: APA (American Psychological Association), MLA (Modern Language Association), or The Chicago Manual of Style .
Now that you know how to write a bibliography, take a look at the Best Websites for Teaching & Learning Writing .
Plus, get all the latest teaching tips and ideas when you sign up for our free newsletters .
Copyright © 2024. All rights reserved. 5335 Gate Parkway, Jacksonville, FL 32256

Writing your Dissertation / Thesis
- Getting started
- Dissertations and theses
- Bibliographic research and literature review
- Citations and bibliography
- Copyright and plagiarism
- Ask a Librarian
Bibliographic research
The search and collection of information from published sources (books, journals, newspapers, etc.) nowadays may include other types of documents, such as websites, reports from bibliographic databases, etc.
Searching for bibliographic sources relevant to your project is an integral and unavoidable part of the thesis work.
To find out how to conduct your bibliographic research, we suggest you consult the Bibliographic Research Guide .
For a start, you can consult the Library books on academic writing (how to write assignments, presentations, theses ...):
Literature review
Literature review is the analysis of the academic literature (articles, books, dissertations, theses, etc.) that you have identified when performing your search on the topic.
A review of the relevant literature for the topic selected is a key element of any academic project (dissertation or PhD thesis, writing an article for an academic journal…) for several reasons:
• it provides you with the conceptual context for your research
• it allows you to acquire, deepen and organize knowledge in the chosen research area
• helps you define or better focus your research objectives
Furthermore, its objectives are:
- describing the state-of-the-art on the given subject (what is the knowledge achieved so far in the research area in which your project fits?)
- identifying strengths and weaknesses, potential gaps in the current knowledge, unexplored empirical issues, or issues that need to be updated
- understanding how the research question is positioned within the field (to what extent does your work provide an original contribution to the research context?)
Want to learn more about the literature review? Explore the Project Planner on SAGE Research Methods .
If you notice that a significant book or resource is not included in the Library collections, please let us know : the Library will consider acquiring it!
- << Previous: Dissertations and theses
- Next: Citations and bibliography >>
- Last Updated: Jan 30, 2024 11:59 AM
- URL: https://unibocconi.libguides.com/dissertation
- Utility Menu
fa3d988da6f218669ec27d6b6019a0cd
A publication of the harvard college writing program.
Harvard Guide to Using Sources
- The Honor Code
- Bibliography
If you are using Chicago style footnotes or endnotes, you should include a bibliography at the end of your paper that provides complete citation information for all of the sources you cite in your paper. Bibliography entries are formatted differently from notes. For bibliography entries, you list the sources alphabetically by last name, so you will list the last name of the author or creator first in each entry. You should single-space within a bibliography entry and double-space between them. When an entry goes longer than one line, use a hanging indent of .5 inches for subsequent lines. Here’s a link to a sample bibliography that shows layout and spacing . You can find a sample of note format here .
Complete note vs. shortened note
Here’s an example of a complete note and a shortened version of a note for a book:
1. Karen Ho, Liquidated: An Ethnography of Wall Street (Durham: Duke University Press, 2009), 27-35.
1. Karen Ho, Liquidated , 27-35.
Note vs. Bibliography entry
The bibliography entry that corresponds with each note is very similar to the longer version of the note, except that the author’s last and first name are reversed in the bibliography entry. To see differences between note and bibliography entries for different types of sources, check this section of the Chicago Manual of Style .
For Liquidated , the bibliography entry would look like this:
Ho, Karen, Liquidated: An Ethnography of Wall Street . Durham: Duke University Press, 2009.
Citing a source with two or three authors
If you are citing a source with two or three authors, list their names in your note in the order they appear in the original source. In the bibliography, invert only the name of the first author and use “and” before the last named author.
1. Melissa Borja and Jacob Gibson, “Internationalism with Evangelical Characteristics: The Case of Evangelical Responses to Southeast Asian Refugees,” The Review of Faith & International Affairs 17, no. 3 (2019): 80-81, https://doi.org/10.1080/15570274.2019.1643983 .
Shortened note:
1. Borja and Gibson, “Internationalism with Evangelical Characteristics,” 80-81.
Bibliography:
Borja, Melissa, and Jacob Gibson. “Internationalism with Evangelical Characteristics: The Case of Evangelical Responses to Southeast Asian Refugees.” The Review of Faith & International Affairs 17. no. 3 (2019): 80–93. https://doi.org/10.1080/15570274.2019.1643983 .
Citing a source with more than three authors
If you are citing a source with more than three authors, include all of them in the bibliography, but only include the first one in the note, followed by et al. ( et al. is the shortened form of the Latin et alia , which means “and others”).
1. Justine M. Nagurney, et al., “Risk Factors for Disability After Emergency Department Discharge in Older Adults,” Academic Emergency Medicine 27, no. 12 (2020): 1271.
Short version of note:
1. Justine M. Nagurney, et al., “Risk Factors for Disability,” 1271.
Nagurney, Justine M., Ling Han, Linda Leo‐Summers, Heather G. Allore, Thomas M. Gill, and Ula Hwang. “Risk Factors for Disability After Emergency Department Discharge in Older Adults.” Academic Emergency Medicine 27, no. 12 (2020): 1270–78. https://doi.org/10.1111/acem.14088 .
Citing a book consulted online
If you are citing a book you consulted online, you should include a URL, DOI, or the name of the database where you found the book.
1. Karen Ho, Liquidated: An Ethnography of Wall Street (Durham: Duke University Press, 2009), 27-35, https://doi-org.ezp-prod1.hul.harvard.edu/10.1215/9780822391371 .
Bibliography entry:
Ho, Karen. Liquidated: An Ethnography of Wall Street . Durham: Duke University Press, 2009. https://doi-org.ezp-prod1.hul.harvard.edu/10.1215/9780822391371 .
Citing an e-book consulted outside of a database
If you are citing an e-book that you accessed outside of a database, you should indicate the format. If you read the book in a format without fixed page numbers (like Kindle, for example), you should not include the page numbers that you saw as you read. Instead, include chapter or section numbers, if possible.
1. Karen Ho, Liquidated: An Ethnography of Wall Street (Durham: Duke University Press, 2009), chap. 2, Kindle.
Ho, Karen. Liquidated: An Ethnography of Wall Street . Durham: Duke University Press, 2009. Kindle.
- Citation Management Tools
- In-Text Citations
- Examples of Commonly Cited Sources
- Frequently Asked Questions about Citing Sources in Chicago Format
- Sample Bibliography
PDFs for This Section
- Citing Sources
- Online Library and Citation Tools

- Citation Generator
- Style Guides
- Chicago/Turabian Format
How to Write an APA Bibliography
APA 7 style guidelines require a reference list of all the sources you included in your research paper. APA references follow the author-date style of citation. You may be asked to create an annotated APA bibliography, however. This could be a separate assignment or part of the larger research project. This goes above and beyond the basic reference list with a brief discussion of each entry.

Reference List Instructions
Start the reference list on the page following your report, after appendices, or any other supporting material. Follow these steps to write the perfect APA bibliography .
Format each citation entry by following these rules :
- List authors by last name, first name initial, and middle name initial (e.g., Doe, J. J.).
- Do not spell out first or middle name(s).
- Capitalize only the first letter of the title and subtitle of the article or book.
- Italicize titles of journals or books.
- Use an ampersand before the final author on works with multiple authors.
Format your bibliography page by following these rules:
- Use References as the title, centered at the top of the page.
- Double-space your text.
- Include the running head (optional for students in APA 7).
- Include the page number.
- Follow the letter by letter alphabetizing method .
Example APA Bibliography Page
AGING BRAIN (Professional Papers Only)
Beal, M. F. (2003). Mitochondria, oxidative damage, and inflammation in Parkinson’s disease. Academic Science 991. 120-13 . Health Informatics Journal , 13 (2), 155-6.
Chase, M. H. (1999, September 24). Too often the elderly don’t get the drugs or care they need. Wall Street Journal . 31.
Kidd, P. M. (1999). A review of nutrients and botanicals in the integrative management of cognitive dysfunction. Alternative Medicine 4 (3). 144-161.
Morrison, J. H., & Hof, P. R. (1997). Life and death of neurons in the aging brain. Science, 278 (5337), 412-419. https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/7012/cafb15a5d6e03caafc71d70d47971ded391b.pdf
Perlmutter, D., & Colman, C. (2004). The better brain book . Riverhead Books.
APA Annotated Bibliography

You may be required to write an APA annotated bibliography . Follow the same formatting rules as above; however, include all sources consulted and add an evaluative or summary annotation of each source listed.
Example Citation Entry
Egendorf, L. K. (Ed.). (2002). An aging population: Opposing viewpoints . Greenhaven Press.
This book on aging in the United States provides twenty-three short essays organized into chapters. Each chapter covers a different theme with writers presenting opposing arguments. For example, there are pro and con articles on whether older people are hurting the economy. This is a good book to read on aspects of the aging population. It is not an in-depth look but provides some good arguments, which lead to further research and discussion.
Follow your teacher’s instructions while writing and researching your APA format school paper even if it’s different than what you’ve learned about formal APA style.
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
Average rating 3.5 / 5. Vote count: 194
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
8 APA Book Reference Examples
Apa citation newspaper article examples, apa annotated bibliography guide with examples, apa citation guidelines.
How to Write a Bibliography (MLA, APA Examples)

Learn how to easily write a bibliography by following the format outlined in this article.
This resource will help your students properly cite different resources in the bibliography of a research paper, and how to format those citations, for books, encyclopedias, films, websites, and people.
| Add to Folder | |
|---|---|
| creative writing | |
| children's book | |
| activities | |
| classroom tools | |
| language arts and writing | |
| vocabulary |
What is a bibliography?
According to Infoplease.com, A bibliography is a list of the types of sources you used to get information for your report. It is included at the end of your report, on the last page (or last few pages).
What are the types of bibliography styles (MLA, APA, etc.)?
The 3 most common bibliography/citation styles are:
- MLA Style: The Modern Language Association works cited page style
- APA Style: The American Psychological Association style
- Chicago Style: The bibliography style defined by the Chicago Manual of Style
We’ll give examples of how to create bibliography entries in various styles further down in this article.
What sources do you put in a bibliography?
An annotated bibliography should include a reference list of any sources you use in writing a research paper. Any printed sources from which you use a text citation, including books, websites, newspaper articles, journal articles, academic writing, online sources (such as PDFs), and magazines should be included in a reference list. In some cases, you may need or want to cite conversations or interviews, works of art, visual works such as movies, television shows, or documentaries - these (and many others) can also be included in a reference list.
How to get started writing your bibliography
You will find it easier to prepare your MLA, APA, or Chicago annotated bibliography if you keep track of each book, encyclopedia, journal article, webpage or online source you use as you are reading and taking notes. Start a preliminary, or draft, bibliography by listing on a separate sheet of paper all your sources. Note down the full title, author’s last name, place of publication, web address, publisher, and date of publication for each source.
Haven't started your paper yet and need an outline? These sample essay outlines include a research paper outline from an actual student paper.
How to write a bibliography step-by-step (with examples)
General Format: Author (last name first). Title of the book. Publisher, Date of publication.
MLA Style: Sibley, David Allen. What It’s Like to Be a Bird. From Flying to Nesting, Eating to Singing, What Birds Are Doing, and Why. Alfred A. Knopf, 2020.
APA Style: Sibley, D.A. (2020). What It’s Like to Be a Bird. From Flying to Nesting, Eating to Singing, What Birds Are Doing, and Why . Alfred A. Knopf.
Notes: Use periods, not commas, to separate the data in the entry. Use a hanging indent if the entry is longer than one line. For APA style, do not use the full author’s first name.
Websites or webpages:
MLA Style: The SB Nation Family of Sites. Pension Plan Puppets: A Toronto Maple Leafs Blog, 2022, www.pensionplanpuppets.com. Accessed 15 Feb. 2022.
APA Style: American Heart Association. (2022, April 11). How to keep your dog’s heart healthy. https://www.heart.org/en/news/2022/04/11/how-to-keep-your-dogs-heart-healthy
Online news article from a newspaper site:
APA Style: Duehren, A. (2022, April 9). Janet Yellen faces challenge to keep pressure on Russia. Wall Street Journal. https://www.wsj.com/articles/janet-yellen-faces-challenge-to-keep-pressure-on-russia-while-addressing-global-consequences-11650366000
Print journal articles:
MLA Style: Booch, Grady. "Patterns in Object-Oriented Design." IEEE Software Engineering, vol. 6, no. 6, 2006, pp. 31-50.
APA Style: Booch, G. (2006). Patterns in object-oriented design. IEEE Software Engineering, 6(6), 31–50.
Note: It is suggested that you include a DOI and a webpage address when referencing either a printed journal article, and electronic journal article, or an journal article that appears in both formats.
MLA Style: Gamma, Eric, and Peter A. Coad. “Exceptions to the Unified Modeling Language in Python Patterns.” IEEE Software Engineering, vol. 2, no. 6, 8 Mar. 2006, pp. 190-194. O’Reilly Software Engineering Library, https://doi.org/10.1006/se.20061. Accessed 26 May 2009.
APA Style: Masters, H., Barron, J., & Chanda, L. (2017). Motivational interviewing techniques for adolescent populations in substance abuse counseling. NAADAC Notes, 7(8), 7–13. https://www.naadac.com/notes/adolescent-techniques
ML:A Style: @Grady_Booch. “That’s a bold leap over plain old battery power cars.” Twitter, 13 Mar. 2013, 12:06 p.m., https://twitter.com/Grady_Booch/status/1516379006727188483.
APA Style: Westborough Library [@WestboroughLib]. (2022, April 12). Calling all 3rd through 5th grade kids! Join us for the Epic Writing Showdown! Winner receives a prize! Space is limited so register, today. loom.ly/ypaTG9Q [Tweet; thumbnail link to article]. Twitter. https://twitter.com/WestboroughLib/status/1516373550415896588.
Print magazine articles:
General format: Author (last name first), "Article Title." Name of magazine. Volume number, (Date): page numbers.
MLA Style: Stiteler, Sharon. "Tracking Red-Breasted Grosbeak Migration." Minnesota Bird Journal, 7 Sept. 2019, pp. 7-11.
APA Style: Jordan, Jennifer, "Filming at the Top of the World." Museum of Science Magazine. Volume 47, No. 1, (Winter 1998): p. 11.
Print newspaper articles:
General format: Author (last name first), "Article Title." Name of newspaper, city, state of publication. (date): edition if available, section, page number(s).
MLA Style: Adelman, Martin. "Augustus Announces Departure from City Manager Post." New York Times, late ed., 15 February 2020, p. A1
APA Style: Adelman, M. (2020, February 15). Augustus announced departure from city manager post. New York Times, A1.
Encyclopedias:
General Format: Encyclopedia Title, Edition Date. Volume Number, "Article Title," page numbers.
MLA Style: “Gorillas.” The Encyclopedia Brittanica. 15th ed. 2010.
APA Style: Encyclopedia Brittanica, Inc. (1997.) Gorillas. In The Encyclopedia Brittanica (15th ed., pp. 50-51). Encyclopedia Brittanica, Inc.
Personal interviews:
General format: Full name (last name first). Personal Interview. (Occupation.) Date of interview.
MLA Style: Smithfield, Joseph. Personal interview. 19 May 2014.
APA Style: APA does not require a formal citation for a personal interview. Published interviews from other sources should be cited accordingly.
Films and movies:
General format: Title, Director, Distributor, Year.
MLA Style: Fury. Directed by David Ayer, performances by Brad Pitt, Shia LaBeouf, Jon Bernthal, Sony Pictures, 2014.
APA Style: Ayer, D. (Director). (2014). Fury [Film]. Sony Pictures.
Featured High School Resources

Related Resources

About the author

TeacherVision Editorial Staff
The TeacherVision editorial team is comprised of teachers, experts, and content professionals dedicated to bringing you the most accurate and relevant information in the teaching space.

- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
How to Write a Bibliography in APA Format
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Emily is a board-certified science editor who has worked with top digital publishing brands like Voices for Biodiversity, Study.com, GoodTherapy, Vox, and Verywell.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Emily-Swaim-1000-0f3197de18f74329aeffb690a177160c.jpg)
- APA Bibliography
- How to Create One
- Why You Need It
Sample Bibliography
An APA format bibliography lists all of the sources that might be used in a paper. A bibliography can be a great tool to help you keep track of information during the research and writing process. In some cases, your instructor may require you to include a bibliography as part of your assignment.
At a Glance
A well-written APA format bibliography can help you keep track of information and sources as you research and write your psychology paper. To create a bibliography, gather up all of the sources that you might use in your paper. Create an APA format reference for each source and then write a brief annotation. Your annotation should be a brief summary of what each reference is about. You can quickly refer to these annotations When writing your paper and determine which to include.
What Is an APA Format Bibliography?
An APA format bibliography is an alphabetical listing of all sources that might be used to write an academic paper, essay, article, or research paper—particularly work that is covering psychology or psychology-related topics. APA format is the official style of the American Psychological Association (APA). This format is used by many psychology professors, students, and researchers.
Even if it is not a required part of your assignment, writing a bibliography can help you keep track of your sources and make it much easier to create your final reference page in proper APA format.
Creating an APA Bibliography
A bibliography is similar in many ways to a reference section , but there are some important differences. While a reference section includes every source that was actually used in your paper, a bibliography may include sources that you considered using but may have dismissed because they were irrelevant or outdated.
Bibliographies can be a great way to keep track of information you might want to use in your paper and to organize the information that you find in different sources. The following are four steps you can follow to create your APA format bibliography.
Start on a New Page
Your working bibliography should be kept separate from the rest of your paper. Start it on a new page, with the title "Bibliography" centered at the top and in bold text. Some people use the title "References" instead, so it's best to check with your professor or instructor about which they prefer you to use.
Gather Your Sources
Compile all the sources you might possibly use in your paper. While you might not use all of these sources in your paper, having a complete list will make it easier later on when you prepare your reference section.
Gathering your sources can be particularly helpful when outlining and writing your paper.
By quickly glancing through your working bibliography, you will be able to get a better idea of which sources will be the most appropriate to support your thesis and main points.
Reference Each Source
Your references should be listed alphabetically by the author’s last name, and they should be double-spaced. The first line of each reference should be flush left, while each additional line of a single reference should be a few spaces to the right of the left margin, which is known as a hanging indent.
The format of each source is as follows for academic journals:
- Last name of first author (followed by their first initial)
- The year the source was published in parentheses
- The title of the source
- The journal that published the source (in italics)
- The volume number, if applicable (in italics)
- The issue number, if applicable
- Page numbers (in parentheses)
- The URL or "doi" in lowercase letters followed by a colon and the doi number, if applicable
The following examples are scholarly articles in academic journals, cited in APA format:
- Kulacaoglu, F., & Kose, S. (2018). Borderline personality disorder (BPD): In the midst of vulnerability, chaos, and awe. Brain sciences , 8 (11), 201. doi:10.3390/brainsci8110201
- Cattane, N., Rossi, R., & Lanfredi, M. (2017). Borderline personality disorder and childhood trauma: exploring the affected biological systems and mechanisms. BMC Psychiatry, 18 (221). doi:10.1186/s12888-017-1383-2
Visit the American Psychological Association's website for more information on citing other types of sources including online media, audiovisual media, and more.
Create an Annotation for Each Source
Normally a bibliography contains only references' information, but in some cases you might decide to create an annotated bibliography. An annotation is a summary or evaluation of the source.
An annotation is a brief description of approximately 150 words describing the information in the source, your evaluation of its credibility, and how it pertains to your topic. Writing one of these for each piece of research will make your writing process faster and easier.
This step helpful in determining which sources to ultimately use in your paper. Your instructor may also require it as part of the assignment so they can assess your thought process and understanding of your topic.
Reasons to Write a Bibliography
One of the biggest reasons to create an APA format bibliography is simply to make the research and writing process easier.
If you do not have a comprehensive list of all of your references, you might find yourself scrambling to figure out where you found certain bits of information that you included in your paper.
A bibliography is also an important tool that your readers can use to access your sources.
While writing an annotated bibliography might not be required for your assignment, it can be a very useful step. The process of writing an annotation helps you learn more about your topic, develop a deeper understanding of the subject, and become better at evaluating various sources of information.
The following is an example of an APA format bibliography by the website EasyBib:
There are many online resources that demonstrate different formats of bibliographies, including the American Psychological Association website . Purdue University's Online Writing Lab also has examples of formatting an APA format bibliography.
Check out this video on their YouTube channel which provides detailed instructions on formatting an APA style bibliography in Microsoft Word.
You can check out the Purdue site for more information on writing an annotated APA bibliography as well.
What This Means For You
If you are taking a psychology class, you may be asked to create a bibliography as part of the research paper writing process. Even if your instructor does not expressly require a bibliography, creating one can be a helpful way to help structure your research and make the writing process more manageable.
For psychology majors , it can be helpful to save any bibliographies you have written throughout your studies so that you can refer back to them later when studying for exams or writing papers for other psychology courses.
American Psychological Association. Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association . 7th Edition. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association; 2020.
Masic I. The importance of proper citation of references in biomedical articles. Acta Inform Med . 2013;21(3):148–155. doi:10.5455/aim.2013.21.148-155
American Psychological Association. How do you format a bibliography in APA Style?
Cornell University Library. How to prepare an annotated bibliography: The annotated bibliography .
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Write a Bibliography
Last Updated: March 12, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Diane Stubbs . Diane Stubbs is a Secondary English Teacher with over 22 years of experience teaching all high school grade levels and AP courses. She specializes in secondary education, classroom management, and educational technology. Diane earned a Bachelor of Arts in English from the University of Delaware and a Master of Education from Wesley College. There are 14 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 665,181 times.
When you write a paper or a book, it's important to include a bibliography. A bibliography tells your reader what sources you've used. It lists all the books, articles, and other references you cited in or used to inform your work. Bibliographies are typically formatted according to one of three styles: American Psychological Association (APA) for scientific papers, Modern Language Association (MLA) for humanities papers, and Chicago Manual of Style (CMS) for the social sciences. Make sure you always check with your superior - whether a professor or boss - about which style they prefer.
Sample Bibliographies

Writing an APA Bibliography

- For example, if the author's name for a source is "John Adams Smith," you would list him as "Smith, J.A.," before listing the title of his piece.

- For example, if one source has twelve authors, and the seventh author is "Smith, J.A." and the twelfth is "Timothy, S.J.," you would list the first six authors, then write "Smith, J.A. ...Timothy, S.J."

- For example, if you have a World Health Organization Report without an author as one of your sources, you would write, "World Health Organization, "Report on Development Strategies in Developing Nations," July 1996."

- For example, an article citation might look like this: Jensen, O. E. (2012). "African Elephants." Savannah Quarterly , 2(1), 88.
- If the periodical the article comes from always begins with page number 1 (these types of periodicals are called “paginated by issue” periodicals, you should include the full page range of the article.
- If the article was retrieved online, end the citation with the words "Retrieved from" followed by the web address.

- Example: Worden, B. L. (1999). Echoing Eden. New York, New York: One Two Press.
- If the title is more than one word long and doesn’t contain any proper nouns, only the first word should be capitalized. Only the first letter of any subtitle should be capitalized as well.
![how to do a bibliographic research Step 9 [8]...](https://www.wikihow.com/images/thumb/6/65/Write-a-Bibliography-Step-9-Version-3.jpg/v4-460px-Write-a-Bibliography-Step-9-Version-3.jpg)
- For example, a cited website might look like this: Quarry, R. R. (May 23, 2010). Wild Skies. Retrieved from https://wildskies.com.
- If no author is available, just start with the title. If no date is available, write "n.d."

Writing a MLA Bibliography

- You shouldn’t use an author’s title or degrees when listing their names in your bibliography. This is true even if they are listed that way on the source.

- For example, a book citation might look like this: Butler, Olivia. Parable of the Flower. Sacramento: Seed Press, 1996.

- For example, an article published in a scholarly journal might look like this: Green, Marsha. "Life in Costa Rica." Science Magazine vol. 1, no. 4, Mar 2013: 1-2.
- If you’re citing an article in a newspaper, you only need the name of the newspaper, followed by the date it was published, and the page number. A citation for that might look like this: Smith, Jennifer. “Tiny Tim Wins Award.” New York Times, 24 Dec 2017, p. A7.

- For example, a website citation might look like this: Jong, June. "How to Write an Essay." Writing Portal. 2 Aug. 2012. University of California. 23 Feb. 2013. <https://writingportal.com>
- Some websites, particularly academic ones, will have what’s called a DOI (digital object identifier). Write “doi:” in front of this number in place of the website’s url if a DOI is available.

Writing a CMS Bibliography

- Example: Skylar Marsh. "Walking on Water." Earth Magazine 4(2001): 23.

- For example, a book entry might look like this: Walter White. Space and Time . New York: London Press, 1982

- Example: University of California. "History of University of California." Last modified April 3, 2013. https://universityofcalifornia.com.
- Unless there is a publication date for the website you’re citing, you don’t need to include an access date. If you do have an access date, it goes at the end of the citation.
Expert Q&A

- Ask your teacher or professor which style they prefer you to use in your paper. Thanks Helpful 6 Not Helpful 2
- Be sure to include each and every source you reference in your work. Thanks Helpful 7 Not Helpful 5
- When writing a bibliography or a reference page, it really comes down to looking at an example and applying it to your own information. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://libguides.reading.ac.uk/citing-references/compilingbibliography
- ↑ https://morningside.libguides.com/APA7/references
- ↑ https://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/560/03/
- ↑ Cite articles
- ↑ https://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/560/08/
- ↑ https://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/560/10/
- ↑ https://www.scribbr.com/mla/works-cited/
- ↑ https://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/747/05/
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/mla_style/mla_formatting_and_style_guide/mla_works_cited_page_basic_format.html
- ↑ https://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/747/06/
- ↑ https://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/747/07/
- ↑ https://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/717/02/
- ↑ https://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/717/03/
- ↑ https://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/717/05/
About This Article

To create an APA bibliography, title a separate page at the end of your paper "References." Then, use the authors' last names to organize your list alphabetically, for example by writing the author John Adam Smith as "Smith, J. A." If a source has more than 7 authors, list the first 7 before adding an ellipses. To cite an article, include the author's name, year of publication, article title, publication title, and page numbers. When citing a book, begin with the author's name, then the date of publication, title in Italics, location of the publisher, and publisher's name. For tips on how to write an MLA or CMS bibliography, keep reading! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Dec 9, 2023
Did this article help you?

Mar 11, 2023
Mar 12, 2020
Braden White
Oct 21, 2020
Oct 12, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles


Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Level up your tech skills and stay ahead of the curve
Writing a Bibliography | Definition, Types & Examples
TK Waters has been an adjunct professor of religion at Western Kentucky University for six years. They have a master's degree in religious studies from Western Kentucky University and a bachelor's degree in English literature and religious studies from Western Kentucky University.
Doresa holds a Ph.D. in Communication Studies.
What should a bibliography look like?
Bibliographies look different depending on the citation style. The bibliography structure always includes citing the author's name, the title of the work, the year of publication, and the publisher for each source one consults for a paper or project. Although specific formatting details differ for each citation style, the basics are universal for each type, with the bibliography alphabetized by the author's last name for each source.
What do you write in a bibliography?
A bibliography is a detailed list of all the sources consulted and cited in a research paper or project. The bibliography structure always includes citing the author's name, the title of the work, the year of publication, and the publisher for each source one consults for a paper or project. Although the formatting details differ for each citation style, the basics are universal, and the bibliography is always alphabetized by the author's last name for each source.
How do you write a bibliography for a website?
A website is cited similarly to a book or article by including the author, title, publisher, date of publication, and URL for the source. The bibliographic entry style varies depending on the utilization of Chicago, APA, or MLA style, but all of these elements are always included when available.
How do you begin a bibliography?
The best way to begin a bibliography is by keeping a list of sources consulted during the research. Upon completion of the study, one should follow the required citation style (usually Chicago, APA, or MLA) and put all of the information about the source, such as author and title, into that format.
How do you write a bibliography?
The bibliography structure always includes citing the author's name, the title of the work, the year of publication, and the publisher for each source one consults for a paper or project. Although the details of how this is formatted differ for each citation style, the basics are universal, with the bibliography alphabetized by the author's last name for each source.
What is a bibliography for an essay?
A bibliography is a list of sources reviewed when writing the essay; this can include references cited in the body of the paper and sources from general information.
Table of Contents
What is a bibliography, types of bibliographies, how to write a bibliography, lesson summary.
Most high schools, colleges, and universities require research papers and projects, so students need to know how to write a bibliography to cite the research sources they use. A bibliography is a list of sources one consults and references in a research paper or project. What does bibliography mean? The word "bibliography" is Greek. The Greek words biblio and graphia literally mean "the writing of/about books."
Bibliographies are required whenever a writer consults a source for their research, whether they directly or indirectly use information from the reference. This application gives credit to the original author of that information. It keeps the person writing the research paper from committing plagiarism or making information from other sources seem like the writer's own idea. While bibliographies originally were lists of books, in the 21st century, bibliographies can include books, journal articles , websites, newspaper articles, films, and even social media pages -anything that the writer consults in their research.
For any paper or project where research transpires, the writer should include a bibliography. The format and title of the bibliography depend on what citation style the writer uses. For example, a writer using Chicago style would use "Bibliography" as the title of their source page; in APA style, this would be "References," while in MLA style it would be "Works Cited." This practice extends to when the writer is researching a topic they might want to do more research on in the future, presenting new information in their field of study, or even critiquing another person's work, such as in a book review.
Bibliographies not only provide a way to cite sources but also help give the writer credibility. A writer can use references and bibliographies to inform their readers which evidence supports their ideas, who or what influenced the writer's ideas and work, and what sources were used if a reader decides to use the writer's work for their research or a critique.
To unlock this lesson you must be a Study.com Member. Create your account

An error occurred trying to load this video.
Try refreshing the page, or contact customer support.
You must c C reate an account to continue watching
Register to view this lesson.
As a member, you'll also get unlimited access to over 88,000 lessons in math, English, science, history, and more. Plus, get practice tests, quizzes, and personalized coaching to help you succeed.
Get unlimited access to over 88,000 lessons.
Already registered? Log in here for access
Resources created by teachers for teachers.
I would definitely recommend Study.com to my colleagues. It’s like a teacher waved a magic wand and did the work for me. I feel like it’s a lifeline.
You're on a roll. Keep up the good work!
Just checking in. are you still watching.
- 0:13 Why Do We Use Bibliographies?
- 2:52 Types of Bibliographies
- 3:47 How Do You Create a…
- 5:25 When Do You Need a…
Although the concept of a bibliography might seem straightforward, many different types of bibliographies exist and are necessary for different situations. These types include, but are not limited to, the following:
- an enumerative/systematic bibliography,
- an annotated bibliography,
- a working bibliography,
- a period bibliography,
- and a subject bibliography.
Enumerative Bibliography
The most commonly used type of bibliography is the enumerative bibliography , sometimes called a systematic bibliography. This type of bibliography is simply a list of the sources consulted and cited in a research paper or project ordered in a particular way, usually alphabetically by each author's last name. Whenever an assignment or instructor requests a "bibliography" without any other details, they typically refer to an enumerative bibliography.
Annotated Bibliography
An annotated bibliography is a type of bibliography usually used early on in research projects. Annotated bibliographies have a list of sources to support a research project and brief "annotations" about each source. These annotations are usually around 150 words each and explain what the source is about and why it would be helpful to consult in the research project.
Working Bibliography
A working bibliography is similar to a rough draft version of a bibliography. A working bibliography is what one uses in drafting a research project or paper. This means that the working bibliography will change over time as new sources are added to it when the author continues their research. A working bibliography is not always a polished version of the bibliography. Depending on the requirements for an assignment, it might not even be in alphabetical order since the author has not finalized the bibliography yet.
Other Bibliographies
Enumerative, annotated, and working bibliographies are the most common types of bibliographies used in academic settings. Depending on the field of study, however, there are other types of bibliographies one might use. One of these is a period bibliography, which includes sources from a specific era, usually to aid in historical research. These bibliographies might accompany a project, but they might also be published separately just as a list of sources for others to consult if they are researching over that period. A subject bibliography works in much the same way as a period bibliography but covers a particular subject instead of a time.
Being able to understand what a bibliography is and how to do a bibliography are entirely different concepts. Many students in high schools, colleges, and even universities might be comfortable writing a research paper but still wonder, "How do you write a bibliography?" The bibliography in a research paper or project is typically one of the last pages of the paper, occurring after the bulk of the writing but before appendices. All bibliographies must include all of the references used to create the paper or project and what bibliographic information is available for a source; this includes:
- the name(s) of the author(s),
- the year of publication,
- the date of publication,
- the publisher,
- the containing work (journal, newspaper, anthology),
- the internet retrieval location (when applicable),
- and other necessary information for someone to be able to find the source.
Different citation styles determine how the bibliography should be formatted. Usually, an instructor or assignment will indicate the required citation style for the class or assignment. The three primary citation styles are the Chicago Manual of Style, the APA Style, and the MLA Style. While the Chicago style uses "bibliography" to refer to the bibliographies in their papers, APA style uses "references" while MLA style uses "works cited." The names refer to the same information, but each style guide has different requirements for formatting.
Chicago Style
The Chicago Manual of Style is the style used most commonly in history, anthropology, religious studies, and other humanities fields. Chicago style uses "Bibliography" to title the list of sources at the end of a paper. In addition to a bibliography, writers should include footnotes or endnotes in the body of their work. As the readers are reading, these notes detail where outside information was used. The basic information in a Chicago style bibliographic entry is as follows and in this order:
- author's last name,
- author's first name,
- title of work,
- publication location,
- and year of publication.
This information varies depending on the source cited, but the general order stays the same in Chicago style. What does a Chicago-style bibliography look like? Here are a few examples of different sources (book, journal article, film, and newspaper article) formatted in Chicago style. The author's last name alphabetizes all sources, only the first line of each entry is aligned to the left margin while subsequent lines are indented, and URLs are included for internet sources. Page ranges for articles appear after the volume number and issue number.
Although the Chicago style is the only formatting style that uses the term "bibliography" for sources, APA and MLA styles are the most commonly used citation styles. APA Style , which the American Psychological Association produced, is a style guide for fields like sociology, psychology, and other social sciences, as well as some natural sciences or scientific journals. Because most of these fields continue developing research and recent work is usually the most up-to-date, APA style puts the year of each source as the secondary focus after the author. In-text and parenthetical citations are in the body of the paper and bibliography, which is titled "References." The basic information in each APA style bibliographic entry includes, in order:
- author's first and middle initials,
- publisher name,
- and DOI (digital object identifier).
There are a few unique aspects that distinguish APA style bibliographic entries from what other citation styles require:
- The year appears directly after the author in parentheses.
- The work's title, whether a book or an article, uses sentence-style capitalization, which means that only the first word, words after colons and semicolons, ending punctuation, and proper nouns are capitalized. While this applies to book and article titles, it does not apply to journal and newspaper titles, which should still use title capitalization and have all major words capitalized.
- In the most recent edition, APA requires all sources to include a DOI (digital object identifier), if available, whether or not they were found on the internet.
- Volume numbers of journals are italicized, while issue numbers are in parentheses with page ranges following. Here are some examples of what APA style looks like on a reference page .
One of the most basic and widely used citation styles is MLA Style . MLA style, created by the Modern Language Association, is usually used in English, modern languages, cultural studies, and film study fields. MLA is one of the most approachable and straightforward to use styles, so it is often the first citation style one uses in an academic setting before learning the other types. In MLA, in-text and parenthetical citations are used to cite information in the body of the paper, while the bibliographic entries are organized on a page called " Works Cited ". MLA bibliographic entries typically include the following in order:
MLA style bibliographies look similar to Chicago style, with some exceptions. In MLA style, the abbreviation "pp." is used before a page range while "vol." and "no." are included before, respectively, a volume number and issue number. MLA also separates items in bibliographic entries primarily with commas instead of periods. One of the unique parts of an MLA entry is the formatting of the publisher's name. While Chicago and APA styles require the full publisher name, MLA style prefers that the publisher name stay short, one or two words if possible. If redundant words like "publisher," "publishing," "press," or "university" are part of the publisher's name, the omitting of these words are appropriate. Here are some examples of MLA bibliographic entries.
A bibliography is used in most academic writing to list works that an author consults in their research. This application gives the author credibility, lets their readers know where the author found the information and gives credit to other authors who have previously written various works. There are a few common types of bibliographies:
- an enumerative bibliography , which is a standard bibliography that lists all of the works and sources the author consulted in their research;
- an annotated bibliography , includes a bibliographic entry for each source an author is considering or has reviewed, along with a brief description and evaluation of the source;
- and a working bibliography , which includes what sources an author has consulted thus far and changes as the author continue researching and writing.
Many citation styles are used in academic settings to cite sources. These citation styles include:
- the Chicago Manual of Style , which is common in history and humanities fields;
- the APA Style , utilized primarily in the psychological and social sciences fields;
- and the MLA Style , commonly used in English, modern language, and film studies fields.
APA and MLA styles are the most commonly used citation styles. Each citation style has unique formatting requirements for how bibliographic entries should be formatted. However, all include basic information like the author's name, the title of the work, and the year of publication.
Video Transcript
Why do we use bibliographies.
Have you ever sat in a chair, looked out on a beautiful sunset and thought, 'what exactly is a bibliography?' Me either, but you may have to write one one day, so let's talk about what a bibliography is and why they are important.
Most often, when the word 'bibliography' is used in an academic setting it's referring to a list of sources used by the author to inform their work on a given topic . This means that you're going to include all the works that were read when researching the topic - whether or not they're used directly in your own writing.
There are several reasons why we use bibliographies. The first major reason for using a bibliography is to inform your reader on how widely you researched the topic on which you're writing. While you may cite only seven or eight sources within a paper, you may have read 25, 50, or even 100 different books, journal articles, or scholarly websites in finding those sources. Showing just how widely you researched your topic provides more credence and credibility to your work.
Another use for a bibliography is to allow your reader to know if you considered a work but chose not to include it within your piece, or if you didn't consult a particular author at all. For instance, I may be completing a research paper on the behavior of chimpanzees both in the wild and in captivity. If someone was reading through my piece and didn't see me cite Jane Goodall, one of the most famous chimpanzee experts of all time, they may be curious. A bibliography would let them know if I considered any of her famous works or if I failed to give her work any consideration at all. This would allow them to critique my own work on a much more informed basis.
One of the largest benefits for you personally in creating a bibliography is that it allows you to keep track of all the research you've consulted on a topic. For instance, when you are first writing a paper that you've researched, you may not initially utilize a source that you consulted. However, after you've done some rewriting and reworking of your paper, you may find that you really did need to include a source after all. Having a bibliography, it would be much easier for you to find the source information; you don't have to start all over again in the search process. Creating a bibliography allows you to build a small database of information on a number of given topics. While you're never going to write the same paper twice in an academic setting, you may write on a similar subject. Having a bibliography that you created as a place to start your research will put you much further ahead in the process.
What are the types on bibliographies? The first type you may find is an annotated bibliography , and that's going to give the citation of each source you consulted along with a brief description and evaluation of the source.
The second type is enumerative. An enumerative bibliography is a list of sources that were consulted, simply citing them in a proper format.
The third type of bibliography is a list of works published during a particular time in history - that's called a period bibliography . These are often used in anthropological, historical, or cultural research.
A subject bibliography is a list of sources on a particular subject, often considered a record of the most important works in any given field of study.
Now that you know the types of bibliography, let's talk about how you create one.
How Do You Create a Bibliography?
One of the first things you have to do in preparing to create a bibliography is to decide in advance what type of bibliography you are going to do - annotated, enumerative, period, or subject. In an academic setting, you are most likely going to do an annotated or enumerative bibliography. The second step is to decide on the citation formatting you're going to be using. The two most common types are APA and MLA, followed by Chicago formatting. The third step is to keep a record of the citations that you're going to be using, as well as keeping them in your chosen format.
Now, on your screen, you're going to see a sample annotated bibliography in APA format. This bibliography sample is provided to us by Purdue University. As you can see, the first step is to cite the source in proper formatting - that's the first paragraph that you see. That is an APA-formatted source: author's last name, year of publication, the title of the book, as well as the publishing information.
The second thing that you see is a brief summary of the work; that's that second paragraph. You see exactly what the book is about. Is it fiction or nonfiction? What is it based on, and what are the basic things that it covers? The final paragraph is a brief critique of the work from this particular researcher's point of view.
When Do You Need a Bibliography?
Now, how do you know when you need a bibliography? A good way to know is if your professor tells you to write one. On those occasions when it isn't clear - or isn't that clear - here are some good rules of thumb for deciding whether or not to utilize a bibliography:
1. When you are researching a topic you may want or need to do further research on in the future, you're going to want to do a bibliography. This includes any papers written in your major or minor field of study.
2. When you are writing a biography of a famous and/or historical person in which there are a lot of sources or a particularly large body of work.
3. When you are presenting new information in a field of study, or your conclusions are contrary or contrasting current trends or norms of the time.
4. When you are providing a critique of another author's piece of work.
5. When you are writing a paper for which others will be critiquing your conclusions.
6. When you have chosen to write on a more advanced topic and have chosen not to provide foundational information. This will allow the reader to know that you have looked at the foundations of the field, but chose to spend your limited writing space on more advanced information.
Lesson Objectives
After watching this lesson, you should be able to:
- Explain what a bibliography is and define the different types
- Describe how to write a bibliography
- Understand why and when you should write a bibliography
Unlock Your Education
See for yourself why 30 million people use study.com, become a study.com member and start learning now..
Already a member? Log In
Recommended Lessons and Courses for You
Related lessons, related courses, recommended lessons for you.

Writing a Bibliography | Definition, Types & Examples Related Study Materials
- Related Topics
Browse by Courses
- American Literature Syllabus Resource & Lesson Plans
- AP English Literature Syllabus Resource & Lesson Plans
- CSET English: Study Guide & Test Prep
- College Composition for Teachers: Professional Development
- Technical Writing for Teachers: Professional Development
- FTCE English 6-12 (013) Prep
- FTCE Middle Grades English 5-9 (014) Prep
- Praxis English Language Arts: Content Knowledge (5038) Prep
- Common Core ELA - Language Grades 9-10: Standards
- Common Core ELA - Literature Grades 11-12: Standards
- 9th Grade English: High School
- 10th Grade English: High School
- ILTS English Language Arts (207): Test Practice and Study Guide
- CAHSEE English Exam: Test Prep & Study Guide
- Common Core ELA Grade 8 - Language: Standards
Browse by Lessons
- Creating a Bibliography: Lesson for Kids
- Enumerative Bibliography: Definition & Examples
- Period Bibliography: Definition & Examples
- Using Bibliographic Sources in a Library Media Program
- Aeschylus Tragedies, Trilogies & Tetralogies | Overview & Summary
- The Sovereignty and Goodness of God by Mary Rowlandson: Summary & Explanation
- The Iliad by Home: Book 1 | Summary, Themes & Analysis
- The Iliad by Homer: Book 3 | Summary, Analysis & Themes
- The Iliad Book 7 Summary
- The Iliad Book 8 Summary
- The Iliad Book 9 Summary
- The Iliad Book 10 Summary
- The Iliad Book 11 Summary
- The Iliad by Homer: Book 12 | Summary, Themes & Analysis
- Assessing Evidence in Informational Writing
Create an account to start this course today Used by over 30 million students worldwide Create an account
Explore our library of over 88,000 lessons
- Foreign Language
- Social Science
- See All College Courses
- Common Core
- High School
- See All High School Courses
- College & Career Guidance Courses
- College Placement Exams
- Entrance Exams
- General Test Prep
- K-8 Courses
- Skills Courses
- Teacher Certification Exams
- See All Other Courses
- Create a Goal
- Create custom courses
- Get your questions answered
Eight tips and questions for your bibliographic study in business and management research
- Open access
- Published: 18 May 2020
- Volume 70 , pages 307–312, ( 2020 )
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- Jörn H. Block 1 , 2 , 3 &
- Christian Fisch 1 , 2
13k Accesses
102 Citations
2 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Management Review Quarterly (MRQ) specializes in systematic literature reviews, meta analyses, replication studies, and bibliographic studies. Previous editorials published in MRQ provide authors with guidelines for performing systematic (narrative) literature reviews (Fisch and Block 2018 ) and replication studies (Block and Kuckertz 2018 ). In this editorial, we focus on bibliographic studies and outline eight tips that help authors to improve their bibliographic studies.
In contrast to systematic literature reviews, meta analyses, and replication studies, little information on best practices and guidelines exist on bibliographic studies (also known as bibliographic literature reviews). Over the last years, we saw a steady increase in the number of bibliographic studies submitted to MRQ. We attribute this rise to the better accessibility of bibliographic data and software packages that specialize in bibliographic analyses. Another antecedent of the increasing prevalence of bibliographic studies is the ongoing differentiation of business and management research into narrowly defined subdisciplines, which calls for studies that are interdisciplinary and ‘break the walls’. Well-conducted bibliographic studies can break those walls. They structure a field and detect links between disciplines, identify topic clusters, literature gaps and academic silos, and show the most impactful authors and their research. Yet, in contrast to narrative literature reviews, bibliographic literature reviews use quantitative and statistical methods to achieve this goal.
We currently observe a considerable heterogeneity in the type and quality of bibliographic studies submitted to MRQ. These submissions range from systematic narrative literature reviews erroneously labeled as bibliographic ones to purely technical citation analyses with little interpretation and discussion of the state of the art in the respective research field. Hence, there seems to be confusion in business and management research as to what a bibliographic study is and what defines its quality. The goal of this editorial is to reduce this confusion and help future authors of MRQ to craft bibliographic studies of high quality. In line with earlier MRQ editorials, we organize this editorial in eight tips and questions. Specifically, we outline suggestions that we perceive as crucial for every bibliographic study published in MRQ. Since bibliographic studies rely on a systematic collection of articles, this editorial shares many similarities with our editorial on systematic narrative literature reviews (Fisch and Block 2018 ) as well as as the editorial’s discussion and extension by Clark et al. ( 2020 ). We summarize the main commonalities and differences of the two forms of literature reviews in Table 1 .
Is your study really a bibliographic study? Although the term ‘bibliographic study’ is widely used in academic research, a clear definition is lacking. MRQ is interested in bibliographic studies, which we define as systematic literature reviews that analyze bibliographic data with bibliometric methods. Bibliographic data include, amongst others, author names, journal names, article titles, article keywords, article abstracts, and article publication years. These bibliographic data are collected and made available by bibliographic databases such as Web of Science (WoS) or Scopus. These databases also provide citation data. Bibliometric methods rely on statistical methods to analyze bibliographic and citation data. As noted above, many manuscripts submitted to MRQ are erroneously labeled as bibliographic studies as they do not use bibliometric (= statistical) methods and only provide lists of important and impactful studies, authors, topics, and journals. Compiling and providing such lists is an essential first step but does not qualify your study as a bibliographic study. Also, bibliographic studies should not be confused with annotated bibliographies, which comprise a list of references to important studies followed by a brief description of their content. MRQ sees annotated bibliographies as an important element of systematic narrative literature reviews.
Is your main research goal really to summarize the structure of a research field? Literature reviews can summarize the content and structure of a particular research field. While a narrative literature review aims to summarize the content of the studies of a particular research field, a bibliographic literature review focuses on assessing the structure of a particular research field. A description and summary of “simple” bibliographic data (e.g., authors, journal names) is too superficial to derive specific answers to particular research questions. Article titles, keywords, and abstracts are already more informative and can, for example, be used to identify topic clusters. Citation data helps to identify impactful articles, authors, and journals. Such data also facilitates the identification of topic clusters and allows the measurement of knowledge diffusion within and between disciplines.
Provide and motivate a research goal and explain why a bibliographic study is needed to achieve this goal. Your article’s abstract and introduction have an important motivational function. As such, carefully begin your study by delineating and motivating your research goal. In particular, carefully explain why you choose a bibliographic literature review to achieve this goal. In other words: inform the reader that the analysis of bibliographic data with bibliometric methods provides important insights regarding your research goal. In general, bibliographic studies are particularly useful to describe the structure of a research field (see tip 2 above) and its development over time because they help to identify topic clusters, author networks, literature gaps, and academic silos.
Identify the relevant literature in a broad, systematic, and reproducible way . A bibliographic study is a particular form of a systematic literature review. Hence, the literature search process should be transparent and reproducible. A detailed account of the search strategy is needed, which includes a description of the databases used, the search terms, and inclusion/exclusion criteria. Footnote 1 In particular, carefully choose your bibliographic database. For example, Scopus often has a broader coverage of journals than WoS and if you leave out some of the most important journals, that’s a problem. Note that the application of screening or inclusion criteria (e.g., only focusing on highly ranked journals) should be well-justified because the screening criteria can have crucial implications for the bibliographic data obtained and the results of the quantitative, bibliometric analysis that follows. Since bibliographic studies rely on a quantitative and objective approach to summarize the structure and trends of a field, the systematic approach to identifying the literature is, in our view, even more important than in interpretative and narrative forms of literature reviews. We also believe that the literature covered should be broader than in narrative literature reviews, for example, with regard to the journals or publication years considered.
Provide a map of the research field. While original empirical research articles typically begin their results section with descriptive statistics, bibliographic studies should commence with a description of the studies under investigation (i.e., a map of the field). For example, a good strategy is to provide a chronological view of the field (e.g., how has the number of studies evolved, how have the topics evolved, how have the outlets evolved), and to give an overview of the most influential authors, journals, and publications. The outline can be sorted by multiple criteria, such as the number of papers or different citation measures. Notice that different types of citation data exist and that you need to defend your approach and source of citation data. In our view, this map of the field is a critical part of any bibliographic study. Yet, a bibliographic study should not stop at that stage. Instead, you should use the map of the field as a starting point to dig deeper into your bibliographic data using bibliometric methods, as outlined in tip 6.
Clearly specify the methodological steps of your bibliometric analysis. As with most empirical and statistical analyses, performing a bibliometric analysis requires taking various methodological choices. For example, authors need to choose a software and need to carefully prepare the data to be used in the analysis, such as the keywords of articles used. Make a sensible choice about which keywords to include in the analysis. For example, including your original search terms as keywords may produce trivial results. While a lot of graphical illustrations exist in the field of bibliographic studies (e.g., to visualize citation clusters or links between authors), sometimes tables can be easier to understand and interpret than figures (which are also often in color and difficult to print). Carefully outline and motivate the choices made in this regard.
Use the full potential and range of bibliometric methods. A bibliographic study should rely on statistical tools to derive results. Hence, you should go beyond simple article and citation counts. Such measures can be used to provide a map of the field (see tip 5), but the main part of the bibliometric analysis should be build on more sophisticated, multivariate statistical analyses. Bibliometric or scientometric analysis has developed into a discipline itself and specialized journals exist, such as Scientometrics and the Journal of Informetrics. Some commonly applied bibliometric methods, which we would like to also see in MRQ manuscripts, include co-citation analysis, co-occurrence analysis, and bibliometric coupling. We require authors of bibliographic studies to use such methods as a basis for their statements about the structure as well as the thematic clusters and gaps in the field. Yet, try to use these tools in a meaningful way. Simply displaying sophisticated tables, figures, and graphs derived from bibliometric software tools can lead to an overly descriptive and confusing picture of the field. Try to identify a relevant and interesting “story” that is supported by your bibliographic data and bibliometric analyses. Good examples of articles that have followed this approach are Aliyev et al. ( 2019 ), Block et al. ( 2019 ), and Kumar et al. ( 2019 ).
The bibliometric analysis needs to serve a purpose and needs to contribute to your research goal. The bibliometric analysis is the core of a bibliographic study. The most common mistake we see in manuscripts submitted to MRQ is that authors perform bibliometric analyses for the sake of performing bibliometric analyses. We are not interested in such manuscripts because they do not structure the knowledge in our field, do not lead to a discussion of where we are and what we know, and do not provide an agenda for future research. Hence, make sure that your bibliometric analysis contributes to the overall goal of MRQ. Like a systematic narrative literature review, bibliographic studies must go beyond a mere descriptive summary of prior literature. They require the authors to interpret and discuss the development and state of the field and give suggestions for meaningful future research.
See Fisch and Block ( 2018 ) and the references cited therein for more tips on systematic literature search.
Aliyev F, Urkmez T, Wagner R (2019) A comprehensive look at luxury brand marketing research from 2000 to 2016: a bibliometric study and content analysis. Manag Rev Q 69(3):233–264
Article Google Scholar
Block J, Kuckertz A (2018) Seven principles of effective replication studies: strengthening the evidence base of management research. Manag Rev Q 68(4):355–359
Block J, Fisch C, Rehan F (2019) Religion and entrepreneurship: a map of the field and a bibliometric analysis. Manag Rev Q. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11301-019-00177-2 (forthcoming)
Clark WR, Clark LA, Raffo DM, Williams RI (2020) Extending Fisch and Block’s (2018) tips for a systematic review in management and business literature. Manag Rev Q. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11301-020-00184-8 (forthcoming)
Fisch C, Block J (2018) Six tips for your (systematic) literature review in business and management research. Manag Rev Q 68(2):103–106
Kumar S, Sureka R, Colombage S (2019) Capital structure of SMEs: a systematic literature review and bibliometric analysis. Manag Rev Q. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11301-019-00175-4E (forthcoming)
Download references
Acknowledgements
Open Access funding provided by Projekt DEAL.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Faculty of Management, Trier University, 54296, Trier, Germany
Jörn H. Block & Christian Fisch
Erasmus School of Economics, Erasmus University Rotterdam, P.O. Box 1738, 3000 DR, Rotterdam, The Netherlands
Wittener Institut für Familienunternehmen (WIFU), Universität Witten/Herdecke, Alfred-Herrhausen-Str. 50, 58448, Witten, Germany
Jörn H. Block
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Jörn H. Block .
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Block, J.H., Fisch, C. Eight tips and questions for your bibliographic study in business and management research. Manag Rev Q 70 , 307–312 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11301-020-00188-4
Download citation
Published : 18 May 2020
Issue Date : August 2020
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11301-020-00188-4
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

Research Process: Bibliographic Information
- Selecting a Topic
- Background Information
- Narrowing the Topic
- Library Terms
- Generating Keywords
- Boolean Operators
- Search Engine Strategies
- Google Searching
- Basic Internet Terms
- Research & The Web
- Search Engines
- Evaluating Books
- Evaluating Articles
- Evaluating Websites
Bibliographic Information
- Off Campus Access
- Periodical Locator
What is a bibliography?
A bibliography is a list of works on a subject or by an author that were used or consulted to write a research paper, book or article. It can also be referred to as a list of works cited. It is usually found at the end of a book, article or research paper.
Gathering Information
Regardless of what citation style is being used, there are key pieces of information that need to be collected in order to create the citation.
For books and/or journals:
- Author name
- Title of publication
- Article title (if using a journal)
- Date of publication
- Place of publication
- Volume number of a journal, magazine or encyclopedia
- Page number(s)
For websites:
- Author and/or editor name
- Title of the website
- Company or organization that owns or posts to the website
- URL (website address)
- Date of access
This section provides two examples of the most common cited sources: a print book and an online journal retrieved from a research database.
Book - Print
For print books, bibliographic information can be found on the TITLE PAGE . This page has the complete title of the book, author(s) and publication information.
The publisher information will vary according to the publisher - sometimes this page will include the name of the publisher, the place of publication and the date.
For this example : Book title: HTML, XHTML, and CSS Bible Author: Steven M. Schafer Publisher: Wiley Publications, Inc.
If you cannot find the place or date of publication on the title page, refer to the COPYRIGHT PAGE for this information. The copyright page is the page behind the title page, usually written in a small font, it carries the copyright notice, edition information, publication information, printing history, cataloging data, and the ISBN number.
For this example : Place of publication: Indianapolis, IN Date of publication: 2010
Article - Academic OneFile Database
In the article view:
Bibliographic information can be found under the article title, at the top of the page. The information provided in this area is NOT formatted according to any style.
Citations can also be found at the bottom of the page; in an area titled SOURCE CITATION . The database does not specify which style is used in creating this citation, so be sure to double check it against the style rules for accuracy.
Article - ProQuest Database
Bibliographic information can be found under the article title, at the top of the page. The information provided in this area is NOT formatted according to any style.
Bibliographic information can also be found at the bottom of the page; in an area titled INDEXING . (Not all the information provided in this area is necessary for creating citations, refer to the rules of the style being used for what information is needed.)
Other databases have similar formats - look for bibliographic information under the article titles and below the article body, towards the bottom of the page.
- << Previous: Plagiarism
- Next: Research Databases >>
- Last Updated: Jan 8, 2024 10:20 AM
- URL: https://pgcc.libguides.com/researchprocess
University Library, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign

Bibliography and Historical Research
Introduction.
- National Bibliography
- Personal Bibliography
- Corporate Bibliography
- Subject Bibliography
- Searching the Catalog for Bibliographies
- Browsing the Catalog for Bibliographies
- Other Tools for Finding Bibliographies
- Return to HPNL Website
Ask a Librarian
This guide created by Geoffrey Ross, May 4, 2017.
A bibliography is a list of documents, usually published documents like books and articles. This type of bibliography is more accurately called "enumerative bibliography". An enumerative bibliography will attempt to be as comprehensive as possible, within whatever parameters established by the bibliographer.
Bibliographies will list both secondary and primary sources. They are perhaps most valuable to historians for identifying primary sources. (They are still useful for finding secondary sources, but increasingly historians rely on electronic resources, like article databases, to locate secondary sources.)
Think of a bibliography as a guide to the source base for a specific field of inquiry. A high quality bibliography will help you understand what kinds of sources are available, but also what kinds of sources are not available (either because they were never preserved, or because they were never created in the first place).
Take for example the following bibliography:
- British Autobiographies: An Annotated Bibliography of British Autobiographies Published or Written before 1951 by William Matthews Call Number: 016.920041 M43BR Publication Date: 1955
Like many bibliographies, this one includes an introduction or prefatory essay that gives a bibliographic overview of the topic. If you were hoping to use autobiographies for a paper on medieval history, the following information from the preface would save you from wasting your time in a fruitless search:

The essay explains that autobiography does not become an important historical source until the early modern period:

Finally, the essay informs us that these early modern autobiographies are predominantly religious in nature--a useful piece of information if we were hoping to use them as evidence of, for example, the early modern textile trade:

All bibliographies are organized differently, but the best include indexes that help you pinpoint the most relevant entries.
A smart researcher will also use the index to obtain an overview of the entire source base: the index as a whole presents a broad outline of the available sources--the extent of available sources, as well as the the strengths and weaknesses of the source base. Browsing the subject index, if there is one, is often an excellent method of choosing a research topic because it enables you quickly to rule out topics that cannot be researched due to lack of primary sources.
The index to British Autobiographies , for example, tells me that I can find many autobiographies that document British social clubs (like White's and Boodle's), especially from the 19th century:

Unlike indexes you might be familiar with from non-fiction books, the indexes in bibliographies usually reference specific entries, not page numbers.
A bibliography's index will often help guide you systematically through the available sources, as in this entry which prompts you to look under related index entries for even more sources:

There are four main types of enumerative bibliography used for historical research:
Click here to learn more about bibliography as a discipline .
- Next: National Bibliography >>
- Last Updated: Jan 4, 2023 2:21 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.illinois.edu/bibliography
Bibliography: Definition and Examples
Glossary of Grammatical and Rhetorical Terms
- An Introduction to Punctuation
- Ph.D., Rhetoric and English, University of Georgia
- M.A., Modern English and American Literature, University of Leicester
- B.A., English, State University of New York
A bibliography is a list of works (such as books and articles) written on a particular subject or by a particular author. Adjective : bibliographic.
Also known as a list of works cited , a bibliography may appear at the end of a book, report , online presentation, or research paper . Students are taught that a bibliography, along with correctly formatted in-text citations, is crucial to properly citing one's research and to avoiding accusations of plagiarism . In formal research, all sources used, whether quoted directly or synopsized, should be included in the bibliography.
An annotated bibliography includes a brief descriptive and evaluative paragraph (the annotation ) for each item in the list. These annotations often give more context about why a certain source may be useful or related to the topic at hand.
- Etymology: From the Greek, "writing about books" ( biblio , "book", graph , "to write")
- Pronunciation: bib-lee-OG-rah-fee
Examples and Observations
"Basic bibliographic information includes title, author or editor, publisher, and the year the current edition was published or copyrighted . Home librarians often like to keep track of when and where they acquired a book, the price, and a personal annotation, which would include their opinions of the book or of the person who gave it to them" (Patricia Jean Wagner, The Bloomsbury Review Booklover's Guide . Owaissa Communications, 1996)
Conventions for Documenting Sources
"It is standard practice in scholarly writing to include at the end of books or chapters and at the end of articles a list of the sources that the writer consulted or cited. Those lists, or bibliographies, often include sources that you will also want to consult. . . . "Established conventions for documenting sources vary from one academic discipline to another. The Modern Language Association (MLA) style of documentation is preferred in literature and languages. For papers in the social sciences the American Psychological Association (APA) style is preferred, whereas papers in history, philosophy, economics, political science, and business disciplines are formatted in the Chicago Manual of Style (CMS) system. The Council of Biology Editors (CBE) recommends varying documentation styles for different natural sciences." (Robert DiYanni and Pat C. Hoy II, The Scribner Handbook for Writers , 3rd ed. Allyn and Bacon, 2001)
APA vs MLA Styles
There are several different styles of citations and bibliographies that you might encounter: MLA, APA, Chicago, Harvard, and more. As described above, each of those styles is often associated with a particular segment of academia and research. Of these, the most widely used are APA and MLA styles. They both include similar information, but arranged and formatted differently.
"In an entry for a book in an APA-style works-cited list, the date (in parentheses) immediately follows the name of the author (whose first name is written only as an initial), just the first word of the title is capitalized, and the publisher's full name is generally provided.
APA Anderson, I. (2007). This is our music: Free jazz, the sixties, and American culture . Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania Press.
By contrast, in an MLA-style entry, the author's name appears as given in the work (normally in full), every important word of the title is capitalized, some words in the publisher's name are abbreviated, the publication date follows the publisher's name, and the medium of publication is recorded. . . . In both styles, the first line of the entry is flush with the left margin, and the second and subsequent lines are indented.
MLA Anderson, Iain. This Is Our Music: Free Jazz, the Sixties, and American Culture . Philadelphia: U of Pennsylvania P, 2007. Print. The Arts and Intellectual Life in Mod. Amer.
( MLA Handbook for Writers of Research Papers , 7th ed. The Modern Language Association of America, 2009)
Finding Bibliographic Information for Online Sources
"For Web sources, some bibliographic information may not be available, but spend time looking for it before assuming that it doesn't exist. When information isn't available on the home page, you may have to drill into the site, following links to interior pages. Look especially for the author's name, the date of publication (or latest update), and the name of any sponsoring organization. Do not omit such information unless it is genuinely unavailable. . . . "Online articles and books sometimes include a DOI (digital object identifier). APA uses the DOI, when available, in place of a URL in reference list entries." (Diana Hacker and Nancy Sommers, A Writer's Reference With Strategies for Online Learners , 7th ed. Bedford/St. Martin's, 2011)
- What Is a Bibliography?
- What Is a Citation?
- MLA Bibliography or Works Cited
- What Is a Senior Thesis?
- MLA Sample Pages
- How to Write a Bibliography For a Science Fair Project
- What Is an Annotated Bibliography?
- What Is a Style Guide and Which One Do You Need?
- Turabian Style Guide With Examples
- APA In-Text Citations
- Tips for Typing an Academic Paper on a Computer
- Definition and Examples of Title Case and Headline Style
- Documentation in Reports and Research Papers
- Writing an Annotated Bibliography for a Paper
- MLA Style Parenthetical Citations
- 140 Key Copyediting Terms and What They Mean
Home / Guides / Citation Guides / Citation Basics / Annotated Bibliography Format & Examples
Annotated Bibliography Format & Examples
A complete guide to the mla & apa annotated bibliography.
If you’ve just received an assignment that requires an MLA or APA annotated bibliography, you may be wondering where to start. This guide will help answer all of your questions and includes step-by-step instructions on how to do an annotated bibliography in MLA style, as well as an APA annotated bibliography. You will also find sample annotated bibliographies, real-life examples, and opportunities to practice what you have learned.
The MLA ( Modern Language Association ) and APA (American Psychological Association) are not associated with this guide. All of the information provided here, however, offers direction for students and researchers who use these citation styles in their work.
The structures and annotated bibliography templates on this page were created by the in-house librarians at EasyBib.com.
If you’re simply looking for an example of an annotated bibliography (both in MLA format and APA format), scroll down toward the bottom of the page. We’ve included links to visuals for those of you who need help with the structure and styling of an annotated bibliography. If you’re looking for a variety of annotated bibliography topics, and you’re truly searching for the answer to, “What is an annotated bibliography?” then continue reading!
Here’s a run-through of everything this page includes:
Table of contents
What is an annotated bibliography, annotations vs. abstract, why include annotations.
- Step 1: Analyze your sources
Step 2: Write the descriptions
- Step 3a: Formatting an MLA style annotated bibliography
- Step 3b: Formatting an APA style annotated bibliography
Annotated Bibliography Templates
Using the easybib annotation tool.
A bibliography is a complete list of the sources that were used to complete a research paper or project.
Depending on the style guide you follow, you may also see this called a Works Cited (also called an MLA bibliography) or Reference List (APA format). Each listed source, or citation , shares information about the author, title, publishing year, and other details that serve to credit the original authors whose work informed your research. These details also help other students and researchers find and read the source materials.
When your research is related to a scholastic assignment, you should always verify your instructor’s requirements for the types and number of sources to include, as well as the style you should adhere to when formatting your paper and bibliography.
An MLA annotated bibliography and an APA format annotated bibliography are bibliographies that include a concise explanation, or annotation , of each listed source. Depending on the assignment, this annotation may be solely descriptive, or analytical.
An abstract and annotation should not be confused; they differ in both their substance as well as their placement in a paper.
Annotations:
- Usually found in bibliographies at the end of a paper
- Are subjective
- Purpose is to summarize and evaluate . It should briefly communicate the work’s main point, but also discuss the background of the author or study, and the strengths/weaknesses of the work.
Abstracts:
- Usually found in journal databases or the beginning of a paper
- Are objective
- Purpose is to summarize . It should provide a short overview of the article and communicate the main points and themes.
If you would like to learn more , this link further explores the difference between an abstract and an annotation.
This resource provides additional information on how to write a bibliography with annotations in other formats. You can also take advantage of the plagiarism checker and bibliography tools that come with EasyBib Plus to help you create your reference lists.
Before you learn how to make an annotated bibliography, you may be wondering why you need to.
Sometimes instructors want you to create and include annotations in your bibliography, either as part of an assignment or as an assignment unto itself. Understanding the purpose of this approach to your reference list can help to ensure that you gain all of the benefits that the annotated bibliography process provides.
As a student, this method will help you develop or hone your research skills, providing you with practice not only in locating sources but also in analyzing and evaluating them for relevance and quality.
Your instructor will gain insight into your research abilities, as well, allowing them to assess your work more thoroughly. If you plan to publish your research, this comprehensive approach to detailing your sources will provide readers and other researchers with a substantial directory of resources to evaluate for their own work.
Whether you’re publishing or submitting your annotated bibliography, make sure your spelling and wording is correct! If you need to brush up on any parts of speech topics, check out our interjection , determiner , and adverb pages!
Step 1: Analyze your sources
Each annotation should be a summarization or analysis of your source. If you have been tasked with writing annotations as part of a research paper or project, begin to create both the citation and notes on the source while you identify and analyze your sources.
Not only will this approach help you to hone your research skills and identify sources that are relevant and useful for your topic, but you will also save time. When done in this manner, both your citations and annotations will be nearly complete before you begin to write the body of your paper.
Analyzing your potential sources requires a two-pronged approach that first evaluates the author, publication, and date, and then examines the content.
When conducting your initial assessment of the source, consider some of the following questions to guide your appraisal:
- What qualifies the author to write on this subject?
- Is the author affiliated with a reputable institution in this field?
- Is the author credentialed or otherwise considered an expert in this field?
- Is this source current?
- Is this the most recent edition?
- Is the publisher reputable?
- Is the journal reputable?
Once your primary evaluation is complete, you will move on the assessing the content itself. Consider some of these elements as you review each source:
- Who is the intended audience?
- Is the author presenting her opinion or interpretation as the truth, or stating facts?
- What supporting evidence does the author provide?
- Did the author perform the research, or curate and present the research of others?
- If the author used the research of others, are the sources the author cites credible?
- Are there errors or omissions of fact?
- Is the author writing objectively and without bias?
Also, consider the value each source provides to you:
- Is the information helpful for your particular assignment?
- Does it help answer your research question(s)?
- Is this source different from your other sources, or does it repeat information you already have?
- Is the source providing you with a different perspective on your topic, or changing your beliefs or thinking about your subject?
To make it easier for you to create your reference page, write your notes in the format you will be using when you construct this part of the assignment (for instance, as short phrases or complete sentences). Once you have identified all of the sources you wish to include, you will merely need to insert what you have already written on the page and write your citation, which is explained in the next section.
Click here for additional information and a supplementary annotated bibliography sample. For an MLA bibliography example (with annotations), check out our visual example of an MLA annotated bibliography .
An annotated bibliography entry may be written either as short phrases or complete sentences. Your instructor will advise you of which approach you are required to take.
Annotations should include either:
- The main points from the source, as well as the topics covered, the approach used, and any findings.
- Or your critical evaluation.
- A standard annotation is approximately one paragraph.
- Take care not to include any unnecessary details, as the goal is to summarize each source as succinctly as possible and, in some cases, evaluate them.
- Your field of study or instructor will determine what format your annotated bibliography will use. In this guide, you’ll find examples of an MLA and an APA annotated bibliography.
Here is an annotated bibliography example MLA annotation for the book The Elements of Eloquence: Secrets of the Perfect Turn of Phrase by UK author and blogger Mark Forsyth:
The author, Mark Forsyth, examines the rhetorical devices used in the English language, analyzing the patterns and formats that create memorable quotes. He traces the history of rhetoric to the Ancient Greeks, and provides an abridged timeline, following their use and evolution through to modern day. The author also explores the broader subject of persuasion and maps out the role that the figures of rhetoric play in it. In all, he examines over thirty devices, dissecting notable passages and phrases from pop music, the plays of William Shakespeare, the Bible, and more to explore the figures of rhetoric at work within each of them. Thorough definitions accompany this examination of structure to demonstrate how these formulas have been used to generate famously memorable expressions as well as how to reproduce their effects.
Notice how the annotated bibliography MLA entry above is descriptive enough so the reader has an idea of what the source is about with just a single paragraph. For more information on annotations, check out this informative site . If you’re looking to strengthen your writing in general, reading these grammar guides could be a good start.
For guidance on creating entries in MLA format , APA format , and more styles , check out the EasyBib library of resources or try the EasyBib annotation tool—we talk about it below!
Step 3a: MLA annotated bibliography format
The MLA Style Center and the current edition of the MLA Handbook provide the following guidance for formatting an MLA annotated bibliography:
- Title your reference page as “Annotated Bibliography” or “Annotated List of Works Cited.”
- Place each annotation after its reference.
- Annotations should typically not exceed a single paragraph.
- Annotations should be indented one inch from the start of your citation.
- Double-space all text on the page.
- 1-inch margins around the page.
Sources in an annotated bibliography can be organized alphabetically by the first word in each reference (as with a normal Works Cited page), by publication date, or by subject.
For a visual example of an annotated bibliography, as well as specific annotation examples, visit the MLA annotated bibliography guide .
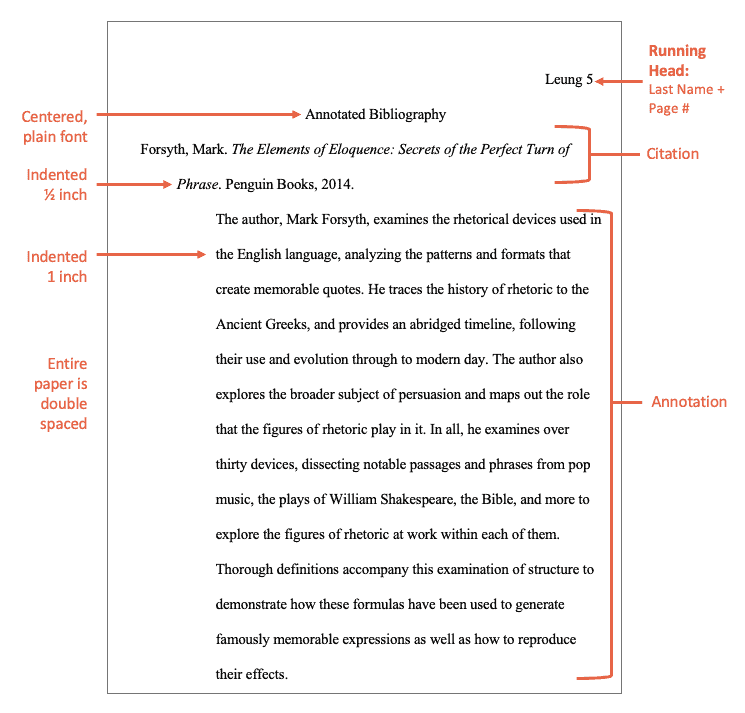
If you are required to share your references in a manner other than in MLA bibliography format, the EasyBib style guides can help you with many common styles. While you’re at it, check out their conjunction , preposition , and pronoun pages to help keep your paper in mint condition!
Step 3b: APA annotated bibliography format
The American Psychological Association states that your instructor should set the guidelines for your annotated bibliography, but asks that the bibliography be formatted according to their standard reference page rules (see Section 9.51 of the Publication Manual ). If your teacher has requested an APA formatted annotated bibliography, first ask them for guidelines. Otherwise, here are some quick rules for you to follow:
- Double space all text on the page.
- Title your page “Annotated Bibliogra phy”. Bold and center the title.
- Organize references alphabetically by the first word of each reference.
- Only the first line of a ref erence is flush with the left margin. Any other lines after the first line should be indented ½ inch from the left.
- Add annotations on the next line after their paired reference.
- Fully indent annotations by a ½ inch from the left.
- Keep annotations short. No more than one paragraph.
For examples of a properly formatted APA annotation, visit this guide on APA annotated bibliographies .
In comparison to the sample annotated bibliography MLA, the APA sample formats its page elements and references differently.

Students and researchers who type their research notes can save time by using an annotated bibliography template in MLA format while reviewing and analyzing sources. By adding the relevant information into a pre-formatted template, you’ll create a resource that helps you when you begin writing your paper in addition to saving time by completing your references and summaries alongside your research.
Students who prefer to take notes by hand can employ a modified version of this approach, with an additional step required to transfer your handwritten and formatted references from your notebook to populate your reference page.
Bibliography Template for MLA
To create an annotated bibliography MLA template, copy the following details into the program in which you will take notes or hand write it on the top margin of a page in your notebook. For each source, use this template to guide you as you identify the necessary details and insert them into your notes:
- Author (Last name, First name).
- Title of source.
- Title of the container ,
- Other contributors (names and roles),
- Publication Date,
- Location of the source (such as URL or page range).
- Summary or Analysis.
The MLA 9 model for MLA works cited entries offers a single format for all source type, and a great deal of flexibility to include the information most relevant to your topic and omit that which isn’t.
Hopefully our visual annotated bibliography example in MLA above has helped. If you still have lingering questions, visit the MLA Style Center online ( linked here ). Also, here’s a guide if you’re looking for more on the related topic of MLA in-text & parenthetical citations .
Bibliography Template for APA
Students and researchers who are still asking themselves how to piece together an annotated bibliography, or still questioning what is an annotated bibliography, could probably benefit from a template, similar to the one above. This one, however, is for those of you who are tasked with creating an annotated bibliography in the style created by the American Psychological Association.
The tricky thing about this specific style though, is that every reference is styled differently. Books, websites, journal articles, newspaper articles, and many others each have their own reference structure.
For most sources though, you should look for the following, basic information:
- Type of source
- Author (last name, first name)
- Title of source/article/web page, etc.
- Title of where source was found (e.g., database name, website name, etc.)
- Other contributors (names and roles)
- Location of the source (such as URL, DOI, or page range)
- Summary or Analysis
We understand it can get tricky, and it’s very different from the Modern Language Association’s structure for references. Take a moment to either use the other handy guides on EasyBib.com or use our automatic generator to form your references in just a few clicks. Our tools help take the pain away from having to rack your brain to form references properly. Capitals, lowercase letters, italics, quotation marks, punctuation in the appropriate places, it can all be quite overwhelming. Do yourself a favor, and use the EasyBib automatic citation generator.
Even though there are a lot of different variations, here’s a commonly used structure for sources:
Author’s Last Name, First initial, Middle initial. (Year the source was published). Title of the source . Retrieved from (insert the website address here)
Underneath the reference, include your summary or analysis paragraph.
Hopefully, this page helped answer all of your “What is an annotated bibliography?” questions. If you’re seeking out an annotated bibliography generator, follow the steps above the annotated bibliography examples.
Looking for additional help with other related topics? Don’t forget about the various beneficial guides on EasyBib.com! Our APA in-text citation guide and our APA parenthetical citation guide are two of our most popular pages. Learn the ins and outs of referencing your work in the body of your paper with our thorough, complete, and reader-friendly guides.
If you are creating a bibliography in MLA format, the EasyBib MLA bibliography generator can help save you time formatting your citations and annotations correctly. You can create entries for websites, books, videos, databases, dictionary articles, and many other types of sources.
In addition to forming the citations, you can also enter your annotation text to produce the complete entry for each source. The process for this is simple. You can follow along below to practice creating one:
- First, select your source type from among the 50+ available options. For this example, we will use the acting career of Keanu Reeves as our research topic and use the movie Point Break from 1991 as our first source. To cite this film, you would select the option for “Film/Online Video.” As you follow along, pick the option that is suitable for your source if you are using a different example.
- Enter the title of your source or, if you are citing a website, you may enter the URL. (Now would be a great time to peek at how to cite websites in MLA ). After you enter the title or URL for your reference, the EasyBib citation tool will scan for titles that match it and provide you with a list of results. Select “Cite this” next to the listing that matches your source.
- You will see a citation form. This gives you the option to add additional relevant or necessary information. For our sample topic, we will specifically cite Keanu Reeves as the performer and Kathryn Bigelow as the director.
- After entering any additional details, you have the option to expand your entry and include an annotation. To do so, select “Add annotation” at the bottom of the page, and a text box will open up.
Then, type your summary or analysis into the text box. If you took notes during the research stage using the format of your paper, this might be as simple as copying and pasting your already written summary or critique. Once you have entered all of the necessary information, select “Create citation” to generate the complete entry. You can then copy and paste this into your MLA bibliography.
Here’s what it’ll look like:
Point Break . Directed by Kathryn Bigelow, performance by Keanu Reeves, 20th Century Fox, 1991.
Reeves’ role as rookie FBI Agent Johnny Utah in Point Break marks the turning point in his Hollywood film career. While he’d risen to fame due to the success of the Bill and Ted franchise, his status today as an action star began when Point Break provided him with the material to establish himself as capable of portraying more than the lovable but unserious characters of his previous starring roles. In a parallel arc, director Kathryn Bigelow’s career also sees a shift beginning with Point Break , establishing her within the traditional action genre as a serious director capable of creating high-action and visually memorable films. While Point Break leaves plenty to be desired in terms of dialogue, it afforded Bigelow and Reeves the opportunities to showcase themselves and their talent in new ways that still echo in their work today.
- Works Cited
Harner, James L. On Compiling an Annotated Bibliography . 2nd ed., Modern Language Association of America, 2000.
MLA Handbook . 9th ed., Modern Language Association of America, 2021.
Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association . 7th ed., American Psychological Association, 2020.
“What Guidance Should I Give My Students for Preparing an Annotated Bibliography?” The MLA Style Center , The Modern Language Association, 4 Nov. 2016, style.mla.org/annotated-bibliographies/.
Visit our EasyBib Twitter feed to discover more citing tips, fun grammar facts, and the latest product updates.
Published October 18, 2015. Updated July 25, 2021.
Written and edited by Michele Kirschenbaum and Elise Barbeau. Michele Kirschenbaum is a school library media specialist and is the in-house librarian at EasyBib.com. Elise Barbeau is the Citation Specialist at Chegg. She has worked in digital marketing, libraries, and publishing.
Citation Guides
- Annotated Bibliography
- Block Quotes
- Citation Examples
- et al Usage
- In-text Citations
- Page Numbers
- Reference Page
- Sample Paper
- APA 7 Updates
- View APA Guide
- Bibliography
- MLA 8 Updates
- View MLA Guide
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
An annotated bibliography is a list containing complete information of sources, such as journals, books, and reports, cited in the text. In addition, it provides a brief description of each source in about 100–150 words. The annotation can explain the topics covered in the source or evaluate the source. The main objective of giving the annotation is to provide the reader the importance, accuracy, and value of the source.
An example of an annotated bibliography in APA style is given below.
Lim, L. (2014). Ideology, rationality and reproduction in education: A critical discourse analysis. Discourse: Studies in the Cultural Politics of Education, 35 (1), 61–76. https://doi:10.1080/01596306.2012.739467
Lim (2014) focuses on issues of power and ideology dominant in curricular discourses of rationality to study a discourse analysis of the goals of one of the most important curricula in the teaching of thinking. He proves that political and class commitments are reproduced in the forms of thinking that are valued in societies. Through his research, Lim asserts that such curricula engage in making our understanding of what thinking and rationality are. It must facilitate the social reproduction of a specific proportion of the middle class.
If you want to evaluate or provide a description of a source you are citing, you can create an annotated bibliography. Write your annotation in 100–150 words and add it below the source for which you are providing your annotation. Remember, your annotation should provide the reader the importance, accuracy, and value of the source. Below are the guidelines and rules to be followed while writing an annotated bibliography for APA style:
Order your reference entries in alphabetical order, similar to how you would order entries in the reference list.
If you want to add an annotation to an entry, add it as a fresh paragraph below the reference entry. The annotation is indented 0.5 inches from the left margin. However, the first line of the annotation is not indented.
To format the annotated bibliography, follow the recommendations given below:
Set the left, right, top, and bottom margins to 1 inch.
Give double-line spacing.
Title the page “Annotated Bibliography.” Set it in bold.
The title should be aligned to the center of the page.
As you format reference entries, left-align all references in the annotated bibliography section. If any entry runs over more than a line, indent the subsequent lines 0.5 inch from the left margin.
Arrange all reference entries alphabetically according to the surname of the authors.
Provide your annotations below the reference entry for which you want to give your annotation. Indent annotations 0.5 inches from the left margin.
Citation Basics
Harvard Referencing
Plagiarism Basics
Plagiarism Checker
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started

Reference Examples
More than 100 reference examples and their corresponding in-text citations are presented in the seventh edition Publication Manual . Examples of the most common works that writers cite are provided on this page; additional examples are available in the Publication Manual .
To find the reference example you need, first select a category (e.g., periodicals) and then choose the appropriate type of work (e.g., journal article ) and follow the relevant example.
When selecting a category, use the webpages and websites category only when a work does not fit better within another category. For example, a report from a government website would use the reports category, whereas a page on a government website that is not a report or other work would use the webpages and websites category.
Also note that print and electronic references are largely the same. For example, to cite both print books and ebooks, use the books and reference works category and then choose the appropriate type of work (i.e., book ) and follow the relevant example (e.g., whole authored book ).
Examples on these pages illustrate the details of reference formats. We make every attempt to show examples that are in keeping with APA Style’s guiding principles of inclusivity and bias-free language. These examples are presented out of context only to demonstrate formatting issues (e.g., which elements to italicize, where punctuation is needed, placement of parentheses). References, including these examples, are not inherently endorsements for the ideas or content of the works themselves. An author may cite a work to support a statement or an idea, to critique that work, or for many other reasons. For more examples, see our sample papers .
Reference examples are covered in the seventh edition APA Style manuals in the Publication Manual Chapter 10 and the Concise Guide Chapter 10
Related handouts
- Common Reference Examples Guide (PDF, 147KB)
- Reference Quick Guide (PDF, 225KB)
Textual Works
Textual works are covered in Sections 10.1–10.8 of the Publication Manual . The most common categories and examples are presented here. For the reviews of other works category, see Section 10.7.
- Journal Article References
- Magazine Article References
- Newspaper Article References
- Blog Post and Blog Comment References
- UpToDate Article References
- Book/Ebook References
- Diagnostic Manual References
- Children’s Book or Other Illustrated Book References
- Classroom Course Pack Material References
- Religious Work References
- Chapter in an Edited Book/Ebook References
- Dictionary Entry References
- Wikipedia Entry References
- Report by a Government Agency References
- Report with Individual Authors References
- Brochure References
- Ethics Code References
- Fact Sheet References
- ISO Standard References
- Press Release References
- White Paper References
- Conference Presentation References
- Conference Proceeding References
- Published Dissertation or Thesis References
- Unpublished Dissertation or Thesis References
- ERIC Database References
- Preprint Article References
Data and Assessments
Data sets are covered in Section 10.9 of the Publication Manual . For the software and tests categories, see Sections 10.10 and 10.11.
- Data Set References
- Toolbox References
Audiovisual Media
Audiovisual media are covered in Sections 10.12–10.14 of the Publication Manual . The most common examples are presented together here. In the manual, these examples and more are separated into categories for audiovisual, audio, and visual media.
- Artwork References
- Clip Art or Stock Image References
- Film and Television References
- Musical Score References
- Online Course or MOOC References
- Podcast References
- PowerPoint Slide or Lecture Note References
- Radio Broadcast References
- TED Talk References
- Transcript of an Audiovisual Work References
- YouTube Video References
Online Media
Online media are covered in Sections 10.15 and 10.16 of the Publication Manual . Please note that blog posts are part of the periodicals category.
- Facebook References
- Instagram References
- LinkedIn References
- Online Forum (e.g., Reddit) References
- TikTok References
- X References
- Webpage on a Website References
- Clinical Practice References
- Open Educational Resource References
- Whole Website References
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Citing sources
- How to Cite a Book | APA, MLA, & Chicago Examples
How to Cite a Book | APA, MLA, & Chicago Examples
Published on February 26, 2021 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on January 17, 2024.
To cite a book, you need a brief in-text citation and a corresponding reference listing the author’s name, the title, the year of publication, and the publisher. The order and format of information depends on the citation style you’re using. The most common styles are APA , MLA , and Chicago style .
Use the interactive example generator to explore the format of book citations in MLA and APA.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Citing a book in mla style, citing a book in apa style, citing a book in chicago style, where to find source information in a book, frequently asked questions about citations.
An MLA book citation includes the author’s name , the book title (in italics, capitalized headline-style), the edition (if specified), the publisher, and the year of publication. If it’s an e-book , write “e-book” (or a more specific description, e.g. “Kindle ed.”) before the publisher name.
The corresponding in-text citation lists the author’s last name and the page number of the passage cited.
| MLA format | Author last name, First name. : Subtitle. Edition, Publisher, Year. |
|---|---|
| Donaldson, Bruce. . 3rd ed., Routledge, 2017. | |
| (Donaldson 73) |
You can also use our free MLA Citation Generator to create your book citations.
Generate accurate MLA citations with Scribbr
Citing a book chapter in mla.
To cite a book chapter , first give the author and title (in quotation marks) of the chapter cited, then information about the book as a whole and the page range of the specific chapter.
The in-text citation lists the author of the chapter and the page number of the relevant passage.
| MLA format | Author last name, First name. “Chapter Title.” : Subtitle, edited by Editor name, Publisher, Year, pp. Page range. |
|---|---|
| Nussbaum, Martha C. “Legal Reasoning.” , edited by John Tasioulas, Cambridge University Press, 2020, pp. 59–77. | |
| (Nussbaum 65) |
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
An APA Style book citation lists the author’s last name and initials, the year of publication, the title and any subtitle (in italics, capitalizing only the first word), the edition (if specified), and the publisher. Add a DOI or URL to the end of the entry if available (e.g. for e-books or books accessed online ).
In an in-text citation, state the author’s last name and the publication year, and a page number if you need to show the location of a specific quote or paraphrase .
| APA format | Author last name, Initials. (Year). : Subtitle (Edition). Publisher. DOI or URL |
|---|---|
| Donaldson, B. (2017). (3rd ed.). Routledge. | |
| (Donaldson, 2017, p. 73) |
You can also use our free APA Citation Generator to automatically generate your book citations. Search for a title, DOI, or ISBN to retrieve the details.
Generate accurate APA citations with Scribbr
Citing a book chapter in apa.
To cite a book chapter , list information about the chapter first, followed by information about the book, including the book’s editor(s) and the chapter’s page range within the book.
The author of the chapter, not the editor of the book, is listed in the in-text citation.
| APA format | Author last name, Initials. (Year). Title of chapter. In Editor initials. Last name (Ed. or Eds.), : Subtitle (pp. Page range). Publisher. |
|---|---|
| Nussbaum, M. C. (2020). Legal reasoning. In Tasioulas, J. (Ed.), (pp. 59–77). Cambridge University Press. | |
| (Nussbaum, 2020, p. 65) |
Chicago notes and bibliography style uses footnotes to cite sources instead of parenthetical citations. These notes refer to a bibliography at the end giving full source details.
A Chicago bibliography entry for a book includes the author’s name, the book title and subtitle, the edition (if stated), the location and name of the publisher, and the year of publication. For an e-book , add the e-book format (e.g. “Kindle”) at the end.
| Chicago format | Author last name, First name. : Subtitle. Edition. Place of publication: Publisher, Year. E-book format. |
|---|---|
| Donaldson, Bruce. . 3rd ed. Abingdon-on-Thames: Routledge, 2017. | |
| 1. Bruce Donaldson, , 3rd ed. (Abingdon-on-Thames: Routledge, 2017), 35. 2. Donaldson, , 73. |
Chicago also has an alternative style, Chicago author-date . You can see examples of book citations in this style here .
Citing a book chapter in Chicago
To cite a book chapter , start with the author and the title of the chapter (in quotation marks), then give the title (in italics) and editor of the book, the page range of the chapter, the location and name of the publisher, and the year of publication.
| Chicago format | Author last name, First name. “Chapter Title.” In : Subtitle, edited by Editor first name Last name, Page range. Place of publication: Publisher, Year. |
|---|---|
| Nussbaum, Martha C. “Legal Reasoning.” In , edited by John Tasioulas, 59–77. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2020. | |
| 1. Martha C. Nussbaum, “Legal Reasoning,” in , ed. John Tasioulas (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press), 60. 2. Nussbaum, “Legal Reasoning,” 65. |
All the information you need for a book citation can usually be found on the book’s title page and copyright page. The main things you’re looking for are:
- the title (and subtitle if present)
- name(s) of the author(s)
- year of publication
- place of publication
You should also check if the book specifies an edition (e.g. 2nd edition, revised edition) and if any other contributors are named (e.g. editor, translator).
The image below shows where to find the relevant information on the title and copyright pages of a typical book.
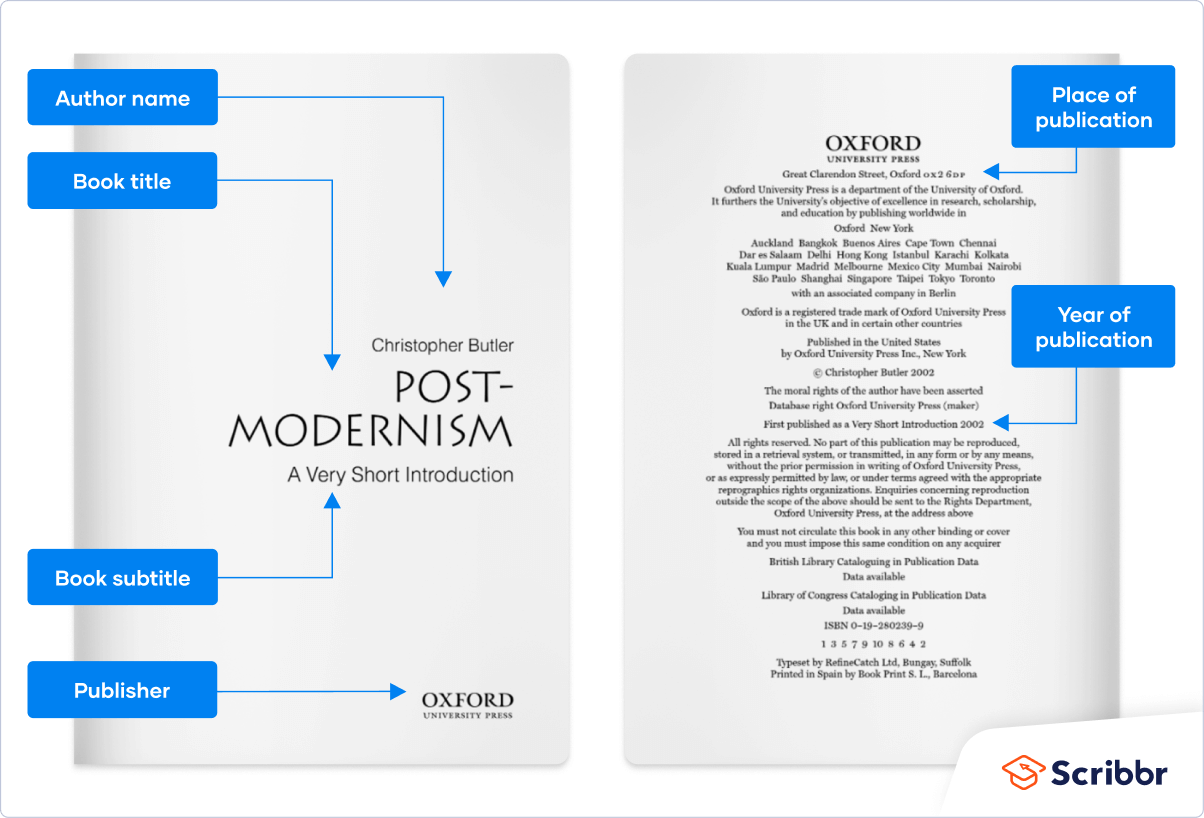
Scribbr Citation Checker New
The AI-powered Citation Checker helps you avoid common mistakes such as:
- Missing commas and periods
- Incorrect usage of “et al.”
- Ampersands (&) in narrative citations
- Missing reference entries

The main elements included in all book citations across APA , MLA , and Chicago style are the author, the title, the year of publication, and the name of the publisher. A page number is also included in in-text citations to highlight the specific passage cited.
In Chicago style and in the 6th edition of APA Style , the location of the publisher is also included, e.g. London: Penguin.
When a book’s chapters are written by different authors, you should cite the specific chapter you are referring to.
When all the chapters are written by the same author (or group of authors), you should usually cite the entire book, but some styles include exceptions to this.
- In APA Style , single-author books should always be cited as a whole, even if you only quote or paraphrase from one chapter.
- In MLA Style , if a single-author book is a collection of stand-alone works (e.g. short stories ), you should cite the individual work.
- In Chicago Style , you may choose to cite a single chapter of a single-author book if you feel it is more appropriate than citing the whole book.
Check if your university or course guidelines specify which citation style to use. If the choice is left up to you, consider which style is most commonly used in your field.
- APA Style is the most popular citation style, widely used in the social and behavioral sciences.
- MLA style is the second most popular, used mainly in the humanities.
- Chicago notes and bibliography style is also popular in the humanities, especially history.
- Chicago author-date style tends to be used in the sciences.
Other more specialized styles exist for certain fields, such as Bluebook and OSCOLA for law.
The most important thing is to choose one style and use it consistently throughout your text.
The abbreviation “ et al. ” (Latin for “and others”) is used to shorten citations of sources with multiple authors.
“Et al.” is used in APA in-text citations of sources with 3+ authors, e.g. (Smith et al., 2019). It is not used in APA reference entries .
Use “et al.” for 3+ authors in MLA in-text citations and Works Cited entries.
Use “et al.” for 4+ authors in a Chicago in-text citation , and for 10+ authors in a Chicago bibliography entry.
When you want to cite a specific passage in a source without page numbers (e.g. an e-book or website ), all the main citation styles recommend using an alternate locator in your in-text citation . You might use a heading or chapter number, e.g. (Smith, 2016, ch. 1)
In APA Style , you can count the paragraph numbers in a text to identify a location by paragraph number. MLA and Chicago recommend that you only use paragraph numbers if they’re explicitly marked in the text.
For audiovisual sources (e.g. videos ), all styles recommend using a timestamp to show a specific point in the video when relevant.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2024, January 17). How to Cite a Book | APA, MLA, & Chicago Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved June 7, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/citing-sources/cite-a-book/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, how to cite an image | photographs, figures, diagrams, how to cite a journal article | apa, mla, & chicago examples, how to cite a lecture | apa, mla & chicago examples, what is your plagiarism score.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Welcome to the Purdue Online Writing Lab

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The Online Writing Lab at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service of the Writing Lab at Purdue. Students, members of the community, and users worldwide will find information to assist with many writing projects. Teachers and trainers may use this material for in-class and out-of-class instruction.
The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives. The Purdue OWL offers global support through online reference materials and services.
A Message From the Assistant Director of Content Development
The Purdue OWL® is committed to supporting students, instructors, and writers by offering a wide range of resources that are developed and revised with them in mind. To do this, the OWL team is always exploring possibilties for a better design, allowing accessibility and user experience to guide our process. As the OWL undergoes some changes, we welcome your feedback and suggestions by email at any time.
Please don't hesitate to contact us via our contact page if you have any questions or comments.
All the best,
Social Media
Facebook twitter.

Adding Items to Zotero
This page describes the various ways to add items (e.g., books, journal articles, web pages, etc.) as items in Zotero. To learn more about adding files (such as PDFs or images), please see the files page.
Via your web browser
To use Zotero properly, you need to install the Zotero Connector for Chrome, Firefox, Edge, or Safari, in addition to the Zotero desktop app.
The Zotero Connector's save button is the most convenient and reliable way to add items with high-quality bibliographic metadata to your Zotero library. As you browse the web, the Zotero Connector will automatically find bibliographic information on webpages you visit and allow you to add it to Zotero with a single click.
For example, if you're on the main page for a journal article, the save button will change to the icon of a journal article (circled in red):

On a library catalog entry for a book, the save button will show a book icon:

Clicking the save button will create an item in Zotero with the information it has identified.
On many sites, Zotero will also save any PDF accessible from the page or an open-access PDF that can be found for the saved item.
- Generic Webpages
Some webpages don't provide any information that Zotero can recognize. On these pages, the save button will show a gray webpage icon. If you click the save button on these pages, Zotero will import the page as a “Web Page” item with a title, URL , and access date. See Saving Webpages below.

If you are viewing a PDF file in your browser, the save button will show a PDF icon. Clicking this button will import the PDF file alone into your library and then automatically attempt to retrieve information about it. While this will often produce good results, it is usually better to use the save button from the publication's abstract page or catalog entry, as described above, if there is one.
If you save a PDF directly and Zotero isn't able to retrieve metadata, it will leave the PDF as a standalone attachment. To add metadata, you'll need to create a parent item, either by saving a regular bibliographic item as described above and dragging the PDF on top of it or by right-clicking on the PDF, choosing Create Parent Item, and entering an identifier such as a DOI or ISBN. If all else fails, you can click Manual Entry after selecting Create Parent Item and manually enter metadata for the item.
- Multiple Results
On some webpages that contain information about multiple items (e.g., a list of Google Scholar search results), the save button will show a folder icon. Clicking this folder icon will open a window where you can select the items that you want to save to Zotero:

- Saving to a Specific Collection or Library
After you click the save button, a popup will appear indicating which Zotero collection the item is being saved to. If you want to save the item to a different collection or library, you can change the selection there, as well as enter tags to assign to the new item.
- Data Quality and Choosing a Translator
The quality of the data Zotero imports is determined by the information supplied on the webpage. Some websites provide very high-quality data using a standard way to provide Zotero with data (via embedded metadata). Other websites provide only limited metadata (e.g., only the title of a blog post) or no metadata at all. For many sites, Zotero has website-specific “translators” to obtain the best quality metadata. Zotero recognizes almost all library catalogs, most news sites, research databases and scientific publishers. (For more information, see our compatible websites list .) By default, translator updates are automatically installed, independent of Zotero updates. Metadata for the same item may vary in quality across sites providing it. For example, importing an item from the publisher website will generally yield much better data than importing from Google Scholar.
Zotero will generally choose the best translator available for each site automatically. You can choose an alternative translator by right-clicking on the Zotero save button (or the page background in Safari) and choosing one of the supplied options. If a website isn't importing properly, please report it on the Zotero Forums and provide the webpage URL .
- Add Item by Identifier
To look up metadata, Zotero uses Library of Congress, WorldCat , and other catalogs for ISBNs, CrossRef and other registries for DOIs, NCBI PubMed for PubMed IDs, arXiv.org for arXiv IDs, and ADS for ADS Bibcodes.
Adding PDFs and Other Files
As explained above, when possible, we recommend saving items using the Save to Zotero button in your browser from the primary webpage (e.g, a journal article's abstract page) rather than adding PDFs directly. The Save to Zotero button will usually save high-quality metadata and also automatically download the relevant PDF if you have access to it.
If there's no primary webpage, you can click the Save to Zotero button while viewing the PDF in your browser to save the PDF directly.

- Standalone Attachments and Parent Items
Attachments can be either child items or standalone attachments. Standalone attachments can't have bibliographic metadata or child notes, so in most cases you'll want to convert them to child items under regular parent items.
When you add a PDF directly, Zotero will initially save it as a standalone attachment and then automatically attempt to retrieve metadata for it and create a parent item. This should work well for most academic PDFs (though it may sometimes yield lower-quality metadata than using the Save to Zotero button on the article page). For other documents, while Zotero can sometimes extract basic information (title, author), you shouldn't expect that — anything can be distributed as a PDF, but that doesn’t mean there’s any standard metadata available for it.
If Zotero isn't able to retrieve metadata for the PDF, you'll be left with just the standalone attachment. You have a few options:
- If you can find a source for metadata online, you can save a regular bibliographic item by using the Save to Zotero button on the article page and drag the attachment item onto the new item.
- If you have a DOI, ISBN, or other identifier, you can right-click on the attachment item, choose Create Parent Item, and enter the identifier to retrieve metadata.
- If all else fails, you can click Manual Entry in the Create Parent Item window to enter metadata manually.
- Saving Webpages
With Zotero, you can create an item from any webpage by clicking the save button in the browser toolbar. If the page isn't recognized by a translator , you'll see the gray webpage icon. If the page does have a recognized translator, you can force Zotero to save a Web Page item instead by right-clicking (click-and-hold in Safari) on the Zotero save button and choosing “Save to Zotero (Web Page with/without Snapshot)”
If “Automatically take snapshots when creating items from web pages” is enabled in the General tab of the Zotero preferences, a copy (or snapshot) of the webpage will be saved to your computer and added as a child item. You can also save a snapshot with this setting disabled by right-clicking (click-and-hold in Safari) on the Zotero save button and choosing the relvant option. To view the saved copy, double-click the item or the snapshot in Zotero.

Double-clicking a Web Page item without a snapshot in your library will take you to the original webpage. Double-clicking a Web Page item with a snapshot will display the snapshot instead. You can also visit the original webpage by clicking the ”URL:” label to the left of the URL field in Zotero's right-hand pane.
- Importing from Other Tools
See Importing from Other Reference Managers .
- Large-Scale Imports from Databases
If you are importing a large number of items from scholarly databases (e.g., if you are conducting a systematic review), databases such as Google Scholar, ProQuest, Web of Science, and others, may lock you out if you use the Zotero save button too frequently or with too many items at once. In such cases, it is better to export the items as a batch in one of the standardized formats listed above (e.g., BibTeX and RIS are common choices) and import this file into Zotero. Web of Science and ProQuest offer the ability to select multiple items from a search results list and export as a batch to various formats. In Google Scholar, you need to first save the items to your Google Scholar library (using the ☆ icon in the search results), then select and export them from the Google Scholar “My Library” page.
- Manually Adding Items
Zotero is designed to help you avoid manual entry whenever possible. As a rule, you should save items to Zotero via your web browser rather than creating them manually. When you save from the web, Zotero will automatically extract high-quality metadata and download PDFs when available, saving you time and reducing errors. Even if you need to make manual corrections, it's best to start with the version that Zotero saves rather than creating an item completely from scratch.
Note: Since it's almost always better to visit a webpage in your browser and use the “Save to Zotero” button, the Web Page item type is not included in the “New Item” menu. However, if you really want to create a webpage item by hand, you create an empty item of another type and switch the item type to Web Page in the right-hand pane.
- Editing Items
When you have selected an item in the center pane, you can view and edit its bibliographic information via the Info tab of the right-hand pane. Most fields can be clicked and edited. Changes are saved automatically as they are made. Some fields have special features, which are discussed below.
Each item can have zero or more creators, of different types, such as authors, editors, etc. To change the creator type, click the creator field label (e.g., Author: ). A creator can be deleted by clicking the minus button at the end of the creator field, and additional creator fields can be added by clicking the plus button at the end of the last creator field. Creators can be reordered by clicking a creator field label and selecting “Move Up” or “Move Down”.
Each name field can be toggled between single and two field mode by clicking the “Switch to single field” / “Switch to two fields” buttons at the end of the creator field. Single field mode should be used to institutions (e.g., when the author is “Company A”), while two field mode (last name, first name) should be used for personal names. If a person has only one name (e.g., “Socrates”), enter this as a Last Name in two field mode. You can switch the order of two field author names by right-clicking on the name and choosing “Swap First/Last Names”
To quickly enter additional creators, type Shift-Enter/Retun to move immediately to a new creator field.
Journal Abbreviations
Journal articles are often cited with the abbreviated journal title. Zotero stores the journal title and journal title abbreviation in separate fields (“Publication” and “Journal Abbr”, respectively). While some citation styles require different abbreviations, most of the variation is in whether or not the abbreviation contain periods (e.g., “PLoS Biol” or “PLoS Biol.”). Because removing periods is more accurate than adding them, we recommend that you store title abbreviations in your Zotero library with periods. Zotero can then reliably strip out the periods in rendered bibliographies when the chosen citation style calls for it.
We recommend that you always store titles in your Zotero library in sentence case. See Sentence Casing for more information.
Clicking the label of the URL (“ URL :”) and DOI (“DOI:”) fields will open up the (DOI-resolved) URL in your web browser.
The Extra field can be used for storing custom item metadata or data that doesn't have a dedicated field in Zotero. If you need to cite an item using a field not supplied by Zotero, you can also store such data in Extra. See Citing Fields from Extra for more details on how to cite these fields. For example, to add a DOI to a Book Section item, add this to the top of Extra: DOI: 10.1234/567890
- Verify and Edit Your Records
When using Zotero — or any other reference manager — for citing, you should always check items for accuracy after saving them to your library.
Zotero will accurately import metadata supplied by most bibliographic databases, library catalogs, publisher sites, and webpages. It will even make adjustments to the metadata to compensate for known quirks (e.g., author names in all upper case) in what the supplier provides.
That said, sometimes the metadata that Zotero receives is incomplete or incorrect. For example, one major academic search site often provides the wrong serial name with otherwise correct metadata. Another scholarly research site's metadata can omit some of the authors' names or present them in the wrong order. Even major publishers sometimes omit important metadata fields.
Some metadata is provided with only author last names and one or two initials when the authors' full names are provided on the full-text version of the article. (For author names to be properly disambiguated in author-date styles, the author's name must be consistently and identically entered across all items they contributed to.)
Publishers have different conventions for the casing of titles. No software can accurately and reliably convert title case to sentence case, so you should always store titles in sentence case and let Zotero convert them to title case as necessary.
You should be aware of these issues and verify that the items in your library are accurate and in the correct format so that Zotero can produce well-formed citations. One of the primary benefits of using a reference manager is that, once you've corrected item data once, your citations will always be correct going forward, in any citation style, no matter how many times you cite them.
If you do consistently receive incorrect information from a particular source, you should report it — with an example URL or identifier — in the Zotero Forums , as Zotero developers may be able to update Zotero to automatically correct the incorrect data.
Table of Contents
- Old revisions
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
- My Bibliography
- Collections
- Citation manager
Save citation to file
Email citation, add to collections.
- Create a new collection
- Add to an existing collection
Add to My Bibliography
Your saved search, create a file for external citation management software, your rss feed, suicidal ideation, affiliations.
- 1 Saginaw Valley State University
- 2 Kaweah Delta Health Care District
- 3 West Virginia University, William R Sharpe Jr Hospital
- 4 Western University/ Kaweah Delta
- PMID: 33351435
- Bookshelf ID: NBK565877
Suicide remains a significant public health issue in the United States, with the age-adjusted suicide rate reaching 14.1 per 100,000 population in 2021. Increasing concern exists regarding deaths categorized as unintentional falls or poisonings, both of which have risen, as they may be misclassified suicides. The age-adjusted suicide rate saw a 36.7% increase between 2000 and 2018. Notably, in the 10 to 24-year-old age group, suicide is the second leading cause of death. While the suicide rate in this demographic was stable from 2001 to 2007, an upward trend was observed through 2021.
The suicide rate in the United States exhibits significant variations across different demographics. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), in 2021, the rate of suicide among men was 4 times higher than that among women. Additionally, individuals aged older than 85 experienced the highest rates of suicide. In the population aged 55 and older, the suicide rate increased with age among men, whereas the rate decreased with age among women. Substantial racial disparities are apparent in suicide rates, with the highest rate observed among American Indian and Alaska Native populations; in contrast, the lowest rate is found in Asians, with the rate among the former being approximately 4 times higher than the latter. According to the CDC, in 2021,12.3 million adults reported experiencing suicidal thoughts, 3.5 million adults made suicide plans, 1.7 million adults attempted suicide, and 48,183 individuals died by suicide.
Suicidal ideation refers to thinking about or formulating plans for suicide. The ideation exists on a spectrum of intensity, beginning with a general desire to die that lacks any concrete method, plan, intention, or action and progressing to active suicidal ideation, which involves a detailed plan and a determined intent to act on the ideas. Suicidal ideation is closely associated with both suicidal attempts and deaths, serving as a significant risk factor for future suicide attempts. Suicidal thoughts and actions are often viewed as a single concept, whereas passive thinking, active planning, and actual behavior are seen as a continuous spectrum. Research indicates that some individuals attempt suicide without prior suicidal ideation, though this is debated due to potential underreporting post-attempt due to stigma. A helpful analogy is to view suicidal ideation as the more significant, unseen portion of an iceberg, with the act of suicide as the visible tip. This perspective emphasizes the need for early identification and targeted intervention of those with suicidal ideation to prevent progression to suicide.
Assessing suicidal ideation is an early warning for subsequent suicidal acts and also offers valuable insights into the patient's level of suffering and their specific needs. This dual purpose underscores the importance of evaluating suicidal ideation comprehensively. Only a subset of patients with suicidal ideation will carry out the act. Nevertheless, suicidal ideation accompanied by intention and a specific plan is a psychiatric emergency and needs to be aggressively managed.
Given that 90% of individuals who die by suicide have a psychiatric illness, with the most common being mood disorder, recognizing suicidal ideation in patients presents a crucial opportunity for a thorough evaluation to understand their challenges, needs, and risk levels. Research shows that 80% of suicide victims had seen primary care clinicians within 1 year of their death, compared to just 25% to 30% who had consulted with psychiatric clinicians in that timeframe. Primary care clinicians are uniquely positioned to manage patients with suicidal ideation, assess suicide risk, and implement appropriate interventions.
Copyright © 2024, StatPearls Publishing LLC.
PubMed Disclaimer
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure: Bonnie Harmer declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
Disclosure: Sarah Lee declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
Disclosure: Abid Rizvi declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
Disclosure: Abdolreza Saadabadi declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
- Continuing Education Activity
- Introduction
- Epidemiology
- History and Physical
- Treatment / Management
- Differential Diagnosis
- Pertinent Studies and Ongoing Trials
- Complications
- Consultations
- Deterrence and Patient Education
- Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
- Review Questions
Similar articles
- Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas. Crider K, Williams J, Qi YP, Gutman J, Yeung L, Mai C, Finkelstain J, Mehta S, Pons-Duran C, Menéndez C, Moraleda C, Rogers L, Daniels K, Green P. Crider K, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1;2(2022):CD014217. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014217. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36321557 Free PMC article.
- Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks. Preuss CV, Kalava A, King KC. Preuss CV, et al. 2023 Apr 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan–. 2023 Apr 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
- Pilot Medical Certification. Matthews MJ, Stretanski MF. Matthews MJ, et al. 2023 Feb 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan–. 2023 Feb 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan–. PMID: 33620822 Free Books & Documents.
- Prevention of suicide and attempted suicide in Denmark. Epidemiological studies of suicide and intervention studies in selected risk groups. Nordentoft M. Nordentoft M. Dan Med Bull. 2007 Nov;54(4):306-69. Dan Med Bull. 2007. PMID: 18208680 Review.
- Evidence Brief: The Quality of Care Provided by Advanced Practice Nurses [Internet]. McCleery E, Christensen V, Peterson K, Humphrey L, Helfand M. McCleery E, et al. Washington (DC): Department of Veterans Affairs (US); 2014 Sep. Washington (DC): Department of Veterans Affairs (US); 2014 Sep. PMID: 27606392 Free Books & Documents. Review.
- Curtin SC, Garnett MF. Suicide and Homicide Death Rates Among Youth and Young Adults Aged 10-24: United States, 2001-2021. NCHS Data Brief. 2023 Jun;(471):1-8. - PubMed
- Garnett MF, Spencer MR, Weeks JD. Suicide Among Adults Age 55 and Older, 2021. NCHS Data Brief. 2023 Nov;(483):1-8. - PubMed
- Garnett MF, Curtin SC. Suicide Mortality in the United States, 2001-2021. NCHS Data Brief. 2023 Apr;(464):1-8. - PubMed
- Han B, Crosby AE, Ortega LA, Parks SE, Compton WM, Gfroerer J. Suicidal ideation, suicide attempt, and occupations among employed adults aged 18-64years in the United States. Compr Psychiatry. 2016 Apr;66:176-86. - PMC - PubMed
- Posner K, Brown GK, Stanley B, Brent DA, Yershova KV, Oquendo MA, Currier GW, Melvin GA, Greenhill L, Shen S, Mann JJ. The Columbia-Suicide Severity Rating Scale: initial validity and internal consistency findings from three multisite studies with adolescents and adults. Am J Psychiatry. 2011 Dec;168(12):1266-77. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
- Search in PubMed
- Search in MeSH
- Add to Search
Related information
- Cited in Books
LinkOut - more resources
Full text sources.
- NCBI Bookshelf

- Citation Manager
NCBI Literature Resources
MeSH PMC Bookshelf Disclaimer
The PubMed wordmark and PubMed logo are registered trademarks of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). Unauthorized use of these marks is strictly prohibited.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Formatting a Harvard style bibliography. Sources are alphabetised by author last name. The heading 'Reference list' or 'Bibliography' appears at the top. Each new source appears on a new line, and when an entry for a single source extends onto a second line, a hanging indent is used: Harvard bibliography example.
A bibliography entry for a book begins with the author's name, which is written in this order: last name, comma, first name, period. After the author's name comes the title of the book. If you are handwriting your bibliography, underline each title. If you are working on a computer, put the book title in italicized type.
How To Write a Bibliography (References) Using APA Style. Here are some general notes on writing an APA reference list: Title your bibliography section "References" and center the title on the top line of the page. Do not center your references; they should be left-aligned. For longer items, subsequent lines should use a hanging indent of 1 ...
Searching for bibliographic sources relevant to your project is an integral and unavoidable part of the thesis work. To find out how to conduct your bibliographic research, we suggest you consult the Bibliographic Research Guide. For a start, you can consult the Library books on academic writing (how to write assignments, presentations, theses
The heading Bibliography is bolded and centred at the top of the page. Unlike the rest of a Chicago format paper, the bibliography is not double-spaced. However, add a single line space between entries. If a bibliography entry extends onto more than one line, subsequent lines should be indented (hanging indent), as seen in the example below ...
For bibliography entries, you list the sources alphabetically by last name, so you will list the last name of the author or creator first in each entry. You should single-space within a bibliography entry and double-space between them. When an entry goes longer than one line, use a hanging indent of .5 inches for subsequent lines.
Start the reference list on the page following your report, after appendices, or any other supporting material. Follow these steps to write the perfect APA bibliography. Step One: Gather your sources together in a preliminary bibliography. Step Two: Format each citation entry by following these rules: List authors by last name, first name ...
Type the last name of the first author listed on the source followed by a comma, then the first author's first name followed by a comma. Then type the word "and" then list the second author's first name and last name in the standard order. Follow the second name with a period.
An annotated bibliography should include a reference list of any sources you use in writing a research paper. Any printed sources from which you use a text citation, including books, websites, newspaper articles, journal articles, academic writing, online sources (such as PDFs), and magazines should be included in a reference list.
To create a bibliography, gather up all of the sources that you might use in your paper. Create an APA format reference for each source and then write a brief annotation. Your annotation should be a brief summary of what each reference is about. You can quickly refer to these annotations When writing your paper and determine which to include.
The bibliographic information for different types of resources are located in different places, so you may need to do some detective work to get all of the information for your bibliography. Try looking in these places: the title page of a book, encyclopedia or dictionary; the heading of an article; the front, second, or editorial page of the ...
6. Cite books. Include the author's last name and first name, separated by a comma and ending with a period. Then the book title comes in italics with a period at the end of the title. The place of publication and the name of the publishing company are separated by a colon, and then a comma and the publication date.
At college level, you must properly cite your sources in all essays, research papers, and other academic texts (except exams and in-class exercises). Add a citation whenever you quote, paraphrase, or summarize information or ideas from a source. You should also give full source details in a bibliography or reference list at the end of your text.
For example, if the study intends to provide a review of the past, present, and future of a research field with a large bibliometric corpus, then a combination of co-citation analysis (past), bibliographic coupling (present), and co-word analysis (e.g., notable words in the implications and future research directions of full texts) (future) can ...
What do you write in a bibliography? A bibliography is a detailed list of all the sources consulted and cited in a research paper or project. The bibliography structure always includes citing the ...
Bibliographies are essential to scientific research, as they provide a comprehensive list of the sources that have been used in the research and writing process. Including a bibliography is important for several reasons. Citations in works submitted for publication are closely scrutinized by reviewers and publishers for the following reasons:
While a narrative literature review aims to summarize the content of the studies of a particular research field, a bibliographic literature review focuses on assessing the structure of a particular research field. A description and summary of "simple" bibliographic data (e.g., authors, journal names) is too superficial to derive specific ...
A bibliography is a list of works on a subject or by an author that were used or consulted to write a research paper, book or article. It can also be referred to as a list of works cited. It is usually found at the end of a book, article or research paper. Gathering Information. Regardless of what citation style is being used, there are key ...
Show how your research addresses a gap or contributes to a debate; Evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of the scholarly debates around your topic. Writing literature reviews is a particularly important skill if you want to apply for graduate school or pursue a career in research. We've written a step-by-step ...
All bibliographies are organized differently, but the best include indexes that help you pinpoint the most relevant entries. A smart researcher will also use the index to obtain an overview of the entire source base: the index as a whole presents a broad outline of the available sources--the extent of available sources, as well as the the strengths and weaknesses of the source base.
A bibliography is a list of works (such as books and articles) written on a particular subject or by a particular author. Adjective: bibliographic. Also known as a list of works cited, a bibliography may appear at the end of a book, report, online presentation, or research paper. Students are taught that a bibliography, along with correctly ...
A bibliography is a complete list of the sources that were used to complete a research paper or project.. Depending on the style guide you follow, you may also see this called a Works Cited (also called an MLA bibliography) or Reference List (APA format).Each listed source, or citation, shares information about the author, title, publishing year, and other details that serve to credit the ...
More than 100 reference examples and their corresponding in-text citations are presented in the seventh edition Publication Manual.Examples of the most common works that writers cite are provided on this page; additional examples are available in the Publication Manual.. To find the reference example you need, first select a category (e.g., periodicals) and then choose the appropriate type of ...
These notes refer to a bibliography at the end giving full source details. A Chicago bibliography entry for a book includes the author's name, the book title and subtitle, the edition (if stated), the location and name of the publisher, and the year of publication. For an e-book, add the e-book format (e.g. "Kindle") at the end.
Mission. The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives.
You can quickly add items to your library if you already know their ISBN, DOI, PubMed ID, arXiv ID, or ADS Bibcode. Click the Add Item by Identifier button () in the toolbar, type or paste in the identifier, and press Enter/Return. To add more than one item, separate identifiers by spaces, commas, or line breaks.
Suicidal ideation refers to thinking about or formulating plans for suicide. The ideation exists on a spectrum of intensity, beginning with a general desire to die that lacks any concrete method, plan, intention, or action and progressing to active suicidal ideation, which involves a detailed plan and a determined intent to act on the ideas.