- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →

Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- AI Essentials for Business
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading Change and Organizational Renewal
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
What Is Creative Problem-Solving & Why Is It Important?

- 01 Feb 2022
One of the biggest hindrances to innovation is complacency—it can be more comfortable to do what you know than venture into the unknown. Business leaders can overcome this barrier by mobilizing creative team members and providing space to innovate.
There are several tools you can use to encourage creativity in the workplace. Creative problem-solving is one of them, which facilitates the development of innovative solutions to difficult problems.
Here’s an overview of creative problem-solving and why it’s important in business.
Access your free e-book today.
What Is Creative Problem-Solving?
Research is necessary when solving a problem. But there are situations where a problem’s specific cause is difficult to pinpoint. This can occur when there’s not enough time to narrow down the problem’s source or there are differing opinions about its root cause.
In such cases, you can use creative problem-solving , which allows you to explore potential solutions regardless of whether a problem has been defined.
Creative problem-solving is less structured than other innovation processes and encourages exploring open-ended solutions. It also focuses on developing new perspectives and fostering creativity in the workplace . Its benefits include:
- Finding creative solutions to complex problems : User research can insufficiently illustrate a situation’s complexity. While other innovation processes rely on this information, creative problem-solving can yield solutions without it.
- Adapting to change : Business is constantly changing, and business leaders need to adapt. Creative problem-solving helps overcome unforeseen challenges and find solutions to unconventional problems.
- Fueling innovation and growth : In addition to solutions, creative problem-solving can spark innovative ideas that drive company growth. These ideas can lead to new product lines, services, or a modified operations structure that improves efficiency.

Creative problem-solving is traditionally based on the following key principles :
1. Balance Divergent and Convergent Thinking
Creative problem-solving uses two primary tools to find solutions: divergence and convergence. Divergence generates ideas in response to a problem, while convergence narrows them down to a shortlist. It balances these two practices and turns ideas into concrete solutions.
2. Reframe Problems as Questions
By framing problems as questions, you shift from focusing on obstacles to solutions. This provides the freedom to brainstorm potential ideas.
3. Defer Judgment of Ideas
When brainstorming, it can be natural to reject or accept ideas right away. Yet, immediate judgments interfere with the idea generation process. Even ideas that seem implausible can turn into outstanding innovations upon further exploration and development.
4. Focus on "Yes, And" Instead of "No, But"
Using negative words like "no" discourages creative thinking. Instead, use positive language to build and maintain an environment that fosters the development of creative and innovative ideas.
Creative Problem-Solving and Design Thinking
Whereas creative problem-solving facilitates developing innovative ideas through a less structured workflow, design thinking takes a far more organized approach.
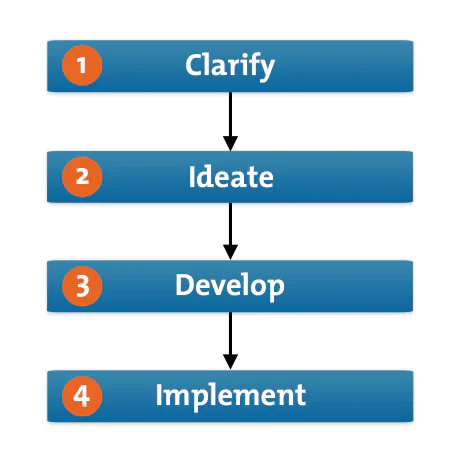
Design thinking is a human-centered, solutions-based process that fosters the ideation and development of solutions. In the online course Design Thinking and Innovation , Harvard Business School Dean Srikant Datar leverages a four-phase framework to explain design thinking.
The four stages are:

- Clarify: The clarification stage allows you to empathize with the user and identify problems. Observations and insights are informed by thorough research. Findings are then reframed as problem statements or questions.
- Ideate: Ideation is the process of coming up with innovative ideas. The divergence of ideas involved with creative problem-solving is a major focus.
- Develop: In the development stage, ideas evolve into experiments and tests. Ideas converge and are explored through prototyping and open critique.
- Implement: Implementation involves continuing to test and experiment to refine the solution and encourage its adoption.
Creative problem-solving primarily operates in the ideate phase of design thinking but can be applied to others. This is because design thinking is an iterative process that moves between the stages as ideas are generated and pursued. This is normal and encouraged, as innovation requires exploring multiple ideas.
Creative Problem-Solving Tools
While there are many useful tools in the creative problem-solving process, here are three you should know:
Creating a Problem Story
One way to innovate is by creating a story about a problem to understand how it affects users and what solutions best fit their needs. Here are the steps you need to take to use this tool properly.
1. Identify a UDP
Create a problem story to identify the undesired phenomena (UDP). For example, consider a company that produces printers that overheat. In this case, the UDP is "our printers overheat."
2. Move Forward in Time
To move forward in time, ask: “Why is this a problem?” For example, minor damage could be one result of the machines overheating. In more extreme cases, printers may catch fire. Don't be afraid to create multiple problem stories if you think of more than one UDP.
3. Move Backward in Time
To move backward in time, ask: “What caused this UDP?” If you can't identify the root problem, think about what typically causes the UDP to occur. For the overheating printers, overuse could be a cause.
Following the three-step framework above helps illustrate a clear problem story:
- The printer is overused.
- The printer overheats.
- The printer breaks down.
You can extend the problem story in either direction if you think of additional cause-and-effect relationships.
4. Break the Chains
By this point, you’ll have multiple UDP storylines. Take two that are similar and focus on breaking the chains connecting them. This can be accomplished through inversion or neutralization.
- Inversion: Inversion changes the relationship between two UDPs so the cause is the same but the effect is the opposite. For example, if the UDP is "the more X happens, the more likely Y is to happen," inversion changes the equation to "the more X happens, the less likely Y is to happen." Using the printer example, inversion would consider: "What if the more a printer is used, the less likely it’s going to overheat?" Innovation requires an open mind. Just because a solution initially seems unlikely doesn't mean it can't be pursued further or spark additional ideas.
- Neutralization: Neutralization completely eliminates the cause-and-effect relationship between X and Y. This changes the above equation to "the more or less X happens has no effect on Y." In the case of the printers, neutralization would rephrase the relationship to "the more or less a printer is used has no effect on whether it overheats."
Even if creating a problem story doesn't provide a solution, it can offer useful context to users’ problems and additional ideas to be explored. Given that divergence is one of the fundamental practices of creative problem-solving, it’s a good idea to incorporate it into each tool you use.
Brainstorming
Brainstorming is a tool that can be highly effective when guided by the iterative qualities of the design thinking process. It involves openly discussing and debating ideas and topics in a group setting. This facilitates idea generation and exploration as different team members consider the same concept from multiple perspectives.
Hosting brainstorming sessions can result in problems, such as groupthink or social loafing. To combat this, leverage a three-step brainstorming method involving divergence and convergence :
- Have each group member come up with as many ideas as possible and write them down to ensure the brainstorming session is productive.
- Continue the divergence of ideas by collectively sharing and exploring each idea as a group. The goal is to create a setting where new ideas are inspired by open discussion.
- Begin the convergence of ideas by narrowing them down to a few explorable options. There’s no "right number of ideas." Don't be afraid to consider exploring all of them, as long as you have the resources to do so.
Alternate Worlds
The alternate worlds tool is an empathetic approach to creative problem-solving. It encourages you to consider how someone in another world would approach your situation.
For example, if you’re concerned that the printers you produce overheat and catch fire, consider how a different industry would approach the problem. How would an automotive expert solve it? How would a firefighter?
Be creative as you consider and research alternate worlds. The purpose is not to nail down a solution right away but to continue the ideation process through diverging and exploring ideas.

Continue Developing Your Skills
Whether you’re an entrepreneur, marketer, or business leader, learning the ropes of design thinking can be an effective way to build your skills and foster creativity and innovation in any setting.
If you're ready to develop your design thinking and creative problem-solving skills, explore Design Thinking and Innovation , one of our online entrepreneurship and innovation courses. If you aren't sure which course is the right fit, download our free course flowchart to determine which best aligns with your goals.

About the Author

How it works
For Business
Join Mind Tools
Article • 10 min read
Creative Problem Solving
Finding Innovative Solutions to Challenges
By the Mind Tools Content Team

Imagine that you're vacuuming your house in a hurry because you've got friends coming over. Frustratingly, you're working hard but you're not getting very far. You kneel down, open up the vacuum cleaner, and pull out the bag. In a cloud of dust, you realize that it's full... again. Coughing, you empty it and wonder why vacuum cleaners with bags still exist!
James Dyson, inventor and founder of Dyson® vacuum cleaners, had exactly the same problem, and he used creative problem solving to find the answer. While many companies focused on developing a better vacuum cleaner filter, he realized that he had to think differently and find a more creative solution. So, he devised a revolutionary way to separate the dirt from the air, and invented the world's first bagless vacuum cleaner. [1]
Creative problem solving (CPS) is a way of solving problems or identifying opportunities when conventional thinking has failed. It encourages you to find fresh perspectives and come up with innovative solutions, so that you can formulate a plan to overcome obstacles and reach your goals.
In this article, we'll explore what CPS is, and we'll look at its key principles. We'll also provide a model that you can use to generate creative solutions.
About Creative Problem Solving
Alex Osborn, founder of the Creative Education Foundation, first developed creative problem solving in the 1940s, along with the term "brainstorming." And, together with Sid Parnes, he developed the Osborn-Parnes Creative Problem Solving Process. Despite its age, this model remains a valuable approach to problem solving. [2]
The early Osborn-Parnes model inspired a number of other tools. One of these is the 2011 CPS Learner's Model, also from the Creative Education Foundation, developed by Dr Gerard J. Puccio, Marie Mance, and co-workers. In this article, we'll use this modern four-step model to explore how you can use CPS to generate innovative, effective solutions.
Why Use Creative Problem Solving?
Dealing with obstacles and challenges is a regular part of working life, and overcoming them isn't always easy. To improve your products, services, communications, and interpersonal skills, and for you and your organization to excel, you need to encourage creative thinking and find innovative solutions that work.
CPS asks you to separate your "divergent" and "convergent" thinking as a way to do this. Divergent thinking is the process of generating lots of potential solutions and possibilities, otherwise known as brainstorming. And convergent thinking involves evaluating those options and choosing the most promising one. Often, we use a combination of the two to develop new ideas or solutions. However, using them simultaneously can result in unbalanced or biased decisions, and can stifle idea generation.
For more on divergent and convergent thinking, and for a useful diagram, see the book "Facilitator's Guide to Participatory Decision-Making." [3]
Core Principles of Creative Problem Solving
CPS has four core principles. Let's explore each one in more detail:
- Divergent and convergent thinking must be balanced. The key to creativity is learning how to identify and balance divergent and convergent thinking (done separately), and knowing when to practice each one.
- Ask problems as questions. When you rephrase problems and challenges as open-ended questions with multiple possibilities, it's easier to come up with solutions. Asking these types of questions generates lots of rich information, while asking closed questions tends to elicit short answers, such as confirmations or disagreements. Problem statements tend to generate limited responses, or none at all.
- Defer or suspend judgment. As Alex Osborn learned from his work on brainstorming, judging solutions early on tends to shut down idea generation. Instead, there's an appropriate and necessary time to judge ideas during the convergence stage.
- Focus on "Yes, and," rather than "No, but." Language matters when you're generating information and ideas. "Yes, and" encourages people to expand their thoughts, which is necessary during certain stages of CPS. Using the word "but" – preceded by "yes" or "no" – ends conversation, and often negates what's come before it.
How to Use the Tool
Let's explore how you can use each of the four steps of the CPS Learner's Model (shown in figure 1, below) to generate innovative ideas and solutions.
Figure 1 – CPS Learner's Model
Explore the Vision
Identify your goal, desire or challenge. This is a crucial first step because it's easy to assume, incorrectly, that you know what the problem is. However, you may have missed something or have failed to understand the issue fully, and defining your objective can provide clarity. Read our article, 5 Whys , for more on getting to the root of a problem quickly.
Gather Data
Once you've identified and understood the problem, you can collect information about it and develop a clear understanding of it. Make a note of details such as who and what is involved, all the relevant facts, and everyone's feelings and opinions.
Formulate Questions
When you've increased your awareness of the challenge or problem you've identified, ask questions that will generate solutions. Think about the obstacles you might face and the opportunities they could present.
Explore Ideas
Generate ideas that answer the challenge questions you identified in step 1. It can be tempting to consider solutions that you've tried before, as our minds tend to return to habitual thinking patterns that stop us from producing new ideas. However, this is a chance to use your creativity .
Brainstorming and Mind Maps are great ways to explore ideas during this divergent stage of CPS. And our articles, Encouraging Team Creativity , Problem Solving , Rolestorming , Hurson's Productive Thinking Model , and The Four-Step Innovation Process , can also help boost your creativity.
See our Brainstorming resources within our Creativity section for more on this.
Formulate Solutions
This is the convergent stage of CPS, where you begin to focus on evaluating all of your possible options and come up with solutions. Analyze whether potential solutions meet your needs and criteria, and decide whether you can implement them successfully. Next, consider how you can strengthen them and determine which ones are the best "fit." Our articles, Critical Thinking and ORAPAPA , are useful here.
4. Implement
Formulate a plan.
Once you've chosen the best solution, it's time to develop a plan of action. Start by identifying resources and actions that will allow you to implement your chosen solution. Next, communicate your plan and make sure that everyone involved understands and accepts it.
There have been many adaptations of CPS since its inception, because nobody owns the idea.
For example, Scott Isaksen and Donald Treffinger formed The Creative Problem Solving Group Inc . and the Center for Creative Learning , and their model has evolved over many versions. Blair Miller, Jonathan Vehar and Roger L. Firestien also created their own version, and Dr Gerard J. Puccio, Mary C. Murdock, and Marie Mance developed CPS: The Thinking Skills Model. [4] Tim Hurson created The Productive Thinking Model , and Paul Reali developed CPS: Competencies Model. [5]
Sid Parnes continued to adapt the CPS model by adding concepts such as imagery and visualization , and he founded the Creative Studies Project to teach CPS. For more information on the evolution and development of the CPS process, see Creative Problem Solving Version 6.1 by Donald J. Treffinger, Scott G. Isaksen, and K. Brian Dorval. [6]
Creative Problem Solving (CPS) Infographic
See our infographic on Creative Problem Solving .

Creative problem solving (CPS) is a way of using your creativity to develop new ideas and solutions to problems. The process is based on separating divergent and convergent thinking styles, so that you can focus your mind on creating at the first stage, and then evaluating at the second stage.
There have been many adaptations of the original Osborn-Parnes model, but they all involve a clear structure of identifying the problem, generating new ideas, evaluating the options, and then formulating a plan for successful implementation.
[1] Entrepreneur (2012). James Dyson on Using Failure to Drive Success [online]. Available here . [Accessed May 27, 2022.]
[2] Creative Education Foundation (2015). The CPS Process [online]. Available here . [Accessed May 26, 2022.]
[3] Kaner, S. et al. (2014). 'Facilitator′s Guide to Participatory Decision–Making,' San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
[4] Puccio, G., Mance, M., and Murdock, M. (2011). 'Creative Leadership: Skils That Drive Change' (2nd Ed.), Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
[5] OmniSkills (2013). Creative Problem Solving [online]. Available here . [Accessed May 26, 2022].
[6] Treffinger, G., Isaksen, S., and Dorval, B. (2010). Creative Problem Solving (CPS Version 6.1). Center for Creative Learning, Inc. & Creative Problem Solving Group, Inc. Available here .
You've accessed 1 of your 2 free resources.
Get unlimited access
Discover more content
Simplex thinking.
8 Steps for Solving Complex Problems
Book Insights
Theory U: Leading From the Future as It Emerges
C. Otto Scharmer
Add comment
Comments (0)
Be the first to comment!

Get 30% off your first year of Mind Tools
Great teams begin with empowered leaders. Our tools and resources offer the support to let you flourish into leadership. Join today!
Sign-up to our newsletter
Subscribing to the Mind Tools newsletter will keep you up-to-date with our latest updates and newest resources.
Subscribe now
Business Skills
Personal Development
Leadership and Management
Member Extras
Most Popular
Latest Updates

The Objective Leader

6 Ways to Energize Your Workplace
Mind Tools Store
About Mind Tools Content
Discover something new today
Generate ideas with scamper.
Brainstorming Improvements to Your Goods and Services
How Emotionally Intelligent Are You?
Boosting Your People Skills
Self-Assessment
What's Your Leadership Style?
Learn About the Strengths and Weaknesses of the Way You Like to Lead
Recommended for you
Ge-mckinsey matrix.
Determining Investment Priorities
Business Operations and Process Management
Strategy Tools
Customer Service
Business Ethics and Values
Handling Information and Data
Project Management
Knowledge Management
Self-Development and Goal Setting
Time Management
Presentation Skills
Learning Skills
Career Skills
Communication Skills
Negotiation, Persuasion and Influence
Working With Others
Difficult Conversations
Creativity Tools
Self-Management
Work-Life Balance
Stress Management and Wellbeing
Coaching and Mentoring
Change Management
Team Management
Managing Conflict
Delegation and Empowerment
Performance Management
Leadership Skills
Developing Your Team
Talent Management
Problem Solving
Decision Making
Member Podcast

- ACADEMIC ADVICE
The Importance of Creativity in Business: A Skill of the Future
- October 18, 2023
Table of Contents
Fast problem-solving, separating your business from the competition, boost in productivity, importance of sustaining creativity in a business, take a walk, broaden your knowledge, analyze everything, why is creativity important in business, how does creativity help in problem-solving for businesses, can businesses benefit from creativity in staying ahead of competitors, does creativity play a role in boosting employee productivity, why is it essential to sustain creativity in a business, how can i develop a creative mindset for business, are there any risks associated with embracing creativity in business.
With software becoming essential for businesses , some companies are more ready for changes brought by digital transformation than others. In addition, besides the general threat to public health, the coronavirus pandemic heavily affected the economy as well. Due to the widespread of the virus, roughly 200.000 U.S. establishments were permanently closed , and many people lost their jobs. According to the International Monetary Fund (IMF) , regardless of the policy support already deployed, the average unemployment rates are up compared to the pre-pandemic average. Why is this data necessary, you may ask.
Seeing how the world struggles to adapt to the changes thrust upon them, the spotlight falls upon business creativity as a skill that may be what saves the day for many companies. How is creativity important in business ? A creative mindset can be what helps business owners overcome challenges and succeed in this day and age. By thinking outside of the box, you can discover innovative solutions to the obstacles you face and prosper in the business world, regardless of the situation.
Why is Creativity Important in Business?
Creative thinking is one of the most demanded skills nowadays. Companies value workers who take innovative and unique approaches to solve problems and overcome challenges. The importance of creativity in business is also what helps employers and employees gain an advantage over competitors and boost productivity.
Even with machine learning and artificial intelligence fostering the power of automation , businesses need creative thinkers who bring new ideas to the table. After all, technology can only be as good as the people who operate it.
Creative thinking is necessary for business problem-solving. This skill enables workers to find opportunities that help improve situations in which finding a solution is difficult. It also helps them see the problems they face from another perspective. This way, they can use their imagination to come up with innovative approaches.
The process of creative thinking for problem-solving is not easy. However, once you merge creativity with interest, effort, and collaboration, you can generate unique and valuable ideas for any dilemma you may face.
Companies use creative approaches to add value to their business and gain an advantage over their competitors. For example, they can achieve this advantage by applying creative ideas in brainstorming for new product development (NPD). If the company provides a better service or product than its competitors, it can increase its profit margins. These unique products or services help the company reach new customers while also retaining the current ones.
Another benefit of creativity and innovation in business is that it helps in boosting productivity . Through coming up with creative ideas, you get to work on new exciting projects, which can be an incentive towards working harder. Business creativity also helps workers feel more appreciated since they get to test their limits and come up with something new. Plus, taking a creative approach encourages more feedback from peers and supervisors. With feedback, you can figure out the areas you need to improve on and work more effectively.
The real challenge of being a creative person working in business is sustaining that creativity. Sometimes, you have to deal with assignments that are monotonous and don’t require new ideas. It makes sense to work with already established work processes and ideas, especially when working in companies that have reached maturity. At that stage, some companies are not willing to take many risks and prefer to shift from experimentation towards stability.
You might never lose your creative side entirely, but you can certainly lose touch with it. Therefore, you should ensure you do not suppress your creativity and find creative ways to improve either your personal performance or pitch ideas that may benefit the entire department or company in which you work.
How Can I Develop a Creative Mindset?
Anyone can improve their ability to generate innovative ideas. Like every other skill , to fully develop your creativity, you must constantly use it. To ensure that creative thinking becomes a habit , you can practice it through the following activities.
According to a study based on the Kaplan theory , nature can enhance creative ways of thinking. This theory suggests that natural environments help recharge directed attention that is required when analyzing and developing ideas. When you are outside, the environment captures your involuntary attention, thus, allowing your voluntary or directed attention to “rest”. Another study also suggests that people are more creative when they are walking in comparison to sitting down.
Every idea you have is a combination of concepts that you already know. That is why the more knowledge you have, the greater your potential of generating unique ideas. You can read books, watch documentaries and films, keep up with the news, take new classes, start new hobbies, and socialize with different types of people to gain more knowledge.
✅ Request information on BAU's programs TODAY!
During your brainstorming session, you might come up with ideas that do not sound that good at first. Do not be discouraged. It is important that you further research every idea and plan until you find the one. The research will help you put new ideas into action, come up with some new ones, and weed out some unnecessary others.
Because we are always around technology, nowadays, distractions are just one click away. However, instead of always having your mind preoccupied with something, try being bored. Results of a study suggested that participants who felt bored performed better on creativity tests than the ones feeling distressed or relaxed. Give yourself the space to be creative.
If you want your business to succeed, you need to be ready to take risks, go out of your comfort zone, and be different. Use your creativity and uniqueness to set yourself and your company apart from others. Do not be afraid to go for it. The greatest creations were once just ideas. Yours could be next!
Frequently Asked Questions
Creativity is vital in business because it enables innovative problem-solving and helps companies find unique solutions to challenges. It also gives businesses a competitive edge and boosts productivity.
Creative thinking allows individuals to approach problems from different angles and generate innovative solutions. It helps in finding opportunities in challenging situations.
Yes, creative approaches can differentiate a business from its competitors. By using creative ideas in product development or service enhancement, a company can increase its profitability and attract new customers while retaining existing ones.
Yes, creativity can boost productivity by motivating employees to work on exciting and innovative projects. It also encourages feedback, helping workers improve and become more effective in their roles.
Sustaining creativity is crucial because some business tasks may become monotonous, but creativity is a valuable asset. It ensures continued innovation and adaptation, vital for a company’s growth and success.
You can develop a creative mindset by engaging in activities like walking in nature, broadening your knowledge through reading and learning, analyzing and researching ideas, and allowing yourself to be bored.
While creativity is valuable, there may be risks involved, such as the potential for ideas to fail or the need to invest resources in new, unproven ventures. However, taking calculated risks and learning from failures is an essential part of fostering creativity in business and driving innovation.
Bay Atlantic University
Leave a reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
You May Also Like
- 4 minute read
Double Majoring: Is Two Always Better Than One
- March 17, 2021
- 6 minute read
How to Take Notes in College: Efficiently and Effectively
- March 23, 2021
Main Differences Between Undergraduate and Graduate School
- June 29, 2020
- 5 minute read
Online Learning Statistics: Is Online Education the Future?
- August 20, 2020
- 20 shares 13 0 7
- 7 minute read
Top 6 Gift Ideas for Teachers
- June 1, 2022
- INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY
- 8 minute read
12 Useful Apps for College Students
- June 3, 2022
Navigate the Levels of English as a Second Language
- April 24, 2024
Learning English as A Second Language: A Comprehensive Guide
Mastering esl teacher skills: a comprehensive guide to success, esl vs. efl: what is the difference, request information on bau's programs today.
What is creative problem-solving?
Table of Contents
An introduction to creative problem-solving.
Creative problem-solving is an essential skill that goes beyond basic brainstorming . It entails a holistic approach to challenges, melding logical processes with imaginative techniques to conceive innovative solutions. As our world becomes increasingly complex and interconnected, the ability to think creatively and solve problems with fresh perspectives becomes invaluable for individuals, businesses, and communities alike.
Importance of divergent and convergent thinking
At the heart of creative problem-solving lies the balance between divergent and convergent thinking. Divergent thinking encourages free-flowing, unrestricted ideation, leading to a plethora of potential solutions. Convergent thinking, on the other hand, is about narrowing down those options to find the most viable solution. This dual approach ensures both breadth and depth in the problem-solving process.
Emphasis on collaboration and diverse perspectives
No single perspective has a monopoly on insight. Collaborating with individuals from different backgrounds, experiences, and areas of expertise offers a richer tapestry of ideas. Embracing diverse perspectives not only broadens the pool of solutions but also ensures more holistic and well-rounded outcomes.
Nurturing a risk-taking and experimental mindset
The fear of failure can be the most significant barrier to any undertaking. It's essential to foster an environment where risk-taking and experimentation are celebrated. This involves viewing failures not as setbacks but as invaluable learning experiences that pave the way for eventual success.
The role of intuition and lateral thinking
Sometimes, the path to a solution is not linear. Lateral thinking and intuition allow for making connections between seemingly unrelated elements. These 'eureka' moments often lead to breakthrough solutions that conventional methods might overlook.
Stages of the creative problem-solving process
The creative problem-solving process is typically broken down into several stages. Each stage plays a crucial role in understanding, addressing, and resolving challenges in innovative ways.
Clarifying: Understanding the real problem or challenge
Before diving into solutions, one must first understand the problem at its core. This involves asking probing questions, gathering data, and viewing the challenge from various angles. A clear comprehension of the problem ensures that effort and resources are channeled correctly.
Ideating: Generating diverse and multiple solutions
Once the problem is clarified, the focus shifts to generating as many solutions as possible. This stage champions quantity over quality, as the aim is to explore the breadth of possibilities without immediately passing judgment.
Developing: Refining and honing promising solutions
With a list of potential solutions in hand, it's time to refine and develop the most promising ones. This involves evaluating each idea's feasibility, potential impact, and any associated risks, then enhancing or combining solutions to maximize effectiveness.
Implementing: Acting on the best solutions
Once a solution has been honed, it's time to put it into action. This involves planning, allocating resources, and monitoring the results to ensure the solution is effectively addressing the problem.
Techniques for creative problem-solving
Solving complex problems in a fresh way can be a daunting task to start on. Here are a few techniques that can help kickstart the process:
Brainstorming
Brainstorming is a widely-used technique that involves generating as many ideas as possible within a set timeframe. Variants like brainwriting (where ideas are written down rather than spoken) and reverse brainstorming (thinking of ways to cause the problem) can offer fresh perspectives and ensure broader participation.
Mind mapping
Mind mapping is a visual tool that helps structure information, making connections between disparate pieces of data. It is particularly useful in organizing thoughts, visualizing relationships, and ensuring a comprehensive approach to a problem.
SCAMPER technique
SCAMPER stands for Substitute, Combine, Adapt, Modify, Put to another use, Eliminate, and Reverse. This technique prompts individuals to look at existing products, services, or processes in new ways, leading to innovative solutions.
Benefits of creative problem-solving
Creative problem-solving offers numerous benefits, both at the individual and organizational levels. Some of the most prominent advantages include:
Finding novel solutions to old problems
Traditional problems that have resisted conventional solutions often succumb to creative approaches. By looking at challenges from fresh angles and blending different techniques, we can unlock novel solutions previously deemed impossible.
Enhanced adaptability in changing environments
In our rapidly evolving world, the ability to adapt is critical. Creative problem-solving equips individuals and organizations with the agility to pivot and adapt to changing circumstances, ensuring resilience and longevity.
Building collaborative and innovative teams
Teams that embrace creative problem-solving tend to be more collaborative and innovative. They value diversity of thought, are open to experimentation, and are more likely to challenge the status quo, leading to groundbreaking results.
Fostering a culture of continuous learning and improvement
Creative problem-solving is not just about finding solutions; it's also about continuous learning and improvement. By encouraging an environment of curiosity and exploration, organizations can ensure that they are always at the cutting edge, ready to tackle future challenges head-on.
Get on board in seconds
Join thousands of teams using Miro to do their best work yet.
How To Foster Creative Thinking at Your Business
Updated: March 11, 2024
Published: April 22, 2023
Creative thinking isn’t just for fiction authors and designers. It’s also a critical skill for business owners in virtually every industry. Sometimes, a problem needs a unique solution to overcome it.

And in some cases, you need an out-of-the-box idea to stand out from the competition. Having creative thinking skills and a mindset that values creativity can help your business develop and maintain a competitive edge.
But how do you develop your creative thinking abilities, especially if you haven’t flexed those muscles in a while? And how do you maintain those skills once you’ve established them so that creativity is second nature to you?
What is creative thinking?
In business, creative thinking is the ability to explore different possibilities to come up with new ideas that can help you achieve goals and overcome roadblocks. It involves looking at things differently, breaking down barriers, and thinking “outside the box.”
Creative thinking can also solve problems, create art, develop new products or services, and even discover new knowledge. It’s useful in almost any situation — from problem-solving to designing creative solutions for everyday tasks.
Critical thinking vs. creative thinking
Critical thinking involves logical reasoning and analysis to come to a solution, while creative thinking requires out-of-the-box thinking to develop new and innovative ideas.
Critical thinking requires you to analyze and evaluate information to make informed decisions. You must review all options and look for the best solution to a problem. It’s a logical process that requires objectivity, fact-checking, and careful consideration of all available evidence. Critical thinking provides a more informed, reasoned approach to problem-solving.
Creative thinking, on the other hand, is much less logical or analytical in nature. It involves creating a unique solution to a problem and exploring different perspectives. Creative thinking encourages divergent thinking — the ability to generate multiple ideas and solutions to a single problem.
Creative thinking is also important for developing new products and services since it promotes fresh and novel ideas.
For example, a small-business owner who needs to increase sales may use critical thinking to look at past sales data and then create a marketing plan targeting their most profitable customers. They might also use creative thinking to ideate a new product or service to attract new customers and boost sales.
It’s important to note that there doesn’t need to be an either-or dichotomy between creative thinking and critical thinking. The truth is that both are essential to successfully running a business, especially in the early days of a startup. By using both critical and creative thinking, small-business owners are better equipped to make decisions that benefit the company.
Creative thinking examples
Using creative thinking keeps your business fresh and competitive. It empowers you to overcome adversities easier and stay ahead of the curve. But what does this look like in the real world?
Promoting teams to be creative
The tech industry relies on innovation to thrive. So having teams that can flex their creative muscles to invent or improve products and features is a must. Tech giants like Google know this, and that’s why in 2000, it introduced what’s called 20% time .
The concept: Employees can spend up to 20% of their working time on projects that are not directly tied to their core responsibilities.
While these projects should be work-related, they don’t need to promise immediate returns for the company. Ideally, they should have the potential to be developed into major opportunities in the future.
And it works — several Google products stemmed from this method, including Google News, Gmail, and AdSense.
Evolving with the times
Are you old enough to remember when Netflix delivered DVDs to your door? It was an excellent idea in an era when you had to drive to Blockbuster or your local movie rental store to get a flick to watch.
But the company didn’t stop there. They later introduced a membership option to be more affordable, which still exists today .
As the infrastructure underpinning the internet became more robust and made faster internet speeds a reality, the company saw another opportunity to elevate its services by providing even more value and convenience to customers through streaming. And now we have what exists today — a streaming service you can watch from any device, anywhere.
The company’s core focus was always on innovation, and its eyes are still on the prize.
Getting everyone involved
Being a small-business owner forces you to wear many hats, but after a while, it becomes overwhelming to be the brains and the brawn of the company.
By leveraging your team’s talent, you can collaborate to find solutions and ideas to propel your business forward.
Four Seasons did this when the CEO built an organization-wide execution strategy to get all hands on deck to redefine luxury as a service . Its golden rule: “to deal with others — partners, customers, coworkers, everyone — as we would want them to deal with us.”
Everyone from the bellhop to the founder is free to serve customers how they see fit to reach the company’s goal of making each customer/employee engagement personalized, sincere, and thoughtful.
The employees seem to love it — for the past 50 years, Four Seasons has made it to Fortune’s 100 Best Companies to Work For list every year.
Thinking waaay outside of the box
Creative thinking in business typically takes two forms. On one hand, there’s iterative creative thinking that builds upon existing ideas and concepts slowly over time. On the other hand, there are the kinds of ideas that have truly never been done before: the ones that start over from scratch in a radically different way. While both are effective, the latter are the ones with the greatest potential to shift paradigms and industries.
For example, just look to some recent restaurant concepts:
- Eating in the dark : Ctaste offers an “Experience Dinner” where you receive a three-course dinner from a surprise menu inside of a dark room. So you won’t know what you’re eating until you take a bite.
- Rude staff : The Wiener’s Circle is a hot-dog joint in Chicago that’s renowned for its rude and offensive staff. But rather than deter diners from its establishment, more flocked to it (and even generated social media buzz). So the restaurant capitalized on this by maintaining a staff of rude workers that intentionally insult patrons.
These examples show that creativity can be bizarre and still drive results. Just make sure to test the waters before diving in.
Creative thinking exercises
Being creative isn’t something you’re born with — it’s something you learn. Here is a list of exercises that you and your team can use to improve your creative thinking abilities.
Implement collaborative brainstorming
Gather your team and discuss an issue or opportunity you’re currently facing. Encourage everyone to share their thoughts and ideas freely, no matter how wild they may seem.
After generating a list of ideas and solutions, narrow them down by evaluating each for feasibility and potential impact.
Try reverse engineering
Select a competitor or industry leader that’s doing well and ask yourself why they’ve made certain decisions or implemented certain strategies. This could give you insight into approaching similar problems from a new perspective.
For example, if your competitor has successfully used social media marketing, figure out which platforms they’re using and what type of content they’re creating — then come up with ideas to achieve similar success, but in your own way.
Use design thinking
Design thinking is a problem-solving technique that focuses on the needs of users — and on creating solutions that meet those needs. It involves brainstorming, prototyping, and testing.
The goal is to develop innovative ideas that meet customer expectations while also creating value for your business. Start by defining the problem, then use creative techniques like brainstorming to generate ideas . After you have a list of potential solutions, create prototypes and test them with customers to find the best one.
This is excellent for technology and ecommerce businesses.
Leverage technology
Technology has the potential to maximize your creative thinking. For example, you might use artificial intelligence to identify patterns and trends, leverage virtual reality simulations to help visualize solutions to problems, and even use meditation apps to help get your brain in a creative flow.
Software-as-a-service (SaaS) platforms like Adobe Creative Cloud empower you to design and create projects using Photoshop, Illustrator, and InDesign tools for a low monthly cost. Canva is another design tool that makes it easy for those without design skills to create creative assets using templates.
Test mind mapping
Mind mapping is a visual brainstorming technique that involves creating a diagram to represent ideas and concepts. Start with a central idea or theme and branch out into subtopics and related ideas. This exercise can generate new ideas and identify connections between seemingly unrelated concepts.
Let's say you’re working on a marketing campaign for a new product and need creative ideas for the campaign that will resonate with your target audience.
You start by:
- Writing the central idea, “Marketing Campaign,” in the center of a piece of paper.
- Then, create branches for subtopics like “Target Audience,” “Messaging,” and “Channels.”
- Under each subtopic, add related ideas like “Social Media Advertising,” “Influencer Marketing,” “Product Demos,” and “Email Campaigns.”
As you continue to add ideas and subtopics to your mind map, you’ll see connections between novel concepts.
Exercising your creativity doesn’t have to occur only in a work setting — the need for out-of-the-box thinking can happen anytime, anywhere. Keep your mind open and look for opportunities to solve problems and reach objectives in a way you wouldn’t normally do. Over time, conjuring up unique solutions to everyday problems will become second nature.
hbspt.cta._relativeUrls=true;hbspt.cta.load(53, 'ad22bdd9-fd50-4b35-a4f5-7586f5a61a1e', {"useNewLoader":"true","region":"na1"});
What did you think of this article .
Give Feedback

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.

Brainstorming Techniques: 15 Creative Activities to Do Solo or as a Team

3 Habits to Boost Creativity & Become a More Prolific Marketer

How to Use Ideation Sessions to Develop Your Best Ideas Yet

The Surprising Relationship Between Stress and Creativity

Creative Work Relies on Failure

4 Strategies to Spark On-Demand Creativity

Why Empathy Is the Key to Being More Creative

Why Virtual Agencies Might Be More Creative

Why You Should Pretend to Work on Projects for Someone Else & 4 Other Science-Backed Ways to Improve Your Creativity

How to Be Creative When You're Not Naturally Creative
Outline your company's marketing strategy in one simple, coherent plan.
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform
Six problem-solving mindsets for very uncertain times
Great problem solvers are made, not born. That’s what we’ve found after decades of problem solving with leaders across business, nonprofit, and policy sectors. These leaders learn to adopt a particularly open and curious mindset, and adhere to a systematic process for cracking even the most inscrutable problems. They’re terrific problem solvers under any conditions. And when conditions of uncertainty are at their peak, they’re at their brilliant best.
Six mutually reinforcing approaches underly their success: (1) being ever-curious about every element of a problem; (2) being imperfectionists , with a high tolerance for ambiguity; (3) having a “dragonfly eye” view of the world, to see through multiple lenses; (4) pursuing occurrent behavior and experimenting relentlessly; (5) tapping into the collective intelligence , acknowledging that the smartest people are not in the room; and (6) practicing “show and tell” because storytelling begets action (exhibit).
Here’s how they do it.
1. Be ever-curious
As any parent knows, four-year-olds are unceasing askers. Think of the never-ending “whys” that make little children so delightful—and relentless. For the very young, everything is new and wildly uncertain. But they’re on a mission of discovery, and they’re determined to figure things out. And they’re good at it! That high-energy inquisitiveness is why we have high shelves and childproof bottles.
When you face radical uncertainty, remember your four-year-old or channel the four-year-old within you. Relentlessly ask, “Why is this so?” Unfortunately, somewhere between preschool and the boardroom, we tend to stop asking. Our brains make sense of massive numbers of data points by imposing patterns that have worked for us and other humans in the past. That’s why a simple technique, worth employing at the beginning of problem solving, is simply to pause and ask why conditions or assumptions are so until you arrive at the root of the problem. 1 This approach was originally developed by Sakichi Toyoda, the founder of Toyota.
Natural human biases in decision making, including confirmation, availability, and anchoring biases, often cause us to shut down the range of solutions too early. 2 Daniel Kahneman, Thinking, Fast and Slow , New York, NY: Farrar, Straus and Giroux, 2011. Better—and more creative—solutions come from being curious about the broader range of potential answers.
One simple suggestion from author and economist Caroline Webb to generate more curiosity in team problem solving is to put a question mark behind your initial hypotheses or first-cut answers. This small artifice is surprisingly powerful: it tends to encourage multiple solution paths and puts the focus, correctly, on assembling evidence. We also like thesis/antithesis, or red team/blue team, sessions, in which you divide a group into opposing teams that argue against the early answers—typically, more traditional conclusions that are more likely to come from a conventional pattern. Why is this solution better? Why not that one? We’ve found that better results come from embracing uncertainty. Curiosity is the engine of creativity.
We have to be comfortable with estimating probabilities to make good decisions, even when these guesses are imperfect. Unfortunately, we have truckloads of evidence showing that human beings aren’t good intuitive statisticians.
2. Tolerate ambiguity—and stay humble!
When we think of problem solvers, many of us tend to picture a poised and brilliant engineer. We may imagine a mastermind who knows what she’s doing and approaches a problem with purpose. The reality, though, is that most good problem solving has a lot of trial and error; it’s more like the apparent randomness of rugby than the precision of linear programming. We form hypotheses, porpoise into the data, and then surface and refine (or throw out) our initial guess at the answer. This above all requires an embrace of imperfection and a tolerance for ambiguity—and a gambler’s sense of probabilities.
The real world is highly uncertain. Reality unfolds as the complex product of stochastic events and human reactions. The impact of COVID-19 is but one example: we address the health and economic effects of the disease, and their complex interactions, with almost no prior knowledge. We have to be comfortable with estimating probabilities to make good decisions, even when these guesses are imperfect. Unfortunately, we have truckloads of evidence showing that human beings aren’t good intuitive statisticians. Guesses based on gut instinct can be wildly wrong. That’s why one of the keys to operating in uncertain environments is epistemic humility, which Erik Angner defines as “the realization that our knowledge is always provisional and incomplete—and that it might require revision in light of new evidence.” 3 Erik Angner, “Epistemic humility—knowing your limits in a pandemic,” Behavioral Scientist , April 13, 2020, behavioralscientist.org.
Recent research shows that we are better at solving problems when we think in terms of odds rather than certainties. 4 Annie Duke, Thinking in Terms of Bets: Making Smarter Decisions When You Don’t Have All the Facts , New York, NY: Portfolio/Penguin, 2018. For example, when the Australian research body Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO), which owned a core patent on the wireless internet protocol, sought royalties from major companies, it was initially rebuffed. The CSIRO bet that it could go to court to protect its intellectual property because it estimated that it needed only 10 percent odds of success for this to be a good wager, given the legal costs and likely payoff. It improved its odds by picking the weakest of the IP violators and selecting a legal jurisdiction that favored plaintiffs. This probabilistic thinking paid off and eventually led to settlements to CSIRO exceeding $500 million. 5 CSIRO briefing to US Government, December 5, 2006. A tolerance for ambiguity and a willingness to play the odds helped the organization feel its way to a good solution path.
To embrace imperfectionism with epistemic humility, start by challenging solutions that imply certainty. You can do that in the nicest way by asking questions such as “What would we have to believe for this to be true?” This brings to the surface implicit assumptions about probabilities and makes it easier to assess alternatives. When uncertainty is high, see if you can make small moves or acquire information at a reasonable cost to edge out into a solution set. Perfect knowledge is in short supply, particularly for complex business and societal problems. Embracing imperfection can lead to more effective problem solving. It’s practically a must in situations of high uncertainty, such as the beginning of a problem-solving process or during an emergency.
Good problem solving typically involves designing experiments to reduce key uncertainties. Each move provides additional information and builds capabilities.
Would you like to learn more about our Strategy & Corporate Finance Practice ?
3. take a dragonfly-eye view.
Dragonfly-eye perception is common to great problem solvers. Dragonflies have large, compound eyes, with thousands of lenses and photoreceptors sensitive to different wavelengths of light. Although we don’t know exactly how their insect brains process all this visual information, by analogy they see multiple perspectives not available to humans. The idea of a dragonfly eye taking in 360 degrees of perception 6 Philip Tetlock and Dan Gardner, Superforecasting: The Art and Science of Prediction , New York, NY: Crown, 2015. is an attribute of “superforecasters”—people, often without domain expertise, who are the best at forecasting events.
Think of this as widening the aperture on a problem or viewing it through multiple lenses. The object is to see beyond the familiar tropes into which our pattern-recognizing brains want to assemble perceptions. By widening the aperture, we can identify threats or opportunities beyond the periphery of vision.
Consider the outbreak of HIV in India in the early 1990s—a major public-health threat. Ashok Alexander, director of the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation’s India Aids Initiative, provided a brilliant example of not just vision but also dragonfly vision. Facing a complex social map with a rapidly increasing infection rate, he widened the problem’s definition, from a traditional epidemiological HIV transmission model at known “hot spots,” to one in which sex workers facing violence were made the centerpiece.
This approach led to the “Avahan solution,” which addressed a broader set of leverage points by including the sociocultural context of sex work. The solution was rolled out to more than 600 communities and eventually credited with preventing 600,000 infections. The narrow medical perspective was sensible and expected, but it didn’t tap into the related issue of violence against sex workers, which yielded a richer solution set. Often, a secret unlocks itself only when one looks at a problem from multiple perspectives, including some that initially seem orthogonal.
The secret to developing a dragonfly-eye view is to “anchor outside” rather than inside when faced with problems of uncertainty and opportunity. Take the broader ecosystem as a starting point. That will encourage you to talk with customers, suppliers, or, better yet, players in a different but related industry or space. Going through the customer journey with design-thinking in mind is another powerful way to get a 360-degree view of a problem. But take note: when decision makers face highly constrained time frames or resources, they may have to narrow the aperture and deliver a tight, conventional answer.

Want better strategies? Become a bulletproof problem solver
4. pursue occurrent behavior.
Occurrent behavior is what actually happens in a time and place, not what was potential or predicted behavior. Complex problems don’t give up their secrets easily. But that shouldn’t deter problem solvers from exploring whether evidence on the facets of a solution can be observed, or running experiments to test hypotheses. You can think of this approach as creating data rather than just looking for what has been collected already. It’s critical for new market entry—or new market creation. It also comes in handy should you find that crunching old data is leading to stale solutions.
Most of the problem-solving teams we are involved with have twin dilemmas of uncertainty and complexity, at times combined as truly “wicked problems.” 7 A term coined in a now famous 1973 article: Horst W. J. Rittel and Melvin Webber, “Dilemmas in a general theory of planning,” Policy Sciences , 1973, Number 4, pp. 155–69. For companies ambitious to win in the great unknown in an emerging segment—such as electric cars or autonomous vehicles, where the market isn’t fully established—good problem solving typically involves designing experiments to reduce key uncertainties, not just relying on existing data. Each move (such as buying IP or acquiring a component supplier) and each experiment (including on-road closed tests) not only provides additional information to make decisions but also builds capabilities and assets that support further steps. Over time, their experiments, including alliances and acquisitions, come to resemble staircases that lead to either the goal or to abandonment of the goal. Problem-solving organizations can “bootstrap” themselves into highly uncertain new spaces, building information, foundational assets, and confidence as they take steps forward.
Risk-embracing problem solvers find a solution path by constantly experimenting. Statisticians use the abbreviation EVPI—the expected value of perfect information—to show the value of gaining additional information that typically comes from samples and experiments, such as responses to price changes in particular markets. A/B testing is a powerful tool for experimenting with prices, promotions, and other features and is particularly useful for digital marketplaces and consumer goods. Online marketplaces make A/B testing easy. Yet most conventional markets also offer opportunities to mimic the market’s segmentation and use it to test different approaches.
The mindset required to be a restless experimenter is consistent with the notion in start-ups of “failing fast.” It means that you get product and customer affirmation or rejection quickly through beta tests and trial offerings. Don’t take a lack of external data as an impediment—it may actually be a gift, since purchasable data is almost always from a conventional way of meeting needs, and is available to your competitors too. Your own experiments allow you to generate your own data; this gives you insights that others don’t have. If it is difficult (or unethical) to experiment, look for the “natural experiments” provided by different policies in similar locations. An example would be to compare outcomes in twin cities, such as Minneapolis–St. Paul.
It’s a mistake to think that your team has the smartest people in the room. They aren’t there. They’re invariably somewhere else. Nor do they need to be there if you can access their intelligence via other means.
5. Tap into collective intelligence and the wisdom of the crowd
Chris Bradley, a coauthor of Strategy Beyond the Hockey Stick , 8 Chris Bradley, Marin Hirt, and Sven Smit, Strategy Beyond the Hockey Stick: People, Probabilities, and Big Moves to Beat the Odds , Hoboken, NJ: Wiley, 2018. observed that “it’s a mistake to think that on your team you have the smartest people in the room. They aren’t there. They’re invariably somewhere else.” 9 For more from Chris Bradley, in a conversation with Rob McLean, see “ Want better strategies? Become a bulletproof problem solver ,” August 2019. Nor do they need to be there if you can access their intelligence via other means. In an ever-changing world where conditions can evolve unpredictably, crowdsourcing invites the smartest people in the world to work with you. For example, in seeking a machine-learning algorithm to identify fish catch species and quantities on fishing boats, the Nature Conservancy (TNC) turned to Kaggle and offered a $150,000 prize for the best algorithm. This offer attracted 2,293 teams from all over the world. TNC now uses the winning algorithm to identify fish types and sizes caught on fishing boats in Asia to protect endangered Pacific tuna and other species.
Crowdsourced problem solving is familiar in another guise: benchmarking. When Sir Rod Carnegie was CEO of Conzinc Riotinto Australia (CRA), he was concerned about the costs of unscheduled downtime with heavy trucks, particularly those requiring tire changes. He asked his management team who was best in the world at changing tires; their answer was Formula One, the auto racing competition. A team traveled to the United Kingdom to learn best practice for tire changes in racetrack pits and then implemented what it learned thousands of miles away, in the Pilbara region of Western Australia. The smartest team for this problem wasn’t in the mining industry at all.
Of course, while crowdsourcing can be useful when conventional thinking yields solutions that are too expensive or incomplete for the challenge at hand, it has its limitations. Good crowdsourcing takes time to set up, can be expensive, and may signal to your competitors what you are up to. Beware of hidden costs, such as inadvertently divulging information and having to sieve through huge volumes of irrelevant, inferior suggestions to find the rare gem of a solution.
Accept that it’s OK to draw on diverse experiences and expertise other than your own. Start with brainstorming sessions that engage people from outside your team. Try broader crowdsourcing competitions to generate ideas. Or bring in deep-learning talent to see what insights exist in your data that conventional approaches haven’t brought to light. The broader the circles of information you access, the more likely it is that your solutions will be novel and creative.
Rookie problem solvers show you their analytic process and math to convince you they are clever. Seasoned problem solvers show you differently.
6. Show and tell to drive action
We started our list of mindsets with a reference to children, and we return to children now, with “show and tell.” As you no doubt remember—back when you were more curious!—show and tell is an elementary-school activity. It’s not usually associated with problem solving, but it probably piqued your interest. In fact, this approach is critical to problem solving. Show and tell is how you connect your audience with the problem and then use combinations of logic and persuasion to get action.
The show-and-tell mindset aims to bring decision makers into a problem-solving domain you have created. A team from the Nature Conservancy, for instance, was presenting a proposal asking a philanthropic foundation to support the restoration of oyster reefs. Before the presentation, the team brought 17 plastic buckets of water into the boardroom and placed them around the perimeter. When the foundation’s staff members entered the room, they immediately wanted to know what the buckets were for. The team explained that oyster-reef restoration massively improves water quality because each oyster filters 17 buckets of water per day. Fish stocks improve, and oysters can also be harvested to help make the economics work. The decision makers were brought into the problem-solving domain through show and tell. They approved the funding requested and loved the physical dimension of the problem they were part of solving.
Rookie problem solvers show you their analytic process and mathematics to convince you that they are clever. That’s sometimes called APK, the anxious parade of knowledge. But seasoned problem solvers show you differently. The most elegant problem solving is that which makes the solution obvious. The late economist Herb Simon put it this way: “Solving a problem simply means representing it so as to make the solution transparent.” 10 Herbert Simon, The Sciences of the Artificial , Cambridge, MA: MIT Press, 1969.
To get better at show and tell, start by being clear about the action that should flow from your problem solving and findings: the governing idea for change. Then find a way to present your logic visually so that the path to answers can be debated and embraced. Present the argument emotionally as well as logically, and show why the preferred action offers an attractive balance between risks and rewards. But don’t stop there. Spell out the risks of inaction, which often have a higher cost than imperfect actions have.
The mindsets of great problem solvers are just as important as the methods they employ. A mindset that encourages curiosity, embraces imperfection, rewards a dragonfly-eye view of the problem, creates new data from experiments and collective intelligence, and drives action through compelling show-and-tell storytelling creates radical new possibilities under high levels of unpredictability. Of course, these approaches can be helpful in a broad range of circumstances, but in times of massive uncertainty, they are essential.
Charles Conn is an alumnus of McKinsey’s Sydney office and is a board member of Patagonia and former CEO of the Rhodes Trust. Robert McLean is an alumnus of the Sydney office and is the advisory-board chair of the Nature Conservancy Australia. They are the authors of Bulletproof Problem Solving: The One Skill That Changes Everything (Wiley, 2018).
This article was edited by David Schwartz, an executive editor in the Tel Aviv office.
Explore a career with us
Related articles.

Strategy to beat the odds

Dwight Eisenhower: Lessons from the ‘balancer in chief’
What is Business Creativity: Unlocking Innovation and Growth in the Workplace
By: Author Paul Jenkins
Posted on June 12, 2023
Categories Creativity , Business
Business creativity is a vital aspect of the modern corporate world, as it drives innovation and enables organizations to stay ahead of their competitors.
Blending knowledge management and basic skills of creativity management, business creativity helps generate novel and valuable ideas that can lead to the development of new products, services, or processes and, ultimately, a company’s growth.
In today’s dynamic market environment, where change is constant, and consumer needs evolve rapidly, fostering business creativity has become crucial for organizations that aim to stay relevant and competitive. It involves identifying opportunities, challenging conventional thinking, and nurturing an environment encouraging experimentation and risk-taking.
The focus is not solely on the individual creative genius but also on an entire organization’s collaborative effort and collective intelligence.
Understanding Business Creativity
Creativity vs. innovation.
Business creativity and innovation may seem similar, but they have distinct differences. Creativity involves generating new ideas, concepts, or solutions that have value.
In a business context, this can mean developing new products, services, or strategies to enhance the organization. On the other hand, innovation is implementing and turning those creative ideas into tangible results.
This often entails refining, testing, and adapting creative ideas to meet the specific needs of the market or customers.
Understanding the distinction between these concepts is essential for businesses to harness their creative potential effectively. While creativity provides the initial spark, innovation is the driving force that ensures those ideas are actualized and generate value for the business.
Role of Creativity in Business
Business creativity plays a crucial role in several aspects of an organization:
- Product Development: A creative approach to product development helps businesses create unique, competitive offerings that cater to customer needs. Creativity allows businesses to think beyond conventional methods and develop innovative ideas that set them apart.
- Problem-Solving: Business creativity can be applied to solving complex challenges within a company. By encouraging and fostering creative thinking, companies can find new ways to overcome obstacles, streamline operations, and improve efficiency.
- Strategic Planning: Creatively-driven organizations often succeed by identifying novel opportunities and crafting strategies that leverage their unique strengths. A creative strategy helps businesses stay ahead of their competition and continuously adapt to changing market conditions.
- Company Culture: Fostering a creative culture within a company can have long-lasting positive effects on employee engagement, motivation, and collaboration. A healthy, creative work environment can enhance overall productivity and employee satisfaction.
In conclusion, understanding business creativity is crucial for organizations to unlock their full potential and drive innovation. By recognizing the importance of creativity in various aspects of a company, businesses can foster a culture that encourages creative thinking, problem-solving, and continuous growth.
Elements of Business Creativity
Creative processes.
Creative processes play a key role in business creativity.
These processes involve generating, evaluating, and implementing new ideas and concepts to create innovative products, services, or solutions. The corporate creativity literature highlights the importance of having a structured process for fostering innovation in an organization.
Some crucial steps in the creative process include idea generation, selection, refinement, and execution.
Companies can use various techniques to support their creative processes, such as brainstorming, design thinking, and open innovation. These approaches help stimulate the flow of ideas and encourage out-of-the-box thinking.
Creative Mindset
A creative mindset is essential for nurturing business creativity. This involves encouraging an entrepreneurial spirit, fostering a culture of innovation, and empowering employees to take risks.
Organizations must provide an environment that supports their employees in developing new ideas and pursuing innovative solutions while being open to failure as a learning opportunity. Some ways to cultivate a creative mindset include:
- Encouraging curiosity and continuous learning
- Recognizing and rewarding creativity
- Supporting experimentation and risk-taking
Collaboration and Teamwork
Innovation is often a result of effective collaboration and teamwork.
Businesses must create an environment encouraging employee collaboration, as diverse perspectives can lead to more innovative products and solutions. Implementing cross-functional teams and providing tools and platforms to facilitate communication can help foster a collaborative culture. Some essential aspects of collaboration and teamwork in business creativity include:
- Encouraging open communication and idea sharing
- Empowering employees to contribute regardless of their background or expertise
- Fostering trust and psychological safety within teams
Observation and Experimentation
Observation and experimentation are crucial aspects of business creativity. Companies need to closely observe market trends, customer behavior, and competitors’ strategies to identify opportunities for innovation.
Taking inspiration from other industries and adopting an external perspective can help businesses identify creative solutions.
Experimentation involves testing new ideas and iterating rapidly based on feedback and results. Companies should be open to trying new approaches, conducting pilot projects, or running experiments in a low-risk environment to identify the most promising innovations.
This iterative process can produce more refined products and services that better meet customer needs and deliver value.
Driving Business Growth Through Creativity
Creating business opportunities.
In the competitive business world, creativity plays a vital role in discovering new organizational opportunities.
Companies that promote creativity among their employees often excel at generating innovative solutions to challenges faced in various industries. By identifying unique ways of meeting market needs, creative organizations can build a strong competitive advantage, better satisfying their customers’ demands and fostering growth.
Creative leaders drive their industry by introducing breakthrough products, offering novel services, and exploring untapped markets.
For instance, companies like Apple have gone beyond the traditional manufacturing sector by creating products that redefine consumer expectations, leading to tremendous business growth and value creation.
Fostering a Creative Culture
Establishing a creative culture within an organization encourages employees to think differently, pushing the boundaries of conventional problem-solving methods. Here are some ways to cultivate such a culture:
- Encourage collaboration: Create an environment where employees from diverse backgrounds and skill sets can collaborate, bringing in holistic perspectives and experiences.
- Provide resources: Provide employees access to the necessary resources, tools, and training to convert their creative ideas into tangible outcomes.
- Celebrate innovation: Recognize and reward creative efforts and accomplishments, motivating employees to continue pushing boundaries.
Encouraging Risk Taking
A core aspect of business creativity is embracing the unknown and taking calculated risks. By encouraging experimentation and risk-taking, companies provide an environment where employees feel empowered to explore innovative solutions.
Organizations that understand the inherent uncertainty of the market and are willing to embrace risk often lead the curve in introducing novel products, services, and solutions.
Embracing Failure
Failure is an inevitable part of the creative process, essential for learning and growth. By accepting the possibility of failure, companies can create a supportive environment that encourages creative thinking and problem-solving.
When organizations foster a culture that embraces failure as an opportunity to grow, they promote ongoing innovation and resilience. This mindset ultimately leads to greater adaptability and better positioning in the face of challenges and changing market conditions.
Leveraging Technology for Business Creativity
Virtual work and collaboration.
The rapid development of technology has enabled businesses to foster creativity and innovation in the workplace. One significant shift is the widespread adoption of virtual work and collaboration tools, which became especially crucial during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Remote work has become more accessible due to communication and collaboration software advancements. Zoom, Microsoft Teams, and Slack allow teams to connect and collaborate from anywhere.
This shift to virtual work has benefits in terms of productivity and efficiency. For instance, it has removed geographical barriers, allowing companies to tap into global talent pools. Additionally, flexible work arrangements can improve employee well-being and lead to higher levels of creativity and innovation.
Automation and Efficiency
Automation technology has also played a significant role in enhancing business creativity. By automating repetitive tasks, companies can allocate more time and resources to focusing on creative problem-solving and strategic thinking. For example, in health care, automation has streamlined administrative processes and improved patient care.
Increased efficiency from automation allows employees to focus on higher-value tasks, which can lead to innovative products and services.
At the same time, automation technologies can open up new markets and business opportunities, driving further innovation and growth.
Innovative Products and Services
Another example of leveraging technology for business creativity is the development of innovative products and services.
Take the Apple iPhone, which revolutionized the smartphone industry and transformed how people communicate and access information. By continuously investing in research and development, Apple has maintained its competitive edge and engaged users with new features and applications.
Innovative products and services not only help businesses stand out in the market, but they also drive industry progress. Companies that embrace emerging technologies can also foster a culture of innovation, as employees are encouraged to experiment with new ideas and adopt a forward-thinking mindset.
This approach can lead to breakthroughs and discoveries that propel businesses to new heights, solidifying their position as market leaders.
Creative Problem-Solving in Business Operations
Adapting business models.
Business creativity starts with solving problems in unique ways. In business operations, companies often experiment with new approaches to adapt their business models to meet shifting economic and market needs.
Entrepreneurs and managers must consider context, market demands, and financial constraints when transitioning.
Some strategies for adapting business models include:
- Diversification of product or service offerings
- Entering new markets or customer segments
- Expanding distribution channels
- Collaborating with industry partners
Pivoting Amid Obstacles
Unexpected challenges can arise in any business operation, requiring creative problem-solving for effective decision-making.
Pivoting is an important process in which an organization changes its direction, strategy, or product offerings to overcome obstacles and achieve growth. The ability to pivot is vital for maintaining engagement and remaining competitive in an ever-evolving marketplace.
Key aspects of successful pivoting include:
- Identifying new opportunities based on market trends or consumer behaviors
- Iterating and refining ideas to develop innovative solutions
- Leveraging strengths and resources to overcome barriers
- Agility and flexibility in transitioning to a new direction
Addressing Market Needs
Meeting market needs is at the core of any successful business. When addressing these needs, companies must focus on innovation-driven thinking and use creativity to develop strategies that resonate with their target audience.
These innovative approaches can involve combining existing ideas, improving existing products or services, or creating new offerings to address unique customer pain points.
An example of addressing market needs is the Forbes Business Council, which fosters collaboration and knowledge sharing among top executives.
By facilitating engagement and supporting innovative solutions, organizations can better anticipate market trends, cater to customer requirements, and ultimately succeed in their industry.
The Impact of Creativity on Marketing Strategies
Thinking outside the box.
In marketing, thinking outside the box means experimenting with innovative ideas rather than using conventional methods. For instance, adopting new technologies or experimenting with different channels can help marketers grab attention and reach more customers.
A creative person would leverage innovative thinking to discover unique marketing approaches to help their business stand out.
Engaging with Customers
Creative marketing strategies prioritize interactions that engage customers with a brand, impacting the success of the overall marketing effort. Brands can use creative storytelling to tap into customer emotions, thus forging a stronger connection.
The rise of Web 2.0 and social media provides a platform for businesses to foster genuine customer interactions and showcase their personality.
Focusing on customer engagement will enable marketers to understand their audience better, refine their product offers, and develop more tailored marketing strategies.
Differentiating from Competitors
A key aim of creative marketing strategies is to differentiate a business from its competitors. Uniqueness can be achieved through various tactics, such as:
- Developing a distinct visual identity
- Highlighting the value proposition
- Utilizing innovative marketing channels
- Adopting customer-centric approaches
By embracing risky and unconventional ideas, companies can stand out in the market and boost their enterprise value. However, it is essential to balance innovation and feasibility, ensuring that creative marketing strategies align with the company’s objectives and capabilities.
Incorporating creativity into marketing strategies not only enhances a brand’s visibility but also fosters a culture of innovation.
Nurturing creative marketing skills improves customer interactions, encourages unique thinking, and helps businesses differentiate themselves from their competitors. Capable of significantly impacting a company’s success, creativity in marketing should be duly acknowledged and rewarded.
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Career Planning
- Skills Development

What Is Creative Thinking?
Definition & Examples of Creative Thinking
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/ADHeadshot-Cropped-b80e40469d5b4852a68f94ad69d6e8bd.jpg)
How Creative Thinking Works
Types of creative thinking, benefits of creative thinking, how to showcase your creative thinking skills.
Melissa Ling / The Balance
Creative thinking is the ability to consider something in a new way. Employers in all industries want employees who can think creatively and bring new perspectives to the workplace.
Creative thinking can involve:
- A new approach to a problem
- A resolution to a conflict between employees
- A new result from a data set
- A previously untried approach to earn revenue
- A new product—or product feature
Find out more about the various types of creative thinking, and why having this ability is very beneficial in the workplace.
Creative thinking means thinking outside the box. Often, creativity involves lateral thinking, which is the ability to perceive patterns that are not obvious.
Creative thinking might mean devising new ways to carry out tasks, solve problems , and meet challenges. It means bringing a fresh, and sometimes unorthodox, perspective to your work. This way of thinking can help departments and organizations be more productive.
Creative thinking isn't limited to artistic types. Creative thinking is a skill that anyone can nurture and develop.
A creative thinker will turn conventional thinking on its head—they'll zig, where others zag.
Opportunities for creative thought in the workplace vary from obvious artistic positions to highly technical ones. Generally, anything that involves an “aha” moment is considered creative. Here are some examples of how to display creative thinking in different jobs.
Artistic Creativity
You don't have to be an artist for your work to have an artistic element. Perhaps you arrange retail displays for maximum impact or shape the path of an enticing hiking trail. Other artistically creative tasks might include designing logos, writing advertising copy, creating the packaging for a product, or drafting a phone script for a fundraising drive.
Creative Problem-Solving
Creative problem-solving stands out as innovative. A creative problem-solver will find new solutions rather than simply identifying and implementing the norm. You might brainstorm new ways to reduce energy use, find new ways to cut costs during a budget crisis, or develop a unique litigation strategy to defend a client.
Creativity in STEM
Some people think of science and engineering as the opposite of art and creativity. That's not true. The fields of science, technology, engineering, and math (STEM) are highly creative. Designing a more efficient assembly line robot, writing an innovative new computer program, or developing a testable hypothesis are all highly creative acts.
The history of science and technology is filled with projects that didn't work, not because of errors in technique or methodology, but because people remained stuck in their assumptions and old habits. STEM fields need creativity to flourish and grow.
Creative thinking is expressed in several ways. Here are some types of creative thinking you might see in the workplace.
Before thinking creatively about something, you first have to be able to understand it. This requires the ability to examine things carefully to know what they mean. Whether you are looking at a text, a data set, a lesson plan, or an equation, you need to be able to analyze it first.
Open-Mindedness
To think creatively, set aside any assumptions or biases you may have, and look at things in a completely new way. By coming to a problem with an open mind, you allow yourself the chance to think creatively.
Problem-Solving
Employers want creative employees who will help them to solve work-related issues. When faced with a problem, consider ways that you can solve it before asking for help. If you need the input of a manager, suggest solutions rather than just presenting problems.
Organization
This might seem counterintuitive: Aren’t creative people known for being somewhat disorganized? Actually, organization is an essential part of creativity. While you might need to get a bit messy when trying out a new idea, you need to organize your ideas so others will understand and follow through with your vision.
Communication
People will only appreciate your creative idea or solution if you communicate it effectively. You need to have strong written and oral communication skills.
Employers want creative thinkers because it benefits their bottom line. Companies that foster creativity may see more revenue growth. Positioning yourself as a creative thinker can make you a more appealing job candidate or leader within your current organization.
When you're applying for a job, think about how your creative nature has helped you in the past and how it might be an asset in the job you're seeking.
Here's how to showcase your creative thinking throughout the application process.
- Add Keywords: In your resume and cover letter, consider including keywords that demonstrate your creativity. For instance, you might try "problem-solving."
- Give examples: In your cover letter, include one or two specific examples of times your creative thinking added value to your employer. Perhaps you came up with a creative way to save your department money, or maybe you developed a new filing system that increased efficiency.
- Tell stories: Come to your interview prepared with examples of how you've demonstrated your creativity. This is especially important if the job description lists creativity or creative thinking as a requirement.
If you're looking for creative opportunities as a means of personal fulfillment, you can find satisfaction in surprising places. Any job that allows you to put your own spin on your work will end up being and feeling creative.
Key Takeaways
- Creative thinking is the ability to consider something in a new way.
- Creative thinking includes analysis, open-mindedness, problem-solving, organization, and communication.
- Many employers value creative thinkers, so consider highlighting your creative thinking skills on your resume and in interviews.
Northeastern University. " The Importance of Creativity in Business ."
Forbes. " The Most Valuable Skill In Difficult Times Is Lateral Thinking—Here’s How To Do It ."
Forrester. " The Creative Dividend ," Page 3.
How to Use Creativity in Problem-Solving

Using creativity in problem-solving is a dynamic process that involves seeing challenges from unique perspectives, generating novel solutions , and redefining the status quo. It requires going beyond traditional methodologies and employing inventive thinking.
Table of Contents
Techniques such as brainstorming, lateral thinking, and mind mapping can help ignite your creative sparks. By cultivating a culture of creativity, you empower yourself and others to tackle issues innovatively, ensuring that the problem-solving process is effective but also exciting and rewarding.
What is the Role of Creativity in Problem-Solving?
Creative problem-solving is an approach that combines imagination, innovation, and a broad sense of flexibility to find solutions to problems. It’s about shunning the traditional mindset that restricts our thoughts to only known and accepted techniques and methods . Instead, it encourages thinking outside the box, leveraging all cognitive resources, and pushing beyond the boundaries of standard methodologies to arrive at unique and often more effective solutions.
At the heart of creative problem-solving is the understanding that problems are often not what they initially appear to be. An issue may seem like a stumbling block. Still, with creative problem-solving , it can be transformed into an opportunity for innovation and growth. It’s about not accepting the immediate, apparent problem at face value but delving deeper into uncovering the root cause and addressing that, often leading to a more comprehensive and long-lasting solution.
Stages of Creative Problem-Solving
To appreciate what is creative problem-solving, it is crucial to recognize its critical stages. First is problem identification, which involves understanding the problem from different angles and perspectives. This stage lays the groundwork for the creative process by opening up many possibilities.
Next comes idea generation. This stage is the crux of the creative process, where traditional thinking is left behind, and innovative ideas can flourish. Techniques like brainstorming, free writing, and mind mapping are commonly used to spur creativity and encourage various possible solutions.
Finally, there’s the evaluation and implementation of the solution. This stage involves critically assessing the proposed solutions, selecting the best one, and implementing them. It’s important to remember that the solution’s effectiveness should be evaluated and adjustments made, if necessary, to ensure the problem is resolved.
In essence, creative problem-solving is a process that welcomes innovation, embraces change, and turns problems into opportunities for creative growth. It’s not about finding a solution but about using creativity to discover the best solution. The beauty of creative problem-solving is that honing this skill is possible and can be developed, ultimately leading to better decision-making and problem-solving abilities in all areas of life.
How to Harness Creativity in Problem-Solving
Harnessing creativity is the cornerstone of innovative problem-solving. This involves challenging our usual thought patterns and opening ourselves to new ways of thinking. But how do we activate this creative engine within us? The answer lies in asking the right creative problem-solving questions.
Creative Problem-Solving Questions
Questions are the fuel that ignites the engine of creativity. They challenge our assumptions, expand our perspectives, and drive us to think outside the box. In problem-solving, creative questions can illuminate unseen possibilities and pathways toward innovative solutions.
The first step in harnessing creativity for problem-solving is understanding the problem in-depth. Questions such as “What is the core issue?” or “Why is this a problem?” can help identify the root cause rather than just dealing with symptoms. Understanding the problem at a granular level often reveals unique angles and opportunities for innovative solutions.
Once we deeply understand the problem, it’s time to generate ideas. Here, creative problem-solving questions are designed to push our thinking beyond usual boundaries. Questions like “What if the impossible were possible?” or “How would this problem be solved in a completely different context?” can spark unconventional ideas and unlock creative potential.
The next stage is about evaluating the solutions. Questions such as “What could be the potential impacts of this solution?” or “How can we improve this idea?” ensure we critically assess the proposed solutions from various angles. It’s vital to constructively challenge each idea’s viability, promoting further creativity and refinement.
Finally, we come to the implementation of the chosen solution. Questions like “What resources are needed to execute this solution?” and “What could be potential roadblocks, and how can we overcome them?” enable us to foresee any practical issues and address them proactively, thus ensuring a smooth execution of the solution.
Asking creative problem-solving questions can help unlock our inherent creative capabilities. By harnessing our creativity, we can drive innovative problem-solving and find solutions that are not just effective but also genuinely novel and groundbreaking. These questions are more than just tools; they are the catalysts that transform problems into opportunities for creative innovation.

What is the Connection between Creativity and Problem-Solving?
Creativity is an invaluable tool in the problem-solving process. It empowers us to develop unique solutions that resolve the issue and provide opportunities for growth and innovation. But how is creativity used in problem-solving? Let’s dive into the nuances of this connection.
At its core, problem-solving is about finding solutions to obstacles or challenges. Traditional problem-solving techniques often focus on logical reasoning and proven methodologies. However, these techniques may only sometimes be sufficient, especially when dealing with complex or unprecedented problems. This is where creativity steps in.
How is Creativity Used in Problem-Solving
Creativity in problem-solving starts with reframing the problem. It prompts us to see beyond the apparent and understand the problem from different perspectives. This is particularly helpful when dealing with intricate issues, as it helps identify underlying patterns and relationships that might not be immediately apparent.
Once the problem is reframed, the next step is idea generation. This is where the power of creativity truly shines. Creative thinking encourages us to break free from conventional thinking patterns and explore a broader spectrum of possibilities. Brainstorming, mind mapping, or even daydreaming can help stimulate creative thoughts and generate innovative ideas.
Creativity also plays a critical role in evaluating and selecting the best solution. It allows us to envision how each potential solution might play out, assess the risks and benefits, and choose the most effective and innovative option.
Finally, creativity is instrumental in the implementation of the solution. It encourages us to think on our feet, adapt to unexpected challenges, and continuously refine the solution until the problem is fully resolved.
Creativity fuels each stage of the problem-solving process, transforming it from a mundane task into an exciting journey of discovery and innovation. So, whether you’re dealing with a minor hiccup or a major hurdle, remember to tap into your creative side. You might be surprised at the great solutions that emerge.
How to Explore Techniques for Fostering Creativity in Problem-Solving
In the dynamic and competitive business world, a creative approach to problem-solving can be a significant differentiator. Now businesses require innovative solutions to keep up with rapidly changing environments and customer expectations. Here, we’ll explore techniques for fostering creative problem-solving in business.
How to Use Creative Problem-Solving in Business
Firstly, it’s crucial to cultivate an environment that encourages creativity. An open-minded culture supporting risk-taking and diverse perspectives can significantly enhance creative thinking. This includes welcoming all ideas during brainstorming sessions, regardless of how unconventional they seem, and celebrating successes and learning opportunities from failures.
Secondly, divergent thinking is a powerful tool for creative problem-solving. It involves generating multiple possible solutions to a problem rather than following a linear, logical path. Techniques like brainstorming or lateral thinking can stimulate divergent thinking, leading to more innovative problem-solving.
Another technique uses creative problem-solving frameworks, like the SCAMPER model (Substitute, Combine, Adapt, Modify, Put to another use, Eliminate, Reverse). These frameworks provide structured methods for thinking creatively and can be particularly useful in a business setting.
Also, fostering creativity requires constant learning and development . Encouraging continuous learning, such as attending seminars, workshops, or online courses on creativity and innovation, can significantly enhance creative problem-solving skills. Also, exposure to different industries, cultures, and ways of thinking can provide new perspectives and ideas.
Creativity can also be enhanced by embracing technology. AI and machine learning, for example, can provide insights and patterns that would be hard to spot otherwise, opening new avenues for creative solutions.
Lastly, it’s essential to recognize the power of rest in fostering creativity. Downtime, hobbies, or simple walks in nature can rejuvenate the mind and often lead to ‘Eureka’ moments when least expected.
Fostering creative problem-solving in business is not a one-size-fits-all process. It requires a blend of culture, techniques, learning, technology, and well-being that suits your team’s unique needs and dynamics. However, the rewards – innovative solutions, competitive advantage, and team satisfaction – make it an investment worth making.

What are Some Successful Implementations of Creativity in Problem-Solving?
Applying creativity in problem-solving has led to groundbreaking solutions in various fields. In this context, we will explore several instances of creative problem-solving that resulted in successful and innovative outcomes.
Examples of Creative Problem-Solving
Accommodation: Let’s look at a classic example from the business world: Airbnb. In its early days, the company needed help to gain traction. The founders identified a key issue: the quality of listing photos could have been better, deterring potential renters. In a creative problem-solving move, they hired professional photographers to take pictures of the rentals. This innovative approach significantly improved the appeal of the listings, and the rest is history. Airbnb’s success illustrates how a creative solution can transform a problem into an opportunity.
Motor Industry: Consider the example of the automobile industry’s Tesla Motors . Confronted with the problem of fossil fuel dependency and its environmental impact, Tesla disrupted the conventional solution of tweaking existing fuel technologies. Instead, they creatively focused on developing high-performance electric vehicles, changing the industry’s perception and leading towards sustainable transportation.
Healthcare: Another example can be found in healthcare, particularly in the fight against polio. In the 1950s, the ‘iron lung’ was the primary treatment for polio-induced respiratory failure. It was a cumbersome and expensive solution. Dr. Bjørn Aage Ibsen , confronted with a polio outbreak, creatively proposed a new method: positive pressure ventilation. This involved manually ventilating the patient with a tube inserted into their trachea. This became the precursor to modern mechanical ventilation, demonstrating the impact of creative problem-solving in healthcare.
Education: Lastly, consider the example from education: the Khan Academy . Recognizing that traditional classroom education could not cater to each student’s pace and learning style, Salman Khan saw an opportunity to teach differently. He used technology creatively to provide free online educational videos, fundamentally transforming the access and delivery of education on a global scale.
The Impact of Creative Problem-Solving
In these cases, the key to successful problem-solving was applying creative thinking. These examples of creative problem-solving underscore the power of innovative thinking in transforming challenges into opportunities for growth and advancement. The ability to think creatively in problem-solving is a valuable skill and, in many cases, a game-changer.
How to Overcome Obstacles in Creativity in Problem-Solving
While creative problem-solving offers incredible potential for innovative solutions, it’s not without its challenges. However, these obstacles can often be overcome with a structured approach, such as the creative problem-solving model (CPS).
Creative Problem-Solving Model
The CPS model, initially developed by Alex Osborn and Sidney Parnes, provides a clear framework for navigating challenges that can arise during creative problem-solving. This model consists of four main steps: Clarify, Ideate, Develop, and Implement.
The first step, ‘Clarify,’ involves identifying the problem accurately and comprehensively. It’s easy to rush into solving a problem based on initial perceptions, which often results in treating symptoms rather than addressing the underlying issue. The CPS model emphasizes the importance of dedicating time to deeply understand the problem before jumping to solutions.
The second step, ‘Ideate,’ is generating various possible solutions. It’s common to experience blocks during this stage, such as sticking to familiar ideas or fearing judgment for unconventional thoughts. This step encourages divergent thinking, pushing past the initial, most apparent ideas to reach more unique and creative solutions.
Next, the ‘Develop’ stage involves converging on the most promising ideas and fleshing them into actionable solutions. Sometimes, the most creative ideas can seem risky or unrealistic. This stage, however, reminds us that these ideas often hold the most potential for innovative solutions and should be explored and developed rather than dismissed.
Finally, ‘Implement’ is about turning the solution into reality. Implementation can face many obstacles, from resistance to change, lack of resources, or unforeseen challenges. But the CPS model treats these not as dead ends but as parts of the problem-solving journey to be creatively overcome.
The creative problem-solving model provides a powerful tool to deal with the challenges of creative thinking. It offers a structured approach that fosters creativity, keeps the problem-solving process on track, and ultimately leads to innovative and effective solutions.

What are Some Tools and Strategies for Enhancing Creativity in Problem-Solving?
Creative problem-solving is a critical skill in today’s dynamic and complex world. It helps us navigate challenges with innovative and effective solutions. Various tools and strategies can enhance this process. Here, we delve into some of these creative problem-solving tools.
Creative Problem-Solving Tools
Brainstorming.
Brainstorming is the most familiar tool. It’s a freewheeling method to generate many ideas without immediate judgment or criticism. It invites and encourages wild and divergent thoughts, which are later sifted and refined. This tool is particularly effective in groups where diverse perspectives can spark unique ideas.
Mind Mapping
Mind Mapping, another powerful tool, visually represents thoughts and their interconnections. You can reveal unexpected connections by mapping the problem and related ideas and fostering innovative solutions. It’s an excellent tool for complex problems that involve multiple dimensions or for situations where a holistic view is needed.
The SCAMPER Method
The SCAMPER method (Substitute, Combine, Adapt, Modify, Put to another use, Eliminate, Reverse) prompts users to ask specific questions about the problem. Each word in the acronym poses a different way to manipulate and think about the problem, leading to fresh insights and solutions.
Six Thinking Hats Technique
Then there’s the Six Thinking Hats technique by Edward de Bono. This tool urges users to assume different ‘hats’ or roles (like the optimist, devil’s advocate, creative, etc.) during problem-solving. This strategy ensures a comprehensive approach, capturing different perspectives and reducing bias in decision-making.
Alongside these tools, specific strategies can cultivate creativity in problem-solving. Encouraging a culture of openness, where diverse thoughts are valued, can lead to more prosperous, more creative problem-solving. Creating a safe space where risks are welcomed is beneficial, and failures are seen as learning opportunities rather than setbacks.
Moreover, taking regular breaks and engaging in different activities can stimulate creativity. Often, stepping away from a problem allows our subconscious minds to work on it, leading to unexpected insights.
Regularly practicing and using these tools and strategies can dramatically improve creative problem-solving abilities. They stimulate innovative thinking and help structure the process, making it more effective and efficient. By leveraging these creative problem-solving tools, we can transform how we approach problems, turning challenges into opportunities for innovation.
What is the Future of Creativity in Problem-Solving?
As we navigate through a world that is becoming progressively more complex and unpredictable, the importance of creativity in problem-solving cannot be overstated. While still valuable, traditional problem-solving methods often must catch up when dealing with unprecedented challenges. Creativity injects flexibility, innovation, and adaptability into problem-solving, making it a vital skill for the future. Here, we explore some trends and predictions of creativity in problem-solving.
Growing Creative Problem-Solving
Firstly, we will likely see greater recognition of the role of creativity in problem-solving across various sectors. From businesses to education systems, there’s a growing understanding that generating and implementing innovative solutions to problems for survival and growth is crucial. We can see more emphasis on fostering creativity in leadership roles and at all levels.
Tech-Enhanced Creative Solutions
Secondly, technology will continue to play a significant role in enhancing creativity in problem-solving. Advanced technologies like AI and machine learning can provide us with more data and insights, enabling us to understand problems better and develop more creative solutions. At the same time, technology can facilitate the creative problem-solving process through tools that stimulate creative thinking and collaboration.
However, as we increasingly rely on technology, there’s also a danger that we might limit our creativity by depending too much on algorithms and predefined solutions. Therefore, balancing technology and human creativity will be essential to future problem-solving.
Additionally, we expect to see more integration of diverse perspectives in problem-solving. As we face global problems across various fields and cultures, it’s becoming clear that the most creative and effective solutions often come from interdisciplinary and diverse teams.
Dynamic Problem Adaptation
Finally, resilience and adaptability in problem-solving will be emphasized as we move toward a more uncertain future. Creative problem-solving will be less about finding the correct answer and more about continuous learning and adapting to evolving situations.
The future of creativity in problem-solving looks bright, promising, and exciting. By recognizing the importance of creativity and harnessing it effectively, we can equip ourselves to navigate future challenges with innovative and effective solutions.
What is the role of creativity in problem-solving?
Creativity in problem-solving allows for the generation of unique, practical solutions. It involves thinking outside the box, challenging traditional assumptions, and viewing the problem from various perspectives. Creativity is crucial in problem-solving as it fosters innovation and adaptability.
How can creativity be harnessed in problem-solving?
Creativity can be harnessed in problem-solving by promoting a culture that supports risk-taking and values diverse perspectives, employing techniques like divergent thinking and creative problem-solving frameworks, engaging in continuous learning and development, embracing technology, and prioritizing well-being and rest.
What is the connection between creativity and effective problem-solving?
Creativity contributes to effective problem-solving by enabling the generation of numerous possible solutions, encouraging novel perspectives, and fostering flexibility and adaptability. These aspects, in turn, lead to more comprehensive and innovative solutions.
What challenges might one encounter in creative problem-solving?
Challenges in creative problem-solving include rushing to solve the problem without fully understanding it, experiencing blocks during the ideation stage, dismissing seemingly unrealistic or risky ideas, and encountering resistance or unforeseen challenges during the implementation stage.
How might the future of creativity in problem-solving look like?
The future will likely see greater recognition of the role of creativity in problem-solving across various sectors. Technology will play a significant role in enhancing creativity, but maintaining a balance with human creativity will be necessary. Integrating diverse perspectives and emphasis on resilience and adaptability will also characterize future problem-solving.

Learn How To Develop Launch-Ready Creative Products
Download How to Turn Your Creativity into a Product, a FREE starter kit.

Advertisement
Create a Memorable Social Media Experience
Get the content planner that makes social media 10x easier.

Invite Your Customers To A Whole New World
Create a unique user experience.

Maximize Your Brand and Make Your Mark
Custom brand assets will take you to new heights.

Content Creation Calendar: How to Choose the Format

Email Marketing: How to Build a Community

Side Hustle: How to Find Your Niche

Branding: How to Thrive in the Marketplace

Headlines: How to Handle the Impact of Clickbait

Content Creation Calendar: What You Need to Know

- Onsite training
3,000,000+ delegates
15,000+ clients
1,000+ locations
- KnowledgePass
- Log a ticket
01344203999 Available 24/7
What is Creative Thinking? An Ultimate Guide
Creative Thinking is the key to unlocking innovative solutions and fostering imagination. This blog covers the essence of Creative Thinking, highlighting its significance in problem-solving and idea generation. Explore how nurturing your creative thinking skills can lead to breakthroughs in various aspects of life, from art and business to everyday challenges.

Exclusive 40% OFF
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Share this Resource
- Leadership Skills Training
- Instructional Design Training
- Design Thinking Course
- Business Development Training
- Leadership and Management Course

In a world constantly reshaped by innovation and imagination, the force driving these transformations is the power of Creative Thinking. But What is Creative Thinking exactly? At its core, it's the ability to perceive the world in new ways. It allows you to find hidden patterns and generate solutions and it's not just reserved for artists and inventors but is a crucial skill for everyone. Want to know how? Read this blog to learn about What is Creative Thinking, its features, examples, its importance as well as tips to unlock your Creative Thinking potential.
Table of Contents
1) Understanding What is Creative Thinking
2) Types of Creative Thinking
3) Importance of Creative Thinking
4) Benefits of Creative Thinking
5) Creative Thinking examples
6) Conclusion
Understanding What is Creative Thinking
Defining Creative Thinking is important before one chooses to explore its depth. Creative Thinking is a crucial aspect of Design Thinking, characterised as the capacity to perceive scenarios, ideas, or challenges in novel, innovative, and often unconventional manners. It necessitates surpassing established patterns or notions, leading to the creation of original and impactful ideas. At its core, it represents the act of venturing beyond conventional boundaries.

Types of Creative Thinking
After you have learned What is Creative Thinking, it’s time to understand its various types. Creative Thinking is multifaceted, and various types can be employed depending on the context or the problem at hand. Here are its five common types:
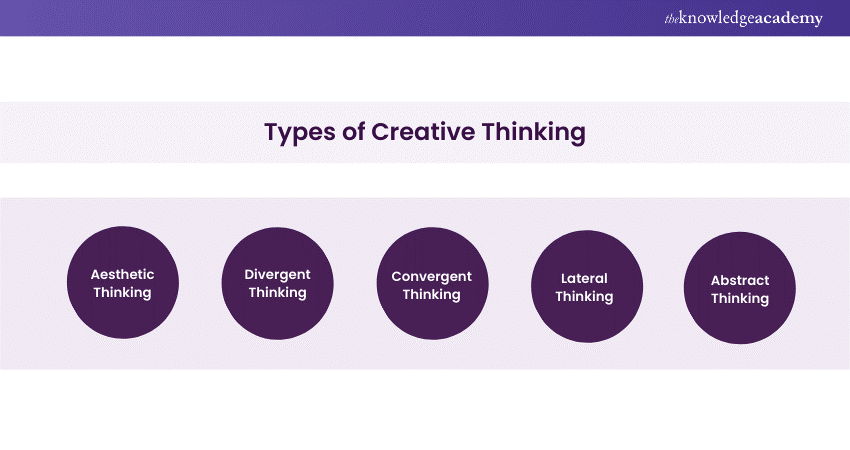
a) Divergent T hinking : This type of Thinking is about generating multiple solutions or ideas from a single starting point. It's similar to brainstorming, where the goal is to come up with as many answers or ideas as possible. Divergent Thinking is expansive, non-linear, and unrestrained, allowing for a wide array of potential solutions.
b) Convergent Thinking: Opposite to Divergent Thinking, Convergent Thinking seeks to narrow down options to find the single best solution to a problem. It involves analytical skills and logic to evaluate the ideas generated by divergent thinking, ultimately arriving at the most suitable answer.
c) Lateral Thinking: Coined by Edward de Bono, Lateral Thinking involves looking at a problem from a completely different perspective. It's about thinking "outside the box" and seeking solutions that might not be immediately obvious. Lateral thinkers often use indirect and creative approaches to problem-solving, making connections between seemingly unrelated concepts.
d) Abstract Thinking: This ability refers to the about concepts, ideas, or objects that are not physically present. It involves understanding complex ideas by breaking them down into their constituent parts and understanding how they relate to one another. Abstract thinkers are often good at seeing the "bigger picture" and understanding overarching themes and patterns.
e) Aesthetic Thinking: Rooted in the appreciation of beauty, art, and nature, Aesthetic Thinking is about recognising and creating harmony, balance, rhythm, and emotion. It's a form of Thinking often employed by artists, designers, musicians, and other creatives who seek to convey emotion, evoke reactions, or represent abstract ideas through their works.
Interested in building skills to guide those around you? Register for our Leadership Skills Courses !
Importance of Creative Thinking
In the contemporary job market, the enduring value of soft skills, such as Creative Thinking, extends across diverse industries. Employers increasingly prioritise adept at developing and experimenting with novel ideas. They actively seek analytical and outside-the-box thinkers, emphasising the iterative nature of Creative Thinking skills. These skills, encompassing creative problem-solving, innovative thinking, and analytical abilities, hold particular significance in workplaces marked by constant evolution and the integration of emerging technologies.
Creative Thinking is a linchpin in the contemporary professional landscape. With the rising importance of soft skills, including resilience, flexibility, agility, motivation, self-awareness, curiosity, and a commitment to lifelong learning, these attributes complement and amplify the impact of Creative Thinking. They reflecting the multifaceted nature of skills demanded in an ever-evolving workplace.
Thus, Creative Thinking is not confined to specific roles or industries but emerges as a cross-cutting competency essential for addressing the complexity of modern challenges. As workplaces grapple with rapid technological advancements and paradigm shifts, professionals with Creative Thinking skills stand out as valuable assets. Their ability to navigate challenges, devise innovative solutions, and adapt to changing market environments aligns with the demands of an era marked by continuous transformation.
Benefits of Creative Thinking
Embracing Creative Thinking isn't confined to professional realms; its transformative impact extends to various facets of life, want to know how?. Here are key benefits that underscore the value of nurturing Creative Thinking skills across personal, academic, and leadership domains:
Improved problem-solving capabilities
Creative Thinking is a versatile problem-solving tool, not limited to workplace challenges. It accelerates problem resolution by introducing diverse thought techniques. The cultivated ability to discern patterns more swiftly broadens the scope of effective solutions, promoting agility in addressing many issues encountered in daily life.
Stronger interpersonal connections
Enhanced communication lies at the heart of Creative Thinking's impact on relationships. Clear articulation of ideas enriches conversations with friends, family, and colleagues. Moreover, collaborative Creative Thinking fosters a collective approach to problem-solving. This, in turn, strengthens bonds and generating innovative solutions through the synergy of diverse perspectives.
Heightened productivity
Contrary to misconceptions, Creative Thinking is not a diversion but a catalyst for productivity. When traditional thought patterns lead to frustration and stagnation, engaging in Creative Thinking strategies becomes a rejuvenating pause. It rekindles motivation, reignites passion, and unlocks new solutions. As a result, it prevents productivity decline by introducing fresh perspectives and approaches.
Higher self-awareness
Creative Thinking acts as a vehicle for self-discovery by encouraging the exploration of diverse perspectives. This process unveils assumptions, biases, and viewpoints that may have remained unnoticed.
By challenging conventional thinking, it nurtures self-awareness and bolsters emotional intelligence. The ability to reframe perspectives and embrace a growth mindset becomes a decisive outcome of this ongoing journey of self-exploration.

Creative Thinking examples
Understanding a concept often becomes simpler when illustrated with tangible examples. To provide a clearer image of what Creative Thinking encompasses, let’s dive deeper into instances from diverse domains:
Salvador Dali, a master of the surreal, gifts the world with his painting, "The Persistence of Memory". At first glance, the work can be disconcerting, with its limp watches draped eerily across a desolate land. But delve deeper, and it's evident that Dali challenges our understanding of time. The melted clocks aren’t just distortions; they're an invitation to view time not as a rigid construct but as a fluid entity. Dali’s work exemplifies how creative thinkers can challenge accepted norms and offer fresh, sometimes revolutionary perspectives.
Business
Apple's unveiling of the iPhone in 2007 was more than just the launch of a new product. While the market was saturated with phones that played music or accessed the internet, Apple's vision was different. They didn’t see these functions as separate entities but imagined a cohesive device that melded them together.
Converging an iPod, a phone, and an Internet communicator into a single device, Apple didn't just create a new product; they reinvented our understanding of what a phone could be. This disruptive innovation, born from a willingness to think differently, altered the trajectory of communication technology.
Problem-solving
Mistakes, in the creative world, are often seen as stepping stones rather than setbacks. A perfect illustration of this mindset is the invention of "Post-it Notes" by 3M. What started as a botched experiment in search of a robust adhesive led to the accidental discovery of a weak, repositionable one.
Where others might have seen failure, 3M spotted opportunity. Instead of discarding the discovery, they embraced its unique qualities, leading to the birth of the Post-it Note. Today, these sticky notes, borne from an unintentional finding, adorn offices, homes, and schools worldwide, reminding us that sometimes thinking creatively means recognising the potential in the unexpected.
Learn to be a dignified figure among your peers by joining our Introduction to Supervising a Team Course !
Conclusion
While asking the question “What is Creative Thinking?", remember that the answer goes beyond just understanding innovation. It delves into the profound realisation of our potential to transform and innovate. As illustrated by numerous examples, such thinking can revolutionise sectors, tackle immense challenges, and enhance personal growth. When confronted with a challenge, embrace this powerful mindset to harness your mind's vast capabilities.
Curious about how the human mind works? Try our Creative and Analytical Thinking Training !
Frequently Asked Questions
To enhance Creative Thinking skills, engage in activities outside your comfort zone, embrace diverse perspectives, and regularly challenge assumptions. Practice brainstorming without self-censorship, explore new hobbies and seek inspiration from various sources. Cultivate a mindset of curiosity and continuous learning, fostering a creative approach to problem-solving
Creative Thinking provides a competitive edge in the job market by enabling innovative problem-solving, fostering adaptability, and enhancing communication skills. Employers value candidates who bring fresh perspectives to challenges, driving creativity and efficiency.
Certifications targeting Creative Thinking offer creativity, innovation, and problem-solving capabilities. While not certifications per se, courses can provide valuable skills and perspectives to strengthen your creative thinking abilities.
The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue , encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA .
The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass , a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
The Knowledge Academy offers various Leadership courses , including Leadership Skills Training and Agile Leadership Course. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Leadership Qualities .
Our Leadership Skills blogs cover a range of topics related to Leadership, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Leadership skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Fri 7th Jun 2024
Fri 2nd Aug 2024
Fri 4th Oct 2024
Fri 6th Dec 2024
Get A Quote
WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
My employer
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry
- Business Analysis
- Lean Six Sigma Certification
Share this course
Our biggest spring sale.

We cannot process your enquiry without contacting you, please tick to confirm your consent to us for contacting you about your enquiry.
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry.
We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Or select from our popular topics
- ITIL® Certification
- Scrum Certification
- Change Management Certification
- Business Analysis Courses
- Microsoft Azure Certification
- Microsoft Excel Courses
- Microsoft Project
- Explore more courses
Press esc to close
Fill out your contact details below and our training experts will be in touch.
Fill out your contact details below
Thank you for your enquiry!
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go over your training requirements.
Back to Course Information
Fill out your contact details below so we can get in touch with you regarding your training requirements.
* WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
Preferred Contact Method
No preference
Back to course information
Fill out your training details below
Fill out your training details below so we have a better idea of what your training requirements are.
HOW MANY DELEGATES NEED TRAINING?
HOW DO YOU WANT THE COURSE DELIVERED?
Online Instructor-led
Online Self-paced
WHEN WOULD YOU LIKE TO TAKE THIS COURSE?
Next 2 - 4 months
WHAT IS YOUR REASON FOR ENQUIRING?
Looking for some information
Looking for a discount
I want to book but have questions
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go overy your training requirements.
Your privacy & cookies!
Like many websites we use cookies. We care about your data and experience, so to give you the best possible experience using our site, we store a very limited amount of your data. Continuing to use this site or clicking “Accept & close” means that you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more about our privacy policy and cookie policy cookie policy .
We use cookies that are essential for our site to work. Please visit our cookie policy for more information. To accept all cookies click 'Accept & close'.

How You Can Use Creative Problem Solving at Work
Lucid Content
Reading time: about 4 min
How many times have you tried to solve a problem only to get stuck in the process? In a business setting, this is a common occurrence. You’re faced with issues that traditional problem solving methods can’t solve. But you still need to find a way to fix the issue to move a project forward or resolve a conflict. This is when you may need to get creative to solve the problem at hand.
What is creative problem solving?
The definition of creative problem solving (CPS) will vary between organizations. At its core, CPS involves approaching a problem in an imaginative, innovative, and unconventional way. The process encourages you to find new, creative ways of thinking that can help you overcome the issue at hand more quickly.
7 steps of the creative problem solving process
The CPS process can be broken down into seven steps.
1. Identify the goal
Before solving the problem, you need to fully understand the problem you’re trying to solve. You may have overlooked or misunderstood some details. Take some time to analyze the conflict and clear up any confusion.
2. Gather data
Once you know what the problem is, you need to learn all you can about it. Who does the problem affect? Who is involved in solving the issue? Gather all the knowledge you can to gain a better understanding of the issue and to solve it.
3. Formulate challenge questions
After you’ve gathered the details, turn the problem into a question. Word the question in a way that encourages suggestions or ideas. It should be short, concise, and only focus on a single issue. Once you’ve created one or two questions, start trying to answer them.
4. Explore ideas
This step is where the brainstorming begins. You’ll be creating possible ideas or solutions to the problem you’re facing. This is usually when the creativity really starts to flow. With so many ideas flowing, it’s crucial that you write each of them down—even the stupid ones. Even if the idea you come up with has little to no chance of working, write it down. Trying to sort out bad ideas from the good ones during this step can squash creativity.
5. Come up with solutions.
Weed out the average ideas from the winners by testing each one. See if the possible solution actually solves the problem and if you can implement it successfully. If the potential solution doesn’t resolve the issue, move on to the next idea. Evaluating each idea will help you zero in on the perfect solution.
6. Create an action plan
Now that you have the perfect solution, you’ll need to create an action plan outlining implementation steps. Consider what resources you’ll need and how long it will take. Then write it all down. Once you create the plan, communicate the approach to the rest of the team so they’re aware of what’s happening.
To help you create an organized and detailed plan, you can use swimlanes in Lucidchart.
7. Take action
With your plan created and your team on board, it’s time to implement your solution and resolve the problem.
CPS techniques
Just knowing the process behind CPS isn’t enough. You’ll want to know about the common creative problem solving ideas or techniques that you can use to be more successful during each phase. Below are a few of the techniques you can use to help you through the CPS process:
Synectics: This technique helps to inspire thoughts that you might not be aware of. It is a way to approach creativity in a logical, rational manner.
TRIZ methodology (Theory of Inventive Problem Solving): This problem solving methodology is based on logic, data, and research—not intuition. It involves adapting existing solutions to your particular problem.
Brainstorming: Using this technique allows you to collect a number of ideas that can be a potential solution to a problem and can be used in either a group or individual setting.
Mind mapping: Mind mapping helps keeps your ideas organized by representing them in a graphical manner.

Reversal of problem: Trying to solve a problem using traditional problem solving methods can sometimes end in roadblocks.This technique forces you to think about a problem from a new perspective.
Looking beyond something’s function: Thinking about how you can use something beyond its typical function is a common CPS technique.
SCAMPER: This acronym can help you come up with new ideas. Each letter stands for a way you can manipulate an original idea to come up with something new:
- S ubstitute
- P ut to other uses
Why use CPS
No matter what profession you’re in, you will face challenges. There will be times when traditional problem solving techniques just don’t do the trick. That’s when you can take advantage of CPS to help uncover the best solution to your problem.
About Lucidchart
Lucidchart, a cloud-based intelligent diagramming application, is a core component of Lucid Software's Visual Collaboration Suite. This intuitive, cloud-based solution empowers teams to collaborate in real-time to build flowcharts, mockups, UML diagrams, customer journey maps, and more. Lucidchart propels teams forward to build the future faster. Lucid is proud to serve top businesses around the world, including customers such as Google, GE, and NBC Universal, and 99% of the Fortune 500. Lucid partners with industry leaders, including Google, Atlassian, and Microsoft. Since its founding, Lucid has received numerous awards for its products, business, and workplace culture. For more information, visit lucidchart.com.
Related articles
How to brainstorm: 4 ways to get the creative juices flowing.
Brainstorming can promote problem-solving and innovative thinking to bring the best ideas forward. Follow these four steps and learn how to brainstorm ideas like a pro.
Affinity Diagrams: Your Key to More Creative Problem Solving
No matter the situation, affinity diagramming will help you to organize your thoughts and overcome your workplace challenges. Use these tips and templates to get started.
Bring your bright ideas to life.
or continue with
- Back to All Programs /
Creative Thinking: Innovative Solutions to Complex Challenges
Learn how to grow a culture of creativity to innovate competitive solutions.
All Start Dates
8:30 AM – 4:30 PM ET
2 consecutive days
Registration Deadline
May 28, 2024
October 8, 2024
Overview: Creative Thinking Skills Course
The tech breakthrough that makes smartphones irrelevant, a new viral ad campaign, your company’s next big revenue generator — ideas like these could be sitting in your brain; all you need are the creative thinking skills and strategies to pull them out.
This interactive program focuses explicitly on the creative thinking skills you need to solve complex problems and design innovative solutions. Learn how to transform your thinking from the standard “why can’t we” to the powerful “how might we.” Crack the code on how to consistently leverage your team’s creative potential in order to drive innovation within your organization. Explore how to build a climate for innovation, remove barriers to creativity, cultivate courage, and create more agile, proactive, and inspired teams.
You will leave this program with new ideas about how to think more productively and how to introduce creative thinking skills into your organization. You can apply key takeaways immediately to implement a new leadership vision, inspire renewed enthusiasm, and enjoy the skills and tools to tackle challenges and seize opportunities.
Innovation experts Anne Manning and Susan Robertson bring to this highly-interactive and powerful program their decades of experience promoting corporate innovation, teaching the art of creative problem solving, and applying the principles of brain science to solve complex challenges.
Who Should Take Creative Thinking Skills Training?
This program is ideal for leaders with at least 3 years of management experience. It is designed for leaders who want to develop new strategies, frameworks, and tools for creative problem solving. Whether you are a team lead, project manager, sales director, or executive, you’ll learn powerful tools to lead your team and your organization to create innovative solutions to complex challenges.
All participants will earn a Certificate of Participation from the Harvard Division of Continuing Education.
Benefits of Creative Thinking Skills Training
The goal of this creative thinking program is to help you develop the strategic concepts and tactical skills to lead creative problem solving for your team and your organization. You will learn to:
- Retrain your brain to avoid negative cognitive biases and long-held beliefs and myths that sabotage creative problem solving and innovation
- Become a more nimble, proactive, and inspired thinker and leader
- Create the type of organizational culture that supports collaboration and nurtures rather than kills ideas
- Gain a practical toolkit for solving the “unsolvable” by incorporating creative thinking into day-to-day processes
- Understand cognitive preferences (yours and others’) to adapt the creative thinking process and drive your team’s success
- Develop techniques that promote effective brainstorming and enable you to reframe problems in a way that inspires innovative solutions
The curriculum in this highly interactive program utilizes research-based methodologies and techniques to build creative thinking skills and stimulate creative problem solving.
Through intensive group discussions and small-group exercises, you will focus on topics such as:
- The Creative Problem Solving process: a researched, learnable, repeatable process for uncovering new and useful ideas. This process includes a “how to” on clarifying, ideating, developing, and implementing new solutions to intractable problems
- The cognitive preferences that drive how we approach problems, and how to leverage those cognitive preferences for individual and team success
- How to develop—and implement— a methodology that overcomes barriers to innovative thinking and fosters the generation of new ideas, strategies, and techniques
- The role of language, including asking the right questions, in reframing problems, challenging assumptions, and driving successful creative problem solving
- Fostering a culture that values, nurtures, and rewards creative solutions
Considering this program?
Send yourself the details.
Related Programs
- Design Thinking: Creating Better Customer Experiences
- Agile Leadership: Transforming Mindsets and Capabilities in Your Organization
June Schedule
- Creative Challenges: A Team Sport
- The Place to Begin: Reframe the Challenge
- Ideas on Demand
- Building a Creative Organization
October Schedule
Instructors, anne manning, susan robertson, certificates of leadership excellence.
The Certificates of Leadership Excellence (CLE) are designed for leaders with the desire to enhance their business acumen, challenge current thinking, and expand their leadership skills.
This program is one of several CLE qualifying programs. Register today and get started earning your certificate.
Harvard Division of Continuing Education
The Division of Continuing Education (DCE) at Harvard University is dedicated to bringing rigorous academics and innovative teaching capabilities to those seeking to improve their lives through education. We make Harvard education accessible to lifelong learners from high school to retirement.

- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
A Cognitive Trick for Solving Problems Creatively
- Theodore Scaltsas

Mental biases can actually help.
Many experts argue that creative thinking requires people to challenge their preconceptions and assumptions about the way the world works. One common claim, for example, is that the mental shortcuts we all rely on to solve problems get in the way of creative thinking. How can you innovate if your thinking is anchored in past experience?
- TS Theodore Scaltsas is a Chaired Professor in Classical Philosophy at the University of Edinburgh in Scotland.
Partner Center

Soft Skills Training Modules: Problem Solving and Critical Thinking
Problem Solving and Critical Thinking: Cultivating analytical and creative thinking for effective decision-making.
Problem solving and critical thinking.
Problem Solving and Critical Thinking are two interlinked skills that form the backbone of decision-making, both personally and professionally. They combine our ability to analyze situations or problems, consider alternatives, and choose the most appropriate course of action.
Let us explore these skills in more depth.
Critical Thinking
Critical thinking refers to the ability to objectively analyze information and make a reasoned judgment. It involves the process of actively and skillfully conceptualizing, applying, analyzing, synthesizing, and evaluating information gathered from observation, experience, or communication.
For example, suppose you are a project manager faced with a project delay due to a sudden shortage of resources. Critical thinking would involve analyzing the cause and extent of the resource shortage, understanding how it affects the project timeline, and considering various options to address the problem.
Problem Solving
Problem solving, on the other hand, is a cognitive process focused on finding solutions to difficult or complex issues. It involves identifying problems, developing potential solutions, making decisions about the best solutions, and implementing them. Divergent thinking (generating many unique ideas) and convergent thinking (combining those ideas into the best result) are central to the problem-solving process.
For instance, continuing with the previous example, after your critical analysis, you might identify several solutions such as reallocating resources from another project, hiring temporary resources, or negotiating for an extended deadline. The problem-solving skill would then involve selecting the best solution and implementing it effectively.
Techniques for Effective Decision-Making
The ability to problem solve and think critically are fundamental to making decisions. Decision-making is a process of making choices from alternatives based on the values and preferences of the decision maker.
Let’s take an example of a business deciding to enter a new market. Critical thinking might involve analyzing the market opportunity, understanding competitors and identifying any regulatory constraints. Problem-solving might entail devising marketing strategies, securing funds, and preparing the business plan.
Pearson’s RED Critical Thinking Model 🔴
Pearson’s Recognize Assumptions, Evaluate Arguments and Draw conclusions (RED) model is a valuable tool for enhancing critical thinking.
- Recognize Assumptions : This involves identifying unstated beliefs and values that affect our thinking and actions. For instance, the assumption that the new market operates the same way as the current one could be flawed.
- Evaluate Arguments : Once assumptions are recognized, the next step involves examining any arguments or propositions to determine their reliability. For example, evaluating the pros and cons of the proposed marketing strategies.
- Draw Conclusions : Finally, after all assumptions and arguments have been analyzed, conclusions are drawn based on this evaluation. For example, deciding whether to enter the new market or not.
In conclusion, mastering problem-solving and critical thinking are integral to efficient and effective decision-making. These skills can be developed and honed, significantly amplifying our personal and professional mastery. For every problem encountered, remember to inspect, reflect, and direct to a solution using critical thinking, problem-solving, and effective decision-making skills.
Root cause analysis techniques
“Did you know that Einstein once said: ‘If I had an hour to solve a problem, I’d spend 55 minutes thinking about the problem and 5 minutes thinking about the solution?’ This quote highlights the importance of deeply understanding a problem before jumping to solutions. One of the most effective ways to do this is through Root Cause Analysis . 🎯
What is Root Cause Analysis?
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) is a method used to identify the underlying cause of a problem rather than addressing the obvious symptoms. Its goal is to eradicate problems by removing the risk of the same issue repeating in the future. A root cause is the deepest underlying cause that can be resolved to forestall future recurrence of a problem.
Let’s explore the various techniques and steps involved in Root Cause Analysis.
Techniques of Root Cause Analysis 🛠
There are a few popular techniques that practitioners use in Root Cause Analysis:
1. The 5 Whys method: The 5 Whys uses counter measures through root cause identification. Its straightforward approach involves asking ‘Why?’ five times, each question building on the answer to the previous one.
2. The Fishbone Diagram (Ishikawa Diagram): Developed by Professor Kaoru Ishikawa in the 1960s, this technique is used to categorize potential causes of problems in an organized way and is a visual way to look at cause and effect.
3. The Pareto Chart: This is a simple graphical synopsis of how significant your problems are. The Pareto Chart helps you focus on the problems that offer the greatest potential for improvement by showing which issues have the largest effect on a problem, and thus which solutions will have the most impact.
📌 These are the main techniques but others like Fault Tree Analysis or Failure Mode and Effects Analysis are also applied based on the nature and criticality of the problem.
How to Conduct Root Cause Analysis
Now let’s have a look at the practical aspects of performing root cause analysis
Step 1: Identify the problem. The first step in performing a root cause analysis is to clearly defining what the problem is. Try to be as specific as possible.
Step 2: Collect data. Data pertinent to the issue needs to be collected. This can involve records, documents, or individuals with knowledge about the problem.
Step 3: Identify potential root causes. Using one of the above mentioned techniques, potential root causes are identified.
Step 4: Analyze & Identify the root cause. After collecting all data and potential root causes, the team should work together to analyze and identify the underlying root cause.
Step 5: Develop, implement and monitor corrective actions. Once the root cause has been identified, a potential solution can be developed, implemented and monitored.
Just keep in mind that RCA is only as good as the actions taken based on its findings. Without applying corrective measures, the value of the analysis is drastically diminished.
Root cause analysis encourages a long-term perspective and a preventative mindset. It strives for a culture where problems are not hidden or ignored, but are seen as opportunities for essential system improvements. ” So, are you ready to discover the truth under the surface of your problems?
To do: Apply root cause analysis techniques to identify and address underlying issues in the project workflow.
Short step-by-step plan:
- Identify the Problem : Select a specific issue to apply root cause analysis, such as frequent delays in project timelines.
- Gather Data : Collect relevant data and information regarding the issue, including project schedules, team communication logs, and any relevant feedback or complaints.
- Generate Possible Causes : Brainstorm potential reasons for the delays, like unclear project priorities, inadequate resources, or miscommunication among team members.
- Narrow Down Causes : Review the list of potential causes and prioritize them based on their likelihood and impact on the issue at hand.
- Investigate Root Causes : Analyze each potential cause in detail, looking for connections or patterns that may point to the underlying root cause.
- Confirm Root Cause : Validate the identified root cause through additional data analysis or team discussions, ensuring that the focus is on addressing the core issue.
- Develop Solutions : Based on the identified root cause, create specific action plans to address and resolve the issue, such as implementing clearer communication protocols or reallocating resources.
- Implement and Monitor : Put the proposed solutions into action and monitor their effectiveness, using measurable indicators to track progress and ensure sustained improvement.
🍏 As a deliverable for this task, create a detailed report outlining the chosen issue, the identified root cause, and the implemented solutions, supported by relevant data and analysis.
Data-driven decision making
Did you know that a stunning 84% of business leaders expect data to inform all or most of their decisions? Yes, that’s right, data-driven decision making (DDD) 📈 is a critical aspect of successful business strategy in every industry today! Let’s dive into the world of DDD, unpack its meaning, and explore its profound implications.
Understanding Data-Driven Decision Making
The heart and soul of DDD is using facts, metrics, and data to guide strategic business decisions, rather than going by intuition or observation alone. This unique intersection of statistical methods with predictive algorithms fuels the engine of DDD. Not only does it enhance accuracy, it also speeds up decision-making while reducing the influence of cognitive biases.
To make this a bit clearer, let’s imagine you’re the manager of an online retail store. Instead of deciding an advertising strategy based on your gut feeling, you look at data on which ads have generated the most traffic in the past. Now, you can make decisions informed by evidence and drive truly impactful business outcomes!
The Benefits of a Data-Driven Approach 📊
With DDD, you’re able to make more strategic, educated decisions. Here are a few benefits:
- Increased Efficiency: By understanding patterns in your data, you can identify areas where your strategies are effective and areas where improvements could be made.
- Enhanced Accuracy: Data reduces guesswork. It presents a more precise, nuanced view of what’s truly going on.
- Optimized Customer Strategy: Consumer behavior data can help you understand customer needs better, and tweak your product or service offerings to match these needs.
The Steps in Data-Driven Decision Making
1. Identify the Decision: The first question you need to answer is – what decision do you need to make? Clearly define what you are trying to achieve. Remember, your goal should be SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound)!
2. Gather Relevant Data: Once you know what you’re trying to achieve, start gathering data relevant to your decision. This might include sales data, website analytics, market research, or any other information that can inform your decision.
3. Analyze the Data: After gathering the data, it’s time to analyze it. Look for patterns or trends. You might find it helpful to use software or other tools to make this process easier.
4. Make the Decision: Based on your analysis, make your decision. Remember, the purpose of DDD isn’t to make the decision for you. Rather, it provides you with more information so you can make a more informed decision.
5. Evaluate the Decision: After the decision has been implemented, gather more data to determine if the decision was effective. If not, use what you’ve learned to make a better decision next time.
Applying these steps to our previous example, imagine you’re trying to improve your online store’s advertising strategy (Step 1). You start gathering data on previous ad campaigns and website traffic (Step 2). You analyze this (Step 3) and realize that Video A generated more click-throughs than Video B. You decide to invest more in advertising like Video A (Step 4). Later, you evaluate the results of this change to assess its impact (Step 5).
Now, consider how you can implement these steps into your own decision-making process. Remember, the goal isn’t to let data make your decisions, but to use data to make more informed decisions. That’s the power of Data-Driven Decision Making 📈.
Aligning your decisions with hard data can undoubtedly transform your decision-making process, strengthen your problem-solving abilities, and more importantly, bring massive success to your business!
To do: Conduct a data-driven decision making process for a marketing campaign.
- Define the decision to be made: Determine the specific marketing challenge and the decision that needs to be made, such as choosing between different advertising channels for an upcoming campaign.
- Gather relevant data: Collect data on past campaign performance, customer demographics, market trends, and competitor activities that can inform the decision.
- Analyze the data: Use statistical methods and data visualization tools to identify patterns, correlations, and insights within the collected data.
- Make a decision based on the data analysis: Use the findings from the data analysis to make an informed decision on the most effective marketing approach for the campaign, considering factors like return on investment, target audience engagement, and market trends.
- Monitor the decision’s outcomes: Implement the chosen marketing strategy and continually track its performance using key performance indicators, such as sales, website traffic, and customer engagement metrics.
🍏 After analyzing the data, I found that focusing on social media advertising for this specific campaign yielded the highest return on investment based on past performance and current market trends.
Creative problem solving methods
Let’s dive right into the world of creative problem-solving methods . 🧠🌟 This style of problem-solving encourages unique, innovative solutions to issues, helping you step out of your comfort zone and think outside the box.
Creative Problem-Solving Methods 💭💡
Creative problem solving is a fantastic skill to develop. It allows us to approach challenges from a new perspective, and is especially useful when we’re faced with problems where traditional methods have fallen short.
Brainstorming 🌩️✍️
One of our first techniques, Brainstorming, is possibly something you’ve run into before. It’s all about creating a safe space where as many ideas as possible are encouraged – no matter how out-of-the-box they may seem! The goal is quantity over quality in this initial stage because even the most outrageous idea can spark inspiration.
For instance, in a brainstorming session, a person might suggest an impractical method to clean up pollution. However, this might inspire another participant to think up an out-of-the-box yet feasible solution.
Reverse Thinking 🔄💭
Want to change it up? Reverse Thinking might be your ticket. Instead of asking how to solve the problem, ask how you could cause it. This method flips our standard logic on its head, allowing us to explore the problem from a totally new angle!
Imagine if you’re trying to increase customer satisfaction. Using reverse thinking, you would ask, “How could we make our customers unsatisfied?” The answers to this question may point out your current mistakes or weaknesses that need addressing.
Mind Mapping 🧠🌐
Another fantastic problem-solving method is Mind Mapping. This approach is visually based and starts with a central concept. From the center, you draw lines or ‘branches’ out to major ideas connected to your main concept, and continue branching out into subtopics.
Let’s say your problem is improving communication within a team. Your “central concept” would then be “communication.” Branches might be “email,” “team meetings,” “one-on-one chats.” Subbranches under “email” could be “response times,” ” clarity,” “tone of voice,” and so on. In this way, you can visually break down complex problems and see potential solutions.
The Six Thinking Hats 🎩🧢
Last, but certainly not least, is the Six Thinking Hats technique, developed by Edward de Bono. This method encourages you to tackle problems from six distinct perspectives or ‘hats’: white (facts), red (feelings), black (negatives), yellow (positives), green (creativity), and blue (management).
Suppose you’re launching a new product. By “wearing each hat,” you force yourself to consider all angles: What are the facts and data regarding the market? What are customers likely to feel about this product? What could the negatives be? The positives? How can the product be improved creatively?
In conclusion, creative problem-solving techniques are a fantastic way of generating innovative solutions. By brainstorming, reverse thinking, mind mapping, and switching ‘thinking hats,’ you can uncover unique and effective methods to address any challenge. 🚀🌠
To do: Practice using the SCAMPER method for creative problem solving.
- Example: Take a problem you’re facing and think of a substitute or alternative solution that could work instead of the current approach.
- Example: Think about how you could combine different ideas or elements to develop a novel solution to a problem you’re currently working on.
- Example: Identify an existing solution and adapt it to better fit the current problem you’re trying to solve.
- Example: Take an existing product or idea and modify it to better suit the needs of your project or the problem you’re addressing.
- Example: Consider how you could put an existing tool or resource to use in a completely different context to solve a problem you’re encountering.
- Example: Take a look at an existing process or approach and consider what steps or elements could be eliminated to streamline the overall solution.
- Example: Consider reversing the order of a particular process or the function of a tool to come up with a fresh perspective on solving a current problem.
🍏 Practice using the SCAMPER method by applying each of its steps to address a specific problem you’re currently facing.
Overcoming cognitive biases
Did you know that every day, your brain is constantly making decisions based on information it receives? Often, these decisions are influenced by cognitive biases. These biases can significantly sway your judgment and lead you to make illogical conclusions. Understanding these biases and learning how to overcome them is paramount in enhancing your problem-solving and critical thinking abilities for effective decision-making.
🧠 What are Cognitive Biases?
Cognitive biases are systematic errors in our thinking that affect the decisions we make. They occur when we rely on our mental shortcuts, known as heuristics, to process information quickly. While these shortcuts can be beneficial in some situations, they often lead us to make irrational decisions in others.
Some common examples of cognitive biases include Confirmation Bias 💡, where we favor information that confirms our preexisting beliefs and ignore contradictory evidence, and Hindsight Bias 👁🗨, the tendency to overestimate our ability to have predicted an event after it has already occurred.
⛔ The Impact of Cognitive Biases on Decision Making
Cognitive biases can have a significant and harmful impact on our decision-making abilities. They can cause us to make irrational decisions, lead us to believe we are more informed or in control than we actually are, and contribute to groupthink, a phenomenon where individuality and dissent are discouraged in group decision-making processes. This can lead to poor decisions and reduced problem-solving abilities.
👥 Ways to Overcome Cognitive Biases
Overcoming cognitive biases is not an easy task, especially since they are often hardwired into our brains as a result of evolutionary adaptations. However, understanding these biases and knowing how they influence our decision-making abilities can help in mitigating their effects. Below are some strategies that can be used:
Awareness 🚦
Knowledge of the existence of cognitive biases is the first step towards overcoming them. By understanding how they work and their possible impacts, one can begin to identify when these biases are influencing their decision-making process.
Seeking Diverse Perspectives 🔭
Overcoming cognitive biases also involves seeking multiple perspectives. Diversifying the opinions and viewpoints you consider when making a decision can reduce bias and result in more balanced decision-making.
Critical Thinking 🔍
Engaging in critical thinking can also help combat cognitive biases. This involves questioning assumptions, verifying facts and evidence, and being open to changing your viewpoints based on new information.
Using Analytical Tools 🛠️
Analytical tools, such as decision trees, pro-con lists, and SWOT analysis, can help make decision-making more objective and balanced. These tools can assist in logically analyzing the decision at hand and reducing the influence of biases.
In conclusion, overcoming cognitive biases can significantly improve your decision-making and problem-solving abilities. By developing your understanding of these biases, seeking diverse perspectives, practicing critical thinking, and utilizing analytical tools, you can begin to mitigate their detrimental effects on your decisions.
To do: Identify and address cognitive biases in decision making.
- Example: Research and identify common cognitive biases such as confirmation bias, anchoring bias, and availability heuristic.
- Example: Reflect on a recent decision you made and consider if any cognitive biases influenced your thinking or choices.
- Example: Engage with colleagues or friends to gain diverse viewpoints on a decision you need to make, helping to counteract potential biases.
- Example: Apply decision-making frameworks like SWOT analysis or decision trees to structure your thinking and reduce the impact of biases.
- Example: Actively question your assumptions and beliefs when making decisions, thus reducing the influence of biases.
- Example: Regularly assess how your cognitive biases may be affecting your judgment and work on addressing them through self-reflection.
- Example: Incorporate mindfulness techniques to increase self-awareness and reduce the impact of cognitive biases on decision making.
- Example: Seek guidance from a mentor or coach to help identify and address cognitive biases in your decision-making process.
🍏 Make use of the step-by-step plan, and customize it as per your specific requirements and cognitive bias challenges.
Developing an analytical mindset
Sure, let’s move on to a very intriguing topic that deals with enhancing our cognitive capabilities. Have you ever considered why some individuals are able to decipher complex problems with apparent ease while others struggle with straightforward tasks? The distinction is often come down to one thing: having an analytical mindset. So, what exactly does it mean and how can we perfect it? Let’s deep dive into this fascinating subject.
🧠 What is an Analytical Mindset?
An Analytical Mindset is an individual’s ability to identify, scrutinize and evaluate an issue in order to reach a logical conclusion. It’s the thinking style that helps us make sense of complex problems by breaking them down into smaller, manageable components. This sort of mindset is not just advantageous, but often crucial in many professional environments, especially in data-driven industries.
🧩 The building blocks of an Analytical Mindset
Before diving into the development process, let’s understand the main components of this type of thinking:
- 🔎 Critical Thinking : The ability to objectively analyze and evaluate a situation or problem, understanding its various components and their interdependencies.
- 💡 Problem-Solving : The process of identifying solutions to specific problems.
- 📊 Data Analysis : Involved in examining and interpreting data to reach conclusions.
🛠 Developing an Analytical Mindset
So, how can we develop or improve our analytical mindset? Here are some steps to help in this journey.
📖 Educating Oneself about Analytical Thinking
Start by gaining a solid understanding of what analytical thinking entails. Read books, attend workshops, or enroll in courses to understand the theoretical aspects of analytical thinking.
🚀 Practice Makes Perfect
Just like any other skill, improving your analytical thinking abilities takes practice. Start by analysing small, day-to-day issues as an exercise. Try breaking the problem down into smaller parts and scrutinise each part.
🌐 Expanding Horizons
Expose yourself to diverse ideas, perspectives, and disciplines. The broader your knowledge base, the better equipped you’ll be to think analytically.
🎯 Setting clear goals
Without clear objectives, it’s hard to achieve anything. When it comes to developing your analytical mindset, set specific goals that are actionable and measurable.
🚦Identifying and Overcoming Obstacles
There will inevitably be barriers in your path to cultivate an analytical mindset. It may be a lack of resources, time constraints, or cognitive biases. Identify these obstacles and devise strategies to overcome them.
Developing an analytical mindset cannot be achieved overnight. It is a lifelong journey that requires persistent effort, curiosity, and learning. However, with these steps, you’ll be well on your way to honing this skill. Good luck on your voyage towards becoming a more analytical thinker!
To do: Practice developing an analytical mindset by solving a real-life problem using data-driven decision making.
- Identify a real-life problem: For example, analyze the sales data of a product to identify factors impacting its performance.
- Gather relevant data: Collect sales figures, customer feedback, and market trends related to the product.
- Conduct data analysis: Utilize statistical tools to identify trends, correlations, and outliers within the gathered data.
- Identify potential causes: Based on the analysis, pinpoint potential factors influencing the product’s performance.
- Generate hypotheses: Formulate possible explanations for the observed patterns in the data.
- Test hypotheses: Gather additional data or conduct experiments to validate or refute the formulated hypotheses.
- Make data-driven decisions: Use the results of the analysis and testing to make informed decisions on how to improve the product’s performance.
🍏 This practical task involves using analytical thinking and data-driven techniques to address a specific problem, allowing for the application of analytical mindset in a real-life context.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Creative problem-solving primarily operates in the ideate phase of design thinking but can be applied to others. This is because design thinking is an iterative process that moves between the stages as ideas are generated and pursued. This is normal and encouraged, as innovation requires exploring multiple ideas.
Also known as creative problem-solving, creative thinking is a valuable and marketable soft skill in a wide variety of careers. Here's what you need to know about creative thinking at work and how to use it to land a job. Creative Thinking Definition. Creative thinking is all about developing innovative solutions to problems.
Creative problem solving (CPS) is a way of solving problems or identifying opportunities when conventional thinking has failed. It encourages you to find fresh perspectives and come up with innovative solutions, so that you can formulate a plan to overcome obstacles and reach your goals. In this article, we'll explore what CPS is, and we'll ...
Fast problem-solving. Creative thinking is necessary for business problem-solving. This skill enables workers to find opportunities that help improve situations in which finding a solution is difficult. It also helps them see the problems they face from another perspective. This way, they can use their imagination to come up with innovative ...
Creative problem-solving is an essential skill that goes beyond basic brainstorming. It entails a holistic approach to challenges, melding logical processes with imaginative techniques to conceive innovative solutions. As our world becomes increasingly complex and interconnected, the ability to think creatively and solve problems with fresh ...
Creative thinking in business typically takes two forms. On one hand, there's iterative creative thinking that builds upon existing ideas and concepts slowly over time. ... Use design thinking. Design thinking is a problem-solving technique that focuses on the needs of users — and on creating solutions that meet those needs. It involves ...
CURT NICKISCH: Design thinking is another really different method essentially for solving problems or coming up with solutions that just aren't arrived at through usual problem-solving or usual ...
Thinking creatively makes you a better problem-solver, which has far-reaching benefits in both your work and personal life. Expressive, creative thinking helps us challenge our own assumptions, discover new things about ourselves and our perspective, stay mentally sharp, and even be more optimistic.
Creativity in the workplace is an ability individuals possess that allows them to develop new and imaginative ideas regarding processes, products or materials. Businesses can use creativity in the workplace to create innovative solutions or more positive and collaborative work environments. The creative process also involves asking questions or ...
That's what we've found after decades of problem solving with leaders across business, nonprofit, and policy sectors. These leaders learn to adopt a particularly open and curious mindset, and adhere to a systematic process for cracking even the most inscrutable problems. They're terrific problem solvers under any conditions.
Problem-Solving: Business creativity can be applied to solving complex challenges within a company. By encouraging and fostering creative thinking, companies can find new ways to overcome obstacles, streamline operations, and improve efficiency. ... By accepting the possibility of failure, companies can create a supportive environment that ...
Creative thinking is the ability to consider something in a new way. Creative thinking includes analysis, open-mindedness, problem-solving, organization, and communication. Many employers value creative thinkers, so consider highlighting your creative thinking skills on your resume and in interviews.
Creativity in problem-solving allows for the generation of unique, practical solutions. It involves thinking outside the box, challenging traditional assumptions, and viewing the problem from various perspectives. Creativity is crucial in problem-solving as it fosters innovation and adaptability.
CPS is a comprehensive system built on our own natural thinking processes that deliberately ignites creative thinking and produces innovative solutions. Through alternating phases of divergent and convergent thinking, CPS provides a process for managing thinking and action, while avoiding premature or inappropriate judgment. It is built upon a ...
Creative Thinking is a versatile problem-solving tool, not limited to workplace challenges. It accelerates problem resolution by introducing diverse thought techniques. The cultivated ability to discern patterns more swiftly broadens the scope of effective solutions, promoting agility in addressing many issues encountered in daily life.
What is creative problem solving? The definition of creative problem solving (CPS) will vary between organizations. At its core, CPS involves approaching a problem in an imaginative, innovative, and unconventional way. The process encourages you to find new, creative ways of thinking that can help you overcome the issue at hand more quickly. 7 ...
The Creative Problem Solving process: a researched, learnable, repeatable process for uncovering new and useful ideas. ... (CLE) are designed for leaders with the desire to enhance their business acumen, challenge current thinking, and expand their leadership skills. This program is one of several CLE qualifying programs. Register today and get ...
A Cognitive Trick for Solving Problems Creatively. Many experts argue that creative thinking requires people to challenge their preconceptions and assumptions about the way the world works. One ...
Creative thinking is the spark that ignites innovation in problem-solving. It allows you to look beyond the obvious and explore a wider range of possibilities.
3 The Process. The process of integrating creative thinking into logical analysis can be thought of as a cycle. It begins with an open-minded exploration of the problem space, where you brainstorm ...
In the complex world of business, problem-solving requires both logical analysis and creative innovation. Effective strategies that marry these two thinking styles can lead to breakthrough ...
According to cognitive psychologists, creativity is a special kind of problem-solving experience, which involves the activation of two opposite but complementary mental processes, convergent thinking and divergent thinking, as well as insight. Creativity as an insight problem experience is a mainly unexplored phenomenon which has attracted ...
Creative problem solving methods. Let's dive right into the world of creative problem-solving methods. 🧠🌟 This style of problem-solving encourages unique, innovative solutions to issues, helping you step out of your comfort zone and think outside the box. Creative Problem-Solving Methods 💭💡. Creative problem solving is a fantastic skill to develop.
Creative thinking inherently involves a higher degree of risk compared to traditional logical approaches. Logical problem-solving aims to minimize uncertainty and risk by relying on data ...
4 Mental Flexibility. Mental flexibility is a cornerstone of creative problem-solving. By regularly practicing creative exercises, such as puzzles that require lateral thinking or tasks that ...
Most suited to 14-16-year-old pupils across the UK in developing their understanding of ethics and careers. In England, Northern Ireland and Wales it is relevant to GCSE business. In Scotland it ...