
Essays About Online Class: Top 5 Examples and 7 Prompts
Essays about online class tell many stories. If you need to write about e-learning, discover the top examples and prompts for the subject in our guide.
With over 5.8 million American students attending in 2021, online classes are now one of the education sector’s most popular and modern learning methods. Although it became prevalent because of the pandemic, it’s believed that the concept of distance learning began in the late 1800s .
Online classes pose many benefits that many still take advantage of even after the pandemic. However, not everyone adjusts well to this technology-centered learning due to no face-to-face contact and difficulty learning without the back-and-forth of lesson question time.
1. My Experience as an Online Student by Debra Sicard
2. how to succeed in online classes essay by anonymous on ivypanda.com, 3. essay on advantages and disadvantages of online classes by anonymous on selfstudymantra.com, 4. online school vs. traditional school essay by anonymous on gradesfixer.com, 5. short essay on online classes by anonymous on byjus.com, 7 helpful prompts on essays about online class, 1. online classes: defined, 2. my experience with online classes during lockdown, 3. how does online class work, 4. the best sites for online class, 5. the pros and cons of enrolling in online class, 6. review of a book about online class, 7. should online classes be the norm.
“I am not a traditional student, so I have non-traditional needs… online classes fit my lifestyle.”
Sicard shares her positive experience with online classes, primarily centering her essay on convenience. She says that with online courses, she can fit more lessons into her schedule, save her money on gas, and have more time with her family. In addition, she mentions she can work and do other things besides taking her credits.
To have a proper perspective of the topic, Sicard also includes the disadvantages of virtual learning, such as devices catching viruses and missing in-real-life interactions with her professors and classmates. But, she believes that an online student can learn as much or even more than what students learn in traditional classes.
“In an online class, a student can only achieve success if he is committed to time management, balancing personal obligations, finding an ideal study environment, asking questions, and applying more effort to completing the course requirements.”
This essay contains steps a non-traditional student can take to avoid failing online classes. The author says that students, especially multitaskers, must know how to manage and balance their time to avoid losing focus. In addition, having a dedicated study spot is necessary to avoid distractions.
“Online classes or online method of learning presents an easy and comfortable method to achieve knowledge. Online classes have now become a great alternative to traditional classes.”
The writer delves into the benefits and drawbacks of online versus traditional learning. Virtual classes offer students freedom regarding their schedules and whereabouts. Some schools also allow students to learn for free. E-learning effectively trains individuals to be responsible and disciplined.
However, individuals who are not computer literate will find online classes frustrating. Plus, electronic devices can be bad for health, and a lack of personal interaction can hinder personality development.
“[Online course] will also help you become more self-motivated, a trait that will make you stand out in the workplace and beyond.”
By listing the similarities and differences between online and traditional schools, the author demonstrates what classes a student should pick. The writer concludes that while traditional schools prepare students for the real world by interacting with diverse people, online schools help students become more self-motivated to stand out.
“The advantages of online classes take over their disadvantages. If students want to learn, then they have immense opportunities to learn from online classes.”
The author defines online classes as a type of education system where students use electronic devices with an internet connection to learn. However, while online learning improves the quality of education, it can also make the student lazy and cultivates a sense of isolation. Ultimately, they believe that to have the best education system, school teachers and officials must learn how to combine the two methods.
If the topic you’re thinking of is still confusing and you don’t know where to start, here are seven easy writing prompts to inspire you:

Explain the topic to your reader and give a brief history of the origins of online classes. Then briefly compare it to the traditional class to make the differences clear. Finally, point out the distinct features of online classes that conventional learning doesn’t offer, such as face-to-face interaction and question-and-answer debates. You can also discuss various online classes schools offer, such as hybrid learning, interactive online courses, etc.
Tell your story if you’re a student with experience with online classes. Narrate how your school switched to virtual classrooms. Relay the challenges you encountered, including how you adapted. Finish your essay by stating your current preference and why.
For example, you favor e-learning because it cuts your transportation expenses, helps you be more responsible for managing your time, and lets you sleep in the mornings.
Relate your experience when your school moved online. Discuss any equipment or devices you need to buy before enrolling in your online class. Explain how your school handles online courses and what it does when there are technical difficulties. Add how these challenges (such as unstable internet connection and sudden power outage), such as attendance and participation, impact a class.
To make your essay more intriguing, add the average price of your online classes and if you think it’s fair. For instance, you can argue that since schools don’t provide computers and save expenses on cleaning and utilities when physical classrooms are unused, they should cut their laboratory or miscellaneous fees. You may also be interested in these articles about back to school .

Zoom, Google Classroom, and Microsoft Team are just three of the most popular online teaching software for online classes. In this prompt, look for the most useful and efficient software sites teachers or schools should incorporate into e-learning. Find examples or reliable data that show the number of students or schools that use them. Finally, ensure the details you add are accurate to make your essay credible.
Do you want to write about technology instead? Check out our essays about technology .
Discussing online classes’ positive and negative effects is a usual essay topic. To make your essay stand out, pick the most impactful points on everyone involved. Don’t just explore the students’ perspectives. Include how virtual learning influences teachers, parents, and businesses.
To give you an idea, you can look into businesses near the campus that closed down when the school shifted to virtual classrooms.
This prompt requires you to search for publications about online classes and share your opinion on them.
For example, John F. Lyons’s book, How to Succeed in an Online Class , published in 2011, introduced technology students encounter in online classes. Suppose you read this book. First, enumerate Lyons’ advice, tips, and learning techniques to prevent a student from failing their online course. Then, briefly explain them individually and include examples or proof that his advice helped.
Online schooling has been around for a long time but has only become widespread because of the pandemic. Use this prompt to write your opinion on whether schools should make virtual learning a permanent option for students. Whatever your answer is, explain your reason to your readers.If you’re interested in learning more about essays, check out our essay writing tips !

Maria Caballero is a freelance writer who has been writing since high school. She believes that to be a writer doesn't only refer to excellent syntax and semantics but also knowing how to weave words together to communicate to any reader effectively.
View all posts
- Essay Samples
- College Essay
- Writing Tools
- Writing guide

Creative samples from the experts
↑ Return to Essay Samples
Argumentative Essay: Online Learning and Educational Access
Conventional learning is evolving with the help of computers and online technology. New ways of learning are now available, and improved access is one of the most important benefits available. People all around the world are experiencing improved mobility as a result of the freedom and potential that online learning provides, and as academic institutions and learning organisations adopt online learning technologies and remote-access learning, formal academic education is becoming increasingly legitimate. This essay argues the contemporary benefits of online learning, and that these benefits significantly outweigh the issues, challenges and disadvantages of online learning.
Online learning is giving people new choices and newfound flexibility with their personal learning and development. Whereas before, formal academic qualifications could only be gained by participating in a full time course on site, the internet has allowed institutions to expand their reach and offer recognized courses on a contact-partial, or totally virtual, basis. Institutions can do so with relatively few extra resources, and for paid courses this constitutes excellent value, and the student benefits with greater educational access and greater flexibility to learn and get qualified even when there lots of other personal commitments to deal with.
Flexibility is certainly one of the most important benefits, but just as important is educational access. On top of the internet’s widespread presence in developed countries, the internet is becoming increasingly available in newly developed and developing countries. Even without considering the general informational exposure that the internet delivers, online academic courses and learning initiatives are becoming more aware of the needs of people from disadvantaged backgrounds, and this means that people from such backgrounds are in a much better position to learn and progress than they used to be.
The biggest argument that raises doubt over online learning is the quality of online courses in comparison to conventional courses. Are such online courses good enough for employers to take notice? The second biggest argument is the current reality that faces many people from disadvantaged backgrounds, despite the improvements made in this area in recent years – they do not have the level of basic access needed to benefit from online learning. In fact, there are numerous sources of evidence that claim disadvantaged students are not receiving anywhere near the sort of benefits that online learning institutions and promoters are trying to instigate. Currently there are many organisations, campaigns and initiatives that are working to expand access to higher education. With such high participation, it can be argued that it is only a matter of time before the benefits are truly realised, but what about the global online infrastructure?
There is another argument that is very difficult to dispel, and that is the response of different types of students to the online learning paradigm. Evidence shows that there are certain groups of students that benefit from college distance learning much more than other groups. In essence, students must be highly motivated and highly disciplined if they are to learn effectively in their own private environment.

Follow Us on Social Media
Get more free essays

Send via email
Most useful resources for students:.
- Free Essays Download
- Writing Tools List
- Proofreading Services
- Universities Rating
Contributors Bio

Find more useful services for students
Free plagiarism check, professional editing, online tutoring, free grammar check.
Advertisement
The effects of online education on academic success: A meta-analysis study
- Published: 06 September 2021
- Volume 27 , pages 429–450, ( 2022 )
Cite this article

- Hakan Ulum ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-1398-6935 1
78k Accesses
26 Citations
11 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
The purpose of this study is to analyze the effect of online education, which has been extensively used on student achievement since the beginning of the pandemic. In line with this purpose, a meta-analysis of the related studies focusing on the effect of online education on students’ academic achievement in several countries between the years 2010 and 2021 was carried out. Furthermore, this study will provide a source to assist future studies with comparing the effect of online education on academic achievement before and after the pandemic. This meta-analysis study consists of 27 studies in total. The meta-analysis involves the studies conducted in the USA, Taiwan, Turkey, China, Philippines, Ireland, and Georgia. The studies included in the meta-analysis are experimental studies, and the total sample size is 1772. In the study, the funnel plot, Duval and Tweedie’s Trip and Fill Analysis, Orwin’s Safe N Analysis, and Egger’s Regression Test were utilized to determine the publication bias, which has been found to be quite low. Besides, Hedge’s g statistic was employed to measure the effect size for the difference between the means performed in accordance with the random effects model. The results of the study show that the effect size of online education on academic achievement is on a medium level. The heterogeneity test results of the meta-analysis study display that the effect size does not differ in terms of class level, country, online education approaches, and lecture moderators.
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction
Information and communication technologies have become a powerful force in transforming the educational settings around the world. The pandemic has been an important factor in transferring traditional physical classrooms settings through adopting information and communication technologies and has also accelerated the transformation. The literature supports that learning environments connected to information and communication technologies highly satisfy students. Therefore, we need to keep interest in technology-based learning environments. Clearly, technology has had a huge impact on young people's online lives. This digital revolution can synergize the educational ambitions and interests of digitally addicted students. In essence, COVID-19 has provided us with an opportunity to embrace online learning as education systems have to keep up with the rapid emergence of new technologies.
Information and communication technologies that have an effect on all spheres of life are also actively included in the education field. With the recent developments, using technology in education has become inevitable due to personal and social reasons (Usta, 2011a ). Online education may be given as an example of using information and communication technologies as a consequence of the technological developments. Also, it is crystal clear that online learning is a popular way of obtaining instruction (Demiralay et al., 2016 ; Pillay et al., 2007 ), which is defined by Horton ( 2000 ) as a way of education that is performed through a web browser or an online application without requiring an extra software or a learning source. Furthermore, online learning is described as a way of utilizing the internet to obtain the related learning sources during the learning process, to interact with the content, the teacher, and other learners, as well as to get support throughout the learning process (Ally, 2004 ). Online learning has such benefits as learning independently at any time and place (Vrasidas & MsIsaac, 2000 ), granting facility (Poole, 2000 ), flexibility (Chizmar & Walbert, 1999 ), self-regulation skills (Usta, 2011b ), learning with collaboration, and opportunity to plan self-learning process.
Even though online education practices have not been comprehensive as it is now, internet and computers have been used in education as alternative learning tools in correlation with the advances in technology. The first distance education attempt in the world was initiated by the ‘Steno Courses’ announcement published in Boston newspaper in 1728. Furthermore, in the nineteenth century, Sweden University started the “Correspondence Composition Courses” for women, and University Correspondence College was afterwards founded for the correspondence courses in 1843 (Arat & Bakan, 2011 ). Recently, distance education has been performed through computers, assisted by the facilities of the internet technologies, and soon, it has evolved into a mobile education practice that is emanating from progress in the speed of internet connection, and the development of mobile devices.
With the emergence of pandemic (Covid-19), face to face education has almost been put to a halt, and online education has gained significant importance. The Microsoft management team declared to have 750 users involved in the online education activities on the 10 th March, just before the pandemic; however, on March 24, they informed that the number of users increased significantly, reaching the number of 138,698 users (OECD, 2020 ). This event supports the view that it is better to commonly use online education rather than using it as a traditional alternative educational tool when students do not have the opportunity to have a face to face education (Geostat, 2019 ). The period of Covid-19 pandemic has emerged as a sudden state of having limited opportunities. Face to face education has stopped in this period for a long time. The global spread of Covid-19 affected more than 850 million students all around the world, and it caused the suspension of face to face education. Different countries have proposed several solutions in order to maintain the education process during the pandemic. Schools have had to change their curriculum, and many countries supported the online education practices soon after the pandemic. In other words, traditional education gave its way to online education practices. At least 96 countries have been motivated to access online libraries, TV broadcasts, instructions, sources, video lectures, and online channels (UNESCO, 2020 ). In such a painful period, educational institutions went through online education practices by the help of huge companies such as Microsoft, Google, Zoom, Skype, FaceTime, and Slack. Thus, online education has been discussed in the education agenda more intensively than ever before.
Although online education approaches were not used as comprehensively as it has been used recently, it was utilized as an alternative learning approach in education for a long time in parallel with the development of technology, internet and computers. The academic achievement of the students is often aimed to be promoted by employing online education approaches. In this regard, academicians in various countries have conducted many studies on the evaluation of online education approaches and published the related results. However, the accumulation of scientific data on online education approaches creates difficulties in keeping, organizing and synthesizing the findings. In this research area, studies are being conducted at an increasing rate making it difficult for scientists to be aware of all the research outside of their expertise. Another problem encountered in the related study area is that online education studies are repetitive. Studies often utilize slightly different methods, measures, and/or examples to avoid duplication. This erroneous approach makes it difficult to distinguish between significant differences in the related results. In other words, if there are significant differences in the results of the studies, it may be difficult to express what variety explains the differences in these results. One obvious solution to these problems is to systematically review the results of various studies and uncover the sources. One method of performing such systematic syntheses is the application of meta-analysis which is a methodological and statistical approach to draw conclusions from the literature. At this point, how effective online education applications are in increasing the academic success is an important detail. Has online education, which is likely to be encountered frequently in the continuing pandemic period, been successful in the last ten years? If successful, how much was the impact? Did different variables have an impact on this effect? Academics across the globe have carried out studies on the evaluation of online education platforms and publishing the related results (Chiao et al., 2018 ). It is quite important to evaluate the results of the studies that have been published up until now, and that will be published in the future. Has the online education been successful? If it has been, how big is the impact? Do the different variables affect this impact? What should we consider in the next coming online education practices? These questions have all motivated us to carry out this study. We have conducted a comprehensive meta-analysis study that tries to provide a discussion platform on how to develop efficient online programs for educators and policy makers by reviewing the related studies on online education, presenting the effect size, and revealing the effect of diverse variables on the general impact.
There have been many critical discussions and comprehensive studies on the differences between online and face to face learning; however, the focus of this paper is different in the sense that it clarifies the magnitude of the effect of online education and teaching process, and it represents what factors should be controlled to help increase the effect size. Indeed, the purpose here is to provide conscious decisions in the implementation of the online education process.
The general impact of online education on the academic achievement will be discovered in the study. Therefore, this will provide an opportunity to get a general overview of the online education which has been practiced and discussed intensively in the pandemic period. Moreover, the general impact of online education on academic achievement will be analyzed, considering different variables. In other words, the current study will allow to totally evaluate the study results from the related literature, and to analyze the results considering several cultures, lectures, and class levels. Considering all the related points, this study seeks to answer the following research questions:
What is the effect size of online education on academic achievement?
How do the effect sizes of online education on academic achievement change according to the moderator variable of the country?
How do the effect sizes of online education on academic achievement change according to the moderator variable of the class level?
How do the effect sizes of online education on academic achievement change according to the moderator variable of the lecture?
How do the effect sizes of online education on academic achievement change according to the moderator variable of the online education approaches?
This study aims at determining the effect size of online education, which has been highly used since the beginning of the pandemic, on students’ academic achievement in different courses by using a meta-analysis method. Meta-analysis is a synthesis method that enables gathering of several study results accurately and efficiently, and getting the total results in the end (Tsagris & Fragkos, 2018 ).
2.1 Selecting and coding the data (studies)
The required literature for the meta-analysis study was reviewed in July, 2020, and the follow-up review was conducted in September, 2020. The purpose of the follow-up review was to include the studies which were published in the conduction period of this study, and which met the related inclusion criteria. However, no study was encountered to be included in the follow-up review.
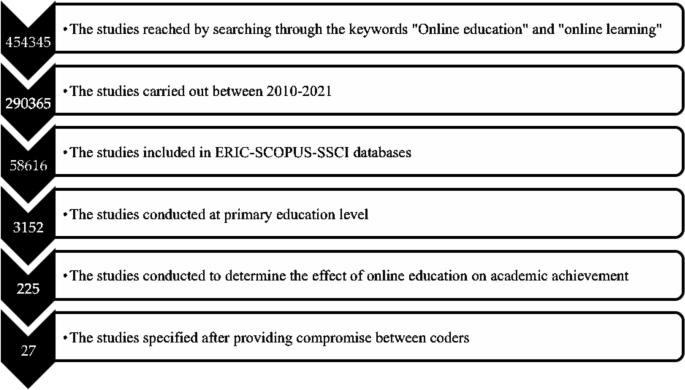
In order to access the studies in the meta-analysis, the databases of Web of Science, ERIC, and SCOPUS were reviewed by utilizing the keywords ‘online learning and online education’. Not every database has a search engine that grants access to the studies by writing the keywords, and this obstacle was considered to be an important problem to be overcome. Therefore, a platform that has a special design was utilized by the researcher. With this purpose, through the open access system of Cukurova University Library, detailed reviews were practiced using EBSCO Information Services (EBSCO) that allow reviewing the whole collection of research through a sole searching box. Since the fundamental variables of this study are online education and online learning, the literature was systematically reviewed in the related databases (Web of Science, ERIC, and SCOPUS) by referring to the keywords. Within this scope, 225 articles were accessed, and the studies were included in the coding key list formed by the researcher. The name of the researchers, the year, the database (Web of Science, ERIC, and SCOPUS), the sample group and size, the lectures that the academic achievement was tested in, the country that the study was conducted in, and the class levels were all included in this coding key.
The following criteria were identified to include 225 research studies which were coded based on the theoretical basis of the meta-analysis study: (1) The studies should be published in the refereed journals between the years 2020 and 2021, (2) The studies should be experimental studies that try to determine the effect of online education and online learning on academic achievement, (3) The values of the stated variables or the required statistics to calculate these values should be stated in the results of the studies, and (4) The sample group of the study should be at a primary education level. These criteria were also used as the exclusion criteria in the sense that the studies that do not meet the required criteria were not included in the present study.
After the inclusion criteria were determined, a systematic review process was conducted, following the year criterion of the study by means of EBSCO. Within this scope, 290,365 studies that analyze the effect of online education and online learning on academic achievement were accordingly accessed. The database (Web of Science, ERIC, and SCOPUS) was also used as a filter by analyzing the inclusion criteria. Hence, the number of the studies that were analyzed was 58,616. Afterwards, the keyword ‘primary education’ was used as the filter and the number of studies included in the study decreased to 3152. Lastly, the literature was reviewed by using the keyword ‘academic achievement’ and 225 studies were accessed. All the information of 225 articles was included in the coding key.
It is necessary for the coders to review the related studies accurately and control the validity, safety, and accuracy of the studies (Stewart & Kamins, 2001 ). Within this scope, the studies that were determined based on the variables used in this study were first reviewed by three researchers from primary education field, then the accessed studies were combined and processed in the coding key by the researcher. All these studies that were processed in the coding key were analyzed in accordance with the inclusion criteria by all the researchers in the meetings, and it was decided that 27 studies met the inclusion criteria (Atici & Polat, 2010 ; Carreon, 2018 ; Ceylan & Elitok Kesici, 2017 ; Chae & Shin, 2016 ; Chiang et al. 2014 ; Ercan, 2014 ; Ercan et al., 2016 ; Gwo-Jen et al., 2018 ; Hayes & Stewart, 2016 ; Hwang et al., 2012 ; Kert et al., 2017 ; Lai & Chen, 2010 ; Lai et al., 2015 ; Meyers et al., 2015 ; Ravenel et al., 2014 ; Sung et al., 2016 ; Wang & Chen, 2013 ; Yu, 2019 ; Yu & Chen, 2014 ; Yu & Pan, 2014 ; Yu et al., 2010 ; Zhong et al., 2017 ). The data from the studies meeting the inclusion criteria were independently processed in the second coding key by three researchers, and consensus meetings were arranged for further discussion. After the meetings, researchers came to an agreement that the data were coded accurately and precisely. Having identified the effect sizes and heterogeneity of the study, moderator variables that will show the differences between the effect sizes were determined. The data related to the determined moderator variables were added to the coding key by three researchers, and a new consensus meeting was arranged. After the meeting, researchers came to an agreement that moderator variables were coded accurately and precisely.
2.2 Study group
27 studies are included in the meta-analysis. The total sample size of the studies that are included in the analysis is 1772. The characteristics of the studies included are given in Table 1 .
2.3 Publication bias
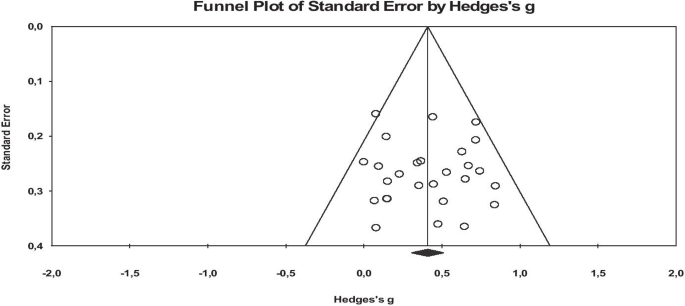
Publication bias is the low capability of published studies on a research subject to represent all completed studies on the same subject (Card, 2011 ; Littell et al., 2008 ). Similarly, publication bias is the state of having a relationship between the probability of the publication of a study on a subject, and the effect size and significance that it produces. Within this scope, publication bias may occur when the researchers do not want to publish the study as a result of failing to obtain the expected results, or not being approved by the scientific journals, and consequently not being included in the study synthesis (Makowski et al., 2019 ). The high possibility of publication bias in a meta-analysis study negatively affects (Pecoraro, 2018 ) the accuracy of the combined effect size, causing the average effect size to be reported differently than it should be (Borenstein et al., 2009 ). For this reason, the possibility of publication bias in the included studies was tested before determining the effect sizes of the relationships between the stated variables. The possibility of publication bias of this meta-analysis study was analyzed by using the funnel plot, Orwin’s Safe N Analysis, Duval and Tweedie’s Trip and Fill Analysis, and Egger’s Regression Test.
2.4 Selecting the model
After determining the probability of publication bias of this meta-analysis study, the statistical model used to calculate the effect sizes was selected. The main approaches used in the effect size calculations according to the differentiation level of inter-study variance are fixed and random effects models (Pigott, 2012 ). Fixed effects model refers to the homogeneity of the characteristics of combined studies apart from the sample sizes, while random effects model refers to the parameter diversity between the studies (Cumming, 2012 ). While calculating the average effect size in the random effects model (Deeks et al., 2008 ) that is based on the assumption that effect predictions of different studies are only the result of a similar distribution, it is necessary to consider several situations such as the effect size apart from the sample error of combined studies, characteristics of the participants, duration, scope, and pattern of the study (Littell et al., 2008 ). While deciding the model in the meta-analysis study, the assumptions on the sample characteristics of the studies included in the analysis and the inferences that the researcher aims to make should be taken into consideration. The fact that the sample characteristics of the studies conducted in the field of social sciences are affected by various parameters shows that using random effects model is more appropriate in this sense. Besides, it is stated that the inferences made with the random effects model are beyond the studies included in the meta-analysis (Field, 2003 ; Field & Gillett, 2010 ). Therefore, using random effects model also contributes to the generalization of research data. The specified criteria for the statistical model selection show that according to the nature of the meta-analysis study, the model should be selected just before the analysis (Borenstein et al., 2007 ; Littell et al., 2008 ). Within this framework, it was decided to make use of the random effects model, considering that the students who are the samples of the studies included in the meta-analysis are from different countries and cultures, the sample characteristics of the studies differ, and the patterns and scopes of the studies vary as well.
2.5 Heterogeneity
Meta-analysis facilitates analyzing the research subject with different parameters by showing the level of diversity between the included studies. Within this frame, whether there is a heterogeneous distribution between the studies included in the study or not has been evaluated in the present study. The heterogeneity of the studies combined in this meta-analysis study has been determined through Q and I 2 tests. Q test evaluates the random distribution probability of the differences between the observed results (Deeks et al., 2008 ). Q value exceeding 2 value calculated according to the degree of freedom and significance, indicates the heterogeneity of the combined effect sizes (Card, 2011 ). I 2 test, which is the complementary of the Q test, shows the heterogeneity amount of the effect sizes (Cleophas & Zwinderman, 2017 ). I 2 value being higher than 75% is explained as high level of heterogeneity.
In case of encountering heterogeneity in the studies included in the meta-analysis, the reasons of heterogeneity can be analyzed by referring to the study characteristics. The study characteristics which may be related to the heterogeneity between the included studies can be interpreted through subgroup analysis or meta-regression analysis (Deeks et al., 2008 ). While determining the moderator variables, the sufficiency of the number of variables, the relationship between the moderators, and the condition to explain the differences between the results of the studies have all been considered in the present study. Within this scope, it was predicted in this meta-analysis study that the heterogeneity can be explained with the country, class level, and lecture moderator variables of the study in terms of the effect of online education, which has been highly used since the beginning of the pandemic, and it has an impact on the students’ academic achievement in different lectures. Some subgroups were evaluated and categorized together, considering that the number of effect sizes of the sub-dimensions of the specified variables is not sufficient to perform moderator analysis (e.g. the countries where the studies were conducted).
2.6 Interpreting the effect sizes
Effect size is a factor that shows how much the independent variable affects the dependent variable positively or negatively in each included study in the meta-analysis (Dinçer, 2014 ). While interpreting the effect sizes obtained from the meta-analysis, the classifications of Cohen et al. ( 2007 ) have been utilized. The case of differentiating the specified relationships of the situation of the country, class level, and school subject variables of the study has been identified through the Q test, degree of freedom, and p significance value Fig. 1 and 2 .
3 Findings and results
The purpose of this study is to determine the effect size of online education on academic achievement. Before determining the effect sizes in the study, the probability of publication bias of this meta-analysis study was analyzed by using the funnel plot, Orwin’s Safe N Analysis, Duval and Tweedie’s Trip and Fill Analysis, and Egger’s Regression Test.
When the funnel plots are examined, it is seen that the studies included in the analysis are distributed symmetrically on both sides of the combined effect size axis, and they are generally collected in the middle and lower sections. The probability of publication bias is low according to the plots. However, since the results of the funnel scatter plots may cause subjective interpretations, they have been supported by additional analyses (Littell et al., 2008 ). Therefore, in order to provide an extra proof for the probability of publication bias, it has been analyzed through Orwin’s Safe N Analysis, Duval and Tweedie’s Trip and Fill Analysis, and Egger’s Regression Test (Table 2 ).
Table 2 consists of the results of the rates of publication bias probability before counting the effect size of online education on academic achievement. According to the table, Orwin Safe N analysis results show that it is not necessary to add new studies to the meta-analysis in order for Hedges g to reach a value outside the range of ± 0.01. The Duval and Tweedie test shows that excluding the studies that negatively affect the symmetry of the funnel scatter plots for each meta-analysis or adding their exact symmetrical equivalents does not significantly differentiate the calculated effect size. The insignificance of the Egger tests results reveals that there is no publication bias in the meta-analysis study. The results of the analysis indicate the high internal validity of the effect sizes and the adequacy of representing the studies conducted on the relevant subject.
In this study, it was aimed to determine the effect size of online education on academic achievement after testing the publication bias. In line with the first purpose of the study, the forest graph regarding the effect size of online education on academic achievement is shown in Fig. 3 , and the statistics regarding the effect size are given in Table 3 .
The flow chart of the scanning and selection process of the studies
Funnel plot graphics representing the effect size of the effects of online education on academic success
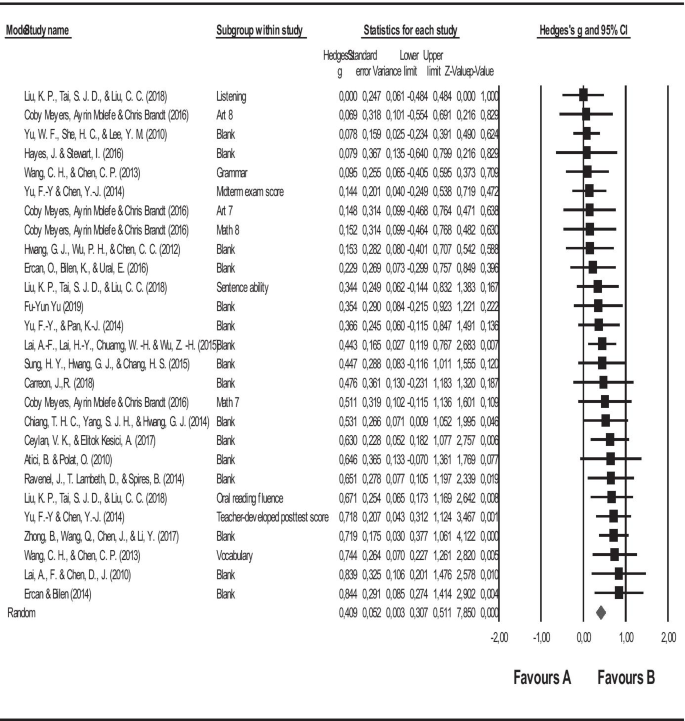
Forest graph related to the effect size of online education on academic success
The square symbols in the forest graph in Fig. 3 represent the effect sizes, while the horizontal lines show the intervals in 95% confidence of the effect sizes, and the diamond symbol shows the overall effect size. When the forest graph is analyzed, it is seen that the lower and upper limits of the combined effect sizes are generally close to each other, and the study loads are similar. This similarity in terms of study loads indicates the similarity of the contribution of the combined studies to the overall effect size.
Figure 3 clearly represents that the study of Liu and others (Liu et al., 2018 ) has the lowest, and the study of Ercan and Bilen ( 2014 ) has the highest effect sizes. The forest graph shows that all the combined studies and the overall effect are positive. Furthermore, it is simply understood from the forest graph in Fig. 3 and the effect size statistics in Table 3 that the results of the meta-analysis study conducted with 27 studies and analyzing the effect of online education on academic achievement illustrate that this relationship is on average level (= 0.409).
After the analysis of the effect size in the study, whether the studies included in the analysis are distributed heterogeneously or not has also been analyzed. The heterogeneity of the combined studies was determined through the Q and I 2 tests. As a result of the heterogeneity test, Q statistical value was calculated as 29.576. With 26 degrees of freedom at 95% significance level in the chi-square table, the critical value is accepted as 38.885. The Q statistical value (29.576) counted in this study is lower than the critical value of 38.885. The I 2 value, which is the complementary of the Q statistics, is 12.100%. This value indicates that the accurate heterogeneity or the total variability that can be attributed to variability between the studies is 12%. Besides, p value is higher than (0.285) p = 0.05. All these values [Q (26) = 29.579, p = 0.285; I2 = 12.100] indicate that there is a homogeneous distribution between the effect sizes, and fixed effects model should be used to interpret these effect sizes. However, some researchers argue that even if the heterogeneity is low, it should be evaluated based on the random effects model (Borenstein et al., 2007 ). Therefore, this study gives information about both models. The heterogeneity of the combined studies has been attempted to be explained with the characteristics of the studies included in the analysis. In this context, the final purpose of the study is to determine the effect of the country, academic level, and year variables on the findings. Accordingly, the statistics regarding the comparison of the stated relations according to the countries where the studies were conducted are given in Table 4 .
As seen in Table 4 , the effect of online education on academic achievement does not differ significantly according to the countries where the studies were conducted in. Q test results indicate the heterogeneity of the relationships between the variables in terms of countries where the studies were conducted in. According to the table, the effect of online education on academic achievement was reported as the highest in other countries, and the lowest in the US. The statistics regarding the comparison of the stated relations according to the class levels are given in Table 5 .
As seen in Table 5 , the effect of online education on academic achievement does not differ according to the class level. However, the effect of online education on academic achievement is the highest in the 4 th class. The statistics regarding the comparison of the stated relations according to the class levels are given in Table 6 .
As seen in Table 6 , the effect of online education on academic achievement does not differ according to the school subjects included in the studies. However, the effect of online education on academic achievement is the highest in ICT subject.
The obtained effect size in the study was formed as a result of the findings attained from primary studies conducted in 7 different countries. In addition, these studies are the ones on different approaches to online education (online learning environments, social networks, blended learning, etc.). In this respect, the results may raise some questions about the validity and generalizability of the results of the study. However, the moderator analyzes, whether for the country variable or for the approaches covered by online education, did not create significant differences in terms of the effect sizes. If significant differences were to occur in terms of effect sizes, we could say that the comparisons we will make by comparing countries under the umbrella of online education would raise doubts in terms of generalizability. Moreover, no study has been found in the literature that is not based on a special approach or does not contain a specific technique conducted under the name of online education alone. For instance, one of the commonly used definitions is blended education which is defined as an educational model in which online education is combined with traditional education method (Colis & Moonen, 2001 ). Similarly, Rasmussen ( 2003 ) defines blended learning as “a distance education method that combines technology (high technology such as television, internet, or low technology such as voice e-mail, conferences) with traditional education and training.” Further, Kerres and Witt (2003) define blended learning as “combining face-to-face learning with technology-assisted learning.” As it is clearly observed, online education, which has a wider scope, includes many approaches.
As seen in Table 7 , the effect of online education on academic achievement does not differ according to online education approaches included in the studies. However, the effect of online education on academic achievement is the highest in Web Based Problem Solving Approach.
4 Conclusions and discussion
Considering the developments during the pandemics, it is thought that the diversity in online education applications as an interdisciplinary pragmatist field will increase, and the learning content and processes will be enriched with the integration of new technologies into online education processes. Another prediction is that more flexible and accessible learning opportunities will be created in online education processes, and in this way, lifelong learning processes will be strengthened. As a result, it is predicted that in the near future, online education and even digital learning with a newer name will turn into the main ground of education instead of being an alternative or having a support function in face-to-face learning. The lessons learned from the early period online learning experience, which was passed with rapid adaptation due to the Covid19 epidemic, will serve to develop this method all over the world, and in the near future, online learning will become the main learning structure through increasing its functionality with the contribution of new technologies and systems. If we look at it from this point of view, there is a necessity to strengthen online education.
In this study, the effect of online learning on academic achievement is at a moderate level. To increase this effect, the implementation of online learning requires support from teachers to prepare learning materials, to design learning appropriately, and to utilize various digital-based media such as websites, software technology and various other tools to support the effectiveness of online learning (Rolisca & Achadiyah, 2014 ). According to research conducted by Rahayu et al. ( 2017 ), it has been proven that the use of various types of software increases the effectiveness and quality of online learning. Implementation of online learning can affect students' ability to adapt to technological developments in that it makes students use various learning resources on the internet to access various types of information, and enables them to get used to performing inquiry learning and active learning (Hart et al., 2019 ; Prestiadi et al., 2019 ). In addition, there may be many reasons for the low level of effect in this study. The moderator variables examined in this study could be a guide in increasing the level of practical effect. However, the effect size did not differ significantly for all moderator variables. Different moderator analyzes can be evaluated in order to increase the level of impact of online education on academic success. If confounding variables that significantly change the effect level are detected, it can be spoken more precisely in order to increase this level. In addition to the technical and financial problems, the level of impact will increase if a few other difficulties are eliminated such as students, lack of interaction with the instructor, response time, and lack of traditional classroom socialization.
In addition, COVID-19 pandemic related social distancing has posed extreme difficulties for all stakeholders to get online as they have to work in time constraints and resource constraints. Adopting the online learning environment is not just a technical issue, it is a pedagogical and instructive challenge as well. Therefore, extensive preparation of teaching materials, curriculum, and assessment is vital in online education. Technology is the delivery tool and requires close cross-collaboration between teaching, content and technology teams (CoSN, 2020 ).
Online education applications have been used for many years. However, it has come to the fore more during the pandemic process. This result of necessity has brought with it the discussion of using online education instead of traditional education methods in the future. However, with this research, it has been revealed that online education applications are moderately effective. The use of online education instead of face-to-face education applications can only be possible with an increase in the level of success. This may have been possible with the experience and knowledge gained during the pandemic process. Therefore, the meta-analysis of experimental studies conducted in the coming years will guide us. In this context, experimental studies using online education applications should be analyzed well. It would be useful to identify variables that can change the level of impacts with different moderators. Moderator analyzes are valuable in meta-analysis studies (for example, the role of moderators in Karl Pearson's typhoid vaccine studies). In this context, each analysis study sheds light on future studies. In meta-analyses to be made about online education, it would be beneficial to go beyond the moderators determined in this study. Thus, the contribution of similar studies to the field will increase more.
The purpose of this study is to determine the effect of online education on academic achievement. In line with this purpose, the studies that analyze the effect of online education approaches on academic achievement have been included in the meta-analysis. The total sample size of the studies included in the meta-analysis is 1772. While the studies included in the meta-analysis were conducted in the US, Taiwan, Turkey, China, Philippines, Ireland, and Georgia, the studies carried out in Europe could not be reached. The reason may be attributed to that there may be more use of quantitative research methods from a positivist perspective in the countries with an American academic tradition. As a result of the study, it was found out that the effect size of online education on academic achievement (g = 0.409) was moderate. In the studies included in the present research, we found that online education approaches were more effective than traditional ones. However, contrary to the present study, the analysis of comparisons between online and traditional education in some studies shows that face-to-face traditional learning is still considered effective compared to online learning (Ahmad et al., 2016 ; Hamdani & Priatna, 2020 ; Wei & Chou, 2020 ). Online education has advantages and disadvantages. The advantages of online learning compared to face-to-face learning in the classroom is the flexibility of learning time in online learning, the learning time does not include a single program, and it can be shaped according to circumstances (Lai et al., 2019 ). The next advantage is the ease of collecting assignments for students, as these can be done without having to talk to the teacher. Despite this, online education has several weaknesses, such as students having difficulty in understanding the material, teachers' inability to control students, and students’ still having difficulty interacting with teachers in case of internet network cuts (Swan, 2007 ). According to Astuti et al ( 2019 ), face-to-face education method is still considered better by students than e-learning because it is easier to understand the material and easier to interact with teachers. The results of the study illustrated that the effect size (g = 0.409) of online education on academic achievement is of medium level. Therefore, the results of the moderator analysis showed that the effect of online education on academic achievement does not differ in terms of country, lecture, class level, and online education approaches variables. After analyzing the literature, several meta-analyses on online education were published (Bernard et al., 2004 ; Machtmes & Asher, 2000 ; Zhao et al., 2005 ). Typically, these meta-analyzes also include the studies of older generation technologies such as audio, video, or satellite transmission. One of the most comprehensive studies on online education was conducted by Bernard et al. ( 2004 ). In this study, 699 independent effect sizes of 232 studies published from 1985 to 2001 were analyzed, and face-to-face education was compared to online education, with respect to success criteria and attitudes of various learners from young children to adults. In this meta-analysis, an overall effect size close to zero was found for the students' achievement (g + = 0.01).
In another meta-analysis study carried out by Zhao et al. ( 2005 ), 98 effect sizes were examined, including 51 studies on online education conducted between 1996 and 2002. According to the study of Bernard et al. ( 2004 ), this meta-analysis focuses on the activities done in online education lectures. As a result of the research, an overall effect size close to zero was found for online education utilizing more than one generation technology for students at different levels. However, the salient point of the meta-analysis study of Zhao et al. is that it takes the average of different types of results used in a study to calculate an overall effect size. This practice is problematic because the factors that develop one type of learner outcome (e.g. learner rehabilitation), particularly course characteristics and practices, may be quite different from those that develop another type of outcome (e.g. learner's achievement), and it may even cause damage to the latter outcome. While mixing the studies with different types of results, this implementation may obscure the relationship between practices and learning.
Some meta-analytical studies have focused on the effectiveness of the new generation distance learning courses accessed through the internet for specific student populations. For instance, Sitzmann and others (Sitzmann et al., 2006 ) reviewed 96 studies published from 1996 to 2005, comparing web-based education of job-related knowledge or skills with face-to-face one. The researchers found that web-based education in general was slightly more effective than face-to-face education, but it is insufficient in terms of applicability ("knowing how to apply"). In addition, Sitzmann et al. ( 2006 ) revealed that Internet-based education has a positive effect on theoretical knowledge in quasi-experimental studies; however, it positively affects face-to-face education in experimental studies performed by random assignment. This moderator analysis emphasizes the need to pay attention to the factors of designs of the studies included in the meta-analysis. The designs of the studies included in this meta-analysis study were ignored. This can be presented as a suggestion to the new studies that will be conducted.
Another meta-analysis study was conducted by Cavanaugh et al. ( 2004 ), in which they focused on online education. In this study on internet-based distance education programs for students under 12 years of age, the researchers combined 116 results from 14 studies published between 1999 and 2004 to calculate an overall effect that was not statistically different from zero. The moderator analysis carried out in this study showed that there was no significant factor affecting the students' success. This meta-analysis used multiple results of the same study, ignoring the fact that different results of the same student would not be independent from each other.
In conclusion, some meta-analytical studies analyzed the consequences of online education for a wide range of students (Bernard et al., 2004 ; Zhao et al., 2005 ), and the effect sizes were generally low in these studies. Furthermore, none of the large-scale meta-analyzes considered the moderators, database quality standards or class levels in the selection of the studies, while some of them just referred to the country and lecture moderators. Advances in internet-based learning tools, the pandemic process, and increasing popularity in different learning contexts have required a precise meta-analysis of students' learning outcomes through online learning. Previous meta-analysis studies were typically based on the studies, involving narrow range of confounding variables. In the present study, common but significant moderators such as class level and lectures during the pandemic process were discussed. For instance, the problems have been experienced especially in terms of eligibility of class levels in online education platforms during the pandemic process. It was found that there is a need to study and make suggestions on whether online education can meet the needs of teachers and students.
Besides, the main forms of online education in the past were to watch the open lectures of famous universities and educational videos of institutions. In addition, online education is mainly a classroom-based teaching implemented by teachers in their own schools during the pandemic period, which is an extension of the original school education. This meta-analysis study will stand as a source to compare the effect size of the online education forms of the past decade with what is done today, and what will be done in the future.
Lastly, the heterogeneity test results of the meta-analysis study display that the effect size does not differ in terms of class level, country, online education approaches, and lecture moderators.
*Studies included in meta-analysis
Ahmad, S., Sumardi, K., & Purnawan, P. (2016). Komparasi Peningkatan Hasil Belajar Antara Pembelajaran Menggunakan Sistem Pembelajaran Online Terpadu Dengan Pembelajaran Klasikal Pada Mata Kuliah Pneumatik Dan Hidrolik. Journal of Mechanical Engineering Education, 2 (2), 286–292.
Article Google Scholar
Ally, M. (2004). Foundations of educational theory for online learning. Theory and Practice of Online Learning, 2 , 15–44. Retrieved on the 11th of September, 2020 from https://eddl.tru.ca/wp-content/uploads/2018/12/01_Anderson_2008-Theory_and_Practice_of_Online_Learning.pdf
Arat, T., & Bakan, Ö. (2011). Uzaktan eğitim ve uygulamaları. Selçuk Üniversitesi Sosyal Bilimler Meslek Yüksek Okulu Dergisi , 14 (1–2), 363–374. https://doi.org/10.29249/selcuksbmyd.540741
Astuti, C. C., Sari, H. M. K., & Azizah, N. L. (2019). Perbandingan Efektifitas Proses Pembelajaran Menggunakan Metode E-Learning dan Konvensional. Proceedings of the ICECRS, 2 (1), 35–40.
*Atici, B., & Polat, O. C. (2010). Influence of the online learning environments and tools on the student achievement and opinions. Educational Research and Reviews, 5 (8), 455–464. Retrieved on the 11th of October, 2020 from https://academicjournals.org/journal/ERR/article-full-text-pdf/4C8DD044180.pdf
Bernard, R. M., Abrami, P. C., Lou, Y., Borokhovski, E., Wade, A., Wozney, L., et al. (2004). How does distance education compare with classroom instruction? A meta- analysis of the empirical literature. Review of Educational Research, 3 (74), 379–439. https://doi.org/10.3102/00346543074003379
Borenstein, M., Hedges, L. V., Higgins, J. P. T., & Rothstein, H. R. (2009). Introduction to meta-analysis . Wiley.
Book Google Scholar
Borenstein, M., Hedges, L., & Rothstein, H. (2007). Meta-analysis: Fixed effect vs. random effects . UK: Wiley.
Card, N. A. (2011). Applied meta-analysis for social science research: Methodology in the social sciences . Guilford.
Google Scholar
*Carreon, J. R. (2018 ). Facebook as integrated blended learning tool in technology and livelihood education exploratory. Retrieved on the 1st of October, 2020 from https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/EJ1197714.pdf
Cavanaugh, C., Gillan, K. J., Kromrey, J., Hess, M., & Blomeyer, R. (2004). The effects of distance education on K-12 student outcomes: A meta-analysis. Learning Point Associates/North Central Regional Educational Laboratory (NCREL) . Retrieved on the 11th of September, 2020 from https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED489533.pdf
*Ceylan, V. K., & Elitok Kesici, A. (2017). Effect of blended learning to academic achievement. Journal of Human Sciences, 14 (1), 308. https://doi.org/10.14687/jhs.v14i1.4141
*Chae, S. E., & Shin, J. H. (2016). Tutoring styles that encourage learner satisfaction, academic engagement, and achievement in an online environment. Interactive Learning Environments, 24(6), 1371–1385. https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2015.1009472
*Chiang, T. H. C., Yang, S. J. H., & Hwang, G. J. (2014). An augmented reality-based mobile learning system to improve students’ learning achievements and motivations in natural science inquiry activities. Educational Technology and Society, 17 (4), 352–365. Retrieved on the 11th of September, 2020 from https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Gwo_Jen_Hwang/publication/287529242_An_Augmented_Reality-based_Mobile_Learning_System_to_Improve_Students'_Learning_Achievements_and_Motivations_in_Natural_Science_Inquiry_Activities/links/57198c4808ae30c3f9f2c4ac.pdf
Chiao, H. M., Chen, Y. L., & Huang, W. H. (2018). Examining the usability of an online virtual tour-guiding platform for cultural tourism education. Journal of Hospitality, Leisure, Sport & Tourism Education, 23 (29–38), 1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhlste.2018.05.002
Chizmar, J. F., & Walbert, M. S. (1999). Web-based learning environments guided by principles of good teaching practice. Journal of Economic Education, 30 (3), 248–264. https://doi.org/10.2307/1183061
Cleophas, T. J., & Zwinderman, A. H. (2017). Modern meta-analysis: Review and update of methodologies . Switzerland: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-55895-0
Cohen, L., Manion, L., & Morrison, K. (2007). Observation. Research Methods in Education, 6 , 396–412. Retrieved on the 11th of September, 2020 from https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Nabil_Ashraf2/post/How_to_get_surface_potential_Vs_Voltage_curve_from_CV_and_GV_measurements_of_MOS_capacitor/attachment/5ac6033cb53d2f63c3c405b4/AS%3A612011817844736%401522926396219/download/Very+important_C-V+characterization+Lehigh+University+thesis.pdf
Colis, B., & Moonen, J. (2001). Flexible Learning in a Digital World: Experiences and Expectations. Open & Distance Learning Series . Stylus Publishing.
CoSN. (2020). COVID-19 Response: Preparing to Take School Online. CoSN. (2020). COVID-19 Response: Preparing to Take School Online. Retrieved on the 3rd of September, 2021 from https://www.cosn.org/sites/default/files/COVID-19%20Member%20Exclusive_0.pdf
Cumming, G. (2012). Understanding new statistics: Effect sizes, confidence intervals, and meta-analysis. New York, USA: Routledge. https://doi.org/10.4324/9780203807002
Deeks, J. J., Higgins, J. P. T., & Altman, D. G. (2008). Analysing data and undertaking meta-analyses . In J. P. T. Higgins & S. Green (Eds.), Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions (pp. 243–296). Sussex: John Wiley & Sons. https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470712184.ch9
Demiralay, R., Bayır, E. A., & Gelibolu, M. F. (2016). Öğrencilerin bireysel yenilikçilik özellikleri ile çevrimiçi öğrenmeye hazır bulunuşlukları ilişkisinin incelenmesi. Eğitim ve Öğretim Araştırmaları Dergisi, 5 (1), 161–168. https://doi.org/10.23891/efdyyu.2017.10
Dinçer, S. (2014). Eğitim bilimlerinde uygulamalı meta-analiz. Pegem Atıf İndeksi, 2014(1), 1–133. https://doi.org/10.14527/pegem.001
*Durak, G., Cankaya, S., Yunkul, E., & Ozturk, G. (2017). The effects of a social learning network on students’ performances and attitudes. European Journal of Education Studies, 3 (3), 312–333. 10.5281/zenodo.292951
*Ercan, O. (2014). Effect of web assisted education supported by six thinking hats on students’ academic achievement in science and technology classes . European Journal of Educational Research, 3 (1), 9–23. https://doi.org/10.12973/eu-jer.3.1.9
Ercan, O., & Bilen, K. (2014). Effect of web assisted education supported by six thinking hats on students’ academic achievement in science and technology classes. European Journal of Educational Research, 3 (1), 9–23.
*Ercan, O., Bilen, K., & Ural, E. (2016). “Earth, sun and moon”: Computer assisted instruction in secondary school science - Achievement and attitudes. Issues in Educational Research, 26 (2), 206–224. https://doi.org/10.12973/eu-jer.3.1.9
Field, A. P. (2003). The problems in using fixed-effects models of meta-analysis on real-world data. Understanding Statistics, 2 (2), 105–124. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15328031us0202_02
Field, A. P., & Gillett, R. (2010). How to do a meta-analysis. British Journal of Mathematical and Statistical Psychology, 63 (3), 665–694. https://doi.org/10.1348/00071010x502733
Geostat. (2019). ‘Share of households with internet access’, National statistics office of Georgia . Retrieved on the 2nd September 2020 from https://www.geostat.ge/en/modules/categories/106/information-and-communication-technologies-usage-in-households
*Gwo-Jen, H., Nien-Ting, T., & Xiao-Ming, W. (2018). Creating interactive e-books through learning by design: The impacts of guided peer-feedback on students’ learning achievements and project outcomes in science courses. Journal of Educational Technology & Society., 21 (1), 25–36. Retrieved on the 2nd of October, 2020 https://ae-uploads.uoregon.edu/ISTE/ISTE2019/PROGRAM_SESSION_MODEL/HANDOUTS/112172923/CreatingInteractiveeBooksthroughLearningbyDesignArticle2018.pdf
Hamdani, A. R., & Priatna, A. (2020). Efektifitas implementasi pembelajaran daring (full online) dimasa pandemi Covid-19 pada jenjang Sekolah Dasar di Kabupaten Subang. Didaktik: Jurnal Ilmiah PGSD STKIP Subang, 6 (1), 1–9.
Hart, C. M., Berger, D., Jacob, B., Loeb, S., & Hill, M. (2019). Online learning, offline outcomes: Online course taking and high school student performance. Aera Open, 5(1).
*Hayes, J., & Stewart, I. (2016). Comparing the effects of derived relational training and computer coding on intellectual potential in school-age children. The British Journal of Educational Psychology, 86 (3), 397–411. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjep.12114
Horton, W. K. (2000). Designing web-based training: How to teach anyone anything anywhere anytime (Vol. 1). Wiley Publishing.
*Hwang, G. J., Wu, P. H., & Chen, C. C. (2012). An online game approach for improving students’ learning performance in web-based problem-solving activities. Computers and Education, 59 (4), 1246–1256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2012.05.009
*Kert, S. B., Köşkeroğlu Büyükimdat, M., Uzun, A., & Çayiroğlu, B. (2017). Comparing active game-playing scores and academic performances of elementary school students. Education 3–13, 45 (5), 532–542. https://doi.org/10.1080/03004279.2016.1140800
*Lai, A. F., & Chen, D. J. (2010). Web-based two-tier diagnostic test and remedial learning experiment. International Journal of Distance Education Technologies, 8 (1), 31–53. https://doi.org/10.4018/jdet.2010010103
*Lai, A. F., Lai, H. Y., Chuang W. H., & Wu, Z.H. (2015). Developing a mobile learning management system for outdoors nature science activities based on 5e learning cycle. Proceedings of the International Conference on e-Learning, ICEL. Proceedings of the International Association for Development of the Information Society (IADIS) International Conference on e-Learning (Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, Spain, July 21–24, 2015). Retrieved on the 14th November 2020 from https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED562095.pdf
Lai, C. H., Lin, H. W., Lin, R. M., & Tho, P. D. (2019). Effect of peer interaction among online learning community on learning engagement and achievement. International Journal of Distance Education Technologies (IJDET), 17 (1), 66–77.
Littell, J. H., Corcoran, J., & Pillai, V. (2008). Systematic reviews and meta-analysis . Oxford University.
*Liu, K. P., Tai, S. J. D., & Liu, C. C. (2018). Enhancing language learning through creation: the effect of digital storytelling on student learning motivation and performance in a school English course. Educational Technology Research and Development, 66 (4), 913–935. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11423-018-9592-z
Machtmes, K., & Asher, J. W. (2000). A meta-analysis of the effectiveness of telecourses in distance education. American Journal of Distance Education, 14 (1), 27–46. https://doi.org/10.1080/08923640009527043
Makowski, D., Piraux, F., & Brun, F. (2019). From experimental network to meta-analysis: Methods and applications with R for agronomic and environmental sciences. Dordrecht: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-024_1696-1
* Meyers, C., Molefe, A., & Brandt, C. (2015). The Impact of the" Enhancing Missouri's Instructional Networked Teaching Strategies"(eMINTS) Program on Student Achievement, 21st-Century Skills, and Academic Engagement--Second-Year Results . Society for Research on Educational Effectiveness. Retrieved on the 14 th November, 2020 from https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED562508.pdf
OECD. (2020). ‘A framework to guide an education response to the COVID-19 Pandemic of 2020 ’. https://doi.org/10.26524/royal.37.6
Pecoraro, V. (2018). Appraising evidence . In G. Biondi-Zoccai (Ed.), Diagnostic meta-analysis: A useful tool for clinical decision-making (pp. 99–114). Cham, Switzerland: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-78966-8_9
Pigott, T. (2012). Advances in meta-analysis . Springer.
Pillay, H. , Irving, K., & Tones, M. (2007). Validation of the diagnostic tool for assessing Tertiary students’ readiness for online learning. Higher Education Research & Development, 26 (2), 217–234. https://doi.org/10.1080/07294360701310821
Prestiadi, D., Zulkarnain, W., & Sumarsono, R. B. (2019). Visionary leadership in total quality management: efforts to improve the quality of education in the industrial revolution 4.0. In the 4th International Conference on Education and Management (COEMA 2019). Atlantis Press
Poole, D. M. (2000). Student participation in a discussion-oriented online course: a case study. Journal of Research on Computing in Education, 33 (2), 162–177. https://doi.org/10.1080/08886504.2000.10782307
Rahayu, F. S., Budiyanto, D., & Palyama, D. (2017). Analisis penerimaan e-learning menggunakan technology acceptance model (Tam)(Studi Kasus: Universitas Atma Jaya Yogyakarta). Jurnal Terapan Teknologi Informasi, 1 (2), 87–98.
Rasmussen, R. C. (2003). The quantity and quality of human interaction in a synchronous blended learning environment . Brigham Young University Press.
*Ravenel, J., T. Lambeth, D., & Spires, B. (2014). Effects of computer-based programs on mathematical achievement scores for fourth-grade students. i-manager’s Journal on School Educational Technology, 10 (1), 8–21. https://doi.org/10.26634/jsch.10.1.2830
Rolisca, R. U. C., & Achadiyah, B. N. (2014). Pengembangan media evaluasi pembelajaran dalam bentuk online berbasis e-learning menggunakan software wondershare quiz creator dalam mata pelajaran akuntansi SMA Brawijaya Smart School (BSS). Jurnal Pendidikan Akuntansi Indonesia, 12(2).
Sitzmann, T., Kraiger, K., Stewart, D., & Wisher, R. (2006). The comparative effective- ness of Web-based and classroom instruction: A meta-analysis . Personnel Psychology, 59 (3), 623–664. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-6570.2006.00049.x
Stewart, D. W., & Kamins, M. A. (2001). Developing a coding scheme and coding study reports. In M. W. Lipsey & D. B. Wilson (Eds.), Practical metaanalysis: Applied social research methods series (Vol. 49, pp. 73–90). Sage.
Swan, K. (2007). Research on online learning. Journal of Asynchronous Learning Networks, 11 (1), 55–59.
*Sung, H. Y., Hwang, G. J., & Chang, Y. C. (2016). Development of a mobile learning system based on a collaborative problem-posing strategy. Interactive Learning Environments, 24 (3), 456–471. https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2013.867889
Tsagris, M., & Fragkos, K. C. (2018). Meta-analyses of clinical trials versus diagnostic test accuracy studies. In G. Biondi-Zoccai (Ed.), Diagnostic meta-analysis: A useful tool for clinical decision-making (pp. 31–42). Cham, Switzerland: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-78966-8_4
UNESCO. (2020, Match 13). COVID-19 educational disruption and response. Retrieved on the 14 th November 2020 from https://en.unesco.org/themes/education-emergencies/ coronavirus-school-closures
Usta, E. (2011a). The effect of web-based learning environments on attitudes of students regarding computer and internet. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 28 (262–269), 1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2011.11.051
Usta, E. (2011b). The examination of online self-regulated learning skills in web-based learning environments in terms of different variables. Turkish Online Journal of Educational Technology-TOJET, 10 (3), 278–286. Retrieved on the 14th November 2020 from https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/EJ944994.pdf
Vrasidas, C. & MsIsaac, M. S. (2000). Principles of pedagogy and evaluation for web-based learning. Educational Media International, 37 (2), 105–111. https://doi.org/10.1080/095239800410405
*Wang, C. H., & Chen, C. P. (2013). Effects of facebook tutoring on learning english as a second language. Proceedings of the International Conference e-Learning 2013, (2009), 135–142. Retrieved on the 15th November 2020 from https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED562299.pdf
Wei, H. C., & Chou, C. (2020). Online learning performance and satisfaction: Do perceptions and readiness matter? Distance Education, 41 (1), 48–69.
*Yu, F. Y. (2019). The learning potential of online student-constructed tests with citing peer-generated questions. Interactive Learning Environments, 27 (2), 226–241. https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2018.1458040
*Yu, F. Y., & Chen, Y. J. (2014). Effects of student-generated questions as the source of online drill-and-practice activities on learning . British Journal of Educational Technology, 45 (2), 316–329. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjet.12036
*Yu, F. Y., & Pan, K. J. (2014). The effects of student question-generation with online prompts on learning. Educational Technology and Society, 17 (3), 267–279. Retrieved on the 15th November 2020 from http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.565.643&rep=rep1&type=pdf
*Yu, W. F., She, H. C., & Lee, Y. M. (2010). The effects of web-based/non-web-based problem-solving instruction and high/low achievement on students’ problem-solving ability and biology achievement. Innovations in Education and Teaching International, 47 (2), 187–199. https://doi.org/10.1080/14703291003718927
Zhao, Y., Lei, J., Yan, B, Lai, C., & Tan, S. (2005). A practical analysis of research on the effectiveness of distance education. Teachers College Record, 107 (8). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9620.2005.00544.x
*Zhong, B., Wang, Q., Chen, J., & Li, Y. (2017). Investigating the period of switching roles in pair programming in a primary school. Educational Technology and Society, 20 (3), 220–233. Retrieved on the 15th November 2020 from https://repository.nie.edu.sg/bitstream/10497/18946/1/ETS-20-3-220.pdf
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Primary Education, Ministry of Turkish National Education, Mersin, Turkey
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Hakan Ulum .
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Ulum, H. The effects of online education on academic success: A meta-analysis study. Educ Inf Technol 27 , 429–450 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-021-10740-8
Download citation
Received : 06 December 2020
Accepted : 30 August 2021
Published : 06 September 2021
Issue Date : January 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-021-10740-8
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Online education
- Student achievement
- Academic success
- Meta-analysis
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Meet top uk universities from the comfort of your home, here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

- School Education /
✍️Essay on Online Classes: Samples in 100, 150, 200 Words
- Updated on
- Oct 20, 2023

Online classes, also known as virtual classes, have over time revolutionized education. They are known for providing students with the flexibility to access educational content and at the same time interact with professors in the comfort of their homes. With time, this mode of learning has gained huge popularity due to its accessibility and the ability to cater to diverse learning styles.

In this digital age, online classes have become a fundamental part of education, enabling all individuals to acquire knowledge, skills etc. Are you looking to gain some more information about online classes? Well, you have come to the right place. Here you will get to read some samples of online classes.
Table of Contents
- 1 What are Online Classes?
- 2 Essay on Online Classes in 100 Words
- 3 Essay on Online Classes in 150 Words
- 4 Essay on Online Classes in 200 Words
Also Read: Online Courses
What are Online Classes?
Online classes are educational courses or learning programs which are conducted over the Internet. They provide students with the opportunity to study and complete their coursework remotely from the comfort of their homes. Online classes are a part of formal education. They can be taken in schools or colleges or can be offered by various online learning platforms.
Online classes may include a variety of digital resources as well as tools. These may include quizzes, assignments, video lectures, discussion forums, connecting with friends via email, chat video calls etc. This type of learning offers the student flexibility in terms of when and where they can access their coursework and study. It is also helpful for those who study part-time have busy schedules and prefer remote learning.
With the onset of COVID-19 , online classes became a huge hit hence the evolution of online classes. It offers one with different levels of education, skill training and much more.
Essay on Online Classes in 100 Words
Online classes have become a central aspect of modern education. They offer flexibility, accessibility, and convenience, allowing students to learn from the comfort of their homes. The rise of online classes was accelerated during the COVID-19 pandemic, making a shift from traditional classrooms to virtual learning environments.
However, there are many disadvantages to online classes. Students may struggle with distractions, lack of in-person interaction, and technical issues. Additionally, they have opened up new avenues for global collaboration and lifelong learning. In an increasingly digital world, online classes are likely to remain a significant part of education.
Essay on Online Classes in 150 Words
Online classes have become a prevalent mode of education, especially in the past two years. These digital platforms offer several advantages. First, they provide flexibility, allowing students to learn from the comfort of their homes. This is especially beneficial for those with busy schedules or who are studying part-time.
Second, online classes often offer a wider range of courses, enabling learners to explore diverse subjects. Additionally, these classes promote self-discipline and time management skills as students must regulate their own study routines.
However, there are challenges associated with online learning. Technical issues can disrupt classes, and the lack of face-to-face interaction may hinder social development. It can also be isolating for some students.
In conclusion, online classes offer convenience and a variety of courses, but they also present challenges related to technology and socialization. The future of education likely involves a blend of traditional and online learning methods, catering to diverse learning needs.
Also Read: Online Learning
Essay on Online Classes in 200 Words
Online classes have become a prevalent mode of education. However, this shift has brought about both advantages and challenges.
One significant benefit of online classes is accessibility. They allow students from diverse backgrounds and locations to access quality education without any constraints. This inclusivity promotes diversity and global learning experiences. Additionally, online classes often offer flexible schedules, enabling students to balance their studies with other responsibilities.
However, online classes present challenges too. Technical issues and a lack of face-to-face interaction can hinder effective learning. Students may even struggle with self-discipline and motivation, leading to a decline in academic performance. Moreover, the absence of physical facilities like libraries and laboratories can limit hands-on learning opportunities.
In conclusion, online classes have revolutionized education by providing accessibility and flexibility. Yet, they also pose challenges related to technical issues, motivation, and practical experiences.
Related Articles
Every student has their own pace of study, and this is where distance learning’s benefits really shine. You can go at your own speed in online classes, go over the material as needed, and complete the work in a method that best suits your learning preferences.
Online courses can be successful provided they are well-designed and delivered, just like any other course or programme. However, this depends from person to person as not every student is meant for online classes.
In online education, students get to study online using a computer/laptop and only need a proper internet connection.
For more information on such interesting topics, visit our essay-writing page and follow Leverage Edu !
Malvika Chawla
Malvika is a content writer cum news freak who comes with a strong background in Journalism and has worked with renowned news websites such as News 9 and The Financial Express to name a few. When not writing, she can be found bringing life to the canvasses by painting on them.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *

Connect With Us

25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today.

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
January 2024
September 2024
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
Have something on your mind?

Make your study abroad dream a reality in January 2022 with
India's Biggest Virtual University Fair

Essex Direct Admission Day
Why attend .

Don't Miss Out
Home — Essay Samples — Education — Online Vs. Traditional Classes — Online Learning vs Face-to-Face
Online Learning Vs Face-to-face
- Categories: Online Vs. Traditional Classes Technology in Education
About this sample

Words: 768 |
Published: Aug 24, 2023
Words: 768 | Pages: 2 | 4 min read
Table of contents
Advantages of online learning, disadvantages of online learning, advantages of face-to-face education, disadvantages of face-to-face education.

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Verified writer
- Expert in: Education Information Science and Technology

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
2 pages / 761 words
1 pages / 628 words
1 pages / 593 words
3 pages / 1347 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Online Vs. Traditional Classes
There is no doubt that education is the only tool to become successful. It gives us the opportunity to become a full-fledged member of a society we belong, by gaining all the necessary abilities. Nowadays there are several [...]
Online education has become an increasingly popular option for students seeking to further their education and obtain a degree. With the advancement of technology, the accessibility and convenience of online education have made [...]
The debate between online education and in-class education has been ongoing for several years, with proponents and detractors arguing the benefits and drawbacks of each mode of learning. The rise of online education has brought [...]
The Society of Jesus, also known as the Jesuits, has played a significant role in the history of education and has had a profound impact on various fields of study. Founded by Saint Ignatius of Loyola in the 16th century, the [...]
10 Minute School is the largest online educational platform of Bangladesh. It was introduced or created by Ayman Sadiq with his goal to destroy all kinds of barriers of ensuring quality education to all across Bangladesh. It can [...]
Online learning has become important of a typical post-secondary or university experience; in fact, about 29 per cent of all Canadian post-secondary students registered for courses online. Its prevalence in institutions of [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
- Open supplemental data
- Reference Manager
- Simple TEXT file
People also looked at
Original research article, insights into students’ experiences and perceptions of remote learning methods: from the covid-19 pandemic to best practice for the future.

- 1 Minerva Schools at Keck Graduate Institute, San Francisco, CA, United States
- 2 Ronin Institute for Independent Scholarship, Montclair, NJ, United States
- 3 Department of Physics, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada
This spring, students across the globe transitioned from in-person classes to remote learning as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic. This unprecedented change to undergraduate education saw institutions adopting multiple online teaching modalities and instructional platforms. We sought to understand students’ experiences with and perspectives on those methods of remote instruction in order to inform pedagogical decisions during the current pandemic and in future development of online courses and virtual learning experiences. Our survey gathered quantitative and qualitative data regarding students’ experiences with synchronous and asynchronous methods of remote learning and specific pedagogical techniques associated with each. A total of 4,789 undergraduate participants representing institutions across 95 countries were recruited via Instagram. We find that most students prefer synchronous online classes, and students whose primary mode of remote instruction has been synchronous report being more engaged and motivated. Our qualitative data show that students miss the social aspects of learning on campus, and it is possible that synchronous learning helps to mitigate some feelings of isolation. Students whose synchronous classes include active-learning techniques (which are inherently more social) report significantly higher levels of engagement, motivation, enjoyment, and satisfaction with instruction. Respondents’ recommendations for changes emphasize increased engagement, interaction, and student participation. We conclude that active-learning methods, which are known to increase motivation, engagement, and learning in traditional classrooms, also have a positive impact in the remote-learning environment. Integrating these elements into online courses will improve the student experience.
Introduction
The COVID-19 pandemic has dramatically changed the demographics of online students. Previously, almost all students engaged in online learning elected the online format, starting with individual online courses in the mid-1990s through today’s robust online degree and certificate programs. These students prioritize convenience, flexibility and ability to work while studying and are older than traditional college age students ( Harris and Martin, 2012 ; Levitz, 2016 ). These students also find asynchronous elements of a course are more useful than synchronous elements ( Gillingham and Molinari, 2012 ). In contrast, students who chose to take courses in-person prioritize face-to-face instruction and connection with others and skew considerably younger ( Harris and Martin, 2012 ). This leaves open the question of whether students who prefer to learn in-person but are forced to learn remotely will prefer synchronous or asynchronous methods. One study of student preferences following a switch to remote learning during the COVID-19 pandemic indicates that students enjoy synchronous over asynchronous course elements and find them more effective ( Gillis and Krull, 2020 ). Now that millions of traditional in-person courses have transitioned online, our survey expands the data on student preferences and explores if those preferences align with pedagogical best practices.
An extensive body of research has explored what instructional methods improve student learning outcomes (Fink. 2013). Considerable evidence indicates that active-learning or student-centered approaches result in better learning outcomes than passive-learning or instructor-centered approaches, both in-person and online ( Freeman et al., 2014 ; Chen et al., 2018 ; Davis et al., 2018 ). Active-learning approaches include student activities or discussion in class, whereas passive-learning approaches emphasize extensive exposition by the instructor ( Freeman et al., 2014 ). Constructivist learning theories argue that students must be active participants in creating their own learning, and that listening to expert explanations is seldom sufficient to trigger the neurological changes necessary for learning ( Bostock, 1998 ; Zull, 2002 ). Some studies conclude that, while students learn more via active learning, they may report greater perceptions of their learning and greater enjoyment when passive approaches are used ( Deslauriers et al., 2019 ). We examine student perceptions of remote learning experiences in light of these previous findings.
In this study, we administered a survey focused on student perceptions of remote learning in late May 2020 through the social media account of @unjadedjade to a global population of English speaking undergraduate students representing institutions across 95 countries. We aim to explore how students were being taught, the relationship between pedagogical methods and student perceptions of their experience, and the reasons behind those perceptions. Here we present an initial analysis of the results and share our data set for further inquiry. We find that positive student perceptions correlate with synchronous courses that employ a variety of interactive pedagogical techniques, and that students overwhelmingly suggest behavioral and pedagogical changes that increase social engagement and interaction. We argue that these results support the importance of active learning in an online environment.
Materials and Methods
Participant pool.
Students were recruited through the Instagram account @unjadedjade. This social media platform, run by influencer Jade Bowler, focuses on education, effective study tips, ethical lifestyle, and promotes a positive mindset. For this reason, the audience is presumably academically inclined, and interested in self-improvement. The survey was posted to her account and received 10,563 responses within the first 36 h. Here we analyze the 4,789 of those responses that came from undergraduates. While we did not collect demographic or identifying information, we suspect that women are overrepresented in these data as followers of @unjadedjade are 80% women. A large minority of respondents were from the United Kingdom as Jade Bowler is a British influencer. Specifically, 43.3% of participants attend United Kingdom institutions, followed by 6.7% attending university in the Netherlands, 6.1% in Germany, 5.8% in the United States and 4.2% in Australia. Ninety additional countries are represented in these data (see Supplementary Figure 1 ).
Survey Design
The purpose of this survey is to learn about students’ instructional experiences following the transition to remote learning in the spring of 2020.
This survey was initially created for a student assignment for the undergraduate course Empirical Analysis at Minerva Schools at KGI. That version served as a robust pre-test and allowed for identification of the primary online platforms used, and the four primary modes of learning: synchronous (live) classes, recorded lectures and videos, uploaded or emailed materials, and chat-based communication. We did not adapt any open-ended questions based on the pre-test survey to avoid biasing the results and only corrected language in questions for clarity. We used these data along with an analysis of common practices in online learning to revise the survey. Our revised survey asked students to identify the synchronous and asynchronous pedagogical methods and platforms that they were using for remote learning. Pedagogical methods were drawn from literature assessing active and passive teaching strategies in North American institutions ( Fink, 2013 ; Chen et al., 2018 ; Davis et al., 2018 ). Open-ended questions asked students to describe why they preferred certain modes of learning and how they could improve their learning experience. Students also reported on their affective response to learning and participation using a Likert scale.
The revised survey also asked whether students had responded to the earlier survey. No significant differences were found between responses of those answering for the first and second times (data not shown). See Supplementary Appendix 1 for survey questions. Survey data was collected from 5/21/20 to 5/23/20.
Qualitative Coding
We applied a qualitative coding framework adapted from Gale et al. (2013) to analyze student responses to open-ended questions. Four researchers read several hundred responses and noted themes that surfaced. We then developed a list of themes inductively from the survey data and deductively from the literature on pedagogical practice ( Garrison et al., 1999 ; Zull, 2002 ; Fink, 2013 ; Freeman et al., 2014 ). The initial codebook was revised collaboratively based on feedback from researchers after coding 20–80 qualitative comments each. Before coding their assigned questions, alignment was examined through coding of 20 additional responses. Researchers aligned in identifying the same major themes. Discrepancies in terms identified were resolved through discussion. Researchers continued to meet weekly to discuss progress and alignment. The majority of responses were coded by a single researcher using the final codebook ( Supplementary Table 1 ). All responses to questions 3 (4,318 responses) and 8 (4,704 responses), and 2,512 of 4,776 responses to question 12 were analyzed. Valence was also indicated where necessary (i.e., positive or negative discussion of terms). This paper focuses on the most prevalent themes from our initial analysis of the qualitative responses. The corresponding author reviewed codes to ensure consistency and accuracy of reported data.
Statistical Analysis
The survey included two sets of Likert-scale questions, one consisting of a set of six statements about students’ perceptions of their experiences following the transition to remote learning ( Table 1 ). For each statement, students indicated their level of agreement with the statement on a five-point scale ranging from 1 (“Strongly Disagree”) to 5 (“Strongly Agree”). The second set asked the students to respond to the same set of statements, but about their retroactive perceptions of their experiences with in-person instruction before the transition to remote learning. This set was not the subject of our analysis but is present in the published survey results. To explore correlations among student responses, we used CrossCat analysis to calculate the probability of dependence between Likert-scale responses ( Mansinghka et al., 2016 ).
Table 1. Likert-scale questions.
Mean values are calculated based on the numerical scores associated with each response. Measures of statistical significance for comparisons between different subgroups of respondents were calculated using a two-sided Mann-Whitney U -test, and p -values reported here are based on this test statistic. We report effect sizes in pairwise comparisons using the common-language effect size, f , which is the probability that the response from a random sample from subgroup 1 is greater than the response from a random sample from subgroup 2. We also examined the effects of different modes of remote learning and technological platforms using ordinal logistic regression. With the exception of the mean values, all of these analyses treat Likert-scale responses as ordinal-scale, rather than interval-scale data.
Students Prefer Synchronous Class Sessions
Students were asked to identify their primary mode of learning given four categories of remote course design that emerged from the pilot survey and across literature on online teaching: live (synchronous) classes, recorded lectures and videos, emailed or uploaded materials, and chats and discussion forums. While 42.7% ( n = 2,045) students identified live classes as their primary mode of learning, 54.6% ( n = 2613) students preferred this mode ( Figure 1 ). Both recorded lectures and live classes were preferred over uploaded materials (6.22%, n = 298) and chat (3.36%, n = 161).
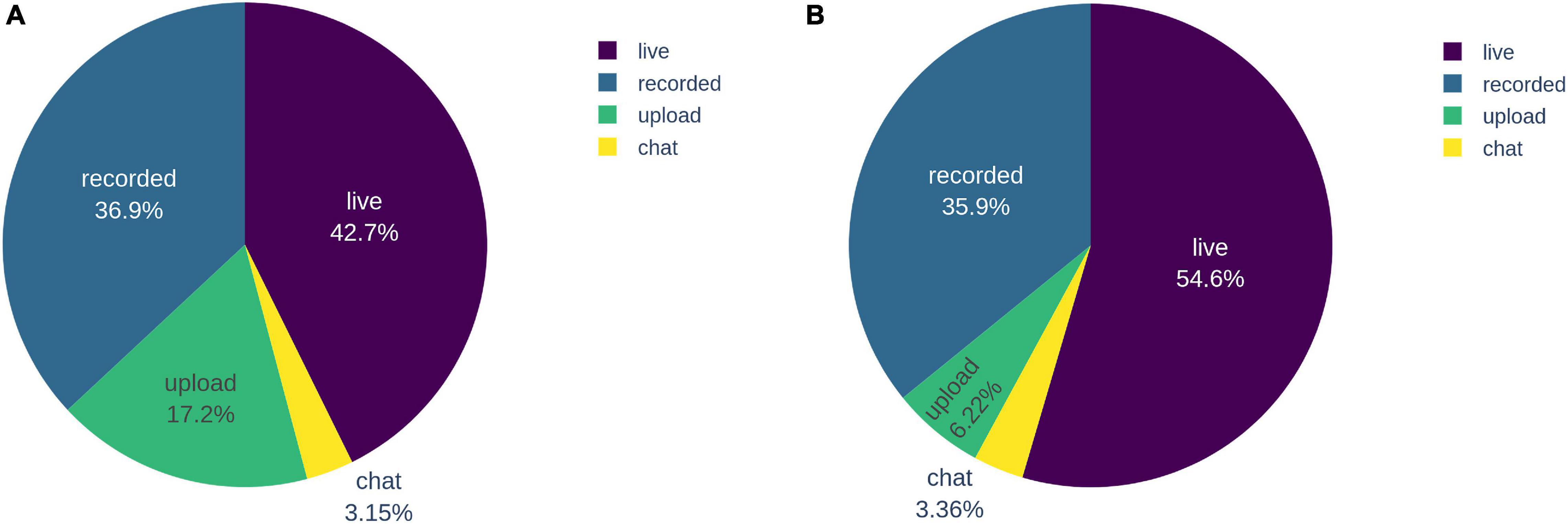
Figure 1. Actual (A) and preferred (B) primary modes of learning.
In addition to a preference for live classes, students whose primary mode was synchronous were more likely to enjoy the class, feel motivated and engaged, be satisfied with instruction and report higher levels of participation ( Table 2 and Supplementary Figure 2 ). Regardless of primary mode, over two-thirds of students reported they are often distracted during remote courses.
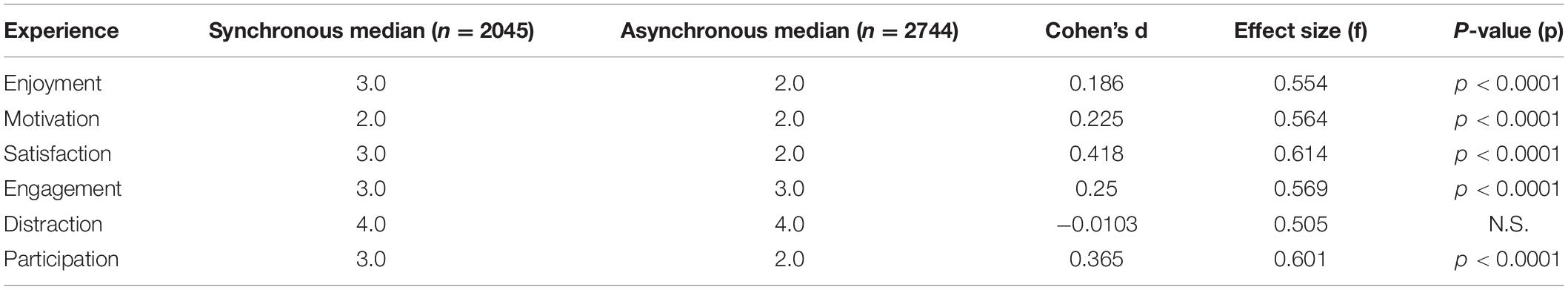
Table 2. The effect of synchronous vs. asynchronous primary modes of learning on student perceptions.
Variation in Pedagogical Techniques for Synchronous Classes Results in More Positive Perceptions of the Student Learning Experience
To survey the use of passive vs. active instructional methods, students reported the pedagogical techniques used in their live classes. Among the synchronous methods, we identify three different categories ( National Research Council, 2000 ; Freeman et al., 2014 ). Passive methods (P) include lectures, presentations, and explanation using diagrams, white boards and/or other media. These methods all rely on instructor delivery rather than student participation. Our next category represents active learning through primarily one-on-one interactions (A). The methods in this group are in-class assessment, question-and-answer (Q&A), and classroom chat. Group interactions (F) included classroom discussions and small-group activities. Given these categories, Mann-Whitney U pairwise comparisons between the 7 possible combinations and Likert scale responses about student experience showed that the use of a variety of methods resulted in higher ratings of experience vs. the use of a single method whether or not that single method was active or passive ( Table 3 ). Indeed, students whose classes used methods from each category (PAF) had higher ratings of enjoyment, motivation, and satisfaction with instruction than those who only chose any single method ( p < 0.0001) and also rated higher rates of participation and engagement compared to students whose only method was passive (P) or active through one-on-one interactions (A) ( p < 0.00001). Student ratings of distraction were not significantly different for any comparison. Given that sets of Likert responses often appeared significant together in these comparisons, we ran a CrossCat analysis to look at the probability of dependence across Likert responses. Responses have a high probability of dependence on each other, limiting what we can claim about any discrete response ( Supplementary Figure 3 ).
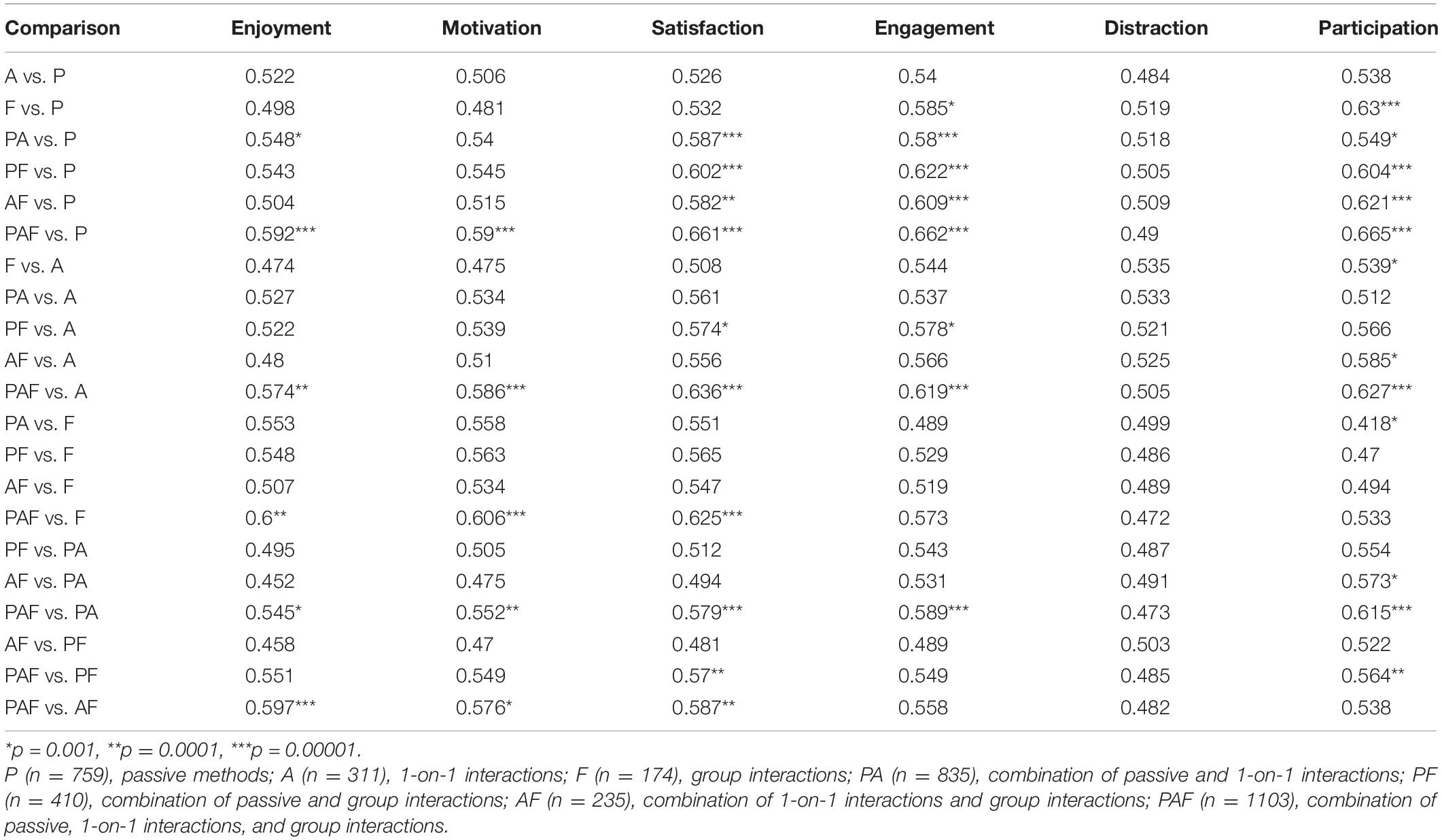
Table 3. Comparison of combinations of synchronous methods on student perceptions. Effect size (f).
Mann-Whitney U pairwise comparisons were also used to check if improvement in student experience was associated with the number of methods used vs. the variety of types of methods. For every comparison, we found that more methods resulted in higher scores on all Likert measures except distraction ( Table 4 ). Even comparison between four or fewer methods and greater than four methods resulted in a 59% chance that the latter enjoyed the courses more ( p < 0.00001) and 60% chance that they felt more motivated to learn ( p < 0.00001). Students who selected more than four methods ( n = 417) were also 65.1% ( p < 0.00001), 62.9% ( p < 0.00001) and 64.3% ( p < 0.00001) more satisfied with instruction, engaged, and actively participating, respectfully. Therefore, there was an overlap between how the number and variety of methods influenced students’ experiences. Since the number of techniques per category is 2–3, we cannot fully disentangle the effect of number vs. variety. Pairwise comparisons to look at subsets of data with 2–3 methods from a single group vs. 2–3 methods across groups controlled for this but had low sample numbers in most groups and resulted in no significant findings (data not shown). Therefore, from the data we have in our survey, there seems to be an interdependence between number and variety of methods on students’ learning experiences.
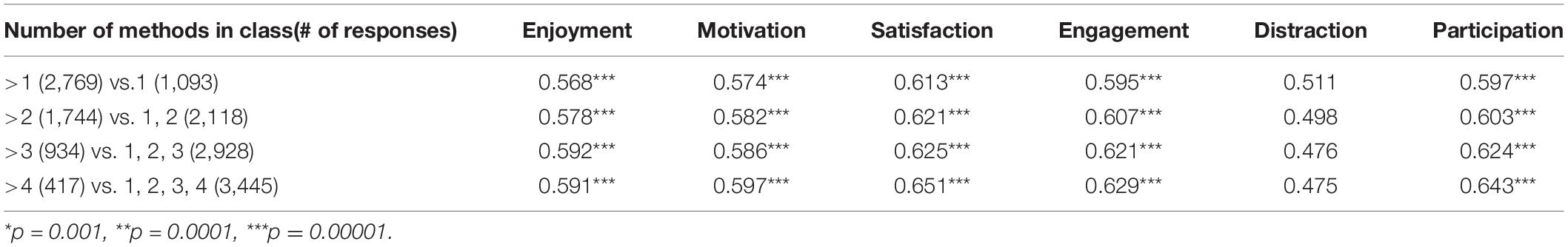
Table 4. Comparison of the number of synchronous methods on student perceptions. Effect size (f).
Variation in Asynchronous Pedagogical Techniques Results in More Positive Perceptions of the Student Learning Experience
Along with synchronous pedagogical methods, students reported the asynchronous methods that were used for their classes. We divided these methods into three main categories and conducted pairwise comparisons. Learning methods include video lectures, video content, and posted study materials. Interacting methods include discussion/chat forums, live office hours, and email Q&A with professors. Testing methods include assignments and exams. Our results again show the importance of variety in students’ perceptions ( Table 5 ). For example, compared to providing learning materials only, providing learning materials, interaction, and testing improved enjoyment ( f = 0.546, p < 0.001), motivation ( f = 0.553, p < 0.0001), satisfaction with instruction ( f = 0.596, p < 0.00001), engagement ( f = 0.572, p < 0.00001) and active participation ( f = 0.563, p < 0.00001) (row 6). Similarly, compared to just being interactive with conversations, the combination of all three methods improved five out of six indicators, except for distraction in class (row 11).
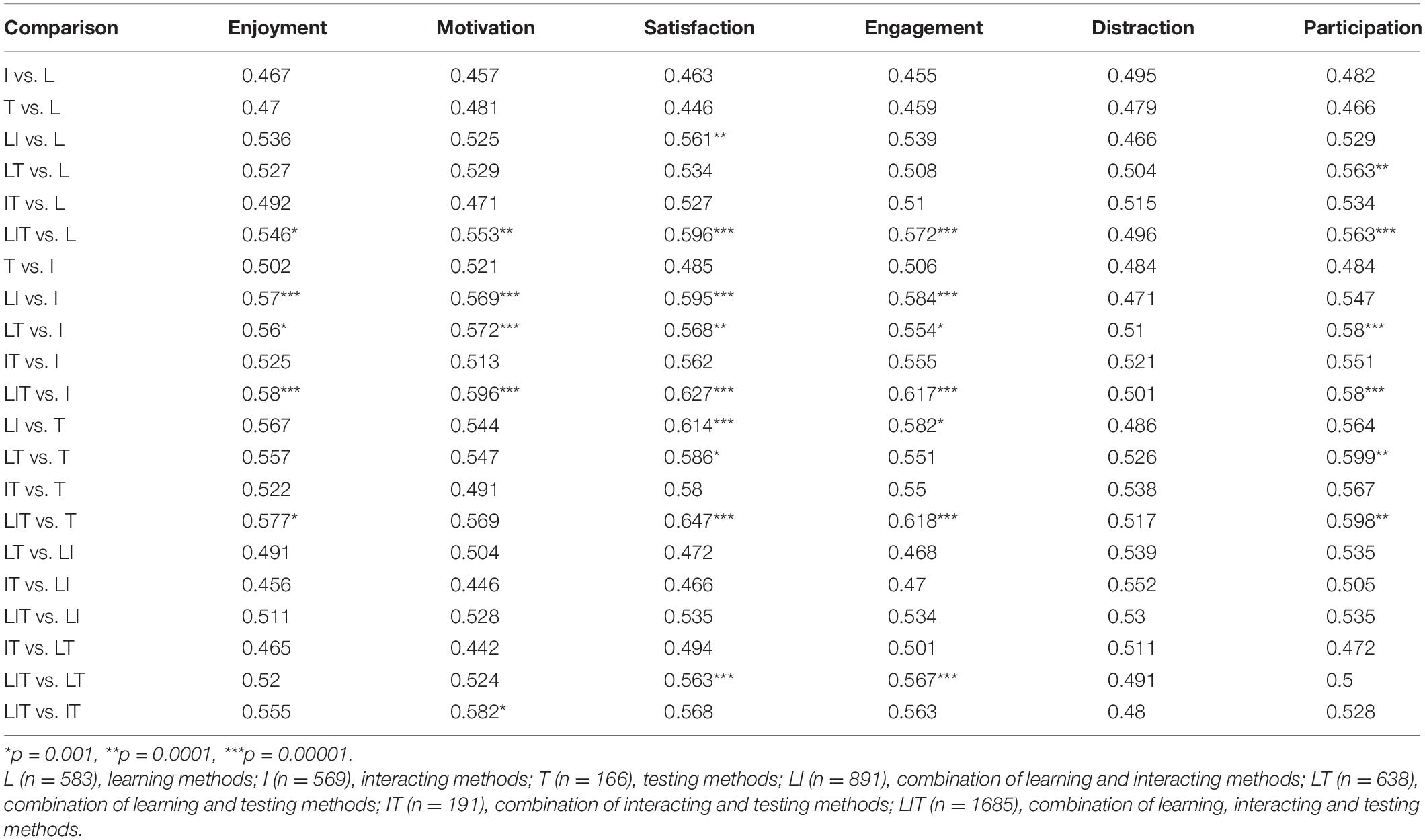
Table 5. Comparison of combinations of asynchronous methods on student perceptions. Effect size (f).
Ordinal logistic regression was used to assess the likelihood that the platforms students used predicted student perceptions ( Supplementary Table 2 ). Platform choices were based on the answers to open-ended questions in the pre-test survey. The synchronous and asynchronous methods used were consistently more predictive of Likert responses than the specific platforms. Likewise, distraction continued to be our outlier with no differences across methods or platforms.
Students Prefer In-Person and Synchronous Online Learning Largely Due to Social-Emotional Reasoning
As expected, 86.1% (4,123) of survey participants report a preference for in-person courses, while 13.9% (666) prefer online courses. When asked to explain the reasons for their preference, students who prefer in-person courses most often mention the importance of social interaction (693 mentions), engagement (639 mentions), and motivation (440 mentions). These students are also more likely to mention a preference for a fixed schedule (185 mentions) vs. a flexible schedule (2 mentions).
In addition to identifying social reasons for their preference for in-person learning, students’ suggestions for improvements in online learning focus primarily on increasing interaction and engagement, with 845 mentions of live classes, 685 mentions of interaction, 126 calls for increased participation and calls for changes related to these topics such as, “Smaller teaching groups for live sessions so that everyone is encouraged to talk as some people don’t say anything and don’t participate in group work,” and “Make it less of the professor reading the pdf that was given to us and more interaction.”
Students who prefer online learning primarily identify independence and flexibility (214 mentions) and reasons related to anxiety and discomfort in in-person settings (41 mentions). Anxiety was only mentioned 12 times in the much larger group that prefers in-person learning.
The preference for synchronous vs. asynchronous modes of learning follows similar trends ( Table 6 ). Students who prefer live classes mention engagement and interaction most often while those who prefer recorded lectures mention flexibility.
Table 6. Most prevalent themes for students based on their preferred mode of remote learning.

Student Perceptions Align With Research on Active Learning
The first, and most robust, conclusion is that incorporation of active-learning methods correlates with more positive student perceptions of affect and engagement. We can see this clearly in the substantial differences on a number of measures, where students whose classes used only passive-learning techniques reported lower levels of engagement, satisfaction, participation, and motivation when compared with students whose classes incorporated at least some active-learning elements. This result is consistent with prior research on the value of active learning ( Freeman et al., 2014 ).
Though research shows that student learning improves in active learning classes, on campus, student perceptions of their learning, enjoyment, and satisfaction with instruction are often lower in active-learning courses ( Deslauriers et al., 2019 ). Our finding that students rate enjoyment and satisfaction with instruction higher for active learning online suggests that the preference for passive lectures on campus relies on elements outside of the lecture itself. That might include the lecture hall environment, the social physical presence of peers, or normalization of passive lectures as the expected mode for on-campus classes. This implies that there may be more buy-in for active learning online vs. in-person.
A second result from our survey is that student perceptions of affect and engagement are associated with students experiencing a greater diversity of learning modalities. We see this in two different results. First, in addition to the fact that classes that include active learning outperform classes that rely solely on passive methods, we find that on all measures besides distraction, the highest student ratings are associated with a combination of active and passive methods. Second, we find that these higher scores are associated with classes that make use of a larger number of different methods.
This second result suggests that students benefit from classes that make use of multiple different techniques, possibly invoking a combination of passive and active methods. However, it is unclear from our data whether this effect is associated specifically with combining active and passive methods, or if it is associated simply with the use of multiple different methods, irrespective of whether those methods are active, passive, or some combination. The problem is that the number of methods used is confounded with the diversity of methods (e.g., it is impossible for a classroom using only one method to use both active and passive methods). In an attempt to address this question, we looked separately at the effect of number and diversity of methods while holding the other constant. Across a large number of such comparisons, we found few statistically significant differences, which may be a consequence of the fact that each comparison focused on a small subset of the data.
Thus, our data suggests that using a greater diversity of learning methods in the classroom may lead to better student outcomes. This is supported by research on student attention span which suggests varying delivery after 10–15 min to retain student’s attention ( Bradbury, 2016 ). It is likely that this is more relevant for online learning where students report high levels of distraction across methods, modalities, and platforms. Given that number and variety are key, and there are few passive learning methods, we can assume that some combination of methods that includes active learning improves student experience. However, it is not clear whether we should predict that this benefit would come simply from increasing the number of different methods used, or if there are benefits specific to combining particular methods. Disentangling these effects would be an interesting avenue for future research.
Students Value Social Presence in Remote Learning
Student responses across our open-ended survey questions show a striking difference in reasons for their preferences compared with traditional online learners who prefer flexibility ( Harris and Martin, 2012 ; Levitz, 2016 ). Students reasons for preferring in-person classes and synchronous remote classes emphasize the desire for social interaction and echo the research on the importance of social presence for learning in online courses.
Short et al. (1976) outlined Social Presence Theory in depicting students’ perceptions of each other as real in different means of telecommunications. These ideas translate directly to questions surrounding online education and pedagogy in regards to educational design in networked learning where connection across learners and instructors improves learning outcomes especially with “Human-Human interaction” ( Goodyear, 2002 , 2005 ; Tu, 2002 ). These ideas play heavily into asynchronous vs. synchronous learning, where Tu reports students having positive responses to both synchronous “real-time discussion in pleasantness, responsiveness and comfort with familiar topics” and real-time discussions edging out asynchronous computer-mediated communications in immediate replies and responsiveness. Tu’s research indicates that students perceive more interaction with synchronous mediums such as discussions because of immediacy which enhances social presence and support the use of active learning techniques ( Gunawardena, 1995 ; Tu, 2002 ). Thus, verbal immediacy and communities with face-to-face interactions, such as those in synchronous learning classrooms, lessen the psychological distance of communicators online and can simultaneously improve instructional satisfaction and reported learning ( Gunawardena and Zittle, 1997 ; Richardson and Swan, 2019 ; Shea et al., 2019 ). While synchronous learning may not be ideal for traditional online students and a subset of our participants, this research suggests that non-traditional online learners are more likely to appreciate the value of social presence.
Social presence also connects to the importance of social connections in learning. Too often, current systems of education emphasize course content in narrow ways that fail to embrace the full humanity of students and instructors ( Gay, 2000 ). With the COVID-19 pandemic leading to further social isolation for many students, the importance of social presence in courses, including live interactions that build social connections with classmates and with instructors, may be increased.
Limitations of These Data
Our undergraduate data consisted of 4,789 responses from 95 different countries, an unprecedented global scale for research on online learning. However, since respondents were followers of @unjadedjade who focuses on learning and wellness, these respondents may not represent the average student. Biases in survey responses are often limited by their recruitment techniques and our bias likely resulted in more robust and thoughtful responses to free-response questions and may have influenced the preference for synchronous classes. It is unlikely that it changed students reporting on remote learning pedagogical methods since those are out of student control.
Though we surveyed a global population, our design was rooted in literature assessing pedagogy in North American institutions. Therefore, our survey may not represent a global array of teaching practices.
This survey was sent out during the initial phase of emergency remote learning for most countries. This has two important implications. First, perceptions of remote learning may be clouded by complications of the pandemic which has increased social, mental, and financial stresses globally. Future research could disaggregate the impact of the pandemic from students’ learning experiences with a more detailed and holistic analysis of the impact of the pandemic on students.
Second, instructors, students and institutions were not able to fully prepare for effective remote education in terms of infrastructure, mentality, curriculum building, and pedagogy. Therefore, student experiences reflect this emergency transition. Single-modality courses may correlate with instructors who lacked the resources or time to learn or integrate more than one modality. Regardless, the main insights of this research align well with the science of teaching and learning and can be used to inform both education during future emergencies and course development for online programs that wish to attract traditional college students.
Global Student Voices Improve Our Understanding of the Experience of Emergency Remote Learning
Our survey shows that global student perspectives on remote learning agree with pedagogical best practices, breaking with the often-found negative reactions of students to these practices in traditional classrooms ( Shekhar et al., 2020 ). Our analysis of open-ended questions and preferences show that a majority of students prefer pedagogical approaches that promote both active learning and social interaction. These results can serve as a guide to instructors as they design online classes, especially for students whose first choice may be in-person learning. Indeed, with the near ubiquitous adoption of remote learning during the COVID-19 pandemic, remote learning may be the default for colleges during temporary emergencies. This has already been used at the K-12 level as snow days become virtual learning days ( Aspergren, 2020 ).
In addition to informing pedagogical decisions, the results of this survey can be used to inform future research. Although we survey a global population, our recruitment method selected for students who are English speakers, likely majority female, and have an interest in self-improvement. Repeating this study with a more diverse and representative sample of university students could improve the generalizability of our findings. While the use of a variety of pedagogical methods is better than a single method, more research is needed to determine what the optimal combinations and implementations are for courses in different disciplines. Though we identified social presence as the major trend in student responses, the over 12,000 open-ended responses from students could be analyzed in greater detail to gain a more nuanced understanding of student preferences and suggestions for improvement. Likewise, outliers could shed light on the diversity of student perspectives that we may encounter in our own classrooms. Beyond this, our findings can inform research that collects demographic data and/or measures learning outcomes to understand the impact of remote learning on different populations.
Importantly, this paper focuses on a subset of responses from the full data set which includes 10,563 students from secondary school, undergraduate, graduate, or professional school and additional questions about in-person learning. Our full data set is available here for anyone to download for continued exploration: https://dataverse.harvard.edu/dataset.xhtml?persistentId= doi: 10.7910/DVN/2TGOPH .
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics Statement
Ethical review and approval was not required for the study on human participants in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The patients/participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author Contributions
GS: project lead, survey design, qualitative coding, writing, review, and editing. TN: data analysis, writing, review, and editing. CN and PB: qualitative coding. JW: data analysis, writing, and editing. CS: writing, review, and editing. EV and KL: original survey design and qualitative coding. PP: data analysis. JB: original survey design and survey distribution. HH: data analysis. MP: writing. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
We want to thank Minerva Schools at KGI for providing funding for summer undergraduate research internships. We also want to thank Josh Fost and Christopher V. H.-H. Chen for discussion that helped shape this project.
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/feduc.2021.647986/full#supplementary-material
Aspergren, E. (2020). Snow Days Canceled Because of COVID-19 Online School? Not in These School Districts.sec. Education. USA Today. Available online at: https://www.usatoday.com/story/news/education/2020/12/15/covid-school-canceled-snow-day-online-learning/3905780001/ (accessed December 15, 2020).
Google Scholar
Bostock, S. J. (1998). Constructivism in mass higher education: a case study. Br. J. Educ. Technol. 29, 225–240. doi: 10.1111/1467-8535.00066
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Bradbury, N. A. (2016). Attention span during lectures: 8 seconds, 10 minutes, or more? Adv. Physiol. Educ. 40, 509–513. doi: 10.1152/advan.00109.2016
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Chen, B., Bastedo, K., and Howard, W. (2018). Exploring best practices for online STEM courses: active learning, interaction & assessment design. Online Learn. 22, 59–75. doi: 10.24059/olj.v22i2.1369
Davis, D., Chen, G., Hauff, C., and Houben, G.-J. (2018). Activating learning at scale: a review of innovations in online learning strategies. Comput. Educ. 125, 327–344. doi: 10.1016/j.compedu.2018.05.019
Deslauriers, L., McCarty, L. S., Miller, K., Callaghan, K., and Kestin, G. (2019). Measuring actual learning versus feeling of learning in response to being actively engaged in the classroom. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 116, 19251–19257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1821936116
Fink, L. D. (2013). Creating Significant Learning Experiences: An Integrated Approach to Designing College Courses. Somerset, NJ: John Wiley & Sons, Incorporated.
Freeman, S., Eddy, S. L., McDonough, M., Smith, M. K., Okoroafor, N., Jordt, H., et al. (2014). Active learning increases student performance in science, engineering, and mathematics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 111, 8410–8415. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1319030111
Gale, N. K., Heath, G., Cameron, E., Rashid, S., and Redwood, S. (2013). Using the framework method for the analysis of qualitative data in multi-disciplinary health research. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 13:117. doi: 10.1186/1471-2288-13-117
Garrison, D. R., Anderson, T., and Archer, W. (1999). Critical inquiry in a text-based environment: computer conferencing in higher education. Internet High. Educ. 2, 87–105. doi: 10.1016/S1096-7516(00)00016-6
Gay, G. (2000). Culturally Responsive Teaching: Theory, Research, and Practice. Multicultural Education Series. New York, NY: Teachers College Press.
Gillingham, and Molinari, C. (2012). Online courses: student preferences survey. Internet Learn. 1, 36–45. doi: 10.18278/il.1.1.4
Gillis, A., and Krull, L. M. (2020). COVID-19 remote learning transition in spring 2020: class structures, student perceptions, and inequality in college courses. Teach. Sociol. 48, 283–299. doi: 10.1177/0092055X20954263
Goodyear, P. (2002). “Psychological foundations for networked learning,” in Networked Learning: Perspectives and Issues. Computer Supported Cooperative Work , eds C. Steeples and C. Jones (London: Springer), 49–75. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4471-0181-9_4
Goodyear, P. (2005). Educational design and networked learning: patterns, pattern languages and design practice. Australas. J. Educ. Technol. 21, 82–101. doi: 10.14742/ajet.1344
Gunawardena, C. N. (1995). Social presence theory and implications for interaction and collaborative learning in computer conferences. Int. J. Educ. Telecommun. 1, 147–166.
Gunawardena, C. N., and Zittle, F. J. (1997). Social presence as a predictor of satisfaction within a computer mediated conferencing environment. Am. J. Distance Educ. 11, 8–26. doi: 10.1080/08923649709526970
Harris, H. S., and Martin, E. (2012). Student motivations for choosing online classes. Int. J. Scholarsh. Teach. Learn. 6, 1–8. doi: 10.20429/ijsotl.2012.060211
Levitz, R. N. (2016). 2015-16 National Online Learners Satisfaction and Priorities Report. Cedar Rapids: Ruffalo Noel Levitz, 12.
Mansinghka, V., Shafto, P., Jonas, E., Petschulat, C., Gasner, M., and Tenenbaum, J. B. (2016). CrossCat: a fully Bayesian nonparametric method for analyzing heterogeneous, high dimensional data. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 17, 1–49. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-69765-9_7
National Research Council (2000). How People Learn: Brain, Mind, Experience, and School: Expanded Edition. Washington, DC: National Academies Press, doi: 10.17226/9853
Richardson, J. C., and Swan, K. (2019). Examining social presence in online courses in relation to students’ perceived learning and satisfaction. Online Learn. 7, 68–88. doi: 10.24059/olj.v7i1.1864
Shea, P., Pickett, A. M., and Pelz, W. E. (2019). A Follow-up investigation of ‘teaching presence’ in the suny learning network. Online Learn. 7, 73–75. doi: 10.24059/olj.v7i2.1856
Shekhar, P., Borrego, M., DeMonbrun, M., Finelli, C., Crockett, C., and Nguyen, K. (2020). Negative student response to active learning in STEM classrooms: a systematic review of underlying reasons. J. Coll. Sci. Teach. 49, 45–54.
Short, J., Williams, E., and Christie, B. (1976). The Social Psychology of Telecommunications. London: John Wiley & Sons.
Tu, C.-H. (2002). The measurement of social presence in an online learning environment. Int. J. E Learn. 1, 34–45. doi: 10.17471/2499-4324/421
Zull, J. E. (2002). The Art of Changing the Brain: Enriching Teaching by Exploring the Biology of Learning , 1st Edn. Sterling, VA: Stylus Publishing.
Keywords : online learning, COVID-19, active learning, higher education, pedagogy, survey, international
Citation: Nguyen T, Netto CLM, Wilkins JF, Bröker P, Vargas EE, Sealfon CD, Puthipiroj P, Li KS, Bowler JE, Hinson HR, Pujar M and Stein GM (2021) Insights Into Students’ Experiences and Perceptions of Remote Learning Methods: From the COVID-19 Pandemic to Best Practice for the Future. Front. Educ. 6:647986. doi: 10.3389/feduc.2021.647986
Received: 30 December 2020; Accepted: 09 March 2021; Published: 09 April 2021.
Reviewed by:
Copyright © 2021 Nguyen, Netto, Wilkins, Bröker, Vargas, Sealfon, Puthipiroj, Li, Bowler, Hinson, Pujar and Stein. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) . The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Geneva M. Stein, [email protected]
This article is part of the Research Topic
Covid-19 and Beyond: From (Forced) Remote Teaching and Learning to ‘The New Normal’ in Higher Education
Home / Essay Samples / Education / Online Courses / The Advantages of Online Learning: Comprehensive Review
The Advantages of Online Learning: Comprehensive Review
- Category: Education
- Topic: E-Learning , Online Courses , Online Vs. Traditional Classes
Pages: 2 (748 words)
- Downloads: -->
--> ⚠️ Remember: This essay was written and uploaded by an--> click here.
Found a great essay sample but want a unique one?
are ready to help you with your essay
You won’t be charged yet!
Indian Education Essays
Academic Interests Essays
Graduation Essays
College Education Essays
Brittany Stinson Essays
Related Essays
We are glad that you like it, but you cannot copy from our website. Just insert your email and this sample will be sent to you.
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Your essay sample has been sent.
In fact, there is a way to get an original essay! Turn to our writers and order a plagiarism-free paper.
samplius.com uses cookies to offer you the best service possible.By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .--> -->