Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center


PROBLEMS AND DIFFICULTIES ENCOUNTERED BY STUDENTS TOWARDS MASTERING LEARNING COMPETENCIES IN MATHEMATICS

Related Papers
Necdet Guner
The aim of this study is to identify whether high school students encounter any difficulties in mathematics and reveal the reasons for such difficulties. The participants of the study, which was a descriptive case study based on qualitative understanding, were a total of 164 students, including 85 students from Anatolian High Schools and 79 students from Science High Schools. Approximately 11% of the participants said they had no difficulties in math, whereas 99% of the students from Anatolian High Schools and 78% of the students from Science High Schools said they had difficulties in mathematic. Their thoughts about the reasons for such difficulties were analyzed by content analysis method considering the type of high school they attended. The findings obtained revealed that the difficulties encountered by the participants in mathematics were teacher-, contentand studentbased. Anatolian High School students stated that they intensely faced teacher-based difficulties, whereas Scienc...
Denniel Gallos
Poshan Niraula
With the rapid development of science and mathematics, many works of the people have become understandable. Despite the development of various technologies, people need mathematical knowledge in everyday tasks. Students are exposed to various problems while teaching mathematics. Themes are explored for why students are experiencing those problems, what may be the solution to those problems, and more. The problems encountered by students during their geometry, arithmetic and algebra learning are presented in a systematic way. Due to inadequate practical content in the curriculum, students have difficulty in learning. Therefore, the curriculum should include practical content.
Zenodo (CERN European Organization for Nuclear Research)
Yuri Gonzaga
Psychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary Journal
Psychology and Education , jeremias E Obina , Danilo E. Derio Jr. , Annie Rose D. Rosa , Jonna Fe Gorit , Jolai G. Bolaños
Mathematics is one of the subjects that is taught in all Schools and Universities. It is usually viewed by students as difficult subject. This study aimed to determine the factors that affect the Mathematics performance of Mathematics major students and the extent of each factor. Further, it sought to determine the challenges encountered by the respondents in learning Mathematics. The study has three research questions and it made used of the explanatory-sequential research design. Relevant literatures were reviewed on theories and findings that emerged from different authors. There were 57 respondents involved in the study, 47 from 1 st year to 3 rd year Mathematics major student and 10 from 4 th year students at Notre Dame of Midsayap College. Data collection was done by using questionnaires. The findings showed that factors that affect Mathematics performance are the sources of the challenges in learning Mathematics. It also indicated that learning Mathematics is affected by numerous factors such as needs, interest, and seriousness of the subject matter, teachers' practices and methodologies, teachers' personality, parental support and home environment. The respondents have encountered challenges in learning Mathematics such as unfavorable teaching practices, lack of time management, lack of motivation, poor internet connectivity, and difficulty to get rapid feedback, lack of knowledge and regulation skills, and limited quotas.
International Journal of Educational Research Review
Omoniyi Oginni
Educational Research and Reviews
Mithat TAKUNYACI
Adriel Roman
Mathematics in the Modern World (MITMW) is one of the general education subjects taught in the new college curriculum in the Philippines. In this study, the self-assessment of students on their acquisition of the competencies set in the MITMW are being described as well as the extent of difficulties and performance. Using descriptive correlational research design, this study hypothesized that the perceived extent of acquisition of the first year college students on the competencies intended for Mathematics in the Modern World and their extent of difficulties experienced provide significant relationship to their performance. Two hundred seventy-one (271) first year college students were surveyed using validated questionnaires. Results revealed that the first year college students have higher extent of acquisitions on the competencies set in the MITMW (knowledge, values, and skills). Students experienced slight difficulties on the different topics of MITMW with satisfactory performanc...
IJESRT Journal
The study was conducted to determine the learning difficulties in Mathematics of the senior students of Cathedral School of La Naval, Naval, Biliran. This utilized a descriptive method of research. Different statistical tools were used in the analysis of data: frequency and percentage for the profiles, number of mistakes and performance. Mean and t-test with alpha level of significance was set at 0.05 to determine the correlation. The findings of the study showed that there is significant difference between the performance and age while there is no difference between performance and sex and parents'/guardians' highest educational attainment with very high correlation. A very high correlation was also found out in terms of performance and learning difficulties, where both variables were significant. The item which incurred the greatest number of mistakes was on Perfect Square Binomial. Mentors should give focus or remediation on topics were students' low performance was identified and further establish friendly ambiance so that they could fill-in the learning gap of the learners with the use of various teaching strategies and materials.
Francesca Gregorio
The huge difficulties related to the transition from secondary to tertiary mathematics are documented by several official data. The analysis of these difficulties is a main issue in educational research at undergraduate level. It is of particular interest the case of the students who choose mathematics as a major. In fact, for the most part, they are students considered excellent in mathematics during secondary school, they seem to have the cognitive resources to succeed, but, in many cases, they encounter several difficulties during their university experience. Therefore, it appears particularly interesting to study also the affective sources and consequences of these difficulties. With this aim, we developed a qualitative and narrative study focused on students’ reflections about their mathematical difficulties in the university experience.
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
- Future Students
- Current Students
- Faculty/Staff

News and Media
- News & Media Home
- Research Stories
- School's In
- In the Media
You are here
Softening the sharp edges in mathematics.

For everyone whose relationship with mathematics is distant or broken, Jo Boaler , a professor at Stanford Graduate School of Education (GSE), has ideas for repairing it. She particularly wants young people to feel comfortable with numbers from the start — to approach the subject with playfulness and curiosity, not anxiety or dread.
“Most people have only ever experienced what I call narrow mathematics — a set of procedures they need to follow, at speed,” Boaler says. “Mathematics should be flexible, conceptual, a place where we play with ideas and make connections. If we open it up and invite more creativity, more diverse thinking, we can completely transform the experience.”

“Mathematics should be flexible, conceptual, a place where we play with ideas and make connections," says Professor Jo Boaler. (Photo: Robert Houser Photography)
Boaler, the Nomellini and Olivier Professor of Education at the GSE, is the co-founder and faculty director of Youcubed , a Stanford research center that provides resources for math learning that has reached more than 230 million students in over 140 countries. In 2013 Boaler, a former high school math teacher, produced “How to Learn Math,” the first massive open online course (MOOC) on mathematics education. She leads workshops and leadership summits for teachers and administrators, and her online courses have been taken by over a million users.
In her new book, Math-ish: Finding Creativity, Diversity, and Meaning in Mathematics , Boaler argues for a broad, inclusive approach to math education, offering strategies and activities for learners at any age. We spoke with her about why creativity is an important part of mathematics, the impact of representing numbers visually and physically, and how what she calls “ishing” a math problem can help students make better sense of the answer.
What do you mean by “math-ish” thinking?
It’s a way of thinking about numbers in the real world, which are usually imprecise estimates. If someone asks how old you are, how warm it is outside, how long it takes to drive to the airport – these are generally answered with what I call “ish” numbers, and that’s very different from the way we use and learn numbers in school.
In the book I share an example of a multiple-choice question from a nationwide exam where students are asked to estimate the sum of two fractions: 12/13 + 7/8. They’re given four choices for the closest answer: 1, 2, 19, or 21. Each of the fractions in the question is very close to 1, so the answer would be 2 — but the most common answer 13-year-olds gave was 19. The second most common was 21.
I’m not surprised, because when students learn fractions, they often don’t learn to think conceptually or to consider the relationship between the numerator or denominator. They learn rules about creating common denominators and adding or subtracting the numerators, without making sense of the fraction as a whole. But stepping back and judging whether a calculation is reasonable might be the most valuable mathematical skill a person can develop.
But don’t you also risk sending the message that mathematical precision isn’t important?
I’m not saying precision isn’t important. What I’m suggesting is that we ask students to estimate before they calculate, so when they come up with a precise answer, they’ll have a real sense for whether it makes sense. This also helps students learn how to move between big-picture and focused thinking, which are two different but equally important modes of reasoning.
Some people ask me, “Isn’t ‘ishing’ just estimating?” It is, but when we ask students to estimate, they often groan, thinking it’s yet another mathematical method. But when we ask them to “ish” a number, they're more willing to offer their thinking.
Ishing helps students develop a sense for numbers and shapes. It can help soften the sharp edges in mathematics, making it easier for kids to jump in and engage. It can buffer students against the dangers of perfectionism, which we know can be a damaging mind-set. I think we all need a little more ish in our lives.
You also argue that mathematics should be taught in more visual ways. What do you mean by that?
For most people, mathematics is an almost entirely symbolic, numerical experience. Any visuals are usually sterile images in a textbook, showing bisecting angles, or circles divided into slices. But the way we function in life is by developing models of things in our minds. Take a stapler: Knowing what it looks like, what it feels and sounds like, how to interact with it, how it changes things — all of that contributes to our understanding of how it works.
There’s an activity we do with middle-school students where we show them an image of a 4 x 4 x 4 cm cube made up of smaller 1 cm cubes, like a Rubik’s Cube. The larger cube is dipped into a can of blue paint, and we ask the students, if they could take apart the little cubes, how many sides would be painted blue? Sometimes we give the students sugar cubes and have them physically build a larger 4 x 4 x 4 cube. This is an activity that leads into algebraic thinking.
Some years back we were interviewing students a year after they’d done that activity in our summer camp and asked what had stayed with them. One student said, ‘I’m in geometry class now, and I still remember that sugar cube, what it looked like and felt like.’ His class had been asked to estimate the volume of their shoes, and he said he’d imagined his shoes filled with 1 cm sugar cubes in order to solve that question. He had built a mental model of a cube.
When we learn about cubes, most of us don’t get to see and manipulate them. When we learn about square roots, we don’t take squares and look at their diagonals. We just manipulate numbers.
I wonder if people consider the physical representations more appropriate for younger kids.
That’s the thing — elementary school teachers are amazing at giving kids those experiences, but it dies out in middle school, and by high school it’s all symbolic. There’s a myth that there’s a hierarchy of sophistication where you start out with visual and physical representations and then build up to the symbolic. But so much of high-level mathematical work now is visual. Here in Silicon Valley, if you look at Tesla engineers, they're drawing, they're sketching, they're building models, and nobody says that's elementary mathematics.
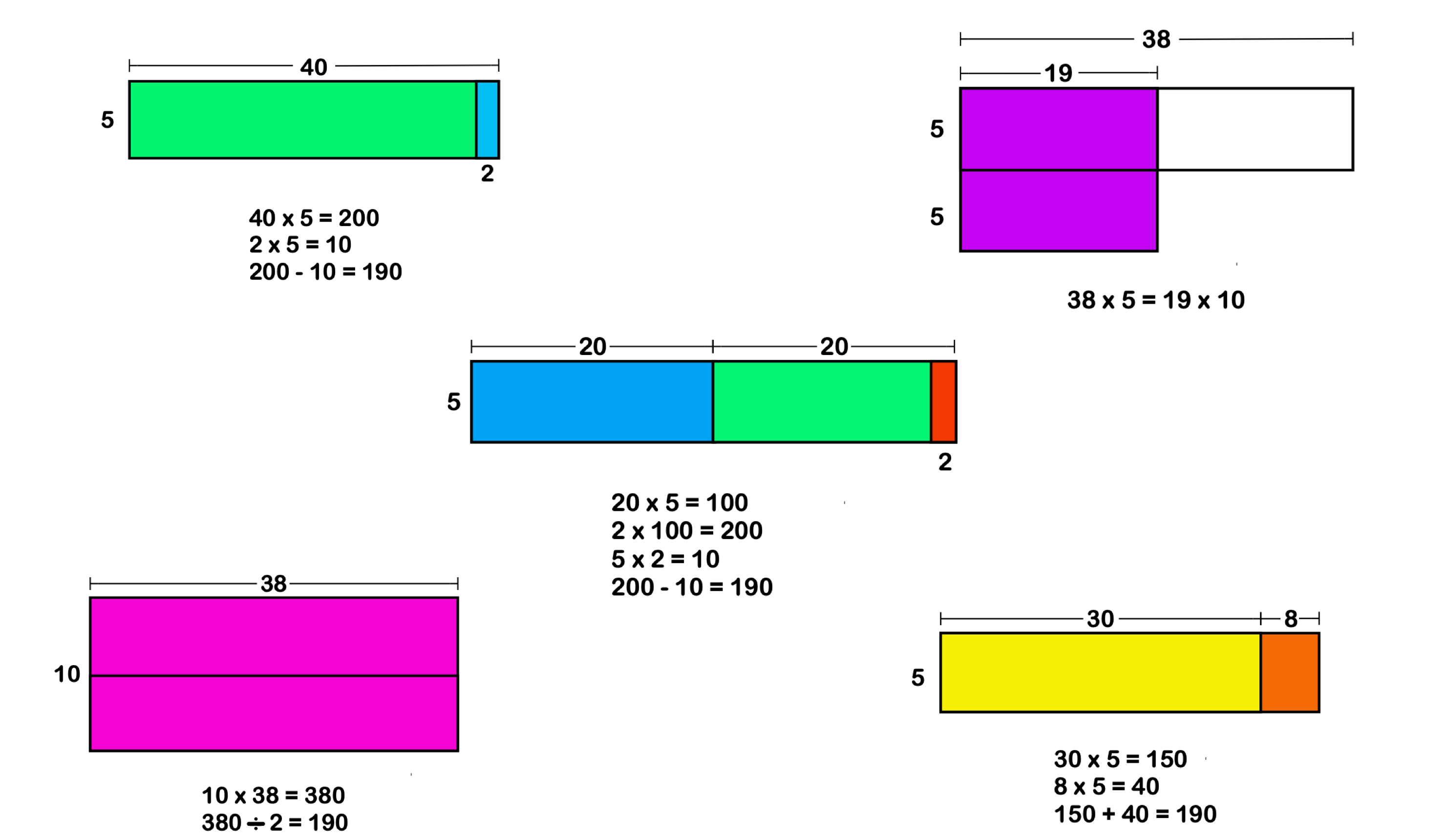
Click to enlarge: A depiction of various ways to calculate 38 x 5, numerically and visually. (Image: Courtesy of Jo Boaler)
There’s an example in the book where you’ve asked students how they would calculate 38 x 5 in their heads, and they come up with several different ways of arriving at the same answer. The creativity is fascinating, but wouldn’t it be easier to teach students one standard method?
That narrow, rigid version of mathematics where there’s only one right approach is what most students experience, and it’s a big part of why people have such math trauma. It keeps them from realizing the full range and power of mathematics. When you only have students blindly memorizing math facts, they’re not developing number sense. They don’t learn how to use numbers flexibly in different situations. It also makes students who think differently believe there’s something wrong with them.
When we open mathematics to acknowledge the different ways a concept or problem can be viewed, we also open the subject to many more students. Mathematical diversity, to me, is a concept that includes both the value of diversity in people and the diverse ways we can see and learn mathematics. When we bring those forms of diversity together, it’s powerful. If we want to value different ways of thinking and problem-solving in the world, we need to embrace mathematical diversity.
More Stories

⟵ Go to all Research Stories
Get the Educator
Subscribe to our monthly newsletter.
Stanford Graduate School of Education
482 Galvez Mall Stanford, CA 94305-3096 Tel: (650) 723-2109
- Contact Admissions
- GSE Leadership
- Site Feedback
- Web Accessibility
- Career Resources
- Faculty Open Positions
- Explore Courses
- Academic Calendar
- Office of the Registrar
- Cubberley Library
- StanfordWho
- StanfordYou
Improving lives through learning

- Stanford Home
- Maps & Directions
- Search Stanford
- Emergency Info
- Terms of Use
- Non-Discrimination
- Accessibility
© Stanford University , Stanford , California 94305 .
Senior Thesis
This page is for Undergraduate Senior Theses. For Ph.D. Theses, see here .
So that Math Department senior theses can more easily benefit other undergraduate, we would like to exhibit more senior theses online (while all theses are available through Harvard University Archives , it would be more convenient to have them online). It is absolutely voluntary, but if you decide to give us your permission, please send an electronic version of your thesis to cindy@math. The format can be in order of preference: DVI, PS, PDF. In the case of submitting a DVI format, make sure to include all EPS figures. You can also submit Latex or MS word source files.
If you are looking for information and advice from students and faculty about writing a senior thesis, look at this document . It was compiled from comments of students and faculty in preparation for, and during, an information session. Let Wes Cain ([email protected]) know if you have any questions not addressed in the document.
share this!
May 13, 2024
This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies . Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
written by researcher(s)
Malawi's school kids are using tablets to improve their reading and math skills
by Nicola Pitchford and Dr. Karen Levesque, The Conversation
Malawi introduced free primary education in 1994. This has significantly improved access to schooling. However, the country—which is one of the poorest in the world —still faces a high learning poverty rate of 87%. Learning poverty is a measure of a child's inability to meet minimum proficiency in reading, numeracy and other skills at the primary school level. Malawi's rate means that 87% of children in standard 4, at age 10, are unable to read .
Only 19% of children aged between 7 and 14 have foundational reading skills and 13% have foundational numeracy skills. This leads to social and financial dependency. It also limits the extent to which individuals can actively participate in society. Children become especially vulnerable to pernicious social issues such as forced marriage, female genital mutilation, and child labor.
The primary education sector also has many challenges . These include overcrowded classrooms, limited learning materials, and a shortage of trained teachers.
There is a pressing need for innovative, transformative approaches to providing foundational education to meet the goals envisioned in Malawi 2063 , the country's long-term national plan. To accomplish this, the government of Malawi is using scientific evidence to enable meaningful and effective learning happen at scale.
This evidence has been generated in parallel by researchers from the University of Nottingham in the UK and the NGO Imagine Worldwide in the US and Africa. We have been testing the efficacy of an interactive educational technology (EdTech) developed by UK-based non-profit onebillion to raise foundational education by different groups of learners in Malawi.
The EdTech delivers personalized, adaptive software that enables each child to learn reading, writing and numeracy at the right level. Children work on tablets through a carefully structured course made up of thousands of engaging activities, games and stories. Over the past 11 years, we have built a complementary and robust evidence base focusing on different aspects of the software and program.
In 2013, I conducted the first pupil-level randomized control trial at a state primary school in Malawi's capital city, Lilongwe. Randomized controlled trials are prospective studies that measure the effectiveness of a new intervention compared to standard practice. They are considered the gold standard in effectiveness research . We wanted to test whether the EdTech could raise young children's numeracy skills. The study showed that after eight weeks of using the EdTech for 30 minutes a day, learners in grades 1–3 (aged 6 to 9) made significant improvements in basic numeracy compared to standard classroom practice. Teachers were also able to put the EdTech to use with ease.
Now, after many studies, Malawi's government, in collaboration with Imagine Worldwide , is embedding the EdTech program in all state primary schools nationwide . This will serve 3.8 million children per year in grades 1–4 across all 6,000 state primary schools in Malawi.
Rigorous testing
After our initial 2013 study, we kept testing the EdTech through rigorous studies. One showed that the EdTech program significantly raised foundational numeracy and literacy skills of early grade learners. Our results showed similar learning gains for girls and boys with the EdTech. This equalizes foundational education across gender.
Another study showed that children with special educational needs and disabilities could interact and learn with the EdTech, albeit at a slower pace than mainstream peers.
The EdTech wasn't just tested in Malawi. We wanted to see if it could address learning poverty in different contexts, thus equalizing all children's opportunities, no matter where they live.
Research in the UK demonstrated that the same EdTech raised the basic numeracy skills of children in the early years of primary schools compared to standard classroom instruction. It was also found to support numeracy acquisition by developmentally young children , including those with Down syndrome.
It was also shown to be effective in a bilingual setting . Brazilian children's basic numeracy skills improved compared to standard practice after instruction with the EdTech delivered in either English, their language of instruction, or their home language, Brazilian-Portuguese.
Alongside the research from the University of Nottingham, Imagine Worldwide undertook a series of studies in Malawi and other countries to investigate how this EdTech could raise foundational skills over longer periods of time and in different languages and contexts, including refugee camps.
Imagine Worldwide conducted six randomized control trials , including two of the longest over eight months and two years. They showed robust learning gains in literacy and numeracy. They also found that children's excitement about school, their attendance, and their confidence as learners improved.
The EdTech program also mitigated against learning loss during school closures. During Imagine's 2-year randomized control trial in Malawi, program delivery was interrupted for seven months by COVID-related closures. Yet, results showed that children who had participated in the EdTech program prior to schools closing returned to school with higher achievement levels than their peers who had received standard instruction only.
Applying the evidence to policy
Malawi's government was pleased with the early results and the program was expanded to about 150 schools, with the help of UK non-profit Voluntary Service Overseas. A national steering committee was established by Malawi's government to monitor the program and review additional emerging research. In 2022 the Education Ministry formally launched the program through which the EdTech will be rolled out; it was introduced in 500 new schools at the start of the 2023/2024 school year, in September 2023.
To achieve the promise of the early research, ongoing implementation research and monitoring is helping to ensure program quality and impacts are sustained as it rolls out nationwide.
Strong evidence
Basic literacy and numeracy are the keys to unlocking a child's potential— improving their health, wealth and social outcomes . Our combined research has shown that child-directed EdTech can deliver high-quality education for millions of marginalized children worldwide. The evidence is strong, diverse and replicable. Now governments need to follow the lead of Malawi to abolish learning poverty and make foundational education a reality for all children, everywhere.
Provided by The Conversation
Explore further
Feedback to editors

DNA analysis reveals that Jamestown Colony residents ate dogs with Indigenous ancestry
4 hours ago
Study shows COVID-related private funding had little effect in 2020 presidential election
6 hours ago

Neutrons open window to explore space glass

Researchers find unique adaptations of fungus associated with bee bread
7 hours ago

Highly sensitive fiber optic gyroscope senses rotational ground motion around active volcano

'Dusty' archives inspire new story about 1886 Charleston earthquake

Study finds widespread 'cell cannibalism' and related phenomena across tree of life
Detecting odors on the edge: Researchers decipher how insects smell more with less

New catalyst transforms carbon dioxide from industrial emissions into commonly used chemicals

Researchers use hydrogel chemistry and microfabrication to miniaturize and integrate components into bioelectronics
Relevant physicsforums posts, graphing trip efficiency - distance over time.
May 20, 2024
Help with Recurrence Equation
May 18, 2024
Numerically how to approximate exponential decay in a discrete signal
May 16, 2024
Flat surface to curved surface
An exact paraxial equation derivation, 100% cartesian, formal definition of multiplication for real and complex numbers.
May 6, 2024
More from General Math
Related Stories

Rise of ChatGPT shows why Australia needs a clearer approach to technology in schools
Feb 16, 2023


Global evidence for how EdTech can support pupils with disabilities is 'thinly spread'
Mar 25, 2021

Motor skills and physical activity practice supports preschoolers' learning, finds researcher
Jun 6, 2023

9 out of 10 kids are not developmentally on track in literacy and numeracy—study of 8 African countries
Apr 10, 2024

Online tutoring helps struggling students catch up
Aug 10, 2021

Learning in two languages: Lessons from francophone Africa on what works best
Feb 22, 2024
Recommended for you

Math discovery provides new method to study cell activity, aging
9 hours ago

First-generation medical students face unique challenges and need more targeted support, say researchers

Mechanistic model shows how much gossip is needed to foster social cooperation
May 15, 2024
Random processes shape science and math: Researchers propose a unified, probabilistic framework
May 9, 2024

Study of new method used to preserve privacy with US census data suggests accuracy has suffered

New study is first to use statistical physics to corroborate 1940s social balance theory
May 3, 2024
Let us know if there is a problem with our content
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form . For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines ).
Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request
Thank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.
E-mail the story
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Phys.org in any form.
Newsletter sign up
Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox. You can unsubscribe at any time and we'll never share your details to third parties.
More information Privacy policy
Donate and enjoy an ad-free experience
We keep our content available to everyone. Consider supporting Science X's mission by getting a premium account.
E-mail newsletter
Ohio State nav bar
The Ohio State University
- BuckeyeLink
- Find People
- Search Ohio State
Careers Planning for IMME Students – Do It Now!

Last week, we had a successful coffee morning for IMME students looking to start making a careers plan. I cannot stress enough how much planning can help you to execute some worthwhile job or research experience.
For those of you who could not make it here are some things to think about in terms of planning.
Something to Do This Summer ? Find a Mentor
Think about looking for a mentor. There are so many free mentoring programs. It is a great idea to jump onto one of these.
Join StudentMentor.org and/or Great Minds in Stem and see if you can find a mentor. NOGLSTP (geared towards Engineering and Science) has a mentoring program but bear in mind it is only open to LGBTQ+ students. SCORE offers free mentoring to entrepreneurs. Women students might apply to the FWA (Financial Women’s Association). Morgan Stanley have great mentoring programs, as do J.P. Morgan Chase .
Next Semester : August
Careers Coaching
Look into Careers Coaching from OSU Arts & Sciences. They can help with: identifying how your major relates to career options; strengthening your resume; orienting you to the Readiness Competencies (RCs); teaching you how to network; and providing tips on how to find internships or other opportunities.
Finding Work or Research Opportunities
- Check out the American Mathematical Society for more applied-type student opportunities.
- If you are looking for paid work, consider applying for work as a peer tutor at OSU ($13 per hour).
- Consider getting involved with Math to Industry which have events and career resources.
- Look out for undergraduate Math job opportunities.
- Keep an eye out for Arts and Sciences job fairs .
- Try to secure an internship for summer 2026 in the fall term, so that you can then apply for an Accelerator Grant to help cover your costs. Here is a helpful guide to finding and negotiating an internship.
- Independent study and thesis projects can be good for showing rigorous analytical and organizational skills via the English department or Mathematics department . Professors who have expressed interest in supervising IMME students include: from English : Prof. Alan B. Farmer , Prof. Molly J. Farrell , Prof. John Jones and Dr. Cathy Ryan ; from Math : Prof. Jim Fowler , Prof. John Johnson , and Prof. Dan Thompson . We can also partner with captains of industry to seek to solve real world problems, for example Dennis Baer who is on the Math Advisory Committee.
Before the Winter Holidays
Consider Study Abroad opportunities in the English department, or prep to apply for a Summer Library Fellowship for the following summer, which will pay you to work on library collections. See Why a Summer Library Fellowship is a Great Idea .
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Teacher, Math - Middle (2024-2025 School Year)
Job posting for teacher, math - middle (2024-2025 school year) at lake county schools.
Apply for this job
Receive alerts for other Teacher, Math - Middle (2024-2025 School Year) job openings
Report this Job
Sign up to receive alerts about other jobs that are on the Teacher, Math - Middle (2024-2025 School Year) career path.
Click the checkbox next to the jobs that you are interested in.
Sign up to receive alerts about other jobs with skills like those required for the Teacher, Math - Middle (2024-2025 School Year) .
Child Psychology Skill
- Special Education Teacher Income Estimation: $49,582 - $82,371
- Teacher Kindergarten Income Estimation: $51,841 - $75,191
Childhood Education Skill
Job openings at Lake County Schools
Not the job you're looking for here are some other teacher, math - middle (2024-2025 school year) jobs in the tavares, fl area that may be a better fit., we don't have any other teacher, math - middle (2024-2025 school year) jobs in the tavares, fl area right now..
7th Grade Math Teacher
Lake Nona Middle School , Orlando, FL
Middle School Math Teacher
All Souls Catholic School , Sanford, FL

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Early math and numeracy skills are skills that are already being used by most young. children daily through play and everyday interactions (Help your child, n.d.). These are skills that begin in early childhood and are the foundation for the rest of elementary math and into. upper level math classes as well.
I have encountered teaching strategies that suggest skills between subject areas, particularly English and math, are unique. Topics regarding syntax and sentence patterns are not typically discussed in a math classroom and implementing strategies could help maximize student performance. The questions that guided my research were 1.
Unlike other subjects that rely on tangible objects, mathematics deals with theoretical constructs and requires a unique set of skills and approaches that makes it difficult to master.
skills in the industry, academia, and the government is still quite appalling (Jang, 2016; Sluijsmans et al., 1998). Hence, there is a need for understanding the kind of mathematical skills needed in today's world and the shifts that should be made in both content and pedagogy for preparing students to acquire relevant 21. st
The high school dropout. rate in 2006 was 6.3% while the chronic truancy rate was at 7.4%. The financial earnings of the teachers and administrators at this district average at. $62, 452 per year. The teachers in this district have been working for an average for 12.5. years.
this thesis aims to explore the impact of establishing conceptual anchors to promote. enduring conceptual understanding and lasting procedural skills with algebraic topics. For the purpose of this research, the conceptual anchor for a specific topic was in the.
Students were able to show mastery of grade-level math skills in two of. the ten math skills tested. Gamification was used in this study to determine if students using gamification would. yield higher mastery of skills and achieve more grade-level skills than students not receiving. gamification.
Abstract. This systematic literature review examines the role of technology in enhancing basic math skills. within the realm of mathematics education. Synthesizing findings from diverse studies ...
problems in mathematics in a form of problem set or worded problems. The problems are composed of items in arithmetic and algebra, trigonometry, geometry, sets, probability, number theory and puzzle problem/logic. Hence, with the main goal of mathematics education to improve students' problem-solving skills in mathematics particularly to
A Master's Thesis Submitted to the Faculty of William Paterson University of New Jersey In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements ... This study investigates the impact of incorporating writing, specifically through math journals, on the problem-solving skills of middle school self-contained special education
The ability to develop, apply, and interpret Mathematics to solve issues in a range of real-world contexts is known as skills in Mathematics. This study was undertaken to identify the level of the ...
THE EFFECT OF THINKING MAPS© ON MATH WORD PROBLEM SOLVING SKILLS OF STUDENTS WITH SPECIFIC LEARNING DISABILITIES _____ A Thesis Presented to the Faculty of California State University, Dominguez Hills _____ In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree Master of Arts in Special Education _____ by Martha Villa Fall 2019
Given the importance of problem solving skills and the well-documented inadequate performance of students with LD and MD, several meta-analyses of mathematics intervention research for students with LD and MD have been conducted (i.e., Gersten, Chard, Jayanthi, Baker, Morphy, & Flojo, 2009; Kroesbergen & Van Luit,
The thesis project proposes that one way to address these educational and economic inequities in manufacturing is to create and implement core modules in math relevant to manufacturing. The math modules are designed foundational skills needed in manufacturing and will be used to prepare potential employees for current positions
Problem solving refers to the elimination of a problem through the use of required information and operations in cognitive processes (reasoning) (Altun, 1995). Reading. Gökhan Özsoy, Faculty of Education, University of Ordu, Ordu, Turkey. E-mail: [email protected], Phone: +90 452 2265200/5565.
He revealed that the extent of mastery of the pupils in the different mathematics skills was determined by the strategies, techiques, approaches, evaluative measures, follow-up activities, and utilization of instructional materials employed by teachers. ... Competencies in Mathematics. Unpublished Master's Thesis. Bataan Polytechnic State ...
Word problems are usually used as a link mathematics and real-world situations so that students can develop skills in applying mathematics [1], [14], [15]. The choice of problems in the form of ...
Ishing helps students develop a sense for numbers and shapes. It can help soften the sharp edges in mathematics, making it easier for kids to jump in and engage. It can buffer students against the dangers of perfectionism, which we know can be a damaging mind-set. I think we all need a little more ish in our lives.
An important objective in teaching mathematics is to develop students' mathematical problem-solving skills. The researcher, a Mathematics Coordinator, considers this endeavor to be of help to school administrators, teachers, parents, and pupils in improving the mathematics performance of learners and to other future researchers. Research Questions
This page is for Undergraduate Senior Theses. For Ph.D. Theses, see here.. So that Math Department senior theses can more easily benefit other undergraduate, we would like to exhibit more senior theses online (while all theses are available through Harvard University Archives, it would be more convenient to have them online).It is absolutely voluntary, but if you decide to give us your ...
in mathematics education and in different fields (Alexander and Winne 2006; Sfard 1991). Mathematics teacher education as a field of inquiry and practice rises as a crossover between teacher education and Mathematics education. Pedagogical approaches to addressing the educational skills for effective classroom teaching (Das, 2019).
Learning poverty is a measure of a child's inability to meet minimum proficiency in reading, numeracy and other skills at the primary school level. Malawi's rate means that 87% of children in ...
Unpublished thesis, Central Mindanao University. ... determine the level of students' mathematical resilience and identify the level of students' critical thinking skills in Mathematics before and ...
Independent study and thesis projects can be good for showing rigorous analytical and organizational skills via the English department or Mathematics department. Professors who have expressed interest in supervising IMME students include: from English: Prof. Alan B. Farmer, Prof. Molly J. Farrell, Prof. John Jones and Dr. Cathy Ryan; from Math ...
involves all important skills such as logical and analytic thinking as well as quantitative reasoning (Devlin, 2012). Developing mathematical thinking is the main goal of mathematics education. In today's information-based society, it is desirable to develop process skills such as innovative ways to find a solution to a problem.
Apply for the Job in Teacher, Math - Middle (2024-2025 School Year) at Tavares, FL. View the job description, responsibilities and qualifications for this position. Research salary, company info, career paths, and top skills for Teacher, Math - Middle (2024-2025 School Year)
Mathematics, as we know, " Mathematics is the Queen and servant of Sciences. Confluent learning, as reemphasized by Loon and Nichol (2015), is holistic, it aims to activate and engage. all of ...