- Privacy Policy

Home » Ethical Considerations – Types, Examples and Writing Guide

Ethical Considerations – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Ethical Considerations
Ethical considerations in research refer to the principles and guidelines that researchers must follow to ensure that their studies are conducted in an ethical and responsible manner. These considerations are designed to protect the rights, safety, and well-being of research participants, as well as the integrity and credibility of the research itself
Some of the key ethical considerations in research include:
- Informed consent: Researchers must obtain informed consent from study participants, which means they must inform participants about the study’s purpose, procedures, risks, benefits, and their right to withdraw at any time.
- Privacy and confidentiality : Researchers must ensure that participants’ privacy and confidentiality are protected. This means that personal information should be kept confidential and not shared without the participant’s consent.
- Harm reduction : Researchers must ensure that the study does not harm the participants physically or psychologically. They must take steps to minimize the risks associated with the study.
- Fairness and equity : Researchers must ensure that the study does not discriminate against any particular group or individual. They should treat all participants equally and fairly.
- Use of deception: Researchers must use deception only if it is necessary to achieve the study’s objectives. They must inform participants of the deception as soon as possible.
- Use of vulnerable populations : Researchers must be especially cautious when working with vulnerable populations, such as children, pregnant women, prisoners, and individuals with cognitive or intellectual disabilities.
- Conflict of interest : Researchers must disclose any potential conflicts of interest that may affect the study’s integrity. This includes financial or personal relationships that could influence the study’s results.
- Data manipulation: Researchers must not manipulate data to support a particular hypothesis or agenda. They should report the results of the study objectively, even if the findings are not consistent with their expectations.
- Intellectual property: Researchers must respect intellectual property rights and give credit to previous studies and research.
- Cultural sensitivity : Researchers must be sensitive to the cultural norms and beliefs of the participants. They should avoid imposing their values and beliefs on the participants and should be respectful of their cultural practices.
Types of Ethical Considerations
Types of Ethical Considerations are as follows:
Research Ethics:
This includes ethical principles and guidelines that govern research involving human or animal subjects, ensuring that the research is conducted in an ethical and responsible manner.
Business Ethics :
This refers to ethical principles and standards that guide business practices and decision-making, such as transparency, honesty, fairness, and social responsibility.
Medical Ethics :
This refers to ethical principles and standards that govern the practice of medicine, including the duty to protect patient autonomy, informed consent, confidentiality, and non-maleficence.
Environmental Ethics :
This involves ethical principles and values that guide our interactions with the natural world, including the obligation to protect the environment, minimize harm, and promote sustainability.
Legal Ethics
This involves ethical principles and standards that guide the conduct of legal professionals, including issues such as confidentiality, conflicts of interest, and professional competence.
Social Ethics
This involves ethical principles and values that guide our interactions with other individuals and society as a whole, including issues such as justice, fairness, and human rights.
Information Ethics
This involves ethical principles and values that govern the use and dissemination of information, including issues such as privacy, accuracy, and intellectual property.
Cultural Ethics
This involves ethical principles and values that govern the relationship between different cultures and communities, including issues such as respect for diversity, cultural sensitivity, and inclusivity.
Technological Ethics
This refers to ethical principles and guidelines that govern the development, use, and impact of technology, including issues such as privacy, security, and social responsibility.
Journalism Ethics
This involves ethical principles and standards that guide the practice of journalism, including issues such as accuracy, fairness, and the public interest.
Educational Ethics
This refers to ethical principles and standards that guide the practice of education, including issues such as academic integrity, fairness, and respect for diversity.
Political Ethics
This involves ethical principles and values that guide political decision-making and behavior, including issues such as accountability, transparency, and the protection of civil liberties.
Professional Ethics
This refers to ethical principles and standards that guide the conduct of professionals in various fields, including issues such as honesty, integrity, and competence.
Personal Ethics
This involves ethical principles and values that guide individual behavior and decision-making, including issues such as personal responsibility, honesty, and respect for others.
Global Ethics
This involves ethical principles and values that guide our interactions with other nations and the global community, including issues such as human rights, environmental protection, and social justice.
Applications of Ethical Considerations
Ethical considerations are important in many areas of society, including medicine, business, law, and technology. Here are some specific applications of ethical considerations:
- Medical research : Ethical considerations are crucial in medical research, particularly when human subjects are involved. Researchers must ensure that their studies are conducted in a way that does not harm participants and that participants give informed consent before participating.
- Business practices: Ethical considerations are also important in business, where companies must make decisions that are socially responsible and avoid activities that are harmful to society. For example, companies must ensure that their products are safe for consumers and that they do not engage in exploitative labor practices.
- Environmental protection: Ethical considerations play a crucial role in environmental protection, as companies and governments must weigh the benefits of economic development against the potential harm to the environment. Decisions about land use, resource allocation, and pollution must be made in an ethical manner that takes into account the long-term consequences for the planet and future generations.
- Technology development : As technology continues to advance rapidly, ethical considerations become increasingly important in areas such as artificial intelligence, robotics, and genetic engineering. Developers must ensure that their creations do not harm humans or the environment and that they are developed in a way that is fair and equitable.
- Legal system : The legal system relies on ethical considerations to ensure that justice is served and that individuals are treated fairly. Lawyers and judges must abide by ethical standards to maintain the integrity of the legal system and to protect the rights of all individuals involved.
Examples of Ethical Considerations
Here are a few examples of ethical considerations in different contexts:
- In healthcare : A doctor must ensure that they provide the best possible care to their patients and avoid causing them harm. They must respect the autonomy of their patients, and obtain informed consent before administering any treatment or procedure. They must also ensure that they maintain patient confidentiality and avoid any conflicts of interest.
- In the workplace: An employer must ensure that they treat their employees fairly and with respect, provide them with a safe working environment, and pay them a fair wage. They must also avoid any discrimination based on race, gender, religion, or any other characteristic protected by law.
- In the media : Journalists must ensure that they report the news accurately and without bias. They must respect the privacy of individuals and avoid causing harm or distress. They must also be transparent about their sources and avoid any conflicts of interest.
- In research: Researchers must ensure that they conduct their studies ethically and with integrity. They must obtain informed consent from participants, protect their privacy, and avoid any harm or discomfort. They must also ensure that their findings are reported accurately and without bias.
- In personal relationships : People must ensure that they treat others with respect and kindness, and avoid causing harm or distress. They must respect the autonomy of others and avoid any actions that would be considered unethical, such as lying or cheating. They must also respect the confidentiality of others and maintain their privacy.
How to Write Ethical Considerations
When writing about research involving human subjects or animals, it is essential to include ethical considerations to ensure that the study is conducted in a manner that is morally responsible and in accordance with professional standards. Here are some steps to help you write ethical considerations:
- Describe the ethical principles: Start by explaining the ethical principles that will guide the research. These could include principles such as respect for persons, beneficence, and justice.
- Discuss informed consent : Informed consent is a critical ethical consideration when conducting research. Explain how you will obtain informed consent from participants, including how you will explain the purpose of the study, potential risks and benefits, and how you will protect their privacy.
- Address confidentiality : Describe how you will protect the confidentiality of the participants’ personal information and data, including any measures you will take to ensure that the data is kept secure and confidential.
- Consider potential risks and benefits : Describe any potential risks or harms to participants that could result from the study and how you will minimize those risks. Also, discuss the potential benefits of the study, both to the participants and to society.
- Discuss the use of animals : If the research involves the use of animals, address the ethical considerations related to animal welfare. Explain how you will minimize any potential harm to the animals and ensure that they are treated ethically.
- Mention the ethical approval : Finally, it’s essential to acknowledge that the research has received ethical approval from the relevant institutional review board or ethics committee. State the name of the committee, the date of approval, and any specific conditions or requirements that were imposed.
When to Write Ethical Considerations
Ethical considerations should be written whenever research involves human subjects or has the potential to impact human beings, animals, or the environment in some way. Ethical considerations are also important when research involves sensitive topics, such as mental health, sexuality, or religion.
In general, ethical considerations should be an integral part of any research project, regardless of the field or subject matter. This means that they should be considered at every stage of the research process, from the initial planning and design phase to data collection, analysis, and dissemination.
Ethical considerations should also be written in accordance with the guidelines and standards set by the relevant regulatory bodies and professional associations. These guidelines may vary depending on the discipline, so it is important to be familiar with the specific requirements of your field.
Purpose of Ethical Considerations
Ethical considerations are an essential aspect of many areas of life, including business, healthcare, research, and social interactions. The primary purposes of ethical considerations are:
- Protection of human rights: Ethical considerations help ensure that people’s rights are respected and protected. This includes respecting their autonomy, ensuring their privacy is respected, and ensuring that they are not subjected to harm or exploitation.
- Promoting fairness and justice: Ethical considerations help ensure that people are treated fairly and justly, without discrimination or bias. This includes ensuring that everyone has equal access to resources and opportunities, and that decisions are made based on merit rather than personal biases or prejudices.
- Promoting honesty and transparency : Ethical considerations help ensure that people are truthful and transparent in their actions and decisions. This includes being open and honest about conflicts of interest, disclosing potential risks, and communicating clearly with others.
- Maintaining public trust: Ethical considerations help maintain public trust in institutions and individuals. This is important for building and maintaining relationships with customers, patients, colleagues, and other stakeholders.
- Ensuring responsible conduct: Ethical considerations help ensure that people act responsibly and are accountable for their actions. This includes adhering to professional standards and codes of conduct, following laws and regulations, and avoiding behaviors that could harm others or damage the environment.
Advantages of Ethical Considerations
Here are some of the advantages of ethical considerations:
- Builds Trust : When individuals or organizations follow ethical considerations, it creates a sense of trust among stakeholders, including customers, clients, and employees. This trust can lead to stronger relationships and long-term loyalty.
- Reputation and Brand Image : Ethical considerations are often linked to a company’s brand image and reputation. By following ethical practices, a company can establish a positive image and reputation that can enhance its brand value.
- Avoids Legal Issues: Ethical considerations can help individuals and organizations avoid legal issues and penalties. By adhering to ethical principles, companies can reduce the risk of facing lawsuits, regulatory investigations, and fines.
- Increases Employee Retention and Motivation: Employees tend to be more satisfied and motivated when they work for an organization that values ethics. Companies that prioritize ethical considerations tend to have higher employee retention rates, leading to lower recruitment costs.
- Enhances Decision-making: Ethical considerations help individuals and organizations make better decisions. By considering the ethical implications of their actions, decision-makers can evaluate the potential consequences and choose the best course of action.
- Positive Impact on Society: Ethical considerations have a positive impact on society as a whole. By following ethical practices, companies can contribute to social and environmental causes, leading to a more sustainable and equitable society.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

How to Cite Research Paper – All Formats and...

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Paper Format – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
6.3 Principles of Research Ethics
There are general ethical principles that guide and underpin the proper conduct of research. The term “ethical principles” refers to those general rules that operate as a foundational rationale for the numerous specific ethical guidelines and assessments of human behaviour. 7 The National Statement on ‘ethical conduct in human research’ states that ethical behaviour entails acting with integrity, motivated by a deep respect and concern for others. 8 Before research can be conducted, it is essential for researchers to develop and submit to a relevant human research ethics committee a research proposal that meets the National Statement’s requirements and is ethically acceptable. There are five key ethical research principles – respect for autonomy, beneficence, non-maleficence, and justice 8, 9 (Figure 6.1). These principles are universal, which means they apply everywhere in the world, without national, cultural, legal, or economic boundaries. Therefore, everyone involved in human research studies should understand and follow these principles.
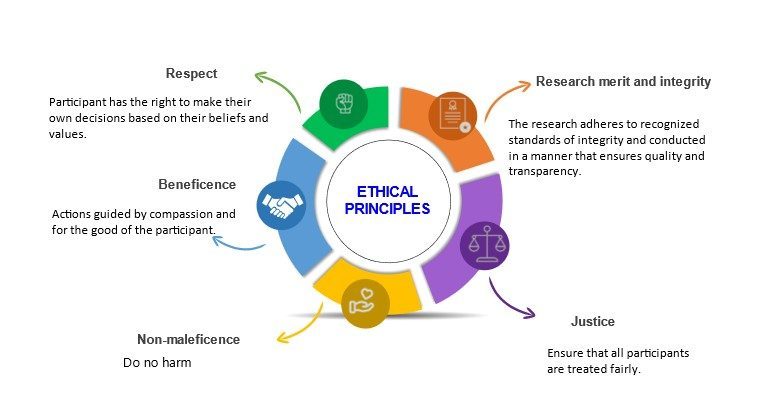
Research merit and integrity
Research merit and integrity relate to the quality or value of a study in contributing to the knowledge base of a particular field or discipline. 8,9 This is determined by the originality and significance of the research question, the soundness and appropriateness of the research methodology, the rigor and reliability of the data analysis, the clarity and coherence of the research findings, and the potential impact of the research on advancing knowledge or solving practical problems. Research must be developed with methods that are appropriate to the study’s objectives, based on a thorough analysis of the relevant literature, and conducted using facilities and resources that are appropriate for the study’s needs. In essence, research must adhere to recognised standards of integrity and be designed, reviewed and conducted in a manner that ensures quality and transparency. 8 Examples of unacceptable practices include plagiarism through appropriation or use of the ideas or intellectual property of others; falsification by creating false data or other aspects of research (including documentation and consent of participants); distortion through improper manipulation and/or selection of data, images and/or consent.
Respect for persons
Respect for humans is an acknowledgement of their inherent worth, and it refers to the moral imperative to regard the autonomy of others. 8,10 Respect entails taking into account the well-being, beliefs, perspectives, practises, and cultural heritage of persons participating in research, individually and collectively. It involves respecting the participants’ privacy, confidentiality, and cultural sensitivity. 8 Respect also entails giving adequate consideration to people to make their judgements throughout the study process. In cases where the participants have limited capacity to make autonomous decisions, respect for them entails protecting them against harm. 8 This means that all participants in research must participate voluntarily without coercion or undue influence, and their rights, dignity and autonomy should be respected and adequately protected.
Beneficence
The ethical principle that requires actions that promote the well-being and interests of others is known as beneficence. 10 It is the fundamental premise underlying all medical health care and research. 8 Beneficence requires the researcher to weigh the prospective benefits and hazards and make certain that projects have the potential for net benefit over harm. 8,10 Researchers are responsible for: (a) structuring the study to minimise the risks of injury or discomfort to participants; (b) explaining the possible benefits and dangers of the research to participants; and (c) the welfare of the participants in the research setting 8. Thus, the study participants must always be prioritised over the research methodology, even if this means invalidating data. 8
Non-maleficence
This is the ethical principle that requires actions that avoid or minimize harm to others. According to the principle of non-maleficence, participating in a study shouldn’t do any harm to the research subject. This principle is closely related to beneficence; however, it may be difficult to keep track of any damage to study participants. 11 Different types of harm could occur, including physical, mental, social, or financial harm. While the physical injury may be quickly recognised and then avoided or reduced, less evident issues such as emotional, social, and economic factors might hurt the subject without the researcher being aware. 11 It is essential to note that all research involve cost to participants even if just their time, and each research study has the potential to hurt participants, hence it is important to ensure that the merit of research outweighs the costs and risks. There are five categories into which studies may be categorised based on the possible amount of injury or discomfort that they may expose the participants to. 11
- No anticipated effects
- Temporary discomfort
- Unusual levels of temporary discomfort
- Risk of permanent damage
- Certainty of permanent damage
The concept of fairness and the application of moral principles to ensure equitable treatment. According to this research tenet, the researcher must treat participants fairly and always prioritise the needs of the research subjects over the study’s aim. 8,11 Research participants must be fairly chosen, and that exclusion and inclusion criteria must be accurately stated in the research’s findings. 8 In addition, there is no unjust hardship associated with participating in research on certain groups, and the participant recruitment method is fair. Furthermore, the rewards for research involvement are fairly distributed; research participants are not exploited, and research rewards are accessible to everybody equally. 8
An Introduction to Research Methods for Undergraduate Health Profession Students Copyright © 2023 by Faith Alele and Bunmi Malau-Aduli is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.

Ethical Considerations
Ethical Considerations can be specified as one of the most important parts of the research. Dissertations may even be doomed to failure if this part is missing.
According to Bryman and Bell (2007) [1] the following ten points represent the most important principles related to ethical considerations in dissertations:
- Research participants should not be subjected to harm in any ways whatsoever.
- Respect for the dignity of research participants should be prioritised.
- Full consent should be obtained from the participants prior to the study.
- The protection of the privacy of research participants has to be ensured.
- Adequate level of confidentiality of the research data should be ensured.
- Anonymity of individuals and organisations participating in the research has to be ensured.
- Any deception or exaggeration about the aims and objectives of the research must be avoided.
- Affiliations in any forms, sources of funding, as well as any possible conflicts of interests have to be declared.
- Any type of communication in relation to the research should be done with honesty and transparency.
- Any type of misleading information, as well as representation of primary data findings in a biased way must be avoided.
In order to address ethical considerations aspect of your dissertation in an effective manner, you will need to expand discussions of each of the following points to at least one paragraph:
1. Voluntary participation of respondents in the research is important. Moreover, participants have rights to withdraw from the study at any stage if they wish to do so.
2. Respondents should participate on the basis of informed consent. The principle of informed consent involves researchers providing sufficient information and assurances about taking part to allow individuals to understand the implications of participation and to reach a fully informed, considered and freely given decision about whether or not to do so, without the exercise of any pressure or coercion. [2]
3. The use of offensive, discriminatory, or other unacceptable language needs to be avoided in the formulation of Questionnaire/Interview/Focus group questions.
4. Privacy and anonymity or respondents is of a paramount importance.
5. Acknowledgement of works of other authors used in any part of the dissertation with the use of Harvard/APA/Vancouver referencing system according to the Dissertation Handbook
6. Maintenance of the highest level of objectivity in discussions and analyses throughout the research
7. Adherence to Data Protection Act (1998) if you are studying in the UK
In studies that do not involve primary data collection, on the other hand, ethical issues are going to be limited to the points d) and e) above.
Most universities have their own Code of Ethical Practice. It is critically important for you to thoroughly adhere to this code in every aspect of your research and declare your adherence in ethical considerations part of your dissertation.
My e-book, The Ultimate Guide to Writing a Dissertation in Business Studies: a step by step assistance offers practical assistance to complete a dissertation with minimum or no stress. The e-book covers all stages of writing a dissertation starting from the selection to the research area to submitting the completed version of the work within the deadline. John Dudovskiy

[1] Bryman, A. & Bell, E. (2007) “Business Research Methods”, 2nd edition. Oxford University Press.
[2] Saunders, M., Lewis, P. & Thornhill, A. (2012) “Research Methods for Business Students” 6th edition, Pearson Education Limited.

What Are the Ethical Considerations in Research Design?
When I began my work on the thesis I was always focused on my research. However, once I began to make my way through research, I realized that research ethics is a core aspect of the research work and the foundation of research design.
Research ethics play a crucial role in ensuring the responsible conduct of research. Here are some key reasons why research ethics matter:

Let us look into some of the major ethical considerations in research design.
Ethical Issues in Research
There are many organizations, like the Committee on Publication Ethics , dedicated to promoting ethics in scientific research. These organizations agree that ethics is not an afterthought or side note to the research study. It is an integral aspect of research that needs to remain at the forefront of our work.
The research design must address specific research questions. Hence, the conclusions of the study must correlate to the questions posed and the results. Also, research ethics demands that the methods used must relate specifically to the research questions.
Voluntary Participation and Consent
An individual should at no point feel any coercion to participate in a study. This includes any type of persuasion or deception in attempting to gain an individual’s trust.
Informed consent states that an individual must give their explicit consent to participate in the study. You can think of consent form as an agreement of trust between the researcher and the participants.
Sampling is the first step in research design . You will need to explain why you want a particular group of participants. You will have to explain why you left out certain people or groups. In addition, if your sample includes children or special needs individuals, you will have additional requirements to address like parental permission.
Confidentiality
The third ethics principle of the Economic and Social Research Council (ESRC) states that: “The confidentiality of the information supplied by research subjects and the anonymity of respondents must be respected.” However, sometimes confidentiality is limited. For example, if a participant is at risk of harm, we must protect them. This might require releasing confidential information.
Risk of Harm
We should do everything in our power to protect study participants. For this, we should focus on the risk to benefit ratio. If possible risks outweigh the benefits, then we should abandon or redesign the study. Risk of harm also requires us to measure the risk to benefit ratio as the study progresses.
Research Methods
We know there are numerous research methods. However, when it comes to ethical considerations, some key questions can help us find the right approach for our studies.
i. Which methods most effectively fit the aims of your research?
ii. What are the strengths and restrictions of a particular method?
iii. Are there potential risks when using a particular research method?
For more guidance, you can refer to the ESRC Framework for Research Ethics .
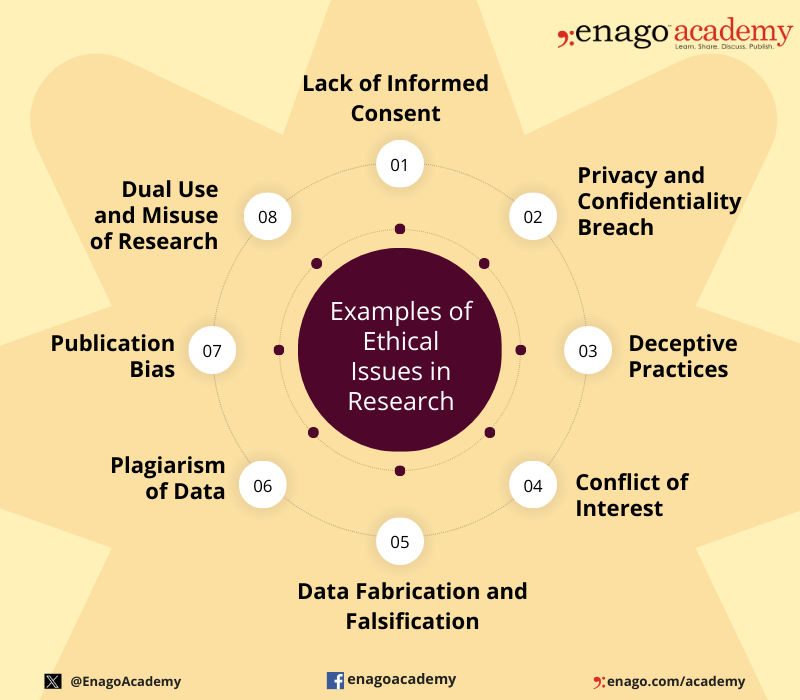
Ethical issues in research can arise at various stages of the research process and involve different aspects of the study. Here are some common examples of ethical issues in research:
Institutional Review Boards
The importance of ethics in research cannot be understated. Following ethical guidelines will ensure your study’s validity and promote its contribution to scientific study. On a personal level, you will strengthen your research and increase your opportunities to gain funding.
To address the need for ethical considerations, most institutions have their own Institutional Review Board (IRB). An IRB secures the safety of human participants and prevents violation of human rights. It reviews the research aims and methodologies to ensure ethical practices are followed. If a research design does not follow the set ethical guidelines, then the researcher will have to amend their study.
Applying for Ethical Approval
Applications for ethical approval will differ across institutions. Regardless, they focus on the benefits of your research and the risk to benefit ratio concerning participants. Therefore, you need to effectively address both in order to get ethical clearence.
Participants
It is vital that you make it clear that individuals are provided with sufficient information in order to make an informed decision on their participation. In addition, you need to demonstrate that the ethical issues of consent, risk of harm, and confidentiality are clearly defined.
Benefits of the Study
You need to prove to the panel that your work is essential and will yield results that contribute to the scientific community. For this, you should demonstrate the following:
i. The conduct of research guarantees the quality and integrity of results.
ii. The research will be properly distributed.
iii. The aims of the research are clear and the methodology is appropriate.
Integrity and transparency are vital in the research. Ethics committees expect you to share any actual or potential conflicts of interest that could affect your work. In addition, you have to be honest and transparent throughout the approval process and the research process.
The Dangers of Unethical Practices
There is a reason to follow ethical guidelines. Without these guidelines, our research will suffer. Moreover, more importantly, people could suffer.
The following are just two examples of infamous cases of unethical research practices that demonstrate the importance of adhering to ethical standards:
- The Stanford Prison Experiment (1971) aimed to investigate the psychological effects of power using the relationship between prisoners and prison officers. Those assigned the role of “prison officers” embraced measures that exposed “prisoners” to psychological and physical harm. In this case, there was voluntary participation. However, there was disregard for welfare of the participants.
- Recently, Chinese scientist He Jiankui announced his work on genetically edited babies . Over 100 Chinese scientists denounced this research, calling it “crazy” and “shocking and unacceptable.” This research shows a troubling attitude of “do first, debate later” and a disregard for the ethical concerns of manipulating the human body Wang Yuedan, a professor of immunology at Peking University, calls this “an ethics disaster for the world” and demands strict punishments for this type of ethics violation.
What are your experiences with research ethics? How have you developed an ethical approach to research design? Please share your thoughts with us in the comments section below.
I love the articulation of reasoning and practical examples of unethical research
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- AI in Academia
- Trending Now
6 Leading AI Detection Tools for Academic Writing — A comparative analysis
The advent of AI content generators, exemplified by advanced models like ChatGPT, Claude AI, and…

- Reporting Research
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for data interpretation
In research, choosing the right approach to understand data is crucial for deriving meaningful insights.…

- Industry News
China’s Ministry of Education Spearheads Efforts to Uphold Academic Integrity
In response to the increase in retractions of research papers submitted by Chinese scholars to…

Comparing Cross Sectional and Longitudinal Studies: 5 steps for choosing the right approach
The process of choosing the right research design can put ourselves at the crossroads of…

- Publishing Research
- Understanding Ethics
Understanding the Difference Between Research Ethics and Compliance
Ethics refers to the principles, values, and moral guidelines that guide individual or group behavior…
Unlocking the Power of Networking in Academic Conferences
Intersectionality in Academia: Dealing with diverse perspectives
Meritocracy and Diversity in Science: Increasing inclusivity in STEM education
Avoiding the AI Trap: Pitfalls of relying on ChatGPT for PhD applications

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Springer Nature - PMC COVID-19 Collection

Ethical Issues in Research: Perceptions of Researchers, Research Ethics Board Members and Research Ethics Experts
Marie-josée drolet.
1 Department of Occupational Therapy (OT), Université du Québec à Trois-Rivières (UQTR), Trois-Rivières (Québec), Canada
Eugénie Rose-Derouin
2 Bachelor OT program, Université du Québec à Trois-Rivières (UQTR), Trois-Rivières (Québec), Canada
Julie-Claude Leblanc
Mélanie ruest, bryn williams-jones.
3 Department of Social and Preventive Medicine, School of Public Health, Université de Montréal, Montréal (Québec), Canada
In the context of academic research, a diversity of ethical issues, conditioned by the different roles of members within these institutions, arise. Previous studies on this topic addressed mainly the perceptions of researchers. However, to our knowledge, no studies have explored the transversal ethical issues from a wider spectrum, including other members of academic institutions as the research ethics board (REB) members, and the research ethics experts. The present study used a descriptive phenomenological approach to document the ethical issues experienced by a heterogeneous group of Canadian researchers, REB members, and research ethics experts. Data collection involved socio-demographic questionnaires and individual semi-structured interviews. Following the triangulation of different perspectives (researchers, REB members and ethics experts), emerging ethical issues were synthesized in ten units of meaning: (1) research integrity, (2) conflicts of interest, (3) respect for research participants, (4) lack of supervision and power imbalances, (5) individualism and performance, (6) inadequate ethical guidance, (7) social injustices, (8) distributive injustices, (9) epistemic injustices, and (10) ethical distress. This study highlighted several problematic elements that can support the identification of future solutions to resolve transversal ethical issues in research that affect the heterogeneous members of the academic community.
Introduction
Research includes a set of activities in which researchers use various structured methods to contribute to the development of knowledge, whether this knowledge is theoretical, fundamental, or applied (Drolet & Ruest, accepted ). University research is carried out in a highly competitive environment that is characterized by ever-increasing demands (i.e., on time, productivity), insufficient access to research funds, and within a market economy that values productivity and speed often to the detriment of quality or rigour – this research context creates a perfect recipe for breaches in research ethics, like research misbehaviour or misconduct (i.e., conduct that is ethically questionable or unacceptable because it contravenes the accepted norms of responsible conduct of research or compromises the respect of core ethical values that are widely held by the research community) (Drolet & Girard, 2020 ; Sieber, 2004 ). Problematic ethics and integrity issues – e.g., conflicts of interest, falsification of data, non-respect of participants’ rights, and plagiarism, to name but a few – have the potential to both undermine the credibility of research and lead to negative consequences for many stakeholders, including researchers, research assistants and personnel, research participants, academic institutions, and society as a whole (Drolet & Girard, 2020 ). It is thus evident that the academic community should be able to identify these different ethical issues in order to evaluate the nature of the risks that they pose (and for whom), and then work towards their prevention or management (i.e., education, enhanced policies and procedures, risk mitigation strategies).
In this article, we define an “ethical issue” as any situation that may compromise, in whole or in part, the respect of at least one moral value (Swisher et al., 2005 ) that is considered socially legitimate and should thus be respected. In general, ethical issues occur at three key moments or stages of the research process: (1) research design (i.e., conception, project planning), (2) research conduct (i.e., data collection, data analysis) and (3) knowledge translation or communication (e.g., publications of results, conferences, press releases) (Drolet & Ruest, accepted ). According to Sieber ( 2004 ), ethical issues in research can be classified into five categories, related to: (a) communication with participants and the community, (b) acquisition and use of research data, (c) external influence on research, (d) risks and benefits of the research, and (e) selection and use of research theories and methods. Many of these issues are related to breaches of research ethics norms, misbehaviour or research misconduct. Bruhn et al., ( 2002 ) developed a typology of misbehaviour and misconduct in academia that can be used to judge the seriousness of different cases. This typology takes into consideration two axes of reflection: (a) the origin of the situation (i.e., is it the researcher’s own fault or due to the organizational context?), and (b) the scope and severity (i.e., is this the first instance or a recurrent behaviour? What is the nature of the situation? What are the consequences, for whom, for how many people, and for which organizations?).
A previous detailed review of the international literature on ethical issues in research revealed several interesting findings (Beauchemin et al., 2021 ). Indeed, the current literature is dominated by descriptive ethics, i.e., the sharing by researchers from various disciplines of the ethical issues they have personally experienced. While such anecdotal documentation is relevant, it is insufficient because it does not provide a global view of the situation. Among the reviewed literature, empirical studies were in the minority (Table 1 ) – only about one fifth of the sample (n = 19) presented empirical research findings on ethical issues in research. The first of these studies was conducted almost 50 years ago (Hunt et al., 1984 ), with the remainder conducted in the 1990s. Eight studies were conducted in the United States (n = 8), five in Canada (n = 5), three in England (n = 3), two in Sweden (n = 2) and one in Ghana (n = 1).
Summary of Empirical Studies on Ethical Issues in Research by the year of publication
Further, the majority of studies in our sample (n = 12) collected the perceptions of a homogeneous group of participants, usually researchers (n = 14) and sometimes health professionals (n = 6). A minority of studies (n = 7) triangulated the perceptions of diverse research stakeholders (i.e., researchers and research participants, or students). To our knowledge, only one study has examined perceptions of ethical issues in research by research ethics board members (REB; Institutional Review Boards [IRB] in the USA), and none to date have documented the perceptions of research ethics experts. Finally, nine studies (n = 9) adopted a qualitative design, seven studies (n = 7) a quantitative design, and three (n = 3) a mixed-methods design.
More studies using empirical research methods are needed to better identify broader trends, to enrich discussions on the values that should govern responsible conduct of research in the academic community, and to evaluate the means by which these values can be supported in practice (Bahn, 2012 ; Beauchemin et al., 2021 ; Bruhn et al., 2002 ; Henderson et al., 2013 ; Resnik & Elliot, 2016; Sieber 2004 ). To this end, we conducted an empirical qualitative study to document the perceptions and experiences of a heterogeneous group of Canadian researchers, REB members, and research ethics experts, to answer the following broad question: What are the ethical issues in research?
Research Methods
Research design.
A qualitative research approach involving individual semi-structured interviews was used to systematically document ethical issues (De Poy & Gitlin, 2010 ; Hammell et al., 2000 ). Specifically, a descriptive phenomenological approach inspired by the philosophy of Husserl was used (Husserl, 1970 , 1999 ), as it is recommended for documenting the perceptions of ethical issues raised by various practices (Hunt & Carnavale, 2011 ).
Ethical considerations
The principal investigator obtained ethics approval for this project from the Research Ethics Board of the Université du Québec à Trois-Rivières (UQTR). All members of the research team signed a confidentiality agreement, and research participants signed the consent form after reading an information letter explaining the nature of the research project.
Sampling and recruitment
As indicated above, three types of participants were sought: (1) researchers from different academic disciplines conducting research (i.e., theoretical, fundamental or empirical) in Canadian universities; (2) REB members working in Canadian organizations responsible for the ethical review, oversight or regulation of research; and (3) research ethics experts, i.e., academics or ethicists who teach research ethics, conduct research in research ethics, or are scholars who have acquired a specialization in research ethics. To be included in the study, participants had to work in Canada, speak and understand English or French, and be willing to participate in the study. Following Thomas and Polio’s (2002) recommendation to recruit between six and twelve participants (for a homogeneous sample) to ensure data saturation, for our heterogeneous sample, we aimed to recruit approximately twelve participants in order to obtain data saturation. Having used this method several times in related projects in professional ethics, data saturation is usually achieved with 10 to 15 participants (Drolet & Goulet, 2018 ; Drolet & Girard, 2020 ; Drolet et al., 2020 ). From experience, larger samples only serve to increase the degree of data saturation, especially in heterogeneous samples (Drolet et al., 2017 , 2019 ; Drolet & Maclure, 2016 ).
Purposive sampling facilitated the identification of participants relevant to documenting the phenomenon in question (Fortin, 2010 ). To ensure a rich and most complete representation of perceptions, we sought participants with varied and complementary characteristics with regards to the social roles they occupy in research practice (Drolet & Girard, 2020 ). A triangulation of sources was used for the recruitment (Bogdan & Biklen, 2006 ). The websites of Canadian universities and Canadian health institution REBs, as well as those of major Canadian granting agencies (i.e., the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada, and the Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council of Canada, Fonds de recherche du Quebec), were searched to identify individuals who might be interested in participating in the study. Further, people known by the research team for their knowledge and sensitivity to ethical issues in research were asked to participate. Research participants were also asked to suggest other individuals who met the study criteria.
Data Collection
Two tools were used for data collecton: (a) a socio-demographic questionnaire, and (b) a semi-structured individual interview guide. English and French versions of these two documents were used and made available, depending on participant preferences. In addition, although the interview guide contained the same questions, they were adapted to participants’ specific roles (i.e., researcher, REB member, research ethics expert). When contacted by email by the research assistant, participants were asked to confirm under which role they wished to participate (because some participants might have multiple, overlapping responsibilities) and they were sent the appropriate interview guide.
The interview guides each had two parts: an introduction and a section on ethical issues. The introduction consisted of general questions to put the participant at ease (i.e., “Tell me what a typical day at work is like for you”). The section on ethical issues was designed to capture the participant’s perceptions through questions such as: “Tell me three stories you have experienced at work that involve an ethical issue?” and “Do you feel that your organization is doing enough to address, manage, and resolve ethical issues in your work?”. Although some interviews were conducted in person, the majority were conducted by videoconference to promote accessibility and because of the COVID-19 pandemic. Interviews were digitally recorded so that the verbatim could be transcribed in full, and varied between 40 and 120 min in duration, with an average of 90 min. Research assistants conducted the interviews and transcribed the verbatim.
Data Analysis
The socio-demographic questionnaires were subjected to simple descriptive statistical analyses (i.e., means and totals), and the semi-structured interviews were subjected to qualitative analysis. The steps proposed by Giorgi ( 1997 ) for a Husserlian phenomenological reduction of the data were used. After collecting, recording, and transcribing the interviews, all verbatim were analyzed by at least two analysts: a research assistant (2nd author of this article) and the principal investigator (1st author) or a postdoctoral fellow (3rd author). The repeated reading of the verbatim allowed the first analyst to write a synopsis, i.e., an initial extraction of units of meaning. The second analyst then read the synopses, which were commented and improved if necessary. Agreement between analysts allowed the final drafting of the interview synopses, which were then analyzed by three analysts to generate and organize the units of meaning that emerged from the qualitative data.
Participants
Sixteen individuals (n = 16) participated in the study, of whom nine (9) identified as female and seven (7) as male (Table 2 ). Participants ranged in age from 22 to 72 years, with a mean age of 47.5 years. Participants had between one (1) and 26 years of experience in the research setting, with an average of 14.3 years of experience. Participants held a variety of roles, including: REB members (n = 11), researchers (n = 10), research ethics experts (n = 4), and research assistant (n = 1). As mentioned previously, seven (7) participants held more than one role, i.e., REB member, research ethics expert, and researcher. The majority (87.5%) of participants were working in Quebec, with the remaining working in other Canadian provinces. Although all participants considered themselves to be francophone, one quarter (n = 4) identified themselves as belonging to a cultural minority group.
Description of Participants
With respect to their academic background, most participants (n = 9) had a PhD, three (3) had a post-doctorate, two (2) had a master’s degree, and two (2) had a bachelor’s degree. Participants came from a variety of disciplines: nine (9) had a specialty in the humanities or social sciences, four (4) in the health sciences and three (3) in the natural sciences. In terms of their knowledge of ethics, five (5) participants reported having taken one university course entirely dedicated to ethics, four (4) reported having taken several university courses entirely dedicated to ethics, three (3) had a university degree dedicated to ethics, while two (2) only had a few hours or days of training in ethics and two (2) reported having no knowledge of ethics.
Ethical issues
As Fig. 1 illustrates, ten units of meaning emerge from the data analysis, namely: (1) research integrity, (2) conflicts of interest, (3) respect for research participants, (4) lack of supervision and power imbalances, (5) individualism and performance, (6) inadequate ethical guidance, (7) social injustices, (8) distributive injustices, (9) epistemic injustices, and (10) ethical distress. To illustrate the results, excerpts from verbatim interviews are presented in the following sub-sections. Most of the excerpts have been translated into English as the majority of interviews were conducted with French-speaking participants.

Ethical issues in research according to the participants
Research Integrity
The research environment is highly competitive and performance-based. Several participants, in particular researchers and research ethics experts, felt that this environment can lead both researchers and research teams to engage in unethical behaviour that reflects a lack of research integrity. For example, as some participants indicated, competition for grants and scientific publications is sometimes so intense that researchers falsify research results or plagiarize from colleagues to achieve their goals.
Some people will lie or exaggerate their research findings in order to get funding. Then, you see it afterwards, you realize: “ah well, it didn’t work, but they exaggerated what they found and what they did” (participant 14). Another problem in research is the identification of authors when there is a publication. Very often, there are authors who don’t even know what the publication is about and that their name is on it. (…) The time that it surprised me the most was just a few months ago when I saw someone I knew who applied for a teaching position. He got it I was super happy for him. Then I looked at his publications and … there was one that caught my attention much more than the others, because I was in it and I didn’t know what that publication was. I was the second author of a publication that I had never read (participant 14). I saw a colleague who had plagiarized another colleague. [When the colleague] found out about it, he complained. So, plagiarism is a serious [ethical breach]. I would also say that there is a certain amount of competition in the university faculties, especially for grants (…). There are people who want to win at all costs or get as much as possible. They are not necessarily going to consider their colleagues. They don’t have much of a collegial spirit (participant 10).
These examples of research misbehaviour or misconduct are sometimes due to or associated with situations of conflicts of interest, which may be poorly managed by certain researchers or research teams, as noted by many participants.
Conflict of interest
The actors and institutions involved in research have diverse interests, like all humans and institutions. As noted in Chap. 7 of the Canadian Tri-Council Policy Statement: Ethical Conduct for Research Involving Humans (TCPS2, 2018),
“researchers and research students hold trust relationships, either directly or indirectly, with participants, research sponsors, institutions, their professional bodies and society. These trust relationships can be put at risk by conflicts of interest that may compromise independence, objectivity or ethical duties of loyalty. Although the potential for such conflicts has always existed, pressures on researchers (i.e., to delay or withhold dissemination of research outcomes or to use inappropriate recruitment strategies) heighten concerns that conflicts of interest may affect ethical behaviour” (p. 92).
The sources of these conflicts are varied and can include interpersonal conflicts, financial partnerships, third-party pressures, academic or economic interests, a researcher holding multiple roles within an institution, or any other incentive that may compromise a researcher’s independence, integrity, and neutrality (TCPS2, 2018). While it is not possible to eliminate all conflicts of interest, it is important to manage them properly and to avoid temptations to behave unethically.
Ethical temptations correspond to situations in which people are tempted to prioritize their own interests to the detriment of the ethical goods that should, in their own context, govern their actions (Swisher et al., 2005 ). In the case of researchers, this refers to situations that undermine independence, integrity, neutrality, or even the set of principles that govern research ethics (TCPS2, 2018) or the responsible conduct of research. According to study participants, these types of ethical issues frequently occur in research. Many participants, especially researchers and REB members, reported that conflicts of interest can arise when members of an organization make decisions to obtain large financial rewards or to increase their academic profile, often at the expense of the interests of members of their research team, research participants, or even the populations affected by their research.
A company that puts money into making its drug work wants its drug to work. So, homeopathy is a good example, because there are not really any consequences of homeopathy, there are not very many side effects, because there are no effects at all. So, it’s not dangerous, but it’s not a good treatment either. But some people will want to make it work. And that’s a big issue when you’re sitting at a table and there are eight researchers, and there are two or three who are like that, and then there are four others who are neutral, and I say to myself, this is not science. I think that this is a very big ethical issue (participant 14). There are also times in some research where there will be more links with pharmaceutical companies. Obviously, there are then large amounts of money that will be very interesting for the health-care institutions because they still receive money for clinical trials. They’re still getting some compensation because its time consuming for the people involved and all that. The pharmaceutical companies have money, so they will compensate, and that is sometimes interesting for the institutions, and since we are a bit caught up in this, in the sense that we have no choice but to accept it. (…) It may not be the best research in the world, there may be a lot of side effects due to the drugs, but it’s good to accept it, we’re going to be part of the clinical trial (participant 3). It is integrity, what we believe should be done or said. Often by the pressure of the environment, integrity is in tension with the pressures of the environment, so it takes resistance, it takes courage in research. (…) There were all the debates there about the problems of research that was funded and then the companies kept control over what was written. That was really troubling for a lot of researchers (participant 5).
Further, these situations sometimes have negative consequences for research participants as reported by some participants.
Respect for research participants
Many research projects, whether they are psychosocial or biomedical in nature, involve human participants. Relationships between the members of research teams and their research participants raise ethical issues that can be complex. Research projects must always be designed to respect the rights and interests of research participants, and not just those of researchers. However, participants in our study – i.e., REB members, researchers, and research ethics experts – noted that some research teams seem to put their own interests ahead of those of research participants. They also emphasized the importance of ensuring the respect, well-being, and safety of research participants. The ethical issues related to this unit of meaning are: respect for free, informed and ongoing consent of research participants; respect for and the well-being of participants; data protection and confidentiality; over-solicitation of participants; ownership of the data collected on participants; the sometimes high cost of scientific innovations and their accessibility; balance between the social benefits of research and the risks to participants (particularly in terms of safety); balance between collective well-being (development of knowledge) and the individual rights of participants; exploitation of participants; paternalism when working with populations in vulnerable situations; and the social acceptability of certain types of research. The following excerpts present some of these issues.
Where it disturbs me ethically is in the medical field – because it’s more in the medical field that we’re going to see this – when consent forms are presented to patients to solicit them as participants, and then [these forms] have an average of 40 pages. That annoys me. When they say that it has to be easy to understand and all that, adapted to the language, and then the hyper-technical language plus there are 40 pages to read, I don’t understand how you’re going to get informed consent after reading 40 pages. (…) For me, it doesn’t work. I read them to evaluate them and I have a certain level of education and experience in ethics, and there are times when I don’t understand anything (participant 2). There is a lot of pressure from researchers who want to recruit research participants (…). The idea that when you enter a health care institution, you become a potential research participant, when you say “yes to a research, you check yes to all research”, then everyone can ask you. I think that researchers really have this fantasy of saying to themselves: “as soon as people walk through the door of our institution, they become potential participants with whom we can communicate and get them involved in all projects”. There’s a kind of idea that, yes, it can be done, but it has to be somewhat supervised to avoid over-solicitation (…). Researchers are very interested in facilitating recruitment and making it more fluid, but perhaps to the detriment of confidentiality, privacy, and respect; sometimes that’s what it is, to think about what type of data you’re going to have in your bank of potential participants? Is it just name and phone number or are you getting into more sensitive information? (participant 9).
In addition, one participant reported that their university does not provide the resources required to respect the confidentiality of research participants.
The issue is as follows: researchers, of course, commit to protecting data with passwords and all that, but we realize that in practice, it is more difficult. It is not always as protected as one might think, because professor-researchers will run out of space. Will the universities make rooms available to researchers, places where they can store these things, especially when they have paper documentation, and is there indeed a guarantee of confidentiality? Some researchers have told me: “Listen; there are even filing cabinets in the corridors”. So, that certainly poses a concrete challenge. How do we go about challenging the administrative authorities? Tell them it’s all very well to have an ethics committee, but you have to help us, you also have to make sure that the necessary infrastructures are in place so that what we are proposing is really put into practice (participant 4).
If the relationships with research participants are likely to raise ethical issues, so too are the relationships with students, notably research assistants. On this topic, several participants discussed the lack of supervision or recognition offered to research assistants by researchers as well as the power imbalances between members of the research team.
Lack of Supervision and Power Imbalances
Many research teams are composed not only of researchers, but also of students who work as research assistants. The relationship between research assistants and other members of research teams can sometimes be problematic and raise ethical issues, particularly because of the inevitable power asymmetries. In the context of this study, several participants – including a research assistant, REB members, and researchers – discussed the lack of supervision or recognition of the work carried out by students, psychological pressure, and the more or less well-founded promises that are sometimes made to students. Participants also mentioned the exploitation of students by certain research teams, which manifest when students are inadequately paid, i.e., not reflective of the number of hours actually worked, not a fair wage, or even a wage at all.
[As a research assistant], it was more of a feeling of distress that I felt then because I didn’t know what to do. (…) I was supposed to get coaching or be supported, but I didn’t get anything in the end. It was like, “fix it by yourself”. (…) All research assistants were supposed to be supervised, but in practice they were not (participant 1). Very often, we have a master’s or doctoral student that we put on a subject and we consider that the project will be well done, while the student is learning. So, it happens that the student will do a lot of work and then we realize that the work is poorly done, and it is not necessarily the student’s fault. He wasn’t necessarily well supervised. There are directors who have 25 students, and they just don’t supervise them (participant 14). I think it’s really the power relationship. I thought to myself, how I saw my doctorate, the beginning of my research career, I really wanted to be in that laboratory, but they are the ones who are going to accept me or not, so what do I do to be accepted? I finally accept their conditions [which was to work for free]. If these are the conditions that are required to enter this lab, I want to go there. So, what do I do, well I accepted. It doesn’t make sense, but I tell myself that I’m still privileged, because I don’t have so many financial worries, one more reason to work for free, even though it doesn’t make sense (participant 1). In research, we have research assistants. (…). The fact of using people… so that’s it, you have to take into account where they are, respect them, but at the same time they have to show that they are there for the research. In English, we say “carry” or take care of people. With research assistants, this is often a problem that I have observed: for grant machines, the person is the last to be found there. Researchers, who will take, use student data, without giving them the recognition for it (participant 5). The problem at our university is that they reserve funding for Canadian students. The doctoral clientele in my field is mostly foreign students. So, our students are poorly funded. I saw one student end up in the shelter, in a situation of poverty. It ended very badly for him because he lacked financial resources. Once you get into that dynamic, it’s very hard to get out. I was made aware of it because the director at the time had taken him under her wing and wanted to try to find a way to get him out of it. So, most of my students didn’t get funded (participant 16). There I wrote “manipulation”, but it’s kind of all promises all the time. I, for example, was promised a lot of advancement, like when I got into the lab as a graduate student, it was said that I had an interest in [this particular area of research]. I think there are a lot of graduate students who must have gone through that, but it is like, “Well, your CV has to be really good, if you want to do a lot of things and big things. If you do this, if you do this research contract, the next year you could be the coordinator of this part of the lab and supervise this person, get more contracts, be paid more. Let’s say: you’ll be invited to go to this conference, this big event”. They were always dangling something, but you have to do that first to get there. But now, when you’ve done that, you have to do this business. It’s like a bit of manipulation, I think. That was very hard to know who is telling the truth and who is not (participant 1).
These ethical issues have significant negative consequences for students. Indeed, they sometimes find themselves at the mercy of researchers, for whom they work, struggling to be recognized and included as authors of an article, for example, or to receive the salary that they are due. For their part, researchers also sometimes find themselves trapped in research structures that can negatively affect their well-being. As many participants reported, researchers work in organizations that set very high productivity standards and in highly competitive contexts, all within a general culture characterized by individualism.
Individualism and performance
Participants, especially researchers, discussed the culture of individualism and performance that characterizes the academic environment. In glorifying excellence, some universities value performance and productivity, often at the expense of psychological well-being and work-life balance (i.e., work overload and burnout). Participants noted that there are ethical silences in their organizations on this issue, and that the culture of individualism and performance is not challenged for fear of retribution or simply to survive, i.e., to perform as expected. Participants felt that this culture can have a significant negative impact on the quality of the research conducted, as research teams try to maximize the quantity of their work (instead of quality) in a highly competitive context, which is then exacerbated by a lack of resources and support, and where everything must be done too quickly.
The work-life balance with the professional ethics related to work in a context where you have too much and you have to do a lot, it is difficult to balance all that and there is a lot of pressure to perform. If you don’t produce enough, that’s it; after that, you can’t get any more funds, so that puts pressure on you to do more and more and more (participant 3). There is a culture, I don’t know where it comes from, and that is extremely bureaucratic. If you dare to raise something, you’re going to have many, many problems. They’re going to make you understand it. So, I don’t talk. It is better: your life will be easier. I think there are times when you have to talk (…) because there are going to be irreparable consequences. (…) I’m not talking about a climate of terror, because that’s exaggerated, it’s not true, people are not afraid. But people close their office door and say nothing because it’s going to make their work impossible and they’re not going to lose their job, they’re not going to lose money, but researchers need time to be focused, so they close their office door and say nothing (participant 16).
Researchers must produce more and more, and they feel little support in terms of how to do such production, ethically, and how much exactly they are expected to produce. As this participant reports, the expectation is an unspoken rule: more is always better.
It’s sometimes the lack of a clear line on what the expectations are as a researcher, like, “ah, we don’t have any specific expectations, but produce, produce, produce, produce.” So, in that context, it’s hard to be able to put the line precisely: “have I done enough for my work?” (participant 3).
Inadequate ethical Guidance
While the productivity expectation is not clear, some participants – including researchers, research ethics experts, and REB members – also felt that the ethical expectations of some REBs were unclear. The issue of the inadequate ethical guidance of research includes the administrative mechanisms to ensure that research projects respect the principles of research ethics. According to those participants, the forms required for both researchers and REB members are increasingly long and numerous, and one participant noted that the standards to be met are sometimes outdated and disconnected from the reality of the field. Multicentre ethics review (by several REBs) was also critiqued by a participant as an inefficient method that encumbers the processes for reviewing research projects. Bureaucratization imposes an ever-increasing number of forms and ethics guidelines that actually hinder researchers’ ethical reflection on the issues at stake, leading the ethics review process to be perceived as purely bureaucratic in nature.
The ethical dimension and the ethical review of projects have become increasingly bureaucratized. (…) When I first started working (…) it was less bureaucratic, less strict then. I would say [there are now] tons of forms to fill out. Of course, we can’t do without it, it’s one of the ways of marking out ethics and ensuring that there are ethical considerations in research, but I wonder if it hasn’t become too bureaucratized, so that it’s become a kind of technical reflex to fill out these forms, and I don’t know if people really do ethical reflection as such anymore (participant 10). The fundamental structural issue, I would say, is the mismatch between the normative requirements and the real risks posed by the research, i.e., we have many, many requirements to meet; we have very long forms to fill out but the research projects we evaluate often pose few risks (participant 8). People [in vulnerable situations] were previously unable to participate because of overly strict research ethics rules that were to protect them, but in the end [these rules] did not protect them. There was a perverse effect, because in the end there was very little research done with these people and that’s why we have very few results, very little evidence [to support practices with these populations] so it didn’t improve the quality of services. (…) We all understand that we have to be careful with that, but when the research is not too risky, we say to ourselves that it would be good because for once a researcher who is interested in that population, because it is not a very popular population, it would be interesting to have results, but often we are blocked by the norms, and then we can’t accept [the project] (participant 2).
Moreover, as one participant noted, accessing ethics training can be a challenge.
There is no course on research ethics. […] Then, I find that it’s boring because you go through university and you come to do your research and you know how to do quantitative and qualitative research, but all the research ethics, where do you get this? I don’t really know (participant 13).
Yet, such training could provide relevant tools to resolve, to some extent, the ethical issues that commonly arise in research. That said, and as noted by many participants, many ethical issues in research are related to social injustices over which research actors have little influence.
Social Injustices
For many participants, notably researchers, the issues that concern social injustices are those related to power asymmetries, stigma, or issues of equity, diversity, and inclusion, i.e., social injustices related to people’s identities (Blais & Drolet, 2022 ). Participants reported experiencing or witnessing discrimination from peers, administration, or lab managers. Such oppression is sometimes cross-sectional and related to a person’s age, cultural background, gender or social status.
I have my African colleague who was quite successful when he arrived but had a backlash from colleagues in the department. I think it’s unconscious, nobody is overtly racist. But I have a young person right now who is the same, who has the same success, who got exactly the same early career award and I don’t see the same backlash. He’s just as happy with what he’s doing. It’s normal, they’re young and they have a lot of success starting out. So, I think there is discrimination. Is it because he is African? Is it because he is black? I think it’s on a subconscious level (participant 16).
Social injustices were experienced or reported by many participants, and included issues related to difficulties in obtaining grants or disseminating research results in one’s native language (i.e., even when there is official bilingualism) or being considered credible and fundable in research when one researcher is a woman.
If you do international research, there are things you can’t talk about (…). It is really a barrier to research to not be able to (…) address this question [i.e. the question of inequalities between men and women]. Women’s inequality is going to be addressed [but not within the country where the research takes place as if this inequality exists elsewhere but not here]. There are a lot of women working on inequality issues, doing work and it’s funny because I was talking to a young woman who works at Cairo University and she said to me: “Listen, I saw what you had written, you’re right. I’m willing to work on this but guarantee me a position at your university with a ticket to go”. So yes, there are still many barriers [for women in research] (participant 16).
Because of the varied contextual characteristics that intervene in their occurrence, these social injustices are also related to distributive injustices, as discussed by many participants.
Distributive Injustices
Although there are several views of distributive justice, a classical definition such as that of Aristotle ( 2012 ), describes distributive justice as consisting in distributing honours, wealth, and other social resources or benefits among the members of a community in proportion to their alleged merit. Justice, then, is about determining an equitable distribution of common goods. Contemporary theories of distributive justice are numerous and varied. Indeed, many authors (e.g., Fraser 2011 ; Mills, 2017 ; Sen, 2011 ; Young, 2011 ) have, since Rawls ( 1971 ), proposed different visions of how social burdens and benefits should be shared within a community to ensure equal respect, fairness, and distribution. In our study, what emerges from participants’ narratives is a definite concern for this type of justice. Women researchers, francophone researchers, early career researchers or researchers belonging to racialized groups all discussed inequities in the distribution of research grants and awards, and the extra work they need to do to somehow prove their worth. These inequities are related to how granting agencies determine which projects will be funded.
These situations make me work 2–3 times harder to prove myself and to show people in power that I have a place as a woman in research (participant 12). Number one: it’s conservative thinking. The older ones control what comes in. So, the younger people have to adapt or they don’t get funded (participant 14).
Whether it is discrimination against stigmatized or marginalized populations or interest in certain hot topics, granting agencies judge research projects according to criteria that are sometimes questionable, according to those participants. Faced with difficulties in obtaining funding for their projects, several strategies – some of which are unethical – are used by researchers in order to cope with these situations.
Sometimes there are subjects that everyone goes to, such as nanotechnology (…), artificial intelligence or (…) the therapeutic use of cannabis, which are very fashionable, and this is sometimes to the detriment of other research that is just as relevant, but which is (…), less sexy, less in the spirit of the time. (…) Sometimes this can lead to inequities in the funding of certain research sectors (participant 9). When we use our funds, we get them given to us, we pretty much say what we think we’re going to do with them, but things change… So, when these things change, sometimes it’s an ethical decision, but by force of circumstances I’m obliged to change the project a little bit (…). Is it ethical to make these changes or should I just let the money go because I couldn’t use it the way I said I would? (participant 3).
Moreover, these distributional injustices are not only linked to social injustices, but also epistemic injustices. Indeed, the way in which research honours and grants are distributed within the academic community depends on the epistemic authority of the researchers, which seems to vary notably according to their language of use, their age or their gender, but also to the research design used (inductive versus deductive), their decision to use (or not use) animals in research, or to conduct activist research.
Epistemic injustices
The philosopher Fricker ( 2007 ) conceptualized the notions of epistemic justice and injustice. Epistemic injustice refers to a form of social inequality that manifests itself in the access, recognition, and production of knowledge as well as the various forms of ignorance that arise (Godrie & Dos Santos, 2017 ). Addressing epistemic injustice necessitates acknowledging the iniquitous wrongs suffered by certain groups of socially stigmatized individuals who have been excluded from knowledge, thus limiting their abilities to interpret, understand, or be heard and account for their experiences. In this study, epistemic injustices were experienced or reported by some participants, notably those related to difficulties in obtaining grants or disseminating research results in one’s native language (i.e., even when there is official bilingualism) or being considered credible and fundable in research when a researcher is a woman or an early career researcher.
I have never sent a grant application to the federal government in English. I have always done it in French, even though I know that when you receive the review, you can see that reviewers didn’t understand anything because they are English-speaking. I didn’t want to get in the boat. It’s not my job to translate, because let’s be honest, I’m not as good in English as I am in French. So, I do them in my first language, which is the language I’m most used to. Then, technically at the administrative level, they are supposed to be able to do it, but they are not good in French. (…) Then, it’s a very big Canadian ethical issue, because basically there are technically two official languages, but Canada is not a bilingual country, it’s a country with two languages, either one or the other. (…) So I was not funded (participant 14).
Researchers who use inductive (or qualitative) methods observed that their projects are sometimes less well reviewed or understood, while research that adopts a hypothetical-deductive (or quantitative) or mixed methods design is better perceived, considered more credible and therefore more easily funded. Of course, regardless of whether a research project adopts an inductive, deductive or mixed-methods scientific design, or whether it deals with qualitative or quantitative data, it must respect a set of scientific criteria. A research project should achieve its objectives by using proven methods that, in the case of inductive research, are credible, reliable, and transferable or, in the case of deductive research, generalizable, objective, representative, and valid (Drolet & Ruest, accepted ). Participants discussing these issues noted that researchers who adopt a qualitative design or those who question the relevance of animal experimentation or are not militant have sometimes been unfairly devalued in their epistemic authority.
There is a mini war between quantitative versus qualitative methods, which I think is silly because science is a method. If you apply the method well, it doesn’t matter what the field is, it’s done well and it’s perfect ” (participant 14). There is also the issue of the place of animals in our lives, because for me, ethics is human ethics, but also animal ethics. Then, there is a great evolution in society on the role of the animal… with the new law that came out in Quebec on the fact that animals are sensitive beings. Then, with the rise of the vegan movement, [we must ask ourselves]: “Do animals still have a place in research?” That’s a big question and it also means that there are practices that need to evolve, but sometimes there’s a disconnection between what’s expected by research ethics boards versus what’s expected in the field (participant 15). In research today, we have more and more research that is militant from an ideological point of view. And so, we have researchers, because they defend values that seem important to them, we’ll talk for example about the fight for equality and social justice. They have pressure to defend a form of moral truth and have the impression that everyone thinks like them or should do so, because they are defending a moral truth. This is something that we see more and more, namely the lack of distance between ideology and science (participant 8).
The combination or intersectionality of these inequities, which seems to be characterized by a lack of ethical support and guidance, is experienced in the highly competitive and individualistic context of research; it provides therefore the perfect recipe for researchers to experience ethical distress.
Ethical distress
The concept of “ethical distress” refers to situations in which people know what they should do to act ethically, but encounter barriers, generally of an organizational or systemic nature, limiting their power to act according to their moral or ethical values (Drolet & Ruest, 2021 ; Jameton, 1984 ; Swisher et al., 2005 ). People then run the risk of finding themselves in a situation where they do not act as their ethical conscience dictates, which in the long term has the potential for exhaustion and distress. The examples reported by participants in this study point to the fact that researchers in particular may be experiencing significant ethical distress. This distress takes place in a context of extreme competition, constant injunctions to perform, and where administrative demands are increasingly numerous and complex to complete, while paradoxically, they lack the time to accomplish all their tasks and responsibilities. Added to these demands are a lack of resources (human, ethical, and financial), a lack of support and recognition, and interpersonal conflicts.
We are in an environment, an elite one, you are part of it, you know what it is: “publish or perish” is the motto. Grants, there is a high level of performance required, to do a lot, to publish, to supervise students, to supervise them well, so yes, it is clear that we are in an environment that is conducive to distress. (…). Overwork, definitely, can lead to distress and eventually to exhaustion. When you know that you should take the time to read the projects before sharing them, but you don’t have the time to do that because you have eight that came in the same day, and then you have others waiting… Then someone rings a bell and says: “ah but there, the protocol is a bit incomplete”. Oh yes, look at that, you’re right. You make up for it, but at the same time it’s a bit because we’re in a hurry, we don’t necessarily have the resources or are able to take the time to do things well from the start, we have to make up for it later. So yes, it can cause distress (participant 9). My organization wanted me to apply in English, and I said no, and everyone in the administration wanted me to apply in English, and I always said no. Some people said: “Listen, I give you the choice”, then some people said: “Listen, I agree with you, but if you’re not [submitting] in English, you won’t be funded”. Then the fact that I am young too, because very often they will look at the CV, they will not look at the project: “ah, his CV is not impressive, we will not finance him”. This is complete nonsense. The person is capable of doing the project, the project is fabulous: we fund the project. So, that happened, organizational barriers: that happened a lot. I was not eligible for Quebec research funds (…). I had big organizational barriers unfortunately (participant 14). At the time of my promotion, some colleagues were not happy with the type of research I was conducting. I learned – you learn this over time when you become friends with people after you enter the university – that someone was against me. He had another candidate in mind, and he was angry about the selection. I was under pressure for the first three years until my contract was renewed. I almost quit at one point, but another colleague told me, “No, stay, nothing will happen”. Nothing happened, but these issues kept me awake at night (participant 16).
This difficult context for many researchers affects not only the conduct of their own research, but also their participation in research. We faced this problem in our study, despite the use of multiple recruitment methods, including more than 200 emails – of which 191 were individual solicitations – sent to potential participants by the two research assistants. REB members and organizations overseeing or supporting research (n = 17) were also approached to see if some of their employees would consider participating. While it was relatively easy to recruit REB members and research ethics experts, our team received a high number of non-responses to emails (n = 175) and some refusals (n = 5), especially by researchers. The reasons given by those who replied were threefold: (a) fear of being easily identified should they take part in the research, (b) being overloaded and lacking time, and (c) the intrusive aspect of certain questions (i.e., “Have you experienced a burnout episode? If so, have you been followed up medically or psychologically?”). In light of these difficulties and concerns, some questions in the socio-demographic questionnaire were removed or modified. Talking about burnout in research remains a taboo for many researchers, which paradoxically can only contribute to the unresolved problem of unhealthy research environments.
Returning to the research question and objective
The question that prompted this research was: What are the ethical issues in research? The purpose of the study was to describe these issues from the perspective of researchers (from different disciplines), research ethics board (REB) members, and research ethics experts. The previous section provided a detailed portrait of the ethical issues experienced by different research stakeholders: these issues are numerous, diverse and were recounted by a range of stakeholders.
The results of the study are generally consistent with the literature. For example, as in our study, the literature discusses the lack of research integrity on the part of some researchers (Al-Hidabi et al., 2018 ; Swazey et al., 1993 ), the numerous conflicts of interest experienced in research (Williams-Jones et al., 2013 ), the issues of recruiting and obtaining the free and informed consent of research participants (Provencher et al., 2014 ; Keogh & Daly, 2009 ), the sometimes difficult relations between researchers and REBs (Drolet & Girard, 2020 ), the epistemological issues experienced in research (Drolet & Ruest, accepted; Sieber 2004 ), as well as the harmful academic context in which researchers evolve, insofar as this is linked to a culture of performance, an overload of work in a context of accountability (Berg & Seeber, 2016 ; FQPPU; 2019 ) that is conducive to ethical distress and even burnout.
If the results of the study are generally in line with those of previous publications on the subject, our findings also bring new elements to the discussion while complementing those already documented. In particular, our results highlight the role of systemic injustices – be they social, distributive or epistemic – within the environments in which research is carried out, at least in Canada. To summarize, the results of our study point to the fact that the relationships between researchers and research participants are likely still to raise worrying ethical issues, despite widely accepted research ethics norms and institutionalized review processes. Further, the context in which research is carried out is not only conducive to breaches of ethical norms and instances of misbehaviour or misconduct, but also likely to be significantly detrimental to the health and well-being of researchers, as well as research assistants. Another element that our research also highlighted is the instrumentalization and even exploitation of students and research assistants, which is another important and worrying social injustice given the inevitable power imbalances between students and researchers.
Moreover, in a context in which ethical issues are often discussed from a micro perspective, our study helps shed light on both the micro- and macro-level ethical dimensions of research (Bronfenbrenner, 1979 ; Glaser 1994 ). However, given that ethical issues in research are not only diverse, but also and above all complex, a broader perspective that encompasses the interplay between the micro and macro dimensions can enable a better understanding of these issues and thereby support the identification of the multiple factors that may be at their origin. Triangulating the perspectives of researchers with those of REB members and research ethics experts enabled us to bring these elements to light, and thus to step back from and critique the way that research is currently conducted. To this end, attention to socio-political elements such as the performance culture in academia or how research funds are distributed, and according to what explicit and implicit criteria, can contribute to identifying the sources of the ethical issues described above.
Contemporary culture characterized by the social acceleration
The German sociologist and philosopher Rosa (2010) argues that late modernity – that is, the period between the 1980s and today – is characterized by a phenomenon of social acceleration that causes various forms of alienation in our relationship to time, space, actions, things, others and ourselves. Rosa distinguishes three types of acceleration: technical acceleration , the acceleration of social changes and the acceleration of the rhythm of life . According to Rosa, social acceleration is the main problem of late modernity, in that the invisible social norm of doing more and faster to supposedly save time operates unchallenged at all levels of individual and collective life, as well as organizational and social life. Although we all, researchers and non-researchers alike, perceive this unspoken pressure to be ever more productive, the process of social acceleration as a new invisible social norm is our blind spot, a kind of tyrant over which we have little control. This conceptualization of the contemporary culture can help us to understand the context in which research is conducted (like other professional practices). To this end, Berg & Seeber ( 2016 ) invite faculty researchers to slow down in order to better reflect and, in the process, take care of their health and their relationships with their colleagues and students. Many women professors encourage their fellow researchers, especially young women researchers, to learn to “say No” in order to protect their mental and physical health and to remain in their academic careers (Allaire & Descheneux, 2022 ). These authors also remind us of the relevance of Kahneman’s ( 2012 ) work which demonstrates that it takes time to think analytically, thoroughly, and logically. Conversely, thinking quickly exposes humans to cognitive and implicit biases that then lead to errors in thinking (e.g., in the analysis of one’s own research data or in the evaluation of grant applications or student curriculum vitae). The phenomenon of social acceleration, which pushes the researcher to think faster and faster, is likely to lead to unethical bad science that can potentially harm humankind. In sum, Rosa’s invitation to contemporary critical theorists to seriously consider the problem of social acceleration is particularly insightful to better understand the ethical issues of research. It provides a lens through which to view the toxic context in which research is conducted today, and one that was shared by the participants in our study.
Clark & Sousa ( 2022 ) note, it is important that other criteria than the volume of researchers’ contributions be valued in research, notably quality. Ultimately, it is the value of the knowledge produced and its influence on the concrete lives of humans and other living beings that matters, not the quantity of publications. An interesting articulation of this view in research governance is seen in a change in practice by Australia’s national health research funder: they now restrict researchers to listing on their curriculum vitae only the top ten publications from the past ten years (rather than all of their publications), in order to evaluate the quality of contributions rather than their quantity. To create environments conducive to the development of quality research, it is important to challenge the phenomenon of social acceleration, which insidiously imposes a quantitative normativity that is both alienating and detrimental to the quality and ethical conduct of research. Based on our experience, we observe that the social norm of acceleration actively disfavours the conduct of empirical research on ethics in research. The fact is that researchers are so busy that it is almost impossible for them to find time to participate in such studies. Further, operating in highly competitive environments, while trying to respect the values and ethical principles of research, creates ethical paradoxes for members of the research community. According to Malherbe ( 1999 ), an ethical paradox is a situation where an individual is confronted by contradictory injunctions (i.e., do more, faster, and better). And eventually, ethical paradoxes lead individuals to situations of distress and burnout, or even to ethical failures (i.e., misbehaviour or misconduct) in the face of the impossibility of responding to contradictory injunctions.
Strengths and Limitations of the study
The triangulation of perceptions and experiences of different actors involved in research is a strength of our study. While there are many studies on the experiences of researchers, rarely are members of REBs and experts in research ethics given the space to discuss their views of what are ethical issues. Giving each of these stakeholders a voice and comparing their different points of view helped shed a different and complementary light on the ethical issues that occur in research. That said, it would have been helpful to also give more space to issues experienced by students or research assistants, as the relationships between researchers and research assistants are at times very worrying, as noted by a participant, and much work still needs to be done to eliminate the exploitative situations that seem to prevail in certain research settings. In addition, no Indigenous or gender diverse researchers participated in the study. Given the ethical issues and systemic injustices that many people from these groups face in Canada (Drolet & Goulet, 2018 ; Nicole & Drolet, in press ), research that gives voice to these researchers would be relevant and contribute to knowledge development, and hopefully also to change in research culture.
Further, although most of the ethical issues discussed in this article may be transferable to the realities experienced by researchers in other countries, the epistemic injustice reported by Francophone researchers who persist in doing research in French in Canada – which is an officially bilingual country but in practice is predominantly English – is likely specific to the Canadian reality. In addition, and as mentioned above, recruitment proved exceedingly difficult, particularly amongst researchers. Despite this difficulty, we obtained data saturation for all but two themes – i.e., exploitation of students and ethical issues of research that uses animals. It follows that further empirical research is needed to improve our understanding of these specific issues, as they may diverge to some extent from those documented here and will likely vary across countries and academic research contexts.
Conclusions
This study, which gave voice to researchers, REB members, and ethics experts, reveals that the ethical issues in research are related to several problematic elements as power imbalances and authority relations. Researchers and research assistants are subject to external pressures that give rise to integrity issues, among others ethical issues. Moreover, the current context of social acceleration influences the definition of the performance indicators valued in academic institutions and has led their members to face several ethical issues, including social, distributive, and epistemic injustices, at different steps of the research process. In this study, ten categories of ethical issues were identified, described and illustrated: (1) research integrity, (2) conflicts of interest, (3) respect for research participants, (4) lack of supervision and power imbalances, (5) individualism and performance, (6) inadequate ethical guidance, (7) social injustices, (8) distributive injustices, (9) epistemic injustices, and (10) ethical distress. The triangulation of the perspectives of different members (i.e., researchers from different disciplines, REB members, research ethics experts, and one research assistant) involved in the research process made it possible to lift the veil on some of these ethical issues. Further, it enabled the identification of additional ethical issues, especially systemic injustices experienced in research. To our knowledge, this is the first time that these injustices (social, distributive, and epistemic injustices) have been clearly identified.
Finally, this study brought to the fore several problematic elements that are important to address if the research community is to develop and implement the solutions needed to resolve the diverse and transversal ethical issues that arise in research institutions. A good starting point is the rejection of the corollary norms of “publish or perish” and “do more, faster, and better” and their replacement with “publish quality instead of quantity”, which necessarily entails “do less, slower, and better”. It is also important to pay more attention to the systemic injustices within which researchers work, because these have the potential to significantly harm the academic careers of many researchers, including women researchers, early career researchers, and those belonging to racialized groups as well as the health, well-being, and respect of students and research participants.

Acknowledgements
The team warmly thanks the participants who took part in the research and who made this study possible. Marie-Josée Drolet thanks the five research assistants who participated in the data collection and analysis: Julie-Claude Leblanc, Élie Beauchemin, Pénéloppe Bernier, Louis-Pierre Côté, and Eugénie Rose-Derouin, all students at the Université du Québec à Trois-Rivières (UQTR), two of whom were active in the writing of this article. MJ Drolet and Bryn Williams-Jones also acknowledge the financial contribution of the Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council of Canada (SSHRC), which supported this research through a grant. We would also like to thank the reviewers of this article who helped us improve it, especially by clarifying and refining our ideas.
Competing Interests and Funding
As noted in the Acknowledgements, this research was supported financially by the Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council of Canada (SSHRC).
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
- Al-Hidabi, Abdulmalek, M. D., & The, P. L. (2018). Multiple Publications: The Main Reason for the Retraction of Papers in Computer Science. In K. Arai, S. Kapoor, & R. Bhatia (eds), Future of Information and Communication Conference (FICC): Advances in Information and Communication, Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing (AISC), Springer, vol. 886, pp. 511–526
- Allaire, S., & Deschenaux, F. (2022). Récits de professeurs d’université à mi-carrière. Si c’était à refaire… . Presses de l’Université du Québec
- Aristotle . Aristotle’s Nicomachean Ethics. Chicago: The University of Chicago Press; 2012. [ Google Scholar ]
- Bahn S. Keeping Academic Field Researchers Safe: Ethical Safeguards. Journal of Academic Ethics. 2012; 10 :83–91. doi: 10.1007/s10805-012-9159-2. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Balk DE. Bereavement Research Using Control Groups: Ethical Obligations and Questions. Death Studies. 1995; 19 :123–138. doi: 10.1080/07481189508252720. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Beauchemin, É., Côté, L. P., Drolet, M. J., & Williams-Jones, B. (2021). Conceptualizing Ethical Issues in the Conduct of Research: Results from a Critical and Systematic Literature Review. Journal of Academic Ethics , Early Online. 10.1007/s10805-021-09411-7
- Berg, M., & Seeber, B. K. (2016). The Slow Professor . University of Toronto Press
- Birchley G, Huxtable R, Murtagh M, Meulen RT, Flach P, Gooberman-Hill R. Smart homes, private homes? An empirical study of technology researchers’ perceptions of ethical issues in developing smart-home health technologies. BMC Medical Ethics. 2017; 18 (23):1–13. doi: 10.1186/s12910-017-0183-z. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Blais, J., & Drolet, M. J. (2022). Les injustices sociales vécues en camp de réfugiés: les comprendre pour mieux intervenir auprès de personnes ayant séjourné dans un camp de réfugiés. Recueil annuel belge d’ergothérapie , 14, 37–48
- Bogdan, R. C., & Biklen, S. K. (2006). Qualitative research in education: An introduction to theory and methods . Allyn & Bacon
- Bouffard C. Le développement des pratiques de la génétique médicale et la construction des normes bioéthiques. Anthropologie et Sociétés. 2000; 24 (2):73–90. doi: 10.7202/015650ar. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bronfenbrenner, U. (1979). The Ecology of Human development. Experiments by nature and design . Harvard University Press
- Bruhn JG, Zajac G, Al-Kazemi AA, Prescott LD. Moral positions and academic conduct: Parameters of tolerance for ethics failure. Journal of Higher Education. 2002; 73 (4):461–493. doi: 10.1353/jhe.2002.0033. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Clark, A., & Sousa (2022). It’s time to end Canada’s obsession with research quantity. University Affairs/Affaires universitaires , February 14th. https://www.universityaffairs.ca/career-advice/effective-successfull-happy-academic/its-time-to-end-canadas-obsession-with-research-quantity/?utm_source=University+Affairs+e-newsletter&utm_campaign=276a847f 70-EMAIL_CAMPAIGN_2022_02_16&utm_medium=email&utm_term=0_314bc2ee29-276a847f70-425259989
- Colnerud G. Ethical dilemmas in research in relation to ethical review: An empirical study. Research Ethics. 2015; 10 (4):238–253. doi: 10.1177/1747016114552339. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Davison J. Dilemmas in Research: Issues of Vulnerability and Disempowerment for the Social Workers/Researcher. Journal of Social Work Practice. 2004; 18 (3):379–393. doi: 10.1080/0265053042000314447. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- DePoy E, Gitlin LN. Introduction to Research. St. Louis: Elsevier Mosby; 2010. [ Google Scholar ]
- Drolet, M. J., & Goulet, M. (2018). Travailler avec des patients autochtones du Canada ? Perceptions d’ergothérapeutes du Québec des enjeux éthiques de cette pratique. Recueil annuel belge francophone d’ergothérapie , 10 , 25–56
- Drolet MJ, Girard K. Les enjeux éthiques de la recherche en ergothérapie: un portrait préoccupant. Revue canadienne de bioéthique. 2020; 3 (3):21–40. doi: 10.7202/1073779ar. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Drolet MJ, Girard K, Gaudet R. Les enjeux éthiques de l’enseignement en ergothérapie: des injustices au sein des départements universitaires. Revue canadienne de bioéthique. 2020; 3 (1):22–36. [ Google Scholar ]
- Drolet MJ, Maclure J. Les enjeux éthiques de la pratique de l’ergothérapie: perceptions d’ergothérapeutes. Revue Approches inductives. 2016; 3 (2):166–196. doi: 10.7202/1037918ar. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Drolet MJ, Pinard C, Gaudet R. Les enjeux éthiques de la pratique privée: des ergothérapeutes du Québec lancent un cri d’alarme. Ethica – Revue interdisciplinaire de recherche en éthique. 2017; 21 (2):173–209. [ Google Scholar ]
- Drolet MJ, Ruest M. De l’éthique à l’ergothérapie: un cadre théorique et une méthode pour soutenir la pratique professionnelle. Québec: Presses de l’Université du Québec; 2021. [ Google Scholar ]
- Drolet, M. J., & Ruest, M. (accepted). Quels sont les enjeux éthiques soulevés par la recherche scientifique? In M. Lalancette & J. Luckerhoff (dir). Initiation au travail intellectuel et à la recherche . Québec: Presses de l’Université du Québec, 18 p
- Drolet MJ, Sauvageau A, Baril N, Gaudet R. Les enjeux éthiques de la formation clinique en ergothérapie. Revue Approches inductives. 2019; 6 (1):148–179. doi: 10.7202/1060048ar. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Fédération québécoise des professeures et des professeurs d’université (FQPPU) Enquête nationale sur la surcharge administrative du corps professoral universitaire québécois. Principaux résultats et pistes d’action. Montréal: FQPPU; 2019. [ Google Scholar ]
- Fortin MH. Fondements et étapes du processus de recherche. Méthodes quantitatives et qualitatives. Montréal, QC: Chenelière éducation; 2010. [ Google Scholar ]
- Fraser DM. Ethical dilemmas and practical problems for the practitioner researcher. Educational Action Research. 1997; 5 (1):161–171. doi: 10.1080/09650799700200014. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Fraser, N. (2011). Qu’est-ce que la justice sociale? Reconnaissance et redistribution . La Découverte
- Fricker, M. (2007). Epistemic Injustice: Power and the Ethics of Knowing . Oxford University Press
- Giorgi A, et al. De la méthode phénoménologique utilisée comme mode de recherche qualitative en sciences humaines: théories, pratique et évaluation. In: Poupart J, Groulx LH, Deslauriers JP, et al., editors. La recherche qualitative: enjeux épistémologiques et méthodologiques. Boucherville, QC: Gaëtan Morin; 1997. pp. 341–364. [ Google Scholar ]
- Giorgini V, Mecca JT, Gibson C, Medeiros K, Mumford MD, Connelly S, Devenport LD. Researcher Perceptions of Ethical Guidelines and Codes of Conduct. Accountability in Research. 2016; 22 (3):123–138. doi: 10.1080/08989621.2014.955607. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Glaser, J. W. (1994). Three realms of ethics: Individual, institutional, societal. Theoretical model and case studies . Kansas Cuty, Sheed & Ward
- Godrie B, Dos Santos M. Présentation: inégalités sociales, production des savoirs et de l’ignorance. Sociologie et sociétés. 2017; 49 (1):7. doi: 10.7202/1042804ar. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hammell KW, Carpenter C, Dyck I. Using Qualitative Research: A Practical Introduction for Occupational and Physical Therapists. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone; 2000. [ Google Scholar ]
- Henderson M, Johnson NF, Auld G. Silences of ethical practice: dilemmas for researchers using social media. Educational Research and Evaluation. 2013; 19 (6):546–560. doi: 10.1080/13803611.2013.805656. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Husserl E. The crisis of European sciences and transcendental phenomenology. Evanston, IL: Northwestern University Press; 1970. [ Google Scholar ]
- Husserl E. The train of thoughts in the lectures. In: Polifroni EC, Welch M, editors. Perspectives on Philosophy of Science in Nursing. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott; 1999. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hunt SD, Chonko LB, Wilcox JB. Ethical problems of marketing researchers. Journal of Marketing Research. 1984; 21 :309–324. doi: 10.1177/002224378402100308. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hunt MR, Carnevale FA. Moral experience: A framework for bioethics research. Journal of Medical Ethics. 2011; 37 (11):658–662. doi: 10.1136/jme.2010.039008. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Jameton, A. (1984). Nursing practice: The ethical issues . Englewood Cliffs, Prentice-Hall
- Jarvis K. Dilemmas in International Research and the Value of Practical Wisdom. Developing World Bioethics. 2017; 17 (1):50–58. doi: 10.1111/dewb.12121. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kahneman D. Système 1, système 2: les deux vitesses de la pensée. Paris: Flammarion; 2012. [ Google Scholar ]
- Keogh B, Daly L. The ethics of conducting research with mental health service users. British Journal of Nursing. 2009; 18 (5):277–281. doi: 10.12968/bjon.2009.18.5.40539. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lierville AL, Grou C, Pelletier JF. Enjeux éthiques potentiels liés aux partenariats patients en psychiatrie: État de situation à l’Institut universitaire en santé mentale de Montréal. Santé mentale au Québec. 2015; 40 (1):119–134. doi: 10.7202/1032386ar. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lynöe N, Sandlund M, Jacobsson L. Research ethics committees: A comparative study of assessment of ethical dilemmas. Scandinavian Journal of Public Health. 1999; 27 (2):152–159. doi: 10.1177/14034948990270020401. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Malherbe JF. Compromis, dilemmes et paradoxes en éthique clinique. Anjou: Éditions Fides; 1999. [ Google Scholar ]
- McGinn R. Discernment and denial: Nanotechnology researchers’ recognition of ethical responsibilities related to their work. NanoEthics. 2013; 7 :93–105. doi: 10.1007/s11569-013-0174-6. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mills, C. W. (2017). Black Rights / White rongs. The Critique of Racial Liberalism . Oxford University Press
- Miyazaki AD, Taylor KA. Researcher interaction biases and business ethics research: Respondent reactions to researcher characteristics. Journal of Business Ethics. 2008; 81 (4):779–795. doi: 10.1007/s10551-007-9547-5. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mondain N, Bologo E. L’intentionnalité du chercheur dans ses pratiques de production des connaissances: les enjeux soulevés par la construction des données en démographie et santé en Afrique. Cahiers de recherche sociologique. 2009; 48 :175–204. doi: 10.7202/039772ar. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Nicole, M., & Drolet, M. J. (in press). Fitting transphobia and cisgenderism in occupational therapy, Occupational Therapy Now
- Pope KS, Vetter VA. Ethical dilemmas encountered by members of the American Psychological Association: A national survey. The American Psychologist. 1992; 47 (3):397–411. doi: 10.1037/0003-066X.47.3.397. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Provencher V, Mortenson WB, Tanguay-Garneau L, Bélanger K, Dagenais M. Challenges and strategies pertaining to recruitment and retention of frail elderly in research studies: A systematic review. Archives of Gerontology and Geriatrics. 2014; 59 (1):18–24. doi: 10.1016/j.archger.2014.03.006. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rawls, J. (1971). A Theory of Justice . Harvard University Press
- Resnik DB, Elliott KC. The Ethical Challenges of Socially Responsible Science. Accountability in Research. 2016; 23 (1):31–46. doi: 10.1080/08989621.2014.1002608. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rosa, H. (2010). Accélération et aliénation. Vers une théorie critique de la modernité tardive . Paris, Découverte
- Sen, A. K. (2011). The Idea of Justice . The Belknap Press of Harvard University Press
- Sen, A. K. (1995). Inegality Reexaminated . Oxford University Press
- Sieber JE. Empirical Research on Research Ethics. Ethics & Behavior. 2004; 14 (4):397–412. doi: 10.1207/s15327019eb1404_9. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sigmon ST. Ethical practices and beliefs of psychopathology researchers. Ethics & Behavior. 1995; 5 (4):295–309. doi: 10.1207/s15327019eb0504_1. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Swazey JP, Anderson MS, Lewis KS. Ethical Problems in Academic Research. American Scientist. 1993; 81 (6):542–553. [ Google Scholar ]
- Swisher LL, Arsalanian LE, Davis CM. The realm-individual-process-situation (RIPS) model of ethical decision-making. HPA Resource. 2005; 5 (3):3–8. [ Google Scholar ]
- Tri-Council Policy Statement (TCPS2) (2018). Ethical Conduct for Research Involving Humans . Government of Canada, Secretariat on Responsible Conduct of Research. https://ethics.gc.ca/eng/documents/tcps2-2018-en-interactive-final.pdf
- Thomas SP, Pollio HR. Listening to Patients: A Phenomenological Approach to Nursing Research and Practice. New York: Springer Publishing Company; 2002. [ Google Scholar ]
- Wiegand DL, Funk M. Consequences of clinical situations that cause critical care nurses to experience moral distress. Nursing Ethics. 2012; 19 (4):479–487. doi: 10.1177/0969733011429342. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Williams-Jones B, Potvin MJ, Mathieu G, Smith E. Barriers to research on research ethics review and conflicts of interest. IRB: Ethics & Human Research. 2013; 35 (5):14–20. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Young, I. M. (2011). Justice and the Politics of difference . Princeton University Press
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- Ethical Considerations in Research | Types & Examples
Ethical Considerations in Research | Types & Examples
Published on 7 May 2022 by Pritha Bhandari .
Ethical considerations in research are a set of principles that guide your research designs and practices. Scientists and researchers must always adhere to a certain code of conduct when collecting data from people.
The goals of human research often include understanding real-life phenomena, studying effective treatments, investigating behaviours, and improving lives in other ways. What you decide to research and how you conduct that research involve key ethical considerations.
These considerations work to:
- Protect the rights of research participants
- Enhance research validity
- Maintain scientific integrity
Table of contents
Why do research ethics matter, getting ethical approval for your study, types of ethical issues, voluntary participation, informed consent, confidentiality, potential for harm, results communication, examples of ethical failures, frequently asked questions about research ethics.
Research ethics matter for scientific integrity, human rights and dignity, and collaboration between science and society. These principles make sure that participation in studies is voluntary, informed, and safe for research subjects.
You’ll balance pursuing important research aims with using ethical research methods and procedures. It’s always necessary to prevent permanent or excessive harm to participants, whether inadvertent or not.
Defying research ethics will also lower the credibility of your research because it’s hard for others to trust your data if your methods are morally questionable.
Even if a research idea is valuable to society, it doesn’t justify violating the human rights or dignity of your study participants.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Before you start any study involving data collection with people, you’ll submit your research proposal to an institutional review board (IRB) .
An IRB is a committee that checks whether your research aims and research design are ethically acceptable and follow your institution’s code of conduct. They check that your research materials and procedures are up to code.
If successful, you’ll receive IRB approval, and you can begin collecting data according to the approved procedures. If you want to make any changes to your procedures or materials, you’ll need to submit a modification application to the IRB for approval.
If unsuccessful, you may be asked to re-submit with modifications or your research proposal may receive a rejection. To get IRB approval, it’s important to explicitly note how you’ll tackle each of the ethical issues that may arise in your study.
There are several ethical issues you should always pay attention to in your research design, and these issues can overlap with each other.
You’ll usually outline ways you’ll deal with each issue in your research proposal if you plan to collect data from participants.
Voluntary participation means that all research subjects are free to choose to participate without any pressure or coercion.
All participants are able to withdraw from, or leave, the study at any point without feeling an obligation to continue. Your participants don’t need to provide a reason for leaving the study.
It’s important to make it clear to participants that there are no negative consequences or repercussions to their refusal to participate. After all, they’re taking the time to help you in the research process, so you should respect their decisions without trying to change their minds.
Voluntary participation is an ethical principle protected by international law and many scientific codes of conduct.
Take special care to ensure there’s no pressure on participants when you’re working with vulnerable groups of people who may find it hard to stop the study even when they want to.
Informed consent refers to a situation in which all potential participants receive and understand all the information they need to decide whether they want to participate. This includes information about the study’s benefits, risks, funding, and institutional approval.
- What the study is about
- The risks and benefits of taking part
- How long the study will take
- Your supervisor’s contact information and the institution’s approval number
Usually, you’ll provide participants with a text for them to read and ask them if they have any questions. If they agree to participate, they can sign or initial the consent form. Note that this may not be sufficient for informed consent when you work with particularly vulnerable groups of people.
If you’re collecting data from people with low literacy, make sure to verbally explain the consent form to them before they agree to participate.
For participants with very limited English proficiency, you should always translate the study materials or work with an interpreter so they have all the information in their first language.
In research with children, you’ll often need informed permission for their participation from their parents or guardians. Although children cannot give informed consent, it’s best to also ask for their assent (agreement) to participate, depending on their age and maturity level.
Anonymity means that you don’t know who the participants are and you can’t link any individual participant to their data.
You can only guarantee anonymity by not collecting any personally identifying information – for example, names, phone numbers, email addresses, IP addresses, physical characteristics, photos, and videos.
In many cases, it may be impossible to truly anonymise data collection. For example, data collected in person or by phone cannot be considered fully anonymous because some personal identifiers (demographic information or phone numbers) are impossible to hide.
You’ll also need to collect some identifying information if you give your participants the option to withdraw their data at a later stage.
Data pseudonymisation is an alternative method where you replace identifying information about participants with pseudonymous, or fake, identifiers. The data can still be linked to participants, but it’s harder to do so because you separate personal information from the study data.
Confidentiality means that you know who the participants are, but you remove all identifying information from your report.
All participants have a right to privacy, so you should protect their personal data for as long as you store or use it. Even when you can’t collect data anonymously, you should secure confidentiality whenever you can.
Some research designs aren’t conducive to confidentiality, but it’s important to make all attempts and inform participants of the risks involved.
As a researcher, you have to consider all possible sources of harm to participants. Harm can come in many different forms.
- Psychological harm: Sensitive questions or tasks may trigger negative emotions such as shame or anxiety.
- Social harm: Participation can involve social risks, public embarrassment, or stigma.
- Physical harm: Pain or injury can result from the study procedures.
- Legal harm: Reporting sensitive data could lead to legal risks or a breach of privacy.
It’s best to consider every possible source of harm in your study, as well as concrete ways to mitigate them. Involve your supervisor to discuss steps for harm reduction.
Make sure to disclose all possible risks of harm to participants before the study to get informed consent. If there is a risk of harm, prepare to provide participants with resources, counselling, or medical services if needed.
Some of these questions may bring up negative emotions, so you inform participants about the sensitive nature of the survey and assure them that their responses will be confidential.
The way you communicate your research results can sometimes involve ethical issues. Good science communication is honest, reliable, and credible. It’s best to make your results as transparent as possible.
Take steps to actively avoid plagiarism and research misconduct wherever possible.
Plagiarism means submitting others’ works as your own. Although it can be unintentional, copying someone else’s work without proper credit amounts to stealing. It’s an ethical problem in research communication because you may benefit by harming other researchers.
Self-plagiarism is when you republish or re-submit parts of your own papers or reports without properly citing your original work.
This is problematic because you may benefit from presenting your ideas as new and original even though they’ve already been published elsewhere in the past. You may also be infringing on your previous publisher’s copyright, violating an ethical code, or wasting time and resources by doing so.
In extreme cases of self-plagiarism, entire datasets or papers are sometimes duplicated. These are major ethical violations because they can skew research findings if taken as original data.
You notice that two published studies have similar characteristics even though they are from different years. Their sample sizes, locations, treatments, and results are highly similar, and the studies share one author in common.
Research misconduct
Research misconduct means making up or falsifying data, manipulating data analyses, or misrepresenting results in research reports. It’s a form of academic fraud.
These actions are committed intentionally and can have serious consequences; research misconduct is not a simple mistake or a point of disagreement about data analyses.
Research misconduct is a serious ethical issue because it can undermine scientific integrity and institutional credibility. It leads to a waste of funding and resources that could have been used for alternative research.
Later investigations revealed that they fabricated and manipulated their data to show a nonexistent link between vaccines and autism. Wakefield also neglected to disclose important conflicts of interest, and his medical license was taken away.
This fraudulent work sparked vaccine hesitancy among parents and caregivers. The rate of MMR vaccinations in children fell sharply, and measles outbreaks became more common due to a lack of herd immunity.
Research scandals with ethical failures are littered throughout history, but some took place not that long ago.
Some scientists in positions of power have historically mistreated or even abused research participants to investigate research problems at any cost. These participants were prisoners, under their care, or otherwise trusted them to treat them with dignity.
To demonstrate the importance of research ethics, we’ll briefly review two research studies that violated human rights in modern history.
These experiments were inhumane and resulted in trauma, permanent disabilities, or death in many cases.
After some Nazi doctors were put on trial for their crimes, the Nuremberg Code of research ethics for human experimentation was developed in 1947 to establish a new standard for human experimentation in medical research.
In reality, the actual goal was to study the effects of the disease when left untreated, and the researchers never informed participants about their diagnoses or the research aims.
Although participants experienced severe health problems, including blindness and other complications, the researchers only pretended to provide medical care.
When treatment became possible in 1943, 11 years after the study began, none of the participants were offered it, despite their health conditions and high risk of death.
Ethical failures like these resulted in severe harm to participants, wasted resources, and lower trust in science and scientists. This is why all research institutions have strict ethical guidelines for performing research.
Ethical considerations in research are a set of principles that guide your research designs and practices. These principles include voluntary participation, informed consent, anonymity, confidentiality, potential for harm, and results communication.
Scientists and researchers must always adhere to a certain code of conduct when collecting data from others .
These considerations protect the rights of research participants, enhance research validity , and maintain scientific integrity.
Research ethics matter for scientific integrity, human rights and dignity, and collaboration between science and society. These principles make sure that participation in studies is voluntary, informed, and safe.
Anonymity means you don’t know who the participants are, while confidentiality means you know who they are but remove identifying information from your research report. Both are important ethical considerations .
You can only guarantee anonymity by not collecting any personally identifying information – for example, names, phone numbers, email addresses, IP addresses, physical characteristics, photos, or videos.
You can keep data confidential by using aggregate information in your research report, so that you only refer to groups of participants rather than individuals.
These actions are committed intentionally and can have serious consequences; research misconduct is not a simple mistake or a point of disagreement but a serious ethical failure.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Bhandari, P. (2022, May 07). Ethical Considerations in Research | Types & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 14 May 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/ethical-considerations/
Is this article helpful?

Pritha Bhandari
Other students also liked, a quick guide to experimental design | 5 steps & examples, data collection methods | step-by-step guide & examples, how to avoid plagiarism | tips on citing sources.

Cultural Relativity and Acceptance of Embryonic Stem Cell Research
Article sidebar.

Main Article Content
There is a debate about the ethical implications of using human embryos in stem cell research, which can be influenced by cultural, moral, and social values. This paper argues for an adaptable framework to accommodate diverse cultural and religious perspectives. By using an adaptive ethics model, research protections can reflect various populations and foster growth in stem cell research possibilities.
INTRODUCTION
Stem cell research combines biology, medicine, and technology, promising to alter health care and the understanding of human development. Yet, ethical contention exists because of individuals’ perceptions of using human embryos based on their various cultural, moral, and social values. While these disagreements concerning policy, use, and general acceptance have prompted the development of an international ethics policy, such a uniform approach can overlook the nuanced ethical landscapes between cultures. With diverse viewpoints in public health, a single global policy, especially one reflecting Western ethics or the ethics prevalent in high-income countries, is impractical. This paper argues for a culturally sensitive, adaptable framework for the use of embryonic stem cells. Stem cell policy should accommodate varying ethical viewpoints and promote an effective global dialogue. With an extension of an ethics model that can adapt to various cultures, we recommend localized guidelines that reflect the moral views of the people those guidelines serve.
Stem cells, characterized by their unique ability to differentiate into various cell types, enable the repair or replacement of damaged tissues. Two primary types of stem cells are somatic stem cells (adult stem cells) and embryonic stem cells. Adult stem cells exist in developed tissues and maintain the body’s repair processes. [1] Embryonic stem cells (ESC) are remarkably pluripotent or versatile, making them valuable in research. [2] However, the use of ESCs has sparked ethics debates. Considering the potential of embryonic stem cells, research guidelines are essential. The International Society for Stem Cell Research (ISSCR) provides international stem cell research guidelines. They call for “public conversations touching on the scientific significance as well as the societal and ethical issues raised by ESC research.” [3] The ISSCR also publishes updates about culturing human embryos 14 days post fertilization, suggesting local policies and regulations should continue to evolve as ESC research develops. [4] Like the ISSCR, which calls for local law and policy to adapt to developing stem cell research given cultural acceptance, this paper highlights the importance of local social factors such as religion and culture.
I. Global Cultural Perspective of Embryonic Stem Cells
Views on ESCs vary throughout the world. Some countries readily embrace stem cell research and therapies, while others have stricter regulations due to ethical concerns surrounding embryonic stem cells and when an embryo becomes entitled to moral consideration. The philosophical issue of when the “someone” begins to be a human after fertilization, in the morally relevant sense, [5] impacts when an embryo becomes not just worthy of protection but morally entitled to it. The process of creating embryonic stem cell lines involves the destruction of the embryos for research. [6] Consequently, global engagement in ESC research depends on social-cultural acceptability.
a. US and Rights-Based Cultures
In the United States, attitudes toward stem cell therapies are diverse. The ethics and social approaches, which value individualism, [7] trigger debates regarding the destruction of human embryos, creating a complex regulatory environment. For example, the 1996 Dickey-Wicker Amendment prohibited federal funding for the creation of embryos for research and the destruction of embryos for “more than allowed for research on fetuses in utero.” [8] Following suit, in 2001, the Bush Administration heavily restricted stem cell lines for research. However, the Stem Cell Research Enhancement Act of 2005 was proposed to help develop ESC research but was ultimately vetoed. [9] Under the Obama administration, in 2009, an executive order lifted restrictions allowing for more development in this field. [10] The flux of research capacity and funding parallels the different cultural perceptions of human dignity of the embryo and how it is socially presented within the country’s research culture. [11]
b. Ubuntu and Collective Cultures
African bioethics differs from Western individualism because of the different traditions and values. African traditions, as described by individuals from South Africa and supported by some studies in other African countries, including Ghana and Kenya, follow the African moral philosophies of Ubuntu or Botho and Ukama , which “advocates for a form of wholeness that comes through one’s relationship and connectedness with other people in the society,” [12] making autonomy a socially collective concept. In this context, for the community to act autonomously, individuals would come together to decide what is best for the collective. Thus, stem cell research would require examining the value of the research to society as a whole and the use of the embryos as a collective societal resource. If society views the source as part of the collective whole, and opposes using stem cells, compromising the cultural values to pursue research may cause social detachment and stunt research growth. [13] Based on local culture and moral philosophy, the permissibility of stem cell research depends on how embryo, stem cell, and cell line therapies relate to the community as a whole. Ubuntu is the expression of humanness, with the person’s identity drawn from the “’I am because we are’” value. [14] The decision in a collectivistic culture becomes one born of cultural context, and individual decisions give deference to others in the society.
Consent differs in cultures where thought and moral philosophy are based on a collective paradigm. So, applying Western bioethical concepts is unrealistic. For one, Africa is a diverse continent with many countries with different belief systems, access to health care, and reliance on traditional or Western medicines. Where traditional medicine is the primary treatment, the “’restrictive focus on biomedically-related bioethics’” [is] problematic in African contexts because it neglects bioethical issues raised by traditional systems.” [15] No single approach applies in all areas or contexts. Rather than evaluating the permissibility of ESC research according to Western concepts such as the four principles approach, different ethics approaches should prevail.
Another consideration is the socio-economic standing of countries. In parts of South Africa, researchers have not focused heavily on contributing to the stem cell discourse, either because it is not considered health care or a health science priority or because resources are unavailable. [16] Each country’s priorities differ given different social, political, and economic factors. In South Africa, for instance, areas such as maternal mortality, non-communicable diseases, telemedicine, and the strength of health systems need improvement and require more focus. [17] Stem cell research could benefit the population, but it also could divert resources from basic medical care. Researchers in South Africa adhere to the National Health Act and Medicines Control Act in South Africa and international guidelines; however, the Act is not strictly enforced, and there is no clear legislation for research conduct or ethical guidelines. [18]
Some parts of Africa condemn stem cell research. For example, 98.2 percent of the Tunisian population is Muslim. [19] Tunisia does not permit stem cell research because of moral conflict with a Fatwa. Religion heavily saturates the regulation and direction of research. [20] Stem cell use became permissible for reproductive purposes only recently, with tight restrictions preventing cells from being used in any research other than procedures concerning ART/IVF. Their use is conditioned on consent, and available only to married couples. [21] The community's receptiveness to stem cell research depends on including communitarian African ethics.
c. Asia
Some Asian countries also have a collective model of ethics and decision making. [22] In China, the ethics model promotes a sincere respect for life or human dignity, [23] based on protective medicine. This model, influenced by Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), [24] recognizes Qi as the vital energy delivered via the meridians of the body; it connects illness to body systems, the body’s entire constitution, and the universe for a holistic bond of nature, health, and quality of life. [25] Following a protective ethics model, and traditional customs of wholeness, investment in stem cell research is heavily desired for its applications in regenerative therapies, disease modeling, and protective medicines. In a survey of medical students and healthcare practitioners, 30.8 percent considered stem cell research morally unacceptable while 63.5 percent accepted medical research using human embryonic stem cells. Of these individuals, 89.9 percent supported increased funding for stem cell research. [26] The scientific community might not reflect the overall population. From 1997 to 2019, China spent a total of $576 million (USD) on stem cell research at 8,050 stem cell programs, increased published presence from 0.6 percent to 14.01 percent of total global stem cell publications as of 2014, and made significant strides in cell-based therapies for various medical conditions. [27] However, while China has made substantial investments in stem cell research and achieved notable progress in clinical applications, concerns linger regarding ethical oversight and transparency. [28] For example, the China Biosecurity Law, promoted by the National Health Commission and China Hospital Association, attempted to mitigate risks by introducing an institutional review board (IRB) in the regulatory bodies. 5800 IRBs registered with the Chinese Clinical Trial Registry since 2021. [29] However, issues still need to be addressed in implementing effective IRB review and approval procedures.
The substantial government funding and focus on scientific advancement have sometimes overshadowed considerations of regional cultures, ethnic minorities, and individual perspectives, particularly evident during the one-child policy era. As government policy adapts to promote public stability, such as the change from the one-child to the two-child policy, [30] research ethics should also adapt to ensure respect for the values of its represented peoples.
Japan is also relatively supportive of stem cell research and therapies. Japan has a more transparent regulatory framework, allowing for faster approval of regenerative medicine products, which has led to several advanced clinical trials and therapies. [31] South Korea is also actively engaged in stem cell research and has a history of breakthroughs in cloning and embryonic stem cells. [32] However, the field is controversial, and there are issues of scientific integrity. For example, the Korean FDA fast-tracked products for approval, [33] and in another instance, the oocyte source was unclear and possibly violated ethical standards. [34] Trust is important in research, as it builds collaborative foundations between colleagues, trial participant comfort, open-mindedness for complicated and sensitive discussions, and supports regulatory procedures for stakeholders. There is a need to respect the culture’s interest, engagement, and for research and clinical trials to be transparent and have ethical oversight to promote global research discourse and trust.
d. Middle East
Countries in the Middle East have varying degrees of acceptance of or restrictions to policies related to using embryonic stem cells due to cultural and religious influences. Saudi Arabia has made significant contributions to stem cell research, and conducts research based on international guidelines for ethical conduct and under strict adherence to guidelines in accordance with Islamic principles. Specifically, the Saudi government and people require ESC research to adhere to Sharia law. In addition to umbilical and placental stem cells, [35] Saudi Arabia permits the use of embryonic stem cells as long as they come from miscarriages, therapeutic abortions permissible by Sharia law, or are left over from in vitro fertilization and donated to research. [36] Laws and ethical guidelines for stem cell research allow the development of research institutions such as the King Abdullah International Medical Research Center, which has a cord blood bank and a stem cell registry with nearly 10,000 donors. [37] Such volume and acceptance are due to the ethical ‘permissibility’ of the donor sources, which do not conflict with religious pillars. However, some researchers err on the side of caution, choosing not to use embryos or fetal tissue as they feel it is unethical to do so. [38]
Jordan has a positive research ethics culture. [39] However, there is a significant issue of lack of trust in researchers, with 45.23 percent (38.66 percent agreeing and 6.57 percent strongly agreeing) of Jordanians holding a low level of trust in researchers, compared to 81.34 percent of Jordanians agreeing that they feel safe to participate in a research trial. [40] Safety testifies to the feeling of confidence that adequate measures are in place to protect participants from harm, whereas trust in researchers could represent the confidence in researchers to act in the participants’ best interests, adhere to ethical guidelines, provide accurate information, and respect participants’ rights and dignity. One method to improve trust would be to address communication issues relevant to ESC. Legislation surrounding stem cell research has adopted specific language, especially concerning clarification “between ‘stem cells’ and ‘embryonic stem cells’” in translation. [41] Furthermore, legislation “mandates the creation of a national committee… laying out specific regulations for stem-cell banking in accordance with international standards.” [42] This broad regulation opens the door for future global engagement and maintains transparency. However, these regulations may also constrain the influence of research direction, pace, and accessibility of research outcomes.
e. Europe
In the European Union (EU), ethics is also principle-based, but the principles of autonomy, dignity, integrity, and vulnerability are interconnected. [43] As such, the opportunity for cohesion and concessions between individuals’ thoughts and ideals allows for a more adaptable ethics model due to the flexible principles that relate to the human experience The EU has put forth a framework in its Convention for the Protection of Human Rights and Dignity of the Human Being allowing member states to take different approaches. Each European state applies these principles to its specific conventions, leading to or reflecting different acceptance levels of stem cell research. [44]
For example, in Germany, Lebenzusammenhang , or the coherence of life, references integrity in the unity of human culture. Namely, the personal sphere “should not be subject to external intervention.” [45] Stem cell interventions could affect this concept of bodily completeness, leading to heavy restrictions. Under the Grundgesetz, human dignity and the right to life with physical integrity are paramount. [46] The Embryo Protection Act of 1991 made producing cell lines illegal. Cell lines can be imported if approved by the Central Ethics Commission for Stem Cell Research only if they were derived before May 2007. [47] Stem cell research respects the integrity of life for the embryo with heavy specifications and intense oversight. This is vastly different in Finland, where the regulatory bodies find research more permissible in IVF excess, but only up to 14 days after fertilization. [48] Spain’s approach differs still, with a comprehensive regulatory framework. [49] Thus, research regulation can be culture-specific due to variations in applied principles. Diverse cultures call for various approaches to ethical permissibility. [50] Only an adaptive-deliberative model can address the cultural constructions of self and achieve positive, culturally sensitive stem cell research practices. [51]
II. Religious Perspectives on ESC
Embryonic stem cell sources are the main consideration within religious contexts. While individuals may not regard their own religious texts as authoritative or factual, religion can shape their foundations or perspectives.
The Qur'an states:
“And indeed We created man from a quintessence of clay. Then We placed within him a small quantity of nutfa (sperm to fertilize) in a safe place. Then We have fashioned the nutfa into an ‘alaqa (clinging clot or cell cluster), then We developed the ‘alaqa into mudgha (a lump of flesh), and We made mudgha into bones, and clothed the bones with flesh, then We brought it into being as a new creation. So Blessed is Allah, the Best of Creators.” [52]
Many scholars of Islam estimate the time of soul installment, marked by the angel breathing in the soul to bring the individual into creation, as 120 days from conception. [53] Personhood begins at this point, and the value of life would prohibit research or experimentation that could harm the individual. If the fetus is more than 120 days old, the time ensoulment is interpreted to occur according to Islamic law, abortion is no longer permissible. [54] There are a few opposing opinions about early embryos in Islamic traditions. According to some Islamic theologians, there is no ensoulment of the early embryo, which is the source of stem cells for ESC research. [55]
In Buddhism, the stance on stem cell research is not settled. The main tenets, the prohibition against harming or destroying others (ahimsa) and the pursuit of knowledge (prajña) and compassion (karuna), leave Buddhist scholars and communities divided. [56] Some scholars argue stem cell research is in accordance with the Buddhist tenet of seeking knowledge and ending human suffering. Others feel it violates the principle of not harming others. Finding the balance between these two points relies on the karmic burden of Buddhist morality. In trying to prevent ahimsa towards the embryo, Buddhist scholars suggest that to comply with Buddhist tenets, research cannot be done as the embryo has personhood at the moment of conception and would reincarnate immediately, harming the individual's ability to build their karmic burden. [57] On the other hand, the Bodhisattvas, those considered to be on the path to enlightenment or Nirvana, have given organs and flesh to others to help alleviate grieving and to benefit all. [58] Acceptance varies on applied beliefs and interpretations.
Catholicism does not support embryonic stem cell research, as it entails creation or destruction of human embryos. This destruction conflicts with the belief in the sanctity of life. For example, in the Old Testament, Genesis describes humanity as being created in God’s image and multiplying on the Earth, referencing the sacred rights to human conception and the purpose of development and life. In the Ten Commandments, the tenet that one should not kill has numerous interpretations where killing could mean murder or shedding of the sanctity of life, demonstrating the high value of human personhood. In other books, the theological conception of when life begins is interpreted as in utero, [59] highlighting the inviolability of life and its formation in vivo to make a religious point for accepting such research as relatively limited, if at all. [60] The Vatican has released ethical directives to help apply a theological basis to modern-day conflicts. The Magisterium of the Church states that “unless there is a moral certainty of not causing harm,” experimentation on fetuses, fertilized cells, stem cells, or embryos constitutes a crime. [61] Such procedures would not respect the human person who exists at these stages, according to Catholicism. Damages to the embryo are considered gravely immoral and illicit. [62] Although the Catholic Church officially opposes abortion, surveys demonstrate that many Catholic people hold pro-choice views, whether due to the context of conception, stage of pregnancy, threat to the mother’s life, or for other reasons, demonstrating that practicing members can also accept some but not all tenets. [63]
Some major Jewish denominations, such as the Reform, Conservative, and Reconstructionist movements, are open to supporting ESC use or research as long as it is for saving a life. [64] Within Judaism, the Talmud, or study, gives personhood to the child at birth and emphasizes that life does not begin at conception: [65]
“If she is found pregnant, until the fortieth day it is mere fluid,” [66]
Whereas most religions prioritize the status of human embryos, the Halakah (Jewish religious law) states that to save one life, most other religious laws can be ignored because it is in pursuit of preservation. [67] Stem cell research is accepted due to application of these religious laws.
We recognize that all religions contain subsets and sects. The variety of environmental and cultural differences within religious groups requires further analysis to respect the flexibility of religious thoughts and practices. We make no presumptions that all cultures require notions of autonomy or morality as under the common morality theory , which asserts a set of universal moral norms that all individuals share provides moral reasoning and guides ethical decisions. [68] We only wish to show that the interaction with morality varies between cultures and countries.
III. A Flexible Ethical Approach
The plurality of different moral approaches described above demonstrates that there can be no universally acceptable uniform law for ESC on a global scale. Instead of developing one standard, flexible ethical applications must be continued. We recommend local guidelines that incorporate important cultural and ethical priorities.
While the Declaration of Helsinki is more relevant to people in clinical trials receiving ESC products, in keeping with the tradition of protections for research subjects, consent of the donor is an ethical requirement for ESC donation in many jurisdictions including the US, Canada, and Europe. [69] The Declaration of Helsinki provides a reference point for regulatory standards and could potentially be used as a universal baseline for obtaining consent prior to gamete or embryo donation.
For instance, in Columbia University’s egg donor program for stem cell research, donors followed standard screening protocols and “underwent counseling sessions that included information as to the purpose of oocyte donation for research, what the oocytes would be used for, the risks and benefits of donation, and process of oocyte stimulation” to ensure transparency for consent. [70] The program helped advance stem cell research and provided clear and safe research methods with paid participants. Though paid participation or covering costs of incidental expenses may not be socially acceptable in every culture or context, [71] and creating embryos for ESC research is illegal in many jurisdictions, Columbia’s program was effective because of the clear and honest communications with donors, IRBs, and related stakeholders. This example demonstrates that cultural acceptance of scientific research and of the idea that an egg or embryo does not have personhood is likely behind societal acceptance of donating eggs for ESC research. As noted, many countries do not permit the creation of embryos for research.
Proper communication and education regarding the process and purpose of stem cell research may bolster comprehension and garner more acceptance. “Given the sensitive subject material, a complete consent process can support voluntary participation through trust, understanding, and ethical norms from the cultures and morals participants value. This can be hard for researchers entering countries of different socioeconomic stability, with different languages and different societal values. [72]
An adequate moral foundation in medical ethics is derived from the cultural and religious basis that informs knowledge and actions. [73] Understanding local cultural and religious values and their impact on research could help researchers develop humility and promote inclusion.
IV. Concerns
Some may argue that if researchers all adhere to one ethics standard, protection will be satisfied across all borders, and the global public will trust researchers. However, defining what needs to be protected and how to define such research standards is very specific to the people to which standards are applied. We suggest that applying one uniform guide cannot accurately protect each individual because we all possess our own perceptions and interpretations of social values. [74] Therefore, the issue of not adjusting to the moral pluralism between peoples in applying one standard of ethics can be resolved by building out ethics models that can be adapted to different cultures and religions.
Other concerns include medical tourism, which may promote health inequities. [75] Some countries may develop and approve products derived from ESC research before others, compromising research ethics or drug approval processes. There are also concerns about the sale of unauthorized stem cell treatments, for example, those without FDA approval in the United States. Countries with robust research infrastructures may be tempted to attract medical tourists, and some customers will have false hopes based on aggressive publicity of unproven treatments. [76]
For example, in China, stem cell clinics can market to foreign clients who are not protected under the regulatory regimes. Companies employ a marketing strategy of “ethically friendly” therapies. Specifically, in the case of Beike, China’s leading stem cell tourism company and sprouting network, ethical oversight of administrators or health bureaus at one site has “the unintended consequence of shifting questionable activities to another node in Beike's diffuse network.” [77] In contrast, Jordan is aware of stem cell research’s potential abuse and its own status as a “health-care hub.” Jordan’s expanded regulations include preserving the interests of individuals in clinical trials and banning private companies from ESC research to preserve transparency and the integrity of research practices. [78]
The social priorities of the community are also a concern. The ISSCR explicitly states that guidelines “should be periodically revised to accommodate scientific advances, new challenges, and evolving social priorities.” [79] The adaptable ethics model extends this consideration further by addressing whether research is warranted given the varying degrees of socioeconomic conditions, political stability, and healthcare accessibilities and limitations. An ethical approach would require discussion about resource allocation and appropriate distribution of funds. [80]
While some religions emphasize the sanctity of life from conception, which may lead to public opposition to ESC research, others encourage ESC research due to its potential for healing and alleviating human pain. Many countries have special regulations that balance local views on embryonic personhood, the benefits of research as individual or societal goods, and the protection of human research subjects. To foster understanding and constructive dialogue, global policy frameworks should prioritize the protection of universal human rights, transparency, and informed consent. In addition to these foundational global policies, we recommend tailoring local guidelines to reflect the diverse cultural and religious perspectives of the populations they govern. Ethics models should be adapted to local populations to effectively establish research protections, growth, and possibilities of stem cell research.
For example, in countries with strong beliefs in the moral sanctity of embryos or heavy religious restrictions, an adaptive model can allow for discussion instead of immediate rejection. In countries with limited individual rights and voice in science policy, an adaptive model ensures cultural, moral, and religious views are taken into consideration, thereby building social inclusion. While this ethical consideration by the government may not give a complete voice to every individual, it will help balance policies and maintain the diverse perspectives of those it affects. Embracing an adaptive ethics model of ESC research promotes open-minded dialogue and respect for the importance of human belief and tradition. By actively engaging with cultural and religious values, researchers can better handle disagreements and promote ethical research practices that benefit each society.
This brief exploration of the religious and cultural differences that impact ESC research reveals the nuances of relative ethics and highlights a need for local policymakers to apply a more intense adaptive model.
[1] Poliwoda, S., Noor, N., Downs, E., Schaaf, A., Cantwell, A., Ganti, L., Kaye, A. D., Mosel, L. I., Carroll, C. B., Viswanath, O., & Urits, I. (2022). Stem cells: a comprehensive review of origins and emerging clinical roles in medical practice. Orthopedic reviews , 14 (3), 37498. https://doi.org/10.52965/001c.37498
[2] Poliwoda, S., Noor, N., Downs, E., Schaaf, A., Cantwell, A., Ganti, L., Kaye, A. D., Mosel, L. I., Carroll, C. B., Viswanath, O., & Urits, I. (2022). Stem cells: a comprehensive review of origins and emerging clinical roles in medical practice. Orthopedic reviews , 14 (3), 37498. https://doi.org/10.52965/001c.37498
[3] International Society for Stem Cell Research. (2023). Laboratory-based human embryonic stem cell research, embryo research, and related research activities . International Society for Stem Cell Research. https://www.isscr.org/guidelines/blog-post-title-one-ed2td-6fcdk ; Kimmelman, J., Hyun, I., Benvenisty, N. et al. Policy: Global standards for stem-cell research. Nature 533 , 311–313 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/533311a
[4] International Society for Stem Cell Research. (2023). Laboratory-based human embryonic stem cell research, embryo research, and related research activities . International Society for Stem Cell Research. https://www.isscr.org/guidelines/blog-post-title-one-ed2td-6fcdk
[5] Concerning the moral philosophies of stem cell research, our paper does not posit a personal moral stance nor delve into the “when” of human life begins. To read further about the philosophical debate, consider the following sources:
Sandel M. J. (2004). Embryo ethics--the moral logic of stem-cell research. The New England journal of medicine , 351 (3), 207–209. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMp048145 ; George, R. P., & Lee, P. (2020, September 26). Acorns and Embryos . The New Atlantis. https://www.thenewatlantis.com/publications/acorns-and-embryos ; Sagan, A., & Singer, P. (2007). The moral status of stem cells. Metaphilosophy , 38 (2/3), 264–284. http://www.jstor.org/stable/24439776 ; McHugh P. R. (2004). Zygote and "clonote"--the ethical use of embryonic stem cells. The New England journal of medicine , 351 (3), 209–211. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMp048147 ; Kurjak, A., & Tripalo, A. (2004). The facts and doubts about beginning of the human life and personality. Bosnian journal of basic medical sciences , 4 (1), 5–14. https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2004.3453
[6] Vazin, T., & Freed, W. J. (2010). Human embryonic stem cells: derivation, culture, and differentiation: a review. Restorative neurology and neuroscience , 28 (4), 589–603. https://doi.org/10.3233/RNN-2010-0543
[7] Socially, at its core, the Western approach to ethics is widely principle-based, autonomy being one of the key factors to ensure a fundamental respect for persons within research. For information regarding autonomy in research, see: Department of Health, Education, and Welfare, & National Commission for the Protection of Human Subjects of Biomedical and Behavioral Research (1978). The Belmont Report. Ethical principles and guidelines for the protection of human subjects of research.; For a more in-depth review of autonomy within the US, see: Beauchamp, T. L., & Childress, J. F. (1994). Principles of Biomedical Ethics . Oxford University Press.
[8] Sherley v. Sebelius , 644 F.3d 388 (D.C. Cir. 2011), citing 45 C.F.R. 46.204(b) and [42 U.S.C. § 289g(b)]. https://www.cadc.uscourts.gov/internet/opinions.nsf/6c690438a9b43dd685257a64004ebf99/$file/11-5241-1391178.pdf
[9] Stem Cell Research Enhancement Act of 2005, H. R. 810, 109 th Cong. (2001). https://www.govtrack.us/congress/bills/109/hr810/text ; Bush, G. W. (2006, July 19). Message to the House of Representatives . National Archives and Records Administration. https://georgewbush-whitehouse.archives.gov/news/releases/2006/07/20060719-5.html
[10] National Archives and Records Administration. (2009, March 9). Executive order 13505 -- removing barriers to responsible scientific research involving human stem cells . National Archives and Records Administration. https://obamawhitehouse.archives.gov/the-press-office/removing-barriers-responsible-scientific-research-involving-human-stem-cells
[11] Hurlbut, W. B. (2006). Science, Religion, and the Politics of Stem Cells. Social Research , 73 (3), 819–834. http://www.jstor.org/stable/40971854
[12] Akpa-Inyang, Francis & Chima, Sylvester. (2021). South African traditional values and beliefs regarding informed consent and limitations of the principle of respect for autonomy in African communities: a cross-cultural qualitative study. BMC Medical Ethics . 22. 10.1186/s12910-021-00678-4.
[13] Source for further reading: Tangwa G. B. (2007). Moral status of embryonic stem cells: perspective of an African villager. Bioethics , 21(8), 449–457. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8519.2007.00582.x , see also Mnisi, F. M. (2020). An African analysis based on ethics of Ubuntu - are human embryonic stem cell patents morally justifiable? African Insight , 49 (4).
[14] Jecker, N. S., & Atuire, C. (2021). Bioethics in Africa: A contextually enlightened analysis of three cases. Developing World Bioethics , 22 (2), 112–122. https://doi.org/10.1111/dewb.12324
[15] Jecker, N. S., & Atuire, C. (2021). Bioethics in Africa: A contextually enlightened analysis of three cases. Developing World Bioethics, 22(2), 112–122. https://doi.org/10.1111/dewb.12324
[16] Jackson, C.S., Pepper, M.S. Opportunities and barriers to establishing a cell therapy programme in South Africa. Stem Cell Res Ther 4 , 54 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1186/scrt204 ; Pew Research Center. (2014, May 1). Public health a major priority in African nations . Pew Research Center’s Global Attitudes Project. https://www.pewresearch.org/global/2014/05/01/public-health-a-major-priority-in-african-nations/
[17] Department of Health Republic of South Africa. (2021). Health Research Priorities (revised) for South Africa 2021-2024 . National Health Research Strategy. https://www.health.gov.za/wp-content/uploads/2022/05/National-Health-Research-Priorities-2021-2024.pdf
[18] Oosthuizen, H. (2013). Legal and Ethical Issues in Stem Cell Research in South Africa. In: Beran, R. (eds) Legal and Forensic Medicine. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-32338-6_80 , see also: Gaobotse G (2018) Stem Cell Research in Africa: Legislation and Challenges. J Regen Med 7:1. doi: 10.4172/2325-9620.1000142
[19] United States Bureau of Citizenship and Immigration Services. (1998). Tunisia: Information on the status of Christian conversions in Tunisia . UNHCR Web Archive. https://webarchive.archive.unhcr.org/20230522142618/https://www.refworld.org/docid/3df0be9a2.html
[20] Gaobotse, G. (2018) Stem Cell Research in Africa: Legislation and Challenges. J Regen Med 7:1. doi: 10.4172/2325-9620.1000142
[21] Kooli, C. Review of assisted reproduction techniques, laws, and regulations in Muslim countries. Middle East Fertil Soc J 24 , 8 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s43043-019-0011-0 ; Gaobotse, G. (2018) Stem Cell Research in Africa: Legislation and Challenges. J Regen Med 7:1. doi: 10.4172/2325-9620.1000142
[22] Pang M. C. (1999). Protective truthfulness: the Chinese way of safeguarding patients in informed treatment decisions. Journal of medical ethics , 25(3), 247–253. https://doi.org/10.1136/jme.25.3.247
[23] Wang, L., Wang, F., & Zhang, W. (2021). Bioethics in China’s biosecurity law: Forms, effects, and unsettled issues. Journal of law and the biosciences , 8(1). https://doi.org/10.1093/jlb/lsab019 https://academic.oup.com/jlb/article/8/1/lsab019/6299199
[24] Wang, Y., Xue, Y., & Guo, H. D. (2022). Intervention effects of traditional Chinese medicine on stem cell therapy of myocardial infarction. Frontiers in pharmacology , 13 , 1013740. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2022.1013740
[25] Li, X.-T., & Zhao, J. (2012). Chapter 4: An Approach to the Nature of Qi in TCM- Qi and Bioenergy. In Recent Advances in Theories and Practice of Chinese Medicine (p. 79). InTech.
[26] Luo, D., Xu, Z., Wang, Z., & Ran, W. (2021). China's Stem Cell Research and Knowledge Levels of Medical Practitioners and Students. Stem cells international , 2021 , 6667743. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/6667743
[27] Luo, D., Xu, Z., Wang, Z., & Ran, W. (2021). China's Stem Cell Research and Knowledge Levels of Medical Practitioners and Students. Stem cells international , 2021 , 6667743. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/6667743
[28] Zhang, J. Y. (2017). Lost in translation? accountability and governance of Clinical Stem Cell Research in China. Regenerative Medicine , 12 (6), 647–656. https://doi.org/10.2217/rme-2017-0035
[29] Wang, L., Wang, F., & Zhang, W. (2021). Bioethics in China’s biosecurity law: Forms, effects, and unsettled issues. Journal of law and the biosciences , 8(1). https://doi.org/10.1093/jlb/lsab019 https://academic.oup.com/jlb/article/8/1/lsab019/6299199
[30] Chen, H., Wei, T., Wang, H. et al. Association of China’s two-child policy with changes in number of births and birth defects rate, 2008–2017. BMC Public Health 22 , 434 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-022-12839-0
[31] Azuma, K. Regulatory Landscape of Regenerative Medicine in Japan. Curr Stem Cell Rep 1 , 118–128 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40778-015-0012-6
[32] Harris, R. (2005, May 19). Researchers Report Advance in Stem Cell Production . NPR. https://www.npr.org/2005/05/19/4658967/researchers-report-advance-in-stem-cell-production
[33] Park, S. (2012). South Korea steps up stem-cell work. Nature . https://doi.org/10.1038/nature.2012.10565
[34] Resnik, D. B., Shamoo, A. E., & Krimsky, S. (2006). Fraudulent human embryonic stem cell research in South Korea: lessons learned. Accountability in research , 13 (1), 101–109. https://doi.org/10.1080/08989620600634193 .
[35] Alahmad, G., Aljohani, S., & Najjar, M. F. (2020). Ethical challenges regarding the use of stem cells: interviews with researchers from Saudi Arabia. BMC medical ethics, 21(1), 35. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12910-020-00482-6
[36] Association for the Advancement of Blood and Biotherapies. https://www.aabb.org/regulatory-and-advocacy/regulatory-affairs/regulatory-for-cellular-therapies/international-competent-authorities/saudi-arabia
[37] Alahmad, G., Aljohani, S., & Najjar, M. F. (2020). Ethical challenges regarding the use of stem cells: Interviews with researchers from Saudi Arabia. BMC medical ethics , 21 (1), 35. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12910-020-00482-6
[38] Alahmad, G., Aljohani, S., & Najjar, M. F. (2020). Ethical challenges regarding the use of stem cells: Interviews with researchers from Saudi Arabia. BMC medical ethics , 21(1), 35. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12910-020-00482-6
Culturally, autonomy practices follow a relational autonomy approach based on a paternalistic deontological health care model. The adherence to strict international research policies and religious pillars within the regulatory environment is a great foundation for research ethics. However, there is a need to develop locally targeted ethics approaches for research (as called for in Alahmad, G., Aljohani, S., & Najjar, M. F. (2020). Ethical challenges regarding the use of stem cells: interviews with researchers from Saudi Arabia. BMC medical ethics, 21(1), 35. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12910-020-00482-6), this decision-making approach may help advise a research decision model. For more on the clinical cultural autonomy approaches, see: Alabdullah, Y. Y., Alzaid, E., Alsaad, S., Alamri, T., Alolayan, S. W., Bah, S., & Aljoudi, A. S. (2022). Autonomy and paternalism in Shared decision‐making in a Saudi Arabian tertiary hospital: A cross‐sectional study. Developing World Bioethics , 23 (3), 260–268. https://doi.org/10.1111/dewb.12355 ; Bukhari, A. A. (2017). Universal Principles of Bioethics and Patient Rights in Saudi Arabia (Doctoral dissertation, Duquesne University). https://dsc.duq.edu/etd/124; Ladha, S., Nakshawani, S. A., Alzaidy, A., & Tarab, B. (2023, October 26). Islam and Bioethics: What We All Need to Know . Columbia University School of Professional Studies. https://sps.columbia.edu/events/islam-and-bioethics-what-we-all-need-know
[39] Ababneh, M. A., Al-Azzam, S. I., Alzoubi, K., Rababa’h, A., & Al Demour, S. (2021). Understanding and attitudes of the Jordanian public about clinical research ethics. Research Ethics , 17 (2), 228-241. https://doi.org/10.1177/1747016120966779
[40] Ababneh, M. A., Al-Azzam, S. I., Alzoubi, K., Rababa’h, A., & Al Demour, S. (2021). Understanding and attitudes of the Jordanian public about clinical research ethics. Research Ethics , 17 (2), 228-241. https://doi.org/10.1177/1747016120966779
[41] Dajani, R. (2014). Jordan’s stem-cell law can guide the Middle East. Nature 510, 189. https://doi.org/10.1038/510189a
[42] Dajani, R. (2014). Jordan’s stem-cell law can guide the Middle East. Nature 510, 189. https://doi.org/10.1038/510189a
[43] The EU’s definition of autonomy relates to the capacity for creating ideas, moral insight, decisions, and actions without constraint, personal responsibility, and informed consent. However, the EU views autonomy as not completely able to protect individuals and depends on other principles, such as dignity, which “expresses the intrinsic worth and fundamental equality of all human beings.” Rendtorff, J.D., Kemp, P. (2019). Four Ethical Principles in European Bioethics and Biolaw: Autonomy, Dignity, Integrity and Vulnerability. In: Valdés, E., Lecaros, J. (eds) Biolaw and Policy in the Twenty-First Century. International Library of Ethics, Law, and the New Medicine, vol 78. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-05903-3_3
[44] Council of Europe. Convention for the protection of Human Rights and Dignity of the Human Being with regard to the Application of Biology and Medicine: Convention on Human Rights and Biomedicine (ETS No. 164) https://www.coe.int/en/web/conventions/full-list?module=treaty-detail&treatynum=164 (forbidding the creation of embryos for research purposes only, and suggests embryos in vitro have protections.); Also see Drabiak-Syed B. K. (2013). New President, New Human Embryonic Stem Cell Research Policy: Comparative International Perspectives and Embryonic Stem Cell Research Laws in France. Biotechnology Law Report , 32 (6), 349–356. https://doi.org/10.1089/blr.2013.9865
[45] Rendtorff, J.D., Kemp, P. (2019). Four Ethical Principles in European Bioethics and Biolaw: Autonomy, Dignity, Integrity and Vulnerability. In: Valdés, E., Lecaros, J. (eds) Biolaw and Policy in the Twenty-First Century. International Library of Ethics, Law, and the New Medicine, vol 78. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-05903-3_3
[46] Tomuschat, C., Currie, D. P., Kommers, D. P., & Kerr, R. (Trans.). (1949, May 23). Basic law for the Federal Republic of Germany. https://www.btg-bestellservice.de/pdf/80201000.pdf
[47] Regulation of Stem Cell Research in Germany . Eurostemcell. (2017, April 26). https://www.eurostemcell.org/regulation-stem-cell-research-germany
[48] Regulation of Stem Cell Research in Finland . Eurostemcell. (2017, April 26). https://www.eurostemcell.org/regulation-stem-cell-research-finland
[49] Regulation of Stem Cell Research in Spain . Eurostemcell. (2017, April 26). https://www.eurostemcell.org/regulation-stem-cell-research-spain
[50] Some sources to consider regarding ethics models or regulatory oversights of other cultures not covered:
Kara MA. Applicability of the principle of respect for autonomy: the perspective of Turkey. J Med Ethics. 2007 Nov;33(11):627-30. doi: 10.1136/jme.2006.017400. PMID: 17971462; PMCID: PMC2598110.
Ugarte, O. N., & Acioly, M. A. (2014). The principle of autonomy in Brazil: one needs to discuss it ... Revista do Colegio Brasileiro de Cirurgioes , 41 (5), 374–377. https://doi.org/10.1590/0100-69912014005013
Bharadwaj, A., & Glasner, P. E. (2012). Local cells, global science: The rise of embryonic stem cell research in India . Routledge.
For further research on specific European countries regarding ethical and regulatory framework, we recommend this database: Regulation of Stem Cell Research in Europe . Eurostemcell. (2017, April 26). https://www.eurostemcell.org/regulation-stem-cell-research-europe
[51] Klitzman, R. (2006). Complications of culture in obtaining informed consent. The American Journal of Bioethics, 6(1), 20–21. https://doi.org/10.1080/15265160500394671 see also: Ekmekci, P. E., & Arda, B. (2017). Interculturalism and Informed Consent: Respecting Cultural Differences without Breaching Human Rights. Cultura (Iasi, Romania) , 14 (2), 159–172.; For why trust is important in research, see also: Gray, B., Hilder, J., Macdonald, L., Tester, R., Dowell, A., & Stubbe, M. (2017). Are research ethics guidelines culturally competent? Research Ethics , 13 (1), 23-41. https://doi.org/10.1177/1747016116650235
[52] The Qur'an (M. Khattab, Trans.). (1965). Al-Mu’minun, 23: 12-14. https://quran.com/23
[53] Lenfest, Y. (2017, December 8). Islam and the beginning of human life . Bill of Health. https://blog.petrieflom.law.harvard.edu/2017/12/08/islam-and-the-beginning-of-human-life/
[54] Aksoy, S. (2005). Making regulations and drawing up legislation in Islamic countries under conditions of uncertainty, with special reference to embryonic stem cell research. Journal of Medical Ethics , 31: 399-403.; see also: Mahmoud, Azza. "Islamic Bioethics: National Regulations and Guidelines of Human Stem Cell Research in the Muslim World." Master's thesis, Chapman University, 2022. https://doi.org/10.36837/ chapman.000386
[55] Rashid, R. (2022). When does Ensoulment occur in the Human Foetus. Journal of the British Islamic Medical Association , 12 (4). ISSN 2634 8071. https://www.jbima.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/01/2-Ethics-3_-Ensoulment_Rafaqat.pdf.
[56] Sivaraman, M. & Noor, S. (2017). Ethics of embryonic stem cell research according to Buddhist, Hindu, Catholic, and Islamic religions: perspective from Malaysia. Asian Biomedicine,8(1) 43-52. https://doi.org/10.5372/1905-7415.0801.260
[57] Jafari, M., Elahi, F., Ozyurt, S. & Wrigley, T. (2007). 4. Religious Perspectives on Embryonic Stem Cell Research. In K. Monroe, R. Miller & J. Tobis (Ed.), Fundamentals of the Stem Cell Debate: The Scientific, Religious, Ethical, and Political Issues (pp. 79-94). Berkeley: University of California Press. https://escholarship.org/content/qt9rj0k7s3/qt9rj0k7s3_noSplash_f9aca2e02c3777c7fb76ea768ba458f0.pdf https://doi.org/10.1525/9780520940994-005
[58] Lecso, P. A. (1991). The Bodhisattva Ideal and Organ Transplantation. Journal of Religion and Health , 30 (1), 35–41. http://www.jstor.org/stable/27510629 ; Bodhisattva, S. (n.d.). The Key of Becoming a Bodhisattva . A Guide to the Bodhisattva Way of Life. http://www.buddhism.org/Sutras/2/BodhisattvaWay.htm
[59] There is no explicit religious reference to when life begins or how to conduct research that interacts with the concept of life. However, these are relevant verses pertaining to how the fetus is viewed. (( King James Bible . (1999). Oxford University Press. (original work published 1769))
Jerimiah 1: 5 “Before I formed thee in the belly I knew thee; and before thou camest forth out of the womb I sanctified thee…”
In prophet Jerimiah’s insight, God set him apart as a person known before childbirth, a theme carried within the Psalm of David.
Psalm 139: 13-14 “…Thou hast covered me in my mother's womb. I will praise thee; for I am fearfully and wonderfully made…”
These verses demonstrate David’s respect for God as an entity that would know of all man’s thoughts and doings even before birth.
[60] It should be noted that abortion is not supported as well.
[61] The Vatican. (1987, February 22). Instruction on Respect for Human Life in Its Origin and on the Dignity of Procreation Replies to Certain Questions of the Day . Congregation For the Doctrine of the Faith. https://www.vatican.va/roman_curia/congregations/cfaith/documents/rc_con_cfaith_doc_19870222_respect-for-human-life_en.html
[62] The Vatican. (2000, August 25). Declaration On the Production and the Scientific and Therapeutic Use of Human Embryonic Stem Cells . Pontifical Academy for Life. https://www.vatican.va/roman_curia/pontifical_academies/acdlife/documents/rc_pa_acdlife_doc_20000824_cellule-staminali_en.html ; Ohara, N. (2003). Ethical Consideration of Experimentation Using Living Human Embryos: The Catholic Church’s Position on Human Embryonic Stem Cell Research and Human Cloning. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology . Retrieved from https://article.imrpress.com/journal/CEOG/30/2-3/pii/2003018/77-81.pdf.
[63] Smith, G. A. (2022, May 23). Like Americans overall, Catholics vary in their abortion views, with regular mass attenders most opposed . Pew Research Center. https://www.pewresearch.org/short-reads/2022/05/23/like-americans-overall-catholics-vary-in-their-abortion-views-with-regular-mass-attenders-most-opposed/
[64] Rosner, F., & Reichman, E. (2002). Embryonic stem cell research in Jewish law. Journal of halacha and contemporary society , (43), 49–68.; Jafari, M., Elahi, F., Ozyurt, S. & Wrigley, T. (2007). 4. Religious Perspectives on Embryonic Stem Cell Research. In K. Monroe, R. Miller & J. Tobis (Ed.), Fundamentals of the Stem Cell Debate: The Scientific, Religious, Ethical, and Political Issues (pp. 79-94). Berkeley: University of California Press. https://escholarship.org/content/qt9rj0k7s3/qt9rj0k7s3_noSplash_f9aca2e02c3777c7fb76ea768ba458f0.pdf https://doi.org/10.1525/9780520940994-005
[65] Schenker J. G. (2008). The beginning of human life: status of embryo. Perspectives in Halakha (Jewish Religious Law). Journal of assisted reproduction and genetics , 25 (6), 271–276. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-008-9221-6
[66] Ruttenberg, D. (2020, May 5). The Torah of Abortion Justice (annotated source sheet) . Sefaria. https://www.sefaria.org/sheets/234926.7?lang=bi&with=all&lang2=en
[67] Jafari, M., Elahi, F., Ozyurt, S. & Wrigley, T. (2007). 4. Religious Perspectives on Embryonic Stem Cell Research. In K. Monroe, R. Miller & J. Tobis (Ed.), Fundamentals of the Stem Cell Debate: The Scientific, Religious, Ethical, and Political Issues (pp. 79-94). Berkeley: University of California Press. https://escholarship.org/content/qt9rj0k7s3/qt9rj0k7s3_noSplash_f9aca2e02c3777c7fb76ea768ba458f0.pdf https://doi.org/10.1525/9780520940994-005
[68] Gert, B. (2007). Common morality: Deciding what to do . Oxford Univ. Press.
[69] World Medical Association (2013). World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects. JAMA , 310(20), 2191–2194. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2013.281053 Declaration of Helsinki – WMA – The World Medical Association .; see also: National Commission for the Protection of Human Subjects of Biomedical and Behavioral Research. (1979). The Belmont report: Ethical principles and guidelines for the protection of human subjects of research . U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. https://www.hhs.gov/ohrp/regulations-and-policy/belmont-report/read-the-belmont-report/index.html
[70] Zakarin Safier, L., Gumer, A., Kline, M., Egli, D., & Sauer, M. V. (2018). Compensating human subjects providing oocytes for stem cell research: 9-year experience and outcomes. Journal of assisted reproduction and genetics , 35 (7), 1219–1225. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-018-1171-z https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6063839/ see also: Riordan, N. H., & Paz Rodríguez, J. (2021). Addressing concerns regarding associated costs, transparency, and integrity of research in recent stem cell trial. Stem Cells Translational Medicine , 10 (12), 1715–1716. https://doi.org/10.1002/sctm.21-0234
[71] Klitzman, R., & Sauer, M. V. (2009). Payment of egg donors in stem cell research in the USA. Reproductive biomedicine online , 18 (5), 603–608. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1472-6483(10)60002-8
[72] Krosin, M. T., Klitzman, R., Levin, B., Cheng, J., & Ranney, M. L. (2006). Problems in comprehension of informed consent in rural and peri-urban Mali, West Africa. Clinical trials (London, England) , 3 (3), 306–313. https://doi.org/10.1191/1740774506cn150oa
[73] Veatch, Robert M. Hippocratic, Religious, and Secular Medical Ethics: The Points of Conflict . Georgetown University Press, 2012.
[74] Msoroka, M. S., & Amundsen, D. (2018). One size fits not quite all: Universal research ethics with diversity. Research Ethics , 14 (3), 1-17. https://doi.org/10.1177/1747016117739939
[75] Pirzada, N. (2022). The Expansion of Turkey’s Medical Tourism Industry. Voices in Bioethics , 8 . https://doi.org/10.52214/vib.v8i.9894
[76] Stem Cell Tourism: False Hope for Real Money . Harvard Stem Cell Institute (HSCI). (2023). https://hsci.harvard.edu/stem-cell-tourism , See also: Bissassar, M. (2017). Transnational Stem Cell Tourism: An ethical analysis. Voices in Bioethics , 3 . https://doi.org/10.7916/vib.v3i.6027
[77] Song, P. (2011) The proliferation of stem cell therapies in post-Mao China: problematizing ethical regulation, New Genetics and Society , 30:2, 141-153, DOI: 10.1080/14636778.2011.574375
[78] Dajani, R. (2014). Jordan’s stem-cell law can guide the Middle East. Nature 510, 189. https://doi.org/10.1038/510189a
[79] International Society for Stem Cell Research. (2024). Standards in stem cell research . International Society for Stem Cell Research. https://www.isscr.org/guidelines/5-standards-in-stem-cell-research
[80] Benjamin, R. (2013). People’s science bodies and rights on the Stem Cell Frontier . Stanford University Press.
Mifrah Hayath
SM Candidate Harvard Medical School, MS Biotechnology Johns Hopkins University
Olivia Bowers
MS Bioethics Columbia University (Disclosure: affiliated with Voices in Bioethics)
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License .
This paper is in the following e-collection/theme issue:
Published on 17.5.2024 in Vol 26 (2024)
Reporting of Ethical Considerations in Qualitative Research Utilizing Social Media Data on Public Health Care: Scoping Review
Authors of this article:

- Yujie Zhang 1, 2 * , MD ;
- Jiaqi Fu 1, 2 * , MD ;
- Jie Lai 1, 2 * , MD ;
- Shisi Deng 1, 2 , MD ;
- Zihan Guo 1, 2 , MD ;
- Chuhan Zhong 1, 2 , MD ;
- Jianyao Tang 1, 2 , MD ;
- Wenqiong Cao 1 , BSc ;
- Yanni Wu 1 , PhD
1 Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China
2 School of Nursing, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China
*these authors contributed equally
Corresponding Author:
Yanni Wu, PhD
Nanfang Hospital
Southern Medical University
No 1838 Guangzhou Avenue North
Baiyun District, Guangdong Province
Guangzhou, 510515
Phone: 86 02061641192
Email: [email protected]
Background: The internet community has become a significant source for researchers to conduct qualitative studies analyzing users’ views, attitudes, and experiences about public health. However, few studies have assessed the ethical issues in qualitative research using social media data.
Objective: This study aims to review the reportage of ethical considerations in qualitative research utilizing social media data on public health care.
Methods: We performed a scoping review of studies mining text from internet communities and published in peer-reviewed journals from 2010 to May 31, 2023. These studies, limited to the English language, were retrieved to evaluate the rates of reporting ethical approval, informed consent, and privacy issues. We searched 5 databases, that is, PubMed, Web of Science, CINAHL, Cochrane, and Embase. Gray literature was supplemented from Google Scholar and OpenGrey websites. Studies using qualitative methods mining text from the internet community focusing on health care topics were deemed eligible. Data extraction was performed using a standardized data extraction spreadsheet. Findings were reported using PRISMA-ScR (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses Extension for Scoping Reviews) guidelines.
Results: After 4674 titles, abstracts, and full texts were screened, 108 studies on mining text from the internet community were included. Nearly half of the studies were published in the United States, with more studies from 2019 to 2022. Only 59.3% (64/108) of the studies sought ethical approval, 45.3% (49/108) mentioned informed consent, and only 12.9% (14/108) of the studies explicitly obtained informed consent. Approximately 86% (12/14) of the studies that reported informed consent obtained digital informed consent from participants/administrators, while 14% (2/14) did not describe the method used to obtain informed consent. Notably, 70.3% (76/108) of the studies contained users’ written content or posts: 68% (52/76) contained verbatim quotes, while 32% (24/76) paraphrased the quotes to prevent traceability. However, 16% (4/24) of the studies that paraphrased the quotes did not report the paraphrasing methods. Moreover, 18.5% (20/108) of the studies used aggregated data analysis to protect users’ privacy. Furthermore, the rates of reporting ethical approval were different between different countries ( P =.02) and between papers that contained users’ written content (both direct and paraphrased quotes) and papers that did not contain users’ written content ( P <.001).
Conclusions: Our scoping review demonstrates that the reporting of ethical considerations is widely neglected in qualitative research studies using social media data; such studies should be more cautious in citing user quotes to maintain user privacy. Further, our review reveals the need for detailed information on the precautions of obtaining informed consent and paraphrasing to reduce the potential bias. A national consensus of ethical considerations such as ethical approval, informed consent, and privacy issues is needed for qualitative research of health care using social media data of internet communities.
Introduction
Social media are web-based computer-mediated tools to collaborate, share, or exchange information, ideas, pictures, or videos in virtual communities and networks such as message boards, communities, chat rooms, forums, Twitter, and Facebook [ 1 ]. Moreover, patients and researchers can use internet communities to provide health care and disseminate health information [ 2 , 3 ]. Health care refers to the efforts made to improve or maintain physical, mental, or emotional well-being, including prevention, diagnosis, treatment, recovery, and other physical and mental impairments [ 4 ]. Currently, with 57% of the global population’s access to social media, more than 40% of the patients and caregivers worldwide utilize the internet community for health care information needs [ 5 ]. With diverse populations accessing internet communities and sharing information about health care topics, researchers have the opportunity to collect and analyze text about health care from a diverse range of participants in the internet community, which was unavailable previously [ 6 ]. Usually, quantitative data are derived from information extraction, which can be analyzed statistically, and the summary results presented cannot be directly linked to individual participants. In contrast, qualitative research within internet community analysis posts and comments qualitatively or thematically involves a more detailed and in-depth analysis and understanding of the full written content [ 7 ]. However, a controversial ethical problem has been raised about conducting qualitative research containing internet users’ verbatim quotes that could lead to traceability of the original post, thereby causing a threat to an individual’s privacy [ 8 ]. Additionally, a previous study investigated public and patients’ views regarding ethics in research using social media data and reported that internet users were aggrieved if they found any of their quotes cited in a medical research paper without obtaining their informed consent [ 9 ]. Further, besides the privacy breach caused by posts being traced, there is greater harm for special groups or vulnerable groups if we do not highlight the importance of the technical standards for text mining and privacy protection in health care. For instance, some unusual postings, abnormal pictures, and interactions that were expressed by individuals with mental disorders in social media can be detected by researchers by using text mining tools without obtaining their consent [ 10 ]. The publication of research on mental disorders, including quotes in posts, can result in a high risk of information harm, which can lead to personal information being revealed and further stigmatization of the condition or disease [ 11 ]. Since 2001, ethical concerns have been debated for decades about ethical approval, informed consent, and how to ensure anonymity and preserve data privacy and confidentiality in qualitative research in the internet community [ 12 - 14 ].
With the rapid development of social media and internet research, some ethical guidelines or standards have been published to ensure that research based on internet communities is conducted ethically. The Association of Internet Researchers (internet research ethical guidelines 2.0 and 3.0) showed that researchers working without the direct approval of ethics review boards would have additional challenges to face, and obtaining informed consent is obviously impracticable in several big data projects. However, with the ethical issues about privacy breaches and harms of risk of discrimination, the Association of Internet Researchers recommended reserving the acquisition of informed consent to the dissemination stage by asking for informed consent from specific participants before publication of their quotes [ 15 , 16 ]. Furthermore, researchers should take responsibility for information confidentiality and anonymity according to the internet research ethics criteria prepared by the National Committee for Research Ethics in the Social Sciences and the Humanities guidelines, which recommend a basic research ethic norm for the analyses, reports, and evaluations that apply to all research [ 17 ]. Moreover, the National Committee for Research Ethics in the Social Sciences and the Humanities guidelines contain more details about the demand for legal consent and privacy standards imposed by the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation. The General Data Protection Regulation is a European Union–wide regulation targeting the project of personal data processing. The General Data Protection Regulation defines personal data as any information relating to an identifiable person (data subject), including name, online identification number, location data, and other factors related to personal, physical, physiological, mental, or social identity [ 18 ]. The General Data Protection Regulation recommends using anonymous data and deleting identifiable information to ensure the confidentiality of the data. Consent should be obtained from the individual for use in scientific research [ 18 , 19 ]. The British Psychological Society guideline does not explicitly refer to the internet community but suggests that researchers may consider paraphrasing the verbatim quotes to reduce the risk of being traced or identified in qualitative research [ 20 ]. When paraphrasing, steps must be put into place to ensure that the original meaning of the message is maintained. Currently, there is no widespread consensus on ethical considerations by social media researchers.
Some researchers have tried to explore the reporting of existing ethical considerations in research papers using social media data. For instance, Sinnenberg et al [ 6 ] reported that only 32% and 12% of the papers mentioned acquiring ethical approval and informed consent, respectively, by utilizing multiple analysis methods, including surveillance, intervention, recruitment, engagement, content analysis, and network analysis with Twitter data before 2015. Thereafter, Takats et al [ 21 ] conducted an updated examination based on Sinnenberg et al’s [ 6 ] study. They found that of 367 studies using different methodological approaches, including sentiment mining, surveillance, and thematic exploration of public health research using Twitter data between 2010 to 2019, 17% of the studies included verbatim tweets and identifiable information about the internet users [ 21 ]. Similarly, Lathan et al [ 22 ] reviewed papers, including both qualitative and quantitative methods, by using Facebook data to explore public health issues and reported that only 48% and 10% of the papers obtained ethical approval and informed consent, respectively. Furthermore, in a study on research using YouTube data or comments, Tanner et al [ 23 ] found that only 26.1% of these studies sought ethical approval, only 1 paper (0.08%) sought informed consent, and 27.7% contained identifiable information. These findings indicate widespread neglect of ethical issues such as ethical approval, informed consent, and privacy issues in research papers using social media data.
Our study focuses on the ethical challenges of qualitative studies utilizing social media data. First, social media can be considered as sources for qualitative data collection because of the low cost, vast amount of available sources about health information, and users’ health behaviors, experiences, and attitudes. Second, qualitative research is context-dependent and mainly contains quotations and written content to support the viewpoint. It is acknowledged that quote materials from social media would potentially be traced back to the original posts and threaten the users’ privacy [ 24 ]. This is supported by findings reported by Ayers et al [ 25 ] who found that online searches of verbatim Twitter quotes in journal papers described as “content analyses” or “coded Twitter postings” can be traced back to individual internet users 84% of the time. Furthermore, Lathan et al [ 22 ] identified that 46% of the studies with verbatim or paraphrased quotes could be traced to the original posts in 10 minutes. Therefore, it is essential to investigate the extent to which ethical oversight is reported in qualitative studies using social media data. Moreover, qualitative research often involves personally sensitive data about health conditions and diseases; hence, anonymity and proper deidentification would be more important for researchers [ 26 , 27 ].
Previous studies have reviewed the ethical challenges and methodological use of social media platforms such as Twitter [ 6 , 21 ], Facebook [ 22 ], and YouTube [ 23 ] for health care research in both qualitative and quantitative studies. Although there is plenty of qualitative data pouring into social media such as blogs, Twitter, Facebook, and Weibo, evidence is lacking on the investigation of ethical considerations targeting qualitative data in different software and web-based discussion forums to provide a more comprehensive understanding of the ethical issues. To address the ethical considerations in qualitative research of different internet communities and draw the attention of researchers and publishers to ethical issues, we conducted this study to evaluate the ethical practices and ethical considerations of qualitative studies on health care by using data of internet communities. This review aims to (1) assess the rates of reporting institutional review board (IRB) approval and informed consent in studies focused on mining text in the internet community and social media, (2) compare these rates according to the year of publication, country conducting the research, website included in the study’s analysis, and journal’s guidelines about ethical approval for the type of study, and (3) describe whether the studies used anonymized/deidentified data.
Research Design
We conducted a scoping review to investigate how qualitative research mining social media data handles ethical approval, informed consent, and confidential issues. We performed this study according to the PRISMA-ScR (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses Extension for Scoping Reviews) guidelines. The completed PRISMA-ScR checklist is provided in Multimedia Appendix 1 .
Search Strategy
All published qualitative studies from 2010 to March 31, 2023, focusing on mining text from online community and social media sources about health care in the following databases were included in this study: PubMed, Web of Science, CINAHL, Cochrane, and Embase. A standardized search string containing Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) and non-MeSH entry terms was used in the search strategy. In addition, the reference lists of the retrieved papers and citation tracking were manually searched as a supplement to database searches to improve comprehensiveness. Gray literature was also identified through internet searches in Google Scholar and OpenGrey websites. The search strategies are represented in Multimedia Appendix 2 .
Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
We divided the criteria into 2 parts. First, we limited the inclusion and exclusion criteria used at the title and abstract screening stage eligible for (1) studies mining existing text and posts from the internet community and social media data focusing on health care topics, (2) studies using qualitative methods or available qualitative parts in mixed methods studies to analyze data, and (3) studies only written in English. Ineligible studies were those related to investigating the use and dissemination of social media in health care, using social media or internet community as an intervention tool, and using social media to conduct web-based interviews, surveys, or focus groups. We also excluded studies published as reviews, case studies, conference abstracts, commentaries, policies, guidelines, and recommendations. Second, at the full screening stage, the specific eligible inclusion criteria were studies focused on mining text about health care topics with full-text papers. Studies that did not have the full text after contacting the authors and that were not originally in the English language were excluded.
Study Selection
All results of the searches were entered into the EndNote library, and duplicates were removed. Two researchers reviewed the titles and abstracts based on the inclusion and exclusion criteria independently. Those studies that were irrelevant to the study topic were discarded, and then the full text was screened to select eligible papers. Any disagreements were discussed and resolved by consensus or a third person.
Data Extraction
Data were extracted between April 2023 and May 2023. Two researchers independently read the full text carefully, and the results were extracted using a standardized data extraction spreadsheet, including research type, first author, study objective, sample size, publication time, country where the research was conducted or country of the first author, website or internet community the studies focus on, type of data collected from social media, language of collected posts or data, privacy level of data (public or privacy posts), study design, research results, published journal, and information about the ethical considerations. Disagreements were resolved by consensus of a third person. The information about ethical considerations was analyzed to investigate the rates of reporting ethical approval, informed consent, and privacy issues: whether IRB review was reported (IRB approval, IRB exemption, unnecessary, not mentioned) and the reason for not requiring IRB approval; whether informed consent was obtained from participants or the websites’ administrators, consent types (digitally informed consent or written informed consent, informed consent is not required, consent was waived by IRB), and the methods used to obtain consent in each study; and whether quoting a post in papers could lead to the identification of internet users in each study. The description of users’ posts (verbatim quote, paraphrase) was recorded. We also analyzed if posts were paraphrased to maintain the original meaning, if actions were taken to deidentify the internet users, and if the posts contained other identifying information (ie, usernames, photos, links, hashtags) attached to the post. As every journal would provide publication ethical considerations and requirements, we also searched the submission guidelines and editorial policies of each journal submission website to check whether the journal contained any ethical guidance targeting studies using data from internet community and social media platforms. Additional information was included about the details of ethical approval, informed consent, and privacy, for example, whether individuals can withdraw their quotes if they want to be excluded from the study at any time without any reprisal and whether the quotations were tested for deidentification via search engines. There was excellent agreement on the primary outcome between the 2 researchers (k>.95 for all).
Data Analysis
Data were analyzed using SPSS software (IBM Corp). The chi-square test or Fisher exact tests (when cell size was less than 5) were used to test for differences between the rates of informed consent and ethical approval according to publication year, website, and different countries. All P values were 2-sided, and P values <.05 indicated significance.
Study Selection for the Review
We reviewed 4674 papers after removing the duplicates. After screening the titles, abstracts, and full-texts, we reviewed 108 eligible papers ( Figure 1 ). The full list of the included papers and all the extracted information are incorporated in Multimedia Appendix 3 [ 28 - 135 ]. Of the 108 studies reviewed, 73 (67.6%) were qualitative studies and 35 (32.4%) were mixed methods studies. All papers had text mined from internet communities or social media for qualitative analysis. The sample size ranged from 32 to 392,962. Approximately 82.4% (89/108) of the studies were published after 2018, and there was a sharp increase in the number of studies from 2019 to 2022. Moreover, nearly half of the studies (55/108, 50.9%) were published in the United States. Regarding the websites for mining text, the most widely used social media platform was Twitter (42/108, 38.9%), followed by Facebook (17/108, 15.7%).

Ethics Approval in These Studies
Our results indicated that of the 108 studies, 78 (72.2%) reported ethics approval. Of the 78 studies, 31 (40%) explicitly stated that ethics approval was obtained before the study was undertaken, 33 (42%) reported that the ethics approval was granted through exemptions by the local IRB, and 14 (18%) explicitly demonstrated that approval by the ethics committee was not required because publicly available data were collected from internet communities and social media platforms. However, 30 (27.8%) of the 108 studies did not mention about obtaining IRB approval ( Table 1 ).
Based on our exploration of the ethical guidelines of each journal to determine whether there were ethical requirements for studies mining social media data, only 36.1% (39/108) of the studies were published in journals that required ethical considerations for studies gathering data from social media platforms by using internet and digital technologies. Of the 39 studies published in 19 journals, 27 (69%) were published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research and its sister journals. The submission guidelines of the Journal of Medical Internet Research state that authors of manuscripts describing studies of internet, digital tools, and technologies are required to verify that they have adhered to local, national, regional, and international laws and regulations, and are required to verify that they complied with informed consent guidelines. Moreover, 2 journals also provided a specific requirement, that is, when researchers interact with individuals or obtain privacy information gathered from social media platforms, they should obtain ethics approval prior to conducting the study and informed consent from anyone who could potentially be identified. Surprisingly, there were no significant differences in the ethics approval reportage between journals with ethics approval guidelines and those that did not have ethics guidelines for researchers gathering data from social media platforms ( P =.08). Notably, the rates of reporting ethics approval were different between different countries ( P =.02). However, there were no statistically significant differences between the rates of reporting ethical approval and different websites or publication years (all P >.05) ( Table 2 ).
Informed Consent
Of the 108 studies, 59 (54.7%) showed that they did not include any information about informed consent and 49 (45.3%) mentioned informed consent. Of the 49 studies that mentioned informed consent, 14 (13%) demonstrated that informed consent was waived by local institutional boards, and 21 (19%) reported that informed consent was not required because this information is publicly available in websites or did not involve human participants. We interpreted this as not seeking informed consent. Only 14 (12.9%) of the 108 studies explicitly indicated that informed consent was obtained ( Table 1 ). Among the 14 studies, 2 (14%) only provided a generic statement that informed consent was obtained but did not report the process of how the informed consent was obtained, while 12 (86%) received digital informed consent. Of the 12 studies that reported receiving digital informed consent, 6 reported that they sought permission from the communities’ or groups’ administrators and by posting a statement of the research objective on the group’s wall, while 5 studies contacted the participants privately via email, commenting below the posts and software to gain consent, and 1 study reported that it had sent a digital version of the informed consent book. Furthermore, among the studies that had obtained informed consent, 7 studies included the statement that the individuals’ posts would be removed if they wanted to be excluded from the study, and they could withdraw from the study whenever they wanted. In addition, the rates of reporting informed consent showed no statistical significance between publication years, different countries, and different websites (all P >.05) ( Table 2 ).
Confidentiality of the Information
All data sources were obtained from anonymous websites or communities, and the majority (104/108, 96.3%) of the data sources did not contain usernames. Notably, only 3.7% (4/108) of the studies contained the participants’ usernames or pseudonyms. One study reported that pseudonyms like Sasha had been used instead of the real name. The other 3 studies contained the expression for usernames but did not state whether pseudonyms were used. Except for 9 studies that used nonnative language quotes and 3 studies that were transcribed into text via video, among the 108 included studies, 76 (70.3%) quoted at least one native language post in their reports. Additionally, 20 studies presenting aggregated analysis or composite accounts did not include any quotation or written content. Of the 76 studies containing internet users’ written content, 52 (68%) contained just verbatim-quoted participants’ posts and 24 (32%) contained paraphrased posts ( Table 1 ). Among the 52 studies containing direct and verbatim quotations, which are likely to be traced to the original posts from users, only 17 (33%) studies took measures to deidentify the users. The 17 studies mentioned that all names or usernames were removed and personal identifying information was removed to maintain privacy, while 42% (22/52) of the studies did not mention any measures that were taken to deidentify the users and maintain confidentiality. Approximately 32% (24/76) of the studies described that they paraphrased posts and removed any explicitly identified personal information to maintain confidentiality to reduce the likelihood of users being identified via search engines. Of the 24 studies, 20 (83%) reported that the quotations were slightly modified or summarized for readability, the symbol information was removed using “…”, and key identifiable information was removed to protect privacy while maintaining the meaning of posts. Four of the 24 (17%) studies did not report the methods and details of paraphrasing. Notably, only 3% (2/76) of the studies containing users’ written content showed that researchers intentionally entered each quote into search engines to ensure that every quote did not lead to the original posts. Moreover, of the 76 studies containing written content, 62 (82%) did not contain other types of identity information attached to the posts, while 14 (18%) included other identifying data (hashtags, emojis, geolocation, photos, links, screenshots) attached to the original posts for analysis ( Table 1 ). Of the 14 studies including other identifying information, 4 (29%) contained photos and screenshots associated with the website pages. Of the 52 studies that disclosed verbatim quotes and other identifiable information, 26 (46%) studies reported informed consent consideration, and only 8 (15%) obtained explicitly informed consent. Additionally, of the 77% (40/52) of the studies that mentioned IRB or ethical review, 38% (15/40) received IRB approval, and 63% (25/40) of the studies were granted exemption. The proportion of reporting ethical approval in studies containing users’ written content was modestly higher than that in studies not containing users’ written content (60/76, 79% vs 14/32, 44%; P <.001) ( Table 2 ).
Principal Findings and Comparison to Prior Work
In this scoping review, we included 108 studies ( Multimedia Appendix 3 ; [ 28 - 135 ]) that focused on mining text from internet community and social media data for health care research, and we reviewed the ethical consideration reportage and outcome reports in these studies. We found that the rates of reporting IRB approval and informed consent in qualitative research on health care utilizing social media data were 59.3% (64/108) and 12.9% (14/108), respectively. Our findings demonstrate that the key ethical considerations for qualitative research in online communities are insufficiently discussed and described. However, the reporting rates of ethical considerations in the papers in our scoping review were much higher than those reported in systematic reviews including multiple analysis methodologies on only 1 social media platform. For example, ethics approval and informed consent were reported in 48% and 10% of research studies using only Facebook data [ 22 ], 32% and 0% from 2006 to 2019 [ 21 ], 40% and 0.9% (only 1 paper) from 2015 to 2016 in public health research using only Twitter data [ 25 ], and 26.1% and 0.8% (only 1 paper) in researches incorporating only YouTube data [ 23 ], respectively. In fact, previous studies were limited to only a few selected websites such as Twitter, Facebook, and YouTube. There is a lack of research that incorporates a variety of different social media data for comparisons. Differences in the reporting of ethical considerations may be attributed to the different methodologies adopted by studies. For example, Lathan et al [ 22 ] analyzed the ethical considerations in studies including predictive or model development, while our research focuses on the ethical considerations in qualitative studies.
Importantly, our findings indicate that there is a need to develop a standardized and apparent approach for the reporting of ethical considerations in qualitative research of data from social media and online communities. Our research demonstrates that the rates of reporting ethics approval are different in different countries ( P =.02). Specifically, a wide variety of national research ethics governing bodies and over 1000 laws, regulations, and standards provide oversight for human subjects research in 130 countries. Obviously, a guideline is needed for best ethical practices for qualitative research involving posts from social media platforms. Surprisingly, there were no significant differences between the rates of reporting ethical approval and those of journals specifying ethical requirements for studies involving text mining ( P =.08). This inconsistent result of publication guidelines and reports of ethical approval consent is similar to previous findings on the ethical standards in COVID-19 human studies [ 136 ]. Although there are journal publication guidelines for studies mining social media data, the reports of ethical approval and consent in the papers published in such journals do not exactly follow the guidelines. Consequently, this finding indicates that more ethical awareness is needed among researchers, editors, and reviewers for qualitative studies on data mining.
Besides the different legal and regulations in different countries, the inconsistency in the ethics approval in published papers may be because social media research is a highly interdisciplinary science, and computer science researchers may be less experienced or may pay less attention to the key ethical issues of protecting human subjects [ 137 ]. Medical and health science researchers may have considered some ethical concerns about gathering social media data but they may not be familiar with the relevant guidelines. For example, the Association of Internet Researchers has a detailed ethical guideline targeting social scientists conducting digital research, while it may be less popular and less well-known among medical and health care researchers. At the institute level, Ferretti et al [ 138 ] noticed that institutionalized review committees, especially the individual IRB institutes for universities and health care systems lack knowledge about the methodology, text mining technical standards, data security, and ethical harms for studies using big data and social media as sources. Because of this lack of knowledge, institutional ethics committees may have inconsistent ethical criteria and perspectives about web-based projects using social media data [ 139 ]. Therefore, some ethics review committees exclude research on internet communities from ethical oversights because their ethics standards are confined only to medical fields. Above all, it is additionally challenging for ethical approval institutions because of the continuous development and dynamic change of studies using social media data. Furthermore, it is necessary for ethics committee members to be trained about the ethical issues in studies mining text from social media. Inviting interdisciplinary researchers to join in the approval process would be an appropriate method to increase the awareness of ethical considerations [ 140 , 141 ].
Interestingly, the reporting rate of obtaining informed consent for mining social media data in qualitative studies was unexpected. The most influential ethical reports such as the Nuremberg Code [ 142 ], Declaration of Helsinki [ 143 ], and the Belmont Report [ 144 ] have demonstrated the principle of informed consent in research involving humans. Our review shows that only 12.9% (14/108) of the studies explicitly obtained informed consent and 32.4% (35/108) of the studies reported that informed consent was exempted by IRB or was not required, as the information was available publicly in websites or did not involve human participants. Our results are similar to those of Wongkoblap et al [ 145 ] who reported that only 16.7% of the studies received informed consent from participants prior to data analysis on data mining of social network data on mental health disorders.
There are multiple reasons for the challenges in obtaining informed consent in an internet setting. First, it is impractical for researchers to gain individual informed consent from a large number of users in an internet community [ 146 ]. Second, members of ethics review boards lack consensus about the need for informed consent from an internet community for qualitative research under the current legal definition [ 147 ]. Moreover, there has been a debate on the criteria of human subject research in using social media data. The federal regulation recommends that if data in the studies are obtained from public social media websites, where data are identifiable and do not require interaction with individuals, such studies do not constitute human subject research, while studies involving the identification of private information or interaction with the individual can be considered as human subject research [ 148 ]. In contrast, some researchers believe that social media and big data research are not ethically exceptional and should be treated in the same manner and with the same rules as those for traditional forms of research [ 149 ]. There is ambiguity as to what is appropriate or should be standard practice for obtaining informed consent.
Currently, it is challenging to maintain privacy and protect the traceability of individuals posting content in the internet community. Our findings indicated that 70.3% (76/108) of the studies contained internet users’ written content, of which 68% (52/76) included verbatim quotations of users’ posts that could lead to identification, and 18% (14/76) of the studies included other identifiable information such as links, screenshots, and emojis linked to original posts, which are similar to the findings of Ayers et al [ 25 ] and Lathan et al [ 22 ]. Usha Lawrance et al [ 150 ] and Wilkinson and Thelwall [ 151 ] argued that using direct quotes to support findings would lead to the identification of users and breach users’ confidentiality in internet community data. Moreover, quoting social media posts or disclosing usernames violate the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors’ ethics standards, which state that identifying information such as written descriptions and photos should not be published unless the information is essential for scientific purposes and the participants give written informed consent for publication [ 152 ]. Furthermore, our study demonstrates that the proportion of studies containing users’ written content (both direct and paraphrased quotations) is higher than that of studies that do not include any quotation or written content (60/76, 79% vs 14/32, 44%; P <.001)——a tentative explanation is that some researchers realized that ethical reportage should be stricter for qualitative papers with quotations from social media posts due to privacy and security issues. This is supported by Boyd and Crawford [ 153 ] who stated that rigorous thinking about the process of mining and anonymizing big data is required for ethics boards to ensure that people are protected. Our findings show that 32% (24/76) of the studies intentionally paraphrased the quotes to ensure that users could not locate them, and 20 studies used aggregated data interconnected with anonymity. Moreover, it is recommended by Wilkinson and Thelwall [ 151 ], Bond et al [ 154 ], and Markham et al [ 155 ] that researchers should not directly quote and work with aggregate data sets and separate texts from their original context, which is more acceptable to participants. In addition, the British Psychological Society guidelines recommend that researchers consider paraphrasing any verbatim quotes to reduce the risk of these being traced to the source [ 20 ]. Notably, 13 of the 25 papers in this study showed that they did not report the precautions taken for paraphrasing. This may be due to the lack of detailed methodology and consensus about paraphrasing quotes to reduce bias and maintaining the original meaning.
Limitations and Strengths
Our scoping review has several limitations. First, our research was limited to qualitative studies and the qualitative parts in mixed methods studies on text mining from social media, and it is unclear whether ethical considerations are critical in quantitative studies among internet communities. Second, we were restricted to studies published in English language and those with the full text available, and therefore, we could be underestimating the number of relevant papers published in other languages. Third, the rates of reporting ethical approval, informed consent, and privacy of this research relied on self-reported data. Thus, it is possible that although certain studies did not report the process of ethical considerations, such considerations may have been followed during the research. Conversely, some studies may have mentioned about the ethical considerations but may not have conducted them in practice. Hence, there is a bias because of the lack of accurate documentation that must be considered.
Social media text mining can be a useful tool for researchers to understand patient experiences of health conditions and health care. However, as illustrated by the absence of ethical discourse in publications, our analysis indicates significant gaps in the ethical considerations and governance of qualitative research of internet posts. Therefore, a complete and consistent consensus guideline of ethical considerations in qualitative research of internet posts is needed to protect users’ data. With the continued advancing development of text-mining techniques, qualitative studies mining text from social media should be more cautious while using user quotations to maintain user privacy and protect the traceability of the internet users posting content. We suggest that authors should report their results by using aggregated findings or deidentified ways like paraphrasing instead of verbatim quotations, which can prevent internet users from being identified through search engines. In addition, authors should provide more detailed information about the precautions taken for obtaining informed consent and paraphrasing to reduce the potential bias. Furthermore, journals and editors should pay more attention to the reporting standards of ethical consideration and privacy issues in qualitative research involving social media data.
Acknowledgments
This project was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (72304131) and the Outstanding Youths Development Scheme of Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University (2023J005). The funders had no role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of this manuscript. We sincerely thank the funders of this study.
Data Availability
All data extracted and analyzed during this study are presented in this paper and in the multimedia appendices.
Authors' Contributions
YW was responsible for the protocol of the research and redrafted the paper critically. YZ and JF performed literature searches. YZ, JL, and WC performed study identification and screening. ZG, SD, CZ, and JT extracted and analyzed the data from the included journals. YZ and JL wrote the first draft of the paper. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
None declared.
PRISMA-ScR (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses Extension for Scoping Reviews) checklist.
Search strategy for each database.
Summary of included literature.
- Obar JA, Wildman S. Social media definition and the governance challenge: An introduction to the special issue. Telecommunications Policy. Oct 2015;39(9):745-750. [ CrossRef ]
- Kaplan AM, Haenlein M. Users of the world, unite! The challenges and opportunities of social media. Business Horizons. Jan 2010;53(1):59-68. [ CrossRef ]
- VanDam C, Kanthawala S, Pratt W, Chai J, Huh J. Detecting clinically related content in online patient posts. J Biomed Inform. Nov 2017;75:96-106. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Health care. Wikipedia. URL: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Health_care [accessed 2023-06-01]
- Moorhead SA, Hazlett DE, Harrison L, Carroll JK, Irwin A, Hoving C. A new dimension of health care: systematic review of the uses, benefits, and limitations of social media for health communication. J Med Internet Res. Apr 23, 2013;15(4):e85. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Sinnenberg L, Buttenheim AM, Padrez K, Mancheno C, Ungar L, Merchant RM. Twitter as a tool for health research: A systematic review. Am J Public Health. Jan 2017;107(1):e1-e8. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Braun V, Clarke V. Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qualitative Research in Psychology. Jan 2006;3(2):77-101. [ CrossRef ]
- Hswen Y, Naslund JA, Brownstein JS, Hawkins JB. Monitoring online discussions about suicide among Twitter users with schizophrenia: exploratory study. JMIR Ment Health. Dec 13, 2018;5(4):e11483. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Golder S, Ahmed S, Norman G, Booth A. Attitudes toward the ethics of research using social media: a systematic review. J Med Internet Res. Jun 06, 2017;19(6):e195. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Athanasopoulou C, Sakellari E. Facebook and health information: content analysis of groups related to schizophrenia. Stud Health Technol Inform. 2015;213:255-258. [ Medline ]
- Conway M, O'Connor D. Social media, big data, and mental health: current advances and ethical implications. Curr Opin Psychol. Jun 2016;9:77-82. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Eysenbach G, Till JE. Ethical issues in qualitative research on internet communities. BMJ. Nov 10, 2001;323(7321):1103-1105. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Heilferty CM. Ethical considerations in the study of online illness narratives: a qualitative review. J Adv Nurs. May 2011;67(5):945-953. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Roberts LD. Ethical issues in conducting qualitative research in online communities. Qualitative Research in Psychology. Apr 20, 2015;12(3):314-325. [ CrossRef ]
- Franzke A, Bechmann A, Zimmer M, Ess C, the Association of Internet Researchers. Internet research: ethical guidelines 3.0. Association of Internet Researchers. 2020. URL: https://aoir.org/reports/ethics3.pdf [accessed 2023-05-30]
- Markham A, Buchanan E. Ethical decision-making and internet research: recommendations from the AoIR ethics working committee (version 2.0). AoIR. 2012. URL: https://aoir.org/reports/ethics2.pdf [accessed 2023-06-05]
- The NCFREITSSH(. Ethical guidelines for internet research. 2022. URL: https://www.forskningsetikk.no/en/guidelines/social-sciences-humanities-law-and-theology/a-guide-to-internet-research-ethics [accessed 2023-06-13]
- Chapter 3: Rights of the data subject. General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). European Commission. Official Journal of the European Union; 2018. URL: https://gdpr-info.eu/chapter-3/ [accessed 2023-11-29]
- Hand DJ. Aspects of data ethics in a changing world: where are we now? Big Data. Sep 01, 2018;6(3):176-190. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- British Psychological Society. Ethics guidelines for internet-mediated research. 2021. URL: https://explore.bps.org.uk/binary/bpsworks/64374754e0c1dd30/5a757d7c2d39a9837f0eedec1b9ba28fa5e9e38f0bffa9950b678ab727803959/rep155_2021.pdf [accessed 2023-05-30]
- Takats C, Kwan A, Wormer R, Goldman D, Jones HE, Romero D. Ethical and methodological considerations of Twitter data for public health research: systematic review. J Med Internet Res. Nov 29, 2022;24(11):e40380. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Lathan HS, Kwan A, Takats C, Tanner JP, Wormer R, Romero D, et al. Ethical considerations and methodological uses of Facebook data in public health research: A systematic review. Soc Sci Med. Apr 2023;322:115807. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Tanner J, Takats C, Lathan H, Kwan A, Wormer R, Romero D, et al. Approaches to research ethics in health research on YouTube: systematic review. J Med Internet Res. Oct 04, 2023;25:e43060. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Stockdale J, Cassell J, Ford E. "Giving something back": A systematic review and ethical enquiry into public views on the use of patient data for research in the United Kingdom and the Republic of Ireland. Wellcome Open Res. 2018;3:6. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Ayers JW, Caputi TL, Nebeker C, Dredze M. Don't quote me: reverse identification of research participants in social media studies. NPJ Digit Med. 2018;1:30. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Aitken M, de St Jorre J, Pagliari C, Jepson R, Cunningham-Burley S. Public responses to the sharing and linkage of health data for research purposes: a systematic review and thematic synthesis of qualitative studies. BMC Med Ethics. Nov 10, 2016;17(1):73. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Hunter RF, Gough A, O’Kane N, McKeown G, Fitzpatrick A, Walker T, et al. Ethical issues in social media research for public health. Am J Public Health. Mar 2018;108(3):343-348. [ CrossRef ]
- Ahmed OH, Sullivan SJ, Schneiders AG, McCrory P. iSupport: do social networking sites have a role to play in concussion awareness? Disabil Rehabil. 2010;32(22):1877-1883. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Bender JL, Jimenez-Marroquin M, Jadad AR. Seeking support on Facebook: a content analysis of breast cancer groups. J Med Internet Res. Feb 04, 2011;13(1):e16. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Gajaria A, Yeung E, Goodale T, Charach A. Beliefs about attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and response to stereotypes: youth postings in Facebook groups. J Adolesc Health. Jul 2011;49(1):15-20. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Degroot JM. Maintaining relational continuity with the deceased on Facebook. Omega (Westport). Nov 01, 2012;65(3):195-212. [ CrossRef ]
- Donelle L, Booth RG. Health tweets: an exploration of health promotion on twitter. Online J Issues Nurs. Sep 30, 2012;17(3):4. [ FREE Full text ] [ Medline ]
- Rui JR, Chen Y, Damiano A. Health organizations providing and seeking social support: a Twitter-based content analysis. Cyberpsychol Behav Soc Netw. Sep 2013;16(9):669-673. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Lyles CR, López A, Pasick R, Sarkar U. "5 mins of uncomfyness is better than dealing with cancer 4 a lifetime": an exploratory qualitative analysis of cervical and breast cancer screening dialogue on Twitter. J Cancer Educ. Mar 2013;28(1):127-133. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Lee JL, DeCamp M, Dredze M, Chisolm MS, Berger ZD. What are health-related users tweeting? A qualitative content analysis of health-related users and their messages on twitter. J Med Internet Res. Oct 15, 2014;16(10):e237. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Ahlwardt K, Heaivilin N, Gibbs J, Page J, Gerbert B, Tsoh JY. Tweeting about pain: comparing self-reported toothache experiences with those of backaches, earaches and headaches. J Am Dent Assoc. Jul 2014;145(7):737-743. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Struik LL, Baskerville NB. The role of Facebook in Crush the Crave, a mobile- and social media-based smoking cessation intervention: qualitative framework analysis of posts. J Med Internet Res. Jul 11, 2014;16(7):e170. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Abdel-Razig S, Anglade P, Ibrahim H. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on a physician group's WhatsApp chat: qualitative content analysis. JMIR Form Res. Dec 07, 2021;5(12):e31791. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Reddy A. Skincare in social media: analyzing prominent themes in online dermatologic discussions. Cureus. May 7, 2021:e14890. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- van der Pijl MSG, Hollander MH, van der Linden T, Verweij R, Holten L, Kingma E, et al. Left powerless: A qualitative social media content analysis of the Dutch #breakthesilence campaign on negative and traumatic experiences of labour and birth. PLoS One. 2020;15(5):e0233114. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Rath L, Vijiaratnam N, Skibina O. Alemtuzumab in multiple sclerosis: lessons from social media in enhancing patient care. Int J MS Care. 2017;19(6):323-328. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Bloom R, Beck S, Chou W, Reblin M, Ellington L. In their own words: experiences of caregivers of adults with cancer as expressed on social media. ONF. Sep 1, 2019;46(5):617-630. [ CrossRef ]
- Grumme V, Gordon S. Social media use by transplant recipients for support and healing. Comput Inform Nurs. Dec 2016;34(12):570-577. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Haug NA, Bielenberg J, Linder SH, Lembke A. Assessment of provider attitudes toward #naloxone on Twitter. Subst Abus. 2016;37(1):35-41. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Oren E, Martinez L, Hensley RE, Jain P, Ahmed T, Purnajo I, et al. Twitter communication during an outbreak of hepatitis A in San Diego, 2016–2018. Am J Public Health. Oct 2020;110(S3):S348-S355. [ CrossRef ]
- Parker C, Zomer E, Liew D, Ayton D. Characterising experiences with acute myeloid leukaemia using an Instagram content analysis. PLoS One. 2021;16(5):e0250641. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Kurko T, Linden K, Kolstela M, Pietilä K, Airaksinen M. Is nicotine replacement therapy overvalued in smoking cessation? Analysis of smokers' and quitters' communication in social media. Health Expect. Dec 2015;18(6):2962-2977. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Reuter K, Lee D. Perspectives toward seeking treatment among patients with psoriasis: protocol for a Twitter content analysis. JMIR Res Protoc. Feb 18, 2021;10(2):e13731. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Mollema L, Harmsen IA, Broekhuizen E, Clijnk R, De Melker H, Paulussen T, et al. Disease detection or public opinion reflection? Content analysis of tweets, other social media, and online newspapers during the measles outbreak in The Netherlands in 2013. J Med Internet Res. May 26, 2015;17(5):e128. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- O'Hagan ET, Traeger AC, Bunzli S, Leake HB, Schabrun SM, Wand BM, et al. What do people post on social media relative to low back pain? A content analysis of Australian data. Musculoskelet Sci Pract. Aug 2021;54:102402. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Zhou F, Zhang W, Cai H, Cao Y. Portrayals of 2v, 4v and 9vHPV vaccines on Chinese social media: a content analysis of hot posts on Sina Weibo. Hum Vaccin Immunother. Nov 02, 2021;17(11):4433-4441. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Golder S, Bach M, O'Connor K, Gross R, Hennessy S, Gonzalez Hernandez G. Public perspectives on anti-diabetic drugs: exploratory analysis of Twitter posts. JMIR Diabetes. Jan 26, 2021;6(1):e24681. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Mercier R, Senter K, Webster R, Henderson RA. Instagram users? experiences of miscarriage. Obstet Gynecol 2020 Jan;? Jan 2020;135(1):166-173. [ CrossRef ]
- Alghamdi A, Abumelha K, Allarakia J, Al-Shehri A. Conversations and misconceptions about chemotherapy in Arabic tweets: content analysis. J Med Internet Res. Jul 29, 2020;22(7):e13979. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Golder S, O'Connor K, Hennessy S, Gross R, Gonzalez-Hernandez G. Assessment of beliefs and attitudes about statins posted on Twitter: a qualitative study. JAMA Netw Open. Jun 01, 2020;3(6):e208953. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Stekelenburg N, Horsham C, O'Hara M, Janda M. Using social media to determine the affective and cognitive components of tweets about sunburn. Dermatology. Feb 27, 2020;236(2):75-80. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Meeking K. Patients' experiences of radiotherapy: Insights from Twitter. Radiography (Lond). Aug 2020;26(3):e146-e151. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Shah S, Bradbury-Jones C, Taylor J. Using Facebook to tell stories of premature ageing and sexual and reproductive healthcare across the life course for women with cerebral palsy in the UK and USA. BMJ Open. Feb 17, 2020;10(2):e032172. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Pretorius K, Choi E, Kang S, Mackert M. Sudden infant death syndrome on Facebook: qualitative descriptive content analysis to guide prevention efforts. J Med Internet Res. Jul 30, 2020;22(7):e18474. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Karmegam D, Mapillairaju B. What people share about the COVID-19 outbreak on Twitter? An exploratory analysis. BMJ Health Care Inform. Nov 2020;27(3):e100133. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Hairston TK, Links AR, Harris V, Tunkel DE, Walsh J, Beach MC, et al. Evaluation of parental perspectives and concerns about pediatric tonsillectomy in social media. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. Jan 01, 2019;145(1):45-52. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Årsand E, Bradway M, Gabarron E. What are diabetes patients versus health care personnel discussing on social media? J Diabetes Sci Technol. Mar 2019;13(2):198-205. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Jiang X, Jiang W, Cai J, Su Q, Zhou Z, He L, et al. Characterizing media content and effects of organ donation on a social media platform: content analysis. J Med Internet Res. Mar 12, 2019;21(3):e13058. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Oser TK, Minnehan KA, Wong G, Parascando J, McGinley E, Radico J, et al. Using social media to broaden understanding of the barriers and facilitators to exercise in adults with type 1 diabetes. J Diabetes Sci Technol. May 2019;13(3):457-465. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Sutton J, Vos SC, Olson MK, Woods C, Cohen E, Gibson CB, et al. Lung cancer messages on Twitter: content analysis and evaluation. J Am Coll Radiol. Jan 2018;15(1 Pt B):210-217. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Thomas J, Prabhu AV, Heron DE, Beriwal S. Twitter and brachytherapy: An analysis of "tweets" over six years by patients and health care professionals. Brachytherapy. 2018;17(6):1004-1010. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Kelly-Hedrick M, Grunberg PH, Brochu F, Zelkowitz P. "It's totally okay to be sad, but never lose hope": content analysis of infertility-related videos on YouTube in relation to viewer preferences. J Med Internet Res. May 23, 2018;20(5):e10199. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Gage-Bouchard EA, LaValley S, Mollica M, Beaupin LK. Cancer communication on social media: examining how cancer caregivers use Facebook for cancer-related communication. Cancer Nurs. 2017;40(4):332-338. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Rael CT, Pierre D, Frye V, Kessler D, Duffy L, Malos N, et al. Evaluating blood donor experiences and barriers/facilitators to blood donation in the United States using YouTube video content. Transfusion. Sep 2021;61(9):2650-2657. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Fisher S, Jehassi A, Ziv M. Hidradenitis suppurativa on Facebook: thematic and content analyses of patient support group. Arch Dermatol Res. Aug 2020;312(6):421-426. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Abdoli S, Hessler D, Vora A, Smither B, Stuckey H. Descriptions of diabetes burnout from individuals with Type 1 diabetes: an analysis of YouTube videos. Diabet Med. Aug 2020;37(8):1344-1351. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Myneni S, Lewis B, Singh T, Paiva K, Kim SM, Cebula AV, et al. Diabetes self-management in the age of social media: large-scale analysis of peer interactions using semiautomated methods. JMIR Med Inform. Jun 30, 2020;8(6):e18441. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Charlie AM, Gao Y, Heller SL. What do patients want to know? questions and concerns regarding mammography expressed through social media. J Am Coll Radiol. Oct 2018;15(10):1478-1486. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Watts G, Christou P, Antonarakis G. Experiences of individuals concerning combined orthodontic and orthognathic surgical treatment: a qualitative Twitter analysis. Med Princ Pract. 2018;27(3):227-235. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Pai RR, Alathur S. Assessing mobile health applications with Twitter analytics. Int J Med Inform. May 2018;113:72-84. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Cheng TY, Liu L, Woo BK. Analyzing Twitter as a platform for Alzheimer-related dementia awareness: thematic analyses of tweets. JMIR Aging. Dec 10, 2018;1(2):e11542. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Bridges N, Howell G, Schmied V. Exploring breastfeeding support on social media. Int Breastfeed J. 2018;13:22. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Anderson JG, Hundt E, Dean M, Keim-Malpass J, Lopez RP. "The Church of Online Support": examining the use of blogs among family caregivers of persons with dementia. J Fam Nurs. Feb 2017;23(1):34-54. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Kearney MD, Selvan P, Hauer MK, Leader AE, Massey PM. Characterizing HPV vaccine sentiments and content on Instagram. Health Educ Behav. Dec 2019;46(2_suppl):37-48. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Davies SH, Langer MD, Klein A, Gonzalez-Hernandez G, Dowshen N. Adolescent perceptions of menstruation on Twitter: opportunities for advocacy and education. J Adolesc Health. Jul 2022;71(1):94-104. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Van Diepen C, Rosales Valdes D. A content analysis on the perceptions of LGBTQ+ (centred) health care on Twitter. Health Expect. Dec 2022;25(6):3238-3245. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Pleasure ZH, Frohwirth LF, Li N, Polis CB. A content analysis of Reddit users' posts about challenges to contraceptive care-seeking during COVID-19-related restrictions in the United States. J Health Commun. Oct 03, 2022;27(10):746-754. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Du Y, Dennis B, Ramirez V, Li C, Wang J, Meireles CL. Experiences and disease self-management in individuals living with chronic kidney disease: qualitative analysis of the National Kidney Foundation's online community. BMC Nephrol. Mar 04, 2022;23(1):88. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Sadek Attalla S, Ow NL, McNarry M, De Simoni A. Experiences of exercise in patients with asthma: a qualitative analysis of discussions in a UK asthma online community. BJGP Open. Apr 29, 2022;6(3):BJGPO.2021.0162. [ CrossRef ]
- Bartmess M, Talbot C, O'Dwyer ST, Lopez RP, Rose KM, Anderson JG. Using Twitter to understand perspectives and experiences of dementia and caregiving at the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic. Dementia (London). Jul 2022;21(5):1734-1752. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Brewer G, Centifanti L, Caicedo JC, Huxley G, Peddie C, Stratton K, et al. Experiences of mental distress during COVID-19: thematic analysis of discussion forum posts for anxiety, depression, and obsessive-compulsive disorder. Illn Crises Loss. Oct 2022;30(4):795-811. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Castillo LIR, Hadjistavropoulos T, Beahm J. Social media discussions about long-term care and the COVID-19 pandemic. J Aging Stud. Dec 2022;63:101076. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Colaceci S, Anderson G, Ricciuto V, Montinaro D, Alazraki G, Mena-Tudela D. Experiences of birth during COVID-19 pandemic in Italy and Spain: A thematic analysis. Int J Environ Res Public Health. Jun 18, 2022;19(12):7488. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Tripathi SD, Parker PD, Prabhu AV, Thomas K, Rodriguez A. An examination of patients and caregivers on Reddit Navigating Brain Cancer: content analysis of the brain tumor Subreddit. JMIR Cancer. Jun 22, 2022;8(2):e35324. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Jina-Pettersen N. Fear, neglect, coercion, and dehumanization: is inpatient psychiatric trauma contributing to a public health crisis? J Patient Exp. 2022;9:23743735221079138. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Rossi NA, Devarajan K, Chokshi SN, Ochoa VJ, Benavidez M, Malaya LT, et al. Social media depictions of cochlear implants: An Instagram and TikTok analysis. Otol Neurotol. 2023;44(1):e13-e21. [ CrossRef ]
- Singh GK, Rego J, Chambers S, Fox J. Health professionals' perspectives of the role of palliative care during COVID-19: content analysis of articles and blogs posted on Twitter. Am J Hosp Palliat Care. Apr 2022;39(4):487-493. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Koly KN, Tasnim Z, Ahmed S, Saba J, Mahmood R, Farin FT, et al. Mental healthcare-seeking behavior of women in Bangladesh: content analysis of a social media platform. BMC Psychiatry. Dec 19, 2022;22(1):797. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Belcher R, Sim D, Meykler M, Owens-Walton J, Hassan N, Rubin R, et al. A qualitative analysis of female Reddit users' experiences with low libido: how do women perceive their changes in sexual desire? J Sex Med. Feb 27, 2023;20(3):287-297. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Culp F, Wu Y, Wu D, Ren Y, Raynor P, Hung P, et al. Understanding alcohol use discourse and stigma patterns in perinatal care on Twitter. Healthcare (Basel). Nov 26, 2022;10(12):2375. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Ferrey A, Ashworth G, Cabling M, Rundblad G, Ismail K. A thematic analysis of YouTube comments on a television documentary titled 'Diabulimia: The world's most dangerous eating disorder'. Diabet Med. May 2023;40(5):e15025. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Watt S, Salway T, Gómez-Ramírez O, Ablona A, Barton L, Chang H, et al. Rumination, risk, and response: a qualitative analysis of sexual health anxiety among online sexual health chat service users. Sex. Health. May 23, 2022;19(3):182-191. [ CrossRef ]
- Naganathan G, Bilgen I, Cleland J, Reel E, Cil T. #COVID19 and #Breastcancer: a qualitative analysis of tweets. Curr Oncol. Nov 08, 2022;29(11):8483-8500. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Potgieter I, Hoare DJ, Fackrell K. Hyperacusis in children: a thematic analysis of discussions in online forums. Am J Audiol. Mar 03, 2022;31(1):166-174. [ CrossRef ]
- Manning Hutson M, Hosking SM, Mantalvanos S, Berk M, Pasco J, Dunning T. What injured workers with complex claims look for in online communities: netnographic analysis. J Med Internet Res. Apr 07, 2022;24(4):e17180. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Lawless MT, Hunter SC, Pinero de Plaza MA, Archibald MM, Kitson AL. "You Are By No Means Alone": a netnographic study of self-care support in an online community for older adults. Qual Health Res. Nov 2022;32(13):1935-1951. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Keim-Malpass J, Mitchell EM, Sun E, Kennedy C. Using Twitter to understand public perceptions regarding the #HPV vaccine: opportunities for public health nurses to engage in social marketing. Public Health Nurs. Jul 2017;34(4):316-323. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Yamada R, Rasmussen KM, Felice JP. "What is 'enough,' and how do I make it?": a qualitative examination of questions mothers ask on social media about pumping and providing an adequate amount of milk for their infants. Breastfeed Med. 2019;14(1):17-21. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Osadchiy V, Mills JN, Eleswarapu SV. Understanding patient anxieties in the social media era: qualitative analysis and natural language processing of an online male infertility community. J Med Internet Res. Mar 10, 2020;22(3):e16728. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Thomas TH, Nauth-Shelley K, Thompson MA, Attai DJ, Katz MS, Graham D, et al. The needs of women treated for ovarian cancer: results from a #gyncsm Twitter chat. J Patient Cent Res Rev. 2018;5(2):149-157. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Mehta N, Zhu L, Lam K, Stall NM, Savage R, Read SH, et al. Health forums and Twitter for dementia research: opportunities and considerations. J Am Geriatr Soc. Dec 2020;68(12):2881-2889. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Gupta R, Ariefdjohan M. Mental illness on Instagram: a mixed method study to characterize public content, sentiments, and trends of antidepressant use. J Ment Health. Aug 2021;30(4):518-525. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- He L, He C, Reynolds T, Bai Q, Huang Y, Li C, et al. Why do people oppose mask wearing? A comprehensive analysis of U.S. tweets during the COVID-19 pandemic. J Am Med Inform Assoc. Jul 14, 2021;28(7):1564-1573. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Loeb S, Mihalcea R, Perez-Rosas V, Xu A, Taylor J, Byrne N, et al. Leveraging social media as a thermometer to gauge patient and caregiver concerns: COVID-19 and prostate cancer. Eur Urol Open Sci. Mar 2021;25:1-4. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Graf I, Gerwing H, Hoefer K, Ehlebracht D, Christ H, Braumann B. Social media and orthodontics: A mixed-methods analysis of orthodontic-related posts on Twitter and Instagram. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. Aug 2020;158(2):221-228. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Boon-Itt S, Skunkan Y. Public perception of the COVID-19 pandemic on Twitter: sentiment analysis and topic modeling study. JMIR Public Health Surveill. Nov 11, 2020;6(4):e21978. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Wang J, Zhou Y, Zhang W, Evans R, Zhu C. Concerns expressed by Chinese social media users during the COVID-19 pandemic: content analysis of Sina Weibo microblogging data. J Med Internet Res. Nov 26, 2020;22(11):e22152. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Wahbeh A, Nasralah T, Al-Ramahi M, El-Gayar O. Mining physicians' opinions on social media to obtain insights into COVID-19: mixed methods analysis. JMIR Public Health Surveill. Jun 18, 2020;6(2):e19276. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Çınar S, Boztepe H, Prof. The use of social media among parents of infants with cleft lip and/or palate. J Pediatr Nurs. 2020;54:e91-e96. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Jiang T, Osadchiy V, Mills JN, Eleswarapu SV. Is It all in my head? self-reported psychogenic erectile dysfunction and depression are common among young men seeking advice on social media. Urology. Aug 2020;142:133-140. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Dzubur E, Khalil C, Almario CV, Noah B, Minhas D, Ishimori M, et al. Patient concerns and perceptions regarding biologic therapies in ankylosing spondylitis: insights from a large-scale survey of social media platforms. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). Feb 2019;71(2):323-330. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Gonzalez G, Vaculik K, Khalil C, Zektser Y, Arnold C, Almario CV, et al. Women's experience with stress urinary incontinence: insights from social media analytics. Journal of Urology. May 2020;203(5):962-968. [ CrossRef ]
- Jha SR, McDonagh J, Prichard R, Newton PJ, Hickman LD, Fung E, et al. #Frailty: A snapshot Twitter report on frailty knowledge translation. Australas J Ageing. Dec 2018;37(4):309-312. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Litchman ML, Snider C, Edelman LS, Wawrzynski SE, Gee PM. Diabetes online community user perceptions of successful aging with diabetes: analysis of a #DSMA Tweet chat. JMIR Aging. Jun 22, 2018;1(1):e10176. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Jones J, Pradhan M, Hosseini M, Kulanthaivel A, Hosseini M. Novel approach to cluster patient-generated data into actionable topics: case study of a web-based breast cancer forum. JMIR Med Inform. Nov 29, 2018;6(4):e45. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Gonzalez G, Vaculik K, Khalil C, Zektser Y, Arnold C, Almario CV, et al. Using large-scale social media analytics to understand patient perspectives about urinary tract infections: thematic analysis. J Med Internet Res. Jan 25, 2022;24(1):e26781. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Sormunen T, Westerbotn M, Aanesen A, Fossum B, Karlgren K. Social media in the infertile community-using a text analysis tool to identify the topics of discussion on the multitude of infertility blogs. Womens Health (Lond). 2021;17:17455065211063280. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Berkovic D, Ackerman IN, Briggs AM, Ayton D. Tweets by people with arthritis during the COVID-19 pandemic: content and sentiment analysis. J Med Internet Res. Dec 03, 2020;22(12):e24550. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Della Rosa S, Sen F. Health topics on Facebook Groups: content analysis of posts in multiple sclerosis communities. Interact J Med Res. Feb 11, 2019;8(1):e10146. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Awofeso N, Imam SA, Ahmed A. Content analysis of media coverage of childhood obesity topics in UAE newspapers and popular social media platforms, 2014-2017. Int J Health Policy Manag. Feb 01, 2019;8(2):81-89. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Smith DJ, Mac VV, Hertzberg VS. Using Twitter for nursing research: a tweet analysis on heat illness and health. J Nurs Scholarsh. May 2021;53(3):343-350. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Green BM, Van Horn KT, Gupte K, Evans M, Hayes S, Bhowmick A. Assessment of adaptive engagement and support model for people with chronic health conditions in online health communities: combined content analysis. J Med Internet Res. Jul 07, 2020;22(7):e17338. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Osakwe ZT, Cortés YI. Impact of COVID-19: a text mining analysis of Twitter data in Spanish language. Hisp Health Care Int. Dec 2021;19(4):239-245. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Sümeyye Yorulmaz D, Karadeniz H. Vaccination refusal debate on social media in Turkey: a content analysis of the comments on Instagram blogs. Iran J Public Health. Mar 2022;51(3):615-623. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Choi E, Becker H, Kim S. A blog text analysis to explore psychosocial support in adolescents and young adults with cancer. Cancer Nurs. Dec 11, 2022;46(2):143-151. [ CrossRef ]
- Jun J, Wickersham K, Zain A, Ford R, Zhang N, Ciccarelli C, et al. Cancer and COVID-19 vaccines on Twitter: the voice and vaccine attitude of cancer community. J Health Commun. Jan 02, 2023;28(1):1-14. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Yashpal S, Raghunath A, Gencerliler N, Burns LE. Exploring public perceptions of dental care affordability in the United States: mixed method analysis via Twitter. JMIR Form Res. Jul 01, 2022;6(7):e36315. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Damier P, Henderson EJ, Romero-Imbroda J, Galimam L, Kronfeld N, Warnecke T. Impact of off-time on quality of life in Parkinson's patients and their caregivers: insights from social media. Parkinsons Dis. 2022;2022:1800567. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Miller WR, Malloy C, Mravec M, Sposato MF, Groves D. Nursing in the spotlight: Talk about nurses and the nursing profession on Twitter during the early COVID-19 pandemic. Nurs Outlook. 2022;70(4):580-589. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Hriberšek M, Eibensteiner F, Kapral L, Teufel A, Nawaz FA, Cenanovic M, et al. "Loved ones are not 'visitors' in a patient's life"-The importance of including loved ones in the patient's hospital stay: An international Twitter study of #HospitalsTalkToLovedOnes in times of COVID-19. Front Public Health. 2023;11:1100280. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- O'Sullivan L, Killeen RP, Doran P, Crowley RK. Adherence with reporting of ethical standards in COVID-19 human studies: a rapid review. BMC Med Ethics. Jun 28, 2021;22(1):80. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Denecke K, Bamidis P, Bond C, Gabarron E, Househ M, Lau AYS, et al. Ethical issues of social media usage in healthcare. Yearb Med Inform. Aug 13, 2015;10(1):137-147. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Ferretti A, Ienca M, Sheehan M, Blasimme A, Dove ES, Farsides B, et al. Ethics review of big data research: What should stay and what should be reformed? BMC Med Ethics. Apr 30, 2021;22(1):51. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Kohn T, Shore C. The Ethics of University Ethics Committees: risk management and the research imagination. Death Public Univ Uncertain Futur High Educ Knowl Econ. May 2017:229-249. [ CrossRef ]
- Friesen P, Redman B, Caplan A. Of straws, camels, research regulation, and IRBs. Ther Innov Regul Sci. Jul 2019;53(4):526-534. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Sellers C, Samuel G, Derrick G. Reasoning "uncharted territory": notions of expertise within ethics review panels assessing research use of social media. J Empir Res Hum Res Ethics. 2020;15(1-2):28-39. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Kious B. The Nuremberg Code: its history and implications. Princet J Bioeth. 2001;4:7-19. [ Medline ]
- World Medical Association. World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects. JAMA. Nov 27, 2013;310(20):2191-2194. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Department of Health‚ Education‚Welfare, National Commission for the Protection of Human Subjects of BiomedicalBehavioral Research. The Belmont Report. Ethical principles and guidelines for the protection of human subjects of research. J Am Coll Dent. 2014;81(3):4-13. [ Medline ]
- Wongkoblap A, Vadillo MA, Curcin V. Researching mental health disorders in the era of social media: systematic review. J Med Internet Res. Jun 29, 2017;19(6):e228. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Alim S. An initial exploration of ethical research practices regarding automated data extraction from online social media user profiles. First Monday. Jul 2014;19(7):105-127. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Vitak J, Proferes N, Shilton K, Ashktorab Z. Ethics regulation in social computing research: examining the role of institutional review boards. J Empir Res Hum Res Ethics. Dec 2017;12(5):372-382. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Moreno MA, Goniu N, Moreno PS, Diekema D. Ethics of social media research: common concerns and practical considerations. Cyberpsychol Behav Soc Netw. Sep 2013;16(9):708-713. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Metcalf J, Crawford K. Where are human subjects in Big Data research? The emerging ethics divide. Big Data & Society. Jun 01, 2016;3(1):205395171665021. [ CrossRef ]
- Usha Lawrance J, Nayahi Jesudhasan JV. Privacy preserving parallel clustering based anonymization for big data using MapReduce framework. Applied Artificial Intelligence. Oct 17, 2021;35(15):1587-1620. [ CrossRef ]
- Wilkinson D, Thelwall M. Researching personal information on the public web. Social Science Computer Review. Aug 17, 2010;29(4):387-401. [ CrossRef ]
- International Committee of Medical Journal Editors. Uniform requirements for manuscripts submitted to biomedical journals: writing and editing for biomedical publication. Croat Med J. Dec 2003;44(6):770-783. [ FREE Full text ] [ Medline ]
- Boyd D, Crawford K. Critical questions for big data. Information, Communication & Society. Jun 2012;15(5):662-679. [ CrossRef ]
- Bond CS, Ahmed OH, Hind M, Thomas B, Hewitt-Taylor J. The conceptual and practical ethical dilemmas of using health discussion board posts as research data. J Med Internet Res. Jun 07, 2013;15(6):e112. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Markham A, Tiidenberg K, Herman A. Ethics as methods: doing ethics in the era of big data research—introduction. Social Media + Society. Jul 19, 2018;4(3):205630511878450-205630511878416. [ CrossRef ]
Abbreviations
Edited by T Leung, T de Azevedo Cardoso; submitted 02.08.23; peer-reviewed by E Zibrowski, J Scheibner; comments to author 06.10.23; revised version received 29.11.23; accepted 16.04.24; published 17.05.24.
©Yujie Zhang, Jiaqi Fu, Jie Lai, Shisi Deng, Zihan Guo, Chuhan Zhong, Jianyao Tang, Wenqiong Cao, Yanni Wu. Originally published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research (https://www.jmir.org), 17.05.2024.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work, first published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research, is properly cited. The complete bibliographic information, a link to the original publication on https://www.jmir.org/, as well as this copyright and license information must be included.
MINI REVIEW article
This article is part of the research topic.
Reviews in Pediatric Urology 2024
Advancements in Surgical Education: Exploring Animal and Simulation Models in Fetal and Neonatal Surgery Training Provisionally Accepted

- 1 University of Wisconsin-Madison, United States
- 2 School of Medicine and Public Health, University of Wisconsin-Madison, United States
The final, formatted version of the article will be published soon.
The use of animal models in surgical training has a long history, dating back to Halsted's introduction in 1889. These models, often utilizing large animals like swine and dogs, offer valuable insights into fetal and neonatal surgeries. They allow for the study of long-term outcomes and the simulation of various diseases and anomalies, providing essential training experiences not readily available in human surgeries. However, there are notable limitations, including anatomical and physiological differences from humans, ethical considerations, and substantial infrastructure and maintenance costs. Simulation-based training offers several benefits, including standardized and safe learning environments without risks to real patients. Bench models, using synthetic materials or non-living animal tissue, provide cost-effective options for skills development. Virtual reality and 3-D printing technologies further enhance simulation experiences, allowing for the replication of complex clinical scenarios and patient-specific anatomies. While these models offer significant advantages, they lack the complexity of biological systems found in animal models. In conclusion, both animal and non-animal simulation models play crucial roles in enhancing surgical education, particularly in fetal and neonatal surgery. While advancements in non-animal technologies are important for ethical reasons, the continued necessity of animal models in certain areas should be acknowledged. By responsibly integrating these models into training programs, surgical education can be further enriched while upholding ethical standards and ensuring optimal patient outcomes.
Keywords: surgical education, Animal Models, surgical simulation, fetal surgical training, neonatal surgical training
Received: 17 Mar 2024; Accepted: 17 May 2024.
Copyright: © 2024 Davidson, Penniston and Farhat. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) . The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) or licensor are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
* Correspondence: Dr. Walid Farhat, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, United States
People also looked at

Ethical Issues in Community and Patient Stakeholder–Engaged Health Research
- © 2023
- Emily E. Anderson ORCID: https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2197-1239 0
Neiswanger Institute for Bioethics, Stritch School of Medicine, Loyola University Chicago, Maywood, USA
You can also search for this editor in PubMed Google Scholar
- First book to cover the full range of ethical issues related to a variety of different forms of stakeholder engagement
- Contains case studies highlighting unique issues that arise in stakeholder engagement relevant to different populations
- Synthesizes current conversations, best practices, and future directions in stakeholder–engaged health research
Part of the book series: Philosophy and Medicine (PHME, volume 146)
2892 Accesses
1 Citations
22 Altmetric
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this book
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Durable hardcover edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Other ways to access
Licence this eBook for your library
Institutional subscriptions
Table of contents (20 chapters)
Front matter, introduction: what we talk about when we talk about the ethics of engaging patient and community stakeholders in health research.
Emily E. Anderson
Theorizing Participatory Research
- Andrew Evans, Angela Potochnik
An Evolving Ethical Framework for Patient and Community-Engaged Research
- Lisa Mikesell
Beyond Good Intentions: Principles for Anti-racist Community-Engaged Research
- Alexis Grant, Andrea L. DaViera
Demystifying How Academic-Community Partnerships Use Reflexivity and Praxis to Promote Participatory Research Principles of Equity and Justice
- Jeni Hebert-Beirne, Sylvia Gonzalez, Melissa Chrusfield, Adlaide Holloway, Jennifer Plascencia Lopez, Dolores Castañeda
Reflexivity: A Strategy for Ethics- and Values-Driven Community Partnerships in Mental Health
- Tommy Chou, Stacy L. Frazier
In the Field
How do you define community and why is it important.
- Laurene Tumiel-Berhalter, Linda Kahn
Community Researchers and Ethical Considerations: Burdens in the Field
- Maghboeba Mosavel, Briona Phillips
Community-Engaged Research with People with Developmental Disabilities: A Conversation with Community Researchers about their Ethical Inclusion
- Brendan Durkin, Micah Fialka-Feldman, Jacob Myers, Ariel Schwartz, Katherine McDonald
Community Conversations about Culturally Responsive Health Research for African American Communities
- Adina Black, Millicent Robinson, Paige Castro-Reyes, Al Richmond, Latajah Lassus, Nancy Shore
The Power of Personal Narrative: My Experience with SACHRP, the FDA, and Bioethics
- Gianna McMillan
Unique Ethical Considerations
Patient advocacy organizations and conflicts of interest in research.
- Lisa Parker, Barbara Mintzes
Representing and Protecting: Gatekeepers in Community-Engaged Research
- Ryan Spellecy
Paying Research Participants and Community and Patient Research Partners: An Engaging Ethical Issue
- Lisa Ballance, Elizabeth Ripley
Rethinking Risks and Benefits in Stakeholder-Engaged Research: Lessons from HIV, Substance Use, and Sexual Health Research with Marginalized Communities
- Adrian Guta, Peter A. Newman, Adam Bourne
Data Decisions and Ethics: The Case of Stakeholder-Engaged Research
- Melody S. Goodman, Kristyn A. Pierce, James M. DuBois, Vetta Sanders Thompson
- Community-engaged Research
- history of codes of ethics
- epistemology and stakeholder engagement
- the Belmont principle
- CIOMS Ethical guidelines
- philosophy of patient engagement
- promoting equitable collaboration
- stakeholder voices in healthcare
- human research protections
About this book
This book provides in-depth analyses of a wide range of topics surrounding ethical issues in community and patient stakeholder–engaged health research, and highlights where consensus exists, is emerging, or remains elusive. Topics in this book cover the history of stakeholder engagement in health research; how codes of ethics and regulations have (or have not) addressed stakeholder engagement; how to promote equitable collaboration; the ethical perspectives of different stakeholders; and the unique challenges posed by stakeholder- engaged research to the protection of human research participants and the research ethics review process. The book includes discussion of unique issues that arise in stakeholder engagement relevant to different populations, settings, and research designs. This book is relevant for anyone with a role or interest in stakeholder-engaged research, including patient and community research partners; academic researchers; research ethics scholars and educators; and funders.
Editors and Affiliations
About the editor.
Emily E. Anderson, PhD, MPH, is Professor in the Neiswanger Institute for Bioethics and Healthcare Leadership at Loyola University Chicago’s Stritch School of Medicine. Dr. Anderson holds a PhD in health care ethics from Saint Louis University and an MPH from University of Illinois Chicago. She teaches courses on research ethics and responsible conduct of research to bioethics and biomedical sciences graduate students as well as medical students. In addition to the ethics of stakeholder engagement in research, her areas of interest and expertise include researcher and physician professionalism and misconduct; ethical issues in research with vulnerable populations; informed consent; institutional review board (IRB) policy; and the application of qualitative research techniques to the study of research ethics. She has published over 50 articles in top journals including the American Journal of Bioethics, Journal of Law, Medicine, and Ethics, Academic Medicine, and IRB: Ethics & Human Research. Dr. Anderson currently serves as associate editor of Narrative Inquiry in Bioethics . Dr. Anderson has been a co-investigator on several federally-funded research and educational projects and recently co-authored the book 100 Questions and Answers about Research Ethics (Sage Publications, 2018) with Dr. Amy Corneli (at Duke University).
Bibliographic Information
Book Title : Ethical Issues in Community and Patient Stakeholder–Engaged Health Research
Editors : Emily E. Anderson
Series Title : Philosophy and Medicine
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-40379-8
Publisher : Springer Cham
eBook Packages : Religion and Philosophy , Philosophy and Religion (R0)
Copyright Information : The Editor(s) (if applicable) and The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG 2023
Hardcover ISBN : 978-3-031-40378-1 Published: 02 October 2023
Softcover ISBN : 978-3-031-40381-1 Due: 31 October 2023
eBook ISBN : 978-3-031-40379-8 Published: 29 September 2023
Series ISSN : 0376-7418
Series E-ISSN : 2215-0080
Edition Number : 1
Number of Pages : XVI, 327
Number of Illustrations : 1 b/w illustrations
Topics : Ethics , Medicine/Public Health, general , Public Health , Community and Environmental Psychology
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Revised on May 9, 2024. Ethical considerations in research are a set of principles that guide your research designs and practices. Scientists and researchers must always adhere to a certain code of conduct when collecting data from people. The goals of human research often include understanding real-life phenomena, studying effective treatments ...
Ethical Considerations. Ethical considerations in research refer to the principles and guidelines that researchers must follow to ensure that their studies are conducted in an ethical and responsible manner. These considerations are designed to protect the rights, safety, and well-being of research participants, as well as the integrity and credibility of the research itself
The chapter begins by presenting four ethical principles—autonomy, non-maleficence, beneficence, and justice—that were first brought to attention by Beauchamp and Childress (Principles of biomedical ethics. Oxford University Press, New York, 2013). These principles form the basis for the protection of the subject in qualitative research.
6.3 Principles of Research Ethics There are general ethical principles that guide and underpin the proper conduct of research. The term "ethical principles" refers to those general rules that operate as a foundational rationale for the numerous specific ethical guidelines and assessments of human behaviour. 7 The National Statement on 'ethical conduct in human research' states that ...
Ethical Considerations T he consideration of ethics in research, and in general business for that matter, is of growing importance. It is, therefore, critical that you ... be asked that, if appropriately answered, will ensure that potential ethical problems are avoided. This chapter is designed to discuss a range of ethical issues. Many of these
• also be aware of the noteworthy issues involved in ethics for qualitative research. Overview Chapter 2 deals with the crucial issue of ethical consideration for research in psy-chology, and more specifically for you, the undergraduate psychology student, about to embark on your first piece of independent research. It is important to
guidance on additional ethical considerations . that may apply to: • the use of human biospecimens in laboratory based research (Chapter 3.2) • genomic research (Chapter 3.3) • xenotransplantation research (Chapter 3.4). This guidance applies to research, but . sometimes the distinction between research
Research ethics are moral principles that need to be adhered to when conducting a research study as well as when writing a scientific article, with the prime aim of avoiding deception or intent to harm study's participants, the scientific community, and society. Practicing and adhering to research ethics is essential for personal integrity as ...
Chapter Four Ethical Considerations in Research marcelle cacciaTTolo F or beginning researchers undertaking their first major research project, can often be a time of mixed emotions . Initial meetings with supervi- ... This matter of ethical research is the basis of this chap-ter . At all times the researcher should ensure that participants are ...
Ethical Considerations in Research Bonnie Rogers, DrPH, RNC, COHN In an age where technology is rapidly advancing and societal values and roles are changing dramatically, ethical issues are becoming increasingly more complex. This is evidenced when human beings are used as subjects of research investigations. What does the conduct of research eth
This chapter considers all of these important ethical con-cerns as associated with research in general and with qualitative research in particular. Chapter 3 Ethical Issues in Research Learning Objectives After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 13. Explain why questionable research practices involving humans signaled the need for ...
The article aims to identify the ethical guidelines which have been f ollowed. recently in the conduction of research and also the issues faced with them, and the unethical practices reported ...
Ethical Considerations can be specified as one of the most important parts of the research. Dissertations may even be doomed to failure if this part is missing. According to Bryman and Bell (2007) [1] the following ten points represent the most important principles related to ethical considerations in dissertations:
For beginning researchers undertaking their first major research project, can often be a time of mixed emotions. Initial meetings with supervisors or research collaborators involve addressing questions around the nature and scope of the research question, the methodological tools that will be used to collect data and the ease with which entry ...
Chapter 3. Research Ethics Conducting research with human subjects Ethics is the area of study that involves investigation, organization and pro-tection of societal concepts of right and wrong behaviour. There are multiple ways in which ethics relates to research. The information that arises from human subjects in research studies may
46 CHAPTER 4 ETHICAL CONSIDERATIONS IN RESEARCH 045-61/SpataCH04 11/18/02 6:23 PM Page 46. The key principles of ethical guidelines regarding the use of human participants can be traced back to the Nuremberg trials that tried the Nazi war criminals following World War II. When the war ended and the Nazi atrocities fully came to light, those ...
The third ethics principle of the Economic and Social Research Council (ESRC) states that: "The confidentiality of the information supplied by research subjects and the anonymity of respondents must be respected.". However, sometimes confidentiality is limited. For example, if a participant is at risk of harm, we must protect them.
Ethical research therefore considers systemic and institutional factors that. are influencing the success with which goals and outcomes can be achieved. In the case of Nhung, there was a need for ...
This chapter is included in the part "Challenges in evaluation policies for social sciences" is meant to explore the ethical challenges for research evaluation.
Introduction. Research includes a set of activities in which researchers use various structured methods to contribute to the development of knowledge, whether this knowledge is theoretical, fundamental, or applied (Drolet & Ruest, accepted).University research is carried out in a highly competitive environment that is characterized by ever-increasing demands (i.e., on time, productivity ...
Ethical considerations in research are a set of principles that guide your research designs and practices. Scientists and researchers must always adhere to a certain code of conduct when collecting data from people. The goals of human research often include understanding real-life phenomena, studying effective treatments, investigating ...
Ethical considerations related to conducting research also involve standards for the storage and analysis of research data so cases like the Schön scandal can be reviewed expeditiously. Generally speaking, all research data, including primary materials and raw data, such as survey questionnaires, measurements, recordings, and computer results, must be stored in secure and durable storage ...
Best ethical practices. 4.3.1. Research design. Research ethics starts with a sound research design. Knight, Chidlow and Minbaeva assert that the research design "sets out the research plan for empirically addressing a research question (s) that aims to develop theory in a feasible way" (2022: 45).
Voices in Bioethics is currently seeking submissions on philosophical and practical topics, both current and timeless. Papers addressing access to healthcare, the bioethical implications of recent Supreme Court rulings, environmental ethics, data privacy, cybersecurity, law and bioethics, economics and bioethics, reproductive ethics, research ethics, and pediatric bioethics are sought.
Careful consideration of the issues of nonmaleficence and how best to facilitate the participant experience was integral to the research design and addressed throughout the ethics approval process ...
Background: The internet community has become a significant source for researchers to conduct qualitative studies analyzing users' views, attitudes, and experiences about public health. However, few studies have assessed the ethical issues in qualitative research using social media data. Objective: This study aims to review the reportage of ethical considerations in qualitative research ...
The cases and chapter themes in this casebook illustrate and provide opportunities for reflection on the importance of a broad, contextually sensitive understanding of research ethics in emergencies. Each chapter includes case studies detailing lived experiences during 2020 and early 2021 to facilitate consideration of the complex ethical ...
The use of animal models in surgical training has a long history, dating back to Halsted's introduction in 1889. These models, often utilizing large animals like swine and dogs, offer valuable insights into fetal and neonatal surgeries. They allow for the study of long-term outcomes and the simulation of various diseases and anomalies, providing essential training experiences not readily ...
This book provides in-depth analyses of a wide range of topics surrounding ethical issues in community and patient stakeholder-engaged health research, and highlights where consensus exists, is emerging, or remains elusive. Topics in this book cover the history of stakeholder engagement in health research; how codes of ethics and regulations ...