- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- Critical Reviews

How to Write an Article Review (With Examples)
Last Updated: April 24, 2024 Fact Checked
Preparing to Write Your Review
Writing the article review, sample article reviews, expert q&a.
This article was co-authored by Jake Adams . Jake Adams is an academic tutor and the owner of Simplifi EDU, a Santa Monica, California based online tutoring business offering learning resources and online tutors for academic subjects K-College, SAT & ACT prep, and college admissions applications. With over 14 years of professional tutoring experience, Jake is dedicated to providing his clients the very best online tutoring experience and access to a network of excellent undergraduate and graduate-level tutors from top colleges all over the nation. Jake holds a BS in International Business and Marketing from Pepperdine University. There are 12 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 3,107,156 times.
An article review is both a summary and an evaluation of another writer's article. Teachers often assign article reviews to introduce students to the work of experts in the field. Experts also are often asked to review the work of other professionals. Understanding the main points and arguments of the article is essential for an accurate summation. Logical evaluation of the article's main theme, supporting arguments, and implications for further research is an important element of a review . Here are a few guidelines for writing an article review.
Education specialist Alexander Peterman recommends: "In the case of a review, your objective should be to reflect on the effectiveness of what has already been written, rather than writing to inform your audience about a subject."
Article Review 101
- Read the article very closely, and then take time to reflect on your evaluation. Consider whether the article effectively achieves what it set out to.
- Write out a full article review by completing your intro, summary, evaluation, and conclusion. Don't forget to add a title, too!
- Proofread your review for mistakes (like grammar and usage), while also cutting down on needless information.

- Article reviews present more than just an opinion. You will engage with the text to create a response to the scholarly writer's ideas. You will respond to and use ideas, theories, and research from your studies. Your critique of the article will be based on proof and your own thoughtful reasoning.
- An article review only responds to the author's research. It typically does not provide any new research. However, if you are correcting misleading or otherwise incorrect points, some new data may be presented.
- An article review both summarizes and evaluates the article.

- Summarize the article. Focus on the important points, claims, and information.
- Discuss the positive aspects of the article. Think about what the author does well, good points she makes, and insightful observations.
- Identify contradictions, gaps, and inconsistencies in the text. Determine if there is enough data or research included to support the author's claims. Find any unanswered questions left in the article.

- Make note of words or issues you don't understand and questions you have.
- Look up terms or concepts you are unfamiliar with, so you can fully understand the article. Read about concepts in-depth to make sure you understand their full context.

- Pay careful attention to the meaning of the article. Make sure you fully understand the article. The only way to write a good article review is to understand the article.

- With either method, make an outline of the main points made in the article and the supporting research or arguments. It is strictly a restatement of the main points of the article and does not include your opinions.
- After putting the article in your own words, decide which parts of the article you want to discuss in your review. You can focus on the theoretical approach, the content, the presentation or interpretation of evidence, or the style. You will always discuss the main issues of the article, but you can sometimes also focus on certain aspects. This comes in handy if you want to focus the review towards the content of a course.
- Review the summary outline to eliminate unnecessary items. Erase or cross out the less important arguments or supplemental information. Your revised summary can serve as the basis for the summary you provide at the beginning of your review.

- What does the article set out to do?
- What is the theoretical framework or assumptions?
- Are the central concepts clearly defined?
- How adequate is the evidence?
- How does the article fit into the literature and field?
- Does it advance the knowledge of the subject?
- How clear is the author's writing? Don't: include superficial opinions or your personal reaction. Do: pay attention to your biases, so you can overcome them.

- For example, in MLA , a citation may look like: Duvall, John N. "The (Super)Marketplace of Images: Television as Unmediated Mediation in DeLillo's White Noise ." Arizona Quarterly 50.3 (1994): 127-53. Print. [9] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source

- For example: The article, "Condom use will increase the spread of AIDS," was written by Anthony Zimmerman, a Catholic priest.

- Your introduction should only be 10-25% of your review.
- End the introduction with your thesis. Your thesis should address the above issues. For example: Although the author has some good points, his article is biased and contains some misinterpretation of data from others’ analysis of the effectiveness of the condom.

- Use direct quotes from the author sparingly.
- Review the summary you have written. Read over your summary many times to ensure that your words are an accurate description of the author's article.

- Support your critique with evidence from the article or other texts.
- The summary portion is very important for your critique. You must make the author's argument clear in the summary section for your evaluation to make sense.
- Remember, this is not where you say if you liked the article or not. You are assessing the significance and relevance of the article.
- Use a topic sentence and supportive arguments for each opinion. For example, you might address a particular strength in the first sentence of the opinion section, followed by several sentences elaborating on the significance of the point.

- This should only be about 10% of your overall essay.
- For example: This critical review has evaluated the article "Condom use will increase the spread of AIDS" by Anthony Zimmerman. The arguments in the article show the presence of bias, prejudice, argumentative writing without supporting details, and misinformation. These points weaken the author’s arguments and reduce his credibility.

- Make sure you have identified and discussed the 3-4 key issues in the article.

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://libguides.cmich.edu/writinghelp/articlereview
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4548566/
- ↑ Jake Adams. Academic Tutor & Test Prep Specialist. Expert Interview. 24 July 2020.
- ↑ https://guides.library.queensu.ca/introduction-research/writing/critical
- ↑ https://www.iup.edu/writingcenter/writing-resources/organization-and-structure/creating-an-outline.html
- ↑ https://writing.umn.edu/sws/assets/pdf/quicktips/titles.pdf
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/mla_style/mla_formatting_and_style_guide/mla_works_cited_periodicals.html
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4548565/
- ↑ https://writingcenter.uconn.edu/wp-content/uploads/sites/593/2014/06/How_to_Summarize_a_Research_Article1.pdf
- ↑ https://www.uis.edu/learning-hub/writing-resources/handouts/learning-hub/how-to-review-a-journal-article
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/editing-and-proofreading/
About This Article

If you have to write an article review, read through the original article closely, taking notes and highlighting important sections as you read. Next, rewrite the article in your own words, either in a long paragraph or as an outline. Open your article review by citing the article, then write an introduction which states the article’s thesis. Next, summarize the article, followed by your opinion about whether the article was clear, thorough, and useful. Finish with a paragraph that summarizes the main points of the article and your opinions. To learn more about what to include in your personal critique of the article, keep reading the article! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Prince Asiedu-Gyan
Apr 22, 2022
Did this article help you?

Sammy James
Sep 12, 2017
Juabin Matey
Aug 30, 2017
Vanita Meghrajani
Jul 21, 2016
Nov 27, 2018

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Develop the tech skills you need for work and life
How to Write an Article Review: Tips and Examples

Did you know that article reviews are not just academic exercises but also a valuable skill in today's information age? In a world inundated with content, being able to dissect and evaluate articles critically can help you separate the wheat from the chaff. Whether you're a student aiming to excel in your coursework or a professional looking to stay well-informed, mastering the art of writing article reviews is an invaluable skill.
Short Description
In this article, our research paper writing service experts will start by unraveling the concept of article reviews and discussing the various types. You'll also gain insights into the art of formatting your review effectively. To ensure you're well-prepared, we'll take you through the pre-writing process, offering tips on setting the stage for your review. But it doesn't stop there. You'll find a practical example of an article review to help you grasp the concepts in action. To complete your journey, we'll guide you through the post-writing process, equipping you with essential proofreading techniques to ensure your work shines with clarity and precision!
What Is an Article Review: Grasping the Concept
A review article is a type of professional paper writing that demands a high level of in-depth analysis and a well-structured presentation of arguments. It is a critical, constructive evaluation of literature in a particular field through summary, classification, analysis, and comparison.
If you write a scientific review, you have to use database searches to portray the research. Your primary goal is to summarize everything and present a clear understanding of the topic you've been working on.
Writing Involves:
- Summarization, classification, analysis, critiques, and comparison.
- The analysis, evaluation, and comparison require the use of theories, ideas, and research relevant to the subject area of the article.
- It is also worth nothing if a review does not introduce new information, but instead presents a response to another writer's work.
- Check out other samples to gain a better understanding of how to review the article.
Types of Review
When it comes to article reviews, there's more than one way to approach the task. Understanding the various types of reviews is like having a versatile toolkit at your disposal. In this section, we'll walk you through the different dimensions of review types, each offering a unique perspective and purpose. Whether you're dissecting a scholarly article, critiquing a piece of literature, or evaluating a product, you'll discover the diverse landscape of article reviews and how to navigate it effectively.
.webp)
Journal Article Review
Just like other types of reviews, a journal article review assesses the merits and shortcomings of a published work. To illustrate, consider a review of an academic paper on climate change, where the writer meticulously analyzes and interprets the article's significance within the context of environmental science.
Research Article Review
Distinguished by its focus on research methodologies, a research article review scrutinizes the techniques used in a study and evaluates them in light of the subsequent analysis and critique. For instance, when reviewing a research article on the effects of a new drug, the reviewer would delve into the methods employed to gather data and assess their reliability.
Science Article Review
In the realm of scientific literature, a science article review encompasses a wide array of subjects. Scientific publications often provide extensive background information, which can be instrumental in conducting a comprehensive analysis. For example, when reviewing an article about the latest breakthroughs in genetics, the reviewer may draw upon the background knowledge provided to facilitate a more in-depth evaluation of the publication.
Need a Hand From Professionals?
Address to Our Writers and Get Assistance in Any Questions!
Formatting an Article Review
The format of the article should always adhere to the citation style required by your professor. If you're not sure, seek clarification on the preferred format and ask him to clarify several other pointers to complete the formatting of an article review adequately.
How Many Publications Should You Review?
- In what format should you cite your articles (MLA, APA, ASA, Chicago, etc.)?
- What length should your review be?
- Should you include a summary, critique, or personal opinion in your assignment?
- Do you need to call attention to a theme or central idea within the articles?
- Does your instructor require background information?
When you know the answers to these questions, you may start writing your assignment. Below are examples of MLA and APA formats, as those are the two most common citation styles.
Using the APA Format
Articles appear most commonly in academic journals, newspapers, and websites. If you write an article review in the APA format, you will need to write bibliographical entries for the sources you use:
- Web : Author [last name], A.A [first and middle initial]. (Year, Month, Date of Publication). Title. Retrieved from {link}
- Journal : Author [last name], A.A [first and middle initial]. (Publication Year). Publication Title. Periodical Title, Volume(Issue), pp.-pp.
- Newspaper : Author [last name], A.A [first and middle initial]. (Year, Month, Date of Publication). Publication Title. Magazine Title, pp. xx-xx.
Using MLA Format
- Web : Last, First Middle Initial. “Publication Title.” Website Title. Website Publisher, Date Month Year Published. Web. Date Month Year Accessed.
- Newspaper : Last, First M. “Publication Title.” Newspaper Title [City] Date, Month, Year Published: Page(s). Print.
- Journal : Last, First M. “Publication Title.” Journal Title Series Volume. Issue (Year Published): Page(s). Database Name. Web. Date Month Year Accessed.
Enhance your writing effortlessly with EssayPro.com , where you can order an article review or any other writing task. Our team of expert writers specializes in various fields, ensuring your work is not just summarized, but deeply analyzed and professionally presented. Ideal for students and professionals alike, EssayPro offers top-notch writing assistance tailored to your needs. Elevate your writing today with our skilled team at your article review writing service !
.jpg)
The Pre-Writing Process
Facing this task for the first time can really get confusing and can leave you unsure of where to begin. To create a top-notch article review, start with a few preparatory steps. Here are the two main stages from our dissertation services to get you started:
Step 1: Define the right organization for your review. Knowing the future setup of your paper will help you define how you should read the article. Here are the steps to follow:
- Summarize the article — seek out the main points, ideas, claims, and general information presented in the article.
- Define the positive points — identify the strong aspects, ideas, and insightful observations the author has made.
- Find the gaps —- determine whether or not the author has any contradictions, gaps, or inconsistencies in the article and evaluate whether or not he or she used a sufficient amount of arguments and information to support his or her ideas.
- Identify unanswered questions — finally, identify if there are any questions left unanswered after reading the piece.
Step 2: Move on and review the article. Here is a small and simple guide to help you do it right:
- Start off by looking at and assessing the title of the piece, its abstract, introductory part, headings and subheadings, opening sentences in its paragraphs, and its conclusion.
- First, read only the beginning and the ending of the piece (introduction and conclusion). These are the parts where authors include all of their key arguments and points. Therefore, if you start with reading these parts, it will give you a good sense of the author's main points.
- Finally, read the article fully.
These three steps make up most of the prewriting process. After you are done with them, you can move on to writing your own review—and we are going to guide you through the writing process as well.
Outline and Template
As you progress with reading your article, organize your thoughts into coherent sections in an outline. As you read, jot down important facts, contributions, or contradictions. Identify the shortcomings and strengths of your publication. Begin to map your outline accordingly.
If your professor does not want a summary section or a personal critique section, then you must alleviate those parts from your writing. Much like other assignments, an article review must contain an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. Thus, you might consider dividing your outline according to these sections as well as subheadings within the body. If you find yourself troubled with the pre-writing and the brainstorming process for this assignment, seek out a sample outline.
Your custom essay must contain these constituent parts:
- Pre-Title Page - Before diving into your review, start with essential details: article type, publication title, and author names with affiliations (position, department, institution, location, and email). Include corresponding author info if needed.
- Running Head - In APA format, use a concise title (under 40 characters) to ensure consistent formatting.
- Summary Page - Optional but useful. Summarize the article in 800 words, covering background, purpose, results, and methodology, avoiding verbatim text or references.
- Title Page - Include the full title, a 250-word abstract, and 4-6 keywords for discoverability.
- Introduction - Set the stage with an engaging overview of the article.
- Body - Organize your analysis with headings and subheadings.
- Works Cited/References - Properly cite all sources used in your review.
- Optional Suggested Reading Page - If permitted, suggest further readings for in-depth exploration.
- Tables and Figure Legends (if instructed by the professor) - Include visuals when requested by your professor for clarity.
Example of an Article Review
You might wonder why we've dedicated a section of this article to discuss an article review sample. Not everyone may realize it, but examining multiple well-constructed examples of review articles is a crucial step in the writing process. In the following section, our essay writing service experts will explain why.
Looking through relevant article review examples can be beneficial for you in the following ways:
- To get you introduced to the key works of experts in your field.
- To help you identify the key people engaged in a particular field of science.
- To help you define what significant discoveries and advances were made in your field.
- To help you unveil the major gaps within the existing knowledge of your field—which contributes to finding fresh solutions.
- To help you find solid references and arguments for your own review.
- To help you generate some ideas about any further field of research.
- To help you gain a better understanding of the area and become an expert in this specific field.
- To get a clear idea of how to write a good review.
View Our Writer’s Sample Before Crafting Your Own!
Why Have There Been No Great Female Artists?
Steps for Writing an Article Review
Here is a guide with critique paper format on how to write a review paper:
.webp)
Step 1: Write the Title
First of all, you need to write a title that reflects the main focus of your work. Respectively, the title can be either interrogative, descriptive, or declarative.
Step 2: Cite the Article
Next, create a proper citation for the reviewed article and input it following the title. At this step, the most important thing to keep in mind is the style of citation specified by your instructor in the requirements for the paper. For example, an article citation in the MLA style should look as follows:
Author's last and first name. "The title of the article." Journal's title and issue(publication date): page(s). Print
Abraham John. "The World of Dreams." Virginia Quarterly 60.2(1991): 125-67. Print.
Step 3: Article Identification
After your citation, you need to include the identification of your reviewed article:
- Title of the article
- Title of the journal
- Year of publication
All of this information should be included in the first paragraph of your paper.
The report "Poverty increases school drop-outs" was written by Brian Faith – a Health officer – in 2000.
Step 4: Introduction
Your organization in an assignment like this is of the utmost importance. Before embarking on your writing process, you should outline your assignment or use an article review template to organize your thoughts coherently.
- If you are wondering how to start an article review, begin with an introduction that mentions the article and your thesis for the review.
- Follow up with a summary of the main points of the article.
- Highlight the positive aspects and facts presented in the publication.
- Critique the publication by identifying gaps, contradictions, disparities in the text, and unanswered questions.
Step 5: Summarize the Article
Make a summary of the article by revisiting what the author has written about. Note any relevant facts and findings from the article. Include the author's conclusions in this section.
Step 6: Critique It
Present the strengths and weaknesses you have found in the publication. Highlight the knowledge that the author has contributed to the field. Also, write about any gaps and/or contradictions you have found in the article. Take a standpoint of either supporting or not supporting the author's assertions, but back up your arguments with facts and relevant theories that are pertinent to that area of knowledge. Rubrics and templates can also be used to evaluate and grade the person who wrote the article.
Step 7: Craft a Conclusion
In this section, revisit the critical points of your piece, your findings in the article, and your critique. Also, write about the accuracy, validity, and relevance of the results of the article review. Present a way forward for future research in the field of study. Before submitting your article, keep these pointers in mind:
- As you read the article, highlight the key points. This will help you pinpoint the article's main argument and the evidence that they used to support that argument.
- While you write your review, use evidence from your sources to make a point. This is best done using direct quotations.
- Select quotes and supporting evidence adequately and use direct quotations sparingly. Take time to analyze the article adequately.
- Every time you reference a publication or use a direct quotation, use a parenthetical citation to avoid accidentally plagiarizing your article.
- Re-read your piece a day after you finish writing it. This will help you to spot grammar mistakes and to notice any flaws in your organization.
- Use a spell-checker and get a second opinion on your paper.
The Post-Writing Process: Proofread Your Work
Finally, when all of the parts of your article review are set and ready, you have one last thing to take care of — proofreading. Although students often neglect this step, proofreading is a vital part of the writing process and will help you polish your paper to ensure that there are no mistakes or inconsistencies.
To proofread your paper properly, start by reading it fully and checking the following points:
- Punctuation
- Other mistakes
Afterward, take a moment to check for any unnecessary information in your paper and, if found, consider removing it to streamline your content. Finally, double-check that you've covered at least 3-4 key points in your discussion.
And remember, if you ever need help with proofreading, rewriting your essay, or even want to buy essay , our friendly team is always here to assist you.
Need an Article REVIEW WRITTEN?
Just send us the requirements to your paper and watch one of our writers crafting an original paper for you.
What Is A Review Article?
How to write an article review, how to write an article review in apa format.

Daniel Parker
is a seasoned educational writer focusing on scholarship guidance, research papers, and various forms of academic essays including reflective and narrative essays. His expertise also extends to detailed case studies. A scholar with a background in English Literature and Education, Daniel’s work on EssayPro blog aims to support students in achieving academic excellence and securing scholarships. His hobbies include reading classic literature and participating in academic forums.

is an expert in nursing and healthcare, with a strong background in history, law, and literature. Holding advanced degrees in nursing and public health, his analytical approach and comprehensive knowledge help students navigate complex topics. On EssayPro blog, Adam provides insightful articles on everything from historical analysis to the intricacies of healthcare policies. In his downtime, he enjoys historical documentaries and volunteering at local clinics.
Related Articles
.webp)
The Tech Edvocate
- Advertisement
- Home Page Five (No Sidebar)
- Home Page Four
- Home Page Three
- Home Page Two
- Icons [No Sidebar]
- Left Sidbear Page
- Lynch Educational Consulting
- My Speaking Page
- Newsletter Sign Up Confirmation
- Newsletter Unsubscription
- Page Example
- Privacy Policy
- Protected Content
- Request a Product Review
- Shortcodes Examples
- Terms and Conditions
- The Edvocate
- The Tech Edvocate Product Guide
- Write For Us
- Dr. Lynch’s Personal Website
- The Edvocate Podcast
- Assistive Technology
- Child Development Tech
- Early Childhood & K-12 EdTech
- EdTech Futures
- EdTech News
- EdTech Policy & Reform
- EdTech Startups & Businesses
- Higher Education EdTech
- Online Learning & eLearning
- Parent & Family Tech
- Personalized Learning
- Product Reviews
- Tech Edvocate Awards
- School Ratings
The Goodness of Fit: Everything You Need to Know
Spain, ireland and norway say they will recognize a palestinian state. why does that matter, world reacts to the death of iran’s president ebrahimraisi, best cities to live in the u.s., according to u.s. news & world report, netanyahu denounces bid to arrest him over gaza war, how does this end with hamas holding firm and fighting back in gaza, israel faces only bad options, trump hush money trial to shape prosecutor alvin bragg’s legacy, judge dismisses felony convictions of 5 retired military officers in u.s. navy bribery case, trump falsely claims us justice department was ready to kill him, majority of americans wrongly believe us is in recession – and most blame biden, how to write an article review (with sample reviews) .

An article review is a critical evaluation of a scholarly or scientific piece, which aims to summarize its main ideas, assess its contributions, and provide constructive feedback. A well-written review not only benefits the author of the article under scrutiny but also serves as a valuable resource for fellow researchers and scholars. Follow these steps to create an effective and informative article review:
1. Understand the purpose: Before diving into the article, it is important to understand the intent of writing a review. This helps in focusing your thoughts, directing your analysis, and ensuring your review adds value to the academic community.
2. Read the article thoroughly: Carefully read the article multiple times to get a complete understanding of its content, arguments, and conclusions. As you read, take notes on key points, supporting evidence, and any areas that require further exploration or clarification.
3. Summarize the main ideas: In your review’s introduction, briefly outline the primary themes and arguments presented by the author(s). Keep it concise but sufficiently informative so that readers can quickly grasp the essence of the article.
4. Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses: In subsequent paragraphs, assess the strengths and limitations of the article based on factors such as methodology, quality of evidence presented, coherence of arguments, and alignment with existing literature in the field. Be fair and objective while providing your critique.
5. Discuss any implications: Deliberate on how this particular piece contributes to or challenges existing knowledge in its discipline. You may also discuss potential improvements for future research or explore real-world applications stemming from this study.
6. Provide recommendations: Finally, offer suggestions for both the author(s) and readers regarding how they can further build on this work or apply its findings in practice.
7. Proofread and revise: Once your initial draft is complete, go through it carefully for clarity, accuracy, and coherence. Revise as necessary, ensuring your review is both informative and engaging for readers.
Sample Review:
A Critical Review of “The Effects of Social Media on Mental Health”
Introduction:
“The Effects of Social Media on Mental Health” is a timely article which investigates the relationship between social media usage and psychological well-being. The authors present compelling evidence to support their argument that excessive use of social media can result in decreased self-esteem, increased anxiety, and a negative impact on interpersonal relationships.
Strengths and weaknesses:
One of the strengths of this article lies in its well-structured methodology utilizing a variety of sources, including quantitative surveys and qualitative interviews. This approach provides a comprehensive view of the topic, allowing for a more nuanced understanding of the effects of social media on mental health. However, it would have been beneficial if the authors included a larger sample size to increase the reliability of their conclusions. Additionally, exploring how different platforms may influence mental health differently could have added depth to the analysis.
Implications:
The findings in this article contribute significantly to ongoing debates surrounding the psychological implications of social media use. It highlights the potential dangers that excessive engagement with online platforms may pose to one’s mental well-being and encourages further research into interventions that could mitigate these risks. The study also offers an opportunity for educators and policy-makers to take note and develop strategies to foster healthier online behavior.
Recommendations:
Future researchers should consider investigating how specific social media platforms impact mental health outcomes, as this could lead to more targeted interventions. For practitioners, implementing educational programs aimed at promoting healthy online habits may be beneficial in mitigating the potential negative consequences associated with excessive social media use.
Conclusion:
Overall, “The Effects of Social Media on Mental Health” is an important and informative piece that raises awareness about a pressing issue in today’s digital age. Given its minor limitations, it provides valuable
3 Ways to Make a Mini Greenhouse ...
3 ways to teach yourself to play ....
Matthew Lynch
Related articles more from author.

How to Clean an Above Ground Pool

3 Easy Ways to Treat an Infected Lip Piercing
How to Use NLP: 10 Steps

3 Ways to Add Templates in Microsoft Word

How to Raise a Mynah Bird
Article Review Examples and Samples
Reviewing an article is not as easy as it sounds: it requires a critical mind and doing some extra research. Check out our article review samples to gain a better understanding of how to review articles yourself.
How to Write an Article Review: A Comprehensive Guide
Writing an article review can be a complex task. It requires a careful summary of the writer’s article, a thorough evaluation of its key arguments, and a clear understanding of the subject area or discipline. This guide provides guidelines and tips for preparing and writing an effective article review.
Understanding an Article Review
An article review is a critique or assessment of another’s work, typically written by experts in the field. It involves summarizing the writer’s piece, evaluating its main points, and providing an analysis of the content. A review article isn’t just a simple summary; it’s a critical assessment that reflects your understanding and interpretation of the writer’s work.
Preparing for an Article Review
Before you start writing, you need to spend time preparing. This involves getting familiar with the author’s work, conducting research, and identifying the main points or central ideas in the text. It’s crucial to understand the subject area or discipline the writer’s article falls under to provide a comprehensive review.
Writing the Summary
The first part of your article review should provide a summary of the writer’s article. This isn’t a simple recounting of the article; it’s an overview or summation that highlights the key arguments and central ideas. It should give the reader a clear understanding of the writer’s main points and the overall structure of the article.
Evaluating the Article
The evaluation or assessment is the heart of your article review. Here, you analyze the writer’s piece, critique their main points, and assess the validity of their arguments. This evaluation should be based on your research and your understanding of the subject area. It’s important to be critical, but fair in your assessment.
Consulting Experts
Consulting experts or professionals in the field can be a valuable part of writing an article review. They can provide insights, add depth to your critique, and validate your evaluation. Remember, an article review is not just about your opinion, but also about how the writer’s piece is perceived by experts in the field.
Writing the Review
Now that you have your summary and evaluation, it’s time to start writing your review. Begin with an introduction that provides a brief overview of the writer’s article and your intended critique. The body of your review should contain your detailed summary and evaluation. Finally, conclude your review by summarizing your critique and providing your final thoughts on the writer’s piece.
Following Guidelines
While writing your article review, it’s important to adhere to the guidelines provided by your instructor or the journal you’re writing for. These recommendations often include specific formatting and structure requirements, as well as suggestions on the tone and style of your review.
Revisiting the Writer’s Article
As you work on your article review, don’t forget to revisit the writer’s article from time to time. This allows you to maintain a fresh perspective on the writer’s piece and ensures that your evaluation is accurate and comprehensive. The ability to relate to the author’s work is crucial in writing an effective critique.
Highlighting the Main Points
The main points or key arguments of the writer’s article should be at the forefront of your review. These central ideas form the crux of the author’s work and are, therefore, essential to your summary and evaluation. Be sure to clearly identify these points and discuss their significance and impact in the context of the field.
Engaging with the Field
An article review isn’t just about the writer’s article – it’s also about the broader subject area or discipline. Engage with the field by discussing relevant research, theories, and debates. This not only adds depth to your review but also positions the writer’s piece within a larger academic conversation.
Incorporating Expert Opinions
Incorporating the opinions of experts or authorities in the field strengthens your review. Experts can provide valuable insights, challenge your assumptions, and help you see the writer’s article from different perspectives. They can also validate your evaluation and lend credibility to your review.
The Role of Research in Your Review
Research plays a vital role in crafting an article review. It informs your understanding of the writer’s article, the main points, and the field. It also provides the necessary context for your evaluation. Be sure to conduct thorough research and incorporate relevant studies and investigations into your review.
Finalizing Your Review
Before submitting your review, take some time to revise and refine your writing. Check for clarity, coherence, and conciseness. Ensure your summary accurately represents the writer’s article and that your evaluation is thorough and fair. Adhere to the guidelines and recommendations provided by your instructor or the journal. If you need to add citations and reference page – don’t forget to include those. You can refer to one of our tools like acm reference generator to help you do everything correctly
In summary, writing an article review is a meticulous process that requires a detailed summary of the writer’s piece, a comprehensive evaluation of its main points, and a deep engagement with the field. By preparing adequately, consulting experts, and conducting thorough research, you can write a critique that is insightful, informed, and impactful.
Psychotherapy and Collaborative Goals Essay Sample, Example
Improving Mental Health Through Collaborative Psychotherapy Initiating psychotherapy is a crucial step towards achieving mental health and wellbeing. It is a process that involves the…
Early Assessment for Depression in Teenagers Essay Sample, Example
Handling Early Teenage Depression Depression is one of the most common mental health disorders in teenagers. According to the National Institute of Mental Health, approximately…
Discussion: Pharmaceuticals and Behavioral Health Essay Sample, Example
The Correlation Between Pharmaceuticals and Behavioral Health Pharmaceuticals and behavioral health are two interconnected fields that have a significant impact on the overall health and…
Human Experience Across the Health-Illness Continuum Essay Sample, Example
The Changing Human Experience in Health and Illness Human experience is a complex and multifaceted concept that encompasses a wide range of emotions, thoughts, behaviors,…
Total Quality Management Essay Sample, Example
Total Quality Management as a Systematic Approach Total Quality Management (TQM) is a management philosophy that focuses on continuous improvement, customer satisfaction, and employee involvement.…
The Lack of Patient Access in a Healthcare Organization Essay Sample, Example
Lack of Patient Access and Its Consequences The lack of patient access in a healthcare organization is a major concern for patients, healthcare providers, and…
Innovation Management and Creativity Essay Sample, Example
Integrating Innovations into Business Management Practices Innovation management and creativity are two concepts that are closely related and have a significant impact on the success…
Background Checks Essay Sample, Example
Performing Background Checks Before Hiring a New Employee In today’s competitive and fast-paced business world, employers are vigilant about hiring the right people. One of…
Evaluating Performance Essay Sample, Example
Performance Evaluation as a Way to Uphold Business Practices to a High Standard Evaluation of performance in management is an essential aspect of organizational success.…
How the city of London shaped Shakespeare Essay Sample, Example
William Shakespeare William Shakespeare is one of the most celebrated and influential playwrights in history, and his works have endured through the ages. Shakespeare spent…
George Washington as Military Leader and President – views and attitudes Essay Sample, Example
George Washington George Washington was a man of many talents, but his greatest achievements were as a military leader and as the first President of…
Factors Affecting Stock Prices Essay Sample, Example
The Impact of Various Factors on Stock Market Valuations Stock prices are influenced by a wide range of factors that can impact the performance of…
Importance of Corporate Budget Essay Sample, Example
The Correlation Between Corporate Budgeting and Business Success Corporate budgeting is the process of creating a financial plan that outlines the expected expenditures and revenues…
COVID-19 and The Challenging Context of International Business, Trade, and Investment Essay Sample, Example
The Influence of COVID-19 on International Business, Trade, and Investment COVID-19 has presented a challenging context for international business, trade, and investment. The pandemic has…
Family Therapy and Group Work Practice in Social Work Essay Sample, Example
Family Therapy and Group Work Practice Family therapy and group work practice are two approaches to psychotherapy that focus on the interpersonal relationships between individuals.…
Group Leadership Skill: Interpersonal Process in Group Counseling and Therapy Essay Sample, Example
Group Leadership Skill As an a Valuable Part of Group Counseling and Therapy Interpersonal process is an essential group leadership skill in group counseling and…
Working with the Military and Veterans Essay Sample, Example
Social Work with the Military, Veterans and Their Families Working with the military and veterans can be a challenging and rewarding experience for social workers.…
Memory, Knowledge, and Language and Their Importance in Social Work Essay Sample, Example
Social Work and Memory, Knowledge, and Language Memory, knowledge, and language are important components in social work. Social work is a field that involves working…
Are Dress Codes a Good Idea for Schools? Essay Sample, Example
School Dress Codes Dress codes have been a topic of discussion in schools for many years. Some people believe that dress codes are a good…
Customer Satisfaction Still at 1970s Levels Essay Sample, Example
Brooks, Chad. Customer Satisfaction Still at 1970s Levels. Business News Daily, 2013. The article draws attention to the problem of relationships between American companies and…
Remember Me
What is your profession ? Student Teacher Writer Other
Forgotten Password?
Username or Email
How to Write an Article Review: Template & Examples
An article review is an academic assignment that invites you to study a piece of academic research closely. Then, you should present its summary and critically evaluate it using the knowledge you’ve gained in class and during your independent study. If you get such a task at college or university, you shouldn’t confuse it with a response paper, which is a distinct assignment with other purposes (we’ll talk about it in detail below).
In this article, prepared by Custom-Writing experts, you’ll find:
- the intricacies of article review writing;
- the difference between an article review and similar assignments;
- a step-by-step algorithm for review composition;
- a couple of samples to guide you throughout the writing process.
So, if you wish to study our article review example and discover helpful writing tips, keep reading.
❓ What Is an Article Review?
- ✍️ Writing Steps
📑 Article Review Format
🔗 references.
An article review is an academic paper that summarizes and critically evaluates the information presented in your selected article.

The first thing you should note when approaching the task of an article review is that not every article is suitable for this assignment. Let’s have a look at the variety of articles to understand what you can choose from.
Popular Vs. Scholarly Articles
In most cases, you’ll be required to review a scholarly, peer-reviewed article – one composed in compliance with rigorous academic standards. Yet, the Web is also full of popular articles that don’t present original scientific value and shouldn’t be selected for a review.
Not sure how to distinguish these two types? Here is a comparative table to help you out.
Article Review vs. Response Paper
Now, let’s consider the difference between an article review and a response paper:
- If you’re assigned to critique a scholarly article , you will need to compose an article review .
- If your subject of analysis is a popular article , you can respond to it with a well-crafted response paper .
The reason for such distinctions is the quality and structure of these two article types. Peer-reviewed, scholarly articles have clear-cut quality criteria, allowing you to conduct and present a structured assessment of the assigned material. Popular magazines have loose or non-existent quality criteria and don’t offer an opportunity for structured evaluation. So, they are only fit for a subjective response, in which you can summarize your reactions and emotions related to the reading material.
All in all, you can structure your response assignments as outlined in the tips below.
✍️ How to Write an Article Review: Step by Step
Here is a tried and tested algorithm for article review writing from our experts. We’ll consider only the critical review variety of this academic assignment. So, let’s get down to the stages you need to cover to get a stellar review.
Read the Article
As with any reviews, reports, and critiques, you must first familiarize yourself with the assigned material. It’s impossible to review something you haven’t read, so set some time for close, careful reading of the article to identify:
- The author’s main points and message.
- The arguments they use to prove their points.
- The methodology they use to approach the subject.
In terms of research type , your article will usually belong to one of three types explained below.
Summarize the Article
Now that you’ve read the text and have a general impression of the content, it’s time to summarize it for your readers. Look into the article’s text closely to determine:
- The thesis statement , or general message of the author.
- Research question, purpose, and context of research.
- Supporting points for the author’s assumptions and claims.
- Major findings and supporting evidence.
As you study the article thoroughly, make notes on the margins or write these elements out on a sheet of paper. You can also apply a different technique: read the text section by section and formulate its gist in one phrase or sentence. Once you’re done, you’ll have a summary skeleton in front of you.
Evaluate the Article
The next step of review is content evaluation. Keep in mind that various research types will require a different set of review questions. Here is a complete list of evaluation points you can include.
Write the Text
After completing the critical review stage, it’s time to compose your article review.
The format of this assignment is standard – you will have an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. The introduction should present your article and summarize its content. The body will contain a structured review according to all four dimensions covered in the previous section. The concluding part will typically recap all the main points you’ve identified during your assessment.
It is essential to note that an article review is, first of all, an academic assignment. Therefore, it should follow all rules and conventions of academic composition, such as:
- No contractions . Don’t use short forms, such as “don’t,” “can’t,” “I’ll,” etc. in academic writing. You need to spell out all those words.
- Formal language and style . Avoid conversational phrasing and words that you would naturally use in blog posts or informal communication. For example, don’t use words like “pretty,” “kind of,” and “like.”
- Third-person narrative . Academic reviews should be written from the third-person point of view, avoiding statements like “I think,” “in my opinion,” and so on.
- No conversational forms . You shouldn’t turn to your readers directly in the text by addressing them with the pronoun “you.” It’s vital to keep the narrative neutral and impersonal.
- Proper abbreviation use . Consult the list of correct abbreviations , like “e.g.” or “i.e.,” for use in your academic writing. If you use informal abbreviations like “FYA” or “f.i.,” your professor will reduce the grade.
- Complete sentences . Make sure your sentences contain the subject and the predicate; avoid shortened or sketch-form phrases suitable for a draft only.
- No conjunctions at the beginning of a sentence . Remember the FANBOYS rule – don’t start a sentence with words like “and” or “but.” They often seem the right way to build a coherent narrative, but academic writing rules disfavor such usage.
- No abbreviations or figures at the beginning of a sentence . Never start a sentence with a number — spell it out if you need to use it anyway. Besides, sentences should never begin with abbreviations like “e.g.”
Finally, a vital rule for an article review is properly formatting the citations. We’ll discuss the correct use of citation styles in the following section.
When composing an article review, keep these points in mind:
- Start with a full reference to the reviewed article so the reader can locate it quickly.
- Ensure correct formatting of in-text references.
- Provide a complete list of used external sources on the last page of the review – your bibliographical entries .
You’ll need to understand the rules of your chosen citation style to meet all these requirements. Below, we’ll discuss the two most common referencing styles – APA and MLA.
Article Review in APA
When you need to compose an article review in the APA format , here is the general bibliographical entry format you should use for journal articles on your reference page:
- Author’s last name, First initial. Middle initial. (Year of Publication). Name of the article. Name of the Journal, volume (number), pp. #-#. https://doi.org/xx.xxx/yyyy
Horigian, V. E., Schmidt, R. D., & Feaster, D. J. (2021). Loneliness, mental health, and substance use among US young adults during COVID-19. Journal of Psychoactive Drugs, 53 (1), pp. 1-9. https://doi.org/10.1080/02791072.2020.1836435
Your in-text citations should follow the author-date format like this:
- If you paraphrase the source and mention the author in the text: According to Horigian et al. (2021), young adults experienced increased levels of loneliness, depression, and anxiety during the pandemic.
- If you paraphrase the source and don’t mention the author in the text: Young adults experienced increased levels of loneliness, depression, and anxiety during the pandemic (Horigian et al., 2021).
- If you quote the source: As Horigian et al. (2021) point out, there were “elevated levels of loneliness, depression, anxiety, alcohol use, and drug use among young adults during COVID-19” (p. 6).
Note that your in-text citations should include “et al.,” as in the examples above, if your article has 3 or more authors. If you have one or two authors, your in-text citations would look like this:
- One author: “According to Smith (2020), depression is…” or “Depression is … (Smith, 2020).”
- Two authors: “According to Smith and Brown (2020), anxiety means…” or “Anxiety means (Smith & Brown, 2020).”
Finally, in case you have to review a book or a website article, here are the general formats for citing these source types on your APA reference list.
Article Review in MLA
If your assignment requires MLA-format referencing, here’s the general format you should use for citing journal articles on your Works Cited page:
- Author’s last name, First name. “Title of an Article.” Title of the Journal , vol. #, no. #, year, pp. #-#.
Horigian, Viviana E., et al. “Loneliness, Mental Health, and Substance Use Among US Young Adults During COVID-19.” Journal of Psychoactive Drugs , vol. 53, no. 1, 2021, pp. 1-9.
In-text citations in the MLA format follow the author-page citation format and look like this:
- According to Horigian et al., young adults experienced increased levels of loneliness, depression, and anxiety during the pandemic (6).
- Young adults experienced increased levels of loneliness, depression, and anxiety during the pandemic (Horigian et al. 6).
Like in APA, the abbreviation “et al.” is only needed in MLA if your article has 3 or more authors.
If you need to cite a book or a website page, here are the general MLA formats for these types of sources.
✅ Article Review Template
Here is a handy, universal article review template to help you move on with any review assignment. We’ve tried to make it as generic as possible to guide you in the academic process.
📝 Article Review Examples
The theory is good, but practice is even better. Thus, we’ve created three brief examples to show you how to write an article review. You can study the full-text samples by following the links.
📃 Men, Women, & Money
This article review examines a famous piece, “Men, Women & Money – How the Sexes Differ with Their Finances,” published by Amy Livingston in 2020. The author of this article claims that men generally spend more money than women. She makes this conclusion from a close analysis of gender-specific expenditures across five main categories: food, clothing, cars, entertainment, and general spending patterns. Livingston also looks at men’s approach to saving to argue that counter to the common perception of women’s light-hearted attitude to money, men are those who spend more on average.
📃 When and Why Nationalism Beats Globalism
This is a review of Jonathan Heidt’s 2016 article titled “When and Why Nationalism Beats Globalism,” written as an advocacy of right-wing populism rising in many Western states. The author illustrates the case with the election of Donald Trump as the US President and the rise of right-wing rhetoric in many Western countries. These examples show how nationalist sentiment represents a reaction to global immigration and a failure of globalization.
📃 Sleep Deprivation
This is a review of the American Heart Association’s article titled “The Dangers of Sleep Deprivation.” It discusses how the national organization concerned with the American population’s cardiovascular health links the lack of high-quality sleep to far-reaching health consequences. The organization’s experts reveal how a consistent lack of sleep leads to Alzheimer’s disease development, obesity, type 2 diabetes, etc.
✏️ Article Review FAQ
A high-quality article review should summarize the assigned article’s content and offer data-backed reactions and evaluations of its quality in terms of the article’s purpose, methodology, and data used to argue the main points. It should be detailed, comprehensive, objective, and evidence-based.
The purpose of writing a review is to allow students to reflect on research quality and showcase their critical thinking and evaluation skills. Students should exhibit their mastery of close reading of research publications and their unbiased assessment.
The content of your article review will be the same in any format, with the only difference in the assignment’s formatting before submission. Ensure you have a separate title page made according to APA standards and cite sources using the parenthetical author-date referencing format.
You need to take a closer look at various dimensions of an assigned article to compose a valuable review. Study the author’s object of analysis, the purpose of their research, the chosen method, data, and findings. Evaluate all these dimensions critically to see whether the author has achieved the initial goals. Finally, offer improvement recommendations to add a critique aspect to your paper.
- Scientific Article Review: Duke University
- Book and Article Reviews: William & Mary, Writing Resources Center
- Sample Format for Reviewing a Journal Article: Boonshoft School of Medicine
- Research Paper Review – Structure and Format Guidelines: New Jersey Institute of Technology
- Article Review: University of Waterloo
- Article Review: University of South Australia
- How to Write a Journal Article Review: University of Newcastle Library Guides
- Writing Help: The Article Review: Central Michigan University Libraries
- Write a Critical Review of a Scientific Journal Article: McLaughlin Library
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to LinkedIn
- Share to email

Short essays answer a specific question on the subject. They usually are anywhere between 250 words and 750 words long. A paper with less than 250 words isn’t considered a finished text, so it doesn’t fall under the category of a short essay. Essays of such format are required for...

High school and college students often face challenges when crafting a compare-and-contrast essay. A well-written paper of this kind needs to be structured appropriately to earn you good grades. Knowing how to organize your ideas allows you to present your ideas in a coherent and logical manner This article by...

If you’re a student, you’ve heard about a formal essay: a factual, research-based paper written in 3rd person. Most students have to produce dozens of them during their educational career. Writing a formal essay may not be the easiest task. But fear not: our custom-writing team is here to guide...

Narrative essays are unlike anything you wrote throughout your academic career. Instead of writing a formal paper, you need to tell a story. Familiar elements such as evidence and arguments are replaced with exposition and character development. The importance of writing an outline for an essay like this is hard...

A précis is a brief synopsis of a written piece. It is used to summarize and analyze a text’s main points. If you need to write a précis for a research paper or the AP Lang exam, you’ve come to the right place. In this comprehensive guide by Custom-Writing.org, you’ll...

A synthesis essay requires you to work with multiple sources. You combine the information gathered from them to present a well-rounded argument on a topic. Are you looking for the ultimate guide on synthesis essay writing? You’ve come to the right place! In this guide by our custom writing team,...

Do you know how to make your essay stand out? One of the easiest ways is to start your introduction with a catchy hook. A hook is a phrase or a sentence that helps to grab the reader’s attention. After reading this article by Custom-Writing.org, you will be able to...

Critical thinking is the process of evaluating and analyzing information. People who use it in everyday life are open to different opinions. They rely on reason and logic when making conclusions about certain issues. A critical thinking essay shows how your thoughts change as you research your topic. This type...

Process analysis is an explanation of how something works or happens. Want to know more? Read the following article prepared by our custom writing specialists and learn about: process analysis and its typesa process analysis outline tipsfree examples and other tips that might be helpful for your college assignment So,...

A visual analysis essay is an academic paper type that history and art students often deal with. It consists of a detailed description of an image or object. It can also include an interpretation or an argument that is supported by visual evidence. In this article, our custom writing experts...

Want to know how to write a reflection paper for college or school? To do that, you need to connect your personal experiences with theoretical knowledge. Usually, students are asked to reflect on a documentary, a text, or their experience. Sometimes one needs to write a paper about a lesson...

A character analysis is an examination of the personalities and actions of protagonists and antagonists that make up a story. It discusses their role in the story, evaluates their traits, and looks at their conflicts and experiences. You might need to write this assignment in school or college. Like any...
Article Review
Article Review Writing: A Complete Step-by-Step Guide with Examples

People also read
Learn How to Write an Editorial on Any Topic
Best Tips on How to Avoid Plagiarism
How to Write a Movie Review - Guide & Examples
A Complete Guide on How to Write a Summary for Students
Write Opinion Essay Like a Pro: A Detailed Guide
Evaluation Essay - Definition, Examples, and Writing Tips
How to Write a Thematic Statement - Tips & Examples
How to Write a Bio - Quick Tips, Structure & Examples
How to Write a Synopsis – A Simple Format & Guide
How to Write a Comparative Essay – A Complete Guide
Visual Analysis Essay - A Writing Guide with Format & Sample
List of Common Social Issues Around the World
Writing Character Analysis - Outline, Steps, and Examples
11 Common Types of Plagiarism Explained Through Examples
A Detailed Guide on How to Write a Poem Step by Step
Detailed Guide on Appendix Writing: With Tips and Examples
Struggling to write a review that people actually want to read? Feeling lost in the details and wondering how to make your analysis stand out?
You're not alone!
Many writers find it tough to navigate the world of article reviews, not sure where to start or how to make their reviews really grab attention.
No worries!
In this blog, we're going to guide you through the process of writing an article review that stands out. We'll also share tips, and examples to make this process easier for you.
Let’s get started.
- 1. What is an Article Review?
- 2. Types of Article Reviews
- 3. Article Review Format
- 4. How to Write an Article Review? 10 Easy Steps
- 5. Article Review Outline
- 6. Article Review Examples
- 7. Tips for Writing an Effective Article Review
What is an Article Review?
An article review is a critical evaluation and analysis of a piece of writing, typically an academic or journalistic article.
It goes beyond summarizing the content; it involves an in-depth examination of the author's ideas, arguments, and methodologies.
The goal is to provide a well-rounded understanding of the article's strengths, weaknesses, and overall contribution to the field.

Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers!
Types of Article Reviews
Article reviews come in various forms, each serving a distinct purpose in the realm of academic or professional discourse. Understanding these types is crucial for tailoring your approach.
Here are some common types of article reviews:
Journal Article Review
A journal article review involves a thorough evaluation of scholarly articles published in academic journals.
It requires summarizing the article's key points, methodology, and findings, emphasizing its contributions to the academic field.
Take a look at the following example to help you understand better.
Example of Journal Article Review
Research Article Review
A research article review focuses on scrutinizing articles with a primary emphasis on research.
This type of review involves evaluating the research design, methodology, results, and their broader implications.
Discussions on the interpretation of results, limitations, and the article's overall contributions are key.
Here is a sample for you to get an idea.
Example of Research Article Review
Science Article Review
A science article review specifically addresses articles within scientific disciplines. It includes summarizing scientific concepts, hypotheses, and experimental methods.
The type of review assesses the reliability of the experimental design, and evaluates the author's interpretation of findings.
Take a look at the following example.
Example of Science Article Review
Critical Review
A critical review involves a balanced critique of a given article. It encompasses providing a comprehensive summary, highlighting key points, and engaging in a critical analysis of strengths and weaknesses.
To get a clearer idea of a critical review, take a look at this example.
Critical Review Example
Article Review Format
When crafting an article review in either APA or MLA format, it's crucial to adhere to the specific guidelines for citing sources.
Below are the bibliographical entries for different types of sources in both APA and MLA styles:
How to Write an Article Review? 10 Easy Steps
Writing an effective article review involves a systematic approach. Follow this step-by-step process to ensure a comprehensive and well-structured analysis.
Step 1: Understand the Assignment
Before diving into the review, carefully read and understand the assignment guidelines.
Pay attention to specific requirements, such as word count, formatting style (APA, MLA), and the aspects your instructor wants you to focus on.
Step 2: Read the Article Thoroughly
Begin by thoroughly reading the article. Take notes on key points, arguments, and evidence presented by the author.
Understand the author's main thesis and the context in which the article was written.
Step 3: Create a Summary
Summarize the main points of the article. Highlight the author's key arguments and findings.
While writing the summary ensure that you capture the essential elements of the article to provide context for your analysis.
Step 4: Identify the Author's Thesis
In this step, pinpoint the author's main thesis or central argument. Understand the purpose of the article and how the author supports their position.
This will serve as a foundation for your critique.
Step 5: Evaluate the Author's Evidence and Methodology
Examine the evidence provided by the author to support their thesis. Assess the reliability and validity of the methodology used.
Consider the sources, data collection methods, and any potential biases.
Step 6: Analyze the Author's Writing Style
Evaluate the author's writing style and how effectively they communicate their ideas.
Consider the clarity of the language, the organization of the content, and the overall persuasiveness of the article.
Step 7: Consider the Article's Contribution
Reflect on the article's contribution to its field of study. Analyze how it fits into the existing literature, its significance, and any potential implications for future research or applications.
Step 8: Write the Introduction
Craft an introduction that includes the article's title, author, publication date, and a brief overview.
State the purpose of your review and your thesis—the main point you'll be analyzing in your review.
Step 9: Develop the Body of the Review
Organize your review by addressing specific aspects such as the author's thesis, methodology, writing style, and the article's contribution.
Use clear paragraphs to structure your analysis logically.
Step 10: Conclude with a Summary and Evaluation
Summarize your main points and restate your overall assessment of the article.
Offer insights into its strengths and weaknesses, and conclude with any recommendations for improvement or suggestions for further research.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
Article Review Outline
Creating a well-organized outline is an essential part of writing a coherent and insightful article review.
This outline given below will guide you through the key sections of your review, ensuring that your analysis is comprehensive and logically structured.
Refer to the following template to understand outlining the article review in detail.
Article Review Format Template
Article Review Examples
Examining article review examples can provide valuable insights into the structure, tone, and depth of analysis expected.
Below are sample article reviews, each illustrating a different approach and focus.
Example of Article Review
Sample of article review assignment pdf
Tips for Writing an Effective Article Review
Crafting an effective article review involves a combination of critical analysis, clarity, and structure.
Here are some valuable tips to guide you through the process:
- Start with a Clear Introduction
Kick off your article review by introducing the article's main points and mentioning the publication date, which you can find on the re-title page. Outline the topics you'll cover in your review.
- Concise Summary with Unanswered Questions
Provide a short summary of the article, emphasizing its main ideas. Highlight any lingering questions, known as "unanswered questions," that the article may have triggered. Use a basic article review template to help structure your thoughts.
- Illustrate with Examples
Use examples from the article to illustrate your points. If there are tables or figures in the article, discuss them to make your review more concrete and easily understandable.
- Organize Clearly with a Summary Section
Keep your review straightforward and well-organized. Begin with the start of the article, express your thoughts on what you liked or didn't like, and conclude with a summary section. This follows a basic plan for clarity.
- Constructive Criticism
When providing criticism, be constructive. If there are elements you don't understand, frame them as "unanswered questions." This approach shows engagement and curiosity.
- Smoothly Connect Your Ideas
Ensure your thoughts flow naturally throughout your review. Use simple words and sentences. If you have questions about the article, let them guide your review organically.
- Revise and Check for Clarity
Before finishing, go through your review. Correct any mistakes and ensure it sounds clear. Check if you followed your plan, used simple words, and incorporated the keywords effectively. This makes your review better and more accessible for others.
In conclusion , writing an effective article review involves a thoughtful balance of summarizing key points, and addressing unanswered questions.
By following a simple and structured approach, you can create a review that not only analyzes the content but also adds value to the reader's understanding.
Remember to organize your thoughts logically, use clear language, and provide examples from the article to support your points.
Ready to elevate your article reviewing skills? Explore the valuable resources and expert assistance at MyPerfectWords.com.
Our team of experienced writers is here to help you with article reviews and other school tasks.
So why wait? Place your " write my essays online " request today!

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Dr. Barbara is a highly experienced writer and author who holds a Ph.D. degree in public health from an Ivy League school. She has worked in the medical field for many years, conducting extensive research on various health topics. Her writing has been featured in several top-tier publications.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading
How to Write an Effective Article Review – Updated 2024 Guide

Purpose of an Article Review
Importance of writing an effective review, read the article thoroughly, identify the main arguments, take notes on key points.
- Evaluate the Author's Credibility
- Assess the Article's Structure and Organization
Examine the Use of Evidence and Examples
Write a concise summary of the article.
- Include the Article's Main Points
Avoid Personal Opinions in the Summary
Identify strengths and weaknesses.
- Evaluate the Article's Logic and Reasoning
- Discuss the Article's Impact and Relevance
Start with an Engaging Introduction
Provide a brief overview of the article.
- Critique the Article's Strengths and Weaknesses
Offer Suggestions for Improvement
Conclude with a summary and recommendation, check for grammar and spelling errors, ensure clarity and coherence of writing, revise for proper formatting and citations, review the overall structure and flow, make final edits and revisions, submit the article review.
Writing an article review can be a challenging task, but it is an essential skill for academics, researchers, and anyone who needs to critically evaluate published work. An article review is a written piece that provides a comprehensive analysis and evaluation of a scholarly article, book, or other published material. It goes beyond a simple summary by offering a critical assessment of the work’s strengths, weaknesses, and overall contribution to the field. In this blog post, we will explore the steps involved in writing an effective article review.
I. Introduction
The primary purpose of an article review is to provide a critical evaluation of a published work. It serves as a means of engaging with the ideas and arguments presented by the author(s) and assessing their validity, significance, and potential impact on the field. An article review allows the reviewer to analyze the work’s merits, identify its limitations, and offer constructive feedback or suggestions for further research or discussion.
Writing an effective article review is crucial for several reasons. First, it demonstrates the reviewer’s ability to critically analyze and synthesize complex information. This skill is highly valued in academic and professional settings, where critical thinking and analytical skills are essential . Second, article reviews contribute to the ongoing scholarly discourse by providing informed perspectives and critiques that can shape future research and discussions. Finally, well-written article reviews can help readers determine whether a particular work is worth reading or exploring further, making them valuable resources for researchers and scholars in the field.
II. Understanding the Article

The first step in writing an article review is to read the article carefully and thoroughly. This may seem obvious, but it is crucial to ensure a comprehensive understanding of the work before attempting to critique it. During the initial reading, focus on grasping the main arguments, key points, and the overall structure of the article. Take note of any unfamiliar concepts, terminology, or references that may require further research or clarification.
As you read the article, pay close attention to the author’s central arguments or thesis statements. Identify the main claims, hypotheses, or research questions that the article attempts to address. Understanding the core arguments is essential for evaluating the effectiveness of the author’s reasoning and the validity of their conclusions.
While reading the article, it is helpful to take notes on the key points, supporting evidence, and any critical or thought-provoking ideas presented by the author(s). These notes will serve as a reference when you begin writing the review and will help you organize your thoughts and critique more effectively.
III. Analyzing the Article
Evaluate the author’s credibility.
When analyzing an article, it is essential to consider the author’s credibility and expertise in the field. Research the author’s background, qualifications, and previous publications to assess their authority on the subject matter. This information can provide valuable context and help you determine the weight and reliability of the arguments presented in the article.
Assess the Article’s Structure and Organization
Evaluate the overall structure and organization of the article. Is the information presented in a logical and coherent manner? Does the article follow a clear progression from introduction to conclusion? Assessing the structure can help you determine whether the author has effectively communicated their ideas and arguments.
Critically examine the evidence and examples used by the author(s) to support their arguments. Are the sources credible and up-to-date? Are the examples relevant and well-chosen? Evaluating the quality and appropriateness of the evidence can help you assess the strength and validity of the author’s claims.
IV. Summarizing the Article
Before delving into your critique, it is essential to provide a concise summary of the article . This summary should briefly outline the article’s main arguments, key points, and conclusions. The goal is to give the reader a clear understanding of the article’s content without adding any personal opinions or critiques at this stage.
Include the Article’s Main Points
In your summary, be sure to include the article’s main points and the evidence or examples used to support them. This will help the reader understand the context and the basis for the author’s arguments, which is crucial for your subsequent critique.
When summarizing the article, it is important to remain objective and avoid injecting personal opinions or critiques. The summary should be a neutral representation of the article’s content, leaving the analysis and evaluation for the critique section.
V. Critiquing the Article

After providing a summary, it is time to analyze and critique the article. Begin by identifying the article’s strengths and weaknesses . Strengths may include well-reasoned arguments, thorough research, innovative ideas, or significant contributions to the field. Weaknesses could include flawed logic, lack of evidence, oversimplification of complex issues, or failure to address counterarguments.
Evaluate the Article’s Logic and Reasoning
Carefully evaluate the author’s logic and reasoning throughout the article. Are the arguments well-supported and logically consistent? Do the conclusions follow naturally from the evidence presented? Identify any logical fallacies, contradictions, or gaps in reasoning that may undermine the author’s arguments.
Discuss the Article’s Impact and Relevance
Consider the article’s potential impact and relevance within the broader context of the field. How does it contribute to existing knowledge or challenge prevailing theories? Does it open up new avenues for research or discussion? Discussing the article’s impact and relevance can help readers understand its significance and importance.
VI. Writing the Article Review

Begin your article review with an engaging introduction that captures the reader’s attention and provides context for the review. Briefly introduce the article, its author(s), and the main topic or research area. You can also include a concise thesis statement that summarizes your overall evaluation or critique of the article.
After the introduction, provide a brief overview or summary of the article. This should be a condensed version of the summary you wrote earlier, highlighting the article’s main arguments, key points, and conclusions. Keep this section concise and focused, as the main critique will follow.
Critique the Article’s Strengths and Weaknesses
In the critique section, present your analysis of the article’s strengths and weaknesses. Discuss the author’s use of evidence, the validity of their arguments, and the overall quality of their reasoning. Support your critique with specific examples and references from the article. Be sure to provide balanced criticism, acknowledging both the positive and negative aspects of the work.
In addition to critiquing the article , consider offering constructive suggestions for improvement. These suggestions could address areas where the author’s arguments were weak or where additional research or discussion is needed. Your suggestions should be specific and actionable, aimed at enhancing the quality and impact of the work.
Conclude your article review by summarizing your main points and providing an overall recommendation or final assessment of the article. This recommendation could be to read or not read the article, to use it as a reference in a specific context, or to consider it as a starting point for further research or discussion.
VII. Editing and Proofreading
After you have completed your initial draft, it is essential to carefully proofread and edit your work. Check for any grammatical errors, spelling mistakes, or typos that may have been overlooked during the writing process. These small errors can detract from the overall quality and professionalism of your review.
In addition to checking for mechanical errors , ensure that your writing is clear, concise, and coherent. Review your sentences and paragraphs for clarity, and make sure that your ideas flow logically from one point to the next. Avoid ambiguous or confusing language that could make your critique difficult to understand.
Depending on the specific requirements or guidelines for your article review, you may need to revise your work to ensure proper formatting and citation styles. Check that you have correctly cited any references or quotes from the article you are reviewing, and that your formatting (e.g., headings, spacing, font) adheres to the specified guidelines.
VIII. Finalizing the Review

Before finalizing your article review , take a step back and review the overall structure and flow of your writing. Ensure that your introduction effectively sets the stage for your critique, and that your body paragraphs logically build upon one another, leading to a well-supported conclusion.
During this final review, consider whether your critique is balanced and objective, presenting both the strengths and weaknesses of the article in a fair and impartial manner. Also, check that you have provided sufficient evidence and examples to support your analysis and that your arguments are clearly articulated.
After reviewing the overall structure and flow, make any necessary final edits and revisions to your article review. This might involve reorganizing or reworking certain sections for better clarity, strengthening your arguments with additional evidence, or refining your writing style for greater impact.
Pay close attention to your choice of words and tone, ensuring that your critique remains respectful and professional, even when addressing the article’s shortcomings. Remember, the goal is to provide a constructive and well-reasoned analysis, not to disparage or attack the author’s work.
Once you are satisfied with your article review, it is time to submit it according to the appropriate guidelines or requirements . This might involve formatting your work in a specific style, adhering to word count or page limits, or following specific submission procedures.
If your article review is intended for publication, be sure to follow the guidelines provided by the journal or publication outlet. This may include submitting your work through an online portal, adhering to specific formatting requirements, or including additional materials such as an abstract or author biography.
Congratulations! By following these steps, you have successfully written a comprehensive and effective article review. Remember, the process of critically evaluating published work is an essential skill that not only demonstrates your ability to analyze and synthesize complex information but also contributes to the ongoing scholarly discourse within your field.
Writing an article review can be a challenging task, but it is a valuable exercise that sharpens your critical thinking, analytical, and communication skills. By carefully reading and understanding the article, assessing its strengths and weaknesses, and providing a well-reasoned critique, you contribute to the advancement of knowledge and foster a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
So, embrace the opportunity to write article reviews, and use each one as a platform to engage with the ideas and arguments presented by scholars and researchers. Your thoughtful and insightful critiques can shape future research, inspire new perspectives, and ultimately drive progress within your field of study.
- RESEARCH PAPER FOR SALE
- RESEARCH PAPER WRITER
- RESEARCH PROPOSAL WRITING SERVICES
- SCHOLARSHIP ESSAY HELP
- SPEECH HELP
- STATISTICS HOMEWORK HELP
- TERM PAPER WRITING HELP
- THESIS EDITING SERVICES
- THESIS PROPOSAL WRITING SERVICE
- TRIGONOMETRY HOMEWORK HELP
- ADMISSION ESSAY WRITING HELP
- BIOLOGY PAPER WRITING SERVICE
- BOOK REPORT WRITING HELP
- BUY BOOK REVIEW
- BUY COURSEWORKS
- BUY DISCUSSION POST
- BUY TERM PAPER
- CAPSTONE PROJECT WRITING SERVICE
- COURSEWORK WRITING SERVICE
- CRITIQUE MY ESSAY
- CUSTOM RESEARCH PAPER
- CUSTOMER CONDUCT
- DISSERTATION EDITING SERVICE
- DISSERTATION WRITERS
- DO MY DISSERTATION FOR ME
- DO MY POWERPOINT PRESENTATION
- EDIT MY PAPER
- English Research Paper Writing Service
- ENGLISH RESEARCH PAPER WRITING SERVICE
- ESSAY WRITING HELP
- ESSAYS FOR SALE
- GRADUATE PAPER WRITING SERVICE
- LAW ASSIGNMENT WRITING HELP
- MARKETING ASSIGNMENT WRITING HELP
- NON-PLAGIARIZED ESSAYS
- NURSING ASSIGNMENT HELP
- PAY FOR COURSEWORK
- PAY FOR ESSAYS
- PAY FOR LITERATURE REVIEW
- PAY FOR PAPERS
- PAY FOR RESEARCH PAPERS
- PERSONAL STATEMENT EDITING SERVICE
- PERSONAL STATEMENT WRITER
- PERSUASIVE ESSAY WRITING HELP
- PERSUASIVE ESSAY WRITING SERVICES
- PHD THESIS WRITING SERVICE
- PROOFREAD MY PAPER
- PSYCHOLOGY ESSAY WRITING SERVICES
- THESIS STATEMENT HELP
- WRITE MY ANNOTATED BIBLIOGRAPHY FOR ME
- WRITE MY CASE STUDY
- WRITE MY DISCUSSION BOARD POST
- WRITE MY LAB REPORT

Get Started
Take the first step and invest in your future.

Online Programs
Offering flexibility & convenience in 51 online degrees & programs.

Prairie Stars
Featuring 15 intercollegiate NCAA Div II athletic teams.

Find your Fit
UIS has over 85 student and 10 greek life organizations, and many volunteer opportunities.

Arts & Culture
Celebrating the arts to create rich cultural experiences on campus.

Give Like a Star
Your generosity helps fuel fundraising for scholarships, programs and new initiatives.

Bragging Rights
UIS was listed No. 1 in Illinois and No. 3 in the Midwest in 2023 rankings.
- Quick links Applicants & Students Important Apps & Links Alumni Faculty and Staff Community Admissions How to Apply Cost & Aid Tuition Calculator Registrar Orientation Visit Campus Academics Register for Class Programs of Study Online Degrees & Programs Graduate Education International Student Services Study Away Student Support Bookstore UIS Life Dining Diversity & Inclusion Get Involved Health & Wellness COVID-19 United in Safety Residence Life Student Life Programs UIS Connection Important Apps UIS Mobile App Advise U Canvas myUIS i-card Balance Pay My Bill - UIS Bursar Self-Service Email Resources Bookstore Box Information Technology Services Library Orbit Policies Webtools Get Connected Area Information Calendar Campus Recreation Departments & Programs (A-Z) Parking UIS Newsroom The Observer Connect & Get Involved Update your Info Alumni Events Alumni Networks & Groups Volunteer Opportunities Alumni Board News & Publications Featured Alumni Alumni News UIS Alumni Magazine Resources Order your Transcripts Give Back Alumni Programs Career Development Services & Support Accessibility Services Campus Services Campus Police Facilities & Services Registrar Faculty & Staff Resources Website Project Request Web Services Training & Tools Academic Impressions Career Connect CSA Reporting Cybersecurity Training Faculty Research FERPA Training Website Login Campus Resources Newsroom Campus Calendar Campus Maps i-Card Human Resources Public Relations Webtools Arts & Events UIS Performing Arts Center Visual Arts Gallery Event Calendar Sangamon Experience Center for Lincoln Studies ECCE Speaker Series Community Engagement Center for State Policy and Leadership Illinois Innocence Project Innovate Springfield Central IL Nonprofit Resource Center NPR Illinois Community Resources Child Protection Training Academy Office of Electronic Media University Archives/IRAD Institute for Illinois Public Finance
Request Info

How to Review a Journal Article

- Request Info Request info for.... Undergraduate/Graduate Online Study Away Continuing & Professional Education International Student Services General Inquiries
For many kinds of assignments, like a literature review , you may be asked to offer a critique or review of a journal article. This is an opportunity for you as a scholar to offer your qualified opinion and evaluation of how another scholar has composed their article, argument, and research. That means you will be expected to go beyond a simple summary of the article and evaluate it on a deeper level. As a college student, this might sound intimidating. However, as you engage with the research process, you are becoming immersed in a particular topic, and your insights about the way that topic is presented are valuable and can contribute to the overall conversation surrounding your topic.
IMPORTANT NOTE!!
Some disciplines, like Criminal Justice, may only want you to summarize the article without including your opinion or evaluation. If your assignment is to summarize the article only, please see our literature review handout.
Before getting started on the critique, it is important to review the article thoroughly and critically. To do this, we recommend take notes, annotating , and reading the article several times before critiquing. As you read, be sure to note important items like the thesis, purpose, research questions, hypotheses, methods, evidence, key findings, major conclusions, tone, and publication information. Depending on your writing context, some of these items may not be applicable.
Questions to Consider
To evaluate a source, consider some of the following questions. They are broken down into different categories, but answering these questions will help you consider what areas to examine. With each category, we recommend identifying the strengths and weaknesses in each since that is a critical part of evaluation.
Evaluating Purpose and Argument
- How well is the purpose made clear in the introduction through background/context and thesis?
- How well does the abstract represent and summarize the article’s major points and argument?
- How well does the objective of the experiment or of the observation fill a need for the field?
- How well is the argument/purpose articulated and discussed throughout the body of the text?
- How well does the discussion maintain cohesion?
Evaluating the Presentation/Organization of Information
- How appropriate and clear is the title of the article?
- Where could the author have benefited from expanding, condensing, or omitting ideas?
- How clear are the author’s statements? Challenge ambiguous statements.
- What underlying assumptions does the author have, and how does this affect the credibility or clarity of their article?
- How objective is the author in his or her discussion of the topic?
- How well does the organization fit the article’s purpose and articulate key goals?
Evaluating Methods
- How appropriate are the study design and methods for the purposes of the study?
- How detailed are the methods being described? Is the author leaving out important steps or considerations?
- Have the procedures been presented in enough detail to enable the reader to duplicate them?
Evaluating Data
- Scan and spot-check calculations. Are the statistical methods appropriate?
- Do you find any content repeated or duplicated?
- How many errors of fact and interpretation does the author include? (You can check on this by looking up the references the author cites).
- What pertinent literature has the author cited, and have they used this literature appropriately?
Following, we have an example of a summary and an evaluation of a research article. Note that in most literature review contexts, the summary and evaluation would be much shorter. This extended example shows the different ways a student can critique and write about an article.
Chik, A. (2012). Digital gameplay for autonomous foreign language learning: Gamers’ and language teachers’ perspectives. In H. Reinders (ed.), Digital games in language learning and teaching (pp. 95-114). Eastbourne, UK: Palgrave Macmillan.
Be sure to include the full citation either in a reference page or near your evaluation if writing an annotated bibliography .
In Chik’s article “Digital Gameplay for Autonomous Foreign Language Learning: Gamers’ and Teachers’ Perspectives”, she explores the ways in which “digital gamers manage gaming and gaming-related activities to assume autonomy in their foreign language learning,” (96) which is presented in contrast to how teachers view the “pedagogical potential” of gaming. The research was described as an “umbrella project” consisting of two parts. The first part examined 34 language teachers’ perspectives who had limited experience with gaming (only five stated they played games regularly) (99). Their data was recorded through a survey, class discussion, and a seven-day gaming trial done by six teachers who recorded their reflections through personal blog posts. The second part explored undergraduate gaming habits of ten Hong Kong students who were regular gamers. Their habits were recorded through language learning histories, videotaped gaming sessions, blog entries of gaming practices, group discussion sessions, stimulated recall sessions on gaming videos, interviews with other gamers, and posts from online discussion forums. The research shows that while students recognize the educational potential of games and have seen benefits of it in their lives, the instructors overall do not see the positive impacts of gaming on foreign language learning.
The summary includes the article’s purpose, methods, results, discussion, and citations when necessary.
This article did a good job representing the undergraduate gamers’ voices through extended quotes and stories. Particularly for the data collection of the undergraduate gamers, there were many opportunities for an in-depth examination of their gaming practices and histories. However, the representation of the teachers in this study was very uneven when compared to the students. Not only were teachers labeled as numbers while the students picked out their own pseudonyms, but also when viewing the data collection, the undergraduate students were more closely examined in comparison to the teachers in the study. While the students have fifteen extended quotes describing their experiences in their research section, the teachers only have two of these instances in their section, which shows just how imbalanced the study is when presenting instructor voices.
Some research methods, like the recorded gaming sessions, were only used with students whereas teachers were only asked to blog about their gaming experiences. This creates a richer narrative for the students while also failing to give instructors the chance to have more nuanced perspectives. This lack of nuance also stems from the emphasis of the non-gamer teachers over the gamer teachers. The non-gamer teachers’ perspectives provide a stark contrast to the undergraduate gamer experiences and fits neatly with the narrative of teachers not valuing gaming as an educational tool. However, the study mentioned five teachers that were regular gamers whose perspectives are left to a short section at the end of the presentation of the teachers’ results. This was an opportunity to give the teacher group a more complex story, and the opportunity was entirely missed.
Additionally, the context of this study was not entirely clear. The instructors were recruited through a master’s level course, but the content of the course and the institution’s background is not discussed. Understanding this context helps us understand the course’s purpose(s) and how those purposes may have influenced the ways in which these teachers interpreted and saw games. It was also unclear how Chik was connected to this masters’ class and to the students. Why these particular teachers and students were recruited was not explicitly defined and also has the potential to skew results in a particular direction.
Overall, I was inclined to agree with the idea that students can benefit from language acquisition through gaming while instructors may not see the instructional value, but I believe the way the research was conducted and portrayed in this article made it very difficult to support Chik’s specific findings.
Some professors like you to begin an evaluation with something positive but isn’t always necessary.
The evaluation is clearly organized and uses transitional phrases when moving to a new topic.
This evaluation includes a summative statement that gives the overall impression of the article at the end, but this can also be placed at the beginning of the evaluation.
This evaluation mainly discusses the representation of data and methods. However, other areas, like organization, are open to critique.
How to Write an Article Review: Practical Tips and Examples
Table of contents
- 1 What Is an Article Review?
- 2 Different Types of Article Review
- 3.1 Critical review
- 3.2 Literature review
- 3.3 Mapping review/systematic map
- 3.4 Meta-analysis
- 3.5 Overview
- 3.6 Qualitative Systematic Review/Qualitative Evidence Synthesis
- 3.7 Rapid review
- 3.8 Scoping review
- 3.9 Systematic review
- 3.10 Umbrella review
- 4 Formatting
- 5 How To Write An Article Review
- 6 Article Review Outline
- 7 10 Tips for Writing an Article Review
- 8 An Article Review Example
What Is an Article Review?
Before you get started, learn what an article review is. It can be defined as a work that combines elements of summary and critical analysis. If you are writing an article review, you should take a close look at another author’s work. Many experts regularly practice evaluating the work of others. The purpose of this is to improve writing skills.
This kind of work belongs to professional pieces of writing because the process of crafting this paper requires reviewing, summarizing, and understanding the topic. Only experts are able to compose really good reviews containing a logical evaluation of a paper as well as a critique.
Your task is not to provide new information. You should process what you have in a certain publication.
Different Types of Article Review
In academic writing, the landscape of article reviews is diverse and nuanced, encompassing a variety of formats that cater to different research purposes and methodologies. Among these, three main types of article reviews stand out due to their distinct approaches and applications:
- Narrative. The basic focus here is the author’s personal experience. Judgments are presented through the prism of experiences and subsequent realizations. Besides, the use of emotional recollections is acceptable.
- Evidence. There is a significant difference from the narrative review. An in-depth study of the subject is assumed, and conclusions are built on arguments. The author may consider theories or concrete facts to support that.
- Systematic. The structure of the piece explains the approach to writing. The answer to what’s a systematic review lies on the surface. The writer should pay special attention to the chronology and logic of the narrative.
Understanding 10 Common Types
Don`t rush looking at meta-analysis vs. systematic review. We recommend that you familiarize yourself with other formats and topics of texts. This will allow you to understand the types of essays better and select them based on your request. For this purpose, we`ll discuss the typology of reviews below.
Critical review
The critical review definition says that the author must be objective and have arguments for each thought. Sometimes, amateur authors believe that they should “criticize” something. However, it is important to understand the difference since objectivity and the absence of emotional judgments are prioritized. The structure of this type of review article is as follows:
- Introduction;
- Conclusion.
“Stuffing” of the text is based on such elements as methodology, argumentation, evidence, and theory base. The subject of study is stated at the beginning of the material. Then follows the transition to the main part (facts). The final word summarizes all the information voiced earlier.
It is a mistake to believe that critical reviews are devoid of evaluation. The author’s art lies in maneuvering between facts. Smooth transition from one argument to another and lays out the conclusions in the reader. That is why such texts are used in science. The critical reviews meaning is especially tangible in medical topics.
Literature review
Literature is the basis for this type of work ─ books, essays, and articles become a source of information. Thus, the author should rethink the voiced information. After that, it is possible to proceed to conclusions. The methodology aims to find interconnections, repetitions, and even “gaps” in the literature. One important item is the referencing of sources. Footnotes are possible in the work itself or the list of resources used.
These types of research reviews often explore myths since there are often inconsistencies in mythology. Sometimes, there is contrary information. In this case, the author has to gather all existing theories. The essence does not always lie in the confirmation of facts. There are other different types of reviews for this purpose. In literary reviews, the object of study may be characters or traditions. This is where the author’s space for discovery opens up. Inconsistencies in the data can tell important details about particular periods or cultures. At the same time, patterns reveal well-established facts. Make sure to outline your work before you write. This will help you with essay writing .
Mapping review/systematic map
A mapping review, also known as a systematic map, is a unique approach to surveying and organizing existing literature, providing a panoramic view of the research landscape. This paper systematically categorizes and maps out the available literature on a particular topic, emphasizing breadth over depth. Its primary goal is to present a comprehensive visual representation of the research distribution, offering insights into the overall scope of a subject.
One of the strengths of systematic reviews is that they deeply focus on a research question with detailed analysis and synthesis, while mapping review prioritizes breadth. It identifies and categorizes a broad range of studies without necessarily providing in-depth critique or content synthesis. This approach allows for a broader understanding of the field, making it especially useful in the early stages of research. Mapping reviews excel in identifying gaps in the existing body of literature.
By systematically mapping the distribution of research, researchers can pinpoint areas where studies are scarce or nonexistent, helping to guide future research directions. This makes mapping reviews a valuable tool for researchers seeking to contribute meaningfully to a field by addressing unexplored or underexplored areas.
Meta-analysis
Meta-analysis is a powerful statistical technique. It systematically combines the results of multiple studies to derive comprehensive and nuanced insights. This method goes beyond the limitations of individual studies, offering a more robust understanding of a particular phenomenon by synthesizing data from diverse sources.
Meta-analysis employs a rigorous methodology. It involves the systematic collection and statistical integration of data from multiple studies. This methodological rigor ensures a standardized and unbiased approach to data synthesis. It is applied across various disciplines, from medicine and psychology to social sciences, providing a quantitative assessment of the overall effect of an intervention or the strength of an association.
In evidence-based fields, where informed decision-making relies on a thorough understanding of existing research, meta-analysis plays a pivotal role. It offers a quantitative overview of the collective evidence, helping researchers, policymakers, and practitioners make more informed decisions. By synthesizing results from diverse studies, meta-analysis contributes to the establishment of robust evidence-based practices, enhancing the reliability and credibility of findings in various fields. To present your research findings in the most readable way possible, learn how to write a summary of article .
If the key purpose of systematic review is to maximize the disclosure of facts, the opposite is true here. Imagine a video shot by a quadcopter from an altitude. The viewer sees a vast area of terrain without focusing on individual details. Overviews follow the same principle. The author gives a general picture of the events or objects described.
These types of reviews often seem simple. However, the role of the researcher becomes a very demanding one. The point is not just to list facts. Here, the search for information comes to the fore. After all, it is such reports that, in the future, will provide the basis for researching issues more narrowly. In essence, you yourself create a new source of information ─ students who worry that somebody may critique the author’s article love this type of material. However, there are no questions for the author; they just set the stage for discussions in different fields.
An example of this type of report would be a collection of research results from scientists. For example, statistics on the treatment of patients with certain diseases. In such a case, reference is made to scientific articles and doctrines. Based on this information, readers can speak about the effectiveness of certain treatment methods.
Qualitative Systematic Review/Qualitative Evidence Synthesis
One of the next types of review articles represents a meticulous effort to synthesize and analyze qualitative studies within a specific research domain.
The focus is synthesizing qualitative studies, employing a systematic and rigorous approach to extract meaningful insights. Its significance lies in its ability to provide a nuanced understanding of complex phenomena, offering a qualitative lens to complement quantitative analyses. Researchers can uncover patterns, themes, and contextual nuances that may elude traditional quantitative approaches by systematically reviewing and synthesizing qualitative data.
Often, you may meet discussion: is a systematic review quantitative or qualitative? The application of qualitative systematic reviews extends across diverse research domains, from healthcare and social sciences to education and psychology. For example, this approach can offer a comprehensive understanding of patient experiences and preferences in healthcare. In social sciences, it can illuminate cultural or societal dynamics. Its versatility makes it a valuable tool for researchers exploring, interpreting, and integrating qualitative findings to enrich their understanding of complex phenomena within their respective fields.
Rapid review
If you don’t know how to write an article review , try starting with this format. It is the complete opposite of everything we talked about above. The key advantage and feature is speed. Quick overviews are used when time is limited. The focus can go to individual details (key). Often, the focus is still on the principal points.
Often, these types of review papers are critically needed in politics. This method helps to communicate important information to the reader quickly. An example can be a comparison of the election programs of two politicians. The author can show the key differences. Or it can make an overview based on the theses of the opponents’ proposals on different topics.
Seeming simplicity becomes power. Such texts allow the reader to make a quick decision. The author’s task is to understand potential interests and needs. Then, highlight and present the most important data as concisely as possible. In addition to politics, such reports are often used in communications, advertising, and marketing. Experienced writers mention the one-minute principle. This means you can count on 60 seconds of the reader’s attention. If you managed to hook them ─ bravo, you have done the job!
Scoping review
If you read the official scoping review definition, you may find similarities with the systematic type of review. However, recall is a sequential and logical study in the second case. It’s like you stack things on a shelf by color, size, and texture.
This type of review can be more difficult to understand. The basic concept is to explore what is called the field of subjects. This means, on the one hand, exploring a particular topic through the existing data about it. The author tries to find gaps or patterns by drawing on sources of information.
Another good comparison between systematic and this type of review is imagining as if drawing a picture. In the first case, you will think through every nuance and detail, why it is there, and how it “moves the story.” In the second case, it is as if you are painting a picture with “broad strokes.” In doing so, you can explain your motives for choosing the primary color. For example: “I chose the emerald color because all the cultural publications say it’s a trend”. The same goes for texts.
Systematic review
Sometimes, you may encounter a battle: narrative review vs. systematic review. The point is not to compare but to understand the different types of papers. Once you understand their purpose, you can present your data better and choose a more readable format. The systematic approach can be called the most scientific. Such a review relies on the following steps:
- Literature search;
- Evaluating the information;
- Data processing;
- Careful analysis of the material.
It is the fourth point that is key. The writer should carefully process the information before using it. However, 80% of your work’s result depends on this stage’s seriousness.
A rigorous approach to data selection produces an array of factual data. That is why this method is so often used in science, education, and social fields. Where accuracy is important. At the same time, the popularity of this approach is growing in other directions.
Systematic reviews allow for using different data and methodologies,, but with one important caveat ─ if the author manages to keep the narrative structured and explain the reason for certain methods. It is not about rigor. The task of this type of review is to preserve the facts, which dictates consistency and rationality.
Umbrella review
An umbrella review is a distinctive approach that involves the review of existing reviews, providing a comprehensive synthesis of evidence on a specific topic. The methodology of an umbrella review entails systematically examining and summarizing findings from multiple systematic reviews and meta-analyses.
This method ensures a rigorous and consolidated analysis of the existing evidence. The application of an umbrella review is broad, spanning various fields such as medicine, public health, and social sciences. It is particularly useful when a substantial body of systematic reviews exists, allowing researchers to draw overarching conclusions from the collective findings.
It allows the summarization of existing reviews and provides a new perspective on individual subtopics of the main object of study. In the context of the umbrella method, the comparison “bird’s eye view” is often cited. A bird in flight can see the whole panorama and shift its gaze to specific objects simultaneously. What becomes relevant at a particular moment? The author will face the same task.
On the one hand, you must delve into the offshoots of the researched topic. On the other hand, focus on the topic or object of study as a whole. Such a concept allows you to open up new perspectives and thoughts.

Different types of formatting styles are used for article review writing. It mainly depends on the guidelines that are provided by the instructor, sometimes, professors even provide an article review template that needs to be followed.
Here are some common types of formatting styles that you should be aware of when you start writing an article review:
- APA (American Psychological Association) – An APA format article review is commonly used for social sciences. It has guidelines for formatting the title, abstract, body paragraphs, and references. For example, the title of an article in APA format is in sentence case, whereas the publication title is in title case.
- MLA (Modern Language Association): This is a formatting style often used in humanities, such as language studies and literature. There are specific guidelines for the formatting of the title page, header, footer, and citation style.
- Chicago Manual of Style: This is one of the most commonly used formatting styles. It is often used for subjects in humanities and social sciences, but also commonly found in a newspaper title. This includes guidelines for formatting the title page, end notes, footnotes, publication title, article citation, and bibliography.
- Harvard Style: Harvard style is commonly used for social sciences and provides specific guidelines for formatting different sections of the pages, including publication title, summary page, website publisher, and more.
To ensure that your article review paper is properly formatted and meets the requirements, it is crucial to adhere to the specific guidelines for the formatting style you are using. This helps you write a good article review.
- Free unlimited checks
- All common file formats
- Accurate results
- Intuitive interface
How To Write An Article Review
There are several steps that must be followed when you are starting to review articles. You need to follow these to make sure that your thoughts are organized properly. In this way, you can present your ideas in a more concise and clear manner. Here are some tips on how to start an article review and how to cater to each writing stage.
- Read the Article Closely: Even before you start to write an article review, it’s important to make sure that you have read the specific article thoroughly. Write down the central points and all the supporting ideas. It’s important also to note any questions or comments that you have about the content.
- Identify the Thesis: Make sure that you understand the author’s main points, and identify the main thesis of the article. This will help you focus on your review and ensure that you are addressing all of the key points.
- Formulate an Introduction: The piece should start with an introduction that has all the necessary background information, possibly in the first paragraph or in the first few paragraphs. This can include a brief summary of the important points or an explanation of the importance.
- Summarize the Article : Summarize the main points when you review the article, and make sure that you include all supporting elements of the author’s thesis.
- Start with Personal Critique : Now is the time to include a personal opinion on the research article or the journal article review. Start with evaluating all the strengths and weaknesses of the reviewed article. Discuss all of the flaws that you found in the author’s evidence and reasoning. Also, point out whether the conclusion provided by the author was well presented or not.
- Add Personal Perspective: Offer your perspective on the original article, do you agree or disagree with the ideas that the article supports or not. Your critical review, in your own words, is an essential part of a good review. Make sure you address all unanswered questions in your review.
- Conclude the Article Review : In this section of the writing process, you need to be very careful and wrap up the whole discussion in a coherent manner. This is should summarize all the main points and offer an overall assessment.
Make sure to stay impartial and provide proof to back up your assessment. By adhering to these guidelines, you can create a reflective and well-structured article review.
Article Review Outline
Here is a basic, detailed outline for an article review you should be aware of as a pre-writing process if you are wondering how to write an article review.
Introduction
- Introduce the article that you are reviewing (author name, publication date, title, etc.) Now provide an overview of the article’s main topic
Summary section
- Summarize the key points in the article as well as any arguments Identify the findings and conclusion
Critical Review
- Assess and evaluate the positive aspects and the drawbacks
- Discuss if the authors arguments were verified by the evidence of the article
- Identify if the text provides substantial information for any future paper or further research
- Assess any gaps in the arguments
- Restate the thesis statement
- Provide a summary for all sections
- Write any recommendations and thoughts that you have on the article
- Never forget to add and cite any references that you used in your article
10 Tips for Writing an Article Review
Have you ever written such an assignment? If not, study the helpful tips for composing a paper. If you follow the recommendations provided here, the process of writing a summary of the article won’t be so time-consuming, and you will be able to write an article in the most effective manner.
The guidelines below will help to make the process of preparing a paper much more productive. Let’s get started!
- Check what kind of information your work should contain. After answering the key question “What is an article review?” you should learn how to structure it the right way. To succeed, you need to know what your work should be based on. An analysis with insightful observations is a must for your piece of writing.
- Identify the central idea: In your first reading, focus on the overall impression. Gather ideas about what the writer wants to tell, and consider whether he or she managed to achieve it.
- Look up unfamiliar terms. Don’t know what certain words and expressions mean? Highlight them, and don’t forget to check what they mean with a reliable source of information.
- Highlight the most important ideas. If you are reading it a second time, use a highlighter to highlight the points that are most important to understanding the passage.
- Write an outline. A well-written outline will make your life a lot easier. All your thoughts will be grouped. Detailed planning helps not to miss anything important. Think about the questions you should answer when writing.
- Brainstorm headline ideas. When choosing a project, remember: it should reflect the main idea. Make it bold and concise.
- Check an article review format example. You should check that you know how to cite an article properly. Note that citation rules are different in APA and MLA formats. Ask your teacher which one to prioritize.
- Write a good introduction. Use only one short paragraph to state the central idea of the work. Emphasize the author’s key concepts and arguments. Add the thesis at the end of the Introduction.
- Write in a formal style. Use the third person, remembering that this assignment should be written in a formal academic writing style.
- Wrap up, offer your critique, and close. Give your opinion on whether the author achieved his goals. Mention the shortcomings of the job, if any, and highlight its strengths.
If you have checked the tips and you still doubt whether you have all the necessary skills and time to prepare this kind of educational work, follow one more tip that guarantees 100% success- ask for professional assistance by asking the custom writing service PapersOwl to craft your paper instead of you. Just submit an order online and get the paper completed by experts.

An Article Review Example
If you have a task to prepare an analysis of a certain piece of literature, have a look at the article review sample. There is an article review example for you to have a clear picture of what it must look like.
Journal Article on Ayn Rand’s Works Review Example
“The purpose of the article is to consider the features of the poetics of Ayn Rand’s novels “Atlas Shrugged,” “We the living,” and “The Fountainhead.” In the analysis of the novels, the structural-semantic and the method of comparative analysis were used.
With the help of these methods, genre features of the novels were revealed, and a single conflict and a cyclic hero were identified.
In-depth reading allows us to more fully reveal the worldview of the author reflected in the novels. It becomes easier to understand the essence of the author’s ideas about the connection between being and consciousness, embodied in cyclic ideas and images of plot twists and heroes. The author did a good job highlighting the strong points of the works and mentioning the reasons for the obvious success of Ayn Rand.“
You can also search for other relevant article review examples before you start.
In conclusion, article reviews play an important role in evaluating and analyzing different scholarly articles. Writing a review requires critical thinking skills and a deep understanding of the article’s content, style, and structure. It is crucial to identify the type of article review and follow the specific guidelines for formatting style provided by the instructor or professor.
The process of writing an article review requires several steps, such as reading the article attentively, identifying the thesis, and formulating an introduction. By following the tips and examples provided in this article, students can write a worthy review that demonstrates their ability to evaluate and critique another writer’s work.
Learning how to write an article review is a critical skill for students and professionals alike. Before diving into the nitty-gritty of reviewing an article, it’s important to understand what an article review is and the elements it should include. An article review is an assessment of a piece of writing that summarizes and evaluates a work. To complete a quality article review, the author should consider the text’s purpose and content, its organization, the author’s style, and how the article fits into a larger conversation. But if you don’t have the time to do all of this work, you can always purchase a literature review from Papers Owl .
Readers also enjoyed

WHY WAIT? PLACE AN ORDER RIGHT NOW!
Just fill out the form, press the button, and have no worries!
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy.
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- CAREER FEATURE
- 04 December 2020
- Correction 09 December 2020
How to write a superb literature review
Andy Tay is a freelance writer based in Singapore.
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Literature reviews are important resources for scientists. They provide historical context for a field while offering opinions on its future trajectory. Creating them can provide inspiration for one’s own research, as well as some practice in writing. But few scientists are trained in how to write a review — or in what constitutes an excellent one. Even picking the appropriate software to use can be an involved decision (see ‘Tools and techniques’). So Nature asked editors and working scientists with well-cited reviews for their tips.
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
24,99 € / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
185,98 € per year
only 3,65 € per issue
Rent or buy this article
Prices vary by article type
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-020-03422-x
Interviews have been edited for length and clarity.
Updates & Corrections
Correction 09 December 2020 : An earlier version of the tables in this article included some incorrect details about the programs Zotero, Endnote and Manubot. These have now been corrected.
Hsing, I.-M., Xu, Y. & Zhao, W. Electroanalysis 19 , 755–768 (2007).
Article Google Scholar
Ledesma, H. A. et al. Nature Nanotechnol. 14 , 645–657 (2019).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Brahlek, M., Koirala, N., Bansal, N. & Oh, S. Solid State Commun. 215–216 , 54–62 (2015).
Choi, Y. & Lee, S. Y. Nature Rev. Chem . https://doi.org/10.1038/s41570-020-00221-w (2020).
Download references
Related Articles

- Research management

Researcher parents are paying a high price for conference travel — here’s how to fix it
Career Column 27 MAY 24

How researchers in remote regions handle the isolation
Career Feature 24 MAY 24

What steps to take when funding starts to run out

Guidelines for academics aim to lessen ethical pitfalls in generative-AI use
Nature Index 22 MAY 24
Who will make AlphaFold3 open source? Scientists race to crack AI model
News 23 MAY 24

Egypt is building a $1-billion mega-museum. Will it bring Egyptology home?
News Feature 22 MAY 24

Pay researchers to spot errors in published papers
World View 21 MAY 24
Sir Run Run Shaw Hospital, School of Medicine, Zhejiang University, Warmly Welcomes Talents Abroad
“Qiushi” Distinguished Scholar, Zhejiang University, including Professor and Physician
No. 3, Qingchun East Road, Hangzhou, Zhejiang (CN)
Sir Run Run Shaw Hospital Affiliated with Zhejiang University School of Medicine

Associate Editor, Nature Briefing
Associate Editor, Nature Briefing Permanent, full time Location: London, UK Closing date: 10th June 2024 Nature, the world’s most authoritative s...
London (Central), London (Greater) (GB)
Springer Nature Ltd
Professor, Division Director, Translational and Clinical Pharmacology
Cincinnati Children’s seeks a director of the Division of Translational and Clinical Pharmacology.
Cincinnati, Ohio
Cincinnati Children's Hospital & Medical Center
Data Analyst for Gene Regulation as an Academic Functional Specialist
The Rheinische Friedrich-Wilhelms-Universität Bonn is an international research university with a broad spectrum of subjects. With 200 years of his...
53113, Bonn (DE)
Rheinische Friedrich-Wilhelms-Universität
Recruitment of Global Talent at the Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (IOZ, CAS)
The Institute of Zoology (IOZ), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), is seeking global talents around the world.
Beijing, China
Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (IOZ, CAS)
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you’re on board with our cookie policy

- A Research Guide
- Writing Guide
- Article Writing
How To Write an Article Review
- Definition of article review
- Why do students write article reviews
- Types of article review
- Structure and outline
- Step-by-step guide
Article review format
- How to write a good article review
- Article review examples
Definition of article review assignments
Why do students write article reviews.
- Article writing is a deeply analytical process that helps students to correct vague terms when and if they are present. Likewise, when composing an article review or an original assignment, such work provides more clarity regarding using appropriate words. If an article has colloquial language or logical gaps, it is one of those aspects to mention in an article review. It also allows writers to determine whether certain terms must be replaced and edited.
- Article review essay writing helps to clarify scientific questions.
- Writing an article review allows students to see and understand how others approach specific issues and what perspectives should be studied regarding the problems at hand. Once a person reads the review, it makes it easier to get rid of bias.
- Article review assignments also provide students with editing and grammar work to help with more accurate papers.
- Most importantly, an article review is a way to encourage better work and provide critical analysis with due criticism and evaluation of the original article.
Types of article review tasks
- Original Research Article Review. The original research article review is close to what is often seen as the literature review. An author must explore the author’s hypothesis and some background studies with due analysis to outline scientific methods. It’s one of the most challenging tasks to write as one must interpret the findings and talk about future implications. This type of work can also get lengthy and be up to 6,000 words in subjects like History or Sociology.
- Critical Analysis. As the name implies, it critically evaluates the author’s work and can be up to 3,000 words.
- Literature Review. It stands for the review of secondary literature sources. As a rule, such reviews do not present much new data and only evaluate the importance of sources and information that supports the author’s arguments.
- Systematic Review. This case stands for research questions and articles that require a deeper synthesis of available facts or certain evidence. The purpose here is to define and evaluate the quality of the data obtained by the author.
- Meta-Analysis Reviews. Once again, it is a systematic review focusing on a specific topic, the literature issues. You must provide a special quantitative estimate for exposure and intervention.
- Clinical Trial Reviews. It means that one must provide a study related to an investigation offered by the author. It can relate to a drug or talk about a sample group of people, thus bringing it into the field of a defined population or a group of participants.
- Perspective or Opinion Article Review. This is where one poses an opinion, meaning things can get biased toward a certain opinion. In writing a good review, a student can look for perspectives and evaluate the importance of the original article. Likewise, posing an opinion is one of the obligatory aspects.
Article review structure and outline
Article review structure.
- Title page.
- An article introduction presenting the main subject and/or a problem.
- Brief article summary.
- Critical article evaluation and/or a summary.
- Conclusion with the moral lesson and discussion on the findings’ pros/cons.
- Bibliography with relevant citations.
Article review outline
- You provide an evaluation and summary of the author’s article.
- Your audience can receive sufficient knowledge regarding the subject.
- You have made points about the strongest arguments of the author.
- You have criticized the author’s work and explained how it contributes to the scientific field.
- You conclude your article review with your original thoughts and opinions without turning to additional research unless the grading rubric required it.
Step-by-step writing guide
Step 1: learn about the article’s agenda., step 2: summarize the main article ideas, step 3: organization aspect of the review, step 4: article preview and take notes, step 5: paraphrasing and analysis, step 6: final evaluation.

- An introduction. The topic of your study must be mentioned here in the first sentence. Indicate what your article contains and talk about the author’s background. Provide an order of the subjects you plan to discuss to explain what your readers expect. The introduction should provide the author’s claims and the main arguments that result in your thesis statement. When writing an introduction, you must determine the main argument.
- Body paragraphs. This is where you provide an evaluation with a summary and write about the author’s work.
- Conclusion. Speak of your reasons for providing a review and talk about whether you could support your thesis and what you have learned.
- Works Cited page. Refer to your grading rubric to identify what citation style must be used.
How to write a good article review?
- Do not write the statements in the first person. It is recommended to use the third person instead by turning to a formal academic tone.
- Your introduction with the information about the original article should take from 10 to 25% of your assignment’s volume.
- An introduction must end with a strong thesis and make an assumption or research the author’s main claim. A typical thesis to start an article review for an assignment may look this way:
- Write down all the important points and share your findings. It will help to show that you have done your homework correctly.
- Discuss how the article supports the claims and whether it provides good evidence.
- Always provide background information about the author.
- Use direct quotes to support your claims by turning to the original article.
- Read your summary twice to evaluate whether it follows the main thesis.
- Talk about the contributions of the author to the academic community.
- Provide reasons for whether you support the author’s view or not. Why or why not?
- Summarize all the important points in a conclusion part.
Why choose article review examples?
- Wright State University’s Journal Article Review Example .
- University of Illinois Springfield’s Article How-to Review Guide .
- UC Merced Library’s Article Review Sample
- Identify recent and important changes in your field of study.
- Determine who works in a specific field of science and why.
- Narrow things down and identify essential information to help you start with research.
- Use obtained information in school debates, and references work.
- Generate new ideas and conduct lab experiments.
- Write an article review through the lens of personal experience and expertise.

Receive paper in 3 Hours!
- Choose the number of pages.
- Select your deadline.
- Complete your order.
Number of Pages
550 words (double spaced)
Deadline: 10 days left
By clicking "Log In", you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We'll occasionally send you account related and promo emails.
Sign Up for your FREE account
How to Write Critical Reviews
When you are asked to write a critical review of a book or article, you will need to identify, summarize, and evaluate the ideas and information the author has presented. In other words, you will be examining another person’s thoughts on a topic from your point of view.
Your stand must go beyond your “gut reaction” to the work and be based on your knowledge (readings, lecture, experience) of the topic as well as on factors such as criteria stated in your assignment or discussed by you and your instructor.
Make your stand clear at the beginning of your review, in your evaluations of specific parts, and in your concluding commentary.
Remember that your goal should be to make a few key points about the book or article, not to discuss everything the author writes.
Understanding the Assignment
To write a good critical review, you will have to engage in the mental processes of analyzing (taking apart) the work–deciding what its major components are and determining how these parts (i.e., paragraphs, sections, or chapters) contribute to the work as a whole.
Analyzing the work will help you focus on how and why the author makes certain points and prevent you from merely summarizing what the author says. Assuming the role of an analytical reader will also help you to determine whether or not the author fulfills the stated purpose of the book or article and enhances your understanding or knowledge of a particular topic.
Be sure to read your assignment thoroughly before you read the article or book. Your instructor may have included specific guidelines for you to follow. Keeping these guidelines in mind as you read the article or book can really help you write your paper!
Also, note where the work connects with what you’ve studied in the course. You can make the most efficient use of your reading and notetaking time if you are an active reader; that is, keep relevant questions in mind and jot down page numbers as well as your responses to ideas that appear to be significant as you read.
Please note: The length of your introduction and overview, the number of points you choose to review, and the length of your conclusion should be proportionate to the page limit stated in your assignment and should reflect the complexity of the material being reviewed as well as the expectations of your reader.
Write the introduction
Below are a few guidelines to help you write the introduction to your critical review.
Introduce your review appropriately
Begin your review with an introduction appropriate to your assignment.
If your assignment asks you to review only one book and not to use outside sources, your introduction will focus on identifying the author, the title, the main topic or issue presented in the book, and the author’s purpose in writing the book.
If your assignment asks you to review the book as it relates to issues or themes discussed in the course, or to review two or more books on the same topic, your introduction must also encompass those expectations.
Explain relationships
For example, before you can review two books on a topic, you must explain to your reader in your introduction how they are related to one another.
Within this shared context (or under this “umbrella”) you can then review comparable aspects of both books, pointing out where the authors agree and differ.
In other words, the more complicated your assignment is, the more your introduction must accomplish.
Finally, the introduction to a book review is always the place for you to establish your position as the reviewer (your thesis about the author’s thesis).
As you write, consider the following questions:
- Is the book a memoir, a treatise, a collection of facts, an extended argument, etc.? Is the article a documentary, a write-up of primary research, a position paper, etc.?
- Who is the author? What does the preface or foreword tell you about the author’s purpose, background, and credentials? What is the author’s approach to the topic (as a journalist? a historian? a researcher?)?
- What is the main topic or problem addressed? How does the work relate to a discipline, to a profession, to a particular audience, or to other works on the topic?
- What is your critical evaluation of the work (your thesis)? Why have you taken that position? What criteria are you basing your position on?
Provide an overview
In your introduction, you will also want to provide an overview. An overview supplies your reader with certain general information not appropriate for including in the introduction but necessary to understanding the body of the review.
Generally, an overview describes your book’s division into chapters, sections, or points of discussion. An overview may also include background information about the topic, about your stand, or about the criteria you will use for evaluation.
The overview and the introduction work together to provide a comprehensive beginning for (a “springboard” into) your review.
- What are the author’s basic premises? What issues are raised, or what themes emerge? What situation (i.e., racism on college campuses) provides a basis for the author’s assertions?
- How informed is my reader? What background information is relevant to the entire book and should be placed here rather than in a body paragraph?
Write the body
The body is the center of your paper, where you draw out your main arguments. Below are some guidelines to help you write it.
Organize using a logical plan
Organize the body of your review according to a logical plan. Here are two options:
- First, summarize, in a series of paragraphs, those major points from the book that you plan to discuss; incorporating each major point into a topic sentence for a paragraph is an effective organizational strategy. Second, discuss and evaluate these points in a following group of paragraphs. (There are two dangers lurking in this pattern–you may allot too many paragraphs to summary and too few to evaluation, or you may re-summarize too many points from the book in your evaluation section.)
- Alternatively, you can summarize and evaluate the major points you have chosen from the book in a point-by-point schema. That means you will discuss and evaluate point one within the same paragraph (or in several if the point is significant and warrants extended discussion) before you summarize and evaluate point two, point three, etc., moving in a logical sequence from point to point to point. Here again, it is effective to use the topic sentence of each paragraph to identify the point from the book that you plan to summarize or evaluate.
Questions to keep in mind as you write
With either organizational pattern, consider the following questions:
- What are the author’s most important points? How do these relate to one another? (Make relationships clear by using transitions: “In contrast,” an equally strong argument,” “moreover,” “a final conclusion,” etc.).
- What types of evidence or information does the author present to support his or her points? Is this evidence convincing, controversial, factual, one-sided, etc.? (Consider the use of primary historical material, case studies, narratives, recent scientific findings, statistics.)
- Where does the author do a good job of conveying factual material as well as personal perspective? Where does the author fail to do so? If solutions to a problem are offered, are they believable, misguided, or promising?
- Which parts of the work (particular arguments, descriptions, chapters, etc.) are most effective and which parts are least effective? Why?
- Where (if at all) does the author convey personal prejudice, support illogical relationships, or present evidence out of its appropriate context?
Keep your opinions distinct and cite your sources
Remember, as you discuss the author’s major points, be sure to distinguish consistently between the author’s opinions and your own.
Keep the summary portions of your discussion concise, remembering that your task as a reviewer is to re-see the author’s work, not to re-tell it.
And, importantly, if you refer to ideas from other books and articles or from lecture and course materials, always document your sources, or else you might wander into the realm of plagiarism.
Include only that material which has relevance for your review and use direct quotations sparingly. The Writing Center has other handouts to help you paraphrase text and introduce quotations.
Write the conclusion
You will want to use the conclusion to state your overall critical evaluation.
You have already discussed the major points the author makes, examined how the author supports arguments, and evaluated the quality or effectiveness of specific aspects of the book or article.
Now you must make an evaluation of the work as a whole, determining such things as whether or not the author achieves the stated or implied purpose and if the work makes a significant contribution to an existing body of knowledge.
Consider the following questions:
- Is the work appropriately subjective or objective according to the author’s purpose?
- How well does the work maintain its stated or implied focus? Does the author present extraneous material? Does the author exclude or ignore relevant information?
- How well has the author achieved the overall purpose of the book or article? What contribution does the work make to an existing body of knowledge or to a specific group of readers? Can you justify the use of this work in a particular course?
- What is the most important final comment you wish to make about the book or article? Do you have any suggestions for the direction of future research in the area? What has reading this work done for you or demonstrated to you?

Academic and Professional Writing
This is an accordion element with a series of buttons that open and close related content panels.
Analysis Papers
Reading Poetry
A Short Guide to Close Reading for Literary Analysis
Using Literary Quotations
Play Reviews
Writing a Rhetorical Précis to Analyze Nonfiction Texts
Incorporating Interview Data
Grant Proposals
Planning and Writing a Grant Proposal: The Basics
Additional Resources for Grants and Proposal Writing
Job Materials and Application Essays
Writing Personal Statements for Ph.D. Programs
- Before you begin: useful tips for writing your essay
- Guided brainstorming exercises
- Get more help with your essay
- Frequently Asked Questions
Resume Writing Tips
CV Writing Tips
Cover Letters
Business Letters
Proposals and Dissertations
Resources for Proposal Writers
Resources for Dissertators
Research Papers
Planning and Writing Research Papers
Quoting and Paraphrasing
Writing Annotated Bibliographies
Creating Poster Presentations
Writing an Abstract for Your Research Paper
Thank-You Notes
Advice for Students Writing Thank-You Notes to Donors
Reading for a Review
Critical Reviews
Writing a Review of Literature
Scientific Reports
Scientific Report Format
Sample Lab Assignment
Writing for the Web
Writing an Effective Blog Post
Writing for Social Media: A Guide for Academics
How to Write an Article Review: Tips, Outline, Format

Have you been assigned an article review paper, but you are unsure where to start, or what is a review article at all? There is no need to worry, as EssayService has put together a top guide for you! Find out all about an article review to master your assignment.
What is an Article Review?
In simple terms, an article review essay is like a summary and evaluation of another professional or expert's work. It may also be referred to as a literature review that includes an outline of the most recent research on the subject, or a critical review that focuses on a specific article with smaller scope. Article review can be used for many reasons; for example, a teacher or lecturer may wish to introduce their students to a new subject by reviewing a professional's piece. You can also learn about the most important works of specialists in your industry by looking at relevant article review examples.
Also, a newspaper article review example could be a journalist writing a critique about another competitor's published work.
In comparison, a book review article example could be critiqued by a fellow author or even a student in the chosen field.
Depending on the critique criteria and the work being reviewed, there could also be certain points asked for addition which should be checked and noted by the lecturer or supervisor. Otherwise, follow the article review guidelines from our write my essay service to complete the assignment in no time.
Key points when writing an article review:
Use the article review template from our paper writing service to get through the assignment as fast as possible so you will not waste any time.

How to Start an Article Review?
- Firstly read the work being reviewed as much as possible and look up key phrases and words that are not understood.
- Discuss the work with other professionals or colleagues to collect more opinions and get a more balanced impression.
- Highlight important sections or sentences and refer this to your knowledge in the topic, do you agree or disagree and what does this contribute to the field?
- Then re-write the key arguments and findings into your own words this will help gain better understanding into the paper. This can be just written as an outline also and will help decide which points are wanted to discuss later.
If you feel you do not have enough time to create a critique worthy of your time, then come to EssayService and order a custom Article review online.
You can order essay independent of type, for example:
- nursing essay;
- law essay writing;
- history essays.
The best way to write an effective essay would be to draw up a plan or outline of what needs to be covered and use it for guidance throughout the critique.

Article Review Formatting
There is no one-fits-all article format you can follow in your review. In fact, the formatting is dictated by the citation style specified by your professor in the task requirements. Thus, be sure to clarify the preferred style before you jump straight to writing to handle the given assignment right.
APA Format Article Review
Writing an APA style article review, you will most likely use articles from journals, websites, and newspapers. For each source, you will have to create properly formatted bibliographical entries.
Here is how to write an article review APA:
- Journal: Author’s last name, First and middle initial. (Year of Publication). Publication Title. Periodical Title, Volume(Issue), pp.-pp.
- Website: Last name, initials. (Date of Publication). Title. Retrieved from {link}
- Newspaper: Last name, initials. (Date of Publication). Title. Magazine Title, pp. xx-xx.
MLA Format Article Review
Tips for citing sources in an article review MLA format:
- Journal: Last name, First name Middle initial. “Title.” Journal Title Series Volume. Issue (Year of Publication): Page(s). Database Name. Web. Date Accessed.
- Website: Last, First M. “Title.” Website Title. Publisher, Date Published. Web. Date Accessed.
- Newspaper: Last, First M. “Title.” Newspaper Title [City] Date of Publication: Page(s). Print.
Article Review Outline
Planning out an outline for your paper will help writing and to put it together so therefore saving you time in the long run.
Some questions to help with the outline of a critique:
- What does the article set out to do or prove?
- Are the main ideas clear and defined?
- How substantial is the evidence?
- Where does the article fit in its specific field?
- Does it provide new knowledge on the topic?
- What are the central theories and assumptions?
- Is the writer conclusive at getting their point across?
Here is a typical article review format to follow:

Use our article review template to get through the assignment as fast as possible so you will not waste any time.
Article Review Title
Firstly start with creating a title for your critique, this should be something to do with the focus of the work that is being reviewed. An approach could be to make it descriptive or also in a more creative way think of something that intrigues the reader. After the title, this is a good place to correctly cite the paper being critiqued and include the important details for example, the author, title of publication, any page references. The style in which the citation is written will depend on which is best for this type of work being reviewed.
Article Review Introduction
The introduction should be a brief glimpse into what the author was writing about and any other details the audience will find interesting. Maybe some background details on the piece that is not already known or something that contributes to the review itself. It is a good idea to start by introducing the work at the start of the paragraph and then include a ' hook '. Include the writer's thesis if there is one and put it at the end but include your own thesis towards the critique near the beginning of this section.
Article Review Body
When constructing the summary section, write down the important points and findings in the piece in your own words. Include how the claims are supported and backed up with evidence but use direct quotes as sparing as possible. Do not put in any information known to professionals in the field or topic, but detail any conclusions the work came to. Make sure the paper is not just copied word for word and is actually summarized by yourself; this will also help the review stage.
To make an accurate critique, break down the work and express opinions on whether it achieves its goals and how useful it is in explaining the topics for an article review. Decide if the paper contributes to its field and is important and credible to the given field. Back up all the claims with evidence from the summary or another source. If using another text, remember to cite it correctly in the bibliography section. Look at how strong the points are and do they contribute to the argument. Try to identify any biases the writer might have and use this to make a fair critique. This part is only for opinions of the piece's significance, not including whether you liked it. Furthermore, the different types of audiences that would benefit from the paper can be mentioned in this section.
Article Review Conclusion
In the conclusion section of the critique, there should only be one or two paragraphs in which a summary of key points and opinions in the piece are included. Also, summarize the paper's significance to its field and how accurate the work is. Depending on the type of critique or work evaluated, it is also possible to include comments on future research or the topic to be discussed further.
If other sources have been used, construct a bibliography section and correctly cite all works utilized in the critique.
The APA format is very common in an article review and stands for American Psychology Association. This will include a 'references list' at the end of the critique and in-text citations, mentioning the author's last name, page number, and publication date.
There are also MLA and Chicago formats for citations with slight differences in a name, like using a 'works cited' page for MLA. More can be found in this guide on the subtle differences between the types of citation methods under the heading 'Creating a bibliography.'
Article Review Example
Article review writing tips.
If you are interested in best scholarships for high school seniors , the following tips will be handy while writing your essay or article:
- Allow enough time to complete the research and writing of the critique. The number one problem with creating a critique is running out of time to make it the best it can be. This can be avoided by effective planning and keeping on time with the deadlines you set out.
- Collect twice more research than you think is needed to write a review. This will help when coming to the writing stage as not all the information collected will be used in the final draft.
- Write in a style that is compatible with the work being critiqued. This will be better for whoever requested the critique and also will make paper easier to construct.
- A summary and evaluation must be written. Do not leave out either part as one complements the other and is vital to create a critique worth reading.
- Be clear and explain well every statement made about the piece . Everything that is unknown to professionals in the field should be explained and all comments should be easy to follow for the reader.
- Do not just describe the work, analyze and interpret it. The critique should be in depth and give the audience some detailed interpretations of the work in a professional way.
- Give an assessment of the quality in the writing and of what standard it is. Evaluate every aspect in the paper so that the audience can see where it fits into the rest of the related works. Give opinions based on fact and do not leave any comments without reason as this will not count for anything.
How to Write an Article Review?
Writing a review article is not that hard if you know what steps to take. Below is a step-by-step guide on how to write a review example quickly and easily.
- Before You Start
Before you start writing your review essay, there are a few pre-writing steps to take. The pre-writing process should consist of the following steps:
- Pick the subject of your review (if it wasn’t specified by your professor);
- Read the article fully multiple times;
- Summarize the main ideas, points, and claims made in the article;
- Define the positive (strong) aspects;
- Identify the gaps or inconsistencies;
- Find the questions that remained unanswered.
All these steps are needed to help you define the direction for your review article and find the main ideas you’d like to cover in it.
After you review articles and define the key ideas, gaps, and other details, map out your future paper by creating a detailed outline.
Here are the core elements that must be included:
- Pre-title page;
- Corresponding author details (optional);
- Running head (only for the APA style);
- Summary page (optional);
- Title page;
- Introduction;
- References/Works Cited;
- Suggested Reading page (optional);
- Tables and Figure Legends (if required by the professor).
This step is vital to organize your thoughts and ensure a proper structure of your work. Thus, be sure not to skip this step.
When you have an outline, students can move on to the writing stage by formulating compelling titles for their article reviews. Titles should be declarative, interrogative, or descriptive to reflect the core focus of the paper.
- Article Citation
After the title should follow a proper citation of the piece you are going to review. Write a citation according to the required style, and feel free to check out a well-written article review example to see how it should look like.
- Article Identification
Start the first paragraph of your review with concise and clear article identification that specifies its title, author, name of the resource (e.g., journal, web, etc.), and the year of publication.
Following the identification, write a short introductory paragraph. It should be to the point and state a clear thesis for your review.
- Summary and Critique
In the main body of your article review, you should first make a detailed but not too extensive summary of the article you reviewed, its main ideas, statements, and findings. In this part, you should also reflect on the conclusion made by the author of the original article.
After a general summary should follow an objective critique. In this part of your paper, you have to state and analyze the main strengths and weaknesses of the article. Also, you need to point out any gaps or unanswered questions that are still there. And clarify your stance on the author’s assertions.
Lastly, you need to craft a compelling conclusion that recaps the key points of your review and gives the final, logical evaluation of the piece that was reviewed.
After this, proofread your work and submit it.
No Time Left For Your Due Assignment
Now we hope you understand how to write a review of an article. However, we know that writing a great article review requires a lot of time to properly research the work. To save your precious time, visit EssayService, where our team of top essay writers will help you. The team can even provide you with the best article review topics! You can learn more at the college essay writing service page where we have free guides with all the essay writing tips and tricks!
Frequently asked questions
She was flawless! first time using a website like this, I've ordered article review and i totally adored it! grammar punctuation, content - everything was on point
This writer is my go to, because whenever I need someone who I can trust my task to - I hire Joy. She wrote almost every paper for me for the last 2 years
Term paper done up to a highest standard, no revisions, perfect communication. 10s across the board!!!!!!!
I send him instructions and that's it. my paper was done 10 hours later, no stupid questions, he nailed it.
Sometimes I wonder if Michael is secretly a professor because he literally knows everything. HE DID SO WELL THAT MY PROF SHOWED MY PAPER AS AN EXAMPLE. unbelievable, many thanks
You Might Also Like

New Posts to Your Inbox!
Stay in touch
When you choose to publish with PLOS, your research makes an impact. Make your work accessible to all, without restrictions, and accelerate scientific discovery with options like preprints and published peer review that make your work more Open.
- PLOS Biology
- PLOS Climate
- PLOS Complex Systems
- PLOS Computational Biology
- PLOS Digital Health
- PLOS Genetics
- PLOS Global Public Health
- PLOS Medicine
- PLOS Mental Health
- PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases
- PLOS Pathogens
- PLOS Sustainability and Transformation
- PLOS Collections
How to Write a Peer Review

When you write a peer review for a manuscript, what should you include in your comments? What should you leave out? And how should the review be formatted?
This guide provides quick tips for writing and organizing your reviewer report.
Review Outline
Use an outline for your reviewer report so it’s easy for the editors and author to follow. This will also help you keep your comments organized.
Think about structuring your review like an inverted pyramid. Put the most important information at the top, followed by details and examples in the center, and any additional points at the very bottom.
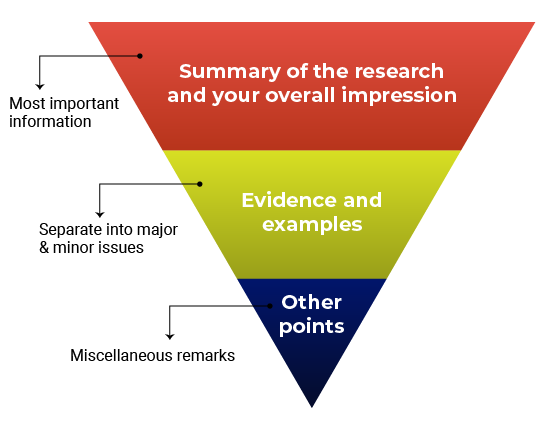
Here’s how your outline might look:
1. Summary of the research and your overall impression
In your own words, summarize what the manuscript claims to report. This shows the editor how you interpreted the manuscript and will highlight any major differences in perspective between you and the other reviewers. Give an overview of the manuscript’s strengths and weaknesses. Think about this as your “take-home” message for the editors. End this section with your recommended course of action.
2. Discussion of specific areas for improvement
It’s helpful to divide this section into two parts: one for major issues and one for minor issues. Within each section, you can talk about the biggest issues first or go systematically figure-by-figure or claim-by-claim. Number each item so that your points are easy to follow (this will also make it easier for the authors to respond to each point). Refer to specific lines, pages, sections, or figure and table numbers so the authors (and editors) know exactly what you’re talking about.
Major vs. minor issues
What’s the difference between a major and minor issue? Major issues should consist of the essential points the authors need to address before the manuscript can proceed. Make sure you focus on what is fundamental for the current study . In other words, it’s not helpful to recommend additional work that would be considered the “next step” in the study. Minor issues are still important but typically will not affect the overall conclusions of the manuscript. Here are some examples of what would might go in the “minor” category:
- Missing references (but depending on what is missing, this could also be a major issue)
- Technical clarifications (e.g., the authors should clarify how a reagent works)
- Data presentation (e.g., the authors should present p-values differently)
- Typos, spelling, grammar, and phrasing issues
3. Any other points
Confidential comments for the editors.
Some journals have a space for reviewers to enter confidential comments about the manuscript. Use this space to mention concerns about the submission that you’d want the editors to consider before sharing your feedback with the authors, such as concerns about ethical guidelines or language quality. Any serious issues should be raised directly and immediately with the journal as well.
This section is also where you will disclose any potentially competing interests, and mention whether you’re willing to look at a revised version of the manuscript.
Do not use this space to critique the manuscript, since comments entered here will not be passed along to the authors. If you’re not sure what should go in the confidential comments, read the reviewer instructions or check with the journal first before submitting your review. If you are reviewing for a journal that does not offer a space for confidential comments, consider writing to the editorial office directly with your concerns.
Get this outline in a template
Giving Feedback
Giving feedback is hard. Giving effective feedback can be even more challenging. Remember that your ultimate goal is to discuss what the authors would need to do in order to qualify for publication. The point is not to nitpick every piece of the manuscript. Your focus should be on providing constructive and critical feedback that the authors can use to improve their study.
If you’ve ever had your own work reviewed, you already know that it’s not always easy to receive feedback. Follow the golden rule: Write the type of review you’d want to receive if you were the author. Even if you decide not to identify yourself in the review, you should write comments that you would be comfortable signing your name to.
In your comments, use phrases like “ the authors’ discussion of X” instead of “ your discussion of X .” This will depersonalize the feedback and keep the focus on the manuscript instead of the authors.
General guidelines for effective feedback

- Justify your recommendation with concrete evidence and specific examples.
- Be specific so the authors know what they need to do to improve.
- Be thorough. This might be the only time you read the manuscript.
- Be professional and respectful. The authors will be reading these comments too.
- Remember to say what you liked about the manuscript!

Don’t
- Recommend additional experiments or unnecessary elements that are out of scope for the study or for the journal criteria.
- Tell the authors exactly how to revise their manuscript—you don’t need to do their work for them.
- Use the review to promote your own research or hypotheses.
- Focus on typos and grammar. If the manuscript needs significant editing for language and writing quality, just mention this in your comments.
- Submit your review without proofreading it and checking everything one more time.
Before and After: Sample Reviewer Comments
Keeping in mind the guidelines above, how do you put your thoughts into words? Here are some sample “before” and “after” reviewer comments
✗ Before
“The authors appear to have no idea what they are talking about. I don’t think they have read any of the literature on this topic.”
✓ After
“The study fails to address how the findings relate to previous research in this area. The authors should rewrite their Introduction and Discussion to reference the related literature, especially recently published work such as Darwin et al.”
“The writing is so bad, it is practically unreadable. I could barely bring myself to finish it.”
“While the study appears to be sound, the language is unclear, making it difficult to follow. I advise the authors work with a writing coach or copyeditor to improve the flow and readability of the text.”
“It’s obvious that this type of experiment should have been included. I have no idea why the authors didn’t use it. This is a big mistake.”
“The authors are off to a good start, however, this study requires additional experiments, particularly [type of experiment]. Alternatively, the authors should include more information that clarifies and justifies their choice of methods.”
Suggested Language for Tricky Situations
You might find yourself in a situation where you’re not sure how to explain the problem or provide feedback in a constructive and respectful way. Here is some suggested language for common issues you might experience.
What you think : The manuscript is fatally flawed. What you could say: “The study does not appear to be sound” or “the authors have missed something crucial”.
What you think : You don’t completely understand the manuscript. What you could say : “The authors should clarify the following sections to avoid confusion…”
What you think : The technical details don’t make sense. What you could say : “The technical details should be expanded and clarified to ensure that readers understand exactly what the researchers studied.”
What you think: The writing is terrible. What you could say : “The authors should revise the language to improve readability.”
What you think : The authors have over-interpreted the findings. What you could say : “The authors aim to demonstrate [XYZ], however, the data does not fully support this conclusion. Specifically…”
What does a good review look like?
Check out the peer review examples at F1000 Research to see how other reviewers write up their reports and give constructive feedback to authors.
Time to Submit the Review!
Be sure you turn in your report on time. Need an extension? Tell the journal so that they know what to expect. If you need a lot of extra time, the journal might need to contact other reviewers or notify the author about the delay.
Tip: Building a relationship with an editor
You’ll be more likely to be asked to review again if you provide high-quality feedback and if you turn in the review on time. Especially if it’s your first review for a journal, it’s important to show that you are reliable. Prove yourself once and you’ll get asked to review again!
- Getting started as a reviewer
- Responding to an invitation
- Reading a manuscript
- Writing a peer review
The contents of the Peer Review Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
The contents of the Writing Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
There’s a lot to consider when deciding where to submit your work. Learn how to choose a journal that will help your study reach its audience, while reflecting your values as a researcher…

Article Review
Ai generator.

Article reviews are an essential part of academic article writing , providing an opportunity to evaluate and analyze published research. A well-written review can help readers understand the simple subject matter and determine the value of the article. In this article, we’ll cover what is an article review, provide step-by-step guidance on how to write one, and answer some common questions.
1. Journal Article Review Form

Size: 84 KB
2. Article Review & Critique

Size: 420 KB
3. Formal Article Review

Size: 188 KB
4. Article Review Guideline

Size: 157 KB
5. Book and Article Reviews

Size: 284 KB
6. Format for Review Article

Size: 71 KB
7. Scientific Article Review

Size: 258 KB
8. Critical Reviews of Journal Articles

Size: 50 KB
9. Research Experience Article Review

Size: 31 KB
10. Review for Article Psychological Bulletin

11. Article Format Guide Review
Size: 449 KB
12. Value Of Review Article

Size: 51 KB
13. Articles for Peer-Review Publications

Size: 181 KB
14. Law Review Article Selection Process

15. Creative Article Review

Size: 46 KB
16. Club Article Review

Size: 77 KB
17. Review of Research Articles

Size: 152 KB
What is an Article Review
An article review is a critical assessment of a scholarly article or research paper. It involves analyzing the content, methodology, and findings of the article and providing an evaluation of its strengths and weaknesses. The review typically includes a summary of the article’s main points, an evaluation of its contribution to the subject, and suggestions for improvement.
How to Write an Article Review
Writing an article review can be a challenging task, but it’s an essential skill for students and researchers alike. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you write an effective article review:
Choose the article to review
Select an article that is relevant to your subject and interests you. Make sure the article is recent, reputable, and published in a peer-reviewed journal.
Read the article carefully
Read the article thoroughly and take notes as you go. Pay attention to the author’s thesis statement, research question, methodology, and findings.
Identify the main points and key arguments
Determine the main points and arguments of the article. Look for evidence that supports the author’s thesis statement.
Evaluate the article’s methodology and research design
Evaluate the methodology and research design used in the article. Determine if the research methods were appropriate and effective in answering the research question.
Assess the article’s strengths and weaknesses
Identify the strengths and weaknesses of the article. Evaluate the quality of the evidence presented and the logic of the arguments made.
Write a summary of the article
Summarize the article in your own words. Include the main points, key arguments, and findings of the article.
Write the main body of the review
In the main body of the review, analyze and evaluate the article. Discuss the strengths and weaknesses of the article and provide evidence to support your claims.
Conclude with a final evaluation and recommendations for improvement
Conclude your review with a final evaluation conclusion of the article. Highlight its strengths and weaknesses and provide recommendations for improvement.
Proofread and edit the review
After completing your review, proofread and edit it carefully. Check for spelling, grammar, and punctuation errors. Make sure your review is clear, concise, and well-organized.
What is the difference between an article review and a literature review?
A literature review is a comprehensive analysis of published research on a particular subject, while an article review focuses specifically on one article.
Can I use first-person sentences in an article review?
It depends on the guidelines given by your instructor or the publication you are submitting the review to. Generally, using the third person is more appropriate for academic writing sentences .
Should I include the abstract of the article in my review?
Yes, including a brief summary of the article’s abstract is usually a good idea.
How long should an article review be?
The length of an article review varies depending on the subject and the publication requirements. Generally, a review should be between 500 and 1000 words.
Writing an effective article review requires careful analysis, evaluation, and critique of the article. By following our step-by-step guide, you can develop the skills to write a comprehensive and insightful review that provides valuable information to readers. Whether you’re reviewing an academic article, book or manuscript , or any other subject, the tips and techniques outlined here will help you write an effective article review.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Article review writing format, steps, examples and illustration PDF Compiled by Mohammed Yismaw

2021, Article review writing format, steps, examples and illustration PDF Compiled by Mohammed Yismaw
The purpose of this document is to help students and researchers understand how a review of an academic journal is conducted and reported in different fields of study. Review articles in academic journals that analyze or discuss researches previously published by others, rather than reporting new research results or findings. Summaries and critiques are two ways to write a review of a scientific journal article. Both types of writing ask you first to read and understand an article from the primary literature about your topic. The summary involves briefly but accurately stating the key points of the article for a reader who has not read the original article. The critique begins by summarizing the article and then analyzes and evaluates the author’s research. Summaries and critiques help you learn to synthesize information from different sources and are usually limited to two pages maximum.
Related Papers
Harald von Kortzfleisch , Christoph Kahle
Neue Technologien und Innovationen stellen heutzutage wichtige Schlüsselelemente der Wachstums und Erfolgssicherung von Unternehmen dar. Durch einen in Geschwindigkeit und Intensität immer schneller zunehmenden Wettbewerb nehmen Innovationen eine immer zentralere Rolle im Praxisalltag von Unternehmen ein. Dieser technische Fortschritt treibt auch in der Wissenschaft das Thema des Innovationsmanagements in den letzten Jahrzehnten immer stärker voran und wird dort ausgiebig diskutiert. Die Bedeutung von Innovationen wächst dabei ebenfalls aus der Sicht der Kunden, welche heutzutage viel differenzierter als früher Produkte und Dienste nachfragen und somit Unternehmen vor neue Herausforderungen stellen. Ãberdies stellen Innovationen heute ein entscheidendes Bindeglied zwischen Marktorientierung und erhofften Unternehmenserfolg dar. Seit einigen Jahren lässt sich eine Ãffnung der Unternehmensgrenzen für externe Quellen wie Kunden, Zulieferer, Universitäten oder teilweise auch M...
SSRN Electronic Journal
Helmut Krcmar
Dominic Lindner
Alexandra Waluszewski
Research Policy
Nuria Gonzalez Alvarez
Creativity and Innovation Management
Matti Pihlajamaa
Firms tap into user knowledge to learn about the users’ needs. While users have been recognized as a valuable source of knowledge for innovation, few studies have investigated how their knowledge is integrated into innovation processes in the context of complex products and systems (CoPS). The purpose of this study is to reveal the practices of CoPS manufacturers to facilitate user knowledge utilization for innovation. We investigate two case companies, a medical device manufacturer and an aircraft manufacturer, and report on seven managerial practices for utilizing user knowledge. We adopt the absorptive capacity model in structuring our findings and elaborate three of the model's sub-capabilities (recognition of the value of user knowledge, acquisition of user knowledge, and assimilation/transformation of user knowledge) by proposing that each is associated with a distinct managerial goal and related practices: (1) Sensitizing the organization to the innovation potential of user knowledge, (2) identifying and gaining access to suitable user knowledge, and (3) analyzing and interpreting user knowledge and integrating it into product development. Our study contributes to the innovation management literature by analyzing the capabilities required to utilize user knowledge throughout the CoPS innovation process.
Information & Management
Diffusion of digital technologies into the manufacturing industry has created new opportunities for innovation that firms must address to remain competitive. We investigate the role of customer and user knowledge in the digital innovation processes of three global B2B manufacturing companies. We find that the B2B manufacturing industry's characteristics influence how users and customers may be leveraged. Customers making the purchasing decisions are considered for knowledge about short-term changes in market needs, while users working directly with the products provide long-term guidance for digital innovation. We identify practices for acquiring, distributing, and using customer and user knowledge for digital innovation.
Journal of business market management
Patricia Sandmeier
Journal of Entrepreneurship, Management and Innovation
Journal of Entrepreneurship, Management and Innovation JEMI
Given the rising role of users in innovation processes and the increasing amount of research in this field the aim of this paper is to explore the limits of our understanding of the user innovation (UI) concept. In doing so, the study addresses four basic questions: (1) Why do users create and share innovation? (2) Who is the user-innovator? (3) What type of innovation do users create? (4) How do users innovate? The results of a systematic literature review identified the main research streams on user innovation, together with weaknesses of past research and perspectives for future studies.
RELATED PAPERS
Gernot Grabher
Journal of Computer‐ …
Petra Schubert , Kathrin Möslein
Mossimo Sesom
Shahab Zare
Arthur Shulman
International Journal of Technology Management
Richard Farr
European Journal of Dental Education
Y.P. CHANDRA
Chandra Yanto
Management Science
John Roberts
Maria Antikainen
Johanna Bragge
intechopen.com
Ivona Vrdoljak Raguz
Service Science
Tuure Tuunanen
Jouni K Juntunen
Benji Decker
Eva Heiskanen
Handbook of Marketing
Jerome Hauser
Service Industries Journal
Christian Kowalkowski
Journal of Engineering Design
Ola Isaksson , Anna Rönnbäck
Journal of Management
Bettina Bastian
International Journal of Innovation Management
Harald von Kortzfleisch
Guido H Baltes
Technology Analysis & Strategic Management
Raimo Lovio
Marco Bertoni , Christian Johansson
Dominik Walcher
Managing Service Quality
Tor W. Andreassen
Journal of Product Innovation Management
Gary Schirr
System Sciences, 2004. …
Ralf Reichwald , Dominik Walcher
Edina Vadovics
Jouni Similä
Luis Cancino Muñoz
Shell Artillery
Ralf Reichwald
Journal of the Academy of …
Ian Wilkinson , Subroto Roy
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
Peer review templates, expert examples and free training courses

Joanna Wilkinson
Learning how to write a constructive peer review is an essential step in helping to safeguard the quality and integrity of published literature. Read on for resources that will get you on the right track, including peer review templates, example reports and the Web of Science™ Academy: our free, online course that teaches you the core competencies of peer review through practical experience ( try it today ).
How to write a peer review
Understanding the principles, forms and functions of peer review will enable you to write solid, actionable review reports. It will form the basis for a comprehensive and well-structured review, and help you comment on the quality, rigor and significance of the research paper. It will also help you identify potential breaches of normal ethical practice.
This may sound daunting but it doesn’t need to be. There are plenty of peer review templates, resources and experts out there to help you, including:
Peer review training courses and in-person workshops
- Peer review templates ( found in our Web of Science Academy )
- Expert examples of peer review reports
- Co-reviewing (sharing the task of peer reviewing with a senior researcher)
Other peer review resources, blogs, and guidelines
We’ll go through each one of these in turn below, but first: a quick word on why learning peer review is so important.
Why learn to peer review?
Peer reviewers and editors are gatekeepers of the research literature used to document and communicate human discovery. Reviewers, therefore, need a sound understanding of their role and obligations to ensure the integrity of this process. This also helps them maintain quality research, and to help protect the public from flawed and misleading research findings.
Learning to peer review is also an important step in improving your own professional development.
You’ll become a better writer and a more successful published author in learning to review. It gives you a critical vantage point and you’ll begin to understand what editors are looking for. It will also help you keep abreast of new research and best-practice methods in your field.
We strongly encourage you to learn the core concepts of peer review by joining a course or workshop. You can attend in-person workshops to learn from and network with experienced reviewers and editors. As an example, Sense about Science offers peer review workshops every year. To learn more about what might be in store at one of these, researcher Laura Chatland shares her experience at one of the workshops in London.
There are also plenty of free, online courses available, including courses in the Web of Science Academy such as ‘Reviewing in the Sciences’, ‘Reviewing in the Humanities’ and ‘An introduction to peer review’
The Web of Science Academy also supports co-reviewing with a mentor to teach peer review through practical experience. You learn by writing reviews of preprints, published papers, or even ‘real’ unpublished manuscripts with guidance from your mentor. You can work with one of our community mentors or your own PhD supervisor or postdoc advisor, or even a senior colleague in your department.
Go to the Web of Science Academy
Peer review templates
Peer review templates are helpful to use as you work your way through a manuscript. As part of our free Web of Science Academy courses, you’ll gain exclusive access to comprehensive guidelines and a peer review report. It offers points to consider for all aspects of the manuscript, including the abstract, methods and results sections. It also teaches you how to structure your review and will get you thinking about the overall strengths and impact of the paper at hand.
- Web of Science Academy template (requires joining one of the free courses)
- PLoS’s review template
- Wiley’s peer review guide (not a template as such, but a thorough guide with questions to consider in the first and second reading of the manuscript)
Beyond following a template, it’s worth asking your editor or checking the journal’s peer review management system. That way, you’ll learn whether you need to follow a formal or specific peer review structure for that particular journal. If no such formal approach exists, try asking the editor for examples of other reviews performed for the journal. This will give you a solid understanding of what they expect from you.
Peer review examples
Understand what a constructive peer review looks like by learning from the experts.
Here’s a sample of pre and post-publication peer reviews displayed on Web of Science publication records to help guide you through your first few reviews. Some of these are transparent peer reviews , which means the entire process is open and visible — from initial review and response through to revision and final publication decision. You may wish to scroll to the bottom of these pages so you can first read the initial reviews, and make your way up the page to read the editor and author’s responses.
- Pre-publication peer review: Patterns and mechanisms in instances of endosymbiont-induced parthenogenesis
- Pre-publication peer review: Can Ciprofloxacin be Used for Precision Treatment of Gonorrhea in Public STD Clinics? Assessment of Ciprofloxacin Susceptibility and an Opportunity for Point-of-Care Testing
- Transparent peer review: Towards a standard model of musical improvisation
- Transparent peer review: Complex mosaic of sexual dichromatism and monochromatism in Pacific robins results from both gains and losses of elaborate coloration
- Post-publication peer review: Brain state monitoring for the future prediction of migraine attacks
- Web of Science Academy peer review: Students’ Perception on Training in Writing Research Article for Publication
F1000 has also put together a nice list of expert reviewer comments pertaining to the various aspects of a review report.
Co-reviewing
Co-reviewing (sharing peer review assignments with senior researchers) is one of the best ways to learn peer review. It gives researchers a hands-on, practical understanding of the process.
In an article in The Scientist , the team at Future of Research argues that co-reviewing can be a valuable learning experience for peer review, as long as it’s done properly and with transparency. The reason there’s a need to call out how co-reviewing works is because it does have its downsides. The practice can leave early-career researchers unaware of the core concepts of peer review. This can make it hard to later join an editor’s reviewer pool if they haven’t received adequate recognition for their share of the review work. (If you are asked to write a peer review on behalf of a senior colleague or researcher, get recognition for your efforts by asking your senior colleague to verify the collaborative co-review on your Web of Science researcher profiles).
The Web of Science Academy course ‘Co-reviewing with a mentor’ is uniquely practical in this sense. You will gain experience in peer review by practicing on real papers and working with a mentor to get feedback on how their peer review can be improved. Students submit their peer review report as their course assignment and after internal evaluation receive a course certificate, an Academy graduate badge on their Web of Science researcher profile and is put in front of top editors in their field through the Reviewer Locator at Clarivate.
Here are some external peer review resources found around the web:
- Peer Review Resources from Sense about Science
- Peer Review: The Nuts and Bolts by Sense about Science
- How to review journal manuscripts by R. M. Rosenfeld for Otolaryngology – Head and Neck Surgery
- Ethical guidelines for peer review from COPE
- An Instructional Guide for Peer Reviewers of Biomedical Manuscripts by Callaham, Schriger & Cooper for Annals of Emergency Medicine (requires Flash or Adobe)
- EQUATOR Network’s reporting guidelines for health researchers
And finally, we’ve written a number of blogs about handy peer review tips. Check out some of our top picks:
- How to Write a Peer Review: 12 things you need to know
- Want To Peer Review? Top 10 Tips To Get Noticed By Editors
- Review a manuscript like a pro: 6 tips from a Web of Science Academy supervisor
- How to write a structured reviewer report: 5 tips from an early-career researcher
Want to learn more? Become a master of peer review and connect with top journal editors. The Web of Science Academy – your free online hub of courses designed by expert reviewers, editors and Nobel Prize winners. Find out more today.
Related posts
Journal citation reports 2024 preview: unified rankings for more inclusive journal assessment.

Introducing the Clarivate Academic AI Platform

Reimagining research impact: Introducing Web of Science Research Intelligence

Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Writing a Literature Review

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays). When we say “literature review” or refer to “the literature,” we are talking about the research ( scholarship ) in a given field. You will often see the terms “the research,” “the scholarship,” and “the literature” used mostly interchangeably.
Where, when, and why would I write a lit review?
There are a number of different situations where you might write a literature review, each with slightly different expectations; different disciplines, too, have field-specific expectations for what a literature review is and does. For instance, in the humanities, authors might include more overt argumentation and interpretation of source material in their literature reviews, whereas in the sciences, authors are more likely to report study designs and results in their literature reviews; these differences reflect these disciplines’ purposes and conventions in scholarship. You should always look at examples from your own discipline and talk to professors or mentors in your field to be sure you understand your discipline’s conventions, for literature reviews as well as for any other genre.
A literature review can be a part of a research paper or scholarly article, usually falling after the introduction and before the research methods sections. In these cases, the lit review just needs to cover scholarship that is important to the issue you are writing about; sometimes it will also cover key sources that informed your research methodology.
Lit reviews can also be standalone pieces, either as assignments in a class or as publications. In a class, a lit review may be assigned to help students familiarize themselves with a topic and with scholarship in their field, get an idea of the other researchers working on the topic they’re interested in, find gaps in existing research in order to propose new projects, and/or develop a theoretical framework and methodology for later research. As a publication, a lit review usually is meant to help make other scholars’ lives easier by collecting and summarizing, synthesizing, and analyzing existing research on a topic. This can be especially helpful for students or scholars getting into a new research area, or for directing an entire community of scholars toward questions that have not yet been answered.
What are the parts of a lit review?
Most lit reviews use a basic introduction-body-conclusion structure; if your lit review is part of a larger paper, the introduction and conclusion pieces may be just a few sentences while you focus most of your attention on the body. If your lit review is a standalone piece, the introduction and conclusion take up more space and give you a place to discuss your goals, research methods, and conclusions separately from where you discuss the literature itself.
Introduction:
- An introductory paragraph that explains what your working topic and thesis is
- A forecast of key topics or texts that will appear in the review
- Potentially, a description of how you found sources and how you analyzed them for inclusion and discussion in the review (more often found in published, standalone literature reviews than in lit review sections in an article or research paper)
- Summarize and synthesize: Give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: Don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically Evaluate: Mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: Use transition words and topic sentence to draw connections, comparisons, and contrasts.
Conclusion:
- Summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance
- Connect it back to your primary research question
How should I organize my lit review?
Lit reviews can take many different organizational patterns depending on what you are trying to accomplish with the review. Here are some examples:
- Chronological : The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time, which helps familiarize the audience with the topic (for instance if you are introducing something that is not commonly known in your field). If you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order. Try to analyze the patterns, turning points, and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred (as mentioned previously, this may not be appropriate in your discipline — check with a teacher or mentor if you’re unsure).
- Thematic : If you have found some recurring central themes that you will continue working with throughout your piece, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic. For example, if you are reviewing literature about women and religion, key themes can include the role of women in churches and the religious attitude towards women.
- Qualitative versus quantitative research
- Empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the research by sociological, historical, or cultural sources
- Theoretical : In many humanities articles, the literature review is the foundation for the theoretical framework. You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts. You can argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach or combine various theorical concepts to create a framework for your research.
What are some strategies or tips I can use while writing my lit review?
Any lit review is only as good as the research it discusses; make sure your sources are well-chosen and your research is thorough. Don’t be afraid to do more research if you discover a new thread as you’re writing. More info on the research process is available in our "Conducting Research" resources .
As you’re doing your research, create an annotated bibliography ( see our page on the this type of document ). Much of the information used in an annotated bibliography can be used also in a literature review, so you’ll be not only partially drafting your lit review as you research, but also developing your sense of the larger conversation going on among scholars, professionals, and any other stakeholders in your topic.
Usually you will need to synthesize research rather than just summarizing it. This means drawing connections between sources to create a picture of the scholarly conversation on a topic over time. Many student writers struggle to synthesize because they feel they don’t have anything to add to the scholars they are citing; here are some strategies to help you:
- It often helps to remember that the point of these kinds of syntheses is to show your readers how you understand your research, to help them read the rest of your paper.
- Writing teachers often say synthesis is like hosting a dinner party: imagine all your sources are together in a room, discussing your topic. What are they saying to each other?
- Look at the in-text citations in each paragraph. Are you citing just one source for each paragraph? This usually indicates summary only. When you have multiple sources cited in a paragraph, you are more likely to be synthesizing them (not always, but often
- Read more about synthesis here.
The most interesting literature reviews are often written as arguments (again, as mentioned at the beginning of the page, this is discipline-specific and doesn’t work for all situations). Often, the literature review is where you can establish your research as filling a particular gap or as relevant in a particular way. You have some chance to do this in your introduction in an article, but the literature review section gives a more extended opportunity to establish the conversation in the way you would like your readers to see it. You can choose the intellectual lineage you would like to be part of and whose definitions matter most to your thinking (mostly humanities-specific, but this goes for sciences as well). In addressing these points, you argue for your place in the conversation, which tends to make the lit review more compelling than a simple reporting of other sources.

How it works
Transform your enterprise with the scalable mindsets, skills, & behavior change that drive performance.
Explore how BetterUp connects to your core business systems.
We pair AI with the latest in human-centered coaching to drive powerful, lasting learning and behavior change.
Build leaders that accelerate team performance and engagement.
Unlock performance potential at scale with AI-powered curated growth journeys.
Build resilience, well-being and agility to drive performance across your entire enterprise.
Transform your business, starting with your sales leaders.
Unlock business impact from the top with executive coaching.
Foster a culture of inclusion and belonging.
Accelerate the performance and potential of your agencies and employees.
See how innovative organizations use BetterUp to build a thriving workforce.
Discover how BetterUp measurably impacts key business outcomes for organizations like yours.
A demo is the first step to transforming your business. Meet with us to develop a plan for attaining your goals.

- What is coaching?
Learn how 1:1 coaching works, who its for, and if it's right for you.
Accelerate your personal and professional growth with the expert guidance of a BetterUp Coach.
Types of Coaching
Navigate career transitions, accelerate your professional growth, and achieve your career goals with expert coaching.
Enhance your communication skills for better personal and professional relationships, with tailored coaching that focuses on your needs.
Find balance, resilience, and well-being in all areas of your life with holistic coaching designed to empower you.
Discover your perfect match : Take our 5-minute assessment and let us pair you with one of our top Coaches tailored just for you.

Research, expert insights, and resources to develop courageous leaders within your organization.
Best practices, research, and tools to fuel individual and business growth.
View on-demand BetterUp events and learn about upcoming live discussions.
The latest insights and ideas for building a high-performing workplace.
- BetterUp Briefing
The online magazine that helps you understand tomorrow's workforce trends, today.
Innovative research featured in peer-reviewed journals, press, and more.
Founded in 2022 to deepen the understanding of the intersection of well-being, purpose, and performance
We're on a mission to help everyone live with clarity, purpose, and passion.
Join us and create impactful change.
Read the buzz about BetterUp.
Meet the leadership that's passionate about empowering your workforce.

For Business
For Individuals
53 performance review examples to boost growth

Jump to section
The importance of performance reviews
53 performance review examples, 3 tips for delivering a performance review to an underperformer, a performance review is an opportunity to foster growth.
Even the most well-intentioned criticism can be hard to hear.
If you need to give feedback to a peer or employee, you might feel nervous. After all, you can probably empathize — most of us have been in their position. You want the person to know where they excel and how to improve, but you don’t want to come off as harsh or lose your authority. It’s a delicate balance.
When sharing professional feedback, you need to achieve that perfect equilibrium to motivate your team to continue doing their best work. Perfect your delivery by studying these 53 performance review examples.
A performance review -– also known as a performance appraisal — evaluates how well an employee is tracking toward goals and upholding the company vision and values . This formal assessment documents strengths and weaknesses , expectations for improvement , and other relevant employee feedback , like kudos for a standout performance.
Performance reviews are essential because they provide managers (or employees assessing their peers) with a set time and structure for delivering in-depth, example-driven feedback. It’s also an opportunity for the reviewer to set metrics-based expectations so the reviewee knows how to improve for next time.
Plus, performance reviews are an excellent opportunity to open lines of communication between peers or a manager and their direct reports. Both sides can clarify questions or concerns about performance, and the reviewer may use this time to motivate the reviewee. These types of workplace conversations build more trusting, engaged, and caring professional relationships.
Unfortunately, typical performance reviews only inspire 14% of employees . In other words, reviewers need to step up their own performance if they want to make an impression during these meetings.
Effective performance reviews are level-headed and honest. They aren’t excuses to scold an employee for a mistake or poor performance . They make time to offer constructive criticism, praise what the team member is doing well, and provide suggested areas for improvement.
To keep the conversation as productive as possible, study our list of performance evaluation examples that provide focused feedback and maintain an upbeat, inspiring tone that doesn’t undermine the seriousness of the commentary.
Here are 53 employee evaluation examples for various scenarios.
Communication
Good workplace communication helps teams clearly express ideas and work through problems effectively. Respectful communication also fosters healthy social relationships between peers, which are essential for a positive work culture.
When you assess a colleague on this interpersonal skill , focus on the politeness of their interactions, the coherence of how they present information, and their ability to listen to others actively .
Use performance evaluation comments like the following when a colleague has done an exceptional job of clearly and respectfully communicating:
1. “I’ve noticed how clearly you communicate complex concepts to clients. I really admire this ability.”
2. “You’re excellent at solving conflicts . Thank you for taking on this responsibility.”
3. “Several of your teammates have told me how pleasant it is to work with you. Thank you for being such a respectful communicator.”
4. “I’ve been observing your standout negotiation skills and will continue to look for opportunities for you to use them.”
5. “I’d like to congratulate you on your clear and easy-to-follow presentations. Would you consider giving a workshop for your teammates?”
Improvement suggestions
Poor communication leads to confusion and fraught interactions. Plus, muddled instructions or explanations can cause project errors, and negative delivery can harm team and stakeholder relationships . It’s important for each team member to have this skill.
Here’s how to cite communication that needs improving:
6. “I’ve noticed that you sometimes miss part of an explanation. I have helpful materials on active listening I recommend taking a look at.”
7. “Clients have noted that your explanations are difficult to understand. You have a strong grasp of complex concepts, but let’s work together on ways to break them down for an unfamiliar audience.”
8. “I’d appreciate it if you could communicate when there’s an issue on a project or you have a question. I’ve seen delays and errors due to a lack of updates.”
9. “Some of your emails to clients have had spelling and grammar errors. Could you make an extra effort to check your work so that we keep our company communication as polished as possible?”
10. “Your teammates have cited rude interactions with you. We must keep communication respectful. Is something going on that’s causing you frustration or prompting these interactions?”
Innovation and creativity
Innovative solutions and creativity allow organizations to generate new products and services, build a more resonant brand image, and connect successfully with their target audience. When giving a performance review, provide positive feedback on how the person contributes to the team or company’s growth.
Teammates who offer fresh ideas for projects or ways to improve company processes to boost efficiency deserve a proverbial pat on the back. Here are five performance appraisal examples that show how to give it:
11. “Last quarter, you saved our team 50 hours of administrative work with your solution for streamlining databases. Thank you for this invaluable idea.”
12. “The marketing campaign you created to target younger audiences has been one of our most successful. Everyone on our team has something to learn from you.”
13. “You’ve been integral to launching one of the most innovative apps on the market. You should be proud of yourself. You’re helping a lot of end users.”
14. “I admire the way you creatively approach complex problems . You resolved a tricky supply chain issue that kept our deliveries on track.”
15. “You deeply understand the brand image and voice. All of your marketing copy and designs represent us well.”

Improvement suggestions
Team members in creativity- and innovation-driven roles may stagnate. Your organization might have a performance review template you can follow to zero on in how to improve in these areas. You can also use the following feedback pieces to push them in the right direction:
16. "You’re one of our most valued graphic designers. However, I’ve noticed that your recent designs have been similar. Let’s talk about ways to innovate.”
17. “Since you’re in a leadership role, I would like it if you took more initiative to offer creative solutions to problems . I have some reading to guide you.”
18. “I’ve noticed that your copy lacks that fresh voice we admire. Have you also tracked this change, and what solutions do you have to liven up the writing?”
19. “You’ve offered some of the most innovative development ideas our company’s seen. But you’ve been quiet in brainstorming sessions lately. Let’s talk about what may be going on.”
20. “Your latest product innovation had flaws resulting from rushed work and a lack of attention to detail. Does that resonate?”
Everyone can be a leader — regardless of their rank at an organization. Team members set examples for their peers, and managers guide reports toward success. Whether you’re giving a performance review for a veteran or an entry-level employee, address their leadership skills where you can.
When an employee exceeds expectations by mentoring others, taking charge of problems, and upholding organizational values , recognize their outstanding work with phrases like the following:
21. “Your positive attitude , willingness to take on more responsibility, and ability to explain concepts to your peers makes you an example to all.”
22. “I appreciate your advances in developing better leadership skills, like clear communication and excellent negotiation tactics. Kudos.”
23. “I know you started here recently, but many people already look up to you. You take initiative, aren’t afraid to share ideas, and treat your peers respectfully.”
24. “Since you’ve become a project manager, the development team consistently delivers quality outputs on time. You’re doing a great job guiding the group.”
25. “When there was a conflict with a client last month, you stepped in to manage it. You have the makings of a great leader.”
If an employee like a project manager or team lead isn’t mentoring others as well as they could, a performance review is the perfect moment to tackle the issue. And if you have a stellar employee who isn’t showing the leadership and initiative required to earn them a promotion, they might need some encouragement to strengthen these skills. Use the following examples as a guide for wording your feedback:
26. “You’ve consistently been an excellent leader, but teammates have reported a lack of mentorship on recent projects, leading to confusion and poor results. What can we do to improve the clarity of your communication and guidance?”
27. “I’ve noticed that you’re stepping back from public speaking opportunities. You’re a strong leader already, but giving talks is an inevitable part of your role. Here’s information on a speaking course I took that could help.”
28. “Some of your teammates have said you’re difficult to approach with a problem. Let’s work to improve your communication skills to make others comfortable asking you for help.”
29. “Your communication and mentorship skills are unmatched, but you still have to improve your time management skills. Several projects have run late, impacting client deliveries.”
30. “You form excellent social relationships with your team, but you may be getting too close. I’m concerned you could lose your authority if you continue to act more like a peer than a mentor.”
Collaboration and teamwork
Teams must work well together — it’s synergy that allows them to accomplish more than they’d be able to alone. Collaboration drives better organizational results and fosters a communicative, innovative work environment. Here’s how to tackle this topic in a performance appraisal.
Certain team members go above and beyond to help peers, manage conflicts, and share their knowledge. Reward them with statements like the following:
31. “You’re an excellent resource for new team members. Thank you for being willing to share what you know.”
32. “Your ability to adapt when obstacles arise and encourage your teammates to do the same has saved us from late deliveries several times. Congratulations, and thank you.”
33. “You didn’t have to navigate that conflict between your peers last week, but you stepped up. I think everyone in your group learned something from you that day.”
34. “I know you’d like to be doing more on projects, but I appreciate that you’re splitting the work with newer teammates so they can learn. Exciting opportunities are coming your way soon.”
35. “Your team traditionally had trouble working together. Thank you for identifying their strengths and guiding them as a leader to use them in harmony.”
Employees resisting participation in a team or creating conflicts must change behaviors to help their peers thrive. Here are a few ways to suggest improvements:
36. “I’ve noticed that you’ve been canceling team meetings and avoiding social events. Let’s talk about what’s going on.”
37. “It’s great to challenge your peers' ideas, but I’ve repeatedly observed you push contrary thoughts when the rest of the team has reached a consensus. This can hold up projects, so I’d like to ask you to be more flexible.”
38. “I know you’ve been very busy, but could you take more time to share your skills with others? There are new team members who could learn from you.”
39. “You’re sometimes quick to nix others’ ideas. Try listening to their suggestions with a more open mind to be a better team player.”
40. “You’re an involved leader, and that’s an excellent trait. But sometimes, you get too close to a project, and your guidance borders on micromanaging . I’d encourage you to try taking a step back when the team is working well together.”
Work ethic and organization
Punctuality, time management , and planning keep work flowing. In performance reviews, ensure all team members understand how their work ethics contribute to overall success.
Show your appreciation to those employees who keep administrative tasks running smoothly. Here are some examples:
41. “Thank you for changing our customer relationship management system. Now everyone can access data more easily, and it’s improved our workflow.”
42. “Your persistence in implementing the Agile project management framework has paid off. We’re delivering better, more timely products to clients.”
43. “You’re never late and sometimes even early. I appreciate your dedication to punctuality. It helps meetings run on time, and the day gets off to a strong start.”
44. “You always answer clients’ emails promptly. Thank you for your dedication to excellent customer service.”
45. “As a project manager, you do a great job resolving teammate’s blockers efficiently. This allows them to perform tasks confidently and keeps projects on track.”
Improvement suggestion
Employees who consistently arrive late or have trouble organizing tasks and following company processes negatively impact others’ ability to work well — not to mention their own. Here are constructive employee review examples for those cases:
46. “You’re often tardy to meetings, which causes your teammates and clients to wait. This can be frustrating for stakeholders. I’d like to share some tips for time management.”
47. “I’ve noticed you consistently turn in work late. I’m concerned you may have too much on your plate. Let’s assess your workload.”
48. “Client emails are falling through the cracks, making us look like we don’t care. Here’s a system I use to ensure I respond to every email quickly.”
49. “I understand the new customer relationship management system is tricky, but we need everyone to get on board. Would it be helpful if I set up an additional training session to walk you through the software?”
50. “You didn’t meet your goals this quarter, so I’m modifying them for the upcoming one. Please let me know if you need tools, skills, or support to make achieving these goals possible.”
Performance review summary examples
Wrap up your review by revisiting what the employee has done well and highlighting the improvements they should make. Here are three examples you can model your performance review summary on:
51. “You’ve improved your communication and public speaking skills this quarter, making you a stronger leader. But you can still work on your task and time management skills by implementing better organizational practices.”
52. “Your first few months at the company have been a success. You’ve learned to use our tools and processes, and your teammates enjoy working with you. Next quarter, I’d like you to take more initiative in brainstorming sessions.”
53. “You’re a long-time valued employee, and you have a unique talent as a graphic designer. Your social media campaign last quarter was top-notch, but others have been stagnant. I know you can tap into your talents and do more innovative work.”

You’re a compassionate leader and never want to hurt anyone’s feelings. But in a performance review , you may have to deliver tricky constructive criticism . You’re giving this feedback with the best intentions, but doing so might make the other person defensive. Keep the conversation productive and focus on framing improvement as a positive with these three tips:
- Start and end on a high note: Open the conversation with what the employee has done well and circle back to this point after giving criticism. This will remind the employee of their value.
- Use metrics: Don’t run a performance review on “gut feelings.” Quantifiable metrics and clear feedback allow you to identify areas of improvement. You must demonstrate specific examples and measurable figures to back up your claims. Otherwise, your criticism can seem unfounded.
- Offer suggestions: An employee may not know how to interpret feedback and translate it into action items. And they might have some concluding performance review questions about how to improve. Offer help and a professional development plan so the person feels inspired, capable, and supported in making the changes you suggest.
Many fear receiving and giving sub-optimal feedback. However, in performance reviews, colleagues inevitably highlight negative aspects of a person’s work.
But if you establish a healthy balance between recognizing an employee’s strengths and offering constructive feedback for improvement (like in our performance review examples), these sessions turn into growth opportunities. Your colleagues take on new challenges, acquire better skills, and become more understanding teammates thanks to criticism.
And guess what? The next performance review will be less nerve-wracking for everyone involved.
Lead with confidence and authenticity
Develop your leadership and strategic management skills with the help of an expert Coach.
Elizabeth Perry, ACC
Elizabeth Perry is a Coach Community Manager at BetterUp. She uses strategic engagement strategies to cultivate a learning community across a global network of Coaches through in-person and virtual experiences, technology-enabled platforms, and strategic coaching industry partnerships. With over 3 years of coaching experience and a certification in transformative leadership and life coaching from Sofia University, Elizabeth leverages transpersonal psychology expertise to help coaches and clients gain awareness of their behavioral and thought patterns, discover their purpose and passions, and elevate their potential. She is a lifelong student of psychology, personal growth, and human potential as well as an ICF-certified ACC transpersonal life and leadership Coach.
What is financial coaching, and why do you need it?
How to coach your team to success: 5 key tips for managers, 7 types of employee coaching (and why you can’t afford to miss out), how coaching drove $10m in additional sales, how professional coaching can be a force multiplier for the military, coaching during crisis: new betterup research shows coaching helps employees navigate change and uncertainty, what to get coaching on here’s what managers are saying, innovations in coaching: growth through connection for an evolving world of work, introducing betterup, and why everyone needs a coach in their corner, similar articles, 31 examples of problem solving performance review phrases, 17 positive feedback examples to develop a winning team, leverage love languages at work to improve your office culture, 10 performance review tips to drastically move the needle, how to give positive comments to your boss, 5 ways to recognize employees, how to praise someone professionally on their work (with examples), 25 performance review questions (and how to use them), 16 constructive feedback examples — and tips for how to use them, stay connected with betterup, get our newsletter, event invites, plus product insights and research..
3100 E 5th Street, Suite 350 Austin, TX 78702
- Platform Overview
- Integrations
- Powered by AI
- BetterUp Lead™
- BetterUp Manage™
- BetterUp Care®
- Sales Performance
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Case Studies
- Why BetterUp?
- About Coaching
- Find your Coach
- Career Coaching
- Communication Coaching
- Life Coaching
- News and Press
- Leadership Team
- Become a BetterUp Coach
- BetterUp Labs
- Center for Purpose & Performance
- Leadership Training
- Business Coaching
- Contact Support
- Contact Sales
- Privacy Policy
- Acceptable Use Policy
- Trust & Security
- Cookie Preferences
- Open access
- Published: 26 May 2024
The sense of coherence scale: psychometric properties in a representative sample of the Czech adult population
- Martin Tušl 1 ,
- Ivana Šípová 2 ,
- Martin Máčel 2 ,
- Kristýna Cetkovská 2 &
- Georg F. Bauer 1
BMC Psychology volume 12 , Article number: 293 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
Metrics details
Sense of coherence (SOC) is a personal resource that reflects the extent to which one perceives the world as comprehensible, manageable, and meaningful. Decades of empirical research consistently show that SOC is an important protective resource for health and well-being. Despite the extensive use of the 13-item measure of SOC, there remains uncertainty regarding its factorial structure. Additionally, a valid and reliable Czech version of the scale is lacking. Therefore, the present study aims to examine the psychometric properties of the SOC-13 scale in a representative sample of Czech adults.
An online survey was completed by 498 Czech adults (18–86 years old) between November 2021 and December 2021. We used confirmatory factor analysis to examine the factorial structure of the scale. Further, we examined the variations in SOC based on age and gender, and we tested the criterion validity of the scale using the short form of the Mental Health Continuum (MHC) scale and the Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) scale as mental health outcomes.
SOC-13 showed an acceptable one- and three-factor fit only with specified residual covariance between items 2 and 3. We tested alternative short versions by systematically removing poorly performing items. The fit significantly improved for all shorter versions with SOC-9 having the best psychometric properties with a clear one-factorialstructure. We found that SOC increases with age and males score higher than females. SOC showed a moderately strong positive correlation with MHC, and a moderately strong negative correlation with GAD. These findings were similar for all tested versions supporting the criterion validity of the SOC scale.
Our findings suggest that shortened versions of the SOC-13 scale have better psychometric properties than the original 13-item version in the Czech adult population. Particularly, SOC-9 emerges as a viable alternative, showing comparable reliability and validity as the 13-item version and a clear one-factorial structure in our sample.
Peer Review reports
Sense of coherence (SOC) was introduced by the sociologist Aaron Antonovsky as the main pillar of his salutogenic theory, which explains how individuals cope with stressors and stay healthy even in case of adverse life situations [ 1 ]. SOC is a personal resource defined as a global orientation to life determining the degree to which one perceives life as comprehensible, manageable, and meaningful [ 2 ]. A strong SOC enables individuals to cope with stressors and manage tension, thus moving to the ease-end of the ease/disease continuum [ 2 , 3 ]. A person’s strength of SOC can be measured with the Orientation to Life Questionnaire commonly referred to as the SOC scale [ 4 ]. The original version is composed of 29 items (SOC-29) and Antonovsky recommended 13 items for the short version of the scale (SOC-13). To date, both versions of the scale have been used across diverse populations in at least 51 languages and 51 countries [ 5 ]. Studies have consistently shown that SOC correlates strongly with different health and well-being outcomes [ 6 , 7 ] and quality of life measures [ 8 ]. In the context of the recent COVID-19 pandemic, SOC has been identified as the most important protective resource in relation to mental health [ 9 ]. Regarding individual differences, SOC has been shown to strengthen over the life course [ 10 ], males usually score higher than females [ 11 ], and some studies indicate that SOC increases with the level of education [ 12 ]. However, despite the extensive evidence on the criterion validity of the scale, there is still a lack of clarity about its underlying factor structure and dimensionality.
The SOC scale was conceptualized as unidimensional suggesting that SOC in its totality, as a global orientation, influences the movement along the ease/dis-ease continuum [ 2 ]. However, the structure of the scale is rather multidimensional as each item is composed of multiple elements. Antonovsky developed the scale according to the facet theory [ 13 , 14 ] which assumes that social phenomena are best understood when they are seen as multidimensional. Facet theory involves the construction of a mapping sentence which consists of the facets and the sentence linking the facets together [ 15 ]. The SOC scale is composed of five facets: (i) the response mode (comprehensibility, manageability, meaningfulness); (ii) the modality of stimulus (instrumental, cognitive, affective), (iii) its source (internal, external, both), (iv) the nature of the demand it poses (concrete, diffuse, affective), (v) and its time reference (past, present, future). For example, item 3 “Has it happened that people whom you counted on disappointed you?” is a manageability item that can be described with the mapping sentence as follows: "Respondent X responds to an instrumental stimulus (“counted on”), which originated from the external environment (“people”), and which poses a diffuse demand (“disappointed”) being in the past (“has it happened”)." Although each item can be categorized along the SOC component comprehensibility, manageability, or meaningfulness, the items also share elements from the other four facets with items within the same, but also within the other SOC components (see 2, Chap. 4 for details). As Antonovsky states [ 2 , p. 87]: “The SOC facet pulls the items apart; the other facets push them together.”
Thus, the multi-facet nature of the scale can create difficulties in identifying the three theorized SOC components using statistical methods such as factor analysis. In fact, both the unidimensional and the three-dimensional SOC-13 rarely yield an acceptable fit without specifying residual covariance between single items (see 5 for an overview). This has been further exemplified in a recent study which examined the dimensionality of SOC-13 using a network perspective. The authors were unable to identify a clear structure and concluded that SOC is composed of multiple elements that are deeply linked and not necessarily distinct [ 16 ]. As a result, several researchers have suggested modified [ 17 ] or abbreviated versions of the scale, such as SOC-12 [ 18 , 19 ], SOC-11 [ 20 , 21 , 22 ], or SOC-9 [ 23 ], which have empirically shown a better factorial structure. This prompts the general question, whether an alternative short version should be preferred over the 13-item version. In fact, looking into the original literature [ 2 ], it is not clear why Antonovsky chose specifically these 13 items from the 29-item scale. We will address this question with the Czech version of the SOC-13 scale.
Salutogenesis in the Czech Republic
Salutogenesis and the SOC scale were introduced to the Czech audience in the early 90s by a Czech psychologist Jaro Křivohlavý. His work included the Czech translation of the SOC-29 scale [ 24 ] and the application of the concept in research on resilience [ 25 ] and behavioral medicine [ 26 ]. Unfortunately, the early Czech translation of the scale by Křivohlavý is not available electronically, nor could we locate it in library repositories. Later studies examined SOC-29 in relation to resilience [ 27 , 28 ] and self-reported health [ 29 , 30 ], however, it is not clear which translation of SOC-29 the authors used in the studies. A new Czech translation of the SOC-13 scale has recently been developed by the authors of this paper to examine the protective role of SOC for mental health during the COVID-19 crisis [ 31 ]. In line with earlier studies [ 9 ], SOC was identified as an important protective resource for individual mental health. This recent Czech translation of the SOC-13 scale [ 31 ] is the subject of the present study.
Present study
Our study aims to investigate the psychometric properties of the SOC-13 scale within a representative sample of the Czech adult population. Specifically, we will examine the factorial structure of the SOC-13 scale to understand its underlying dimensions and evaluate its internal consistency to ensure its reliability as a measure of SOC. Additionally, we aim to assess criterion validity by examining the scale’s association with established measures of positive and negative mental health outcomes - the Mental Health Continuum [ 32 ] and Generalized Anxiety Disorder [ 33 ]. We anticipate a strong correlation between these measures and the SOC construct [ 6 ]. Furthermore, we will investigate demographic variations in SOC, considering factors such as age, gender, and education. Understanding these variations will provide valuable insights into the applicability of the SOC-13 scale across different population subgroups. Finally, we will explore whether alternative short versions of the SOC scale should be preferred over the 13-item version. This analysis will help determine the most efficient version of the SOC scale for future research.
Study design and data collection
Our study design is a cross-sectional online survey of the Czech adult population. We contracted a professional agency DataCollect ( www.datacollect.cz ) to collect data from a representative sample for our study. Participants were recruited using quota sampling. The inclusion criteria were: being of adult age (18+), speaking the Czech language, and having permanent residence in the Czech Republic. Exclusion criteria related to study participation were predetermined to minimize the risk of biases in the collected data. The order of items in all measures was randomized and we implemented two attention checks in the questionnaire (e.g. “Please, choose option number 2”). Participants were excluded if they did not finish the survey, completed the survey in less than five minutes, did not pass the attention checks, or gave the same answer to more than 10 consecutive items. Data collection was conducted via the online platform Survey Monkey between November 2021 and December 2021.
Translation into the Czech language
Translation of the SOC scale was carried out by the authors of the paper with the help of a qualified translator. We followed the translation guidelines provided on the website of the Society for Research and Theory on Salutogenesis ( www.stars-society.org ), where the original English version of the SOC scale is available for download. Two translations were conducted independently, then compared and checked for differences. Based on this comparison, the agreed version of the scale was back translated into English by a Czech-English translator. The final version was checked for resemblance to the original version in content and in form. Although we used only the short version of the scale in our study (i.e., SOC-13), the translation included the full SOC-29 scale. The Czech translation of the full SOC scale is available as supplementary material.
Sense of coherence. We used the short version of the Orientation to Life Questionnaire [ 3 ] to assess SOC. The measure consists of 13 items evaluated on a 7-point Likert-type scale with different response options. Five items measure comprehensibility (e.g., “Does it happen that you experience feelings that you would rather not have to endure?”), four items measure manageability (e.g., “Has it happened that people whom you counted on disappointed you?”), and four items measure meaningfulness (e.g., “Do you have the feeling that you really don’t care about what is going on around you?”). In our sample, Cronbach’s alpha for the full scale was α = 0.88, for comprehensibility α = 0.76, manageability α = 0.72, and meaningfulness α = 0.70.
Mental health continuum - short form (MHC-SF; 32). This scale consists of 14 items that capture three dimensions of well-being: (i) emotional (e.g. “During the past month, how often did you feel interested in life?”); (ii) social (e.g. “During the past month, how often did you feel that the way our society works makes sense to you?”); (iii) psychological (e.g. “During the past month, how often did you feel confident to think or express your own ideas and opinions?”). The items assess the experiences the participants had over the past two weeks, the response options ranged from 1 (never) to 6 (every day). Internal consistency of the scale was α = 0.90.
Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD; 33). The scale consists of seven items that measure symptoms of anxiety over the past two weeks. Sample items include, e.g. “Over the past two weeks, how often have you been bothered by the following problems?” (i) “feeling nervous, anxious, or on edge”, (ii) “worrying too much about different things”, (iii) “becoming easily annoyed or irritable”. The response options ranged from 0 (not at all) to 3 (almost every day). Internal consistency of the scale was α = 0.92.
Sociodemographic characteristics included age, gender, and level of education (i.e., primary/vocational, secondary, tertiary).
Analytical procedure
Data analysis was conducted in R [ 34 ]. For confirmatory factor analysis, we used the cfa function of the lavaan package 0.6–16 [ 35 ]. We compared a one-factor model of SOC-13 to a correlated three-factor model (correlated latent factors comprehensibility, manageability, and meaningfulness) and a bi-factor model (general SOC dimension and specific dimensions comprehensibility, manageability, meaningfulness). Based on the empirical findings we further assessed the fit of alternative shorter versions of the SOC scale. We assessed the model fit using the comparative-fit index (CFI), Tucker-Lewis index (TLI), root mean square error of approximation (RMSEA), and standardized root mean square residual (SRMR) with the conventional cut-off values. The goodness-of-fit values for CFI and TLI surpassing 0.90 indicate an acceptable fit and exceeding 0.95 a good fit [ 36 ]. A value under 0.08 for RMSEA and SRMR indicates a good fit [ 37 ]. Nested models were compared using chi-square difference tests and the Bayesian Information Criterion (BIC). Models with lower BIC values should be preferred over models with higher BIC values [ 38 ]. All models were fitted using maximum likelihood estimation.
Further, we used the cor function of the stats package 4.3.2 [ 34 ] for Pearson correlation analysis to explore the association between SOC-13 and age, the t.test function of the same package for between groups t-test for differences based on gender, and the aov function with posthoc tests of the same package for one-way between-subjects ANOVA to test for differences based on level of education. To examine the criterion validity of the scale, we used the cor function for Pearson correlation analysis to examine the associations between SOC-13, MHC-SF, and GAD. We conducted the same analyses for the alternative short versions of the scale.
Participants
The median survey completion time was 11 min. In total, 676 participants started the survey and 557 completed it. Of those, 56 were excluded due to exclusion criteria. One additional respondent was excluded because of dubious responses on demographic items (e.g., 100 years old and a student), and two respondents were excluded for not meeting the inclusion criteria (under 18 years old). The final sample included N = 498 participants. Of those, 53.4% were female, the average age was 49 years ( SD = 16.6; range = 18–86), 43% had completed primary, 35% secondary, and 22% tertiary education. The sample is a good representation of the Czech adult population Footnote 1 with regard to gender (51% females), age ( M = 50 years), and education level (44% primary, 33% secondary, 18% tertiary). Representativeness was tested using chi-squared test which yielded non-significant results for all domains.
Descriptive statistics
In Table 1 , we present an inter-item correlation matrix along with skewness, kurtosis, means and standard deviations of single items for SOC-13. Item correlations ranged from r = 0.07 (items 2 and 4) to r = 0.67 (items 8 and 9). Strong and moderately strong correlations were found also across the three SOC dimensions (e.g., r = 0.77 comprehensibility and manageability).
- Confirmatory factor analysis
A one-factor model showed inadequate fit to the data [χ2(65) = 338.2, CFI = 0.889, TLI = 0.867, RMSEA = 0.092, SRMR = 0.062]. Based on existing evidence [ 6 ], we specified residual covariance between items 2 and 3 and tested a modified one-factor model. The model showed an acceptable fit to the data [χ2(64) = 242.6, CFI = 0.927, TLI = 0.911, RMSEA = 0.075, SRMR = 0.050], and it was superior to the one-factor model (Δχ2 = 95.5, Δ df = 1, p < 0.001).
A correlated three-factor model showed an acceptable fit considering CFI and SRMR [χ2(63) = 286.6, CFI = 0.909, TLI = 0.885, RMSEA = 0.085, SRMR = 0.058]. The model was superior to the one-factor model (Δχ2 = 51.5, Δ df = 2, p < 0.001), however, it was inferior to the modified one-factor model (ΔBIC = -56). We further tested a modified three-factor model with residual covariance between items 2 and 3 which showed an acceptable fit to the data based on CFI and TLI and a good fit based on RMSEA and SRMR [χ2(62) = 191.7, CFI = 0.947, TLI = 0.932, RMSEA = 0.066, SRMR = 0.046]. The model was superior to the three-factor model (Δχ2 = 97.1, Δ df = 1, p < 0.001) as well as to the modified one-factor model (Δχ2 = 50.9, Δ df = 3, p < 0.001). See Fig. 1 for a detailed illustration of the model.
Finally, we tested a bi-factor model with one general SOC factor and three specific factors (comprehensibility, manageability, meaningfulness), however, the model was not identified.
Correlated three-factor model of SOC-13 with residual covariance between item 2 and item 3
Alternative short versions of the SOC scale
We further tested the fit of alternative shorter versions of the SOC scale by systematically removing poorly performing items. In SOC-12, item 2 was excluded (“Has it happened in the past that you were surprised by the behavior of people whom you thought you knew well?”). This item measures comprehensibility, hence SOC-12 has even distribution of items for each dimension (i.e., comprehensibility, manageability, meaningfulness). Item 2 has previously been identified as problematic [ 6 ] and also in our sample it did not perform well in any of the fitted SOC-13 models (i.e., low factor loading and explained variance). A one-factor SOC-12 model showed an acceptable fit to the data based on CFI and TLI and a good fit based on RMSEA and SRMR [χ2(54) = 221.1, CFI = 0.927, RMSEA = 0.079, SRMR = 0.048]. A correlated three-factor model showed an acceptable fit based on CFI and TLI and a good fit based on RMSEA and SRMR [χ2(52) = 171.1, CFI = 0.948, TLI = 0.932, RMSEA = 0.069 SRMR = 0.043]. The model was superior to the one-factor model (Δχ2 = 50, Δ df = 3, p < 0.001). Bi-factor model was not identified.
In SOC-11, we removed item 3 (“Has it happened that people whom you counted on disappointed you?”), which measures manageability. The item had the lowest factor loading and the lowest explained variance in the one-factor SOC-12. A one-factor SOC-11 model showed a good fit to the data [χ2 (44) = 138.5, CFI = 0.955, TLI = 0.944, RMSEA = 0.066, SRMR = 0.038]. A correlated three-factor model was identified but not acceptable due to covariance between comprehensibility and manageability higher than 1 (i.e., Heywood case; 39).
In SOC-10, we removed item 1 (“Do you have the feeling that you don’t really care about what goes on around you?”), which measures meaningfulness. The item had the lowest factor loading and the lowest explained variance in one-factor SOC-11. A one-factor SOC-10 model showed a good fit to the data [χ2 (35) = 126.6, CFI = 0.956, TLI = 0.943, RMSEA = 0.072, SRMR = 0.039]. As in the case of SOC-11, a correlated three-factor model was identified but not acceptable due to covariance between comprehensibility and manageability higher than 1.
Finally, in SOC-9, we removed item 11 (“When something happened, have you generally found that… you overestimated or underestimated its importance / you saw the things in the right proportion”), which measures comprehensibility. The item had the lowest factor loading and the lowest explained variance in one-factor SOC-10. SOC-9 has an even distribution of three items for each dimension. A one-factor model showed a good fit to the data [χ2 (27) = 105.6, CFI = 0.959, TLI = 0.946, RMSEA = 0.076, SRMR = 0.038]. As in the previous models, a correlated three-factor model was identified but not acceptable due to covariance between comprehensibility and manageability higher than 1. See Fig. 2 for an illustration of one-factor SOC-9 model. Detailed results of the confirmatory factor analysis are shown in Table 2 . In Table 3 , we present the items of the SOC-13 (and SOC-9) scale with details about their facet structure.
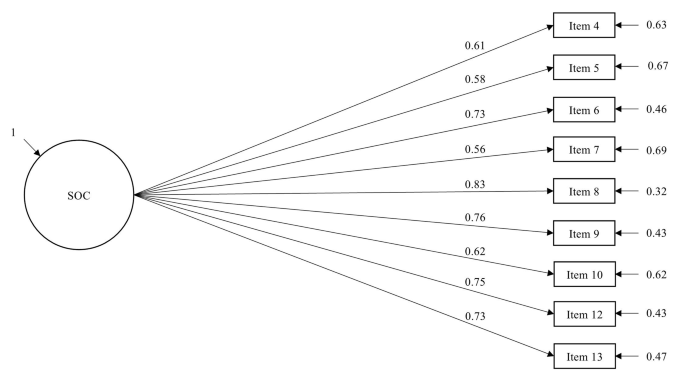
One-factor model of SOC-9
Differences by gender, age, and education
Correlation analysis indicated that SOC-13 increases with age ( r = 0.32, p < 0.001), this finding was identical for all alternative short versions of the SOC scale (see Table 2 ). Further, the results of the two-tailed t-test showed that males ( M = 4.8, SD = 1.08) had a significantly higher SOC-13 score [ t (497) = 3.06, p = 0.002, d = 0.27] than females ( M = 4.5, SD = 1.07). A one-way between-subjects ANOVA did not show any significant effect of level of education on SOC-13 score [F(2, 497) = 1.78, p = 0.169, η p 2 = 0.022]. These results were similar for all alternative short versions of the SOC scale.
Criterion validity
We found a moderately strong positive correlation ( r = 0.61, p < 0.001) between SOC-13 and the positive mental health measure MHC, and a moderately strong negative correlation between SOC-13 and the negative mental health measure GAD ( r = -0.68, p < 0.001). These findings were similar for all alternative short versions of the SOC scale (see Table 4 ).
Our study examined the psychometric properties of the SOC-13 scale and its alternative short versions SOC-12, SOC-11, SOC-10, and SOC-9 in a representative sample of the Czech adult population. In line with existing studies [ 40 ], we found that SOC increases with age and that males score higher than females. In contrast to some prior findings [ 12 ], we did not find any significant differences in SOC based on the level of education. Further, we tested criterion validity using both positive and negative mental health outcomes (i.e., MHC and GAD). SOC had a strong positive correlation with MHC and a strong negative correlation with GAD, thus adding to the evidence about the criterion validity of the scale [ 6 , 40 ].
Analysis of the factor structure showed that a one-factor SOC-13 had an inadequate fit to our data, however, an acceptable fit was achieved for a modified one-factor model with specified residual covariance between item 2 (“Has it happened in the past that you were surprised by the behavior of people whom you thought you knew well?”) and item 3 (“Has it happened that people whom you counted on disappointed you?”). A correlated three factor model with latent factors comprehensibility, manageability, and meaningfulness showed a better fit than the one factor-model. However, it was also necessary to specify residual covariance between item 2 and item 3 to reach an acceptable fit for all fit indices. A recent Slovenian study [ 41 ] found a similar result and several prior studies (see 6 for an overview) have noted that items 2 and 3 of the SOC-13 scale are problematic. Although the items pertain to different SOC dimensions (item 2 to comprehensibility, item 3 to manageability), multiple studies [e.g., 20 , 42 , 43 ] have reported moderately strong correlation between them and this is also the case in our study ( r = 0.5, p < 0.001). The two items aptly illustrate the facet theory behind the scale construction as the SOC component represents only one building block of each item. Although items 2 and 3 theoretically pertain to different SOC components, they share the same elements from the other four facets (i.e., modality, source, demand, and time) which is reflected in the similarity of their wording. Therefore, they will necessarily share residual variance and this needs to be specified to achieve a good model fit. Drageset and Haugan [ 18 ] explain this similarity in that the people whom we know well are usually the ones that we count on, and feeling disappointed and surprised by the behavior of people we know well is closely related. Therefore, it should be theoretically justifiable to specify residual covariance between item 2 and item 3 as a possible solution to improve the fit. As we could show in our sample, the model fit significantly improved for both one-factor and three-factor solutions.
In addition, we examined the fit of alternative short versions of the SOC scale by systematically removing single items that performed poorly. First, in line with previous studies [ 6 ], we addressed the issue of residual covariance in SOC-13 by removing item 2, examining the factor structure of SOC-12. The remaining 12 items were equally distributed within the three SOC components with four items per each component. Interestingly, a one-factor model reached an acceptable fit and the fit further improved for a correlated three-factor model with latent factors of comprehensibility, manageability, and meaningfulness. Although correlated three-factor models were superior to one-factor models, we observed extreme covariances between latent variables, especially in case of comprehensibility and manageability (cov = 0.98). This suggests that the SOC components are not empirically separable and that, indeed, SOC is rather a one-dimensional global orientation with multiple components that are dynamically interrelated as Antonovsky proposed [ 2 ]. This notion was supported in a recent study that explored the dimensionality of the scale using a network perspective [ 16 ]. Our examination of SOC-11, SOC-10 and SOC-9 provided further support for a one-factor structure of the scale. All shorter versions yielded a good one-dimensional fit, however, we could not identify a correlated three-factor model fit due to the Heywood case. This refers to the situation when a solution that otherwise is satisfactory produces communality greater than one explained by the latent factor, which implies that the residual variance of the variable is negative [ 39 ]. In our case, this was true for the latent factors comprehensibility and manageability. However, we demonstrated that we could attain a good one-dimensional fit for all alternative short versions of SOC, and, importantly, they all showed comparable reliability and validity metrics to their longer counterpart SOC-13. In particular, SOC-9 shows very good fit indices and it performs equally well in validity analyses as SOC-13. Given these findings and existing evidence [ 5 ], we propose that future investigations may consider utilizing the SOC-9 scale instead of the SOC-13. It is interesting to point out that the majority of items that were removed for the shorter versions of the scale are negatively worded or reverse-scored (expect for item 11). This is in line with the latest research suggesting that such items can cause problems in model identification as they create additional method factors [ 44 , 45 , 46 ].
Finally, it is important to highlight that Antonovsky did not provide any information about the selection of the 13 items for the short version of the SOC scale [ 2 ]. For example, a detailed examination of the facet structure reveals that none of the items included in SOC-13 refers to future which is part of facet referring to time (i.e., past, present, future). Hence, considering the absence of explicit criteria for item selection in the SOC-13 scale, it would be interesting to gather data from diverse populations utilizing the full SOC-29 scale. Subsequently, through exploratory factor analysis, researchers could derive a new, theory- and empirical-driven, short version of the SOC scale.
Strengths and limitations
A clear strength of our study is that our findings are based on a representative sample that accurately reflects the Czech adult population. Moreover, we implemented rigorous data cleaning procedures, meticulously excluding participants who provided potentially careless or low-quality responses. By doing so, we ensured that our conclusions are based on high-quality data and that they are generalizable to our target population of Czech adults. Finally, we conducted a thorough back-translation procedure to achieve an accurate Czech version of the SOC scale and we carried out systematic testing of different short versions of the SOC scale.
However, our study also has some limitations. First, our conclusions are based on data from a culturally specific country and they may not be generalizable to other populations. It is important to note, however, that most of our findings are in line with multiple existing studies which supports the validity of our conclusions. Second, the data were collected during a later stage of the COVID-19 pandemic, which may have impacted particularly the mental health outcomes we used for criterion validity. It would be worthwhile to investigate whether the data replicate in our population outside of this exceptional situation. Third, it should be noted that we did not examine test-retest reliability of the scale due to the cross-sectional design of our study. Finally, self-reported data are subject to common method biases such as social desirability, recall bias, or consistency motive [ 47 ]. We aimed to minimize this risk by implementing various strategies in the questionnaire, such as randomization of items and the use of disqualifying items (e.g. “Please, choose option number 2”) to disqualify careless answers.
Our study contributes to decades of ongoing research on SOC, the main pillar of the theory of salutogenesis. In line with existing research, we found evidence for the validity of the SOC as a construct, but we could not identify a clear factorial structure of the SOC-13 scale. However, following Antonovsky’s conception of the scale, we believe it is theoretically sound to aim for a one-factor solution of the scale and we could show that this is possible with shorter versions of the SOC scale. We particularly recommend using the SOC-9 scale in future research which shows an excellent one-factor fit and validity indices comparable to SOC-13. Finally, since Antonovsky does not explain how he selected the items of the SOC-13 scale, it would be interesting to examine the possibility of developing a new one-dimensional short version based on exploratory factor analysis of the original SOC-29 scale.
Data availability
The datasets used and analyzed during the current study and the R code used for the statistical analysis are available as supplementary material.
www.czso.cz .
Antonovsky A. The salutogenic model as a theory to guide health promotion. Health Promot Int. 1996;11(1).
Antonovsky A. Unraveling the mystery of Health how people manage stress and stay well. Jossey-Bass; 1987.
Antonovsky A. Health stress and coping. Jossey-Bass; 1979.
Antonovsky A. The structure and Properties of the sense of coherence scale. Soc Sci Med. 1993;36(6):125–733.
Article Google Scholar
Eriksson M, Contu P. The sense of coherence: Measurement issues. The Handbook of Salutogenesis. Springer International Publishing; 2022. pp. 79–91.
Eriksson M. The sense of coherence: the Concept and its relationship to Health. The Handbook of Salutogenesis. Springer International Publishing; 2022. pp. 61–8.
Eriksson M, Lindström B. Antonovsky’s sense of coherence scale and the relation with health: a systematic review. J Epidemiol Community Health (1978). 2006;60(5):376–81.
Eriksson M, Lindström B. Antonovsky’s sense of coherence scale and its relation with quality of life: a systematic review. J Epidemiol Community Health. 2007;61(11):938–44.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Mana A, Super S, Sardu C, Juvinya Canal D, Moran N, Sagy S. Individual, social and national coping resources and their relationships with mental health and anxiety: A comparative study in Israel, Italy, Spain, and the Netherlands during the Coronavirus pandemic. Glob Health Promot [Internet]. 2021;28(2):17–26.
Silverstein M, Heap J. Sense of coherence changes with aging over the second half of life. Adv Life Course Res. 2015;23:98–107.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Rivera F, García-Moya I, Moreno C, Ramos P. Developmental contexts and sense of coherence in adolescence: a systematic review. J Health Psychol. 2013;18(6):800–12.
Volanen SM, Lahelma E, Silventoinen K, Suominen S. Factors contributing to sense of coherence among men and women. Eur J Public Health [Internet]. 2004;14(3):322–30.
Guttman L. Measurement as structural theory. Psychometrika. 1971;3(4):329–47.
Guttman R, Greenbaum CW. Facet theory: its development and current status. Eur Psychol. 1998;3(1):13–36.
Shye S. Theory Construction and Data Analysis in the behavioral sciences. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass; 1978.
Google Scholar
Portoghese I, Sardu C, Bauer G, Galletta M, Castaldi S, Nichetti E, Petrocelli L, Tassini M, Tidone E, Mereu A, Contu P. A network perspective to the measurement of sense of coherence (SOC): an exploratory graph analysis approach. Current Psychology. 2024;12:1-3.
Bachem R, Maercker A. Development and psychometric evaluation of a revised sense of coherence scale. Eur J Psychol Assess. 2016;34(3):206–15.
Drageset J, Haugan G. Psychometric properties of the orientation to Life Questionnaire in nursing home residents. Scand J Caring Sci. 2016;30(3):623–30.
Kanhai J, Harrison VE, Suominen AL, Knuuttila M, Uutela A, Bernabé E. Sense of coherence and incidence of periodontal disease in adults. J Clin Periodontol. 2014;41(8):760–5.
Naaldenberg J, Tobi H, van den Esker F, Vaandrager L. Psychometric properties of the OLQ-13 scale to measure sense of coherence in a community-dwelling older population. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2011;9.
Luyckx K, Goossens E, Apers S, Rassart J, Klimstra T, Dezutter J et al. The 13-item sense of coherence scale in Dutch-speaking adolescents and young adults: structural validity, age trends, and chronic disease. Psychol Belg. 2012;52(4):351–68.
Lerdal A, Opheim R, Gay CL, Moum B, Fagermoen MS, Kottorp A. Psychometric limitations of the 13-item sense of coherence scale assessed by Rasch analysis. BMC Psychol. 2017;5(1).
Klepp OM, Mastekaasa A, Sørensen T, Sandanger I, Kleiner R. Structure analysis of Antonovsky’s sense of coherence from an epidemiological mental health survey with a brief nine-item sense of coherence scale. Int J Methods Psychiatr Res. 2007;16(1):11–22.
Křivohlavý J. Sense of coherence: methods and first results. II. Sense of coherence and cancer. Czechoslovak Psychol. 1990;34:511–7.
Křivohlavý J. Nezdolnost v pojetí SOC. Czechoslovak Psychol. 1990;34(6).
Křivohlavý J. Salutogenesis and behavioral medicine. Cas Lek Cesk. 1990;126(36):1121–4.
Kebza V, Šolcová I. Hlavní Koncepce psychické odolnosti. Czechoslovak Psychol. 2008;52(1):1–19.
Šolcová I, Blatný M, Kebza V, Jelínek M. Relation of toddler temperament and perceived parenting styles to adult resilience. Czechoslovak Psychol. 2016;60(1):61–70.
Šolcová I, Kebza V, Kodl M, Kernová V. Self-reported health status predicting resilience and burnout in longitudinal study. Cent Eur J Public Health. 2017;25(3):222–7.
Šolcová I, Kebza V. Subjective health: current state of knowledge and results of two Czech studies. Czechoslovak Psychol. 2006;501:1–15.
Šípová I, Máčel M, Zubková A, Tušl M. Association between coping resources and mental health during the COVID-19 pandemic: a cross-sectional study in the Czech Republic. Int J Environ Health Res. 2022;1–9.
Keyes CLM. The Mental Health Continuum: from languishing to flourishing in life. J Health Soc Behav. 2002;43(2):207–22.
Löwe B, Decker O, Müller S, Brähler E, Schellberg D, Herzog W, et al. Validation and standardization of the generalized anxiety disorder screener (GAD-7) in the General Population. Med Care. 2008;46(3):266–74.
R Core Team. R: a language and environment for statistical computing. Vienna, Austria: R Foundation for Statistical Computing; 2022.
Rosseel Y. Lavaan: an R Package for Structural equation modeling. J Stat Softw. 2012;48(2):1–36.
Bentler PM, Bonett DG. Significance tests and goodness of fit in the analysis of covariance structures. Psychol Bull. 1980;88(3):588–606.
Beauducel A, Wittmann WW. Simulation study on fit indexes in CFA based on data with slightly distorted simple structure. Struct Equ Model. 2005;12(1):41–75.
Raftery AE. Bayesian model selection in Social Research. Sociol Methodol. 1995;25:111–63.
Farooq R. Heywood cases: possible causes and solutions. Int J Data Anal Techniques Strategies. 2022;14(1):79.
Eriksson M, Lindström B. Validity of Antonovsky’s sense of coherence scale: a systematic review. J Epidemiol Community Health (1978). 2005;59(6):460–6.
Stern B, Socan G, Rener-Sitar K, Kukec A, Zaletel-Kragelj L. Validation of the Slovenian version of short sense of coherence questionnaire (SOC-13) in multiple sclerosis patients. Zdr Varst. 2019;58(1):31–9.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Bernabé E, Tsakos G, Watt RG, Suominen-Taipale AL, Uutela A, Vahtera J, et al. Structure of the sense of coherence scale in a nationally representative sample: the Finnish Health 2000 survey. Qual Life Res. 2009;18(5):629–36.
Sardu C, Mereu A, Sotgiu A, Andrissi L, Jacobson MK, Contu P. Antonovsky’s sense of coherence scale: cultural validation of soc questionnaire and socio-demographic patterns in an Italian Population. Clin Pract Epidemiol Mental Health. 2012;8:1–6.
Chyung SY, Barkin JR, Shamsy JA. Evidence-based Survey Design: the Use of negatively worded items in surveys. Perform Improv. 2018;57(3):16–25.
Suárez-Alvarez J, Pedrosa I, Lozano LM, García-Cueto E, Cuesta M, Muñiz J. Using reversed items in likert scales: a questionable practice. Psicothema. 2018;30(2):149–58.
PubMed Google Scholar
van Sonderen E, Sanderman R, Coyne JC. Ineffectiveness of reverse wording of questionnaire items: let’s learn from cows in the rain. PLoS ONE. 2013;8(7).
Podsakoff PM, MacKenzie SB, Lee JY, Podsakoff NP. Common method biases in behavioral research: a critical review of the literature and recommended remedies. J Appl Psychol. 2003;88(5):879–903.
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank to the team of Center of Salutogenesis at the University of Zurich for their helpful comments on the adapted version of the SOC scale.
MT received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program under the Marie Skłodowska-Curie grant agreement No 801076, through the SSPH + Global PhD Fellowship Program in Public Health Sciences (GlobalP3HS) of the Swiss School of Public Health. Data collection was supported by the Charles University Strategic Partnerships Fund 2021. The University of Zurich Foundation supported the contribution of GB.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Division of Public and Organizational Health, Center of Salutogenesis, Epidemiology, Biostatistics and Prevention Institute, University of Zurich, Hirschengraben 84, Zurich, 8001, Switzerland
Martin Tušl & Georg F. Bauer
Department of Psychology, Faculty of Arts, Charles University, Prague, Czech Republic
Ivana Šípová, Martin Máčel & Kristýna Cetkovská
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
All authors contributed to the conception and design of the study. MT wrote the manuscript, conducted data analysis, and contributed to data collection. MM and IS conducted data collection, contributed to data analysis, interpretation of results, edited and commented on the manuscript. KC and GB contributed to interpretation of results, edited and commented on the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Martin Tušl .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
The study was conducted in accordance with the general principles of the Declaration of Helsinki and with the ethical principles defined by the university and by the national law ( https://cuni.cz/UK-5317.html ). Informed consent was obtained from all participants prior to the completion of the survey. Participation was voluntary and participants could withdraw from the study at any time without any consequences. For anonymous online surveys in adult population no ethical review by an ethics committee was necessary under national law and university rules. See: https://www.muni.cz/en/about-us/organizational-structure/boards-and-committees/research-ethics-committee/evaluation-request .
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Material 1
Supplementary material 2, supplementary material 3, rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Tušl, M., Šípová, I., Máčel, M. et al. The sense of coherence scale: psychometric properties in a representative sample of the Czech adult population. BMC Psychol 12 , 293 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40359-024-01805-7
Download citation
Received : 22 March 2023
Accepted : 21 May 2024
Published : 26 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s40359-024-01805-7
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Salutogenesis
- Sense of coherence
- Psychometrics
- Czech adult population
- Mental health
BMC Psychology
ISSN: 2050-7283
- General enquiries: [email protected]
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
What Really Motivates You at Work?
- Carrie Ott-Holland

To get the recognition that matters most to you, start by identifying exactly what that looks like.
When we work hard, we generally expect our efforts to be recognized by our employer. And most employers will do just that — showering someone with praise at a company meeting, taking a team to a nice dinner, or quietly delivering a cash bonus. But sometimes an employer’s broader recognition strategy does not align with what its individual workers want and need. Some workers may be incentivized by more paid time off, while others may appreciate a gift card to a local shop. And some workers may be motivated by monetary rewards, while others hope to be assigned the role of team lead on the next high-stakes project. In this article, the author offers five practical techniques you can start using today to increase the likelihood of getting the rewards and recognition you value most.
Most of us want to feel rewarded and recognized for a job well done. And most employers want to incentivize their workers to perform well and stay engaged. While these two things should align, employers unfortunately don’t always get it right. A team dinner can be a fun culmination of a group project, or it can feel like a frustrating stand-in if you were hoping for a monetary reward. On the flip side, a cash bonus quietly appearing in your inbox may feel strange if you expected public recognition for a heroic work accomplishment. Yet some people would rather call in sick than stand in front of their colleagues to receive an award.
- Carrie Ott-Holland works as principal people analyst at Klaviyo. She has worked in people analytics and talent management in the tech industry for the past decade and is an organizational psychologist by training.
Partner Center
To revisit this article, visit My Profile, then View saved stories .

The New Billie Eilish Record Is the Uninhibited Billie We’ve Been Waiting For
By Suzy Exposito

“People say I look happy / Just because I got skinny,” Billie Eilish sings in “Skinny,” the lead track off her new album, Hit Me Hard and Soft . “But the old me is still me / And maybe the real me / And I think she’s pretty.”
Are we entering a new era of Eilish ? The singer-songwriter may only be 22 years old, but her 22 is not just anybody’s 22. She is, after all, a performer whose breakthrough work came out before she even graduated from high school. At the age when most people are finishing college, she has (with her brother and collaborator Finneas O’Connell) claimed nine Grammys and two Academy Awards.
In her macabre debut, 2019’s When We All Fall Asleep, Where Do We Go?, Eilish’s most sincere moments were overshadowed by her villainous alt-pop persona. In her sophomore LP, 2021’s Happier Than Ever , the edgy teen phenom had been poked, prodded, and surveilled into a more subdued songstress. Although she confronted music-industry predators in “Your Power” (from the second album), it was with painstakingly hushed condemnations: “Will you only feel bad when they find out?”
Perhaps no genre of her evolution has attracted more attention than her shifting attitude toward her body. Known initially for her baggy, tomboy apparel, in 2020 she appeared on the cover of British Vogue in an Alexander McQueen corset and other high-femme finery, in part to prove to body-shamers that she could pull it off. “If I wear what is comfortable, I am not a woman,” she recited coldly in the spoken-word video “Not My Responsibility” from the same year, her voice lingering a decibel below a whisper. “If I shed the layers, I’m a slut. Is my value based only on your perception? Or is your opinion of me not my responsibility?”

By Marie Bladt

By Jeanne Ballion

By Ana Morales
But in Hit Me , Eilish rips off the psychic bodice and noticeably cranks up the volume in her vocals, as well as her own desires. After inadvertently coming out as bisexual in a 2023 interview with Variety —“Wasn’t it obvious?” she later stated —she gets giddily explicit about her attraction to women on the slinky pop track “Lunch.” In the music video, she reverts back to her skater-boy steez, cocking her baseball cap to the side and cheekily wedging a cherry between her lips. “I could eat that girl for lunch / Yeah, she dances on my tongue / Tastes like she might be the one,” she sings.
It’s no coincidence that Eilish is learning what it is to love women as she comes around to loving her own body. In the classic feminist text Our Bodies, Ourselves , the authors urged women of yesteryear to do body-affirming mirror exercises and relish their physical forms like unique works of art. In a 2024 interview with Rolling Stone , Billie extolled the virtues of her own lustier version of the exercise: making love to herself in front of a mirror. This way, her body is no longer an adversary nor a receptacle of shame; her body is more like a friend she’s getting to know better.
“I can’t stress it enough, as somebody with extreme body issues and dysmorphia that I’ve had my entire life,” Eilish told Rolling Stone . “I have learned that looking at myself and watching myself feel pleasure has been an extreme help in loving myself and accepting myself, and feeling empowered and comfortable.”
Hit Me arrives the same year that Tracy Chapman and Boygenius made headlines at the Grammys and Reneé Rapp and Chappell Roan stole hearts with their bubblegum-flavored lesbian anthems at Coachella. Eilish’s contribution to the queer-pop-girlie canon is a delicious prelude to a lusty, unapologetic sapphic pop summer.
This effervescent new wave of queer pop—which implores fans to connect with their bodies through dance, dress, and sex—has become more politically urgent than ever. Eilish lambasted the Supreme Court’s decision to overturn Roe v. Wade onstage at the Glastonbury Festival in 2022: “Today is a really, really dark day for women in the US,” she told the crowd in the UK. And with the prevalence of image-based social media platforms like Instagram and TikTok, young Americans report feeling lonelier and more unsettled in their bodies than ever before. In a study cited by Surgeon General Vivek Murthy , 46% of adolescents aged 13 to 17 report that social media makes them feel worse about themselves. Public-health experts at Harvard have also correlated chronic social media use with symptoms of body dysmorphia , eating disorders, and suicidal ideation in youth.
But what Eilish imparts in her new songs is a lesson that not only women nor LGBTQ people can appreciate: In learning how to be a loving partner to your body, your true empowerment can begin.
Panasonic S9 initial review

Product images by Dale Baskin/Mitchell Clark
The Panasonic Lumix S9 is the newest addition to Panasonic's line of full-frame mirrorless cameras, though it differs considerably from previous models. It's the first in the series to diverge from the traditional DSLR form factor. More significantly, it's the first full-frame Lumix camera aimed squarely at social media content creators.
The basic premise of the S9 is that it's designed to simplify and speed-up the social media workflow. The goal is to allow content creators to generate photos or videos ready to publish straight out of the camera without additional editing in other applications.
Key specifications
- 24MP BSI CMOS sensor with on-sensor phase detection
- 4K 3:2 open-gate video in 25 or 30p (4:2:0 10-bit) with new 'MP4 (Lite)' codec
- 6K 3:2 open-gate video at up to 30p (4:2:0 10-bit)
- 6K or DCI/UHD 4K from full sensor width up to 30p
- DCI/UHD 4K up to 60p (with APS-C crop)
- Dedicated LUT button to apply LUTs in real time (photos and video)
- Tight integration with the new LumixLab smartphone app
- Dual conversion gain sensor with explicit 'Dual Native ISO' gain selection
- UHS-II card slot
- 1.84M dot fully-articulating LCD
The Lumix S9 will be available from the end of May 2024 at a suggested retail price of $1499. Four color options are available: night blue, dark olive, crimson red and jet black.
Alongside the S9, Panasonic also announced a new L-mount lens designed to pair with the camera. The Lumix S 26mm F8 is a fixed-aperture, manual focus 'pancake' style lens with a suggested retail price of $199.
- What's new?
How it compares
- Body and controls
Initial impressions
- Sample gallery
- Specifications
- Press release
What's new:
Under the hood, the Panasonic S9 is largely the same camera as the Panasonic S5II. However, by necessity, it omits some of that camera's hardware features in the interest of size, including an EVF, a second main command dial, a joystick, a second card slot and an integrated fan. And while the two cameras share a common technology platform, the S9 is not intended to be a more compact version of the S5II: the cameras have very different design philosophies and are aimed at different types of users.
Social media-focused workflow
The S9 is specifically designed with a social media workflow in mind. This means providing social media creators with the tools necessary to generate a unique, signature look to their photos and videos straight out of the camera without requiring any editing skills. Panasonic describes this as the ability to "Shoot, edit and share in 30 seconds." While 30 seconds may be a bit optimistic, it's important to understand that this social media workflow underpins the camera's features and design choices.
In essence, the S9 is intended to provide social media creators with a camera-to-social-media workflow that can be executed quickly and easily, wherever they may be, without relying on a computer or any third-party software. Although the camera can support an enthusiast photographer's workflow, it's not optimized around that use case in the same way as a camera like the S5II and lacks features that dedicated photographers are likely to value, such as a dedicated viewfinder, a second command dial and direct controls for features such as AF mode and area.
Expanded use of 'Real Time' LUTs
A core feature of the S9's social media workflow is Panasonic's 'Real Time' LUT system, first introduced on the S5II. This does more or less what it sounds like: it lets you instantly apply a look-up table (LUT) color transformation to a photo or video as they're captured to provide a custom look that would otherwise require additional editing to achieve.
LUTs have been a standard method of applying color transformations in the video world for years, but Panasonic has expanded their use to broadly apply to both stills and video. It promises that this LUT-based workflow will let you skip the editing step entirely because you can use LUTs to achieve whatever look you want straight out of the camera.
LUTs are such an essential part of the S9's identity that it has a dedicated LUT button next to the AF-On button on the back of the camera. Tapping this button allows you to quickly cycle through all the LUTs loaded into the camera to select the look you want to achieve.
In addition to a dedicated LUT button, the camera improves upon the system found on the S5II in several ways. The S9 can store up to 39 LUTs in memory, up from ten on the S5II, and LUTs can now be applied to any of the camera's photo styles; previously, LUTs could only be applied to the V-Log style. Users now have the ability to control LUT opacity, ranging from 10-100%, and it's even possible to apply two LUTs at once by creating a 'My Photo Style', which lets you choose a base photo style and apply one or two LUTs on top of it.
The result is a virtually limitless combination of looks that can be created and stored in-camera for quick access at the touch of a button.
New LUTs can be added to the camera quickly and easily using a companion smartphone app, though it's also possible to add a LUT in .cube or .vlt format from an SD card if desired.
LumixLab app
Alongside the S9, Panasonic is launching a new smartphone app called LumixLab, specifically intended to support the S9's social media workflow. Unlike most smartphone apps for cameras, which serve as an optional tool, LumixLab is fundamental to the S9 user experience, to the point that the camera's headline feature of using real time LUTs depends on it.
LumixLab allows you to apply LUTs to photos and to manage the LUTs installed on your camera. However, the real power of LumixLab is the ability to quickly and easily create your own custom looks and generate custom LUTs based on those looks. The app includes various editing tools, including exposure, color, HSL, tone curve, split toning, sharpening, noise reduction, sharpness, and even simulated film grain. If you edit an image or video clip and get a look that you want to reproduce in the future, you can instantly save a custom LUT based on your edits and load it into one of the camera's 39 memory banks.
The idea is to allow you to create a signature look that you can automatically apply to any media you capture in the future simply by selecting your custom LUT using the camera's LUT button.
LumixLab also includes a library of ready-to-use LUTs, including LUTs created by Panasonic and LUTs shared by other social media content creators. This means you have many creative options to choose from, even without having to make LUTs yourself.
It's worth noting that LumixLab doesn't replicate all of the features of Panasonic's existing Image App, such as the ability to control your camera remotely. Panasonic tells us the two apps will coexist for a while but that it eventually plans to merge them. LumixLab will be available for download from the Apple App Store and Google Play Store on May 29.
4K open-gate recording and MP4 (Lite) codec
The S9's default video mode is 4K open-gate video, downsampled from 6K, using the entire area of the camera's sensor rather than a 16:9 region, as most cameras do. This makes it easier to generate horizontal and vertical video from the same master clip but with smaller file sizes that transfer more quickly to a smartphone than full-resolution 6K open-gate video. Interestingly, this default mode supports 25p and 30p recording but not 24p.
This default video mode uses a new codec, which Panasonic calls 'MP4 (Lite)', which records at 50 Mbps. This may seem low compared to the higher bit rates we've become accustomed to in recent years, but it significantly speeds up transfers between the camera and smartphone and is probably sufficient for most social media, where video is heavily compressed for streaming.
*Open gate 4K recording is the default video mode for camera
The default video mode even gets its own slot on the camera's Q menu, separate from all other video settings. You still have access to most of Panasonic's other video settings, right up to 6K open-gate video, but you'll need to switch out of the default video mode to use them.
Similarly, you get access to Panasonic's excellent video features like waveform monitor, shutter angle, zebras, Log view assist, record frame indicator, and the other usual suspects. However, the camera does have a 15-minute recording limit.
Panasonic's pitching this camera squarely at creators who are still mainly shooting with their phones. If it wants the S9 to woo them, it has to do two things: be almost as convenient to carry around and shoot with as a phone, while producing much higher-quality images. The camera's compact size, along with the revamped app, are plays at making it convenient, while its full-frame sensor should provide enough raw photo and video quality to stand out in a crowd of smartphone images.
Of course, the S9 isn't the only choice for creators looking to step up to a dedicated camera. Sony's ZV-E1 is a direct rival that's focused on meeting the needs of creators. We've also included the Panasonic DC-S5II, the company's more photographer-friendly model underpinned by similar hardware.
Finally, the Sigma fp is admittedly a slightly left-field comparison but its lack of viewfinder, reliance on electronic shutter and use of the same sensor makes it an interesting point of comparison.
For its price and size, the S9 has a pretty impressive spec sheet for a mid-level camera, largely owing to its high-res, full-frame sensor, and its ample video features. The company's stabilization tech and autofocus are also competitive, though Sony still holds the crown in the later category.
Which makes the comparison with the Sony ZV-E1 interesting. It too aims to make creators' lives easier, but through different means. The S9's forte is making it easy to find or create a look for your images, while the ZV-E1 is tuned to make filming yourself easier. Its "Auto Framing" feature will automatically crop your video so that it follows your subject and it includes a "product showcase" mode that'll specifically focus on items that you're holding up to the camera, both making it suited to single-person operation. Its sensor is also better matched for video, so it can record 4K at 60fps without any crop or 120p with a slight crop.
That sensor's lower megapixel count puts the ZV-E1 at a disadvantage when it comes to shooting photos, though, and while it does have its own custom LUT feature, it's mostly focused on video instead of photos. The MSRP is also substantially higher than the S9's.
The S9's focus on creators means there are plenty of features that could push enthusiast and more photo-focused buyers towards more expensive cameras like the S5II. The S9's bigger cousin has a second SD card slot and, of course, an EVF. It's also better-equipped for video, with a full-size HDMI port versus a fragile micro one and a dedicated headphone socket (with the ability to record to an SSD on the more expensive S5II X model). The S5II's extra features come at a cost though, both figurative and literal; it's over 50% heavier and its MSRP is $500 higher than the S9's, both factors that could be dealbreakers for on-the-go content creators or people who are just starting out.
Body and handling
The S9 has a very sleek design, reminiscent of old rangefinder film cameras. Its face is a mostly flat surface, a leatherette cover that comes in four colors. (Real ones too; it's nice that Panasonic hasn't skimped on saturation like many gadget-makers are these days.) Unlike Panasonic's higher-end offerings, the S9 doesn't have any programmable buttons up front.
The camera is relatively compact for housing a full-frame sensor; it's smaller and lighter than Panasonic's four thirds-equipped G9II. However, the S9 is still not a small object, and we felt its thickness, rounded edges, and lack of ergonomic affordances made it difficult to confidently shoot it one-handed, like you can with cameras like the S5II or GH5II. Its surface finishes are relatively slick, and it doesn't have any front grip to speak of. (There is a leatherette-covered thumbrest, but it can only do so much.)
At the top of the camera is the mode dial, along with a programmable command dial that runs around the shutter button. There's also a programmable red button that, by default, will start recording video even if you're in a photo mode, though in a limited set of resolutions and framerates. (It'll start recording in MP4 Lite, standard MP4, or MOV, but you'll have to switch to video mode to shoot above 4K.) Finally, there's a cold shoe mount, which could be useful for accessories like vlogging microphones or on-camera lights as long as they can provide their own power.
Moving to the back of the camera, there's the flip-out touchscreen, which is the S9's only display. Unlike most other cameras in the current Lumix S or G lineup, there's no EVF to be found. The display is also the main way to select your focus points, as there's no joystick or directional pad. It's responsive, crisp and clear at 3.0" and 1.84 million dots (960 x 640px), but it's susceptible to glare even on relatively overcast days.
Above the display, you'll find the LUT and AF On buttons, both of which are programmable and easy to reach while shooting. Down to the right is the control wheel, along with the rest of the camera's buttons. We found the dial to be quite sensitive, which limited our choices while choosing its function; it's no fun looking down at your camera and discovering that you accidentally changed to a black and white photo style, or adjusted your white balance.
That sensitivity does help you zip around menus, but it doesn't make it any easier to use the wheel when you're one-handing the camera. It's placed such that you'll have to remove your thumb from the thumbrest to make adjustments, something that will almost certainly unbalance the camera unless you're supporting it with a second hand.
Photographers that spend most of their time in manual mode, or who ever want to control their primary parameter while also having access to exposure compensation, will probably wish for an extra command dial, and those who hate diving into menus will likely want an extra programmable button or two. However, it's definitely possible to get by with the controls included on the S9, especially if you take the time to customize the Q menu and "My Menu" systems. The main menus of the camera are also reasonably easy to navigate, and you can control them with either dial, or using the touchscreen.
The S9 uses Panasonic's 16 Wh DMW-BLK22 battery, the same one found in the S5II, G9II, and GH5II. It's rated to give you around 470 shots per charge, though as always that number is likely well below what you'll get during real-world use. That's quite a good showing, especially for a camera of this size; that's enough power that most photographers could head out for a weekend of shooting without worrying about bringing a second battery, unless you plan on shooting a lot of video.
The S9 doesn't come with a power adapter or battery charger, but it has a USB-C port that you can use with standard charging bricks. According to Panasonic, you should be able to keep it topped up with a battery bank, provided it and your USB cable support outputting at 9V at 3A.
By Dale Baskin
The Lumix S9 is a significant departure from Panasonic’s previous full-frame mirrorless cameras, not only in terms of its physical design but also the entire design philosophy behind the camera. After using it for a week, I feel like I’ve developed a pretty good sense of not only what the camera is but also what it isn’t. And that’s an important distinction.
If you learned photography on a dedicated camera, chances are the S9 wasn’t designed for you... if you learned photography on a camera that could also make phone calls, it’s entirely possible it was
It’s tempting to look at the S9 and see a more compact version of the S5II. (Or, possibly even a supersized version of the Lumix GM1 , a tiny Micro Four Thirds camera from a decade ago.) It’s a stylish camera, and the technology underpinning both models is essentially the same. But don’t let the rangefinder-esque styling and slightly retro looks fool you: the S9 is a very different camera than the S5II, designed for people with different priorities.
In fact, if you learned photography on a dedicated camera – possibly even one with a passing resemblance to the S9 – chances are pretty good that the S9 wasn’t designed for you. You might wish it were, but it’s probably not. On the other hand, if you learned photography on a camera shaped like a flat slab of glass that could also make phone calls, it’s entirely possible this camera was made for you.
Panasonic says it expects people to use it for photos as much as they will for video. However, if you’re looking for a traditional photo shooting experience, you’ll likely find the camera’s design frustrating.
There’s no EVF, which purist photographers will surely miss, and it can be a real challenge to use the LCD outdoors in bright light. It lacks a second command dial and has few custom buttons, so you’ll go menu-diving to change settings, and the lack of a mechanical shutter limits its ability to use flash and could introduce rolling shutter artifacts. As attractive as the camera is, carrying it around like a stills camera for long periods is fatiguing. It’s telling that at the launch event in Osaka, Panasonic provided members of the media with an accessory grip made by SmallRig that screws into the camera’s tripod socket.
As much as it looks like it might be designed for enthusiast photographers, its superpowers lie elsewhere.
The story is different as a tool for social media creation. We’ve seen plenty of cameras that claim to be made for social media users, including from Panasonic itself , but it’s often not entirely clear what value those cameras have added to a content creator’s workflow.
What I appreciate about Panasonic’s approach with the S9 is that it didn’t simply create a new camera with a selfie screen and declare it to be the perfect social media camera, mostly “Because we said so.” Instead, Panasonic seems to have made a pretty good attempt at understanding a real workflow issue that makes it challenging for social media creators to adopt a dedicated camera for their work.
Most social media content creators aren’t worried about the same things as enthusiast or professional photographers. They’re less concerned about resolution and dynamic range than they are about being able to create something with a unique look straight out of the camera and getting it online quickly, no matter where they are. Providing a workflow that allows them to do that, without having to do any additional editing, goes a long way to solving that problem.
The S9 costs $1499, about $500 less than the S5II, and while they're very similar from a technology perspective, the choice between them isn’t as much about price as it is about the problem you’re trying to solve. If you’re a purist photographer looking for a traditional camera experience and workflow, the S5II has you covered. But if you’re the type of person whose priorities include an efficient workflow for social media with as little post-production as possible, the S9 could be a good fit.
Sample Gallery
Please do not reproduce any of these images on a website or any newsletter/magazine without prior permission ( see our copyright page ). We make the originals available for private users to download to their own machines for personal examination or printing (in conjunction with this review); we do so in good faith, so please don't abuse it.
- 1 Initial review
- 2 Specifications
- 3 Press Release
Gear in this story

- Discuss in the forums
- See full product details
- View sample images
When you use DPReview links to buy products, the site may earn a commission.

Reminds me a bit of a 35mm GF1, a hundred grams heavier. The pancake lens offered is not likley to be as good as the GF1's M4/3rds 20mm 1.7. Its the same weight as a GX9. Woud miss a viewfinder, but the GF1 didn't have one either. F.
History doesn't repeat itself, but it rhymes. The logic of the original GF1 and GF2 etc was that the "content creators" of the time didn't need or want an EVF. Gradually Panasonic introduced them on their smaller cameras. A lot of compromises for a stills shooter, They seem to have made it as difficult as possible. Might go for a G100 instead.
If you are not satisfied with the Lumix S9, then buy a Leica M11 or Q3 and be happy. If Panasonic did everything completely and charged $6,000, you'd be complaining about the price. This Lumix S9 for $1,500 is a bargain. Much better than the more expensive DLux 8 rubbish.
Honestly, for $1500 I'd be MUCH more likely to get a new high-end phone and blog with that.
If Panasonic release FF version of LX100 for still photography : 1. LUTs button 2. 24MP BSI CMOS sensor with on-sensor phase detection 3. 2.36M-dot OLED electronic viewfinder 4. Mechanical shutter 5. FAS screen It should not rocket science
They should not rocket science that idea, I agree.
Why should cost $3000? 2.36M-dot OLED EVF is low end EVF used in $699 Fuji X-T200 FAS screen also used in $699 Fuji X-T200
$1499 Panasonic S9 already use 24MP BSI CMOS sensor with on-sensor phase detection
"However, the camera does have a 15-minute recording limit."
Is this insane? And this camera is designed for bloggers? Even if a YouTube video is 15 minutes, does Panasonic realise that the blogger records many minutes of video which is edited down during video editing?
How could DPReview report the 15 minute recording limit for a vlogging camera without expressing outrage?
How many 15m long individual takes do you really make?
In classic Panasonic fashion they seem to be rather under promising here. Looks like you can basically take 5-10 clips indefinitely without any overheating issues.
If you need longer, get a S5ii
Arrrrgh - if only it had an eye level EVF Id preorder immediately. shame really! what were they thinking?
Leica Q3 ou M11
They were thinking that they were making a video camera.
"The S9 costs $1499, about $500 less than the S5II, and while they're very similar from a technology perspective". They're anything but similar IMO. No viewfinder, no mechanical shutter, no way to use any flash whatsoever. OK, it has a FFsensor. Does someone who doesn't need a VF, flash and mechanical shutter really care about FF sensor?
You would have thought the vlogging crowd would care much more about a 15 minute recording limit than IQ differences between FF and MFT. Then again, I'm not a TikTokker or YouTuber - who knows what they're being told to buy by the sponsored-up influencers they blindly follow.
I guess this camera isn't for me. I wouldn't normally buy even a compact camera without a view finder. But, I learnt photography back in the films day, back when it was all manual everything.
After a few days the most interesting feature of this camera seems to be the crisis of online-reviewers it has disclosed. The over the top marketing effort Panasonic has undertaken financing expensive trips for online reviewers to push the sales of that half-baked camera looks like a disaster for both the reviewers and Panasonic.
I wouldn't call it an over the top approach when it's something that literally all brands do, definitely mismanaged tho.
Yes, but it was never so obvious. The disproportion between the camera that is obviously flawed and badly engineered and the praises of too many „influencers“ shortly after its release is just to embarrassing.
Having calmed down enough to give this some thought, I've changed my position somewhat:
The S9 is the most interesting camera release in a long time. It reminded me of something ... I'd seen this design before... then it hit me: the S9 is a dead ringer for the Nikon J5! Seriously, look it up in Google images: the shape, style, control layout, right down to the position of the lens release button. The J5 has a pop-up flash instead of the cold shoe and is missing the two buttons above the LCD, but the likeness is undeniable - the S9 is the J5 reborn with a FF sensor! Say what you want that's a ballsy move by Panasonic: essentially commoditizing FF, saying no, it's no big deal that it has a FF sensor, use it like a cheap and simple compact - have fun with it.
One big difference, Nikon 1 bodies pioneered fast sensor readouts, and you could argue they kinda failed before Nikon pushed the toy cam angle... Meanwhile the S9 lacks the fast readout to make a stills camera functional without it, so it's a toy video camera that sells for more than a phone and the form factor changes drastically once you attach any lens that gives it an advantage vs a phone. Good luck with that imo...
It would've made more sense to bundle it with the 24/3.5 DN than with the 26/8 tbh... I know they wouldn't bundle a Sigma lens, but it's gonna shine a lot more with something like that or the 45/2.8.
The goofy kit lens is "fit for purpose" considering the fun/casual image the S9 aims for, though the combo effectively undercuts any advantage of having a FF sensor.
And that's my final critique: That the S9 didn't need, doesn't benefit from, and is in some ways suffering as a result of, the decision to make it a FF camera.
And do you even know Pentax K01 ;) ?
Calm down, Panasonic didn't steal the J5 design. The S9 takes its lines from Panasonic’s own GM5, which itself was an iteration on the GM1.
I think it's closer to the J5 than the GM5 or the GM1 or even the Fuji X-A/M and Olympus E-P/PL bodies, but whatever: they are all in the same ballpark. The point is no one has made one of *those* cameras with a FF sensor before.
After MFT Camera in FF body (G9-2) next FF camera in Micro body :)))
This camera does not need EVF to be interesting for many people but a compact lens with reasonably f4 /f4.5 aperture will make it very interesting proposition for street shooters. I would buy this camera instead of GRIII with such a lens.
Sigma makes those lenses, but I'm not sure the slow readout makes sense for street stills shooting, gonna get a lot of rolling shutter distortion.
The whole problem with targeting niche markets is you won't sell very many cameras. But that might be the only customers that the camera makers have left today.
The x100vi is for a niche market too, fixed focal length, street photography dominant, premium priced rangefinder style camera. Surprisingly popular, though I feel that it’s not largely being bought by street photographers, but more by the fashion, style and TikTok inspired crowd.
The “creator” market is not niche. Out of curiosity I searched for number of YouTube channels with 1000+ subscribers. Over 10 million. That's just YouTube, other platforms are even more popular with the younger generation. That is massive compared to the serious photographer market.
I too would love to see something for more serious hybrid shooters but can’t fault Panasonic for taking a risk to appeal to the biggest audience .
For better or for worse, the S9 is likely to be a runaway sales success, provided Panasonic can get that other lens into production quickly. It's the most polarising camera announcement in years, which pretty much ensures that.
Not for me....... just not in the target niche. I'm sure it will keep content creators happy, but I'm into photography.
My friend has a car. He cannot go off-road. It is very noisy. The consumption is too high. It is difficult to park his car in narrow places. All in all, he loves his Ferrari. Looking at some comments it looks like this new camera release is the worst in the history of photography. Panasonic is aiming for a specific niche and they are providing a FF sensor in a very compact size with interesting features like the zooming or the LUTs. For people who hate post processing, for people who want a compact camera, for people who love THE best stabilization in the market, for people who don’t want to talk for half hour saying nothing…looks like there is a market for this camera. I really appreciate the transparency on how they communicated the recoding times which is way different to other manufacturers who are really good in autofocus but at the price of holding their hot bodies in your hand. Hope they can bring a similar idea to MFT as it will be easy to implement most of these ”needs”.
I thought all these kind of cameras were aimed at people who do talk for half an hour saying nothing!
Maybe the record limits will have the positive impact of reducing the amount of waffle spoken on talking head videos…
The reviews always seem to show the ugliest side of humanity. The world is ending. How could Company XYZ make such a mistake. Etc. Insert eyeroll here. But my thought in this case is thank you Panasonic for nailing some solutions to extremely important pain points. I love the LUT solution to enable us to create and apply our own signature fit and finish to some or all of oir creations, OOTB. That is awesome. A big high five for that. And simplifying the workflow is another huge pain point for any photographer or videographer, not just people who would be labeled or would identify as a content creator. It is the one of the very reasons why we all pull out our phones instead of using a dedicated device. Camera vendors are finally coming forward with real useful solutions to this camera device island problem as I see it. Kudos to Sony for their latest Sony smartphone / Sony camera integrations too
Would have thought that Panasonic could quite easily offer a stills-centric sister version of this camera which would sell quite well without spending a lot more on R & D. Joystick, EFCS, 14-bit raw, corner or hot-shoe EVF, add-on grip etc.
Seems like they've missed a trick making this such a pure social media camera. And I'm not sure the form factor is that great for vlogging anyway.
I think it would be easy for them, as they have most of what they need from previous cameras, GX8 evf, and adding an extra control dial isn’t a huge burden. What is uncertain is who would buy it if released at a higher price than the S5ii. People would say you should buy the S5ii, unless you must have the form factor. You would also need to overcome the unconscious association of bigger being better, and why something more compact and smaller would be more expensive. The xpro-3 seems to be the most anyone would want to pay for a rangefinder style camera, before they make the immediate jump to Leica. And I don’t think that was super popular.
In the current market, a gx10 m43 camera at £999 with 24mp pdaf sensor, a better viewfinder, and a LUT button would be a killer camera. Package it with a 15mm 1.7 or 20mm f1.7 for £1200-£1299.
The S9 is an interesting camera. However, as probably others may have commented, without a VF - it is not the camera for me.
Everyone is def talking about how this is not the camera for you. It’s all the rage right now!
Agreed! Which is why I waited 10 years for Pany to launch an updated version of the superb GX8. But they didn't. So I bought another one in silver on eBay a month ago. Love it! As responsive & modern as a 2024 camera, which shows how bad Sony, Panasonic, Nikon and Canon, but not Fuji, have been at releasing ergonomically superior street / social media photography/videography cameras over the last decade. Embarrassing Panasonic have launched this ergonomically flawed S9, after the brilliant S1/S2 series. I never ever shoot using the screen! You cannot check focus or proper exposure! I have the best camera phone out there, the Samsung Fold5 (better IQ than the GX8, being a 10 year more modern sensor), but composing without a VF is a bag of hurt, full size sensor or not. Please stop the dumbing down of street & social cams Sony, Panasonic, Nikon and Canon! Ergonomics, ergonomics, ergonomics! I want knobs, a VF, forward facing screen, USB-C in camera charging FF sensor. GX8 Mk2? /rant
Leica Q3 or M11
Dale and Mitchell, I have three questions:
1) If one were to mount an APS-C L-mount lens on the S9, would the camera default to crop mode like its S5 brethren?
2) If one has not yet downloaded custom LUTs to the S9, does the camera’s menu include traditional white balance and scene modes like the S5? Or is one forced to go the LUT route?
3) How easy or difficult is it to see and compose with the S9’s rear scene in bright sunlight?
Is everyone here old? You're too obsessed with outdated features. The iPhone doesn't have an EVF or a shutter. This camera offers a large sensor, a better and simpler design, and a variety of lenses. Nobody cares about distortion nowadays, especially on social media. Do you understand?
I'm incredibly old. A stills photographer. I can't see a phone screen for the glare so I want a viewfinder. I like a shutter button so I don't jerk the camera. A phone is hard to hold without it slipping out of my hand. This seems like a good camera except for the lack of an evf.
An iPhone has no EVF and shutter button because where would you put them?
Also, the S9 has a 3", 1.84M dots screen. How does that compare to an iPhone's?
Do you understand?
Nobody cares about full frame sensor on social media either. The person buying this camera wants something that phones don’t have. That’s why they’re not using a phone.
If what a phone offers was good enough, they would use the phone they already have.
This camera offers…very outdated features. A far worse screen than your phone, no VF and stops recording after 10 minutes, while your phone records 4k for hours. No headphone output? Ahh it’s wireless like every phone today. Wait…
iPhone has a shutter, every camera has a shutter. Be it mechanical or electronic.
The phone can shoot more than 10 minutes, it doesn't crop to half the screen area if you want 60p. and one of the reasons to go away from the phone for many is a viewfinder. Kudos to Panasonic for releasing something different but that doesn't mean we should ignore the drawbacks and compromises I love the idea of a compact FX body, especially with interchangeable lenses but this doesn't have the video features or the stills features to make it very useful. If I was already in the Lumix FX world I might get it, just in case for being better than nothing but I doubt it. The one thing I would say is, in the table above, the size and weight of the S5ii deserve red in this company.
The iPhone doesn't need a mechanical shutter because it has a sensor readout that's many times faster (an order of magnitude faster) so it doesn't suffer from rolling shutter distortion, every modern phone does. If you care about stills rather than video that's gonna matter.
Just to be a bit pedantic: iPhones actually do have a shutter button (at least all mine have had one). Just use the volume up button, perfect.
Using the volume up button jerks the phone. Unless I press it slowly. Then I get a series of shots. Phones are not cameras and probably never will be.
This was so close. Cool looking camera but missing key features for many enthusiast photographers.
The LUTs are such a great idea, a bit like "universal presets".
A EV compensation dial and a joystick for the AF would've improved the appeal for many photographers looking for a fun, easy to carry, with great IQ camera.
Will add in S9 mark II :)
That, and the ability to control a flash. Even if it only synced to 1/60 like my old film cameras, it would still be better than nothing. If they're gonna go cold shoe they should also go PC socket.
Nevermind the editing, does it make sharing any easier? Eg, tap twice in-camera and off it goes onto your Instagram?
You can't share directly from the camera, but sharing is very easy. You can set up the camera to automatically transfer images to your phone, and they will automatically appear in your camera roll. (At least on iOS – I haven't had a chance to test on Android yet.)
Within a few seconds of shooting a photo, you can open your phone and share it just as easily as if it had been captured using your phone's camera.
Panasonic S9 is another proof of why companies need to stop listening to consumers, and while a lot of people here commenting in DPReview may feel their voices have not been heard, listen.
You are in the minority, thats just a fact, most people who buy cameras, are people who put it on auto, shoots JPEG's, these people have very little interest in equipment, they just want a good picture and Panasonic knows exactly who to reach with this camera, its in the same ball park as the Canon R10, its simple, its minimal, its perfect for the common TikToker who's attention span matches a gold fish.
And honestly, Panasonic does need a mainstream camera that can break even cause right now, Panasonic, Fuji, Olympus all these small camera companies barely make 10% of the marketshare, together.
People who buy cameras are in the minority, most people just don't anymore. The days of mass market plastic DSLR's being bought, set to auto, then left in a drawer ended around 2012. The cannon R10 is £999 , has pancake lenses with autofocus, is 100g lighter, and has an EVF. Whereas the cheapest functional S9 kit (if you want an autofocusing lens) is £1799... do you think that's an appropriate price point for "people who put it on auto, shoots JPEG's, these people have very little interest in equipment"?
I think this camera is partly aimed at people like me. I don't want to buy a new system (Z, R, or E), and having a fleet of optics and the main S1R camera, I need an everyday compact camera. Moreover, a compact 18-40mm f/4.5-6.3 zoom lens appeared on the roadmap. I often don't take my camera with me because of its size and weight, but with the S9, I won't have to worry about that.
Nice to see some competition in the compact FF mirrorless market, although lack of an EVF makes this more competitive with the Sigma FP and Sony ZV-E1 than with Sony's A7C line. Perhaps we'll soon finally see still-friendly versions with EVFs?
I hardly use the evf now, dslr you really need it, milc not so much. I prefer holding the camera off my face now. In rare situation when it is super bright, maybe. got the panny gx850 and nikon z30 no real issues. I do use my cellphone a lot too for photos. If the cold shot was hot and had connection maybe they could add an eye piece option.
For a certain section of the market an EVF isn't crucial, but if you care about stills a mechanical shutter or a faster readout is and I feel that's what's really holding back this smaller form factor... My GX850 has a very quiet mechanical shutter that only goes to 1/500, but that's still incredibly useful.
Then again, the S9 isn't much smaller than an A7C (EFCS to 1/4000) or a Pana GX9, definitely larger than an fp...
The success of this camera will be based on how well the in camera editing and sharing functions work.
Camera companies have really struggled with implementing smartphone level touch screen functionality and apps into their cameras. Even Sony has struggled to get their smartphone division and camera division to come up with a solution.
I think Zeiss' ZX1 made a good effort but the editing and sharing functions are just too slow and buggy. For the S9 to take off its going to need to take the next step in this regard.
Seems unbelievable no manufacturer has really cracked this. Take a shot and in-camera tap a filter, tap share (to email, to Instagram, to Facebook, to Twitter etc...) All of sign-ins/contacts etc could be programmed into an app on the phone and transferred/updated to the camera, or just kept in the phone app (tap share in-camera, image transferred to phone if not already there and app whisks it away to whatever contact or platform you selected in-camera)
The perfect implementation would keep your phone in your pocket as a modem, so you do EVERYTHING on the camera and hit "send". At that stage, it will overcome the issues.
Or even using a WiFi network when you get into range. It's the pairing hassle that has always killed these things. Well, and the price of the Zeiss...
Ideally they have Bluetooth auto connect and sync properly. Just like every time I get in the car my phone auto connects and begins playing. I think easier to enter/get info from the phone rather than type all of your contacts, passwords, logins etc into the little camera screen. And maybe use the phone for more sophisticated edits, but beyond that everything in - camera, snap, filter/edit, tap share, to where/which contact. Boom.
My Nikon Zf has auto connect to my phone via wifi and bluetooth but the problem is still the same that I had with my Sony a7RIV and Fuji X-T5 which is that the connection is unreliable and often slow to sync.
The phone connects to the camera just fine it's the sync that is the problem. I'd say 2 out 5 times I lose connection during the syncing process. This is better than my previous cameras but still not good enough to make it a viable workflow process for easy camera to social media posting.
What I like to do if I'm shooting and it's gotta go to the Socials quickly, is I take my tablet with me, and between sets of the show I pair it with my camera and select the keepers to transfer. Once that's done, I can use the tablet to Instagram whatever I'd like. BONUS: the Insta app is buggy too! So even if I manage to get my sometimes recalcitrant Fuji to connect (to be fair, it has gotten much better in the last year or so) the Insta app will crash and lose my last 15 minutes of selections and edits GRRRR.
So it's not one tap and done, but it does work and I like the sitting down to think about my selections aspect as well.
What color is this review unit? When you say there are four color options, I'm expected to see the photos of them all.
You’ll find they actually take the same photos.
There's actually five colour in some markets! Silver, black, blue, green, red. Photos in this review look like the blue version.
... and in Japan, you can also get blue/silver, green/silver and red/silver. That's eight different colour schemes. Nice. Blue/silver for the win!
If there is Leica version of this camera using this size+weight combine with some of Leica CL's features, it will be a great upgrade for Leica CL.
Leica CL has a finder ...
Lack of EVF is a push back for me. Otherwise, this camera have a lot of attractions which make me to consider to upgrade from Leica CL. However, the simplicity of buttons in Leica CL seems not around in this model.
When you download a LUT with Lumix Lab, do you get to keep it? As in, offload it onto your computer in case the creator decides to pull it from the app? Or this LUT store a rental situation like music streaming?
This is a great question! It turns out the answer is yes. (At least on iOS, which is what I'm using for testing.)
In the LumixLab app, you can share any LUTs in your library, including those you've downloaded. It exports a .zip file that contains a standard .cube file. Kudos to Panasonic for thinking of this.
Awesome! Let the LUT collection begin...
The vast majority wanted a small, almost pocket-size full-frame camera to take photos, and not this thing. No viewfinder, no classic controls. Seriously, who decides to make these things? Pay me half the salary of the person who decided to do this thing and I will make them millions.
You might rephrase this to say, "The vast majority of DPReview readers wanted a small, almost pocket-size full-frame camera to take photos, and not this thing."
Panasonic serves many markets, and this camera is aimed at a slightly different demographic than your typical DPReview user. However, I can understand why DPReview readers are frustrated that it's not quite the camera they hoped for.
I think new generations buy smartphones or professional cameras. Not this compromise.
Dale, we already had that in the Sony RX1. That thing is really tiny! Just put an A mount on it, and you have the perfect full frame compact ILC.
@Marty4650 The thing is that I want a 28 mm. And, sorry if I am wrong but the Sony RX1 does not have interchangeable optics. Of course, I really like the Sony Sony RX1. We also have the sony a7c but it is horrible. They could make it with a vintage design. And well, improve the colors that Sony gives...
@Dale Baskin
Let's see how much they sell of this model... I find it hard to think that a blogger would spend $1700 on a camera. And yes, I'm frustrated ;)
Panasonic needs to release an MFT version of this camera, in the same body, with the same AF and as good or better IBIS, the same video codecs, the same LUT function, but with a mechanical shutter, unlimited video recording times and a headphone jack, and at a lower price.
This should be doable because the MFT sensor needs less room and creates less heat in the camera body.
(And we could use the better, already existing Panasonic MFT pancake lenses on it, with AF.)
Panasonic G100 is already a similar size to the S9 yet it packs way more features, has a mechanical shutter, since the G100M2 is leaked to be the next camera to be announced and then the LX200, well it would seem that your wish is coming true, the G100M2 would be infinitely better camera though, its size and weight makes it superior because it alone has more controls and EVF + mechanical shutter, imo
Eyeing the Fuji X-T50 with its kit lens to replace my X-T20 as my travel camera. But I would seriously consider an evolution of the G100 or LX100. I never used a MFT cameras but was always happy with Panasonic compacts or superzooms (all things considered).
Panasonic seems to be spreading themselves pretty thin tbh... Reusing FF body form factors on M4/3, killing off or de-prioritizing *both* their lower end M4/3 bodies (GX) and their higher end FF ones (S1)... That all made sense when the end goal was the S5 II, but the S9 is not it and I'm not sure the video content creator market is gonna embrace it the way they hope. They're not really asking for ultra portable ILCs full of compromises, that's what they've got phones for.
I'd entertain the conversation of a G100 M2 or an LX200 as a smaller EDC or travel camera.
Social media creators. And full frame camera? Hmmm.
No EVF? No deal.
Bonjour, …I have just phoned my supplier of many, many years. He doesn't believe in the future of the S9. Except for the petit bourgeois who want to look good. ...I don't either. Youtoubeurs aren't going to spend 2,000 €/$ to publish on the Web. Right now, they're filming with a smartphone, a Sony, etc. Nor are any of the advertised lenses luminous. How can you photograph or film indoors with a lens opening at F/4.5 or F/8.0 ? A true professional will use a S5, S5II, GH5, GH6, Etc. The difference in size is not that important... I forgot... ...For more than 10 years, Panasonic has consistently failed to listen to its users. Go to the forums and elsewhere. Many photographers and videographers were longing for a GX10 or LX100III with Microphone + headphone connectivity... ...Depending on how you use it, shooting with a M43 or Full Frame makes little difference. But especially when you know that it ends up on a living-room TV or a PC screen... Cheers,
Yep. I am assuming those who keep saying "you aren't the market" don't realize that those of us that were the market have seen this from Lumix before. The GX8 and GX85 would have been game changers with 3.5" mic jack and in camera charging and a headphone jack.
Lumix is missing out when it should have been the leader...
My GX9 as still some beautiful days ahead!
Hey Lumix, I am going to help you out... Put all of your S5II features (Sensor, IBIS, Luts, etc) into the GX8 body with a full compliment of ports, and you have your "vloggers" camera.
(What almost no one is mentioning is that "vlogging" is slowly becoming passe, ie does this market even exist anymore)
I have Rode Stereo VideoMic Pro with this Rycote mount, which I got for environmental shooting. And it's a disaster. Pure marketing. In reality it's wobbling a lot, making loud snuffing noise. So as the wire. And while you can find a way to fix the wire the way that it won't touch the body of the microphone, that Rycote mount is unfixable. The worst part of this all is that Rode didn't bother make detachable cable and put 1/4" thread on the bottom for hard mount.
So may be it could work in static, but on the move that Rycote is completely unusable.
I could be terribly wrong, but why social media creators need full frame format?? To post tiny pics on IG? To upload cropped video on Youtube? I feel this camera is totally mis-purposed.
The FF will give better "bokeh", low light performance, and dynamic range.... but I don't think TikTokers care about this, which means their phone is still the best place for them to go.
I agree with you 100%...
A camera cannot have more than one function? Just because it's marketed towards content creators, it's just as good for photography and everything else.
@Andyyy What does it do so special for photography? LUT customization?
Customizable / future expandable film simulation (via upload New LUTs)
Fun fact, Flickr is a social media site, and so is the one you're typing this comment on.
DGrinb: Does it have to do anything special? It's a small camera, easy to travel with. Some people here talk like the camera is unusable for photos.
Andyyy Maybe you're right. Maybe it's just not for me.
Why do most photographers need full frame? Most photographers are hobbyists. Most photographers also mostly post only on social media and rarely ever print.
Ganesh 8055, Because it's a hype. Not everyone knows what to do with that though.... Same as RAW, most professionals are shooting with. But with introduction with LUT and in-camera presets, people go back to JPEG.
This is a bold and out of the box move by Panasonic. It appeals to me as a small, unobtrusive lightweight high quality stills camera for travelling. A few small f2 primes and I would be done
Yet it is heavier than R8 which has viewfinder and the small primes you wish for.
@vit adamek R8 has a terrible battery, lacks ibis, and bulky, nobody is stopping you from getting it.
I certainly consider IBIS to be more critical than an EVF. I like an EVF, but it doesn't increase my shooting envelope the way IBIS does, especially in low-light. And more than that, I find that for a lot of people using the EVF actually constrains their creativity in how they frame photos, since they are far less likely to try interesting angles that depart from just an eye-level view.
And yeah, the fact that this camera gets more than twice the battery life of the Canon R8 is definitely a factor, too.
I yet have to use more than two batteries in my day to day shooting with R8. R8 is hardly bulky, it is about the same size but greater depth thanks to grip and EVF hump makes it taller.
Yep, ibis is nice to have feature, for static subjects where you want to use slower than the usual focal length equivalent SS. Not a dealbreaker for me, I used to own many cameras without IBIS in the past, including A7 mk I, few Panasonics, Canons, Nikons, Fujis... etc.
Many would argue that EVF is better for framing unless you need low to the ground or high above head angles. Looking through EVF makes you more aware of potential clutter in your composition. This is emphasised in bright sunlight where the LCD is hard to use. It is also a third point of contact to stabilise your camera more effectively.
Hahah, the 3rd point of contact argument is mostly relevant when you don't have IBIS, though, or are trying to get sharp shots at like 1/4s shutter speed or slower with IBIS.
your f2 primes are out of place with this camera as it has no mechanical shutter or flash shoe (or evf for better viewing in the sunlight).
This "R8 has terrible battery" is from those who never tried the camera and go after CIPA ratings. In real life is totally fine.
Do you have winter where you live? Battery life matters a lot more when you're shooting in sub-zero temperatures (which also often produce great photographic opportunities)
@Andyyy the battery is 1080mah @ 7v, LP-E17, that's significantly less than the LP-E6 found in the R5, R6 and all the full frame DSLR's, and that produces 1800ish @ 7v. Panasonic is 2200 @ 7v, and not a budget model battery. There's a reason why Canon wont embarrass themselves putting that battery inside of an R5 or R6.
It has nothing to do with embarrassment omg 🤦♂️ It is simple market segmentation. The battery life is fine, I can take 1000+ shots on single battery if I do burst for i.e. birds in flight. I don't have a need for 3rd battery yet. If used on tripod for video or time lapse and similarly, I can power it through USB-C compatible powerbank or mains adapter.
Vit Adamek is super hyped on his R8. If it had IBIS and third party lenses I'd more seriously consider it as the price point is quite attractive. However I doubt it has the tank-like build of my X-H1, which has already trained me to carry extra batteries :-D And IBIS really does matter, it makes a big difference.
X-H1 is great body, great control scheme and ergonomics.
Nice try, but things don’t fit. They take important things away that could make it interesting for photographers - even those coming from phones. But in the video department it can’t record 4k longer than minutes before overheating? In 2024, really? And all that cropping. And it’s larger than a A7c that has a VF and doesn’t overheat. Least they surprise beginners who expect an all-in-one solution that does everything in Auto with a fixed aperture manual focus lens. What were they thinking?
Saying it's "larger than an A7c" is very, very weird.
It's 2mm different in height and width which is impossible to notice, but is an inch smaller in depth because doesn't have the protruding grip and eyecup on the A7C which are the things that actually get snagged on a camera when you're trying to slip it into a tight bag.
(Source: my GX7, which is roughly identical in size to the A7C)
@Androole granted it would be fairer to say it’s barely any smaller than the A7C (or A7Cii). But that’s still not great when you lose the mechanical shutter, EVF, and a whole bunch of other stuff.
“an inch smaller in depth” because of the grip: As soon as a lens is attached this doesn’t matter anymore. No VF, no eyecup! We have a winner here 😎
Almost as if the absence of features like the EVF are compromises with both pros (thinner, lower cost) and cons (loss of functionality in bright light, different shooting experience).
Of course it’s a compromise, everything in camera design is a compromise, but here I think many would question whether the compromises are worth it. It’s simply not that much thinner, or cheaper for that matter. I suspect if Sony had made the same choices with the A7C they’d have ended up with something even smaller certainly, but notably they didn’t do that - they produced the highly successful A7C we know today instead.
This would make more sense being a m4/3 camera, instead it's held back by big lenses and bad rolling shutter
See the gx100 for the m43 version...
It looks to me that Pana tried hard to make this camera appear desirable. Aesthetics is a cultural thing. I don't know what culture they targeted but it doesn't do it for me like the Fuji X100. No doubt, the retro look of the Fuji appeals to us old photographers. Perhaps the plastic look appeals to young phone users but I don't think so. I would have thought a titanium shell would have been more appealing than blue and black plastic.
As a photographer who loves shooting jpegs and avoiding the editing, the LUT idea really appeals to me. I like the size and styling too. Unfortunately literally everything else about the camera is a turn-off - especially the distortion prone e-shutter and lack of EVF. I think Panasonic have probably missed the mark on this from all the feedback I’ve seen, but I hope they realise they’ve got the germ of a great product here and try again soon.
As a side note Panasonic paid travel expenses to Japan for content creators to do reviews, which is too lavish, briberish. I like how everyone is saying their opinion is not influenced by this ... I have anti bribery trainings at work very often, so had urge to comment on this.
Ah - I do wish Clarence Thomas and a whole lot of other people had your insight and personal ethical reservations. Bravo!
This is not my insight, I am just interpreting information that we are fed with in anti bribery trainings (I work for US company). I also used that vocabulary - lavish gifts, etc. It would be interesting if in the beginning of video or article they put information how many dollars were provided by Panasonic as gift for that creator - it is thousands, that is too much.
What's more telling is that no one overwhelmingly recommended the camera, even with all the greasing of the wheels. I am clear Lumix has no idea how to capitalize off this market because they built the ideal camera in the GX-8.
@Trk @jhunna On these press trips, the company usually pays for the air fare (usually same class as their own employees get) and the hotel, plus travel to locations. (And if it’s a Japanese company, you might well be expected to be up at 7 in the morning for the first presentation or briefing.) That’s it. No pocket money, no other expenses paid, no free cameras to take home. (Not, I suppose, that anyone’s going to believe me: the fallacy’s now too entrenched.)
@photo-opinion The youtubers all received cameras to take home. Do they need to send them back? I don't know. But they all left the S9 by virtue of the at home samples they shared.
I have to be honest, some of the LUT shots are gorgeous!
Sony has done the same for years
Sure, this only shows how camera business is dishonest. Value of these things is too high, imagine if this happened in pharma where they would pay this to doctors for some conference about medicines - such an act would have severe ramifications. Camera manufacturers - bribery and lack of ethics at its highest.
Paid press trips isn't just a camera industry thing, it happens in many industries when companies are launching new products.
Regarding camera "gifts", I don't know about social media influencers, but review publications like DPR usually receive loaner units which must be returned to the manufacturer.
The issue lies in the fact that many YouTubers are not part of the press, nor are they independent journalists. Consequently, they lack the same level of accountability and ethical standards. When these YouTubers fail to comply with certain expectations or requests, they face severe consequences – such as losing access to sponsored trips or sample cameras. This disturbing practice as been reported by several content creators. Moreover, there has been a recent scandal involving Insta cameras. This incident sheds light on the unethical practices within the camera industry. Camera companies, unfortunately, are not immune to such behavior, and we witness their questionable actions on a daily basis. It’s disheartening to see how some camera companies prioritize their interests over transparency and ethical conduct. It is probably reason camera companies are choosing YouTubers, they can manipulate and extort them to their will.
Ok, so Gerald Undone made an interesting video that shows how this problem with corruption is serious. Truth is now uncovered with Panasonic event.
@TRK Pharma reps totally bribe the doctors, in the USA anyway. Doctors can get all manner of travel and free stuff and meals and etc. I knew a pharma rep for awhile, she verified this.
This S9 is basically the same price as an S5II, there is literally only £100 difference with the 20-60 kit offers. £1799 vs £1899. It's not bad looking, but it's not a £1500 camera. I'd put it around £999. £1299 with lens maybe.
Don't worry , it will be soon offered for this price
Approx 360 posts and I haven't spotted a "pre-ordered" or "I will buy". Cleary the comment section does not represent the market, but no a good sign for this camera either ...
@ThomasRnp Some of the market is represented here. Lumix just doesn't know how to make the camera they say they are making.
So, if you want use any other lens apart from the near useless pancake lens, you would need the additional grip by Sirui. can't see how you're going to balance the S9 with the L lens. The Sigma DA C prime lens, the Pana 1.8 prime lens would be alright but other lens would require this grip . there goes your compact camera. Just get the S5ii, excellent camera.
why cant camera manufacturers just give us sun light viewable rear lcd just like our phones.
dpreview: "This is not the camera you're looking for."
I know, I get it, but I hate that it looks like the camera I was looking for! It holds out the tantalizing possibility of a full-frame E-X4 before snatching it away due to what I'm confident will prove to be ill-judged market segmentation.
Right. Also, while it obviously is not the camera we're looking for, it is frustrating to see how easily it could have made to be just that – without making it any worse for what it is targeted to be, for that matter.
The problem might be that with the profit margin they expect from the existing S9, such a camera would be unlikely to be available for less than $2,000.
The design - the "Leicabrick" that Panasonic has always done well - is everything that one might want from a "Zf" styled in classic rangefinder. Everyone on this forum can clearly envision what this camera should have been - a retro-styled, photo-centric version of the S5 ii with solid video specs if you need them - it's truly one of life's mysteries that the people at Panasonic could completely miss it.
So true. Wrong turn. Took away the photocentric features and left a brick that states: VIDEO, but overheats after minutes in 2024, crops like hell and has no headphone output. Love that luts concept.
Really... slow sensor with no shutter, no EVF to drive off still shooters, overheating after trivial minutes to drive off video shooters. Is this only for the few "form over function" people out there?
I'm occasionally tempted to add a FF to my hughe M43 and small Fujifilm set, particularly with smaller FF options available. A real FF take on the GM5 might have done it, but it's not this.
The S5II is just $300 more, brand new, and is a very compelling option. It can control a flash, in addition to having great ergos and all day long video capabilities. And it can be primed with different LUTs.
@Mr Bolton, so what, if someone wants a photographer's camera but doesn't want an SLR-size camera?
@Hubertus Bigend well Panasonic had the chance with this one and I was kinda rootin' for 'em.. but I guess just get on the wait list for an X-100VI.
I like the idea of shooting photos with log gamma and luts, then edit them in Resolve just like videos. But 8bit JPEG is not good enough for v-log, there will be banding. I hope they can add 10 bit 4:2:2 HEIF (.hif) file format for this purpose. Especially after Resolve added support for 10 bit 4:2:2 HEIF files recently.
You can shoot S-log3 HEIF photo with new Sony cameras, but you can't preview or embed custom LUTs in photo mode.
I learned this the hard way after buying an S5M2 specifically to use, modify and create LUTs for stills. I can't believe Panasonic didn't use the S9 launch to introduce HEIF support, which tells me they probably never will. But I hope Lumix Lab is a hit and encourages Sony to enable LUTs for photos via firmware update.
@tilted_horizon You can try Silkypix Panasonic version for free. I read somewhere that it can decode RAW files to v-log photos in 16bit tif files. The color science of that software is a little different compared to Panny in-camera processing pipeline, but close enough at least in sunlight (not so sure in artificial lighting condition). If you tried, I'm happy to hear the result.
Also, Lightroom has v-log camera profiles for supported Panny cameras, but that's almost unusable.
A can of worms opening: “I’m working on my own LUT’s, and I’ll have them available soon,” says one Youtuber. For a price, no doubt. (Yes, I’m cynical—I used to work in a profession noted for it—but perhaps that’s why that particular reviewer was so very enthusiastic about this camera—and even THAT lens?) As if we didn’t have enough of them flogging presets for the first five minutes of every video as it is.
I have a slight (enormous) allergy to the words 'content creator'. Are not all cameras able to create content? And while LUT seems to be handy, with Canon DPP and Picture Styles I've been able forever to edit a photo to my liking and export the settings via a Picture Style to my camera.
You’re not the only one with that allergy. If there’s ‘content’ what’s the ‘container’? It makes me think of someone (or a robot now) on a production line shovelling peas into a tin. I’m expecting any day to find out someone writing a book isn’t an author any more, they’re a ‘content creator’ whose job is just to fill the space between the covers.
The comment from @Photo-opinion reminded me of something. Yesterday I read an article titled something like: "Pixar is laying off X% of its workforce as Disney scales back content".
And I just got this gross feeling... So Pixar movies are just "content" ? Just the same content as someone's generic walkaround VLOG. When referring to something as "content" it's honestly so disrespectful for the creator of the more time-intensive "content".
It's like saying everything is *just* a building. A single parking garage tower however can never be measured to a Sagrada Familia Cathedral. But they are both buildings. In the same way a perfectly timed landscape photo of a once-in-a-liftetime event is the same as someone's snapshot of the sunset. They are both "content" today it seems.
To the streaming services, yes, movies, music, games really are just "content", a source of revenue. And sometimes it's probably very frustrating for the creators. Look how Netflix has become a graveyard for (sometimes excellent) shows that only got one season, because not enough people happened to watch them during the launch week. A slow burner never gets the chance to shine.
yes yes yes! We need more compact full frame cameras (also for photogs), way to go Panasonic!
Although i think hi-res sensors will make them much more viable for photography, since a small+fast prime lens = relevant digital zoom option (35mmf2 60MP, 70mmf4 15MP).
I just wish they realised that a light compact body isn't just for vlogging. A just in case backup body for travel that doubles to make a minimalist walking around outfit.
You may also like
Latest sample galleries.

Latest in-depth reviews

The Sony a9 III is the world's first full-frame mirrorless camera to feature a global electronic shutter with simultaneous readout. After extensive testing of this 120 fps sports camera, to see what you gain (and, perhaps, lose).

The Fujifilm X100VI is the sixth iteration of Fujifilm's classically-styled large sensor compact. A 40MP X-Trans sensor, in-body stabilization and 6.2K video are the major updates, but do they make the camera better?

The Panasonic Lumix S5II launched the second generation of Panasonic’s full-frame mirrorless camera system and was the first Panasonic to feature phase detect autofocus. As our review reveals, it’s a heck of an all-around camera for both still and video shooters.

The fourth camera in Leica's SL series of full-frame mirrorless cameras sees the 60MP BSI sensor from the Q3 and M11 models arrive with a significant interface redesign.

The Nikon Zf is a 24MP full-frame mirrorless camera with classic looks that brings significant improvements to Nikon's mid-price cameras. We just shot a sample reel to get a better feel for its video features and have added our impressions to the review.
Latest buying guides

What’s the best camera for around $2000? This price point gives you access to some of the most all-round capable cameras available. Excellent image quality, powerful autofocus and great looking video are the least you can expect. We've picked the models that really stand out.

What's the best camera for travel? Good travel cameras should be small, versatile, and offer good image quality. In this buying guide we've rounded-up several great cameras for travel and recommended the best.

If you want a compact camera that produces great quality photos without the hassle of changing lenses, there are plenty of choices available for every budget. Read on to find out which portable enthusiast compacts are our favorites.

'What's the best mirrorless camera?' We're glad you asked.

Above $2500 cameras tend to become increasingly specialized, making it difficult to select a 'best' option. We case our eye over the options costing more than $2500 but less than $4000, to find the best all-rounder.

Every week, we ask newsletter subscribers a question about gear, creativity or life. Recently we wanted to know: If you could go back to your 20-year-old self, what camera related advice would you give yourself?

We had a chance to shoot with the Fujifilm X-T50 for quite a while, so we put together a first-look video, outlining what it can offer, as well as shooting a sample gallery using a variety of Film Simulations.

Setting up your new camera is a rite of passage for all photographers. Avoid mistakes, adjust these settings first.

Leica has announced it will introduce the D-Lux 8, an enthusiast zoom compact based around a four thirds type sensor.

We had the opportunity to use the new Panasonic S9 for several days at Panasonic's Lumix Summit in Osaka, Japan. In this short video, we take a closer look at the camera, who it's designed for, and the philosophy behind its LUT-based workflow.

The best of the best from the DPReview community, see our favorite photos you made from the "for the birds" challenge.

The Lumix S9 is Panasonic's newest full-frame mirrorless camera. It allows users to create their own custom looks for out-of-camera colors and is the first full-frame Lumix camera aimed squarely at social media content creators.

Panasonic has announced a manual focus, fixed aperture 26mm F8 lens to go with the S9, it's also said it's working on an 18-40mm F4.5-6.3 wide-angle zoom.

Now in its seventh year, the annual awards recognize some of the best astrophotography of the year.

Furthering its quest to implement AI across its product line, Adobe is bringing Adobe Firefly's 'Generative' tool to Lightroom. Also announced today: expanded tethering for Sony cameras and an updated toolbar for the mobile version.

Every week, we ask newsletter subscribers a question about gear, creativity or life. This week we wanted to know: if you could only pick one lens, what would it be and why?

We got a chance to take Fujifilm's new premium kit zoom to Stockholm, to get a sense of how it looks on a 40MP sensor.

Leaping lemurs and enchanting baobab trees, nature photographer Erez Marom takes us through the national parks of Madagascar.

On this day in history, in the year 2000, Canon's EOS D30 became the first-ever multi-megapixel CMOS sensor used in a production camera. It also helped usher in the then-new era of 'prosumer' cameras.

Sigma has announced an updated 24-70mm F2.8 as part of its Art series of lenses. The 24-70mm F2.8 DG DN II

Fujifilm has announced the X-T50, a mid-range 40MP APS-C mirrorless camera that gains image stabilization, subject recognition AF and a host of high-res video features.

Fujifilm has replaced one of our favorite kit zooms with the XF16-50mm F2.8-4.8 R LM WR, a wider, lighter but less bright premium kit lens.

Fujifilm has announced the GFX 100S II, an upgraded version of its more compact, affordable 100MP medium format mirrorless camera, with a better viewfinder and upgraded capabilities.

Fujifilm has announced the GF 500mm F5.6 R LM OIS WR, a relatively compact super-telephoto prime for its GFX medium format system.

Fujifilm has joined C2PA and CAI, the two groups leading efforts to add cryptographic proof of authenticity to photos.
![article reviews samples Canon announces EOS R1 development [Updated]](https://1.img-dpreview.com/files/p/E~C148x0S888x888T72x72~articles/0785314321/Canon_EOS_R1_with_lens.jpeg)
Canon has announced it is developing (and is currently testing) the EOS R1, the "first flagship model for [the] EOS R system."

In late February, Sigma announced the 15mm F1.4 DG DN Diagonal Fisheye lens, and we put it into the hands of a professional astrophotographer for a shoot in the Canadian sub-arctic. Check out his gallery and see how it performs under the night sky.

With retro-inspired design, China-based upstart Thypoch is hoping to catch eyes with its pair of lenses for Z, X, E and RF mounts.

Announced in April, the $340 16mm lens joins the collection of 24mm, 35mm and 55mm lenses that came before it.
The Pixel 8a is the newest member of Google's Pixel 8 smartphone family. It uses the same cameras as its predecessor, the Pixel 7a, but gets the more powerful processor and features found in the Pixel 8 and 8 Pro. We took it for a spin to see how it performs.

Every week, we ask newsletter subscribers a question about gear, creativity or life. This week, feeling nostalgic over our past 25 years, we want to ask about the one that got away, or rather, the one that you let get away.

This year is DPReview's 25th anniversary. Naturally, we've been thinking a lot about cameras from the past quarter century and even beyond. The current DPReview editors reminisced about what cameras got them started in photography. For good measure, we also looked to the archives to compile some former DPReview editors' historical answers.

When shooting landscapes, it's easy to chase classic scenes involving bold sunrises and moody clouds. In this article, we explore an alternative approach that looks beyond sweeping vistas to focus on smaller moments that are less likely to be replicated by other photographers.

At its "Let Loose" event on Tuesday, Apple introduced new iPad Pros with OLED displays, a pro-oriented camera app for shooting video, an updated version of Final Cut Pro for iPad and more.
- Gear Patrol
- Work for us
- Advertise with us
- Feedback / Contact us
- Camera reviews
- Lens reviews
- Printer reviews
- Buying guides
- Sample images
- Editorial enquiries
- Camera search
- Camera comparison
- Lens search
- Product timeline
- Browse all products
- Community Guidelines
- My Settings
- My GearList
Help | Advanced Search
Computer Science > Software Engineering
Title: streamlining software reviews: efficient predictive modeling with minimal examples.
Abstract: This paper proposes a new challenge problem for software analytics. In the process we shall call "software review", a panel of SMEs (subject matter experts) review examples of software behavior to recommend how to improve that's software's operation. SME time is usually extremely limited so, ideally, this panel can complete this optimization task after looking at just a small number of very informative, examples. To support this review process, we explore methods that train a predictive model to guess if some oracle will like/dislike the next example. Such a predictive model can work with the SMEs to guide them in their exploration of all the examples. Also, after the panelists leave, that model can be used as an oracle in place of the panel (to handle new examples, while the panelists are busy, elsewhere). In 31 case studies (ranging from from high-level decisions about software processes to low-level decisions about how to configure video encoding software), we show that such predictive models can be built using as few as 12 to 30 labels. To the best of our knowledge, this paper's success with only a handful of examples (and no large language model) is unprecedented. In accordance with the principles of open science, we offer all our code and data at this https URL so that others can repeat/refute/improve these results.
Submission history
Access paper:.
- HTML (experimental)
- Other Formats
References & Citations
- Google Scholar
- Semantic Scholar
BibTeX formatted citation
Bibliographic and Citation Tools
Code, data and media associated with this article, recommenders and search tools.
- Institution
arXivLabs: experimental projects with community collaborators
arXivLabs is a framework that allows collaborators to develop and share new arXiv features directly on our website.
Both individuals and organizations that work with arXivLabs have embraced and accepted our values of openness, community, excellence, and user data privacy. arXiv is committed to these values and only works with partners that adhere to them.
Have an idea for a project that will add value for arXiv's community? Learn more about arXivLabs .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A comprehensive guide on how to approach, write, and format an article reviewAn article review is both a summary and an evaluation of another writer's article. Teachers often assign article reviews to introduce students to the work of...
Learn how to write an article review with expert tips and real-world examples. Master the art of critical analysis in this comprehensive guide!
An article review is a critical evaluation of a scholarly or scientific piece, which aims to summarize its main ideas, assess its contributions, and provide constructive feedback. A well-written review not only benefits the author of the article under scrutiny but also serves as a valuable resource for fellow researchers and scholars. Follow these steps to create an effective and informative ...
An article review is a critique or assessment of another's work, typically written by experts in the field. It involves summarizing the writer's piece, evaluating its main points, and providing an analysis of the content. A review article isn't just a simple summary; it's a critical assessment that reflects your understanding and ...
Wondering how to write an article review? 👉 Check out our step-by-step guide! You'll find the article review format, template, & examples.
Feeling stuck writing an article review? No need to worry. This guide provides a step-by-step process on crafting a standout review, along with examples.
A comprehensive guide on how to write an effective article review. Learn the step-by-step process, from understanding the article to analyzing its strengths and weaknesses, and crafting a well-structured critique. Master this essential skill for academics, researchers, and critical thinkers.
For many kinds of assignments, like a literature review, you may be asked to offer a critique or review of a journal article. This is an opportunity for you as a scholar to offer your qualified opinion and evaluation of how another scholar has composed their article, argument, and research. That means you will be expected to go beyond a simple summary of the article and evaluate it on a deeper ...
Here is a basic, detailed outline for an article review you should be aware of as a pre-writing process if you are wondering how to write an article review. Introduction. Introduce the article that you are reviewing (author name, publication date, title, etc.) Now provide an overview of the article's main topic.
The best proposals are timely and clearly explain why readers should pay attention to the proposed topic. It is not enough for a review to be a summary of the latest growth in the literature: the ...
Don't know what an article review is and worry because of it? Just relax! We've prepared an ultimate guide with cool ideas and examples to follow!
Writing a critical article review requires that you to read the selected article in detail as well as other related articles so you can present an objective and educated evaluation.
When asked to write an article review, it is only natural to feel confused about the purpose and definition, especially if you are only learning how to write a good article review. In simple terms, this type of academic writing represents certain work where you have to provide an analysis and summary of an article already written by another individual. It is safe to say that we are dealing ...
Summaries and critiques are two ways to write a review of a scientific journal article. Both types of writing ask you first to read and understand an article from the primary literature about your topic. The summary involves briefly but accurately stating the key points of the article for a reader who has not read the original article. The critique begins by summarizing the article and then ...
Overview When you are asked to write a critical review of a book or article, you will need to identify, summarize, and evaluate the ideas and information the author has presented. In other words, you will be examining another person's thoughts on a topic from your point of view. Your stand must go beyond your…
To review an article, you must summarize, evaluate and analyze to bring out the most important points of view. Read about article outline, tips & formatting.
When you write a peer review for a manuscript, what should you include in your comments? What should you leave out? And how should the review be formatted?
A literature review is a survey of scholarly knowledge on a topic. Our guide with examples, video, and templates can help you write yours.
Here, I provide tips on planning and writing a review article, with examples of well-crafted review articles published in The FEBS Journal.
Learn how to write an effective article review with our step-by-step guide. Explore article examples, literature reviews, article writing, book and manuscript reviews, and much more. Discover the key elements of a review, common FAQs, and get started today.
Article review writing Introduction The purpose of this document is to help students and researchers understand how review of an academic journal is conducted and reported in different fields of study.
Learning how to write a constructive peer review is an essential step in helping to safeguard the quality and integrity of published literature. Read on for resources that will get you on the right track, including peer review templates, example reports and the Web of Science™ Academy: our free, online course that teaches you the core competencies of peer review through practical experience ...
A literature review can be a part of a research paper or scholarly article, usually falling after the introduction and before the research methods sections. In these cases, the lit review just needs to cover scholarship that is important to the issue you are writing about; sometimes it will also cover key sources that informed your research methodology.
Use these 53 performance review examples to deliver clear and thoughtful messages to employees. Foster a culture of improvement, growth, and recognition.
Our findings suggest that shortened versions of the SOC-13 scale have better psychometric properties than the original 13-item version in the Czech adult population. Particularly, SOC-9 emerges as a viable alternative, showing comparable reliability and validity as the 13-item version and a clear one-factorial structure in our sample.
New study finds that people consistently rate reviews written in the present tense as being more helpful than those written in the past or future tense.
What Really Motivates You at Work? Summary. When we work hard, we generally expect our efforts to be recognized by our employer. And most employers will do just that — showering someone with ...
In 'Hit Me Hard and Soft,' Eilish rips off the psychic bodice and cranks up the volume in her vocals, as well as her own desires.
The Lumix S9 is Panasonic's newest full-frame mirrorless camera. It allows users to create their own custom looks for out-of-camera colors and is the first full-frame Lumix camera aimed squarely at social media content creators.
Streamlining Software Reviews: Efficient Predictive Modeling with Minimal Examples. This paper proposes a new challenge problem for software analytics. In the process we shall call "software review", a panel of SMEs (subject matter experts) review examples of software behavior to recommend how to improve that's software's operation. SME time is ...