- All Articles
- Let's Connect
- Fundamentals
- Soft Skills
- Side Projects

A Guide to Problem-Solving for Software Developers with Examples
If I ask you, out of the blue, what’s the role of a developer, what would you answer? Coding all day? Drinking coffee? Complaining about the management?
To me, a developer is first and foremost a problem solver, simply because solving problem is the most important (and the most difficult) part of our job. After all, even if our code is perfect, clear, performing great, a masterpiece of form and meaning, it’s useless if it doesn’t solve the problem it was meant to solve.
So, let’s dive into problem-solving today. More specifically, we’ll see in this article:
- How to define a problem, and the difference sometimes made between problem-solving and decision-making.
- Why some problems should not be solved.
- The two wide categories of problems you can encounter.
- Why it’s important to correctly define the problem, and how to do so.
- How to explore the solution space.
- Why deferring a problem might be the best decision to make in specific situations.
- Why reflecting on the whole process afterward can help you in the future.
This article is mostly based on my own experience, even if I apply here some ideas I found in books and papers.
We have our plan. Now, it’s time to dive deep into the difficult, but rewarding, process of problem-solving.
Problem-Solving and Decision-Making
“When I use a word,” Humpty Dumpty said in rather a scornful tone, “it means just what I choose it to mean — neither more nor less.” “The question is,” said Alice, “whether you can make words mean so many different things.” “The question is,” said Humpty Dumpty, “which is to be master — that’s all.” Lewis Caroll Source
Words are ambiguous; they can mean different things for each of us. So let’s first begin to agree on the definition of “problem-solving” here, to be sure we’re on the same page.
Let’s first look at the definition of the word “problem” in a dictionary:
- According to the American Heritage Dictionary , a problem is “a question to be considered, solved, or answered”.
- According to the Oxford Learner’s dictionary , a problem is “a thing that is difficult to deal with or to understand”.
In short, in any problem, there is some degree of uncertainty. If you’re certain of the solution, the problem is already solved. Nothing would need to be “considered, solved, or answered”.
Information is useful to reduce this uncertainty. The quantity is often not the most important, but the quality will be decisive. If I tell you that 90% of my readers are extremely intelligent, would it help you to solve a problem in your daily job? I bet it wouldn’t. It’s information nonetheless, but its usefulness for you is close to zero.
This is an extreme example, but it highlights an important point: before collecting any data, define your problem clearly; then, according to the problem, decide what data you need. Yet, many companies out there begin to collect the data and then decide what problem to solve. We’ll come back to that soon in this article.
So, to summarize, a problem is a situation with some degree of uncertainty. Sometimes, this uncertainty needs to be reduced to come up with an appropriate solution, or, at least, a decision to move forward to your specific goal.
Is there a Problem to Solve?
Whenever you (or somebody else) see a problem, you should always ask yourself this simple question first: is it really a problem, and should we solve it now ?
In other words, ask yourself the following questions:
- Why is this problem important to solve?
- Would be solving the problem creates some value? What value?
- What would happen if the problem was not solved?
- What desired outcome do we expect by solving the problem?
If the problem doesn’t bother anybody and solving it doesn’t create any value, why allocating effort and time to solve it?
It sounds obvious, but it’s an important point nonetheless. More often than not, I see developers heading first in solving problems without asking themselves if they should solve them at the first place.
The most common examples I can think of are useless refactoring. I saw developers refactoring parts of codebases which never change, or is rarely executed at runtime. In the mind of the developer, the code itself is the problem: refactoring is the solution.
I remember a similar case: a developer refactored part of the codebase which was basically never used. We discovered, months later, when we had more and more users using this specific part of the codebase, that the refactoring didn’t really simplify anything. To the contrary; we had to refactor the code again. The first refactoring tried to solve a problem which didn’t exists.
Of course, the developer could argue that the value created is a “cleaner” codebase, but it’s arguable, especially when the code is neither often modified nor used. The value created here is not clear, and it would have been easier if the first refactoring never happened. In this specific situation, I recommend refactoring when you actively change part of the codebase for another reason (implementing a new feature for example).
Whether a problem is worthy to be solved is subjective. It also depends on the problem: if the solution is clear and straightforward, it might be useful to solve it, if the consequences of the solution are also clearly known and the risks are low. Unfortunately, these kinds of problems, in practice, are quite rare.
Types of Problems
I would define here two wide categories of problems: the problems with a (or multiple) clear solution (what the literature call “problem-solving”), and the problems without clear solution (it’s sometimes called “decision-making” instead of “problem-solving”).
In fact, if the problem you’re trying to solve has a clear, accepted answer, it’s very likely it has been solved already. It’s often the case for mechanical, technical problems. For example, let’s say that you need to order a list; you just have to search on the wild Internet how to do so in your programming language of choice, and you’re done! You can ask an “AI” too, or stack overflow, or whatever.
In my experience, most technical problems have one (or multiple) accepted solution. I won’t speak about these kinds of problems at length in this article, since they’re the easiest to solve.
When you’re in front of a problem which has no clear solution (even after doing some research), it’s where things get more complicated. I’d argue that most problems you’ll face, as a software developer, are of this category. Problems which are directly linked to the domain of the company you work with are often specific (because they depend on the domain), and complex.
For example, I’m working for a company providing a learning platform for medical students who want to become doctors, among other services. This context is changing because the real world is changing; medicine is no exception.
Recently, we had to create new data structures for the knowledge we provide; these data structures are directly linked to the domain (medicine) here. But what data structures to create? How can they adapt to the ever-changing environment? How to capture the data in the most meaningful way, with understandable naming for other developers?
Decisions had to be made, and when there are no clear solutions, you need to come up with a couple of hypothesizes. They won’t feel necessary like solutions , but rather decisions to take to move forward toward the desired outcome. It often ends up in compromises, especially if you’re working in a team where the members have different opinions .
Also, architectural decisions have often no clear solutions because they depend, again, on the changing context. How to be sure that an architectural decision is good today and in three months? How can we make the architecture flexible enough to adapt to the blurry future?
As developers, we deal with complex codebases, which are somewhat linked to the even more complex real world. It’s difficult to know beforehand the consequences of our decisions, as well as the benefits, the drawback, and the potential bugs we introduce.
Before jumping into the solution space however, we first need a good detour in the problem space.
Defining the Problem
Correctly stating the problem.
After determining that we indeed have some kind of problem, it’s tempting to try to find a solution directly. Be patient: it’s better to look at the problem more closely first.
If you don’t specify well the problem, you might not solve it entirely. It’s also possible that you end up solving the wrong problem, or the symptoms of a problem, that is, other minor problems created by a root problem. Often, the ideal scenario is to find the root problem, even if you don’t want to tackle it first. In any case, it’s always useful information.
For example, not long ago, our users didn’t find the content they were searching for, using our search functionality on our learning platform.
We could have directly solved the problem by asking the search team to adjust that for us, but this problem was only a symptom. It wasn’t the first time that we had to spend time and energy trying to communicate to the search team what we wanted to fix; the real root problem here was that we didn’t have any ownership of our search results.
The solution: we created a better API communicating with the search team, to be able to adjust ourselves the search results in a more flexible manner.
When looking at a problem, a good first step is to write it down. Don’t do it once; try to find different formulations for the same problem.
Writing is nice (I love it!), but other ways to represent ideas can be really useful too. You can try to draw what you understand from the problem: a drawing, a diagram, or even a picture can help you understand the problem.
From there, you can ask yourself: do you have enough information to take a decision? The answer will be mostly based on the experience of the problem solver, there is no magical formula to be sure that you can and will solve the problem.
You should also try to look at the problem from different angles, to really frame it correctly. The best way to do so is to solve problems as a team.
Solving Problems in a Team
Trying to describe and think about a problem is a great beginning, but it’s even better if you do it as a team. You can exchange experience, opinions, and it’s easier to look at a problem from multiple angles when multiple developers are involved.
First, make sure that everybody in the team is aware of the problem. Defining it altogether is the best. If you have a doubt that somebody is not on the same page, you can re-explain it using different words. It might bring more insights and ideas to the discussion.
Don’t assume that everybody understands the problem equally. Words are powerful, but they are also ambiguous; never hesitate to ask questions (even if they seem stupid at first), and encourage the team to do the same. If your colleagues see that you’re not afraid to ask, it will give them confidence to do the same.
The ambiguity can also build overtime, after the problem was discussed. That’s why it’s really important to document the whole process, for anybody to be able to look at it again and fix the possible creeping misconceptions. Don’t try to describe everything, but try to be specific enough. It’s a delicate balance, and you’ll get better at it with experience.
If you don’t like writing, I’d recommend you to try anyway: this is a powerful skill which will be useful in many areas of your life.
Regarding the team of problem solvers, diversity is important. Diversity of opinion, experience, background, you name it. The more diverse the opinions and ideas are, the more chances you’ll have to solve the problem satisfyingly (more on that later). If the members of the team have enough respect, humility, and know how to listen to their colleagues , you’re in the perfect environment to solve problems.
As developers, we’re dealing with moving systems, because they need to reflect the ever-changing business domain of the company you’re working with. These problems are unique, and even if similar problems might have been solved in the past, they’re never the exactly same. The differences can have an impact on the solution, sometimes insignificant (allowing you to re-apply the solution found previously), sometimes important enough to change the solution entirely.
Exploring the Solution Space
Now that we’ve defined the problem, thought about it with our team, tried to look at it from different angles, it’s time to try to find solutions, or at least to make a decision.
What is a good decision? The one which will bring you closer to your desired outcome. It sounds obvious, but there can be some ego involved in discussions, which will push us to try to be right even if it’s not the best solution in the current context. Our personal incentives can conflict with the company’s best interest; it’s always good to try to stay aware of that.
The solution should also be the simplest possible, while still moving forward to the desired outcome. It should also have an acceptable level of risk when we decide to apply the solution. In my experience, complicated solutions are the ones which come up first: don’t stop there. Take some time trying to find the best solution with your team.
For example, here’s what we do with my actual team:
- We define the problem altogether.
- We try to think about different hypothesizes. Not only one, but a couple of them.
- We write the benefits and drawbacks of each hypothesis (which can lead to more ideas, and possibly more hypothesizes).
- We commit to a hypothesis, which then needs to be implemented.
What I meant by “hypothesis” here is a solution which might work; but only the implementation of the hypothesis can be considered as a solution. Before the implementation, it’s just an informed guess. Many things can go wrong during an implementation.
This process looks simple, but when you have multiple developers involved, it’s not. Again, if each member of the team have good soft skills and some experience, it can be an enjoyable and rewarding process. But you need a good team for it to work efficiently (that’s why it’s so important to ask the good questions when joining a company). It’s even better if the members of the team are used to swim in uncertainty, and take it as a challenge more than a chore.
The process described above is just an example; in practice it’s often more chaotic. For example, even when a decision is made, your brain might still continue to process the problem passively. If you find some flaws in the hypothesis you’ve committed to, congratulations! You have now a brand-new problem.
I can’t emphasize it enough: try to be as detached as possible from your ideas, opinions, and preferred hypothesizes. The goal is not for you to be right and feel good, but for your company to move in the good direction. It’s hard, but with practice it gets easier.
I also want to underline the importance of finding both benefits and drawbacks for the different hypothesizes you (and your team) came up with.
To find good solutions, we might also need to reduce the uncertainty around their possible consequences. Doing some external research can help, like gathering data around the problem and the possible hypothesizes. In the best case scenario, if you can find enough data, and if you feel confident that you can move forward with a hypothesis, that’s already a great victory.
If you don’t have enough external information to reduce the uncertainty to a level you feel comfortable with, look at your past experience. Try to find problems similar to the one your deal with in the present, and try to think about the solutions applied at the time, to see if they could also be applied in your current case. But be careful with this approach: complex problems are context-sensitive, and the context you were in the past will never be exactly the same as the present and future contexts.
For example, I recently changed the way we display search results in our system, because we had some data indicating that some users had difficulties to find what they really wanted to find. The problem: users have difficulties to find the good information; it’s a recurrent problem which might never be 100% solved. That said, thanks to the data gathered, we found an easy way to improve the situation.
The data was very clear and specific, but it’s not always the case. More often than not, your data won’t really prove anything. It might only show correlations without clear causality. It will be even more true if you begin by gathering data without defining first the problem you try to solve. You can find problems looking at some data, that’s true, but it needs care and deep understanding of what you’re doing; looking at data when you know exactly what you want to solve works better.
Using this kind of process, the hypothesis is often some sort of compromise. That’s fine; committing to a hypothesis is not the end of the process, and there will be other occasions to revisit and refine the solution.
If you don’t feel comfortable with the level of uncertainty of the problem (or the risk involved by applying your hypothesis), you need to dig more. Writing a prototype can be useful for example, if you hesitate between two or more approaches. If your prototype is convincing enough, it can also be useful to gather feedback from your users, even if the ones testing your hypothesis will always be more invested if they test a real-life functionality, instead of a prototype which might use dummy data, or be in a context which is too remote from the “real” context.
In my opinion, prototypes are not always useful for complex problems, because a prototype only test a new feature at time T, but doesn’t allow you to see if the solution stay flexible enough overtime. That’s often a big concern: how will the solution evolve?
But prototyping can still help gather information and reduce the uncertainty of the problem, even if the prototype doesn’t really give you the solution on a silver platter. It’s also great for A/B testing, when you’re in the (likely) case when you have not much information about the real needs of your users. You could ask them of course, but nothing guarantee that they know themselves what these needs are.
If you don’t find any satisfying hypothesis to your problem, you might also challenge the desired outcome. Maybe a similar, simplest hypothesis, with slightly different outcomes, could work better? If it makes things easier, faster, and less complex, it could be the best solution. Don’t hesitate to challenge your stakeholders directly on the desired outcomes.
Deferring the Problem
In some cases, you might be hesitant to try to solve a problem if there is still too much uncertainty around it. In that case, it might be best to defer solving the problem altogether.
Deferring the problem means that you don’t solve it now ; you keep things as they are, until you get more information to reduce the uncertainty enough.
We had a problem in the company I worked with some time ago: we have dosages which can be discovered in articles, but users didn’t really find them, and nobody really knew why. Because of this lack of information, the problem was not tackled right away, but differed. From there, data have been collected overtime, allowing us to understand the scope of the problem better.
Don’t forget that deferring a problem is already taking a decision. It might be the less disruptive decision for the application and its codebase, but it’s s decision nonetheless, and it can have consequences. Seeing a differed problem as a decision will push you to think about the possible consequences of your inaction, and you’ll look at it as a partial “solution”, with some uncertainty and risk associated to it.
In my experience, deferring the problem works well only when you try to actively seek more data to solve it later. It can be some monitoring to see how the problem evolves, or some data taken from users’ actions. Sometimes, simply waiting can also give you important information about the nature of the problem.
What you shouldn’t do is try to forget the problem. It might come back in force to haunt your sleepless nightmares later. Avoiding a problem is not deferring it.
Here’s another example: we began recently to build some CMS tooling for medical editors, for them to write and edit content on our learning platform. We had one GraphQL API endpoint at the beginning, providing data to two different part of the application:
- Our CMS for medical editors.
- Our learning platform for medical students.
We knew that using one single GraphQL endpoint for these two types of users could cause some problems.
But we didn’t do anything about it, mostly because we didn’t see any real, concrete problem, at least at first. When a minor symptom, related to this unique endpoint, popped up, we spoke about it, and we still chose not to do anything. We preferred deferring the problem once more, to try to solve the real problem (one API for two different kinds of applications) later.
Finally, when we had enough symptoms and some frustration, we decided to split our graphQL API in two different endpoints. It was the best moment to do so: we had enough information to come up with a good decision, we applied it, and we stayed vigilant, to see how our applied hypothesis would evolve.
Moving fast and breaking things is not always the best solution. In some situations, waiting a bit and see how things evolve can allow you to solve your problems in a more effective way. But, as always, it depends on the problem, its context, and so on.
Reading this article, you might have wondered: how much information is enough to be comfortable enough to apply a solution? Well, again, your experience will be the best judge here. You’ll also need to consider carefully risks, benefits, and drawbacks. It doesn’t mean that you need to chicken out if you don’t have 100% certainty about a problem and some hypothesizes; being a software developer implies to have some courage and accept that mistakes will be made. It’s not an easy task, and there is no general process to follow in any possible case.
In short: use your brain. Even if you’re totally wrong, you’ll have the opportunity to fix the bad decisions you’ve made before the implementation, during the implementation, and even after it. We don’t code in stone.
The Implementation: The Value of Iteration
You’ve gathered with your team, tried to define the problem, found multiple hypothesizes, and agreed to try one of them. Great! Problem solved.
Not so fast! We still need to apply the hypothesis, and hope that it will become a good solution to the problem. Doing so, you’ll gather more information along the way, which might change your perspective on the problem, on your hypothesizes, and can even create some baby problems on its own.
It’s where the agile methodology is useful: since we’ll never have 100% certainty regarding a problem and its possible solution, we’ll learn more about both while implementing the hypothesis. That’s why it’s so valuable to iterate on the implementation: it gives you more information to possibly adjust your code, or even the problem, or even switching hypothesizes altogether. Who knows? A solution which is not implemented is just a guess.
If the hypothesis applied is not the ones you would have personally preferred (compromising, or even giving up on your preferred solution is common in a team), only applying it will tell you if you’re right or wrong; that is, if the hypothesis can become a solution solving the problem, at least in the present context.
If you’re worried about how a specific solution will evolve overtime, it’s more complicated, because an implementation won’t give you the information you seek. Still, implementing a hypothesis can be a great source of learning (the most valuable to me is when I’m wrong, because I learn even more). If you think that your hypothesis can have better outcome at time T, you might also try to implement it and compare it. Again, it’s where prototyping is useful.
When applying the solution, you need to look at the details of the implementation, as well as the big picture, to judge if the solution you’re creating is appropriate (leading to the desired outcome). This is a difficult exercise. In general, a developer should be able to reason on different levels of abstraction, more or less at the same time. Again, if you’re aware of it, your experience will help you here, and you can also push yourself to think of all the possible risks and consequences at different levels.
If you work in a team, try to participate (at least a bit) into the implementation of the solution. It’s not good to create silos in teams (that is, only a couple of members have some information others don’t have).
You can go as far as looking at other projects, and ask yourselves these questions:
- Did we had similar problems on these other projects? How did we solve them?
- What was the context of these projects? Is it similar to our current context?
- What did we learn from these other problems, and their implementation? Is the implementation similar to what we’re doing now?
In any case, I would definitely recommend you to write a development journal. I write mine for years, and it has been valuable in many cases. I basically write in there:
- The interesting problems I had.
- The decisions made.
- How the implementation of the solution evolved overtime.
- The possible mistakes we made along the way.
It’s a great resource when you have a problem and you want to look at your past experience.
To evaluate your decisions overtime, nothing will beat a good monitoring process: logs, tests, and so on. It’s what the book Building Evolutionary Architecture call “fitness functions” for example, some monitoring allowing you to measure how healthy your architecture stays overtime. It doesn’t have to stop to the architecture; you can think about different monitoring system to see how something evolve, especially if the solution has still a lot of uncertainty regarding its benefits, drawbacks, and risks.
You can also do that retrospectively: looking at how the code complexity evolve overtime using Git for example.
Retrospective on the Process
We defined the problem, implemented a solution iteratively, and now the problem is gone. That’s it! We made it! Are we done now?
Decisions are sometimes not optimal, and implementing a solution successfully doesn’t mean that there wasn’t a better (simpler) one to begin with. That’s why it can be beneficial to look back and understand what went right, and what went wrong. For example, we can ask ourselves these questions:
- Looking at what we learned during the whole process, is there a potentially better hypothesis to solve the problem in a simpler, more robust way?
- What are the benefits and drawbacks we missed when speaking about the different hypothesizes, but we discovered during the implementation? Why we didn’t think about them beforehand?
- What other problems did we encounter during the implementation? Did we solve them? Did we differ some? What should be the next steps regarding these new problems?
- What kind of monitoring did we put in place to make sure that the solution won’t have undesired outcomes overtime? Can we learn something with this data?
Reflecting on past solutions is a difficult thing to do. There is no way to logically assess that the decision taken was better than others, since we didn’t implement the other hypothesizes, and we didn’t look at them overtime to appreciate their consequences. But you can still look at the implementation of the solution overtime, and write in your developer journal each time there is a bug which seems directly related to the solution. Would the bugs be the same if another solution would had been applied?
Bugs are often not an option; they will pop up, eventually. Nonetheless, it’s important to make sure that you can fix them in a reasonable amount of time, and that you don’t see them creeping back in the codebase after being solved. Some metrics, from the DevOps movement (like MTTR for example) can help here. Sometimes, bugs will show you a better, more refined solution to the original problem; after all, bugs can also give you some useful information. They are also the most direct result of the implementation of your solution.
If you want to know more about measuring complexity (which can be also used to measure complexity overtime after applying a solution), I wrote a couple of articles on the subject .
Humility in Problem-Solving
It’s time to do a little summary. What did we see in this article?
- We need to ensure that the problem we found is really a problem we need to solve. Is there any value to solve the problem? Is it even a problem?
- Try to determine what kind of problem you have: a problem which can have multiple, specific, known answers (like a technical problem), or a problem which depends on the real-life context, without known solutions?
- Defining the problem is important. Try to define it using different words. Write these definitions down. Does everybody in your team understand the problem equally?
- It’s time to explore the solution space. Draft a couple of hypothesizes, their benefits, drawbacks, and risks. You can also do some prototyping if you think it would give you more information to take the best decision.
- Do you have enough information to implement a hypothesis, becoming effectively a solution? If it’s not the case, it might be better to keep the status quo and try to solve the problem later, when you’ll have more information. But don’t forget the problem!
- If you decide to implement a solution, do it step by step, especially if you’re unsure about the consequences of your decisions. Implement an independent part of the hypothesis, look at the consequences, adjust if necessary, and re-iterate.
- When the solution is implemented, it’s time to reflect on the whole process: did we solve the problem? What other problems did we encounter? Maybe another solution would have been better? Why?
As I was writing above, most problems you’ll encounter will be complex ones, embedded into a changing environment with different moving parts. As a result, it’s difficult to train to solve problems in a vacuum; the only good training I know is solving real life problems. That’s why your experience is so important.
Experience build your intuition, which in turn increase your expertise.
You’ll never have 100% certainty that a solution will bring you the desired outcome, especially if you are in front of a complex problem with a blurry context. If you are absolutely convinced that you have the good solution without even beginning to implement it, I’d advise you to stay humber in front of the Gods of Complexity, or they will show you how little you know.
- How to solve it
- Hammock Driven Development
- When Deferring Decisions Leads to Better Codebases
- Lean Development - deferring decision
What Is Problem Solving? How Software Engineers Approach Complex Challenges

From debugging an existing system to designing an entirely new software application, a day in the life of a software engineer is filled with various challenges and complexities. The one skill that glues these disparate tasks together and makes them manageable? Problem solving .
Throughout this blog post, we’ll explore why problem-solving skills are so critical for software engineers, delve into the techniques they use to address complex challenges, and discuss how hiring managers can identify these skills during the hiring process.
What Is Problem Solving?
But what exactly is problem solving in the context of software engineering? How does it work, and why is it so important?
Problem solving, in the simplest terms, is the process of identifying a problem, analyzing it, and finding the most effective solution to overcome it. For software engineers, this process is deeply embedded in their daily workflow. It could be something as simple as figuring out why a piece of code isn’t working as expected, or something as complex as designing the architecture for a new software system.
In a world where technology is evolving at a blistering pace, the complexity and volume of problems that software engineers face are also growing. As such, the ability to tackle these issues head-on and find innovative solutions is not only a handy skill — it’s a necessity.
The Importance of Problem-Solving Skills for Software Engineers
Problem-solving isn’t just another ability that software engineers pull out of their toolkits when they encounter a bug or a system failure. It’s a constant, ongoing process that’s intrinsic to every aspect of their work. Let’s break down why this skill is so critical.
Driving Development Forward
Without problem solving, software development would hit a standstill. Every new feature, every optimization, and every bug fix is a problem that needs solving. Whether it’s a performance issue that needs diagnosing or a user interface that needs improving, the capacity to tackle and solve these problems is what keeps the wheels of development turning.
It’s estimated that 60% of software development lifecycle costs are related to maintenance tasks, including debugging and problem solving. This highlights how pivotal this skill is to the everyday functioning and advancement of software systems.
Innovation and Optimization
The importance of problem solving isn’t confined to reactive scenarios; it also plays a major role in proactive, innovative initiatives . Software engineers often need to think outside the box to come up with creative solutions, whether it’s optimizing an algorithm to run faster or designing a new feature to meet customer needs. These are all forms of problem solving.
Consider the development of the modern smartphone. It wasn’t born out of a pre-existing issue but was a solution to a problem people didn’t realize they had — a device that combined communication, entertainment, and productivity into one handheld tool.
Increasing Efficiency and Productivity
Good problem-solving skills can save a lot of time and resources. Effective problem-solvers are adept at dissecting an issue to understand its root cause, thus reducing the time spent on trial and error. This efficiency means projects move faster, releases happen sooner, and businesses stay ahead of their competition.
Improving Software Quality
Problem solving also plays a significant role in enhancing the quality of the end product. By tackling the root causes of bugs and system failures, software engineers can deliver reliable, high-performing software. This is critical because, according to the Consortium for Information and Software Quality, poor quality software in the U.S. in 2022 cost at least $2.41 trillion in operational issues, wasted developer time, and other related problems.
Problem-Solving Techniques in Software Engineering
So how do software engineers go about tackling these complex challenges? Let’s explore some of the key problem-solving techniques, theories, and processes they commonly use.
Decomposition
Breaking down a problem into smaller, manageable parts is one of the first steps in the problem-solving process. It’s like dealing with a complicated puzzle. You don’t try to solve it all at once. Instead, you separate the pieces, group them based on similarities, and then start working on the smaller sets. This method allows software engineers to handle complex issues without being overwhelmed and makes it easier to identify where things might be going wrong.
Abstraction
In the realm of software engineering, abstraction means focusing on the necessary information only and ignoring irrelevant details. It is a way of simplifying complex systems to make them easier to understand and manage. For instance, a software engineer might ignore the details of how a database works to focus on the information it holds and how to retrieve or modify that information.
Algorithmic Thinking
At its core, software engineering is about creating algorithms — step-by-step procedures to solve a problem or accomplish a goal. Algorithmic thinking involves conceiving and expressing these procedures clearly and accurately and viewing every problem through an algorithmic lens. A well-designed algorithm not only solves the problem at hand but also does so efficiently, saving computational resources.
Parallel Thinking
Parallel thinking is a structured process where team members think in the same direction at the same time, allowing for more organized discussion and collaboration. It’s an approach popularized by Edward de Bono with the “ Six Thinking Hats ” technique, where each “hat” represents a different style of thinking.
In the context of software engineering, parallel thinking can be highly effective for problem solving. For instance, when dealing with a complex issue, the team can use the “White Hat” to focus solely on the data and facts about the problem, then the “Black Hat” to consider potential problems with a proposed solution, and so on. This structured approach can lead to more comprehensive analysis and more effective solutions, and it ensures that everyone’s perspectives are considered.
This is the process of identifying and fixing errors in code . Debugging involves carefully reviewing the code, reproducing and analyzing the error, and then making necessary modifications to rectify the problem. It’s a key part of maintaining and improving software quality.
Testing and Validation
Testing is an essential part of problem solving in software engineering. Engineers use a variety of tests to verify that their code works as expected and to uncover any potential issues. These range from unit tests that check individual components of the code to integration tests that ensure the pieces work well together. Validation, on the other hand, ensures that the solution not only works but also fulfills the intended requirements and objectives.
Explore verified tech roles & skills.
The definitive directory of tech roles, backed by machine learning and skills intelligence.
Explore all roles
Evaluating Problem-Solving Skills
We’ve examined the importance of problem-solving in the work of a software engineer and explored various techniques software engineers employ to approach complex challenges. Now, let’s delve into how hiring teams can identify and evaluate problem-solving skills during the hiring process.
Recognizing Problem-Solving Skills in Candidates
How can you tell if a candidate is a good problem solver? Look for these indicators:
- Previous Experience: A history of dealing with complex, challenging projects is often a good sign. Ask the candidate to discuss a difficult problem they faced in a previous role and how they solved it.
- Problem-Solving Questions: During interviews, pose hypothetical scenarios or present real problems your company has faced. Ask candidates to explain how they would tackle these issues. You’re not just looking for a correct solution but the thought process that led them there.
- Technical Tests: Coding challenges and other technical tests can provide insight into a candidate’s problem-solving abilities. Consider leveraging a platform for assessing these skills in a realistic, job-related context.
Assessing Problem-Solving Skills
Once you’ve identified potential problem solvers, here are a few ways you can assess their skills:
- Solution Effectiveness: Did the candidate solve the problem? How efficient and effective is their solution?
- Approach and Process: Go beyond whether or not they solved the problem and examine how they arrived at their solution. Did they break the problem down into manageable parts? Did they consider different perspectives and possibilities?
- Communication: A good problem solver can explain their thought process clearly. Can the candidate effectively communicate how they arrived at their solution and why they chose it?
- Adaptability: Problem-solving often involves a degree of trial and error. How does the candidate handle roadblocks? Do they adapt their approach based on new information or feedback?
Hiring managers play a crucial role in identifying and fostering problem-solving skills within their teams. By focusing on these abilities during the hiring process, companies can build teams that are more capable, innovative, and resilient.
Key Takeaways
As you can see, problem solving plays a pivotal role in software engineering. Far from being an occasional requirement, it is the lifeblood that drives development forward, catalyzes innovation, and delivers of quality software.
By leveraging problem-solving techniques, software engineers employ a powerful suite of strategies to overcome complex challenges. But mastering these techniques isn’t simple feat. It requires a learning mindset, regular practice, collaboration, reflective thinking, resilience, and a commitment to staying updated with industry trends.
For hiring managers and team leads, recognizing these skills and fostering a culture that values and nurtures problem solving is key. It’s this emphasis on problem solving that can differentiate an average team from a high-performing one and an ordinary product from an industry-leading one.
At the end of the day, software engineering is fundamentally about solving problems — problems that matter to businesses, to users, and to the wider society. And it’s the proficient problem solvers who stand at the forefront of this dynamic field, turning challenges into opportunities, and ideas into reality.
This article was written with the help of AI. Can you tell which parts?
Get started with HackerRank
Over 2,500 companies and 40% of developers worldwide use HackerRank to hire tech talent and sharpen their skills.
Recommended topics
- Hire Developers
- Problem Solving
Does a College Degree Still Matter for Developers in 2024?
35 problem-solving techniques and methods for solving complex problems

Design your next session with SessionLab
Join the 150,000+ facilitators using SessionLab.
Recommended Articles
A step-by-step guide to planning a workshop, how to create an unforgettable training session in 8 simple steps, 47 useful online tools for workshop planning and meeting facilitation.
All teams and organizations encounter challenges as they grow. There are problems that might occur for teams when it comes to miscommunication or resolving business-critical issues . You may face challenges around growth , design , user engagement, and even team culture and happiness. In short, problem-solving techniques should be part of every team’s skillset.
Problem-solving methods are primarily designed to help a group or team through a process of first identifying problems and challenges , ideating possible solutions , and then evaluating the most suitable .
Finding effective solutions to complex problems isn’t easy, but by using the right process and techniques, you can help your team be more efficient in the process.
So how do you develop strategies that are engaging, and empower your team to solve problems effectively?
In this blog post, we share a series of problem-solving tools you can use in your next workshop or team meeting. You’ll also find some tips for facilitating the process and how to enable others to solve complex problems.
Let’s get started!
How do you identify problems?
How do you identify the right solution.
- Tips for more effective problem-solving
Complete problem-solving methods
- Problem-solving techniques to identify and analyze problems
- Problem-solving techniques for developing solutions
Problem-solving warm-up activities
Closing activities for a problem-solving process.
Before you can move towards finding the right solution for a given problem, you first need to identify and define the problem you wish to solve.
Here, you want to clearly articulate what the problem is and allow your group to do the same. Remember that everyone in a group is likely to have differing perspectives and alignment is necessary in order to help the group move forward.
Identifying a problem accurately also requires that all members of a group are able to contribute their views in an open and safe manner. It can be scary for people to stand up and contribute, especially if the problems or challenges are emotive or personal in nature. Be sure to try and create a psychologically safe space for these kinds of discussions.
Remember that problem analysis and further discussion are also important. Not taking the time to fully analyze and discuss a challenge can result in the development of solutions that are not fit for purpose or do not address the underlying issue.
Successfully identifying and then analyzing a problem means facilitating a group through activities designed to help them clearly and honestly articulate their thoughts and produce usable insight.
With this data, you might then produce a problem statement that clearly describes the problem you wish to be addressed and also state the goal of any process you undertake to tackle this issue.
Finding solutions is the end goal of any process. Complex organizational challenges can only be solved with an appropriate solution but discovering them requires using the right problem-solving tool.
After you’ve explored a problem and discussed ideas, you need to help a team discuss and choose the right solution. Consensus tools and methods such as those below help a group explore possible solutions before then voting for the best. They’re a great way to tap into the collective intelligence of the group for great results!
Remember that the process is often iterative. Great problem solvers often roadtest a viable solution in a measured way to see what works too. While you might not get the right solution on your first try, the methods below help teams land on the most likely to succeed solution while also holding space for improvement.
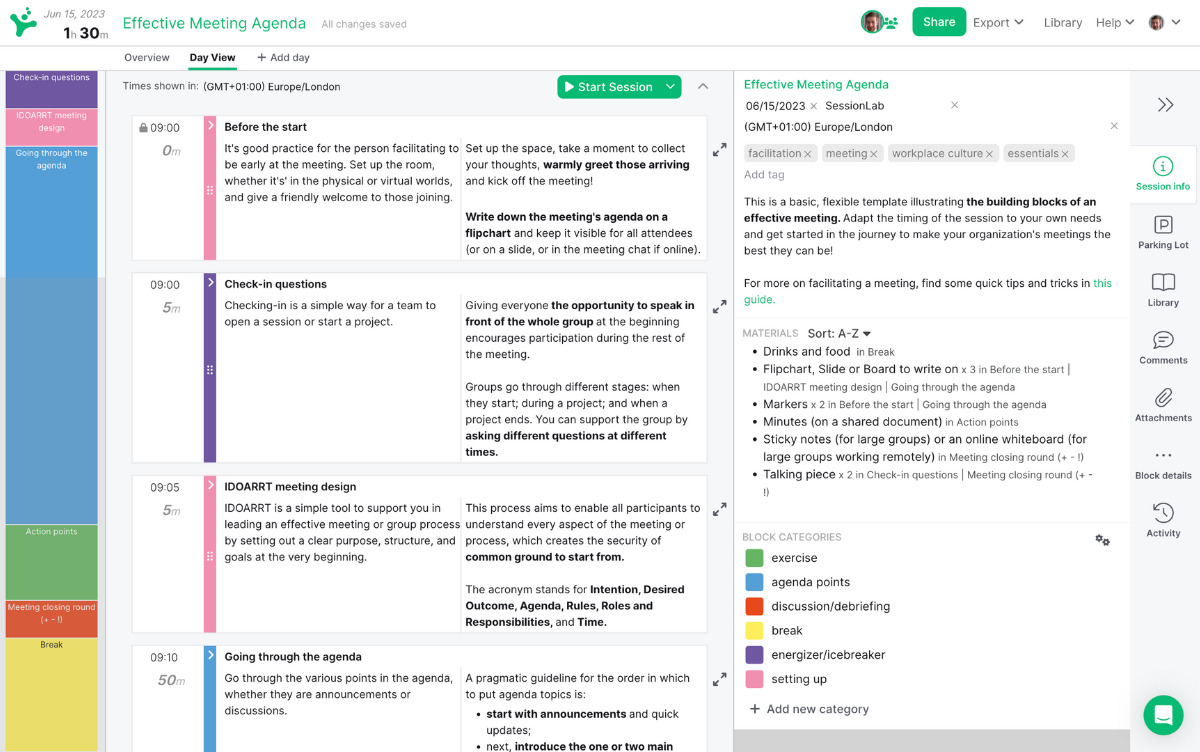
Every effective problem solving process begins with an agenda . A well-structured workshop is one of the best methods for successfully guiding a group from exploring a problem to implementing a solution.
In SessionLab, it’s easy to go from an idea to a complete agenda . Start by dragging and dropping your core problem solving activities into place . Add timings, breaks and necessary materials before sharing your agenda with your colleagues.
The resulting agenda will be your guide to an effective and productive problem solving session that will also help you stay organized on the day!
Tips for more effective problem solving
Problem-solving activities are only one part of the puzzle. While a great method can help unlock your team’s ability to solve problems, without a thoughtful approach and strong facilitation the solutions may not be fit for purpose.
Let’s take a look at some problem-solving tips you can apply to any process to help it be a success!
Clearly define the problem
Jumping straight to solutions can be tempting, though without first clearly articulating a problem, the solution might not be the right one. Many of the problem-solving activities below include sections where the problem is explored and clearly defined before moving on.
This is a vital part of the problem-solving process and taking the time to fully define an issue can save time and effort later. A clear definition helps identify irrelevant information and it also ensures that your team sets off on the right track.
Don’t jump to conclusions
It’s easy for groups to exhibit cognitive bias or have preconceived ideas about both problems and potential solutions. Be sure to back up any problem statements or potential solutions with facts, research, and adequate forethought.
The best techniques ask participants to be methodical and challenge preconceived notions. Make sure you give the group enough time and space to collect relevant information and consider the problem in a new way. By approaching the process with a clear, rational mindset, you’ll often find that better solutions are more forthcoming.
Try different approaches
Problems come in all shapes and sizes and so too should the methods you use to solve them. If you find that one approach isn’t yielding results and your team isn’t finding different solutions, try mixing it up. You’ll be surprised at how using a new creative activity can unblock your team and generate great solutions.
Don’t take it personally
Depending on the nature of your team or organizational problems, it’s easy for conversations to get heated. While it’s good for participants to be engaged in the discussions, ensure that emotions don’t run too high and that blame isn’t thrown around while finding solutions.
You’re all in it together, and even if your team or area is seeing problems, that isn’t necessarily a disparagement of you personally. Using facilitation skills to manage group dynamics is one effective method of helping conversations be more constructive.
Get the right people in the room
Your problem-solving method is often only as effective as the group using it. Getting the right people on the job and managing the number of people present is important too!
If the group is too small, you may not get enough different perspectives to effectively solve a problem. If the group is too large, you can go round and round during the ideation stages.
Creating the right group makeup is also important in ensuring you have the necessary expertise and skillset to both identify and follow up on potential solutions. Carefully consider who to include at each stage to help ensure your problem-solving method is followed and positioned for success.
Document everything
The best solutions can take refinement, iteration, and reflection to come out. Get into a habit of documenting your process in order to keep all the learnings from the session and to allow ideas to mature and develop. Many of the methods below involve the creation of documents or shared resources. Be sure to keep and share these so everyone can benefit from the work done!
Bring a facilitator
Facilitation is all about making group processes easier. With a subject as potentially emotive and important as problem-solving, having an impartial third party in the form of a facilitator can make all the difference in finding great solutions and keeping the process moving. Consider bringing a facilitator to your problem-solving session to get better results and generate meaningful solutions!
Develop your problem-solving skills
It takes time and practice to be an effective problem solver. While some roles or participants might more naturally gravitate towards problem-solving, it can take development and planning to help everyone create better solutions.
You might develop a training program, run a problem-solving workshop or simply ask your team to practice using the techniques below. Check out our post on problem-solving skills to see how you and your group can develop the right mental process and be more resilient to issues too!
Design a great agenda
Workshops are a great format for solving problems. With the right approach, you can focus a group and help them find the solutions to their own problems. But designing a process can be time-consuming and finding the right activities can be difficult.
Check out our workshop planning guide to level-up your agenda design and start running more effective workshops. Need inspiration? Check out templates designed by expert facilitators to help you kickstart your process!
In this section, we’ll look at in-depth problem-solving methods that provide a complete end-to-end process for developing effective solutions. These will help guide your team from the discovery and definition of a problem through to delivering the right solution.
If you’re looking for an all-encompassing method or problem-solving model, these processes are a great place to start. They’ll ask your team to challenge preconceived ideas and adopt a mindset for solving problems more effectively.
- Six Thinking Hats
- Lightning Decision Jam
- Problem Definition Process
- Discovery & Action Dialogue
Design Sprint 2.0
- Open Space Technology
1. Six Thinking Hats
Individual approaches to solving a problem can be very different based on what team or role an individual holds. It can be easy for existing biases or perspectives to find their way into the mix, or for internal politics to direct a conversation.
Six Thinking Hats is a classic method for identifying the problems that need to be solved and enables your team to consider them from different angles, whether that is by focusing on facts and data, creative solutions, or by considering why a particular solution might not work.
Like all problem-solving frameworks, Six Thinking Hats is effective at helping teams remove roadblocks from a conversation or discussion and come to terms with all the aspects necessary to solve complex problems.
2. Lightning Decision Jam
Featured courtesy of Jonathan Courtney of AJ&Smart Berlin, Lightning Decision Jam is one of those strategies that should be in every facilitation toolbox. Exploring problems and finding solutions is often creative in nature, though as with any creative process, there is the potential to lose focus and get lost.
Unstructured discussions might get you there in the end, but it’s much more effective to use a method that creates a clear process and team focus.
In Lightning Decision Jam, participants are invited to begin by writing challenges, concerns, or mistakes on post-its without discussing them before then being invited by the moderator to present them to the group.
From there, the team vote on which problems to solve and are guided through steps that will allow them to reframe those problems, create solutions and then decide what to execute on.
By deciding the problems that need to be solved as a team before moving on, this group process is great for ensuring the whole team is aligned and can take ownership over the next stages.
Lightning Decision Jam (LDJ) #action #decision making #problem solving #issue analysis #innovation #design #remote-friendly The problem with anything that requires creative thinking is that it’s easy to get lost—lose focus and fall into the trap of having useless, open-ended, unstructured discussions. Here’s the most effective solution I’ve found: Replace all open, unstructured discussion with a clear process. What to use this exercise for: Anything which requires a group of people to make decisions, solve problems or discuss challenges. It’s always good to frame an LDJ session with a broad topic, here are some examples: The conversion flow of our checkout Our internal design process How we organise events Keeping up with our competition Improving sales flow
3. Problem Definition Process
While problems can be complex, the problem-solving methods you use to identify and solve those problems can often be simple in design.
By taking the time to truly identify and define a problem before asking the group to reframe the challenge as an opportunity, this method is a great way to enable change.
Begin by identifying a focus question and exploring the ways in which it manifests before splitting into five teams who will each consider the problem using a different method: escape, reversal, exaggeration, distortion or wishful. Teams develop a problem objective and create ideas in line with their method before then feeding them back to the group.
This method is great for enabling in-depth discussions while also creating space for finding creative solutions too!
Problem Definition #problem solving #idea generation #creativity #online #remote-friendly A problem solving technique to define a problem, challenge or opportunity and to generate ideas.
4. The 5 Whys
Sometimes, a group needs to go further with their strategies and analyze the root cause at the heart of organizational issues. An RCA or root cause analysis is the process of identifying what is at the heart of business problems or recurring challenges.
The 5 Whys is a simple and effective method of helping a group go find the root cause of any problem or challenge and conduct analysis that will deliver results.
By beginning with the creation of a problem statement and going through five stages to refine it, The 5 Whys provides everything you need to truly discover the cause of an issue.
The 5 Whys #hyperisland #innovation This simple and powerful method is useful for getting to the core of a problem or challenge. As the title suggests, the group defines a problems, then asks the question “why” five times, often using the resulting explanation as a starting point for creative problem solving.
5. World Cafe
World Cafe is a simple but powerful facilitation technique to help bigger groups to focus their energy and attention on solving complex problems.
World Cafe enables this approach by creating a relaxed atmosphere where participants are able to self-organize and explore topics relevant and important to them which are themed around a central problem-solving purpose. Create the right atmosphere by modeling your space after a cafe and after guiding the group through the method, let them take the lead!
Making problem-solving a part of your organization’s culture in the long term can be a difficult undertaking. More approachable formats like World Cafe can be especially effective in bringing people unfamiliar with workshops into the fold.
World Cafe #hyperisland #innovation #issue analysis World Café is a simple yet powerful method, originated by Juanita Brown, for enabling meaningful conversations driven completely by participants and the topics that are relevant and important to them. Facilitators create a cafe-style space and provide simple guidelines. Participants then self-organize and explore a set of relevant topics or questions for conversation.
6. Discovery & Action Dialogue (DAD)
One of the best approaches is to create a safe space for a group to share and discover practices and behaviors that can help them find their own solutions.
With DAD, you can help a group choose which problems they wish to solve and which approaches they will take to do so. It’s great at helping remove resistance to change and can help get buy-in at every level too!
This process of enabling frontline ownership is great in ensuring follow-through and is one of the methods you will want in your toolbox as a facilitator.
Discovery & Action Dialogue (DAD) #idea generation #liberating structures #action #issue analysis #remote-friendly DADs make it easy for a group or community to discover practices and behaviors that enable some individuals (without access to special resources and facing the same constraints) to find better solutions than their peers to common problems. These are called positive deviant (PD) behaviors and practices. DADs make it possible for people in the group, unit, or community to discover by themselves these PD practices. DADs also create favorable conditions for stimulating participants’ creativity in spaces where they can feel safe to invent new and more effective practices. Resistance to change evaporates as participants are unleashed to choose freely which practices they will adopt or try and which problems they will tackle. DADs make it possible to achieve frontline ownership of solutions.
7. Design Sprint 2.0
Want to see how a team can solve big problems and move forward with prototyping and testing solutions in a few days? The Design Sprint 2.0 template from Jake Knapp, author of Sprint, is a complete agenda for a with proven results.
Developing the right agenda can involve difficult but necessary planning. Ensuring all the correct steps are followed can also be stressful or time-consuming depending on your level of experience.
Use this complete 4-day workshop template if you are finding there is no obvious solution to your challenge and want to focus your team around a specific problem that might require a shortcut to launching a minimum viable product or waiting for the organization-wide implementation of a solution.
8. Open space technology
Open space technology- developed by Harrison Owen – creates a space where large groups are invited to take ownership of their problem solving and lead individual sessions. Open space technology is a great format when you have a great deal of expertise and insight in the room and want to allow for different takes and approaches on a particular theme or problem you need to be solved.
Start by bringing your participants together to align around a central theme and focus their efforts. Explain the ground rules to help guide the problem-solving process and then invite members to identify any issue connecting to the central theme that they are interested in and are prepared to take responsibility for.
Once participants have decided on their approach to the core theme, they write their issue on a piece of paper, announce it to the group, pick a session time and place, and post the paper on the wall. As the wall fills up with sessions, the group is then invited to join the sessions that interest them the most and which they can contribute to, then you’re ready to begin!
Everyone joins the problem-solving group they’ve signed up to, record the discussion and if appropriate, findings can then be shared with the rest of the group afterward.
Open Space Technology #action plan #idea generation #problem solving #issue analysis #large group #online #remote-friendly Open Space is a methodology for large groups to create their agenda discerning important topics for discussion, suitable for conferences, community gatherings and whole system facilitation
Techniques to identify and analyze problems
Using a problem-solving method to help a team identify and analyze a problem can be a quick and effective addition to any workshop or meeting.
While further actions are always necessary, you can generate momentum and alignment easily, and these activities are a great place to get started.
We’ve put together this list of techniques to help you and your team with problem identification, analysis, and discussion that sets the foundation for developing effective solutions.
Let’s take a look!
- The Creativity Dice
- Fishbone Analysis
- Problem Tree
- SWOT Analysis
- Agreement-Certainty Matrix
- The Journalistic Six
- LEGO Challenge
- What, So What, Now What?
- Journalists
Individual and group perspectives are incredibly important, but what happens if people are set in their minds and need a change of perspective in order to approach a problem more effectively?
Flip It is a method we love because it is both simple to understand and run, and allows groups to understand how their perspectives and biases are formed.
Participants in Flip It are first invited to consider concerns, issues, or problems from a perspective of fear and write them on a flip chart. Then, the group is asked to consider those same issues from a perspective of hope and flip their understanding.
No problem and solution is free from existing bias and by changing perspectives with Flip It, you can then develop a problem solving model quickly and effectively.
Flip It! #gamestorming #problem solving #action Often, a change in a problem or situation comes simply from a change in our perspectives. Flip It! is a quick game designed to show players that perspectives are made, not born.
10. The Creativity Dice
One of the most useful problem solving skills you can teach your team is of approaching challenges with creativity, flexibility, and openness. Games like The Creativity Dice allow teams to overcome the potential hurdle of too much linear thinking and approach the process with a sense of fun and speed.
In The Creativity Dice, participants are organized around a topic and roll a dice to determine what they will work on for a period of 3 minutes at a time. They might roll a 3 and work on investigating factual information on the chosen topic. They might roll a 1 and work on identifying the specific goals, standards, or criteria for the session.
Encouraging rapid work and iteration while asking participants to be flexible are great skills to cultivate. Having a stage for idea incubation in this game is also important. Moments of pause can help ensure the ideas that are put forward are the most suitable.
The Creativity Dice #creativity #problem solving #thiagi #issue analysis Too much linear thinking is hazardous to creative problem solving. To be creative, you should approach the problem (or the opportunity) from different points of view. You should leave a thought hanging in mid-air and move to another. This skipping around prevents premature closure and lets your brain incubate one line of thought while you consciously pursue another.
11. Fishbone Analysis
Organizational or team challenges are rarely simple, and it’s important to remember that one problem can be an indication of something that goes deeper and may require further consideration to be solved.
Fishbone Analysis helps groups to dig deeper and understand the origins of a problem. It’s a great example of a root cause analysis method that is simple for everyone on a team to get their head around.
Participants in this activity are asked to annotate a diagram of a fish, first adding the problem or issue to be worked on at the head of a fish before then brainstorming the root causes of the problem and adding them as bones on the fish.
Using abstractions such as a diagram of a fish can really help a team break out of their regular thinking and develop a creative approach.
Fishbone Analysis #problem solving ##root cause analysis #decision making #online facilitation A process to help identify and understand the origins of problems, issues or observations.
12. Problem Tree
Encouraging visual thinking can be an essential part of many strategies. By simply reframing and clarifying problems, a group can move towards developing a problem solving model that works for them.
In Problem Tree, groups are asked to first brainstorm a list of problems – these can be design problems, team problems or larger business problems – and then organize them into a hierarchy. The hierarchy could be from most important to least important or abstract to practical, though the key thing with problem solving games that involve this aspect is that your group has some way of managing and sorting all the issues that are raised.
Once you have a list of problems that need to be solved and have organized them accordingly, you’re then well-positioned for the next problem solving steps.
Problem tree #define intentions #create #design #issue analysis A problem tree is a tool to clarify the hierarchy of problems addressed by the team within a design project; it represents high level problems or related sublevel problems.
13. SWOT Analysis
Chances are you’ve heard of the SWOT Analysis before. This problem-solving method focuses on identifying strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats is a tried and tested method for both individuals and teams.
Start by creating a desired end state or outcome and bare this in mind – any process solving model is made more effective by knowing what you are moving towards. Create a quadrant made up of the four categories of a SWOT analysis and ask participants to generate ideas based on each of those quadrants.
Once you have those ideas assembled in their quadrants, cluster them together based on their affinity with other ideas. These clusters are then used to facilitate group conversations and move things forward.
SWOT analysis #gamestorming #problem solving #action #meeting facilitation The SWOT Analysis is a long-standing technique of looking at what we have, with respect to the desired end state, as well as what we could improve on. It gives us an opportunity to gauge approaching opportunities and dangers, and assess the seriousness of the conditions that affect our future. When we understand those conditions, we can influence what comes next.
14. Agreement-Certainty Matrix
Not every problem-solving approach is right for every challenge, and deciding on the right method for the challenge at hand is a key part of being an effective team.
The Agreement Certainty matrix helps teams align on the nature of the challenges facing them. By sorting problems from simple to chaotic, your team can understand what methods are suitable for each problem and what they can do to ensure effective results.
If you are already using Liberating Structures techniques as part of your problem-solving strategy, the Agreement-Certainty Matrix can be an invaluable addition to your process. We’ve found it particularly if you are having issues with recurring problems in your organization and want to go deeper in understanding the root cause.
Agreement-Certainty Matrix #issue analysis #liberating structures #problem solving You can help individuals or groups avoid the frequent mistake of trying to solve a problem with methods that are not adapted to the nature of their challenge. The combination of two questions makes it possible to easily sort challenges into four categories: simple, complicated, complex , and chaotic . A problem is simple when it can be solved reliably with practices that are easy to duplicate. It is complicated when experts are required to devise a sophisticated solution that will yield the desired results predictably. A problem is complex when there are several valid ways to proceed but outcomes are not predictable in detail. Chaotic is when the context is too turbulent to identify a path forward. A loose analogy may be used to describe these differences: simple is like following a recipe, complicated like sending a rocket to the moon, complex like raising a child, and chaotic is like the game “Pin the Tail on the Donkey.” The Liberating Structures Matching Matrix in Chapter 5 can be used as the first step to clarify the nature of a challenge and avoid the mismatches between problems and solutions that are frequently at the root of chronic, recurring problems.
Organizing and charting a team’s progress can be important in ensuring its success. SQUID (Sequential Question and Insight Diagram) is a great model that allows a team to effectively switch between giving questions and answers and develop the skills they need to stay on track throughout the process.
Begin with two different colored sticky notes – one for questions and one for answers – and with your central topic (the head of the squid) on the board. Ask the group to first come up with a series of questions connected to their best guess of how to approach the topic. Ask the group to come up with answers to those questions, fix them to the board and connect them with a line. After some discussion, go back to question mode by responding to the generated answers or other points on the board.
It’s rewarding to see a diagram grow throughout the exercise, and a completed SQUID can provide a visual resource for future effort and as an example for other teams.
SQUID #gamestorming #project planning #issue analysis #problem solving When exploring an information space, it’s important for a group to know where they are at any given time. By using SQUID, a group charts out the territory as they go and can navigate accordingly. SQUID stands for Sequential Question and Insight Diagram.
16. Speed Boat
To continue with our nautical theme, Speed Boat is a short and sweet activity that can help a team quickly identify what employees, clients or service users might have a problem with and analyze what might be standing in the way of achieving a solution.
Methods that allow for a group to make observations, have insights and obtain those eureka moments quickly are invaluable when trying to solve complex problems.
In Speed Boat, the approach is to first consider what anchors and challenges might be holding an organization (or boat) back. Bonus points if you are able to identify any sharks in the water and develop ideas that can also deal with competitors!
Speed Boat #gamestorming #problem solving #action Speedboat is a short and sweet way to identify what your employees or clients don’t like about your product/service or what’s standing in the way of a desired goal.
17. The Journalistic Six
Some of the most effective ways of solving problems is by encouraging teams to be more inclusive and diverse in their thinking.
Based on the six key questions journalism students are taught to answer in articles and news stories, The Journalistic Six helps create teams to see the whole picture. By using who, what, when, where, why, and how to facilitate the conversation and encourage creative thinking, your team can make sure that the problem identification and problem analysis stages of the are covered exhaustively and thoughtfully. Reporter’s notebook and dictaphone optional.
The Journalistic Six – Who What When Where Why How #idea generation #issue analysis #problem solving #online #creative thinking #remote-friendly A questioning method for generating, explaining, investigating ideas.
18. LEGO Challenge
Now for an activity that is a little out of the (toy) box. LEGO Serious Play is a facilitation methodology that can be used to improve creative thinking and problem-solving skills.
The LEGO Challenge includes giving each member of the team an assignment that is hidden from the rest of the group while they create a structure without speaking.
What the LEGO challenge brings to the table is a fun working example of working with stakeholders who might not be on the same page to solve problems. Also, it’s LEGO! Who doesn’t love LEGO!
LEGO Challenge #hyperisland #team A team-building activity in which groups must work together to build a structure out of LEGO, but each individual has a secret “assignment” which makes the collaborative process more challenging. It emphasizes group communication, leadership dynamics, conflict, cooperation, patience and problem solving strategy.
19. What, So What, Now What?
If not carefully managed, the problem identification and problem analysis stages of the problem-solving process can actually create more problems and misunderstandings.
The What, So What, Now What? problem-solving activity is designed to help collect insights and move forward while also eliminating the possibility of disagreement when it comes to identifying, clarifying, and analyzing organizational or work problems.
Facilitation is all about bringing groups together so that might work on a shared goal and the best problem-solving strategies ensure that teams are aligned in purpose, if not initially in opinion or insight.
Throughout the three steps of this game, you give everyone on a team to reflect on a problem by asking what happened, why it is important, and what actions should then be taken.
This can be a great activity for bringing our individual perceptions about a problem or challenge and contextualizing it in a larger group setting. This is one of the most important problem-solving skills you can bring to your organization.
W³ – What, So What, Now What? #issue analysis #innovation #liberating structures You can help groups reflect on a shared experience in a way that builds understanding and spurs coordinated action while avoiding unproductive conflict. It is possible for every voice to be heard while simultaneously sifting for insights and shaping new direction. Progressing in stages makes this practical—from collecting facts about What Happened to making sense of these facts with So What and finally to what actions logically follow with Now What . The shared progression eliminates most of the misunderstandings that otherwise fuel disagreements about what to do. Voila!
20. Journalists
Problem analysis can be one of the most important and decisive stages of all problem-solving tools. Sometimes, a team can become bogged down in the details and are unable to move forward.
Journalists is an activity that can avoid a group from getting stuck in the problem identification or problem analysis stages of the process.
In Journalists, the group is invited to draft the front page of a fictional newspaper and figure out what stories deserve to be on the cover and what headlines those stories will have. By reframing how your problems and challenges are approached, you can help a team move productively through the process and be better prepared for the steps to follow.
Journalists #vision #big picture #issue analysis #remote-friendly This is an exercise to use when the group gets stuck in details and struggles to see the big picture. Also good for defining a vision.
Problem-solving techniques for developing solutions
The success of any problem-solving process can be measured by the solutions it produces. After you’ve defined the issue, explored existing ideas, and ideated, it’s time to narrow down to the correct solution.
Use these problem-solving techniques when you want to help your team find consensus, compare possible solutions, and move towards taking action on a particular problem.
- Improved Solutions
- Four-Step Sketch
- 15% Solutions
- How-Now-Wow matrix
- Impact Effort Matrix
21. Mindspin
Brainstorming is part of the bread and butter of the problem-solving process and all problem-solving strategies benefit from getting ideas out and challenging a team to generate solutions quickly.
With Mindspin, participants are encouraged not only to generate ideas but to do so under time constraints and by slamming down cards and passing them on. By doing multiple rounds, your team can begin with a free generation of possible solutions before moving on to developing those solutions and encouraging further ideation.
This is one of our favorite problem-solving activities and can be great for keeping the energy up throughout the workshop. Remember the importance of helping people become engaged in the process – energizing problem-solving techniques like Mindspin can help ensure your team stays engaged and happy, even when the problems they’re coming together to solve are complex.
MindSpin #teampedia #idea generation #problem solving #action A fast and loud method to enhance brainstorming within a team. Since this activity has more than round ideas that are repetitive can be ruled out leaving more creative and innovative answers to the challenge.
22. Improved Solutions
After a team has successfully identified a problem and come up with a few solutions, it can be tempting to call the work of the problem-solving process complete. That said, the first solution is not necessarily the best, and by including a further review and reflection activity into your problem-solving model, you can ensure your group reaches the best possible result.
One of a number of problem-solving games from Thiagi Group, Improved Solutions helps you go the extra mile and develop suggested solutions with close consideration and peer review. By supporting the discussion of several problems at once and by shifting team roles throughout, this problem-solving technique is a dynamic way of finding the best solution.
Improved Solutions #creativity #thiagi #problem solving #action #team You can improve any solution by objectively reviewing its strengths and weaknesses and making suitable adjustments. In this creativity framegame, you improve the solutions to several problems. To maintain objective detachment, you deal with a different problem during each of six rounds and assume different roles (problem owner, consultant, basher, booster, enhancer, and evaluator) during each round. At the conclusion of the activity, each player ends up with two solutions to her problem.
23. Four Step Sketch
Creative thinking and visual ideation does not need to be confined to the opening stages of your problem-solving strategies. Exercises that include sketching and prototyping on paper can be effective at the solution finding and development stage of the process, and can be great for keeping a team engaged.
By going from simple notes to a crazy 8s round that involves rapidly sketching 8 variations on their ideas before then producing a final solution sketch, the group is able to iterate quickly and visually. Problem-solving techniques like Four-Step Sketch are great if you have a group of different thinkers and want to change things up from a more textual or discussion-based approach.
Four-Step Sketch #design sprint #innovation #idea generation #remote-friendly The four-step sketch is an exercise that helps people to create well-formed concepts through a structured process that includes: Review key information Start design work on paper, Consider multiple variations , Create a detailed solution . This exercise is preceded by a set of other activities allowing the group to clarify the challenge they want to solve. See how the Four Step Sketch exercise fits into a Design Sprint
24. 15% Solutions
Some problems are simpler than others and with the right problem-solving activities, you can empower people to take immediate actions that can help create organizational change.
Part of the liberating structures toolkit, 15% solutions is a problem-solving technique that focuses on finding and implementing solutions quickly. A process of iterating and making small changes quickly can help generate momentum and an appetite for solving complex problems.
Problem-solving strategies can live and die on whether people are onboard. Getting some quick wins is a great way of getting people behind the process.
It can be extremely empowering for a team to realize that problem-solving techniques can be deployed quickly and easily and delineate between things they can positively impact and those things they cannot change.
15% Solutions #action #liberating structures #remote-friendly You can reveal the actions, however small, that everyone can do immediately. At a minimum, these will create momentum, and that may make a BIG difference. 15% Solutions show that there is no reason to wait around, feel powerless, or fearful. They help people pick it up a level. They get individuals and the group to focus on what is within their discretion instead of what they cannot change. With a very simple question, you can flip the conversation to what can be done and find solutions to big problems that are often distributed widely in places not known in advance. Shifting a few grains of sand may trigger a landslide and change the whole landscape.
25. How-Now-Wow Matrix
The problem-solving process is often creative, as complex problems usually require a change of thinking and creative response in order to find the best solutions. While it’s common for the first stages to encourage creative thinking, groups can often gravitate to familiar solutions when it comes to the end of the process.
When selecting solutions, you don’t want to lose your creative energy! The How-Now-Wow Matrix from Gamestorming is a great problem-solving activity that enables a group to stay creative and think out of the box when it comes to selecting the right solution for a given problem.
Problem-solving techniques that encourage creative thinking and the ideation and selection of new solutions can be the most effective in organisational change. Give the How-Now-Wow Matrix a go, and not just for how pleasant it is to say out loud.
How-Now-Wow Matrix #gamestorming #idea generation #remote-friendly When people want to develop new ideas, they most often think out of the box in the brainstorming or divergent phase. However, when it comes to convergence, people often end up picking ideas that are most familiar to them. This is called a ‘creative paradox’ or a ‘creadox’. The How-Now-Wow matrix is an idea selection tool that breaks the creadox by forcing people to weigh each idea on 2 parameters.
26. Impact and Effort Matrix
All problem-solving techniques hope to not only find solutions to a given problem or challenge but to find the best solution. When it comes to finding a solution, groups are invited to put on their decision-making hats and really think about how a proposed idea would work in practice.
The Impact and Effort Matrix is one of the problem-solving techniques that fall into this camp, empowering participants to first generate ideas and then categorize them into a 2×2 matrix based on impact and effort.
Activities that invite critical thinking while remaining simple are invaluable. Use the Impact and Effort Matrix to move from ideation and towards evaluating potential solutions before then committing to them.
Impact and Effort Matrix #gamestorming #decision making #action #remote-friendly In this decision-making exercise, possible actions are mapped based on two factors: effort required to implement and potential impact. Categorizing ideas along these lines is a useful technique in decision making, as it obliges contributors to balance and evaluate suggested actions before committing to them.
27. Dotmocracy
If you’ve followed each of the problem-solving steps with your group successfully, you should move towards the end of your process with heaps of possible solutions developed with a specific problem in mind. But how do you help a group go from ideation to putting a solution into action?
Dotmocracy – or Dot Voting -is a tried and tested method of helping a team in the problem-solving process make decisions and put actions in place with a degree of oversight and consensus.
One of the problem-solving techniques that should be in every facilitator’s toolbox, Dot Voting is fast and effective and can help identify the most popular and best solutions and help bring a group to a decision effectively.
Dotmocracy #action #decision making #group prioritization #hyperisland #remote-friendly Dotmocracy is a simple method for group prioritization or decision-making. It is not an activity on its own, but a method to use in processes where prioritization or decision-making is the aim. The method supports a group to quickly see which options are most popular or relevant. The options or ideas are written on post-its and stuck up on a wall for the whole group to see. Each person votes for the options they think are the strongest, and that information is used to inform a decision.
All facilitators know that warm-ups and icebreakers are useful for any workshop or group process. Problem-solving workshops are no different.
Use these problem-solving techniques to warm up a group and prepare them for the rest of the process. Activating your group by tapping into some of the top problem-solving skills can be one of the best ways to see great outcomes from your session.
- Check-in/Check-out
- Doodling Together
- Show and Tell
- Constellations
- Draw a Tree
28. Check-in / Check-out
Solid processes are planned from beginning to end, and the best facilitators know that setting the tone and establishing a safe, open environment can be integral to a successful problem-solving process.
Check-in / Check-out is a great way to begin and/or bookend a problem-solving workshop. Checking in to a session emphasizes that everyone will be seen, heard, and expected to contribute.
If you are running a series of meetings, setting a consistent pattern of checking in and checking out can really help your team get into a groove. We recommend this opening-closing activity for small to medium-sized groups though it can work with large groups if they’re disciplined!
Check-in / Check-out #team #opening #closing #hyperisland #remote-friendly Either checking-in or checking-out is a simple way for a team to open or close a process, symbolically and in a collaborative way. Checking-in/out invites each member in a group to be present, seen and heard, and to express a reflection or a feeling. Checking-in emphasizes presence, focus and group commitment; checking-out emphasizes reflection and symbolic closure.
29. Doodling Together
Thinking creatively and not being afraid to make suggestions are important problem-solving skills for any group or team, and warming up by encouraging these behaviors is a great way to start.
Doodling Together is one of our favorite creative ice breaker games – it’s quick, effective, and fun and can make all following problem-solving steps easier by encouraging a group to collaborate visually. By passing cards and adding additional items as they go, the workshop group gets into a groove of co-creation and idea development that is crucial to finding solutions to problems.
Doodling Together #collaboration #creativity #teamwork #fun #team #visual methods #energiser #icebreaker #remote-friendly Create wild, weird and often funny postcards together & establish a group’s creative confidence.
30. Show and Tell
You might remember some version of Show and Tell from being a kid in school and it’s a great problem-solving activity to kick off a session.
Asking participants to prepare a little something before a workshop by bringing an object for show and tell can help them warm up before the session has even begun! Games that include a physical object can also help encourage early engagement before moving onto more big-picture thinking.
By asking your participants to tell stories about why they chose to bring a particular item to the group, you can help teams see things from new perspectives and see both differences and similarities in the way they approach a topic. Great groundwork for approaching a problem-solving process as a team!
Show and Tell #gamestorming #action #opening #meeting facilitation Show and Tell taps into the power of metaphors to reveal players’ underlying assumptions and associations around a topic The aim of the game is to get a deeper understanding of stakeholders’ perspectives on anything—a new project, an organizational restructuring, a shift in the company’s vision or team dynamic.
31. Constellations
Who doesn’t love stars? Constellations is a great warm-up activity for any workshop as it gets people up off their feet, energized, and ready to engage in new ways with established topics. It’s also great for showing existing beliefs, biases, and patterns that can come into play as part of your session.
Using warm-up games that help build trust and connection while also allowing for non-verbal responses can be great for easing people into the problem-solving process and encouraging engagement from everyone in the group. Constellations is great in large spaces that allow for movement and is definitely a practical exercise to allow the group to see patterns that are otherwise invisible.
Constellations #trust #connection #opening #coaching #patterns #system Individuals express their response to a statement or idea by standing closer or further from a central object. Used with teams to reveal system, hidden patterns, perspectives.
32. Draw a Tree
Problem-solving games that help raise group awareness through a central, unifying metaphor can be effective ways to warm-up a group in any problem-solving model.
Draw a Tree is a simple warm-up activity you can use in any group and which can provide a quick jolt of energy. Start by asking your participants to draw a tree in just 45 seconds – they can choose whether it will be abstract or realistic.
Once the timer is up, ask the group how many people included the roots of the tree and use this as a means to discuss how we can ignore important parts of any system simply because they are not visible.
All problem-solving strategies are made more effective by thinking of problems critically and by exposing things that may not normally come to light. Warm-up games like Draw a Tree are great in that they quickly demonstrate some key problem-solving skills in an accessible and effective way.
Draw a Tree #thiagi #opening #perspectives #remote-friendly With this game you can raise awarness about being more mindful, and aware of the environment we live in.
Each step of the problem-solving workshop benefits from an intelligent deployment of activities, games, and techniques. Bringing your session to an effective close helps ensure that solutions are followed through on and that you also celebrate what has been achieved.
Here are some problem-solving activities you can use to effectively close a workshop or meeting and ensure the great work you’ve done can continue afterward.
- One Breath Feedback
- Who What When Matrix
- Response Cards
How do I conclude a problem-solving process?
All good things must come to an end. With the bulk of the work done, it can be tempting to conclude your workshop swiftly and without a moment to debrief and align. This can be problematic in that it doesn’t allow your team to fully process the results or reflect on the process.
At the end of an effective session, your team will have gone through a process that, while productive, can be exhausting. It’s important to give your group a moment to take a breath, ensure that they are clear on future actions, and provide short feedback before leaving the space.
The primary purpose of any problem-solving method is to generate solutions and then implement them. Be sure to take the opportunity to ensure everyone is aligned and ready to effectively implement the solutions you produced in the workshop.
Remember that every process can be improved and by giving a short moment to collect feedback in the session, you can further refine your problem-solving methods and see further success in the future too.
33. One Breath Feedback
Maintaining attention and focus during the closing stages of a problem-solving workshop can be tricky and so being concise when giving feedback can be important. It’s easy to incur “death by feedback” should some team members go on for too long sharing their perspectives in a quick feedback round.
One Breath Feedback is a great closing activity for workshops. You give everyone an opportunity to provide feedback on what they’ve done but only in the space of a single breath. This keeps feedback short and to the point and means that everyone is encouraged to provide the most important piece of feedback to them.
One breath feedback #closing #feedback #action This is a feedback round in just one breath that excels in maintaining attention: each participants is able to speak during just one breath … for most people that’s around 20 to 25 seconds … unless of course you’ve been a deep sea diver in which case you’ll be able to do it for longer.
34. Who What When Matrix
Matrices feature as part of many effective problem-solving strategies and with good reason. They are easily recognizable, simple to use, and generate results.
The Who What When Matrix is a great tool to use when closing your problem-solving session by attributing a who, what and when to the actions and solutions you have decided upon. The resulting matrix is a simple, easy-to-follow way of ensuring your team can move forward.
Great solutions can’t be enacted without action and ownership. Your problem-solving process should include a stage for allocating tasks to individuals or teams and creating a realistic timeframe for those solutions to be implemented or checked out. Use this method to keep the solution implementation process clear and simple for all involved.
Who/What/When Matrix #gamestorming #action #project planning With Who/What/When matrix, you can connect people with clear actions they have defined and have committed to.
35. Response cards
Group discussion can comprise the bulk of most problem-solving activities and by the end of the process, you might find that your team is talked out!
Providing a means for your team to give feedback with short written notes can ensure everyone is head and can contribute without the need to stand up and talk. Depending on the needs of the group, giving an alternative can help ensure everyone can contribute to your problem-solving model in the way that makes the most sense for them.
Response Cards is a great way to close a workshop if you are looking for a gentle warm-down and want to get some swift discussion around some of the feedback that is raised.
Response Cards #debriefing #closing #structured sharing #questions and answers #thiagi #action It can be hard to involve everyone during a closing of a session. Some might stay in the background or get unheard because of louder participants. However, with the use of Response Cards, everyone will be involved in providing feedback or clarify questions at the end of a session.
Save time and effort discovering the right solutions
A structured problem solving process is a surefire way of solving tough problems, discovering creative solutions and driving organizational change. But how can you design for successful outcomes?
With SessionLab, it’s easy to design engaging workshops that deliver results. Drag, drop and reorder blocks to build your agenda. When you make changes or update your agenda, your session timing adjusts automatically , saving you time on manual adjustments.
Collaborating with stakeholders or clients? Share your agenda with a single click and collaborate in real-time. No more sending documents back and forth over email.
Explore how to use SessionLab to design effective problem solving workshops or watch this five minute video to see the planner in action!

Over to you
The problem-solving process can often be as complicated and multifaceted as the problems they are set-up to solve. With the right problem-solving techniques and a mix of creative exercises designed to guide discussion and generate purposeful ideas, we hope we’ve given you the tools to find the best solutions as simply and easily as possible.
Is there a problem-solving technique that you are missing here? Do you have a favorite activity or method you use when facilitating? Let us know in the comments below, we’d love to hear from you!
thank you very much for these excellent techniques
Certainly wonderful article, very detailed. Shared!
Your list of techniques for problem solving can be helpfully extended by adding TRIZ to the list of techniques. TRIZ has 40 problem solving techniques derived from methods inventros and patent holders used to get new patents. About 10-12 are general approaches. many organization sponsor classes in TRIZ that are used to solve business problems or general organiztational problems. You can take a look at TRIZ and dwonload a free internet booklet to see if you feel it shound be included per your selection process.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Going from a mere idea to a workshop that delivers results for your clients can feel like a daunting task. In this piece, we will shine a light on all the work behind the scenes and help you learn how to plan a workshop from start to finish. On a good day, facilitation can feel like effortless magic, but that is mostly the result of backstage work, foresight, and a lot of careful planning. Read on to learn a step-by-step approach to breaking the process of planning a workshop into small, manageable chunks. The flow starts with the first meeting with a client to define the purposes of a workshop.…

How does learning work? A clever 9-year-old once told me: “I know I am learning something new when I am surprised.” The science of adult learning tells us that, in order to learn new skills (which, unsurprisingly, is harder for adults to do than kids) grown-ups need to first get into a specific headspace. In a business, this approach is often employed in a training session where employees learn new skills or work on professional development. But how do you ensure your training is effective? In this guide, we'll explore how to create an effective training session plan and run engaging training sessions. As team leader, project manager, or consultant,…

Effective online tools are a necessity for smooth and engaging virtual workshops and meetings. But how do you choose the right ones? Do you sometimes feel that the good old pen and paper or MS Office toolkit and email leaves you struggling to stay on top of managing and delivering your workshop? Fortunately, there are plenty of online tools to make your life easier when you need to facilitate a meeting and lead workshops. In this post, we’ll share our favorite online tools you can use to make your job as a facilitator easier. In fact, there are plenty of free online workshop tools and meeting facilitation software you can…
Design your next workshop with SessionLab
Join the 150,000 facilitators using SessionLab
Sign up for free
- Latest Articles
- Top Articles
- Posting/Update Guidelines
- Article Help Forum
- View Unanswered Questions
- View All Questions
- View C# questions
- View C++ questions
- View Javascript questions
- View Visual Basic questions
- View Python questions
- CodeProject.AI Server
- All Message Boards...
- Running a Business
- Sales / Marketing
- Collaboration / Beta Testing
- Work Issues
- Design and Architecture
- Artificial Intelligence
- Internet of Things
- ATL / WTL / STL
- Managed C++/CLI
- Objective-C and Swift
- System Admin
- Hosting and Servers
- Linux Programming
- .NET (Core and Framework)
- Visual Basic
- Web Development
- Site Bugs / Suggestions
- Spam and Abuse Watch
- Competitions
- The Insider Newsletter
- The Daily Build Newsletter
- Newsletter archive
- CodeProject Stuff
- Most Valuable Professionals
- The Lounge
- The CodeProject Blog
- Where I Am: Member Photos
- The Insider News
- The Weird & The Wonderful
- What is 'CodeProject'?
- General FAQ
- Ask a Question
- Bugs and Suggestions
Problem Solving for Software Engineers

Introduction
The work of the software engineer is a never-ending effort of solving complex logical problems with ever-changing tools and technologies. We spend a great deal of time learning trending technologies and keeping up with new frameworks and methodologies. Yet, we frequently neglect to develop the very core skill of our profession, the ability of thinking critically and creatively about problems and their solutions.
In 1945, the Hungarian mathematician George Pólya published “How to solve it”, a very unique and insightful book on heuristic, the art of reasoning upon a problem. While mostly focused on mathematics, many of the guidelines provided in this small volume are generic in nature and can be applied to any logical problem. Following is my attempt to ‘flavor’ these key problem solving concepts based on my experience as a developer.
There are four main phases that are clearly identifiable in the process of solving problems:
Understanding the problem, Devising the plan, Carrying out the plan and Retrospection.
Understanding The Problem
It may seem obvious that in order to be able to solve a problem, we have to first understand it. Nothing is farther from reality in the IT business. It is not uncommon in my profession to see entire applications and architectures flawed and crippled by initial misunderstandings of a problem or requirement. While spending time to deeply understand what we have to build may not sound like the most ‘agile’ thing to do, the price to pay for a faulty start could be quite high.
We usually start learning about the problem when analyzing software requirements that explain how things should work from the user’s perspective.
a. Understand the statement of the problem
This is a sanity check to make sure that the software specifications are correctly stated:
- Are the specifications precise enough to be coded and tested?
- Is there a clear relationship between input and output?
- Are all the use-cases covered?
- Can we see potential contradictions/collisions of constraints or goals?
- Are there arbitrary concepts or sentences subject to interpretation? Are the terms of the requirements measurable? Can we see fuzzy words like ‘probably’, ‘usually’, ‘fast’, ‘many’, ‘almost’, etc.?
b. Understand the goals
Here we question the goals and outputs of the project to ensure that they are sound, but also to reveal and explicit all the problems that we may have to face while undertaking the project.
- Which goals are mandatory and which ones are desirable?
- Which ones are mission-critical and which ones are ancillaries from the business standpoint?
- What are the most challenging goals and what makes them difficult to achieve?
- How can we measure if the goals have been successfully reached?
- What are the risks that can jeopardize the goals? What would be the impact of a defect or a downtime?
- How are the goals of the software expected to expand or change overtime?
- Which external factors or dependencies can prevent the achievement of the goals?
c. Understand the data
Here, we question the inputs of the software and all the data provided upfront or expected to be available for the software to be properly functional.
- Is there any unused input/data provided? If so, why is it provided? Can some data be derived, calculated or inferred?
- What assumptions can be safely made about the correctness and integrity of the input?
- What is the level of concurrency in accessing or changing the data? What are the boundaries and volume of the transactions?
- Are the relationships between data elements easy to be used? Is the format of the data convenient for processing?
- What is the value of the data? What are the related security threats to be expected?
- Will the data be available during development? Can it be simulated in a realistic way?
- How is the size of the data expected to grow over time? Can the old data be purged?
- What happens if the data is unavailable for a time, due to maintenance or emergency situations?
- Can the data be distributed or centralized? If not, why not?
d. Understand the conditions
Here we question all the assumptions, constraints and conditions specified for the software, such as validations, business rules, quality, usability, security and performance requirements, etc.
- Are the constraints realistic? Why are they all necessary? Are they hiding other problems?
- Can additional constraints be derived from the existing ones (dependencies between functionalities, external dependencies, unavoidable sequentiality of steps, etc.)?
- Are there conditions based on wrong or unverified assumptions (e. g., the customer may think that a certain feature would be easier or cheaper by adding some limitations)?
- Can more constraints be added, even if not necessary, to simplify some scenarios?
- Can some constraints be removed by modifying processes or workflows?
- Could there be unnecessary, self-imposed conditions used implicitly or explicitly and perhaps based on a fallacious mental model of a process or functionality?
e. Build a Model
Geometric problems are easier to understand and reason upon if we can visualize them in a drawing or a 3-D Model. Software functionalities are also easy to understand and reason upon if we build simplified models, wire-frames or prototypes that can help us visualizing relevant aspects. This can give confidence on the most challenging or critical tasks and an advantageous intimacy with the problems that we will have to solve with much more hard work in the real solution. Models are great helpers to reason on problems and solutions within the technical team or with all the stakeholders.
Devising the Plan
Once the problem has been properly understood, we enter the core phase of problem solving: planning. This is the phase where we evaluate and devise the different solution strategies; here comes the time to brainstorm and breed the ideas that will allow us to produce quality software and achieve the project goals. In this phase, Pólya reminds us that there is no infallible methodology to solve a problem, by stating the following Rules of Discovery:
- Have brain and good luck
- Sit tight and wait until you get a bright idea
While there are no mechanical rules to solve problems, Pólya also observes that there are heuristic procedures, mental operation, stereotyped questions and suggestions that can hint solutions to intelligent people. In this article, I will examine a non-exhaustive list of four strategies: Analogy, Decomposing and Recombining, Variation of the Problem, and Working Backwards. While these strategies will be presented individually for the sake of clarity, in real scenarios they are likely to be combined to derive a solution.
Analogy is a strategy of using the knowledge from previously solved problems that are closely related to the one at hand or at least share some commonalities. In order to be able to use the known solution to a related problem, it is frequently necessary to introduce auxiliary elements that can adapt such solution to our goals and needs.
Hints: Do you know a related problem? Can you think of a familiar problem having the same or similar solution? How can you use it?
In Software Engineering… Before tackling a complex problem, a good software engineer should spend some time researching well-known solutions to well-known problems that fall under the same category. We would likely find books, blogs and articles discussing different ideas and approaches, code snippets, open source projects, commercial components, etc. Even if our problem is such that we cannot entirely use any of the solutions that we find, we may still be able to adapt some algorithms or pieces of code to well serve our needs. If nothing else, we would at least acquire more knowledge of the problem and have a term of comparison for our design choices.
Decomposing and Recombining
To solve a complex problem, we may try to decompose it into other problems that are both easier to solve and that can be used as a stepping stones to reach our original goals.
Hints: Could you solve a part of the problem? Can you separate the various parts of the conditions?
In Software Engineering… Software engineers are grand masters in this mental operation and they perform it all the time. We break complex applications into small, focused components that we then aggregate and wire up to form an organic complex solution. Object Oriented Analysis, Functional Decomposition and design patterns (e. g., MVC, MVVM, etc.) are all examples of decomposing problems and recombining solutions. Most of our design principles and procedures can be seen as practices to decompose the complexity of problems: separation of concerns, separation of state and behavior (functional programming), dependency inversion, Law of Demeter, etc. Decomposing and recombining is not only useful to tame complexity but also to facilitate reusability by taking components used in a previous solution and aggregating them differently to solve different problems, much like lego pieces. Other notable examples are the map-reduce big data pattern, which is a decomposition for parallel computation; the decomposition for testability, which is encouraged by TDD/BDD; and also the decomposition of the SDLC itself into small iteration, to reduce project risks.
Variation of the Problem
When a problem seems too complex to be solved, we instead solve an auxiliary problem derived from the original through different types of alterations. The purpose of the alterations is to obtain a different problem, simpler or more familiar, in the hope that its solution may help us with the original problem, or at least give some useful insights.
Hints: Can you think of more accessible goals? Can you make the goals more accessible by altering the input or the constraints?
Here are some typical types of problem variation:
- Auxiliary Elements When we do not know how to solve a certain problem, we try can always try to solve a related one. Adding auxiliary elements can help bridging the solution of the related problem to the solution of more difficult problem. Hints: Can we introduce auxiliary elements to make use of a known solution or a more accessible problem? In Software Engineering… Inheritance is a common example of how we can extend a basic functionality to more perform more specific or complex tasks. Applying design patterns such as proxy or decorator are also examples of achieving a complex solution by adding elements on top of a simpler one. For instance, we can obtain a secure functionality by implementing the plain functionality (simpler problem) and then wrapping it with a data encryption decorator (auxiliary element). Adapters can also be seen as auxiliary elements to be able to fit other components into the design of our solution.
Removing Elements When we are stuck on a difficult obstacle that is slowing down our progress, we may pretend to make the obstacle disappearing with an imaginary magic wand. Great problem solvers use this mental operation to throw their mind over the obstacle, to explore what would happened next if the impediments where suddenly resolved. Mentally removing an obstacle may force our brain to step back and look at the impediments under the light of a broader context. Hints: What would you do if the obstacle was not there? In Software Engineering… Developers are easily obsessed by impediments such as high level of optimization, without considering what they are really gaining (or losing) as result of their effort. If we are asked to build an easy-to-carry luggage, we may struggle and spend all our time and energy trying to obtain light and durable construction materials. But if we pretend for a moment that we already have the lightest and most durable material, then we stop being obsessed with this aspect and we perhaps can see that the weight of the luggage will always be at least the weight of its content. We can finally move on and consider alternatives, such as putting wheels underneath the luggage.
- Generalization The more ambitious plan may have more chances of success. This idea is also known as the Inventor’s Paradox. With generalization, instead of solving a specific problem, we solve a broader and more generic one whose solution includes the solution of the specific problem that we need to solve. Mathematical induction is a popular example of solving a problem by generalizing it. Hints: Is the complexity of the problem at hand caused by its excessive specificity? In Software Engineering… Generic solutions can be, in some cases, much simpler. Such is the case when specificity leads to nested, complicated conditional logic and flaky code that needs to be frequently and significantly altered to accommodate new business rules, with an elevated risk of breaking something. For example, let us consider a validation engine whose implementation is based upon hundreds of configuration parameters. Each parameter may have different possible values expressing what kind of validation rule should be applied or skipped. Moreover, some dependencies between rules are identified: if a validation rule A is skipped, then also another rule B should be skipped, etc. If we try to build a prototype of a specific solution, implementing only a small subset of configuration rules, we would likely be horrified by the jungle of switches and if statements that we will have to write. We may then use an analogy with software firewalls that can validate multiple complex conditions by decomposing the problem into prioritized cascading rules that can be dynamically defined (instead of having all the possible variations hardcoded with static configuration values). The complexity is reduced by implementing a generic validation engine.
- Specialization Opposite to the generalization, this mental operation can be very useful for exploratory purposes. When a problem complexity is caused by its generality and the high number of variables, we may decide to try to solve special, extreme cases. We do this to explore the boundaries of the problem in the hope to obtain more knowledge or some hints of solution. If lucky, we may reuse the solution of the special problem, or at least find out if we are going in the wrong direction. Hints: Can you imagine a more accessible related problem? A special problem? Can you use it? Could you use its result, perhaps by introducing auxiliary elements? In Software Engineering… QA and testing engineers habitually consider special inputs that can break code or cause incorrect results. Stress testing is also an example of building extreme cases that can reveal performance bottlenecks and weaknesses of an application. When designing software, it is always useful to think about malicious special cases, like security vulnerabilities or potential issues caused by race conditions while accessing shared resources. Generally speaking, every good software engineer should exploit the code by considering all the things that can potentially go wrong, checking for unwanted side effects, causes for invalid states, etc.
Working Backwards
When we have no clue on how to reach a solution from the given data/conditions, we can try examining the last point that we have reached in the analysis and retrace our steps backward until we discover a path between the data and the goal. Finding a solution in reverse is not intuitive and presents some psychological difficulties, since we devise steps that are bringing us away from our goals (the starting point), instead of moving us towards them.
Hints: What characteristics can you see in the goals? How can they be derived? Can you think of a related solution that can achieve the same goals using different data and conditions?
In Software Engineering… There are many complex problems that have a crystal clear input and a crystal clear goal but do not have any obvious deterministic solution. Expert systems solve problems by emulating the judgment of a subject expert (human being) in different situations. Similarly, the design of genetic algorithms starts from the end result to determine which fitness function to use. For this broad category of engineering problems, thinking backwards is a regular practice and sometimes the only option. Consider this problem: given any home page (HTML file) of a company website, find the company logo image. Without assumptions about the input, we may not have any straightforward solution strategy, so we start thinking from the end. Examining many manually identified (by a live person) company logos, we can collect many useful measurable properties: geometrical attributes (position, size and proportions), markup properties (names and attributes of the image), graphic properties (format, file size, number of colors), etc. Using a quantitative analysis we can build the steps backward to identify the set of rules that are effective to derive the known result. Finally, we plan the first steps to extract the needed properties from the html.
Some Additional Thoughts on Perspective
The brightest ideas to solve problems usually come by looking at them from the right perspective. The Ptolemaic model describes the orbits of the planets through complex equations and artificial constructions (epicycles). The Copernican model describes the very same orbits with outstanding simplicity by shifting the point of view from Earth to the Sun. The best perspective is frequently the most natural (closest to reality) and it is also the one that greatly simplifies the way we think of a problem.
Carrying out the Plan
Devising a plan requires analytic skills, good ideas and heuristic reasoning. The plan is what Pólya calls the “scaffolding of the bridge” that we need to build to solve complex problems. Scaffolding is essential but temporary in nature, and all the intuitions, assumptions and plausible arguments that we used in our plan needs now to be slowly replaced by solid working software. Carrying out the plan is a work of synthesis, rigorous and scrupulous execution. We need to painstakingly verify and prove each step without losing sight of the connections and relationships between all the steps.
a. Top-Down Execution
Nobody knows better than a software engineer that the devil is in the details. A top-down order is very relevant when digging into the details of the solution. Before to tackle the minor aspects, we need first to work out the major ones to make sure that they are sound. Starting to code immediately is tempting but also risky when the big picture is fuzzy; therefore, we should first resolve all the important doubts and verify the major assumptions that can significantly affect the outcome of our work. Coding the details can be extremely time-consuming; it would be costly to find out later that our magnificent code implements a wrong or unwanted functionality.
b. Importance and Challenge
Risk is another essential factor in determining the execution order. Some tasks are more important than others in the big picture. Some tasks also present a higher challenge then others. If a step is both important and challenging at the same time, then we should make an effort to prioritize it due to the great impact that it may have on the overall plan.
c. Breaking Dependencies
Steps may naturally depend upon each other. Each software component usually relies on others to achieve its goals. In software engineering, it is sometimes possible and convenient to cheat what seems to be a natural execution order by creating mock or fake dependencies that allow skipping the less relevant details (that can be addressed later) and focus on the high priority tasks that give us the highest level of confidence on the whole solution. This strategy is also useful for organizational purposes (e. g., coding in parallel modules that depend upon each other).
d. Consolidating the Efforts
Complex software solutions can be carried out by many developers and many teams, eventually spread out in different geographical locations. This scenario poses the risk of multiplying the independent efforts of solving similar problems. To consolidate the execution efforts, the following steps can be taken:
- Architects/Technical leads should make each developer aware of the context of his/her work within the high level solution. Typically, this is done through kick off presentations and providing solution background documents.
- The main structure of the source code should reserve specific physical locations to store components that can have a broader utilization other than the specific task for which they were created.
- Common components should be documented and submitted to code review sessions. When ready, they should be advertised to all the developers to make them aware of their existence.
e. Bottom-Up Testing
The mathematician demonstrates a theorem by formally proving each and every step, from the hypotheses to the thesis. Likewise, the engineer proves that a software solution works by writing formal tests. Testing is usually a bottom-up process that starts by writing unit tests and then moves up to functional tests for modules, integration tests, all the way up to the whole solution. The advantage of the bottom-up testing is that if a low level test fails, we can immediately pinpoint the defect; on the other hand, if a high level test fails we can concentrate in finding defects in the wiring and interactions between major components. Low level tests should in fact be created as soon as possible (by the developers) to avoid the time-consuming and expensive bug-fixing that is typically associated with logical defects. Written tests are usually automated to ensure the correctness against future changes (regression testing).
f. Pedantry and Mastery
Pólya described two opposite attitudes towards rules that apply quite well in the context of modern software design and development methodologies. The pedant software engineer relies conscientiously and indiscriminately on a limited, well-known set of tools, patterns and practices that are proven to be successful in most cases. Such type of engineer strictly applies standards and follows verbatim a methodology. The master engineer instead focuses on the purposes of patterns and methodologies, seizing the opportunities and judging case by case the tools that best fit each situation.
Retrospection
Pólya teaches us that complex problems are never completely exhausted. The final phase of problem solving is looking back at our completed solution to expand its potentials and consolidate our knowledge. In software engineering, this process usually starts with code reviews, agile retrospectives and postmortem meetings. Following are some of the major goals that can be achieved with retrospection:
a. Clean Up
To sharpen our solution, we need to remove duplication, redundancy, and code verbosity. Simplicity and clarity are also important goals of the clean-up phase: removing dead code and unnecessary steps, replacing convoluted algorithms with equivalent but more straightforward ones, selecting more meaningful names for classes, modules, etc. This helps to make the solution more intuitive and easy to see at glance.
b. Maintenance and Scalability
Good software solutions need to be able to cope with future changes. Therefore, we need to verify that the impact of reasonably expected maintenance conforms to the initial expectations. Retrospection is also the right phase to exploit performance bottlenecks that may affect our scalability plans.
The main objective of modular software is to be able to reuse as much as possible its components in different contexts. Retrospection can reveal opportunities to generalize or adapt pieces of the solution to be employed in other projects, performing similar tasks.
d. Compare and Improve
Authoring a solution gives us a point of view on the problem that we solved. Our point of view may not necessarily the best; nevertheless, it is always a valuable term of comparison with other solutions. Surveying the solution can consolidate our knowledge of a business domain and identify which areas of our solution can be further improved. Writing an informal document can be an exceptionally useful to record a high level description of the strategies adopted, the strong points, the identified limitations, and any interesting idea or suggestion that emerge during the retrospection.
This article, along with any associated source code and files, is licensed under The Code Project Open License (CPOL)

Comments and Discussions
Use Ctrl+Left/Right to switch messages, Ctrl+Up/Down to switch threads, Ctrl+Shift+Left/Right to switch pages.
- Best "Everything Else" Article of January 2015 : Second Prize
How to Develop Problem-Solving Skills on Software Engineering
Gimena Aguerreberry May 20, 2021

Developing software is a rewarding endeavor because you create an efficient and easy-to-use program that solves people's problems. However, you have to be a good problem solver before getting to this end goal and launching your project.
Experienced developers will tell you that there's no way to prepare for the amount of tech issues, bugs, and human error that will come up during the development process. You have to learn how to think fast and solve problems collaboratively with others.
There are many things you can do to hone your problem-solving skills. Check out our top tips for becoming a problem solver, and you'll learn how to become a more effective software engineer quickly.
Take time to Research
Before you begin solving all your software's problems, you need to understand the problem head-on and your options available. This is where using a traditional development process can help.
In traditional problem-solving setups, the first step of problem-solving is learning more about the problem, researching it, and understanding it. Researching the topic is an essential part of this process, as you may begin to see solutions you hadn't previously recognized.
What have other developers said about this coding or framework structure bug? You can read programming books or even check out forums like r/Programming and even Quora.
Break Down Bigger Problems into Manageable Chunks
Once you better understand the problem, exercise your ability to break it down into manageable pieces. Think of it like this: an entire mountain is intimidating. But taking a step is doable. You don't need to conquer the mountain all at once. Take it one step at a time.
When we use our ability to break down a problem into simpler tasks, we not only work effectively but build our confidence and understanding of the problem. This part of the development process will improve your perspective of the problem and work like experienced developers.
Visualize Data Flows
Another method of problem-solving skills is to think in terms of data flows for your development process. Point A is the problem you start with, and you need to move it to the destination at the end: the solution.
Between the start of the process and destination, there are the arrows the data flows through, and then the boxes. Each box represents a sub-goal. If something doesn't work, you can set a new path and sub-goal.
The data will need to move through a flow chart and hit all the sub-goals to get to the destination. Each goal represents how the data will be somehow changed and manipulated.
The end of the flow is your main goal. By thinking through a data flow, you can follow the data through each transformation, easily set sub-goals, and understand how they contribute to reaching the ultimate solution!
Apply Parallel Task Management
Once you break down the problem into manageable tasks, consider when you'll need to complete each one.
One approach is to work on one task at a time. However, this can be inefficient. A more efficient approach, particularly if you're working with a team, is to work on two tasks that don't overlap.
For example, if you can do task number 3 before task 2 is finished, but you can't move onto task 4 without tasks 2 and 3 being completed, 2 and 3 can be grouped. Working on these tasks in tandem can keep you working and thinking about the problem overall.
When you don't group tasks, you may find yourself stuck on something in one task. And it can be hard to keep up your momentum. By finding tasks that complement each other, you'll learn more about your project, and working on one task could help you with the other!
Use (and Re-Use) Solutions That Already Work
Software development isn't always about reinventing the wheel. Experienced developers often take advantage of existing solutions rather than waste energy creating new solutions to old problems.
A clear example of this is with open source software development. You can save yourself time and the headache of creating hundreds of solutions and programming language algorithms that don't work like you need them to.
You can also re-use your own past successes or those of your colleagues. As you face new problems, you don't need to find novel solutions consistently. If the information is readily available, take advantage of it.
Every software engineer develops their problem-solving skills over time and improves with every project. As long as you are utilizing a process, work towards improving your skills (even if slowly doing so), and reflecting on your successes and failures, you will grow in your problem-solving skills and become an even better software engineer.
Need to develop your software with problem-solving skills that work? Our team at SOPHiLABS can take the pressure off. We have experience working through complex software engineering development issues with clients. We'll take a look at your project and work with your team to come up with efficient problem-solving solutions.
Get in touch with us today to learn more about how we can help with your software development project.

Myths About Software Development
Whether you're frustrated that the software engineers for your project won't just add features or the development process generally mystifies you, we're sure you've heard some myths about software development.

Useful Tips for Your App Strategy
Mobile app development isn't just about making a great product. You also need a marketing strategy that sets your product apart from the rest and even the best specialists don't get the formula right sometimes.

Mitigating Risks in Software Development
The world of software development is becoming more advanced. But with greater capability comes greater risk, and if your software stops working as it should, it can have a devastating effect on your business.
Photo by Hitesh Choudhary .
We are Sophilabs
A software design and development agency that helps companies build and grow products by delivering high-quality software through agile practices and perfectionist teams.
.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:42px;color:#F5F4F3;}@media (max-width: 1120px){.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:12px;}} AI that works. Coming June 5, Asana redefines work management—again. .css-1ixh9fn{display:inline-block;}@media (max-width: 480px){.css-1ixh9fn{display:block;margin-top:12px;}} .css-1uaoevr-heading-6{font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-1uaoevr-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} .css-ora5nu-heading-6{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-box-pack:start;-ms-flex-pack:start;-webkit-justify-content:flex-start;justify-content:flex-start;color:#0D0E10;-webkit-transition:all 0.3s;transition:all 0.3s;position:relative;font-size:16px;line-height:28px;padding:0;font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{border-bottom:0;color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover path{fill:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div{border-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div:before{border-left-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active{border-bottom:0;background-color:#EBE8E8;color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active path{fill:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div{border-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div:before{border-left-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} Get early access .css-1k6cidy{width:11px;height:11px;margin-left:8px;}.css-1k6cidy path{fill:currentColor;}
- Product overview
- All features
- App integrations
CAPABILITIES
- project icon Project management
- Project views
- Custom fields
- Status updates
- goal icon Goals and reporting
- Reporting dashboards
- workflow icon Workflows and automation
- portfolio icon Resource management
- Time tracking
- my-task icon Admin and security
- Admin console
- asana-intelligence icon Asana Intelligence
- list icon Personal
- premium icon Starter
- briefcase icon Advanced
- Goal management
- Organizational planning
- Campaign management
- Creative production
- Marketing strategic planning
- Request tracking
- Resource planning
- Project intake
- View all uses arrow-right icon
- Project plans
- Team goals & objectives
- Team continuity
- Meeting agenda
- View all templates arrow-right icon
- Work management resources Discover best practices, watch webinars, get insights
- What's new Learn about the latest and greatest from Asana
- Customer stories See how the world's best organizations drive work innovation with Asana
- Help Center Get lots of tips, tricks, and advice to get the most from Asana
- Asana Academy Sign up for interactive courses and webinars to learn Asana
- Developers Learn more about building apps on the Asana platform
- Community programs Connect with and learn from Asana customers around the world
- Events Find out about upcoming events near you
- Partners Learn more about our partner programs
- Support Need help? Contact the Asana support team
- Asana for nonprofits Get more information on our nonprofit discount program, and apply.
Featured Reads

- Project planning |
- How to solve problems using the design ...
How to solve problems using the design thinking process

The design thinking process is a problem-solving design methodology that helps you develop solutions in a human-focused way. Initially designed at Stanford’s d.school, the five stage design thinking method can help solve ambiguous questions, or more open-ended problems. Learn how these five steps can help your team create innovative solutions to complex problems.
As humans, we’re approached with problems every single day. But how often do we come up with solutions to everyday problems that put the needs of individual humans first?
This is how the design thinking process started.
What is the design thinking process?
The design thinking process is a problem-solving design methodology that helps you tackle complex problems by framing the issue in a human-centric way. The design thinking process works especially well for problems that are not clearly defined or have a more ambiguous goal.
One of the first individuals to write about design thinking was John E. Arnold, a mechanical engineering professor at Stanford. Arnold wrote about four major areas of design thinking in his book, “Creative Engineering” in 1959. His work was later taught at Stanford’s Hasso-Plattner Institute of Design (also known as d.school), a design institute that pioneered the design thinking process.
This eventually led Nobel Prize laureate Herbert Simon to outline one of the first iterations of the design thinking process in his 1969 book, “The Sciences of the Artificial.” While there are many different variations of design thinking, “The Sciences of the Artificial” is often credited as the basis.
Anatomy of Work Special Report: How to spot—and overcome—the most crucial enterprise challenges
Learn how enterprises can improve processes and productivity, no matter how complex your organization is. With fewer redundancies, leaders and their teams can hit goals faster.
![problem solving strategies in software design [Resource Card] AOW Blog Image](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/fdc408f5-063d-4ea7-8d73-cb3ec61704fc/Global-AOW23-Black-Hole?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
A non-linear design thinking approach
Design thinking is not a linear process. It’s important to understand that each stage of the process can (and should) inform the other steps. For example, when you’re going through user testing, you may learn about a new problem that didn’t come up during any of the previous stages. You may learn more about your target personas during the final testing phase, or discover that your initial problem statement can actually help solve even more problems, so you need to redefine the statement to include those as well.
Why use the design thinking process
The design thinking process is not the most intuitive way to solve a problem, but the results that come from it are worth the effort. Here are a few other reasons why implementing the design thinking process for your team is worth it.
Focus on problem solving
As human beings, we often don’t go out of our way to find problems. Since there’s always an abundance of problems to solve, we’re used to solving problems as they occur. The design thinking process forces you to look at problems from many different points of view.
The design thinking process requires focusing on human needs and behaviors, and how to create a solution to match those needs. This focus on problem solving can help your design team come up with creative solutions for complex problems.
Encourages collaboration and teamwork
The design thinking process cannot happen in a silo. It requires many different viewpoints from designers, future customers, and other stakeholders . Brainstorming sessions and collaboration are the backbone of the design thinking process.
Foster innovation
The design thinking process focuses on finding creative solutions that cater to human needs. This means your team is looking to find creative solutions for hyper specific and complex problems. If they’re solving unique problems, then the solutions they’re creating must be equally unique.
The iterative process of the design thinking process means that the innovation doesn’t have to end—your team can continue to update the usability of your product to ensure that your target audience’s problems are effectively solved.
The 5 stages of design thinking
Currently, one of the more popular models of design thinking is the model proposed by the Hasso-Plattner Institute of Design (or d.school) at Stanford. The main reason for its popularity is because of the success this process had in successful companies like Google, Apple, Toyota, and Nike. Here are the five steps designated by the d.school model that have helped many companies succeed.
1. Empathize stage
The first stage of the design thinking process is to look at the problem you’re trying to solve in an empathetic manner. To get an accurate representation of how the problem affects people, actively look for people who encountered this problem previously. Asking them how they would have liked to have the issue resolved is a good place to start, especially because of the human-centric nature of the design thinking process.
Empathy is an incredibly important aspect of the design thinking process. The design thinking process requires the designers to put aside any assumptions and unconscious biases they may have about the situation and put themselves in someone else’s shoes.
For example, if your team is looking to fix the employee onboarding process at your company, you may interview recent new hires to see how their onboarding experience went. Another option is to have a more tenured team member go through the onboarding process so they can experience exactly what a new hire experiences.
2. Define stage
Sometimes a designer will encounter a situation when there’s a general issue, but not a specific problem that needs to be solved. One way to help designers clearly define and outline a problem is to create human-centric problem statements.
A problem statement helps frame a problem in a way that provides relevant context in an easy to comprehend way. The main goal of a problem statement is to guide designers working on possible solutions for this problem. A problem statement frames the problem in a way that easily highlights the gap between the current state of things and the end goal.
Tip: Problem statements are best framed as a need for a specific individual. The more specific you are with your problem statement, the better designers can create a human-centric solution to the problem.
Examples of good problem statements:
We need to decrease the number of clicks a potential customer takes to go through the sign-up process.
We need to decrease the new subscriber unsubscribe rate by 10%.
We need to increase the Android app adoption rate by 20%.
3. Ideate stage
This is the stage where designers create potential solutions to solve the problem outlined in the problem statement. Use brainstorming techniques with your team to identify the human-centric solution to the problem defined in step two.
Here are a few brainstorming strategies you can use with your team to come up with a solution:
Standard brainstorm session: Your team gathers together and verbally discusses different ideas out loud.
Brainwrite: Everyone writes their ideas down on a piece of paper or a sticky note and each team member puts their ideas up on the whiteboard.
Worst possible idea: The inverse of your end goal. Your team produces the most goofy idea so nobody will look silly. This takes out the rigidity of other brainstorming techniques. This technique also helps you identify areas that you can improve upon in your actual solution by looking at the worst parts of an absurd solution.
It’s important that you don’t discount any ideas during the ideation phase of brainstorming. You want to have as many potential solutions as possible, as new ideas can help trigger even better ideas. Sometimes the most creative solution to a problem is the combination of many different ideas put together.
4. Prototype stage
During the prototype phase, you and your team design a few different variations of inexpensive or scaled down versions of the potential solution to the problem. Having different versions of the prototype gives your team opportunities to test out the solution and make any refinements.
Prototypes are often tested by other designers, team members outside of the initial design department, and trusted customers or members of the target audience. Having multiple versions of the product gives your team the opportunity to tweak and refine the design before testing with real users. During this process, it’s important to document the testers using the end product. This will give you valuable information as to what parts of the solution are good, and which require more changes.
After testing different prototypes out with teasers, your team should have different solutions for how your product can be improved. The testing and prototyping phase is an iterative process—so much so that it’s possible that some design projects never end.
After designers take the time to test, reiterate, and redesign new products, they may find new problems, different solutions, and gain an overall better understanding of the end-user. The design thinking framework is flexible and non-linear, so it’s totally normal for the process itself to influence the end design.
Tips for incorporating the design thinking process into your team
If you want your team to start using the design thinking process, but you’re unsure of how to start, here are a few tips to help you out.
Start small: Similar to how you would test a prototype on a small group of people, you want to test out the design thinking process with a smaller team to see how your team functions. Give this test team some small projects to work on so you can see how this team reacts. If it works out, you can slowly start rolling this process out to other teams.
Incorporate cross-functional team members : The design thinking process works best when your team members collaborate and brainstorm together. Identify who your designer’s key stakeholders are and ensure they’re included in the small test team.
Organize work in a collaborative project management software : Keep important design project documents such as user research, wireframes, and brainstorms in a collaborative tool like Asana . This way, team members will have one central source of truth for anything relating to the project they’re working on.
Foster collaborative design thinking with Asana
The design thinking process works best when your team works collaboratively. You don’t want something as simple as miscommunication to hinder your projects. Instead, compile all of the information your team needs about a design project in one place with Asana.
Related resources
How to track utilization rate and drive team profitability

How to accomplish big things with long-term goals
Smooth product launches are simpler than you think

What is stakeholder analysis and why is it important?
- Reviews / Why join our community?
- For companies
- Frequently asked questions
Design Thinking (DT)
What is design thinking (dt).
Design thinking is a non-linear, iterative process that teams use to understand users, challenge assumptions, redefine problems and create innovative solutions to prototype and test. It is most useful to tackle ill-defined or unknown problems and involves five phases: Empathize, Define, Ideate, Prototype and Test.
- Transcript loading…
Why Is Design Thinking so Important?
“Design thinking is a human-centered approach to innovation that draws from the designer's toolkit to integrate the needs of people, the possibilities of technology, and the requirements for business success.”
— Tim Brown, CEO of IDEO
Design thinking fosters innovation . Companies must innovate to survive and remain competitive in a rapidly changing environment. In design thinking, cross-functional teams work together to understand user needs and create solutions that address those needs. Moreover, the design thinking process helps unearth creative solutions.
Design teams use design thinking to tackle ill-defined/unknown problems (aka wicked problems ). Alan Dix, Professor of Human-Computer Interaction, explains what wicked problems are in this video.
Wicked problems demand teams to think outside the box, take action immediately, and constantly iterate—all hallmarks of design thinking.
Don Norman, a pioneer of user experience design, explains why the designer’s way of thinking is so powerful when it comes to such complex problems.
Design thinking offers practical methods and tools that major companies like Google, Apple and Airbnb use to drive innovation. From architecture and engineering to technology and services, companies across industries have embraced the methodology to drive innovation and address complex problems.
The End Goal of Design Thinking: Be Desirable, Feasible and Viable
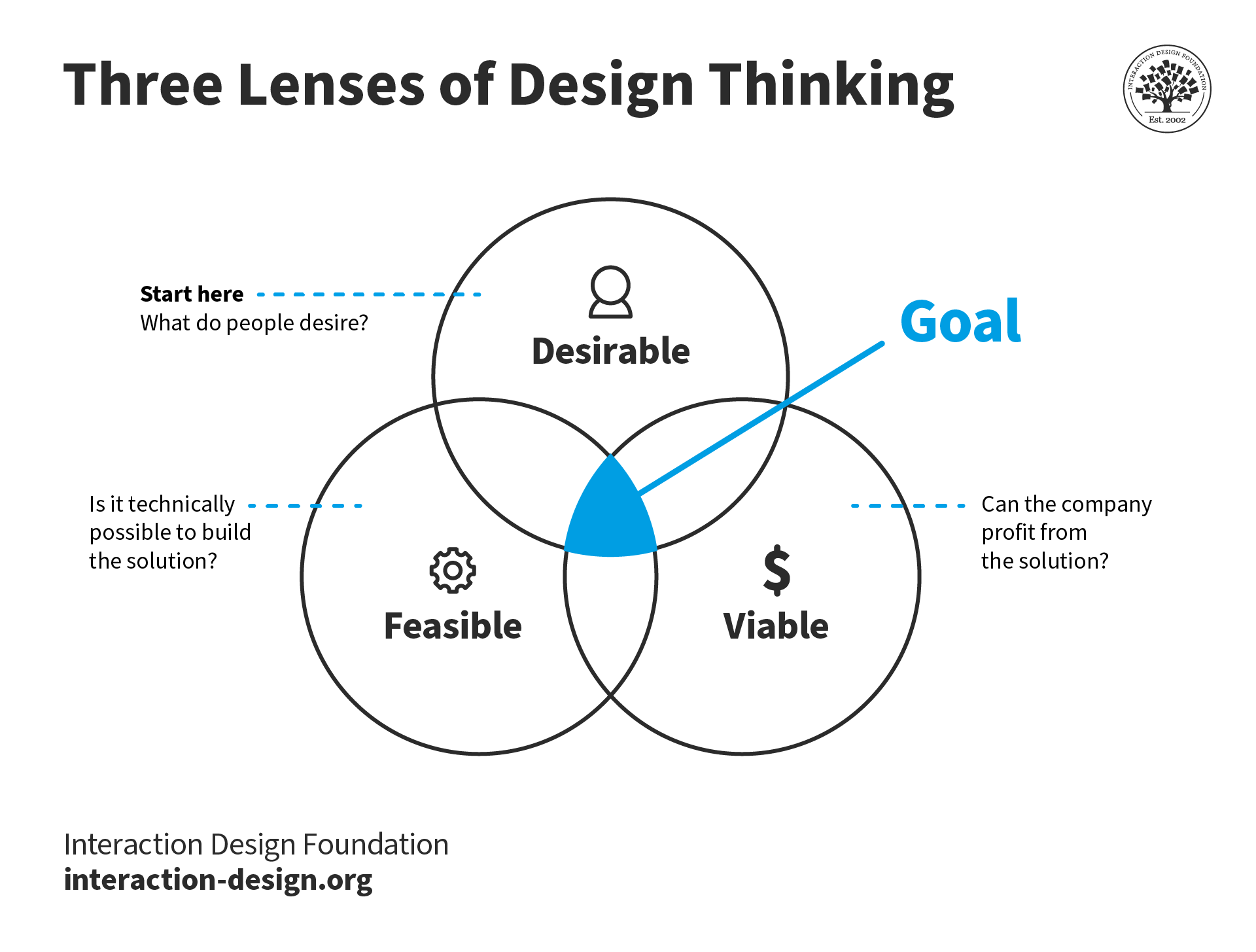
The design thinking process aims to satisfy three criteria: desirability (what do people desire?), feasibility (is it technically possible to build the solution?) and viability (can the company profit from the solution?). Teams begin with desirability and then bring in the other two lenses.
© Interaction Design Foundation, CC BY-SA 4.0

Desirability: Meet People’s Needs
The design thinking process starts by looking at the needs, dreams and behaviors of people—the end users. The team listens with empathy to understand what people want, not what the organization thinks they want or need. The team then thinks about solutions to satisfy these needs from the end user’s point of view.
Feasibility: Be Technologically Possible
Once the team identifies one or more solutions, they determine whether the organization can implement them. In theory, any solution is feasible if the organization has infinite resources and time to develop the solution. However, given the team’s current (or future resources), the team evaluates if the solution is worth pursuing. The team may iterate on the solution to make it more feasible or plan to increase its resources (say, hire more people or acquire specialized machinery).
At the beginning of the design thinking process, teams should not get too caught up in the technical implementation. If teams begin with technical constraints, they might restrict innovation.
Viability: Generate Profits
A desirable and technically feasible product isn’t enough. The organization must be able to generate revenues and profits from the solution. The viability lens is essential not only for commercial organizations but also for non-profits.
Traditionally, companies begin with feasibility or viability and then try to find a problem to fit the solution and push it to the market. Design thinking reverses this process and advocates that teams begin with desirability and bring in the other two lenses later.
The Five Stages of Design Thinking
Stanford University’s Hasso Plattner Institute of Design, commonly known as the d.school, is renowned for its pioneering approach to design thinking. Their design process has five phases: Empathize, Define, Ideate, Prototype, and Test. These stages are not always sequential. Teams often run them in parallel, out of order, and repeat them as needed.
Stage 1: Empathize —Research Users' Needs
The team aims to understand the problem, typically through user research. Empathy is crucial to design thinking because it allows designers to set aside your assumptions about the world and gain insight into users and their needs.
Stage 2: Define—State Users' Needs and Problems
Once the team accumulates the information, they analyze the observations and synthesize them to define the core problems. These definitions are called problem statements . The team may create personas to help keep efforts human-centered.
Stage 3: Ideate—Challenge Assumptions and Create Ideas
With the foundation ready, teams gear up to “think outside the box.” They brainstorm alternative ways to view the problem and identify innovative solutions to the problem statement.
Stage 4: Prototype—Start to Create Solutions
This is an experimental phase. The aim is to identify the best possible solution for each problem. The team produces inexpensive, scaled-down versions of the product (or specific features found within the product) to investigate the ideas. This may be as simple as paper prototypes .
Stage 5: Test—Try the Solutions Out
The team tests these prototypes with real users to evaluate if they solve the problem. The test might throw up new insights, based on which the team might refine the prototype or even go back to the Define stage to revisit the problem.
These stages are different modes that contribute to the entire design project rather than sequential steps. The goal is to gain a deep understanding of the users and their ideal solution/product.
Design Thinking Frameworks
There is no single definition or process for design thinking. The five-stage design thinking methodology described above is just one of several frameworks.
Hasso-Platner Institute Panorama
Ludwig Wilhelm Wall, CC BY-SA 3.0 , via Wikimedia Commons
Innovation doesn’t follow a linear path or have a clear-cut formula. Global design leaders and consultants have interpreted the abstract design process in different ways and have proposed other frameworks of design thinking.
Head, Heart and Hand by the American Institution of Graphic Arts (AIGA)
The Head, Heart, and Hand approach by AIGA (American Institute of Graphic Arts) is a holistic perspective on design. It integrates the intellectual, emotional, and practical aspects of the creative process.

More than a process, the Head, Heart and Hand framework outlines the different roles that designers must perform to create great results.
© American Institute of Graphic Arts, Fair Use
“ Head ” symbolizes the intellectual component. The team focuses on strategic thinking, problem-solving and the cognitive aspects of design. It involves research and analytical thinking to ensure that design decisions are purposeful.
“ Heart ” represents the emotional dimension. It emphasizes empathy, passion, and human-centeredness. This aspect is crucial in understanding the users’ needs, desires, and experiences to ensure that designs resonate on a deeper, more personal level.
“ Hand ” signifies the practical execution of ideas, the craftsmanship, and the skills necessary to turn concepts into tangible solutions. This includes the mastery of tools, techniques, and materials, as well as the ability to implement and execute design ideas effectively.
Inspire, Ideate, Implement by IDEO
IDEO is a leading design consultancy and has developed its own version of the design thinking framework.

IDEO’s design thinking process is a cyclical three-step process that involves Inspiration, Ideation and Implementation.
© IDEO, Public License
In the “ Inspire ” phase, the team focuses on understanding users’ needs, behaviors, and motivations. The team empathizes with people through observation and user interviews to gather deep insights.
In the “ Ideate ” phase, the team synthesizes the insights gained to brainstorm a wide array of creative solutions. This stage encourages divergent thinking, where teams focus on quantity and variety of ideas over immediate practicality. The goal is to explore as many possibilities as possible without constraints.
In the “ Implement ” phase, the team brings these ideas to life through prototypes. The team tests, iterates and refines these ideas based on user feedback. This stage is crucial for translating abstract concepts into tangible, viable products, services, or experiences.
The methodology emphasizes collaboration and a multidisciplinary approach throughout each phase to ensure solutions are innovative and deeply rooted in real human needs and contexts.
The Double Diamond by the Design Council
In the book Designing Social Systems in a Changing World , Béla Heinrich Bánáthy, Professor at San Jose State University and UC Berkeley, created a “divergence-convergence model” diagram. The British Design Council interpreted this diagram to create the Double Diamond design process model.

As the name suggests, the double diamond model consists of two diamonds—one for the problem space and the other for the solution space. The model uses diamonds to represent the alternating diverging and converging activities.
© Design Council, CC BY 4.0
In the diverging “ Discover ” phase, designers gather insights and empathize with users’ needs. The team then converges in the “ Define ” phase to identify the problem.
The second, solution-related diamond, begins with “ Develop ,” where the team brainstorms ideas. The final stage is “ Deliver ,” where the team tests the concepts and implements the most viable solution.
This model balances expansive thinking with focused execution to ensure that design solutions are both creative and practical. It underscores the importance of understanding the problem thoroughly and carefully crafting the solution, making it a staple in many design and innovation processes.
With the widespread adoption of the double diamond framework, Design Council’s simple visual evolved.
In this expanded and annotated version, the framework emphasizes four design principles:
Be people-centered.
Communicate (visually and inclusively).
Collaborate and co-create.
Iterate, iterate, iterate!
The updated version also highlights the importance of leadership (to create an environment that allows innovation) and engagement (to connect with different stakeholders and involve them in the design process).
Common Elements of Design Thinking Frameworks
On the surface, design thinking frameworks look very different—they use alternative names and have different numbers of steps. However, at a fundamental level, they share several common traits.
Start with empathy . Focus on the people to come up with solutions that work best for individuals, business, and society.
Reframe the problem or challenge at hand . Don’t rush into a solution. Explore the problem space and look at the issue through multiple perspectives to gain a more holistic, nuanced understanding.
Initially, employ a divergent style of thinking (analyze) . In the problem space, gather as many insights as possible. In the solution space, encourage team members to generate and explore as many solutions as possible in an open, judgment-free ideation space.
Later, employ a convergent style of thinking (synthesize) . In the problem space, synthesize all data points to define the problem. In the solution space, whittle down all the ideas—isolate, combine and refine potential solutions to create more mature ideas.
Create and test prototypes . Solutions that make it through the previous stages get tested further to remove potential issues.
Iterate . As the team progresses through the various stages, they revisit different stages and may redefine the challenge based on new insights.
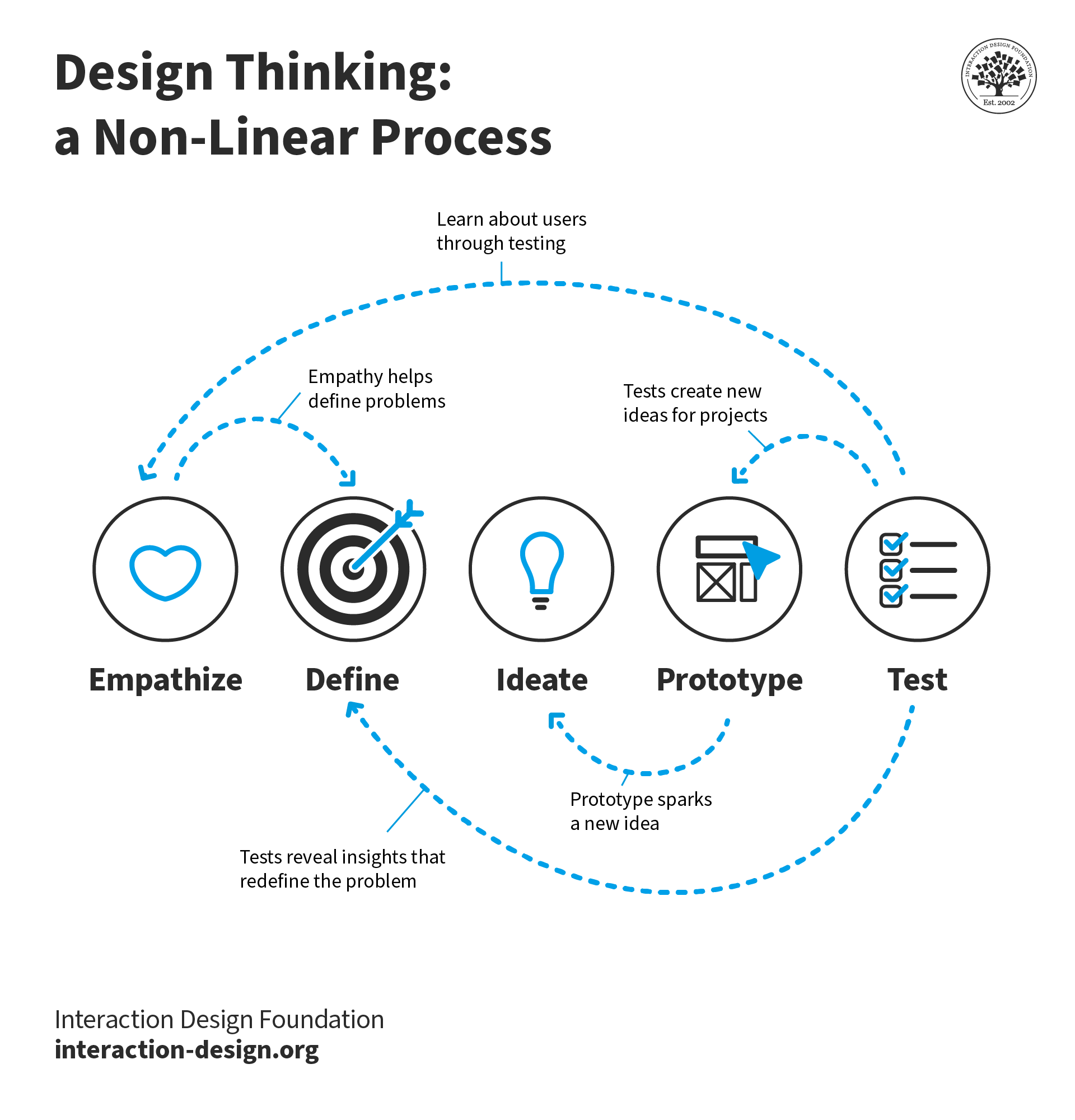
Design thinking is a non-linear process. For example, teams may jump from the test stage to the define stage if the tests reveal insights that redefine the problem. Or, a prototype might spark a new idea, prompting the team to step back into the ideate stage. Tests may also create new ideas for projects or reveal insights about users.
Design Thinking Mindsets: More than a Process

A mindset is a characteristic mental attitude that determines how one interprets and responds to situations . Design thinking mindsets are how individuals think , feel and express themselves during design thinking activities. It includes people’s expectations and orientations during a design project.
Without the right mindset, it can be very challenging to change how we work and think.
The key mindsets that ensure a team can successfully implement design thinking are.
Be empathetic: Empathy is the ability to place yourself, your thinking and feelings in another person’s shoes. Design thinking begins from a deep understanding of the needs and motivations of people—the parents, neighbors, children, colleagues, and strangers who make up a community.
Be collaborative: No one person is responsible for the outcome when you work in a team. Several great minds are always stronger than just one. Design thinking benefits from the views of multiple perspectives and lets others’ creativity bolster your own.
Be optimistic: Be confident about achieving favorable outcomes. Design thinking is the fundamental belief that we can all create change—no matter how big a problem, how little time, or how small a budget. Designing can be a powerful process no matter what constraints exist around you.
Embrace ambiguity: Get comfortable with ambiguous and complex situations. If you expect perfection, it is difficult to take risks, which limits your ability to create radical change. Design thinking is all about experimenting and learning by doing. It gives you the confidence to believe that new, better things are possible and that you can help make them a reality.
Be curious: Be open to different ideas. Recognize that you are not the user.
Reframe: Challenge and reframe assumptions associated with a given situation or problem. Don’t take problems at face value. Humans are primed to look for patterns. The unfortunate side effect of these patterns is that we form (often false and sometimes dangerous) stereotypes and assumptions. Design thinking aims to help you break through any preconceived notions and biases and reframe challenges.
Embrace diversity: Work with and engage people with different cultural backgrounds, experiences, and ways of thinking and working. Everyone brings a unique perspective to the team. When you include diverse voices in a team, you learn from each other’s experiences, further helping you break through your assumptions.
Make tangible: When you make ideas tangible, it is faster and easier for everyone on the team to be on the same page. For example, sketching an idea or enacting a scenario is far more convenient and easy to interpret than an elaborate presentation or document.
Take action: Run experiments and learn from them.
Design Thinking vs Agile Methodology
Teams often use design thinking and agile methodologies in project management, product development, and software development. These methodologies have distinct approaches but share some common principles.
Similarities between Design Thinking and Agile
Iterative process.
Both methodologies emphasize iterative development. In design thinking, teams may jump from one phase to another, not necessarily in a set cyclical or linear order. For example, on testing a prototype, teams may discover something new about their users and realize that they must redefine the problem. Agile teams iterate through development sprints.
User-Centered
The agile and design thinking methodologies focus on the end user. All design thinking activities—from empathizing to prototyping and testing—keep the end users front and center. Agile teams continually integrate user feedback into development cycles.
Collaboration and Teamwork
Both methodologies rely heavily on collaboration among cross-functional teams and encourage diverse perspectives and expertise.
Flexibility and Adaptability
With its focus on user research, prototyping and testing, design thinking ensures teams remain in touch with users and get continuous feedback. Similarly, agile teams monitor user feedback and refine the product in a reasonably quick time.
In this video, Laura Klein, author of Build Better Products , describes a typical challenge designers face on agile teams. She encourages designers to get comfortable with the idea of a design not being perfect. Notice the many parallels between Laura’s advice for designers on agile teams and the mindsets of design thinking.
Differences between Design Thinking and Agile
While design thinking and agile teams share principles like iteration, user focus, and collaboration, they are neither interchangeable nor mutually exclusive. A team can apply both methodologies without any conflict.
From a user experience design perspective, design thinking applies to the more abstract elements of strategy and scope. At the same time, agile is more relevant to the more concrete elements of UX: structure, skeleton and surface. For quick reference, here’s an overview of the five elements of user experience.
Design thinking is more about exploring and defining the right problem and solution, whereas agile is about efficiently executing and delivering a product.
Here are the key differences between design thinking and agile.
Design Sprint: A Condensed Version of Design Thinking
A design sprint is a 5-day intensive workshop where cross-functional teams aim to develop innovative solutions.
The design sprint is a very structured version of design thinking that fits into the timeline of a sprint (a sprint is a short timeframe in which agile teams work to produce deliverables). Developed by Google Ventures, the design sprint seeks to fast-track innovation.
In this video, user researcher Ditte Hvas Mortensen explains the design sprint in detail.
Learn More about Design Thinking
Design consultancy IDEO’s designkit is an excellent repository of design thinking tools and case studies.
To keep up with recent developments in design thinking, read IDEO CEO Tim Brown’s blog .
Enroll in our course Design Thinking: The Ultimate Guide —an excellent guide to get you started on your design thinking projects.
Questions related to Design Thinking
You don’t need any certification to practice design thinking. However, learning about the nuances of the methodology can help you:
Pick the appropriate methods and tailor the process to suit the unique needs of your project.
Avoid common pitfalls when you apply the methods.
Better lead a team and facilitate workshops.
Increase the chances of coming up with innovative solutions.
IxDF has a comprehensive course to help you gain the most from the methodology: Design Thinking: The Ultimate Guide .
Anyone can apply design thinking to solve problems. Despite what the name suggests, non-designers can use the methodology in non-design-related scenarios. The methodology helps you think about problems from the end user’s perspective. Some areas where you can apply this process:
Develop new products with greater chances of success.
Address community-related issues (such as education, healthcare and environment) to improve society and living standards.
Innovate/enhance existing products to gain an advantage over the competition.
Achieve greater efficiencies in operations and reduce costs.
Use the Design Thinking: The Ultimate Guide course to apply design thinking to your context today.
A framework is the basic structure underlying a system, concept, or text. There are several design thinking frameworks with slight differences. However, all the frameworks share some traits. Each framework:
Begins with empathy.
Reframes the problem or challenge at hand.
Initially employs divergent styles of thinking to generate ideas.
Later, it employs convergent styles of thinking to narrow down the best ideas,
Creates and tests prototypes.
Iterates based on the tests.
Some of the design thinking frameworks are:
5-stage design process by d.school
7-step early traditional design process by Herbert Simon
The 5-Stage DeepDive™ by IDEO
The “Double Diamond” Design Process Model by the Design Council
Collective Action Toolkit (CAT) by Frog Design
The LUMA System of Innovation by LUMA Institute
For details about each of these frameworks, see 10 Insightful Design Thinking Frameworks: A Quick Overview .
IDEO’s 3-Stage Design Thinking Process consists of inspiration, ideation and implementation:
Inspire : The problem or opportunity inspires and motivates the search for a solution.
Ideate : A process of synthesis distills insights which can lead to solutions or opportunities for change.
Implement : The best ideas are turned into a concrete, fully conceived action plan.
IDEO is a leader in applying design thinking and has developed many frameworks. Find out more in 10 Insightful Design Thinking Frameworks: A Quick Overview .
Design Council's Double Diamond diagram depicts the divergent and convergent stages of the design process.
Béla H. Bánáthy, founder of the White Stag Leadership Development Program, created the “divergence-convergence” model in 1996. In the mid-2000s, the British Design Council made this famous as the Double Diamond model.
The Double Diamond diagram graphically represents a design thinking process. It highlights the divergent and convergent styles of thinking in the design process. It has four distinct phases:
Discover: Initial idea or inspiration based on user needs.
Define: Interpret user needs and align them with business objectives.
Develop: Develop, iterate and test design-led solutions.
Deliver: Finalize and launch the end product into the market.
Double Diamond is one of several design thinking frameworks. Find out more in 10 Insightful Design Thinking Frameworks: A Quick Overview .
There are several design thinking methods that you can choose from, depending on what stage of the process you’re in. Here are a few common design thinking methods:
User Interviews: to understand user needs, pain points, attitudes and behaviors.
5 Whys Method: to dig deeper into problems to diagnose the root cause.
User Observations: to understand how users behave in real life (as opposed to what they say they do).
Affinity Diagramming: to organize research findings.
Empathy Mapping: to empathize with users based on research insights.
Journey Mapping: to visualize a user’s experience as they solve a problem.
6 Thinking Hats: to encourage a group to think about a problem or solution from multiple perspectives.
Brainstorming: to generate ideas.
Prototyping: to make abstract ideas more tangible and test them.
Dot Voting: to select ideas.
Start applying these methods to your work today with the Design Thinking template bundle .

For most of the design thinking process, you will need basic office stationery:
Pen and paper
Sticky notes
Whiteboard and markers
Print-outs of templates and canvases as needed (such as empathy maps, journey maps, feedback capture grid etc.) You can also draw these out manually.
Prototyping materials such as UI stencils, string, clay, Lego bricks, sticky tapes, scissors and glue.
A space to work in.
You can conduct design thinking workshops remotely by:
Using collaborative software to simulate the whiteboard and sticky notes.
Using digital templates instead of printed canvases.
Download print-ready templates you can share with your team to practice design thinking today.
Design thinking is a problem-solving methodology that helps teams better identify, understand, and solve business and customer problems.
When businesses prioritize and empathize with customers, they can create solutions catering to their needs. Happier customers are more likely to be loyal and organically advocate for the product.
Design thinking helps businesses develop innovative solutions that give them a competitive advantage.
Gain a competitive advantage in your business with Design Thinking: The Ultimate Guide .
The evolution of Design Thinking can be summarised in 8 key events from the 1960s to 2004.
© Interaction Design Foundation, CC BY-SA 4.0.
Herbert Simon’s 1969 book, "The Sciences of the Artificial," has one of the earliest references to design thinking. David Kelley, founder of the design consultancy IDEO, coined the term “design thinking” and helped make it popular.
For a more comprehensive discussion on the origins of design thinking, see The History of Design Thinking .
Some organizations that have employed design thinking successfully are:
Airbnb: Airbnb used design thinking to create a platform for people to rent out their homes to travelers. The company focused on the needs of both hosts and guests . The result was a user-friendly platform to help people find and book accommodations.
PillPack: PillPack is a prescription home-delivery system. The company focused on the needs of people who take multiple medications and created a system that organizes pills by date and time. Amazon bought PillPack in 2018 for $1 billion .
Google Creative Lab: Google Creative Lab collaborated with IDEO to discover how kids physically play and learn. The team used design thinking to create Project Bloks . The project helps children develop foundational problem-solving skills "through coding experiences that are playful, tactile and collaborative.”
See more examples of design thinking and learn practical methods in Design Thinking: The Ultimate Guide .
Innovation essentially means a new idea. Design thinking is a problem-solving methodology that helps teams develop new ideas. In other words, design thinking can lead to innovation.
Human-Centered Design is a newer term for User-Centered Design
“Human-centred design is an approach to interactive systems development that aims to make systems usable and useful by focusing on the users, their needs and requirements, and by applying human factors/ergonomics, and usability knowledge and techniques. This approach enhances effectiveness and efficiency, improves human well-being, user satisfaction, accessibility and sustainability; and counteracts possible adverse effects of use on human health, safety and performance.”
— ISO 9241-210:2019(en), ISO (the International Organization for Standardization)
User experience expert Don Norman describes human-centered design (HCD) as a more evolved form of user-centered design (UCD). The word "users" removes their importance and treats them more like objects than people. By replacing “user” with “human,” designers can empathize better with the people for whom they are designing. Don Norman takes HCD a step further and prefers the term People-Centered Design.
Design thinking has a broader scope and takes HCD beyond the design discipline to drive innovation.
People sometimes use design thinking and human-centered design to mean the same thing. However, they are not the same. HCD is a formal discipline with a specific process used only by designers and usability engineers to design products. Design thinking borrows the design methods and applies them to problems in general.
Design Sprint condenses design thinking into a 1-week structured workshop
Google Ventures condensed the design thinking framework into a time-constrained 5-day workshop format called the Design Sprint. The sprint follows one step per day of the week:
Monday: Unpack
Tuesday: Sketch
Wednesday: Decide
Thursday: Prototype
Friday: Test
Learn more about the design sprint in Make Your UX Design Process Agile Using Google’s Methodology .
Systems Thinking is a distinct discipline with a broader approach to problem-solving
“Systems thinking is a way of exploring and developing effective action by looking at connected wholes rather than separate parts.”
— Introduction to Systems thinking, Report of GSE and GORS seminar, Civil Service Live
Both HCD and Systems Thinking are formal disciplines. Designers and usability engineers primarily use HCD. Systems thinking has applications in various fields, such as medical, environmental, political, economic, human resources, and educational systems.
HCD has a much narrower focus and aims to create and improve products. Systems thinking looks at the larger picture and aims to change entire systems.
Don Norman encourages designers to incorporate systems thinking in their work. Instead of looking at people and problems in isolation, designers must look at them from a systems point of view.
In summary, UCD and HCD refer to the same field, with the latter being a preferred phrase.
Design thinking is a broader framework that borrows methods from human-centered design to approach problems beyond the design discipline. It encourages people with different backgrounds and expertise to work together and apply the designer’s way of thinking to generate innovative solutions to problems.
Systems thinking is another approach to problem-solving that looks at the big picture instead of specific problems in isolation.
The design sprint is Google Ventures’ version of the design thinking process, structured to fit the design process in 1 week.
There are multiple design thinking frameworks, each with a different number of steps and phase names. One of the most popular frameworks is the Stanford d.School 5-stage process.
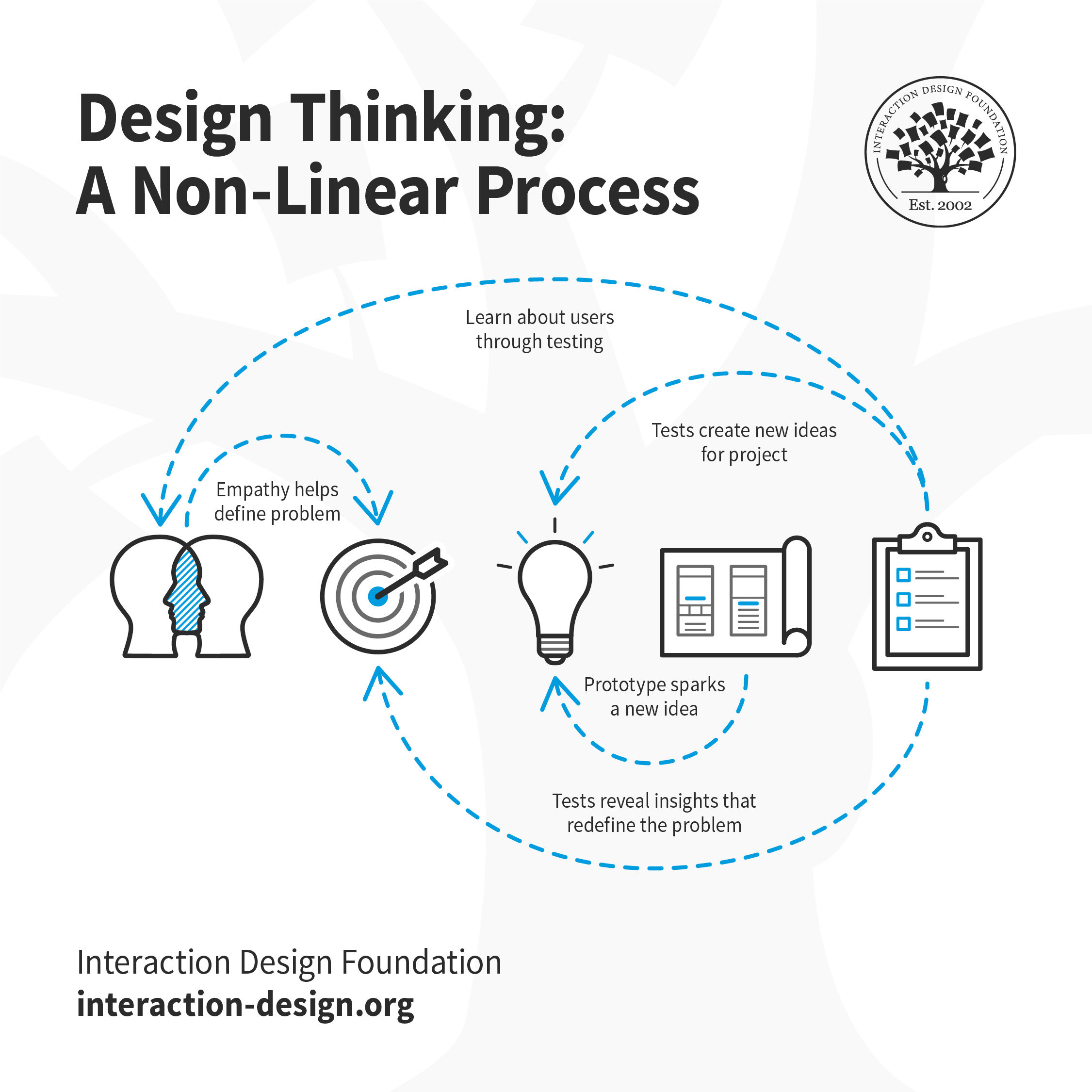
Design thinking is an iterative and non-linear process. It contains five phases: 1. Empathize, 2. Define, 3. Ideate, 4. Prototype and 5. Test. It is important to note the five stages of design thinking are not always sequential. They do not have to follow a specific order, and they can often occur in parallel or be repeated iteratively. The stages should be understood as different modes which contribute to the entire design project, rather than sequential steps.
For more details, see The 5 Stages in the Design Thinking Process .
IDEO is a leading design consultancy and has developed its own version of the design thinking framework and adds the dimension of implementation in the process.
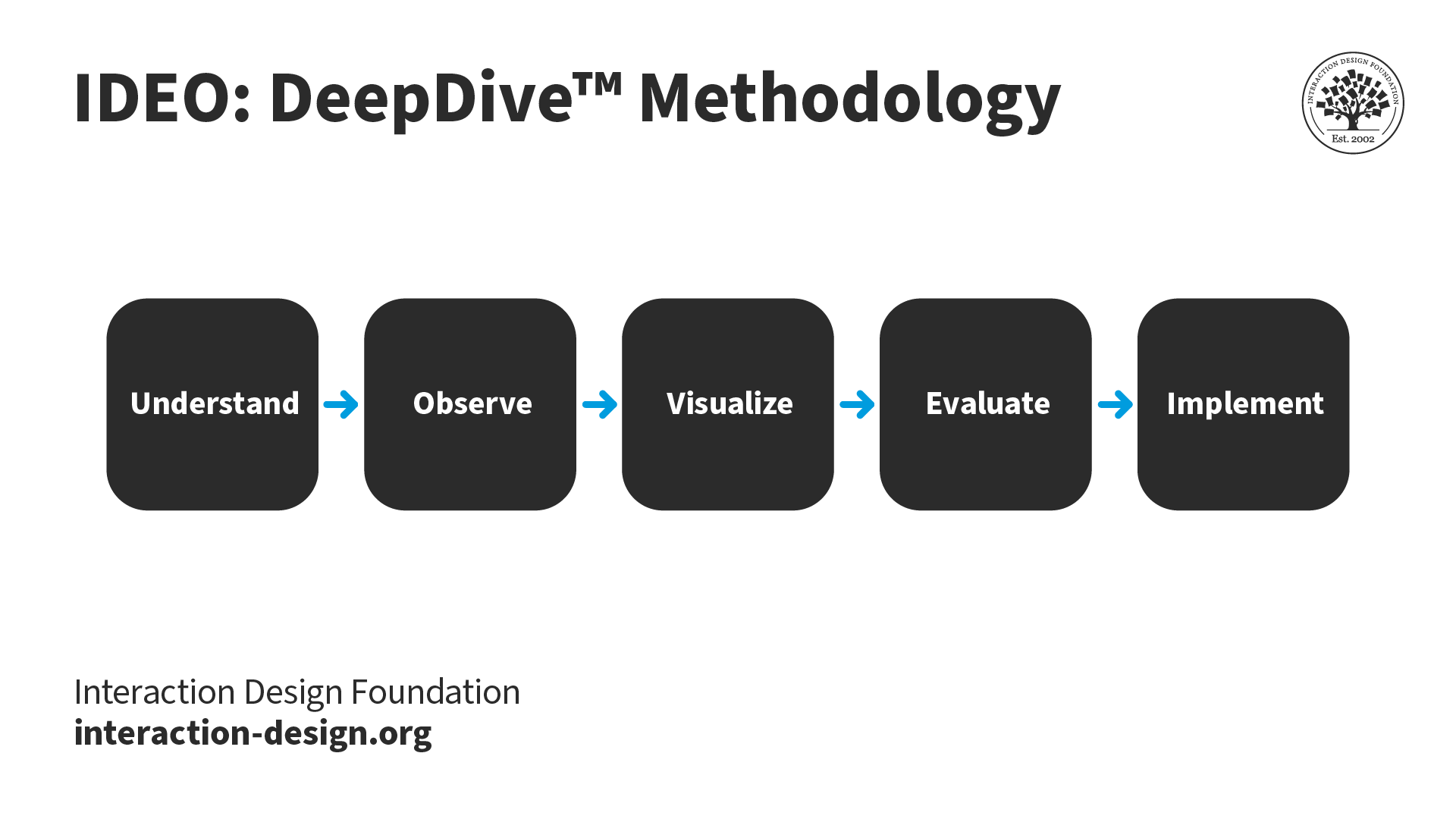
IDEO’s framework uses slightly different terms than d.school’s design thinking process and adds an extra dimension of implementation. The steps in the DeepDive™ Methodology are: Understand, Observe, Visualize, Evaluate and Implement.
IDEO’s DeepDive™ Methodology includes the following steps:
Understand: Conduct research and identify what the client needs and the market landscape
Observe: Similar to the Empathize step, teams observe people in live scenarios and conduct user research to identify their needs and pain points.
Visualize: In this step, the team visualizes new concepts. Similar to the Ideate phase, teams focus on creative, out-of-the-box and novel ideas.
Evaluate: The team prototypes ideas and evaluates them. After refining the prototypes, the team picks the most suitable one.
Implement: The team then sets about to develop the new concept for commercial use.
IDEO’s DeepDive™ is one of several design thinking frameworks. Find out more in 10 Insightful Design Thinking Frameworks: A Quick Overview .
Answer a Short Quiz to Earn a Gift
What are the stages in the design thinking process?
- Brainstorm, Prototype, Design, Launch, Test
- Define, Ideate, Research, Design, Test
- Empathize, Define, Ideate, Prototype, Test
Why is empathy critical in the design thinking process?
- It allows designers to understand and address the real needs of users.
- It helps designers maintain control over the creative process.
- It makes sure the solution is inexpensive and easy to create.
What is the primary purpose of the prototyping phase in design thinking?
- To explore potential solutions and how they might work in real-world situations
- To finalize the product design for mass production
- To sell the idea to stakeholders with a high-fidelity (hi-fi) demonstration
What is a "wicked problem" in design thinking?
- Problems that are complex, ill-defined and have no single correct answer.
- Problems that are straightforward and have a clear, single solution.
- Problems that are tricky, but can be solved quickly with conventional methods.
Why is the iterative process important in design thinking?
- It allows design teams to use up all available resources.
- It allows for the improvement of solutions based on user feedback and testing.
- It makes sure the solution remains unchanged throughout development.
Better luck next time!
Do you want to improve your UX / UI Design skills? Join us now
Congratulations! You did amazing
You earned your gift with a perfect score! Let us send it to you.
Check Your Inbox
We’ve emailed your gift to [email protected] .
Literature on Design Thinking (DT)
Here’s the entire UX literature on Design Thinking (DT) by the Interaction Design Foundation, collated in one place:
Learn more about Design Thinking (DT)
Take a deep dive into Design Thinking (DT) with our course Design Thinking: The Ultimate Guide .
Some of the world’s leading brands, such as Apple, Google, Samsung, and General Electric, have rapidly adopted the design thinking approach, and design thinking is being taught at leading universities around the world, including Stanford d.school, Harvard, and MIT. What is design thinking, and why is it so popular and effective?
Design Thinking is not exclusive to designers —all great innovators in literature, art, music, science, engineering and business have practiced it. So, why call it Design Thinking? Well, that’s because design work processes help us systematically extract, teach, learn and apply human-centered techniques to solve problems in a creative and innovative way—in our designs, businesses, countries and lives. And that’s what makes it so special.
The overall goal of this design thinking course is to help you design better products, services, processes, strategies, spaces, architecture, and experiences. Design thinking helps you and your team develop practical and innovative solutions for your problems. It is a human-focused , prototype-driven , innovative design process . Through this course, you will develop a solid understanding of the fundamental phases and methods in design thinking, and you will learn how to implement your newfound knowledge in your professional work life. We will give you lots of examples; we will go into case studies, videos, and other useful material, all of which will help you dive further into design thinking. In fact, this course also includes exclusive video content that we've produced in partnership with design leaders like Alan Dix, William Hudson and Frank Spillers!
This course contains a series of practical exercises that build on one another to create a complete design thinking project. The exercises are optional, but you’ll get invaluable hands-on experience with the methods you encounter in this course if you complete them, because they will teach you to take your first steps as a design thinking practitioner. What’s equally important is you can use your work as a case study for your portfolio to showcase your abilities to future employers! A portfolio is essential if you want to step into or move ahead in a career in the world of human-centered design.
Design thinking methods and strategies belong at every level of the design process . However, design thinking is not an exclusive property of designers—all great innovators in literature, art, music, science, engineering, and business have practiced it. What’s special about design thinking is that designers and designers’ work processes can help us systematically extract, teach, learn, and apply these human-centered techniques in solving problems in a creative and innovative way—in our designs, in our businesses, in our countries, and in our lives.
That means that design thinking is not only for designers but also for creative employees , freelancers , and business leaders . It’s for anyone who seeks to infuse an approach to innovation that is powerful, effective and broadly accessible, one that can be integrated into every level of an organization, product, or service so as to drive new alternatives for businesses and society.
You earn a verifiable and industry-trusted Course Certificate once you complete the course. You can highlight them on your resume, CV, LinkedIn profile or your website .
All open-source articles on Design Thinking (DT)
What is design thinking and why is it so popular.
- 1.6k shares
Personas – A Simple Introduction

- 1.5k shares
Stage 2 in the Design Thinking Process: Define the Problem and Interpret the Results

- 1.3k shares
What is Ideation – and How to Prepare for Ideation Sessions
- 1.2k shares
Affinity Diagrams: How to Cluster Your Ideas and Reveal Insights

- 2 years ago
Stage 3 in the Design Thinking Process: Ideate

- 4 years ago
Stage 4 in the Design Thinking Process: Prototype

- 3 years ago
Stage 1 in the Design Thinking Process: Empathise with Your Users
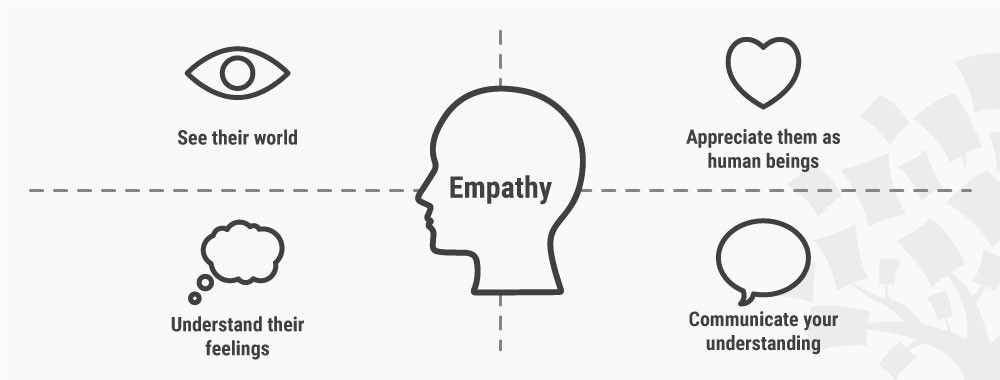
Empathy Map – Why and How to Use It
What Is Empathy and Why Is It So Important in Design Thinking?
10 Insightful Design Thinking Frameworks: A Quick Overview
Define and Frame Your Design Challenge by Creating Your Point Of View and Ask “How Might We”

- 1.1k shares
Design Thinking: Get Started with Prototyping

5 Common Low-Fidelity Prototypes and Their Best Practices

Design Thinking: New Innovative Thinking for New Problems

Test Your Prototypes: How to Gather Feedback and Maximize Learning

The History of Design Thinking
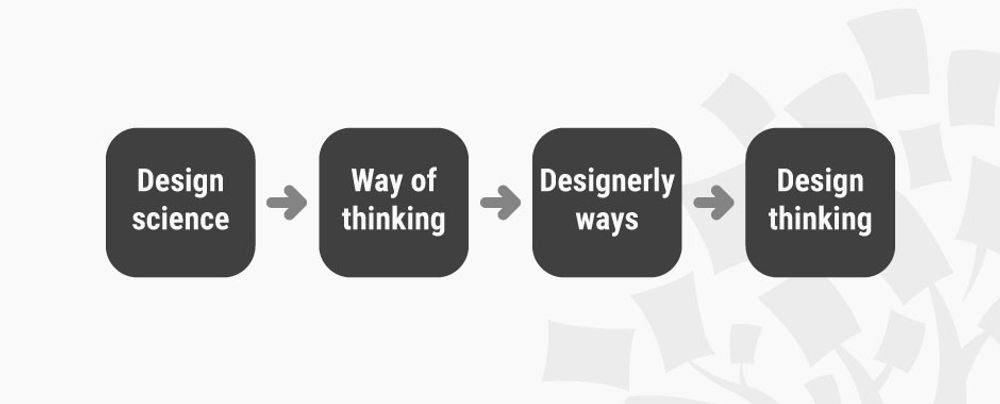
The Ultimate Guide to Understanding UX Roles and Which One You Should Go For
Stage 5 in the Design Thinking Process: Test

What Are Wicked Problems and How Might We Solve Them?
Open Access—Link to us!
We believe in Open Access and the democratization of knowledge . Unfortunately, world-class educational materials such as this page are normally hidden behind paywalls or in expensive textbooks.
If you want this to change , cite this page , link to us, or join us to help us democratize design knowledge !
Privacy Settings
Our digital services use necessary tracking technologies, including third-party cookies, for security, functionality, and to uphold user rights. Optional cookies offer enhanced features, and analytics.
Experience the full potential of our site that remembers your preferences and supports secure sign-in.
Governs the storage of data necessary for maintaining website security, user authentication, and fraud prevention mechanisms.
Enhanced Functionality
Saves your settings and preferences, like your location, for a more personalized experience.
Referral Program
We use cookies to enable our referral program, giving you and your friends discounts.
Error Reporting
We share user ID with Bugsnag and NewRelic to help us track errors and fix issues.
Optimize your experience by allowing us to monitor site usage. You’ll enjoy a smoother, more personalized journey without compromising your privacy.
Analytics Storage
Collects anonymous data on how you navigate and interact, helping us make informed improvements.
Differentiates real visitors from automated bots, ensuring accurate usage data and improving your website experience.
Lets us tailor your digital ads to match your interests, making them more relevant and useful to you.
Advertising Storage
Stores information for better-targeted advertising, enhancing your online ad experience.
Personalization Storage
Permits storing data to personalize content and ads across Google services based on user behavior, enhancing overall user experience.
Advertising Personalization
Allows for content and ad personalization across Google services based on user behavior. This consent enhances user experiences.
Enables personalizing ads based on user data and interactions, allowing for more relevant advertising experiences across Google services.
Receive more relevant advertisements by sharing your interests and behavior with our trusted advertising partners.
Enables better ad targeting and measurement on Meta platforms, making ads you see more relevant.
Allows for improved ad effectiveness and measurement through Meta’s Conversions API, ensuring privacy-compliant data sharing.
LinkedIn Insights
Tracks conversions, retargeting, and web analytics for LinkedIn ad campaigns, enhancing ad relevance and performance.
LinkedIn CAPI
Enhances LinkedIn advertising through server-side event tracking, offering more accurate measurement and personalization.
Google Ads Tag
Tracks ad performance and user engagement, helping deliver ads that are most useful to you.
Share Knowledge, Get Respect!
or copy link
Cite according to academic standards
Simply copy and paste the text below into your bibliographic reference list, onto your blog, or anywhere else. You can also just hyperlink to this page.
New to UX Design? We’re Giving You a Free ebook!

Download our free ebook The Basics of User Experience Design to learn about core concepts of UX design.
In 9 chapters, we’ll cover: conducting user interviews, design thinking, interaction design, mobile UX design, usability, UX research, and many more!
- Book a Demo
Struggling to overcome challenges in your life? We all face problems, big and small, on a regular basis.
So how do you tackle them effectively? What are some key problem-solving strategies and skills that can guide you?
Effective problem-solving requires breaking issues down logically, generating solutions creatively, weighing choices critically, and adapting plans flexibly based on outcomes. Useful strategies range from leveraging past solutions that have worked to visualizing problems through diagrams. Core skills include analytical abilities, innovative thinking, and collaboration.
Want to improve your problem-solving skills? Keep reading to find out 17 effective problem-solving strategies, key skills, common obstacles to watch for, and tips on improving your overall problem-solving skills.
Key Takeaways:
- Effective problem-solving requires breaking down issues logically, generating multiple solutions creatively, weighing choices critically, and adapting plans based on outcomes.
- Useful problem-solving strategies range from leveraging past solutions to brainstorming with groups to visualizing problems through diagrams and models.
- Core skills include analytical abilities, innovative thinking, decision-making, and team collaboration to solve problems.
- Common obstacles include fear of failure, information gaps, fixed mindsets, confirmation bias, and groupthink.
- Boosting problem-solving skills involves learning from experts, actively practicing, soliciting feedback, and analyzing others’ success.
- Onethread’s project management capabilities align with effective problem-solving tenets – facilitating structured solutions, tracking progress, and capturing lessons learned.
What Is Problem-Solving?
Problem-solving is the process of understanding an issue, situation, or challenge that needs to be addressed and then systematically working through possible solutions to arrive at the best outcome.
It involves critical thinking, analysis, logic, creativity, research, planning, reflection, and patience in order to overcome obstacles and find effective answers to complex questions or problems.
The ultimate goal is to implement the chosen solution successfully.
What Are Problem-Solving Strategies?
Problem-solving strategies are like frameworks or methodologies that help us solve tricky puzzles or problems we face in the workplace, at home, or with friends.
Imagine you have a big jigsaw puzzle. One strategy might be to start with the corner pieces. Another could be looking for pieces with the same colors.
Just like in puzzles, in real life, we use different plans or steps to find solutions to problems. These strategies help us think clearly, make good choices, and find the best answers without getting too stressed or giving up.
Why Is It Important To Know Different Problem-Solving Strategies?
Knowing different problem-solving strategies is important because different types of problems often require different approaches to solve them effectively. Having a variety of strategies to choose from allows you to select the best method for the specific problem you are trying to solve.
This improves your ability to analyze issues thoroughly, develop solutions creatively, and tackle problems from multiple angles. Knowing multiple strategies also aids in overcoming roadblocks if your initial approach is not working.
Here are some reasons why you need to know different problem-solving strategies:
- Different Problems Require Different Tools: Just like you can’t use a hammer to fix everything, some problems need specific strategies to solve them.
- Improves Creativity: Knowing various strategies helps you think outside the box and come up with creative solutions.
- Saves Time: With the right strategy, you can solve problems faster instead of trying things that don’t work.
- Reduces Stress: When you know how to tackle a problem, it feels less scary and you feel more confident.
- Better Outcomes: Using the right strategy can lead to better solutions, making things work out better in the end.
- Learning and Growth: Each time you solve a problem, you learn something new, which makes you smarter and better at solving future problems.
Knowing different ways to solve problems helps you tackle anything that comes your way, making life a bit easier and more fun!
17 Effective Problem-Solving Strategies
Effective problem-solving strategies include breaking the problem into smaller parts, brainstorming multiple solutions, evaluating the pros and cons of each, and choosing the most viable option.
Critical thinking and creativity are essential in developing innovative solutions. Collaboration with others can also provide diverse perspectives and ideas.
By applying these strategies, you can tackle complex issues more effectively.
Now, consider a challenge you’re dealing with. Which strategy could help you find a solution? Here we will discuss key problem strategies in detail.
1. Use a Past Solution That Worked

This strategy involves looking back at previous similar problems you have faced and the solutions that were effective in solving them.
It is useful when you are facing a problem that is very similar to something you have already solved. The main benefit is that you don’t have to come up with a brand new solution – you already know the method that worked before will likely work again.
However, the limitation is that the current problem may have some unique aspects or differences that mean your old solution is not fully applicable.
The ideal process is to thoroughly analyze the new challenge, identify the key similarities and differences versus the past case, adapt the old solution as needed to align with the current context, and then pilot it carefully before full implementation.
An example is using the same negotiation tactics from purchasing your previous home when putting in an offer on a new house. Key terms would be adjusted but overall it can save significant time versus developing a brand new strategy.
2. Brainstorm Solutions

This involves gathering a group of people together to generate as many potential solutions to a problem as possible.
It is effective when you need creative ideas to solve a complex or challenging issue. By getting input from multiple people with diverse perspectives, you increase the likelihood of finding an innovative solution.
The main limitation is that brainstorming sessions can sometimes turn into unproductive gripe sessions or discussions rather than focusing on productive ideation —so they need to be properly facilitated.
The key to an effective brainstorming session is setting some basic ground rules upfront and having an experienced facilitator guide the discussion. Rules often include encouraging wild ideas, avoiding criticism of ideas during the ideation phase, and building on others’ ideas.
For instance, a struggling startup might hold a session where ideas for turnaround plans are generated and then formalized with financials and metrics.
3. Work Backward from the Solution

This technique involves envisioning that the problem has already been solved and then working step-by-step backward toward the current state.
This strategy is particularly helpful for long-term, multi-step problems. By starting from the imagined solution and identifying all the steps required to reach it, you can systematically determine the actions needed. It lets you tackle a big hairy problem through smaller, reversible steps.
A limitation is that this approach may not be possible if you cannot accurately envision the solution state to start with.
The approach helps drive logical systematic thinking for complex problem-solving, but should still be combined with creative brainstorming of alternative scenarios and solutions.
An example is planning for an event – you would imagine the successful event occurring, then determine the tasks needed the week before, two weeks before, etc. all the way back to the present.
4. Use the Kipling Method
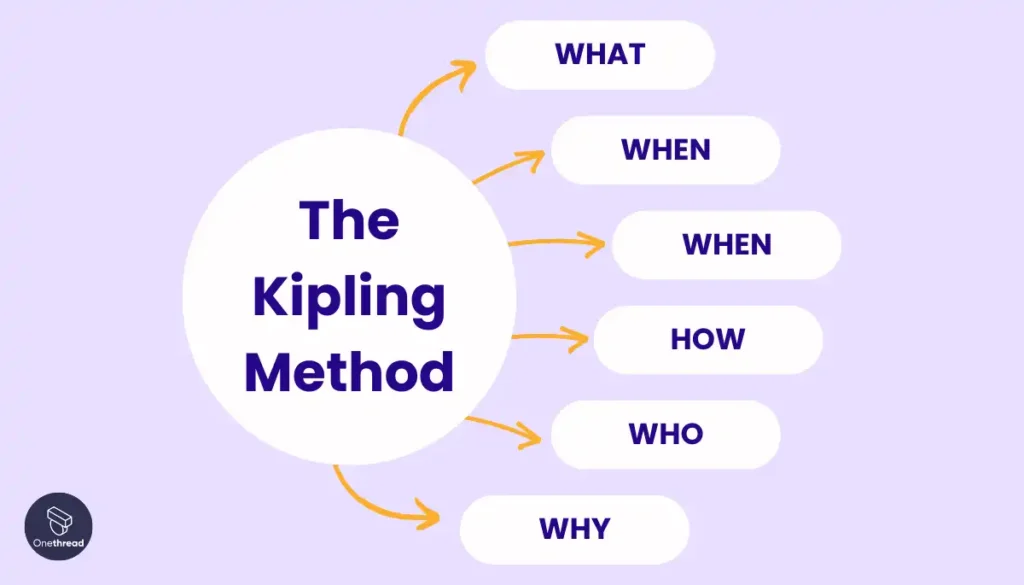
This method, named after author Rudyard Kipling, provides a framework for thoroughly analyzing a problem before jumping into solutions.
It consists of answering six fundamental questions: What, Where, When, How, Who, and Why about the challenge. Clearly defining these core elements of the problem sets the stage for generating targeted solutions.
The Kipling method enables a deep understanding of problem parameters and root causes before solution identification. By jumping to brainstorm solutions too early, critical information can be missed or the problem is loosely defined, reducing solution quality.
Answering the six fundamental questions illuminates all angles of the issue. This takes time but pays dividends in generating optimal solutions later tuned precisely to the true underlying problem.
The limitation is that meticulously working through numerous questions before addressing solutions can slow progress.
The best approach blends structured problem decomposition techniques like the Kipling method with spurring innovative solution ideation from a diverse team.
An example is using this technique after a technical process failure – the team would systematically detail What failed, Where/When did it fail, How it failed (sequence of events), Who was involved, and Why it likely failed before exploring preventative solutions.
5. Try Different Solutions Until One Works (Trial and Error)

This technique involves attempting various potential solutions sequentially until finding one that successfully solves the problem.
Trial and error works best when facing a concrete, bounded challenge with clear solution criteria and a small number of discrete options to try. By methodically testing solutions, you can determine the faulty component.
A limitation is that it can be time-intensive if the working solution set is large.
The key is limiting the variable set first. For technical problems, this boundary is inherent and each element can be iteratively tested. But for business issues, artificial constraints may be required – setting decision rules upfront to reduce options before testing.
Furthermore, hypothesis-driven experimentation is far superior to blind trial and error – have logic for why Option A may outperform Option B.
Examples include fixing printer jams by testing different paper tray and cable configurations or resolving website errors by tweaking CSS/HTML line-by-line until the code functions properly.
6. Use Proven Formulas or Frameworks (Heuristics)
Heuristics refers to applying existing problem-solving formulas or frameworks rather than addressing issues completely from scratch.
This allows leveraging established best practices rather than reinventing the wheel each time.
It is effective when facing recurrent, common challenges where proven structured approaches exist.
However, heuristics may force-fit solutions to non-standard problems.
For example, a cost-benefit analysis can be used instead of custom weighting schemes to analyze potential process improvements.
Onethread allows teams to define, save, and replicate configurable project templates so proven workflows can be reliably applied across problems with some consistency rather than fully custom one-off approaches each time.
Try One thread
Experience One thread full potential, with all its features unlocked. Sign up now to start your 14-day free trial!
7. Trust Your Instincts (Insight Problem-Solving)

Insight is a problem-solving technique that involves waiting patiently for an unexpected “aha moment” when the solution pops into your mind.
It works well for personal challenges that require intuitive realizations over calculated logic. The unconscious mind makes connections leading to flashes of insight when relaxing or doing mundane tasks unrelated to the actual problem.
Benefits include out-of-the-box creative solutions. However, the limitations are that insights can’t be forced and may never come at all if too complex. Critical analysis is still required after initial insights.
A real-life example would be a writer struggling with how to end a novel. Despite extensive brainstorming, they feel stuck. Eventually while gardening one day, a perfect unexpected plot twist sparks an ideal conclusion. However, once written they still carefully review if the ending flows logically from the rest of the story.
8. Reverse Engineer the Problem

This approach involves deconstructing a problem in reverse sequential order from the current undesirable outcome back to the initial root causes.
By mapping the chain of events backward, you can identify the origin of where things went wrong and establish the critical junctures for solving it moving ahead. Reverse engineering provides diagnostic clarity on multi-step problems.
However, the limitation is that it focuses heavily on autopsying the past versus innovating improved future solutions.
An example is tracing back from a server outage, through the cascade of infrastructure failures that led to it finally terminating at the initial script error that triggered the crisis. This root cause would then inform the preventative measure.
9. Break Down Obstacles Between Current and Goal State (Means-End Analysis)

This technique defines the current problem state and the desired end goal state, then systematically identifies obstacles in the way of getting from one to the other.
By mapping the barriers or gaps, you can then develop solutions to address each one. This methodically connects the problem to solutions.
A limitation is that some obstacles may be unknown upfront and only emerge later.
For example, you can list down all the steps required for a new product launch – current state through production, marketing, sales, distribution, etc. to full launch (goal state) – to highlight where resource constraints or other blocks exist so they can be addressed.
Onethread allows dividing big-picture projects into discrete, manageable phases, milestones, and tasks to simplify execution just as problems can be decomposed into more achievable components. Features like dependency mapping further reinforce interconnections.
Using Onethread’s issues and subtasks feature, messy problems can be decomposed into manageable chunks.
10. Ask “Why” Five Times to Identify the Root Cause (The 5 Whys)

This technique involves asking “Why did this problem occur?” and then responding with an answer that is again met with asking “Why?” This process repeats five times until the root cause is revealed.
Continually asking why digs deeper from surface symptoms to underlying systemic issues.
It is effective for getting to the source of problems originating from human error or process breakdowns.
However, some complex issues may have multiple tangled root causes not solvable through this approach alone.
An example is a retail store experiencing a sudden decline in customers. Successively asking why five times may trace an initial drop to parking challenges, stemming from a city construction project – the true starting point to address.
11. Evaluate Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats (SWOT Analysis)

This involves analyzing a problem or proposed solution by categorizing internal and external factors into a 2×2 matrix: Strengths, Weaknesses as the internal rows; Opportunities and Threats as the external columns.
Systematically identifying these elements provides balanced insight to evaluate options and risks. It is impactful when evaluating alternative solutions or developing strategy amid complexity or uncertainty.
The key benefit of SWOT analysis is enabling multi-dimensional thinking when rationally evaluating options. Rather than getting anchored on just the upsides or the existing way of operating, it urges a systematic assessment through four different lenses:
- Internal Strengths: Our core competencies/advantages able to deliver success
- Internal Weaknesses: Gaps/vulnerabilities we need to manage
- External Opportunities: Ways we can differentiate/drive additional value
- External Threats: Risks we must navigate or mitigate
Multiperspective analysis provides the needed holistic view of the balanced risk vs. reward equation for strategic decision making amid uncertainty.
However, SWOT can feel restrictive if not tailored and evolved for different issue types.
Teams should view SWOT analysis as a starting point, augmenting it further for distinct scenarios.
An example is performing a SWOT analysis on whether a small business should expand into a new market – evaluating internal capabilities to execute vs. risks in the external competitive and demand environment to inform the growth decision with eyes wide open.
12. Compare Current vs Expected Performance (Gap Analysis)

This technique involves comparing the current state of performance, output, or results to the desired or expected levels to highlight shortfalls.
By quantifying the gaps, you can identify problem areas and prioritize address solutions.
Gap analysis is based on the simple principle – “you can’t improve what you don’t measure.” It enables facts-driven problem diagnosis by highlighting delta to goals, not just vague dissatisfaction that something seems wrong. And measurement immediately suggests improvement opportunities – address the biggest gaps first.
This data orientation also supports ROI analysis on fixing issues – the return from closing larger gaps outweighs narrowly targeting smaller performance deficiencies.
However, the approach is only effective if robust standards and metrics exist as the benchmark to evaluate against. Organizations should invest upfront in establishing performance frameworks.
Furthermore, while numbers are invaluable, the human context behind problems should not be ignored – quantitative versus qualitative gap assessment is optimally blended.
For example, if usage declines are noted during software gap analysis, this could be used as a signal to improve user experience through design.
13. Observe Processes from the Frontline (Gemba Walk)
A Gemba walk involves going to the actual place where work is done, directly observing the process, engaging with employees, and finding areas for improvement.
By experiencing firsthand rather than solely reviewing abstract reports, practical problems and ideas emerge.
The limitation is Gemba walks provide anecdotes not statistically significant data. It complements but does not replace comprehensive performance measurement.
An example is a factory manager inspecting the production line to spot jam areas based on direct reality rather than relying on throughput dashboards alone back in her office. Frontline insights prove invaluable.
14. Analyze Competitive Forces (Porter’s Five Forces)
This involves assessing the marketplace around a problem or business situation via five key factors: competitors, new entrants, substitute offerings, suppliers, and customer power.
Evaluating these forces illuminates risks and opportunities for strategy development and issue resolution. It is effective for understanding dynamic external threats and opportunities when operating in a contested space.
However, over-indexing on only external factors can overlook the internal capabilities needed to execute solutions.
A startup CEO, for example, may analyze market entry barriers, whitespace opportunities, and disruption risks across these five forces to shape new product rollout strategies and marketing approaches.
15. Think from Different Perspectives (Six Thinking Hats)
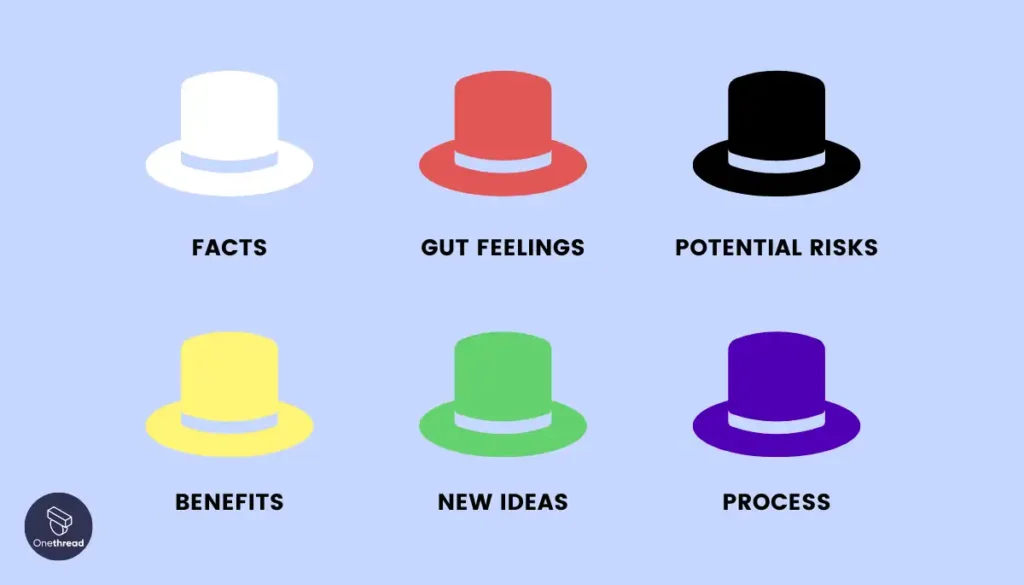
The Six Thinking Hats is a technique developed by Edward de Bono that encourages people to think about a problem from six different perspectives, each represented by a colored “thinking hat.”
The key benefit of this strategy is that it pushes team members to move outside their usual thinking style and consider new angles. This brings more diverse ideas and solutions to the table.
It works best for complex problems that require innovative solutions and when a team is stuck in an unproductive debate. The structured framework keeps the conversation flowing in a positive direction.
Limitations are that it requires training on the method itself and may feel unnatural at first. Team dynamics can also influence success – some members may dominate certain “hats” while others remain quiet.
A real-life example is a software company debating whether to build a new feature. The white hat focuses on facts, red on gut feelings, black on potential risks, yellow on benefits, green on new ideas, and blue on process. This exposes more balanced perspectives before deciding.
Onethread centralizes diverse stakeholder communication onto one platform, ensuring all voices are incorporated when evaluating project tradeoffs, just as problem-solving should consider multifaceted solutions.
16. Visualize the Problem (Draw it Out)
Drawing out a problem involves creating visual representations like diagrams, flowcharts, and maps to work through challenging issues.
This strategy is helpful when dealing with complex situations with lots of interconnected components. The visuals simplify the complexity so you can thoroughly understand the problem and all its nuances.
Key benefits are that it allows more stakeholders to get on the same page regarding root causes and it sparks new creative solutions as connections are made visually.
However, simple problems with few variables don’t require extensive diagrams. Additionally, some challenges are so multidimensional that fully capturing every aspect is difficult.
A real-life example would be mapping out all the possible causes leading to decreased client satisfaction at a law firm. An intricate fishbone diagram with branches for issues like service delivery, technology, facilities, culture, and vendor partnerships allows the team to trace problems back to their origins and brainstorm targeted fixes.
17. Follow a Step-by-Step Procedure (Algorithms)

An algorithm is a predefined step-by-step process that is guaranteed to produce the correct solution if implemented properly.
Using algorithms is effective when facing problems that have clear, binary right and wrong answers. Algorithms work for mathematical calculations, computer code, manufacturing assembly lines, and scientific experiments.
Key benefits are consistency, accuracy, and efficiency. However, they require extensive upfront development and only apply to scenarios with strict parameters. Additionally, human error can lead to mistakes.
For example, crew members of fast food chains like McDonald’s follow specific algorithms for food prep – from grill times to ingredient amounts in sandwiches, to order fulfillment procedures. This ensures uniform quality and service across all locations. However, if a step is missed, errors occur.
The Problem-Solving Process
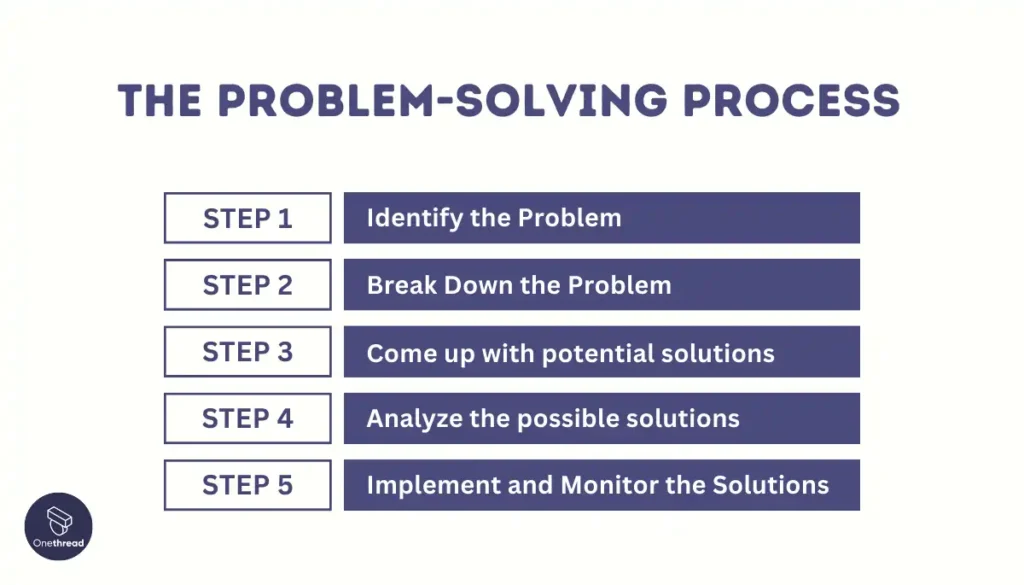
The problem-solving process typically includes defining the issue, analyzing details, creating solutions, weighing choices, acting, and reviewing results.
In the above, we have discussed several problem-solving strategies. For every problem-solving strategy, you have to follow these processes. Here’s a detailed step-by-step process of effective problem-solving:
Step 1: Identify the Problem
The problem-solving process starts with identifying the problem. This step involves understanding the issue’s nature, its scope, and its impact. Once the problem is clearly defined, it sets the foundation for finding effective solutions.
Identifying the problem is crucial. It means figuring out exactly what needs fixing. This involves looking at the situation closely, understanding what’s wrong, and knowing how it affects things. It’s about asking the right questions to get a clear picture of the issue.
This step is important because it guides the rest of the problem-solving process. Without a clear understanding of the problem, finding a solution is much harder. It’s like diagnosing an illness before treating it. Once the problem is identified accurately, you can move on to exploring possible solutions and deciding on the best course of action.
Step 2: Break Down the Problem
Breaking down the problem is a key step in the problem-solving process. It involves dividing the main issue into smaller, more manageable parts. This makes it easier to understand and tackle each component one by one.
After identifying the problem, the next step is to break it down. This means splitting the big issue into smaller pieces. It’s like solving a puzzle by handling one piece at a time.
By doing this, you can focus on each part without feeling overwhelmed. It also helps in identifying the root causes of the problem. Breaking down the problem allows for a clearer analysis and makes finding solutions more straightforward.
Each smaller problem can be addressed individually, leading to an effective resolution of the overall issue. This approach not only simplifies complex problems but also aids in developing a systematic plan to solve them.
Step 3: Come up with potential solutions
Coming up with potential solutions is the third step in the problem-solving process. It involves brainstorming various options to address the problem, considering creativity and feasibility to find the best approach.
After breaking down the problem, it’s time to think of ways to solve it. This stage is about brainstorming different solutions. You look at the smaller issues you’ve identified and start thinking of ways to fix them. This is where creativity comes in.
You want to come up with as many ideas as possible, no matter how out-of-the-box they seem. It’s important to consider all options and evaluate their pros and cons. This process allows you to gather a range of possible solutions.
Later, you can narrow these down to the most practical and effective ones. This step is crucial because it sets the stage for deciding on the best solution to implement. It’s about being open-minded and innovative to tackle the problem effectively.
Step 4: Analyze the possible solutions
Analyzing the possible solutions is the fourth step in the problem-solving process. It involves evaluating each proposed solution’s advantages and disadvantages to determine the most effective and feasible option.
After coming up with potential solutions, the next step is to analyze them. This means looking closely at each idea to see how well it solves the problem. You weigh the pros and cons of every solution.
Consider factors like cost, time, resources, and potential outcomes. This analysis helps in understanding the implications of each option. It’s about being critical and objective, ensuring that the chosen solution is not only effective but also practical.
This step is vital because it guides you towards making an informed decision. It involves comparing the solutions against each other and selecting the one that best addresses the problem.
By thoroughly analyzing the options, you can move forward with confidence, knowing you’ve chosen the best path to solve the issue.
Step 5: Implement and Monitor the Solutions
Implementing and monitoring the solutions is the final step in the problem-solving process. It involves putting the chosen solution into action and observing its effectiveness, making adjustments as necessary.
Once you’ve selected the best solution, it’s time to put it into practice. This step is about action. You implement the chosen solution and then keep an eye on how it works. Monitoring is crucial because it tells you if the solution is solving the problem as expected.
If things don’t go as planned, you may need to make some changes. This could mean tweaking the current solution or trying a different one. The goal is to ensure the problem is fully resolved.
This step is critical because it involves real-world application. It’s not just about planning; it’s about doing and adjusting based on results. By effectively implementing and monitoring the solutions, you can achieve the desired outcome and solve the problem successfully.
Why This Process is Important
Following a defined process to solve problems is important because it provides a systematic, structured approach instead of a haphazard one. Having clear steps guides logical thinking, analysis, and decision-making to increase effectiveness. Key reasons it helps are:
- Clear Direction: This process gives you a clear path to follow, which can make solving problems less overwhelming.
- Better Solutions: Thoughtful analysis of root causes, iterative testing of solutions, and learning orientation lead to addressing the heart of issues rather than just symptoms.
- Saves Time and Energy: Instead of guessing or trying random things, this process helps you find a solution more efficiently.
- Improves Skills: The more you use this process, the better you get at solving problems. It’s like practicing a sport. The more you practice, the better you play.
- Maximizes collaboration: Involving various stakeholders in the process enables broader inputs. Their communication and coordination are streamlined through organized brainstorming and evaluation.
- Provides consistency: Standard methodology across problems enables building institutional problem-solving capabilities over time. Patterns emerge on effective techniques to apply to different situations.
The problem-solving process is a powerful tool that can help us tackle any challenge we face. By following these steps, we can find solutions that work and learn important skills along the way.
Key Skills for Efficient Problem Solving

Efficient problem-solving requires breaking down issues logically, evaluating options, and implementing practical solutions.
Key skills include critical thinking to understand root causes, creativity to brainstorm innovative ideas, communication abilities to collaborate with others, and decision-making to select the best way forward. Staying adaptable, reflecting on outcomes, and applying lessons learned are also essential.
With practice, these capacities will lead to increased personal and team effectiveness in systematically addressing any problem.
Let’s explore the powers you need to become a problem-solving hero!
Critical Thinking and Analytical Skills
Critical thinking and analytical skills are vital for efficient problem-solving as they enable individuals to objectively evaluate information, identify key issues, and generate effective solutions.
These skills facilitate a deeper understanding of problems, leading to logical, well-reasoned decisions. By systematically breaking down complex issues and considering various perspectives, individuals can develop more innovative and practical solutions, enhancing their problem-solving effectiveness.
Communication Skills
Effective communication skills are essential for efficient problem-solving as they facilitate clear sharing of information, ensuring all team members understand the problem and proposed solutions.
These skills enable individuals to articulate issues, listen actively, and collaborate effectively, fostering a productive environment where diverse ideas can be exchanged and refined. By enhancing mutual understanding, communication skills contribute significantly to identifying and implementing the most viable solutions.
Decision-Making
Strong decision-making skills are crucial for efficient problem-solving, as they enable individuals to choose the best course of action from multiple alternatives.
These skills involve evaluating the potential outcomes of different solutions, considering the risks and benefits, and making informed choices. Effective decision-making leads to the implementation of solutions that are likely to resolve problems effectively, ensuring resources are used efficiently and goals are achieved.
Planning and Prioritization
Planning and prioritization are key for efficient problem-solving, ensuring resources are allocated effectively to address the most critical issues first. This approach helps in organizing tasks according to their urgency and impact, streamlining efforts towards achieving the desired outcome efficiently.
Emotional Intelligence
Emotional intelligence enhances problem-solving by allowing individuals to manage emotions, understand others, and navigate social complexities. It fosters a positive, collaborative environment, essential for generating creative solutions and making informed, empathetic decisions.
Leadership skills drive efficient problem-solving by inspiring and guiding teams toward common goals. Effective leaders motivate their teams, foster innovation, and navigate challenges, ensuring collective efforts are focused and productive in addressing problems.
Time Management
Time management is crucial in problem-solving, enabling individuals to allocate appropriate time to each task. By efficiently managing time, one can ensure that critical problems are addressed promptly without neglecting other responsibilities.
Data Analysis
Data analysis skills are essential for problem-solving, as they enable individuals to sift through data, identify trends, and extract actionable insights. This analytical approach supports evidence-based decision-making, leading to more accurate and effective solutions.
Research Skills
Research skills are vital for efficient problem-solving, allowing individuals to gather relevant information, explore various solutions, and understand the problem’s context. This thorough exploration aids in developing well-informed, innovative solutions.
Becoming a great problem solver takes practice, but with these skills, you’re on your way to becoming a problem-solving hero.
How to Improve Your Problem-Solving Skills?

Improving your problem-solving skills can make you a master at overcoming challenges. Learn from experts, practice regularly, welcome feedback, try new methods, experiment, and study others’ success to become better.
Learning from Experts
Improving problem-solving skills by learning from experts involves seeking mentorship, attending workshops, and studying case studies. Experts provide insights and techniques that refine your approach, enhancing your ability to tackle complex problems effectively.
To enhance your problem-solving skills, learning from experts can be incredibly beneficial. Engaging with mentors, participating in specialized workshops, and analyzing case studies from seasoned professionals can offer valuable perspectives and strategies.
Experts share their experiences, mistakes, and successes, providing practical knowledge that can be applied to your own problem-solving process. This exposure not only broadens your understanding but also introduces you to diverse methods and approaches, enabling you to tackle challenges more efficiently and creatively.
Improving problem-solving skills through practice involves tackling a variety of challenges regularly. This hands-on approach helps in refining techniques and strategies, making you more adept at identifying and solving problems efficiently.
One of the most effective ways to enhance your problem-solving skills is through consistent practice. By engaging with different types of problems on a regular basis, you develop a deeper understanding of various strategies and how they can be applied.
This hands-on experience allows you to experiment with different approaches, learn from mistakes, and build confidence in your ability to tackle challenges.
Regular practice not only sharpens your analytical and critical thinking skills but also encourages adaptability and innovation, key components of effective problem-solving.
Openness to Feedback
Being open to feedback is like unlocking a secret level in a game. It helps you boost your problem-solving skills. Improving problem-solving skills through openness to feedback involves actively seeking and constructively responding to critiques.
This receptivity enables you to refine your strategies and approaches based on insights from others, leading to more effective solutions.
Learning New Approaches and Methodologies
Learning new approaches and methodologies is like adding new tools to your toolbox. It makes you a smarter problem-solver. Enhancing problem-solving skills by learning new approaches and methodologies involves staying updated with the latest trends and techniques in your field.
This continuous learning expands your toolkit, enabling innovative solutions and a fresh perspective on challenges.
Experimentation
Experimentation is like being a scientist of your own problems. It’s a powerful way to improve your problem-solving skills. Boosting problem-solving skills through experimentation means trying out different solutions to see what works best. This trial-and-error approach fosters creativity and can lead to unique solutions that wouldn’t have been considered otherwise.
Analyzing Competitors’ Success
Analyzing competitors’ success is like being a detective. It’s a smart way to boost your problem-solving skills. Improving problem-solving skills by analyzing competitors’ success involves studying their strategies and outcomes. Understanding what worked for them can provide valuable insights and inspire effective solutions for your own challenges.
Challenges in Problem-Solving
Facing obstacles when solving problems is common. Recognizing these barriers, like fear of failure or lack of information, helps us find ways around them for better solutions.
Fear of Failure
Fear of failure is like a big, scary monster that stops us from solving problems. It’s a challenge many face. Because being afraid of making mistakes can make us too scared to try new solutions.
How can we overcome this? First, understand that it’s okay to fail. Failure is not the opposite of success; it’s part of learning. Every time we fail, we discover one more way not to solve a problem, getting us closer to the right solution. Treat each attempt like an experiment. It’s not about failing; it’s about testing and learning.
Lack of Information
Lack of information is like trying to solve a puzzle with missing pieces. It’s a big challenge in problem-solving. Because without all the necessary details, finding a solution is much harder.
How can we fix this? Start by gathering as much information as you can. Ask questions, do research, or talk to experts. Think of yourself as a detective looking for clues. The more information you collect, the clearer the picture becomes. Then, use what you’ve learned to think of solutions.
Fixed Mindset
A fixed mindset is like being stuck in quicksand; it makes solving problems harder. It means thinking you can’t improve or learn new ways to solve issues.
How can we change this? First, believe that you can grow and learn from challenges. Think of your brain as a muscle that gets stronger every time you use it. When you face a problem, instead of saying “I can’t do this,” try thinking, “I can’t do this yet.” Look for lessons in every challenge and celebrate small wins.
Everyone starts somewhere, and mistakes are just steps on the path to getting better. By shifting to a growth mindset, you’ll see problems as opportunities to grow. Keep trying, keep learning, and your problem-solving skills will soar!
Jumping to Conclusions
Jumping to conclusions is like trying to finish a race before it starts. It’s a challenge in problem-solving. That means making a decision too quickly without looking at all the facts.
How can we avoid this? First, take a deep breath and slow down. Think about the problem like a puzzle. You need to see all the pieces before you know where they go. Ask questions, gather information, and consider different possibilities. Don’t choose the first solution that comes to mind. Instead, compare a few options.
Feeling Overwhelmed
Feeling overwhelmed is like being buried under a mountain of puzzles. It’s a big challenge in problem-solving. When we’re overwhelmed, everything seems too hard to handle.
How can we deal with this? Start by taking a step back. Breathe deeply and focus on one thing at a time. Break the big problem into smaller pieces, like sorting puzzle pieces by color. Tackle each small piece one by one. It’s also okay to ask for help. Sometimes, talking to someone else can give you a new perspective.
Confirmation Bias
Confirmation bias is like wearing glasses that only let you see what you want to see. It’s a challenge in problem-solving. Because it makes us focus only on information that agrees with what we already believe, ignoring anything that doesn’t.
How can we overcome this? First, be aware that you might be doing it. It’s like checking if your glasses are on right. Then, purposely look for information that challenges your views. It’s like trying on a different pair of glasses to see a new perspective. Ask questions and listen to answers, even if they don’t fit what you thought before.
Groupthink is like everyone in a group deciding to wear the same outfit without asking why. It’s a challenge in problem-solving. It means making decisions just because everyone else agrees, without really thinking it through.
How can we avoid this? First, encourage everyone in the group to share their ideas, even if they’re different. It’s like inviting everyone to show their unique style of clothes.
Listen to all opinions and discuss them. It’s okay to disagree; it helps us think of better solutions. Also, sometimes, ask someone outside the group for their thoughts. They might see something everyone in the group missed.
Overcoming obstacles in problem-solving requires patience, openness, and a willingness to learn from mistakes. By recognizing these barriers, we can develop strategies to navigate around them, leading to more effective and creative solutions.
What are the most common problem-solving techniques?
The most common techniques include brainstorming, the 5 Whys, mind mapping, SWOT analysis, and using algorithms or heuristics. Each approach has its strengths, suitable for different types of problems.
What’s the best problem-solving strategy for every situation?
There’s no one-size-fits-all strategy. The best approach depends on the problem’s complexity, available resources, and time constraints. Combining multiple techniques often yields the best results.
How can I improve my problem-solving skills?
Improve your problem-solving skills by practicing regularly, learning from experts, staying open to feedback, and continuously updating your knowledge on new approaches and methodologies.
Are there any tools or resources to help with problem-solving?
Yes, tools like mind mapping software, online courses on critical thinking, and books on problem-solving techniques can be very helpful. Joining forums or groups focused on problem-solving can also provide support and insights.
What are some common mistakes people make when solving problems?
Common mistakes include jumping to conclusions without fully understanding the problem, ignoring valuable feedback, sticking to familiar solutions without considering alternatives, and not breaking down complex problems into manageable parts.
Final Words
Mastering problem-solving strategies equips us with the tools to tackle challenges across all areas of life. By understanding and applying these techniques, embracing a growth mindset, and learning from both successes and obstacles, we can transform problems into opportunities for growth. Continuously improving these skills ensures we’re prepared to face and solve future challenges more effectively.

Let's Get Started with Onethread
Onethread empowers you to plan, organise, and track projects with ease, ensuring you meet deadlines, allocate resources efficiently, and keep progress transparent.
By subscribing you agree to our Privacy Policy .
Giving modern marketing teams superpowers with short links that stand out.
- Live Product Demo
© Copyright 2023 Onethread, Inc

- Software Engineering Tutorial
- Software Engineering Home
- Software Engineering Overview
- Software Development Life Cycle
- Software Project Management
- Software Requirements
- Software Design Basics
- Analysis & Design Tools
Software Design Strategies
- Software User Interface Design
- Software Design Complexity
- Software Implementation
- Software Testing Overview
- Software Maintenance
- CASE Tools Overview
- S/W - Exams Questions with Answers
- SE - Exams Questions with Answers
- S/W Engineering Resources
- SE - Interview Questions
- SE - Useful Resources
- SE - Quick Guide
- SE - Android App
- Selected Reading
- UPSC IAS Exams Notes
- Developer's Best Practices
- Questions and Answers
- Effective Resume Writing
- HR Interview Questions
- Computer Glossary
Software design is a process to conceptualize the software requirements into software implementation. Software design takes the user requirements as challenges and tries to find optimum solution. While the software is being conceptualized, a plan is chalked out to find the best possible design for implementing the intended solution.
There are multiple variants of software design. Let us study them briefly:
Structured Design
Structured design is a conceptualization of problem into several well-organized elements of solution. It is basically concerned with the solution design. Benefit of structured design is, it gives better understanding of how the problem is being solved. Structured design also makes it simpler for designer to concentrate on the problem more accurately.
Structured design is mostly based on ‘divide and conquer’ strategy where a problem is broken into several small problems and each small problem is individually solved until the whole problem is solved.
The small pieces of problem are solved by means of solution modules. Structured design emphasis that these modules be well organized in order to achieve precise solution.
These modules are arranged in hierarchy. They communicate with each other. A good structured design always follows some rules for communication among multiple modules, namely -
Cohesion - grouping of all functionally related elements.
Coupling - communication between different modules.
A good structured design has high cohesion and low coupling arrangements.
Function Oriented Design
In function-oriented design, the system is comprised of many smaller sub-systems known as functions. These functions are capable of performing significant task in the system. The system is considered as top view of all functions.
Function oriented design inherits some properties of structured design where divide and conquer methodology is used.
This design mechanism divides the whole system into smaller functions, which provides means of abstraction by concealing the information and their operation.. These functional modules can share information among themselves by means of information passing and using information available globally.
Another characteristic of functions is that when a program calls a function, the function changes the state of the program, which sometimes is not acceptable by other modules. Function oriented design works well where the system state does not matter and program/functions work on input rather than on a state.
Design Process
- The whole system is seen as how data flows in the system by means of data flow diagram.
- DFD depicts how functions changes data and state of entire system.
- The entire system is logically broken down into smaller units known as functions on the basis of their operation in the system.
- Each function is then described at large.
Object Oriented Design
Object oriented design works around the entities and their characteristics instead of functions involved in the software system. This design strategies focuses on entities and its characteristics. The whole concept of software solution revolves around the engaged entities.
Let us see the important concepts of Object Oriented Design:
- Objects - All entities involved in the solution design are known as objects. For example, person, banks, company and customers are treated as objects. Every entity has some attributes associated to it and has some methods to perform on the attributes.
Classes - A class is a generalized description of an object. An object is an instance of a class. Class defines all the attributes, which an object can have and methods, which defines the functionality of the object.
- Encapsulation - In OOD, the attributes (data variables) and methods (operation on the data) are bundled together is called encapsulation. Encapsulation not only bundles important information of an object together, but also restricts access of the data and methods from the outside world. This is called information hiding.
- Inheritance - OOD allows similar classes to stack up in hierarchical manner where the lower or sub-classes can import, implement and re-use allowed variables and methods from their immediate super classes. This property of OOD is known as inheritance. This makes it easier to define specific class and to create generalized classes from specific ones.
- Polymorphism - OOD languages provide a mechanism where methods performing similar tasks but vary in arguments, can be assigned same name. This is called polymorphism, which allows a single interface performing tasks for different types. Depending upon how the function is invoked, respective portion of the code gets executed.
Software design process can be perceived as series of well-defined steps. Though it varies according to design approach (function oriented or object oriented, yet It may have the following steps involved:
- A solution design is created from requirement or previous used system and/or system sequence diagram.
- Objects are identified and grouped into classes on behalf of similarity in attribute characteristics.
- Class hierarchy and relation among them is defined.
- Application framework is defined.
Software Design Approaches
Here are two generic approaches for software designing:
Top Down Design
We know that a system is composed of more than one sub-systems and it contains a number of components. Further, these sub-systems and components may have their on set of sub-system and components and creates hierarchical structure in the system.
Top-down design takes the whole software system as one entity and then decomposes it to achieve more than one sub-system or component based on some characteristics. Each sub-system or component is then treated as a system and decomposed further. This process keeps on running until the lowest level of system in the top-down hierarchy is achieved.
Top-down design starts with a generalized model of system and keeps on defining the more specific part of it. When all components are composed the whole system comes into existence.
Top-down design is more suitable when the software solution needs to be designed from scratch and specific details are unknown.
Bottom-up Design
The bottom up design model starts with most specific and basic components. It proceeds with composing higher level of components by using basic or lower level components. It keeps creating higher level components until the desired system is not evolved as one single component. With each higher level, the amount of abstraction is increased.
Bottom-up strategy is more suitable when a system needs to be created from some existing system, where the basic primitives can be used in the newer system.
Both, top-down and bottom-up approaches are not practical individually. Instead, a good combination of both is used.
To Continue Learning Please Login
Design Thinking as a Problem Solving Tool
- First Online: 05 August 2022
Cite this chapter

- Rouxelle de Villiers 2
2448 Accesses
In chapter 10 we covered thirteen ideation tools. We dedicate this chapter to Design Thinking (DT), as a procedure to generate and test ideas, and even more importantly as a creative problem-solving methodology. DT is a human-centred process that will help designers, innovators, entrepreneurs and business executives to systematically solve complex problems, not only in product design and businesses processes, systems and other sticky organizational problems, but also in our communities and our everyday lives. Some leading global brands, such as Apple™, Google™ and Samsung™ have adopted the DT approach to complex problem-solving.
As DT is a shift in our way of thinking and a collection of hands-on methods and tools, we devote this chapter to this highly useful, well-honed 5-stage process. The chapter first covers the history of and thinking modalities involved in DT, then examines how various design thinking schools and leading universities (e.g., Stanford, Harvard and MIT) apply the DT principles using models with three to eight stages. Finally this chapter covers the 5-stage DT iterative process we propose for business executives – those who lead multi-disciplinary teams of innovators, ideators, intrapreneurs and others in business problem-solving roles.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Abductive reasoning is a form of logical inference formulated from inconclusive or incomplete information, relying on inference or intuition, and is directly aided and assisted by personal experience.
Tangibilize – make it tangible or concrete; an equivalent term is ‘concretize’.
Cooper R, Junginger S, Lookwood T. Design thinking and design management: a research and practice perspective. Des Manag Rev. 2009;20(2):46–55.
Article Google Scholar
Kimbell L, ed. Beyond design thinking: design as-practice and designs-in-practice. The CRESC Conference, Manchester; 2009.
Google Scholar
Simon RS. Junging types and creativity of professional fine artists. (Doctoral dissertation), United States International University (University Microfilms 7924570); 1979.
Schön DA. The reflective practitioner: how professionals think in action. Basic books; 1983.
Brown T. Design thinking. Harv Bus Rev. 2008;86(6):84–92.
Brown T. Change by design: how design thinking can transform organizations and inspire innovation. New York: HarperCollins Publishers; 2009.
Kelley T. The art of innovation: lessons in creativity from IDEO. New York: Doubleday; 2001.
Lockwood T. Design thinking, integrating innovation, customer experience and brand value. New York: Allworth Press; 2010.
Brown T. Video Stanford executive briefings blob Kanopy: Kanopy; 2017. Available from: https://aut.kanopy.com/e83b95aa-4355-4f15-8ea6-f165987601a9
Hassi L, Laakso M, eds. Design thinking in the management discourse: defining the elements of the concept. IN: 18th international product development management conference, IPDMC; 2011.
Paparo M, Dosi C, Vignoli M, eds. Towards a DT mindset tool evaluation: factors identification from theory and practice. In: 21st international conference on engineering design (ICED17); 2017.
Boland RJ, Collopy F. Design matters for management’. In: Boland RJ, Collopy F (eds) Managing as designing. Stanford: Stanford University Press; 2004. p. 3–18
Dew N. Abduction: a pre-condition for the intelligent design of strategy. J Bus Strateg. 2007;28(4):38–45.
Holloway M. How tangible is your strategy? How design thinking can turn your strategy into reality. J Bus Strateg. 2009;30(2):50–6.
Carlgren L, Rauth I, Elmguist M. Framing design thinking: the concept in idea and enactment. Creat Innov Manag. 2016;25(1):38–57.
Clark K, Smith R. Unleashing the power of design thinking. Des Manag Rev. 2008;19(3):8–15.
Guterman J. How to become a better manager … by thinking like a designer. Interview with Nancy Duarte and Garr Reynolds. MIT Sloan Manag Rev. 2009;50(4):39-42.
Schweitzer J, Groeger L, Sobel L. The design thinking mindset: an assessment of what we know and what we see in practice journal of design. Bus Soc. 2016;2(1):71–94.
Grots A, Creuznacher I. Design thinking: process or culture?. In: Design thinking for innovation. Cham: Springer; 2016 p. 183–91.
Fraser HM. Designing business: new models for success. Des Manag Rev. 2009;20(2):56–65.
Kashdan TB, Gallagher MW, Silvia PJ, Winterstein BP, Breen WE, Terhar D, et al. The curiosity and exploration inventory-II: development, factor structure, and psychometrics. J Res Pers. 2009;43(6):987–98.
Yeager DS, Romero C, Paunesku D, Hulleman CS, Schneider B, Hinojosa C, et al. Using design thinking to improve psychological interventions: the case of the growth mindset during the transition to high school. J Educ Psychol. 2016;108(3):374–91.
McLain DL. Evidence of the properties of an ambiguity tolerance measure: the multiple stimulus types ambiguity tolerance scale–II (MSTAT–II). Psychol Rep. 2009;105(3):975–88.
Fraser HM. The practice of breakthrough strategies by design. J Bus Strateg. 2007;28(4):66–74.
Razzouk R, Shute VJ. What is design thinking and why is it important? Rev Educ Res. 2012;82(3):330–48.
Köppen E, Meinel C. Empathy via design thinking: creation of sense and knowledge. In: Plattner H, Meinel C, Leifer L, editors. Design thinking research: building innovators. Springer; 2015. p. 15–28.
Moore TW, Snider JB, Luchini M. Thinking style and emotional intelligence: an empirical investigation. J Behav Stud Bus. 2012;5:1.
Liedtka J. Perspective: linking design thinking with innovation outcomes through cognitive bias reduction. J Prod Innov Manag. 2015;32(6):925–38.
Fraser HM. Business design: becoming a bilateral thinker. Rotman Magaz. 2011:71–3.
Rylander A. Design thinking as knowledge work: epistemological foundations and practical implications. Des Manag J. 2009;4(1):7–19.
Howard Z. Understanding design thinking in practice: a qualitative study of design led professionals working with large organisations. Melbourne: Swinburne University of Technology; 2015.
Beckman SLS, Barry M. Innovation as a learning process: embedding design thinking. Calif Manag Rev. 2007;50(1):25–56.
Amabile TM. The social psychology of creativity: a componential conceptualization. J Pers Soc Psychol. 1983;45(2):357.
Kelley T, Kelley D. Creative confidence: unleashing the creative potential within us all. New York: Crown Business; 2012.
Dobni BC. Measuring innovation culture in organizations: the development of a generalized innovation culture construct using exploratory factor analysis. Eur J Innov Manag. 2008;11(4):539–59.
Drews C. Unleashing the full potential of design thinking as a business method. Des Manag Rev. 2009;20(3):39–44.
Junginger S. Learning to design: giving purpose to heart, hand and mind. J Bus Strateg. 2007;28(4):59–65.
Martin RL. The opposable mind: how successful leaders win through integrative thinking. Harvard Business Press; 2009.
Dunne D, Martin R. Design thinking and how it will change management education: an interview and discussion. Acad Manag Learn Educ. 2006;5(4):512–23.
Lockwood T. Transition: how to become a more design-minded organization. Des Manag Rev. 2009;20:28–37.
Sato S. Beyond good: great innovations through design. J Bus Strateg. 2009;30(2):40–9.
Porcini M. Your new design process is not enough—hire design thinkers! Des Manag Rev. 2009;20(3):6–18.
Carr SD, Halliday A, King AC, Liedtka J, Lookwood T. The influence of design thinking in business: some preliminary observations. Des Manag Rev. 2010;21(3):58–63.
Sato S, Lucente S, Meyer D, Mrazek D. Design thinking to make organization change and development more responsive. Des Manag Rev. 2010;21(2):44–52.
Ward A, Runcie E, Morris E. Embedding innovation: design thinking for small enterprises. J Bus Strateg. 2009;30(2):78–84.
Kolko J. Abductive thinking and sensemaking: the drivers of design synthesis. Des Issues. 2010;26(1):15–28.
Dong A, Lovallo D, Mounarath R. The effect of abductive reasoning on concept selection decisions. Des Stud. 2015;37:37–58.
TEDGlobal. Designers – THINK BIG! 2009.
Rajesh C. Change by design: Tim Brown 2016. Available from: https://medium.com/agileconnexions/change-by-design-tim-brown-2ed3271f6f19
Gray D. Empathy map canvas. Gamestorming; 2017.
Lee D. Design thinking in the classroom. Berkley: Ulysses Press; 2018.
Andersen E. Start the New Year like Albert Einstein forbes leadership: www.forbes.com ; 2011. Available from: https://www.forbes.com/sites/erikaandersen/2011/12/30/start-the-new-year-like-albert-einstein/#6c0b71293e12
Dam RF, Siang TY. Personas – a simple introduction. Interaction design foundation; 2020. Available from: https://www.interaction-design.org/literature/article/personas-why-and-how-you-should-use-them
123RF. Persona stock photos and images: 123RF. Available from: https://www.123rf.com/clipart-vector/persona.html?sti=o0j50e4s1bz6cjknld|
Bechter C, Farinelli G, Daniel R-D, Frey M. Advertising between archetype and brand personality. Administ Sci. 2016;6(5):1–12.
Dam RF, Teo YS. Essential ideation techniques 2020. Available from: https://www.interaction-design.org/literature/article/introduction-to-the-essential-ideation-techniques-which-are-the-heart-of-design-thinking
Chasanidou D, Gasparini A, Lee E. Design thinking methods and tools for innovation in multidisciplinary teams. Workshop Innovation in HCI; 2014.
Belski I, Hourani A, Valentine A, Belski A, eds. Can simple ideation techniques enhance idea generation? In: 25th annual conference of the Australasian Association for Engineering Education: engineering the knowledge economy: collaboration, engagement & employability. School of Engineering & Advanced Technology, Massey University; 2014.
Levy J. The brain power workout: 300 ways to improve your memory and creativity. New York: CICO Books; 2010.
Griffiths C, Costi M. The creative thinking handbook: your step-by-step guide to problem solving in business. New York: Kogan Page Ltd; 2019.
Dam RF, Siang TY. Stage 4 in the design thinking process: prototype 2020. Available from: https://www.interaction-design.org/literature/article/stage-4-in-the-design-thinking-process-prototype
Mortensen D. User research: what it is and why you should do it. https://www.interaction-design.org/literature/article/user-research-what-it-is-and-why-you-should-do-it2020 [1]. Available from: https://www.interaction-design.org/literature/article/user-research-what-it-is-and-why-you-should-do-it
Irwin L. Cultivating curiosity: Tirian. Available from: http://whokilledcreativity.com/articles/cultivating-curiosity/
Seidel VP, Fixson SK. Adopting design thinking in novice multidisciplinary teams: the application and limits of design methods and reflexive practices. J Prod Innov Manag. 2013;30:19–33.
Liedtka J, Ogilvie T. Designing for growth: a design thinking tool kit for managers. New York: Columbia University Press; 2011.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Auckland University of Technology, Auckland, New Zealand
Rouxelle de Villiers
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Rouxelle de Villiers .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations, creativity laboratory, 1.1 activity i: cognitive biases.
Explain how the DT process will overcome any four of the nine cognitive biases listed below. (Answers can be found in the paper by Jeanne Liedka ( [ 28 ], p. 930-931) (Table 11.4 )
1.2 Activity II: Empathy Map
Use the empathy map provided in Fig. 11.5 to consider a project or idea you need to “sell” to an antagonist. Try to “wear their/his/her shoes” for a day. Consider their pain points and the gains they might desire. Place yourself entirely in their shoes as you complete this map below. (You might like to copy a bigger version and consider a few rival positions or “enemies of the idea”). How does understanding their motivational drivers and their goals change the way you think about the way you might persuade them to buy into your idea?
Empathy map to facilitate persuasive idea sharing
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
de Villiers, R. (2022). Design Thinking as a Problem Solving Tool. In: de Villiers, R. (eds) The Handbook of Creativity & Innovation in Business. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-2180-3_11
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-2180-3_11
Published : 05 August 2022
Publisher Name : Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN : 978-981-19-2179-7
Online ISBN : 978-981-19-2180-3
eBook Packages : Business and Management Business and Management (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
Analysis of Algorithms
- Backtracking
- Dynamic Programming
- Divide and Conquer
- Geometric Algorithms
- Mathematical Algorithms
- Pattern Searching
- Bitwise Algorithms
- Branch & Bound
- Randomized Algorithms
- Algorithms Tutorial
- What is Algorithm | Introduction to Algorithms
- Definition, Types, Complexity and Examples of Algorithm
Algorithms Design Techniques
- Why the Analysis of Algorithm is important?
- Asymptotic Notation and Analysis (Based on input size) in Complexity Analysis of Algorithms
- Worst, Average and Best Case Analysis of Algorithms
- Types of Asymptotic Notations in Complexity Analysis of Algorithms
- How to Analyse Loops for Complexity Analysis of Algorithms
- How to analyse Complexity of Recurrence Relation
- Introduction to Amortized Analysis
Types of Algorithms
- Sorting Algorithms
- Searching Algorithms
- Greedy Algorithms
- Dynamic Programming or DP
- What is Pattern Searching ?
- Backtracking Algorithm
- Divide and Conquer Algorithm
- Graph Data Structure And Algorithms
- Branch and Bound Algorithm
- The Role of Algorithms in Computing
- Most important type of Algorithms
What is an algorithm? An Algorithm is a procedure to solve a particular problem in a finite number of steps for a finite-sized input. The algorithms can be classified in various ways. They are:
- Implementation Method
- Design Method
- Design Approaches
- Other Classifications
In this article, the different algorithms in each classification method are discussed.
The classification of algorithms is important for several reasons:
Organization: Algorithms can be very complex and by classifying them, it becomes easier to organize, understand, and compare different algorithms.
Problem Solving: Different problems require different algorithms, and by having a classification, it can help identify the best algorithm for a particular problem.
Performance Comparison: By classifying algorithms, it is possible to compare their performance in terms of time and space complexity, making it easier to choose the best algorithm for a particular use case.
Reusability: By classifying algorithms, it becomes easier to re-use existing algorithms for similar problems, thereby reducing development time and improving efficiency.
Research: Classifying algorithms is essential for research and development in computer science, as it helps to identify new algorithms and improve existing ones.
Overall, the classification of algorithms plays a crucial role in computer science and helps to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of solving problems. Classification by Implementation Method: There are primarily three main categories into which an algorithm can be named in this type of classification. They are:
- Recursion or Iteration: A recursive algorithm is an algorithm which calls itself again and again until a base condition is achieved whereas iterative algorithms use loops and/or data structures like stacks , queues to solve any problem. Every recursive solution can be implemented as an iterative solution and vice versa. Example: The Tower of Hanoi is implemented in a recursive fashion while Stock Span problem is implemented iteratively.
- Exact or Approximate: Algorithms that are capable of finding an optimal solution for any problem are known as the exact algorithm. For all those problems, where it is not possible to find the most optimized solution, an approximation algorithm is used. Approximate algorithms are the type of algorithms that find the result as an average outcome of sub outcomes to a problem. Example: For NP-Hard Problems , approximation algorithms are used. Sorting algorithms are the exact algorithms.
- Serial or Parallel or Distributed Algorithms: In serial algorithms, one instruction is executed at a time while parallel algorithms are those in which we divide the problem into subproblems and execute them on different processors. If parallel algorithms are distributed on different machines, then they are known as distributed algorithms.
Classification by Design Method: There are primarily three main categories into which an algorithm can be named in this type of classification. They are:
- Greedy Method: In the greedy method , at each step, a decision is made to choose the local optimum , without thinking about the future consequences. Example: Fractional Knapsack , Activity Selection .
- Divide and Conquer: The Divide and Conquer strategy involves dividing the problem into sub-problem, recursively solving them, and then recombining them for the final answer. Example: Merge sort , Quicksort .
- Dynamic Programming: The approach of Dynamic programming is similar to divide and conquer . The difference is that whenever we have recursive function calls with the same result, instead of calling them again we try to store the result in a data structure in the form of a table and retrieve the results from the table. Thus, the overall time complexity is reduced. “Dynamic” means we dynamically decide, whether to call a function or retrieve values from the table. Example: 0-1 Knapsack , subset-sum problem .
- Linear Programming: In Linear Programming, there are inequalities in terms of inputs and maximizing or minimizing some linear functions of inputs. Example: Maximum flow of Directed Graph
- Reduction(Transform and Conquer): In this method, we solve a difficult problem by transforming it into a known problem for which we have an optimal solution. Basically, the goal is to find a reducing algorithm whose complexity is not dominated by the resulting reduced algorithms. Example: Selection algorithm for finding the median in a list involves first sorting the list and then finding out the middle element in the sorted list. These techniques are also called transform and conquer.
- Backtracking: This technique is very useful in solving combinatorial problems that have a single unique solution . Where we have to find the correct combination of steps that lead to fulfillment of the task. Such problems have multiple stages and there are multiple options at each stage. This approach is based on exploring each available option at every stage one-by-one. While exploring an option if a point is reached that doesn’t seem to lead to the solution, the program control backtracks one step, and starts exploring the next option. In this way, the program explores all possible course of actions and finds the route that leads to the solution. Example: N-queen problem, maize problem.
- Branch and Bound: This technique is very useful in solving combinatorial optimization problem that have multiple solutions and we are interested in find the most optimum solution. In this approach, the entire solution space is represented in the form of a state space tree. As the program progresses each state combination is explored, and the previous solution is replaced by new one if it is not the optimal than the current solution. Example: Job sequencing, Travelling salesman problem.
Classification by Design Approaches : There are two approaches for designing an algorithm. these approaches include
- Top-Down Approach :
- Bottom-up approach
- Top-Down Approach: In the top-down approach, a large problem is divided into small sub-problem. and keep repeating the process of decomposing problems until the complex problem is solved.
- Bottom-up approach: The bottom-up approach is also known as the reverse of top-down approaches. In approach different, part of a complex program is solved using a programming language and then this is combined into a complete program.
Top-Down Approach:
Breaking down a complex problem into smaller, more manageable sub-problems and solving each sub-problem individually. Designing a system starting from the highest level of abstraction and moving towards the lower levels. Bottom-Up Approach:
Building a system by starting with the individual components and gradually integrating them to form a larger system. Solving sub-problems first and then using the solutions to build up to a solution of a larger problem. Note: Both approaches have their own advantages and disadvantages and the choice between them often depends on the specific problem being solved.
Here are examples of the Top-Down and Bottom-Up approaches in code:
Bottom-Up Approach (in Python):
Other Classifications: Apart from classifying the algorithms into the above broad categories, the algorithm can be classified into other broad categories like:
- Randomized Algorithms: Algorithms that make random choices for faster solutions are known as randomized algorithms . Example: Randomized Quicksort Algorithm .
- Classification by complexity: Algorithms that are classified on the basis of time taken to get a solution to any problem for input size. This analysis is known as time complexity analysis . Example: Some algorithms take O(n), while some take exponential time.
- Classification by Research Area: In CS each field has its own problems and needs efficient algorithms. Example: Sorting Algorithm, Searching Algorithm, Machine Learning etc.
- Branch and Bound Enumeration and Backtracking: These are mostly used in Artificial Intelligence.
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads, improve your coding skills with practice.
What kind of Experience do you want to share?

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Write out the problem. Your problem won't always come right out and say: "It's me, hi. I'm the problem, it's me.". In fact, something that often gets in the way of solving a problem is that we zero in on the wrong problem. When pinpointing a problem, you can try borrowing a UX research technique that's part of the design thinking ...
Software developers work on a range of tasks, from pure coding to system-level design and troubleshooting. Much of an engineer's time is spent "debugging" — that is, detecting and correcting errors and bugs in the code that cause the program to break or behave unexpectedly. Using a computer language is a lot like writing; understanding ...
It's even better if the members of the team are used to swim in uncertainty, and take it as a challenge more than a chore. The process described above is just an example; in practice it's often more chaotic. For example, even when a decision is made, your brain might still continue to process the problem passively.
To train the problem-solving side of your brain, these four tips and strategies can help you improve your abilities: 1. Make problem-solving a part of your life. Never restrict yourself to working on problems only during work hours. Don't make it a chore, but, instead, do things that make problem-solving look fun.
As you can see, problem solving plays a pivotal role in software engineering. Far from being an occasional requirement, it is the lifeblood that drives development forward, catalyzes innovation, and delivers of quality software. By leveraging problem-solving techniques, software engineers employ a powerful suite of strategies to overcome ...
1. Photo by Vardan Papikyan on Unsplash. Solving complex problems is one of the main attractions of software engineering for me. The combination of creativity and critical, logical thinking keeps me sharp and engaged in my work. Maybe it is the same for you. I love to dig into a problem and develop an elegant solution to a complex problem.
6. Discovery & Action Dialogue (DAD) One of the best approaches is to create a safe space for a group to share and discover practices and behaviors that can help them find their own solutions. With DAD, you can help a group choose which problems they wish to solve and which approaches they will take to do so.
Once the problem has been properly understood, we enter the core phase of problem solving: planning. This is the phase where we evaluate and devise the different solution strategies; here comes the time to brainstorm and breed the ideas that will allow us to produce quality software and achieve the project goals.
Visualize Data Flows. Another method of problem-solving skills is to think in terms of data flows for your development process. Point A is the problem you start with, and you need to move it to the destination at the end: the solution. Between the start of the process and destination, there are the arrows the data flows through, and then the boxes.
Software developers solve a diverse and wide range of problems. While software engineering research often focuses on tools to support this problem solving, the strategies that developers use to solve problems are at least as important. In this paper, we offer a novel approach for enabling developers to follow explicit programming strategies that describe how an expert tackles a common ...
January 10th, 2024 6 min read. Summary. The design thinking process is a problem-solving design methodology that helps you develop solutions in a human-focused way. Initially designed at Stanford's d.school, the five stage design thinking method can help solve ambiguous questions, or more open-ended problems. Learn how these five steps can ...
Use a systematic approach. 2. Explain your reasoning. Be the first to add your personal experience. 3. Learn from feedback. 4. Seek new challenges. Be the first to add your personal experience.
It primarily originates from software development and borrows from disciplines such as manufacturing and project management. ... Design thinking is a problem-solving methodology that helps teams better identify, understand, and solve business and customer problems. ... Design thinking methods and strategies belong at every level of the design ...
1Assess your skills. The first step is to identify your strengths and weaknesses as a problem solver. You can use self-assessment tools, such as online quizzes, surveys, or tests, to measure your ...
And design thinking is one way to make these interactions easy and intuitive. Design thinking restructures how a business executes ideas, plans strategies, and solves problems by repurposing its understanding of the end users. It identifies what they need the most by highlighting problem areas and empowers employees to address the issues ...
In software development, DT has been using as a problem-solving approach to support the understanding of the problem to be solved, to propose and to validate solutions that meet the users' needs (Alhazmi and Huang, 2020, Martins et al., 2019, Kuula et al., 2020), collaborating from early stages of software activities—from the elicitation of requirements (Hehn et al., 2020) to the creation ...
Step 1: Identify the Problem. The problem-solving process starts with identifying the problem. This step involves understanding the issue's nature, its scope, and its impact. Once the problem is clearly defined, it sets the foundation for finding effective solutions.
Problem-Solving Approach to Strategy Design and Implementation. The problem-solving approach to designing and implementing a strategy includes eight steps (see. Figure A): 1. Identify the Problem. 2. Analyze the Problem and Diagnose Its Causes. 3. Develop a Theory of Action.
Advertisements. Software Design Strategies - Software design is a process to conceptualize the software requirements into software implementation. Software design takes the user requirements as challenges and tries to find optimum solution. While the software is being conceptualized, a plan is chalked out to find the best possible design for i.
Abstract. In chapter 10 we covered thirteen ideation tools. We dedicate this chapter to Design Thinking (DT), as a procedure to generate and test ideas, and even more importantly as a creative problem-solving methodology. DT is a human-centred process that will help designers, innovators, entrepreneurs and business executives to systematically ...
Classification by Design Approaches : There are two approaches for designing an algorithm. these approaches include. Top-Down Approach: In the top-down approach, a large problem is divided into small sub-problem. and keep repeating the process of decomposing problems until the complex problem is solved.
Finding a suitable solution for issues can be accomplished by following the basic four-step problem-solving process and methodology outlined below. Step. Characteristics. 1. Define the problem. Differentiate fact from opinion. Specify underlying causes. Consult each faction involved for information. State the problem specifically.
C This paper is structured as follows. Section 2 explains the term complex problem solving and introduces associated challenges. Section 3 presents the course design for teaching complex problem solving in an engineering degree program. Section 4 con-trasts our work with related approaches.