- You are here:
- American Chemical Society
- Discover Chemistry

Recent advancements in water treatment
For immediate release, acs news service weekly presspac: january 19, 2022.
Generating clean, safe water is becoming increasingly difficult. Water sources themselves can be contaminated, but in addition, some purification methods can cause unintended harmful byproducts to form. And not all treatment processes are created equal with regard to their ability to remove impurities or pollutants. Below are some recent papers published in ACS journals that report insights into how well water treatment methods work and the quality of the resulting water. Reporters can request free access to these papers by emailing newsroom@acs.org .
“Drivers of Disinfection Byproduct Cytotoxicity in U.S. Drinking Water: Should Other DBPs Be Considered for Regulation?” Environmental Science & Technology Dec.15, 2021
In this paper, researchers surveyed both conventional and advanced disinfection processes in the U.S., testing the quality of their drinking waters. Treatment plants with advanced removal technologies, such as activated carbon, formed fewer types and lower levels of harmful disinfection byproducts (known as DBPs) in their water. Based on the prevalence and cytotoxicity of haloacetonitriles and iodoacetic acids within some of the treated waters, the researchers recommend that these two groups be considered when forming future water quality regulations.
“Complete System to Generate Clean Water from a Contaminated Water Body by a Handmade Flower-like Light Absorber” ACS Omega Dec. 9, 2021 As a step toward a low-cost water purification technology, researchers crocheted a coated black yarn into a flower-like pattern. When the flower was placed in dirty or salty water, the water wicked up the yarn. Sunlight caused the water to evaporate, leaving the contaminants in the yarn, and a clean vapor condensed and was collected. People in rural locations could easily make this material for desalination or cleaning polluted water, the researchers say.
“Data Analytics Determines Co-occurrence of Odorants in Raw Water and Evaluates Drinking Water Treatment Removal Strategies” Environmental Science & Technology Dec. 2, 2021
Sometimes drinking water smells foul or “off,” even after treatment. In this first-of-its-kind study, researchers identified the major odorants in raw water. They also report that treatment plants using a combination of ozonation and activated carbon remove more of the odor compounds responsible for the stink compared to a conventional process. However, both methods generated some odorants not originally present in the water.
“Self-Powered Water Flow-Triggered Piezocatalytic Generation of Reactive Oxygen Species for Water Purification in Simulated Water Drainage” ACS ES&T Engineering Nov. 23, 2021
Here, researchers harvested energy from the movement of water to break down chemical contaminants. As microscopic sheets of molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) swirled inside a spiral tube filled with dirty water, the MoS2 particles generated electric charges. The charges reacted with water and created reactive oxygen species, which decomposed pollutant compounds, including benzotriazole and antibiotics. The researchers say these self-powered catalysts are a “green” energy resource for water purification.
The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. ACS’ mission is to advance the broader chemistry enterprise and its practitioners for the benefit of Earth and all its people. The Society is a global leader in promoting excellence in science education and providing access to chemistry-related information and research through its multiple research solutions, peer-reviewed journals, scientific conferences, eBooks and weekly news periodical Chemical & Engineering News . ACS journals are among the most cited, most trusted and most read within the scientific literature; however, ACS itself does not conduct chemical research. As a leader in scientific information solutions, its CAS division partners with global innovators to accelerate breakthroughs by curating, connecting and analyzing the world’s scientific knowledge. ACS’ main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
To automatically receive press releases from the American Chemical Society, contact newsroom@acs.org .
Note: ACS does not conduct research, but publishes and publicizes peer-reviewed scientific studies.
Media Contact
ACS Newsroom newsroom@acs.org

Discover Chemistry —Menu
- News Releases
- ACS in the News
Accept & Close The ACS takes your privacy seriously as it relates to cookies. We use cookies to remember users, better understand ways to serve them, improve our value proposition, and optimize their experience. Learn more about managing your cookies at Cookies Policy .
1155 Sixteenth Street, NW, Washington, DC 20036, USA | service@acs.org | 1-800-333-9511 (US and Canada) | 614-447-3776 (outside North America)
- Terms of Use
- Accessibility
Copyright © 2024 American Chemical Society
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Published: 22 March 2021
Sustainable implementation of innovative technologies for water purification
- Bart Van der Bruggen ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-3921-7472 1 , 2
Nature Reviews Chemistry volume 5 , pages 217–218 ( 2021 ) Cite this article
10k Accesses
75 Citations
3 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Environmental sciences
- Scientific community
One of the sustainable development goals set by the United Nations General Assembly is to ensure the availability and sustainable management of water and sanitation for all. This requires investment in water purification technologies. World Water Day offers an opportunity to discuss whether such investment will help achieve this laudable goal.
Wastewater and seawater have long been considered as potential sources from which to produce freshwater. Several technologies have been developed over the past few decades aimed at their reuse and recycle, but unfortunately the treatment of both sources may have perfidious effects.
Of the approaches presently available, desalination seems to have the greatest potential, given that seawater is a nearly unlimited resource. However, desalination is an energy-intensive process. The state-of-the-art technology, seawater reverse osmosis (SWRO), has undergone huge improvements over the past five decades: the specific energy consumption of SWRO was reduced from 20 kWh m −3 in 1970 to only 2.5 kWh m −3 in 2010. It has been estimated that a further 0.69–0.79 kWh m −3 might be saved by a smart process integration with intrinsic heat recovery 1 , but desalination of typical seawater (with an average salt concentration of 35 g l −1 ) requires a minimum of 1.07 kWh m −3 , offering only a little room for improvement. This limit is the foundation of the water–energy nexus and prompts further research on renewable energy sources for desalination, which remain scarce. In a case study, Delgado-Torres and co-workers 2 used tidal and solar energy for desalination at a semi-arid location in Broome, Australia. Similar studies focus on desalination driven by wind energy, photovoltaics or solar thermal energy. Although such approaches to water desalination may be viable to supply clean water in small or spatially confined communities — as was demonstrated in the island of Aruba 3 — they offer very little for the water challenges of large cities such as Beijing, Cairo or Cape Town.

In a cost–benefit analysis, wastewater recycling is more favourable than seawater desalination, because the former does not require the expensive separation of salts from water. This may seem surprising given that reverse osmosis is the key technology in both cases. The difference is that wastewater recycling would operate at much lower pressure. Such recycling has been practised for more than half a century in Windhoek, Namibia, and is accepted practice in water-scarce places such as Singapore 4 . Southern California is presently implementing a large-scale scheme to use recycled water as a potable source 5 and other countries and locations will surely follow. This trend pushes researchers to develop fouling-resistant, high-flux membranes for reverse osmosis and related membrane processes such as nano- or ultrafiltration. However, new challenges also arise. The production of (polymer) membranes for purification typically requires the use of polar aprotic solvents such as N,N -dimethylformamide (DMF), N,N -dimethylacetamide (DMA), 1,4-dioxane and tetrahydrofuran (THF). These solvents have a considerable environmental impact and significant effort is invested in their replacement with ‘greener’ solvents such as organic carbonates 6 or dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) 7 . Another limitation for present membrane technologies lies in the availability, processing and scale-up of materials for their manufacture. For example, two 2006 reports describe how incorporating carbon nanotubes into membranes affords permeabilities one to two orders of magnitude larger than those of conventional membranes. However, scaling up the synthesis of such membranes was not expected to be easy 8 — and, indeed, it has, so far, not happened. Since these reports emerged, there have been numerous studies on mixed-matrix membranes combining other nanostructures with polymeric matrices but, thus far, none has yet been applied on a large scale. Typically, good results are obtained in the laboratory, but the cost of producing the required nanostructures or issues associated with toxicity or leaching of nanoparticles from membranes have proven prohibitive for industrial use. Researchers need to place greater focus on the development of realistic membranes rather than just better membranes.
Closing the water cycle by either desalination or wastewater purification promises to provide virtually unlimited volumes of freshwater: in principle, it would enable an increase in water consumption by a factor equal to the inverse of the recycled fraction. However, we must be cognizant of unintended consequences. Water availability is one of the limiting factors for population growth and greater availability would certainly stimulate population growth. History has shown that humankind naturally makes use of available resources, sometimes with dramatic consequences, as exemplified by the agricultural and industrial revolutions 9 . A historical, sociological and demographic analysis by Harari shows that if water recycling is practised on a large scale, water consumption per capita may remain the same but our population will grow by the inverse of the recycled fraction 9 . This would then automatically lead to new challenges. A disenchanting example is the present SARS-CoV-2 virus: the scale of the outbreak would have been much more contained in a modest, local society without overpopulation. Water technologies may catalyse global growth more than any other technology because water is one of very few commodities that humankind cannot do without. This is of course not the case for industrialized countries, where water is not a limiting factor, but in most parts of the world it is. Harari was criticized for being unfamiliar with technologies, and, while this may be a fair criticism, warnings from other disciplines should not be summarily dismissed by technology developers.
In conclusion, the scope of water technologies may need to be reconsidered. There is no need for a major technological breakthrough in water recycling or desalination. What is really needed is for present technologies to be available to children growing up without access to clean water sources, as stated in the United Nations sustainable development goals . This will require dedicated, embedded actions towards maintaining the demographic status quo while respecting the basic human rights of all. The goals then are a useful tool to monitor progress but must be considered in context because the indicators that are used can result in tunnel vision 10 . Furthermore, lifestyle choices in terms of water — reduce, reuse and recycle — need to be thoroughly considered and be more than just a hollow slogan.
Park, K., Kim, J. B., Yang, D. R. & Hong, S. K. Towards a low-energy seawater reverse osmosis desalination plant: a review and theoretical analysis for future directions. J. Membr. Sci. 595 , 117607 (2020).
Article CAS Google Scholar
Delgado-Torres, A. M., García-Rodríguez, L. & Jiménez del Moral, M. Preliminary assessment of innovative seawater reverse osmosis (SWRO) desalination powered by a hybrid solar photovoltaic (PV) - tidal range energy system. Desalination 477 , 114247 (2020).
Brendel, L. P. M., Shah, V. M., Groll, E. A. & Braun, J. E. A methodology for analyzing renewable energy opportunities for desalination and its application to Aruba. Desalination 493 , 114613 (2020).
Lafforgue, M. & Lenouvel, V. Closing the urban water loop: lessons from Singapore and Windhoek. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 1 , 622–631 (2015).
Article Google Scholar
Chalmers, R. B., Tremblay, M. & Soni, R. A new water source for Southern California: the regional recycled water program. J. AWWA 112 , 6–19 (2020).
Rasool, M. A., Pescarmona, P. P. & Vankelecom, I. F. J. Applicability of organic carbonates as green solvents for membrane preparation. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 7 , 13774–13785 (2019).
Evenepoel, N., Wen, S., Tsehaye, M. T. & Van der Bruggen, B. Potential of DMSO as greener solvent for PES ultra- and nanofiltration membrane preparation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 135 , 46494 (2018).
Sholl, D. S. & Johnson, J. K. Making high-flux membranes with carbon nanotubes. Science 312 , 1003–1004 (2006).
Harari, Y. N. Sapiens: A Brief History of Humankind (Harper Collins, 2015).
Weststrate, J., Dijkstra, G., Eshuis, J., Gianoli, A. & Rusca, M. The sustainable development goal on water and sanitation: learning from the millennium development goals. Soc. Indic. Res. 143 , 795–810 (2019).
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Chemical Engineering, KU Leuven, Leuven, Belgium
Bart Van der Bruggen
Faculty of Engineering and the Built Environment, Tshwane University of Technology, Pretoria, South Africa
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Bart Van der Bruggen .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The author declares no competing interests.
Additional information
Related links.
United Nations sustainable development goals: https://sdgs.un.org/goals
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Van der Bruggen, B. Sustainable implementation of innovative technologies for water purification. Nat Rev Chem 5 , 217–218 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41570-021-00264-7
Download citation
Published : 22 March 2021
Issue Date : April 2021
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s41570-021-00264-7
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
This article is cited by
Benefits and limitations of recycled water systems in the building sector: a review.
- Zhonghao Chen
- Pow-Seng Yap
Environmental Chemistry Letters (2024)
Nature-inspired wood-based solar evaporation system for efficient desalination and water purification
Journal of Materials Science (2023)
Superhydrophobicity-improved Ethanol-Water Separation
- Linfeng Chen
Chemical Research in Chinese Universities (2023)
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Wastewater Treatment and Reuse: a Review of its Applications and Health Implications
- Open access
- Published: 10 May 2021
- Volume 232 , article number 208 , ( 2021 )
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- Kavindra Kumar Kesari ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-3622-9555 1 na1 ,
- Ramendra Soni 2 na1 ,
- Qazi Mohammad Sajid Jamal 3 ,
- Pooja Tripathi 4 ,
- Jonathan A. Lal 2 ,
- Niraj Kumar Jha 5 ,
- Mohammed Haris Siddiqui 6 ,
- Pradeep Kumar 7 ,
- Vijay Tripathi 2 &
- Janne Ruokolainen 1
56k Accesses
135 Citations
4 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
Water scarcity is one of the major problems in the world and millions of people have no access to freshwater. Untreated wastewater is widely used for agriculture in many countries. This is one of the world-leading serious environmental and public health concerns. Instead of using untreated wastewater, treated wastewater has been found more applicable and ecofriendly option. Moreover, environmental toxicity due to solid waste exposures is also one of the leading health concerns. Therefore, intending to combat the problems associated with the use of untreated wastewater, we propose in this review a multidisciplinary approach to handle wastewater as a potential resource for use in agriculture. We propose a model showing the efficient methods for wastewater treatment and the utilization of solid wastes in fertilizers. The study also points out the associated health concern for farmers, who are working in wastewater-irrigated fields along with the harmful effects of untreated wastewater. The consumption of crop irrigated by wastewater has leading health implications also discussed in this review paper. This review further reveals that our current understanding of the wastewater treatment and use in agriculture with addressing advancements in treatment methods has great future possibilities.
Similar content being viewed by others
Wastewater Application in Agriculture-A Review

Wastewater Reuse in Peri-Urban Agriculture Ecosystem: Current Scenario, Consequences, and Control Measures
Wastewater reclamation and reuse potentials in agriculture: towards environmental sustainability
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction
Rapidly depleting and elevating the level of freshwater demand, though wastewater reclamation or reuse is one of the most important necessities of the current scenario. Total water consumption worldwide for agriculture accounts 92% (Clemmens et al., 2008 ; Hoekstra & Mekonnen, 2012 ; Tanji & Kielen, 2002 ). Out of which about 70% of freshwater is used for irrigation (WRI, 2020 ), which comes from the rivers and underground water sources (Pedrero et al., 2010 ). The statistics shows serious concern for the countries facing water crisis. Shen et al. ( 2014 ) reported that 40% of the global population is situated in heavy water–stressed basins, which represents the water crisis for irrigation. Therefore, wastewater reuse in agriculture is an ideal resource to replace freshwater use in agriculture (Contreras et al., 2017 ). Treated wastewater is generally applied for non-potable purposes, like agriculture, land, irrigation, groundwater recharge, golf course irrigation, vehicle washing, toilet flushes, firefighting, and building construction activities. It can also be used for cooling purposes in thermal power plants (Katsoyiannis et al., 2017 ; Mohsen, 2004 ; Smith, 1995 ; Yang et al., 2017 ). At global level, treated wastewater irrigation supports agricultural yield and the livelihoods of millions of smallholder farmers (Sato et al., 2013 ). Global reuse of treated wastewater for agricultural purposes shows wide variability ranging from 1.5 to 6.6% (Sato et al., 2013 ; Ungureanu et al., 2018 ). More than 10% of the global population consumes agriculture-based products, which are cultivated by wastewater irrigation (WHO, 2006 ). Treated wastewater reuse has experienced very rapid growth and the volumes have been increased ~10 to 29% per year in Europe, the USA, China, and up to 41% in Australia (Aziz & Farissi, 2014 ). China stands out as the leading country in Asia for the reuse of wastewater with an estimated 1.3 M ha area including Vietnam, India, and Pakistan (Zhang & Shen, 2017 ). Presently, it has been estimated that, only 37.6% of the urban wastewater in India is getting treated (Singh et al., 2019 ). By utilizing 90% of reclaimed water, Israel is the largest user of treated wastewater for agriculture land irrigation (Angelakis & Snyder, 2015 ). The detail information related to the utilization of freshwater and treated wastewater is compiled in Table 1 .
Many low-income countries in Africa, Asia, and Latin America use untreated wastewater as a source of irrigation (Jiménez & Asano, 2008 ). On the other hand, middle-income countries, such as Tunisia, Jordan, and Saudi Arabia, use treated wastewater for irrigation (Al-Nakshabandi et al., 1997 ; Balkhair, 2016a ; Balkhair, 2016b ; Qadir et al., 2010 ; Sato et al., 2013 ).
Domestic water and treated wastewater contains various type of nutrients such as phosphorus, nitrogen, potassium, and sulfur, but the major amount of nitrogen and phosphorous available in wastewater can be easily accumulated by the plants, that’s why it is widely used for the irrigation (Drechsel et al., 2010 ; Duncan, 2009 ; Poustie et al., 2020 ; Sengupta et al., 2015 ). The rich availability of nutrients in reclaimed wastewater reduces the use of fertilizers, increases crop productivity, improves soil fertility, and at the same time, it may also decrease the cost of crop production (Chen et al., 2013 a; Jeong et al., 2016 ). The data of high nutritional values in treated wastewater is shown in Fig. 1 .
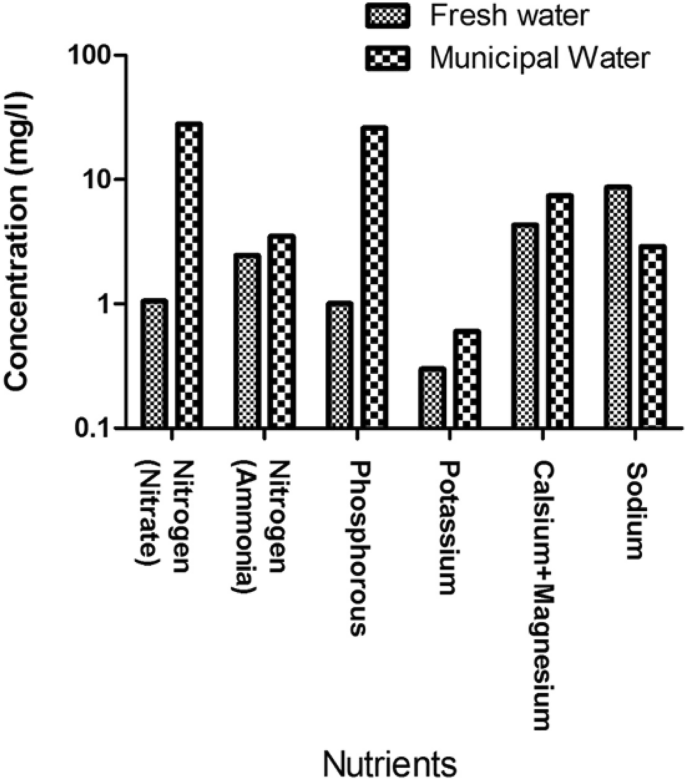
Nutrient concentrations (mg/L) of freshwater/wastewater (Yadav et al., 2002 )
Wastewater reuse for crop irrigation showed several health concerns (Ungureanu et al., 2020 ). Irrigation with the industrial wastewater either directly or mixing with domestic water showed higher risk (Chen et al., 2013). Risk factors are higher due to heavy metal and pathogens contamination because heavy metals are non-biodegradable and have a long biological half-life (Chaoua et al., 2019 ; WHO, 2006 ). It contains several toxic elements, i.e., Cu, Cr, Mn, Fe, Pb, Zn, and Ni (Mahfooz et al., 2020 ). These heavy metals accumulate in topsoil (at a depth of 20 cm) and sourcing through plant roots; they enter the human and animal body through leafy vegetables consumption and inhalation of contaminated soils (Mahmood et al., 2014 ). Therefore, health risk assessment of such wastewater irrigation is important especially in adults (Mehmood et al., 2019 ; Njuguna et al., 2019 ; Xiao et al., 2017 ). For this, an advanced wastewater treatment method should be applied before release of wastewater in the river, agriculture land, and soils. Therefore, this review also proposed an advance wastewater treatment model, which has been tasted partially at laboratory scale by Kesari and Behari ( 2008 ), Kesari et al. ( 2011a , b ), and Kumar et al. ( 2010 ).
For a decade, reuse of wastewater has also become one of the global health concerns linking to public health and the environment (Dang et al., 2019 ; Narain et al., 2020 ). The World Health Organization (WHO) drafted guidelines in 1973 to protect the public health by facilitating the conditions for the use of wastewater and excreta in agriculture and aquaculture (WHO, 1973 ). Later in 2005, the initial guidelines were drafted in the absence of epidemiological studies with minimal risk approach (Carr, 2005 ). Although, Adegoke et al. ( 2018 ) reviewed the epidemiological shreds of evidence and health risks associated with reuse of wastewater for irrigation. Wastewater or graywater reuse has adverse health risks associated with microbial hazards (i.e., infectious pathogens) and chemicals or pharmaceuticals exposures (Adegoke et al., 2016 ; Adegoke et al., 2017 ; Busgang et al., 2018 ; Marcussen et al., 2007 ; Panthi et al., 2019 ). Researchers have reported that the exposure to wastewater may cause infectious (helminth infection) diseases, which are linked to anemia and impaired physical and cognitive development (Amoah et al., 2018 ; Bos et al., 2010 ; Pham-Duc et al., 2014 ; WHO, 2006 ).
Owing to an increasing population and a growing imbalance in the demand and supply of water, the use of wastewater has been expected to increase in the coming years (World Bank, 2010 ). The use of treated wastewater in developed nations follows strict rules and regulations. However, the direct use of untreated wastewater without any sound regulatory policies is evident in developing nations, which leads to serious environmental and public health concerns (Dickin et al., 2016 ). Because of these issues, we present in this review, a brief discussion on the risk associated with the untreated wastewater exposures and advanced methods for its treatment, reuse possibilities of the treated wastewater in agriculture.
2 Environmental Toxicity of Untreated Wastewater
Treated wastewater carries larger applicability such as irrigation, groundwater recharge, toilet flushing, and firefighting. Municipal wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) are the major collection point for the different toxic elements, pathogenic microorganisms, and heavy metals. It collects wastewater from divergent sources like household sewage, industrial, clinical or hospital wastewater, and urban runoff (Soni et al., 2020 ). Alghobar et al. ( 2014 ) reported that grass and crops irrigated with sewage and treated wastewater are rich in heavy metals in comparison with groundwater (GW) irrigation. Although, heavy metals classified as toxic elements and listed as cadmium, lead, mercury, copper, and iron. An exceeding dose or exposures of these heavy metals could be hazardous for health (Duan et al., 2017 ) and ecological risks (Tytła, 2019 ). The major sources of these heavy metals come from drinking water. This might be due to the release of wastewater into river or through soil contamination reaches to ground water. Table 2 presenting the permissible limits of heavy metals presented in drinking water and its impact on human health after an exceeding the amount in drinking water, along with the route of exposure of heavy metals to human body.
Direct release in river or reuse of wastewater for irrigation purposes may create short-term implications like heavy metal and microbial contamination and pathogenic interaction in soil and crops. It has also long-term influence like soil salinity, which grows with regular use of untreated wastewater (Smith, 1995 ). Improper use of wastewater for irrigation makes it unsafe and environment threatening. Irrigation with several different types of wastewater, i.e., industrial effluents, municipal and agricultural wastewaters, and sewage liquid sludge transfers the heavy metals to the soil, which leads to accumulation in crops due to improper practices. This has been identified as a significant route of heavy metals into aquatic resources (Agoro et al., 2020 ). Hussain et al. ( 2019 ) investigated the concentration of heavy metals (except for Cd) was higher in the soil irrigated with treated wastewater (large-scale sewage treatment plant) than the normal ground water, also reported by Khaskhoussy et al. ( 2015 ).
In other words, irrigation with wastewater mitigates the quality of crops and enhances health risks. Excess amount of copper causes anemia, liver and kidney damage, vomiting, headache, and nausea in children (Bent & Bohm, 1995 ; Madsen et al., 1990 ; Salem et al., 2000 ). A higher concentration of arsenic may lead to bone and kidney cancer (Jarup, 2003 ) and results in osteopenia or osteoporosis (Puzas et al., 2004 ). Cadmium gives rise to musculoskeletal diseases (Fukushima et al., 1970 ), whereas mercury directly affects the nervous system (Azevedo et al., 2014 ).
3 Spread of Antibiotic Resistance
Currently, antibiotics are highly used for human disease treatment; however, uses in poultries, animal husbandries, biochemical industries, and agriculture are common practices these days. Extensive use and/or misuse of antibiotics have given rise to multi-resistant bacteria, which carry multiple resistance genes (Icgen & Yilmaz, 2014 ; Lv et al., 2015 ; Tripathi & Tripathi, 2017 ; Xu et al., 2017 ). These multidrug-resistant bacteria discharged through the sewage network and get collected into the wastewater treatment plants. Therefore, it can be inferred that the WWTPs serve as the hotspot of antibiotic-resistant bacteria (ARB) and antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs). Though, these antibiotic-resistant bacteria can be disseminated to the different bacterial species through the mobile genetic elements and horizontal gene transfer (Gupta et al., 2018 ). Previous studies indicated that certain pathogens might survive in wastewater, even during and after the treatment processes, including methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE) (Börjesson et al., 2009 ; Caplin et al., 2008 ). The use of treated wastewater in irrigation provides favorable conditions for the growth and persistence of total coliforms and fecal coliforms (Akponikpe et al., 2011 ; Sacks & Bernstein, 2011 ). Furthermore, few studies have also reported the presence of various bacterial pathogens, such as Clostridium , Salmonella , Streptococci , Viruses, Protozoa, and Helminths in crops irrigated with treated wastewater (Carey et al., 2004 ; Mañas et al., 2009 ; Samie et al., 2009 ). Goldstein ( 2013 ) investigated the survival of ARB in secondary treated wastewater and proved that it causes serious health risks to the individuals, who are exposed to reclaimed water. The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the World Health Organization (WHO) have already declared the ARBs as the imminent hazard to human health. According to the list published by WHO, regarding the development of new antimicrobial agents, the ESKAPE ( Enterococcus faecium , S. aureus , Klebsiella pneumoniae , Acinetobacter baumannii , Pseudomonas aeruginosa , and Enterobacter species) pathogens were designated to be “priority status” as their occurrence in the food chain is considered as the potential and major threat for the human health (Tacconelli et al., 2018 ).
These ESKAPE pathogens have acquired the multi drug resistance mechanisms against oxazolidinones, lipopeptides, macrolides, fluoroquinolones, tetracyclines, β-lactams, β-lactam–β-lactamase inhibitor combinations, and even those antibiotics that are considered as the last line of defense, including carbapenems and glycopeptides (Giddins et al., 2017 ; Herc et al., 2017 ; Iguchi et al., 2016 ; Naylor et al., 2018 ; Zaman et al., 2017 ), by the means of genetic mutation and mobile genetic elements. These cluster of ESKAPE pathogens are mainly responsible for lethal nosocomial infections (Founou et al., 2017 ; Santajit & Indrawattana, 2016 ).
Due to the wide application of antibiotics in animal husbandry and inefficient capability of wastewater treatment plants, the multidrug-resistant bacteria such as tetracyclines, sulfonamides, β-lactam, aminoglycoside, colistin, and vancomycin in major are disseminated in the receiving water bodies, which ultimately results in the accumulation of ARGs in the irrigated crops (He et al., 2020 ).
4 Toxic Contaminations in Wastewater Impacting Human Health
The release of untreated wastewater into the river may pose serious health implications (König et al., 2017 ; Odigie, 2014 ; Westcot, 1997 ). It has been already discussed about the household and municipal sewage which contains a major amount of organic materials and pathogenic microorganisms and these infectious microorganisms are capable of spreading various diseases like typhoid, dysentery, diarrhea, vomiting, and malabsorption (Jia & Zhang, 2020 ; Numberger et al., 2019 ; Soni et al., 2020 ). Additionally, pharmaceutical industries also play a key role in the regulation and discharge of biologically toxic agents. The untreated wastewater also contains a group of contaminants, which are toxic to humans. These toxic contaminations have been classified into two major groups: (i) chemical contamination and (ii) microbial contamination.
4.1 Chemical Contamination
Mostly, various types of chemical compounds released from industries, tanneries, workshops, irrigated lands, and household wastewaters are responsible for several diseases. These contaminants can be organic materials, hydrocarbons, volatile compounds, pesticides, and heavy metals. Exposure to such contaminants may cause infectious diseases like chronic dermatoses and skin cancer, lung infection, and eye irritation. Most of them are non-biodegradable and intractable. Therefore, they can persist in the water bodies for a very long period and could be easily accumulated in our food chain system. Several pharmaceutical personal care products (PPCPs) and surfactants are available that may contain toxic compounds like nonylphenol, estrone, estradiol, and ethinylestradiol. These compounds are endocrine-disrupting chemicals (Bolong et al., 2009 ), and the existence of these compounds in the human body even in the trace amounts can be highly hazardous. Also, the occurrence of perfluorinated compounds (PFCs) in wastewater, which is toxic in nature, has been significantly reported worldwide (Templeton et al., 2009 ). Furthermore, PFCs cause severe health menaces like pre-eclampsia, birth defects, reduced human fertility (Webster, 2010 ), immunotoxicity (Dewitt et al., 2012 ), neurotoxicity (Lee & Viberg, 2013 ), and carcinogenesis (Bonefeld-Jorgensen et al., 2011 ).
4.2 Microbial Contamination
Researchers have reported serious health risks associated with the microbial contaminants in untreated wastewater. The diverse group of microorganisms causes severe health implications like campylobacteriosis, diarrhea, encephalitis, typhoid, giardiasis, hepatitis A, poliomyelitis, salmonellosis, and gastroenteritis (ISDH, 2009 ; Okoh et al., 2010 ). Few bacterial species like P. aeruginosa , Salmonella typhimurium , Vibrio cholerae , G. intestinales , Legionella spp., E. coli , Shigella sonnei have been reported for the spreading of waterborne diseases, and acute illness in human being (Craun et al., 2006 ; Craun et al., 2010 ). These aforementioned microorganisms may release in the environment from municipal sewage water network, animal husbandries, or hospitals and enter the food chain via public water supply systems.
5 Wastewater Impact on Agriculture
The agriculture sector is well known for the largest user of water, accounting for nearly 70% of global water usage (Winpenny et al., 2010 ). The fact that an estimated 20 million hectares worldwide are irrigated with wastewater suggests a major source for irrigation (Ecosse, 2001 ). However, maximum wastewater that is used for irrigation is untreated (Jiménez & Asano, 2008 ; Scott et al., 2004 ). Mostly in developing countries, partially treated or untreated wastewater is used for irrigation purpose (Scott et al., 2009 ). Untreated wastewater often contains a large range of chemical contaminants from waste sites, chemical wastes from industrial discharges, heavy metals, fertilizers, textile, leather, paper, sewage waste, food processing waste, and pesticides. World Health Organization (WHO) has warned significant health implications due to the direct use of wastewater for irrigation purposes (WHO, 2006 ). These contaminants pose health risks to communities (farmers, agricultural workers, their families, and the consumers of wastewater-irrigated crops) living in the proximity of wastewater sources and areas irrigated with untreated wastewater (Qadir et al., 2010 ). Wastewater also contains a wide variety of organic compounds. Some of them are toxic or cancer-causing and have harmful effects on an embryo (Jarup, 2003 ; Shakir et al., 2016 ). The pathway of untreated wastewater used in irrigation and associated health effects are shown in Fig. 2 .
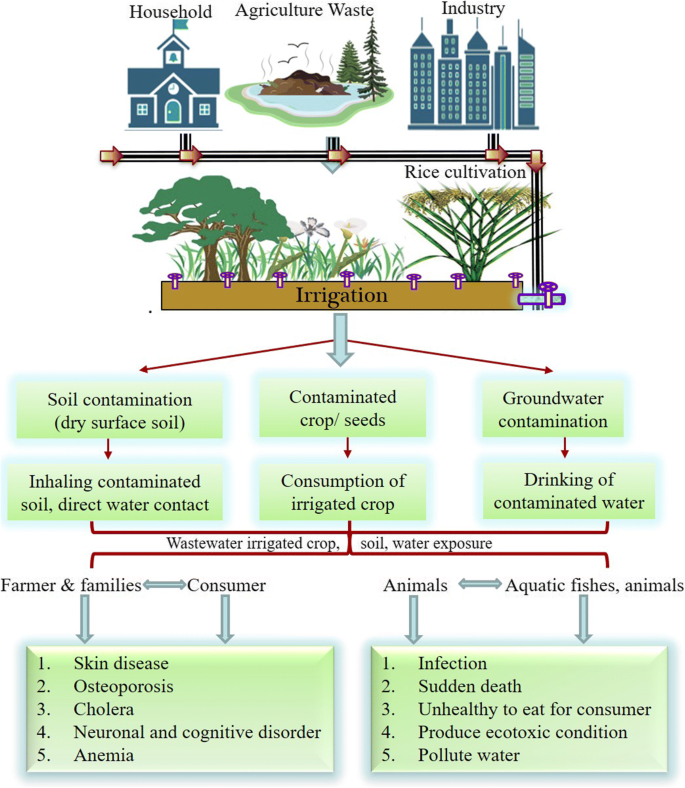
Exposure pathway representing serious health concerns from wastewater-irrigated crops
Alternatively, in developing countries, due to the limited availability of treatment facilities, untreated wastewater is discharged into the existing waterbodies (Qadir et al., 2010 ). The direct use of wastewater in agriculture or irrigation obstructs the growth of natural plants and grasses, which in turn causes the loss of biodiversity. Shuval et al. ( 1985 ) reported one of the earliest evidences connecting to agricultural wastewater reuse with the occurrence of diseases. Application of untreated wastewater in irrigation increases soil salinity, land sealing followed by sodium accumulation, which results in soil erosion. Increased soil salinity and sodium accumulation deteriorates the soil and decreases the soil permeability, which inhibits the nutrients intake of crops from the soil. These causes have been considered the long-term impact of wastewater reuse in agriculture (Halliwell et al., 2001 ). Moreover, wastewater contaminated soils are a major source of intestinal parasites (helminths—nematodes and tapeworms) that are transmitted through the fecal–oral route (Toze, 1997 ). Already known, the helminth infections are linked to blood deficiency and behavioral or cognitive development (Bos et al., 2010 ). One of the major sources of helminth infections around the world is the use of raw or partially treated sewage effluent and sludge for the irrigation of food crops (WHO, 1989 ). Wastewater-irrigated crops contain heavy metal contamination, which originates from mining, foundries, and metal-based industries (Fazeli et al., 1998 ). Exposure to heavy metals including arsenic, cadmium, lead, and mercury in wastewater-irrigated crops is a cause for various health problems. For example, the consumption of high amounts of cadmium causes osteoporosis in humans (Dickin et al., 2016 ). The uptake of heavy metals by the rice crop irrigated with untreated effluent from a paper mill has been reported to cause serious health concerns (Fazeli et al., 1998 ). Irrigating rice paddies with highly contaminated water containing heavy metals leads to the outbreak of Itai-itai disease in Japan (Jarup, 2003 ).
Owing to these widespread health risks, the WHO published the third edition of its guidelines for the safe use of wastewater in irrigating crops (WHO, 2006 ) and made recommendations for threshold contaminant levels in wastewater. The quality of wastewater for agricultural reuse have been classified based on the availability of nutrients, trace elements, microorganisms, and chemicals contamination levels. The level of contamination differs widely depending on the type of source, household sewage, pharmaceutical, chemical, paper, or textile industries effluents. The standard measures of water quality for irrigation are internationally reported (CCREM, 1987 ; FAO, 1985 ; FEPA, 1991 ; US EPA, 2004 , 2012 ; WHO, 2006 ), where the recommended levels of trace elements, metals, COD, BOD, nitrogen, and phosphorus are set at certain limits. Researchers reviewed the status of wastewater reuse for agriculture, based on its standards and guidelines for water quality (Angelakis et al., 1999 ; Brissaud, 2008 ; Kalavrouziotis et al., 2015 ). Based on these recommendations and guidelines, it is evident that greater awareness is required for the treatment of wastewater safely.
6 Wastewater Treatment Techniques
6.1 primary treatment.
This initial step is designed to remove gross, suspended and floating solids from raw wastewater. It includes screening to trap solid objects and sedimentation by gravity to remove suspended solids. This physical solid/liquid separation is a mechanical process, although chemicals can be used sometimes to accelerate the sedimentation process. This phase of the treatment reduces the BOD of the incoming wastewater by 20–30% and the total suspended solids by nearly 50–60%.
6.2 Secondary (Biological) Treatment
This stage helps eliminate the dissolved organic matter that escapes primary treatment. Microbes consume the organic matter as food, and converting it to carbondioxide, water, and energy for their own growth. Additional settling to remove more of the suspended solids then follows the biological process. Nearly 85% of the suspended solids and biological oxygen demand (BOD) can be removed with secondary treatment. This process also removes carbonaceous pollutants that settle down in the secondary settling tank, thus separating the biological sludge from the clear water. This sludge can be fed as a co-substrate with other wastes in a biogas plant to obtain biogas, a mixture of CH 4 and CO 2 . It generates heat and electricity for further energy distribution. The leftover, clear water is then processed for nitrification or denitrification for the removal of carbon and nitrogen. Furthermore, the water is passed through a sedimentation basin for treatment with chlorine. At this stage, the water may still contain several types of microbial, chemical, and metal contaminations. Therefore, to make the water reusable, e.g., for irrigation, it further needs to pass through filtration and then into a disinfection tank. Here, sodium hypochlorite is used to disinfect the wastewater. After this process, the treated water is considered safe to use for irrigation purposes. Solid wastes generated during primary and secondary treatment processes are processed further in the gravity-thickening tank under a continuous supply of air. The solid waste is then passed into a centrifuge dewatering tank and finally to a lime stabilization tank. Treated solid waste is obtained at this stage and it can be processed further for several uses such as landfilling, fertilizers and as a building.
Other than the activated sludge process of wastewater treatment, there are several other methods developed and being used in full-scale reactors such as ponds (aerobic, anaerobic, facultative, and maturation), trickling filters, anaerobic treatments like up-flow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) reactors, artificial wetlands, microbial fuel cells, and methanogenic reactors.
UASB reactors are being applied for wastewater treatment from a very long period. Behling et al. ( 1996 ) examined the performance of the UASB reactor without any external heat supply. In their study, the COD loading rate was maintained at 1.21 kg COD/m 3 /day, after 200 days of trial. They achieved an average of 85% of COD removal. Von-Sperling and Chernicharo ( 2005 ) presented a combined model consisted of an Up-flow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket-Activated Sludge reactor (UASB–AS system), using the low strength domestic wastewater with a BOD 5 amounting to 340 mg/l. Outcomes of their experiment have shown a 60% reduction in sludge construction and a 40% reduction in aeration energy consumption. In another experiment, Rizvi et al. ( 2015 ) seeded UASB reactor with cow manure dung to treat domestic wastewater; they observed 81%, 75%, and 76% reduction in COD, TSS, and total sulfate removal, respectively, in their results.
6.3 Tertiary or Advanced Treatment Processes
The tertiary treatment process is employed when specific constituents, substances, or contaminants cannot be completely removed after the secondary treatment process. The tertiary treatment processes, therefore, ensure that nearly 99% of all impurities are removed from wastewater. To make the treated water safe for drinking purposes, water is treated individually or in combination with advanced methods like the US (ultrasonication), UV (ultraviolet light treatment), and O 3 (exposure to ozone). This process helps to remove bacteria and heavy metal contaminations remaining in the treated water. For the purpose, the secondarily treated water is first made to undergo ultrasonication and it is subsequently exposed to UV light and passed through an ozone chamber for the complete removal of contaminations. The possible mechanisms by which cells are rendered inviable during the US include free-radical attack and physical disruption of cell membranes (Phull et al., 1997 ; Scherba et al., 1991 ). The combined treatment of US + UV + O 3 produces free radicals, which are attached to cell membranes of the biological contaminants. Once the cell membrane is sheared, chemical oxidants can enter the cell and attack internal structures. Thus, the US alone or in combination facilitates the deagglomeration of microorganisms and increases the efficiency of other chemical disinfectants (Hua & Thompson, 2000 ; Kesari et al., 2011a , b ; Petrier et al., 1992 ; Phull et al., 1997 ; Scherba et al., 1991 ). A combined treatment method was also considered by Pesoutova et al. ( 2011 ) and reported a very effective method for textile wastewater treatment. The effectiveness of ultrasound application as a pre-treatment step in combination with ultraviolet rays (Blume & Neis, 2004 ; Naddeo et al., 2009 ), or also compared it with various other combinations of both ultrasound and UV radiation with TiO 2 photocatalysis (Paleologou et al., 2007 ), and ozone (Jyoti & Pandit, 2004 ) to optimize wastewater disinfection process.
An important aspect of our wastewater treatment model (Fig. 3 ) is that at each step of the treatment process, we recommend the measurement of the quality of treated water. After ensuring that the proper purification standards are met, the treated water can be made available for irrigation, drinking or other domestic uses.
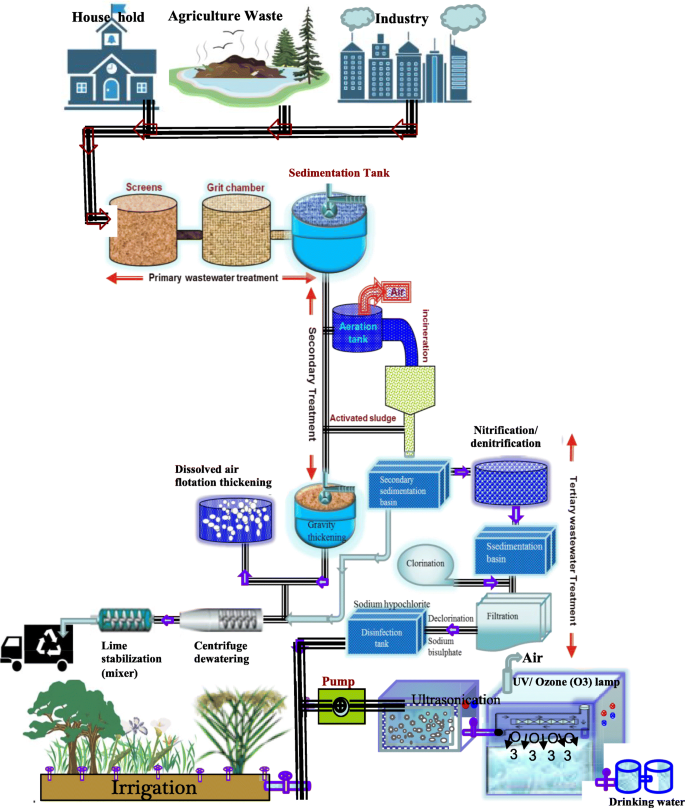
A wastewater treatment schematic highlighting the various methods that result in a progressively improved quality of the wastewater from the source to the intended use of the treated wastewater for irrigation purposes
6.4 Nanotechnology as Tertiary Treatment of Wastewater Converting Drinking Water Alike
Considering the emerging trends of nanotechnology, nanofillers can be used as a viable method for the tertiary treatment of wastewater. Due to the very small pore size, 1–5-nm nanofillers may eliminate the organic–inorganic pollutants, heavy metals, as well as pathogenic microorganisms and pharmaceutically active compounds (PhACs) (Mohammad et al., 2015 ; Vergili, 2013 ). Over the recent years, nanofillers have been largely accepted in the textile industry for the treatment of pulp bleaching pharmaceutical industry, dairy industry, microbial elimination, and removal of heavy metals from wastewater (Abdel-Fatah, 2018 ). Srivastava et al. ( 2004 ) synthesized very efficient and reusable water filters from carbon nanotubes, which exhibited effective elimination of bacterial pathogens ( E. coli and S. aureus ), and Poliovirus sabin-1 from wastewater.
Nanofiltration requires lower operating pressure and lesser energy consumption in comparison of RO and higher rejection of organic compounds compared to UF. Therefore, it can be applied as the tertiary treatment of wastewater (Abdel-Fatah, 2018 ). Apart from nanofilters, there are various kinds of nanoparticles like metal nanoparticles, metal oxide nanoparticles, carbon nanotubes, graphene nanosheets, and polymer-based nanosorbents, which may play a different role in wastewater treatment based on their properties. Kocabas et al. ( 2012 ) analyzed the potential of different metal oxide nanoparticles and observed that nanopowders of TiO 2 , FeO 3 , ZnO 2 , and NiO can exhibit the exceeding amount of removal of arsenate from wastewater. Cadmium contamination in wastewater, which poses a serious health risk, can be overcome by using ZnO nanoparticles (Kumar & Chawla, 2014 ). Latterly, Vélez et al. ( 2016 ) investigated that the 70% removal of mercury from wastewater through iron oxide nanoparticles successfully performed. Sheet et al. ( 2014 ) used graphite oxide nanoparticles for the removal of nickel from wastewater. An exceeding amount of copper causes liver cirrhosis, anemia, liver, and kidney damage, which can be removed by carbon nanotubes, pyromellitic acid dianhydride (PMDA) and phenyl aminomethyl trimethoxysilane (PAMTMS) (Liu et al., 2010 ).
Nanomaterials are efficiently being used for microbial purification from wastewater. Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are broadly applied for the treatment of wastewater contaminated with E. coli , Salmonella , and a wide range of microorganisms (Akasaka & Watari, 2009 ). In addition, silver nanoparticles reveal very effective results against the microorganisms present in wastewater. Hence, it is extensively being used for microbial elimination from wastewater (Inoue et al., 2002 ). Moreover, CNTs exhibit high binding affinity to bacterial cells and possess magnetic properties (Pan & Xing, 2008 ). Melanta ( 2008 ) confirmed and recommended the applicability of CNTs for the removal of E. coli contamination from wastewater. Mostafaii et al. ( 2017 ) suggested that the ZnO nanoparticles could be the potential antibacterial agent for the removal of total coliform bacteria from municipal wastewater. Apart from the previously mentioned, applicability of the nanotechnology, the related drawbacks and challenges cannot be neglected. Most of the nanoengineered techniques are currently either in research scale or pilot scale performing well (Gehrke et al., 2015 ). Nevertheless, as discussed above, nanotechnology and nanomaterials exhibit exceptional properties for the removal of contaminants and purification of water. Therefore, it can be adapted as the prominent solution for the wastewater treatment (Zekić et al., 2018 ) and further use for drinking purposes.
6.5 Wastewater Treatment by Using Plant Species
Some of the naturally growing plants can be a potential source for wastewater treatment as they remove pollutants and contaminants by utilizing them as a nutrient source (Zimmels et al., 2004 ). Application of plant species in wastewater treatment may be cost-effective, energy-saving, and provides ease of operation. At the same time, it can be used as in situ, where the wastewater is being produced (Vogelmann et al., 2016 ). Nizam et al. ( 2020 ) analyzed the phytoremediation efficiency of five plant species ( Centella asiatica , Ipomoea aquatica , Salvinia molesta , Eichhornia crassipes , and Pistia stratiotes ) and achieved the drastic decrease in the amount of three pollutants viz. total suspended solids (TSS), ammoniacal nitrogen (NH 3 -N), and phosphate levels . All the five species found to be efficient removal of the level of 63.9-98% of NH 3 -N, TSS, and phosphate. Coleman et al. ( 2001 ) examined the physiological effects of domestic wastewater treatment by three common Appalachian plant species: common rush or soft rush ( Juncus effuses L.), gray club-rush ( Scirpus Validus L.), and broadleaf cattail or bulrush ( Typha latifolia L.). They observed in their experiments about 70% of reduction in total suspended solids (TSS) and biochemical oxygen demand (BOD), 50% to 60% of reduction in nitrogen, ammonia, and phosphate levels, and a significant reduction in feacal coliform populations. Whereas, Zamora et al. ( 2019 ) found the removal efficiency of chemical oxygen demand (COD), total solids suspended (TSS), nitrogen as ammonium (N-NH 4 ) and nitrate (N-NO 3 ), and phosphate (P-PO 4 ) up to 20–60% higher using the three ornamental species of plants viz. Canna indica , Cyperus papyrus , and Hedychium coronarium . The list of various plant species applied for the wastewater treatment is shown in Table 3 .
6.6 Wastewater Treatment by Using Microorganisms
There is a diverse group of bacteria like Pseudomonas fluorescens , Pseudomonas putida , and different Bacillus strains, which are capable to use in biological wastewater systems. These bacteria work in the cluster forms as a floc, biofilm, or granule during the wastewater treatment. Furthermore, after the recognition of bacterial exopolysaccharides (EPS) as an efficient adsorption material, it may be applied in a revolutionary manner for the heavy metal elimination (Gupta & Diwan, 2017 ). There are few examples of EPS, which are commercially available, i.e., alginate ( P. aeruginosa , Azotobacter vinelandii ), gellan (Sphingomonas paucimobilis ), hyaluronan ( . aeruginosa , Pasteurella multocida , Streptococci attenuated strains ), xanthan (Xanthomonas campestris ), and galactopol ( Pseudomonas oleovorans ) (Freitas et al., 2009 ; Freitas, Alves, & Reis, 2011a ; Freitas, Alves, Torres, et al., 2011b ). Similarly, Hesnawi et al. ( 2014 ) experimented biodegradation of municipal wastewater using local and commercial bacteria (Sludge Hammer), where they achieved a significant decrease in synthetic wastewater, i.e., 70%, 54%, 52%, 42% for the Sludge Hammer, B. subtilis , B. laterosponus , and P. aeruginosa , respectively. Therefore, based on the above studies, it can be concluded that bioaugmentation of wastewater treatment reactor with selective and mixed strains can ameliorate the treatment. During recent years, microalgae have attracted the attention of researchers as an alternative system, due to their applicability in wastewater treatment. Algae are the unicellular or multicellular photosynthetic microorganism that grows on water surfaces, salt water, or moist soil. They utilize the exceeding amount of nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and carbon for their growth and metabolism process through their anaerobic system. This property of algae also inhibits eutrophication; that is to avoid over-deposit of nutrients in water bodies. During the nutrient digestion process, algae produce oxygen that is constructive for the heterotrophic aerobic bacteria, which may further be utilized to degrade the organic and inorganic pollutants. Kim et al. ( 2014 ) observed a total decrease in the levels of COD (86%), total nitrogen (93%), and total phosphorus (83%) after using algae in the municipal wastewater consortium. Nmaya et al. ( 2017 ) reported the heavy metal removal efficiency of microalga Scenedesmus sp. from contaminated river water in the Melaka River, Malaysia. They observed the effective removal of Zn (97-99%) on the 3 rd and 7 th day of the experiment. The categorized list of microorganisms used for wastewater treatment is presented in Table 4 .
7 The Computational Approach in Wastewater Treatment
7.1 bioinformatics and genome sequencing.
A computational approach is accessible in wastewater treatment. Several tools and techniques are in use such as, sequencing platforms (Hall, 2007 ; Marsh, 2007 ), metagenome sequencing strategies (Schloss & Handelsman, 2005 ; Schmeisser et al., 2007 ; Tringe et al., 2005 ), bioinformatics tools and techniques (Chen & Pachter, 2005 ; Foerstner et al., 2006 ; Raes et al., 2007 ), and the genome analysis of complex microbial communities (Fig. 4 ). Most of the biological database contains microorganisms and taxonomical information. Thus, these can provide extensive details and supports for further utilization in wastewater treatment–related research and development (Siezen & Galardini, 2008 ). Balcom et al. ( 2016 ) explored that the microbial population residing in the plant roots immersed in the wastewater of an ecological WWTP and showed the evidence of the capacity for micro-pollutant biodegradation using whole metagenome sequencing (WMS). Similarly, Kumar et al. ( 2016 ) revealed that bioremediation of highly polluted wastewater from textile dyes by two novel strains were found to highly decolorize Joyfix Red. They were identified as Lysinibacillus sphaericus (KF032717) and Aeromonas hydrophila (KF032718) through 16S rDNA analysis. More recently, Leddy et al. ( 2018 ) reported that research scientists are making strides to advance the safety and application of potable water reuse with metagenomics for water quality analysis. The application of the bio-computational approach has also been implemented in the advancements of wastewater treatment and disease detection.
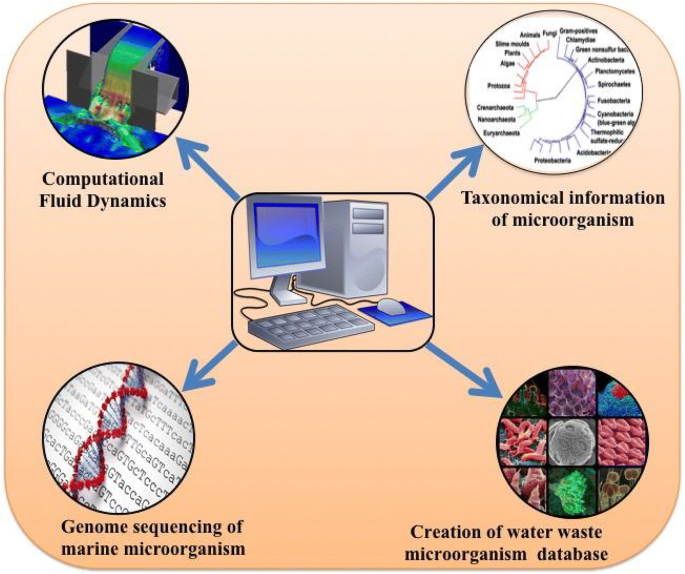
A schematic showing the overall conceptual framework on which depicting the computational approach in wastewater treatment

7.2 Computational Fluid Dynamics in Wastewater Treatment
In recent years, computational fluid dynamics (CFD), a broadly used method, has been applied to biological wastewater treatment. It has exposed the inner flow state that is the hydraulic condition of a biological reactor (Peng et al., 2014 ). CFD is the application of powerful predictive modeling and simulation tools. It may calculate the multiple interactions between all the water quality and process design parameters. CFD modeling tools have already been widely used in other industries, but their application in the water industry is quite recent. CFD modeling has great applications in water and wastewater treatment, where it mechanically works by using hydrodynamic and mass transfer performance of single or two-phase flow reactors (Do-Quang et al., 1998 ). The level of CFD’s capability varies between different process units. It has a high frequency of application in the areas of final sedimentation, activated sludge basin modeling, disinfection, and greater needs in primary sedimentation and anaerobic digestion (Samstag et al., 2016 ). Now, researchers are enhancing the CFD modeling with a developed 3D model of the anoxic zone to evaluate further hydrodynamic performance (Elshaw et al., 2016 ). The overall conceptual framework and the applications of the computational approach in wastewater treatment are presented in Fig. 4 .
7.3 Computational Artificial Intelligence Approach in Wastewater Treatment
Several studies were obtained by researchers to implement computer-based artificial techniques, which provide fast and rapid automated monitoring of water quality tests such as BOD and COD. Recently, Nourani et al. ( 2018 ) explores the possibility of wastewater treatment plant by using three different kinds of artificial intelligence methods, i.e., feedforward neural network (FFNN), adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS), and support vector machine (SVM). Several measurements were done in terms of effluent to tests BOD, COD, and total nitrogen in the Nicosia wastewater treatment plant (NWWTP) and reported high-performance efficiency of artificial intelligence (Nourani et al., 2018 ).
7.4 Remote sensing and Geographical Information System
Since the implementation of satellite technology, the initiation of new methods and tools became popular nowadays. The futuristic approach of remote sensing and GIS technology plays a crucial role in the identification and locating of the water polluted area through satellite imaginary and spatial data. GIS analysis may provide a quick and reasonable solution to develop atmospheric correction methods. Moreover, it provides a user-friendly environment, which may support complex spatial operations to get the best quality information on water quality parameters through remote sensing (Ramadas & Samantaray, 2018 ).
8 Applications of Treated Wastewater
8.1 scope in crop irrigation.
Several studies have assessed the impact of the reuse of recycled/treated wastewater in major sectors. These are agriculture, landscapes, public parks, golf course irrigation, cooling water for power plants and oil refineries, processing water for mills, plants, toilet flushing, dust control, construction activities, concrete mixing, and artificial lakes (Table 5 ). Although the treated wastewater after secondary treatment is adequate for reuse since the level of heavy metals in the effluent is similar to that in nature (Ayers & Westcot, 1985 ), experimental evidences have been found and evaluated the effects of irrigation with treated wastewater on soil fertility and chemical characteristics, where it has been concluded that secondary treated wastewater can improve soil fertility parameters (Mohammad & Mazahreh, 2003 ). The proposed model (Fig. 3 ) is tested partially previously at a laboratory scale by treating the wastewater (from sewage, sugar, and paper industry) in an ultrasonic bath (Kesari et al., 2011a , b ; Kesari & Behari, 2008 ; Kumar et al., 2010 ). Advancing it with ultraviolet and ozone treatment has modified this in the proposed model. A recent study shows that the treated water passed quality measures suited for crop irrigation (Bhatnagar et al., 2016 ). In Fig. 3 , a model is proposed including all three (UV, US, nanoparticle, and ozone) techniques, which have been tested individually as well as in combination (US and nanoparticle) (Kesari et al., 2011a , b ) to obtain the highest water quality standards acceptable for irrigation and even drinking purposes.
A wastewater-irrigated field is a major source of essential and non-essential metals contaminants such as lead, copper, zinc, boron, cobalt, chromium, arsenic, molybdenum, and manganese. While crops need some of these, the others are non-essential metals, toxic to plants, animals, and humans. Kanwar and Sandha ( 2000 ) reported that heavy metal concentrations in plants grown in wastewater-irrigated soils were significantly higher than in plants grown in the reference soil in their study. Yaqub et al. ( 2012 ) suggest that the use of US is very effective in removing heavy or toxic metals and organic pollutants from industrial wastewater. However, it has been also observed that the metals were removed efficiently, when UV light was combined with ozone (Samarghandi et al., 2007 ). Ozone exposure is a potent method for the removal of metal or toxic compounds from wastewater as also reported earlier (Park et al., 2008 ). Application of US, UV, and O 3 in combination lead to the formation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) that oxidize certain organics, metal ions and kill pathogens. In the process of advanced oxidizing process (AOP) primarily oxidants, electricity, light, catalysts etc. are implied to produce extremely reactive free radicals (such as OH) for the breakdown of organic matters (Oturan & Aaron, 2014 ). Among the other AOPs, ozone oxidization process is more promising and effective for the decomposition of complex organic contaminants (Xu et al., 2020 ). Ozone oxidizes the heavy metal to their higher oxidation state to form metallic oxides or hydroxides in which they generally form limited soluble oxides and gets precipitated, which are easy to be filtered by filtration process. Ozone oxidization found to be efficient for the removal of heavy metals like cadmium, chromium, cobalt, copper, lead, manganese, nickel, and zinc from the water source (Upadhyay & Srivastava, 2005 ). Ultrasonic-treated sludge leads to the disintegration of biological cells and kills bacteria in treated wastewater (Kesari, Kumar, et al., 2011a ; Kesari, Verma, & Behari, 2011b ). This has been found that combined treatment with ultrasound and nanoparticles is more effective (Kesari, Kumar, et al., 2011a ). Ultrasonication has the physical effects of cavitation inactivate and lyse bacteria (Broekman et al., 2010 ). The induced effect of US, US, or ozone may destroy the pathogens and especially during ultrasound irradiation including free-radical attack, hydroxyl radical attack, and physical disruption of cell membranes (Kesari, Kumar, et al., 2011a ; Phull et al., 1997 ; Scherba et al., 1991 ).
8.2 Energy and Economy Management
Municipal wastewater treatment plants play a major role in wastewater sanitation and public health protection. However, domestic wastewater has been considered as a resource or valuable products instead of waste, because it has been playing a significant role in the recovery of energy and resource for the plant-fertilizing nutrients like phosphorus and nitrogen. Use of domestic wastewater is widely accepted for the crop irrigation in agriculture and industrial consumption to avoid the water crisis. It has also been found as a source of energy through the anaerobic conversion of the organic content of wastewater into methane gas. However, most of the wastewater treatment plants are using traditional technology, as anaerobic sludge digestion to treat wastewater, which results in more consumption of energy. Therefore, through these conventional technologies, only a fraction of the energy of wastewater has been captured. In order to solve these issues, the next generation of municipal wastewater treatment plants is approaching total retrieval of the energy potential of water and nutrients, mostly nitrogen and phosphorus. These plants also play an important role in the removal and recovery of emerging pollutants and valuable products of different nature like heavy and radioactive metals, fertilizers hormones, and pharma compounds. Moreover, there are still few possibilities of improvement in wastewater treatment plants to retrieve and reuse of these compounds. There are several methods under development to convert the organic matter into bioenergy such as biohydrogen, biodiesel, bioethanol, and microbial fuel cell. These methods are capable to produce electricity from wastewater but still need an appropriate development. Energy development through wastewater is a great driver to regulate the wastewater energy because it produces 10 times more energy than chemical, thermal, and hydraulic forms. Vermicomposting can be utilized for stabilization of sludge from the wastewater treatment plant. Kesari and Jamal ( 2017 ) have reported the significant, economical, and ecofriendly role of the vermicomposting method for the conversion of solid waste materials into organic fertilizers as presented in Fig. 5 . Solid waste may come from several sources of municipal and industrial sludge, for example, textile industry, paper mill, sugarcane, pulp industry, dairy, and intensively housed livestock. These solid wastes or sewage sludges have been treated successfully by composting and/or vermicomposting (Contreras-Ramos et al., 2005 ; Elvira et al., 1998 ; Fraser-Quick, 2002 ; Ndegwa & Thompson, 2001 ; Sinha et al., 2010 ) Although collection of solid wastes materials from sewage or wastewater and further drying is one of the important concerns, processing of dried municipal sewage sludge (Contreras-Ramos et al., 2005 ) and management (Ayilara et al., 2020 ) for vermicomposting could be possible way of generating organic fertilizers for future research. Vermicomposting of household solid wastes, agriculture wastes, or pulp and sugarcane industry wastes shows greater potential as fertilizer for higher crop yielding (Bhatnagar et al., 2016 ; Kesari & Jamal, 2017 ). The higher amount of solid waste comes from agricultural land and instead of utilizing it, this biomass is processed by burning, which causes severe diseases (Kesari & Jamal, 2017 ). Figure 3 shows the proper utilization of solid waste after removal from wastewater; however, Fig. 5 showing greater possibility in fertilizer conversion which has also been discussed in detail elsewhere (Bhatnagar et al., 2016 ; Nagavallemma et al., 2006 )
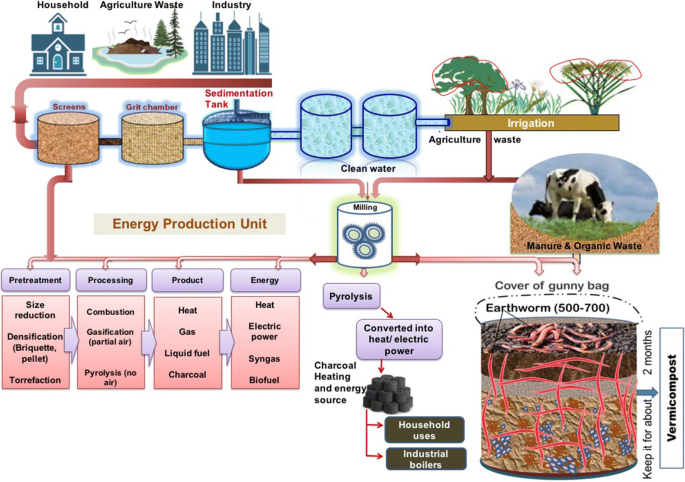
Energy production through wastewater (reproduced from Bhatnagar et al., 2016 ; Kesari & Jamal, 2017 )
9 Conclusions and future perspectives
In this paper, we have reviewed environmental and public health issues associated with the use of untreated wastewater in agriculture. We have focused on the current state of affairs concerning the wastewater treatment model and computational approach. Given the dire need for holistic approaches for cultivation, we proposed the ideas to tackle the issues related to wastewater treatment and the reuse potential of the treated water. Water resources are under threat because of the growing population. Increasing generation of wastewater (municipal, industrial, and agricultural) in developing countries especially in India and other Asian countries has the potential to serve as an alternative of freshwater resources for reuse in rice agriculture, provide appropriate treatment, and distribution measures are adopted. Wastewater treatment is one of the big challenges for many countries because increasing levels of undesired or unknown pollutants are very harmful to health as well as environment. Therefore, this review explores the ideas based on current and future research. Wastewater treatment includes very traditional methods by following primary, secondary, and tertiary treatment procedures, but the implementation of advanced techniques is always giving us a big possibility of good water quality. In this paper, we have proposed combined methods for the wastewater treatment, where the concept of the proposed model works on the various types of wastewater effluents. The proposed model not only useful for wastewater treatment but also for the utilization of solid wastes as fertilizer. An appropriate method for the treatment of wastewater and further utilization for drinking water is the main futuristic outcome. It is also highly recommendable to follow the standard methods and available guidelines provided WHO. In this paper, the proposed role of the computational model, i.e., artificial intelligence, fluid dynamics, and GIS, in wastewater treatment could be useful in future studies. In this review, health concerns associated with wastewater irrigation for farmers and irrigated crops consumers have been discussed.
The crisis of freshwater is one of the growing concerns in the twenty-first century. Globaly, about 330 km 3 of municipal wastewater is generated annually (Hernández-Sancho et al., 2015 ). This data provides a better understanding of why the reuse of treated wastewater is important to solve the issues of the water crisis. The use of treated wastewater (industrial or municipal wastewater or Seawater) for irrigation has a better future for the fulfillment of water demand. Currently, in developing countries, farmers are using wastewater directly for irrigation, which may cause several health issues for both farmers and consumers (crops or vegetables). Therefore, it is very imperative to implement standard and advanced methods for wastewater treatment. A local assessment of the environmental and health impacts of wastewater irrigation is required because most of the developed and developing countries are not using the proper guidelines. Therefore, it is highly required to establish concrete policies and practices to encourage safe water reuse to take advantage of all its potential benefits in agriculture and for farmers.
Abdel-Fatah, M. A. (2018). Nanofiltration systems and applications in wastewater treatment: Review article. Ain Shams Engineering Journal, 9 , 3077–3092.
Google Scholar
Adegoke, A. A., Faleye, A. C., Singh, G., & Stenström, T. A. (2016). Antibiotic resistant superbugs: Assessment of the interrelationship of occurrence in clinical settings and environmental niches. Molecules, 22 , E29.
Adegoke, A. A., Stenström, T. A., & Okoh, A. I. (2017). Stenotrophomonas maltophilia as an emerging ubiquitous pathogen: Looking beyond contemporary antibiotic therapy. Frontiers in Microbiology, 8 , 2276.
Adegoke, A. A., Amoah, I. D., Stenström, T. A., Verbyla, M. E., & Mihelcic, J. R. (2018). Epidemiological evidence and health risks associated with agricultural reuse of partially treated and untreated wastewater: A review. Frontiers in Public Health, 6 , 337.
Adewumia, J. R., Ilemobadea, A. A., & Vanzyl, J. E. (2010). Treated wastewater reuse in South Africa: Overview, potential, and challenges. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 55 , 221–231.
Agoro, M. A., Adeniji, A. O., Adefisoye, M. A., & Okoh, O. O. (2020). Heavy metals in wastewater and sewage sludge from selected municipal treatment plants in Eastern Cape Province, South Africa. Water, 12 , 2746.
CAS Google Scholar
Akasaka, T., & Watari, F. (2009). Capture of bacteria by flexible carbon nanotubes. Acta Biomaterialia, 5 , 607–612.
Akponikpe, P., Wima, K., Yakouba, H., & Mermoud, A. (2011). Reuse of domestic wastewater treated in macrophyte ponds to irrigate tomato and eggplants in semi-arid West-Africa: Benefits and risks. Agricultural Water Management, 98 , 834–840.
Alghobar, M. A., Ramachandra, L., & Suresha, S. (2014). Effect of sewage water irrigation on soil properties and evaluation of the accumulation of elements in Grass crop in Mysore city, Karnataka, India. American Journal of Environmental Protection, 3 , 283–291.
Al-Nakshabandi, G. A., Saqqar, M. M., Shatanawi, M. R., Fayyad, M., & Al-Horani, H. (1997). Some environmental problems associated with the use of treated wastewater for irrigation in Jordan. Agricultural Water Management, 34 , 81–94.
Amabilis-Sosa, L. E., Vázquez-López, E., García Rojas, J. L., Roé-Sosa, A., & Moeller-Chávez, G. E. (2018). Efficient bacteria inactivation by ultrasound in municipal wastewater. Environments, 5 , 47.
Amoah, I. D., Adegoke, A. A., & Stenström, T. A. (2018). Soil-transmitted helminth infections associated with wastewater and sludge reuse: A review of current evidence. Tropical Medicine & International Health, 23 (7), 692–703.
Anastasi, A., Spina, F., Prigione, V., Tigini, V., Giansanti, P., & Varese, G. C. (2010). Scale-up of a bioprocess for textile wastewater treatment using Bjerkandera adusta. Bioresource Technology, 101 , 3067–3075.
Angelakis, A., & Snyder, S. (2015). Wastewater treatment and reuse: Past, present, and future. Water, 7 , 87–95.
Angelakis, A. N., Marecos do Monte, M. H. F., Bontoux, L., & Asano, T. (1999). The status of wastewater reuse practice in the Mediterranean basin: Need for guidelines. Water Research, 33 , 2201–2217.
Asaithambi, P., & Matheswaran, M. (2016). Electrochemical treatment of simulated sugar industrial effluent: Optimization and modeling using a response surface methodology. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 9 , S981–S987.
Ayers, R. S., & Westcot, D. W. (1985). Water quality for agriculture; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United . Nations.
Ayilara, M. S., Olanrewaju, O. S., Babalola, O. O., & Odeyemi, O. (2020). Waste management through composting: Challenges and potentials. Sustainability, 12 , 4456.
Azevedo, B. F., Furieri, L. B., Peçanha, F. M., Wiggers, G. A., Vassallo, P. F., Simões, M. R., et al. (2014). Toxic effects of mercury on the cardiovascular and central nervous systems. Journal of Preventive Medicine and Public Health, 47 , 74–83.
Aziz, F., & Farissi, M. (2014). Reuse of treated wastewater in agriculture: solving water deficit problems in arid areas. Annals of West University of Timişoara Series of Biology, 17 , 95–110.
Balcom, I. N., Driscoll, H., Vincent, J., & Leduc, M. (2016). Metagenomic analysis of an ecological wastewater treatment plant’s microbial communities and their potential to metabolize pharmaceuticals. F1000 Research, 5 , 1881.
Balkhair, K. S. (2016a). Microbial contamination of vegetable crop and soil profile in arid regions under controlled application of domestic wastewater. Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences, 23 (1), S83–S92.
Balkhair, K. S. (2016b). Impact of treated wastewater on soil hydraulic properties and vegetable crop under irrigation with treated wastewater, field study and statistical analysis. Journal of Environmental Biology, 37 (5), 1143–1152.
Balkhair, K. S., & Ashraf, M. A. (2016). Field accumulation risks of heavy metals in soil and vegetable crop irrigated with sewage water in western region of Saudi Arabia. Saudi Journal of Biological Science, 23 , S32–S44.
Behling, E., Diaz, A., Colina, G., Herrera, M., Gutierrez, E., Chacin, E., et al. (1996). Domestic wastewater treatment using a UASB reactor. Bioresource Technology, 61 , 239–245.
Bent, S., & Bohm, K. (1995). Copper induced liver cirrhosis in a 13-month-old boy. Gesundheitswesen (health system in German), 57 , 667–669.
Bhatnagar, A., Kesari, K. K., & Shurpali, N. (2016). Multidisciplinary approaches to handling wastes in sugar industries. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 11 , 1–30.
Blume, T., & Neis, U. (2004). Improved wastewater disinfection by ultrasonic pre-treatment. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 11 , 333–336.
Bolong, N., Ismail, A. F., Salim, M. R., & Matsuura, T. (2009). A review of the effects of emerging contaminants in wastewater and options for their removal. Desalination, 239 , 229–246.
Bonefeld-Jorgensen, E. C., Long, M., Bossi, R., Ayotte, P., Asmund, G., Kruger, T., et al. (2011). Perfluorinated compounds are related to breast cancer risk in Greenlandic Inuit: A case control study. Environmental Health Perspectives, 10 , 88–95.
Börjesson, S., Melin, S., Matussek, A., & Lindgren, P. E. (2009). A seasonal study of the mecA gene and Staphylococcus aureus including methicillin-resistant S. aureus in a municipal wastewater treatment plant. Water Research, 43 , 925–932.
Bos, R., Carr, R., & Keraita, B. (2010). Assessing and mitigating wastewater-related health risks in low income countries: An introduction. In P. Drechsel, C. A. Scott, L. Raschid-Sally, M. Redwood, & A. Bahri (Eds.), In: Wastewater irrigation and health: Assessing and mitigating risk in low-income countries (pp. 29–47). Earthscan.
Briffa, J., Sinagra, E., & Blundell, R. (2020). Heavy metal pollution in the environment and their toxicological effects on humans. Heliyon, 6 , e04691.
Brissaud, F. (2008). Criteria for water recycling and reuse in the Mediterranean countries. Desalination, 218 , 24–33.
Broekman, S., Pohlmann, O., Beardwood, E. S., & de Meulenaer, E. C. (2010). Ultrasonic treatment for microbiological control of water systems. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 17 , 1041–1048.
Brumer, L. (2000). Use of aquatic macrophytes to improve the quality of effluents after chlorination. Ph.D. Dissertation, Technion Israel Institute of Technology, Haifa.
Busgang, A., Friedler, E., Gilboa, Y., & Gross, A. (2018). Quantitative microbial risk analysis for various bacterial exposure scenarios involving greywater reuse for irrigation. Water, 10 , 413.
Caplin, J. L., Hanlon, G. W., & Taylor, H. D. (2008). Presence of vancomycin and ampicillin-resistant Enterococcus faecium of epidemic clonal complex-17 in wastewaters from the south coast of England. Environmental Microbiology, 10 , 885–892.
Carey, C., Lee, H., & Trevors, J. (2004). Biology, persistence and detection of Cryptosporidium parvum and Cryptosporidium homynis oocyst. Water Research, 38 , 818–868.
Carr, R. (2005). WHO guidelines for safe wastewater use-more than just numbers. Irrigation and Drainage, 54 , 103–111.
CCREM. (1987). Canadian Water Quality Guidelines . Prepared by the Task Force on Water Quality Guidelines of the Canadian Council of Resource and Environment Ministers.
Chang, J. S., Chou, C., & Chen, S. Y. (2001). Decolorization of azo dyes with immobilized Pseudomonas luteola. Process Biochemistry, 36 , 757–763.
Chaoua, S., Boussaa, S., Gharmali, A. E., & Boumezzough, A. (2019). Impact of irrigation with wastewater on accumulation of heavy metals in soil and crops in the region of Marrakech in Morocco. Journal of the Saudi Society of Agricultural Sciences, 18, 429–436.
Chen, K., & Pachter, L. (2005). Bioinformatics for whole-genome shotgun sequencing of microbial communities. PLoS Computational Biology, 1 , 106–112.
Chen, W., Lu, S., Pan, N., & Jiao, W. (2013). Impacts of long-term reclaimed water irrigation on soil salinity accumulation in urban green land in Beijing. Water Resources Research, 49 , 7401–7410.
City of Cape Town (CoCT). 2007 Water services Development plan 2007/2008. www.capetown.gov.za/en/Water/WaterservicesDevPlan/Pages/WaterServDevPlan200708.aspx Accessed 12 June 2008.
Clemmens, A. J., Allen, R. G., & Burt, C. M. (2008). Technical concepts related to conservation of irrigation and rainwater in agricultural systems. Water Resources Research, 44 , 1–16.
Coleman, J., Hench, K., Garbutt, K., Sexstone, A., Bissonnette, B., & Skousen, J. (2001). Treatment of domestic wastewater by three plant species in constructed wetlands. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 3 , 283–295.
Contreras, J. D., Meza, R., Siebe, C., Rodríguez-Dozal, S., López-Vidal, Y. A., Castillo-Rojas, G., et al. (2017). Health risks from exposure to untreated wastewater used for irrigation in the Mezquital Valley, Mexico: A 25-year update. Water Research, 123 , 834–850.
Contreras-Ramos, S. M., Escamilla-Silva, E. M., & Dendooven, L. (2005). Vermicomposting of biosolids with cow manure and wheat straw. Biological Fertility of Soils, 41 , 190–198.
Craun, M. F., Craun, G. F., Calderon, R. L., & Beach, M. J. (2006). Waterborne outbreaks in the United States. Journal of Water and Health, 4 (suppl 2), 19–30.
Craun, G. F., Brunkard, J. M., Yoder, J. S., Roberts, V. A., Carpenter, J., Wade, T., et al. (2010). Causes of outbreaks associated with drinking water in the United States from 1971 to 2006. Clinical Microbiology Reviews, 23 , 507–528.
Dang, Q., Tan, W., Zhao, X., Li, D., Li, Y., Yang, T., et al. (2019). Linking the response of soil microbial community structure in soils to long-term wastewater irrigation and soil depth. The Science of the total environment, 688, 26–36.
Delgado, A., Anselmo, A. M., & Novais, J. M. (1998). Heavy metal biosorption by dried powdered mycelium of Fusarium Flocci ferum. Water Environmental Research, 70 , 370.
Dewitt, J. C., Peden-Adams, M. M., Keller, J. M., & Germolec, D. R. (2012). Immunotoxicity of perfluorinated compounds: Recent developments. Toxicologic Pathology, 40 , 300–311.
Dickin, S. K., Schuster-Wallace, C. J., Qadir, M., & Pizzacalla, K. (2016). A review of health risks and pathways for exposure to wastewater use in agriculture. Environmental Health Perspectives, 124 , 900–909.
Do-Quang, Z., Cockx, A., Line, A., & Roustan, M. (1998). Computational fluid dynamics applied to water and wastewater treatment facility modeling. Environmental Engineering and Policy, 1 , 137–147.
Drechsel, P., Scott, A., Sally, R., Redwood, M., Bachir, A. (2010). Wastewater Irrigation and Health: Assessing and Mitigating Risk in Low-Income Countries; International Water Management Institute, Ed.; Earthscan: London, UK.
Duan, J. J., Zhao, J. N., Xue, L. H., & Yang, L. Z. (2016). Nutrient removal of a floating plant system receiving low- pollution wastewater: Effects of plant species and influent concentration. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 41 , 1.
Duan, B., Zhang, W., Zheng, H., Wu, C., Zhang, Q., & Bu, Y. (2017). Comparison of health risk assessments of heavy metals and as in sewage sludge from wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) for adults and children in the Urban district of Taiyuan, China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 14 , 1194.
Duncan, M. (2009). Waste stabilization ponds: Past, present and future. Desalination and Water Treatment, 4 , 85–88.
Ecosse, D. (2001). Alternative techniques in order to meet the shortage of water in the world. Mem DESS Quality and Management of Water, Fac. Science, Amiens 62.
EEA CSI (2018). https://www.eea.europa.eu/themes/water/water-resources/water-use-by-sectors . Accessed 3 Oct 2019.
EPA (Environmental Protection Agency) (2002).National Recommended Water Quality Criteria: 2002. Office of Water, Office of Science and Technology. EPA-822-R-02-047.
Elshaw, A., Hassan, N. M. S., Khan, M. M. K. (2016). CFD modelling and optimisation of a wastewater treatment plant bioreactor—A case study. In Proceedings of the 2016 3rd Asia-Pacific World Congress on Computer science and Engineering (APWC on CSE), 232–239 https://doi.org/10.1109/APWC-on-CSE.2016.046 .
Elvira, C., Sampedro, L., Benitez, E., & Nogales, R. (1998). Vermicomposting of sludges from paper mills and dairy industries with Elsenia anderi. A pilot scale study. Journal of Bioresource Technology, 63 , 205–211.
Falkenberg, T., & Saxena, D. (2018). Impact of wastewater-irrigated urban agriculture on diarrhea incidence in Ahmedabad, India. Indian Journal of Community Medicine, 43 , 102–106.
FAO, (1985) Water Quality for Agriculture. Irrigation and Drainage Paper No. 29, Rev. 1. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Rome.
Fazeli, M. S., Khosravan, F., Hossini, M., Sathyanarayan, S., & Satish, P. N. (1998). Enrichment of heavy metals in paddy crops irrigated by paper mill effluents near Nanjangud, Mysore District, Karnataka, India. Environmental Geology, 34 , 297–302.
FEPA. (1991). Proposed National Water Quality Standards . Federal Environmental Protection Agency.
Foerstner, K. U., Von-Mering, C., & Bork, P. (2006). Comparative analysis of environmental sequences: potential and challenges. Philosophical transactions of the Royal Society of London Series B, Biological sciences, 361 , 519–523.
Founou, R. C., Founou, L. L., & Essack, S. Y. (2017). Clinical and economic impact of antibiotic resistance in developing countries: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One, 12 , e0189621. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0189621 .
Article CAS Google Scholar
Fraser-Quick, G. (2002). Vermiculture – A sustainable total waste management solution. What’s New in Waste Management?, 4 , 13–16.
Freitas, F., Alves, V. D., Pais, J., Costa, N., Oliveira, C., & Mafra, L. (2009). Characterization of an extracellular polysaccharide produced by a Pseudomonas strain grown on glycerol. Bioresource Technology, 100 , 859–865.
Freitas, F., Alves, V. D., & Reis, M. A. (2011a). Advances in bacterial exopolysaccharides: From production to biotechnological applications. Trends in Biotechnology, 29 , 388–398.
Freitas, F., Alves, V. D., Torres, C. A., Cruz, M., Sousa, I., & Melo, M. J. (2011b). Fucose-containing exopolysaccharide produced by the newly isolated Enterobacter strain A47 DSM 23139. Carbohydrate Polymers, 83 , 159–165.
Frontistis, Z., Xekoukoulotakis, N. P., Hapeshi, E., Venieri, D., Fatta-Kassinos, D., & Mantzavinos, D. (2011). Fast degradation of estrogen hormones in environmental matrices by photo-Fenton oxidation under simulated solar radiation. Chemical Engineering Journal, 178 (15), 175–182.
Fukushima, M., Ishizaki, A., & Sakamoto, M. (1970). On distribution of heavy metals in rice field soil in the “Itai-itai” disease epidemic district. Japanese Journal of Hygiene, 24 , 526–535.
Gatta, G., Libutti, A., Gagliardi, A., Disciglio, G., Beneduce, L., d’Antuono, M., Rendina, M., & Tarantino, E. (2015a). Effects of treated agro-industrial wastewater irrigation on tomato processing quality. Italian Journal of Agronomy, 10 (2), 97–100.
Gatta, G., Libutti, A., Gagliardi, A., Beneduce, L., Borruso, L., Disciglio, G., & Tarantino, G. (2015b). Treated agro-industrial wastewater irrigation of tomato crop: Effects on qualitative/quantitative characteristics of production and microbiological properties of the soil. Agricultural Water Management, 149 , 33–43.
Gehrke, I., Geiser, A., & Somborn-Schulz, A. (2015). Innovations in nanotechnology for water treatment. Nanotechnology, Science and Applications, 8 , 1–17.
Genchi, G., Sinicropi, M. S., Lauria, G., Carocci, A., & Catalano, A. (2020). The effects of cadmium toxicity. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17 , 3782.
Giddins, M. J., Macesic, N., Annavajhala, M. K., Stump, S., Khan, S., McConville, T. H., Mehta, M., Gomez-Simmonds, A., & Uhlemann, A. C. (2017). Successive emergence of ceftazidime-avibactam resistance through distinct genomic adaptations in bla(KPC-2)-harboring Klebsiella pneumoniae sequence type 307 isolates. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 62 , e02101–e02117.
Goel, J., Kadirvelu, K., Rajagopal, C., Kumar, G., & V. (2005). Removal of lead (II) by adsorption using treated granular activated carbon: Batch and column studies. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 125 (1-3), 211–220.
Goldstein, R. E. R. (2013). Antibiotic-resistant bacteria in wastewater and potential human exposure through wastewater reuse. PhD Dissertation, University of Maryland.
Gupta, P., & Diwan, B. (2017). Bacterial Exopolysaccharide mediated heavy metal removal: A review on biosynthesis, mechanism and remediation strategies. Biotechnology Reports, 13 , 58–71.
Gupta, S. K., Shin, H., Han, D., Hur, H. G., & Unno, T. (2018). Metagenomic analysis reveals the prevalence and persistence of antibiotic- and heavy metal-resistance genes in wastewater treatment. Plant Journal of Microbiology, 56 , 408–415.
GWI Global Water Intelligence. (2009). PUB study: Perspectives of water reuse . GWI Publishing.
Hall, N. (2007). Advanced sequencing technologies and their wider impact in microbiology. Journal of Experimental Biology, 210 , 1518–1525.
Halliwell, D. J., Barlow, K. M., & Nash, D. M. (2001). A review of the effects of wastewater sodium on soil physical properties and their implications for irrigation systems. Australian Journal of Soil Research, 39 , 1259–1267.
He, Y., Yuan, Q., Mathieu, J., Stadler, L., Senehi, N., Sun, R., & Alvarez, P. J. J. (2020). Antibiotic resistance genes from livestock waste: Occurrence, dissemination and treatment. npj Clean Water, 3 , 4.
Herc, E. S., Kauffman, C. A., Marini, B. L., Perissinotti, A. J., & Miceli, M. H. (2017). Daptomycin nonsusceptible vancomycin resistant Enterococcus bloodstream infections in patients with hematological malignancies: Risk factors and outcomes. Leukemia & Lymphoma, 58 , 2852–2858.
Hernández-Sancho, F., Lamizana-Diallo, B., Mateo-Sagasta, J., & Qadeer, M. (2015). Economic valuation of wastewater –The cost of action and the cost of no action . United Nations Environment Programme.
Hesnawi, R., Dahmani, K., Al-Swayah, A., Mohamed, S., & Mohammed, S. A. (2014). Biodegradation of municipal wastewater with local and commercial bacteria. Procedia Engineering, 70 , 810–814.
Hoekstra, A. Y., & Mekonnen, M. M. (2012). The water footprint of humanity. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 109 , 3232–3237.
Hua, I., & Thompson, J. E. (2000). Inactivation of E. coli by sonication at discrete ultrasonic frequencies. Water Research, 34 , 3888–3893.
Hussain, A., Priyadarshi, M., & Dubey, S. (2019). Experimental study on accumulation of heavy metals in vegetables irrigated with treated wastewater. Applied Water Science, 9 , 122.
Icgen, B., & Yilmaz, F. (2014). Co-occurrence of antibiotic and heavy metal resistance in Kizilirmak River isolates. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 93 , 735–743.
Iguchi, S., Mizutani, T., Hiramatsu, K., & Kikuchi, K. (2016). Rapid acquisition of linezolid resistance in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: Role of hypermutation and homologous recombination. PLoS One, 11 , e0155512.
Indiana State Department of Health, 2009. Diseases Involving Sewage. https://www.in.gov/isdh/22963.htm
Inoue, Y., Hoshino, M., Takahashi, H., Noguchi, T., Murata, T., & Kanzaki, Y. (2002). Bactericidal activity of Ag-zeolite mediated by reactive oxygen species under aerated conditions. Journal of Inorganic Biochemistry, 92 , 37–42.
Jacquez, R. B., Walner, H. Z. (1985). Combining nutrient removal with protein synthesis using a water hyacinth-freshwater prawn polyculture wastewater treatment system. New Mexico Water Resources Research Institute . 92.
Jaishankar, M., Tseten, T., Anbalagan, N., Mathew, B. B., & Beeregowda, K. N. (2014). Toxicity, mechanism and health effects of some heavy metals. Interdisciplinary Toxicology, 7 (2), 60–72.
Jarup, L. (2003). Hazards of heavy metal contamination. British Medical Bulletin, 68 , 167–182.
Jeong, H., Kim, H., & Jang, J. (2016). Irrigation water quality standards for indirect wastewater reuse in agriculture: A contribution toward sustainable wastewater reuse in South Korea. Water, 8 , 169.
Jia, S., Zhang, X. (2020). Biological HRPs in wastewater. In High-risk pollutants in wastewater. Eds. Ren, H. and Zhang, X. 41-67.
Jiménez, B., & Asano, T. (2008). Water reclamation and reuse around the world. In B. Jiménez & T. Asano (Eds.), In: Water reuse: An International Survey of Current Practice, Issues and Needs (pp. 3–26). IWA Publishing .
Jindal, A., Kamat, S. (2011). Water recycling and reuse for domestic and industrial sectors. Chemical Engineering World , 52-62.
Jyothi, N.R. (2020). Heavy metal sources and their effects on human health, heavy metals - Their environmental impacts and mitigation. Ed. Nazal, M. 95370.
Jyothi, N.R. and Farook, N.A.M. (2020). Mercury toxicity in public health, Heavy Metal Toxicity in Public Health. 1-12.
Jyoti, K. K., & Pandit, A. B. (2004). Ozone and cavitation for water disinfection. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 38 , 2249–2258.
Kalavrouziotis, I. K., Kokkinos, P., Oron, G., Fatone, F., Bolzonella, D., Vatyliotou, M., et al. (2015). Current status in wastewater treatment, reuse and research in some mediterranean countries. Desalination and Water Treatment, 53 , 2015–2030.
Kanwar, J., & Sandha, M. (2000). Waste water pollution injury to vegetable crops: A review. Agricultural Research Communication Centre, India, 21 , 133–136.
Katsoyiannis, I. A., Gkotsis, P., Castellana, M., Cartechini, F., & Zouboulis, A. I. (2017). Production of demineralized water for use in thermal power stations by advanced treatment of secondary wastewater effluent. Journal of Environmental Management, 1 (190), 132–139.
Kenny, J. F., Barber, N. L., Hutson, S. S., Linsey, K. S., Lovelace, J. K., & Maupin, M. A. (2009). Estimated use of water in the United States in 2005. U.S. Geological Survey Circular, 1344 , 52.
Kesari, K. K., & Behari, J. (2008). Ultrasonic impact on bacterial population in sewage sample. International Journal of Environment and Waste Management, 2 , 233–244.
Kesari, K. K., Jamal, Q. M. S. (2017). Review Processing, properties and applications of agricultural solid waste: Effect of an open burning in environmental toxicology. In: Kesari K. (eds) Perspectives in Environmental Toxicology. Environmental Science and Engineering . Springer, Cham. Chapter 8:161-181.
Kesari, K. K., Kumar, S., Verma, H. N., & Behari, J. (2011a). Influence of ultrasonic treatment in sewage sludge. Hydrology: Current Research, 2 , 115.
Kesari, K. K., Verma, H. N., & Behari, J. (2011b). Physical methods in wastewater treatment. International Journal of Environmental Technology and Management, 14 , 43–66.
Khaskhoussy, K., Kahlaoui, B., Messoudi, N. B., Jozdan, O., Dakheel, A., & Hachicha, M. (2015). Effect of treated wastewater irrigation on heavy metals distribution in a Tunisian soil. Engineering Technology and Applied Science Research, 5 , 805–810.
Kim, S. Y., Kim, J. H., Kim, C. J., & Oh, D. K. (1996). Metal adsorption of the polysaccharide produced from Methylobacterium organophilum. Biotechnology Letters, 18 , 1161–1164.
Kim, B. H., Kang, Z., Ramanan, R., Choi, J. E., Cho, D. H., Oh, H. M., et al. (2014). Nutrient removal and biofuel production in high rate algal pond using real municipal wastewater. Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 24 , 1123–1132.
Kinuthia, G. K., Ngure, V., Beti, D., Lugalia, R., Wangila, A., & Kamau, L. (2020). Levels of heavy metals in wastewater and soil samples from open drainage channels in Nairobi, Kenya: community health implication. Scientific Reports, 10 , 8434 .
Kocabas, Z. O., Aciksoz, B., Yurum, Y. (2012). Binding mechanisms of As(III) on activated carbon/titanium dioxide nanocomposites: a potential method for arsenic removal from water, MRS online proceedings library. Published online by Cambridge University Press 1449.
König, M., Escher, B. I., Neale, P. A., Krauss, M., Hilscherová, K., Novák, J., et al. (2017). Impact of untreated wastewater on a major European river evaluated with a combination of in vitro bioassays and chemical analysis. Environmental Pollution, 220 (Part B), 1220–1230.
Kumar, R., & Chawla, J. (2014). Removal of cadmium ion from water/wastewater by nano-metal oxides. Water Quality Exposure and Health, 5 , 4.
Kumar, M., Kesari, K. K., & Behari, J. (2010). Low frequency ultrasonic irradiation of activated sludge. International Journal of Environment and Pollution, 43 , 52–65.
Kumar, S. S., Shantkriti, S., Muruganandham, T., Murugesh, E., Rane, N., & Govindwar, N. P. (2016). Bioinformatics aided microbial approach for bioremediation of wastewater containing textile dyes. Ecological Informatics, 31 , 112–121.
Kumar, A., Ali, M., Kumar, R., Kumar, M., Sagar, P., Pandey, R. K., et al. (2021). Arsenic exposure in Indo Gangetic plains of Bihar causing increased cancer risk. Scientific Reports, 11 , 2376.
Leddy, M. B., Plumlee, M. H., Kantor, R. S., Nelson, K. L., Miller, S. E., Kennedy, L. C., et al. (2018). High-throughput DNA sequencing to profile microbial water quality of potable reuse. Water online, 1-4.
Lee, I., & Viberg, H. (2013). A single neonatal exposure to perfluorohexane sulfonate (PFHxS) affects the levels of important neuroproteins in the developing mouse brain. Neurotoxicology, 37 , 190–196.
Libutti, A., Gatta, G., Gagliardi, A., Vergine, P., Pollice, A., Beneduce, L., Disciglio, G., & Tarantino, E. (2018). Agro-industrial wastewater reuse for irrigation of a vegetable crop succession under Mediterranean conditions. Agricultural Water Management, 196 , 1–14.
Liu, J., Ma, Y., Xu, T., & Shao, G. (2010). Preparation of zwitterionic hybrid polymer and its application for the removal of heavy metal ions from water. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 178 , 1021–1029.
Lv, L., Yu, X., Xu, Q., & Ye, C. (2015). Induction of bacterial antibiotic resistance by mutagenic halogenated nitrogenous disinfection byproducts. Environmental Pollution, 205 , 291–298.
Madsen, H., Poultsen, L., & Grandjean, P. (1990). Risk of high copper content in drinking water. Ugeskr Laeger (Journal of the Danish Medical Association), 152 (25), 1806–1809.
Mahendran, R., Ramli, N. H., & Abdurrahman, H. N. (2014). Study the effect of using ultrasonic membrane anaerobic system in treating sugarcane waste and methane gas production. International Journal of Research in Engineering and Technology, 3 , 299–303.
Mahfooz, Y., Yasar, A., Guijian, L., Islam, Q. U., Akhtar, A. B. T., Rasheed, R., Irshad, S., & Naeem, U. (2020). Critical risk analysis of metals toxicity in wastewater irrigated soil and crops: a study of a semi-arid developing region. Scientific Reports, 10 , 12845.
Mahmood, A., & Malik, R. N. (2014). Human health risk assessment of heavy metals via consumption of contaminated vegetables collected from different irrigation sources in Lahore. Pakistan, Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 7 (1), 91–99.
Mañas, P., Castro, E., & Heras, J. (2009). Irrigation with treated wastewater: effects on soil, lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) crop and dynamics of microorganisms. Journal of Environmental Science and Health, 44 , 1261.
Marchal, M., Briandet, R., Koechler, S., Kammerer, B., & Bertin, P. N. (2010). Effect of arsenite on swimming motility delays surface colonization in Herminiimona sarsenicoxydans. Microbiology, 156 , 2336–2342.
Marcussen, H., Holm, P. E., Ha, L. T., & Dalsgaard, A. (2007). Food safety aspects of toxic element accumulation in fish from wastewater-feed ponds in Hanoi, Vietnam . Tropical Medicine & International Health, 12 , 34–39.
Marsh, S. (2007). Pyrosequencing applications. Methods in Molecular Biology, 373 , 15–24.
Meehan, C., Bjourson, A. J., & McMullan, G. (2001). Paeni bacillus azoreducens sp. nov., a synthetic azo dye decolorizing bacterium from industrial wastewater. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 51 , 1681–1685.
Mehmood, A., Mirza, A. S., Choudhary, M. A., Kim, K. H., Raza, W., Raza, N., Lee, S. S., Zhang, M., Lee, J. H., & Sarfraz, M. (2019). Spatial distribution of heavy metals in crops in a wastewater irrigated zone and health risk assessment. Environmental Research, 168 , 382–388.
Melanta, S. (2008). Aquatic bacteria removal using carbon nanotubes. Biological and Agricultural Engineering Undergraduate Thesis . University of Arkansas.
Mohammad, M., & Mazahreh, N. (2003). Changes in soil fertility parameters in response to irrigation of forage crops with secondary treated wastewater. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 34 , 181–1294.
Mohammad, A. W., Teow, Y. H., Ang, W. L., Chung, Y. T., Oatley-Radcliffe, D. L., & Hila, N. (2015). Nanofiltration membranes review: Recent advances and future prospects. Desalination, 356 , 226–254.
Mohsen, M. S. (2004). Treatment and reuse of industrial effluents: Case study of a thermal power plant. Desalination, 167 , 75–86.
Mostafaii, G., Chimehi, E., Gilasi, H. R., & Iranshahi, L. (2017). Investigation of zinc oxide nanoparticles effects on removal of total coliform bacteria in activated sludge process effluent of municipal wastewater. Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 1 , 49–55.
Naddeo, V., Belgiorno, V., Ricco, D., & Kassinos, D. (2009). Degradation of diclofenac by sonolysis, ozonation and their simultaneous application. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 16 , 790–794.
Nagavallemma, K. P., Wani, S. P., Lacroix, S., Padmaja, V. V., Vineela, C., Babu, R. M., & Sahrawat, K. L. (2006). Vermicomposting: recycling wastes into valuable organic fertilizer. SAT eJournal, 2 , 1–16.
Narain, D. M., Bartholomeus, R. P., Dekker, S. C., & Van Wezel, A. P. (2020). Natural purification through soils: Risks and opportunities of sewage effluent reuse in sub-surface irrigation. In In: Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology (Continuation of Residue Reviews) (pp. 1–33). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/398_2020_49 .
Naylor, N. R., Atun, R., Zhu, N., Kulasabanathan, K., Silva, S., Chatterjee, A., Knight, G. M., & Robotham, J. V. (2018). Estimating the burden of antimicrobial resistance: a systematic literature review. Antimicrobial Resistance and Infection Control, 7 , 58.
Ndegwa, P. M., & Thompson, S. A. (2001). Integrated composting and vermicomposting in the treatment and bioconversion of biosolids. Bioresource Technology, 76 , 107–112.
Nizam, N. U. M., Hanafiah, M. M., Noor, I. M., & Karim, H. I. A. (2020). Efficiency of five selected aquatic plants in phytoremediation of aquaculture wastewater. Applied Sciences, 10 , 2712.
Njuguna, S. M., Makokha, V. A., Yan, X., Gituru, R. W., Wang, Q., & Wang, J. (2019). Health risk assessment by consumption of vegetables irrigated with reclaimed wastewater: A case study in Thika (Kenya). Journal of Environmental Management, 231 , 576–581.
Nmaya, M. M., Agam, M. A., Matias-Peralta, H. M., Yabagi, J. A., & Kimpa, M. I. (2017). Freshwater green microalga for bioremediation of river melaka heavy metals contamination. Journal of Science and Technology, 9 , 118–123.
Nour, A. H., & Zainal, Z. (2014). Membrane fouling control by ultrasonic membrane anaerobic system (UMAS) to produce methane gas. International Journal of Engineering Science Research Technology, 3 , 487–497.
Nourani, V., Elkiran, G., & Abba, S. I. (2018). Wastewater treatment plant performance analysis using artificial intelligence – An ensemble approach. Water Science and Technology, 78 (10), 2064–2076.
Numberger, D., Ganzert, L., Zoccarato, L., Mühldorfer, K., Sauer, S., & Grossart, H. P. (2019). Characterization of bacterial communities in wastewater with enhanced taxonomic resolution by full-length 16S rRNA sequencing. Scientific Reports, 9 , 9673.
Odigie, J. O. (2014). Harmful effects of wastewater disposal into water bodies: A case review of the Ikpoba river, Benin city, Nigeria. Tropical Freshwater Biology, 23 , 87–101.
Oilgae Guide to Algae-based Wastewater Treatment. (2014). Commonly used algae strains for wastewater treatment. http://www.oilgae.com/blog/2014/01/commonly-used-algae-strains-for-waste-water-treatment.html . Accessed 5 May 2021
Okoh, A. I., Sibanda, T., & Gusha, S. S. (2010). Inadequately treated wastewater as a source of human enteric viruses in the environment. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 7 , 2620–2637.
Oturan, M. A., & Aaron, J. J. (2014). Advanced oxidation processes in water/wastewater treatment: Principles and applications. A review. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 44 , 2577–2641.
Paleologou, A., Marakas, H., Xekoukoulotakis, N. P., Moya, A., Vergara, Y., Kalogerakis, N., Gikas, P., & Mantzavinos, D. (2007). Disinfection of water and wastewater by TiO2 photocatalysis, sonolysis and UV-C irradiation. Catalysis Today, 129 , 136–142.
Pan, B., & Xing, B. S. (2008). Adsorption mechanisms of organic chemicals on carbon nanotubes. Environmental Science and Technology, 42 , 9005–9013.
Panthi, S., Sapkota, A. R., Raspanti, G., Allard, S. M., Bui, A., Craddock, H. A., Murray, R., et al. (2019). Pharmaceuticals, herbicides, and disinfectants in agricultural water sources. Environmental Research, 174 , 1–8.
Park, K. Y., Maeng, S. K., Song, K. G., & Ahn, K. H. (2008). Ozone treatment of wastewater sludge for reduction and stabilization. Journal Environmental Science Health. Part A, Toxic/Hazardous Substances & Environmental Engineering, 43 , 1546–1550.
Pedrero, F., Kalavrouziotis, I., Alarcón, J. J., Koukoulakis, P., & Asano, T. (2010). Use of treated municipal wastewater in irrigated agriculture. Review of some practices in Spain and Greece. Agricultural Water Management, 97 , 1233–1241.
Peng, S. M., Chen, Y. D., Guo, W. Q., Yang, S. S., Wu, Q. L., Luo, H. C., & Ren, N. Q. (2014). The Application of computational fluid dynamics (CFD) in wastewater biological treatment field. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 507 , 711–715.
Pesoutova, R., Hlavinek, P., & Matysikova, J. (2011). Use of advanced oxidation processes for textile wastewater treatment- A review. Food and Environmental Safety, 10 , 59–65.
Petrier, C., Jeunet, A., Luche, J. L., & Reverdy, G. (1992). Unexpected frequency effects on the rate of oxidative processes induced by ultrasound. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 25 , 148–3150.
Pham-Duc, P., Nguyen-Viet, H., Hattendorf, J., et al. (2014). Diarrhoeal diseases among adult population in an agricultural community Hanam province, Vietnam, with high wastewater and excreta reuse. BMC Public Health, 14 , 978.
Phull, S. S., Newman, A. P., Lorimer, J. P., Pollet, T. J., & Mason, T. J. (1997). The development and evaluation of ultrasound in the biocidal treatment of water. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 4 , 157–164.
Poustie, A., Yang, Y., Verburg, P., Pagilla, K., & Hanigan, D. (2020). Reclaimed wastewater as a viable water source for agricultural irrigation: A review of food crop growth inhibition and promotion in the context of environmental change. Science of the Total Environment, 739 , 139756.
Punshon, T., Jackson, B. P., Meharg, A. A., Warczack, T., Scheckel, K., & Guerinot, M. L. (2017). Understanding arsenic dynamics in agronomic systems to predict and prevent uptake by crop plants. Science of the Total Environment, 581–582 , 209–220.
Puzas, J. E., Campbell, J., O’Keefe, R. J., & Rosier, R. N. (2004). Lead toxicity in the skeleton and its role in osteoporosis. In Nutrition and Bone Health (pp. 373–376). Humana Press.
Qadir, M., Wichelns, D., Raschid-Sally, L., McCornick, P. G., Drechsel, P., Bahri, A., et al. (2010). The challenges of wastewater irrigation in developing countries. Agricultural Water Management, 97 , 561–568.
Raes, J., Foerstner, K. U., & Bork, P. (2007). Get the most out of your metagenome: Computational analysis of environmental sequence data. Current Opinion in Microbiology, 10 , 490–498.
Ramadas, M., & Samantaray, A. K. (2018). Applications of remote sensing and GIS in water quality monitoring and remediation: A state-of-the-art review. In S. Bhattacharya, A. Gupta, A. Gupta, & A. Pandey (Eds.), Water remediation. Energy, Environment, and Sustainability . Springer.
Rizvi, H., Ahmad, N., Abbas, F., Bukhari, I. H., Yasar, A., Ali, S., Yasmeen, T., & Riaz, M. (2015). Start-up of UASB reactors treating municipal wastewater and effect of temperature/sludge age and hydraulic retention time (HRT) on its performance. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 8 , 780–786.
Russ, R., Rau, J., & Stolz, A. (2000). The function of cytoplasmic flavin reductases in the reduction of azodyes by bacteria. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 66 , 1429–1434.
Sacks, M., & Bernstein, N. (2011). Utilization of reclaimed wastewater for irrigation of field-grown melons by surface and subsurface drip irrigation. Israel Journal of Plant Sciences, 59 , 159–169.
Sağ, Y. (2001). Biosorption of heavy metals by fungal biomass and modeling of fungal biosorption: A review. Separation and Purification Reviews, 30 , 1–48.
Salem, H. M., Eweida, E. A., & Farag, A. (2000). Heavy metals in drinking water and their environmental impact on human health (pp. 542–556). ICEHM .
Samarghandi, M. R., Nouri, J., Mesdaghinia, A. R., Mahvi, A. H., Nasseri, S., & Vaezi, F. (2007). Efficiency removal of phenol, lead and cadmium by means of UV/TiO2/H2O2 processes. International journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 4 , 19–25.
Samie, A., Obi, L., Igumbor, O., & Momba, B. (2009). Focus on 14 sewage treatment plants in the Mpumalanga province, South Africa in order to gauge the efficiency of wastewater treatment. African Journal of Microbiology Research, 8 , 3276–3285.
Samstag, R. W., Ducoste, J. J., Griborio, A., Nopens, I., Batstone, D. J., Wicks, J., & Laurent, J. (2016). CFD for wastewater treatment: An overview. Water Science and Technology, 74 , 549–563.
Santajit, S., & Indrawattana, N. (2016). Mechanisms of antimicrobial resistance in ESKAPE pathogens. BioMed Research International, 2016 , 2475067.
Sato, T., Qadir, M., Yamamoto, S., Endo, T., & Zahoor, A. (2013). Global, regional, and country level need for data on wastewater generation, treatment, and use. Agricultural Water Management, 130 , 1–13.
Scherba, G., Weigel, R. M., & Obrien, W. D. (1991). Quantitative assessment of the germicidal efficacy of ultrasonic energy. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 57 , 2079–2084.
Schloss, P. D., & Handelsman, J. (2005). Metagenomics for studying unculturable microorganisms: Cutting the Gordian knot. Genome Biology, 6 , 229.
Schmeisser, C., Steele, H., & Streit, W. R. (2007). Metagenomics, biotechnology with non-culturable microbes. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 75 , 955–962.
Scott, C. A., Faruqui, N. I., & Raschid-Sally, L. (2004). Wastewater use in irrigated agriculture: Management challenges in developing countries. In C. A. Scott, N. I. Faruqui, & L. Raschid-Sally (Eds.), Wastewater use in irrigated agriculture: Confronting the livelihood and environmental realities (pp. 1–10). CABI Publishing.
Scott, C. A., Drechsel, P., Raschid-Sally, L., Bahri, A., Mara, D., Redwood, M., et al. (2009). Wastewater irrigation and health: Challenges and Outlook for mitigating risks in low-income countries. In P. Drechsel, C. A. Scott, L. Raschid-Sally, M. Redwood, & A. Bahri (Eds.), In: Wastewater irrigation and health: Assessing and mitigating risk in low-income countries (pp. 381–394). Earthscan .
Sengupta, S., Nawaz, T., & Beaudry, J. (2015). Nitrogen and phosphorus recovery from wastewater. Current Pollution Reports, 1 , 155–166.
Shakir, R., Davis, S., Norrving, B., Grisold, W., Carroll, W. M., Feigin, V., & Hachinski, V. (2016). Revising the ICD: Stroke is a brain disease. Lancet, 19 , 2475–2476.
Sharma, N. K., Bhardwaj, S., Srivastava, P. K., Thanki, Y. J., Gadhia, P. K., & Gadhia, M. (2012). Soil chemical changes resulting from irrigating with petrochemical effluents. International journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 9 , 361–370.
Sheet, I., Kabbani, A., & Holail, H. (2014). Removal of heavy metals using nanostructured graphite oxide, silica nanoparticles and silica/ graphite oxide composite. Energy Procedia, 50 , 130–138.
Shen, Y., Oki, T., Kanae, S., Hanasaki, N., Utsumi, N., & Kiguchi, M. (2014). Projection of future world water resources under SRES scenarios: An integrated assessment. Hydrological Sciences Journal, 59 , 1775–1793.
Shuval, H. I., Yekutiel, P., & Fattal, B. (1985). Epidemiological evidence for helminth and cholera transmission by vegetables irrigated with wastewater. Jerusalem - Case study. Water Science and Technology, 17 , 433–442.
Siezen, R. J., & Galardini, M. (2008). Genomics of biological wastewater treatment. Microbial Biotechnology, 1 , 333–340.
Singh, A., Sawant, M., Kamble, S. J., Herlekar, M., Starkl, M., Aymerich, E., et al. (2019). Performance evaluation of a decentralized wastewater treatment system in India. Environmental Science and Pollution, 26 , 21172–21188.
Sinha, R. K., Herat, S., Bharambe, G., & Brahambhatt, A. (2010). Vermistabilization of sewage sludge (biosolids) by earthworms: Converting a potential biohazard destined for land disposal into a pathogen free, nutritive and safe biofertilizer for farms. Waste Management and Research, 28 , 872–881.
Smith, R. G. (1995). Water reclamation and reuse. Water Environment Research, 67 , 488–495.
Soni, R., Pal, A. K., Tripathi, P., Lal, J. A., Kesari, K., & Tripathi, V. (2020). An overview of nanoscale materials on the removal of wastewater contaminants. Applied Water Science, 10 , 189.
Spina, F., Anastasi, A., Prigione, V., Tigini, V., & Varese, G. C. (2012). Biological treatment of industrial wastewaters: A fungal approach. Chemical Engineering Transactions, 27 , 175–180.
Srivastava, A., Srivastava, O. N., Talapatra, S., Vajtai, R., & Ajayan, P. M. (2004). Carbon nanotube filters. Nature Materials, 3 , 610–614.
SWRCB (2011) Order No. R3-2011-0222: waste discharge requirements NPDES general permit for discharges of highly treated groundwater to surface waters, NPDES NO. CAG993002, California State Water Quality Control Board.
Tacconelli, E., Carrara, E., Savoldi, A., Harbarth, S., Mendelson, M., Monnet, D. L., et al. (2018). Discovery, research, and development of new antibiotics: The WHO priority list of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and tuberculosis. The Lancet Infectious Diseases, 18 , 318–327.
Tanji, K. K., & Kielen, N. C. (2002). Agricultural drainage water management in arid and semi-arid areas. In FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper (p. 61). Food and Agriculture Organization.
Taylor, A. A., Tsuji, J. S., Garry, M. R., McArdle, M. E., Goodfellow Jr., W. L., Adams, W. J., et al. (2020). Critical review of exposure and effects: Implications for setting regulatory health criteria for ingested copper. Environmental Management, 65 , 131–159.
Templeton, M. R., Graham, N., & Voulvoulis, N. (2009). Emerging chemical contaminants in water and wastewater. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A, 367 , 3873–3875.
Toze, S. (1997). Microbial pathogens in wastewater. CSIRO Land and Water Technical report 1/97.
Tringe, S. G., Von-Merling, C., Kobayashi, A., Salamov, A. A., Chen, K., & Chang, H. W. (2005). Comparative metagenomics of microbial communities. Science, 308 , 554–557.
Tripathi, V., Tripathi, P. (2017). Antibiotic resistance genes: An emerging environmental pollutant. K.K. Kesari (ed.), Perspectives in Environmental Toxicology , 183-201.
Tsagarakis, K. P., Tsoumanis, P., Chartzoulakis, K., & Angelakis, A. N. (2001). Water resources status including wastewater treatment and reuse in Greece. Water International, 26 , 252–258.
Tytła, M. (2019). Assessment of heavy metal pollution and potential ecological risk in sewage sludge from municipal wastewater treatment plant located in the most industrialized region in Poland—Case study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16 , 2430.
Ungureanu, N., Vlăduț, V., Dincă, M., Zăbavă, B. Ș. (2018). Reuse of wastewater for irrigation, a sustainable practice in arid and semi-arid regions. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Thermal Equipment, Renewable Energy and Rural Development (TE-RE-RD), Drobeta-Turnu Severin, Romania, 31 May–2 June. pp. 379–384.
Ungureanu, N., Vlăduț, V., & Voicu, G. (2020). Water Scarcity and wastewater reuse in crop irrigation. Sustainability, 12 (21), 9055.
Upadhyay, K., & Srivastava, J. K. (2005). Application of ozone in the treatment of industrial and municipal wastewater. Journal of Industrial Pollution Control, 21 , 235–245.
US EPA. (2004). Guidelines for Water Reuse 625/R-04/108 . Environmental Protection Agency.
US EPA. (2012). Guidelines for Water Reuse 600/R-12/618 . Environmental Protection Agency.
Vélez, E., Campillo, G. E., Morales, G., Hincapié, C., Osorio, J., Arnache, O., et al. (2016). Mercury removal in wastewater by iron oxide nanoparticles. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 687 , 012050.
Vergili, I. (2013). Application of nanofiltration for the removal of carbamazepine, diclofenac and ibuprofen from drinking water sources. Journal of Environmental Management, 127 , 177–187.
Vogelmann, E. S., Awe, G. O., & Prevedello, J. (2016). Selection of plant species used in wastewater treatment. In Wastewater treatment and reuse for metropolitan regions and small cities in developing countries (pp. 1–10). Publisher.
Volesky, B. (1994). Advances in biosorption of metals: Selection of biomass types. FEMS Microbiology Reviews (Amsterdam), 14 , 291–302.
Von-Sperling, M., & Chernicharo, C. A. L. (2005). Biological Wastewater treatment in warm climate regions (1st ed.p. 810). IWA Publishing.
Wani, A. L., Ara, A., & Usmani, J. A. (2015). Lead toxicity: a review. Interdisciplinary Toxicology, 8 , 55–64.
Webster, G. M. (2010). Chemicals, Health and Pregnancy Study (CHirP). Vancouver, BC: University of British Columbia, Centre for Health and Environment Research (CHER) and School for Occupational and Environmental Hygiene (SOEH). http://www.ncceh.ca/sites/default/files/Health_effects_PFCs_Oct_2010.pdf . Accessed Sept 2019.
Westcot, D. W. (1997). Quality control of wastewater for irrigated crop production. In In Chapter 2 - Health risks associated with wastewater use FAO Water Report (10th ed., p. 86).
WHO (1973) WHO meeting of experts on the reuse of effluents: Methods of wastewater treatment and health safeguards & World Health Organization. Reuse of effluents: Methods of wastewater treatment and health safeguards, report of a WHO meeting of experts [meeting held in Geneva from 30 November to 6 December 1971].
WHO. (1989) Health guidelines for the use of wastewater in agriculture and aquaculture. Technical Report Series No. 74. World Health Organization, Geneva.
WHO (2003).Copper in drinking-water. Background document for preparation of WHO Guidelines for drinking-water quality. Geneva, World Health Organization (WHO/SDE/WSH/03.04/88).
WHO-World Health Organization. (2006). Guidelines for the Safe Use of Wastewater, Excreta and Greywater . In Wastewater Use in Agriculture (2nd ed.). WHO-World Health Organization.
Winpenny, J., Heinz, I., Koo-Oshima, S., Salgot, M., Collado, J., Hernandex, F., et al. (2010). The Wealth of waste: The economics of wastewater use in agriculture. In Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (p. 35). FAO Water Reports .
World Bank. (2010). Improving wastewater use in agriculture: An emerging priority (p. 169). A report of the Water Partnership Program.
World Resources Institute (WRI), (2020) Aqueduct country rankings. Available online: https://www.wri.org/applications/aqueduct/country-rankings/ Accessed 3 Sept 2020.
Xiao, R., Wang, S., Li, R., Wang, J. J., & Zhang, Z. (2017). Ecotoxicology and environmental safety soil heavy metal contamination and health risks associated with artisanal gold mining in Tongguan, Shaanxi, China. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 141 , 17–24.
Xu, Y. B., Hou, M., Li, Y. F., Huang, L., Ruan, J. J., Zheng, L., et al. (2017). Distribution of tetracycline resistance genes and AmpC β-lactamase genes in representative non-urban sewage plants and correlations with treatment processes and heavy metals. Chemosphere, 170 , 274–281.
Xu, S., Yan, N., Cui, M., & Liu, H. (2020). Decomplexation of Cu(II)/Ni(II)-EDTA by ozone-oxidation process. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27 , 812–822.
Yadav, R. K., Goyal, B., Sharma, R. K., Dubey, S. K., & Minhas, P. S. (2002). Post-irrigation impact of domestic sewage effluent on composition of soils, crops and ground water—A case study. Environment International, 28 , 481–486.
Yang, J., Jia, R., Gao, Y., Wang, W., & Cao, P. (2017). The reliability evaluation of reclaimed water reused in power plant project. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 100 , 012189.
Yaqub, A., Ajab, H., Isa, M. H., Jusoh, H., Junaid, M., & Farooq, R. (2012). Effect of ultrasound and electrode material on electrochemical treatment of industrial wastewater. Journal of New Materials for Electrochemical Systems, 15 , 289–292.
Yuen, H. W., & Becker, W. (2020). Iron toxicity. [Updated 2020 Jun 30]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing; Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459224/ .
Zahmatkesh, M., Spanjers, H., Jules, B., & Lier, V. (2018). A novel approach for application of white rot fungi in wastewater treatment under non-sterile conditions: Immobilization of fungi on sorghum. Environmental Technology, 39 (16), 2030–2040.
Zaman, S. B., Hussain, M. A., Nye, R., Mehta, V., Mamun, K. T., & Hossain, N. (2017). A review on antibiotic resistance: Alarm bells are ringing. Cureus, 9 , e1403.
Zamora, S., Marín-Muñíz, J. L., Nakase-Rodríguez, C., Fernández-Lambert, G., & Sandoval, L. (2019). Wastewater treatment by constructed wetland eco-technology: Influence of mineral and plastic materials as filter media and tropical ornamental plants. Water, 11 , 2344.
Zekić, E., Vuković, Z., & Halkijević, I. (2018). Application of nanotechnology in wastewater treatment. GRAĐEVINAR, 70 , 315–323.
Zhang, H., & Reynolds, M. (2019). Cadmium exposure in living organisms: A short review. Science of the Total Environment, 678 , 761–767.
Zhang, Y., & Shen, Y. (2017). Wastewater irrigation: Past, present, and future. Wastewater treatment: Aims and challenges. Water, 6 (3), e1234. https://doi.org/10.1002/wat2.1234 .
Article Google Scholar
Zhou, X., & Wang, G. (2010). Nutrient concentration variations during Oenantheja vanica growth and decay in the ecological floating bed system. Journal of Environmental Sciences (China), 22 , 1710–1717.
Zhu, L., Li, Z., & Ketola, T. (2011). Biomass accumulations and nutrient uptake of plants cultivated on artificial floating beds in China’s rural area. Ecological Engineering, 37 , 1460–1466.
Zimmels, Y., Kirzhner, F., & Roitman, S. (2004). Use of naturally growing aquatic plants for wastewater purification. Water Environmental Research, 76 , 220.
Download references
Acknowledgements
All the authors are highly grateful to the authority of the respective departments and institutions for their support in doing this research. The author VT would like to thank Science & Engineering Research Board, New Delhi, India (Grant #ECR/2017/001809). The Author RS is thankful to the University Grants Commission for the National Fellowship (201819-NFO-2018-19-OBC-UTT-78476).
Open access funding provided by Aalto University.
Author information
Kavindra Kumar Kesari and Ramendra Soni contributed equally to this work.
Authors and Affiliations
Department of Applied Physics, Aalto University, Espoo, Finland
Kavindra Kumar Kesari & Janne Ruokolainen
Department of Molecular and Cellular Engineering, Sam Higginbottom University of Agriculture, Technology and Sciences, Naini, Allahabad, India
Ramendra Soni, Jonathan A. Lal & Vijay Tripathi
Department of Health Informatics, College of Public Health and Health Informatics, Qassim University, Al Bukayriyah, Saudi Arabia
Qazi Mohammad Sajid Jamal
Department of Computational Biology and Bioinformatics, Sam Higginbottom University of Agriculture, Technology and Sciences, Naini, Allahabad, India
Pooja Tripathi
Department of Biotechnology, School of Engineering & Technology, Sharda University, Greater Noida, UP, India
Niraj Kumar Jha
Department of Bioengineering, Faculty of Engineering, Integral University, Lucknow, India
Mohammed Haris Siddiqui
Department of Forestry, NERIST, Nirjuli, Arunachal Pradesh, India
Pradeep Kumar
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding authors
Correspondence to Kavindra Kumar Kesari , Mohammed Haris Siddiqui or Vijay Tripathi .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Kesari, K.K., Soni, R., Jamal, Q.M.S. et al. Wastewater Treatment and Reuse: a Review of its Applications and Health Implications. Water Air Soil Pollut 232 , 208 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-021-05154-8
Download citation
Received : 12 January 2020
Accepted : 25 April 2021
Published : 10 May 2021
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-021-05154-8
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Bio-computation
- Environmental pollution
- Human health
- Sustainable agriculture
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
A - Z Topics
167 Water Essay Topics & Research Questions about Water
Looking for a research title about water shortage, conservation, pollution, or treatment? Whatever your area of interest is, you will definitely find a good writing idea in this list of titles for water essays! Topics we’ve collected here are fresh, unique, and current. Go ahead and read them below!
🏆 Best Essay Topics on Water
💡 simple water essay titles, 👍 good water research topics & essay examples, 📌 easy water essay topics, 🎓 most interesting water topics for project, ❓ research questions about water.
- Water Accessibility and Quality
- Water Pollution Causes, Effects and Solutions
- The Water Cycle and the Impact of Human Activity on It
- Effects of Water Pollution on Human Health
- Water in the Atmosphere
- How Access to Clean Water Influences the Problem of Poverty
- Don’t Ship Air and Don’t Ship Water Strategies
- The Importance of Water for Body Water is important for all the structural elements of our body and their efficient functioning. A person is not able to feel healthy if he does not consume water.
- Water and Soil Management Maintaining soil water balance has a long history and is practiced in many countries, arguing that human activities are threatening the quality of water and soil.
- Water Quality and Contamination Experiment Report This paper seeks to provide a detailed report on what should be done to ensure quality water for human consumption.
- The Environmental Impact of Bottled Water This paper examines the real situational effects on production of the bottled water to environmental degradation.
- Garbage Pollution’s Impact on Air, Water and Land Garbage pollutes the planet, and to stop this adverse effect, the authorities’ involvement is needed. One solution lies in the plane of economics and politics.
- New Evian Water Product and Customers Analysis As the new Evian water product is a more ecological option, customers concerned about the environment could also represent the client base of the product.
- Activation Energy for Viscous Flow of Water, Acetone, Toluene, and o-Xylene The aim of the research was to investigate the hypothesis that the activation energy of a substance depends on intermolecular forces that arise in this substance.
- Impact of Food Waste and Water Use on Earth The paper explores how food waste and water use affect the food system and how agriculture affects the environment.
- Glacéau Company: Vitamin Water Ethics The business practice of this paper is the production and sale of vitamin water by Glacéau in which the company states that the water being sold has been “enriched” with vitamins.
- Water and Its Properties Water is the most abundant liquid on the universe comprising over 70% of earth’s composition. It exists in three forms namely liquid, solid, and gaseous states.
- Water Recycling: Why Is It Important? Different countries face varying challenges in as far as provision of clean water to its population is concerned depending with its economic development level and geographic location.
- Cooling Water System Overview Water towers can reduce temperatures more than any other devices using air only to reject heat hence are more cost-effective.
- FIJI Water Company’s Success The business owners of FIJI Water embarked on a very active marketing campaign aimed at the promotion of the water, as well as the establishment and maintenance of FIJI Water’s brand.
- Water Scarcity as Effect of Climate Change Climate change is the cause of variability in the water cycle, which also reduces the predictability of water availability, demand, and quality, aggravating water scarcity.
- Land Usage and Water Quality in Saudi Arabia The effect of land use in Saudi Arabian water quality has intensified the region’s water crisis, causing economic, ecological, and social challenges.
- The Problem of Water Scarcity The paper states that although the problem of scarcity of water is severe, it is crucial to take measures to solve it since they can improve the situation.
- Water Management in Sustainable Engineering The current essay demonstrates the significance of sustainable engineering on the example of wastewater treatment and consequent water reuse.
- Benefits of Water Birth Overview Waterbirth remains to be a controversial approach. The studies examined in this paper provide some evidence for the benefits that waterbirth has.
- Basic Functions of Minerals and Water in the Body This paper discusses the functions and sources of minerals, the function of water in the body, and the general effect of dehydration on the body.
- Fiji Water Quality: Biology Lab Experiment Since Fiji water is among the popular brands in the US, it is essential to evaluate whether it is clean, that is, safe for human consumption.
- Water Quality Improvement for Global Health This proposal determines the necessity of water quality from the perspective of global health. The funding will be provided by the government and non-governmental organizations.
- All About Water: Problems and Solutions In addition to explaining water benefits, the paper has also shown that many people globally struggle with water shortages or exposure to contaminated water.
- Bottled Water Impacts on Environment As the use of bottled water continue to rise steadily around the world, many critics have focused on its impacts on the environment, economy and other social implications related to the use.
- The Problem of Environmental Water Pollution This paper discusses a public health concern by explaining the causes of water pollution, how it affects human communities, and the possible strategies.
- “Bling H2O” Bottled Water in the Australian Market Bling H2O water is the world’s most expensive bottled water. The brand’s creator targeted to sell it to the celebrities who highly esteem their bottled water.
- Water Intake and Output: Mechanisms of Regulation For healthy function, the human body requires water balance as one of the key mechanisms, where the average daily water intake and output are relatively equal.
- Studying the Venturi Effect Through Water Flow Calculation The Venturi effect is of particular importance in fluid dynamics, characterizing the pressure drop of a fluid as it flows through narrow spaces.
- Solutions for Food and Water Security Issue With many nations encountering food and water security problems, the consequences of such events have become global, giving rise to multiple outcomes this insecurity.
- Fiji Water Case Study Analysis Brandon Miller aims to establish a business that is the distribution of Fiji water for Monroe and Wayne market areas.
- Baxter Water Treatment Plants and Public Health The Baxter Water Treatment Plant is the largest water treatment facility in Philadelphia, supplying about 60 percent of the city’s drinking water.
- Water: An Often Overlooked Essential Element in Our Environment The freshwater required for growing food and livestock is also in great demand by the large numbers of inhabitants in the world’s cities and towns.
- Virtual Water Trade and Savings in Agriculture This essay discusses the savings associated with virtual water trade in agriculture and touches on the effects of a shift to local agricultural production on global water savings.
- Substances Influence on Water The objective of the experiment will be to find if the freezing rate of water changes when different substances are added.
- Human Energy Consumption and Water Power Human energy use is significantly low compared to natural energy flow. Waterpower is not significant in energy flow because it is renewable energy.
- Biogeochemical Cycles: Carbon, Nitrogen, and Water The most common biogeochemical cycles are carbon, nitrogen, and water cycles. The purpose of this paper was to summarize these three cycles.
- Food and Water Security Management The purpose of this article is to evaluate the current methodologies for addressing food and water security issues and propose sustainable solutions based on scholarly evidence.
- Water Scarcity Due to Climate Change This paper focuses on the adverse impact that water scarcity has brought today with the view that water is the most valuable element in running critical processes.
- The Problem of Environmental Pollution: Fresh Water One of the more important concerns that are fast becoming a major threat is pollution and no form of pollution seemed to be bigger than that of freshwater pollution.
- Multidisciplinary Approach to Water Pollution This paper shows how the multidisciplinary approach addresses water pollution as a public health issue. It is important to understand what the model entails.
- Combating Arsenic Contamination in Water The well known fact is that water is the most valuable natural resource that exists and without which survival of life is impossible.
- Changes in the Global Water Cycle Changes in the climate brought about by global warming have a much bigger likelihood of impacting negatively on the global hydrological cycle.
- Water Buffalo Days: Growing Up in Vietnam by Nhuong The book Water Buffalo Days: Growing Up in Vietnam by Nhuong tells the story of a young boy in a central village in Vietnam. The story presents unique characteristics of Vietnam society and culture.
- Water Management and Ecology Issues The paper studies water management, its various implications and explains why this area is important on examples of environmental issues.
- Bottled Water Impact on Environment This paper seeks to amplify the need for regulation of the used water bottles. It is quite obvious that water bottles are the highest in a number of all bottles thrown away after use.
- Aspects of Global Pollution of Water Global pollution of water resources has devasting effects on the environment that include the destruction of the ocean ecosystem and biodiversity.
- Water Pollution in the Florida State The researchers claimed that plastic pollution was caused by the tourists and citizens who live along the coastline and dumping from the industries.
- The Water Shortage Supply in Las Vegas The water shortage supply in Las Vegas is a major problem due to the city’s reliance on Lake Mead and Colorado Rivers, which are drying up due to droughts.
- Is Bottled Water Safe for Public Health? Bottled water is just water but is marketed in such a way that makes it appear as healthy because it is positioned as “bottles water is healthy”.
- Water Quality Assessment. Environmental Impact Maintaining good water quality is essential to human health; thus, the recent decades have outstandingly worsened the water across communities worldwide by pollution.
- Water Quality and Supply The main problem on the way to the solution of environmental issues is a violation of generally accepted rules.
- The Global Water Crisis: Issues and Solutions The water crisis has now been associated with the reduction in food quantity besides the scarcity of safe drinking water.
- Water Sector Privatisation in Saudi Arabia The paper explores the decision by the Ministry of Water and Electricity in Saudi Arabia to form the National Water Company to facilitate the privatization process and oversee the regional operations.
- Green Infrastructure in Water Management This paper evaluates the utility of water management in urban areas from the aspect of perception and interpretation of green infrastructure in water management.
- Relocation of Solar Power System to Easy Life Water Ventures The paper states that having an effective power source will help the organization operate smoothly and sustainably and increase its reputation.
- Resolutions to Fight Water Scarcity The World Health Organization outlines water scarcity as a global crisis affecting more than 2.8 billion people.
- Effects of Climate Variability on Water Resources, Food Security, and Human Health Evaluating the effects of climate variability on water, food, and health will help identify the areas for improvement and offer solutions to current environmental challenges.
- The Issue of Food and Water Security The global issue for the analysis is food and water security. This is a topical problem nowadays, especially in light of climate change and population growth.
- Food and Water Security as Globalization Issues Globalization has several implications for the business environment, among which are the expanded access to resources, and the interdependence of international companies.
- Lake Mattoon: Recreational Site and Water Reservoir Lake Mattoon remains one of Coles county’s best recreation sites and major water reservoirs; it is a big, man-made lake with lush green shores and big fish populations.
- Water Pollution Effects on Human Health The paper describes the effects of water pollution on human health from the perspective of existing findings on this topic and the assessment of information.
- Is Bottled Water Dangerous for People and the Environment? The purpose of this paper is to discuss alternative perspectives on bottled water and whether it is dangerous for people and the planet.
- Pressurized Water Reactors: An Analysis The paper describes the operations of a Pressurised Water Reactors (PWR) plant in-depth, discusses the functions of PWR plants, their advantages and disadvantages.
- First Nations Communities Water Resources Drinking water is by no means an infinite resource, but there are places in the world where women and children spend hours each day just to collect it.
- Bottled Water: Environmental and Cultural Impact The consumption of bottled water has an impact on society. Appropriate strategies must be implemented to ensure that the hazards associated with bottled water are reduced.
- Water Treatments and Maximum Plant Height The first research question was how different water treatments affect maximum plant height. The experiment involved 12 plants – 6 plants for each type of water.
- “Erin Brockovich” Film and 2014 Flint Water Crisis This paper analyzes the movie “Erin Brockovich” and compares it with the current situation in Flint, which started in April 2014.
- Agriculture, Water, and Food Security in Tanzania This paper evaluates the strategies applicable to the development and further maintenance of agriculture, water, and food security in Tanzania.
- High-Quality Water Supply in the United States The American community has become more conscious about their health and general physical condition. Consequently, a high-quality water supply stays a priority in many households.
- Assessment: Dubai Electricity and Water Authority As a key component of Dubai’s economy, DEWA is critical in assisting the Emirate’s growth and transition to a zero-economy economy.
- Hyponatremia: How Much Water Do You Actually Need? Some schools, like Mississippi State, do hydration tests before each practice to ensure their players are adequately hydrated.
- Analyzing the Use of Water in Danticat, Roumain, and Marshall The use of water in the three novels Roumain’s “Masters of the Dew,” Danticat’s “Krik? Krak!” and Paul’s “Praise Song for the Widow” has a symbolic meaning.
- Water Pollution and How to Address It A person must protect nature – in particular water resources. After all, the possibilities of water resources are not unlimited and sooner or later, they may end.
- Water Pollution: Effects and Treatment Pollution of water bodies is a serious hazard to humans and the aquatic ecology, and population growth is hastening climate change.
- Examining Solutions for Mitigating the Food and Water Security Issue Hunger, malnutrition, and decreased resource distribution manifest in communities having issues with food and water security, which decreases the well-being of individuals.
- Impact of Water Pollution: Water Challenges of an Urbanizing World Water is a source of life on Earth, and it is one of the very first needs of living beings. It is a vital resource for the development of the economic and social sectors.
- Environment: There’s Something in the Water Environmental racism hurts the natural image of landscapes and negatively affects the atmosphere and reduces the quality and duration of life for minorities.
- Evaluation of Articles on Food and Water Security The two resources chosen for this discussion pertain to food and water security solutions. The scholarly source is visually distinct from the popular source due to its structure.
- The Clean Water Network Support Statement Fresh water has become one of the most valuable resources in the world, around which regional or even global wars may occur in the future.
- Global Societal Issue: Food and Water Security According to research, food and water security is a pertinent global problem in the current decade, with access to food and water becoming scarce in certain world regions.
- Climate Change and Accessibility to Safe Water The paper discusses climate change’s effect on water accessibility, providing graphs on water scarcity and freshwater use and resources.
- The High Heat Capacity of Water The heat capacity of water greatly affects the planet’s climate. At high temperatures, water absorbs heat, and when it gets colder, it gives it away.
- Exploring the Agenda for Fresh Water Supply in Remote Regions The fundamental thesis of this entire paper is that scientific and technological advances catalyze the development of technologies to deliver fresh water to remote areas of Texas.
- What Is Water-Related Terrorism and How to Cope With It? Water-related terrorism includes damaging government facilities, and since water resources are vital for human existence, it is profitable for terrorists to attack them.
- Whirlpool in the Sea off the Coast of Scotland Near Ayrshire Due to Waste Water Stunning drone images near Lendalfoot in South Ayrshire captured a glimpse of a mammoth whirlpool off the Scottish west coast.
- Fresh Water Toxins: Serious Threat to Health This paper discusses fresh water toxins as a serious threat to health, analyzes Los Angeles drinking water, access to clean water and sanitation.
- Safe Drinking Water: Current Status and Recommendations The study proposes the usage of agricultural waste as a sustainable biosorbent for toxic metal ions removal from contaminated water.
- Essentials of Water in Supporting Biological Systems Water is essential in supporting the biological system in various ways; the properties of water help in understanding its importance.
- Underground Water Contamination in St. Louis Mo City In St. Louis Mo City of Missouri State, contamination of underground water is most likely and that is why the water supply is a subject to government policies.
- Twitter Campaign: Impact of Water Runoff Water runoff can cause flooding, which means property damage and mold formation in damp basements and more. This paper is a twitter campaign about the impact of water runoff.
- Water Pollution of New York City Rivers The aim of the analysis was to assess the effects of CSOs on water quality and the environment at different sites along the Harlem River.
- Water Cooling Tower Construction Site’s Problems The paper highlights three major problems at the construction site. They are security, scheduling, and safety problems.
- Recent Water Treatment and Production Developments This study attempts to investigate whether inorganic filters are more suitable for industrial and water treatment processes when compared to organic filters.
- Chemistry: Partitioning Coefficient of the Water The partitioning coefficient of the water solutions with of diuron, decadienal, atrazine, fluoranthene, and desethylatrazine compounds are calculated in accordance with the formula.
- Study of Local Water Resources Quality This laboratory report aims to summarize the results obtained during the study oxygen consumption, BOD, and detecting dissolved suspended solids in Hong Kong water.
- Developing Suspension Carbon Nano-Tubes in Water This paper has discussed nano-tubes and suspension as well as stabilization which make use of Multi-Wall-Carbon-Nanotubes by the function of concentrated SDS.
- A Cartographic History of Water Infrastructure and Urbanism in Rome The freshwater available to the city was a huge cultural and economic boon to Roman citizens. Some of this ancient water infrastructure is operational to this day.
- Integrated Water Strategies From Website Water Recycling The website http://waterrecycling.com/ is a front-end of their company showing various services that the company offers in the field of water recycling.
- The Causes of Water Pollution Water pollution is a significant decrease in water resources’ quality due to the ingress of various chemicals and solid waste. The causes of pollution are related to human activities.
- Bottle Water Industry in Current Economic UK Climate The research question is whether bottled water is a necessity or a luxury with regard to the current economic climate in the United Kingdom.
- Political Ecology and Water Wars in Bolivia The given critical assessment will primarily focus on bringing a new perspective to the issue from the standpoint of political ecology.
- The Influence of Water on the Growth of Popcorn Plants The information from the study would aid farmers in identifying appropriate seasons to cultivate popcorn plants based on data of meteorological forecasts.
- Boiling Is a Process That Cools the Water This paper tells that bringing water to a boil while making tea is a progression that cools it since the process lessens the overall temperature.
- Water Conservation Practice in Olympia Olympia city has a comprehensive water conservation program that involves many projects. The city puts much effort into the conservation of water.
- Protecting the Current and Future Water Supply for Rio de Janiero In the current rate of use, as well as the consensus reached by the governing officials in Rio de Janeiro, there will be enough potable water until 2025.
- Water Conservation Practice in Houston From the treatment of wastewater to the reduction of the consumption of the same Houston is an epitome of the increasing need to conserve resources, especially water.
- Burning Issue of Water Pollution in Washington The problem of polluted drinking water in Washington should be solved immediately despite various obstacles, such as pressure for money, etc.
- Drinking-Water in Third World Countries The shortage of drinking water in countries of Third World and the public controversy, surrounding the issue, illustrates the validity of this thesis better then anything else.
- Bottled Water Status in the UK With the current economic climate in the UK, the issue of whether bottled water has become a luxury or a necessity.
- Underground Water Overdraft in Southern California In California, the overuse of underground water reserves and the resultant overexploitation (overdraft) led to a serious water resources deficit.
- Water and Soil Pollution: Effects on the Environment Water and soil pollution is the process of contaminating water and soil. In this project, we will investigate the apparent main pollutants of the Spring Mill Lake.
- Bottled Water: Culture and Environmental Impact Bottled water as a particular branch of industrial growth in countries throughout the world represents the source of environmental pollution.
- Alternative Energy Sources: A Collaborative Approach in Water Management With the increasingly high prices of gasoline in particular and fossil fuels in general there is a need to find an alternative source of energy.
- Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons Effect on Water Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) constitute one of the largest groups of compounds that produce widespread organic environmental pollution posing a risk to marine biota
- Lack of Water in California as an Environmental Issue California can run out of water because of technological and social problems that affected the region. Defining water resources’ “development” is critically important.
- Water Scarcity in the Middle East The Arab region has always had issues with the water supply but as the population continues to grow steadily, this issue has become even more alarming
- Potential Threats to Water Supplies in Ottawa The purpose of the research is to identify the distribution of threats to drinking water in the city and determine who might benefit and who might be harmed in the process.
- Water Quality in Savannah, Georgia The City of Savannah Water Supply and Treatment Department conducts numerous annual tests to ensure that drinking water in the region is safe for human consumption.
- Water Pollution Index of Batujai Reservoir, Central Lombok Regency-Indonesia Despite having 6% of the world’s water resources, Indonesia’s environmental policies have not only been raising concerns but also pushed the country to the brink of water crisis.
- Dream Water Company’s Product Marketing The core product is the main benefit that the product brings to the consumer. For Dream Water, the core product is the medication against insomnia.
- Water Resources in Australia: Usage and Management Australia is one of the driest continents in the world. Various governmental and non-governmental institutions have teamed up to face the challenges facing people as far as water is concerned.
- Water Management in the “Flow” Documentary The documentary “Flow” discusses and describes two significant things that are preventing people from having access to freshwater.
- Water Sanitation Program in Saudi Arabia In the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, as the demand for water continues to increase without an equivalent increase in the supply, the level of hygiene may soon become a problem.
- Virtual Water Content and Global Water Savings The Virtual Water Content concept was the byproduct of discussions regarding the need to provide food in countries suffering from drought or plagued with perpetual water scarcity.
- Active Remediation Algorithm for Water Service in Flint The Active Remediation algorithm aims to inspect the water service in Flint, Michigan, and identify those lead pipes that need to be replaced by copper pipes.
- Water Savings and Virtual Trade in Agriculture Water trade in agriculture is not a practice that is unique to the modern generation. The practice was common long before the emergence of the Egyptian Empire.
- Virtual Water Trade of Agricultural Products Virtual water trade is a concept associated with globalization and the global economy. Its rise was motivated by growing water scarcity in arid areas around the world.
- Virtual Water Savings and Trade in Agriculture The idea of virtual water was initially created as a method for assessing how water-rare nations could offer food, clothing, and other water-intensive products to their residents.
- Environmental Legislation: Clean Water Act Clean Water Act determines water quality standards, serves as a basis for the enactment of pollution control programs, and regulates the presence of contaminants in surface water.
- Third-Party Logistics, Water Transportation, Pipelines Transportation plays a crucial role in today’s business world. This work shows the benefits and limitations of third-party logistics providers, water transportation, and pipelines.
- Water Quality and Contamination In this paper, carries out detailed experiments on the bottled and tap water available to consumers to establish whether it is worthwhile to purchase bottled water.
- Oil, Water and Corruption in Central Asian States The region of Central Asia has been a focus of the world’s political and economic attention due to its rich oil and gas resources. Corruption is the main curse of Central Asian states.
- Water Scarcity Issue and Environment The paper answers the question why to be worried about running out of drinking water even though the earth’s surface is mostly made of water.
- Environmental Studies: Water Recycling Different countries face varying challenges in as far as the provision of clean water to its population is concerned depending on its economic development level and geographic location.
- Water Pollution This essay seeks to examine the concept of water pollution, its causes, effects and solutions to water pollution.
- How Does Water Pollution Affect Human Health?
- Are Sports Drinks Better for Athletes Than Water?
- What Happens if You Don’t Filter Your Water?
- Can Game Theory Help to Mitigate Water Conflicts in the Syrdarya Basin?
- How Can We Reduce Water Scarcity?
- Are Water Filters Really That Important?
- How Much Water Do We Need to Feed the World?
- Why Is Water Important for Food Production?
- Can Markets Improve Water Allocation in Rural America?
- How Can We Reduce Water Consumption in Food Industry?
- Can Public Sector Reforms Improve the Efficiency of Public Water Utilities?
- What Are the Modern Technologies Used to Treat Water?
- How Does Water Pollution Affect Global Warming?
- Can Sea Water Generate Usable Energy?
- What Are the Steps Taken by the Government to Reduce Water Pollution?
- Can Sugar Help Lower the Freezing Point of Water?
- Do We Need More Laws to Control Water Pollution?
- Can the Global Community Successfully Confront the Global Water Shortage?
- What Is the Government Doing to Save Water?
- Can Virtual Water ‘Trade’ Reduce Water Scarcity in Semi-arid Countries?
- Does Urbanization Improve Industrial Water Consumption Efficiency?
- How Has Technology Helped Us Save Water?
- Does Piped Water Improve Household Welfare?
- Can Water Pollution Policy Be Efficient?
- How Does Green Infrastructure Improve Water Quality?
Cite this post
- Chicago (N-B)
- Chicago (A-D)
StudyCorgi. (2021, September 9). 167 Water Essay Topics & Research Questions about Water. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/water-essay-topics/
"167 Water Essay Topics & Research Questions about Water." StudyCorgi , 9 Sept. 2021, studycorgi.com/ideas/water-essay-topics/.
StudyCorgi . (2021) '167 Water Essay Topics & Research Questions about Water'. 9 September.
1. StudyCorgi . "167 Water Essay Topics & Research Questions about Water." September 9, 2021. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/water-essay-topics/.
Bibliography
StudyCorgi . "167 Water Essay Topics & Research Questions about Water." September 9, 2021. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/water-essay-topics/.
StudyCorgi . 2021. "167 Water Essay Topics & Research Questions about Water." September 9, 2021. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/water-essay-topics/.
These essay examples and topics on Water were carefully selected by the StudyCorgi editorial team. They meet our highest standards in terms of grammar, punctuation, style, and fact accuracy. Please ensure you properly reference the materials if you’re using them to write your assignment.
This essay topic collection was updated on January 9, 2024 .
wastewater treatment Recently Published Documents
Total documents.
- Latest Documents
- Most Cited Documents
- Contributed Authors
- Related Sources
- Related Keywords
Metagenomic insights into the profile of antibiotic resistomes in sediments of aquaculture wastewater treatment system
Corrigendum to ’beyond treatment technology: understanding motivations and barriers for wastewater treatment and reuse in unconventional energy production’, improving the efficiency of wastewater treatment and microalgae production for biofuels, hybrid zeolite-based ion-exchange and sulfur oxidizing denitrification for advanced slaughterhouse wastewater treatment, advanced wastewater treatment process using algal photo-bioreactor associated with dissolved-air flotation system: a pilot-scale demonstration, cometabolic biodegradation of antibiotics by ammonia oxidizing microorganisms during wastewater treatment processes, synergistic effects of oxidation, coagulation and adsorption in the integrated fenton-based process for wastewater treatment: a review, fate evaluation of pharmaceuticals in solid and liquid phases at biological process of full-scale municipal wastewater treatment plants, impact of different inoculum sources on the performance of membrane bioreactors for municipal wastewater treatment: dynamic membrane versus ultrafiltration membrane, enhancement of wastewater treatment performance using 3d printed structures: a major focus on material composition, performance, challenges, and sustainable assessment, export citation format, share document.

An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock A locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
JavaScript appears to be disabled on this computer. Please click here to see any active alerts .
- Wastewater Research

Wastewater management is a critical part of the anthropogenic water cycle that helps ensure that water is clean, safe to use, and protective of ecosystems. Wet weather runoff that flows from urban communities into wastewater collection systems is a significant challenge. Runoff from unpredictable strong storms or continuous heavy rain events can result in rapid changes in flow rates and volumes of wastewater that must be collected and treated, and can exceed design flows for treatment processes at the utility. In addition, the pipe system carrying the water to the facility can exceed its holding capacity, resulting sewer overflows. EPA's wastewater research includes development of methods for detecting and treating contaminants, assessment of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) in wastewater, and the development of methods to monitor municipal wastewater for SARS-CoV2 and other contaminants.
Sign Up for Invites & Updates
Webinar Invites Receive emails for upcoming webinars
Science Matters Newsletter Stay current with research highlights
Research Topics
- Wastewater Contaminants
- Alternative Wastewater Disinfectant Research
- Water Reuse
- Stormwater Management and Green Infrastructure
- Enhanced Aquifer Recharge
Models, Methods, and Tools
- EPA Science Models and Research Tools (SMaRT) Search
- Environmental Technologies Design Option Tool (ETDOT)
- Non-potable Environmental and economic Water Reuse calculator (NEWR)
- PFAS Analytical Methods Development and Sampling Research
- Water Modeling Tools for Decision Support
- Method 1622: Cryptosporidium in Water by Filtration/IMS/FA (2005)
- Method 1623: Giardia Report Form (pdf)
- Method 1622/1623 Spiking Suspension Enumeration Form: Cryptosporidium Giardia (pdf)
- Hemacytometer Data Sheet for Cryptosporidium Giardia (Circle One), July 1998 (1998) (pdf)
Related Resources
- EPA information on Municipal Wastewater
- EPA information on Industrial Wastewater
- Water Research Webinar: SARS CoV-2 in Wastewater Monitoring: Linking Research and Application to Meet Immediate Needs (September 20, 2020)
- Water Research Home
- Watersheds Research
- Nutrients and Harmful Algal Blooms Research
- Drinking Water Research
- Alternative Water Sources Research
- Stormwater Management Research
- PFAS Research
- Technical Support for Communities
- Water Research Grants
- Research Outputs
- Training, Outreach, and Engagement

From The Editor | September 26, 2014
The 10 hottest topics in wastewater—what you need to know.

By Laura Martin
Behind on what's hot in the wastewater industry? Get up-to-date with this list of Water Online articles on the industry trends and challenges that everyone is talking about. Read on and you'll be sure to impress your colleagues.
1) Energy Production And Conservation
Finding the ideal balance between energy and water consumption has always been a challenge. Energy use at a water or wastewater utility can be 30 percent to 50 percent of the municipality’s total electricity consumption. In addition, the energy industry itself requires a significant amount of water to operate. But a water-energy nexus solution is on the horizon, as more energy-efficient technologies and alternative energy production methods are developed.
Stories On Energy From Water Online:
Can Co-Locating Utilities Solve The Water-Energy Nexus?
5 Reasons To Harvest The Power Of Biogas
2) Nutrient Management
Changing regulations and increasingly stringent effluent limits have brought nutrient management to the forefront of the wastewater industry.
Stories On Nutrient Management From Water Online
'Peecycle' Please: Will Urine Separation For Nutrient Recovery Take Off?
3 Alternative Nutrient-Removal Techniques
What Everyone Should Know About Enhanced Biological Phosphorus Removal
3) Residuals and Biosolids
The management and removal of residuals, sludge, and biosolids, has historically been a burden on wastewater utilities, accounting for nearly 50 percent of treatment costs. But this “waste” may hold the key to additional revenue if reclaimed and sold.
Stories On Residuals and Biosolids From Water Online:
Revolutionary Sludge Management Comes To America
Bio-Dredging: Cost-Saving Sludge Digestion For Lagoons
4) Water Reclamation And Reuse
There is a growing trend of reusing treated wastewater effluent for both drinking water and industrial applications. On the drinking water side, water shortages have made direct potable reuse (DPR) and indirect potable reuse applications a necessity in parts of the country. Pressure to use less water on the industrial sector has resulted in innovative reuse applications as well.
Stories On Water Reuse From Water Online:
Texas Leads The Way With First Direct Potable Reuse Facilities In U.S.
Fit-for-Purpose Water Reuse And The Road Toward Water Security
New Indirect Potable Reuse Regulations — What To Expect
5) Water Supply And Water Management
In water-scarce areas, managing water supply can be challenging. First, it can be difficult to even determine how much water is available, via groundwater, surface water, reuse, and other sources. Then, there is the challenge of figuring out how water should be allocated between consumers and industrial applications, and how much needs to remain untouched for the sake of the environment. If there isn’t enough to go around, conservation techniques or usage restrictions may have to be considered.
Stories On Water Supply And Management From Water Online:
Tackling The Drought: The Relationship Between Water Law And Water Budget
Why Engineers Can't Solve The Water Shortage With Supply-Side Solutions
6) Stormwater, Green Infrastructure, And Wet Weather Management
Stormwater management is a growing focus for the wastewater industry. Heavy wet-weather events often overwhelm wastewater systems — which are often too small for a growing population — and untreated sewage ends up overflowing into local water bodies. Green infrastructure solutions and growing regulation offer solutions.
Stories On Stormwater From Water Online:
EPA Stormwater Ruling: How Will It Impact Utilities?
Save The Rain: Preventing Combined Sewer Overflows
7) ‘Flushable’ Wipes And Collection Systems
Recently, collection systems have been in the spotlight. The increased attention is thanks (or no thanks) to “flushables,” non-dispersible cleansing cloths that are wreaking havoc on headworks all over the country.
Stories On “Flushables” From Water Online:
Nondispersibles' Turning Sewers Into Nightmares Nationwide
Looming In The Sewers: Nonwovens Are Weaving A Tangled Web
8) Industrial Wastewater
Oil and gas, agriculture, pharmaceuticals, mining, food and beverage processing—the list of industries with growing wastewater challenges goes on and on. Water Online has reported on the modeling, design, and operation of industrial wastewater treatment systems, anaerobic and biological industrial treatment processes, regulatory impacts, and more.
Stories On Industrial Wastewater From Water Online:
The Importance Of An Industrial Water Treatment Program
Has Fracking Gone ‘Green'?
9) Utility Management
Utility executives and managers have a wide range of challenges to overcome. Their workforce is aging and their budgets are shrinking. Public outreach is more important than ever before, and regulations and government oversight are increasing.
Stories On Utility Management From Water Online
New Standard Applies To Every Water Manager, Everywhere
How To Deliver Better Water And Increase Consumer Confidence Simultaneously
10) Innovative Technology
Change is needed in the wastewater industry. Cutting-edge products and services focused on everything from resource recovery and big data management, to innovative green infrastructure solutions are coming to the forefront.
Stories On Innovation From Water Online:
The Top 12 Water Technology Hotspots In America
Ontario's Water Tech Acceleration Project: Fighting For The Future Of Water
Like what you are reading?
Sign up for our free newsletter, newsletter signup.

- Program Finder
- Admissions Services
- Course Directory
- Academic Calendar
- Hybrid Campus
- Lecture Series
- Convocation
- Strategy and Development
- Implementation and Impact
- Integrity and Oversight
- In the School
- In the Field
- In Baltimore
- Resources for Practitioners
- Articles & News Releases
- In The News
- Statements & Announcements
- At a Glance
- Student Life
- Strategic Priorities
- Inclusion, Diversity, Anti-Racism, and Equity (IDARE)
- What is Public Health?
research@BSPH
The School’s research endeavors aim to improve the public’s health in the U.S. and throughout the world.
- Funding Opportunities and Support
- Faculty Innovation Award Winners
Conducting Research That Addresses Public Health Issues Worldwide
Systematic and rigorous inquiry allows us to discover the fundamental mechanisms and causes of disease and disparities. At our Office of Research ( research@BSPH), we translate that knowledge to develop, evaluate, and disseminate treatment and prevention strategies and inform public health practice. Research along this entire spectrum represents a fundamental mission of the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.
From laboratories at Baltimore’s Wolfe Street building, to Bangladesh maternity wards in densely packed neighborhoods, to field studies in rural Botswana, Bloomberg School faculty lead research that directly addresses the most critical public health issues worldwide. Research spans from molecules to societies and relies on methodologies as diverse as bench science and epidemiology. That research is translated into impact, from discovering ways to eliminate malaria, increase healthy behavior, reduce the toll of chronic disease, improve the health of mothers and infants, or change the biology of aging.
120+ countries
engaged in research activity by BSPH faculty and teams.
of all federal grants and contracts awarded to schools of public health are awarded to BSPH.
citations on publications where BSPH was listed in the authors' affiliation in 2019-2023.
publications where BSPH was listed in the authors' affiliation in 2019-2023.
Departments
Our 10 departments offer faculty and students the flexibility to focus on a variety of public health disciplines
Centers and Institutes Directory
Our 80+ Centers and Institutes provide a unique combination of breadth and depth, and rich opportunities for collaboration
Institutional Review Board (IRB)
The Institutional Review Board (IRB) oversees two IRBs registered with the U.S. Office of Human Research Protections, IRB X and IRB FC, which meet weekly to review human subjects research applications for Bloomberg School faculty and students
Generosity helps our community think outside the traditional boundaries of public health, working across disciplines and industries, to translate research into innovative health interventions and practices
Introducing the research@BSPH Ecosystem
The research@BSPH ecosystem aims to foster an interdependent sense of community among faculty researchers, their research teams, administration, and staff that leverages knowledge and develops shared responses to challenges. The ultimate goal is to work collectively to reduce administrative and bureaucratic barriers related to conducting experiments, recruiting participants, analyzing data, hiring staff, and more, so that faculty can focus on their core academic pursuits.

Research at the Bloomberg School is a team sport.
In order to provide extensive guidance, infrastructure, and support in pursuit of its research mission, research@BSPH employs three core areas: strategy and development, implementation and impact, and integrity and oversight. Our exceptional research teams comprised of faculty, postdoctoral fellows, students, and committed staff are united in our collaborative, collegial, and entrepreneurial approach to problem solving. T he Bloomberg School ensures that our research is accomplished according to the highest ethical standards and complies with all regulatory requirements. In addition to our institutional review board (IRB) which provides oversight for human subjects research, basic science studies employee techniques to ensure the reproducibility of research.
Research@BSPH in the News
Four bloomberg school faculty elected to national academy of medicine.
Considered one of the highest honors in the fields of health and medicine, NAM membership recognizes outstanding professional achievements and commitment to service.
The Maryland Maternal Health Innovation Program Grant Renewed with Johns Hopkins
Lerner center for public health advocacy announces inaugural sommer klag advocacy impact award winners.
Bloomberg School faculty Nadia Akseer and Cass Crifasi selected winners at Advocacy Impact Awards Pitch Competition

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
In a News & Views in June 2023 4 we highlighted a paper studying the fundamental aspects of water transport in reverse osmosis membranes 5. Among the papers we published, a clear example is the ...
The 12 research contributions highlight various processes and technologies that can achieve the effective treatment and purification of wastewater and drinking water, aiming (occasionally) for ...
Dec.15, 2021. In this paper, researchers surveyed both conventional and advanced disinfection processes in the U.S., testing the quality of their drinking waters. Treatment plants with advanced removal technologies, such as activated carbon, formed fewer types and lower levels of harmful disinfection byproducts (known as DBPs) in their water.
Feature papers represent the most advanced research with significant potential for high impact in the field. ... SI discusses state-of-the-art wastewater and water treatment technologies that could be used to develop a sustainable treatment method in the future. On this topic, studies have focused on measurements, modeling, and experiments ...
The current trends in membrane-based water and wastewater treatment technologies have been discussed in this review, along with their merits and challenges. These topics are reviewed to highlight the contribution of membrane-based water and wastewater treatment technologies to the achievement of SDGs and their role in the circular economy.
One of the sustainable development goals set by the United Nations General Assembly is to ensure the availability and sustainable management of water and sanitation for all. This requires ...
Water Research publishes refereed, original research papers on all aspects of the science and technology of the anthropogenic water cycle, water quality, and its management worldwide. A broad outline of the journal's scope includes: •Treatment processes for water and wastewaters (municipal, agricultural, industrial, and on-site treatment ...
The present special issue collected articles that address the very important topic of innovative approaches in water and wastewater treatment technologies. Thirteen articles are published, ten research paper and three review articles. The papers can be divided in four major categories, namely, membrane treatment, adsorption studies, advanced oxidation processes and wastewater treatment ...
Urban Water Network Planning and Management: Perspectives and Solutions in the Transition Towards Smart Systems from the City to the End-use Scale. Filippo Mazzoni. Shweta Rathi. Valentina Marsili. Nehal Elshaboury.
Water Resources Research is an AGU hydrology journal publishing original research ... water reclamation and reuse, (5) distributed water treatment, (6) heat recovery, (7) organic ... But clearly translating research results in ways that make them policy relevant is also needed. Research results presented in WRR papers, for example, need to be ...
sustainable resource management by improving the supply of clean water, and minimizing pressur e. on natural resources, energy recovery, and agricultural support. W astewater treatment pr ovides ...
Water pollution is one of the most urgent environmental issues among the different pollution risks, having a direct negative impact on human health and other biological populations [1,2].The key to properly addressing the issues of water pollution and water scarcity is to treat and recycle wastewater [].The research has reported that there are various methods for treating wastewater, including ...
Water scarcity is one of the major problems in the world and millions of people have no access to freshwater. Untreated wastewater is widely used for agriculture in many countries. This is one of the world-leading serious environmental and public health concerns. Instead of using untreated wastewater, treated wastewater has been found more applicable and ecofriendly option. Moreover ...
Abstract. Lawrence K. Wang and Mu-Hao Sung Wang (2023). New Technologies for Water and Wastewater Treatment" In: "Evolutionary Progress in Science, Technology, Engineering, Arts, and Mathematics ...
Fu et al. (Citation 2013) indicated that the main research related to drinking water in the period 1992-2011included water treatment methods and related contaminants; however, the trend in these research topics has not changed for this last decade. In this same period, ozonation and chlorination in disinfection and adsorption were common ...
The treatment units of this plant include wastewater basin, sedimentation basin, sludge thickener and sludge dewatering facility. In this study, the treatment efficiency of SS and turbidity were 48.35-99.68% and 24.15-99.36%, respectively, showing the significant removal efficiency of the wastewater process.
Water in brewing. M. Eumann, in Brewing: New Technologies, 2006 9.5 Future trends. Brewery water treatment systems of the future will be very flexible, allowing breweries to tailor-make their water for different products. At the same time, these future water treatment systems will aim to achieve optimum efficiency in terms of operating cost and especially wastewater produced.
A - Z Topics | The Water Research Foundation. Advanced Treatment. Asset Management. Biosolids. Climate Change. Constituents of Emerging Concern (CECs) Cyanobacteria & Cyanotoxins. Disinfection Byproducts (DBPs) Energy Optimization.
This paper analyzes the movie "Erin Brockovich" and compares it with the current situation in Flint, which started in April 2014. Biogeochemical Cycles: Carbon, Nitrogen, and Water. The most common biogeochemical cycles are carbon, nitrogen, and water cycles. The purpose of this paper was to summarize these three cycles.
Hybrid zeolite-based ion-exchange and sulfur oxidizing denitrification for advanced slaughterhouse wastewater treatment. Journal of Environmental Sciences . 10.1016/j.jes.2021.06.002 . 2022 . Vol 113 . pp. 219-230. Author (s): Shuang Tong . Shaoxiang Zhang .
Wastewater Research. Wastewater management is a critical part of the anthropogenic water cycle that helps ensure that water is clean, safe to use, and protective of ecosystems. Wet weather runoff that flows from urban communities into wastewater collection systems is a significant challenge. Runoff from unpredictable strong storms or continuous ...
3 Alternative Nutrient-Removal Techniques. What Everyone Should Know About Enhanced Biological Phosphorus Removal. 3) Residuals and Biosolids. The management and removal of residuals, sludge, and biosolids, has historically been a burden on wastewater utilities, accounting for nearly 50 percent of treatment costs.
Systematic and rigorous inquiry allows us to discover the fundamental mechanisms and causes of disease and disparities. At our Office of Research (research@BSPH), we translate that knowledge to develop, evaluate, and disseminate treatment and prevention strategies and inform public health practice.Research along this entire spectrum represents a fundamental mission of the Johns Hopkins ...